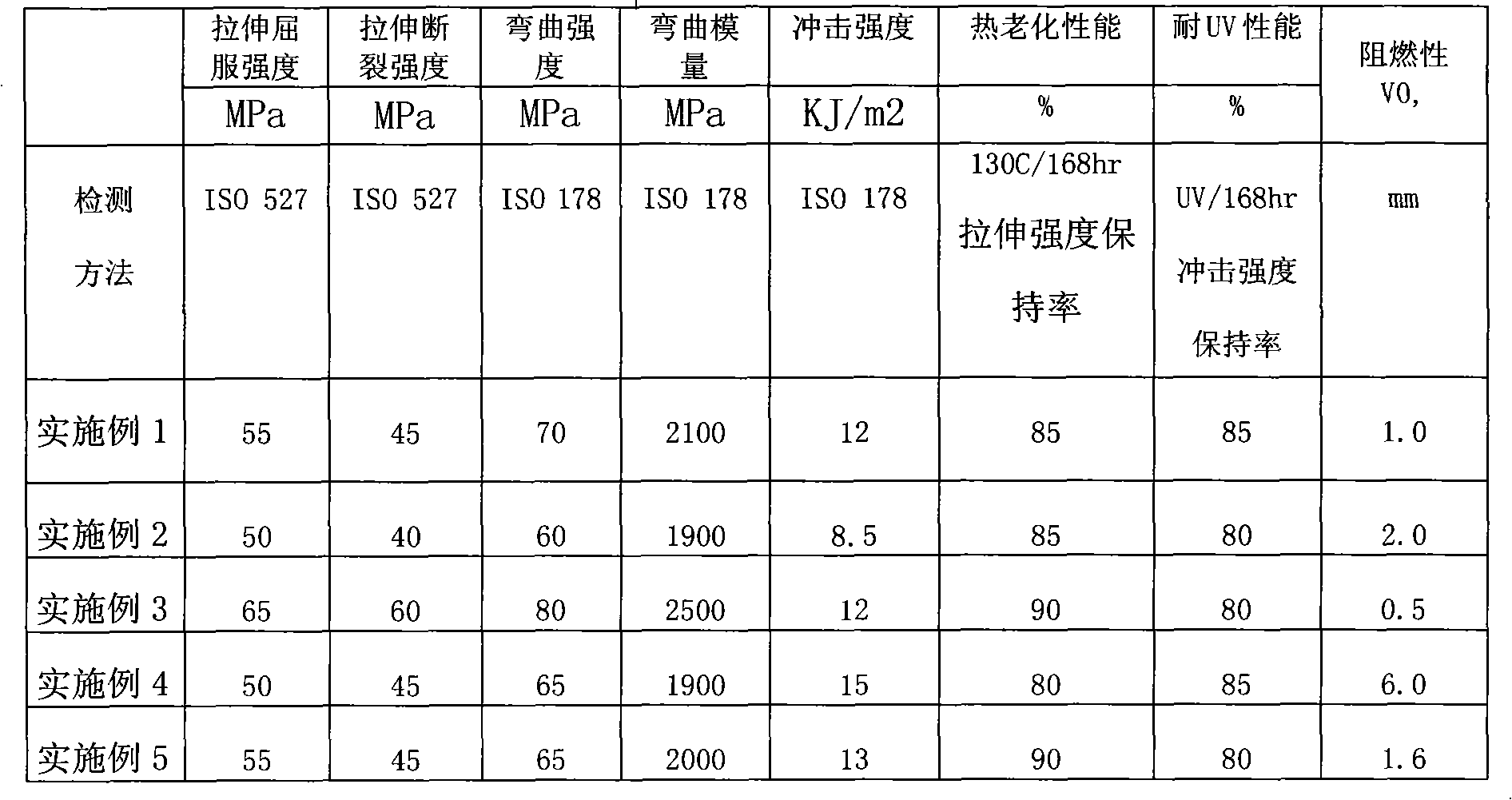
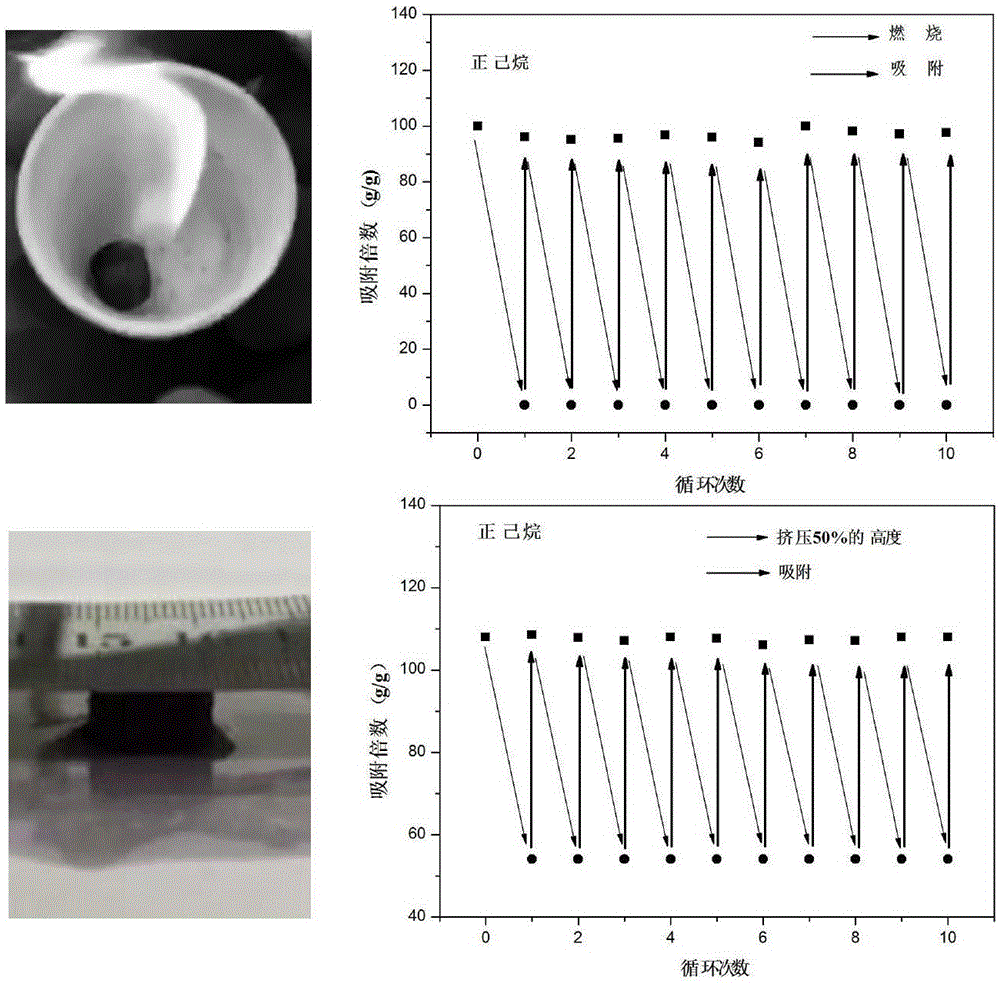
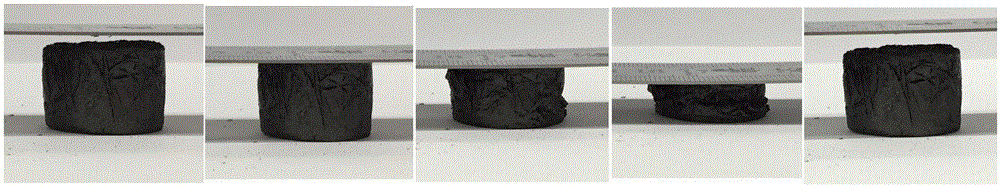
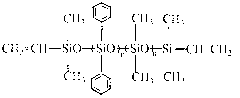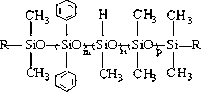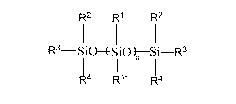Patents
Literature
1226results about How to "Guaranteed toughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
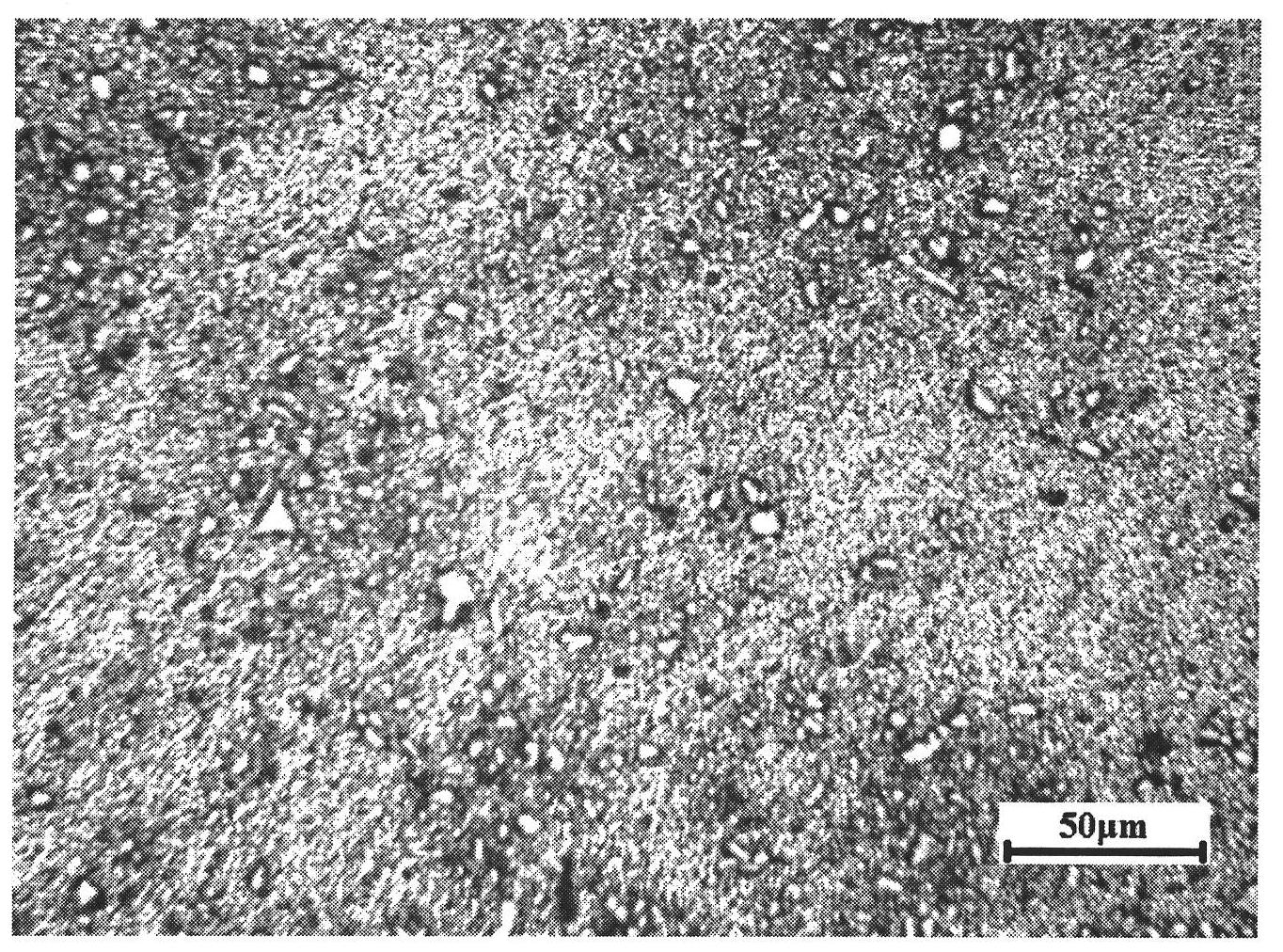
Silicon rubber with high refractive index and high transparency for optical encapsulation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103122149AHigh refractive indexImprove mechanical propertiesSemiconductor devicesHydrogenPolymer science
The invention relates to silicon rubber with high refractive index and high transparency for optical encapsulation and a preparation method thereof. The silicon rubber is prepared from a phenyl vinyl polysiloxane component A, a silicon resin component B containing phenyl vinyl, a phenyl component C containing hydrogen polyoxyalkylene, a platinum catalyst component D, a catalytic inhibitor component E, a modified polysiloxane component F, and a water remover component G in a mixing manner. The silicon rubber not only has over 1.50 of refractive index, but also is good in transparency, excellent in adhesion, and stable in performance, can resist heat and ultraviolet radiation for a long period of time, can meet various requirements of LED (light-emitting diode) encapsulation, and is an ideal encapsulation material of the LED. The silicon rubber can be packaged into a bi-component product; the product has good storage stability; and high transparency is still kept after the product is stored for over 6 months.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
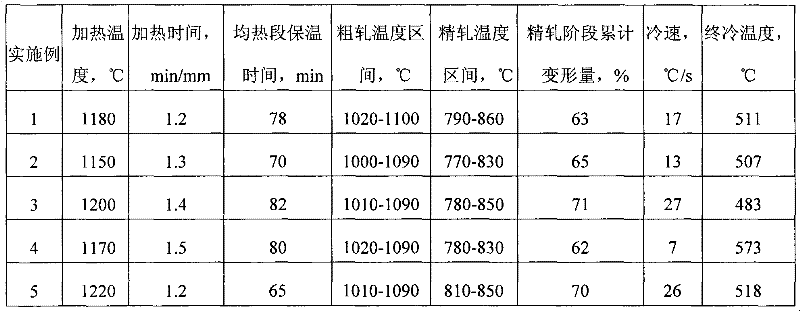
Hot rolled steel plate with excellent low-temperature toughness for thick submerged pipeline and production method of hot rolled steel plate
ActiveCN102409224AGuaranteed toughnessSuitable for solderabilityRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsHydrogenChemical composition
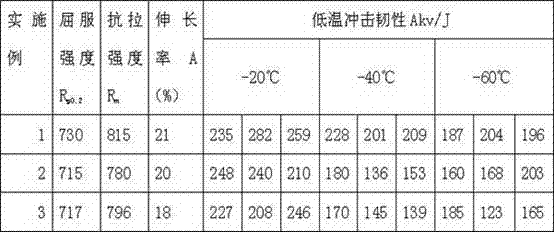
The invention provides a hot rolled steel plate with excellent low-temperature toughness for a thick submerged pipeline and a production method of the hot rolled steel plate. The hot rolled steel plate comprises the following chemical components by weight percentage: 0.02%-0.07% of C, 0.15%-0.40% of Si, 1.0%-1.70% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.003% of S, less than or equal to 0.06% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.025% of Ti, less than or equal to 0.06% of V, less than or equal to 0.20% of Mo, less than or equal to 0.25% of Cu, 0.10%-0.30% of Ni, less than orequal to 0.25% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.008% of N, 0.010%-0.040% of Al, more than or equal to 2 of Al / N and the rest Fe and inevitable impurities. According to the steel for the submerged pipeline with the thickness being over 28mm, disclosed by the invention, the transversal and longitudinal bending strength can reach over 480MPa or 510MPa, the transversal and longitudinal tensile strengthcan reach over 560MPa or 600 MPa, the transversal impact toughness at the temperature of 60 DEG below zero is larger than or equal to 400 J, the transversal DWTT (Drop-Weight Tear Test) shearing areaat the temperature of 25 DEG C below zero is larger than or equal to 85%, simultaneously, the corrosion resistant of the steel plate is excellent, and the result of a 96-hour HIC (Hydrogen Induced Cracking) test conforms to the requirements of the standard 0284 of the NACE (National Association of Corrosion Engineers). The hot rolled steel plate is suitable to be as a raw material for manufacturing a pipeline for submerged oil and gas transmission.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
High-strength high ductility gas protecting welding stick
InactiveCN101234457ASimple welding processStable welding wire qualityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaChemical compositionUltra fine
The invention relates to a gas shielded welding wire with high strength and high toughness, which solves the defects that the existing strength grade in the technical field is unsuitable for market demand and is of high cost. The technical scheme of the invention is that the components of the welding wire (according to the weight percentage) are as follows: 0.04 to 0.10 of C, 0.30 to 0.80 of Si, 1.30 to 2.0 of Mn, 0.40 to 0.89 of Ni, 0.20 to 0.50 of Cr, 0.20 to 0.60 of Mo, 0.56 to 0.80 of Cu, 0.05 to 0.20 of Ti, 0.002 to 0.010 of B, less than 0.020 of P, less than 0.015 of S, less than 0.03 of Als and the rest of Fe and inevitable impurities. The welding wire of the invention has stable quality. The mechanical property of a deposited metal is that Rel is equal to 810MPa; Rm is equal to 840MPa; A is equal to 16 percent and Z is equal to 66 percent. The average impact power AKV in minus 20 DEG C is 141J; and the average impact power AKV in minus 40 DEG C is 128J; and the average impact power AKV in minus 60 DEG C is 70J. The welding wire is suitable for gas shielded welding of 800MPa grade of ultra-fine steel; as the content of Ni is reduced, the cost of the welding wire is reduced dramatically and the implementation is easy.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Low-temperature high-strength, high-toughness steel and preparing method therefor
InactiveCN101024870AHigh strengthGuaranteed toughnessHeat treatment process controlLift systemThermal treatment
The invention relates to a low-temperature, high-intensity, high-toughness steel and the making method thereof, applicable to the environment down to -60 deg.C, adopting low-carbon Cr-Ni-Si-Mn-Mo-V alloy, and its chemical composition includes in mass percent (mass%): C: 0.16-0.24,Si:1.0-1.4, Mn:1.10-1.50,Cr:0.80-1.20,Ni:1.00- 1.40,Mo:0.20-0.40,V:0.05-0.20,S=<0.035,P=<0.035,Cu =<0.050, and the rest Fe. And its making method comprises: (1) smelting; (2) forging: heating at 1280-1320deg.C, where initial forging temperature: 1100-1250deg.C, final forging temperature >=850deg.C; annealing after forging, where heating temperature: 700+-30deg.C, and tapping temperature =<300deg.C; (3) thermal treatment: normalizing: air cooling at 930-950deg.C; tempering: air cooling at 790-720deg.C; quenching: oil cooling at 900-930deg.C; and tempering: air cooling at 200-260deg.C; (4) supersonic crack detection and magnetic particle crack detection. And it is especially applied to the materials for flying rings, hocks, pin shafts, etc, in the lifting systems of mechanical facilities.
Owner:RG PETRO MACHINERY GROUP
Structural steel for welding with ultra-great heat input and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102080193AGuaranteed toughnessTemperature control deviceManufacturing convertersChemical compositionSheet steel
A structural steel for welding with ultra-great heat input and a manufacturing method thereof. The invention belongs to the technical field of high-strength steel plate for welding. The steel plate comprises, by mass percent, the following chemical compositions: 0.03-0.12 wt% of C, 0.01-0.30 wt% of Si, 1.2-2.0 wt% of Mn, not more than 0.015 wt% of P, not more than 0.008 wt% of S, not more than 0.03 wt% of Al, not more than 0.5 wt% of Cr, not more than 0.5 wt% of Mo, not more than 0.03 wt% of Nb, 0.005-0.03 wt% of Ti, 0.01-1.0 wt% of Ni, 0.01-1.0 wt% of Cu, 0.002-0.007 wt% of N, and 0.001-0.006 wt% of O, and also comprises one or more elements selected from Mg, Ca, B, Zr, Ta, or REM with the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities, and the carbon equivalent of the steel plate is less than 0.40%. The type, size and quantity of the inclusions are controlled by controlling the alloy addition method during the refining phase, and the steel plate for welding with great heat input is manufactured by controlled rolling and controlled cooling process. The advantages are that the steel plate has high strength and good toughness, can endure a welding heat input of 400-1000 kJ / cm, still has excellent low-temperature toughness after welding, and has an average impact energy value of above 70 J at -20 DEG C.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Series flux cord welding rod used for pile-up welding reparing and remanufacturing large type medium high carbon steel parts
InactiveCN100999041AImprove crack resistanceHigh carbon contentArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsHigh carbonRare earth
The present invention discloses a series flux-cored wire for reparation and refabrication of large-size medium-high carbon steel components and parts. Its chemical composition includes (wt%) 5-10 of fluorite, 25-45% of high-carbon ferrochrome, 2-10% of high-carbon manganese iron, 5-8% of tantiron, 10-15% of ferro-molybdenum, 8-14% of rare earth oxide, 5-15% of metal nickel, 2-5% of ferrovanadium, 0.5-2% of graphite, 2-4% of chloride and 1-2.5% of aluminium-magnesium alloy. Its external covering adopts low-carbon steel tape.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO WEIERDE SPECIAL WELDING IND
Composite metal carbide wear-resistant coating and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to a composite metal carbide wear-resistant coating and a preparation process thereof, and belongs to a wear-resistant coating and a preparation process thereof. The composite metal carbide wear-resistant coating consists of adhesive coated tungsten carbide and other carbides, wherein the adhesive coated tungsten carbide has the grain size of WC-Co or WC-Ni; and the other carbides comprise chromium carbide, vanadium carbide, iron carbide, titanium carbide and the like. The preparation process comprises the following steps of: mixing the adhesive coated tungsten carbide and one or more kinds of the carbide powder; and performing spray coating (welding) or plasma spray coating (welding) on the surface of a medium-carbon steel part through supersonic flame to form the wear-resistant coating, wherein the carbon content of the medium-carbon steel is 0.35 to 0.55 weight percent (wt); the medium-carbon steel is subjected to the thermal refining state of quenching and high-temperature tempering; and the supersonic flame spray coating (welding) or plasma spray coating (welding) process sequentially comprises steps of performing sand blasting and rust removal on the surface of the medium-carbon steel, spraying a Ni-5 percent Al alloy adhesive coating and spraying a composite carbide wear-resistant coating. The composite carbide wear-resistant coating has Vickers hardness (HV) of 1,200 to 1,800, bonding force of more than 60 Mpa, and high mechanical property, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Wicker treatment agent for wickerwork
InactiveCN104026161AGuaranteed toughnessIncrease the degree of immersion in the liquidBiocidePest repellentsMedicineChrysanthemum cinerariifolium
The invention relates to a wicker treatment agent for wickerwork. The wicker treatment agent comprises coptis chinensis, radix scutellariae, realgar, borneol, fructus evodiae, clove, pyrethrum, lemon and mint. The wicker treatment agent provided by the invention is a pure traditional Chinese medicine preparation, toxic substances are not released in the using process, the wicker treatment agent has a good insect-resistant and anti-mould effect, the using time of wickerwork is greatly prolonged, the anti-insect anti-mould time can be over 5 years, the wickerwork product has a fragrant taste, and the wicker treatment agent does not have a side effect on a human body.
Owner:阜南腾强工艺品有限公司
Polyphenylene oxide composition used for photovoltaic junction box
ActiveCN102399433AImprove liquidityGuaranteed toughnessHazardous substanceComparative Tracking Index
The invention provides a polyphenylene oxide composition used for a photovoltaic junction box. The composition comprises the following components by weight: 55-95 parts of polyphenylene oxide, 45-5 parts of styrene resin, 2-10 parts of a flexibilizer, 5-20 parts of a phosphate fire retardant, 0.5-2.5 parts of an acid absorbent, 0.2-0.6 part of a hindered phenol main antioxidant, 0.2-0.6 part of a phosphite auxiliary antioxidant, 0.3-1.5 parts of an ultraviolet absorbent, 0.3-1.5 parts of a hindered amine light stabilizer, 0.1-0.5 part of a lubricating agent, and 0.1-1.0 part of toner. With the characteristics of good flame resistance, thermo-oxidative aging resistance, UV (ultraviolet) resistance, excellent electrical performances, the composition of the invention has flame retardancy up to grade UL945VA, RTI (relative temperature index)=110DEG C, CTI (comparative tracking index) PLC ( programmable logic controller)=2, and GWIT (glow wire ignition temperature)=750DEG C, thus satisfying the requirements in ROHS (restriction of hazardous substances) standard. Thus, the composition provided in the invention can be used for electronic and electrical component production of solar photovoltaic junction boxes, etc.
Owner:广东瑞能新材料有限公司
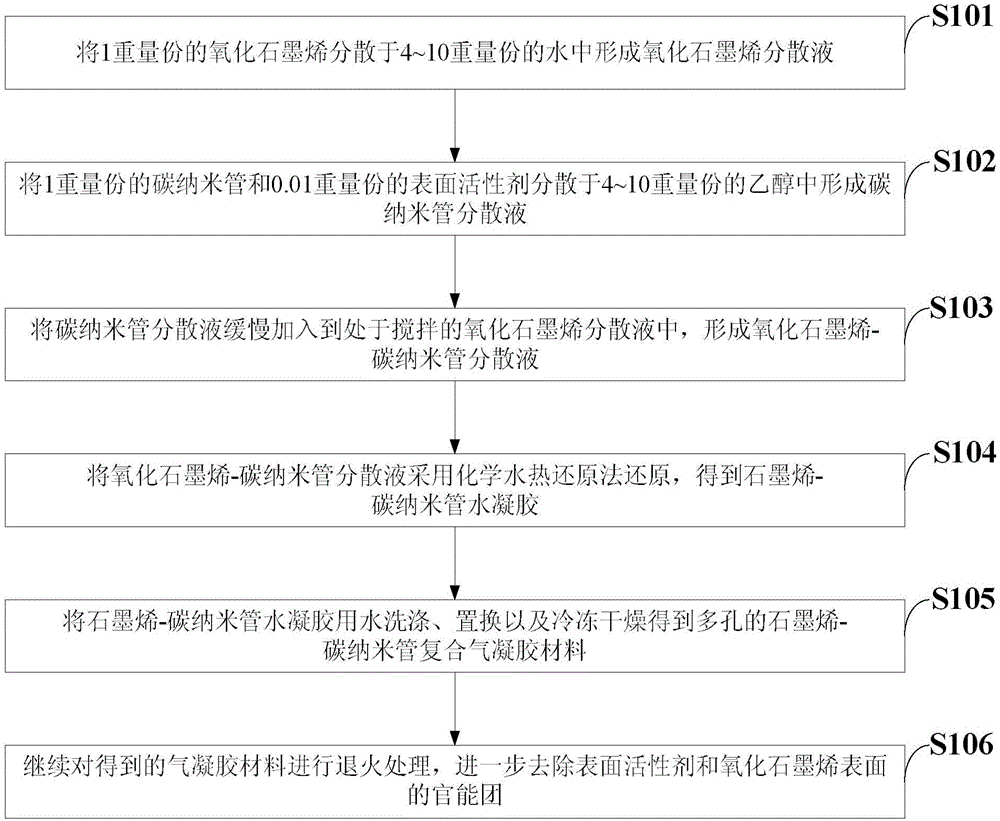
Preparation method for efficient oil absorption carbon aerogel material
ActiveCN104998589AEffective dispersionGuaranteed toughnessOther chemical processesColloidal chemistry detailsFreeze-dryingCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a preparation method for an efficient oil absorption carbon aerogel material. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly 1 part by weight of carbon nano tubes and 0.01 part of a surface active agent are dispersed into 4-10 parts of ethyl alcohol to obtain carbon nano tube dispersion liquid; next, the carbon nano tube dispersion liquid is slowly added into stirring graphene oxide dispersion liquid to form graphene oxide-carbon nano tube dispersion liquid; then reduction is conducted on the graphene oxide-carbon nano tube dispersion liquid by the adoption of a chemical hydrothermal reduction method to obtain graphene oxide-carbon nano tube hydrogel; finally, freeze drying is conducted on the hydrogel to obtain aerogel. According to the preparation method for the efficient oil absorption carbon aerogel material, firstly, the carbon nano tubes are dispersed into the dispersion liquid containing the ethyl alcohol and the surface active agent, then self-assembly is conducted with the high-dispersibility graphene oxide, the technology is simple, the obtain three-dimensional graphene oxide-carbon nano tube effectively combines advantages of the graphene oxide with advantages of the carbon nano tubes, good adsorption performance and mechanical strength are achieved, and the wide application prospect in the field of oil and gas fields is achieved.
Owner:四川旭航新材料有限公司
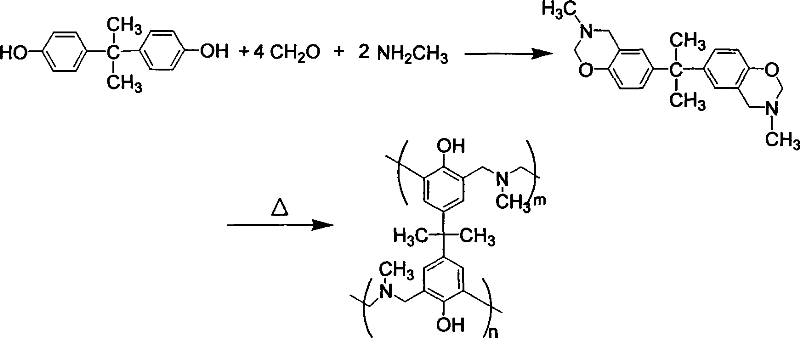
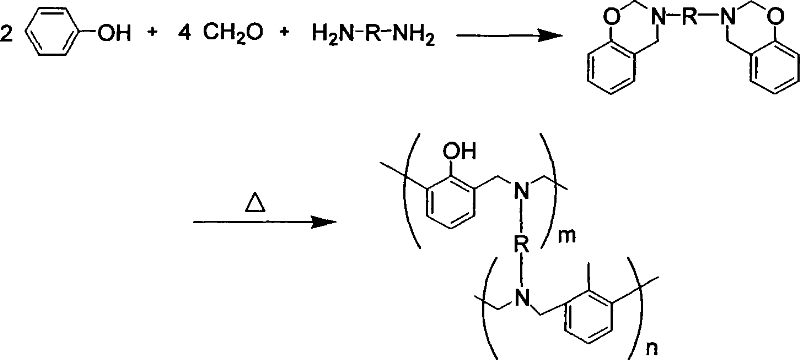
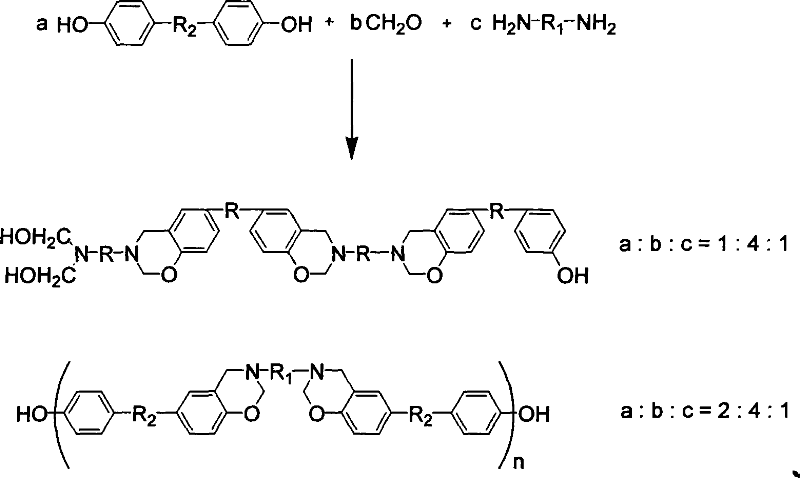
Preparation method of benzoxazine intermediate containing active function groups
The invention discloses a making method of benzoxazine intermediate with active functional group, which is characterized by the following: adopting diamine, dihydric phenol and formaldehyde as raw material; introducing the unit of diamine and dihydric phenol into the intermediate of benzoxazine; polymerizing under heating condition; reducing the ring-opening polymerizing temperature of benzoxazine; fitting for making high-property structural material, electric insulating material, electronic packing material, flame-proof material or braking material with temperature over 155 deg.c.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Slurry for photo-curing 3D-printing dental implant as well as preparation method and application of slurry
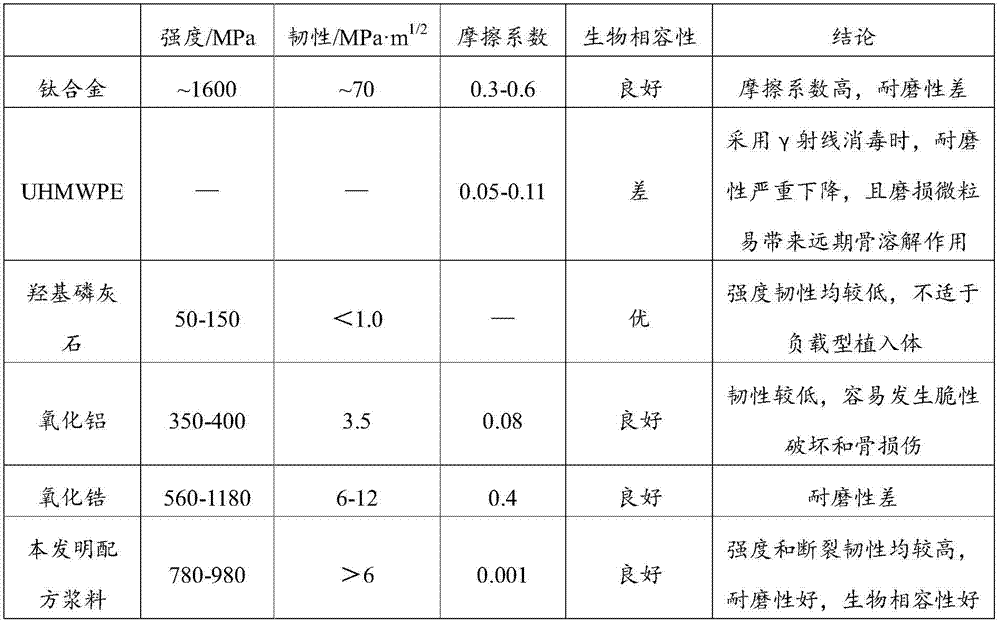
InactiveCN107158474AOvercome performance shortcomingsGuaranteed StrengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingDiluent
The invention discloses slurry for a photo-curing 3D-printing dental implant as well as a preparation method and application of the slurry. The slurry contains the following raw material components: silicon nitride ceramic powder, photosensitive resin, a photoinitiator, an active diluent, a dispersing agent and an aid, wherein the volume ratio of the photosensitive resin to the silicon nitride ceramic powder is (3 to 7)-(1 to 9), the adding proportion of the photoinitiator is 0.1wt%-1.5wt% of the photosensitive resin, the adding proportion of the active diluent is 15wt%-30wt% of the photosensitive resin, the adding proportion of the dispersing agent is 0.1wt%-1.5wt% of the silicon nitride ceramic powder, and the adding proportion of the aid is 0.1%-1% of total mass of the slurry. The dental implant prepared from the slurry has good biocompatibility, and besides, the strength, breaking tenacity and wear resistance of the dental implant are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG RES & DESIGN ACADEMY OF IND CERAMICS
Method and device for preparing high-silicon silicon steel thin strip under magnetic field through powder diffusion method
PendingCN107282928AAvoid processing difficultiesEnhanced diffusionContinuous operationNear net shape
The invention discloses a method and a device for preparing a high-silicon silicon steel thin strip under a magnetic field through a powder diffusion method. According to the method, holes are formed in a low-silicon steel strip to be machined, then surface reinforcing treatment is carried out on the low-silicon steel strip to be machined, the holes are filled with an iron-silicon alloy powder and rolling forming is carried out on the powder, and then heat treatment is carried out on the powder in a magnetic field environment to obtain the high-silicon silicon steel thin strip with certain orientation, a silicon content of 6.5wt%Si and excellent magnetic performance. According to the method and the device, long-size and continuous operation can be realized; and moreover, a near-net-shape thin strip can be prepared, and therefore, a preparation cost can be remarkably lowered.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF TECH
Ceramic grid enhanced metal matrix composite perform and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a ceramic grid enhanced metal matrix composite perform and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing ceramic particles with the particle sizes of 8-30 meshes and self-fluxing alloy powder in polyvinyl alcohol to obtain a mixture; filling the mixture in a grid cavity, prepressing for preparing ceramic grids, filling the self-fluxing alloy powder into grid holes after the grids leave from a mold, wherein the monolithic material is pressed with 100-300 kilogram force, molding and demolding, placing and drying a biscuit and a mold cavity bottom plate in a 150 DEG C drying oven for 2 hours; placing the dried biscuit and the mold cavity bottom plate in a vacuum furnace, sintering for 30-90 minutes under the conditions that the temperature is 1000-1300 DEG C, and the vacuum degree is 0.1 Pa, and cooling and discharging to obtain the ceramic grid enhanced metal matrix composite perform. The ceramic grid enhanced metal matrix composite perform prepared by the method has the advantages of high density, uniform distribution of ceramic particles, good wear resistance and high grinding efficiency.
Owner:NANTONG GAOXIN ANTIWEAR MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Single-action double-pipe coring overburden drill tool for air down-the-hole hammer
InactiveCN104295232AEliminate disadvantagesReduce frictional resistanceBorehole drivesCore removalBall bearingGeological survey
The invention relates to a single-action double-pipe coring overburden drill tool for an air down-the-hole hammer. The single-action double-pipe coring overburden drill tool comprises a central coring drill tool and an overburden drill tool. The central coring drill tool is a single-action double-pipe coring drill tool and comprises a single-action vibration reduction mechanism, an inner pipe adjusting mechanism and a coring mechanism with a bayonet device; the single-action vibration reduction mechanism comprises an impact connector, a disc spring, a bearing block, a connecting shaft, a thrust ball bearing and a radial ball bearing; the inner pipe adjusting mechanism comprises a connecting shaft, a core pipe connector, an inner pipe and a nut; the coring mechanism with the bayonet device comprises an outer pipe, an inner pipe, a connecting shaft, a core pipe connector, a coring drill bit, a rolling needle, a pawl spring seat and a pawl spring; the overburden drill tool comprises a casing, a casing connector, a casing shoe, a clamp ring and a casing drill bit. The single-action double-pipe coring overburden drill tool for the air down-the-hole hammer is applicable to relevant fields such as geological mineral exploration and engineering geological survey for complex formation with loose sand, cobbles, gravel, fracture, breakage and the like.
Owner:江苏省南京工程高等职业学校
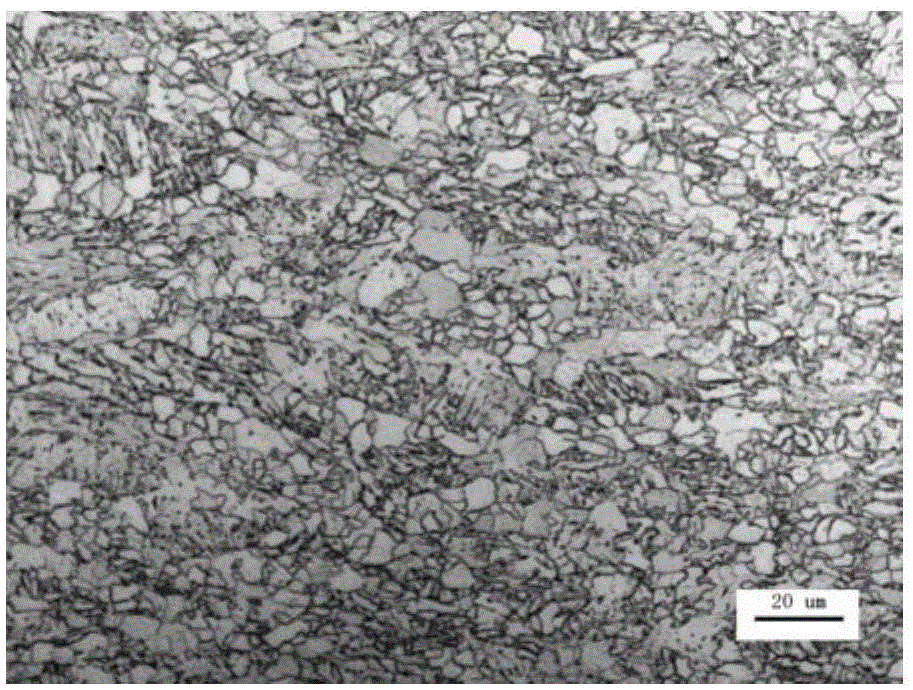
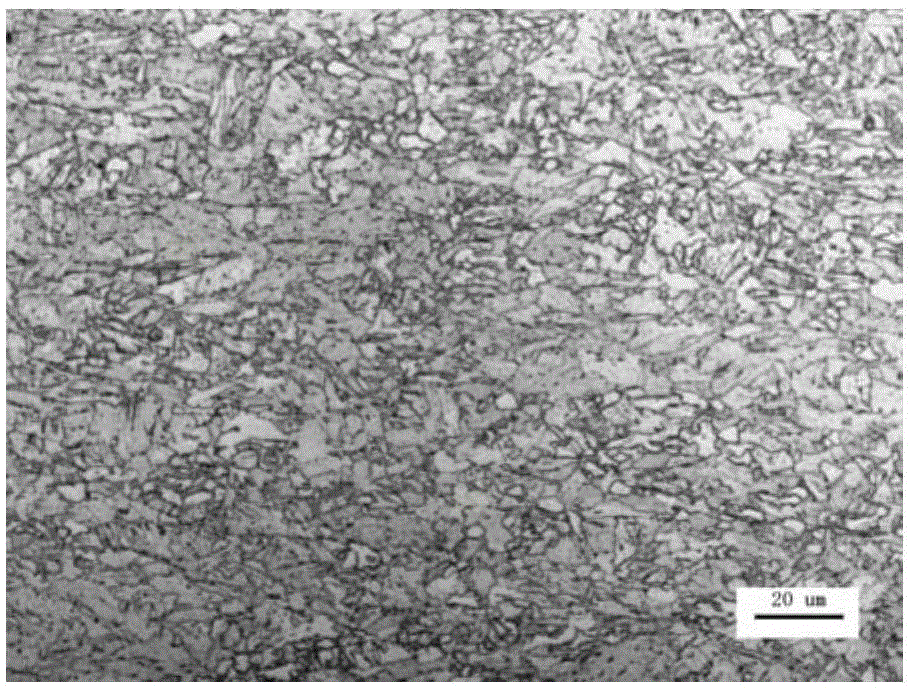
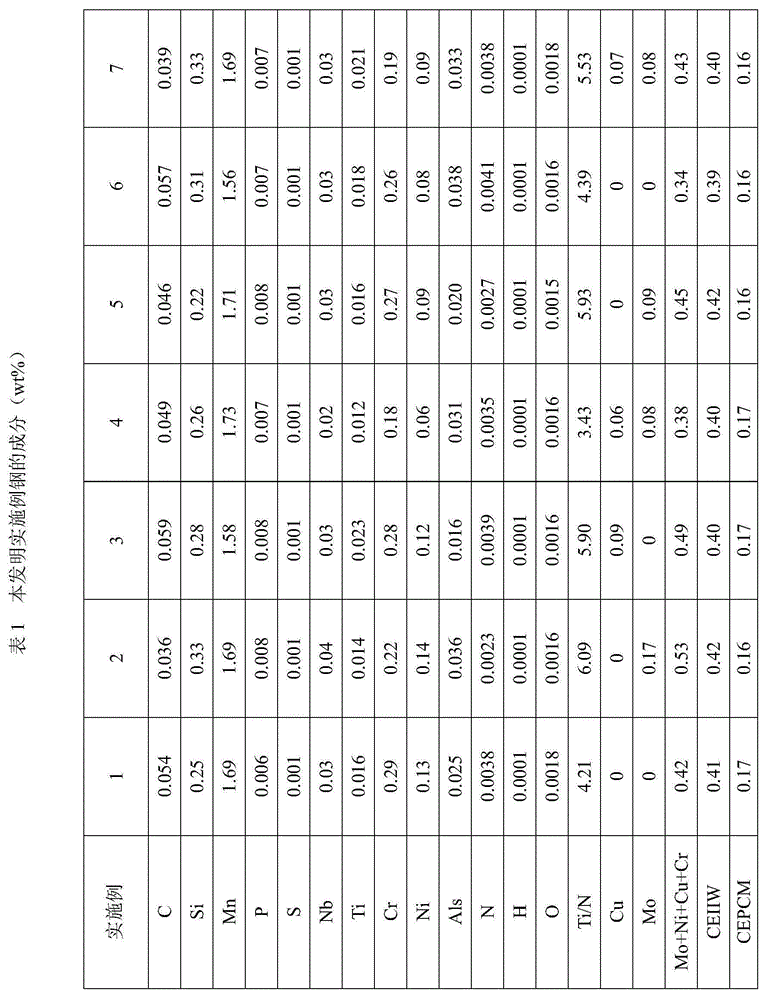
Hot-rolled wide and thick plate with good ductility and toughness for low temperature pipelines and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides a hot-rolled wide and thick plate with good ductility and toughness for low temperature pipelines and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel plate comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.035 to 0.060% of C, 0.20 to 0.35% of Si, 1.56 to 1.74% of Mn, 0.01 to 0.04% of Nb, 0.011 to 0.025% of Ti, 0.18 to 0.30% of Cr, 0.06 to 0.15% of Ni, 0.015 to 0.040% of Als, 0 to 0.10% of Cu, 0 to 0.19% of Mo, 0.0020 to 0.0045% of N, not more than 0.009% of P, not more than 0.001% of S, not more than 0.0015% of H, not more than 0.0020% of O, and the balance being iron and inevitable impurities; wherein the total percentage of Mo, Ni, Cu, and Cr is in a range of 0.32 to 0.55%, and the ratio of Ti and N is in a range of 3.42 to 6.10. At the same time, CEIIW is controlled in a range of 0.385 to 0.430%, and CEPcm is controlled in a range of 0.159 to 0.175%. The manufacturing method comprises steps of molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, external refining, continuous casting, casting blank reheating, rolling, and cooling. The provided wide and thick plate can be used as a raw material to prepare large diameter (not less than 1420 mm) thick wall low temperature steel pipelines, and the ductility and toughness are good.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Manufacturing method for high-speed steel working roll at hot continuous rolling finish rolling rear section
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a high-speed steel working roll at a hot continuous rolling finish rolling rear section. The working layer of a roll body comprises the following chemical components in percentages by weight: 2.00-3.50% of C, 0.40-2.00% of Si, 0.50-1.20% of Mn, 1.50-4.50% of Cr, 2.00-5.00% of Ni, 2.00-10.00% of Mo, V, W and Nb, 0-0.05% of S, 0-0.10% of P, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of smelting, inoculation and spheroidizing and pouring, and heat treatment. Through the alloy compositions with reasonable design and the production technology, a special graphite and metallographic structure is obtained. According to the high-carbon high-speed steel roll at the hot continuous rolling finish rolling rear section, the quality of rear surface of a machine under the roll can be effectively controlled, and meanwhile the abrasive resistance and heat cracking resistance of the roll are improved.
Owner:SINOSTEEL XINGTAI MACHINERY & MILL ROLL
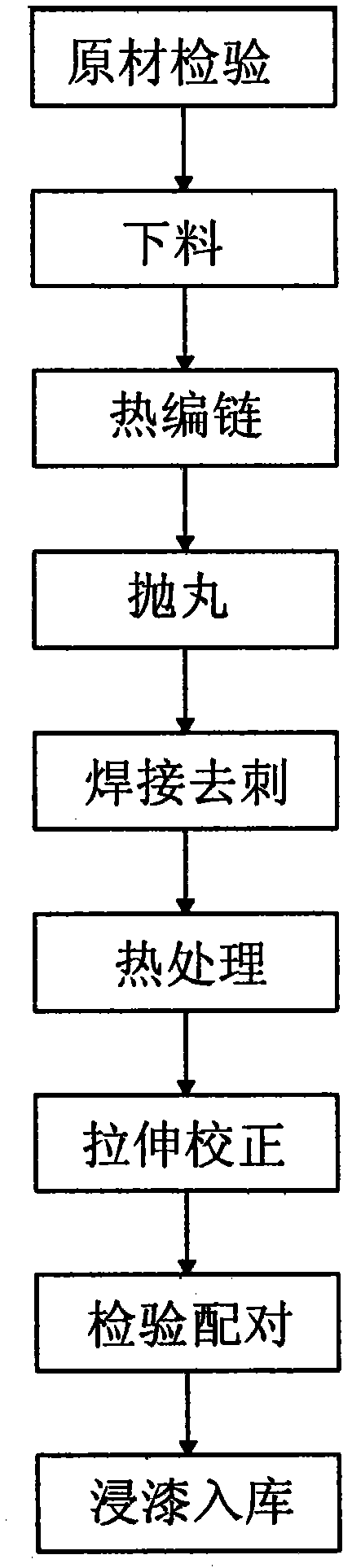
Method for producing round-link chain
The invention discloses a method for producing a round-link chain, which comprises the following steps: A1) raw material selecting: adopting high-quality alloy steel 23MnNiMoCr54; A2) baiting, wherein baiting demands are as follows: being capable of standing, being free from burr and chamfer, and keeping a length error of a bar stock being plus / minus 0.5mm; A3) hotly chaining: bending the bar stock into a chain in a given size under the action of hydraulic power of a chaining machine; A4) ball blast: removing an oxide skin from the surface, preparing for the next process and ensuring the welding quality; A5) welding and removing the burs; A6) heat treatment; A7) stretching and calibrating: once stretching under a stretching load being 80% of a fracture load; and A8) checking, pairing, painting and placing the chain into a storage. By using the method, the efficiency of producing the round-link chain is increased and the cost is lowered. The fracture load, a coefficient of elongation under a test load, a fracture elongation coefficient and a fatigue life of the round-link chain all meet the national standard.
Owner:SHANDONG LIANGDA FASING ROUND LINK CHAINS
Composite material coated with SiC-Fe based alloy layer and preparation method of composite material
InactiveCN102218857ALow costGood value for moneyMolten spray coatingMetal layered productsHardnessPrice ratio
The invention discloses a composite material coated with a SiC-Fe based alloy layer and a preparation method of the composite material. The composite material coated with the SiC-Fe based alloy layer is formed by coating the SiC-Fe based alloy layer on the surface of a steel base material, wherein the steel base material is carbon steel or alloy steel of which the carbon content is 0.2 to 0.7 weight percent, and the raw material of a SiC-Fe composite material layer is SiC powder and iron-based autolytic alloy powder. The preparation method of the composite material comprises the following steps of: mixing the iron-based autolytic alloy powder with the SiC powder; and spraying the mixture on the surface of the steel base material. The composite material coated with the SiC-Fe based alloy layer has excellent performances of high hardness, good wearing resistance, low brittleness, capability of being subjected to heat treatment and machining, low cost, high performance price ratio and the like, and can obviously improve the surface property of the steel base material.
Owner:HEFEI JINSIDA TECH
Superfine extra-high-strength steel wire, steel wire rod, and production method of steel wire rod
ActiveCN110230008AGuaranteed StrengthGuaranteed toughnessFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlVacuum induction meltingChemical composition
The invention discloses a superfine extra-high-strength steel wire, a steel wire rod for the superfine extra-high-strength steel wire, and a production method of the steel wire rod. The superfine extra-high-strength steel wire is prepared from the chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.90 to 0.96 percent of C, 0.12 to 0.30 percent of Si, 0.30 to 0.65 percent of Mn, 0.10 to 0.30 percent of Cr, less than or equal to 0.004 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.001 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of Cu, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of Ni, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.0006 percent of O, less than or equal to 0.0006 percent of N, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurity elements, whereinthe size of an occluded foreign substance is less than or equal to 4mum, and the average density of the brittle occluded foreign substance is less than or equal to 2pieces / mm<2>. The steel wire rod for the superfine extra-high-strength steel wire can be used as base metal for producing the superfine extra-high-strength steel wire with the diameter being 50 to 60mum and the tensile strength beinglarger than or equal to 4500MPa, and the mileage without wire breakage is larger than or equal to 300km in the process of drawing to prepare the superfine extra-high-strength steel wire. The production method comprises the steps of vacuum induction melting, remelting, forging and steel rolling.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE +1
Ceramic particle reinforced aluminum-based gradient composite material and preparation method thereof and jetting precipitation device for preparing material
The invention belongs to the field of aluminum-based composite material and preparation technology thereof and in particular discloses a ceramic particle reinforced aluminum-based gradient composite material, a preparation method thereof and a device used by the method. The composite material uses aluminum alloy as a matrix; the volume fractions of ceramic particles serving as a reinforcement material in the surface layer and the bottom layer are between 30 and 40 percent and between 0 and 5 percent respectively; the ceramic particles perform continuous gradient variation from the surface layer to the bottom layer; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: introducing the ceramic reinforced particles to a high-pressure airflow channel by a discharge amount regulation device to form a solid phase flow and a gas phase flow; atomizing molten aluminum alloy liquid, mixing the molten aluminum alloy liquid and the ceramic particles of the solid phase flow and the gas phase flow, and precipitating the mixture on a deposition matrix to prepare a deposition billet; and controlling the discharge amount regulation device and output air pressure through a programmable logic controller according to the height information of the deposition billet to obtain the ceramic particle reinforced aluminum-based gradient composite material. The preparation method of the invention has convenient operation and high automation degree; and the prepared composite material has the advantages of light weight, high wear resistance and anticorrosion of the surface and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Fire retardant coating for steel structure surface of nuclear power plant
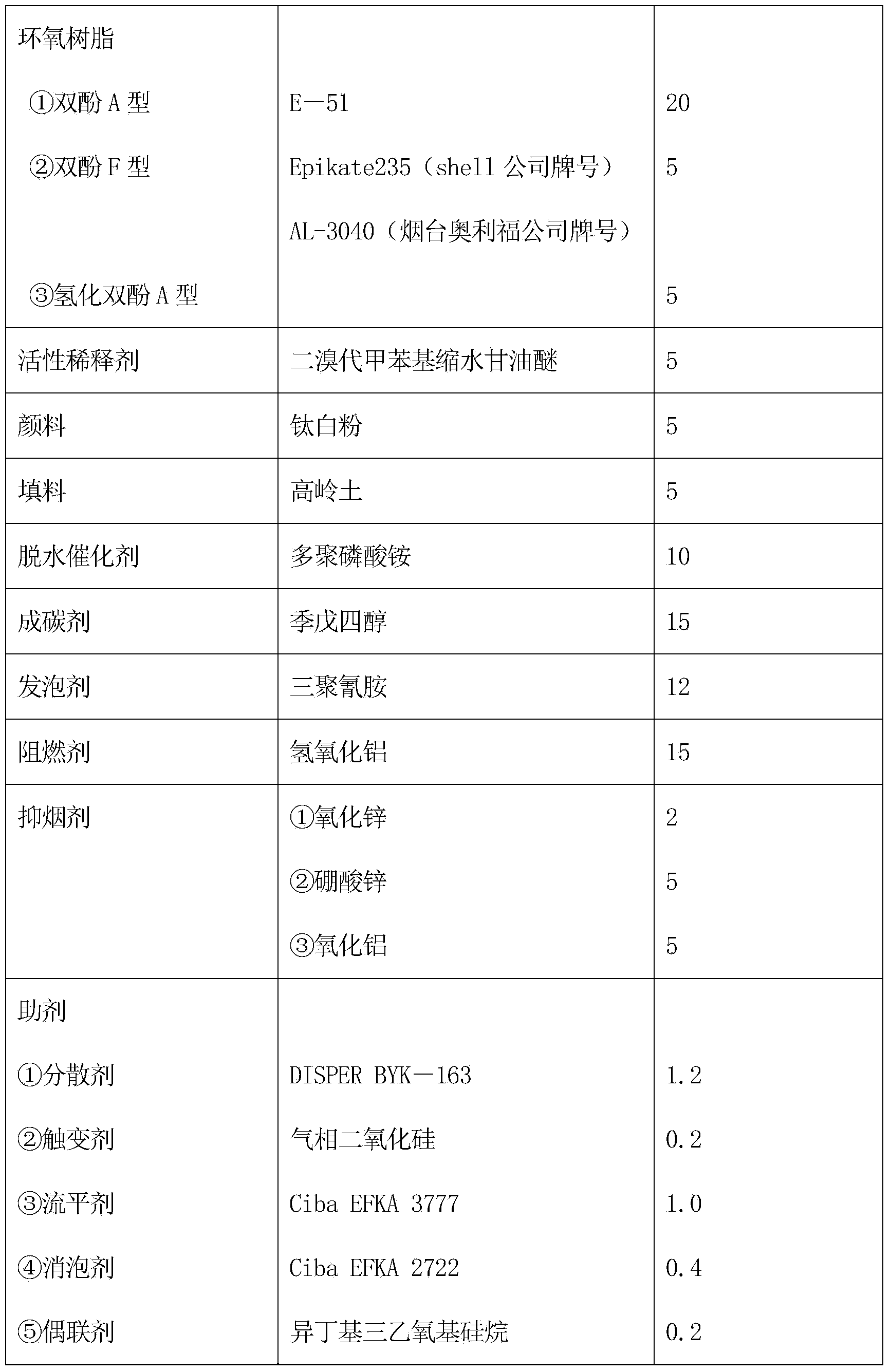
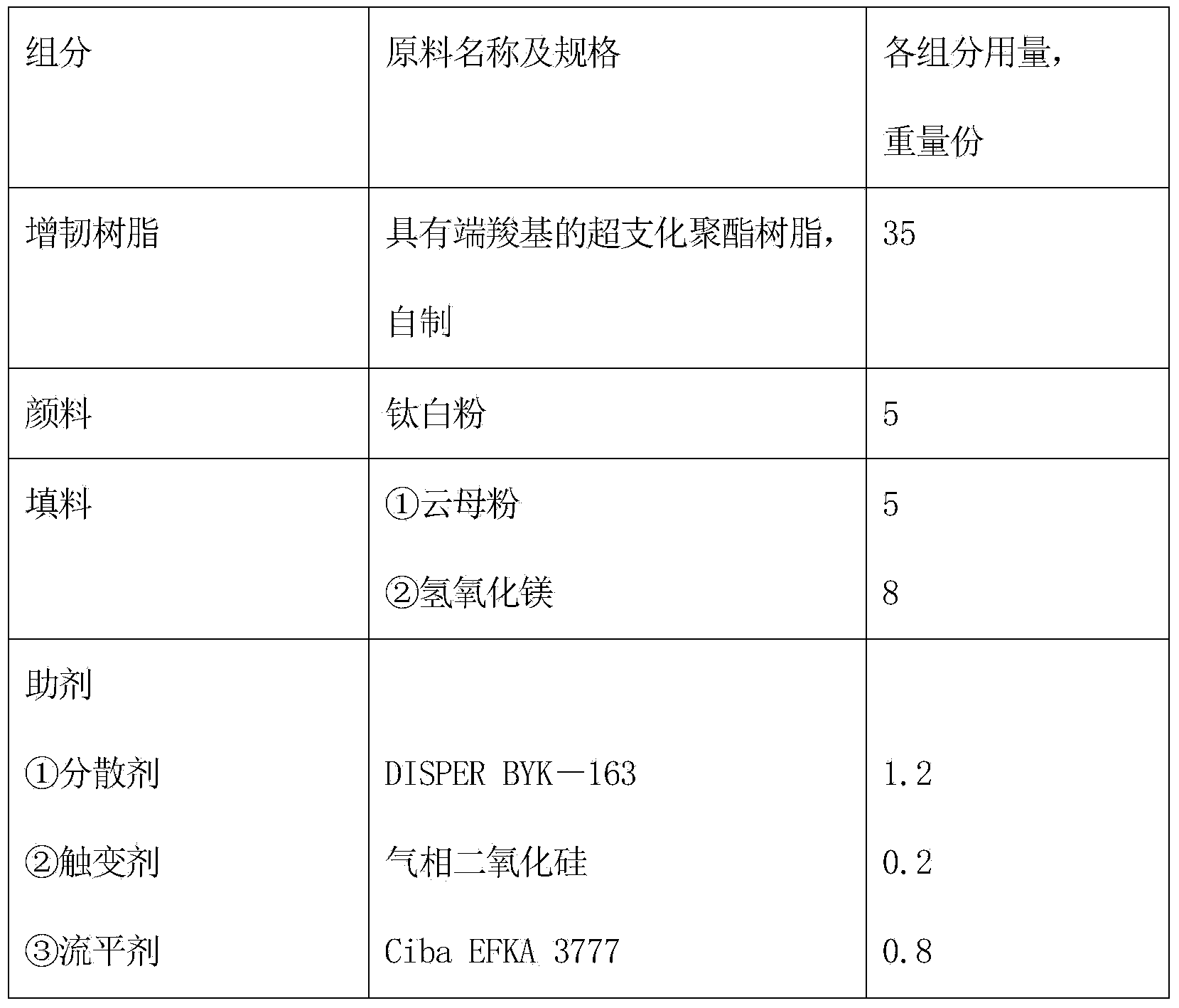
InactiveCN103709899AChemically resistantFlame retardantFireproof paintsEpoxy resin coatingsFoaming agentHyperbranched polyester
The invention relates to a fire retardant coating for a steel structure surface of a nuclear power plant. The fire retardant coating consists of components A, B and C at a weight ratio of (4-6): 1: 1, wherein the component A is a mixture composed of 15-35 parts of epoxy resin, 2-10 parts of reactive diluent, 5-15 parts of dehydration catalyst, 10-30 parts of carbonizing agent, 5-20 parts of foaming agent, 15-35 parts of fire retardant, 5-15 parts of smoke inhibitor, 10-30 parts of pigment and filler and 2-10 parts of auxiliaries; the component B is a mixture composed of 10-50 parts of toughened resin, 10-30 parts of pigment and filler and 2-10 parts of auxiliaries; the C component is an amine curing agent; and the toughened resin in the component B is hyper-branched polyester resin with a terminal carboxyl group. The fire retardant coating disclosed by the invention is more excellent than a normal intumescence fire retardant coating in binding strength, freezing and thawing cycle resistance, acid and base resistance, and fire retardant limit, and is specifically up to fire resistance requirements of the steel structure surface of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +3
Preparation method of composite hard alloy used as cutter material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite hard alloy used as a cutter material. The composite hard alloy material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 35-40 parts of nano titanium carbide, 5-15 parts of nano titanium nitride, 7-9 parts of tungsten carbide, 5-8 parts of niobium carbide, 3-7 parts of silicon carbide, 3-5 parts of cobalt powder, 1-3 parts of yttrium oxide, 1-3 parts of boron carbide and 1-5 parts of copper powder. The method comprises the following steps: preparing materials, preparing carbon-depleted alloy powder, preparing a presintering matrix, carrying out carbonization and carrying out firing step by step. The composite hard alloy prepared by the preparation method has high strength, good toughness and good wear resistance and thermal shock resistance.
Owner:CHENGDU BANGPU CUTTING TOOLS CO LTD
Manufacturing method of vermicular cast iron piston ring
InactiveCN103451510AMeet performance needsHigh tensile strengthPiston ringsFoundry mouldsWear resistanceToughness
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a vermicular cast iron piston ring. The material of the vermicular cast iron piston ring comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 3.4-4.0% of C, 2.4-3.2% of Si, not more than 0.3% of Mn, 0.2-0.4% of Cr, 0.2-0.6% of Mo, 0.5-1.0% of Cu, 0.05-0.15% of Ti, not more than 0.1% of P, not more than 0.05% of S, 0.009-0.02% of Mg and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The manufacturing method of the vermicular cast iron piston ring comprises the following technical steps of moulding, smelting, casting, shaking out, shot blasting, mechanical processing, surface treatment and the like. By adopting the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, the thinning of the piston ring is achieved, the production process is relatively simple, and the manufactured vermicular cast iron piston ring is high in elasticity, strength, toughness and wear resistance.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG JINGANG KAIYUAN POWER SCI & TECH
Steel plate with low welding crack sensitivity and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105441790AReduce manufacturing costGood welding performanceTemperingUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a steel plate with low welding crack sensitivity and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel plate is composed of, by weight, 0.03%-0.09% of C, 0.20%-0.60% of Si, 1.40%-1.80% of Mn, 0-0.020% of P, 0-0.005% of S, 0.15%-0.45% of Cr, 0.03%-0.06% of Nb, 0.006%-0.04% of Ti, 0.015%-0.04% of Als, 0.0008%-0.003% of B, 0-0.04% of As, 0-0.03% of Sn, 0-0.005% of N, 0-0.003% of O, 0-0.0002% of H, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. By the adoption of the technologies of controlled rolling, relaxation and quick cooling, the heat treatment procedure of quenching and tempering or the heat treatment procedure of tempering or the like is not needed, the ultrafine bainite plate is obtained, and working procedure cost is reduced while strength, toughness and welding performance are guaranteed.
Owner:SGIS SONGSHAN CO LTD
Super-high-strength martensite aging stainless steel resistant to seawater corrosion
ActiveCN107653421AGuaranteed toughnessGuaranteed corrosion resistanceChemical compositionHigh intensity
The invention belongs to the field of high-strength stainless steel and provides martensite aging stainless steel which is high in toughness and good in corrosion resistance. The strength of the martensite aging stainless steel reaches 2000 MPa or above. The specific chemical constituents of the martensite aging stainless steel comprise, by weight percentage, less than or equal to 0.03% of C, 13.0-14.0% of Cr, 5.5-7.0% of Ni, 5.5-7.5% of Co, 3.0-5.0% of Mo, 1.9-2.5% of Ti, less than or equal to 0.1% of Si, less than or equal to 0.1% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.01% of P, less than or equal to 0.01% of S and the balance Fe. The stainless steel has the excellent seawater corrosion resistance; the pitting potential Epit is greater than or equal to 0.15 V, and high tough fit is achieved; sigma b is greater than or equal to 2000 MPa, sigma 0.2 is greater than or equal to 1700 MPa, delta is greater than or equal to 8%, and psi is greater than or equal to 40%; the martensite aging stainlesssteel is applicable to manufacturing of high-strength and high-toughness structural components used in a chloridion-containing rigorous corrosion environment such as seawater; the content of preciousmetal Co in the steel is low; material production cost is effectively lowered; and wide application prospect is achieved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Regeneration technique for jean cotton cloth
ActiveCN102071509AReduce usageIncrease profitDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesTextile disintegration and recoveryPollutionCarding
The invention discloses a regeneration technique for jean cotton cloth, which is used for recovering leftover bits and pieces of jean. The regeneration technique for the jean cotton cloth comprises the following steps of: removing impurities from the leftover bits and pieces of jean and cutting the leftover bits and pieces of jean into pieces; desizing the pieces, namely placing the pieces in warm water with the temperature of 60 DEG C, adding alkali oil and desizing powder into the water for soaking the pieces for 10 minutes, and discharging the water soaking the pieces; repeating the step for one time; dewatering, namely discharging water from the pieces; drying the pieces, namely drying the pieces in an environment with the temperature of 100 DEG C; loosening the pieces; and after extracting the cotton material from the pieces, blowing, carding, drawing, spinning and weaving the cotton material to obtain the regenerated jean. In the process of recovering the regenerated cloth, the utilization of a chemical additive is avoided as much as possible, so that the environment is protected; the physical properties of the cotton material, such as toughness, strength and the like, are kept; the regenerated woven cloth can be used for manufacturing the products of the same grade as the product manufactured from the original cloth material; the utilization rate of the cloth is improved; and the pollution to the environment is reduced at the same time.
Owner:中山益达服装有限公司
Ceramic composite material bullet-proof chest board and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104949581AImprove structural impact resistanceGuaranteed bonding strengthSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsCeramic compositeMetallurgy
The invention discloses a ceramic composite material bullet-proof chest board and a preparation method thereof. The ceramic composite material bullet-proof chest board is composed of a carbon fiber composite surface rigid layer, a ceramic composite material sheet combination layer, a bullet-proof fiber composite material body layer and a back elastic surface carbon fiber composite back-convex-proof layer. The ceramic composite material sheet combination layer is made of special fiber reinforced ceramic matrix materials and is of a needling insertion type combined structure or a three-dimensional crazing-prevention framework structure; a composite cementing and micropore riveting combined technology is adopted between the ceramic composite material layer and the bullet-proof body layer; finally, the ceramic composite material sheet combination layer and the bullet-proof fiber composite material body layer are wrapped in a rigid structure composed of the carbon fiber composite surface rigid layer and the back-convex-proof layer to form a whole. The ceramic composite material bullet-proof chest board has various advantages of being light, low in back convex, stable in high and low temperature structure, long in service life and the like. Meanwhile, the problem that a seam bullet-proof characteristic in a traditional splicing structure of ceramic sheets is poor is effectively avoided, and the ceramic composite material bullet-proof chest board has the overall characteristics of multiple bullet-proof materials.
Owner:山东宽原新材料科技有限公司
Wide and heavy steel plate for high-strength high-toughness and low-yield-ratio hot-bending bend and production method of wide and heavy steel plate
The invention provides a wide and heavy steel plate for a high-strength high-toughness and low-yield-ratio hot-bending bend and a production method of the wide and heavy steel plate. The steel plate comprises, by weight percentage, 0.055%-0.080% of C, 0.16%-0.30% of Si, 1.76%-1.95% of Mn, 0.051%-0.080% of Nb, 0.010%-0.025% of Ti, 0.09%-0.13% of V, 0.25%-0.45% of Cr, 0.20%-0.35% of Mo, less than 0.25% of Ni, less than 0.25% of Cu, 0.010%-0.035% of Al, not larger than 0.010% of P, not larger than 0.002% of S, 0.001%-0.004% of N and the balance iron and inevitable impurities, wherein (Mo+Ni+Cr+Cu) is controlled within the range of 0.6%-1.0%, CEIIW is controlled within the range of 0.50%-0.55%, and CEPcm is controlled within the range of 0.19%-0.23%. The production method includes the steps ofmolten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, external refining, continuous casting, heating, rolling, cooling and heat treatment. The microstructure of the wide and heavy steel plate is a compositestructure of bainite and ferrite, and the performance meets the requirement of manufacturing X90-grade hot-bending bends with ultra-wide and thick walls in a low-temperature environment.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
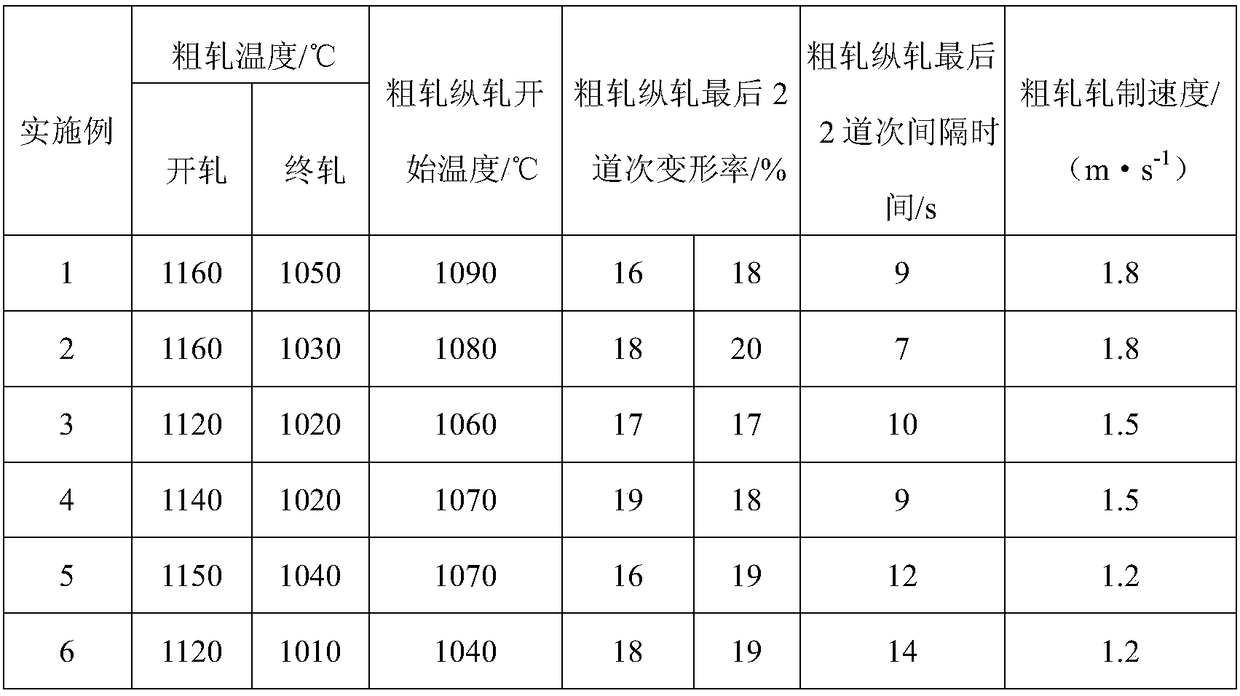
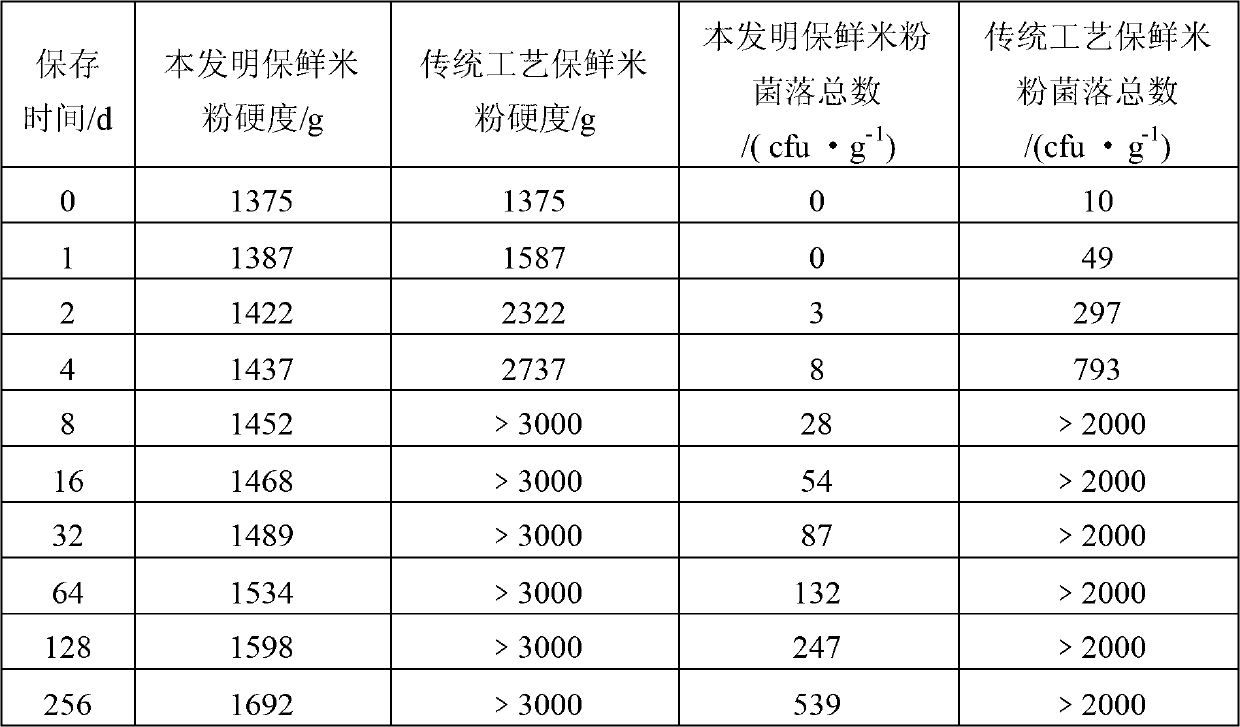
High-quality fresh-keeping convenient rice flour and processing method thereof
InactiveCN102805293AControl agingRapid coolingClimate change adaptationFood preservationChemistryEconomic shortage
The invention relates to high-quality fresh-keeping convenient rice flour and a processing method thereof. The processing method for the high-quality fresh-keeping convenient rice flour comprises the following steps of: cleaning out sand from machine-made rice, burdening, grinding powder, humidifying, extruding, gelatinizing, discharging filaments, cooling, ageing, slitting, cooking, dipping, rinsing, packaging once, sterilizing, cooling, testing and packaging. The processing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple technology, small equipment investment and short processing period. The obtained product is convenient to eat and is durable in storage. On the basis of keeping the original taste of wet rice flour, auxiliary materials are added in the raw material rice so as to delay ageing, improve the taste and shorten rehydration time. According to the processing method disclosed by the invention, the shortages of long period and the like of the traditional production technology are broken through, the food eating convenience is realized, and the rice flour which is the traditional food gradually tends to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:江西华达昌食品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com