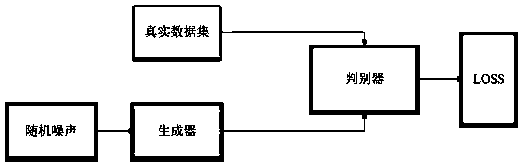
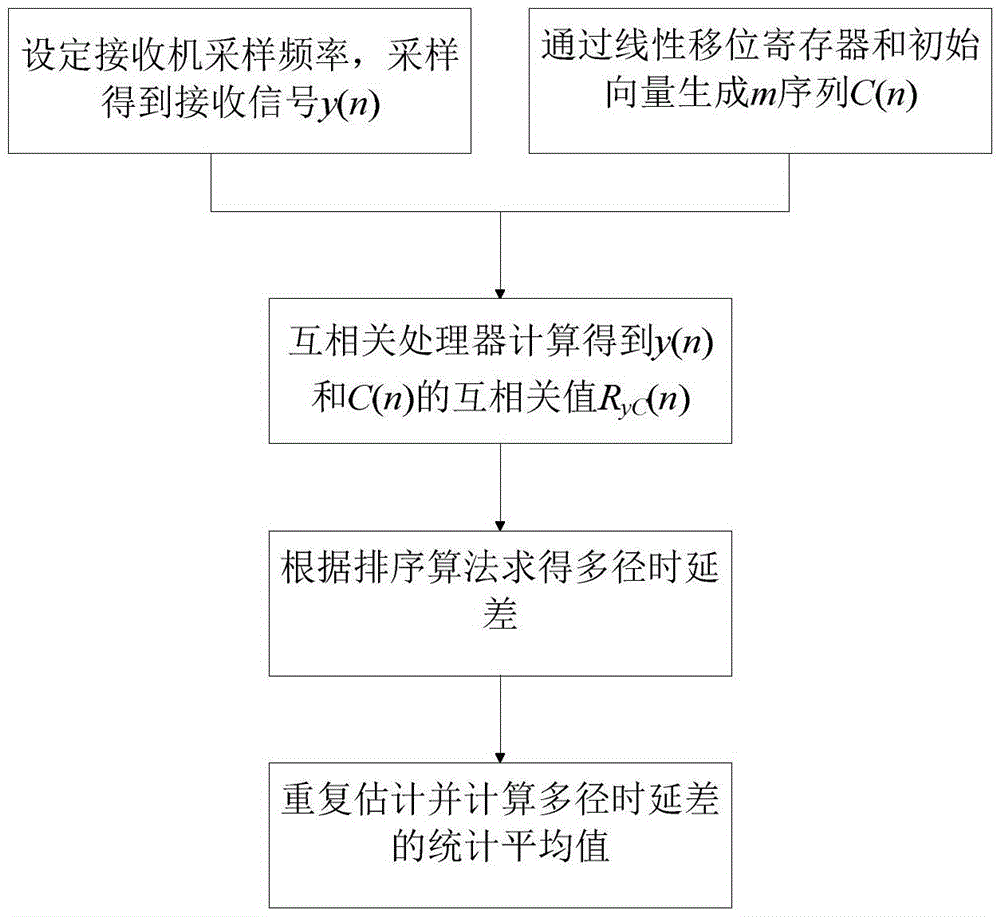
Patents
Literature
253results about How to "Reduce detection efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
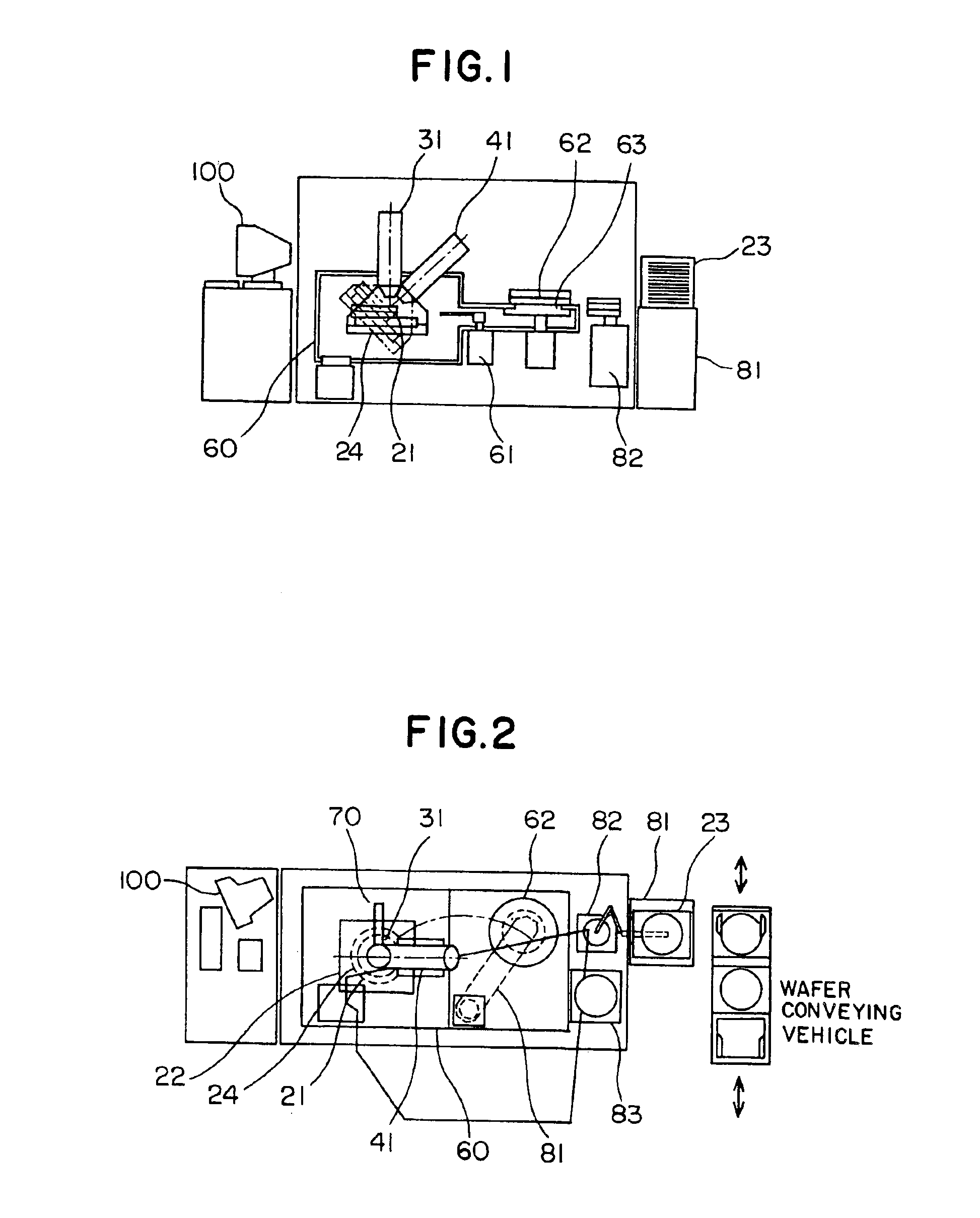
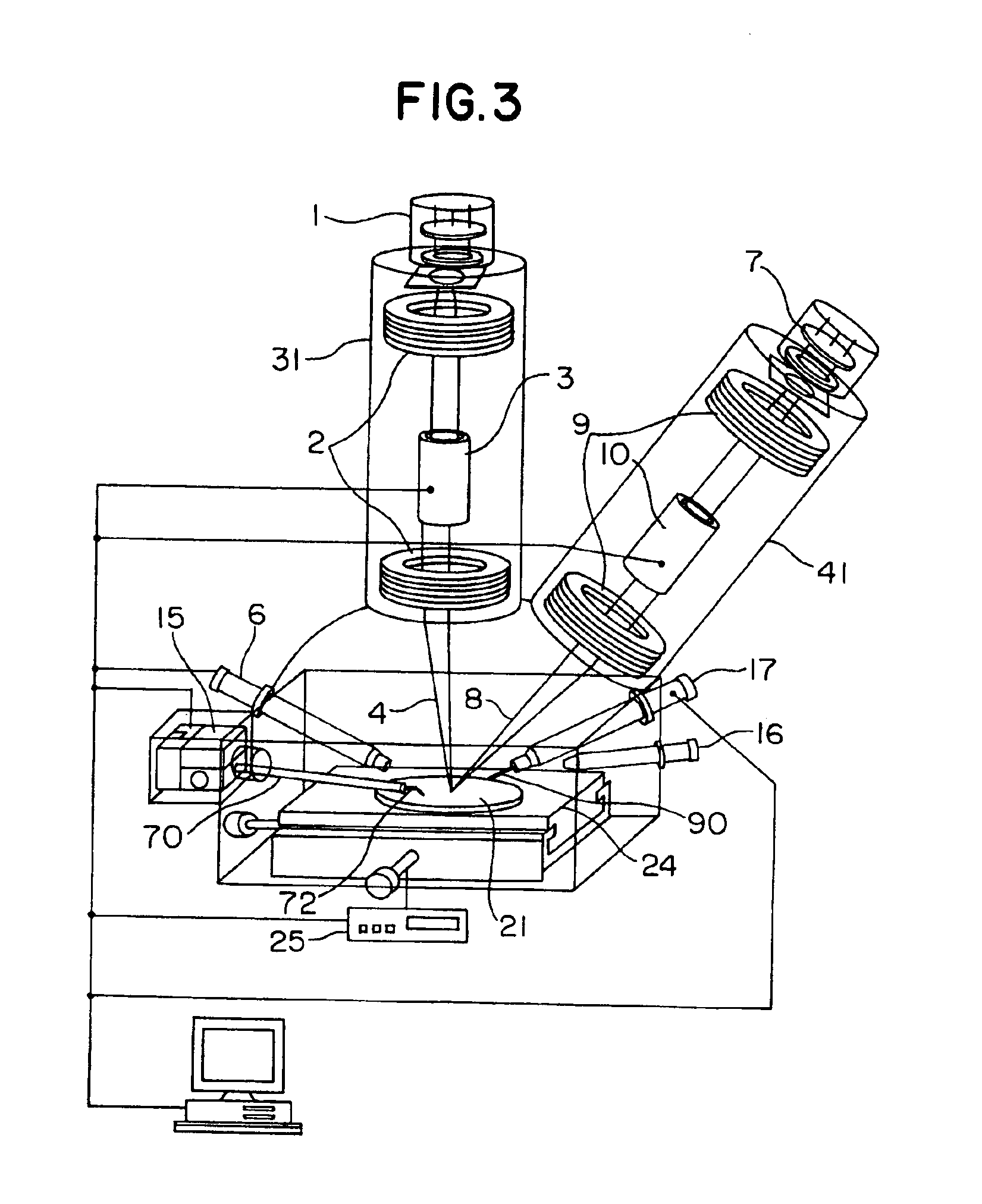
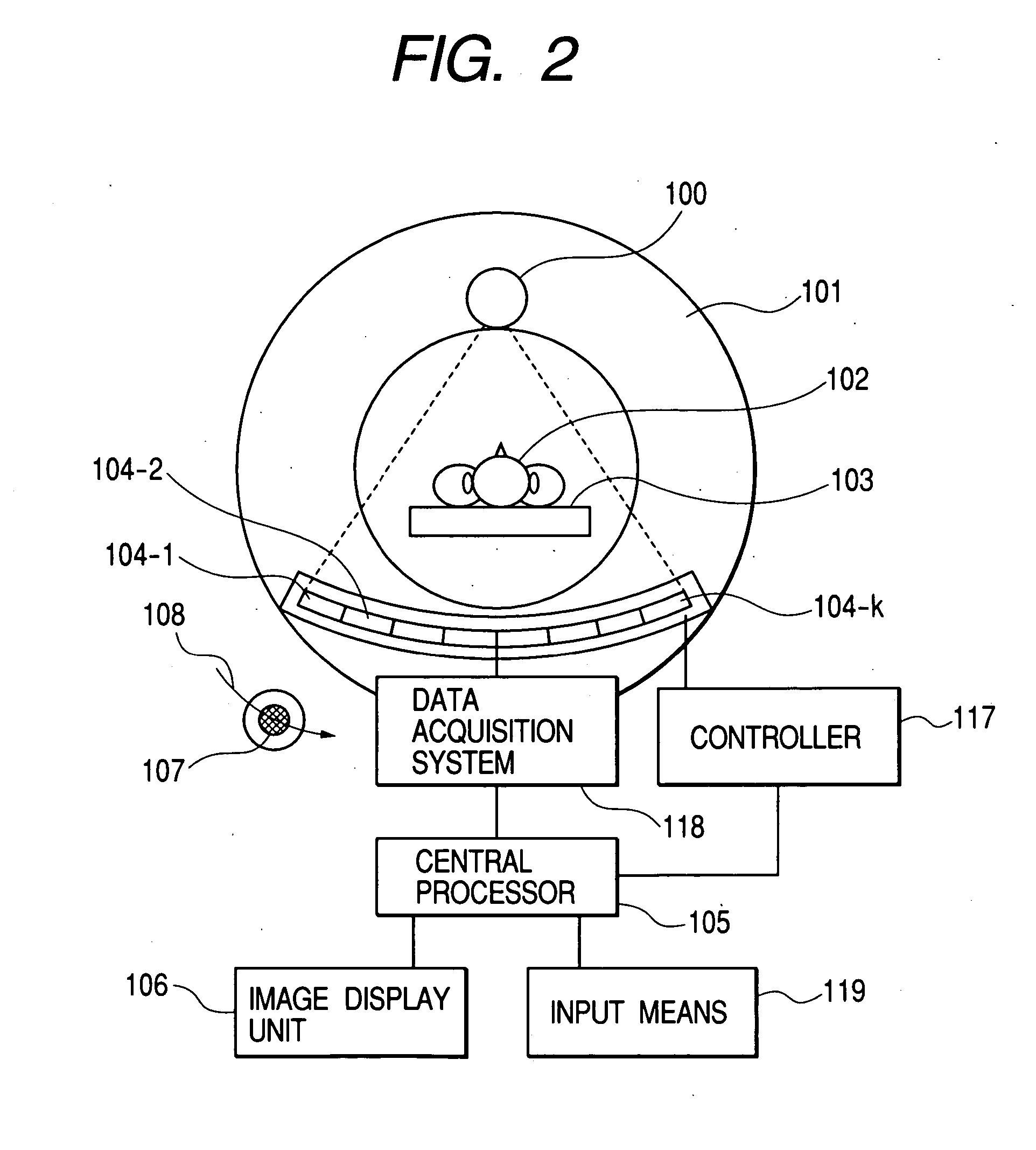
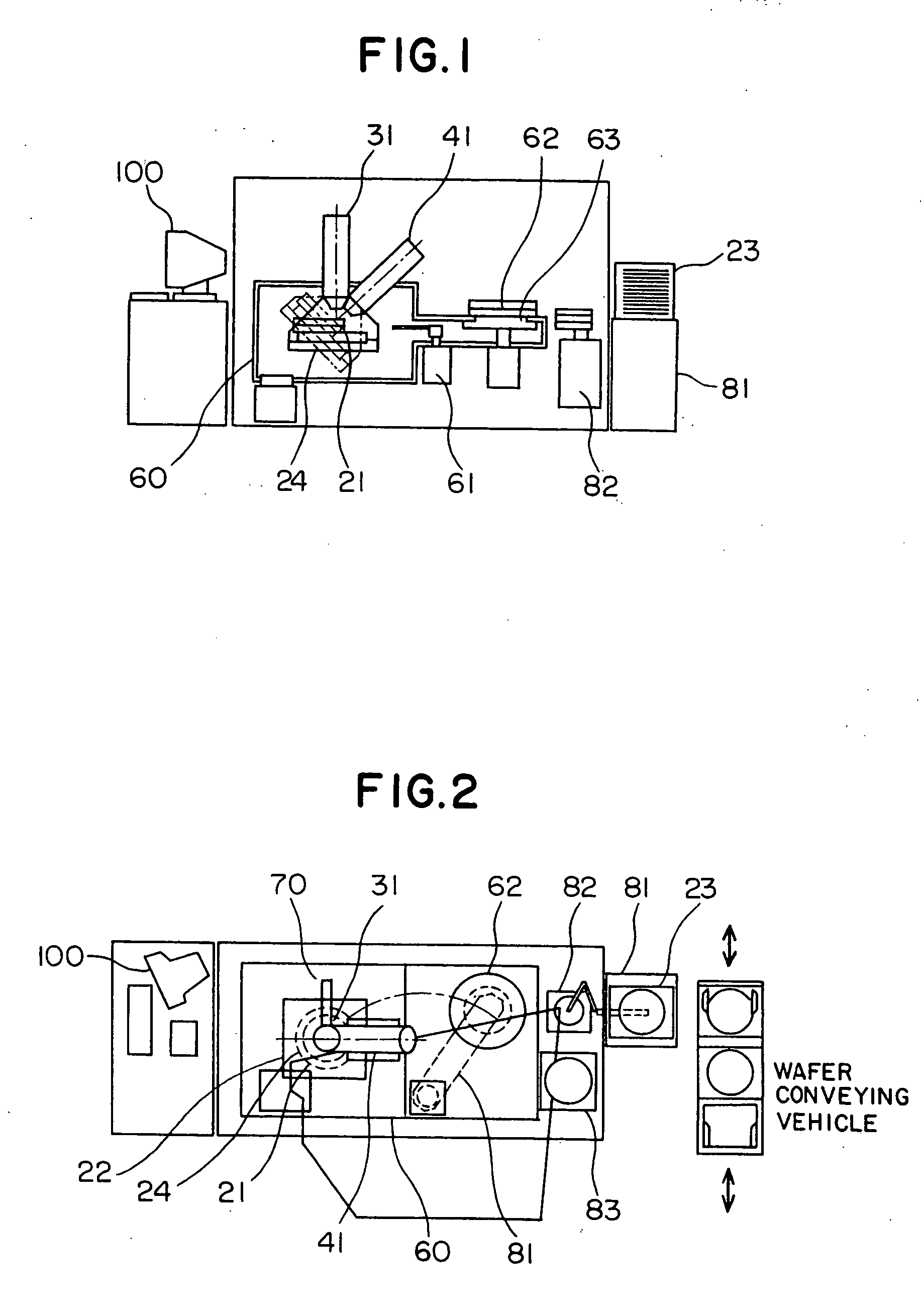
Method and apparatus for processing a micro sample
InactiveUS6927391B2Reduce resolutionGood for observationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementHigh fluxIon beam
Owner:HITACHI LTD
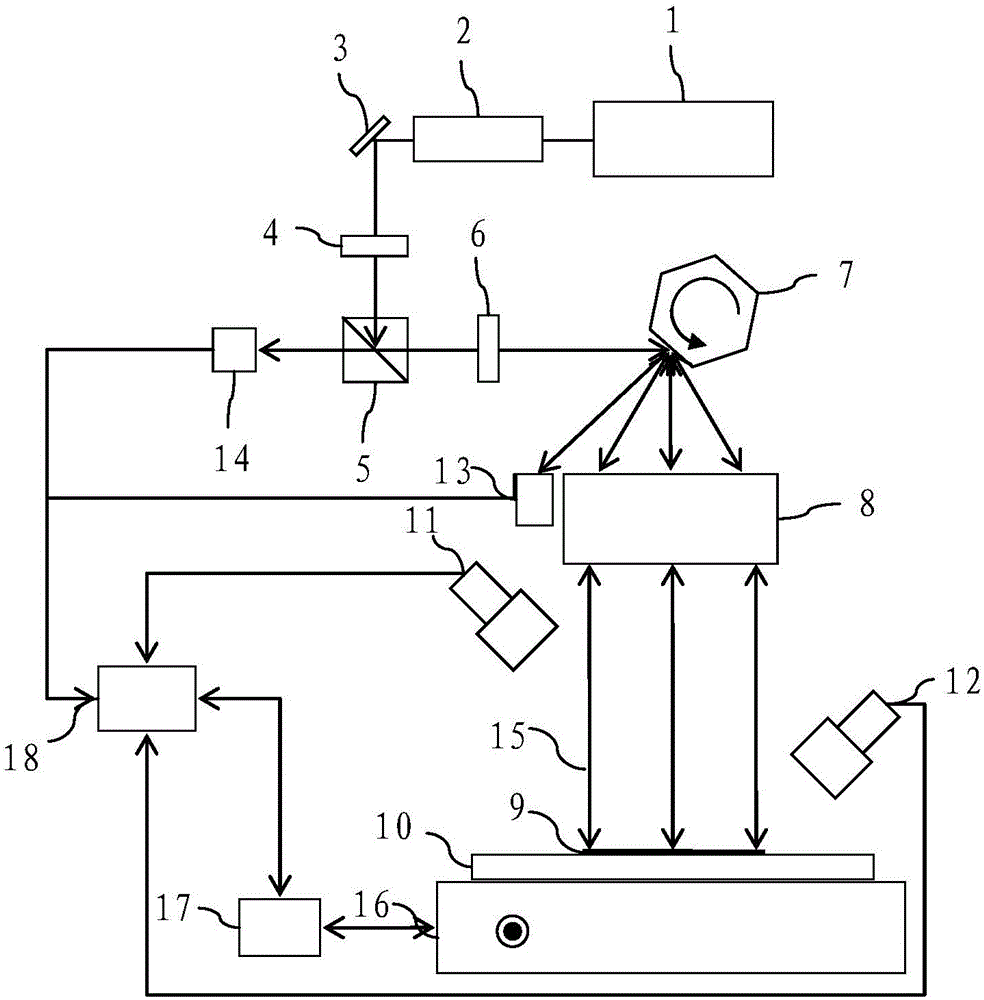
Large-aperture ultra-smooth surface defect detection device and method
ActiveCN106442564AImprove detection efficiencyShorten detection timeOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPolarizerHigh angle
The invention provides a large-aperture ultra-smooth surface defect detection device and method. The device mainly comprises a laser device, a laser beam expanding system, a high-reflectivity mirror, a polarizer, a polarization splitting prism, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a rotary prism, a telecentric field lens, a high-angle-scattering light detector, a low-angle-scattering light detector, a line triggering detector, a reflection light detector, a precise display platform and a computer. Detection efficiency of a large-aperture optical element can be remarkably improved, and the situation that detection results are severely influenced by vibration, axial jumping and the like, caused by high-speed rotation, of the large-aperture optical element is avoided. Surface defects can be classified, and it can be recognized whether the detected defects are pits, scratches, protruding dust, fibers and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
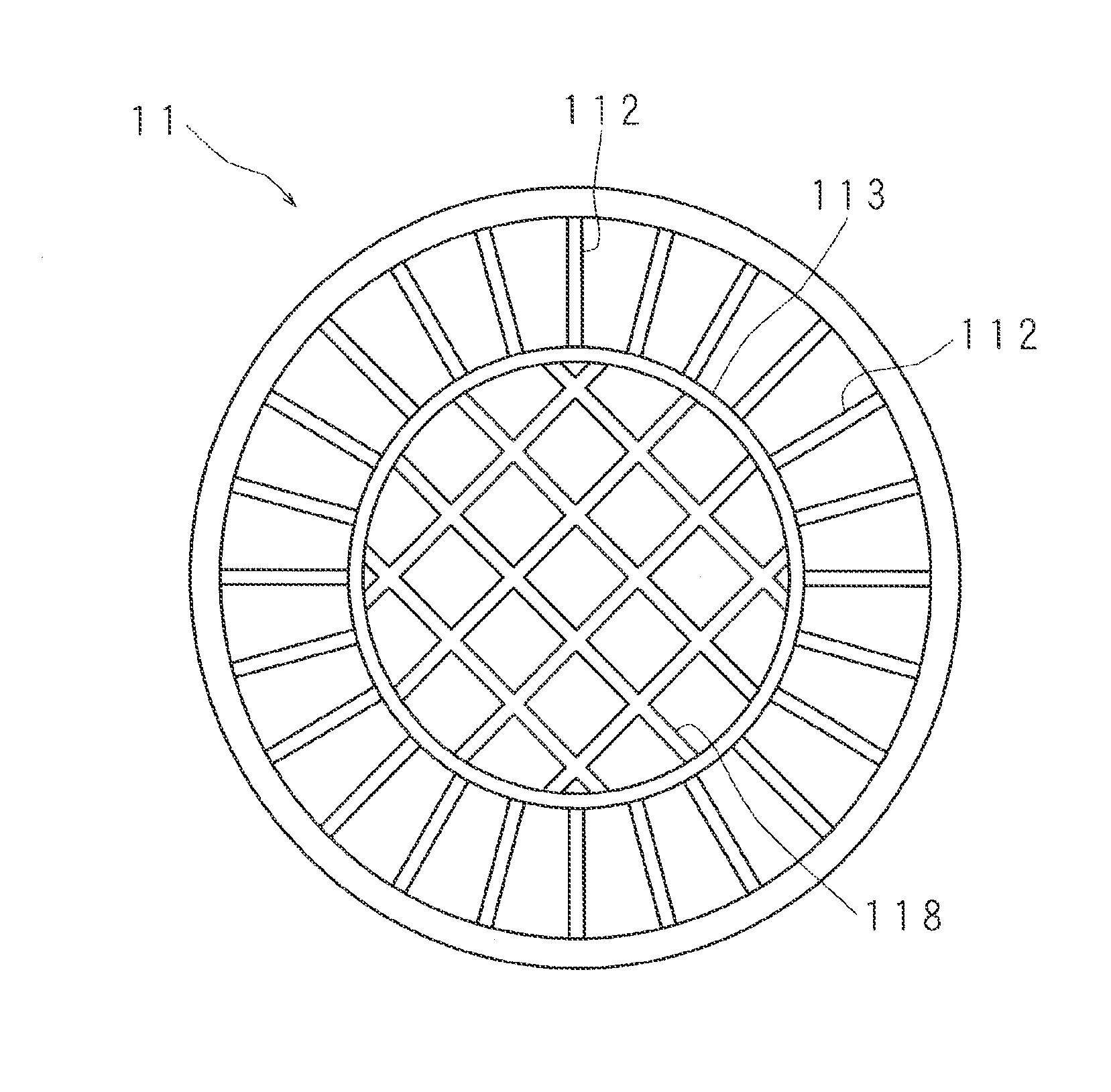
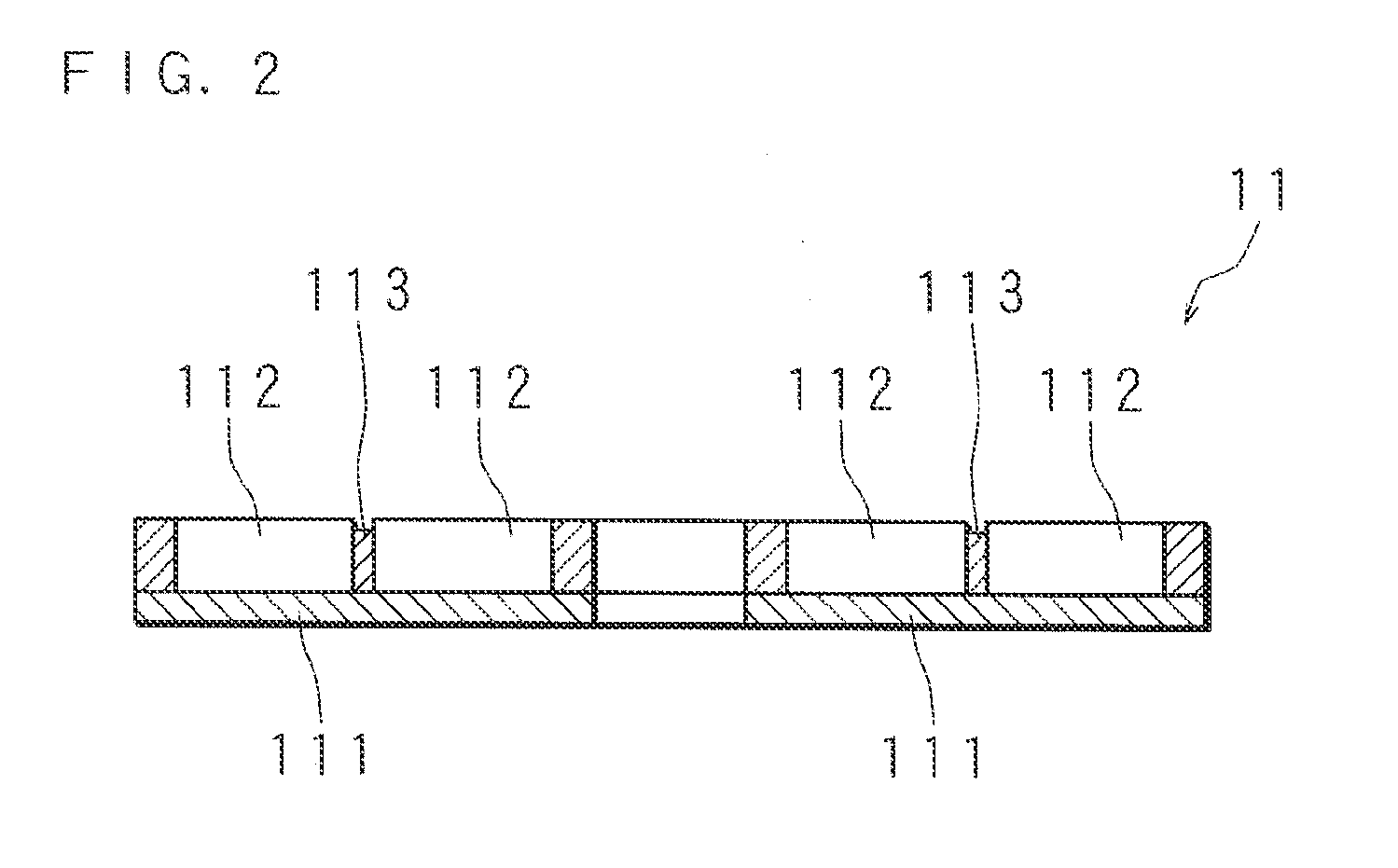
Xray detector having tiled photosensitive modules and Xray system
InactiveUS20040136493A1High priceReduce in quantityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayImage resolution
There are provided an X-ray detector which can realize a larger area without lowering resolution and reducing X-ray detective efficiency when obtaining a matrix construction having a large number of X-ray detecting elements by tiling and a system using the same. An X-ray detector 104 has a construction in which a plurality of photo-electric modules 111 having a plurality of X-ray detecting elements 110 located in a two-dimensional manner are pasted onto a distribution module 113. The X-ray detecting element 110 has scintillators 112, transparent means 121 and photo-electric means 114. These are optically connected to each other. On the edge of the transparent means 121 on one of the photo-electric modules 111 mounted on the distribution module to be adjacent to each other is formed a cutaway part 120 so that the area of an output surface 211 outputting a light to the photo-electric means 114 is smaller than that of an incident surface 210 upon which a light is incident from the scintillators 112. A space caused by the cutaway part 120 is located wiring between the photo-electric module 111 and the distribution module 113 or wiring between the photo-electric modules 111 adjacent to each other.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
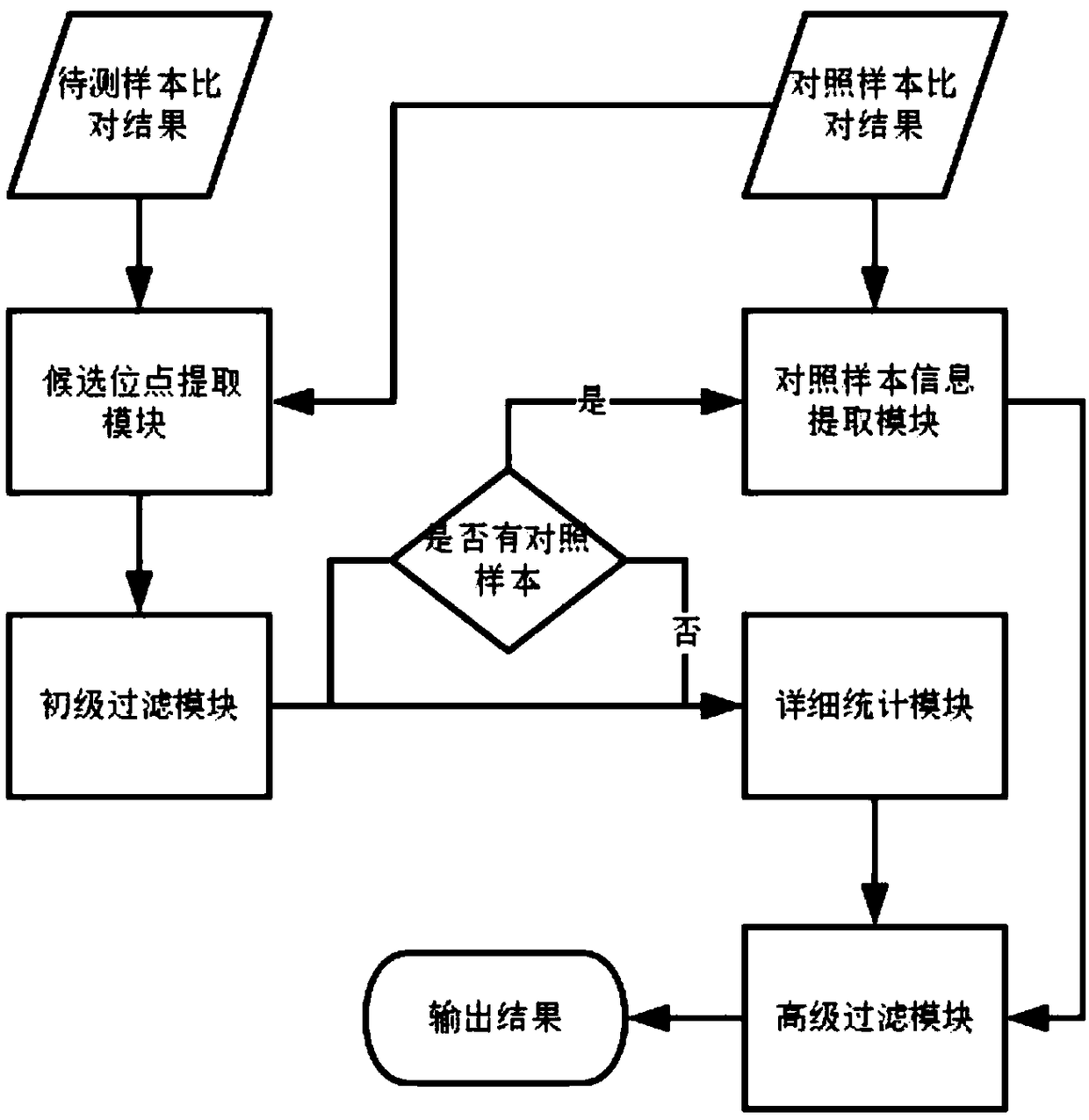
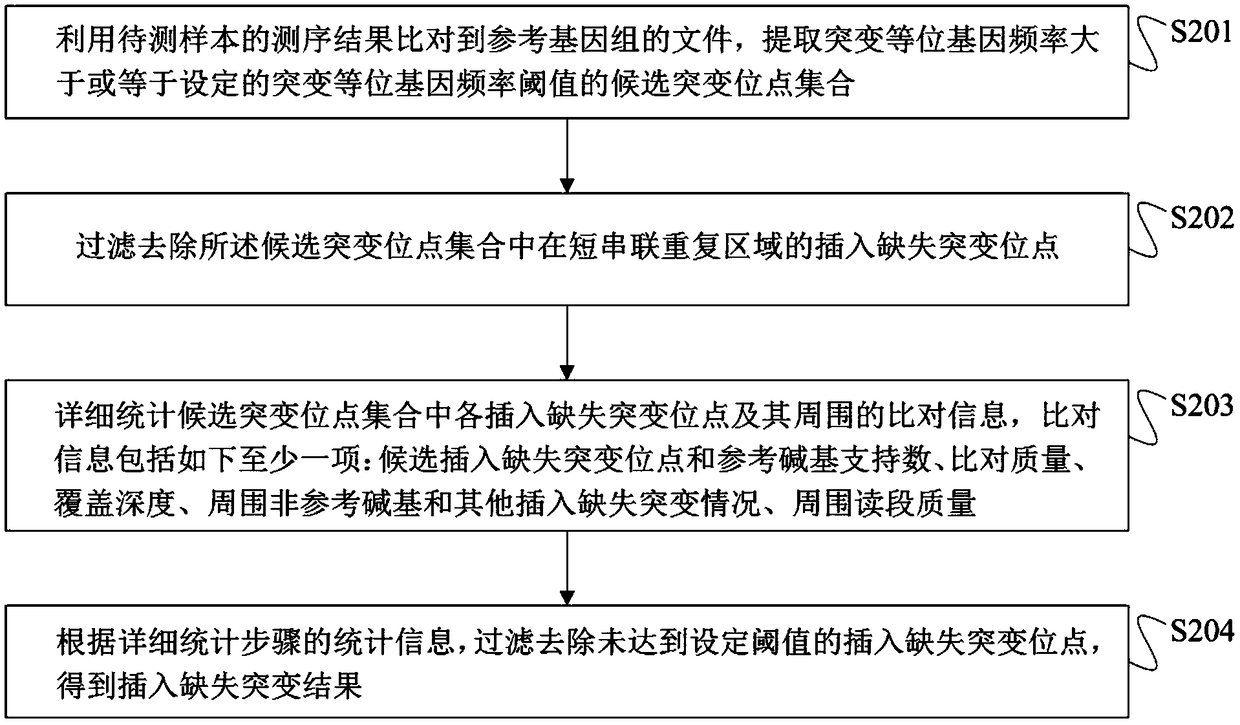
Method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, device and storage medium
ActiveCN108690871AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsInsertion deletionAllele frequency
The present application discloses a method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, a device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps:comparing a sample to be tested with a file of a reference genome to extract a set of candidate mutation sites with mutation allele frequency being greater than or equal to a threshold; filtering to remove sites in a short tandem repeat region; making detail statistics of comparison information of the mutation sites and comparison information surrounding the mutation sites, wherein the comparisoninformation includes InDel site and reference base support number, comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non-reference base and other insertion deletion mutations, surrounding read quality;and filtering to remove sites that do not reach the set threshold according to statistical information to obtain mutation results. The method does not require partial assembly, and filters second-generation sequencing data in advance to quickly eliminate most of false positive results caused by the comparison, reduces detection running time and computing resources, improves detection efficiency, has strong sensitivity and specificity, and can quickly and accurately detect InDel mutations.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
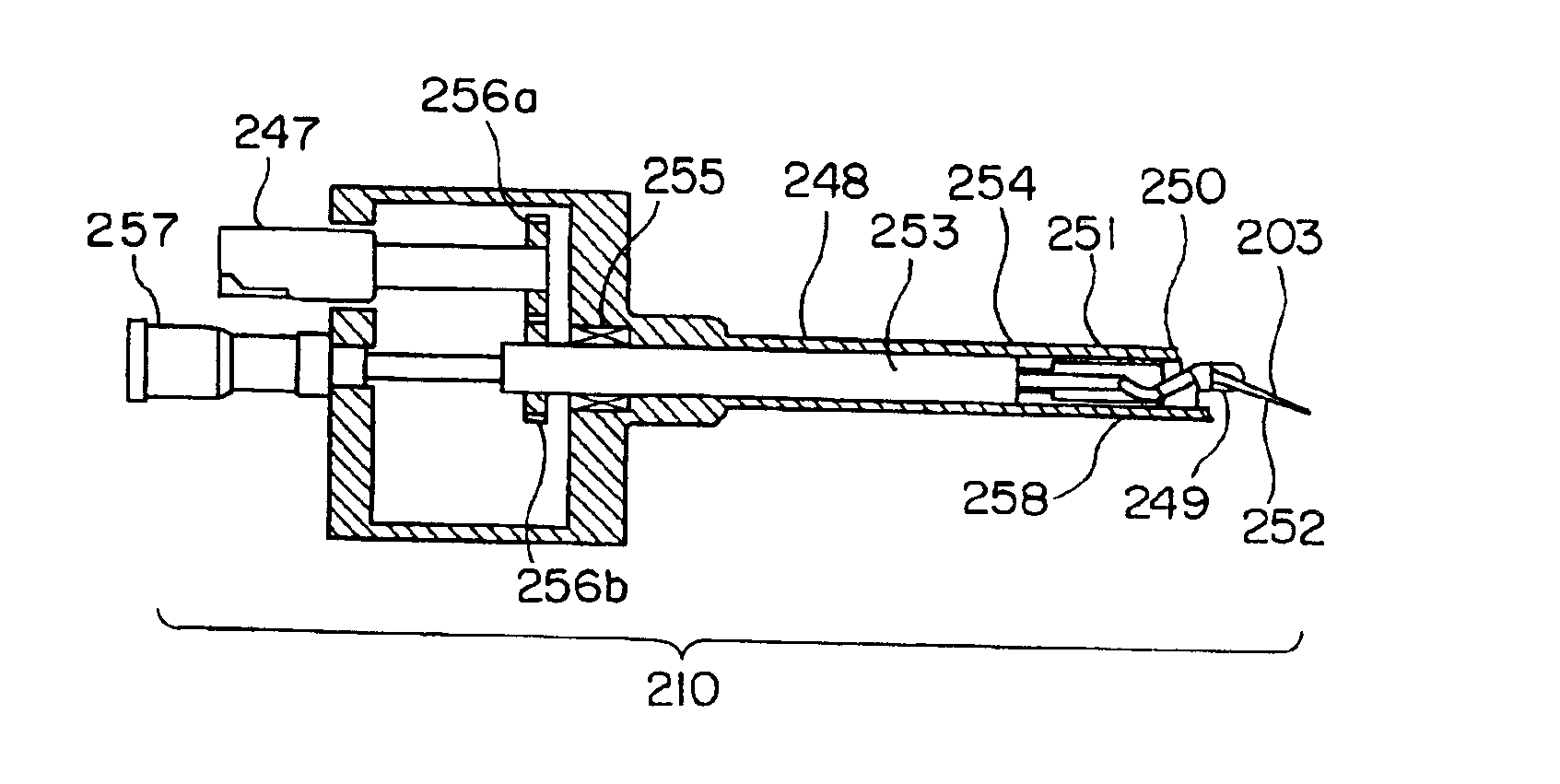
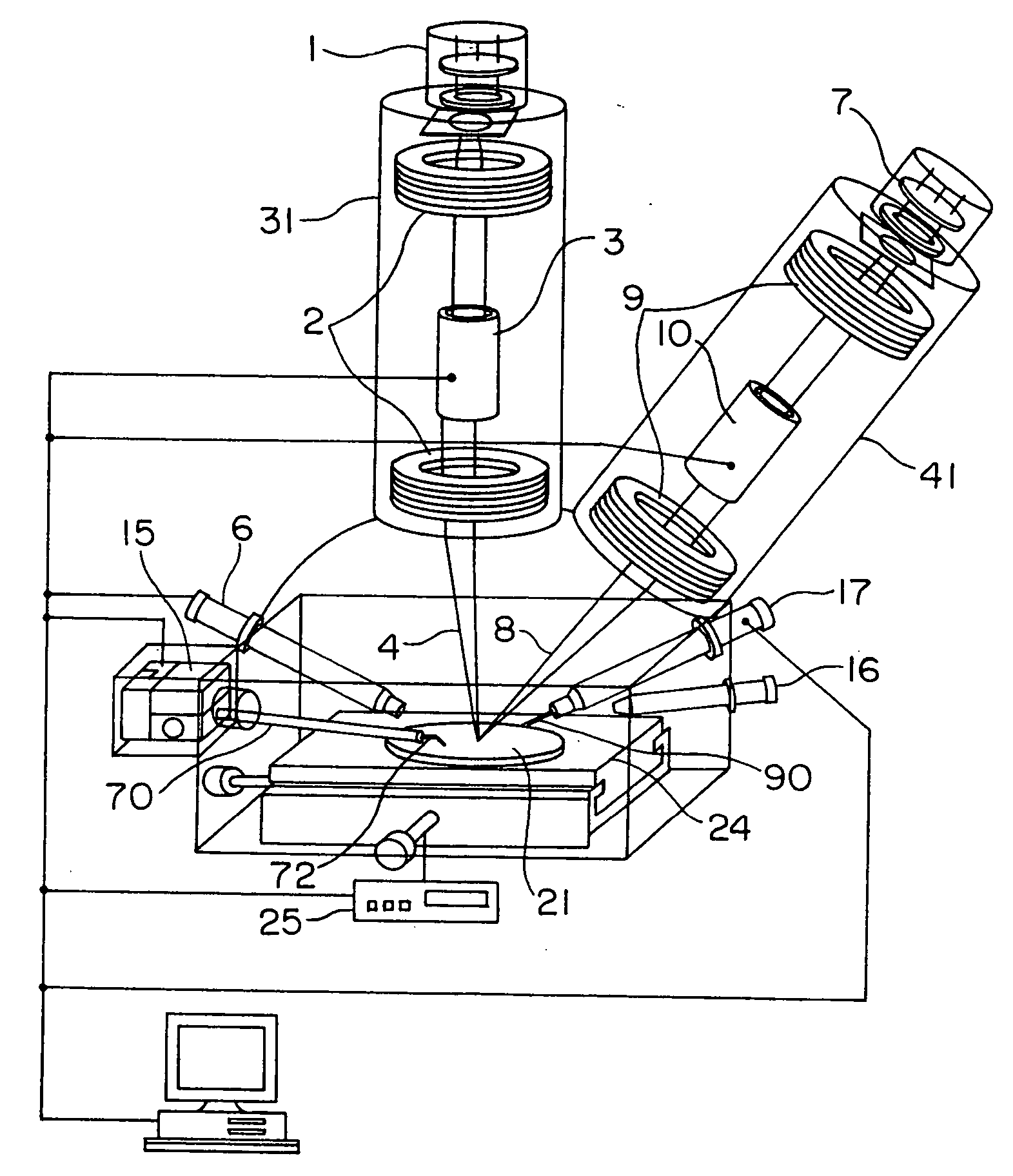
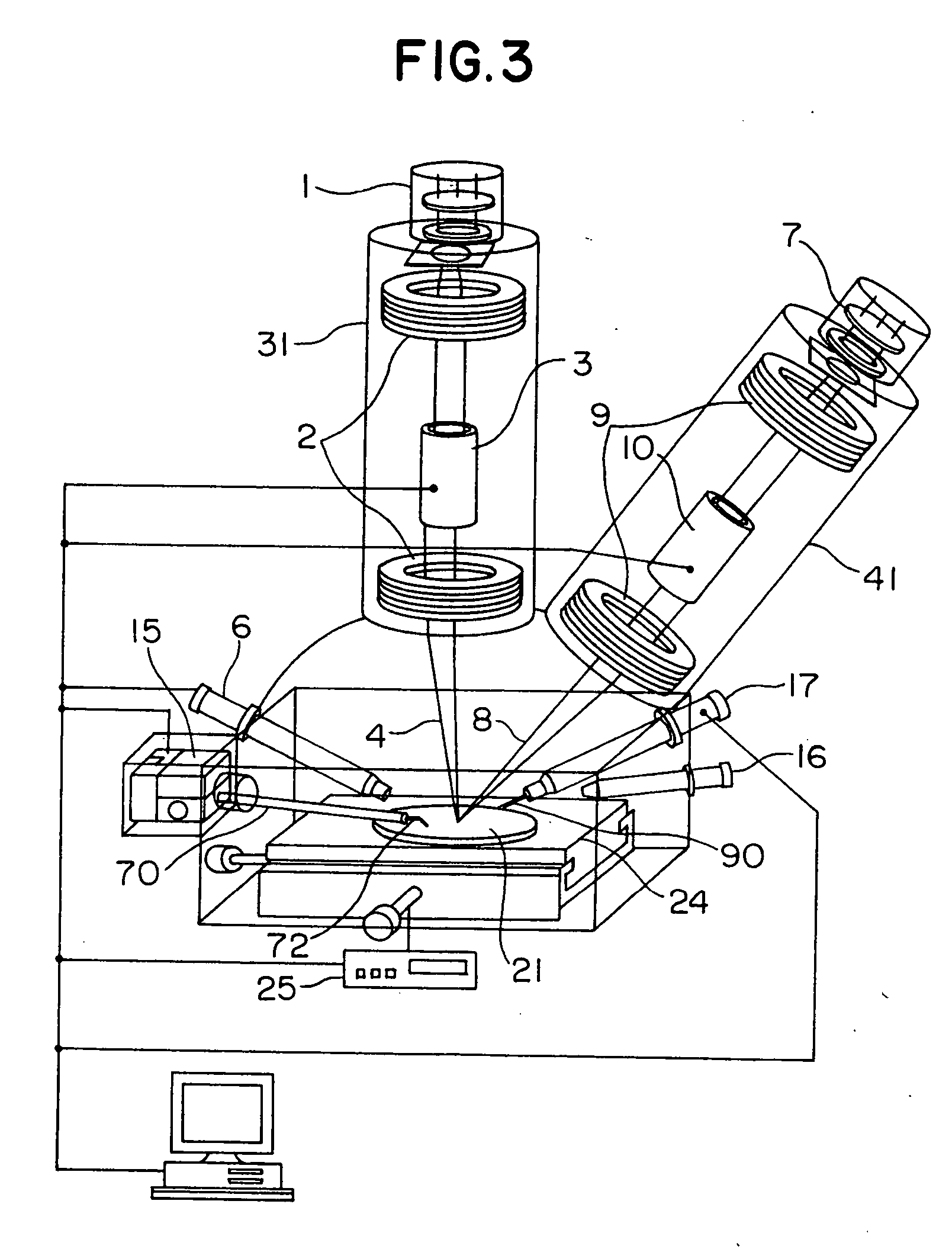
Method and apparatus for processing a micro sample
InactiveUS20050001164A1High resolutionImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementHigh fluxIon beam
An object of the invention is to realize a method and an apparatus for processing and observing a minute sample which can observe a section of a wafer in horizontal to vertical directions with high resolution, high accuracy and high throughput without splitting any wafer which is a sample. In an apparatus of the invention, there are included a focused ion beam optical system and an electron optical system in one vacuum container, and a minute sample containing a desired area of the sample is separated by forming processing with a charged particle beam, and there are included a manipulator for extracting the separated minute sample, and a manipulator controller for driving the manipulator independently of a wafer sample stage.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Integrated droplet microfluidic chip structure, preparation method and microfluidic chip assembly
PendingCN109825426AHighly integratedHigh degree of automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPositive pressureFluorescence
The invention provides an integrated droplet microfluidic chip structure. All functional modules of droplet generation, amplification and detection are integrated on the same microfluidic chip to achieve the whole enclosed process from the droplet generation to fluorescence detection. The invention also relates to an integrated droplet microfluidic chip structure preparation method and a microfluidic chip assembly. The structure is compatible with the positive pressure or negative pressure drive mode, the pressure response time is short, the rapid droplet generation can be achieved, and the sample preparation time is greatly reduced. Droplet generation oil is not required to be filled in advance, the operation is simple, and popularization and application in the technical field of digitalPCR are facilitated.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
SAR image iron tower target detection method based on deep learning
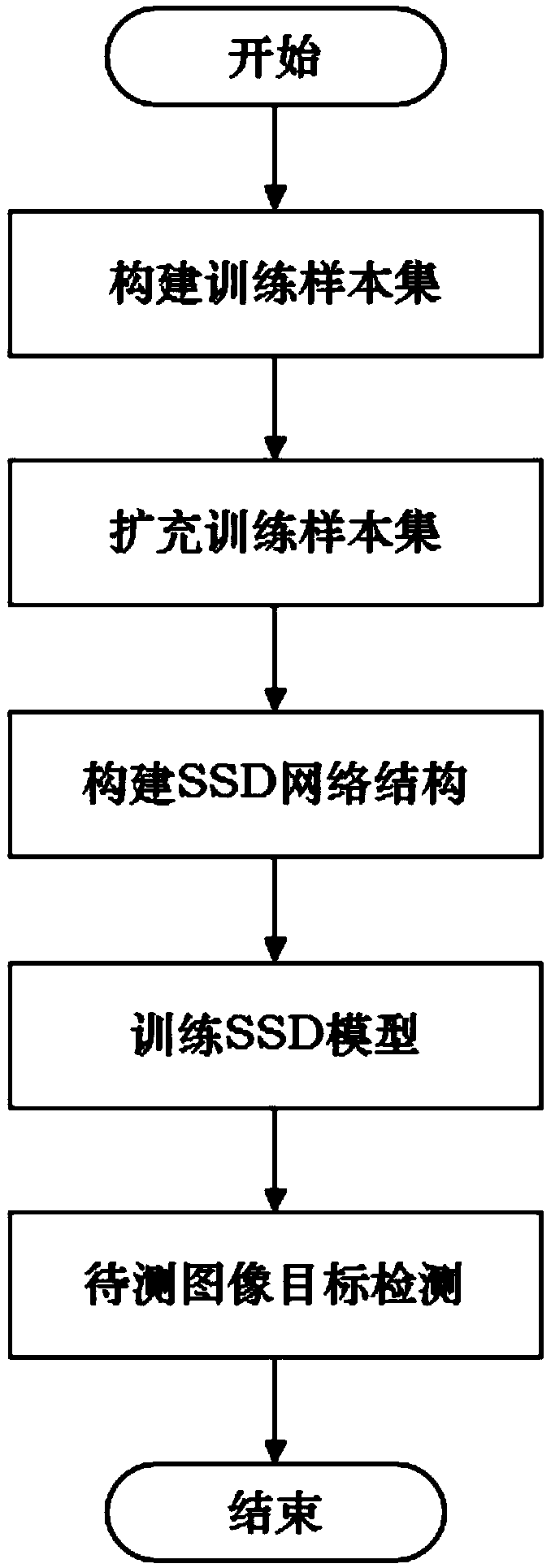
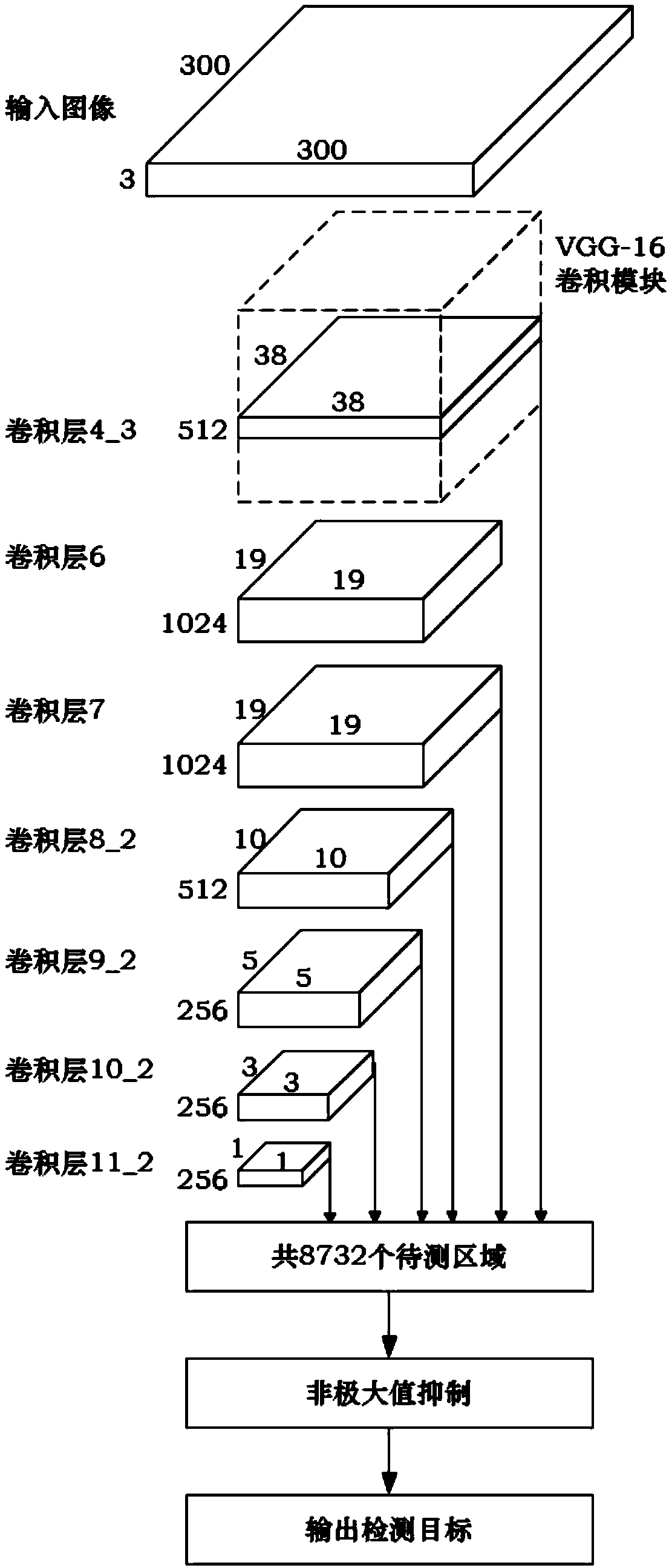
The invention relates to a SAR image iron tower target detection method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps of randomly extracting a plurality of SAR images from a SAR data set, segmenting and obtaining sample slices, setting sample labels for each sample slice and constructing a training sample set; processing each sample slice in the training sample set to generate aplurality of different artificial sample slices, and adding the training sample set after labeling the sample slices to expand the training sample set; constructing an SSD model; inputting the expanded training sample set into the constructed SSD model, and using the gradient descent method to train the SSD model; cutting the data to be measured into a plurality of slices which are the same sizeas the sample slices, and inputting the trained SSD model to obtain the target detection results of the data to be measured. The method of the invention has the advantages of strong robustness, fast running speed, high detection performance and easy migration, and can be used for detection under complex scenes without high contrast between the target and the background.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Digital imaging acquisition system for aggregate grading detection and acquisition method thereof
InactiveCN101929943AQuick collectionHigh detection costVolume/mass flow measurementParticle size analysisDigital imagingPoor Quality Image
The invention discloses a digital imaging acquisition system for aggregate grading detection. The system consists of an aggregate sampling device, an image acquiring device, an optical processing optimizer and communication and storage equipment, wherein the aggregate sampling device comprises a material dividing plate, a distance adjusting rod and an angle adjusting rod; the image acquiring device comprises an infrared laser, a linear array camera and an image acquiring card; the optical processing optimizer comprises a filter device and a diffuse coating layer; and the communication and storage equipment comprises a data line and a computer. A digital imaging acquisition method for aggregate grading detection comprises the following steps of: setting the aggregate sampling device; setting the image acquiring device; setting the communication and storage equipment; acquiring an image of a sampled aggregate; and transmitting and storing the image. An aggregate stream is sampled and acquired by arranging the material dividing plate, so the problem that the image of a falling stream of the aggregate must be completely acquired is solved and the defects of poor quality of the acquired image, difficult separation of particles and a large amount of processing data are overcome.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Fast detection method and instrument for microbe content in food
InactiveCN1847405AShort detection timeChange concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementTesting foodCarbon dioxideFood sample
The fast detection method and instrument for microbe content in food has two parallel sample detecting systems adopted, including one for food sample detection and the other for detecting contrast. These two systems are in the same environment conditions and heated with the same heating element, the CO2 these two systems generate is detected separately in two identical CO2 detecting devices, and the detected data are analyzed and processed to obtain the detection result. The present invention has short detection period, simple structure, low cost and other advantages, and is suitable for fast site detection.
Owner:何宗彦
Method and device for detecting network speed
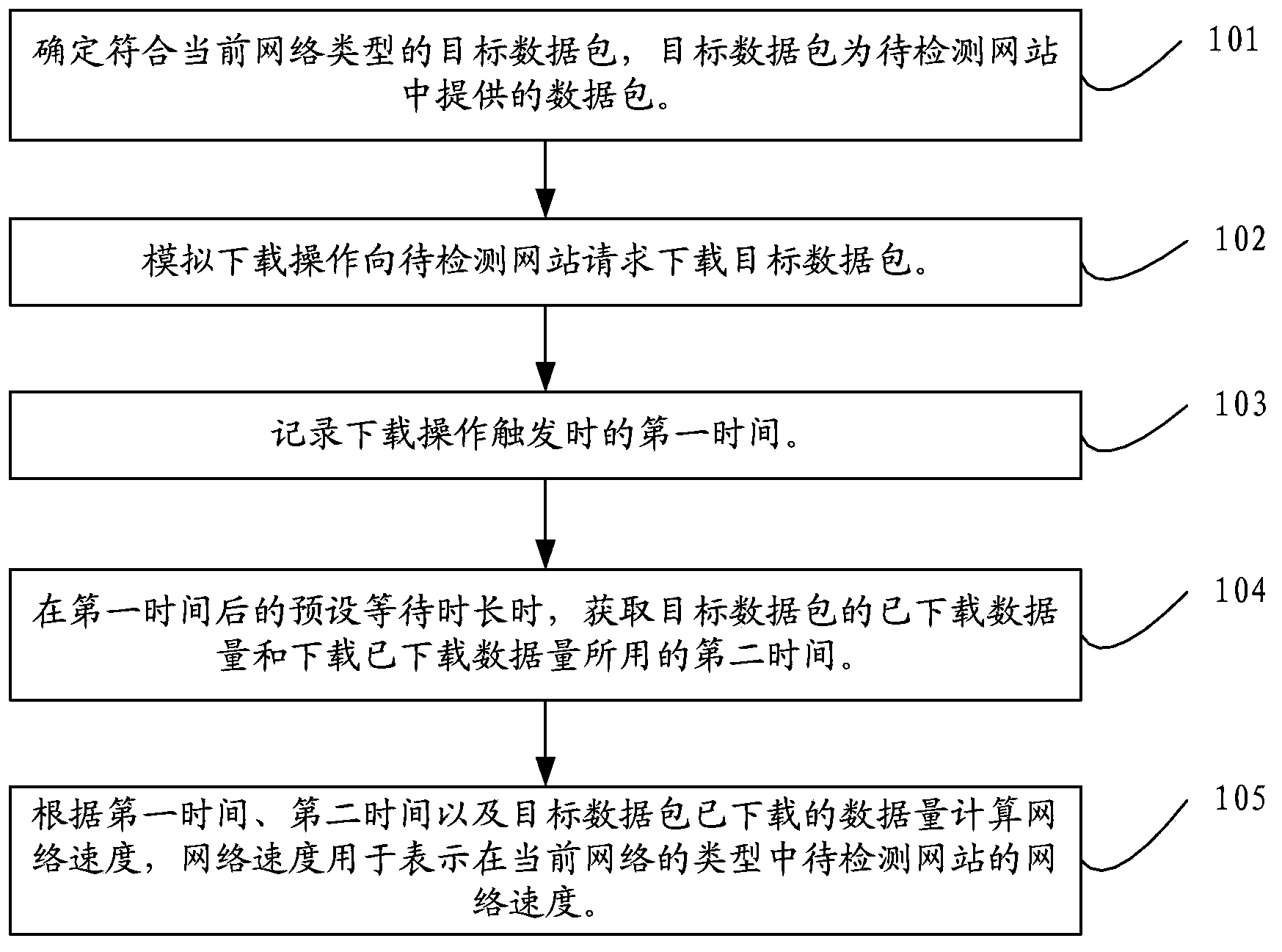
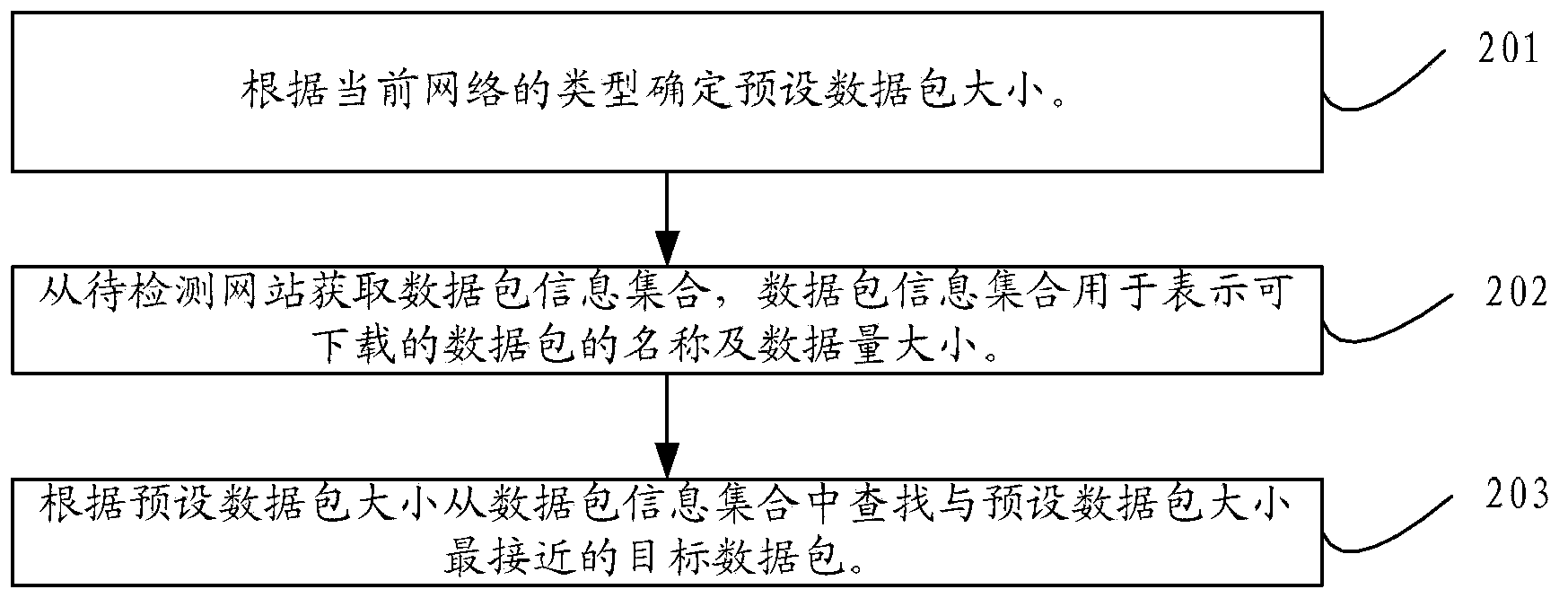
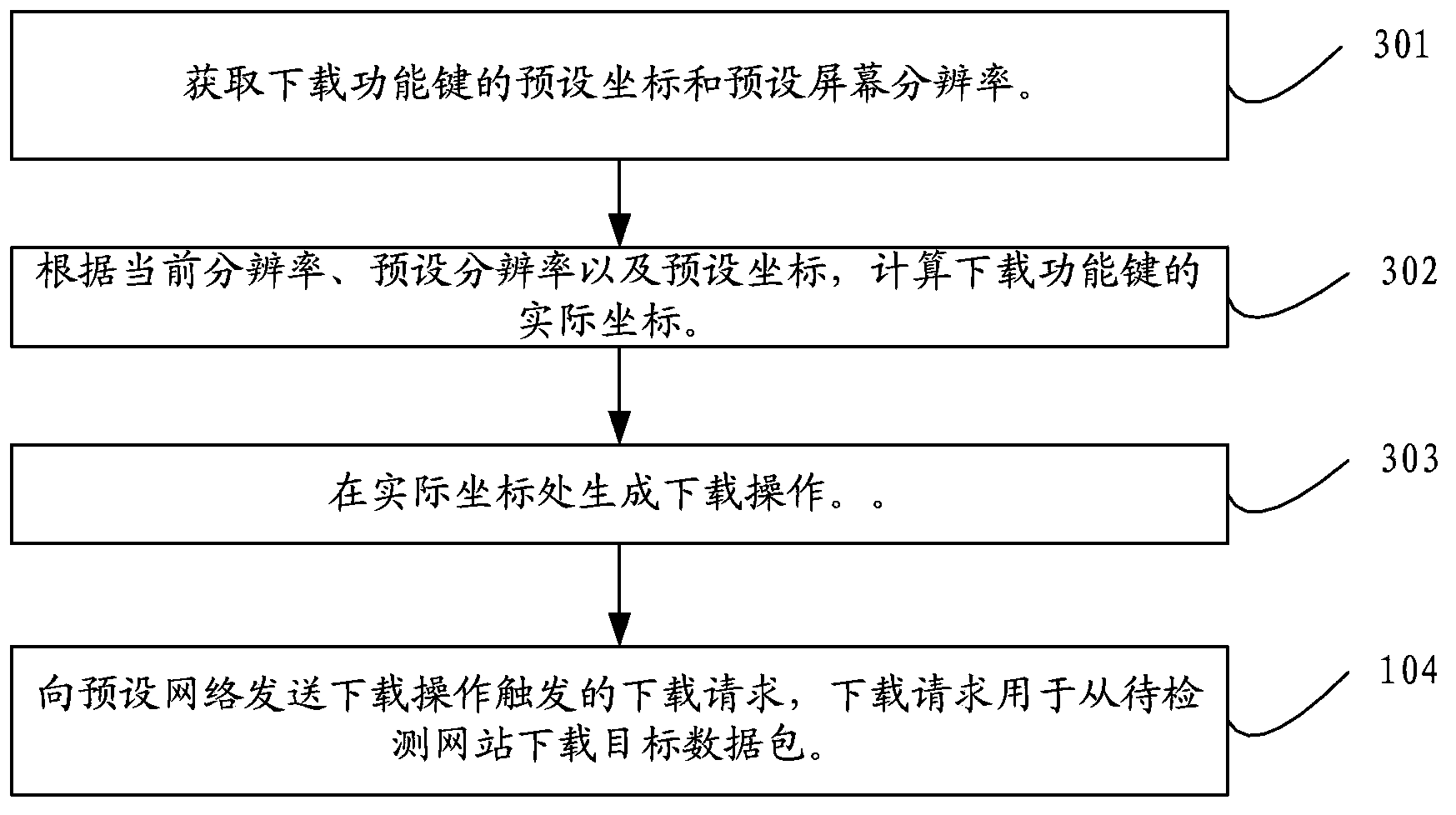
ActiveCN104348680AEfficient data processing capabilityAvoid errorsData switching networksNetwork packetThe Internet
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting network speed and relates to the technical field of the Internet. The method and the device can be used for solving the problem that the detection efficiency is relatively low during manual detection. The method comprises the steps: determining a target packet meeting the type of a current network, wherein the target packet is a packet provided by a website to be detected; requesting the website to be detected to download the target packet by simulating downloading operation; recording a first time when the downloading operation is triggered; after a preset waiting time after the first time, acquiring the amount of downloaded data of the target packet and a second time consumed for downloading the amount of downloaded data; calculating the network speed according to the first time, the second time and the amount of downloaded data of the target packet, wherein the network speed is used for representing the network speed of the website to be detected in the type of the current network. The method and the device are mainly applied to a network maintenance process.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Radiolucent window, radiation detector and radiation detection apparatus
ActiveUS20150235726A1Improve detection efficiencyReduce detection efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayLight beam
Linear ribs are formed radially with a center at a through-hole on one face of an X-ray transmissive film (radiolucent film) in an X-ray transmissive window (radiolucent window) to be used for an X-ray detector (radiation detector). The X-ray transmissive window faces a sample. A beam for irradiation to the sample passes through the through-hole, and X-rays (radiation) are radially emitted on a line extending through the through-hole and enter the X-ray transmissive window. Since the linear ribs are formed radially with the center at the through-hole, even X-rays entering at shallow angles with respect to the X-ray transmissive window are transmitted through the X-ray transmissive window at a probability equivalent to X-rays entering at deep angles. More X-rays are transmitted through the X-ray transmissive window, and thus the X-ray detector can detect X-rays with high efficiency.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Method of detecting and passivating a defect in a solar cell
InactiveUS7979969B2Reduce detection efficiencyImprove efficiencyPhotovoltaic monitoringStatic indicating devicesPower flowGrid pattern
Owner:SOLOPOWER
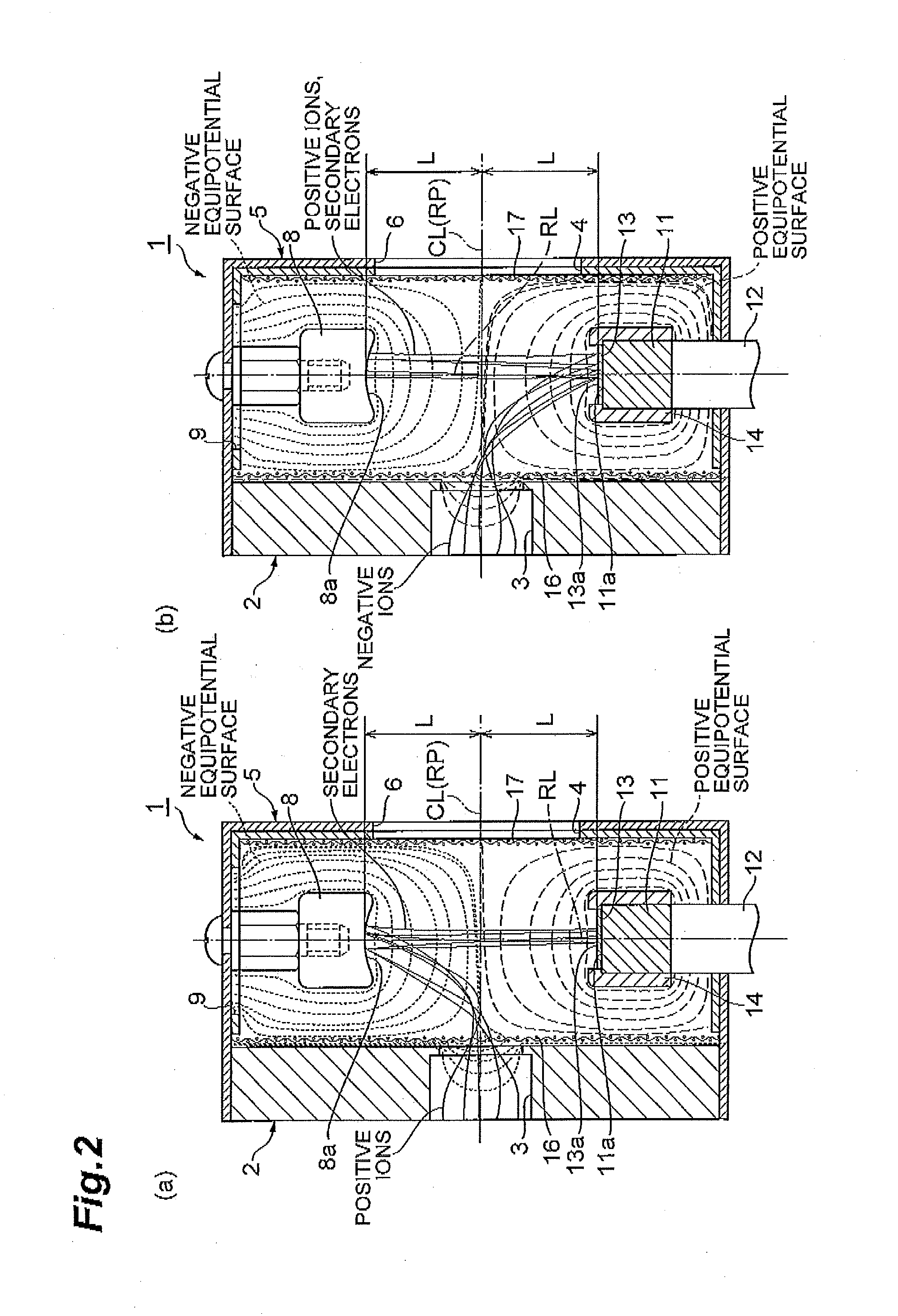
Ion detector
ActiveUS20120025085A1Improve incident efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioThermometer detailsParticle separator tubesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An ion detector for detecting positive ions and negative ions, includes a housing provided with an ion entrance to make the positive ions and the negative ions enter, a conversion dynode which is disposed in the housing and to which a negative potential is applied, a scintillator which is disposed in the housing and has an electron incident surface which is opposed to the conversion dynode and into which secondary electrons emitted from the conversion dynode are made incident, a conductive layer which is formed on the electron incident surface and to which a positive potential is applied, and a photodetector which detects light emitted by the scintillator in response to incidence of the secondary electrons.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Urinalysis device and method for intelligent toilet
ActiveCN107632016AReduce detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLavatory sanitorySlide platePulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a urinalysis device for an intelligent toilet. A fixing assembly comprises a mounting bottom plate, a sliding plate and a mounting top plate, wherein the mounting bottom plateis fixedly connected with the toilet, and the sliding plate is mounted on the mounting bottom plate; one end of the sliding plate faces a toilet bowl; the mounting top plate is mounted above the sliding plate, and a void space for mounting a telescopic mechanism is reserved between the sliding plate and the mounting top plate; a paper feeding mechanism is mounted on the mounting top plate; a testpaper slot is glidingly formed in the sliding plate; a detection mechanism is mounted on the mounting top plate; a paper discharging mechanism comprises a flushing pipe and a flushing device; a dryingmechanism comprises an air guide pipe and an air blowing device, one end of the air guide pipe is communicated with the test paper slot, and the other end of the air guide pipe is communicated with the air blowing device. The problems of user discomfort and poor user experience which are easily caused by the fact that a urinalysis device for a toilet in the prior art is complex in structure and larger in size and occupies more space, urine pollution is easily produced to affect detection results and detection efficiency is low as a result of manual replacement of the urine detection test paper are solved.
Owner:重庆恭逸科技有限公司
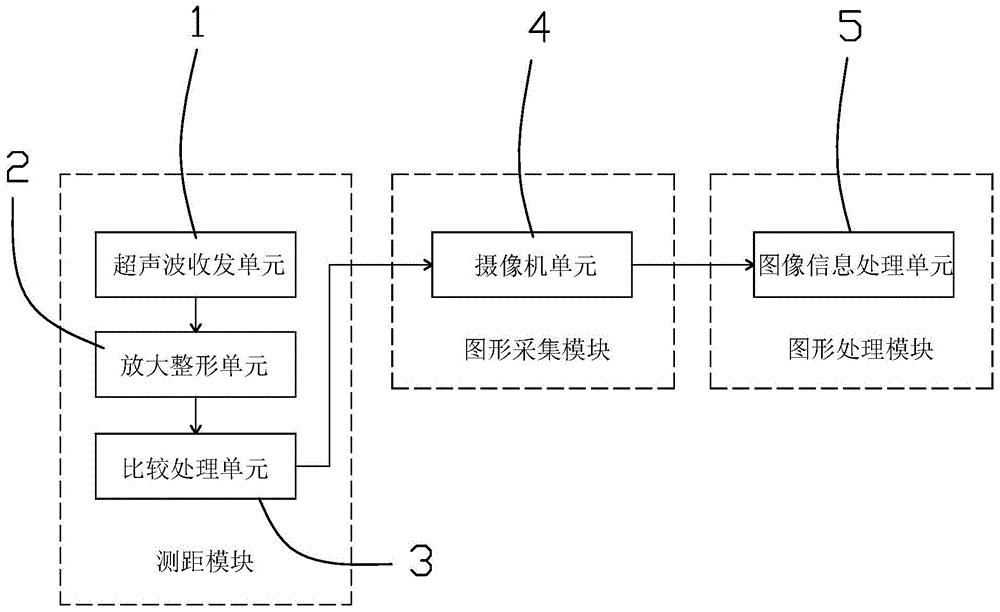
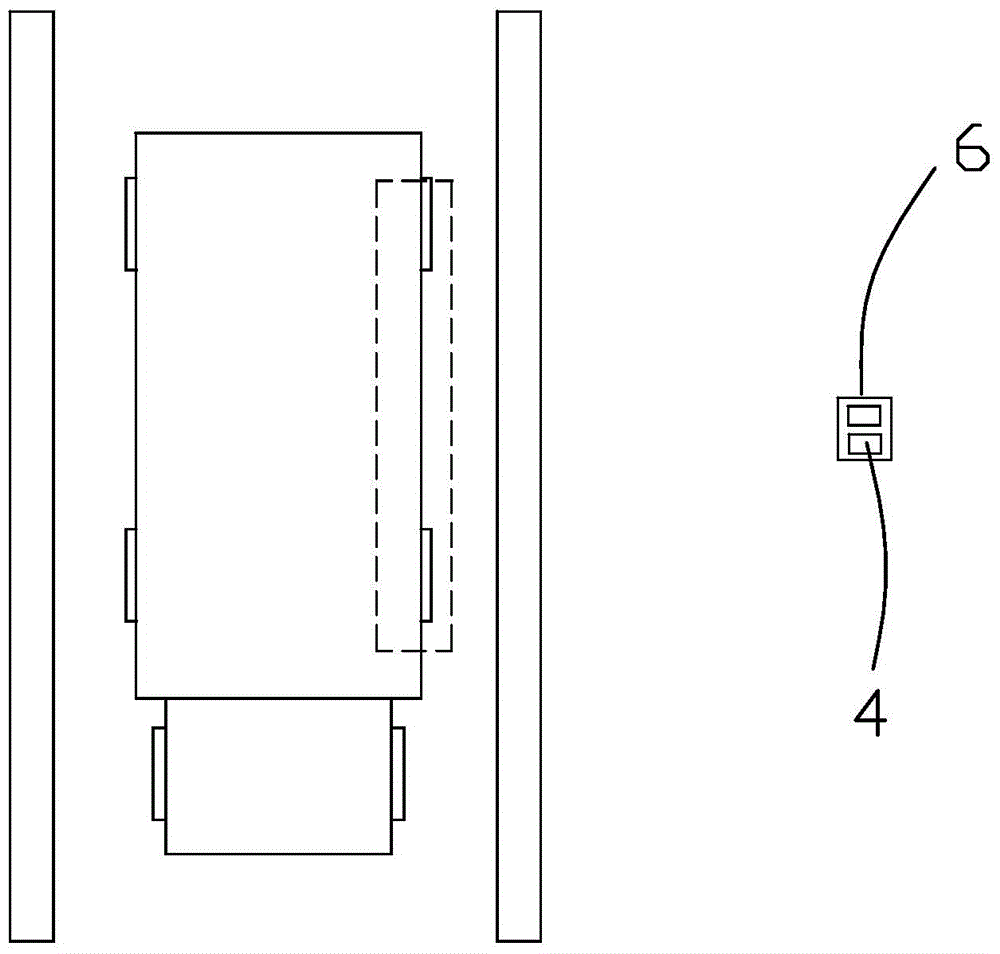
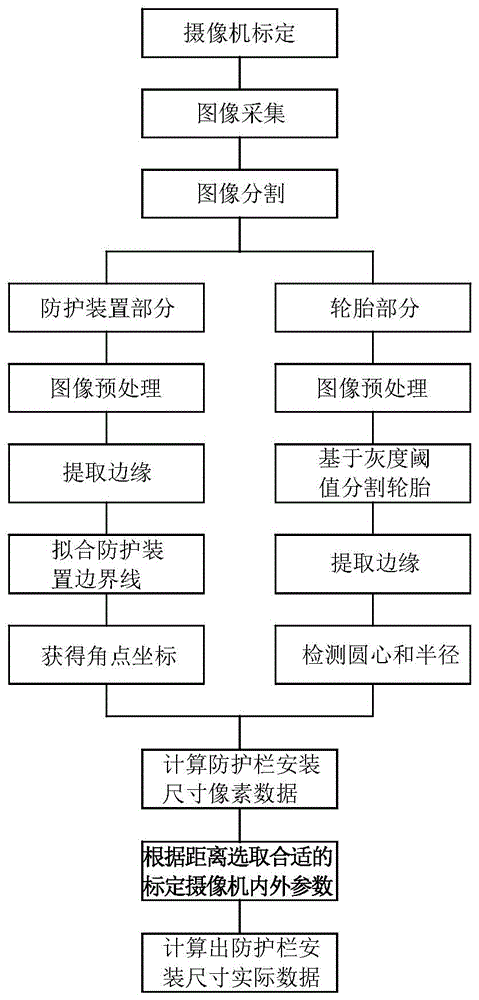
Truck side guard rail mounting size measurement system and method based on machine vision technology
InactiveCN105021126AQuick and effective installation sizeEfficient measurementUsing optical meansInformation processingGraphics
The invention relates to a truck side guard rail mounting size measurement system and a method based on a machine vision technology, so as to solve problems that as the truck guard rail is detected manually in the prior art, random errors such as a reading error and an environment error exist, the measurement result is influenced, and the measurement efficiency is low. The system comprises a ranging module, a graph acquisition module and a graph processing module, wherein the graph acquisition module comprises a camera unit, the ranging module is connected with the camera unit, the graph processing module comprises an image information processing unit, and the camera unit is connected with the image information processing unit. The system acquires two-dimensional image information of the side surface of the truck via the image acquisition module, the image is analyzed and processed via the image processing module, and mounting size information of the truck side guard rail is obtained. The system and the method of the invention have the advantages that a truck side guard device does not need to be touched, the mounting size of the truck side guard device can be quickly and effectively measured, and the detection efficiency is higher.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Low-frequency array eddy current detection device and detection method for corrosion defects of steel pipe inner wall
ActiveCN107941905AEliminate distractionsEasy to call analysisMaterial magnetic variablesDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention relates to a low-frequency array eddy current detection device and a detection method for corrosion defects of a steel pipe inner wall. According to the technical scheme, the low-frequency array eddy current detection device comprises an eddy current detection main machine, a connecting wire and a low-frequency array eddy current probe, wherein the eddy current detection main machineis connected with the low-frequency array eddy current probe through the connecting wire; a main machine shell body is provided with a display device and a probe connection socket respectively; the shell body is internally provided with a low-frequency oscillator, a lithium battery, a controller, an amplifier, a balance filter, a phase shifter, a gain adjustable amplifier and a digital to analogconverter respectively. According to the low-frequency array eddy current detection device, the interference of space scattering leakage magnetic flux is eliminated through a magnetic shielding technology of a magnetic tank and shielding coils and the defect resolution is improved; eight detection coils can be used for imaging independently in a detection process and the detection sensitivity keeps consistent all the time so that leak detection of the defects is avoided; the defects of the steel pipe inner wall of a heated surface covered with the probe can be detected in one-step operation and reciprocated operation is not needed; the low-frequency array eddy current detection device is convenient to use and has a good effect.
Owner:CENT CHINA BRANCH OF CHINA DATANG CORP SCI & TECH RES INST CO LTD
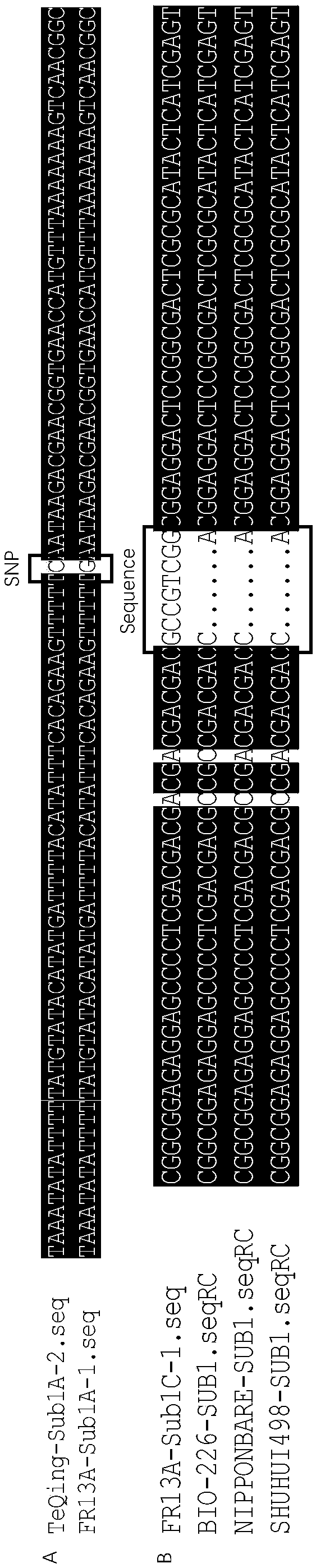
Rice flooding-tolerant gene Sub1 co-dominant molecular marker and application
ActiveCN109468315AShorten the breeding cycleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCO-DOMINANTAgricultural science
The invention provides a rice flooding-tolerant gene Sub1 co-dominant molecular marker and application. The molecular marker comprises an SNP marker and an InDel marker which are separately located onrice No. 9 chromosome genes Sub1A and Sub1C, wherein the polymorphic site of the SNP marker on the gene Sub1A is G / C; and the polymorphic site of the InDel marker on the gene Sub1C is 5'-GCCGTCG-3' / 5'-CA-3'. For the molecular marker, specific amplification primers are designed, and Sub1 genotype detection is carried out through PCR amplification. The provided molecular marker and an amplificationprimer thereof for Sub1 can be used for identifying the genotype of rice Sub1, a flooding-tolerant rice resource is bred, the rice flooding-tolerant gene Sub1 co-dominant molecular marker has the advantages of high identification accuracy, simplicity in operation, low cost and the like, the breeding period of the flooding-tolerant rice can be shortened, and the breeding cost is reduced.
Owner:YUAN LONGPING HIGH TECH AGRI CO LTD +2
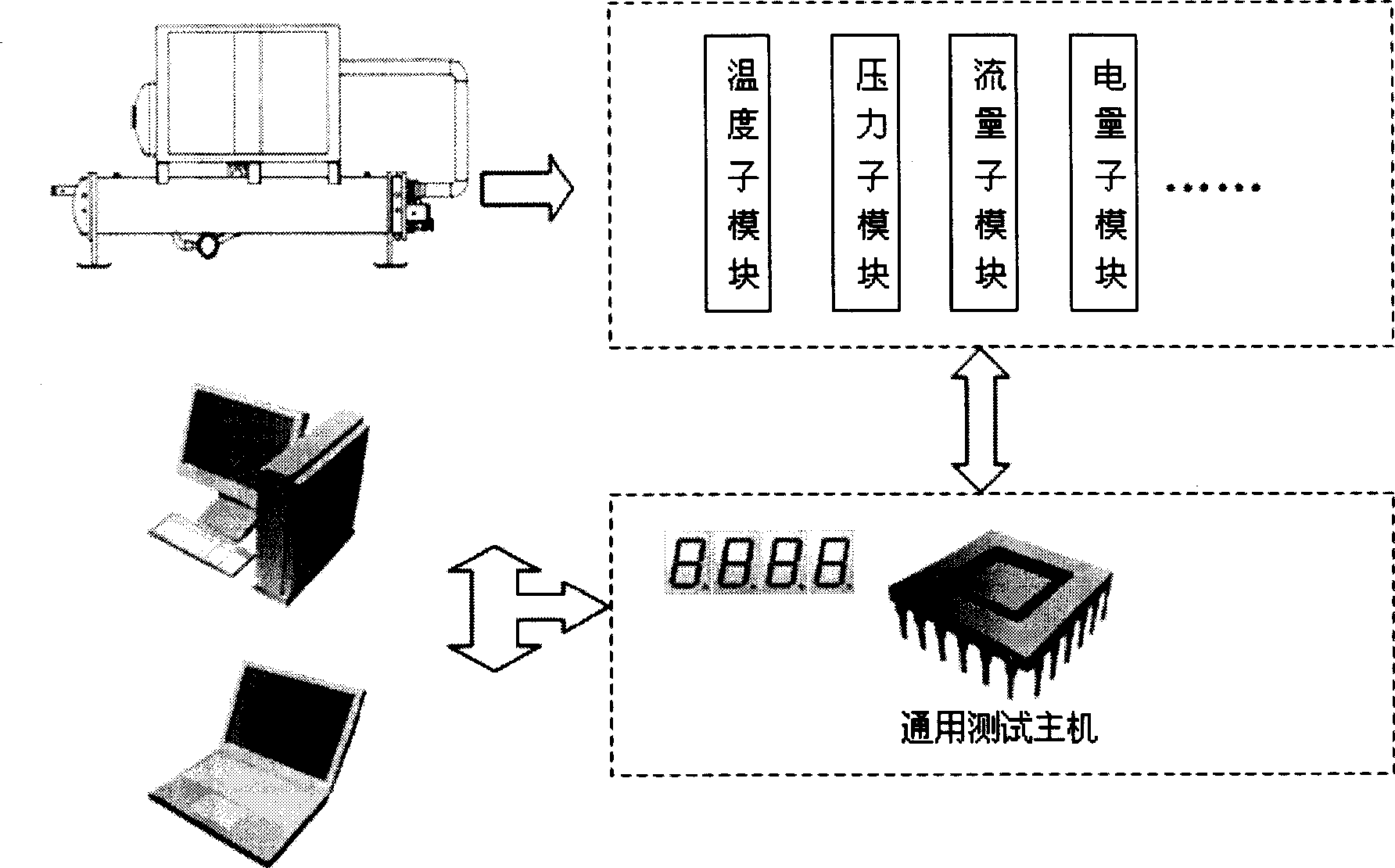
Universal module system used for on-site detection of refrigeration air conditioning system
InactiveCN101498623AShorten the timeIncrease flexibilityElectric testing/monitoringStructural/machines measurementExtensibilityEngineering
The invention relates to a general module system for on-site detection of an air-conditioner refrigeration system, belonging to the technical field of detection technology. The system comprises a general test host, a temperature test submodule, a pressure test submodule, a flow test submodule and an electric quantity test submodule as well as a signal transmitting detecting module and upper computer software which are specially used for detecting other relative parameters. The invention is suitable for performance detection, fault diagnosis, and scientific research of an air-conditioner refrigeration system on the spot in industry application. During the on-site test process, different special detection module systems can be chosen to form a suitable test system according to the test requirement. The invention can flexibly build the test system aiming at different application locale, thereby having convenient use, effectively reducing the test cost, enhancing the commonality of the test system and greatly enhancing the expandability and the secondary development performance of the test system.
Owner:曹勇 +2
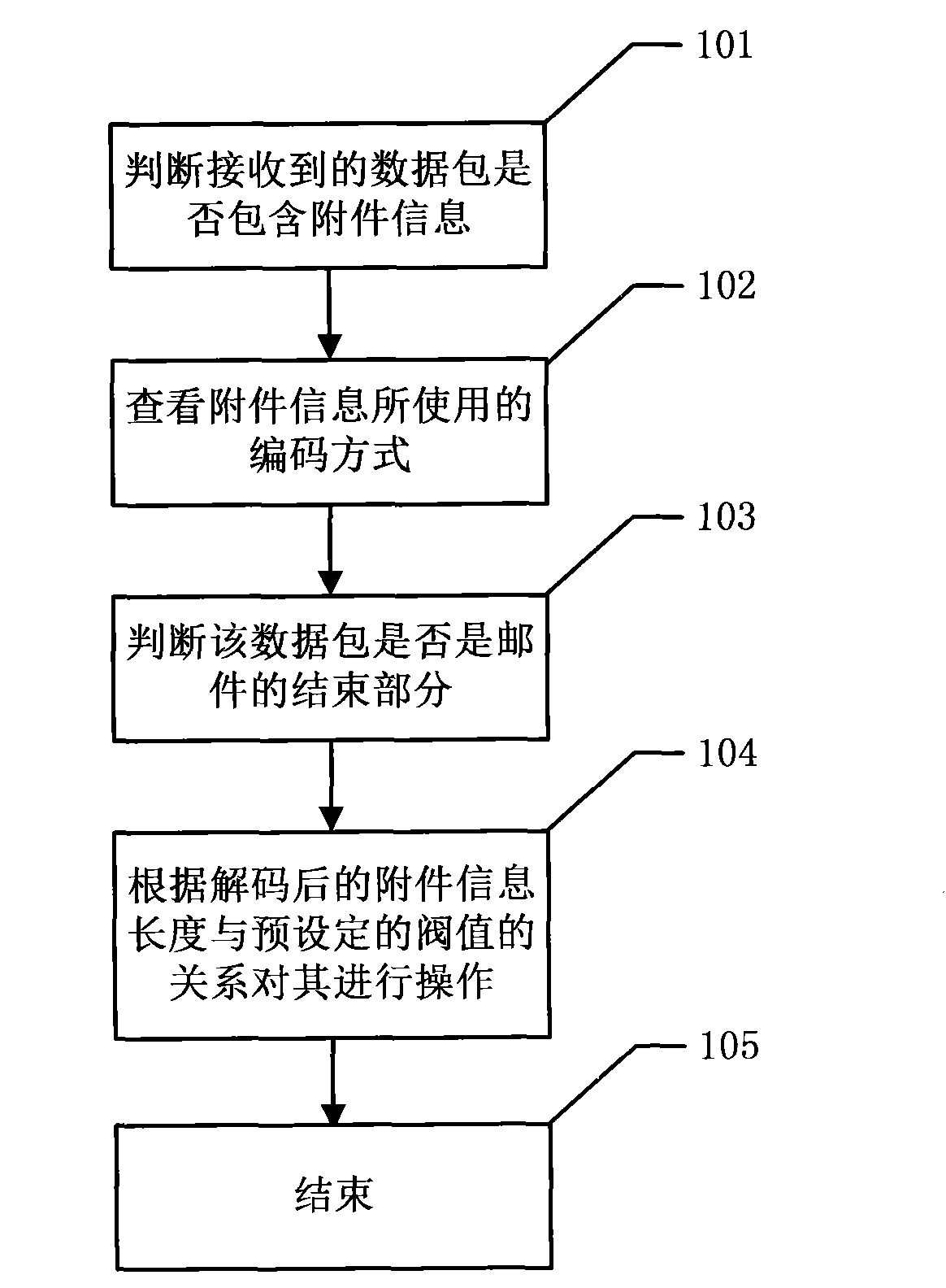
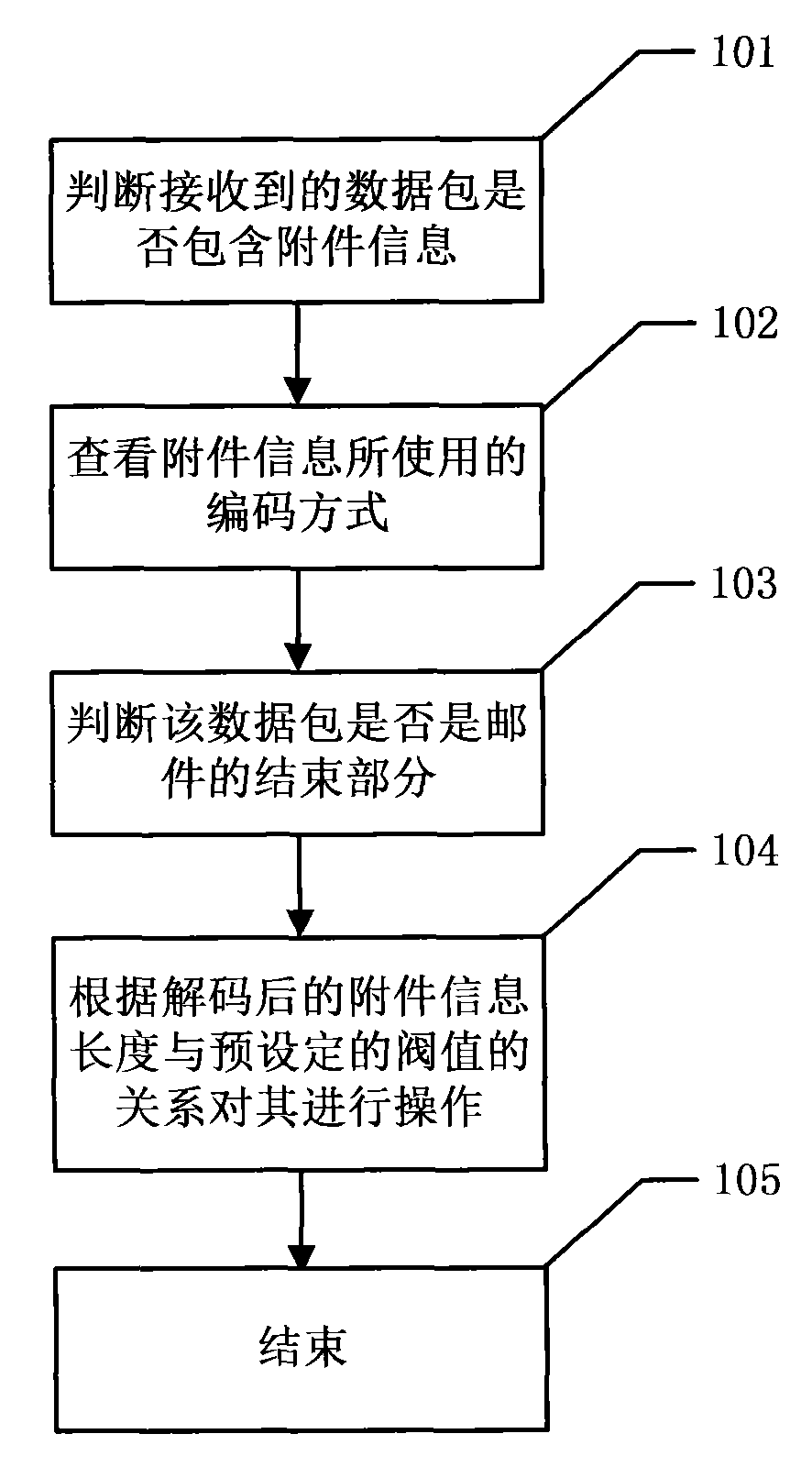
Packet-level dynamic mail attachment virus detection method
ActiveCN101789105AReduce sizeImprove memory usageOffice automationData switching networksInternal memoryNetwork packet
The invention discloses a packet-level dynamic mail attachment virus detection method and relates to website security technical field. The method includes that: the received packet is judged if containing attachment information; the encoding mode of the attachment information is checked; the packet is judged if the packet is the end part of the mail; the packet is processed according to the relationship of decoded attachment information length and the preset threshold. The packet-level dynamic mail attachment virus detection method can improve the internal memory utilization rate and the virus detection efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING ANTIY NETWORK SAFETY TECH CO LTD
Gas tightness detection device and detection method
InactiveCN107677429AAccurate measurementReduce leakageMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateDifferential pressureEngineering
The invention provides a gas tightness detection device and a detection method. The detection method comprises the following steps of opening a gas source and a valve body, and inputting gas with samepressure into a test object and a standard object through a gas pipe and the valve body; and closing the valve body, using a differential pressure sensor to measure a differential pressure value between the test object and the standard object, and in preset time, if the differential pressure value is determined to be greater than a preset differential pressure threshold, emitting an alarm by an alarm apparatus connected to the differential pressure sensor. Whether the test object is qualified is determined through determining whether the differential pressure value in the preset time exceedsthe preset differential pressure threshold. By using a traditional gas tightness detection method, manual observation is needed, detection efficiency is low or input air pressure is high so that detection precision is low. Compared with the traditional gas tightness detection method, by using the gas tightness detection method of the invention, a short detection period and high efficiency are realized; the high precision differential pressure sensor with a low measuring range is used and a reference comparison method is adopted so that the test object with a large size and a small leakage ratecan be accurately measured; and measurement precision is increased.
Owner:HUNAN JUNCHENG TECH
Static railway track assembly overall dimension and damage optical detection system
ActiveCN105507099AConfirm the extent of damageWhether it is loose or notTrack superstructureMeasuring apparatusImaging processingEngineering
The invention provides a static railway track assembly overall dimension and damage optical detection system which comprises linear hard light sources, annular hard light sources, high-speed cameras for optical detection, an image processing card, a computer, data and power source cables, walking type machine frameworks and mileage sensors installed on wheels of the walking type machine frameworks. A track assembly comprises steel rails, steel rail fastener combinations, sleepers, sleeper plates and railway ballasts. Each high-speed camera for optical detection and the corresponding linear hard light source which are installed on the corresponding walking type machine framework and located on the same side of the same corresponding steel rail and are higher than the rail surface form a steel rail and steel rail fastener combination contour section dimension optical detecting set. By means of the technology, the functions of detecting the steel rail overall dimension, the steel rail top face corrugated abrasion and rail bottom slopes and the functions of detecting steel rail fastener gland nut loosening, failures and missing are achieved.
Owner:李社军
Detection equipment for intelligent manufacturing
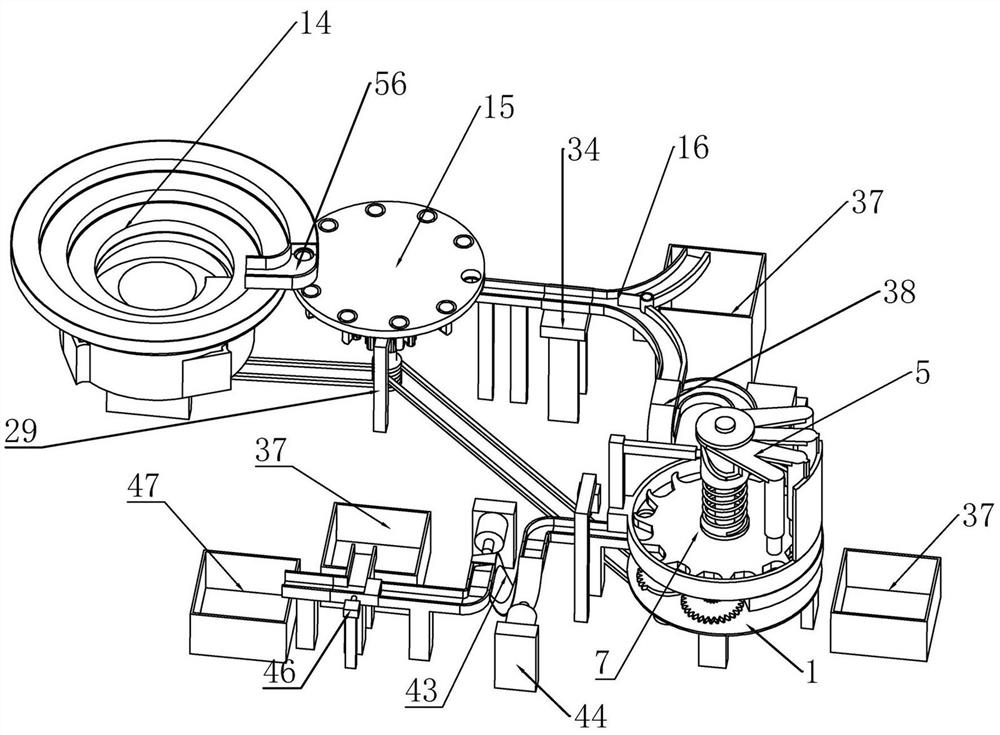
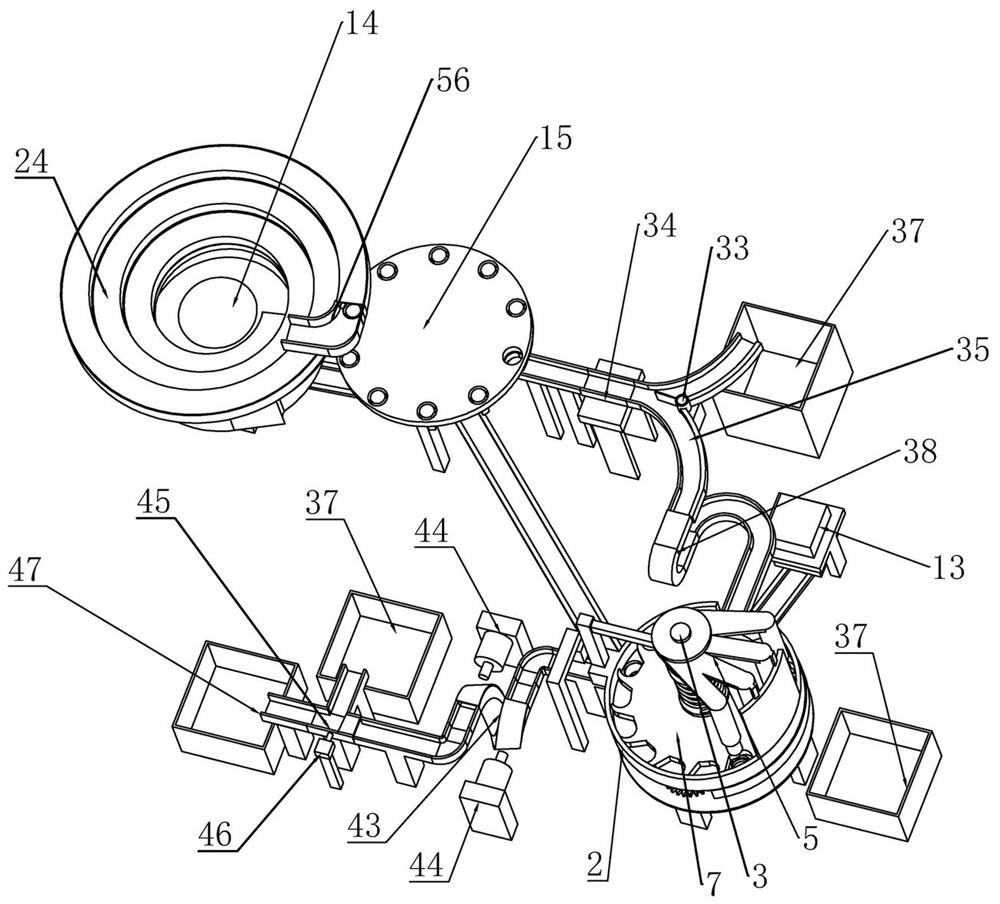
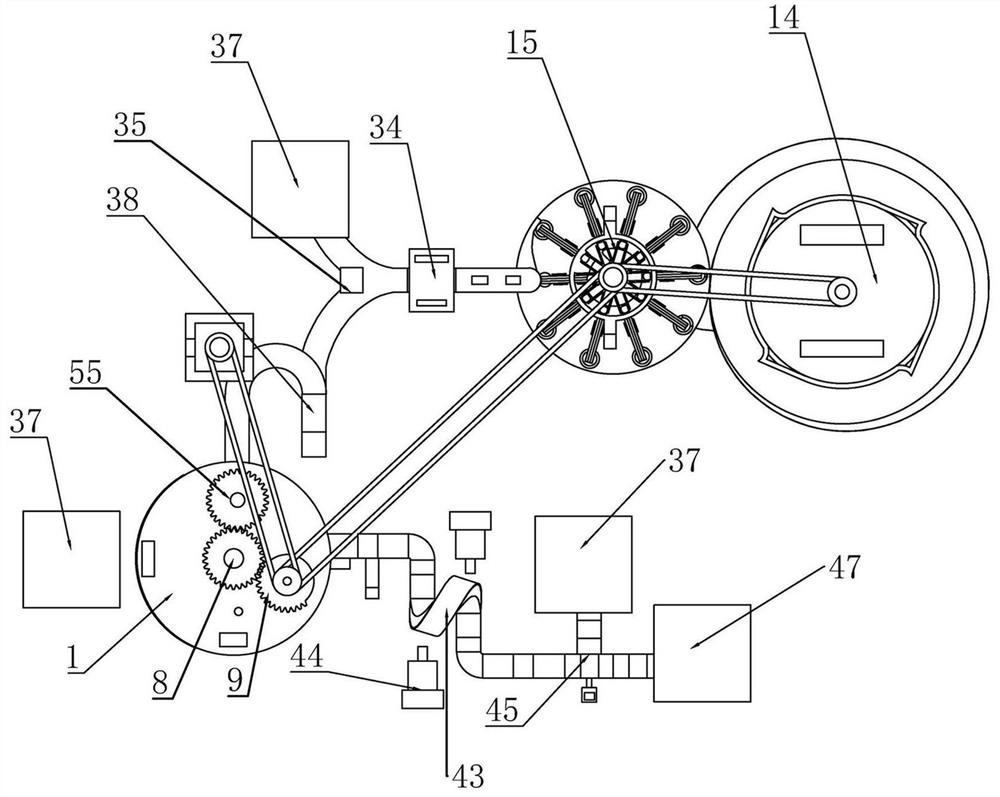
InactiveCN111906046ARealize one by one screeningConvenient air tightness testingSortingStructural engineeringAssembly line
The invention relates to detection equipment for intelligent manufacturing. Through the detection equipment, the problems that existing equipment is low in detection precision and influences product quality, the detection efficiency of bottle cap airtightness is low, and operation is tedious are effectively solved. According to the technical scheme, an airtight rotating trough is fixed above a supporting plate, an airtight lifting shaft is rotationally connected into the airtight rotating trough, a space lifting cylindrical cam is arranged on the airtight lifting shaft in a coaxial rotation mode, airtight detection rods are rotationally arranged on the space lifting cylindrical cam, a lifting guide rod is arranged in a sliding groove of the space lifting cylindrical cam, a claw-type feeding disc is arranged below the space lifting cylindrical cam and is coaxially arranged on the airtight lifting shaft in a sleeving mode, and the space lifting cylindrical cam is connected with the claw-type feeding disc through a spring; According to the detection equipment, unqualified products can be screened and gathered respectively, subsequent recovery is facilitated, all bottle caps on an assembly line can be detected and screened, the detection efficiency is high, and the detection equipment has high practicability and universality.
Owner:XINXIANG VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Infrared thermal image nondestructive testing method based on convolutional neural network
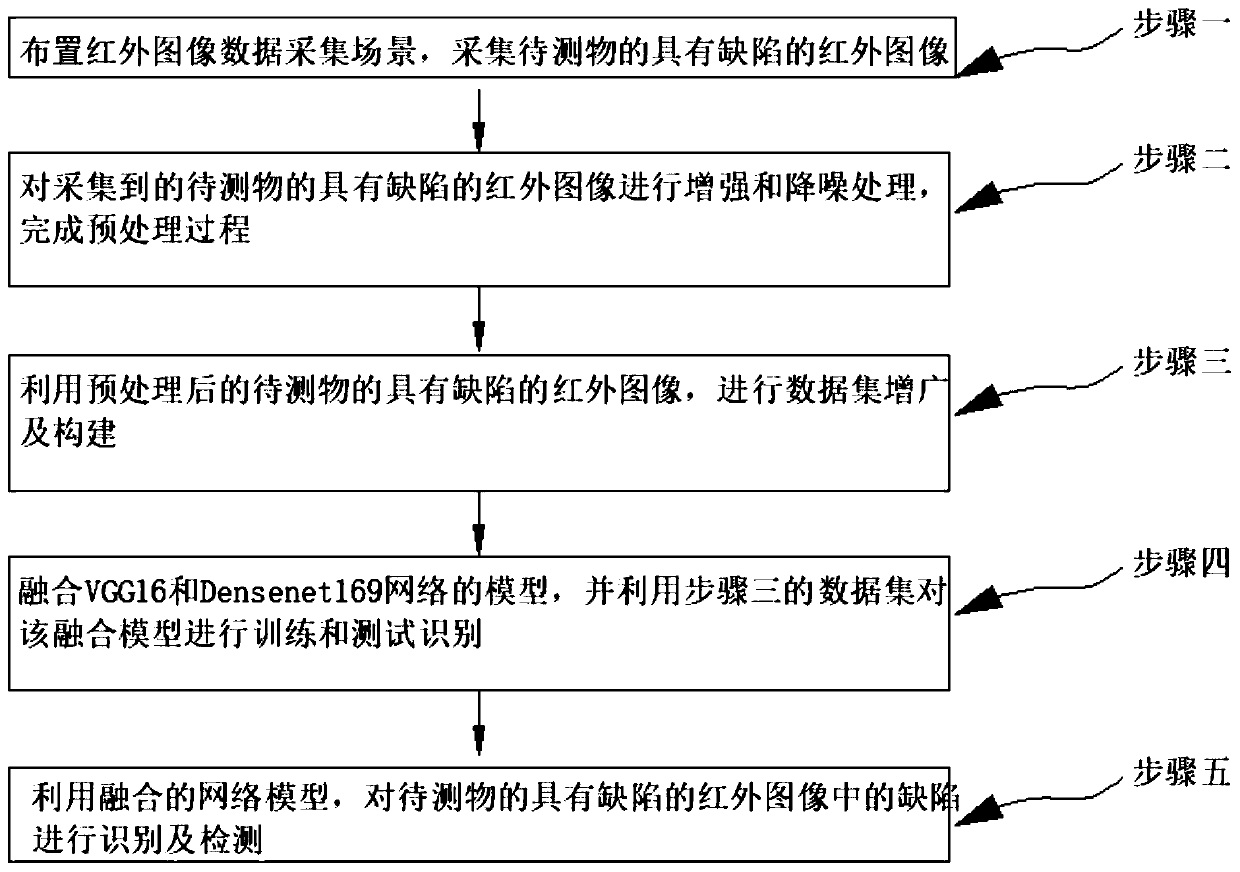
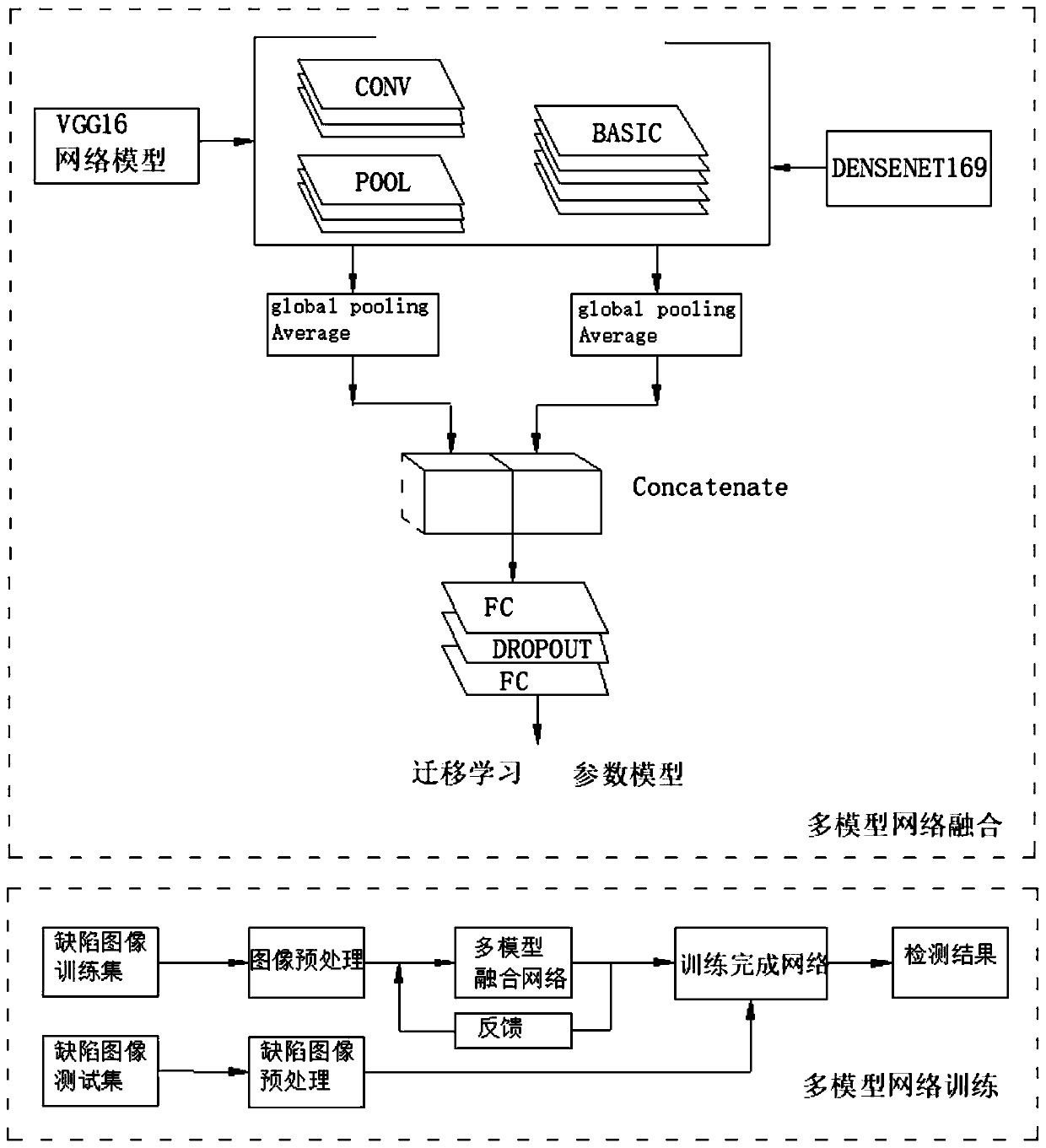
PendingCN111325748AObserve clearlyNo coupling requiredImage enhancementImage analysisData setEngineering
The invention discloses an infrared thermal image nondestructive testing method based on a convolutional neural network, and belongs to the field of image recognition. The problem that nondestructivetesting of an existing convolutional neural network cannot be applied to infrared imaging is solved. An infrared thermal image nondestructive testing method based on a convolutional neural network comprises the following steps: arranging an infrared image data acquisition scene, and acquiring an infrared image with defects of a to-be-tested object; performing enhancement and noise reduction processing on the acquired defective infrared image of the to-be-detected object to complete a preprocessing process; carrying out data set augmentation and construction by utilizing the preprocessed defective infrared image of the to-be-detected object; fusing the models of the VGG16 network and the DenseNet169 network, and training, testing and identifying the fused model by using the data set; and identifying and detecting defects in the defective infrared image of the to-be-detected object by using the fused network model. The identification precision of the detection method provided by the invention reaches 98.5%.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Measurement method for permanganate index and application
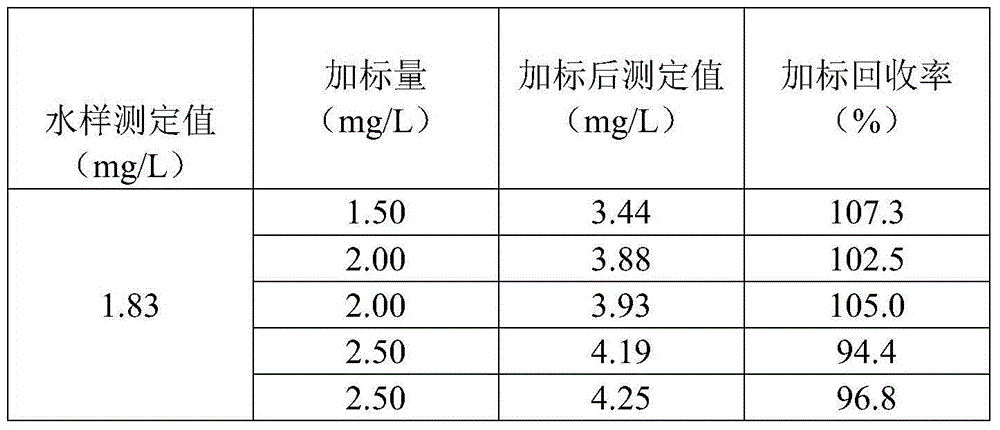
ActiveCN104792714AIncrease dosageReduce dosageColor/spectral properties measurementsSulfosalicylic acidDigestion
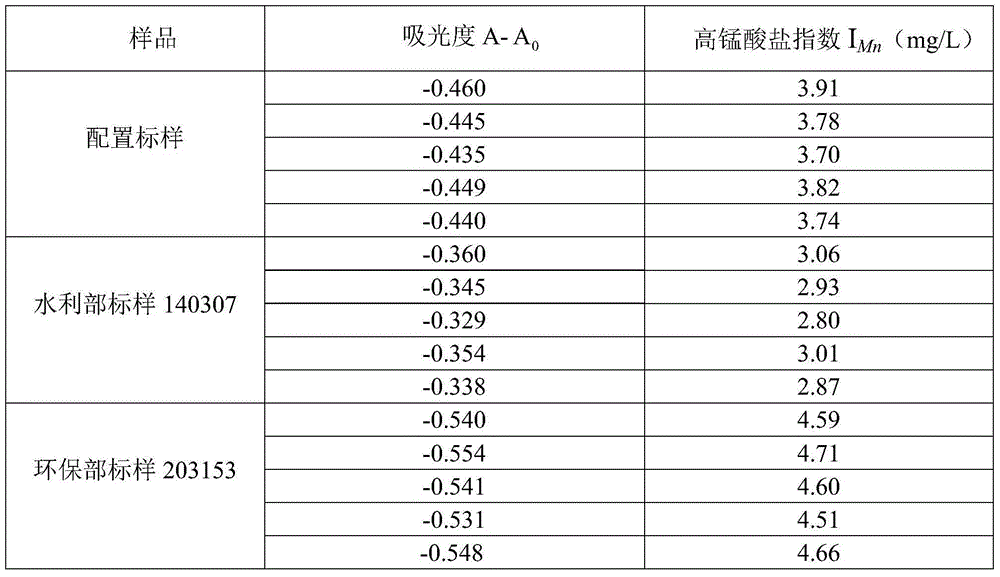
The invention discloses a measurement method for a permanganate index. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a to-be-measured water sample into a colorimetric tube provided with a plug, adding (1+10) sulfuric acid for acidification, adding a potassium permanganate solution, and shaking uniformly; (2) digesting the water sample in the step (1) under a certain condition and quickly cooling to a room temperature; (3) adding an excessive ammonium ferrous sulfate solution into a digestion solution in the step (2), and shaking uniformly; (4) adding a proper amount of a sulfosalicylic acid aqueous solution into a reaction solution in the step (3) for producing a color development reaction; (5) performing absorbance testing on the water sample in the step (4) by taking de-ionized water as a reference at the wavelength of 510 nm, and calculating the permanganate index of the water sample by a formula IMn=-8.5*(A-A0), wherein in the formula, IMn is the permanganate index of the water sample, A is the absorbance of the water sample, and A0 is the absorbance of a blank solution. The measurement method is quick and accurate in detection, suitable for batch measurement and simple to operate, and can be widely applied to laboratory detection and outdoor emergency detection.
Owner:北京连华永兴科技发展有限公司
Method for calculating contents of three effective components in curcuma longa product through relative correction factor
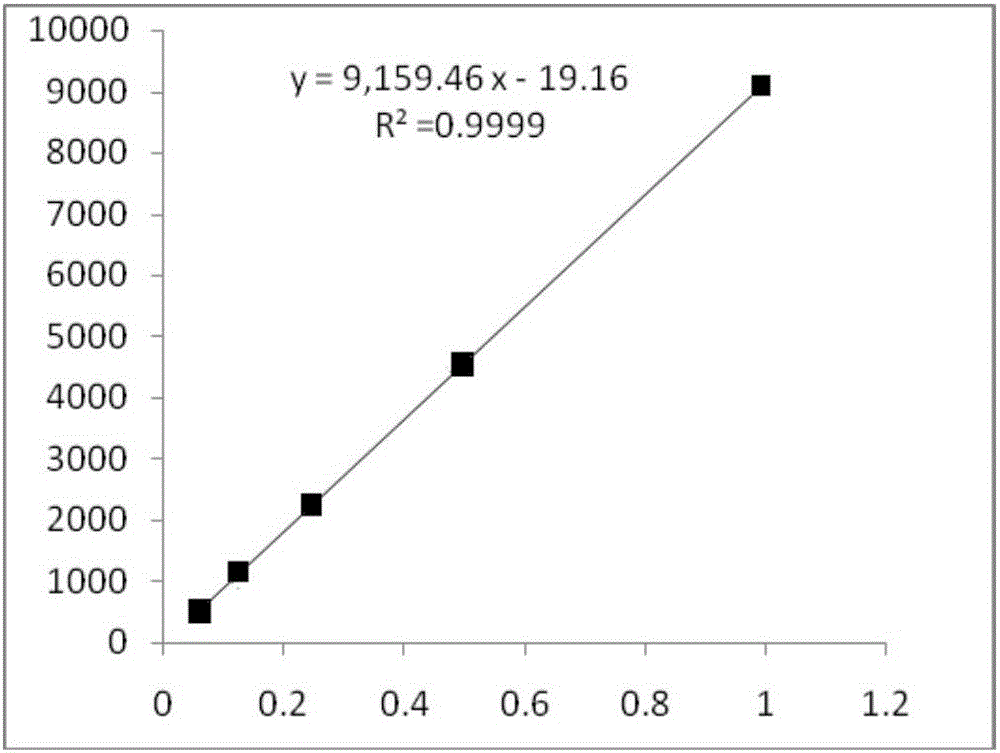
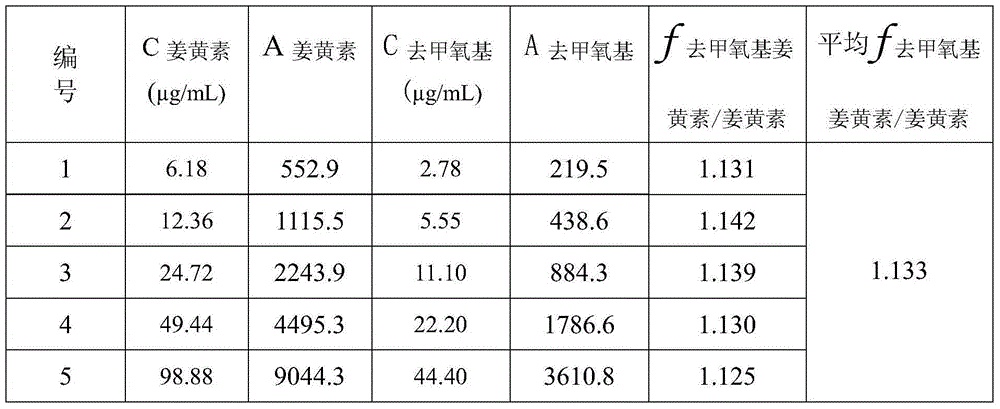
InactiveCN105116061AReduce the number of weighings with the balanceReduce wasteComponent separationMedicineBisdemethoxycurcumin
The invention relates to a method for calculating the contents of three effective components in a curcuma longa product through a relative correction factor, and belongs to the technical field of drug quality determination. The method comprises: (1) preparing a reference substance stock solution; (2) preparing a reference substance solution; (3) preparing a sample solution; (4) determining through high performance liquid chromatography; (5) determining the relative correction factor value; (6) calculating the curcumin content; and (7) calculating the demethoxycurcumin content and the bisdemethoxycurcumin content. According to the present invention, the relative correction factor is used to detect the contents of the three effective components in the curcuma longa product, such that the demethoxycurcumin reference substance preparation and the bisdemethoxycurcumin reference substance preparation in each experiment are eliminated, the detection cost is reduced, and the detection efficiency is improved; the relative correction factor f is verified under different detection equipment, different chromatographic columns, different detection wavelengths, different column temperatures, different flow rates and different flow relative ratios; and the method has characteristics of rapidness, efficiency, high precision, low cost and the like, and is the feasible and effective detection method.
Owner:SICHUAN NEO GREEN PHARMA TECH DEV
Active mobile vehicle bottom dangerous goods detection device based on deep learning algorithm
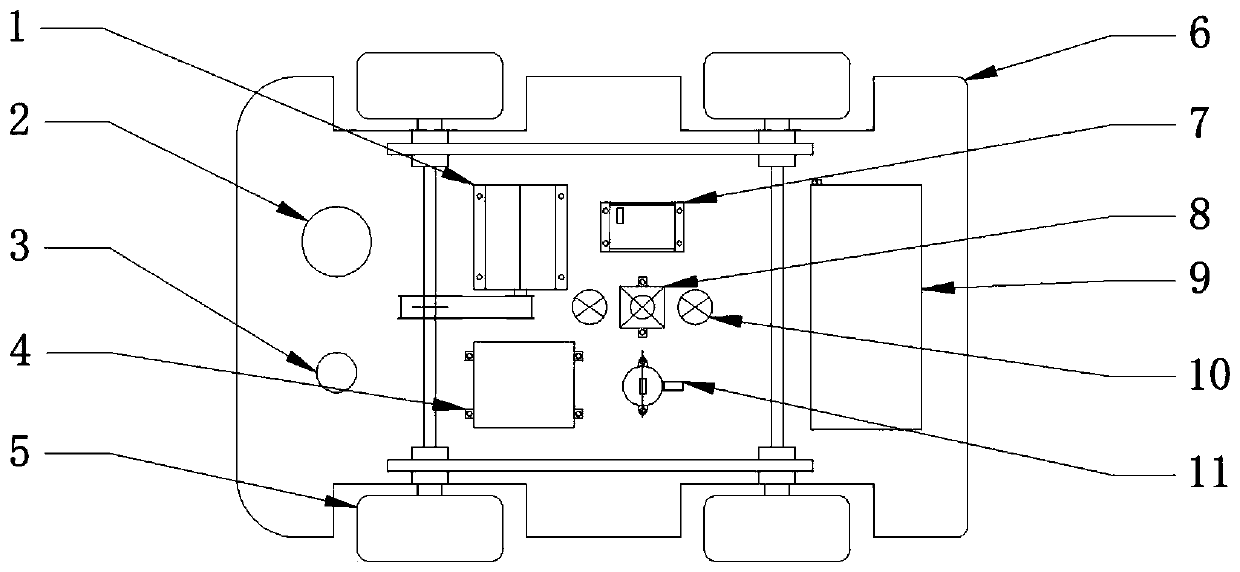
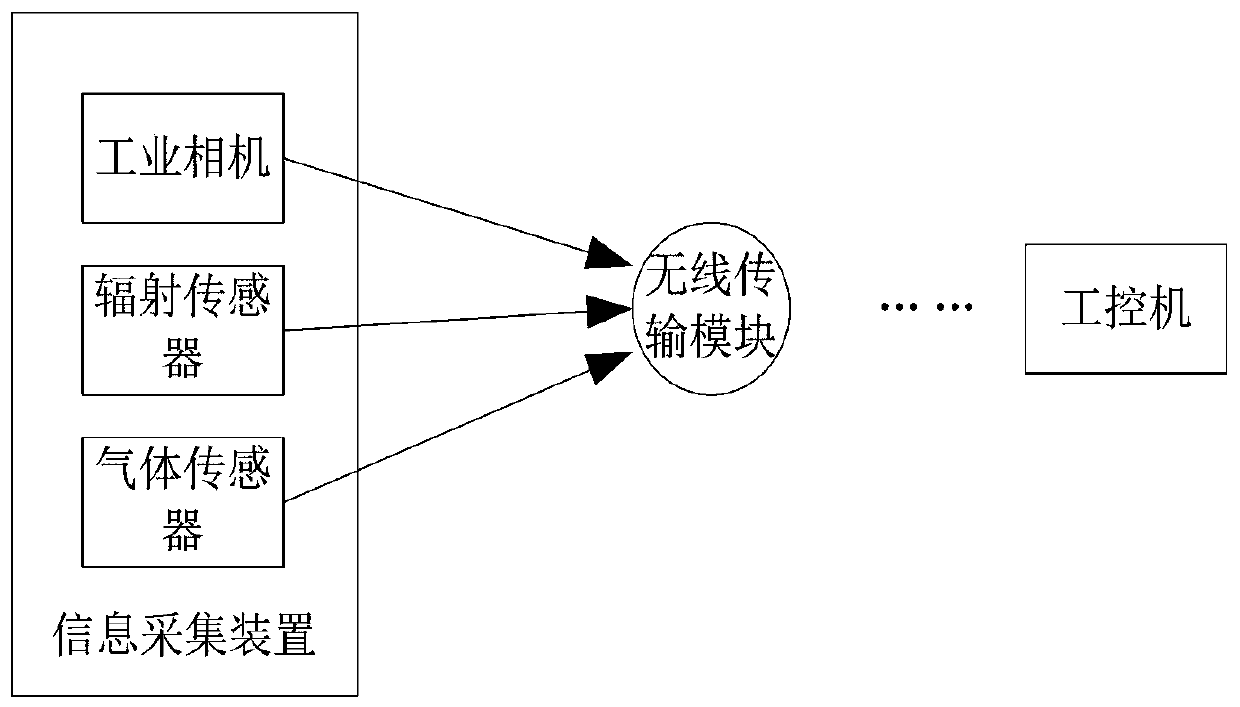
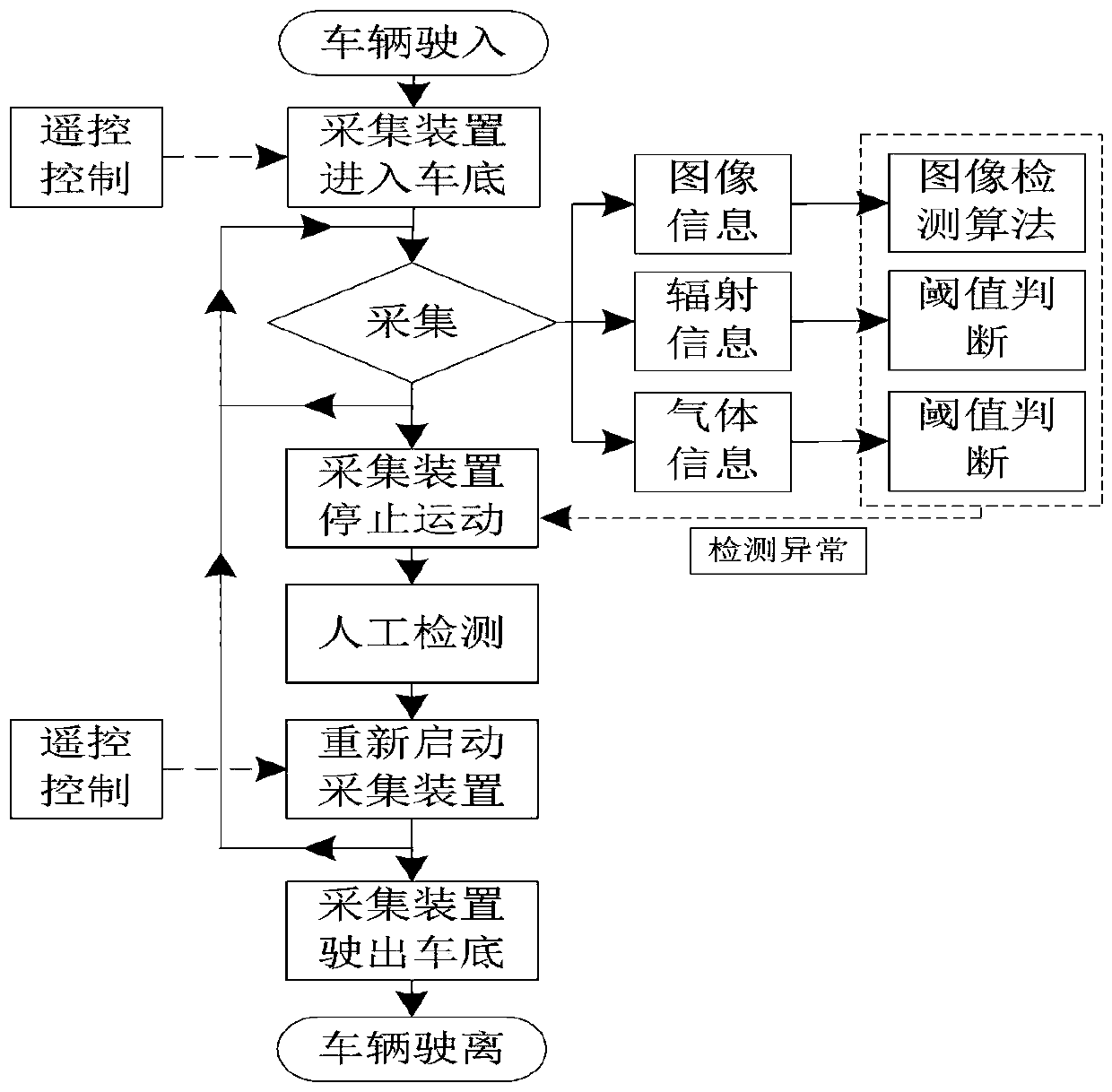
ActiveCN110414391AComprehensive detectionEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionGeological measurementsPersonal computerReal-time computing
The invention relates to an active mobile vehicle bottom dangerous goods detection device based on a deep learning algorithm. The system comprises an information acquisition device and an industrial personal computer. The information acquisition device is in wireless communication with the industrial personal computer. The information acquisition device comprises an industrial camera, a light supplementing lamp, a radiation sensor, a gas sensor and a wireless transmission module. The information acquisition device further comprises a mobile platform, the mobile platform comprises a motion controller, an infrared wireless module and a remote controller, and the mobile platform is controlled by the remote controller to traverse the vehicle bottom through a U-shaped route. The controller is connected with a remote controller through an infrared wireless module. An industrial camera is installed on the upper surface of a machine body of the mobile platform. Light supplementing lamps are symmetrically arranged on the machine body on the front side and the rear side of the industrial camera, and a deep learning algorithm is loaded in the industrial personal computer. The device is an active mobile detection device, that is, after parking, the mobile detection device is actively operated to enter the vehicle bottom for detection, dangerous target detection can be better achieved, andthe detection precision is high.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Sample observing method and scanning electron microscope
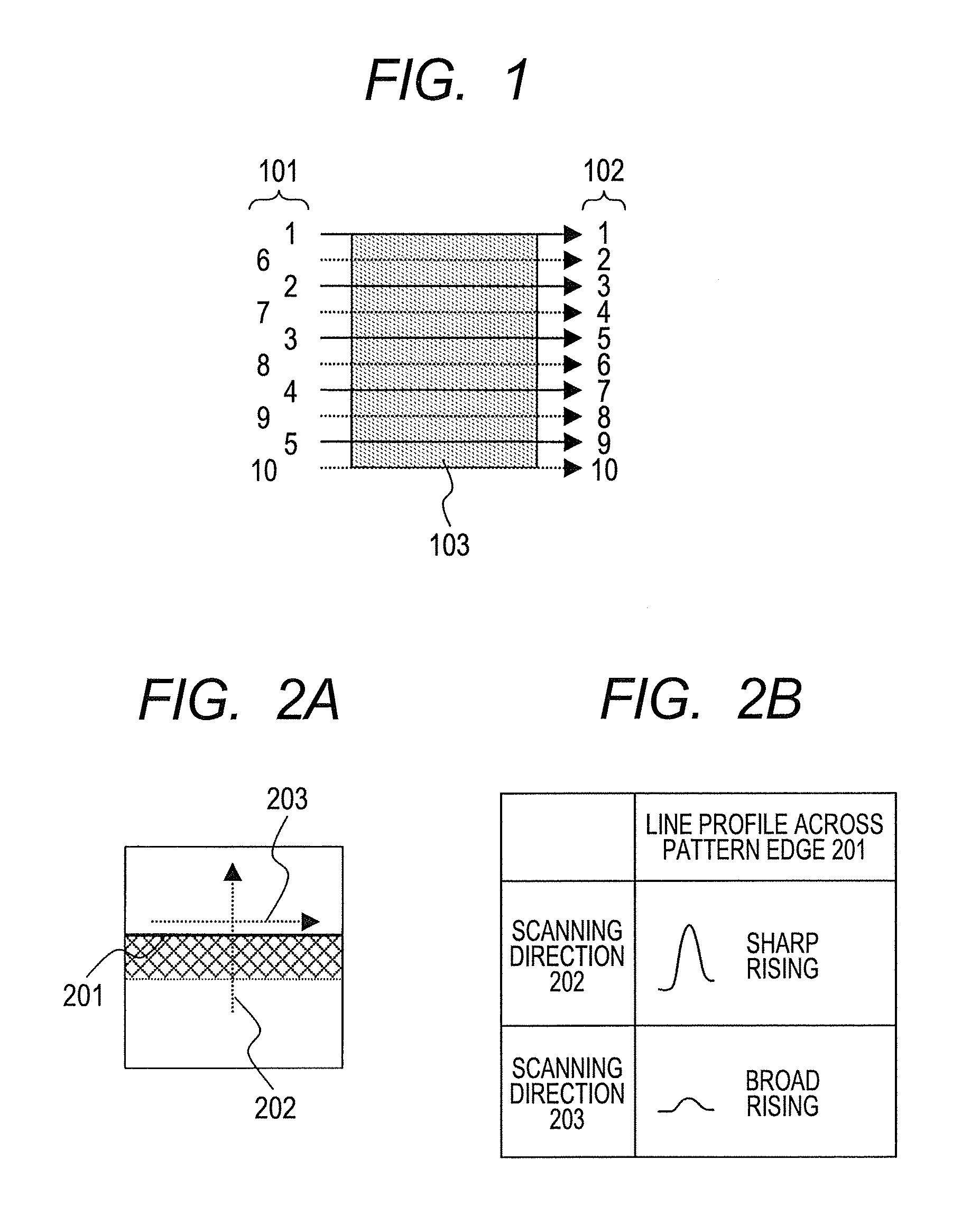
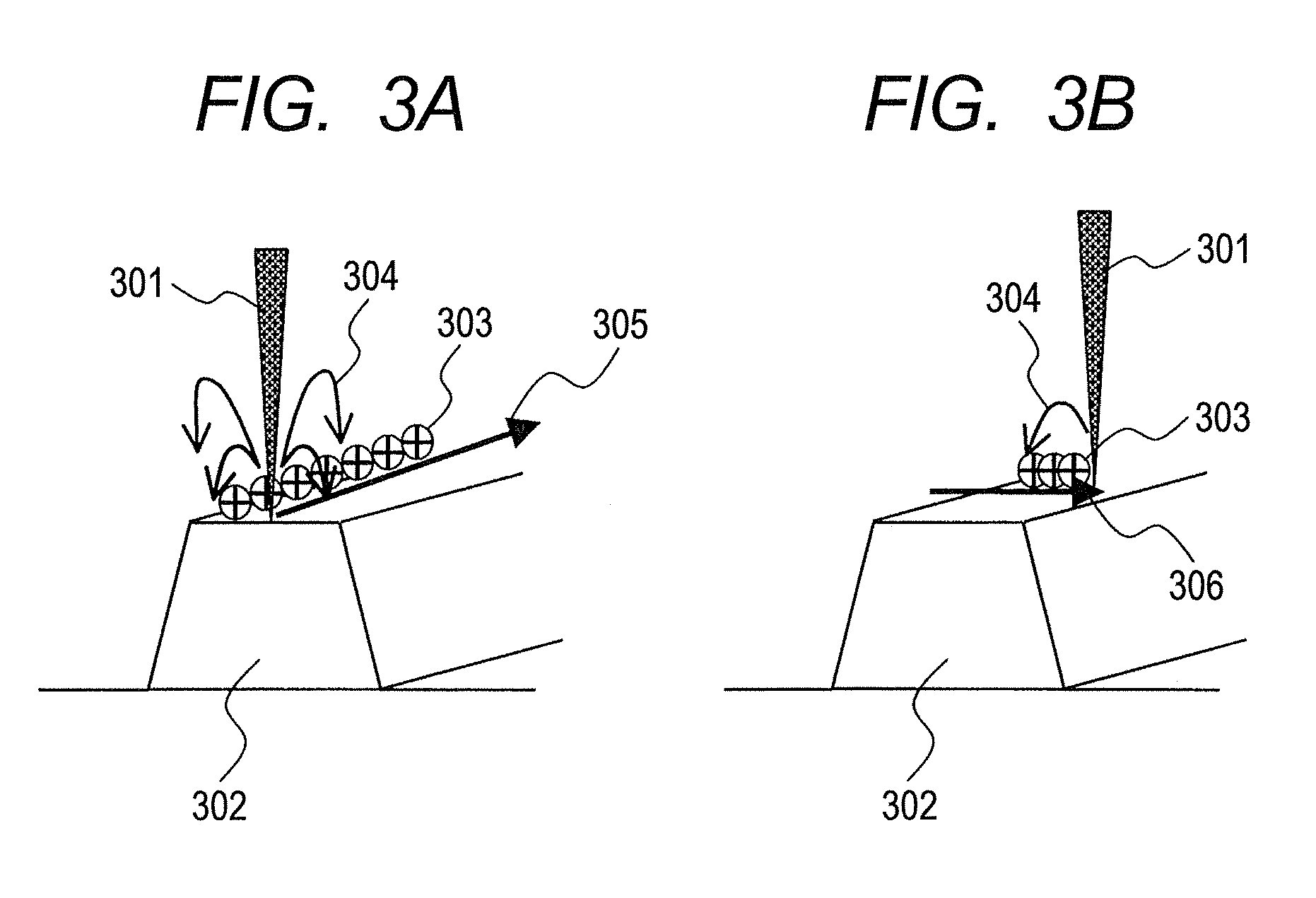
ActiveUS20110303843A1Reduce detection efficiencyDifficult to extractPhotoelectric discharge tubesUsing wave/particle radiation meansPre doseScanning tunneling microscope
Provided is a sample observing method wherein the effect on throughput is minimized, and a pattern profile can be obtained at high accuracy even in a complicated LSI pattern, regardless of the scanning direction of an electron beam. In the sample observing method, the presence or absence of an edge parallel to a scanning direction (707) of an electron beam is judged regarding an edge (708) of a pattern to be observed (S702); if the edge is present, an area in the vicinity of the pattern edge is designated as a local pre-dose area (709) (S703); a local pre-dose of an electron beam is performed, so that the initial charged state is controlled not to return secondary electrons generated by irradiation of an electron beam when an image is captured, to the surface of a sample.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Primary user emulation attack detection method based on channel multipath delay differences
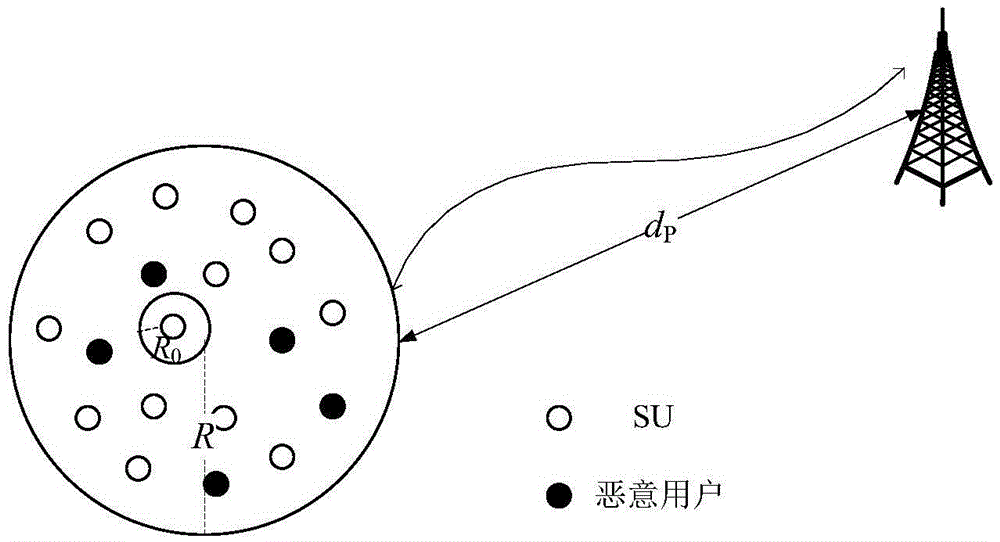
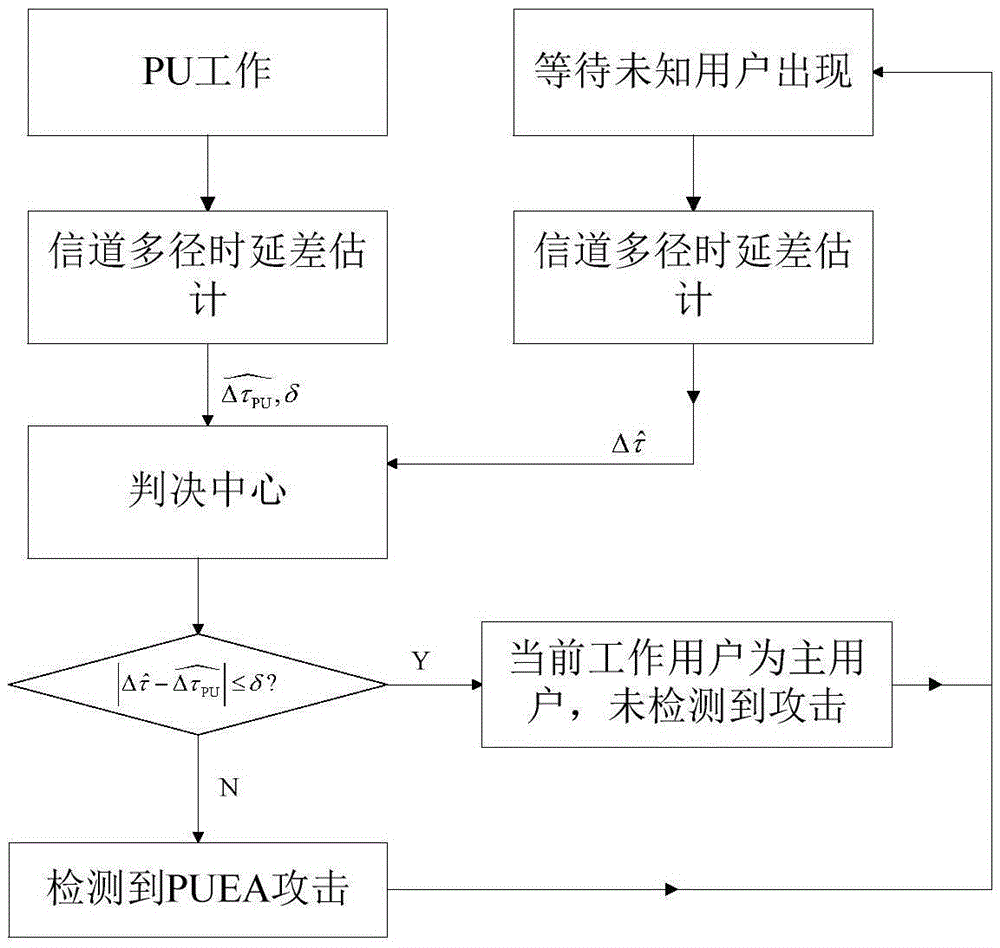
ActiveCN105554739AReduce detection efficiencyRecognition time is shortTransmission monitoringSecurity arrangementPrior informationPresent method
The invention relates to a primary user emulation attack detection method based on channel multipath delay differences. In a present method, when a PUE user can obtain prior information of a PU and has a reconfiguration capability, the detection efficiency greatly decreases. The method provided by the invention is characterized in that channel estimation is carried out to obtain small-scale fading characteristics of channels, and a binary hypothesis detection method is utilized to realize primary user emulation attack detection according to the characteristics. Specifically, the method comprises the steps that: according to a multipath fading model of the channels under a fixed scene, a cognitive radio user utilizes lead code information of the master user to carry out relative operation on received signals and synchronous sequences so as to obtain the multipath delay differences of the channels, then the multipath delay difference of two paths largest in amplitude is selected as a binary hypothesis detection object, and a decision is made. According to the invention, only the lead code information of the primary user is needed, background noise power of the channels are not needed, and normal work is available when the primary user emulation user successfully emulates large-scale and middle-scale fading characteristics of the primary user.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
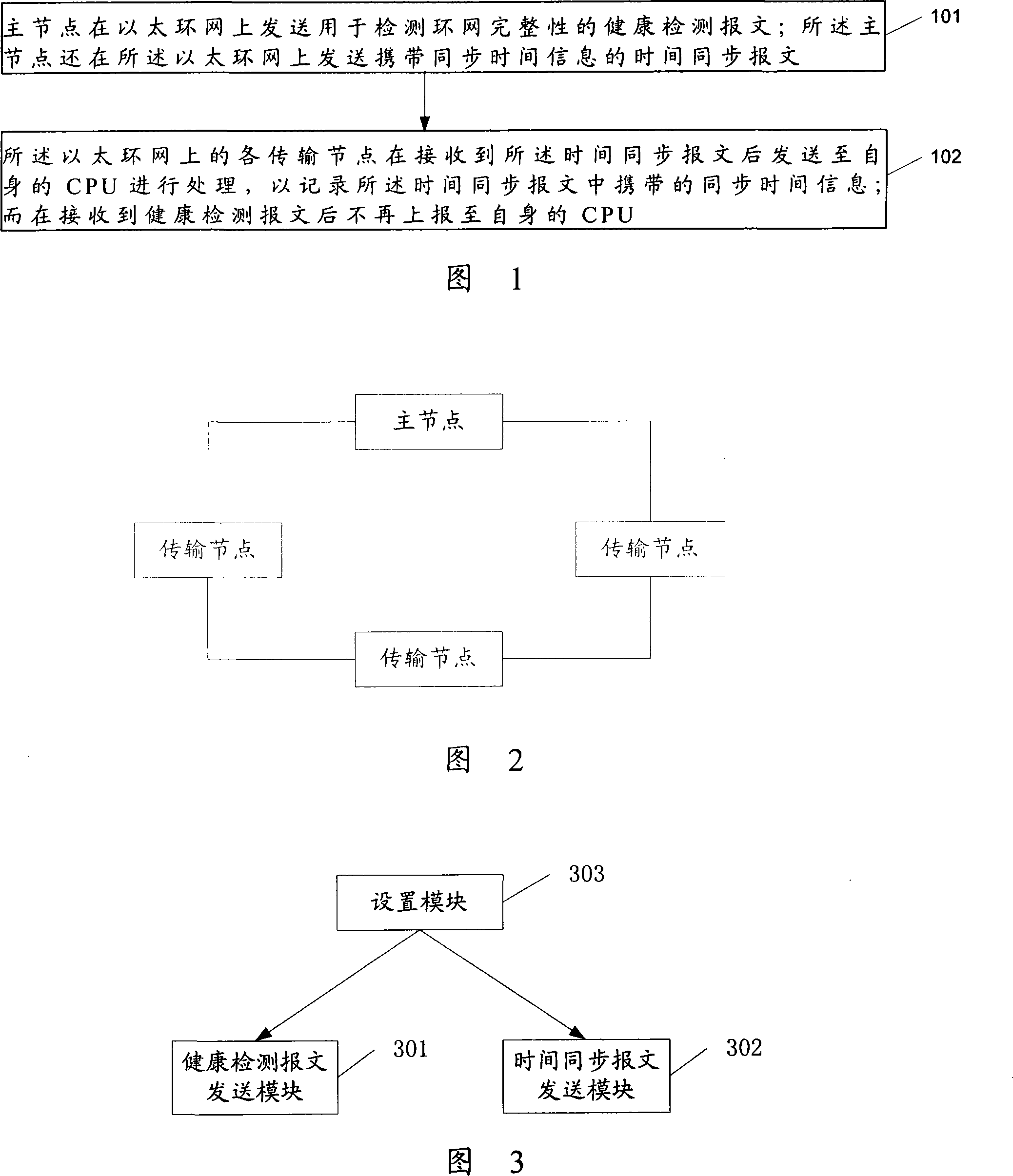
Time synchronization method in Ethernet ring network and Ethernet ring system
ActiveCN101237319AReduced integrity detection efficiencyReduce detection efficiencyError preventionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTime informationRing network
The invention discloses a time synchronism method in an Ethernet ring network, comprising the following steps that: a health detection message which is used for detecting the integrity of the ring network is transmitted on the Ethernet ring network; a time synchronism message which carries over synchronizing time information is transmitted on the Ethernet ring network, and the synchronizing time information can be then informed to various transmission nodes on the Ethernet ring network. Moreover, the invention also discloses another time synchronism method in the Ethernet ring network, an Ethernet ring network system and a main node in the Ethernet ring network. By adoption the technical proposal of the invention, time synchronism in the ring network can be realized without the necessity for utilization of the health detection message, thereby reduction of the CPU efficiency of the transmission nodes and reduction of the detection efficiency of the integrity of the ring network are avoided.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Circular orbit robot for nondestructive testing of large workpiece
InactiveCN104589303AReduce detection efficiencyLow degree of automationManipulatorCircular orbitNondestructive testing
The invention relates to a circular orbit robot for nondestructive testing of a large workpiece. According to the technical scheme, for the large workpiece complex in appearance and large in testing workload, a circular orbit capable of moving up and down is arranged on the periphery of the workpiece, and the industrial robot walks on the orbit and can arrive at different positions; a portable nondestructive testing device is installed on a mechanical arm, each small part is tested in a movable mode, and the nondestructive testing of the large workpiece is completed; meanwhile, the device is connected with a control center, receives the position information transmitted by the control center and returns nondestructive testing results of the corresponding positions back. By means of the method, the limitation on the workpiece and the requirement for labor of a traditional nondestructive testing device are broken through, the nondestructive testing of the large workpiece can be achieved with low cost, and the circular orbit robot is especially suitable for the nondestructive testing of large workpieces many in batch, large in quantity and small in single batch quantity.
Owner:安徽省库仑动力自动化科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com