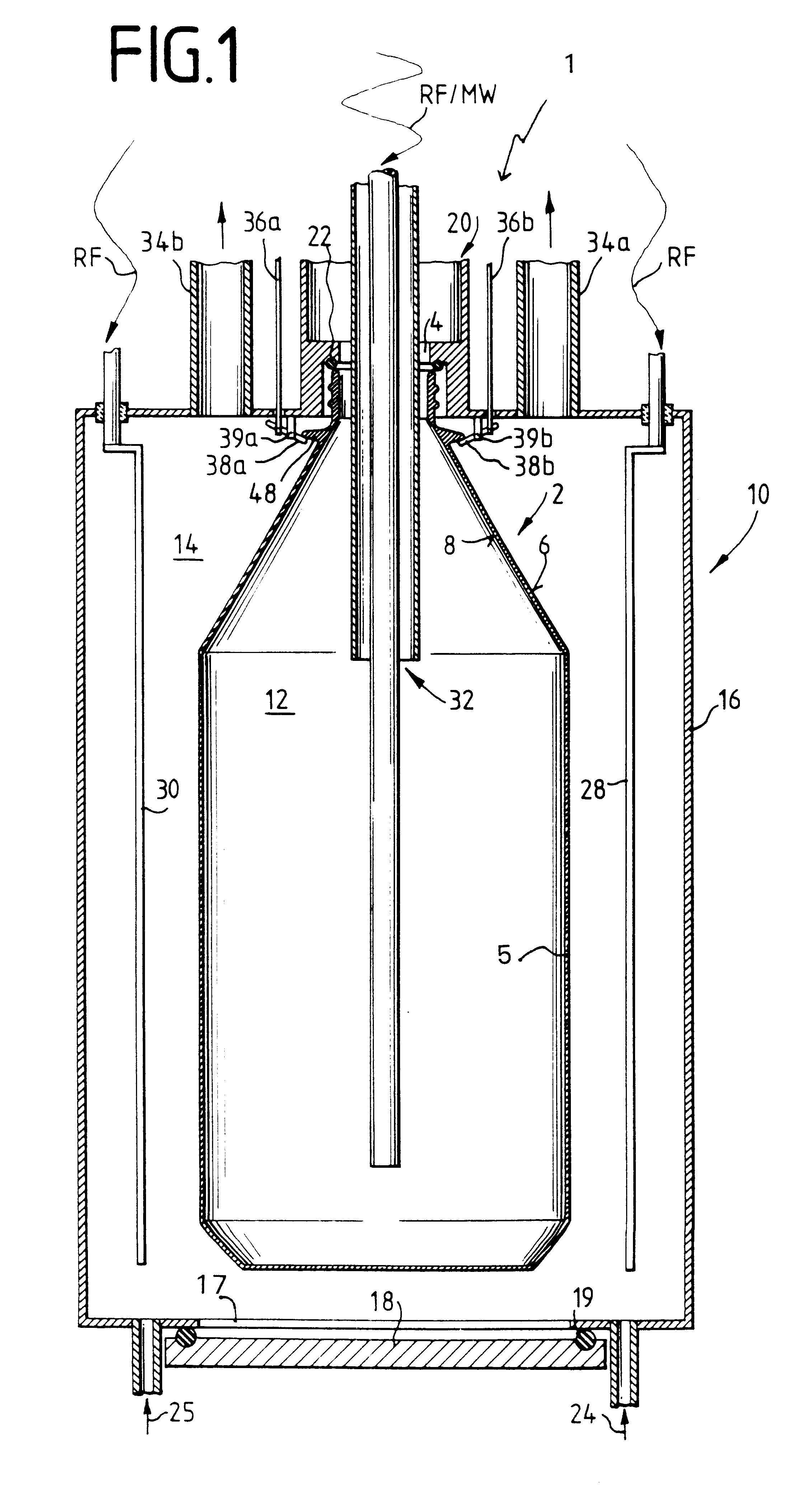
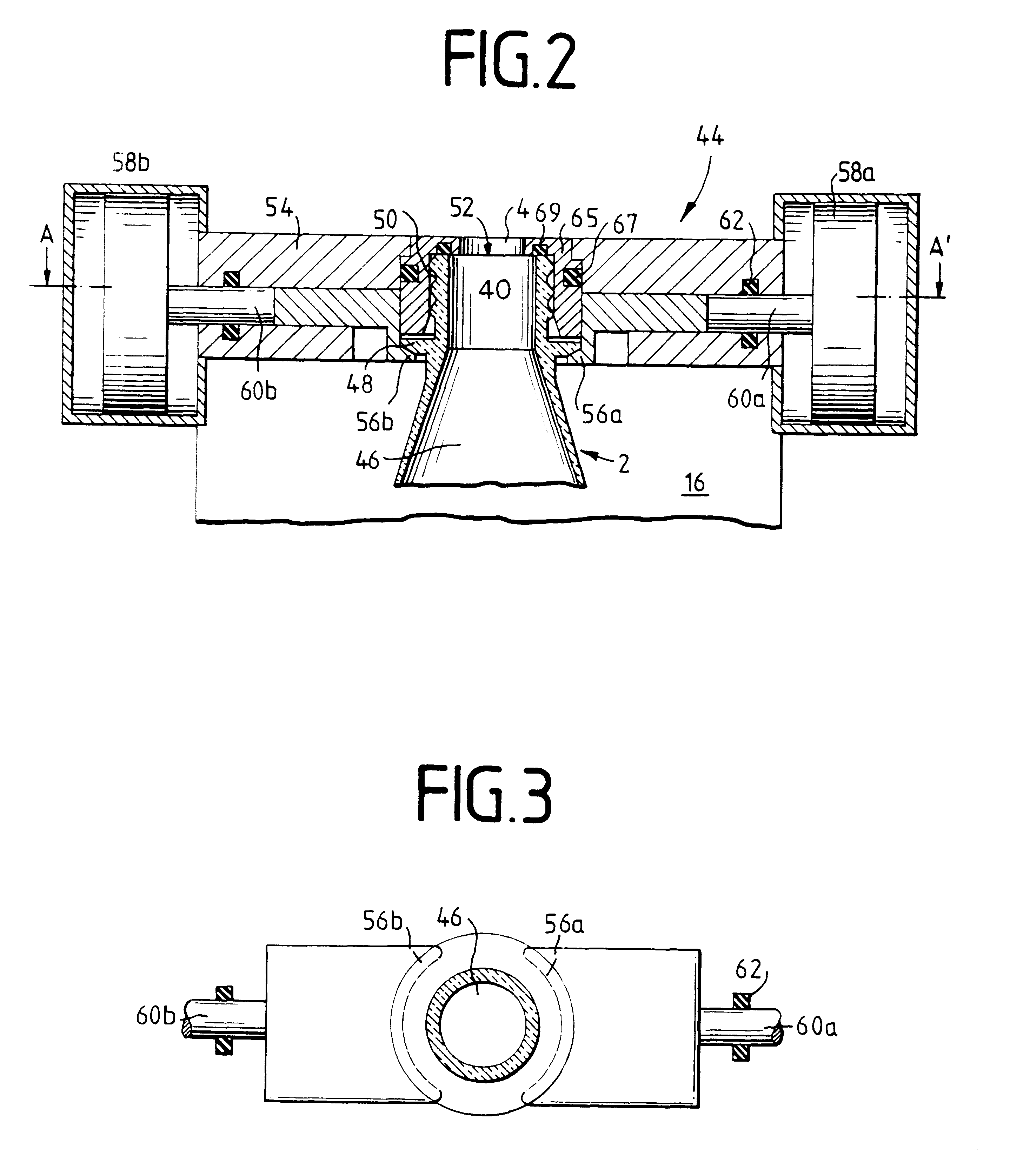
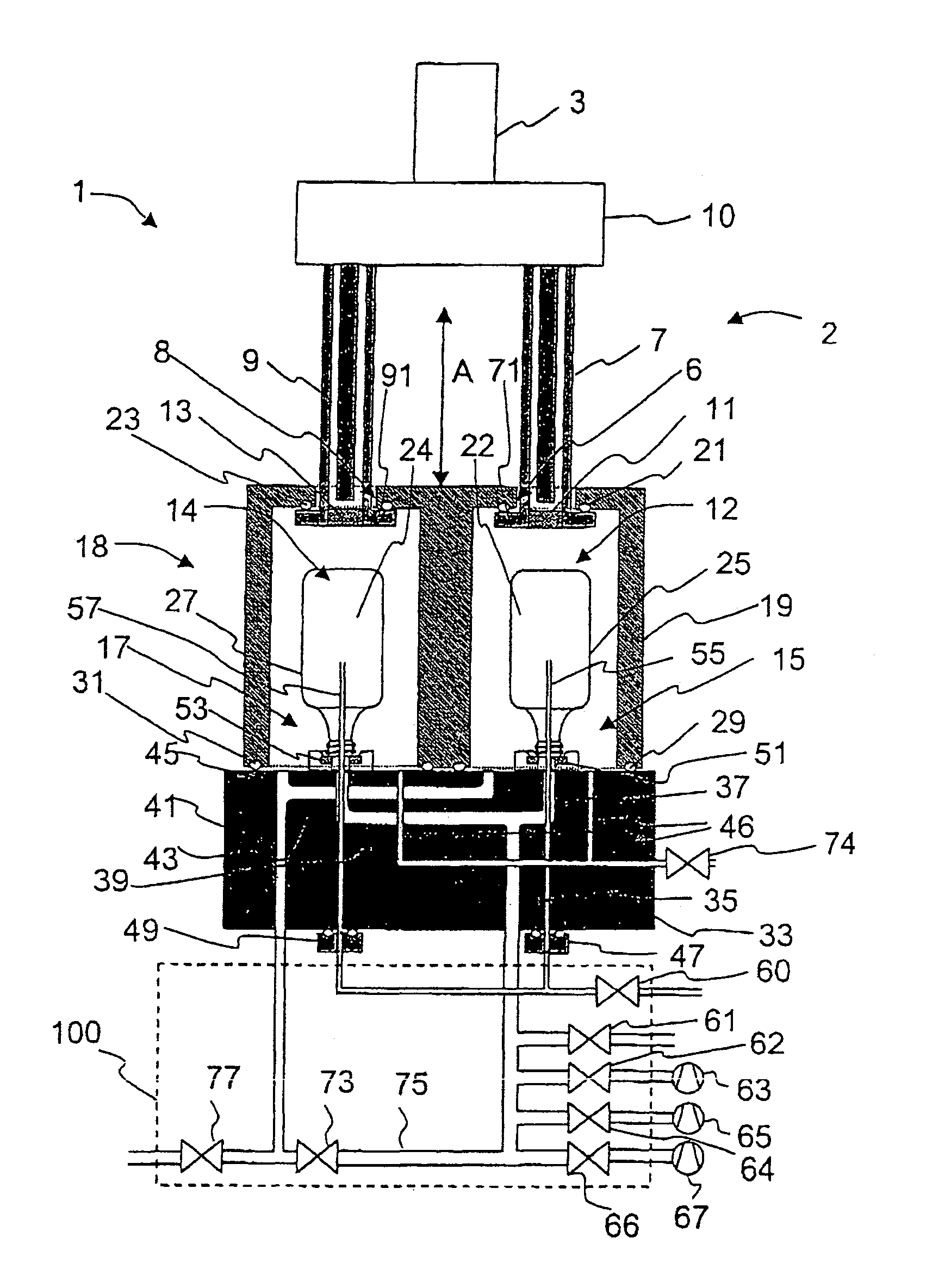
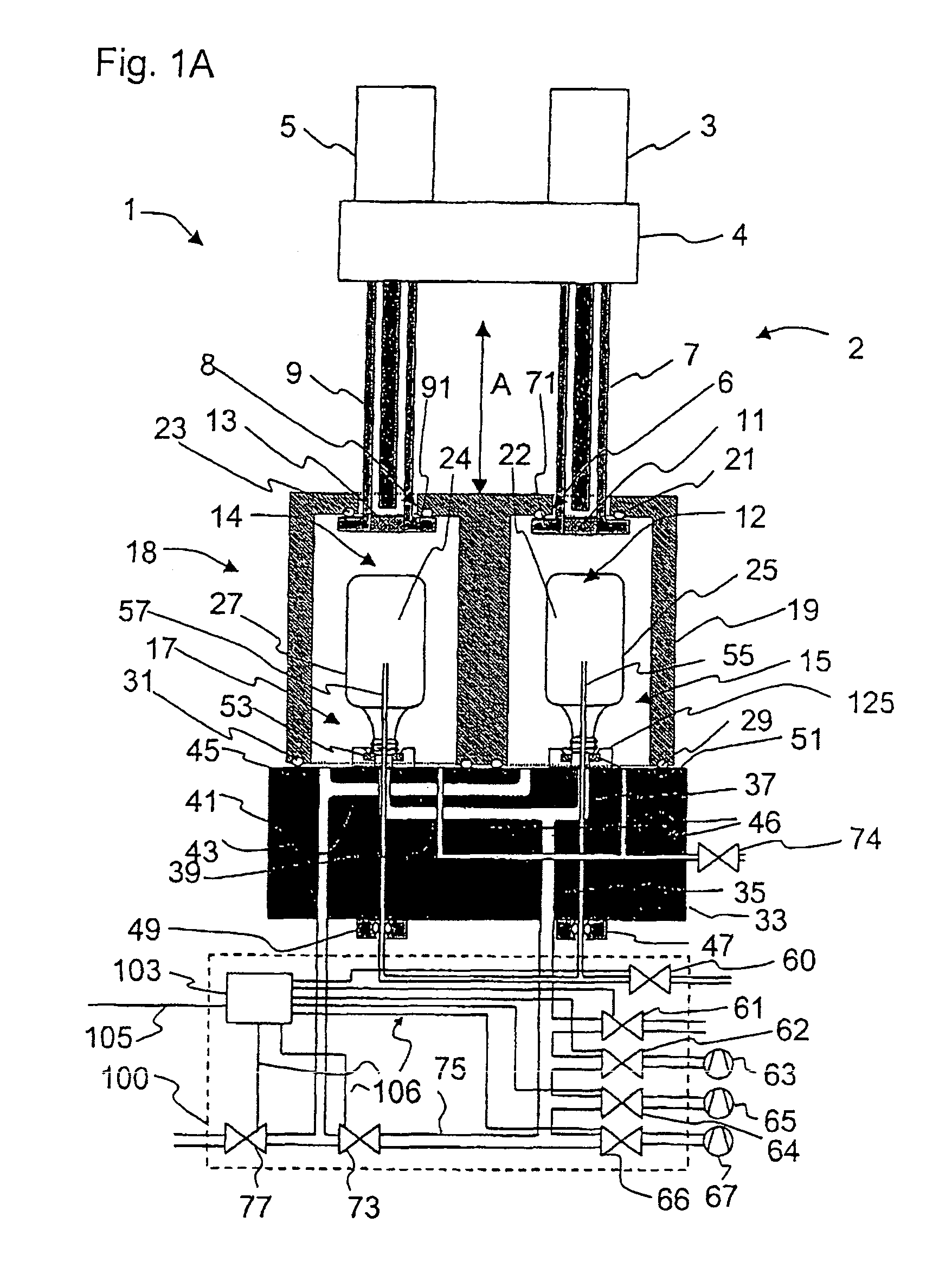
Patents
Literature
256 results about "Plasma coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
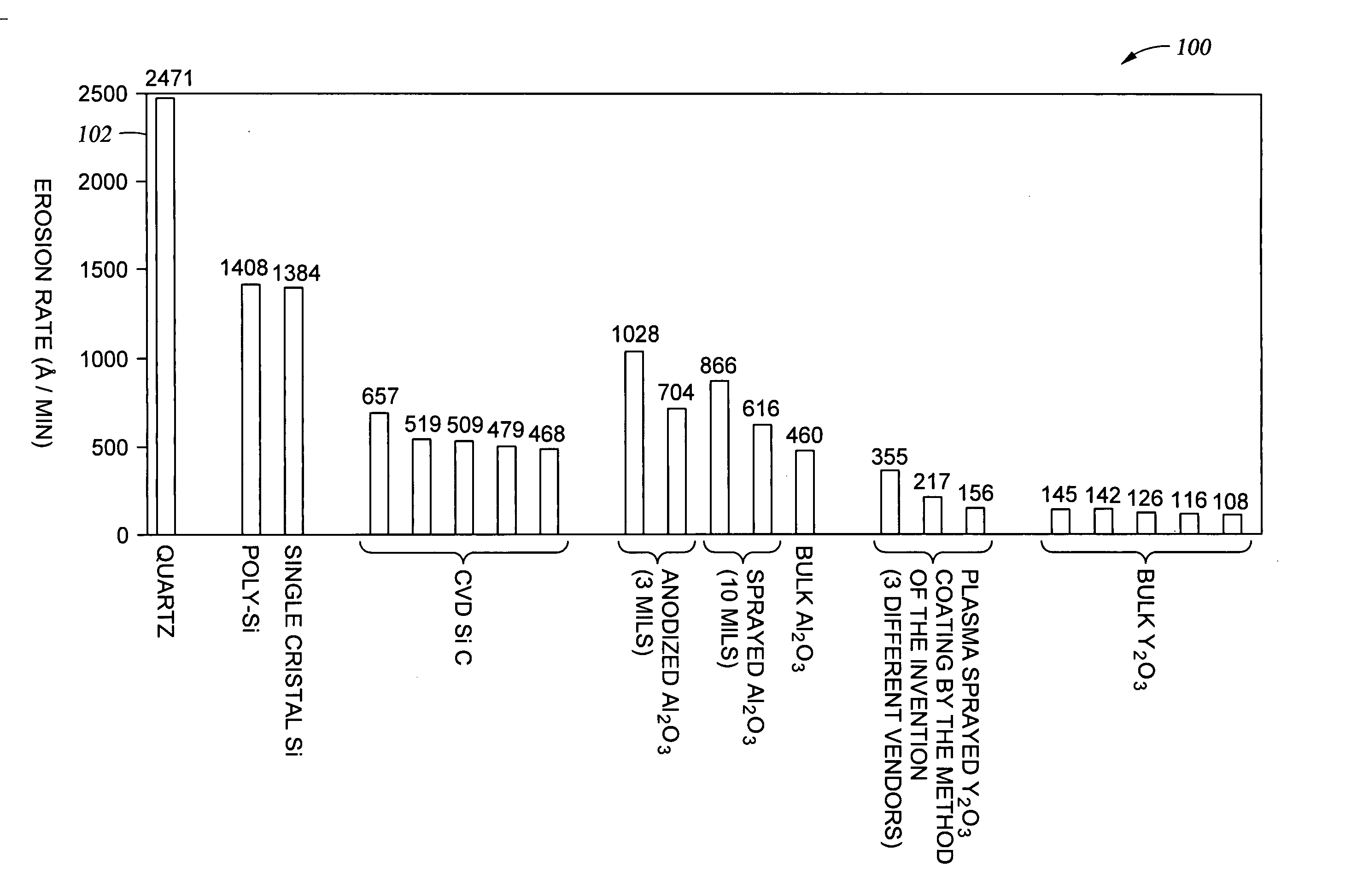
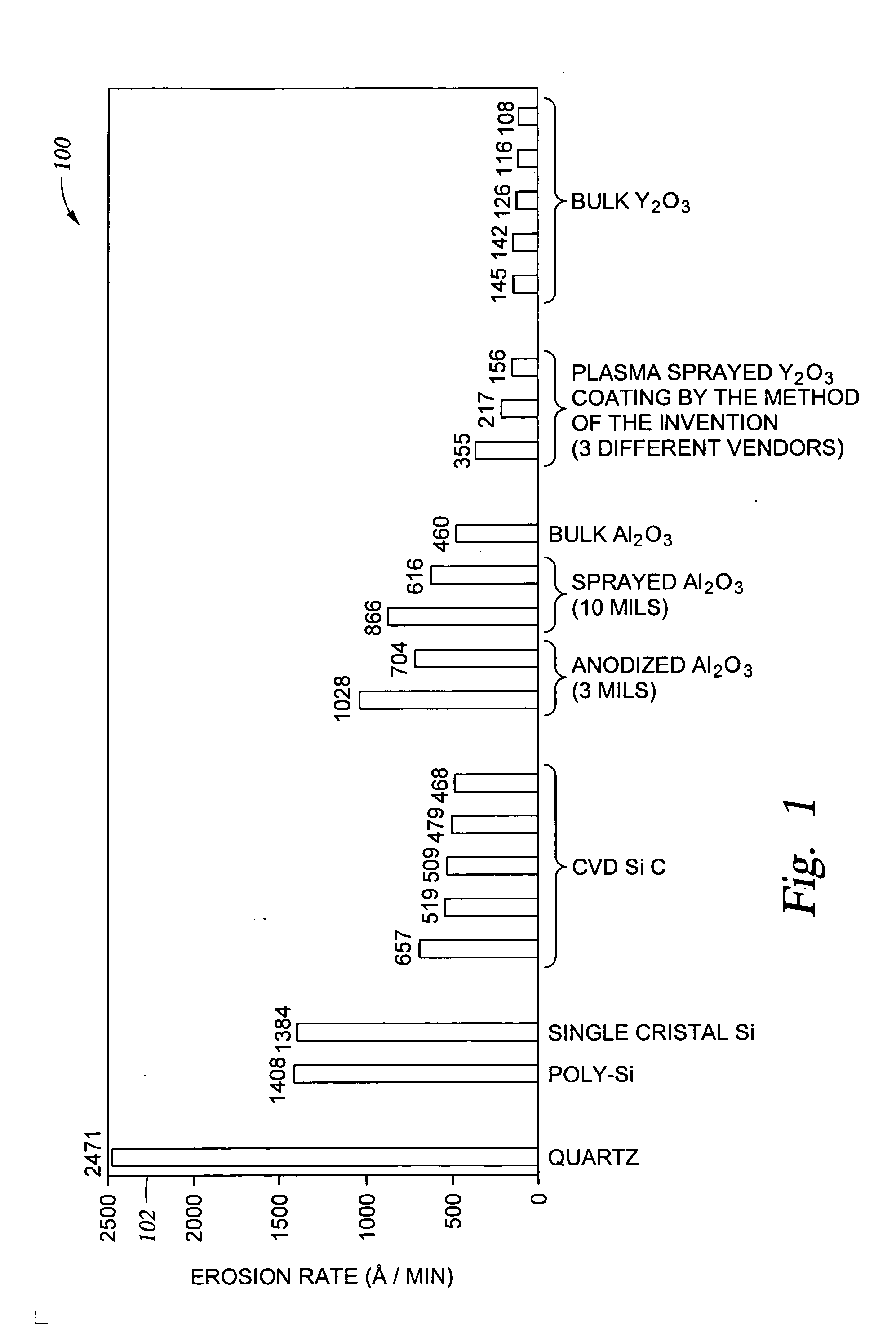
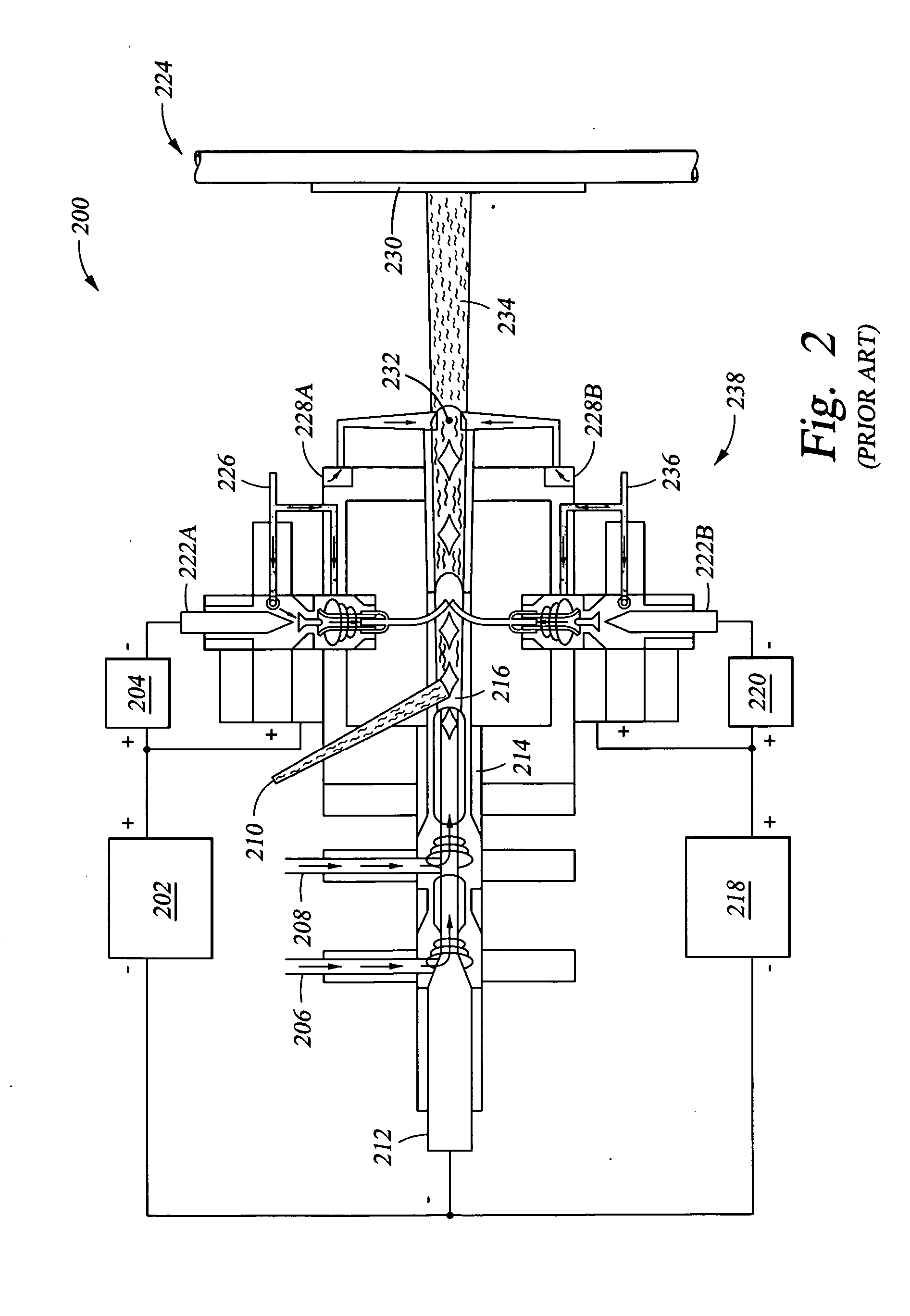
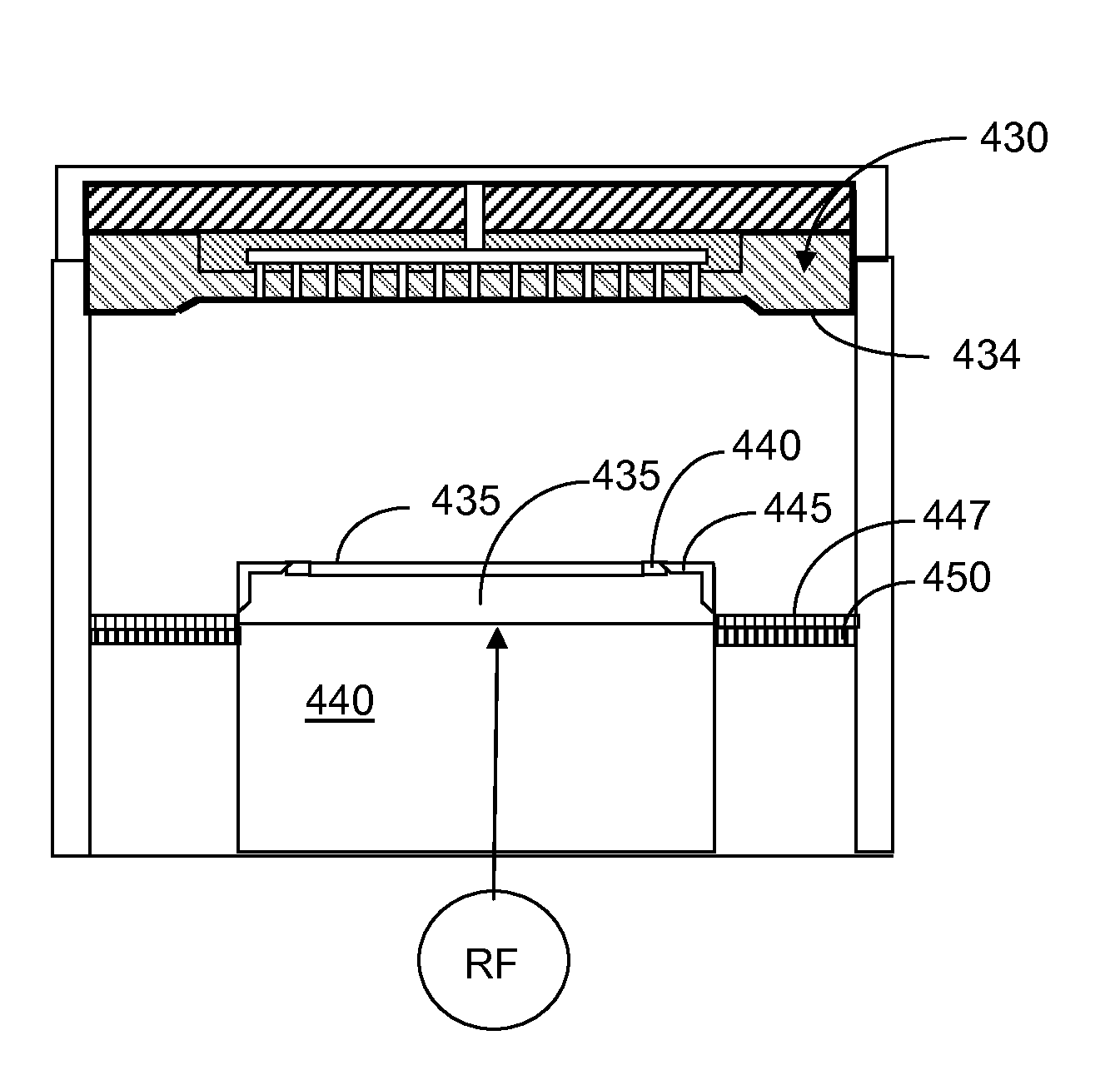
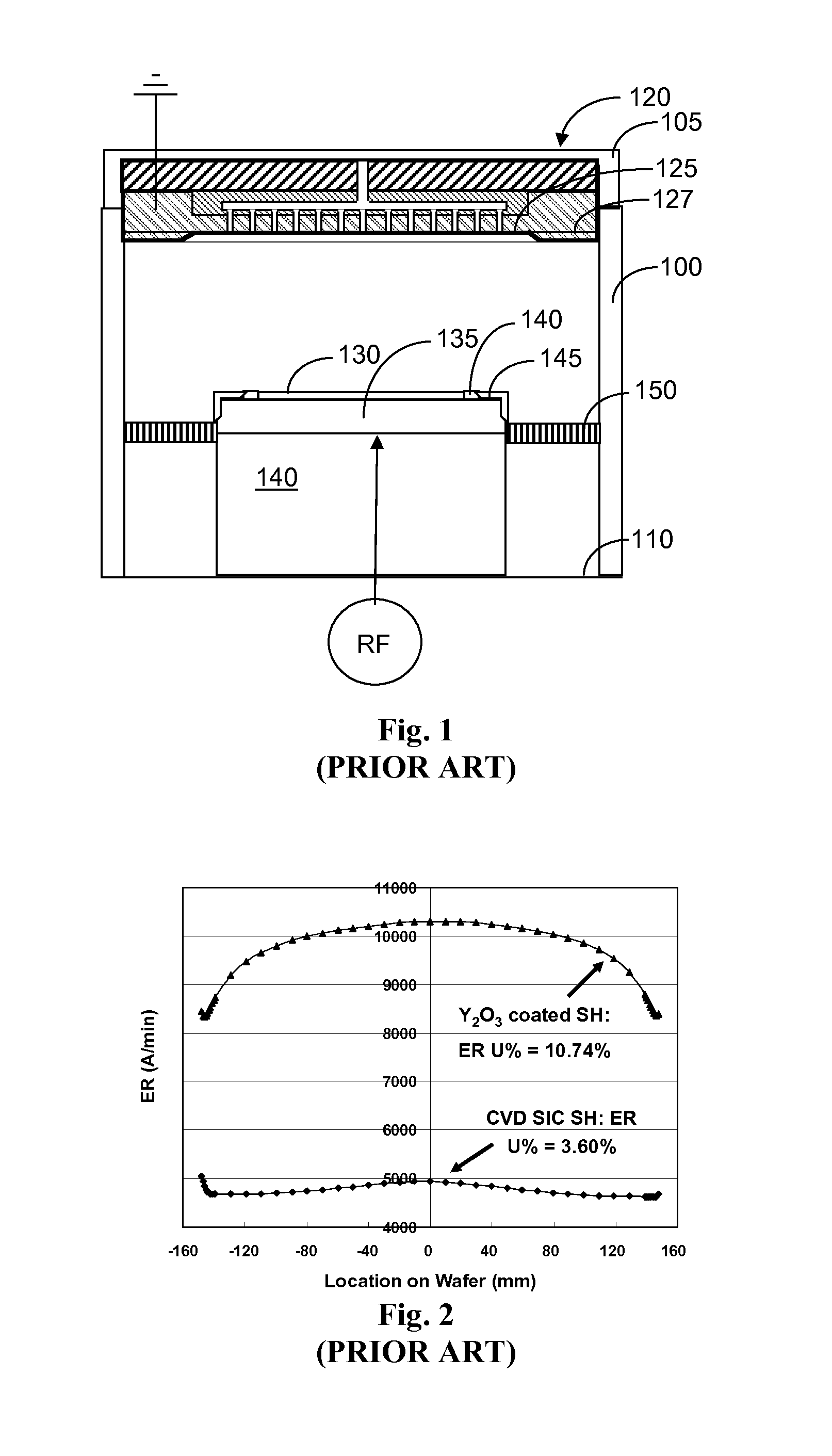
Clean, dense yttrium oxide coating protecting semiconductor processing apparatus
ActiveUS20050037193A1Extended service lifeExcellent plasma corrosion-resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma coatingChemical vapor deposition
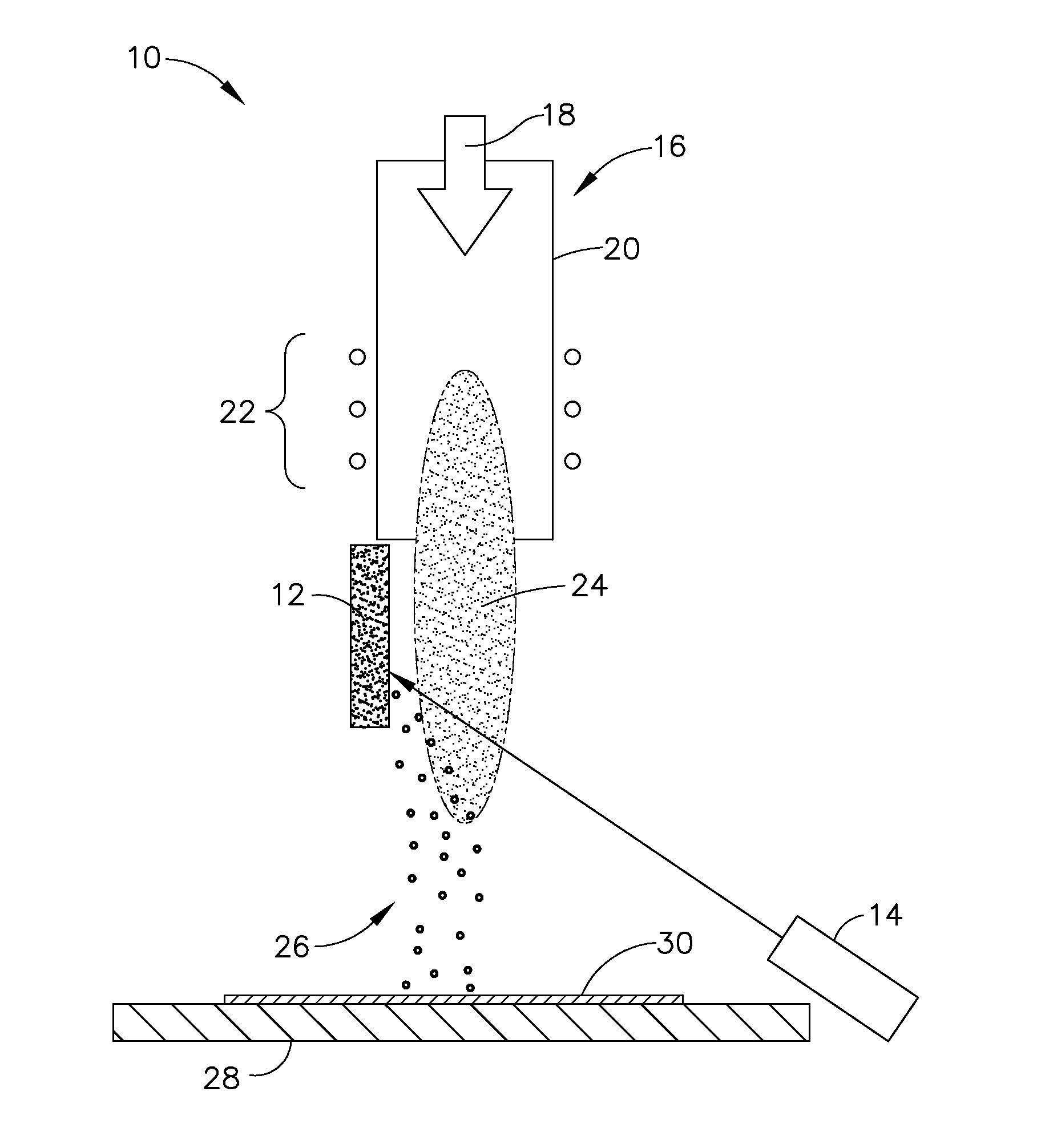
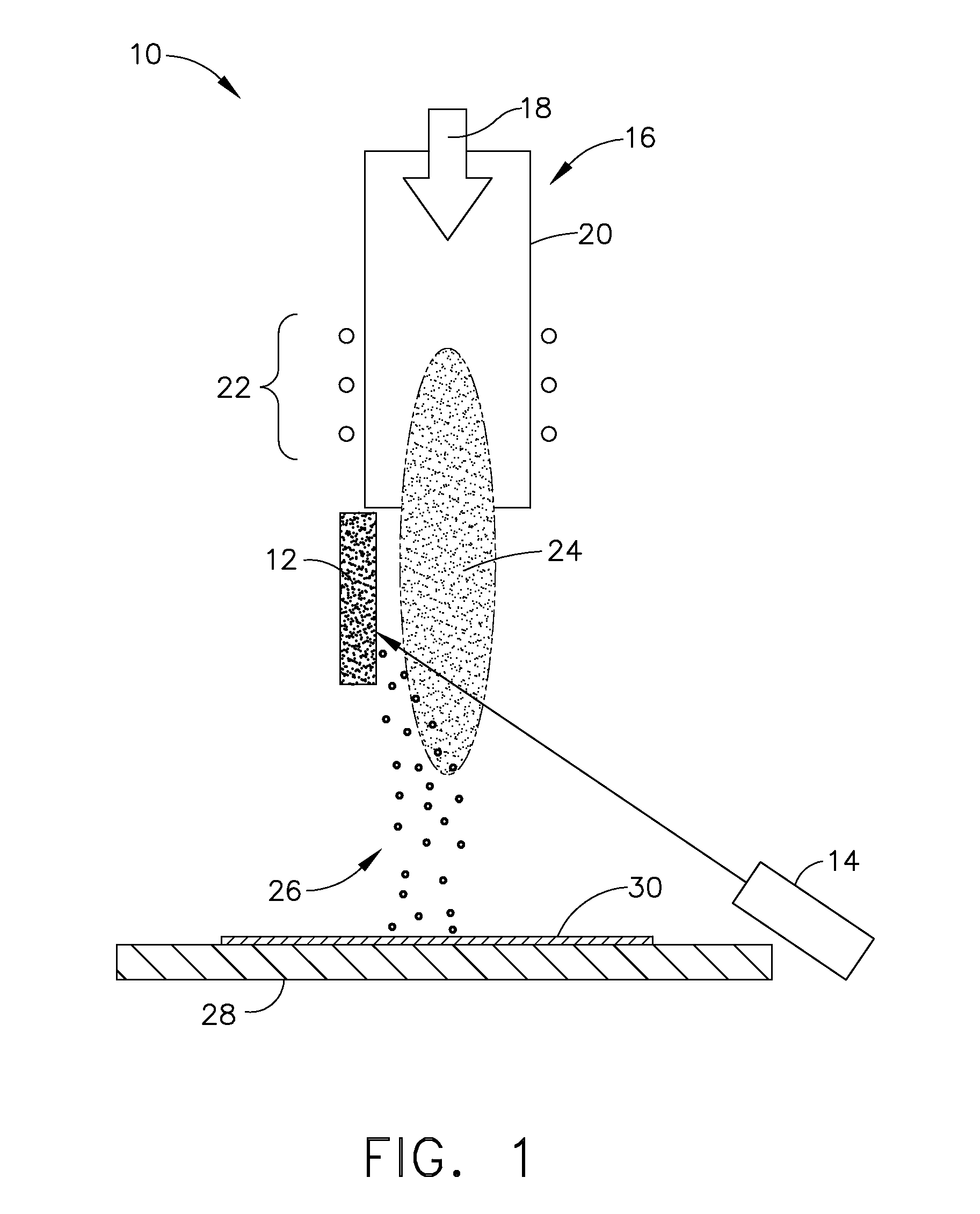
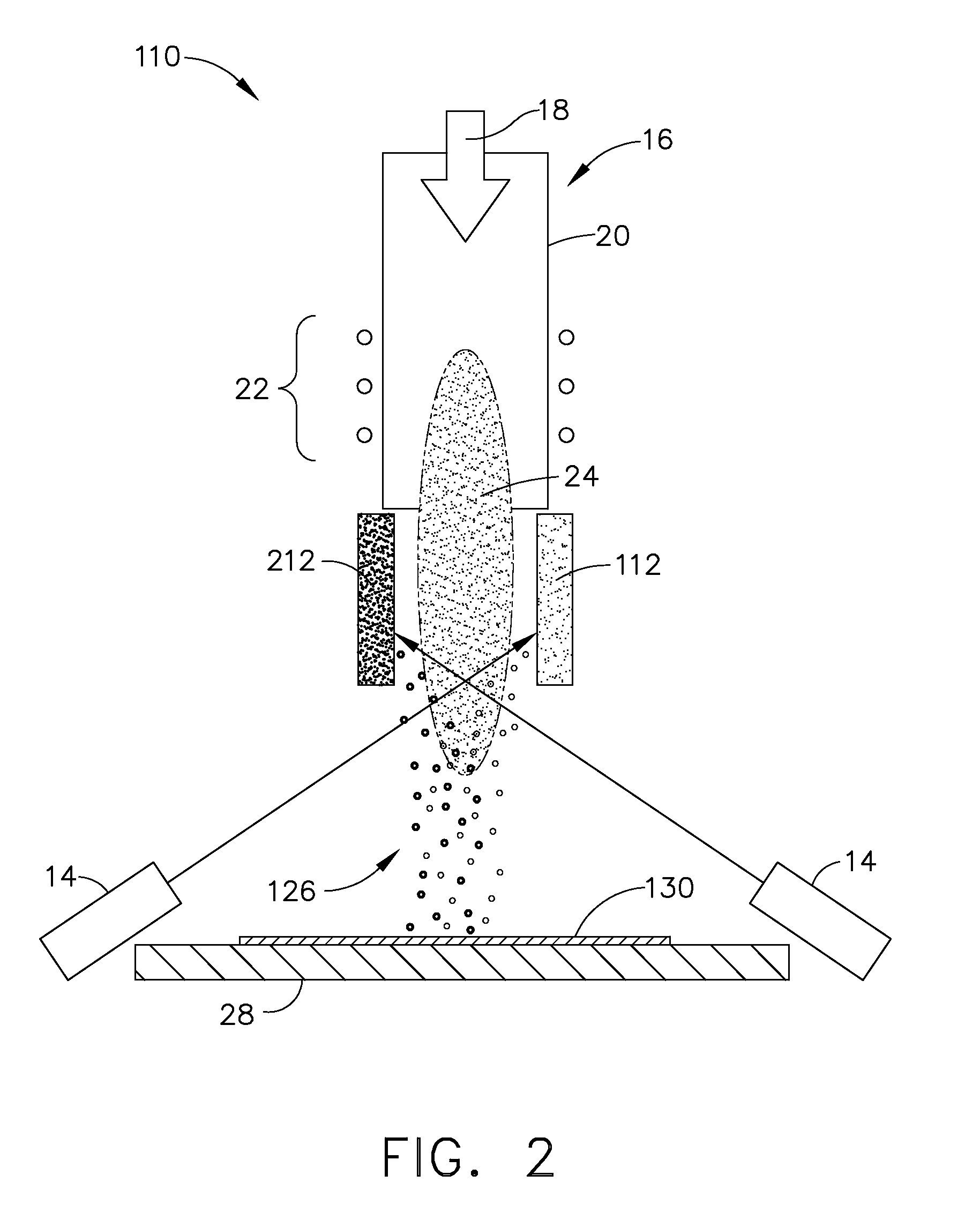
Disclosed herein is a method for applying plasma-resistant coatings for use in semiconductor processing apparatus. The coatings are applied over a substrate which typically comprises an aluminum alloy of the 2000 series or the 5000 through 7000 series. The coating typically comprises an oxide or a fluoride of Y, Sc, La, Ce, Eu, Dy, or the like, or yttrium-aluminum-garnet (YAG). The coating may further comprise about 20 volume % or less of Al2O3. The coatings are typically applied to a surface of an aluminum alloy substrate or an anodized aluminum alloy substrate using a technique selected from the group consisting of thermal / flame spraying, plasma spraying, sputtering, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). To provide the desired corrosion resistance, it is necessary to place the coating in compression. This is accomplished by controlling deposition conditions during application of the coating.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
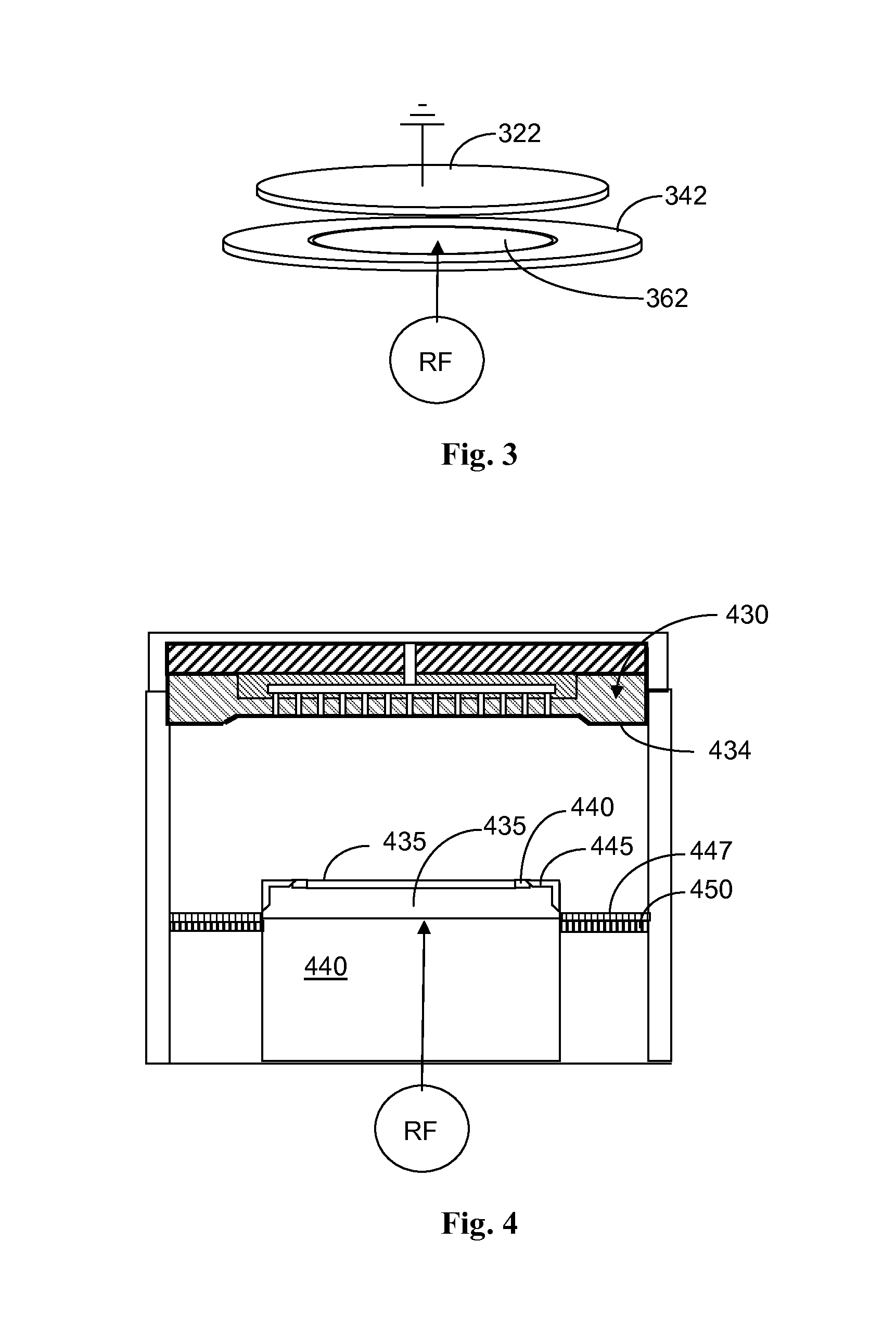
Coating for performance enhancement of semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS20140116338A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingPerformance enhancementPlasma coating
A plasma processing chamber having advanced coating for the showerhead and for an extended bottom electrode. The extended bottom electrode can be formed by one or more of the focus ring, cover ring, and plasma confinement ring. The extended electrode can be formed using a one-piece composite cover ring. The composite cover ring may be made of Al2O3 and include a Y2O3 plasma resistant coating. The plasma confinement ring may include a flow equalization ion shield that may also be provided with the plasma resistant coating. The plasma resistant coating of the extended electrode may have elements matching that of the showerhead.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
Methods of Coating Substrate With Plasma Resistant Coatings and Related Coated Substrates
InactiveUS20110135915A1Reduced particulationLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingWaferingPlasma coating
The invention includes a method of coating a substrate with a plasma etch-resistant layer that exhibits reduced particulation comprising applying an coating layer to a substrate wherein coating layer has a thickness of about 20 microns or less and wherein the coating layer, after exposure to a fluorine based plasma for an amount of time, is substantially free of any cracks or fissures that span the cross section of the coating layer.A coated substrate prepared by the methods described. Also included in the invention are coated substrates for use as a structural element in a fluorine-based semiconductor wafer processing protocol, wherein the coating is a coating layer having a thickness of about 20 microns or less and wherein the coating layer, after exposure to a fluorine based plasma for an amount of time, is substantially free of any cracks or fissures that span the cross section of the coating layer and exhibits reduced particulation.Included are structural elements used in a fluorine-based semiconductor wafer processing protocol, wherein at least a portion of a surface of a structural element is coated with a coating layer that having a thickness of about 20 microns or less and wherein the coating layer, after exposure to a fluorine based plasma for an amount of time, is substantially free of any cracks or fissures that span the cross section of the coating layer and exhibits reduced particulation.
Owner:GREENE TWEED TECH
Plasma coated sutures
InactiveUS7294357B2Improve handlingImprove balanceSuture equipmentsFibre treatmentMedicinePlasma coating
Suture filaments coated by a plasma polymerization process exhibit a good balance of knot run down and knot security characteristics, superior tissue drag characteristics, and improved fray resistance.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP +1
Flash evaporation-plasma coating deposition method
The present invention provides a method for the formation of an organic coating on a substrate. The method includes: providing a substrate in a vacuum; providing at least one vaporized organic material comprising at least one component from at least one source, wherein the vaporized organic material is capable of condensing in a vacuum of less than about 130 Pa; providing a plasma from at least one source other than the source of the vaporized organic material; directing the vaporized organic material and the plasma toward the substrate; and causing the vaporized organic material to condense and polymerize on the substrate in the presence of the plasma to form an organic coating.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
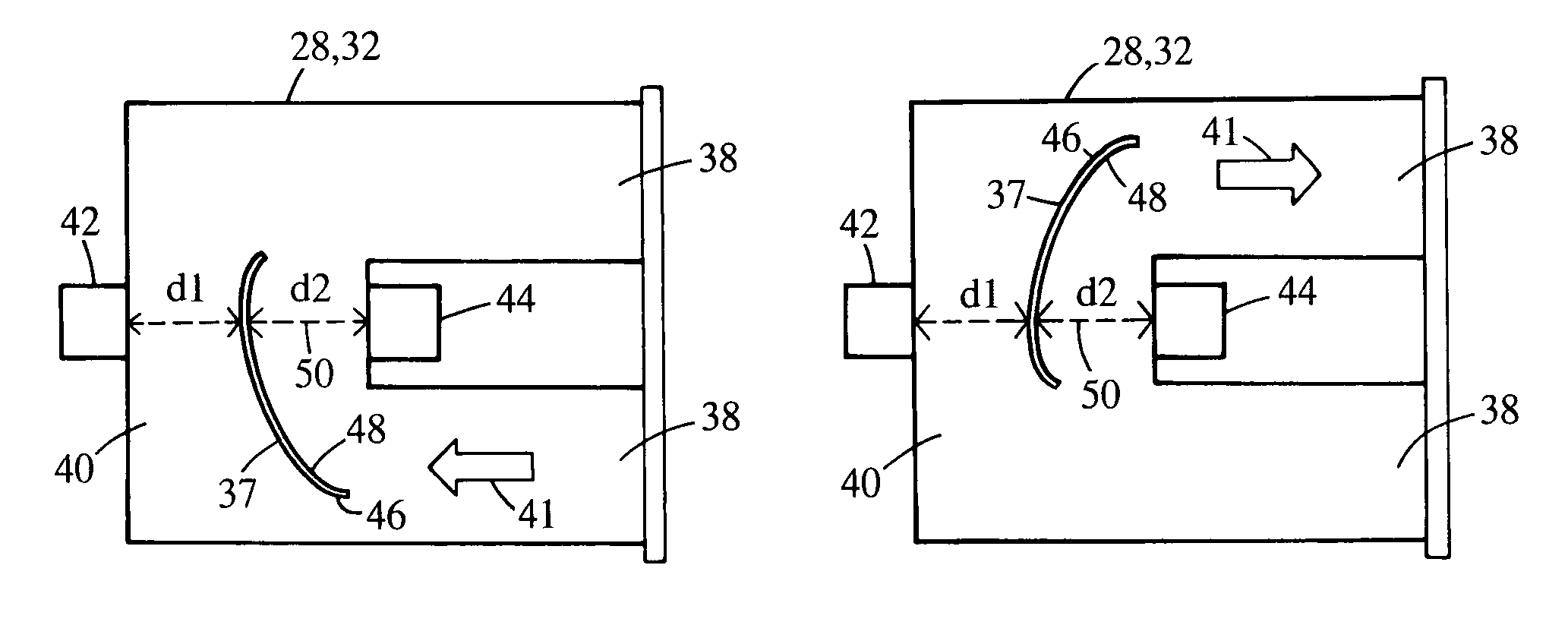
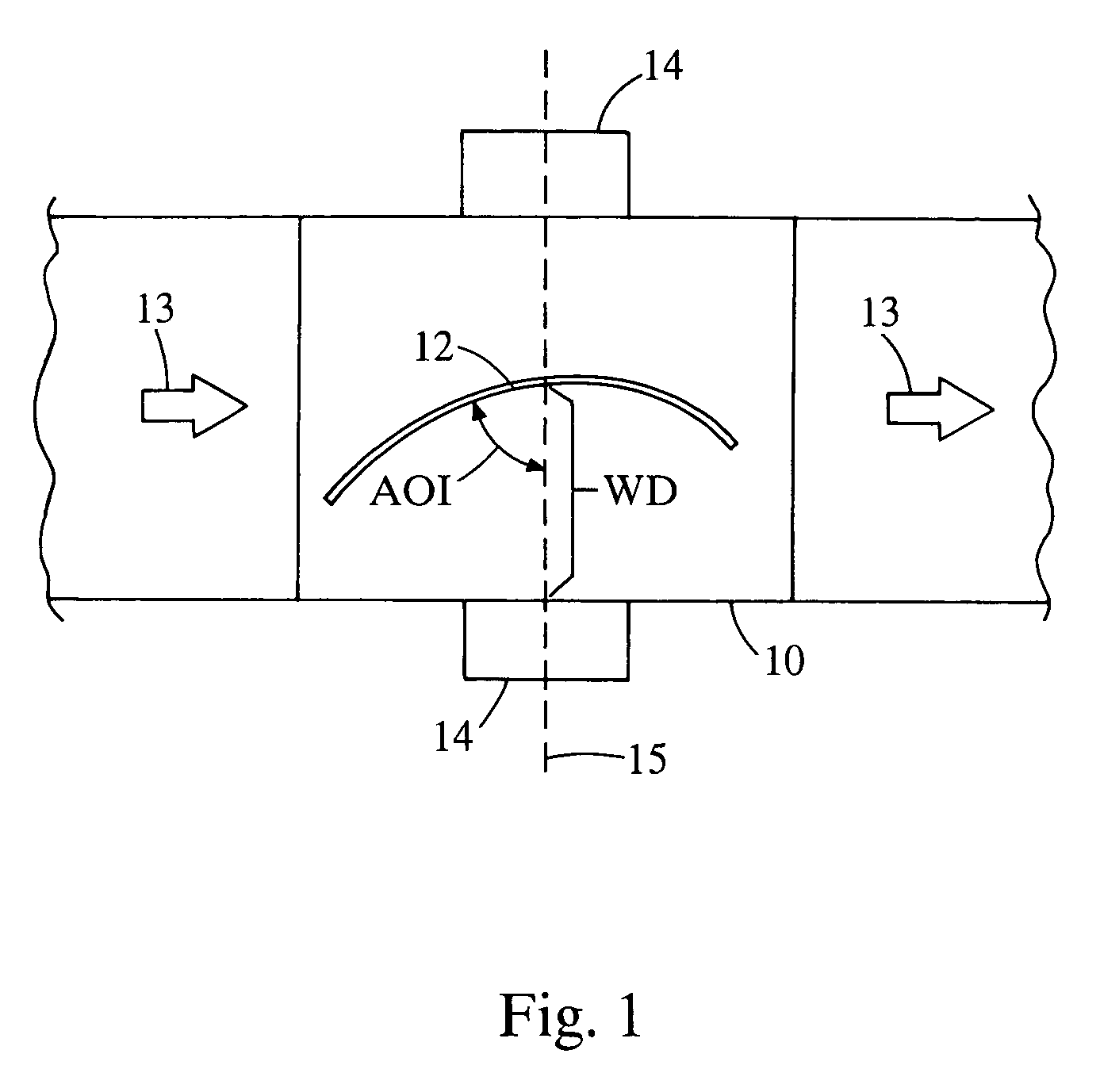
Lens plasma coating system
The invention provides a system and method for plasma coating of an optical lens, particularly lenses made of silicone-containing polymer. A system of the invention comprises an entry chamber, a coating chamber downstream from the entry chamber, and an exit chamber downstream from the coating chamber. The coating chamber includes a pair of spaced apart electrodes disposed therein. A system of the invention is configured in a way so that a lens may enter, pass through and exit the system without requiring the coating chamber to be repeatedly pressurized and depressurized.
Owner:ALCON INC
Sealed plasma coatings
InactiveUS20100323124A1Low shrinkageMolten spray coatingElectric discharge tubesInterior spacePolymer science
A processing device includes a plurality of walls defining an interior space configured to be exposed to plasma and a surface coating on the interior surface of at least one of the plurality of walls. The surface coating includes pores forming interconnected porosity. The processing device further includes a sealant residing in at least a portion of the pores of the surface coating. In an embodiment, the sealant can be a thermally cured sealant having a cure temperature not greater than about 100° C. In another embodiment, the sealant can be an epoxy sealant having a viscosity of not greater than 500 cP in liquid precursor form. In yet another embodiment, the sealant can be a low shrinkage sealant characterized by a solidification shrinkage of not greater than 8%.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
Process for Plasma Coating
InactiveUS20070281108A1Effective barrier against gas transmissionImprove barrier propertiesElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingPolyolefinPlasma coating
The present invention describes a method for plasma coating the inside surface of a polyolefin or a polylactic acid container to provide an effective barrier against gas transmission. The method provides a way to deposit rapidly and uniformly very thin, adherent and nearly defect-free layers of polyorganosiloxane and silicon oxide (or amorphous carbon) on the inner surface of the container to achieve more than an order of magnitude increase in barrier properties.
Owner:WEIKART CHRISTOPHERM +1
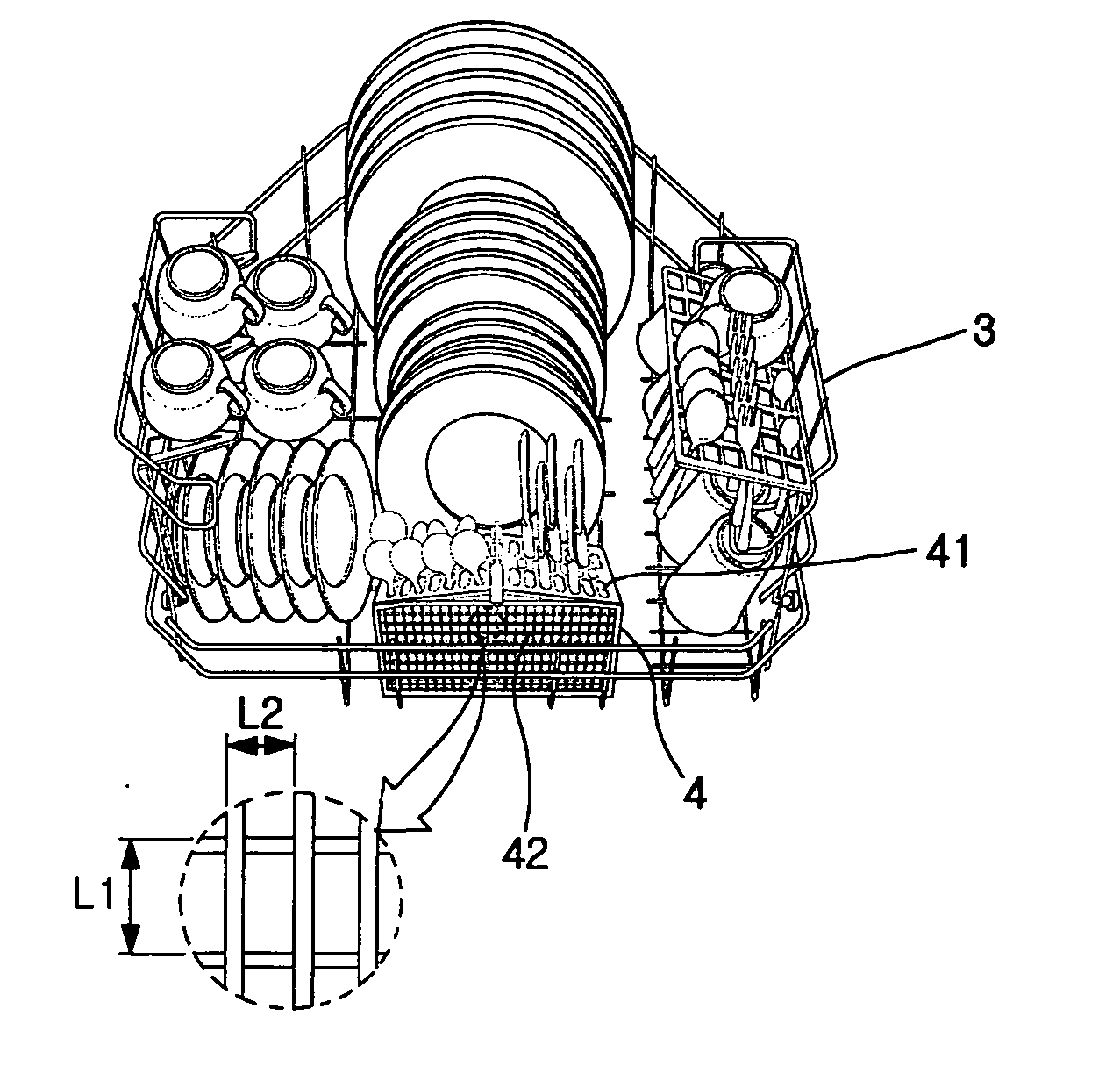
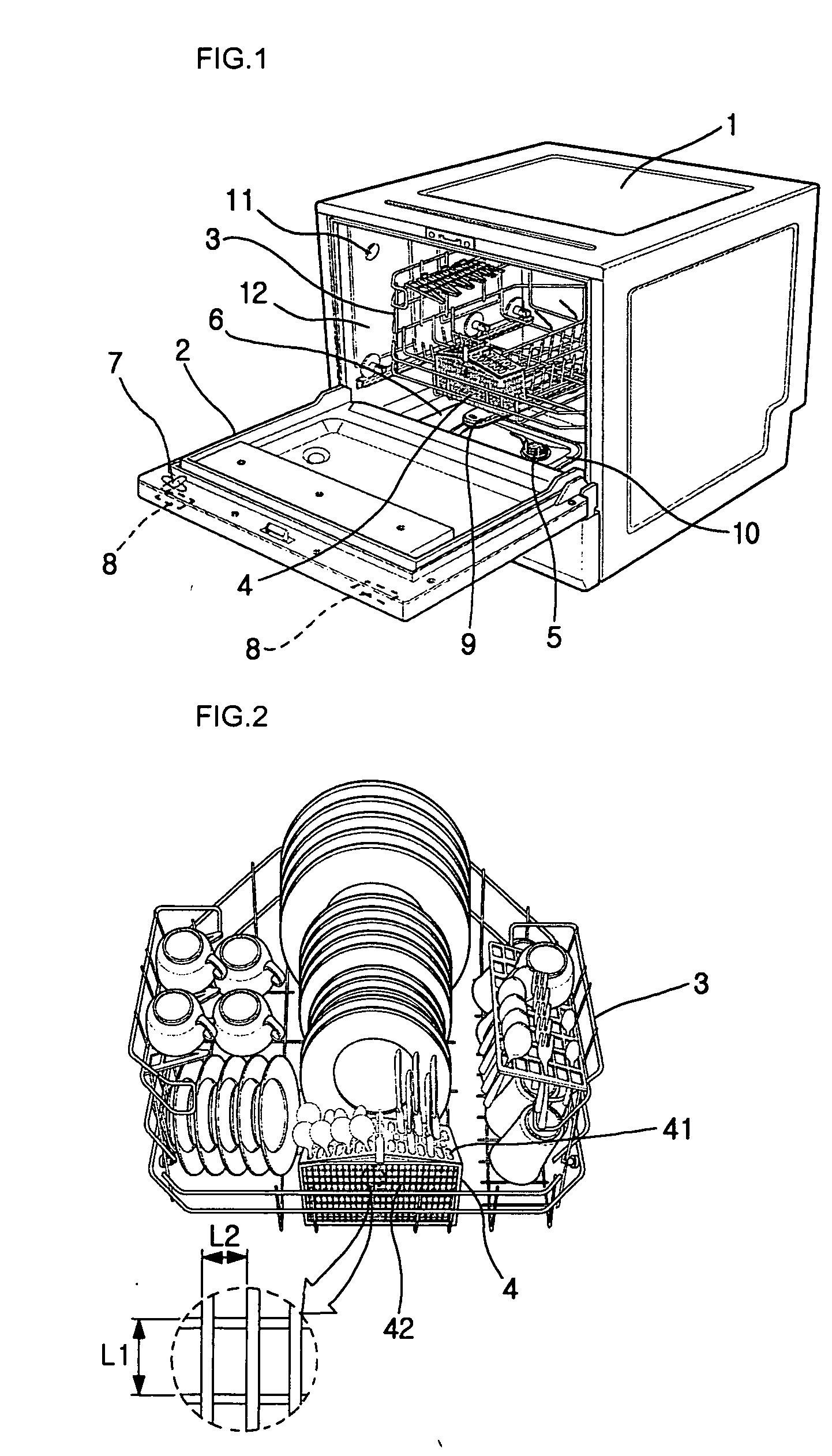
Dish washing machine
InactiveUS20050150528A1Improve hygieneEliminating bad smellTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsElectrostatic cleaningPlasma coatingProcess engineering
A dish washing includes a cabinet having a washing room formed in the cabinet to receive dishes, an injection arm for injecting a washing water toward the dishes, and many components contacted with the washing water. In order to improve the utilization efficiency of the dish washing machine, the machine also includes a plasma coating layer formed on an outer surface of each of the components, a heater for heating the washing water, an air ventilation hole for discharge humid air while the dishes are dried, and a discharge fan for forcibly flowing air through the air ventilation hole.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Plasma modified medical devices and methods
InactiveUS20130046375A1Increased apoptosisGood biocompatibilitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismActive agentThrombus
Coatings, devices and methods are provided, wherein the contacting surface of a medical device with at least one contacting surface for contacting a bodily fluid or tissue, wherein long-lasting and durable bioactive agents or functional groups are deposited on the contacting surface through a unique two-step plasma coating process with deposition of a thin layer of plasma coating using a silicon-containing monomer in the first step and plasma surface modification using a mixture of nitrogen-containing molecules and oxygen-containing molecules in the second step. The two-step plasma coating process enables the implantable medical device to prevent both restenosis and thrombosis under clinical conditions. The invention also relates to surface treatment of metallic and polymeric biomaterials used for making of medical devices with significantly improved clinical performance and durability.
Owner:CHEN MENG
Sers substrates
InactiveUS20120287427A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPlatinumSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrate device, including a base substrate, a single or multiple layered nanostructure that contains metals, and a plasma coating. The nanostructure metal is selected from the group including silver, gold, platinum, copper, titanium, chromium, and combinations thereof. The plasma coating has a thickness of 1-200 nm and may locate on the nanostructure layer or on the base substrate. The plasma coating can precisely control the surface characteristics, including surface energy, hydrophilicity, and contact angle, of the SERS device and may then help to regulate the SERS substrate with well defined and uniform water / oil contact angle with small standard deviation. The water contact angle of the SERS substrate may range from 20 to 140 degrees.
Owner:LI HAO +2
Surface composite coating of turbomachine rotor blade and preparation method thereof
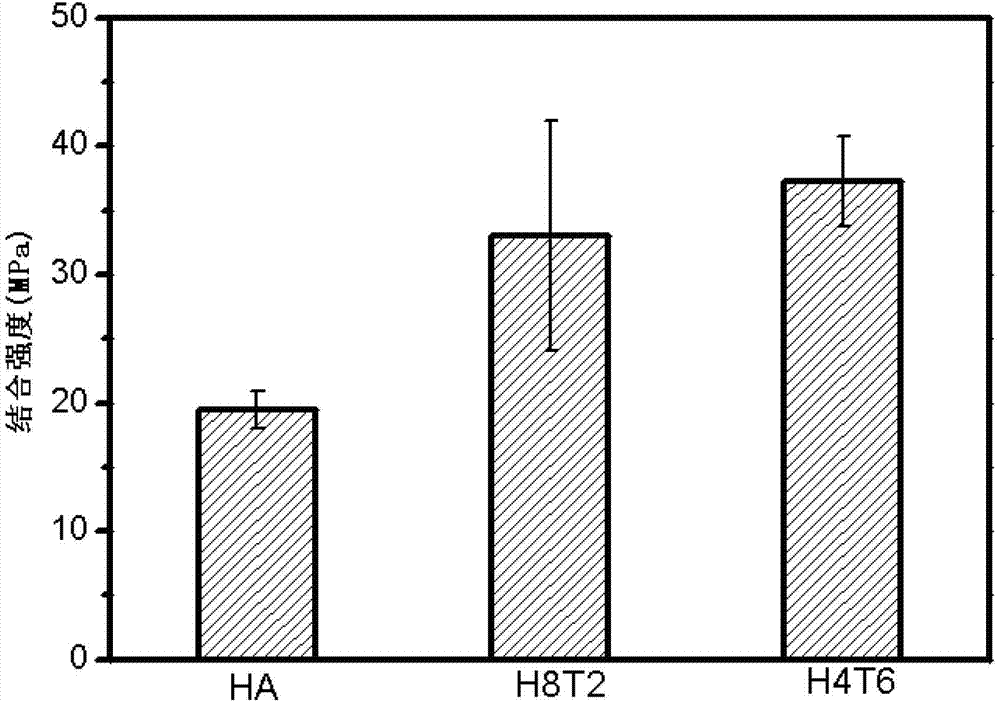
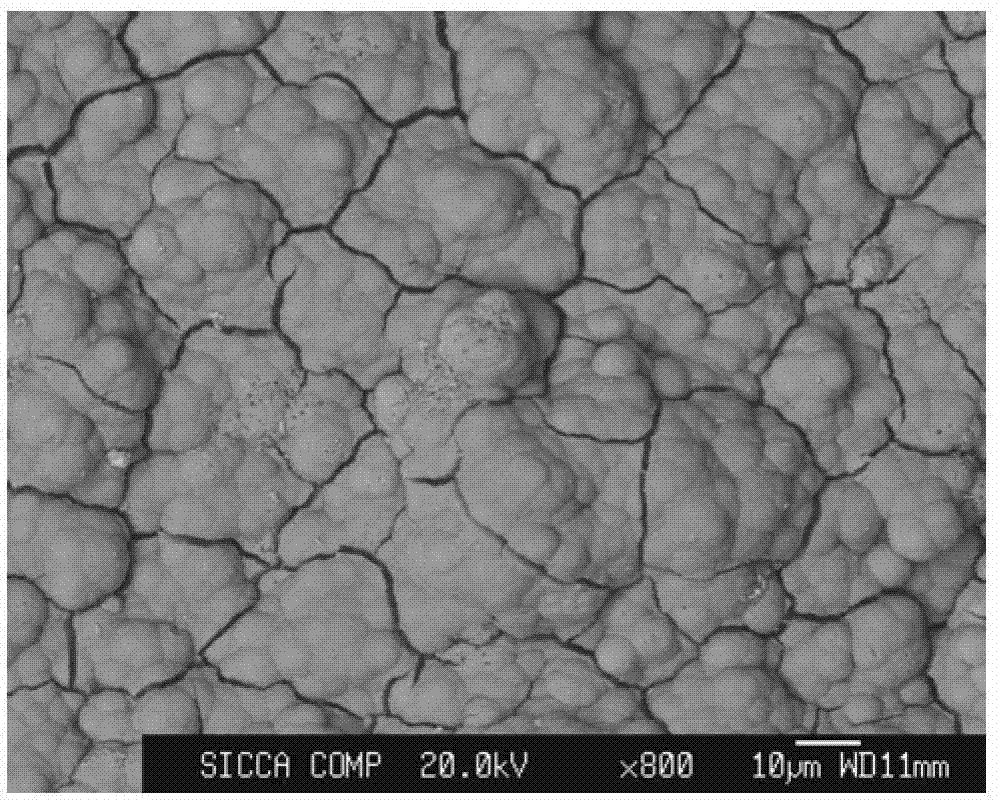
ActiveCN101008324AAlleviate mechanical property mismatchImprove dynamic binding strengthMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesCorrosion resistant alloyHigh energy
The invention discloses a surface composite coat of the blade on rotor and relative production, wherein, the composite coat is divided into adhesive bottom, middle corrosion-resistance alloy layer and metal ceramic rigid abrasion-resistance layer. The invention utilizes high-energy plasma coater and ultrasonic plasma injector, via ultrasonic plasma coating technique to coat aforementioned three layers on the base of blade; then seal the outer face via macromolecule sealing agent as polyurethane or acrylic acid. The thickness of metal ceramic rigid abrasion-resistance layer is 0.12mm, the thickness of middle corrosion-resistant alloy layer is 0.08mm, and the thickness of bottom adhesive layer is 0.05mm. The invention can improve the corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance of blade.
Owner:XIAN SHAANGU POWER
Hydrophobic structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN1990899AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingManufacturing cost reductionPlasma coating
The invention relates to a hydrophobic structure and the method for preparing the same. The method comprises forming coarse hard costing layer and hydrophobic layer on surface of base material by using atmospheric plasma coating technique. The structure in this invention is characterized by increased hardness and wear resistance, improved tranparancy, hydrophobic property, and lower cost because of usage of atmospheric plasma coating technique.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
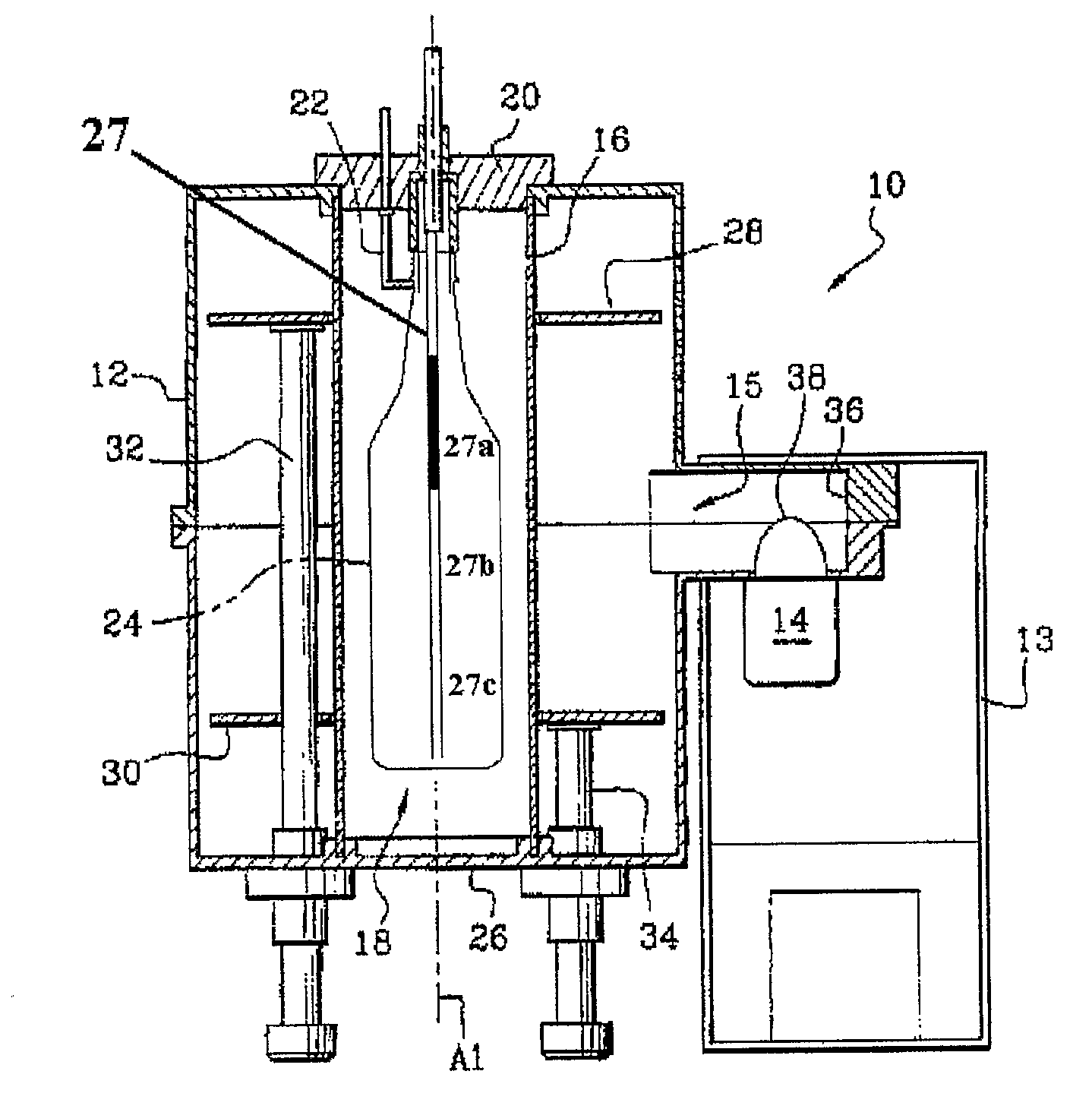
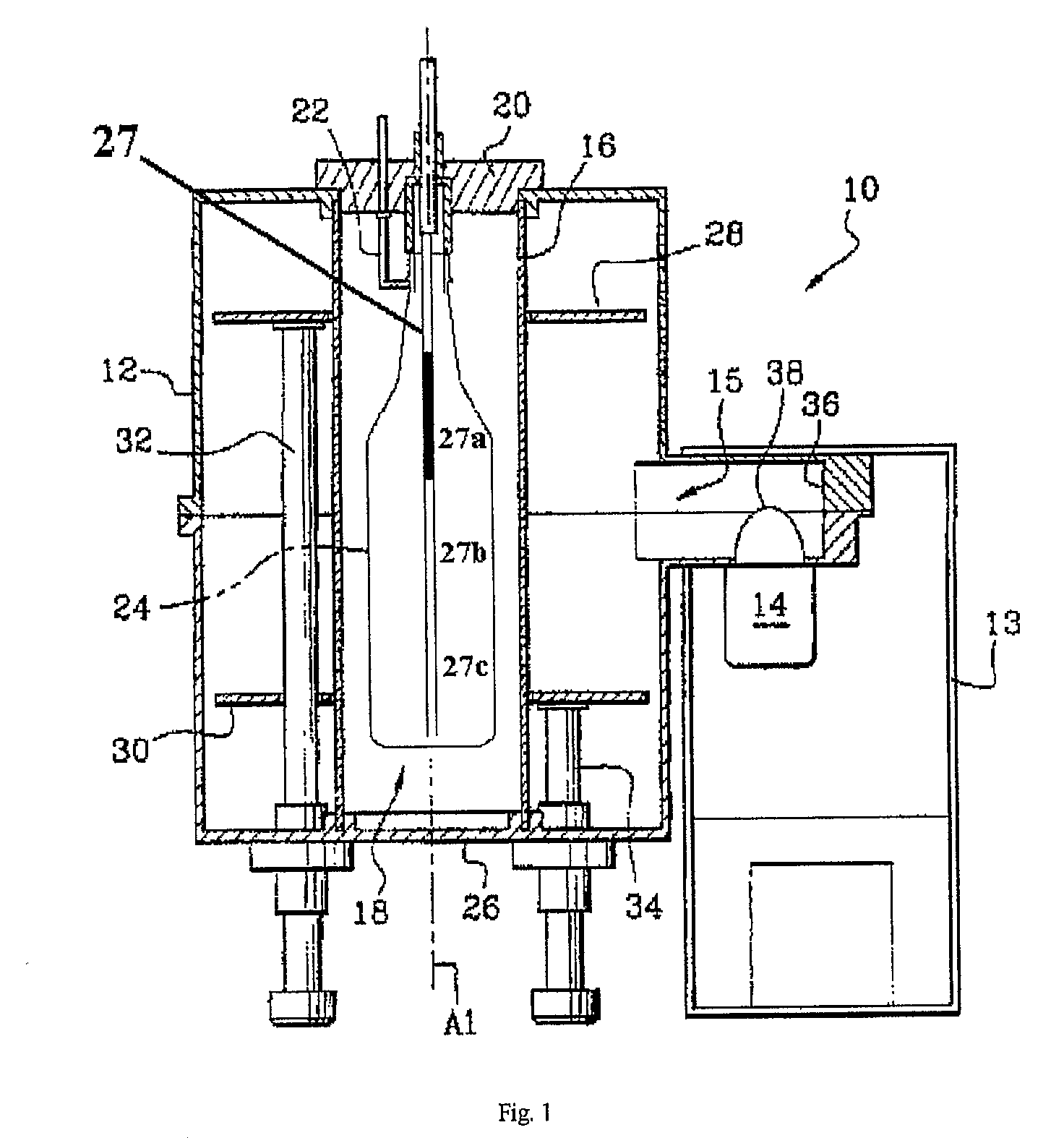
Device and Process for Plasma Coating/Sterilization
InactiveUS20080032059A1Simple designImprove efficiencyElectric shock equipmentsElectric discharge tubesPlasma coatingEngineering
A device for treating containers such as bottles, preferably PET containers, such as PET bottles, with a plasma, whereby the device is designed for sterilizing and / or coating the containers. In addition, the device also relates to a method for treating containers, preferably PET containers such as PET bottles, with a plasma, whereby the treatment comprises sterilization and / or the coating of the containers. Also provided is an airlock for containers such as bottles, in particular PET containers such as PET bottles, having cells to receive the containers, at least one cell being designed to receive at least two containers.
Owner:KRONES AG
Linerless label media cutting mechanism
InactiveUS6155732AReduce maintenanceOther printing apparatusMetal working apparatusComputer printingPlasma coating
A linerless label media cutting apparatus adapted for receiving linerless label media from a printer is provided. The apparatus includes a cutting assembly and a cutter mount. The cutting assembly has a first cutting blade and a second cutting blade that cooperate to sever at least one label. The cutter mount supports the cutting assembly and is mountable to the printer. A drive actuator assembly may be included. The cutter mount may include mounting structure to facilitate mounting and alignment to the printer. The cutter mount may also include a blade carrier and base plate for supporting the cutting blades. The base plate may define a cavity for receipt of linerless label media. The apparatus may also include a blade lubricator. In an alternate embodiment, the apparatus includes an input guide for guiding linerless label media travel. The input guide may be plasma coated. A method for preparing labels is disclosed.
Owner:DATAMAX
Conductive metal thin coatings for implantable medical sensing devices
InactiveUS20100057179A1Small diameterMaximize homogeneityConductive layers on insulating-supportsElectric discharge tubesCell adhesionIn vivo
Thin conductive metal coatings suitable for flexible nonmetal fine wires and leads are described. Polymer clad silica fiber cores are produced by plasma coating with dual layers of metals such as silver, gold or titanium to provide micro thin leads such as those used for pacemakers that are resistant to flexing breakage, and are conductive. The metal surfaces can be engineered to promote cell adhesion so that tissue scarring in vivo is greatly reduced. Nanostructure and thickness of the metal coating can be controlled to provide radiopaque surfaces on nonmetal medical devices and lead wires.
Owner:METASCAPE
Device and method for measuring radar reflection characteristic of plasma coating material
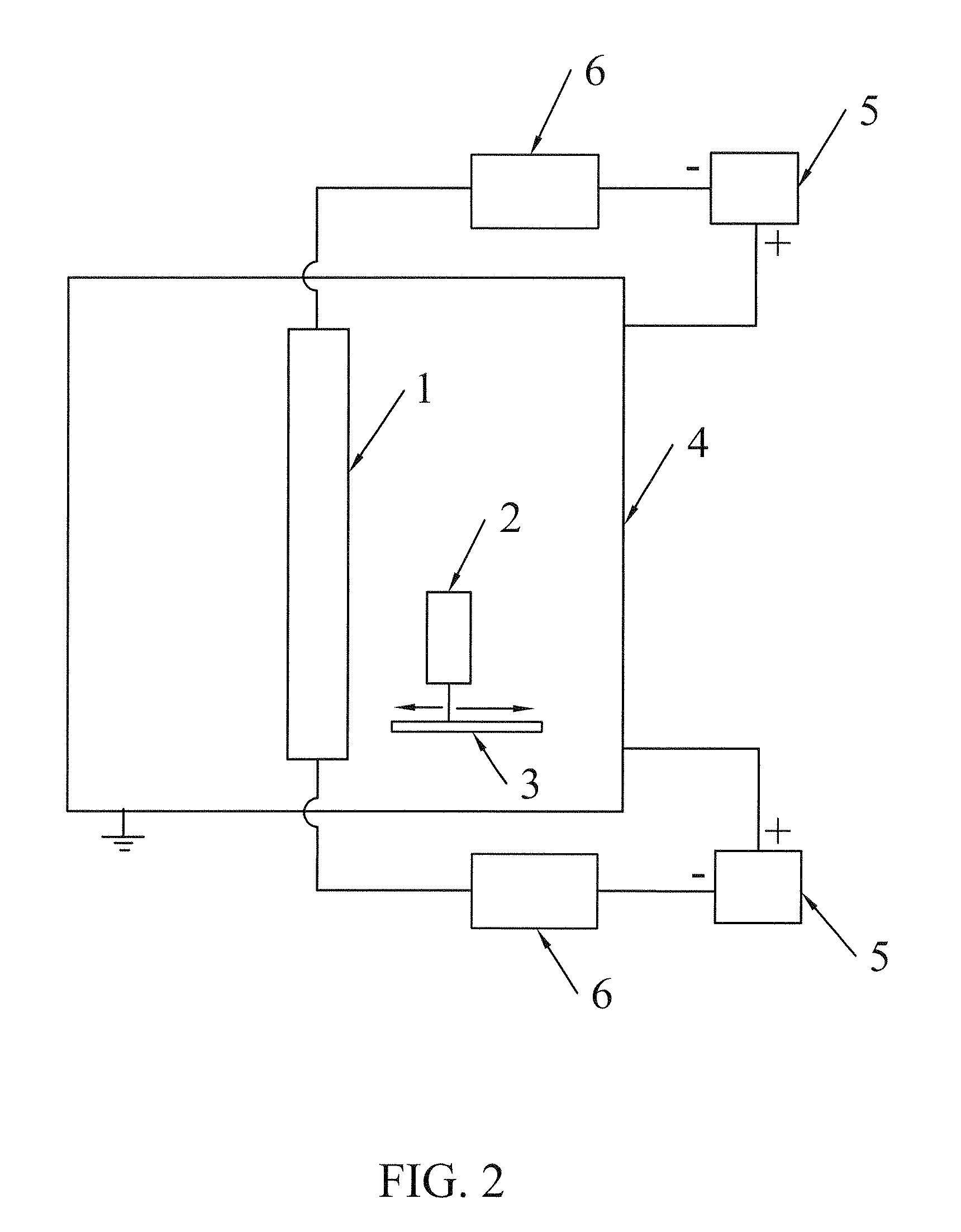
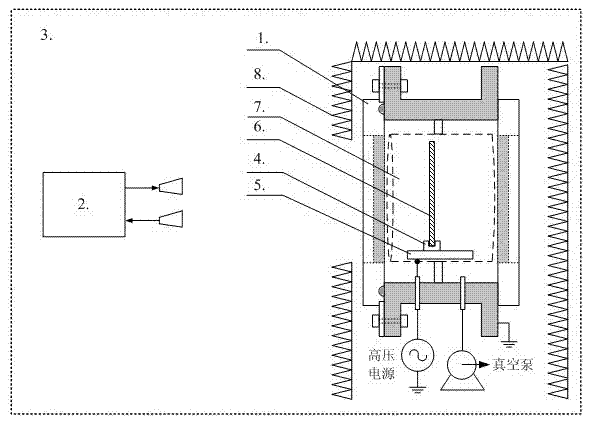
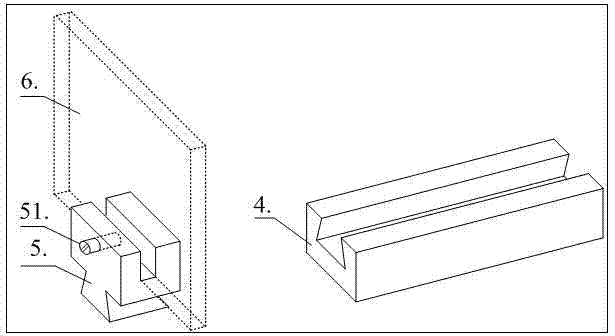
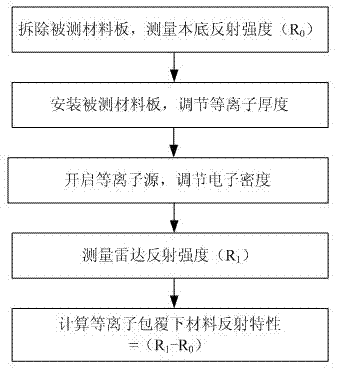
ActiveCN102809577ACoated evenlyPlasma Thickness AdjustmentPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using microwave meansMicrowavePlasma coating
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the radar reflection characteristic of a plasma coating material. The device comprises a large-area uniform unmagnetized plasma generation unit, a radar cross section measurement mechanism, a microwave unreflected chamber, a supporting guide rail, a supporting sliding block, a measured material plate and a wave-absorbing material, wherein the large-area uniform unmagnetized plasma generation unit and the radar cross section measurement mechanism are fixed in the microwave unreflected chamber; the large-area uniform unmagnetized plasma generation unit is surrounded in a space by the wave-absorbing material; and the wave-absorbing material is provided with a window, so that the measured material plate of the large-area uniform unmagnetized plasma generation unit directly faces the radar cross section measurement mechanism. By the device and the method, plasma can be coated on the surface of a measured material, and the adjustment of the thickness of the plasma and the weakening of the radar echo reflection of a body are further realized, so that the development of the experimental measurement of the radar reflection characteristic of the plasma coating material is met.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Components of plasma processing chambers having textured plasma resistant coatings
InactiveUS20130102156A1Electric discharge tubesLayered productsPlasma coatingInductively coupled plasma
A component of a plasma processing chamber includes a three dimensional body having a highly dense plasma resistant coating thereon wherein a plasma exposed surface of the coating has a texture which inhibits particle generation from film buildup on the plasma exposed surface. The component can be a window of an inductively coupled plasma reactor wherein the window includes a textured yttria coating. The texture can be provided by contacting the plasma exposed surface with a polishing pad having a grit size effective to provide intersecting scratches with a depth of 1 to 2 microns.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
WC composite guide roller and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101695713AGuaranteed toughnessGuaranteed StrengthRollsMetal rolling arrangementsFragilityPlasma coating
The invention discloses a WC composite guide roller and a manufacturing method thereof. A composite layer is arranged on the surface of matrix steel of the composite guide roller. The WC composite guide roller is characterized in that the matrix steel is carbon steel or alloy steel containing 0.2-0.7 percent by weight of carbon; the composite layer comprises the following material components in percentage by weight: 10-50 percent of WC, 0.2-0.8 percent of C, 0-3.0 percent of Cr, 0-2.0 percent of Mo, 0-2.0 percent of Mn, 0.11-0.5 percent of RE, not more than 5 percent of other metallic and non-metallic elements and the balance of Fe. The manufacturing method of the WC composite guide roller comprises the following steps of: coating composite powder on the surface of the matrix steel by using an plasma coating method and enabling the composite powder to be remelted together with the matrix steel by using an argon arc remelting method so as to form the composite layer on the surface of the matrix steel; or directly spraying the composite powder on the surface of the matrix steel and enabling the composite powder to be remelted together with the matrix steel by using the argon arc remelting method. The composite guide roller has high rigidity, good abrasion resistance, low fragility, capability of thermal treatment and mechanical machining, low cost and high cost performance.
Owner:合肥上雅电子科技有限公司
Process for coating plastic containers or glass containers by means of a PCVD coating process
InactiveUS6242053B1Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesPlasma coatingBiomedical engineering
Owner:LEYBOLD SYST
Multi-place coating apparatus and process for plasma coating
ActiveUS7926446B2Simplify the delivery processImprove throughputLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesPlasma coatingEngineering
A coating apparatus is provided for simplifying the introduction and removal of workpieces into and from a reactor for plasma coating and to increase the throughput. The coating apparatus has a reactor with a moveable sleeve part and a base element, at least one sealed coating chamber being defined between sleeve part and base element when the latter two parts are fitted onto one another. The coating apparatus also has a device for introducing electromagnetic energy into the at least one coating chamber. The reactor has at least two coating places.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Non-stick coated electrosurgical instruments and method for manufacturing the same
An end effector assembly for use with an electrosurgical instrument is provided. The electrosurgical instrument includes a handle having a shaft that extends therefrom, an end effector disposed at a distal end of the shaft, at least one electrode operably coupled to the end effector and adapted to couple to a source of electrosurgical energy, a chromium nitride coating covering at least a portion of the electrode, and a hexamethyldisiloxane plasma coating covering at least a portion of the chromium nitride coating.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methods of laser assisted plasma coating at atmospheric pressure and superalloy substrates comprising coatings made using the same
Methods of laser assisted plasma coating at atmospheric pressure including providing a plasma, at least one target, at least one laser, and a superalloy substrate, operably directing the laser toward the target to liberate atomic particles from the target and feed the atomic particles into the plasma, and depositing the atomic particles onto the superalloy substrate using the plasma to produce a thermal barrier coating having a column width of from about 0.5 microns to about 60 microns, and an intra column porosity of from about 0% to about 9%.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Plasma Booster for Plasma Treatment Installation
ActiveUS20130040072A1Increase plasma densityGood dissociation and excitationElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingCharge carrierPlasma coating
Owner:OERLIKON SURFACE SOLUTIONS AG PFAFFIKON
Atmospheric plasma coating for ophthalmic devices
ActiveUS20120137635A1Reliable coatingDurable plasma hydrophilic coatingOptical articlesPackaging under special atmospheric conditionsPlasma coatingProduct gas
The invention provides a method of coating and thereby affecting the surface properties of a substrate such as a contact lens or other ophthalmic device. The method comprises the steps of generating an atmospheric plasma flow from a working gas and controlling the continuity of the atmospheric plasma flow with a power generator, and, introducing the atmospheric plasma flow to a substrate surface.
Owner:ALCON INC
Medicinal implant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101961507AHigh porosityIncrease roughnessMolten spray coatingProsthesisPorosityCeramic composite
The invention discloses a medicinal implant and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the fields of medicinal biology and material processing. The medicinal implant comprises an implant and a coating. The medicinal implant is characterized in that: the tantalum coating is coated on the surface of the implant, and the tantalum coating is made of one of tantalum elemental material and tantalum alloy material or tantalum / ceramic composite coating material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing sandblast pretreatment and cleaning on a to-be-coated area of the implant by adopting a sandblast apparatus; and then coating the tantalum coating to the to-be-coated area of the implant by adopting a plasma coating device. The medicinal implant has the advantages of good biocompatibility, simple preparation process, high production efficiency, low production cost, wide matrix selection range, good process controllability, low influence of matrix tissues, high coating roughness, high thickness and wide porosity.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF MATERIALS & TECH
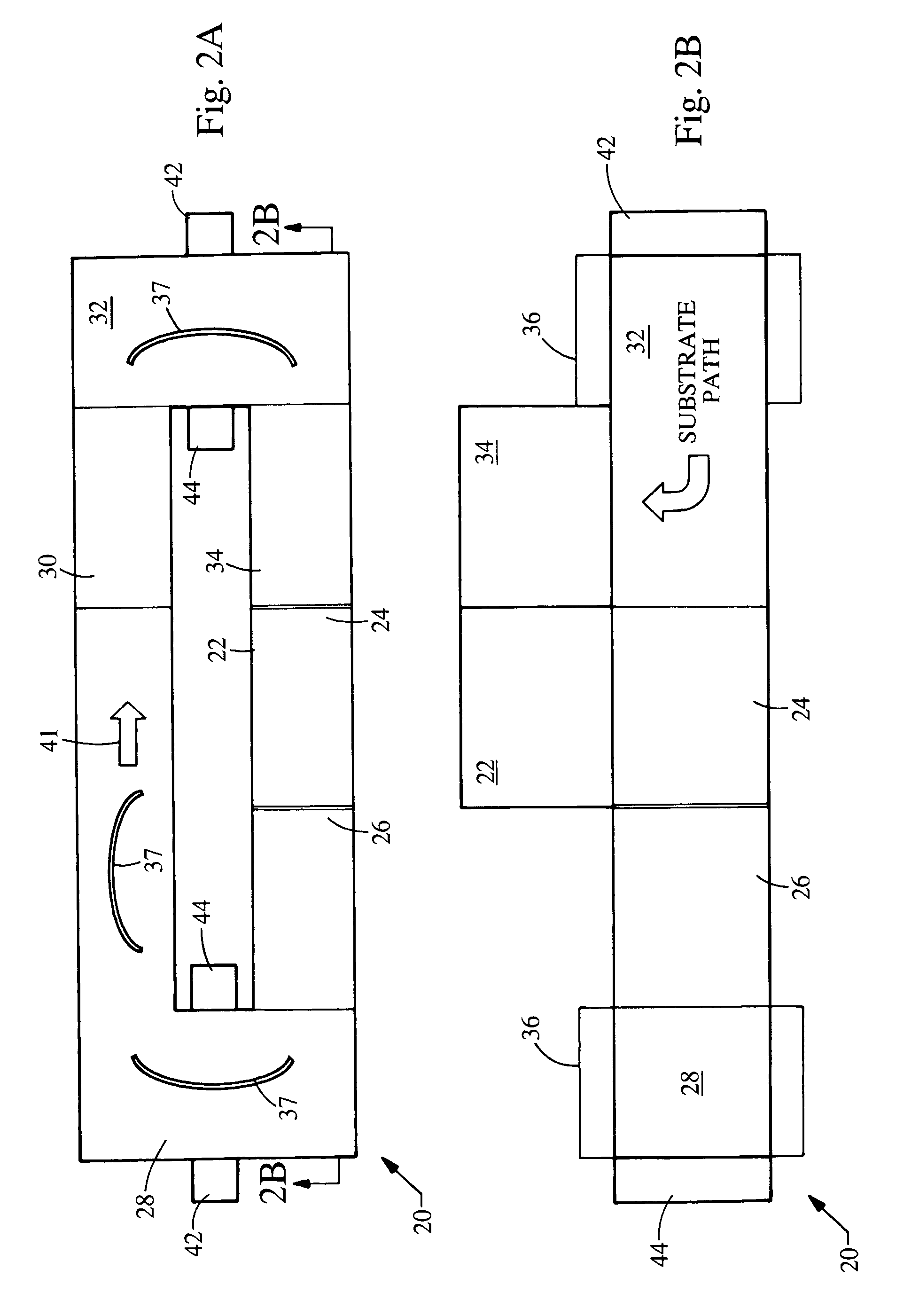
Plasma coating system for accommodating substrates of different shapes
A plasma coating system includes at least one coating station with a first side and a second side defining a pathway with at least one bend. The coating station also includes a first plasma arc that provides a plasma jet directed towards a substrate. The first plasma arc is positioned on either the first side or the second side of the bend.
Owner:EXATEC LLC
Hard tissue substitute material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102921042ASuitable for growthImprove biological activityCoatingsProsthesisCell adhesionHard tissue
The invention discloses a hard tissue substitute material and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises a coating and a base material, wherein the base material is medical metal or medical metal alloy; and the coating is attached over the base material and consists of tantalum-hydroxyapatite powder. The preparation method of the material comprises the following steps: preparing tantalum-hydroxyapatite powder; and preparing a tantalum-hydroxyapatite coating on the base which is subjected to surface pretreatment by a vacuum plasma coating technology. The hard tissue substitute material is provided with a composite coating surface which is suitable for cell adhesion and growth and fixing an implant in a hard tissue; the composite coating is excellent in bioactivity, has strong combining strength and stability with the metal base material; and quick and stable combination between the implant and the bone tissue and subsequent long-term use can be favored. The hard tissue substitute material has the advantages of being simple in preparation process, high in efficiency, good in repeatability, suitable for large-scale industrial production and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for Plasma Coating a Nanocomposite Object
A process for preparing a coating on an object by plasma polymerizing a first compound under conditions to deposit a layer onto the object, the object comprising a nanocomposite polymer. In addition, the object so coated.
Owner:BRASKEM AMERICA
Lens molds having atmospheric plasma coatings thereon
ActiveUS20120139137A1Improve hydrophobicityReducing separation forceOptical articlesCoatingsShell moldingPlasma coating
The invention provides a method of making ophthalmic lenses with an enhanced quality and enhanced yield achieved by reducing mold separation force and lens-mold adhesion. The method comprises the steps of generating an atmospheric plasma flow from a working gas and controlling the continuity of the atmospheric plasma flow with a power generator, and, introducing the atmospheric plasma flow to a molding surface of a mold for making an ophthalmic lens (preferably contact lens, more preferably a silicone hydrogel contact lens) and increasing the surface hydrophobicity of the molding surface of the mold and thereby to reduce a mold separation force after molding a lens formulation in the mold.
Owner:ALCON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com