Patents
Literature
1248 results about "Genetic marker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
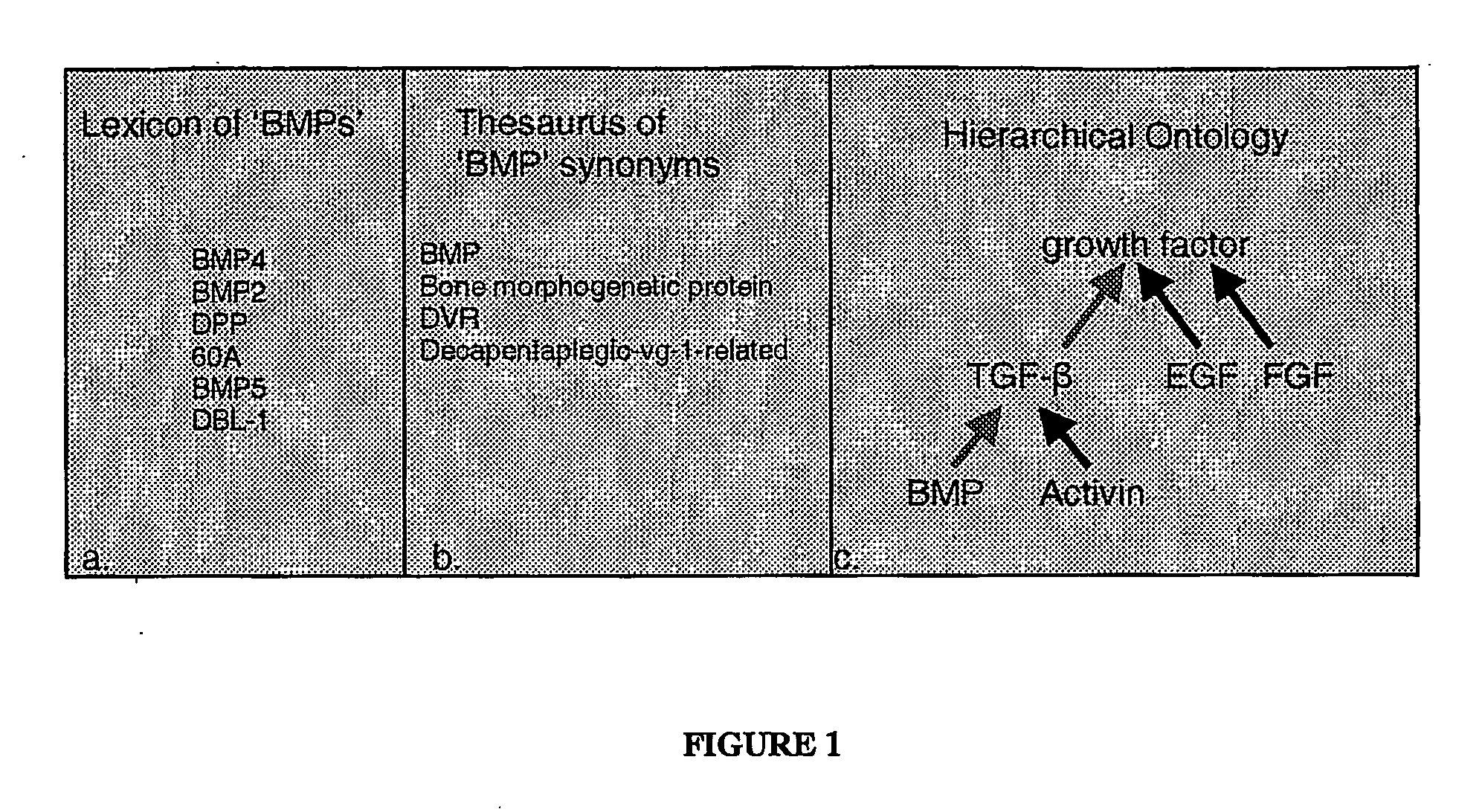
A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be observed. A genetic marker may be a short DNA sequence, such as a sequence surrounding a single base-pair change (single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP), or a long one, like minisatellites.
Non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits
InactiveUS20050164241A1Facilitates non-invasive detectionComponent separationOther chemical processesPregnancyNon invasive
Blood plasma of pregnant women contains fetal and (generally>90%) maternal circulatory extracellular DNA. Most of said fetal DNA contains ≦500 base pairs, said maternal DNA having a greater size. Separation of circulatory extracellular DNA of <500 base pairs results in separation of fetal from maternal DNA. A fraction of a blood plasma or serum sample of a pregnant woman containing, due to size separation (e.g. by chromatography, density gradient centrifugation or nanotechnological methods), extracellular DNA substantially comprising ≦500 base pairs is useful for non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits (including the fetal RhD gene in pregnancies at risk for HDN; fetal Y chromosome-specific sequences in pregnancies at risk for X chromosome-linked disorders; chromosomal aberrations; hereditary Mendelian genetic disorders and corresponding genetic markers; and traits decisive for paternity determination) by e.g. PCR, ligand chain reaction or probe hybridization techniques, or nucleic acid arrays.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits
ActiveUS20080071076A1Facilitates non-invasive detectionSugar derivativesOther chemical processesPregnancyNon invasive
Blood plasma of pregnant women contains fetal and (generally>90%) maternal circulatory extracellular DNA. Most of said fetal DNA contains .Itoreq.500 base pairs, said maternal DNA having a greater size. Separation of circulatory extracellular DNA of .Itoreq.500 base pairs results in separation of fetal from maternal DNA. A fraction of a blood plasma or serum sample of a pregnant woman containing, due to size separation (e.g. by chromatography, density gradient centrifugation or nanotechnological methods), extracellular DNA substantially comprising .Itoreq.500 base pairs is useful for non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits (including the fetal RhD gene in pregnancies at risk for HDN; fetal Y chromosome-specific sequences in pregnancies at risk for X chromosome-linked disorders; chromosomal aberrations; hereditary Mendelian genetic disorders and corresponding genetic markers; and traits decisive for paternity determination) by e.g. PCR, ligand chain reaction or probe hybridization techniques, or nucleic acid arrays.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS7035739B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Plant breeding method
InactiveUS20050144664A1Other foreign material introduction processesAgricultureNumeral systemPlant variety
Methods for using genetic marker genotype (e.g., gene sequence diversity information) to improve the process of developing plant varieties (e.g., single cross hybrids) with improved phenotypic performance are provided. Methods for predicting the value of a phenotypic trait in a plant are provided. The methods use genotypic, phenotypic, and optionally family relationship information for a first plant population to identify an association between at least one genetic marker and the phenotypic trait, and then use the association to predict the value of the phenotypic trait in one or more members of a second, target population of known marker genotype. Methods for identifying new allelic variants affecting the trait are also provided. Plants selected, provided, or produced by any of the methods herein, transgenic plants created by any of the methods herein, and digital systems for performing the methods herein are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Method for detecting chromosomal aneuploidy
The present invention relates to a new, non-invasive method for detecting chromosomal aneuploidy by analyzing a sample from a pregnant woman. The detection is based on the ratio between the amount of a fetal methylation marker located on a chromosome relevant to the aneuploidy and the amount of a fetal genetic marker located on a reference chromosome, offering improved accuracy.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods and compositions for evaluating genetic markers
PendingUS20120165202A1Increase variabilityDisproportionate representationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationMultiplexNucleic acid sequencing
Aspects of the invention relates to methods and compositions that are useful to reduce bias and increase the reproducibility of multiplex analysis of genetic loci. In some configurations, predetermined preparative steps and / or nucleic acid sequence analysis techniques are used in multiplex analyses for a plurality of genetic loci in a plurality of samples.
Owner:MOLECULAR LOOP BIOSOLUTIONS LLC
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS20030224394A1Improve artBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
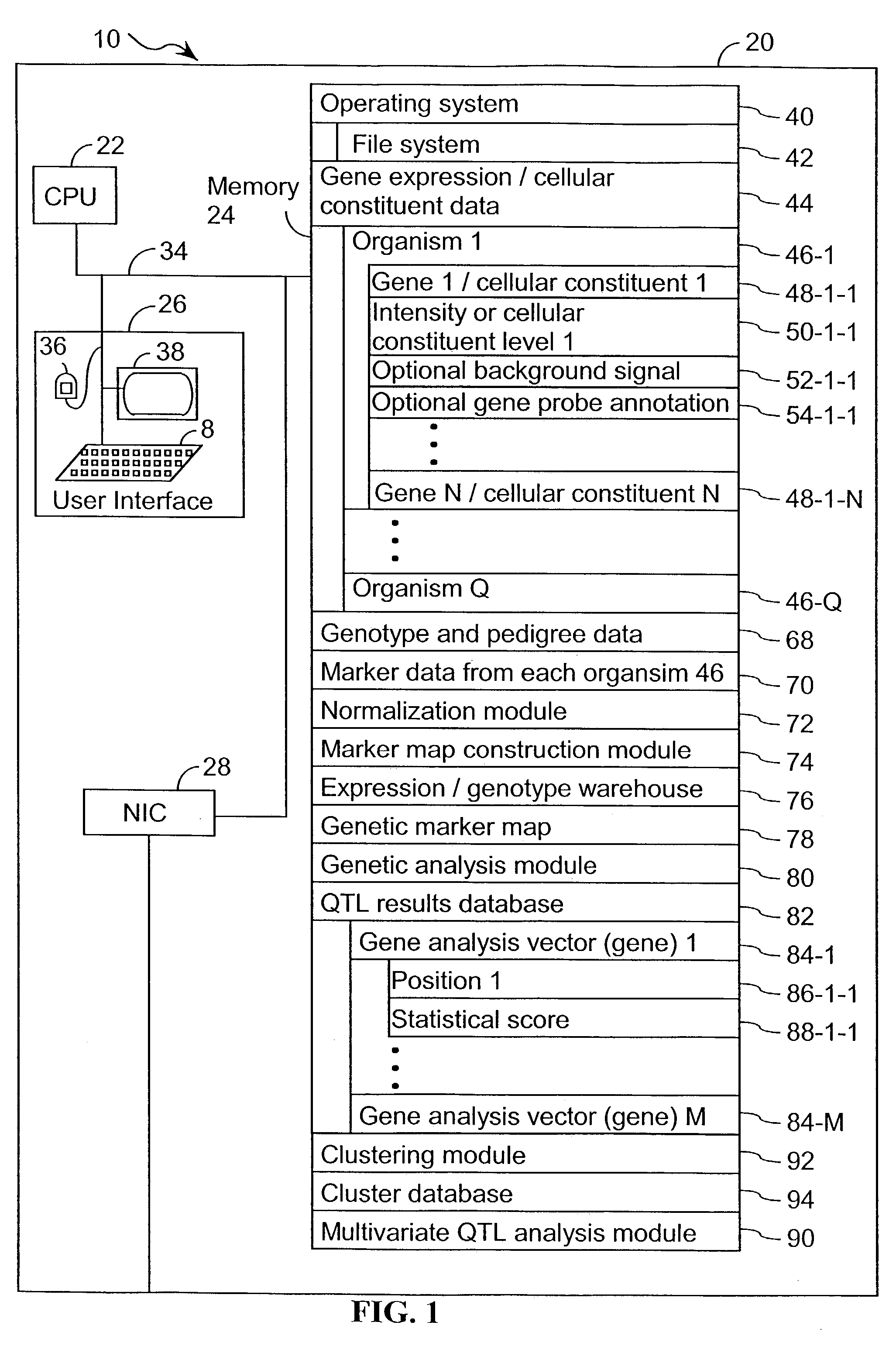
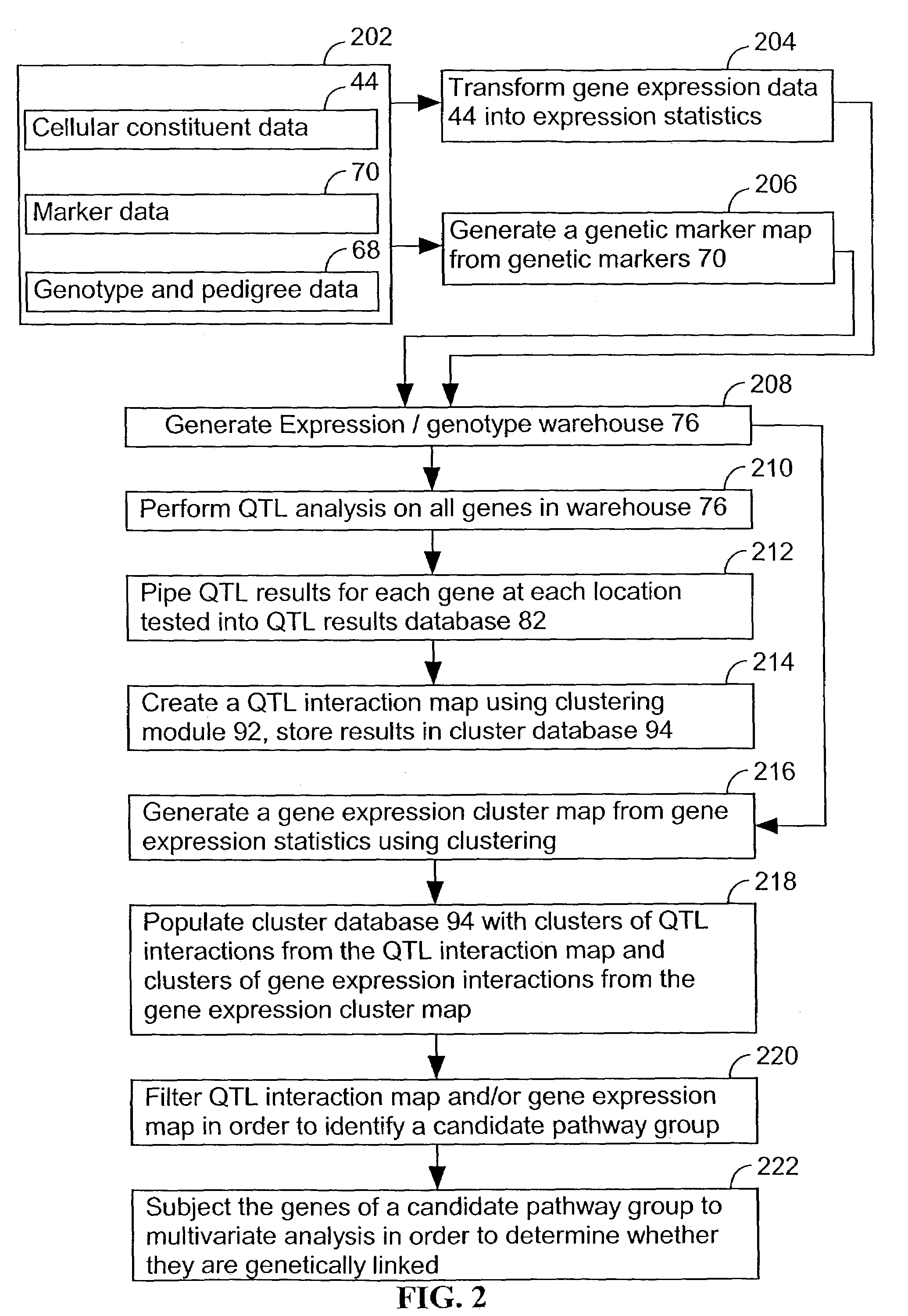
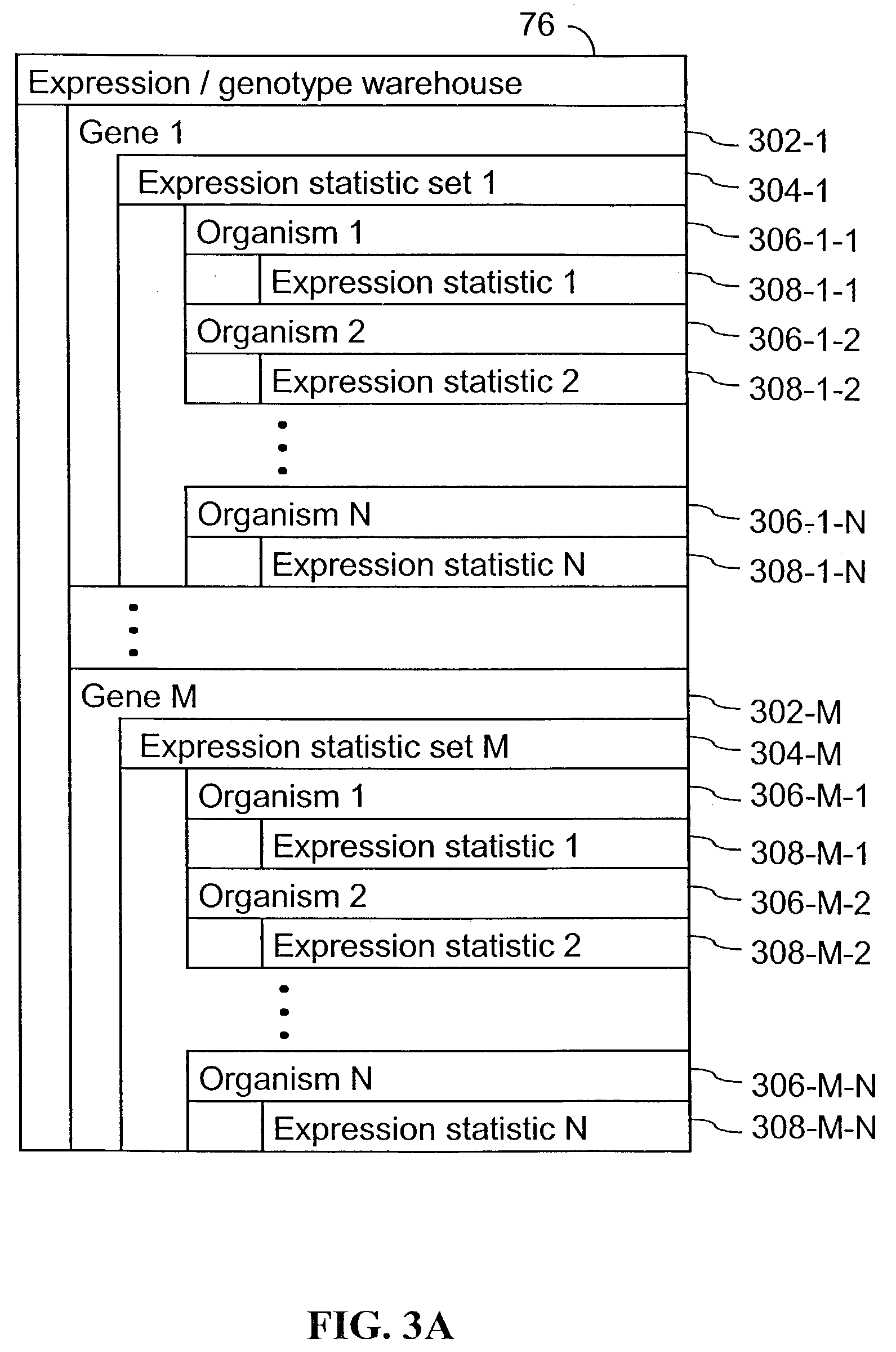
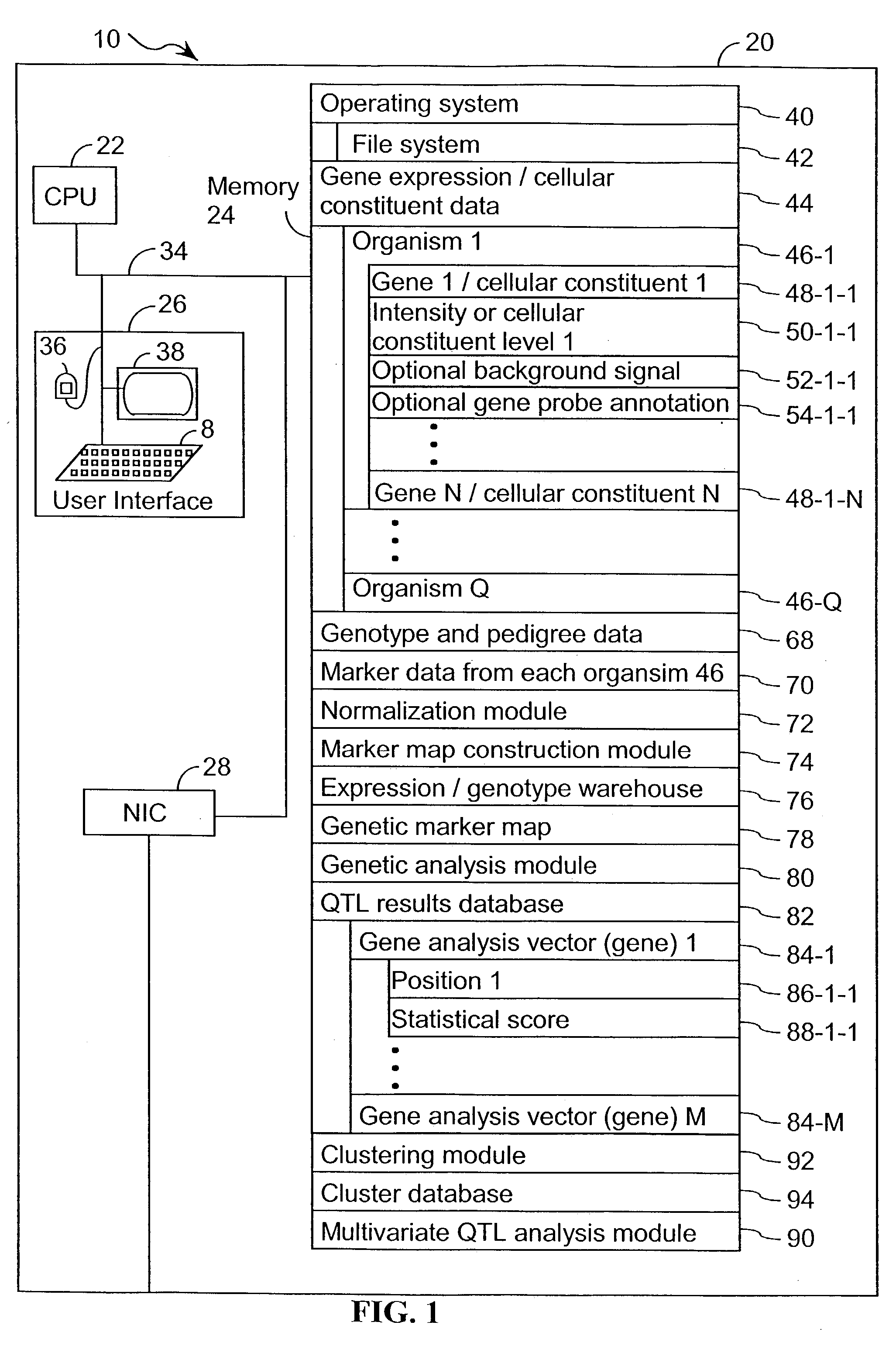
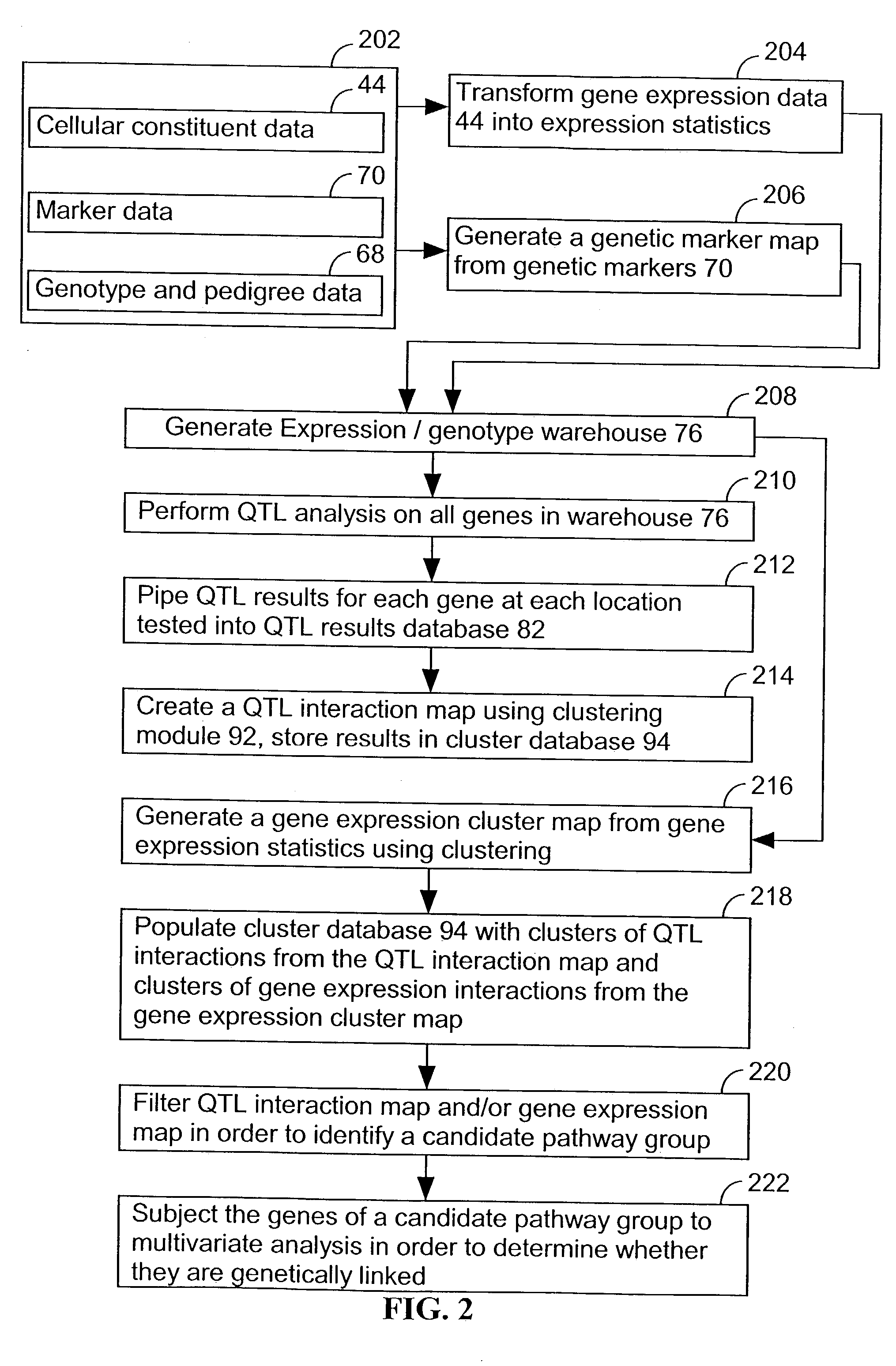
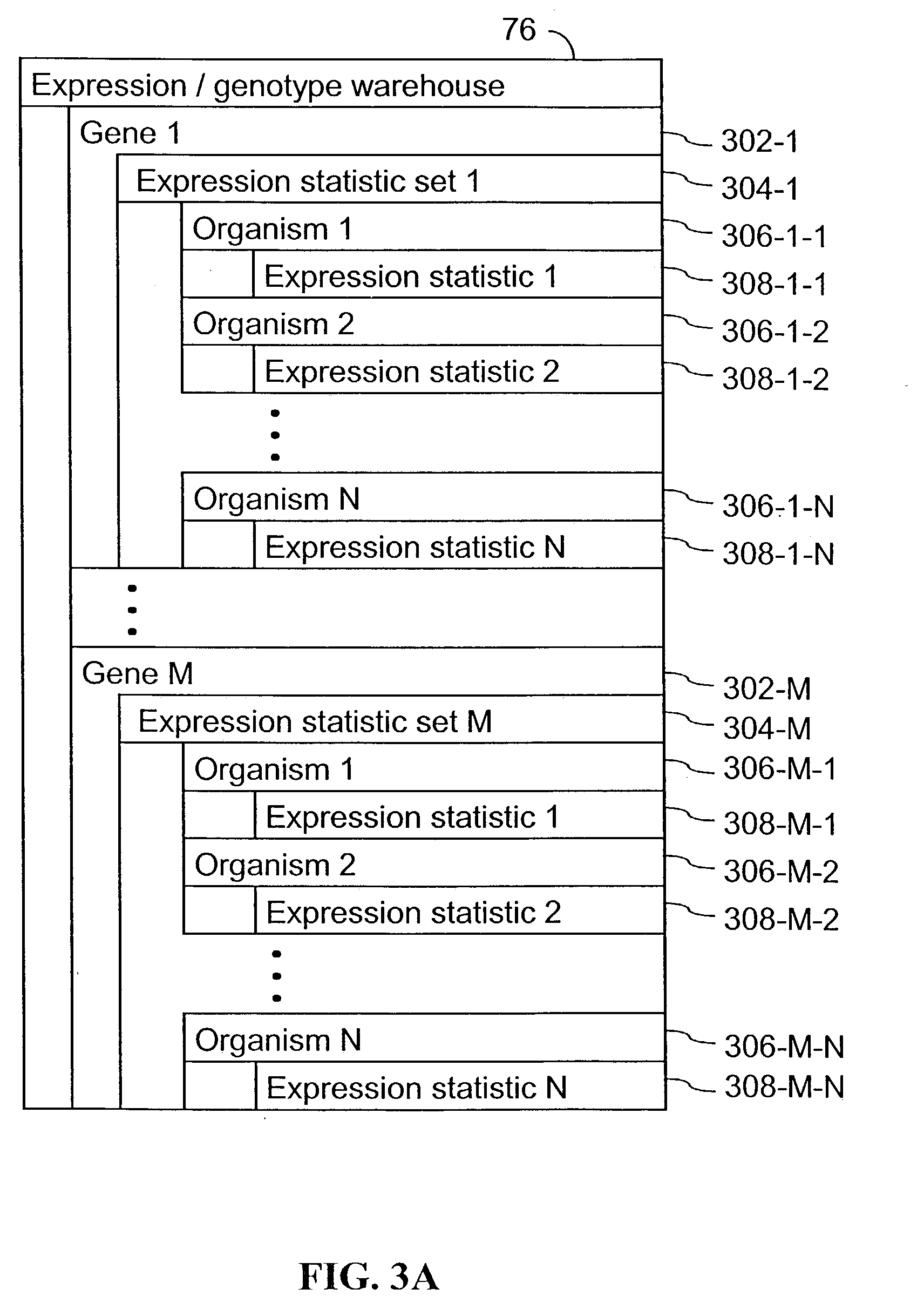
A method for associating a gene with a trait exhibited by one or more organisms in a plurality of organisms from a species. A genetic marker map is constructed from a set of genetic markers associated with the plurality of organisms. For each gene in a plurality of genes, a quantitative trait locus analysis is performed using the genetic marker map and a quantitative trait. The quantitative trait locus analysis produces quantitative trait locus data. A quantitative trait comprises an expression statistic for a gene. The expression statistic for a gene is derived from a cellular constituent level that corresponds to the gene in each organism in the plurality of organisms. The quantitative trait locus data are clustered from each quantitative trait locus analysis to form a quantitative trait locus interaction map. Clusters of genes in the map are identified as a candidate pathway group. An expression cluster map is used to refine the candidate pathway group. Multivariate analysis is used to validate the candidate pathway group as a set of genes that are genetically interacting.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
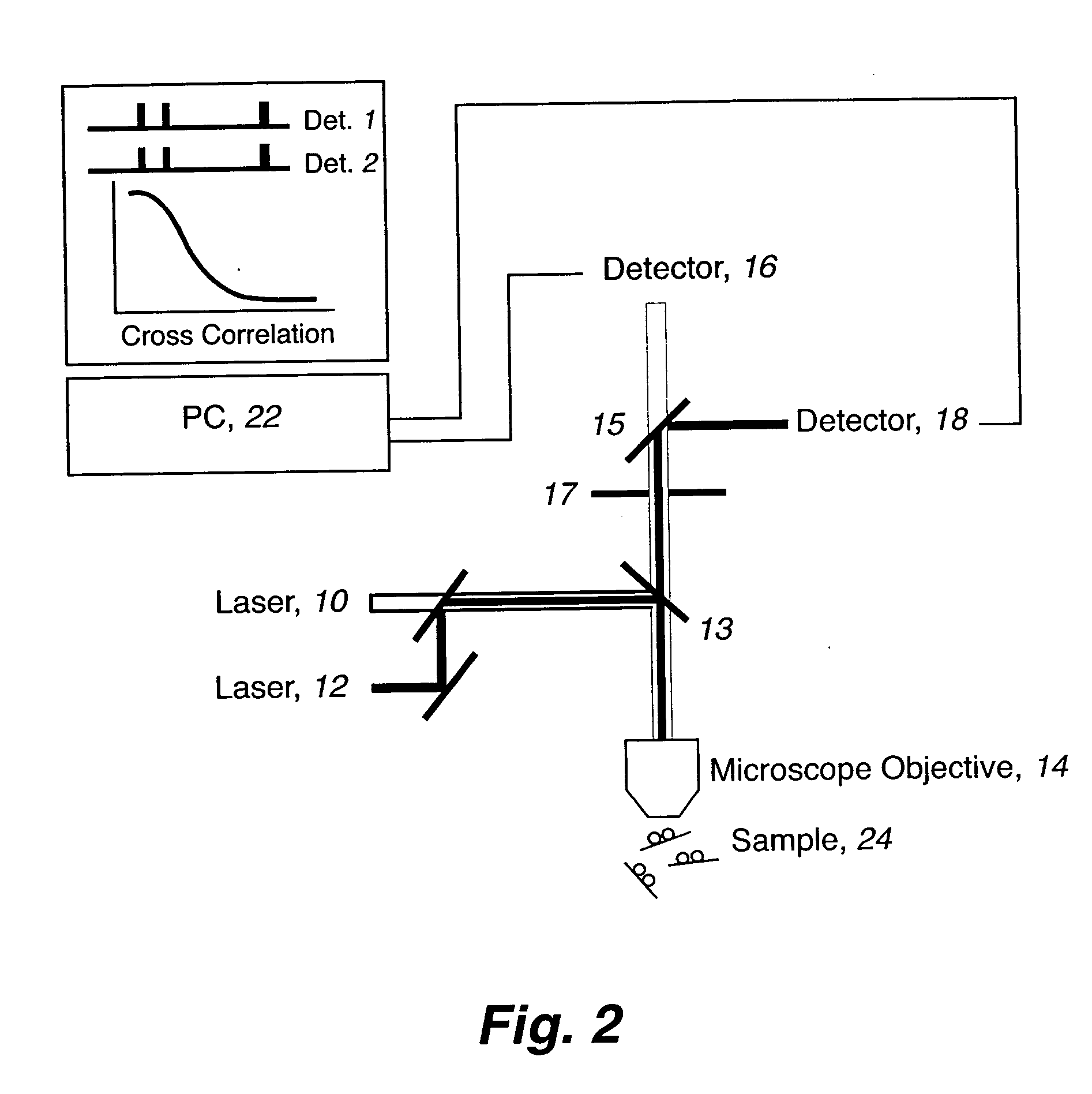
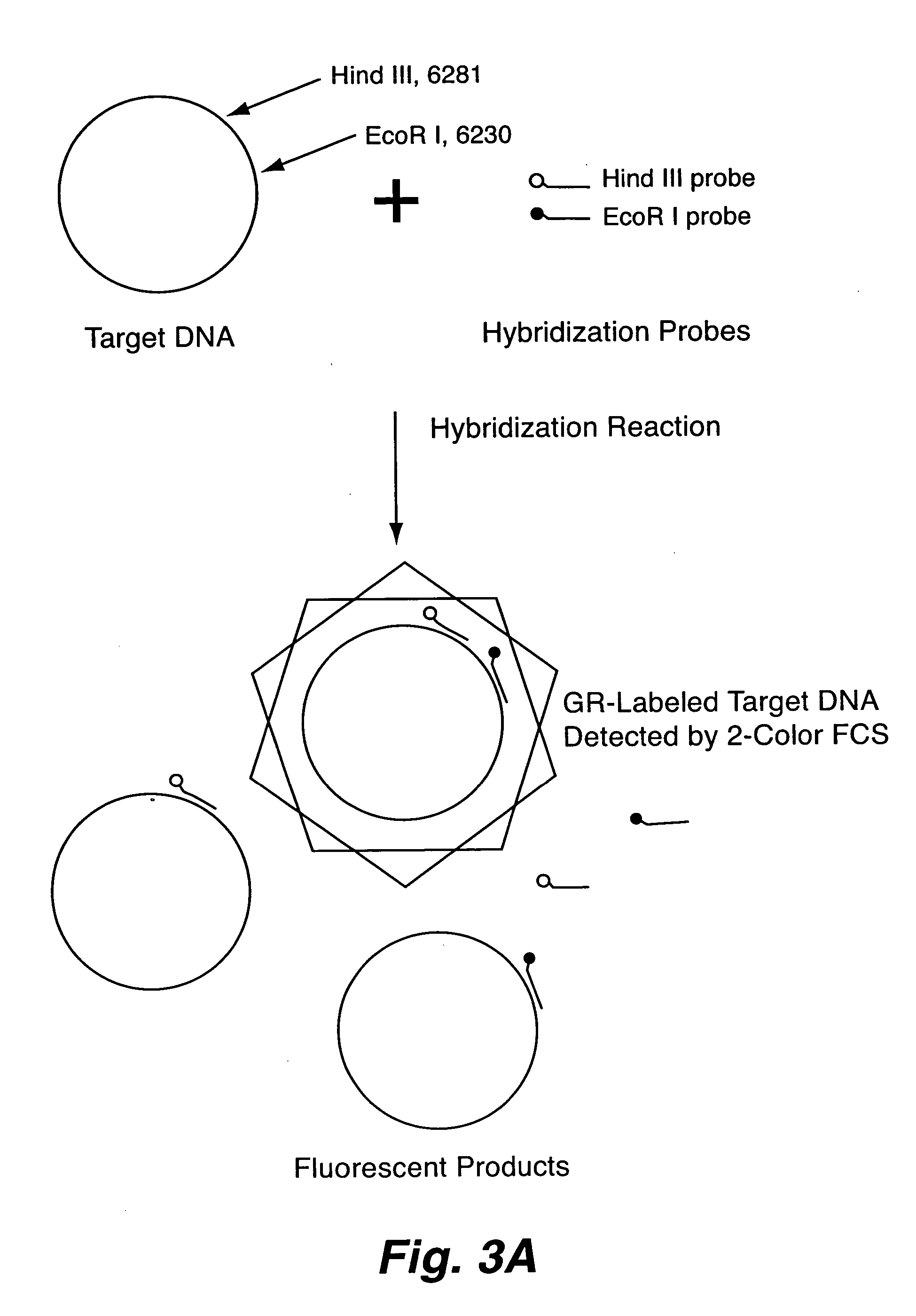
Rapid haplotyping by single molecule detection
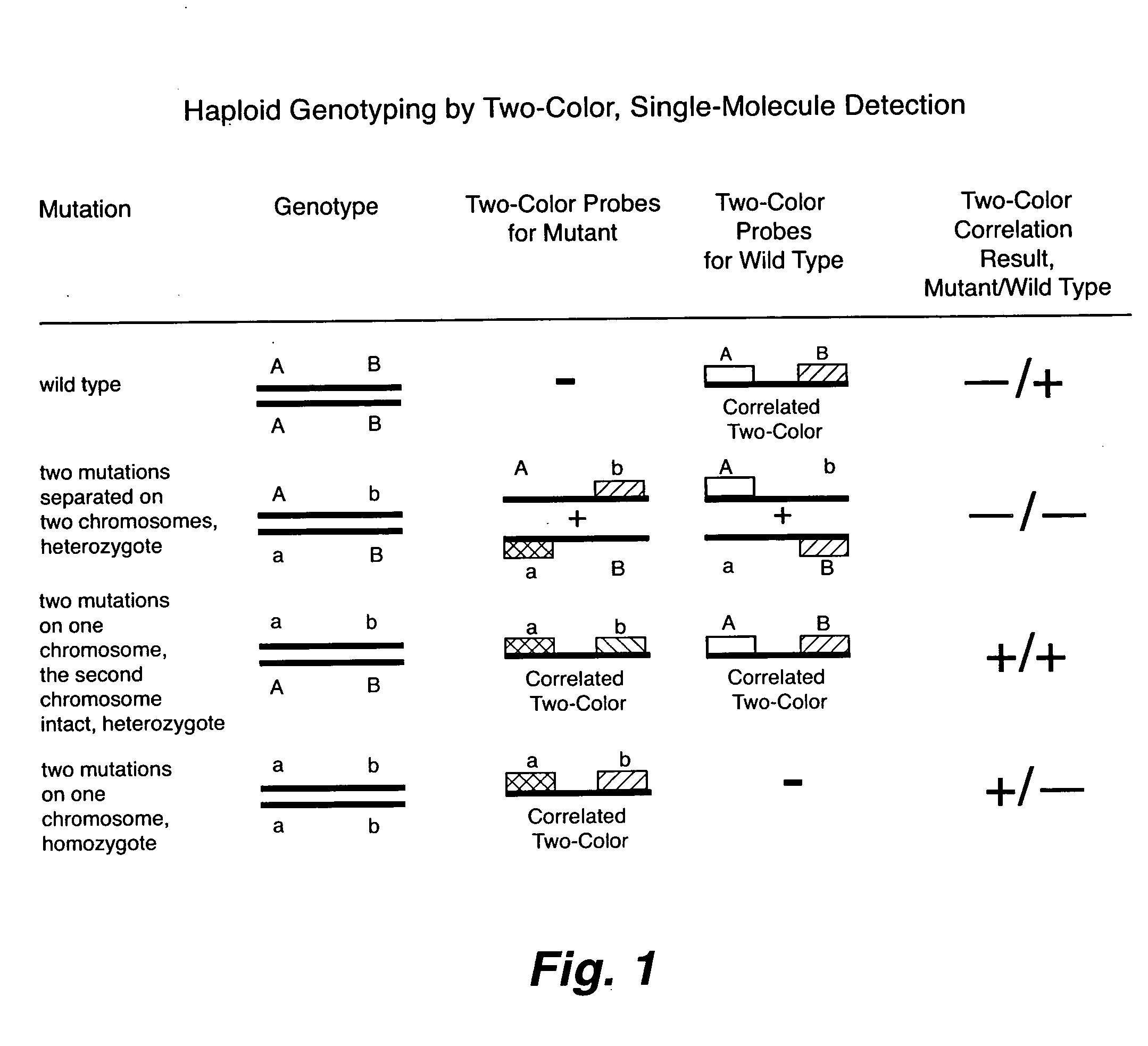
The present invention includes a method for rapid haplotyping a DNA or RNA segment. Two or more target sites on a segment of DNA or RNA are labeled with separate distinguishable luminescent hybridization probes, where the targets are selected genetic markers. A dilute solution is formed containing the labeled DNA or RNA segments. Each DNA or RNA segment is illuminated with light beams effective to excite each luminescent hybridization probe, when present. The presence or absence of each luminescent hybridization probe on each DNA or RNA segment is detected to determine the haplotype of each DNA or RNA segment.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Disease-associated genetic variations and methods for obtaining and using same
InactiveUS20100196898A1Rapid, unbiased, and accurateTumor rejection antigen precursorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease causeVariation (Genetics)
The invention provides a comprehensive, rapid, unbiased, and accurate method for identifying and / or discovering disease-associated genetic variations, e.g., disease-associated variations. The present invention further provides novel disease-associated genetic variations for use as genetic markers of disease, e.g., cancer. The invention further provides methods for assessing an individual's risk for developing a disease, e.g., cancer, by detecting the presence the novel disease-associated genetic variations of the invention.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Hppd-inhibitor herbicide tolerance
ActiveUS20110185445A1Negatively impactingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePlant cell
This invention relates generally to the detection of genetic differences among soybeans. More particularly, the invention relates to soybean quantitative trait loci (QTL) for tolerance or sensitivity to HPPD-inhibitor herbicides, such as mesotrione and isoxazole herbicides, to soybean plants possessing these QTLs, which map to a novel chromosomal region, and to genetic markers that are indicative of phenotypes associated with tolerance, improved tolerance, susceptibility, or increased susceptibility. Methods and compositions for use of these markers in genotyping of soybean and selection are also disclosed, as are methods and compositions for use of these markers in selection and use of herbicides for weed control. Also disclosed are isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides relating to such tolerance or sensitivity and methods of introgressing such tolerance into a plant by breeding or transgenically or by a combination thereof. Plant cells, plants, and seeds produced are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods of selection, reporting and analysis of genetic markers using borad-based genetic profiling applications
ActiveUS20070042369A1Economical and effective genetic profilingGuaranteed economic efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomePhenotype
Owner:FABRIC GENOMICS INC
Disease-associated genetic variations and methods for obtaining and using same
InactiveUS20120214163A1Rapid, unbiased, and accurateFungiTumor rejection antigen precursorsCvd riskVariation (Genetics)
The invention provides a comprehensive, rapid, unbiased, and accurate method for identifying and / or discovering disease-associated genetic variations, e.g., disease-associated variations. The present invention further provides novel disease-associated genetic variations for use as genetic markers of disease, e.g., cancer. The invention further provides methods for assessing an individual's risk for developing a disease, e.g., cancer, by detecting the presence the novel disease-associated genetic variations of the invention.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Method and compositions for highly sensitive detection of molecules
InactiveUS20090234202A1Detection moreImprove the level ofElectrocardiographyMicrobiological testing/measurementVascular endothelial growth factorPhysiological markers
The present invention discloses methods for the detection and monitoring of a condition in a subject using highly sensitive detection of molecules. The invention provides a method for detecting or monitoring a condition in a subject, comprising detecting a first marker in a first sample from the subject and detecting a second marker, wherein the first marker comprises a biomarker, e.g., Cardiac Troponin-I (cTnI) or Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), and wherein the limit of detection of the first marker is less than about 10 pg / ml. The second marker can be a biomarker, physiological marker, a molecular marker or a genetic marker.
Owner:SINGULEX
Method of genotyping by determination of allele copy number
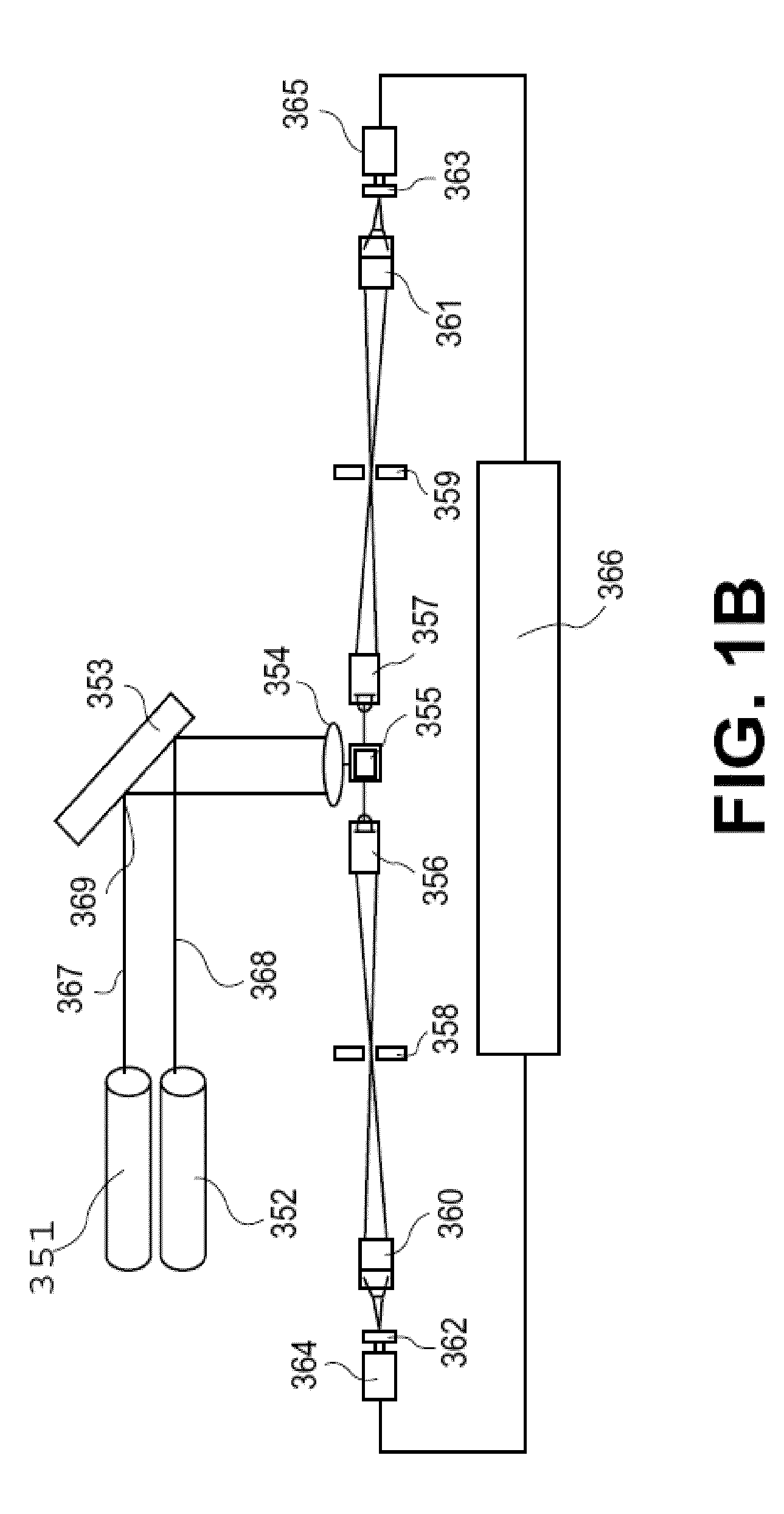
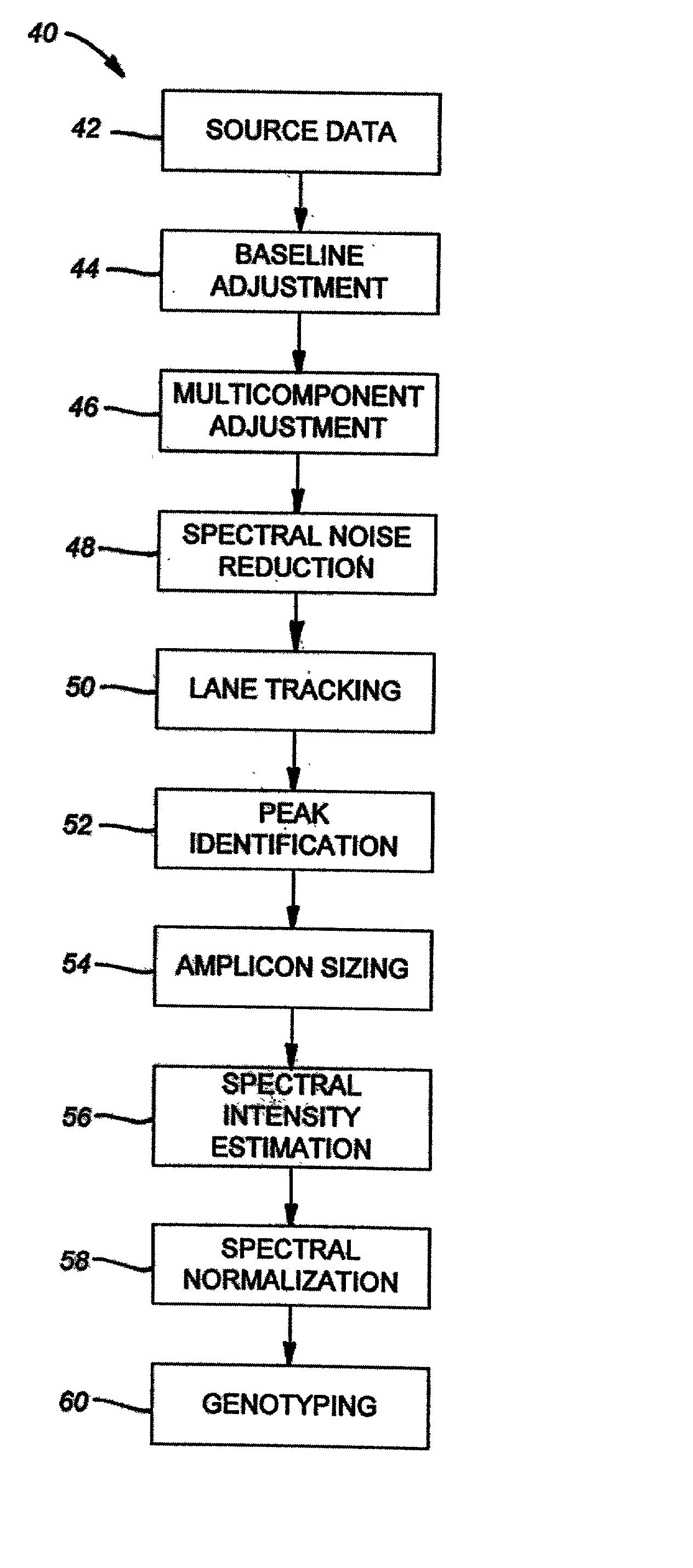
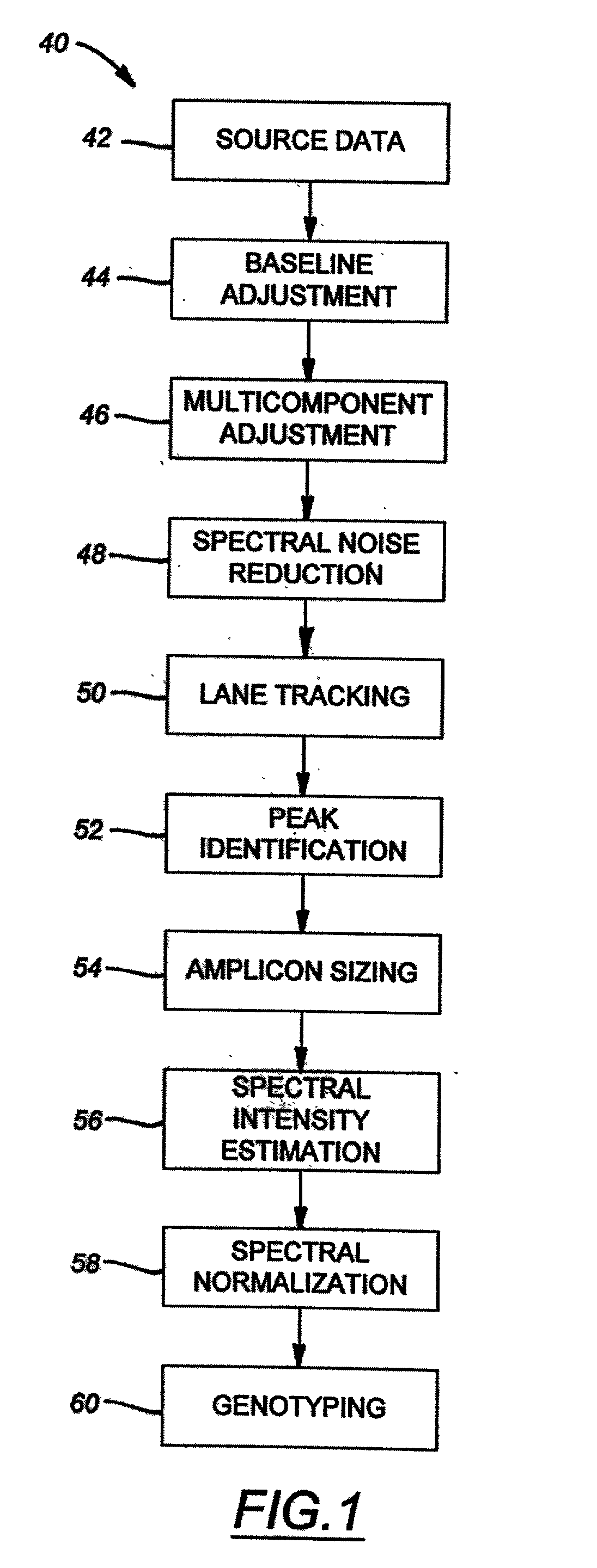
The majority of PCR-based fingerprinting technologies generate dominant genetic markers; homozygote present and heterozygote genotypes cannot be distinguished using conventional detection methods. In contrast, codominant genetic markers provide an unambiguous distinction among each genotype. A genotyping method is described that includes procedures implemented in software. This method quantifies allele copy number and enables recovery of codominant genotypes from markers expressing ostensibly dominant phenotypes. These procedures are designed and implemented to (1) greatly reduce variability attributable to sample assay and detector noise, (2) accurately estimate allele size and copy number, (3) provide normalization criteria for intra- and inter-marker comparisons, and (4) scale the resulting data to determine the genotype of individual markers.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
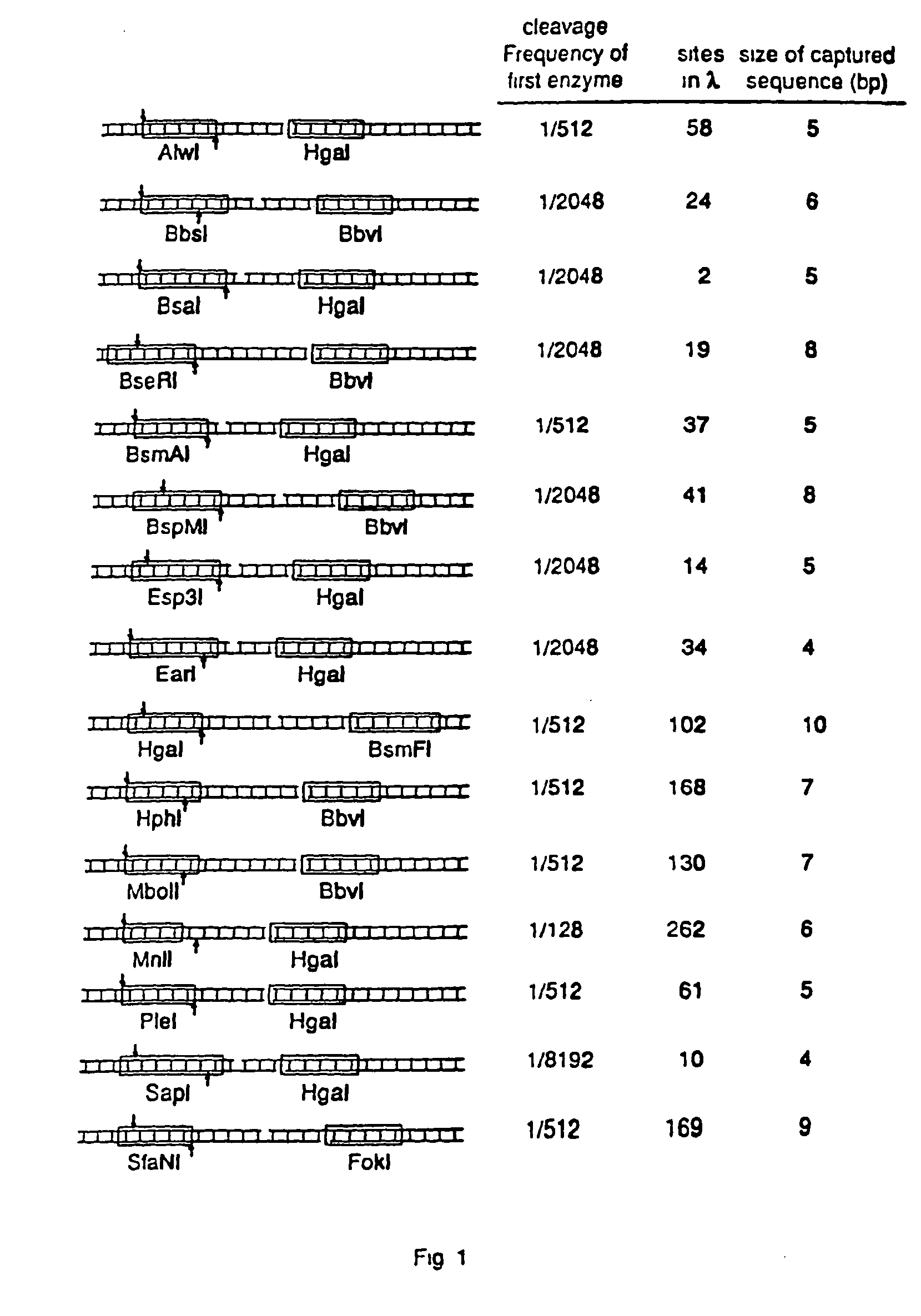
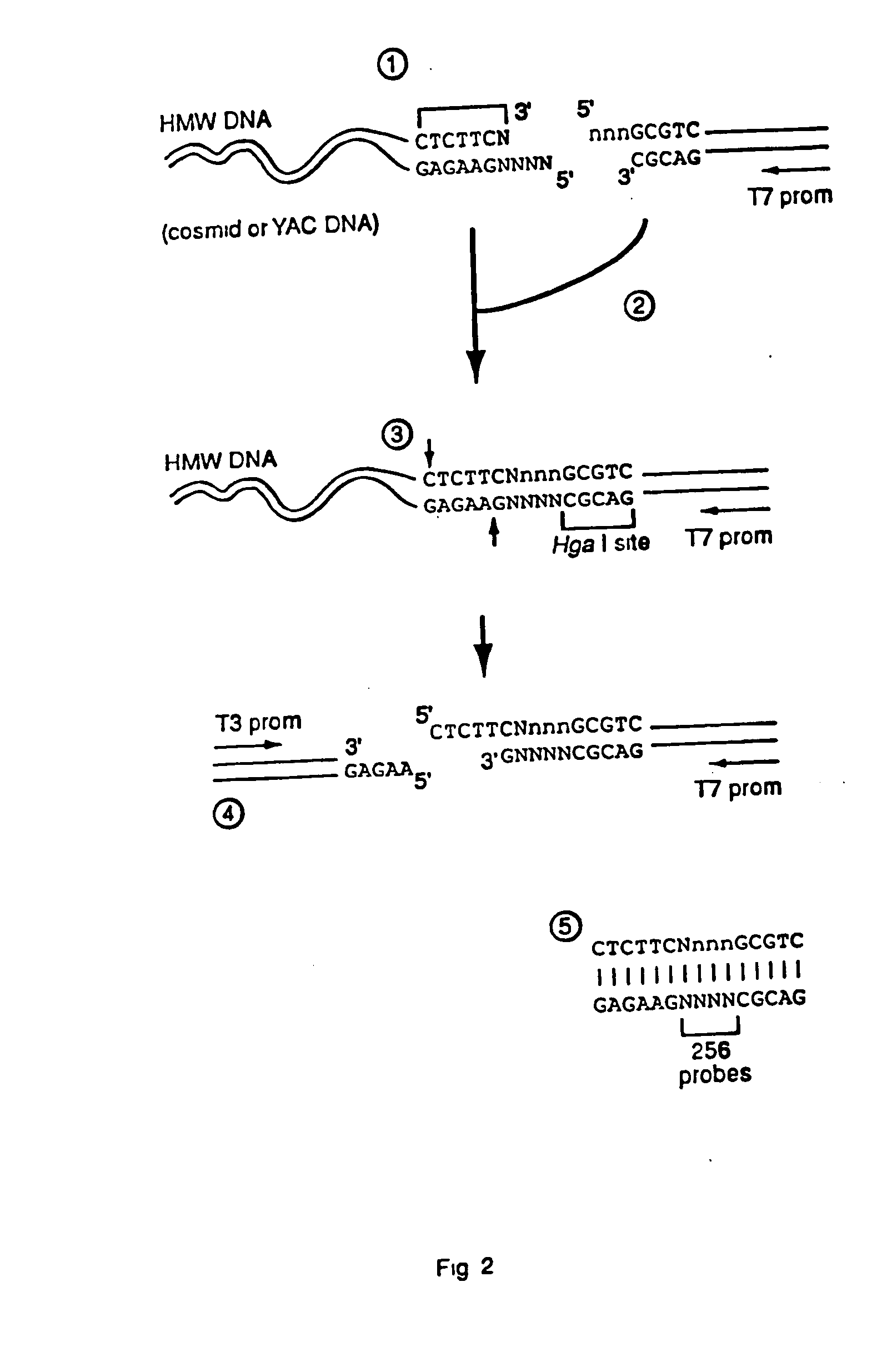
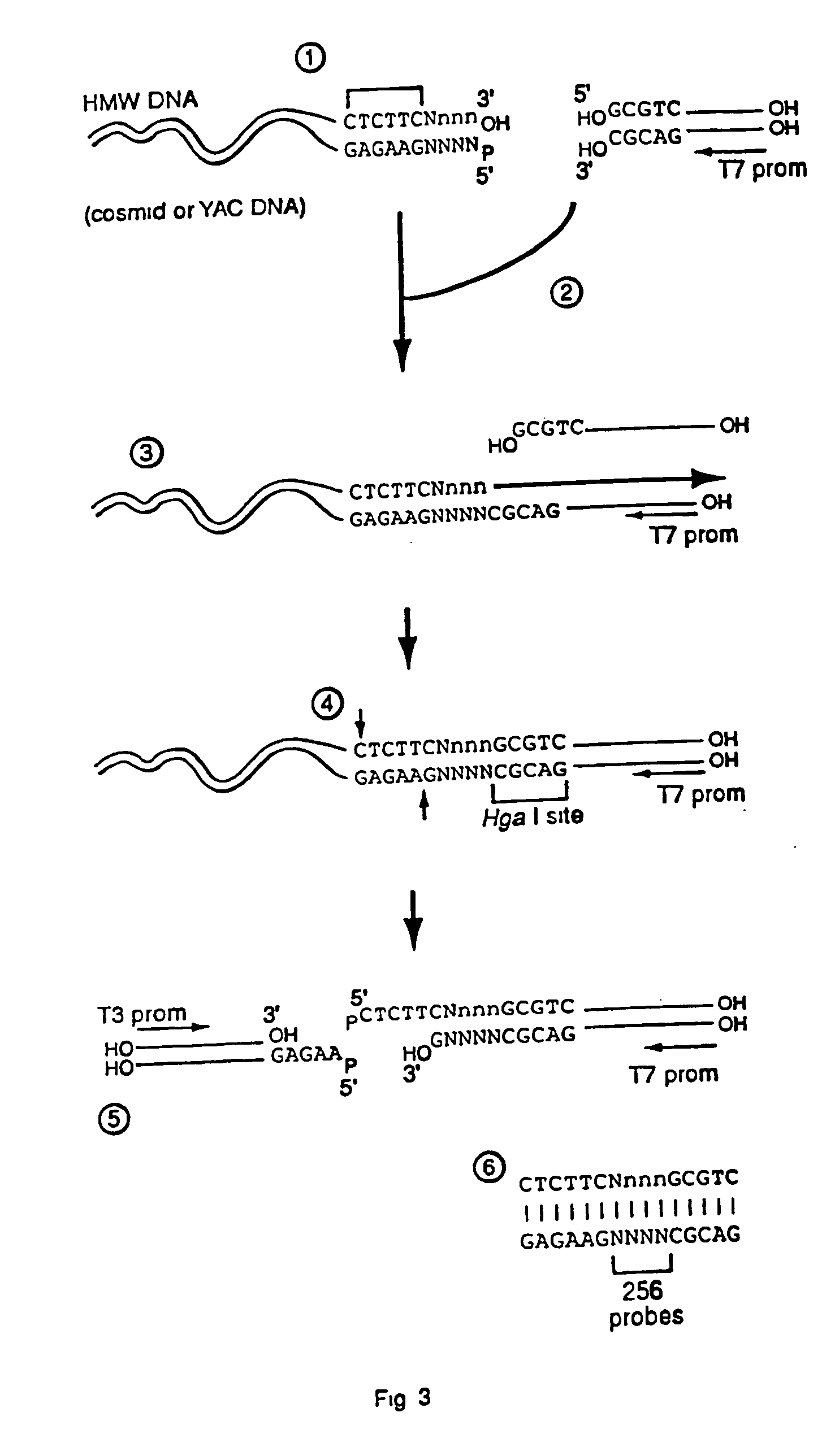
Capturing sequences adjacent to type-IIS restriction sites for genomic library mapping
InactiveUS20060223097A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningOligonucleotideGenetic marker
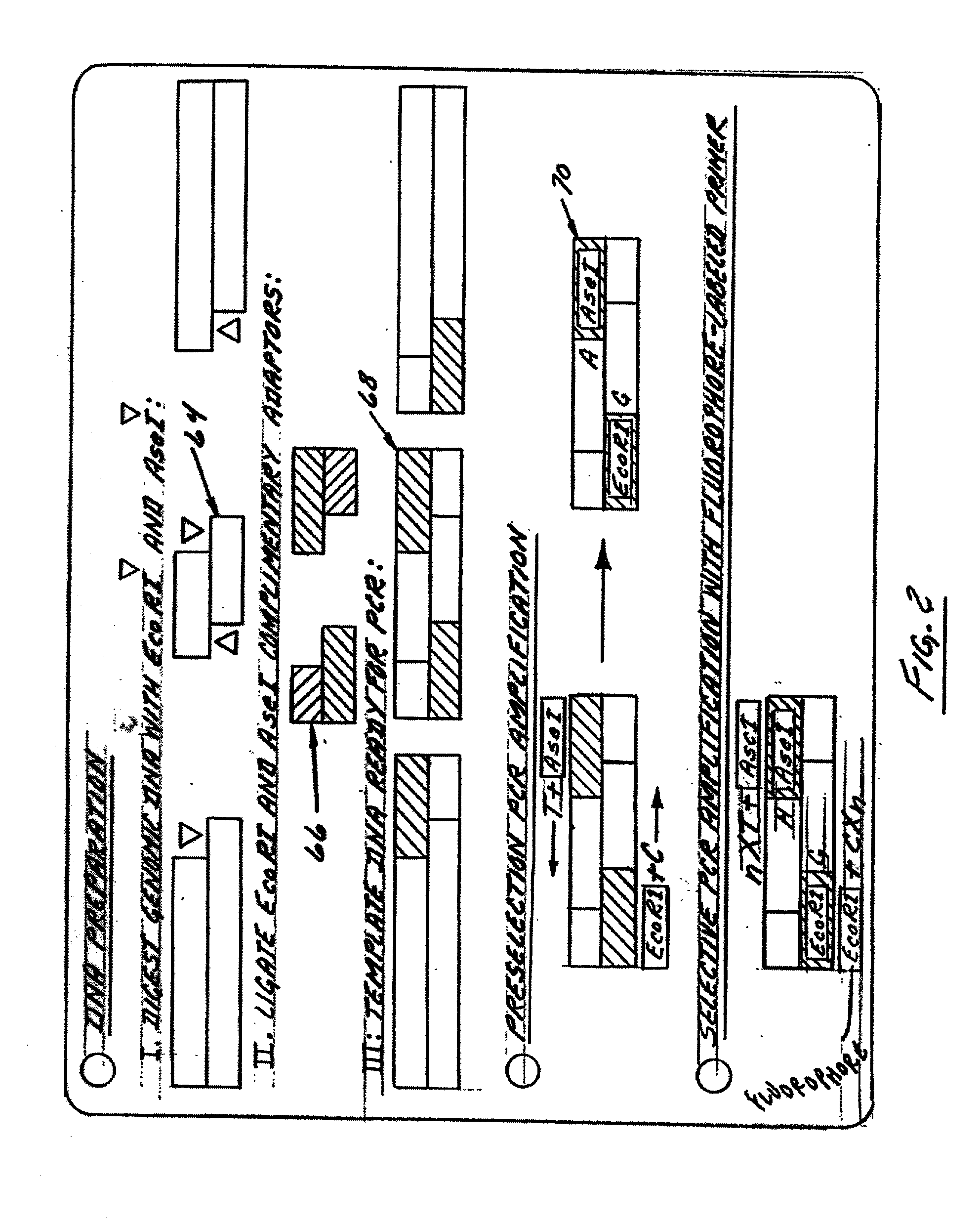
The present invention relates to novel methods for sequencing and mapping genetic markers in polynucleotide sequences using Type-IIs restriction endonucleases. The methods herein described result in the “capturing” and determination of specific oligonucleotide sequences located adjacent to Type-IIs restriction sites. The resulting sequences are useful as effective markers for use in genetic napping, screening and manipulation.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Genetic markers for predicting disease and treatment outcome
InactiveUS20060115827A1Reduce and delay recurrenceProlong survival timeBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesIncreased risk
The invention provides compositions and methods for determining the increased risk for recurrence of certain cancers and the likelihood of successful treatment with one or both of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. The methods comprise determining the type of genomic polymorphism present in a predetermined region of the gene of interest isolated from the subject or patient. Also provided are nucleic acid probes and kits for determining a patient's cancer risk and treatment response.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Risk assessment for adverse drug reactions
The present invention provides a method of predicting the risk of a patient for developing adverse drug reactions, particularly SJS or TEN. It was discovered that an HLA-B allele, HLA-B* 1502, is associated with SJS / TEN that is induced by a variety of drugs. The correlation with HLA-B* 1502 is most significant for carbamazepine-induced SJS / TEN, wherein all the patients tested have the HLA-B* 1502 allele. In addition, another HLA-B allele, HLA-B*5801, is particularly associated with SJS / TEN induced by allopurinol. Milder cutaneous reactions, such as maculopapular rash, erythema multiforme (EM), urticaria, and fixed drug eruption, are particularly associated with a third allele, HLA-B *4601. For any of the alleles, genetic markers (e.g., HLA markers, microsatellite, or single nucleotide polymorphism markers) located between DRB1 and HLA-A region of the specific HLA-B haplotype can also be used for the test.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
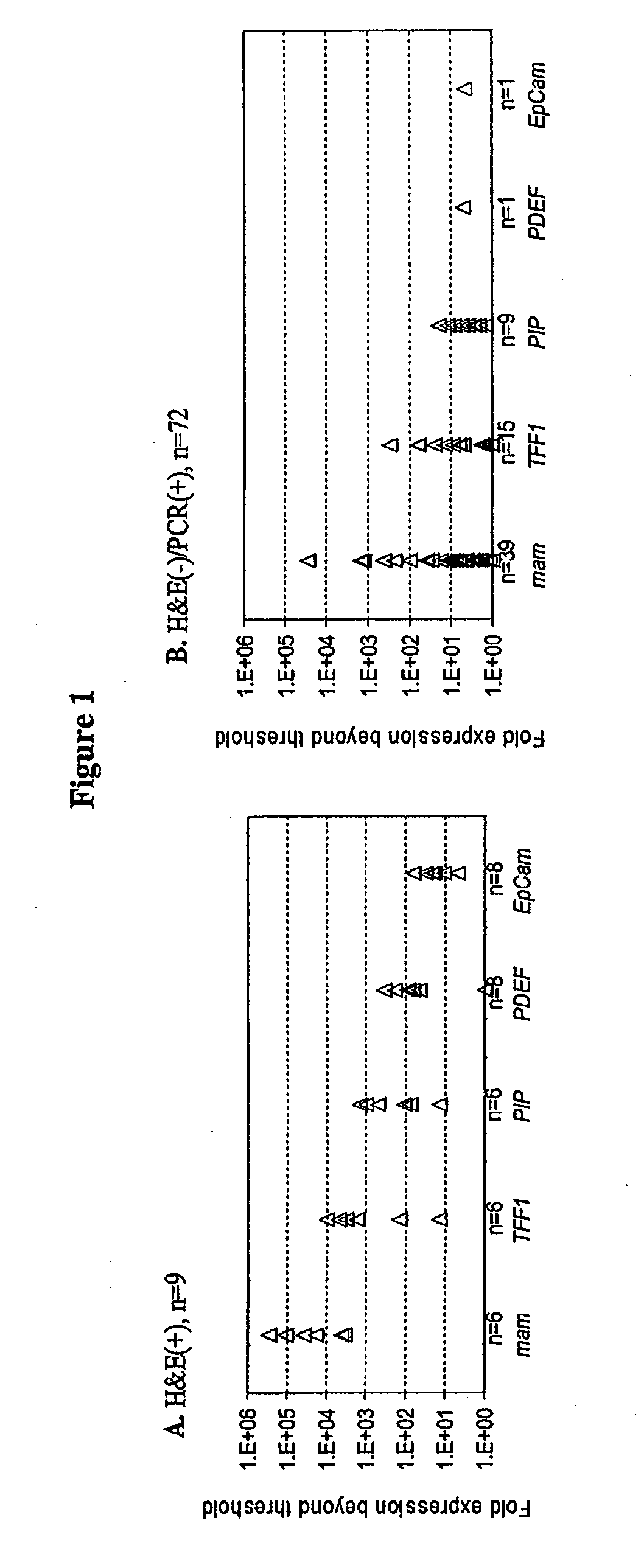
Methods for the detection and treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20070231822A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseLymphatic Spread
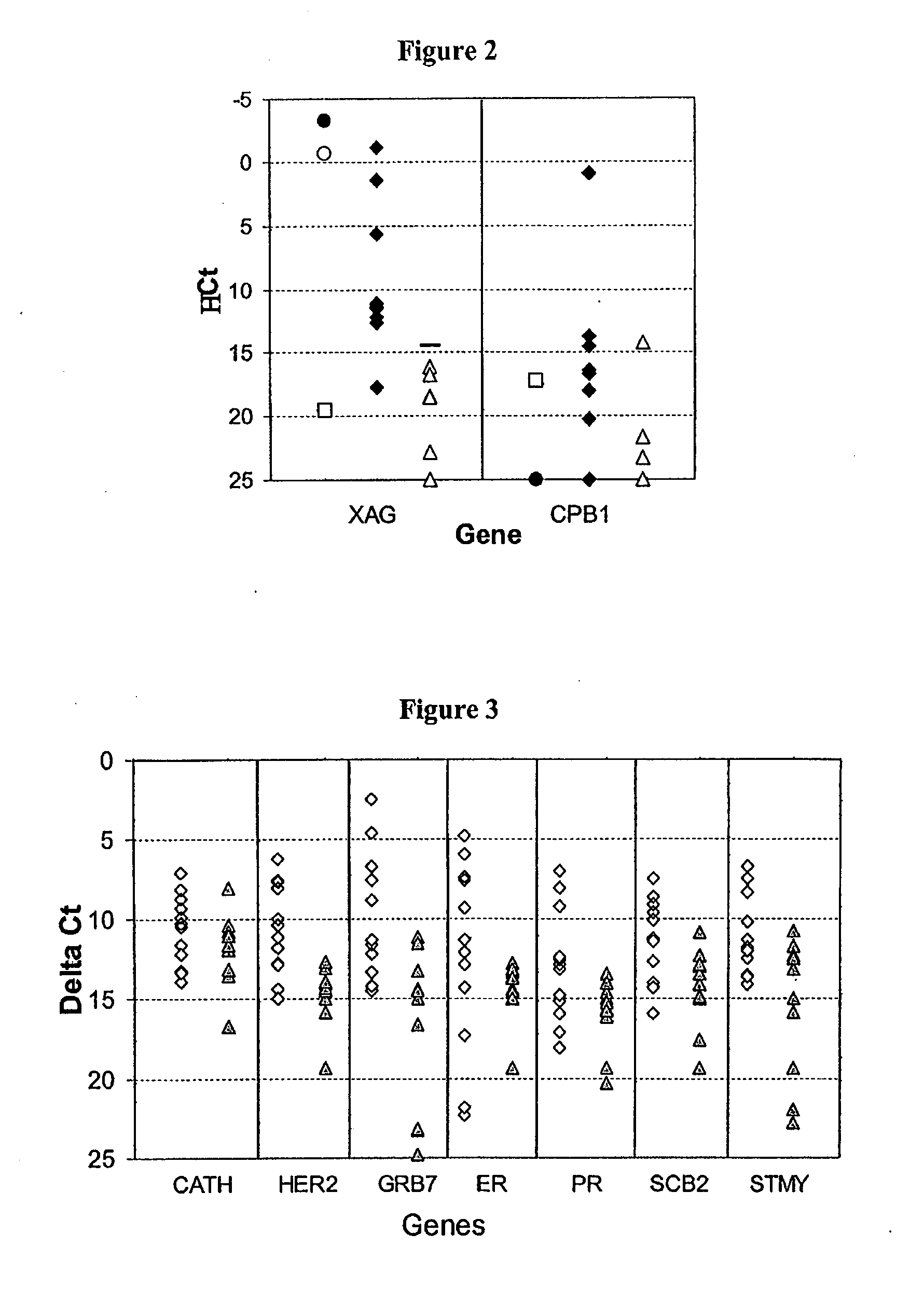
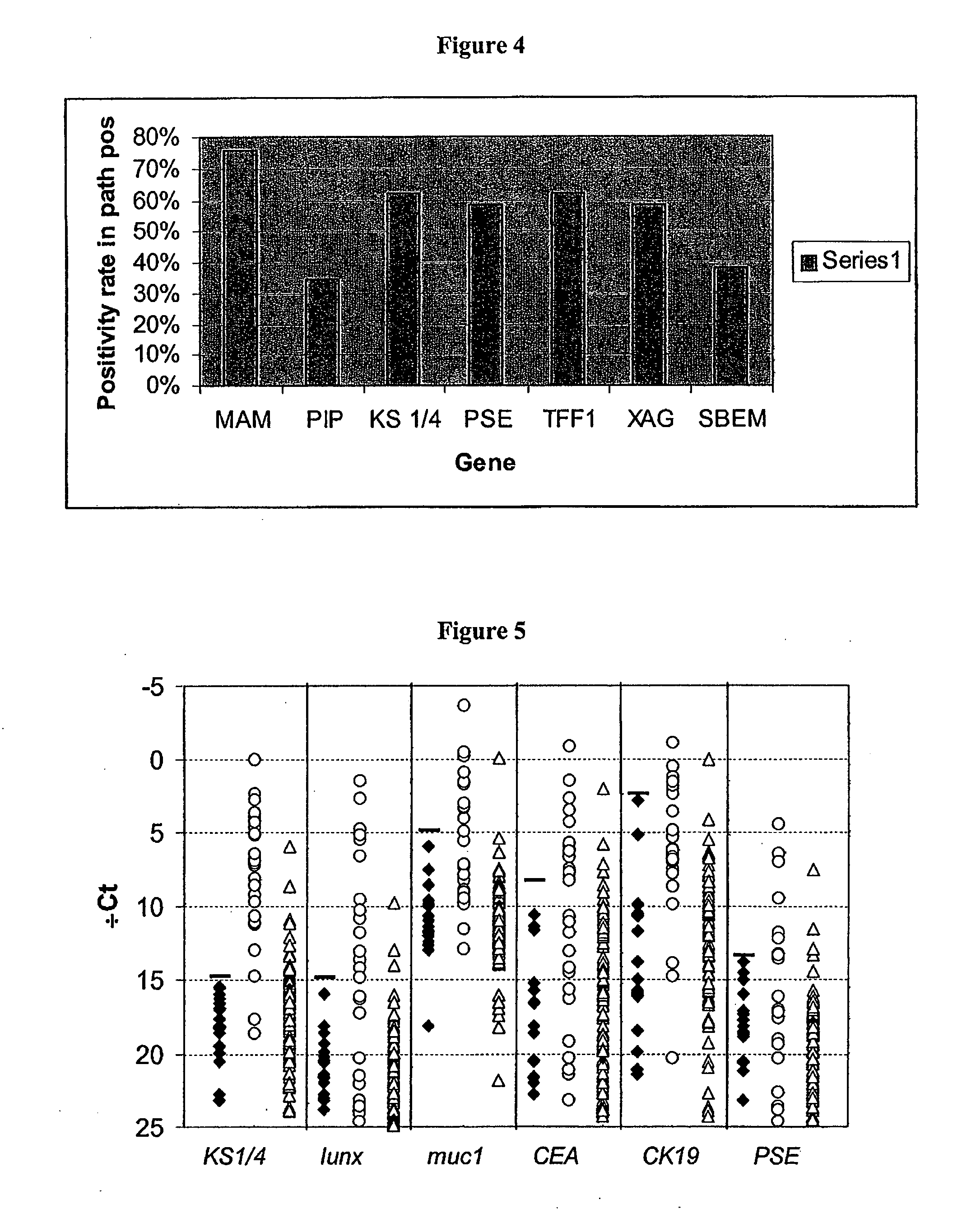
Methods are provided for the detection of and determining prognosis of metastatic breast, lung, prostate, and / or pancreatic cancer using various genetic markers, including markers for gene clusters linked by Esx. In one method, breast cancer micrometastases and non-small cell lung cancer metastases or micrometastases are detected in a patient by determining whether the AGR2 or TFF1 genes are overexpressed in a cell sample compared to control lymph node tissue cells. In a further method, the likelihood that a patient diagnosed with breast cancer will respond to hormonal therapy is predicted by determining a higher expression level of the AGR2 gene compared to a control gene. In a further method, a decreased probability of survival for a patient diagnosed with early stage non-small cell lung cancer is predicted by determining a higher expression level of the AGR2 gene compared to a control gene. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided. Methods are also provided for the identification of markers for which overexpression is indicative of the presence of micrometastatic disease.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
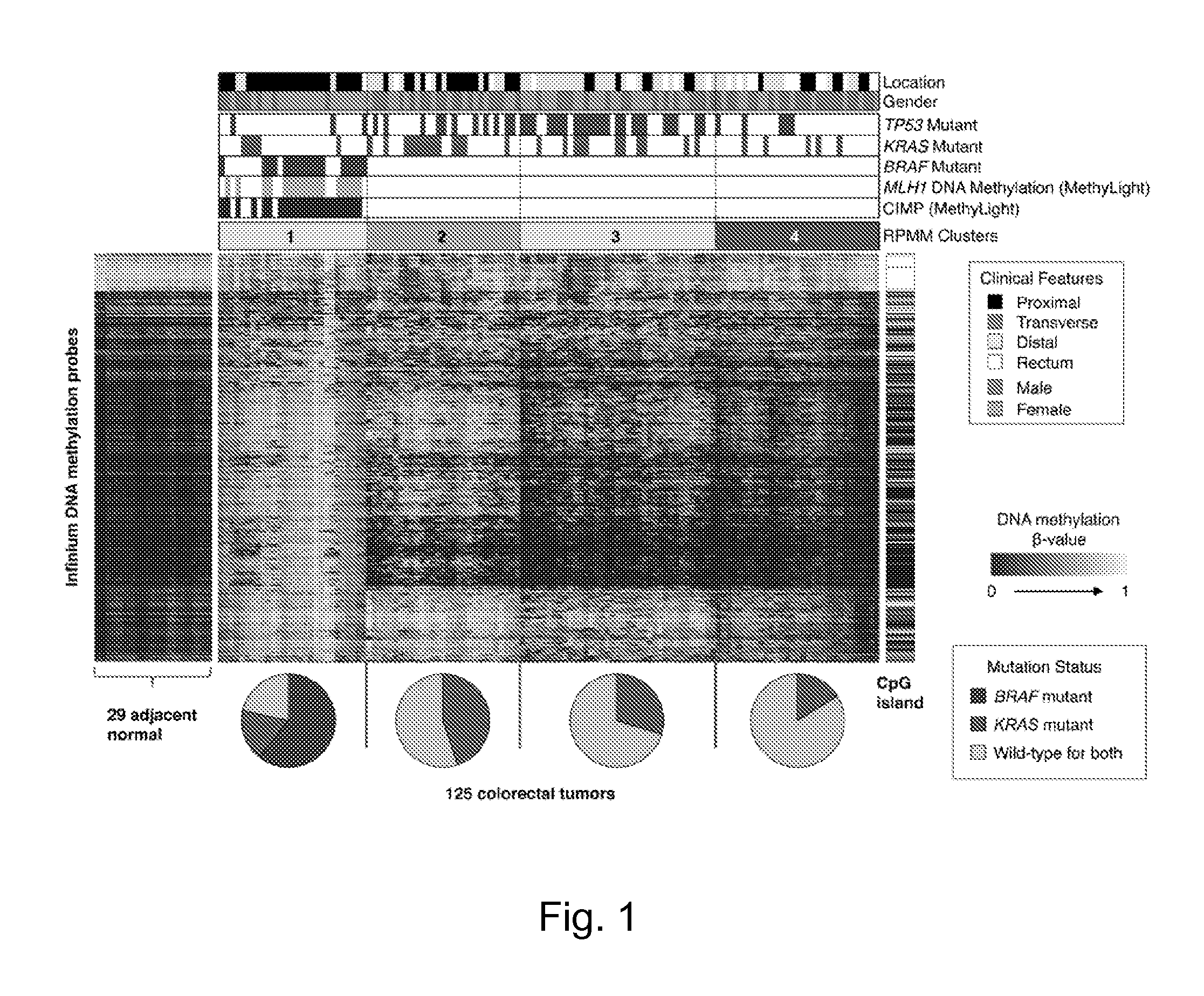
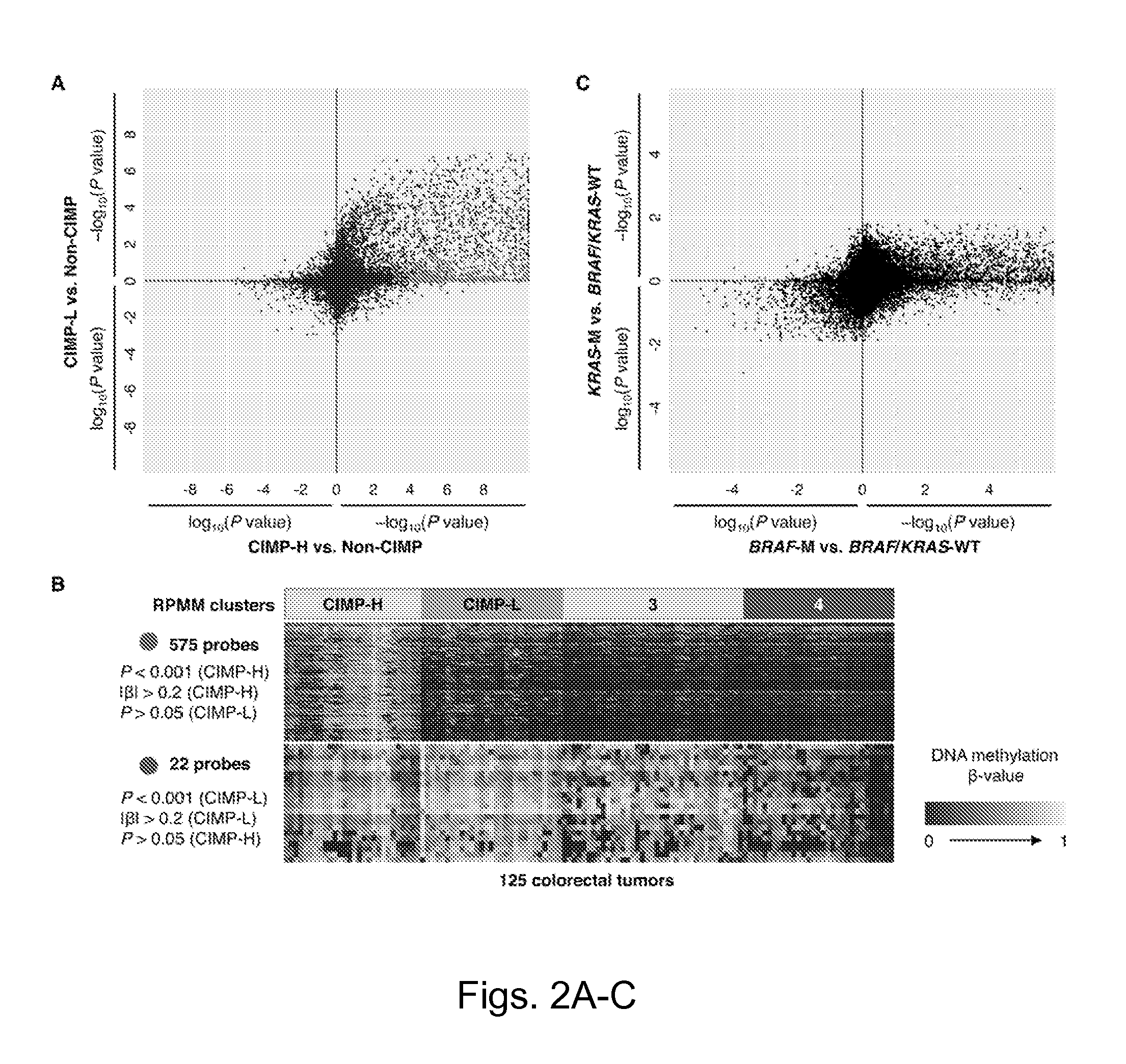
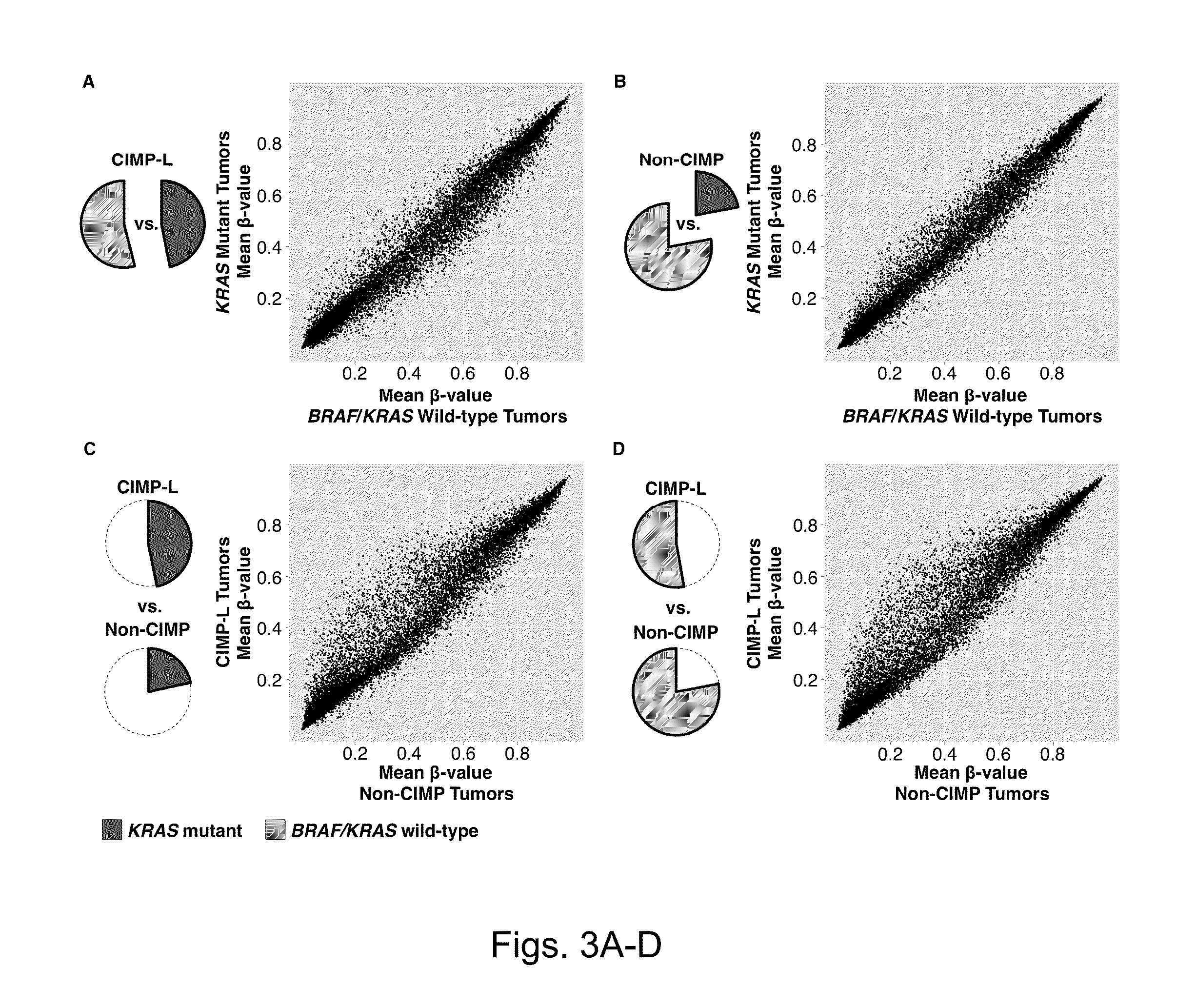
Genome-scale analysis of aberrant DNA methylation in colorectal cancer
Particular aspects provide methods and compositions (e.g., gene marker panels) having substantial utility for at least one of diagnosis, identification and classification of colorectal cancer (CRC) (e.g., tumors) relating to distinctive DNA methylation-based subgroups of CRC including CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) groups (e.g., CIMP-H and CIMP-L) and non-CIMP groups. Exemplary marker panels include: B3GAT2, FOXL2, KCNK13, RAB31 and SLIT1 (CIMP marker panel); and FAM78A, FSTL1, KCNC1, MYOCD, and SLC6A4 (CIMP-H marker panel). Further aspects relate to genetic mutations, and other epigenetic markers relating to said CRC subgroups that can be used in combination with the gene marker panels for at least one of diagnosis, identification and classification of colorectal cancer (CRC) (e.g., tumors) relating to distinctive CIMP and non-CIMP groups.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
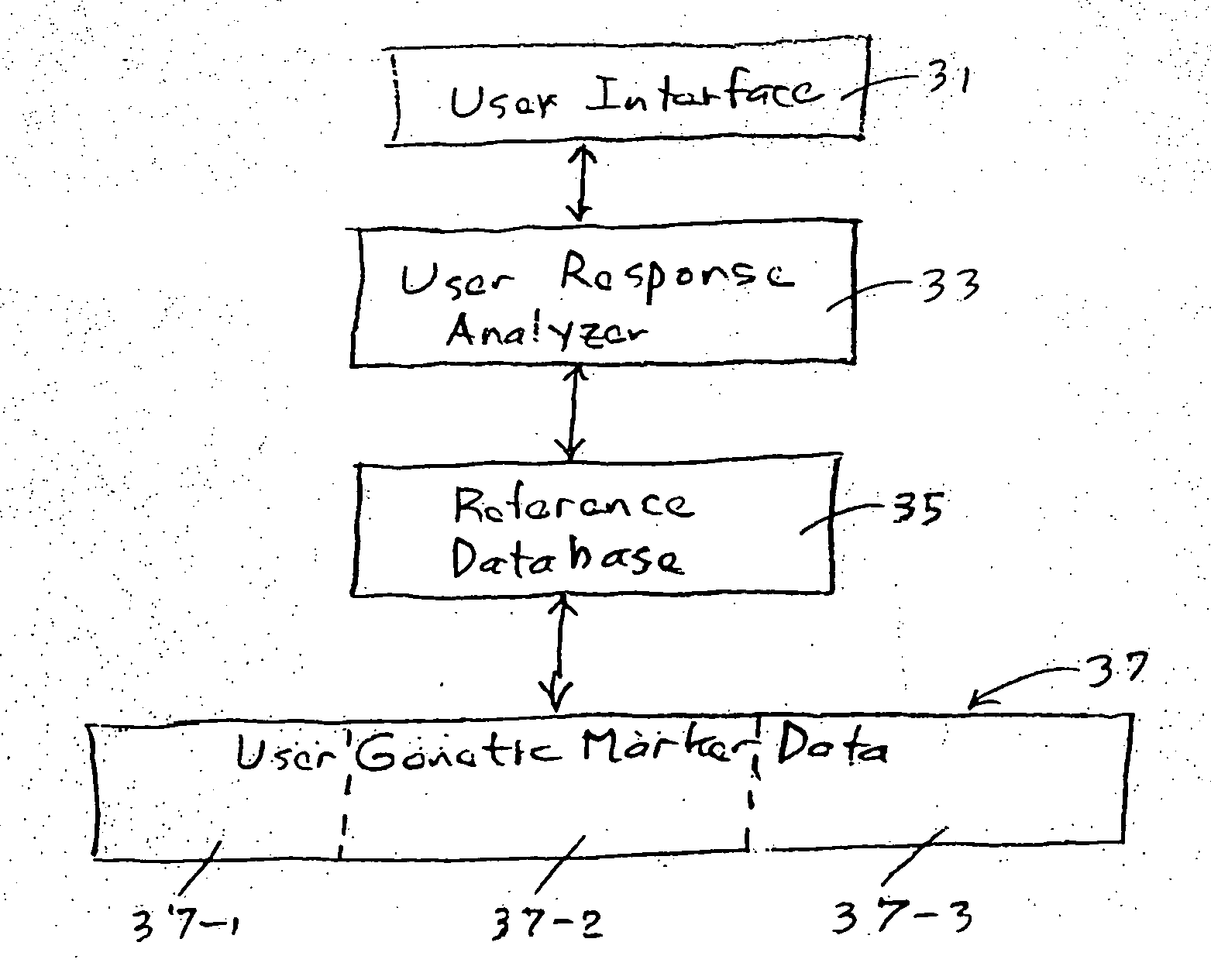
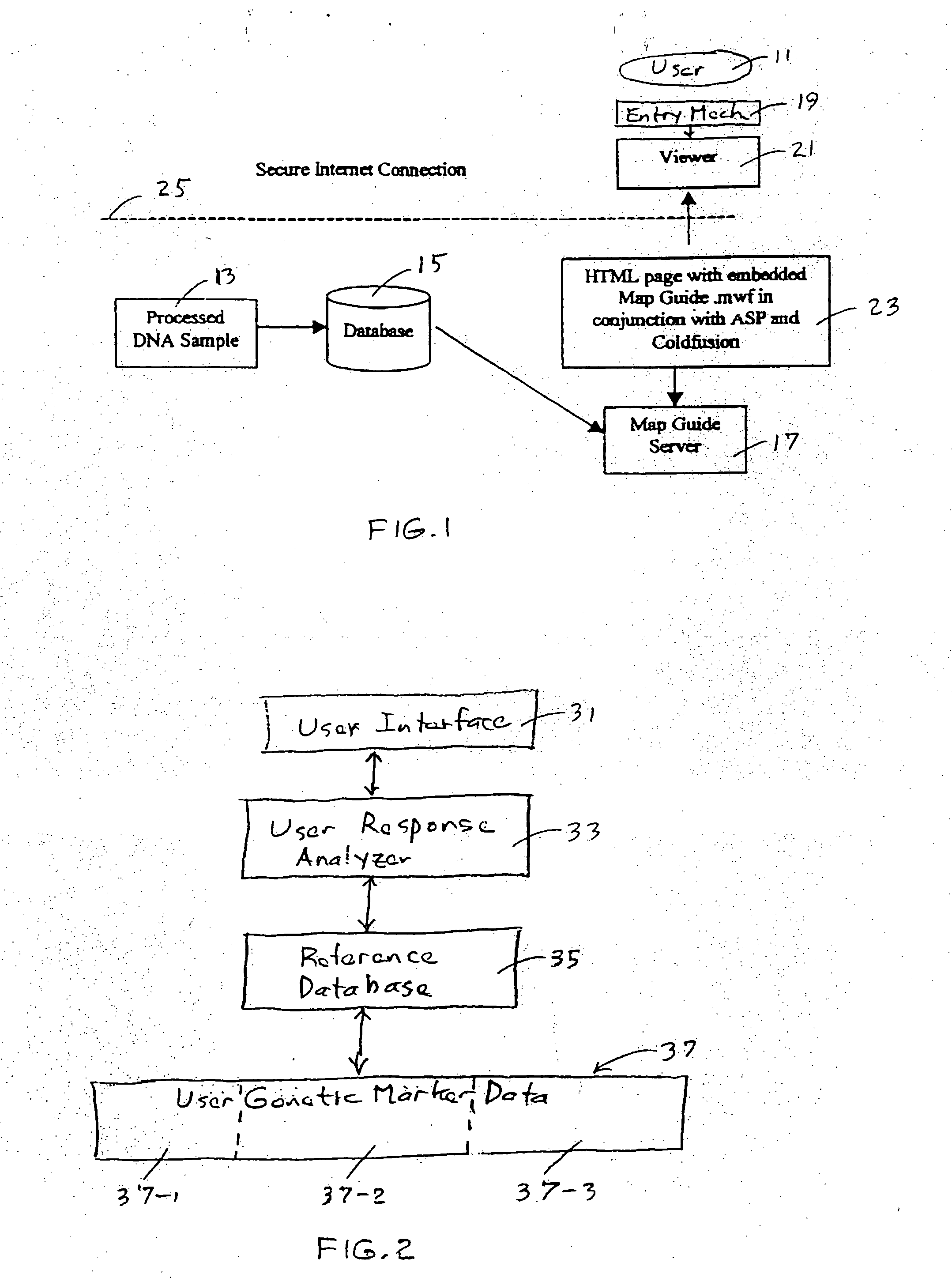
Method for preparing and using personal and genetic profiles
Method and system for preparing a personal genetic profile includes collecting genetic data from an individual, assigning the data to a coordinate system, storing the data, and providing access for retrieval by the individual from whom the genetic data were collected, after receipt of an Identifier that adequately authenticates the identity of the data requestor. Locations of genetic markers are provided as three-dimensional coordinates, described with matrix relationships that are consistent with the primary and secondary chemical structure of molecular constituents of a DNA chain for the individual.
Owner:RATHJEN ALICEMARIE G +9
Reducing error in predicted genetic relationships
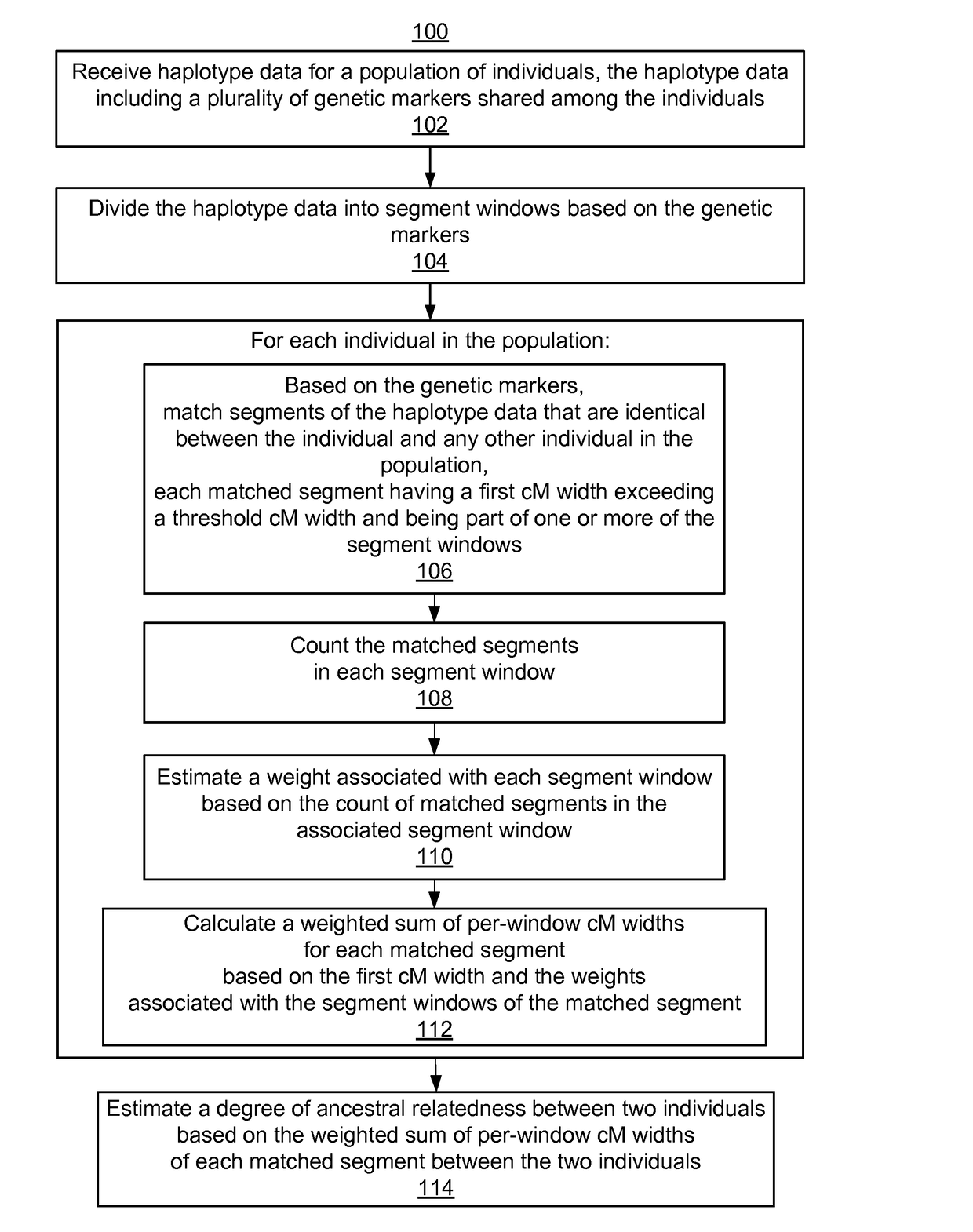
ActiveUS20170220738A1Computationally efficientComputationally scalableMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic markerPopulation
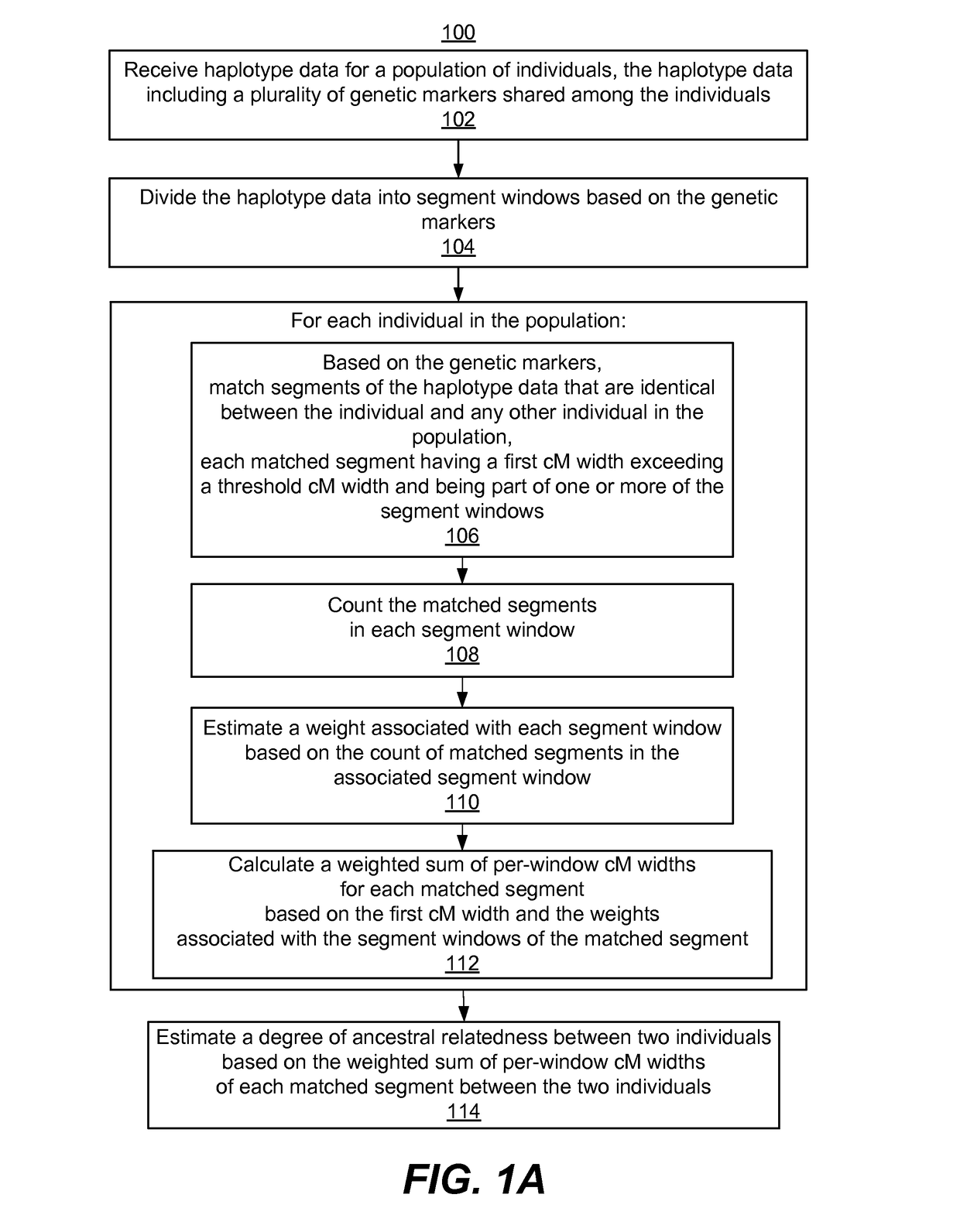
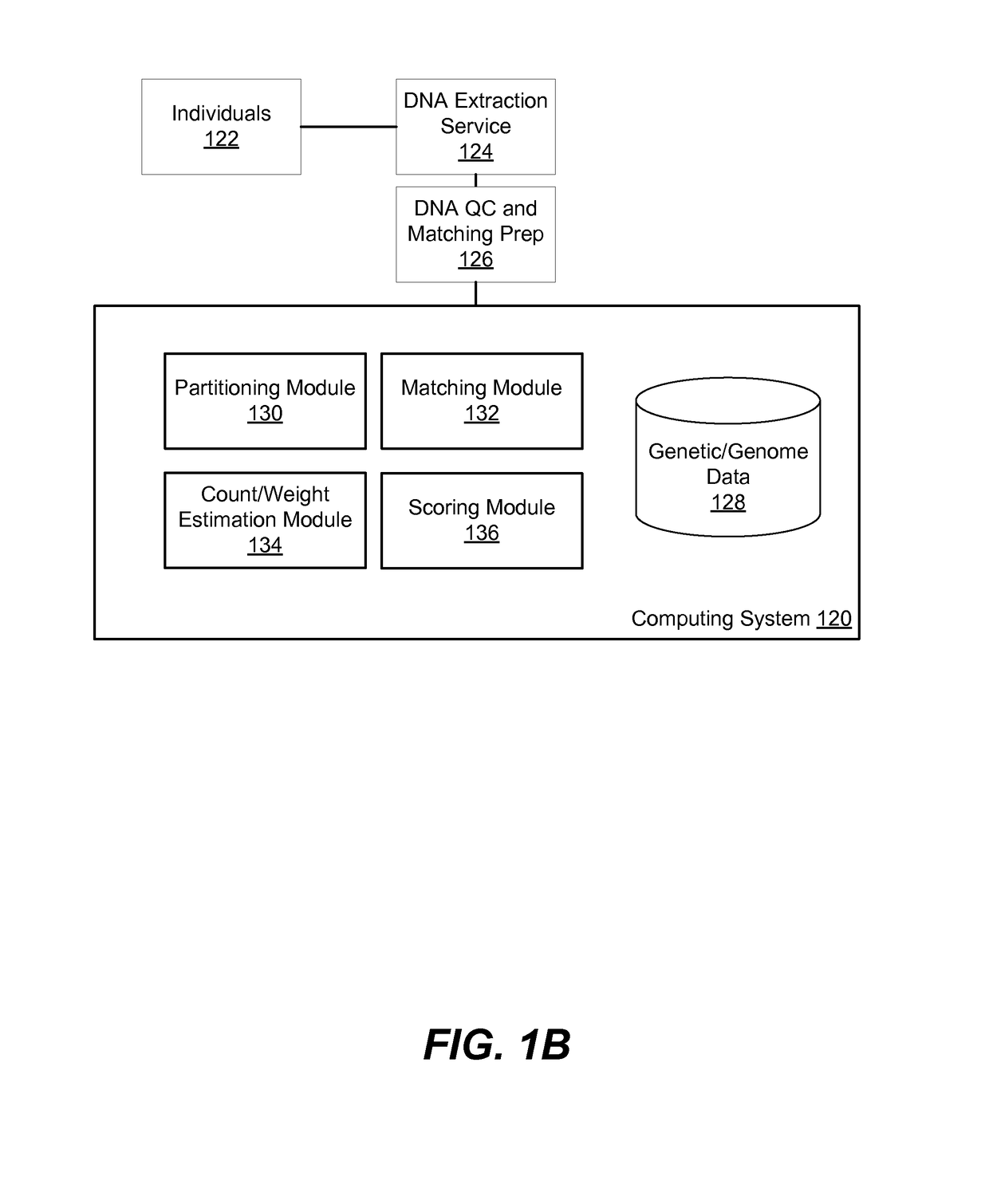
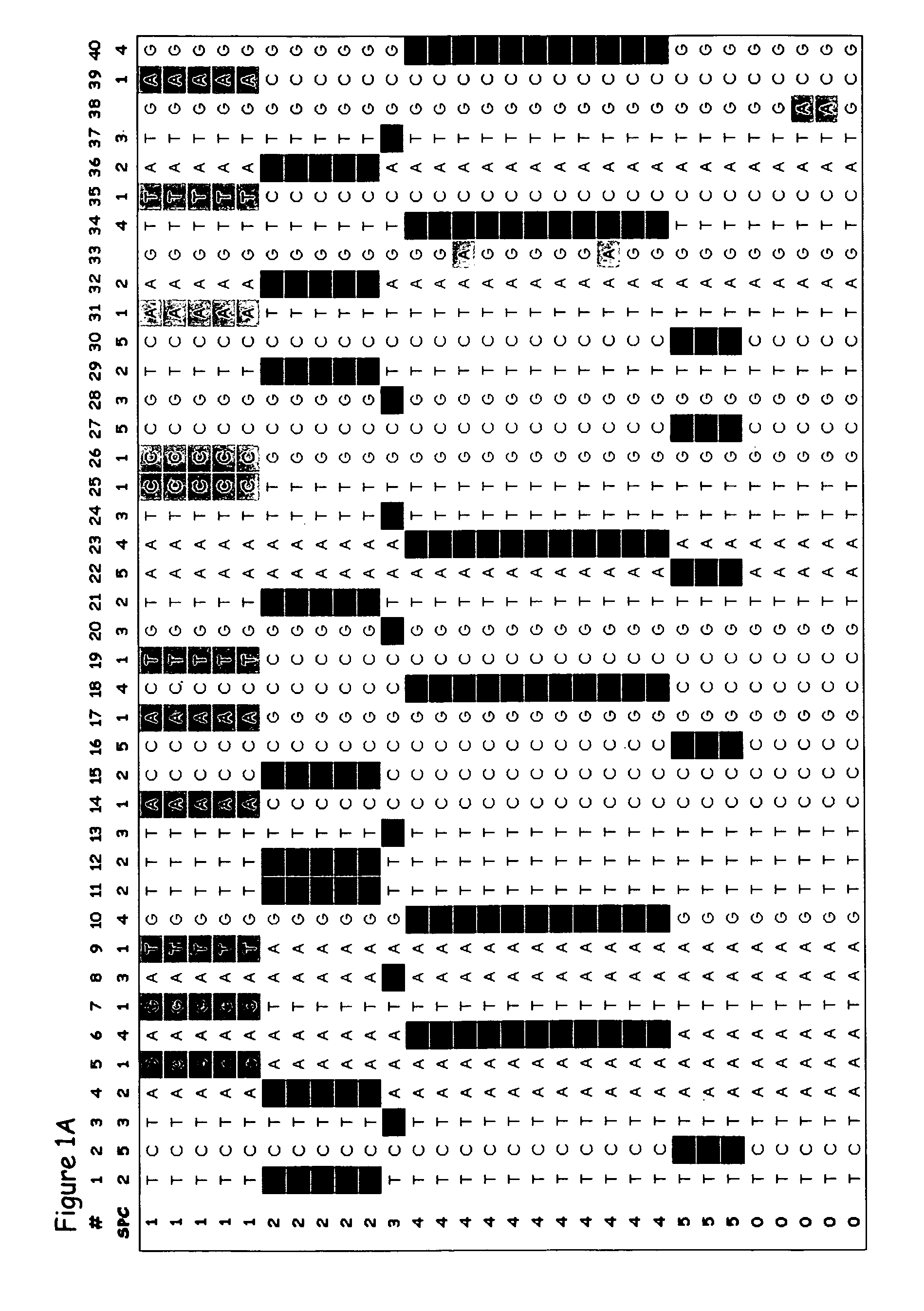
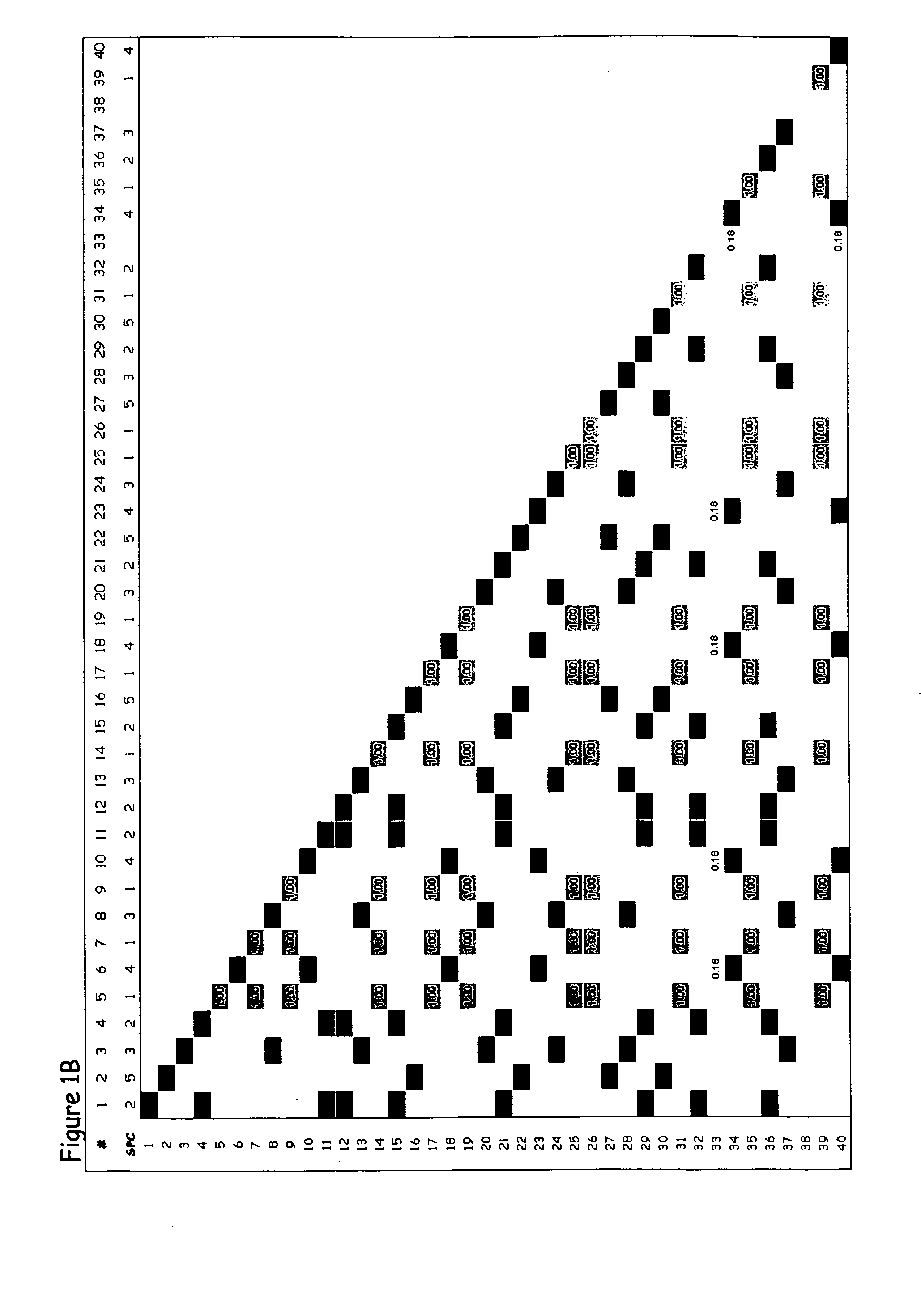
System, computer program products, and methods are disclosed for estimating a degree of ancestral relatedness between two individuals. The haplotype data for a population of individuals is divided into segment windows based on genetic markers, and matched segments for the haplotype data are generated. Each matched segment having a first cM width that exceeds a threshold cM width is included in counting the matched segments in each segment window. A weight associated with each segment window is estimated based on the count of matched segments in the associated segment window. A weighted sum of per-window cM widths for each matched segment is calculated based on the first cM width and the weights associated with the segment windows of the matched segment. The weighted sum of per-window cM widths are used to estimate a degree of ancestral relatedness between two individuals.
Owner:ANCESTRY COM DNA
Genetic diagnosis using multiple sequence variant analysis
The present invention is in the field of nucleic acid-based genetic analysis. More particularly, it discloses novel insights into the overall structure of genetic variation in all living species. The structure can be revealed with the use of any data set of genetic variants from a particular locus. The invention is useful to define the subset of variations that are most suited as genetic markers to search for correlations with certain phenotypic traits. Additionally, the insights are useful for the development of algorithms and computer programs that convert genotype data into the constituent haplotypes that are laborious and costly to derive in an experimental way. The invention is useful in areas such as (i) genome-wide association studies, (ii) clinical in vitro diagnosis, (iii) plant and animal breeding, (iv) the identification of micro-organisms.
Owner:METHEXIS GENOMICS
Temperature sensing male fertile gene and use thereof
ActiveCN101333533AImprove selection efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
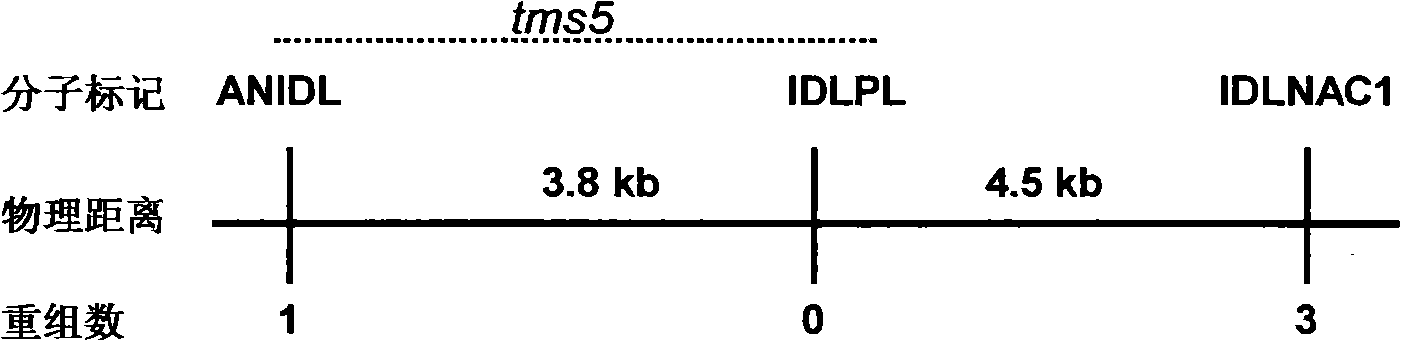
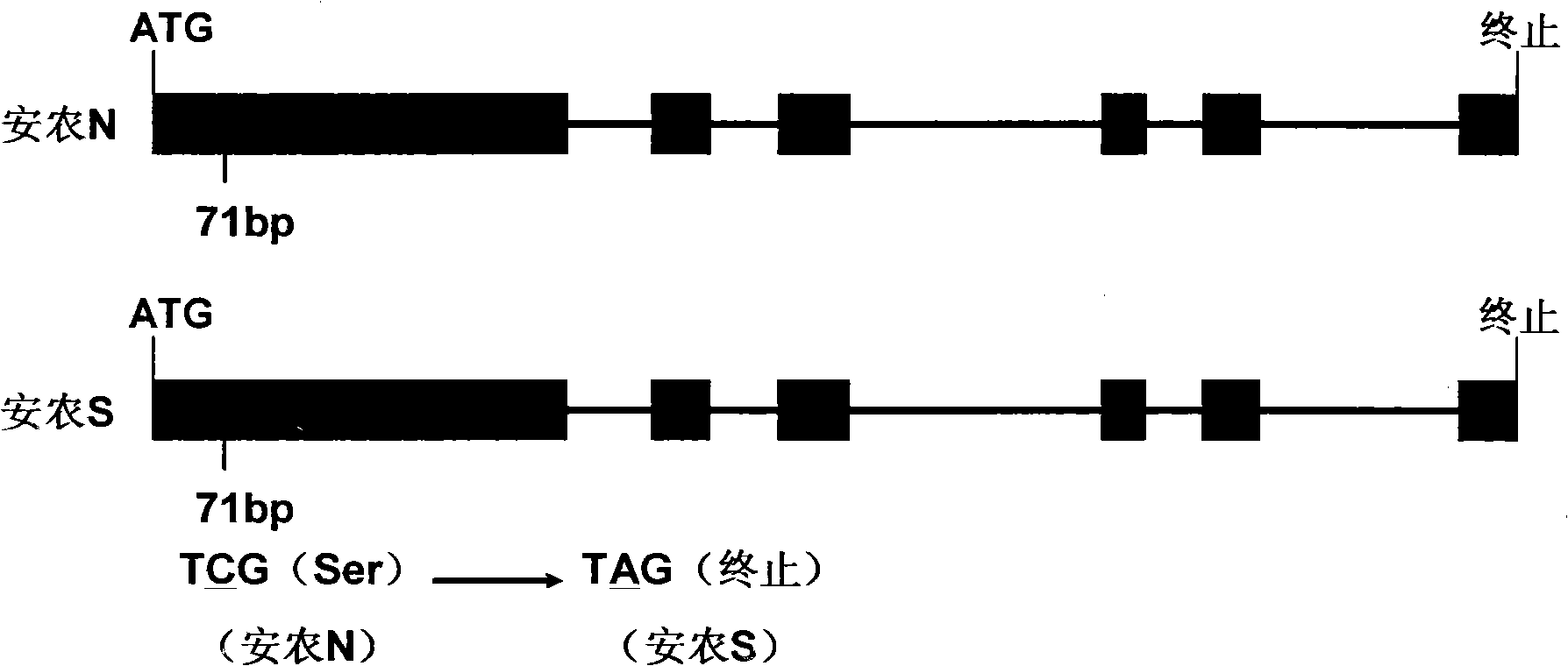
The invention discloses a thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and an application thereof and also discloses a genetic marker of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene, and provides a protein coded by the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a carrier containing the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a recombinant microorganism. The invention also discloses the application of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene in cultivating a thermo-sensitive male sterile line and an application of the genetic marker in rice breeding. The thermo-sensitive fertility gene TSSNR is acquired through the map-based cloning technique of Annong S-1 thermo-sensitive sterility gene locus tms5, functions of the gene are validated through transgene experiments, and the transgene technique of RNAi or antisense RNA or the over-expression dominant negative principle is provided, functions of the TSSRZ gene in normal rice varieties are incapable, so as to cultivate the thermo-sensitive male sterile line, and the application value is significant.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Forensic medicine compound detection kit based on Y chromosome SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genetic marker
ActiveCN103131787AFast personal identificationGood polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementAlleleForensic science
The invention belongs to the field of forensic medicine genetics and in particular relates to a forensic medicine compound detection kit based on a Y chromosome SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genetic marker for individual recognition and genetic relationship identification by a legal medical expert. The forensic medicine compound detection kit provided by the invention is used for carrying out forensic medicine genetic relationship identification and individual recognition on human biology detection materials by utilizing a Y chromosome SNP genetic marker. According to the technical scheme for solving the technical problem, the forensic medicine compound detection kit based on the Y chromosome SNP genetic marker comprises a separated and packaged compound amplification primer mixture, a multiple single-basic-group extension reaction primer mixture, an allele typing standard mixture, a compound amplification reaction mixture and a single-basic-group extension reaction mixture. The kit provided by the invention can be applied to detection of common degradable materials in forensic medicine.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
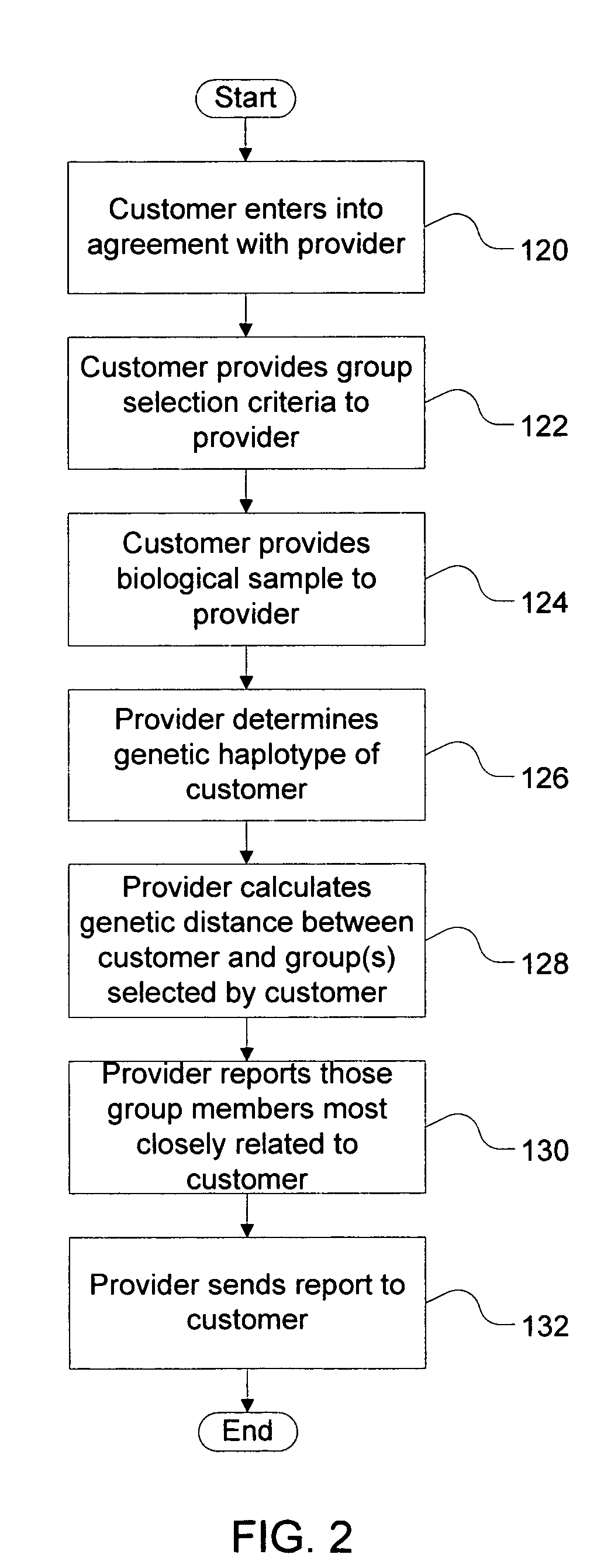
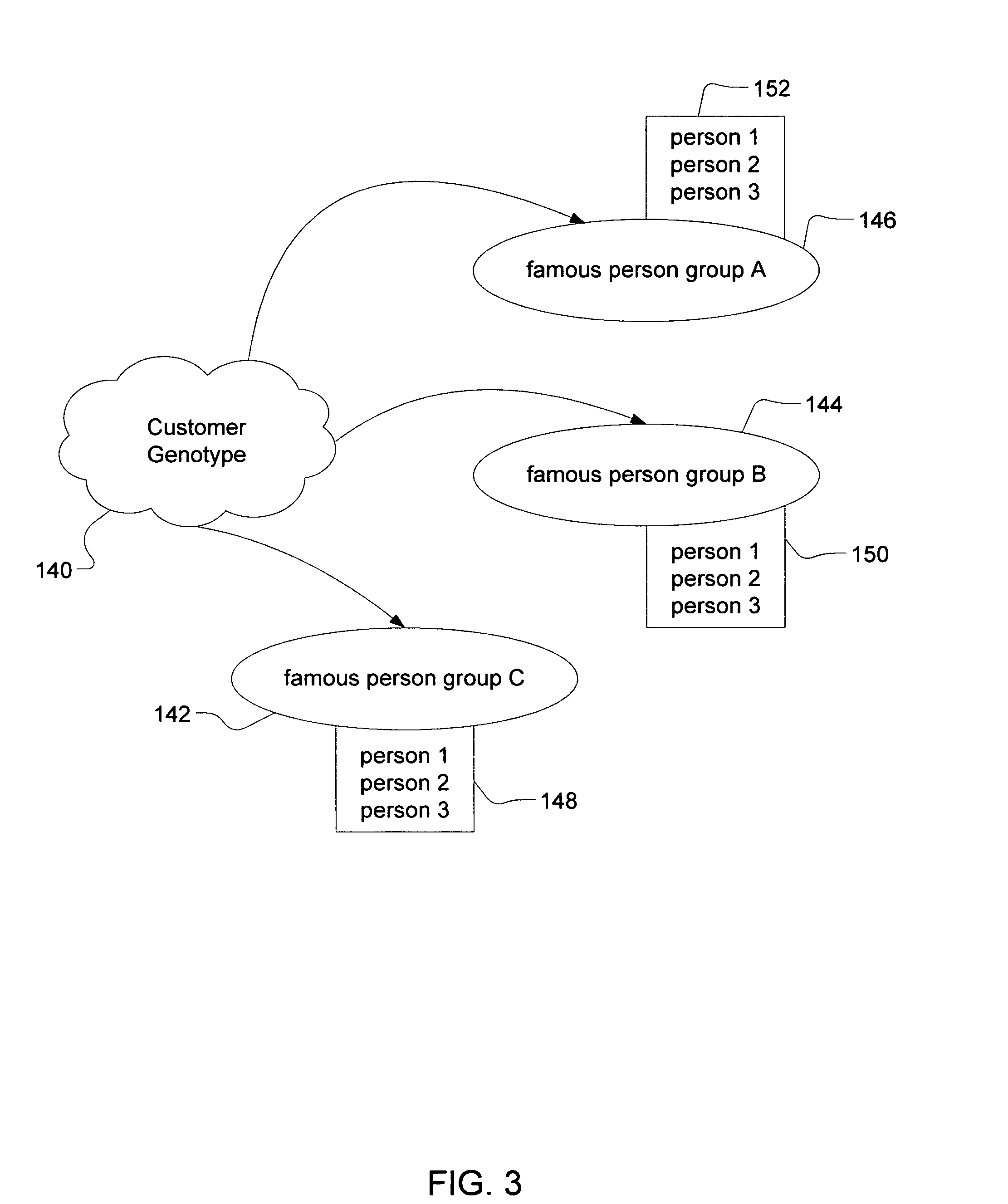
Method of determining a genetic relationship to at least one individual in a group of famous individuals using a combination of genetic markers
A method for quantifying the genetic relationship of a customer to at least one individual of at least one group of famous individuals, the method includes the following steps. First, receiving genetic information and famous individual group selection criteria from a customer, next, calculating the genetic distance of the customer to at least one individual within the group and finally, reporting the results to the customer.
Owner:EGLINGTON CHRIS
Data Structures and Methods for Genealogical Research
InactiveUS20070168368A1Improve abilitiesData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsImproved methodStudy methods
Improved methods of genealogical research utilize databases with fields that more uniquely identify individuals and relationships for the purpose of tracing and identifying ancestors or living relations. In selected embodiments, the fields represent genetic markers on the mitochondrial DNA and biographic or historical data useful in tracing matriarchal heritage. In other embodiments, the fields represent ownership records or conveyances of property between related or unrelated individuals. In other aspects of the invention methods of searching account for the evolution of geographic and political divisions in searching genealogical database, as well as the alternative spelling of names and nickname.
Owner:STONE JOSEPH S
Specific molecular markers of related genes of brassica napus grain weight and application thereof
InactiveCN101962640ASpeed up the processOvercome the downside of choosingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceCandidate Gene Association Study
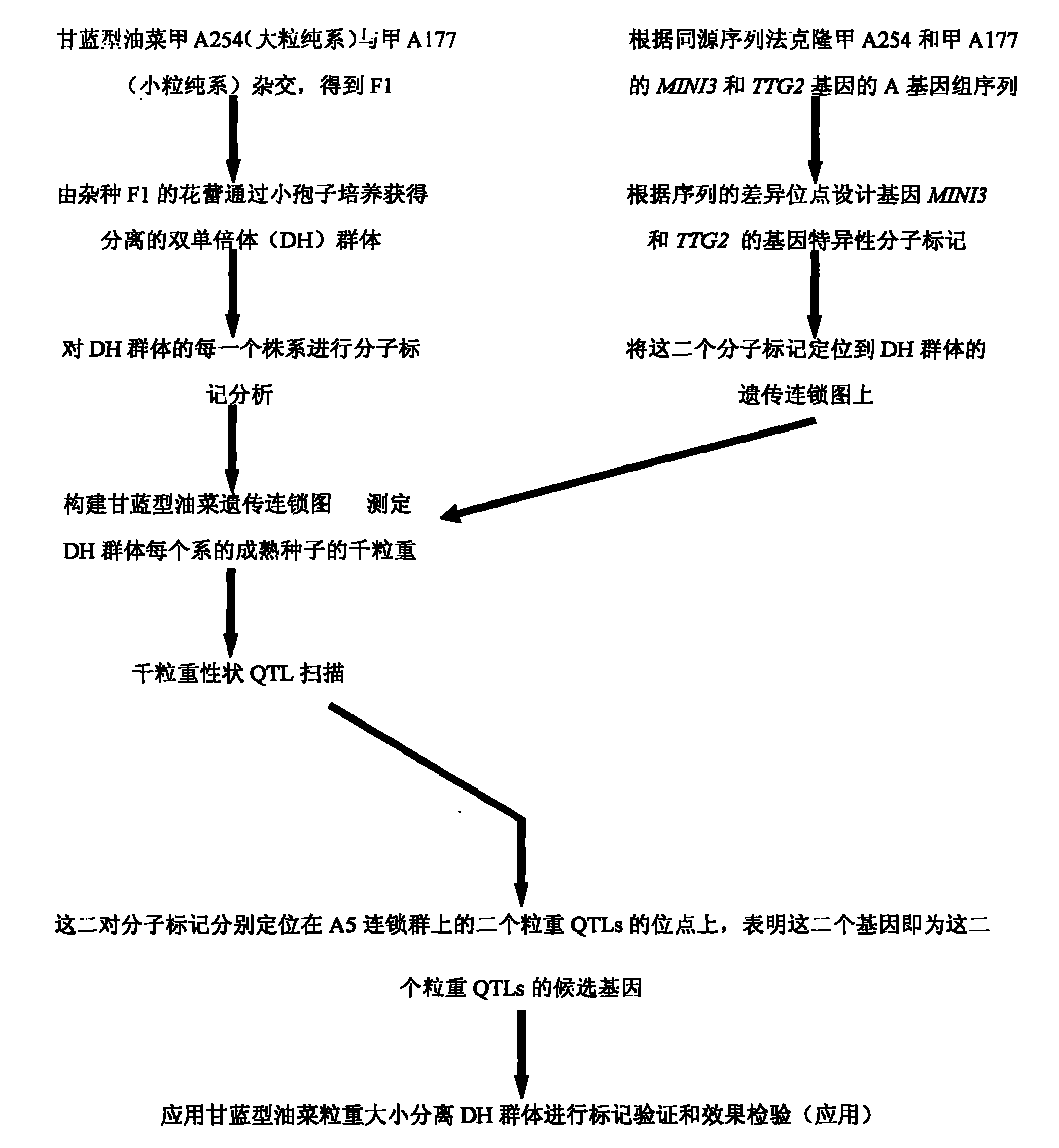
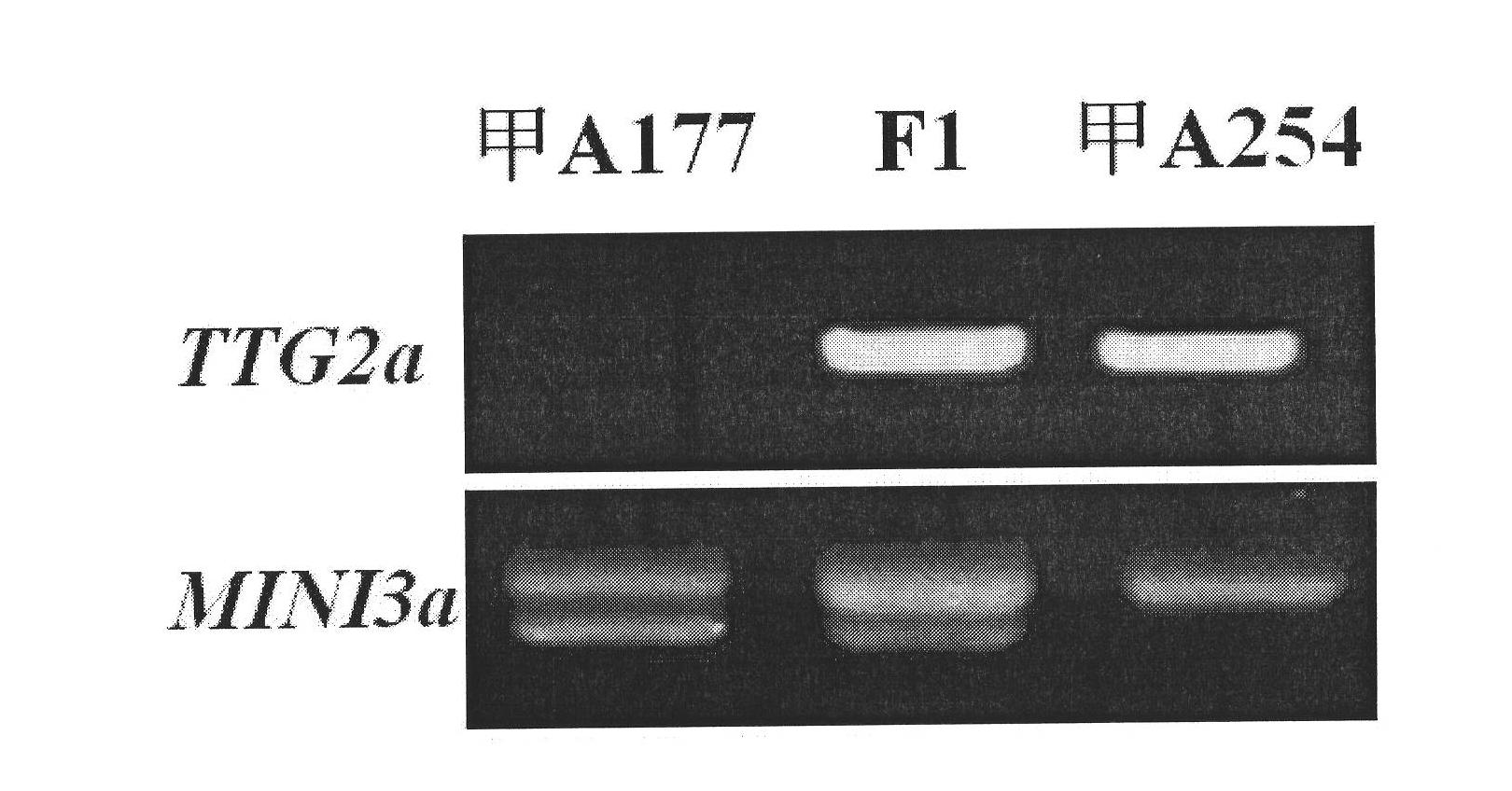
The invention belongs to the field of rape molecular breeding, and relates to preparation of specific molecular markers of related genes MINI3 and TTG2 of the brassica napus grain weight. Double haploid colony (DH) is constructed with brassica napus I A 254 as a female parent and a brassica napus I A 177 as a male parent through hybridization, and the DH colony genotype and the thousand seed weight data are analyzed to obtain a QTLs locus of grain weight character. The MINI3 and the TTG2 genes of the IA254 and the IA177 are cloned by using a homology based candidate gene method, specific molecular markers MINI3a and TTG2a of the MINI3 and the TTG2 genes are designed according to sequence different locuses, and the molecular markers MINI3a and TTG2a are located on two grain weight QTLs locus of an A5 linkage colony for related verification and application, which proves that the molecular marker prepared by the invention is a novel genetic marker. The gene sequence is obtained firstly. The invention provides a novel marker for the molecular breeding of the brassica napus grain weight, and also provides useful information for candidate gene clone and marker auxiliary selection of thethousand seed weight character locuses of the brassica napus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
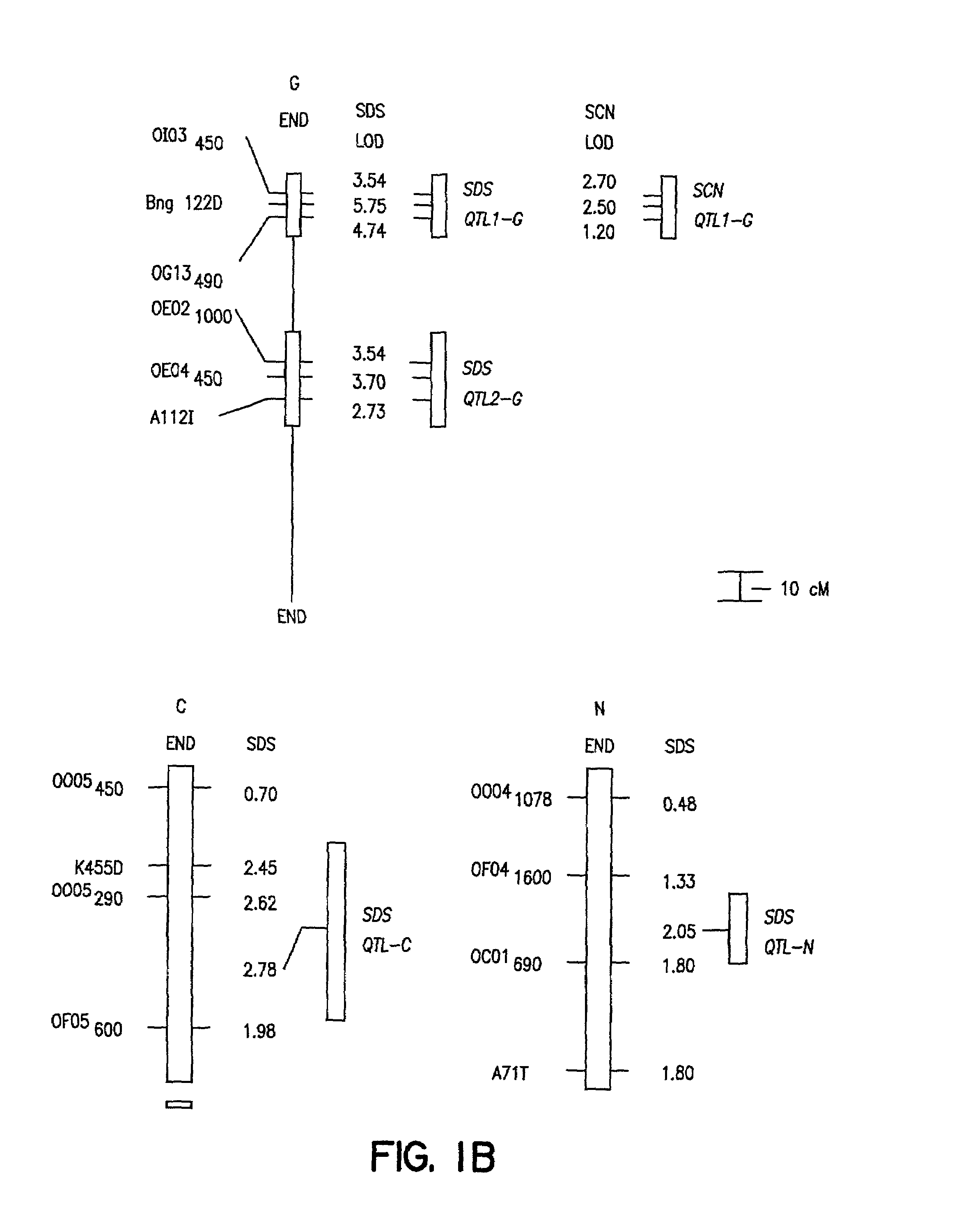
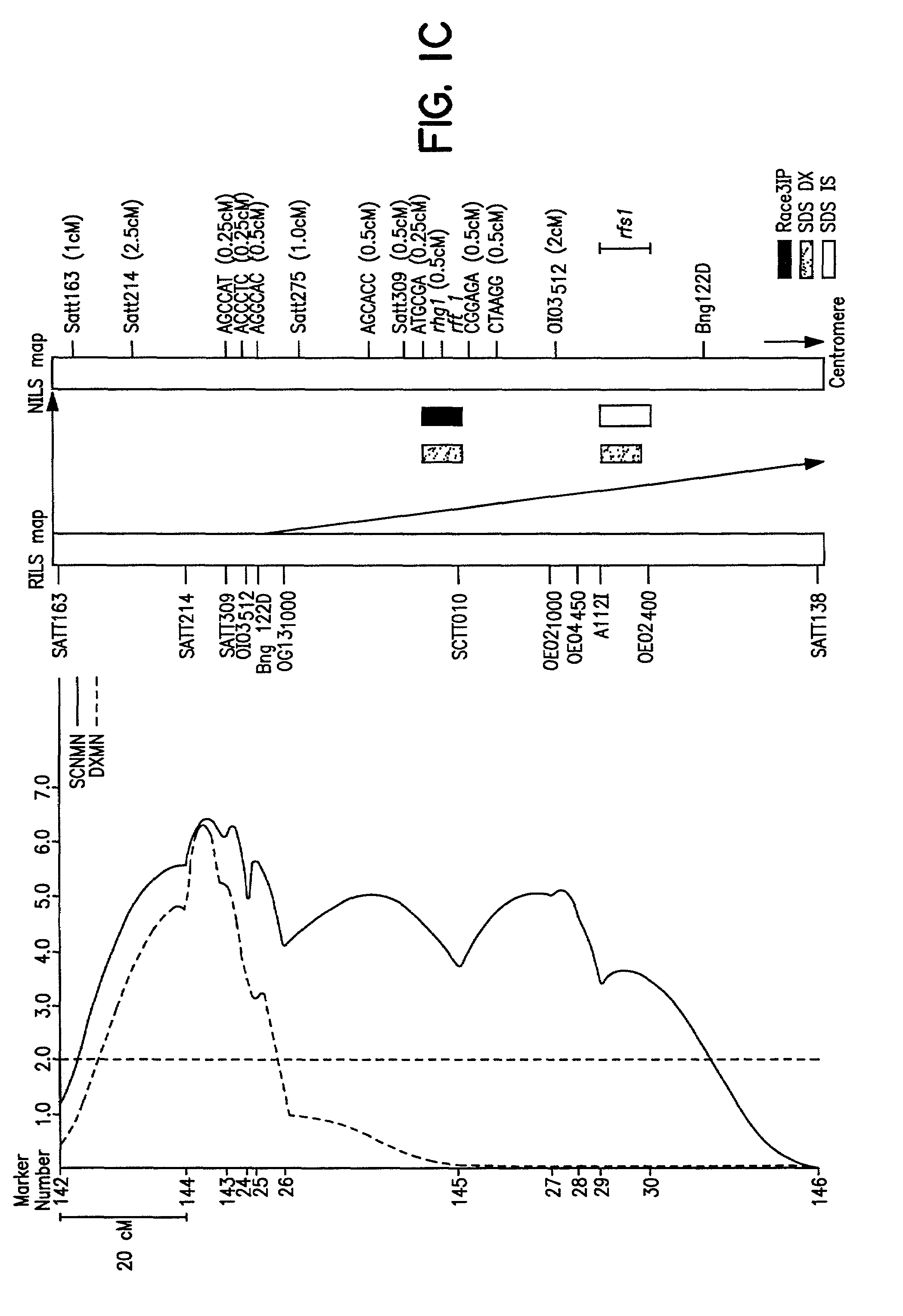
Method of determining soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in a soybean plant
InactiveUS7288386B2Solves the problem quickly and cheaply selecting resistant cultivarsImprove selection for SDS and SCN resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell culture mediaBacterial growth
A method of determining the presence of soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in the soybean plant in a greenhouse setting, the method comprising the steps of: (a) inoculating soil with a low density inoculum of Fusarium solani; (b) planting a soybean plant in said inoculated soil; (c) growing said plant in said soil in a greenhouse; (d) isolating Fusarium solani-infected tissue from said plant; (e) culturing said infected tissue for a period of time sufficient to allow for fungal colony forming unit growth; (f) scoring at least one of disease severity and infection severity in said plant using the number of said fungal colony forming units; and (g) correlating at least one of said disease severity and said infection severity to at least one of disease severity and infection severity data from genetic markers associated with soybean sudden death syndrome resistance to identify a correlation, wherein a statistically significant correlation indicates presence of soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in said soybean plant. Also provided is a method of characterizing resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in a soybean plant, the method comprising the steps of: (a) isolating roots from a soybean plant infected by Fusariurn solani; (b) culturing the root on a culture plate including a restrictive growth medium that provides for slow fungal growth and restricted bacterial growth; (c) determining root infection severity by statistically evaluating the number of Fusarium solani colony forming units on said culture plate; and (d) characterizing resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in said soybean plant based on said determined root infection severity.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
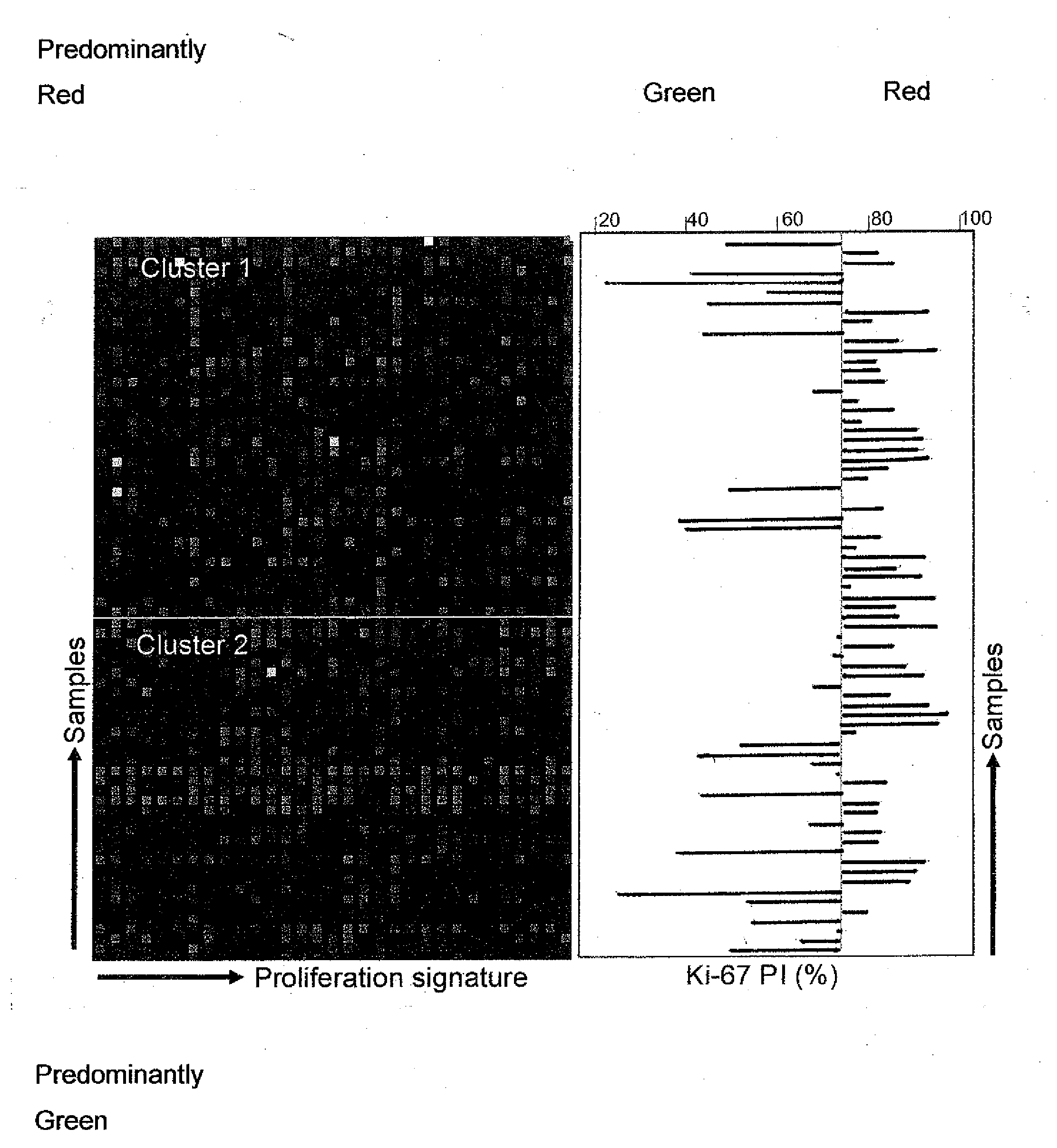
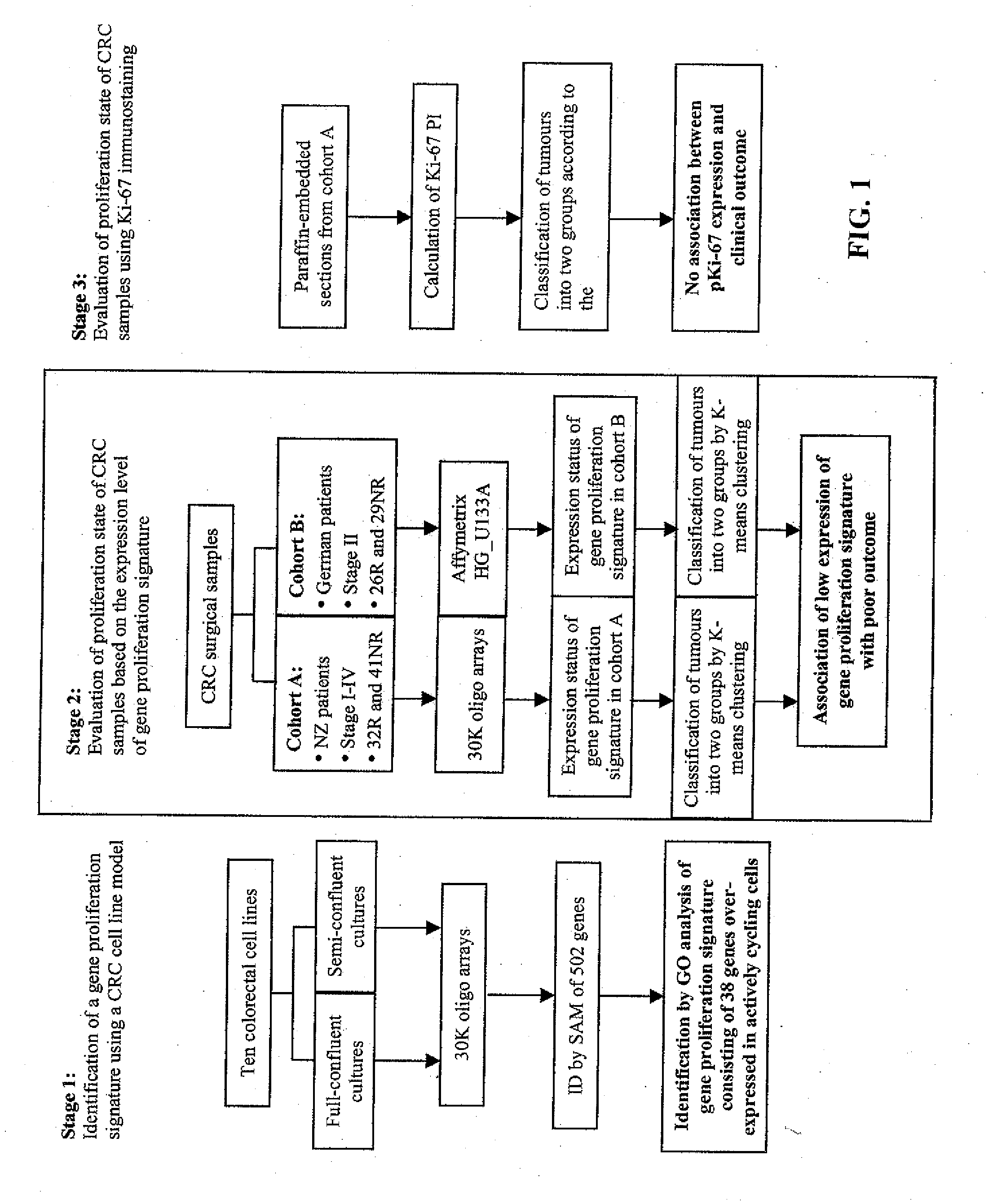
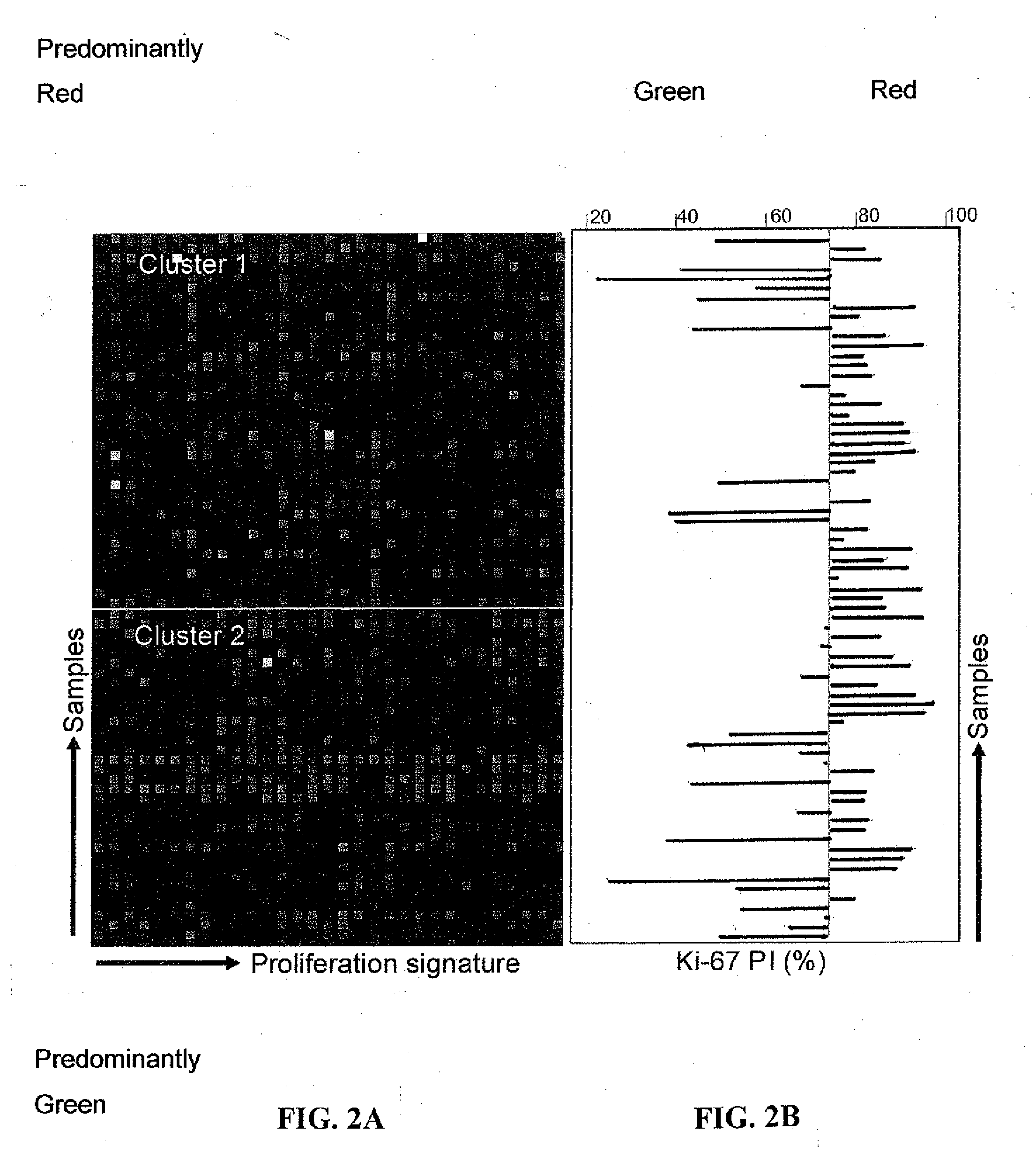
Proliferation Signatures and Prognosis for Gastrointestinal Cancer
This invention relates to methods and compositions for determining the prognosis of cancer in a patient, particularly for gastrointestinal cancer, such as gastric or colorectal cancer. Specifically, this invention relates to the use of genetic markers for the prediction of the prognosis of cancer, such as gastric or colorectal cancer, based on cell proliferation signatures. In various aspects, the invention relates to a method of predicting the likelihood of long-term survival of a cancer patient, a method of determining a treatment regime for a cancer patient, a method of preparing a personalized genomics profile for a cancer patient, among other methods as well as kits and devices for carrying out these methods.
Owner:PACIFIC EDGE
Identification of genetic markers associated with parkinson disease
The present invention provides methods and compositions for screening a subject for Parkinson disease, for increased risk of developing Parkinson disease and / or for an earlier or later age of developing Parkinson disease, comprising detecting the presence of a genetic marker associated with Parkinson disease.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com