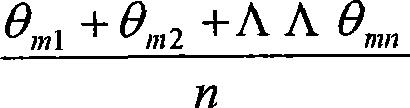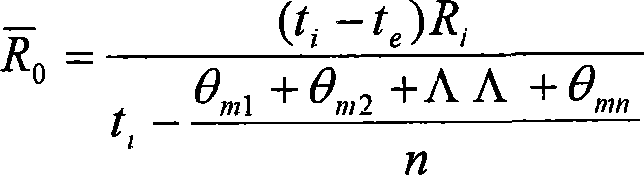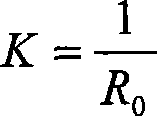Patents
Literature
136 results about "Hot box" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A hot box is the term used when an axle bearing overheats on a piece of railway rolling stock. The term is derived from the journal-bearing trucks used before the mid-20th century. The axle bearings were housed in a box that used oil-soaked rags or cotton (collectively called "packing") to reduce the friction of the axle against the truck frame. When the oil leaked or dried out, the bearings overheated, often starting a fire that could destroy the entire railroad car (and cars coupled to it) if not detected early enough.
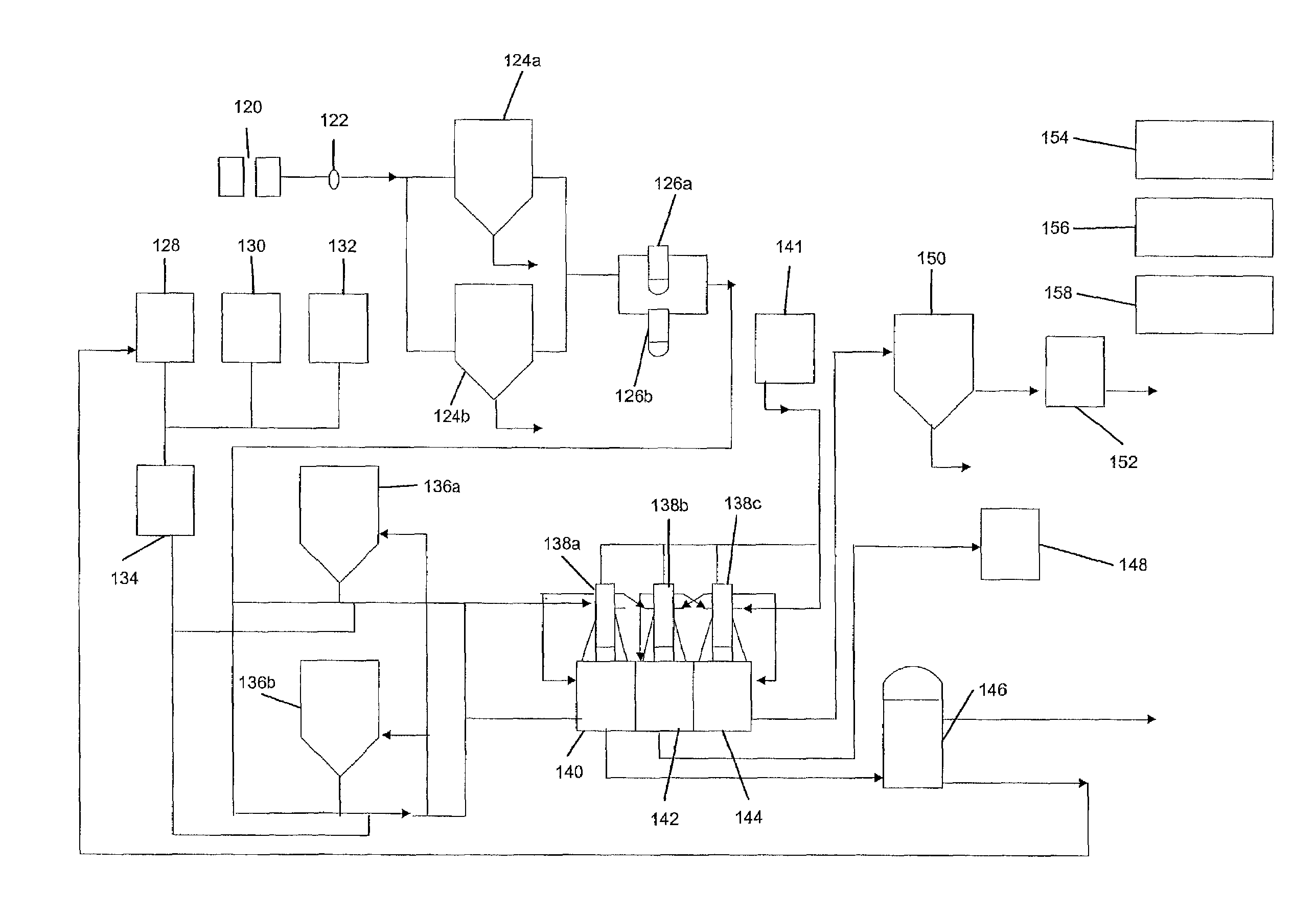
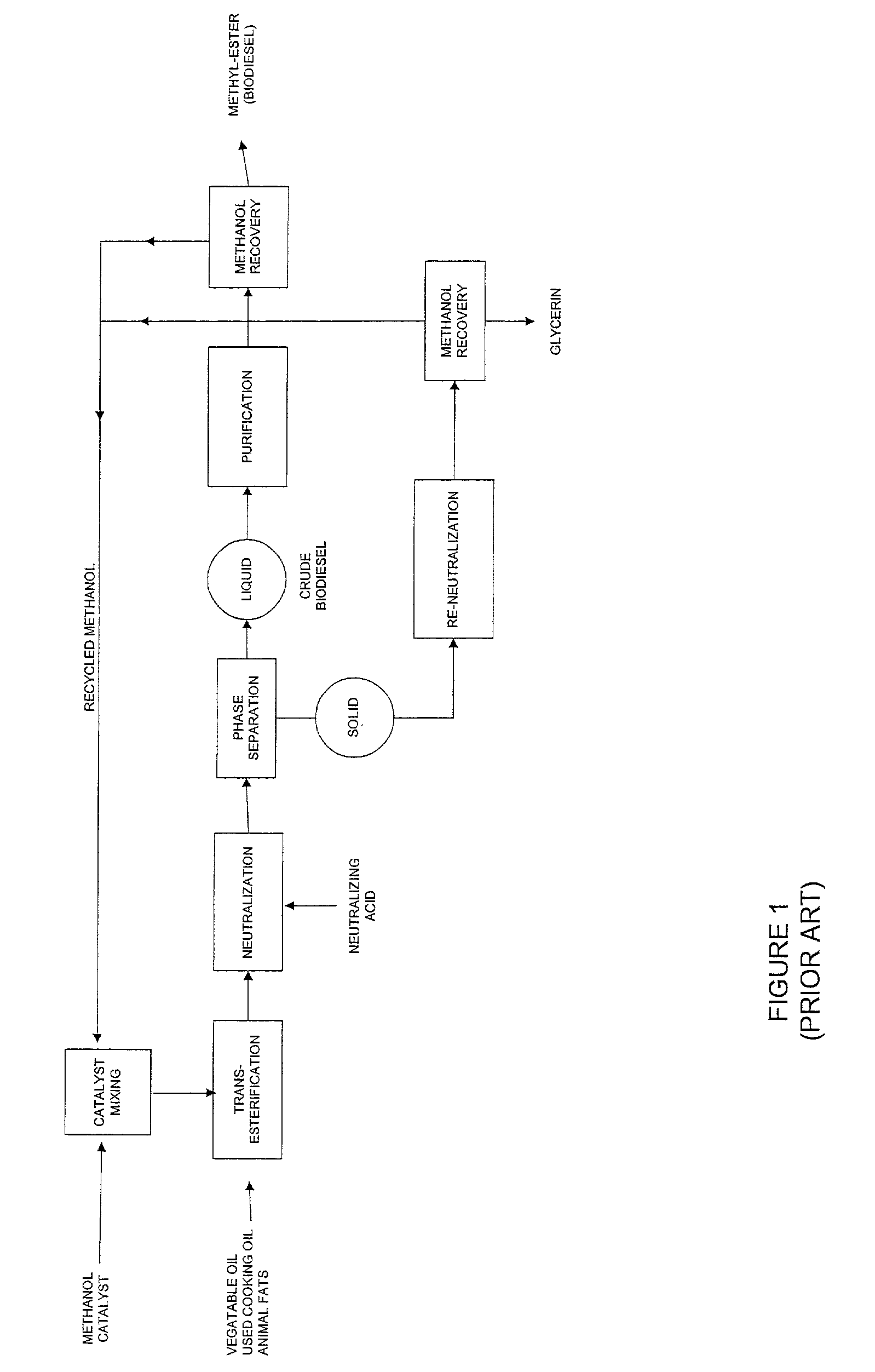
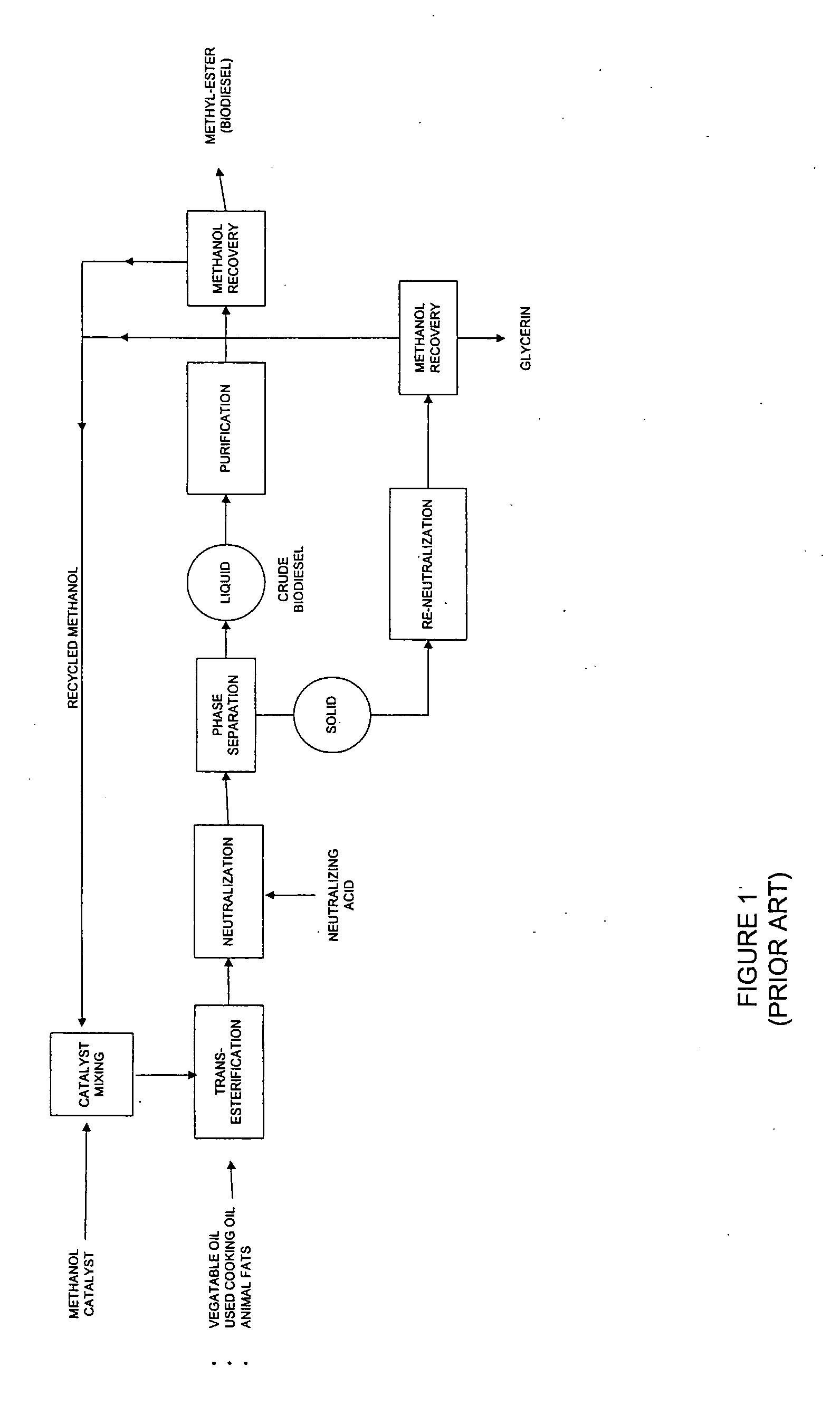
Biodiesel production unit
In a first aspect, systems and methods for producing biodiesel fuel include a modular production unit incorporated onto a single platform or into a housing for ease of relocatability. The modular production unit preferably includes a mixing unit, a reactor unit, a separation unit, a distillation unit, and a filtering unit, all incorporated onto or into a self-contained platform or housing that is able to be easily relocated. In a second aspect, the modular production unit is combined with additional fixed and / or relocatable components to provide a biodiesel processing plant. In a third aspect, a raw materials processing system and method includes a roller barrel adapted for recovery, transportation, and introduction of recycled oil feedstock into a biodiesel manufacturing process. The raw materials processing system preferably includes a hot box for filtering and heating the raw recycled oil feedstock.
Owner:BIODIESEL IND
Production system and method
In a first aspect, systems and methods for producing biodiesel fuel include a modular production unit incorporated onto a single platform or into a housing for ease of relocatability. The modular production unit preferably includes a mixing unit, a reactor unit, a separation unit, a distillation unit, and a filtering unit, all incorporated onto or into a self-contained platform or housing that is able to be easily relocated. In a second aspect, the modular production unit is combined with additional fixed and / or relocatable components to provide a biodiesel processing plant. In a third aspect, a raw materials processing system and method includes a roller barrel adapted for recovery, transportation, and introduction of recycled oil feedstock into a biodiesel manufacturing process. The raw materials processing system preferably includes a hot box for filtering and heating the raw recycled oil feedstock.
Owner:BIODIESEL IND
Predicting method for lithiumion cell heat safety performance
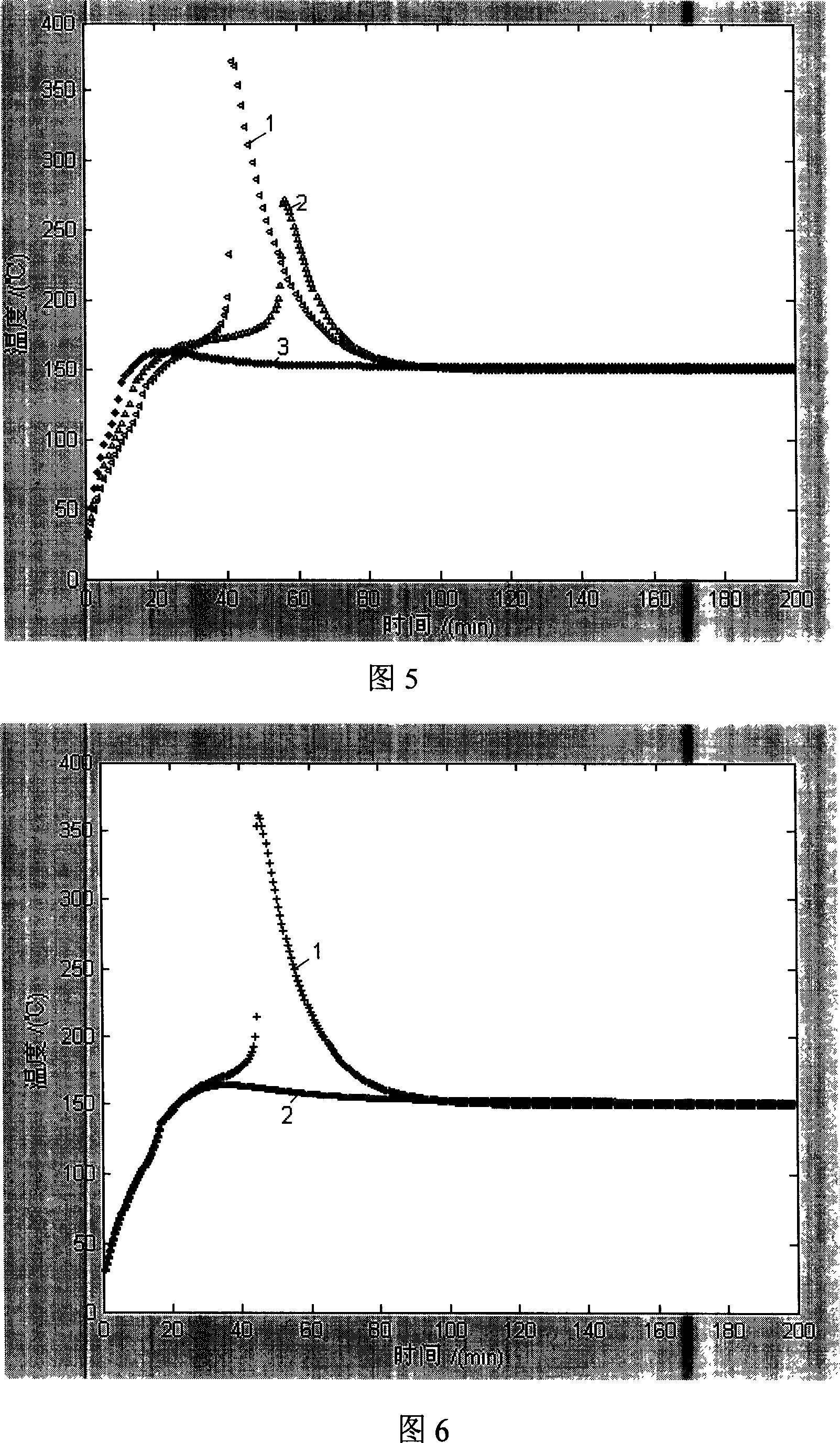
The core of the technique is that the method builds thermal model of lithium ion battery under condition of abuse (for ex. hot box, short circuit, and overcharge) based on law of conservation of energy and Fourier law. Using thermal insulation technique for measuring heat determines kinetic parameter of internal heat source item in model; and other parameters come from documents and experiments. Using the model can forecast safety performance of battery under condition of abuse. Modifying model parameter obtains thermo-safety factors influencing lithium ion battery so as to provide theory basis of predicting safety critical value including size of battery, application temperature and material of battery for safety design of battery. The method reduces fussy working procedures for estimating safety performance of material and new battery by making actual battery and carrying out performance test. Advantages are: avoiding waste of resources and time, quick test speed, and low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN LISHEN BATTERY
Method for manufacturing nylon/spandex air-textured yarn by false twist texturing machine one-step method
The present invention provides a method for making nylon-polyurethane fiber blended yarn by utilizing false-twist texturing machine and adopting one-step process. Said method includes the following steps: (A), making nylon raw yarn be drawn out from raw yarn frame, and making said nylon raw yarn be fed into first roller by means of first yam-cutting device of false-twist texturing machine, then fed into a texturing hot-box, and passed through a cooling device and a false-twister, then attracted by suction gun; (B), making polyurethane fiber yarn be drawn out from polyurethane fiber roller, and making said polyurethane fiber yarn be passed through second yarn-cutting device and second yarn-detector, then be attracted by suction gun, then combined with nylon yarn; and (C), making the combined two yarns be passed through intermediate roller, air-entanglement jet device, second auxiliary roller and first yarn detector, and be reached to oiling roller, finally passed through winding roller and winding to make formation.
Owner:WUXI HONGYUAN ELECTROMECHANICAL TECH
Building glass steady state heat resistance measuring equipment
InactiveCN101241091AHigh precisionUniform temperatureMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHot boxProcess systems
A device special for determining stable state thermal resistance of architecture glass which is a necessary determining device for quality control and product acceptance in energy-saving architecture glass produce is provided. The present invention comprises of heat flux sensor, internal and external guarding heat-box, cold-box (including refrigerating unit), precision temperature measurement and computer data collecting process system, and frame mounted rise-and-fall glass carrying stage and vacuum acetabula glass fixation mechanism. The present invention is not only used for detecting state thermal resistance of energy-saving architecture glass such as vacuum glass, hollow glass, and so on, but also used for detecting heat insulation and heat preservation capacity of other plate architecture material such as polystyrene board, steel (aluminium) plastic compound heat preserving board and so on.
Owner:BEIJING QINRUN GLASS
Preparation method of novel wool-like differential fibers
The invention discloses a preparation method of novel wool-like differential fibers, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) adopting polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) as a raw material to prepare a pre-oriented yarn (a); 2) adopting modified high-shrinkage polyester as a raw material to prepare fully-drawn high boiling water shrinkage fibers (b); and 3) on a DTY machine, passing the pre-oriented yarn (a) through a roller, a hot box and a cooling plate, performing drawing false twisting on the pre-oriented yarn on a false twister, converging the pre-oriented yarn with the high boiling water shrinkage fibers (b) in front of two rollers, and performing network compounding on the pre-oriented yarn and the high boiling water shrinkage fibers, and then passing the pre-oriented yarn and the high boiling water shrinkage fibers through two hot boxes to obtain a composite yarn product. The preparation method develops the novel wool-like differential fibers, the PTT fibers floating on the surface layer are much closer to wool fibers in performance and are superior to common wool-like products in the performance of elastic recovery, handfeel, antistatic property, dyeing and the like, and simultaneously, the treatment of forming different sections of the two raw materials ensures that the products have significant improvements on luster and fibrillation resistance.
Owner:嘉兴逸鹏化纤有限公司
Method for detecting heat transfer resistance/heat transfer factor of building enclosure structure by infrared thermal imaging system
InactiveCN101246137AAccurate thermal resistance/heat transfer coefficientReal-time shootingMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHot boxHeat flow
The present invention relates to a method which uses the infrared thermal imaging system for quantitative-detecting the heat conducting resistance / heat transfer coefficient of the building enclosure structure. The energized electric heating wire is used for identifying on the selected area of the surface of the enclosure structure; the electric thermoscope is used for measuring the temperature of the identified area; taking the picture of the identified area with the infrared thermal imaging system and the infrared thermal image atlas of the area is obtained, measuring the indoor and outdoor temperature with the electronic thermoscope and recording; executing analysis process to the infrared thermal image atlas with the image analyzing software of the infrared thermal imaging system to obtain the value of (1), substituting into the formula (2) and the average heat conducting resistance R0 of the building enclosure structure is obtained, and the average heat transfer coefficient of the enclosure structure is calculated with the formula (3). The invention has the advantages of flexible infrared thermal image shooting, low requirement to the experiment condition, quick testing, accurate data, overcoming the defect of big error when the data is tested with heat flow meter method and the requirement to the batch meter and insulating box in the hot box method.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
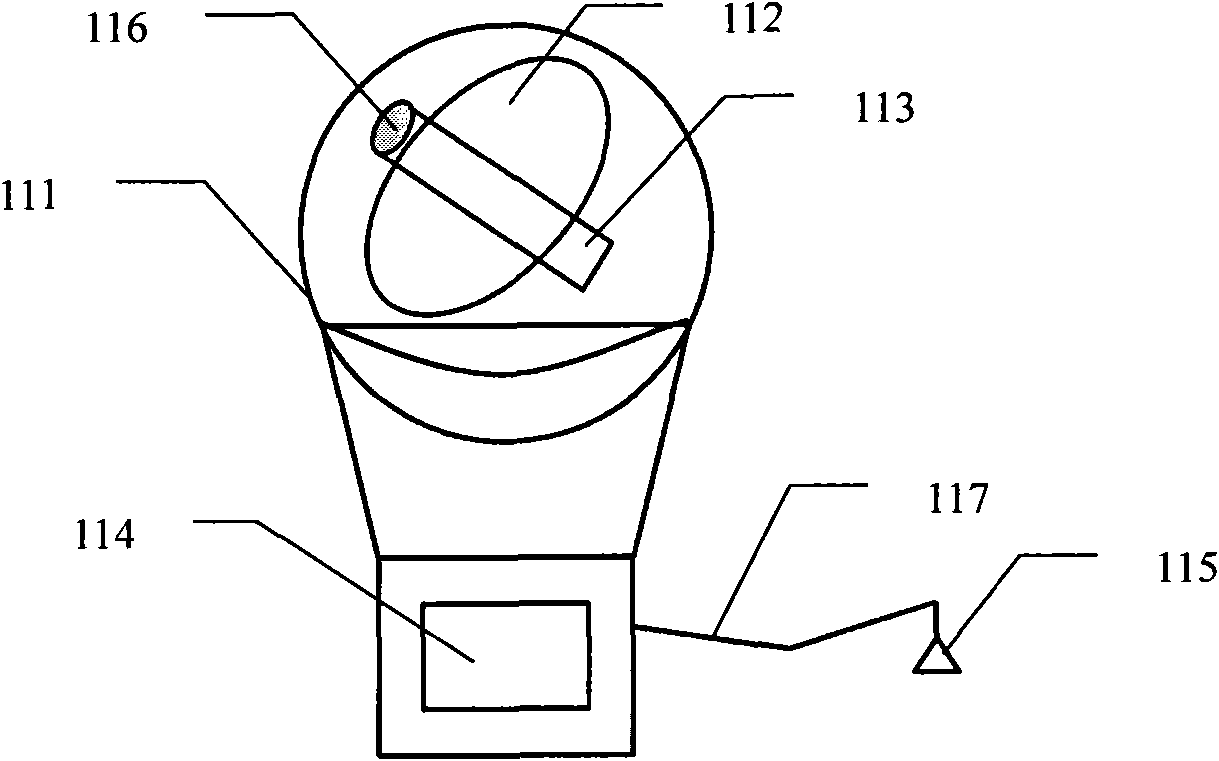
Equipment and method for detecting energy-saving effect of building sun-shading device using imported sunlight
ActiveCN101793849AAvoid the influence of unfavorable factorsStable lightingMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHot boxContinuous light
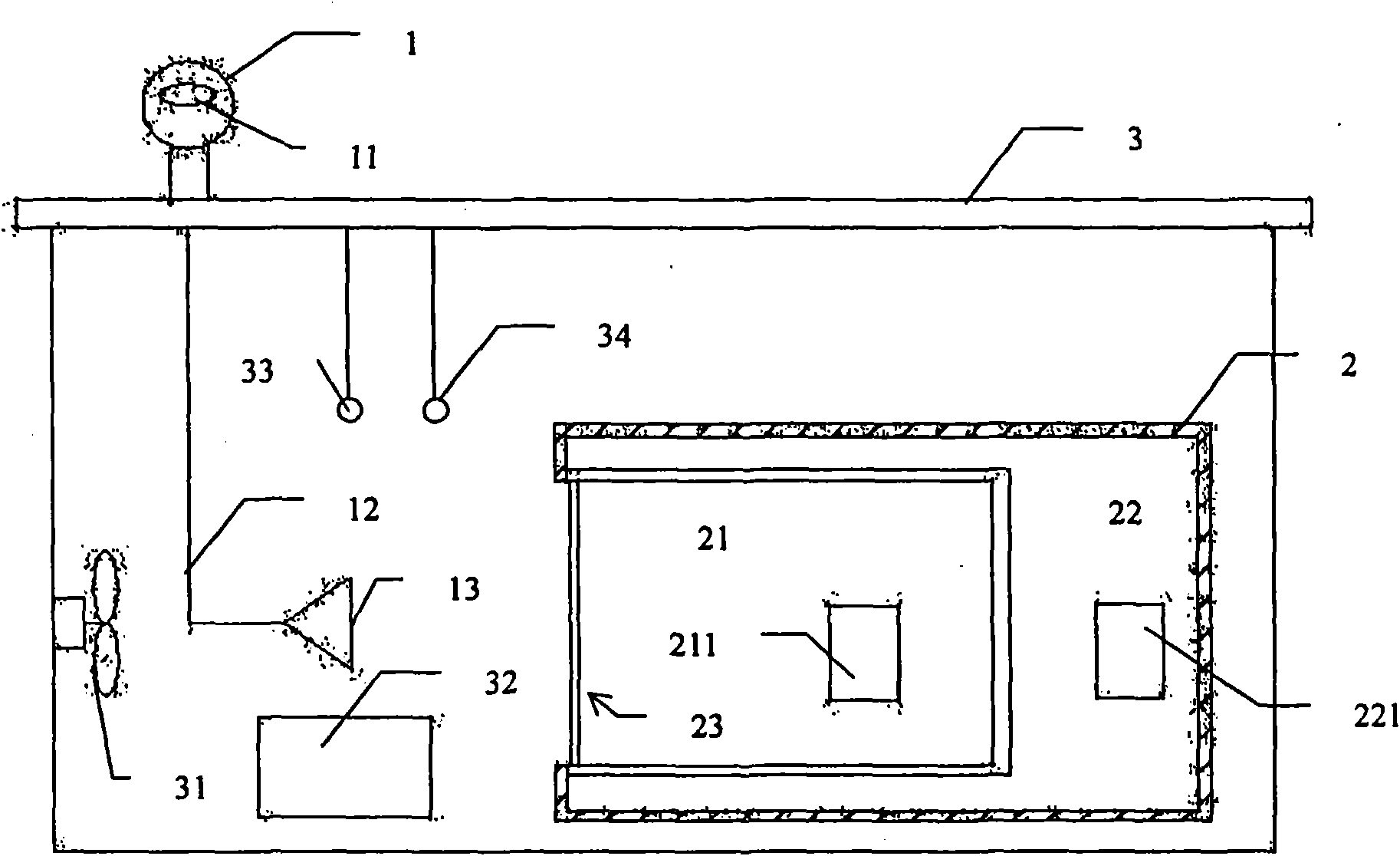
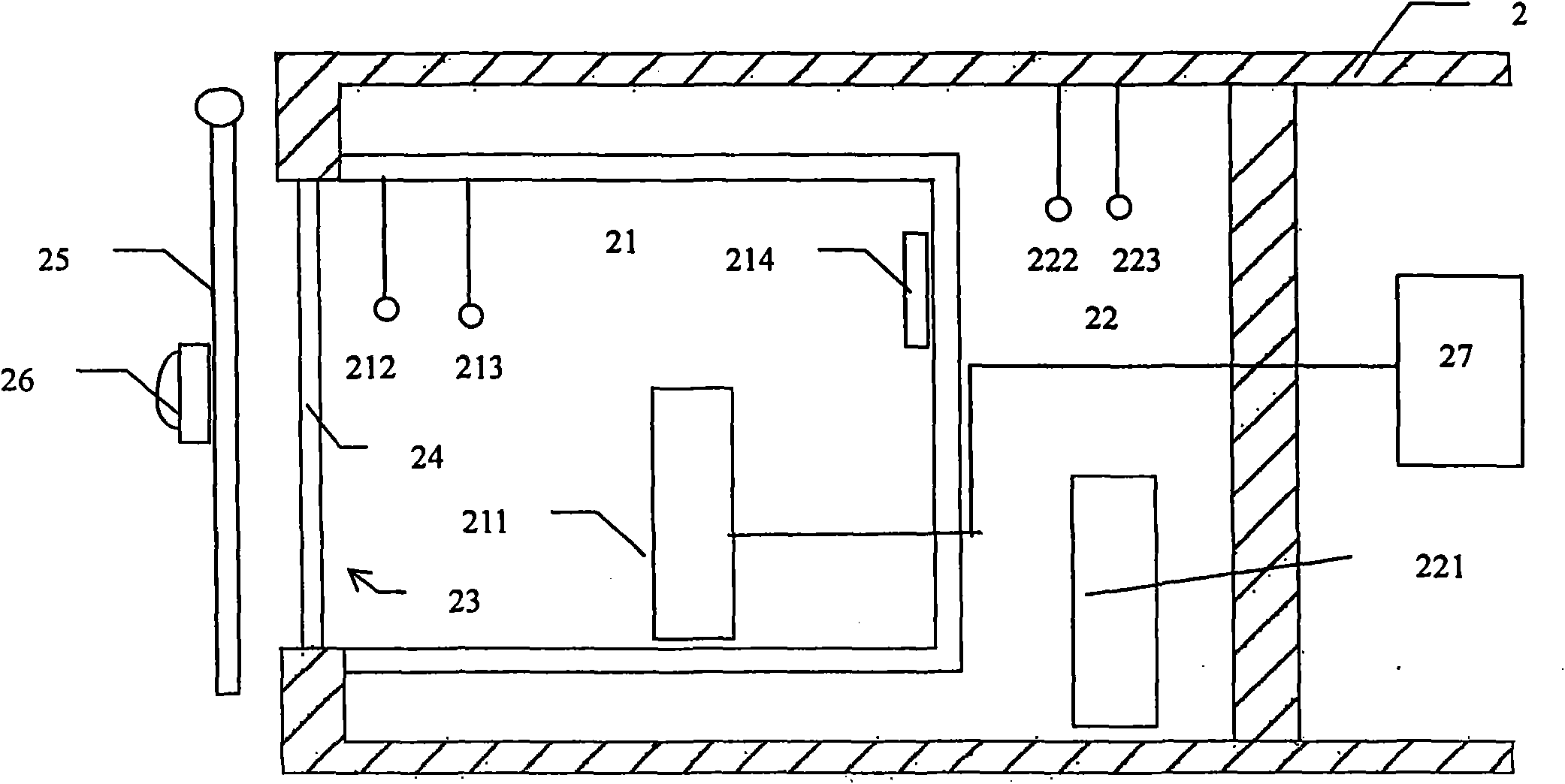
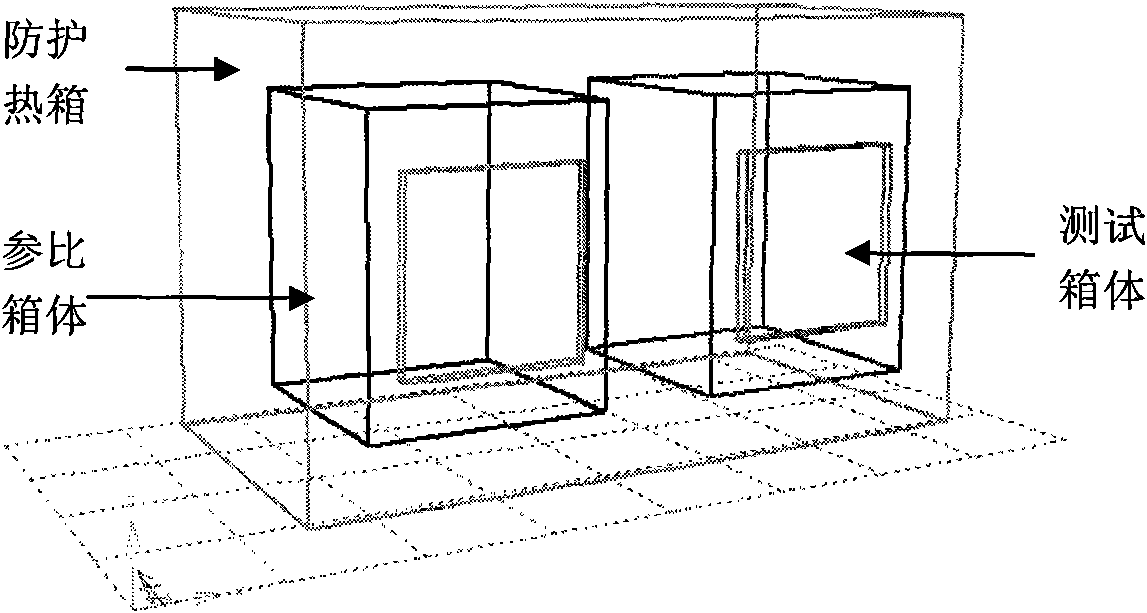
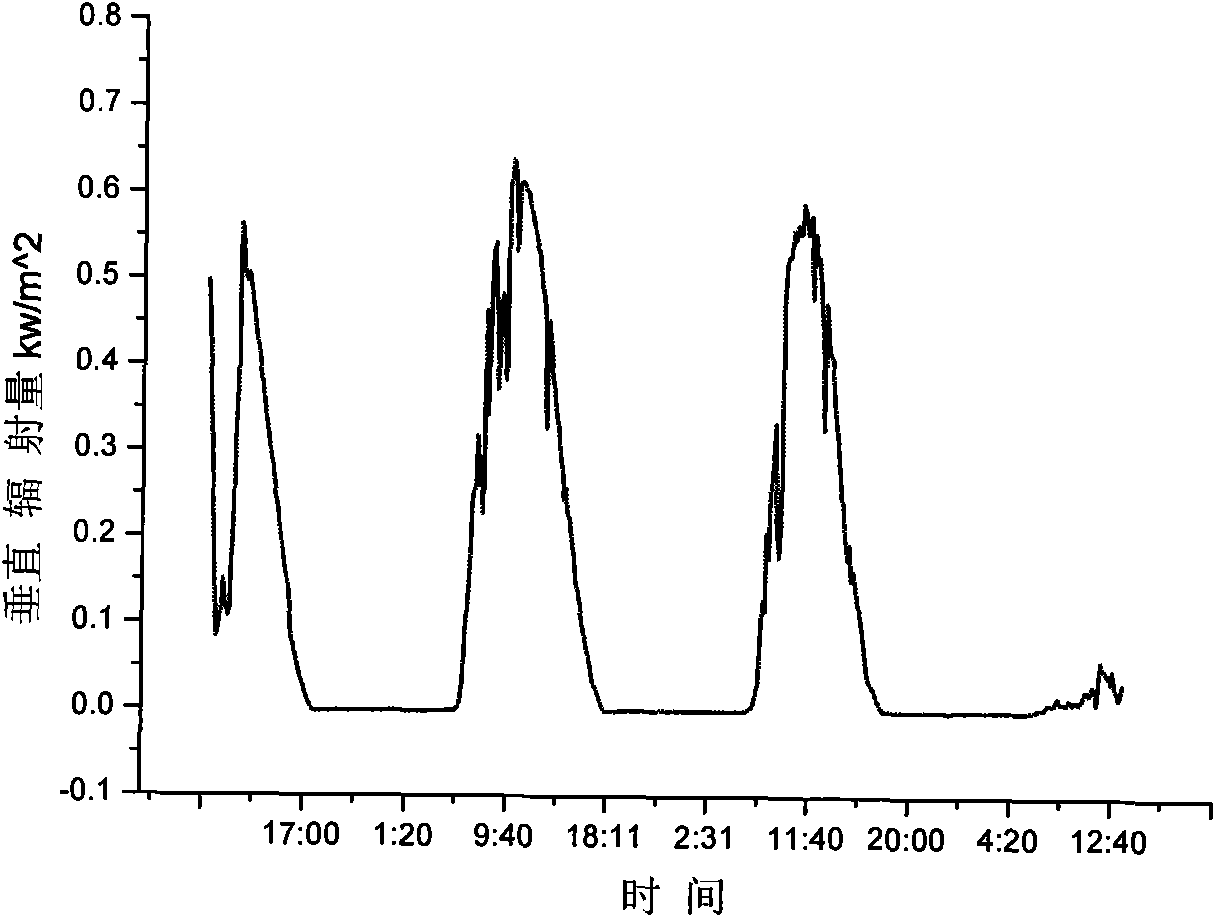
The invention provides equipment and a method for detecting an energy-saving effect of a building sun-shading device using imported sunlight, and relates to the field of the detection of the sun-shading energy-saving effect of building sun-shading products. The equipment consists of three parts: a sunlight imported system, a protected hot box and an environmental box respectively, wherein the sunlight imported system provides a stable and continuous light source for the detection, and by combining the protected hot box method, the defect that the detection can be affected by various outdoor negative factors and the defect that the use of an xenon lamp in the detection is extremely expensive are overcome, and a novel solution for detecting the energy-saving effect of the building sun-shading device is provided.
Owner:CHINA TEST & CERTIFICATION INT GRP CO LTD
Outdoor dynamic testing method for heat-insulation property of heat-insulation coating at outer wall of building
InactiveCN101576519AThe test result is accurateMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHot boxBuilding energy
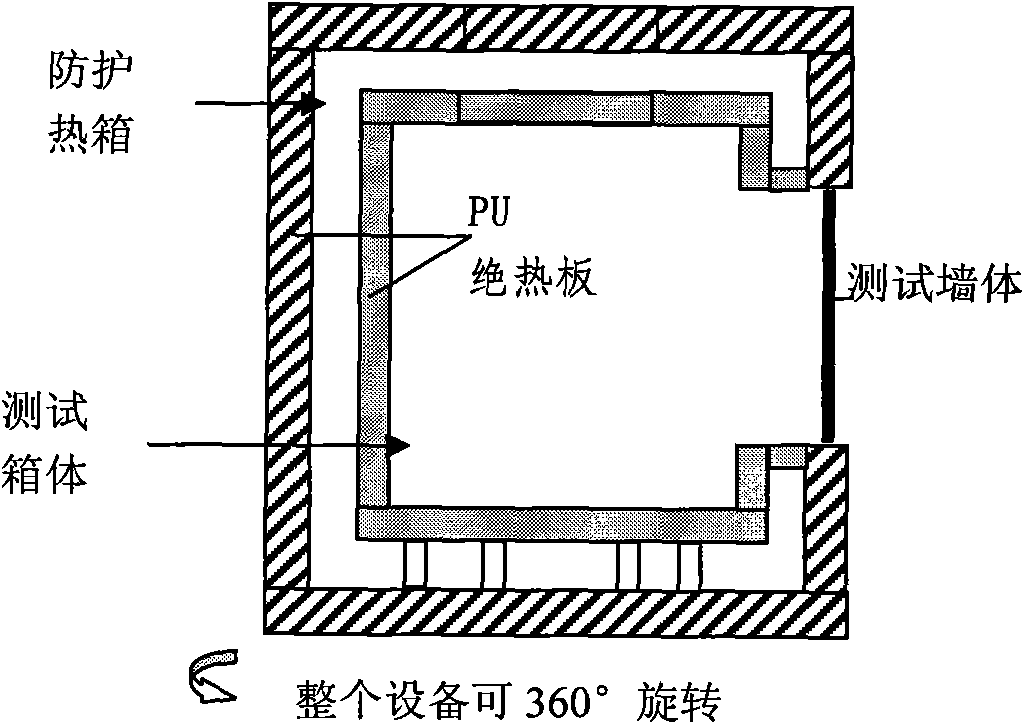
The invention discloses an outdoor dynamic testing method for heat-insulation property of heat-insulation coating at the outer wall of a building, comprising the steps of: placing a test board containing a protective hot box on a rotating disc capable of rotating by 360 degrees; placing a testing box body and a reference box body in the protective hot box; manufacturing a testing wall body adhered with the heat-insulation coating on the testing surface of the testing box body, and manufacturing a reference wall body adhered with the reference coating on the testing surface of the reference box body; regulating and controlling the interior temperature of the testing box body, the reference box body and the protected hot box to be 24 DEG C; regulating and controlling the internal surfaces of the surfaces of the testing box body and the reference box body to be less than 0.3m / s; and obtaining the heat-insulation property of the heat-insulation coating. The testing method takes the effects of solar radiation into consideration, can test and analyze the effect of the heat-insulation coating on the building energy consumption, and can obtain an accurate measurement result for the heat engineering performance of the wall body or the roofing under practical winter and summer climatic conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF BUILDING SCI CO LTD
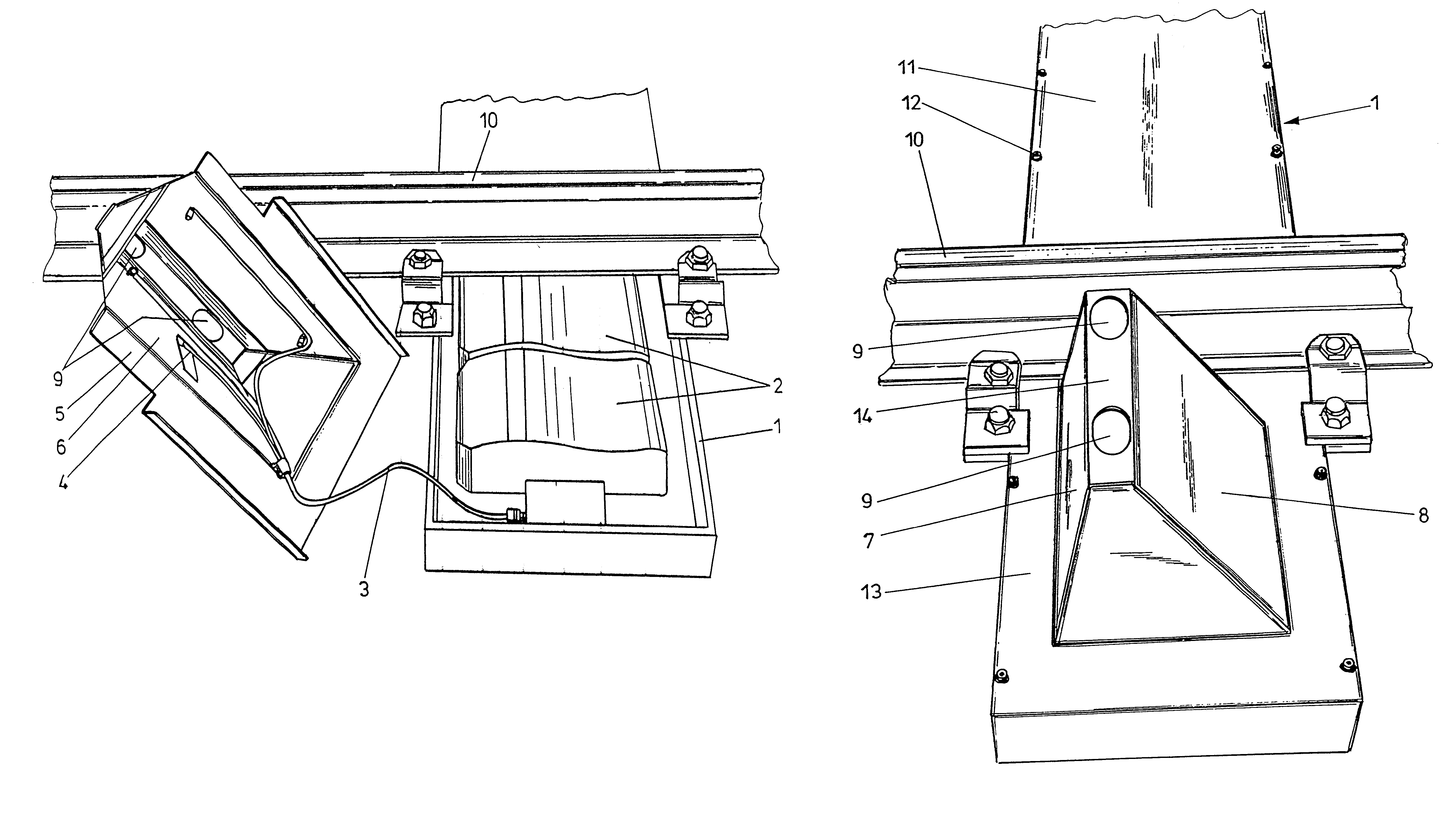
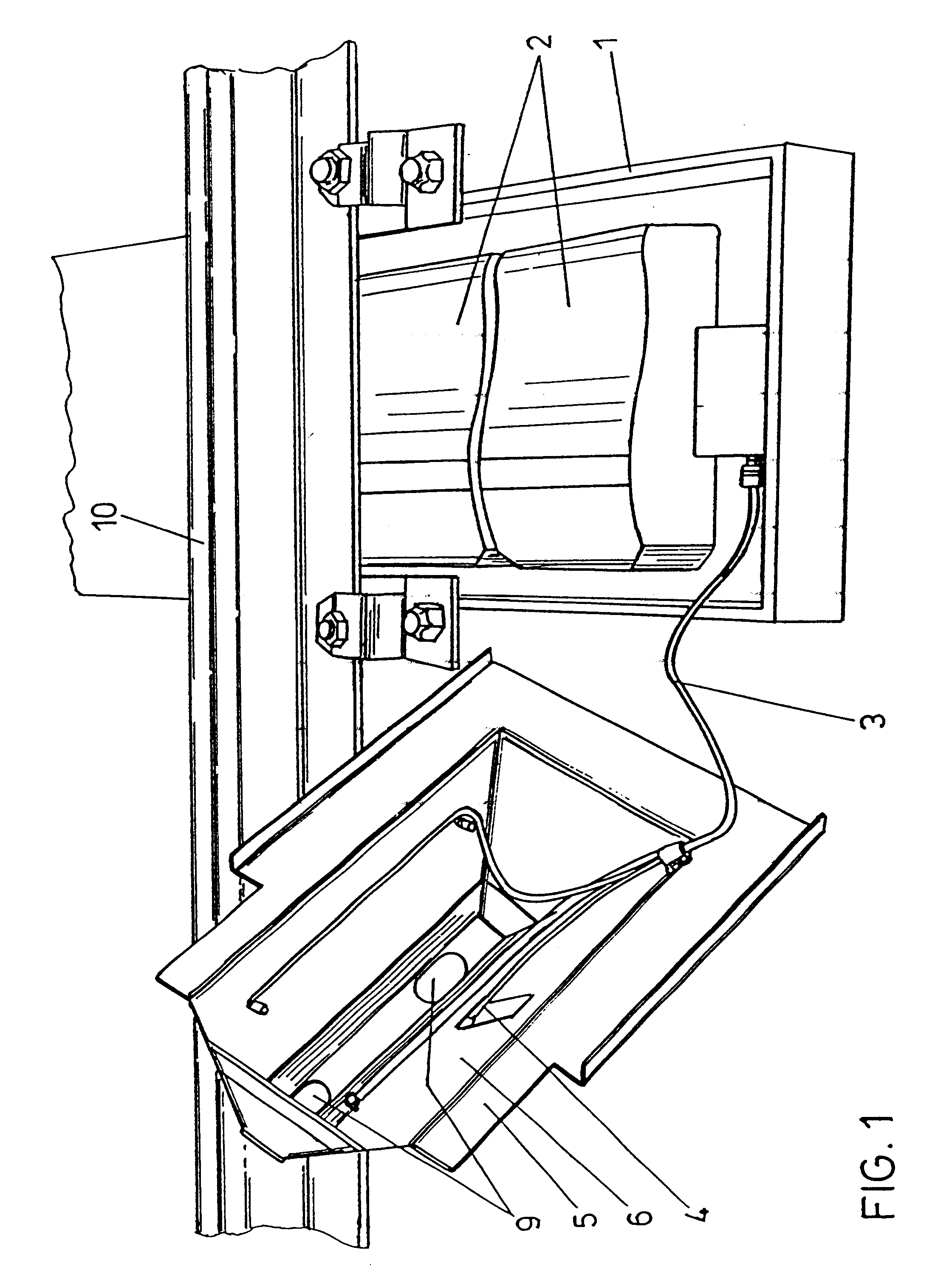
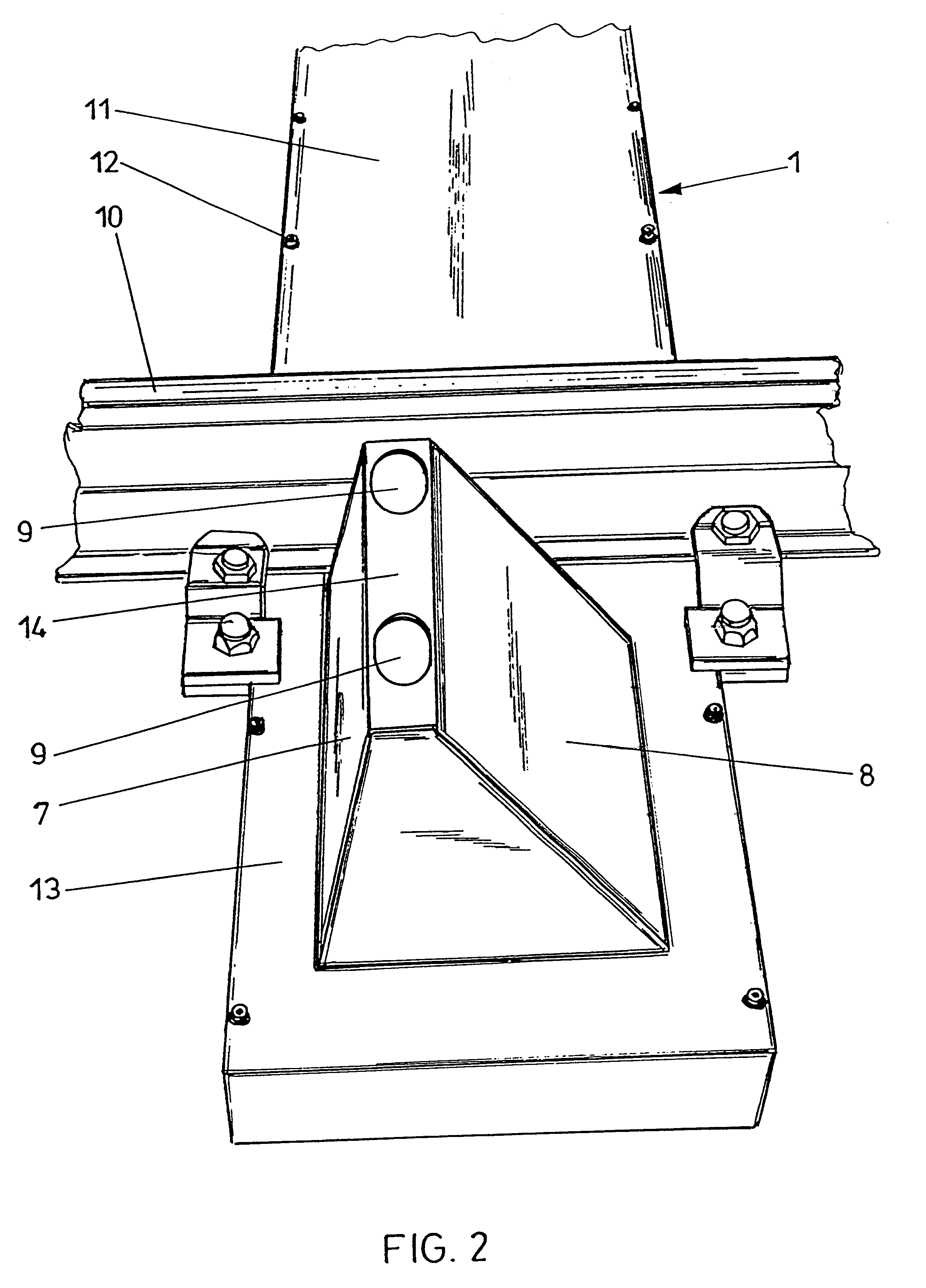
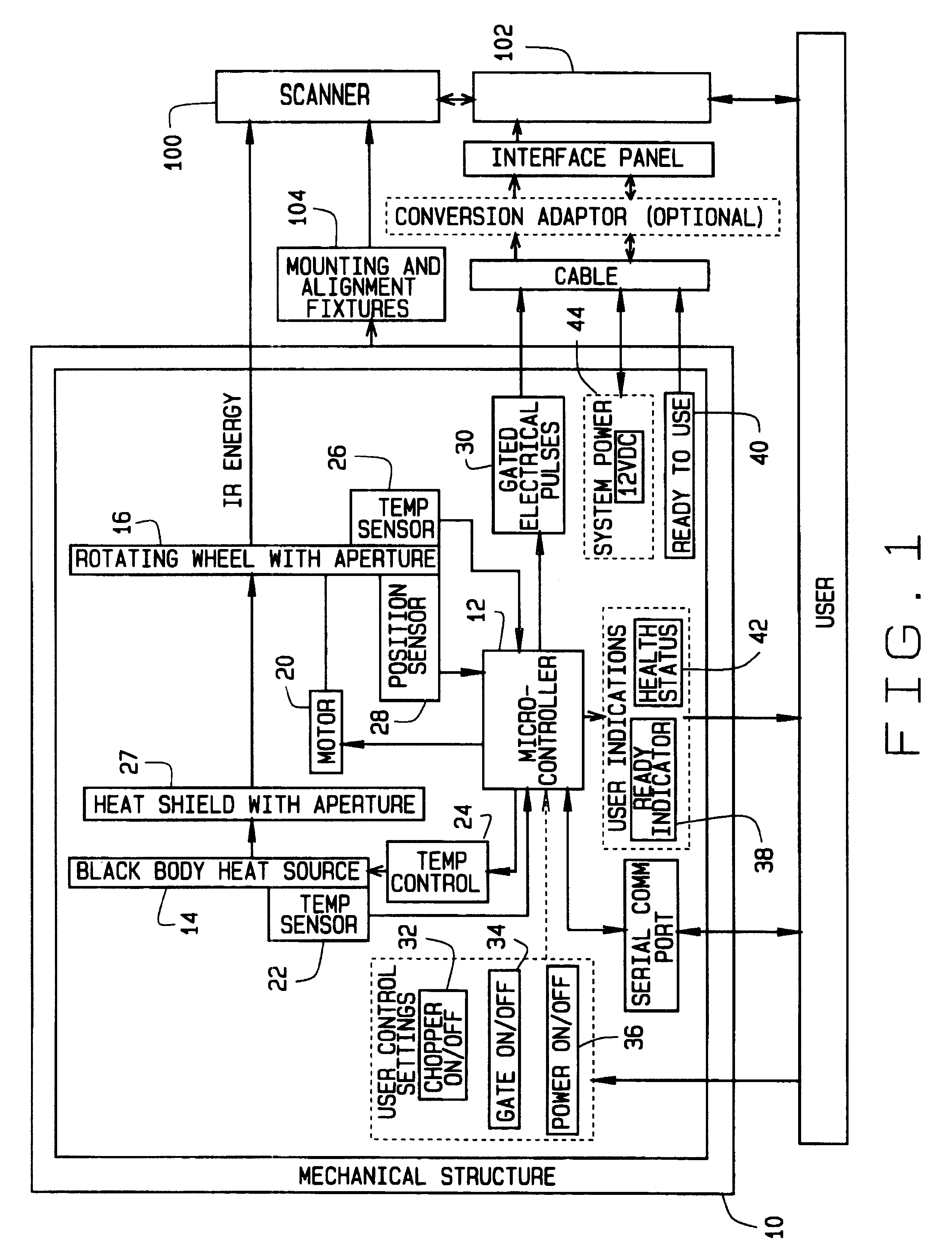
Casing for a hot box or blocked brake detection scanner
InactiveUS6241196B1Easy to useAvoid collectingRoute devices for controlling vehiclesRailway auxillary equipmentHot boxEngineering
The invention relates to a casing for a hot box or blocked brake detection scanner (2) comprising infrared detectors and a heating means, wherein the casing is comprised of a casing lower part and a lid (5), the lid (5) is designed as a chimney top with lateral surfaces (7, 8) converging towards the upper edge and carrying an electrical heating means (4) on their inner sides (6), and the lid (5) includes openings (9) for the scanning geometry of the infrared detector(s) on its upper edge or near its upper edge.
Owner:VAE AG
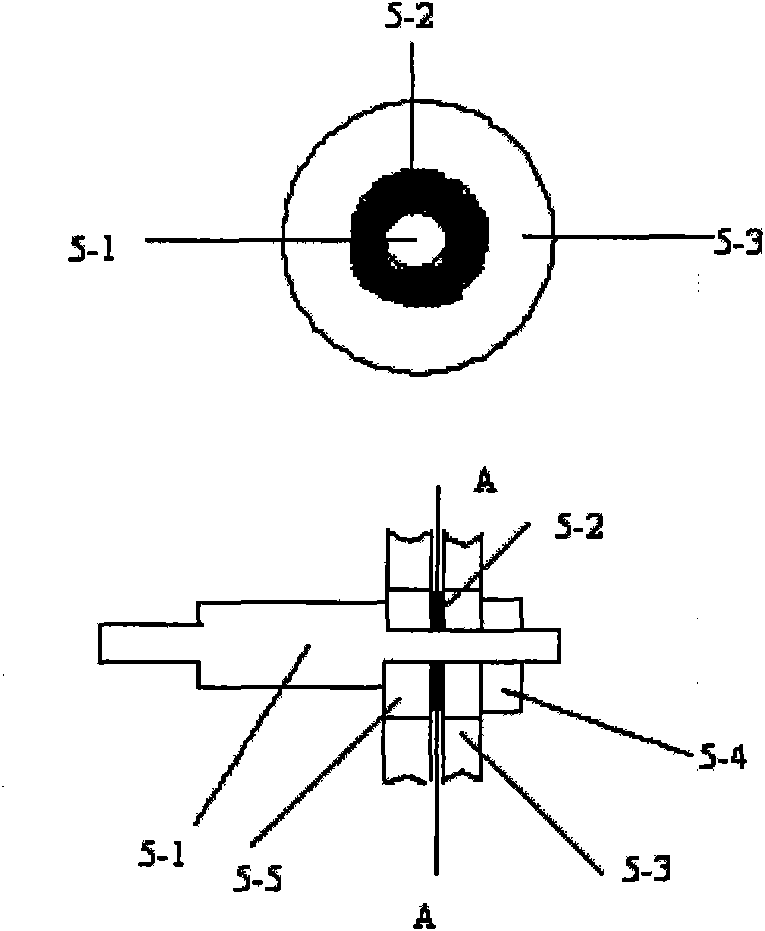
Method for manufacturing superfine denier modified terylene torque-less false twist textured yarn and special thread guide
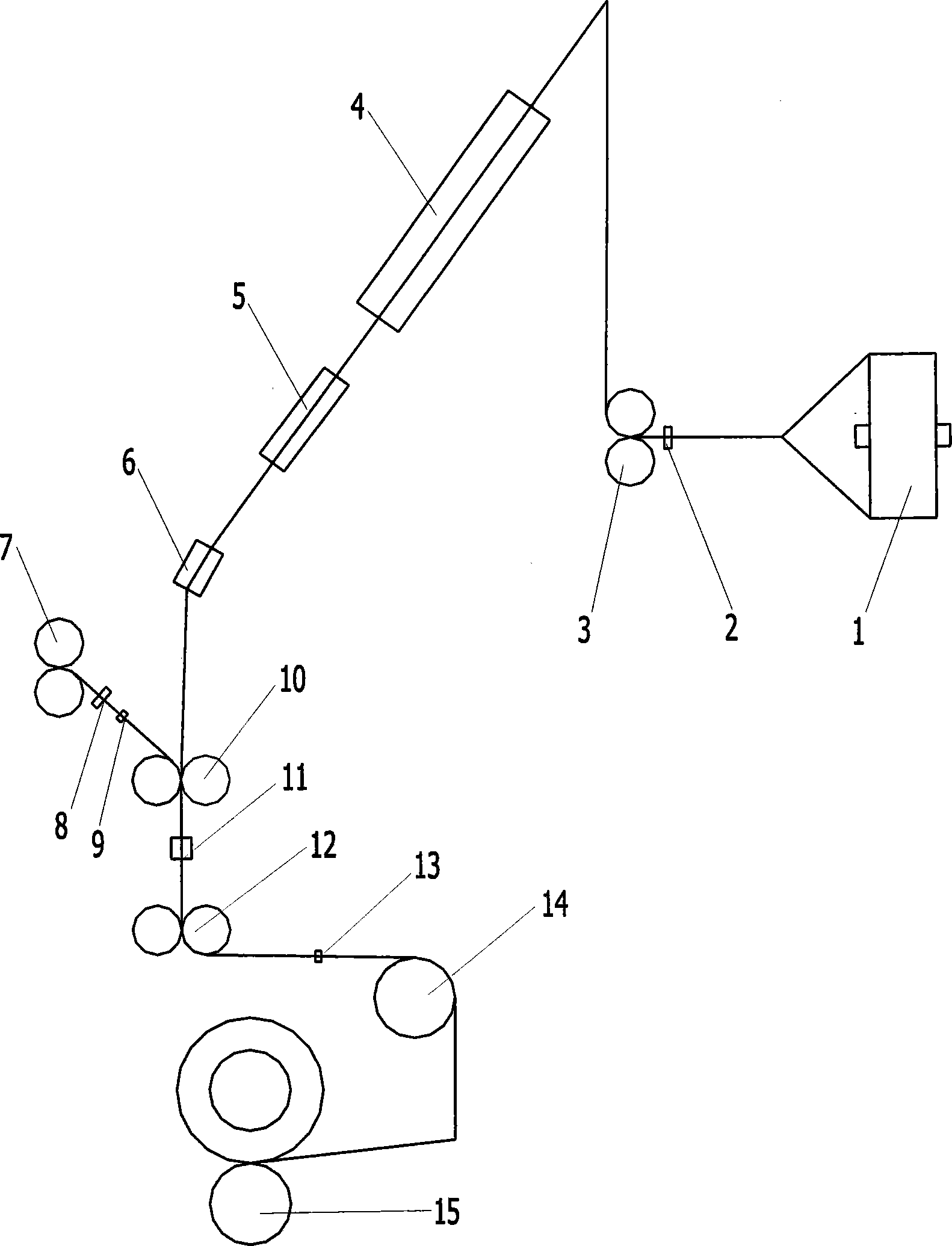
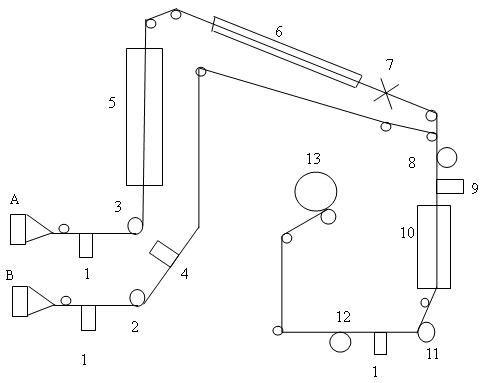
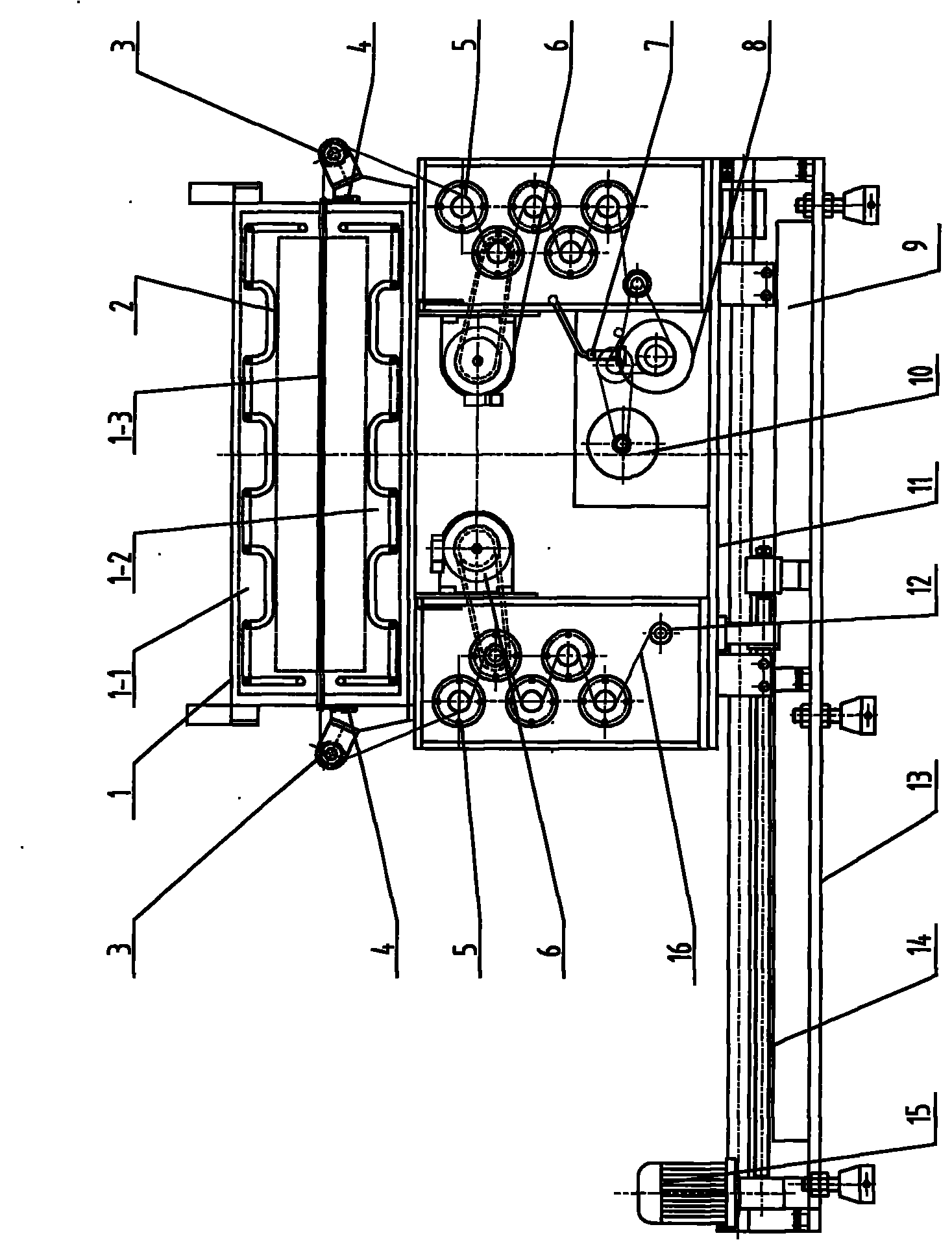
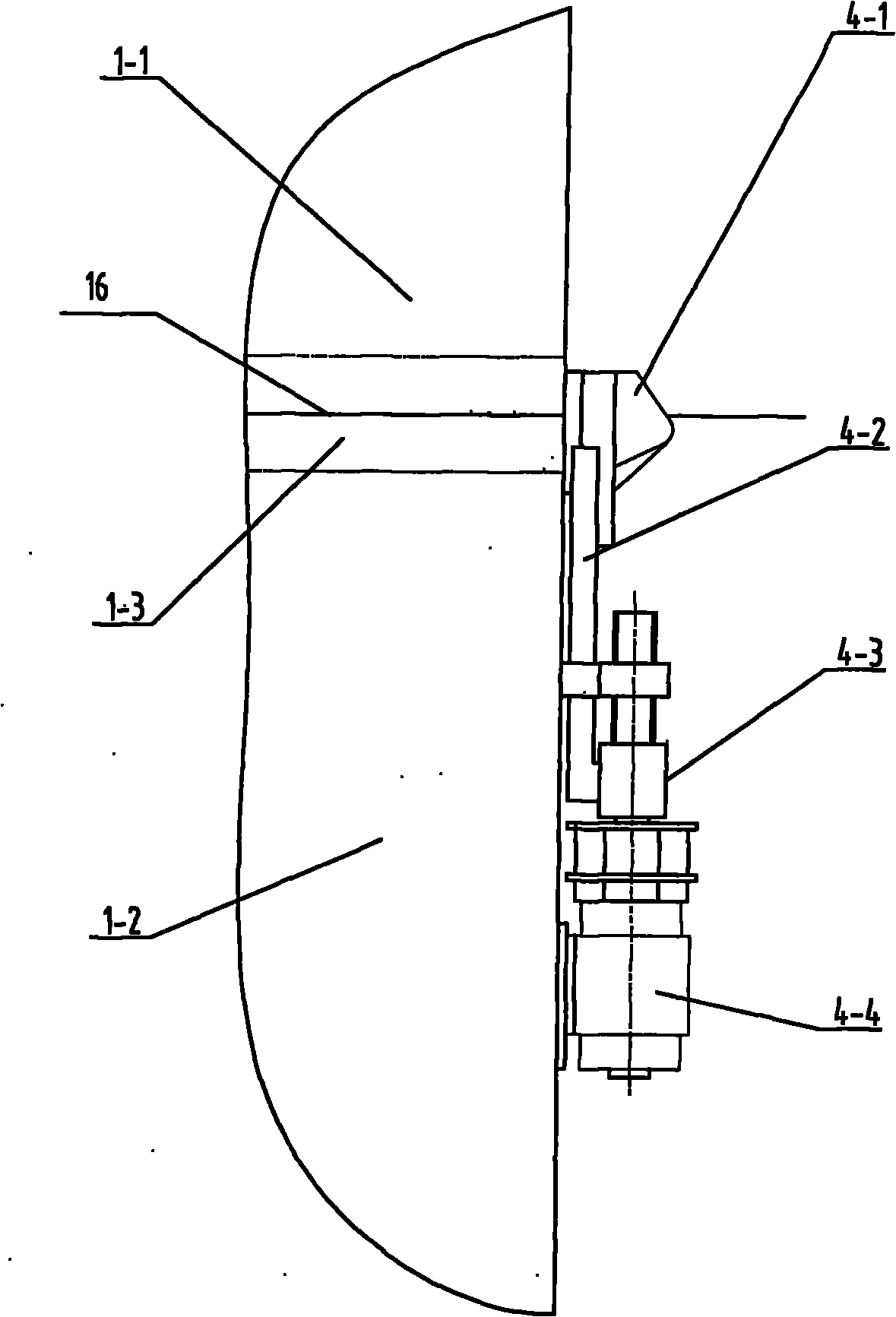
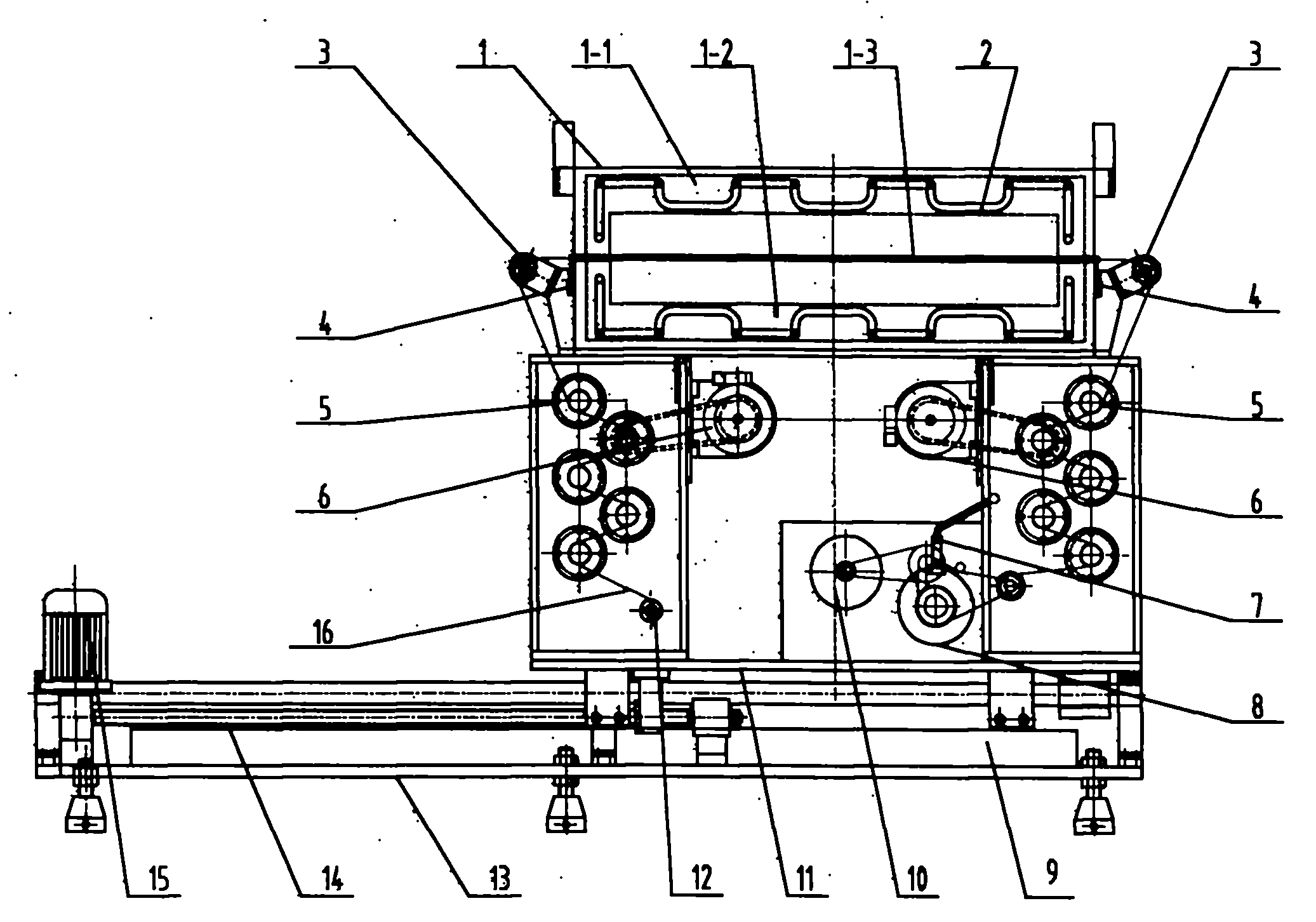
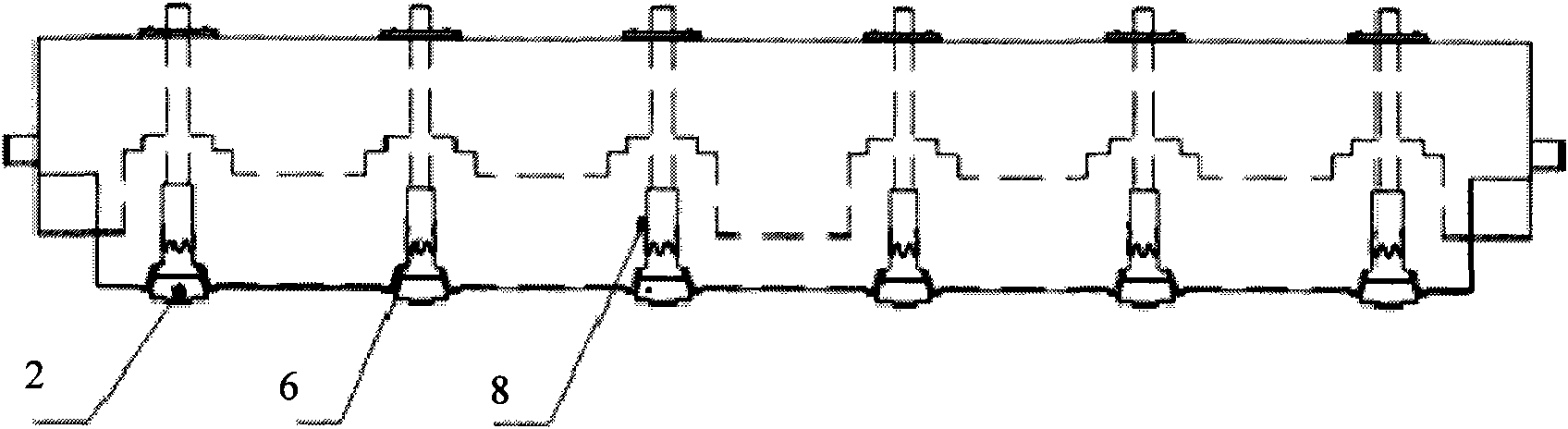
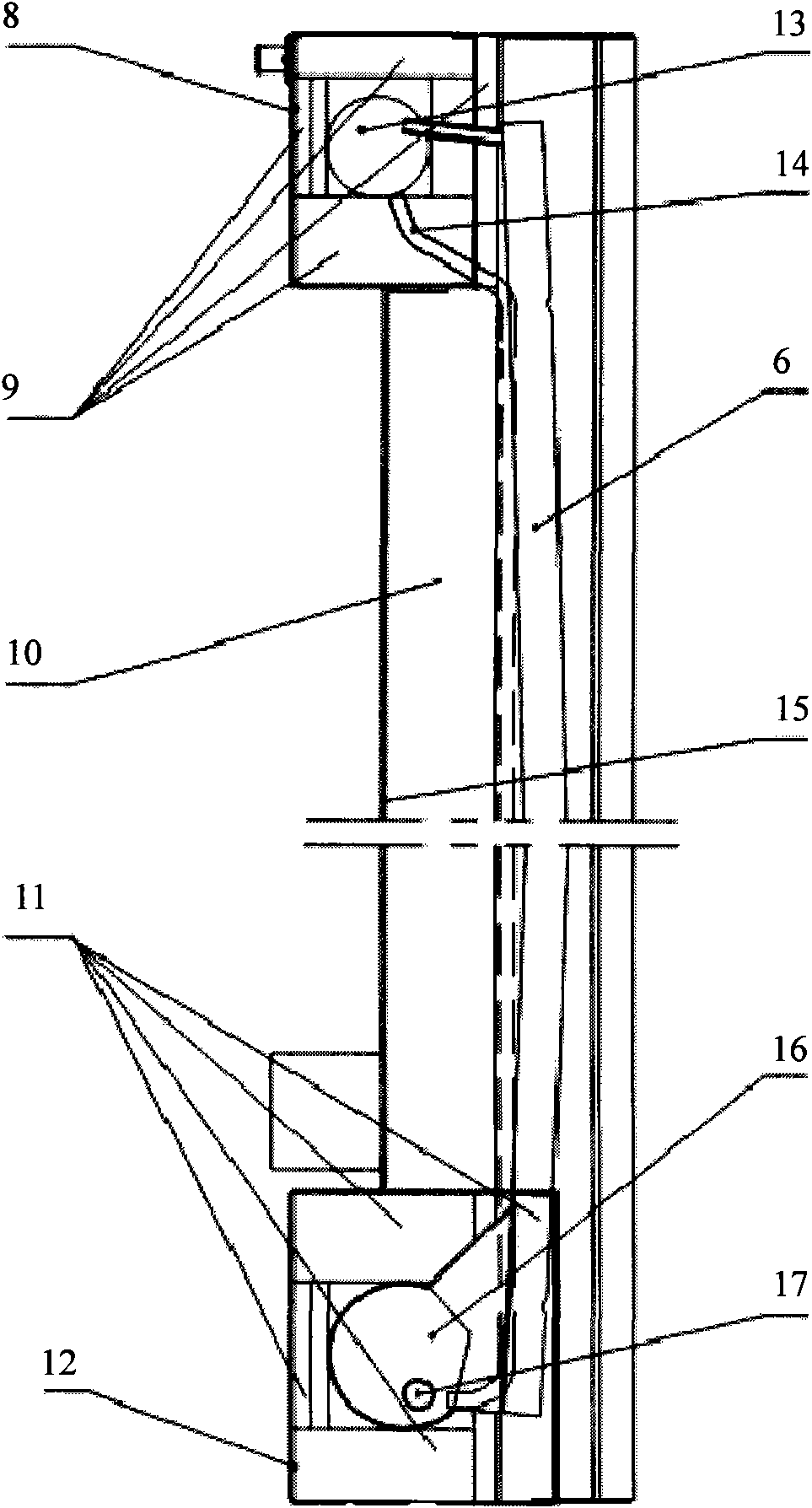
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a superfine denier modified terylene torque-less false twist textured yarn and a special thread guide. The invention aims to solve the technical problem of providing a special thread guide and a manufacturing method using the thread guide. The thread guide comprises two thread rollers (5-3) on the thread guide shaft (5-1), wherein the two thread rollers can rotate independently, and a gap is reserved between the two thread rollers. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps that: two threads (11) get into a front thread-separation thread guide (1) of a first roller along the respective thread path; then the threads pass through a roller (2), a first hot box inlet thread guide (3), a first hot box (4), a special double-thread free-rotation thread guide (5), a special turning double-thread free-rotation thread guide (6), a cooling plate (7), a false twister (8), a second roller (9) and a network nozzle (10) in turn for stranding; and then the threads get into a second hot box (12) to perform heat shaping and obtain the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGYI GRP CO LTD +3
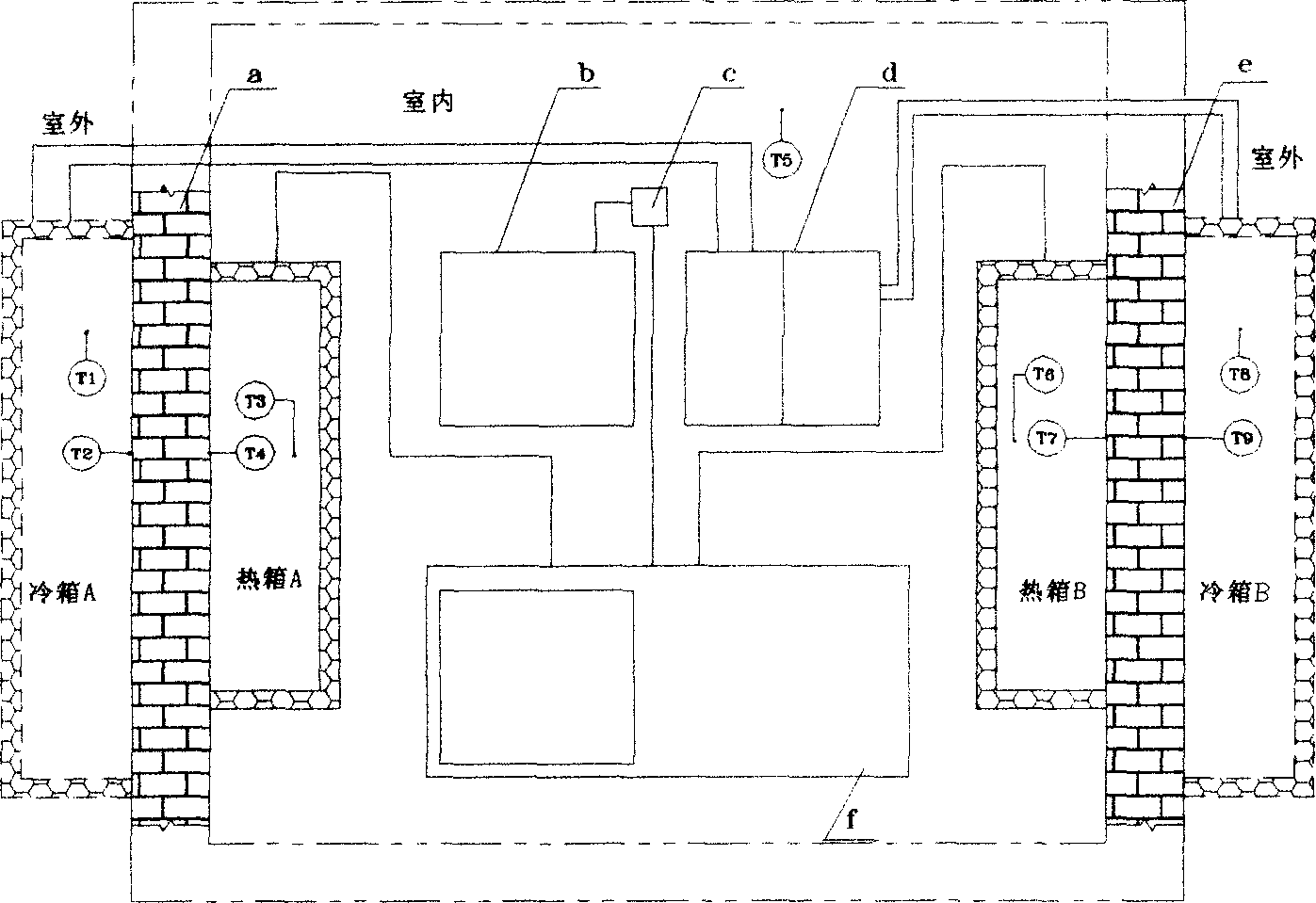
Cold-hot box type heat transfer coefficient detecting instrument
ActiveCN1815209AImprove reliabilityRealize the detection of heat transfer coefficient of on-site enclosure structureMaterial thermal conductivityHot boxSystems design
Present invention refers to Cold heat tank type heat transmission coefficient detect instrument, belonging to energy-saving site equipment for detecting building fender structure heat transmission coefficient. Detection instrument includes heat box, cold box, control apparatus, refrigerator, and heater etc. The require solved problems are 1, building fender structure site detection must be done at all seasons. 2, air temperature in heat box outer-sync with indoor air temperature makes large error of test result. Air temperature in heat box is finely controlled. 4, instrumental interference-resisting ability should be enhanced. Solution scheme is 1, adopting cold box reducing outdoor testing air temperature, 2, Adopting same error high precision temperature sensor, 3, heat box temperature control system adopting PID temperature control regulatory system and blur rule operation, adopting high-speed, high resolution AD conversion system as power consumption counting device, 4, system design adopting modular structure and separating strong and weak electricity.
Owner:北京中建建筑科学技术研究院 +1
High-performance fiber synchrotron radiation in-situ testing machine
ActiveCN101831719AGuarantee product qualityReasonable structureInspecting textilesArtificial filament heat treatmentHot boxFiber
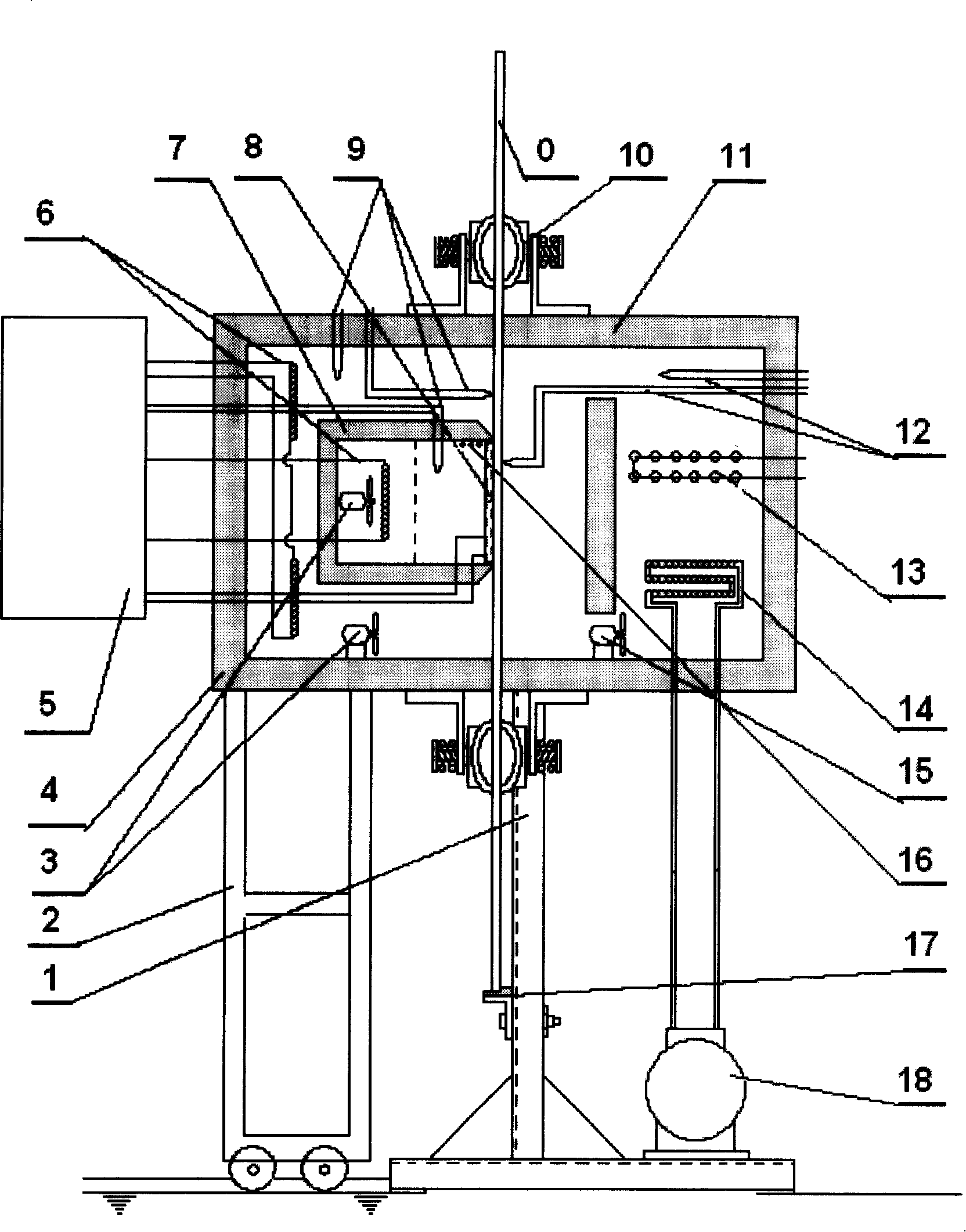
The invention provides a high-performance fiber synchrotron radiation in-situ testing machine. The testing machine comprises a base, a chassis, a drafting hot box, a front drafting mechanism, a back drafting mechanism, a winding mechanism and a translating mechanism, wherein the drafting hot box is used to heat fibre tows, one side of the box body opposite to the heat fibre tows is provided with a working gap; the front and back drafting mechanisms are used to provide drafting force for drafting the heated heat fibre tows; the winding mechanism is used to wind the heat fibre tows after hot stretching; and the translating mechanism is used to move the chassis horizontally and contains a translation motor, a turn-screw and a slideway. The testing machine has reasonable structure and convenient operation and is used commonly with the synchrotron radiation device so as to timely and accurately test the molecular changes of the high-strength and high-modulus polyethylene fibre tows under hot stretching, provide powerful technical support for the hyperploid hot stretching technology of the production of high-performance fiber, shorten debugging period and ensure the quality of fiber products.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENTAI SCI & TECH DEV
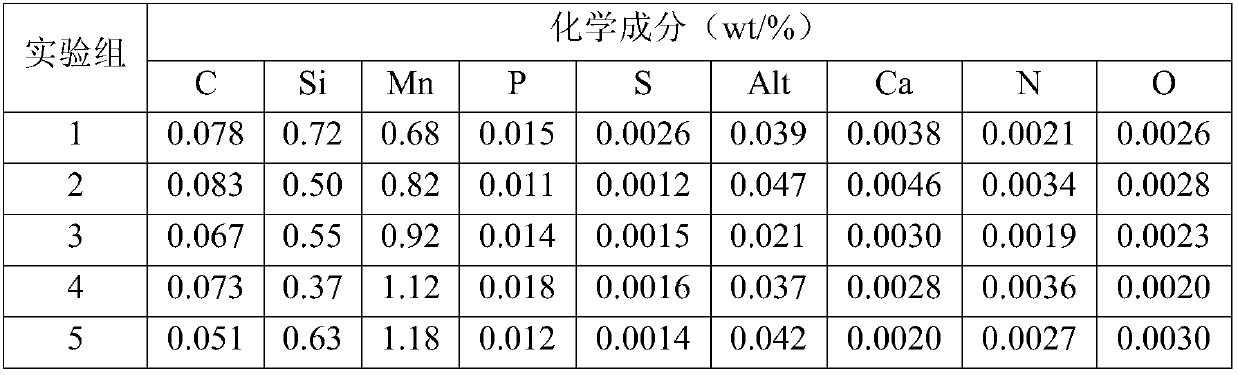
450MPa economical type high-surface-quality highly-reamed steel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses 450MPa economical type high-surface-quality highly-reamed steel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy and calendaring. The450MPa economical type high-surface-quality highly-reamed steel comprises, by weight, 0.045-0.085% of C, 0.30-0.80% of Si, 0.60-1.30% of Mn, 0.010-0.020% of P, 0-0.003% of S, 0.010-0.050% of Alt, 0.0010-0.0050% of Ca, 0-0.0050% of N, 0-0.0040% of O, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein C*Mn*104 is smaller than or equal to 0.10, {P+10*S}*102 is smaller than or equal to 0.04, and Ca / S is greater than or equal to 0.3. The preparation method comprises the following steps of smelting, continuous casting, heating, rough rolling, hot box coiling, finish rolling, laminar cooling, coiling, slow cooling, acid pickling and coiling. The 450MPa economical type high-surface-quality highly-reamed steel has the characteristics of being low in cost and excellent in performance, and can meet the requirements of steel for car chassis and complex stamping parts.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Casting sand core hot box and sand core molding method
ActiveCN104162632AShorten molding timeAvoid Fragile PhenomenaFoundry moulding apparatusHot boxRefractory
The invention discloses a casting sand core hot box and a sand core molding method. According to the hot box, the middle of a movable mold cavity is fixedly connected with a short part of a conical bar; a long part of the conical bar is a conical cylinder; the long part of the conical bar is connected with a filling piece; the filling piece is connected to the conical bar; a conical columnar hole is formed in the middle position of the filling piece; the filling piece is connected with the conical bar through the conical columnar hole; a center line of the conical bar is perpendicular to a mold clamping line of the hot box, and the sand core is molded according to a sequence of adding the filling piece, clamping the mold, sand adding, sand ejection, heating, swinging and rotating, cooling, opening the clamp and taking out the mold. With the adoption of refractory matters and other intermediate filling pieces, a small amount of laminating core sand is used, the production cost is reduced, exhaust is promoted in the casting process, defects are reduced, and the yield of the product is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG BAODING HEAVY IND
Method for producing warp knitting coral velvet polyester filament yarn
InactiveCN101476188AAdjustable fine structureFine structure stabilityTextiles and paperHot boxEngineering
The invention provides a method for producing warp knitting coralon leather polyester filament. The processed POY protofilament is removed to false twist after being detected and balanced, the process flow is that: POY protofilament - a roller feeding in - a hot box for heating distortion - cooling - false twist - two rollers feeding in - two hot boxes for heating and forming - three rollers feeding out - oiling - DTY winding forming, a pre-network working procedure is added between the ROY protofilament and a roller feeding in. The method solves problem that coralon leather fabric processed by normal polyester has defects of no-soft hand touch, adhesive hair, down pile making, without coralon leather style, and can cover the prior art shortage.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
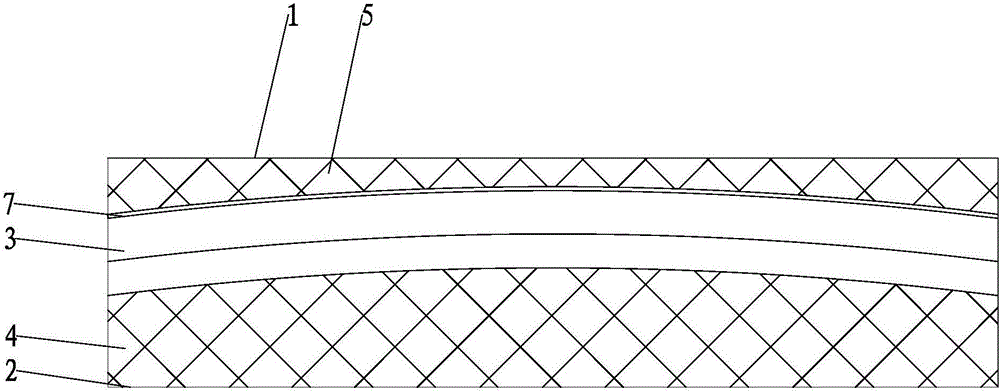
Contact type deformation heat box for elasticizer
The invention relates to a deformation heat box, in particular to a contact type deformation heat box for an elasticizer, and belongs to the technical field of elasticizers. The deformation heat box comprises a heat door, a heat box body and a heat rail, wherein the upper end face of the heat box body is matched with the upper end face of the heat rail, and a certain gap is reserved between the upper end face of the heat box body and a bulged face of the heat rail; the heat door is arranged at the upper end of the heat rail, and is rotationally connected to the heat box body; one end face, towards the heat box body, of the heat door is matched with the upper end face of the heat box body, so that the surface of the heat door is closely attached to the upper end face of the heat box body. According to the deformation heat box, the heat door lower surface and the heat box body lower surface both matched with the heat rail surface are adopted, so that the heat rail is enabled to be closely attached to the heat door lower surface and the heat box body lower surface; meanwhile, the heat door and the heat box body are filled with composite heat-insulation felt inside, so that the heat insulation effect is improved, the heat conductivity is effectively reduced, and a relatively good energy-saving effect is achieved.
Owner:戚其杰
Self-Crosslinking Alkyd Dispersion
A coating composition is produced by forming an aqueous dispersion of a crosslinking agent and a resin that comprises the reaction product of an alkyd polymer, an optional surfalkyd, diacetone acrylamide, another acrylate monomer and optionally aromatic monomers wherein the reaction product is neutralized with either ammonia or an amine. A coating of the aqueous dispersion on wood exhibits at least some of the following desired properties: rapid dry time, good tannin blocking, good resistance to picking up dirt, good hot box stability and good exterior durability. Additionally, the inventive coatings appear to provide improved crosslinking compared to coatings comprising resins not neutralized with an amine or ammonia and / or not containing a surfalkyd.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
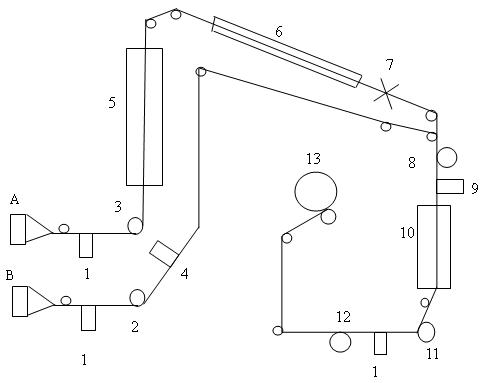
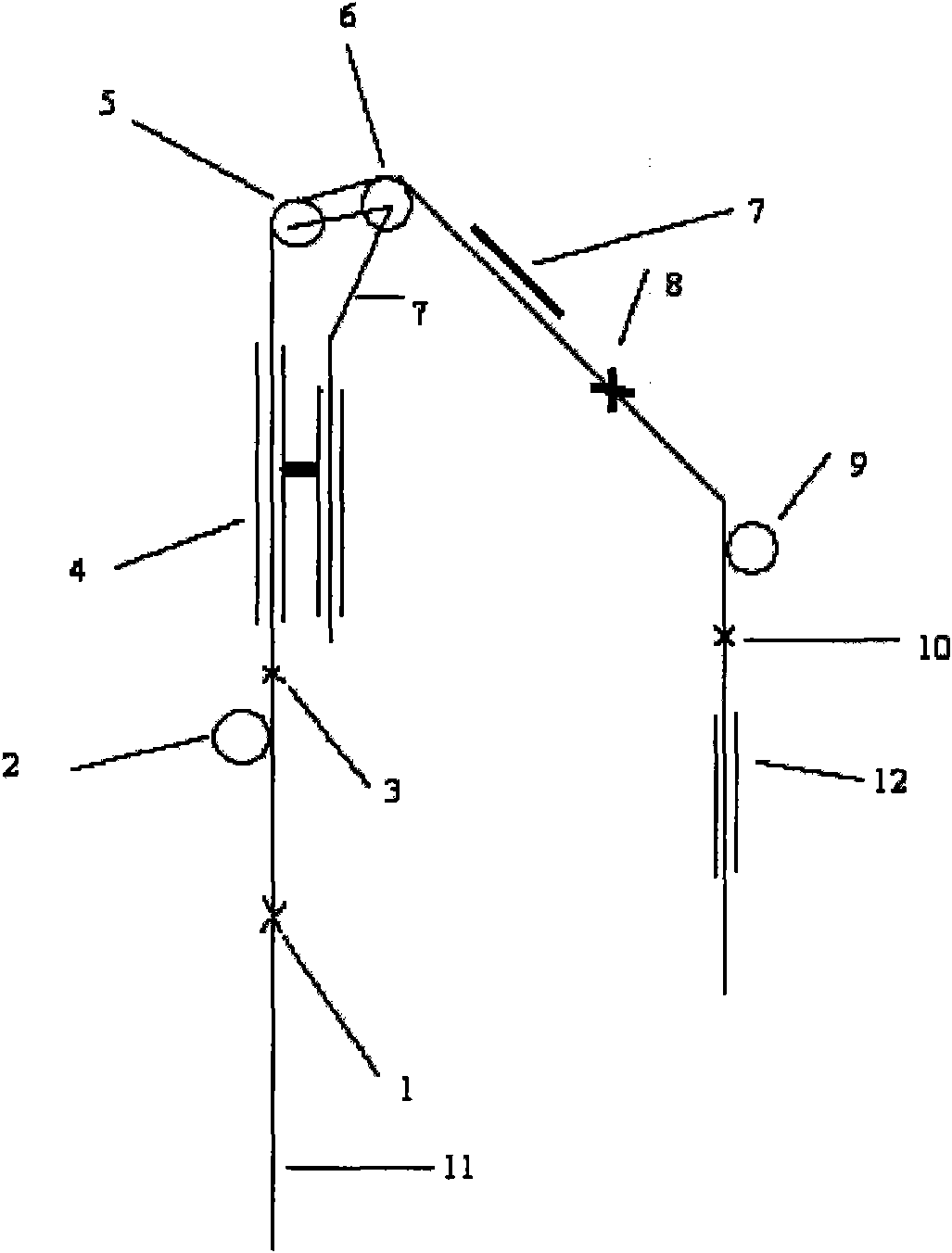
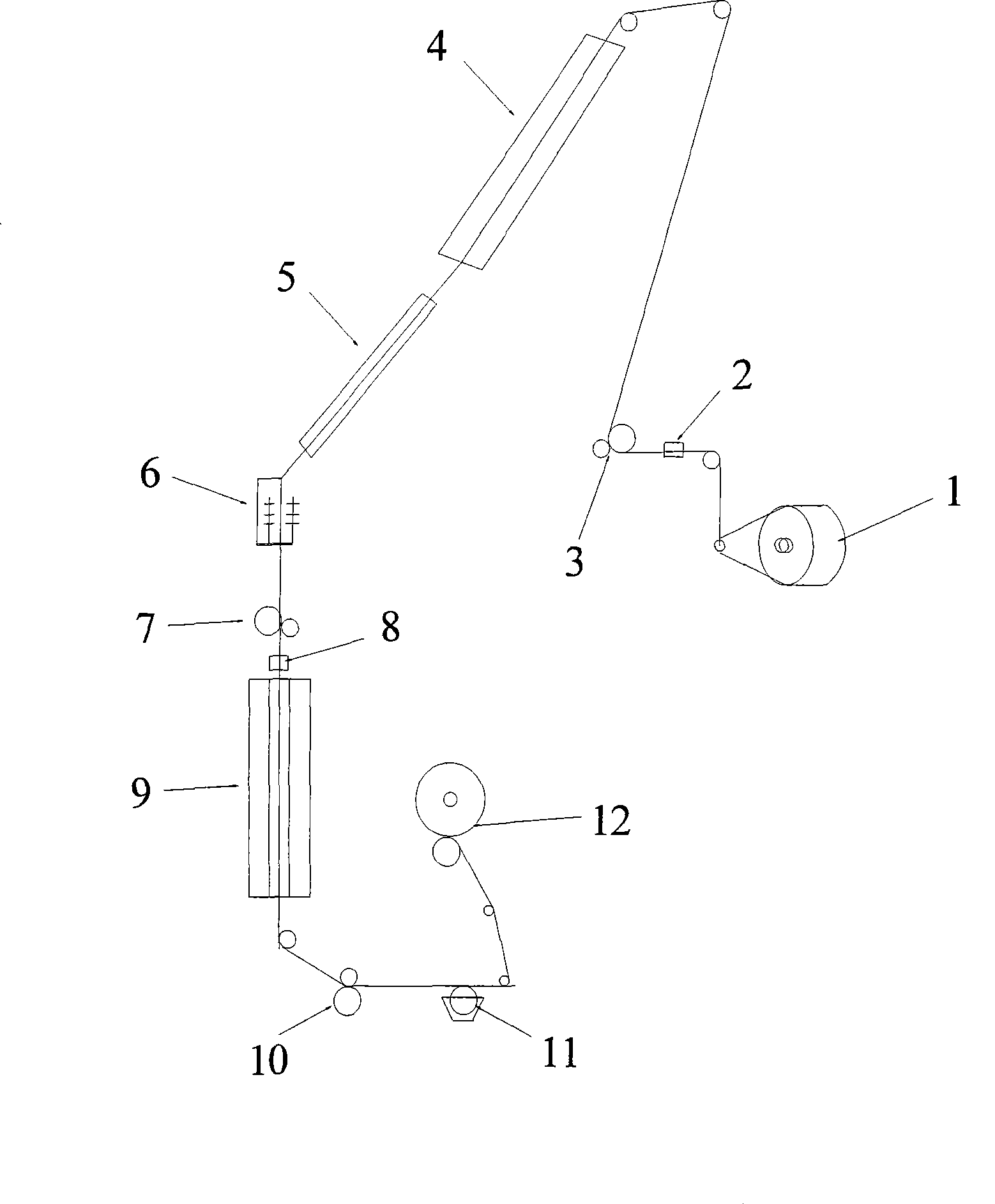
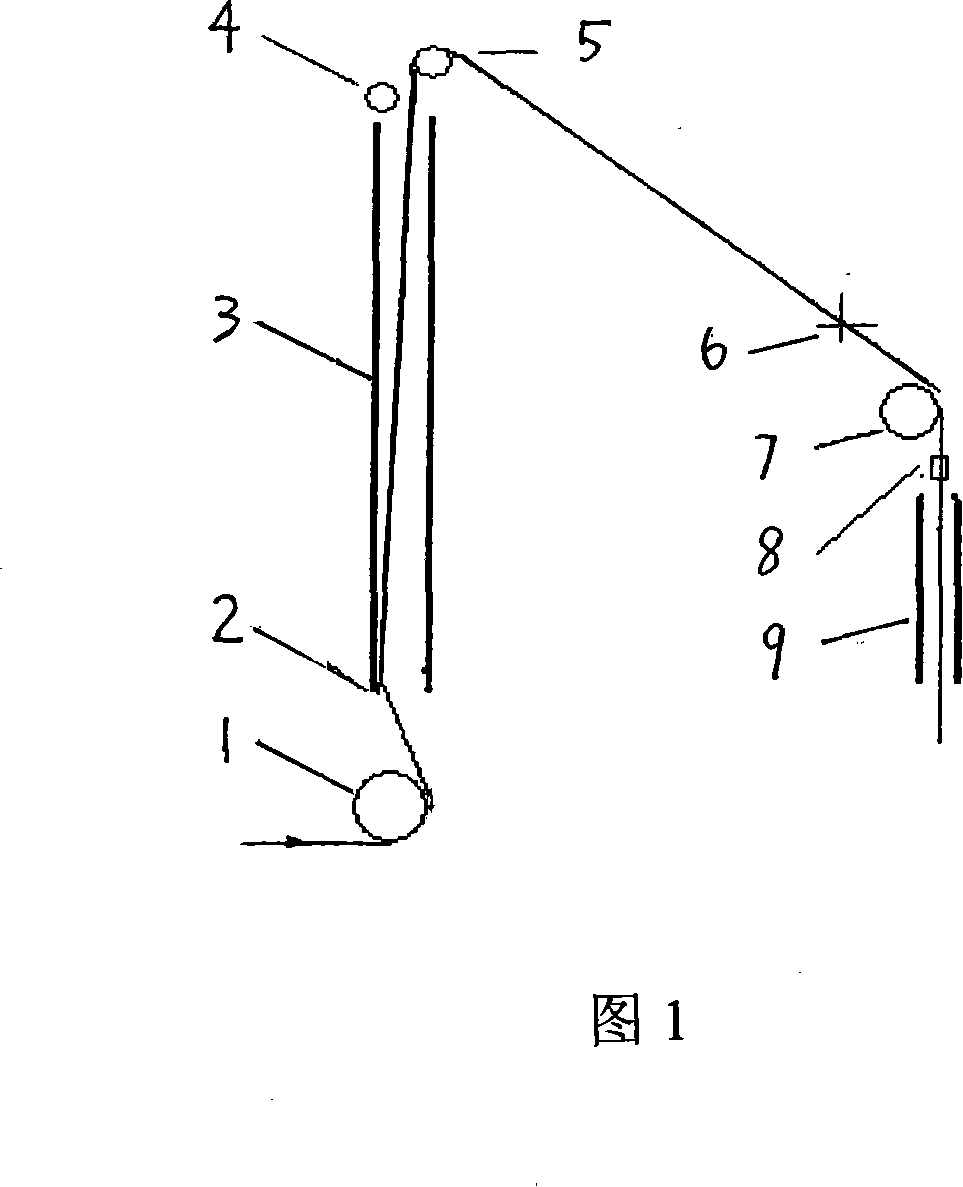
Technique for producing polyester filament yarn using false twisting distortion elasticizer
ActiveCN101250784AHigh fidelity requirementsGood hollownessTextiles and paperHot boxEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing polyester fiber filament by using a false twisting deformation elastic-adding machine, which is characterized in that raw material strand silk which is from a roller (1) passes through an inlet silk guide (2), then directly passes through a hot box(3) and is heated by the mode of non-contact heating, then moves to a turning silk guide (5), (or passes through a twisting machine 6), then passes through a two-roller (7) and reaches to a network jet nozzle (8) and is manufactured to obtain fully drawn yarn FDY (or shape preserving performances with high requirements such as profile degree, degree of hollowness and the like) polyester fiber filament, The process has the advantages of without altering the device, simple process adjustment and the like, and the switching of the two product processes is flexible and convenient, and the process efficiently extends the using range of the false twisting deformation elastic-adding machine and has obvious economic benefits.
Owner:杭州逸暻化纤有限公司
Production method of superfine denier polyester low stretch yarns
The invention discloses a production method of superfine denier polyester low stretch yarns. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: feeding polyester filament yarns serving as a raw material through a pre-collector, a yarn cutter, a first feeding roller, a first hot box, a cooling plate, a false twister, a second feeding roller, a collector, a second hot box, a third roller, a yarn detector and an oil applying system in sequence; winding. Superfine denier polyester low stretch yarns produced by using the production method of the superfine denier polyester low stretch yarns have good performance and stable quality, and are much superior to the existing commercially-available polyester low stretch yarns in quality; the breaking strength is 3.7cN / dt, and the elongation at break is 21 percent.
Owner:SUZHOU YUCHEN FIBER TECH
Energy-saving environment-friendly type multi-functional handrail style vehicle-mounted cold and hot box
InactiveCN103963600AAdjustable body balanceGood for healthAir-treating devicesPassenger spaceHot boxIn vehicle
The invention discloses an energy-saving environment-friendly type multi-functional handrail style vehicle-mounted cold and hot box, which comprises a handrail box body and a cooling and heating device. The energy-saving environment-friendly type multi-functional handrail style vehicle-mounted cold and hot box is suitable for being mounted and used in the existing all types of SUVs, cars, commercial vehicles, passenger cars and other vehicles, fully utilizes the limited space in vehicles, improves the configuration level in vehicles, and life of people in vehicles is more comfortable and full of humanization.
Owner:NANJING HIZOOM ENERGY RESOURCES TECH
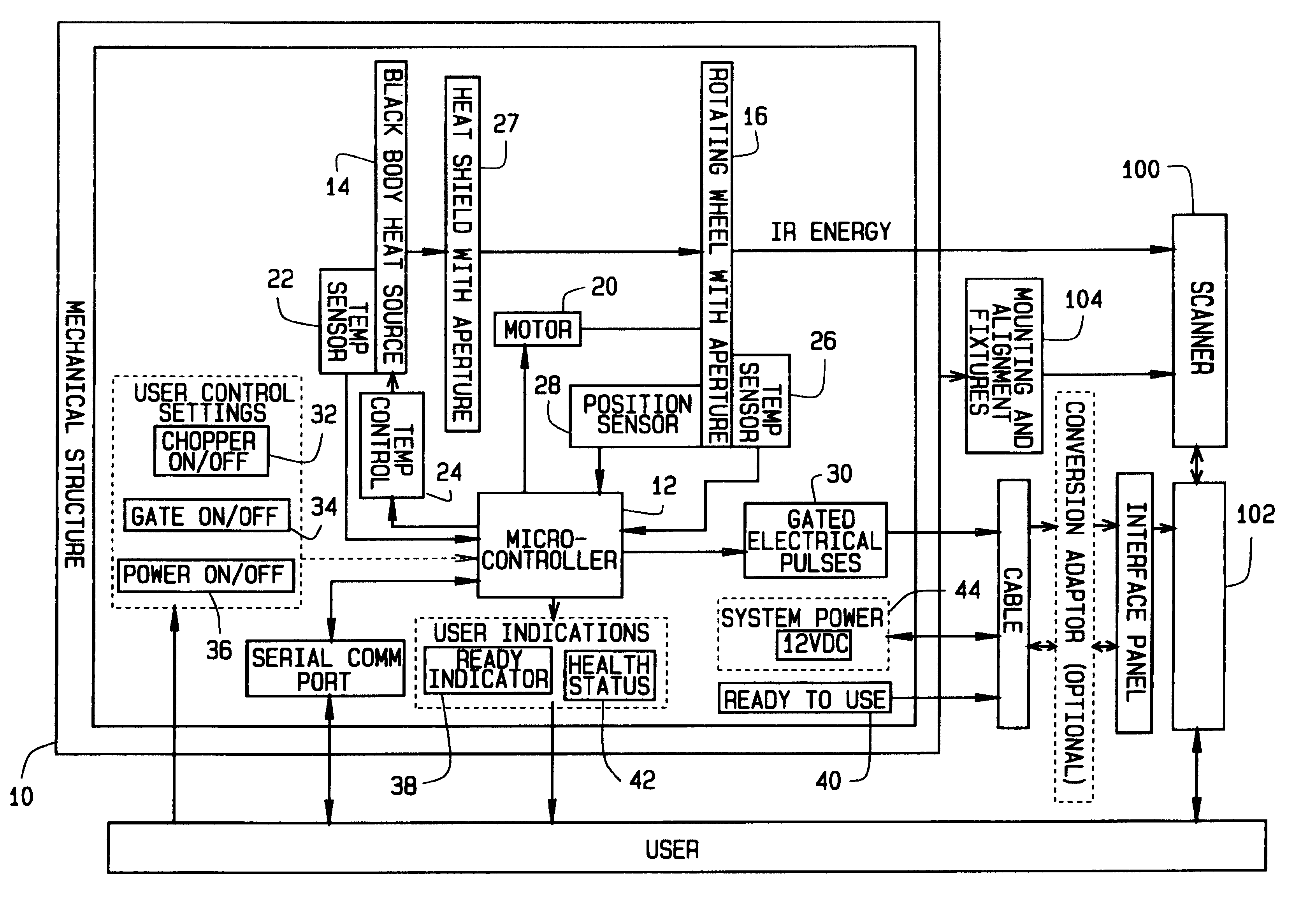
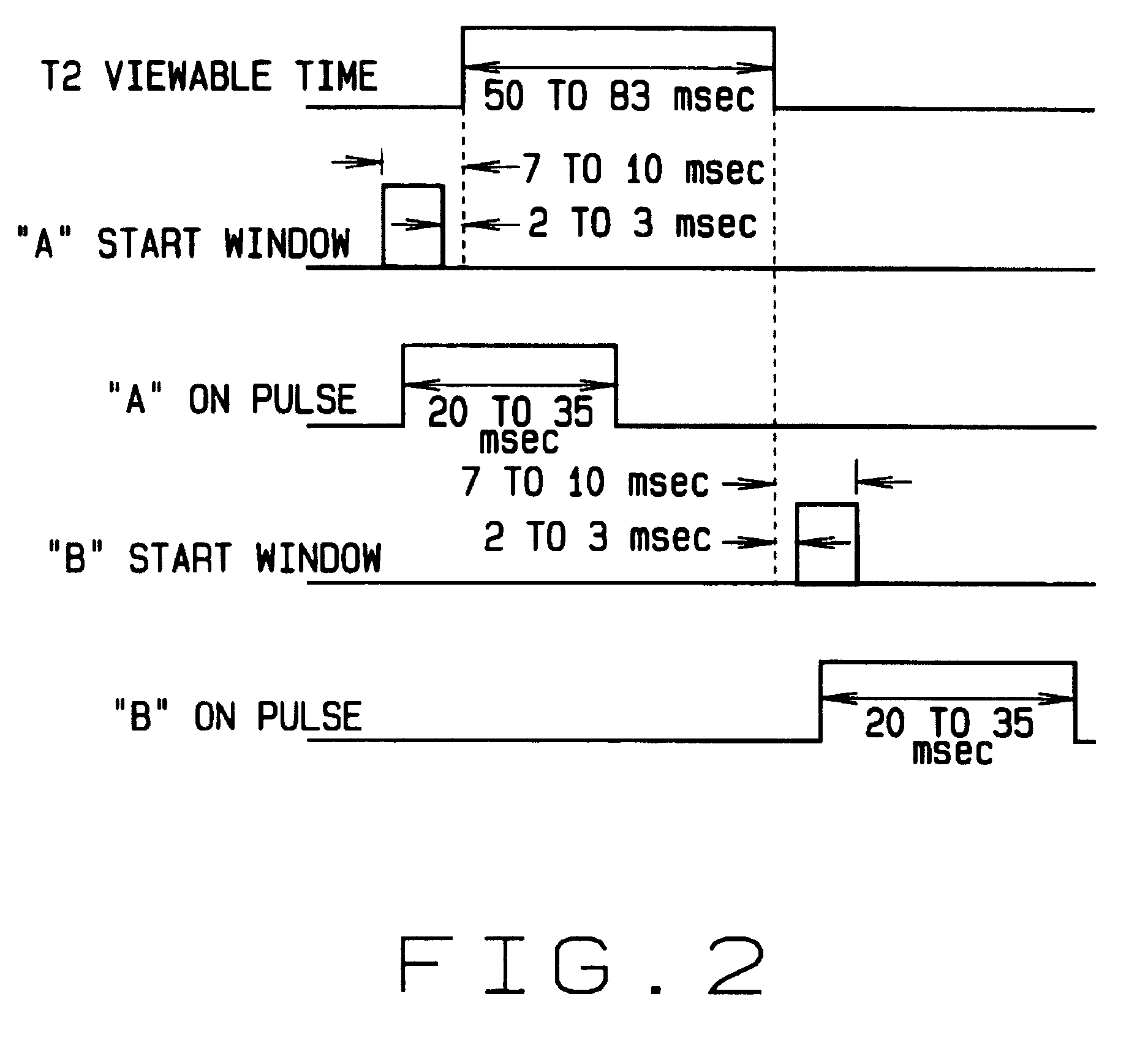
Method and apparatus for time-phased constant IR energy delta source
The present invention comprises apparatus for calibrating a railway infrared hot box or hot wheel detector by delivering a desired radiant energy delta to the hot box detector. The apparatus comprises a solid state radiant energy source adapted to be positioned adjacent to the hot box detector being calibrated for emitting radiant energy along a path toward the hot box detector and a processor to cycle the solid state radiant energy source at a desired frequency and intensity between an on state and an off state to achieve the desired radiant energy delta.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
Multifunctional elasticizer
The invention discloses a multifunctional elasticizer which comprises a raw silk frame, a secondary machine frame device, a deforming hotbox, a main machine frame device and a pedaling plate device, wherein the raw silk frame is positioned outside the multifunctional elasticizer; the secondary machine frame device is positioned between the raw silk frame and the main machine frame device; the deforming hotbox is positioned between the main machine frame device and the secondary machine frame device, and two ends of the deforming hotbox are respectively connected with a main machine frame and a secondary machine frame; and the pedaling plate device is positioned between the main machine frame device and the secondary machine frame device. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the multifunctional elasticizer is simple in structure, low in cost, capable of directly processing a raw silk into an elastic silk with low and middle elasticity, high in production efficiency, wide in variety of products, and high in quality of produced products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YUEJIAN INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD
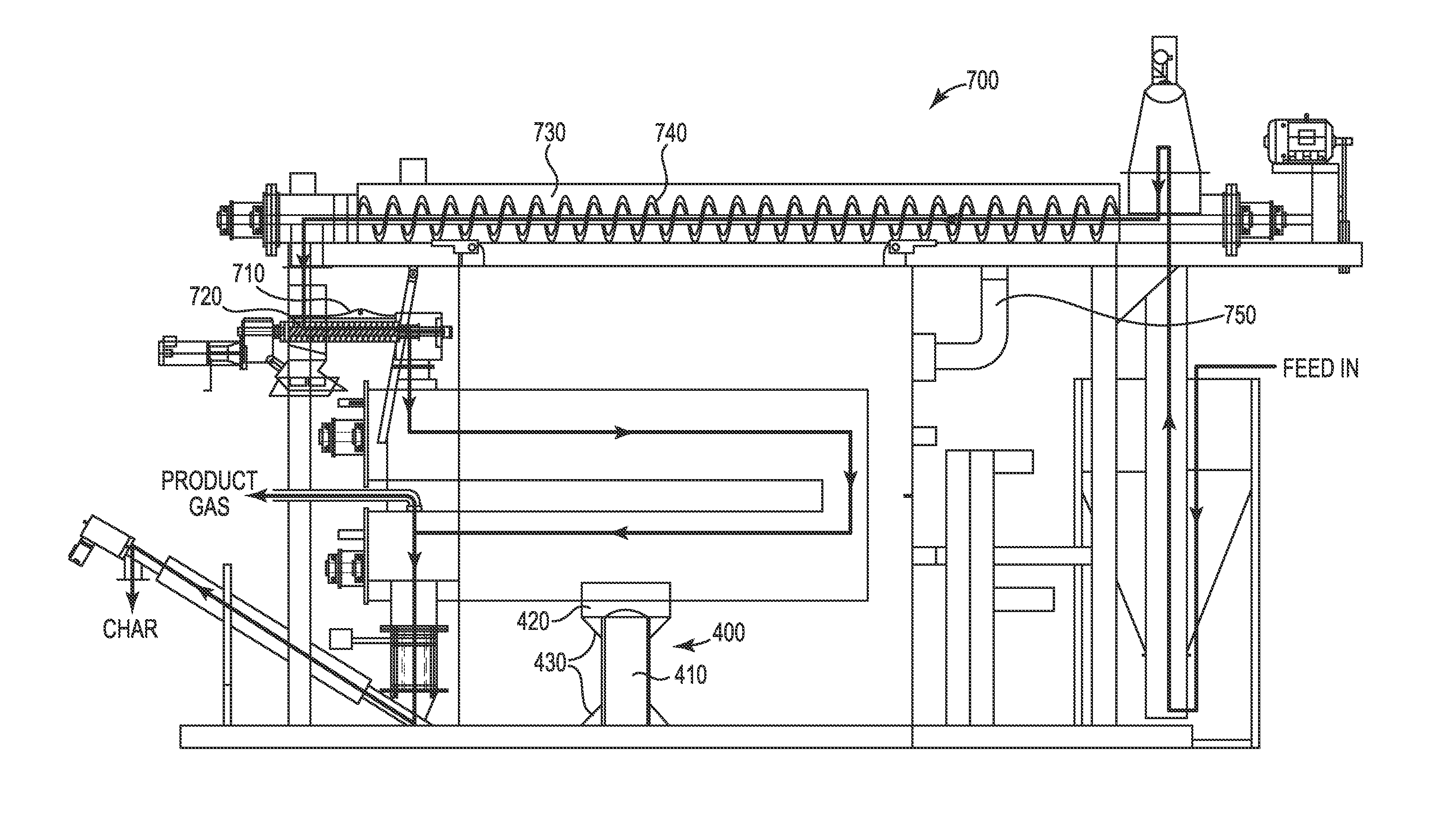
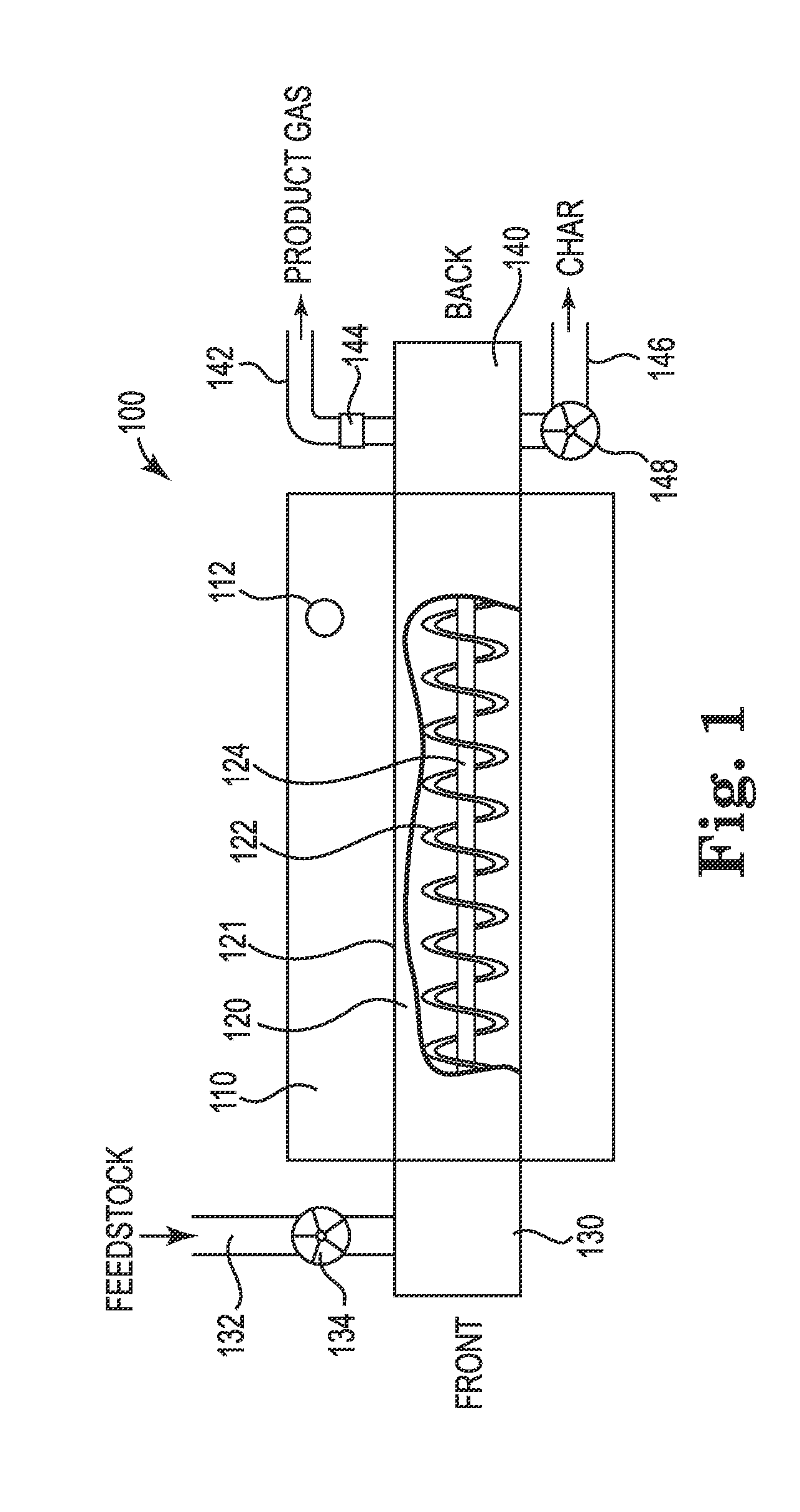
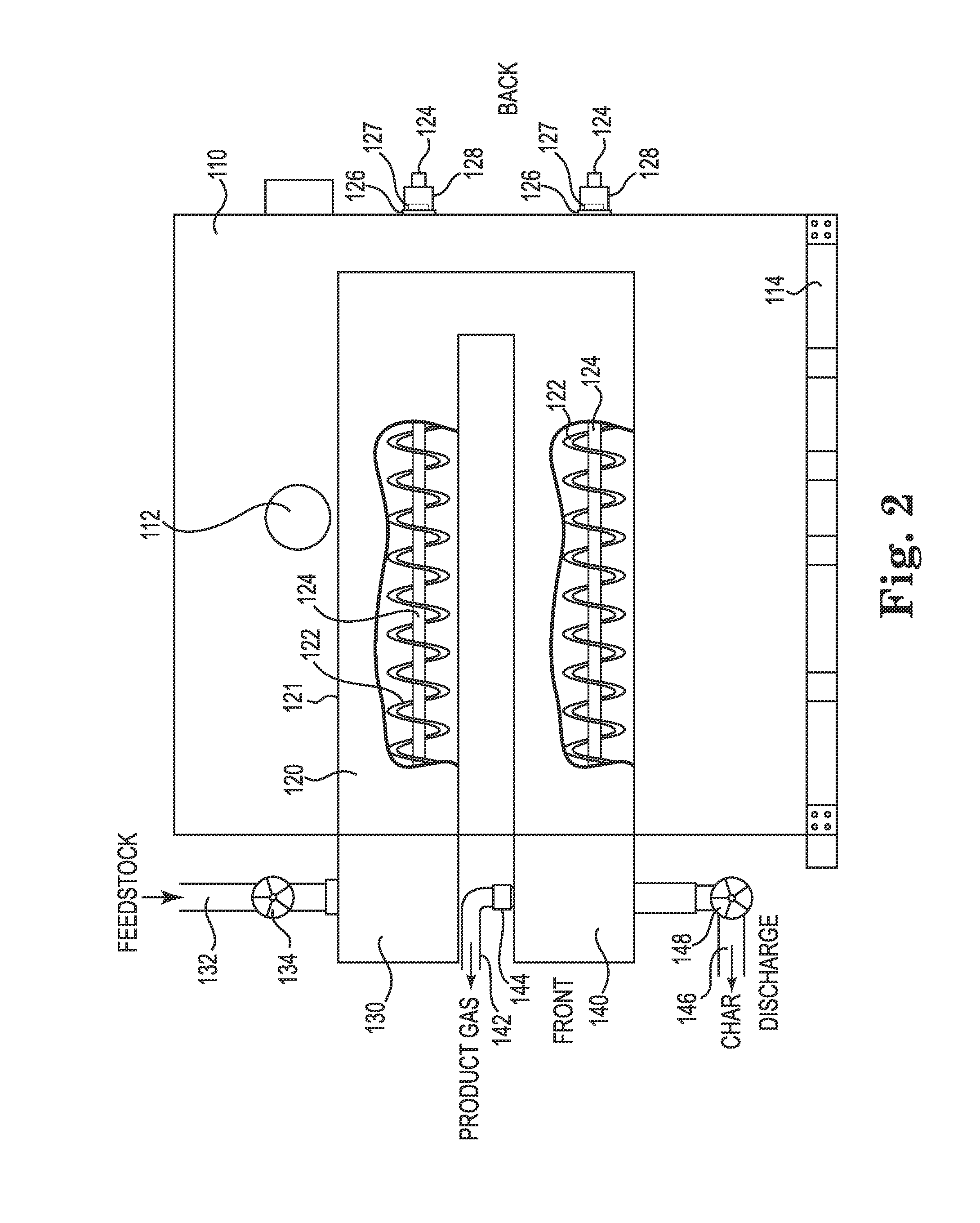
System and Method Using a Horizontal Sublimation Chamber for Production of Fuel From a Carbon-Containing Feedstock
Systems and methods for producing product gas fuel and solid char fuel from a carbon-containing feedstock are described. Feedstock is introduced into and transported through at least one substantially horizontal sublimation reaction chamber. An initial and final sublimation temperature is maintained within less than ±10° C. in an atmosphere free from external oxygen and externally supplied catalyst. The system is configured to not have any product gas leak out of the reaction chamber or oxygen leak into a hot box configured to heat the reaction chamber.
Owner:TEKGAR
Nickel base gamma/ gamma' superalloy with multiple reactive elements and use of said superalloy in complex material systems
InactiveCN102414331AImprove ductilityAvoid uncertaintyBlade accessoriesTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesRare-earth elementHot box
The present invention relates to a nickel-base Gamma / Gamma' superalloy with a unique blend of at most moderate cost, high oxidation resistance, high hot corrosion resistance, moderate strengthening, adequate alloy stability, and comparatively good weldability. The said alloy comprises: Up to 20 wt% of the sum of Co and Fe, between 17 and 21 wt% Cr, between 0.5 and 3 wt% of the sum of Mo and W, at most 2 wt% Mo, between 4.8 and 6 wt% Al, between 1.5 and 5 wt% Ta, between 0.01 and 0.2 wt% of the sum of C and B, between 0.01 and 0.2 wt% Zr, between 0.05 and 1.5 wt% Hf, between 0.05 and 1.0 wt% Si, and between 0.01 and 0.5 wt% of the sum of rare earths such as Sc, Y, the actinides and the lanthanides, such that at least two of these rare earths are present in the alloy, and no more than 0.3 wt% of any of these rare earths. It further relates to its use in hot components such as, but not restricted to, blades, vanes, heat shields, sealings and combustor parts in gas turbines. It further relates to its use as filler alloy for repair welding and / or cladding of such hot components. It further relates to its use as protective coating and / or bond coat in a TBC system on such hot components. It further relates to its dual use as coating and / or bond coat, and, for repair and / or cladding on such hot components. It further relates to its use as intermediate layer between the base alloy and another coating and / or bond coat on such hot components. It further relates to its use in polycrystalline, directionally solidified or single crystal form in such components. It further relates to its production by processes such as, but not restricted to, precision casting, laser welding / cladding, hot box welding, laser sintering, cold spraying, explosion welding and vacuum plasma spraying. It further relates to its production by low S processing. It further relates to its use as part of material systems as exemplified above produced by low S processing.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
High temp. hot case of false twist texturing machine
The invention relates a to false-twist texturing machine high temperature box. It is made up of box body, heat rail, heat transmitter, and heat insulating material. Electrical bar and heat rail is in heat transmitter and fixed in box body. The heat rail is formed by two parallel long and short heat rails. The box body is set thermal detector. The invention has the advantages of short preheating time, fast heating, safe, reliable, and the 625 centigrade degree maximum working temperature; small box body size; short yarn waling length; and good quality and performance stretch yarn.
Owner:王兆海
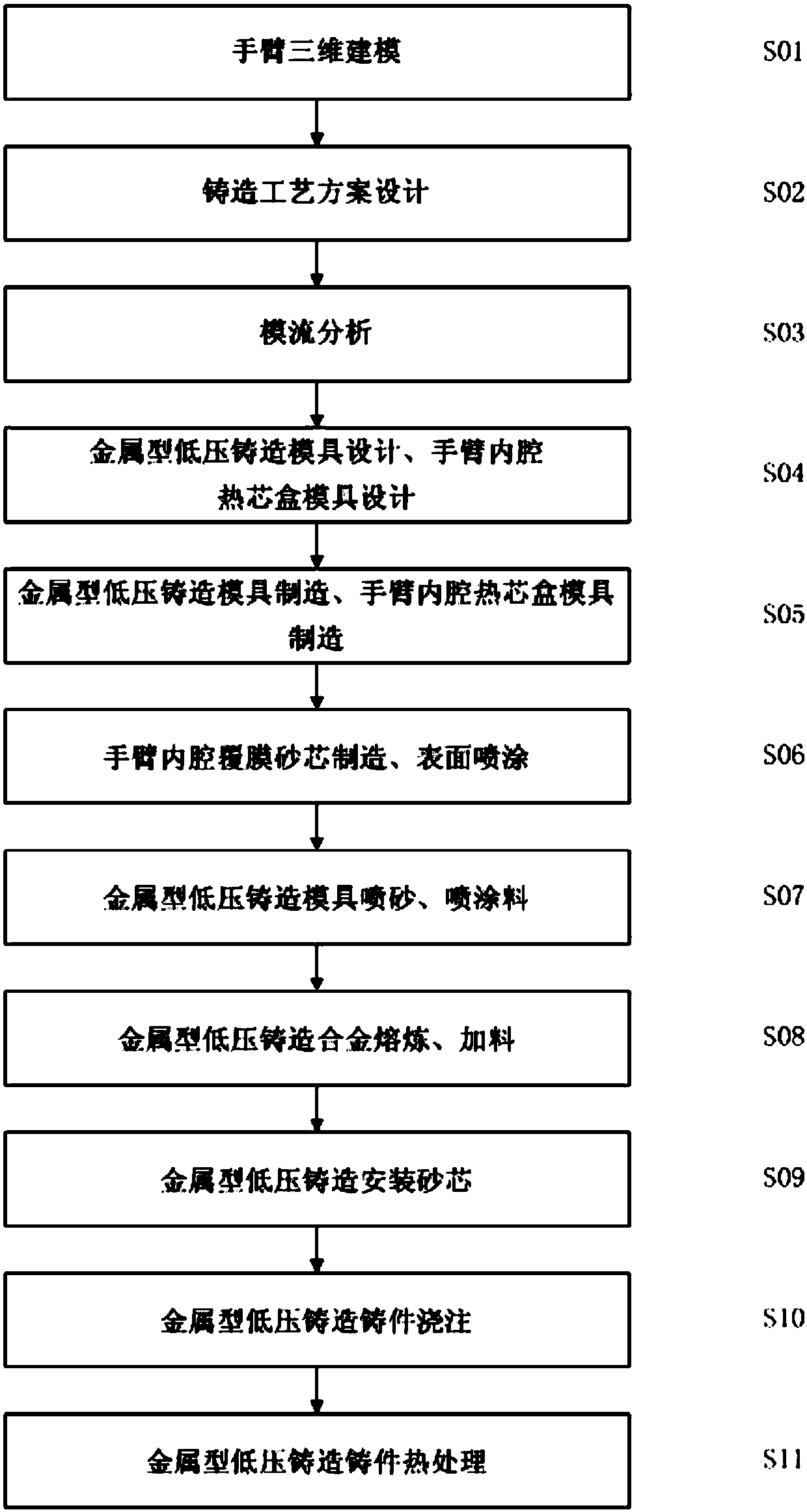
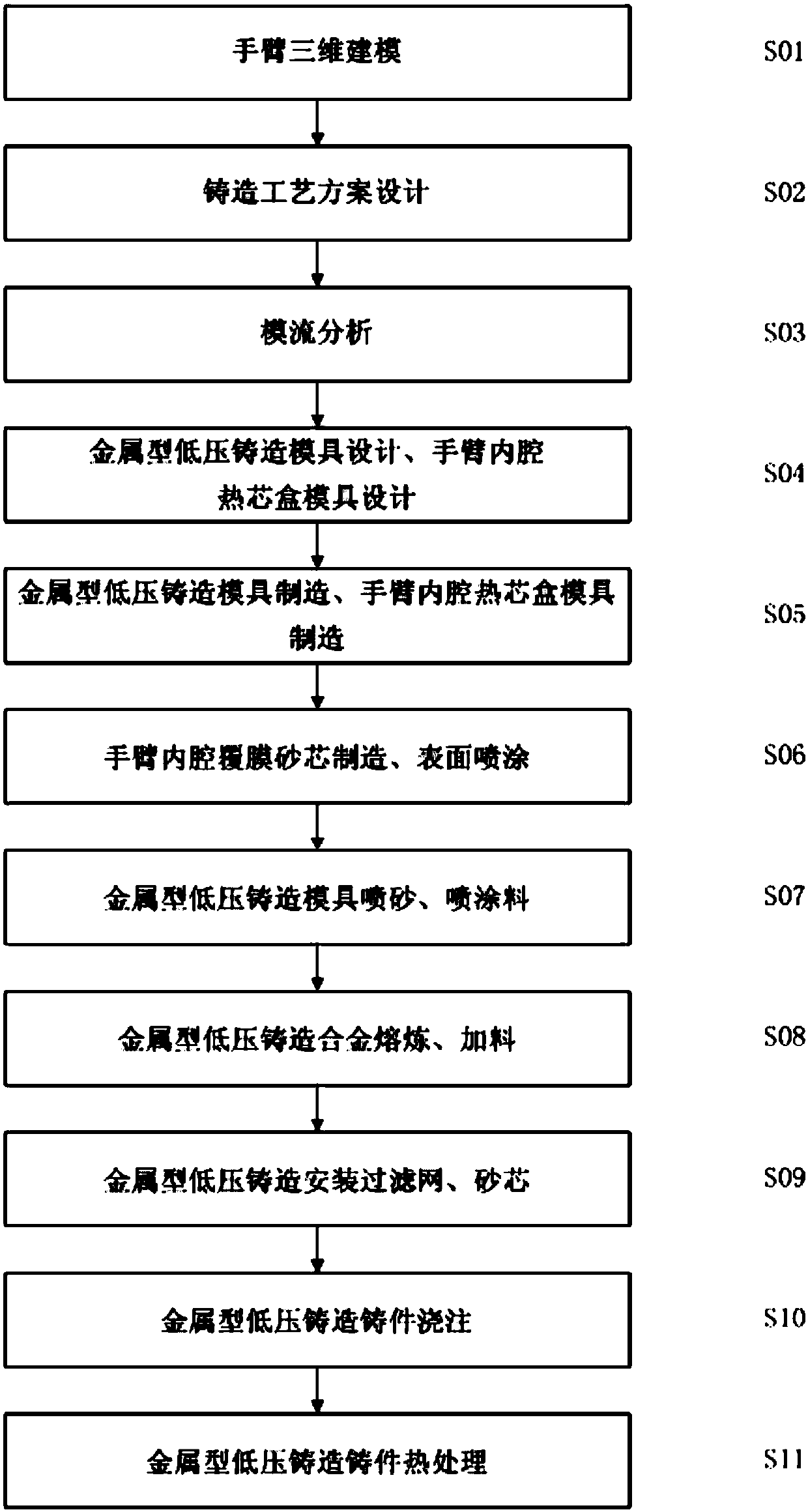
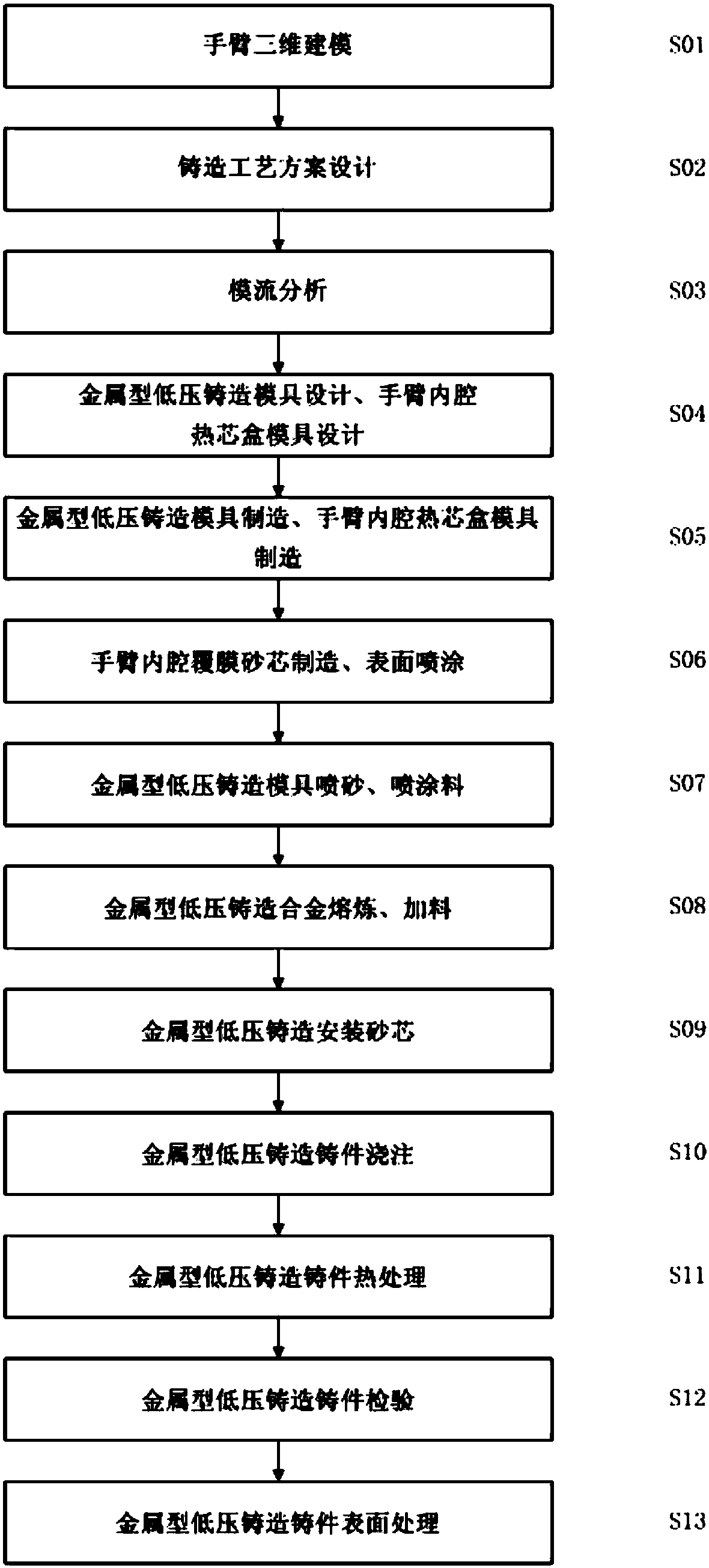
Aluminum alloy metal mold low-pressure casting technological method for collaborative robot arm
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy metal mold low-pressure casting technological method for a collaborative robot arm. The method comprises the following steps of 1, three-dimensional modelingof the arm; 2, design of a casting technological scheme; 3, mold flow analysis; 4, design of a metal mold low-pressure casting mold and an arm inner chamber hot box mold; 5, manufacturing of the metalmold low-pressure casting mold and the arm inner chamber hot box mold; 6, manufacturing of an arm inner chamber film-coated sand core, and surface coating; 7, sand blasting and paint spraying of themetal mold low-pressure casting mold; 8, smelting and feeding of a metal mold low-pressure casting alloy; 9, mounting of the sand core through metal mold low-pressure casting; 10, pouring of metal mold low-pressure casting castings; and 11, heat treatment of the metal mold low-pressure casting castings. The collaborative robot arm manufactured through the method has the beneficial effects of beingsmall in weight, high in rigidity, high in inner chamber precision and attractive and delicate in outer surface.
Owner:张希波
Device and method for detecting heat insulating properties of building doors and windows
ActiveCN108490023AEasy to installIncreased efficiency of mounting into specimen framesMaterial heat developmentHot boxTest room
The invention discloses a device and method for detecting heat insulating properties of building doors and windows, and solves the problem that the mounting efficiency of test pieces of doors and windows at the present stage is low. The main points of the technical scheme are that the device for detecting the heat insulating properties of the building doors and windows comprises a test room, and ahot box and a cold box which are mounted in the test room and adhered to each other; a detecting opening is formed between the hot box and the cold box, and a test piece frame is mounted at the detecting opening; the device for detecting the heat insulating properties of the building doors and windows is also provided with a test piece pre-assembled assembly; the test piece pre-assembled assemblycomprises a pre-assembled outer frame which is adhered to the test piece frame, a pre-assembled inner frame which is adhered to the test pieces of the doors and windows, a supporting piece which is supported between the pre-assembled outer frame and the pre-assembled inner frame, and a filling piece which fills between the pre-assembled inner frame and the pre-assembled outer frame; after the adoption of the device for detecting the heat insulating properties of the building doors and windows, the mounting efficiency of the test pieces of the doors and windows can be improved, so that the detecting efficiency of the heat insulating properties of the overall test pieces of the doors and the windows can be improved.
Owner:宁波和邦检测研究有限公司
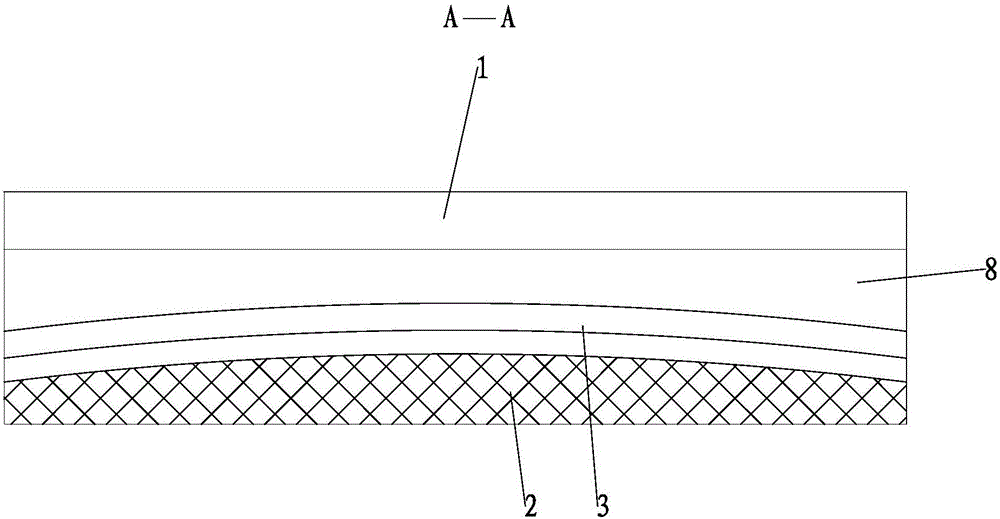
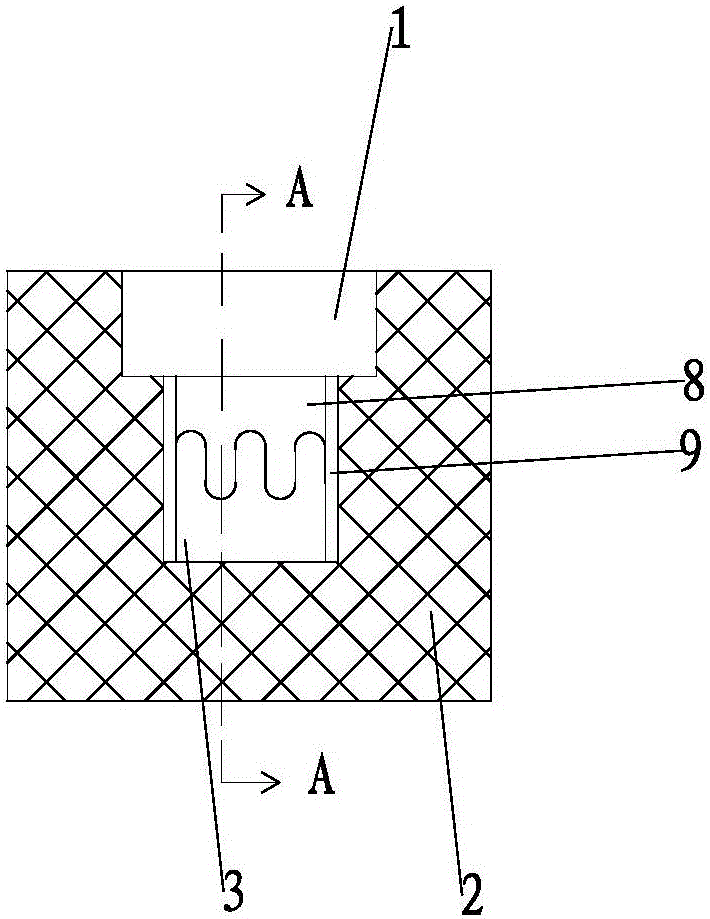
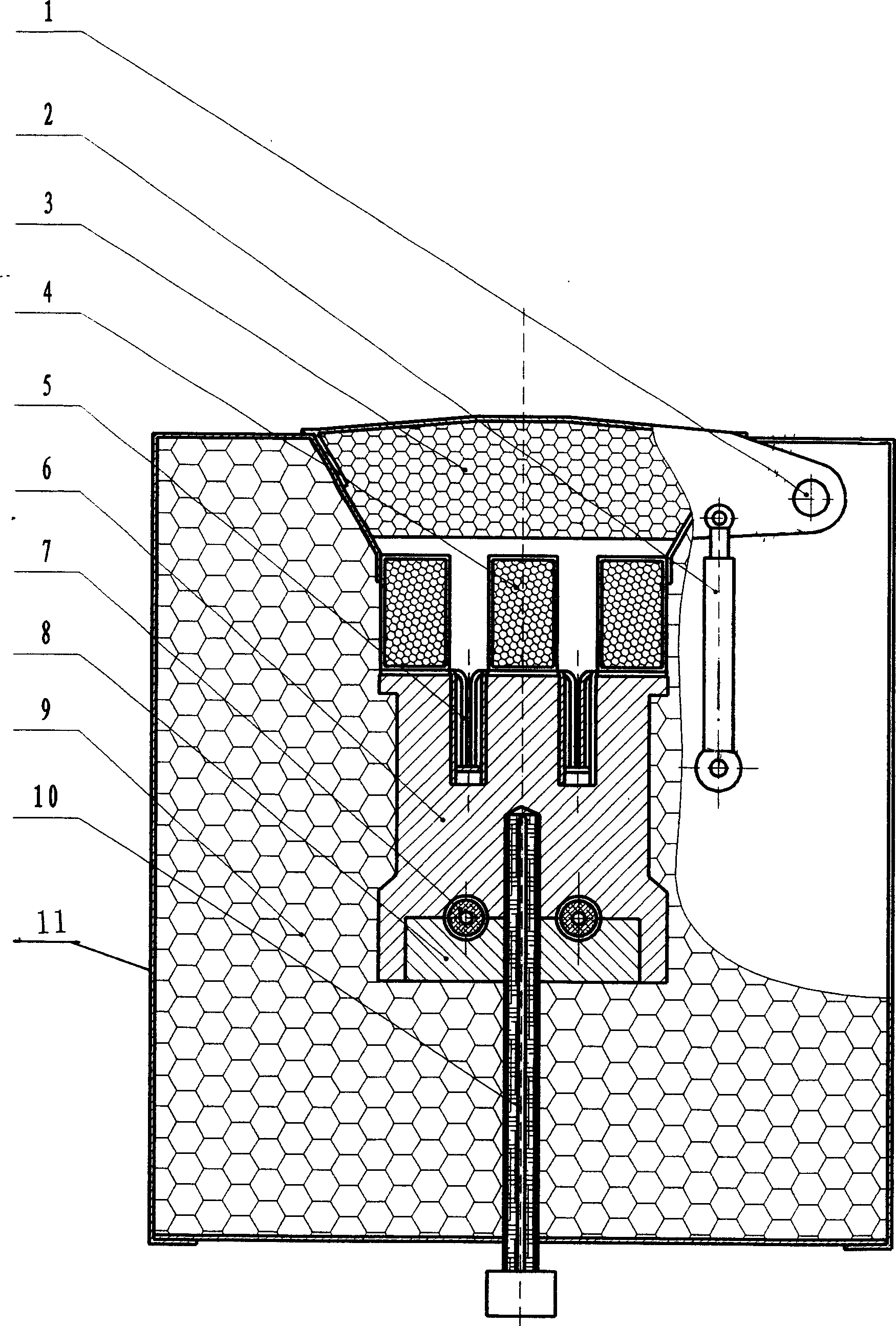
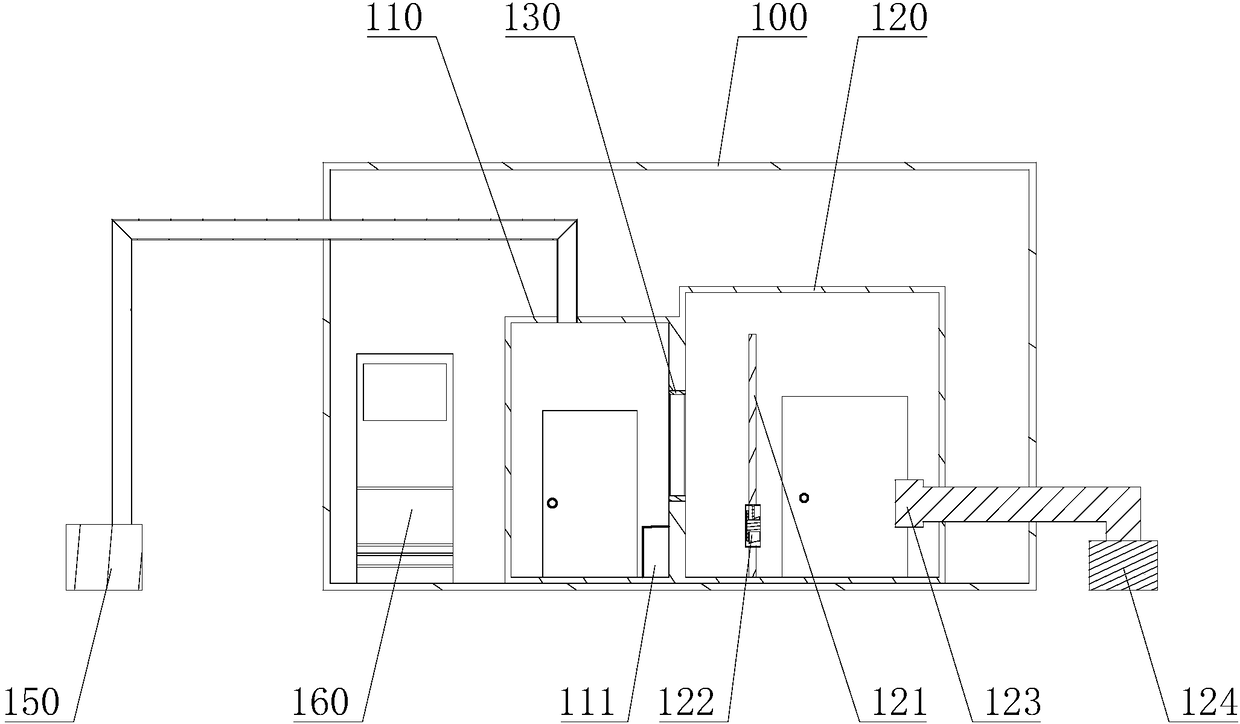
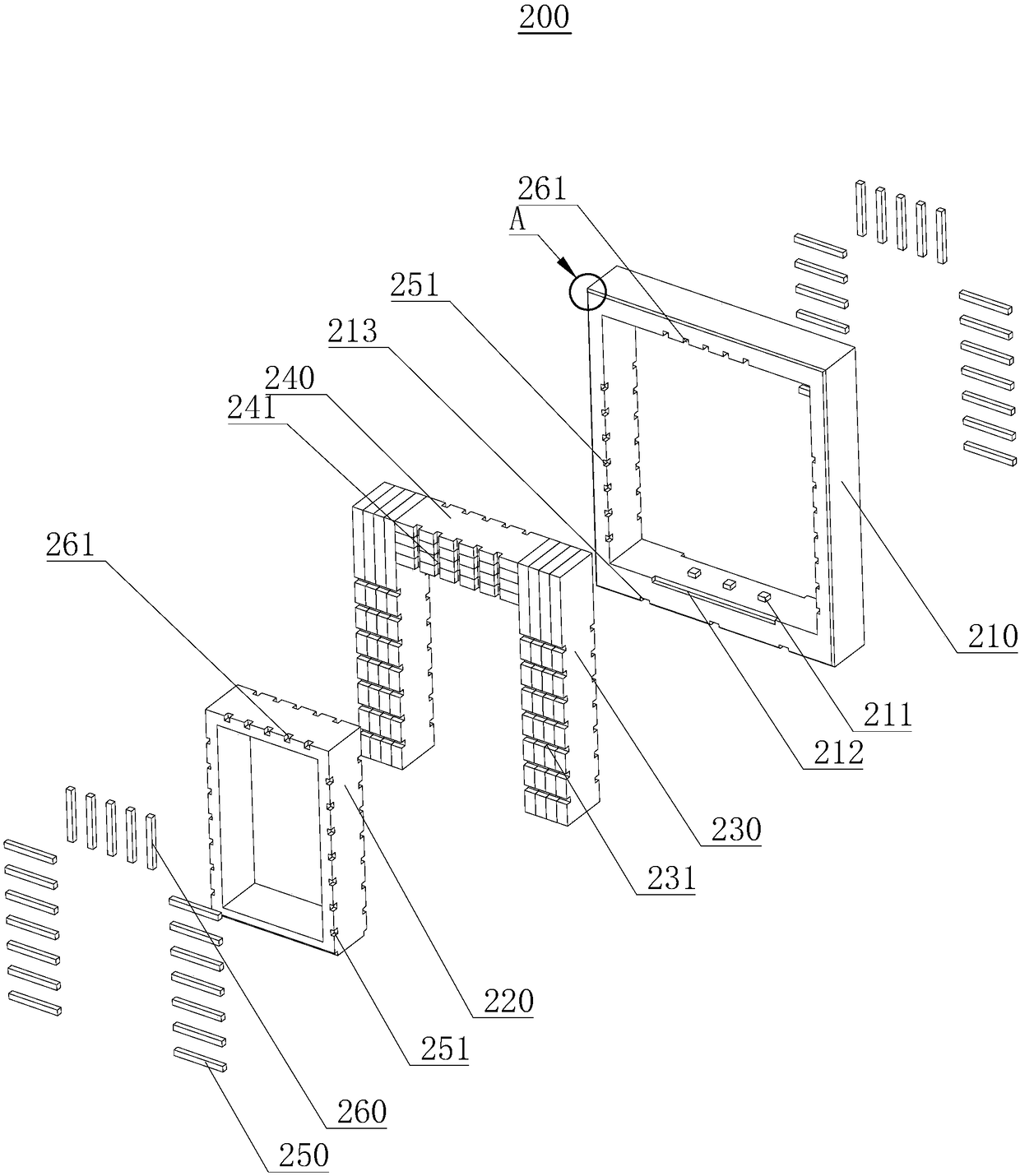
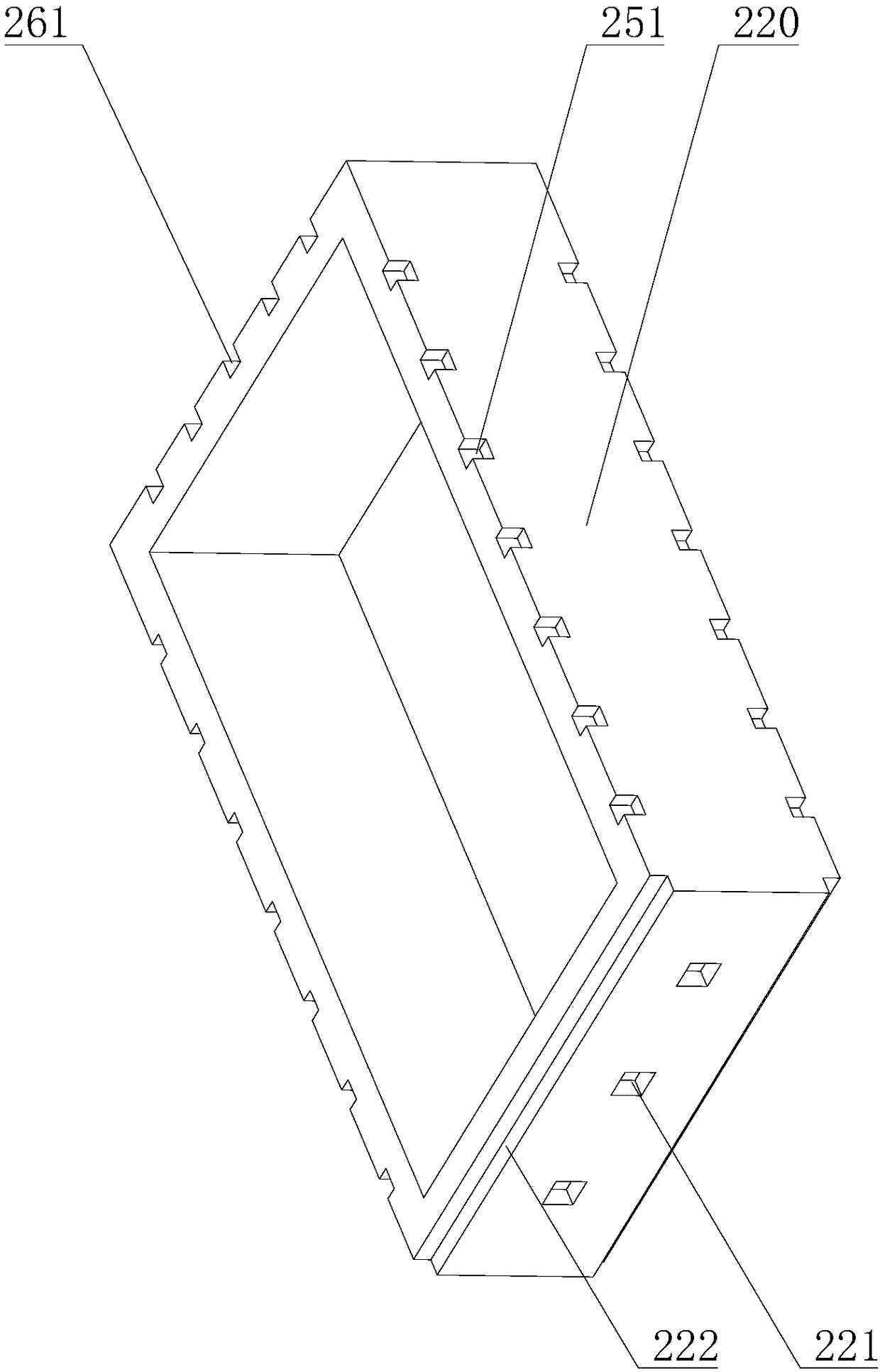
Deformation hot box
The invention relates to a deformation hot box. The deformation hot box comprises a box body, a heating track, a liquid-filling tube, a condensing tube, an electrical bar and a liquid return tube, wherein the heating track, the liquid-filling tube, the condensing tube, the electrical bar and the liquid return tube are installed in the box body; the box body comprises an upper shield plate combination piece, a lower shield plate combination piece, a left shield plate combination piece, a right shield plate combination piece, a front cover plate combination piece, a back cover plate combination piece and a heating track door combination piece, the internal side of the heating track door combination piece is provided with a plurality of heating tracks, the external side of the heating tracks is provided with an insulating block, the insulating block is used for preventing the heat generated by the heating tracks from dissipating so as to reduce the heat dissipation speed of the deformation hot box and generate the heat preservation effect, thereby the energy consumption cost is reduced and the quality of filamentization is improved.
Owner:WUXI HONGYUAN ELECTROMECHANICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com