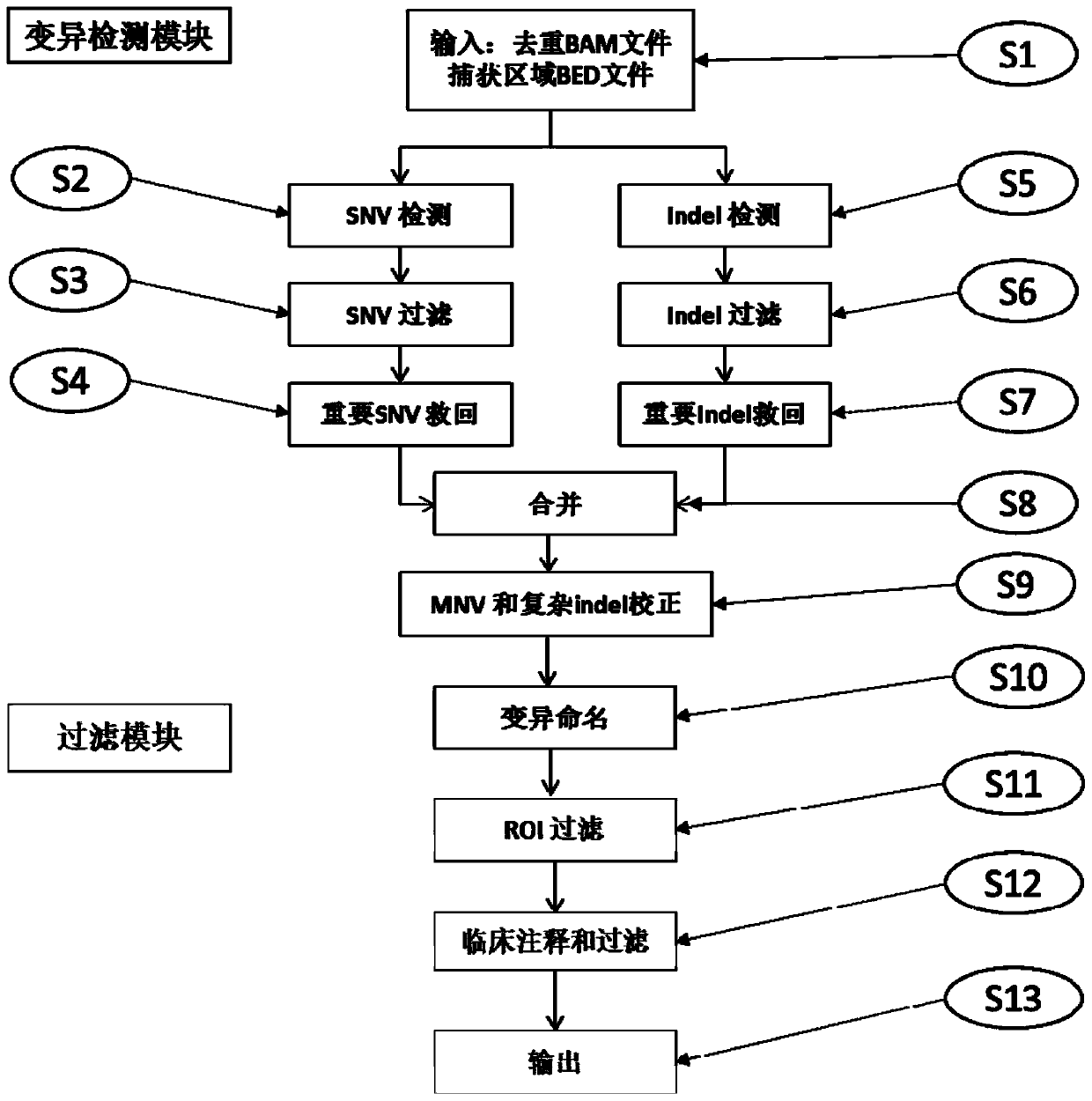
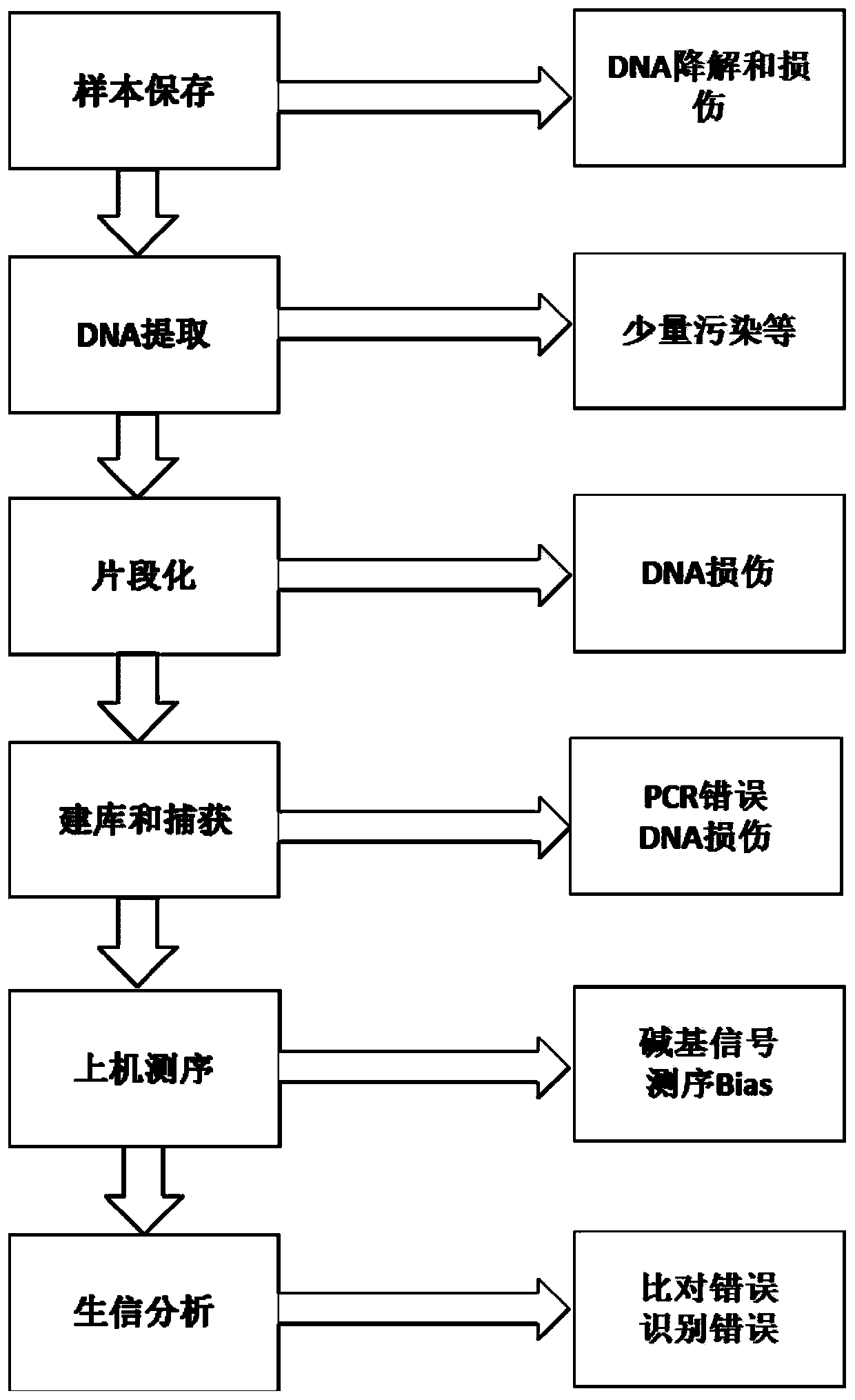
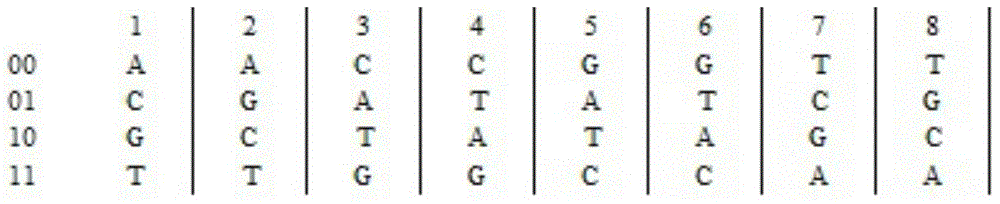
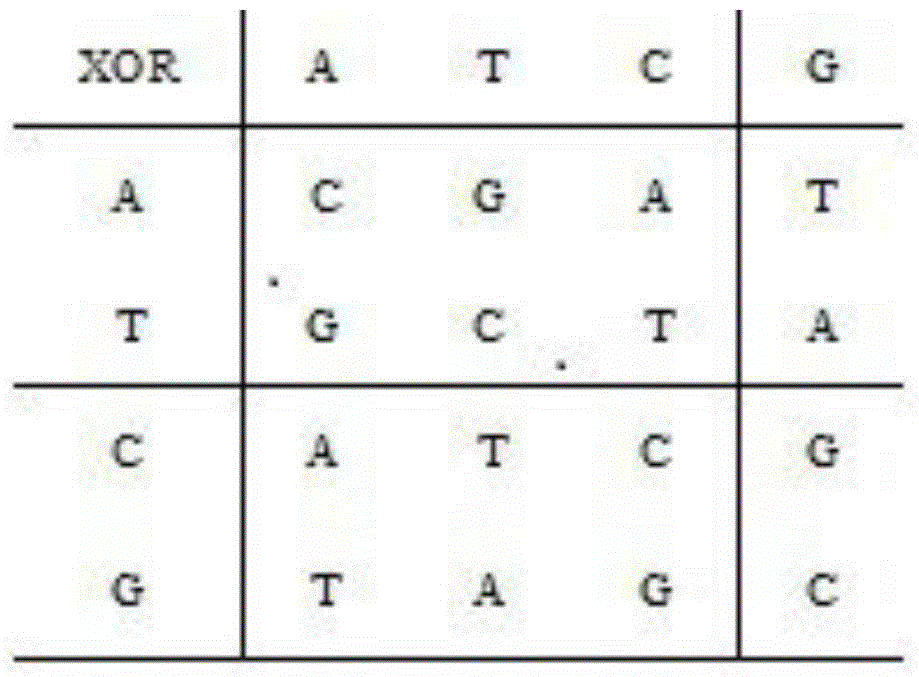
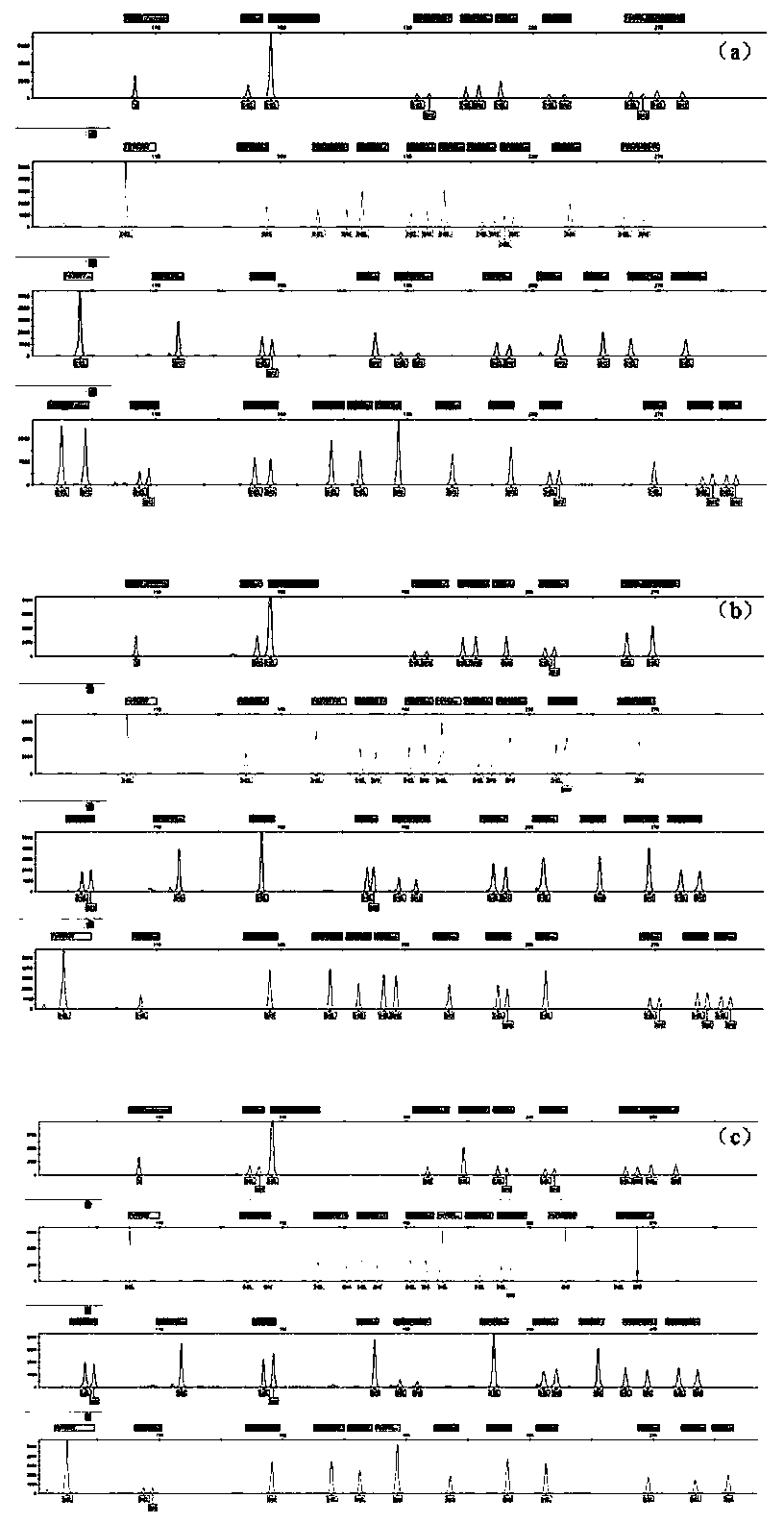
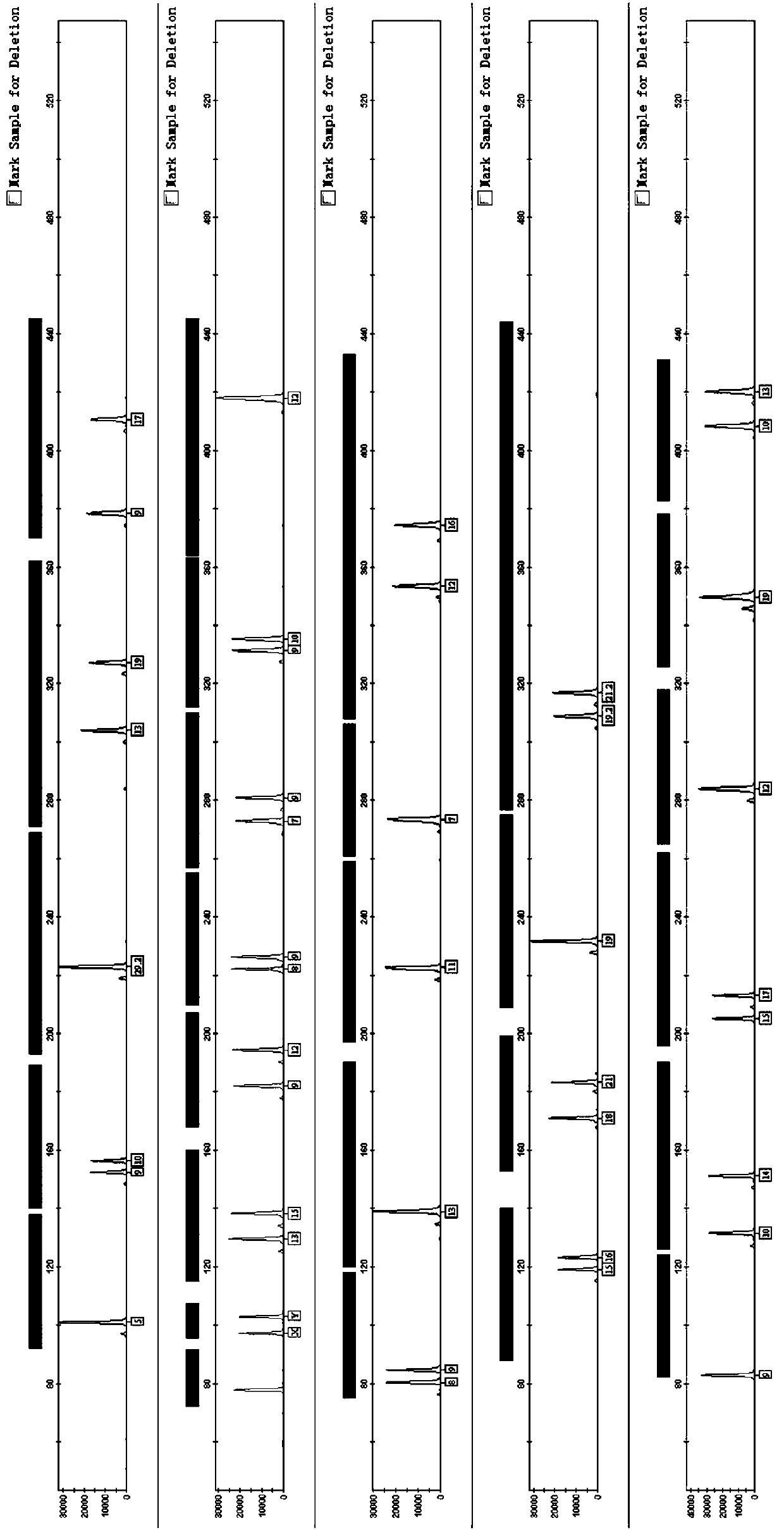
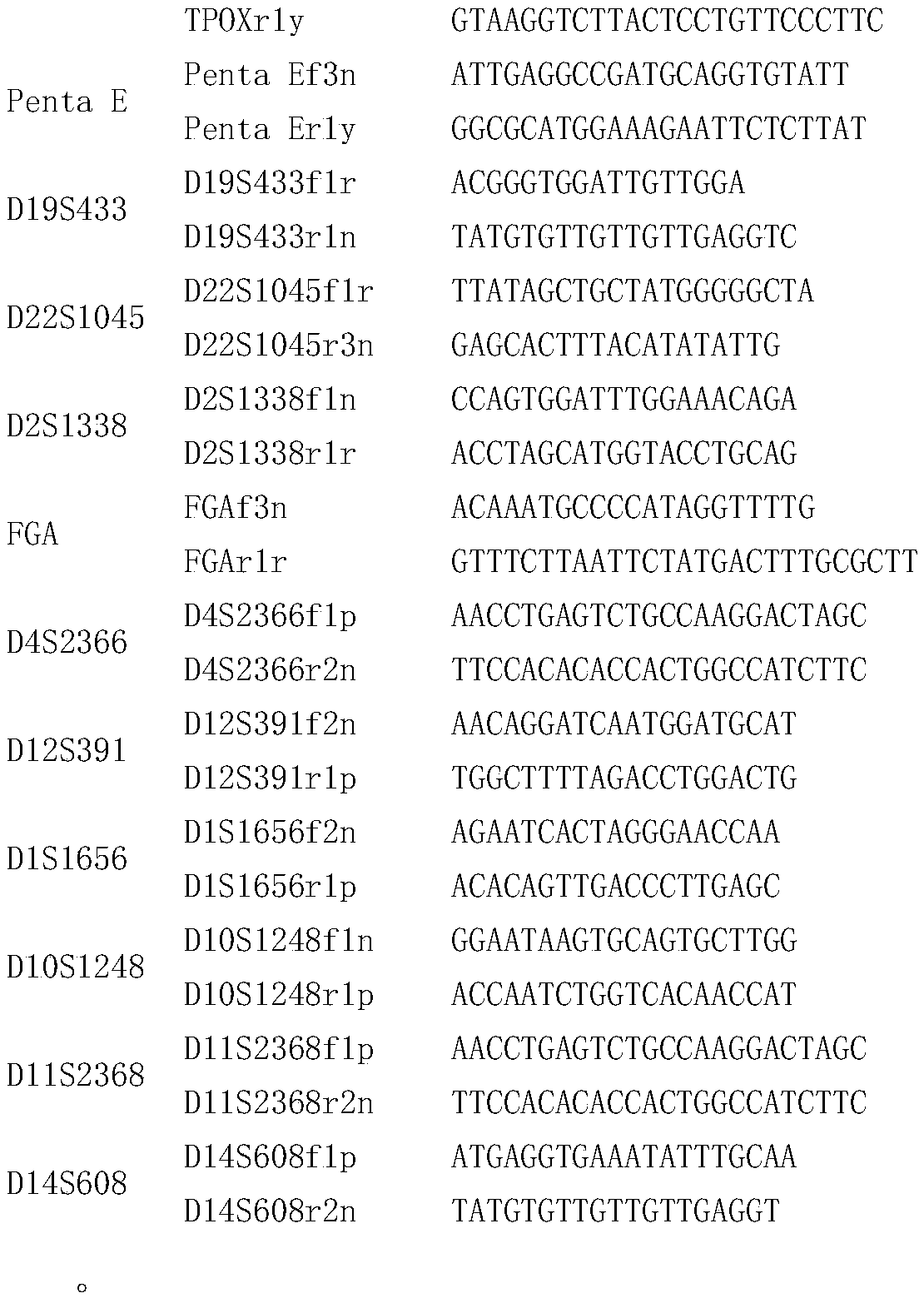
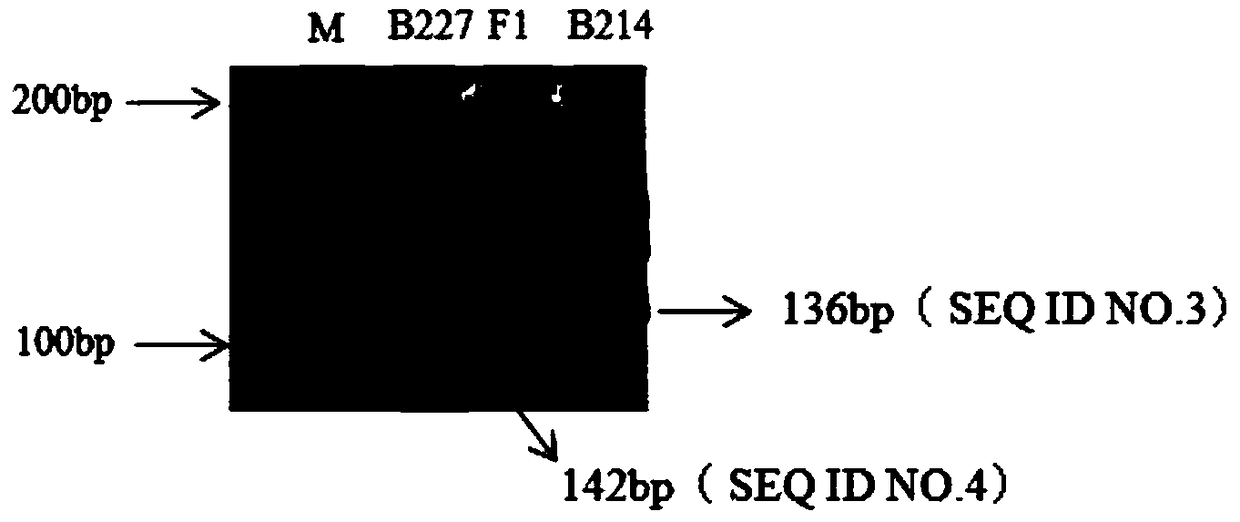
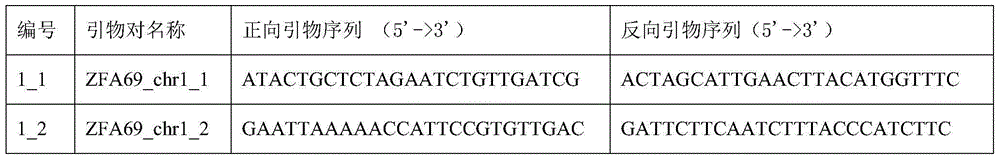Patents
Literature
67 results about "Insertion deletion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Insertion and deletion mutations can be as small as one nucleotide, to thousands of nucleotides long. These long insertion or deletion mutations normally occur when one part of a chromosome crosses over and changes genetic information with a different chromosome.
Method for rapidly detecting human genome single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion
ActiveCN104762402AReduce memory requirementsShort analysis timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsInsertion deletionHuman DNA sequencing
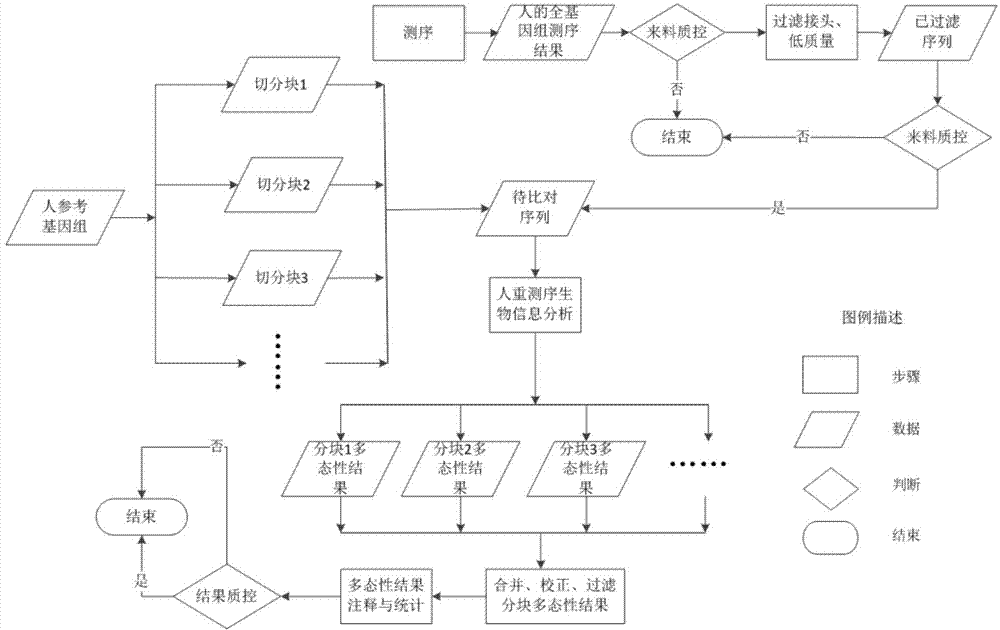
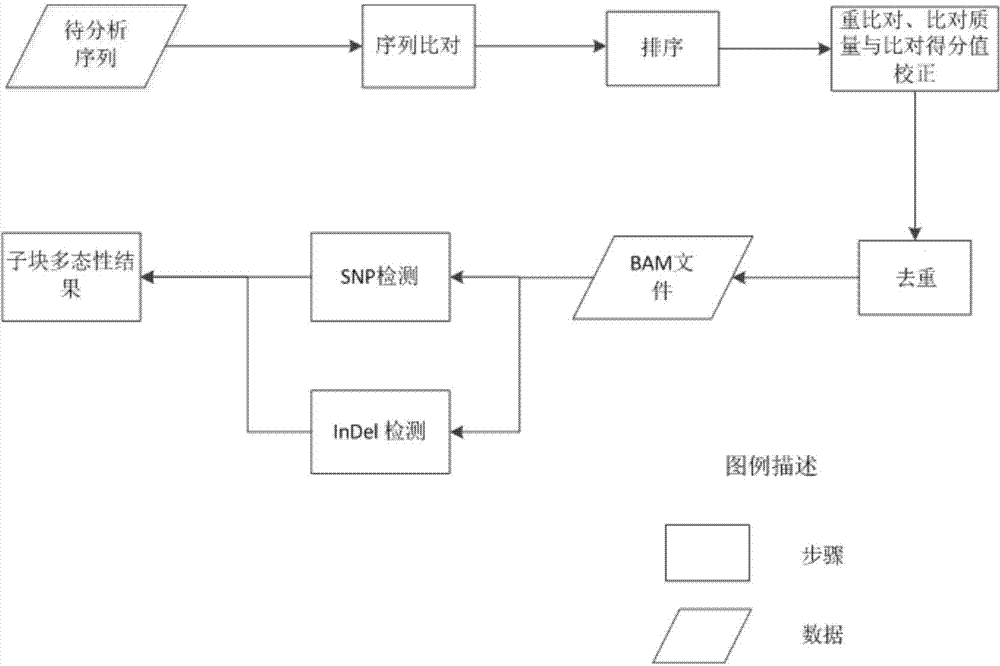
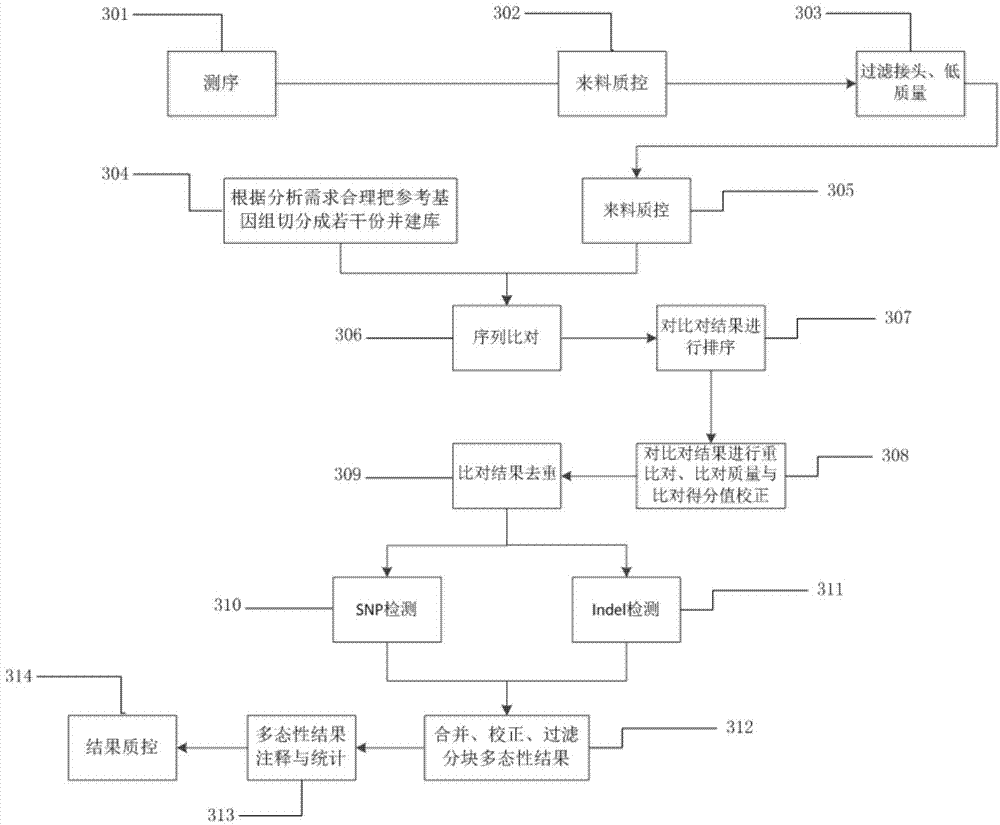
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting human genome single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion. The method is a feasible method for rapidly detecting single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion from a human genome DNA sequencing result. According to the invention, a human reference genome sequence is scientifically and effectively split into small sub reference sequence blocks; almost all steps (including steps with relatively long analysis time) of human resequencing are divided into sub task blocks with greatly reduced computational complexity, wherein the sub task blocks do not influence each other; polymorphism information obtained from the sub reference sequence blocks is subjected to redundancy-removing, correction and filtering, such that the polymorphism information needed by an original human resequencing process is obtained. With the method provided by the invention, a problem of long human resequencing biological information analysis time is solved, and a novel analysis mode is created.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGDING INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, device and storage medium
ActiveCN108690871AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsInsertion deletionAllele frequency
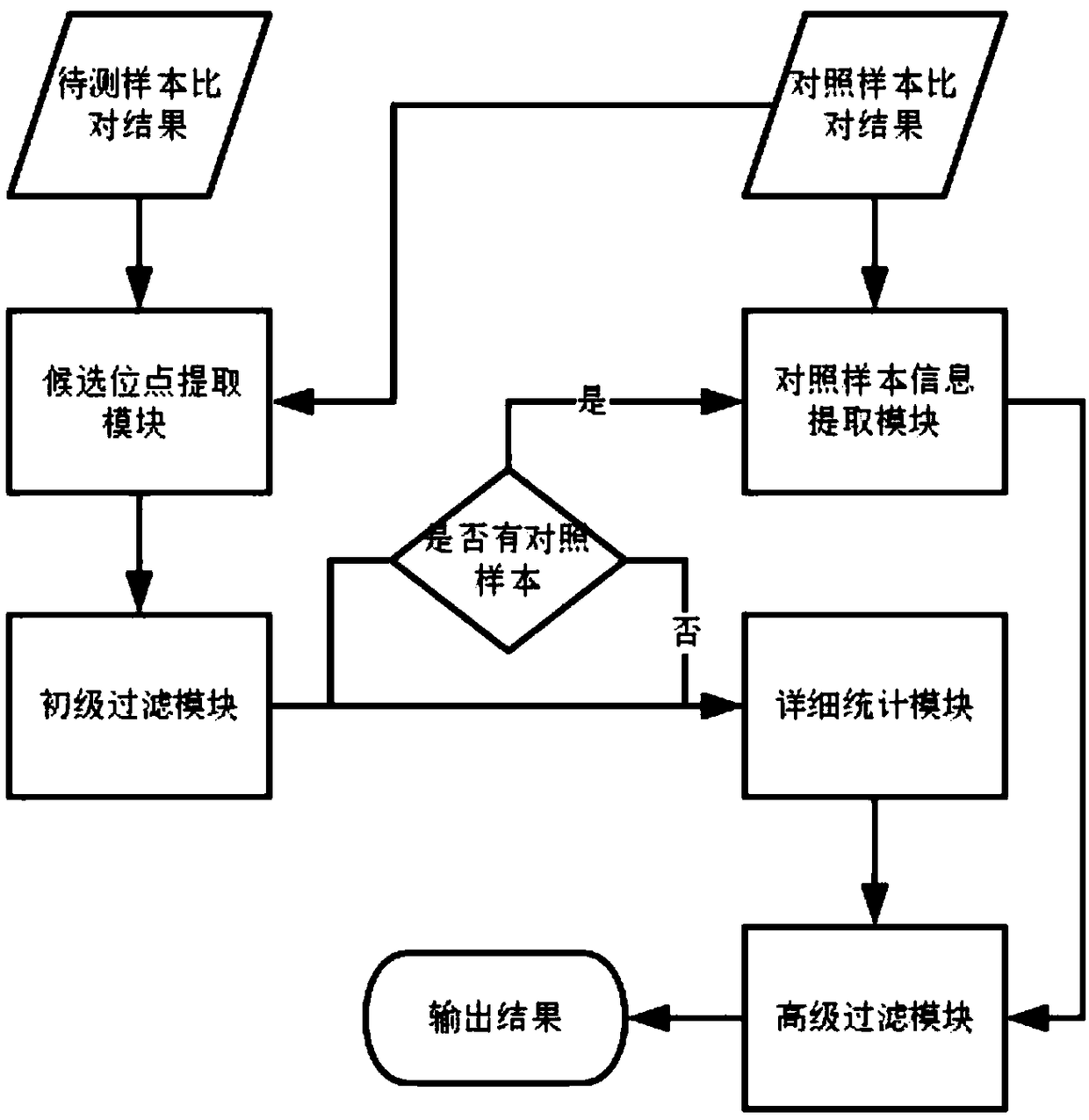
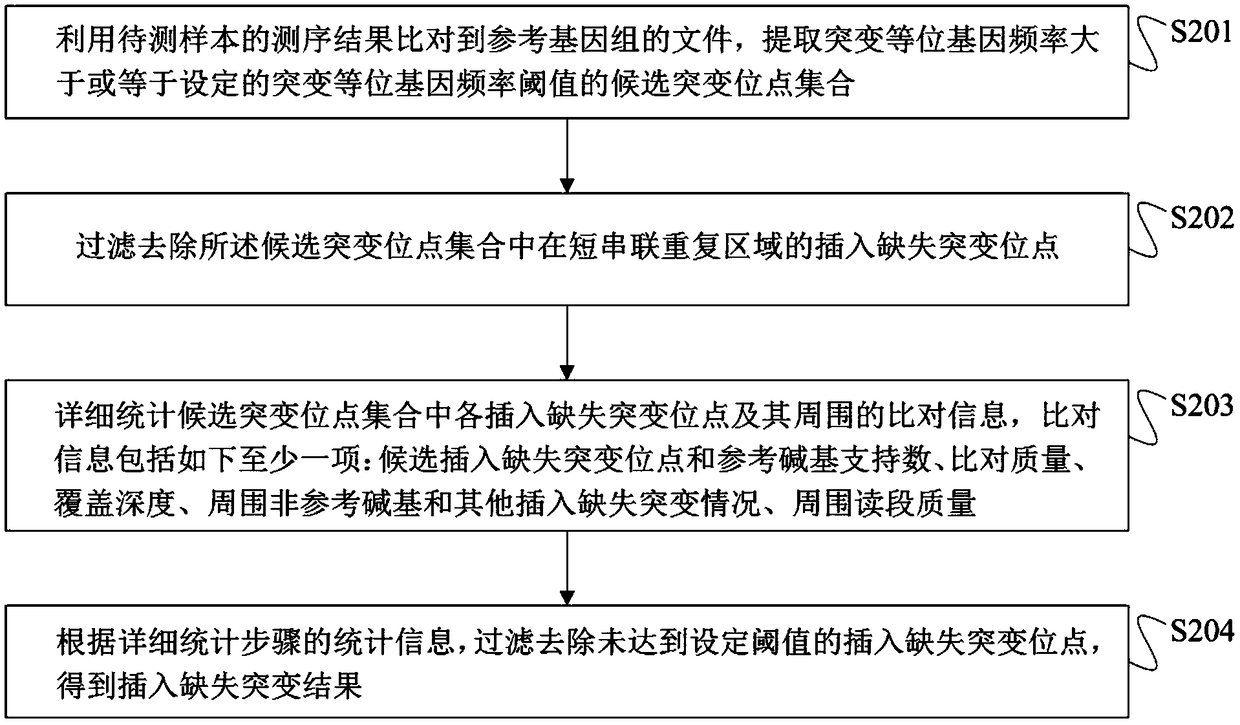
The present application discloses a method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, a device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps:comparing a sample to be tested with a file of a reference genome to extract a set of candidate mutation sites with mutation allele frequency being greater than or equal to a threshold; filtering to remove sites in a short tandem repeat region; making detail statistics of comparison information of the mutation sites and comparison information surrounding the mutation sites, wherein the comparisoninformation includes InDel site and reference base support number, comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non-reference base and other insertion deletion mutations, surrounding read quality;and filtering to remove sites that do not reach the set threshold according to statistical information to obtain mutation results. The method does not require partial assembly, and filters second-generation sequencing data in advance to quickly eliminate most of false positive results caused by the comparison, reduces detection running time and computing resources, improves detection efficiency, has strong sensitivity and specificity, and can quickly and accurately detect InDel mutations.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Tumor mutation analysis method and system, terminal and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110570904APrecision therapyAutomatic detectionProteomicsGenomicsInsertion deletionGenomic sequencing
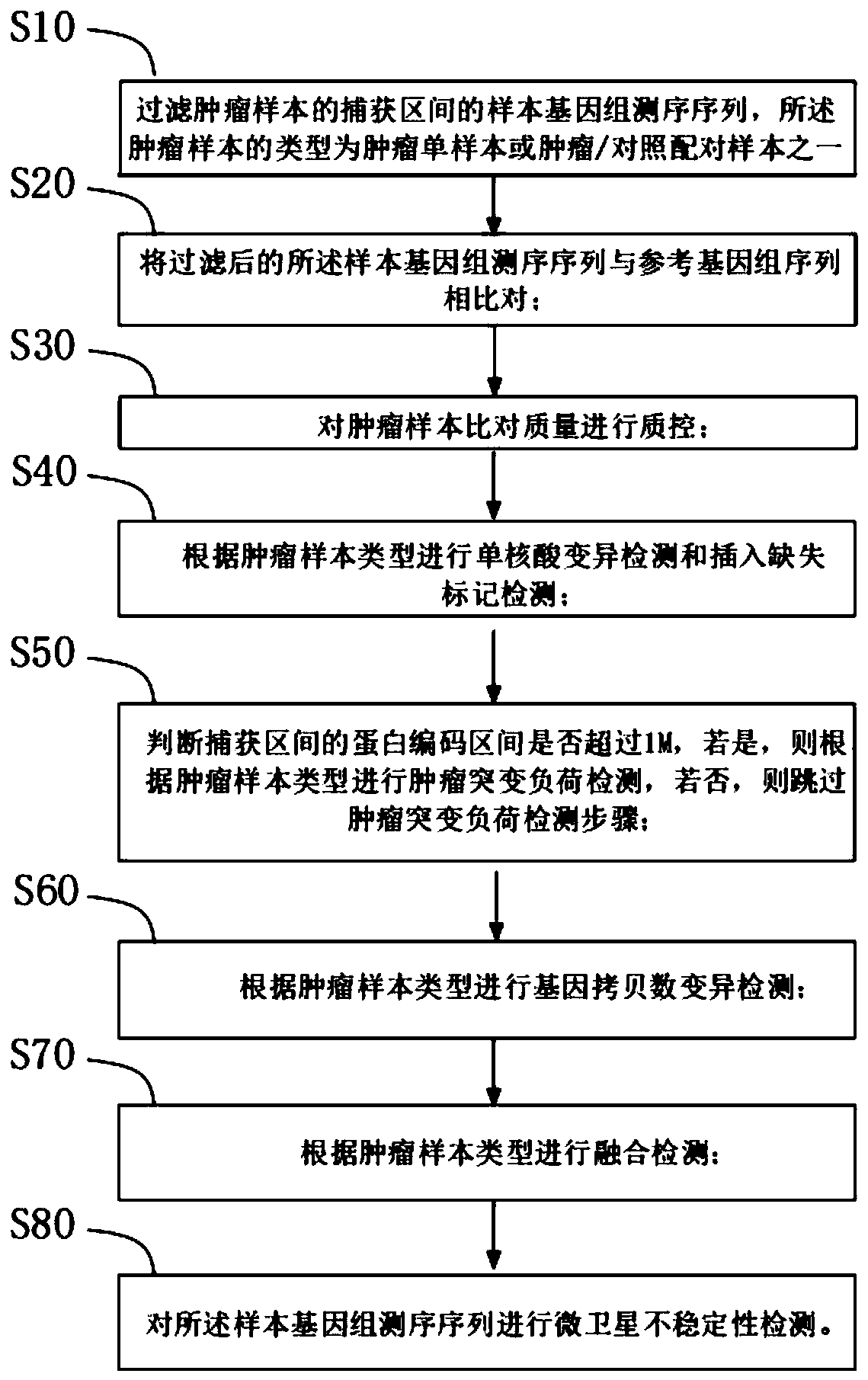
A tumor mutation analysis method based on next-generation sequencing is characterized by comprising filtering a sample genome sequencing sequence; comparing the filtered sample genome sequencing sequence with a reference genome sequence; controlling the tumor sample comparison quality, wherein the type of the tumor sample is one of a tumor single sample or a tumor / control paired sample; performingsingle nucleic acid variation detection and insertion deletion marker detection according to the type of the tumor sample; and performing fusion detection according to the type of the tumor sample. The present invention provides an automated process for tumor variation biological information analysis, which can quickly and automatically detect variation markers such as SNV (single nucleic acid variation), indel (insertion deletion marker), fusion, CNV (gene copy number variation), TMB (tumor mutation load) and MSI, can obtain more information about the precise target of tumor treatment, and provides more help for patients to select targeted drugs with potential benefits.
Owner:深圳百诺精准医疗科技有限公司
High-flux sequencing data analysis method and device
ActiveCN109767810AAccurate calculationVariation detection is fastProteomicsGenomicsInsertion deletionReference genome sequence
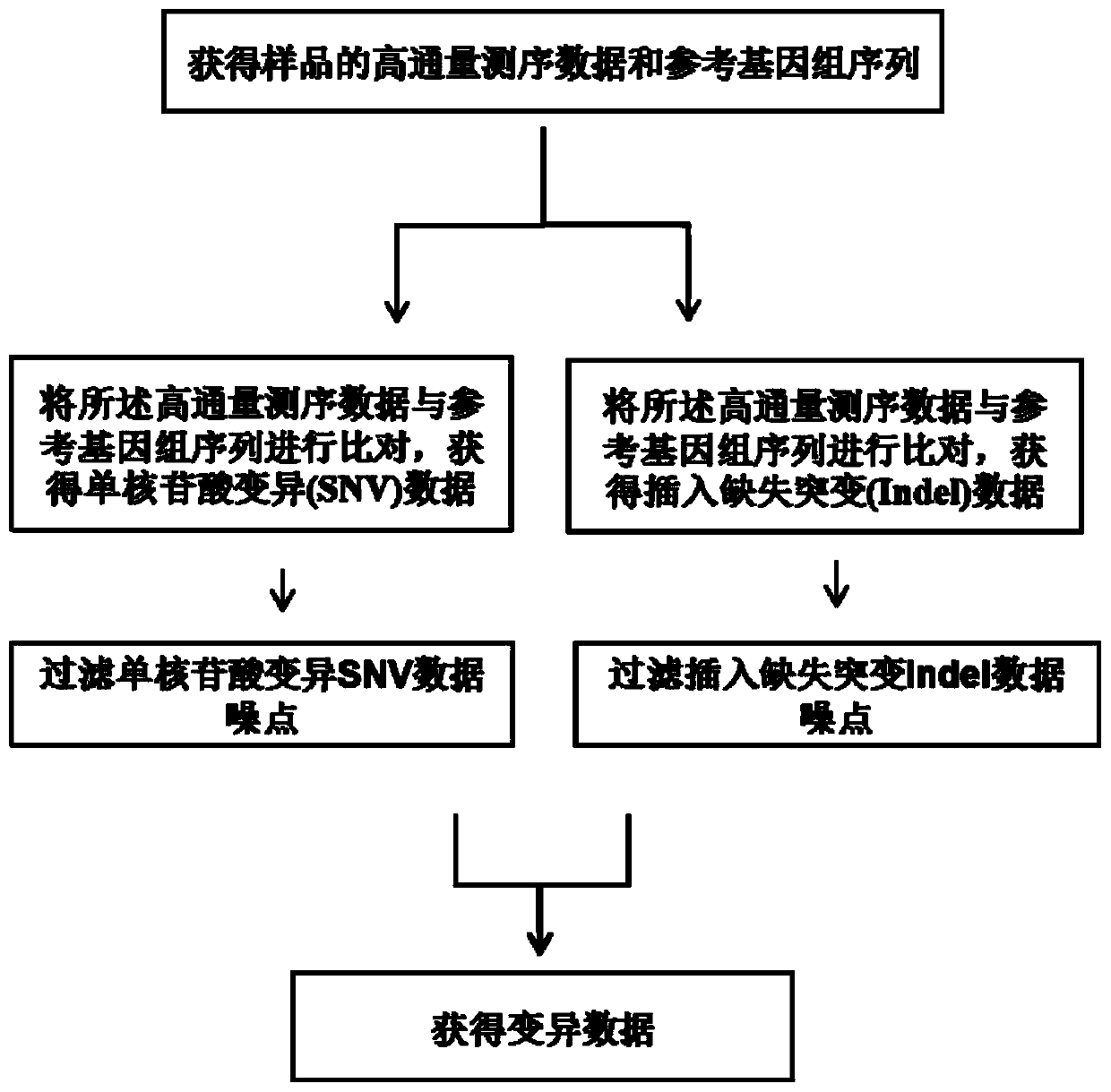
The invention relates to a high-flux sequencing data analysis method and a device. The high-flux sequencing data analysis method comprises the steps of acquiring high-flux sequencing data of a sampleand a reference genome sequence, comparing the high-flux sequencing data with the reference genome sequence, and respectively acquiring locus data of single nucleotide variation (SNV) and locus data of insertion deletion mutation (Indel), and respectively filtering noise points of the SNV data and the Indel data through comparing the difference substantial degrees of the variation and the background, thereby obtaining the variation data. The invention further provides a device for analyzing the high-flux sequencing data and a computer-readable storage medium for storing instructions.
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Image encryption method based on chaotic system and insertion-deletion model
ActiveCN104574259AStrong parallel computing abilityImprove storage densityImage data processing detailsInsertion deletionGeneration process
The invention relates to the field of image encryption, and designs an image encryption method based on a chaotic system and an insertion-deletion model. According to the method, the Hamming distance, the Hamming inverse distance and the Hamming feeding distance are introduced into the generating process of initial values of the chaotic system; in addition, when the method is used for encrypting or decrypting an image, positions of image pixel values are scrambled through the insertion-deletion model; finally, XOR operation of a DNA sequence is applied to diffusing the image pixel values. It can be obtained from simulation results and safety analysis that the method has the good encryption effect and can resist various attacks of an intruder. According to the problem emphatically solved, the basic thought of the insertion-deletion model in DNA calculation is applied to image encryption.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
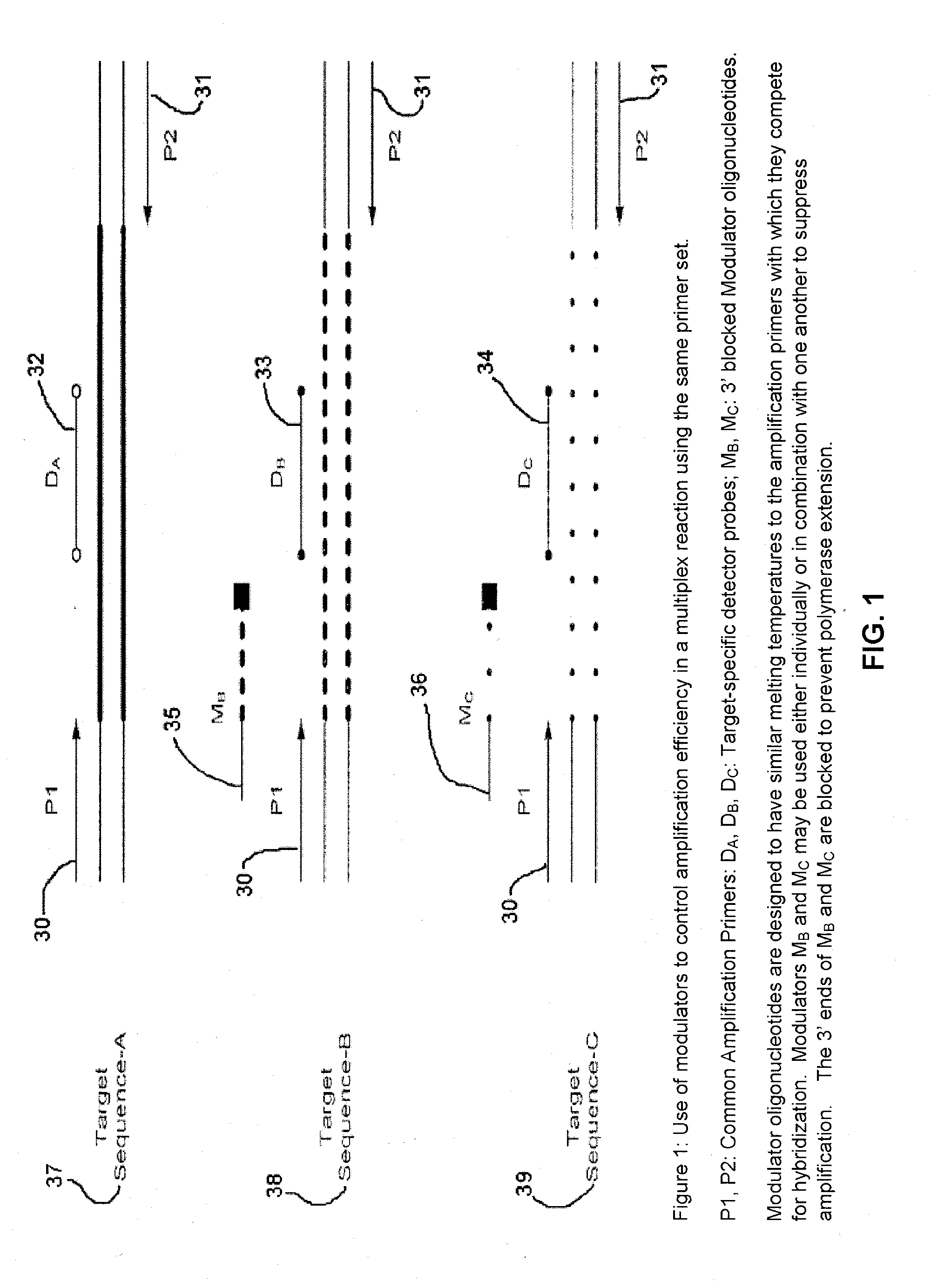
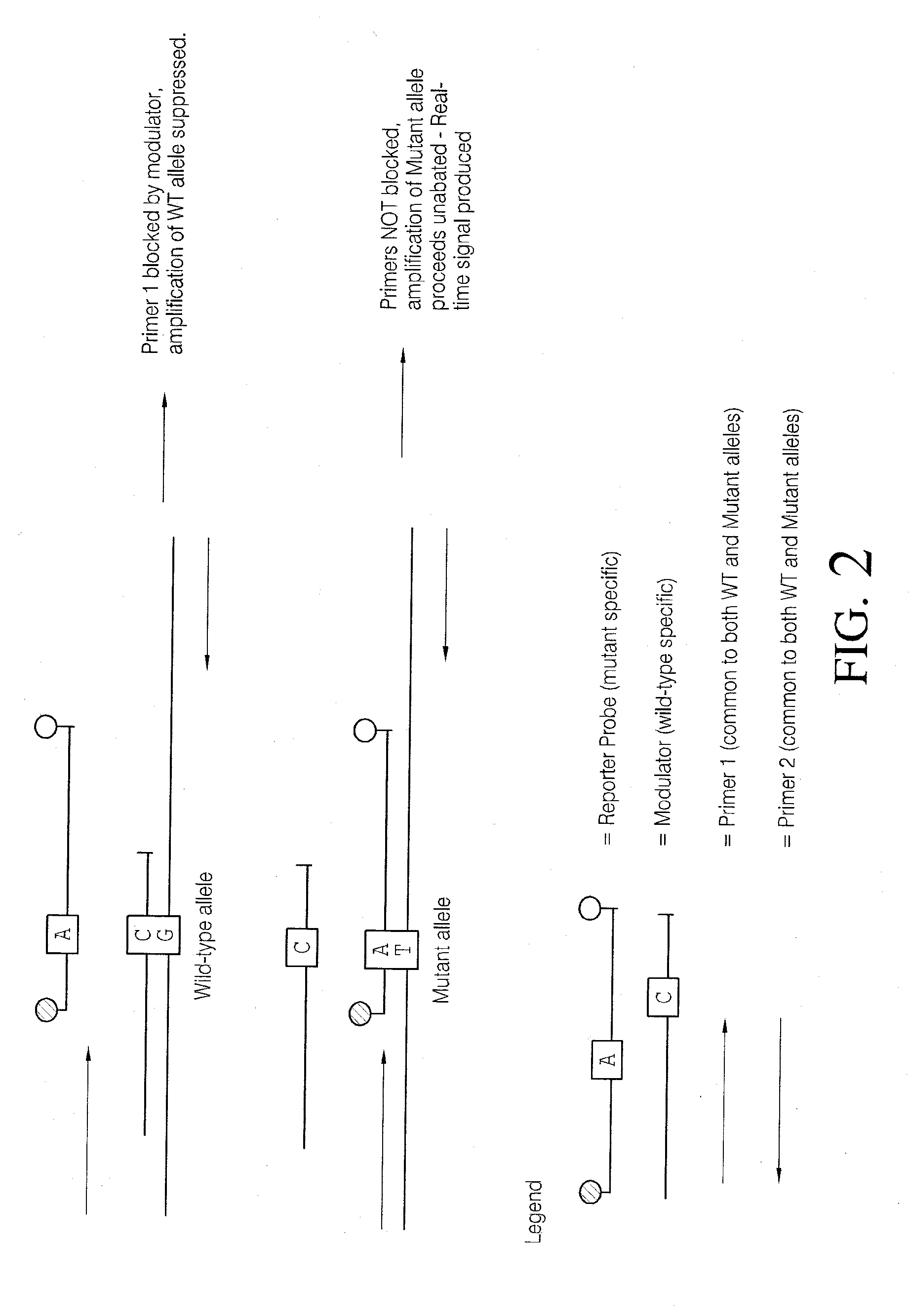
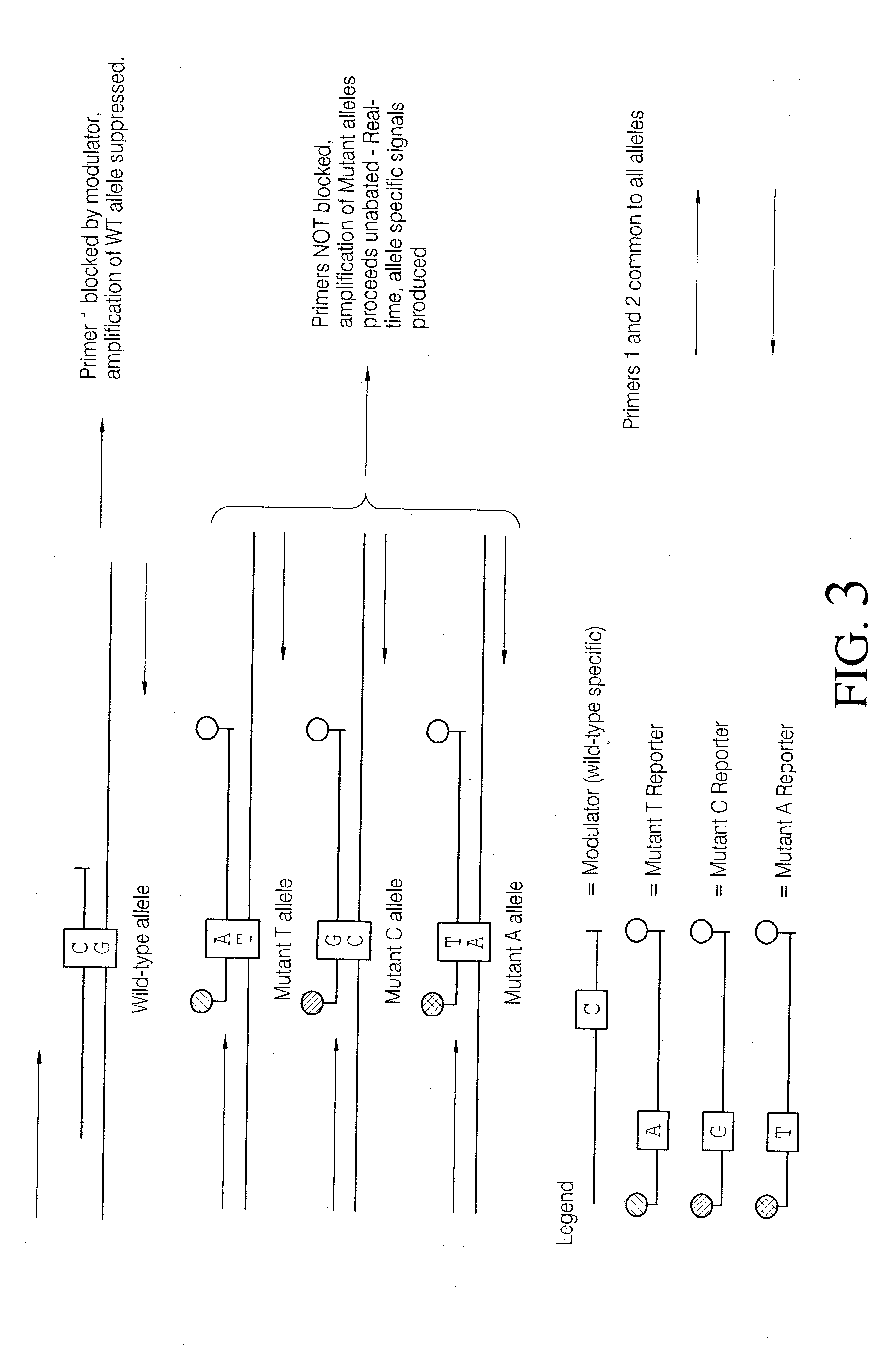
Methods and compositions for modulation of amplification efficiency
Provided herein are methods and kits for modulating the amplification efficiency of nucleic acids, which are useful in multiplex reactions where the amplification efficiency of one or more nucleic acids in the mixture are desired to be modulated relative to one or more other nucleic acids. Embodiments relate to molecular diagnostics, including detecting sequence variants, such as SNPs, insertions deletions, and altered methylation patterns, as well as the modulation of the amplification efficiency of internal control sequences to provide more accurate control sequences for amplification reactions.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
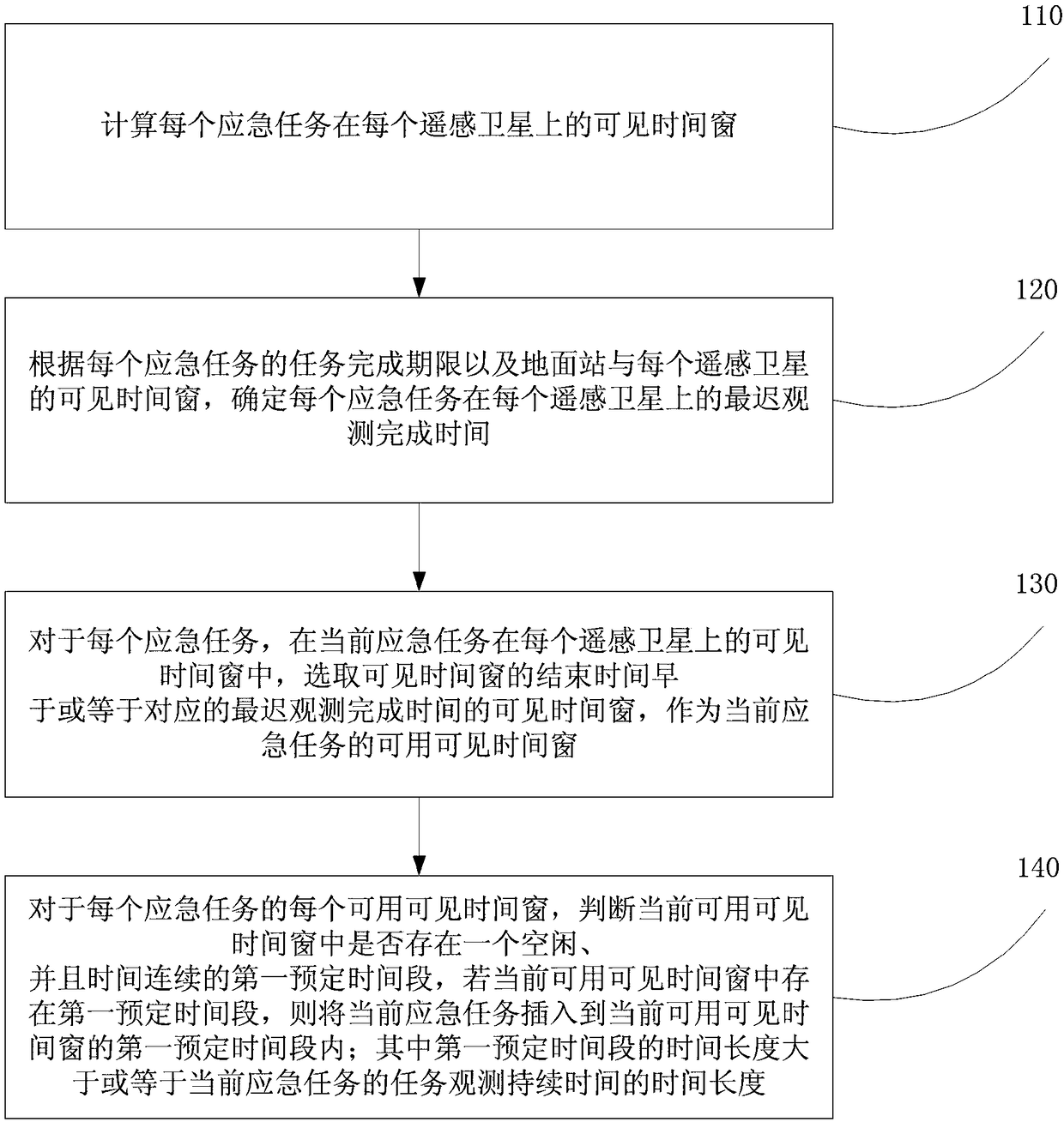
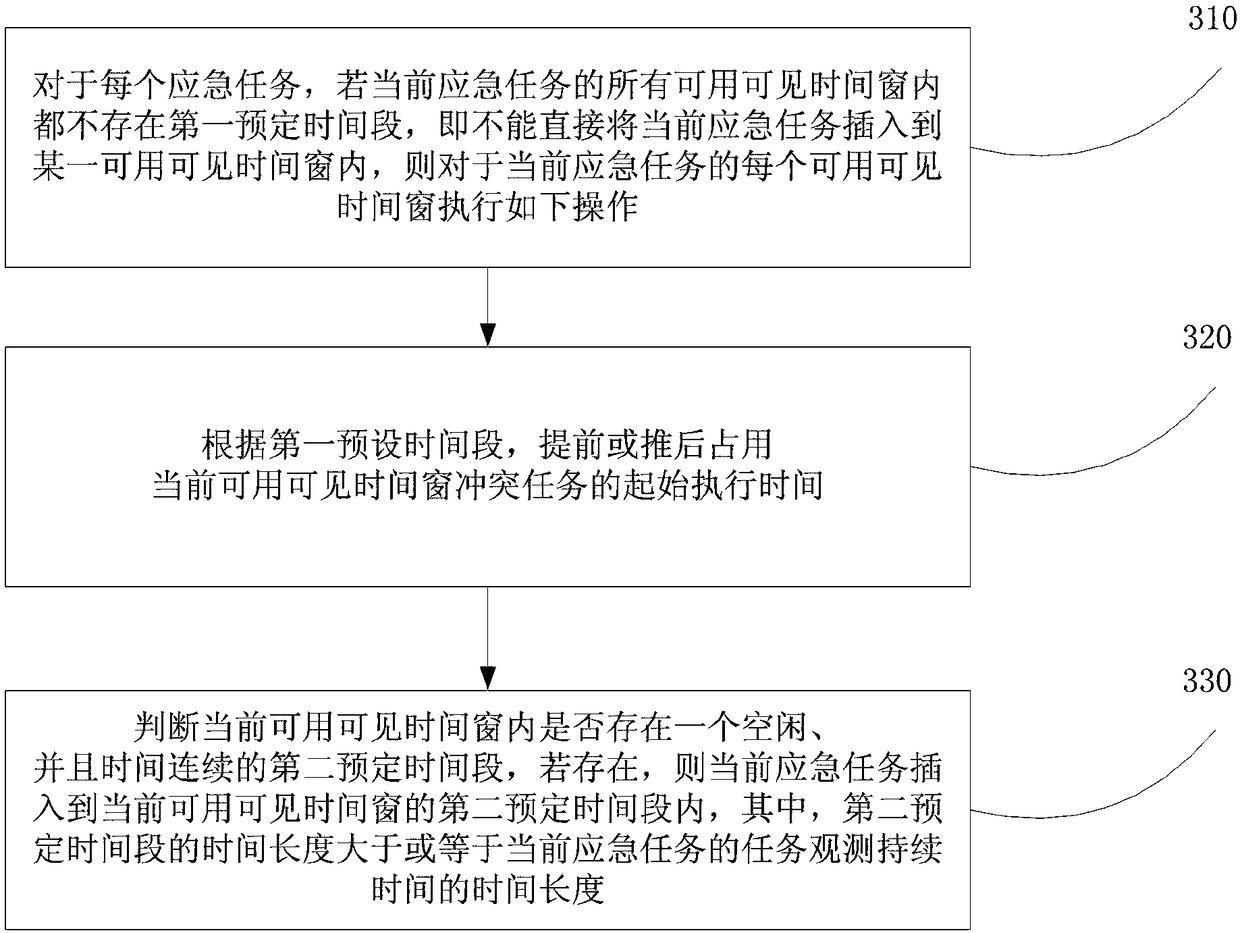
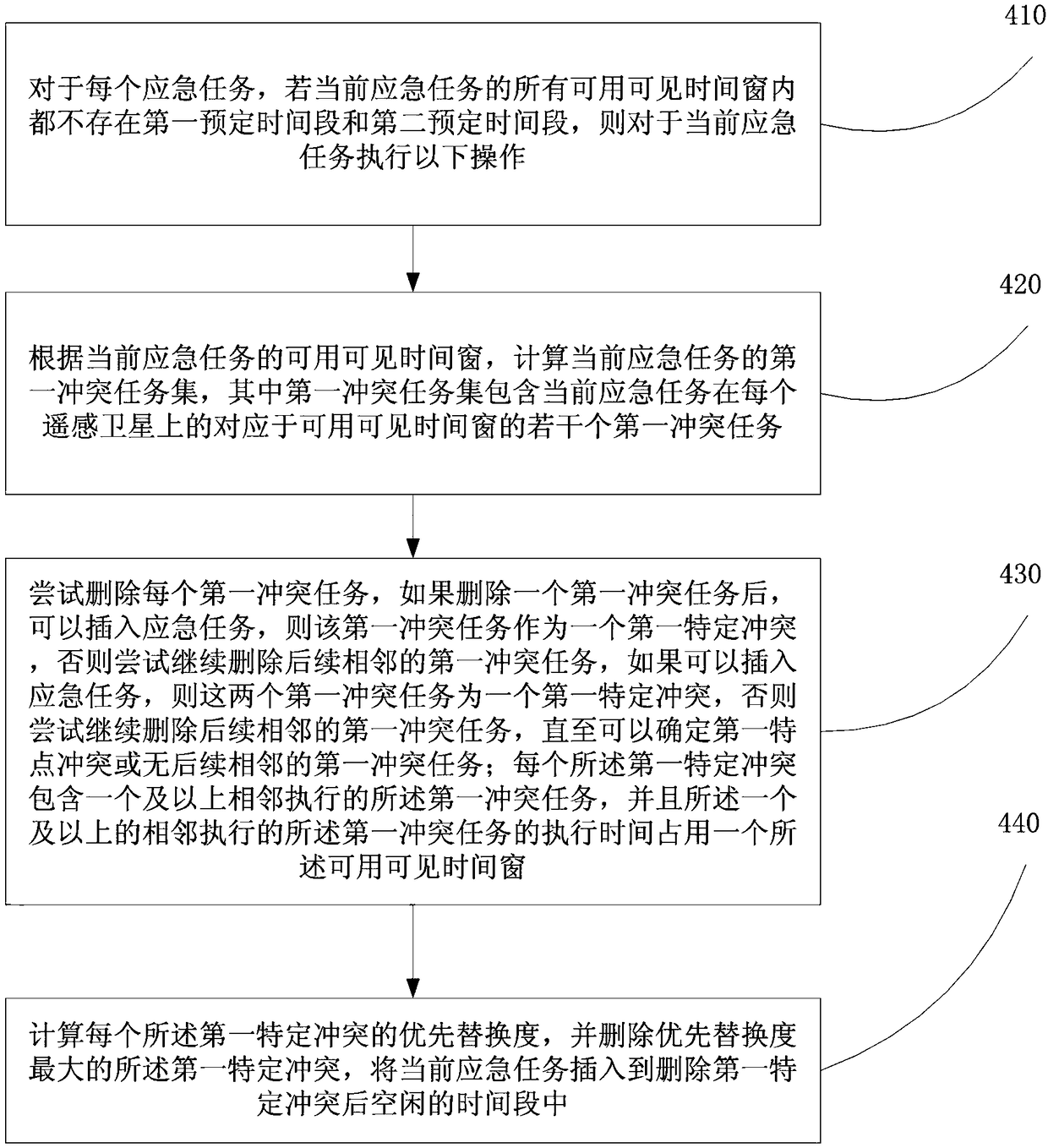
Multi-star emergent task planning method and device
ActiveCN108090630AIncrease chance of insertionIncrease incomeForecastingInsertion deletionTask completion
The embodiment of the invention provides a multi-star emergent task planning method and device. The method comprises the steps that according to the task completion time limit of an emergent task, a ground station and a visible time window of each remote sensing satellite, the latest observation completion time of each emergent task on each remote sensing satellite, then, according to the latest observation completion time, the usable visible time window for observing the emergent task is screened out, finally, the emergent task is inserted into the usable visible time window where the emergent task can be inserted, and therefore the task completion time limit for the emergent task is applied to an emergent task plan so as to ensure that the emergent task can be completed before the task completion time limit; compared with an existing scheme, the method is more reasonable. In addition, when the emergent task cannot be directly inserted, conflict insertion deletion is designed according to the conflict priority substitution degree, one or more conflict tasks are deleted, the emergent task and conventional task insertion probability is increased, and the benefits of the whole schemeare increased.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Compound amplification detection kit containing forty InDel genetic polymorphic sites of human X chromosome
ActiveCN110578009ALow mutation rateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionX chromosome
The invention discloses a compound amplification detection kit containing forty InDel genetic polymorphic sites of human X chromosome. The forty InDel sites of the X chromosome and an individual identification location point are amplified simultaneously by a primer group. Compared with a traditional STR genetic marker, an insertion deletion genetic marker used in the compound amplification detection kit has the advantages of low mutation rate and high sensitivity; and the polymorphism detection sites involved in the compound amplification detection kit combine the advantages of an InDel genetic marker and the special genetic characteristics of the X chromosome, and effective supplementary means can be provided for identification of difficult or special cases.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUAMEI ZHONGYUAN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +2
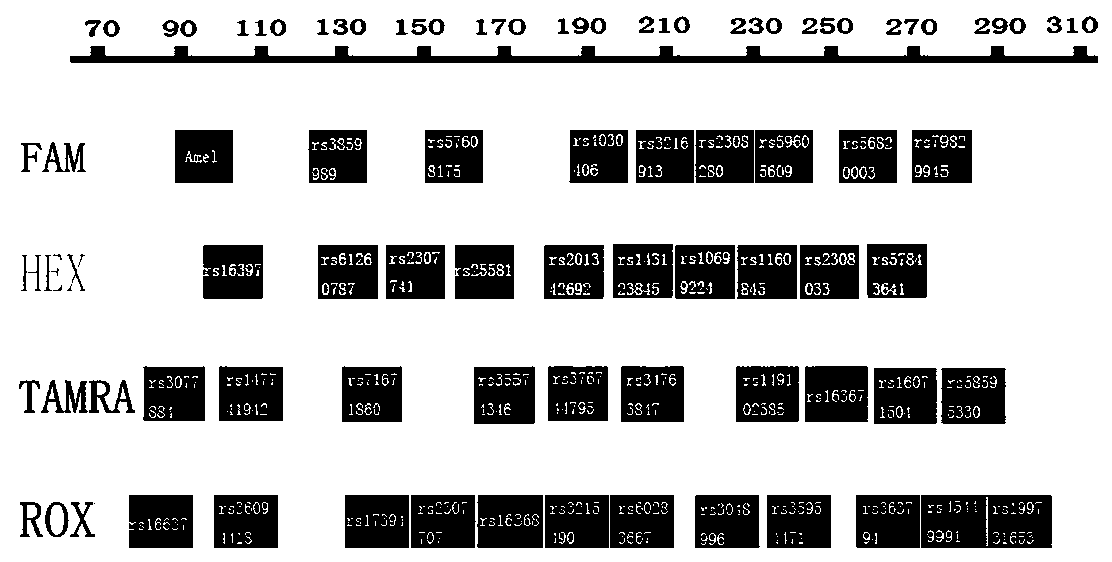
Fluorescently-labeled X-InDel locus composite amplification system and application thereof
ActiveCN104131067AHigh sensitivityHigh individual recognition rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceInsertion deletionDNA paternity testing
The invention provides a fluorescently-labeled X-InDel locus composite amplification system. By means of the system, eighteen insertion-deletion genetic polymorphism loci on an X chromosome can be compositely amplified, wherein the eighteen loci are respectively labeled with three fluoresceins FAM, HEX and TAMRA. The composite amplification system is high in sensitivity and individual identification rate, is high in polymorphism, is good in stability and repeatability, is accurate in typing results and can satisfy a practical requirement. A kit can be manufactured on the basis of the composite amplification system, can be used for paternity test, dyad paternity test, grandparent and grandchild test, sibling test and individual identification. New technologies can be provided for the fields such as anthropology, medical genetics and the like.
Owner:ACADEMY OF FORENSIC SCIENCE
Composite amplification system of 28 short tandem repeats, kit and application thereof
InactiveCN107841567AImprove individual recognitionHigh rate of non-parent exclusionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionGenetic diversity
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and relates to a composite amplification system of 28 short tandem repeats, a kit and an application thereof. The composite amplification system comprises 28 pairs of primers, and can be used for amplifying 28 sites at the same time; and the invention also discloses a primer sequence aiming at the 28 sites. By means of a research of geneticdiversity of a STR locus, 28 sites which contain 22 new CODIS sites, 4 sites with high discrimination power (D4S2366, D6S1043, D11S2368, D14S608) and one gender recognition site Amel, and one Y chromosome insertion-deletion site Y-indel are selected. The sites have higher discrimination power, excluding probability of paternity and polymorphism information content, and other characteristics, so that paternity test and discrimination power system effectiveness can reach a higher level.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROREAD GENETICS
Indel (Insertion-deletion) molecular marker primer for exocarpium benincasae color gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108866226AStrong specificityAssisted breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionCO-DOMINANT
The invention discloses an indel (Insertion-deletion) molecular marker primer for controlling an exocarpium benincasae color gene. The primer can produce a black skin material specific marker and a yellow skin material specific marker (co-dominant markers), and is good in repeatability and high in specificity. The invention also discloses an identification method of an exocarpium benincasae color.The method is accurate, quick, low in cost, short in identification period, and simple and convenient to operate. The invention further discloses application of the indel molecular marker primer controlling the exocarpium benincasae color gene in identifying the exocarpium benincasae color gene.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Resolving genome fractions using polymorphism counts
ActiveCN103797129AMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationRe sequencingInsertion deletion
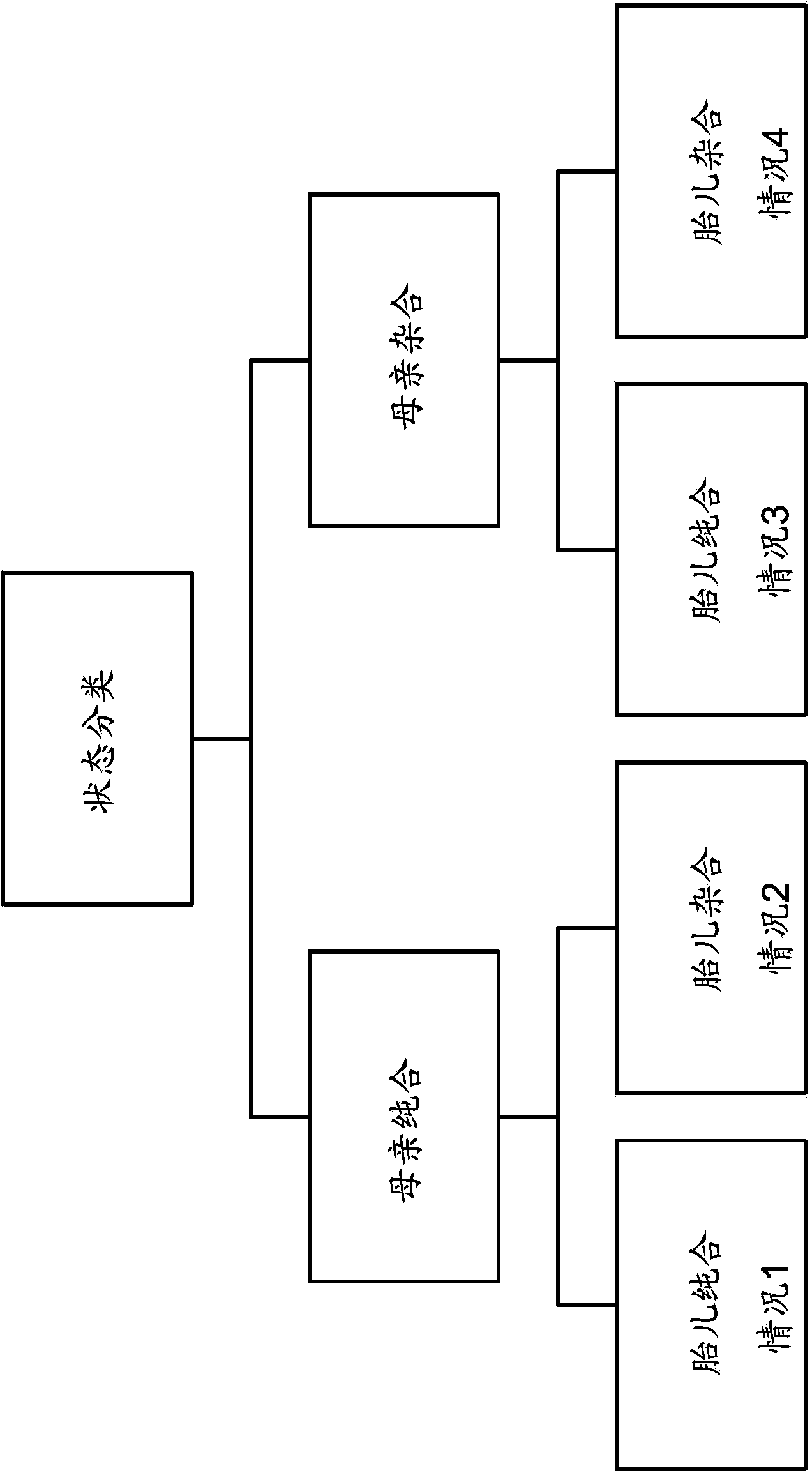
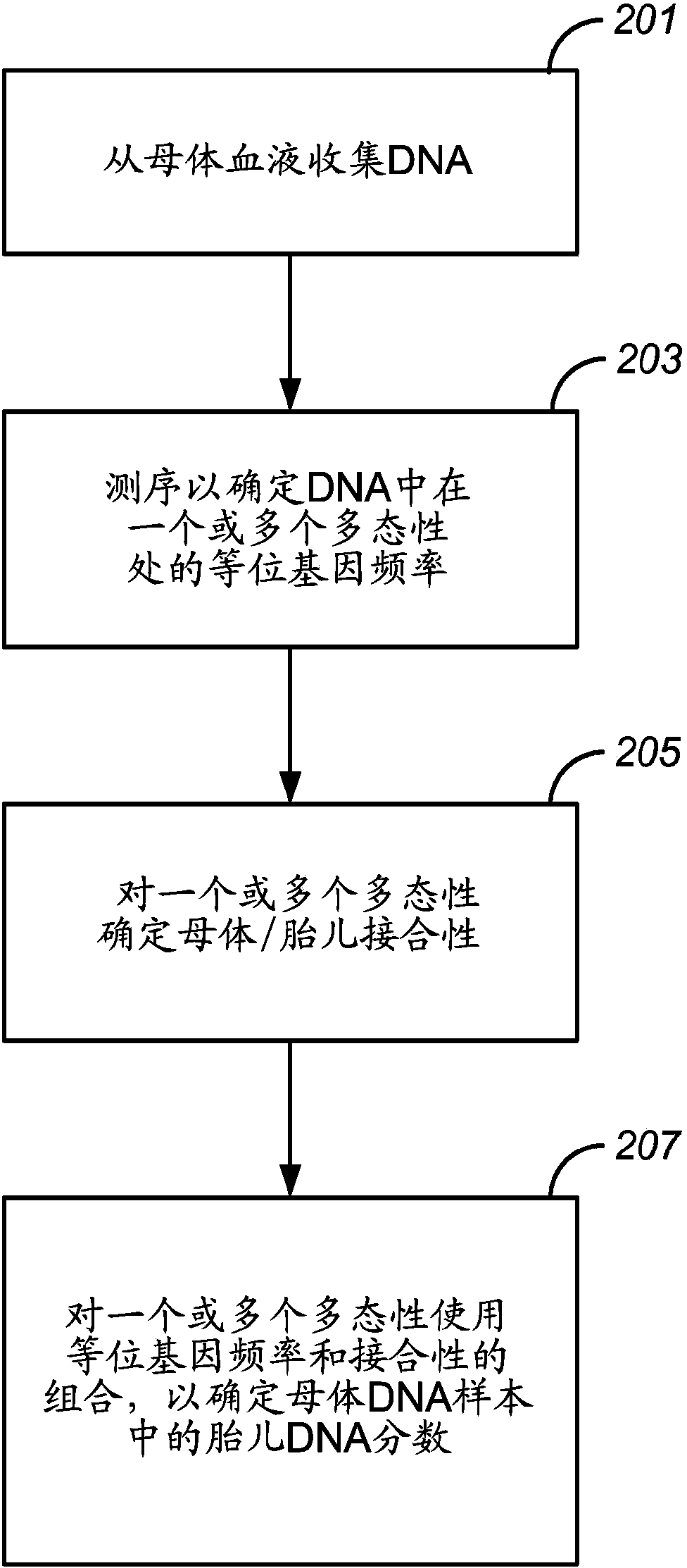
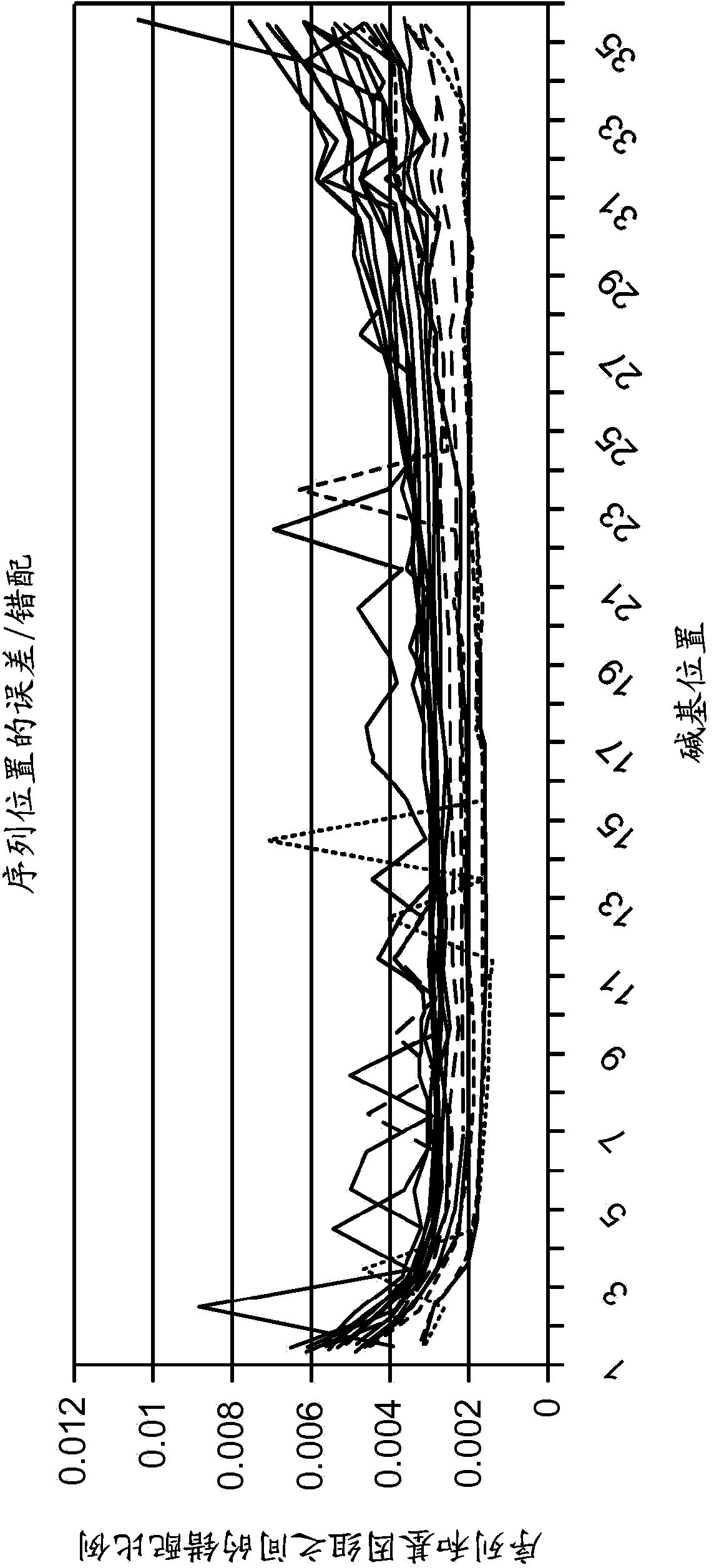
Methods of reliably estimating genomic fraction (e.g., fetal fraction) from polymorphisms such as small base variations or insertions-deletions are disclosed. Sequenced data from a multigenomic source is used to determine allele counts for one or more of the polymorphisms. For one or more of the polymorphisms, zygosity is assigned, and genomic fraction is determined from the zygosity and allele counts. Certain embodiments employ SNPs as the relevant polymorphism. The disclosed methods can be applied as part of an intentional, pre-designed re-sequencing study targeted against known polymorphisms or can be used in a retrospective analysis of variations found by coincidence in overlapping sequences generated from maternal plasma (or any other setting where a mixture of DNA from several people are present).
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
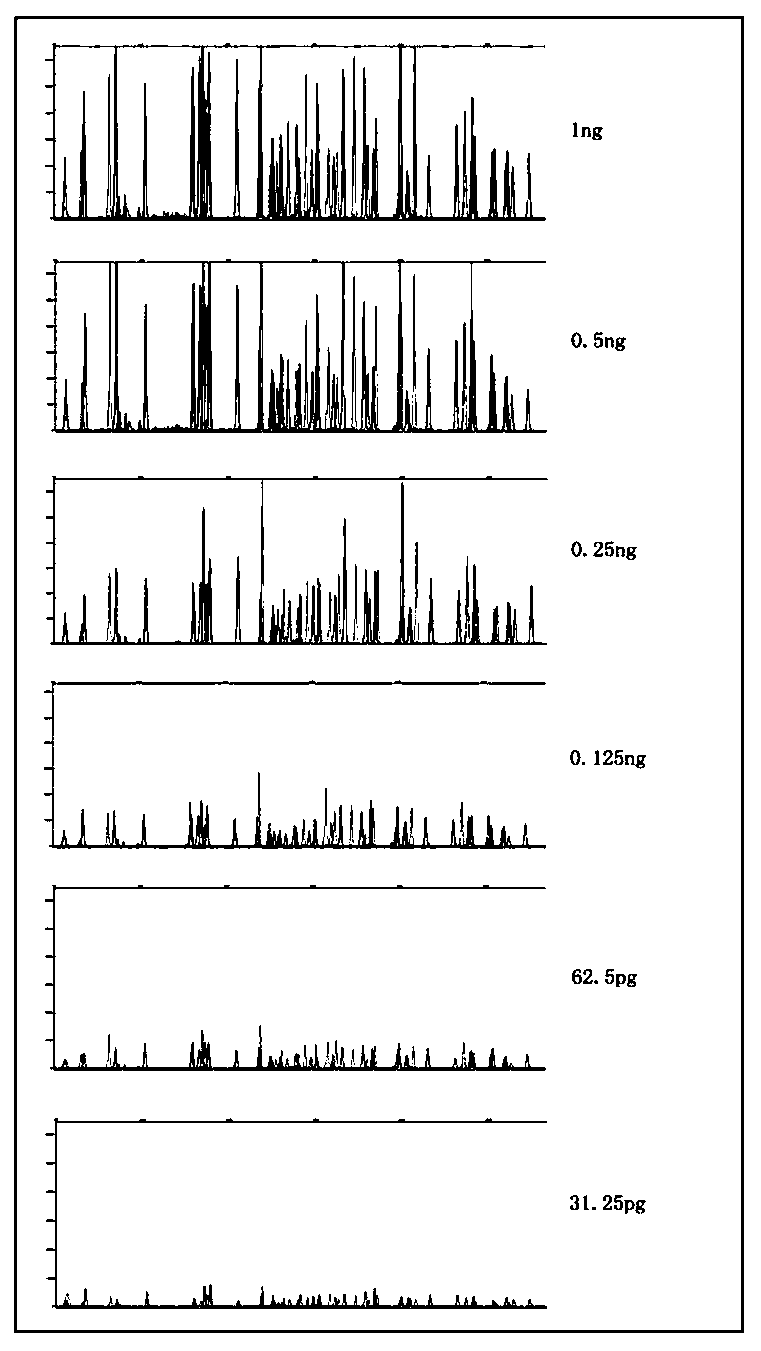
Fluorescent labeling complex amplification kit for insertion-deletion (InDel) polymorphism detection, and application of kit
ActiveCN108060240AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionIndel polymorphism
The invention discloses a fluorescent labeling complex amplification kit for insertion-deletion (InDel) polymorphism detection, and application of the kit. The kit comprises thirty-four InDel polymorphic sites and a sex locus (amelogenin). The fluorescent labeling complex amplification kit can be used for detecting the thirty-four InDel polymorphic sites and the one sex locus (amelogenin) at the same time; the kit can be used for detecting and genotyping 456 unrelated individuals from different ethnic groups from all over the country, has a cumulative personal identification rate reaching 0.99999985, and has a cumulative non-parent exclusion rate of 0.9989; the results prove that the kit is accurate in genotyping results, good in repeatability, high in sensitivity and accurate in genotyping results; therefore, a new method is provided for genetic relationship identification, sibling identification, individual identification, medical diagnosis, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU SUPERBIO LIFE SCI CO LTD +1
Molecule marker linked with brassica compestris color gene of brassica compestris and application of molecule marker
ActiveCN110093346AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaInsertion deletion
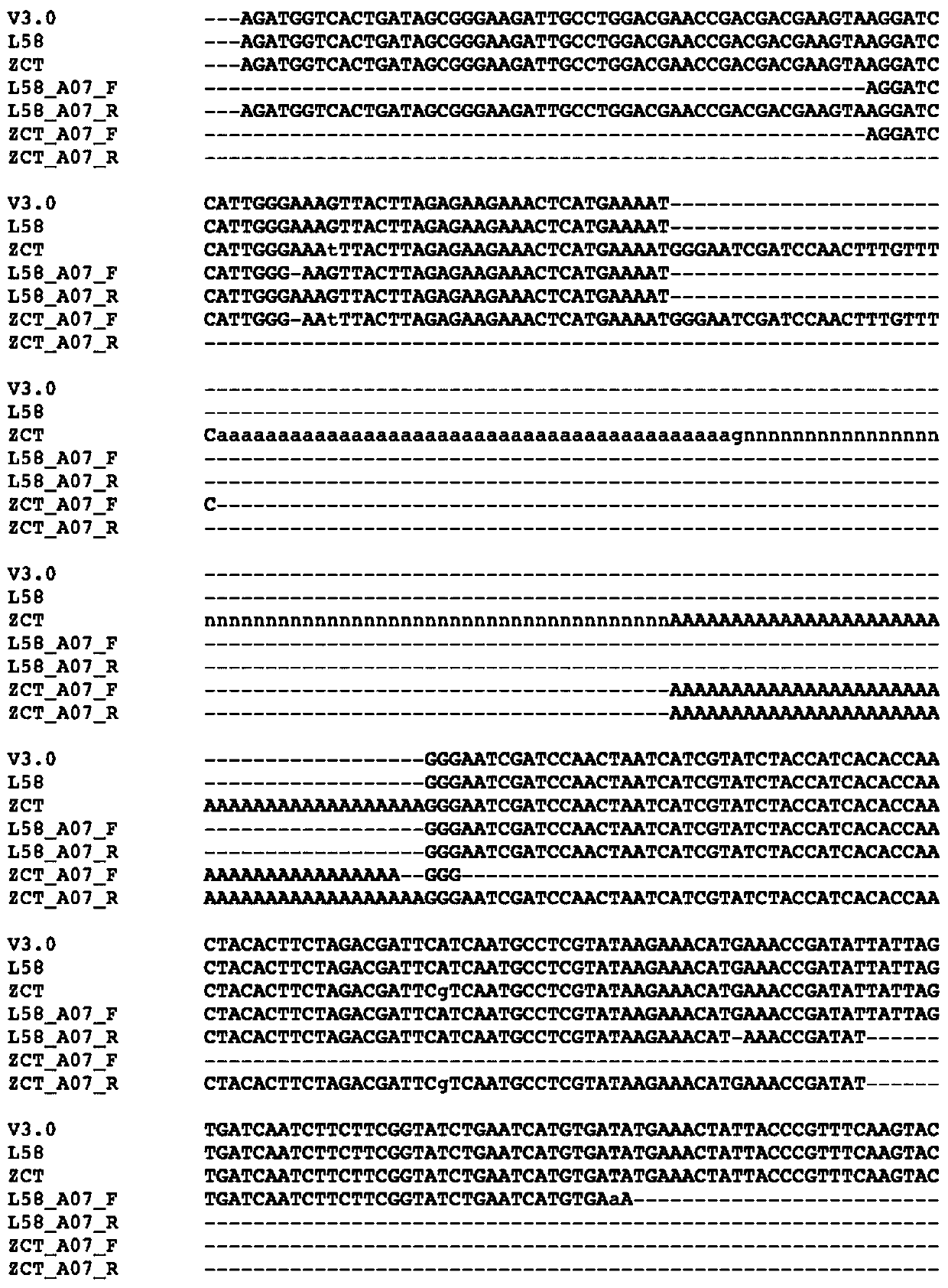
The invention discloses a molecule marker linked with a brassica compestris color gene of brassica compestris and an application of the molecule marker. The gene related to the brassica compestris color gene of brassica compestris is positioned at a No. 7 chromosome. A Chinese cabbage 3.0 edition is used as reference, and the gene insertion-deletion (Indel) is at a position between 25181252nd-25181356th from a 5' end of the No. 7 chromosome. The molecule marker disclosed by the invention can be used for identifying the brassica compestris or genotypes thereof, and further can be used for biological technology assisted breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying reality and purity of pepper male sterile three-line mating hybrids based on InDel (insertion-deletion) molecular markers
ActiveCN108893555AReduce filter rangeIdentification achievedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionCO-DOMINANT
The invention provides a method for identifying reality and purity of pepper male sterile three-line mating hybrids based on InDel (insertion-deletion) molecular markers. The method includes the steps: culturing the pepper hybrids and parents to a bud and seedling stage; extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); screening the hybrids and the parents by core primers. Primers of co-dominant markers can serve as molecular markers for identifying the reality of the hybrids, and co-dominant markers of the pepper hybrids and the parents continues to be screened by combining a secondary core primer library until the co-dominant markers are screened out if the co-dominant markers of the pepper hybrids and the parents cannot be screened out in a core primer library. According to the method, a systemcapable of rapidly and simultaneously identifying the reality and the purity of the pepper male sterile three-line mating hybrids is built and cannot be limited by time and seasons, indoor rapid identification of the reality and the purity of the hybrids is achieved, and molecular biology bases are provided for protection and market supervision of the pepper male sterile three-line mating hybrids.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Standard substance for extensive oncogene detection and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111334505AFit closelyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionCancer genome
The invention provides a standard substance for extensive oncogene detection. The standard substance includes 13 mutation sites verified by Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) and 500X high-throughput whole exome sequencing verified site information, has more than 700 variation sites of over 330 genes, also includes common structural variations of cancer genomes, such as common gene SNV, base insertion deletion and the like, has corresponding mutation site frequencies within a range of 1% to 100%, and is wide in application scene and platform. The standard substance can be used for evaluating stability, specificity and sensitivity of the working flow from sample extraction to biological information analysis, evaluating each sample treatment method and detecting performance differences among platforms. The standard substance belongs to a major innovation in the industry, and has wide application prospect and great industrial application value.
Owner:菁良科技(深圳)有限公司
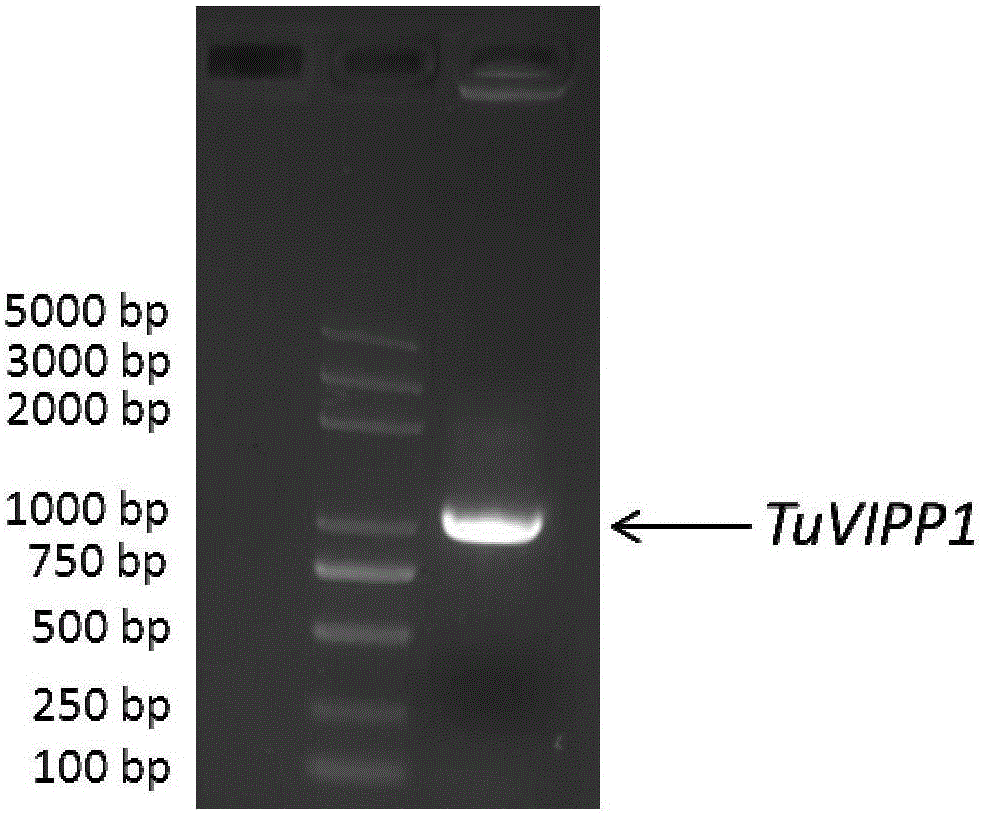
TuVIPP1 protein and encoding gene and application of TuVIPP1 protein
The invention discloses TuVIPP1 protein and an encoding gene and application of the TuVIPP1 protein. The protein is the protein in (1) or (2). The protein in (1) is composed of amino acid residues shown in the sequence 2 in a sequence table; the protein in (2) has the same function, is derived from (1) and is obtained after an amino acid sequence residue sequence in the sequence 2 in the sequence table is subjected to replacing and / or deleting and / or adding of one or more amino acid residues. Experiment results show that the TuVIPP1 gene is cloned in diploid Urartu wheat, the key function of the gene in inner capsule generation is verified by transgenic complementary of arabidopsis thaliana Atvipp1T-DNA insertion deletion mutant, plant photosynthesis can be promoted, and albino plants are greened.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hybrid capture kit and method for detecting tumor individually-medicated sixteen gene hot spots
ActiveCN107858426AComprehensive tumor individualized drug selectionComprehensive genetic testingMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionMutation frequency
The invention discloses a hybrid capture kit for detecting tumor individually-medicated sixteen gene hot spots. The hybrid capture kit comprises a hybridization reagent, a PCR amplification reagent and an enrichment degree detection reagent, wherein the hybridization reagent comprises an SEQ NO.1 to SEQ NO.396 probe mixture, a molar ratio of every two probes is 1:1, and the use volume of the probemixture with the concentration being 10 nM each during detection is 1 [mu]l. The kit is gene detection based on a second-generation sequencing technology, can detect three variation types (mutation,insertion deletion and fusion) one time, and uses a high sequencing depth to cover micro-scale gene variation in order to accurately detect the mutation condition of a patient on the premise of limited samples, and the mutation frequency of 1% can be accurately detected. Polygene and high-sensitivity parallel detection improves the detection rate of medicated gene variation, so the medication opportunity is not missed; and hot spots, rare and even unknown gene variation cane be detected during one-time detection, and relevant drug-resistant mutations (such as KRAS and ALK point mutation) are detected when drug-sensitive variation is found, so the sensitivity and drug resistance information of the medicated patient is accurately reflected.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Identification method of group of genomic characteristic mutation fingerprints associated with homologous recombination repair defects
The present invention discloses a genomic characteristic mutation fingerprint related to hHRD type homologous recombination repair defects and comprises a combination characteristic of a single nucleotide variation (SNV) and insertion deletion (Indel) genomic fingerprint, and an identification method thereof. The fingerprint characteristics can be subjected to high-throughput whole-genome resequencing, bioinformatics software analysis and statistical correlation analysis and are used to identify infectious diseases or tumors with the characteristic mutation fingerprints, especially hepatitis Bvirus infection and related diseases, including liver cirrhosis, liver fibrosis and liver cancer. The mutation fingerprint can also be used to guide methods and uses of treatments of targeted drugs targeting the homologous recombination defects on a variety of the various tumors with the hHRD homologous recombination repair defects, including but not limited to breast cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, endometrioid carcinoma, ovarian clear cell carcinoma, prostate cancer, gastric cancer, skin cancer, hepatitis B virus infection or related liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and bile duct cell cancer.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN +1
Broad specificity DNA damage endonuclease
InactiveUS7060455B1Simple structurePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesInsertion deletionSchizosaccharomyces pombe
The present disclosure describes DNA damage endonucleases which exhibit broad specificity with respect to the types of structural aberrations in double stranded DNA. These enzymes recognize double stranded DNA with distortions in structure, wherein the distortions result from photoproducts, alkylation, intercalation, abasic sites, mismatched base pairs, insertion deletion loops, cisplatin adducts and other types of base damage (for example, uracil resulting from cytosine deamination). The UVDE (Uve1p) of Schizosaccharomyces pombe, certain truncated forms of that UVDE (lacking from about 100 to about 250 amino acids of N-terminal sequence) and certain endonucleases from Homo sapiens, Neurospora crassa, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus anthracis, Methanococcus jannaschii, and Deinococcus radiodurans. The present disclosure further provides methods for cleaving double stranded DNA having structural distortions as set forth herein using the exemplified endonucleases or their stable, functional truncated derivatives.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
New mutant pathogenic gene SLC12A3 of Gitelman syndrome as well as encoded protein and application thereof
ActiveCN105861514ARich resource libraryTo achieve the purpose of prenatal and postnatal screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansInsertion deletionPrenatal diagnosis
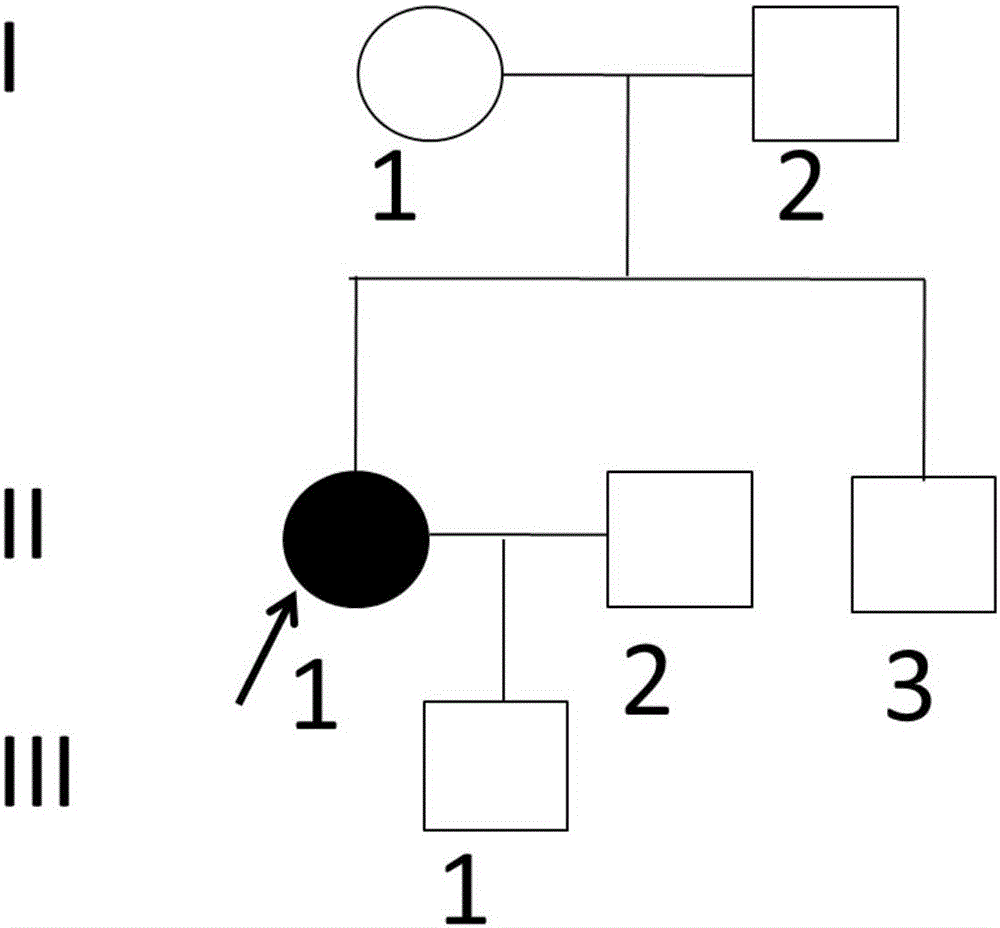
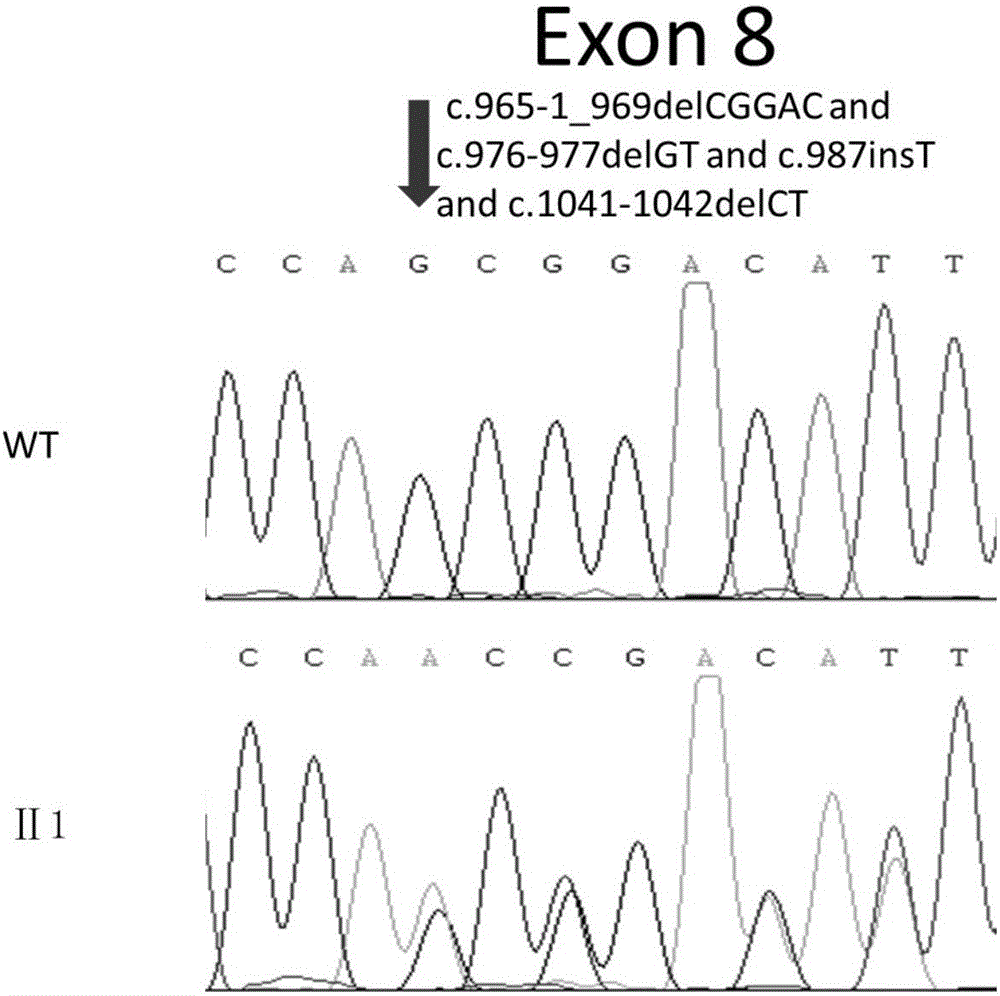
The invention relates to a new mutant pathogenic gene SLC12A3 of Gitelman syndrome as well as an encoded protein and application thereof. In the invention, through gene screening and follow-up visit of a recently treated GS patient and family members thereof, a mutant SLC12A3 gene is identified; and compared with the sequence of a wild SLC12A3 gene, the 8th exon in the mutant sequence has one insertion-deletion frame-shift mutation. According to comparison between the mutant SLC12A3 encoded protein and the wild SLC12A3 protein, frame shift appears since the 332nd-site codon. In the invention, a new site can be provided for the gene diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome, the resource library of mutant sites related to the disease is enriched, and more bases are provided for patient diagnosis in future. The disease can be diagnosed and typed by detecting the SLC12A3 gene sequence of the Gitelman syndrome patient, and reasonable prenatal diagnosis can be carried out for fetuses to achieve an aim of healthy child-bearing and child-rearing screening.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Method for detecting insertion-deletions polymorphism of sheep FTH-1 (ferritin heavy polypeptide1) genes by utilizing PCR-SSCP (polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism) and application thereof
ActiveCN106701930AExcellent genetic resourcesAccurately estimate breeding valuesMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention discloses a method for detecting insertion-deletions polymorphism of sheep FTH-1 (ferritin heavy polypeptide1) genes by utilizing PCR-SSCP (polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism) and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: taking to-be-detected sheep whole genome DNA containing FTH-1 genes as a template, performing PCR amplification on the sheep FTH-1 gene segments, and performing detection and genotyping on the PCR product by utilizing the SSCP technology; and identifying the 639th locus insertion-deletions polymorphism of the sheep FTH-1 genes according to electrophoretic results. The method is a method for screening and detecting a molecular genetic marker which is closely related to reproductive performances of sheep on the DNA level so as to be used for assistant selection and molecular breeding of the sheep and acceleration of sheep stock breeding.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
Insertion deletion marker site for identifying shape of watermelon fruit, primer and application
ActiveCN107619875AAccurate identificationEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionNucleotide
The invention discloses an insertion deletion marker site for identifying a shape of a watermelon fruit, a primer and application, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The insertion deletionsite is located in an 159bp area between nucleotide 26847023 and nucleotide 26847181 of a third chromosome of a watermelon genome 97103, and a sequence of the insertion deletion area is shown as SEQID NO. (sequence identifier number) 1. The invention further discloses a PCR amplification primer pair for identifying the shape of the watermelon fruit, a method of identifying the shape of the watermelon fruit, and application of the method. The insertion deletion marker site is developed on a basis of a candidate gene and tightly linked with the length and circularity of the fruit; and an insertion deletion marker can be used for accurately and quickly identifying the shape of the watermelon fruit in a seedling stage and has the advantages of convenient detection and stable amplification products.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
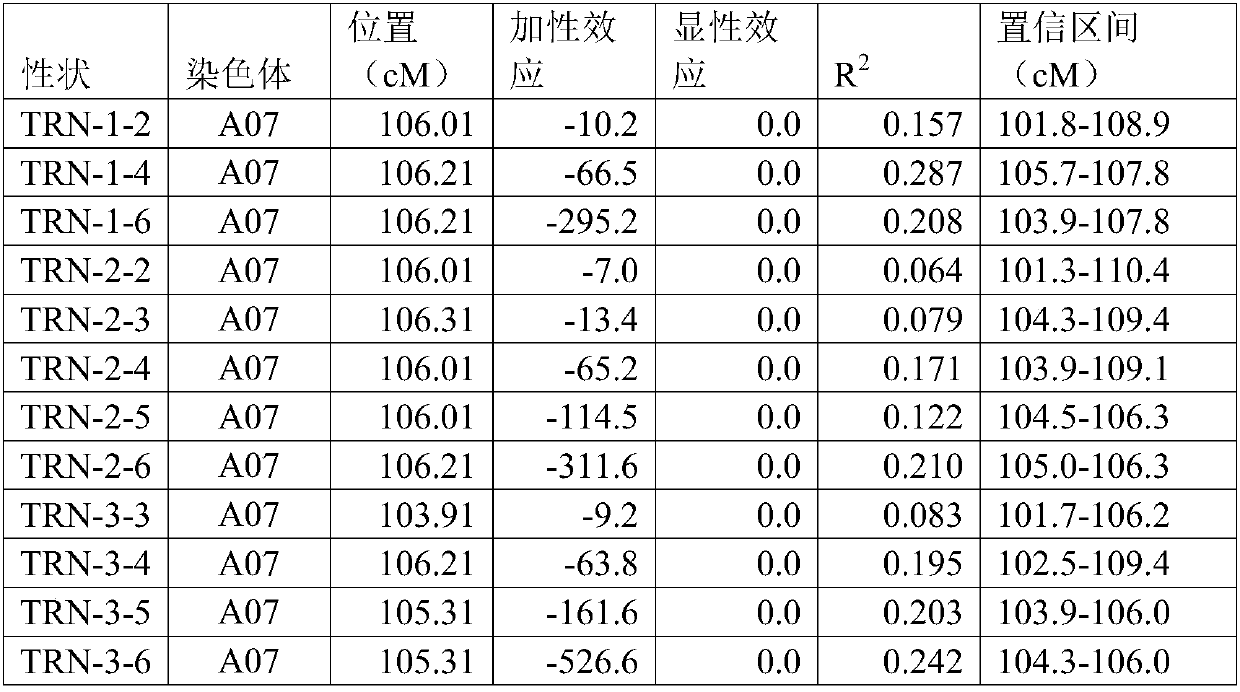
Molecular marker closely linked with major QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) RtA07-2 of lateral root number of rape and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN108048599AConfiguration genetic improvementSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationInsertion deletionQuantitative trait locus
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with a major QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) Rt.A07-2 of lateral root number of rape and application of the molecular marker. The invention locates a major gene locus Rt.A07-2 for controlling the lateral root number of the rape on a rape A07 linkage group for the first time, and 28.7% phenotypic variance can be explained. The locus is closely linked with insertion-deletion (Indel) molecular markers P323 and I42. The lateral root number of the rape can be predicted by checking the molecular markers P323 and I42 related to the traits of the lateral root number of the rape, thereby quickly and accurately screening fine individual plants with more lateral roots.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
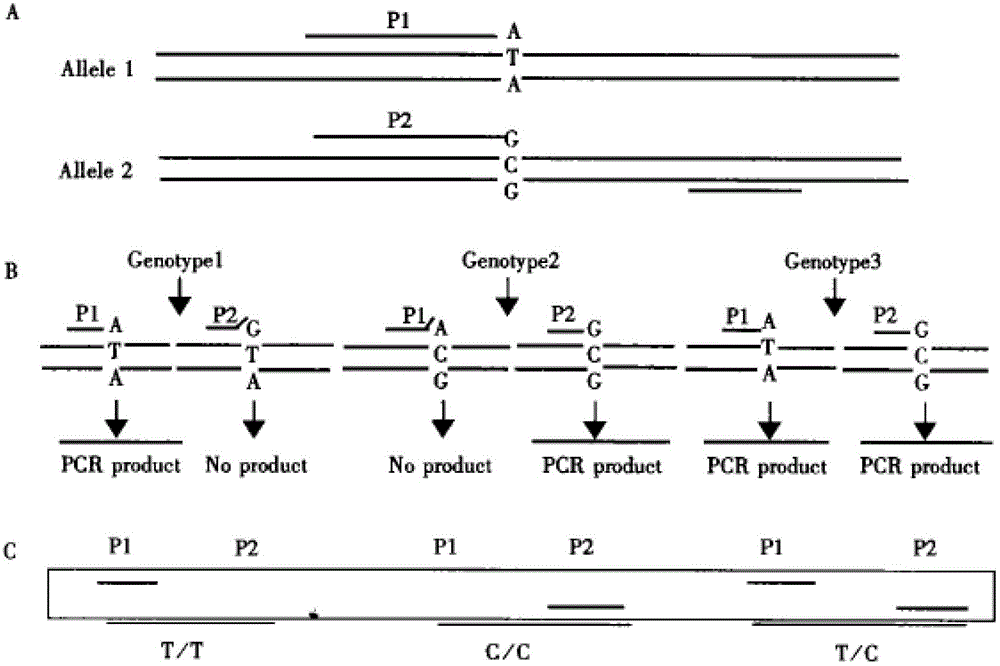
Method for designing SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker with base substitution or insertion deletion
InactiveCN103146823AEasy to knowEfficient use ofMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for designing an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker with base substitution or insertion deletion. Since common TaqDNA polymerase needs normal amplification, 5' does not need to be completely paired with the template, and 3' needs complete pairing. Thus, the discovered SNP site can be specifically designed in the 3' position of the primer; the primer designed according to the mutant gene and the wild gene can form 3' terminal mispairing, resulting in incapability of normal amplification; and similarly, the primer designed according to the wild gene and the 3' terminal of the mutant gene generate mispairing, resulting in incapability of normal amplification in the mutant individual genome. By carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) twice and detecting the PCR result by a specific technique, the invention can conveniently determine the genotype of the individual SNP site.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
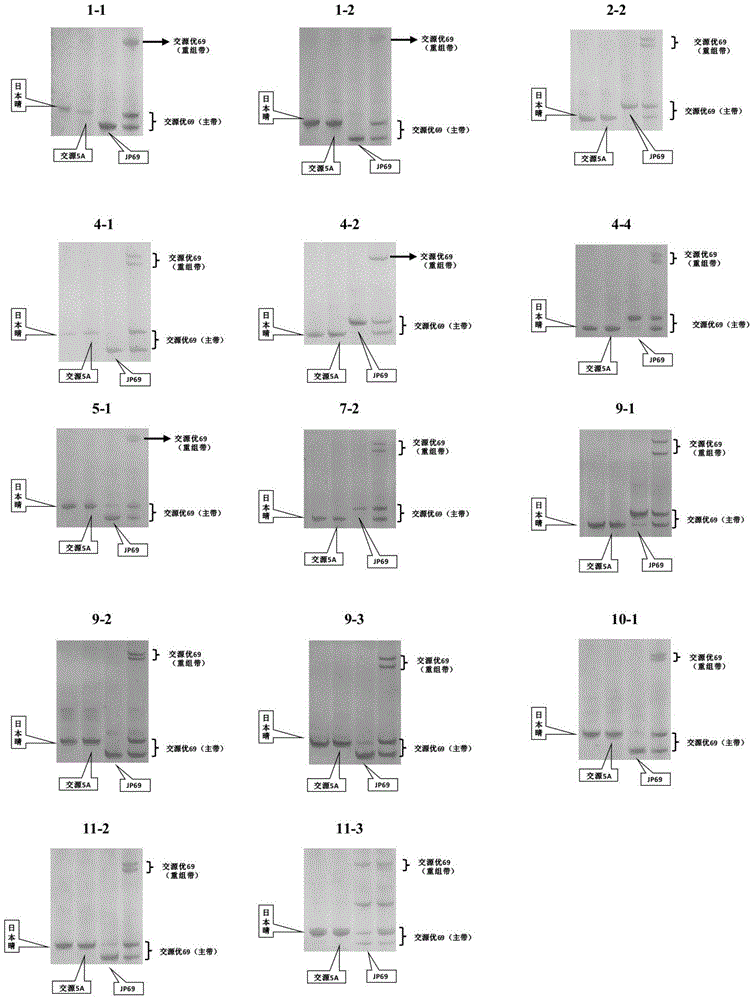
Identification method for hybrid rice variety hybrid source superior 69 based on InDel (insertion-deletion length polymorphism) marker
ActiveCN104789671AReduce dosageAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionDNA fragmentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of creature identification, and particularly relates to an identification method for a hybrid rice variety hybrid source superior 69 based on an InDel (insertion-deletion length polymorphism) marker. In the method, the whole genome DNA sequence of a japonica rice variety Nipponbare and the whole genome DNA sequence of an indica type rice variety 93-11 are compared to obtain 14 pairs of specific DNA primers designed for an insertion / deletion differential fragment; the hybrid source superior 69 and parent hybrid sources 5A and JP69 of the hybrid source superior 69 are subjected to DNA extraction, DNA fragment amplification and electrophoretic separation, and the electrophoretogram is analyzed for identifying the hybrid source superior 69; to be specific, a finger-print spectrum obtained through polymerase chain reaction and gel vertical slab electrophoresis is analyzed by virtue of the combination of the 14 pairs of InDel primers, and further, whether the variety is the hybrid rice variety hybrid source superior 69 or not is determined according to the electrophoretic band type of 14 InDel sites. According to the invention, the sample amount required to be detected is small, the method is simple, convenient and quick, and the identification result is accurate, so that the method can be applied to the variety identification of the hybrid source superior 69 on the market.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
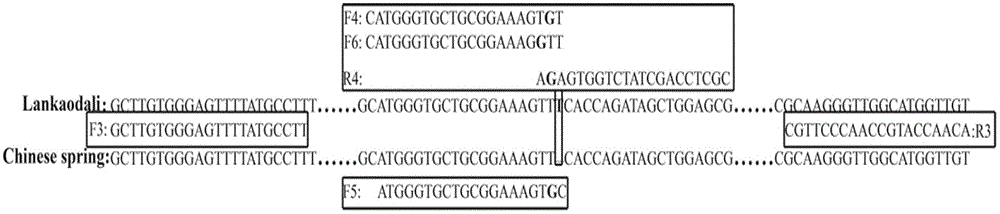
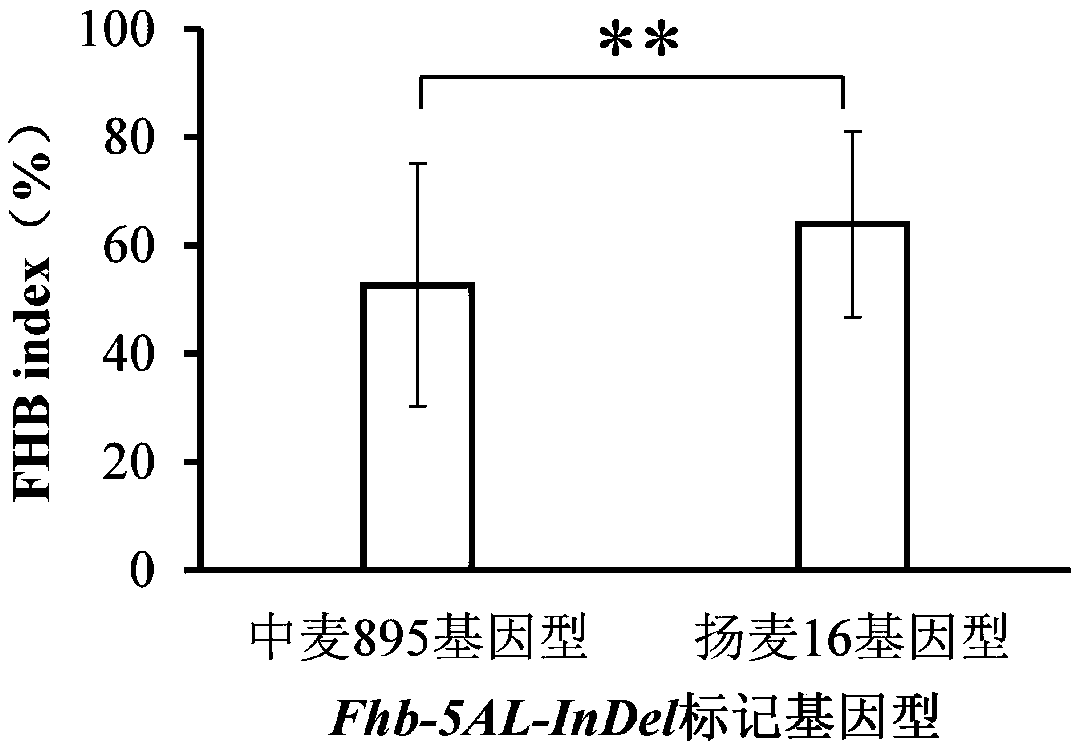
Molecular marker used for detecting zhongmai 895 fusarium head blight resistance QTL and use method
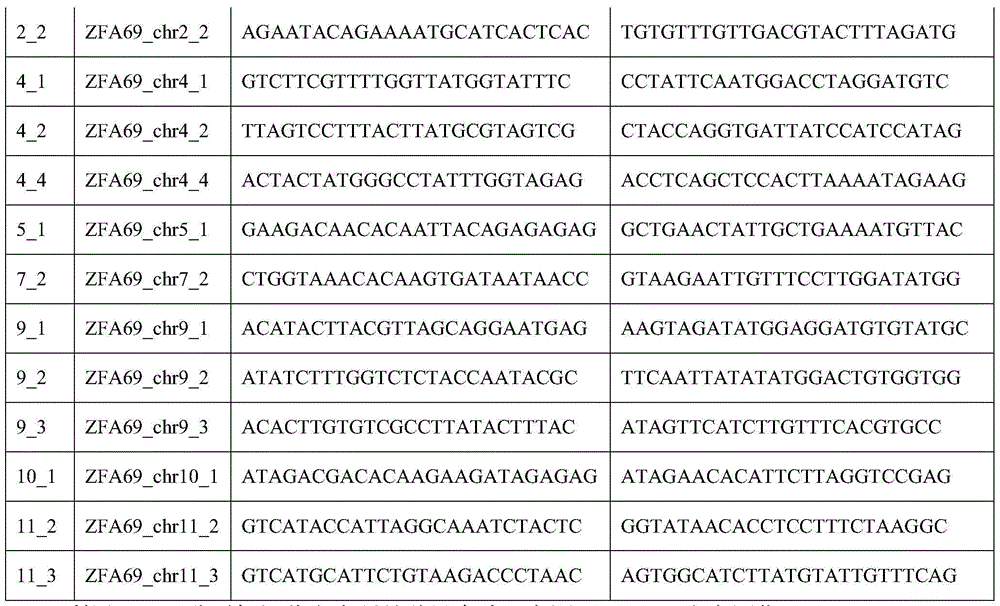
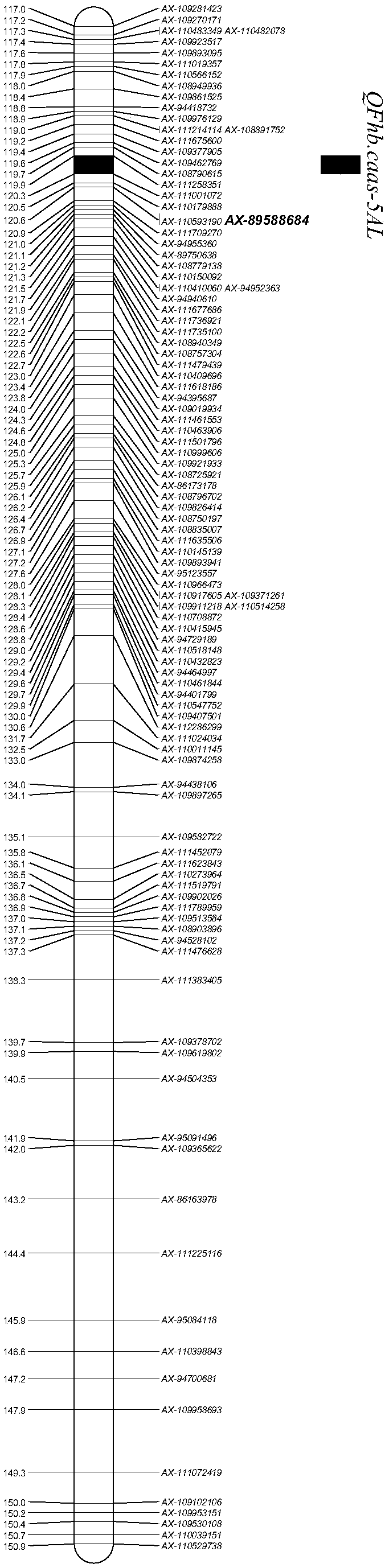
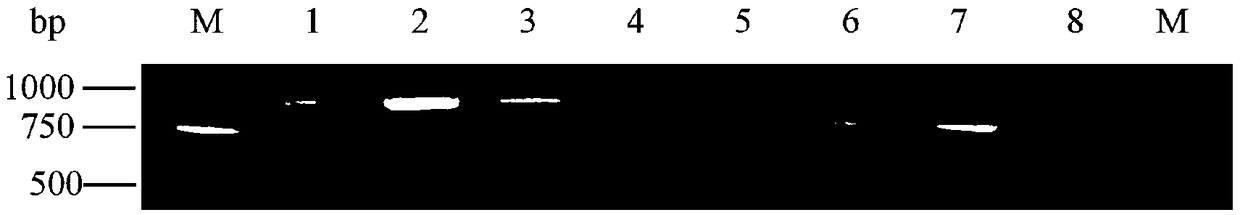
The invention discloses a molecular marker used for detecting a zhongmai 895 fusarium head blight resistance QTL and a use method. According to the molecular marker used for detecting the zhongmai 895fusarium head blight resistance QTL, by conducting fusarium head blight resistance QTL (quantitative trait locus) positioning on a DH (double haploid) group built through production application varieties yangmai 16 and zhongmai 895, the fusarium head blight resistance QTL QFhb.caas-5AL is found on a 5A chromosome long arm, an LOD value is 2.8-9.4, explained phenotypic variation is 2.4%-9.0%, markers on the two sides are AX-111258351 and AX-111001072, and a disease resistance allele comes from the zhongmai 895. On the basis, an InDel (insertion deletion) marker Fhb-5AL-InDel in close linkage with the QFhb.caas-5AL is developed, and a good tool is provided for fusarium head blight resistance breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
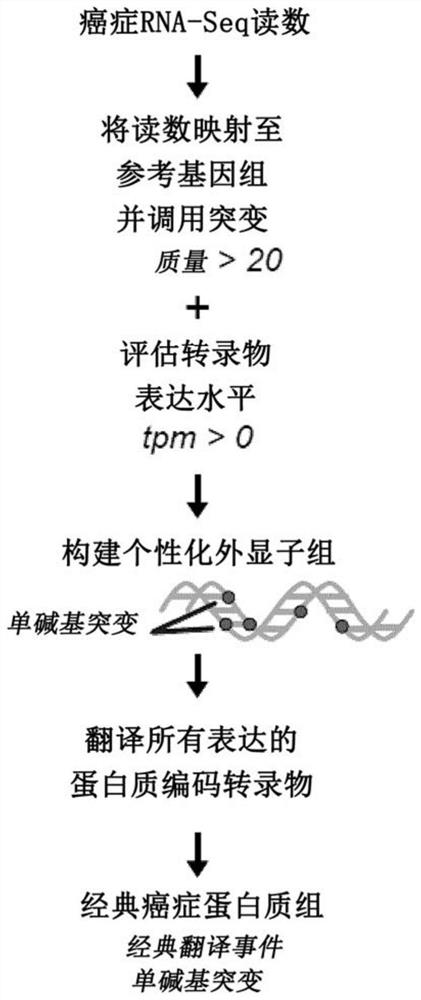
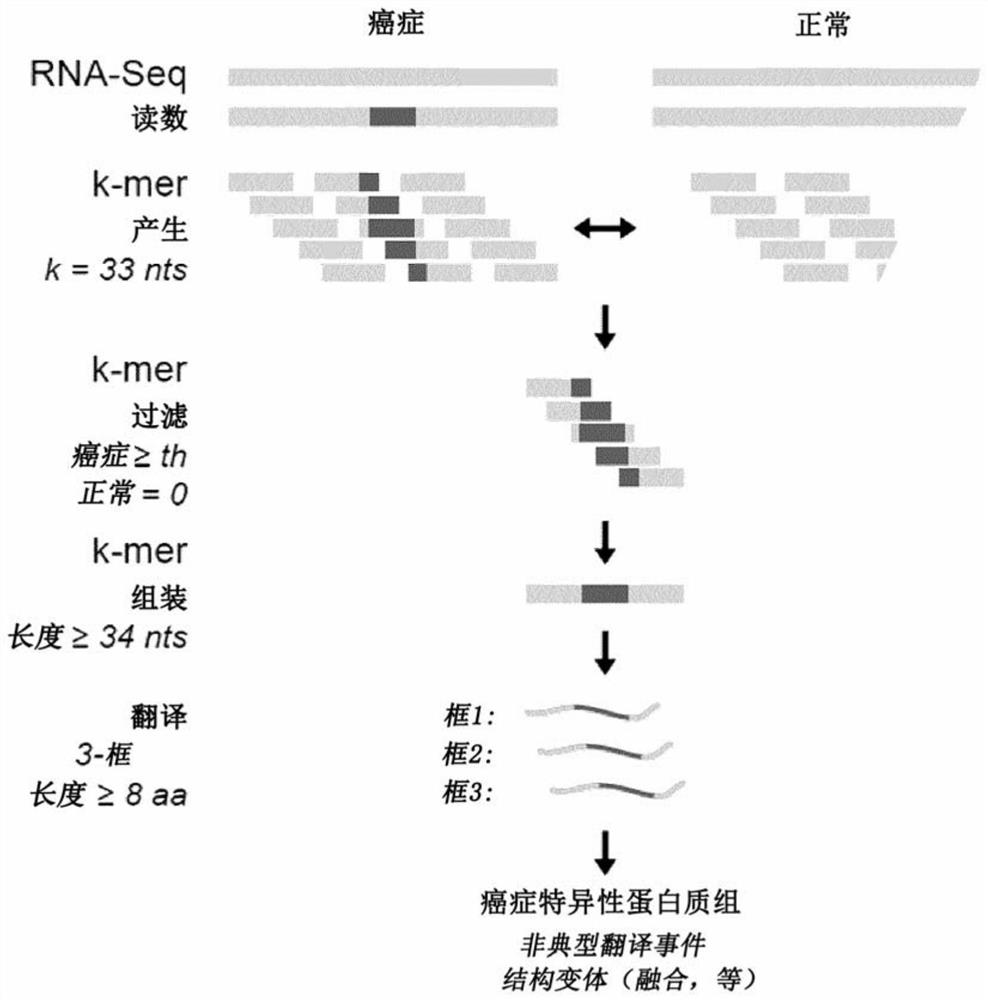
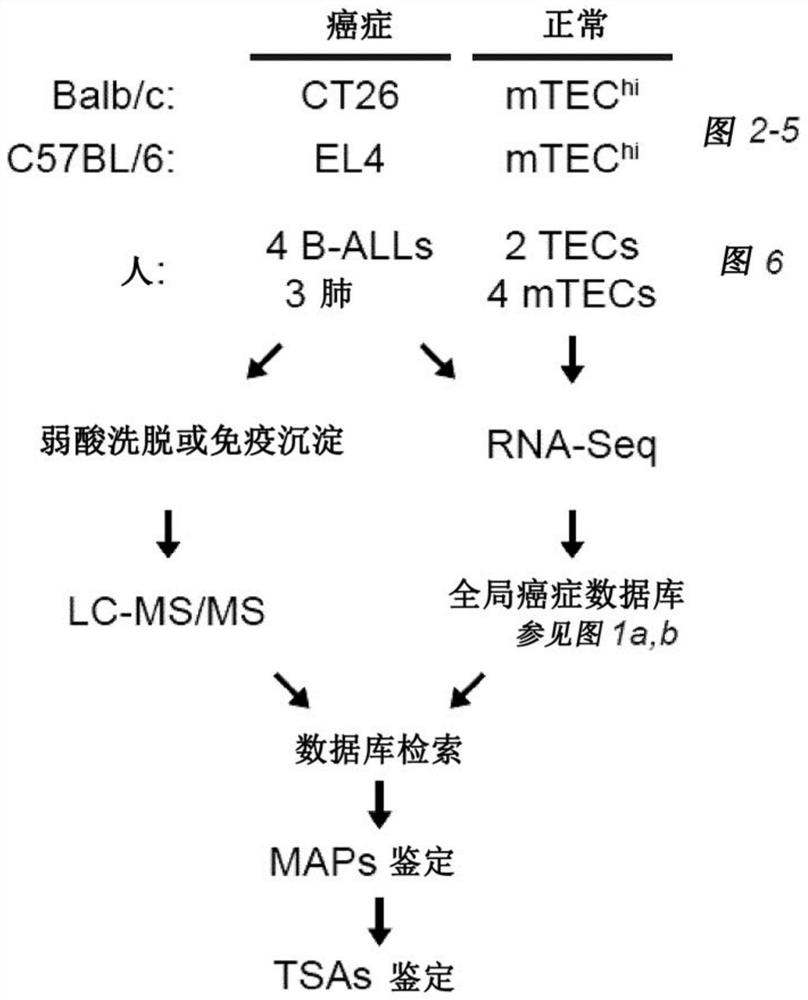
Proteogenomic-based method for identifying tumor-specific antigens
T cells, notably CD8 T cells, are known to be essential players in tumor eradication as the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in several cancers positively correlates with a good prognosis. To eliminate tumor cells, CD8 T cells recognize tumor antigens, which are MHC I-associated peptides present at the surface of tumor cells, with no or very low expression on normal cells. Described herein a proteogenomic approach using RNA-sequencing data from cancer and normal-matched mTEChi samples in order to identify non-tolerogenic tumor-specific antigens derived from (i) coding and non-coding regions of the genome, (ii) non-synonymous single-base mutations or short insertion / deletions and more complex rearrangements as well as (iii) endogenous retroelements, which works regardless of the sample's mutational load or complexity.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Capture probe for DNA sample containing INDEL region, kit and library construction method
PendingCN110564818AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionA-DNA
The invention provides a capture probe for a DNA sample containing an INDEL region, a kit and a library construction method. The capture probe comprises a first section of probe sequence which is complementarily paired with the left side of the INDEL region, a second section of probe sequence which is complementarily paired with the right side of the INDEL region, and a third section of probe sequence which is completely complementarily paired with the INDEL region. According to Indel (insertion-deletion fragment) of a target region, a mutated gene sequence is used as a reference sequence, andthree probes are designed for the Indel region and are respectively an Indel left side probe sequence, an Indel right side probe sequence and a probe sequence covering an Indel mutation site. The capture specificity and sensitivity of the three probes to the target Indel sequence are greatly improved, and the problems of low capture efficiency and low enrichment level of the Indel region of an important gene at present are effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
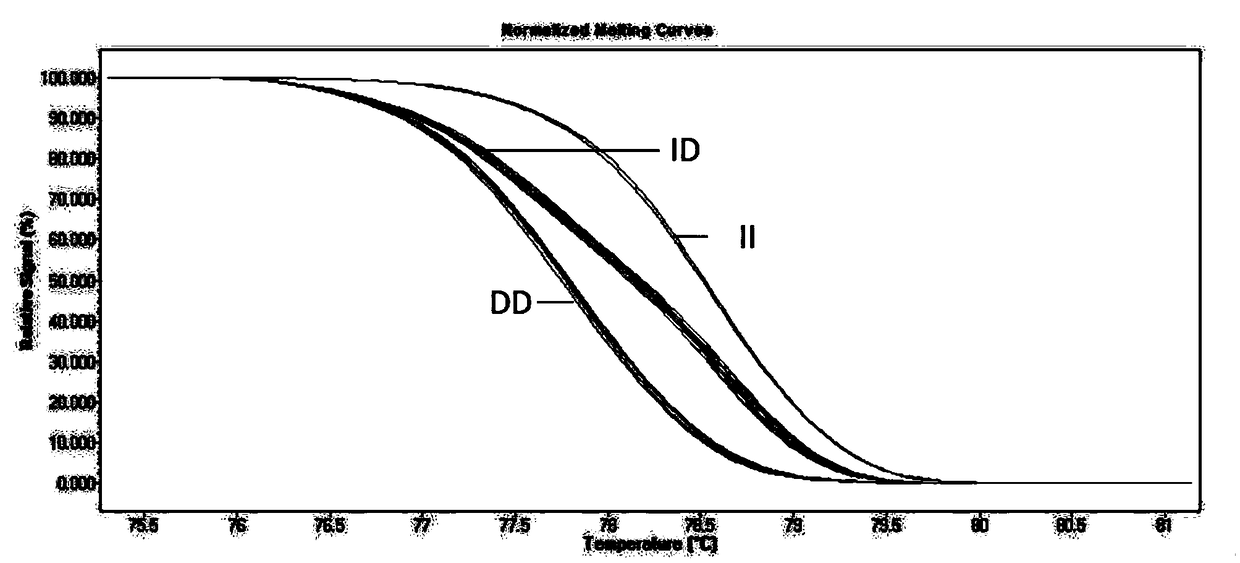
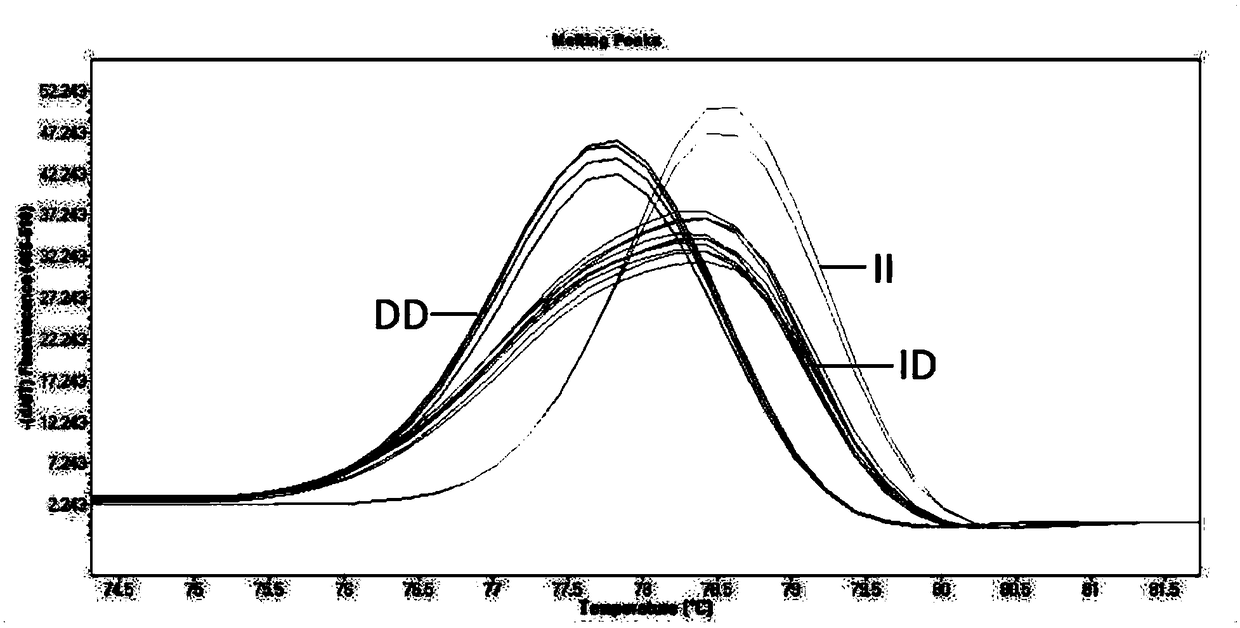
Method for identifying genotype of insertion deletion locus of animal gene with HRM
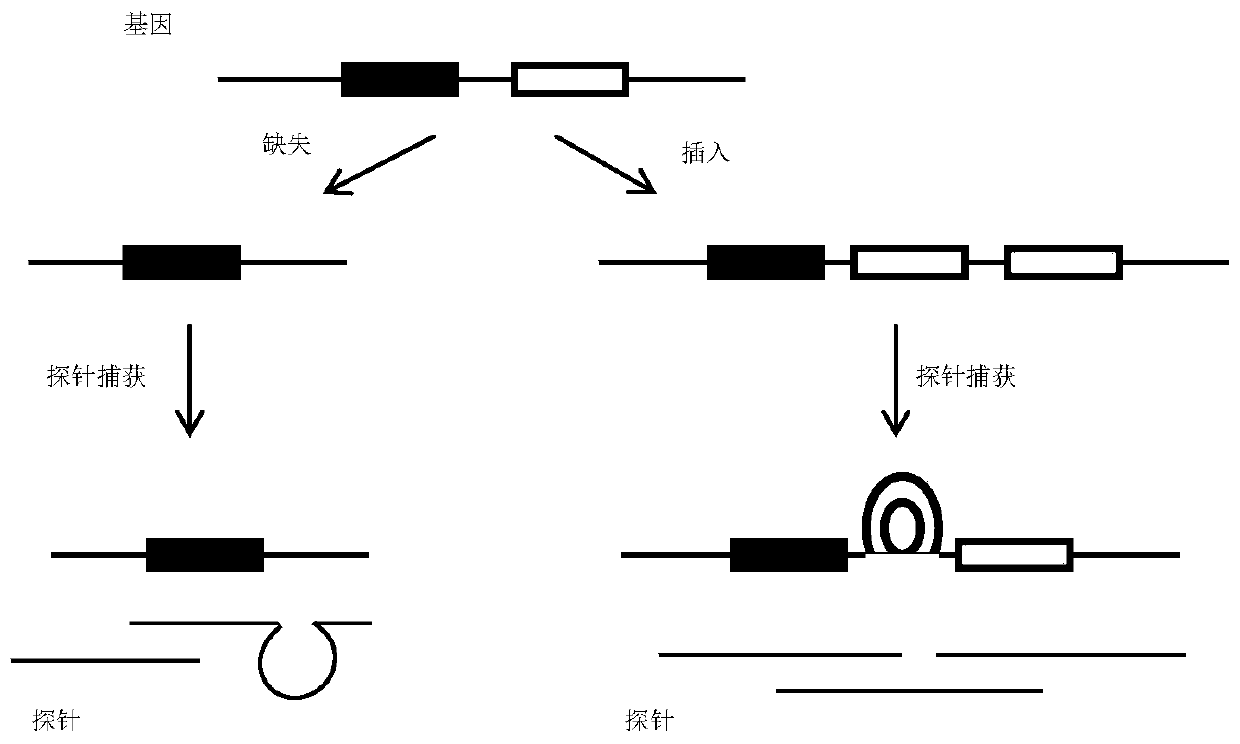
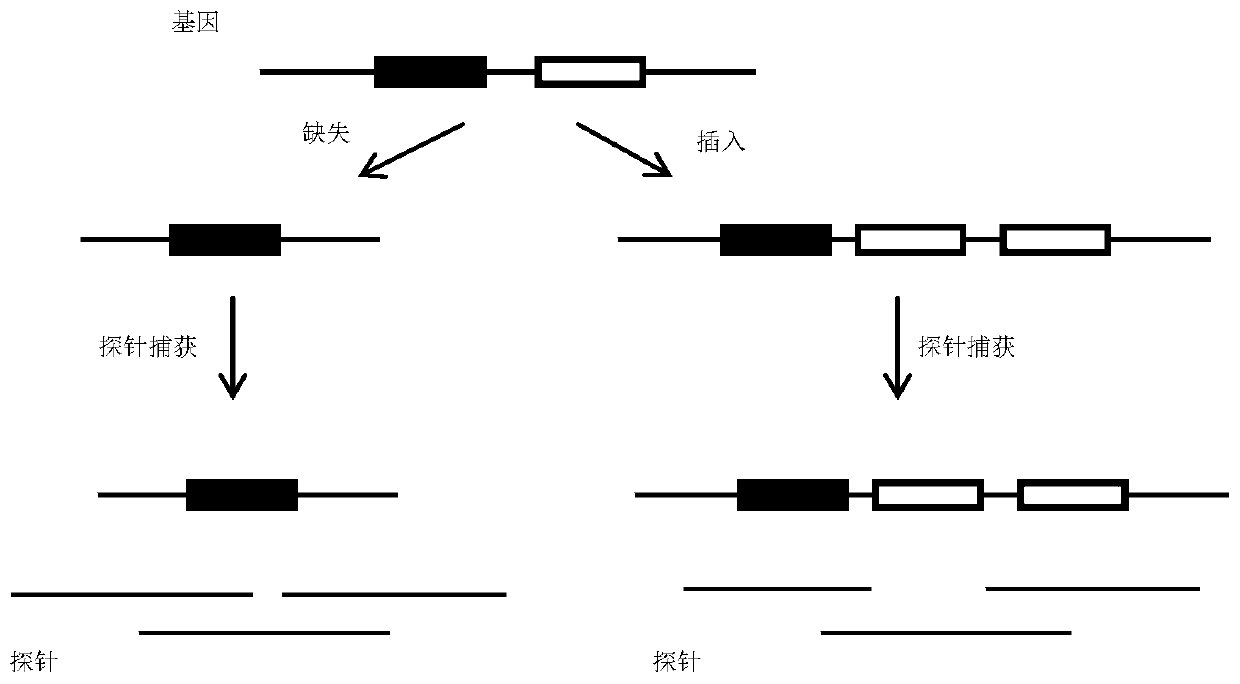
InactiveCN108866160ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionBiology
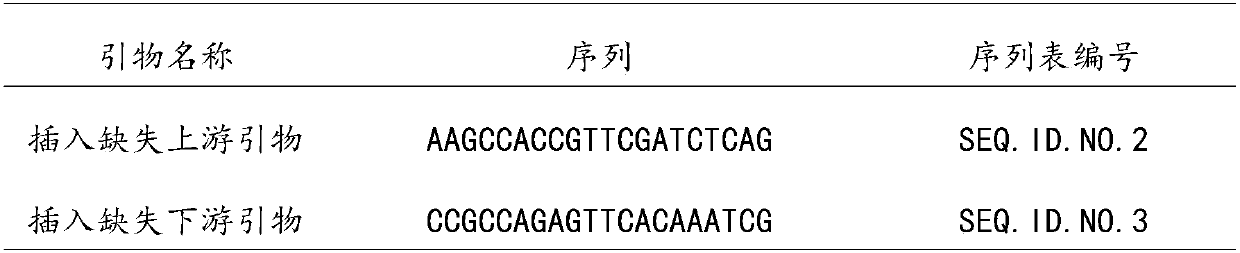
The invention discloses a method for identifying a genotype of an insertion deletion locus of an animal gene with HRM. The method comprises the following steps of searching potential gene insertion deletion locus information through an NCBI database, intercepting an upstream and a downstream of an insertion deletion fragment to design a specific primer, performing DNA mixed pool PCR amplificationsequencing, determining a real insertion deletion locus, performing no-other polymorphic site determination on the real existing insertion deletion locus, utilizing a high resolution melting curve (HRM) to perform individual genotype identification on an animal large group, and then performing PAGE verification and sequencing verification on an identification result through sampling. By adopting the method, the detection accuracy of gene insertion deletion is obviously improved, and the genotype identification efficiency is improved by about 3-5 times. Proved by a PCR and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis method, typing performed by the method is reliable and effective. The method provides richer identification means to molecular marker detection work and provides a new reliable evaluation method to animal breeding work.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com