Patents
Literature
1074 results about "Austenite grain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
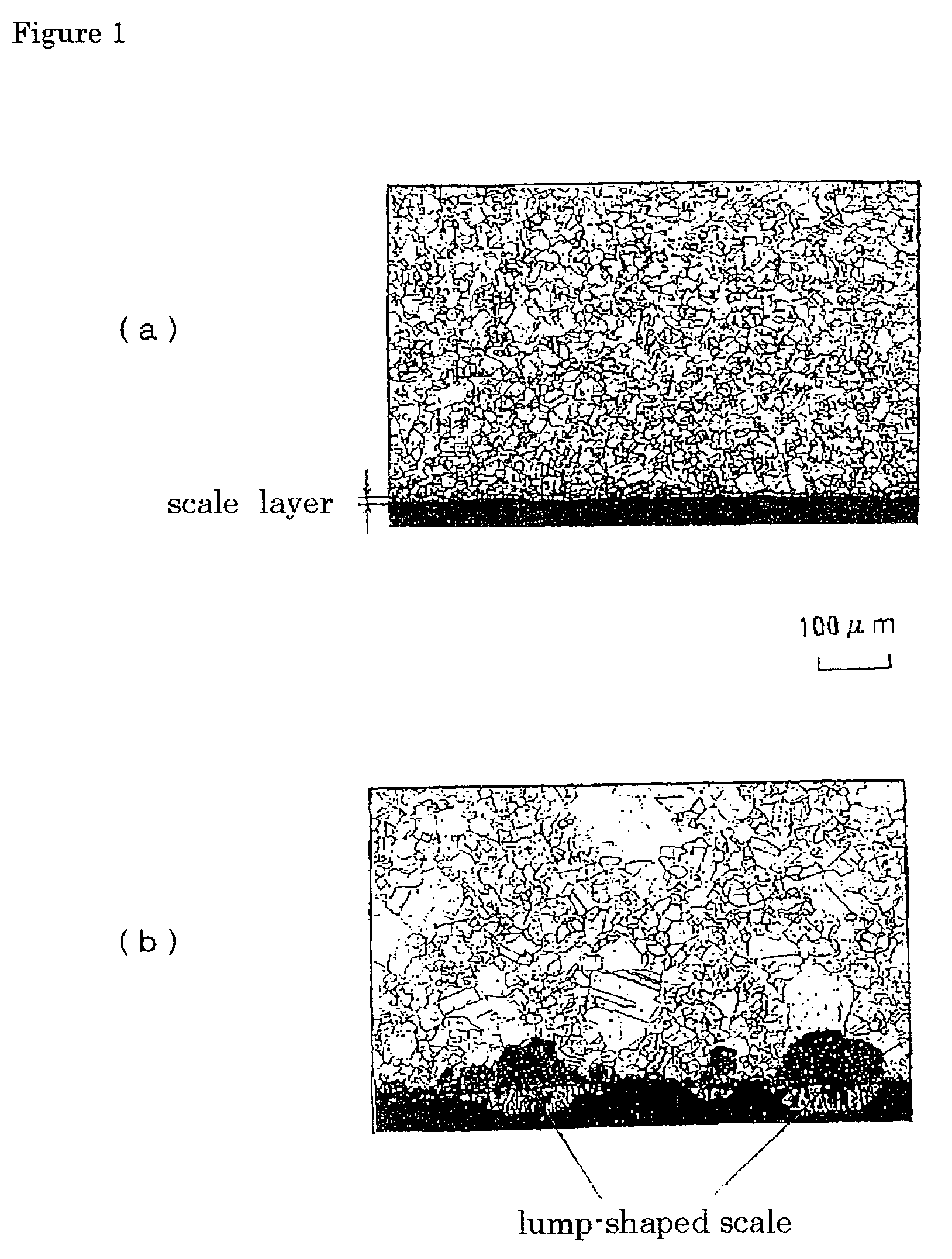
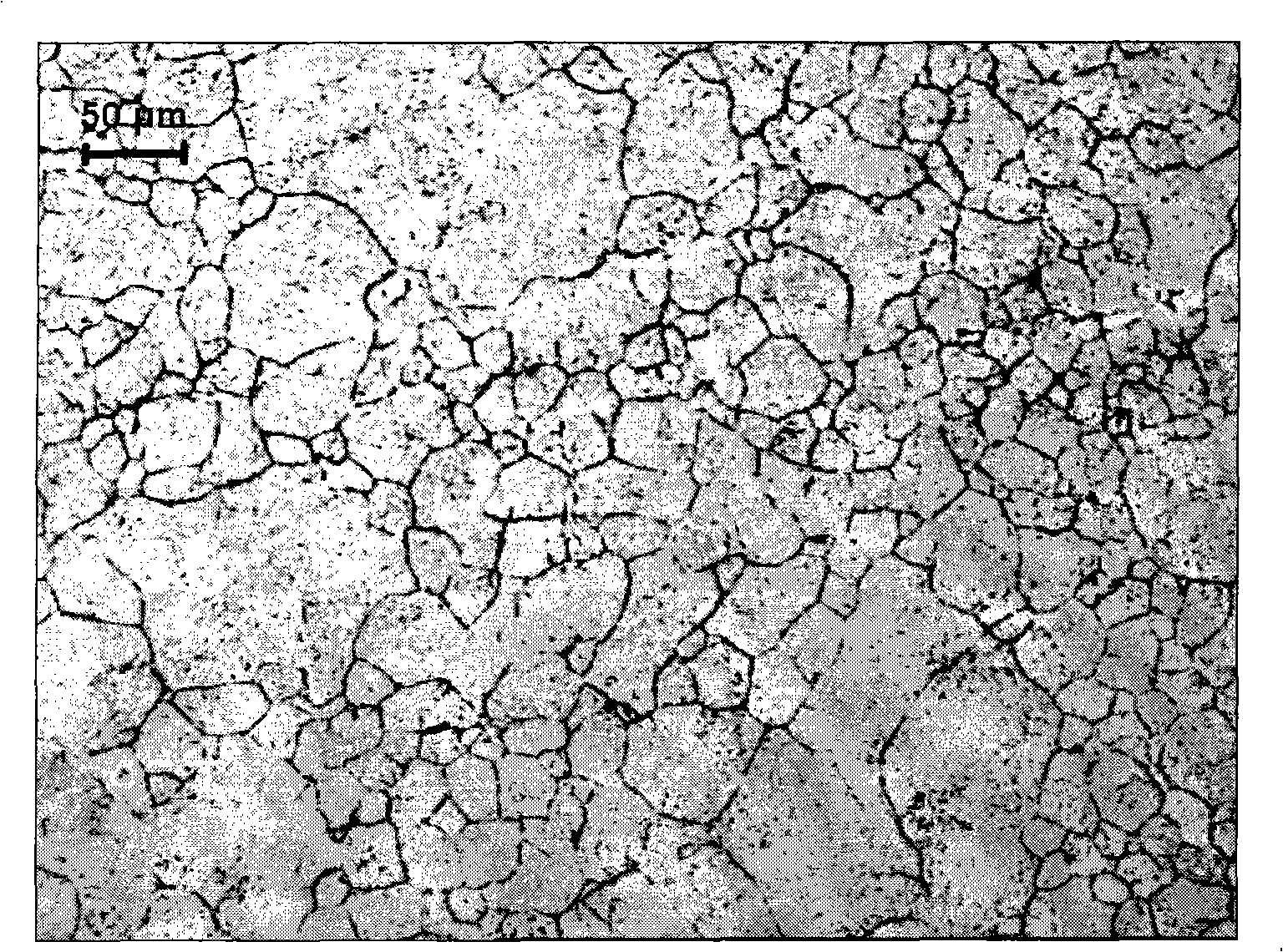
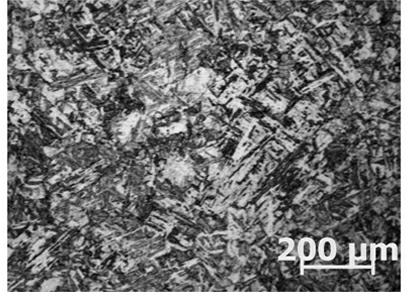
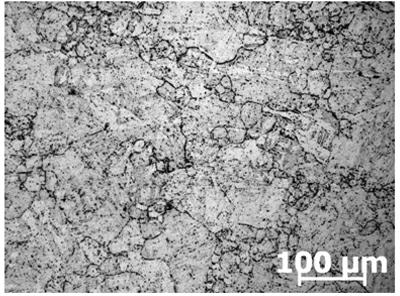
Austenite grain growth does not only play an important role in determining the mechanical properties of steel, but certain surface defects encountered in the continuous casting industry have also been attributed to the formation of large austenite grains.
High toughness steel material and method of producing steel pipes using same
InactiveUS6958099B2Improve toughnessReduce hardenabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesProduction rateAustenite grain
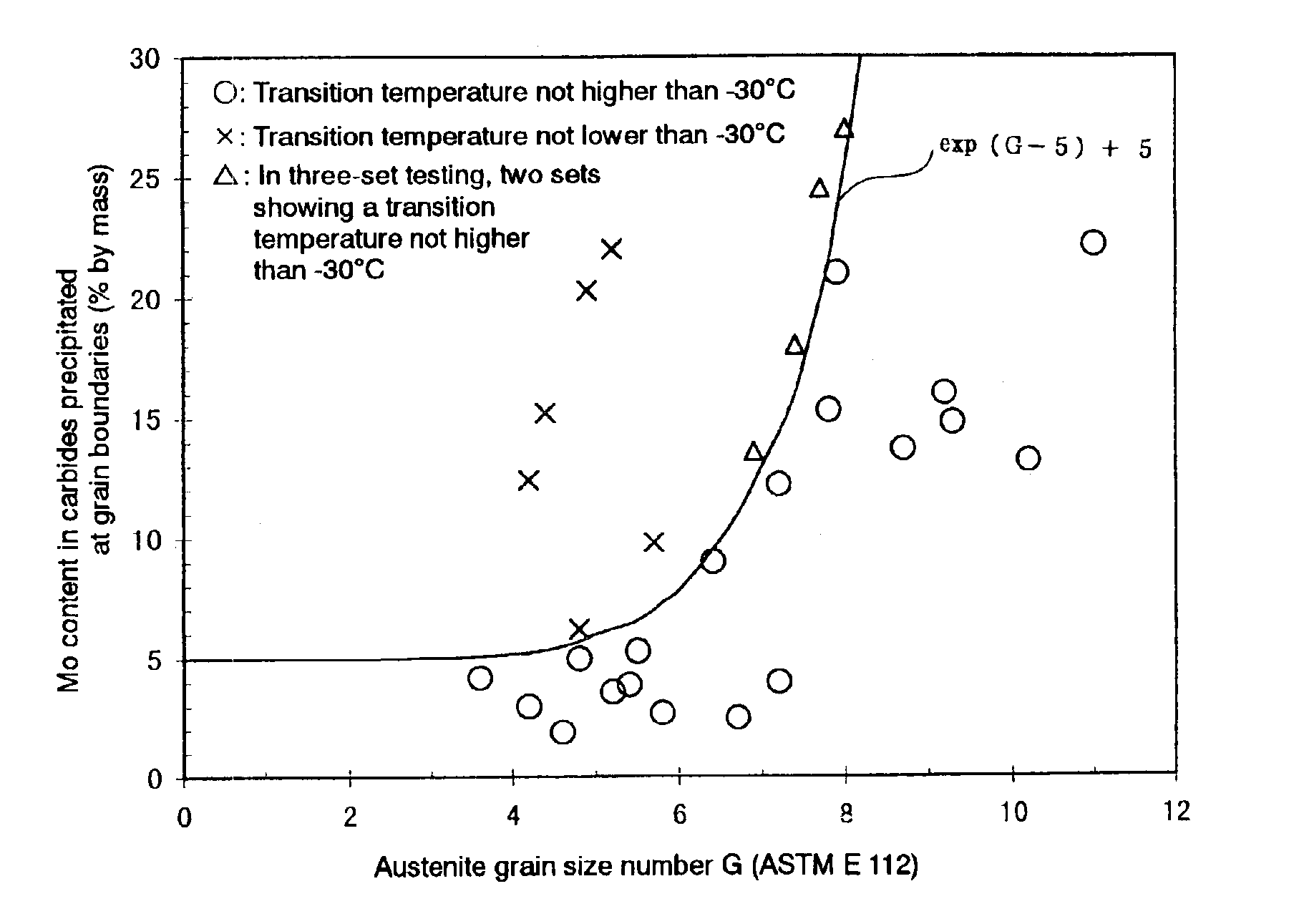
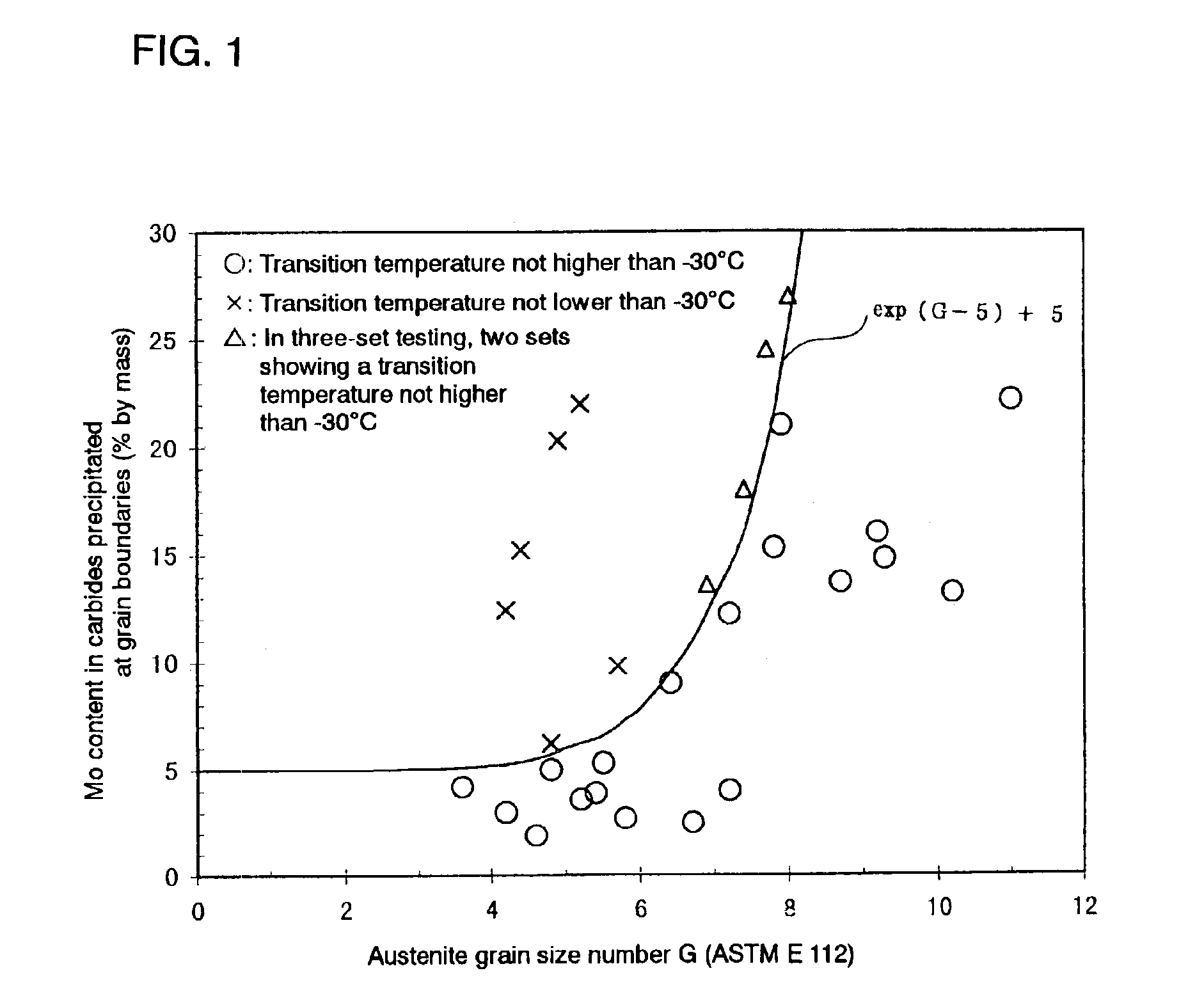
A steel material and a steel pipe made by using the same are provided which are to be used in severe oil well environments. Such a highly tough oil well steel pipe can be produced by rolling the base material, quenching the rolling product from the austenite region and tempering the same so that the relationship between the content of Mo [Mo] in the carbides precipitated at austenite grain boundaries and the austenite grain size (according to ASTM E 112) can be defined by the formula (a) given below. In this manner, steel pipes suited for use even under oil well environments becoming more and more severe can be produced while satisfying the requirements that the cost should be rationalized, the productivity improved and energy saved.[Mo]≦exp(G−5)+5 (a)
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
700MPa high strength hot rolling Q&P steel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103215516AHigh strengthPrevent precipitationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainChemical composition
The invention relates to 700MPa high strength hot rolling Q&P steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel has the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.15-0.40% of C, 1.0-2.0% of Si, 1.5-3.0% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, less than or equal to 0.005% of S, 0.3-1.0% of Al, less than or equal to 0.0065% of N, 0.005-0.015% of Ti and the balance of Fe. The yield strength is greater than or equal to 70MPa, the strength of extension is greater than or equal to 1300MPa, and the ductility is greater than 10%. According to the invention, through a reasonable compound design, based on common C-Mn steel components, austenite crystal is refined by micro Ti treatment by improving the content of Si to inhibit separation of cementite, so that the austenite transformation kinetics in the air cooling process is accelerated by improving the content of Al. Meanwhile, a hot continuous rolling process is matched with a sectional cooling process, so that proeutectoid ferrite+martensite+retained austenite tissues are obtained. The cost of the alloy is greatly lowered.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel tube excellent in steam oxidation resistance and a manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7014720B2Excellent in steam oxidation resistanceHigh-temperature bendingFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainOxygen
The present invention provides an austenitic stainless steel tube with a uniform fine grained structure of regular grains, which is not changed to a coarse structure and the steam oxidation resistance is maintained even if the tube is subjected to a high temperature reheating during welding and high temperature bending working. The austenitic stainless steel tube consists of, by mass %, C: 0.03–0.12%, Si: 0.1–0.9%, Mn: 0.1–2%, Cr: 15–22%, Ni: 8–15%, Ti: 0.002–0.05%, Nb: 0.3–1.5%, sol. Al: 0.0005–0.03%, N: 0.005–0.2% and O (oxygen): 0.001–0.008%, and the balance Fe and impurities, the austenitic stainless steel tube having austenitic grain size number of 7 or more and a mixed grain ratio of preferably 10% or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Easy-to-weld superfine austenite crystal steel with superhigh intensity and high tenacity and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101481780ARoll mill control devicesProcess efficiency improvementAustenite grainChemical composition
The invention discloses an ultra-thin austenitic grained steel with ultrahigh strength, high toughness and easy welding and a manufacturing method thereof. The chemical compositions of the steel are as follows in terms of weigh percentage: 0.04 to 0.14 of C, 0.50 to 1.75 of Mn, 0.10 to 0.50 of Si, no more than 0.010 of S, no more than 0.012 of P, no more than 0.50 of Ni, no more than 1.00 of Cr, no more than 0,80 of Mo, no more than 0.10 of V, 0.10 to 0.30 of Cu, 0.010 to 0.050 of Al, 0.010 to 0.050 of Ti, no more than 0.050 of Nb, 0.0005 to 0.0020 of B, no more than 0.0090 of (O+N), no more than 0.15 of Pb+Sn+As+Sb+Bi and the balance of Fe and impurities. The equivalent carbon content CEQ (%) is no more than 0.60 and the crack sensitivity index PCM (%) is no more than 0.30. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: low-temperature short-time tempering pretreatment, short-time heat preservation after extremely fast and integral heating to more than Ac3, then holding the temperature, and extremely fast quenching to the room temperature. The austenitic grain of the steel has the average size of less than or equal to 6.5Mum, the yield strength of more than or equal to 840MPa, the tensile strength of more than or equal to 945MPa and tough-brittle transition temperature of less than or equal to minus 60 DEG C. The method is particularly suitable for heat treatment of working pieces with thin specification.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method for displaying high-strength vessel slab original austenite crystal grain
ActiveCN101368889ADeep corrosionImprove solubilitySurface/boundary effectPreparing sample for investigationMaterials scienceDodecylbenzenesulfonic acid
The invention relates to a display method used for preparing high-intensity ship plate metallographic samples and the original austenite grains, belonging to the technical field of metallographic sample preparation. The invention has the following technological steps: coarse grinding, fine grinding, polishing and corrosion; the polished specimen is put in the etching solution at 70-80 DEG C; the formula of the etching solution comprises 100ml of distilled water, 5-7g of picric acid, 0.5-1.5ml of hydrochloric acid, 3-5g of SDBS, 5-15g of Seagull paste shampoo and 0.3-1ml of hydrogen peroxide; after being etched for 1-2 minutes, the surface of the specimen is dimmed, and the specimen is taken out, cleaned with alcohol and then dried; and the relatively clear original austenite structure can be observed under a microscope. The invention has the advantages of solving the problem of different display of the high-intensity ship plate austenite grains and clearly displaying the austenite structure; besides, the invention is easy and simple to implement.
Owner:NANTONG WANBAO IND
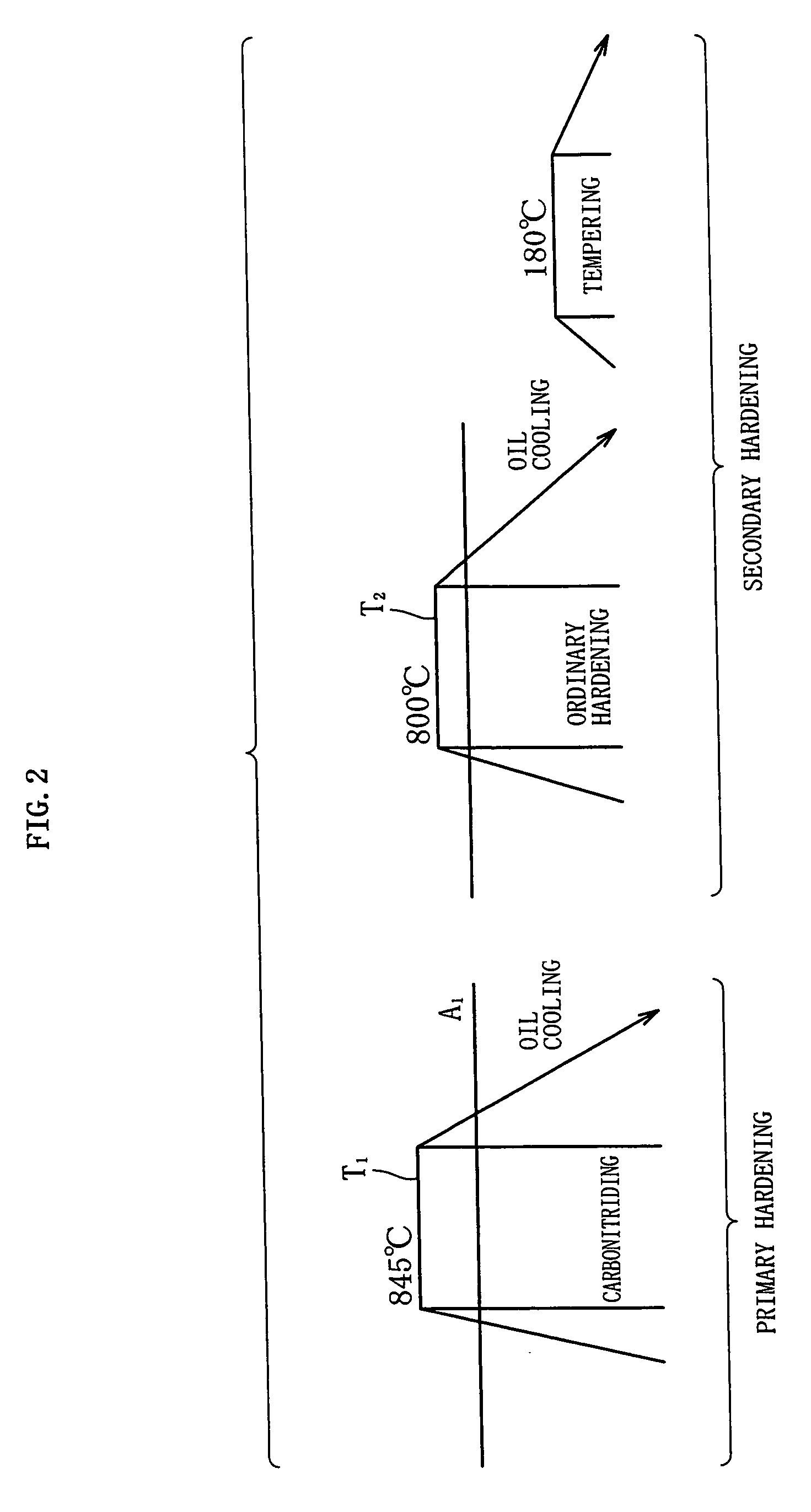
Controlled-forging controlled-cooling processing technology of bearing ring prepared by GCr15
The invention relates to a controlled-forging controlled-cooling processing technology of a bearing ring prepared by GCr15, comprising the following steps of: quenching the bearing ring in cooling fluid at final forging temperature of 850-950 DEG C and at fluid outlet temperature of 350-550 DEG C; when heating the bearing ring to the temperature of 450-550 DEG C, after preserving the temperature for 1h-3h, discharging the bearing ring from a boiler and cooling the bearing ring to room temperature; when heating the bearing ring to the temperature of 650-690 DEG C again, preserving the temperature for 1h; when continuously heating the bearing ring to the temperature of 740-780 DEG C, after preserving the temperature for 2-3h, cooling the bearing ring to the temperature of 680-690 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 2-4 hours; finally, when cooling the bearing ring to the temperature of 550-600 DEG C at the speed of 10 DEG C / h, cooling o the bearing ring to the room temperature along with the boiler by air; quenching a machined semi-finished bearing ring; when heating to the temperature of 810-830 DEG C, after preserving the temperature for 45-60min, discharging the machined semi-finished bearing ring from the boiler and quenching the machined semi-finished bearing ring in oil; and when heating the machined semi-finished bearing ring to the temperature of 160-200 DEG C after being quenched, preserving the temperature of the machined semi-finished bearing ring for 4h, discharging the machined semi-finished bearing ring from the boiler and cooling the machined semi-finished bearing ring to the room temperature by air. According to the invention, carbides, martensite crystals and austenite crystals of the bearing ring are refined, network carbides are improved or eliminated and impact ductility and fatigue life are improved.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING RES INST CO LTD
High strength thin steel sheet having high hydrogen embrittlement resisting property
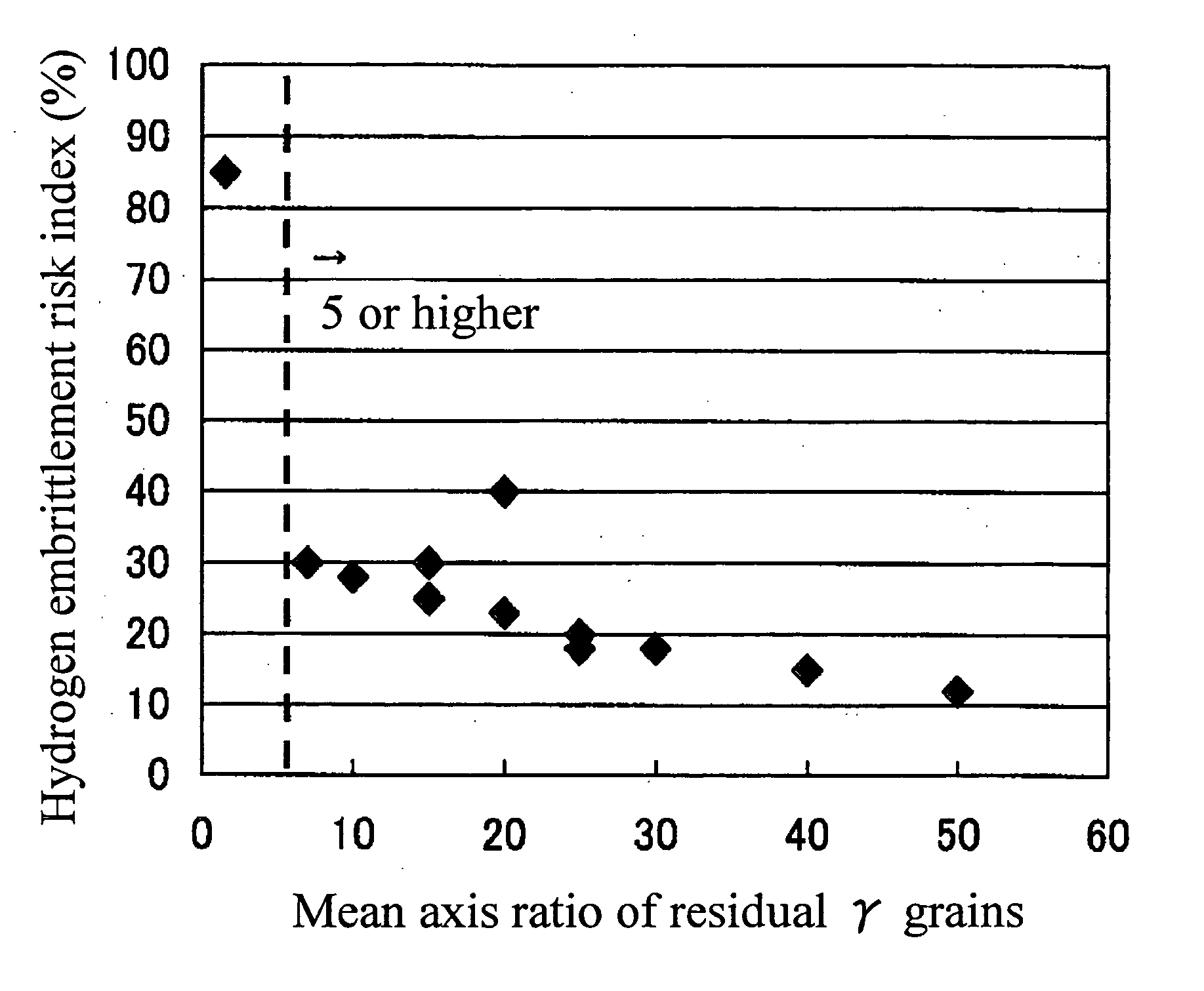
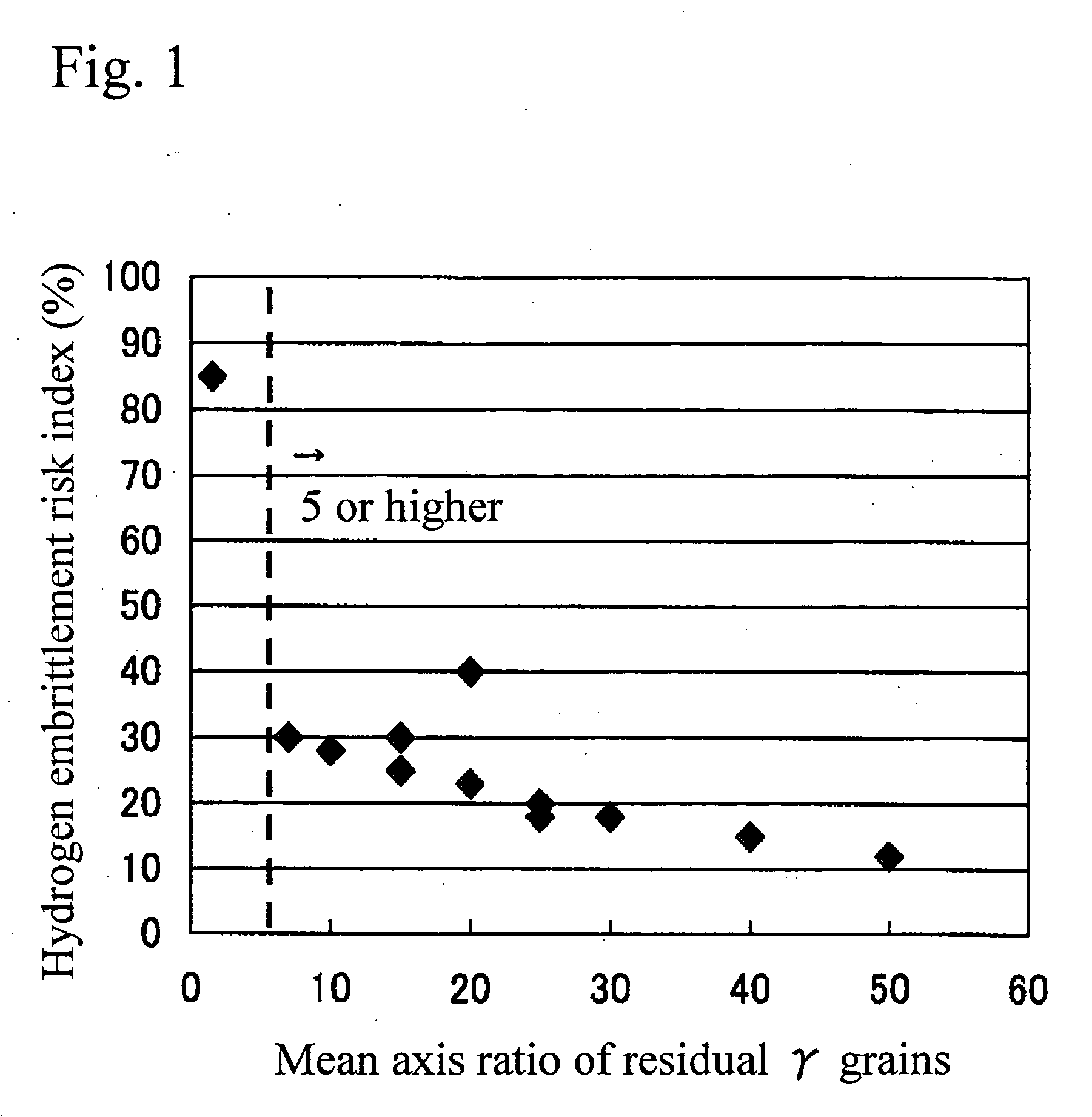
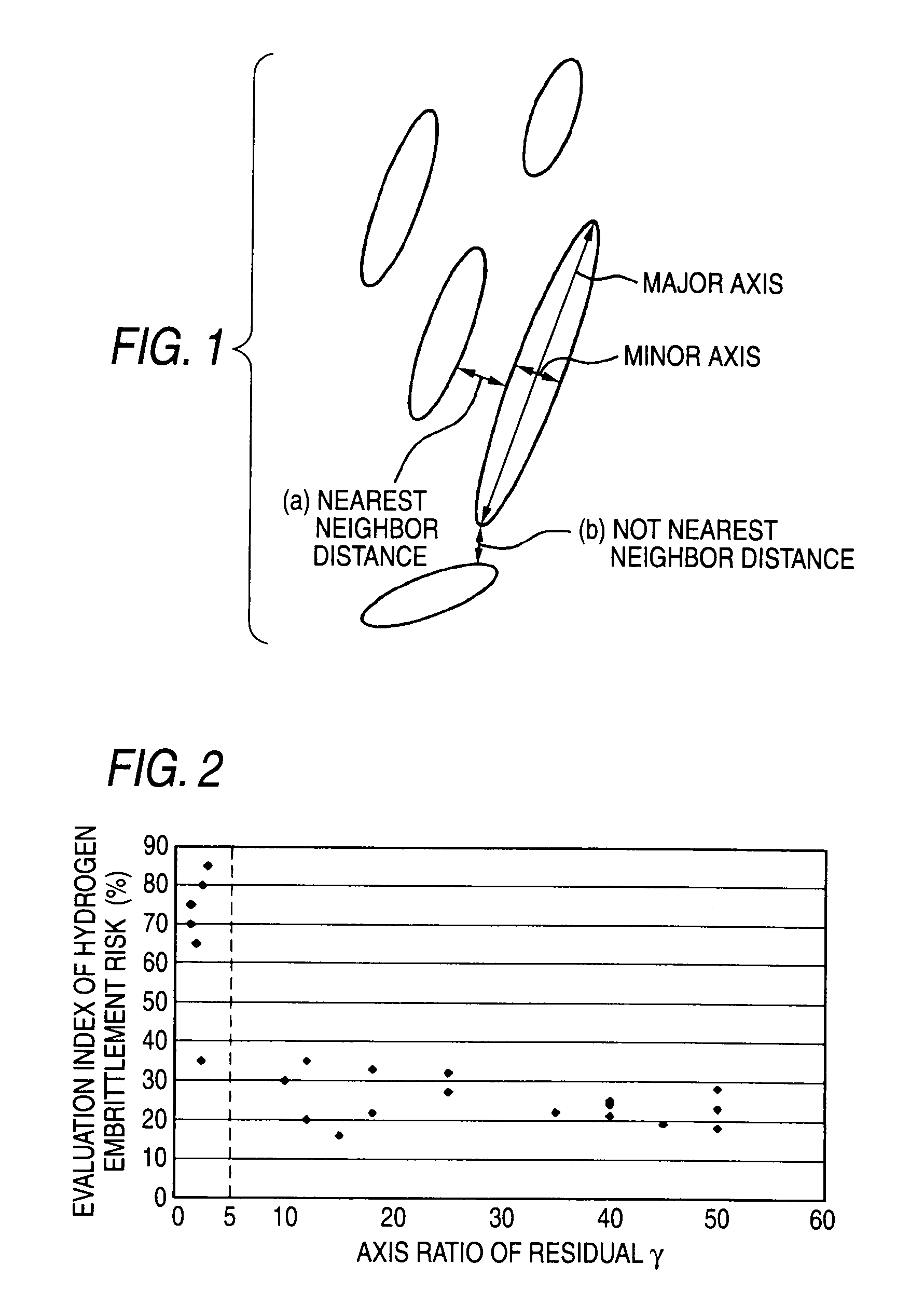
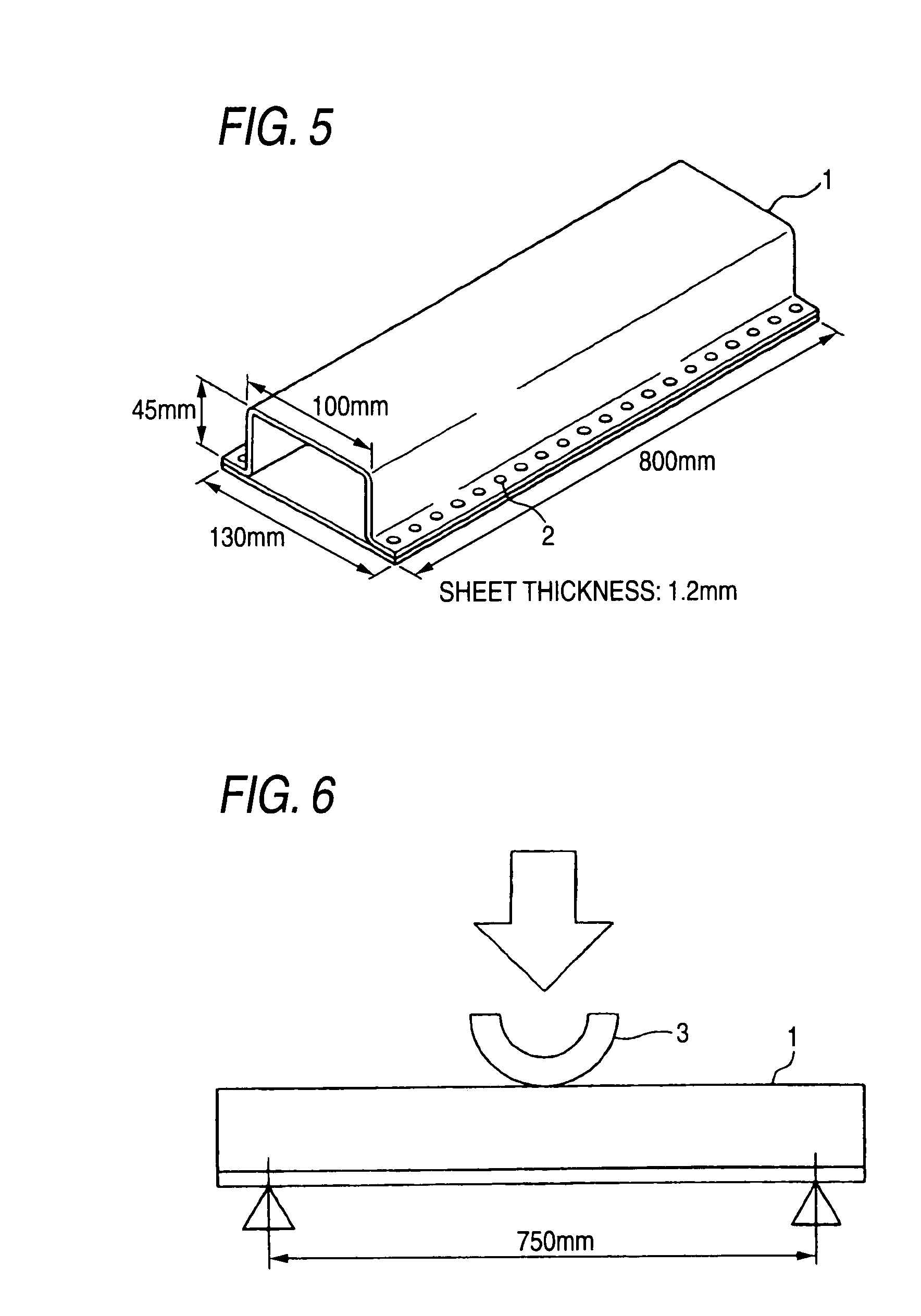
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a high strength thin steel sheet that has high hydrogen embrittlement resisting property. In order to achieve the above purpose, a high strength thin steel sheet having high hydrogen embrittlement resisting property comprises: C: 0.10 to 0.25%; Si: 1.0 to 3.0%; Mn: 1.0 to 3.5%; P: 0.15% or less; S: 0.02% or less; and Al: 1.5% or less (higher than 0%) in terms of percentage by weight, with balance of iron and inevitable impurities; and the metal structure comprises: residual austenite; 1% by area or more in proportion to the entire structure; bainitic ferrite and martensite: 80% or more in total; and ferrite and pearlite: 9% or less (may be 0%) in total, while the mean axis ratio (major axis / minor axis) of said residual austenite grains is 5 or higher, and the steel has tensile strength of 1180 MPa or higher.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low-yield-ratio high-strength hot-rolled Q&P steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to low-yield-ratio high-strength hot-rolled Q&P steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises the chemical components of 0.20-0.40% of C, 1.0-2.0% of Si, 1.5-3.0% of Mn, no more than 0.015% of P, no more than 0.005% of S, 0.02-0.08% of Al, no more than 0.006% of N, 0.005-0.015% of Ti, and balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. According to the invention, through low-cost component design, on a basis of common C-Mn steel, Si content is increased such that cementite precipitation is inhibited, and austenite grains are micronized through micro-Ti treatment. Also, with a combination of hot continuous rolling process and sectioned cooling process, a structure comprising proeutectoid ferrite, martensite, and residual austenite is obtained. The yield strength is lower than 700MPa, a tensile strength is higher than 1000MPa, a yield ratio is 0.50-0.60, and alloy cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Cold-rolled hot-galvanized dual-phase steel plate with flanging property and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a cold-rolled hot-galvanized dual-phase steel plate with a flanging property and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel plate comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: 0.06% to 0.095% of C, 0.3% to 0.6% of Si, 1.4% to 1.8% of Mn, greater than 0% and less than or equal to 0.02% of P, greater than 0% and less than or equal to 0.01% of S, 0.02% to 0.05% of Al, 0.35% to 0.55% of Cr, 0.02% to 0.04% of Nb, greater than 0% and less than or equal to 0.005% of N and the balance of Fe. According to the steel plate provided by the invention, the austenite is dispersedly distributed in a ferrite matrix via the refining of austenite grains by adding the Nb element and controlling temperatures during hot rolling and finish rolling and a rolling temperature; the amount of the austenite after annealing is increased by limiting the content of C and carrying out high-temperature annealing in a continuous hot-galvanized annealing furnace, so that tissues in low-C martensite are obtained after quenching. Thus, the hardness of the martensite is decreased. As a result, a hardness difference between the martensite phase and the ferrite phase is reduced.
Owner:ANSC TKS GALVANIZING
Ultrahigh-strength steel sheet
ActiveUS20090238713A1Improve hydrogen embrittlement resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainUltimate tensile strength
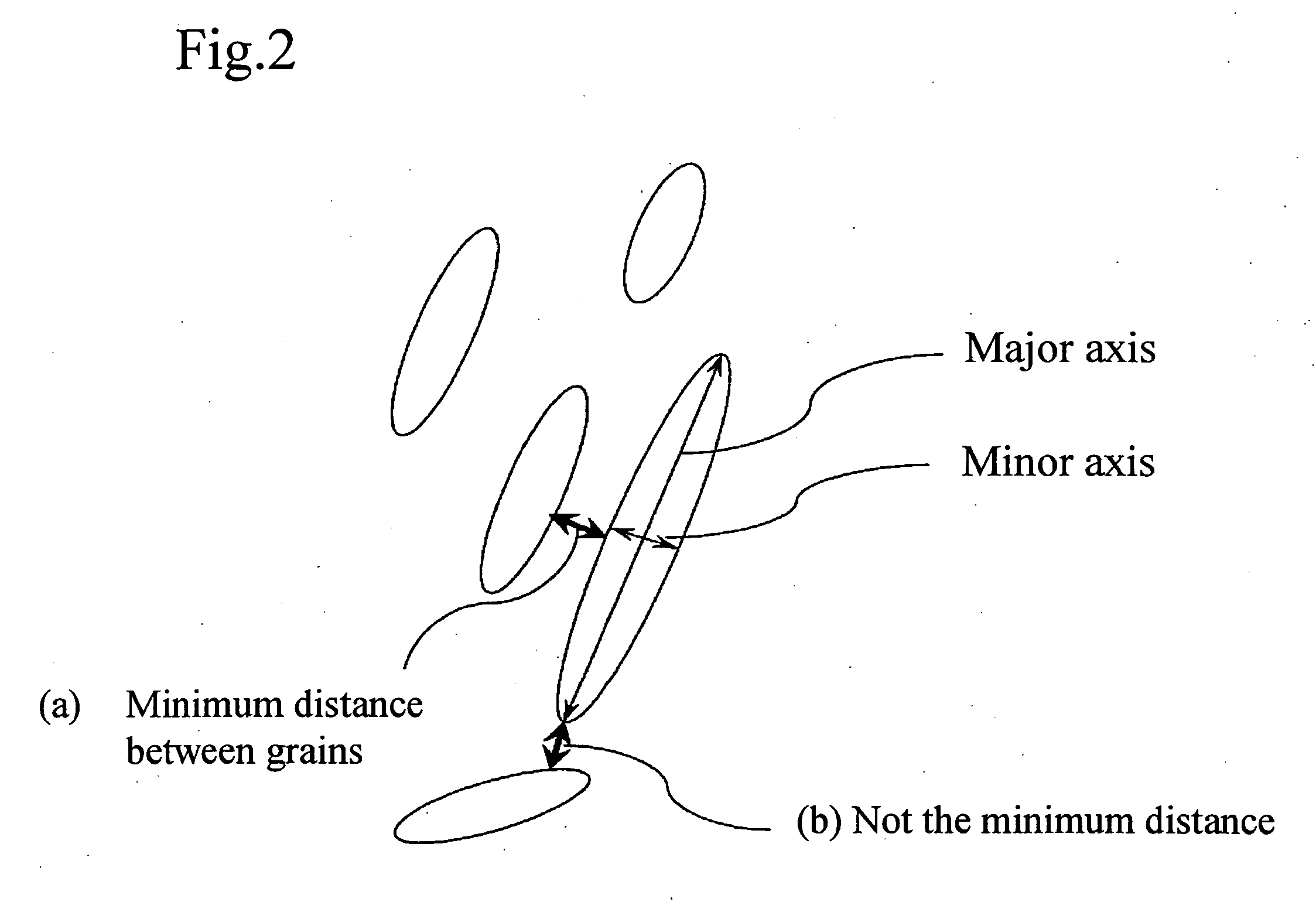
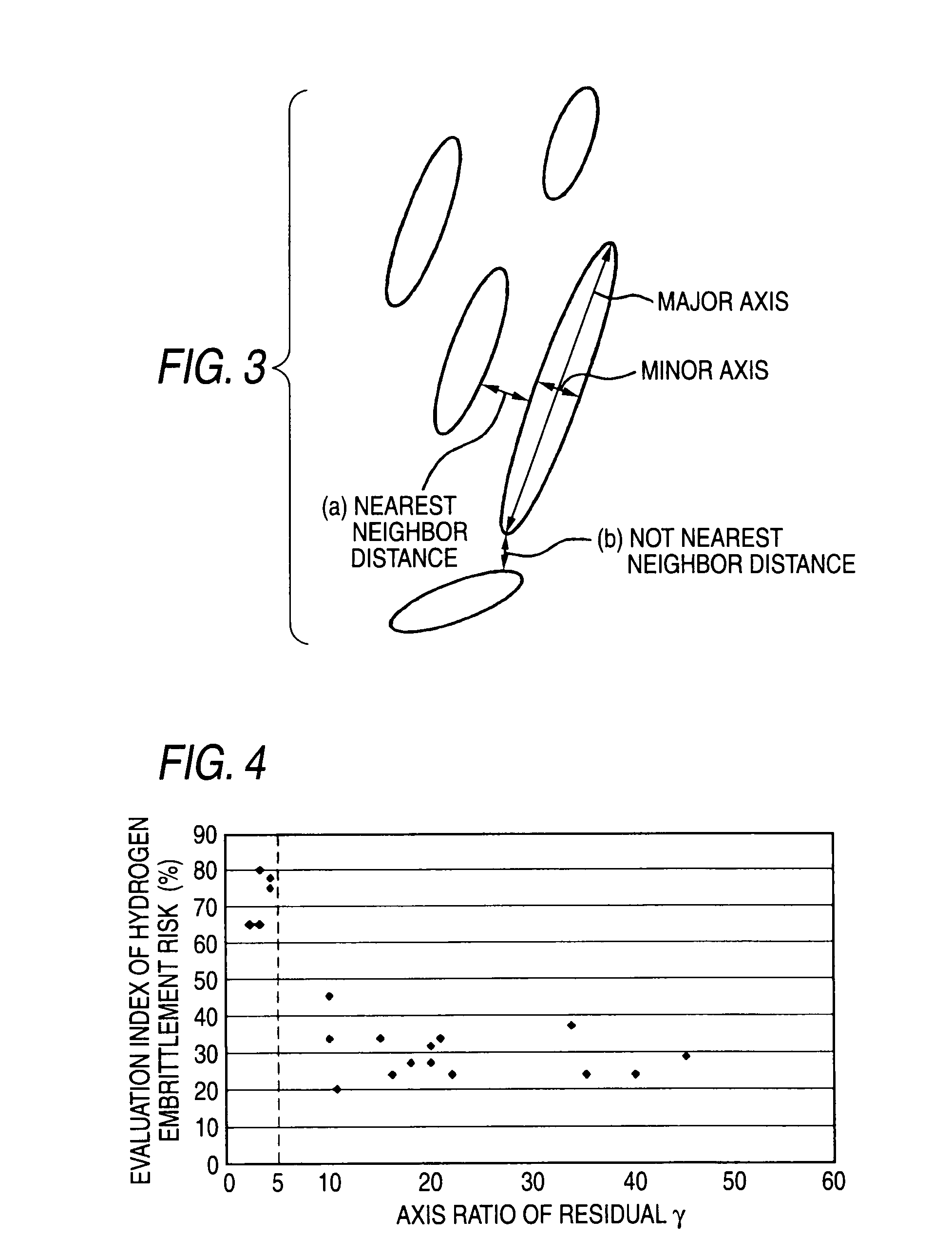
The invention relates to an ultrahigh-strength thin steel sheet excellent in the hydrogen embrittlement resistance, the steel sheet including, by weight %, 0.10 to 0.60% of C, 1.0 to 3.0% of Si, 1.0 to 3.5% of Mn, 0.15% or less of P, 0.02% or less of S, 1.5% or less of Al, 0.003 to 2.0% of Cr, and a balance including iron and inevitable impurities; in which grains of residual austenite have an average axis ratio (major axis / minor axis) of 5 or more, the grains of the residual austenite have an average minor axis length of 1 μm or less, and the grains of the residual austenite have a nearest-neighbor distance between the grains of 1 μm or less.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Hot-stamp-molded article, process for production of steel sheet for hot stamping, and process for production of hot-stamp-molded article
ActiveCN102939399AAchieve lightweightHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHot stampingAustenite grain
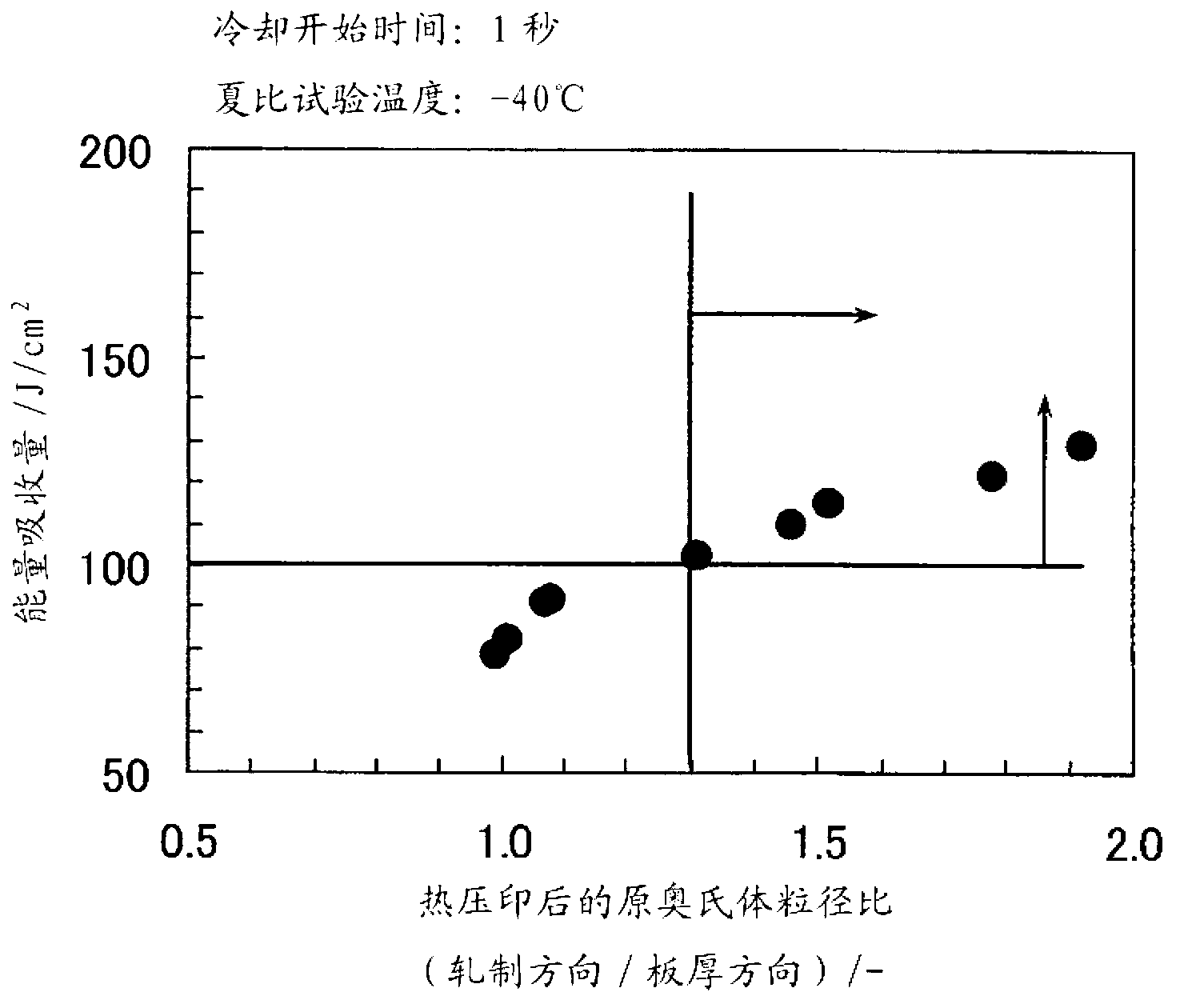
A hot-stamp-molded article comprises, in mass%, 0.20 to 0.35% of C, 0.1 to 0.5% of Si, at least one element selected from Mn and Cr in the total amount of 1 to 3%, 0.005 to 0.06% of Al, 0.002 to 0.1% of Ti, 0.002 to 0.1% of Nb, 0.003 to 0.007% of O, 0.015% or less of P, 0.01% or less of S, 0.004% or less of N, and a remainder made up by Fe and unavoidable impurities, wherein the dimensional ratio of the length of a prior austenite grain in the rolling direction to that in the thicknesswise direction is 1.3 to 2.5 inclusive, the prior austenite grain has an average particle diameter of 6 [mu]m or less, martensite is contained at a proportion of 98% or more, and the tensile strength is 1470 MPa or more.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Zinc-plated hot-formed steel plate or steel strip with excellent cold bending performance and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN109371325AGood cold bending performanceHot-dipping/immersion processesSheet steelAustenite grain
The invention discloses a zinc-plated hot-formed steel plate or steel strip with excellent cold bending performance and a manufacturing method thereof. The zinc-plated hot-formed steel plate or steelstrip comprises a base plate with a surface decarburization layer thickness of 20 [mu]m or below and a zinc coating with an adhesion amount of 10-100 g / m<2> on the base plate. The constituent weight percentage of the base plate is C: 0.1-0.8%, Si: 0.05-2.0%, Mn: 0.5-3.0%, P: <=0.1%, S: <=0.05%, Al: <=0.1%, N: <=0.01%, and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities. The average size of original austenite grains of the base plate is 15 [mu]m or below. The hot-formed steel plate or steel strip has a continuous and complete coating, no cracks extending to the base plate and excellent cold bending performance on the basis of meeting the conditions that the tensile strength of the base plate after hot-forming is 1500 MPa and the elongation after breaking is 5%.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High strength spring steel having excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance
InactiveUS20060169367A1High strengthLow priceFurnace typesOhmic-resistance heatingAustenite grainHigh intensity
The present invention provides a high strength steel used for spring steel that has excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance. The high strength steel which spring steel having excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance comprises 0.20 to 0.60% of C, 1.0 to 3.0% of Si, 1.0 to 3.5% of Mn, higher than 0% and not higher than 1.5% of Al, 0.15% or less P, 0.02% or less S, and balance of iron and inevitable impurities and the structure includes: 1% or more residual austenite; 80% or more in total of bainitic ferrite and martensite; and 10% or less (may be 0%) in total content of ferrite and pearlite in the proportion of area to the entire structure, and also the mean axis ratio (major axis / minor axis) of the residual austenite grains is 5 or higher and the steel tensile strength is 1860 MPa or higher.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD +1
Ultra-supercritical steel organization display method
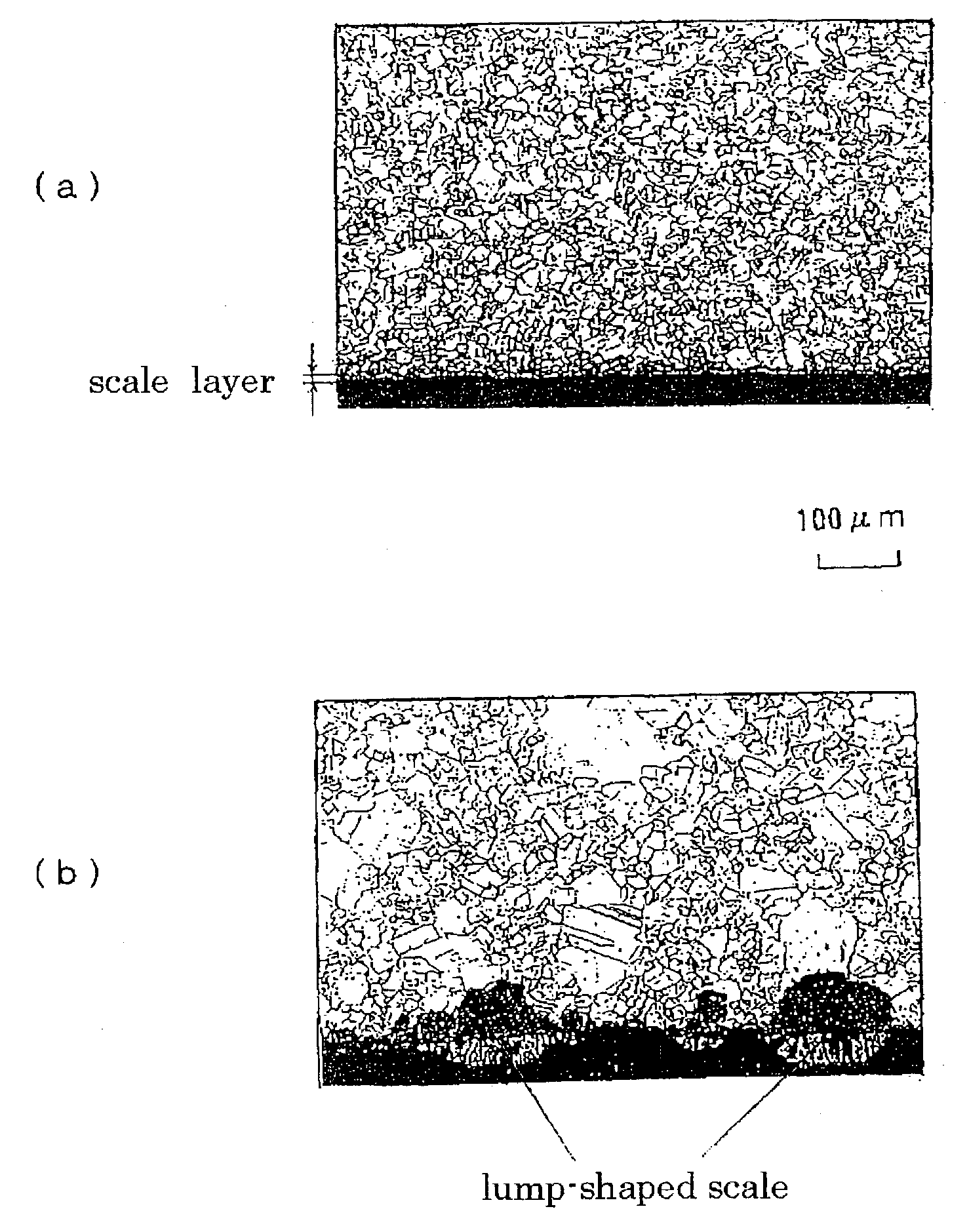
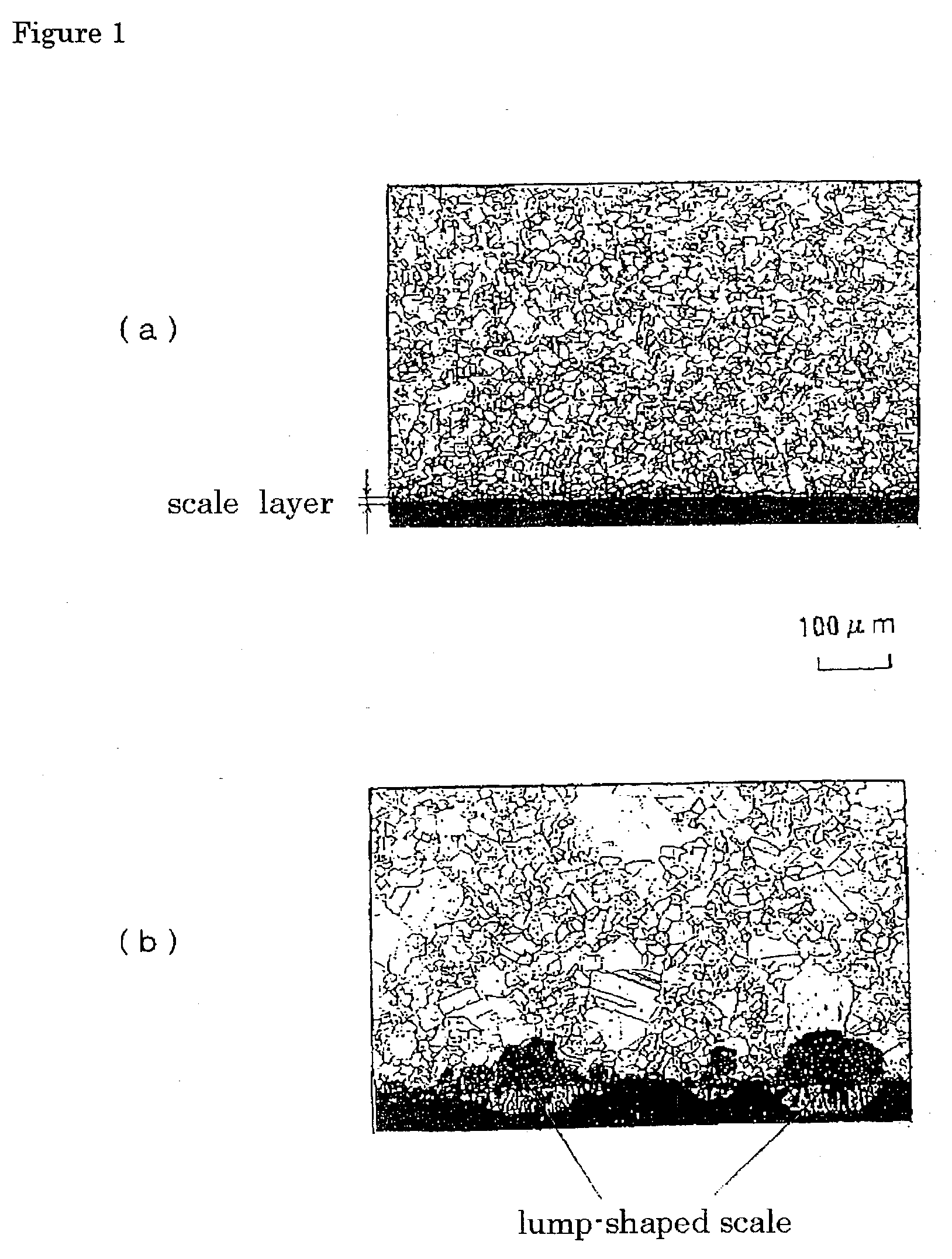
ActiveCN101270498ASolve the thicknessSolve for uniformityPreparing sample for investigationEtchingElectrolysis
The invention relates to the technical field of metallographical sample preparation and tissue observation. The invention relates to a tissue display method for ultra-supercritical steel with the advantages of high alloy content, high anti-corrosion and excellent oxidation resistance in particular. The technique steps of the method includes: firstly adopting a standard grinding-polishing method on an ultra-supercritical steel sample; then selecting a commonly used electrolyte to carry out electrolytic etching with high voltage and high current on the sample; finally combining a mechanical polishing method to finally display a clear original austenite crystal grain boundary. The invention can clearly, completely and independently display the original austenite crystal grain boundary of the ultra-supercritical steel; thereby being able to fully reflect the size and the distribution of the original austenite crystal grain and solving the problem of being harder to precisely assess the thickness and the uniformity of the ultra-supercritical steel tissue.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metallographic etched process for displaying G Cr15 original austenite grain border
InactiveCN101187606AShorten the timeGood reproducibilitySurface/boundary effectPreparing sample for investigationAlcoholMetallography
A metallographic corrosion method for displaying a GCr15 original austenitic grain boundary comprises adding picric acid 5g into distilled water100ml and mixing continuously, then adding sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate 5ml 50% and mixing, finally adding ferric chloride 2g, and using after placing for 24 hours. A sample is grinded roughly, grinded finely, polished, cleared, dried, immersed into caustic erodent for 2-5 minutes according to normal method under a quenching tempering condition until etched surface is changed into silver grey, cleaned up through flowing water, cleaned with alcohol 95%, and dried. If the sample is over-corroded, polishing paste W0.5-1.0 or metallographic polishing egent0.5-1.0 is added on silk polishing cloth, the sample is polished slightly with hands, then cleaned with alcohol 95%, and dried. According to practical condition, grain granularity measurement can adopt methods of picture contrast, grid, intercept, quantitative metallography, and the like, to assess according to relevant standards.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel tube excellent in steam oxidation resistance and a manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20030231976A1Excellent in steam oxidation resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainReduction ratio
The present invention provides an austenitic stainless steel tube with a uniform fine grained structure of regular grains, which is not changed to a coarse structure and the steam oxidation resistance is maintained even if the tube is subjected to a high temperature reheating during welding and high temperature bending working. The austenitic stainless steel tube consists of, by mass %, C: 0.03-0.12%, Si: 0.1-0.9%, Mn: 0.1-2%, Cr: 15-22%, Ni: 8-15%, Ti: 0.002-0.05%, Nb: 0.3-1.5%, sol. Al: 0.0005-0.03%, N: 0.005-0.2% and O (oxygen): 0.001-0.008%, and the balance Fe and impurities, the austenitic stainless steel tube having austenitic grain size number of 7 or more and a mixed grain ratio of preferably 10% or less. The present invention also provide a method of manufacturing the austenitic stainless steel tube comprising the following steps: (a) heating an austenitic steel tube at 1100-1350° C. and maintaining the temperature, and cooling at a cooling ratio of 0.25° C. / sec; (b) working by cross-sectional reduction ratio of 10% or more at a temperature range of 500° C. or less; and (c) heating at a temperature range of 1050-1300° C. and at a temperature of lower by 10° C. or more than the heating temperature in the step(a).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
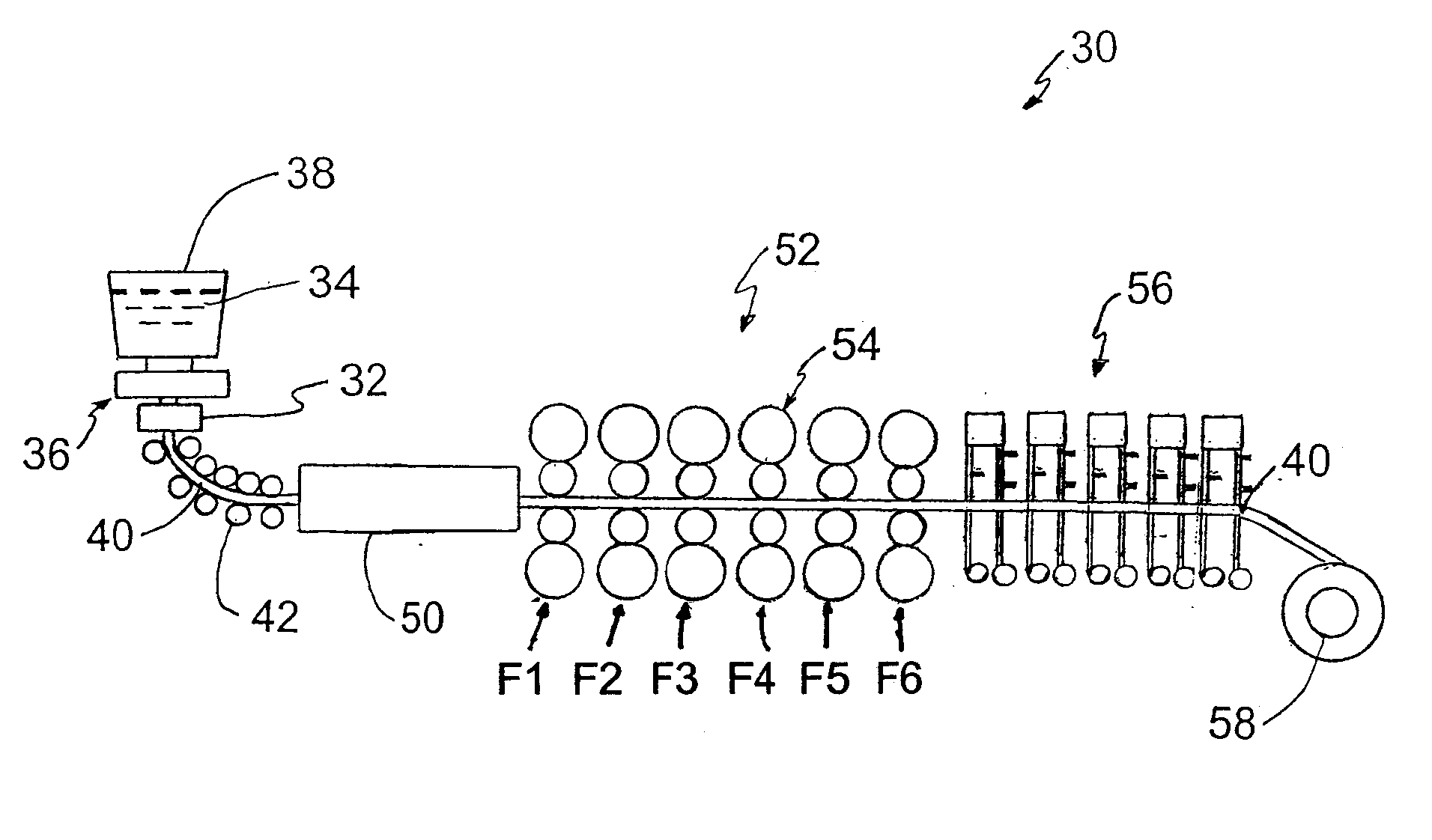
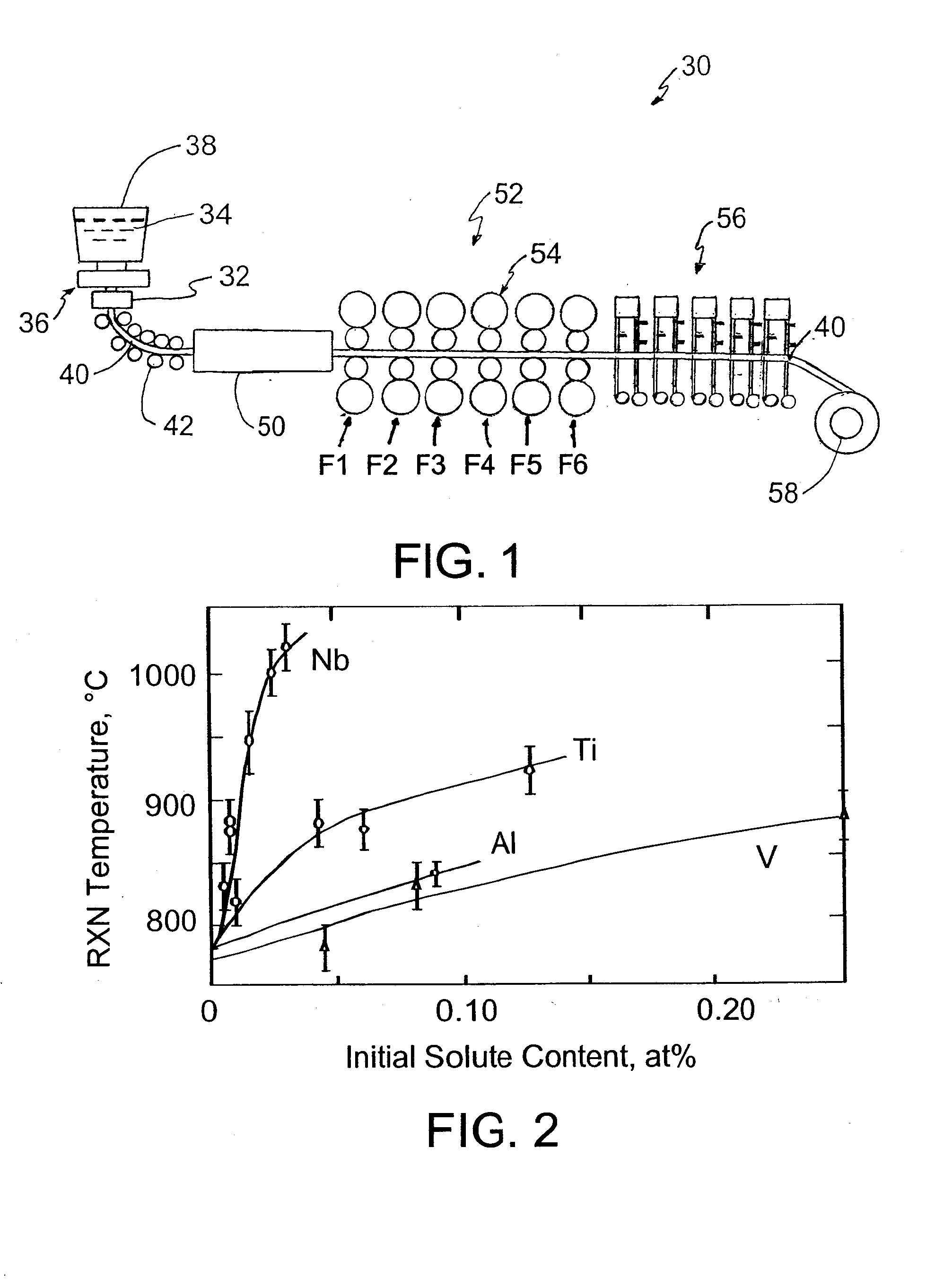
Thermomechanical processing routes in compact strip production of high-strength low-alloy steel
InactiveUS20050115649A1Accurate ultrasonic testingTime allowedMetal rolling arrangementsAustenite grainThin slab
Process for hot rolling of high-strength low-alloy steel cast in Compact Strip Production as a thin slab. The strain and temperature at initial roll stands where deformation occurs allows full recrystallization, and at latest roll stands where deformation occurs there is no recrystallization. Deformation is absent at strains and temperatures where partial recrystallization would occur, allowing increased recrystallization over conventional CSP rolling. The result may be beneficial for microalloyed high-strength low-alloy steel in permitting accurate ultrasonic testing of welds. The time allowed between deformation at passes through roll stands may be increased by eliminating deformation at one or more central roll stands. Combined with increased strain at the initial roll stands where the temperature of the steel is in the full recrystallization region, the process may result in a relatively fine and uniform austenite grain size.
Owner:NUCOR CORP
Method for manufacturing steel plate with high strength and high toughness by using hot-rolling coiled plate
The invention relates to a manufacture method for manufacturing a steel plate with high strength and high toughness by using a hot-rolling coiled plate. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, after a hot-rolling coiled plate is leveled on a leveling machine set, refining heat treatment is carried out on the hot-rolling coiled plate, i.e. the hot-rolling coiled plate is heated in induction heating equipment, the heating time is within 60-140s, and the hot-rolling coiled plate is heated to 910DEG C to 960DEG C and austenized; then, the hot-rolling coiled plate enters a water-cooling or steam-cooling quenching machine set to carry out quenching, the quenching and cooling speed of the hot-rolling coiled plate is greater than or equal to 5DEG C / s, and a quenched martensite organization is obtained after quenching; tempering is carried out after quenching, induction heating is carried out by adopting the induction heating equipment in the tempering, the heating temperature of the quenched martensite organization is 220DEG C to 440DEG C, the tempering time is 80 to 180s, and a tempered martensite organization is obtained; and finally, straightening, flaw detection, surface inspection and sampling inspection are carried out to finally obtain the steel plate with excellent performance, high strength and high toughness. The invention has the advantages that as refining treatment adopts an induction heating method, the heating time is short, austenite crystal grains are fine, the mechanical property is superior to that of a similar product produced by the traditional technology, the plate type of the steel plate is good, and the invention has high production efficiency, low equipment investment, little maintenance cost of the equipment, small occupation area and little environmental pollution.
Owner:武汉武钢实业机电材料工程有限公司
High-heat-input welding thick steel plate and manufacturing method thereof
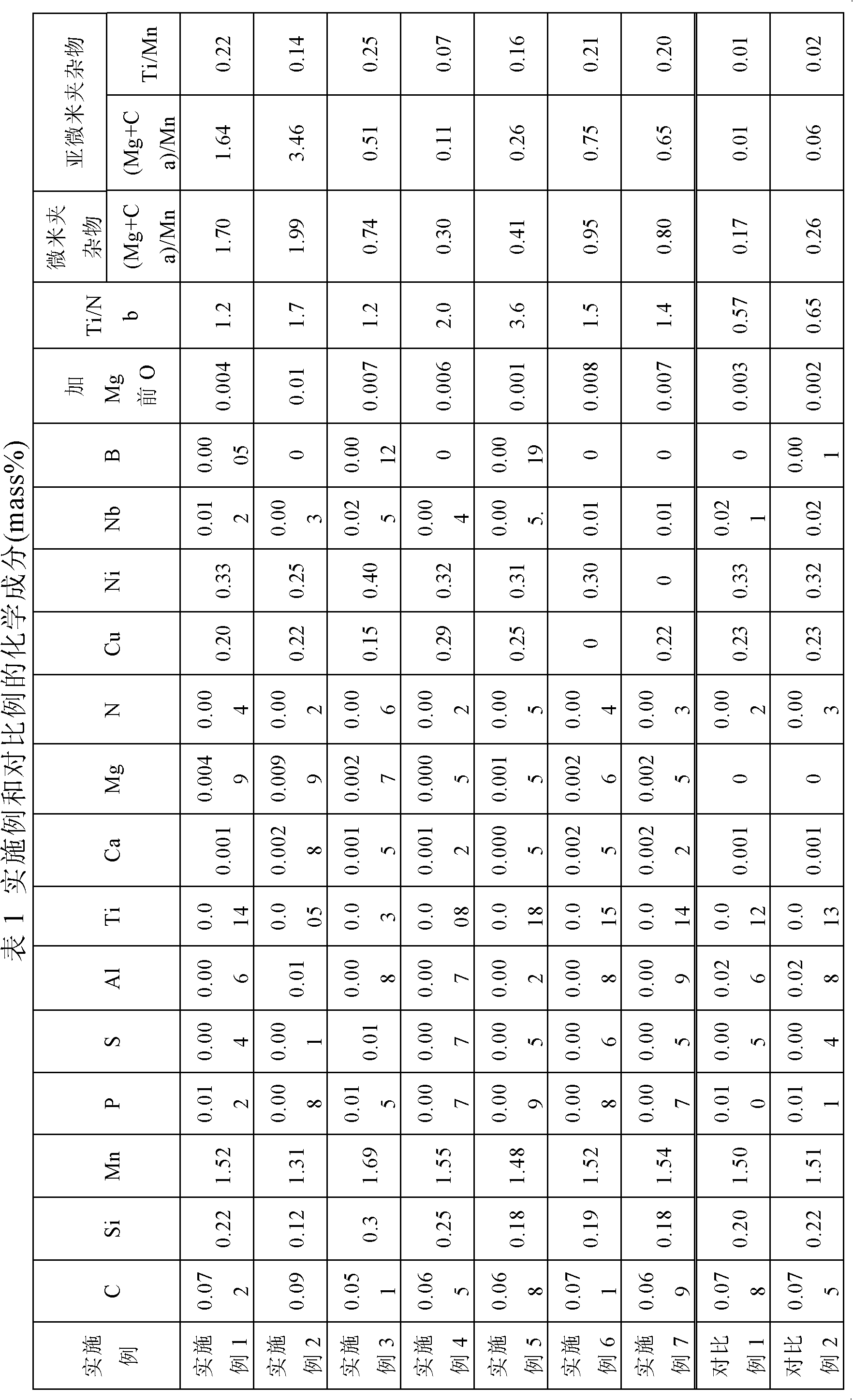
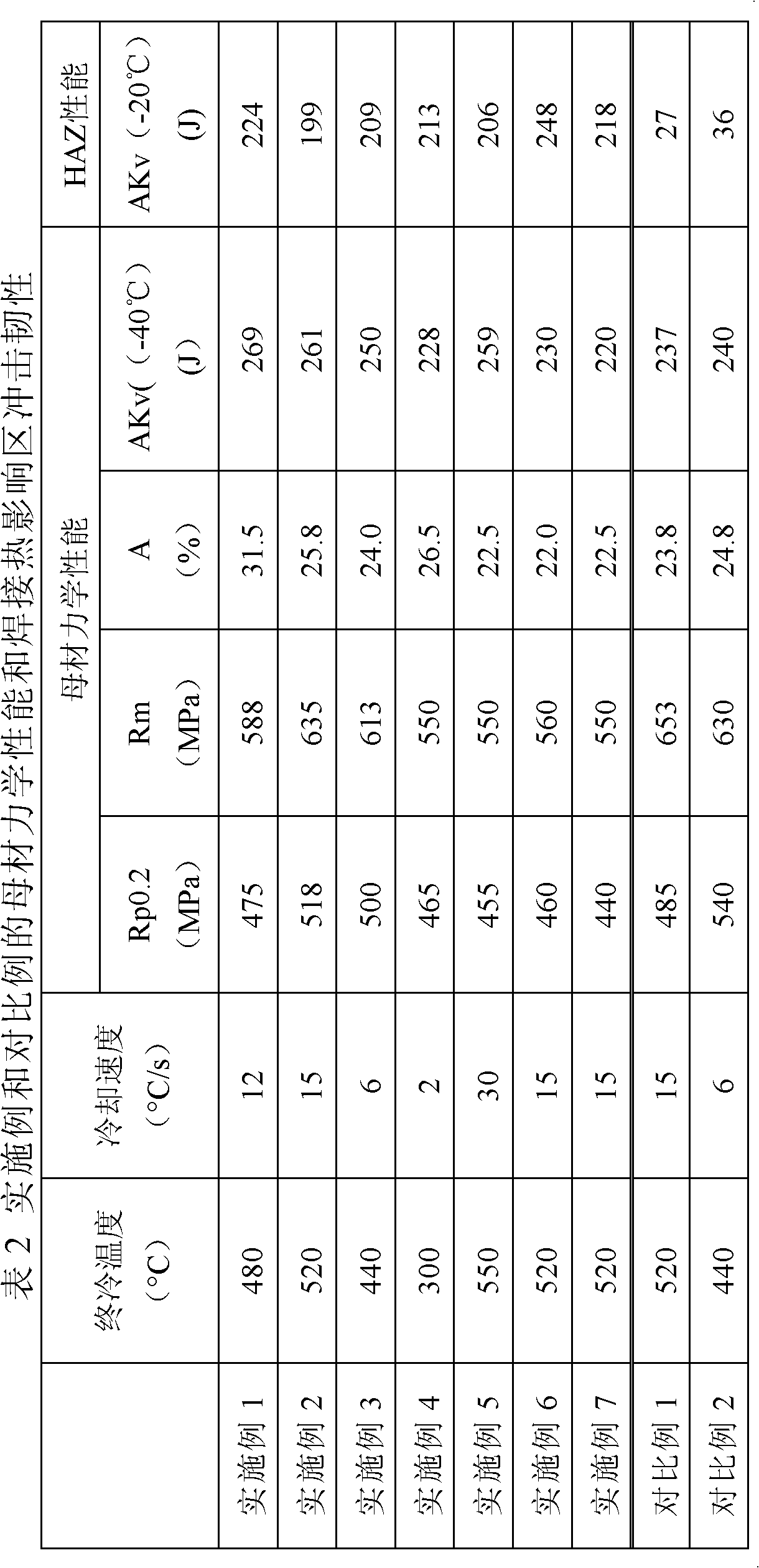
Disclosed are a high-heat-input welding thick steel plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method includes following steps: a) smelting, refining and continuous casting; b) rolling; and c) cooling. Steel consists of components including, by weight percentage, from 0.05 to 0.09% of C, from 0.10 to 0.30% of Si, from 1.3 to 1.7% of Mn, from 0.005 to 0.03% of Ti, from 0.003 to 0.025% of Nb, from 0.001 to 0.01% of S, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.006% of N, from 0.0005 to 0.01% of Mg, smaller than or equal to 0.01% of Al, smaller than or equal to 0.003% of Ca, more than one of smaller than or equal to 0.3% of Cu, smaller than or equal to 0.4% of Ni and smaller than or equal to 0.002% of B, and the balance Fe; and Ti / Nb is larger than or equal to 1.2, deoxidant Mn, Si, Al, Ti, Ca and Mg are successively added in a steel liquid deoxidizing process, wherein (Mg+Ca) / Mn is larger than or equal to 0.3 for micrometer impurities with the grain size larger than or equal to 1.0 micrometer in the steel, (Mg+Ca) / Mn is larger than or equal to 0.1 for sub-micron impurities with the grain size ranging from 0.1 micrometer to 1.0 micrometer in the steel, and Ti / Mn is larger than or equal to 0.07. A large quantity of impurities which are distributed in a dispersion manner are formed, growth of austenite grains in a welding heat affected zone can be restrained, growth of intra-granular ferrite is promoted, and the high-heat-input welding performance of the thick plate is greatly improved.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
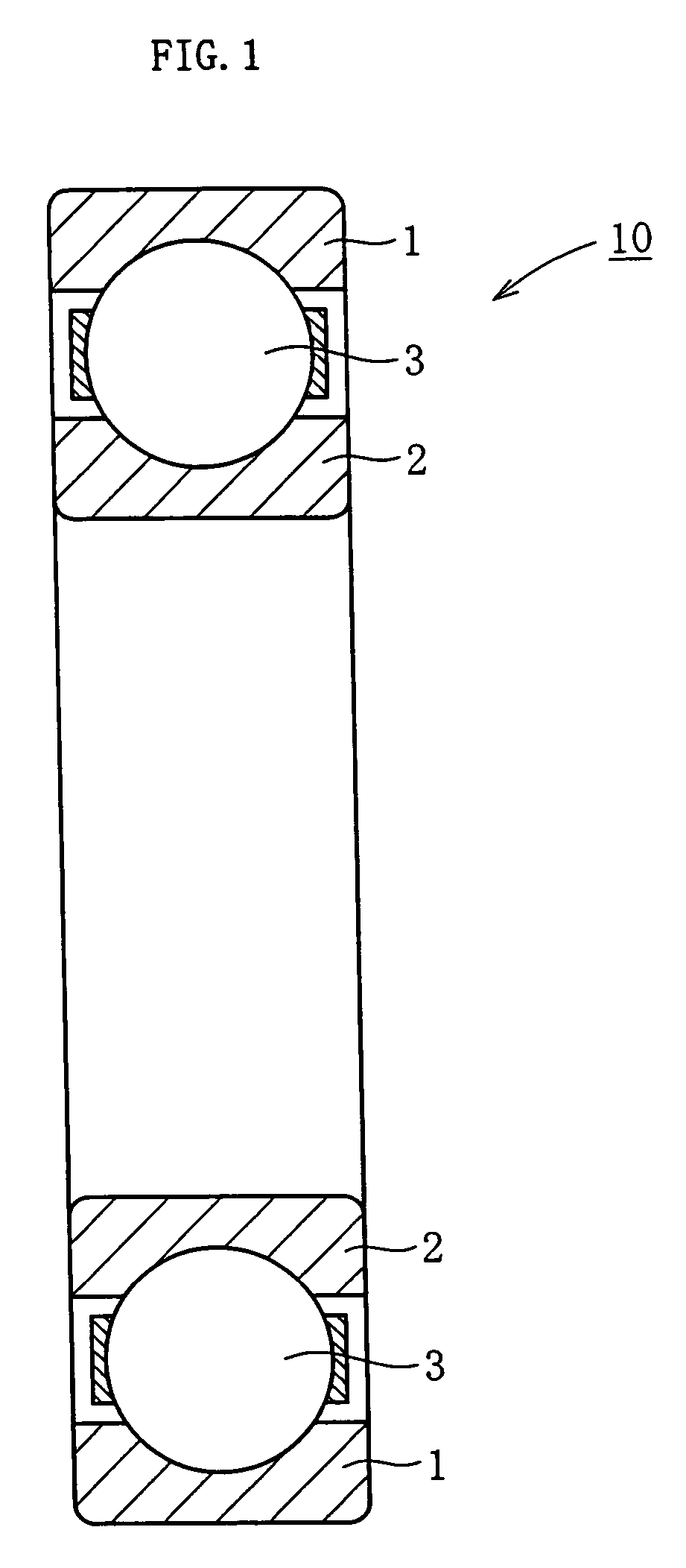
Rolling bearing
ActiveUS20070151633A1High dimensional stabilityImprove fatigue lifeBearing componentsSolid state diffusion coatingAustenite grainRolling-element bearing
A rolling bearing (10) having an outer ring (1), an inner ring (2), and a plurality of rolling elements, wherein at least one of the members, the outer ring (1), inner ring (2) and rolling elements (3), has a nitrogen rich layer and the grain size number of austenite crystal grains is in the range exceeding the number 10.
Owner:NTN CORP
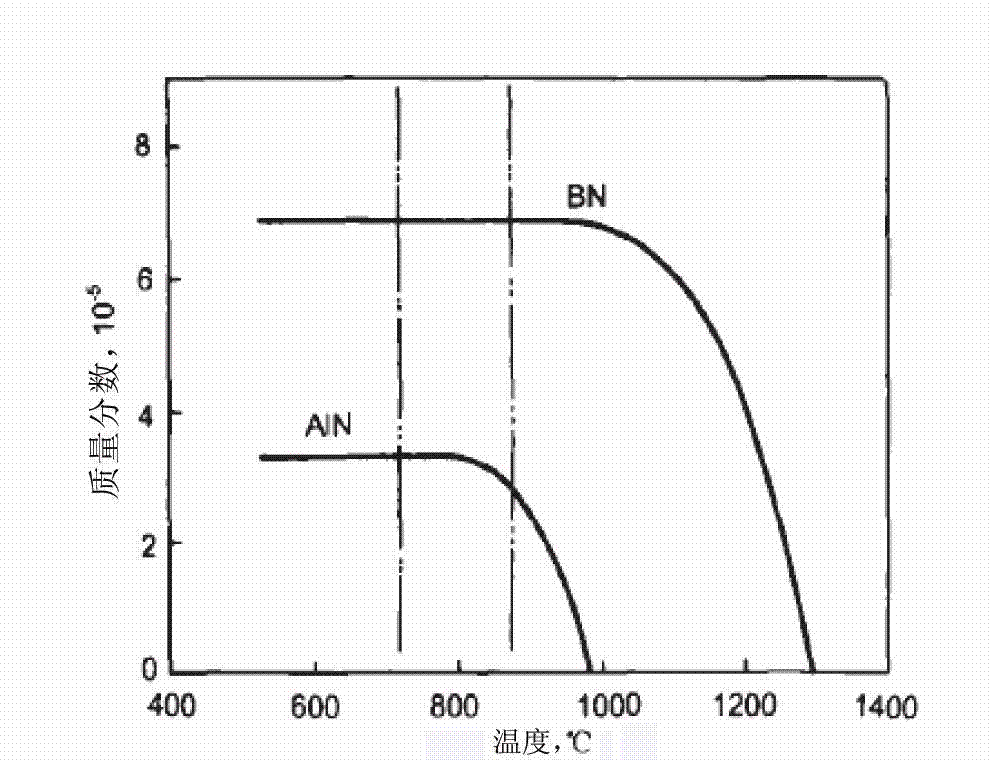
Boron-containing weather-proof thin strip steel and manufacturing method thereof
Provided are boron-containing weather-proof thin strip steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises performing double roller thin strip continuous casting to produce boron-containing weather-proof steel; after a cast strip is processed through a crystallizing roller, adopting a mode of spraying dry ice to perform uniform strengthened cooling on the cast strip, rapidly cooling the cast strip to below 1,280 DEG C, and enabling the cooling speed to be 200-300 DEG C / s, so that precipitation of thick and large BN in the cooling mode is promoted, emergency of low-melting-point-phase B203 and precipitation of tiny AlN are avoided, and the aims of homogenizing austenite grains and reducing yield ratio are achieved; then performing austenite on-line recrystallization rolling; then performing anti-oxidizing rapid cooling to cool the strip steel undergoing hot rolling, and enabling the cooling temperature to be 80-200 DEG C / s; and enabling coiling temperature to be 500-600 DEG C. Steel with low yield ratio can be obtained through the manufacturing method, and the problems that steel produced by thin strip continuous casting are universally uneven in structure, high in yield ratio and difficult to form and cannot meet the requirements for cold rolling materials are effectively solved.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
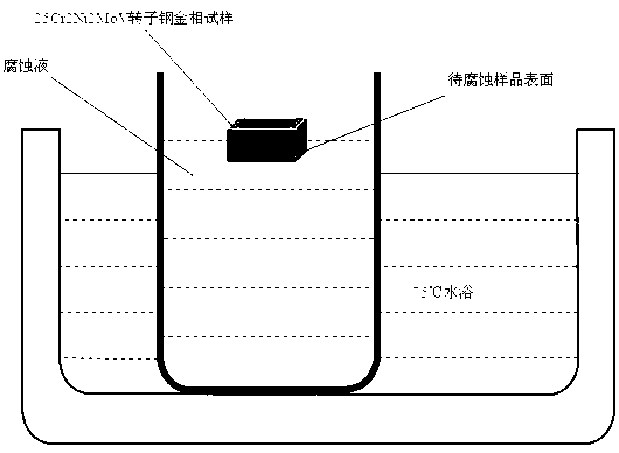
Metallographic corrosion method for clearly displaying original austenite grain boundary of NiCrMoV type rotor steel
The invention relates to a metallographic corrosion method for clearly displaying the original austenite grain boundary of a NiCrMoV type rotor steel, and belongs to the field of metallographic sample preparation. The method comprises the steps of: coarse grinding, fine grinding, polishing and corroding; putting a polished sample into a corrosive liquid of 75 DEG C, wherein the formula of the corrosive liquid comprises 200ml of distilled water, 5g of picric acid, 2ml of 5% diluted hydrochloric acid and 4g of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate; etching for 2minutes, taking the sample out, cleaning the sample with flowing water, cleaning the sample with alcohol and drying; and observing the clear original austenite grain boundary through an optical microscope. The method has the advantages that a difficult displaying problem of the original austenite grains of the NiCrMoV type rotor steel is solved, the original austenite grain boundary can be very clearly displayed, and the method is simple and practicable.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Method for making super-low carbon steel gold-phase sample and displaying its tissue
InactiveCN101025391AImprove the display effectEasy to manufactureSurface/boundary effectPreparing sample for investigationAustenite grainCarbon steel
The invention relates to a method of preparing dead mild steel ultra-low-carbon steel golden phase sample and indicating structure, it belongs to preparation technology field of golden phase sample. The invention includes the following steps: thick grinding, thin grinding-polishing, eroding, arranging corrosion fluid. Its advantages are that: solves the difficult display problems of dead mild steel ultra-low-carbon steel austenite grain, obtains the clear photograph of austenite grain, The implementation of this invention is simple, it can easily prepare dead mild steel ultra-low-carbon steel golden phase sample.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Austenitic stainless steel metallographic etchant, preparing method and use thereof
InactiveCN101353794ADisplay clearErosion effect is goodPreparing sample for investigationHydrofluoric acidAlcohol
The invention discloses a metallographic-phase aggressive agent of an austenitic stainless steel, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The metallographic-phase aggressive agent comprises the mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, calculated by volume ratio, the proportion of each component of the agent is that hydrofluoric acid : nitric acid : water is equal to 2 : 1 : 7. The preparation method thereof is carried out according to the following steps of: taking 70ml of water first, then taking 10ml of analytically pure nitric acid and finally taking 20ml of analytically pure hydrofluoric acid, which are then evenly mixed. The application method thereof comprises the following steps of: putting a simple of the austenitic stainless steel in the metallographic-phase aggressive agent of the austenitic stainless steel and observing the color change of the surface of the sample by time, taking out the sample of the austenitic stainless steel when metallographic-phase surface of the sample is corroded to darker silver gray, washing the sample with water which is then neutralized with alkaline solution and finally washing with water and absolute ethyl alcohol. The technical effects thereof are represented by good corrosion effect, clear austenite grain boundary, slow corrosion speed, easy control, no pollution and other aspects.
Owner:董加坤
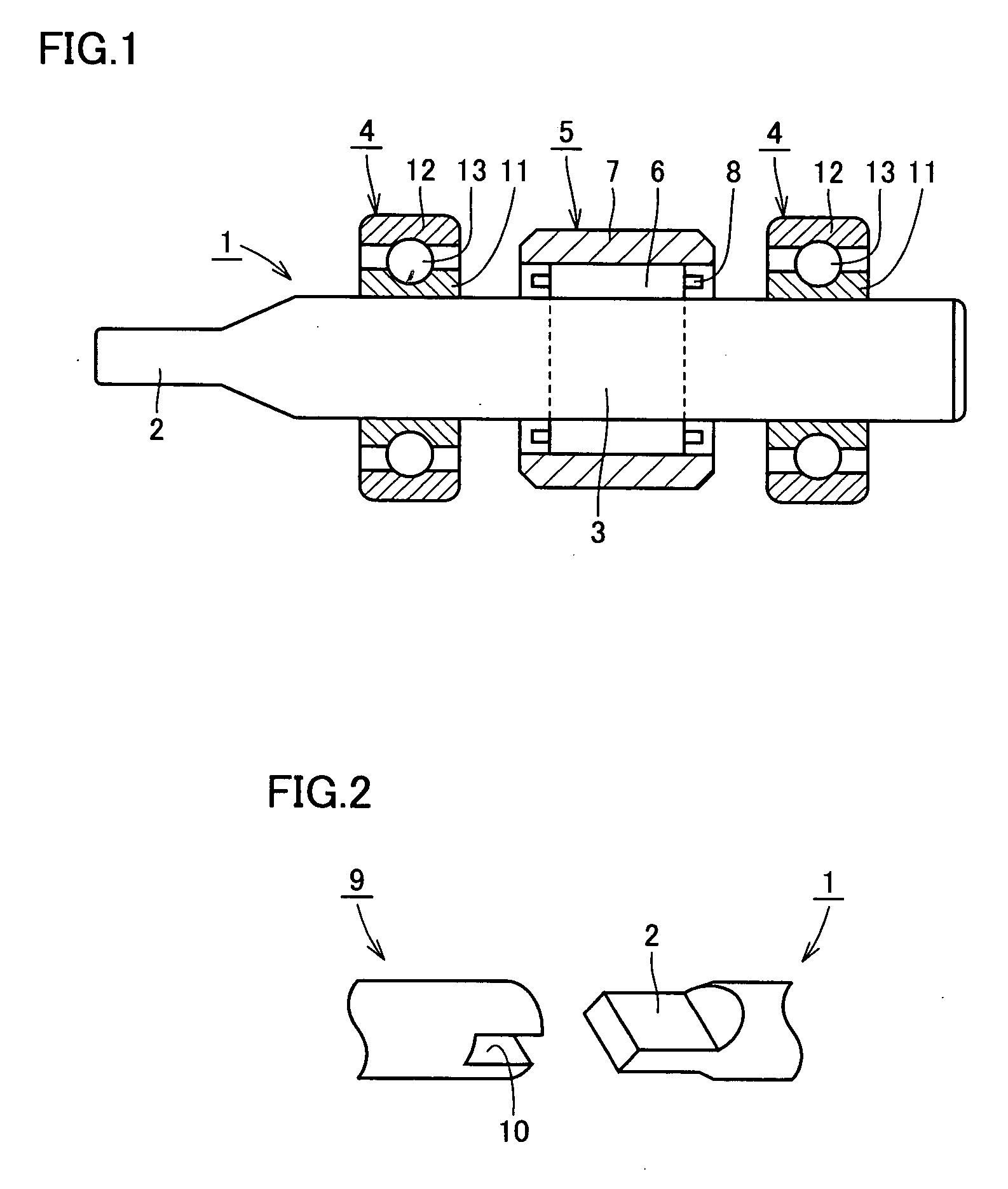
Rolling-contact shaft with joint claw
ActiveUS20070034301A1Improve contact fatigue lifeShaftsBearing componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A steel-made rolling-contact shaft with a joint claw improved in both the rolling contact fatigue life at the raceway and the static fracture strength (torsional strength) at the claw includes a joint claw at one end, and has a portion of the outer cylindrical surface functioning as a raceway of a needle roller qualified as a rolling element of a needle bearing. The joint claw is subjected to tempering by induction heating. A nitrogen-enriched layer is formed at the surface layer of the rolling-contact shaft with a joint claw. The grain size number of austenite grains in the nitrogen-enriched layer exceeds number 10. The hydrogen content of the rolling-contact shaft with ajoint claw is not more than 0.5 ppm.
Owner:NTN CORP
Corrosive agent for displaying 9% Cr steel original austenite grain boundary and application thereof
ActiveCN102517586AEasy grain size ratingGood effectPreparing sample for investigationAustenite grainDodecylsulfonic acid
The invention discloses a corrosive agent for displaying 9% Cr steel original austenite grain boundary and an application thereof. The corrosive agent is prepared by fully mixing the following components of: 60-80ml of H2O, 4-8ml of 36 wt% HCl, 2-4g of FeCl3, 0.2-0.5g of picric acid, and 1.0-2.0g of sodium dodecanesulphonate. The corrosive agent provided by the invention can be used as a reagent for 9% Cr steel grain boundary to clearly display the original austenite grain boundary of large crystal grain, large and small mixed crystal grain and small crystal grain of a sample. Under 100 times, it is easy to carry out grain size rating and the effect is good.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOILER WORKS
Method for producing annealing-free hot rolling S50C plate and strip
The invention relates to a method for producing an annealing-free hot rolling S50C plate and strip, belonging to the technical field of hot rolled plates and strips. The invention adopts the technical scheme that austenite rolling is adopted in rough rolling, a deformation-induced ferrite rolling and warm rolling combined process is adopted in finish rolling, temperature in a rough rolling region is controlled to be 960-1150 DEG C, accumulated screwdown rate is more than 50%, an intermediate blank obtained by the rough rolling is cooled by water and then enters into a finish rolling mill group, opening rolling temperature of a finish rolling mill is 760-850 DEG C, finished rolling temperature of the finish rolling mill is 650-750 DEG C, the accumulated screwdown rate is more than 50%, cooling rate after rolling is controlled to be 0.1-25 DEG C / s, and coiling temperature is controlled to be 550-700 DEG C. The austenite rolling during rough rolling is carried out, thus austenite crystals are refined; the deformation-induced ferrite rolling and warm rolling during finish rolling are carried out, thus ferrite is excessively separated out, carbide is modified in a deformation process, plasticity and toughness of steel are improved, the aim of direct moulding while annealing is eliminated is achieved, and a spheroidizing process before cold forming is eliminated.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Secondary cooling method for controlling surface-layer solidification structure of continuous cast slab
The invention relates to a secondary cooling method for effectively controlling the surface-layer solidification structure of a continuous cast slab. After the continuous cast slab is discharged out of a crystallizer, the casting machine vertical section is cooled at the cooling speed of 3-10 DEG C / s for 50-160 s, the secondary cooling water quantity in the cooling section corresponding to the time period is increased to 2-5 times larger than the original water quantity, i.e. the broadside water quantity is 260-600 L / min, and the narrow side water quantity is 50-125 L / min. After the intensive cooling of the casting machine vertical section is finished, the subsequent cooling sections adopt the secondary cooling mode with the specific water flow of 0.55-0.8 L / kg. Shown by practices, the surface-layer structure of the cast slab poured in the secondary cooling mode is compact, the grain size is 10-100 mum, precipitates at grain boundary are few and uniform, and the original austenite grain boundary at high temperature is not obvious. High-temperature plasticity tests on steel show that the plasticity of the steel is obviously improved, which is beneficial to elimination of crack defects of the cast slab.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Cooling method of heavy and medium plate controlled rolling intermediate blank
InactiveCN101829688ALess investmentImprove applicabilityTemperature control deviceWater qualityWater cycling
The invention belongs to a producing and cooling technique of rolled steel, relating to a cooling method of a heavy and medium plate controlled rolling intermediate blank, which can be realized by both a single-stand heavy and medium plate roll and a double-stand heavy and medium plate roll. The cooling method comprises the following steps of: transmitting a roughly rolled intermediate blank with the thickness range of 30-110 mm in an austenite recrystallization zone into an intermediate controlled cooling zone from a transmission roller way for rapidly cooling to 800-950 DEG C, and then transmitting the intermediate blank into the roll for rolling in a non- recrystallization zone after short-time air cooling and temperature evening. In the intermediate cooling process, an upper collecting pipe and a lower collecting pipe with high density or ultra-high density are adopted to impact, jet and cool the intermediate blank, and specific technological parameters are accurately controlled by a computer. Water is cooling water for the roll with the pressure of 0.3-1.0 MPa in a common water circulating system for workshops. The intermediate cooling holding time is 30-70% shorter than that of the conventional process so that the production efficiency is improved, and due to austenite grain refinement after intermediate controlled cooling, the mechanical properties of a steel plate can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
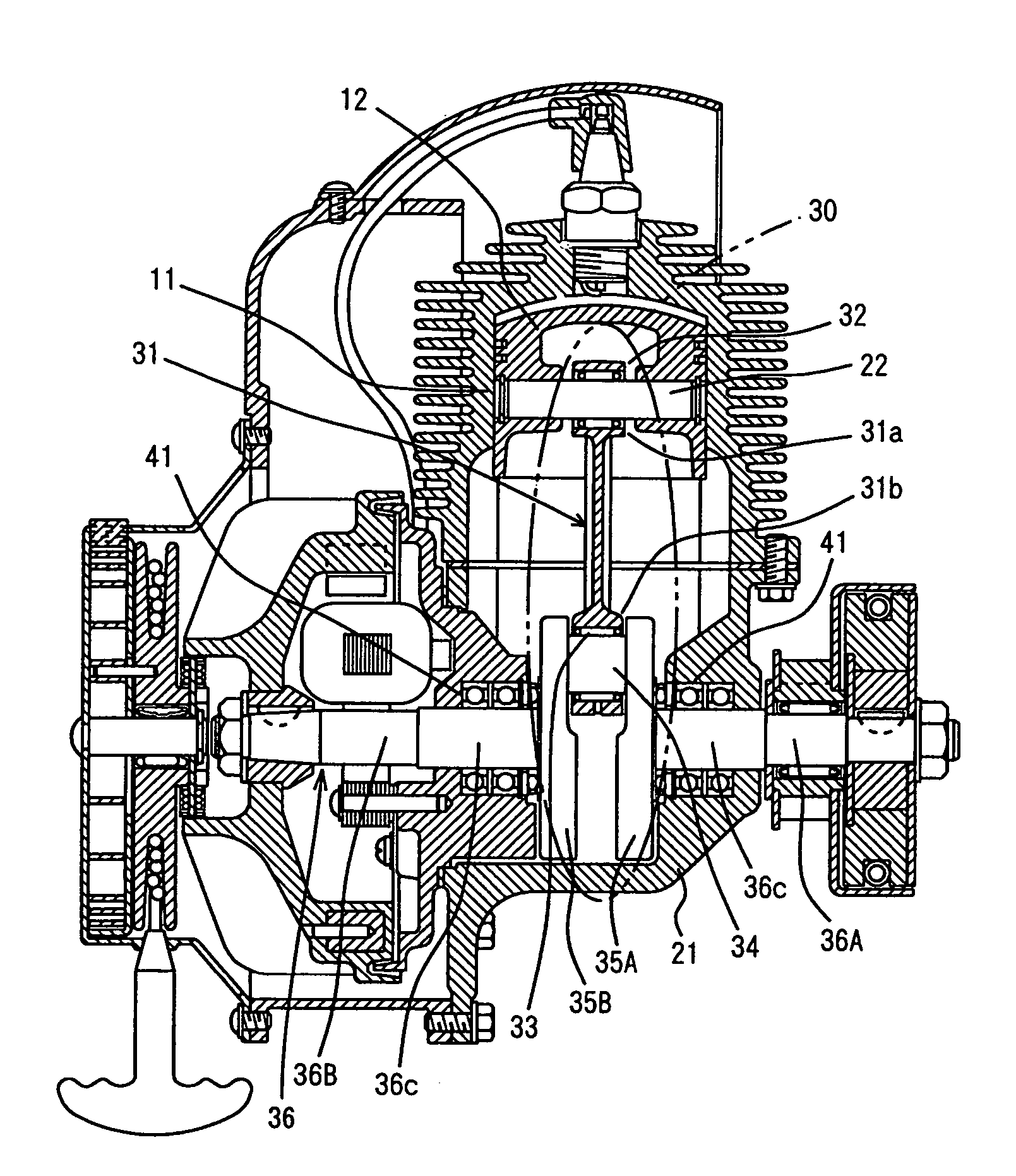
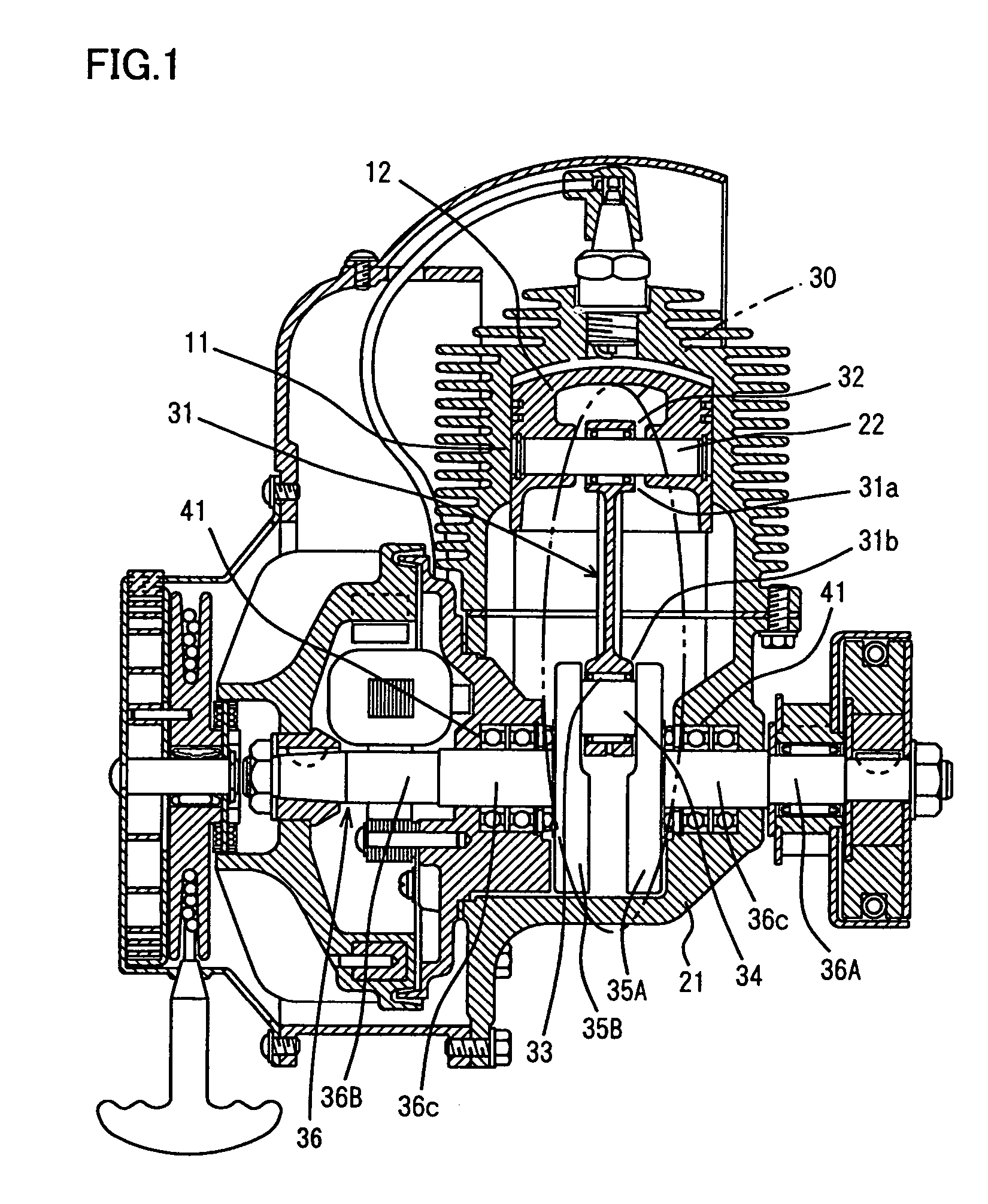
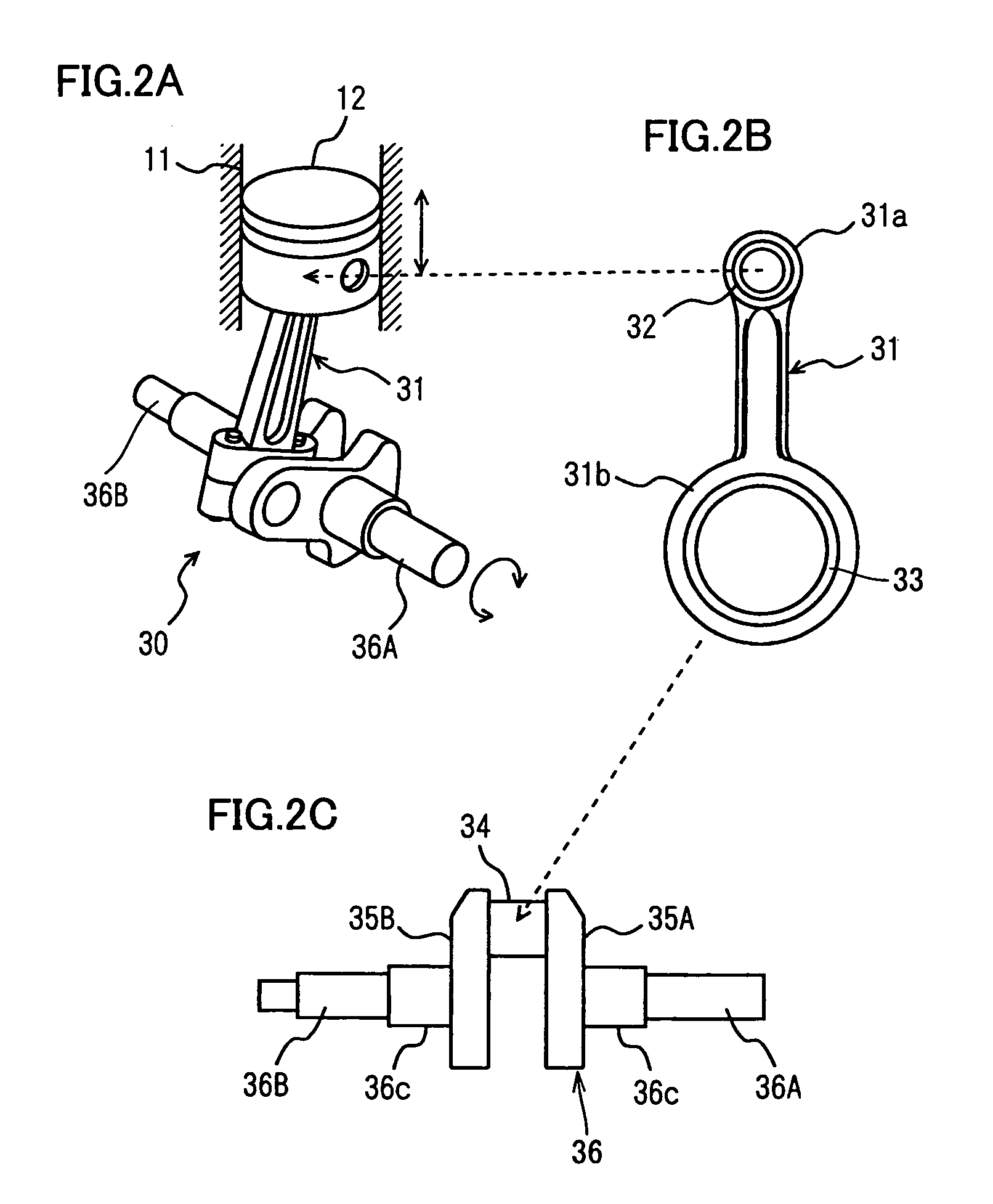
Support structure in crank mechanism and component constituting crank mechanism
InactiveUS7147382B2High strengthSuppressing an increase in rate of secular dimensional changeCrankshaftsConnecting rodsAustenite grainReciprocating motion
A component of a crank mechanism is incorporated in the crank mechanism that converts reciprocating motion of a piston to rotary motion by means of a crank pin, a crank arm and a crank shaft via a connecting bar, and has a hydrogen content of no more than 0.5 ppm, austenite crystal grains of a grain size number exceeding 10, or a fracture stress value of no less than 2650 MPa. Thus, a support structure in and a component of a crank mechanism ensuring a long fatigue life, high anti-crack strength, and a reduced rate of secular dimensional change to improve dimensional stability, can be obtained.
Owner:NTN CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com