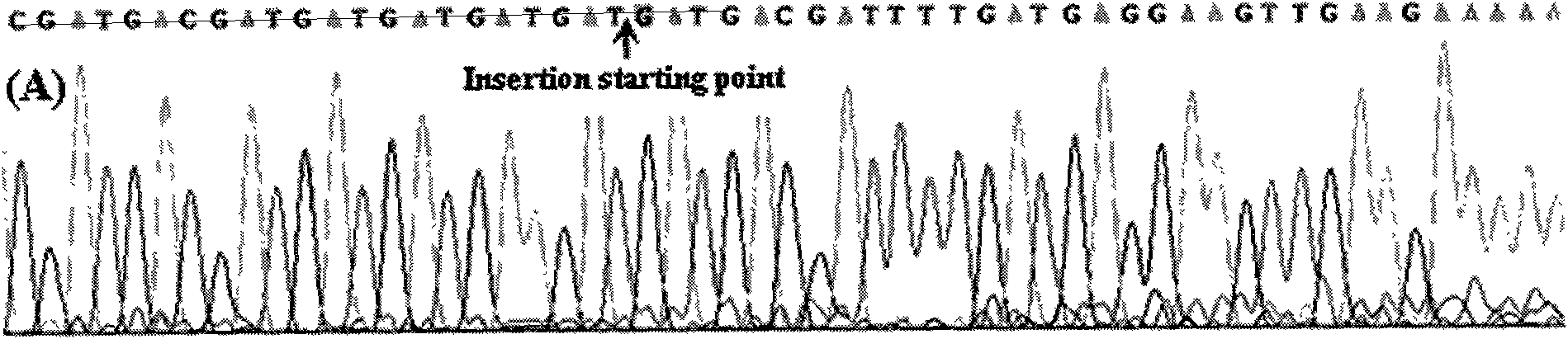
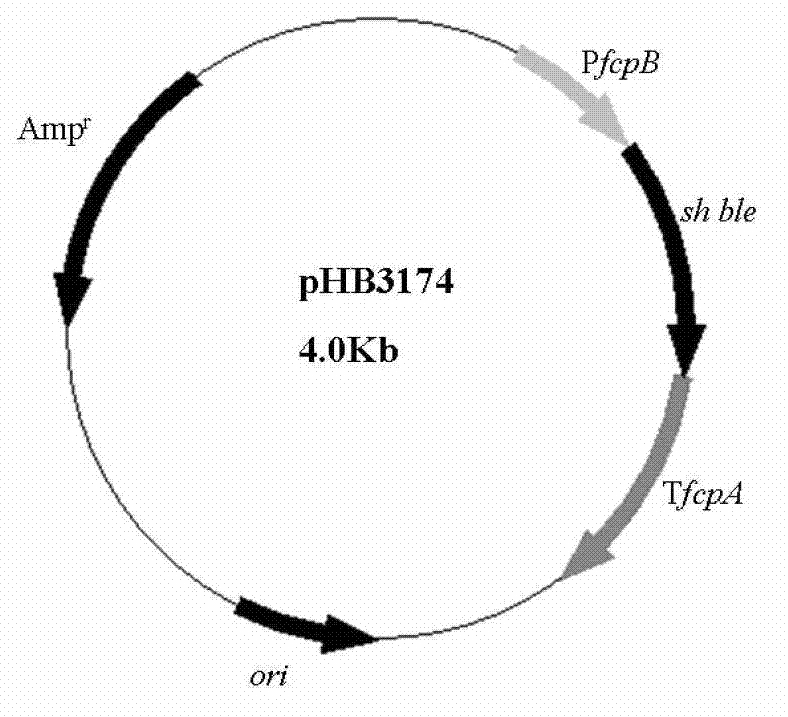
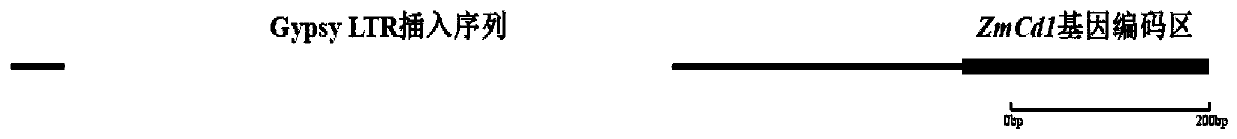Patents
Literature
100 results about "Insertional mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Insertion mutations are a type of mutation wherein one or more nucleotide base pairs are inserted to a chromosome or a DNA sequence. They result from the addition of extra nucleotides in a DNA sequence or chromosome.
Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for beta-thalassemia mutation
InactiveCN102851366AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlBeta thalassemia
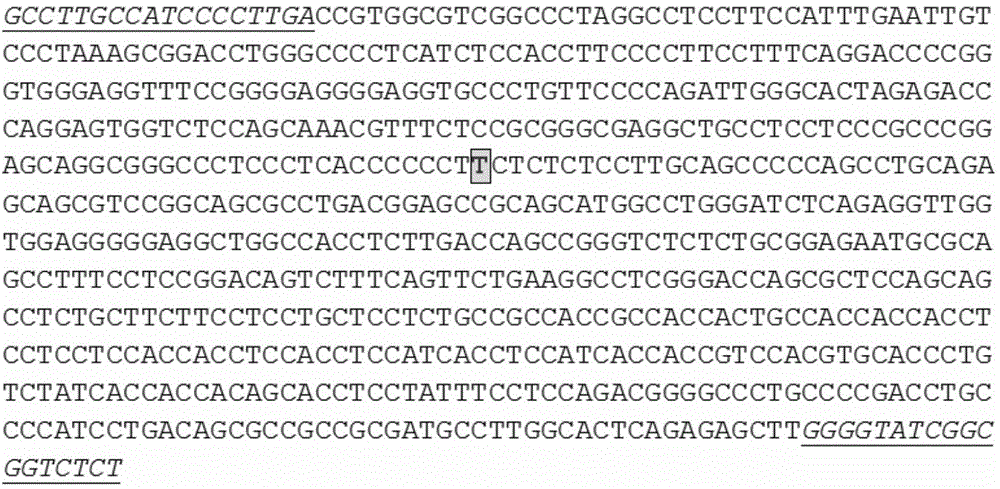
The invention relates to a fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for beta-thalassemia mutation. The kit comprises a PCR mixing reaction liquid, a positive control and fluorescence probes for detecting beta-thalassemia mutation genotype, wherein the PCR mixing reaction liquid contains PCR primers for amplifying a gene fragment on which a mutation site is positioned, and the mutation site is at least one mutation site selected from deletion mutation of a base corresponding to the site 41 / 42 amino acid of beta-globin gene, C-to-T mutation of a base corresponding to the site 654 amino acid of the second intron of beta-globin gene, A-to-T mutation of a base corresponding to the site 17 amino acid of beta-globin gene, A-to-G mutation of a base corresponding to the site 28 amino acid on the upstream of the promoter of beta-globin gene, A base insertion mutation of a base corresponding to the site 71 / 72 amino acid of beta-globin gene, and G-to-C mutation of a base corresponding to the site 5 amino acid of the first intron of beta-globin gene. With the technical scheme of the present invention, rapid, accurate and high sensitivity detection of mutation conditions of beta-thalassemia gene can be achieved, and especially 6 special site mutations of beta-thalassemia gene can be detected, wherein the 6 special site mutations are common in Chinese.
Owner:广州达健生物科技有限公司
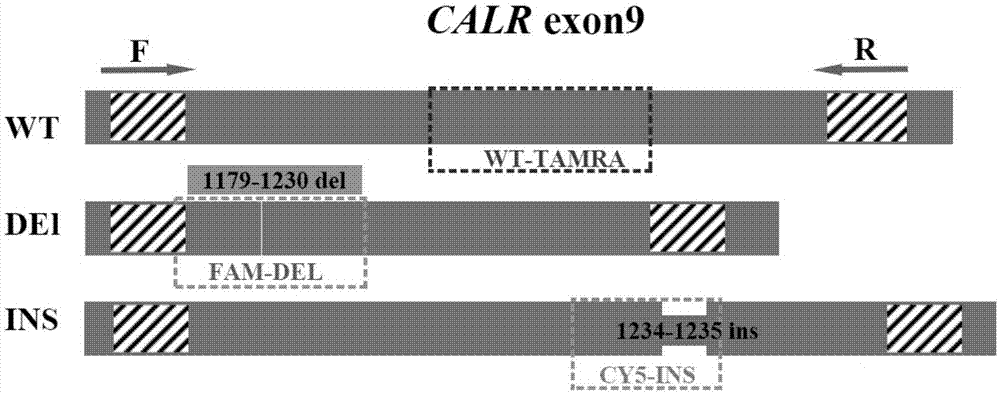
Detection method for CALR (Calreticulin) gene deletion and insertion mutation and kit
InactiveCN105441562AAccurate detectionImmediate observation of test resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCalr geneSpecific detection
The invention provides a detection method for deletion and insertion mutation of L367fs*46 (c.1179-1230del) and K385fs*4(c.1234-1235insTTGTC) of the ninth exon of a CALR (Calreticulin) gene. Universal amplification primers are designed according to deletion and insertion mutation areas of the ninth exon of the CALR gene, specific detection fluorescence probes are designed according to amplified fragments, real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is performed on a to-be-detected sample, and deletion and insertion mutation of the CALR gene are identified through multiple single-tube reactions. The invention further provides applications of the universal amplification primers and the specific detection fluorescence probes in preparation of myeloproliferative neoplasm detection reagents as well as a kit for detecting myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST SHANGHAI
Anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana
ActiveCN102140131AAccording to Mendelian inheritanceIn line with the law of inheritancePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideWild type
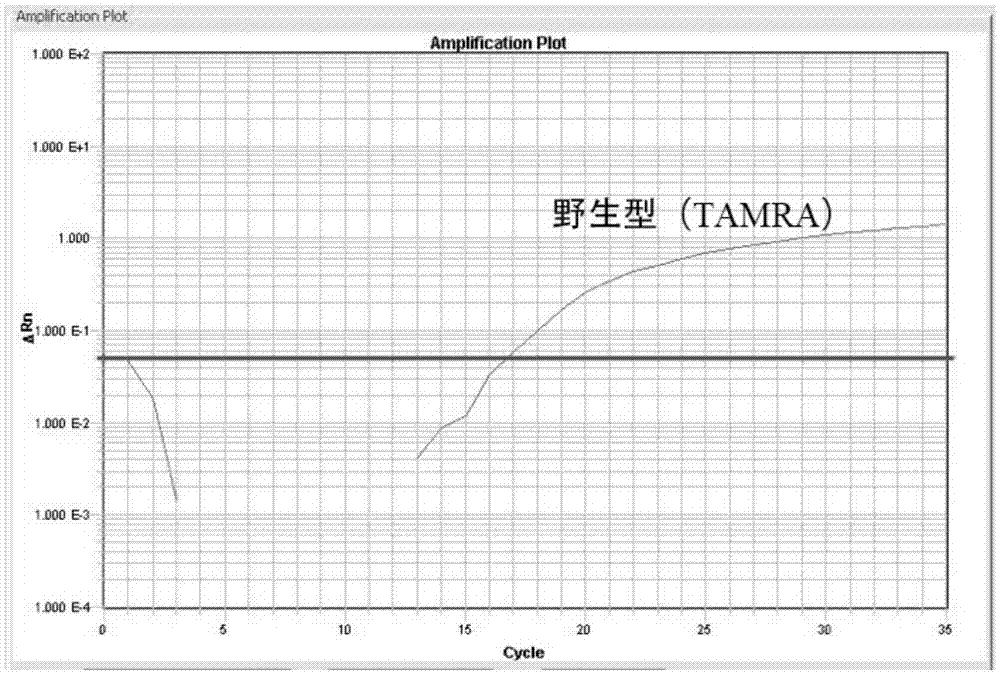
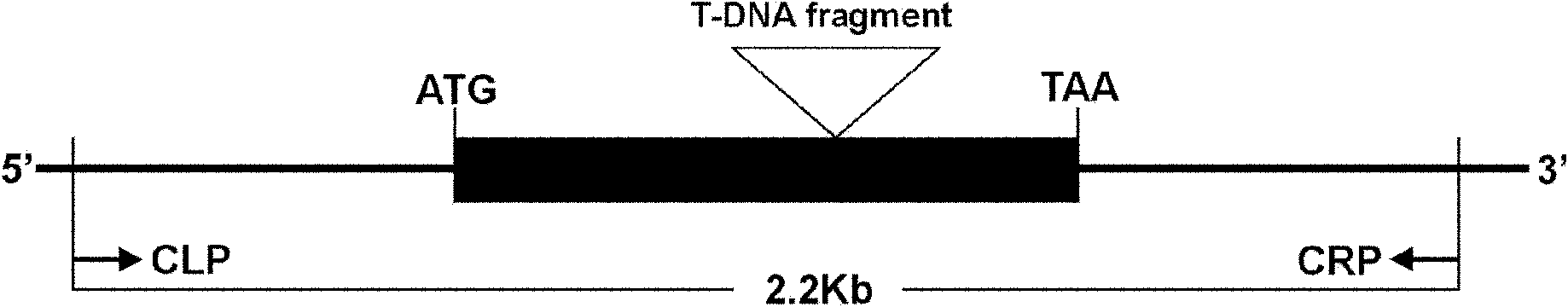
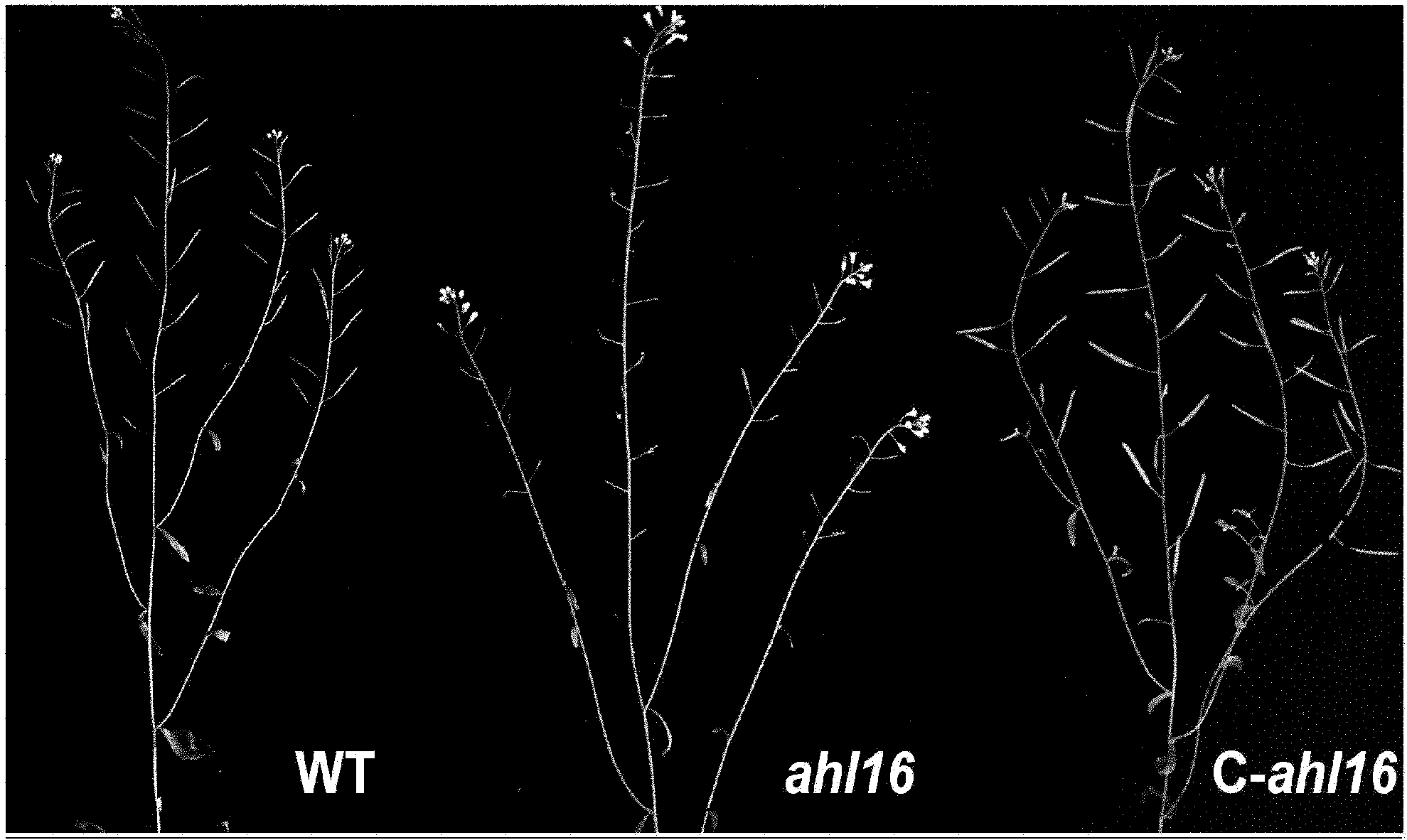
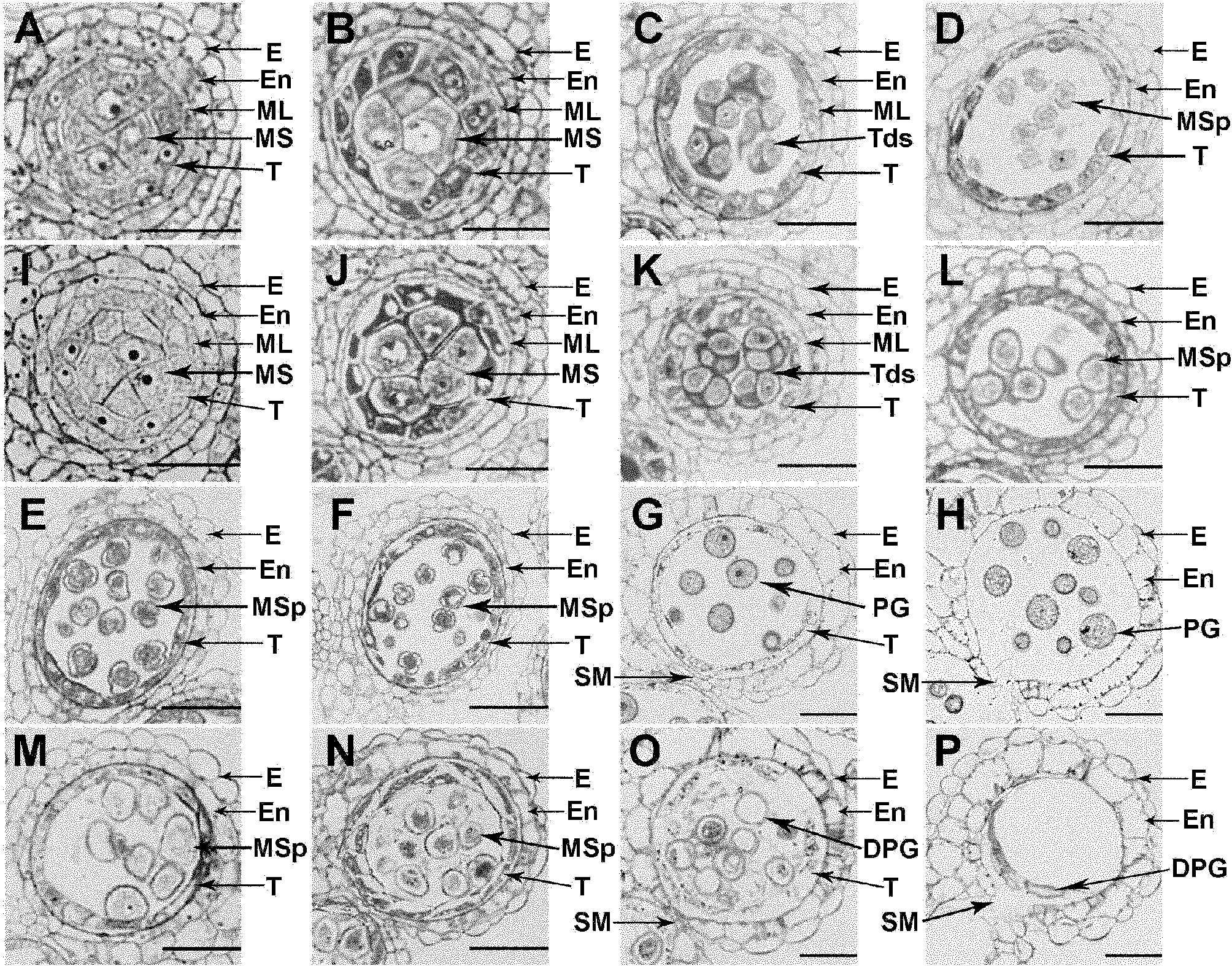
The invention relates to an anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana. An Arabidopsis thaliana male sterile mutant ahl16 is screened out from T-DNA-inserted mutant population, a gene AHL16 controlling the fertility of Arabidopsis thaliana is cloned and identified, the nucleotide sequence of the gene AHL16 is represented by SEQ ID N0.1, and genetic complement experiments prove that the AHL16 gene in a wild type can restore the male sterile phenotype. Amino acid sequence analysis and subcellular localization experiments indicate that the AHL16 gene codes proteins of an AT-hookmotif nuclear localized protein family and is located in the nucleus. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the mutation of the gene leads to complete male sterility. The gene has a very important application value in aspects of explanation of influences of the growth of the inner layers of the outer walls of microspores and the structures of the inner walls on the fertility of plants and improvement on yield by hybrid seed production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Fungus virulence new gene MgKIN17 coming from pyricularia gisea and its use
The present invention provides one new gene MgKIN17 from Pyricularia gisea, and the gene features that it has the amino acid sequence from the site 1 to the site 3544 in the SEQ ID No. 1, the cDNA with the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 2, the promoter with the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 4, and coded protein with the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 3. The insertion mutation and gene complementation of the present invention shows that the destruction of the gene leads the formation of Pyricularia gisea infecting organ and reduced lesion capacity of rice. Wheat bakanae fungus, corn stalk rot and other pathogenic fungus have homogenous protein with homogeneity over 40 % to MgKIN17 and maybe similar biological function. The gene of the present invention and its protein expression and modification may be used as the target site for designing and screening antifungal medicines.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Genetic hypermutability of plants for gene discovery and diagnosis
InactiveUS20030143586A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyInsertional mutation
The invention provides methods for identifying polymorphic markers for herbicide resistance in weeds and for generating herbicide susceptible and herbicide resistant weeds by mutagenizing weeds and comparing genetic differences between herbicide resistant and herbicide susceptible weeds. The methods may involve the inhibition of mismatch repair in the weeds through the introduction of dominant negative alleles of mismatch repair genes, through T-DNA insertional mutations, or the use of chemical inhibitors of mismatch repair. The invention also provides polymorphic markers of herbicide resistance and methods and kits to screen for herbicide resistant weeds, such as horseweed, goosegrass and rye grass.
Owner:MORPHOTEX INC
Rice blast bacterium nontoxic gene Avr-Pib and application
InactiveCN101240282AAvoid infectionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNon toxicity
A rice blast bacterium innocuity gene Avr-Pib is obtained by separation and appraising in T-DNA insertion mutation. The out-knocking mutant of the gene can cause susceptibility of rice breed variety containing Pib disease-resistant gene. The out-knocking mutant and field susceptibility individual plant can recover non-toxicity by function complementation experiment and the breed variety is disease-resistant. The gene can be used as molecule target of newly pesticides and paddy rice disease-resistant genetic engineering.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method of typing gene polymorphisms
InactiveCN1671841AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingInsertional mutationDeletion mutation
Accurate and highly reproducible means of detecting a base substitution mutation (for example, SNP), an insertion mutation or a deletion mutation with the use of a nucleic acid sample in a trace amount and a method of typing gene polymorphisms using the means.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Method for using CRISPR/Cas9 for preparing recombinant pseudorabies virus
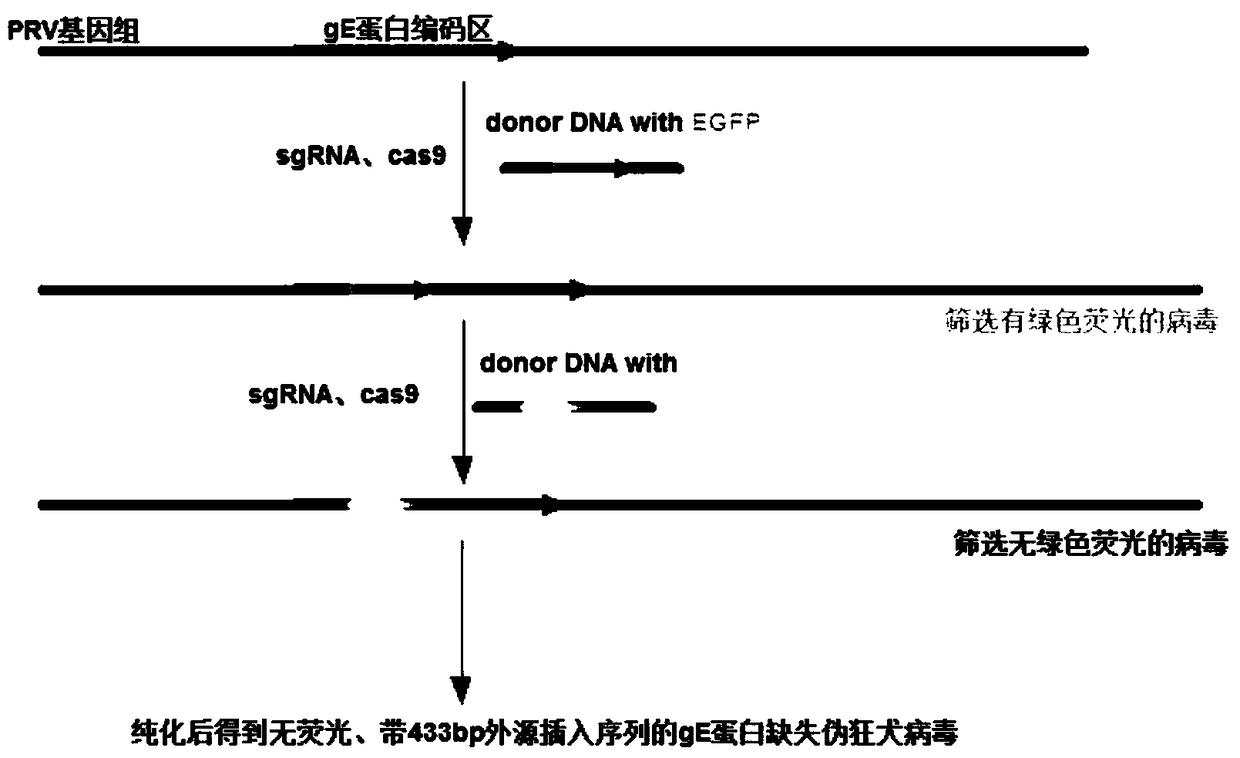
InactiveCN109321571AImprove screening efficiencyReduce workloadVirus peptidesStable introduction of DNAScreening proceduresFluorescent protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly discloses a method for using CRISPR / Cas9 for preparing recombinant pseudorabies virus. According to the method, the gene editing technology CRISPR / Cas9 is used, a coded sequence of fluorescent protein is introduced into a gE editing area of PRV, and after positive recombinant virus is screened out successfully, thesame technology is used for replacing a fluorescent protein gene with an irrelevant sequence (LysC sequence with 500 bp) to form insertion mutation, so that gE protein expression deletion of the PRV is achieved. According to the method for using the CRISPR / Cas9 for preparing the recombinant pseudorabies virus, visible screening of the fluorescent protein from nothing to something and then from something to nothing is used, a screening procedure is simplified, the recombinant virus construction efficiency is improved, and an experiment cycle is shortened; moreover, by introducing insertion mutation into the gE editing area of the pseudorabies virus (PRV), the prepared recombinant virus can be used for researching and developing PRV attenuated vaccine, and meanwhile, the irrelevant sequencecan be used for identifying and judging immunotoxicity and natural toxicity.
Owner:WUHAN KEQIAN BIOLOGY CO LTD
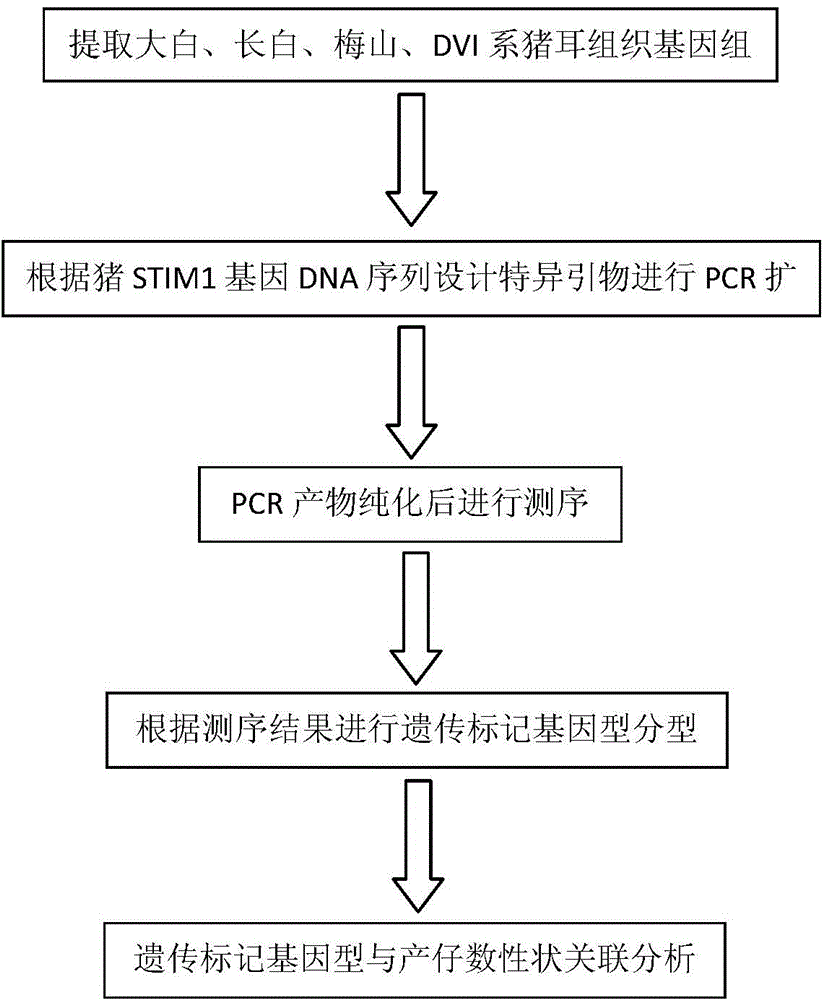
Genetic marker for porcine litter size character and application of genetic marker
ActiveCN104313156AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMolecular genetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of the preparation of livestock molecular genetic markers and particularly relates to a genetic marker for a porcine litter size character and an application of the genetic marker. A T base insertion / deletion mutation of a tenth intron tail end sequence of a porcine STIM1 gene is taken as a genetic marker related to the porcine litter size character. According to the genetic marker provided by the invention, the genetic marker related to the porcine litter size character is obtained through preparation, wherein a nucleotide sequence of the genetic marker of a Yorkshire pig is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and a T base insertion mutation exists at 256bp of the sequence; a nucleotide sequence of the genetic marker of a Meishan pig is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and a T base deletion mutation exists at 256bp of the sequence; and the mutations can obviously influence the porcine litter size character. The invention further discloses a preparation method for the genetic marker and an application of the genetic marker to the association analysis of the porcine litter size character. A new genetic marker is provided for the molecular marker auxiliary breeding of the porcine litter size character.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Shewanella loihica genetic engineering strain capable of producing high-yield hemoglobin and construction method of genetic engineering strain
ActiveCN109609427AGenetic manipulation is simpleWon't breakBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMass spectrometryShewanella putrefaciens
The invention discloses a shewanella loihica genetic engineering strain capable of producing high-yield hemoglobin and a construction method of the genetic engineering strain. According to the method,a Shewanella loihica mutant strain with a deep red phenotype is obtained by random insertion mutation of a transposon. Genetic identification and genetic complementation experiments confirm that a ypiD gene is inactivated by insertional mutation and accumulation of extracellular red matter is caused. The red substance is identified as hemoglobin by mass spectrometry, and then the ypiD gene is knocked out by homologous recombination, so that the shewanella loihica genetic engineering strain ypjD-knockout PV-4 capable of producing high-yield hemoglobin is obtained, the strain can secrete a large amount of hemoglobin extracellularly, and the biomass (OD600) reaches 2.4-2.6 under shake flask culture conditions, and the hemoglobin production is 90-120 mg / L, and great application value is provided.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Molecular marker of low-cadmium-accumulation control gene ZmCd1 of corn kernel and application
ActiveCN111254142AGenetic improvementQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesInsertional mutationCandidate Gene Association Study
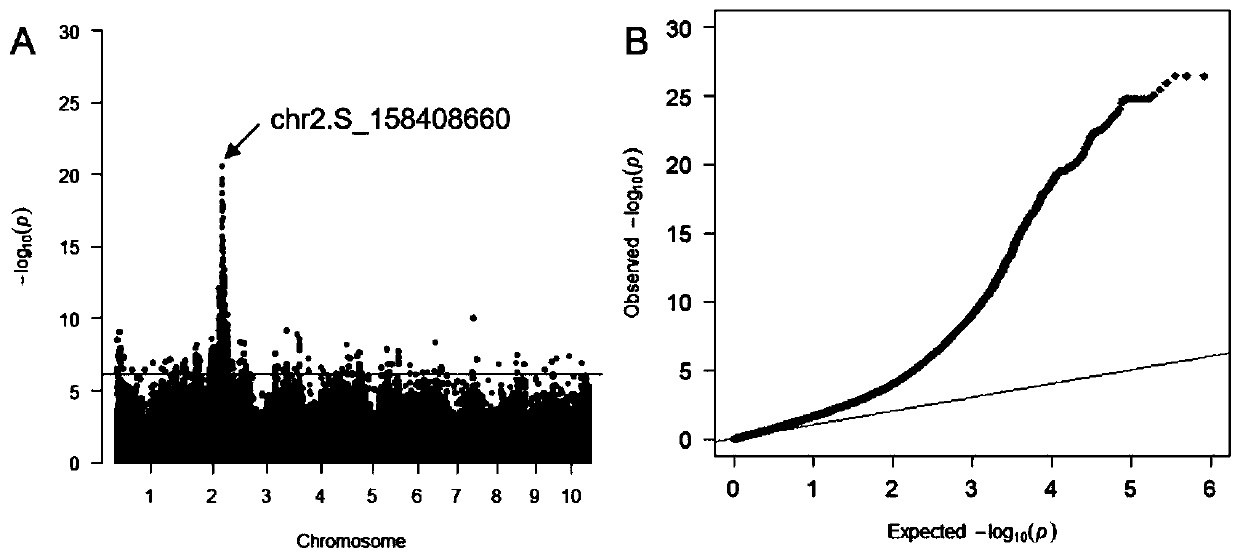
The invention provides a molecular marker of low-cadmium-accumulation control gene ZmCd1 of a corn kernel and an application thereof. The invention comprises the following steps of: performing geneticanalysis on the cadmium content character of the corn kernels by taking a correlated group consisting of 436 parts of corn self-bred lines as basic materials, screening candidate genes for regulatingand controlling the cadmium content of the corn kernels in a range of 100kb of flanking sequences of significant SNP sites, and locking the candidate genes named ZmCd1; conducting sequence comparisonanalysis, wherein analysis results show that 7520bp deletion and 604bp of Gypsy type LTR retrotransposon insertion mutation exist in a promoter position of the ZmCd1 gene of the high-cadmium-accumulation corn self-bred lines compared with the low-cadmium-accumulation corn self-bred lines; and developing a functional molecular marker PCR-ZmCd1 based on PCR according to the difference sequence of the promoter position. The molecular marker can be used for early prediction, screening and breeding of low-cadmium-accumulation corn.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Design method for primers and probe for amplifying low-concentration mutation target sequence
ActiveCN105861678ALow amplification efficiencyAvoid combiningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationForward primerFluorescence
The invention discloses a design method for primers and a probe for amplifying a low-concentration mutation target sequence. The design method includes the steps that the mutation position (a mutational site, namely a 0 site) of a target sequence to be amplified is determined; a 15-25 bp nucleic acid fragment including the 0 site base is selected in the negative direction of the mutational site to serve as the forward primer, and a 12-25 bp nucleic acid sequence is selected from the 1 site base or the 0 site base in the positive direction of the mutational site to serve as a probe sequence of an amplification system; the reverse primer is designed at the suitable position of the 3'direction downstream of the probe sequence according to a conventional method. According to the design method for the primers and the probe, the target fragment can be effectively (with high specificity and efficiency) amplified under the background of a high-content wild type template particularly for point mutation, deletion mutation and insertion mutation in gene mutation, a fluorescence real-time PCR technology is combined, and the problem that at present, sensitivity is poor in clinic tumor detection and drug susceptibility detection can be solved effectively.
Owner:CREATIVE BIOSCIENCES (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
Specific primer used for separating and identifying activator/dissociator (Ac/Ds) transposons flanking sequences
InactiveCN102649959AEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBase JInsertional mutation
The invention relates to a primer and method used for separating and identifying activator / dissociator (Ac / Ds) transposons flanking sequences. The primer is shown as follows: a-, an Ac terminal specific primer used for separating Ac / Ds 5' flanking sequences is a base sequence shown by SEQIDNO:1-SEQIDNO:7; b-, an Ac terminal specific primer used for separating Ac / Ds 3' flanking sequences is a base sequence shown by SEQIDNO:8-SEQIDNO:14. The invention relates to a specific primer and method used for identifying and distinguishing the Ac and Ds flanking sequences. The invention is characterized in that the primer is the base sequence shown by SEQIDNO:15-SEQIDNO:18. The Ac specific primers can be well amplified to obtain the Ac or Ds flanking sequences in a genome. The detection method is simple in operation and is an important technical means for obtaining the Ac flanking sequences of Ac mutants on a large scale and separating genes of Ac insertion mutants.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
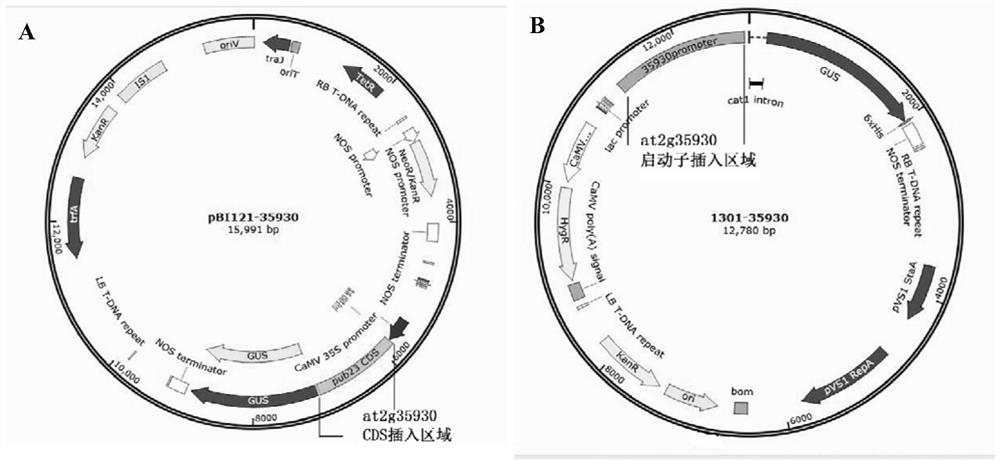
Arabidopsis thaliana clubroot infection candidate gene AT2G35930 and application thereof
The invention discloses an arabidopsis thaliana clubroot infection candidate gene AT2G35930 and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the candidate gene AT2G35930 is a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The T-DNA insertion mutant material of the gene is more resistant to clubroot than Columbia type wild arabidopsisthaliana, AT2G35930 with an enhanced promoter is transformed into arabidopsis thaliana through agrobacterium infection, an AT2G35930 overexpression arabidopsis thaliana strain is obtained, the resultshows that overexpression of AT2G35930 can cause that arabidopsis thaliana is more susceptible to clubroot, and the phenotype is specifically generated due to the fact that the gene participates in supporting growth and development of pathogens at the roots of plants. The gene is closely related to clubroot, the gene and homologous genes of the gene in other cruciferae plants can be applied to cruciferae plant breeding, and good application prospects are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
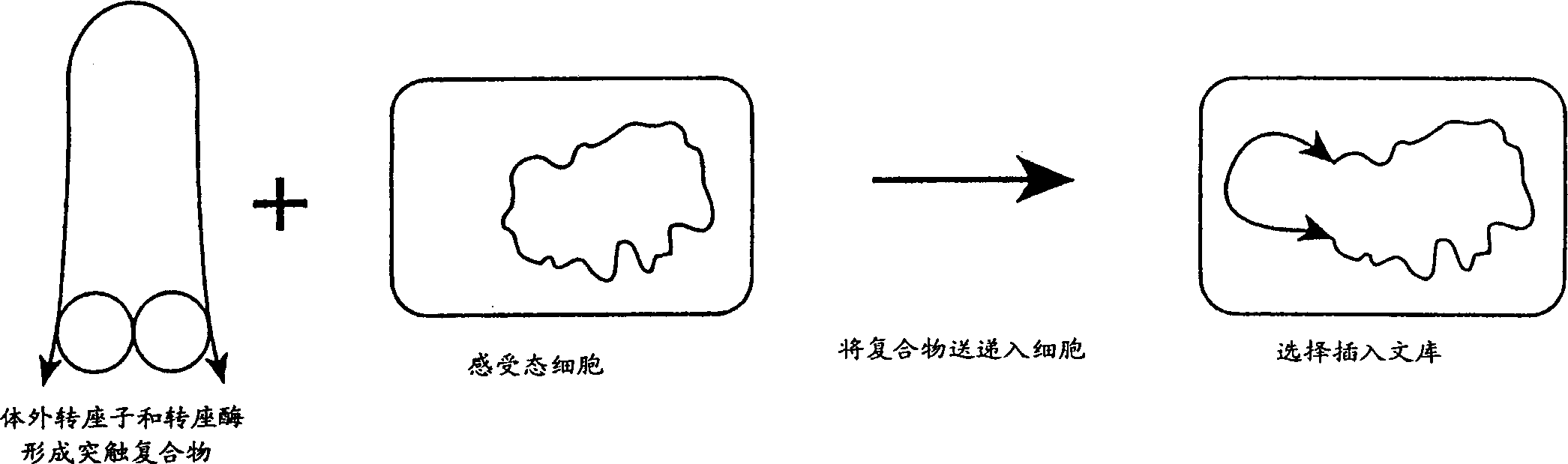
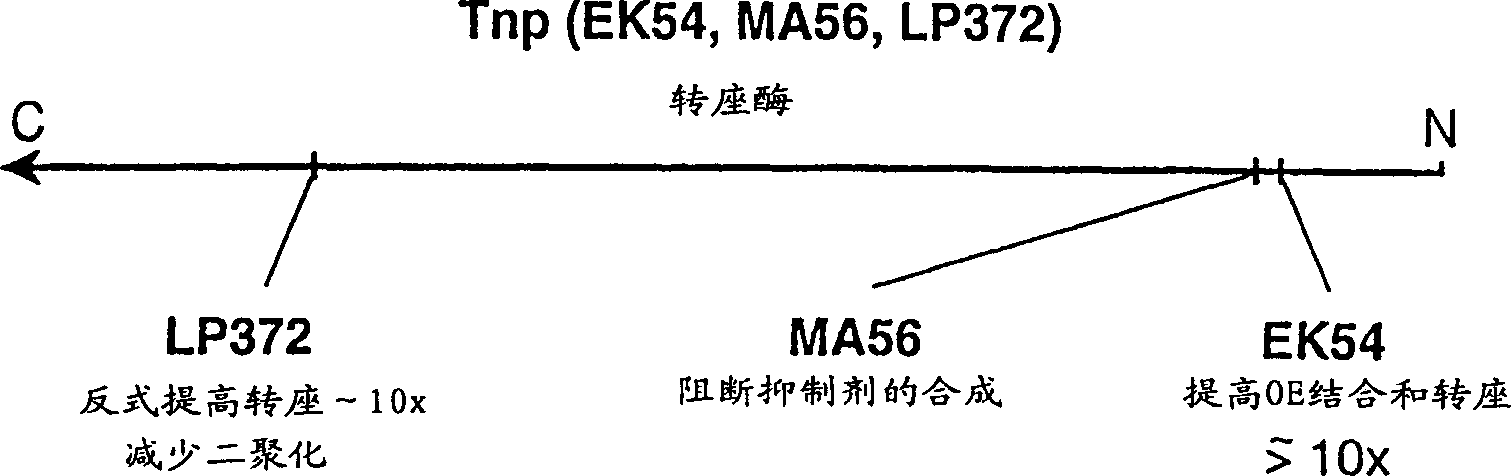
Method for making insertional mutations
InactiveCN1319135AIncreased transpositionEasy to manufactureHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementTn5 transposaseNucleotide
A method for making insertional mutations at random or quasi-random locations in the chromosomal or extra-chromosomal nucleic acid of a target cell includes the step of combining, in the target cell, cellular nucleic acid with a synaptic complex that comprises (a) a Tn5 transposase protein and (b) a polynucleotide that comprises a pair of nucleotide sequences adapted for operably interacting with Tn5 transposase and a transposable nucleotide sequence therebetween, under conditions that mediate transpositions into the cellular DNA. In the method, the synaptic complex is formed in vitro under conditions that disfavor or prevent the synaptic complexes from undergoing productive transposition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
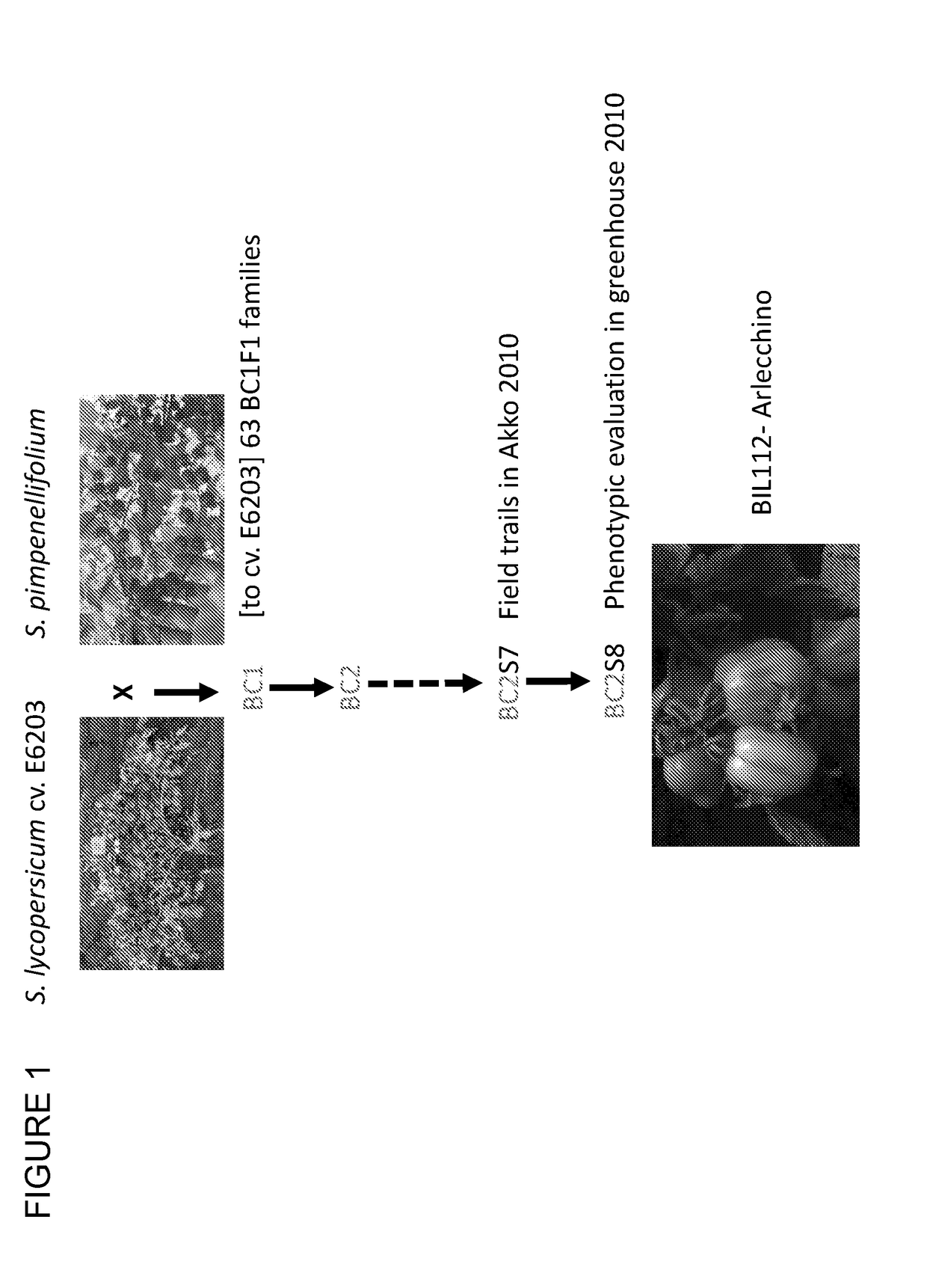
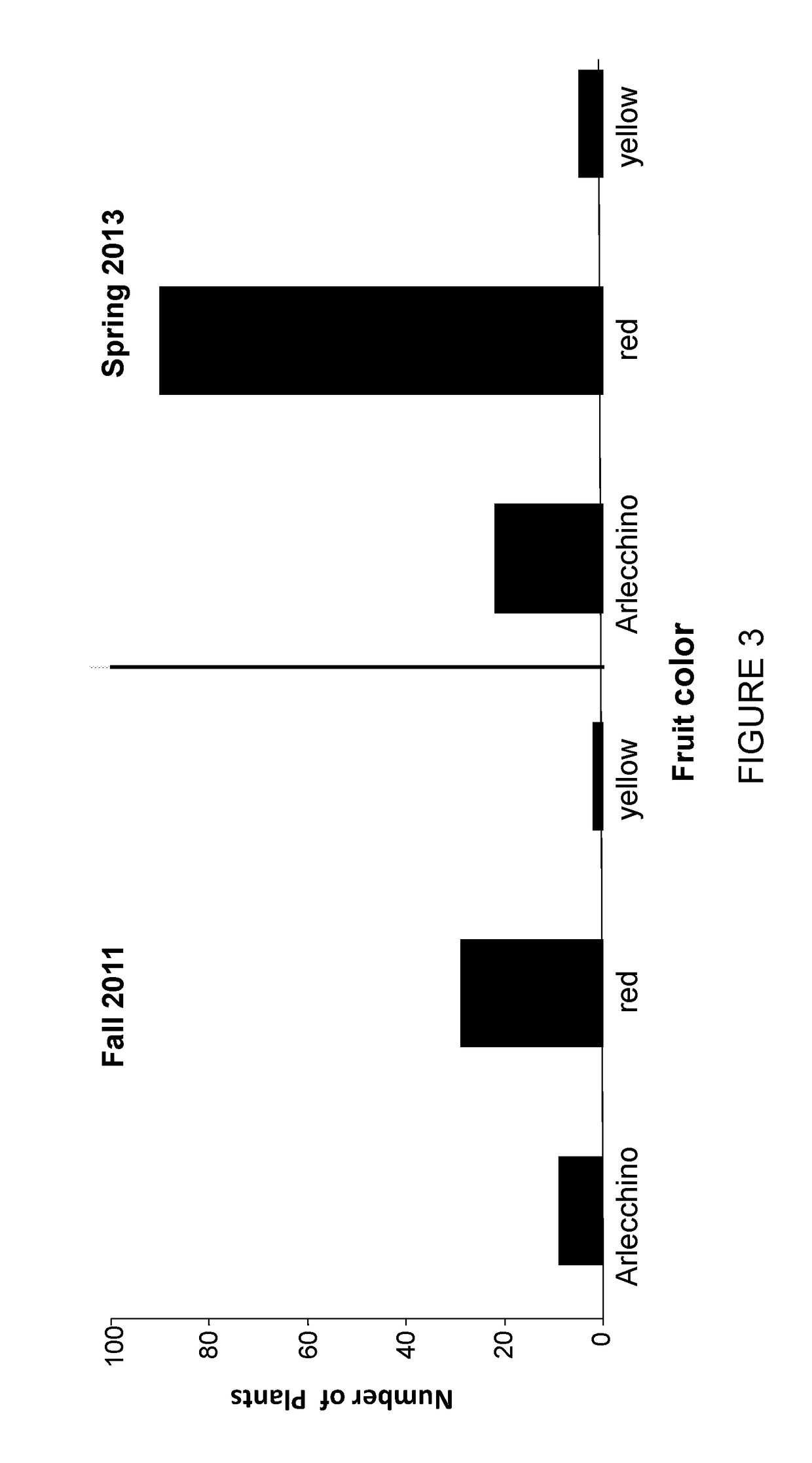
Tomato plants having fruit with yellow and red segments
Provided are tomato plants having fruit with red and yellow segments that appear across the fruit from the internal seed area to the most external layer of the epidermis. The present invention discloses that this phenotype, designated Arlecchino, is linked to insertion mutation within the Phytoene synthase 1 (Psy1) gene.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Method for detecting inserting mutation polymorphism of ox NPM1 gene
InactiveCN101671725AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPolymorphism DetectionNPM1
The invention discloses a method for detecting the inserting mutation polymorphism of an ox NPM1 gene, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out PCR amplification by adopting an NPM1 gene-contained ox gene group to be detected as a template and adopting a primer P as a primer; (2) carrying out polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis detection on a fragment after PCR amplification; carryingout electrophoresis for 50-60 minutes with the voltage of 200V and then carrying out EB dyeing; and (3) parting the inserting mutation polymorphism of the NPM1 gene according to a polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis detecting result. The invention provides a method for detecting the polymorphism of the ox NPM1 gene, which is relevant to economic characteristics; aiming at the gene polymorphism withchanged coding protein conformation, which is caused by the inserting mutation of 12bp existing on an NPM1 gene coding area site, after the specific primer PCR amplification is set, the gene type isparted according to the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis result, thereby providing technical support for detecting the genetic variation of the local ox NPM1 gene in China.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Specific sub sequence for separating Ac/Ds flanking sequence and separation method thereof
The invention relates to a specific sub sequence for separating an Ac / Ds transposon flanking sequence in a corn Ac / Ds transposition mutant and a separation method thereof. The sub sequence is base sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:4. The Ac / Ds flanking sequence in a genome can be well amplified and obtained by using an Ac specific primer and a specific primer of the sub sequence after these sub sequences are connected with corresponding Ac / Ds transposon deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) subjected to restrictive incision enzyme digestion. The detection method is simple to operate, and important technical means is provided for large-scale obtaining of the Ac flanking sequence of the Ac mutant and separation of the gene of an Ac insertion mutant.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
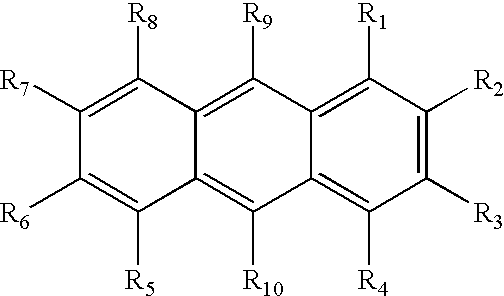
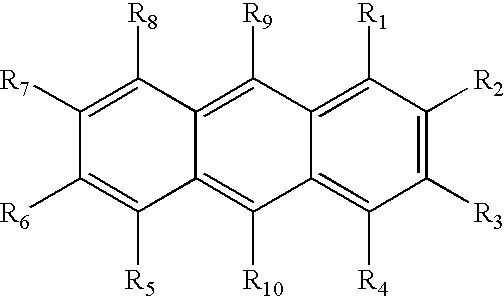
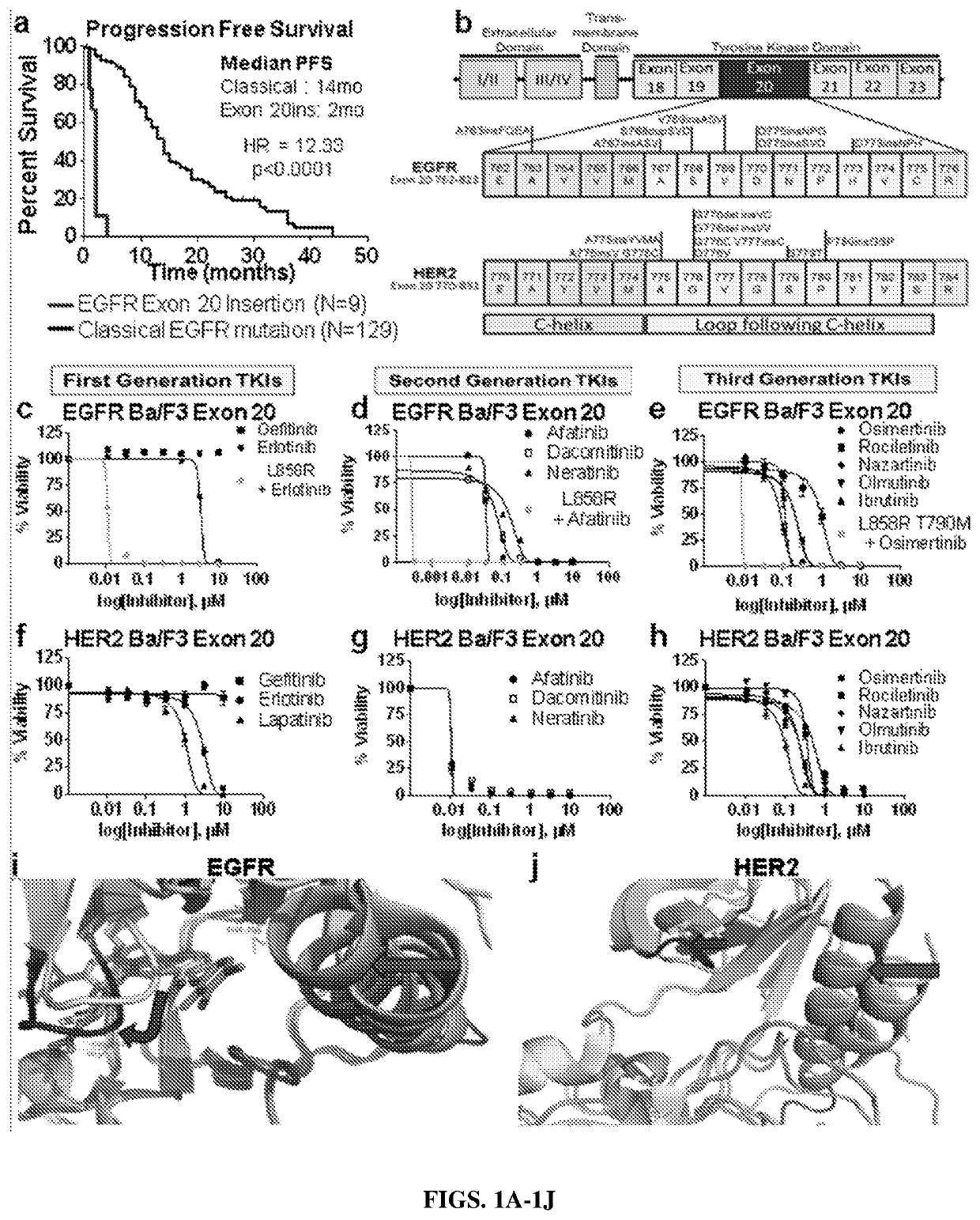
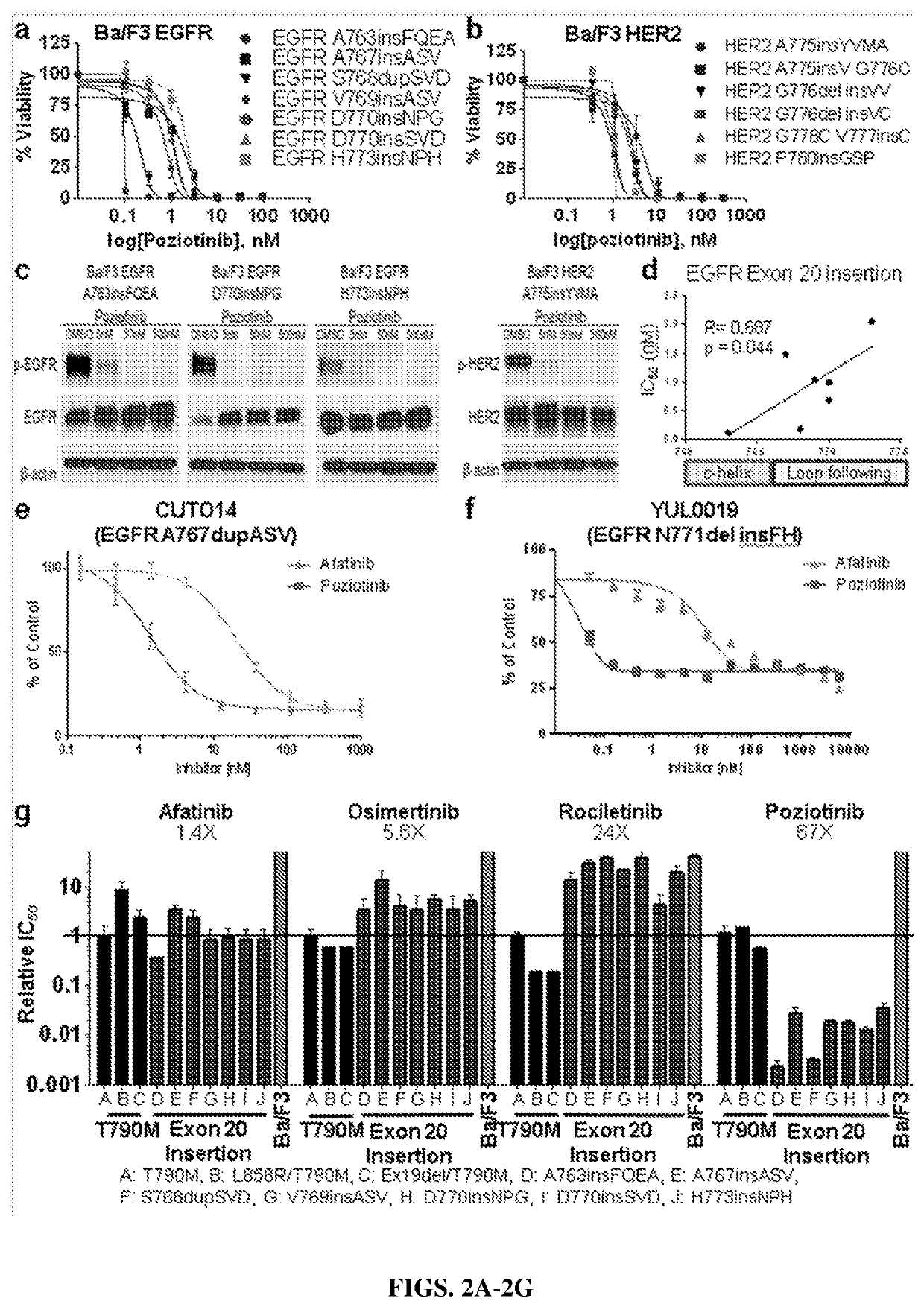
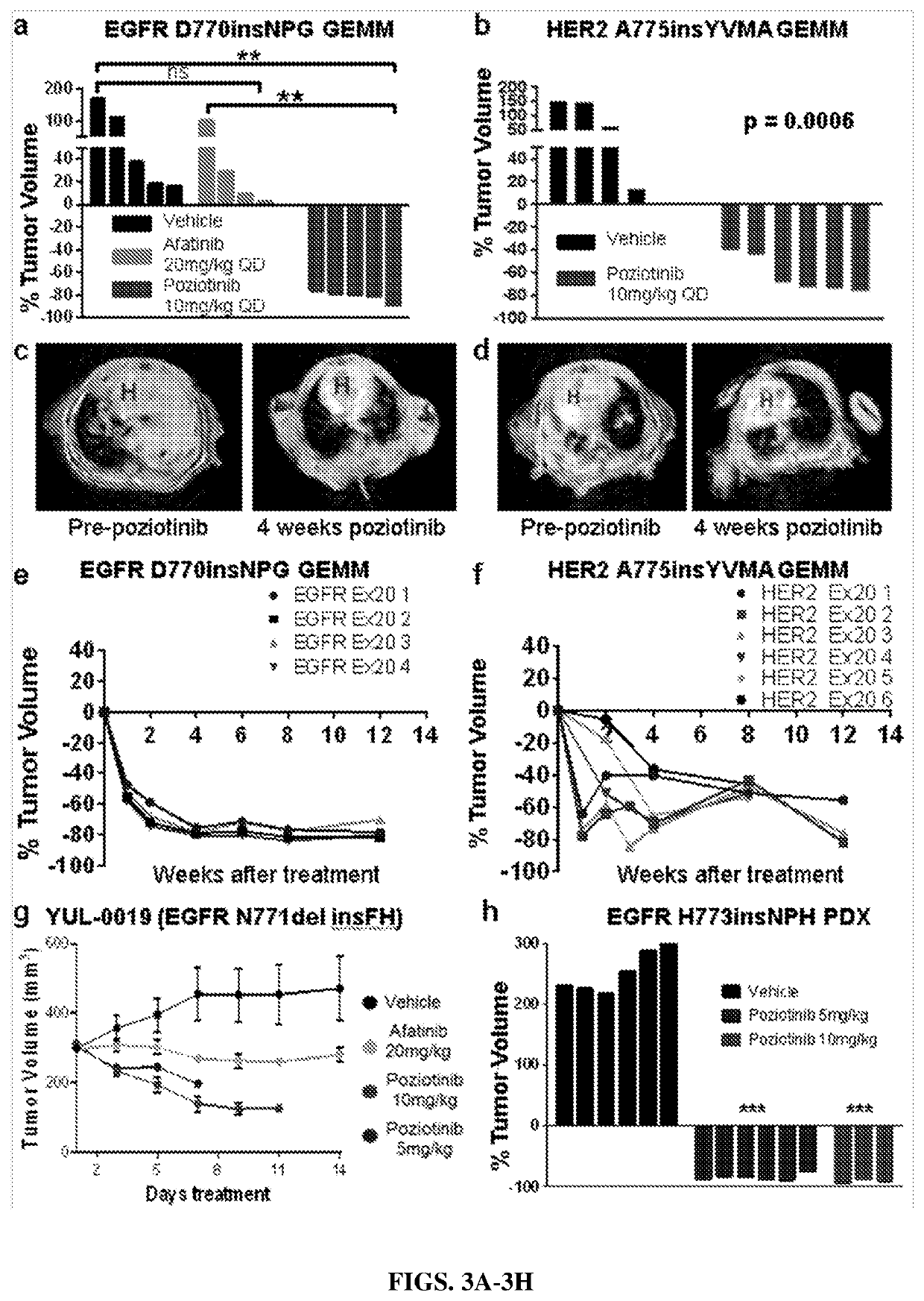
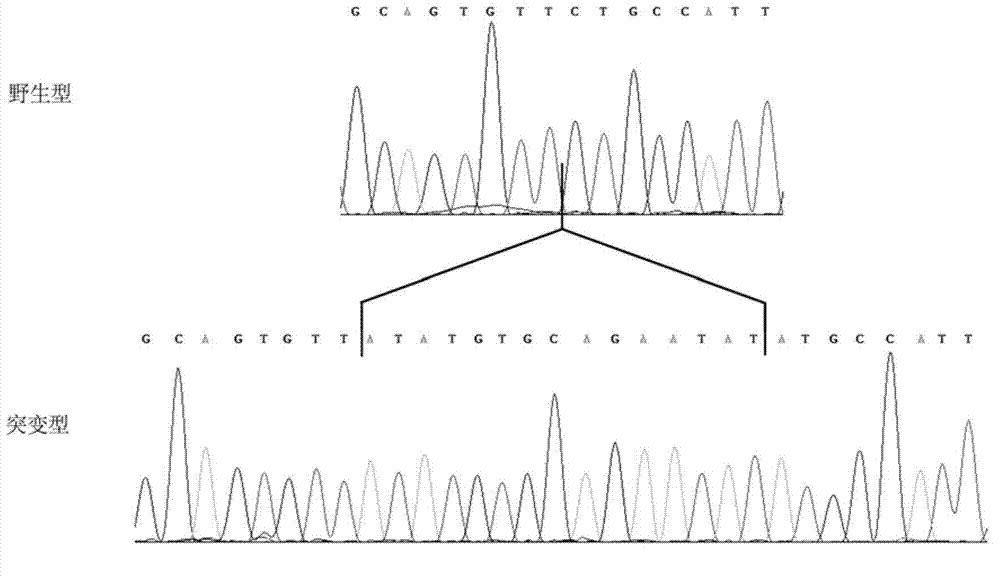
Compounds with Anti-tumor activity against cancer cells bearing EGFR or her2 exon 20 mutations
ActiveUS20200316071A1Improve responseReduce the burden onOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Kit for detecting 15bp insertion mutation in ninth exon of bovine coagulation factor XI gene
InactiveCN102776288AImprove accuracyPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationElectrophoresisWild type
The invention provides a kit for detecting 15bp insertion mutation in a ninth exon of a bovine coagulation factor XI gene. The kit comprises a primer combination shown as SEQ ID NO. 1-4. Based on the position of a 15bp insertion fragment in the ninth exon of the bovine coagulation factor XI gene, two pairs of primers across a 15bp insertion fragment area are designed, based on which a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection system is established. The first pair of primers (Seq ID No. 1 and 2) only specifically amplify a wild type allele, and the second pair of primers (Seq ID No.3 and 4) only specifically amplify a mutant allele; the length difference between two PCR products is 94bp, different genotypes can be sensitively distinguished by shorter-timer electrophoresis by using low-concentration agarose gel, and thus carriers of genetic defects are accurately screened out.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Gene mutant of low-cadmium-accumulation control gene ZmCd1 of corn grains, molecular marker for gene mutant and application of gene mutant
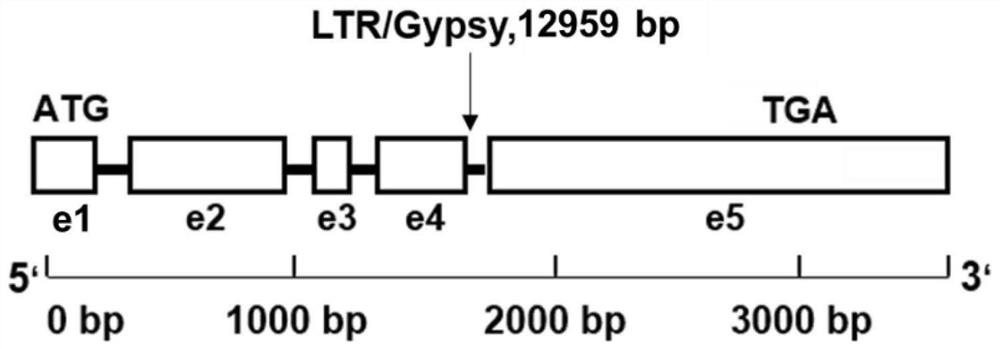
ActiveCN112063628AShorten the breeding processImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention relates to the technical field of botanical molecular biology and particularly relates to a gene mutant of a low-cadmium-accumulation control gene ZmCd1 of corn grains, a molecular marker for the gene mutant and application of the gene mutant. According to the gene mutant ZmCd1-2 of the corn ZmCd1, provided by the invention, compared with a wild type gene ZmCd1, transposon-12959bp insertion mutation presents after a ninth base of a fourth intron, and the mutation is related to high cadmium accumulation of corn. The invention provides the molecular marker for detecting the mutation and a specific primer for detecting the molecular marker, and the molecular marker and the specific primer can be applied to screening and identification of ZmCd1-2-mutation-type high-cadmium-accumulation corn and can also be applied to cadmium-accumulation improvement breeding of ZmCd1-2-type corn grains.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Resource library of rat with gene mutation and preparation method thereof
PendingCN106521638ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant Germ CellsDrug target
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a resource library of rat strains with gene mutation and a preparation method thereof. The rats with gene mutation in the resource library can be obtained from rat spermatogonial stem cells, embryonic stem cells or fertilized ovum with piggyBac transposon insertion mutation. The rats with gene mutation in the resource library also can be obtained from shifting the transposon in germ cells of male rats with mutation. The library can be applied to animal phenotype analysis, gene function research, human disease simulation, medicament screening and drug target development.
Owner:浙江耶大生物医药有限公司
Bleomycin resistance reporter gene mutant, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103981175AIncreased sensitivitySimple methodBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses bleomycin resistance reporter gene mutant, and a preparation method and application thereof. A heterogenous target sequence nucleotide fragment with a certain length is inserted between an initiation codon ATG and a subsequent first amino acid codon GCC of bleomycin gene, and the heterogenous nucleotide fragment with a certain length is a heterogenous target sequence nucleotide fragment with a certain length more than or equal to 1 bp base and less than integer multiple or non-integer multiple of 3 of 1 kb base. By performing insertion mutation on bleomycin resistance reporter gene, a double-resistance plasmid for detecting nuclease activity is constructed. By observing existing or non-existing of bacterium colonies with different resistance or survival and death of cells, evaluation on nuclease activity and off-target effect are performed. Compared with conventional detection technologies, the method has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, simple, and low in cost, and especially, the highlight is that the new method is far higher in sensitivity than that of the prior art.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Intact hepatitis c virus and the method for culturing it in a vitro cell culture
InactiveUS20040166488A1Easy to transcribeImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCell
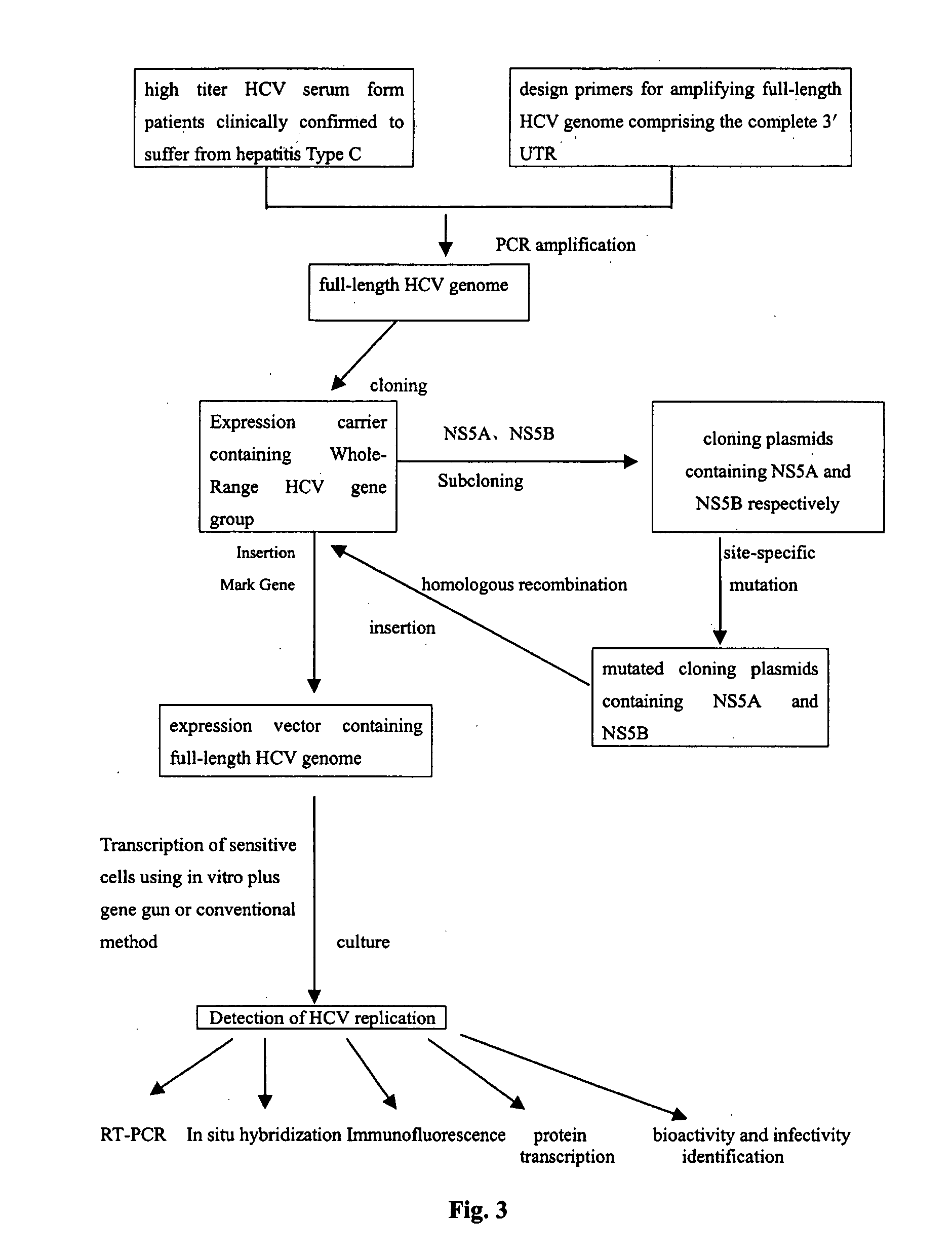
The present invention relates to the establishment of an in vitro cell culture system for culturing the whole HCV proliferating virus by using molecular biology and gene recombinant technology. Said method comprises the step of amplifying from the serum of HCV patients the full-length HCV genome comprising the 98 nucleotides at the 3' end of the genome; site-specific mutating the NS5A and NS5B of HCV genome; inserting a marker gene IRES-GFP expression cassette into the NS5B 3' end in the mutated HCV genome; and transfecting the sensitive cells and culturing, to obtain the infectious HCV offspring virus.
Owner:YANGLING DAIYING BIOLOGICAL ENG
Plant-anthocyanin synthesis control gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108018290AImprove detection accuracyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceIntein
The invention discloses a plant-anthocyanin synthesis control gene and application thereof. The sequence of the disclosed gene is shown in the SEQ ID No.1. A 3,772-bp klenow-fragment insertion mutation of the gene exists in first intron of white heading brassica rapa, and the gDNA sequence of the mutation is shown in the SEQ ID No.5. According to the mutation in the intron in the gDNA nucleotide sequence of the gene, three specificity PCR primers of the Marker 1, the Marker 2 and the Marker 8 are designed, wherein the Marker 1 and the Marker 2 are co-dominant markers, and the Marker 8 is a maternal marker. The DNA of the target brassica rapa is subjected to PCR amplification and identified through agarose gel electrophoresis, drinamyl hybrid strains and homozygous strains in segregation population can be rapidly identified through the Marker 1 and the Marker 2, and the drinamyl hybrid strains and the homozygous strains in the segregation population can also be distinguished through theMarker 8 in cooperation with the heading characteristics.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Primer for identifying rhizoma atractylodis medicinal species by using chloroplast genes, and applications thereof
ActiveCN111004860AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyGenetic diversity
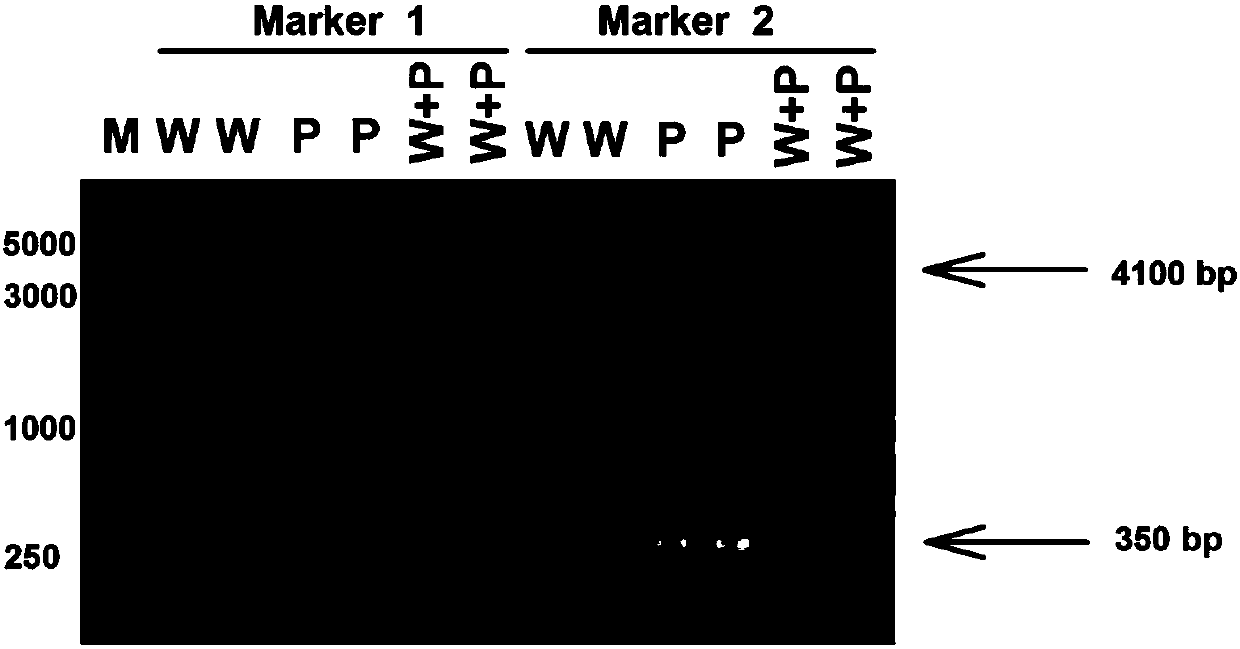
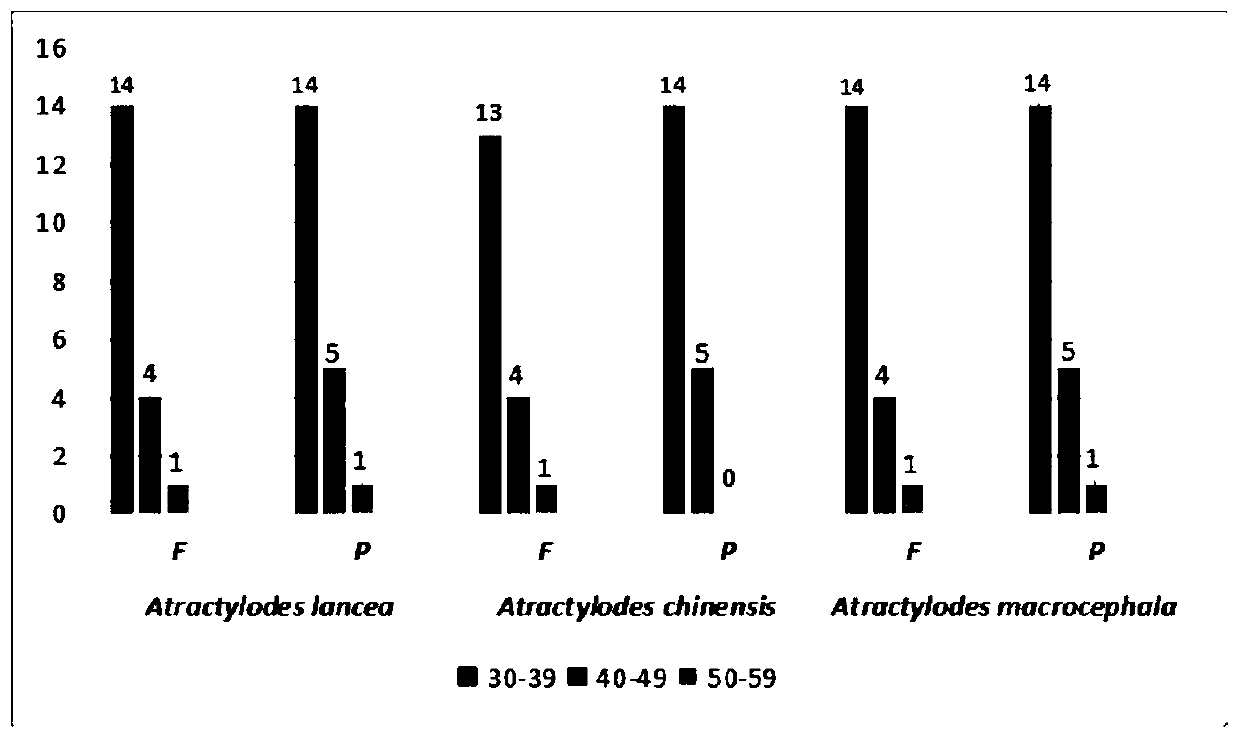
The invention discloses a primer for identifying rhizoma atractylodis medicinal species of Atractylodes macrocephala, Atractylodes lancea and Atractylodes chinensis by using chloroplast genes, and applications thereof. According to the invention, a sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1 / SEQ ID NO.2 is used as a primer to amplify the chloroplast genome sequences of Atractylodes macrocephala, Atractylodes lancea and Atractylodes chinensis, and the comparison results after PCR strip sequencing show that the target strip of the Atractylodes lancea has 5 bps tatat insertion mutation, and the target strip of the Atractylodes macrocephala has 6 bps tcttac insertion mutation; and the chloroplast genome molecular marker successfully distinguishes three species of Atractylodes macrocephala, Atractylodes lancea and Atractylodes chinensis, and provides a technical means for genetic diversity, phylogenetic evolution and taxonomy research of rhizoma atractylodis plants.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for improving genetic characteristics in diatom oil production
InactiveCN102827856AEasy to shapeNo harmUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiodieselStaining
The invention discloses a method for improving genetic characteristics in diatom oil production, and relates to the genetic breeding method of diatom. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing karyogene transformation plasmid; (2) transferring the transformation plasmid into the genome of the diatom to establish a random inserting mutant library; (3) sorting high oil-producing mutant strains in the mutant library through a Nile red fluorescence staining ratio method; (4) measuring triglyceride in the cell, analyzing the fatty acid; and (5) measuring the growth. With adoption of the method, fine varieties can be selected and cultivated by randomly inserting mutation; and the method can be applied to any diatom in which a genetic material transfer system is successfully established; the strains with good comprehensive performance can be successfully sieved easier than gene expression or silence; compared with the methods of chemical mutagenesis and irradiation mutagenesis, the method has no harm to the human body. According to the method, the oil accumulation of the sorted high oil-producing mutant strains is increased, and moreover, the ratio of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the triglyceride can be reduced, so that the triglyceride can be served as the raw material for producing biodiesel without being subject to saturation modification.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA +1
Method of typing gene polymorphisms
InactiveUS20060199178A1Accurate detectionGood reproducibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertional mutationTrace Amounts
Accurate and highly reproducible means of detecting a base substitution mutation (for example, SNP), an insertion mutation or a deletion mutation with the use of a nucleic acid sample in a trace amount and a method of typing gene polymorphisms using the means.
Owner:KOBAYASHI EIJI +6
Transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) target gene editing and optimizing method taking IDLV as template
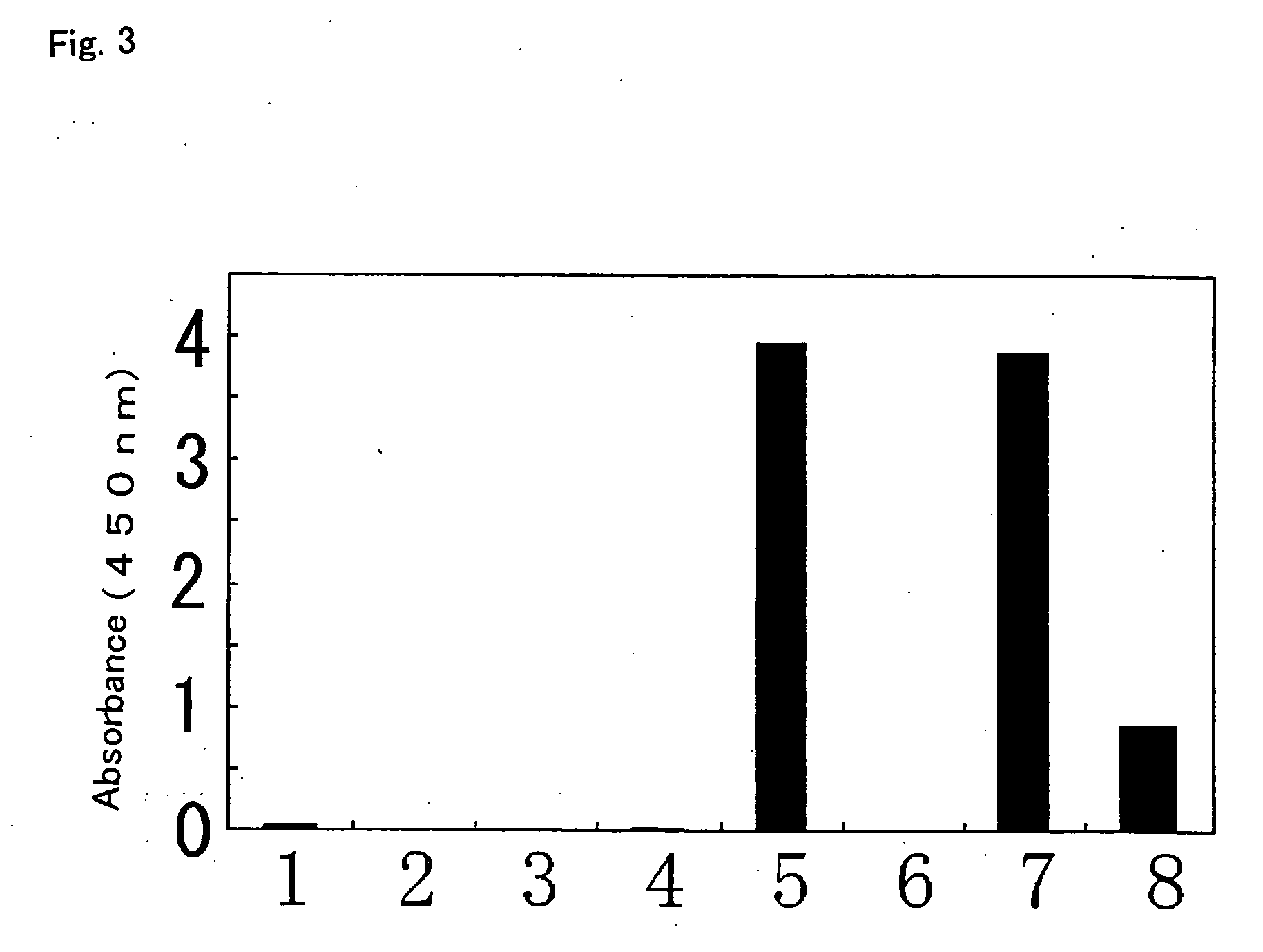
The invention provides a transcription activator-like effector Nuclease (TALEN) target gene editing and optimizing method taking IDLV as a template. A homologous recombination template is inserted into a lentiviral vector, the intracellular delivery efficiency of the homologous recombination template is improved by using efficient transduction efficiency of lentivirus, so as to improve the efficiency of a TALEN target gene editing technique. The lentivirus is packaged by using packaging plasmids with integrase defect, the lentiviral vector containing the template is not integrated into a chromosome, insertion mutation is avoided and the safety of the target gene editing technique is ensured. A complete set of TALEN target gene editing and optimizing method in which the lentivirus with integrase defect is used as an intracellular import tool of the homologous recombination template is provided. Different TALENs and homologous recombination template sequences are designed according to the research targets by the method, and efficient target editing of any gene sequence is expected to be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
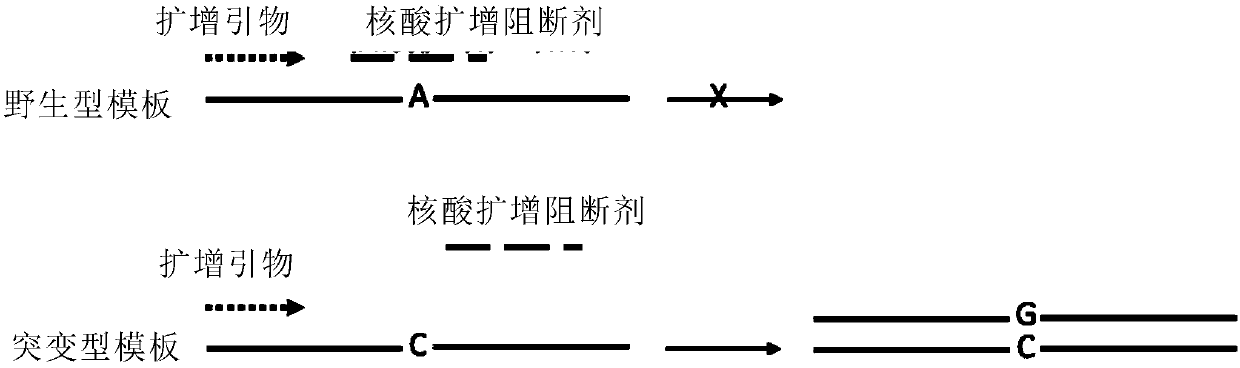
Nucleic acid amplification blocking agent for detecting low-abundance mutant sequences and application
InactiveCN109652410AHigh affinityBase modification position is flexibleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertional mutationWild type
The invention discloses a design principle of a nucleic acid amplification blocking agent for detecting low-abundance mutant sequences, and relates to the field of detection of mutant genes. The nucleic acid amplification blocking agent is oligonucleotide modified by locked nucleic acid (LNA), and a pairing region of the nucleic acid amplification blocking agent is located between amplification sequences and completely paired with wild-type gene sequences, and has at least one mispairing with the mutant sequences. The invention further discloses application of the nucleic acid amplification blocking agent in detecting the low-abundance mutant sequences. According to the nucleic acid amplification blocking agent and the application, the affinity between the nucleic acid amplification blocking agent modified by locked nucleic acid and the mutant nucleic acid sequences / wild-type nucleic acid sequences has a huge difference, and the purpose of highly-selective amplification / enrichment of the mutant sequences in a sample is achieved; the nucleic acid blocking agent has the advantages of being high in affinity, flexible in basic group modification position, good in heat stability, cheapin price and the like, and has a more significant detection effect on deletion mutation and insertion mutation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAG GENE NANOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com