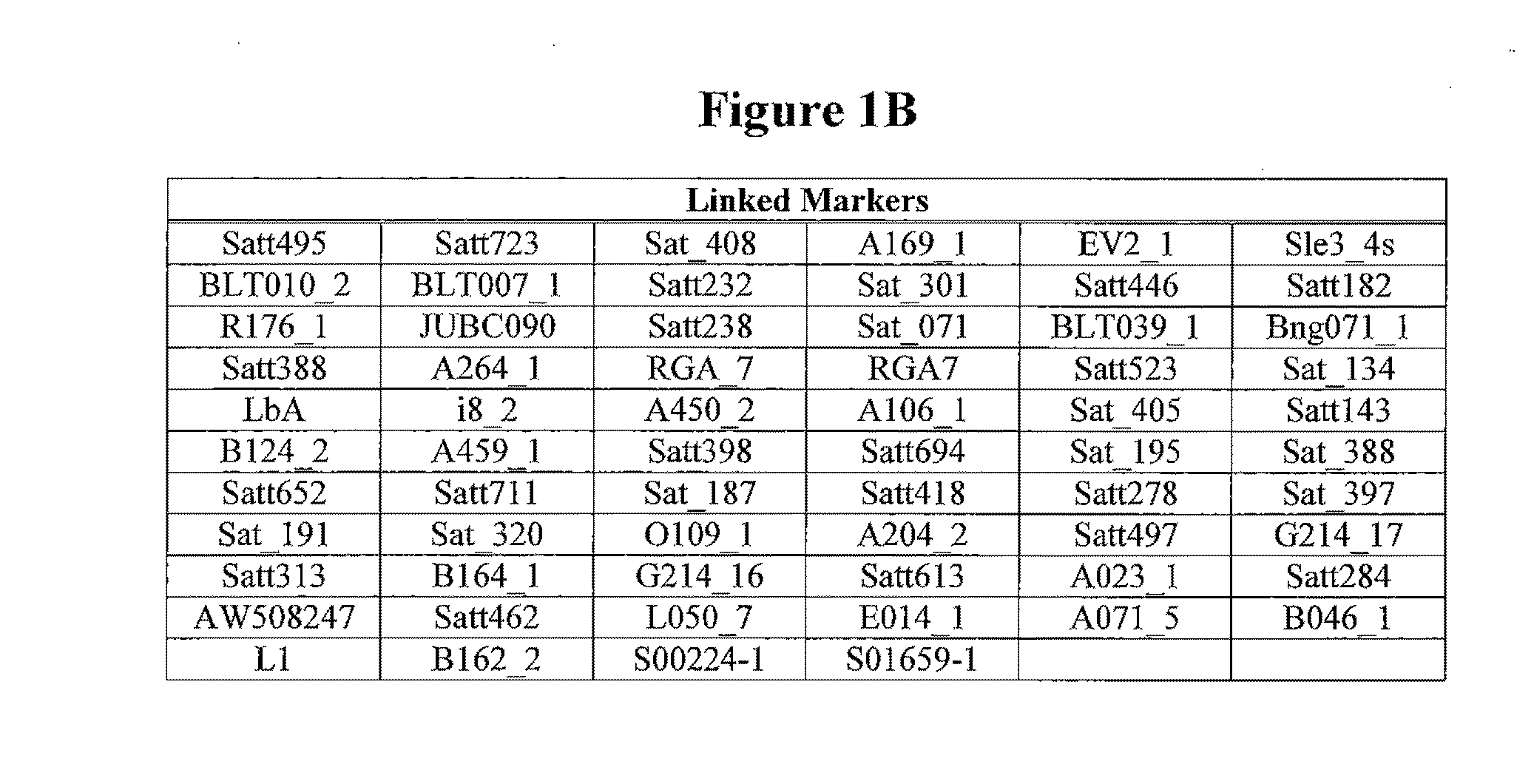
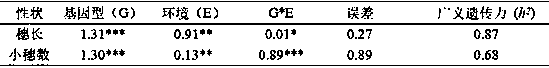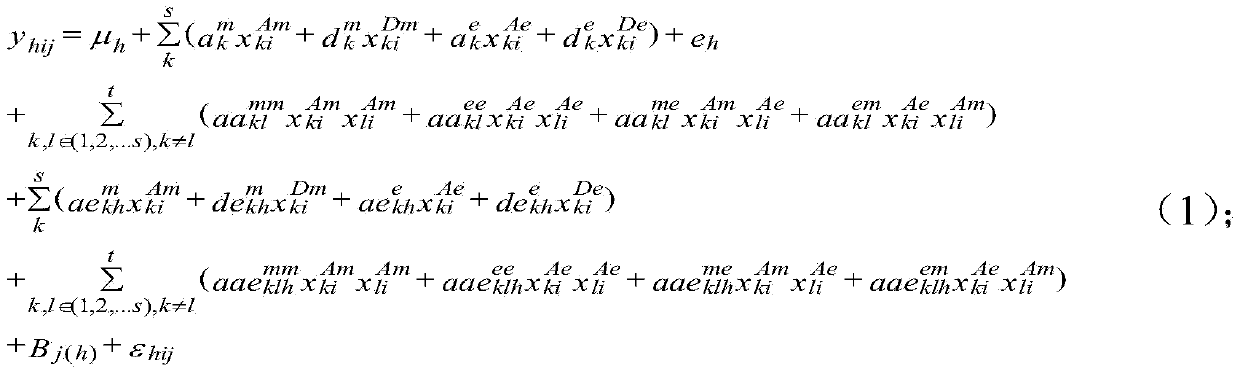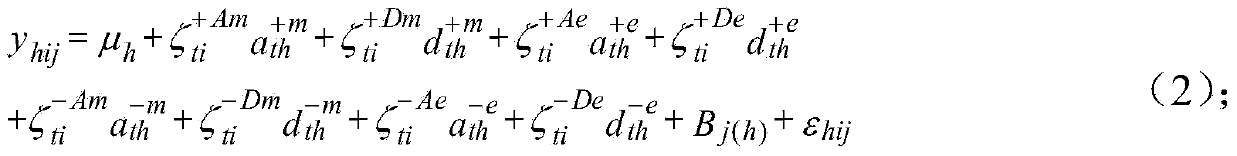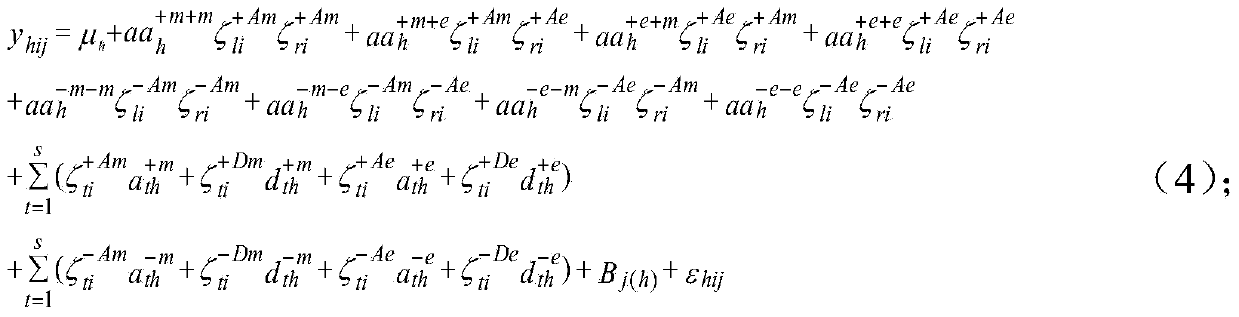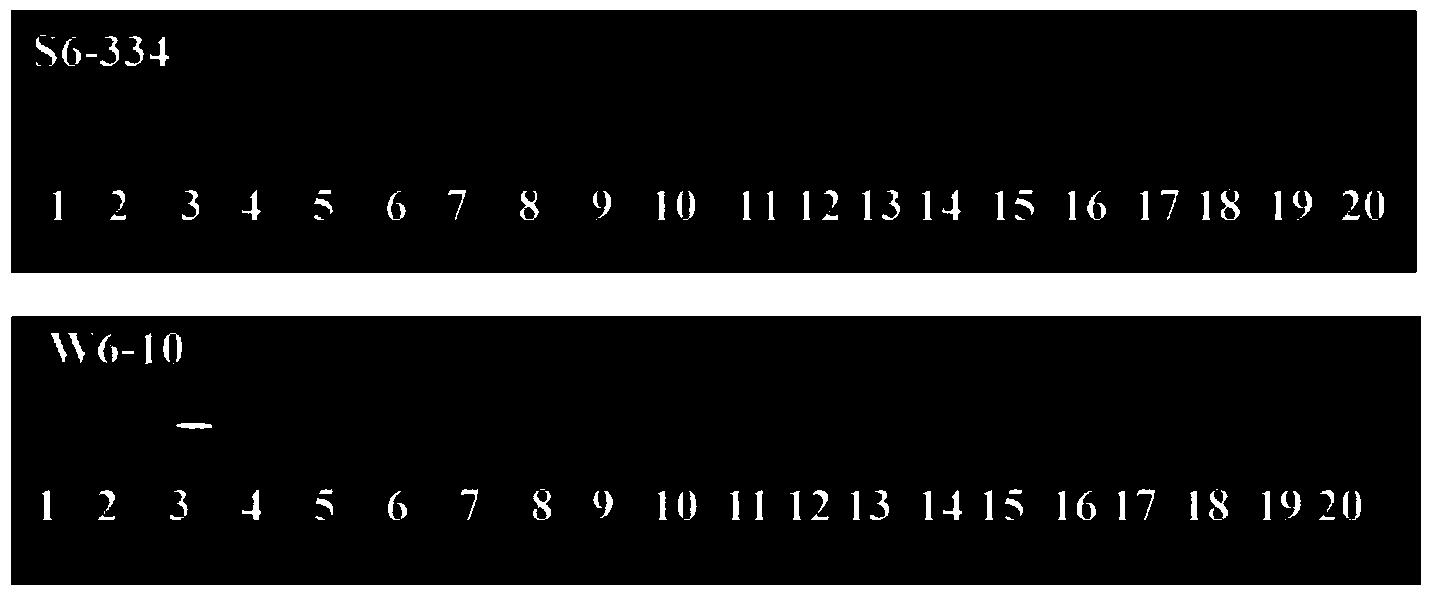Patents
Literature
194 results about "Quantitative trait locus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying and sequencing the actual genes that cause the trait variation.
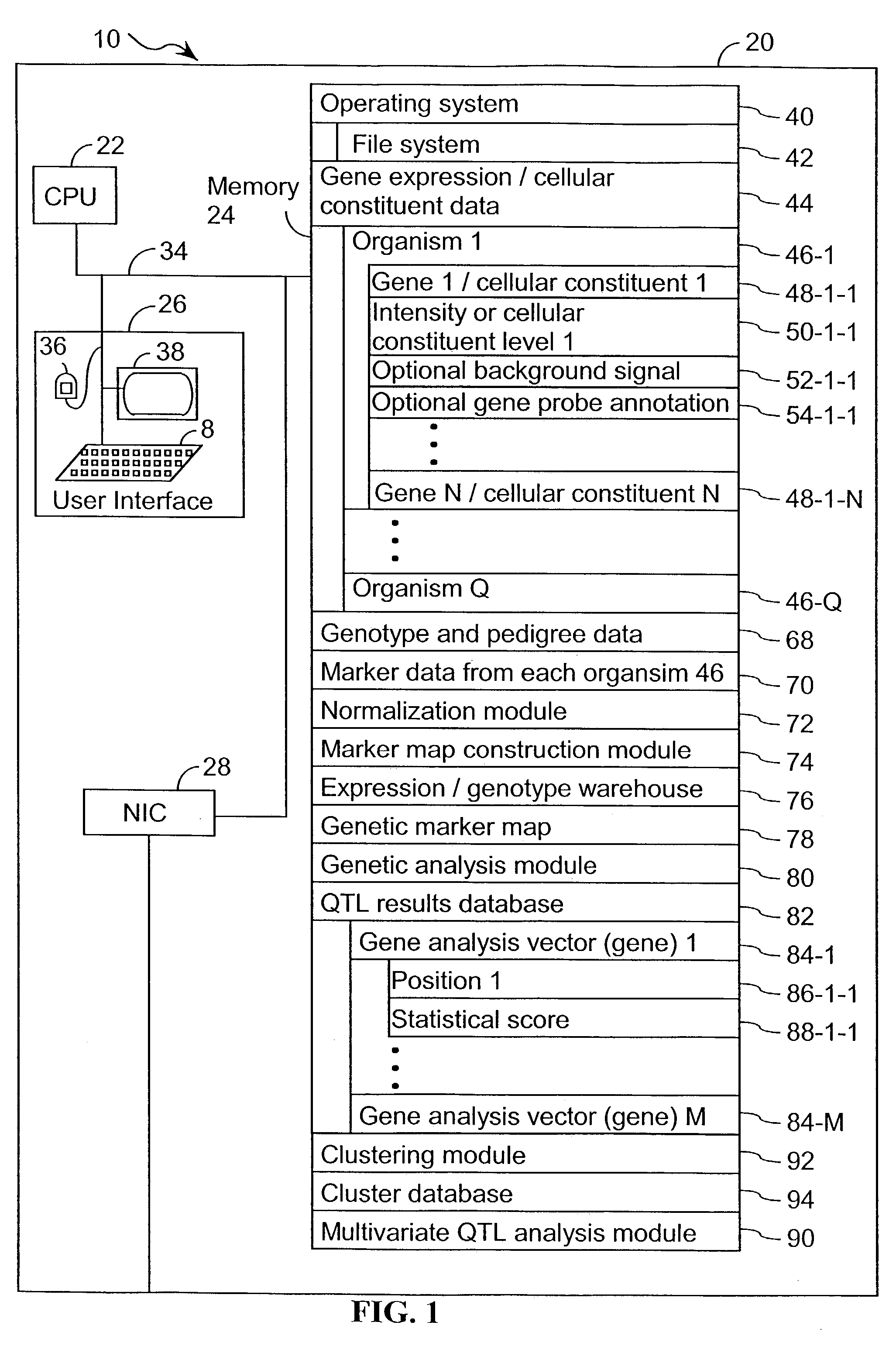
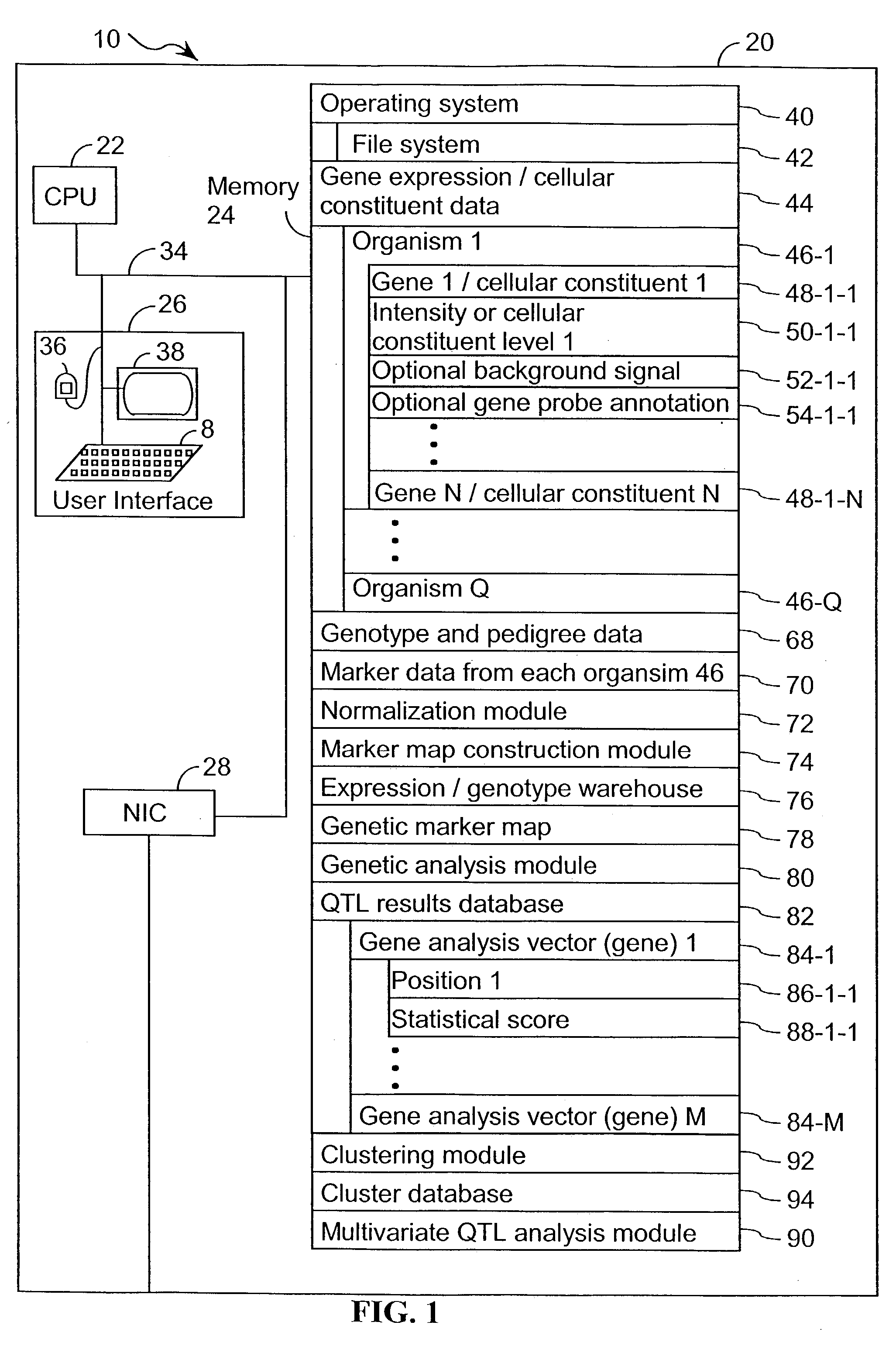
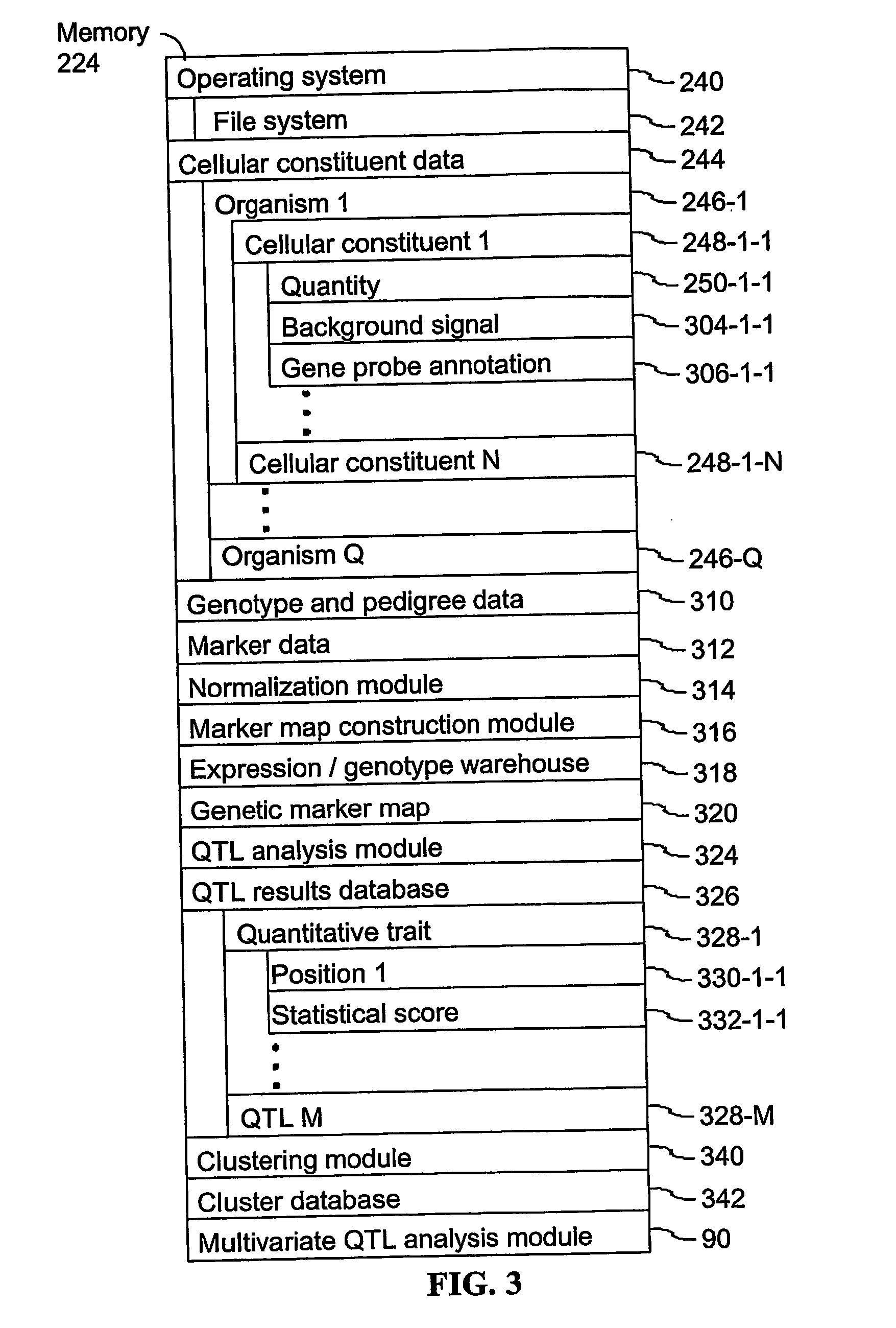
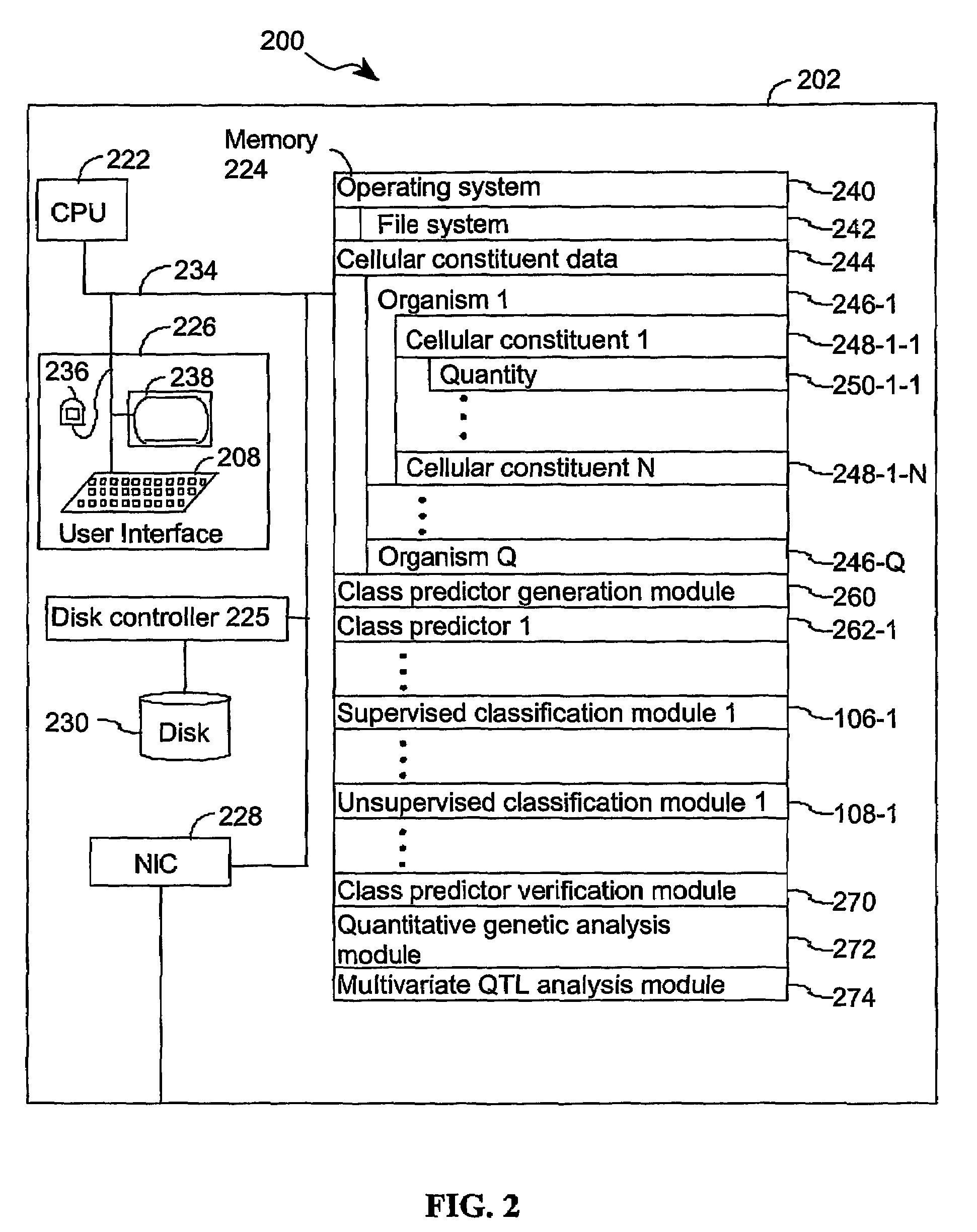
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS7035739B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS20030224394A1Improve artBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
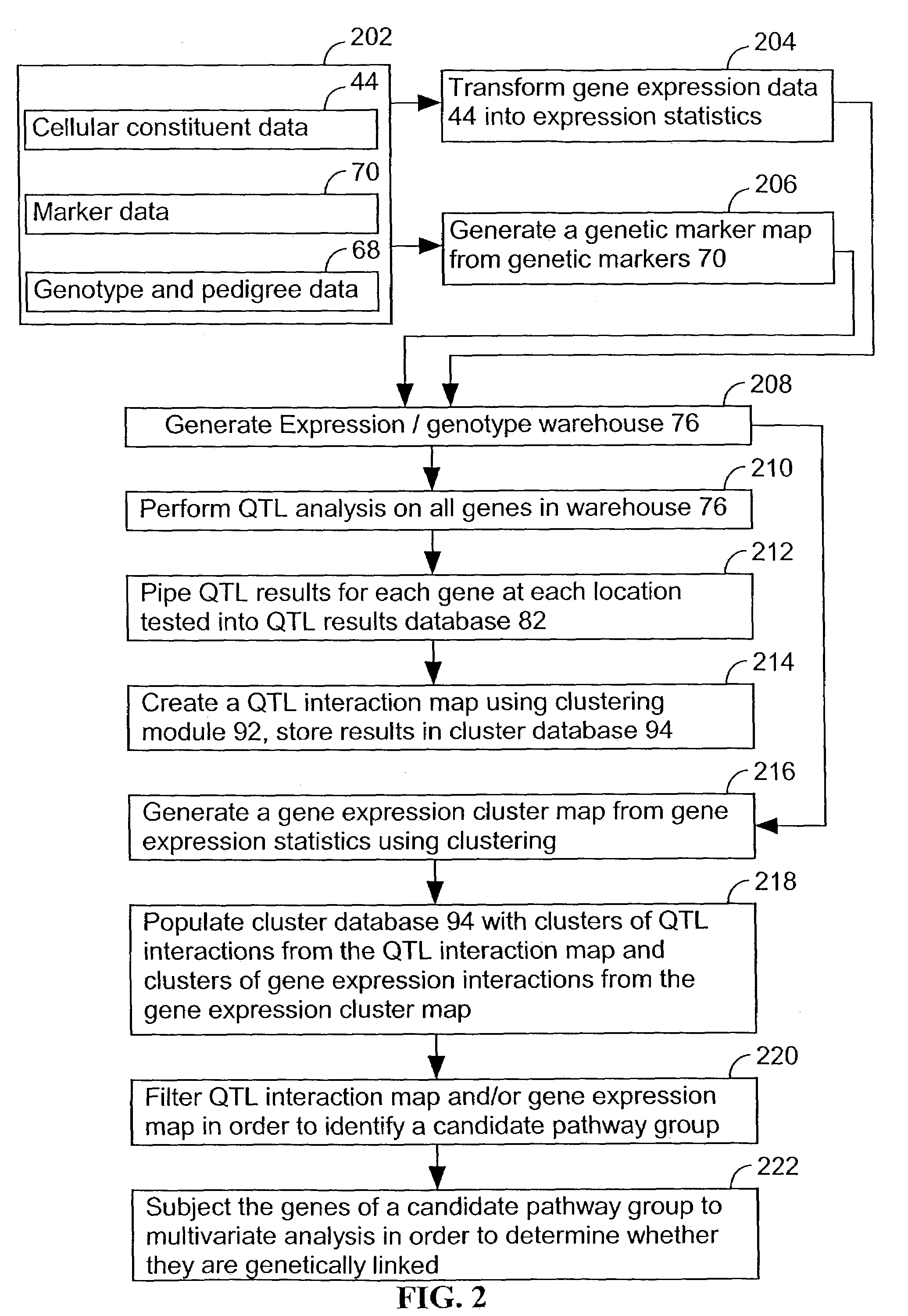
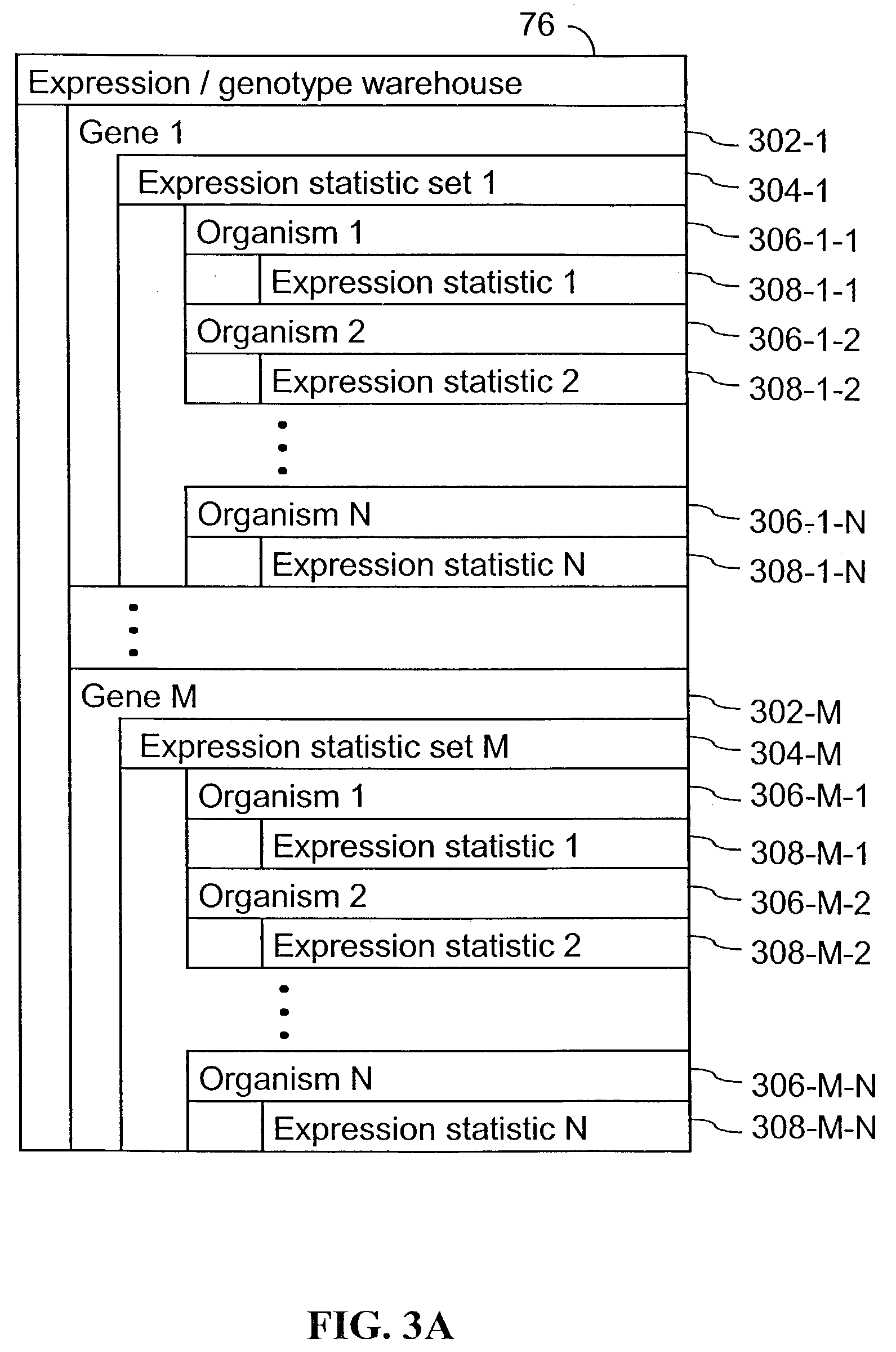
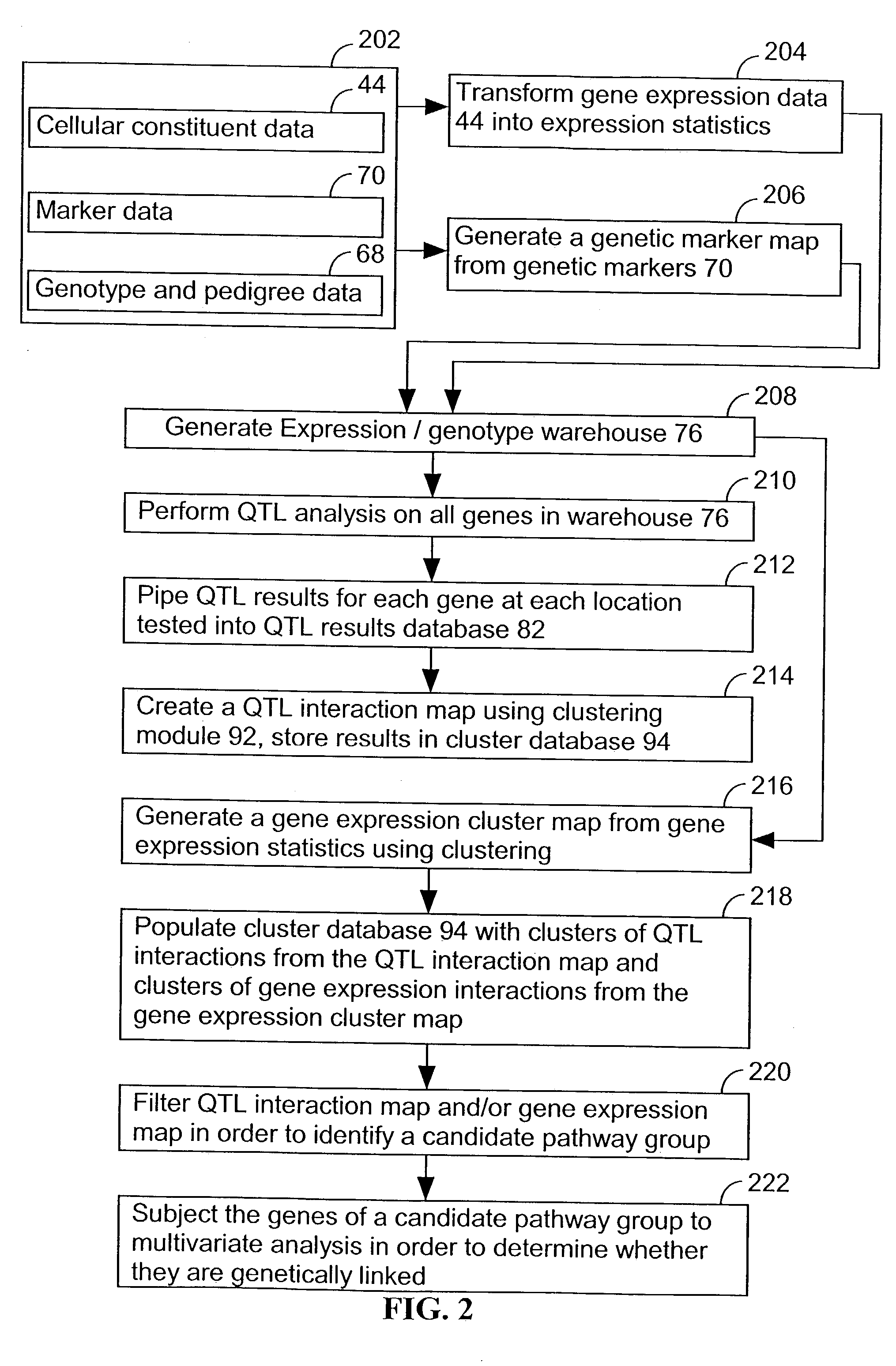
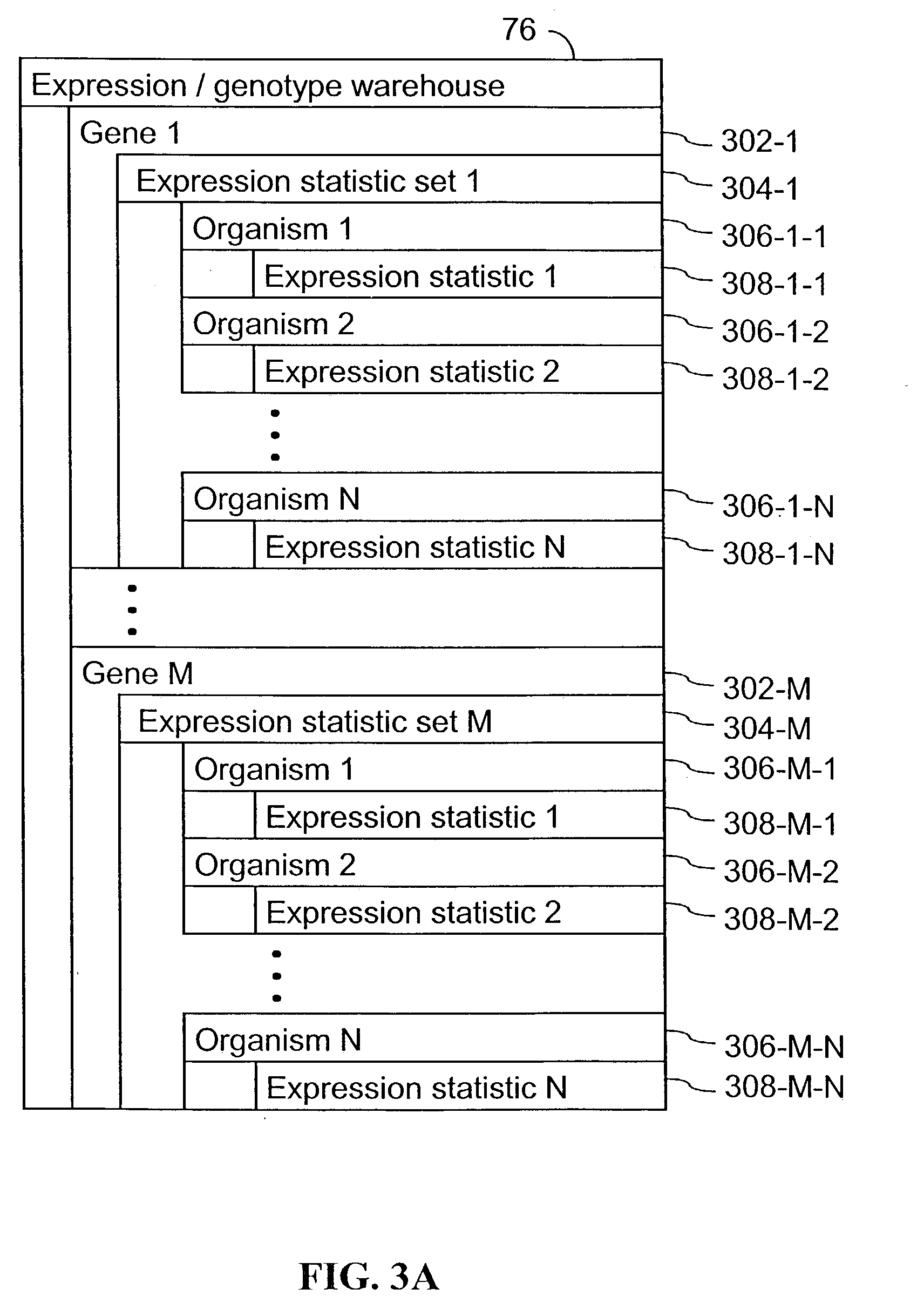
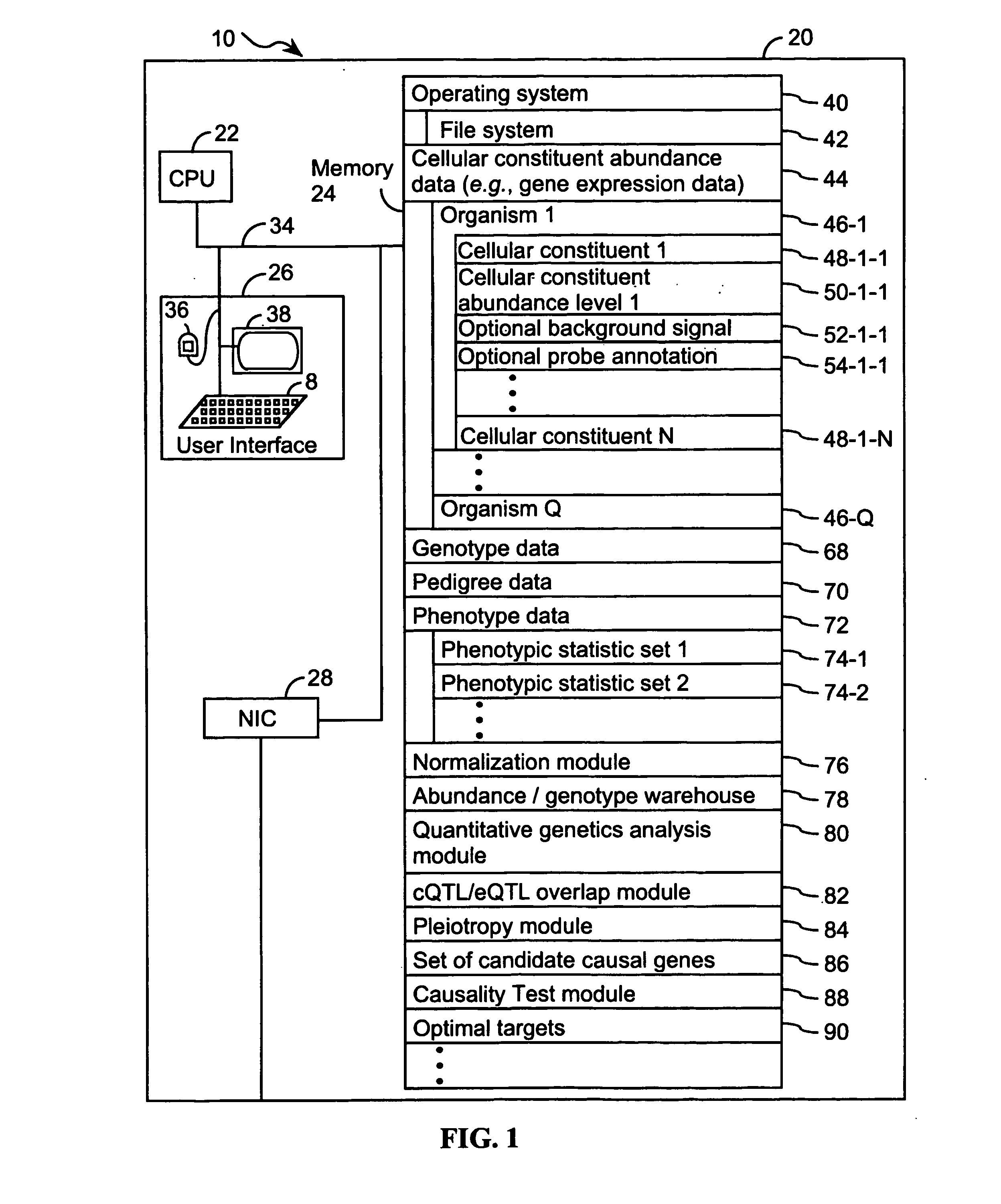
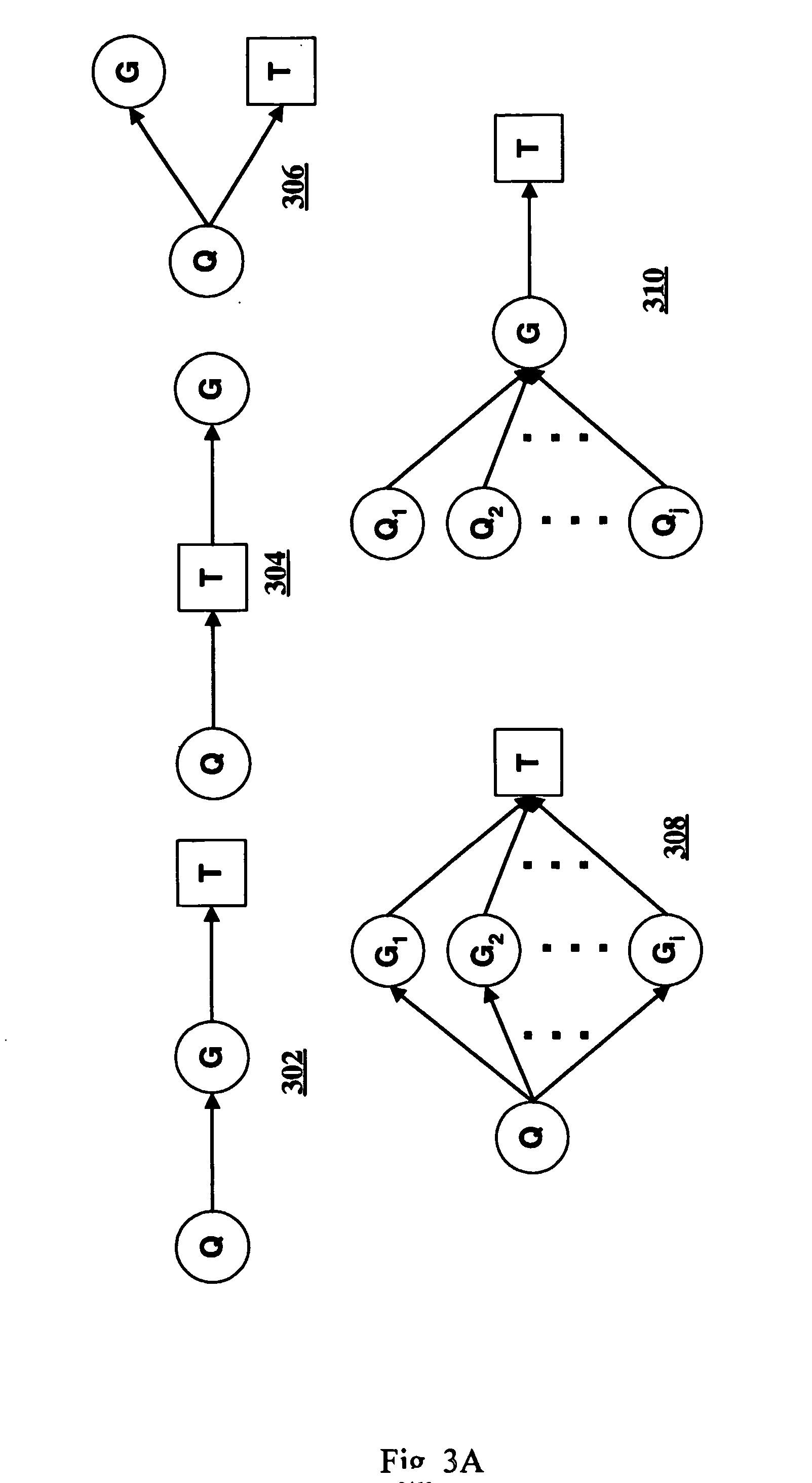
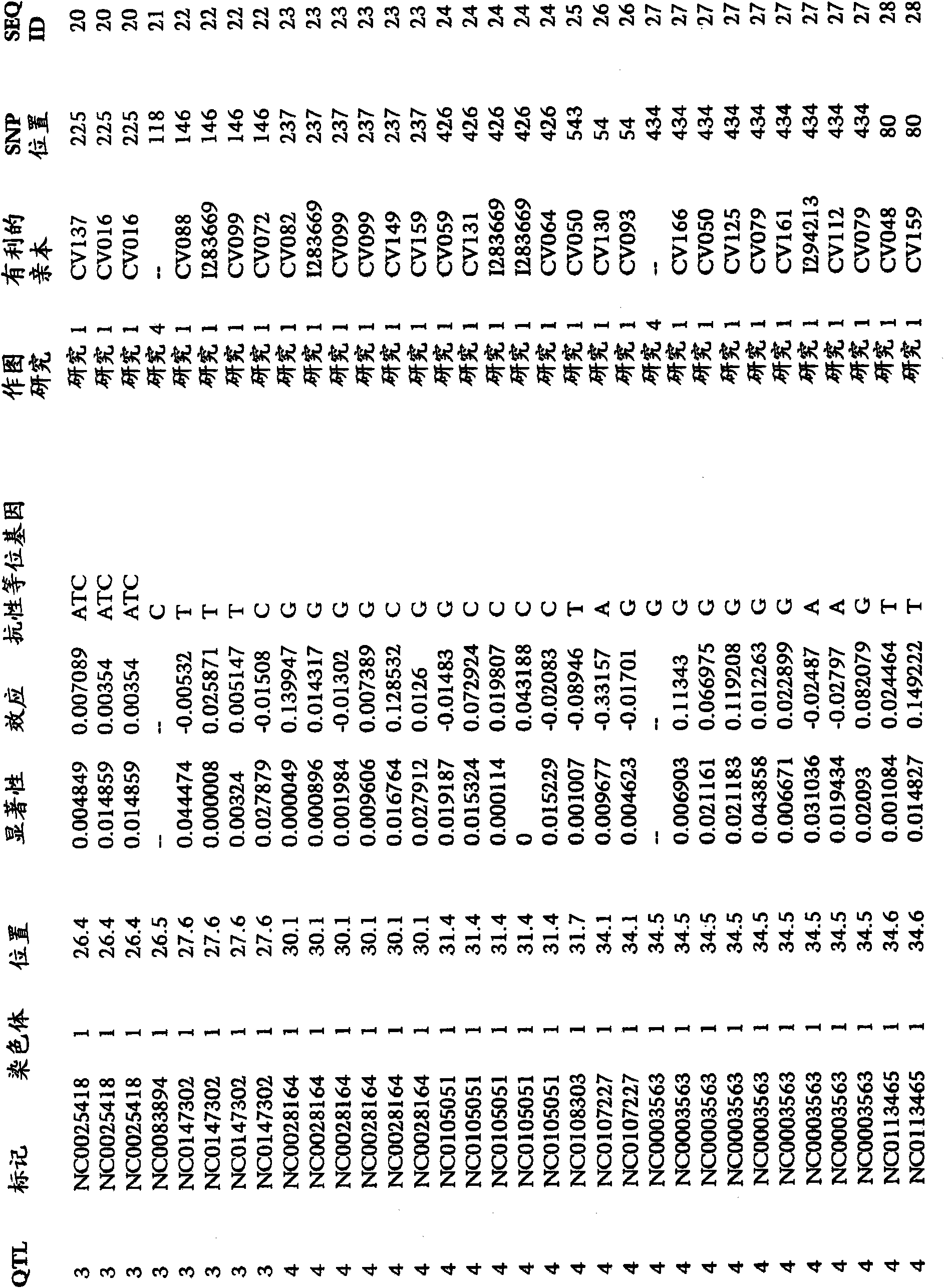
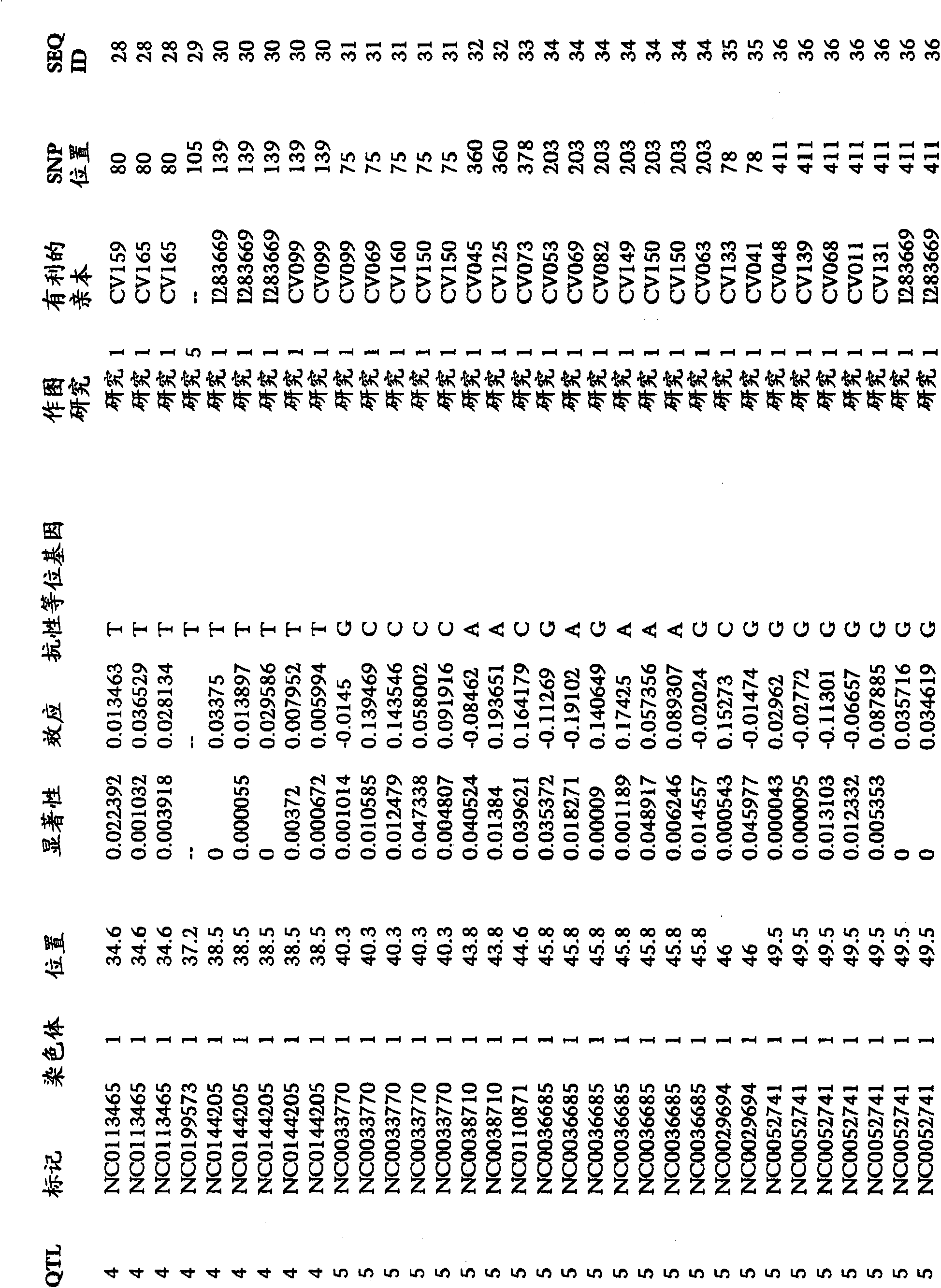
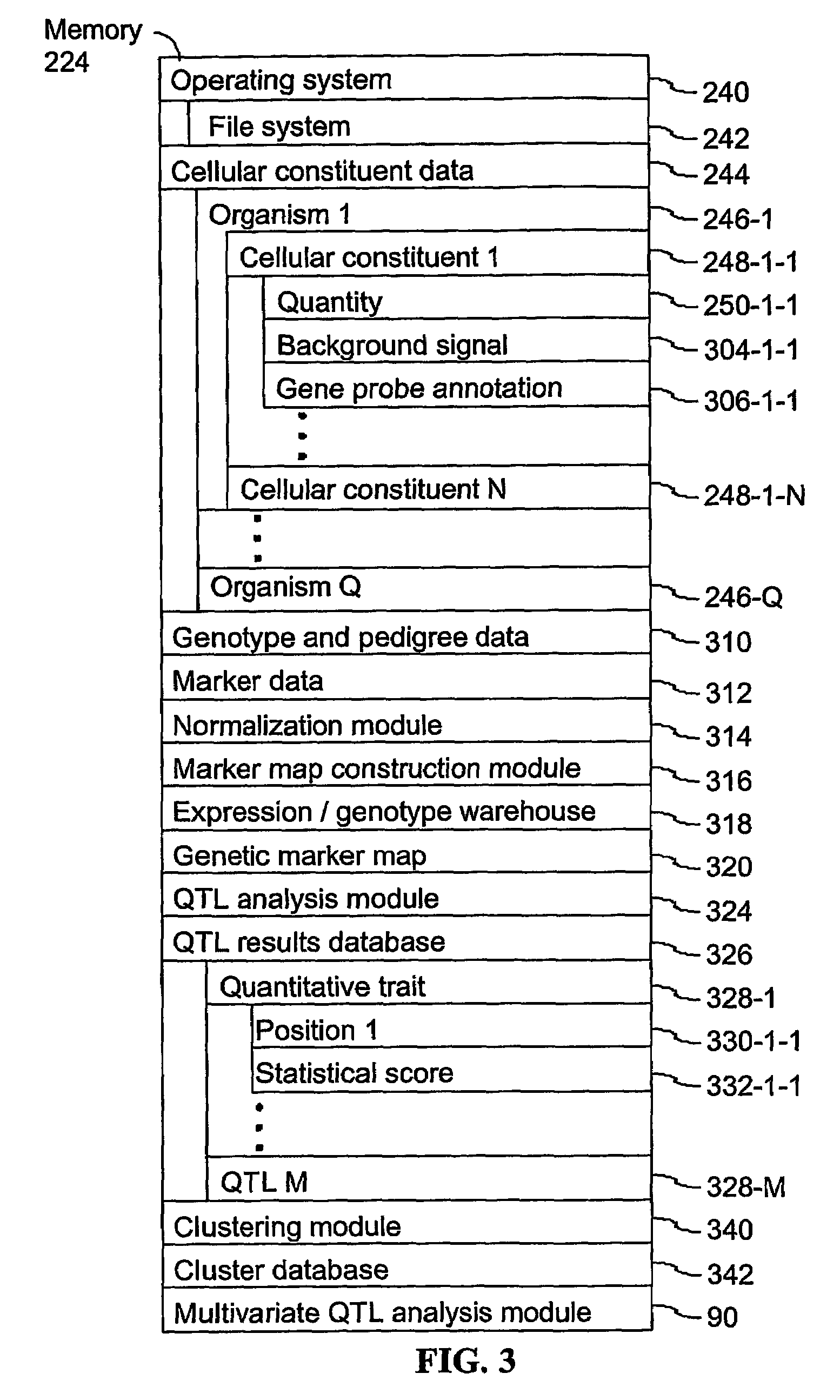
A method for associating a gene with a trait exhibited by one or more organisms in a plurality of organisms from a species. A genetic marker map is constructed from a set of genetic markers associated with the plurality of organisms. For each gene in a plurality of genes, a quantitative trait locus analysis is performed using the genetic marker map and a quantitative trait. The quantitative trait locus analysis produces quantitative trait locus data. A quantitative trait comprises an expression statistic for a gene. The expression statistic for a gene is derived from a cellular constituent level that corresponds to the gene in each organism in the plurality of organisms. The quantitative trait locus data are clustered from each quantitative trait locus analysis to form a quantitative trait locus interaction map. Clusters of genes in the map are identified as a candidate pathway group. An expression cluster map is used to refine the candidate pathway group. Multivariate analysis is used to validate the candidate pathway group as a set of genes that are genetically interacting.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Hppd-inhibitor herbicide tolerance
ActiveUS20110185445A1Negatively impactingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePlant cell
This invention relates generally to the detection of genetic differences among soybeans. More particularly, the invention relates to soybean quantitative trait loci (QTL) for tolerance or sensitivity to HPPD-inhibitor herbicides, such as mesotrione and isoxazole herbicides, to soybean plants possessing these QTLs, which map to a novel chromosomal region, and to genetic markers that are indicative of phenotypes associated with tolerance, improved tolerance, susceptibility, or increased susceptibility. Methods and compositions for use of these markers in genotyping of soybean and selection are also disclosed, as are methods and compositions for use of these markers in selection and use of herbicides for weed control. Also disclosed are isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides relating to such tolerance or sensitivity and methods of introgressing such tolerance into a plant by breeding or transgenically or by a combination thereof. Plant cells, plants, and seeds produced are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Computer systems and methods for inferring casuality from cellular constituent abundance data
InactiveUS20070038386A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCellular componentBiological body
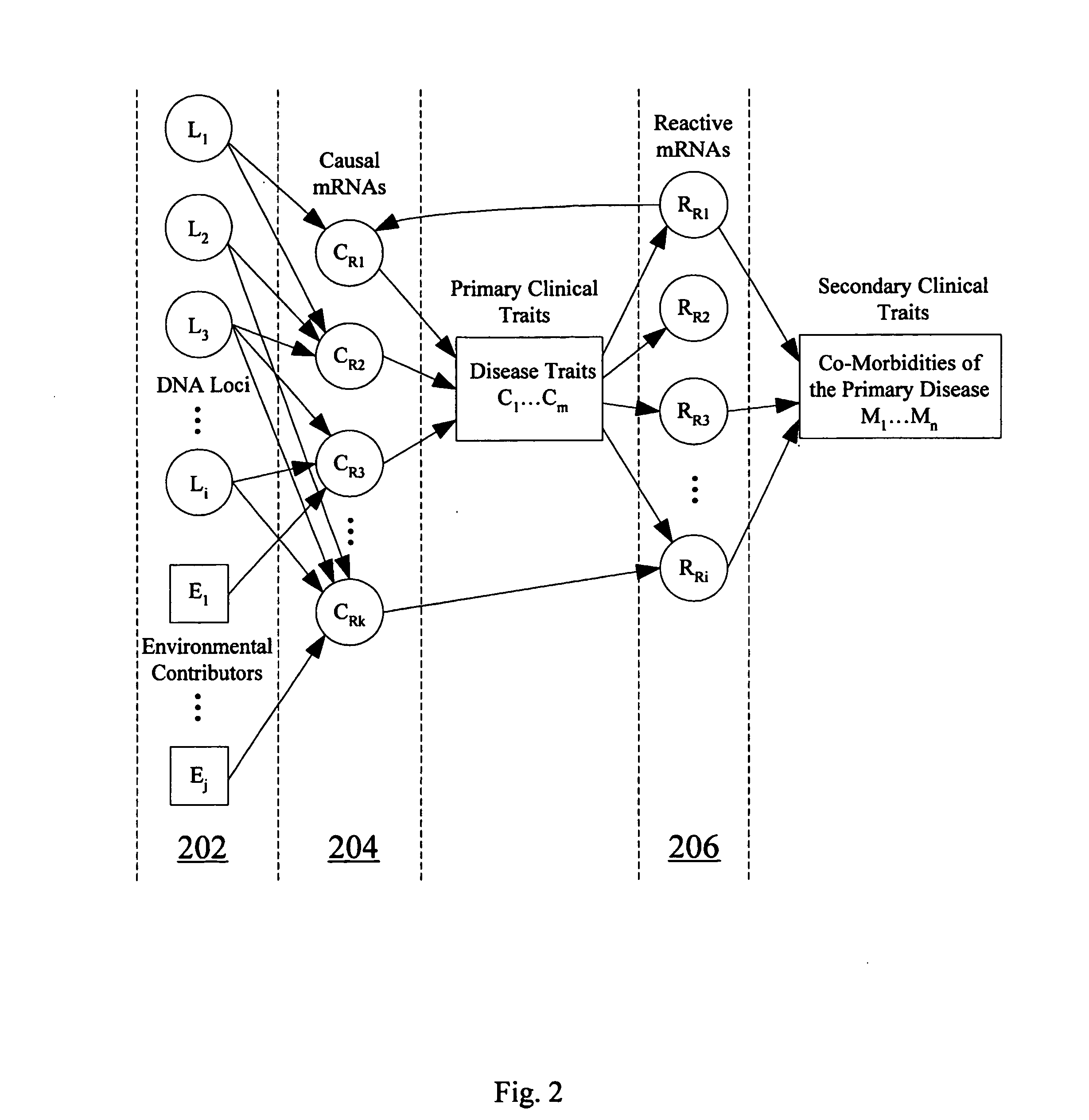
Methods, computer program products, and systems are provided for associating a cellular constituent with a trait T exhibited by a species. A cellular constituent i that has at least one abundance quantitative trait locus (eQTL) coincident with a respective clinical quantitative trait locus (cQTL) for the trait of interest T is identified. For each eQTL, a determination is made as to whether (i) the genetic variation of the eQTL and (ii) the variation of the trait of interest T across the plurality of organisms are correlated conditional on an abundance pattern of the cellular constituent i across the plurality of organisms. When the genetic variation of (i) one of the eQTL and (ii) the variation of the trait of interest T across the plurality of organisms are uncorrelated conditional on the abundance pattern of the cellular constituent i, the cellular constituent i is considered causal for, and is therefore associated with, the trait of interest T.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Salt-tolerance determining method for barley at seedling stage
InactiveCN102860159AReduce the impactSimple methodSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention relates to a determining method for indicating salt tolerance of different varieties of barleys at seedling stages and belongs to the field of agriculture. The determining method includes adopting a water culturing manner to simulate salt environment artificially, investigating salt damage degree of samples to be tested under the condition of salt stress compared with the blank control condition by measuring seedling height, root length and fresh weight of each seedling of different treatment, and finally determining salt tolerance of the variety. The determining method can be widely applied to screening and evaluation of plant stress resistance genetic resources, particularly used for screening of barley salt-tolerance variety resources, salt-tolerance QTL (quantitative trait locus) genetic analysis, salt-tolerance gene positioning and seed selection of salt-tolerance barley varieties. The determining method has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in mastering and reliable results, the whole salt-tolerance determining process is under control and is slightly affected by the environment, requirements for equipment are low so that only one common illumination culturing box is required.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Methods and compositions for breeding for preferred traits
ActiveCN101821409AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringClavibacter michiganenseFungal disease
The present invention relates to the field of plant breeding. More specifically, the present invention includes a method of using haploid plants for genetic mapping of traits such as disease resistance. Further, the invention includes a method for breeding corn plants containing quantitative trait loci (QTL) that are associated with resistance to Gray Leaf Spot (GLS), a fungal disease associated with Cercospora spp. The invention further includes a method for breeding corn plants containing QTL that are associated with Goss' Wilt, a bacterial disease associated with Clavibacter michiganense spp.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
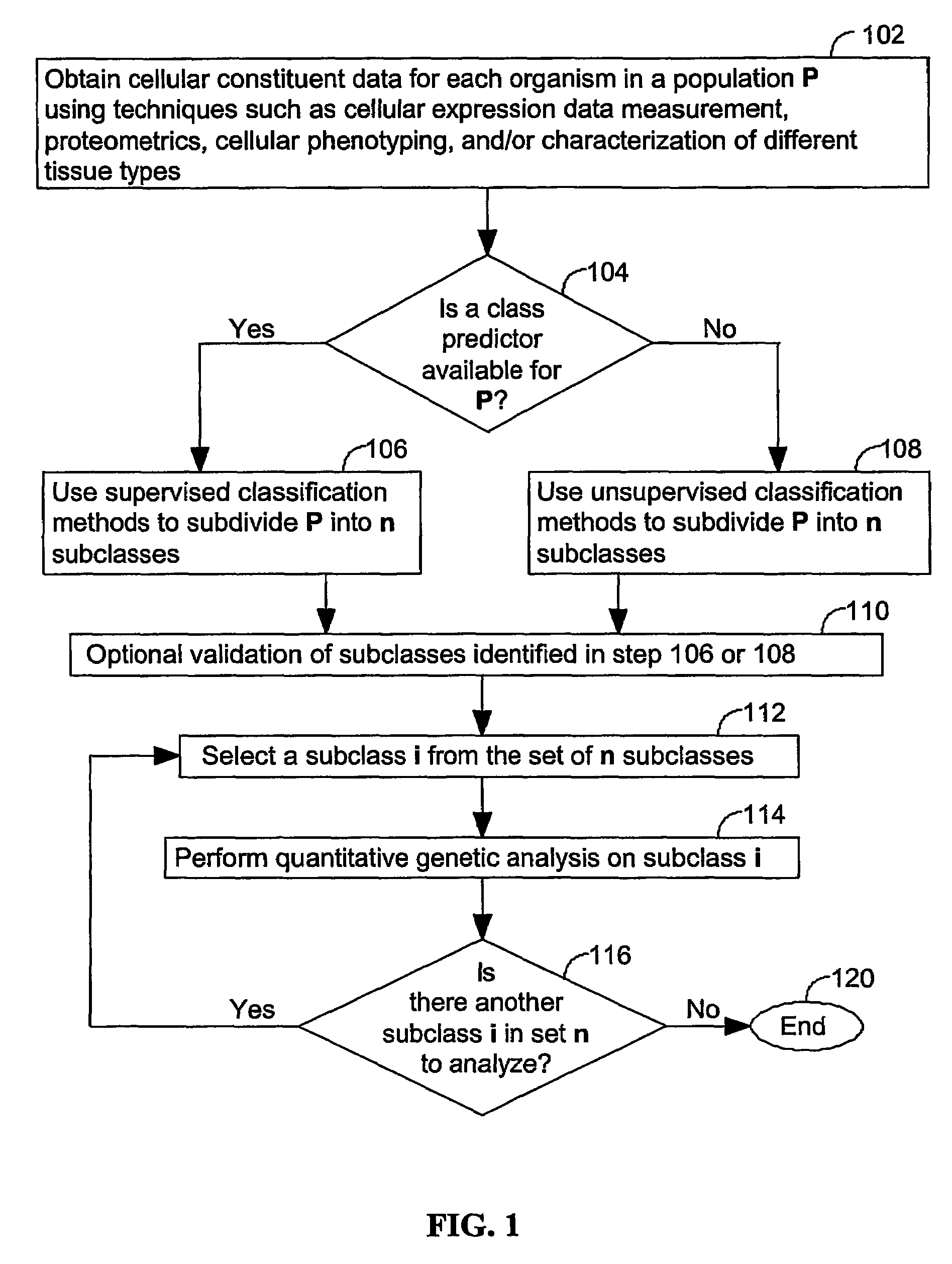
Computer systems and methods for subdividing a complex disease into component diseases
ActiveUS20060122816A1Low heterogeneityImprove accuracy and reliabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
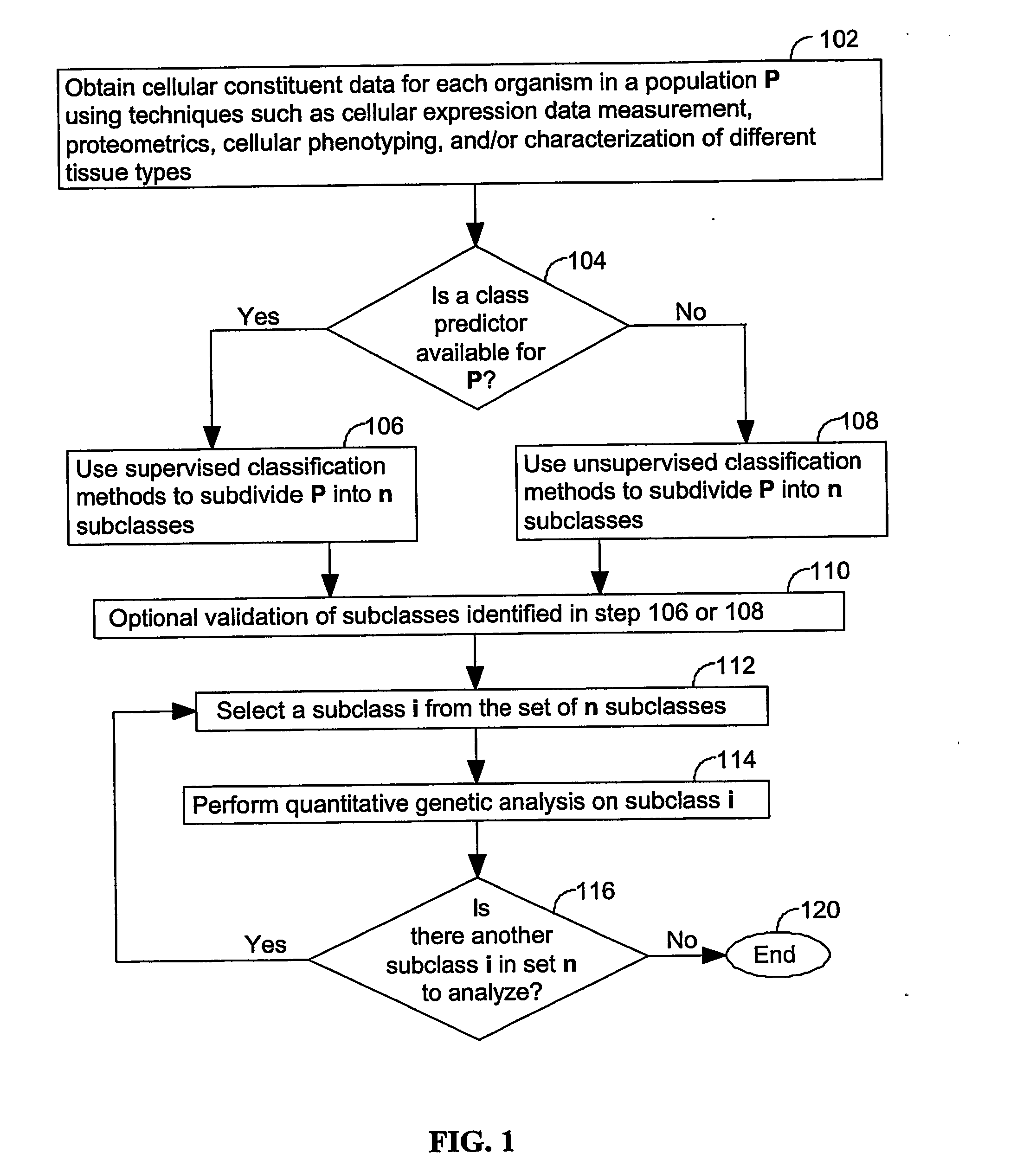
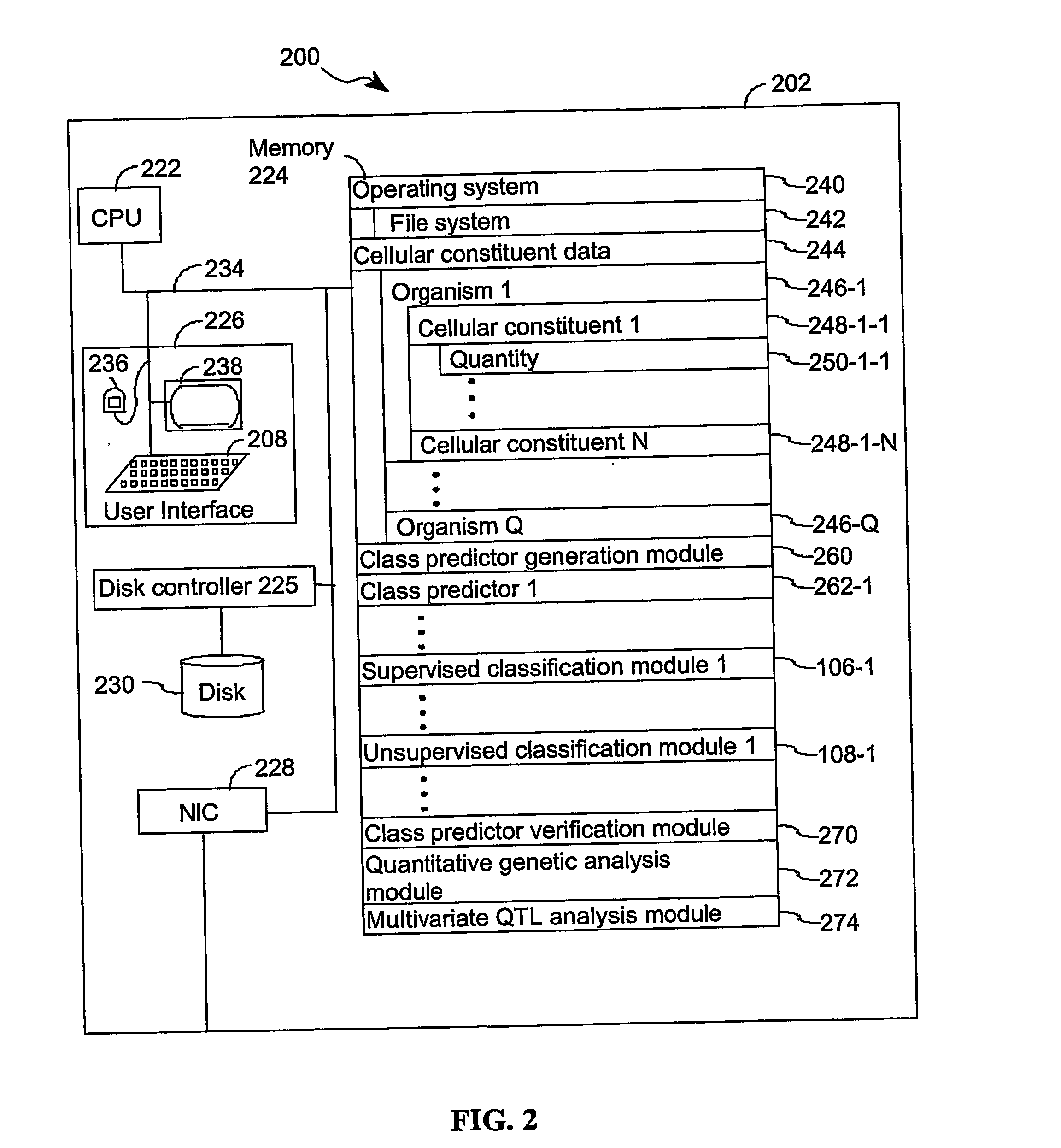
A method for identifying a quantitative trait loci for a complex trait that is exhibited by a plurality of organisms in a population. The population is divided into a plurality of sub-populations using a classification scheme. Depending on what is known about the population, either a supervised or unsupervised classification is used. The classification scheme is derived from a plurality of cellular constituent measurements obtained from each organism in the population. For each sub-population in the plurality of sub-populations, a quantitative genetic analysis is performed on the sub-population in order to identify one or more quantitative trait loci for the complex trait.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Method to identify disease resistant quantitative trait loci in soybean and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20080166699A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycineQuantitative trait locus
The present invention is in the field of plant breeding and genetics, particularly as it pertains to the genus, Glycine. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for screening soybean plants containing one or more quantitative trait loci for disease resistance, species of Glycine having such loci and methods for breeding for and screening of Glycine with such loci. The invention further relates to the use of exotic germplasm in a breeding program.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
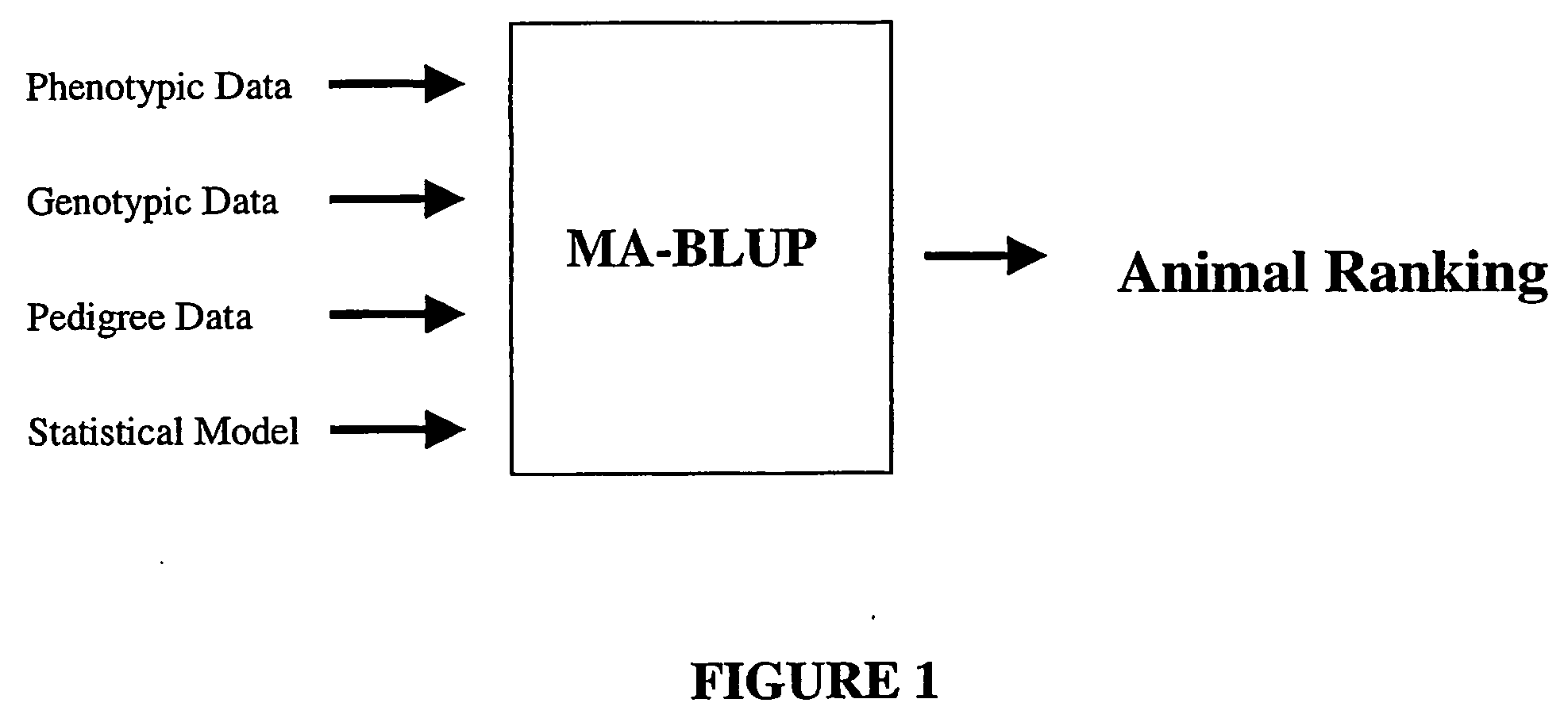
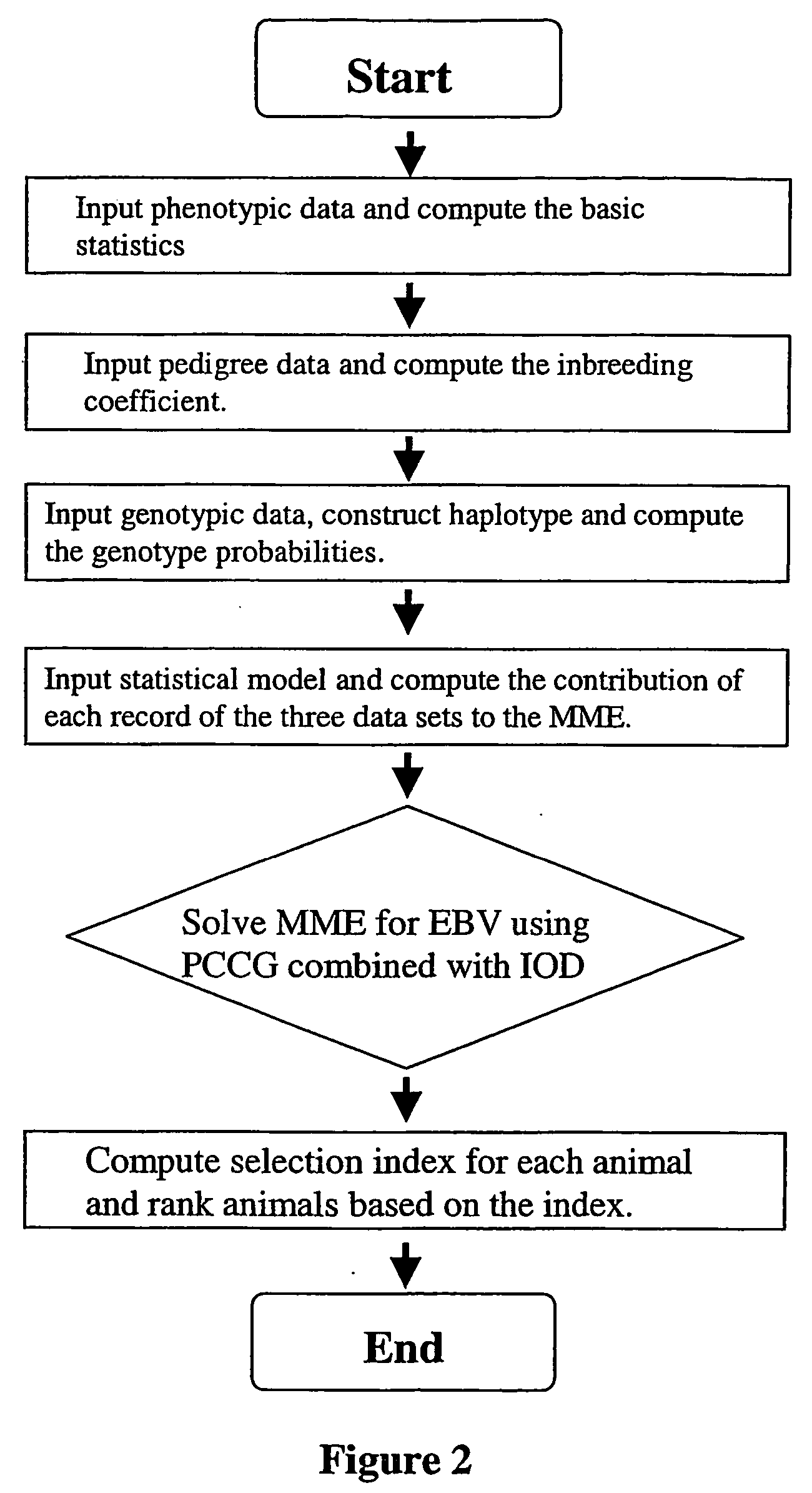
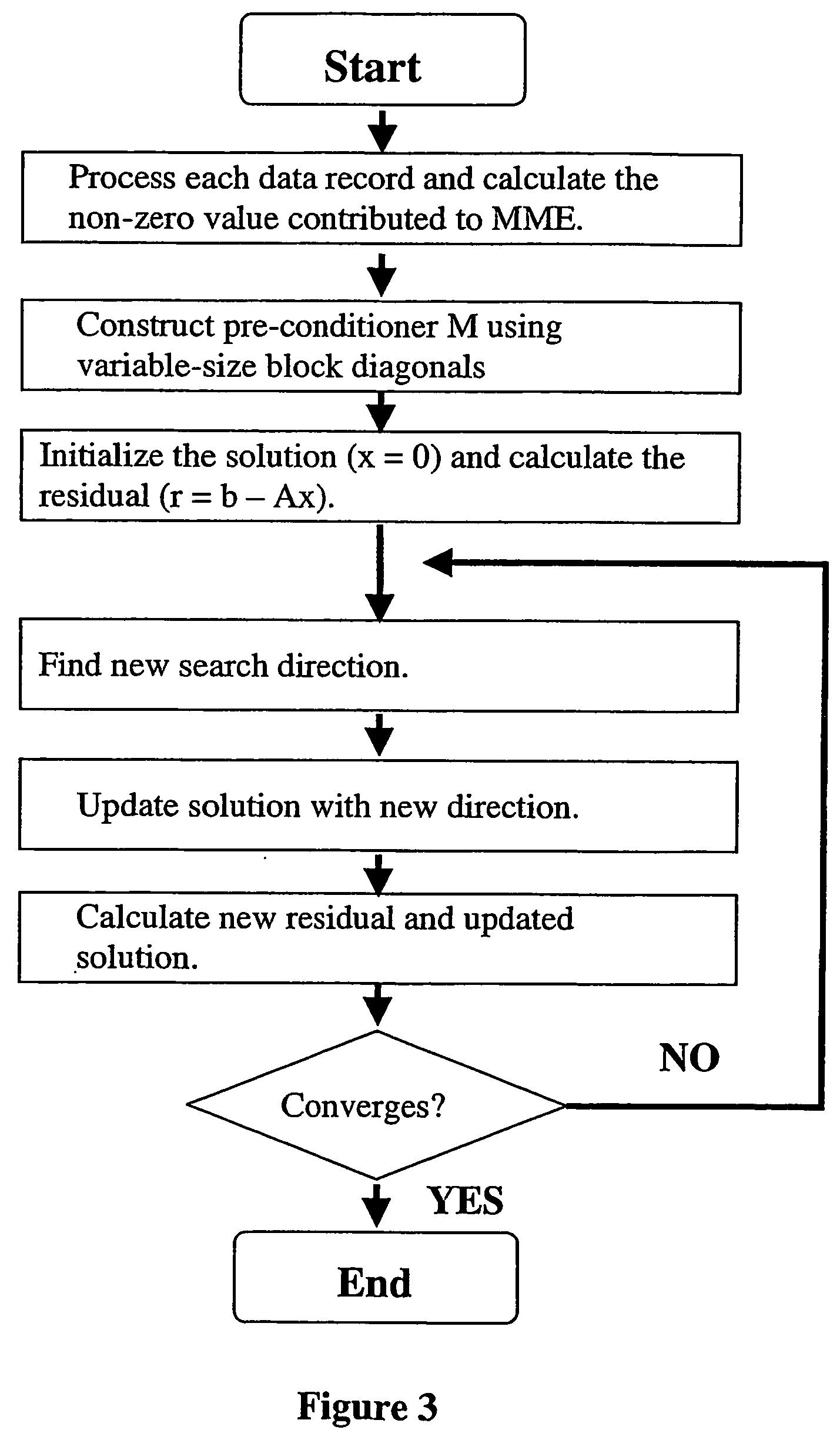
Marker assisted best linear unbiased prediction (ma-blup): software adaptions for large breeding populations in farm animal species
InactiveUS20070105107A1Genetic responseReduce memory requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsQuantitative trait locusHerd
The invention provides methodologies for improved molecular genetic analysis of individual animals and animal populations. The invention includes methods and systems for identifying those animals in a population that are most likely to heritably pass on desirable traits. Provided are means for evaluating the estimated breeding values and increasing the average genetic merit for animals in a population. For each trait, the instant invention provides methods for evaluating the relative effect of one or more quantitative trait loci (QTL) and three or more molecular genetic markers for each QTL The relationship between these various markers and the pre-selected trait and QTL is calculated, along with the contribution of other factors such as pedigree and known measures with respect to quantitative trait, and these data are used to calculate estimated breeding values for the animals in the herd and to rank the animals according to these estimated breeding values.
Owner:SCIDERA
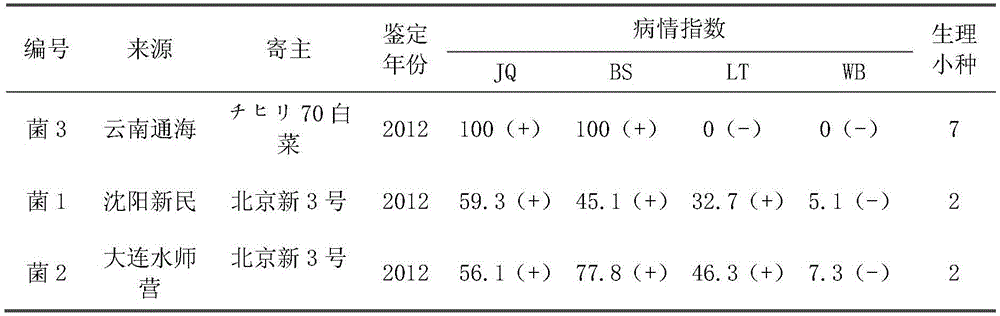
InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof
InactiveCN105543391AAccurate and reliable identification resultsReduce labor costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyForward primer
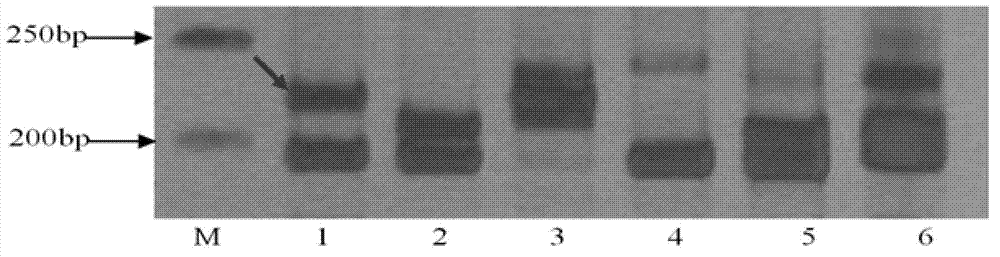
The invention discloses an InDel molecular marker for identifying clubroot-resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) located on Chinese cabbage A03 chromosome and application thereof. The invention provides a method for identifying or auxiliarily identifying whether a Chinese cabbage is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage, which comprises the following steps: carrying out amplification by using genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the Chinese cabbage to be identified as a template, a single-stranded DNA disclosed as SEQ ID No.2 as a forward primer and a single-stranded DNA disclosed as SEQ ID No.3 as a reverse primer; detecting the size of the amplification product; and determining whether the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage according to the size of the amplification product: if the amplification product of the Chinese cabbage to be identified contains a 201bp strip, the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage or candidate clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage; and if the amplification product of the Chinese cabbage to be identified does not contain any 201bp strip, the Chinese cabbage to be identified is a non-clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage or non-candidate clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
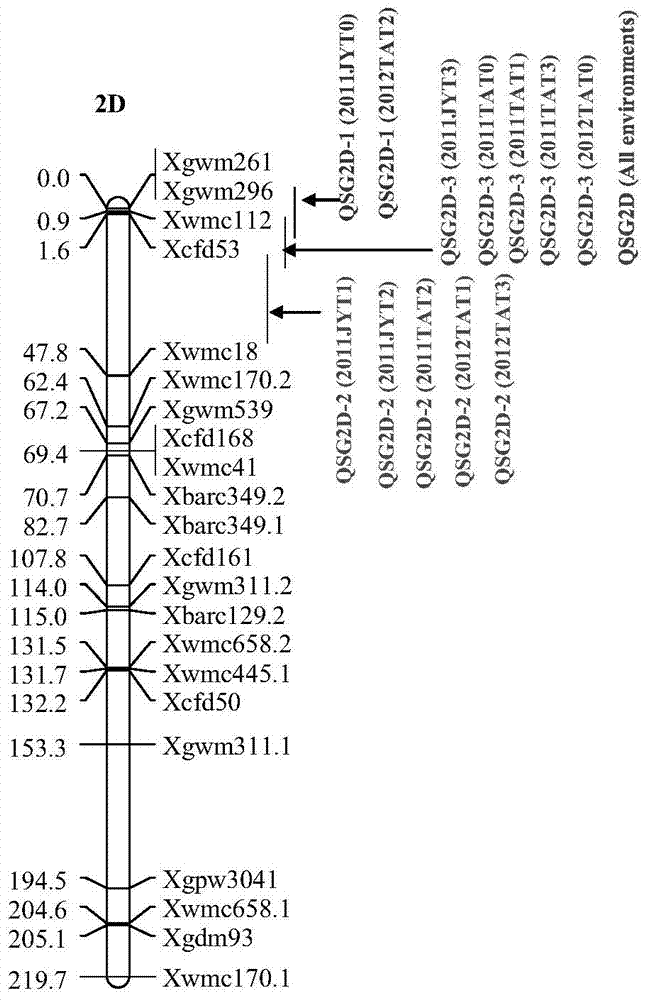
Detection primers for molecular markers in close linkage with major QTL of wheat ear length and application of detection primers
InactiveCN103882143AQuick filterSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
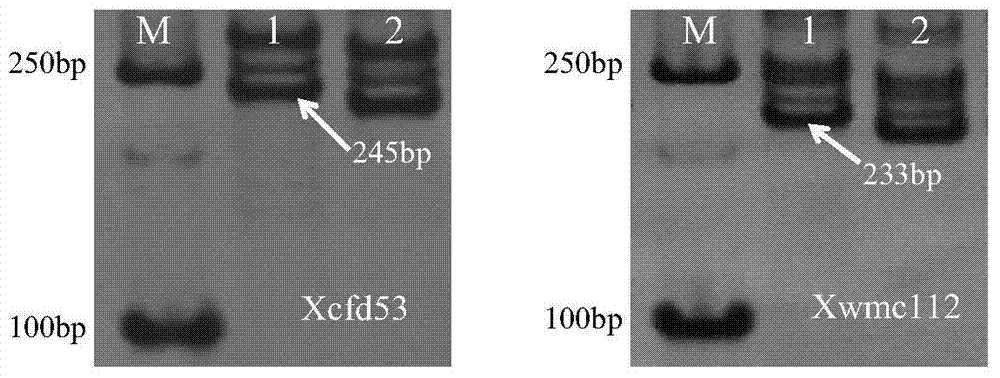
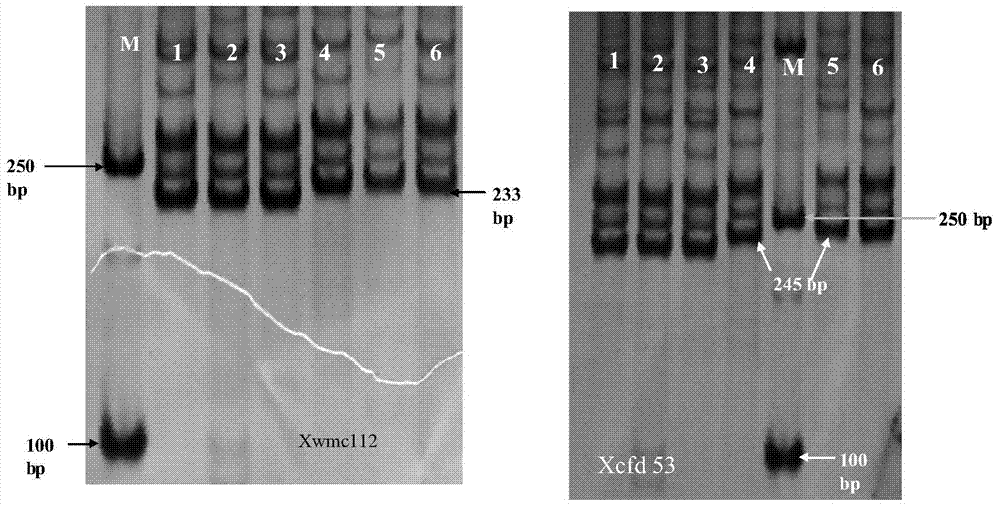
The invention relates to detection primers for molecular markers in close linkage with a major QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) of wheat ear length and an application of the detection primers. The detection primers for the molecular markers include an upstream primer, having a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, of the molecular marker XWMC112 and a downstream primer, having a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, of the molecular marker XWMC112, and an upstream primer, having a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3, of the molecular marker XCFD53 and a downstream primer, having a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.4, of the molecular marker XCFD53. The molecular marker XWMC112 and the molecular marker XCFD53 are studied and found for the first time, and can be used for quickly determining whether a wheat variety or strain has the QTL of the ear length, and thus quickly screening out the wheat variety or strain having the QTL for increasing the ear length, and therefore, the breeding progress of a high-yield wheat variety can be accelerated.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Computer systems and methods for subdividing a complex disease into component diseases
ActiveUS7653491B2Low heterogeneityImprove accuracy and reliabilityRead-only memoriesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansQuantitative trait locusSub populations
A method for identifying a quantitative trait loci for a complex trait that is exhibited by a plurality of organisms in a population. The population is divided into a plurality of sub-populations using a classification scheme. Depending on what is known about the population, either a supervised or unsupervised classification is used. The classification scheme is derived from a plurality of cellular constituent measurements obtained from each organism in the population. For each sub-population in the plurality of sub-populations, a quantitative genetic analysis is performed on the sub-population in order to identify one or more quantitative trait loci for the complex trait.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
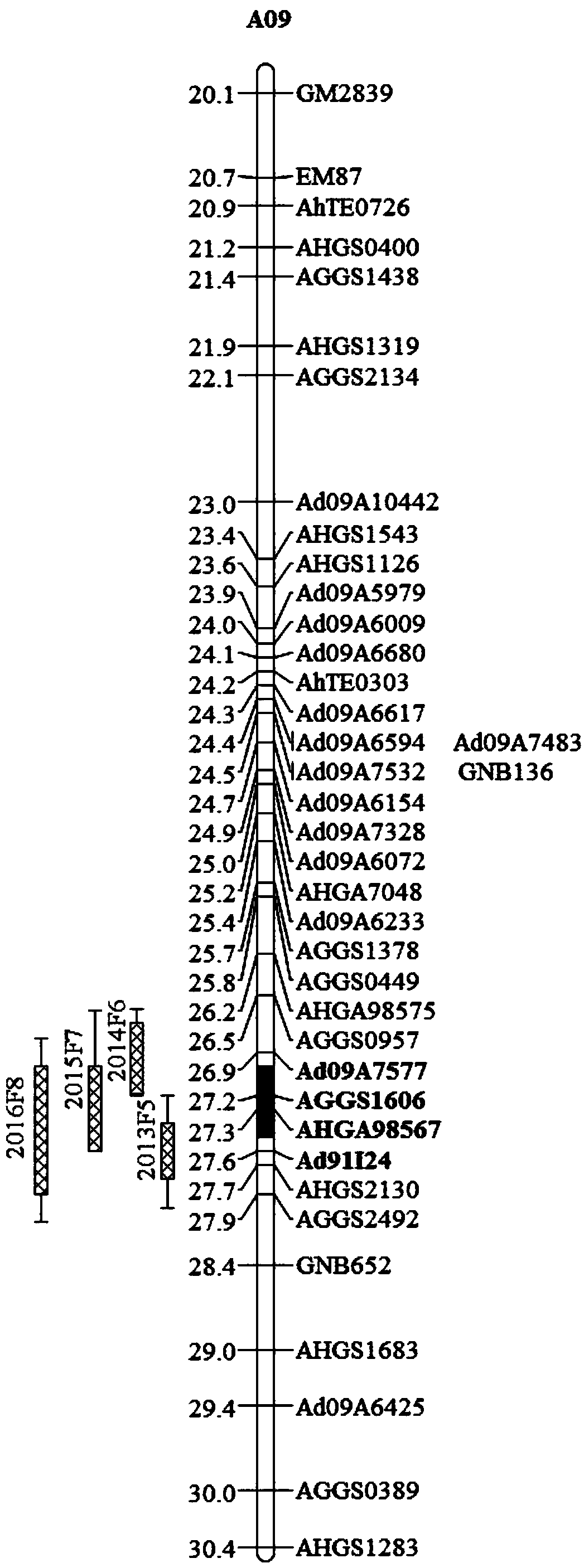
Molecular markers for peanut kernel yield major QTL (quantitative trait locus) and application thereof
ActiveCN108374053AConducive to the promotion of breedingImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationQuantitative trait locusElectrophoresis
The invention belongs to the field of molecular genetic breeding and particularly relates to molecular markers for peanut kernel yield major QTL (quantitative trait locus) and application thereof. Themolecular markers include Ad09A7577, AGGS1606, AHGA98567 and Ad91I24; one or more of primer pairs of the molecular markers Ad09A7577, AGGS1606, AHGA98567 and Ad91I24 are used to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on DNA of peanut material under identification, the amplified product is subjected to electrophoretic detection; if a DNA fragment of corresponding size is obtained byamplifying, it is shown that kernel yield major QTL cqSPA09 is present, and pods have high kernel yield.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
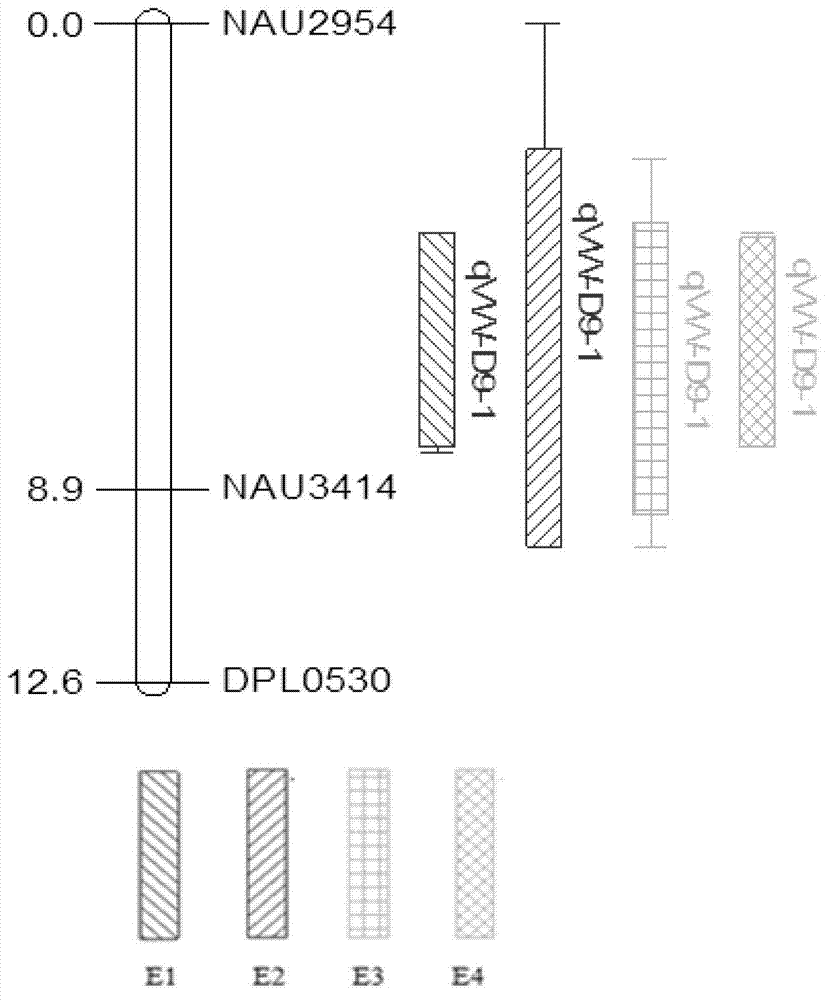
Cotton highly-verticillium wilt resistant major QTL (quantitative trait locus) and SSR molecular marker thereof
ActiveCN102925436AIncrease Verticillium wilt resistance levelStable resistance performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention discloses a cotton highly-verticillium wilt resistant major QTL (quantitative trait locus) and an SSR molecular marker thereof. The cotton highly-verticillium wilt resistant major QTL is located on the cotton D9 chromosome, 16.95-65.53% of phenotypic variation can be explained in the RIL (recombinant inbred line) colony from the highly-verticillium wilt resistant germplasm systems Prema and 86-1, and the following three SSR markers are in close linkage therewith: SSR / NAU2954209, SSR / NAU3414258 and SR / DPL0530220. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is used for screening or identifying the verticillium wilt-resistant cotton variety. The invention is favorable for solving the problem of slow progress of the cotton verticillium wilt resistance breeding of the country, and is favorable for overcoming the defects of high cost, long time, low stability and the like of the existing breeding technology in verticillium wilt resistance identification; and the highly-verticillium wilt resistant cotton new variety breeding and seed industrialization progresses of the country are greatly accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Resistance to gray leaf spot in maize
ActiveUS20100146657A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationFungal diseaseDisease
The present invention is in the field of plant breeding and disease resistance. More specifically, the invention includes a method for breeding corn plants containing quantitative trait loci that are associated with resistance to gray leaf spot, a fungal disease associated with Cercospora spp. The invention further includes germplasm and the use of germplasm containing quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring disease resistance for introgression into elite germplasm in a breeding program for resistance to gray leaf spot.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
SSCP marker closely linked with major wheat scab resistance QTL and application thereof
InactiveCN101892307AReduce the waste of manpower and material resourcesImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismSequence analysis
The invention relates to a single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) marker closely linked with a major wheat scab resistance quantitative trait locus (QTL). The SSCP marker is characterized in that: scab resistance candidate genes of a scab resistance QTL in a 3BS area of a wheat variety or strain resisting scab is PCR amplified by using a primer; after denaturalization, a PCR-amplified product has different single strand conformation; and the SSCP marker closely linked with the major wheat scab resistance QTL is established for detecting a genotype of the wheat variety or strain during breeding. The SSCP marker has the advantages of: overcoming the disadvantages that the wheat scab resistance screening can only be authenticated in a flowering period and is easily influenced by the environment in conventional breeding, predicting and screening wheat plants with the scab resistance by detecting a molecular marker at a seedling stage, eliminating disease plants, reducing waste of labor and materials and improving the breeding efficiency. Compared with an ABI DNA sequence analysis meter-based marker, the SSCP marker closely linked with the major wheat scab resistance QTL has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, low cost and same sensitivity.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
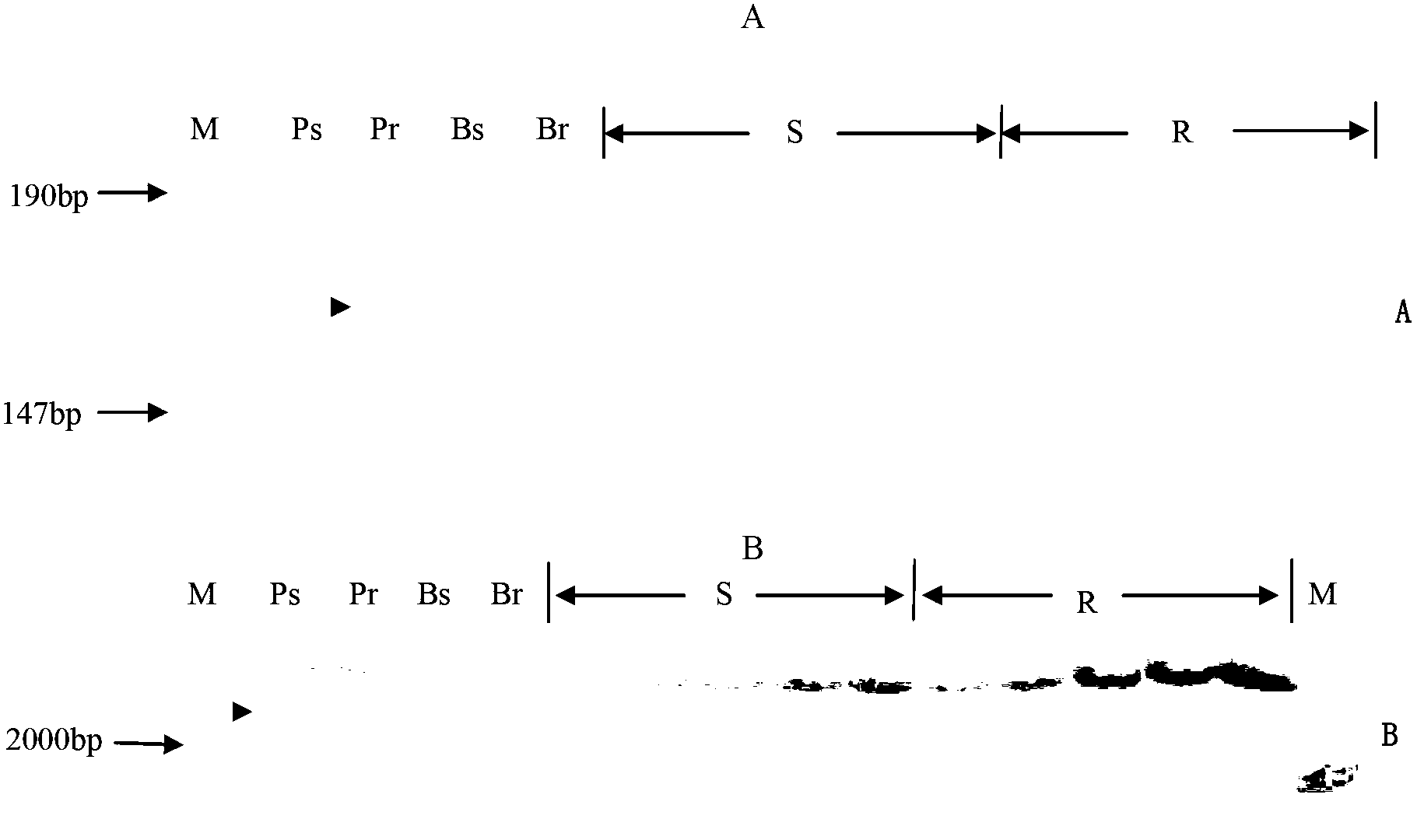
Molecular marker closely linked with major quantitative trait locus (QTL) of thousand-grain weight and grain length of wheat and obtaining method and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN102690822AQuick filterSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
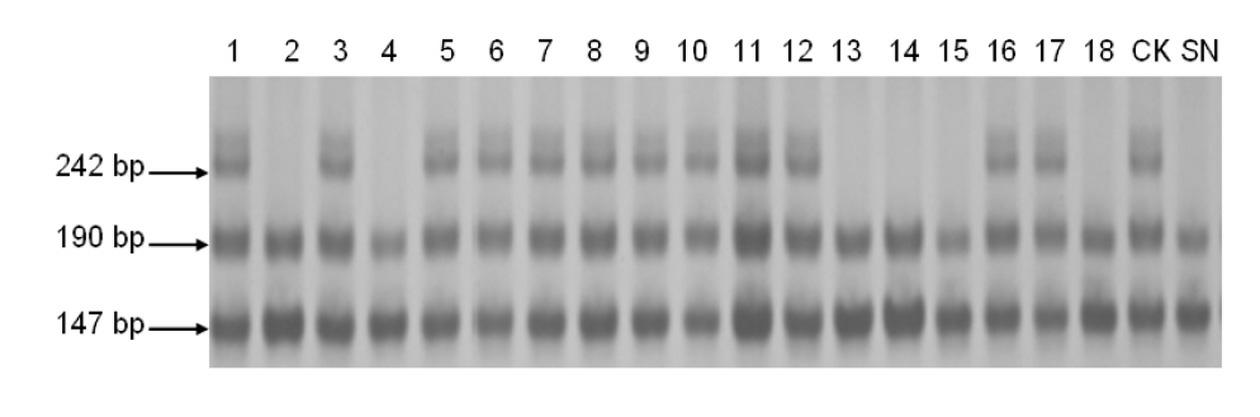
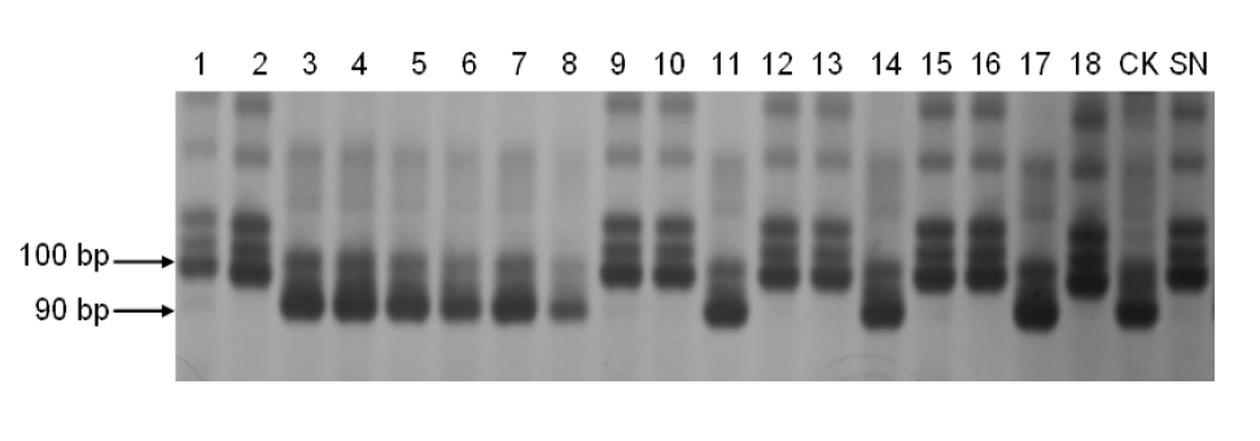
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with a major quantitative trait locus (QTL) of the thousand-grain weight and grain length of wheat and an obtaining method and application of the molecular marker. A labeling primer wmc386 and barc216 are adopted to carry out polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on the DNA of a wheat line Shannong 0431; and after the electrophoretic separation of the amplification product on 8% polyacrylamide gel, the molecular weights of the obtained amplification product are 190 bp and 100 bp respectively, i.e., the molecular marker of the major QTL of the thousand-grain weight and the grain length of the wheat. The molecular marker of the major QTL of the thousand-grain weight and the grain length of the wheat can be used for detecting whether the QTL for increasing the thousand-grain weight and the grain length is contained in a wheat variety or a wheat line, in order to fast screen out the wheat variety or the wheat line containing the QTL for increasing the thousand-grain weight and the grain length for breading; therefore, the selective breeding process for high-yield wheat varieties is much faster.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
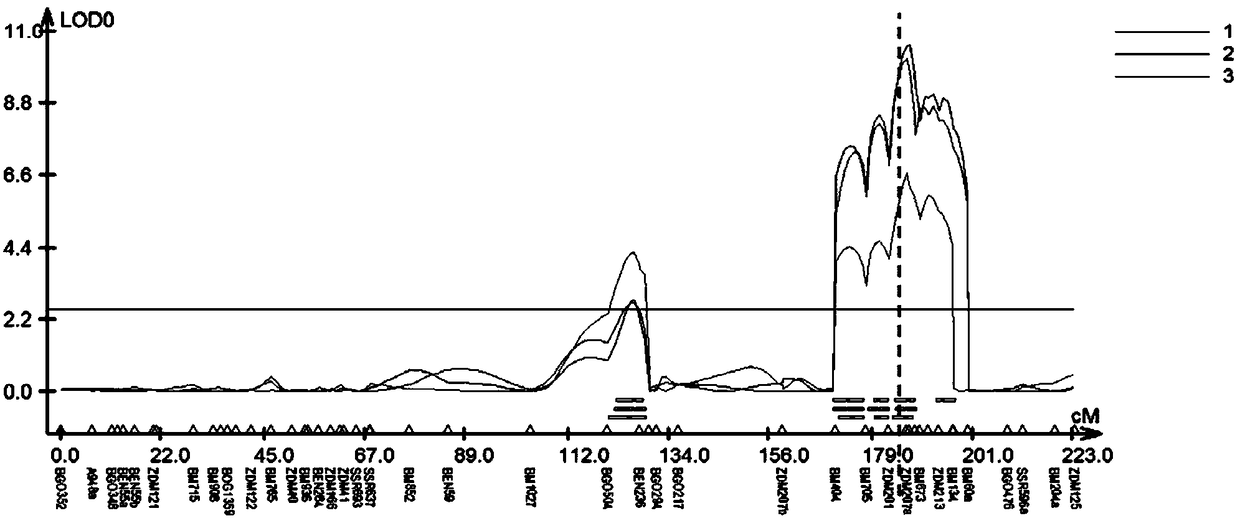
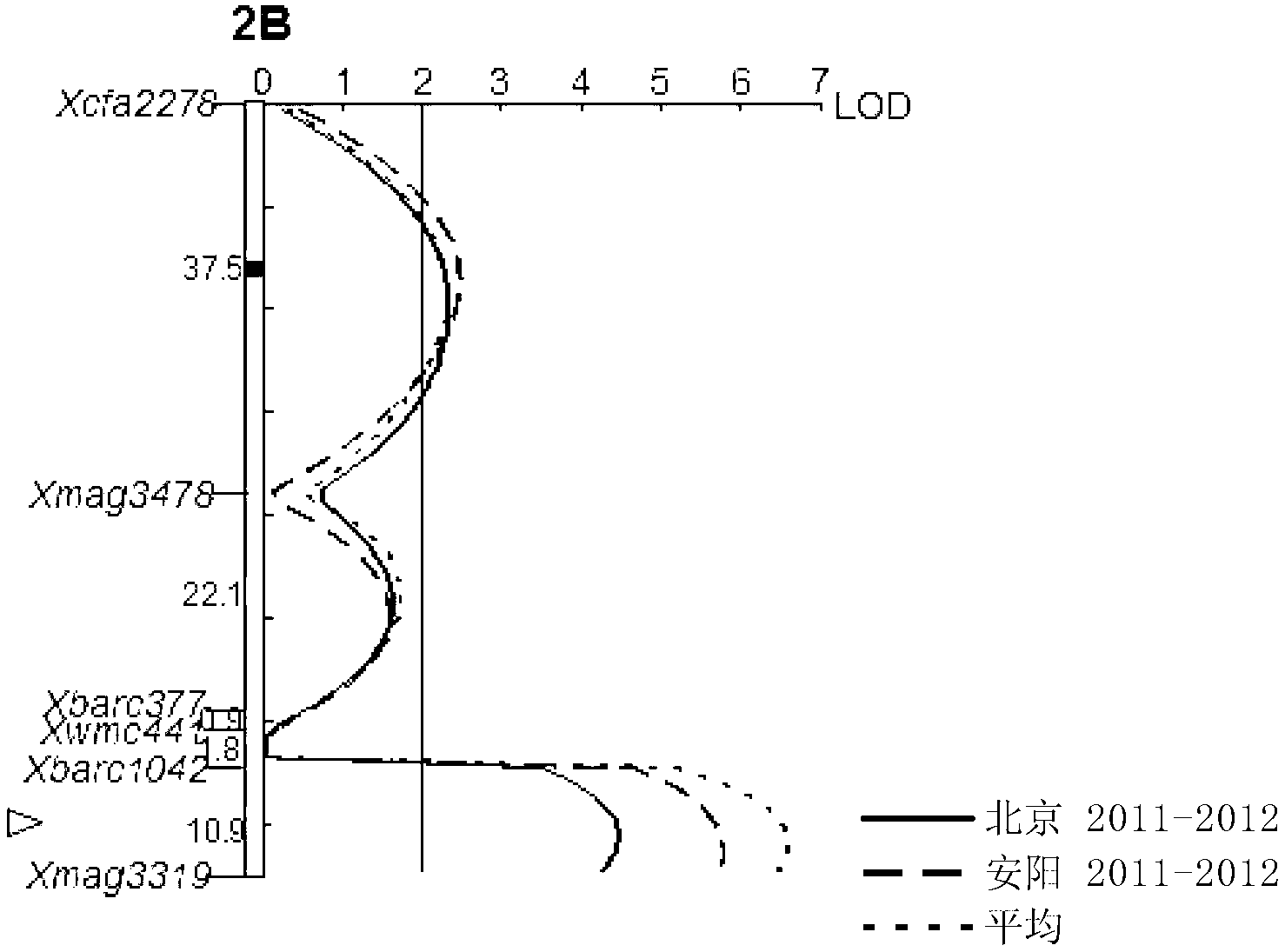
Major QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) capable of influencing wheat ear length and application thereof
ActiveCN109402284AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTriticeaeCandidate Gene Association Study
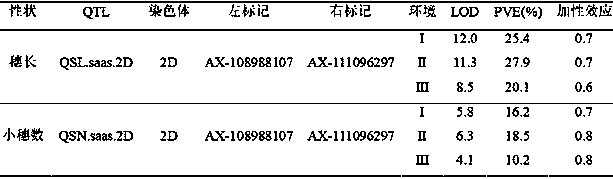
The invention belongs to the field of wheat genetic breeding, and provides major QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) capable of influencing the wheat ear length. The major QTL are located on a 2D (Two-Dimensional) chromosome short arm, and are located between a left marker AX-108988107 and a right marker AX-111096297 of an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker; the major QTL can affect the spikelet number at the same time; the QTL have a candidate gene for encoding IAA (Indoleacetic Acid)-amino acid hydrolase; phenotypic variation explanation rates of the QTL on the ear length and the grain number per ear are respectively 27.9 to 20.1 percent and 18.5 to 10.2 percent; positive allelic variation of the QTL are sourced from parent varieties-Banmangzi, and the QTL have huge application valuein wheat breeding.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Maize water-logging tolerance-related transcription factor gene zm-bRLZ, molecular marker and application
InactiveCN101974537AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideCandidate Gene Association Study
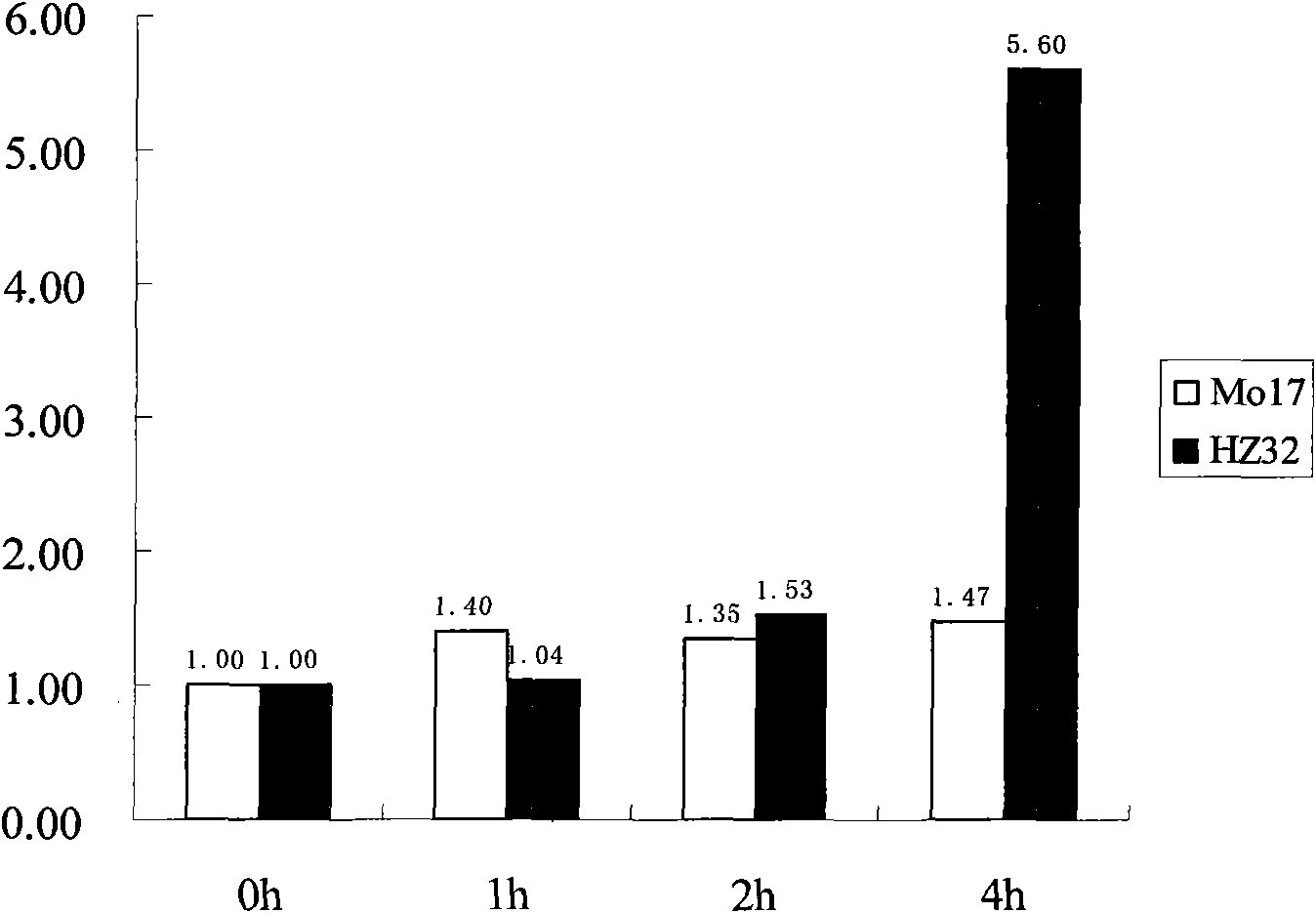
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, and relates to clone and application of a maize water-logging tolerance-related transcription factor gene zm-bRLZ. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the gene has a total length of 4,027bp and comprises 6 exons. The cDNA sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2, and 282 amino acids are encoded on the gene. In flooding stress, the expression of the gene in maize inbred line Hz32 seedling roots is up-regulated and the expression level of the gene in the Mo17 is kept unchanged. The in-vitro combination of a gene protein product and an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) promoter anaerobic response factor shows that the zm-bRLZ gene has a regulation and control effect on an anaerobic induced gene. A pair of cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) markers is developed by utilizing zm-bRLZ gene sequence difference of the maize water-logging tolerance inbred line Hz32 and high-sensitivity K12. The gene is positioned at a water-logging tolerance quantitative trait locus (QTL) peak part of 9.04bin by utilizing K12*Hz32 F2 group. A candidate gene correlation analysis proves that a zm-bRLZ gene promoter region and a plurality of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites at a 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) are all obviously associated with a plurality of water-logging tolerance indexes.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cabbage type rape high oleic acid QTL and molecular marker closely linked thereto
ActiveCN108239674ASpeed up the optimization processImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of rapeseed molecular markers and particularly relates to cabbage type rape high oleic acid QTL and a molecular marker closely linked to theQTL. Through screening, a novel molecular marker BnA129 closely linked to oleic acid content QTL is obtained and has a nucleotide sequence shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO: 3 and / or 4. A primer BnA129 of a detection molecular marker OLEA9 is constructed and has a nucleotide sequence shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO: 1 and 2 in the sequence table. The quantitative trait locus OLEA9 and molecular markers can be used in molecular marker-assisted selection in the improvement of high oleic acid content characters of cabbage type rape and fine mapping and map cloning of oleic acid character sites.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
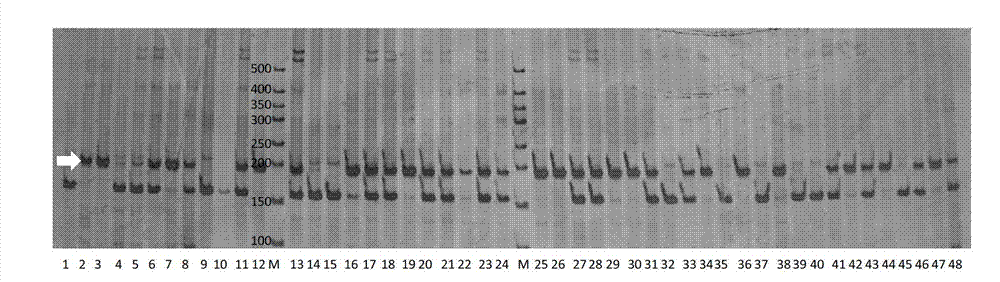
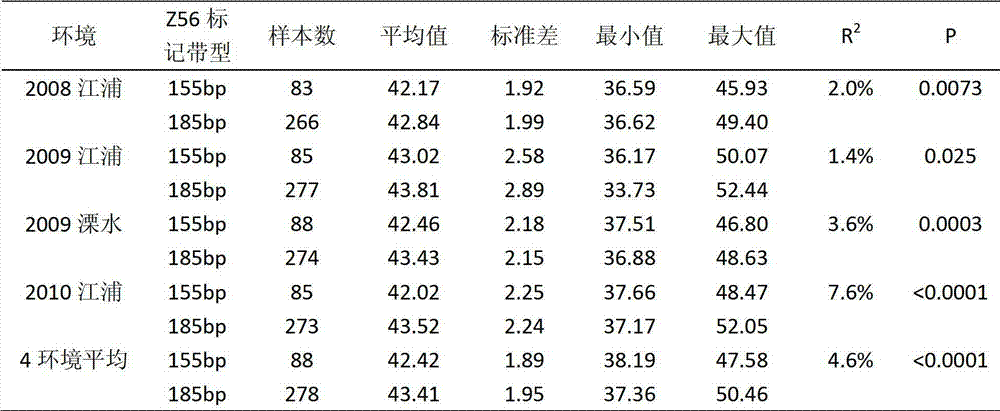
Molecular marker of major QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) of soybean seed protein content and application thereof
InactiveCN103045588AGood correlationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerBiotechnology
The invention discloses a molecular marker of the major QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) of soybean seed protein content and application thereof. The major QTL locus of the soybean seed protein content is positioned on the No. eight chromosome Gm08:13000-17000 kb of a soybean. The forward primer sequence of the molecular marker is SEQ ID NO.1, the reverse primer sequence of the molecular marker is SEQ ID NO.2. In newly allocated hybridized combination, a Z56 primer pair is used for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking the genomic DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of an F2 individual soybean seed to be measured as a template, amplification products are detected, and the soybean to be measured, which is included in the amplification products and has a specific DNA fragment with the size of 180-190bp, is a candidate material with high seed protein content. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for easily and fast screening the soybean seed high-protein materials and can accelerate the soybean seed high-protein content breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Seed quantitative trait locus positioning method based on mixed linear model
ActiveCN103632067AQuick estimateImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsQuantitative trait locusPhenotypic trait
The invention discloses a seed quantitative trait locus positioning method based on a mixed linear model. The method comprises the step of establishing a statistics genetic model, the step of searching the range of a whole genome for all candidate label sections in which an OTL probably exists, the step of regarding the candidate label sections as a concomitant variable, and searching the range of the whole genome for obvious QTLs and a two interaction label section, the step of regarding the QTLs and the two interaction label section as the concomitant variables and searching an obvious interaction label section for obvious loca of a two interaction epistasis, and the step of obtaining coefficients of various effects in the statistics genetic model based on the QTLs and the loca of the two interaction epistasis and calculating the effect of the loca and estimating the heritability of all loca according to the statistics genetic model. The seeds are divided into diploid seeds and triploid seeds according to the traits of the seeds, the epistasis effect and the effect of interaction of genes and the environment are taken into consideration, and the positions of the seed quantitative trait loca and various effects can be fast estimated in an unbiased mode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
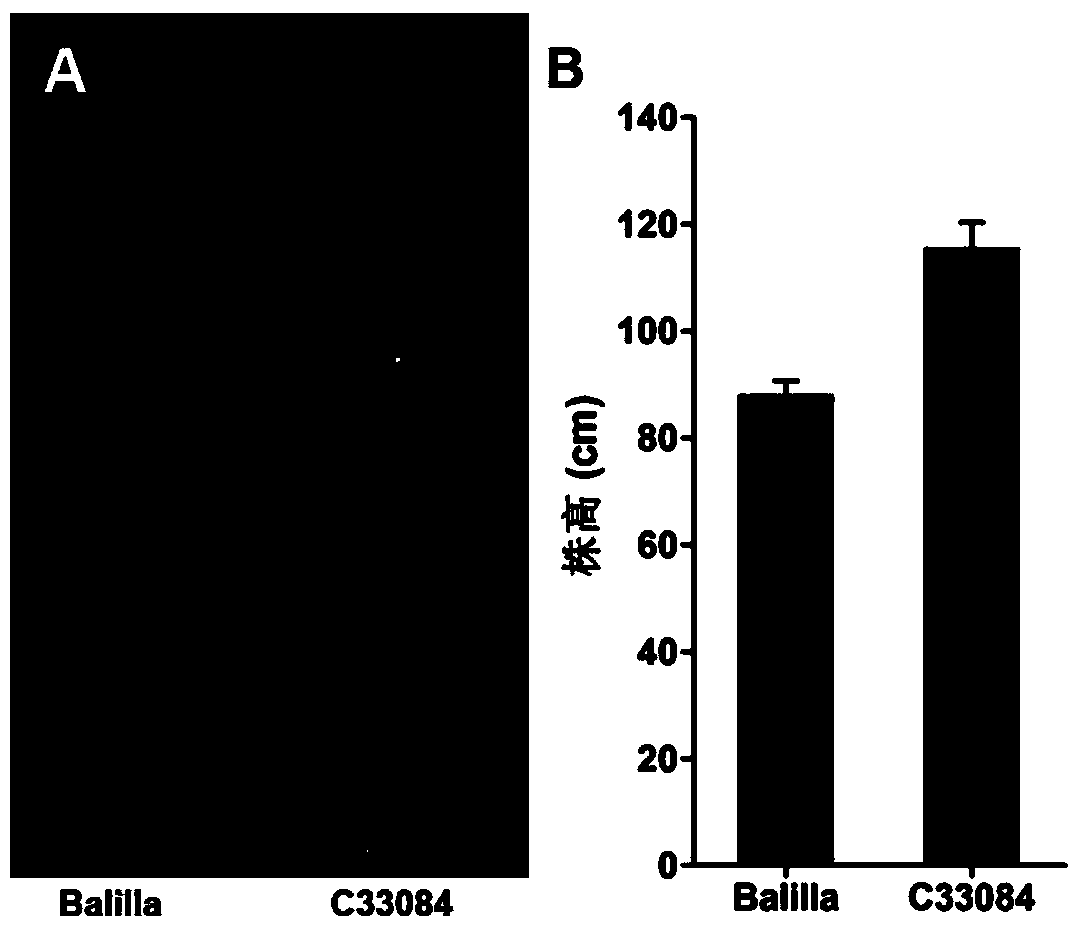
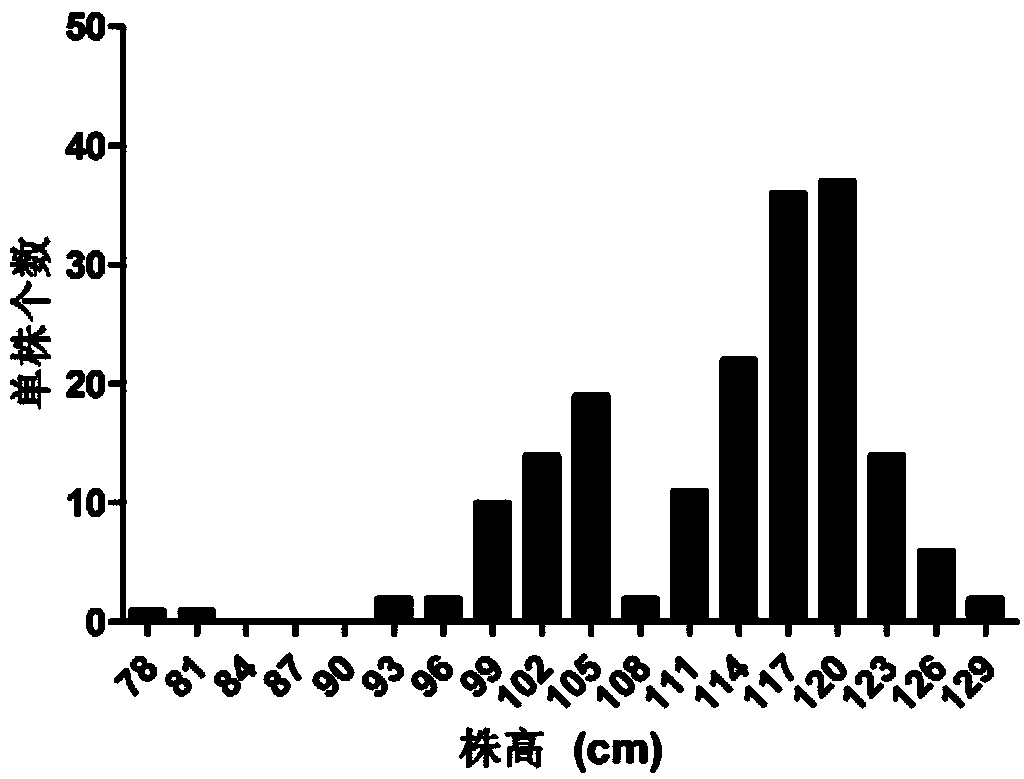
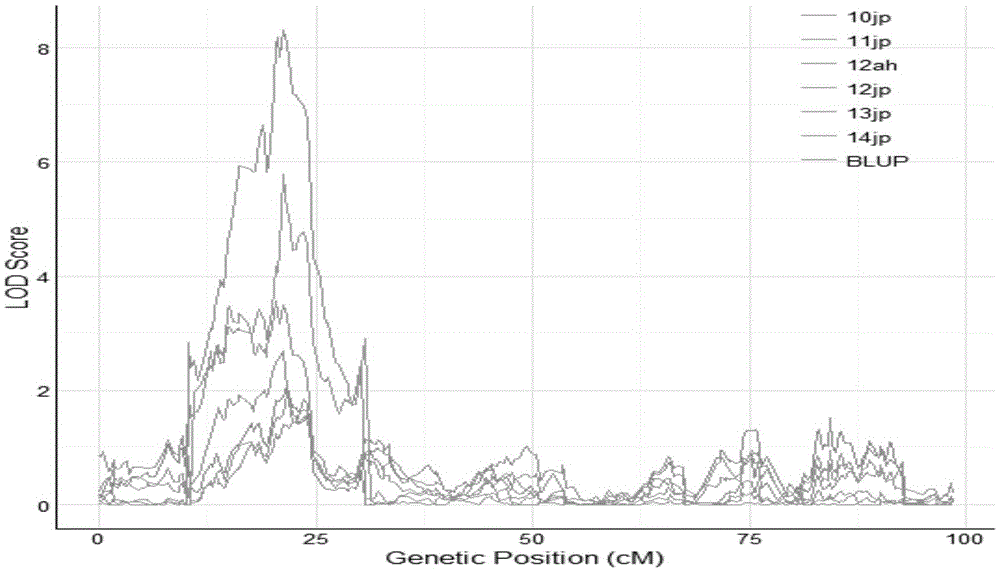
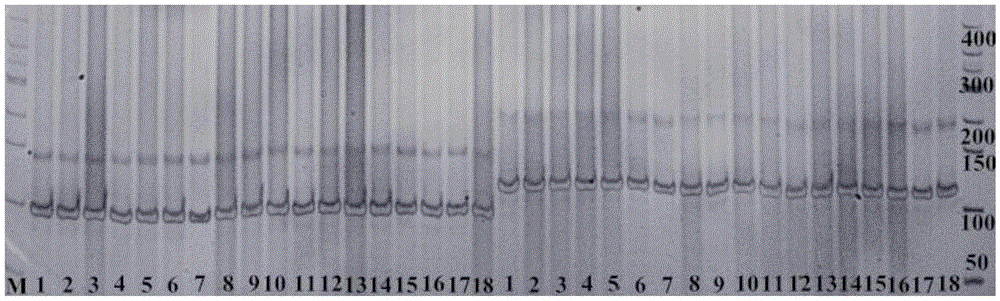
Molecular markers of main effect QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) qPH6 locus of plant height of rice and application thereof
InactiveCN103820444AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLong armAgricultural science
The invention relates to molecular markers of a main effect QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) qPH6 locus of plant height of rice and an application thereof. The molecular markers are S6-334 and S6-10 which are compactly interlinked with the qPH6 locus and can be applied to identifying and breeding dwarf species of rice. According to the molecular marker method of the main effect QTL qPH6 locus of plant height of rice provided by the invention, the main effect QTL novel locus qPH6 which is from Balilla to control the plant height on the long arm of the sixth chromosome is firstly positioned internationally, and InDel markers S6-334 and S6-10 which are compactly interlinked are obtained. By just detecting the characteristics of the amplification stripes of the markers, whether variation of the main effect QTL qPH6 locus of plant height exists or not can be judged to predict the plant height phenotype of rice for guiding breeding work of improvement of plant height of rice.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
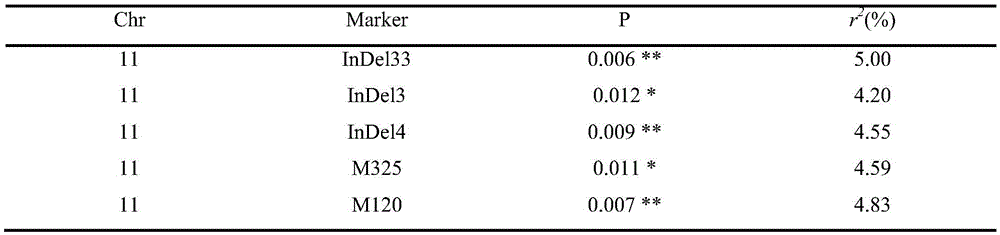
Molecular marker InDeL_33 of main-effect QTL (quantitative trait locus) of soybean hundred-grain weight and application of molecular marker InDeL_33
InactiveCN105543222AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyQuantitative trait locus
The invention discloses a molecular marker InDeL_33 of a main-effect QTL (quantitative trait locus) of soybean hundred-grain weight and an application of the molecular marker InDeL_33. The main-effect QTL of the soybean hundred-grain weight is located on a NO.11 chromosome Gm11:2261898bp-6577664bp of the soybean; an upstream primer sequence of the molecular marker InDeL_33 is represented as Seq ID NO.1, and a downstream primer sequence is represented as Seq ID NO.2. In a built secondary group, to-be-detected F2 single-plant genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is taken as a template, an InDeL_33 primer pair is adopted to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, an amplification product is detected, and a to-be-detected material with a specific DNA fragment in the size of 120bp in the amplification product is a candidate small-grain soybean material. By the aid of the molecular marker, large-grain and small-grain soybean materials can be screened simply and conveniently, and the small-grain soybean breeding process can be accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
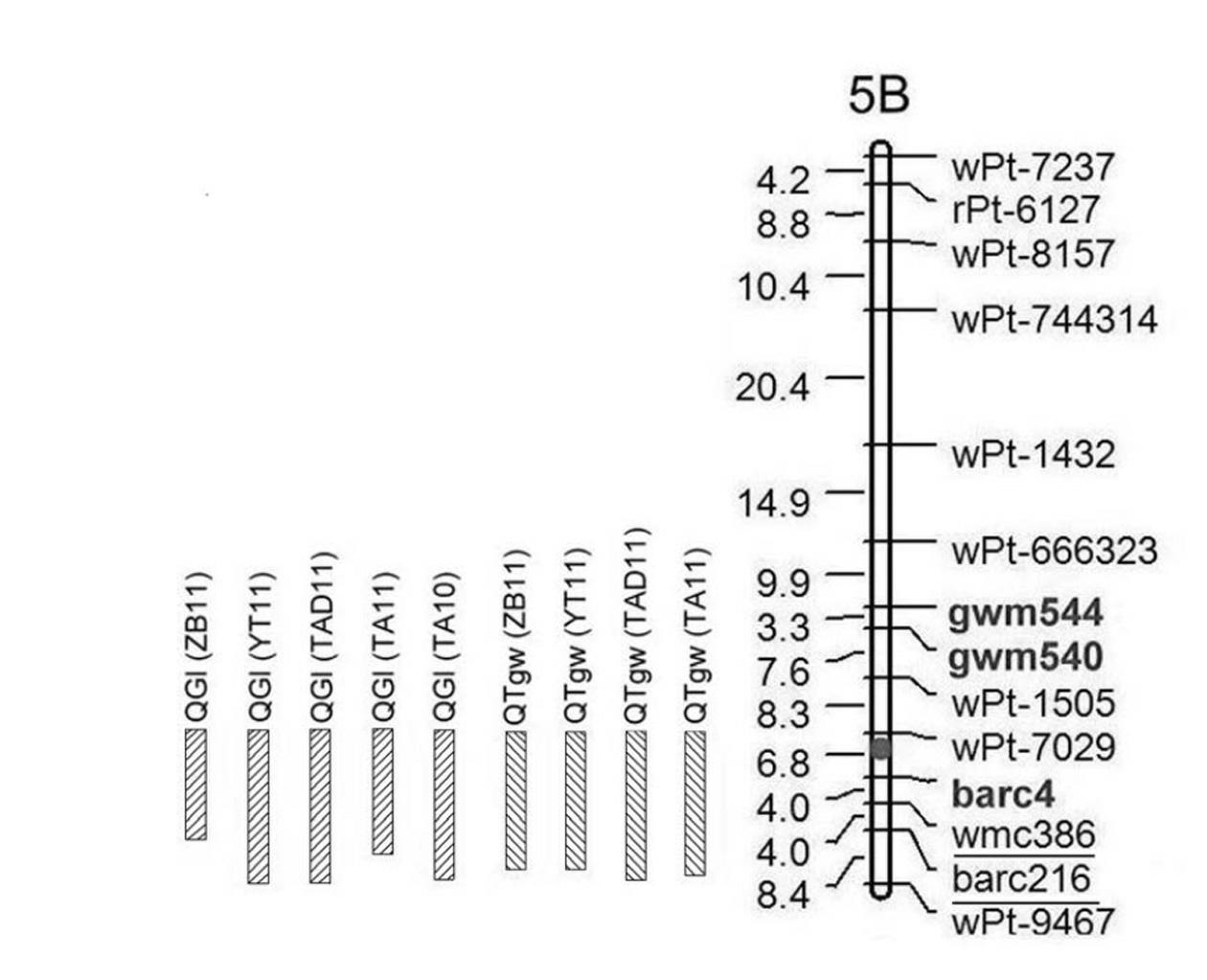
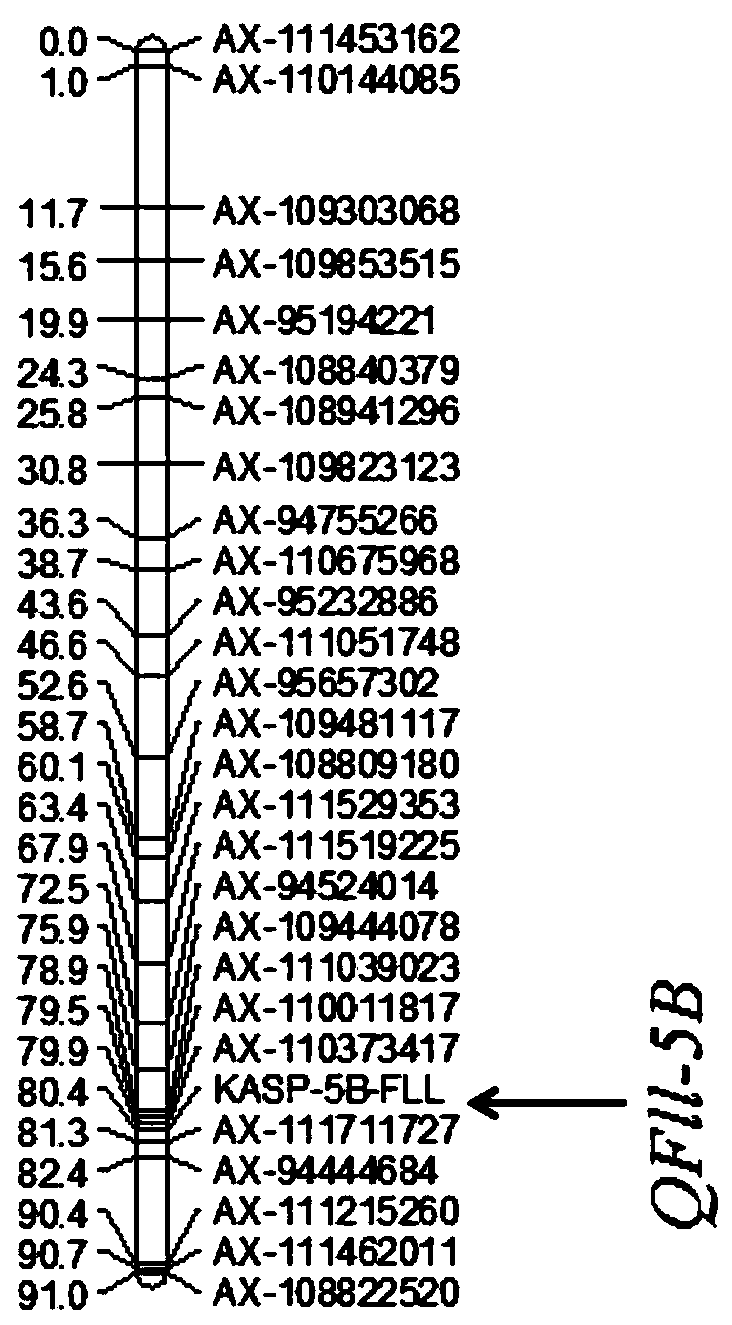
Triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length quantitative trait locus (QTL) linked molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN110499387AHigh linkageImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyLong arm
The invention relates to the field of triticum aestivum L. molecular breeding, and particularly discloses a triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length quantitative trait locus (QTL) linked molecular markerand application thereof. The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker linked with triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length QTL QFll-5B is provided and located on a 5B chromosome long arm ofa RefSeqv1.0 genome edition, and is the 51st of a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.31, polymorphism is C / T, and the SNP molecular marker can be obtained by amplification of a primer shown in a nucleotidesequence such as SEQ ID NO.1-3. The SNP molecular marker can accurately trace the triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length QTL QFll-5B, and predict the flag leaf length characteristics of triticum aestivum L., and molecular design breeding is convenient. The invention further discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker. The prediction accuracy of the flag leaf length can be enhanced by using the method, so that varieties or strains of the triticum aestivum L. with increased the flag leaf length are conveniently and rapidly screened for breeding, and the breeding progress of the varieties of the triticum aestivum L. with a high yield can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Soybean having epistatic genes affecting yield
InactiveCN1261252AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationQuantitative trait locusPlant variety
A method of plant breeding applicable to self-pollinating plants, and plants produced by use of the method, includes the use of molecular markers linked to interacting loci that affect traits of agronomic value. The method allows one to identify a first molecular marker linked to a quantitative trait locus (QTL) and a second molecular marker linked to a modifying locus having an epistatic effect in combination with the QTL. Conventional breeding steps can then be used to introgress the interacting loci into other plant varieties.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Methods and compositions to select cotton plants resistant to cotton root knot nematode
InactiveUS20110173713A1Increase productionReduce allergiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyQuantitative trait locus
The present invention is in the field of plant breeding and disease resistance. More specifically, the invention provides a method for breeding cotton plants containing one or more quantitative trait loci that are associated with resistance to Root Knot Nematode(RKN), a disease associated with Meloidogyne incognita. The invention further provides germplasm and the use of germplasm containing quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring disease resistance for introgression into elite germplasm in a breeding program, thus producing novel elite germplasm comprising one or more RKN resistance QTL.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method and special primer for screening or auxiliary screening of wheat with high pre-harvest sprouting resistance
InactiveCN103160584ASpeed up the breeding processGermination Resistance ImprovementMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationQuantitative trait locusAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method and a special primer for screening or auxiliary screening of wheat with high pre-harvest sprouting resistance. The special primer for screening or auxiliary screening of the wheat with high pre-harvest sprouting resistance consists of a primer pair 1 and a primer pair 2 as follows: the primer pair 1 consists of single-stranded DNA molecules shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table and single-stranded DNA molecules shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table, and the primer pair 2 consists of single-stranded DNA molecules shown in sequence 3 in the sequence table and single-stranded DNA molecules shown in sequence 4 in the sequence table. According to the invention, the experiment proves that the invention provides the special primer which utilizes an offspring group produced by CA0431 / CA0306 for QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) mapping to find out a molecular marker QTL (QPhs.caas-2BL) which is closely linked with a CA0431 pre-harvest sprouting resistance gene, and screens out the special primer for auxiliary screening of the wheat with the pre-harvest sprouting resistance based on the main effect QTL. The special primer can be utilized for screening or auxiliary screening of the wheat with pre-harvest sprouting resistance so as to cultivate pre-harvest sprouting resistant varieties.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
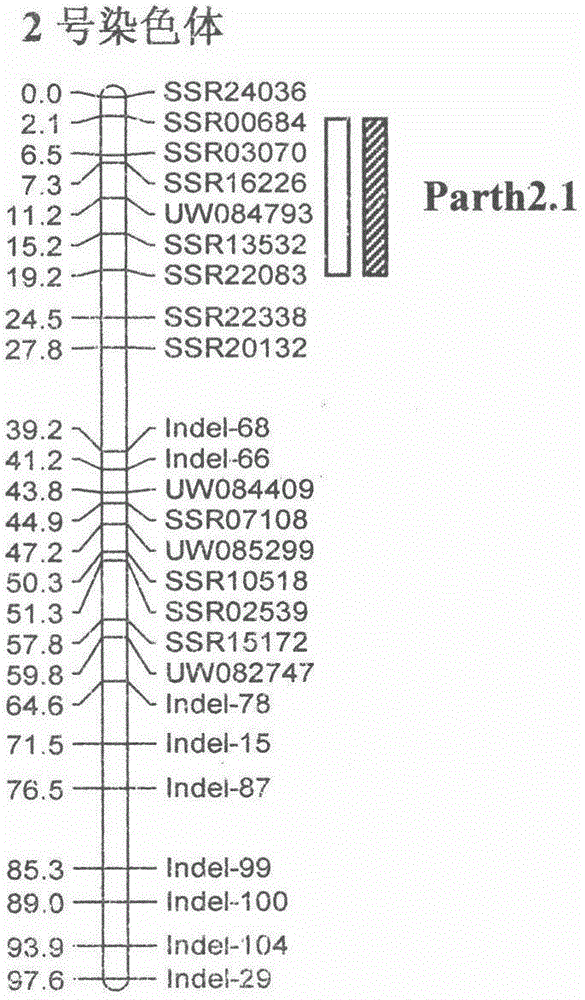
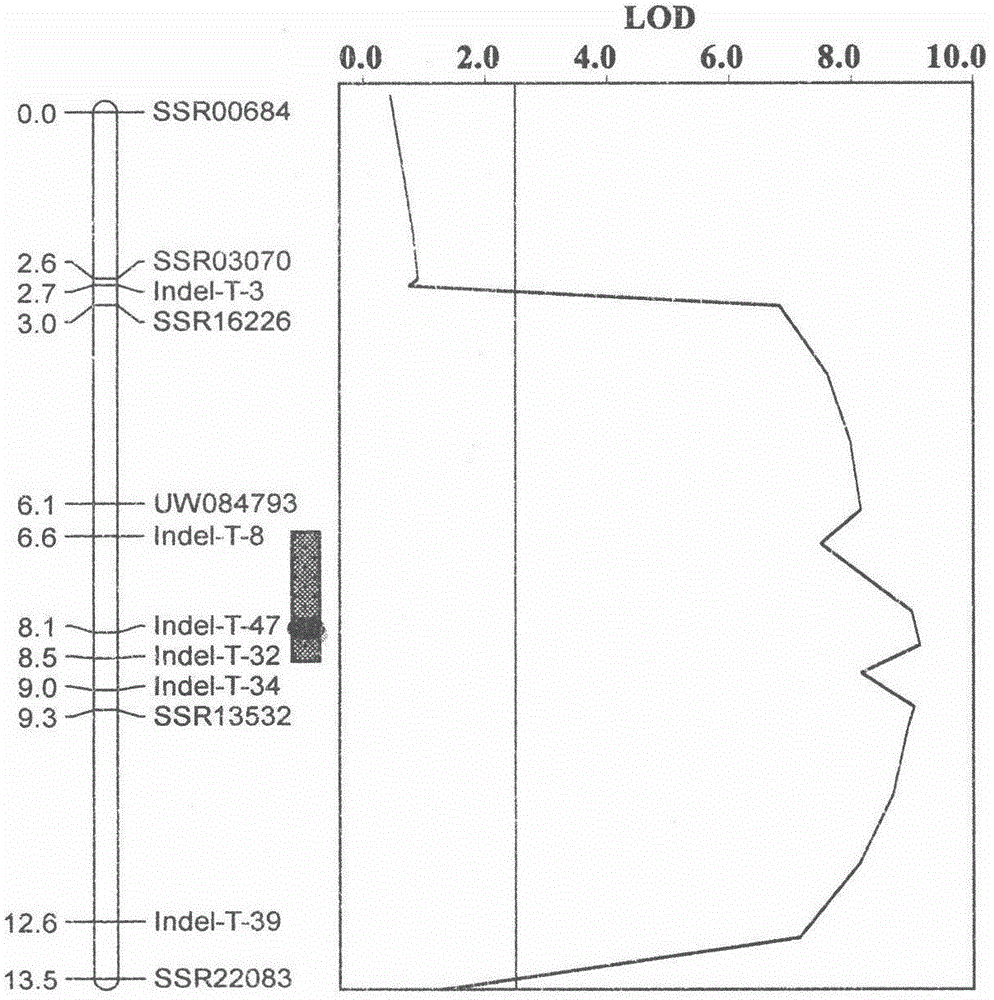
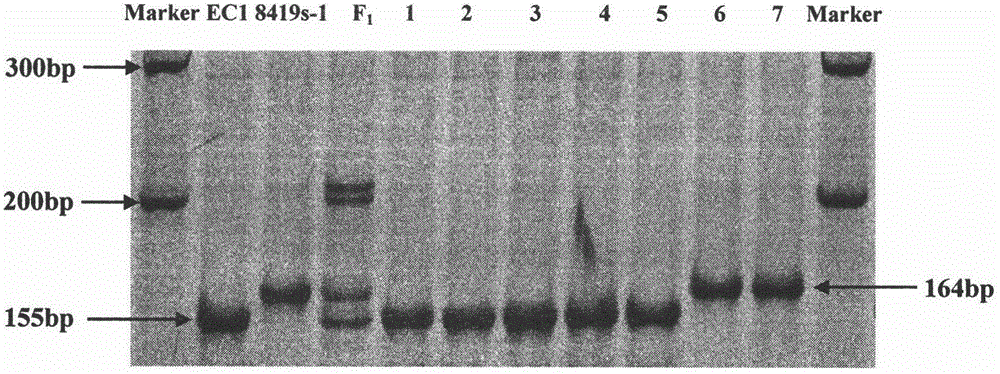
Molecular marker Indel-T-47 for close linkage with cucumber parthenocarpic main-effect QTL (quantitative trait loci)
InactiveCN104789562ASimple methodStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention discloses a molecular marker Indel-T-47 for close linkage with cucumber parthenocarpic main-effect QTL (quantitative trait loci), and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention firstly discloses a molecular marker Indel-T-47 for close linkage with QTL Parth2.1, and further discloses a primer Indexl-T-47F / Indel-T-47R of the marker. In a segregating population containing Parth2.1, the marker is significantly related to parthenocarpy; in an all-female selfing line material containing the Parth2.1, a 155bp product can be amplified from a strong parthenocarpy strain by the marker primer Index-T-47F / Index-T-47R; the marker primer Index-T-47F / Index-T-47R is a peak marker of the Parth2.1, and is closely linked with the Parth2.1. The molecular marker for close linkage with the Parth2.1 disclosed by the invention can be applied to assistant breeding of an all-female cucumber parthenocarpy molecular marker.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com