Patents
Literature
74 results about "Single-strand conformation polymorphism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
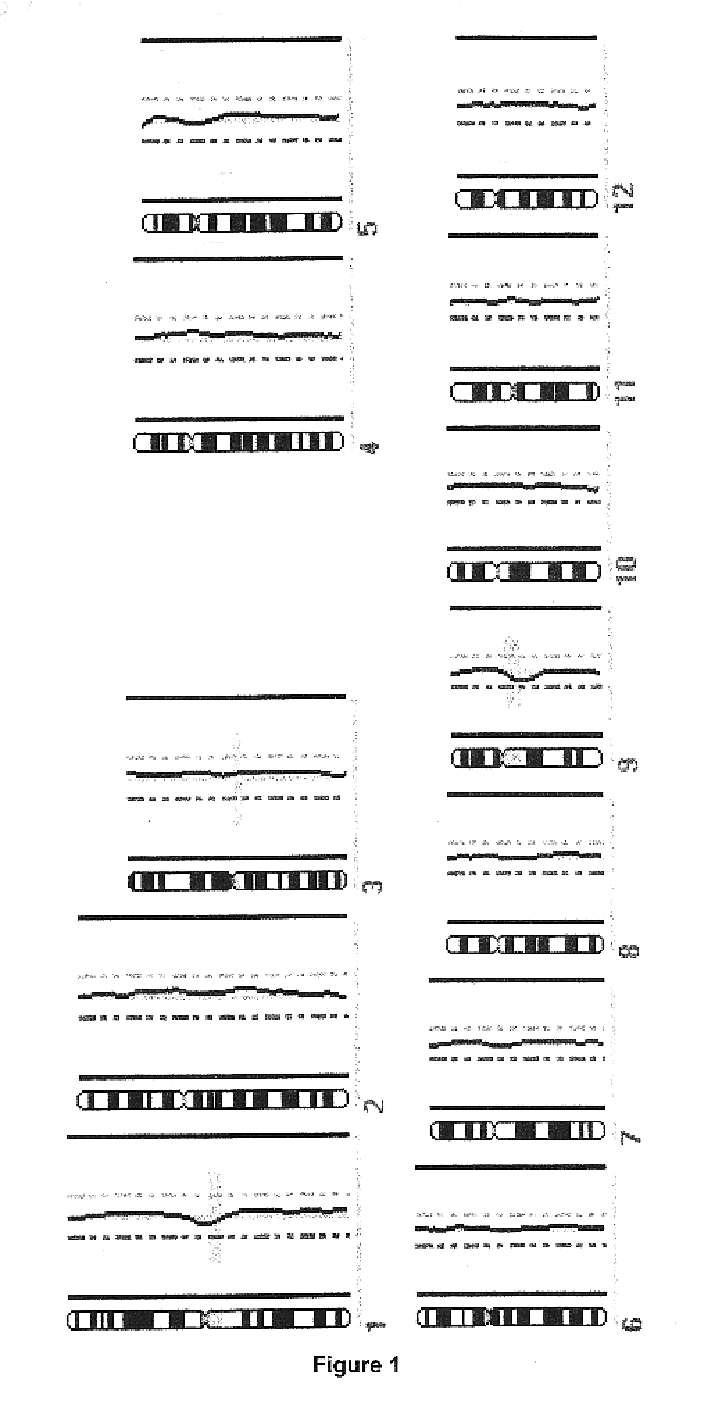
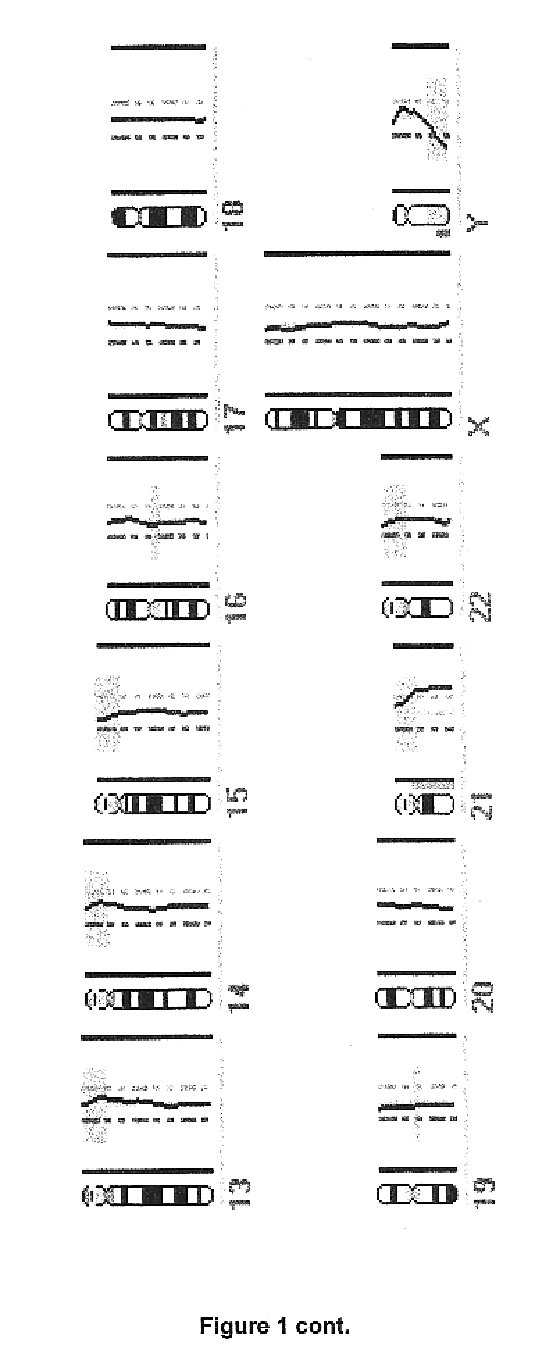
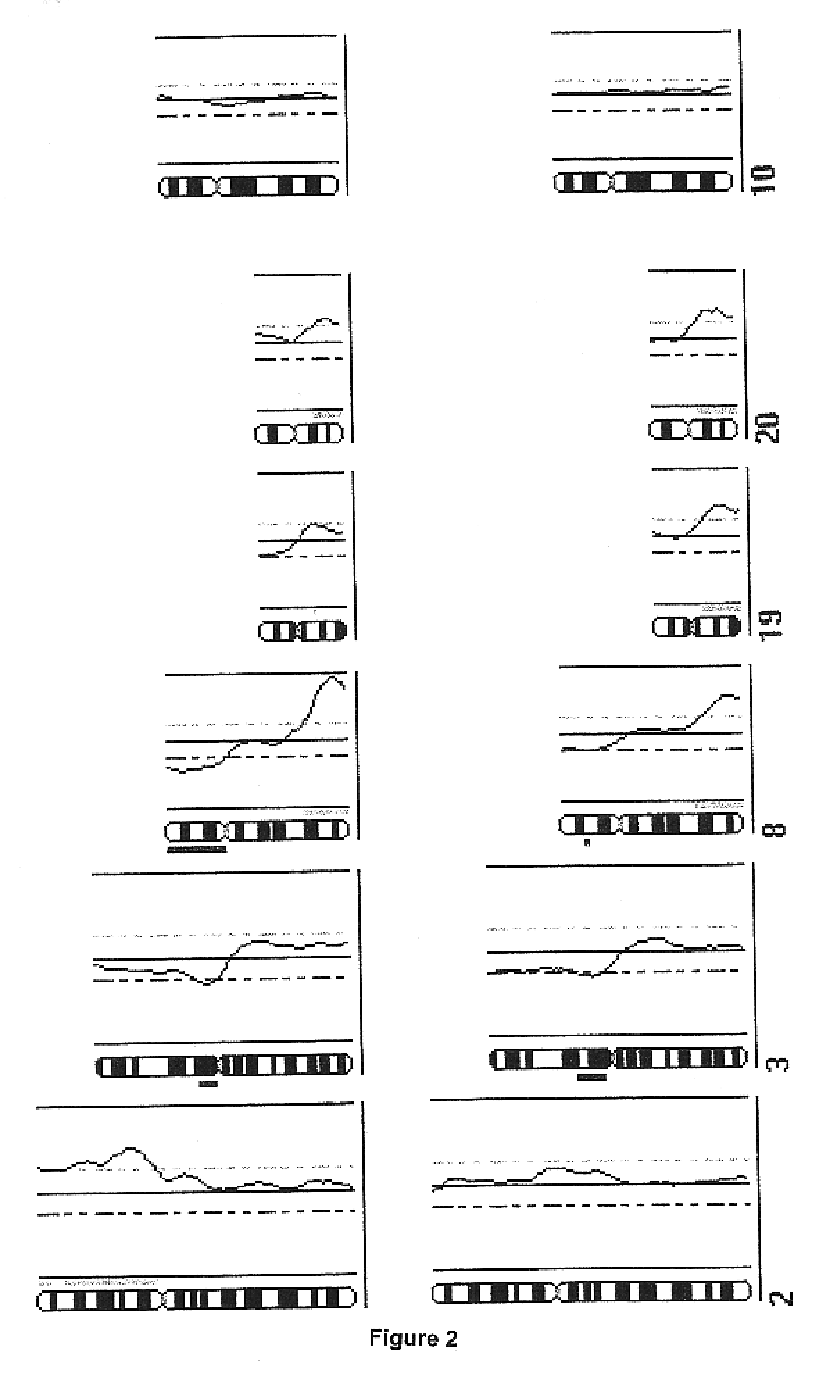
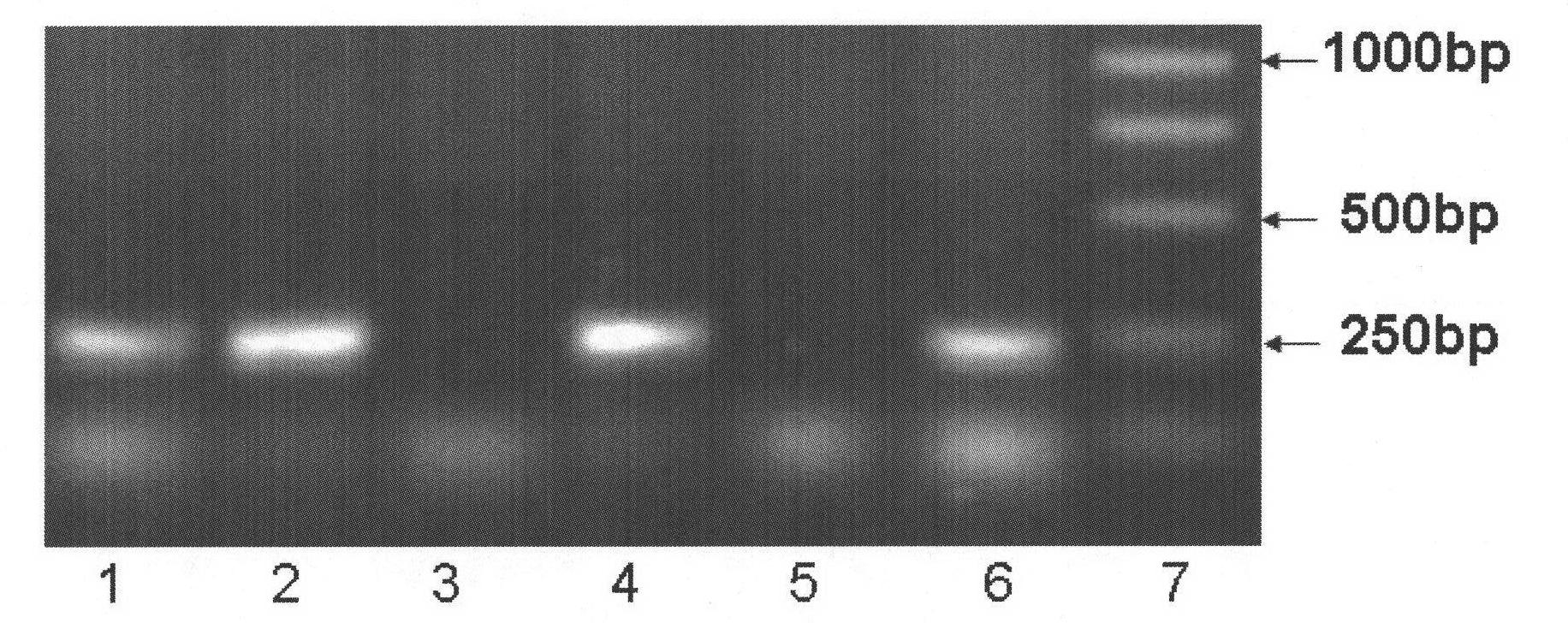
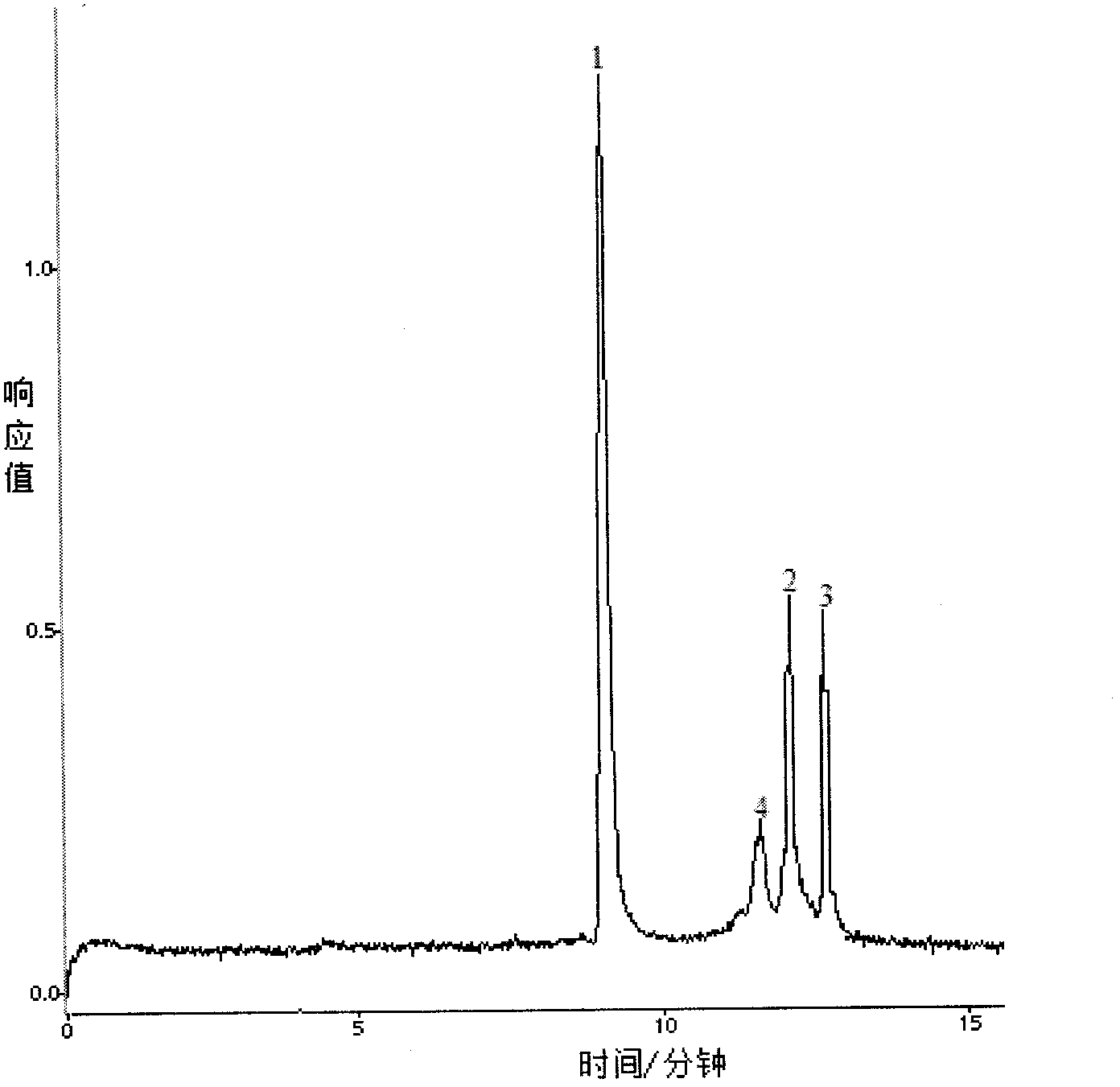
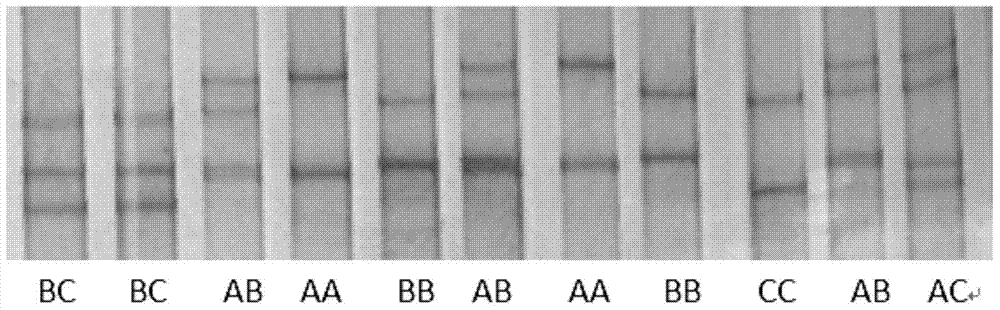
Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP), or single-strand chain polymorphism, is defined as a conformational difference of single-stranded nucleotide sequences of identical length as induced by differences in the sequences under certain experimental conditions. This property allows sequences to be distinguished by means of gel electrophoresis, which separates fragments according to their different conformations.
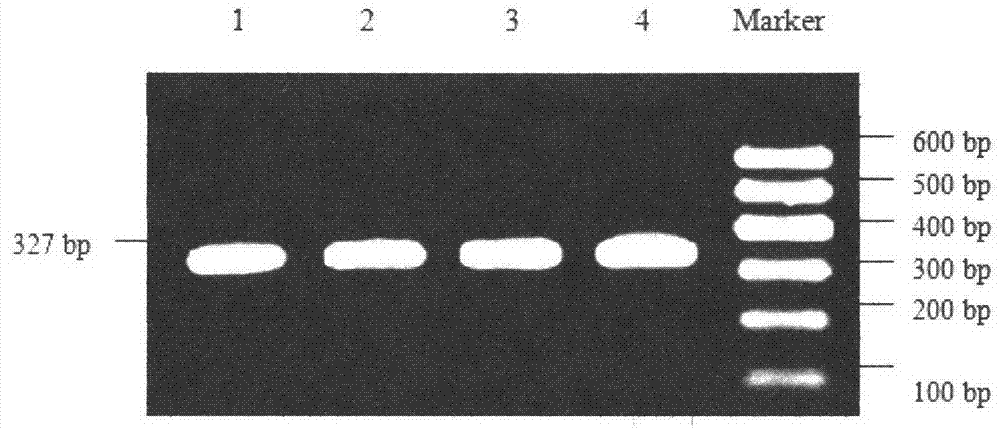
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
SSCP marker closely linked with major wheat scab resistance QTL and application thereof
InactiveCN101892307AReduce the waste of manpower and material resourcesImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismSequence analysis
The invention relates to a single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) marker closely linked with a major wheat scab resistance quantitative trait locus (QTL). The SSCP marker is characterized in that: scab resistance candidate genes of a scab resistance QTL in a 3BS area of a wheat variety or strain resisting scab is PCR amplified by using a primer; after denaturalization, a PCR-amplified product has different single strand conformation; and the SSCP marker closely linked with the major wheat scab resistance QTL is established for detecting a genotype of the wheat variety or strain during breeding. The SSCP marker has the advantages of: overcoming the disadvantages that the wheat scab resistance screening can only be authenticated in a flowering period and is easily influenced by the environment in conventional breeding, predicting and screening wheat plants with the scab resistance by detecting a molecular marker at a seedling stage, eliminating disease plants, reducing waste of labor and materials and improving the breeding efficiency. Compared with an ABI DNA sequence analysis meter-based marker, the SSCP marker closely linked with the major wheat scab resistance QTL has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, low cost and same sensitivity.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveCN102559916AVerify reliabilityExperiment operation is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismIsoniazid resistance
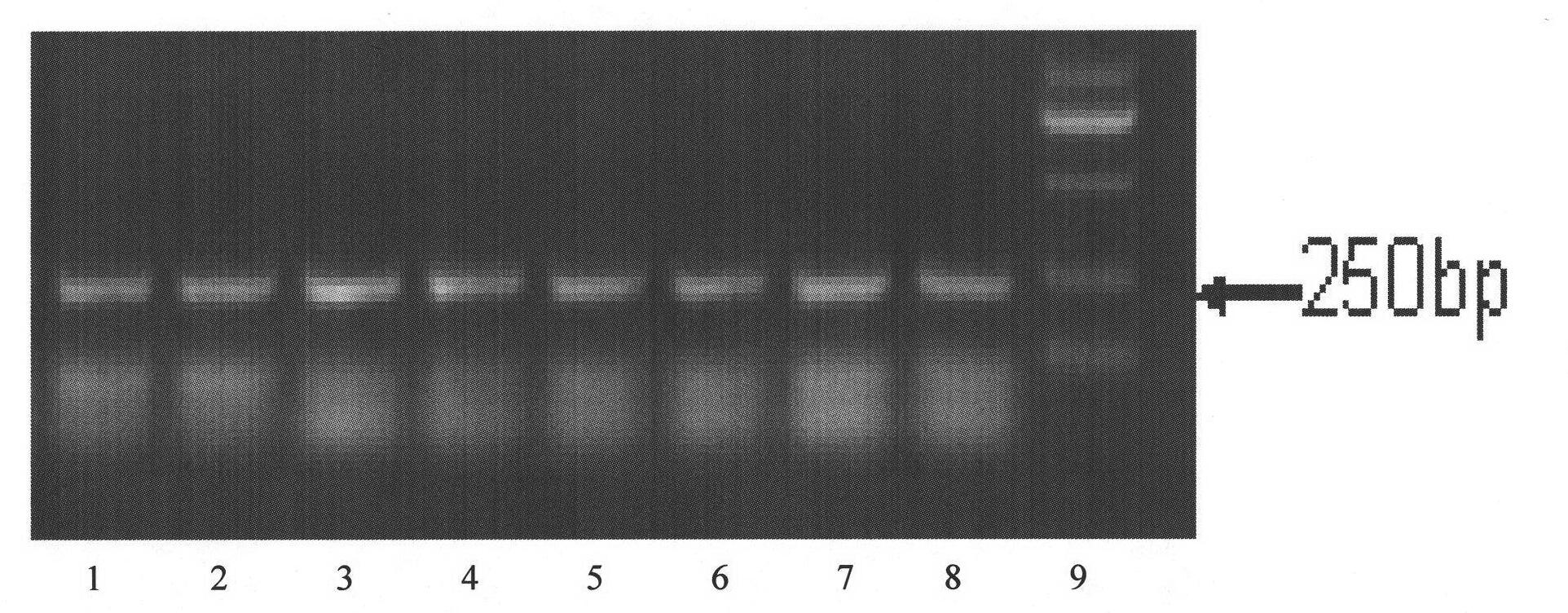
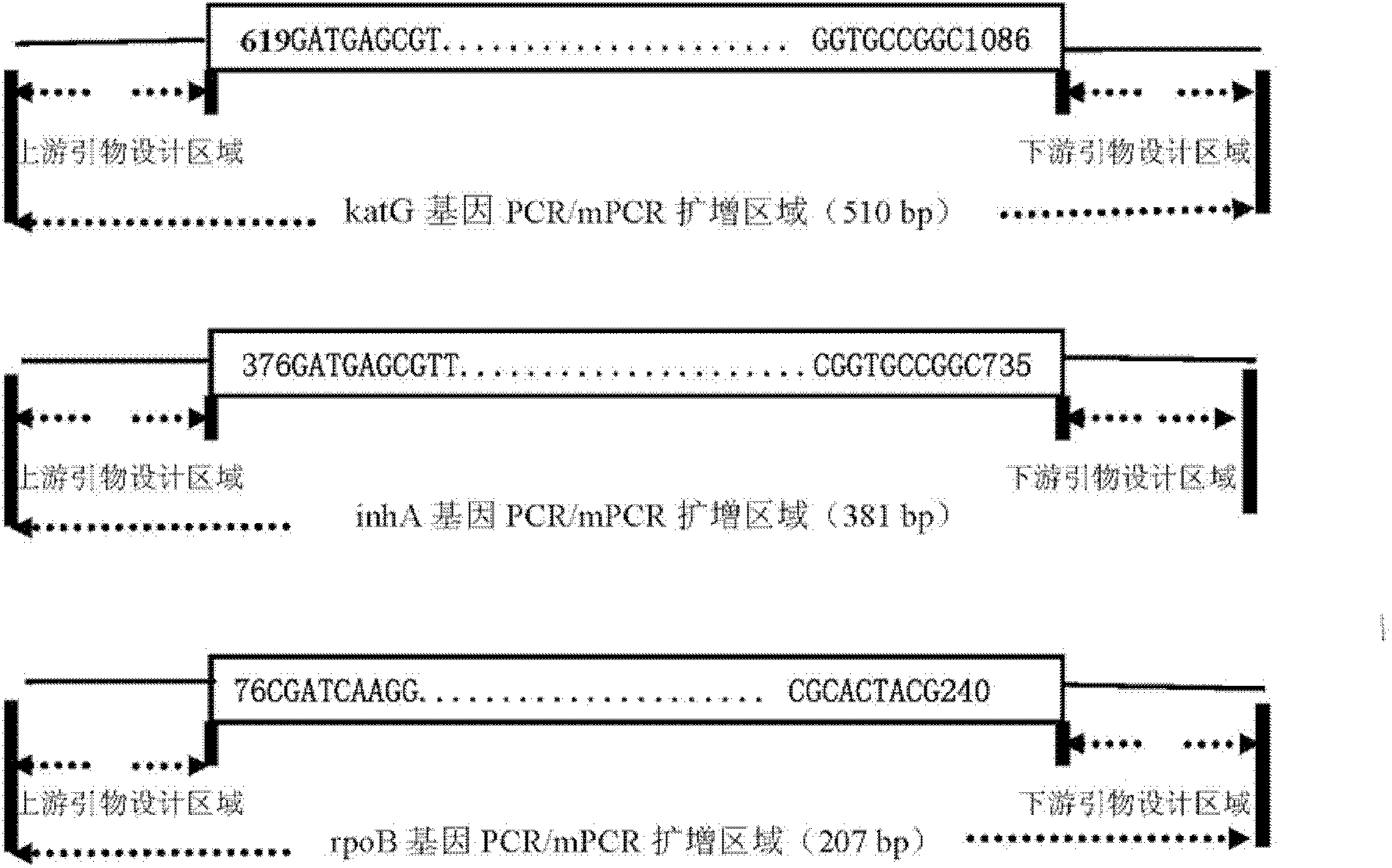
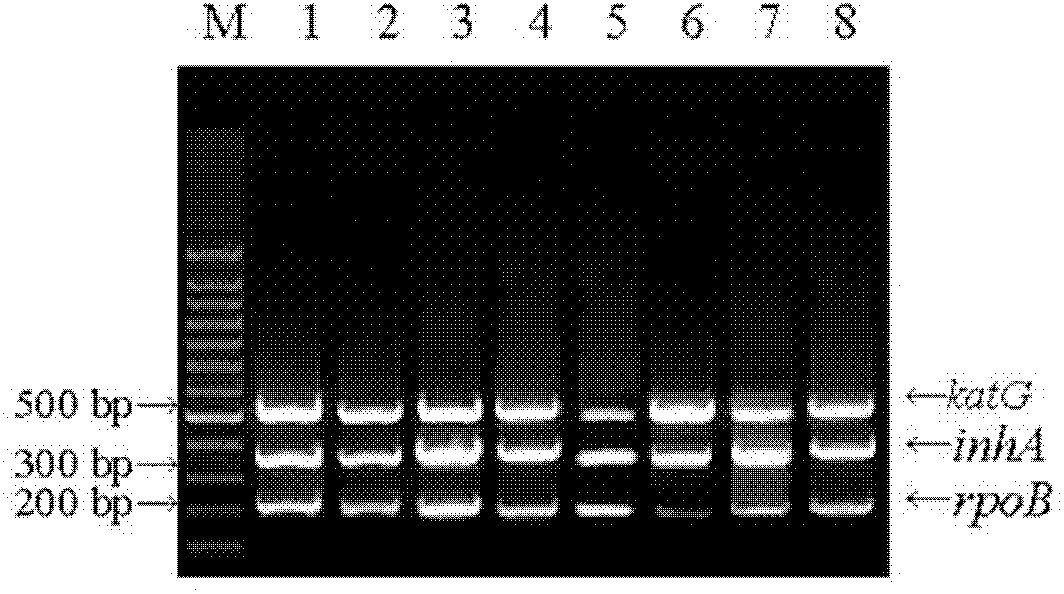
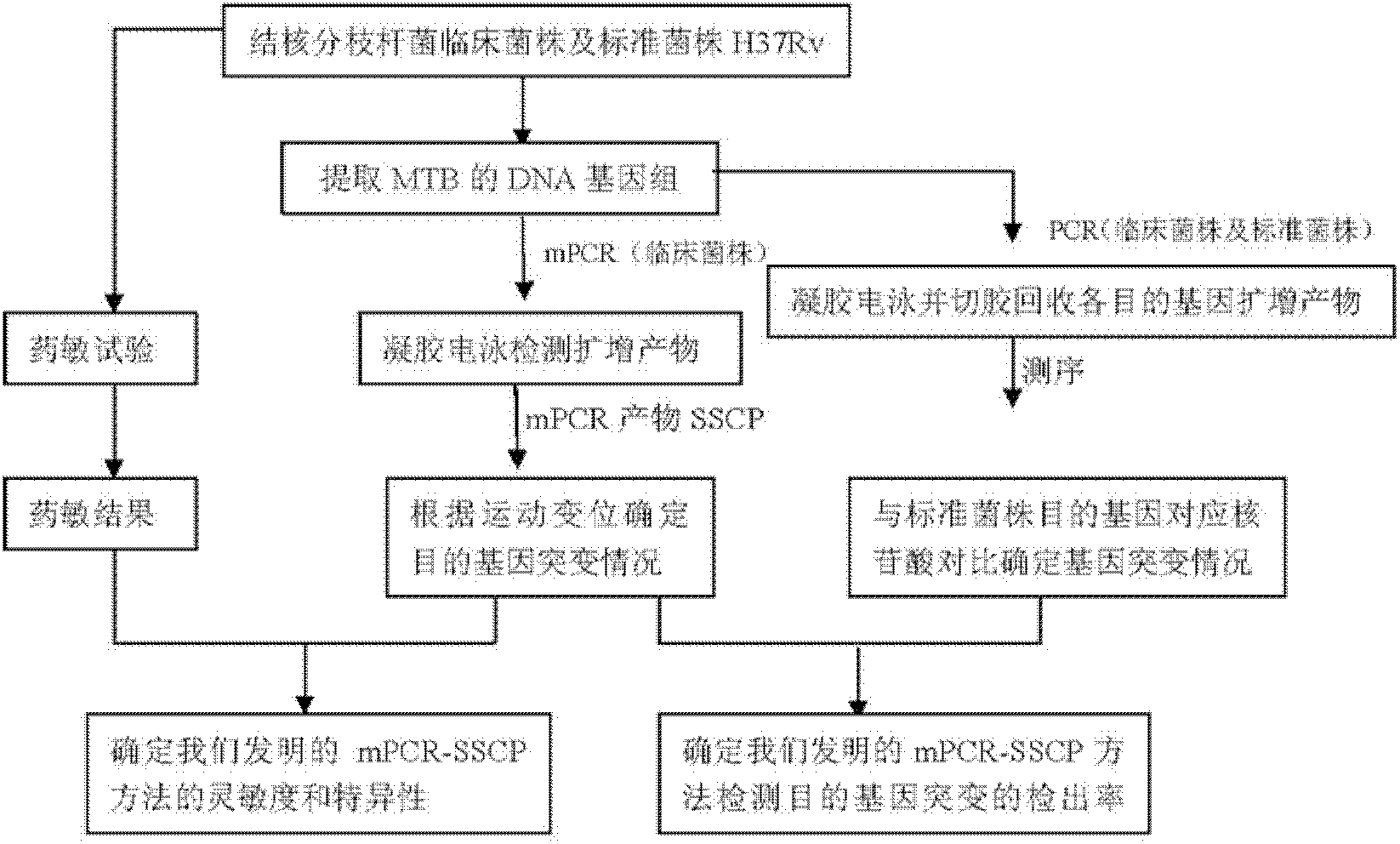
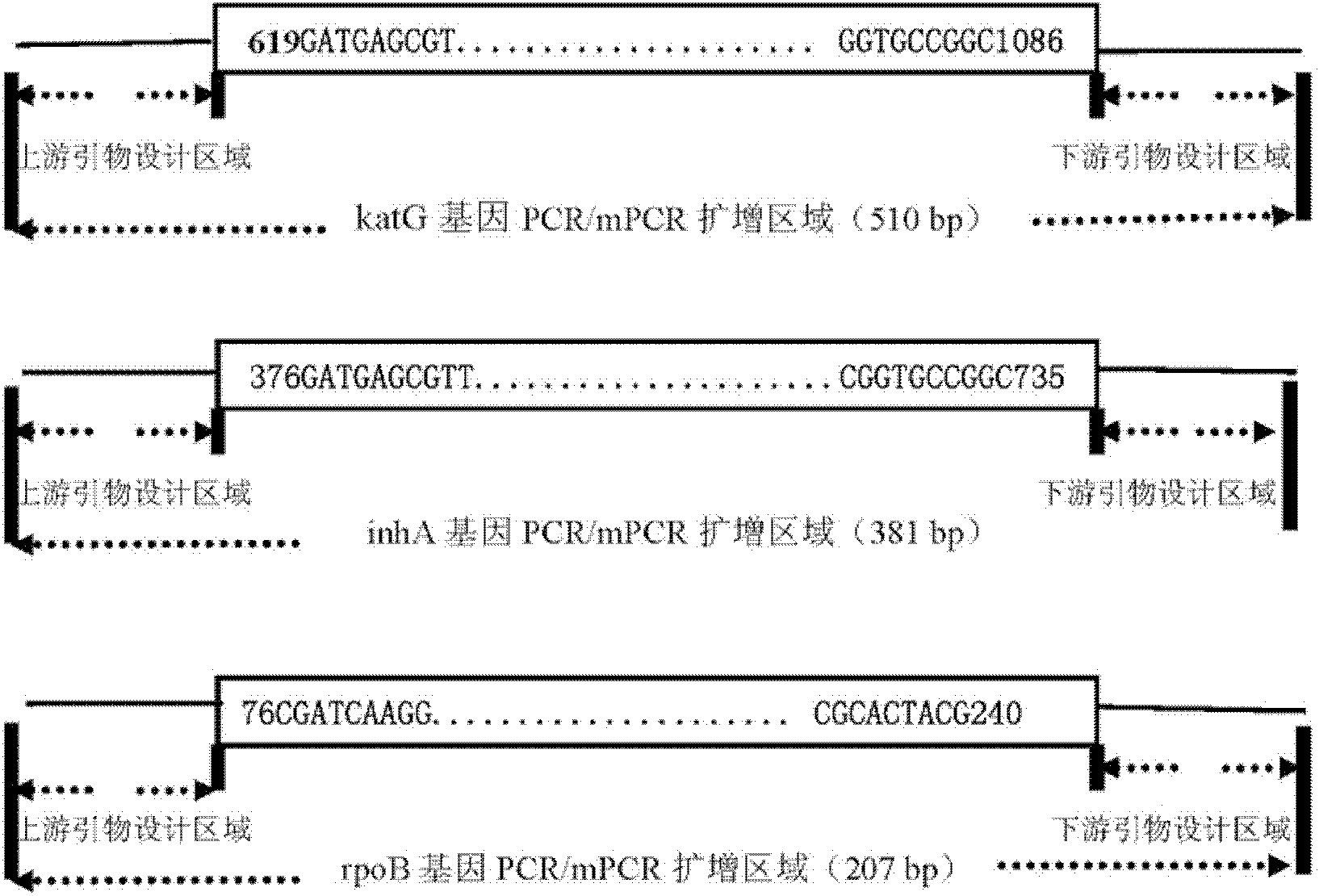
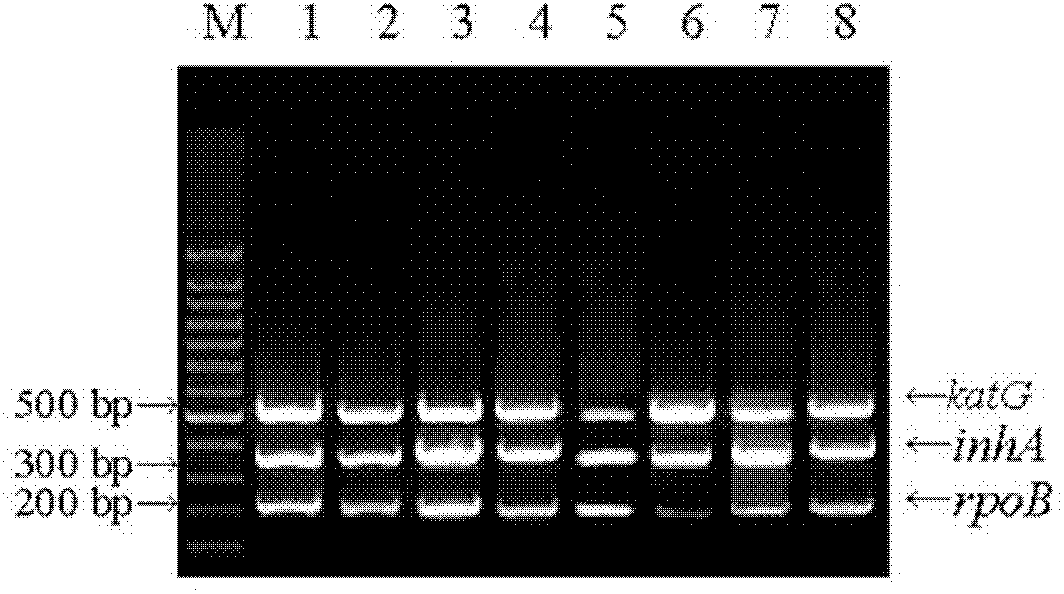
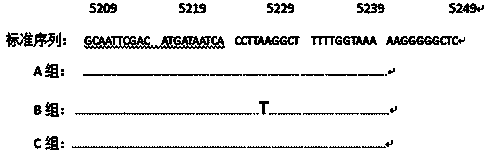
The invention relates to a method for detecting multi-drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which aims at detecting the resistance of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis to isoniazid and rifampicin at the same time and has the characteristics of high specificity and sensitivity, quickness in detection, and easiness and convenience in operation. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: A, establishing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) templates of an MTB clinical strain and a standard strain H37Rv; B, designing three pairs of primers of katG, inhA and rpoB gene fragments which are closely related to the isoniazid resistance and the rifampin resistance, performing mPCR amplification on katG, inhA and rpoB genes of the clinical strain, and performing PCR amplification on katG, inhA and rpoB genes of the clinical strain and the standard strain H37Rv; and C, detecting the mutation conditions of related INH-resistant and RFP-resistant 3 genes of the clinical strain at the same time by a single-strand conformation polymorphism detection method.
Owner:孙爱华 +2
Molecular marker method for breeding meat performance of Aletail sheep and application thereof
ActiveCN103525920AImprove meat performanceIncrease economic incomeMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a molecular marker method for breeding meat performance of Altay sheep and application thereof. The molecular marker method comprises the following steps: using a MyoD1 (Myogenic Determination) gene as a candidate gene which influences meat yield of the Altay sheep; detecting a genetic structure of the MyoD1 gene in the Altay sheep variety by utilizing a PCR-SSCP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Single-strand Conformation Polymorphism) technology; analyzing and judging a correlation between the genetic structure of the MyoD1 gene and the meat yield of the sheet; by a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence of the MyoD1 gene of the sheet, self-designing two pairs of specific primers; carrying out polymorphism detection on the MyoD1 gene of the Altay sheep in Sinkiang province by utilizing the PCR-SSCP technology; and carrying out correlation analysis with meat performance so as to find a molecular marker which is obviously related to the meat yield of the Altay sheep. The molecular marker method is used for improving meat performance of the Altay sheep to greatly improve the speed of improving and recovering excellent meat performance of the Altay sheep and has important significance and practical application value for improving economic income of farmers and herdsmen and quickening development of the mutton sheep industry in Sinkiang province.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Method and kit for detecting correlated mutation allele of total farrow number of sow as well as application
InactiveCN101892318AIncrease in total litter sizeAccurate genotypingMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismGene type
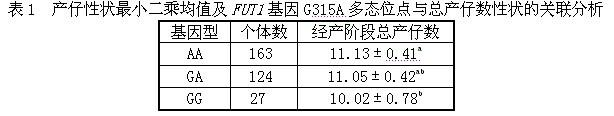
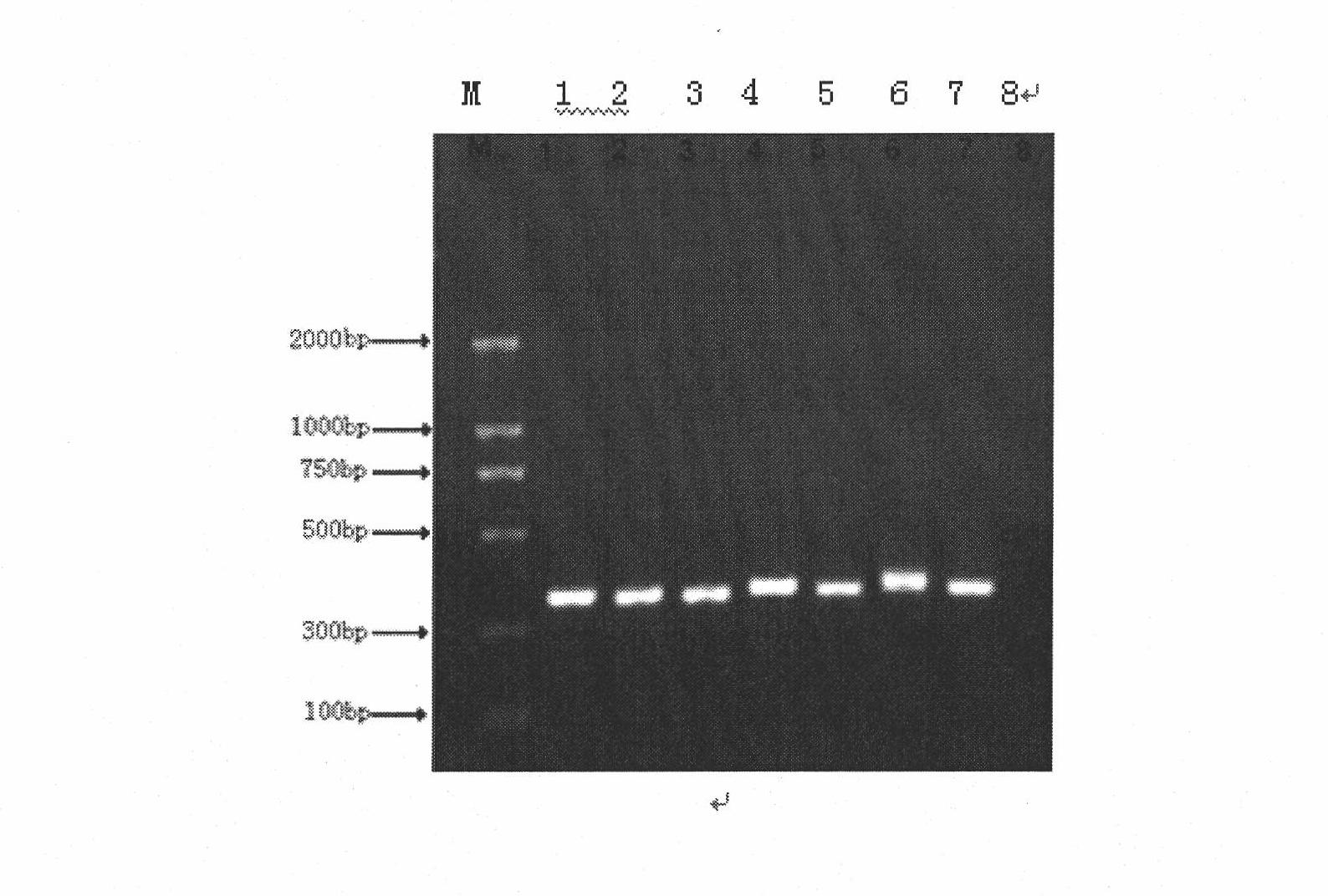
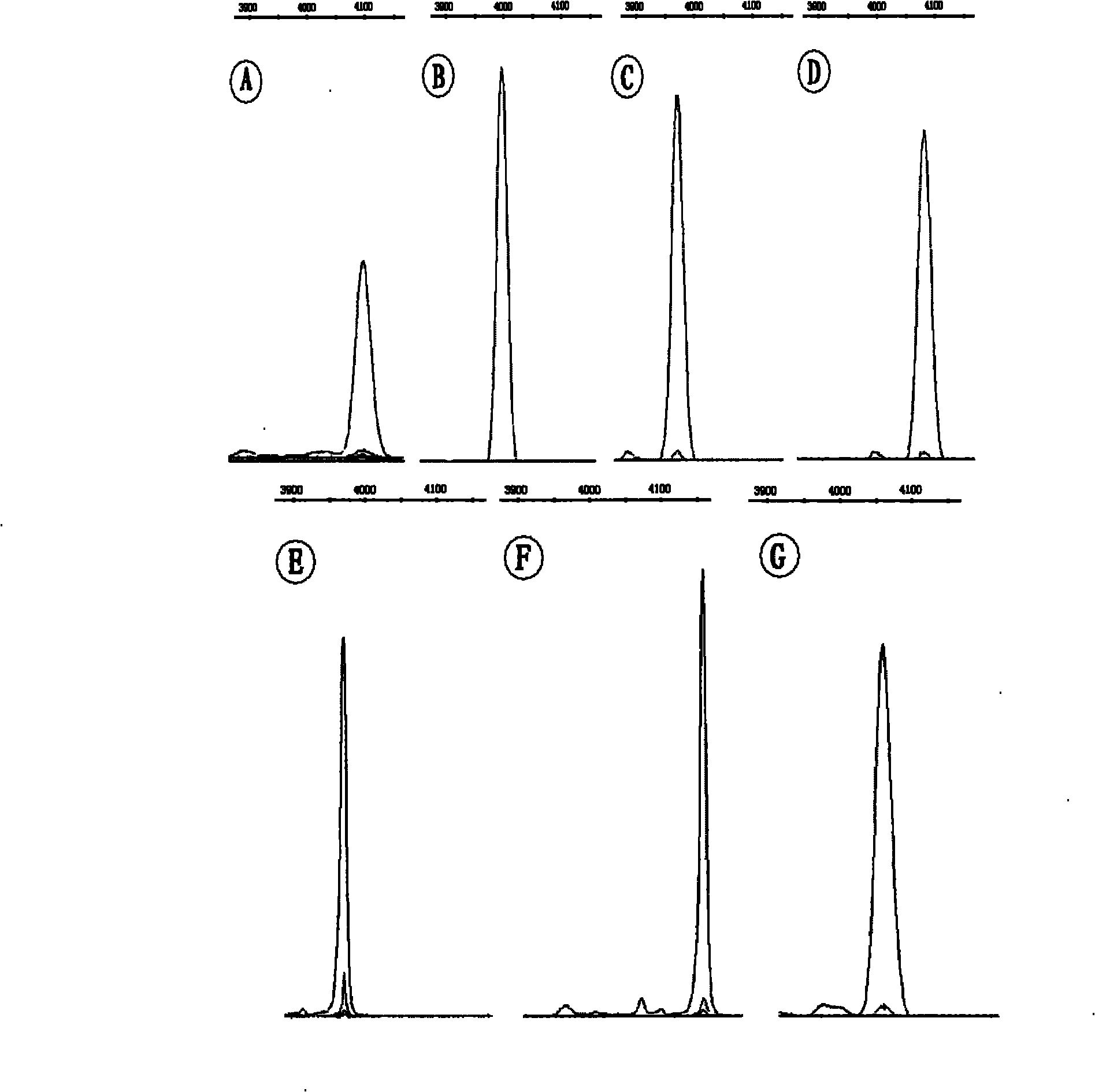
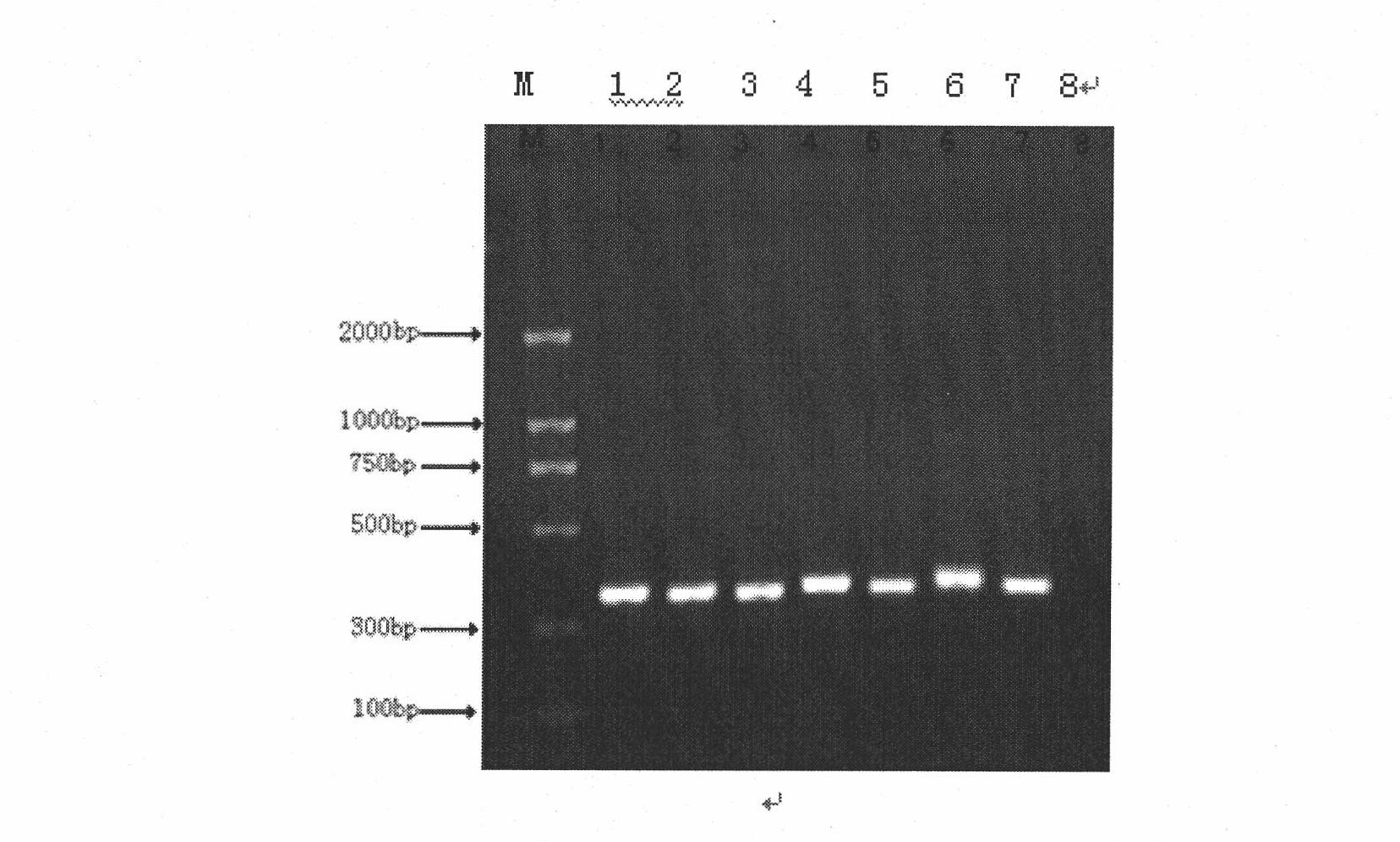
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting the correlated mutation allele of a total farrow number of a sow as well as the application. The method adopts a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)-SSCP (Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism) method, PCR augmentation comprises a section from 315-bit deoxyribonucleotide at the 5' terminal of Gen Bank Accession Number AX752829, PCR augmentation products are detected by gel electrophoresis, and the gene type of the sow to be detected is confirmed according to an electrophoresis result: the gene type of the sow to be detected can be GG or AA which means a homozygote if the electrophoresis result presents two straps, and the gene type of the sow to be detected can be GA which means a heterozygote if the electrophoresis result presents three straps. The detection method of the invention has simple operation, low expense and high accuracy, can realize the automatic direct detection and has higher practical breeding application values. The method and the kit of the invention can be applied to breed grices, early select grices to be selected, effectively solve the problem of long time for selecting excellent grices in practical production, decrease the breeding expense, increase the total sow farrow number and improve the economic benefits.
Owner:BEIJING HEILIU ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TECH
Utilization of nucleotide probes for the measurement of specific mRNA for the molecular diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy
InactiveUS20030049627A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismNucleotide
The present invention concerns the development of a quantitative method for the molecular diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) by measuring the amount of cytosolic mRNA from human muscle cells. Both the procedure using radioactive material and the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) nonradioactive method were developed using 32P-dCTP labeled and biotinylated nucleotide probes. The results obtained demonstrate that the measurement of mRNA could be used as a quantitative method for the molecular diagnosis of SMA. There was a perfect concordance of the results obtained between the procedure using radioactive material, the ELISA method and the single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis regarding the negative and positive SMA samples. The methods developed in this study may be applicable to the diagnosis (detection of homozygous and heterozygous deletions in exons 7 and 8 of the SMN gene) and the control of mRNA concentrations in the future gene therapy of patients with SMA.
Owner:NGUYEN HUYNH MAI THI
Rapid detection method of blood pathogenic bacteria based on CE-SSCP (Capillary Electrophoresis-Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism)
InactiveCN101824470AQuick checkStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention discloses a rapid detection method of blood pathogenic bacteria based on CE-SSCP (Capillary Electrophoresis-Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism). In the rapid detection method, specific to conserved regions of 16SrRNA genes of staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus epidermidis, klebsiella pneumoniae, enterococcus faecalis and streptococcus pneumoniae which are infected by blood, a corresponding PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) general primer is designed and subjected to fluorescence labeling, and then PCR is adopted to carry out amplification and electrophoresis detection on pathogenic bacteria in a blood sample, wherein the length of the designed general primer is suitable to the span of the amplification and has high complementary degree with the DNA of a pathogenic bacteria template in the blood sample to be tested, which enables an amplification product to have good specificity and favorable suitability to same kind of bacterium of different bacterial strains. The method has good repeatability and high sensitivity, can detect trace amount of the DNA of a pathogenic bacteria genome and is very suitable to wide application clinically.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Goat SH2B1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism loci and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102703440AAvoid instabilityLeak detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle-strand conformation polymorphismA-DNA
The invention discloses goat SH2B1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci and a detection method of the loci. The goat SH2B1 gene is subjected to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with the goat full-genome DNA to be detected comprising the SH2B1 gene as a template and a primer pair of P1 and P2 as primers, and SSCP (single-strand conformation polymorphism) detection is carried out. The gene polymorphism loci comprise the polymorphism that the 4356th site of the goat SH2B1 gene is T or C base, and the polymorphism that the 6033th site of the goat SH2B1 gene is G or A base. According to the goat SH2B1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci and a detection method of the loci provided by the invention, PCR product mixed sequencing for screening SNP and PCR-SSCP are combined, so that the SSCP instability is solved and the missed detection of the mutant site is eliminated; and the detection method is simple, rapid, low in cost, high in precision, and convenient for popularization and application, can be used for screening and detecting genetic markers closely related to goat growth traits on a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) level, and can be used for assisted selection and molecule breeding of the goat.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting tumor mutant gene in blood
InactiveCN102251046AGuaranteed accuracyGood temperature control systemMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAbnormal tissue growthSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention relates to a method for detecting a tumor mutant gene in blood. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a polyethylene oxide sieving medium containing TBE (Tetrabromoethane); (2) extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in a blood sample; (3) amplifying a gene target fragment needing to be detected: performing conventional PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking the genome DNA as an amplifying template to obtain a p53 gene PCR amplification sample and a k-ras gene PCR amplification sample; (4) treating the samples: performing denaturation or enzyme digestion on the p53 gene PCR amplification sample and the k-ras gene PCR amplification sample to obtain a denatured sample solution and an enzyme digestion solution respectively; and (5) detecting the samples: adding a 10*SYBR Green I fluorescence dye and the genome DNA into the denatured sample solution and the enzyme digestion solution respectively, uniformly mixing, adding deionized water till a system is 30-50 mu l, automatically filling the polyethylene oxide sieving medium by using a capillary electrophoresis apparatus pressure system and performing CE-SSCP (Capillary Electrophoresis-Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism) detection or CE-RFLP (Capillary Electrophoresis-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) detection respectively. The method is easy to operate, and has high repeatability.
Owner:王荣
Yak meat tenderness candidate gene detection kit and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103866002AImproved meat tendernessRapid responseMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle-strand conformation polymorphismCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention relates to a yak molecular marker-assisted breeding technology in the technical field of animal biology and specifically relates to a yak meat tenderness candidate gene detection kit. The yak meat tenderness candidate gene PCR (polymerase chain reaction)-SSCP (single-strand conformation polymorphism) detection kit is characterized by comprising a PCR solution, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) standard samples of CAPN3*B and CAPN3*C, an SSCP detection reagent, deionized water, 10% of ammonium persulfate, a loading denaturation buffer solution, TEMED (N, N, N', N'-tetramethylethylenediamine) and 12% of non-denatured polyacrylamide gel, wherein Arc: Bis in the non-denatured polyacrylamide gel is 37.5: 1; the loading denaturation buffer solution comprises 98% of deionized formamide, 0.025% of bromophenol blue, 0.025% of xylene cyanol FF and 10mmol / L of EDTA (ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid) with pH value of 8.0. The yak meat tenderness candidate gene detection kit provided by the invention has the characteristics of high speed in molecular marker breeding of yak, high sensitivity, low cost and the like.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting depression sheep fecundity
InactiveCN102643914AMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismGenotype determination
The invention discloses a method for predicating the depression sheep fecundity by Fec genes. According to the method, the 746th site nucleotide of the Fec genes in the depression sheep genome to be detected is detected, so the genotype of depression sheep is determined, and then, the depression sheep fecundity is determined through the genotype; when the 746th site nucleotide of the Fec genes in the depression sheep genome is A, the homozygote genotype is ++, and when the 746th site nucleotide of the Fec genes in the depression sheep genome is G, the homozygote genotype is BB; the heterozygote genotype is B+; the fecundity of the BB genotype is higher that of the B+ genotype, and the fecundity of the B+ genotype is higher than that of ++ type. The method has the advantages that the depression sheep fecundity is determined through polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) and PCR-restricted fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) genetic marker polymorphism, the depression sheep fecundity can be fast, simply and conveniently detected, and a method for accurately, simply and conveniently detecting the depression sheep fecundity is provided for the depression sheep breeding.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for detecting CVM deleterious gene of oxen
InactiveCN1958810AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSingle-strand conformation polymorphismAgricultural science
This invention provides a method for detecting genes related to milk cow complex vertebral malformation (CVM). The method comprises: (1) designing and synthesizing a pair of primers shown in SEQ ID No.1 and 2; (2) performing PCR on a bovine DNA sample with the primers, and annealing at 57 deg.C to obtain the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3; (3) performing single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis, and determining according to the result of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The method is simple, rapid ad accurate. According to the method, relevant test kit can be developed. This invention can be used for dividing and screening the genes related to milk cow CVM, and breeding milk cows.
Owner:北京奶牛中心
Separation and identification method of cow mastitis pathogens
InactiveCN103642925AEfficient identificationIdentification is simple and economicalMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismSequence analysis
The invention relates to a separation and identification method of cow mastitis pathogens. Separation and identification on the Chinese Holstein cow mastitis pathogens are carried out by adopting a traditional bacterial culture method and a sequence analysis method and a double-primer polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) technology on the basis of pathogen 16S rRNA (ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid) genes. The identification result of the double-primer PCR-SSCP technology is basically the same as that of the sequence analysis method. The result of the double-primer PCR-SSCP technology is good in polymorphism, and is similar to the sequence analysis result. The separation and identification method is an efficient, simple and economic method for identifying the pathogens, and a theoretical foundation is provided for rapid identification of the Chinese Holstein cow mastitis pathogens. Thus, a theoretical basis is provided for diagnosis and treatment of cow mastitis.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Detection method and detection kit for goat LMCD1 gene mononucleotide polymorphism sites
InactiveCN104450934ALow costHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a detection method and detection kit for goat LMCD1 gene mononucleotide polymorphism sites. The method comprises the following steps: by using to-be-detected goat genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of containing LMCD1 gene as a template, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the goat LMCD1 gene, and carrying out SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) polymorphism detection. The gene polymorphism sites comprise the following base polymorphisms: the 681st site of the goat LMCD1 gene is A or G; and the 2825th site of the goat LMCD1 gene is C or T. The invention provides a simple quick low-cost high-precision detection method, which can be conveniently applied to screening and detecting of genetic markers closely related to goat growth traits at the DNA level and can be used for assisted selection and molecular breeding of goat.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
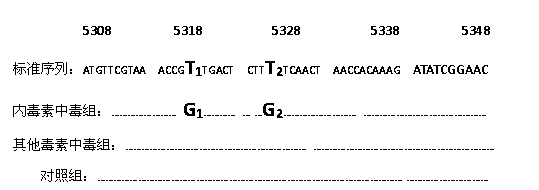
Method for detecting endotoxin poisoning of livestock by mutation of host liver mitochondrial gene
InactiveCN103993080AReduce testing costsLower risk of deathMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a method for detecting endotoxin poisoning of livestock by mutation of host liver mitochondrial gene, which saves time and effort and has credible results. According to the method, host liver mitochondrial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is extracted, a gene specific primer of mitochondria cytochrome C oxidase (COI) is designed, and a liver COI gene segment is analyzed and sequenced by a PCR-SSCP (polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism) technology; and if a sample PCR stripe of a livestock poisoned by endotoxin swims abnormally, and the sequenced COI gene segment is subjected to T-G replacement point mutation simultaneously at 5322 and 5331, the host body is poisoned by the endotoxin and has toxic effect. The method has good repeatability, specificity and sensibility, and has good application value.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
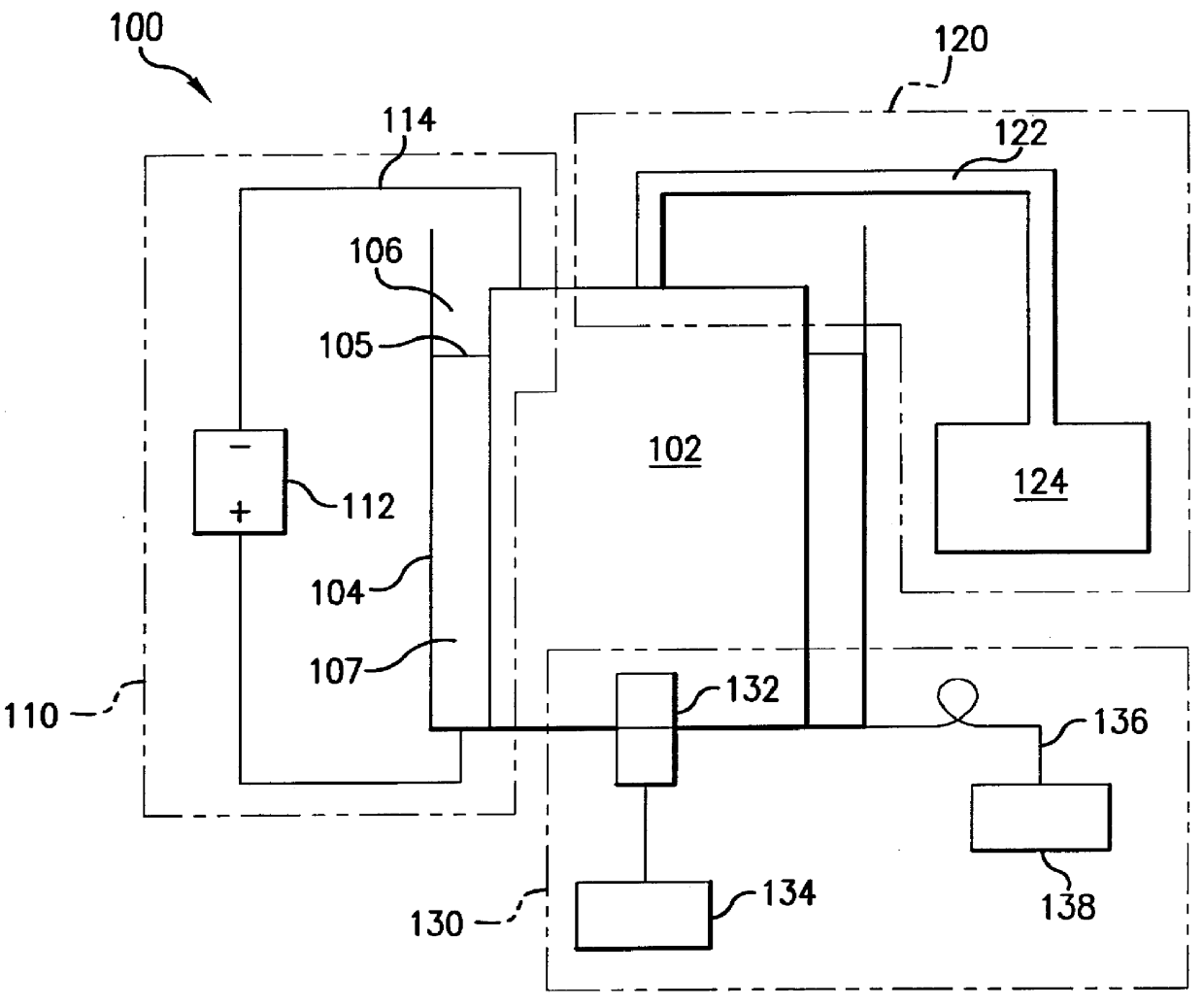
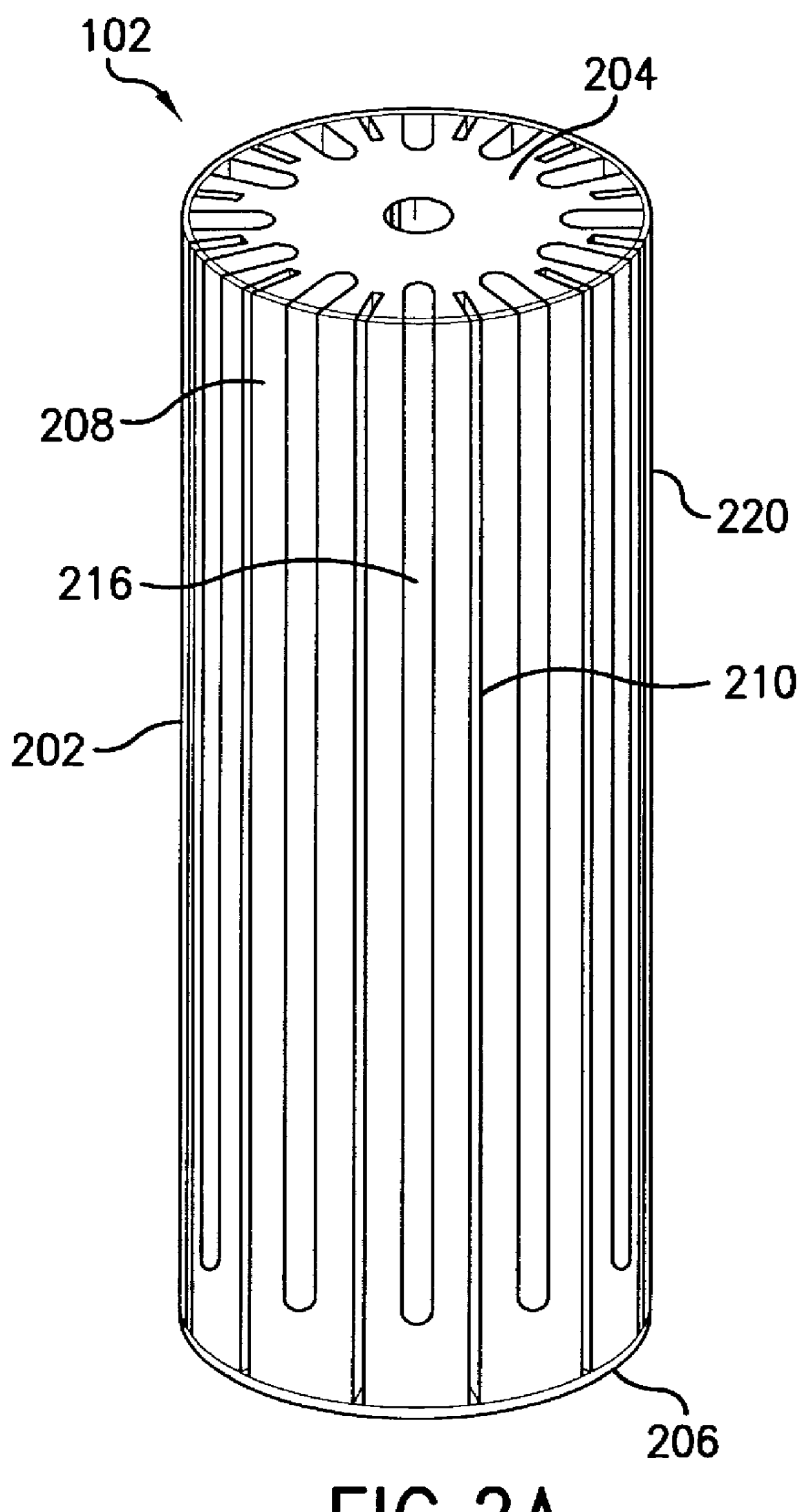
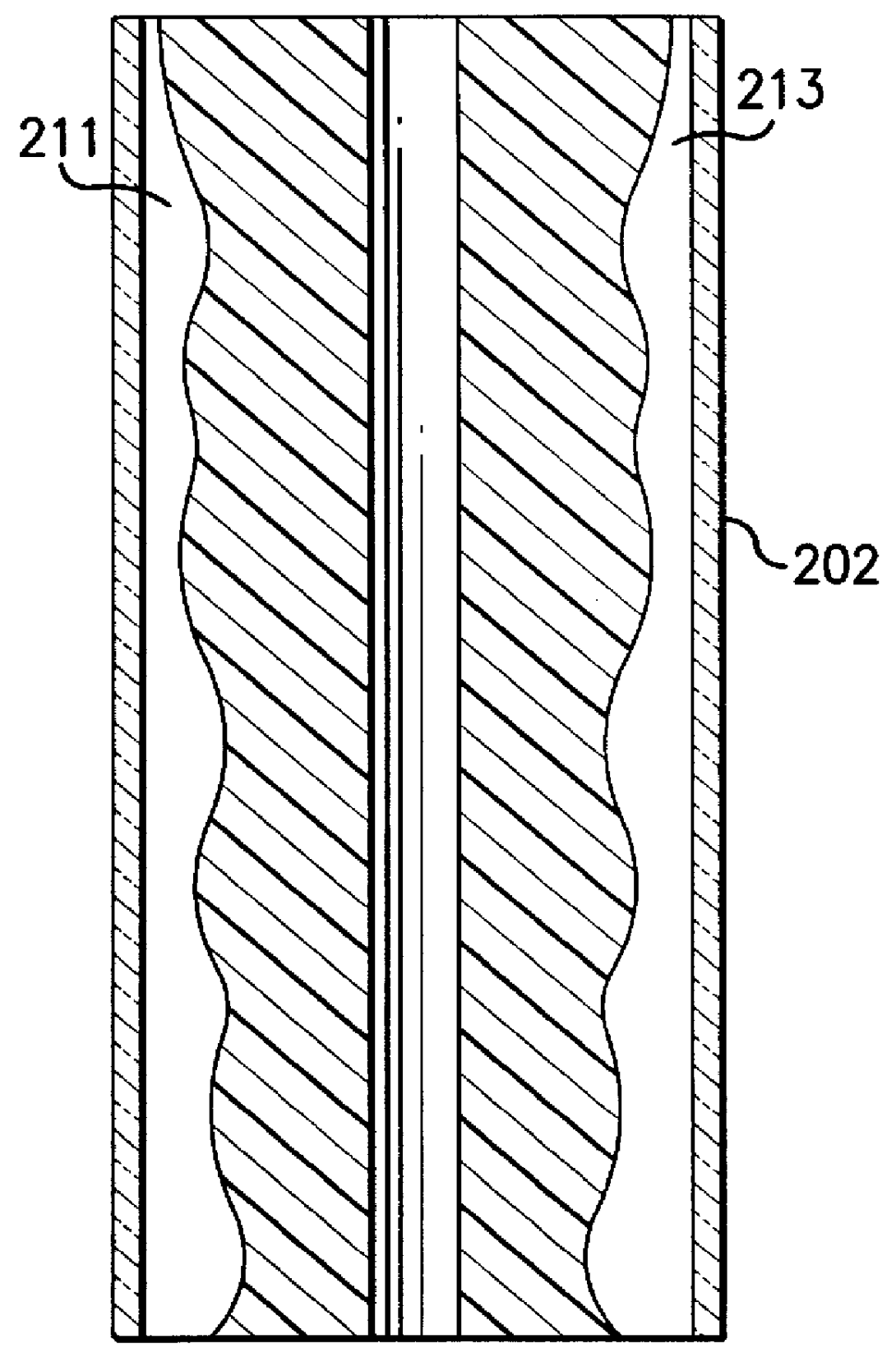
Electrophoresis sequencing apparatus
InactiveUS6113767AAvoid short lengthHigh resolutionCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismFluorescence
A compact, low cost, automated electrophoresis apparatus provides for the optical detection of multiple DNA samples. A substantially cylindrical gel cartridge houses multiple sample lanes that are sealed on the outer periphery by a shrink tube, which allows for straightforward gel casting, as well as for the pre-casting of sequencing gels. The radial column design of the gel cartridge also facilitates the use of a light source to illuminate one or more sample lanes at the same time. The radial column design further provides for an increased sample lane depth that allows for reading through a greater optical path length of the migrated samples, yielding greater optical signal strength, and an increased signal to noise ratio. The gel lanes can be designed to vary in depth as a function of longitudinal length, allowing for a variable current density. Additionally, this radial design allows for different types of optical detection techniques to be performed on the sample, including transmittance and fluorescence. A system of cooling channels incorporated into the radial column design allows for a coolant to be recirculated in the cooling channels between the actual running sample lanes for better lane-to-lane thermal control. This cooling system allows higher operating voltages and facilitates the use of multiple thermal zones, as required, for instance, for single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) applications.
Owner:APOGEE DESIGNS
Specific primers and typing method of class II MHC (major histocompatibility complex) genes for antibacterial potential detection of alligator sinensis
InactiveCN105316409AAvoid wastingShort experiment cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention relates to a pair of single-locus specific primers for amplifying class II major histocompatibility complex genes for antibacterial potential detection of the alligator sinensis and a typing method, wherein the specific sequences of the primers are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-SEQ ID NO. 2. The amplification primers disclosed by the invention are stable in single-locus specific amplification capacity in an alligator sinensis population; a product obtained from amplification can conduct genotyping on various individuals through a subsequent single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) experiment, so that the polymorphism of the class II MHC genes of alligator sinensis individuals in the population is assessed and the potential of the alligator sinensis individuals in resisting bacterial diseases is detected; therefore, an important reference is provided for such operations of new population founder selection, reintroduction individual selection, artificial mating selection and the like in alligator sinensis protection work.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection method by using PRSS2 gene as lactoprotein content molecular marker
ActiveCN105567863AHighly linkedAvoid cumbersomenessMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismCorrelation analysis
The invention discloses a detection method by using a PRSS2 gene as a lactoprotein content molecular marker. The method comprises the following steps: 1. carrying out whole genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction on bovine blood, and inspecting the DNA quality by agarose gel electrophoresis; 2. carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the bovine PRSS2 gene segment by using the whole genome DNA as a template and a primer A as the primer; 3. carrying out mixed-cell PCR on the whole genome DNA to detect the polymorphism sites; and 4. carrying out sequencing on an individual sample, and carrying out polymorphism correlation analysis according to the sequencing result. The method is utilized to detect the relevance between 5 SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) sites and lactoprotein traits in the bovine milk quality. The invention provides a simple quick genetic marker for screening and detecting close relevance to bovine milk quality traits on the DNA level, and the genetic marker can be used for bovine molecular breeding. The method solves the problem of high complexity in the SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) and PCR-PFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) techniques, and enhances the accuracy and precision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Molecular marking method for indicating Qinchuan cattle meat tenderness and water-holding capacity by utilizing THRSP (thyroid hormone responsive spot) genes
InactiveCN103740830AFast improvementBroad development prospectsMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismThyroid hormones
The invention relates to a molecular marking method for indicating Qinchuan cattle meat tenderness and water-holding capacity by utilizing THRSP (thyroid hormone responsive spot) genes. The method comprises the steps of designing a pair of primers according to a cattle THRSP gene sequence, executing the SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) band type detection on Qinchuan cattle whole-blood genomic group DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) after PCR proliferation, and determining the Qinchuan cattle meat tenderness and the water-holding capacity by analyzing the band type. By adopting the PCR-SSCP technology and analyzing and comparing the variation point gene type, the meat quality of the cattle can be predicted and determined; the molecular marking method is simple to operate, low in expense, high in precision and capable of realizing rapid detection.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveCN102559916BVerify reliabilityExperiment operation is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismIsoniazid resistance
The invention relates to a method for detecting multi-drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which aims at detecting the resistance of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis to isoniazid and rifampicin at the same time and has the characteristics of high specificity and sensitivity, quickness in detection, and easiness and convenience in operation. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: A, establishing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) templates of an MTB clinical strain and a standard strain H37Rv; B, designing three pairs of primers of katG, inhA and rpoB gene fragments which are closely related to the isoniazid resistance and the rifampin resistance, performing mPCR amplification on katG, inhA and rpoB genes of the clinical strain, and performing PCR amplification on katG, inhA and rpoB genes of the clinical strain and the standard strain H37Rv; and C, detecting the mutation conditions of related INH-resistant and RFP-resistant 3 genes of the clinical strain at the same time by a single-strand conformation polymorphism detection method.
Owner:孙爱华 +2
SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) detecting method for animal liver bacterial toxin contamination
InactiveCN103993086AEnsure safetyImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismMotility
The invention discloses an SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) detecting method for animal liver bacterial toxin contamination, relates to the biological technical field and particularly relates to a detecting method for animal liver bacterial toxin contamination. According to the method, an SSCP technology is utilized to detect gene mutation of animal liver mitochondria contaminated by bacterial toxin, so that the technology is applied to evaluating and identifying animal food safety. Main steps comprise extracting host liver mitochondria DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), amplifying the liver mitochondria tRNACys-Tyr gene segment by applying PCR(polymerase chain reaction)-SSCP technology, detecting a stripe with abnormal swimming motility by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, sequencing after purifying the stripe, and indicating that the animal food is contaminated by the bacterial toxin if the tRNACys -Tyr gene segment is inserted with insertion mutation of a basic group T at the 5238th and 5239th basic groups. The SSCP detecting method disclosed by the invention can be used for solving the defects of the conventional detecting method, and is quick, accurate, specific, sensitive, good in repeatability, low in detecting cost and easy for popularization and application.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
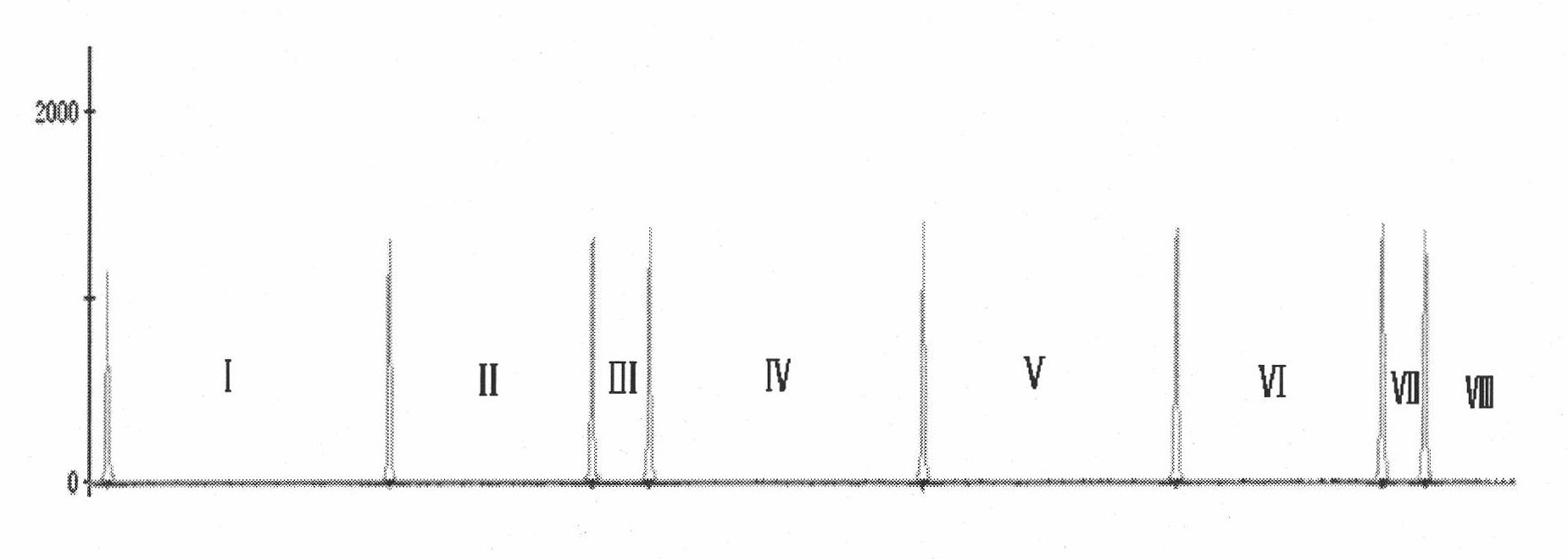
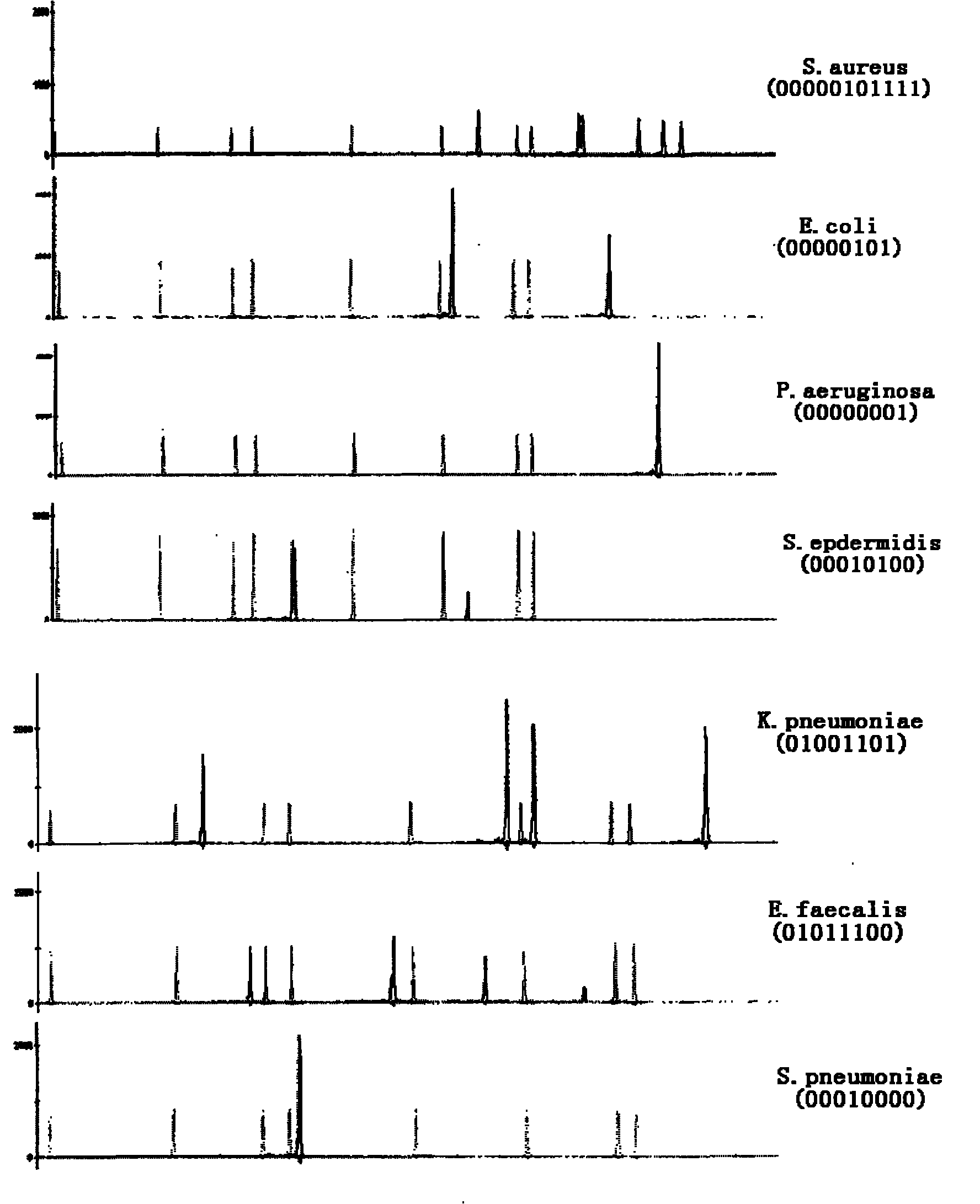
Method for quickly detecting pathogenic bacteria in blood based on machine code recognition technology
InactiveCN101805789AAppropriate lengthSuitable expansion spanMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting pathogenic bacteria in blood based on a machine code recognition technology, comprising the following steps of: designing corresponding universal primers aiming at conserved regions of 16SrDNA and 23SrDNA of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus pneumoniae infected by blood, and carrying out fluorescence labeling; then, respectively carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and CE-SSCP (Capillary Electrophoresis Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism) detection on the DNA of the reference cultures of the seven pathogenic bacteria and the genome DNA of the bacteria of the blood sample to be detected byadopting PCR reaction; and recognizing the detection results by machine codes (binary and decimal codes), and carrying out comparison. The detection method has good repeatability and high sensitivity, can detect the trace genome DNA of pathogenic bacteria, has obvious detection results, and is very suitable for wide application in clinic.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)-SSCP (Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism) detection kit and detection method for growth-rate-related gene Leptin of Gansu alpine fine-wool sheep
ActiveCN103882115AProductivity improvementRapid responseMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismPolyacrylamide
The invention relates to a sheep growth rate molecular marker assisted breeding technique in the technical field of animal biology and particularly relates to a detection kit for an allelic gene of growth-rate-related gene Leptin of Gansu alpine fine-wool sheep. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)-SSCP (Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism) detection kit for the growth-rate-related gene Leptin of Gansu alpine fine-wool sheep is characterized by comprising PCR reactant liquid, a DNA standard sample of Leptin*C, an SSCP detection reagent, deionized water, 10% ammonium persulfate, a sampling denaturing buffer solution, TEMED (Tetramethylethylenediamine) and 12% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel of which Arc: Bis=37.5:1, wherein the sampling denaturing buffer solution comprises 98% of deionized formamide, 0.025% of bromophenol blue, 0.025% of xylene cyanol and 10mmol / L of EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) of which the pH is 8.0. The detection kit disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of rapidness, high sensitivity, low cost and the like when used in the molecular marker breeding of the Gansu alpine fine-wool sheep.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Marking method for resistance gene homologues based on EST(Expressed Sequence Tag) data mining
InactiveCN102747154AAccelerate the breeding process for disease resistanceIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsSingle-strand conformation polymorphismR protein
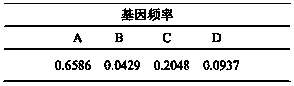
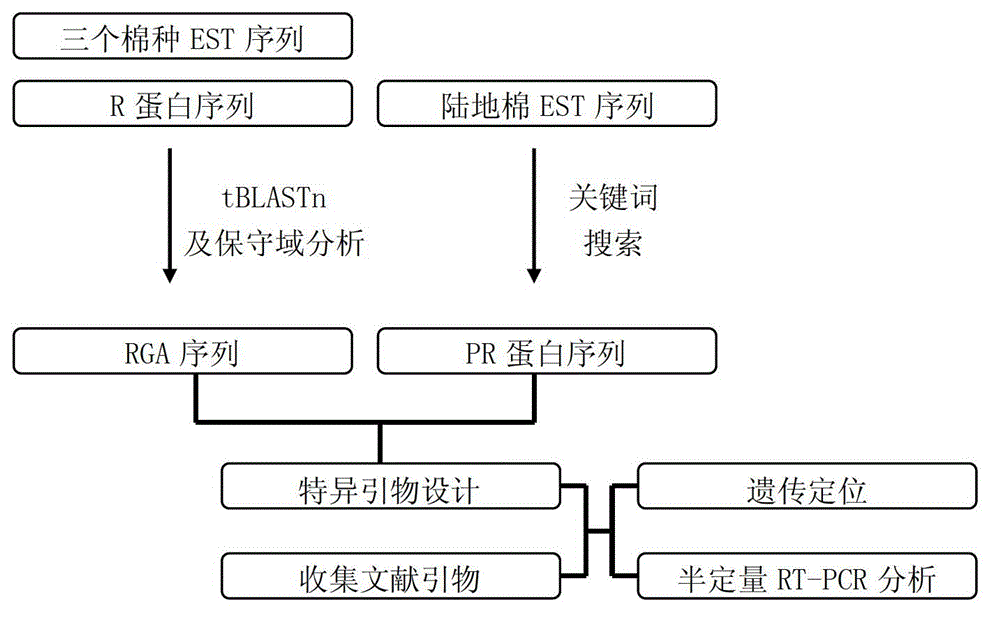
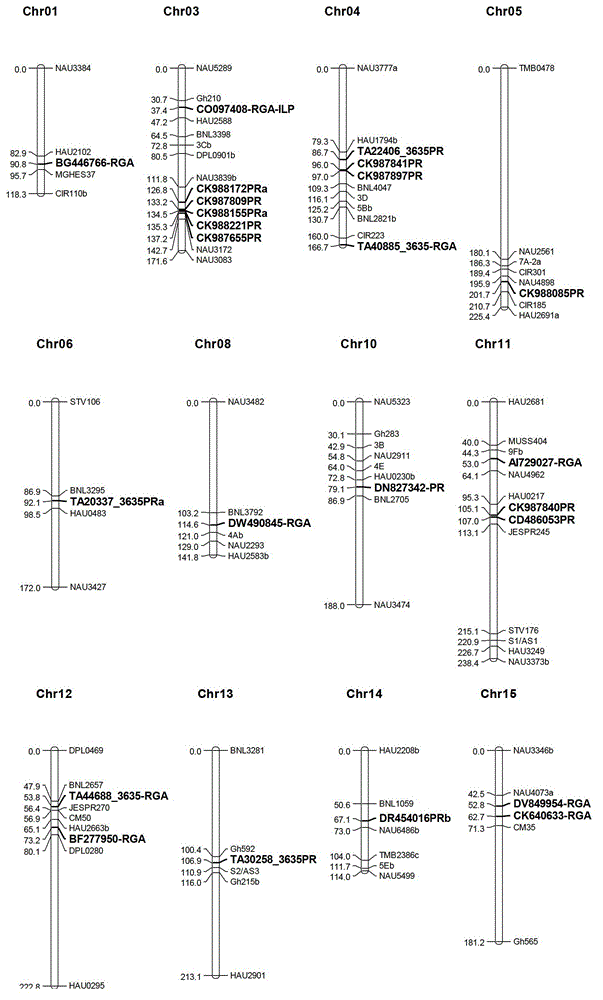
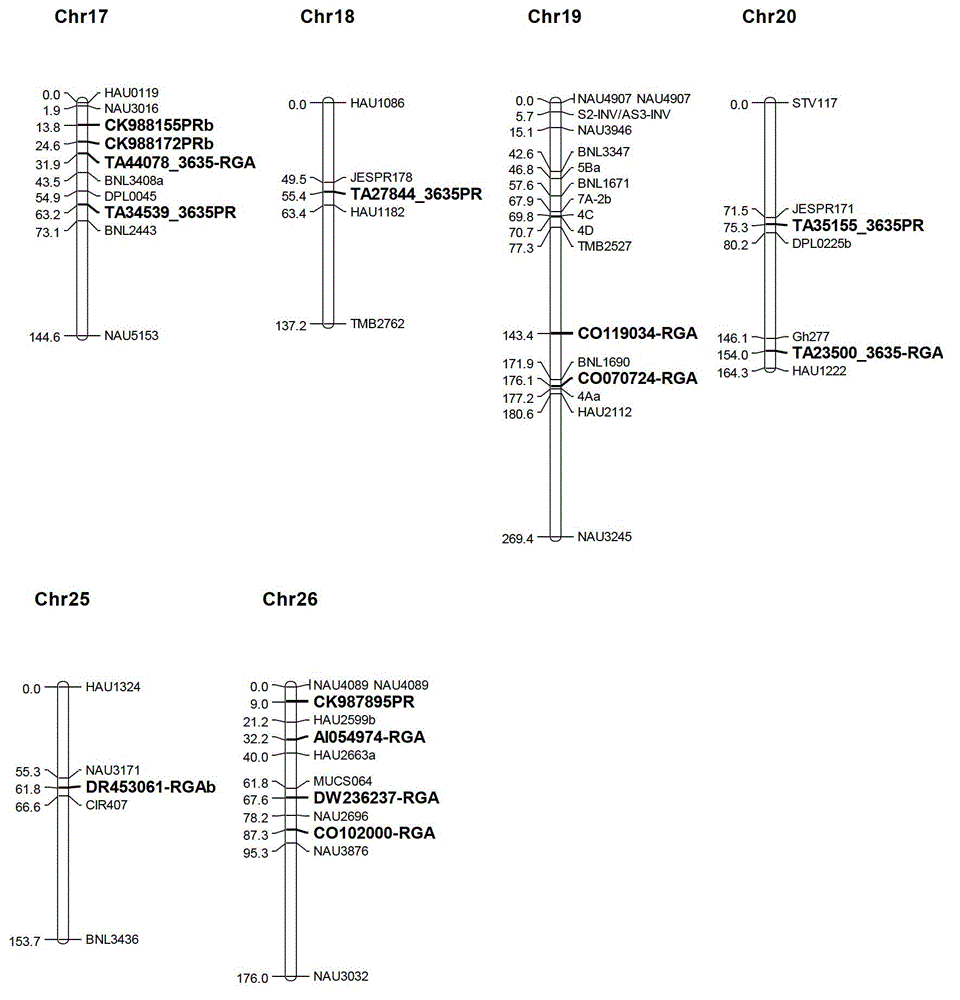
The invention discloses a marking method for resistance gene homologues based on EST data mining. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sequence mining and primer designing; (2) RGA sequence mining and primer designing, wherein 96 R protein sequences of different species are collected through literature, 196 R protein sequences of Arabidopis thaliana are downloaded at the same time, and EST data of three cotton species are downloaded from TIGR; and (3) genetic mapping of developed markers, wherein a BC1 population between Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense is used, then polymorphism is screened by using the parent of Hubei cotton-22 and 3-79 under the condition of electrophoresis of single-strand conformation polymorphism, screened polymorphism markers are used for polymorphism analysis of the BC1 population, and obtained data are introduced into JoinMap3.0 for construction. The method provided in the invention has the advantages of low cost, no need for cost for amplification of degenerate primers and considerable monoclonal sequencing, a greater number of obtained sequences, more abundant sequence varieties and capacity of providing effective molecular markers for molecular breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Utilization of nucleotide probes for the measurement of specific mRNA for the molecular diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy
InactiveUS6924102B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismAssay
The present invention concerns the development of a quantitative method for the molecular diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) by measuring the amount of cytosolic mRNA from human muscle cells. Both the procedure using radioactive material and the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) nonradioactive method were developed using 32P-dCTP labeled and biotinylated nucleotide probes. The results obtained demonstrate that the measurement of mRNA could be used as a quantitative method for the molecular diagnosis of SMA. There was a perfect concordance of the results obtained between the procedure using radioactive material, the ELISA method and the single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis regarding the negative and positive SMA samples. The methods developed in this study may be applicable to the diagnosis (detection of homozygous and heterozygous deletions in exons 7 and 8 of the SMN gene) and the control of mRNA concentrations in the future gene therapy of patients with SMA.
Owner:NGUYEN HUYNH MAI THI
Method for detecting insertion-deletions polymorphism of sheep FTH-1 (ferritin heavy polypeptide1) genes by utilizing PCR-SSCP (polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism) and application thereof
ActiveCN106701930AExcellent genetic resourcesAccurately estimate breeding valuesMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention discloses a method for detecting insertion-deletions polymorphism of sheep FTH-1 (ferritin heavy polypeptide1) genes by utilizing PCR-SSCP (polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism) and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: taking to-be-detected sheep whole genome DNA containing FTH-1 genes as a template, performing PCR amplification on the sheep FTH-1 gene segments, and performing detection and genotyping on the PCR product by utilizing the SSCP technology; and identifying the 639th locus insertion-deletions polymorphism of the sheep FTH-1 genes according to electrophoretic results. The method is a method for screening and detecting a molecular genetic marker which is closely related to reproductive performances of sheep on the DNA level so as to be used for assistant selection and molecular breeding of the sheep and acceleration of sheep stock breeding.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
Method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of cattle PPARGC1A genes
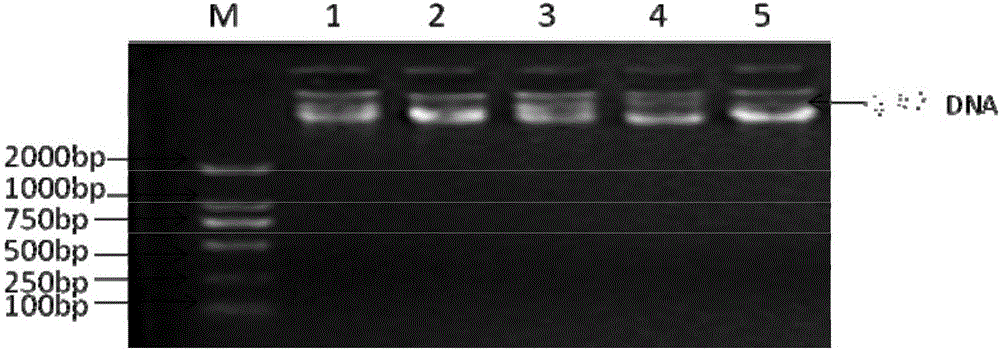
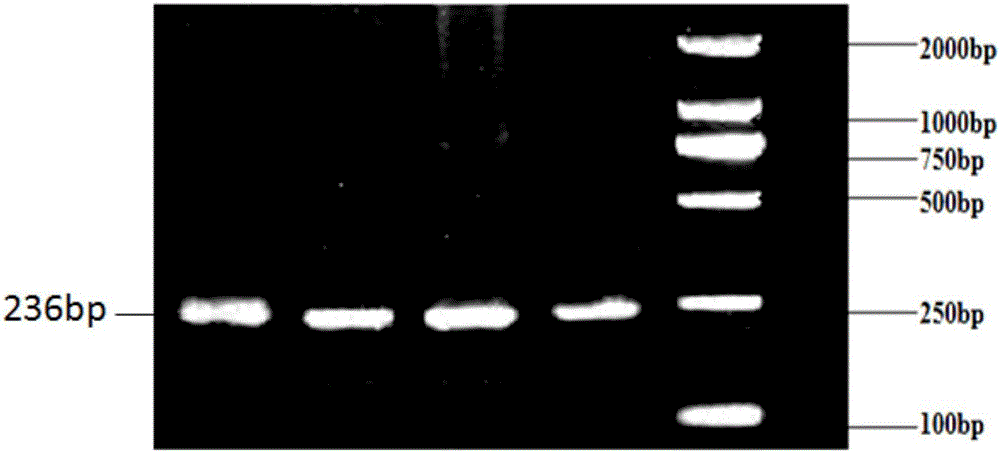
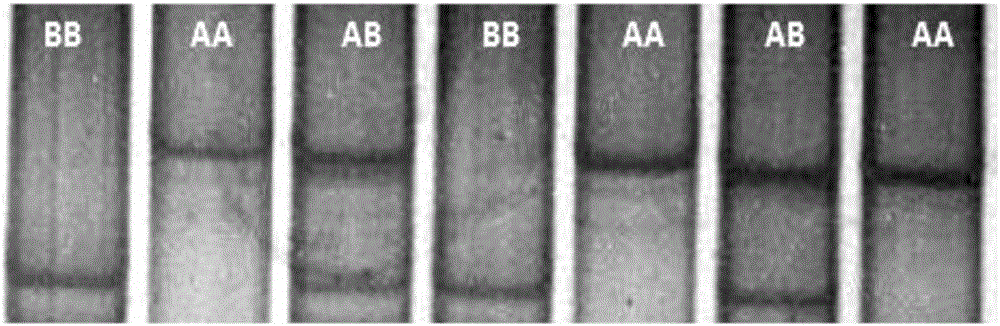
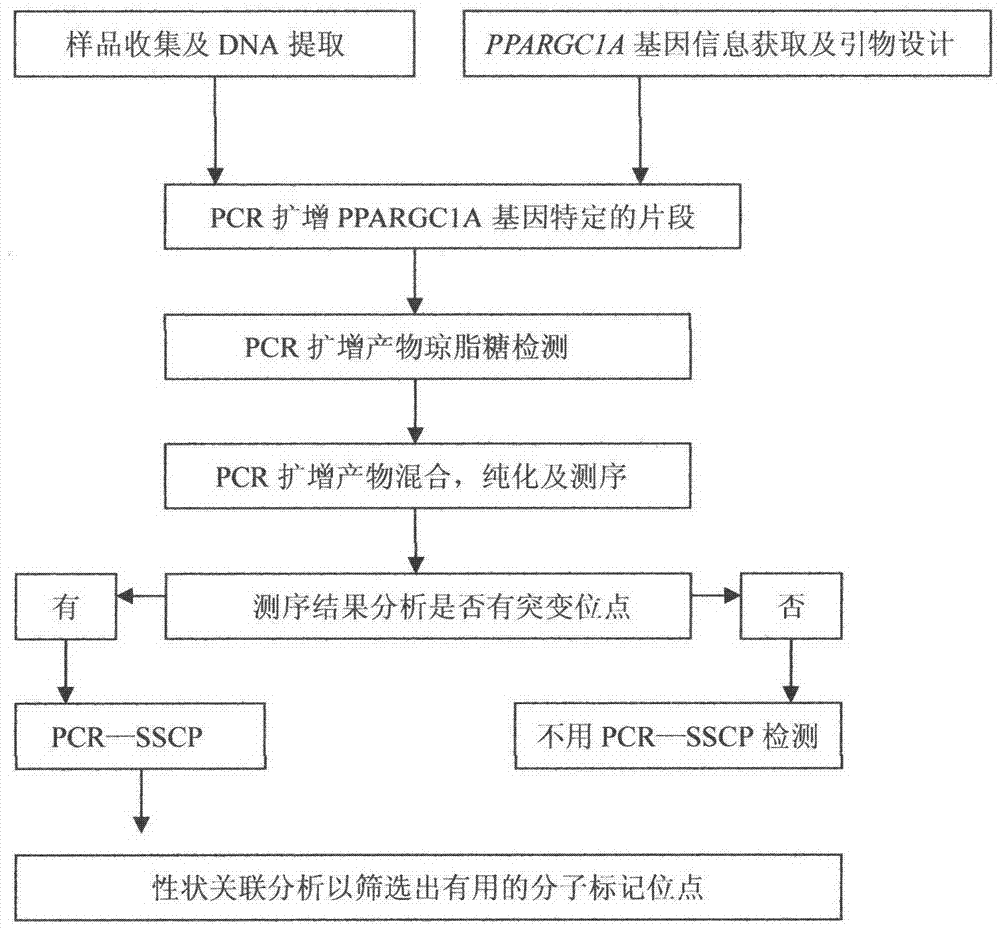
InactiveCN102888451AEasy to detectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of cattle PPARGC1A genes. The method comprises the steps: taking to-be-detected cattle genomic DNA containing PPARGC1A genes as a formwork and a primer pair P as a primer, conducting PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) application to the cattle PPARGC1A genes, and then carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the size of the amplified product segment; and detecting the SSCP (Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism). The method is used for screening and detecting molecular genetic marker closely related with growth traits of cattle on the DNA level, and therefore, the detection method provided by the invention can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection of Chinese cattle beef and growth traits, so that cattle crowds with excellent genetic resources can be further established.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Specific primer of I-class MHC gene for Alligator sinensis antiviral potential detection and typing method
ActiveCN105349535AImplement polymorphic evaluationFast sequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTyping methodsSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention relates to a single-locus specific primer of I-class main tissue compatibility compound gene sequence for amplified Alligator sinensis antiviral potention detection and a typing method. A specific sequence of the primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.8. The amplified primer has stable single-locus specific amplifying capability in Alligator sinensis populations, a product obtained by amplifying the amplified primer can be used for genotyping of different individuals through subsequent single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) experiments, evaluation of I-class MHC gene polymorphism of Alligator sinensis individuals in the populations can be realized, potential, of the Alligator sinensis individuals, in resisting viral diseases can be detected, and important reference can be provided for new population founder selection, wildness reintroduction individual selection and artificial matching in Alligator sinensis protection work.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
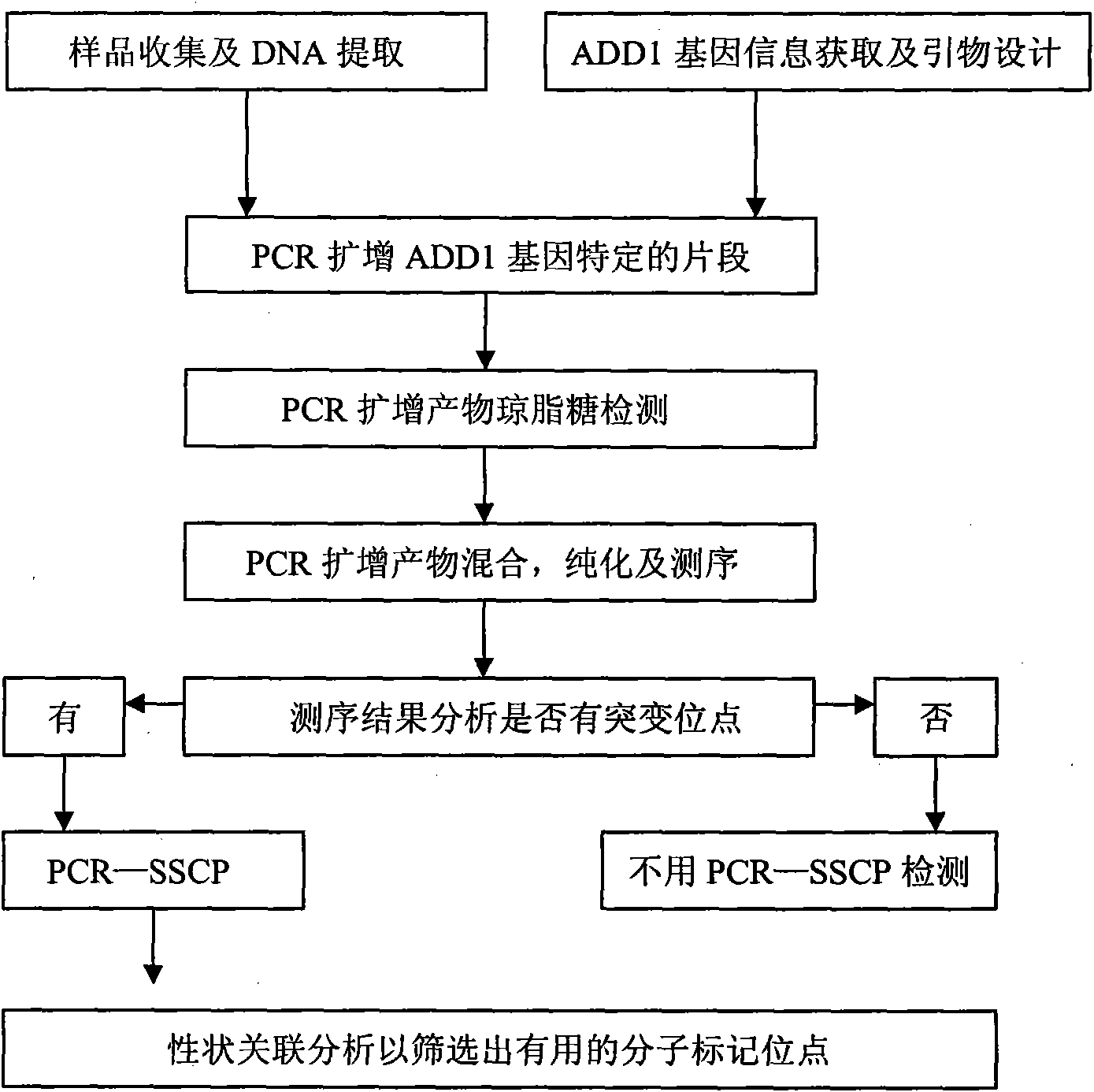
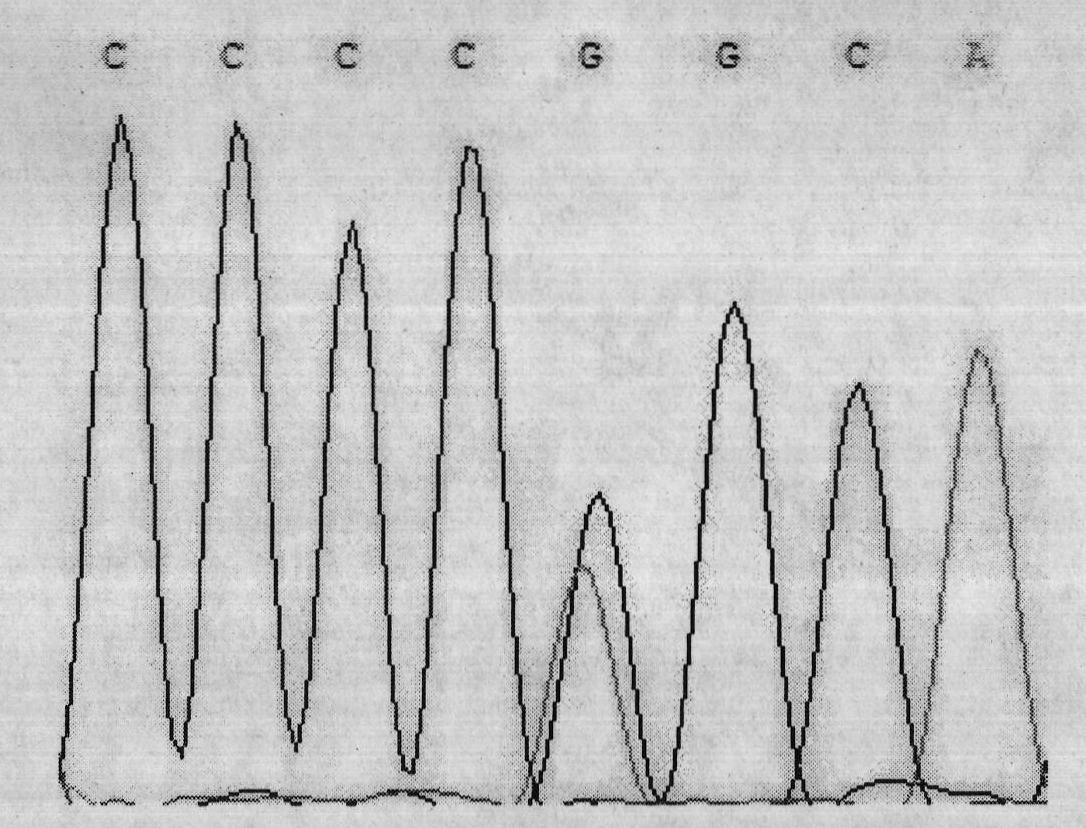
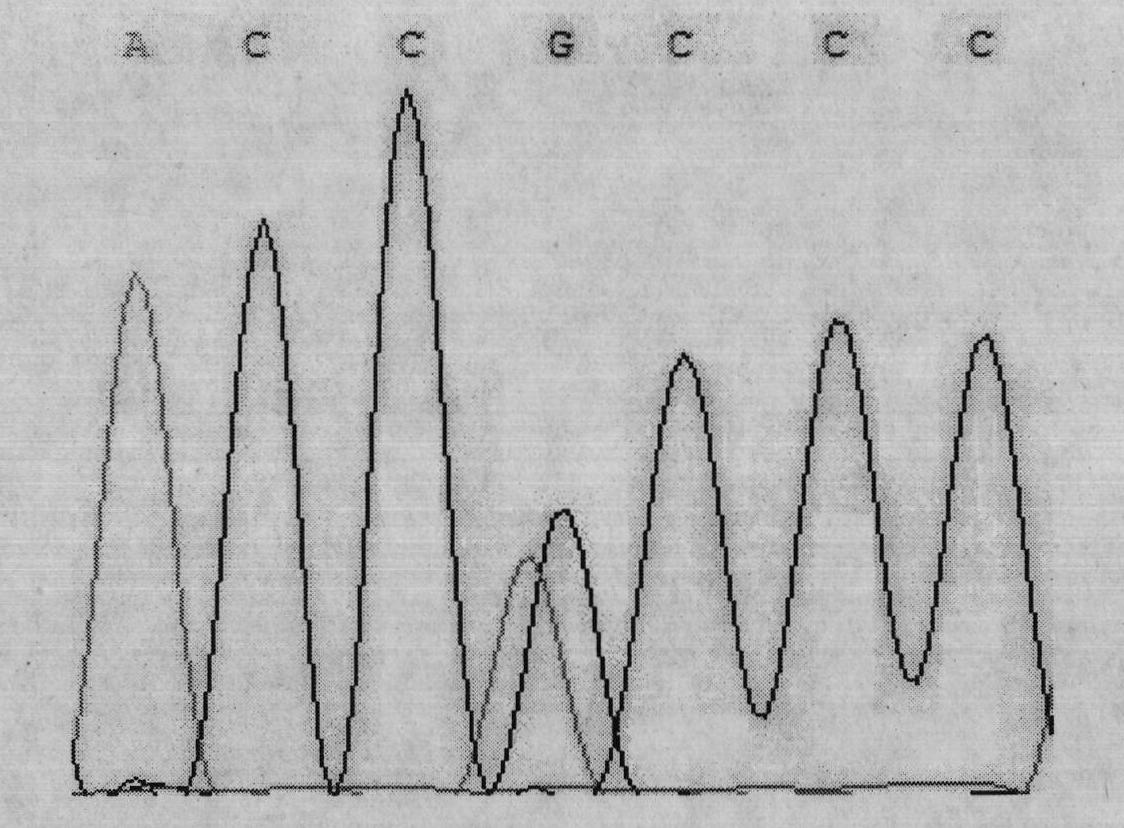
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of ADD1 gene of cattle and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102031304AAvoid instabilityLeak detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of an ADD1 gene of cattle, which comprises the following steps: through taking a genomic DNA of cattle containing an ADD1 gene as a template and taking a primer mix P as a primer, the ADD1 gene of cattle is amplified through PCR (polymerase chain reaction), then the segment size of the obtained product is amplified through AGE (agarose gel electrophoresis) detection; and then, the detection on SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) is performed. The polymorphism of the gene comprises a base polymorphism that the 70027th bit in an ADD1 gene sequence table SEQID No.8 of cattle is G or A, and a base polymorphism that the 70051th bit in the ADD1 gene sequence table SEQID No.8 of cattle is G or A. The analysis on the correlation between the SSCP polymorphism and the production performance shows that: a certain correlation exits between the polymorphic site and the production performance, therefore, the weight of a Qinchuan cattle (genotype: BB) is significantly higher than that of a cattle (genotype: AA). The method is used for the auxiliary selection and molecular breeding of cattle through screening and detecting molecular genetic markers closely relating to the growth properties of cattle on a DNA level, therefore, the method plays a vital role in improving the production performance of cattle.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
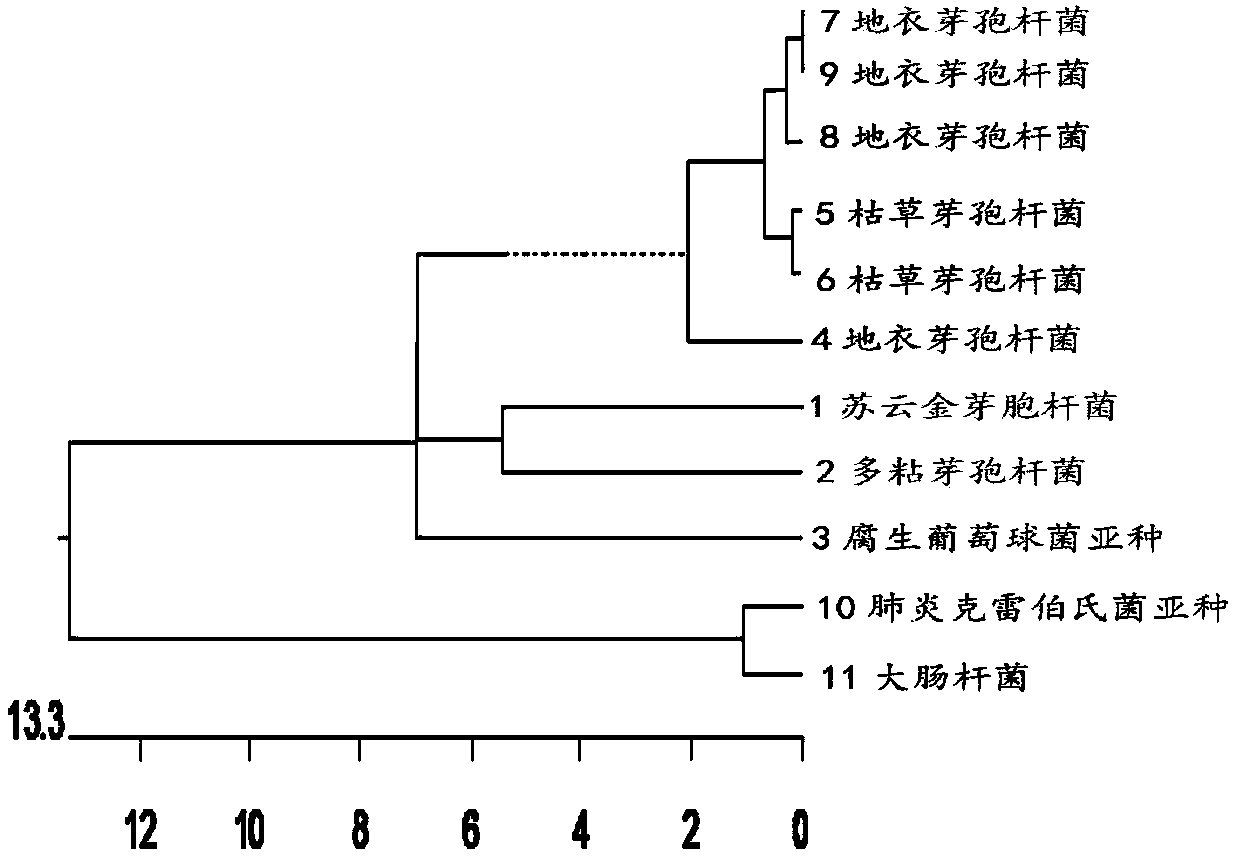
Method for analyzing structure composition of microorganism community by employing single-chain conformation polymorphism technique
InactiveCN101210262AImprove operational efficiencyKeep abreast of changesMicrobiological testing/measurementProcess systemsSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention relates to a method for analyzing microbial community structure and composition using single-strand conformation polymorphism technology, which solves the problem that the existing biological assay and analysis methods are difficult to analyze the composition and structure of microbial community. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting DNA of a microbial community; (2) performing PCR amplification; (3) removing antisense strand with restriction endonuclease; (4) performing gel electrophoresis; (5) purifying DNA; and (6) analyzing the composition and structure of the microbial community. The invention can rapidly and accurately analyze the composition and structure of a complex microbial community in a process system, resolve succession of the community, master the variation of the microbial community in the process system, guide the process, and improve the operating efficiency of the process system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com