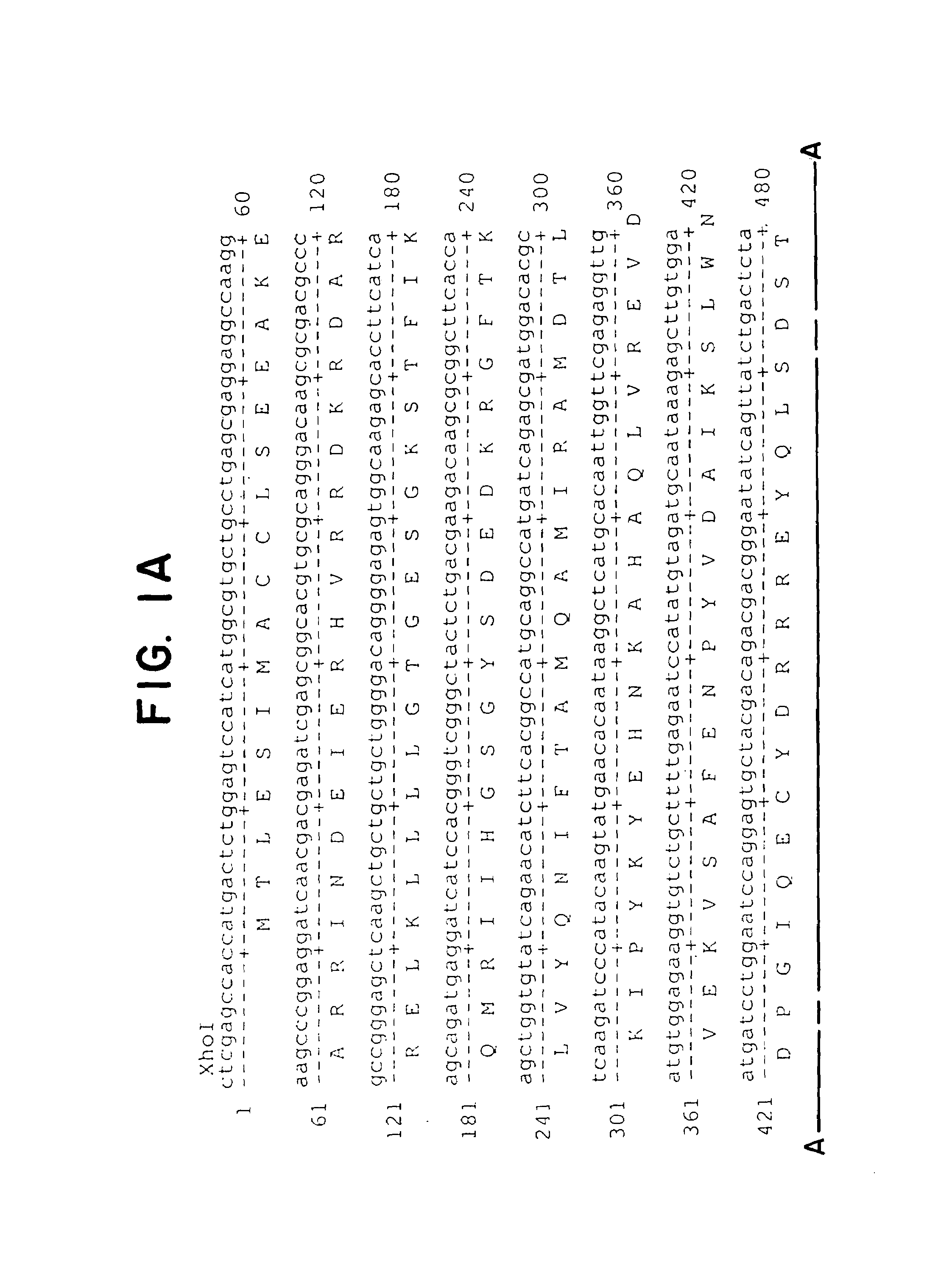
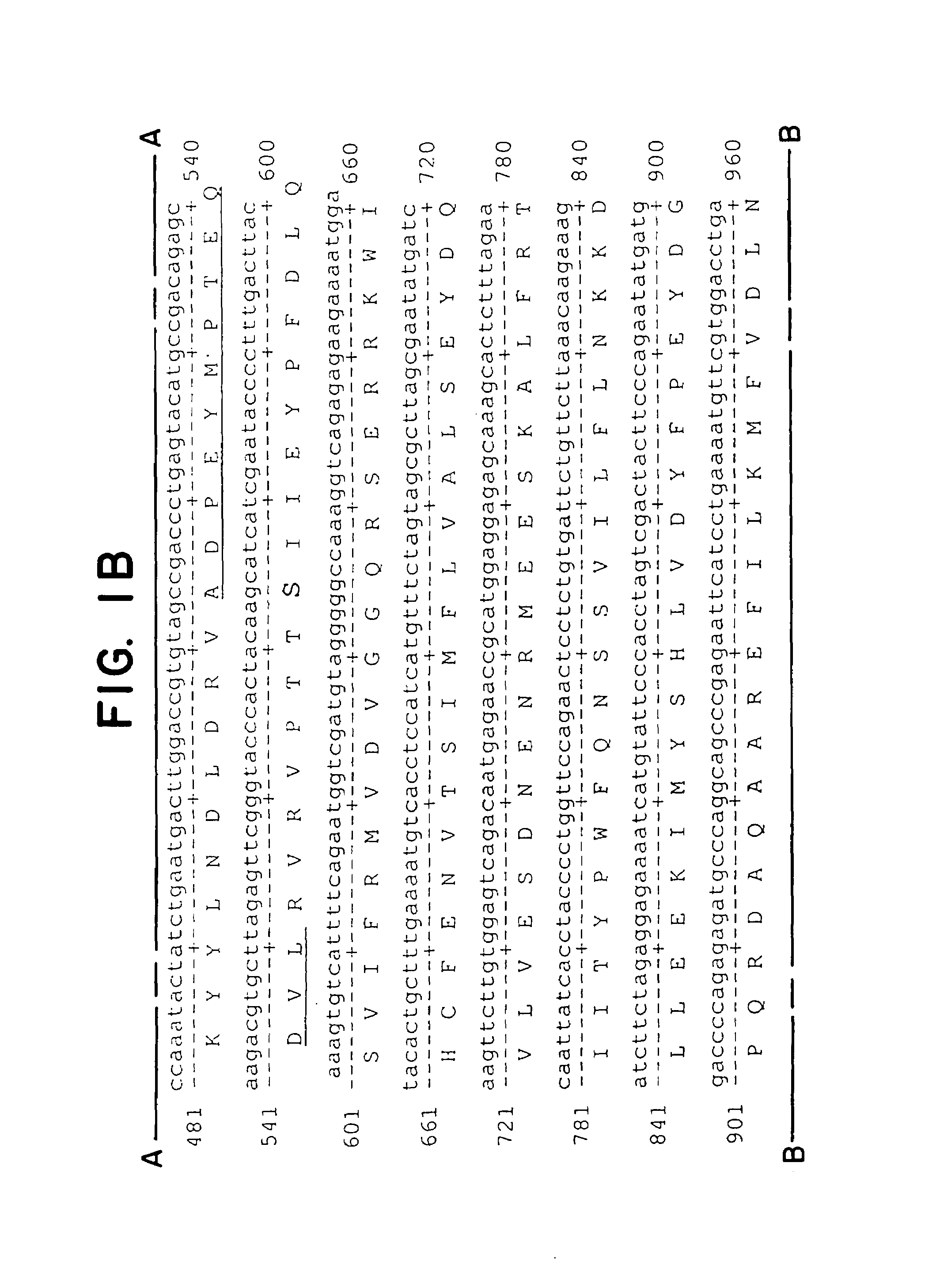
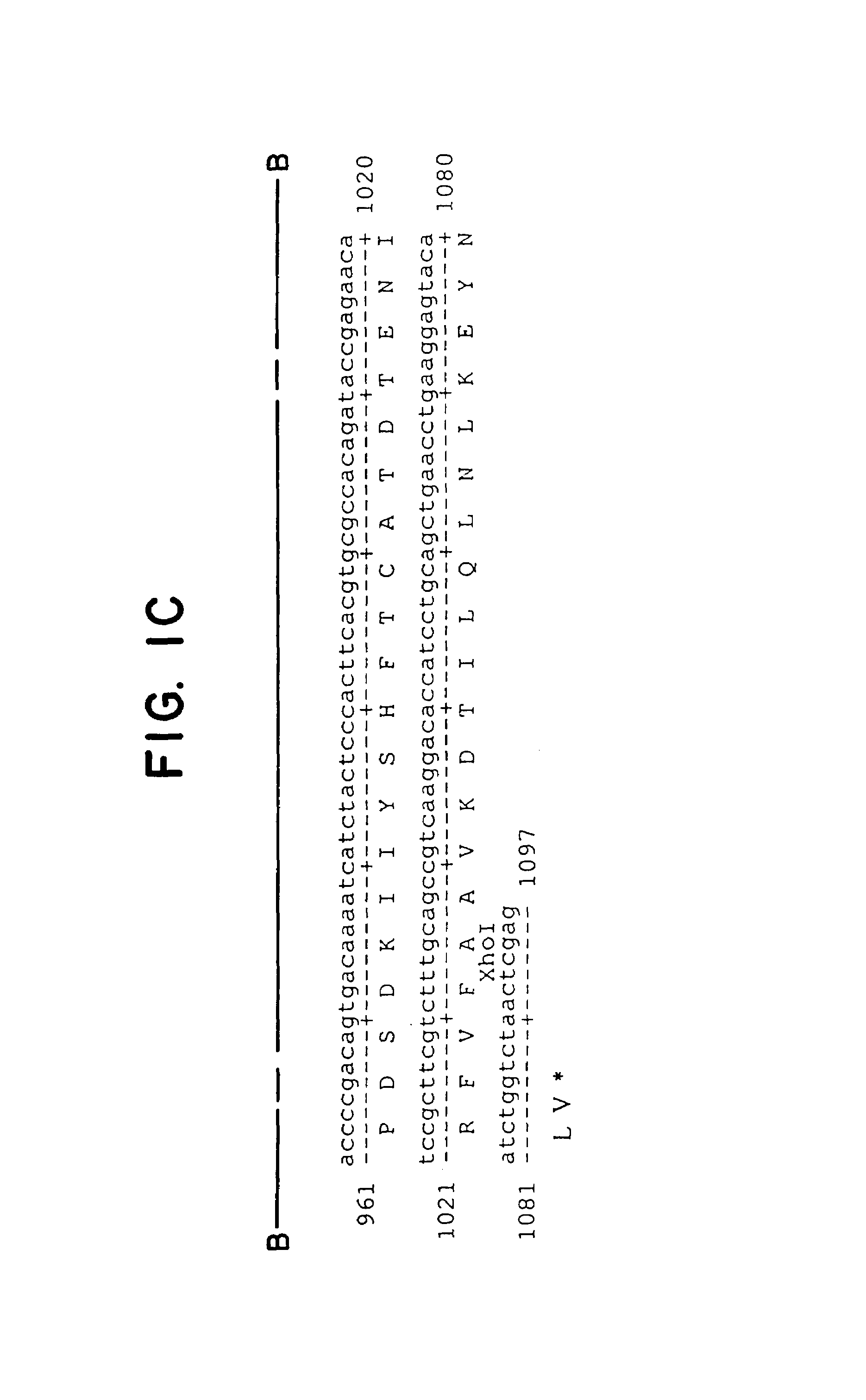
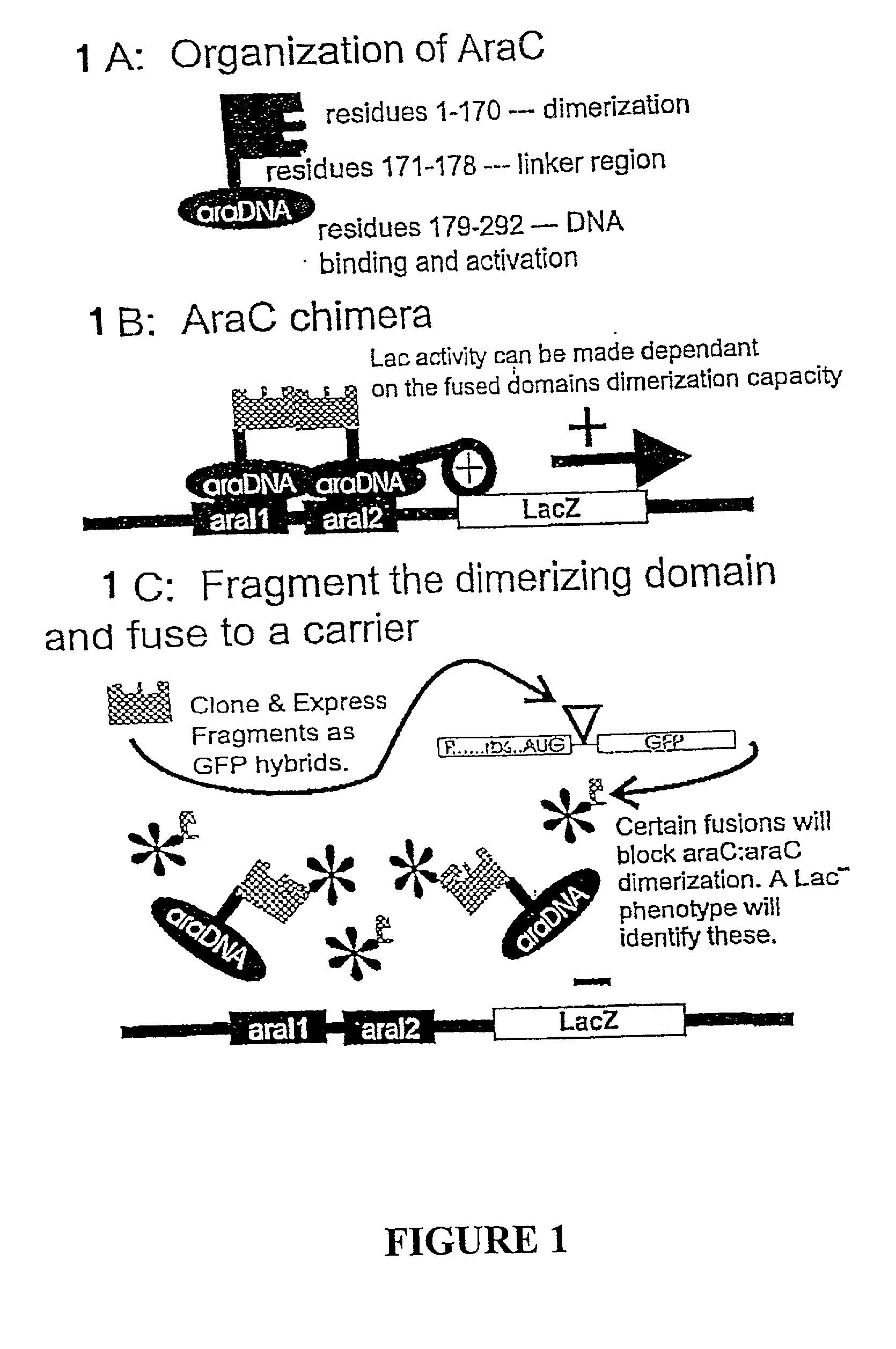
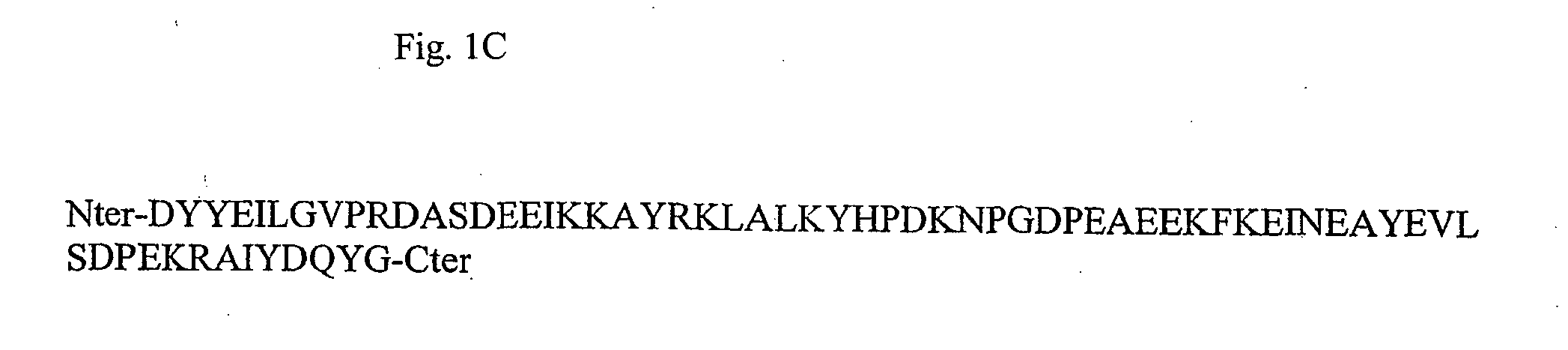Patents
Literature
136 results about "Dominant negative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dominant negative. A mutation whose gene product adversely affects the normal, wild-type gene product within the same cell. This usually occurs if the product can still interact with the same elements as the wild-type product, but block some aspect of its function.Examples: 1.
Disease treatment via antimicrobial peptides or their inhibitors
The invention provides methods for the treatment of disease and promotion of healing that include providing a therapeutically effective amount of a mammalian antimicrobial peptide (AMP) or analog thereof, in particular a cathelicidin or cathelicidin fragment or cathelicidin analog, thereby treating the disease in the subject in need thereof. The invention also provides specific analogs or fragments of cathelicidin that function as agonists, as do endogenous cathelicidins, or as either dominant negatives or as inhibitors to endogenous cathelicidin or to other endogenous AMPs or that compete with pro-inflammatory agents or fragments of AMPs on cognate receptors without inducing disease.
Owner:HILLMAN YITZCHAK
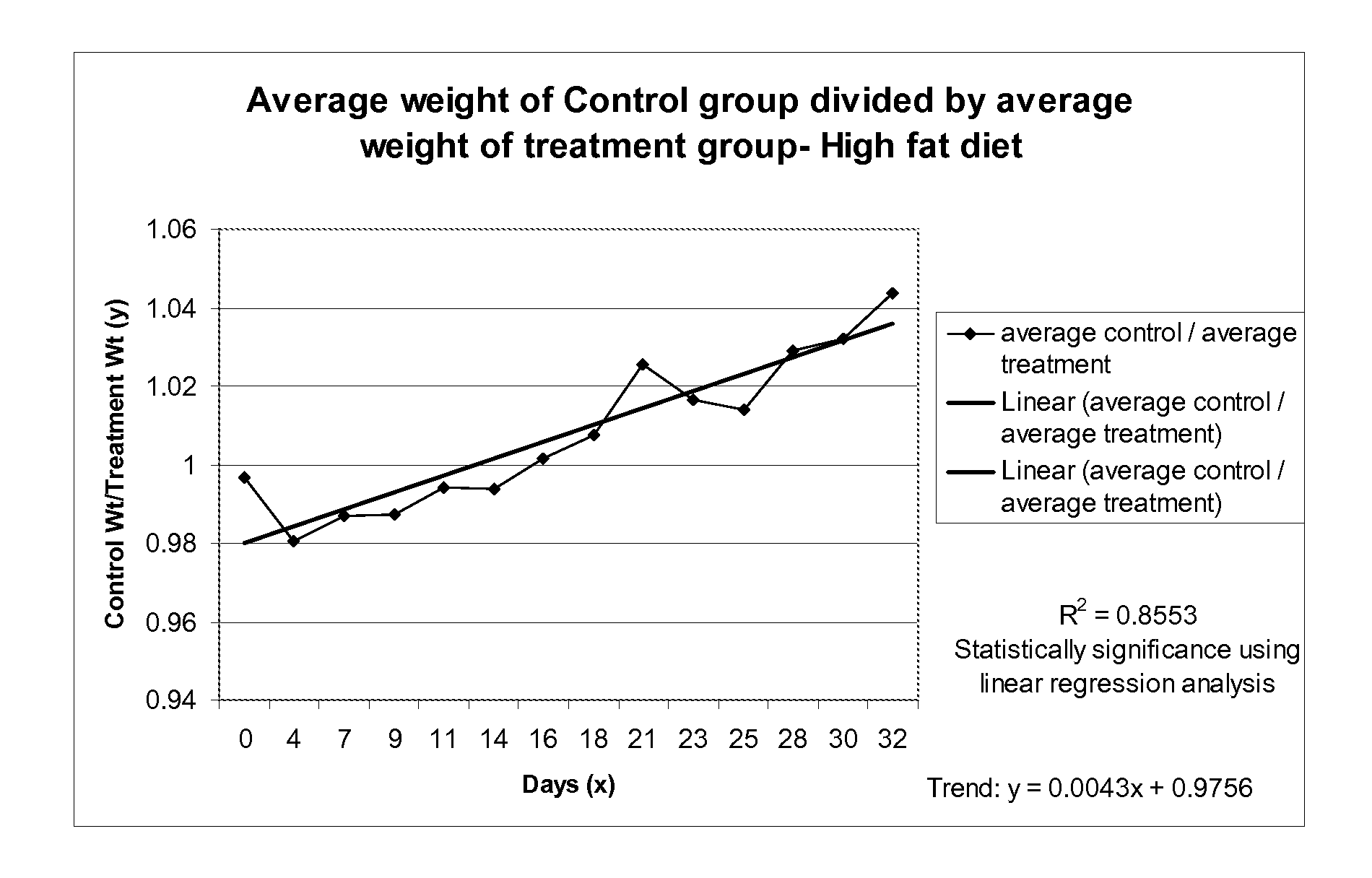
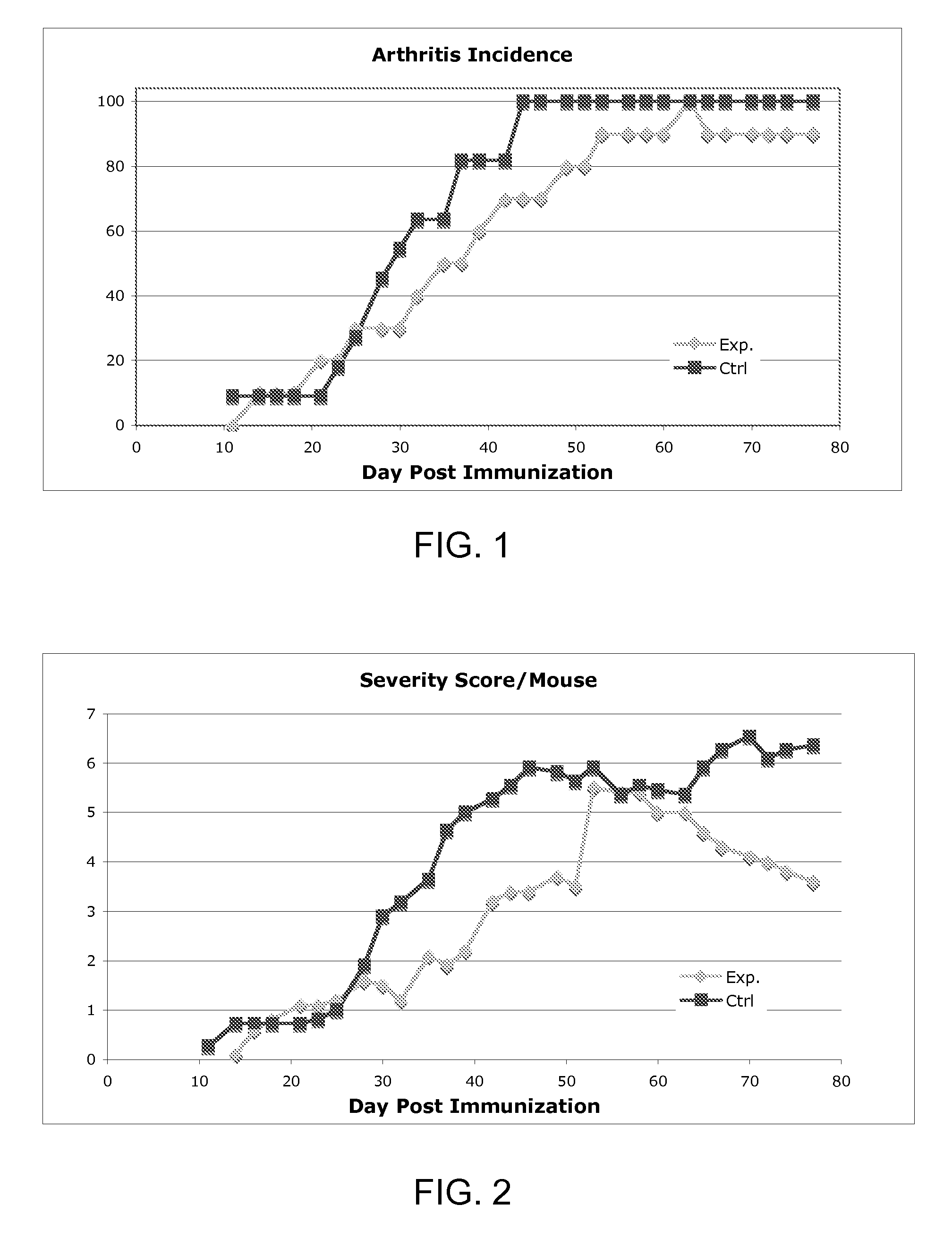
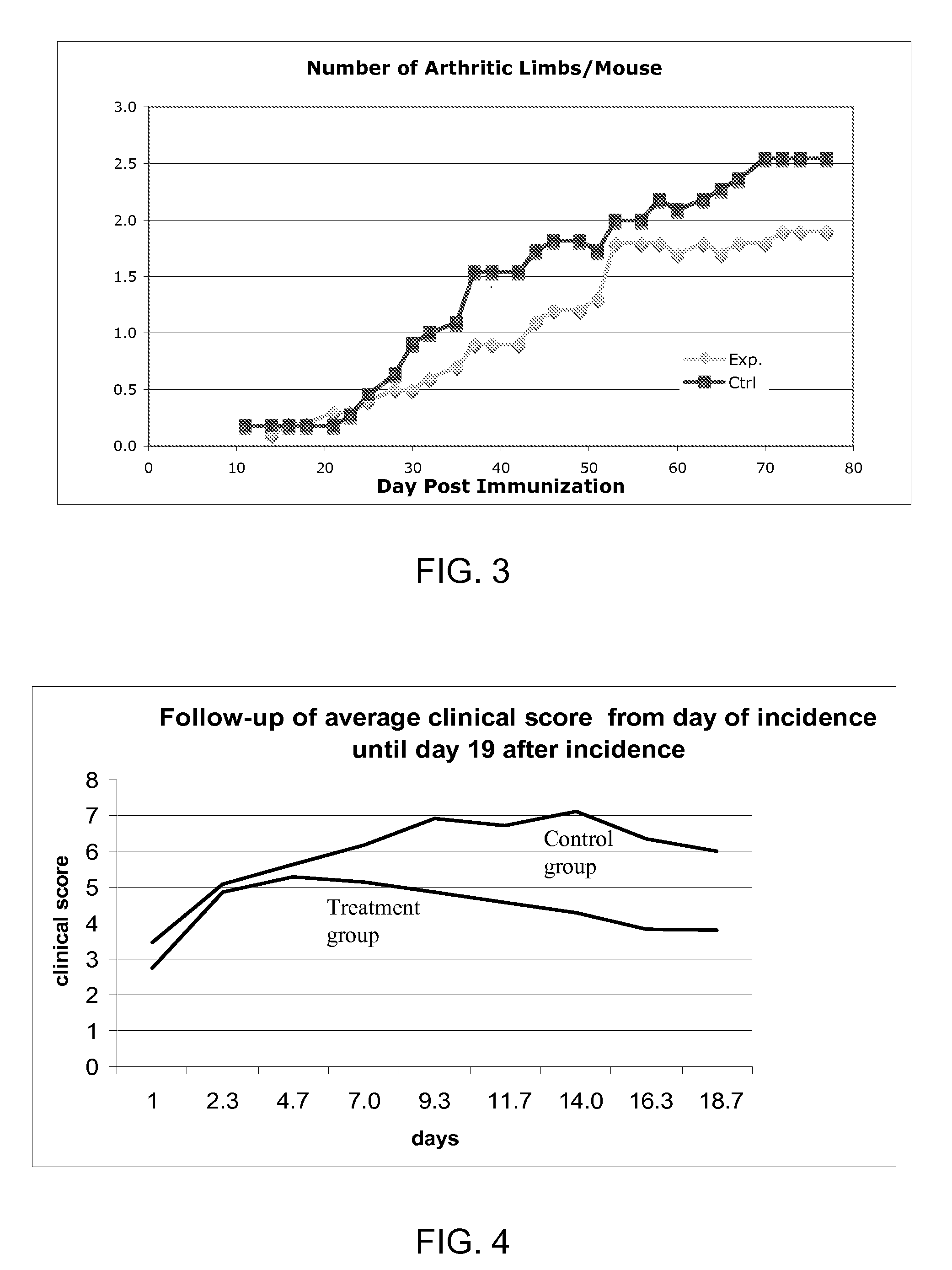
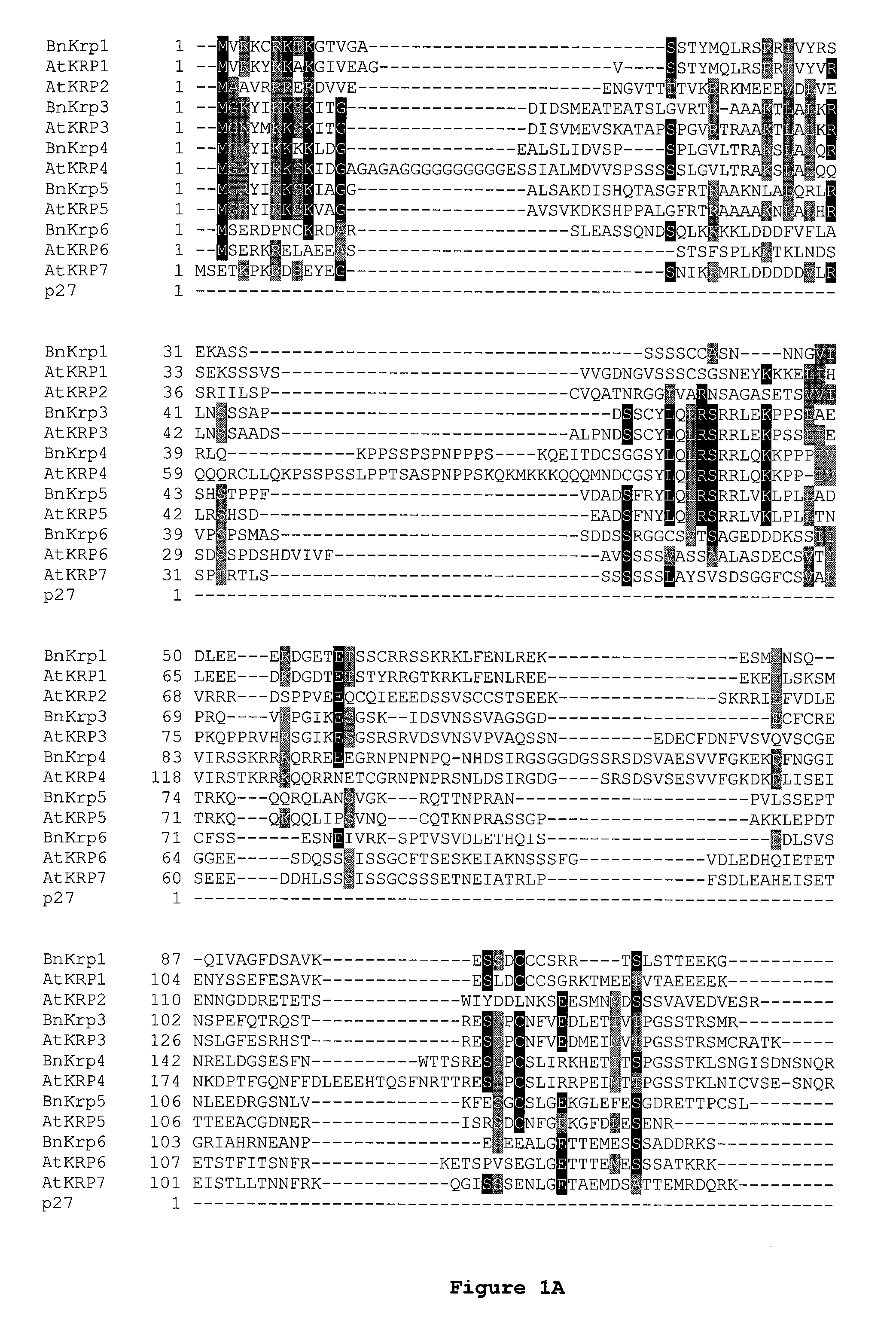
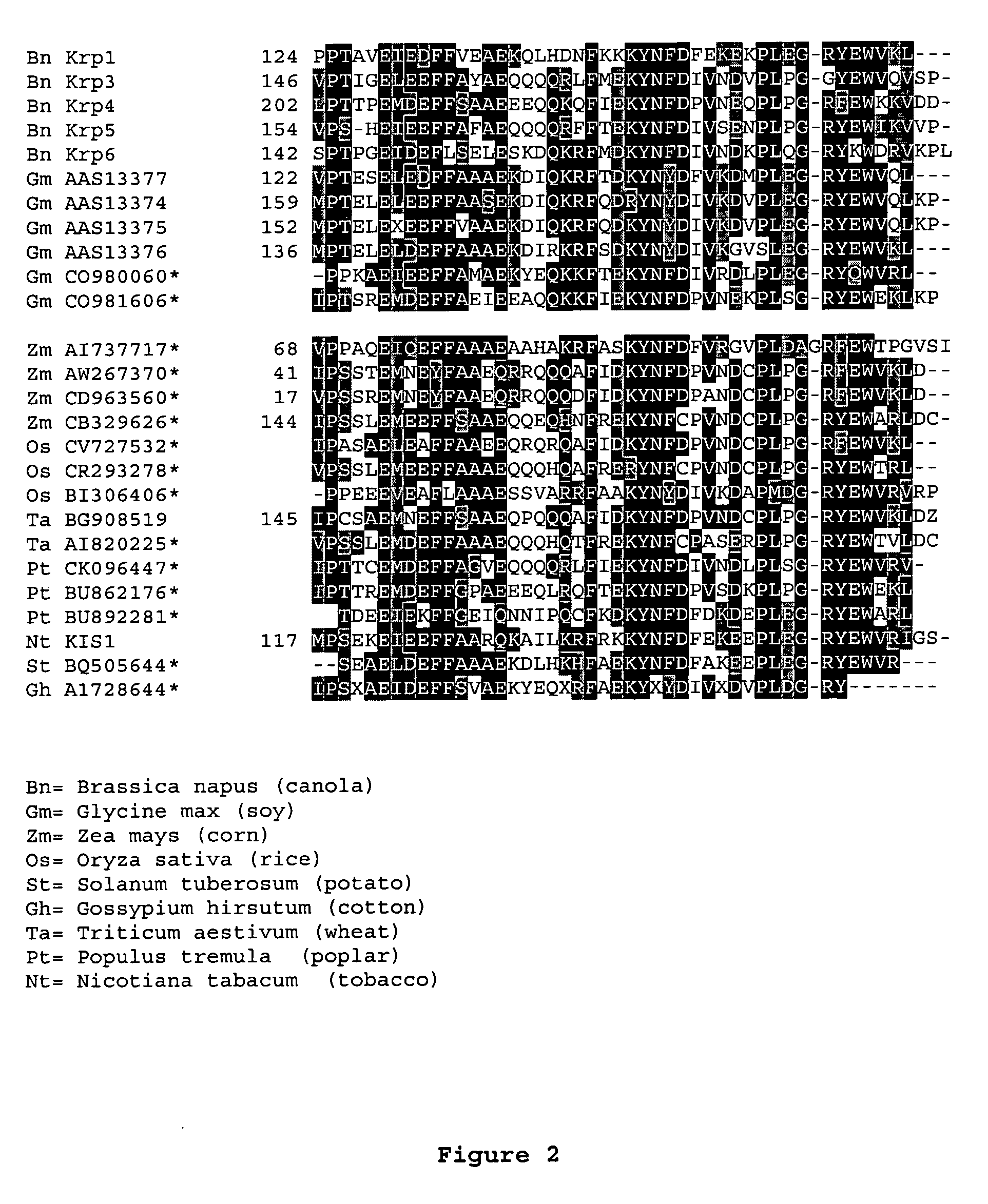
Dominant negative mutant krp protein protection of active cyclin-cdk complex inhibition by wild-type krp
InactiveUS20070056058A1Speed upIncreasing cell proliferationBacteriaSugar derivativesMutated proteinPlant cell
Disclosed are mutant CDK inhibitor (CKI) polypeptides having dominant negative antagonist activity against wild-type CKI proteins, as well as related compositions, including nucleic acids and vectors encoding the mutant CKI polypeptides and transformed host cells and transgenic plants comprising such nucleic acids and vectors. Also disclosed are related methods for using the mutant proteins to modulate cell division in cells, particularly plant cells.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH
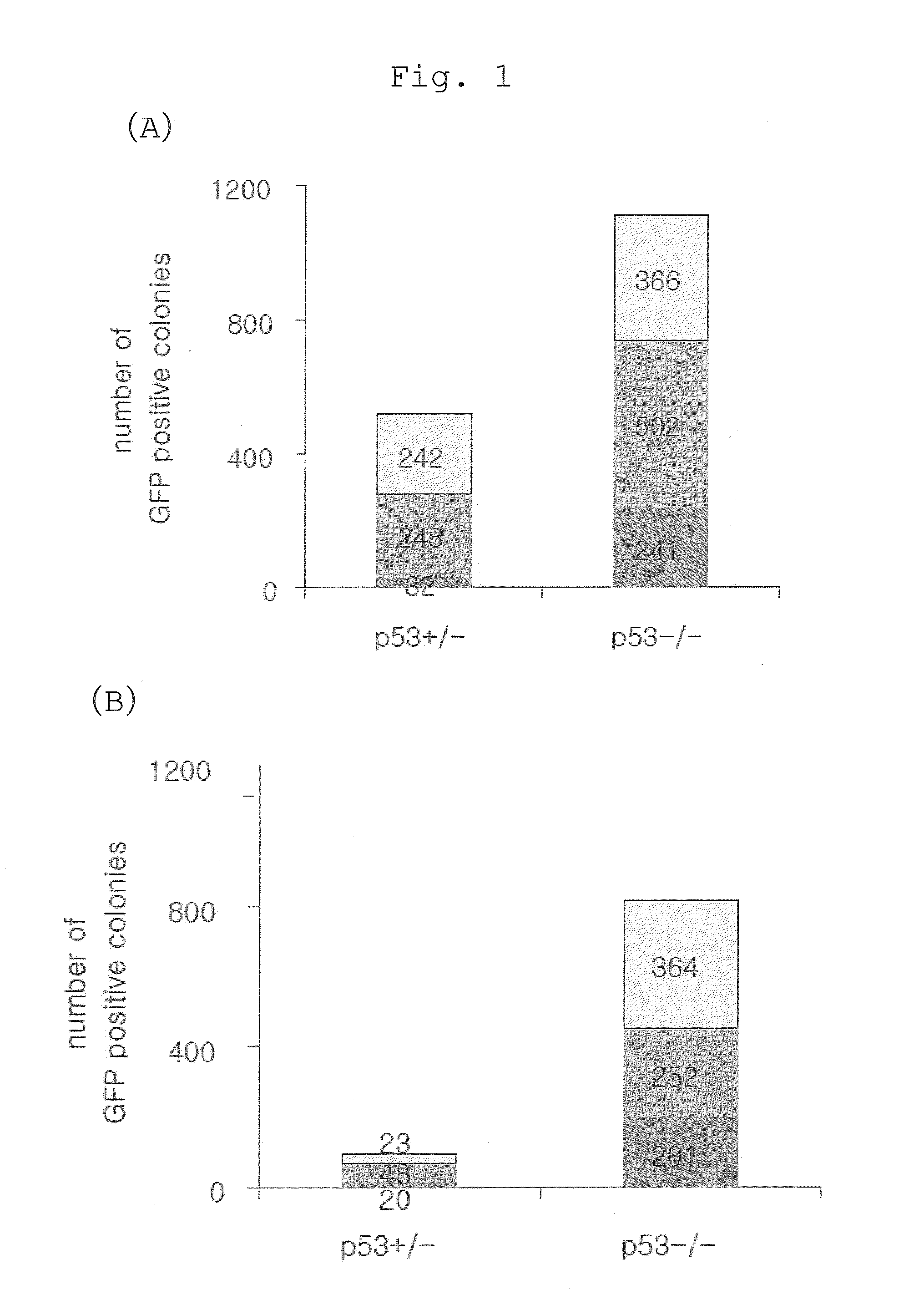
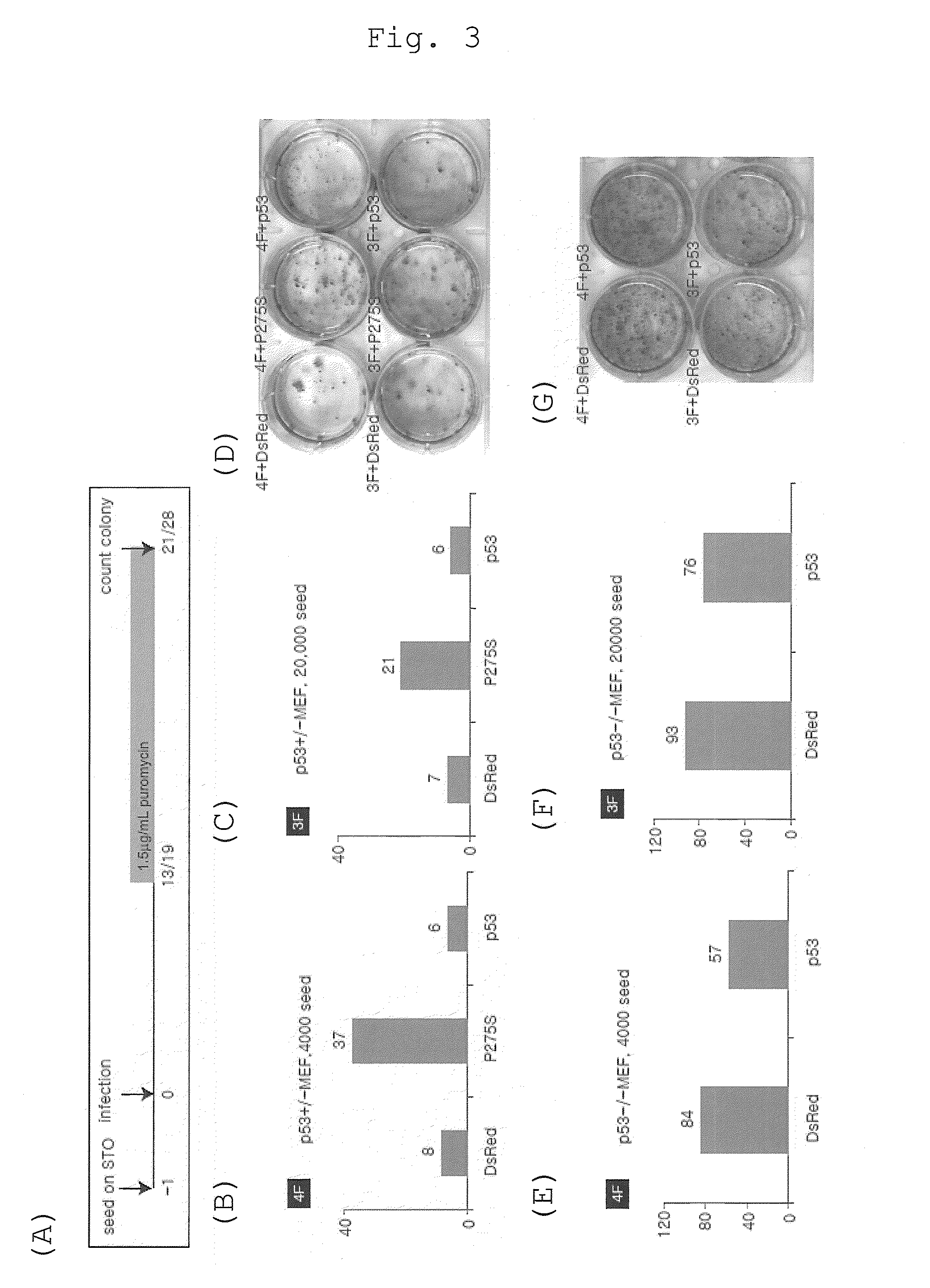
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20110223669A1Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
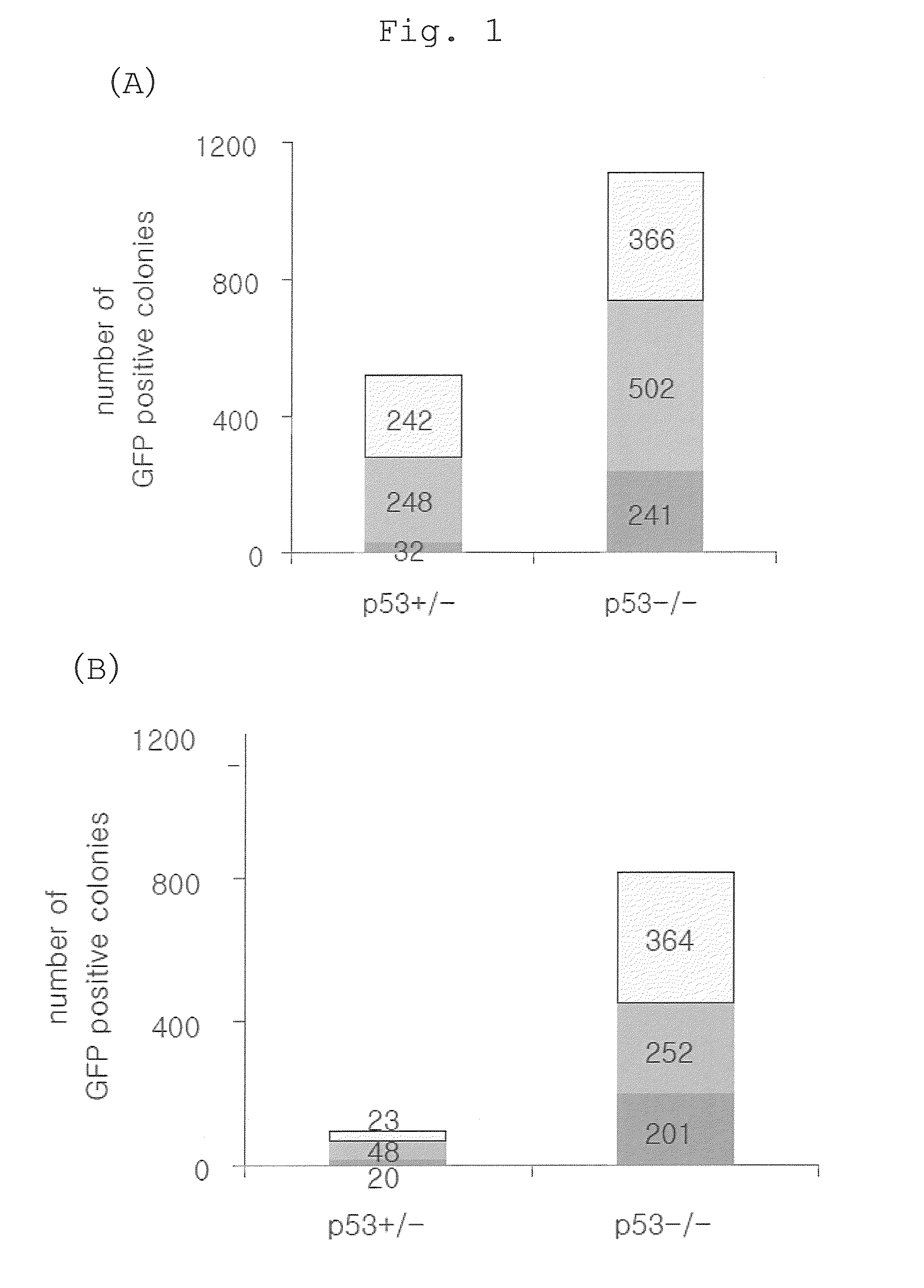
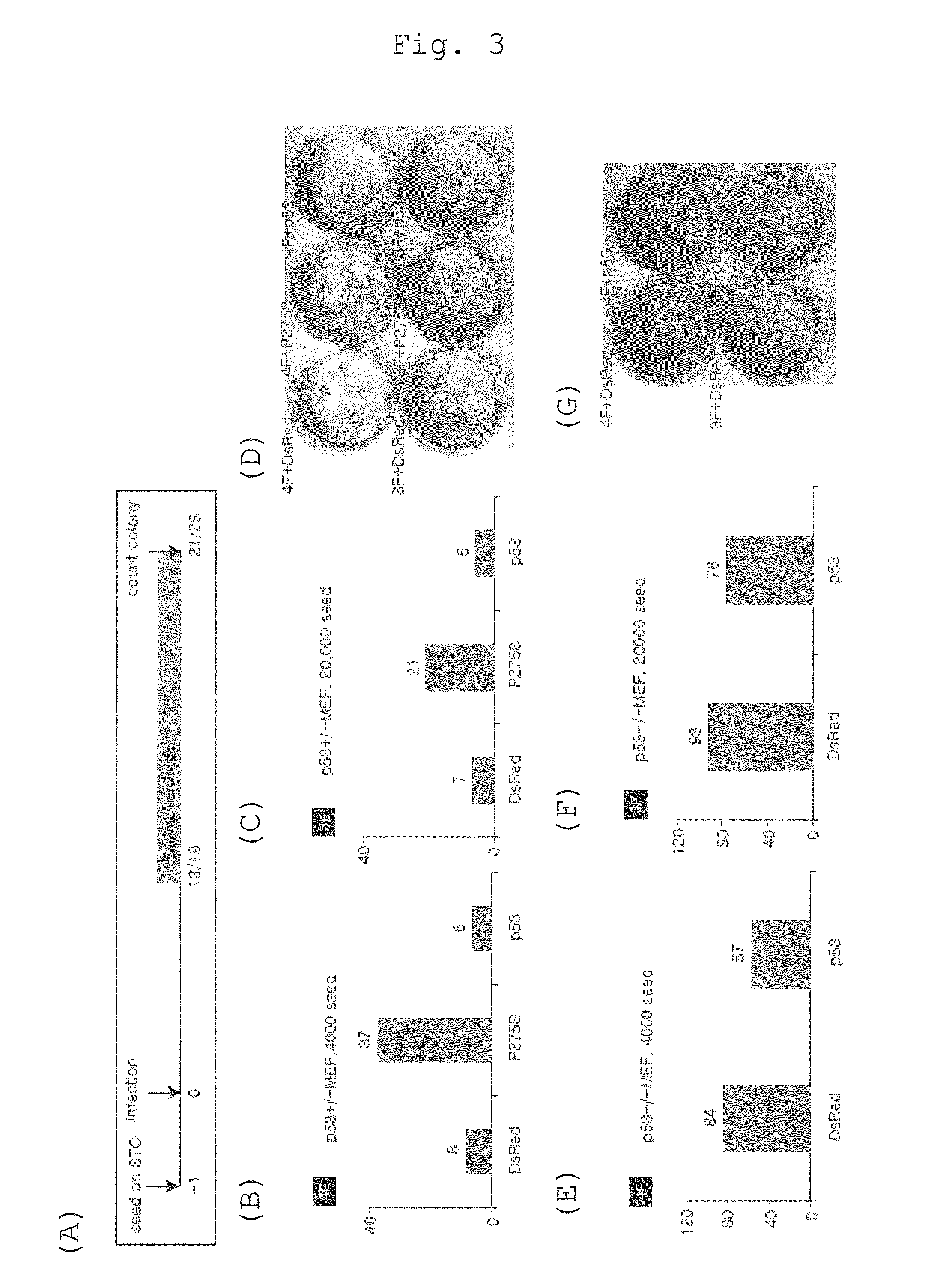
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
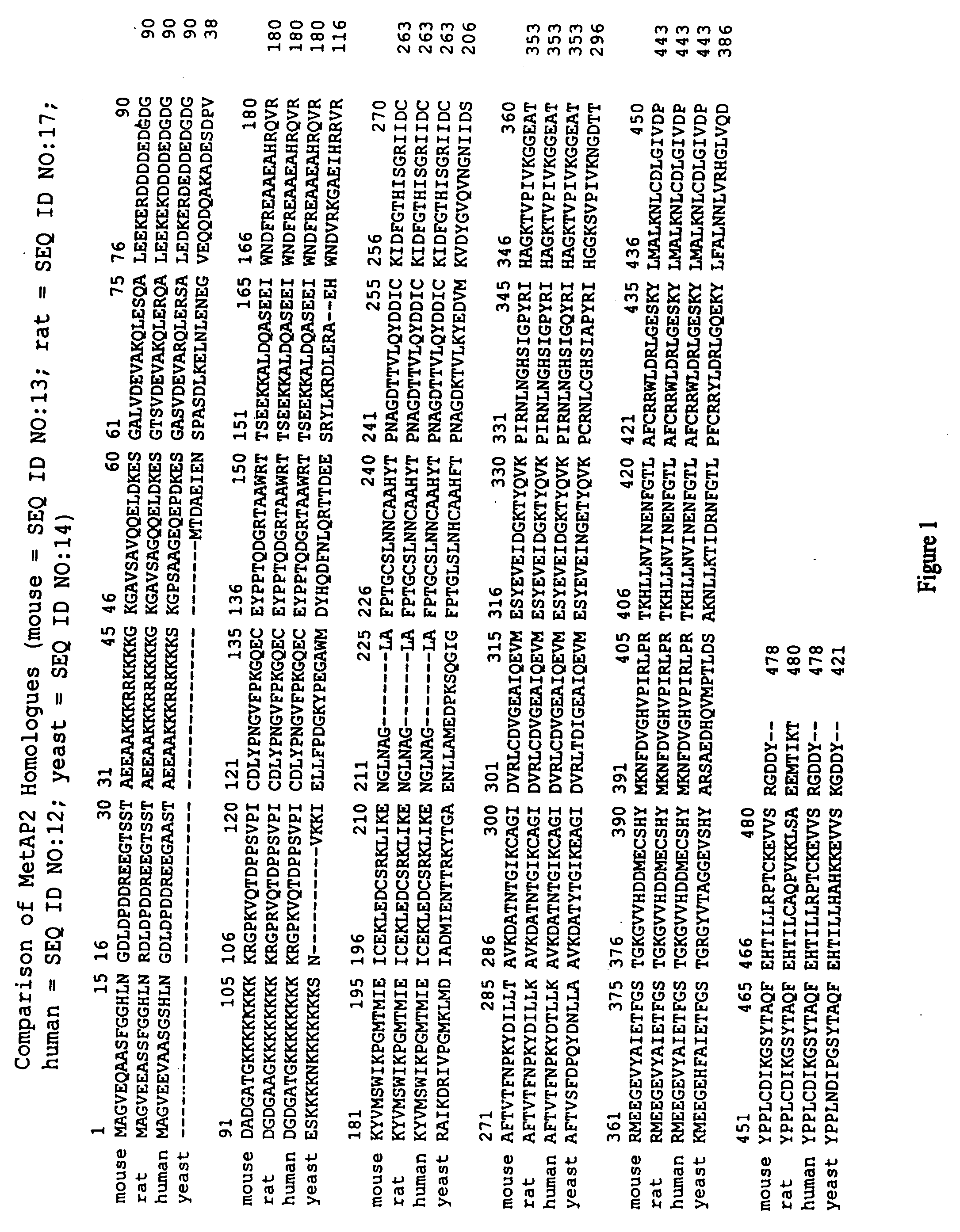
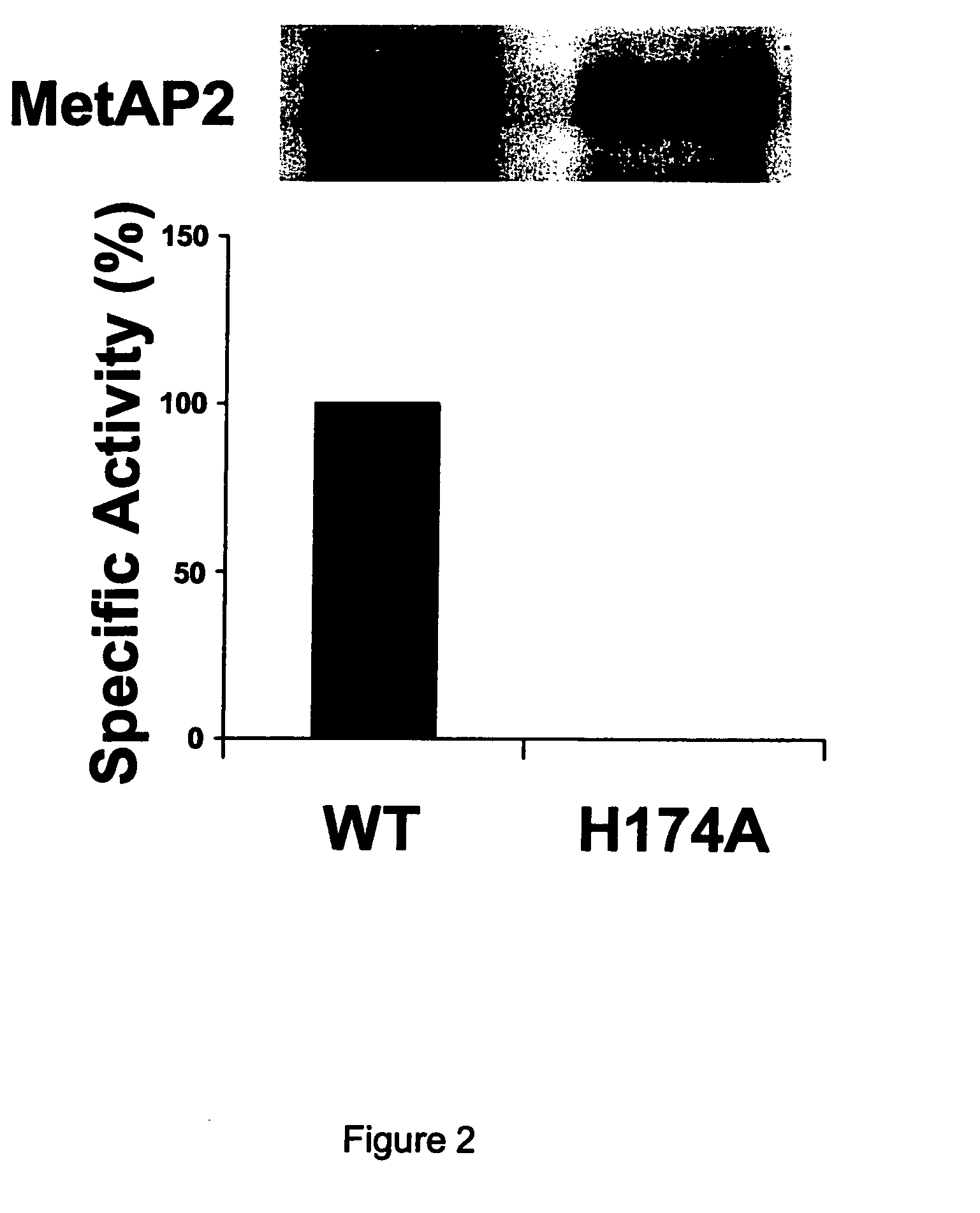
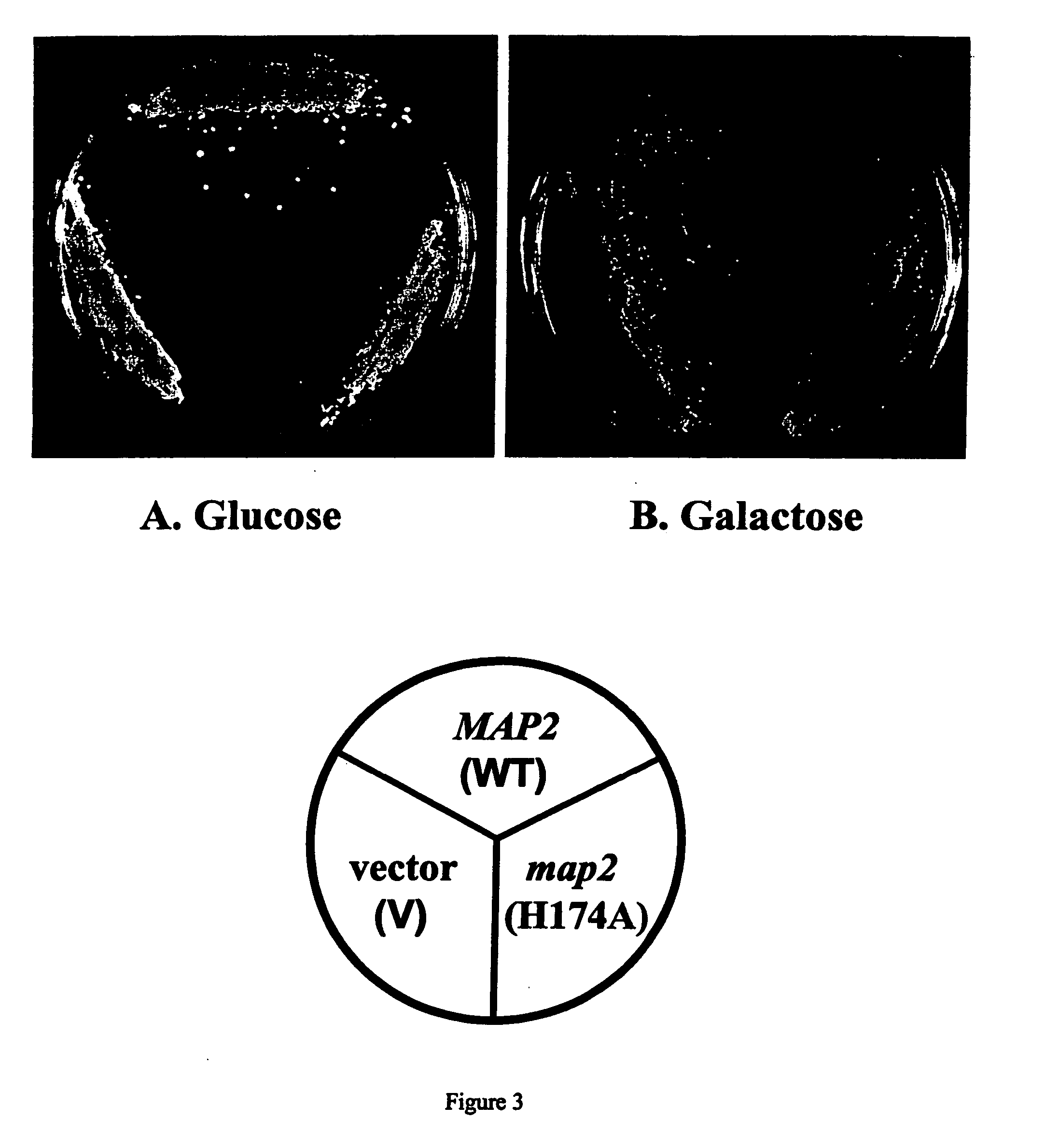
Dominant negative variants of methionine aminopeptidase 2 (MetAP2) and clinical uses thereof
InactiveUS20050032221A1Increase ratingsEliminate negative effectsBiocideCompound screeningMethionine aminopeptidaseMethionine biosynthesis
Inhibitors of type 2 methionine aminopeptidases (“MetAP2”), specifically dominant negative variants of MetAP2, both polypeptides and encoding polynucleotides, are provided. Also provided are methods of treating subjects suffering from cancer, diseases mediated by the immune system or opportunistic infections using inhibitors of MetAP2. Also provided are high through put screens and assays to detect and identify inhibitors of MetAP2 and downstream effectors of MetAP2.
Owner:CHANG YIE HWA +2
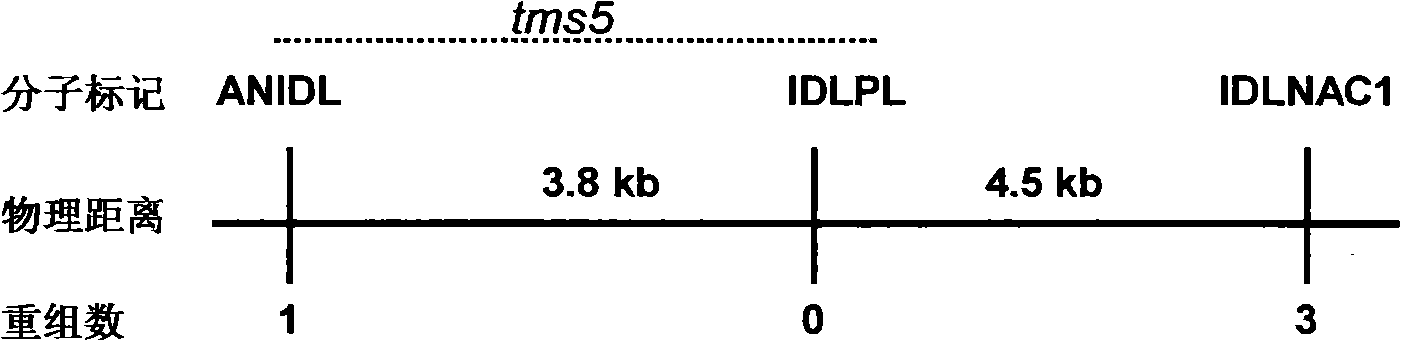
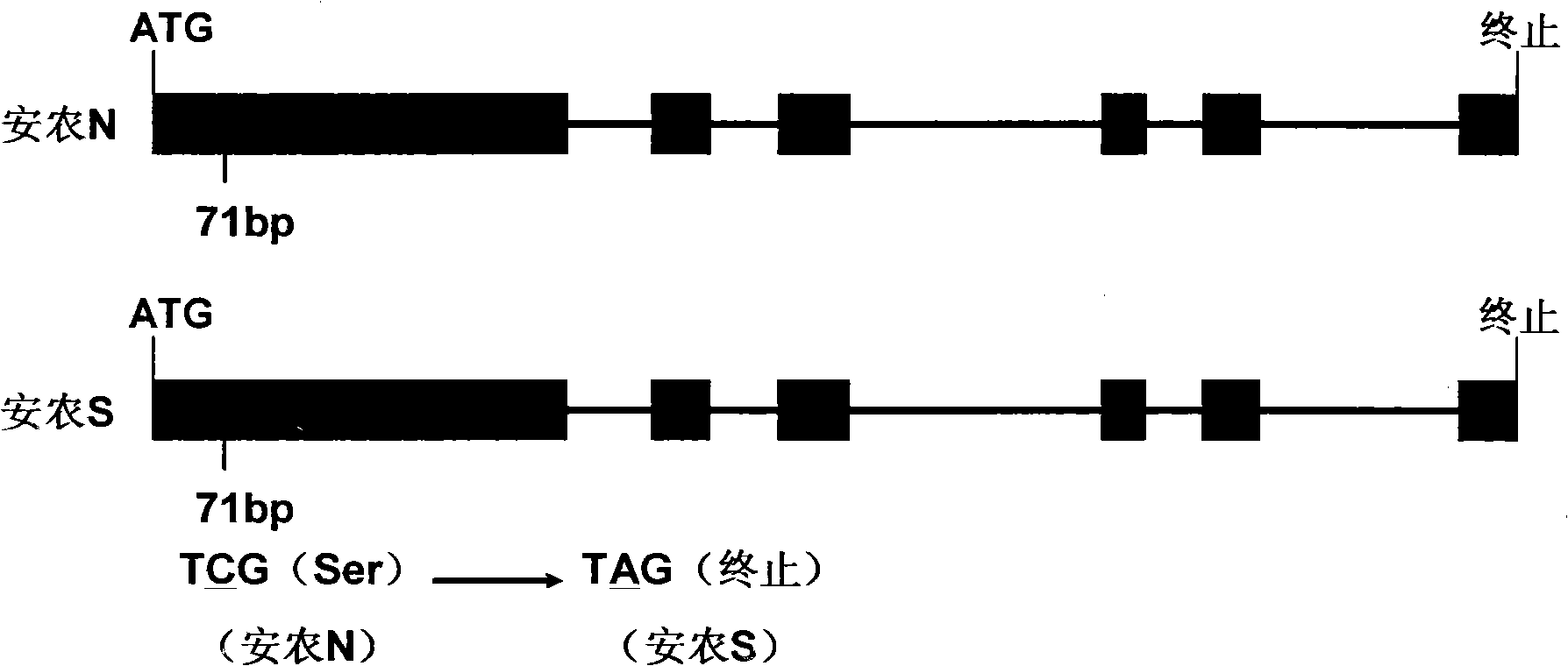
Temperature sensing male fertile gene and use thereof
ActiveCN101333533AImprove selection efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and an application thereof and also discloses a genetic marker of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene, and provides a protein coded by the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a carrier containing the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a recombinant microorganism. The invention also discloses the application of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene in cultivating a thermo-sensitive male sterile line and an application of the genetic marker in rice breeding. The thermo-sensitive fertility gene TSSNR is acquired through the map-based cloning technique of Annong S-1 thermo-sensitive sterility gene locus tms5, functions of the gene are validated through transgene experiments, and the transgene technique of RNAi or antisense RNA or the over-expression dominant negative principle is provided, functions of the TSSRZ gene in normal rice varieties are incapable, so as to cultivate the thermo-sensitive male sterile line, and the application value is significant.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Cell regulatory genes, encoded products, and uses related thereto
InactiveUS6946256B1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSuppressorApoptosis
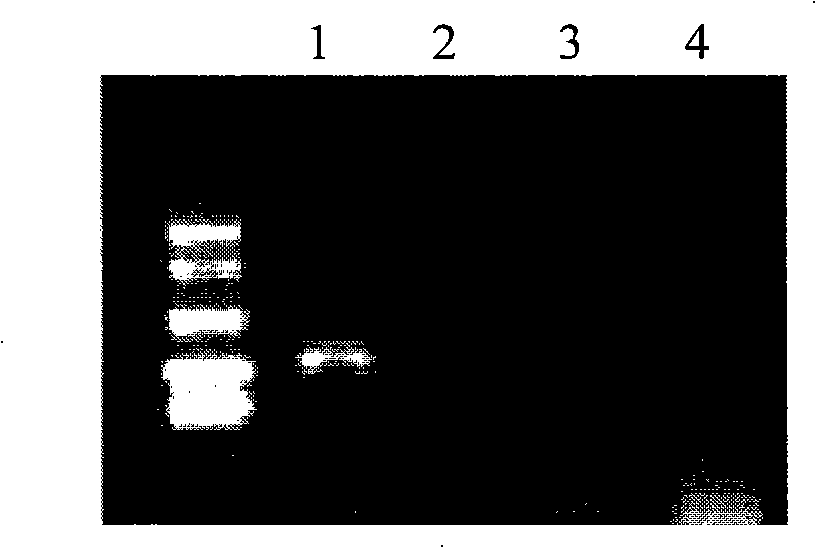
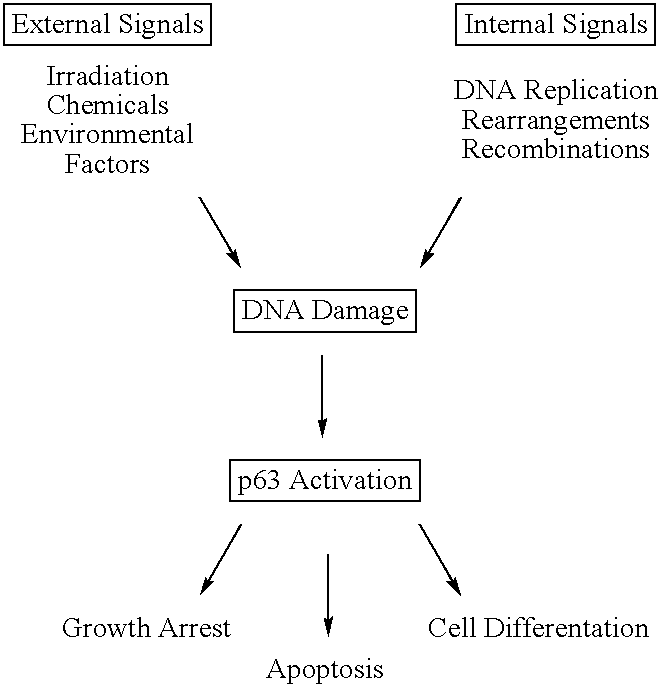
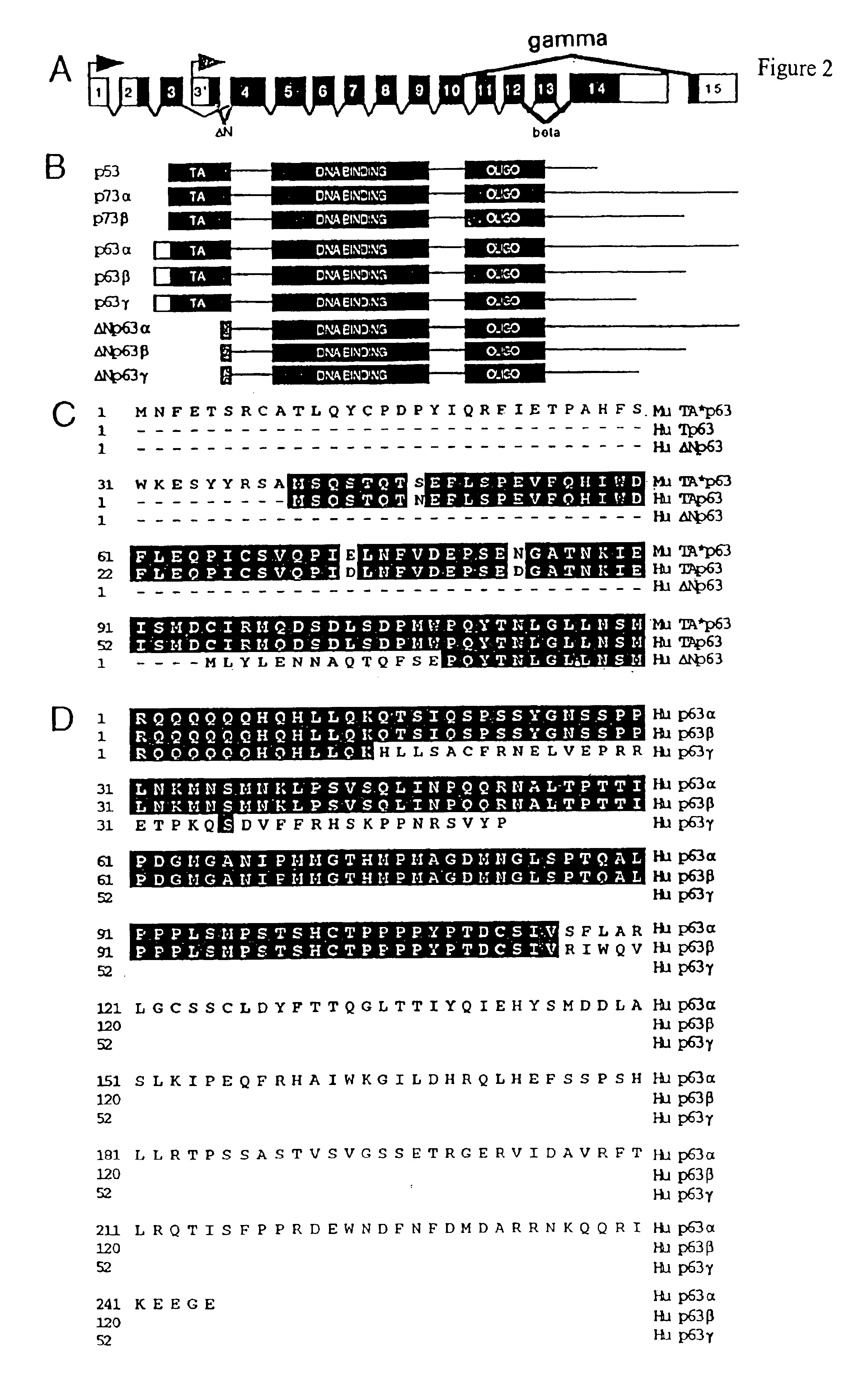
This application describes the cloning of p63, a gene at chromosome 3q27-29, that bears homology to the tumor suppressor p53. The p63 gene encodes at least six different isotypes. p63 was detected in a variety of human and mouse tissue and demonstrates remarkably divergent activities, such as the ability to transactivate p53 reporter genes and induce apoptosis. Isotopes of p63 lacking a transactivation domain act as dominant negatives towards the transactivation by p53 and p63.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +2
Compounds and methods for the treatment and prevention of bacterial infection
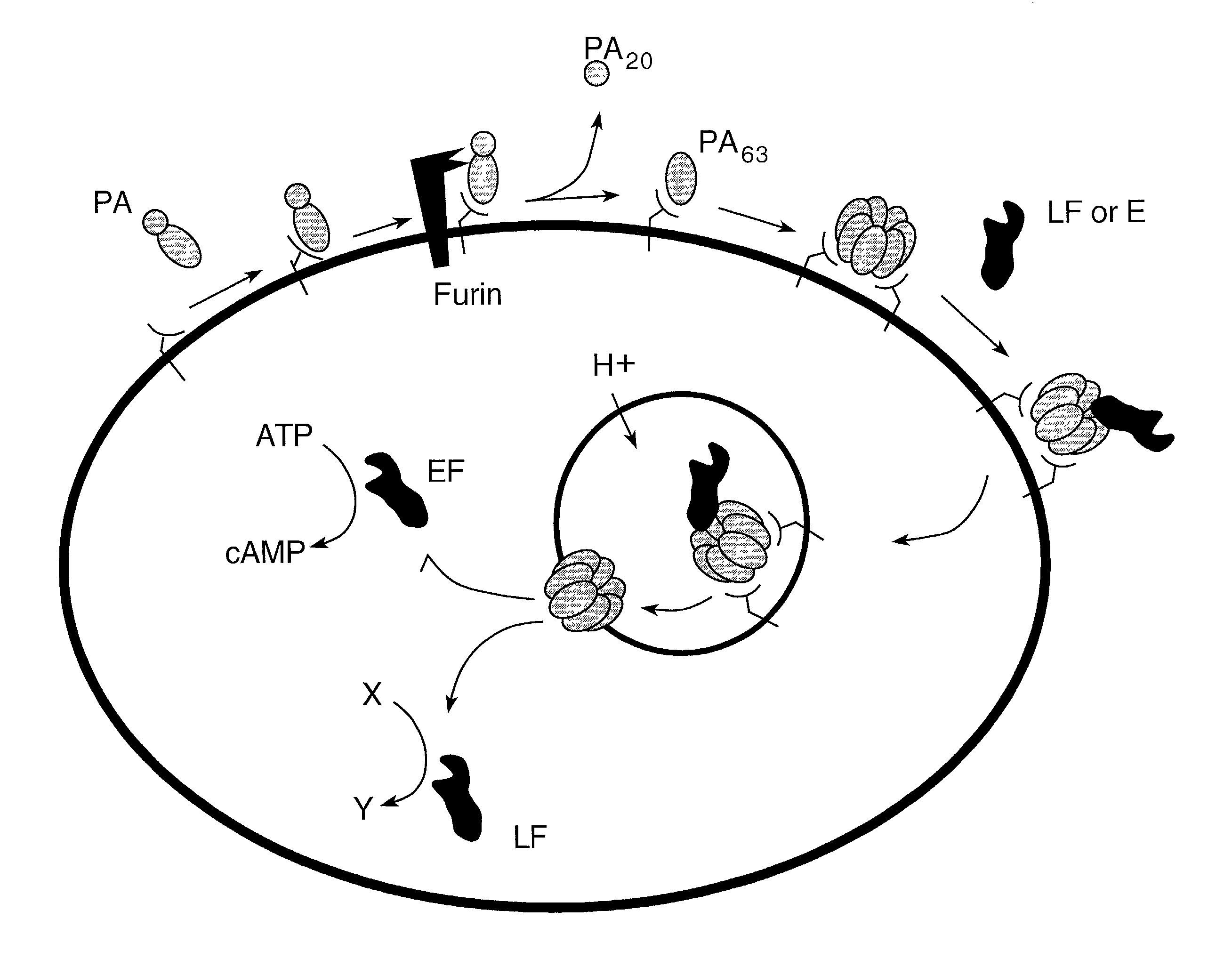
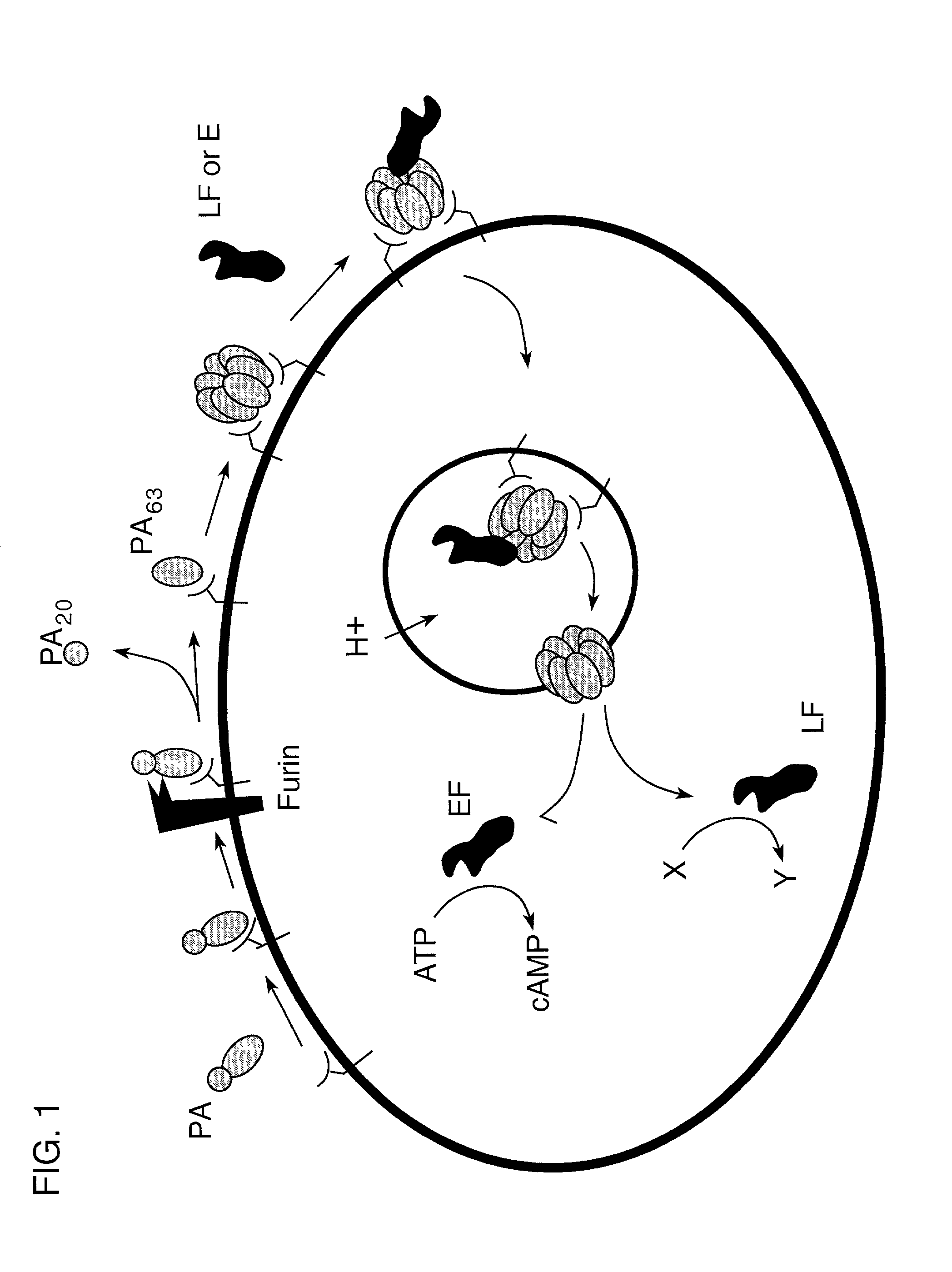
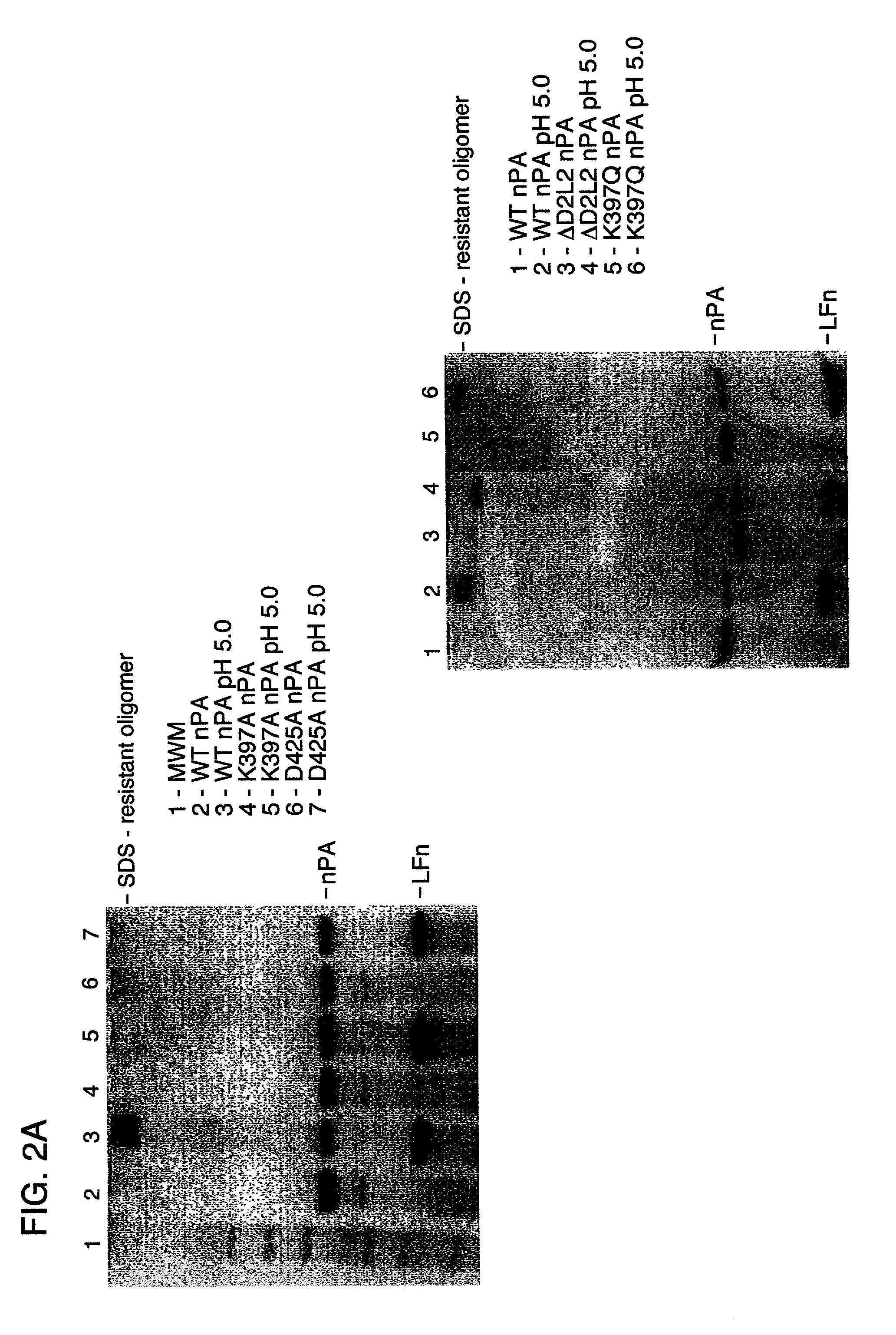
InactiveUS7037503B2Reduced ability to form poreInhibit pore-forming abilityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDominant-Negative MutantDominant negative
The invention provides mutant forms of pore-forming toxins. These mutant toxins may be used in vaccines for the prevention of bacterial infection. Additionally, dominant negative mutants may be administered as therapeutics for the treatment of bacterial infection.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Immune cell compositions and methods of use
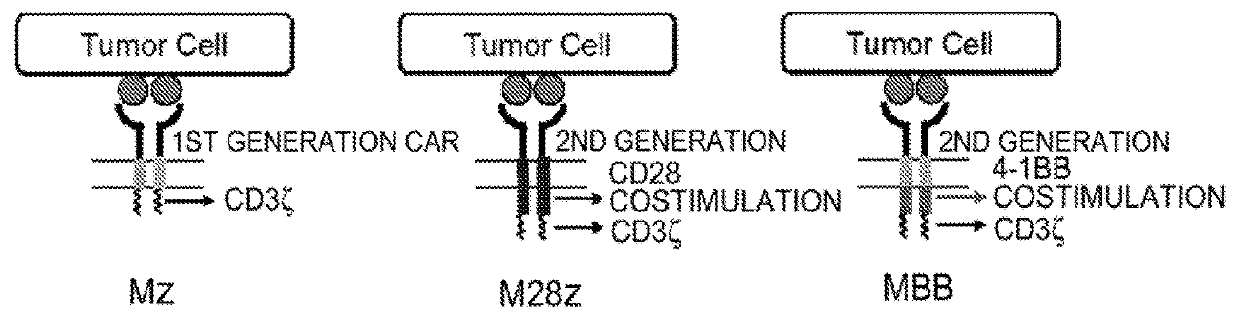
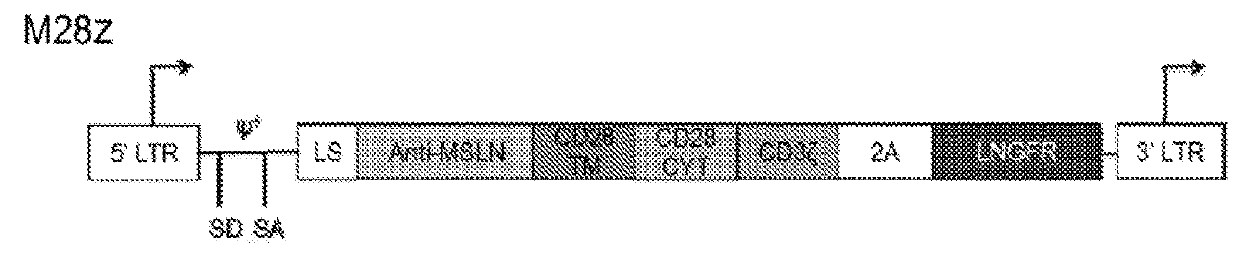
ActiveUS20180273601A1Restores effector functionEnhances tumor burden controlPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorT cell mediated immunity
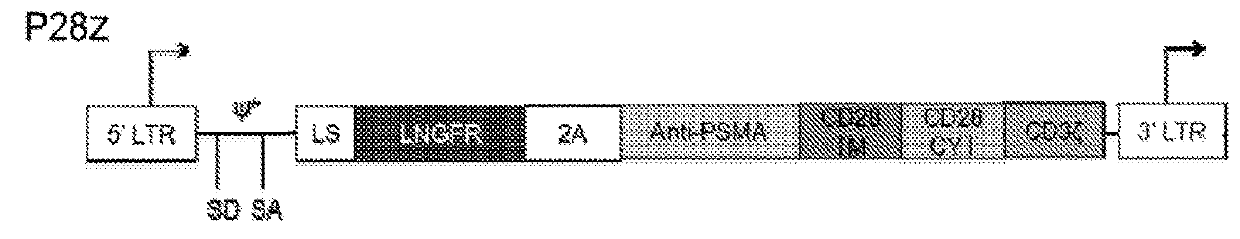
Disclosed herein are cells that are immune cells or precursor cells thereof, which cells recombinantly express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), and a dominant negative form of an inhibitor of a cell-mediated immune response of the immune cell, wherein the CAR binds to a cancer antigen. Also disclosed herein are T cells that recognize and are sensitized to a cancer antigen, which T cells recombinantly express a dominant negative form of an inhibitor of a T cell-mediated immune response. Additionally provided are methods of using such cells to treat cancer in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS8530238B2Genetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsNuclear reprogrammingCancer research
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Donor yeast strain for transfer of genetic material
InactiveUS20060105361A1Reduce needSimple methodFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsBiotechnology
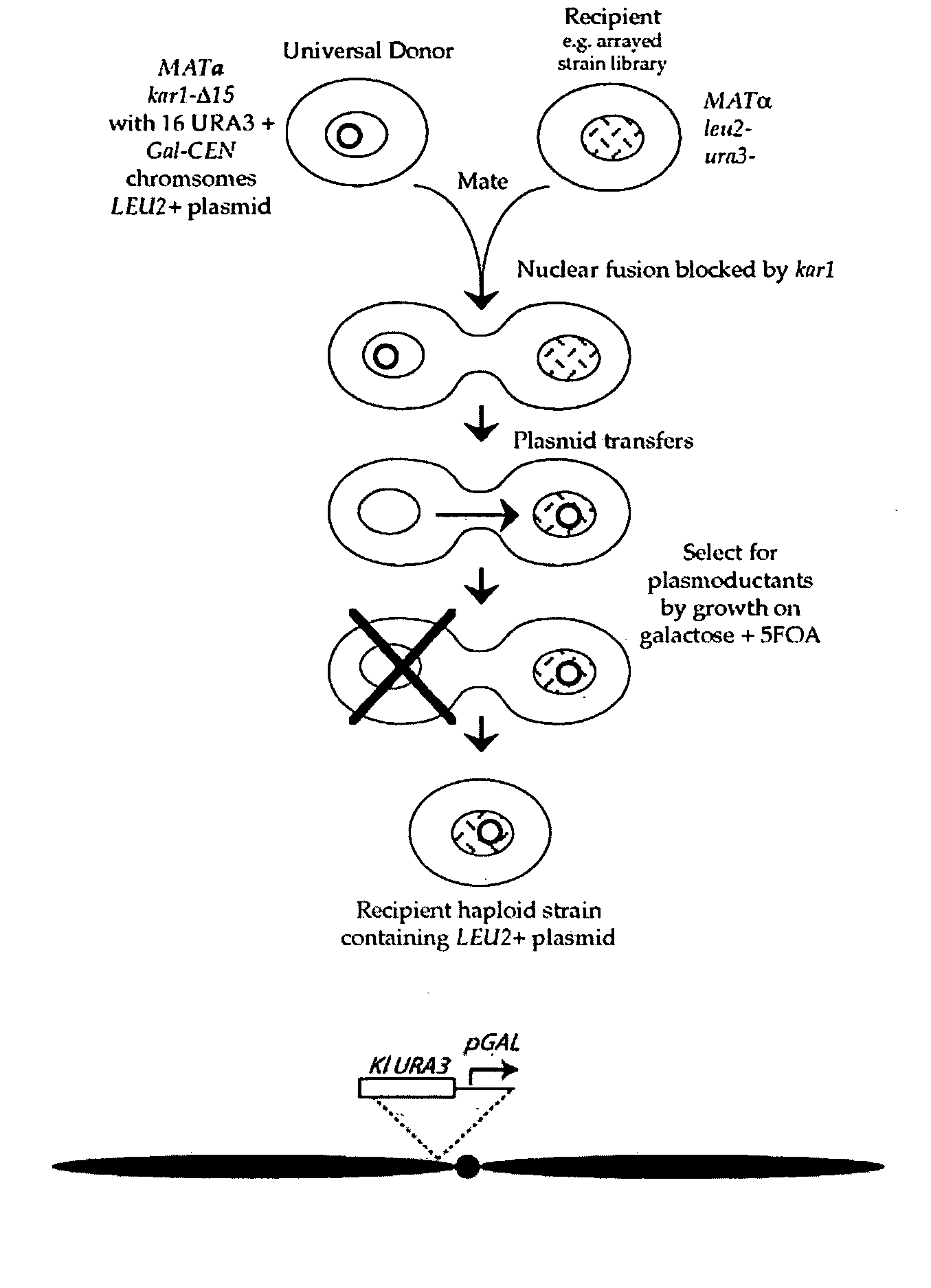
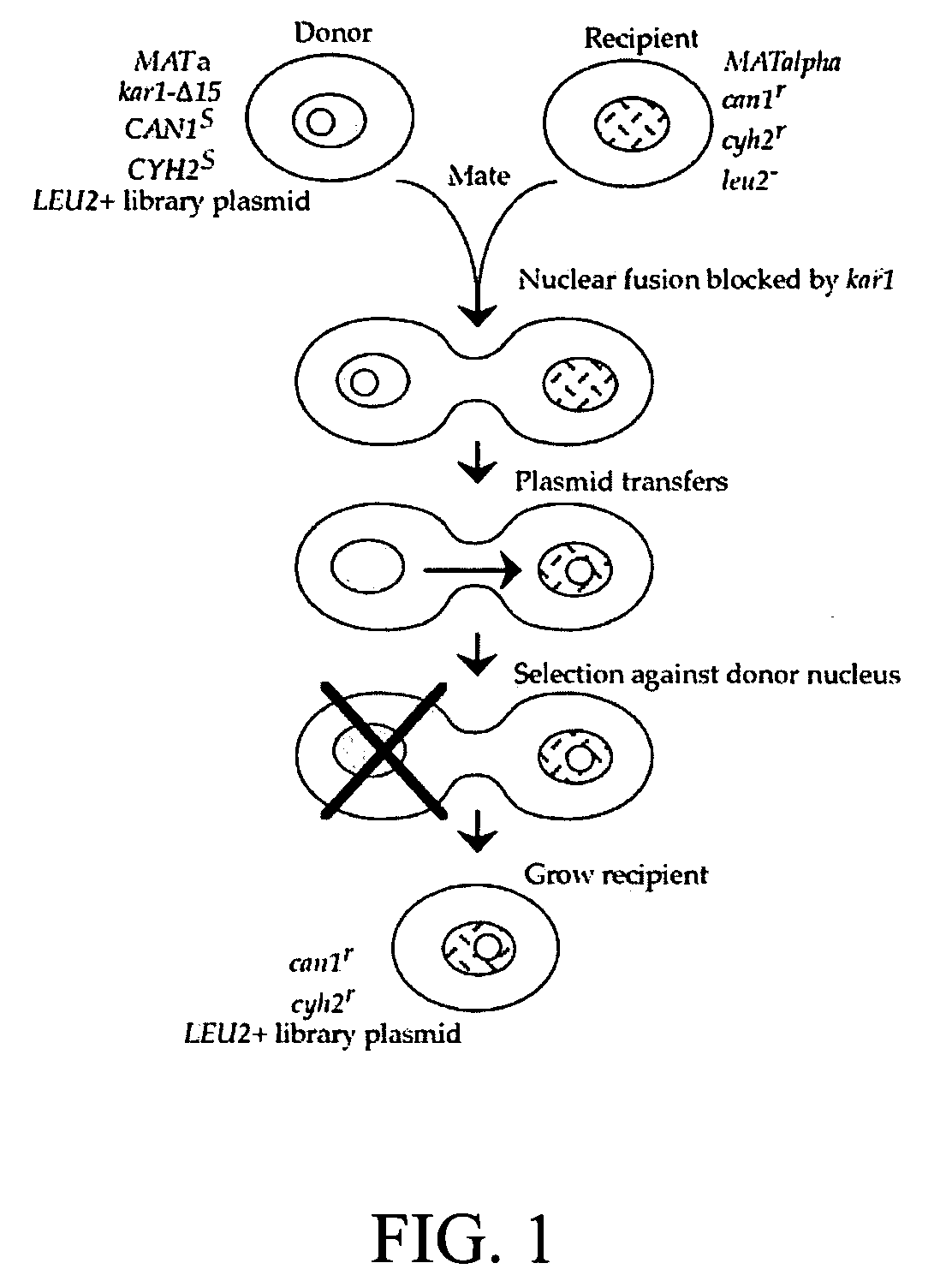
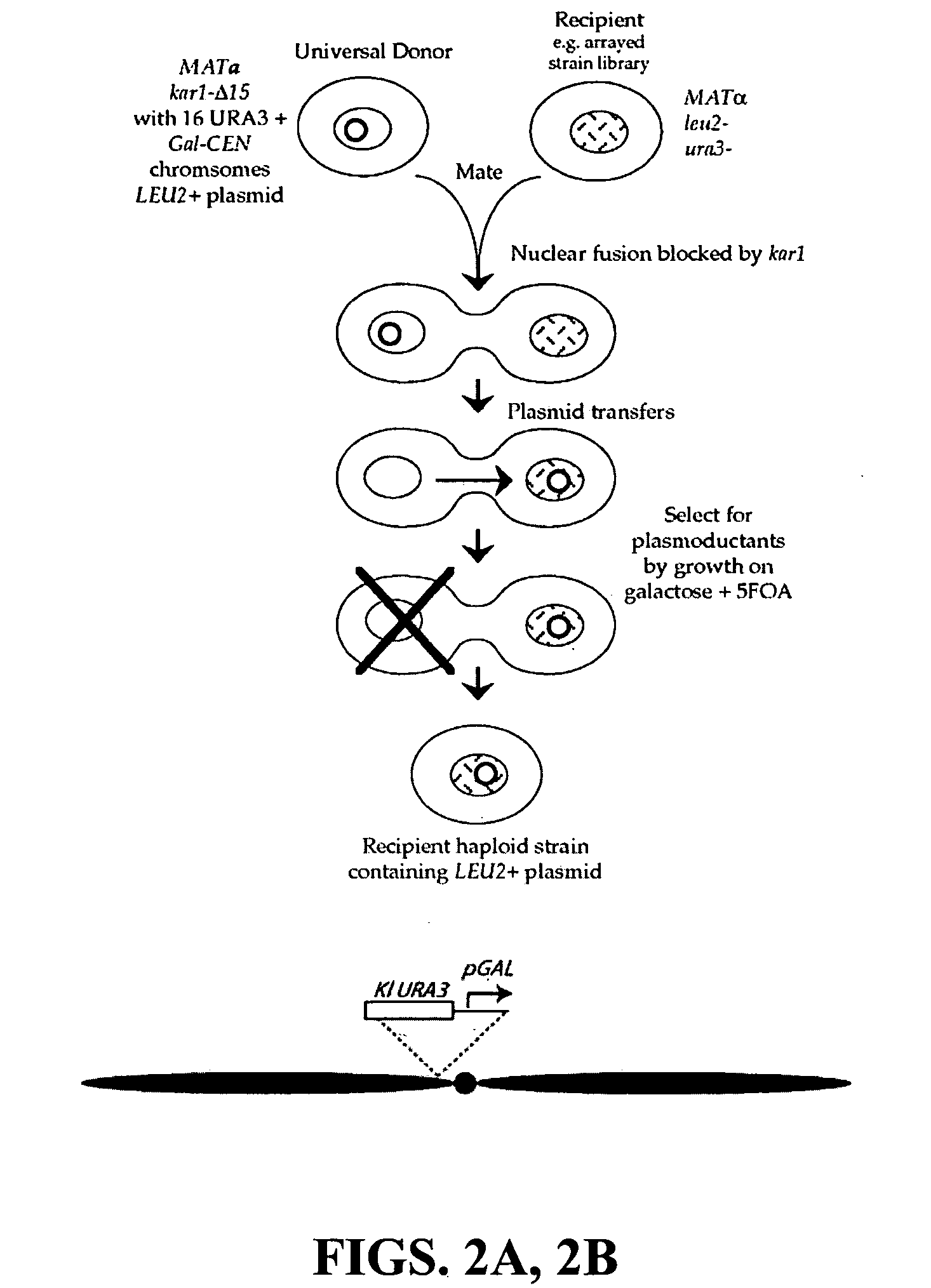
The invention provides a universal yeast donor strain that contains a conditional centromere and a URA3 allele on every chromosome. This strain was constructed in four rounds of crosses of individual conditional chromosome strains using a novel tetrad-based screen to identify segregants in which all marked chromosomes were contained in the same spore. The invention also provides an improved high efficiency method to transfer extrachromosomal genetic material such as plasmid DNA into any Saccharomyces strain for use with the current gene disruption libraries. The method of transfer is mating-based method which uses a kar1 plasmid donor strain that can initiate mating but cannot form a diploid and allows plasmid transfer (plasmoduction) between nuclei in the heterokaryon. kar1 matings have been used to transfer YACs between yeast strains, but previous methods required specialized genetic backgrounds in the recipient strains and suffered from high rates of spurious chromosome transfer (Hugerat, Y., et al. 1994. Genomics 22:108). Plasmoduction with the universal donor strain only requires that the recipient strain be ura3, GAL+ and have another marker available for selection of the transferred plasmid. Counterselection against every donor chromosome also limits the amount of spurious allele transfer. The universal donor strain and the method of the invention are used to screen the yeast gene disruption library with plasmid-based dominant negative alleles of various genes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Generation of potent dominant negative transcriptional inhibitors
The present invention provides methods and compositions for regulating gene expression using transcription factors linked to proteins that localize to the transcriptional machinery.
Owner:ADVANCED GENETIC SYST +1
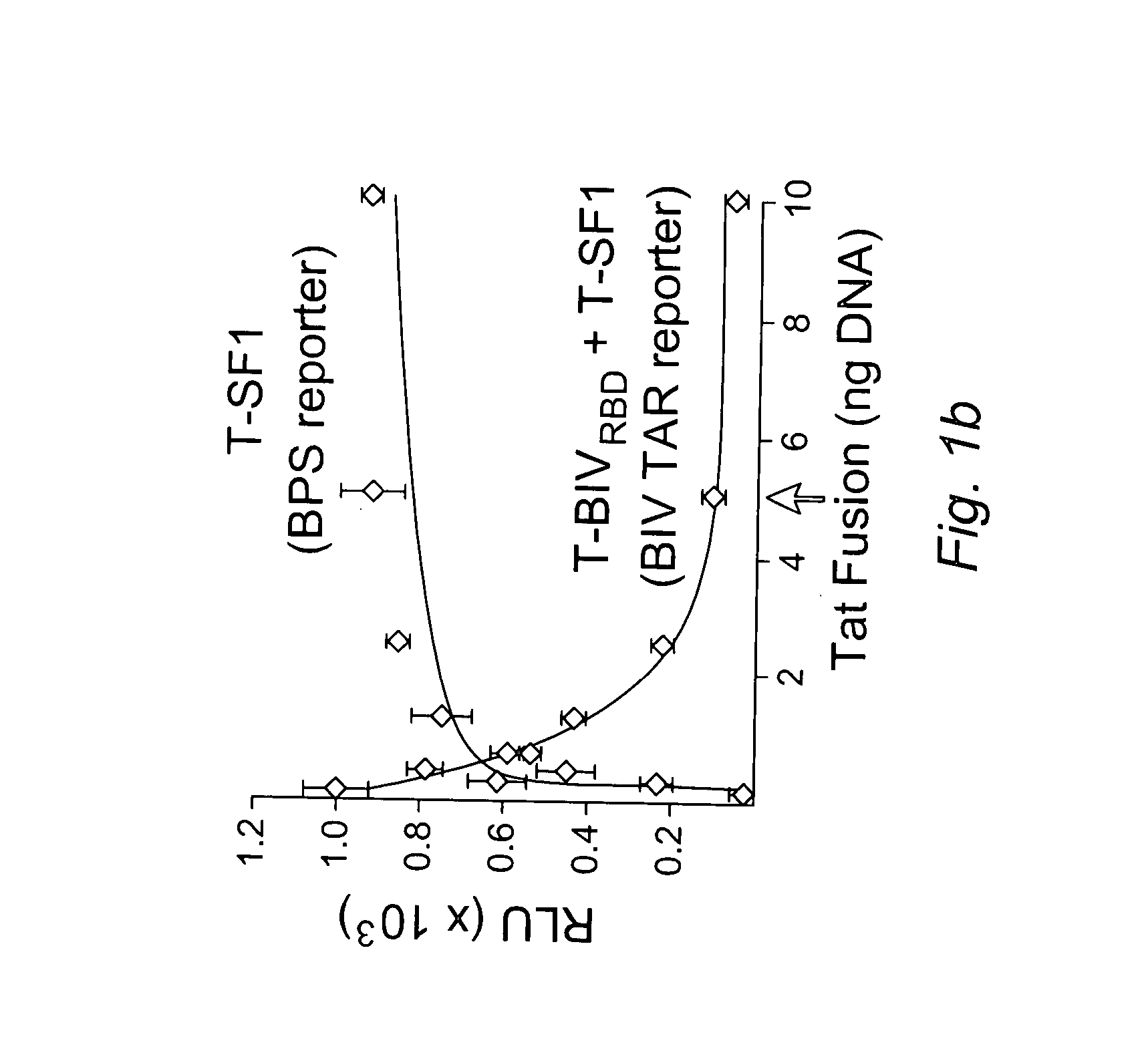
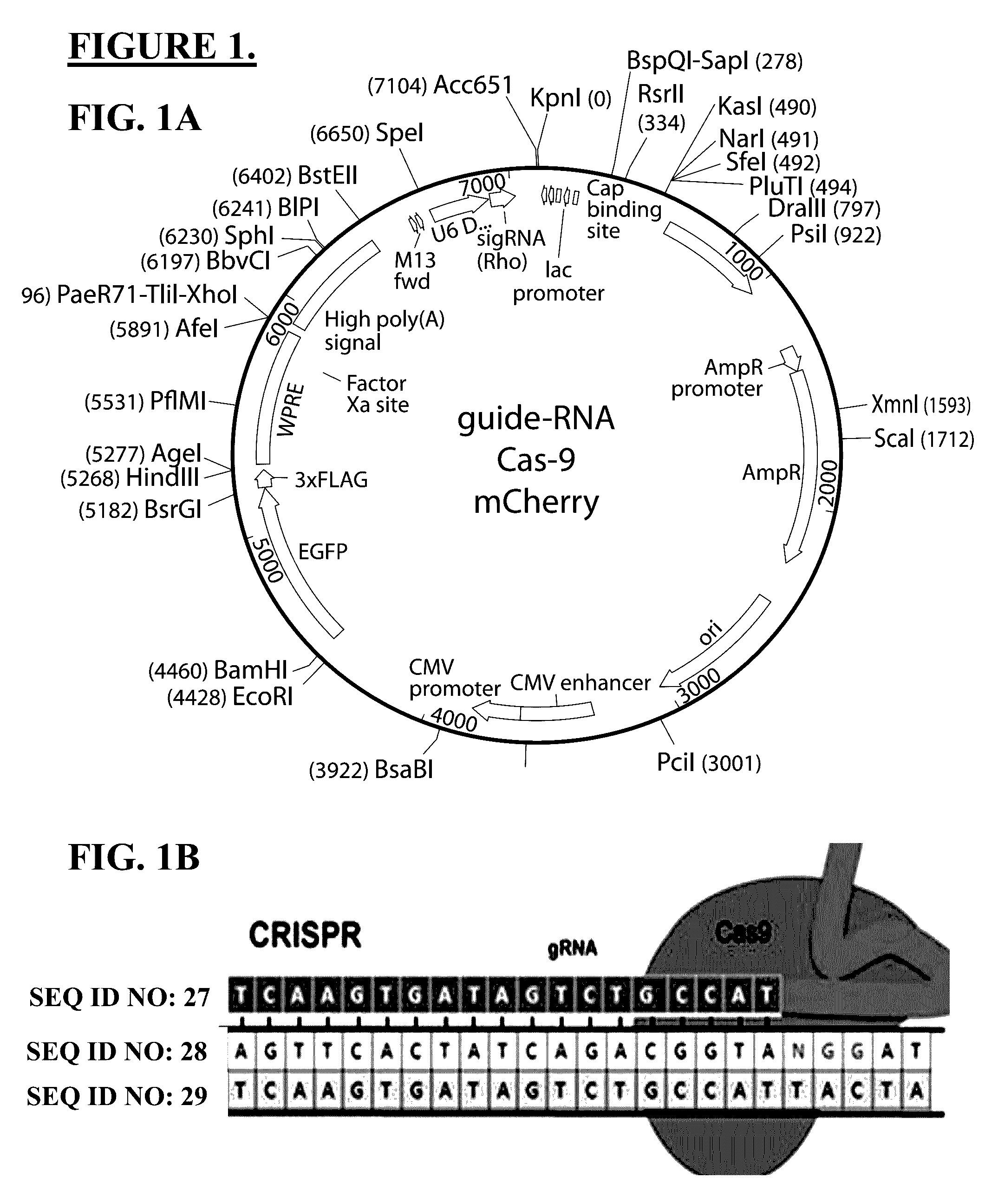
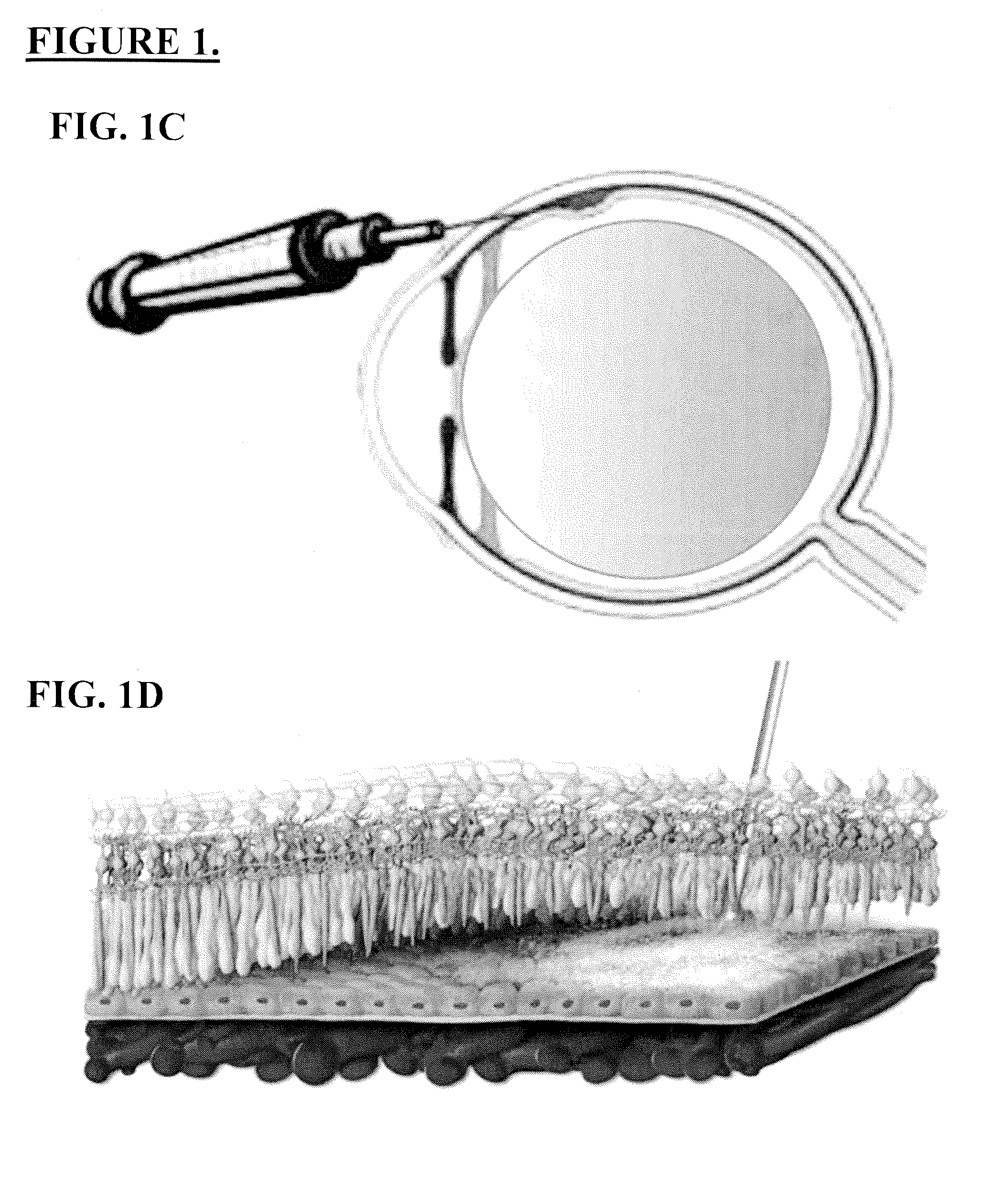
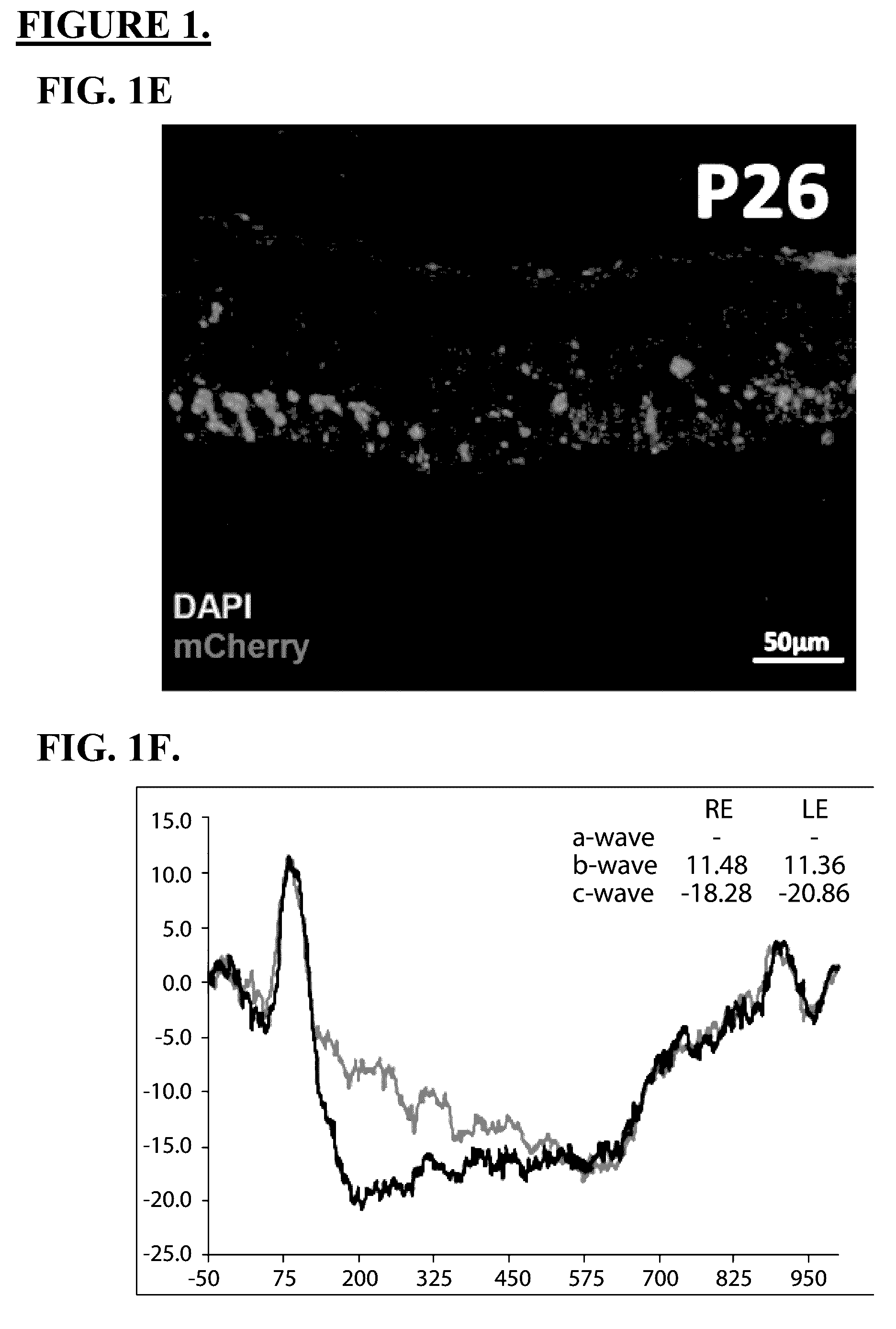
Use of crispr/cas9 as in vivo gene therapy to generate targeted genomic disruptions in genes bearing dominant mutations for retinitis pigmentosa
PendingUS20160324987A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseIn vivo
Described herein are methods and compositions for genomic editing. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic (CRISPR) allows for highly selective targeting and alteration of genetic loci. Here, the Inventors demonstrate CRISPR as capable of being used in living animals to prophylactically prevent a genetic disease from manifesting. Targeting and disruption of mutated rhodopsin gene prevents progression of retinitis pigmentosa in the retinal cells of a transgenic rat model. Such techniques allow for treatment methods in subjects with dominant genetic mutations, often associated with lack of a gene product, or a toxic gene product. The described technology effectively abrogates deleterious effects due to the presence of a mutated gene copy allowing the normal function of the wild-type protein to prevent cell and vision loss. The efficacy of these in vivo mechanisms are widely extensible to similar dominant negative gene mutations causing disease, or other types of genetic disease.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
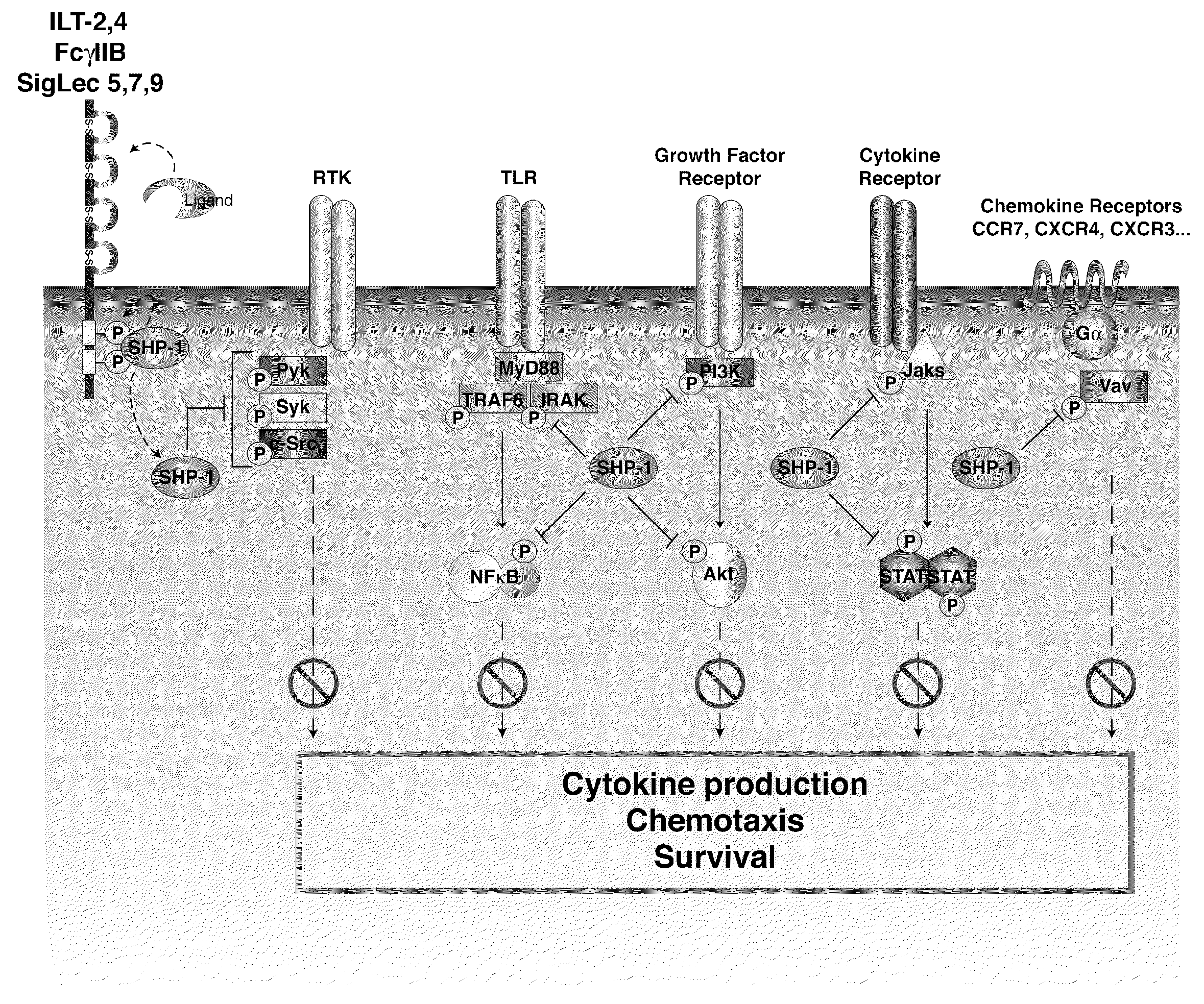
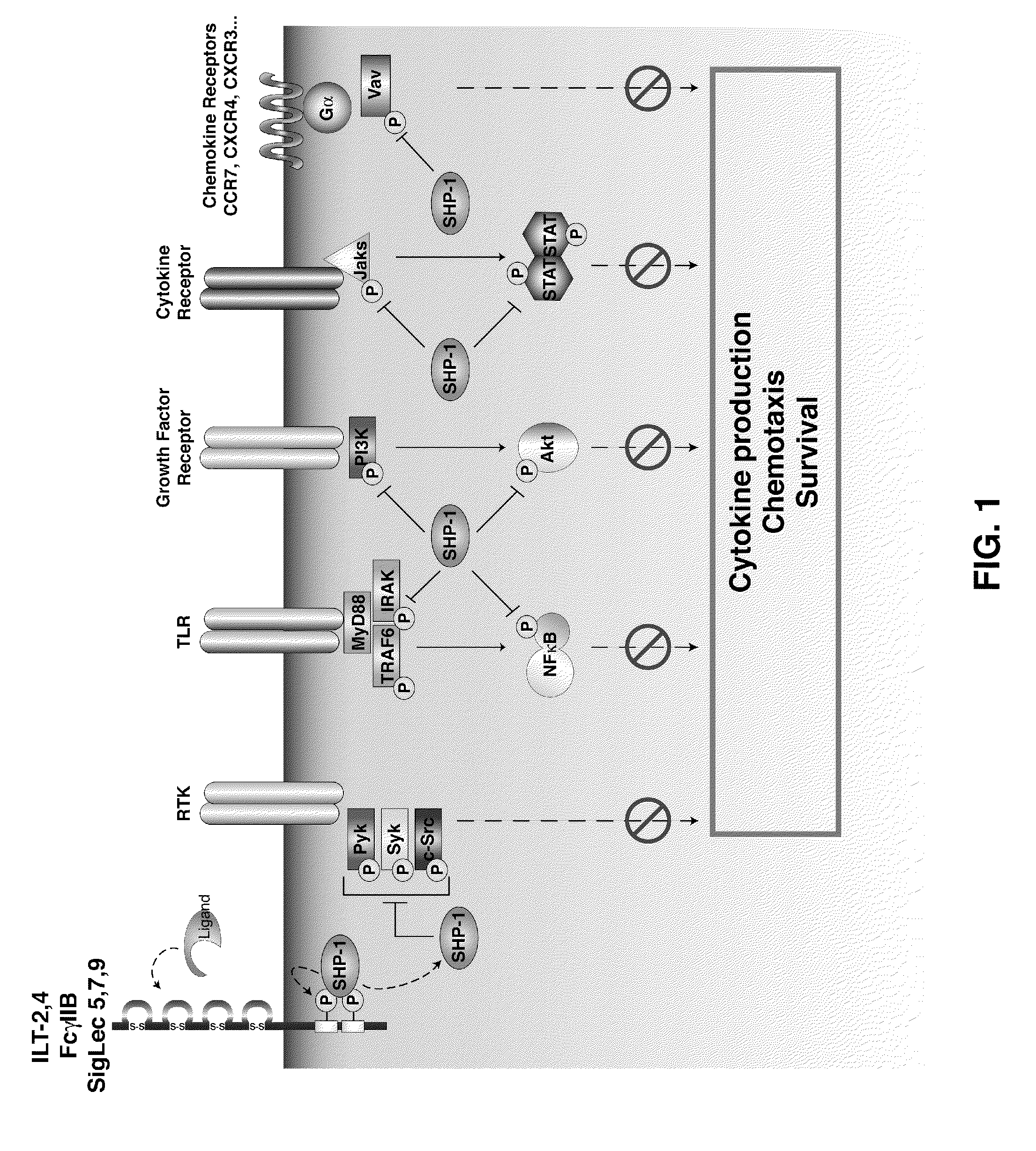
Inhibition of the sh2-domain containing protein tyr-phosphatase, shp-1, to enhance vaccines
The invention describes the use of dendritic cell vaccines, wherein SHP-1 expression or activity is modulated in the dendritic cell. In particular, the invention provides dendritic cells (DC) transduced with an SHP1-shRNA adenovirus, or dominant negative (dn-SHP-1) or constitutively active (ca-SHP-1), and pulsed with an antigen. The methods and compositions of the invention are used for the prevention and / or treatment of cancers, other cell proliferation diseases and conditions, diseases caused by a pathogen, or autoimmune disorders.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
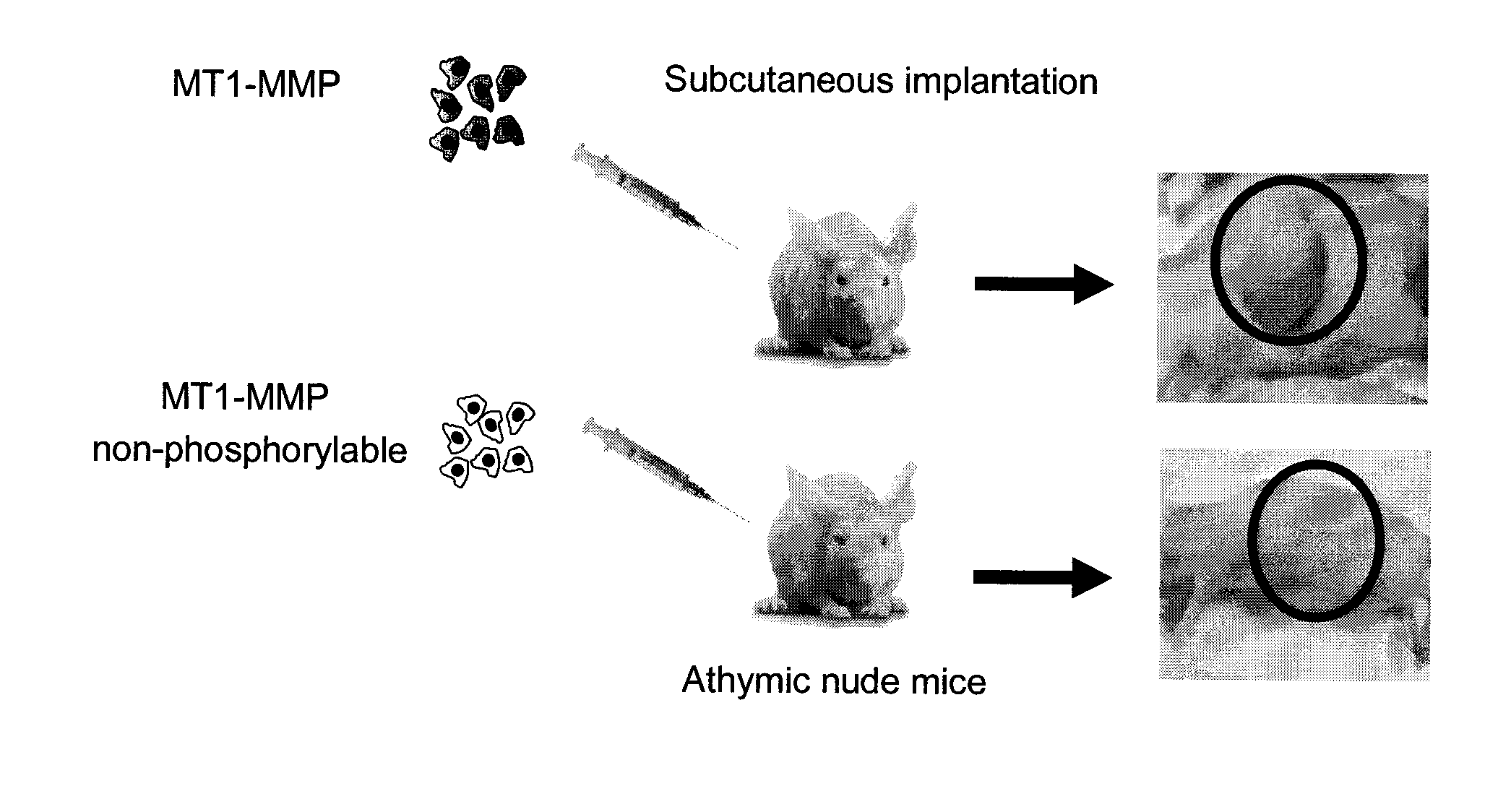
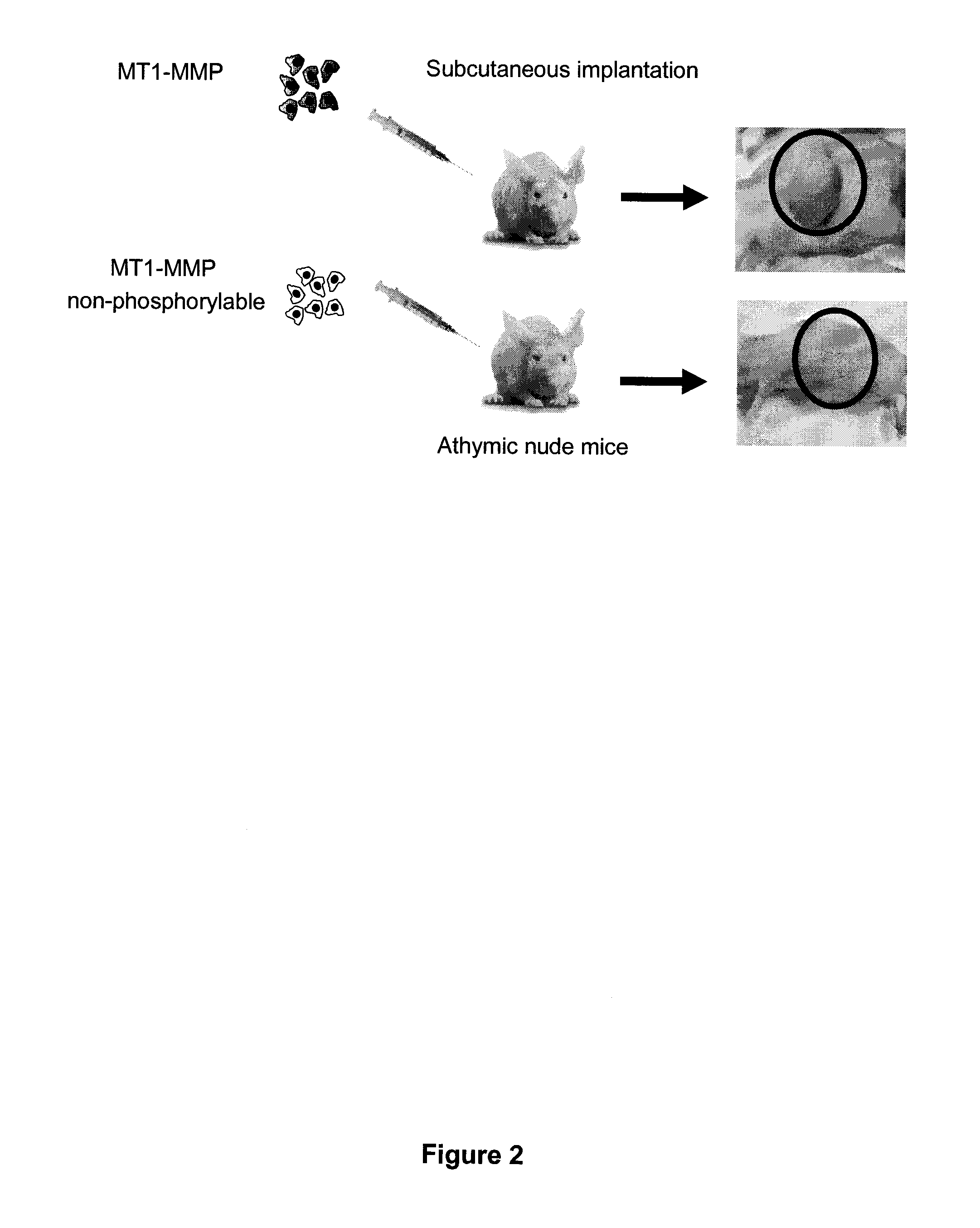
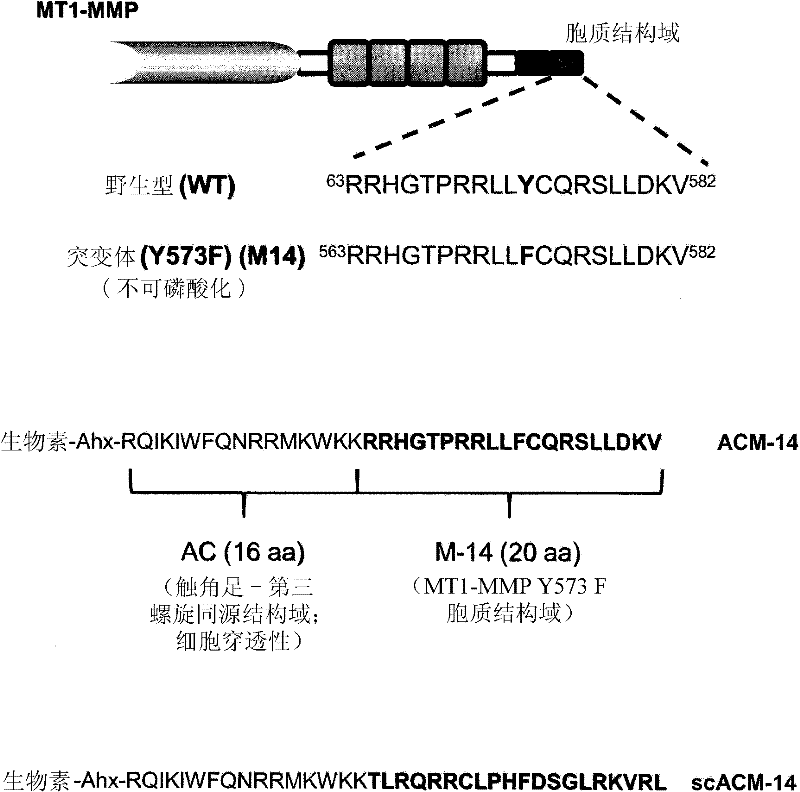
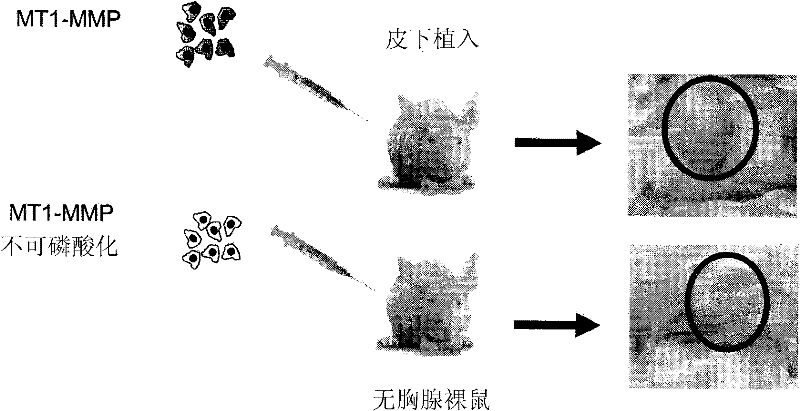
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloprotein inhibitors and uses thereof
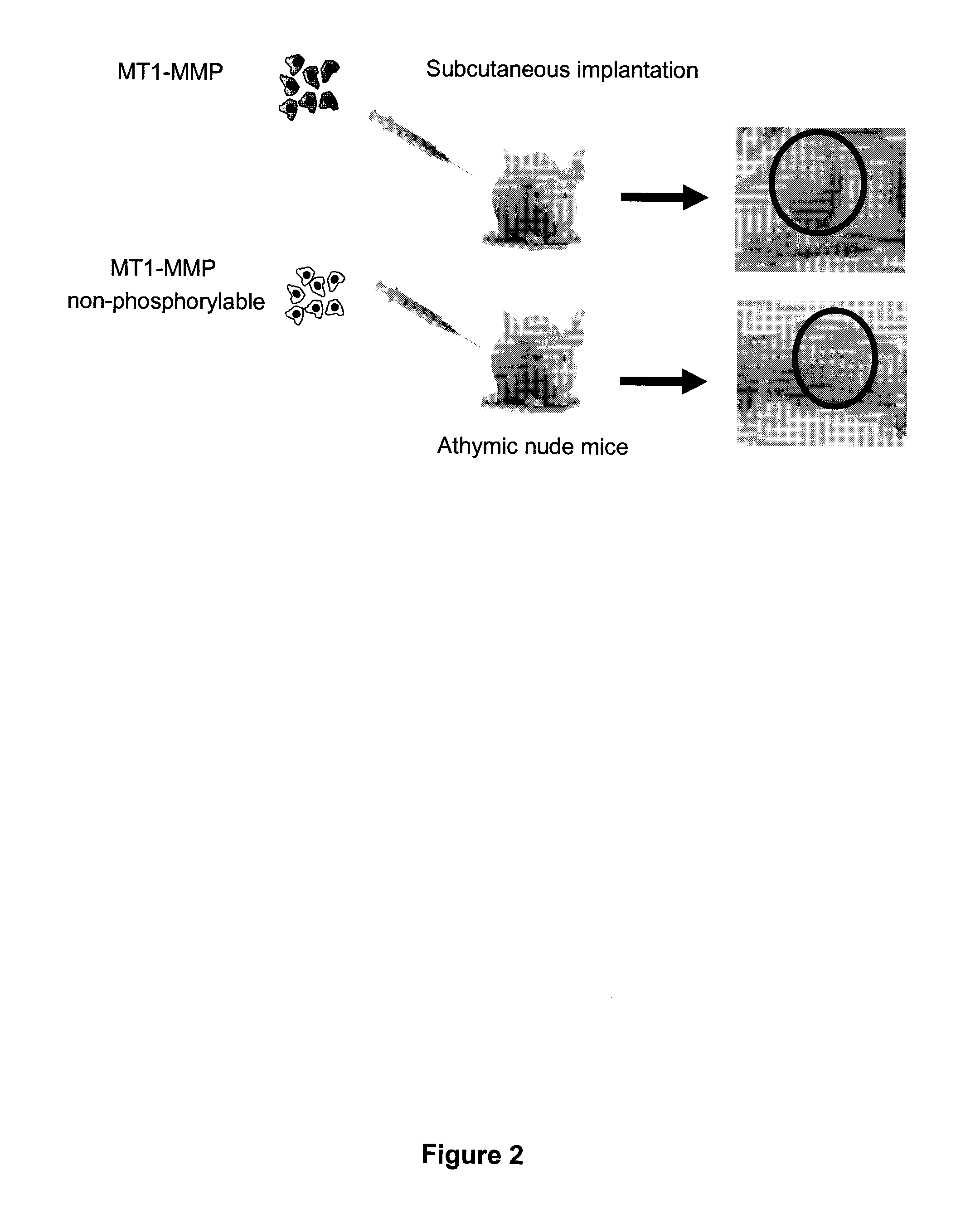
InactiveUS20110305750A1Reduce the frequency of occurrenceReduce severityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseasePhosphorylation
Based on the discovery that a soluble polypeptide including a nonphosphorylatable form of the cytoplasmic domain is capable of inhibiting in a dominant negative manner, the present invention provides compositions including MT1-MMP inhibitors such as peptide inhibitors, and methods for treating diseases associated with MT1-MMP activity. Such diseases include cancer, arthritis, and heart disease, and vascular disease.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Disease treatment via antimicrobial peptides or their inhibitors
The invention provides methods for the treatment of disease and promotion of healing that include providing a therapeutically effective amount of a mammalian antimicrobial peptide (AMP) or analog thereof, in particular a cathelicidin or cathelicidin fragment or cathelicidin analog, thereby treating the disease in the subject in need thereof. The invention also provides specific analogs or fragments of cathelicidin that function as agonists, as do endogenous cathelicidins, or as either dominant negatives or as inhibitors to endogenous cathelicidin or to other endogenous AMPs or that compete with pro-inflammatory agents or fragments of AMPs on cognate receptors without inducing disease.
Owner:HILLMAN YITZCHAK
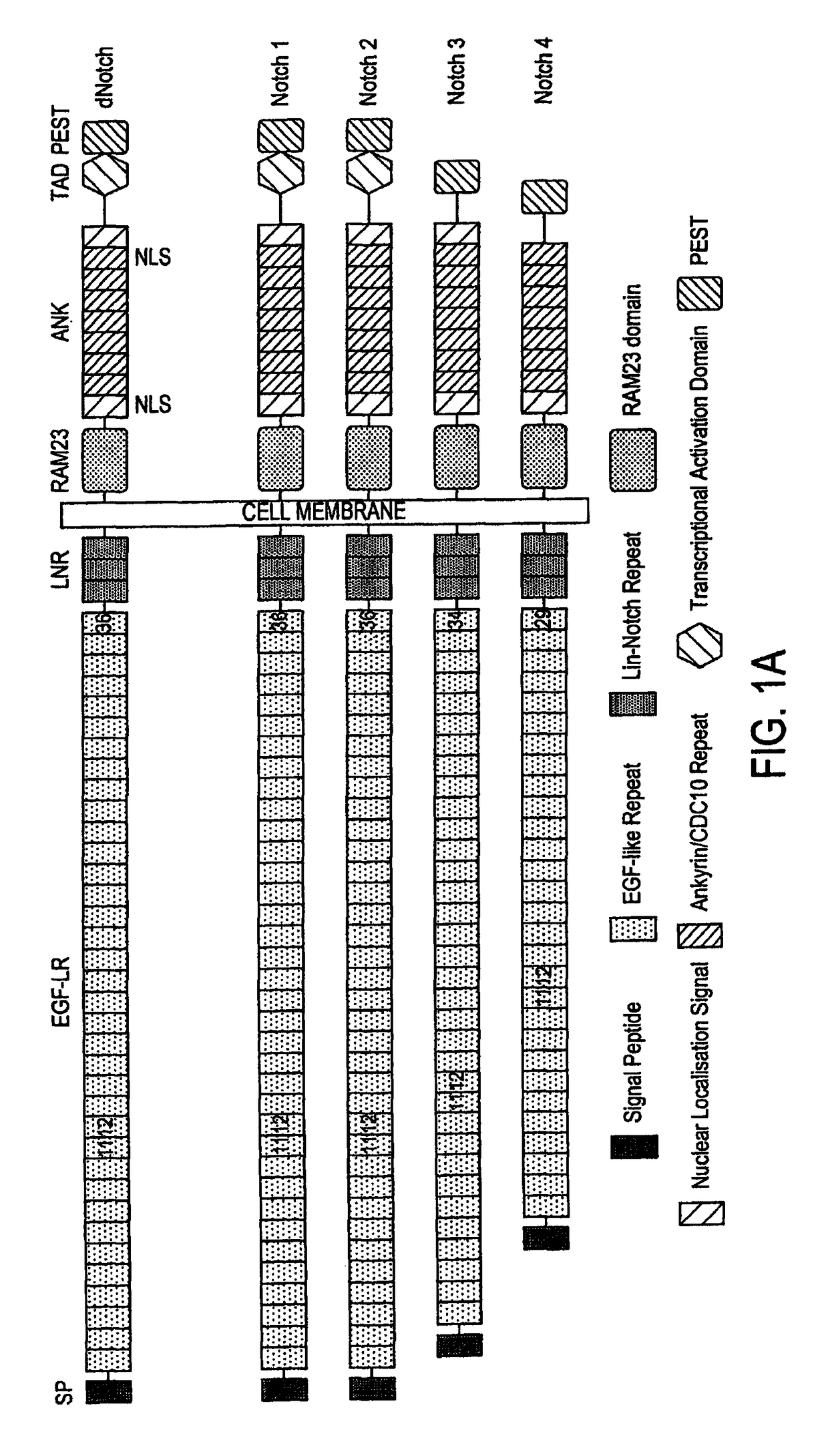
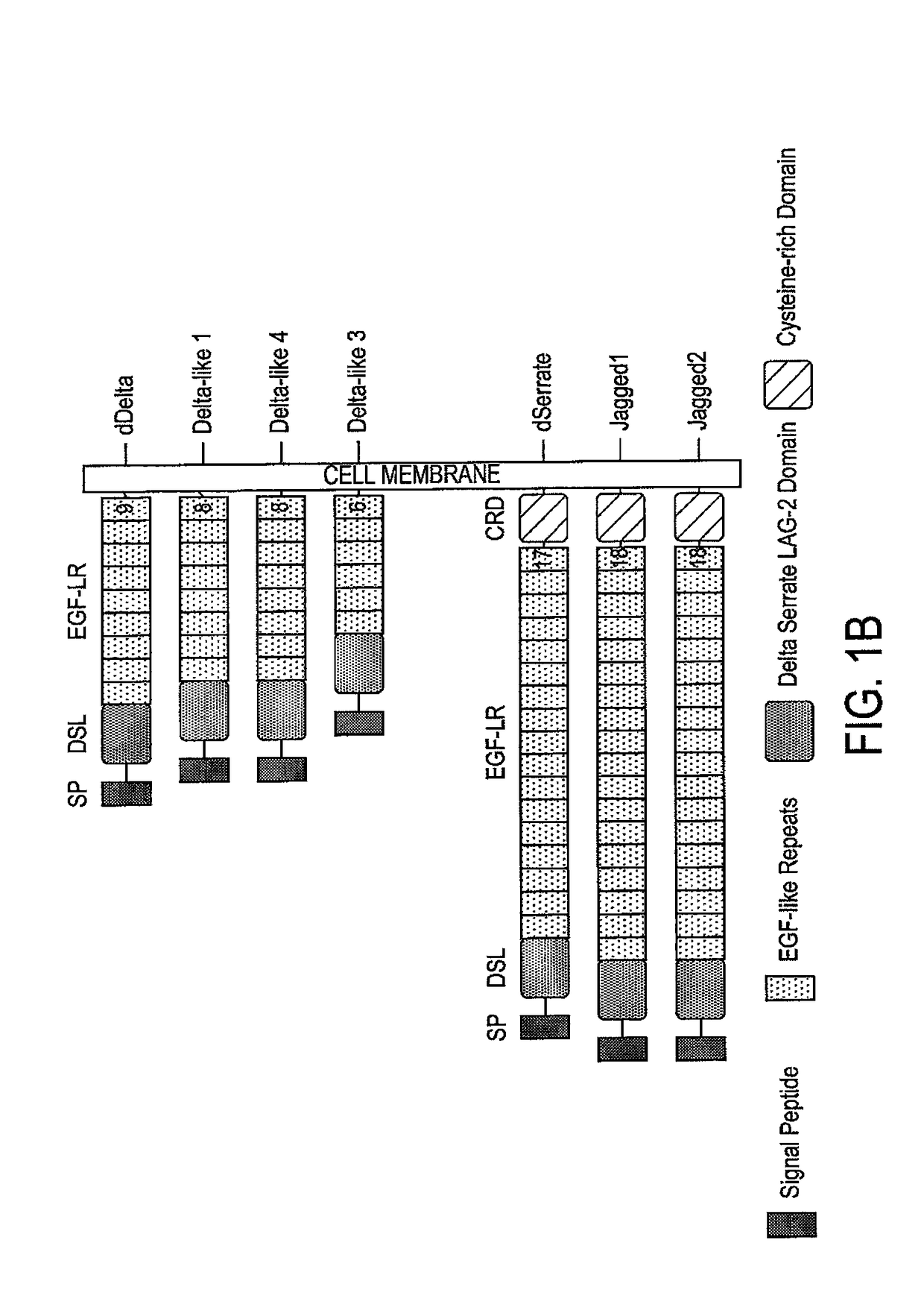
Antennapedia-dominant negative mastermind-like construct
ActiveUS8119366B2Peptide/protein ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesNotch signalling pathwayCancer research
The present invention is based on the discovery that the Notch signaling pathway is associated with cancer. Accordingly, the invention provides methods and compositions for treating cancer. Also provided are methods of modulating the expression and / or activity of proteins in the Notch signaling pathway for use in diagnoses and treatment of cancer in a subject.
Owner:ANASTASIS BIOTEC LTD
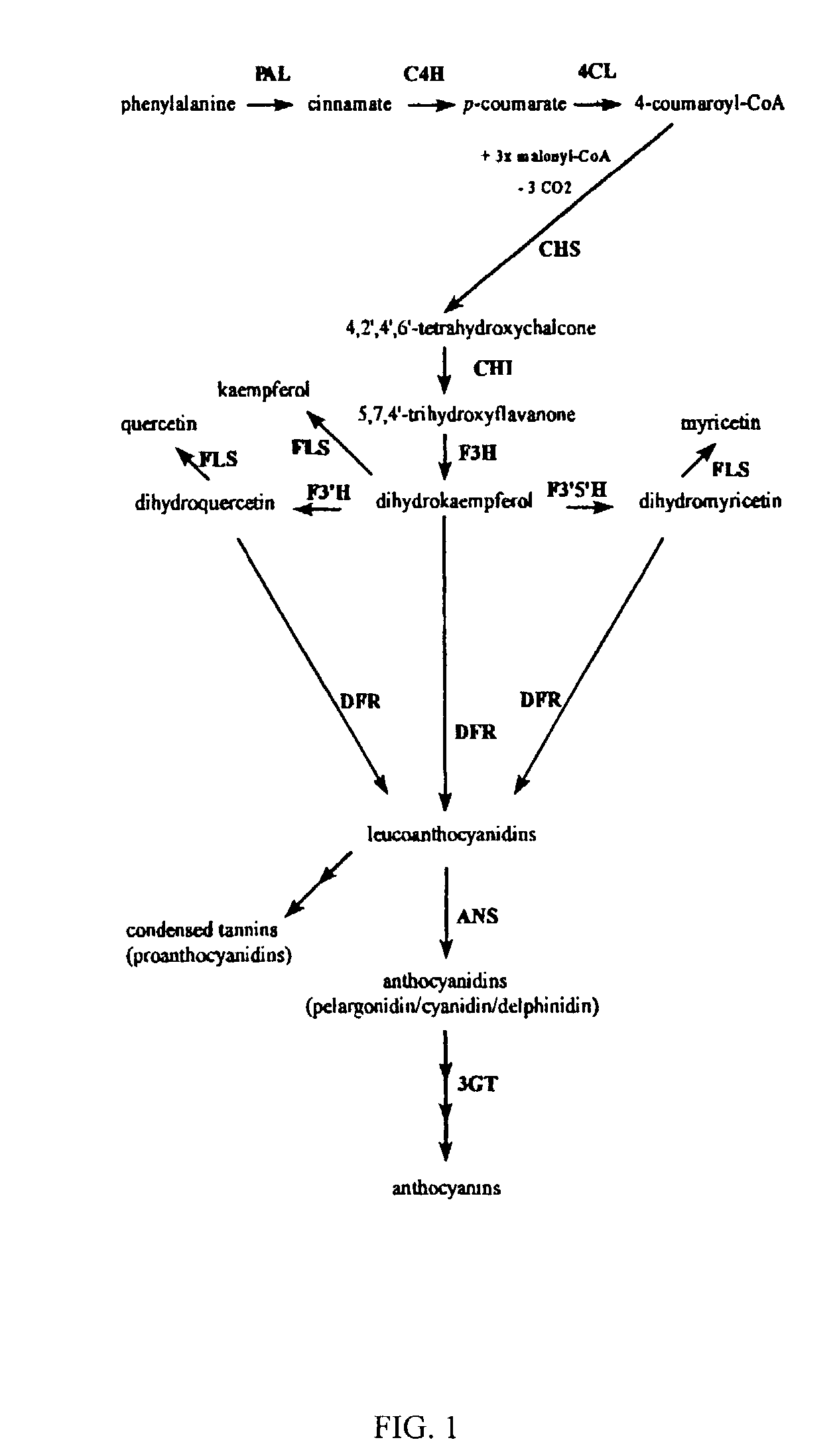
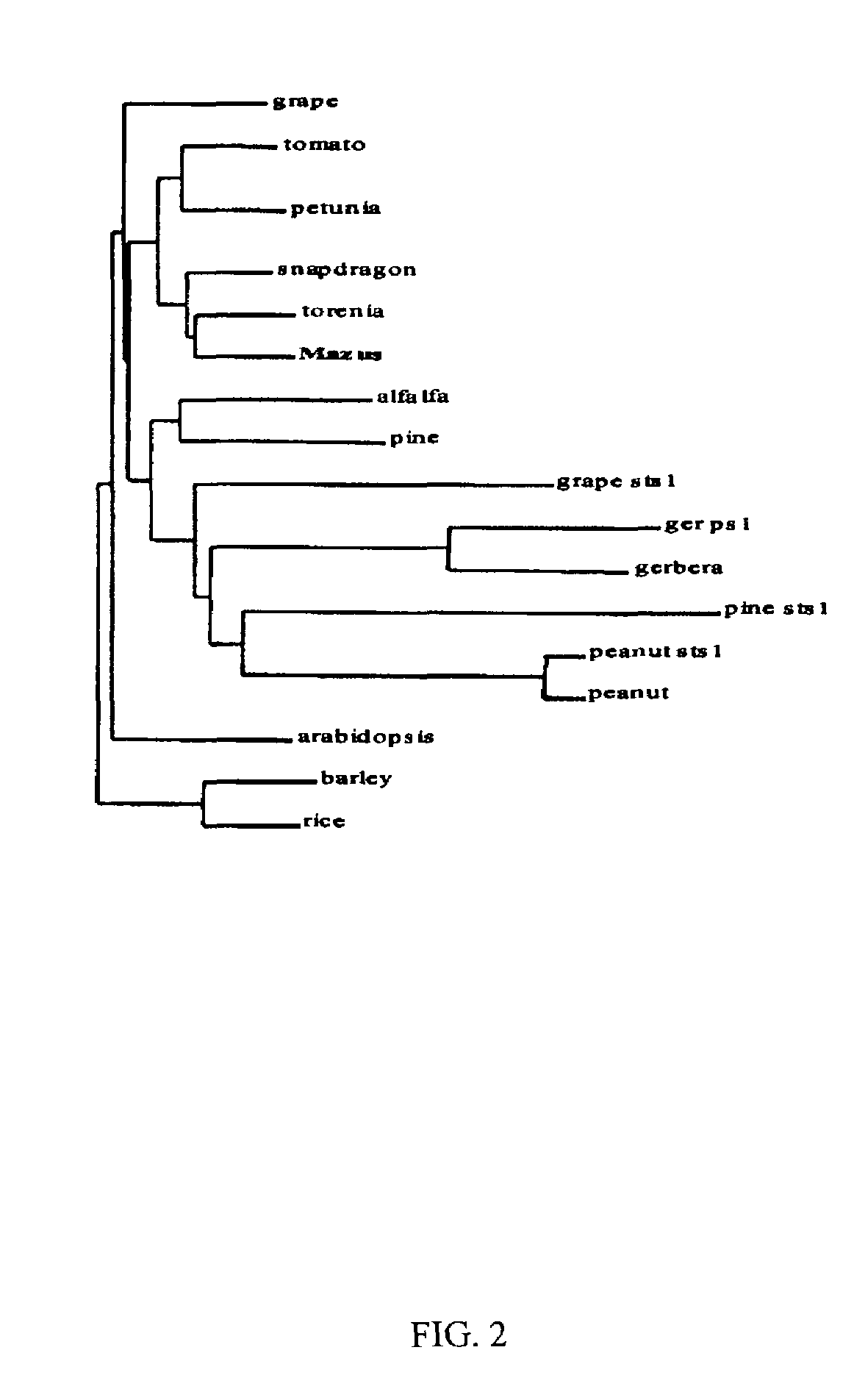
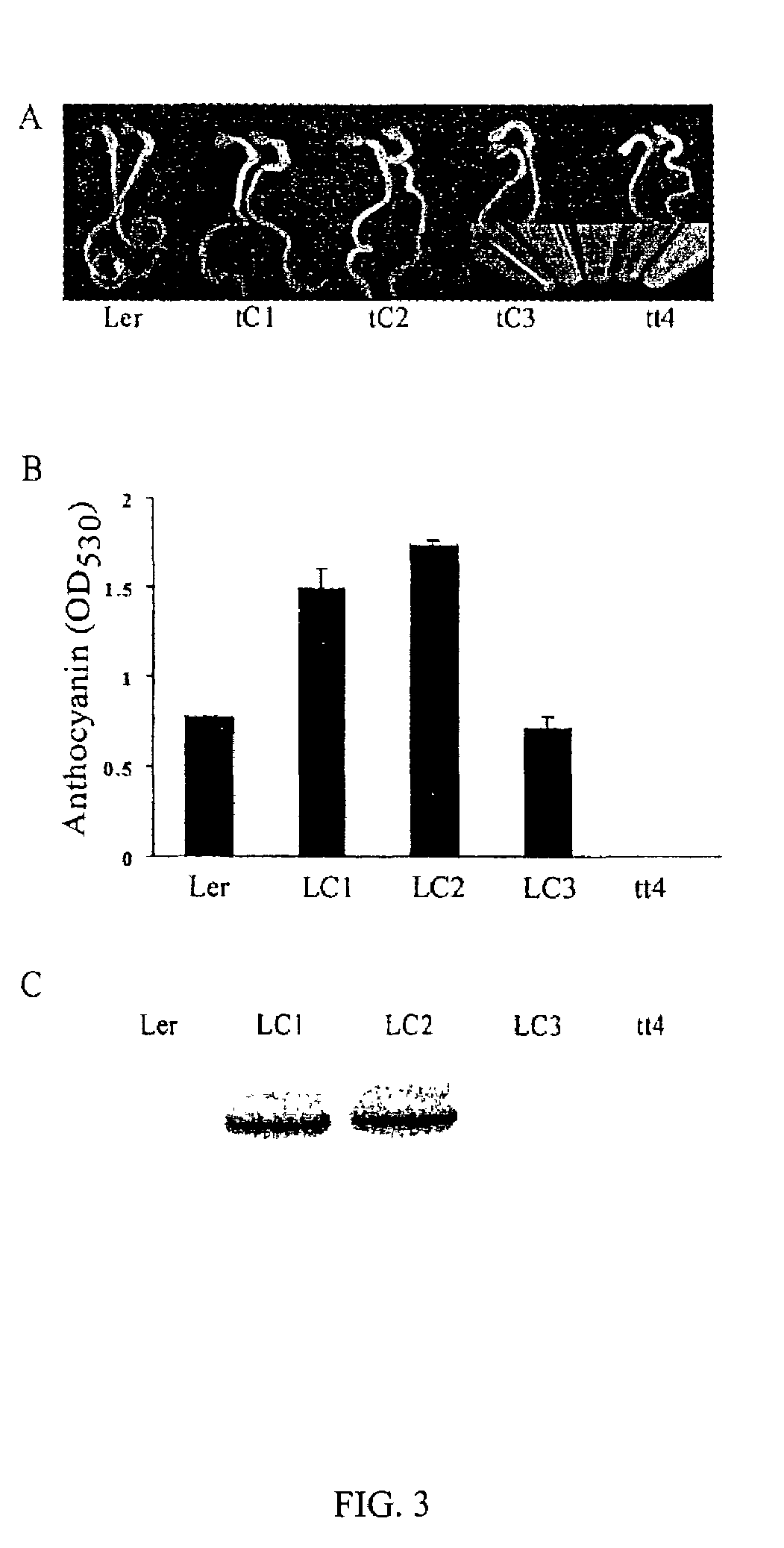
Genetic sequences encoding dominant-negative chalcone synthase and uses therefore
The invention includes modified Mazus chalcone synthase (CHS) nucleic acids, which encode a modified chalcone synthase that has alanine instead of cysteine at the 165th amino acid of Mazus CHS and either glycine or lysine instead of methionine at the 138th amino acid of Mazus CHS. The property of the encoded modified Mazus CHS is characterized by its dominant-negative inhibition of CHS. The invention also includes plants having at least one cell expressing the modified Mazus CHS. Such plants are characterized by the decreased content of anthocyanins. The invention also includes vectors comprising at least a portion of the modified Mazus CHS nucleic acids. The invention also includes methods using such vectors for producing plants having the decreased content of anthocyanins.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Trp inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention, relates to methods including compounds, derivatives, antibodies, interfering RNA, biologies, polypeptides, dominant negative effectors, and their use in the treatment of neuropathic pain by inhibition of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. In another embodiment, this invention relates to inhibitors, antagonists, and agonists of TRPC4. TRPC4 therapeutic agents and modulators include but are not limited to small molecule inhibitors, compounds, amino acid derivatives, polypeptides, RNA interference agents, natural chemicals, ligand derivatives, and ions. TRPC4 therapeutic agents and modulators are developed for the treatment of neuropathic pain, including but not limited to pain sensations such as nociception, hyperalgesia, allodynia, and loss of sensory function.
Owner:POSEIDA THERAPEUTICS INC
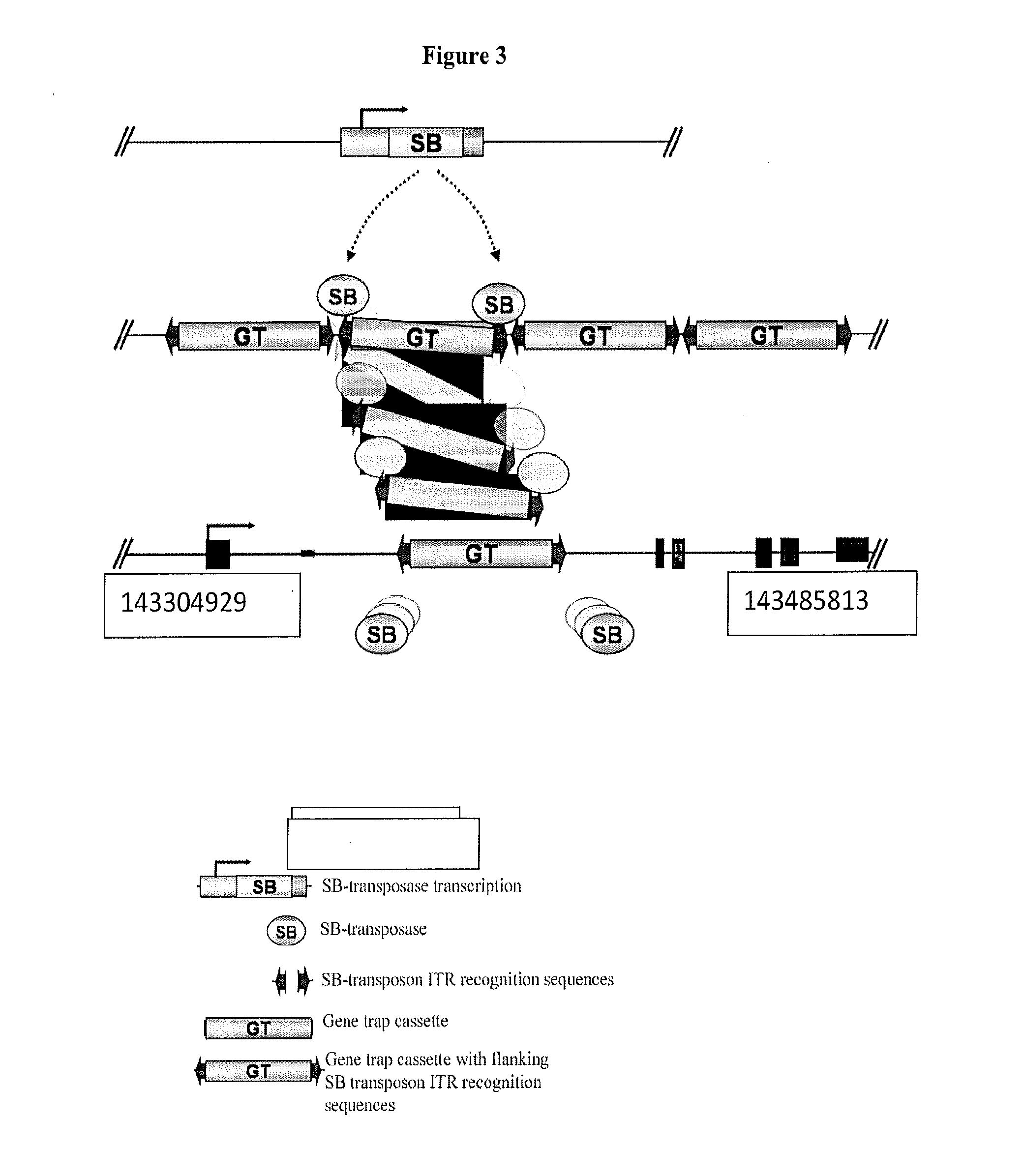
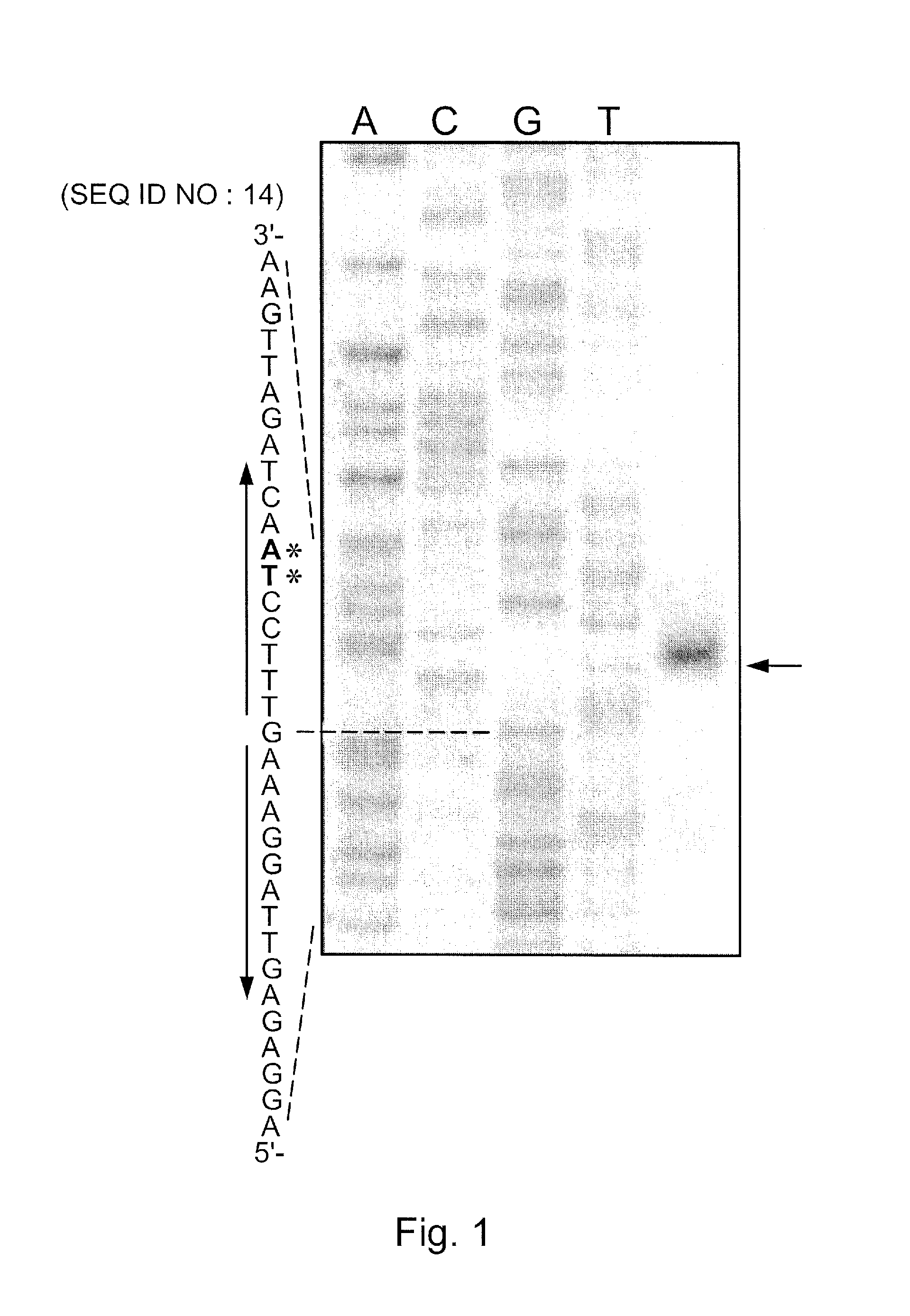
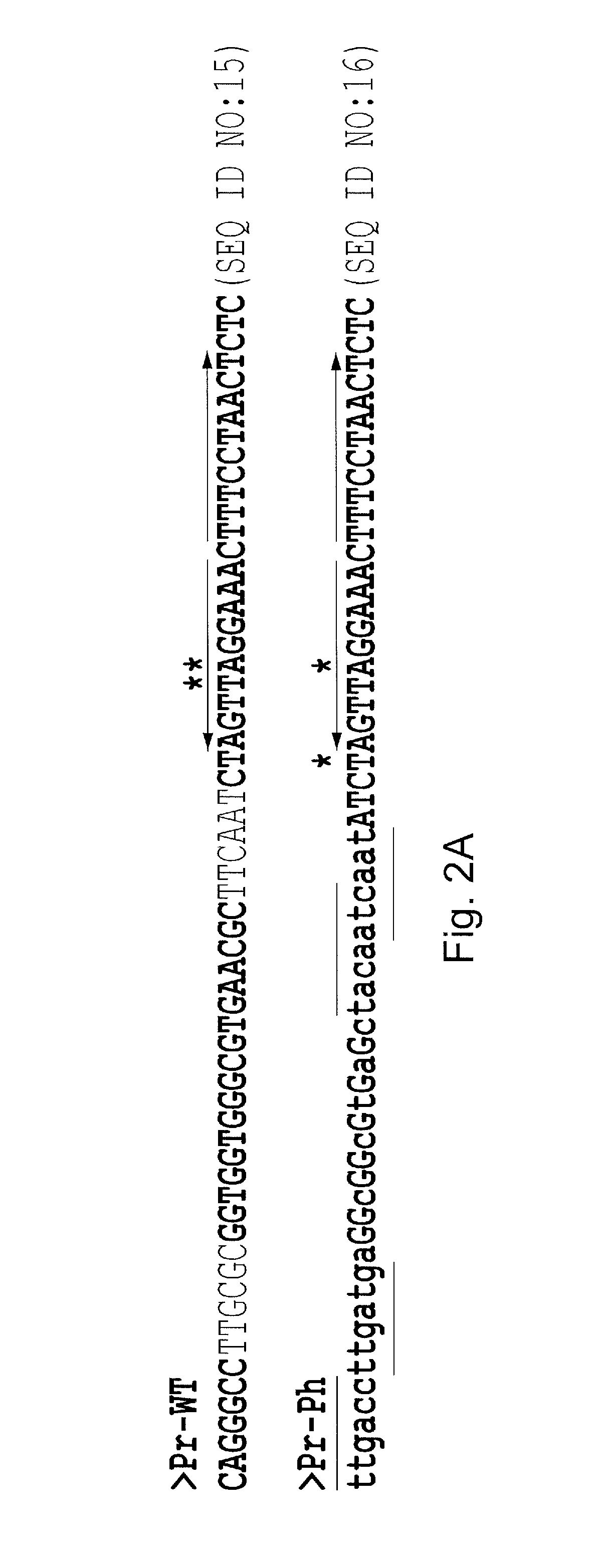
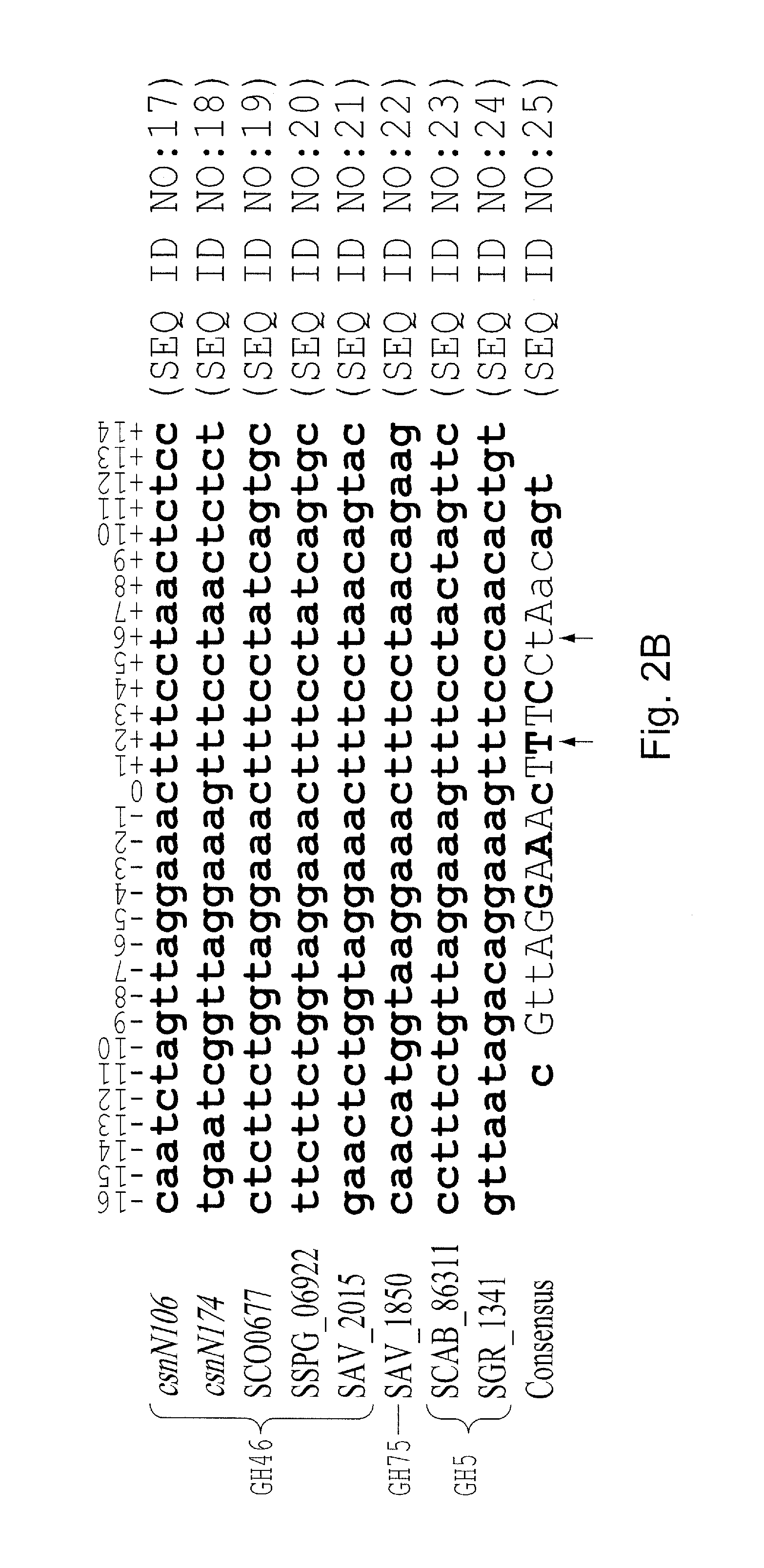
Csnr-deficient actinobacteria for the production of an enzyme having chitosanase activity
The present invention relates to genetically modified actinobacteria for the production of an enzyme having chitosanase activity. The genetically modified actinobacteria have a reduced (or abolished) activity of the CsnR polypeptide. Such reduced activity can be obtained by reducing the capacity of expressing the csnR gene, its corresponding transcript or expressing a dominant-negative CsnR polypeptide. Such genetically modified actinobacteria are less dependent (and, in some embodiment, totally independent) on the presence of chitosan in the culture medium for producing an enzyme having chitosanase activity. In addition, the genetically modified bacteria produce less proteases in the culture medium and ultimately provide a chitosanase end-product with higher purity.
Owner:SCOPRA SCI & GENIE SEC
Transgenic animal
A transgenic rat containing in its genome a nucleotide sequence encoding a Ga subunit protein, which Ga protein subunit is uncoupled from regulation by Regulators of G-Protein Signaling (RGS) proteins, which Gx subunit protein is eventually the dominant-negative G188S mutant of Gax9, which nucleotide sequence is operatively associated with a neuron-specific expression control sequence, wherein the transgenic rat expresses the GA subunit protein in neural cells resulting in extended D-protein coupled receptor signaling mediated by the Ga subunit protein.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Methods and compositions for the determination of protein function and identification of modulators thereof
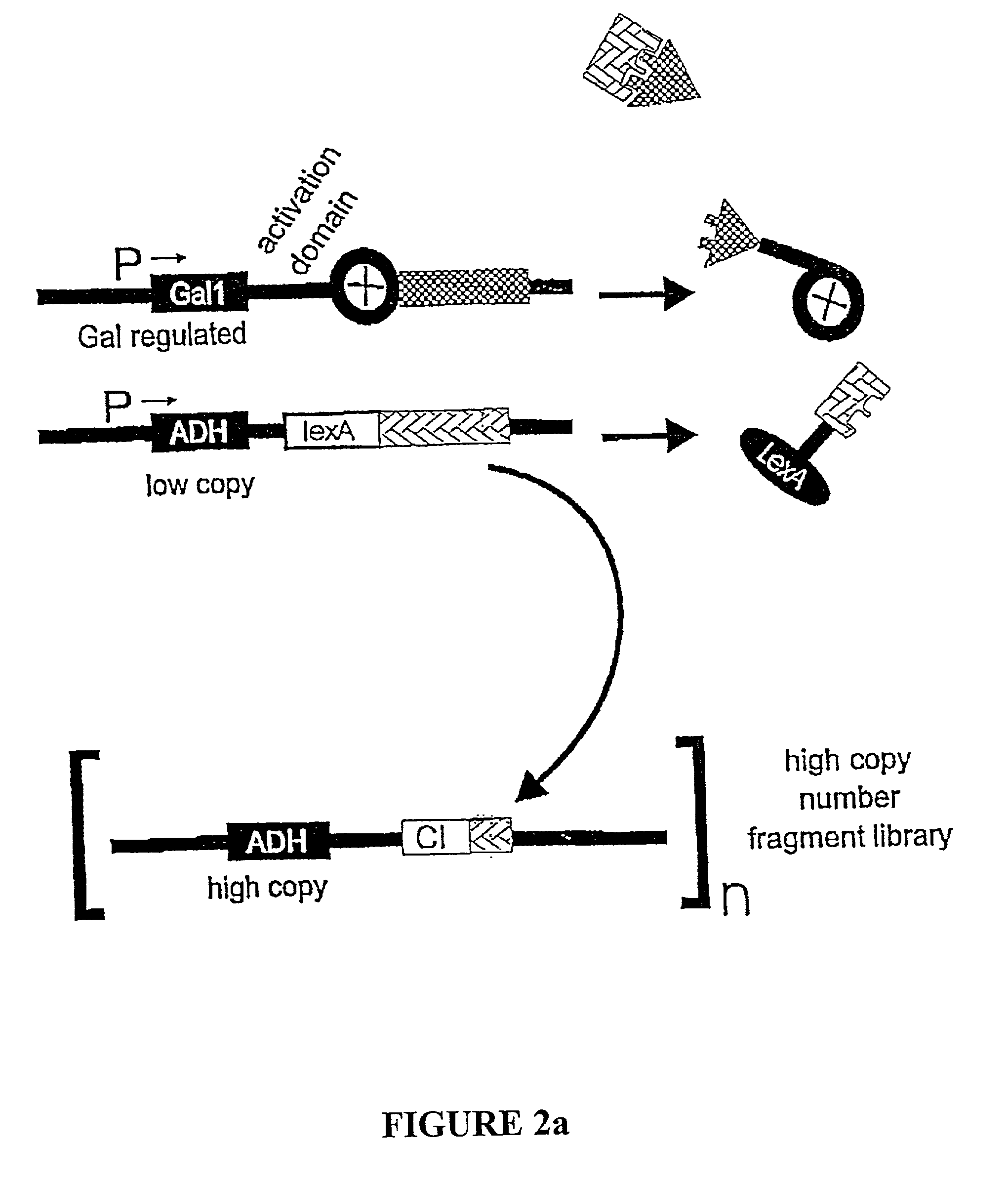
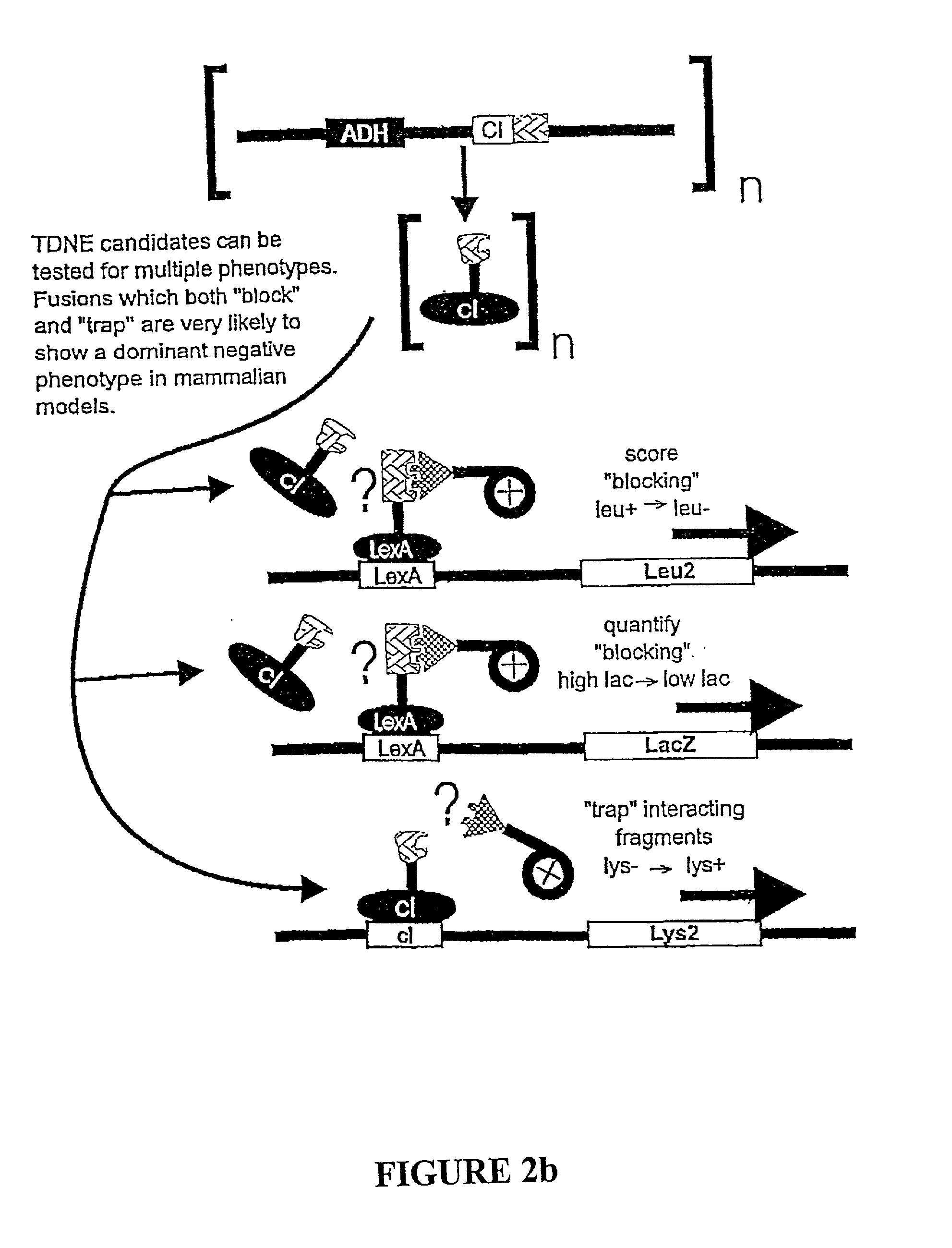
InactiveUS20030003449A1Enhanced inhibitory effectAlter formationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesProtein targetDrug biological activity
The present invention provides libraries of tag dominant-negative elements (TDNE) and methods the identification specific TDNEs that act as dominant-negative elements on a target protein of interest. The present invention further relates to the use of such TDNEs and dominant-negative elements for the identification of protein-protein interactions, and the determination of a target protein's biological activity and function. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the development of means, including small molecule compounds, for disrupting the target protein's biological function and activity.
Owner:MORPHOCHEM INC
Method for generating hypermutable plants
InactiveUS6900370B2Other foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyTransgene
Blockade of mismatch repair in a plant can lead to hypermutation and a new genotype and / or phenotype. One approach used to generate hypermutable plants is through the expression of dominant negative alleles of mismatch repair genes in transgenic plants or derived cells. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic plants, new cell lines and plant varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. Moreover, methods to inhibit the expression and activity of endogenous plant MMR genes and their encoded products are also useful to generate hypermutable plants.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloprotein inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS8853353B2Easy to transportReduce frequencyHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePhosphorylation
Based on the discovery that a soluble polypeptide including a nonphosphorylatable form of the MT1-MMP cytoplasmic domain is capable of inhibiting MT1-MMP in a dominant negative manner, the present invention provides compositions including MT1-MMP inhibitors such as peptide inhibitors, and methods for treating diseases associated with MT1-MMP activity. Such diseases include cancer, arthritis, and heart disease, and vascular disease.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloprotein inhibitors and uses thereof
Based on the discovery that a soluble polypeptide including a nonphosphorylatable form of the MT1-MMP cytoplasmic domain is capable of inhibiting MT1-MMP in a dominant negative manner, the present invention provides compositions including MT1-MMP inhibitors such as peptide inhibitors, and methods for treating diseases associated with MT1-MMP activity. Such diseases include cancer, arthritis, and heart disease, and vascular disease.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Genetic hypermutability of plants for gene discovery and diagnosis
InactiveUS20030143586A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyInsertional mutation
The invention provides methods for identifying polymorphic markers for herbicide resistance in weeds and for generating herbicide susceptible and herbicide resistant weeds by mutagenizing weeds and comparing genetic differences between herbicide resistant and herbicide susceptible weeds. The methods may involve the inhibition of mismatch repair in the weeds through the introduction of dominant negative alleles of mismatch repair genes, through T-DNA insertional mutations, or the use of chemical inhibitors of mismatch repair. The invention also provides polymorphic markers of herbicide resistance and methods and kits to screen for herbicide resistant weeds, such as horseweed, goosegrass and rye grass.
Owner:MORPHOTEX INC
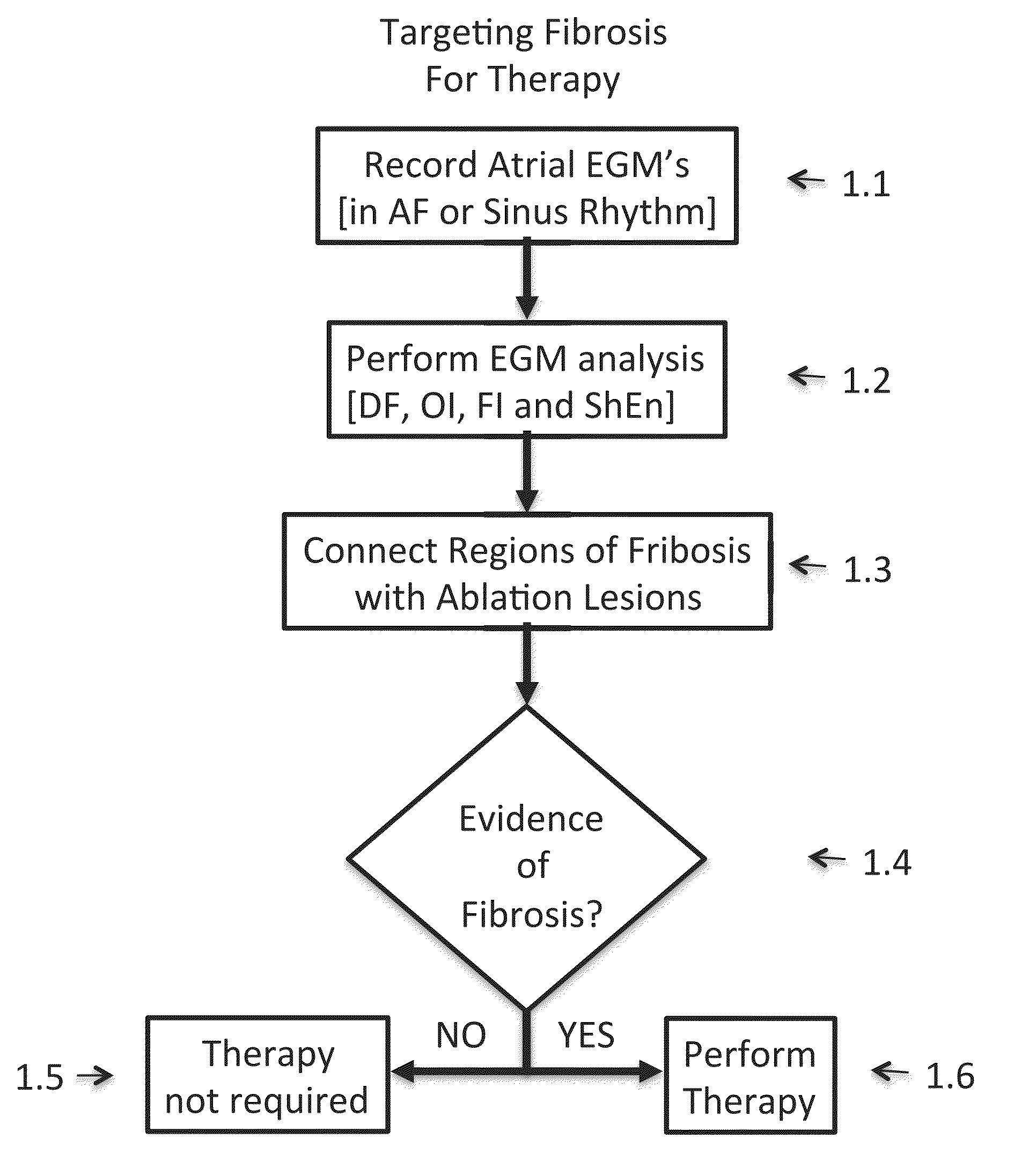
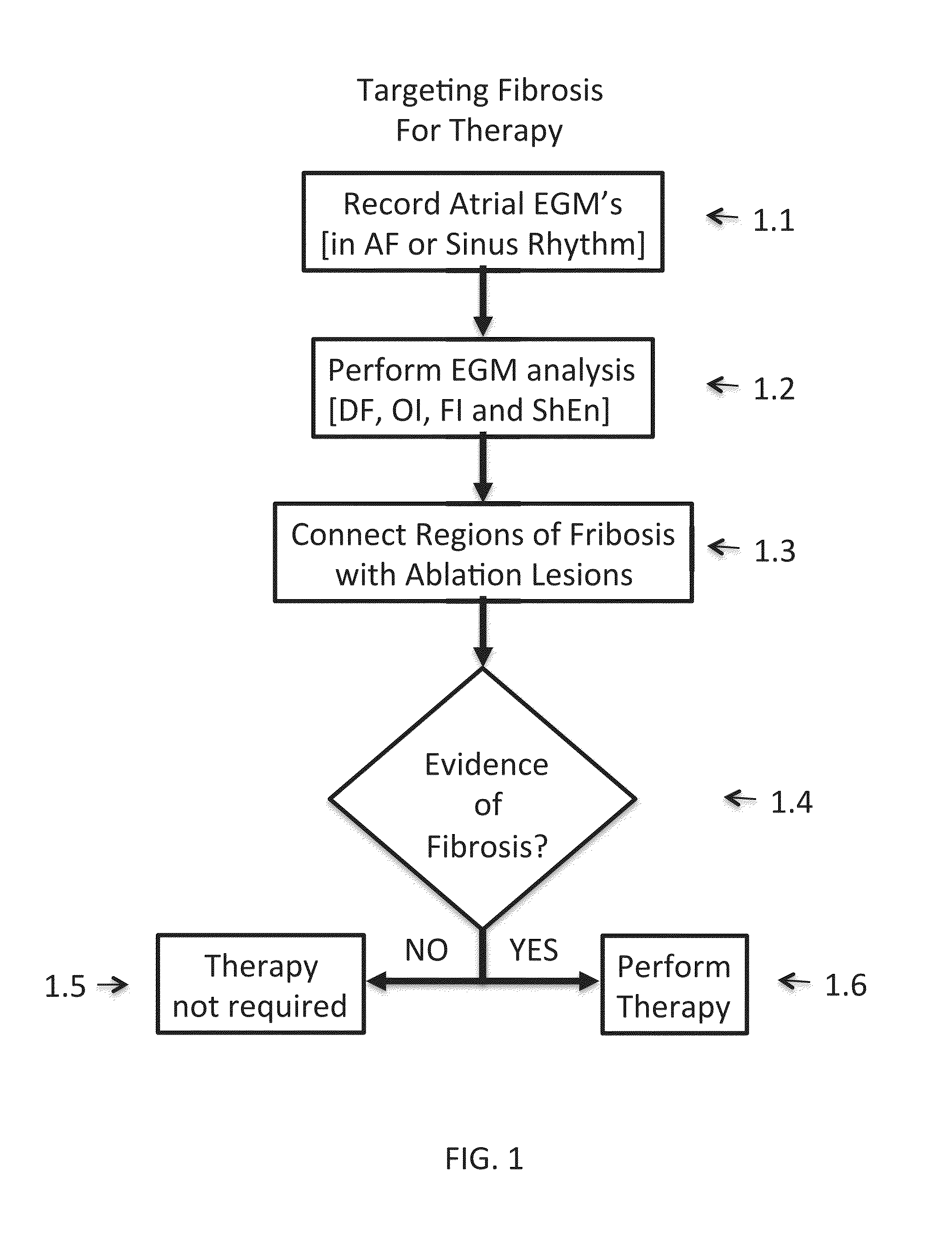
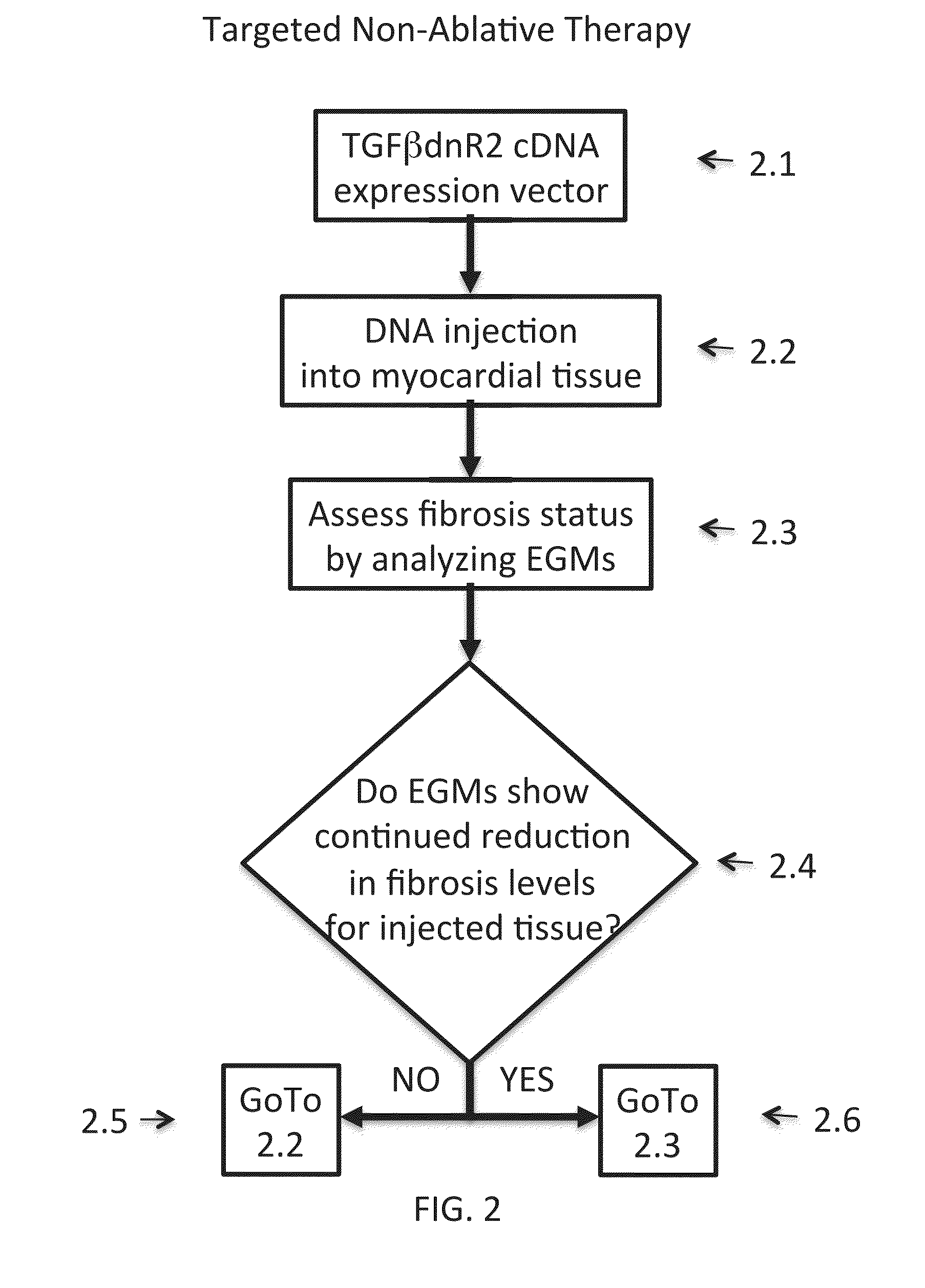
Inhibition of fibrosis and af by tgf-beta inhibition in the posterior left atrium (PLA)
ActiveUS20140037545A1Reducing AF fibrosisElectrocardiographyPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisProviding material
The disclosed methods pertain to diagnosing whether a non-ablative, gene therapy is needed for reducing AF fibrosis in a subject, and if so, methods of reducing AF fibrosis in a subject using gene therapy with a dominant negative TGF-β R2 cDNA expression vector. Kits and computer program products are also described, wherein the kits provide materials for diagnosing and treating AF fibrosis, and the computer program products include a computer readable medium having computer readable program code for monitoring the efficacy of therapeutic ablation of fibrosis in a subject using a gene therapy method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Screening Methods and Transgenic Animals for the Treatment of Beta-Globin Related Disease and Conditions
InactiveUS20080008651A1High expressionIncrease transcriptionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDevelopmental stageBeta globin
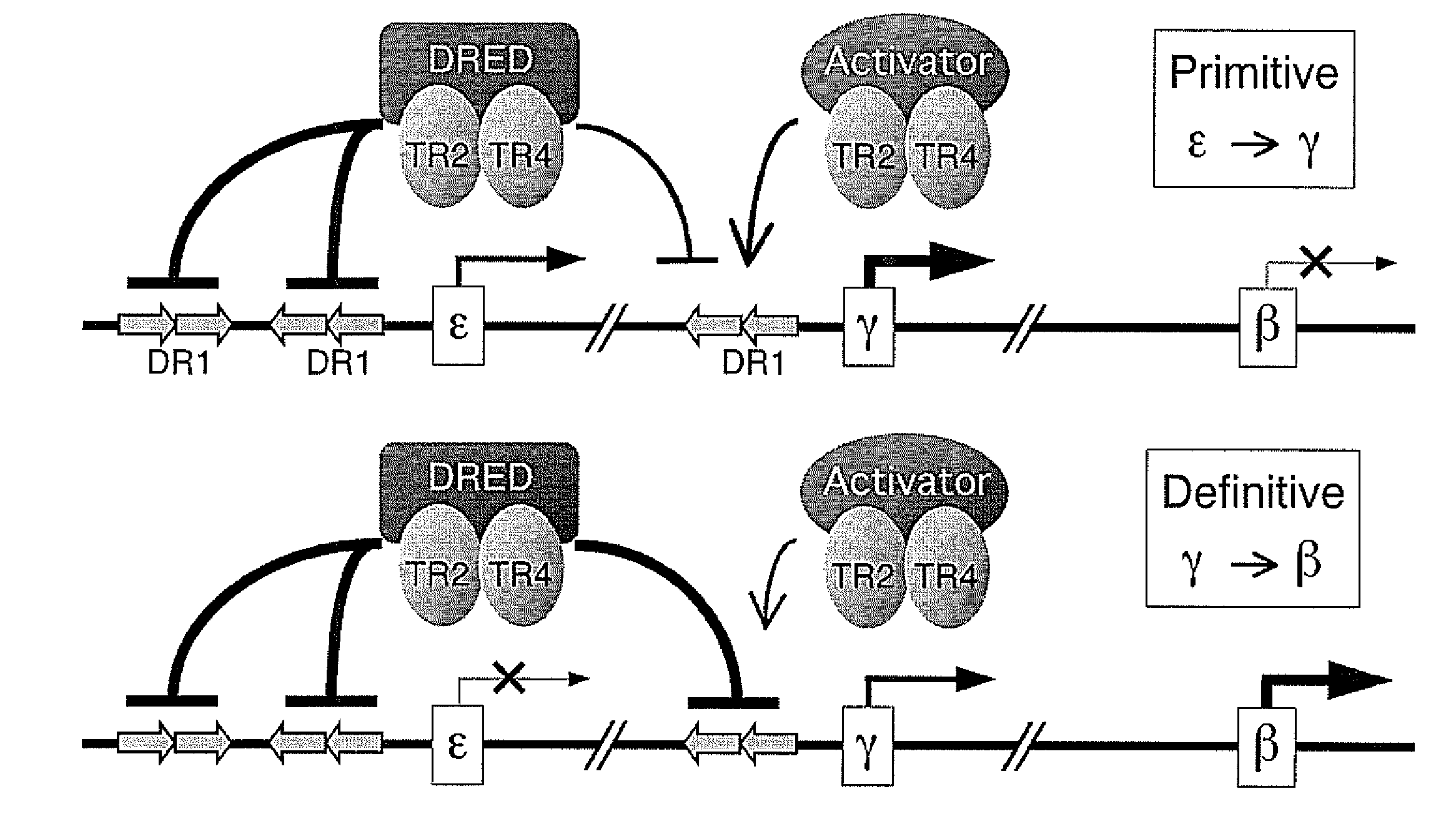
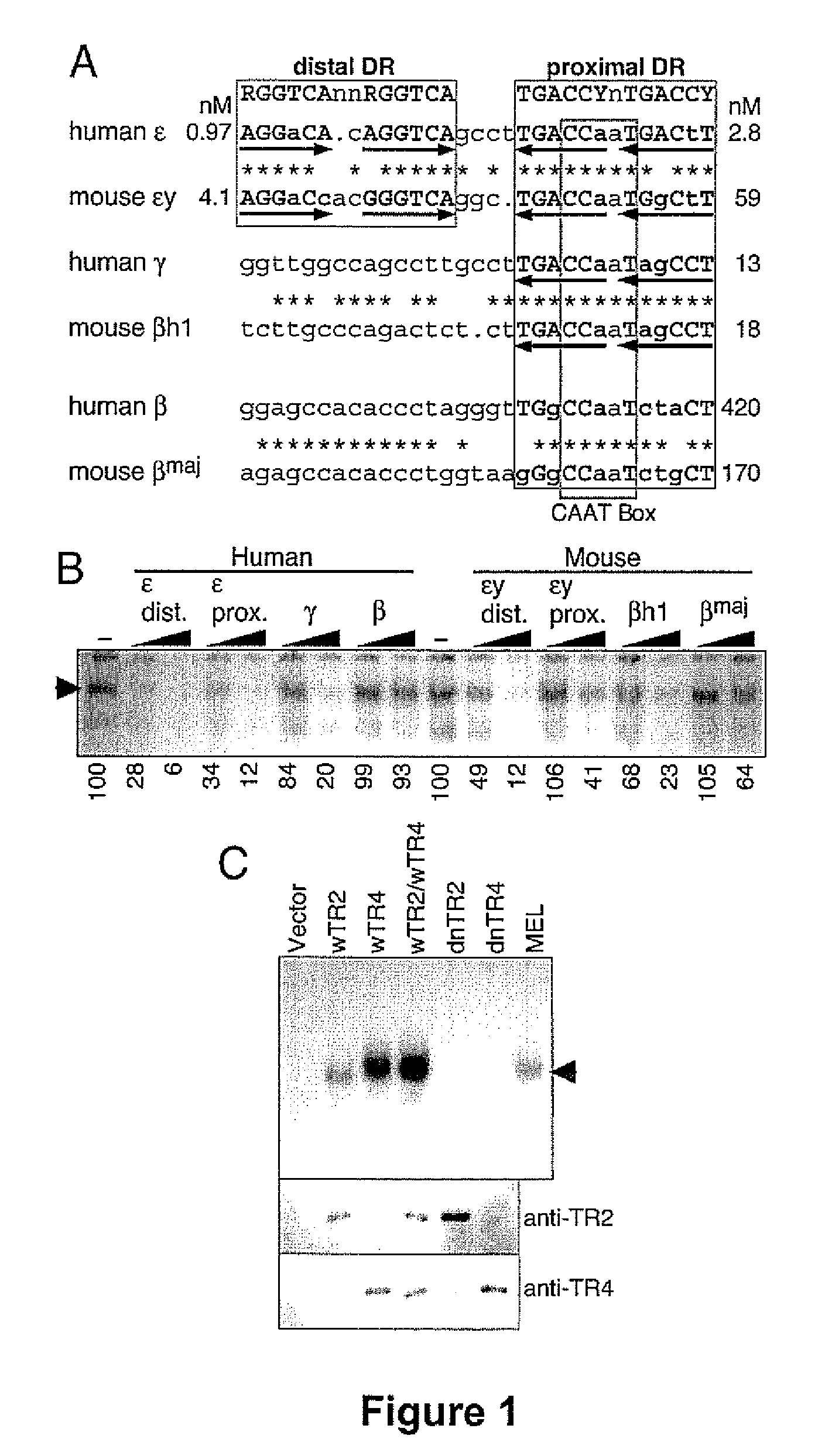
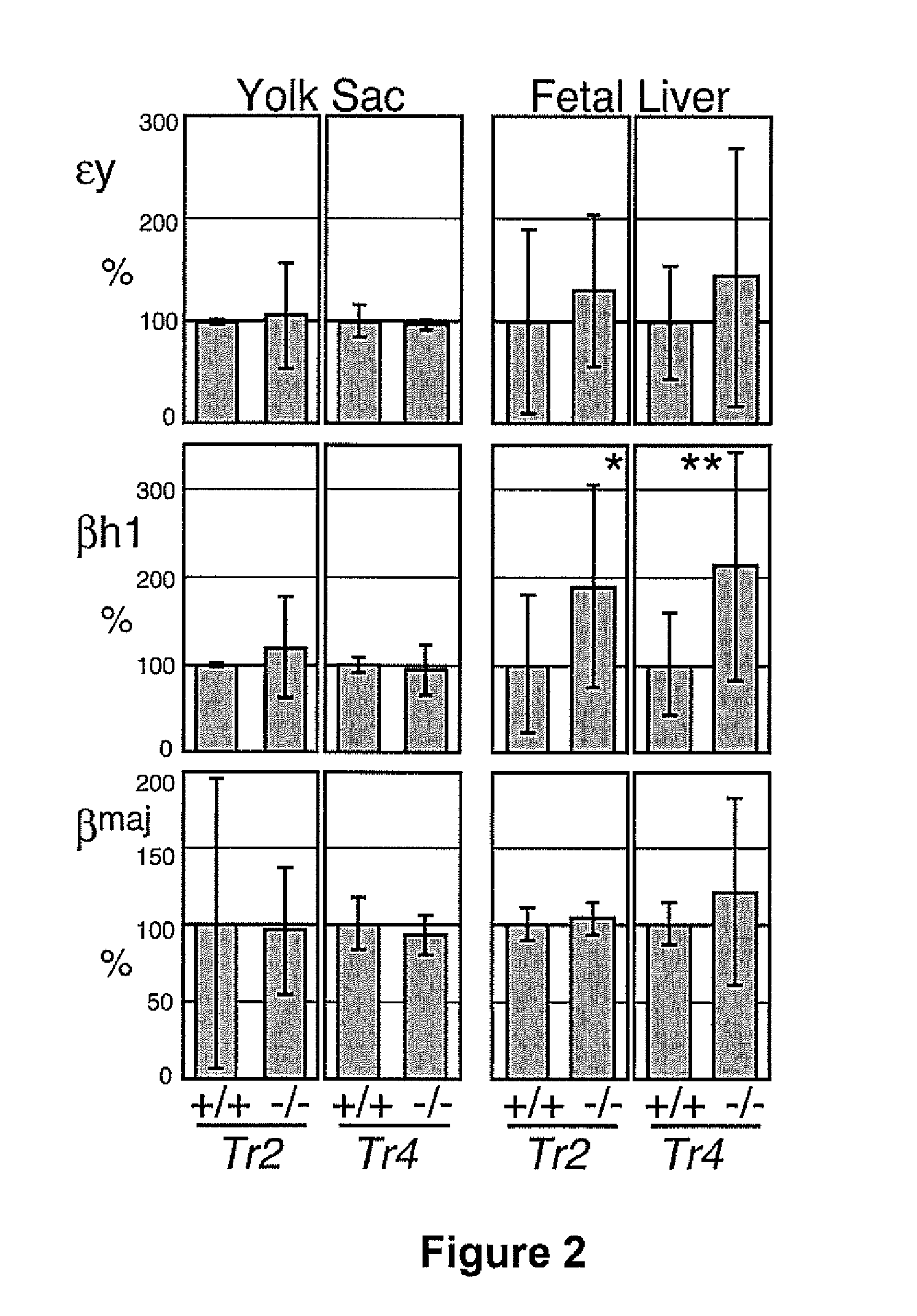
The orphan nuclear receptors TR2 and TR4 together constitute the DNA binding core of the 540 kDa DRED complex, a putative repressor of the human embryonic ε- and fetal γ-globin genes. Here the functional consequences of TR2 and TR4 germ line loss of function were examined, transgenic gain of function and dominant negative gain of function on human and murine β-type globin gene expression throughout development. ε-globin transcription responded in a manner consistent with the hypothesis that TR2 / TR4 is a constitutive erythroid ε-globin repressor. In contrast, parallel experiments show that TR2 / TR4 is a definitive stage-selective γ-globin repressor. This developmental stage-specific, gene-selective repression of the ε- and γ-globin genes by TR2 / TR4 establishes, when considered in concert with the competition hypothesis, a coherent molecular rationale for hemoglobin switching (temporally specific, sequential activation of all the β-type globin genes) during vertebrate development.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
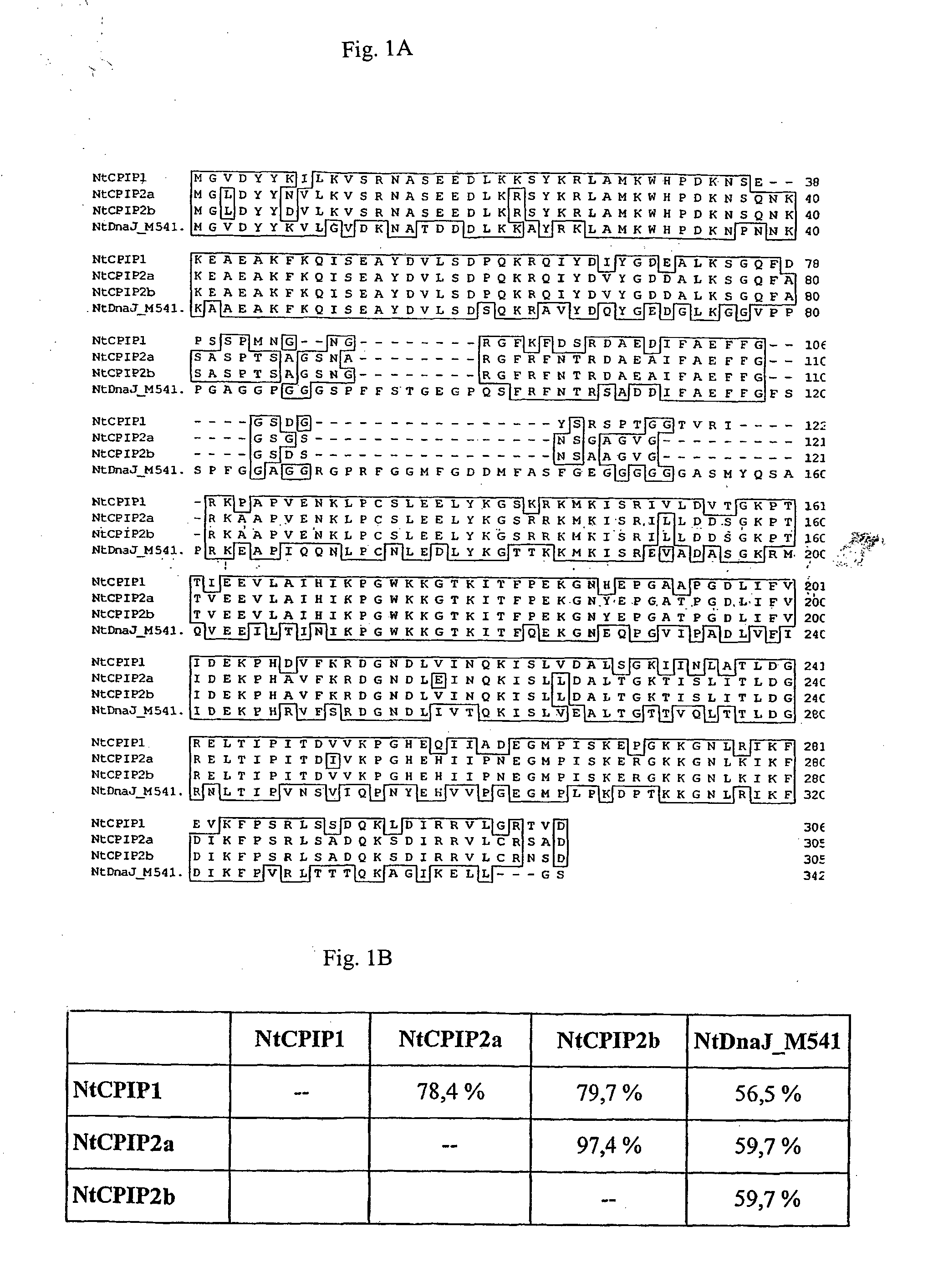
Method for the production of transgenic plants with increased virus resistance by silencing vegetable DnaJ-like proteins
InactiveUS20050251879A1Good antiviral effectEasily put into practiceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellGMO Plants
The invention relates to plants and plant cells which have a transient or permanent virus resistance as a result of modulation of the gene expression and / or binding behavior of vegetable DnaJ-like proteins. The invention also relates to methods for the production of transgenic plants with increased virus resistance, wherein the expression of vegetable DnaJ-like proteins which interact with viral components is substantially prevented by silencing the DnaJ-like proteins. The invention further relates to methods for the production of transgenic plants with increased virus resistance, wherein the interaction of viral components with vegetable DnaJ-like proteins is substantially prevented by expression of dominant-negative mutants of the DnaJ-like proteins, by antibodies against DnaJ-like proteins or by specific inhibitors.
Owner:HOFIUS DANIEL +2
Adenoviral Vector Capable of Infecting Tumor Cells and Eliminating the Function of STAT3
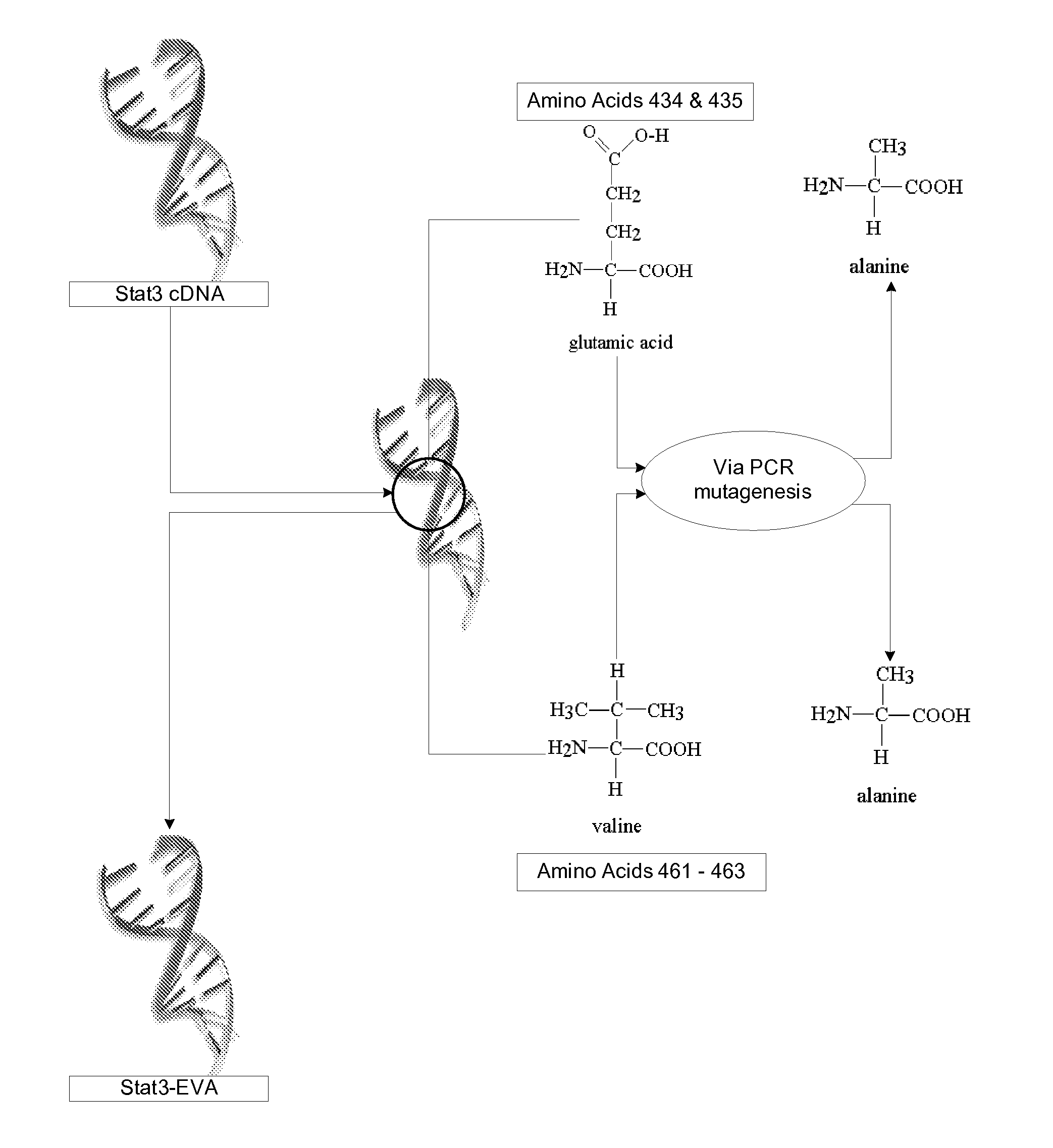
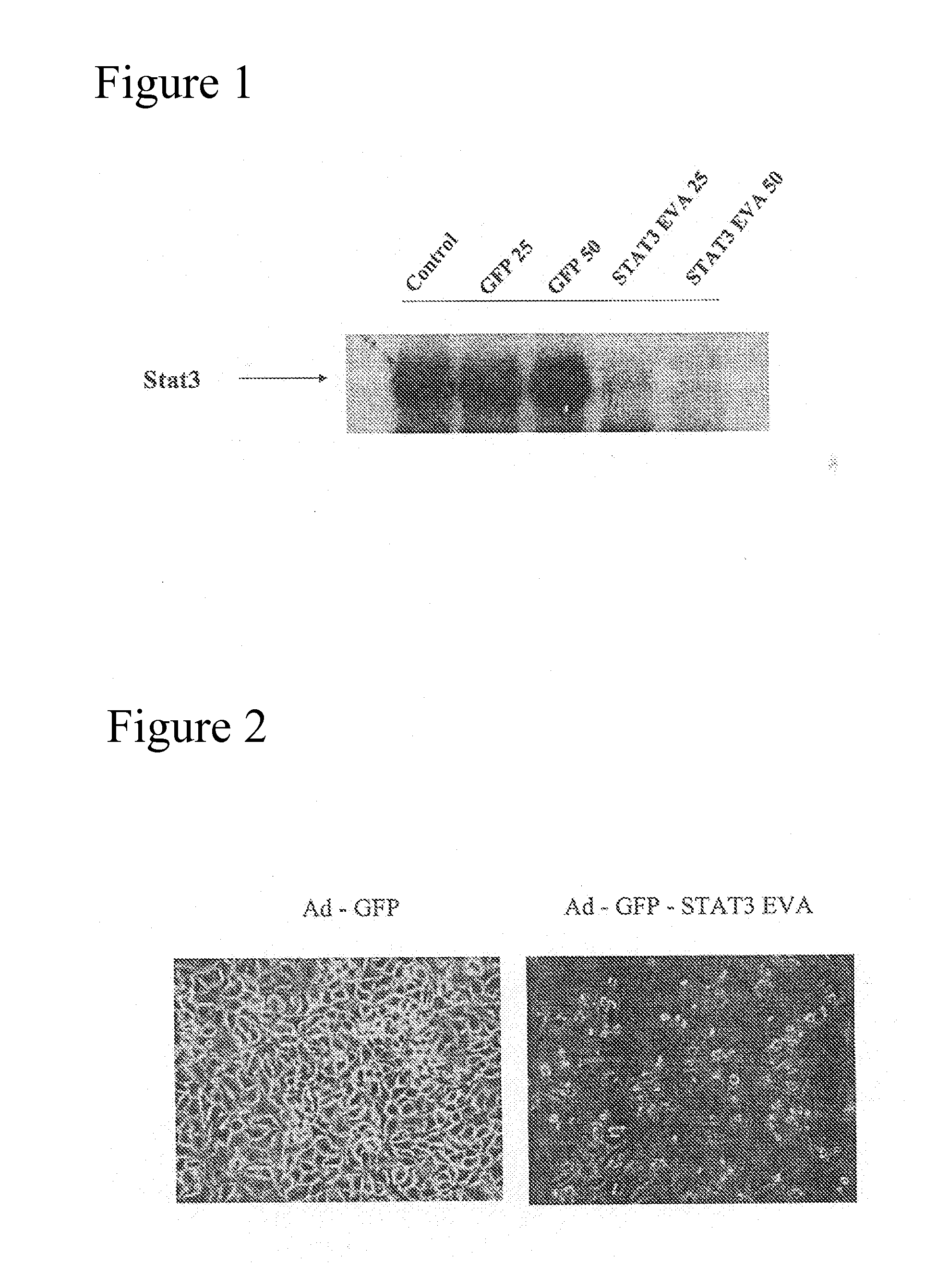
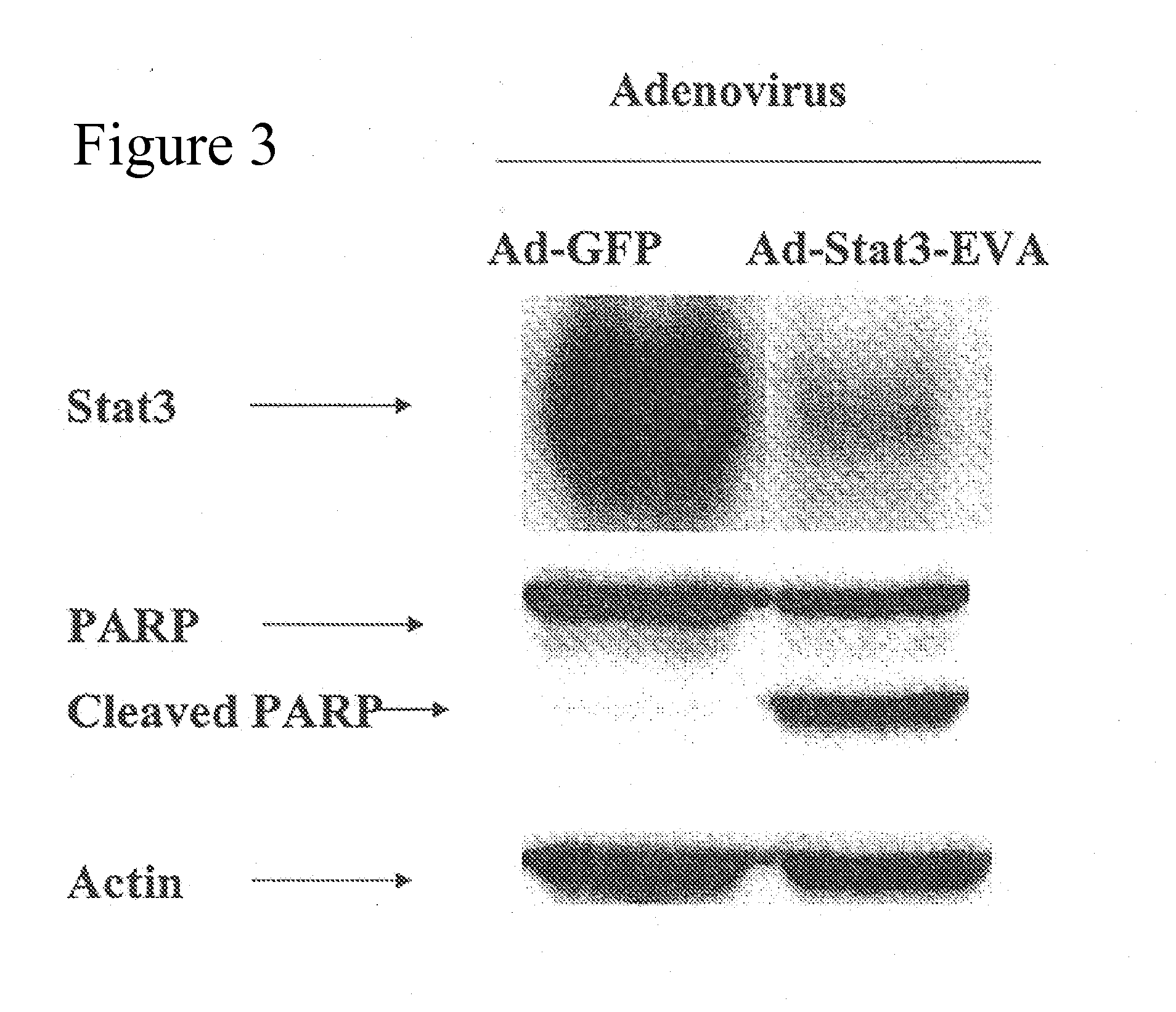
An adenoviral vector which expresses a dominant negative form of Stat3 called Stat3-EVA for the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma. This construct has two mutations in the DNA binding site of Stat3 which prevents binding to DNA but has no effect on tyrosine phosphorylation or dimerization.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Compositions and methods for inhibiting tumor cells by inhibiting the transcription factor atf5
InactiveUS20160046686A1Treating and preventing tumorPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosisWilms' tumor
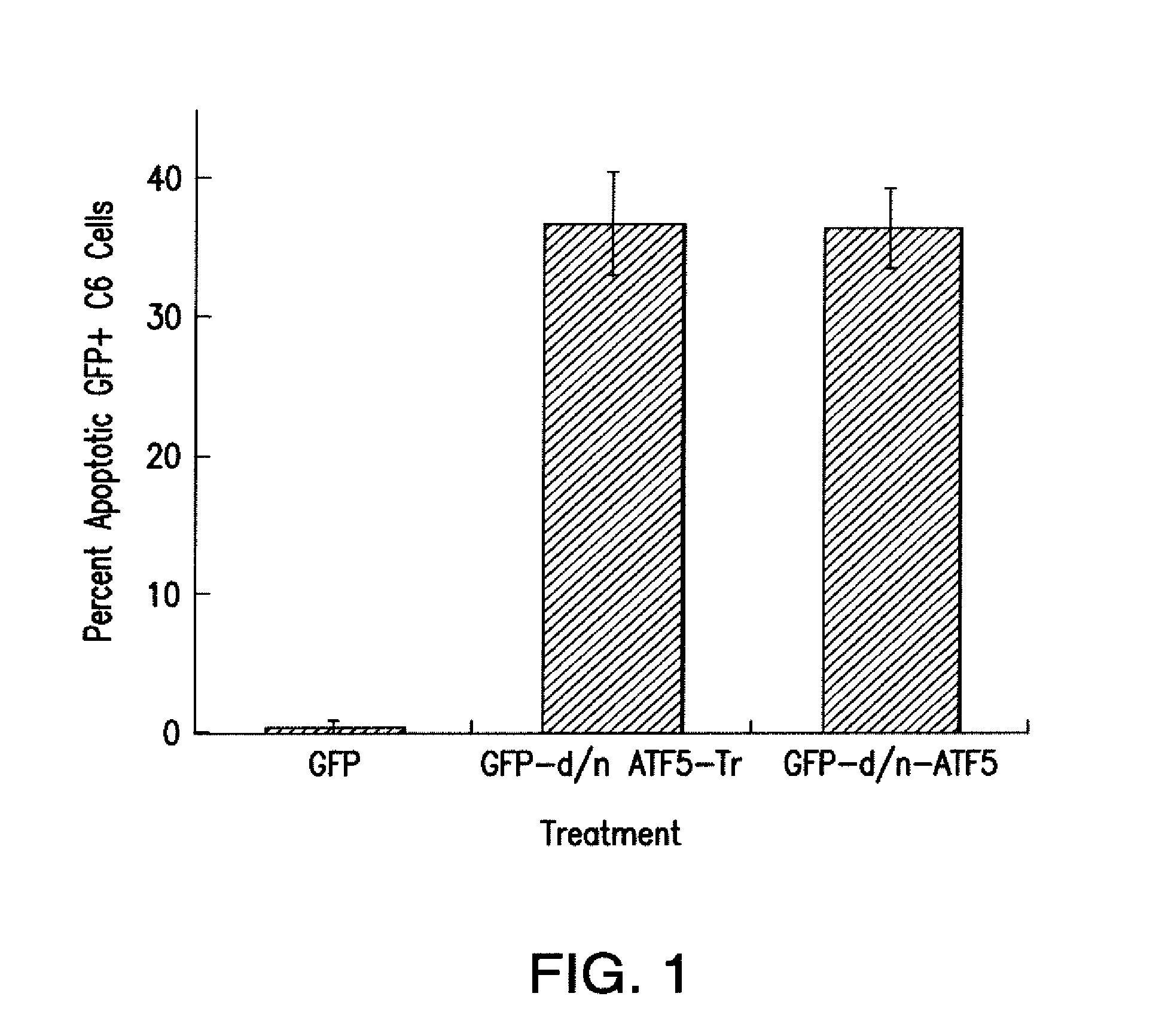
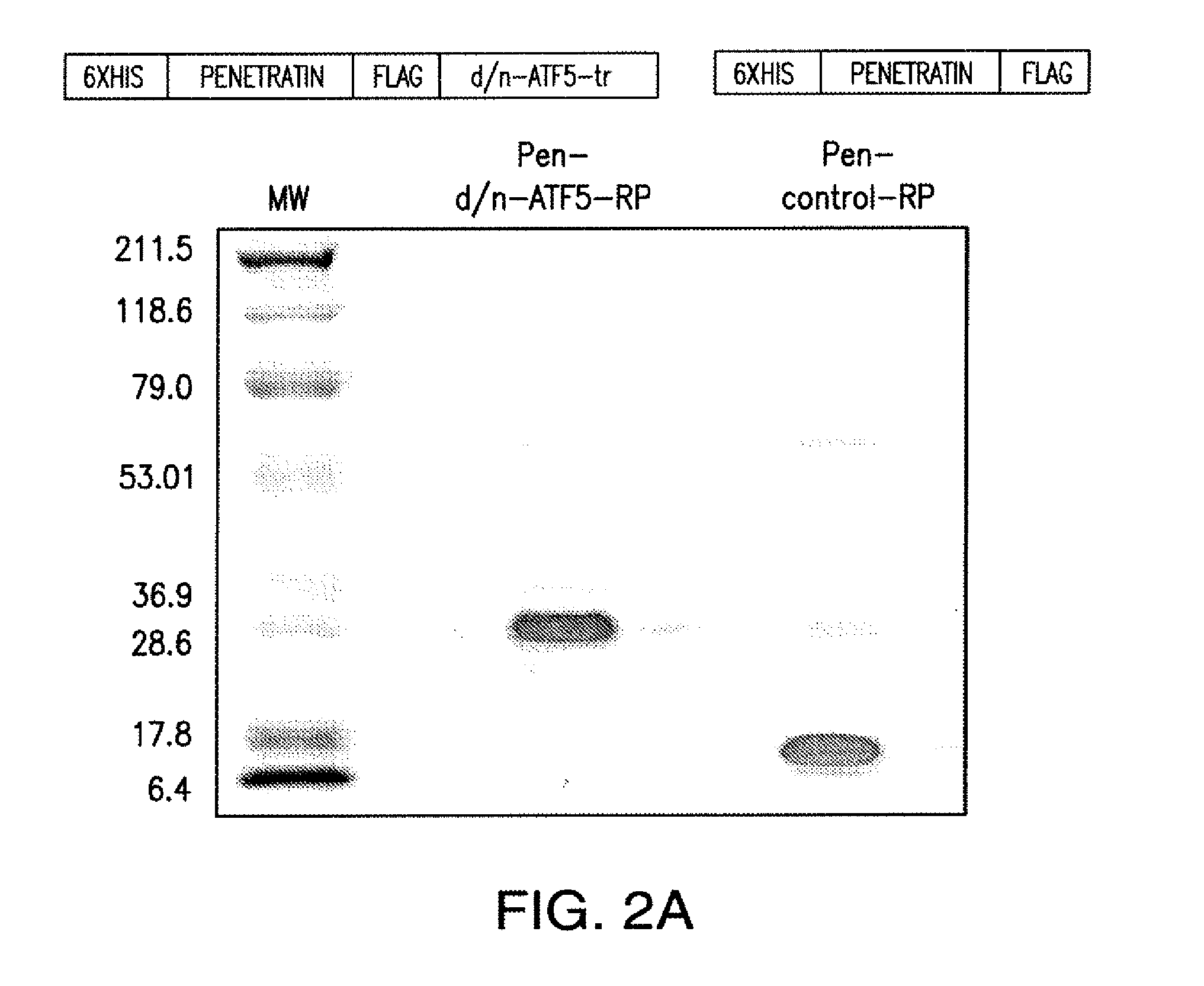
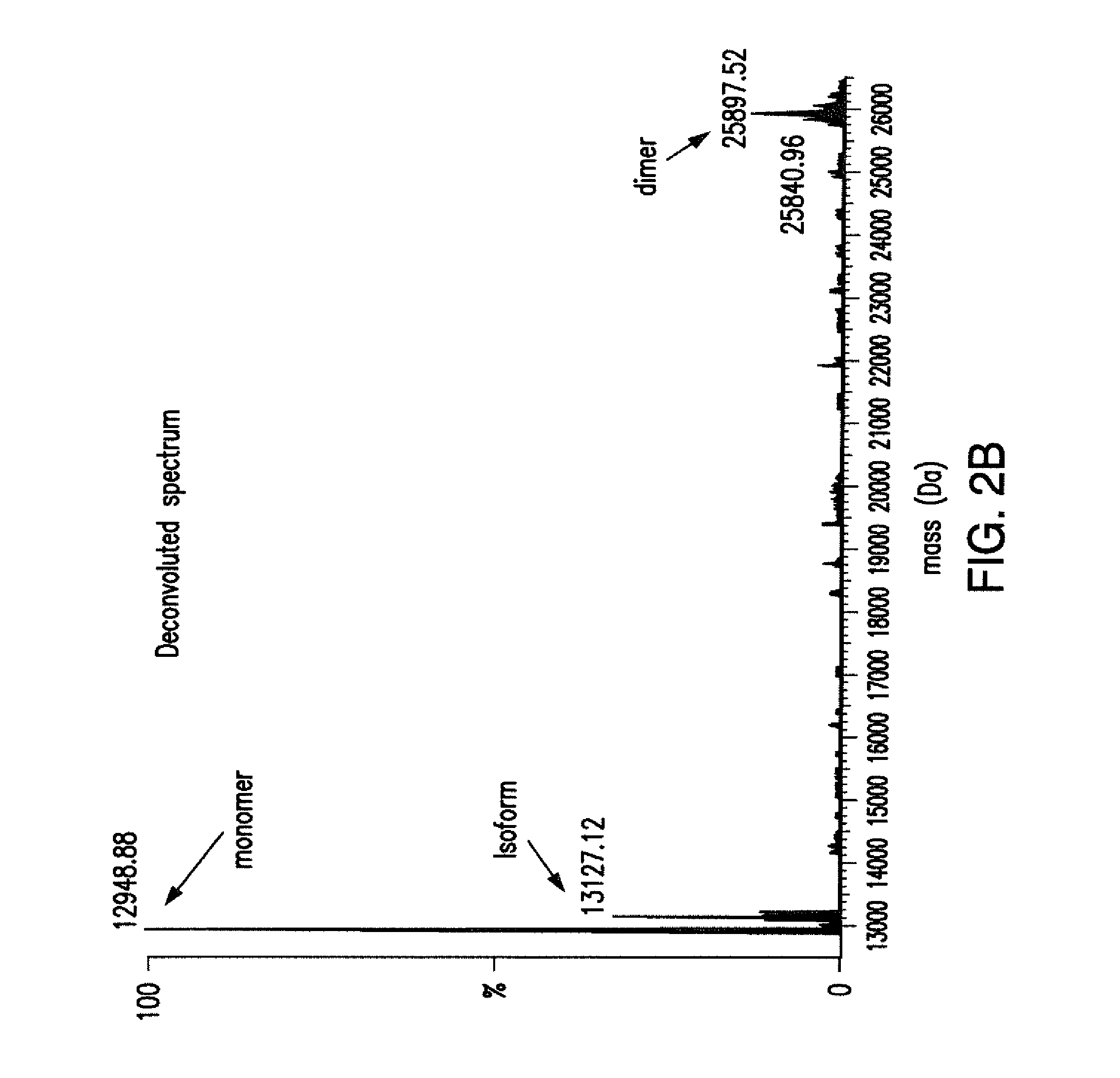
The present invention relates to methods for treating and / or preventing tumors and / or promoting apoptosis in a neoplastic cell comprising contacting the neoplastic cell with an cell-penetrating dominant-negative ATF5 (“CP-d / n-ATF5”), wherein the CP-d / n-ATF5 is capable of inhibiting ATF5 function and / or activity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com