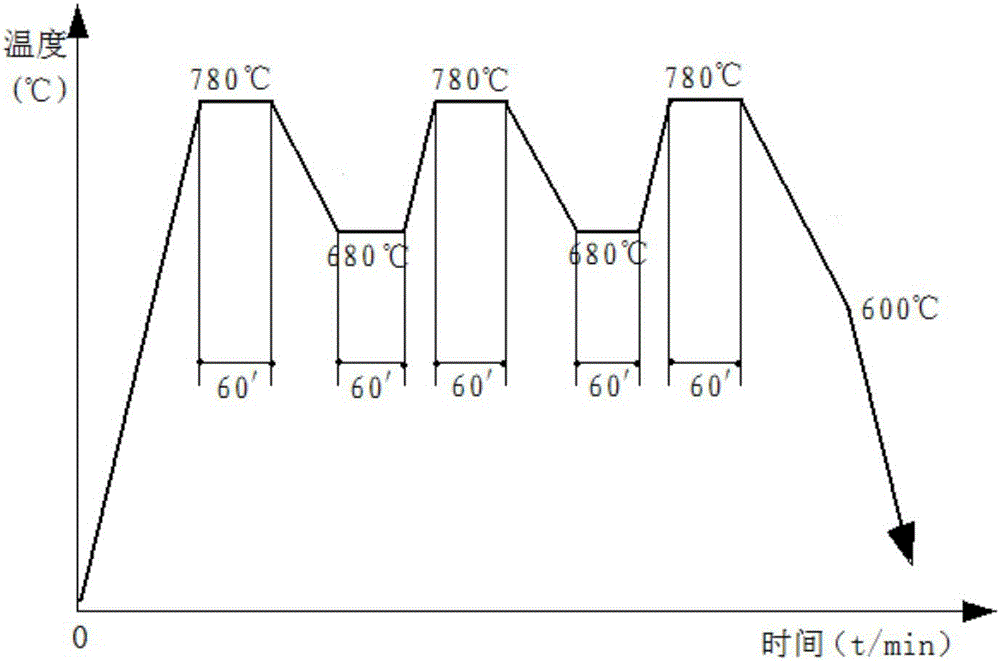
Patents
Literature
106 results about "Metallography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metallography is the study of the physical structure and components of metals, by using microscopy. Ceramic and polymeric materials may also be prepared using metallographic techniques, hence the terms ceramography, plastography and, collectively, materialography.
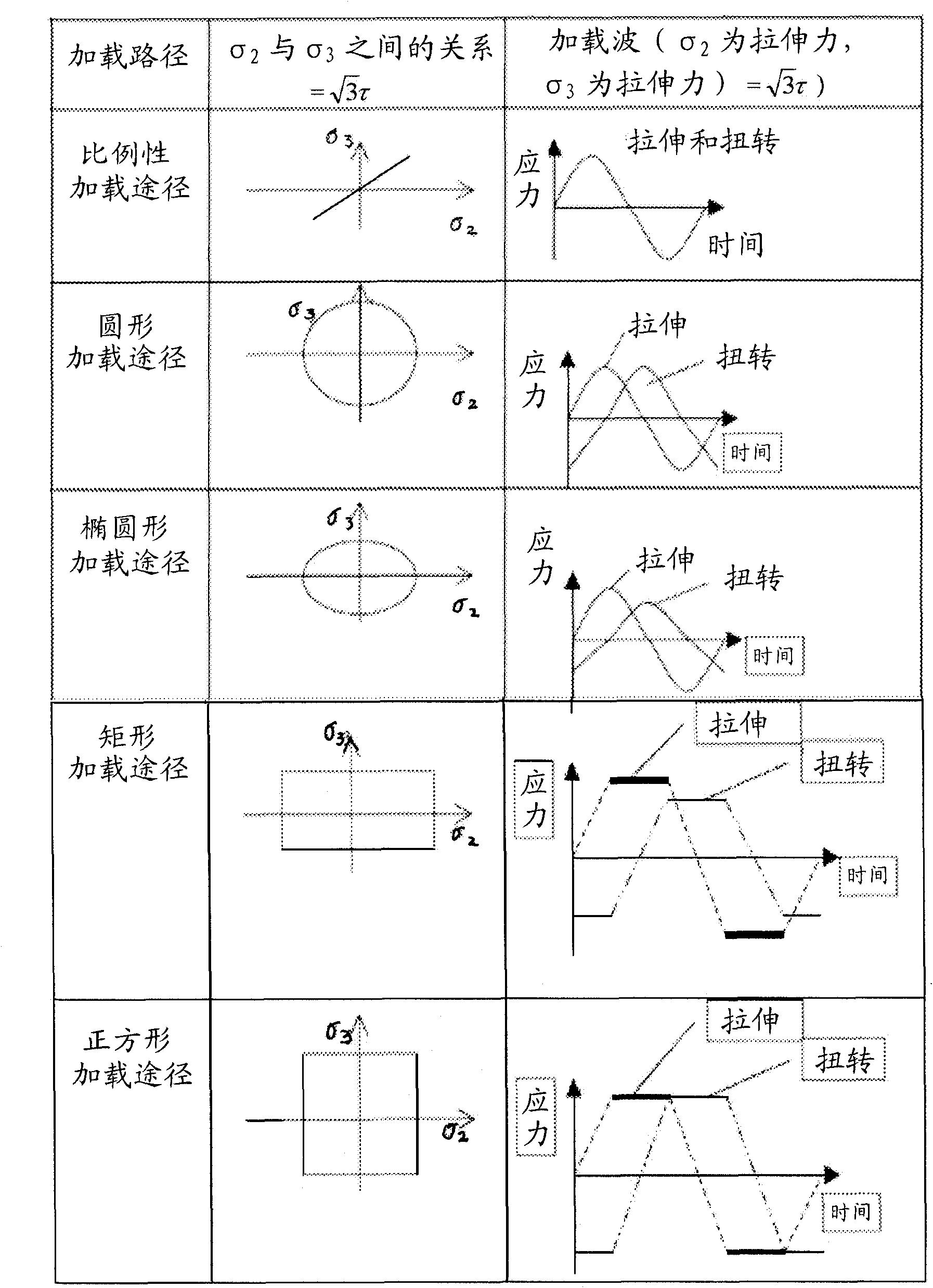
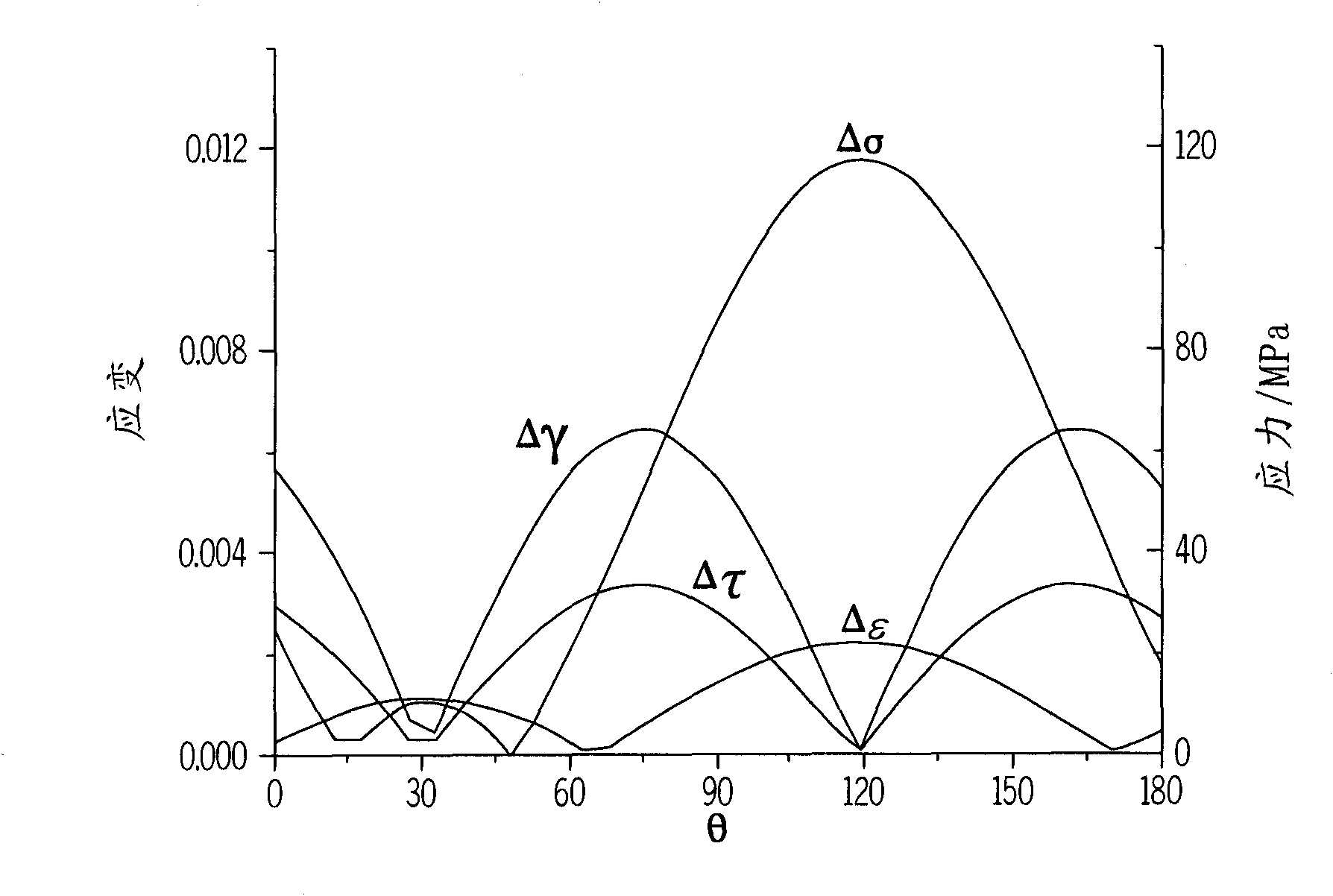
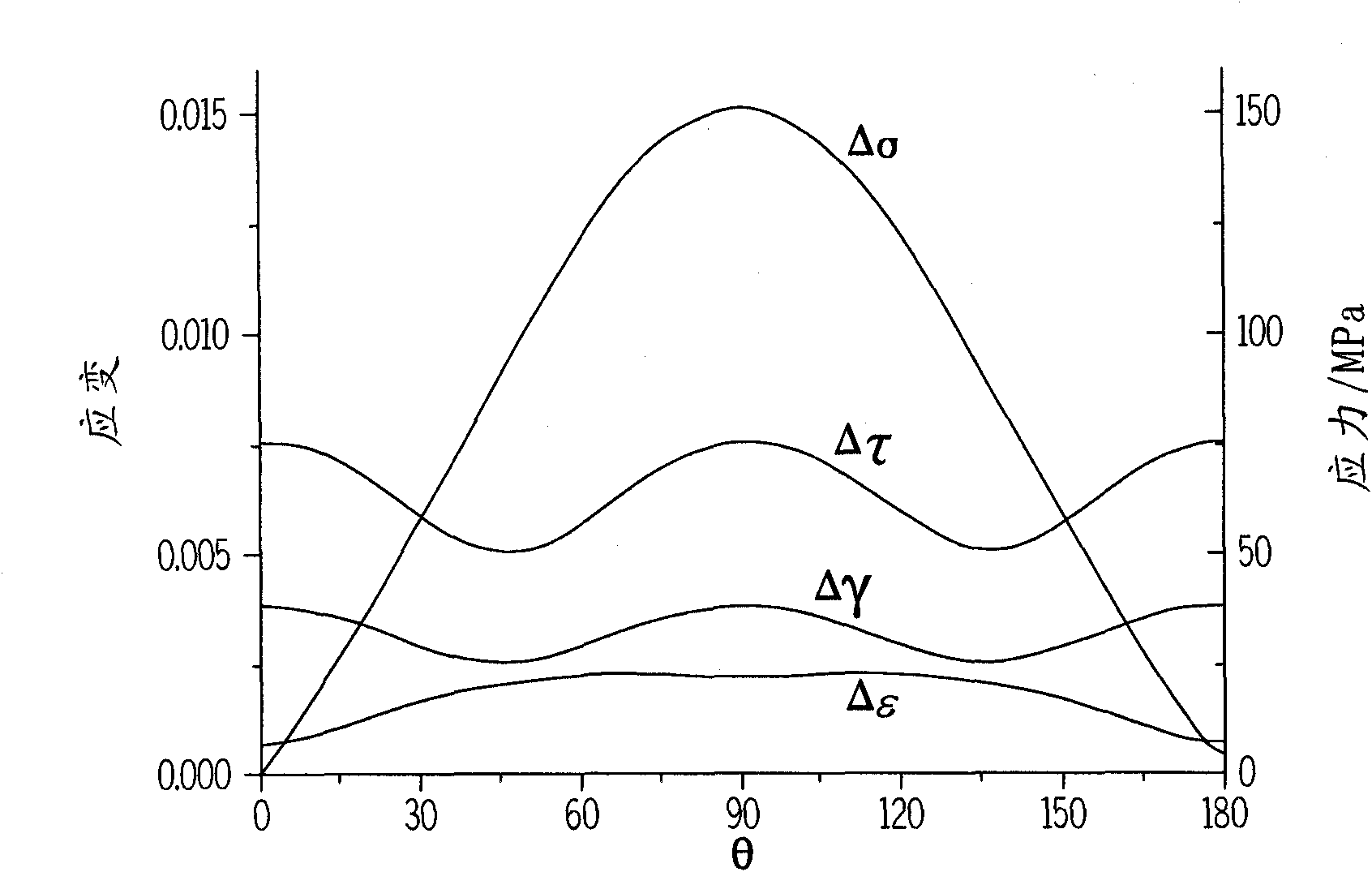
Systems and methods to predict fatigue lives of aluminum alloys under multiaxial loading
A system to predict a fatigue life of an aluminum alloy is disclosed herein. The system comprises a computer-readable medium cooperative with micromechanics-based fatigue life models for cyclic multiaxial loading. The fatigue life models predict the fatigue life by processing information received by the system relating to the aluminum alloy and the stress state present in the aluminum alloy. The received information comprises at least one of: a critical shear plane, a damage factor, a hardening factor defined by at least one of a plurality of uniaxial cyclic hardening factor parameters related to probabilistics of defects and microstructure characteristics in the aluminum alloy, an additional hardening factor related to non-proportionality, and thermophysical and mechanical properties of the aluminum alloy. The defects and microstructure characteristics can be calculated using mathematical modeling of casting, solidification and heat treatment processes or by an extreme value statistics based on metallography measurements.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Metallographic etched process for displaying G Cr15 original austenite grain border
InactiveCN101187606AShorten the timeGood reproducibilitySurface/boundary effectPreparing sample for investigationAlcoholMetallography
A metallographic corrosion method for displaying a GCr15 original austenitic grain boundary comprises adding picric acid 5g into distilled water100ml and mixing continuously, then adding sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate 5ml 50% and mixing, finally adding ferric chloride 2g, and using after placing for 24 hours. A sample is grinded roughly, grinded finely, polished, cleared, dried, immersed into caustic erodent for 2-5 minutes according to normal method under a quenching tempering condition until etched surface is changed into silver grey, cleaned up through flowing water, cleaned with alcohol 95%, and dried. If the sample is over-corroded, polishing paste W0.5-1.0 or metallographic polishing egent0.5-1.0 is added on silk polishing cloth, the sample is polished slightly with hands, then cleaned with alcohol 95%, and dried. According to practical condition, grain granularity measurement can adopt methods of picture contrast, grid, intercept, quantitative metallography, and the like, to assess according to relevant standards.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing aluminum/lead system laminar composite material metallic phase example and display organization
InactiveCN101319974AAvoid pollutionAvoid dangerPreparing sample for investigationMetallographyLead system
A method for preparing a metallography sample and a display tissue of a softer substrate aluminum / lead laminar composite is characterized by including the special working procedures of sample intercepting and besetting, manual kibbling, mechanical fine grinding, rough polishing, fine polishing, etc. The invention successfully prepares a sample which can be used for observing the metallography of the laminar composite of an aluminum-lead system as well as scanning the combining situation of the interface tissues of an electron microscope. The method of the invention has the advantages that the sample preparing method is simpler and more convenient and relates to a technology which can obtain a very clear and complete microscopic tissue.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
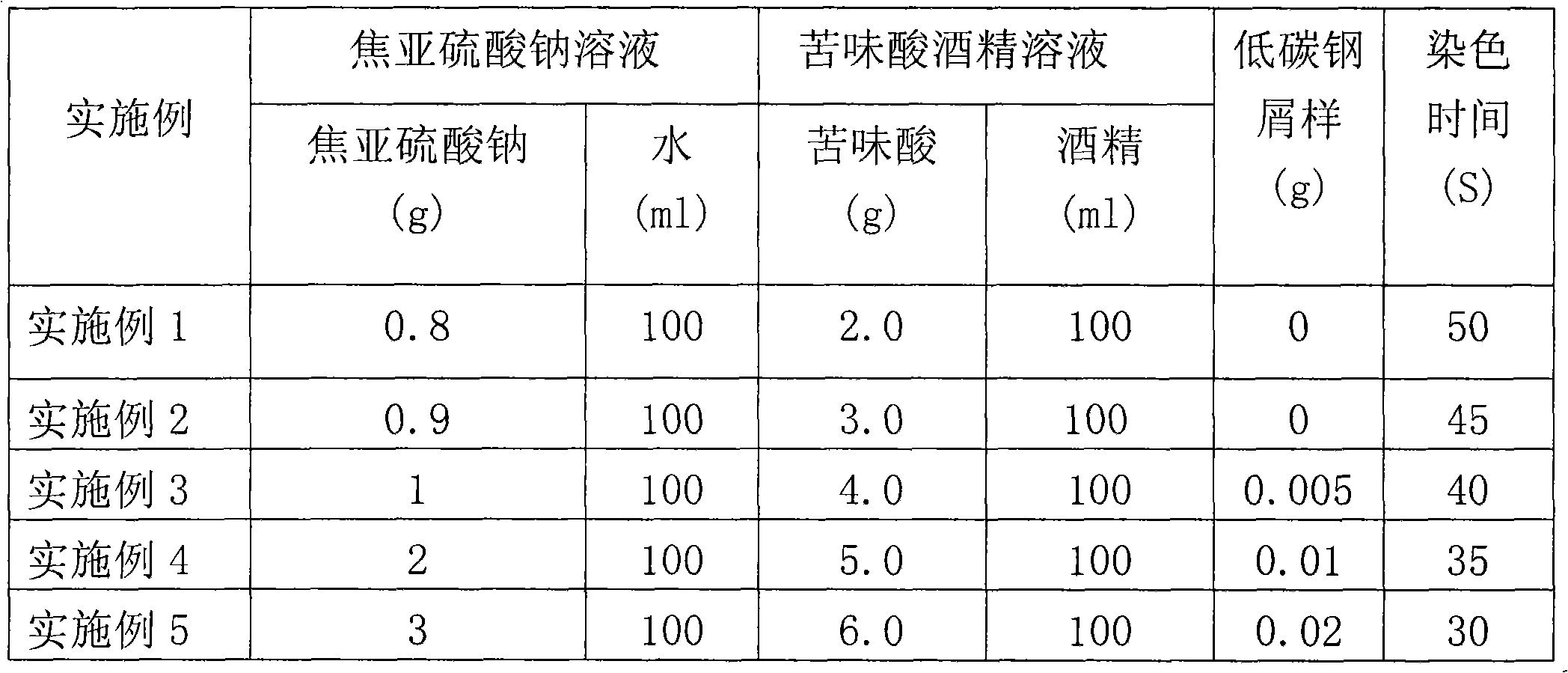
Dual-phase steel color metallographic coloring agent and color display method thereof
ActiveCN102011119AImprove performanceNovel ideaPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansColor imageMaterials science
The invention discloses a dual-phase steel color metallographic coloring agent and a color display method thereof, belongs to a decoration agent for steel material metallographic display, and in particular relates to a decoration agent for steel color metallography and a color metallographic display method. The color metallographic coloring agent is prepared by mixing 40 to 60 volume percent of 0.8 to 3.0 percent sodium pyrosulfite solution and 40 to 60 volume percent of 2.0 to 6.0 percent picral and adding 0 to 0.02g of low-carbon steel scrap sample at the constant temperature of between 30 and 40 DEG C, and is prepared by the steps of sampling, coarse grinding, fine grinding, coarse polishing, fine polishing, coloring agent solution preparation, coloring, microstructure observation, color image acquisition and black-and-white image acquisition. The invention has the advantages that: the concept is novel, the coloring agent solution has stable performance, and the coloring process issimple and reliable; and the coloring agent solution can clearly distinguish bainite or island martensite and a polygonal ferritic structure in dual-phase steel, provides guarantee for the identification and quantitative detection of a microstructure in the steel, facilitates the research and development of products and achieves obvious economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
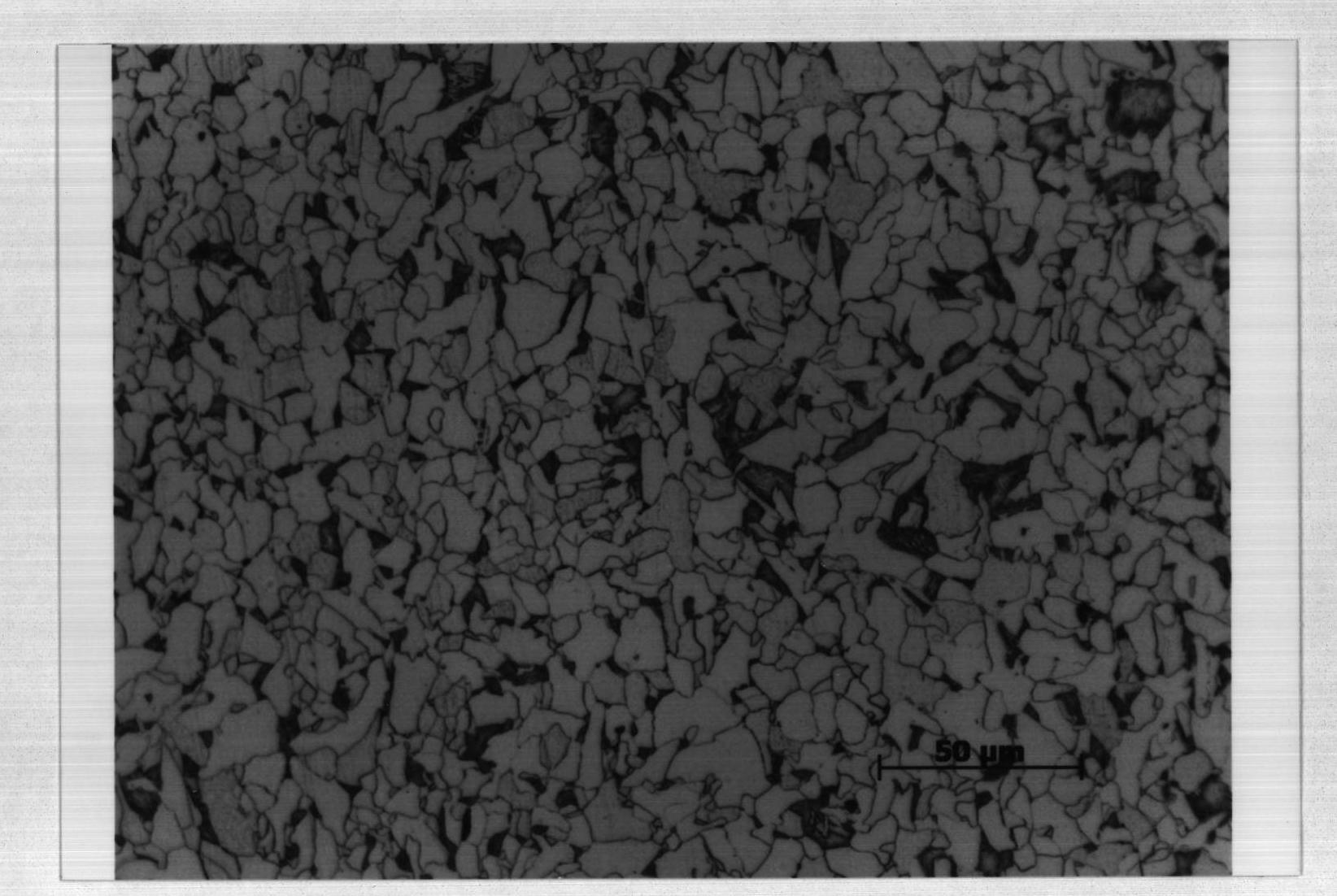
Metallic phase automatic detection method for stainless steel casting blank foreign matter
InactiveCN101403678AGuaranteed to be clearly visibleRelatively small errorSurface/boundary effectOptically investigating flaws/contaminationForeign matterSteel casting
The invention discloses a stainless steel casting inclusions metallography automatic detection method aims to be simple, practical and to be provided with the comparative small error. The invention firstly makes samples and then adopts a horizontalizer to press the sample into horizontal form; then the sample is arranged on an automatic carrier; the microscope is adopted to observe the sample; the CCD is adopted to shoot the inclusions image into the image frame of an inclusion analysis software; after the image is regulated well the standard ASTM E1245 adopted by the automatic image analysis to measure the inclusions quantity in steel and other metals is adopted to set the characteristic value of the inclusions; the characteristic values of the inclusions of sulfide and oxide are also set; and the inclusion analysis software is adopted to detect the inclusions in the sample and the detection results are output in a report form.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Method for producing special fastener
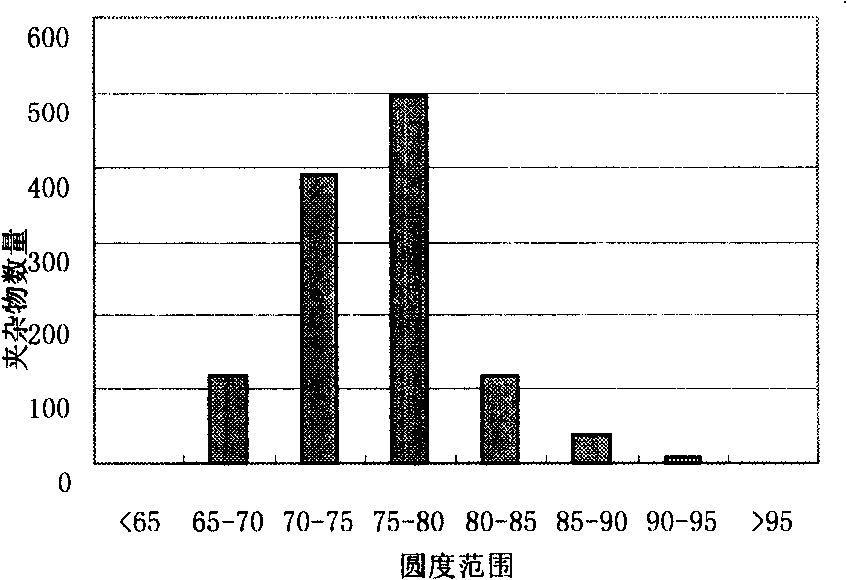
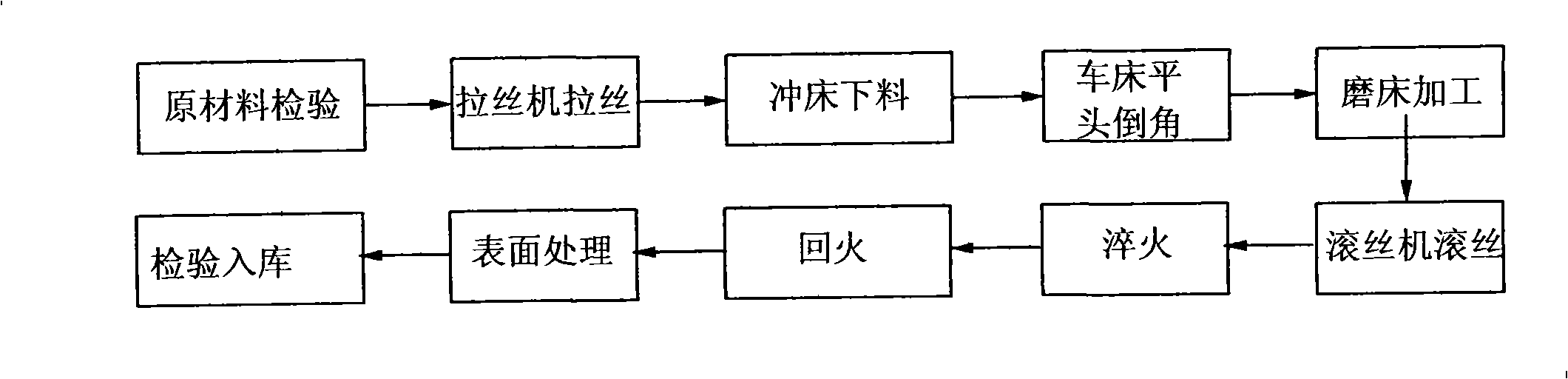
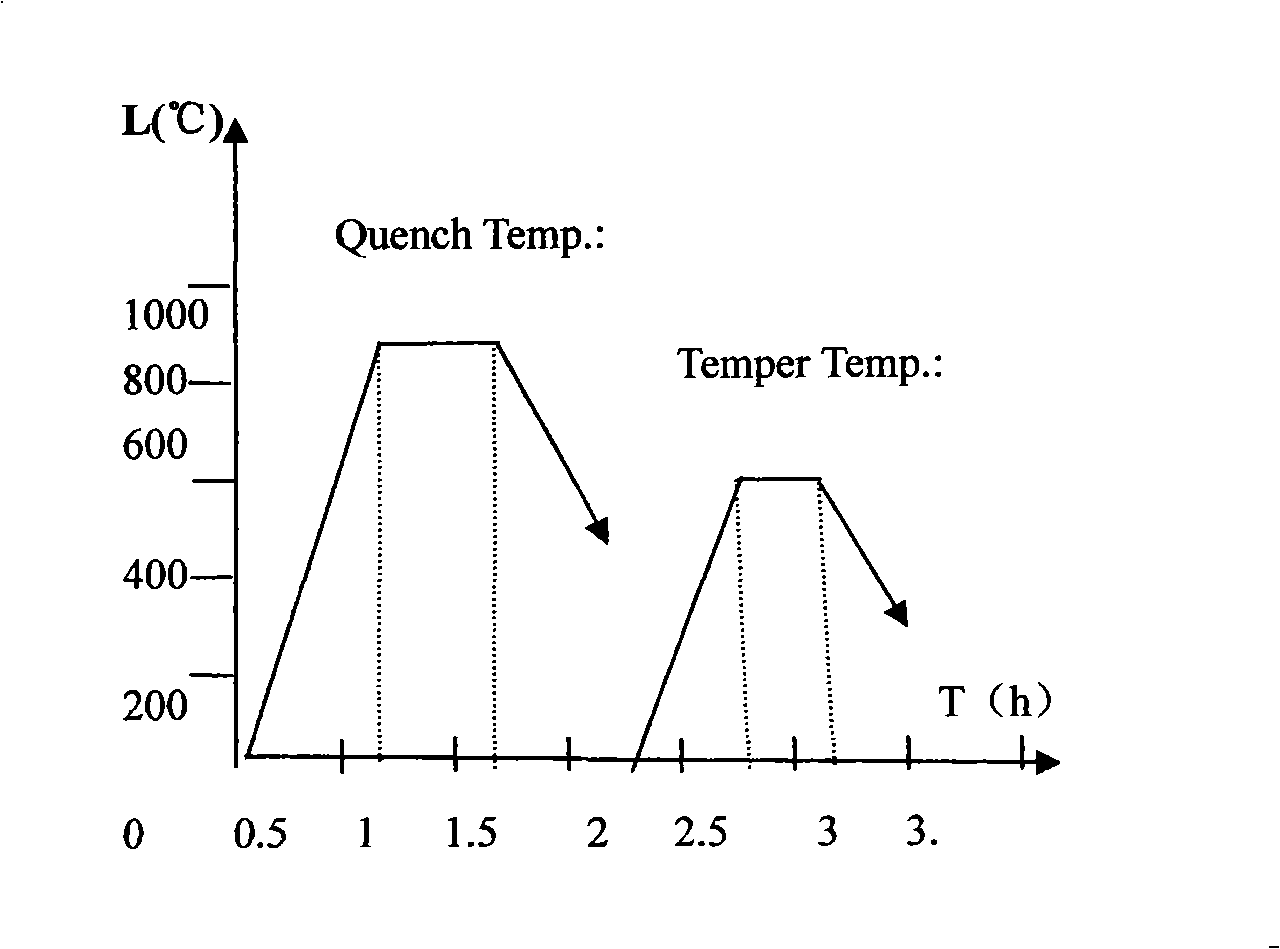
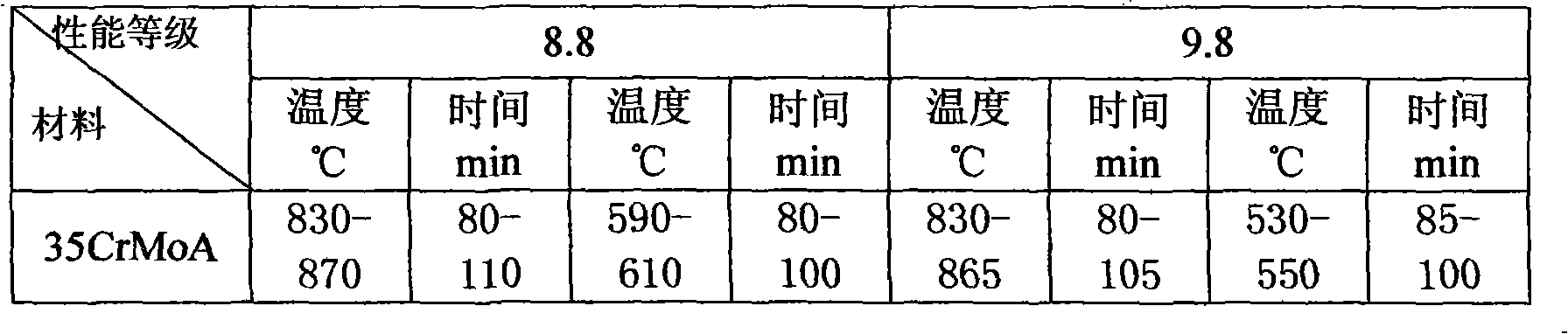
The invention discloses a fabrication method of special fastener, comprising a blank preparation, a heat treatment technology, a surface treatment technology and inspection of finish product. The invention utilizes 42CrMoA which is made in China as raw material, adopts a controllable atmosphere quenching furnace, and obtains the ideal temperature and time of quenching and tempering in heat treatment technology via massive theory instruction and test data. By strictly controlling the temperature and the time as well as carrying out the qualitative investigation of metallography and the test of entire mechanical performance, the invention can greatly strengthen the comprehensive performance of material and promote the corrosion resistance of products by coordinating with the special surface treatment technology. By examined, the special fastener which is prepared by using the invention can have the mechanical performance of 8.8 / 8 levels and above, the impact energy of the low temperature impact property of more than 40 Joule at minus 101 DEG C, the salt spray resistance of more than 4000 hours, and has the advantages of the high strength, the low temperature resistance and the corrosion resistance.
Owner:浙江高强度紧固件有限公司
Casting technique for low-temperature high-tenacity nodular cast iron butterfly valve body
ActiveCN105385802AMeet the operating requirements of low temperature environmentGood spherical effectProcess efficiency improvementMaterials preparationChemical composition
The invention relates to a casting technique for a low-temperature high-tenacity nodular cast iron butterfly valve body. The casting technique for the low-temperature high-tenacity nodular cast iron butterfly valve body comprises the first procedure of smelting, the second procedure of nodularization and inoculation, the third procedure of pouring and pulling out of a box, and the fourth procedure of heat treatment. The procedure of smelling comprises the first step of material preparation and the second step of smelling. According to the casting technique, strict material proportioning is conducted, material feeding for fusion is conducted in batches by two times, silicon carbide is added in the time interval between the two times of material feeding, and a traditional melting process is changed; a nodulizing agent is protected by combining a dam type nodulizing bag and a compacted nucleating agent, so that the nodulizing time and the nodulizing way are controlled; in addition, nodulization is conducted in batches, then mixing is conducted, and thus an ideal nodulizing effect is achieved; the chemical elements of a final product discharged out of a furnace are ideal, the metallography detection index is excellent, the mechanical property is excellent, and the requirement for operation of a valve in a low-temperature environment is completely met.
Owner:HEBEI YULONG CASTING
Heat treatment method for diesel engine cam
InactiveCN101476029AReduce distortionReach hardnessSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesMechanical equipmentCam
The invention discloses a diesel engine cam thermal treatment method comprising a carburizing step, a quenching step and a tempering step.After the carburizing step, a pit cooling method is adopted for reducing the deformation of the cam because of the heat treatment process, two times of alkaline bath quenching are adopted for not only reducing thermal stress and deformation, but also having functions of thinning heart crystal grains and eliminating network carbide for satisfying metallography requirement in the first quenching process of the cam, and having a function of assuring to obtain cryptocrystal martensite, residual austenite and partial of granule carbide on the surface for satisfying performance requirements of rigidity, wearing resistance property, contact fatigue degree and the like of the cam surface in the second quenching process of the cam;simultaneously, the cam heart can obtain lath martensite and fine homogeneous ferrite, and the mechanical property of the cam heart can be improved; according to the invention, design requirements of heat rigidity, wearing resistance property, fatigue strength, mechanical property of the cam heart and deflection can all be satisfied, therefore, the manufactured cams can be extensively used in large-scale heavy-duty mechanical equipment.
Owner:CHONGQING YUEJIN MACHINERY
Martensite high-alloy heat resistant steel metallography detection polishing agent and application thereof
InactiveCN101831653AThe preparation method is simple and easyImprove polishing effectPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEMetallography
The invention relates to a Martensite high-alloy heat resistant steel metallography detection polishing agent, and the polishing agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1.8-2.2 parts of oxalic acid, 0.8-1.2 parts of hydrofluoric acid, 10-30 parts of water and 30-50 parts of hydrogen peroxide. The invention also relates to the application of the polishing agent in metallography detection, which comprises the following steps: (1) abrading; (2) polishing; (3) corrosion: a test surface of Martensite high-alloy heat resistant steel is corroded by chemical etchant, thus displaying a microscopic metallographic structure; (4) replication: a medical film is applied to the test surface of the Martensite high-alloy heat resistant steel, and micro morphology of the metallographic structure is extracted; and (5) observation: taking pictures and evaluation. The Martensite high-alloy heat resistant steel metallography detection polishing agent and the application have scientific compatibility, simple fabrication process, good polishing effect and high innovation and can effectively prevent pseudophase from generating in polishing.
Owner:STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER +1
Manufacturing method for large driving wheel forged pieces
ActiveCN104858344AExtended service lifeImprove consistencyMetal-working apparatusWheelsMetallographyPunching
A manufacturing method for large driving wheel forged pieces includes the first step of blank forming including blanking, heating and blank forming, the second step of hammer forging including heating and hammer forging, the third step of trimming, punching and shaping, the fourth step of thermal treatment including suspended hardening and tempering, hardness detection and metallography detection, the fifth step of finishing including cleaning and grinding, and the sixth step of inspection including fluorescent magnetic particle flaw detection, dimension inspection and appearance inspection. The large driving wheels are forced integrally in a hammer forging mode, so that the driving wheels are good in strength; an annular intermediate billet is used, and the utilization rate of materials is high; all teeth of the driving wheels are cut at a time in the step of trimming, punching and shaping, and are of good consistency; the driving wheels are subjected to suspended hardening and tempering and thermal treatment, so that deformation caused in the thermal treatment process is effectively reduced; by adoption of integral forging, the production process is simple, the production cycle is short, the production cost is low relatively, reliability is good, and quality is stable.
Owner:FIRST TRACTOR
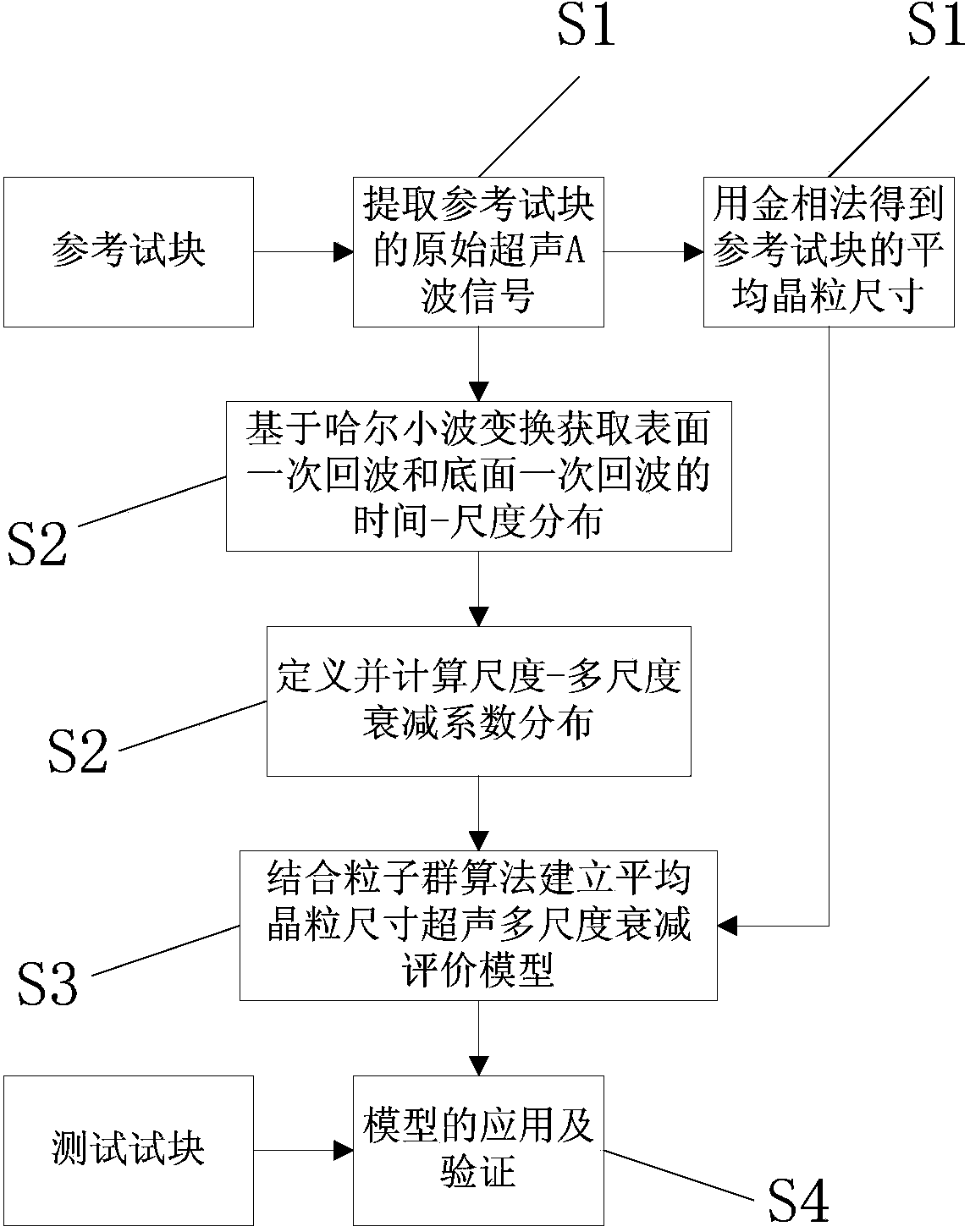
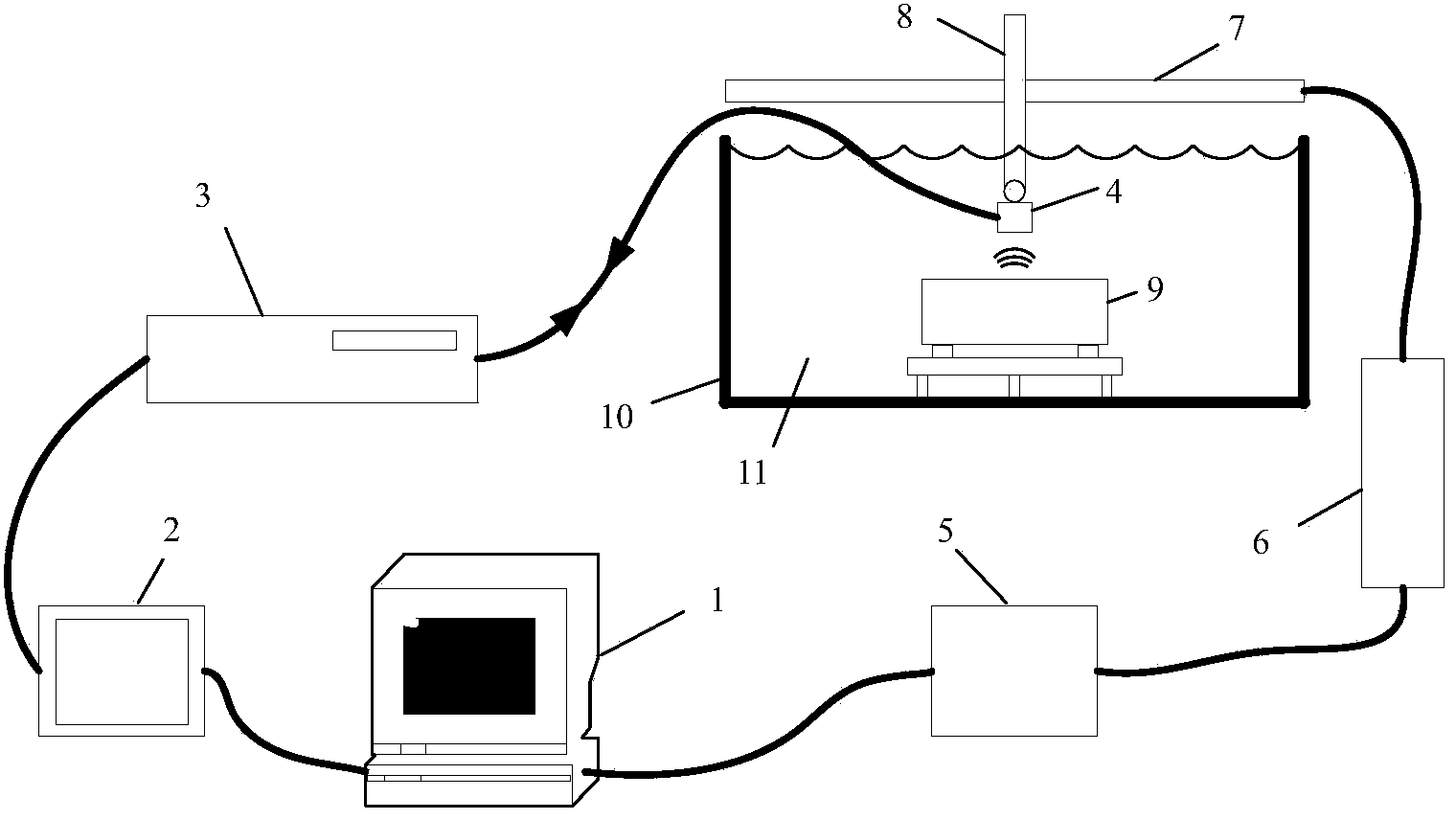
Grain size nondestructive evaluation method based on haar wavelet
ActiveCN104101651ASuppress random errorsReduce mistakesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationData acquisition
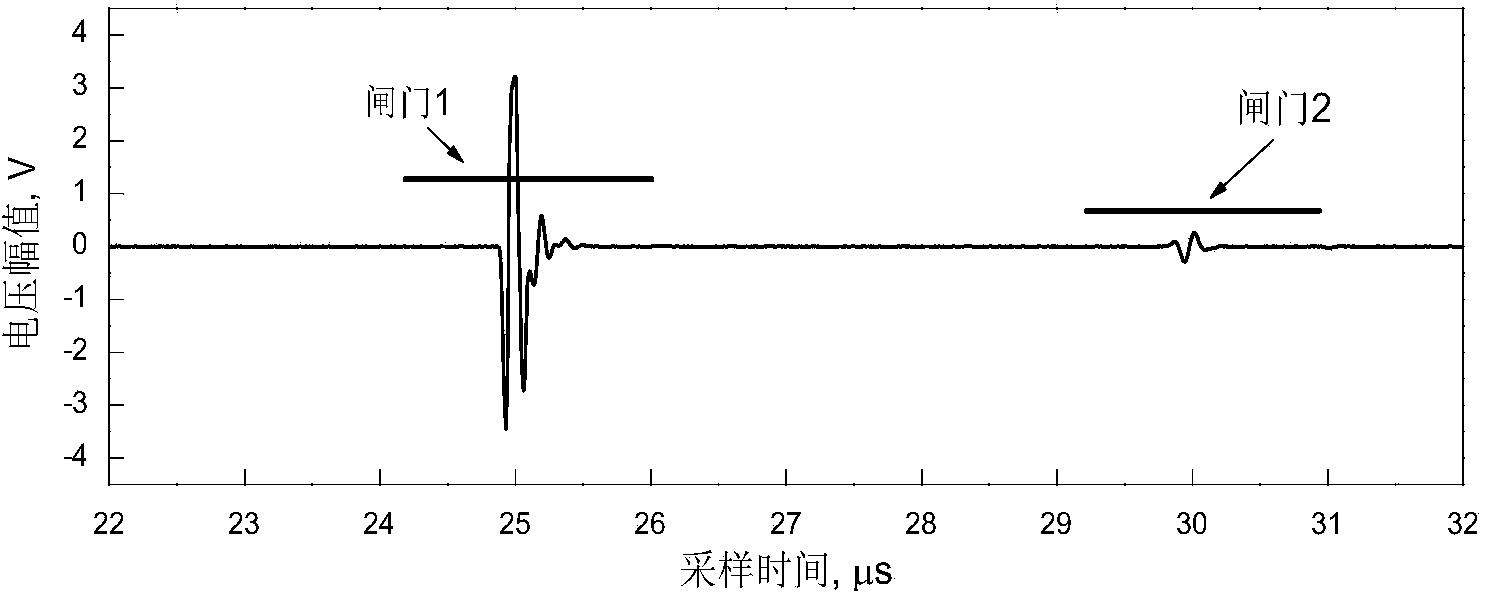
The invention discloses a grain size nondestructive evaluation method based on haar wavelet. The method comprises the following steps: data acquisition is conducted on a reference test block, time-size distribution is obtained by utilizing haar wavelet transform, furthermore, the average multi-scale attenuation coefficient of all reference blocks is calculated, an ultrasonic multi-scale attenuation evaluation model for the average grain size is built according to the preset size assembly and the preset normalized weight, and finally grain size evaluation of the test block of which the grain size is unknown is realized through the built ultrasonic multi-scale attenuation evaluation model of the average grain size. The method reduces system errors in grain size measurement; for test blocks of which the average grain size is 103.5 [mu]m measured by adopting metallography, the evaluation result is 101.7 [mu]m, and the error is controlled to be + / -2%. Therefore, through multi-scale analysis of original ultrasonic A signals, the method provided by the invention can discover more rich grain size information in the original ultrasonic A signals, and further improves the nondestructive evaluation precision of the grain size.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Color metallography coloring method of aluminum alloy
InactiveCN103471897AThe method steps are simpleGood coloring effectPreparing sample for investigationMetallographyAlcohol
The invention discloses a color metallography coloring method of an aluminum alloy. The color metallography coloring method comprises the following steps of (1) pre-etching, namely immersing a polished aluminum alloy metallographic specimen in an etching liquid for 1-10 minutes, after ending etching, washing with running water, cleaning with ethyl alcohol, and drying, wherein the etching liquid is a solution obtained by dissolving potassium chloride or sodium chloride in phosphoric acid or a solution prepared by phosphoric acid, nitric acid and water; and (2) coloring. The color metallography coloring method has the advantages that steps are simple, the coloring effect is good, and a clear grain structure can be obtained, namely, the clear microstructure can be obtained without adopting polarized light and sensitive hue for observation.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for measuring martensite content in heat rolling dual-phase steel
InactiveCN103411815AIncrease contrastAchieve complete statisticsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectronMaterials science
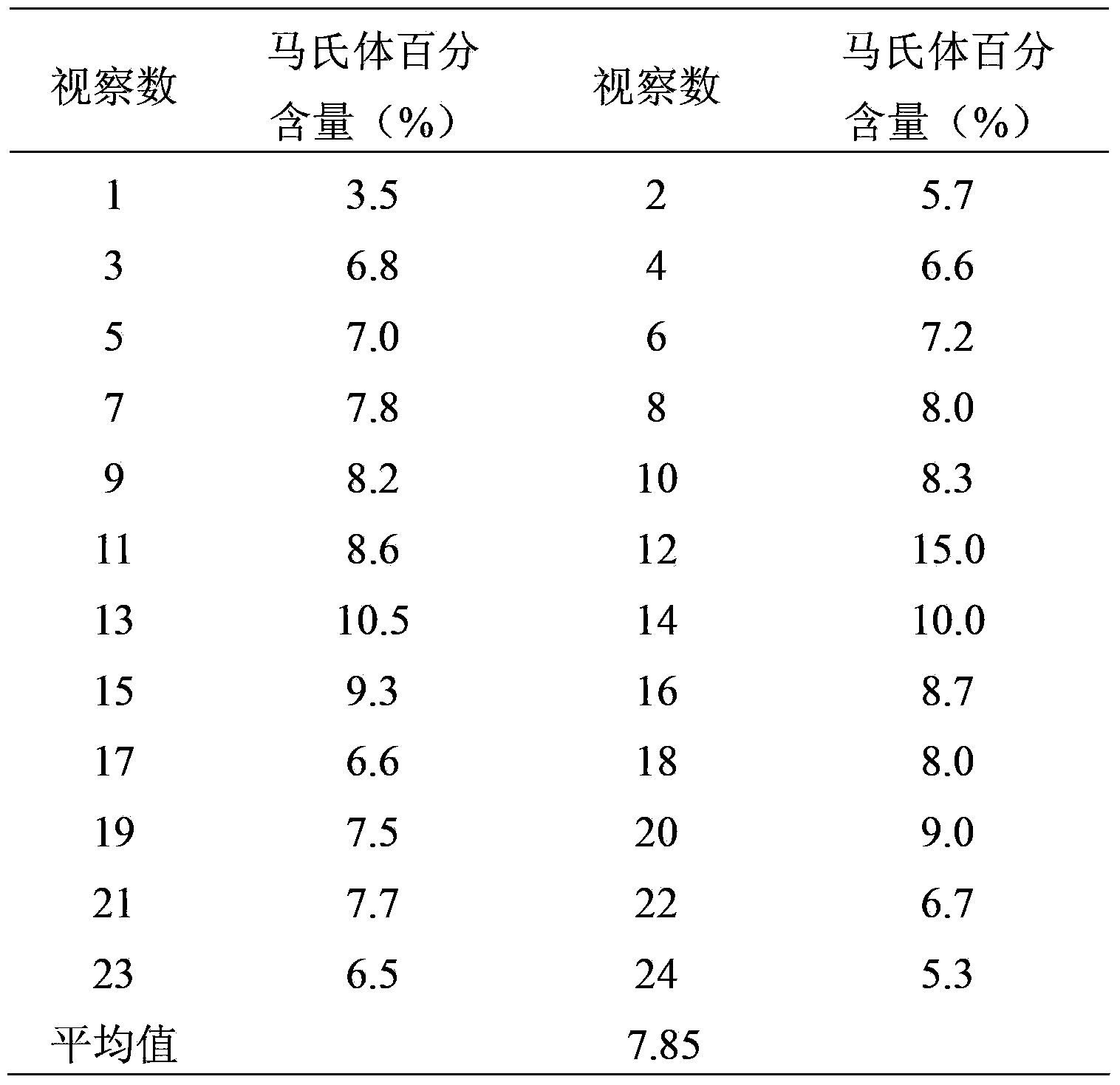
The invention provides a method for measuring martensite content in heat rolling dual-phase steel. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: forming a sample to be measured of the heat rolling dual-phase steel with a smooth surface; performing grinding and burnishing on the sample to be measured, and placing the sample to be measured into a mixed solution for corrosion, wherein the mixed solution is prepared by mixing a water solution of sodium metabisulfite with the mass concentration of 0.85-1.4% and a alcoholic solution of trinitrophenol with the mass concentration of 3.9-4.2% according to the volume ratio of (0.9-1.1):1; cleaning and drying the sample to be measured; shooting a plurality of electronic photos in the thickness direction of the sample to be measured; using metallography image analysis software to process the plurality of electronic photos to obtain the martensite content of the sample to be measured. The invention has the advantages that the method can realize complete statistics for a differential view field, can increase contrast degree of grayness of each tissue, and can accurately measure the martensite content in the heat rolling dual-phase steel.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Display method of tempered martensitic steel carbide colour metallography and electrothermal metallographic chromogenic device special for display method
ActiveCN102364323ADisplay clearEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationMetallographyCarbide
The invention discloses a display method of tempered martensitic steel carbide colour metallography, comprising the following steps of: (1) grinding and polishing the surface of a tempered martensitic steel sample to obtain a tempered martensitic steel metallographic sample; (2) heating the tempered martensitic steel metallographic sample in the oxidation atmosphere to 400-500 DEG C, keeping warm for 6-15 minutes, and forming an interference oxide-film, which makes the microstructure of metal and alloy to present different colors by the action of light, on the surface of the tempered martensitic steel sample, so as to display the tempered martensitic steel carbide color metallography. The method provided by the invention can be used to effectively display and raise the contrast between the T91 steel carbide and the matrix microstructure, so as to effectively observe the microstructure form of the martensitic steel.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
Austenitic stainless steel metallography corrosion agent and austenitic stainless steel metallography display method
InactiveCN104532242AEasy to getReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationAcetic acidHydrofluoric acid
The invention provides an austenitic stainless steel metallography corrosion agent with good erosion effect, and an austenitic stainless steel metallography display method. The corrosion agent has the advantages of simple preparation, convenient operation and small pollution, and the display method had the advantages of good stability and reappearance, and rapid, uniform and clear display of the microstructure. The display method comprises the following steps: mixing 1 part by volume of nitric acid with the mass concentration of 65-68% with 3 parts by volume of hydrochloric acid with the mass concentration of 36-38%, 1.5-3 parts by volume of acetic acid with the mass concentration of 36% and 1 part by volume of hydrofluoric acid with the mass concentration of 40% or more, slightly stirring by using a stirring bar for 20s, standing for 30min to prepare the corrosion agent; immersing a polished austenitic stainless steel sample in the corrosion agent, making the corrosion surface of the sample vertical to the surface of the corrosion agent during immersion, slightly stirring the sample, and allowing the sample to be immersed for 35-60s until the corrosion surface is argenteous; and taking out the immersed sample, flushing by using clear water, carrying out spray washing by using anhydrous ethanol, and carrying out blow drying to obtain the austenitic stainless steel structure to be observed.
Owner:ZHENSHI GROUP EASTERN SPECIAL STEEL
Second-level system progress control method and device of hot rolled strip rolling mill
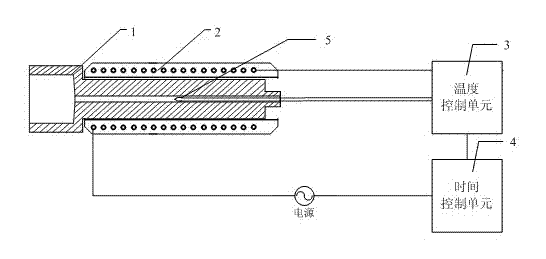
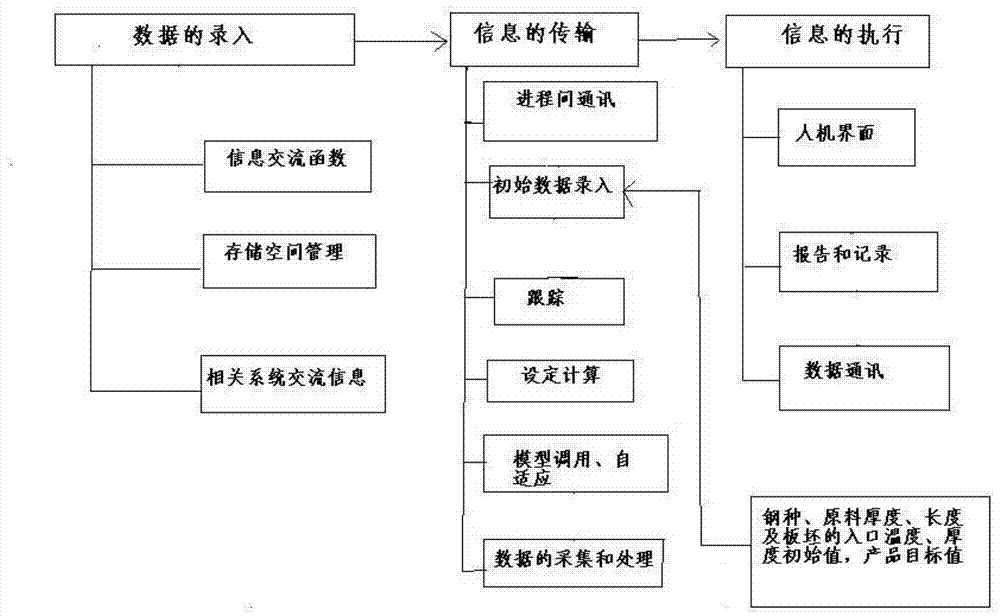
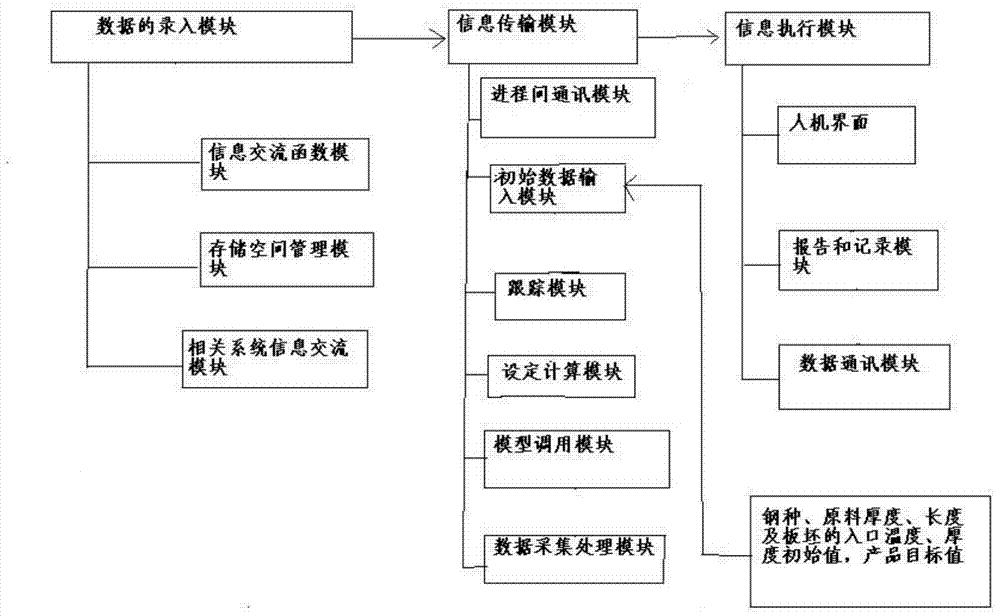
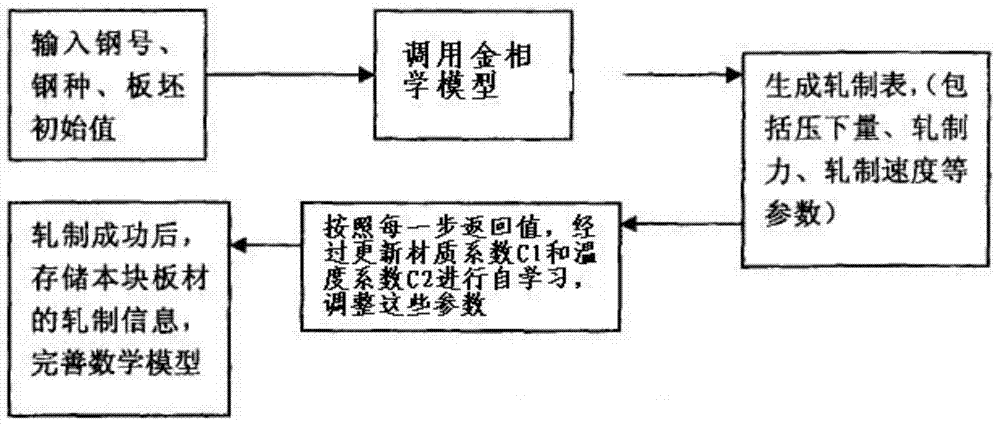
ActiveCN104281088AProgram error location is fastFast error locationNumerical controlSoftware engineeringInter-process communication
The invention relates to a second-level system progress control method and device of a hot rolled strip rolling mill. According to the method, OpenVMS system software is converted to a windows platform, and the method mainly includes the steps that an information exchange function is modified; storage space management is rewritten; windows communication foundation and a remote procedure call frame on the basis of c++ compiling are adopted for rewriting inter-process communication; a program of a minicomputer second-level system is modified to communicate with other systems, and other systems are not modified; a roll steel model and steel mill data are combined with software engineering through a metallography model. Because the OpenVMS system software is converted to the windows platform, visual studio c++ of Microsoft can be used for visual programming, and meanwhile a lot of class libraries provided by Microsoft are used for greatly improving programming efficiency. Due to the fact that visual studio c++ is used for visual programming, the readability of the program is remarkably improved, and a debugging tool provided by Microsoft can be adopted for conveniently and rapidly positioning a program error and greatly improving debugging efficiency. Due to the convenient visual debugging tool, error search time can be shortened to 5-6 minutes from 20-30 minutes, and then working efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU JINHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
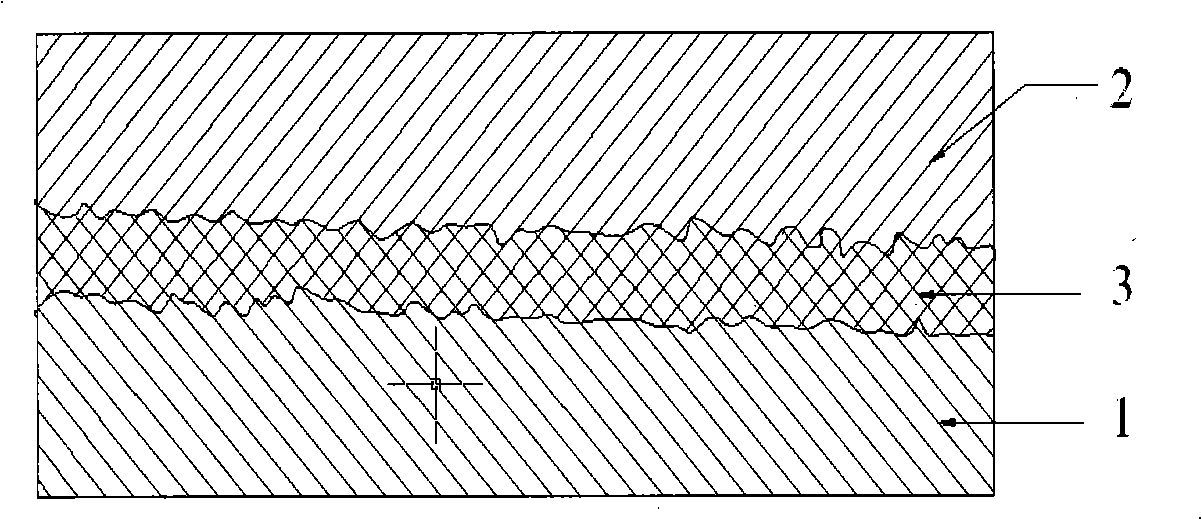
Metallography detection method for bonding interface having honeycomb sandwich structure
InactiveCN102928433AWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMetallographyBond interface
The present invention relates to a metallography detection method for a bonding interface having a honeycomb sandwich structure, wherein a sample is cut from a honeycomb structure or a performance test part, cold inlaying is performed, a metallography sample is grinded, and a bonding state of a glue film and a honeycomb is observed through a metallurgical microscope. According to the present invention, if the honeycomb inserts into the glue film deep and the glue film climbs on the surface of the honeycomb, the bonding strength is high and the bonding quality is good, if the honeycomb inserts into the glue film deep and the glue film does not climb on the surface of the honeycomb, or the honeycomb inserts into the glue film shallowly and even does not enter the glue film and the glue film climb on the surface of the honeycomb less or does not climb, the bonding strength is low and the bonding quality is poor, and the bonding is the weak bonding or the virtual bonding, wherein the bonding quality is related to a temperature, pressure and a pressurization time during a curing process.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Coloring method for wrought aluminum alloy welded joint color metallography
ActiveCN104359742AHigh contrast displayClear grain boundariesPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansAcid etchingMetallography
The invention provides a coloring method for wrought aluminum alloy welded joint color metallography. The method comprises pre-etching and coloring, wherein the pre-etching comprises an acid etching processing step which comprises procedures as follows: an acid etching solution is heated to 55-65 DEG C, dripped on a workpiece surface for 50 s-60 s, flushed by a large amount of deionized water and dried by hot air, and the acid etching solution adopts an aqueous solution comprising 0.3-0.5 mol / L of Cl<->, 1.4-1.8 mol / L of H<+> and 0.3-0.5 mol / L of PO4<3->; and according to the coloring, a test piece after etching processing is soaked in a Weck reagent completely, shaken slightly for 5-10 s, flushed by a large amount of deionized water after surface coloring and dried by hot air. With adoption of the method, the success rate for test piece preparation is high, the repeatability is high, the cost is low, and the wrought aluminum alloy welded joint color metallography processed with the method has the advantages of high contrast display, clear grain boundary and high test result accuracy.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG CO LTD
In-situ structure analytical method for nodular cast iron metal material before and after impact fracture
InactiveCN104406847AStrength propertiesMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMicro structureMetallography
The invention belongs to the metallographic field and particularly relates to an observing and analyzing method of researching a micro structure metallograph of nodular cast iron before and after impact fracture at different temperatures. The method comprises the following steps: coarsely grinding, finely grinding, polishing and corroding two side faces of a V-shaped notch of a nodular cast iron impact test sample; observing under a microscope; selecting a classical region near the V-shaped notch; pressing a microhardness indentation at the center of the region as a mark, and photographing and storing; then, carrying out a Charpy notch impact test at different temperatures ranging from 20 DEG C to minus 80 DEG C; finally, combining the microhardness indentation and surrounding graphite nodule morphology features to obtain micro structure photos of a same region before and after impact so as to achieve comparative analysis of detail change of the nodular cast iron structure behind and after impact. The method is an in-situ structure analytical method which is wide in application range, simple to operate and high in reliability.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Device and method for detecting abrasion resistance of honeycomb-shaped ceramic-metal composite material
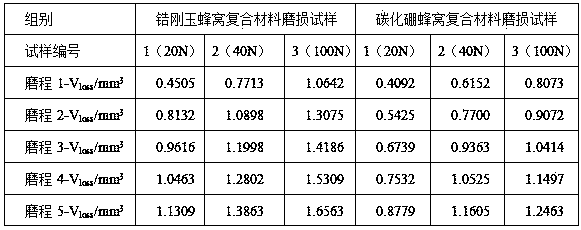
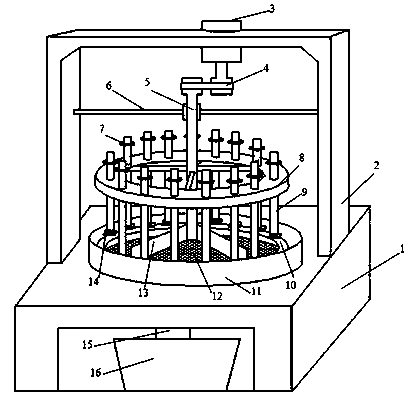
ActiveCN104880374AImprove detection efficiencyReduce detection efficiencyInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceMetallographyHoneycomb
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting the abrasion resistance of a honeycomb-shaped ceramic-metal composite material, and belongs to the field of metal based composite materials. The device comprises a workbench, a motor support, a speed adjustable motor, a conveying belt, a rotation main shaft, a rotation shaft support, a weight table, a rotation ring, a specimen rotation shaft, an abrasion rail, a baffle ring, a ground material screen, a material collecting plate, a fixture, a ground material funnel, a ground material recycling cylinder, a toughness metal column, an abrasion-resistant compounding region, a specimen clamping step, a charge oblique surface, a sclerometer electronic output meter, a quantitative metallography microscopic electronic output meter, a precise scale electronic output meter and a computer. According to the device and method, a plurality of abraded specimens are detected under different loads and the same abrasion environment condition; superfine ground materials are filtered, so that the ground materials are kept in a reasonable range, further the accuracy of the detection result is facilitated; the unique abrasion resistance advantage of the structure of the honeycomb-shaped ceramic-metal composite material in the abrasion process is reflected reliably.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Normalizing method for forging waste heat of steel
ActiveCN105886717AImprove hardenabilityExtended service lifeMetal-working apparatusAusteniteMechanical property
The invention discloses a normalizing method for forging waste heat of steel. The normalizing method is characterized in that online controlled forging and cooling isothermal normalizing treatment for forging waste heat is implemented. The normalizing method comprises the following steps of controlled forging of the steel: controlling the forging temperature and the forging deformation degree of the steel, and refining grains by deforming and recrystallizing austenite; controlled cooling of the steel: controlling cooling rates, cooling uniformity and cooling efficiency of the steel at of all critical temperatures according to the principles of metallography and heat treatment; cooling the steel to a critical temperature and keeping the isothermality; finishing transformation of super-cooled austenite within the temperature range, thus obtaining fine grain structures; and after isothermal keeping, performing controlled cooling, namely controlling the cooling rate, the cooling uniformity, the cooling efficiency and a cooling final temperature after isothermal keeping, thus obtaining the normalizing method with structure and mechanical properties up to standards. According to the normalizing method disclosed by the invention, energy sources and resources can be saved, the normalizing treatment quality is improved, the normalizing treatment cost is reduced, the labor intensity of workers is reduced, labor productivity is improved, and the construction period is shortened.
Owner:王中忞
Full-field statistical & characterizing method of fluid micro-explored strain for alloy microstructure
The invention relates to a full-field statistical & characterizing method of fluid micro-explored strain for alloy microstructure, comprising the following steps: a. grinding and polishing the surface of an alloy sample to mirror with no grinding defects, and then determining a to-be-measured area on the surface of the alloy sample; b. utilizing a white light interferometry 3D surface profiler to perform initial morphology measurement on the surface of an alloy sample; c. utilizing an isostatic pressing technology to obtain the microstructure deformation on the surface of the alloy sample, and then utilizing a white light interferometry 3D surface profiler to perform deformed morphology measurement on the surface of the alloy sample to obtain a changing spectrum of micro morphology of the microstructures on the surface of the alloy; and d. performing trans-scale and rapid quantitative statistical distribution characterization on the morphology change before and after isostatic pressing of the microstructures in the to-be-measured area of the alloy, so as to obtain a corresponding full-field metallography. In the present invention, the sample pretreatment is simple, the analysis speed is rapid, the scanning area is large, and the requirement of high throughput trans-scale analysis can be satisfied, so as to instruct the extraction of the material metallography feature unit.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Bainite steel rail welding joint, and post-weld heat treatment method for controlling 'white block' structure of bainite steel rail welding joint
ActiveCN109457101AImprove mechanical propertiesSmall white defect sizeFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesThree levelMetallography
The invention provides a bainite steel rail welding joint. From microscopic metallography, the welding joint comprises a welding seam structure and white block structures distributed on a welding seamand the periphery of the welding seam, wherein the size of each white block structure is smaller than or equal to 2000mum. The invention adopts a specific post-weld heat treatment method for the bainite steel rail welding joint, so that through a three-level cooling manner of the specific process, the bainite steel rail welding joint with a small white block defect size and less content is obtained. According to the bainite steel rail welding joint and the post-weld heat treatment method for the bainite steel rail welding joint provided by the invention, through the specific post-weld heat treatment process, the number of 'white block' defects in a microscopic structure of the welding joint can be remarkably reduced, the occurrence of the phenomenon of crack propagation of the welding joint caused by the defects of the welding area is avoided, the mechanical property of the bainite steel rail welding joint is favorably improved, the 'saddle' wear and the wheel rail impact caused by low hardness of a steel rail welding area during the railway line running process are further improved, the service life of a steel rail is prolonged, and the railway running safety is ensured.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Production method of vermicular graphite cast iron
The invention relates to a production method of a cast iron, and especially relates to a production method of a vermicular graphite caste iron. The method comprises the following steps: (1) feeding: adding titanium iron into a furnace along with the first batch of furnace charge, wherein the titanium iron accounts for 0.1 to 0.3% of the weight of the furnace charge; (2) smelting: controlling the temperature below 1380 DEG C during the smelting process, wherein the sampling temperature is 1460 to 1480 DEG C, and the overheating temperature is 1500 to 1510 DEG C; (3) embedding: adding a vermiculizer in one side of a vermicular bag, firmly pressing, covering the vermiculizer with an inoculant, then covering the inoculant with 1% to 2% of steel debris until the inoculant is firmly and fully covered, placing 0.5% to 0.8% of copper on the end that molten iron flows in; (4) rapidly discharging iron for one time, wherein the iron discharging temperature is 1470 to 1490, an inoculant slot is not used, and the molten iron is introduced into the system from the side that is not provided with the vermiculizer; (5) carrying out vermicular reactions, and finally removing the slag after the vermicular reactions. The method is unique, and the equipment for on-the-spot metallography detection is not needed to achieve the stable vermicular graphite rate.
Owner:KOCEL GROUP +1
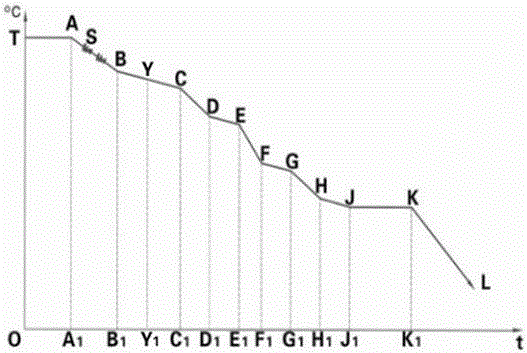
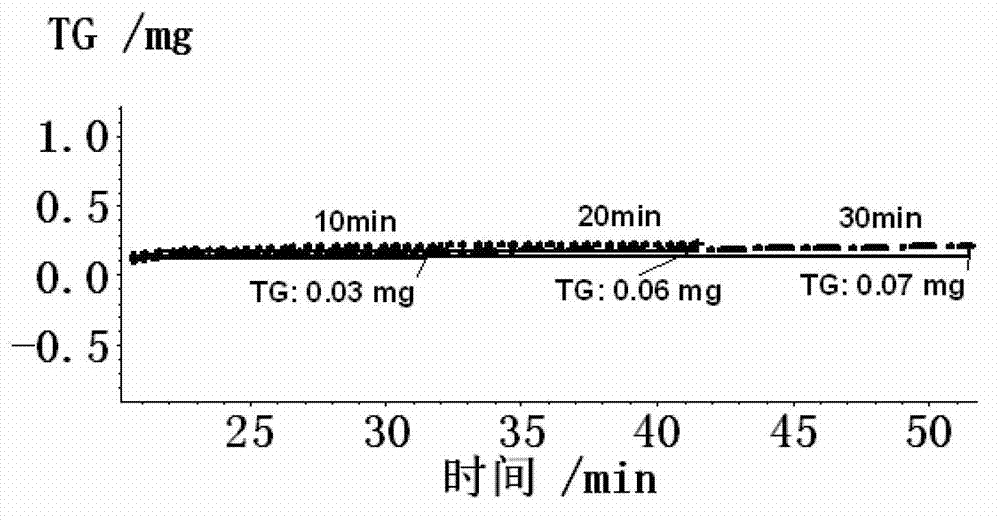
Test method for simulating oxidation and decarbonization of steel
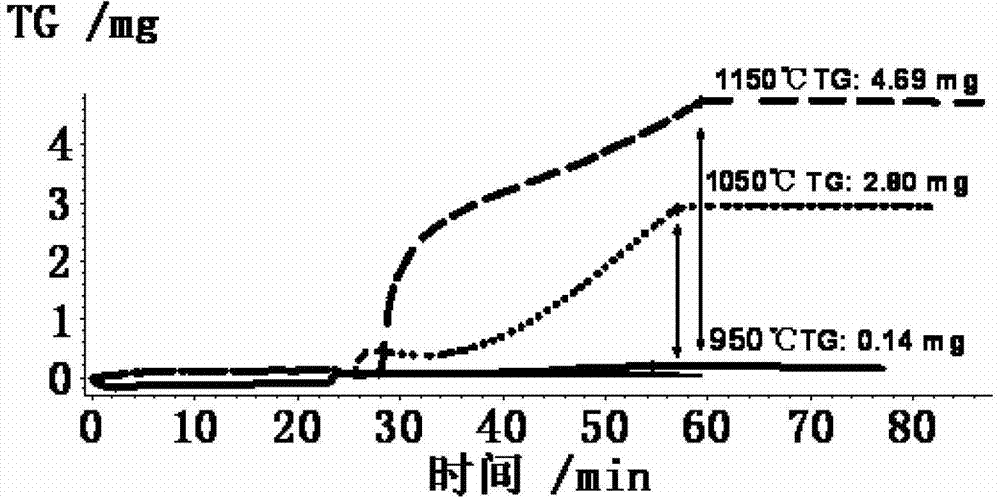
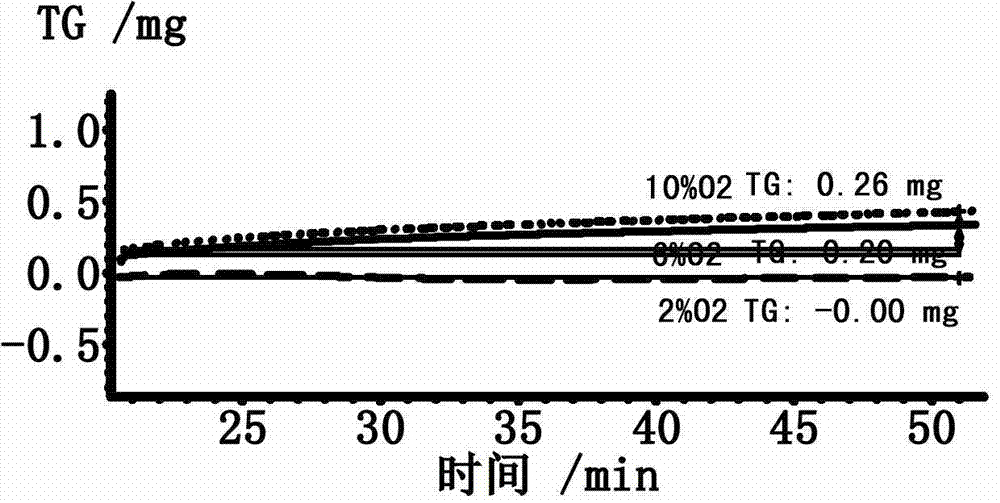
InactiveCN103045826AIn situ testing for oxidative decarburizationEnriching Oxidative Decarburization Research MethodsHeat treatment process controlMetallographyMegasonic cleaning
The invention discloses a test method for simulating oxidation and decarbonization of steel, and belongs to the technical field of steel and iron material surface quality inspection. The test method comprises the steps that a sample for simulating the oxidation and decarbonization is prepared by linear cutting; the sample is subjected to grinding, polishing, and ultrasonic cleaning treatment, and then placed into a dynamic thermogravimetric analyzer comprising a plurality of gas circuits; steel sample heating, heat preservation and cooling are achieved; thermogravimetric curves of different holding times, different heating temperatures and different gas atmospheres and the sample for simulating the oxidation and decarbonization are obtained; the depth of decarburization of the steel is determined and analyzed according to GB / T 224-2008 Determination of Depth of Decarburization of Steels by metallography; and surface decarburization of the steel is obtained. The test method has the advantages that the test method is simple, quick and effective, and enriches steel oxidation and decarbonization research methods.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Camera lens capable of conveniently connecting with microscope lens cone
The invention provides a scheme that a digital video body composed of a camera video / camera lens of a general digital video is matched with a universal microscope lens cone (an eyepiece end), wherein the digital video body and the universal microscope lens cone are combined into an incompact whole, which is used for replacing an appropriative micro digital video, can be convenient for not only microcosmic shooting in the relevant fields, such as microorganism, medicine, mineralogy, metallography, melting point microscopy and the like for basic units and amateurs, but also scientific popularization and learning activities in schools in the microscopic field. Because the digital video (digital camera), a computer (or a TV, a display and a projector) and a microscope are universal, cost is greatly lowered. A connecting kit of the lens can be two magnetic coils and can be a pair of thread bushings, plugins and fixtures. The drawing illustration comprises an internal thread bushing 1, the lens cone (the eyepiece end), two internal thread bushings 3, an internal thread bushing 3, a magnetic coil 5, a fixture 6, an eyepiece 7 and a digital camera 8.
Owner:刘汉生
Ultra-fine austempering nodular iron material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ultra-fine austempering nodular iron material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that after molten iron is drawn through a vertical continuous casting method to form a profile blank, metallography detection is conducted, then cyclic nodulizing annealing treatment is conducted, austempering treatment is conducted after rough machining or semifinishing machining is conducted, and the ultra-fine austempering nodular iron material is obtained finally through metallography detection. The requirements of the metallography detection are that within the layer depth 25 mm inwards from the surface of a profile, the nodularity of graphite is more than 90%, and the diameter of graphite nodules is not larger than 0.03 mm and is not larger than 0.02 mm within the layer depth of 10 mm; and the density of the graphite nodules is larger than or equal to 400 per mm<2> within the layer depth of 15 mm, and is 200-400 per mm<2> within the layer depth of 15-25 mm. The fineness degree of a substrate structure of the ultra-fine austempering nodular iron material exceeds the existing ADI industrial standard, and the ultra-fine austempering nodular iron material is suitable for being used for manufacturing rolling bearings with the self-lubrication function, and rigid wheels, flexible wheels and flexible bearings in harmonic reducers.
Owner:SHAN XI TONGXIN LIANZHU PIPE IND
Method for quantitative analysis of wire rod sorbite content by using imager standard sample method
ActiveCN102901729AImprove analysis accuracyEliminate Analytical ErrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansWire rodMetallography
The present invention relates to a method for quantitative analysis of wire rod sorbite content by using an imager standard sample method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting a standard sample having suitable wire rod sorbite content; 2) treating a wire rod sample requiring analysis to provide a spare use for sorbite content analysis; 3) carrying out calibration on an analysis condition Tmi by using a sorbite percentage content standard value of the standard sample to obtain a calibration gradation threshold Gs under a calibration analysis condition Tm; and 4) maintaining the constant calibration analysis condition Tm, and adopting the calibration gradation threshold Gs to carry out quantitative analysis on the sorbite content of the wire rod requiring analysis. According to the method for obtaining the wire rod sorbite content by combination of the standard sample and the image analyzer, the steel wire rod sorbite content can be accurately and quantitatively analyzed, the distribution metallography of the wire rod sample sorbite structure can be exactly observed and analyzed, and analysis error caused by different analysis conditions is eliminated, such that experiment data has good traceability and good reproducibility, and an experiment process is simple and easy to performed, and has good operability.
Owner:TIANJIN IRON & STEEL GRP
Moulded parts made of pmma powder as simple dosing aid in the manufacture of dental prostheses
Owner:HERAEUS KULZER GMBH
Display method of austenitic grain boundary of medium-manganese steel for automobile
ActiveCN105823671AAvoid cumbersome corrosion methodsAvoid Corrosion MethodsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansMetallographyAlcohol
The invention relates to a display method of an austenitic grain boundary of medium-manganese steel for an automobile, and belongs to the technical field of metallography sample preparation and austenitic grain boundary display. The method comprises the following steps that a metallography sample is processed and subjected to thermal deformation treatment, the metallography sample section is cut and inlaid, rough grinding, fine grinding and polishing treatment are conducted, etching is conducted on the polished metallography sample with sodium bisulfite etchant and nitric acid alcohol etchant successively, and observation is conducted; the etching time is reasonably controlled till the austenitic grain boundary is displayed clearly. According to the display method of the austenitic grain boundary of the medium-manganese steel for the automobile, the operation process is simple and convenient, the austenitic grain boundary of the medium-manganese steel for the automobile can be clearly and fully displayed, and therefore accurate grain size statistical results are obtained, and a key technology is provided for research on the rolling property of the medium-manganese steel for the automobile at high temperature.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com