Patents
Literature
487 results about "Explosion welding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Explosion welding (EXW) is a solid state (solid-phase) process where welding is accomplished by accelerating one of the components at extremely high velocity through the use of chemical explosives. This process is most commonly utilized to clad carbon steel plate with a thin layer of corrosion resistant material (e.g., stainless steel, nickel alloy, titanium, or zirconium). Due to the nature of this process, producible geometries are very limited. Typical geometries produced include plates, tubing and tube sheets.
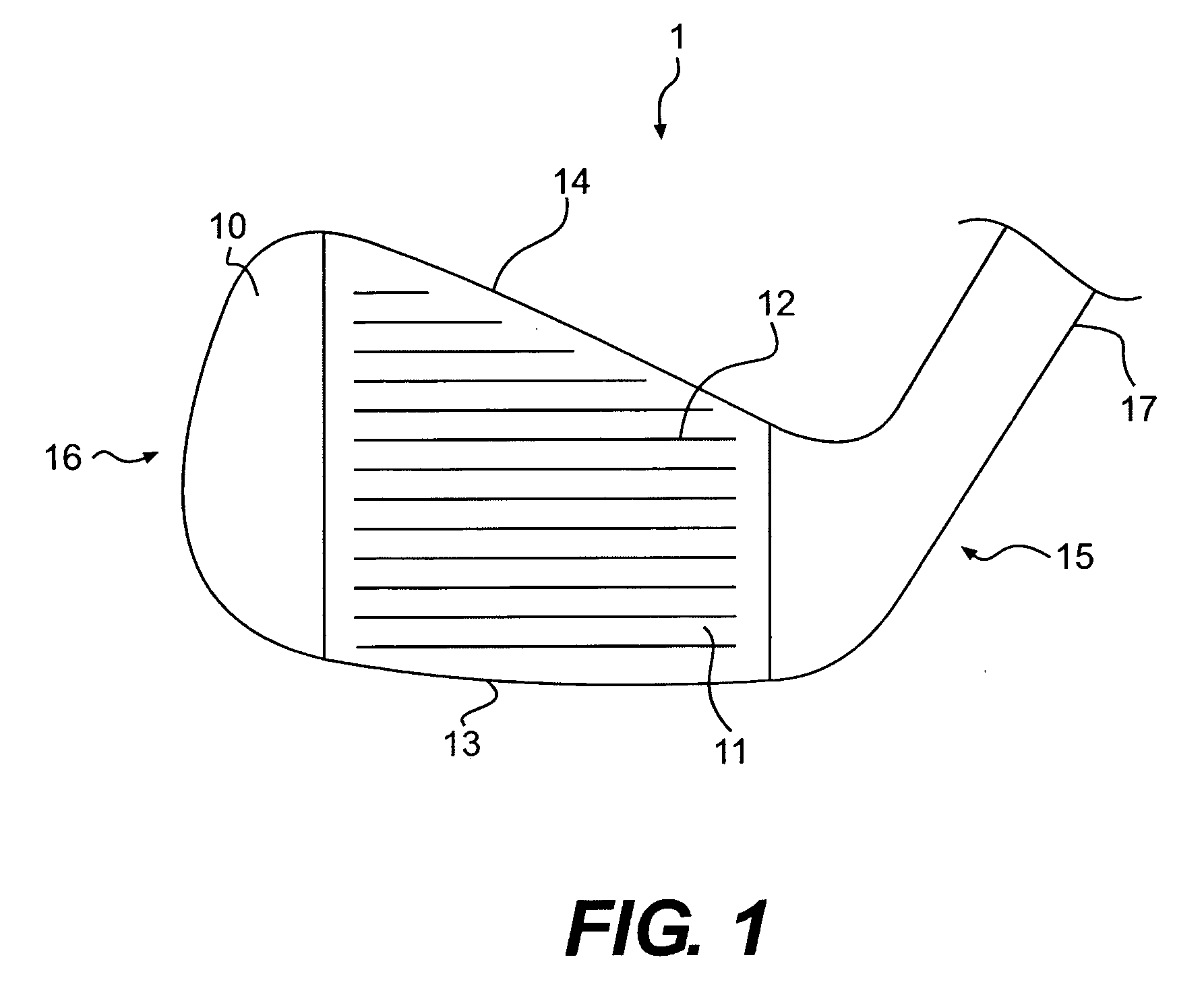
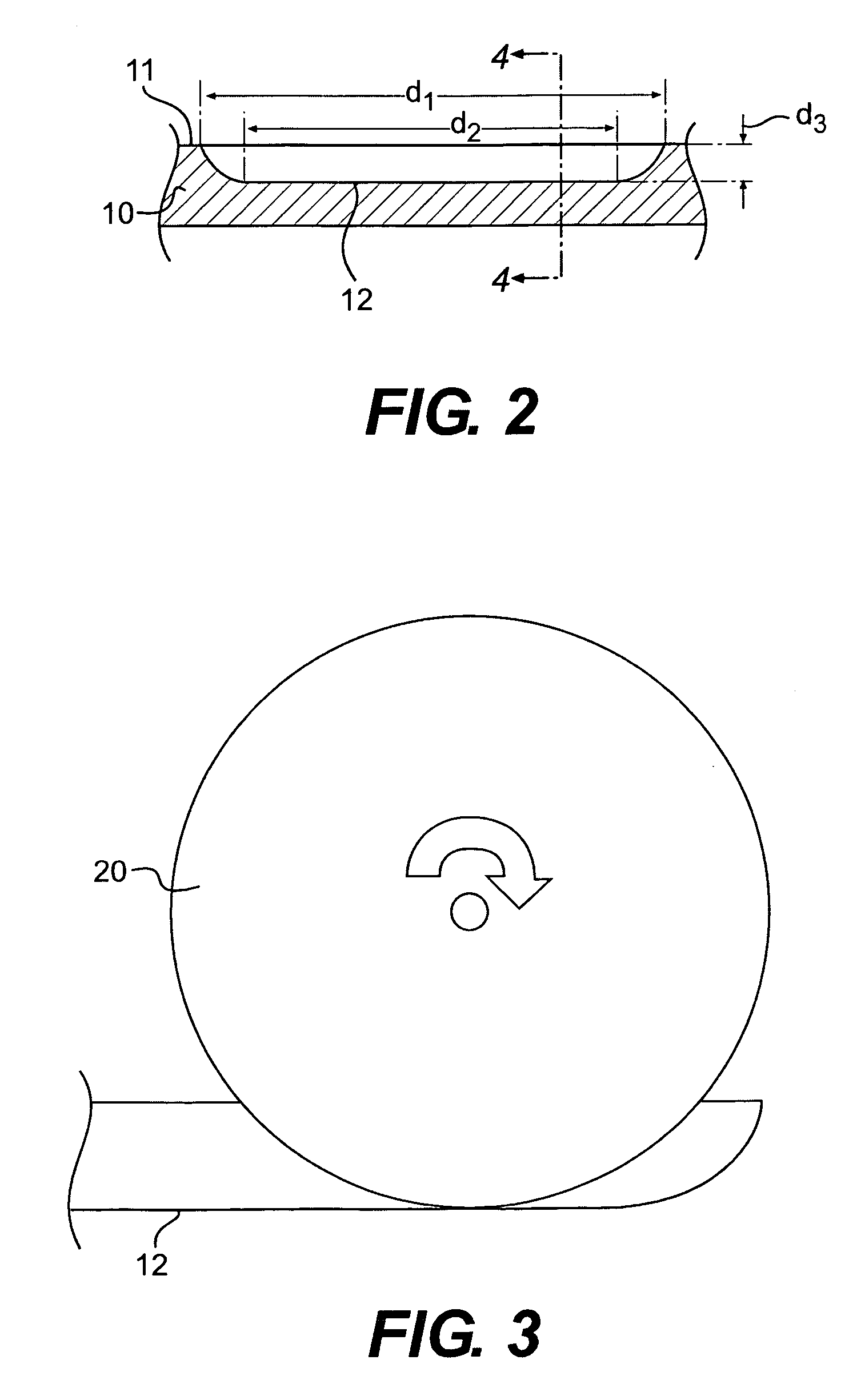
Golf club head
InactiveUS7846039B2Feel goodImprove wear resistanceGolf clubsRacket sportsMulti materialWear resistant
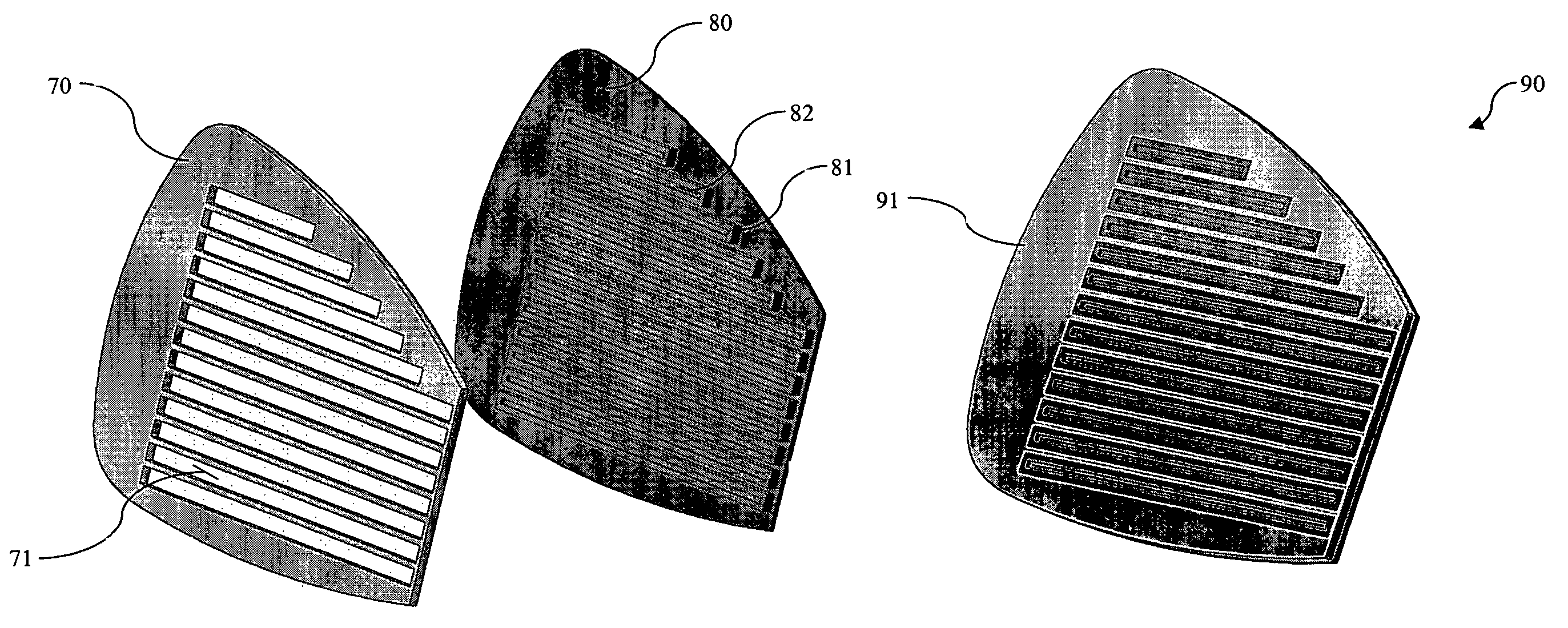
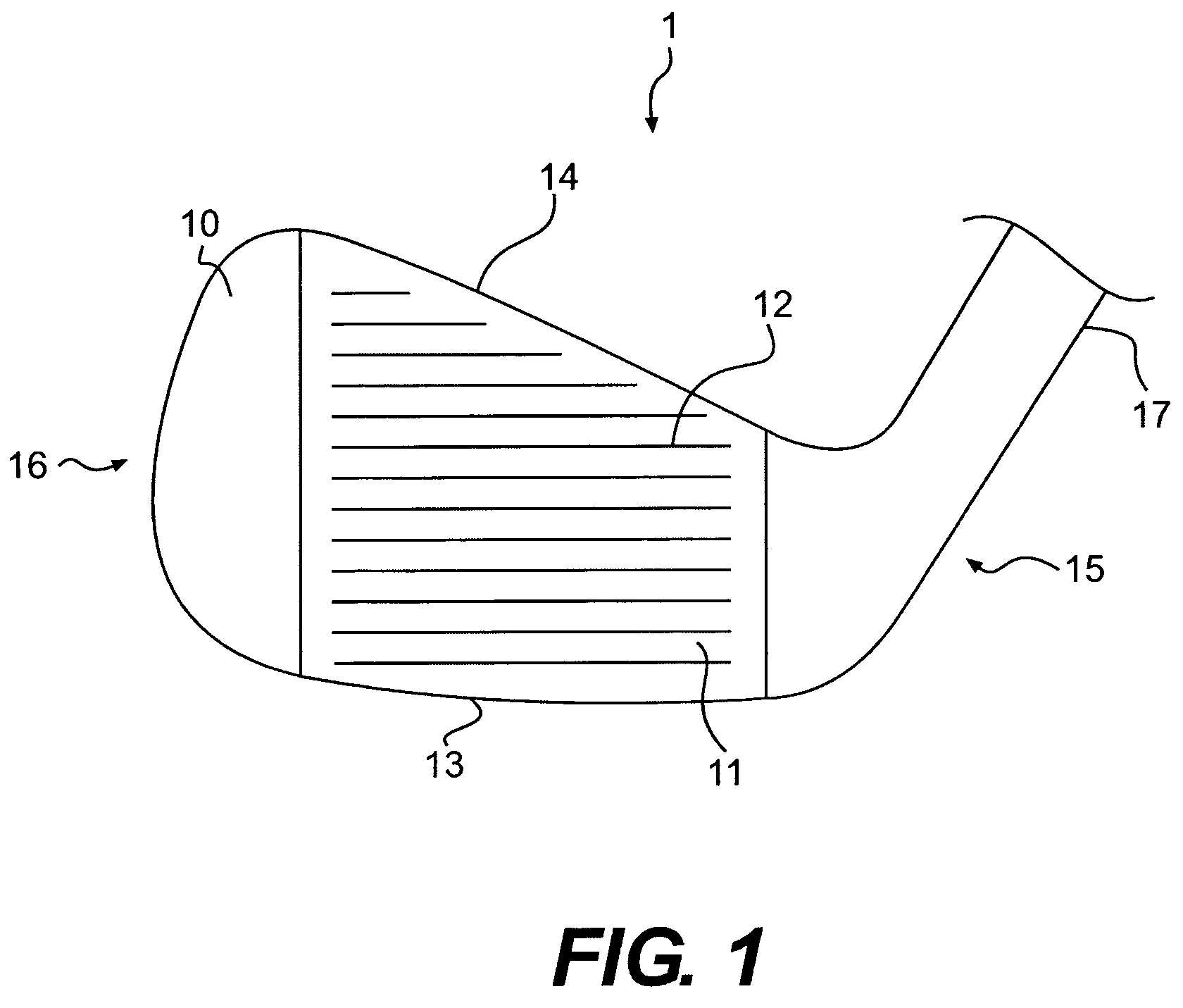
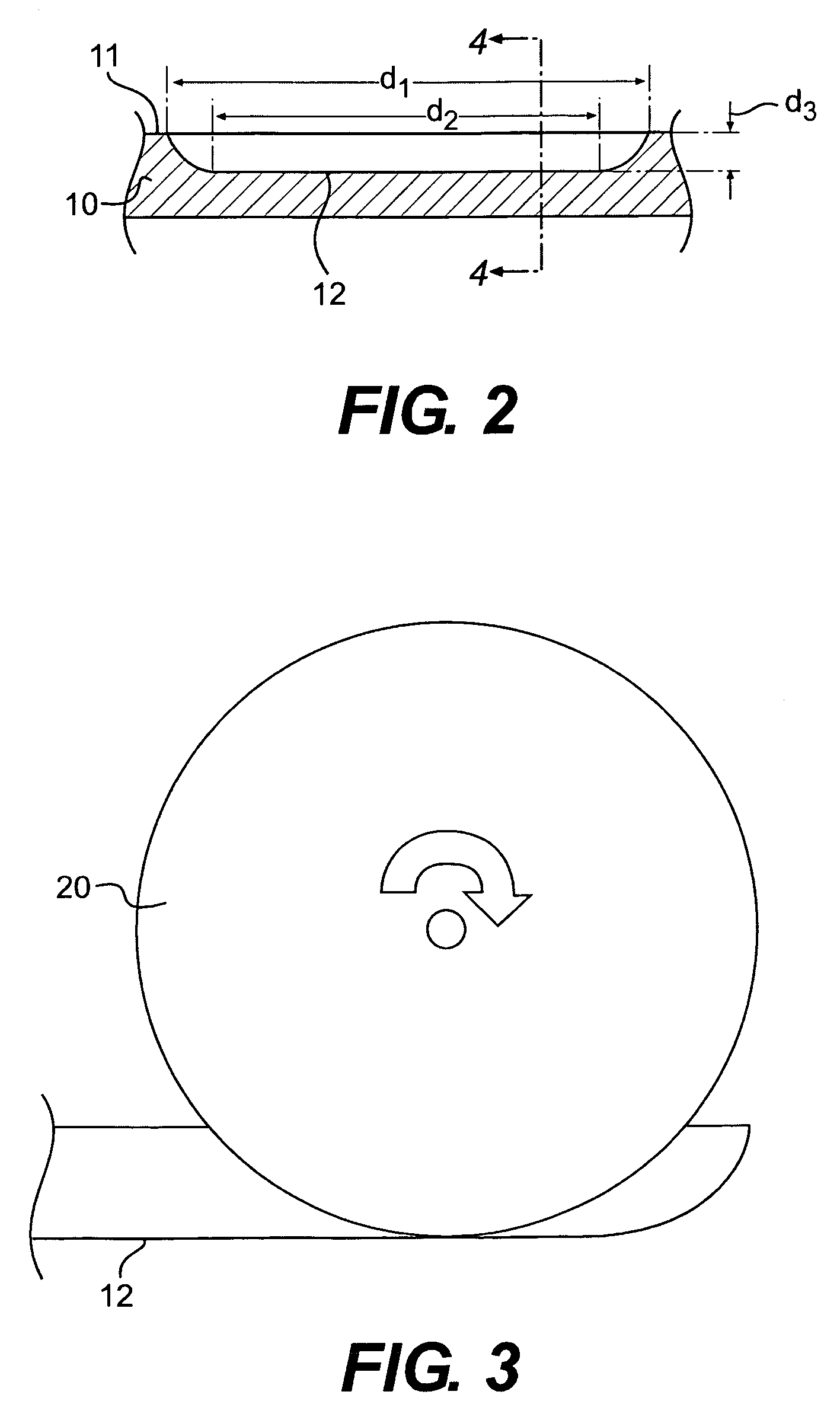
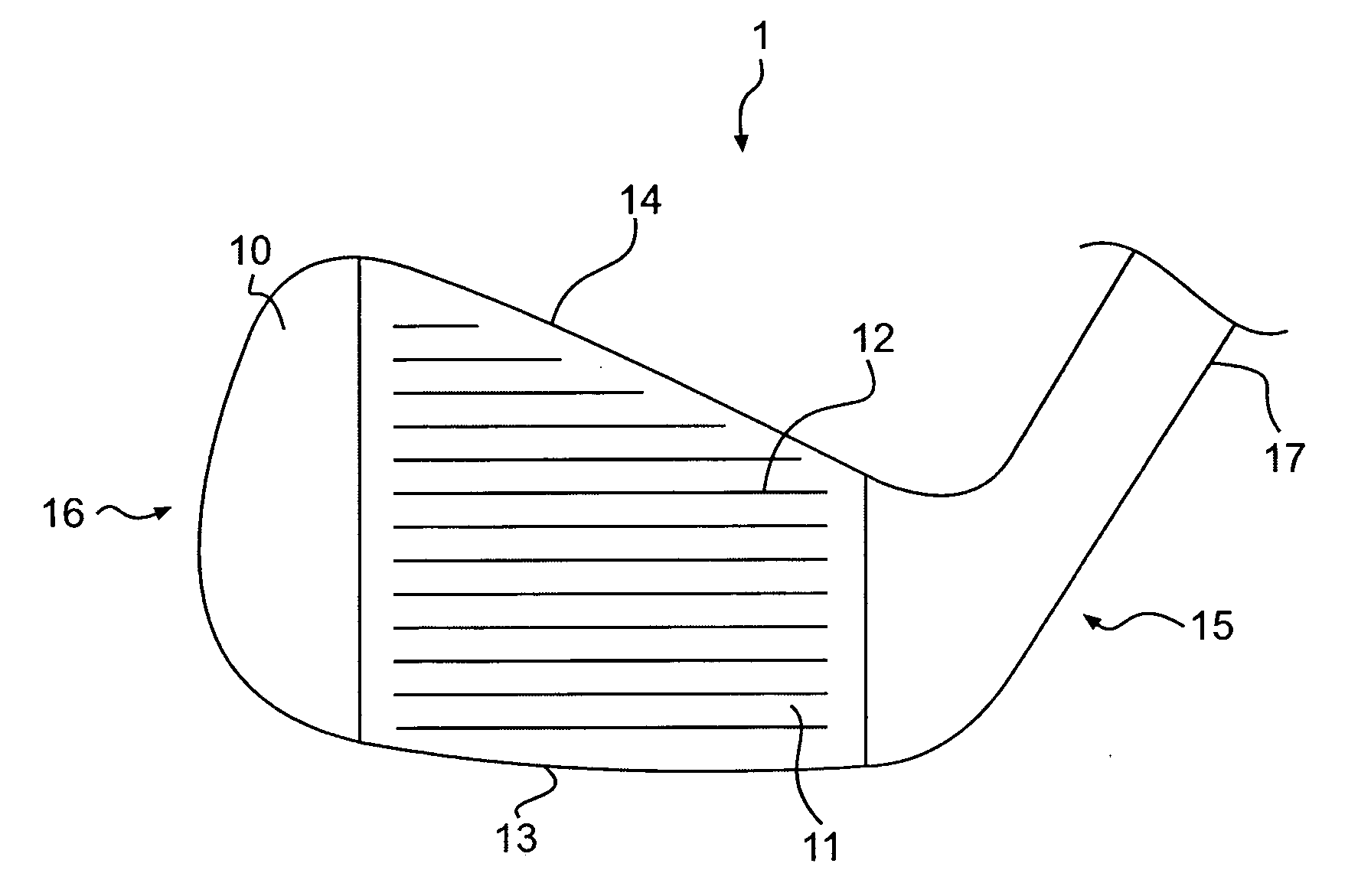
A golf club head having a multi-material face is disclosed and claimed. The face is formed by explosion welding, allowing materials having substantially different properties to be uniformly joined. Explosion welding allows the materials to be joined together via a cold-working process, allowing them to joined without losing their pre-bonded properties. Thus, the golf club head have a hard, wear resistant material as the ball-impacting face surface explosion welded to a softer material, allowing the multi-material face to be joined to a soft body material such that the body can be bent and customized. The multi-material face also allows for improved playing characteristics by allowing the club designer to use a thinner face and lighter body material while still providing improved face wear resistance and durability.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf club head
InactiveUS20070010346A1Feel goodImprove wear resistanceGolf clubsRacket sportsMulti materialWear resistant
A golf club head having a multi-material face is disclosed and claimed. The face is formed by explosion welding, allowing materials having substantially different properties to be uniformly joined. Explosion welding allows the materials to be joined together via a cold-working process, allowing them to joined without losing their pre-bonded properties. Thus, the golf club head have a hard, wear resistant material as the ball-impacting face surface explosion welded to a softer material, allowing the multi-material face to be joined to a soft body material such that the body can be bent and customized. The multi-material face also allows for improved playing characteristics by allowing the club designer to use a thinner face and lighter body material while still providing improved face wear resistance and durability.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Composite steel plate and manufacturing method for same
ActiveCN102430900AExtended service lifeReduce fire accidentsMetal layered productsNon-electric welding apparatusMicrometerSurface roughness
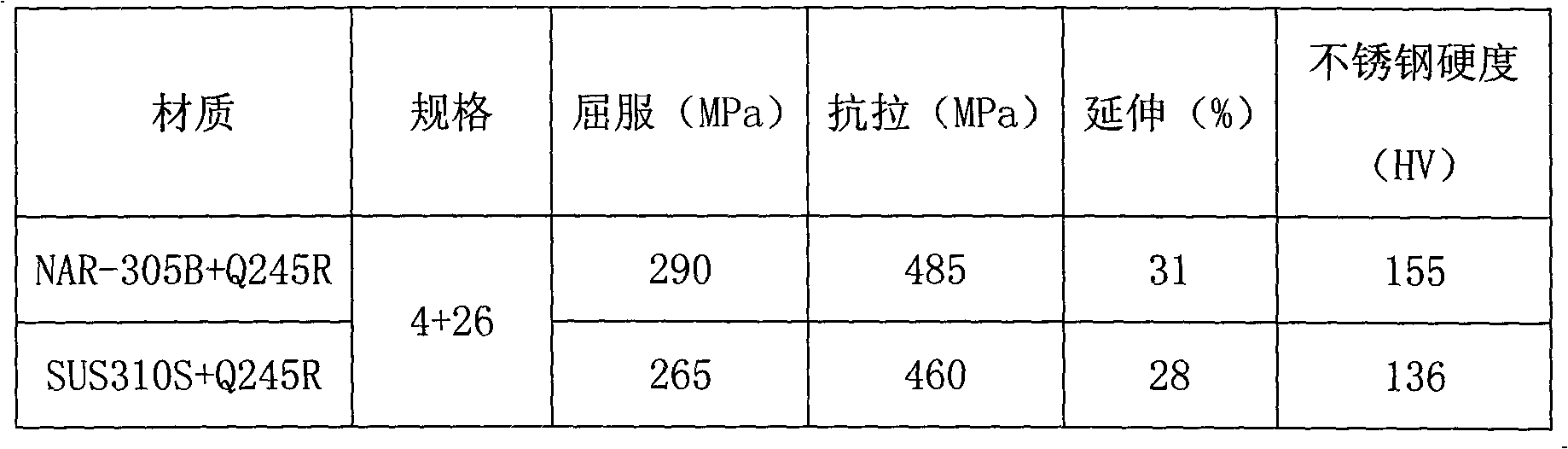
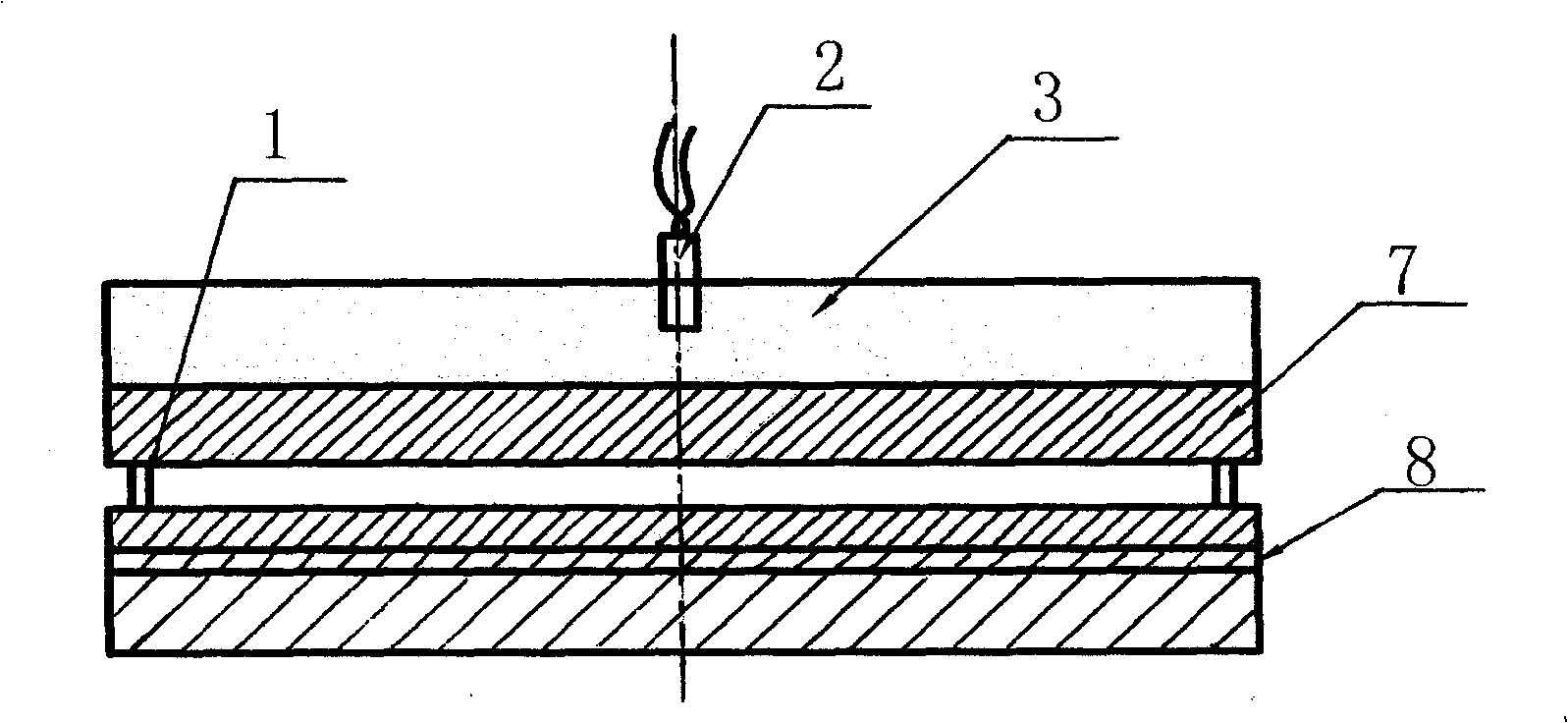
The invention relates to a composite steel plate and a manufacturing method for same. The composite steel plate comprises a Q245R base plate and an NAR-305B composite plate. The manufacturing method includes the successive steps: I, assembling the base plate and the composite plate in a matched manner; II, grinding a joint surface of the surface base plate so that surface roughness is no more than Ra 25 micrometers; III, laying explosion welding explosives on the composite plate, igniting the explosives, and welding the base plate together with the composite plate by means of explosion; IV, welding unwelded points by means of surface repair welding; V, performing heat treatment at the temperature of 900-920 DEG C and preserving heat for 15-20 minutes; VI, cutting the composite steel plate into the size of a finished composite steel plate; VII, testing mechanical properties of the composite steel plate according to GB / T6396-2008; VIII, performing 100% ultrasonic flaw detection for the composite steel plate according to NB / T47002-2009; and IX, grinding the surface of the composite steel plate so that surface roughness is no more than Ra 2 micrometers. The composite steel plate manufactured by the manufacturing method for the composite steel plate is corrosion-resistant and long in service life.
Owner:太原钢铁(集团)有限公司
Apparatus comprising armor
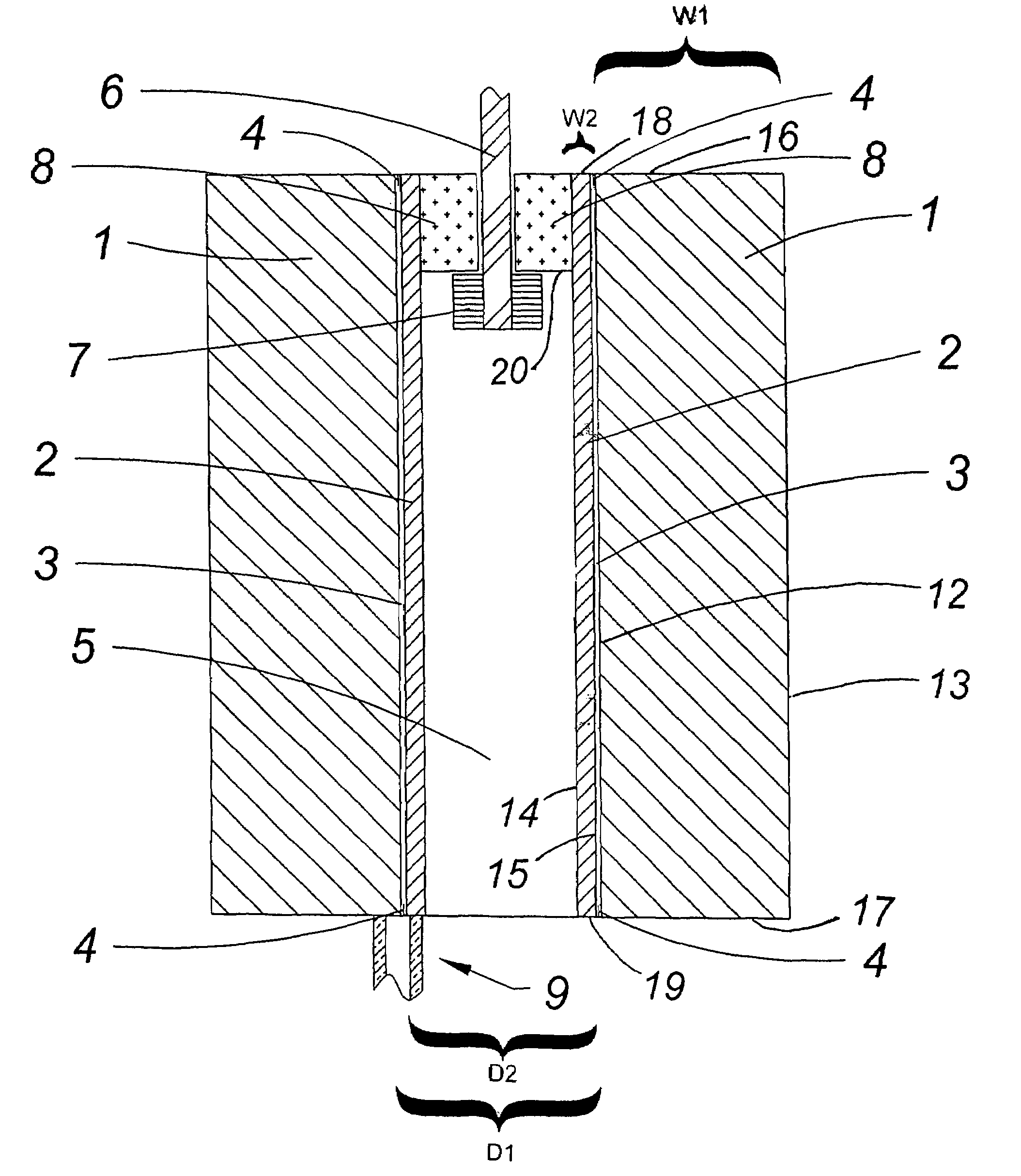
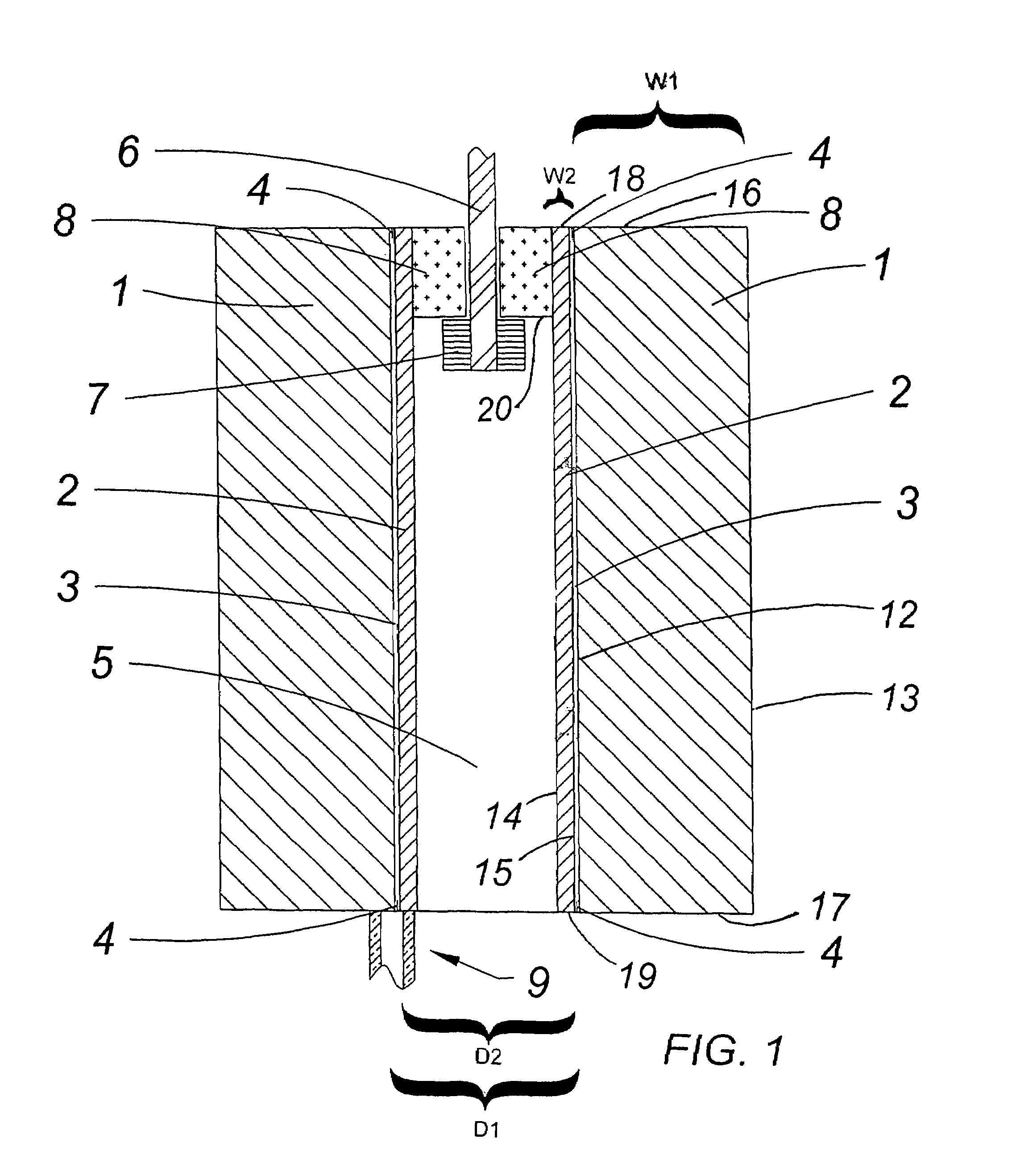
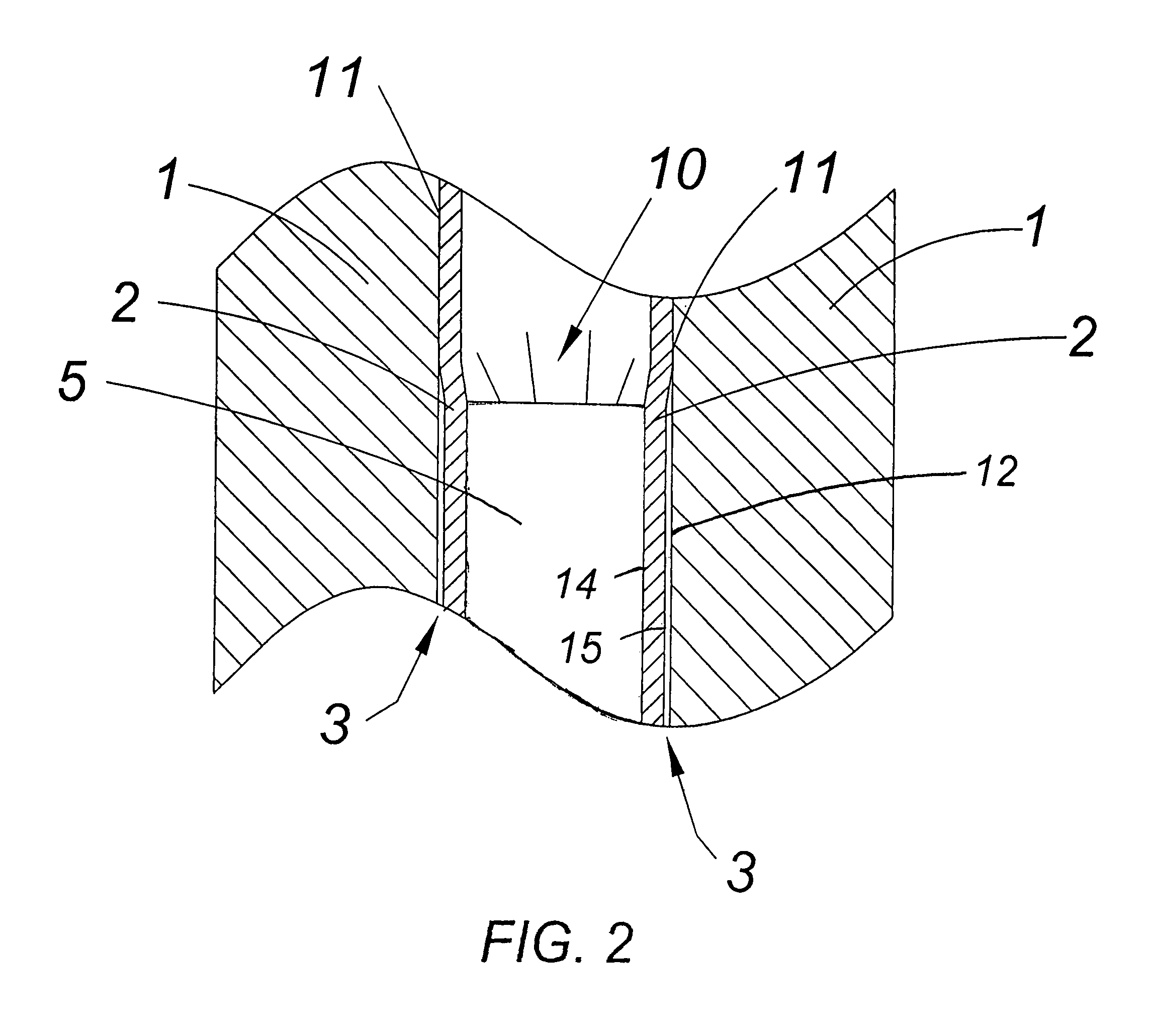
InactiveUS7406909B2Limited effectReduce the possibilityAmmunition storageBlastingSilicone GelsEngineering
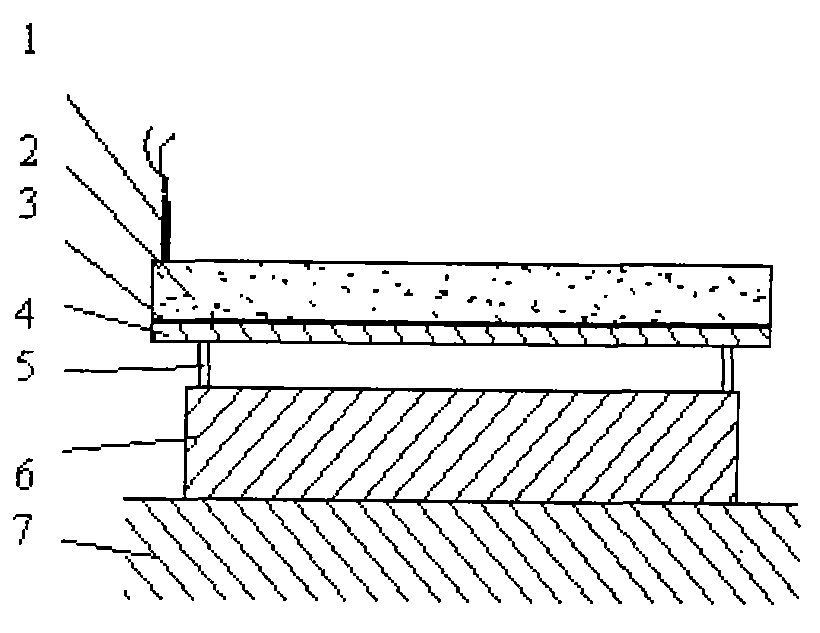
An armor that is used, for example, in multi-cell missile launchers is disclosed. In some embodiments, the armor includes three layers. The inner-most layer undergoes explosive welding when exposed to a pressure wave from an explosion. An intermediate layer in-elastically deforms when exposed to the explosion. The third and outer-most layer includes a plurality of elongated, pressurized tubes that contain fire retardant, among other chemicals. Silicone gel is interposed between the tubes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for producing stainless steel composite steel plate
ActiveCN101352805AUniform thicknessIncrease binding rateMetal rolling arrangementsNon-electric welding apparatusSanderSheet steel
A method for manufacturing a compound steel plate of stainless steel includes the following steps in turn: I, matching two stainless steel plates with a common carbon steel plate and carrying out fitting up according to the demands of a final finished product and rolling; II, welding carbon steel strips on the surrounding of the compound plate: welding the common carbon steel strips with a thickness of 6-8mm and a width of 60mm on the surrounding of the non-junction surface of the compound plate; III, polishing: using a sander to remove the impurities like oxide on the junction surface; IV, explosion welding: welding the compound plate of A surface on a basic plate firstly, and then welding the compound plate of B surface in an explosion way; V, fault detection: using an ultrasonic defectoscope to carry out fault detection; the area junction rate between the compound plate and the basic plate is not less than 99 percent; VI, carrying out defected weldseams on the surrounding fault; VII, carrying out hot rolling on the compound steel plate; feeding the compound steel plate into a hot milling roll to be rolled into a hot rolling compound steel bend with a thickness not more than 3mm; VIII, carrying out hot rolling, solid solution and acid cleaning on the steel plate and finally finishing the steel plate. The manufacture method of the invention can be used for manufacturing the compound steel plate of stainless steel with a total thickness of 0.8mm to 2mm.
Owner:TAIYUAN IRON & STEEL GROUP
Vacuum hot rolling compounding method of titanium alloy plate and stainless steel plate
InactiveCN101288877AAvoid the problem of severe embrittlementReduce the degree of diffusionTemperature control deviceWork treatment devicesLiquid metalCopper foil
The invention provides a vacuum hot-rolled composite method of a titanium alloy plate and a stainless steel plate, which relates to a composite method for the titanium alloy plate and the stainless steel plate. Aiming at the problems that intense mixing of liquid metal and high welding stress are generated during the melt welding of the titanium alloy plate and the stainless steel plate, the contradiction between the diffusion and the controlling of volume fraction of compounds in connection interface metals is boosted to ensure the connection during the vacuum diffusion welding and the explosion weld joint is difficult to be applied to high-temperature and corrosive temperature, the method is characterized in that the stainless steel plate (1) and the titanium alloy plate (2) are used; furthermore, a copper foil or aluminium foil (3) is used; the surfaces of the two plates are milled flatly and the copper foil or the aluminium foil (3) is laminated and fix between the two plates, so as form a specimen; the specimen is arranged in a vacuum loading chamber (5); when the vacuum degree in a vacuum heating furnace (6) is (1-3)*10<-3> Pa and the temperature is 600-1100 DEG C, the specimen is delivered into the vacuum heating furnace for heating and heat preservation, and then welded by a roller (7) and cooled. The method of the invention has small welding stress, can control the volume fraction of compounds in the metals with high hardness and large brittleness; furthermore, the weld joint can be applied to the high-temperature and corrosive environment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Explosion welding method for composite material of aluminum-steel
ActiveCN101152684AQuality improvementRealize large area explosive weldingExplosivesNon-electric welding apparatusSheet steelHigh intensity
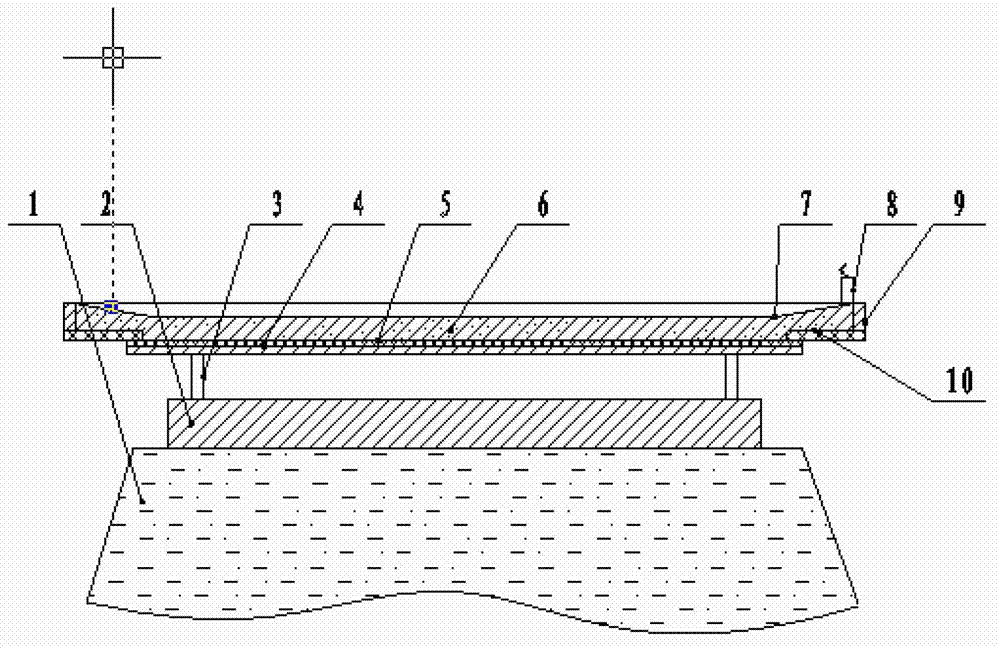
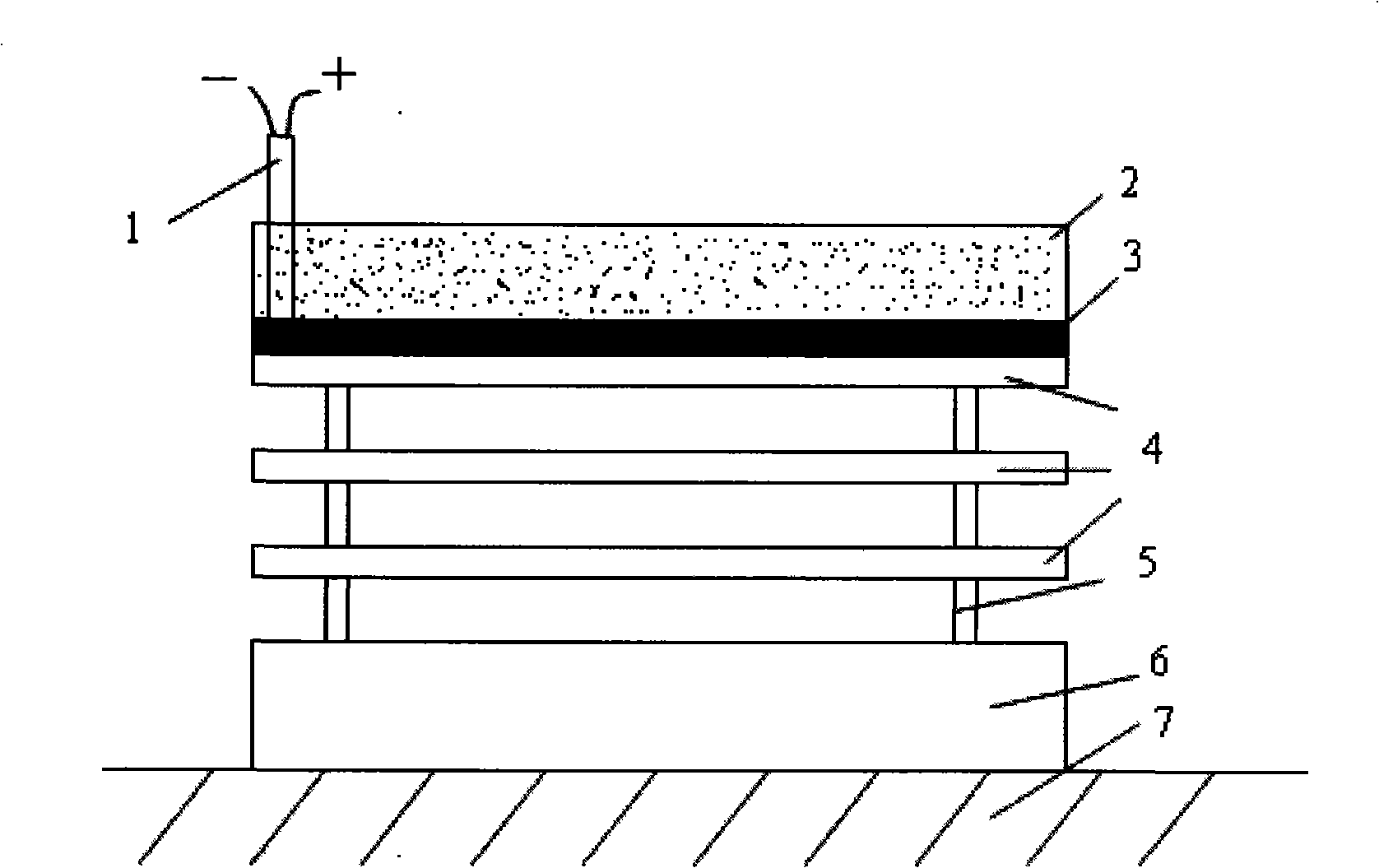
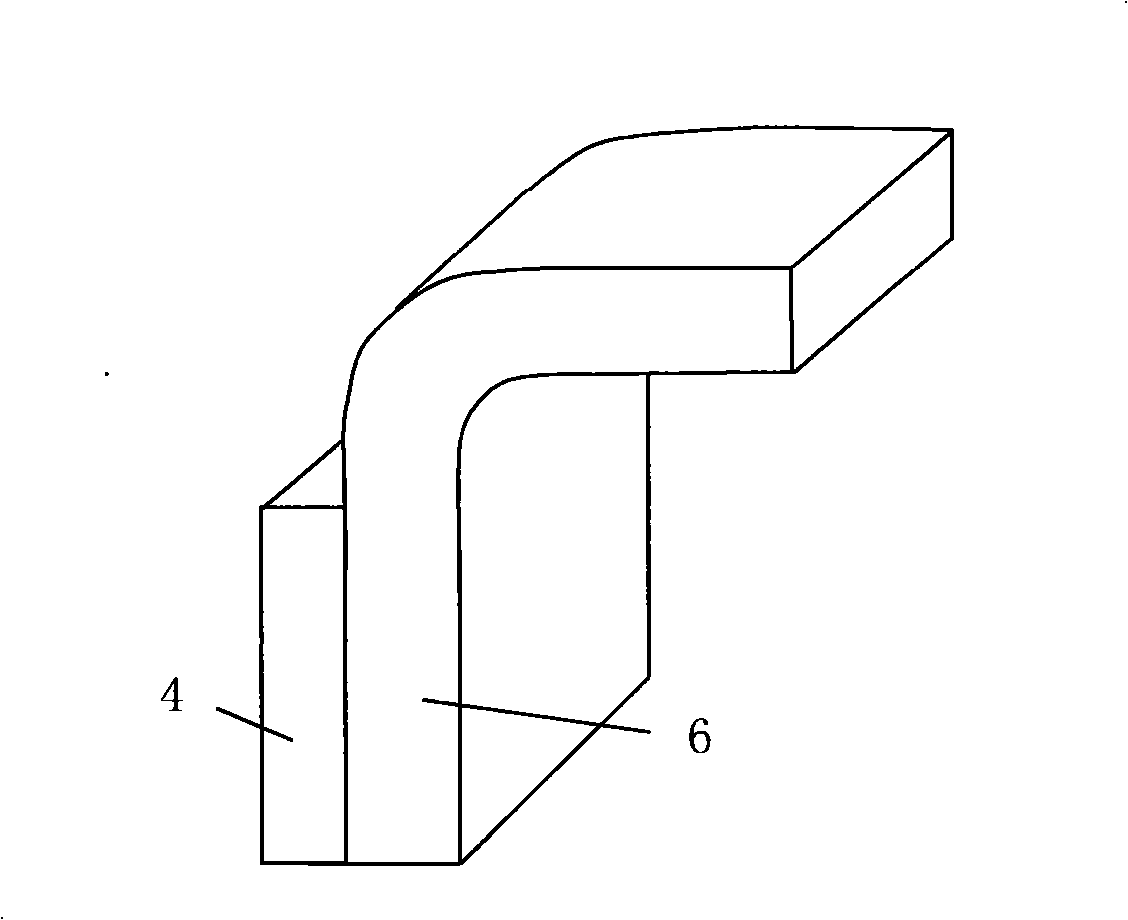
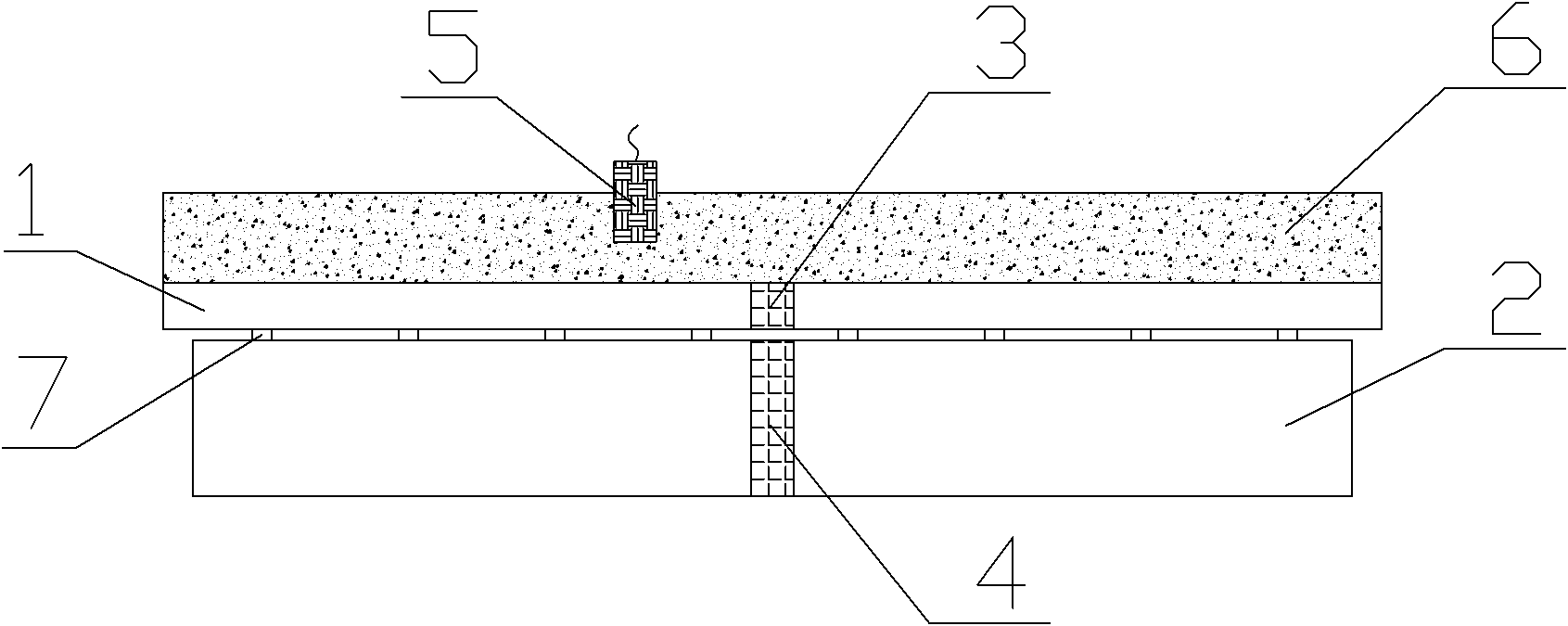
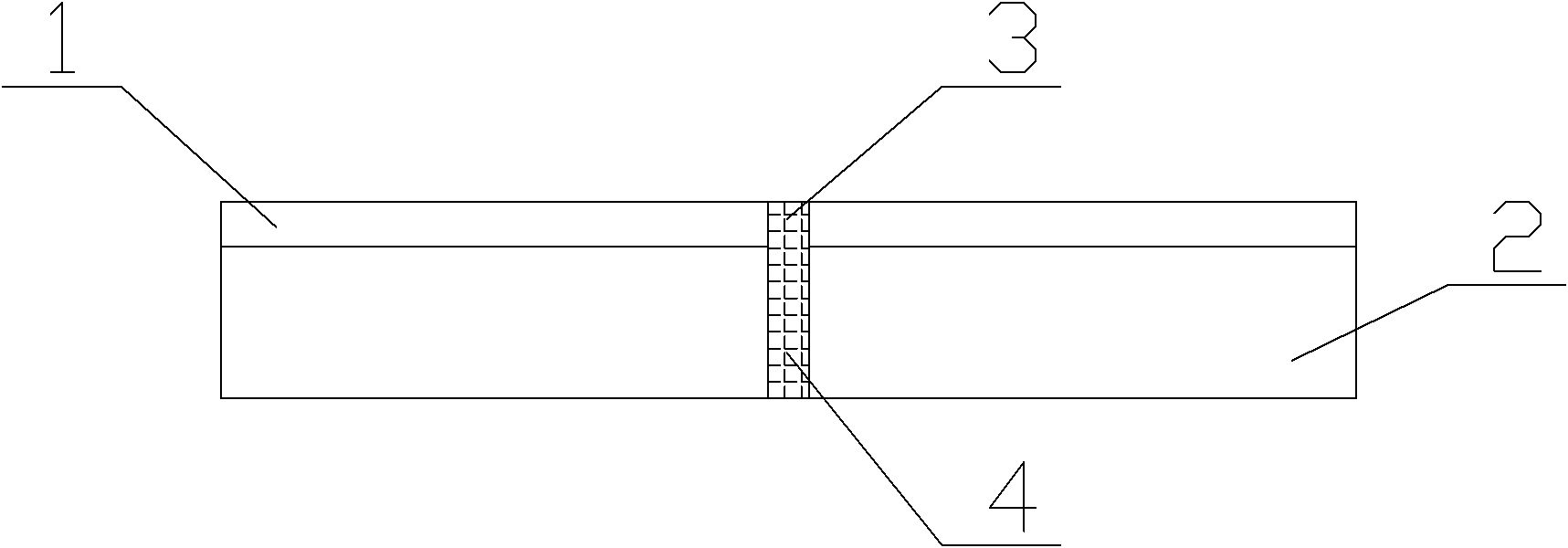
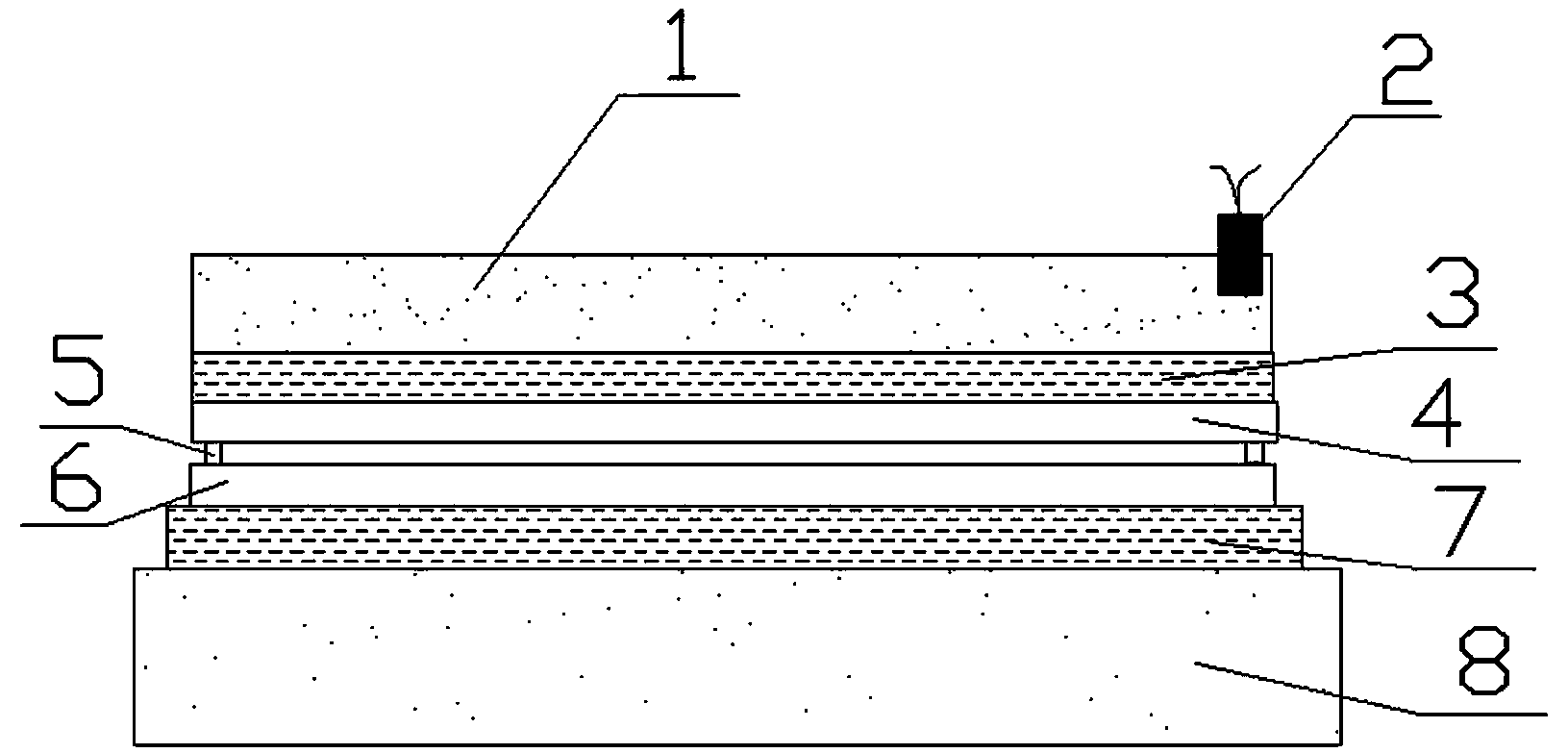
The present invention discloses an explosion welding method with aluminum-steel composite materials; a double-layer aluminum plate (4) is arranged on a basic level steel plate (6) through a support (5); a buffer protecting layer is paved on the surface of the double-layer aluminum plate; an explosive (2) is placed on the surface of the buffer protecting layer in the way of stage gradient style, so that per unit area explosive capacity is stepped gradually decreased from the center of the double-layer aluminum plate to two ends; a large acreage of the aluminum - steel composite materials is gained through the explosion welding method; per unit area explosive capacity is stepped gradually decreased from the center of the double-layer aluminum plate to two ends; the material of the basic level steel plate is a carbon steel or a low alloy steel; the material of the double-layer aluminum plate is a pure aluminum or an aluminum alloy with less or equal to 0.1 percent of Mg. The explosion welding method of the present invention has the advantages of high intensity and equal strength in composite bonding, no excessive melting, delaminating, or non-compounding phenomenon at an interface, being capable of making thick double-layer aluminum plate composite materials through once explosion welding, convenient in production and higher in efficiency.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Explosive welding forming method of magnesium and aluminum alloy composite plates
InactiveCN103586574AImprove compactnessAdvancedMetal working apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusAlloy compositeFuel oil
The invention relates to an explosive welding forming method of magnesium and aluminum alloy composite plates. The explosive welding is performed according to the performance requirements of the magnesium and aluminum alloy composite plates, ammonium nitrate fuel oil mixture is adopted, and long-distance instantaneous explosive form is performed on a ground sand base. The welding method is high in forming speed, welding line is firm and is good in metallographic structure compactness, the combined rate is up to 99.5%, the interfacial shear strength is 120MPa, on the premise of strict operation, the welding process is safe and reliable, and the method is reliable and effective in magnesium and aluminum alloy composite plate production.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Production method for ultralong thin titanium/steel compound plate
InactiveCN102441769AEasy to useGuaranteed lengthAuxillary arrangementsMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelTitanium
The invention provides a production method for an ultralong thin titanium / steel compound plate, which comprises the following steps: firstly, correcting the shape of a multi-layer titanium plate and performing heat treatment; secondly, cleaning and polishing a basic-layer steel plate and the multi-layer titanium plate after the heat treatment; thirdly, explosively welding the basic-layer steel plate with the multi-layer titanium plate to prepare a compound plate; fourthly, leveling the compound plate and mechanically cutting to guarantee that the compound plate binding fraction gets to 100%; fifthly, relatively superposing and assembling the steel surfaces of two qualified compound plates with the same sizes, and welding to obtain a blank; sixthly, rolling the blank; and seventhly, leveling and machining to obtain the ultralong thin titanium / steel compound plate. The method provided by the invention is lower in production cost and high in production efficiency; and the method adopts a combination method of the explosive welding process and the superposing rolling process, so that the using performance of the compound plate can be guaranteed and the length and the thickness of the compound plate also can be guaranteed. Therefore, the qualified ultralong thin titanium / steel compound plate can be produced by using a general rolling process only.
Owner:XIAN TIANLI CLAD METAL MATERIALS
Explosive welding process for super-long and super-wide composite boards
InactiveCN102240845AImprove corrosion resistanceAchieve perfect unityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusIt equipmentEngineering
The invention relates to an explosive welding process for super-long and super-wide composite boards, and provides a method which is convenient, economical and piratical, wherein an explosive is distributed in a three-section different-explosion-velocity manner and compacted at periphery; therefore, the explosive welding of super-long and super-wide TA2 / Q345R is realized, the problems that the side of the composite board is not composited or the bond strength of part of the composite board is too low in the explosive welding process of the super-long and super-wide TA2 / Q345R composite board are solved, and the requirement of our equipment manufacture industry on the super-long and super-wide TA2 / Q345R composite board is satisfied.
Owner:舞钢神州重工金属复合材料有限公司
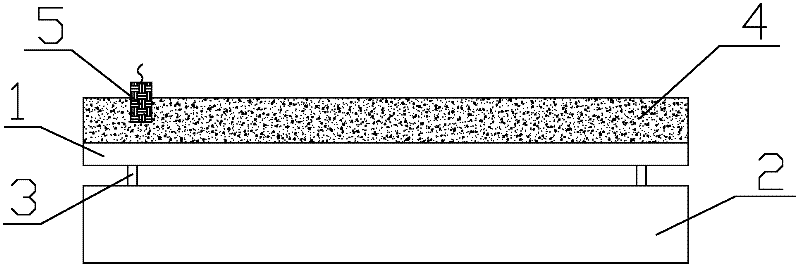
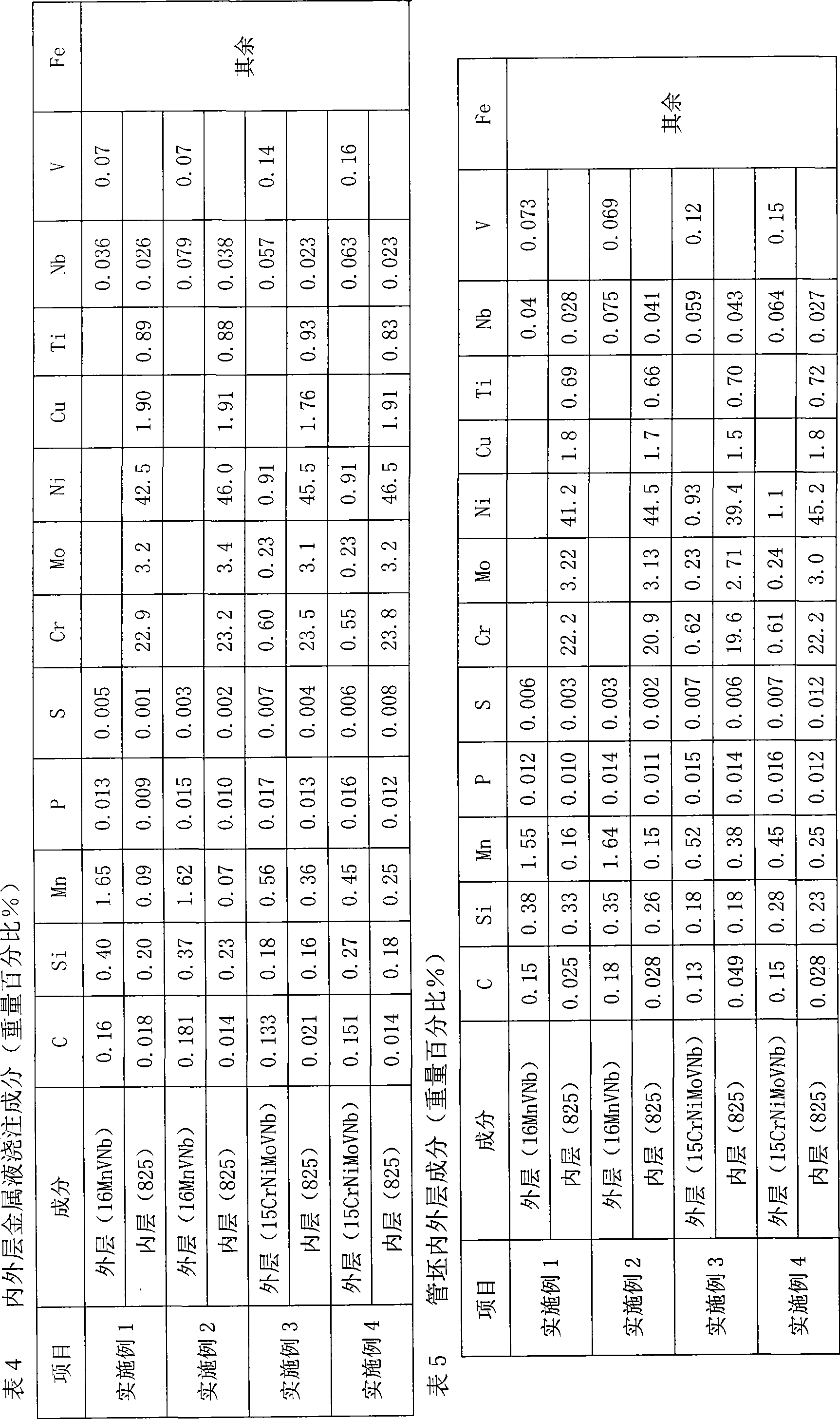
Corrosion-resistant dual metal clad tube blank and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101530898ANot easy to layerImprove securityRigid pipesExplosion weldingCorrosion resistant
A manufacturing method of a corrosion-resistant dual metal clad tube blank comprises the following steps: outer-layer molten metal is pumped into a pipe die for centrifugal pouring, the molten metal is cooled after pouring, and inner-layer molten metal is poured when internal surface temperature of the outer layer is cooled to be lower than 50-70 DEG C which is the melting point of the outer-layer molten metal; inner-layer molten metal is pumped into the pipe die for centrifugal pouring, the molten metal is cooled after pouring; cooling is stopped after the outer layer and the inner layer are completely solidified, at the moment, the inner layer and the outer layer achieve complete metallurgical bonding; wherein, the outer layer is made of X52 or X60 steel and the inner layer is made of 825 steel. A metallurgical bonding layer of a production tube obtained by carrying out extrusion or hot rolling on the tube blank manufactured by the method is several times or dozens of times as thick as a bonding layer of the dual metal tube obtained by the explosive welding process; the transition of the ingredients on the inner and outer layers is gentle, thus greatly relieving the interfacial stress between the inner layer and the outer layer, facilitating the inner layer and the outer layer not to be layered easily, improving the safety of the use of the production tube and prolonging the service life of the production tube.
Owner:HANDAN XINXING SPECIAL TUBING CO LTD
Explosive welding method for large-area lead-steel composite board
ActiveCN102059445ASolve the problem of too soft and hard to supportFree from burnsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusBoundary effectsUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an explosive welding method for a large-area lead-steel composite board, in which a base steel board and a composite lead board are adopted. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a high-strength metal board on the surface of the composite lead board, and bonding the composite lead board and the high-strength metal board together with adhesives; and proportioning special explosive as follows: 45-48 parts of expanded ammonium nitrate, 48-51 parts of sodium chloride and 4-6 parts of pearlite, ensuring a detonation velocity range of 1200m / s-1500m / s and adopting slop type explosive distribution at a far end. The method disclosed in the invention realizes the support of the lead board so that the explosive welding of the large-area lead-steel composite board can be implemented; and the method has the advantages of eliminating negative effects of surface burn and boundary effect on explosive composite, ensuring that the lead-steel composite board has the primary composite rate being higher than 98% and higher bond strength.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Explosion welding repair method of infusible uncommon metal composite board
InactiveCN101108444ARealize continuous weldingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusFire pointExplosion welding
An explode welding repairing method which is hard to dilute metal compound board, firstly, the thickness of hard-diluting metal board is larger than the original board material by 0.5 to 1mm, the area of board material is larger than a defect zone by 20 to 60 mm2; secondly, proceed fine polishing to the compound board at the position under epair; thirdly, put rare metals on the surface under epair, the compound board under epair is made as the lower layer of base board; fourthly, the rare metal board and a placode under epair, the enlarged supporting gas between the two boards adopts edge supporting, the gap is of 7 to 10mm and laid in parallel; fifthly, the rare metal board surface after protecting is distributed with explode evenly, the protecting layer uses lubricate resin adding thinner, the thickness of the protecting layer equals to 0.5 to 1mm; sixthly, the size of the fire point is controlled below the diameter of 15mm; seventhly, after exploding compound, the invention is level to the main material after heat process, flattening and repairing and abrasion of the connection edge.
Owner:南京三邦新材料科技有限公司
Method for preparing non-brazing seam thin compound layer titanium/steel composite board
InactiveCN101406899AHigh bonding strengthGuaranteed Thickness RequirementsRoll mill control devicesFurnace typesSheet steelExplosive cladding
The invention discloses a method for preparing seamless thin multilayer titanium / steel composite plate and relates to a method for preparing the seamless titanium / steel composite plate with large specifications and a thin multilayer through a combined process of explosive welding plus hot rolling. The method is characterized in that after explosive cladding, a titanium plate and a steel plate form the composite plate through hot rolling. The method adopts a combined process of explosive welding plus hot rolling to prepare the seamless titanium / steel composite plate with the large specifications, an overall length over 10, 000mm and the thin multilayer, thereby not only ensuring the binding property and the specification requirements of the composite plate, but also meeting the demand on the seamless titanium / steel composite plate with the large specifications and the thin multilayer of large-scale pressure equipment.
Owner:XIAN TIANLI CLAD METAL MATERIALS
Explosive welding method of aluminum/titanium/steel three-layer composite material
InactiveCN101537531AImprove mechanical propertiesAvoid the difficult problem of parameter selectionWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusSheet steelTitanium
The invention relates to an explosive welding method of an aluminum / titanium / steel three-layer composite material, belonging to the technical field of metal composite materials. The explosive welding method is characterized in that a multi-layer aluminum (4) and a multi-layer titanium (5) are arranged on a steel plate (6) through a metal strutting (1), explosives (3) are distributed on the surface of the multi-layer aluminum (4), and an aluminum / titanium / steel composite material (8) is obtained by first-time explosive welding; a multi-layer aluminum (7) is arranged on the aluminum / titanium / steel composite material (8) by the metal strutting (1), and the aluminum / titanium / steel three-layer composite material with heavy-section multi-layer aluminum is obtained by second-time explosive welding; materials of a base plate are plain carbon steel or low alloyed steel, the thickness of the multi-layer titanium (5) ranges from 1 mm to 2 mm, and the thickness of the multi-layer aluminum (4) can reach 25mm. The invention has the advantages of high combination strength of a composite interface, no melting, layering and compositing phenomenon on the composite interface, and one time explosive welding is carried out on three layers, thereby preventing explosive welding technique parameters from being difficult to control because the multi-layer titanium (5) is extreme thin.
Owner:大连船舶重工集团爆炸加工研究所有限公司
Clad steel plate for nuclear power engineering and manufacturing method of clad steel plate
ActiveCN102825858AUniform corrosion resistance on the surfaceImprove mechanical propertiesMetal layered productsNon-electric welding apparatusTemperingNuclear power
The invention relates to a clad steel plate for nuclear power engineering. The clad steel plate comprises a base plate and a cladding plate, wherein the base plate is a killed steel plate, the cladding plate is a nickel-chromium austenitic stainless steel plate, and the base plate and the cladding plate are combined to form the clad steel plate; the base plate comprises the following components: not larger than 0.25% of C, 1.00-1.80% of Mn, not larger than 0.015% of P, not larger than 0.015% of S, 0.10-0.50% of Si, 0.35-0.70% of Mo, 0.30-0.80% of Ni, not larger than 0.125% of Cu, not larger than 0.25% of Cr, not larger than 0.06% of V, not larger than 0.02% of Nb, not larger than 0.03% of Ti, not larger than 0.25% of Co, not less than 0.02% of Al, and the balance of iron and unavoidable impurities; and the cladding plate comprises the following components: not larger than 0.035% of C, not larger than 2.00% of Mn, not larger than 0.015% of P, not larger than 0.015% of S, not larger than 0.80% of Si, 7.00-12.5% of Ni, not larger than 0.12% of Cu, 17.50-20.50% of Cr, not larger than 0.06% of V, not larger than 0.05% of Co, not larger than 0.11% of N and the balance of iron and unavoidable impurities. The invention further discloses a method for manufacturing of the clad steel plate. The method comprises the following step of (1) surface treatment; (2) explosion welding; and (3) thermal treatment: keeping 920-940 DEG C after the clad steel plate is subjected to the explosion welding in the step of (2), ventilating nitrogen after heating the clad steel plate to be 750-770 DEG C, cooling and carrying out high-temperature tempering to obtain the clad steel plate.
Owner:太原钢铁(集团)有限公司
Method for explosive bonding of tubular metal liners
ActiveUS7530485B1Avoid accumulationUniform travelMetal working apparatusTubular articlesEngineeringExplosion welding
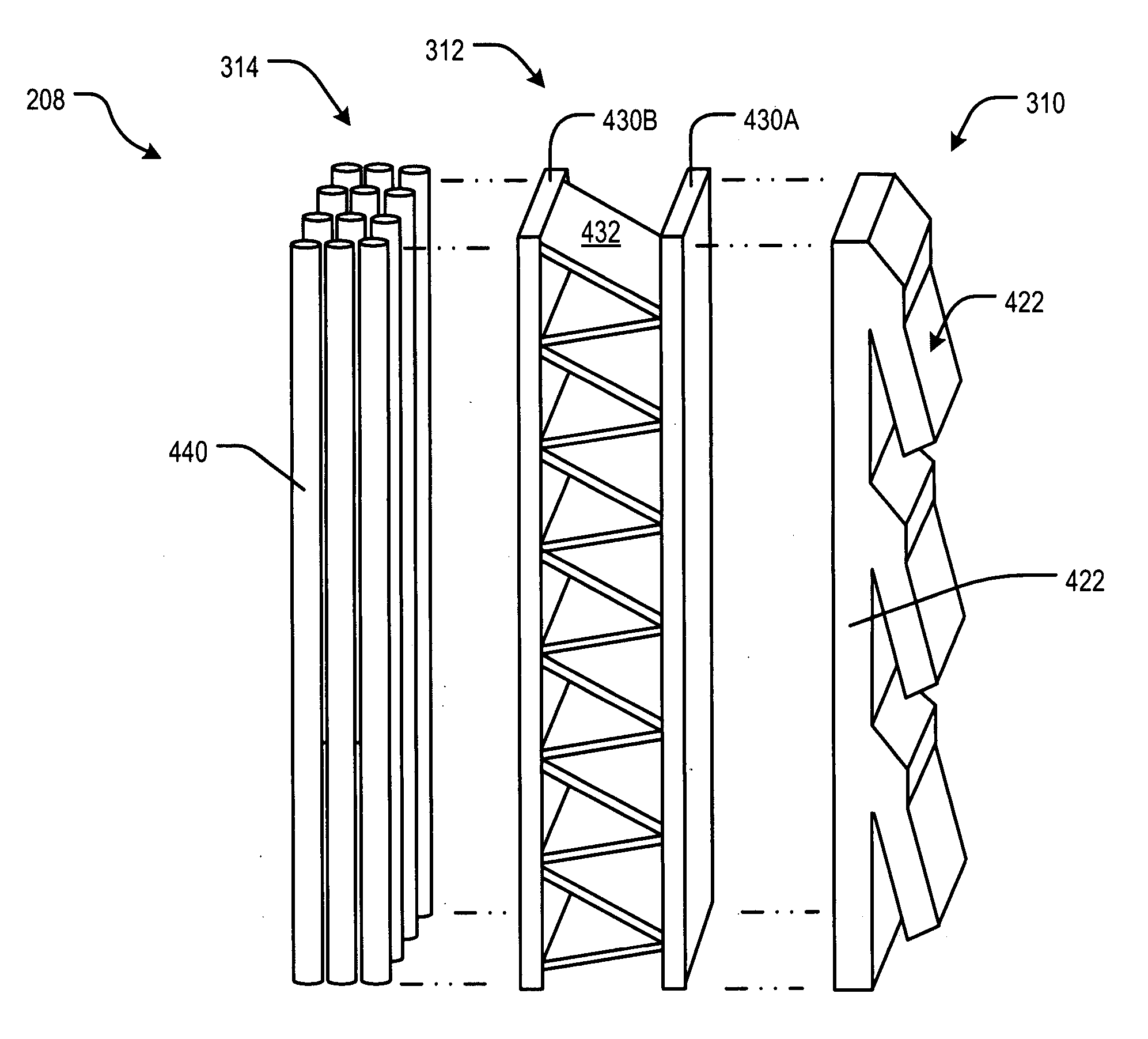
An explosion welding method for metal tube liners in which a metal tube of smaller outside diameter is positioned coaxially within a metal tube of larger inside diameter with one or more shims inserted at opposed tube ends to form a uniform annular gap. The tubes are vertically positioned on a flat surface, and the smaller tube is filled with explosive material detonated from its top surface. The detonation initiates a uniform explosive front traveling down the smaller tube expanding the internal surface of the smaller tube with sufficient velocity to weld the tubes. A vacuum may be formed within the annular gap and / or gas(es) introduced therein to prevent build-up of excessive heat at the explosive front.
Owner:HIGH ENERGY METALS
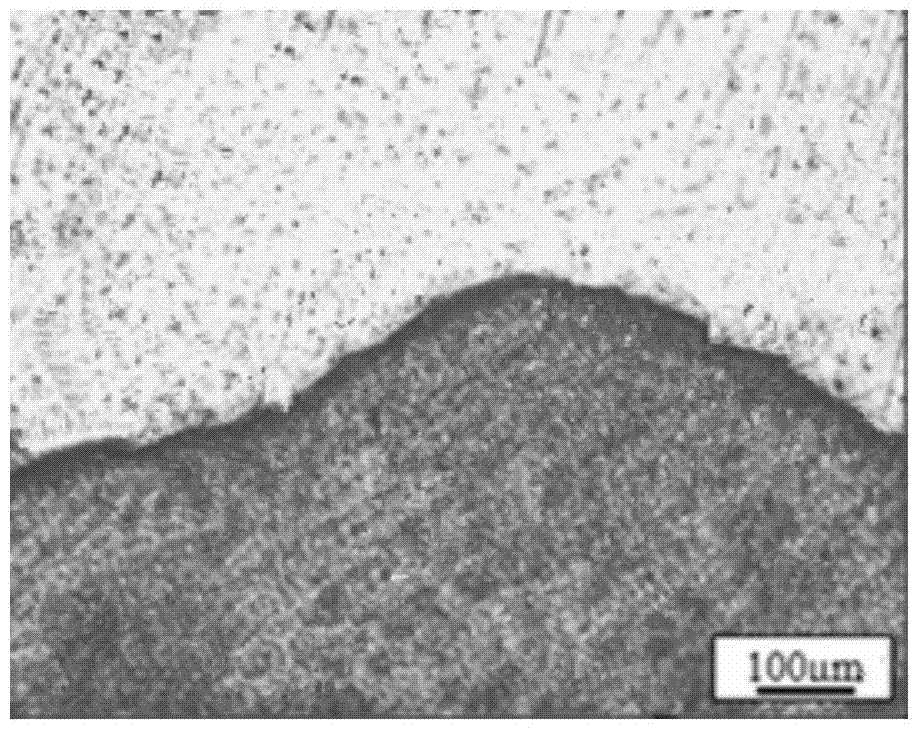
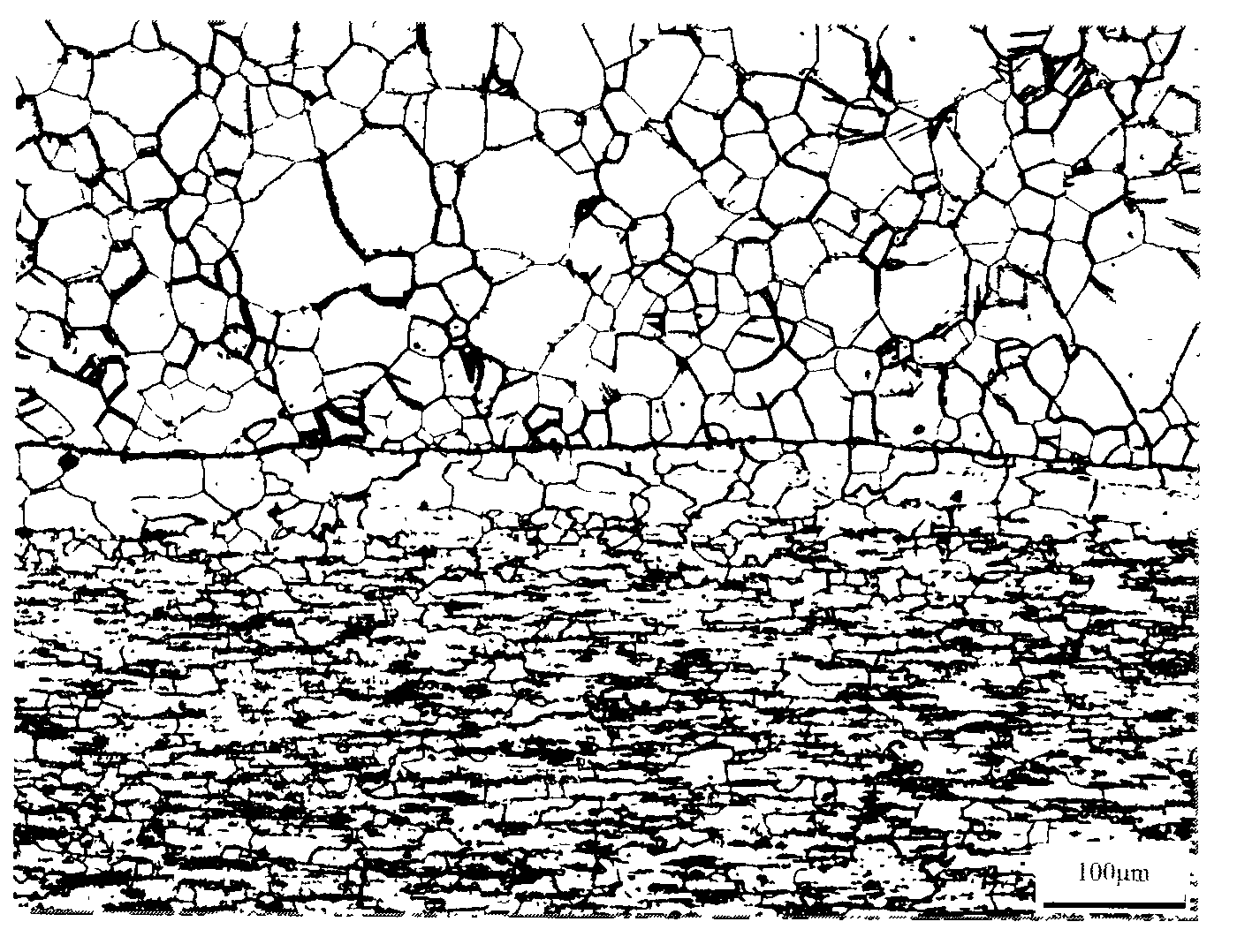
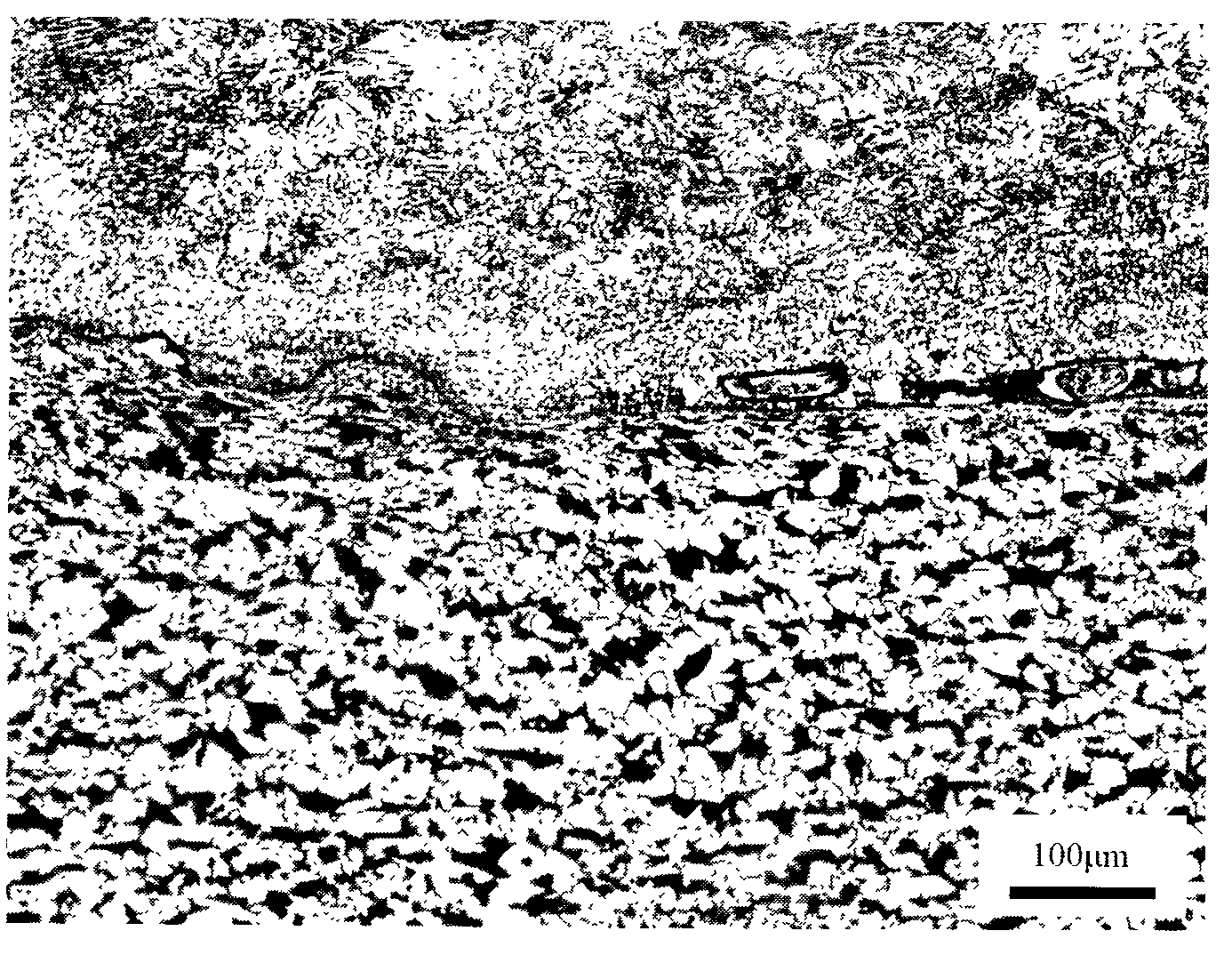
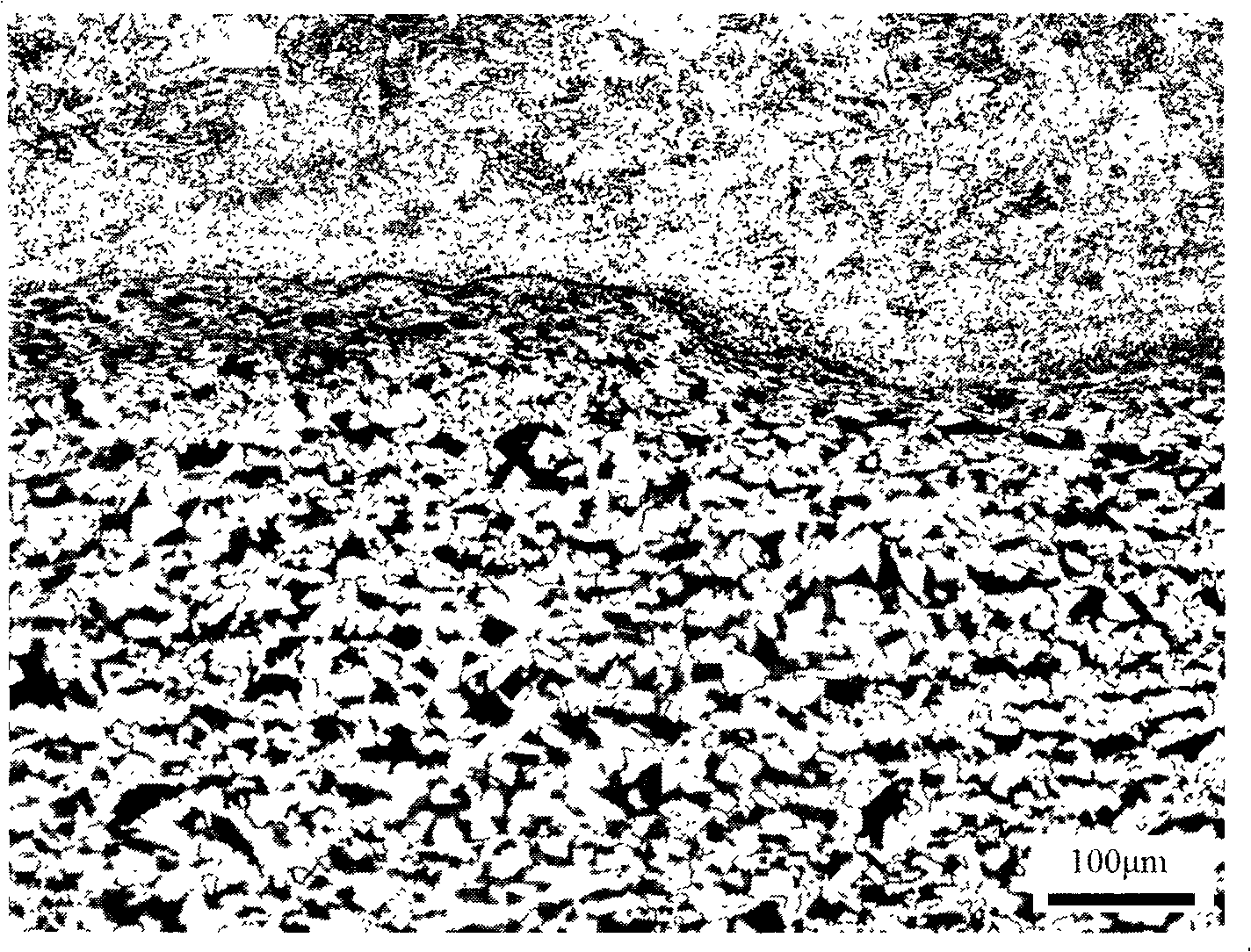
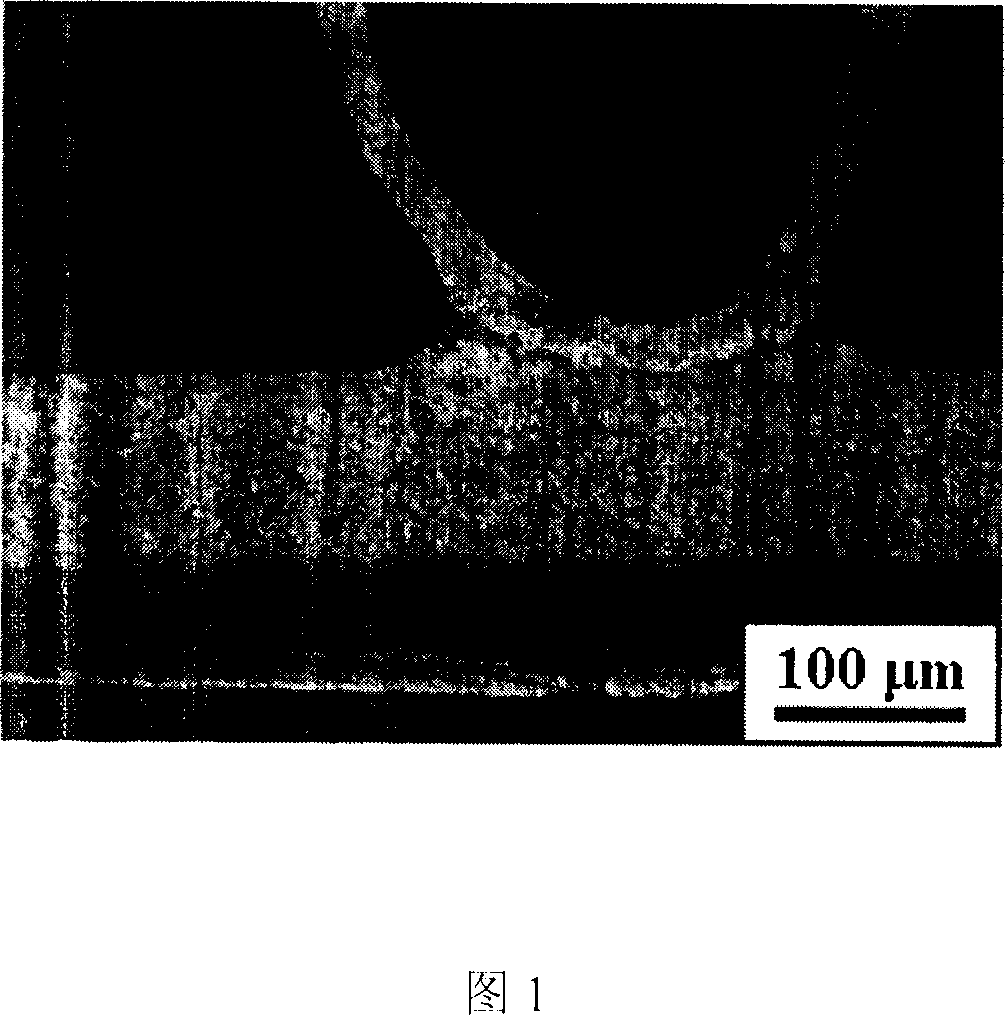
Method for observing metallographic structure on titanium/steel explosion welding interface
InactiveCN102072834AMake up for the lack of grindingAvoid the effects of corrosionPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringTitanium
The present invention discloses a method for observing a metallographic structure on a titanium / steel explosion welding interface, which comprises the following steps: 1, machining a metallographic structure observation plane on the titanium / steel explosion welding interface; 2, grinding the metallographic structure observation plane; 3, carrying out pickling with HF solution; 4, carrying out mechanical polishing; 5, eroding titanium and polishing steel; and 6, carrying out observation. The method is easy to operate, the metallographic structure on the titanium / steel explosion welding interface can be observed clearly by adopting the method, and no special equipment is needed.
Owner:WESTERN METAL MATERIAL
Method for producing copper alloy plate composite steel plate
InactiveCN101372065AGuaranteed stiffnessReliable weldingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusSheet steelHardness
The invention provides a method used for manufacturing a copper alloy composite steel plate; the substrate material is carbon steel plate and the composite plate is copper alloy plate; the manufacture method comprises the manufacture steps as follows: I matching: copper alloy composite plate and normal carbon steel plate which comply with the national standard and usage technical requirement according to the detection are combined in pairs according to the requirement of final products; II: stress troughs of 8-10mm deep and 10-12mm wide are arranged at the circumference of the copper alloy composite plate; III: grinding the surface: oxides and sundries on the explosive combination surface of the substrate and the composite plate are removed; subsequently, a protection layer is uniformly coated on the contact surface of composite plate and dynamite; IV explosive welding: the composite plate and the substrate are supported by copper fulcrum or aluminium fulcrum and welded together by virtue of explosive welding. The combination rate of the manufacture method of the copper alloy plate and the composite steel is more than 99%, with the hardness of HB130-150, thus completely meeting the requirement of copper motor plate on the hardness.
Owner:太原钢铁(集团)有限公司
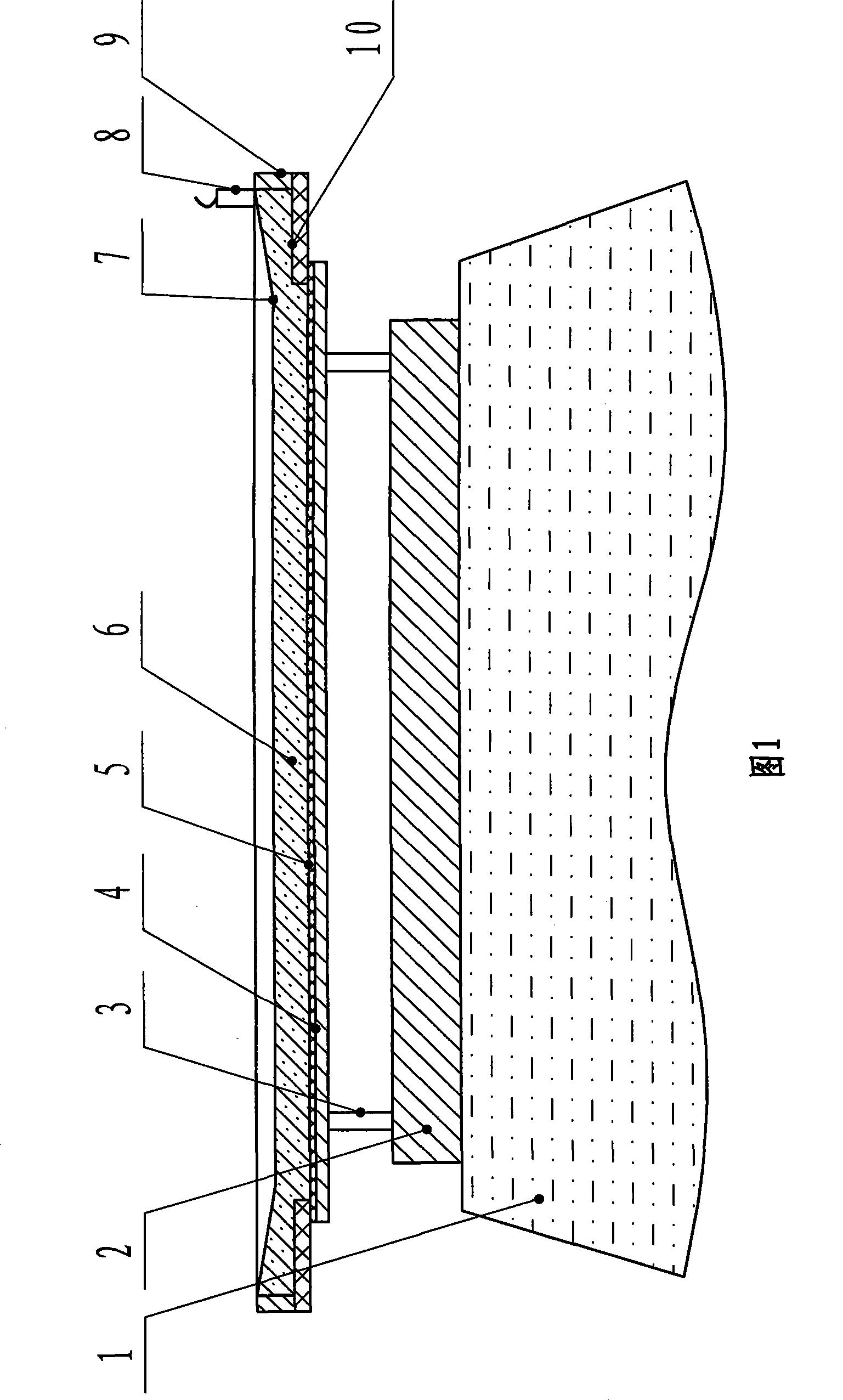
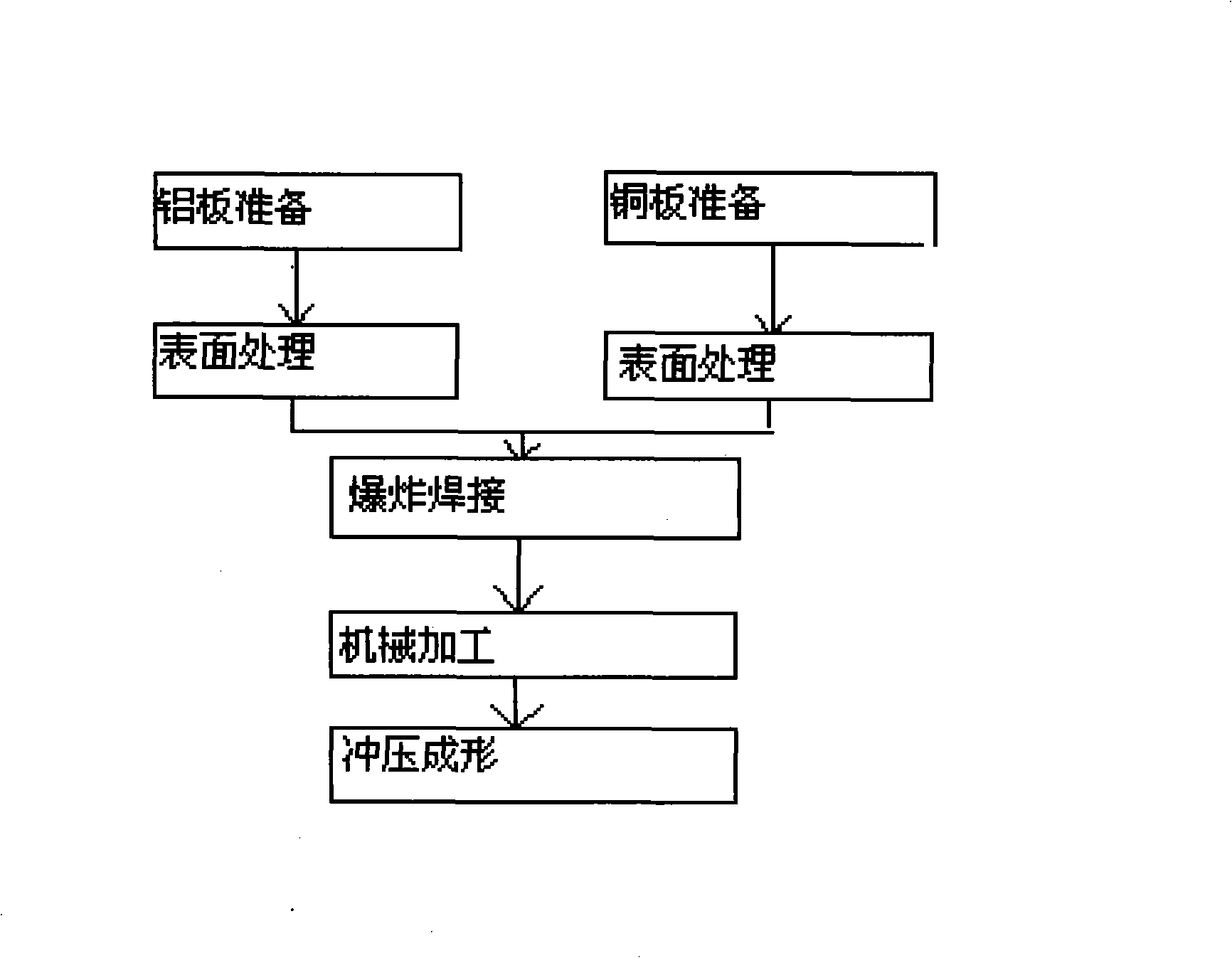
Method for producing aluminum-copper duplex metal compound weldment
InactiveCN101347867AEasy to produceImprove efficiencyWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusCopperExplosion welding
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an aluminium-copper double metal composite weldment, which comprises the following steps: a composite aluminium plate (4) is supported layer by layer by a support (5) and is arranged on a base copper plate (6); a buffering protective layer (3) is stuck on a first layer of aluminium plate (4); explosives (2) are distributed on the surface of the buffering protective layer (3); the explosive load on a unit area is controlled according to the requirement of design strictly; the aluminium-copper double metal composite material with high quality is obtained by integrating explosion, welding and composition, the composite interface has high and uniform bonding strength; the interface does not have excessive melting and composite layering, does not lead the resistance of the interface to increase, can realize explosion and welding on a large area, is convenient to product and improves the efficiency.
Owner:LUOYANG SHUANGRUI METAL COMPOSITE MATERIAL
Preparation method of ultra-thick titanium/steel composite tube plate with large area and high properties
InactiveCN102049626AMeet GB8547-2006Fulfil requirementsWelding apparatusHeat conductingStress relieving
The invention provides a preparation method of an ultra-thick titanium / steel composite tube plate with large area and high properties, which comprises the following steps: 1. adopting a TIG welding method to prepare a multi-layer titanium plate through split welding; 2. adopting an automatic submerged arc welding method to prepare a base-layer steel plate through the split welding; 3. carrying out the leveling treatment on the base-layer steel plate; 4. polishing the combination surface; 5. assembling the base-layer steel plate and the multi-layer titanium plate; 6. preparing the composite tube plate through explosive welding; and 7. carrying out the annealing heat treatment on the composite tube plate to relieve the stress and obtain the ultra-thick titanium / steel composite tube plate with large area and high properties through mechanical processing. The ultra-thick titanium / steel composite tube plate with large area and high properties prepared by the invention has the excellent strength, heat conducting property and welding property of the steel plate, and simultaneously has the corrosion-resistant property of titanium. The composite tube plate prepared by the invention has the combination rate and properties achieving the standard requirements, can be safely applied to the production and basically solves the limit of the composite tube plate dimension to the standards of large-sized equipment.
Owner:XIAN TIANLI CLAD METAL MATERIALS
Method for producing exploded/rolled big area titanium steel composite plate
InactiveCN102225510AMeet different size requirementsImprove toughnessWelding/cutting auxillary devicesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsHeat-affected zoneDetonation
The invention introduces a method for producing an exploded / rolled big area titanium steel composite plate. The method including includes the steps of titanium plate splicing, nondestructive testing after welding, explosive welding, nondestructive testing after explosive welding, rolling, nondestructive testing after rolling, and tissue and performance detecting, wherein, when the titanium plate is not more than 7 mm in thickness, the titanium plate is welded by adopting plasma arc welding, thereby finishing the step for titanium plate splicing; when the titanium plate is more than 7 mm in thickness, performing backing weld by using plasma arc welding and then welding the cover surface by employing automatic argon tungsten-arc welding, thereby finishing the step for titanium plate splicing. The method capable of meeting the demands of users for the titanium steel composite plates with different sizes, is unlimited to supply sizes of titanium materials in the current market, less in welding workload, low in production cost and beautiful in welding seam formation; the joints with good toughness can bear the action of great impact of a detonation wave during the explosive welding process and repeated rolling during the rolling process; the heat affected zone of welding is small; and the welding seam is good in quality. By using the process, the problem of the composite layer titanium for the exploded / rolled big area titanium steel composite plate in which the joints are split after the composite plate is exploded and rolled, is solved successfully.
Owner:LUOYANG SHUANGRUI METAL COMPOSITE MATERIAL
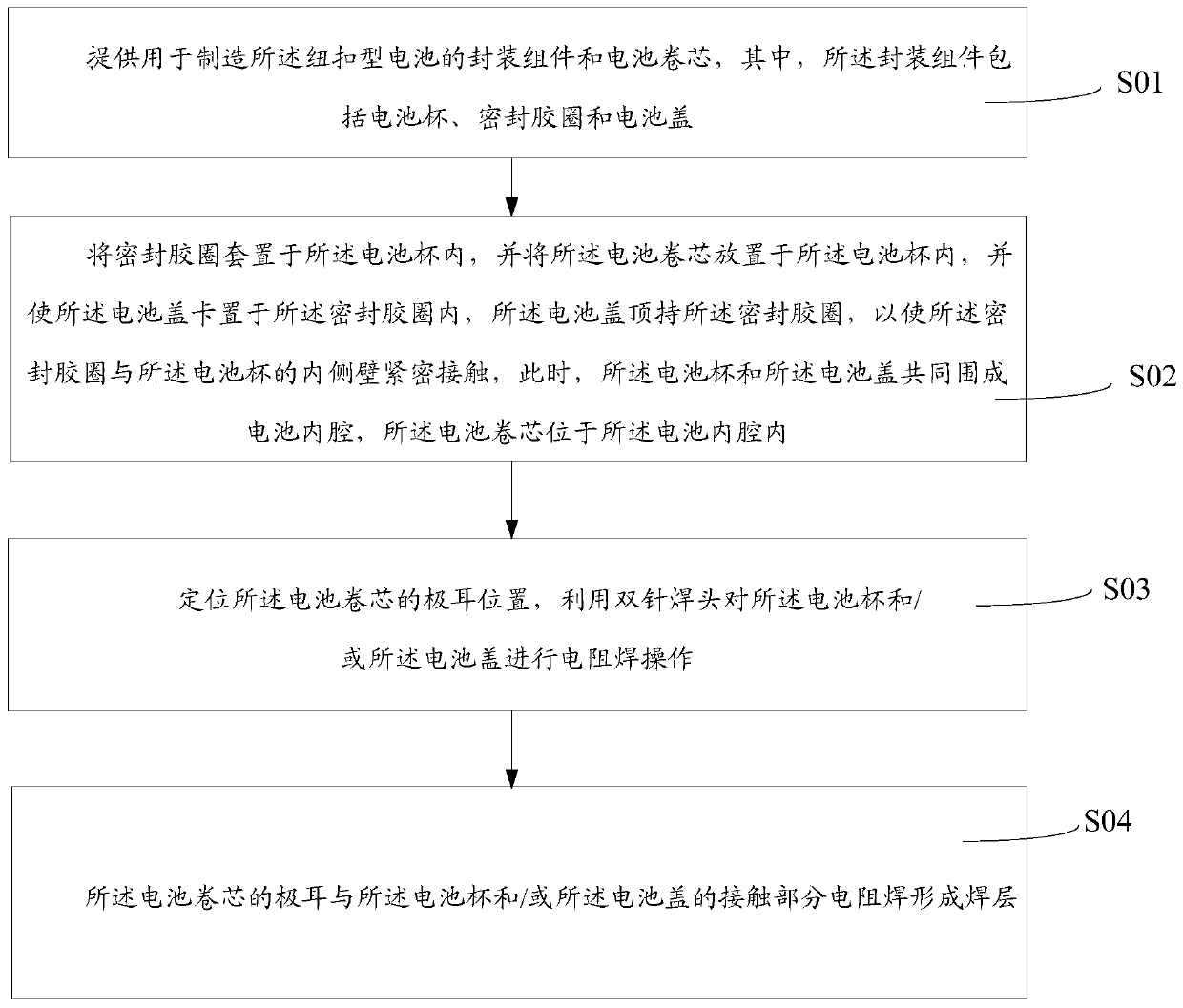
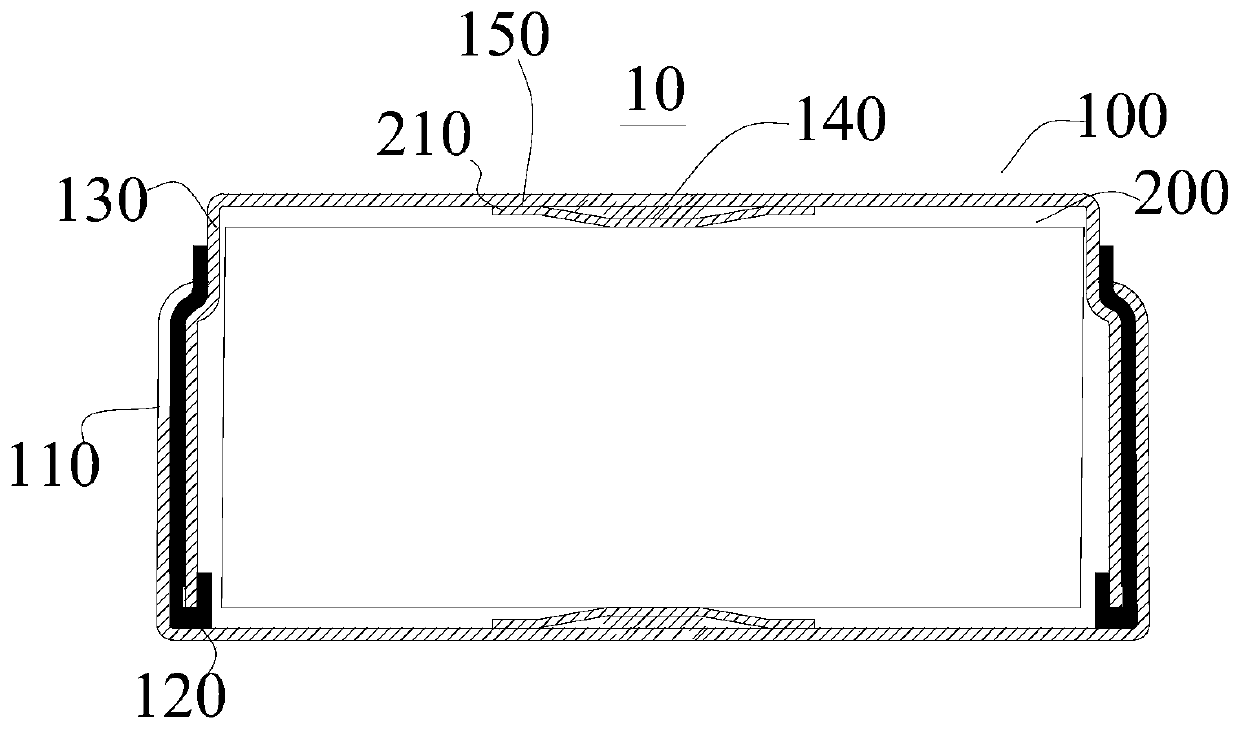
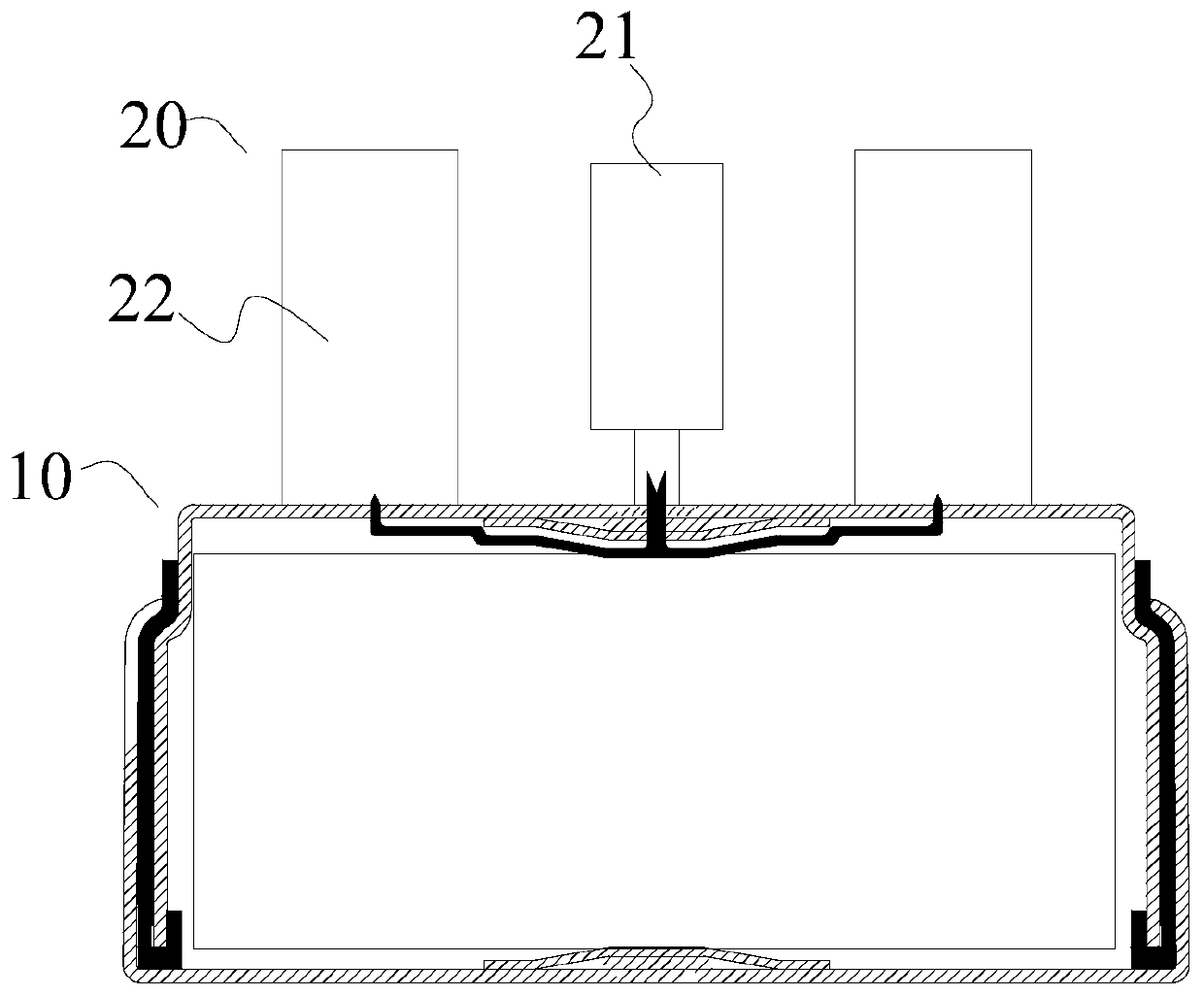
Button cell and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN110336065APlay a protective effectPlay the role of sealing and waterproofFinal product manufactureCylindrical casing cells/batteryRubber ringButton battery
The invention provides a button cell and a manufacturing method thereof. The button cell comprises a package assembly and a battery roll core. In the actual application process, a battery cup and a battery cover play a protection role; a seal rubber ring plays a sealing and waterproofing function; besides, when a tab needs to be welded, the tab is positioned, and electric resistance welding operation is carried out on the battery cup and / or the battery cover, so that the electric resistance welding is carried out on the contact portion between the tab in the center position of the battery roll core and the battery cup and / or the battery cover to form a center welding layer, and the electric resistance welding is carried out on the contact portion between the tab at the edge position of the battery roll core and the battery cup and / or the battery cover to form an edge welding layer; the center welding layer and the edge welding layer can prevent the phenomenon of "explosion welding"occurred in the tabs, thereby greatly improving welding stability of the tabs; and compared with a conventional laser welding mode, the provided welding mode is higher in welding safety factor, and there is no risk that the laser directly breaks down the battery cup or the battery cover.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIC POWER NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Cold spray-coating method for composite solder of conduit and fin of aluminium alloy heat exchanger
InactiveCN1962941AIncrease productivityQuality improvementWelding/cutting media/materialsHeat exchange apparatusSpray coatingAlclad
The invention discloses a preparing method of automobile aluminium alloy exchanger, which comprises the following steps: 1. blending Al-Si and Zn powder and brazing flux with weight rate at 9: 3-4: 0.5-4; drying; preparing cold spraying powder; 2. cleaning the conductor and fin surface; drying to make cold spraying powder; adopting cold-spraying method to sediment powder on the surface of conductor and fin; 3. assembling the base conductor; brazing according to NOCOLOK technique to obtain the product.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Explosive welding method for copper-aluminum composite material
ActiveCN103706940AReduce direct impactEvenly distributedWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusEngineeringAluminum composites
The invention relates to an explosive welding method for a copper-aluminum composite material. An aluminum composite plate (4) is arranged on a copper substrate (6) in a parallel mode through a supporting object (5), a rubber buffering layer (3) is laid on the aluminum composite plate (4), rock ammonium nitrate explosive cloth number two is arranged on a rubber buffering layer (3), the copper substrate (6) is arranged on a rubber cushion layer (7), a medium-fine sand foundation (8) is located below the rubber cushion layer (7), and the copper-aluminum composite material is obtained through explosive welding. A copper-aluminum composite plate produced through the explosive welding method can achieve 100% welding composite rate, is evenly formed in a composite mode without the phenomena of layering, swelling, vortex and the like.
Owner:HUNAN FORHOME COMPOSITE MATERIALS CO LTD
Explosive welding method for bimetal composite boards with special quality requirements
InactiveCN103056508AReliable weldingMeet welding quality requirementsNon-electric welding apparatusBond interfaceCharged body
The invention discloses an explosive welding method for bimetal composite boards with special quality requirements. The explosive welding method includes preprocessing blanks; charging powder; and performing explosive welding. In a powder charging procedure, 'basin'-shaped powder charge bodies are arranged on shroud plates and extension plates, upper and lower surfaces of the powder charge bodies are parallel to the shroud plates and the extension plates, and powder charging quantities are acquired by computing according to a formula. The welded rate of the composite boards welded by the explosive welding method reaches 100%, the bonding strength of welded surfaces of the bimetal composite boards meet a bimetal solid-phase metallurgical bonding strength law, bonding interfaces of the bimetal composite boards are finely wavy and are excellent in quality, and accordingly the quality requirements of critical equipment of thermonuclear fusion power generation test reactors on the composite boards are met.
Owner:中国人民解放军理工大学野战工程学院 +2
Explosion welding method for low melting point metal composite plate
InactiveCN1586785AQuality improvementLow deposition heatNon-electric welding apparatusAlloyComposite plate
The present invention belongs to the field of explosion welding technology and provides one kind of explosion welding method for low melting point alloy plates. After one thin transition metal layer is set between the covering plate of low melting point metal and the base plate, once explosion welding is performed to manufacture composite low melting point metal plate. The present invention may be sued in manufacturing composite plate of Al, Mg, Pb, Sn and their alloy, and has the advantages of making thick composite low melting point alloy plate in once explosion, low cost, high production efficiency, raised upper explosion limit, increased welding parameter range and high finished product rate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Layered aluminum copper composite plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101746088ALight weightImprove conductivityExplosivesMetal layered productsCopper coatingFuel oil
The invention discloses a layered aluminum copper composite plate and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of preparing composite plates. The layered aluminum copper composite plate is prepared by the preparation method comprising the following steps of: coating a pure copper layer on a pure aluminum substrate, wherein the pure aluminum substrate is a pure aluminum plate with the thickness of 5.0 to 10.0 mm, and the pure copper coating layer is a pure copper plate with the thickness of 1.0 to 2.0 mm; selecting the pure copper plate and the pure aluminum plate; polishing the surfaces to be compounded of the pure copper plate and the pure aluminum plate; assembling the well-polished pure copper plate and the pure aluminum plate, flatly spreading a prepared ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive mixture on the upper surface of the pure copper plate, and performing explosive welding; performing annealing after the explosive welding; levelling the composite plate after the annealing; and examining the aluminum copper composite plate after levelling, and cutting out uncompounded or cracked parts on four edges of the composite plate to obtain the layered aluminum copper composite plate. Because the aluminum layer replaces part of the copper layer, compared with a copper plate with the same thickness, the aluminum copper composite plate has the characteristics of lighter specific weight and excellent electric conductivity of copper.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG +1
Explosive welding method of SAF2507 alloy composite steel plate
ActiveCN101837511AQuality improvementWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusSheet steelAlloy composite
The invention discloses an explosive welding method of an SAF2507 composite steel plate. The method comprises the following steps of: leveling to enable the flatness of the steel plate to be less than 3mm / m; treating the composite material to ensure that the plate flatness of the SAF2507 alloy is less than 5mm / m; brushing and pairing: brushing the composite material protective agent on the SAF2507 alloy plate, and paring with the steel plate; and explosively compositing: placing the steel plate flatly on the explosive table, and arranging the SAF2507 alloy plate on the steel plate in parallel, arranging a V shaped support between the steel plate and the SAF2507 alloy plate, uniformly arranging the explosive on the outer surface of the SAF2507 alloy plate, detonating the explosive via the detonator, and tightly bonding the surface of the SAF2507 alloy plate and that of the steel plate together under the high brake pressure. The invention provides an SAF2507 super-duplex stainless steel plate with the higher quality and wider application range.
Owner:黄山顺钛新材料科技有限公司
Apparatus comprising armor
InactiveUS20070089595A1Limited effectReduce the possibilityAmmunition storageBlastingSilicone GelsEngineering
An armor that is used, for example, in multi-cell missile launchers is disclosed. In some embodiments, the armor includes three layers. The inner-most layer undergoes explosive welding when exposed to a pressure wave from an explosion. An intermediate layer in-elastically deforms when exposed to the explosion. The third and outer-most layer includes a plurality of elongated, pressurized tubes that contain fire retardant, among other chemicals. Silicone gel is interposed between the tubes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com