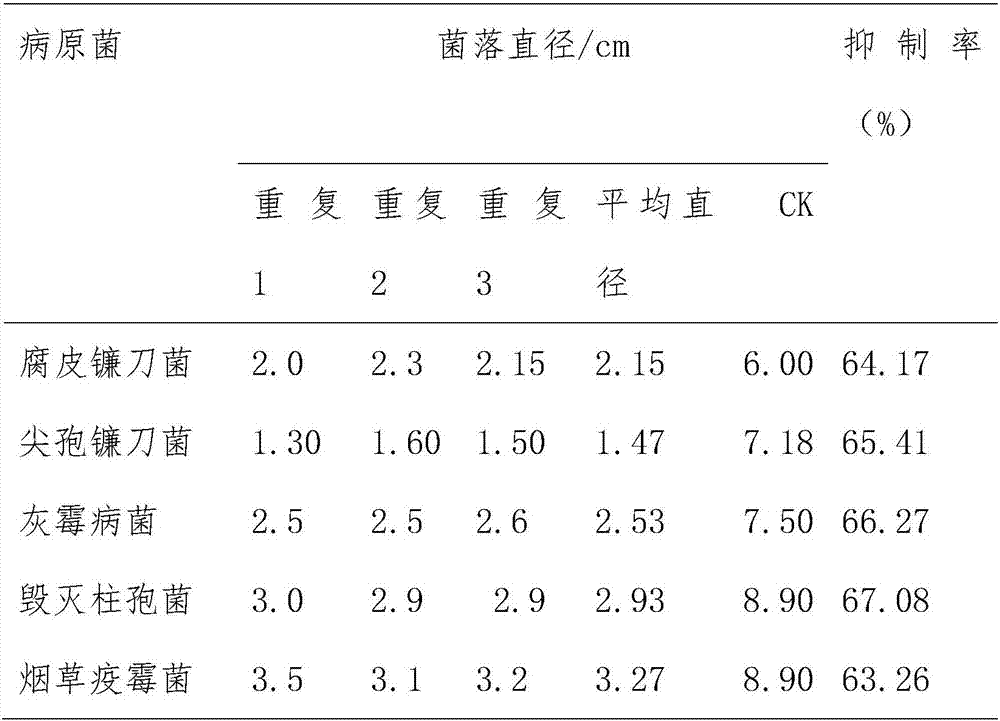
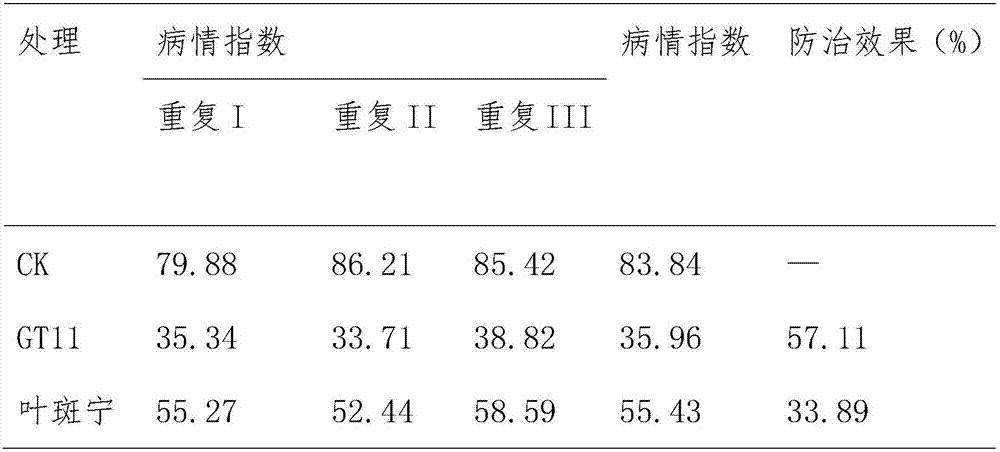
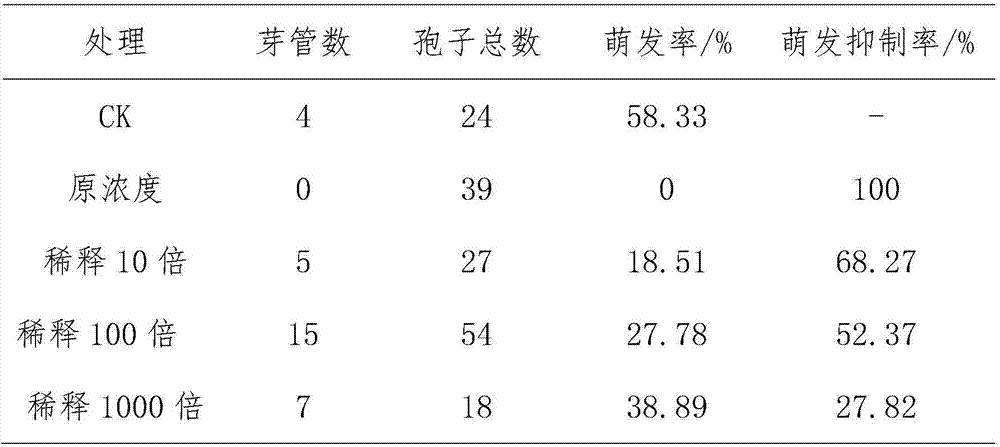
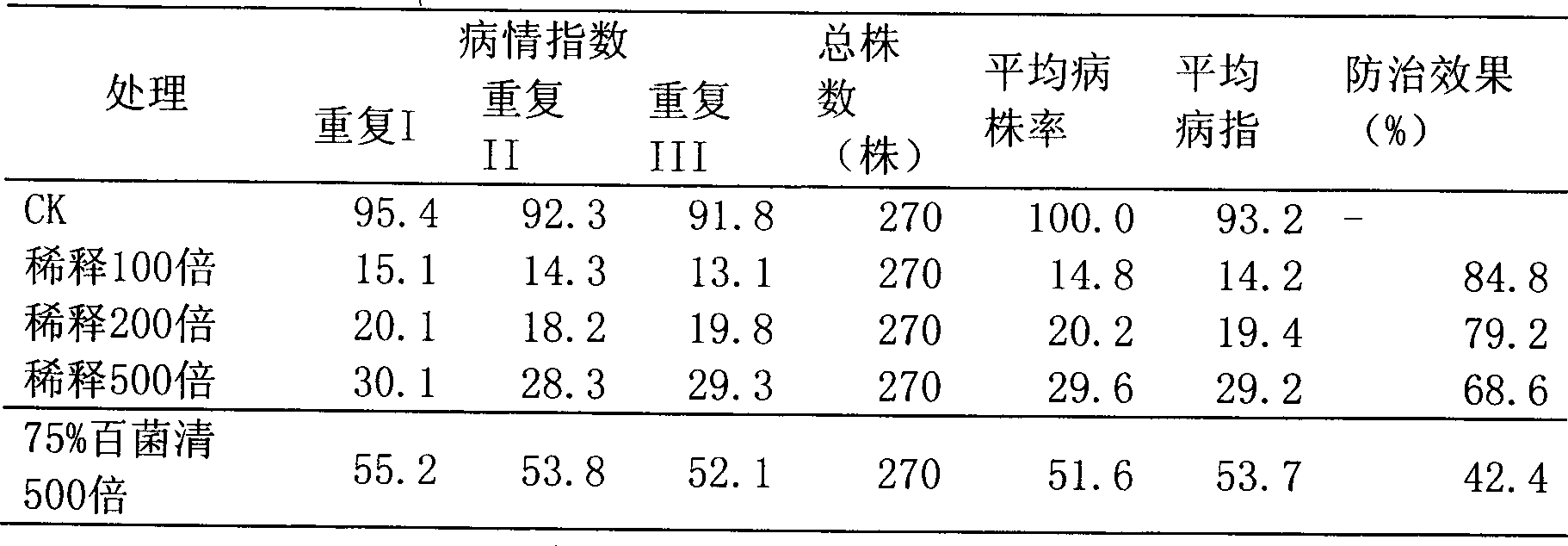
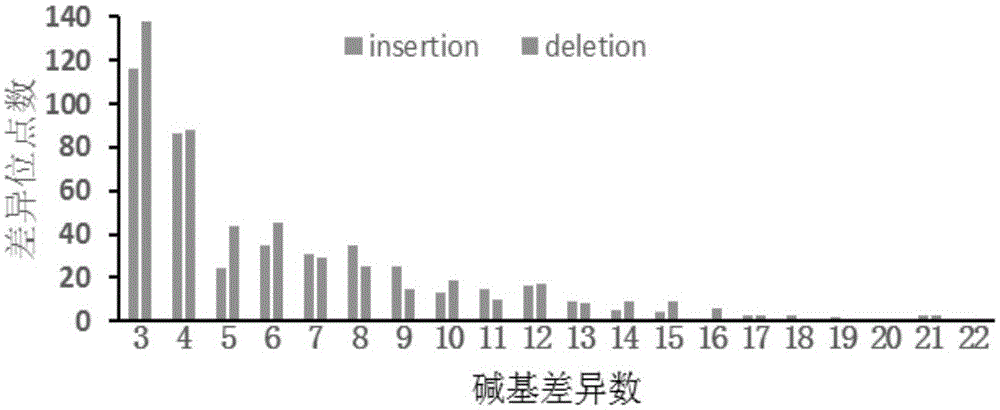
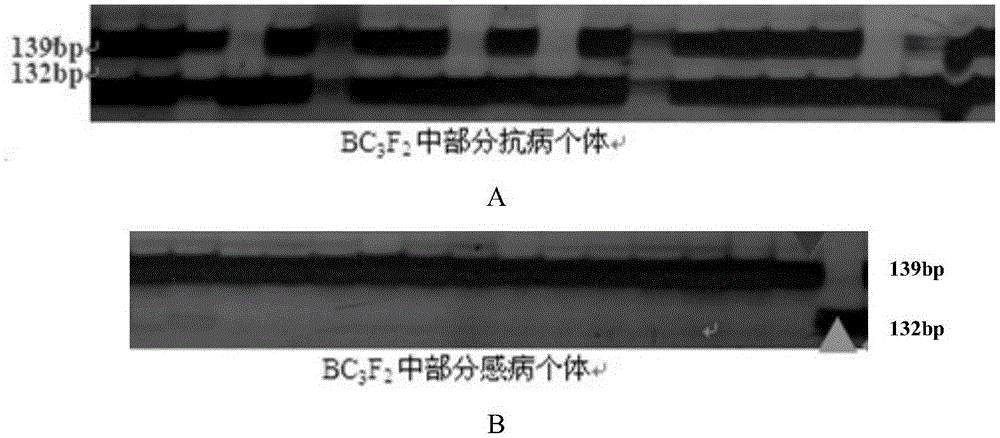
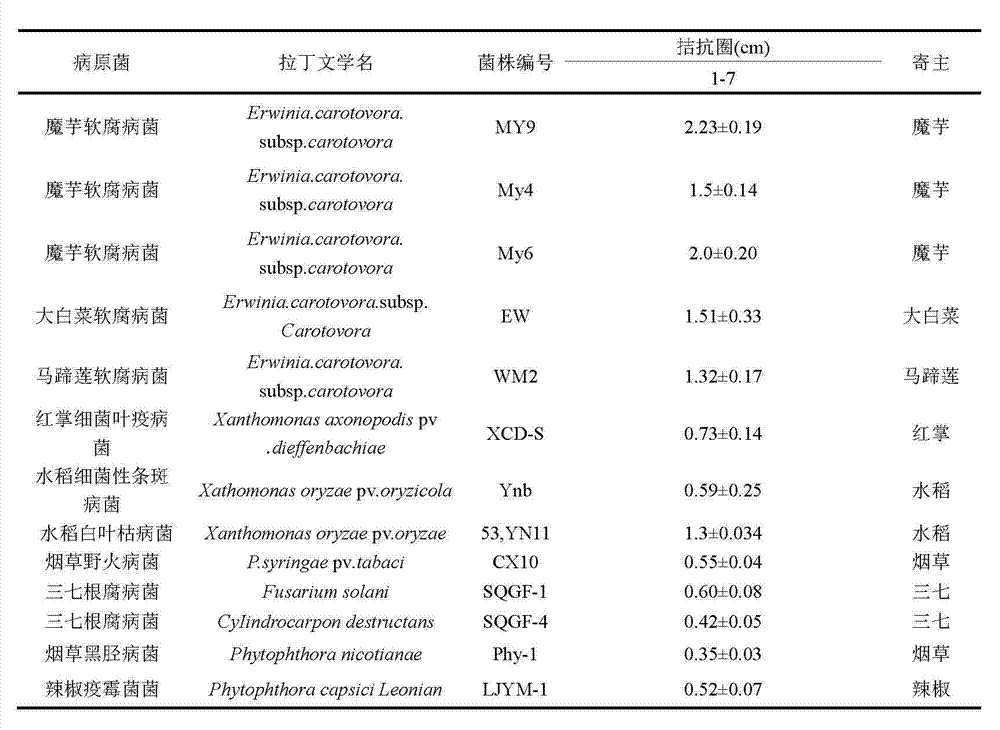
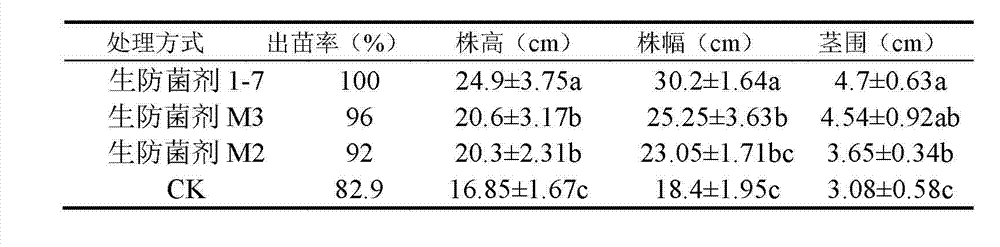
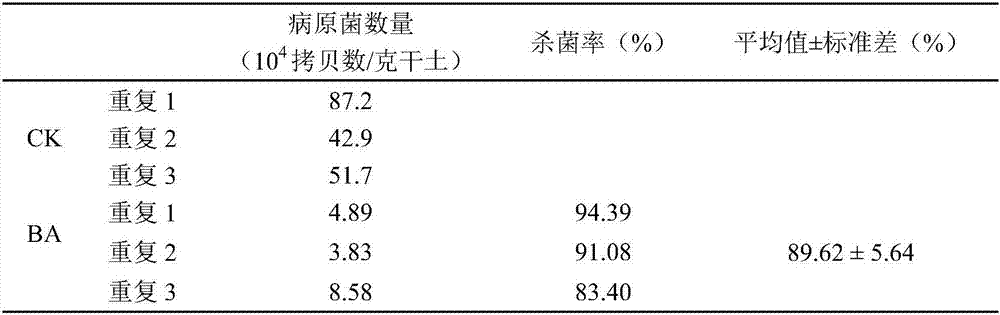
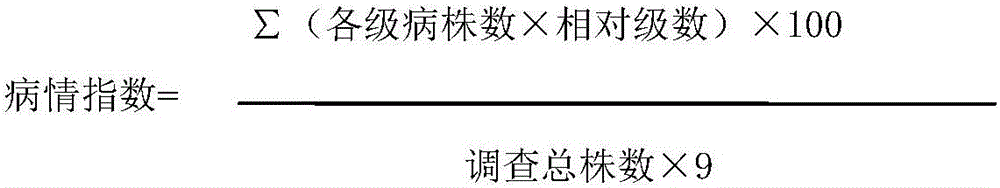
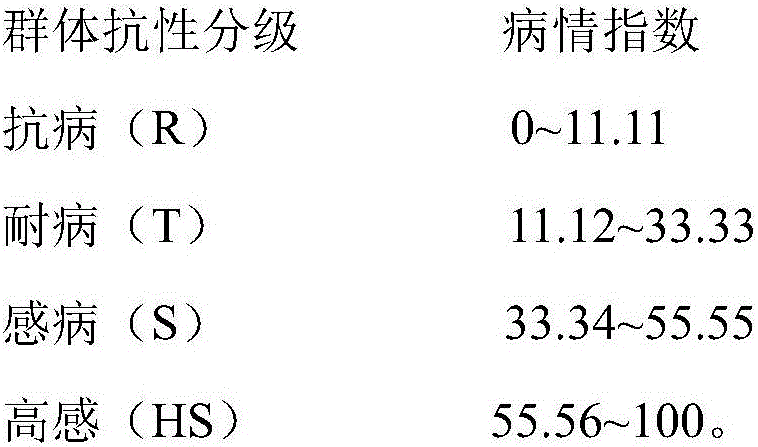
Patents
Literature
268 results about "Clubroot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clubroot is a common disease of cabbages, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, radishes, turnips, stocks, wallflowers and other plants of the family Brassicaceae (Cruciferae). It is caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae, which was once considered a slime mold but is now put in the group Phytomyxea. It is the first phytomyxean for which the genome has been sequenced. It has as many as thirteen races. Gall formation or distortion takes place on latent roots and gives the shape of a club or spindle. In the cabbage such attacks on the roots cause undeveloped heads or a failure to head at all, followed often by decline in vigor or by death. It is an important disease, affecting an estimated 10% of the total cultured area worldwide.
Bacillus belleus GT11 and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus belleus GT11 and application thereof. The bacillus belleus CT11 is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 13th, 2016; the collection number is CGMCC No.13446; the bacillus belleus CT11 can be prepared into water agent, wettable powder or coating material and can be used for preventing and controlling the root rot diseases of pseudo-ginseng and plukenetia volubilis and Chinese cabbage clubroot. The invention provides an efficient, nontoxic, safe, non-residual and conveniently used biological agent for preventing and controlling the diseases such as root rot and clubroot; the effective active ingredient is bacillus belleus CT11 strain; the strain can generate the secondary metabolite antimicrobial active matter, is capable of degrading the cell wall of pathogenic bacteria and has an excellent growth-promoting effect for the crops, such as, plukenetia volubilis, pseudo-ginseng and Chinese cabbage; besides, the bacillus belleus CT11 has a better antibacterial effect for pseudo-ginseng phytophthora sojae, pseudo-ginseng fusarium solani, plukenetia volubilis gray mold, paddy bacterial mycosphaerella, and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biological preparation capable of preventing and treating cruciferae club root and use thereof
InactiveCN101416641AGood control effectSolve prevention and control problemsBiocideBacteriaSucroseRussulaceae
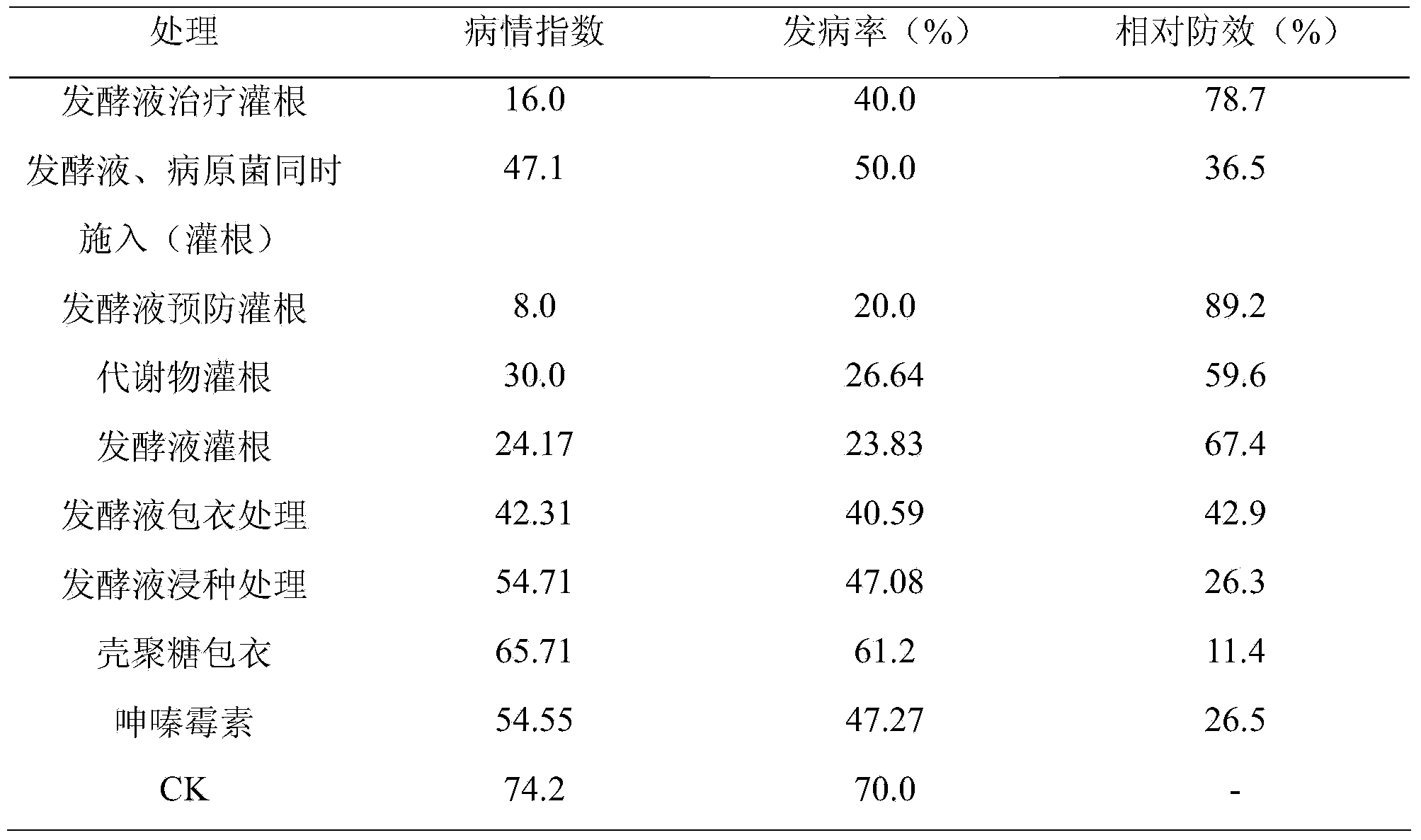
The invention relates to a biological agent against crucifer club root and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of bio-pesticide. The strain for production is Bacillus subtilis XF-1, whose preserving number is CGMCC NO.2357. The stain has the characteristics as follows: (1) the primary colony on the LB culture substrate is white and round having a wet surface; the later colony is light yellow having uneven edge with dry and crimple surface; observed from the microscope, the strain is short-bar shaped and movable with spore, peritricha and dimension of 0.7 - 0.8 * 2.0-2.4 mum; (2) the strain is Gram-positive and aerobic and makes use of glycogen, sugar, citrate, gelatin hydrolysate, starch and casein, but does not make use of cellulose, tyrosine and catalase positive; (3) the stain has the function of sterilization, disease prevention, and yield improvement. The embodiment of the invention is as follows: using the test tube of Bacillus subtilis XF-1 stain, shake cultivation, and culture solution for fermentation to prepare biological agent, then applying the biological agent to the rhizosphere soil of crucifer crops, thereby having good effect in preventing and treating, and simple production.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Ho/ll canola with resistance to clubroot disease
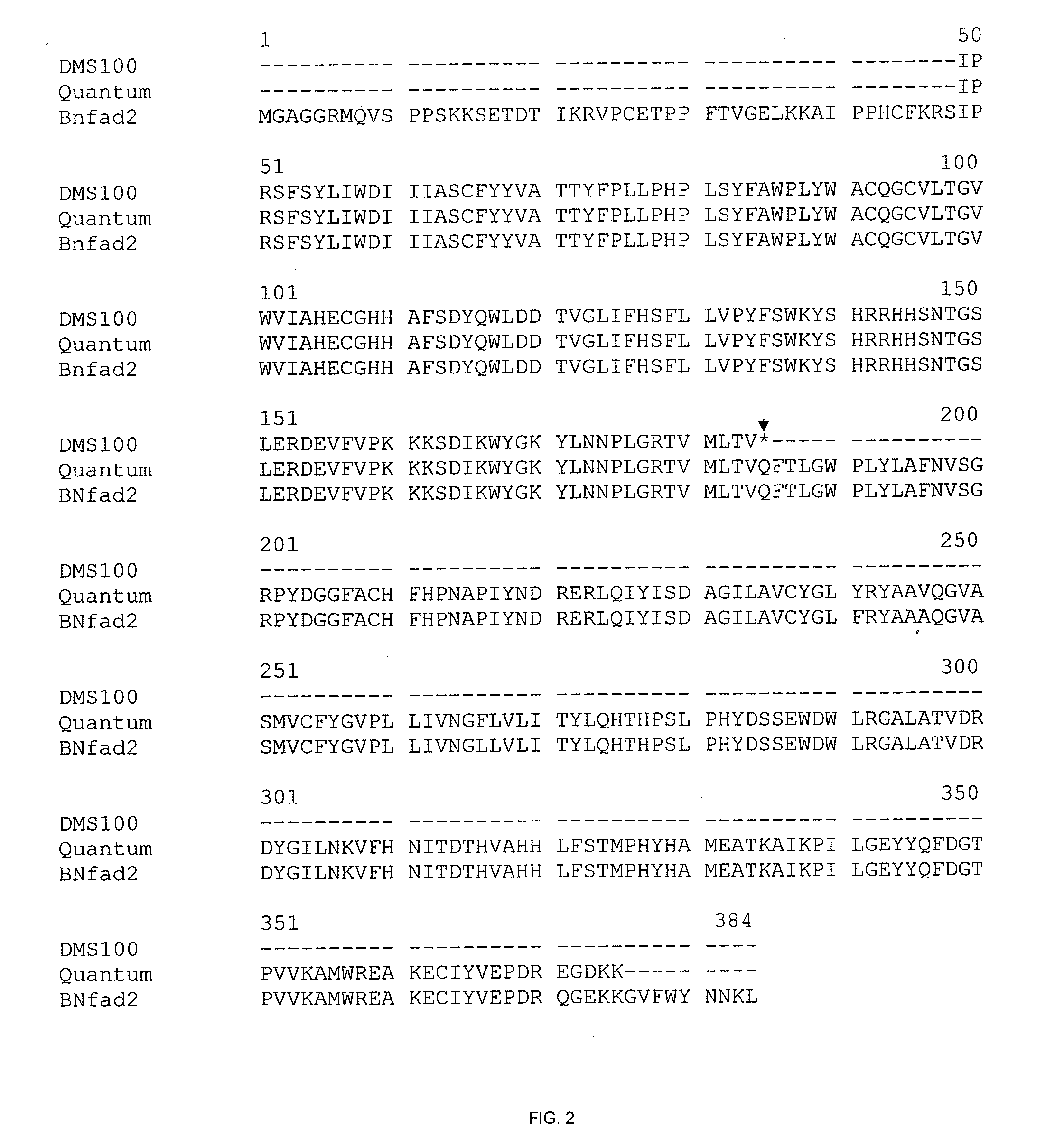
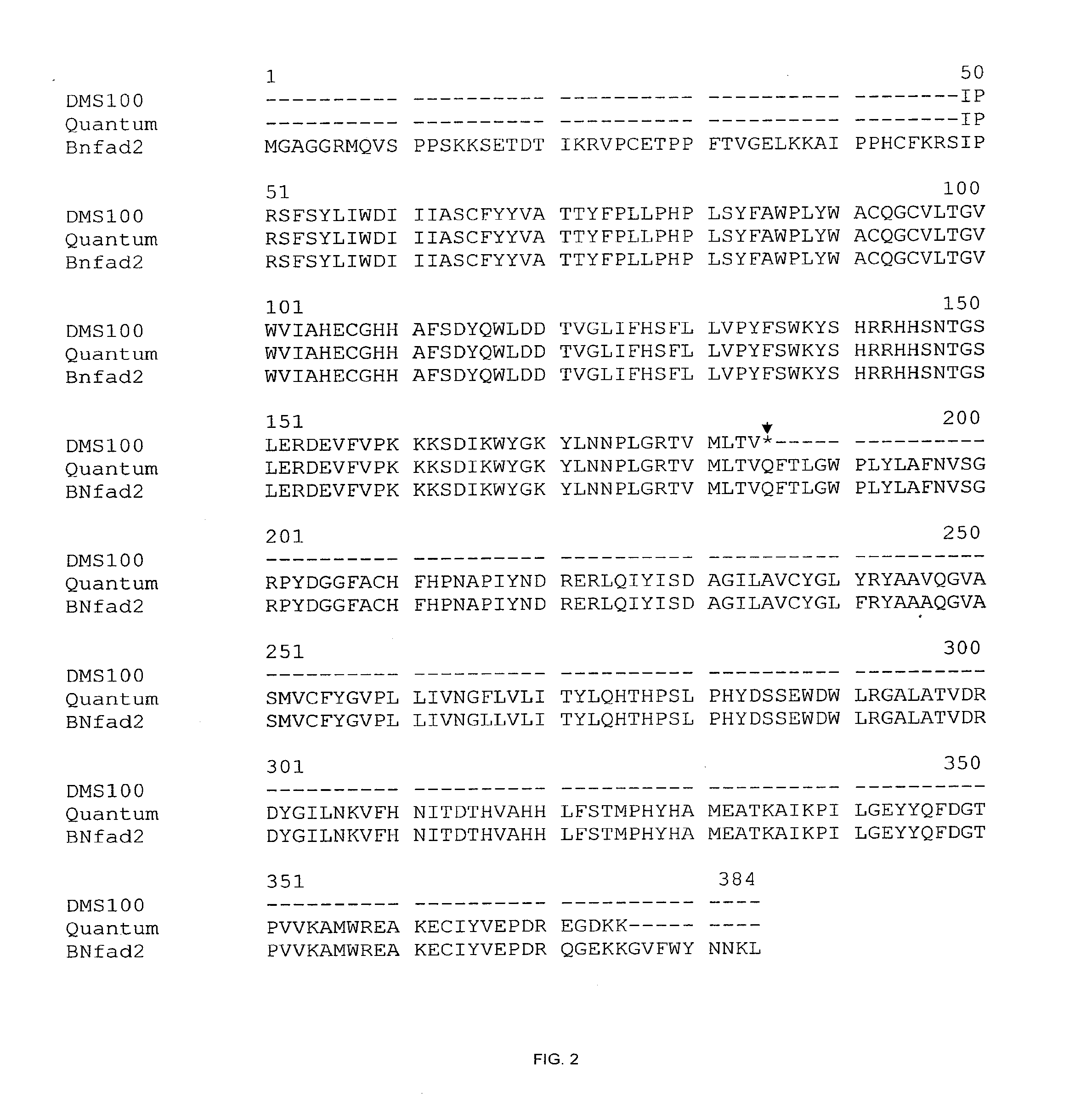
This disclosure concerns a plant of the genus, Brassica, or parts thereof, which comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of high oleic acid content, low linolenic acid content, increased herbicide resistance, restorer of cytoplasmic male sterility, and increased clubroot disease (Plasmodiophora brassicae) resistance, compared to a wild-type plant of the same species. This disclosure further relates to wild-type and mutant alleles of genes involved in these traits, molecular markers linked thereto, and methods of their use.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Ho/ll canola with resistance to clubroot disease
ActiveUS20130298279A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyMutant allele
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Bacillus subtilis M3 and application thereof
InactiveCN103451135AGood control effectGood growth promoting effectBiocideBacteriaBiological activationPlant disease
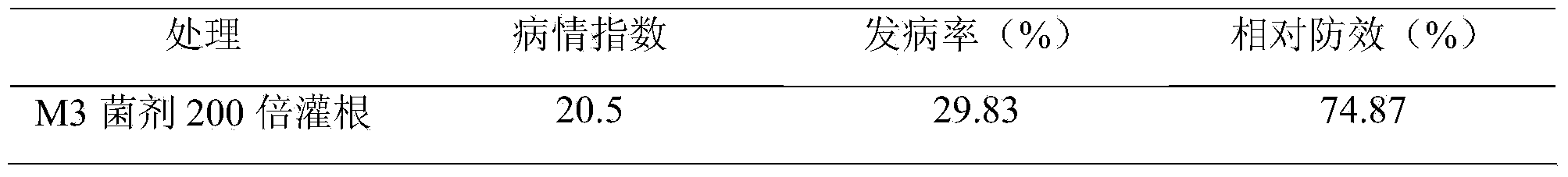
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis M3 and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides. The produced strain is the bacillus subtilis M3; the preservation unit is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; the address is Zhongguancun, Beijing, China; the preservation date is July 11, 2013; the preservation number is CGMCC NO.7911. The application of the bacillus subtilis M3 as a preparation for preventing and controlling Chinese cabbage clubroot, tomato scab, tomato root knot nematode diseases and konjak bacterial soft rot is also disclosed. The bacillus subtilis M3 disclosed by the invention achieves an obvious and stable prevention and control effect on the diseases, can be used for preparing the preparation for preventing and controlling the Chinese cabbage clubroot, the tomato scab, the tomato root knot nematode diseases and the konjak bacterial soft rot and has the advantages of high efficiency, nontoxicity, safety, no residue, bacteria activation, disease control, better growth promotion effect, better comprehensive character and easiness for industrialized production.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
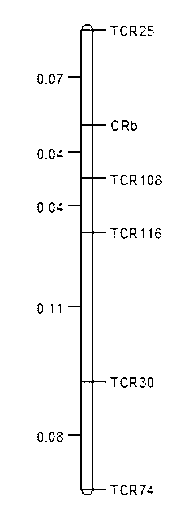
Clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage gene CRb closely-linked molecular markers, primers and selection method of clubroot-resistant plant
InactiveCN103275972AImprove breeding efficiencyShorten the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention provides 5 clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage gene CRb closely-linked molecular markers, primers and a selection method of a clubroot CRb-resistant plant. The 5 clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage gene CRb closely-linked molecular markers comprise TCR25, TCR108, TCR116, TCR30 and TCR74. Distances of the gene CRb respectively to the TCR25, the TCR108, the TCR116, the TCR30 and the TCR74 are 0.07cM, 0.04cM, 0.08cM, 0.19cM and 0.27cM. The 5 clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage gene CRb closely-linked molecular markers can be used for molecular marker-assistant selection of clubroot-resistant genes of brassica such as Chinese cabbage and Shanghai Bak choi. In assistant selection, the 5 clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage gene CRb closely-linked molecular markers are used simultaneously so that theoretical selection accuracy is 100%. The 5 clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage gene CRb closely-linked molecular markers have good repeatability, high reliability and a low detection cost and saves time and labor.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof
InactiveCN105543391AAccurate and reliable identification resultsReduce labor costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyForward primer
The invention discloses an InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof. The invention provides a method for identifying or auxiliarily identifying whether a Chinese cabbage is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage, which comprises the following steps: carrying out amplification by using genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the Chinese cabbage to be identified as a template, a single-stranded DNA disclosed as SEQ ID No.2 as a forward primer and a single-stranded DNA disclosed as SEQ ID No.3 as a reverse primer; detecting the size of the amplification product; and determining whether the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage according to the size of the amplification product: if the amplification product of the Chinese cabbage to be identified contains a 201bp strip, the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage or candidate clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage; and if the amplification product of the Chinese cabbage to be identified does not contain any 201bp strip, the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a non-clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage or non-candidate clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
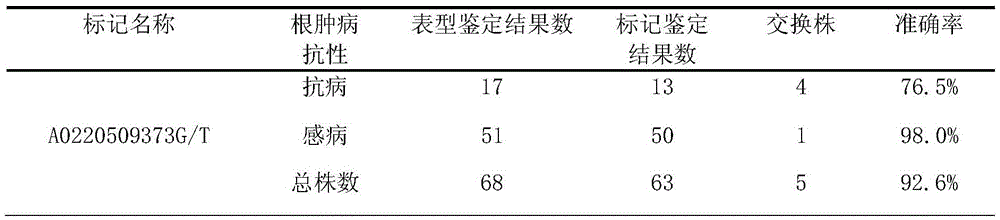
Specific SNP molecular marker for identifying cabbage clubroot 4# physiological race resistance and application
ActiveCN105525024AAccurate and reliable identification resultsReduce labor costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceTyping
The invention discloses a specific SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker for identifying cabbage clubroot 4# physiological race resistance and application. The invention provides application of an A0220509373G / T site in any one aspect as follows: A, application to identification or auxiliary identification of cabbage clubroot resistance; B, application to breeding of cabbage-clubroot-resistant varieties; C, application to cabbage breeding; D, application to prediction of cabbage clubroot resistance; E, application to preparing a product for identification or auxiliary identification of cabbage clubroot resistance; and F, application to preparation of a product for predicting cabbage clubroot resistance. Experiments prove that the A0220509373G / T site and a specific primer of the A0220509373G / T site can realize good typing on the cabbage clubroot; a good application value is realized; and the selection in advance and the auxiliary breeding on materials resisting the clubroot inheritance can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Bacillus velezensis and application thereof in preventing and treating clubroot of cruciferae
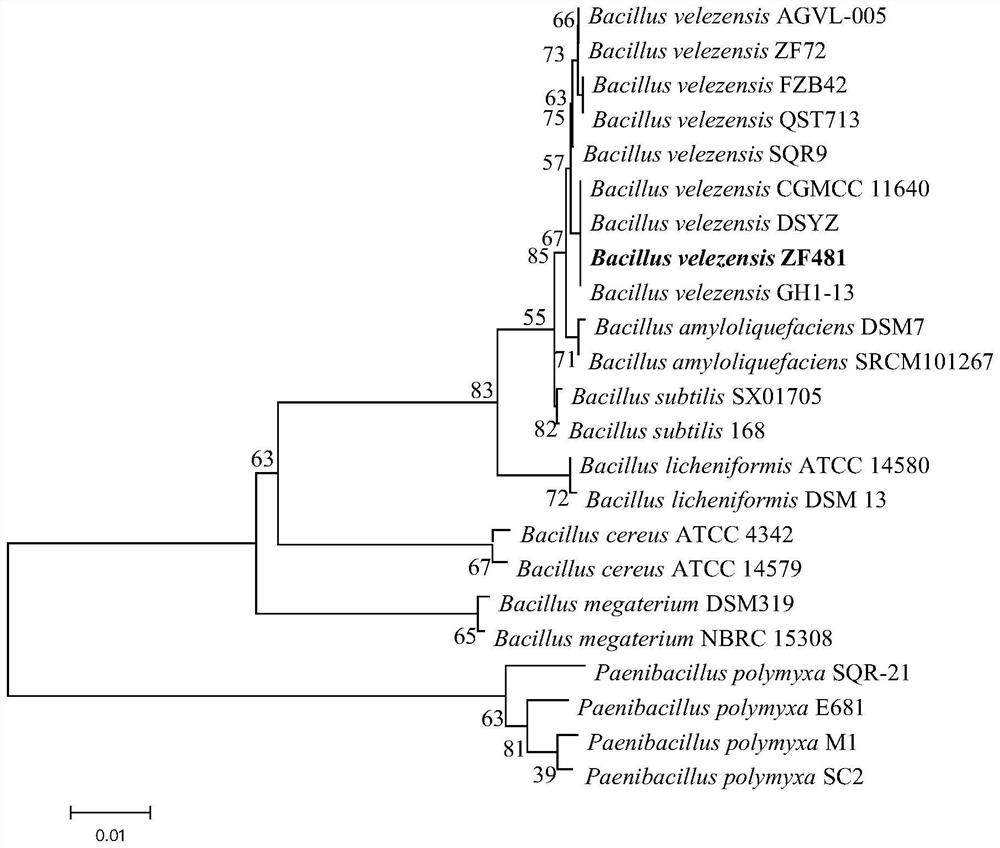
The invention discloses bacillus velezensis ZF481 and application thereof. The strain number of the bacillus velezensis is ZF481, the bacillus velezensis is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 8, 2020, and the registration number of the bacillus velezensis is CGMCC No.20320. The bacillus velezensis ZF481 or / and the metabolite of the bacillus velezensis ZF481 can be used for preventing and / or treating the plant clubroot, or preparing a product for preventing and / or treating the plant clubroot. The strain has an inhibiting effect on the activity and germination of plasmodiophora brassicae resting spores, has a good growth promoting effect on brassicaceous crops such as Chinese cabbage and the like, and also has a good antibacterial effect on phytophthora capsici, stemphylium solani, fusarium oxysporum, alternaria solani, corynespora, Botryis cinerea, rhizoctonia solani and the like.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for producing cruciferous plant resistant to clubroot
InactiveUS20130254929A1Efficient techniquePromote efficient breedingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneClubroot
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG
Soil conditioner for preventing and curing Cruciferae crop clubroot and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101058729ASufficient sourceVery popularAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersSoil conditionerBoron
The invention discloses a soil adjuster to prevent Cruciferae crop from clubroot, which comprises the following parts: 10-50% organics, 10-60% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 15-80% carbonate, 0. 8-5% potassium, 0. 8-5% magnesium, 0. 8-5% zinc, 0. 8-5% boron, wherein the wild or cultivated organics adopts Tagetes plant as raw material; the wild plant can be harvested during blossom period, which is dried and grinded into powder. The invention can avoid the clubroot to 80-95%, which is economic, safe, high-effective and convenient.
Owner:赵国晶
Molecular marker of brassica napus anti-clubroot gene and application of molecular marker to anti-clubroot breeding
ActiveCN105063033AImprove breeding efficiencyShorten the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRe sequencingAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a brassica napus anti-clubroot gene PbBa8.1 and a method for applying the molecular marker to anti-clubroot breeding through re-sequencing. The DNA molecular marker, capable of distinguishing anti-clubroot brassica napus and brassica napus being not resistant to clubroot, is obtained by conducting polymorphic analysis on sequences, around a PbBa8.1 locus, of two parents, and carrying out primer development design by utilizing the flanking sequences of an Indel locus. Primers, namely F A08-300: 5'-GTAGTGCGGGCCACAAAAT-3' and R A08-300: 5'-CACAATGGAGTGTTGAAATTCACT-3', aimed at the molecular marker are designed, and can be used for improving the anti-clubroot gene breeding speed and identification efficiency. The method is easy to carry out, high in repeatability, operability and identification speed, and low in detection cost, time consumption and labor cost, and has the advantages that the workload of selecting an anti-clubroot singleplant through phenotype identification in a field is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 and application
InactiveCN102899266AGood growth promoting effectGood characterBiocideBacteriaBacterial soft rotMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to a Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 and an application, which belongs to the biology technical field. The Pantoea agglomerans1-7 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 28th, 2012 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.6160. The Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 is used for preparing the preparations used for preventing and treating bacterial soft rot of konjak and clubroot disease on cruciferous vegetable club root in fields. The Konjak endophytic bacteria Pantoea agglomerans bacterial strain1-7 has the advantages of high efficiency, no toxicity, safety and no residue, the bacterial strain1-7 has the characteristics of good disease control, better growth promotion effect, better comprehensive characters and easy industrial production, and the Pantoea agglomerans1-7 can be applied to preparation of preparations for controlling cruciferous vegetable club root in fields.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Long-acting biological medicine fertilizer for peanuts and preparation method of long-acting biological medicine fertilizer
The invention discloses long-acting biological medicine fertilizer for peanuts and a preparation method of the long-acting biological medicine fertilizer. The long-acting biological medicine fertilizer is prepared from, by weight, 0.5-1 part of paenibacillus polymyxa, 1-10 parts of chlorpyrifos-carbosulfan suspension microcapsules, 25-35 parts of urea, 30-40 parts of monoammonium phosphate and 30-40 parts of potassium sulphate, and the number of viable bacteria of the paenibacillus polymyxa is 900-1100 million cfu / g. The medicine fertilizer can keep the pesticide effect during the whole processes of sowing of the peanuts and hardening of peanut shells, can conduct insect prevention and can prevent bacterial wilt, blight, root rot, clubroot and other soil-borne diseases, the yield is raised, and the whole course of control over prevention of diseases and insect pests is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG JINHONGYUAN ECOLOGICAL AGRI
SSR molecular marker in linkage with radish clubroot-resisting QTL and applications of SSR molecular marker
InactiveCN109280716ANo pollution in the processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerGenomic sequencing
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker in linkage with radish clubroot-resisting QTL. The radish clubroot-resisting QTL has 5 sites, respectively RsCr1, RsCr2, RsCr3, RsCr4 and RsCr5. The sequences of a forward primer and a reverse primer of the molecular marker are SEQ ID NO.1 and 2. The invention further discloses an acquiring method of the SSR molecular marker. The method comprises thefollowing steps: simplifying genomic sequencing, constructing a radish high-density SNP genetic map, carrying out phenotype identification on the clubroot resistance of the radish F3 family, carryingout radish clubroot-resisting QTL analysis, and developing and screening the SSR molecular marker. The SSR molecular marker provided by the invention can be directly utilized for identifying the clubroot resistance of radish and molecular marker assistant breeding, and has great significance in prevention and treatment research of radish clubroot.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Organic preparation for controlling cruciferous vegetable club root and application thereof
InactiveCN107987838AHigh incidenceReduce morbidityBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesContinuous croppingDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural sustainable development, relates to preparation of organic preparations and in particular relates to an organic preparation for controllingcruciferous vegetable club root and application thereof. The organic preparation is composed of organic raw materials and decomposition-promoting ingredients, wherein the organic materials include but not limited to one or more of crop straws, saw dust and other solid organic materials and molasses, alcoholic fermentation liquor and other liquid organic materials; the decomposition-promoting ingredients include but not limited to one or more of special microbes and organic catalysts; and a ratio (mass) of the organic raw materials to the decomposition-promoting ingredients is (95-100):(5-0).The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the organic preparation. The organic preparation disclosed by the invention is ecologically environment-friendly and is applicable to soil with high incidence of club root after continuous cropping of various cruciferous vegetables. The quantity of plasmodiophora brassicae woron in soil and the incidence rate of the club rootof crops can be effectively reduced after treatment, the sterilization rate and the club root control rate respectively reach 60-90%, and the yield of the crops is obviously increased.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIV CHANGZHOU INST OF INNOVATION & DEV
Identification method for clubroot resistance of alpine radish at seedling stage
InactiveCN106520908AStrong disease resistanceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseTheoretical research
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Identification method for clubroot resistance of non-heading cabbages
InactiveCN104404124AIncreased sensitivityStrong anti-infection effectMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDisease resistantSeedling
The invention discloses an identification method for clubroot resistance of non-heading cabbages. The identification method comprises the following steps: preparing a clubroot bacterium suspension with the concentration of 1*10<7> to 2*10<8>bacteria / mL; when seedlings of the non-heading cabbage grow to have three leaves and one heart, uniformly irrigating the roots of the seedlings with the prepared clubroot bacterium suspension so as to soak the roots of the seedlings in the clubroot bacterium suspension for 3-4 days; taking the seedlings out of the clubroot bacterium suspension, culturing the seedlings for 40-50 days by a conventional method, and identifying and screening non-heading cabbages which are not infected by clubroot. By the identification method, when the seedlings of the non-heading cabbages grow to have three leaves and one heart, the seedlings are inoculated with clubroot bacteria by a root dipping method; by investigating the illness occurrence situation of plants, the disease-resistant or infected non-heading cabbages are identified.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Identification method for clubroot disease resistance of high mountain radishes in field
InactiveCN106508336AAccurate Disease IndexIdentification method is simpleCultivating equipmentsPlant cultivationDiseaseBlack spot
The invention discloses an identification method for clubroot disease resistance of high mountain radishes in a field. The identification method comprises the following steps: selecting experimental radish varieties, enriching bacterium sources of a clubroot disease nursery in a high mountain region, and sowing radishes; grading clubroot disease morbidity degree of full-grown radishes to obtain disease condition grades of the radishes; calculating radish variety disease condition indexes according to the disease condition grades of the radishes and a radish variety disease condition index general formula; and evaluating the resistance type of each radish variety to the clubroot disease by combining a radish disease resistance evaluation standard according to a calculation result. According to the identification method, the disease condition grading of the radishes which are infected with a disease is simplified; the influence on radish clubroot disease condition grading caused by black spots and black scars on the radishes is excluded; the existing grading mode is changed essentially; the overall identification process and the result processing analysis become simple, and meanwhile, the clubroot disease resistance of different radish varieties is judged rigorously and accurately.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Integrated control method for cruciferous vegetable clubroot
InactiveCN105075738APromote germination and strong seedlingsImprove disease resistancePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsDiseaseMedicine
The invention relates to an integrated control method for cruciferous vegetable clubroot, which comprises the following steps: 1. ecological treatment: a. applying HYT, namely applying HYT-A 200-250ml, HYT-B 250-350ml and HYT-C 100-120g every Mu, and operate the procedure 2-4 times during the whole growing period; b. applying traditional Chinese medicine microscale fertilizer one month before the cruciferous vegetable ripe, and apply the traditional Chinese medicine microscale fertilizer 20-25g every Mu; 2. agriculture control; 3. plant quarantine; 4. biological control; 5. physical control; and 6. chemical control. The method comprises the steps of ecological treatment, agriculture control, plant quarantine, physical control chemical control, therefore, the incidence of disease of the cruciferous vegetable clubroot is greatly reduced; the effect is good; and the output and the quality of the cruciferous vegetable is improved.
Owner:李美琼
Soil conditioner for preventing and treating clubroot diseases of cruciferae crops, and preparing method and application of soil conditioner
ActiveCN104004526AEffective pH adjustmentPromote germinationAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesAlkalinityFood safety
The invention provides a soil conditioner for preventing and treating clubroot diseases of cruciferae crops and application of the soil conditioner. The soil conditioner comprises, by weight, 70-80 parts of water-soluble calcium, 0.1-1 part of water-soluble magnesium, 4-5 parts of organic nitrogen, 8-15 parts of humus, 6-15 parts of pellet binders and 20-25 parts of sustained-release preparations. The invention further provides a preparation method of the soil conditioner. The soil conditioner can have a good effect on preventing and treating the clubroot diseases of the cruciferae crops and solve the problem of the clubroot diseases of the cruciferae crops fundamentally; the soil conditioner is free of environmental pollution, beneficial to environmental protection and food safety, safe and convenient to use, particularly suitable for the rice planting season of a paddy-upland rotation region, capable of achieving the double functions of slowly and evenly up-regulating soil acidity and alkalinity and providing nitrogenous fertilizer required by rice in the green-turning period, and good in application and popularization prospect.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection technology of brassicaceous vegetable plasmodiophoromycetes, and its application
InactiveCN103966307AHigh specificityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceIts regionStandard curve
The invention relates to a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection technology of plasmodiophoromycetes, and its application. The technology is used for rapidly and accurately quantitatively detecting brassicaceous vegetable plasmodiophoromycetes. The technology comprises the following steps: extracting DNA from a sample, designing a specific primer, carrying out real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection on the ITS region gene fragment of the plasmodiophoromycetes by applying an SYBRGreen I based dye process fluorescent quantitative PCR technique, constructing a standard curve, and calculating the copy number of the ITS region gene fragment in the sample and the concentration of the plasmodiophoromycetes. The detection technology has the advantages of simple and rapid operation, strong specificity and high sensitivity, realizes a highest detection sensitivity reaching 24 copy numbers per reaction, and can also realize the analysis of large batch samples. The technology provides a good basis for the early-stage prediction forecasting of diseases, so the technology is adapted to be widely applied in the plant disease diagnosis detection field.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for evaluating resistance of brassica plants on club root
InactiveCN102511368ASave landAccurate and reliable identification resultsCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
Owner:云南省农业科学院园艺作物研究所
Method for preventing and treating celery cabbage clubroot
InactiveCN103314749APrevention and treatment of clubrootIncrease productionSeed and root treatmentHorticultureSteelmakingWaste converter
The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating celery cabbage clubroot. The method includes the following steps of 1) species selection and seed pretreatment, 2) sowing, 3) large field soil preparation and fertilization, 4) hole excavation and application of organic bacterial manure and basic converter steelmaking slag mixture, 5) cabbage seedling planting and 6) field management including 6.1) additional fertilizer application and 6.2) pest control. By applying the organic bacterial manure in a large field, pathogenic bacteria can be removed, and beneficial bacteria are multiplied. Micro elements of the basic converter steelmaking slag with M0 larger than 1 are utilized to improve acid soil and prevent and treat the celery cabbage clubroot, application quantity of chemical pesticide can be reduced, and the waste converter steelmaking slag can be turned into wealth. The method is a harmless celery cabbage clubroot preventing and treating technology. By means of the method, celery cabbage yield and quality are improved, and remarkable economical, social and ecological benefits can be obtained.
Owner:ZHENJIANG SUIHAN AGRI
Seedling substrate for preventing and controlling cabbage clubroot
InactiveCN103238509AFormula flexibleEasy material selectionCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationDiseaseShoot
The invention discloses a seedling substrate for preventing and controlling cabbage clubroot, and belongs to the technical field of vegetable culture. The seedling substrate is obtained by the steps: a, measuring organic substrates (humic soil or turf or coco coir or bagasse or wood dust), cow dung and plant ash according to the volume ratio of 8:2:1 and pouring the organic substrates, the cow dung and the plant ash into a stirrer / stirring machine; b, grinding weighed 2.1-2.5kg / m<3> of urea and 1.5-1.8kg / m<3> of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate into powder, adding the powder along with 1.5-1.8kg / m<3> of calcined lime into the stirrer / stirring machine; c, adding 1.2-1.5kg / m<3> of wettable powder with 75% of chlorothalonil into the stirrer / stirring machine; and d, starting the machine, uniformly stirring the powder and sub-packaging the powder. The seedling substrate has the advantages that vegetable shoots are fine in quality, the clubroot is avoided, diseases are relieved after planting, control effect is long, the seedling substrate is not limited by physiological race, and environmental side effects are avoided.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
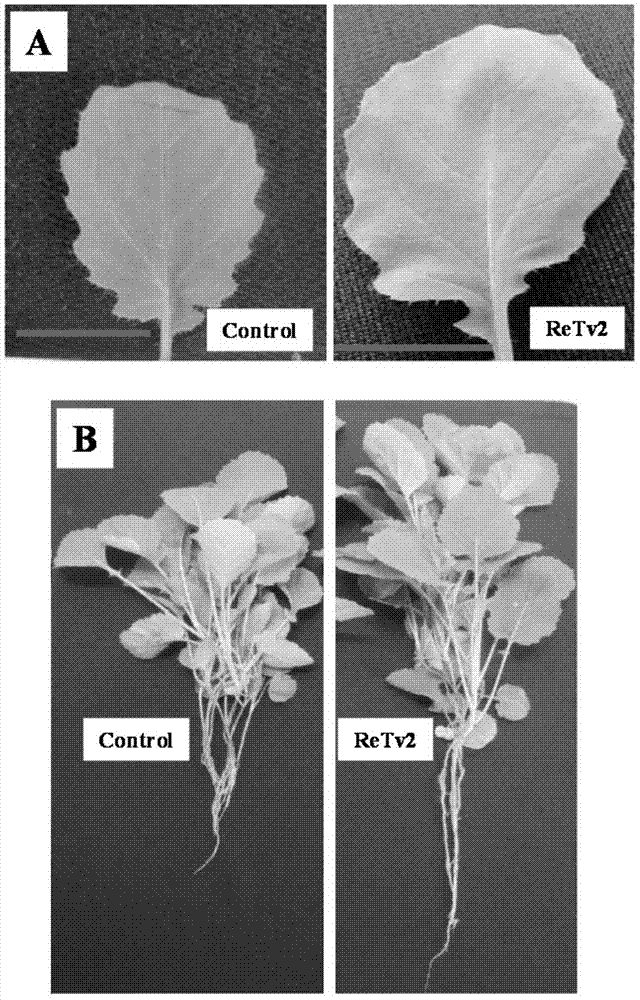
Rapeseed endogenous trichoderma atroviride ReTv2 strain and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a rapeseed endogenous trichoderma atroviride ReTv2 strain and a preparation method and application thereof. The trichoderma atroviride ReTv2 strain is separated from a rapeseed root tissue by the applicant, and the number CCTCC NO is M2014407. The ReTv2 strain is activated and cultured in a PDA culture medium at the temperature of 28 DEG C for 2-4d to obtain conidiospores, and the spores are inoculated into a PDB culture medium for enlarged culture for 6d, wherein the content of the conidiospores can achieve 1.0*10<9> / mL. The trichoderma atroviride ReTv2 strain disclosed by the invention is the rapeseed endogenous strain, can be successfully colonized at the root of rapeseed and has an effect on promoting growth of the rapeseed, a fermentation broth has an obvious effect on inhibiting germination of resting spores of pathogenic bacteria of rapeseed clubroot, and the control effect of the strain against the rapeseed clubroot achieves 66.4%; furthermore, the ReTv2 strain can be directly applied during seeding, is simple in an application method, can save labor force and further has the property of being safe to people and animals of biological pesticides.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for acquiring non-heading Chinese cabbage clubroot resistance germplasm resources
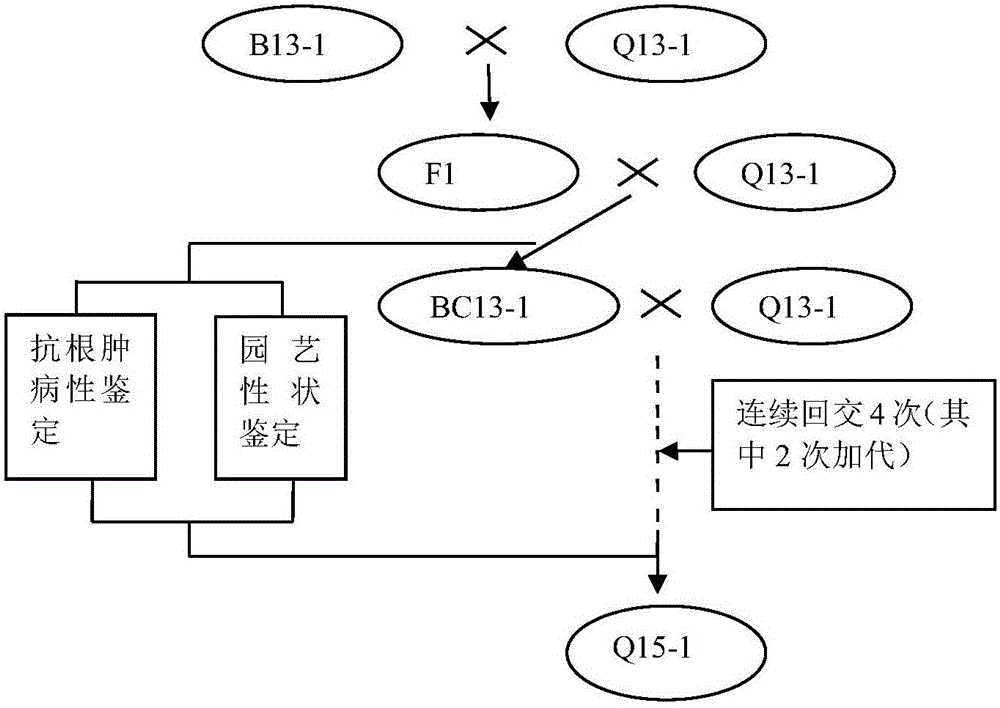
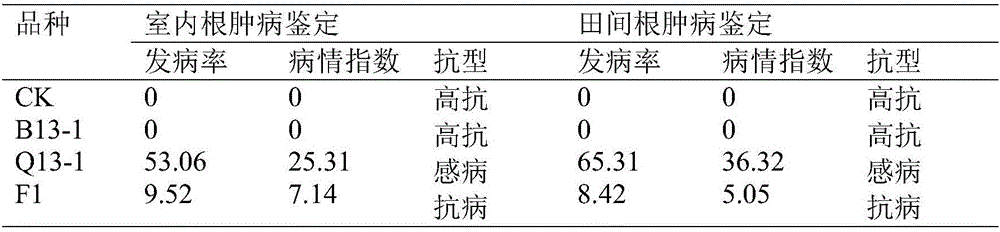
InactiveCN105850717ADig extensivelyExclusion of biohazardsPlant genotype modificationInterspecific hybridizationPhenotypic trait
The invention discloses a method for obtaining germplasm resources of non-heading Chinese cabbage resistant to clubroot, comprising: selecting introduced Chinese cabbage resistant to clubroot and susceptible non-heading Chinese cabbage with excellent agronomic properties; Interspecific hybridization was used to obtain F1 seeds of the first generation of hybridization; the screened F1 generation was continuously backcrossed for 4 generations, and a new non-heading Chinese cabbage resistant germplasm Q15‑1 with stable phenotype and resistance to clubroot was initially obtained. The present invention adopts the method of interspecific hybridization, and carries out artificial inoculation identification on each backcross offspring, screens the resistant single plant of clubroot disease, and finally obtains new germplasm. The present invention utilizes Brassicaceae Chinese cabbage The hybrid vigor between the two varieties of non-heading Chinese cabbage and its variant non-heading Chinese cabbage, the resistance gene of clubroot Chinese cabbage is transferred to non-heading Chinese cabbage through hybridization and backcrossing at the bud stage, which is simple and easy. Biological risks caused by other methods such as genetic modification and genetic engineering technology are excluded.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Specific pcr detection method of clubroot pathogen in soil
ActiveCN102296120ASensitive PCR detection methodQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPlasmodiophora brassicaeClubroot
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 for preventing and treating plasmodiophora brassicae
ActiveCN105230664ALow application concentrationReduce doseBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyBrassicaceae
The invention provides an application method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 for preventing and treating plasmodiophora brassicae. The method comprises the following two methods: the method I comprises: carrying out root-irrigation treatment on a cruciferae crop by a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 bacterial liquid with the amount of 80-100 ml per time per strain, and carrying out treatment for at least three times, wherein the treatment times are the first day, the seventh day and the fifteenth day after transplanting; the method II comprises: carrying out spraying treatment on the cruciferae crop by a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 bacterial liquid with the amount of 150-200 ml per square meter, and carrying out treatment for at least three times, wherein the treatment times are the first day, the seventh day and the fourteenth day after seeding. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 provided by the invention is simple in using method, the application concentration of the bacterial liquid is less and the application dosage of the bacterial liquid is less.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
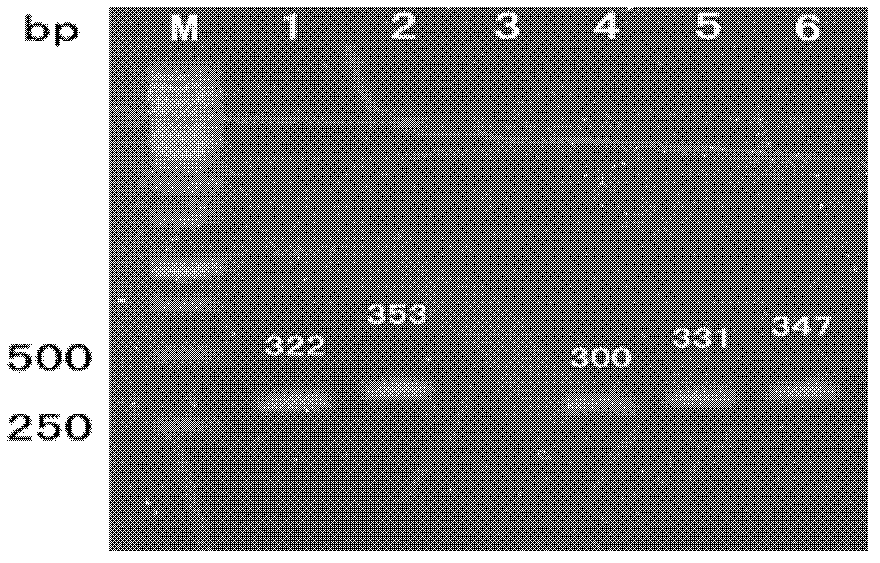
Breeding method of Chinese cabbages resistant to clubroot
ActiveCN106508669AQuick filterAvoid spreadingMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationF1 generationEmbryo
The invention provides a breeding method of Chinese cabbages resistant to clubroot. The breeding method comprises the following steps: 1) a to-be-transferred parent A and a transfer source parent B are hybridized and F1-generaiton seeds are obtained; 2) young embryos of the F1-generation seeds are germinated and sown and cultured after being vernalized; 3) F1-generation plants and the to-be-transferred parent A are subjected to backcrossing, and BC1-generation seeds are obtained; 4) young embryos of the BC1-generation seeds are germinated and sown and cultured after being vernalized; 5) BC1-generation plants are screened by means of a molecular marker, and a BC1-generation disease-resistant single plant is obtained; 6) the BC1 disease-resistant single plant and the to-be-transferred parent A are subjected to backcrossing, and BC2-generation seeds are obtained; 7) the young embryos of the BC2-generation seeds are taken as a treatment object, germination, vernalization, sowing, screening and backcrossing in the step 4), the step 5) and the step 6) are repeated four times, and BC6-generation seeds are obtained; 8) a BC6-generation plant is self-crossed, a BC6-generation self-crossed progeny is obtained, and a transfer single plant with homozygous clubroot resistance is obtained.
Owner:QINGDAO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com