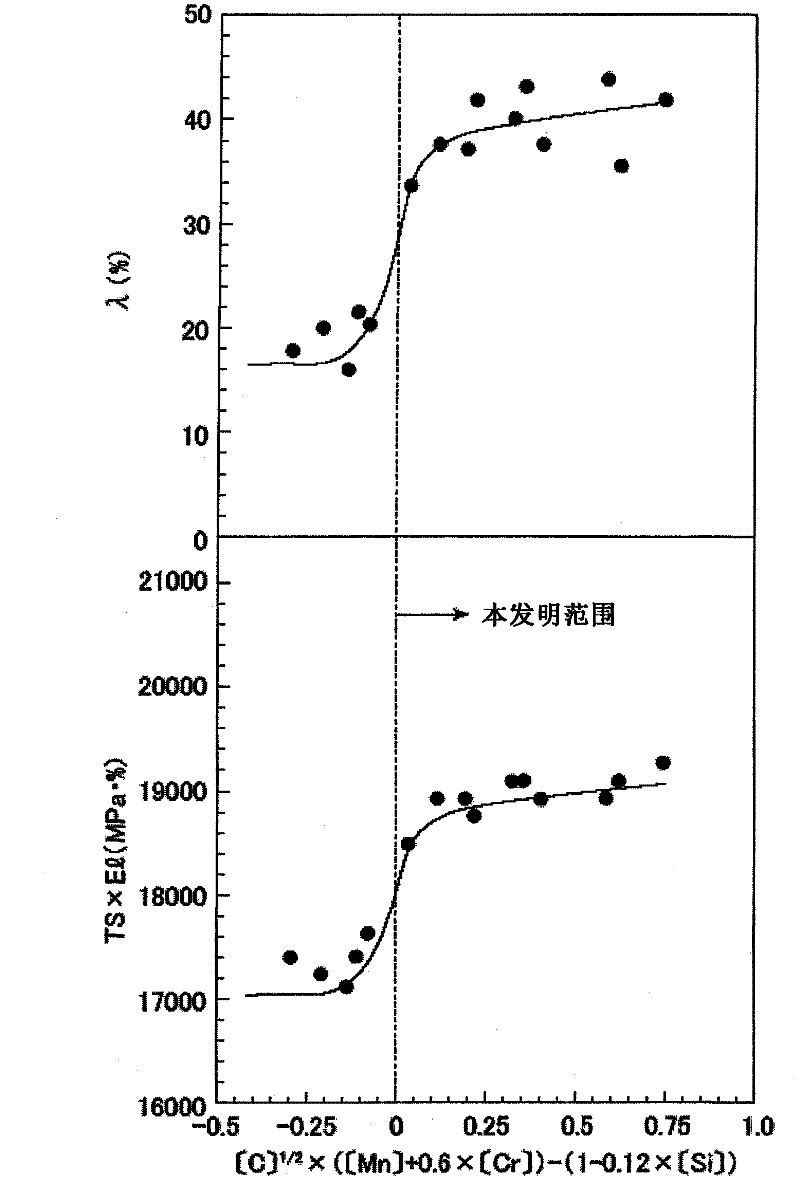
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent workability, molten galvanized high-strength steel sheet, and method for producing same
A technology of hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and cold-rolled steel sheet, which is applied in the field of high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet and high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet, which can solve the problems of steel sheet hole expandability and lower bendability, and achieve excellent hole expandability and bendability , Excellent formability, and the effect of ensuring safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
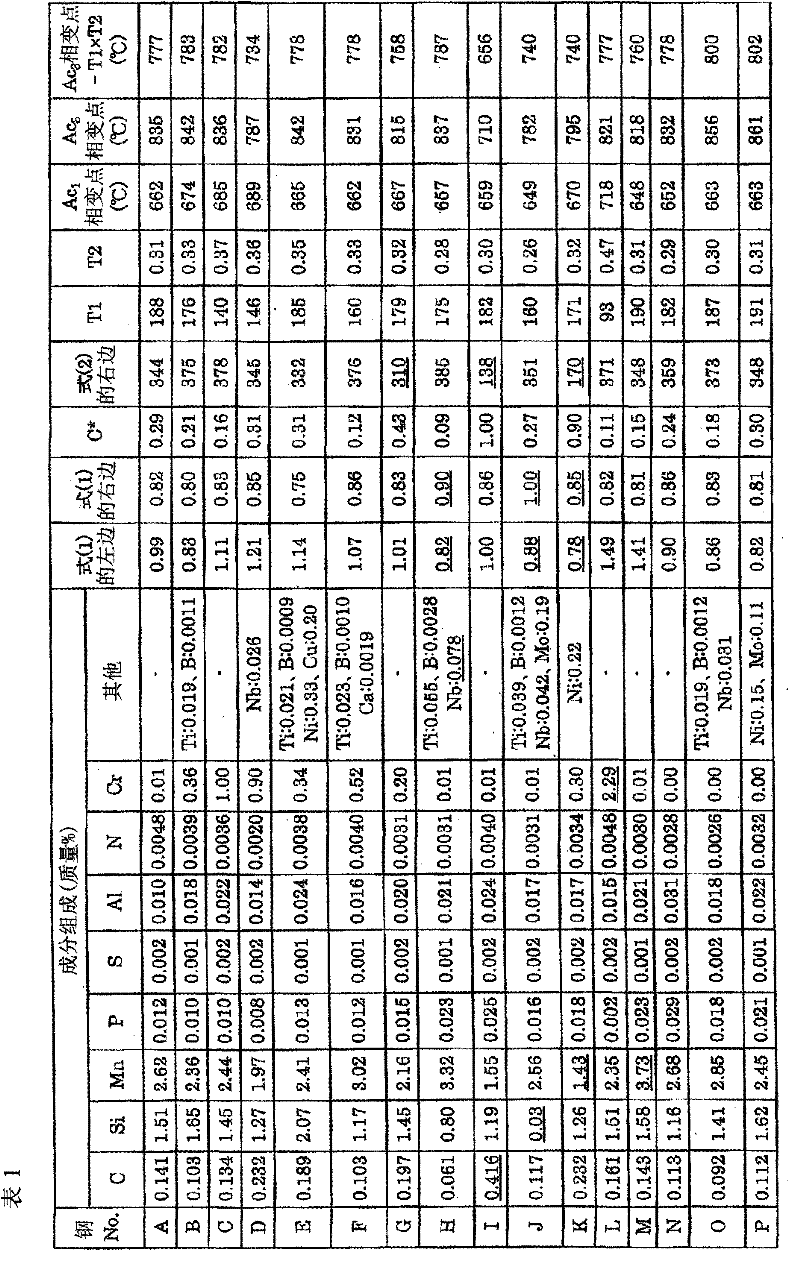
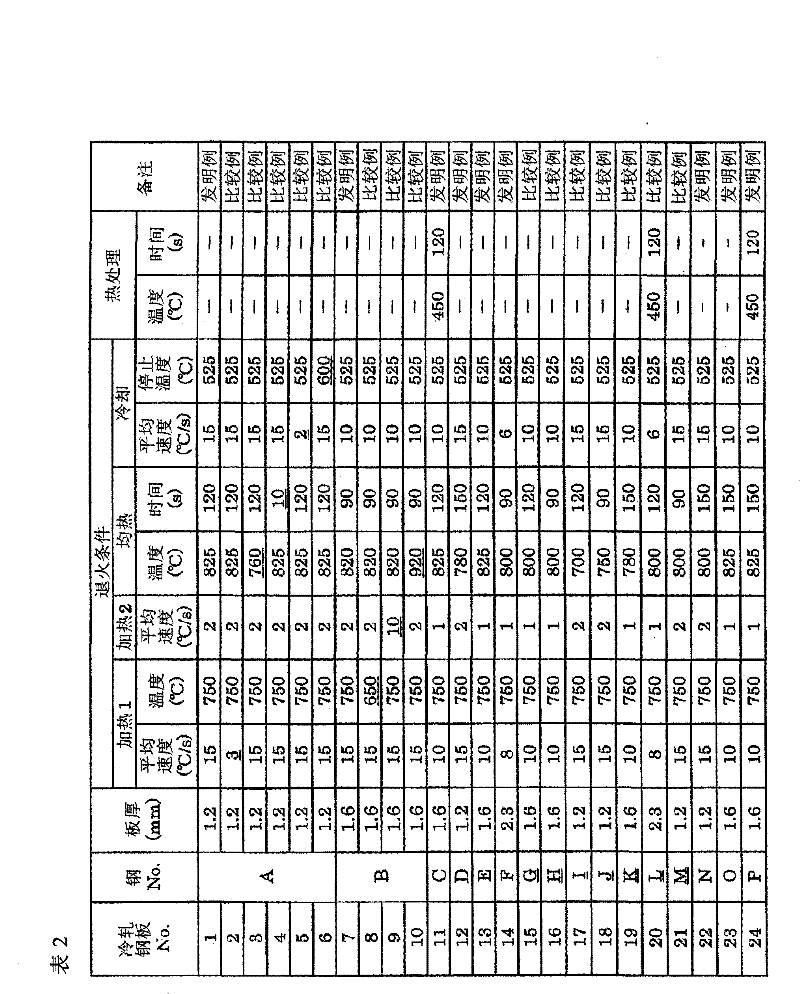
[0112] Steel Nos. A to P having the compositions shown in Table 1 were smelted in a converter, and steel slabs were produced by a continuous casting method. These billets were heated to 1200°C, hot rolled at a finishing temperature of 850 to 920°C, and coiled at a coiling temperature of 600°C. Then, after pickling, it was cold-rolled at a rolling reduction rate of 50% to the plate thickness shown in Table 2, and annealed under the annealing conditions shown in Table 2 through a continuous annealing line to produce cold-rolled steel sheets No. 1 to 24. . Then, the area ratio of the ferrite phase of the obtained cold-rolled steel sheet, the area ratio of the martensite phase obtained by combining the tempered martensite phase and the untempered martensite phase, and the martensite The ratio of the area of the ferrite phase to the area of the ferrite phase, the average grain size of the martensite phase, the area ratio of the tempered martensite phase in the entire martensit...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Steel Nos. A to P having the compositions shown in Table 4 were smelted in a converter, and steel slabs were produced by a continuous casting method. These billets were heated to 1200°C, hot rolled at a finishing temperature of 850 to 920°C, and coiled at a coiling temperature of 600°C. Then, after pickling, cold rolling at a rolling ratio of 50% to the plate thickness shown in Table 5, and after annealing in the annealing conditions shown in Table 5 through a continuous hot-dip galvanizing line, some steel sheets were subjected to heat treatment at 400°C. Heat treatment for the time shown in Table 5, followed by immersion in a 475°C zinc plating bath containing 0.13% Al for 3 seconds to form a coating with a deposition weight of 45g / m 2 The galvanized layer was alloyed at the temperature shown in Table 5 to make galvanized steel sheets No.1-26. In addition, as shown in Table 5, some galvanized steel sheets were not alloyed. Then, the same investigation as in Example ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com