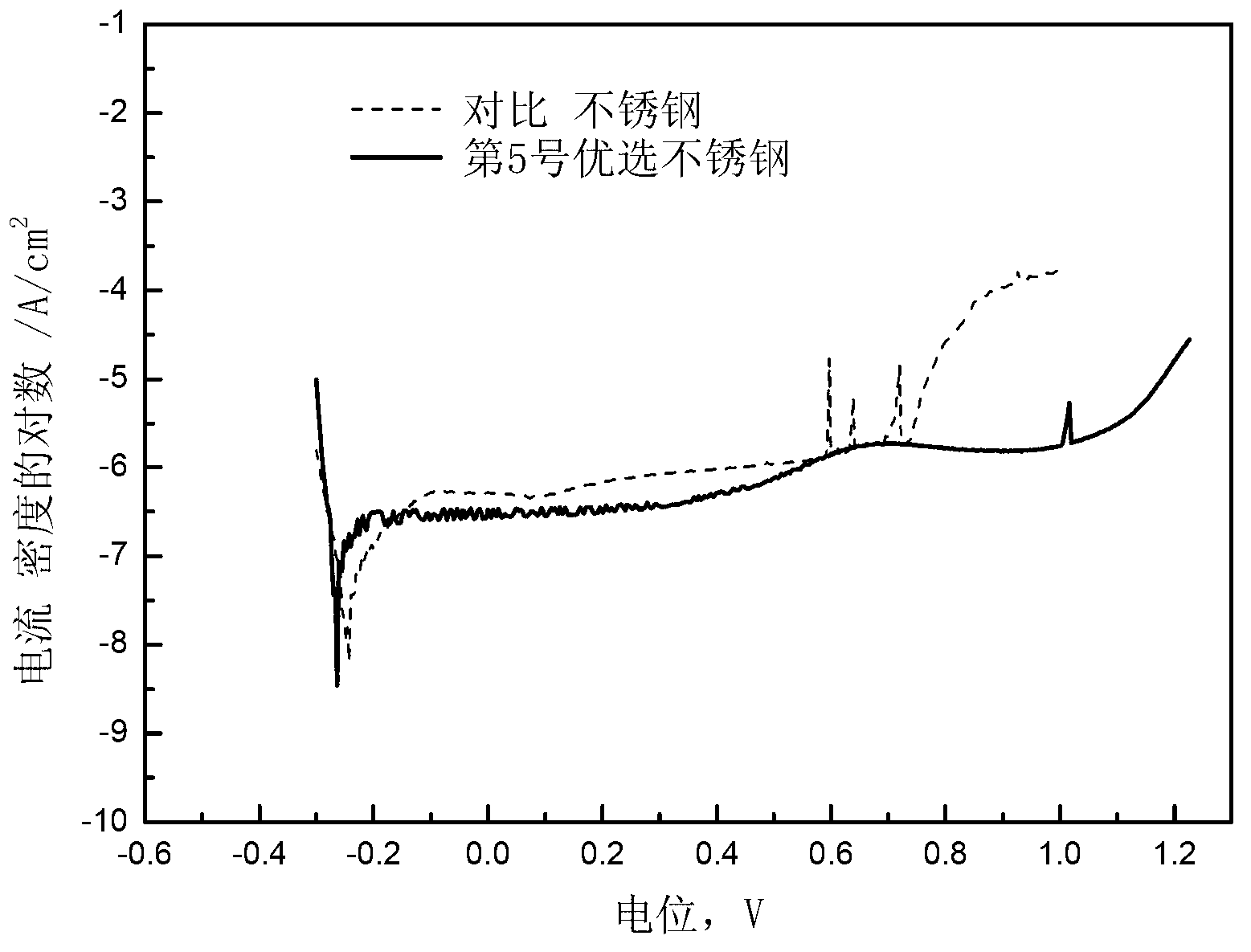
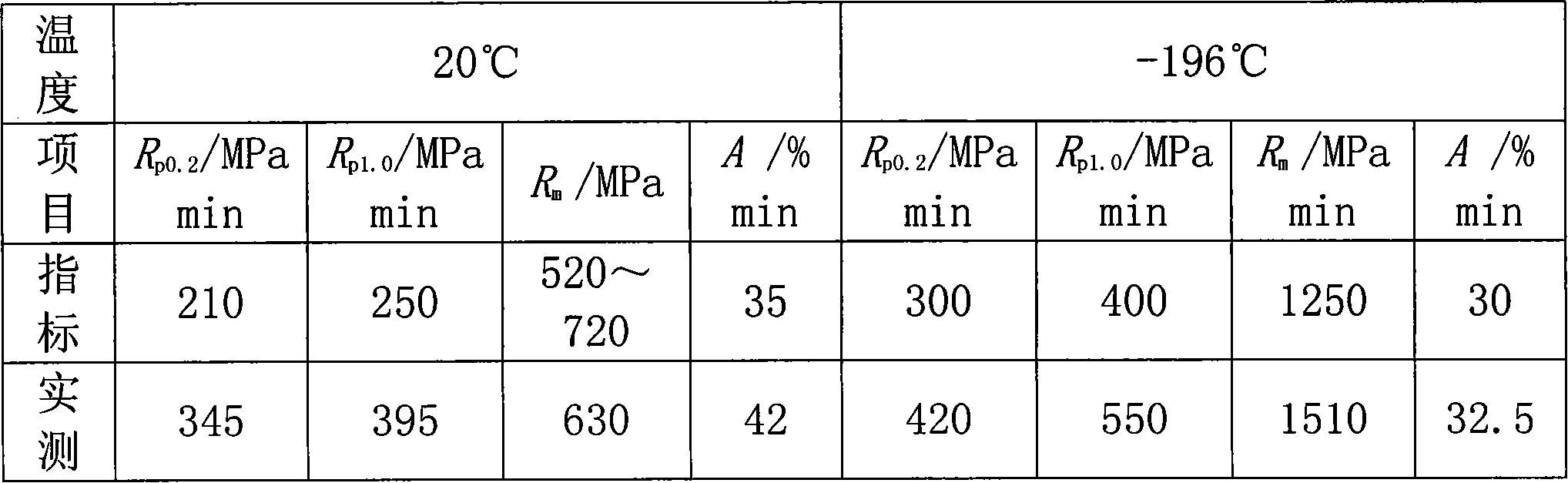
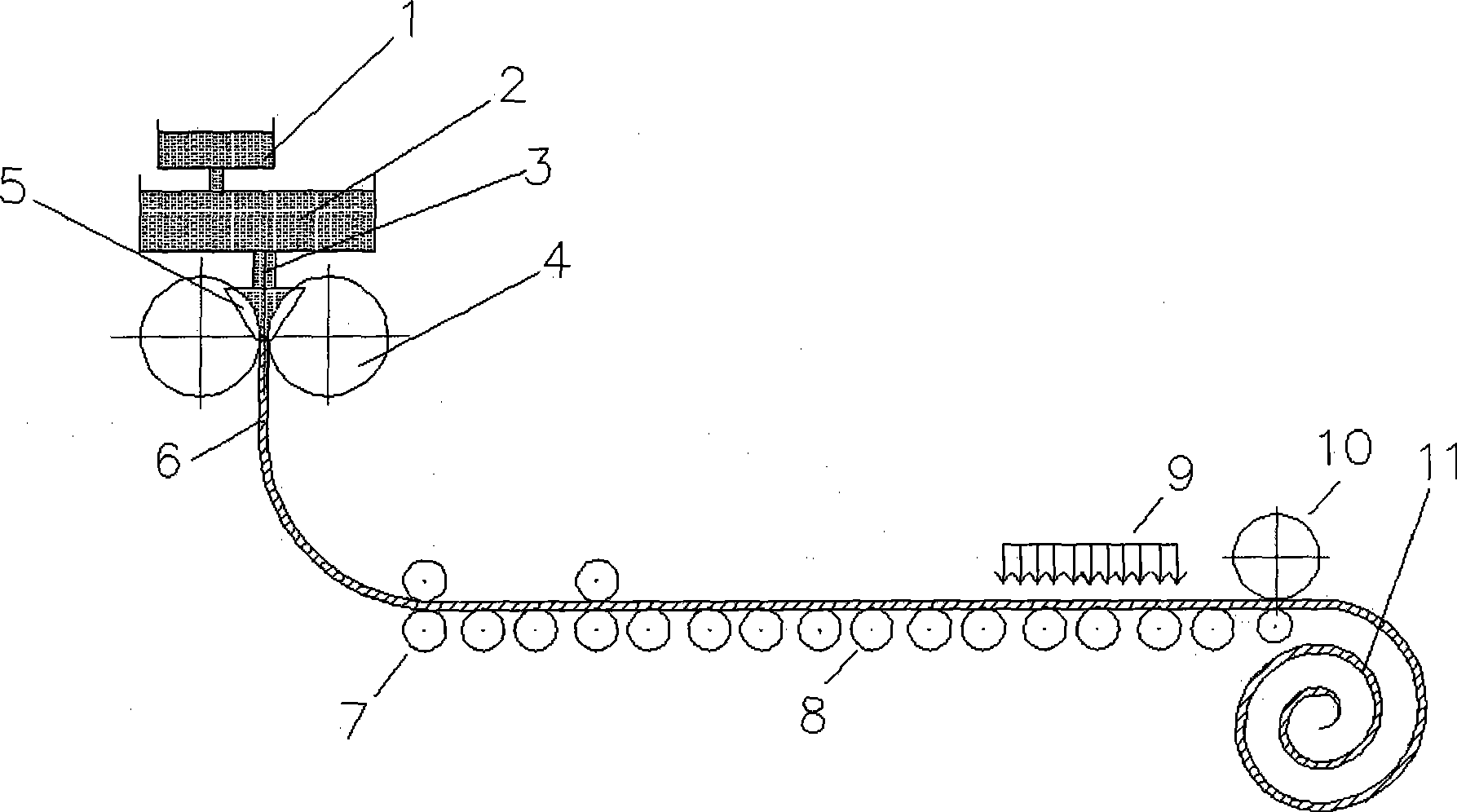
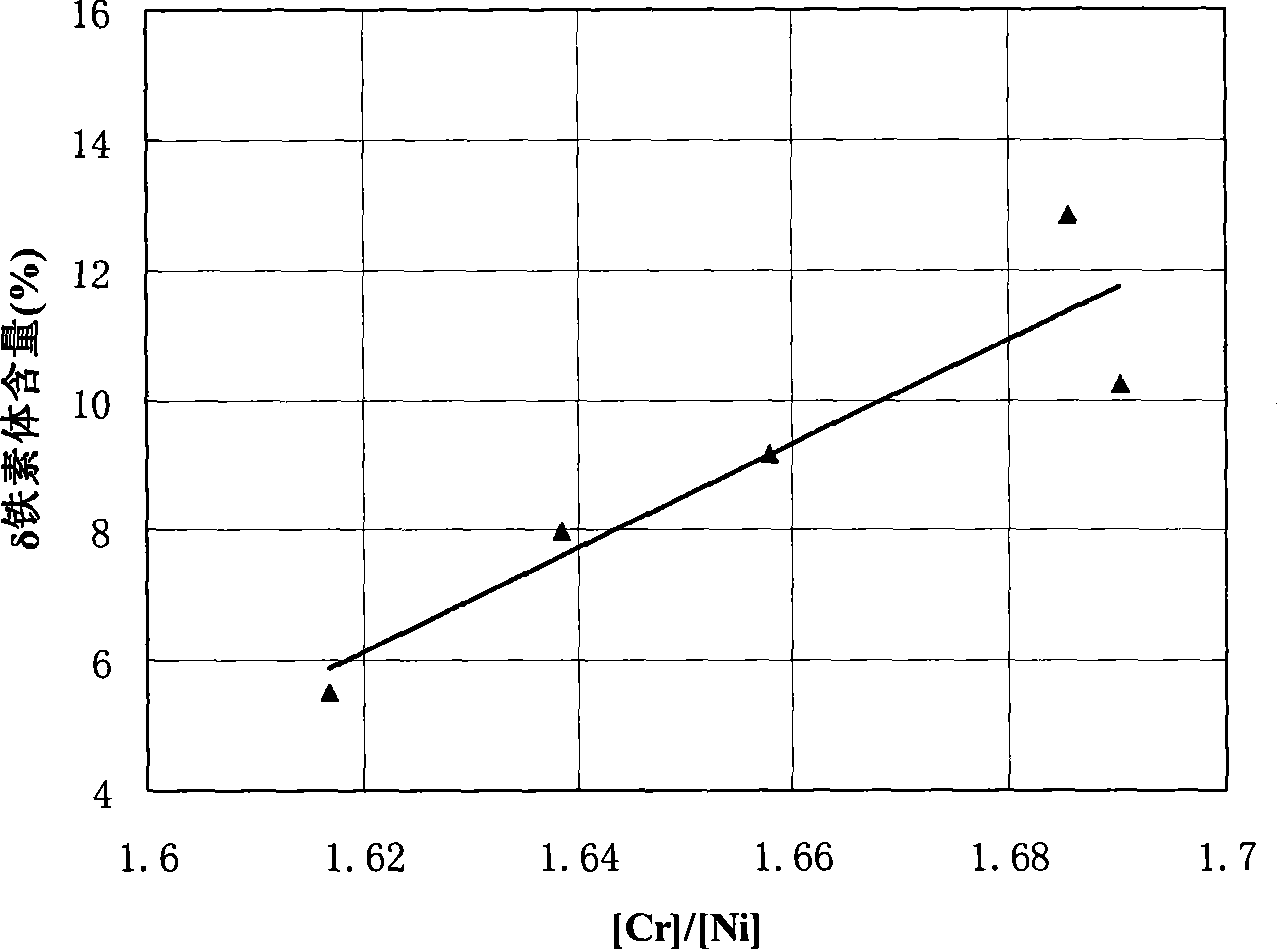
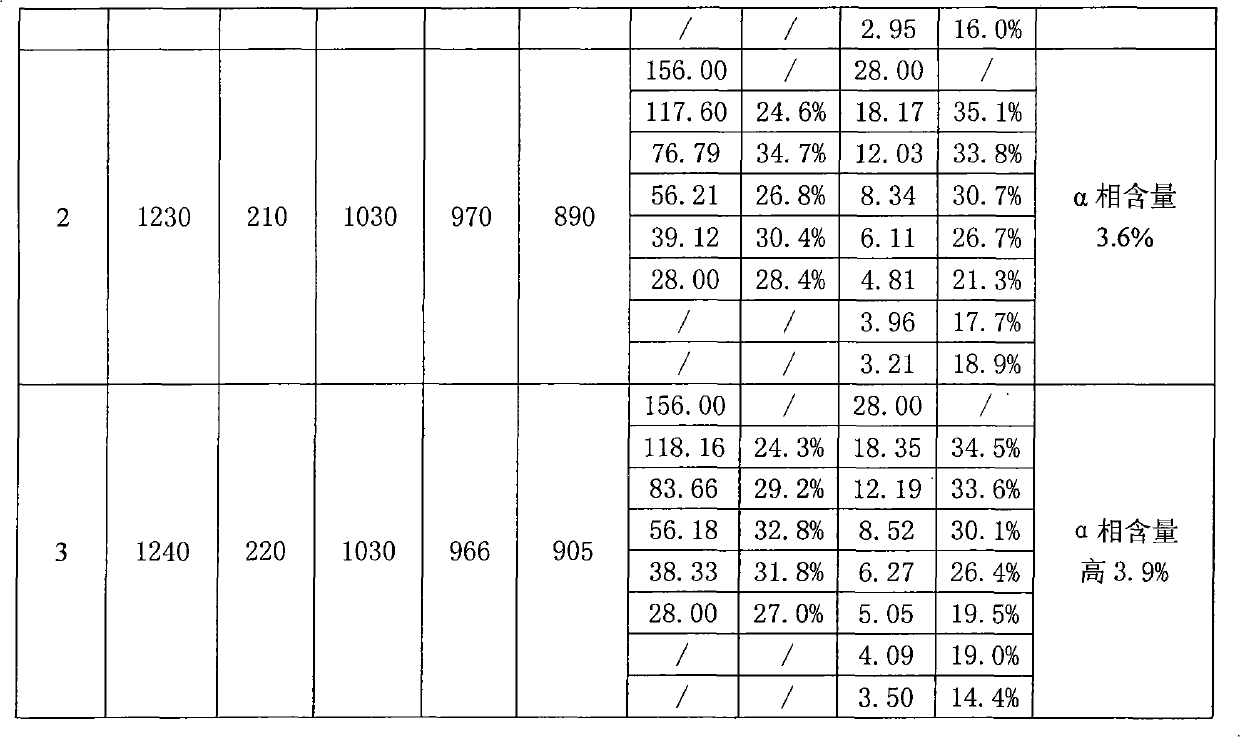
Patents
Literature
3435 results about "Austenitic stainless steel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Austenitic stainless steel is a specific type of stainless steel alloy. Stainless steels may be classified by their crystalline structure into four main types: austenitic, ferritic, martensitic and duplex. Austenitic stainless steels possess austenite as their primary crystalline structure (face centered cubic). This austenite crystalline structure is achieved by sufficient additions of the austenite stabilizing elements nickel, manganese and nitrogen. Due to their crystalline structure, austenitic steels are not hardenable by heat treatment and are essentially non-magnetic.
Austenoferritic stainless steel having a very low nickel content and a high tensile elongation
InactiveUS6096441ALow nickel contentImproved general propertyHeat treatment process controlElectric furnaceSulfurManganese
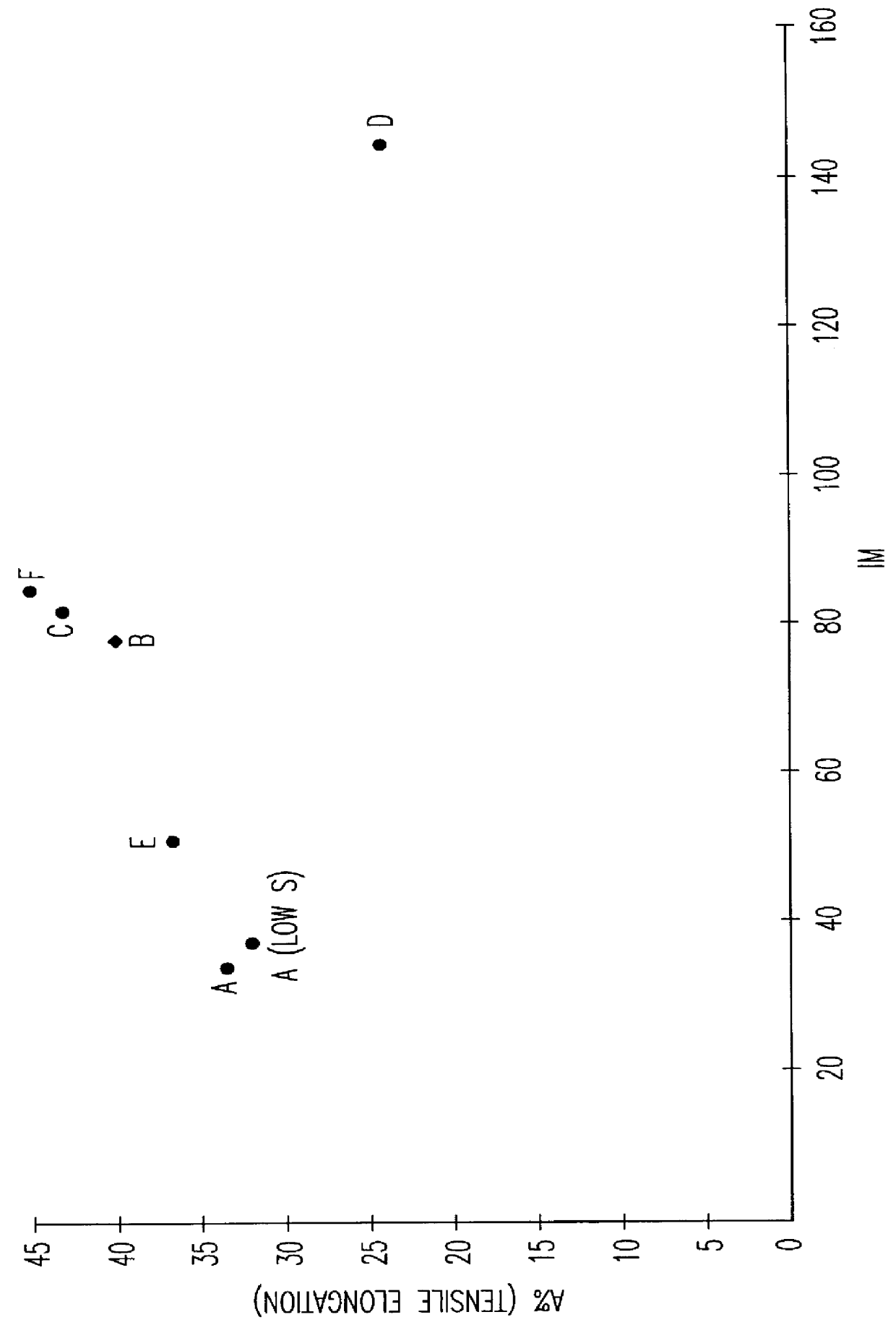
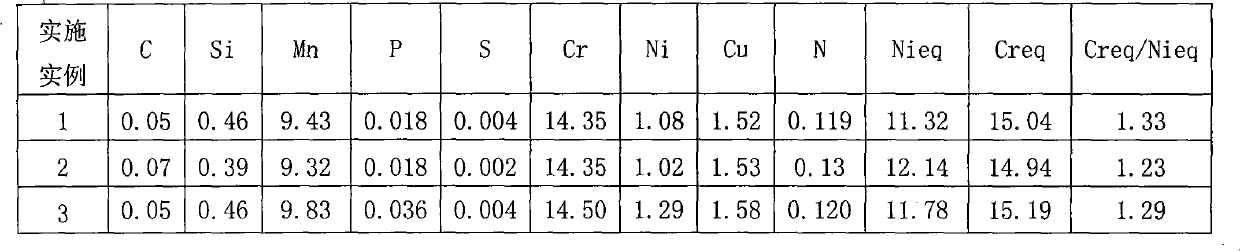
An austenoferritic stainless steel with high tensile elongation includes iron and the following elements in the indicated weight amounts based on total weight: carbon<0.04% 0.4%<silicon<1.2% 2%<manganese<4% 0.1%<nickel<1% 18%<chromium<22% 0.05%<copper<4% sulfur<0.03% phosphorus<0.1% 0.1%<nitrogen<0.3% molybdenum<3% the steel having a two-phase structure of austenite and ferrite and comprising between 30% and 70% of austenite, wherein Creq=Cr %+Mo %+1.5 Si % Nieq=Ni %+0.33 Cu %+0.5 Mn %+30 C %+30 N % and Creq / Nieq is from 2.3 to 2.75, and wherein IM=551-805(C+N)%-8.52 Si %-8.57 Mn %-12.51 Cr %-36 Ni %-34.5 Cu %-14 Mo %, IM being from 40 to 115.
Owner:UGITECH
Austenitic stainless steel, steel tube thereof and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101633999AImprove high temperature creep resistanceExcellent resistance to high temperature steam corrosionTemperature control deviceManufacturing convertersSS - Stainless steelIngot
The invention relates to an austenitic stainless steel, a steel tube thereof and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the austenitic stainless steel and the stainless steel tube comprise the components by mass percent: 0.060-0.14% of C, more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.50% of Si, more than 0 and less than or equal to 1.00% of Mn, less than 0.040% of P, less than 0.015% of S, 17.00-20.00% of Cr, 8.00-11.00% of Ni, 2.50-4.00% of Cu, 0.30-0.60% of Nb, 0.15-0.50% of Mo, 0.15-0.50% of Co, 0.05-0.14% of N, 0.001-0.01% of B, the rest of Fe and unavoidable impurity. The manufacturing method of the steel tube comprises: smelting and pouring to form steel ingots or continuously cast bloom, processing bar material, preparing tubular billet and further processing the steel tube; the method comprises the steps: the heating temperature of processing the bar material is 1250-1270 DEG C, heating temperature of preparing the tubular billet is 1100-1220 DEG C, and the finished product solid solution temperature is 1120-1190 DEG C. The austenitic stainless steel tube has high temperature creep strength and corrosion resisting performance at the high temperature.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG ENG TECH +1
Austenitic stainless steel
An austenitic stainless steel improved in creep strength, creep ductility, weldability and also hot workability. The steel, consisting of, by mass %, C: 0.05-0.15 %, Si: not more than 2 %, Mn: 0.1-3%, P: 0.05-0.30 %, S: not more than 0.03 %, Cr: 15-28 %, Ni: 8-55 %, Cu: 0-3.0 %, Ti: 0.05-0.6 %, REM: 0.001-0.5 %, sol. Al: 0.001-0.1%, N: not more than 0.03 %, and the balance being Fe and incidental impurities. This steel may contain one or more of Mo, W, B, Nb, V, Co, Zr, Hf, Ta, Mg and Ca. It is preferable that REM is Nd.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel
ActiveUS20080107559A1Careful analysisAvoid dissociationHeat exchange apparatusMetallurgyProtective oxide
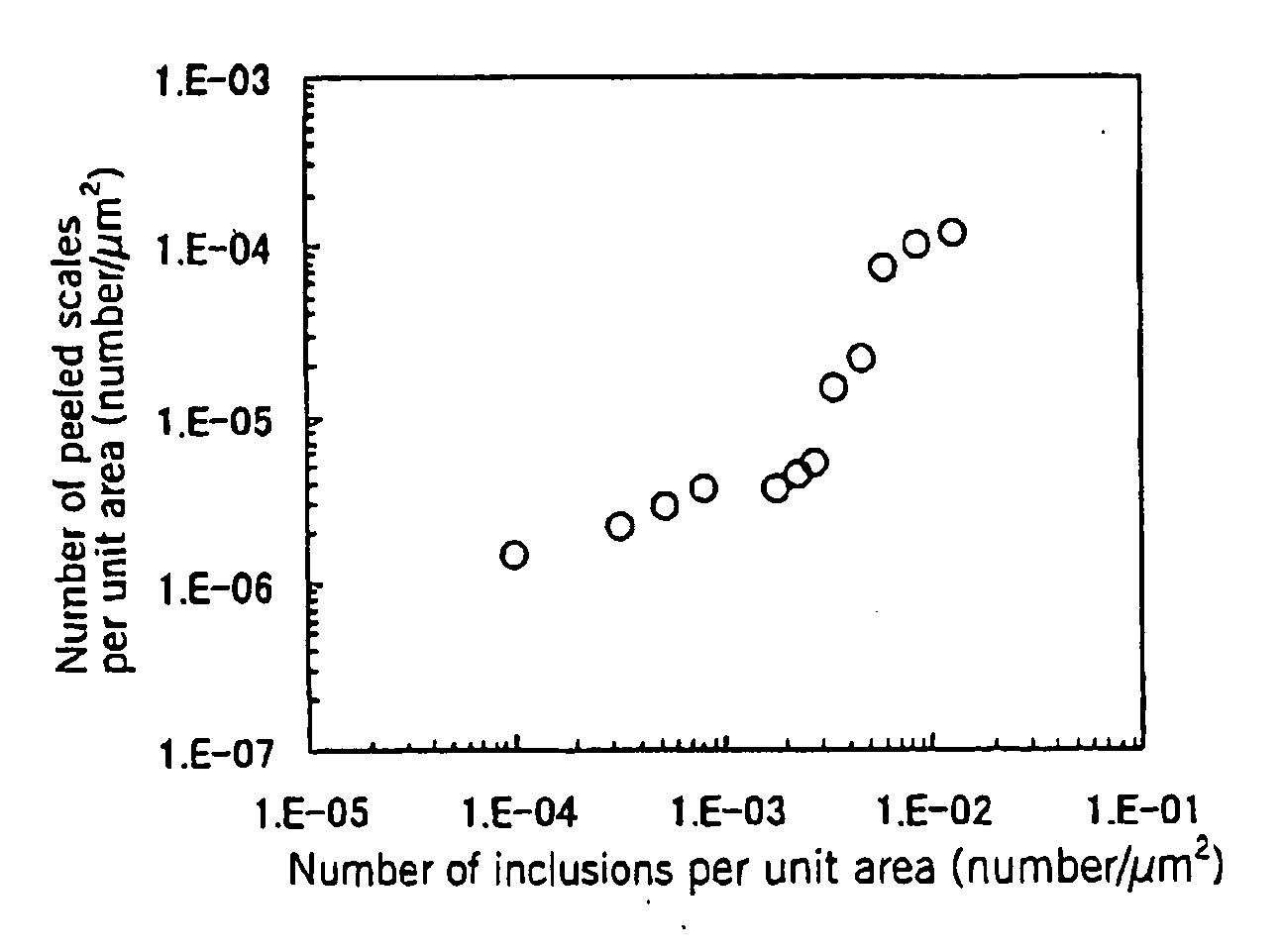
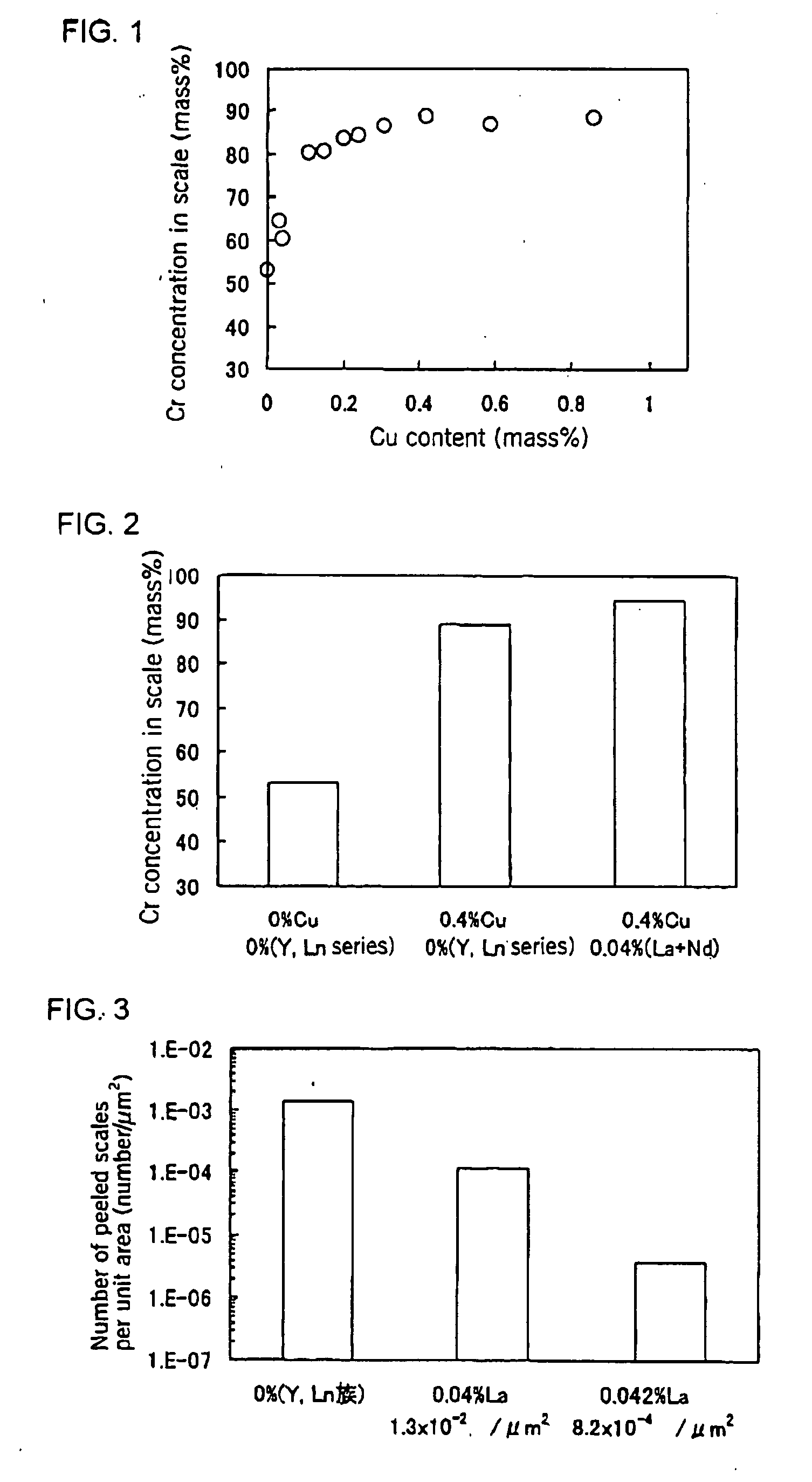
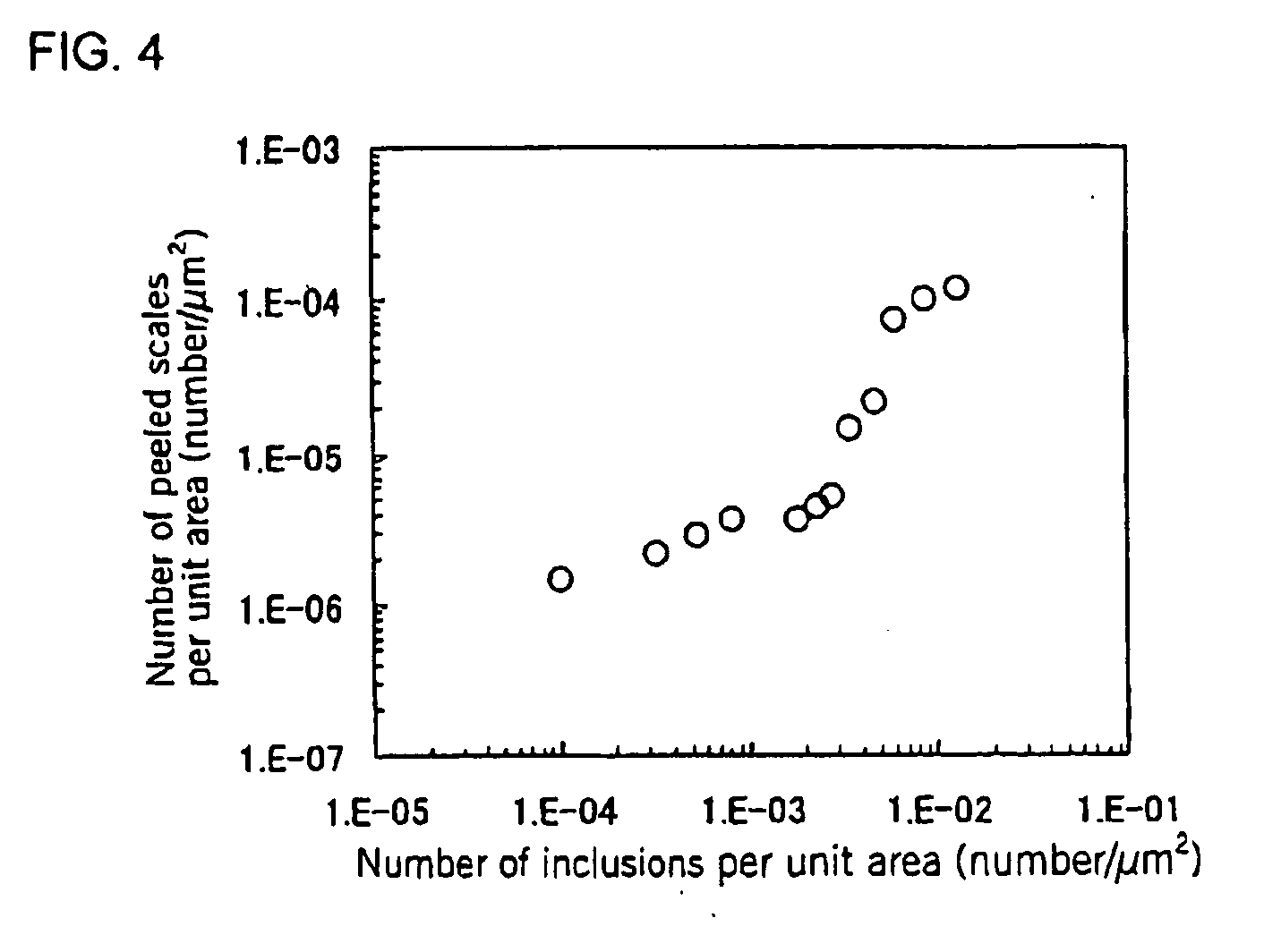
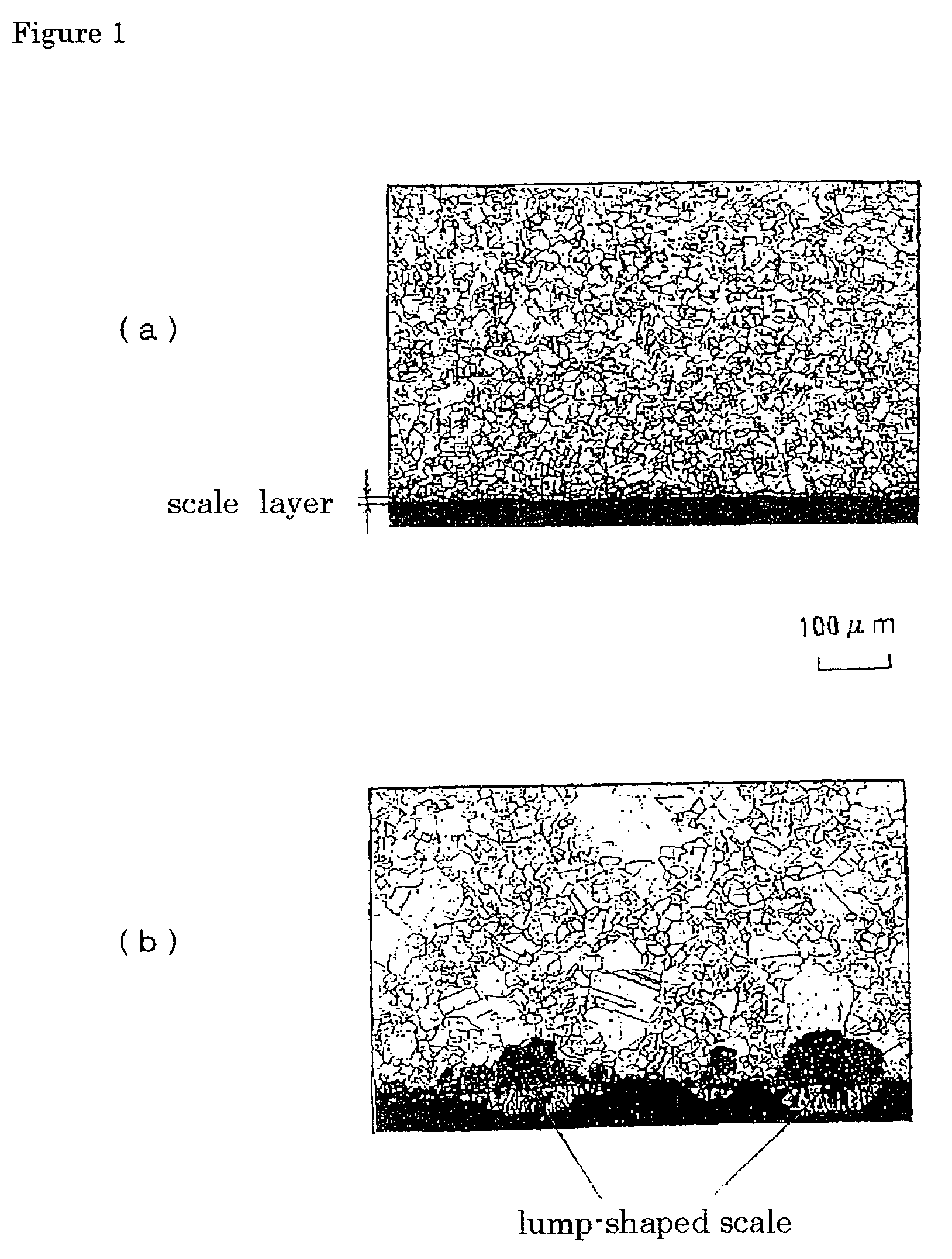
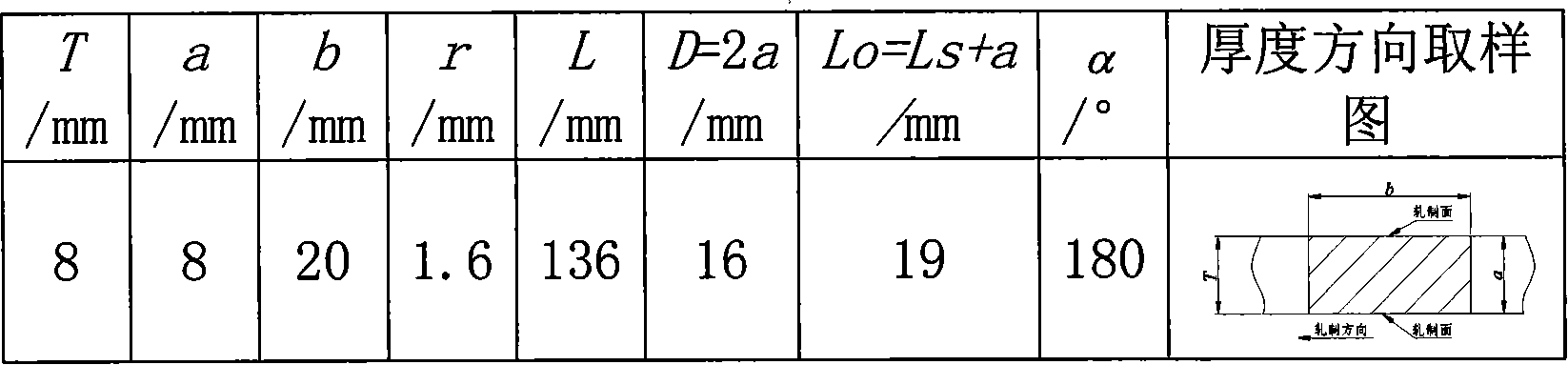
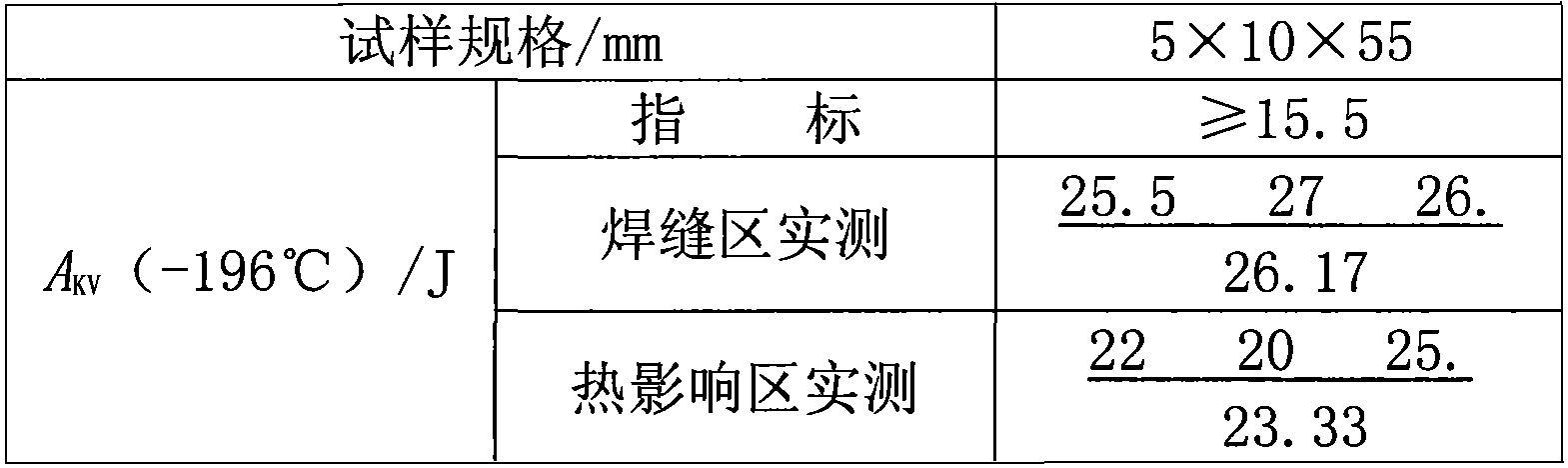
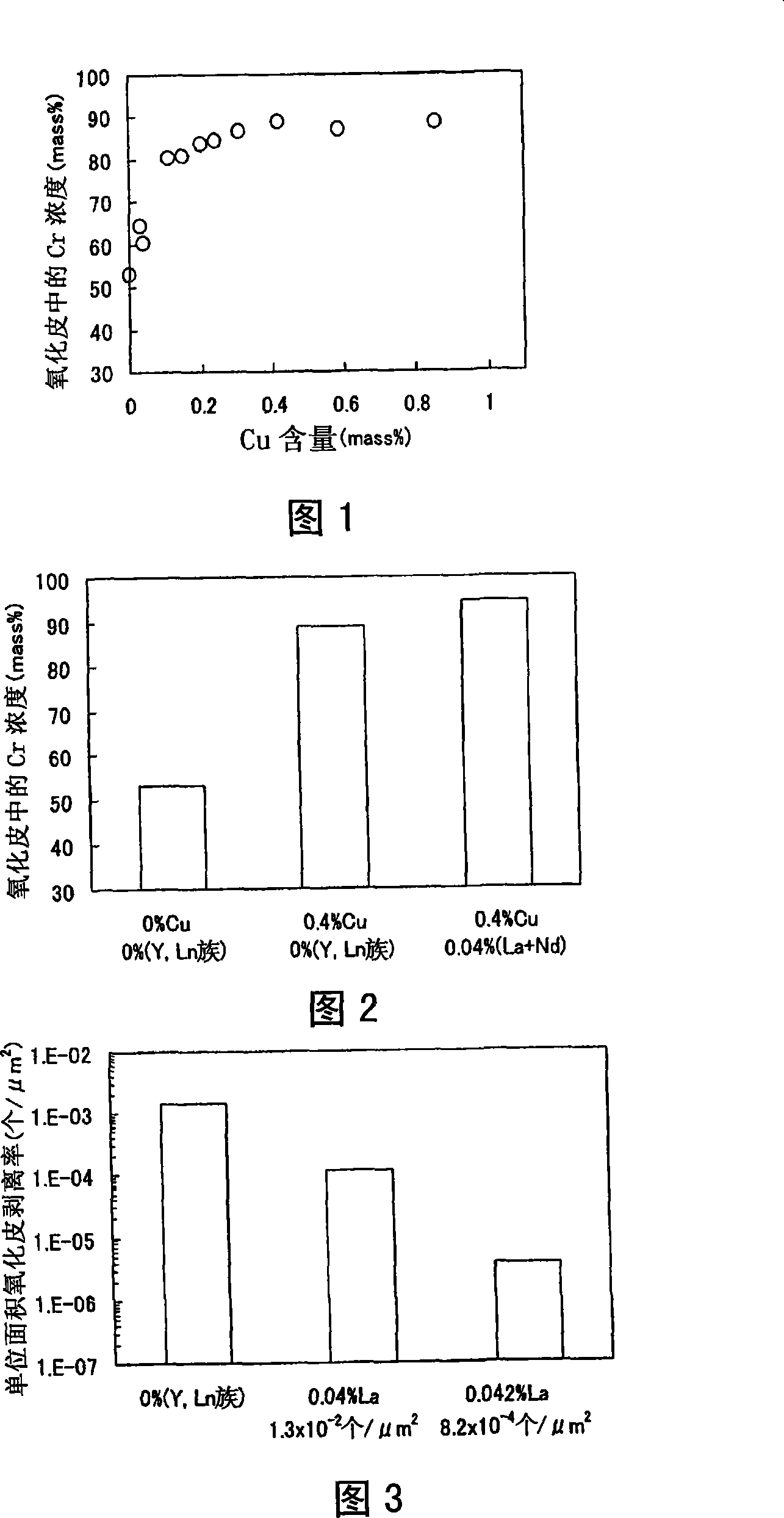
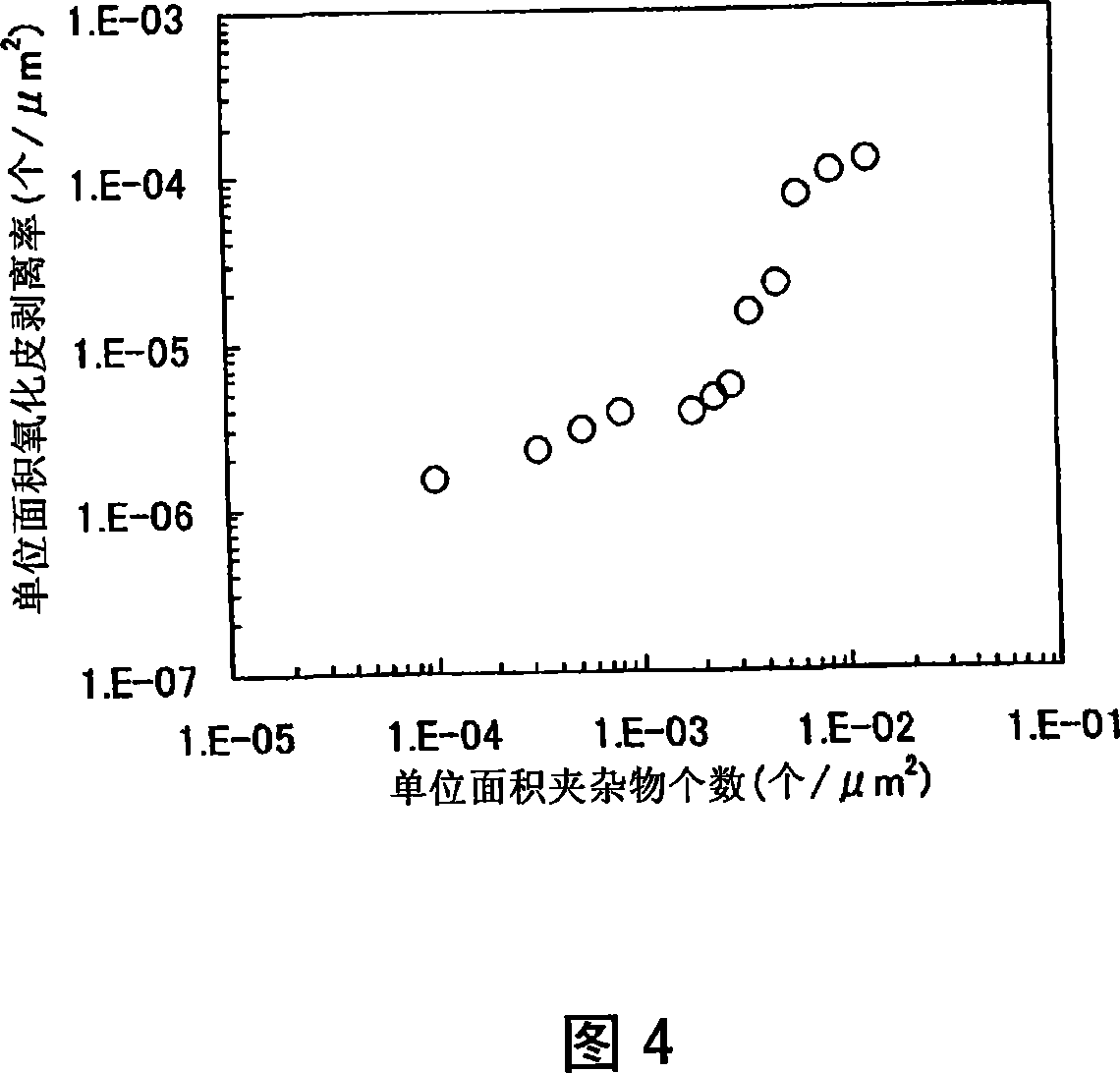
An austenitic stainless steel having excellent resistance to scale peeling which can suppress peeling of a protective oxide scale which is formed on the steel surface even when the steel undergoes repeated cycles of high temperature heating and cooling and which is suitable for use in a high temperature, humidified gas environment at a high temperature and particularly at 1023 K or above has a steel composition consisting essentially of C: 0.01-0.15%, Si: 0.01-3%, Mn: 0.01-2%, Cu: 0.1-2.5%, Cr: 23-30%, Ni: 16-25%, Al: 0.005-0.20%, N: 0.001-0.40%, P: at most 0.04%, S: at most 0.01%, at least one of Y and Ln series elements: a total of 0.005-0.1%, and a balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities, with the number of inclusions containing Y and Ln series elements in the steel surface being at most 5×10−3 / μm2.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel tube excellent in steam oxidation resistance and a manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7014720B2Excellent in steam oxidation resistanceHigh-temperature bendingFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainOxygen
The present invention provides an austenitic stainless steel tube with a uniform fine grained structure of regular grains, which is not changed to a coarse structure and the steam oxidation resistance is maintained even if the tube is subjected to a high temperature reheating during welding and high temperature bending working. The austenitic stainless steel tube consists of, by mass %, C: 0.03–0.12%, Si: 0.1–0.9%, Mn: 0.1–2%, Cr: 15–22%, Ni: 8–15%, Ti: 0.002–0.05%, Nb: 0.3–1.5%, sol. Al: 0.0005–0.03%, N: 0.005–0.2% and O (oxygen): 0.001–0.008%, and the balance Fe and impurities, the austenitic stainless steel tube having austenitic grain size number of 7 or more and a mixed grain ratio of preferably 10% or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel
ActiveCN101784687AHigh strengthExcellent resistance to embrittlement crackingCrack resistanceMaterials science
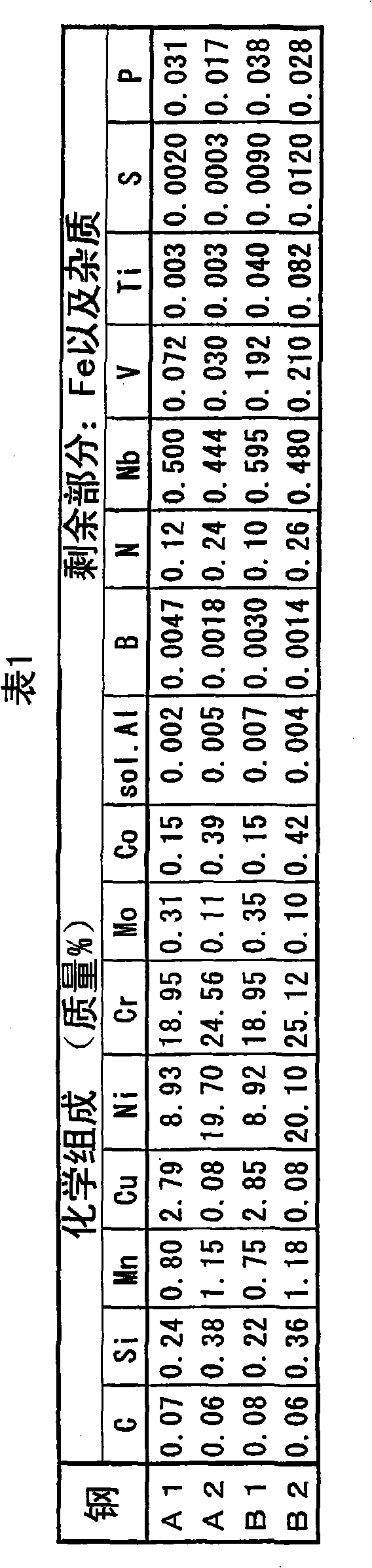
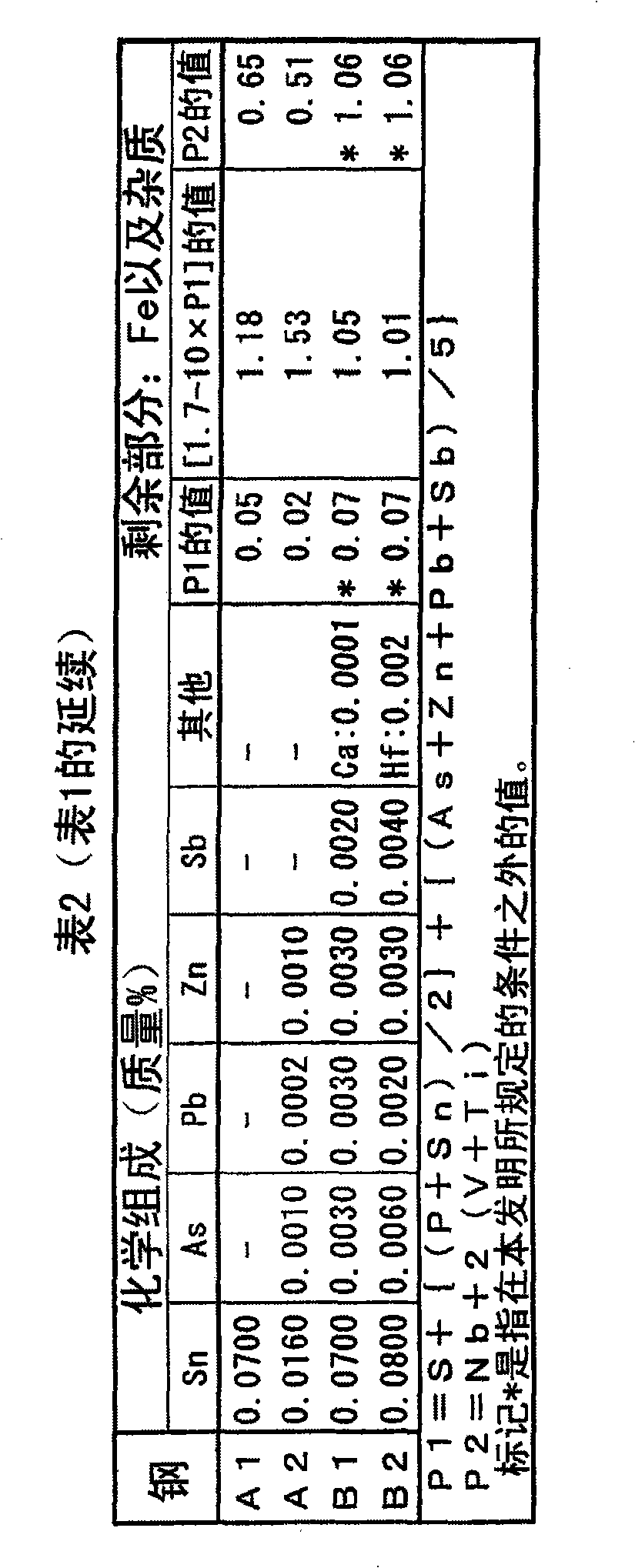
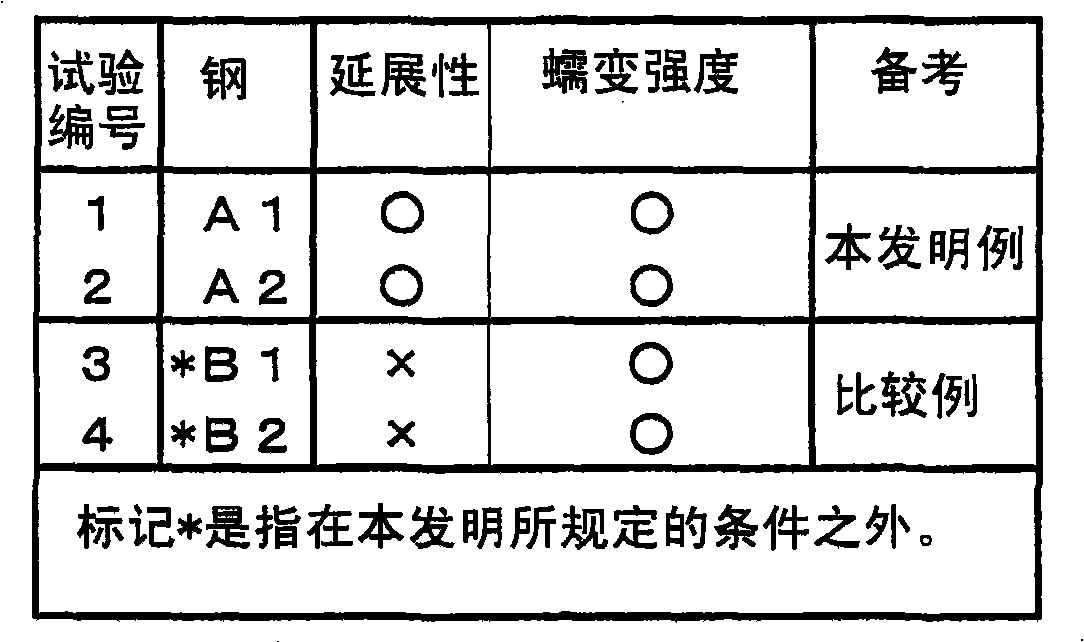
Disclosed is an austenitic stainless steel which comprises the following components: C: 0.04-0.18%, Si: 1.5% or less, Mn: 2.0% or less, Ni: 6-30%, Cr: 15-30%, N: 0.03-0.35%, and sol.Al: 0.03% or less, and which further comprises at least one component selected from 1.0% or less of Nb, 0.5% or less of V and 0.5% or less of Ti, with the remainder being Fe and impurities, wherein the impurities contain the following components: P: 0.04% or less, S: 0.03% or less, Sn: 0.1% or less, As: 0.01% or less, Zn: 0.01% or less, Pb: 0.01% or less and Sb: 0.01% or less, and wherein the following formulae are fulfilled: P1 = S+[(P+Sn) / 2]+[(As+Zn+Pb+Sb) / 5] = 0.06; and 0.2 = Nb+2(V+Ti) = 1.7-10xP1. The austenitic stainless steel has high strength and, when used in a welded part, can exhibit excellent embrittlement crack resistance during being used at a high temperature. The steel is suitable as a material for an instrument that is intended to be used at a high temperature for a long period, such as a boiler for power generation.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Nitrogen-containing nickel-free stainless steel and metallurgy forming process for powder thereof
The invention provides a nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel and a powder-metallurgical molding technology, relating to the field of stainless steel production. Nitrogenous stainless steel powder and a prepared cementing agent are mixed evenly in a mixing machine and then crashed to injection molding feedstock; injection molding blanks with smooth surfaces and without macro defects are obtained by an injection molder under appropriate injection temperature and injection pressure; after degreasing by chlorylene solvent, thermal degreasing and presintering are carried out to the injection molding blanks, thermal degreasing blanks with certain strength and without defects are obtained; the thermal degreasing blanks are sintered and densified in nitrogen based atmosphere, therefore, products with higher density and more excellent performance can be obtained. The nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel of the invention can solve the problems that resource price of the nickel-contained stainless steel is expensive and the contained nickel thereof is harmful to human health and the like, extends the application scope of nitrogenous austenitic stainless steel. The materials prepared by using the nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel of the invention are better than traditionally smelted austenitic stainless steel in terms of performance and the nitrogenous nickel-free stainless steel of the invention is resource saving and environmentally friendly.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
High-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel for vascular stent and application thereof
The invention provides a high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel material for a vascular stent, which comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 16-20% of Cr, 12-20% of Mn, 1-3% of Mo, 0.5-2% of Cu, no more than 0.05% of Ni, 0.7-1.2% of N, 0.5-8% of W, 0.05-0.5% of RE, no more than 0.08% of C, 0.3-4% of Si, no more than 0.010% of S, no more than 0.02% of P and the balance of Fe, wherein RE is a rare-earth element. The high-nitrogen stainless steel provided by the invention is mainly used for vascular stent processing; the elements of copper, nitrogen and rare earth are added to increase the blood compatibility of the stainless steel; and the tungsten alloy is added to increase the density of the stainless steel. The stainless steel has excellent visibility under X rays, contains no potential toxic element nickel, can be used in the aspects of surgical implants, medical appliances, food and catering appliances, jewelry and other stainless steel products which are always in contact with a human body, and can also be used in the fields of chemical engineering, environment protection and the like.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIAN MEDICAL TECH BEIJING CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel buried arc welding wire for low-temperature equipment
ActiveCN101244494AEasy to rollImprove low temperature resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSteelmakingChemical composition
The invention relates to a welding wire, in particular to a welding wire applying to austenitic submerged arc welding for low-temperature equipments, in terms of chemical composition and weight percent, comprising Cr: 19.0 to 23.0%, Ni: 9.0 to 12.0%, C: <=0.03%, Mn: 1.60 to 2.50%, Si: 0.30 to 0.60%, Mo: <=0.30%, Cu: <=0.30%, Co: <=0.20%, Ti: <=0.015%, Nb: <=0.05%, V: <=0.10%, B: <=0.005% and Fe as allowance. The welding wire has the advantages that: the welding wire steelmaking craft is stable; the drawing performance is good; the invention meets the welding technical requirements of the high-intensity, high-toughness and anti-corrosion steel with low temperature and low temperature equipments; the invention can apply to the steel of 500 to 750MPa strength level; the invention is suitable for large range of welding current and no blowhole; the moulding is beautiful; the weld joint can be well matched with the base material.
Owner:哈焊所华通(常州)焊业股份有限公司
Austenite-type stainless steel hot-rolling steel material with excellent corrosion resistance, proof-stress, and low-temperature toughness and production method thereof
InactiveUS20060243356A1Improve corrosion resistanceReduce contentRoom temperatureSS - Stainless steel
An austenitic stainless steel hot-rolled steel material can be provided which has sea-water resistance and strength superior to conventional steel. Low-temperature toughness can be maintained, which is preferable in a structural member of speedy craft. The steel material can include an austenitic stainless steel hot-rolled steel material which excels in the properties of corrosion resistance, proof stress, and low-temperature toughness. In such austenitic stainless steel hot-rolling steel material, e.g., PI[=Cr+3.3(Mo+0.5W)+16N] ranges from 35 to 40, δ cal [=2.9 (Cr+0.3Si+Mo+0.5W)−2.6 (Ni+0.3Mn+0.25Cu+35C+20N)−18] ranges from −6 to +2, and a 0.2% proof stress at room temperature is not less than 550 MPa, Charpy impact value measured using a V-notch test piece at −40° C. is not less than 100 J / cm2, and the pitting potential measured in a deaerated aqueous solution of 10% NaCl at 50° C. (Vc′100) is not less than 500 mV (as it relates to saturated Ag / AgCl).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Austenitic stainless steel
ActiveCN101194037APrevent peelingIncreased durabilityHeat exchange apparatusRare-earth elementSS - Stainless steel
Even after repeated high-temperature heating-cooling cycles, it still has excellent scale peeling resistance that can inhibit the peeling of protective oxide scales formed on the steel surface, and can be used in high temperature, especially high temperature humidified gas environments above 1023K. System stainless steel with the following steel composition: C: 0.01-0.15%, Si: 0.01-3%, Mn: 0.01-2%, Cu: 0.1-2.5%, Cr: 23-30%, Ni: 16-25% , Al: 0.005 to 0.20%, N: 0.001 to 0.40%, P: 0.04% or less, S: 0.01% or less, and one or more rare earth elements selected from the Y and Ln groups: total 0.005 to 0.1%, the balance is substantially composed of Fe and unavoidable impurities, and the inclusions containing Y and Ln group elements on the steel surface are 5×10-3 / μm2 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Welding process for stainless steel piping
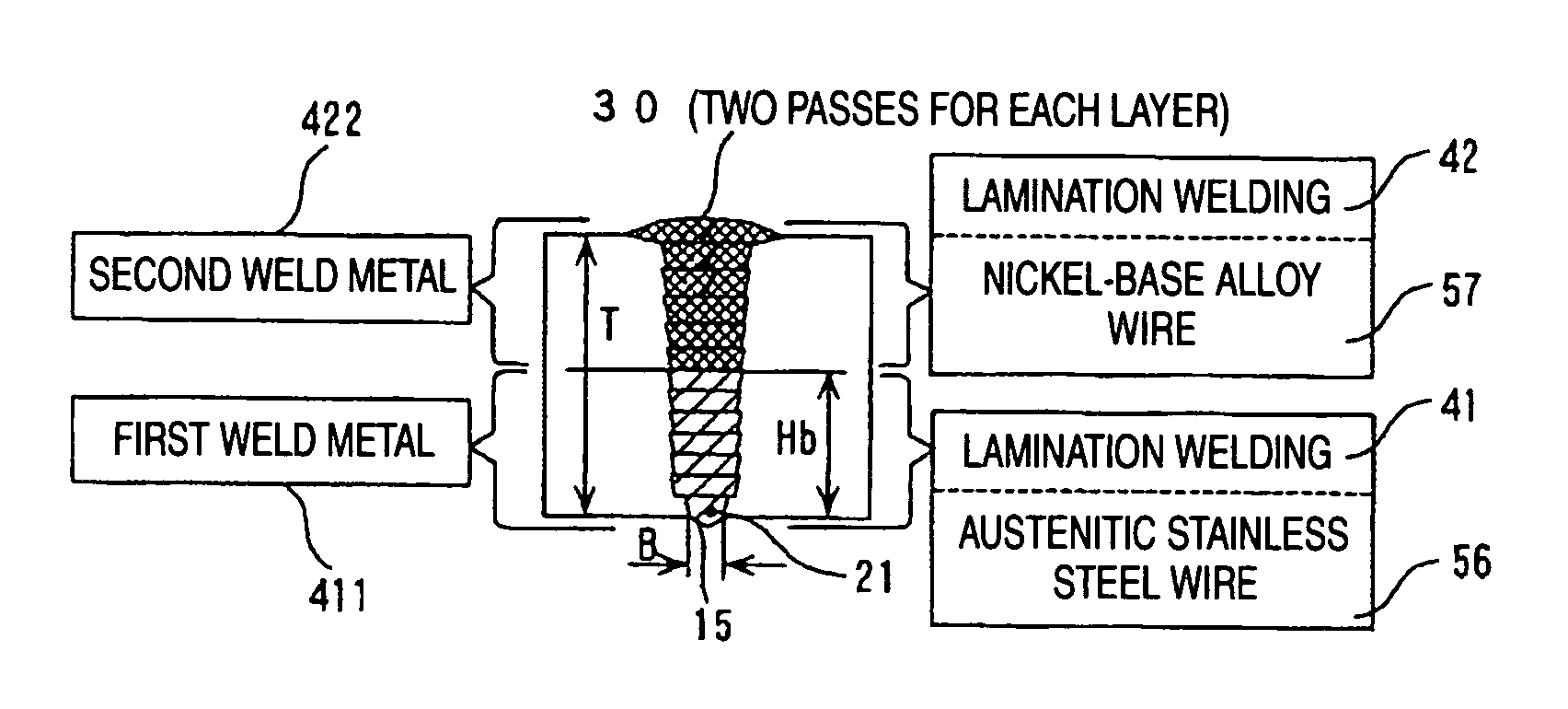
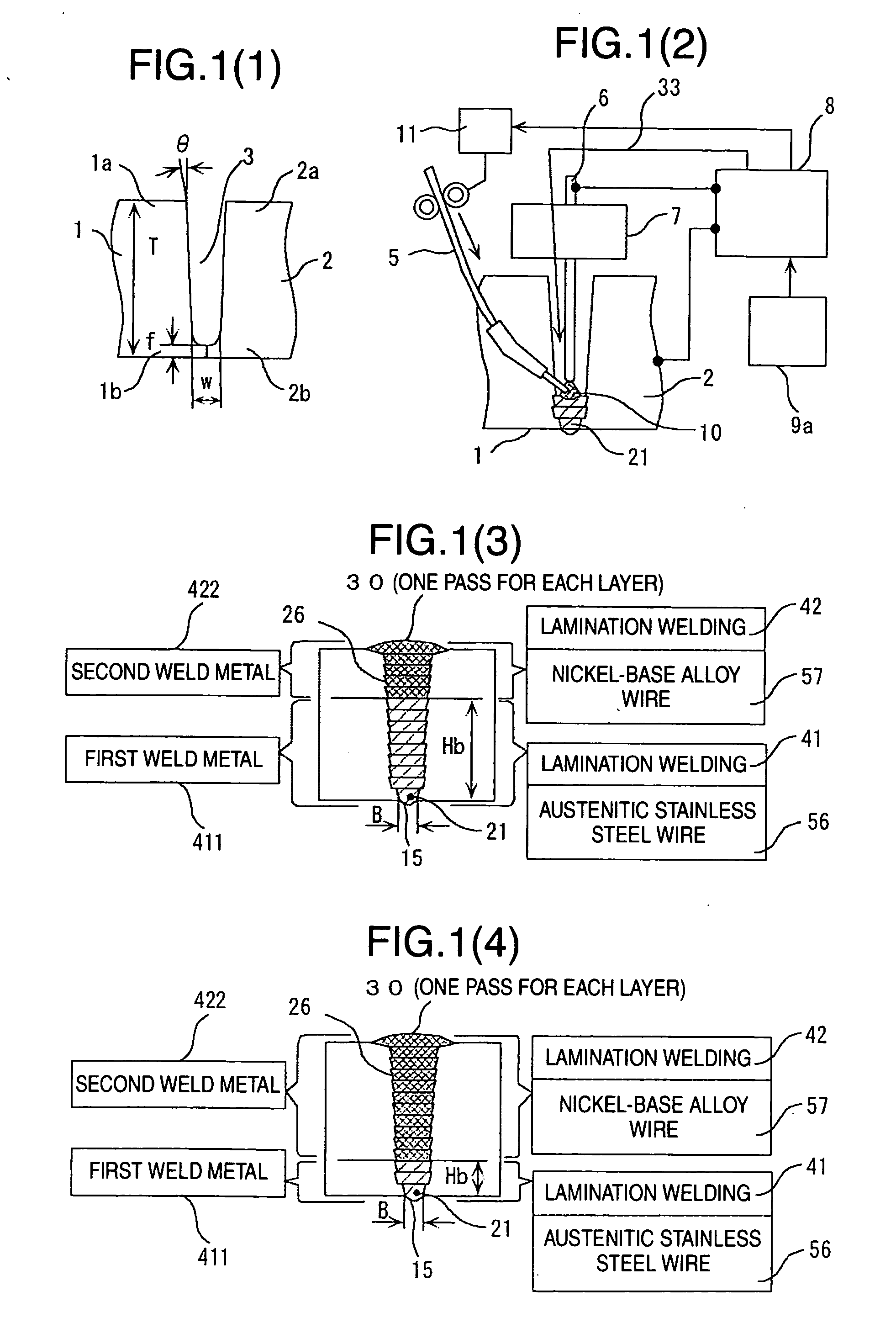
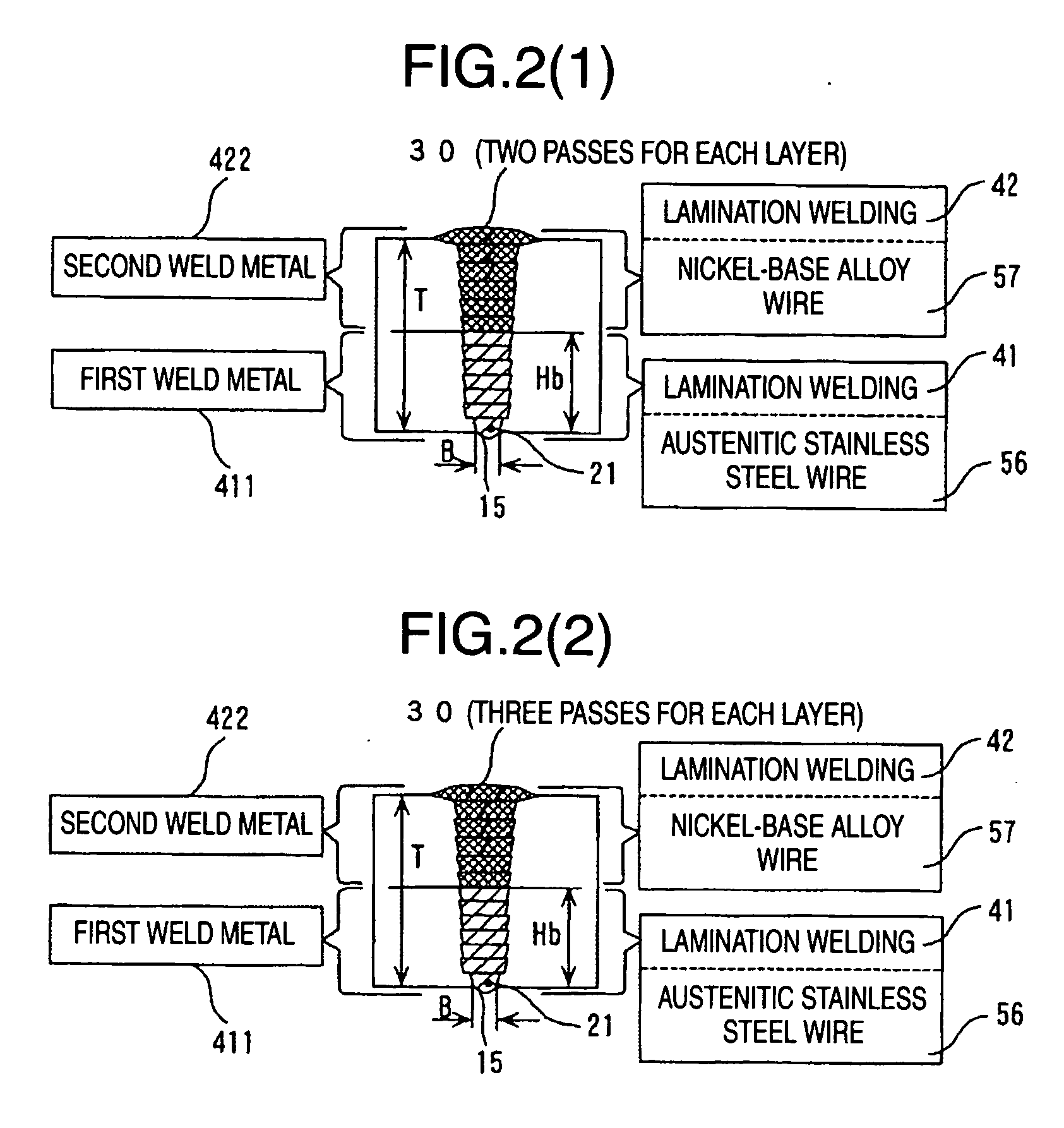
InactiveUS20060201915A1Suppresses stress corrosion crackingReduce residual stressArc welding apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesAlloyAustenite
The present invention has an object to reduce residual stress in a tensile direction of a weld on the inner side in contact with reactor water of austenitic stainless steel piping, and to change the residual stress into compressive stress, to reduce stress corrosive cracking. The present invention provides a welding process for stainless steel piping of laminating two types of welding wire made of different materials in a groove of austenitic stainless steel piping, including at least one of a first layer penetration welding step of performing a predetermined back bead width on the back side of the groove bottom and a tack welding step, a first lamination welding step of lamination welding of austenitic stainless steel wire from the bottom to the top of the groove, and a second lamination welding step of lamination welding of nickel-base alloy wire to a final layer at the top of the groove.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Manufacture of fine-type stainless steel plate heat exchanger
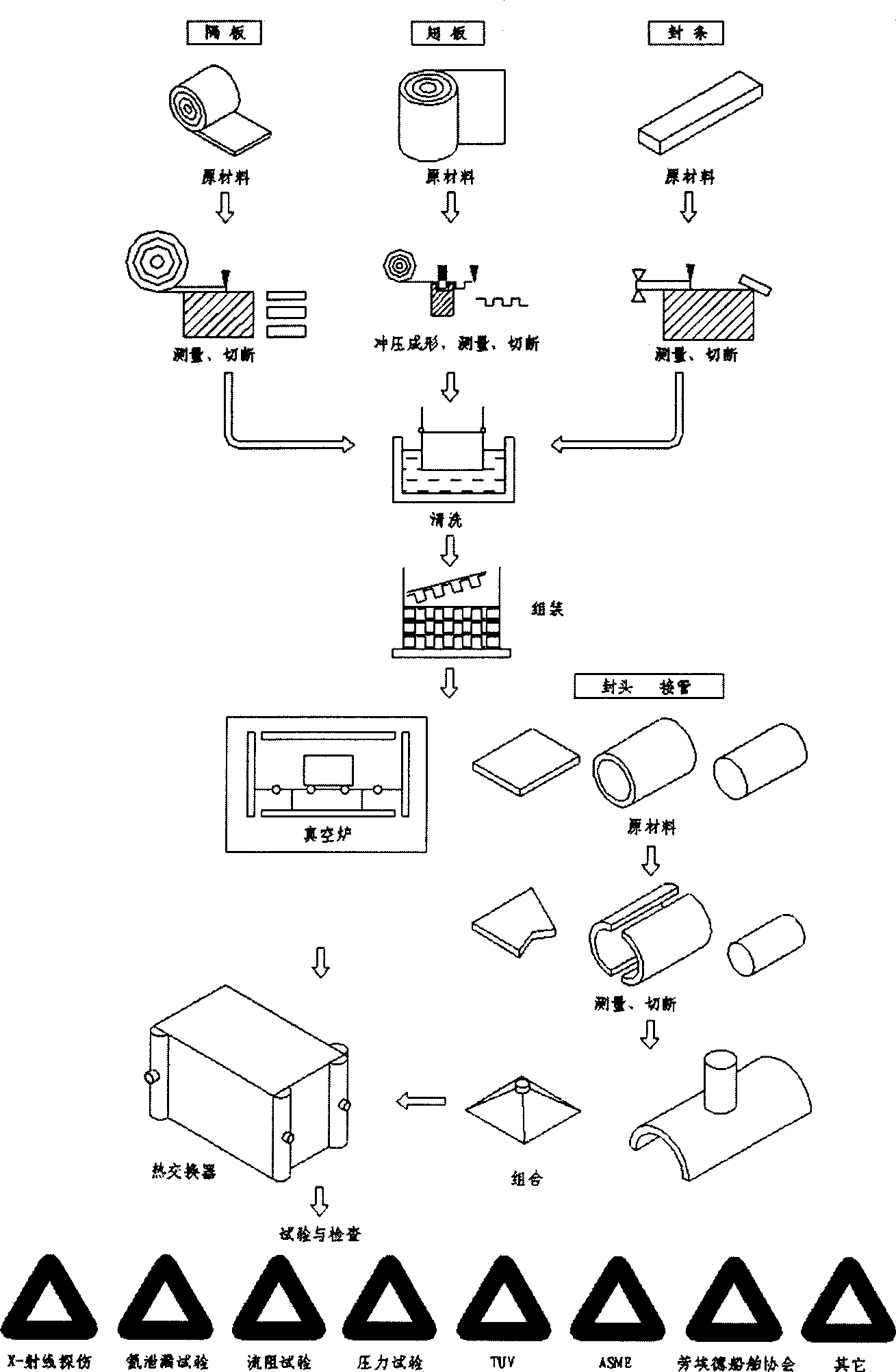
InactiveCN1375374AImprove wettabilityIngredients evenly distributedSoldering apparatusX-rayHigh pressure water
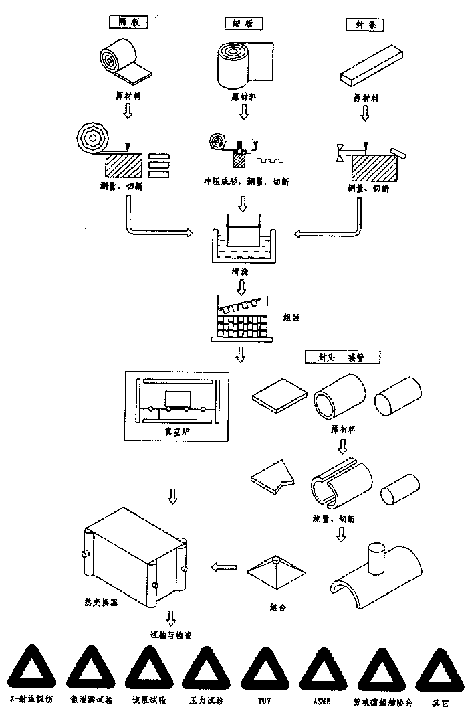
The production method of austenitic stainless steel plate fin heat exchanger includes the following steps: part preparation: partition, sealing strip, fin, sealing head and connecting pipe preparation; cleaning before welding; acid pickling to remove oil, dirt and oxide, and using high-pressure water to wash; element assembling and holding; vacuum braze welding, adopting argon arc welding to weldscaling head and connecting pipe, making general assembly; test and inspection, making x-ray inspection, helium leak detection, flow resistance test, pressure test, TUV, ASME and other test and inspection. Said invented process raise the production quality of said stainless steel plate fin heat exchanger, tensile-strength of connector and its service life.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Austenitic-ferritic stainless steel with excellent formability
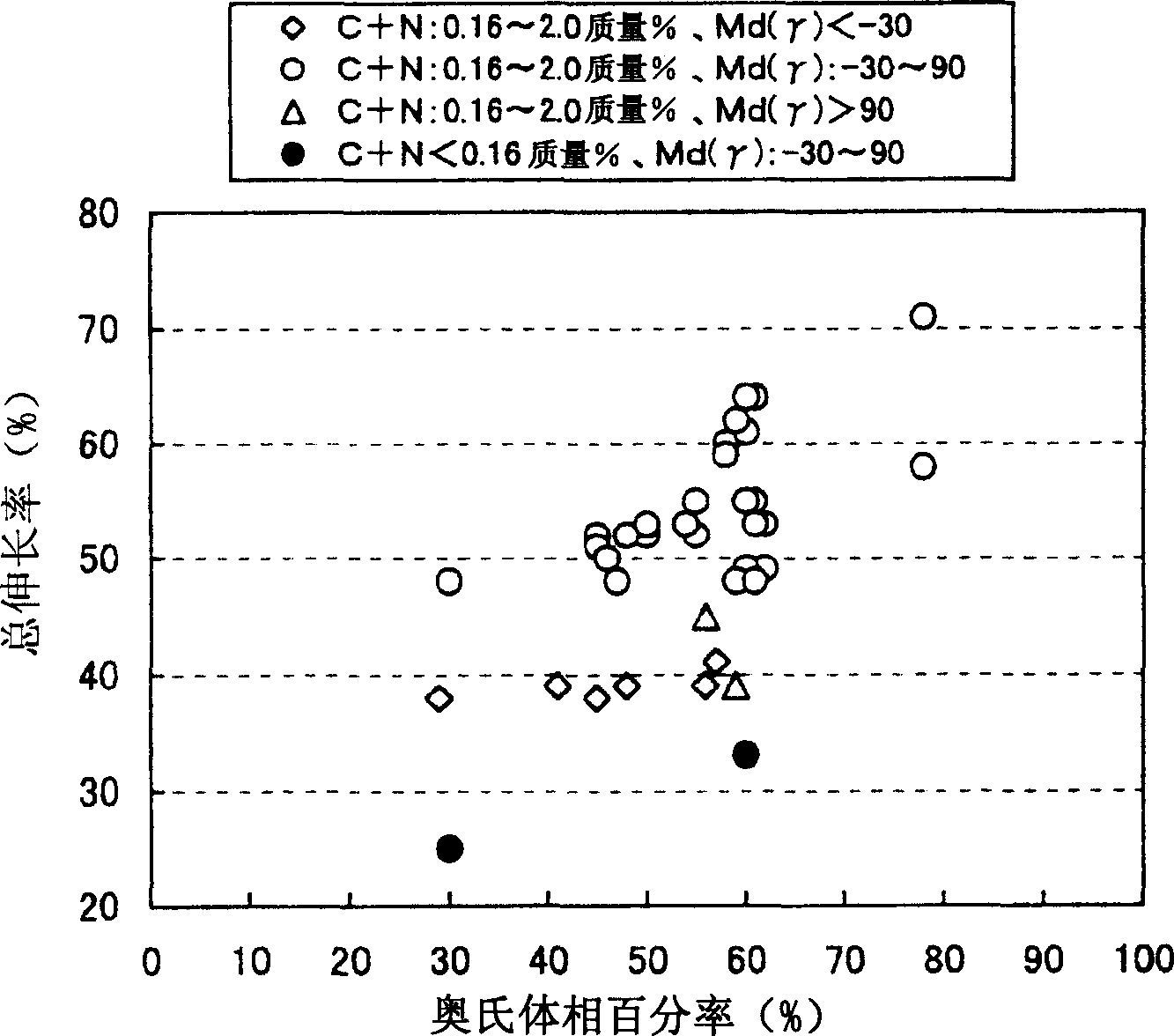
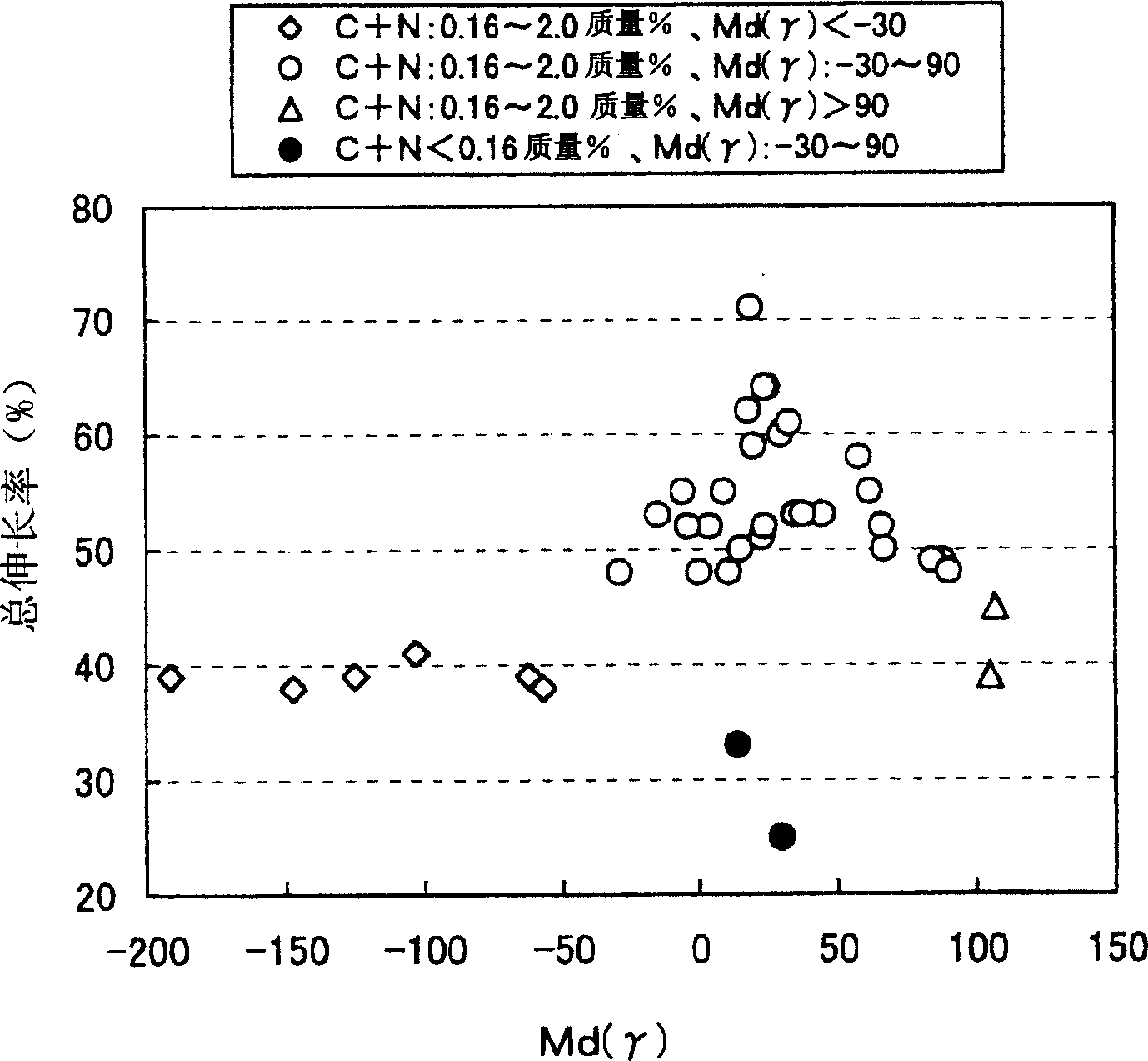
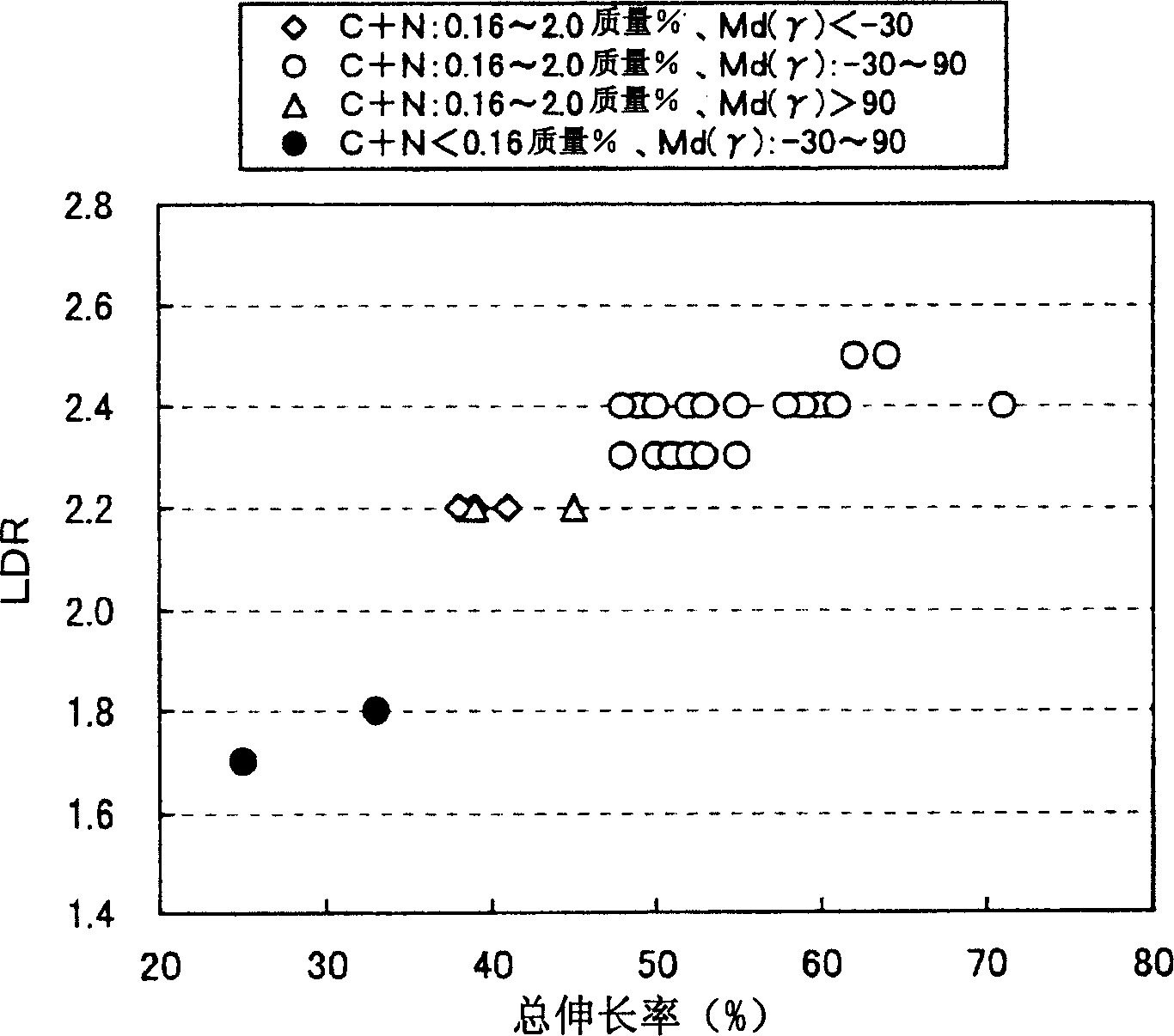
An austenitic-ferritic stainless steel having a low Ni content and a high N content is provided. A stainless steel which contains, in mass %, 0.2 % or less of C, 4 % or less of Si, 12 % or less of Mn, 0.1 % or less of P, 0.03 % or less of S, 15 to 35 % of Cr, 3 % or less of Ni, and 0.05 to 0.6 % of N, and is mainly composed of an austenite phase and a ferrite phase, wherein the proportion of said austenite phase is 10 to 85 volume %. The above austenitic-ferritic stainless steel exhibits good formability and high punch stretch formability, and is excellent in the resistance to crevice corrosion, to the corrosion of a welded zone and to intergranular corrosion. The above austenitic-ferritic stainless steel wherein the austenite phase contains C and N in a total amount of 0.16 to 2 mass % exhibits further improved formability.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
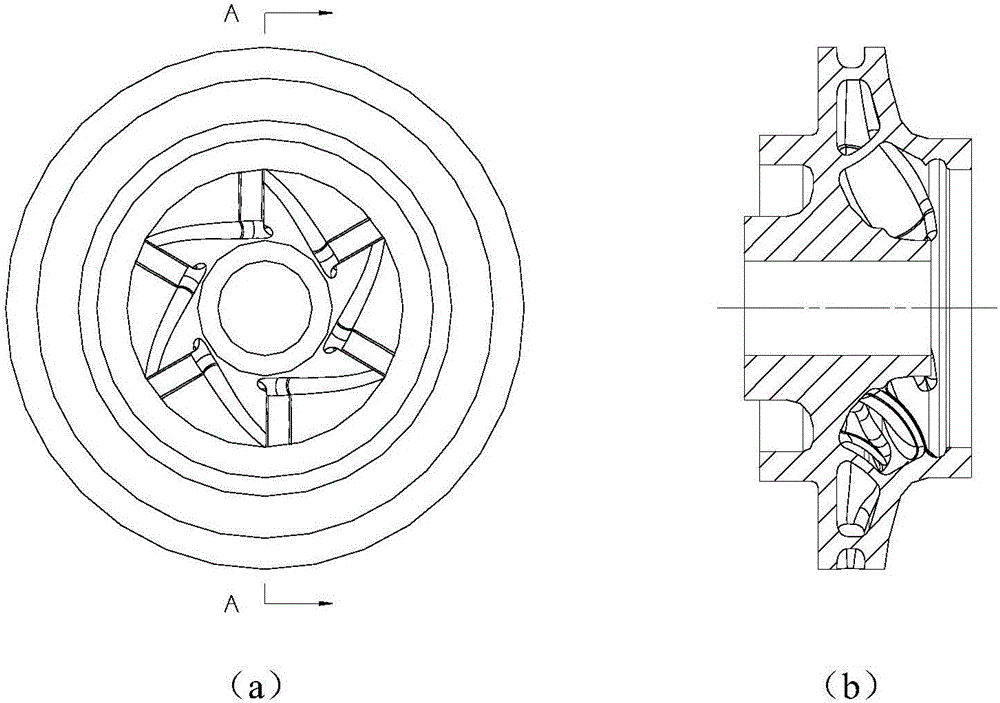
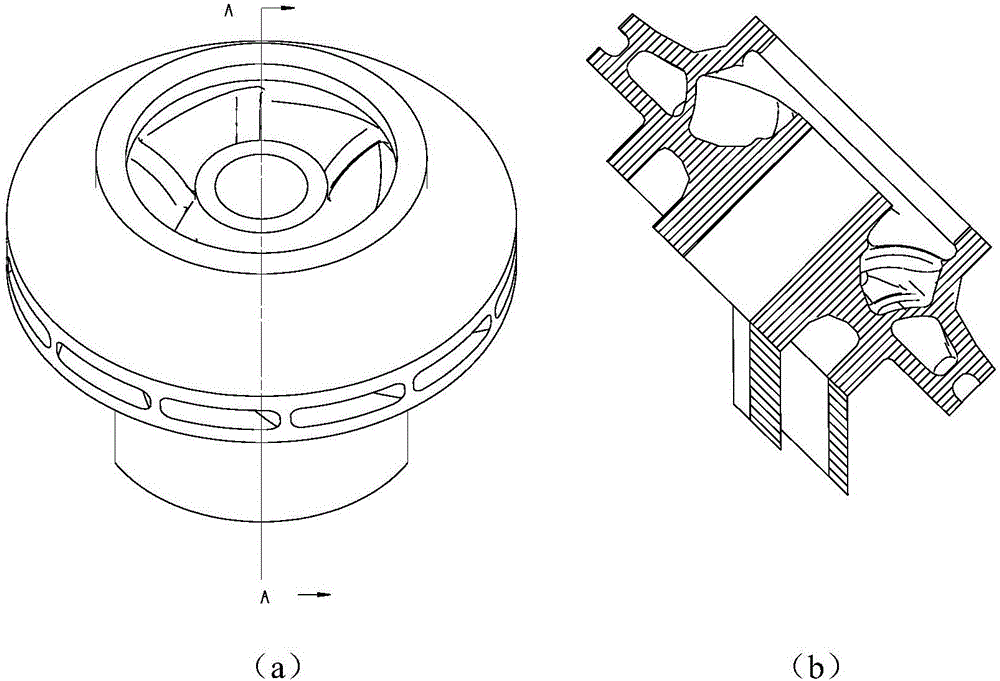
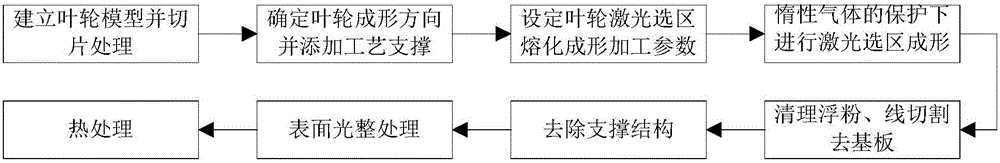
Integral manufacturing method of S-04/S-08 high-strength stainless steel three-dimensional flow shrouded impeller
ActiveCN106077643AShorten the manufacturing cycleCompact structureAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngine manufactureMaterials scienceAustenitic stainless steel
The invention provides an integral manufacturing method of an S-04 / S-08 high-strength stainless steel three-dimensional flow shrouded impeller. The integral manufacturing method comprises the steps of firstly, establishing an impeller three-dimensional model, and carrying out slicing treatment; determining the forming direction and support adding positions according to structural characteristics of the impeller; setting parameters of a laser selective melting forming processing technology according to characteristics of a high-strength stainless steel material; forming under protection of an inert gas; after forming, cleaning floating powder, removing a base plate through linear cutting, and removing supports; and finally, carrying out follow-up treatment such as surface treatment and thermal treatment on the impeller. According to the integral manufacturing method, complex cutters or fixtures do not need to be designed, materials can be directly added for part manufacturing only through the three-dimensional model of the impeller, the manufacturing cycle is greatly shortened, and the integral manufacturing method is applicable to trial manufacturing and middle and small-batch production in the development stage.
Owner:XIAN SPACE ENGINE CO LTD
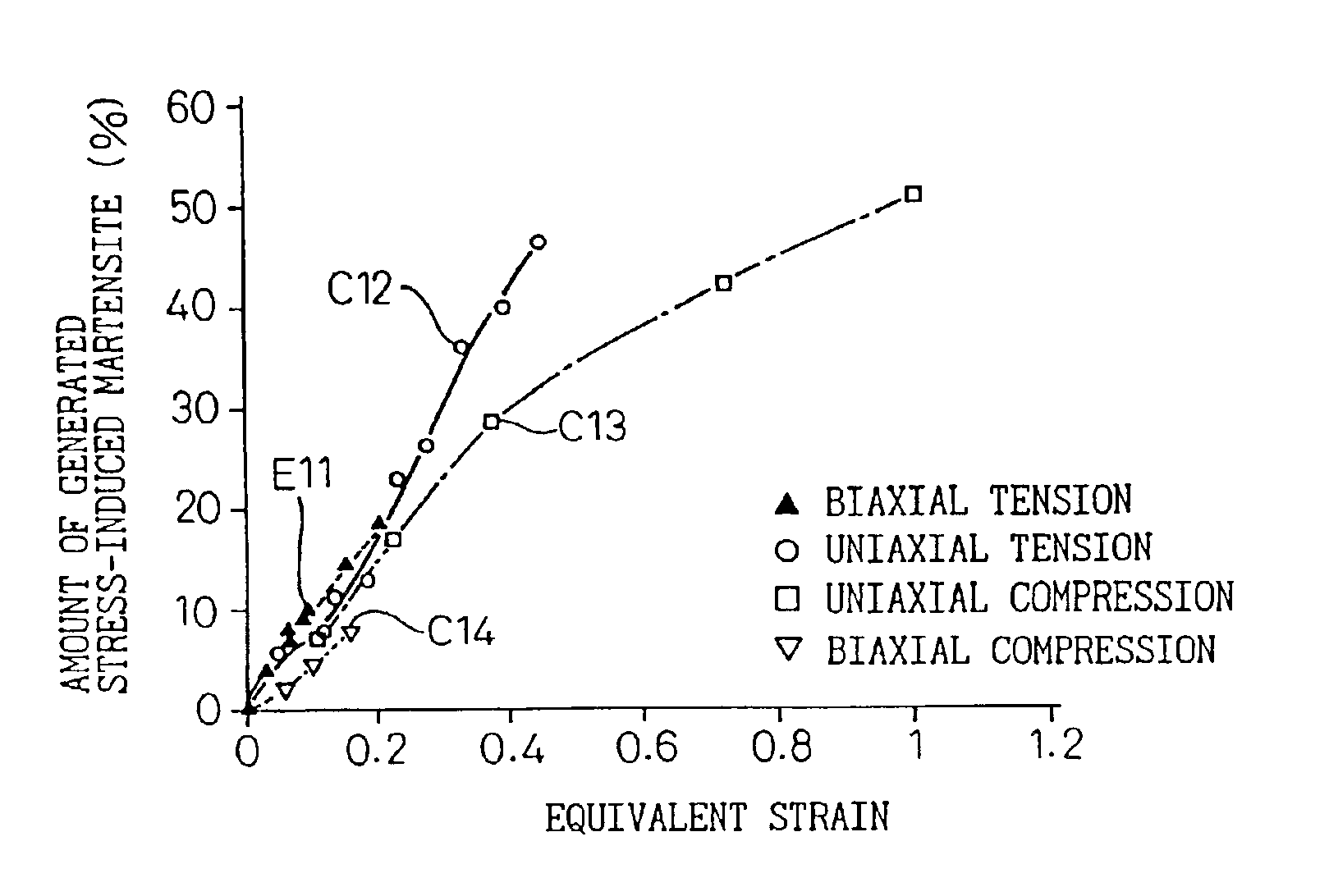
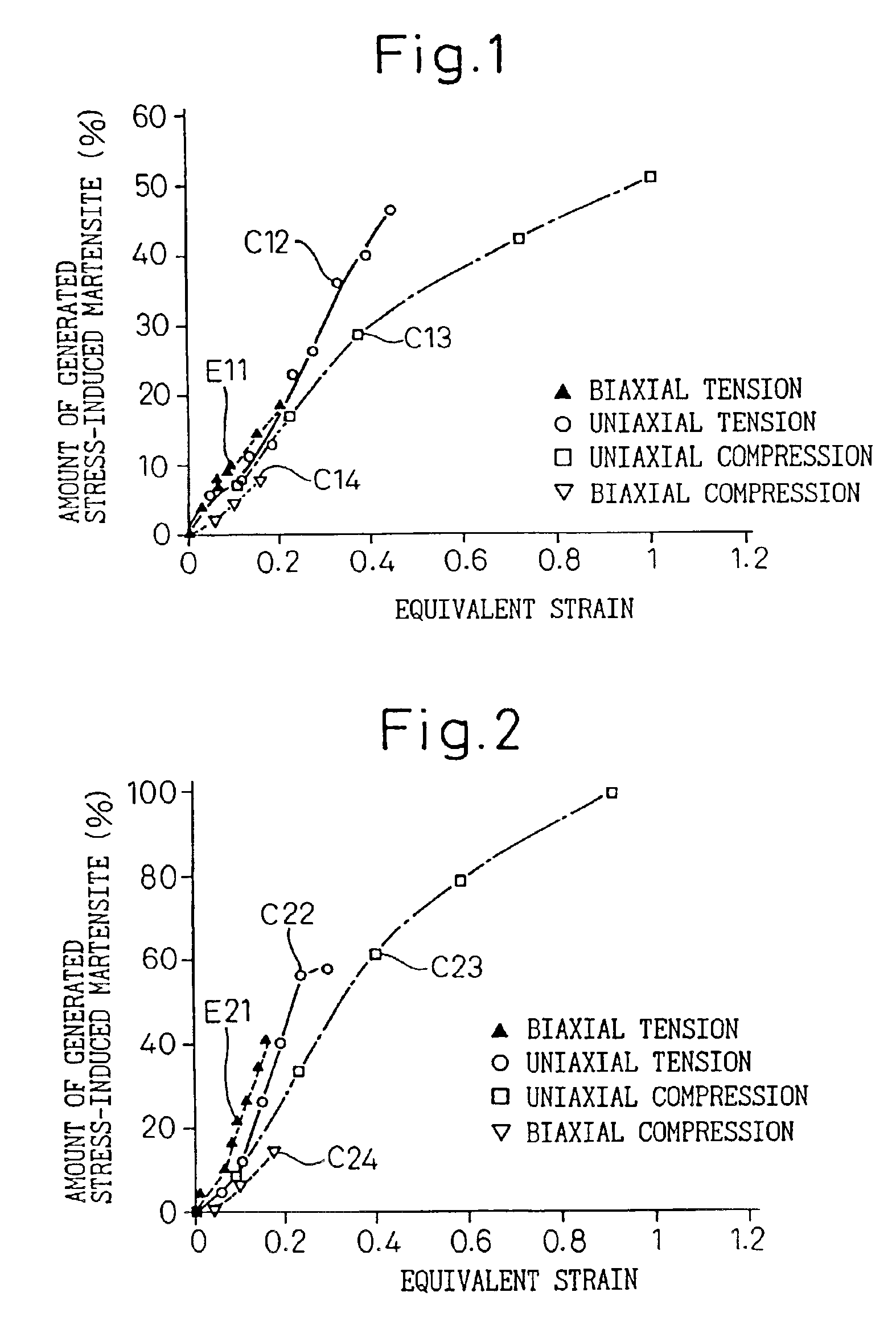
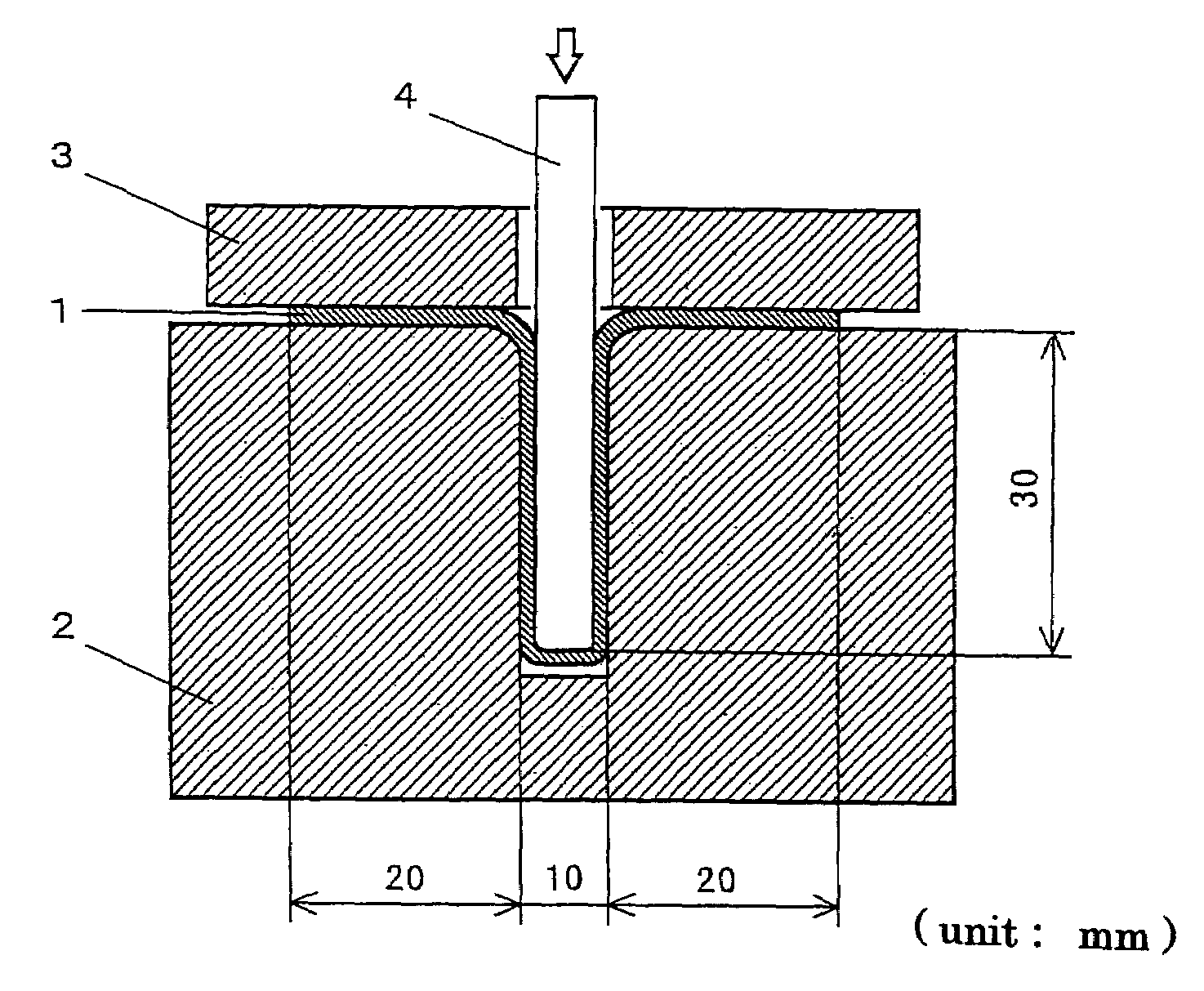
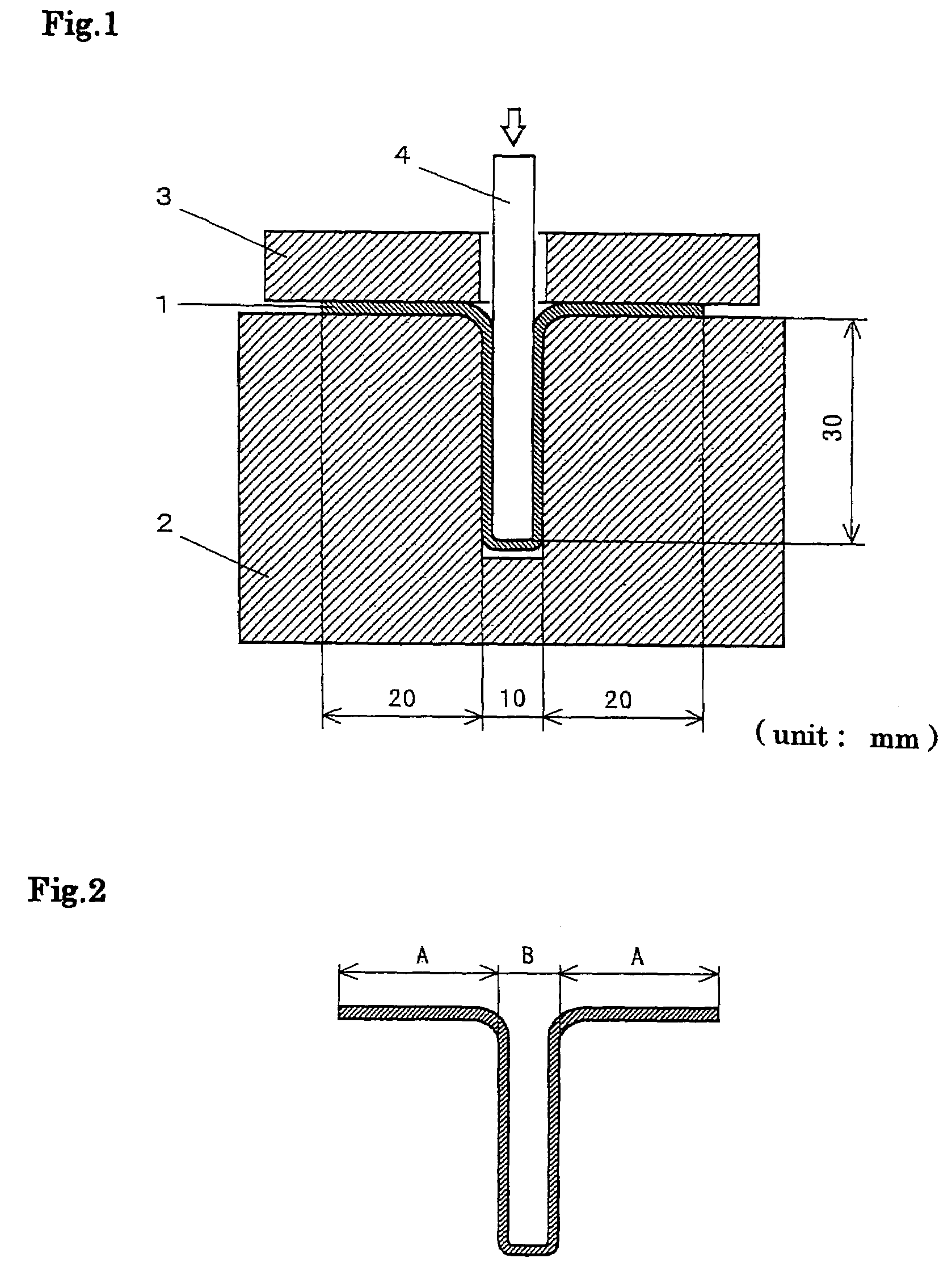
Method of stress inducing transformation of austenite stainless steel and method of producing composite magnetic members
InactiveUS6949148B2Increase generation ratioEasy to mass produceInorganic material magnetismStress inducedMetallurgy
A method of stress inducing transformation from the austenite phase to the martensite phase by conducting cold working on material of austenite stainless steel in the temperature range from the point Ms to the point Md. The above cold working is a biaxial tensing. An intermediately formed hollow body is made, which includes a ferromagnetic portion and a non-magnetic portion contracting inward. Then, the intermediately formed body is subjected to a stress removing process in which residual tensile stress is removed from an intermediately formed body. In the stress removing process, it is preferable that a punch is press-fitted into the intermediately formed body so as to expand a non-magnetic portion and then the intermediately formed body is drawn with ironing while the punch is inserted so that the residual tensile stress can be changed into the residual compressive stress in the non-magnetic portion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Austenitic stainless steel
An austenitic stainless steel with minimized deformation by heating and cooling treatment after cold working, which consists of, % by mass, C: 0.03% or less, Si: 2 to 4%, Mn: 0.1 to 2%, P: 0.03% or less, S: 0.03% or less, Ni: 9 to 15%, Cr: 15 to 20%, N: 0.02 to 0.2%, Nb: 0.03% or less, each of Mo and Cu or a total of Mo and Cu: 0.2 to 4%, and the balance Fe and impurities, and satisfies the following formulas (1) and (2). This steel can also have good weldability when the following formula (3) is also satisfied in addition to the formulas (1) and (2);16.9+6.9Ni+12.5Cu−1.3Cr+3.2Mn+9.3Mo−205C−38.5N−6.5Si−120Nb≧40 (1)450−440(C+N)−12.2Si−9.5Mn−13.5Cr−20(Cu+Ni)−18.5Mo≦−90 (2)8.2+30(C+N)+0.5Mn+Ni−1.1(1.5Si+Cr+Mo)+2.5Nb≦−0.8 (3)wherein each element symbol in the formulas (1), (2) and (3) represents the content, % by mass, of each element included in the steel.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel welding wire and welding structure
ActiveUS20060243719A1Improve corrosion resistanceIncreased durabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaAusteniteMaterials science
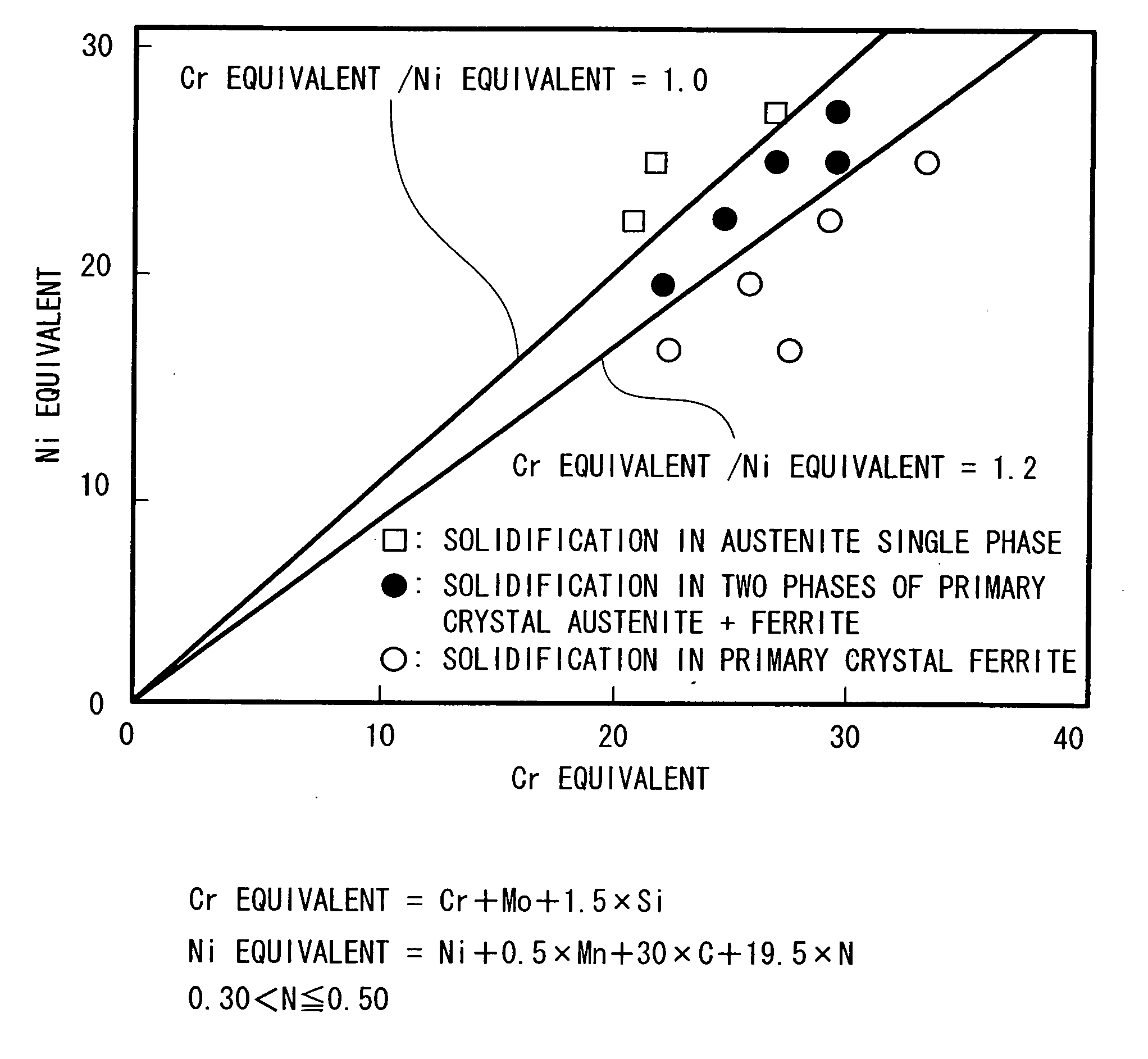
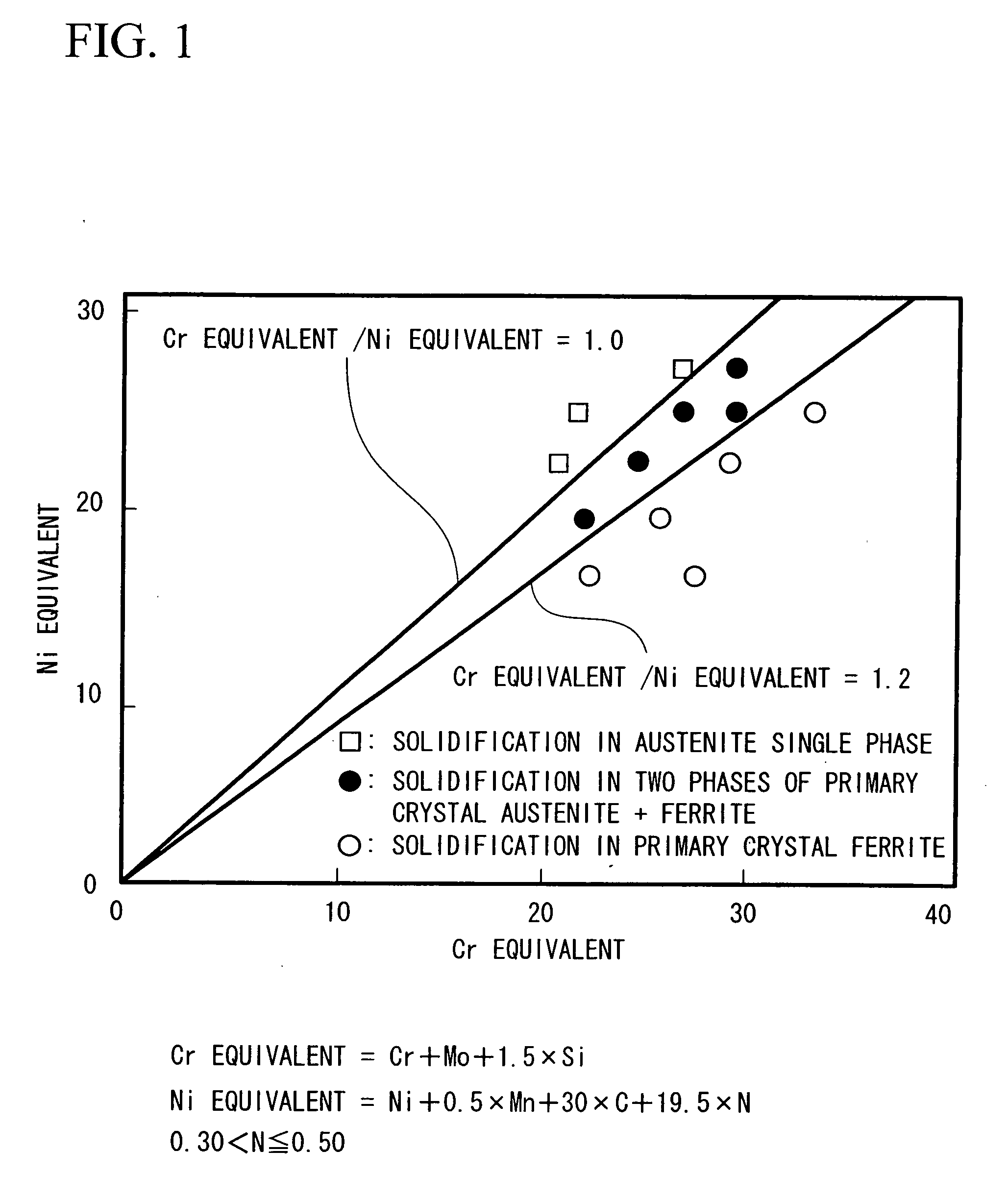
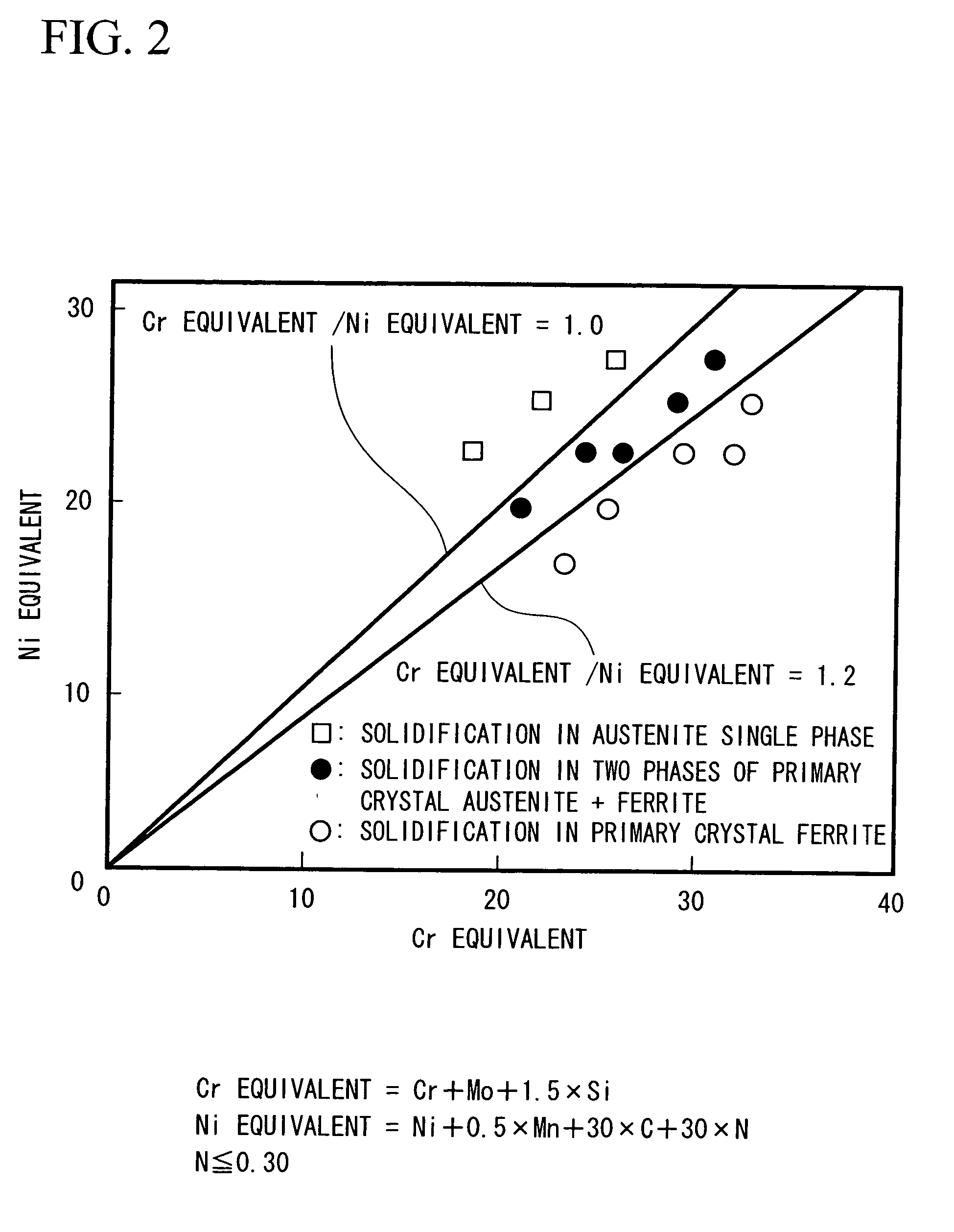
A welding wire for austenitic stainless steel welding contains, in percent by mass, C: 0.005 through 0.05%, Si: 0.1 through 1.0%, Mn: 1.0 through 3.5%, Cr: 25.0 through 28.0%, Ni: 16.0 through 23.9%, Mo: 1.6 through 3.0%, Cu: 0.1 through 0.5%, Al: 0.001 through 0.02%, and N: more than 0.30 through 0.50%, limiting 0 to 0.03% or less, P to 0.03% or less, and S to 0.005% or less, and having a ratio of a Cr equivalent to Ni equivalent (Cr equivalent / Ni equivalent) within a range between 0.85 and 1.2 and a PI value of 35 or more, the remainder being iron and unavoidable impurities.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL STAINLESS STEEL CORP
Girth welding technology for vacuum container
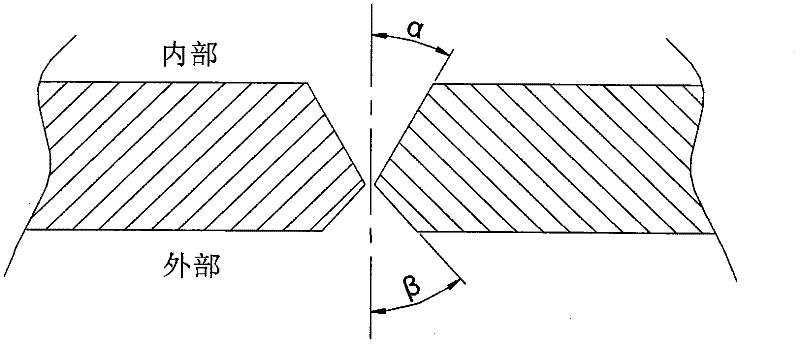
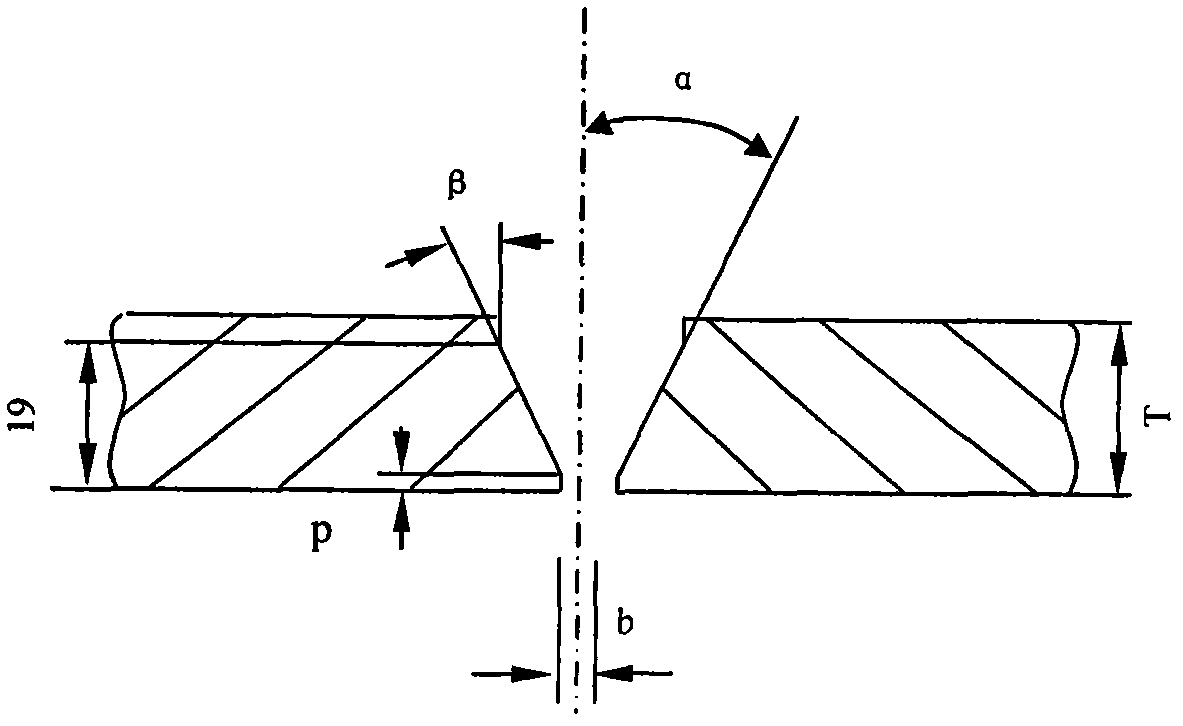
ActiveCN102357741AGuaranteed absolute penetrationAvoid the phenomenon of localized high temperatureArc welding apparatusWorkpiece edge portionsShielded metal arc weldingButt welding
The invention discloses a girth welding technology for a vacuum container, which comprises the following steps: processing beveled edges, assembling and welding. In the step of processing the beveled edges, a 14mm thick 0Cr18Ni9 austenitic stainless steel material is selected as a cylinder base material, X-shaped beveled edges are adopted, an inside beveled edge is processed for 10mm with a single-side angle of 32.5 degrees, an outside beveled edge is processed for 4mm with a single-side angle of 35 degrees, and no truncated edge is left. In the step of assembling, reserved clearances of 2.0-2.5mm are assembled, argon tungsten-arc welding is adopted to position, a positioning welding length is 10-15mm, an interval is 200mm, and then a 'strut having a shape of Chinese character 'mi' which is used for adjusting the roundness of a cylinder is welded in the cylinder. In the step of welding, an argon arc welding double-gun butt-welding method is used for bottoming the interior of the cylinder, two layers are filled in an inner welding bead of the cylinder in the manner of manual arc welding, an external welding bead is covered in the manner of submerged-arc welding, and finally, the inner welding bead is covered in the manner of manual arc welding. The girth welding technology can be used for controlling the welding deformation and has the advantages that the method is simple and is easy to realize.
Owner:无锡市创新低温环模设备科技有限公司
Alloy powder used for laser remanufacturing of martensitic stainless steel parts and preparation method
ActiveCN105039869ASolve and improve formabilitySolve and improve crack resistanceMetallic material coating processesSlagMartensitic stainless steel
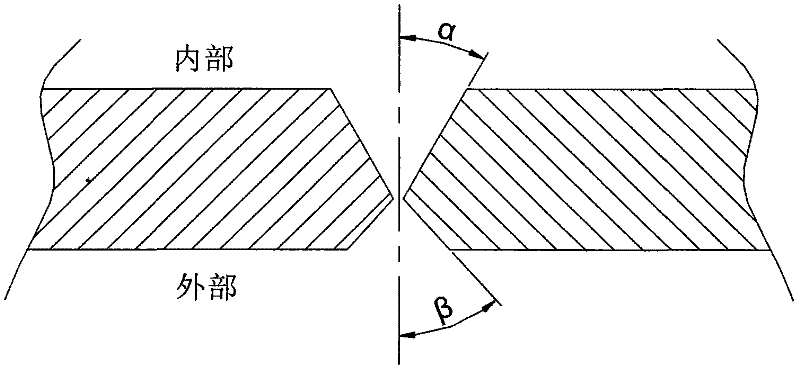
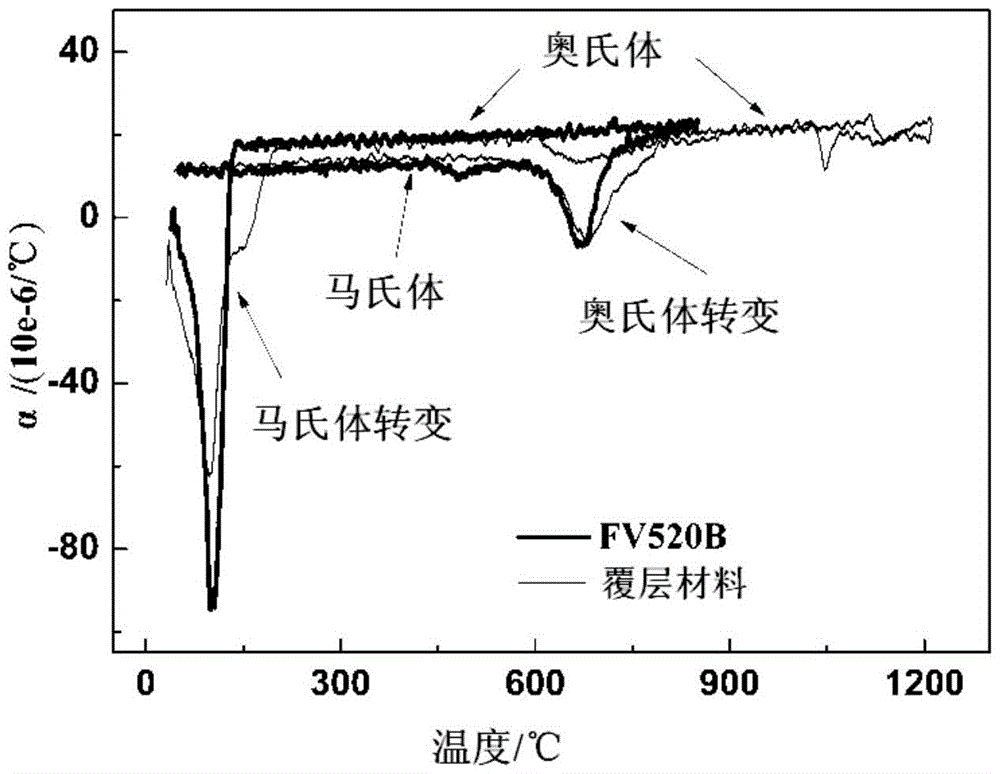
The invention provides alloy powder used for laser remanufacturing of FV520B martensitic stainless steel parts and a preparation method. The chemical components of the alloy powder include, by weight percentage, 0.01-0.3% of C, 12-17% of Cr, 3-7% of Ni, 0.4-2% of Mo, 0.1-2% of Mn, 0.15-0.55% of Nb, 0-3% of Cu, 0.05-2% of Si, 0-1.6% of B and the balance Fe. The preparation method of the alloy powder is a vacuum melting-high pressure gas atomization method. The alloy powder can have the density and the thermal expansion coefficient which are similar to those of FV520B materials when precipitation hardening elements, deoxygenation slag forming elements and elements used for lowering the martensite phase transformation point are added and the weight percent content of all the elements are regulated; the residual stress level is lowered through the martensite phase transformation accompanying effect; and therefore the problems of cracks, deformation and the like are greatly relieved, and the forming property, the anti-cracking property and the process stability are achieved and improved when the FV520B parts are subjected to laser remanufacturing through the alloy powder.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Austenitic stainless steels
InactiveCN1540026AHigh strengthImprove hot workabilityBook coversHeat exchange apparatusUltimate tensile strengthAustenite
An austenitic stainless steel excellent in high temperature strength, high temperature ductility and hot workability, consisting of, by mass %, C: more than 0.05% to 0.15%, Si: 2% or less, Mn: 0.1 to 3%, P: 0.04% or less, S: 0.01% or less, Cr: more than 20% to less than 28%, Ni: more than 15% to 55%, Cu: more than 2% to 6%, Nb: 0.1 to 0.8%, V: 0.02 to 1.5%, sol. Al: 0.001 to 0.1%, but sol.Al<=0.4xN, N: more than 0.05% to 0.3% and O (Oxygen): 0.006% or less, but O<=1 / (60xCu), and the balance Fe and impurities. The austenitic stainless steel may contain at least one of Co, Mo, W, Ti, B, Zr, Hf, Ta, Re, Ir, Pd, Pt and Ag, and / or at least one of Mg, Ca, Y, La, Ce, Nd and Sc.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenic stainless steel strip and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101481778AReduce dosageReduce the amount of ferriteTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsSolution treatmentStrip steel
The invention discloses an austenitic stainless steel belt and a manufacturing method thereof. The invention is characterized by comprising the following chemical elements in terms of weight percentage: 0.04 to 0.12 percent of C, 0.4 to 1. percent of Si, 0.8 to 2 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.04 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of S, 17 to 19 percent of Cr, 7 to 10 percent of Ni, 0.25 to 0.5 percent of Cu and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: smelting; continuous casting with thin belts; control of cooling and winding; acid pickling, direct cold rolling and annealing; acid pickling again and cold rolling to achieve the thickness of a finished product; annealing after achieving the thickness of the finished belt steel, acid pickling, leveling, and length cutting into a finished coil. By utilizing the element of Cu, the invention reduces the use amount of Ni in the steel, reduces the production cost, simultaneously reduces the content of the residual ferrite in the steel, improves the wearing resistance of the steel, adopts direct cold rolling to match the high-temperature annealing procedure, and saves the procedures of hot rolling and solution treatment so as to lead the production process to be simple and stable.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Production technology for inhibiting nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel hot-rolled plate edge crack
InactiveCN101947549AImprove plasticityEliminate edge cracksTemperature control deviceHeat treatment process controlSS - Stainless steelHeating temperature
The invention relates to production technology for inhibiting nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel hot-rolled plate edge crack, which comprises the following steps of: smelting and continuous casting, grinding plate blanks, heating blanks, rolling and the like. By controlling N content in steel below 0.13 percent, controlling Creq / Nieq within 1.35, controlling alpha-phase content in a casting blank texture within 4 percent, setting the reasonable heating temperature of plate blanks by combining on-site reality, and adopting the plate blank one-pass descaling box and frame final-pass descaling descaling technology, in particular the rolling technology of tightly combining hot-rolled rolling pass deformation and blank temperature, the production technology has the advantages of avoiding the edge crack of the produced stainless steel hot-rolled plates, obviously improving the yield, solving the problem of edge crack quality for steel coils in the rolling process through a steckel mill, guaranteeing the edge quality of the hot-rolled steel coils and improving the width yield of finished rolled plates.
Owner:SHANDONG TAISHAN STEEL GROUP
Process for welding duplex stainless steel
ActiveCN101972878AOvercome adverse defectsGood welding effectArc welding apparatusShielding gasPetrochemical
The invention relates to a process for welding duplex stainless steel, in particular to the process for welding the duplex stainless steel used for high-sulfur content refining equipment, highly-corrosive petrochemical equipment and pipelines, high-parameter power devices, and the chloridion-corroded environments of seawater and the like. In the process, a specific protective gas favorable for the welding of the duplex stainless steel is adopted, and simultaneously limited linear energy and inter-layer temperature are regulated in the welding process, so that the unfavorable defects of the conventional welding process can be overcome, and a metallographic structure with the ferrite content of 30 to 70 percent and a ferritic phase in percentage equivalent to that of an austenitic phase is obtained. A welding joint obtained by the welding process has high mechanical properties, high strength and hardness, particularly high yield strength which is about twice that of austenitic stainless steel, high thermal fatigue resistance, pitting corrosion resistance, crevice corrosion resistance, intercrystalline corrosion resistance and high weldability.
Owner:CHINA NAT CHEM ENG NO 7 CONSTR
Flux-cored wire for austenitic stainless steel welding
ActiveCN102451961AReduce carbon contentImprove oxidation capacityArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsManganeseRutile
The invention discloses a flux-cored wire for austenitic stainless steel welding. The flux-cored wire consists of a flux core and an external steel belt; the external steel belt is an austenitic stainless steel belt of which the carbon content is less than 0.025 percent; the carbon content of the flux core is not greater than 0.04 percent and carbon accounts for 18.0 to 24.0 percent based on the total weight of the flux-cored wire; the flux core comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 18.5 to 25.0 percent of metal chromium powder, 8.0 to 10.0 percent of metal nickel powder, 2.0 to 5.0 percent of electrolytic manganese metal, 1.0 to 3.0 percent of aluminum magnesium alloy, 28.0 to 35.0 percent of rutile, 3.0 to 5.0 percent of quartz, 2.0 to 5.0 percent of zircon sand, 2.0 to 5.0 percent of feldspar, 1.0 to 2.0 percent of cryolite, 2.0 to 5.0 percent of arc stabilizer and the balance of iron powder; and the arc stabilizer consists of K2O, Na2O and TiO2 in a weight ratio of (6.0-8.0):(8.0-10.0):(68.0-70.0), and the water content is not greater than 400 ppm.
Owner:CHINA JINGYE ENG TECH CO LTD +1
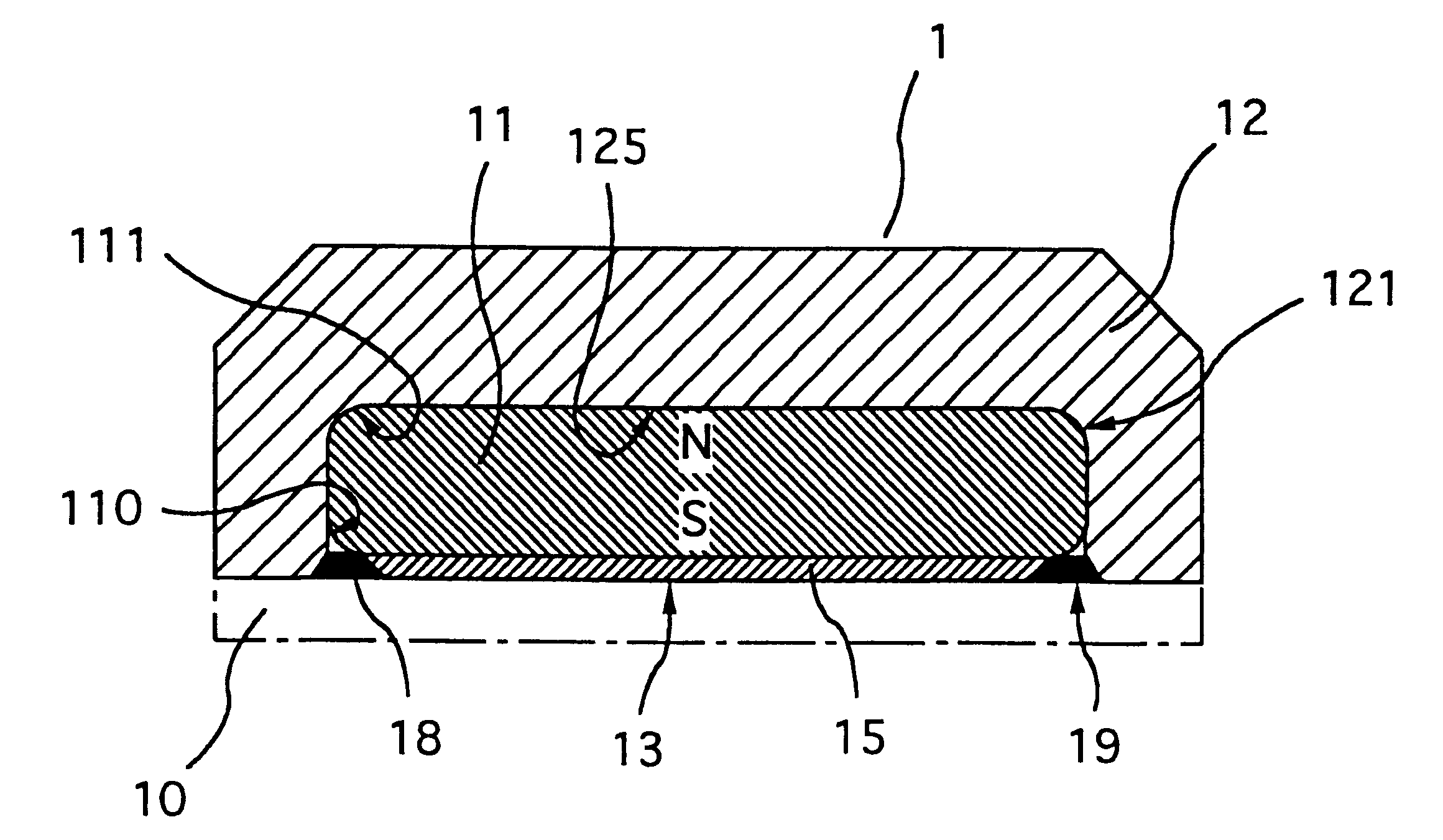
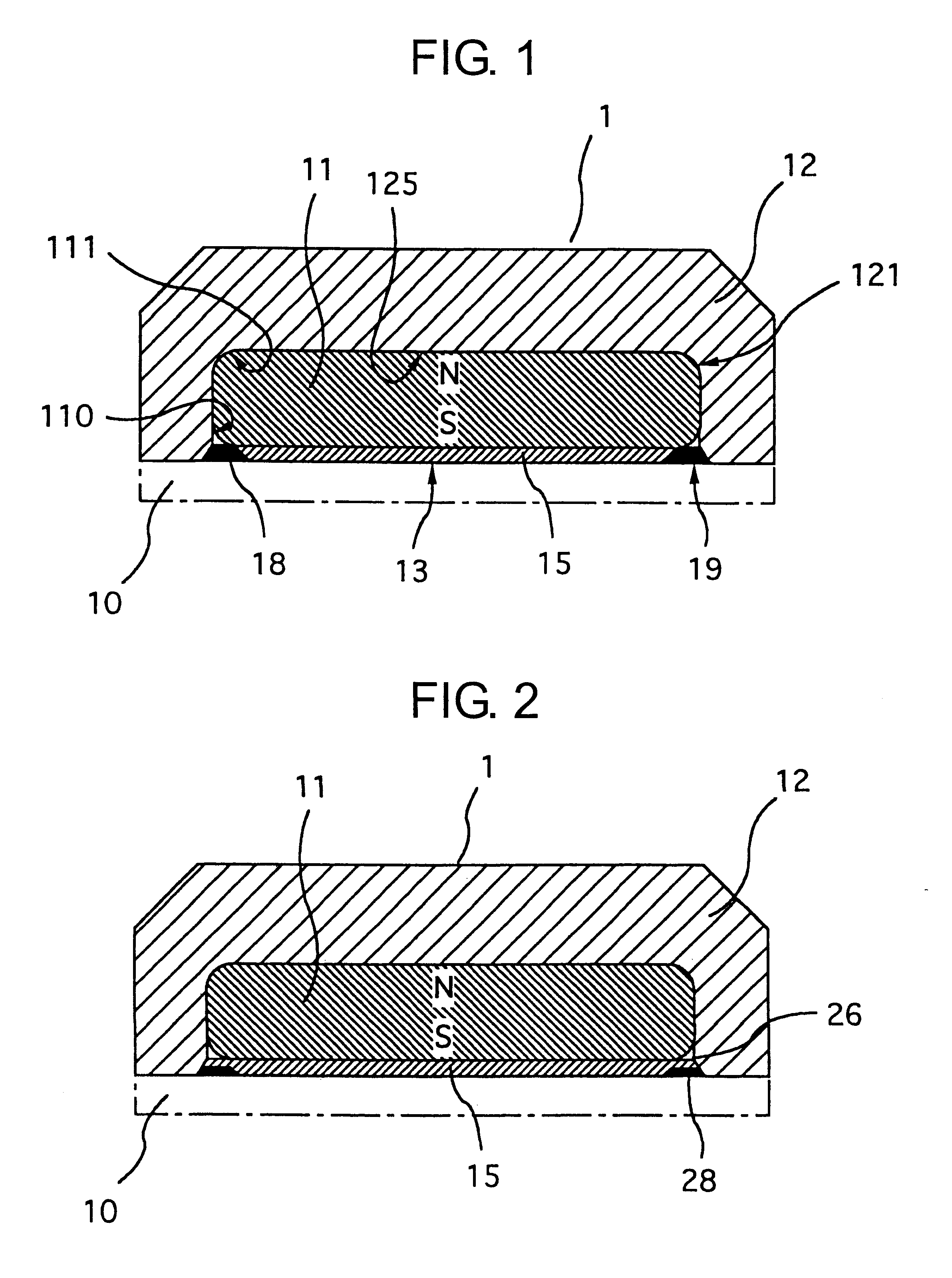
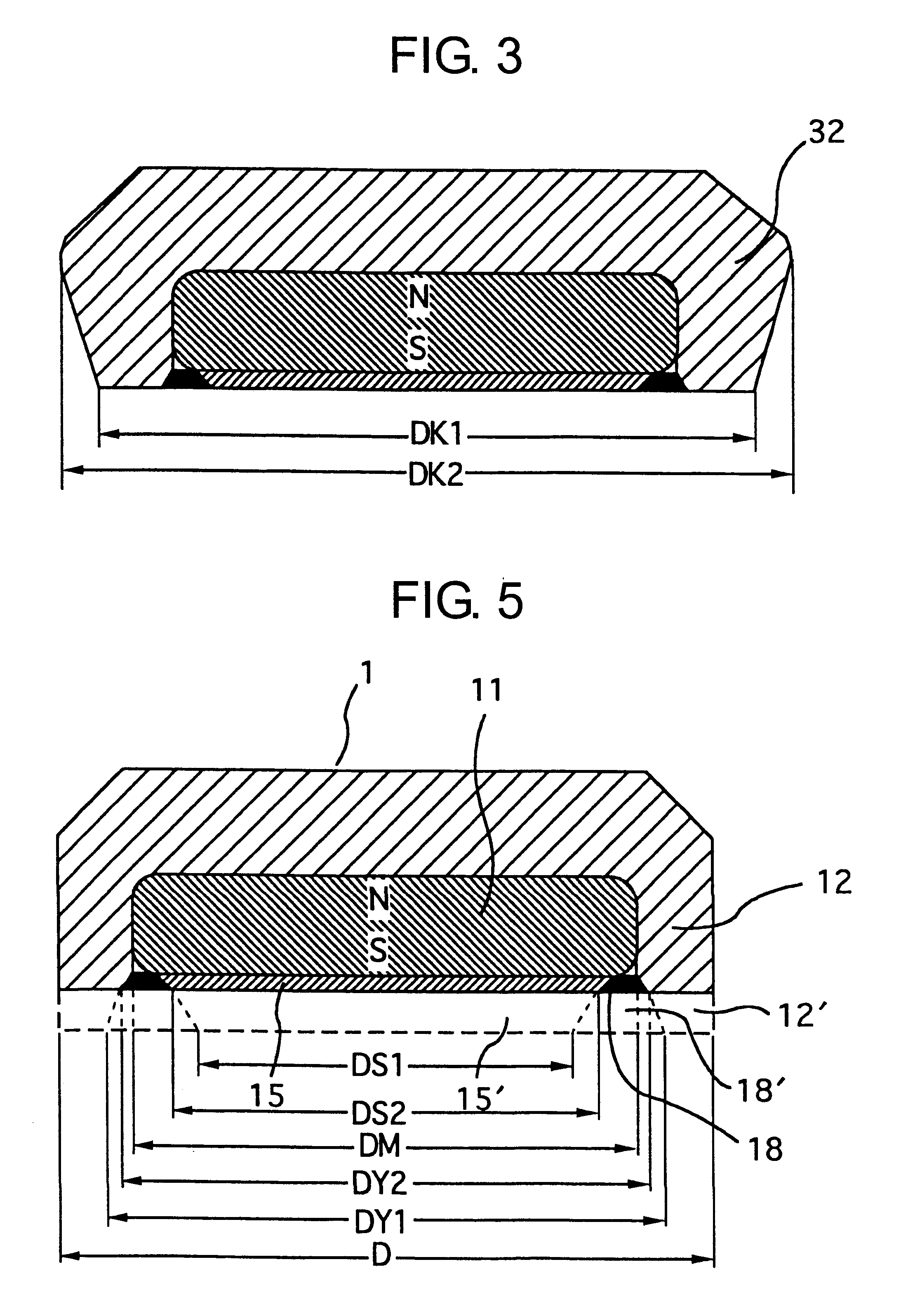
Dental magnetic attachment
A dental magnetic attachment which has a superior magnetic attractive force with a small nonmagnetic welded part and a flat welded surface to be polished. The dental magnetic attachment including a magnet, a yoke with a pit to hold the magnet, a sealing disk placed on the opening of the pit to cover the magnet and a nonmagnetic welded part between the yoke and the disk. The yoke and the disk are made from soft magnetic material. The nonmagnetic welded part, which joins the yoke and the disk, is formed by welding the yoke, the sealing disk, the sealing ring made from nonmagnetic austenitic stainless steel and a Ni coat between the sealing disk and the sealing ring together. Here, it is preferably that there remains a part of the nonmagnetic sealing ring. The welded surface of the dental magnetic attachment is polished to be flat.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Ultrapurification high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel and its preparation method
A superpure high-nitrogen stainless austenite steel contains Cr (17-19 wt.%), Mn (12-16 wt.%), Mo (2-3 wt.%), Cu (0.5-1.5 wt.%), Ni (0-0.2 wt.%), N (0.4-0.6 wt.%), C (0-0.05 wt.%), Si (0-0.5 wt.%), S (0-0.009 wt.%), P (0-0.009 wt.%) and Fe (rest). It is smelted by vacuum induction furnace, where nitrogen is added in FeCrN, CrN or MnN mode.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cold-rolled double-surface stainless steel composite plate having excellent comprehensive performances and manufacturing method
ActiveCN105296854AUniform tissueNo surface yield pattern defectsMetal rolling arrangementsRoom temperatureComposite plate
The invention discloses a cold-rolled double-surface stainless steel composite plate having excellent comprehensive performances and a manufacturing method. The composite plate comprises a basal plate and a compound plate, wherein the upper and lower surfaces of the basal plate are wholly and continuously coated with the compound plate; the basal plate and the compound plate are formed to the cold-rolled double-surface stainless steel composite plate through an atomic diffusion metallurgical bonding method, wherein the basal plate is ultralow carbon aluminum killed steel; and the compound plate is 304 type austenitic stainless steel. The prepared cold-rolled double-surface stainless steel composite plate is excellent in surface quality and uniform in base material structure of carbon steel, has the room-temperature elongation above 45%, is excellent in corrosion resistance and stable in material performance, has the use performance of pure stainless steel, can largely reduce the cost, can serve as a substitute good of 304 stainless steel, and is widely applied to decoration panels and fields with higher forming requirements.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL +1
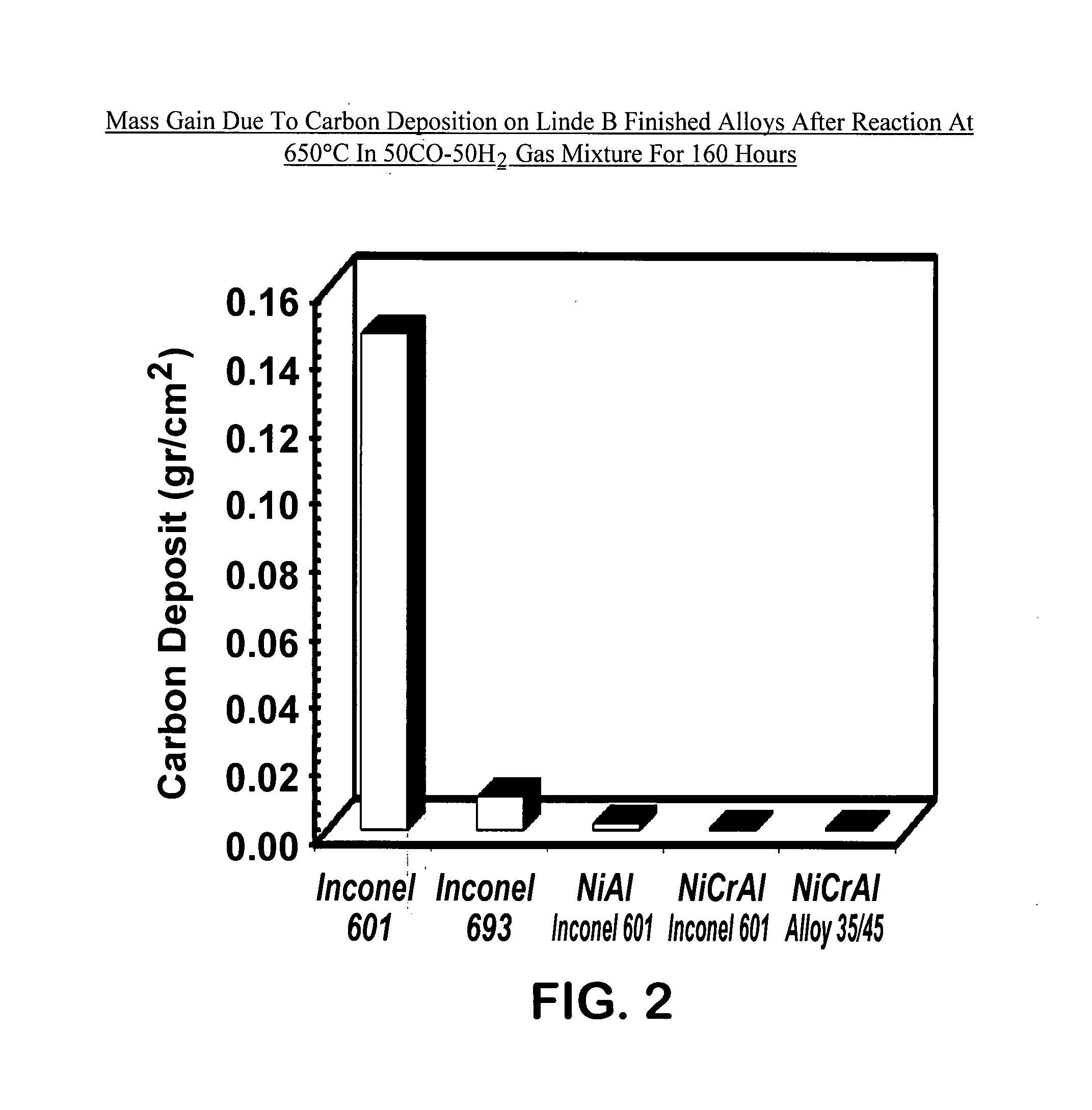
High performance coated material with improved metal dusting corrosion resistance
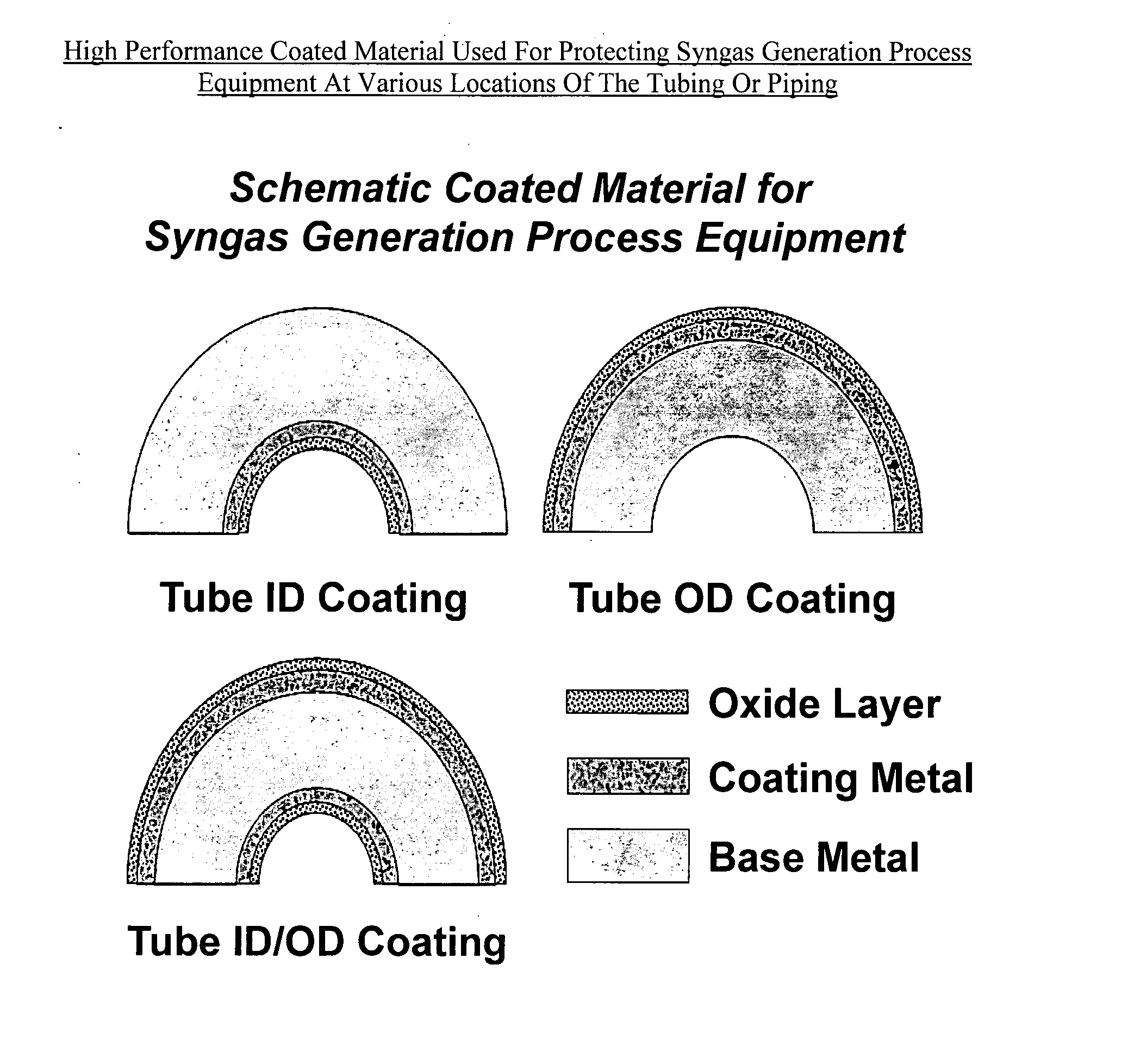
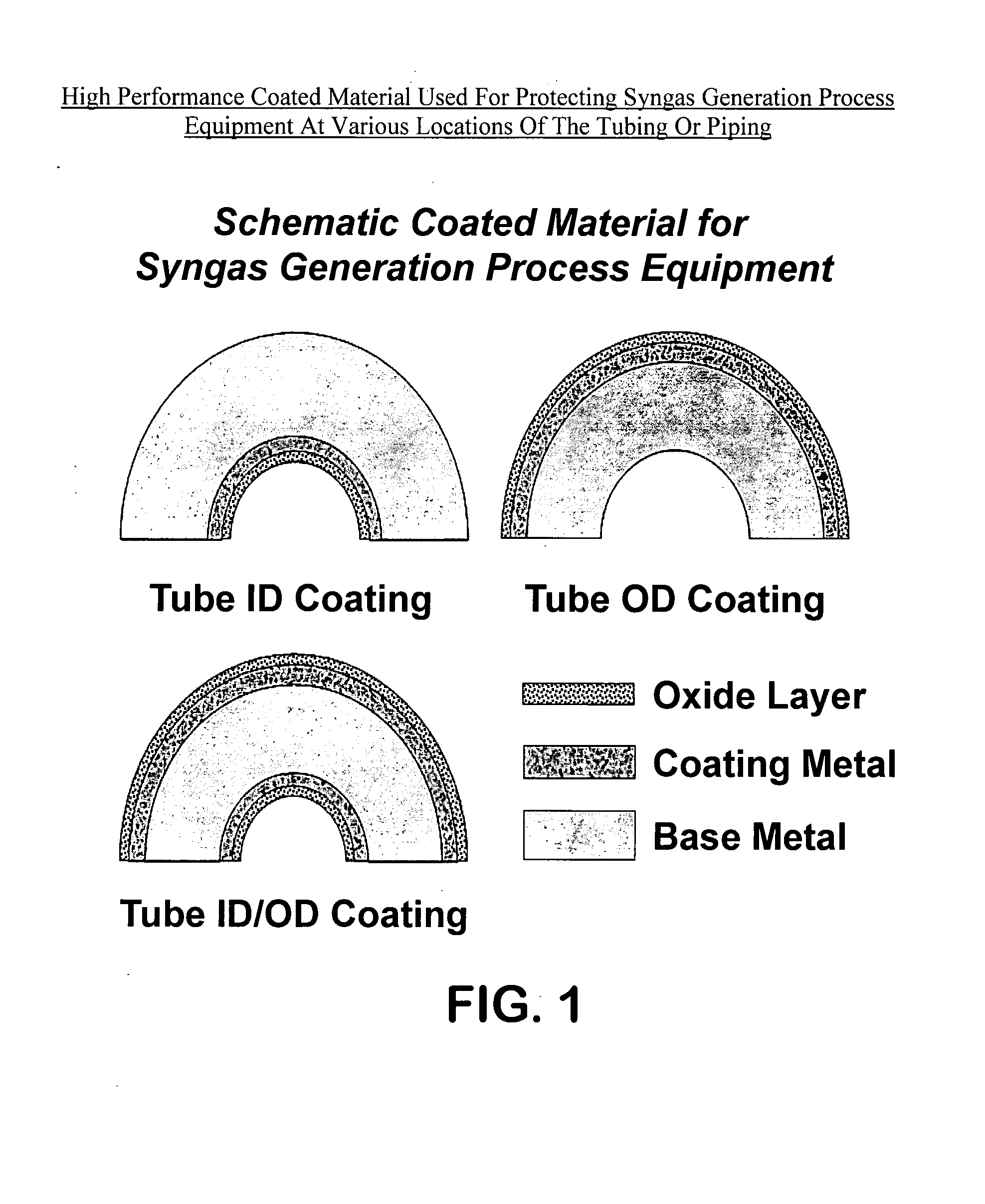
InactiveUS20080020216A1Improve the immunityReduce carbon depositionAnodisationLiquid surface applicatorsMulliteInconel
High performance coated metal compositions resistant to metal dusting corrosion and methods of providing such compositions are provided by the present invention. The coated metal compositions are represented by the structure (PQR), wherein P is an oxide layer at the surface of (PQR), Q is a coating metal layer interposed between P and R, and R is a base metal. P includes alumina, chromia, silica, mullite or mixtures thereof. Q includes Ni and Al, and at least one element selected from the group consisting of Cr, Si, Mn, Fe, Co, B, C, N, P, Ga, Ge, As, In, Sn, Sb, Pb, Sc, La, Y, Ce, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, Ru, Rh, Ir, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au and mixtures thereof. R is selected from the group consisting of carbon steels, low chromium steels, ferritic stainless steels, austenetic stainless steels, duplex stainless steels, Inconel alloys, Incoloy alloys, Fe—Ni based alloys, Ni-based alloys and Co-based alloys. Advantages exhibited by the disclosed coated metal compositions include improved metal dusting corrosion resistance at high temperatures in carbon-supersaturated environments having relatively low oxygen partial pressures. The coated metal compositions are suitable for use in syngas generation process equipment.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
High carbon high silicon martensite stainless steel billet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101967610AGuaranteed performanceSmall temperature fluctuationsProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceStress concentrationElectric arc furnace
The invention provides a high carbon high silicon martensite stainless steel billet. The steel billet is characterized by comprising the following components by weight percent: 0.41-0.47% of C, 2.80-3.20% of Si, 0.50-0.80% of Mn, 8.50-9.20% of Cr, 0.30% or less of Ni, 0.028% or less of P, 0.005% or less of S, 0.20% or less of W, 0.20% or less of Mo, 0.15% or less of V, 0.015% or less of Nb, 0.015% or less of Ti, 0.010% or less of Al and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The invention also provides a preparation method of the high carbon high silicon martensite stainless steel billet. The method comprises the following steps: performing primary smelting with an electric arc furnace (EAF), performing argon-oxygen decarburization (AOD) smelting, refining with a low frequency (LF) furnace, performing continuous casting, annealing and rolling. The method of the invention has simple operation, can stably control the quality of the continuous casting billet, completely suppresse cracks, overcome the defect of concentration of stress and increase the casting yield and quality stability of the martensite stainless steel.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com