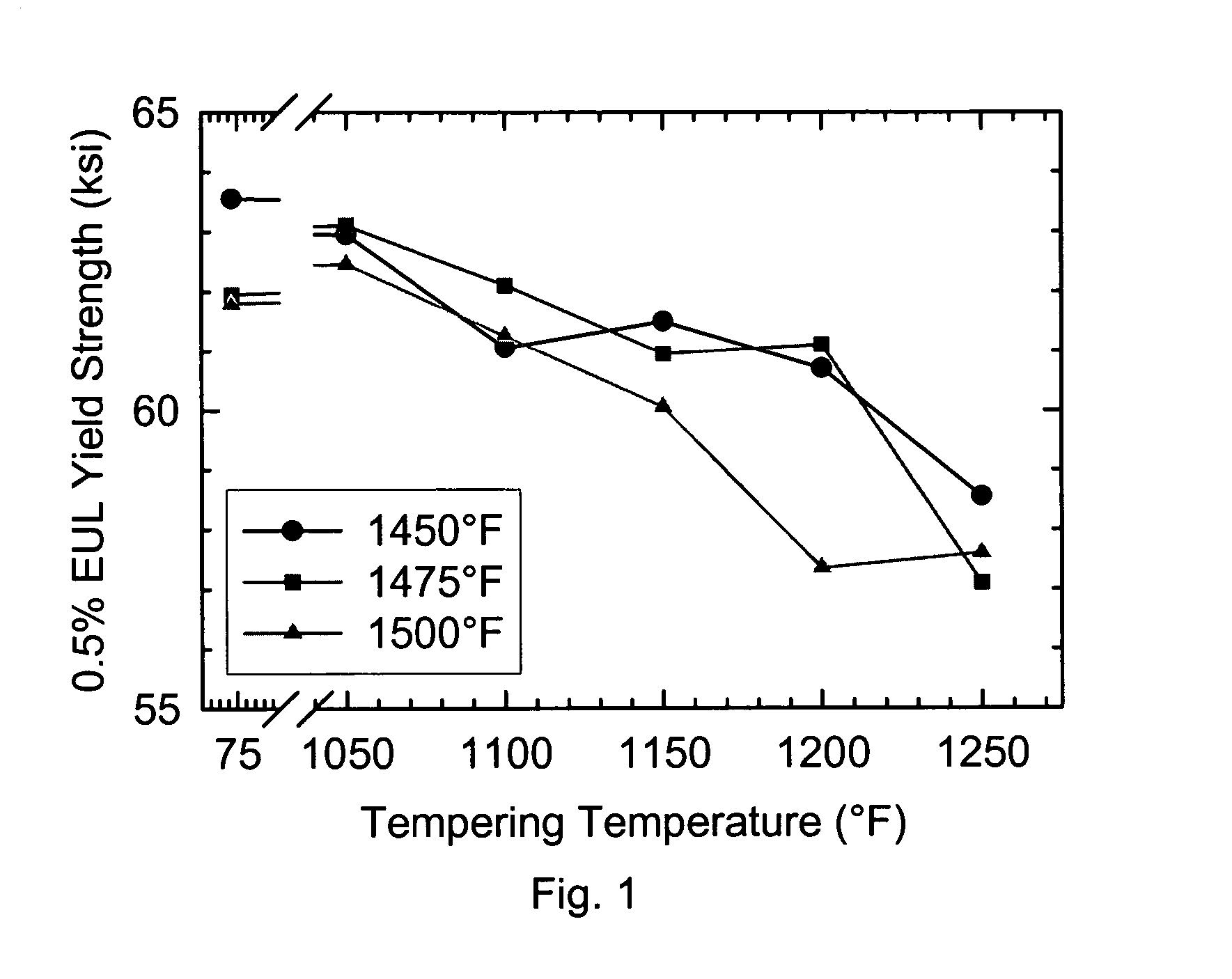
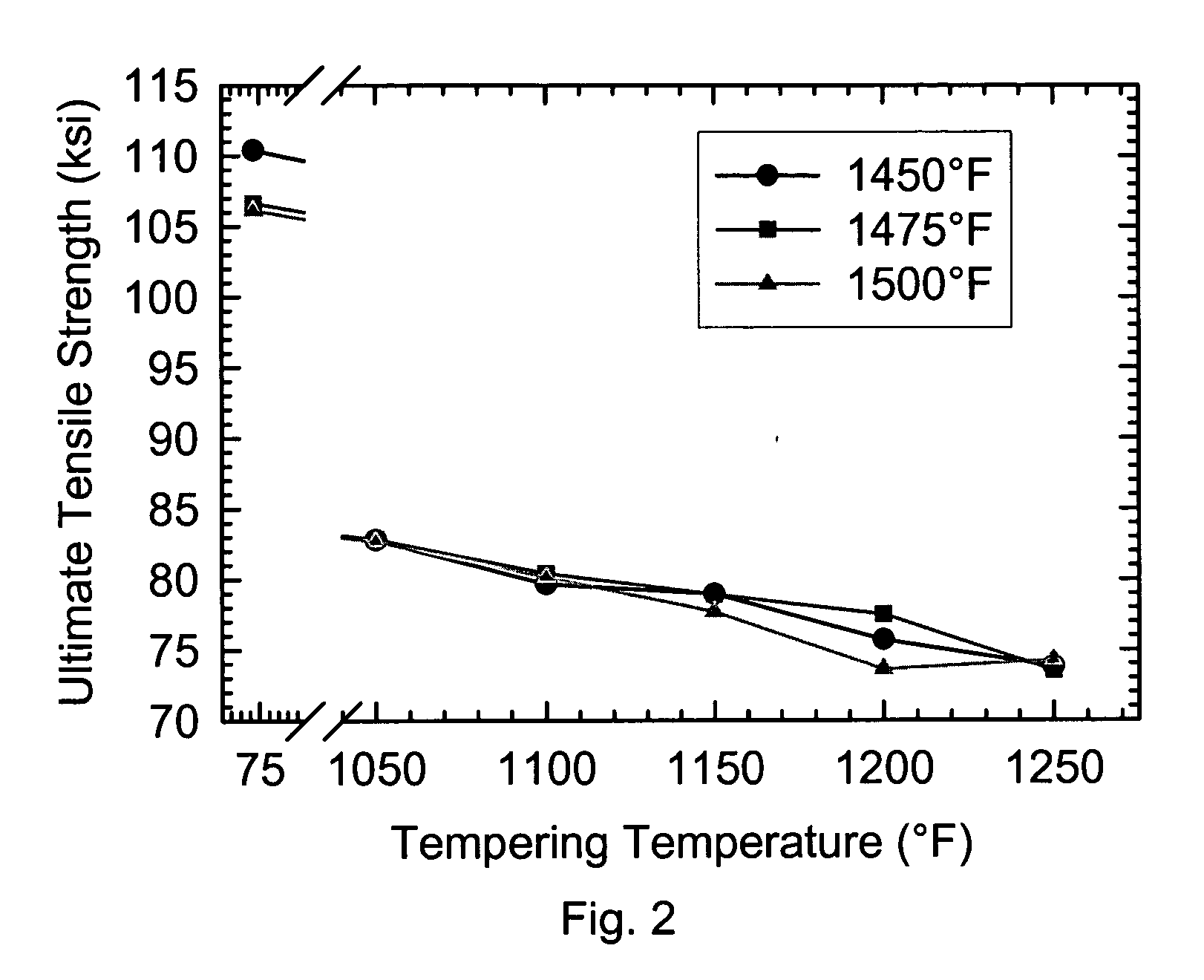
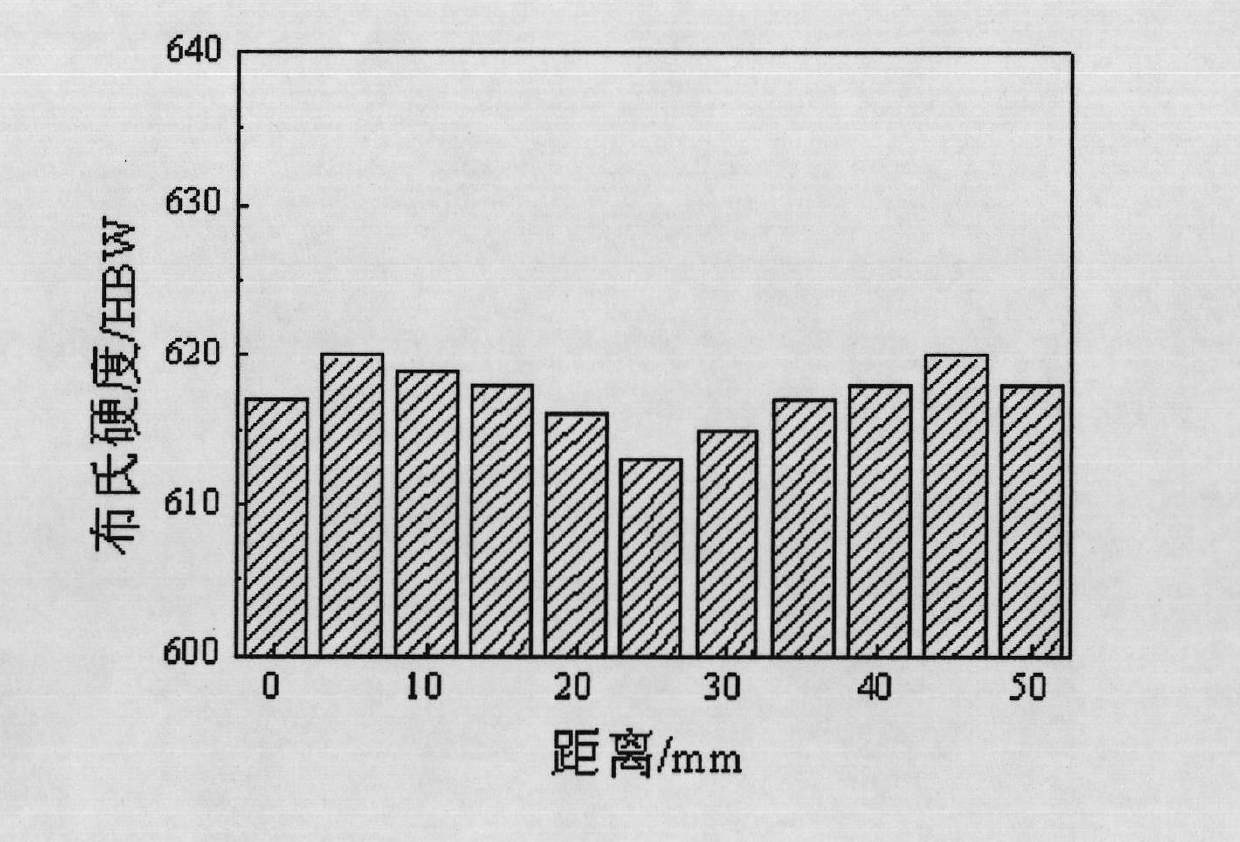
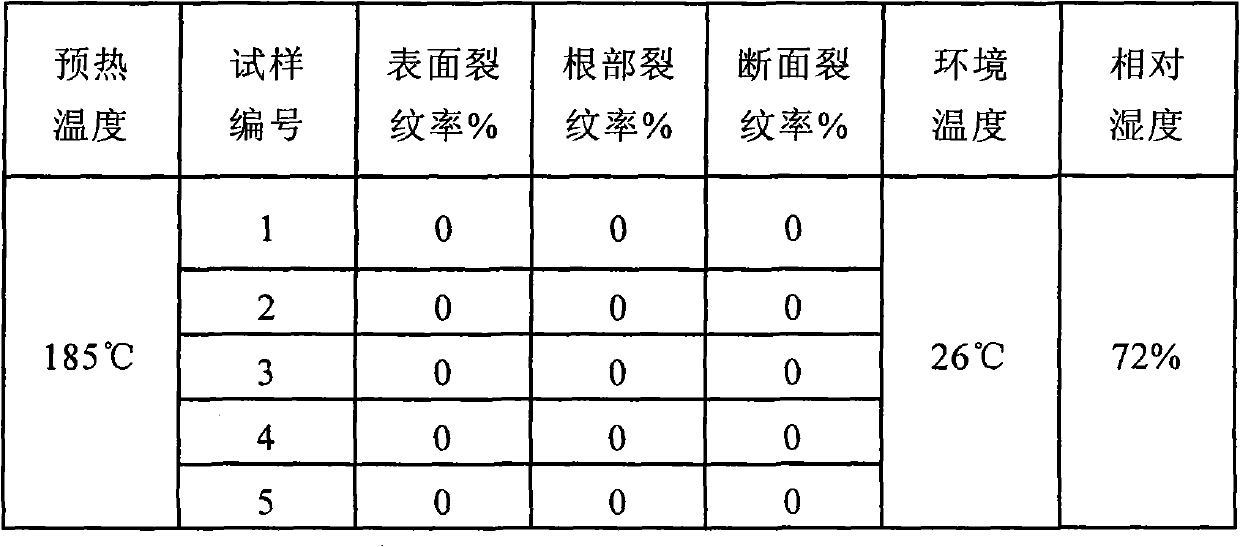
Patents
Literature
2869 results about "Martensite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
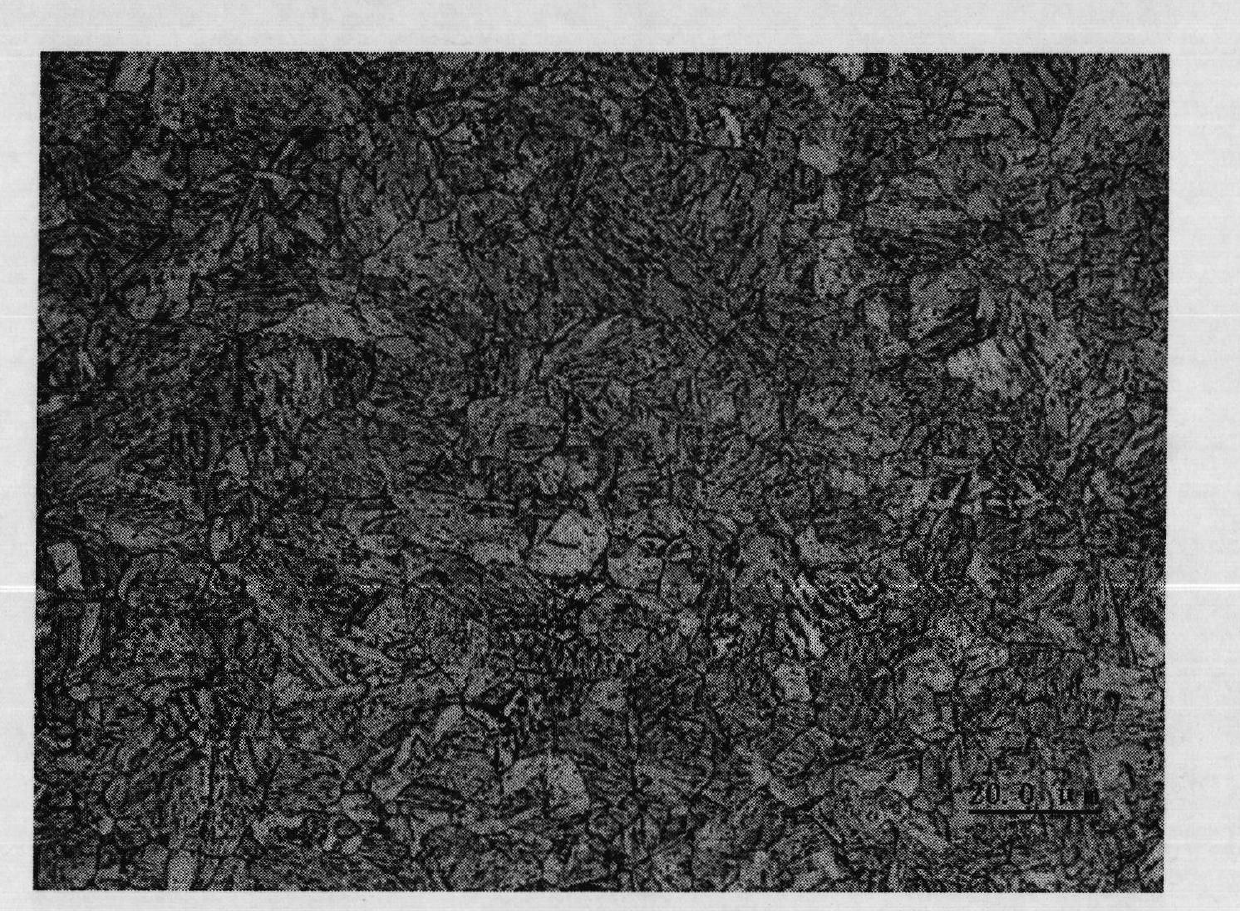
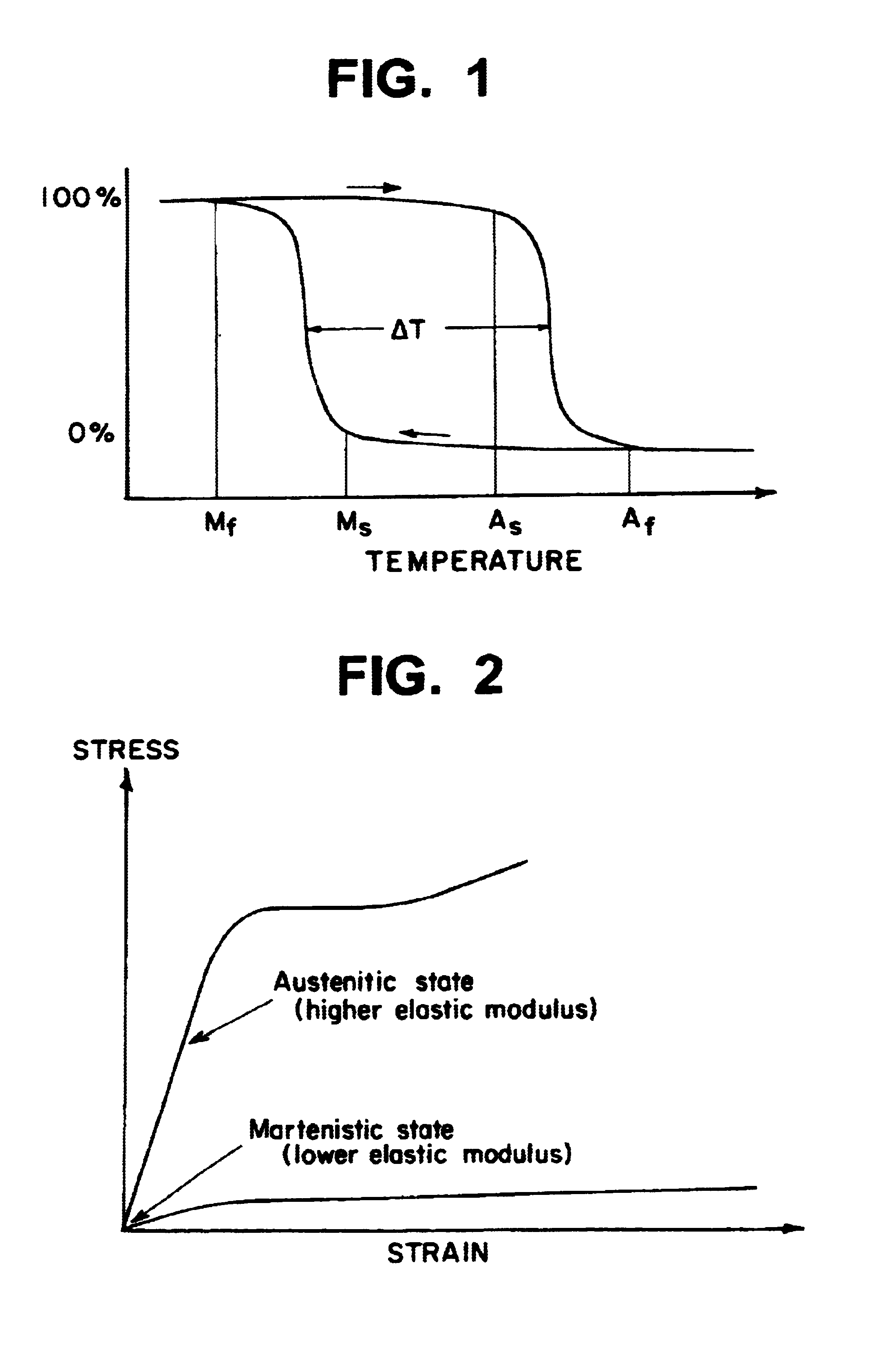
Martensite is a very hard form of steel crystalline structure. It is named after the German metallurgist Adolf Martens (1850–1914). By analogy the term can also refer to any crystal structure that is formed by diffusionless transformation. Martensite includes a class of hard minerals that occur as lath- or plate-shaped crystal grains.
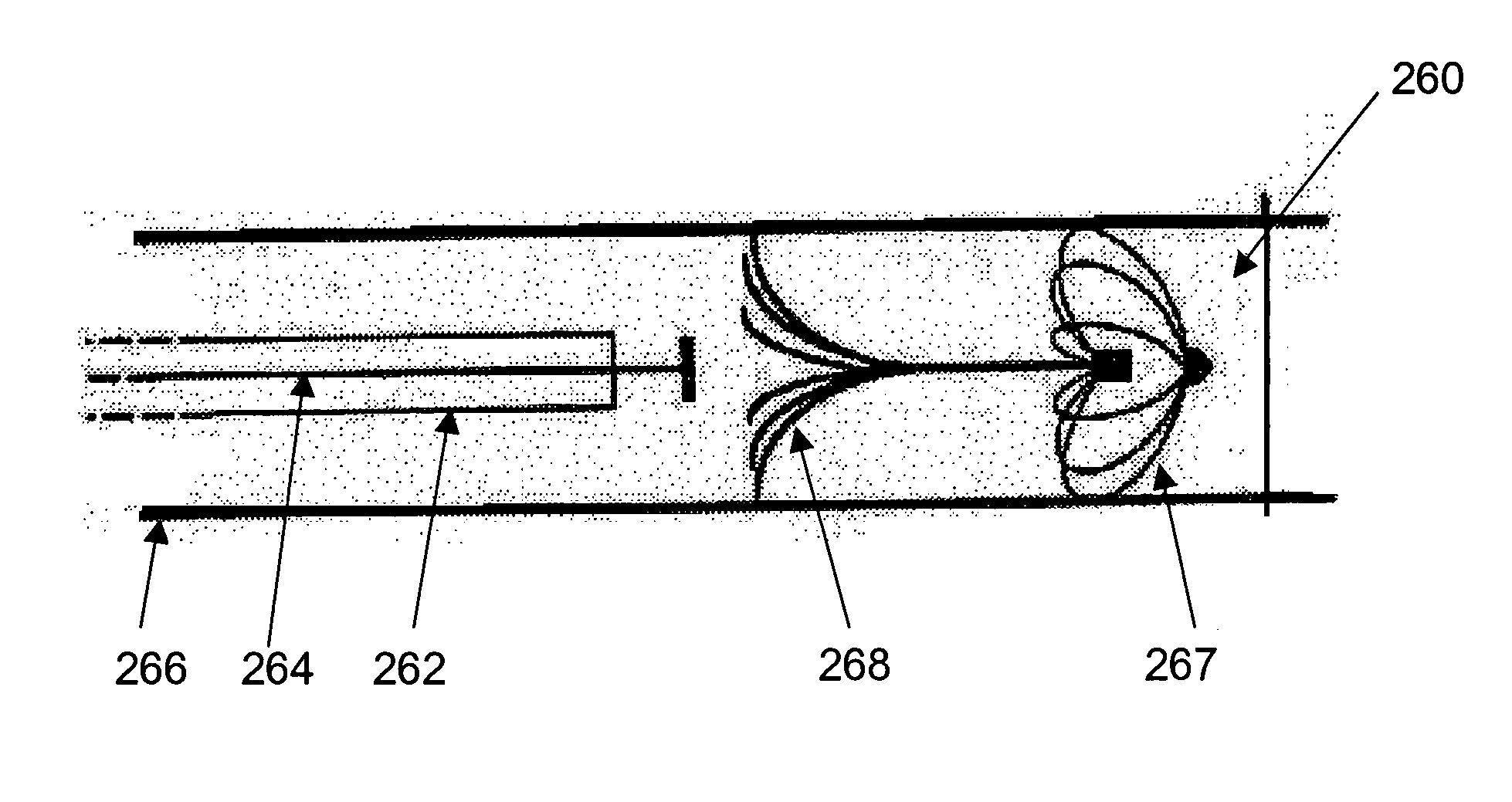
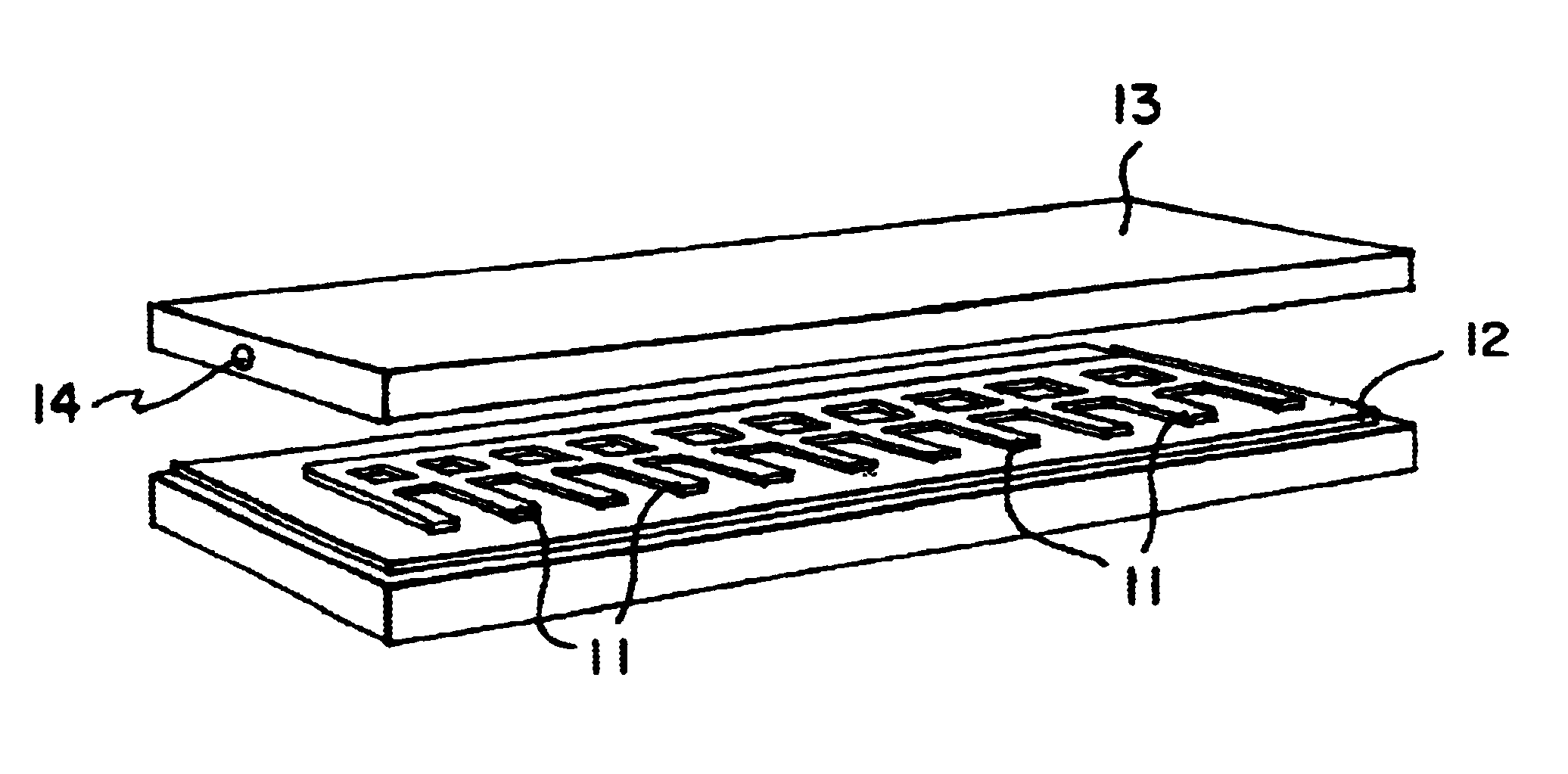
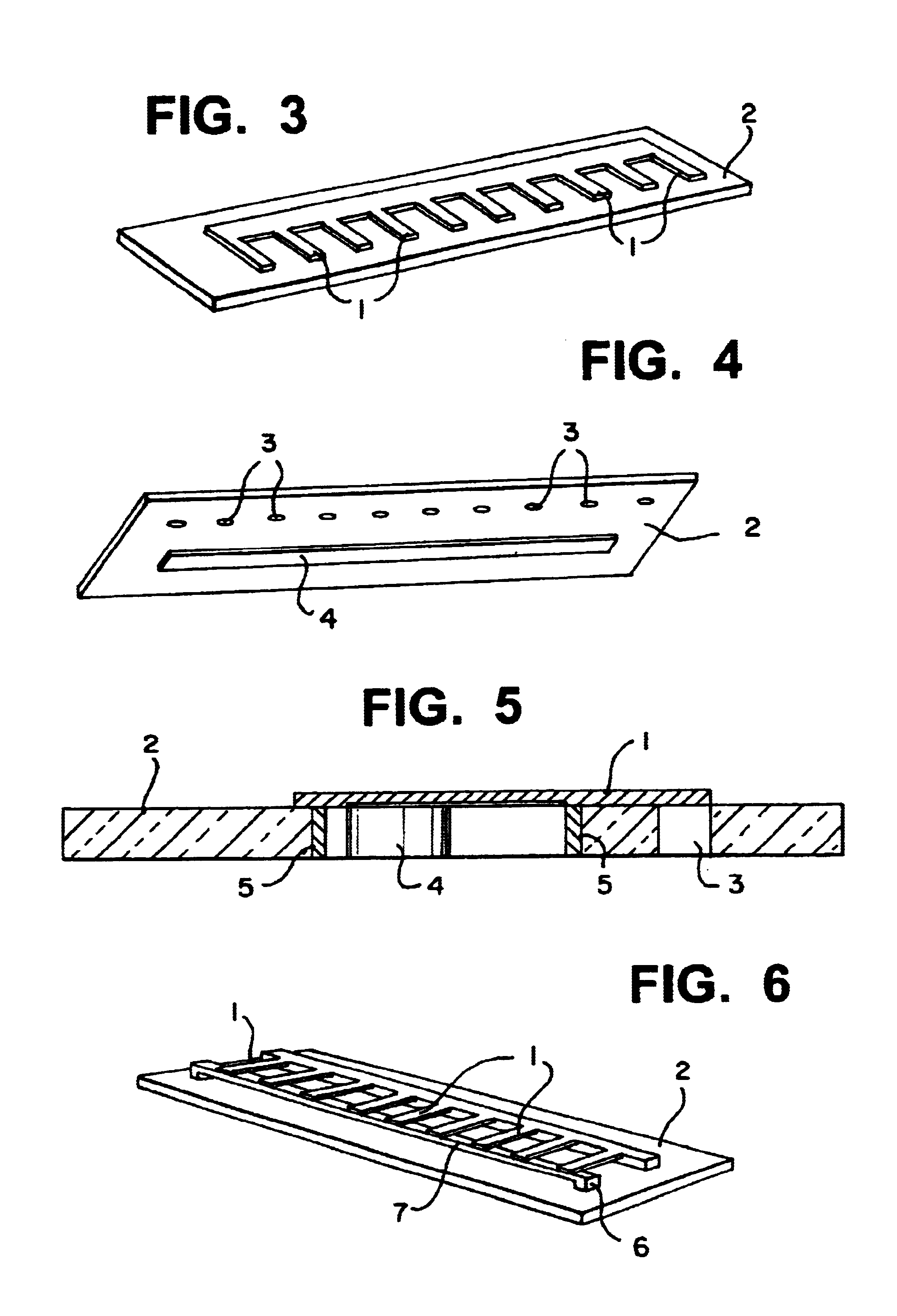
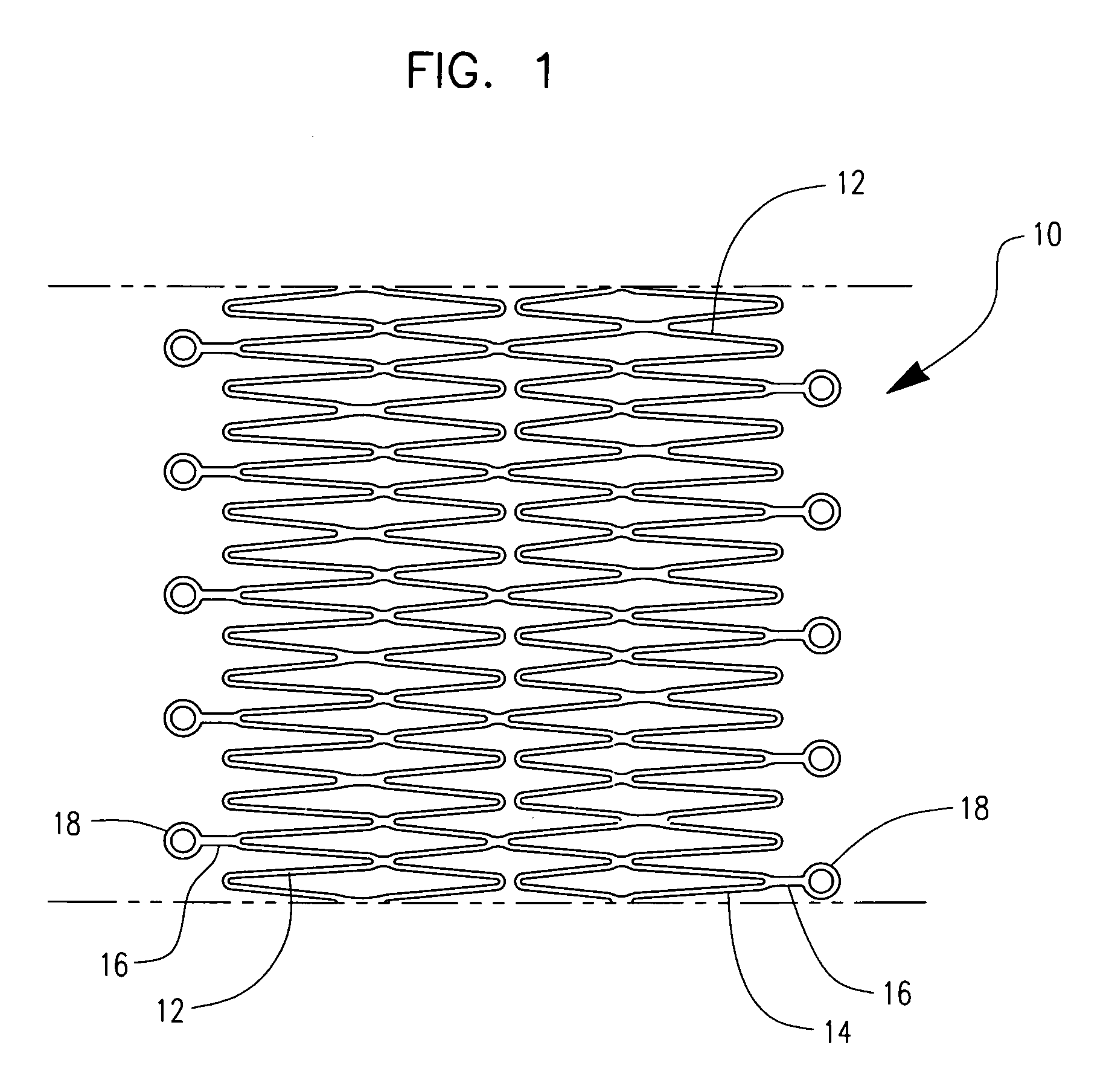
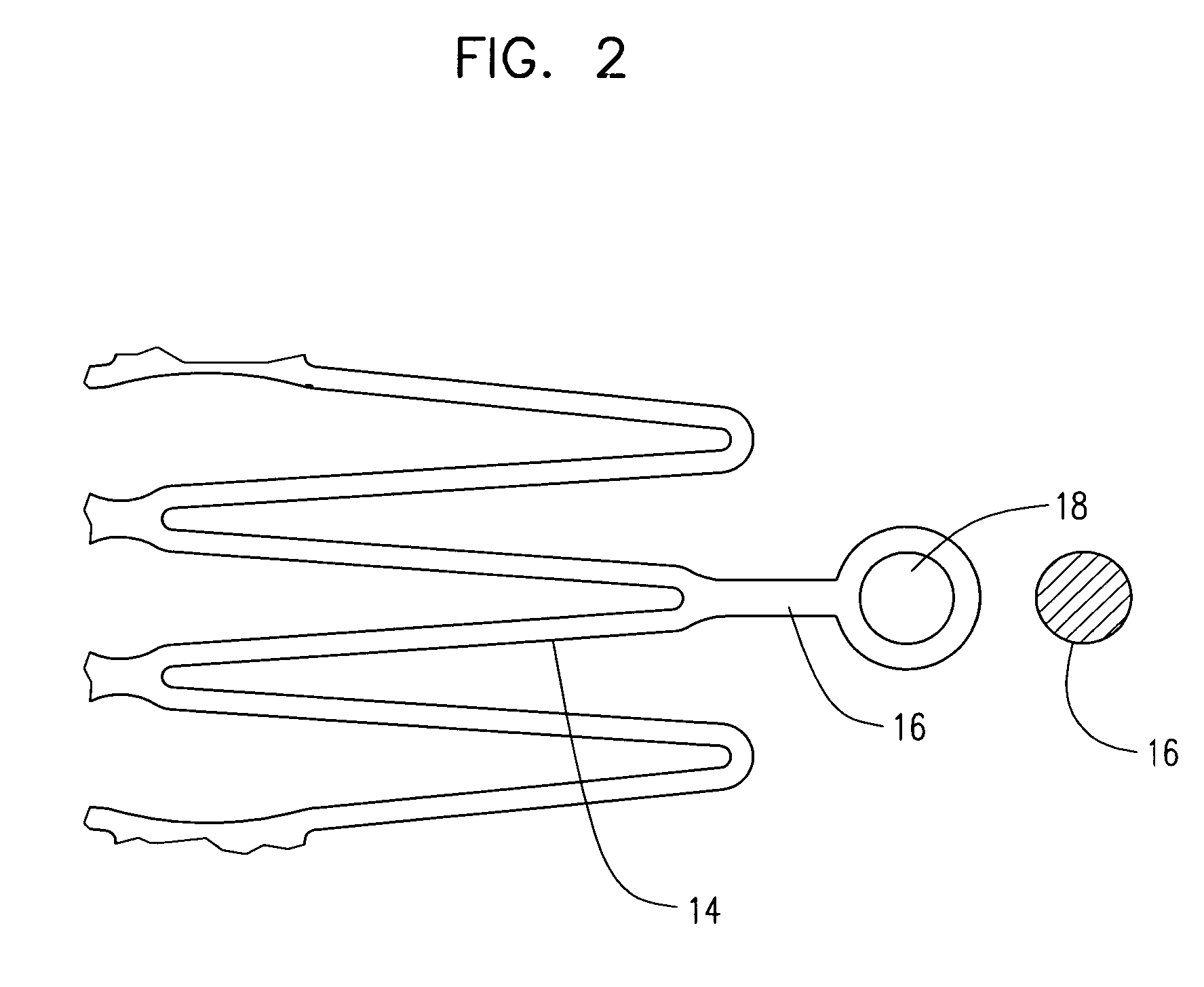
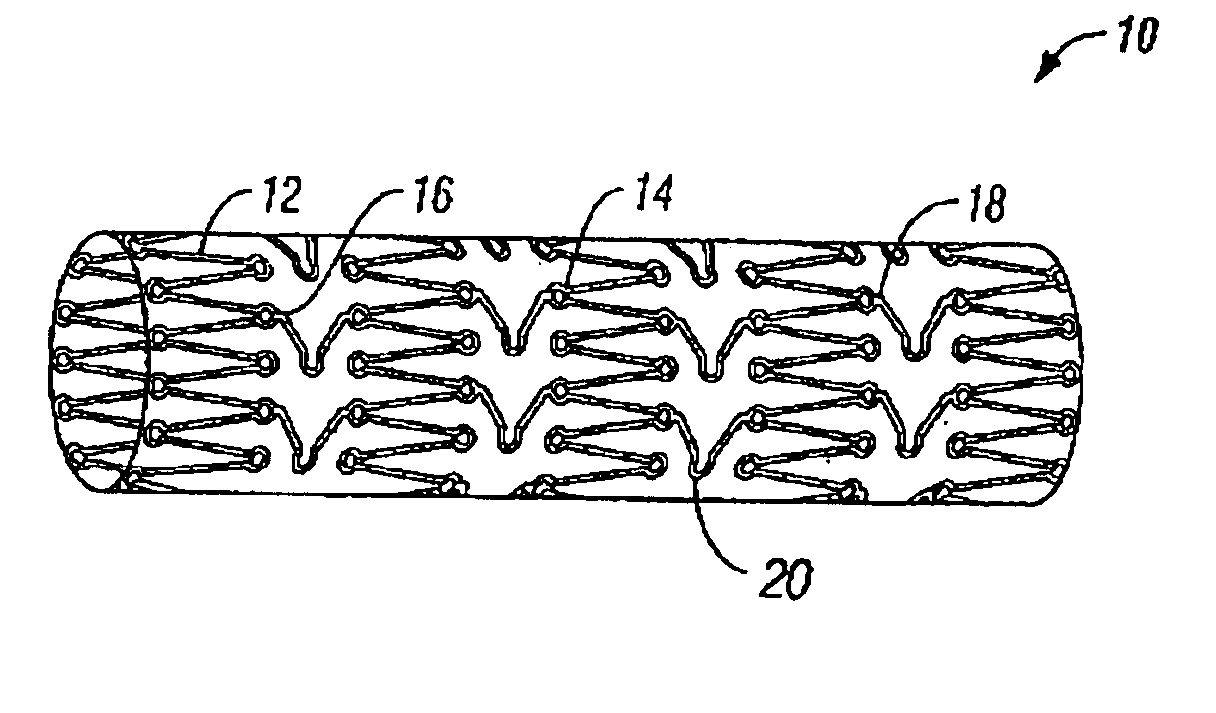
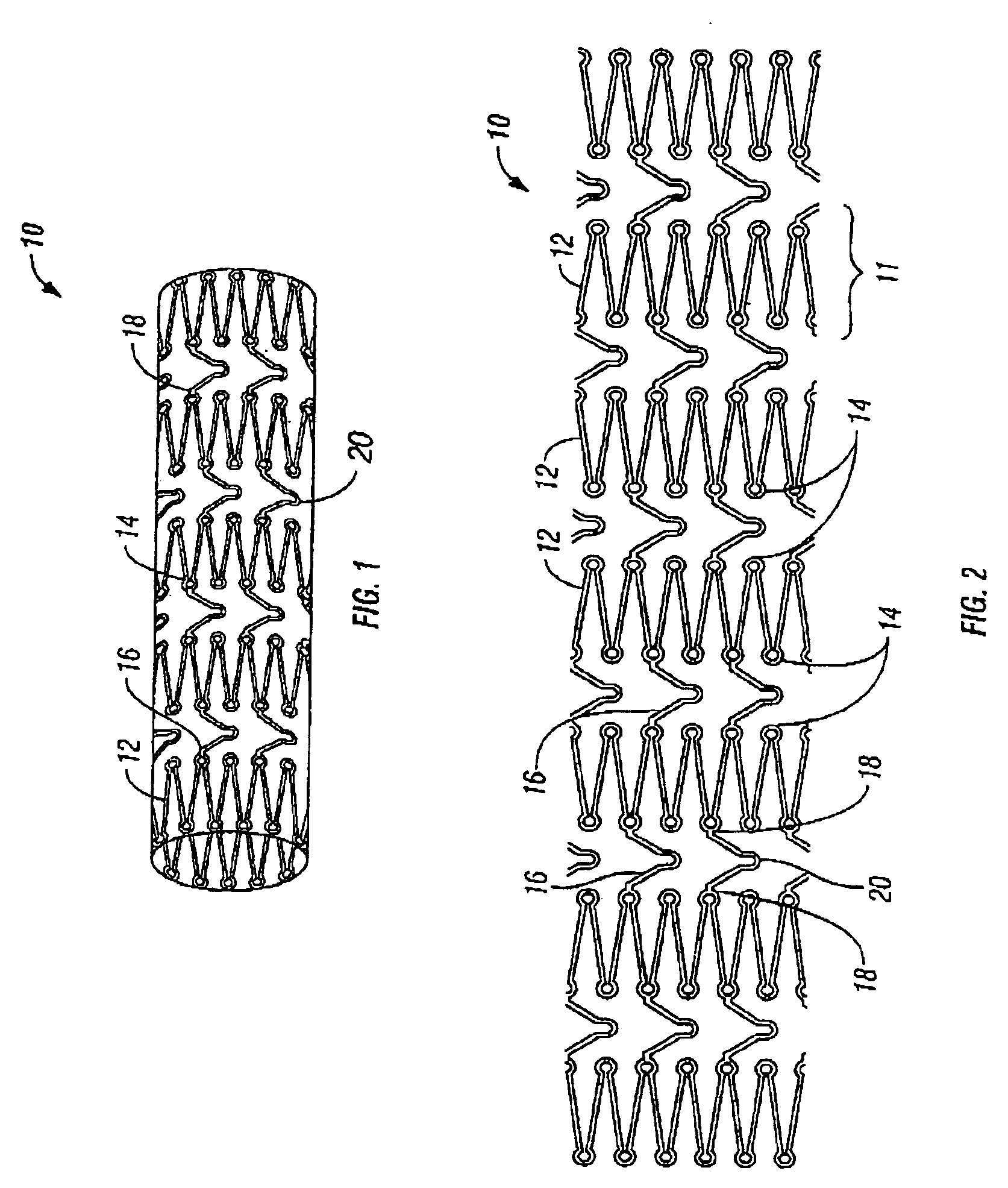
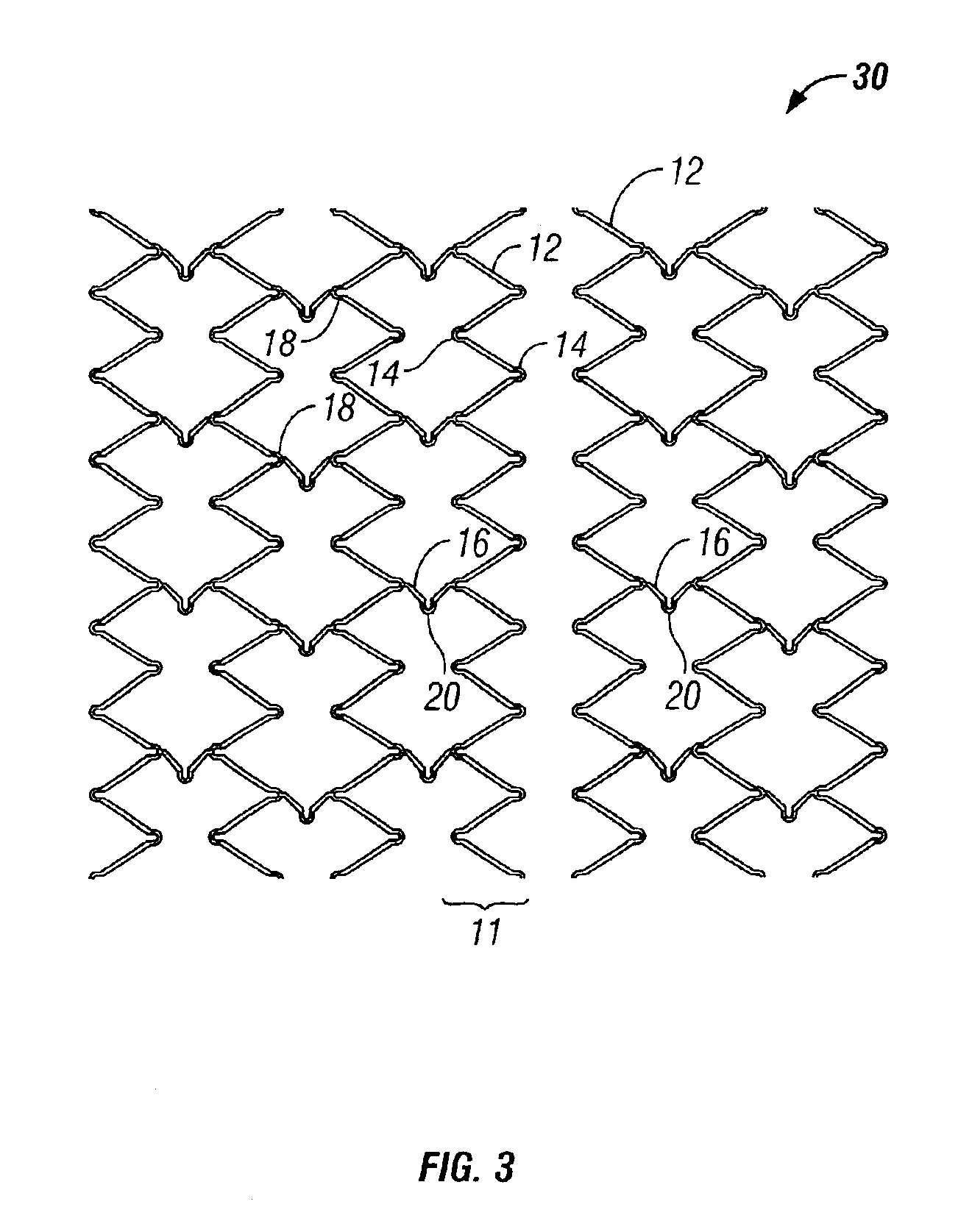
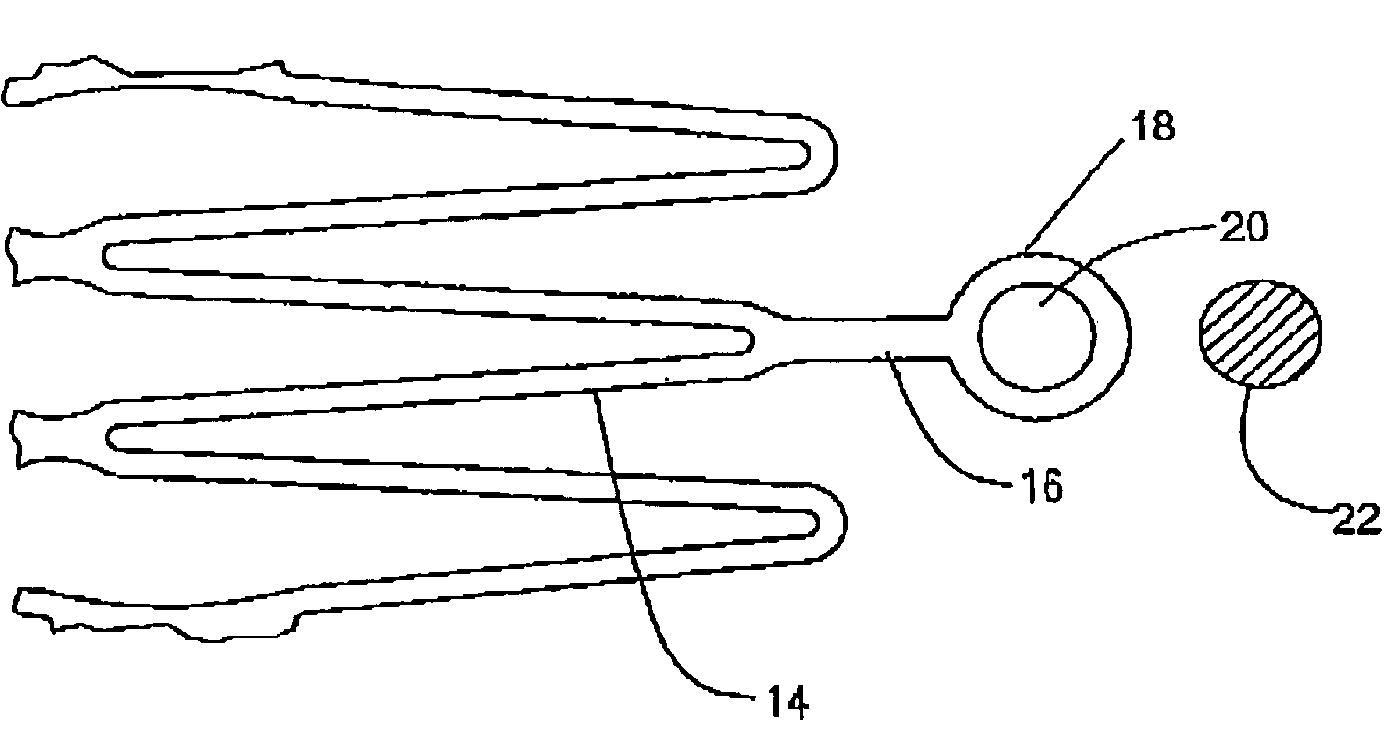
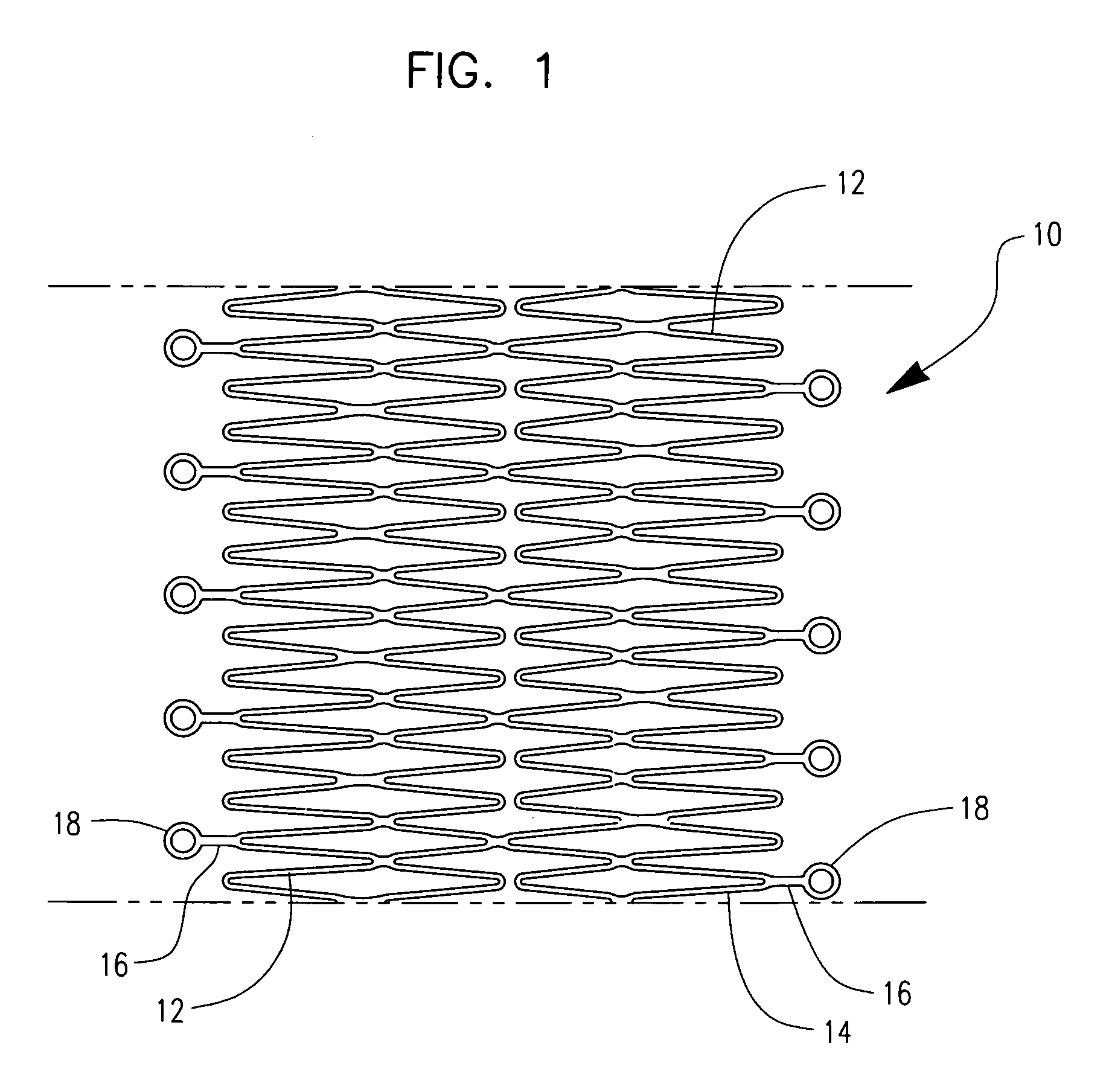
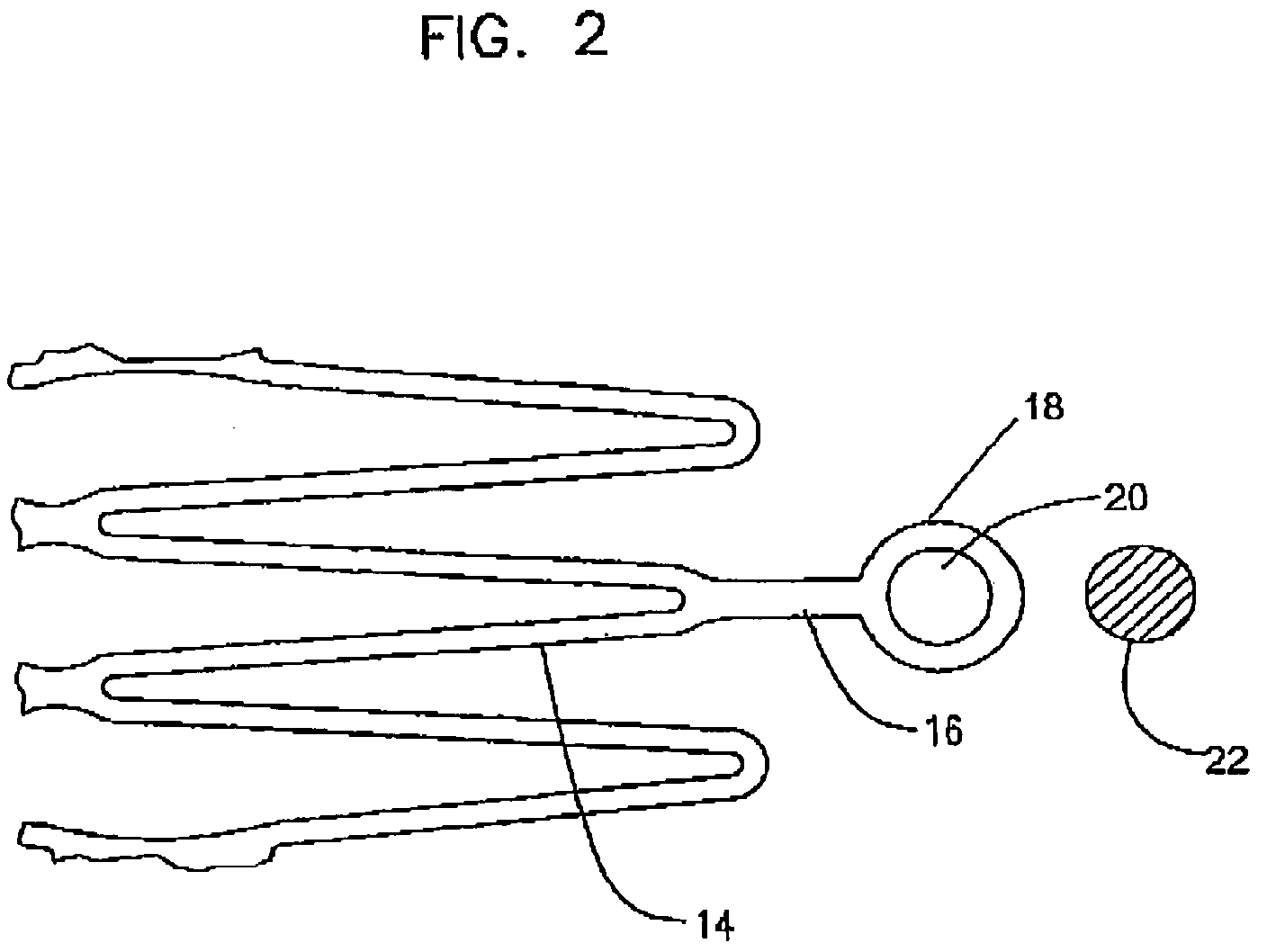
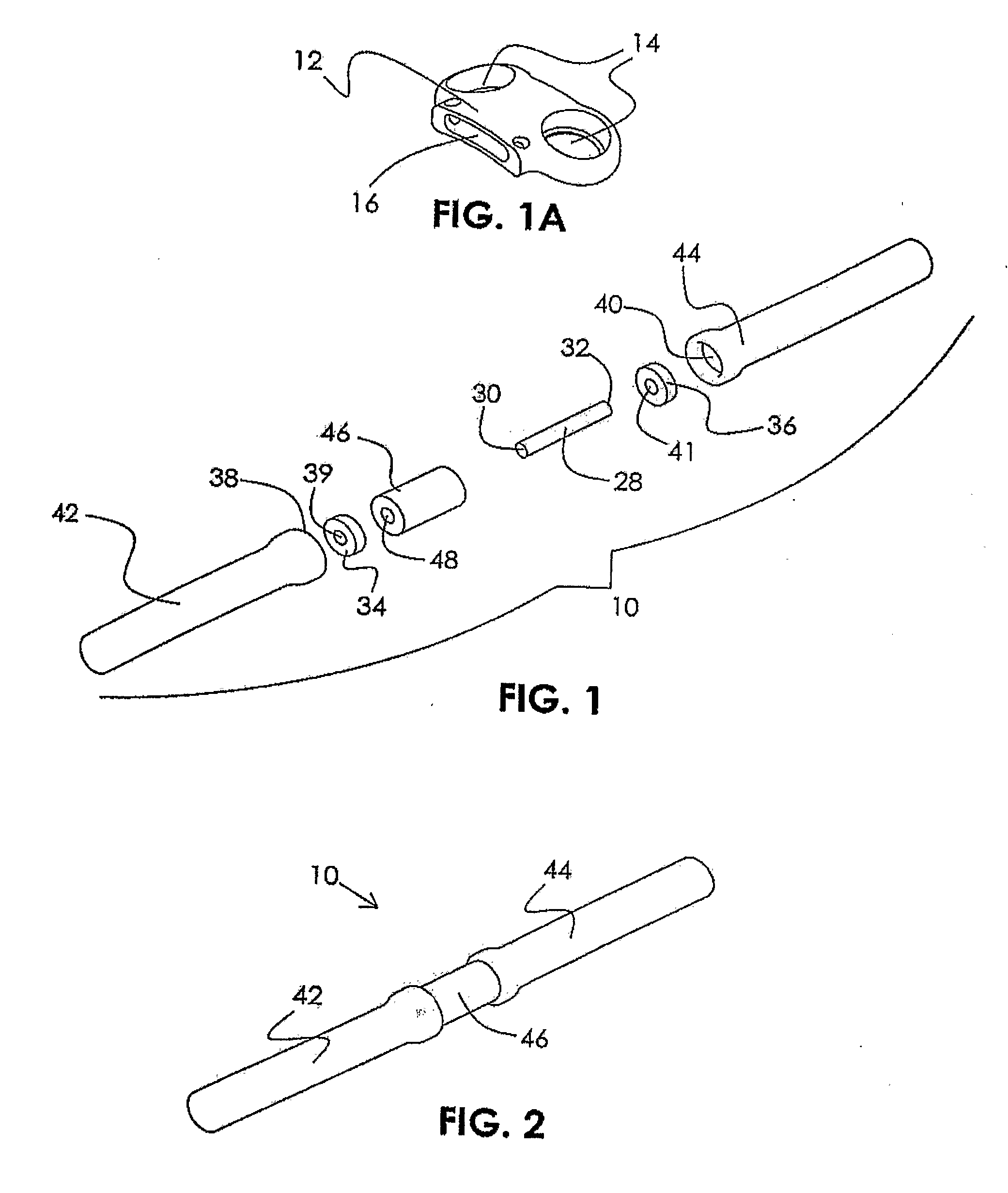
Medical devices formed from shape memory alloys displaying a stress-retained martensitic state and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20050043757A1Good body shapePromote recoverySuture equipmentsDental implantsManufactured formShape-memory alloy
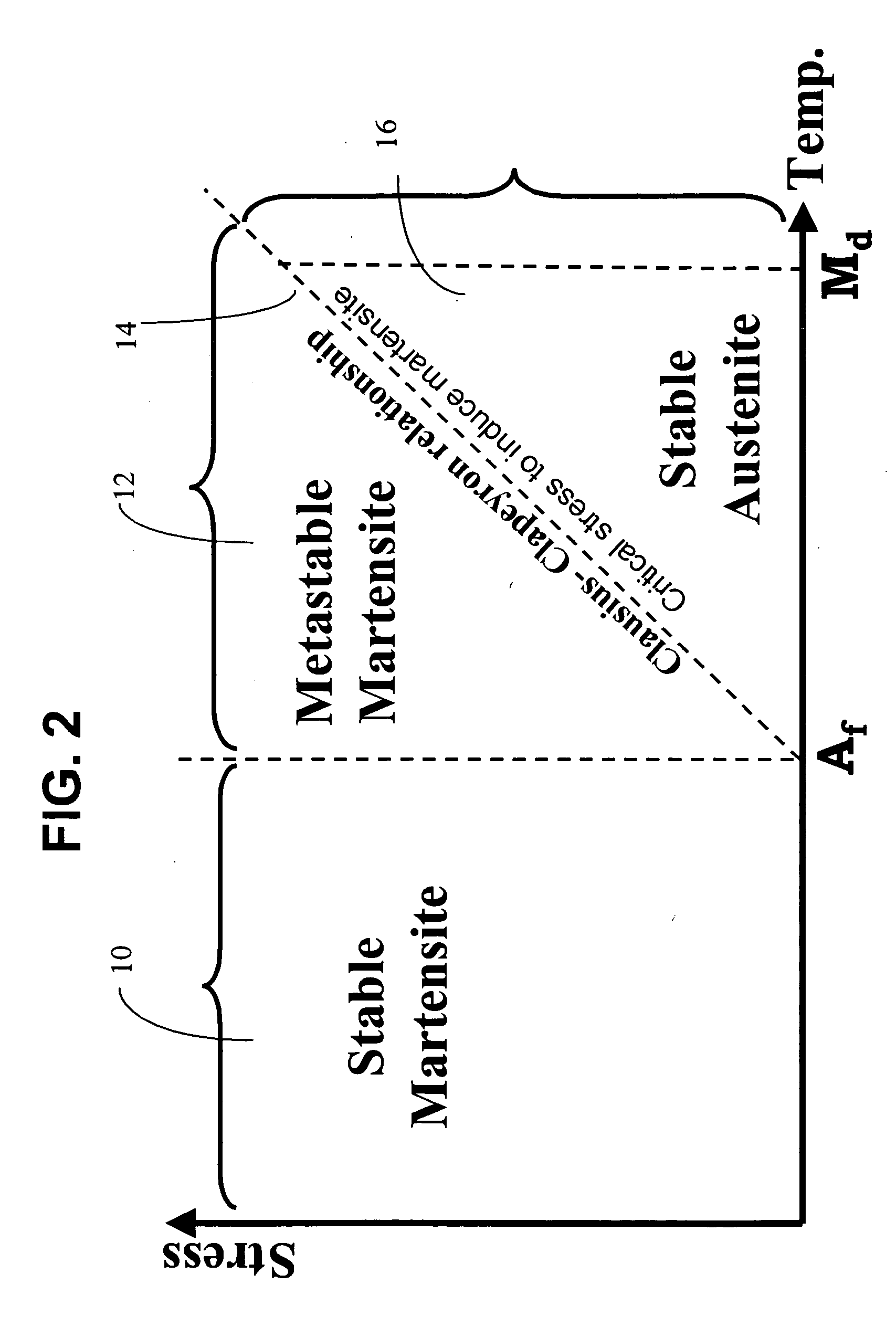
A method is disclosed for utilizing a deformable article of manufacture formed at least partly of a shape memory alloy. The method includes the steps of deforming the article from a first predetermined configuration to a second predetermined configuration while the shape memory alloy is, at least partially, in its stable martensitic state and at a first temperature. A resisting force is applied to the deformed article of manufacture using a restraining means and the article is heated from the first temperature to a second temperature in the presence of the resisting force. The stable martensitic state is transformed to a metastable stress-retained martensitic state. The resisting force is then removed allowing the alloy to transform to its austenitic state and the shape of the article to be restored substantially to its first configuration. Devices primarily medical devices operative by employing this method are also disclosed.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Mitral valve device using conditioned shape memory alloy
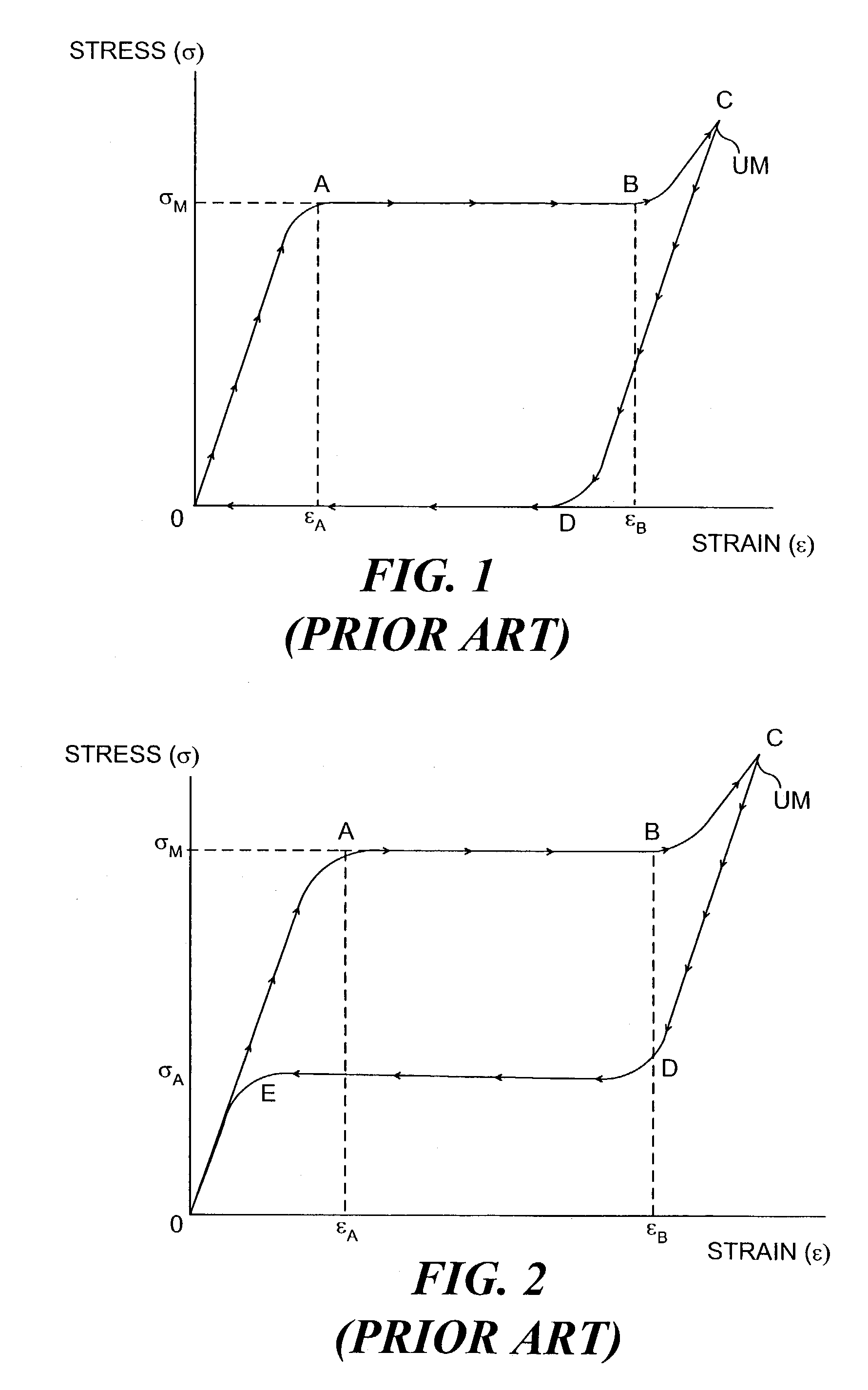
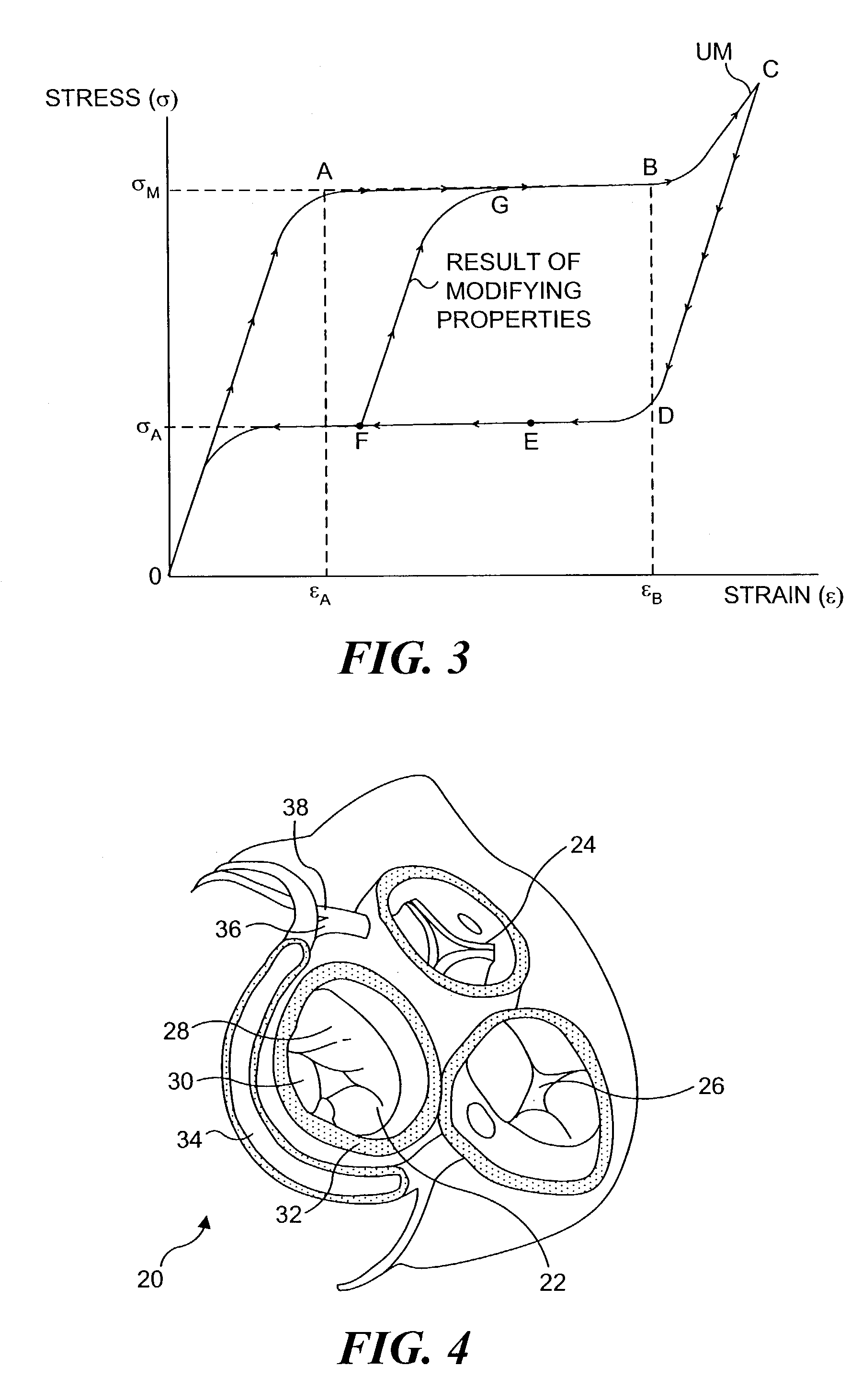
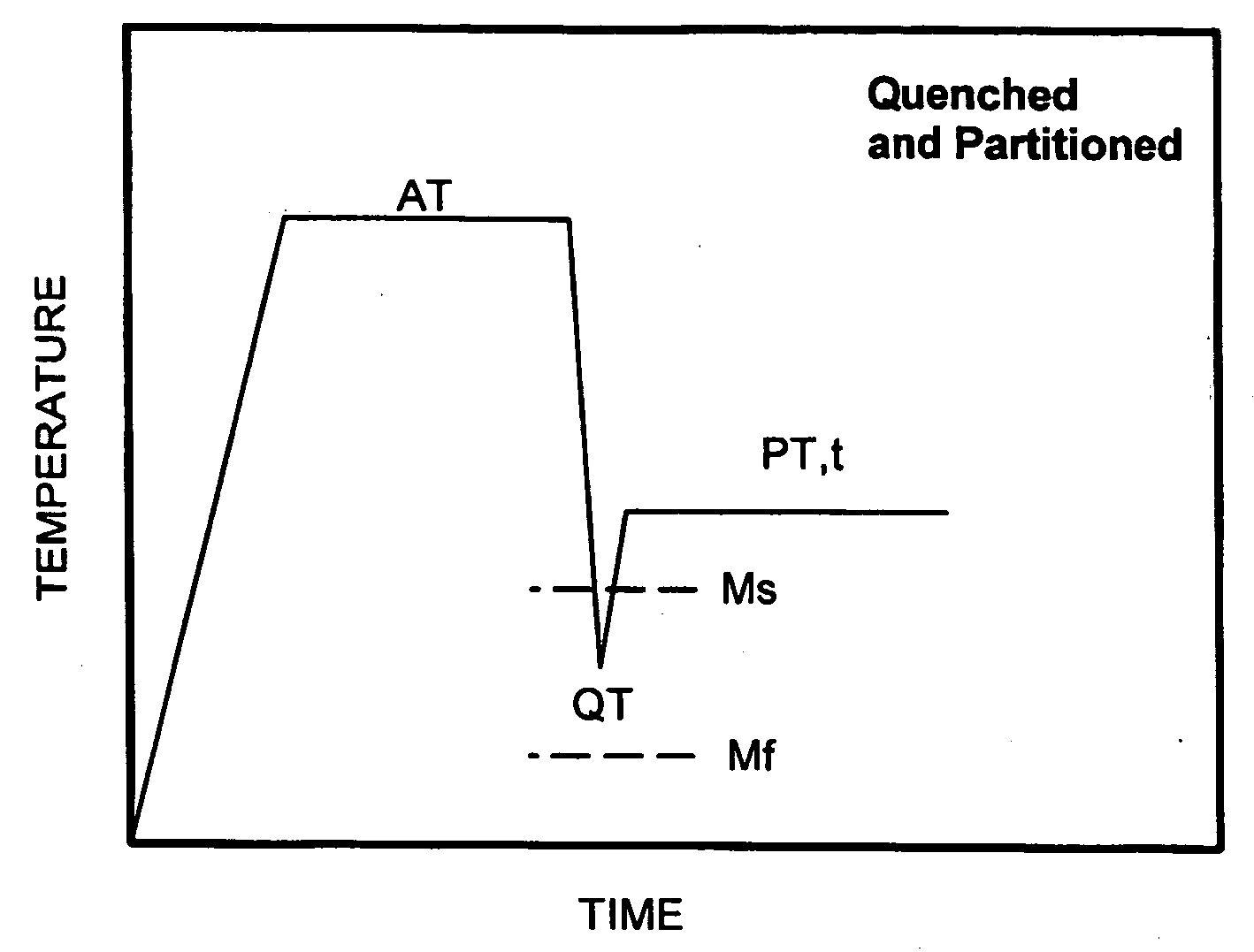
A mitral valve annulus reshaping device includes at least a portion that is formed of a biocompatible shape memory alloy SMA having a characteristic temperature, Af, that is preferably below body temperature. The device is constrained in an unstable martensite (UM) state while being introduced through a catheter that passes through the venous system and into the coronary sinus of the heart. The reshaping device is deployed adjacent to the mitral valve annulus of the heart as it is forced from the catheter. When released from the constraint of the catheter, the SMA of the device at least partially converts from the UM state to an austenitic state and attempts to change to a programmed shape that exerts a force on the adjacent tissue and modifies the shape of the annulus. The strain of the SMA can be varied when the device is within the coronary sinus.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
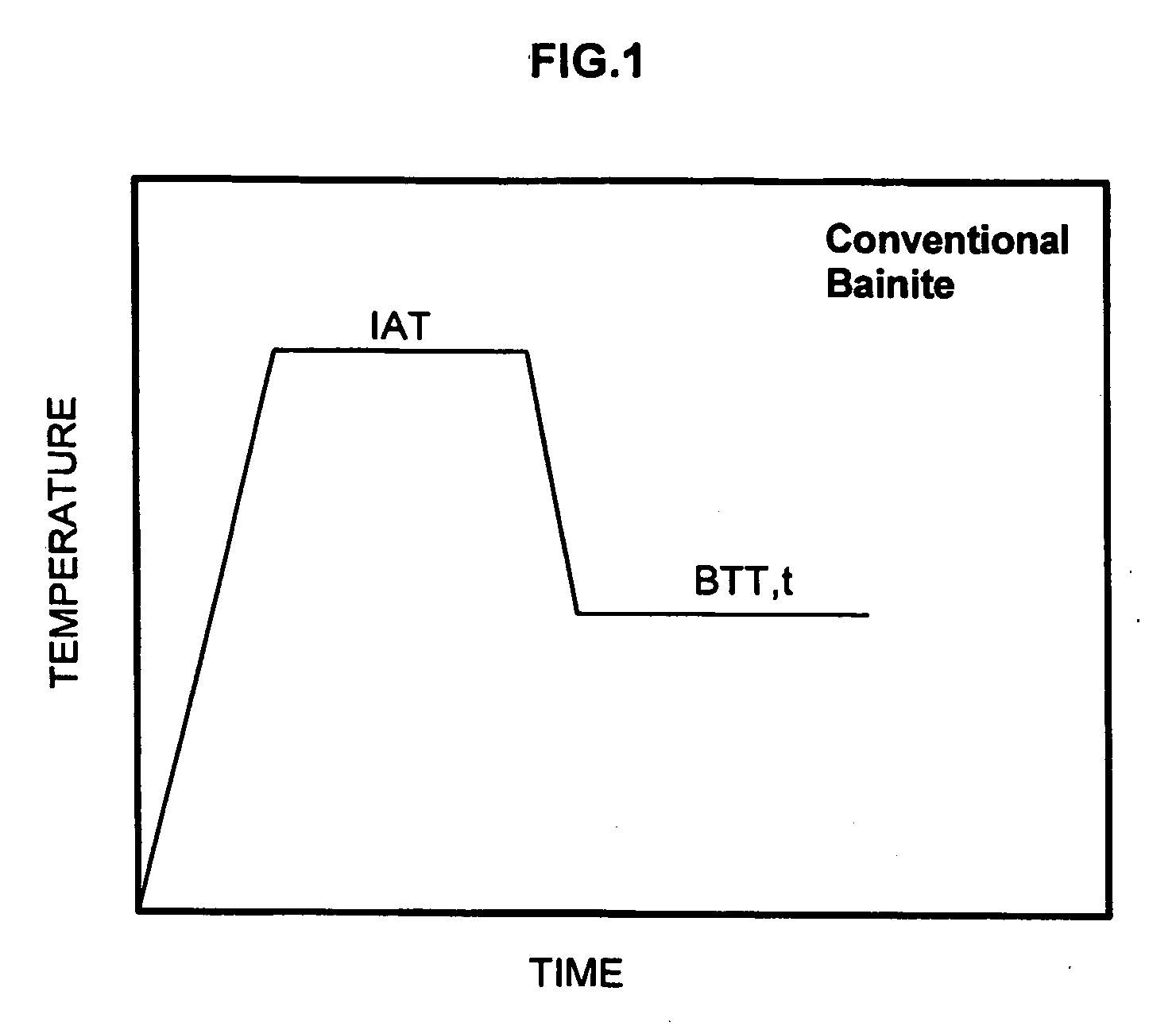
Method for producing steel with retained austenite
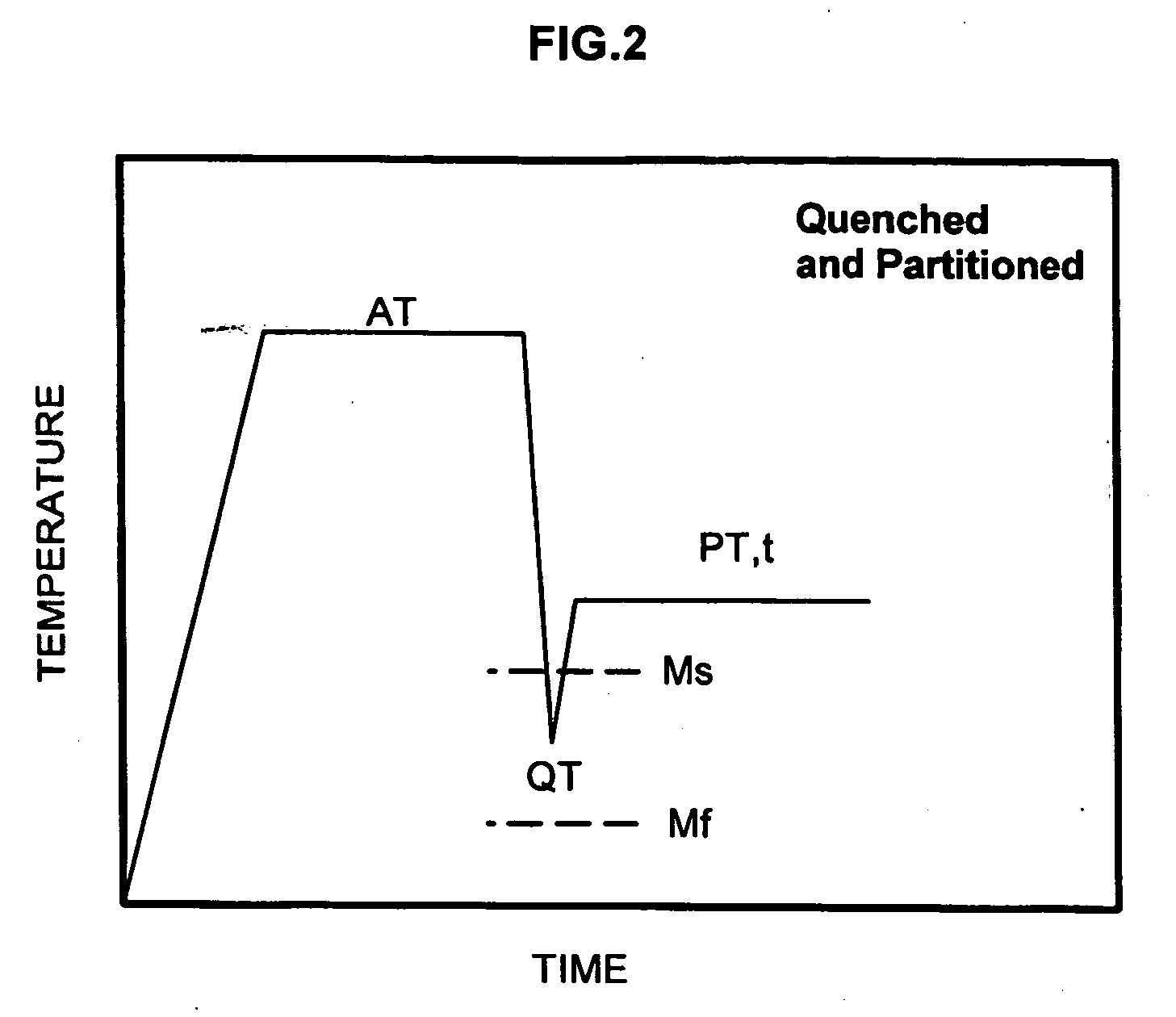
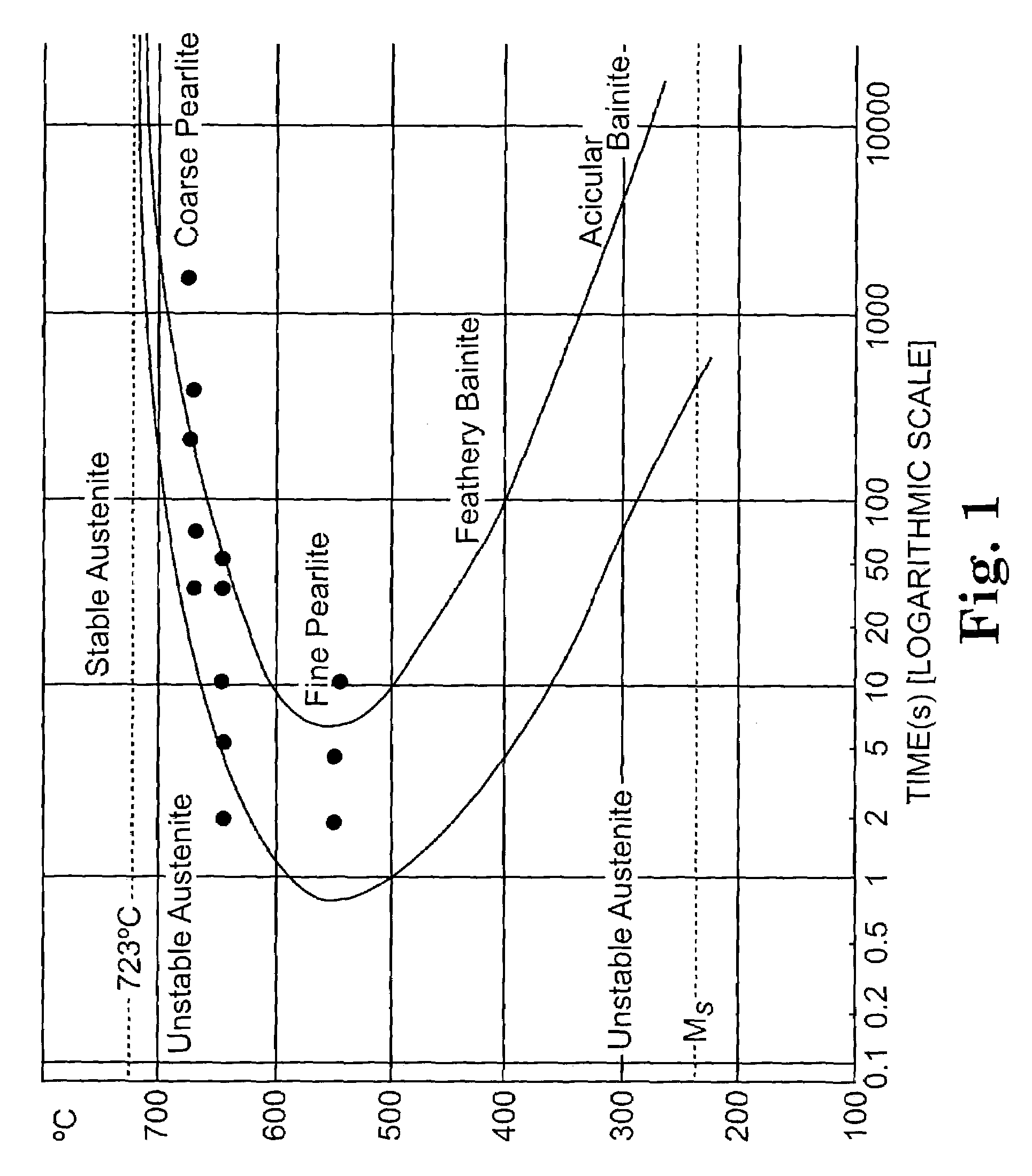
The present invention relates to a process for producing steel with retained austenite. In one embodiment, the process comprises the steps of heating a steel alloy to produce austenite, quenching the steel to produce martensite, and carbon partitioning to transfer carbon from the martensite to the austenite.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
Seam-welded metal pipe and method of making the same without seam anneal
InactiveUS7032809B1Efficient processingEliminates annealing stepArc welding apparatusFurnace typesSufficient timeWeld seam
An apparatus and method for making a seam-welded steel pipe free of untempered martensite without seam anneal. The method includes selecting a steel containing a carbon concentration below a predetermined level, for example, 0.14% or 0.12% by weight. The method also includes flooding both outside and inside of the strip with a coolant while the weld seam is being formed, and continuing to immerse the welded strip for a sufficient time after the weld seam is formed to prevent the formation of untempered martensite. The apparatus includes a heater capable of heating the strip to a temperature sufficient to form a welded seam, a cooling module configured to supply a coolant to the welded seam both inside and outside of the strip as the weld seam is being formed, and another cooling module configured to immerse the welded strip in a coolant after the weld seam is formed for a sufficient length of time to prevent the formation of untempered martensite.
Owner:STEEL VENTURES
Method of setting and actuating a multi-stable micro valve and adjustable micro valve
InactiveUS6926246B2Less sensitive to blockageOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsShape-memory alloyEngineering
A micro valve and a method for setting or actuating a micro valve for use in fluidic applications includes cooling an array of actuating members made of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) material. The SMA material is cooled to a temperature equal to or below the temperature at which a transformation from austenitic to martensitic state occurs so that the entire array of SMA actuating members is either fully or partially in the martensitic state. At least one of the actuating member is selected to correspond to a pre-determined opening pressure or flow resistance. Each of the actuating members are heated individually, except the previously selected one, to a temperature equal to or above the temperature at which a transformation from the martensitic state to the austensitic state occurs.
Owner:MEDOS
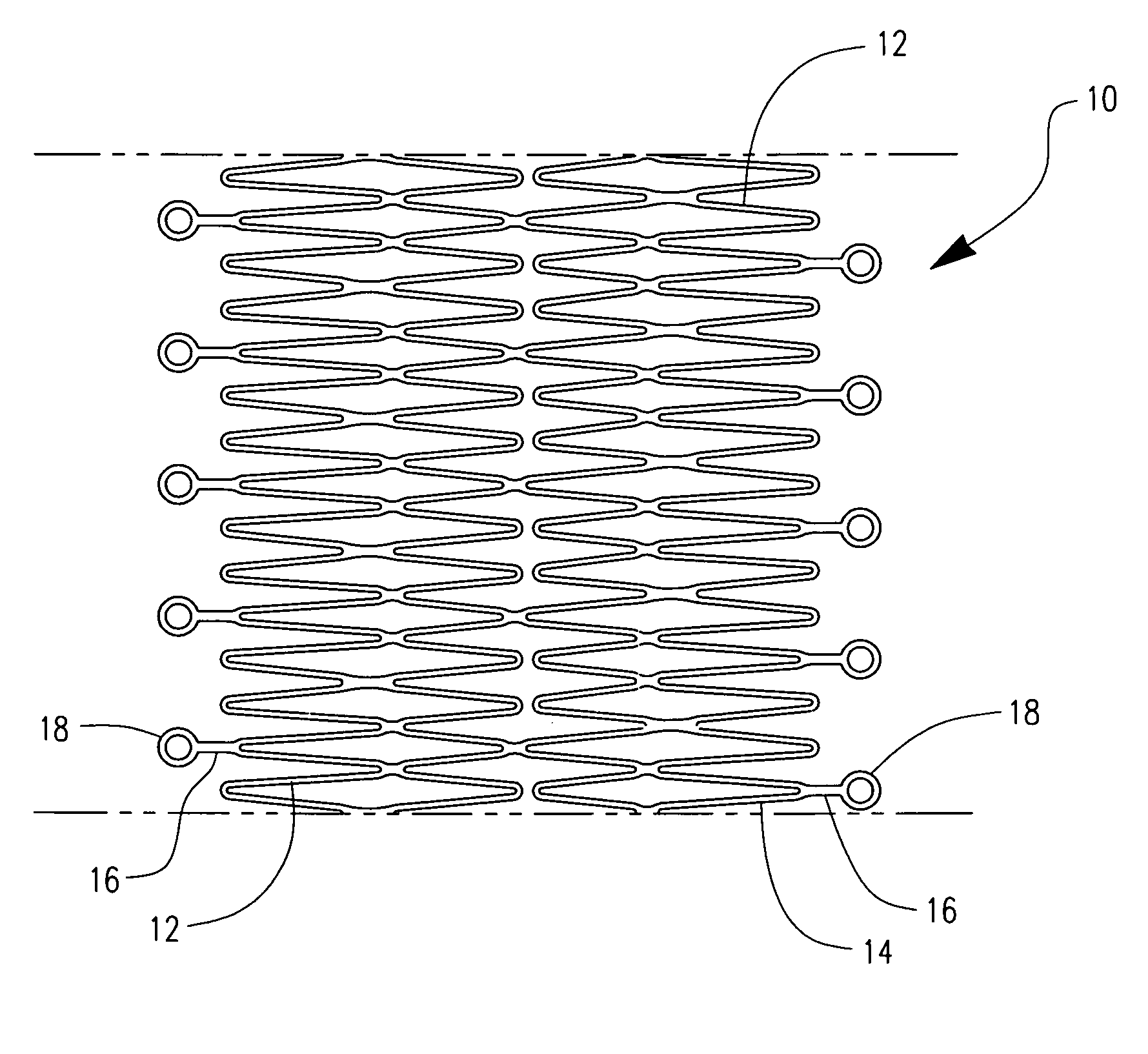
Process method for attaching radio opaque markers to shape memory stent
A process comprising the steps of providing a precursor for an implantable medical device, at least a portion of the precursor made of a shape memory material, the shape memory material having a receptacle for receiving a marker therein, the shape memory material having an austenitic and a martensitic phase; enlarging the receptacle while the shape memory material is in the martensitic phase; inserting a marker in the receptacle while the shape memory material is in the martensitic phase; and thereafter transforming the precursor to the austenitic phase.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
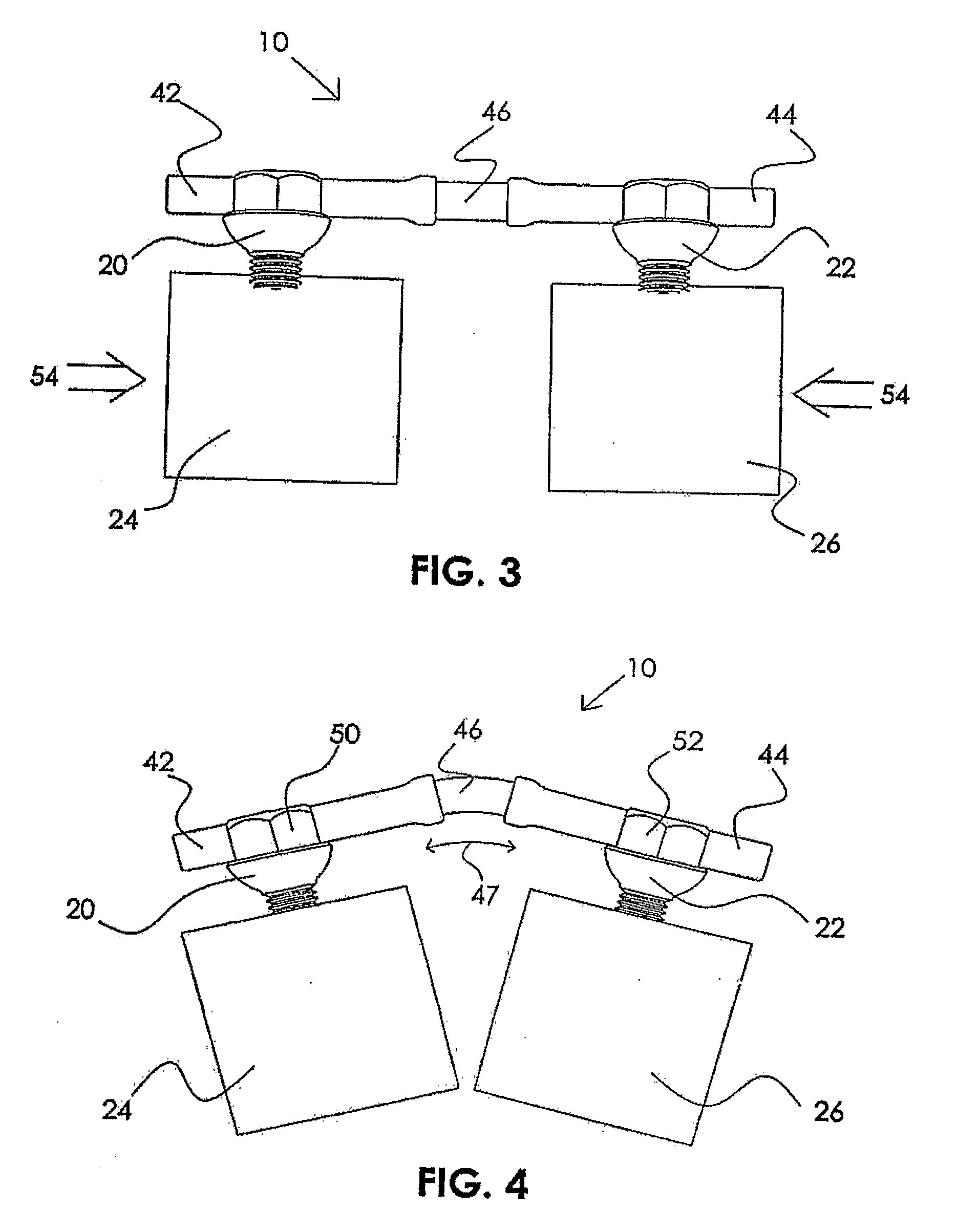
Implantable expandable medical devices having regions of differential mechanical properties and methods of making same
InactiveUS6923829B2Minimizing unwanted vascular injuryMinimizing vascular injuryStentsSurgeryIn vivoMartensite
An implantable expandable medical device in which selected regions of the device are in a martensite phase and selected regions are in an austenite phase. The martensitic regions exhibit pseudoplastic behavior in vivo and may be deformed without recovery under in vivo body conditions. In contrast the austenitic regions exhibit superelastic behavior in vivo and will recover their pre-programmed configuration upon deformation or release of an applied strain
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Process method for attaching radio opaque markers to shape memory stent
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Low-alloy super-strength multiphase steel and heat treatment method thereof
The invention discloses a low-alloy superhigh-intensity diphase steel and the heat treatment method, which is characterized in that: the components of the diphase steel (wt %) are C of 0.3 to 0.7, Si of 0.01 to 3.0, Al of 0.0 to 2.0, Nb of 0.0 to 0.25, V of 0.0 to 0.3, Mo of 0.0 to 2.0, Ni of 0.0 to 4.0, Mn of 0.05 to 3.0, Cr of 0.00 to 3.0, Co of 0.00 to 2.0, W of 0.0 to 2.0, S less than 0.04, P less than 0.04 and Fe of balance; the heat treatment method is that: a workpiece is first heated to 800 to 1000 degree centigrade to process the austenite treatment, and then the workpiece is quickly quenched into a liquid quenching medium of 50 to 250 degree centigrade, and then the workpiece is partitioned in a liquid quenching medium of 250 to 450 degree centigrade, and then the workpiece is quickly quenched into a liquid quenching medium of 100 to 250 degree centigrade for holding, finally the workpiece is quenched into water, and then the workpiece has a three-phase organization with martensite, nanometer ferrito martensite and remaining austenite with rich carbon. The low-alloy superhigh-intensity diphase steel and the heat treatment method has an advantage of increasing the intensity and plasticity of workpieces.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and production thereof
InactiveUS6312536B1High strengthGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelHigh intensity
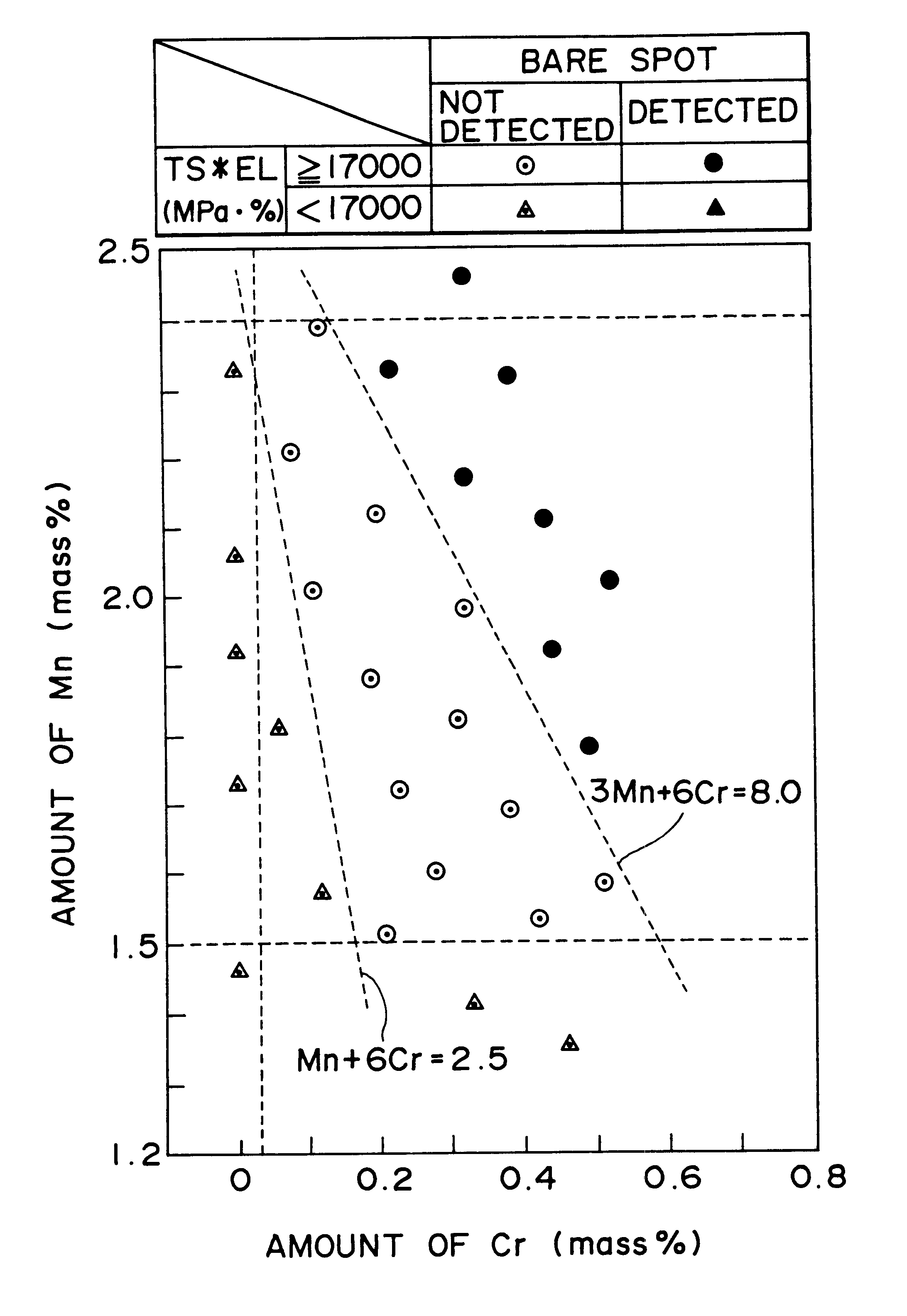
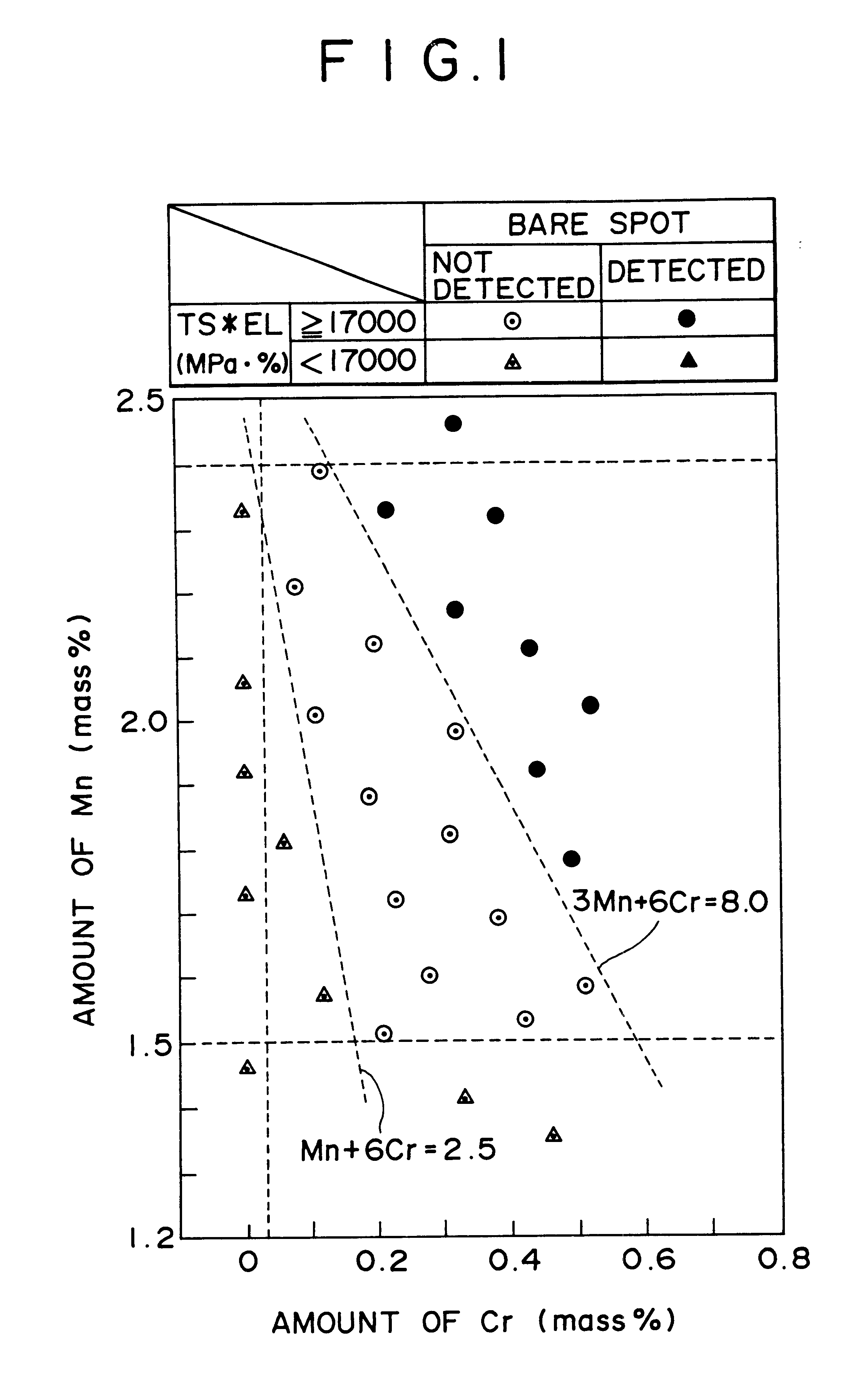
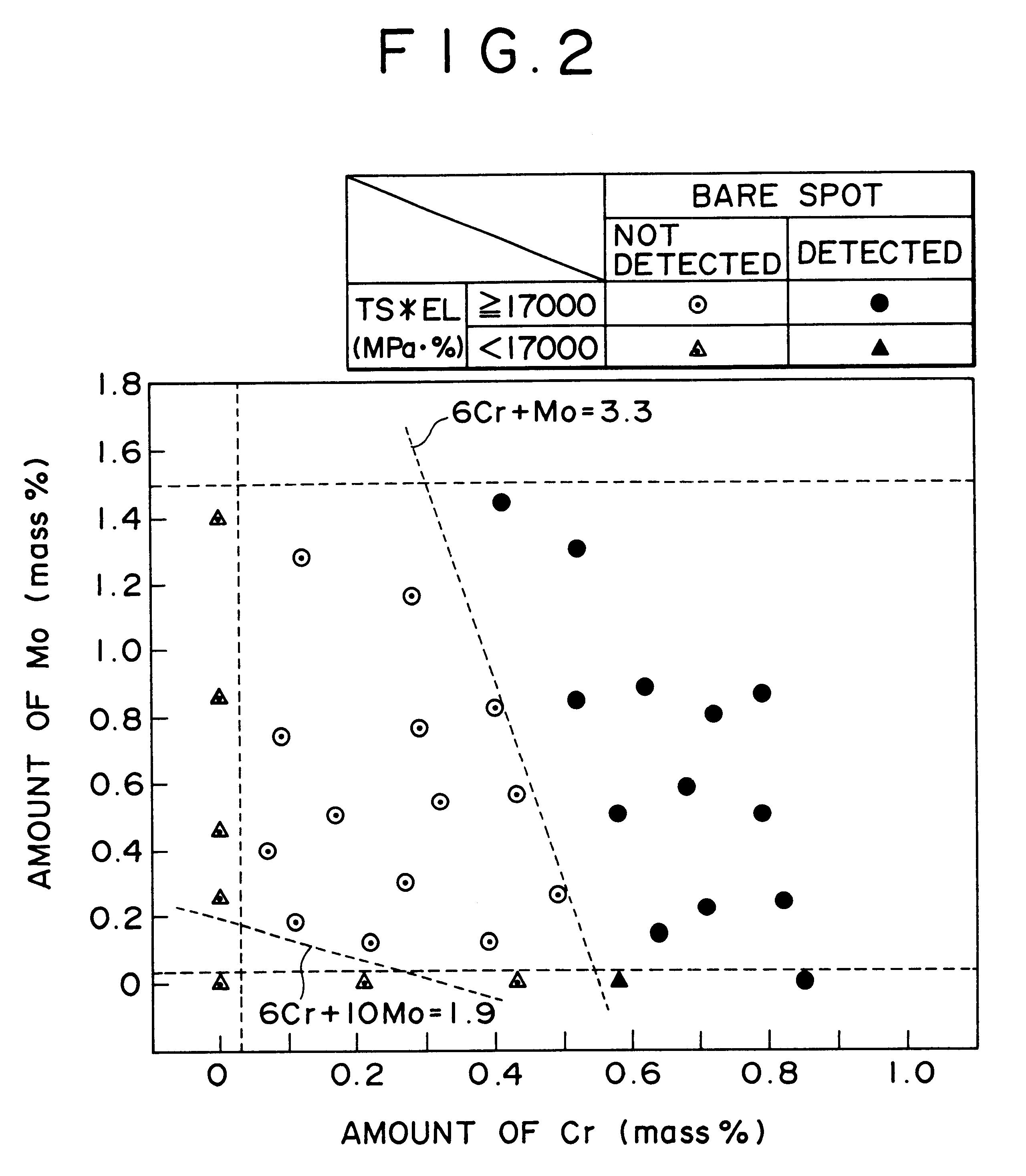
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having both high strength and good formability. A process for producing said hot-dip galvanized steel sheet without requiring additional steps of surface grinding and pre-plating.The hot-dip galvanized steel sheet is produced by forming a hot-dip galvanizing layer on a base cold-rolled steel sheet composed of C (0.02-0.20 mass %), Mn (1.50-2.40 mass %), Cr (0.03-1.50 mass %), Mo (0.03-1.50 mass %), 3Mn+6Cr+Mo (no more than 8.1 mass %), Mn+6Cr+10 Mo (no less than 3.5 mass %), Al (0.010-0.150 mass %), and Fe as the principal component, with Ti limited to 0.01 mass % or less, Si limited to 0.04 mass % or less, P limited to 0.060 mass % or less, and S limited to 0.030 mass % or less, and said base steel sheet having the composite microstructure composed mainly of ferrite and martensite.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Steel plate for stamping and quenching and thermoforming method of steel plate
ActiveCN102031456ASimple compositionPlay the effect of weight reduction and energy savingHot stampingSimple component
The invention discloses a steel plate for stamping and quenching and a thermoforming method of the steel plate. The steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.14-0.28% of C, less than 0.40% of Si, 0.4-2.0% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.010% of P, less than or equal to 0.004% of S, 0.016-0.040% of Al, 0.15-0.8% of Cr, 0.015-0.12% of Ti, 0.0001-0.005% of B, less than or equal to 0.005% of N, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The thermoforming method comprises the following steps: blanking by shearing the steel plate, and heating at Ac3 to (Ac3+80) DEG C to carry out austenization; after insulating for 5-10 minutes in the heating furnace, immediately transferring the steel plate to a metal mold the inside of which is cooled by introducing water, and stamping at the high temperature of 650-850 DEG C; cooling the formed workpiece in the closed mold, and cooling the mold by water circulation in the mold, wherein the cooling rate is greater than the critical cooling rate when austenite forms martensite, and the temperature of the workpiece leaving the hot stamping production line is below 150 DEG C; and carrying out air-cooling to room temperature. The steel plate has the advantages of simple component system and favorable hardenability; and the substrate tissues, which are ferrite and pearlite, are processed by hot stamping andquenching to obtain the all martensitic structure. The tensile strength of the steel plate can be higher than 1300 N / mm<2>.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Composite structure type high tensile strength steel plate, plated plate of composite structure type high tensile strength steel and method for their production
InactiveUS20030129444A1Lower yield stressImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingSheet steelHigh intensity
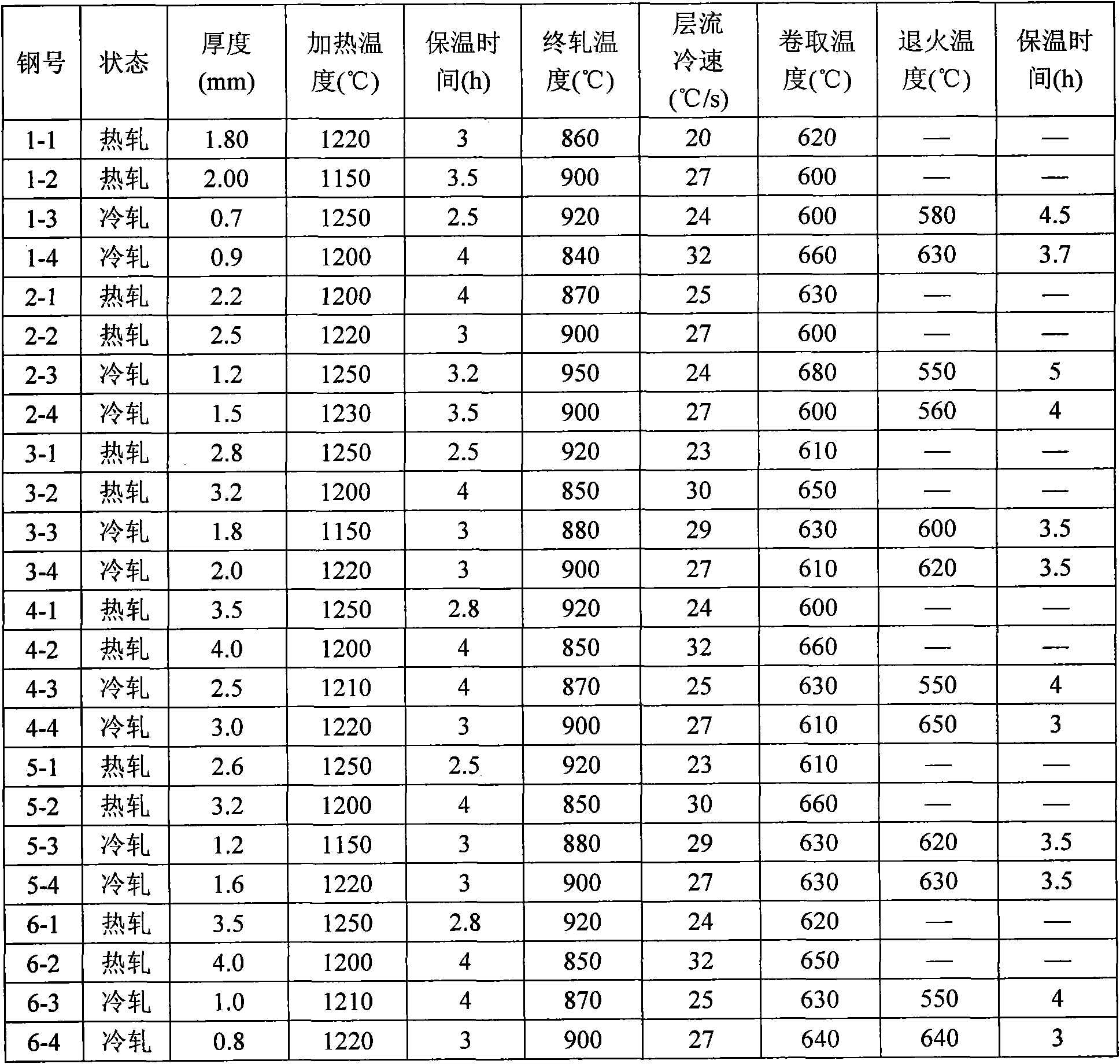
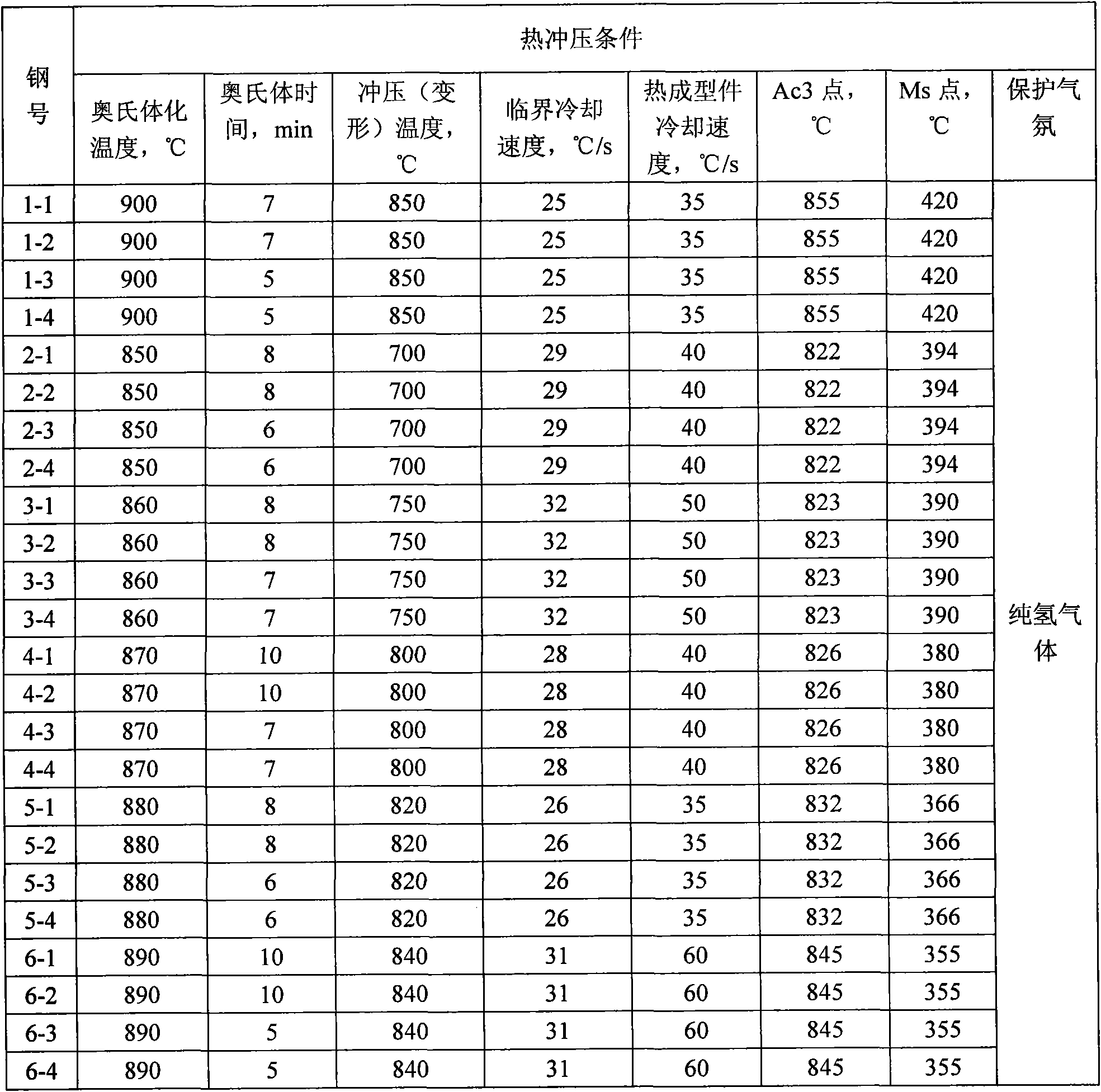
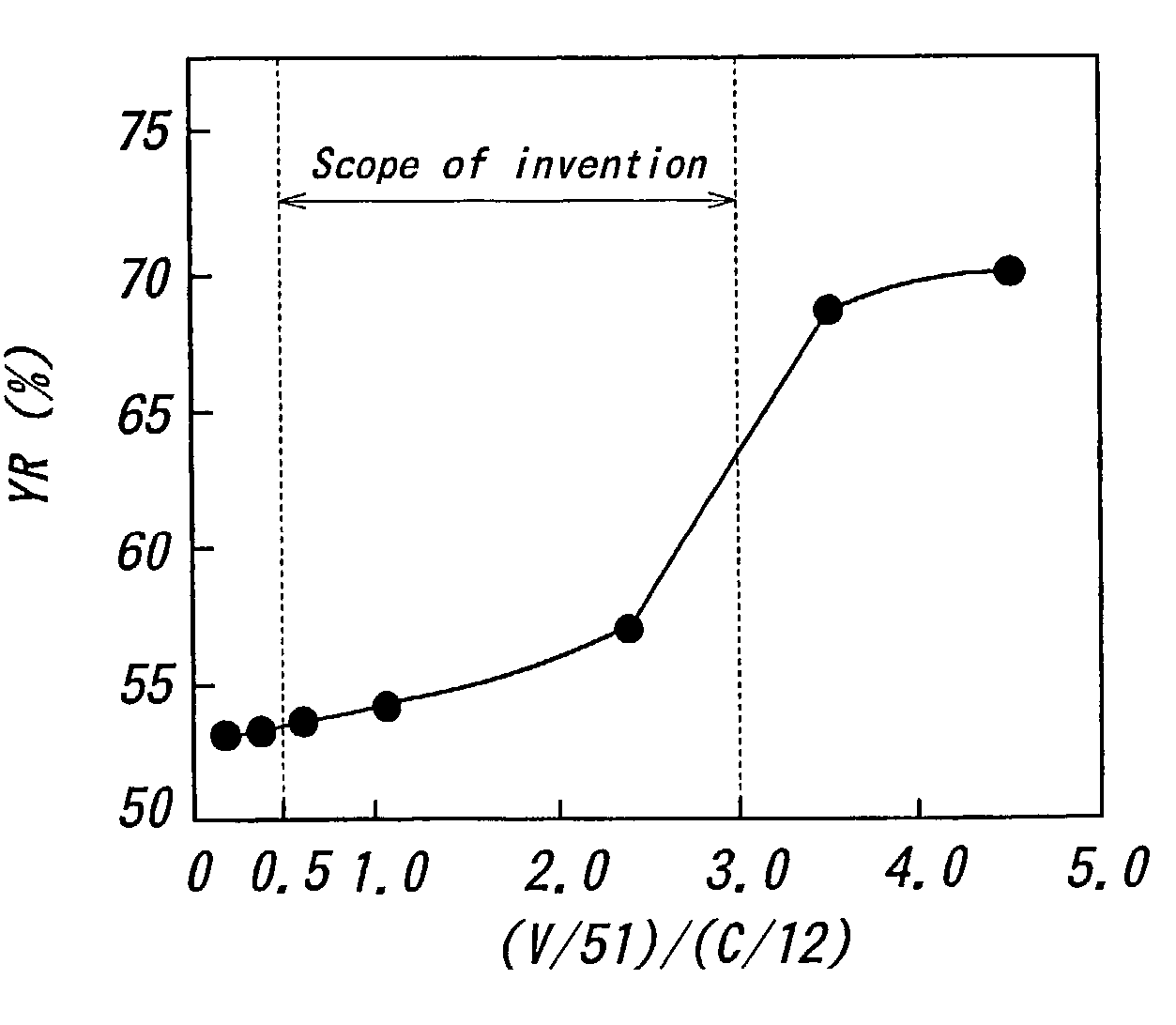
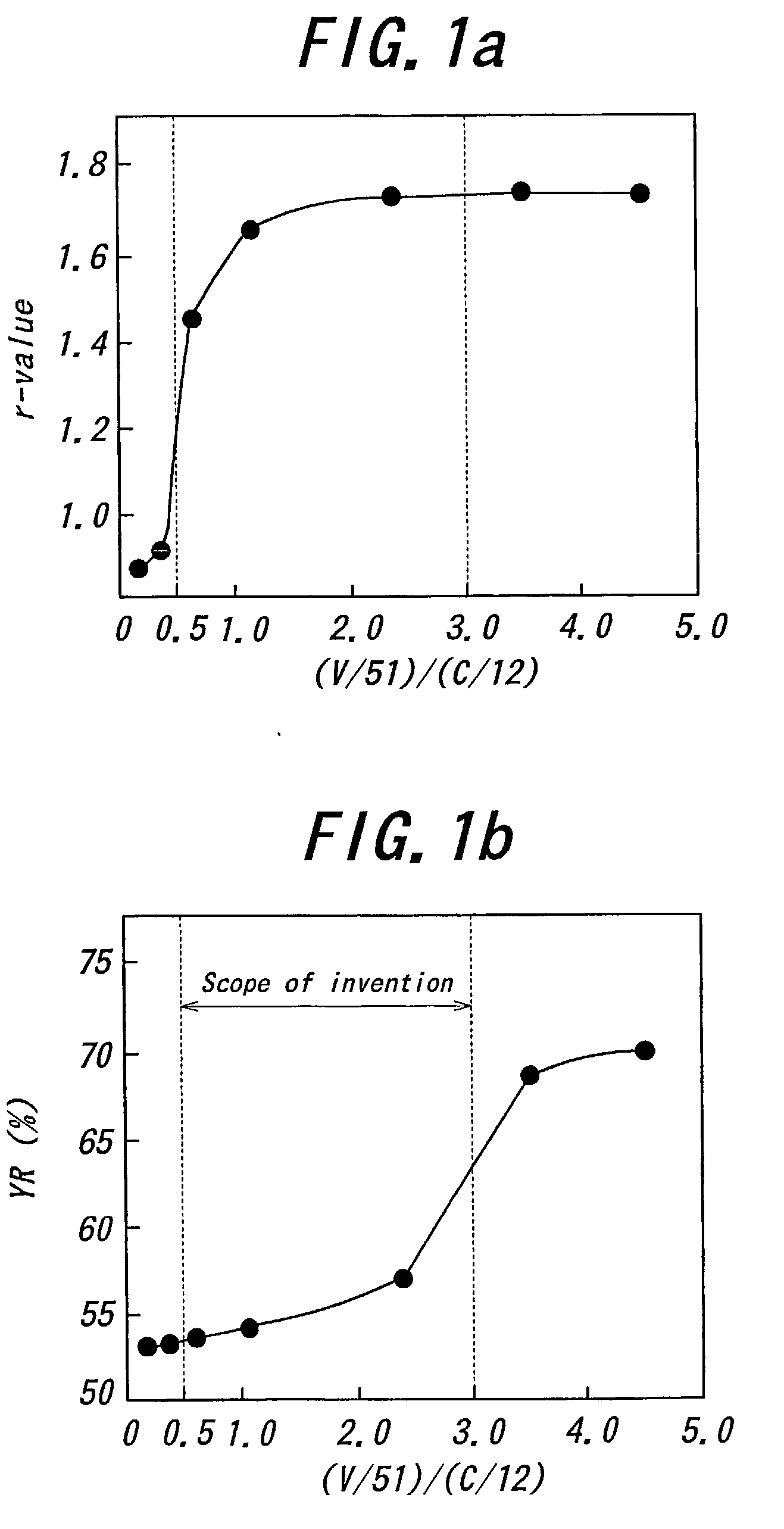
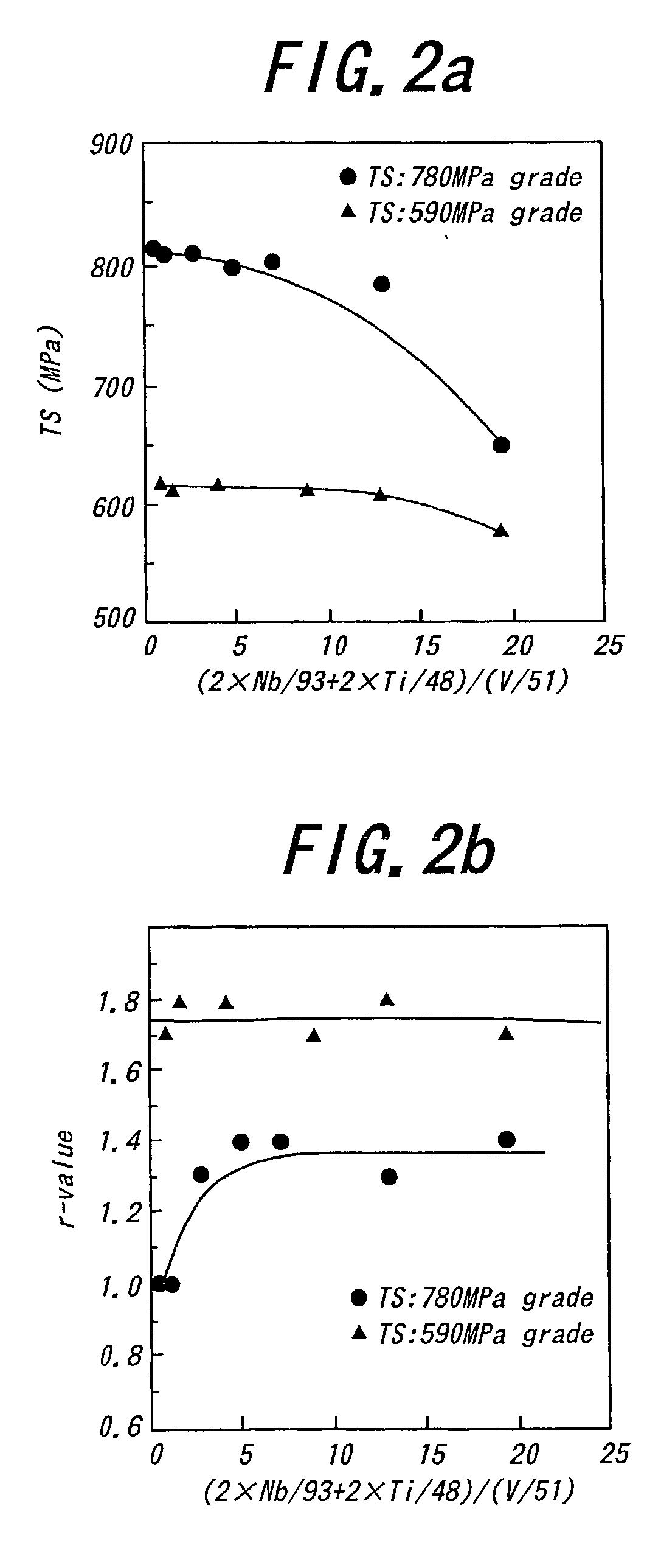
The invention proposes a high-strength dual-phase cold rolled steel sheet having an excellent deep drawability, wherein the steel sheet has a composition comprising C: 0.01-0.08 mass %, Si: not more than 2.0 mass %, Mn: not more than 3.0 mass %, P: not more than 0.10 mass %, S: not more than 0.02 mass %, A1: 0.005-0.20 mass %, N: not more than 0.02 mass % and V: 0.01-0.5 mass %, provided that V and C satisfy a relationship of 0.5xC / 12<=V / 51<=3xC / 12, and the remainder being Fe and inevitable impurities, and has a microstructure consisting of a ferrite phase as a primary phase and a secondary phase including martensite phase at an area ratio of not less than 1% to a whole of the microstructure and a high-strength dual-phase galvanized steel sheet comprising a galvanized coating on the above steel sheet as well as a method of producing the same.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Shape memory alloy temperature sensor
InactiveUS6837620B2Avoid attenuationInhibition of contractionThermometers using material expansion/contactionThermometers using weight distributionShape changeShape-memory alloy
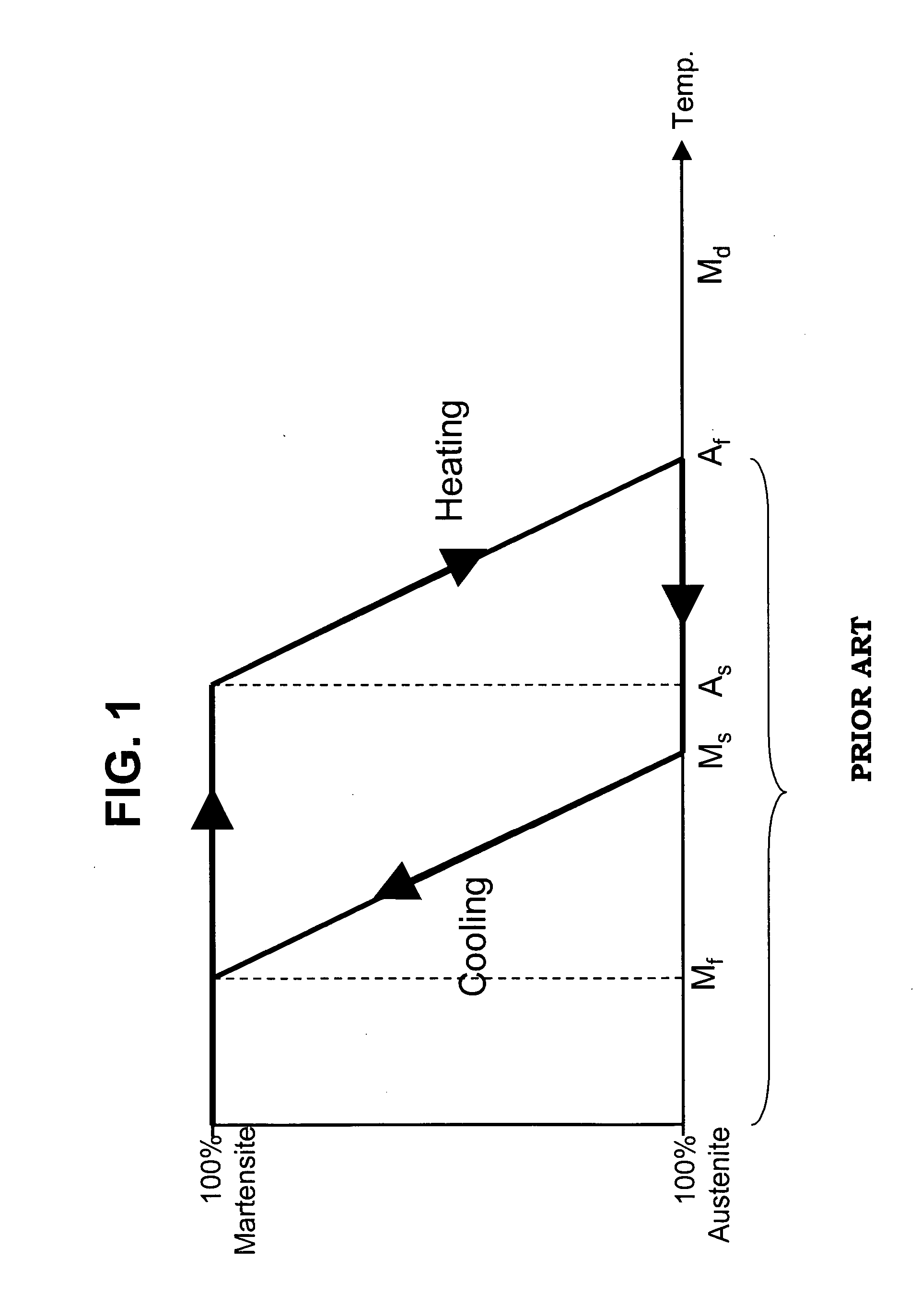
A sensor provides a persistent indication that it has been exposed to temperatures below a certain critical temperature for a predetermined time period. An element of the sensor made from shape memory alloy changes shape when exposed, even temporarily, to temperatures below the Austenitic start temperature As and well into Martensite finish temperature Mf off the shape memory alloy. The shape change of the SMA element causes the sensor to change between two readily distinguishable states. The sensor includes a one-way stop element that creates a persistent indication of the temperature history, allowing the sensor to be manufactured and stored at temperatures above the Austenitic temperature without causing the indication of an over-temperature event.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN
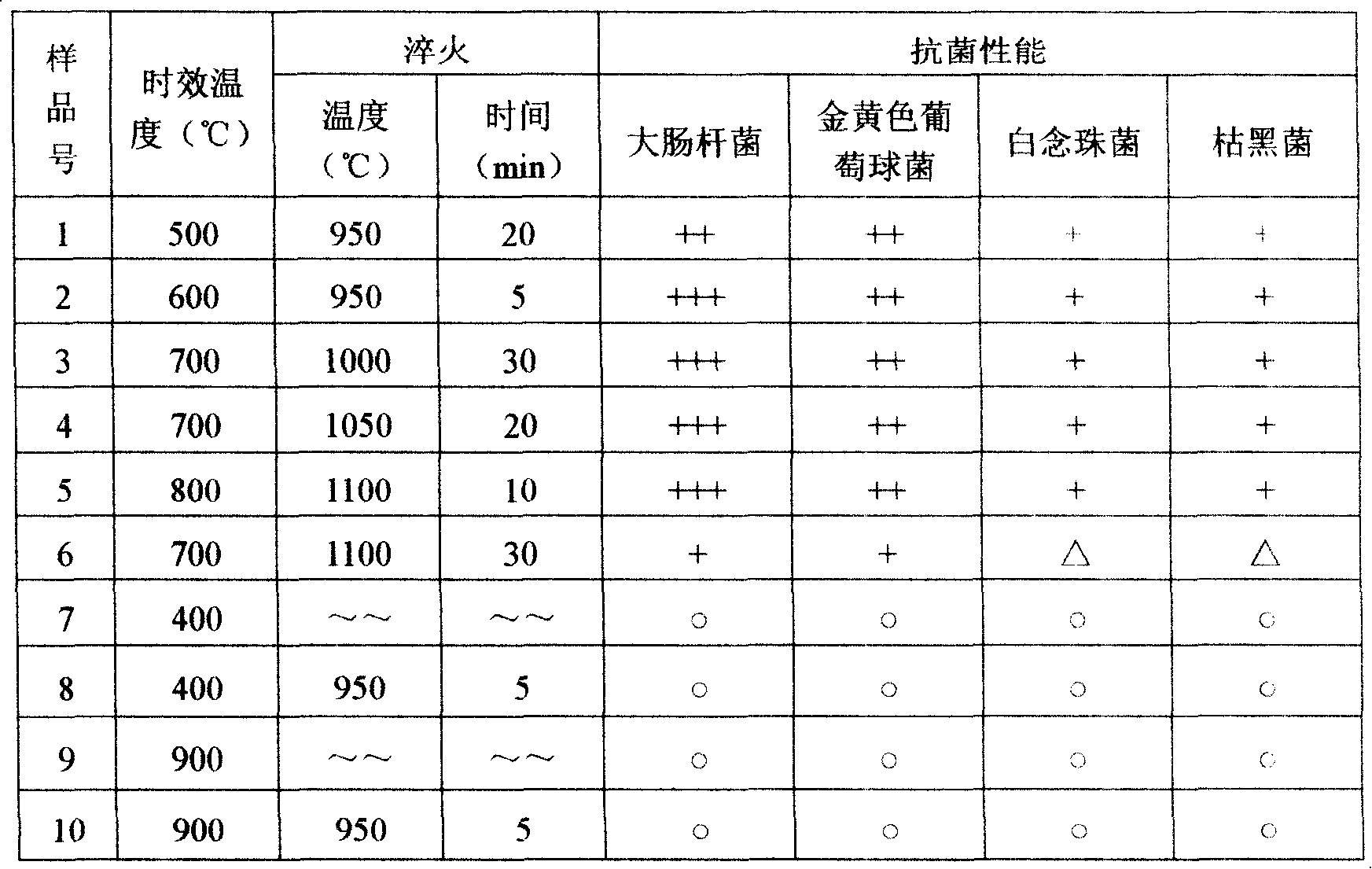
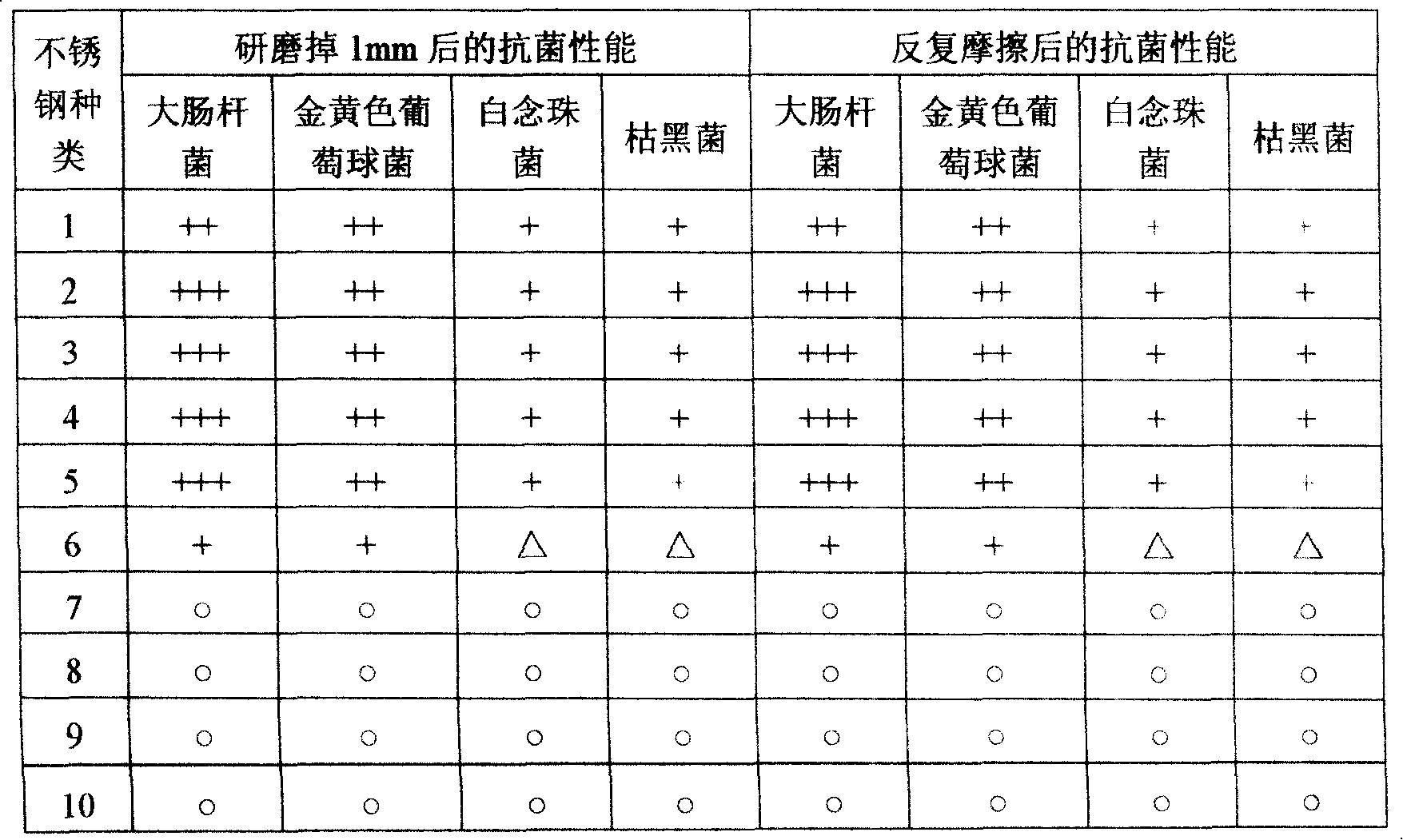
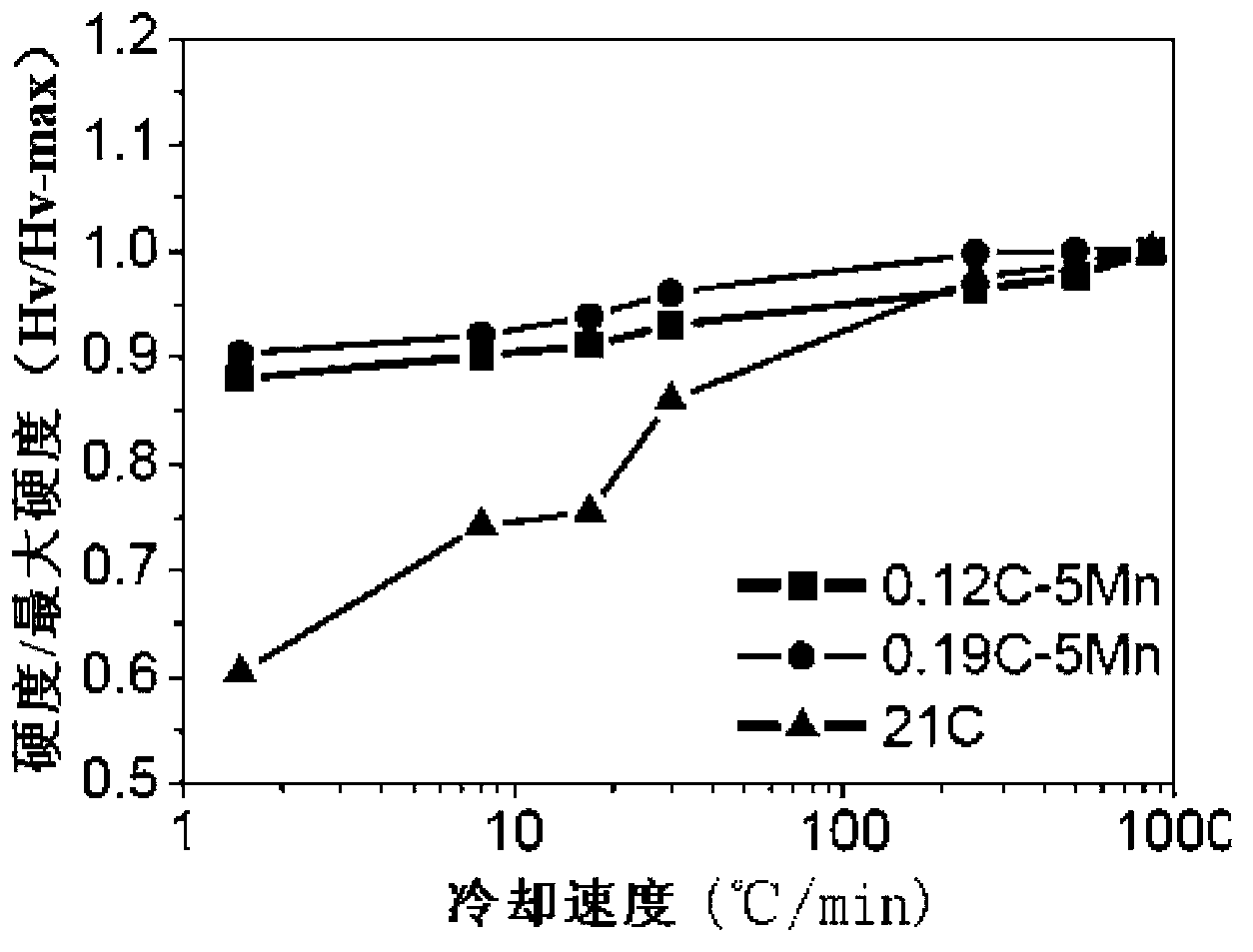
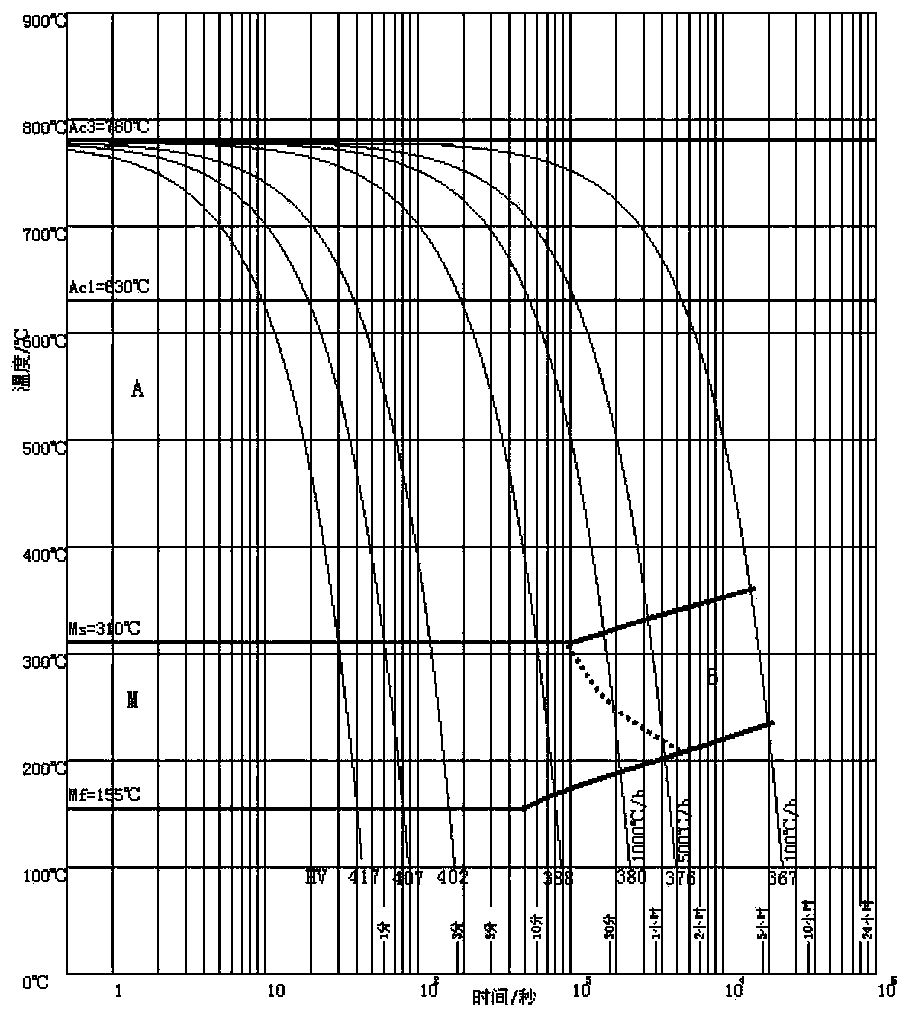
Martensitic antibiotic stainless steel and thermal treatment method thereof
ActiveCN101205592AImprove mechanical propertiesAntibacterial property does not decreaseHeat treatment process controlProcess efficiency improvementChemical compositionThermal treatment
The invention discloses martensite antibacterial stainless steel, the weight percentage compositions of which are: 0.05 to 1.0 percent by weight of C, less than or equal to 3 percent by weight of Si, less than or equal to 1.5 percent by weight of Mn, 10 to 30 percent by weight of Cr, less than or equal to 1 percent by weight of Ni, 0.5 to 5 percent by weight of Cu, less than or equal to 1 percent by weight of Nb, less than or equal to 1 percent by weight of Ti, uniformly dispersed nano-precipitation phases epsilon-cu, and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities. The invention also discloses a hot treatment method of the martensite antibacterial stainless steel, which comprising the following steps of: firstly, performing hot rolling and cold rolling, followed by antibacterial treatment on the martensite antibacterial stainless steel to making an antibacterial part of the martensite antibacterial stainless steel; and then performing quenching and tempering sequentially. The invention has a broad spectrum antibacterial property, rapid sterilization property and a long-lasting antibacterial property, maintains good mechanical performance of the materials and has significant economic and social value.
Owner:华南生物医用材料(深圳)有限公司
Martensite series wear-resistant steel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to martensite series wear-resistant steel and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of wear-resistant steel. The steel comprises the following chemical components: 0.05-0.51wt% of C, 2.0-10wt% of Mn, 0-1.5wt% of Al, 0-1.5wt% of Si, 0-1.5wt% of Cr, 0-1.5wt% of Cu, 0-1.5wt% of Ni and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein the Mn / C ratio is not less than 9. Based on this, the following one or more composite elements can be optionally added: 0.02-0.50wt% of Mo, 0.02-0.50wt% of V, 0.02-0.50wt% of Nb, 0.01-0.5wt% of Ti, 0.02-0.50wt% of B and 0.02-0.50wt% of RE. The wear-resistant steel provided by the invention is easy to produce, low in cost and high in performance. The invention is applicable to the technical field of wear-resistant materials for mines, energy, transportation, agricultural machinery, engineering machinery and other industries.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Fatigue resistant medical devices
A flexible device comprises a metallic element including high strain portions and lesser strain portions, wherein the high strain portions are to be subjected to levels of strain during use increased with respect to strain levels in the lesser strain portions. The high strain portions comprise a material which, under predetermined operating conditions, is stabilized in a martensite phase and the lesser strain portions comprise a material which, under the predetermined operating conditions, is in an austenite phase. A method of forming an element of a medical device comprises the steps of forming an element of the device of Nitinol and impressing a memorized shape on the element, wherein the memorized shape is a shape the element is to assume when in an operational configuration. A high strain portion of the element is treated so that it is substantially Martensite phase stabilized under expected operating conditions of the device, wherein untreated portions of the element are in a substantially austenitic phase under the expected operating conditions.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Mobile spine stabilization device
InactiveUS20090131981A1Limited rangeFlexible limitSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnMedicine
An orthopedic device is described for stabilizing the spinal column between first and second vertebral bodies. The device has first and second screws adapted for fixation to the first and second vertebral bodies, respectively. The device further includes an elongated ligament with a first end connected to the first screw and the second end operatively connected with the second screw. The ligament is made preferably of a nickel titanium alloy selected to have ductile inelastic properties at body temperature and is capable of plastic deformation to allow relative constrained motion between the vertebral bodies. The preferred nickel titanium has a martensite / austenite transition temperature above body temperature. In a preferred embodiment, the second pedicle screw includes a bearing for receiving the ligament in a slidably engageable relationship. The device further includes optional first and second dampening members surrounding the ligament for restraining the spinal column during flexion and extension.
Owner:WHITE PATRICK
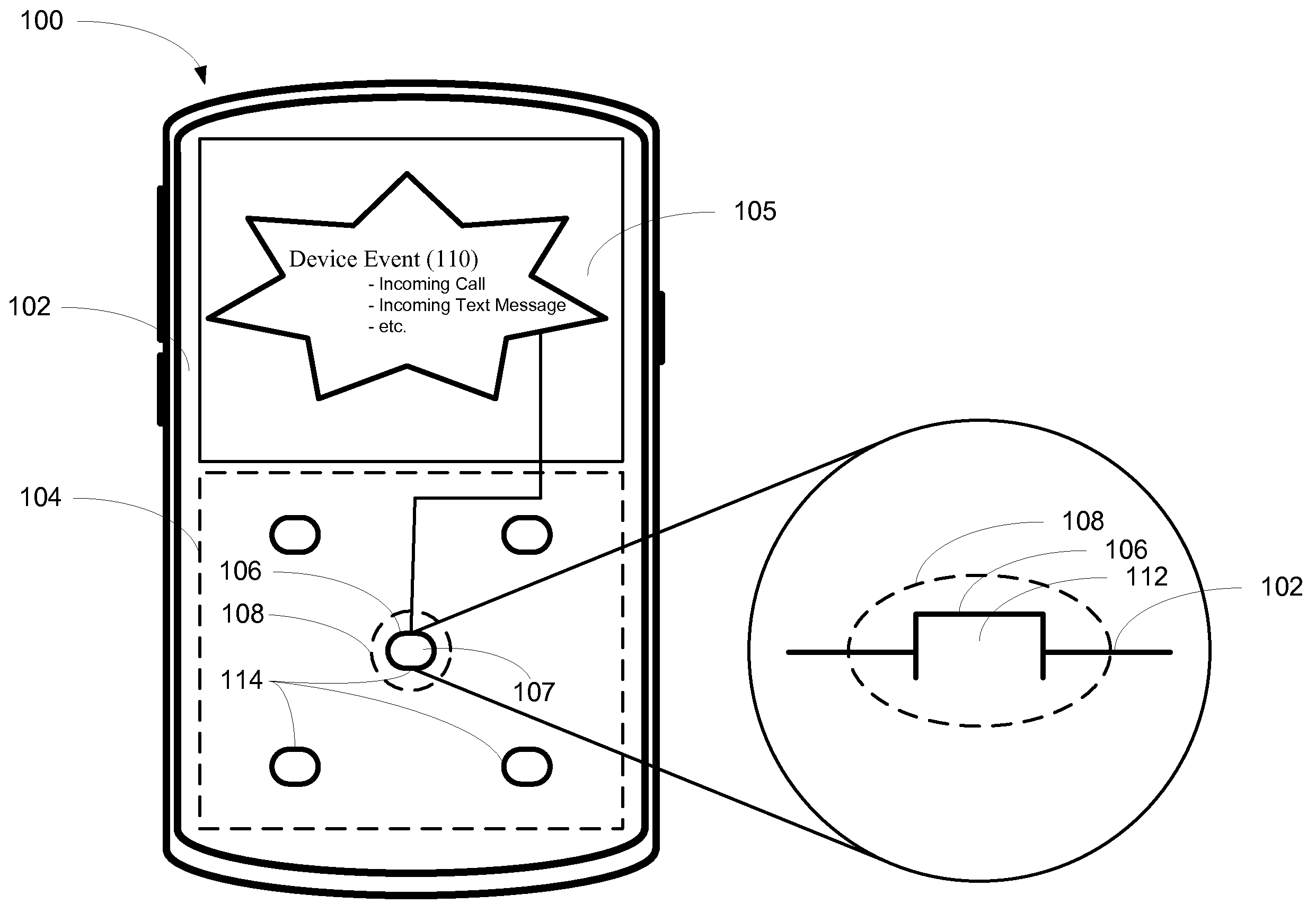
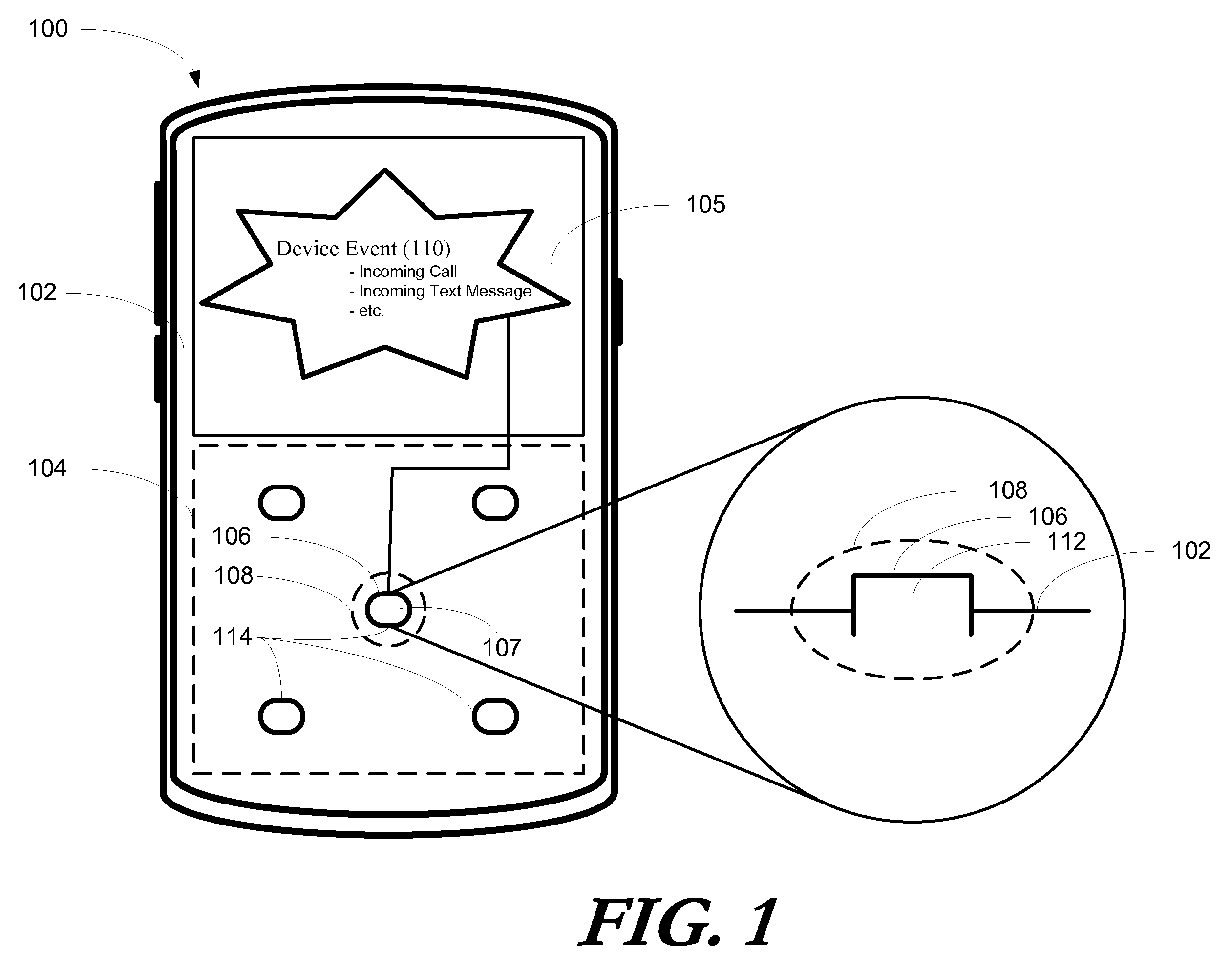
Electronic Device with Physical Alert
InactiveUS20090015547A1Current supply arrangementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsShape-memory alloyEngineering
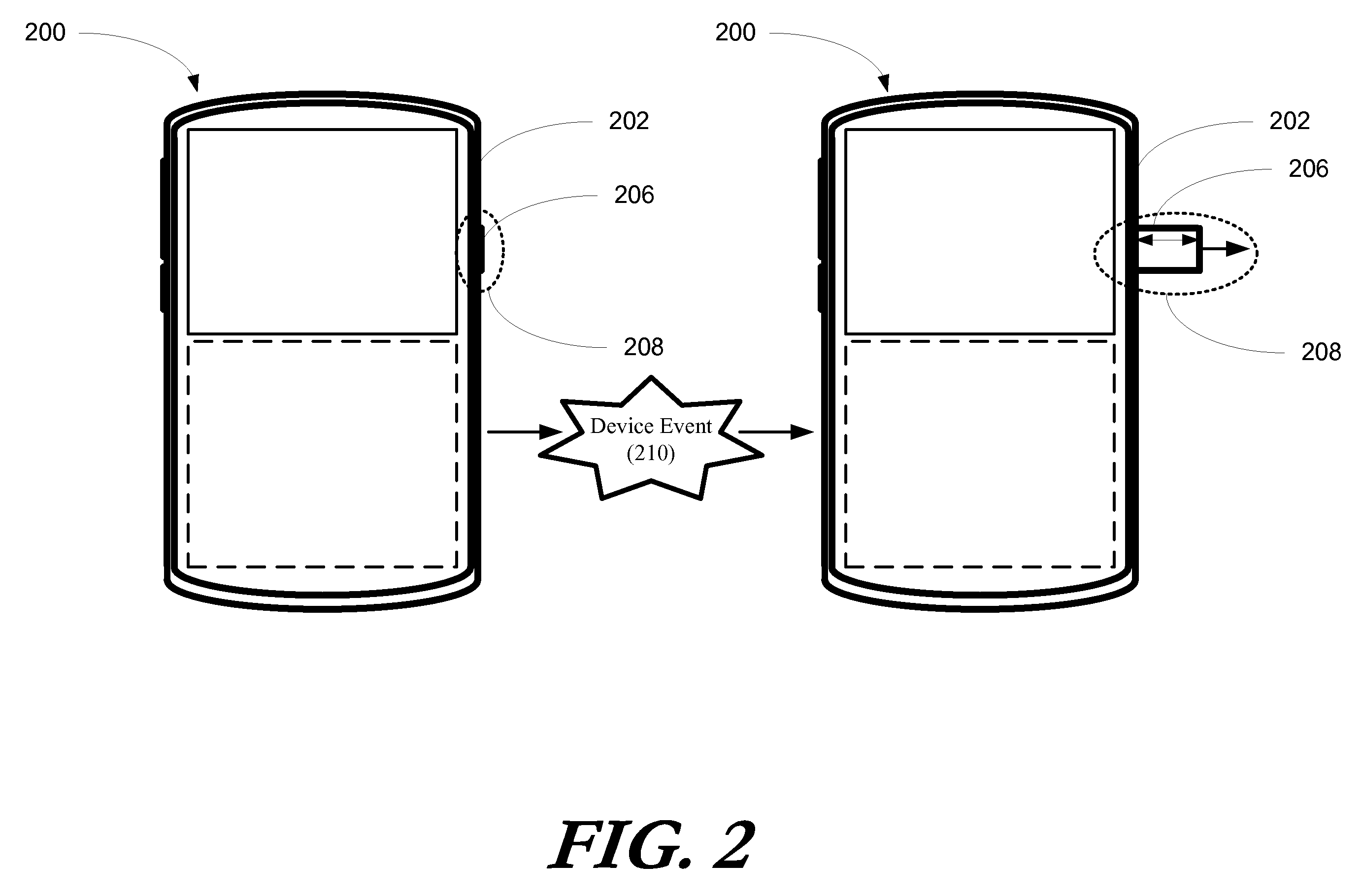
An electronic device (100) includes an actuation element (106) configured to alter an actuation element profile (108) of the actuation element (106) with respect to a housing (102) in response to a device event (110). Altering the actuation element profile (108) may include distally extending or changing the form factor of the actuation element (106). Device events, for example where the electronic device (100) is a radiotelephone (300), may include receipt of an incoming communication (310). When such an event occurs, the actuation element profile (108) of a call activation key (306) is altered. In response to the actuation element profile (108) being altered, a user (620) is alerted to the incoming communication (310). Shape memory alloy elements such as martensite, actuation element profile drivers such as electromagnetic driver (700), or actuation element profile motors such as a cam and follower motor (800) a may additionally be used to alter the actuation element profile (108).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method of manufacturing a dental instrument
Method for manufacturing a dental instrument having a desired machined configuration, without twisting the instrument. A blank of superelastic material is brought to an annealed state comprising a phase structure including a rhombohedral phase alone or in combination with austenite and / or martensite, or a combination of martensite and austenite. In this annealed state, a portion of the annealed material is removed at low temperature, for example less than about 100° C., and advantageously at ambient temperature, to form a final machined configuration for the instrument. The instrument is then heat treated and rapidly quenched to a superelastic condition.
Owner:ORMCO CORP
High-strength steel sheet with yield strength of 1100MPa and manufacturing method thereof
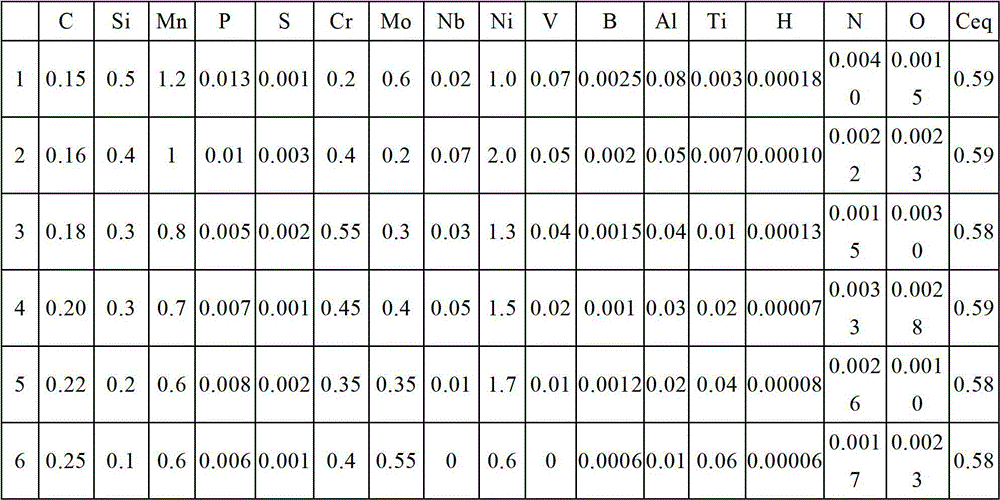
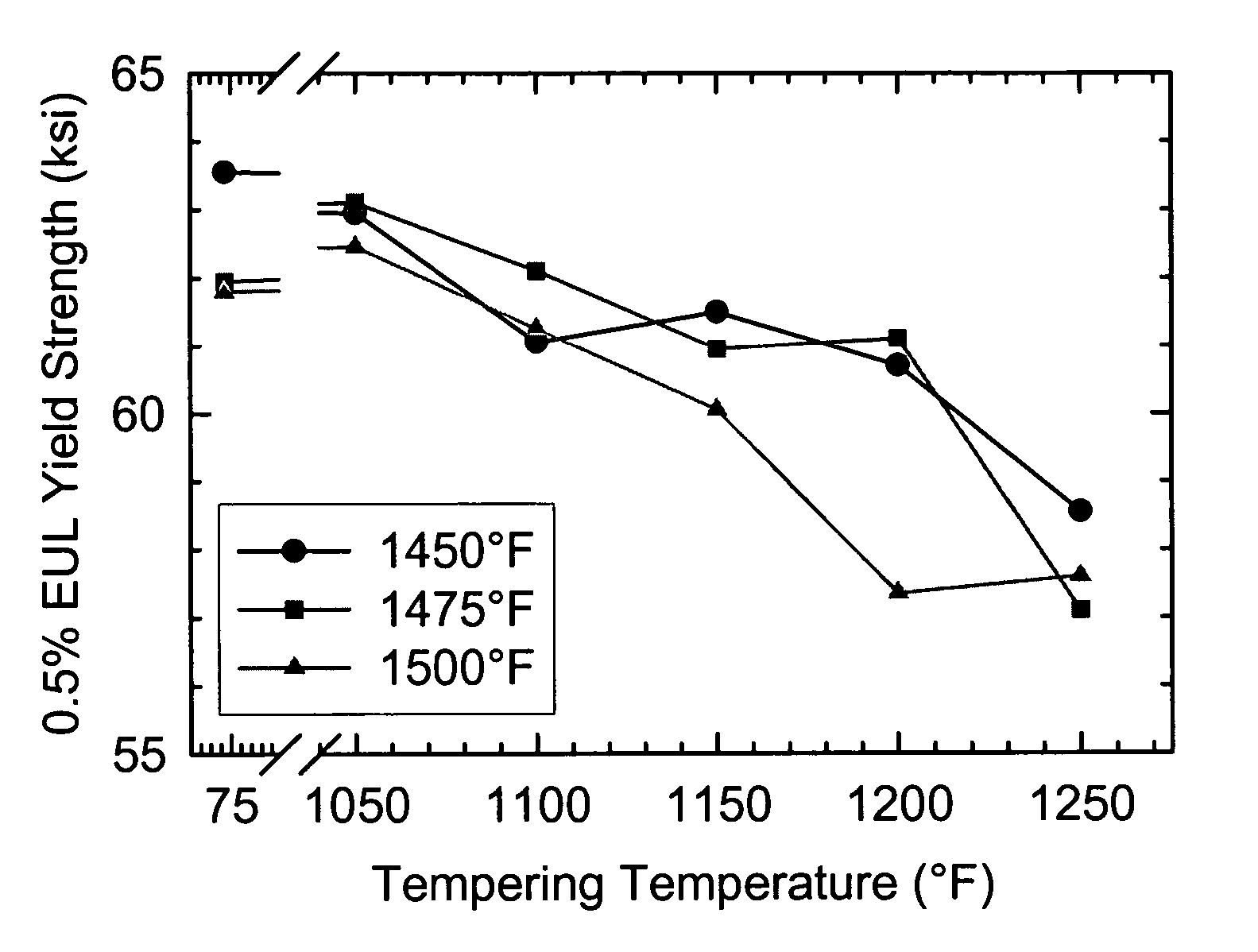
A high-strength steel sheet with yield strength of 1100MPa and a manufacturing method thereof. The high-strength steel sheet comprises, based on the weight percentage, 0.15-0.25% of C, 0.10-0.50% of Si, 0.60-1.20% of Mn, no more than 0.013% of P, no more than 0.003% of S, 0.20-0.55% of Cr, 0.20-0.70% of Mo, 0.60-2% of Ni, 0-0.07% of Nb, 0-0.07% of V, 0.0006-0.0025% of B, 0.01-0.08% of Al, 0.003-0.06% of Ti, no more than 0.00018% of H, no more than 0.0040% of N, no more than 0.0030% of O, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities; and the carbon equivalent CEQ is no more than 0.60%. A quenching and a tempering heat treatment are employed to obtain a tempered martensite tissue. The steel provided by the present invention has yield strength no less than 1100MPa, tensile strength no less than 1250MPa, Charpy ballistic work Akv (-40 DEG C) no less than 50J, and good strength and toughness.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for producing line pipe
A method for producing steel line pipe having low yield strength to tensile strength ratio in order to improve the capability of steel line pipe to undergo reeling into coil form and unreeling therefrom. The method includes (a) providing a steel pipe having a composition consisting essentially of in weight percent: C 0.01 to 0.40, Mn 0.25 to 2.0, P residual to less than 0.5, S residual to less than 0.020, Si residual to 2.0, Cu residual to 1.0, Ni residual to 1.0, Cr residual to 2.0, Mo residual to 1.0, Al 0.010 minimum to less than 1.0, N residual to 0.030, V residual to less than 0.5, B residual to less than 0.02, Ti residual to less than 0.3, and Nb residual to less than 0.3, balance iron and incidental impurities. The pipe is heated to a temperature within the intercritical Ac1 to Ac3 temperature range, cooled to a temperature below the Ms (martensite start) temperature in order to obtain martensite, reheated to a temperature below the Ac1 temperature for a time sufficient to obtain the desired yield strength, tensile strength and yield strength to tensile strength ratio, and then air cooled.
Owner:NITED STATES STEEL CORP
600HB-grade wear resistant steel plate and its manufacturing method
Disclosed is a 600HB-grade wear resistant steel plate, comprising, by weight, 0.41 to 0.50% of C, 0.10 to 0.60% of Si, 0.20 to 1.20% of Mn, no more than 0.050% of P, no more than 0.030% of S, 0.01 to 1.50% of Cr, 0.01 to 1.00% of Mo, 0.01 to 1.50% of Ni, 0.001 to 0.10% of Ti, 0.001 to 0.10% of Al, 0.001 to 0.10% of RE, 0.01 to 1.00% of W, 0.0005 to 0.0040% of B, 0.001 to 0.010% of Ca, the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities. The 600HB-grade wear resistant steel plate provided in the invention has high hardness (no less than 600HB), good toughness and plasticity, high abrasion resistance and excellent processability and weldability; the microstructure is martensite or martensite and retained austenite. Therefore, the 600HB-grade wear resistant steel plate is extremely suitable for being used in high abrasion environment, especially for being used in vehicles or equipment which contact with such materials of high hardness as high strength ores, for example, a bucket, or the compartment of an electric wheel self-discharging truck for mining, etc.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength hot-dip zinc plated steel sheet excellent in workability and process for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101821419AImprove balanceExcellent stretch flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelHigh intensity
The invention provides a high-strength hot-dip zinc plated steel sheet which exhibits high TS-El balance, excellent stretch frangeability, excellent workability due to low YR, and excellent impact characteristics, and a process for manufacturing the same. A high-strength hot-dip zinc plated steel sheet excellent in workability and impact characteristics, having a composition which contains by mass C: 0.05 to 0.3%, Si: 0.01 to 2.5%, Mn: 0.5 to 3.5%, P: 0.003 to 0.100%, S: 0.02% or below, Al: 0.010 to 1.5%, and N: 0.007% or below and further contains at least one element selected from among Ti, Nb and V in a total amount of 0.01 to 0.2% with the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities and a microstructure which comprises, in terms of area fraction, 20 to 87% of ferrite, 3 to 10% (in total) of martensite and retained austenite, and 10 to 60% of tempered martensite and in which the average grain diameter of the second phase consisting of the martensite, retained austenite, and tempered martensite is 3[mu]m or below.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
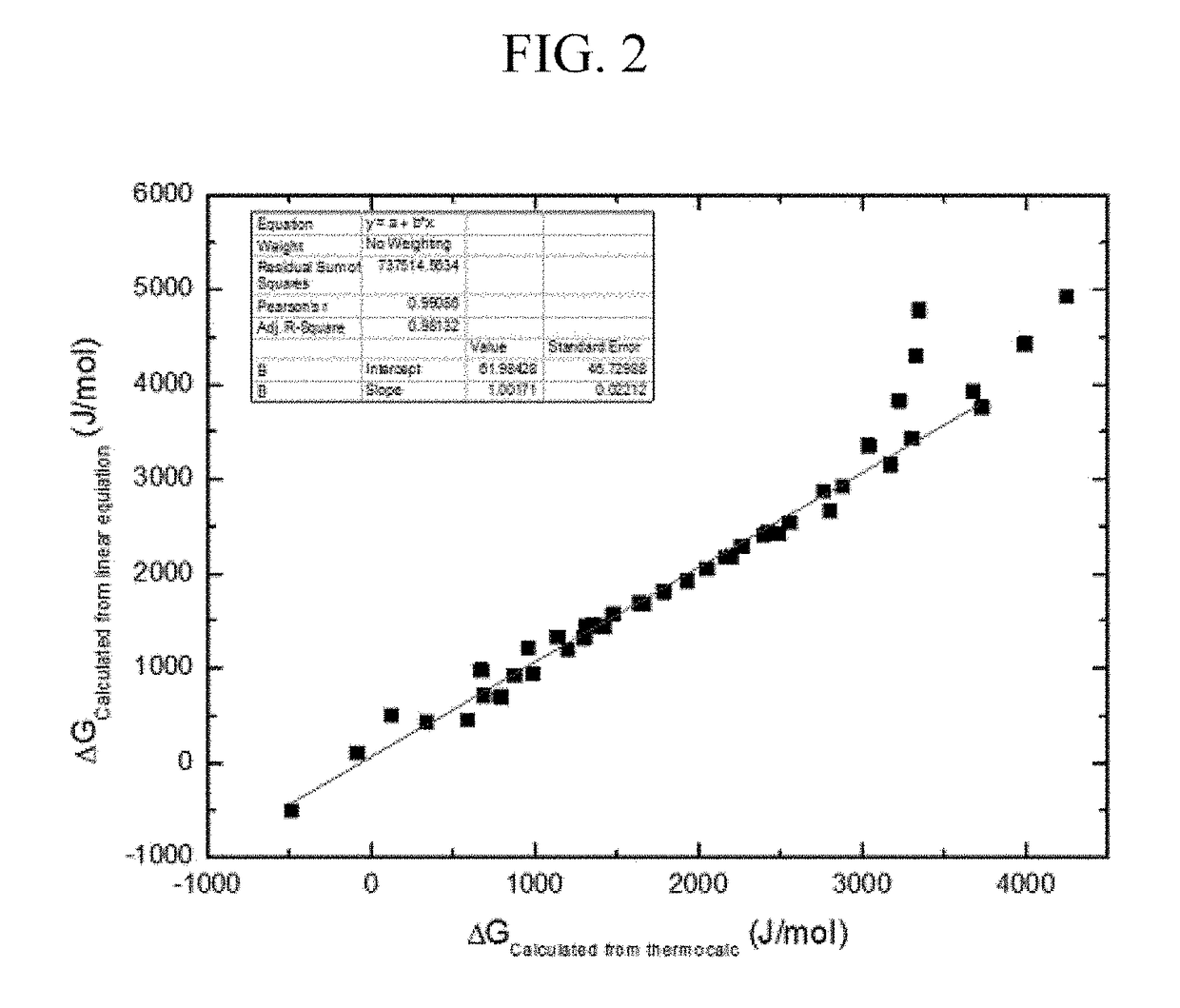
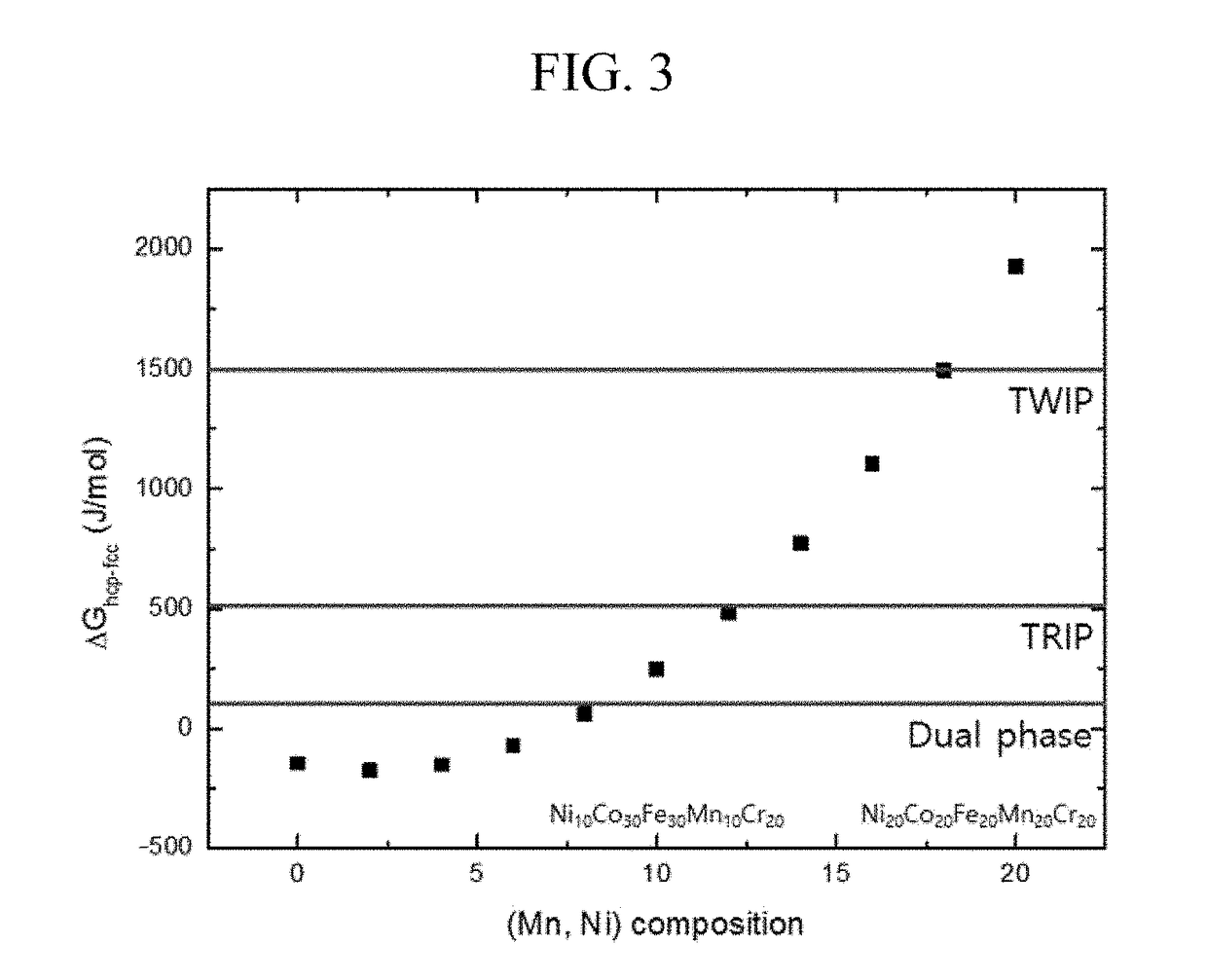
High entropy alloy having twip/trip property and manufacturing method for the same
The present invention relates to a high entropy alloy having more improved mechanical properties by controlling contents of additive elements in a NiCoFeMnCr 5-element alloy to control stacking fault energy, thereby controlling stability of a γ austenite phase to control a transformation mechanism, wherein the stacking fault energy is controlled in a composition range of NiaCobFecMndCre (a+b+c+d+e=100, 1≦a≦50, 1≦b≦50, 1≦c≦50, 1≦d≦50, 10≦e≦25, and 77a−42b−22c+73d−100e+2186≦1500), and thus, the γ austenite phase exhibits a twin-induced plasticity (TWIP) property or a transformation induced-plasticity (TRIP) property in which the γ austenite phase is subjected to phase transformation into an ε martensite phase or an α′ martensite phase, under stress, thereby having improved strength and elongation at the same time to have excellent mechanical properties.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Reusable, spring driven autoinjector
The present invention provides a reusable spring driven autoinjector. The drive mechanism of the autoinjector of the present invention includes one or more drive springs formed of a shape memory alloy. Therefore, by alternating the shape memory alloy forming the one or more drive springs between austenite phase before an injection and a martensite phase after injection, the reusable autoinjector of the present invention is capable of providing an injection force that is higher than the compressive force required to cock the drive mechanism in preparation for a subsequent injection operation.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Oxide dispersion strengthening low activity martensitic steel material and preparation thereof
The invention discloses an oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel. A substrate is a CLAM steel and contains 0.2 to 0.5 percent of Y2O3 and 0.10 to 0.50 percent of Ti. The method comprises the following steps that: CLAM steel powder, Y2O3 powder and Ti powder are evenly mixed and put in a sealed container for degassing, subjected to mechanical alloying, hot isostatic pressing or hot-pressing sintering and densification molding under the protection of high-purity argon gas, then subjected to hot squeezing or forging and rolling and other machining and molding processes, and the needed section material is prepared; and finally, the section material is subjected to the treatment of quenching and tempering to prepare the oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel ODS-CLAM. The oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel has the advantages that: the low-activation martensitic steel realizes a martensite-based alloy with oxide strengthening phases evenly dispersed and distributed and crystal grains of a reasonable size, can be used as a structural steel material, has the characteristics of strong neutron irradiation resistance, good high-temperature performance, low activation, etc. and is suitable for a fusion reactor and other environments with strong neutron irradiation and high-temperature.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-safe high-precision producing method of thermoforming martensitic steel parts
InactiveCN101280352AGuaranteed Hardenability RequirementsLow yield ratioShaping toolsHot stampingSheet steel
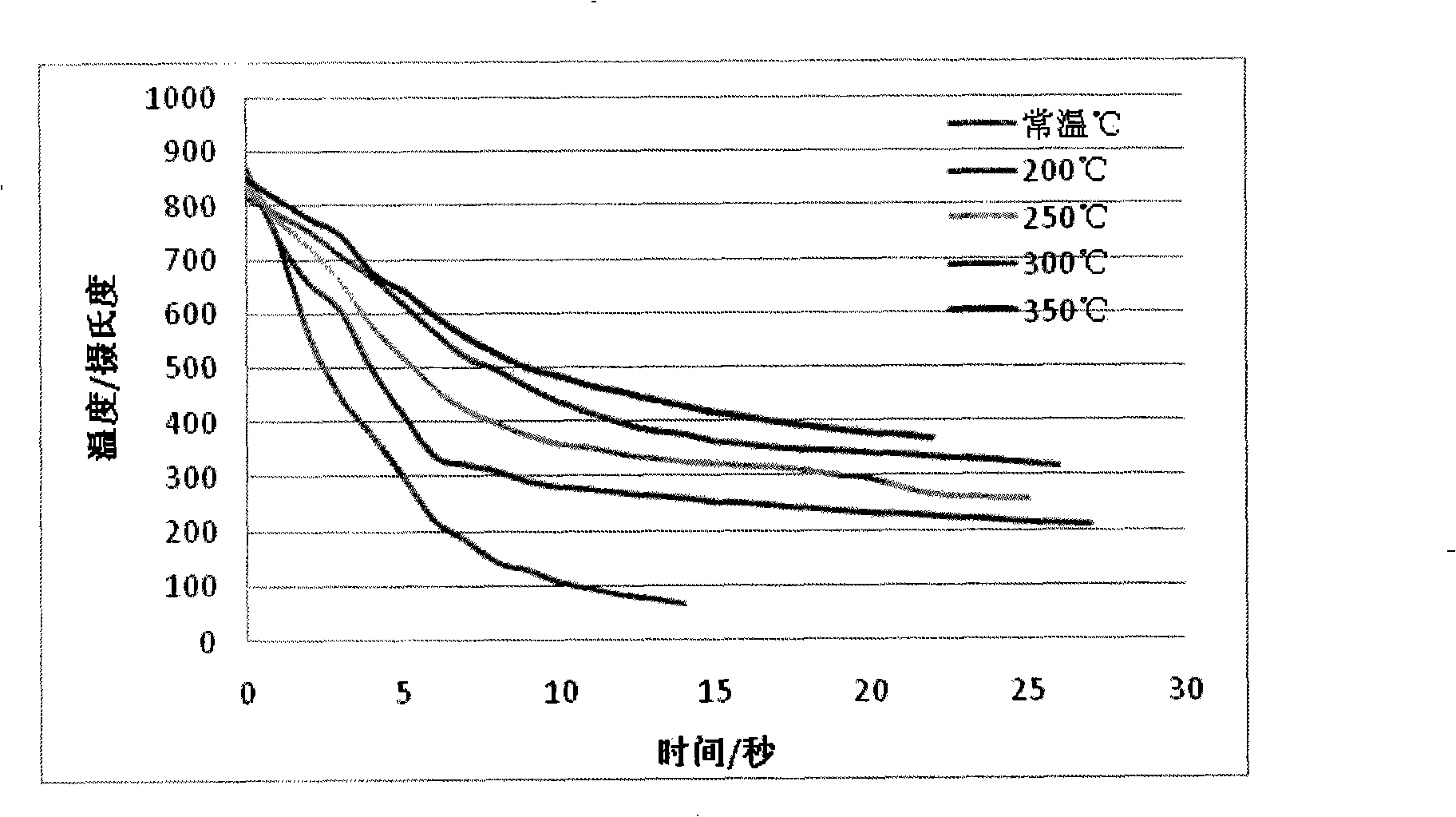
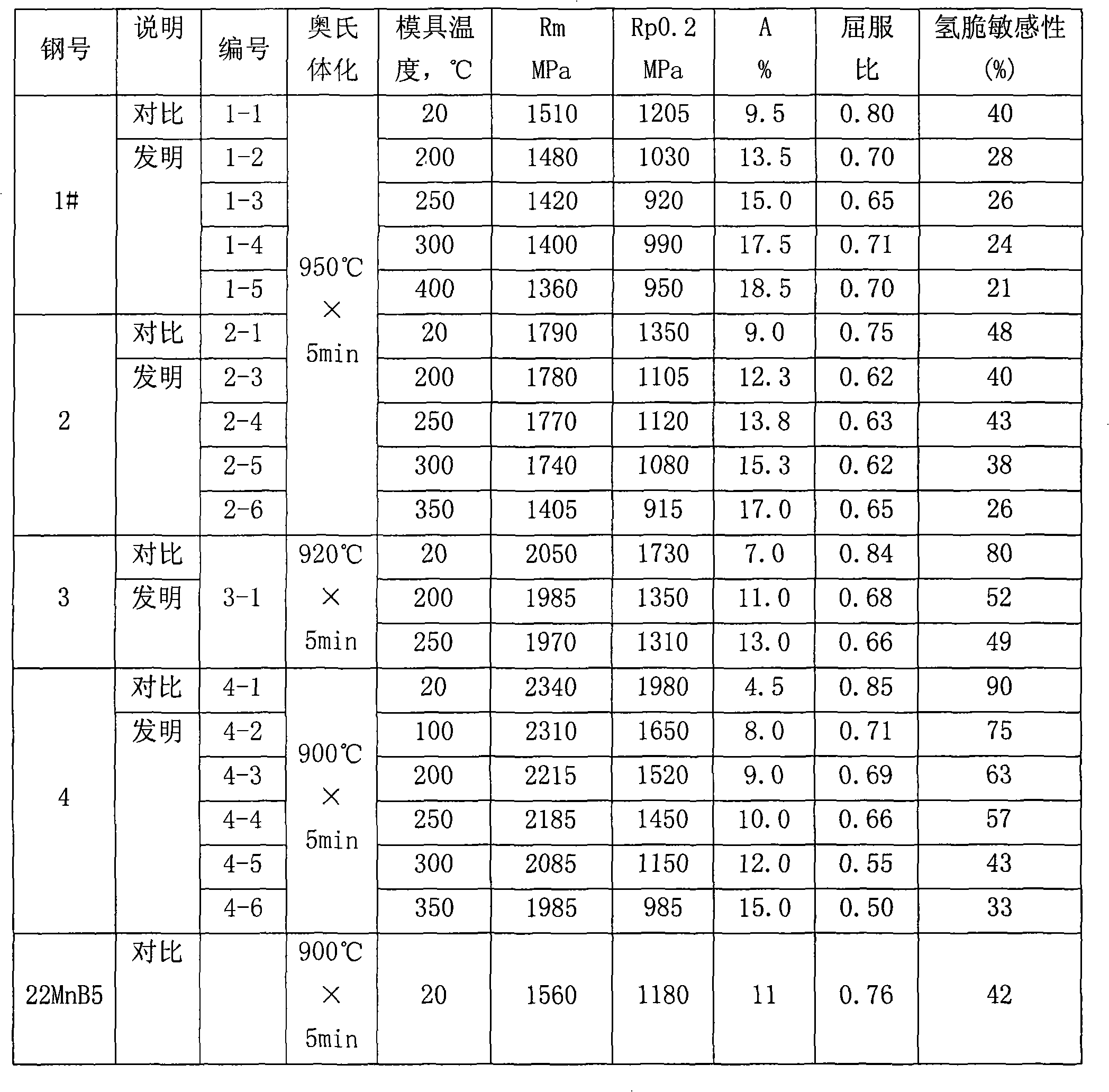
The invention provides a high security, high accuracy and thermal forming martensite steel part preparing method, which belongs to the field of obtaining controlling and cooling technology of the hot stamping forming part of the alloy steel plate, the martensite works as the matrix structure of the alloy steel plate. The method adopts the processes as follows: a steel plate is heated to 20 to 250 DEG C above the Ac3 temperature, therefore an austenite structure can be obtained, then the steel plate is transferred to the stamping die for forming by stamping; simultaneously, the temperature of the stamping die is controlled in a range of 100 to 400 DEG C, 5 to 60 seconds later after stamping forming, the formed component parts can be taken out of the stamping die. The method has the advantages that a well ductility and security can be obtained, and the anti-susceptibility of the steel can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
High yield ratio and high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet excellent in workability and production method thereof
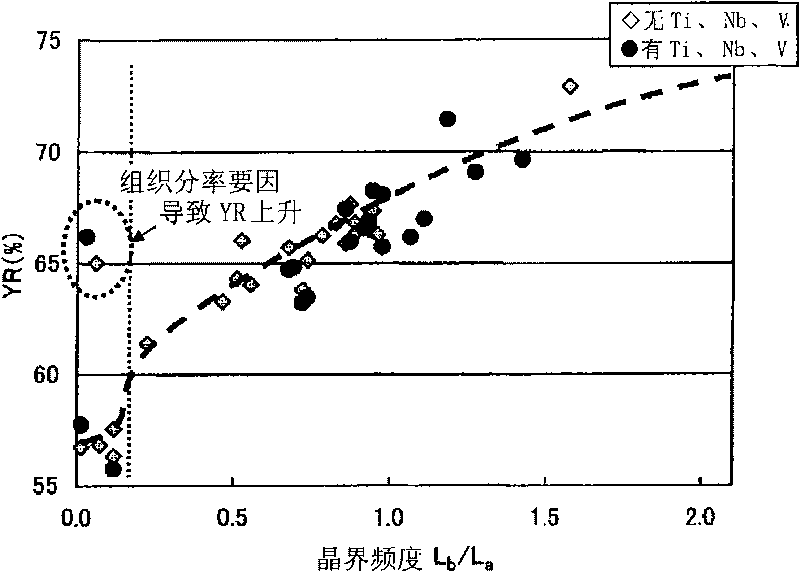
InactiveCN101724776AHigh yield ratioHigh elongationHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelCrystal orientation
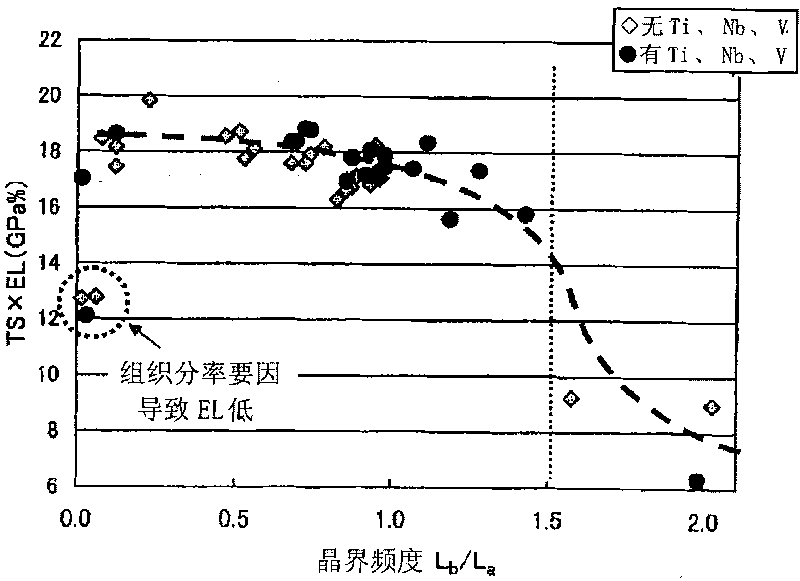
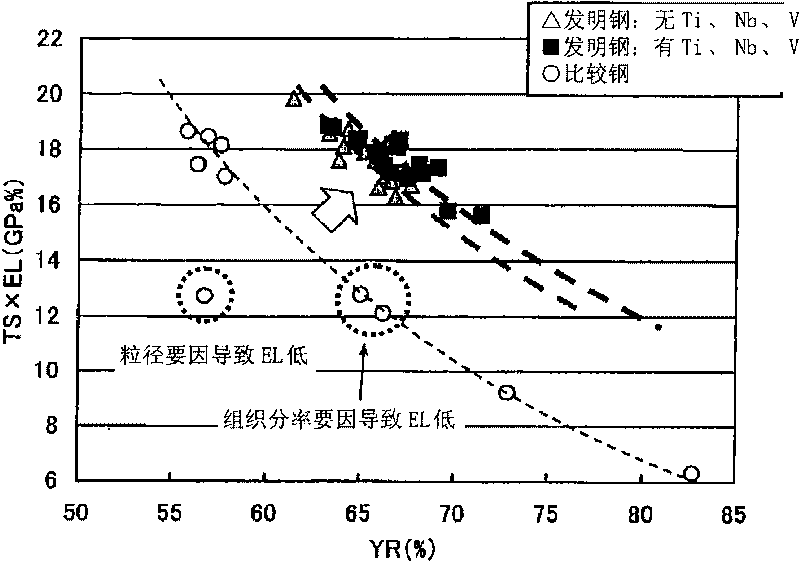
A high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet excellent in workability according to the present invention: contains C, Si, Mn and other elements; has a dual phase structure containing ferrite and martensite as the metallographic structure; and, in the ferrite structure, satisfies the expression 0.2<=(Lb / La)<=1.5 when the length per unit area of the grain boundaries of crystal grains the crystal orientation differences of which are 10 degrees or more is defined as La and the length per unit area of the grain boundaries of crystal grains the crystal orientation differences of which are less than 10 degrees is defined as Lb and further satisfies the requirements that the average value of D is 25 [mu]m or less and the area ratio of crystal grains satisfying the expression D<=30 [mu]m in the ferrite grains surrounded by the grain boundaries of crystal grains the crystal orientation differences of which are 10 degrees or more is 50% or more when the circle equivalent diameter of each of ferrite grains surrounded by the grain boundaries of crystal grains the crystal orientation differences of which are 10 degrees or more is defined as D; and has a tensile strength of 980 MPa or more.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method for preparing seamless steel tubes made of martensite precipitation hardening stainless steel
InactiveCN101612700AAvoid Surface Quality IssuesReduce lossFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsSolution treatmentProduct inspection
The invention discloses a method for preparing seamless steel tubes made of martensite precipitation hardening stainless steel, which comprises the following steps of billets, peeling, blanking, heating, hot punching, cooling, finishing, acid cleaning, lubricating, degreasing, heat treatment, straightening, tube cutting, acid cleaning, inspection, and packaging and warehousing. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that: pierced billets after hot punching are cooled in a pile so as to reduce working procedures and cost; the intermediate heat treatment adopts solution treatment, has short time and high efficiency, and improves surface quality; the tubes all adopt cold rolling process to improve yield; and vacuum aging treatment is adopted to improve the comprehensive mechanical property, the finished product inspection qualified rate reach 95 percent, and the yield from the billets to the finished products reach 51.31 percent.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent workability, molten galvanized high-strength steel sheet, and method for producing same
ActiveCN102227511AExcellent hole expandabilityImprove bending performanceHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesUltimate tensile strengthMartensite
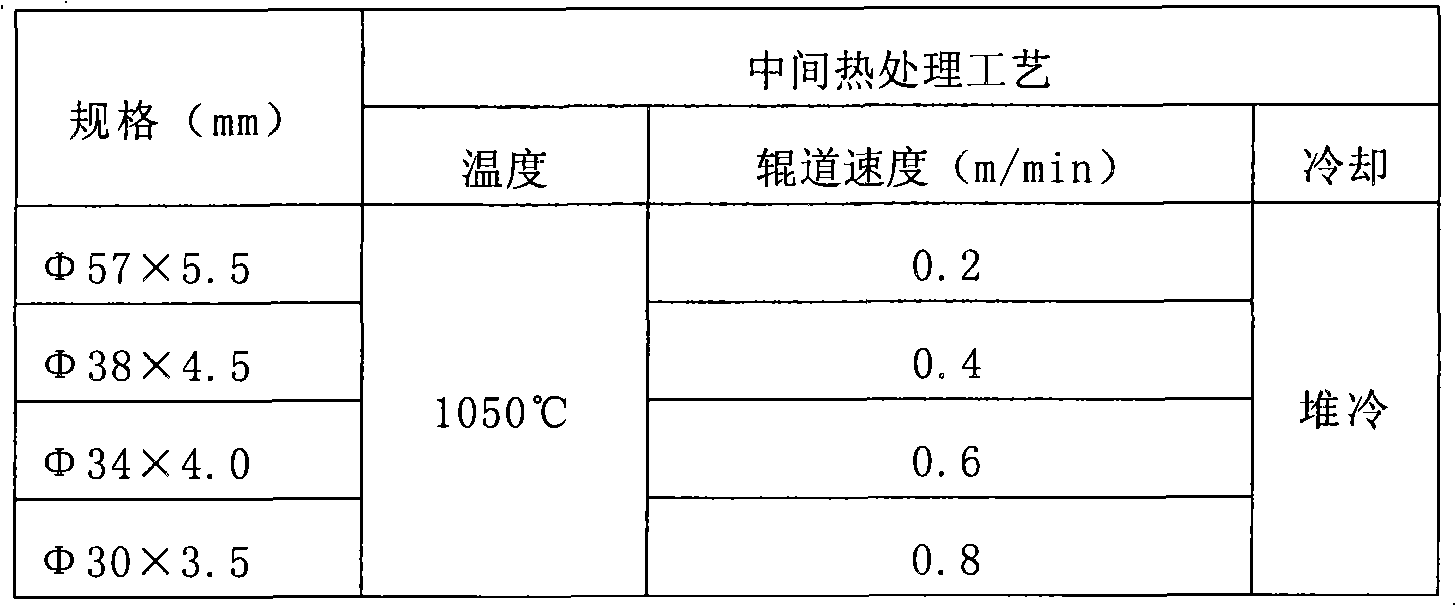
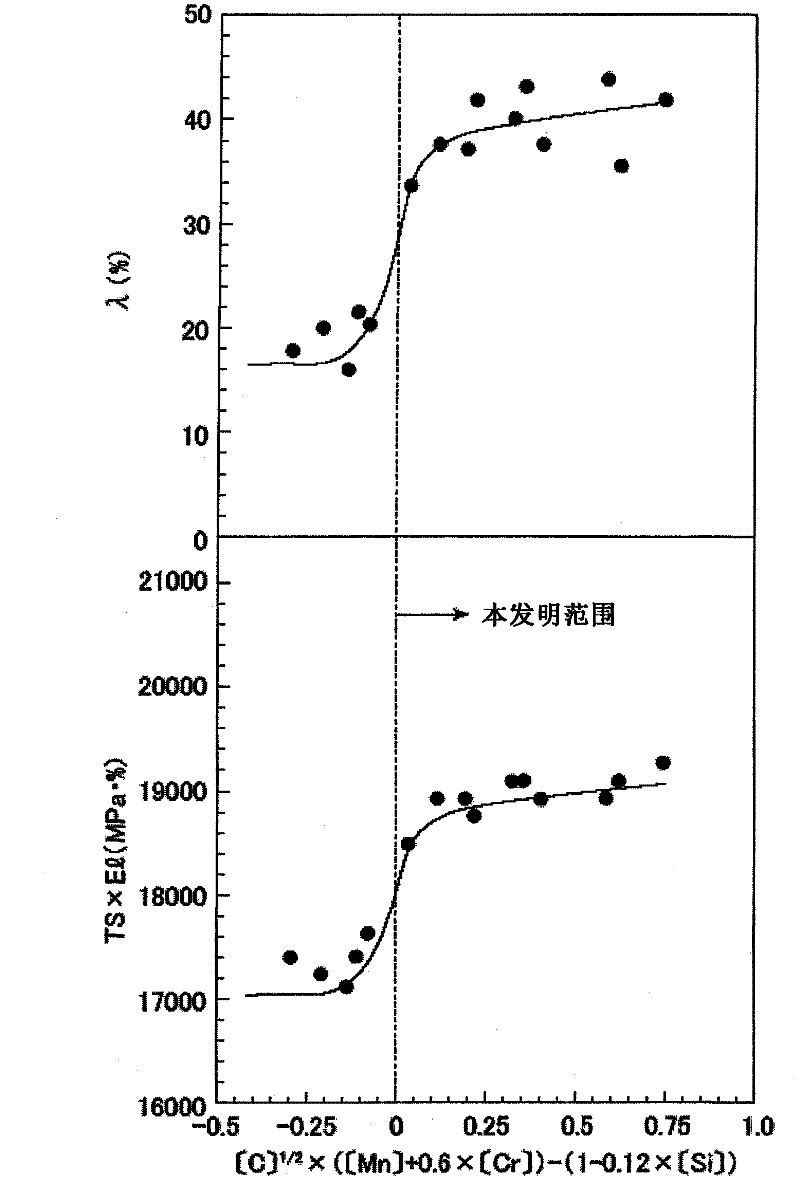
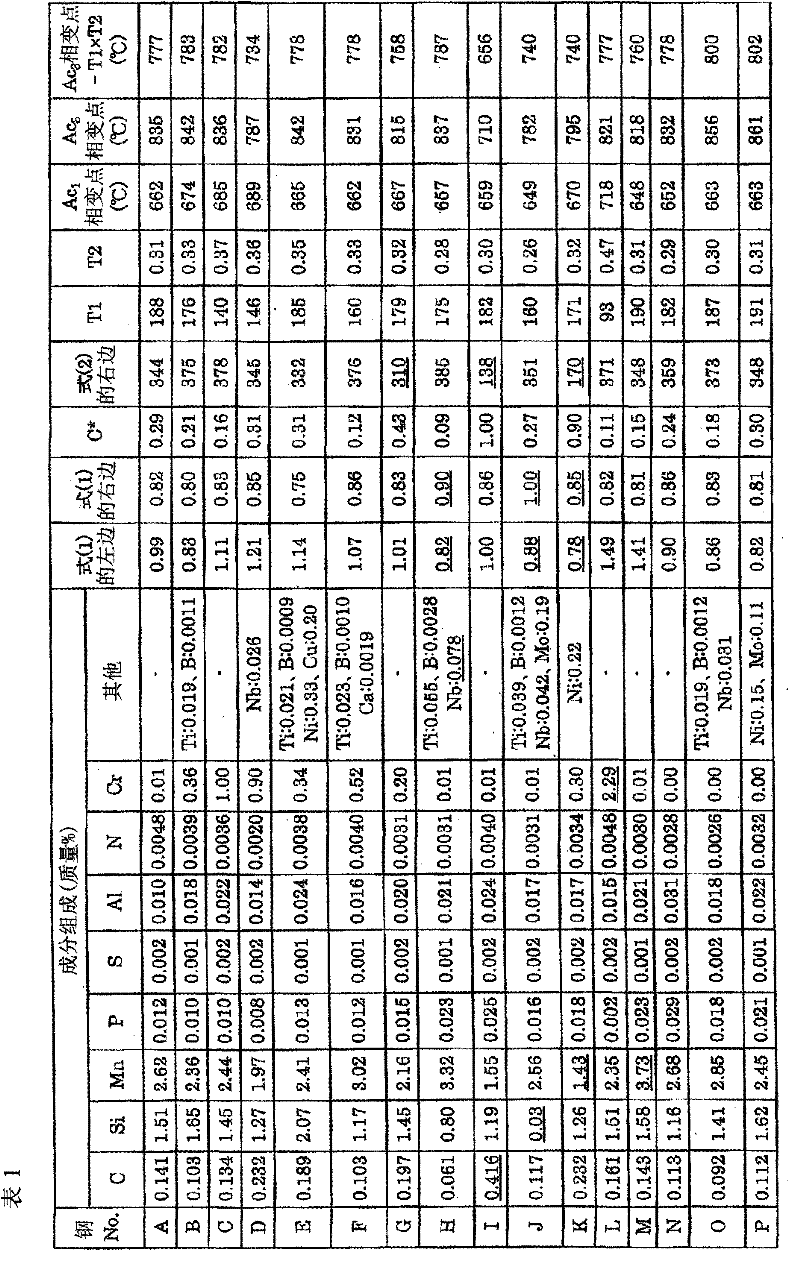
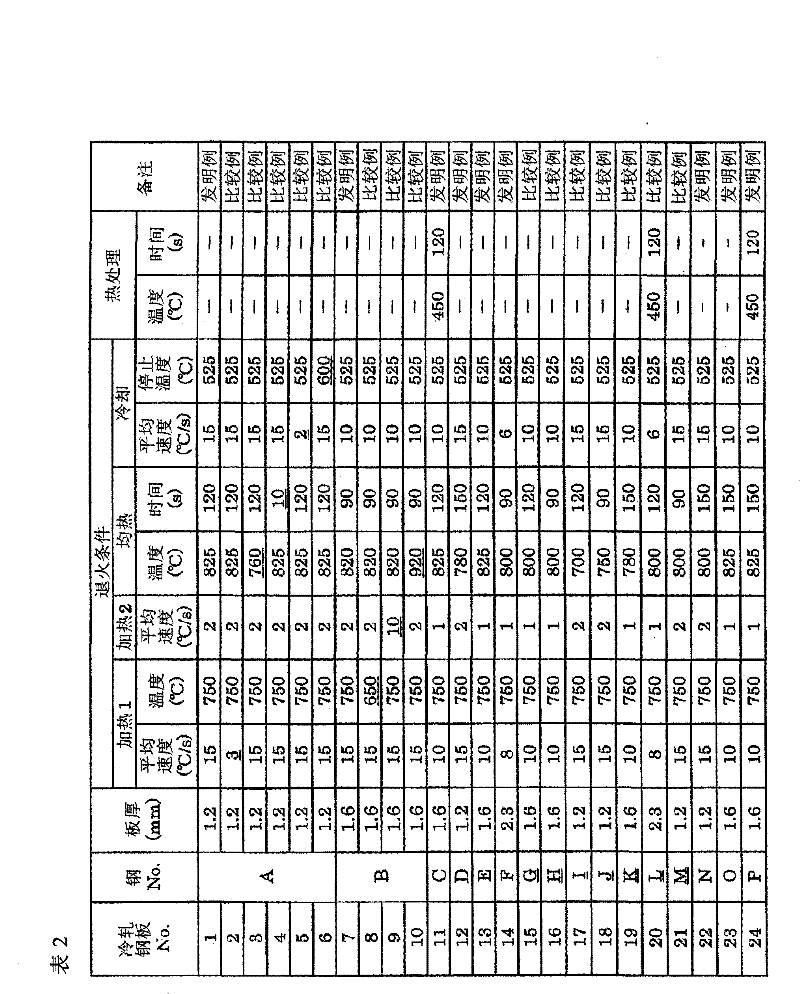
The invention provides a high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having a TS of 1,180 MPa or greater and excellent workability, such as stretch flange workability and bendability. Also provided are a molten galvanized high-strength steel sheet, and a method for producing the same. The high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent workability has a composition that comprises, by mass%, C: 0.05 to 0.3, Si: 0.5 to 2.5, Mn: 1.5 to 3.5, P: 0.001 to 0.05, S: 0.0001 to 0.01, Al: 0.001 to 0.1, N: 0.0005 to 0.01, and Cr: 1.5 or less (including 0) and satisfies formulas (1) and (2), with the balance being Fe and inevitable impurities. The steel sheet has a microtexture wherein there is a ferrite phase and a martensite phase, the percentage of the texture total surface area occupied by martensite phase is 30% or greater, (the surface area occupied by martensite phase) / (surface area occupied by ferrite phase) exceeds 0.45 but is less than 1.5, and the average particle diameter of the martensite phase is 2 microns or larger. [C]1 / 2*([Mn]+0.6*[Cr])> / =1-0.12*[Si] (1), and 550-350*C*-40*[Mn]-20*[Cr]+30*[Al]> / =340 (2), wherein C*=[C] / (1.3*[C]+0.4*[Mn]+0.45*[Cr]-0.75).
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com