InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof
A technology for Chinese cabbage clubroot and clubroot resistance, applied in recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory control effects, achieve accurate and reliable identification results, and speed up large-scale production. The progress of cabbage resistance to clubroot breeding and the effect of reducing labor costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1, the identification of physiological race of Plasmodium brassicae
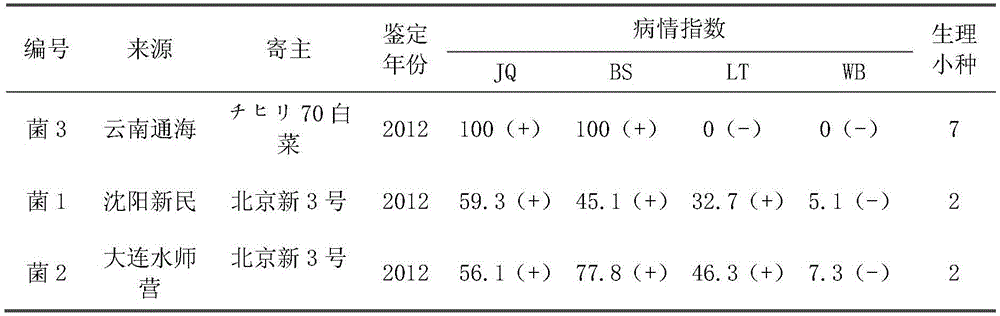
[0051] The Williams identification system was used to identify the physiological races of Plasmodium brassicae collected from Yunnan Tonghai, Shenyang Xinmin, and Dalian Shuishiying Chinese cabbage production areas. The inoculation, investigation and physiological race identification methods refer to the literature "Wang Weihong et al. (2013) , Physiological race identification and resistance source screening of Brassicaceae clubroot bacteria in Changyang County, Hubei Province, Chinese vegetables". The results showed (Table 1): the pathogenic bacteria of Chinese cabbage clubroot from Tonghai, Yunnan Province was Physiological Race No. 7, and the pathogenic bacteria of Chinese cabbage clubroot from Shenyang Xinmin and Dalian Shuishiying was Plasmodium brassicae Race 2.
[0052] Table 1: Race identification results of Plasmodium brassicae from different sources
[0053]
[0054] Note: +...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2, Chinese cabbage clubroot disease-resistant parents and BC 2 f 2 group acquisition
[0056] 1. Acquisition of Chinese cabbage clubroot disease-resistant parent "CR-Weimin A"
[0057] The Chinese cabbage clubroot inbred line "CR-Weimin" was obtained by self-segregation of the Chinese cabbage hybrid "CR-Weimin" for 6 consecutive generations showing resistance to Plasmodium brassica races 2 and 7 A".
[0058] Two, BC 2 f 2 group acquisition
[0059] Chinese cabbage "CR-Weimin A" was used as the disease-resistant parent (female parent) and Chinese cabbage "Beijing Xin No. 3" was used as the susceptible parent (male parent) for hybridization, and the F1 generation seeds were harvested. Plant F1 generation seeds to obtain F1 generation Chinese cabbage plants, backcross the F1 generation Chinese cabbage with the susceptible parent "Beijing Xin 3", and harvest BC 2 f 2 group seeds.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3, BC 2 f 2 Phenotype identification and molecular marker verification of clubroot disease in Chinese cabbage
[0061] 1. BC 2 f 2 Phenotypic Identification of Clubroot Disease Resistance in Chinese Cabbage
[0062] With the BC obtained in Example 2 2 f 2 Populations were used as materials. After sowing, they were inoculated with Plasmodium brassicae from Tonghai, Shenyang, and Shuishiying, Dalian. The inoculation and investigation methods were referred to in the literature "Wang Weihong et al. (2013), Clubroot of Cruciferous Vegetables in Changyang County, Hubei Province Physiological race identification of pathogens and source of resistance screening, the method described in "Chinese Vegetables". Investigate the condition according to the 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 disease classification standards, and calculate the disease index (the disease index = ∑ (the representative value of the disease level × the number of diseased plants) / the total number of investigate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com