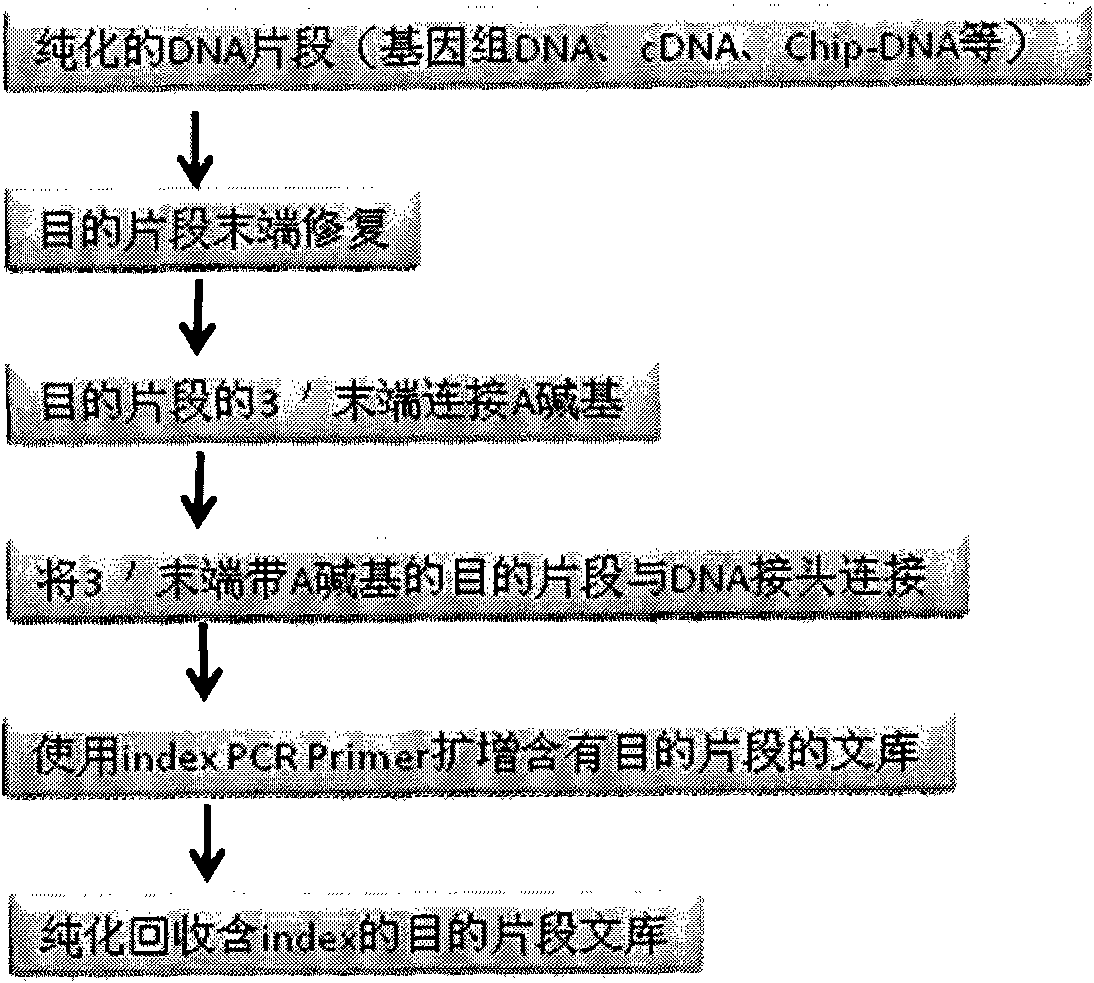Patents
Literature
1159 results about "Real-time polymerase chain reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR), also known as quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (quantitative real-time PCR) and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules) (semi-quantitative real-time PCR).
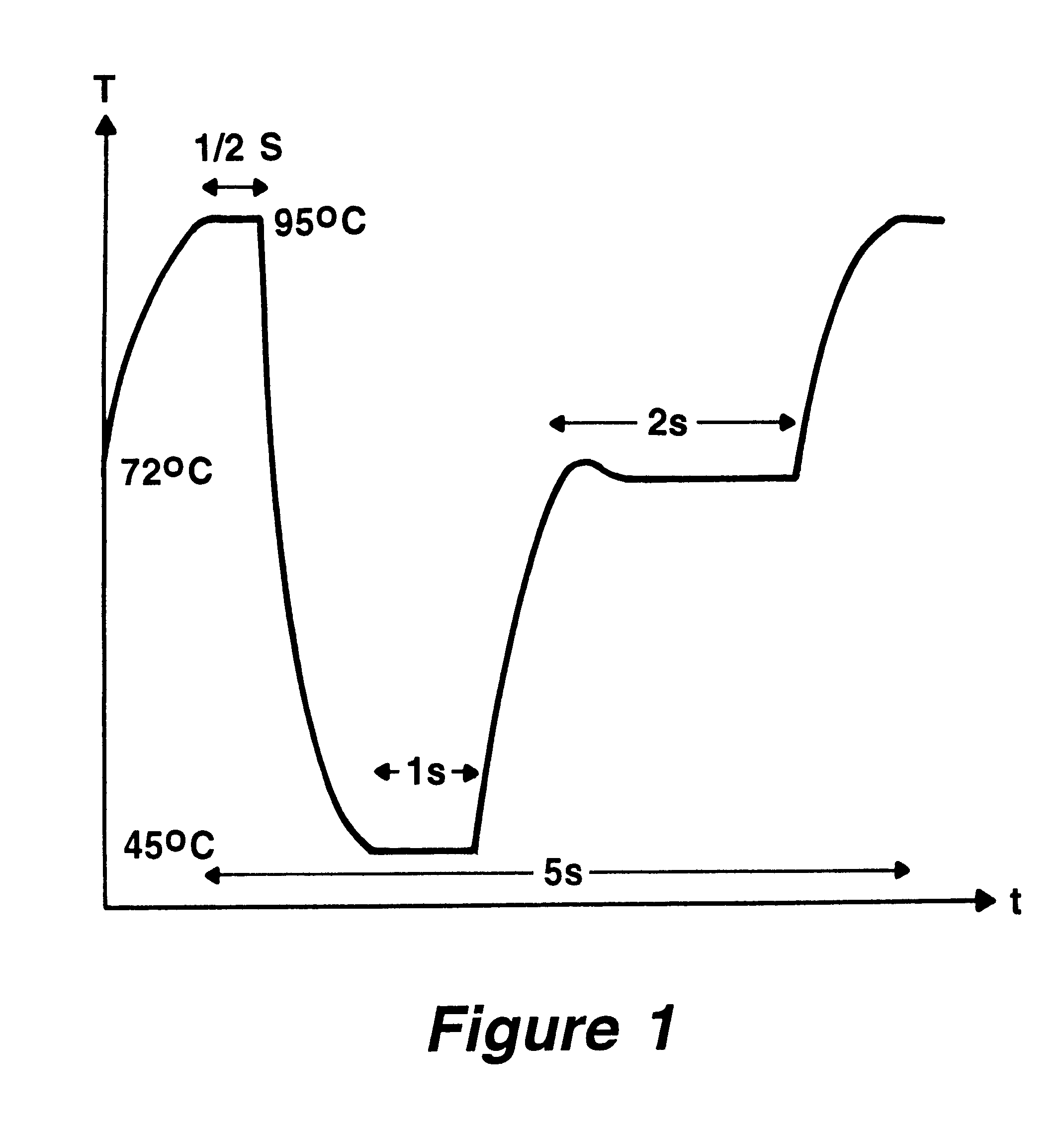
Method and devices for extremely fast DNA replication by polymerase chain reactions (PCR)
InactiveUS6180372B1Shorten cycle timeHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechPolymerase LBiological materials
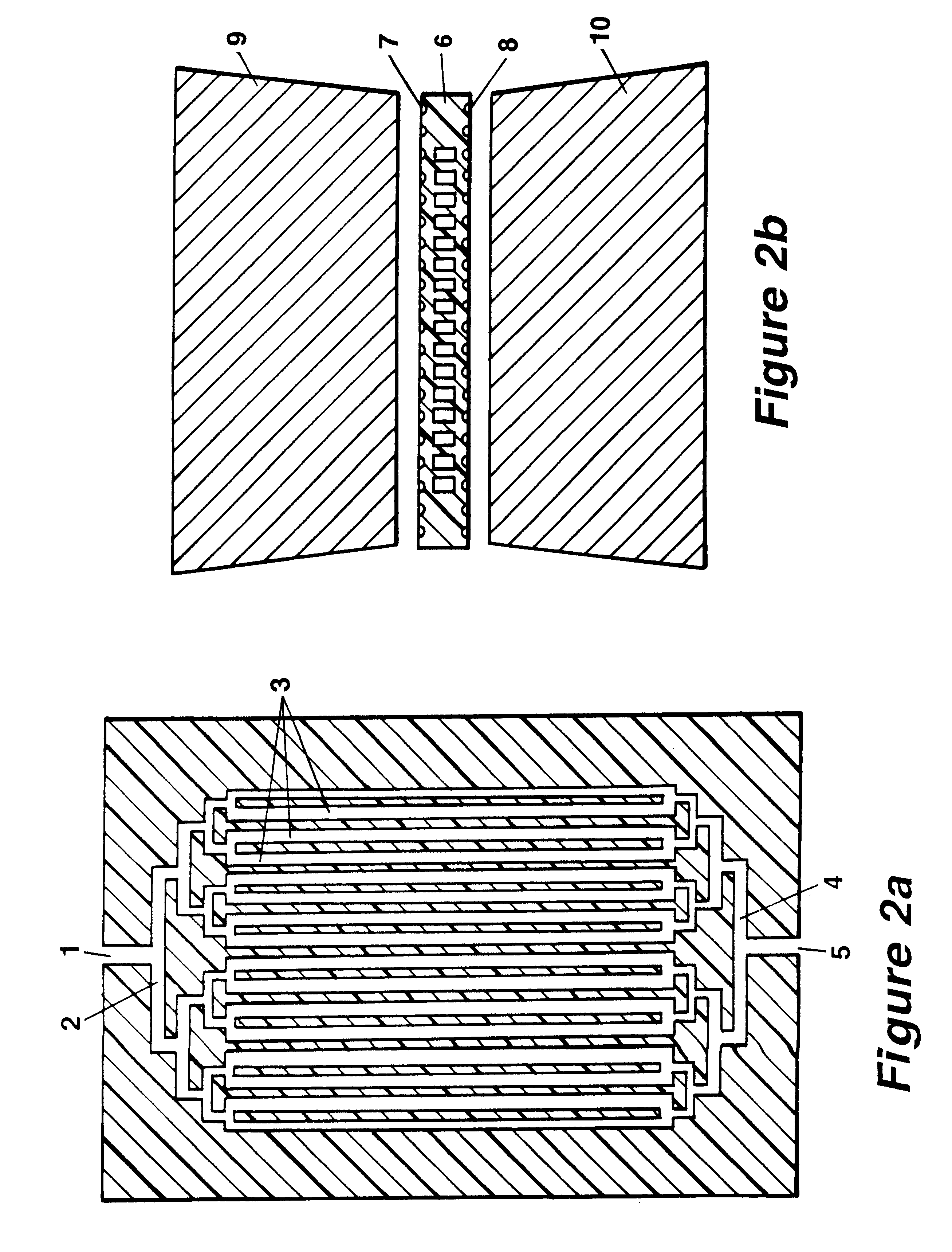
The invention concerns methods and instruments for fast, selective replication of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from biomaterial through the known polymerase chain reaction (PCR), working in individual duplication thermocycles. The invention consists of extremely brief cycle times of only a few seconds for the PCR reactions, generated, on the one hand, by reaction chambers for the reception of the reaction solution constructed of a pattern of fine capillaries in close proximity to heating and cooling elements in order to optimally accelerate the temperature setting in the reaction solution for the three temperature phases of the PCR duplication cycles and, on the other hand, by keeping the flow rates in the capillaries to a minimum during the amplification phase so that the polymerase reaction is not disturbed. The capillary pattern can be simply produced by means of microsystern technology.
Owner:BRUKER FRANZEN ANALYTIK
Method for monitoring molecular species within a medium
InactiveUS7097973B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayGas phase
Apparatus and methods for monitoring, analyzing, and / or discriminating molecular species, preferably a biomolecule, within a medium using a multisensor array (MSA) and multivariate processing. Biological compounds such as nucleotides and polynucleotides can be detected and analyzed. A reaction process such as an accumulation cycle of nucleic acids can be monitored, analyzed, and controlled using a multisensor array (MSA) and multivariate processing. Monitoring a biomolecule includes interrogating the medium, and preferably its gas phase, by coupling a sensor responsive to any changes of the medium and or biomolecule and its secondary products when, for example, an amplification reaction is proceeded. It is also a scope of the present invention to use direct detection and monitoring of biomolecular reactions in real-time without radioactive or fluorescent labeling. A preferred application is real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection.
Owner:ALPHA MOS
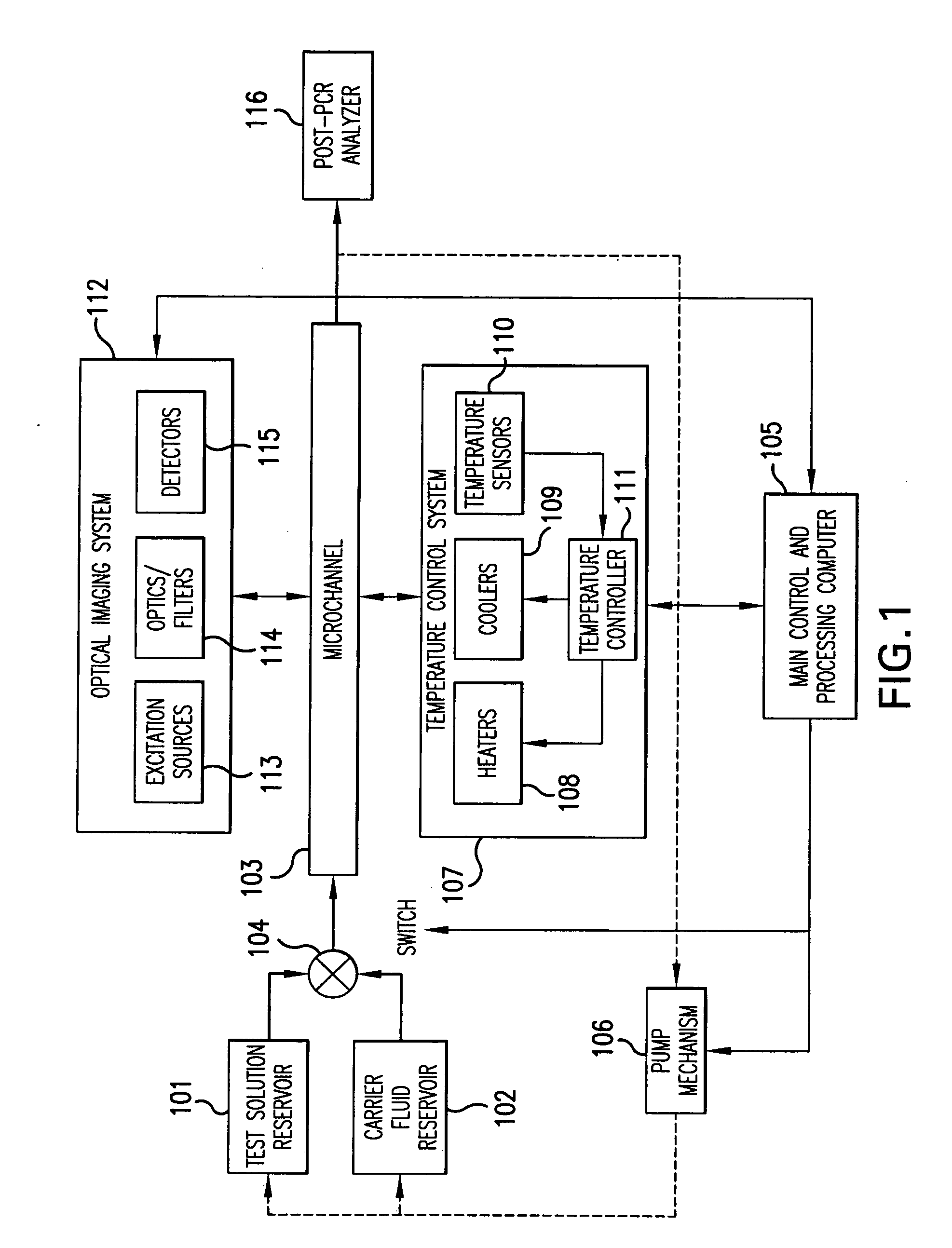
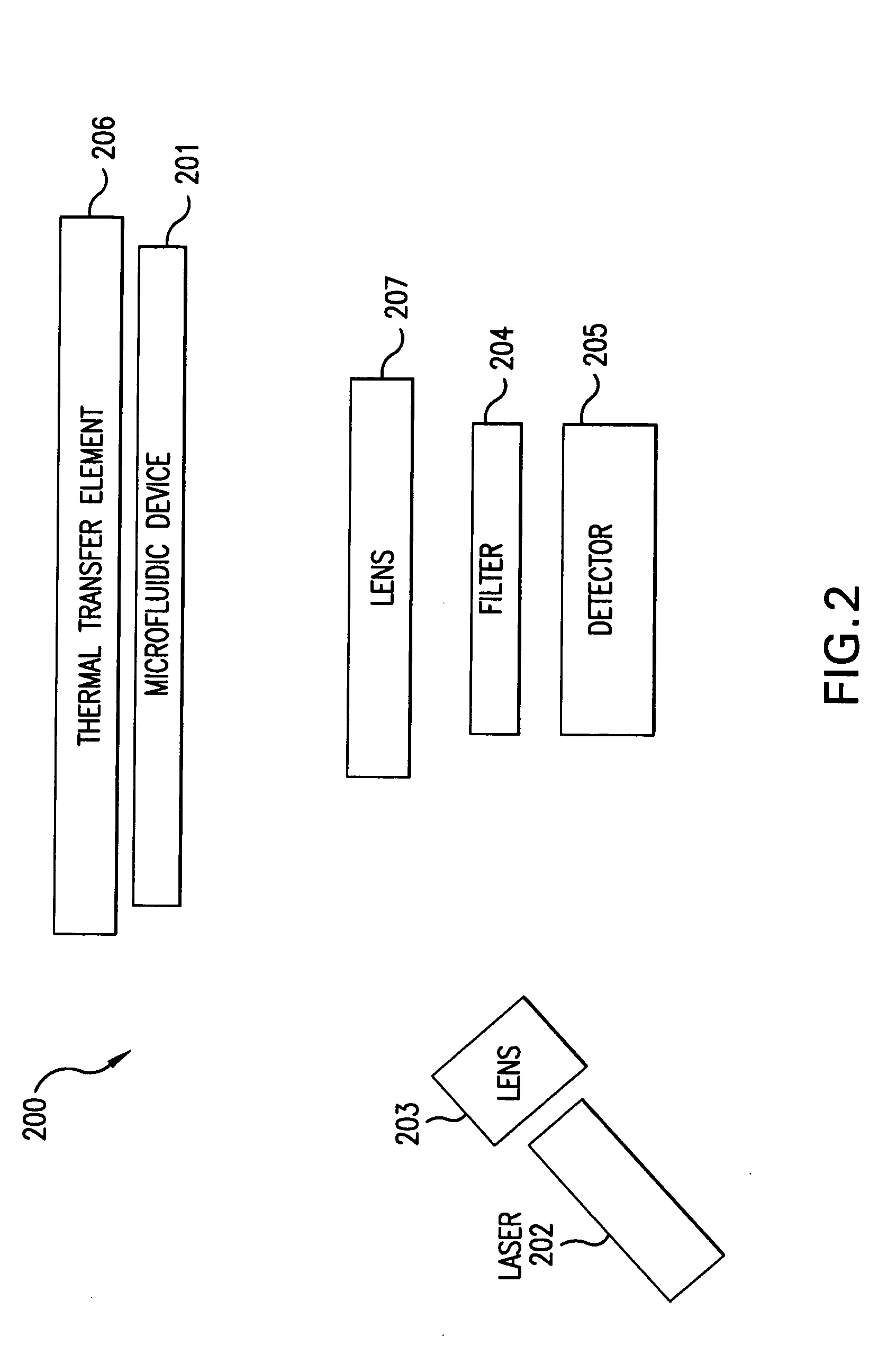
Real-time PCR in micro-channels
The present invention relates to methods for amplifying nucleic acids in micro-channels. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods for performing a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in a continuous-flow microfluidic system and to methods for monitoring real-time PCR in such systems.
Owner:CANON USA
Polymerase chain reaction of DNA of which base sequence is completely unidentified
The present invention relates to a process for amplifying DNA of an organism. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process for amplifying DNA of an organism through Polymerase Chain Reaction(PCR) without any information regarding a primer needed for amplifying DNA of an organism.
Owner:BIONEER
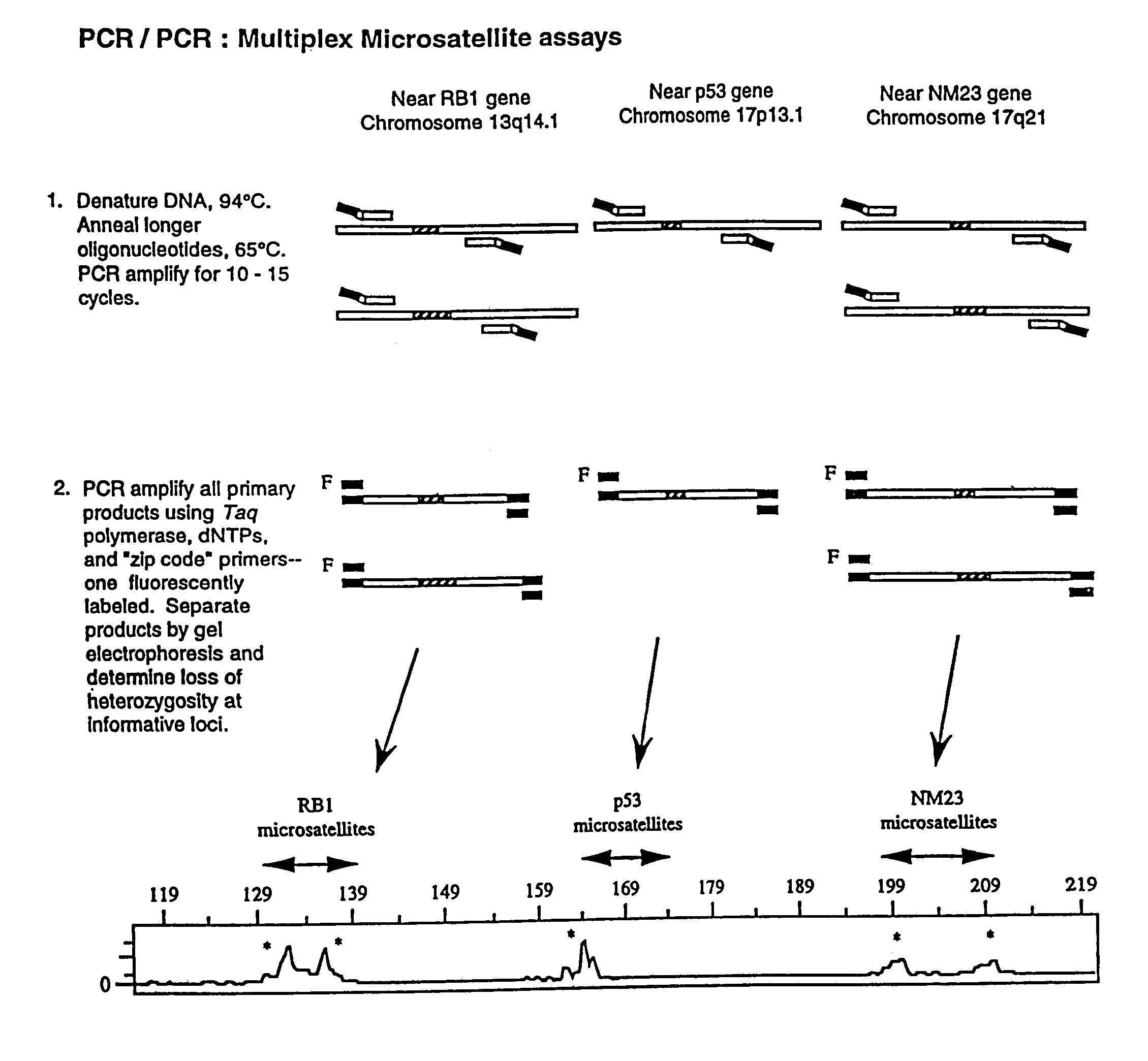
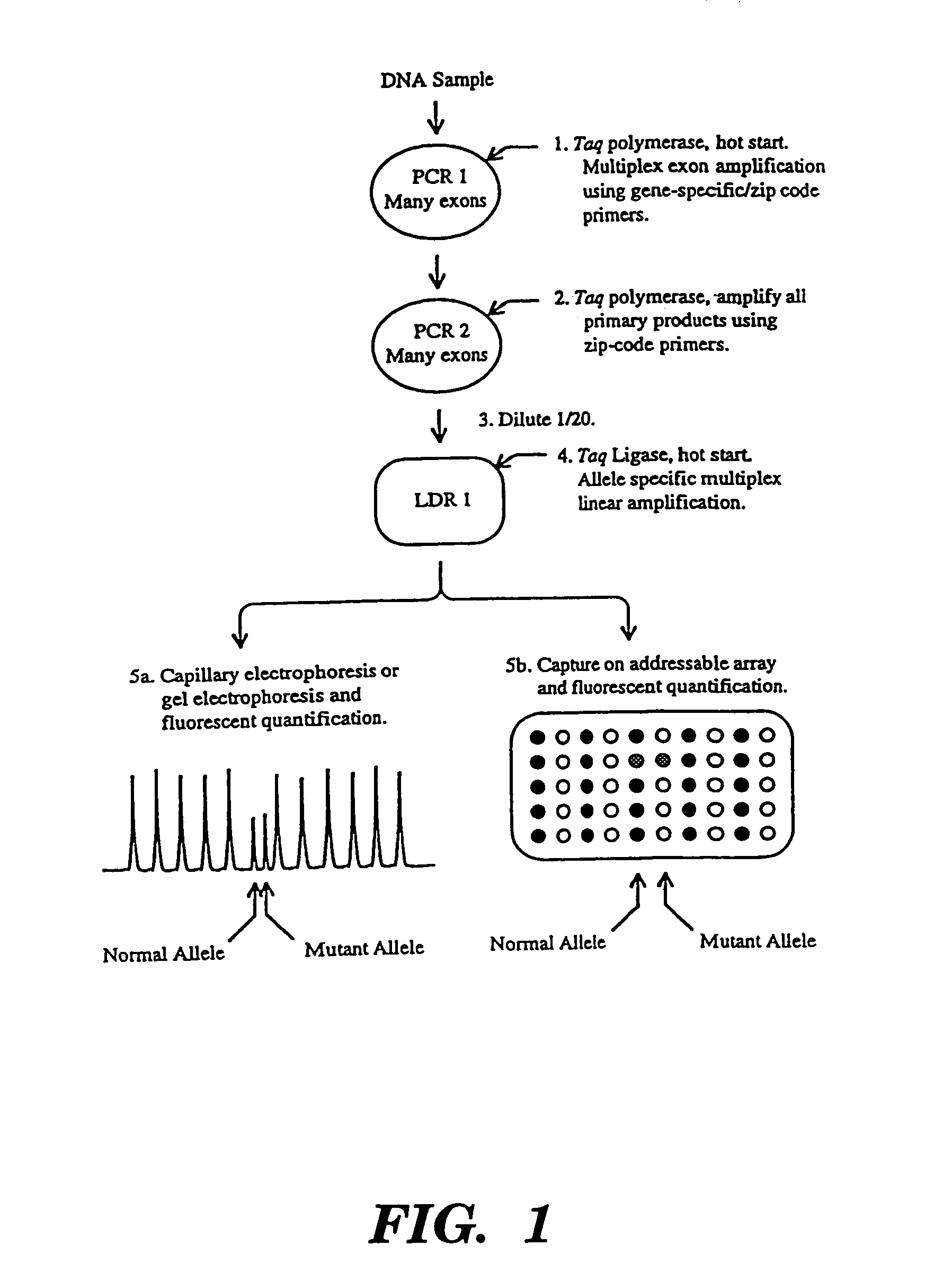
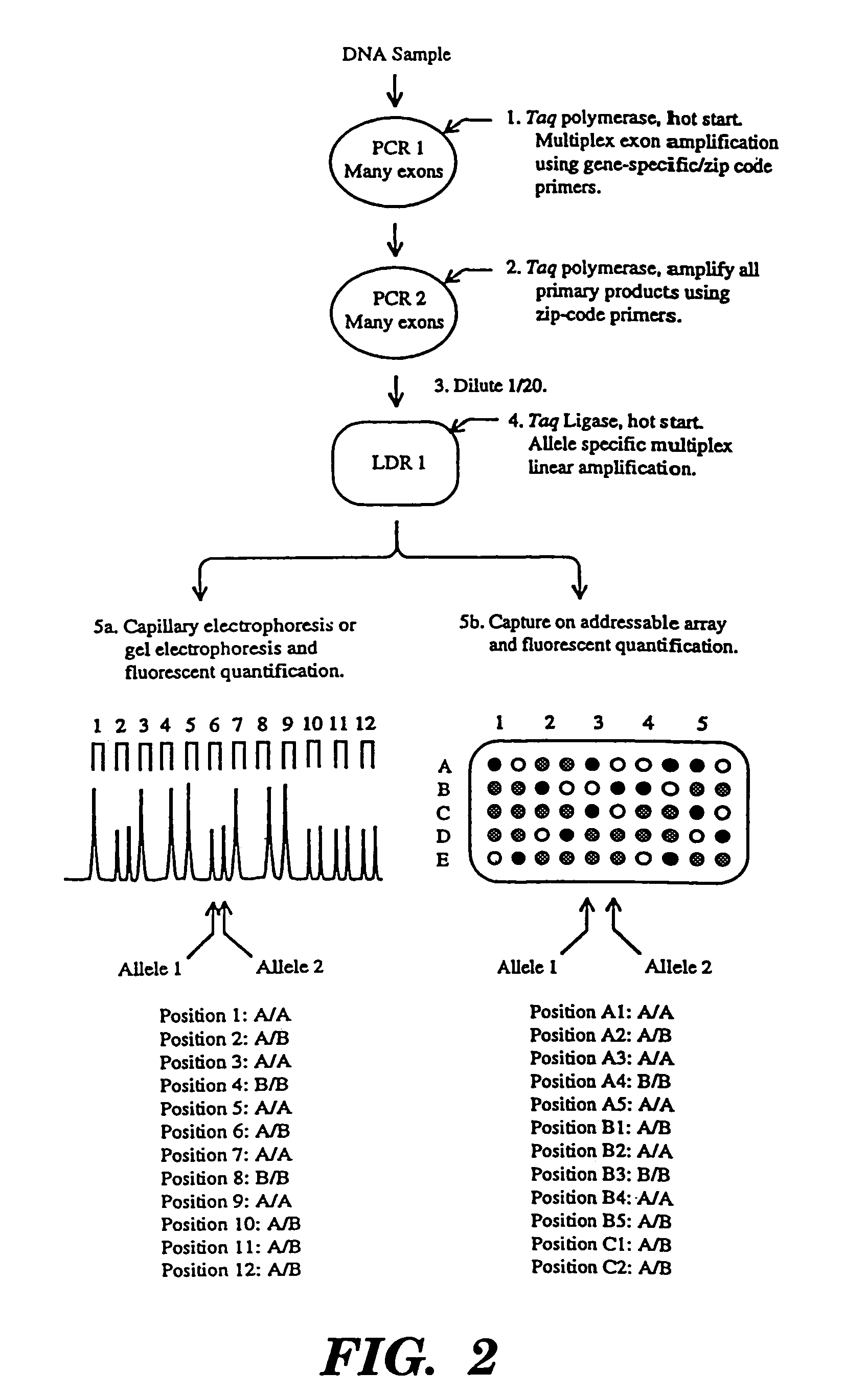
Detection of nucleic acid sequence differences using coupled ligase detection and polymerase chain reactions
InactiveUS7097980B2Maximize productionLess primerMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyNucleotideCoupling
The present invention relates to the detection of nucleic acid sequence differences using coupled ligase detection reaction and polymerase chain reaction. One aspect of the present invention involves use of a ligase detection reaction coupled to a polymerase chain reaction. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of a primary polymerase chain reaction coupled to a secondary polymerase chain reaction coupled to a ligase detection reaction. A third aspect of the present invention involves a primary polymerase chain reaction coupled to a secondary polymerase chain reaction. Such coupling of the ligase detection reaction and the polymerase chain reaction permits multiplex detection of nucleic acid sequence differences.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
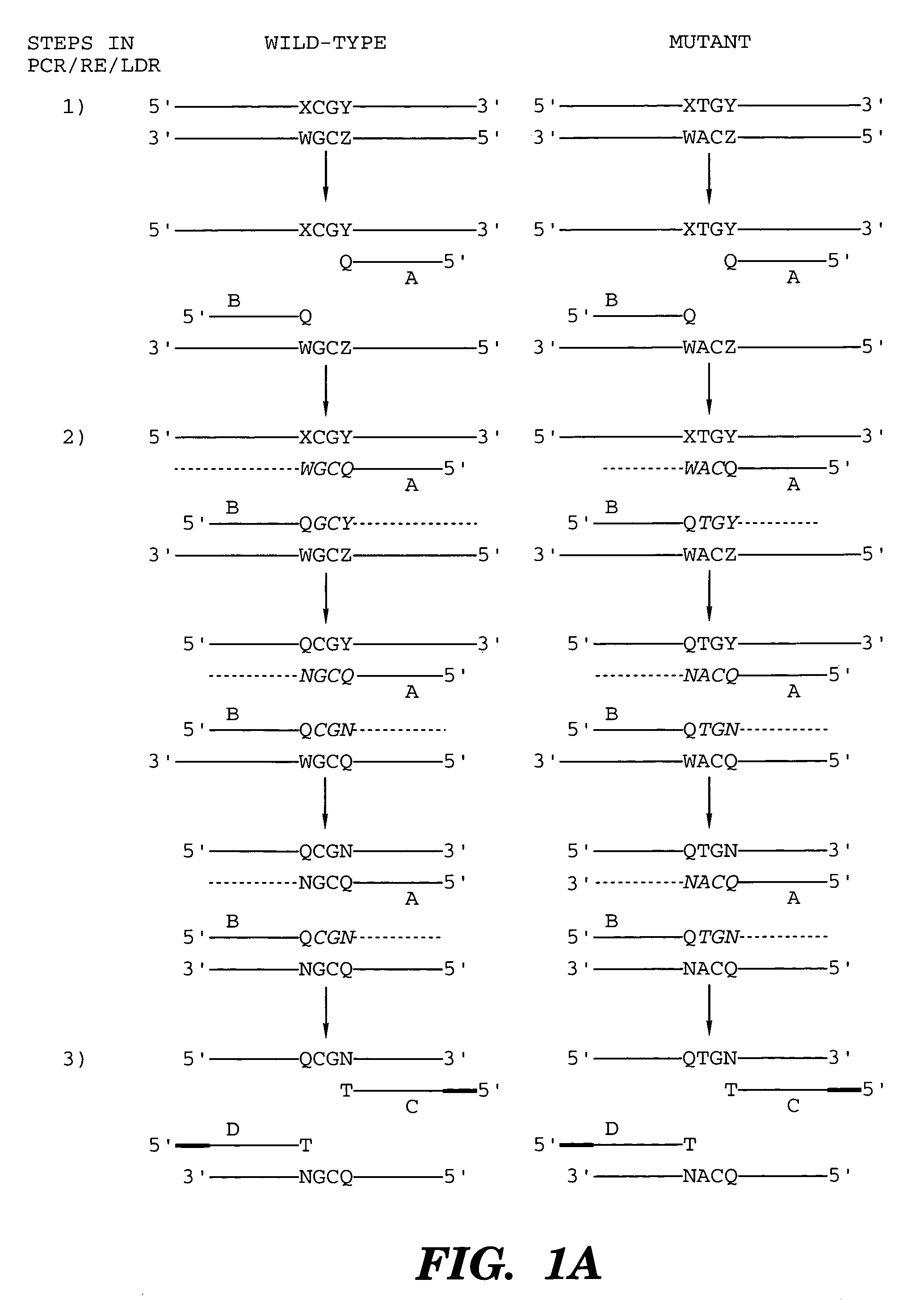
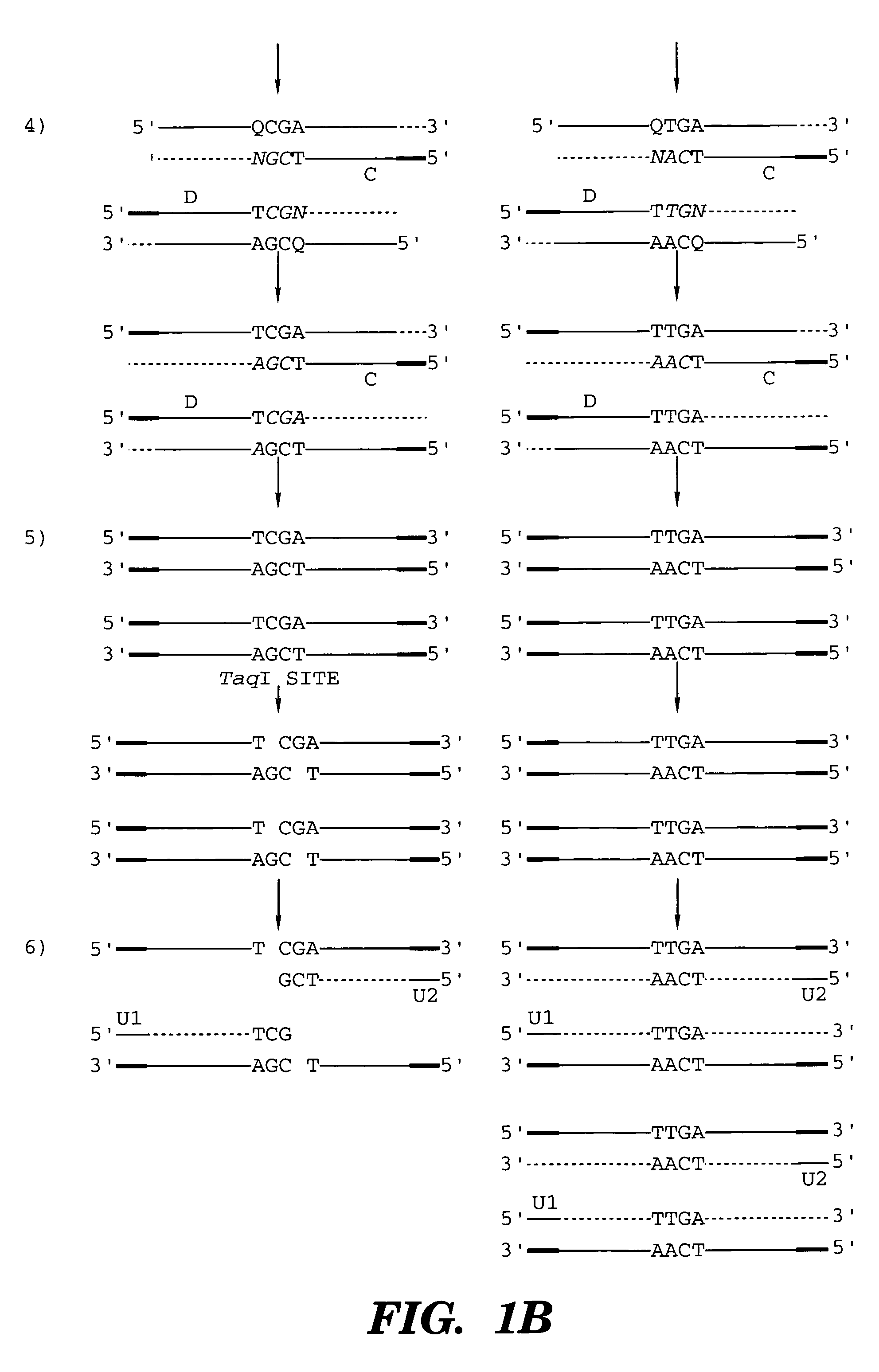
Coupled polymerase chain reaction-restriction-endonuclease digestion-ligase detection reaction process
InactiveUS7014994B1Sensitive highOptimizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention provides a method for identifying one or more low abundance sequences differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, or deletions, from a high abundance sequence in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The high abundance wild-type sequence is selectively removed using high fidelity polymerase chain reaction analog conversion, facilitated by optimal buffer conditions, to create a restriction endonuclease site in the high abundance wild-type gene, but not in the low abundance mutant gene. This allows for digestion of the high abundance DNA. Subsequently the low abundant mutant DNA is amplified and detected by the ligase detection reaction assay. The present invention also relates to a kit for carrying out this procedure.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
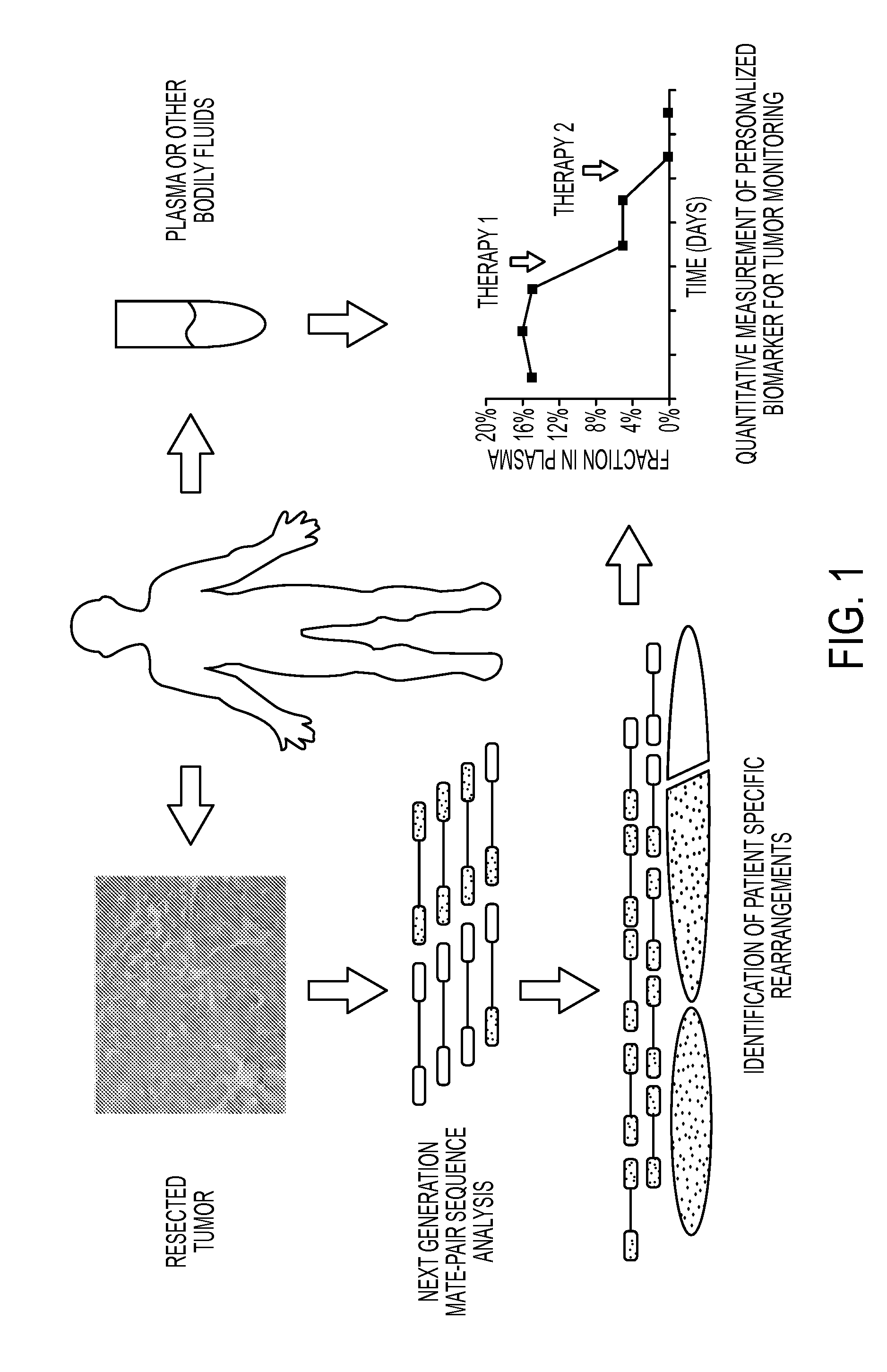
Personalized Tumor Biomarkers
ActiveUS20150344970A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBlood plasmaWilms' tumor
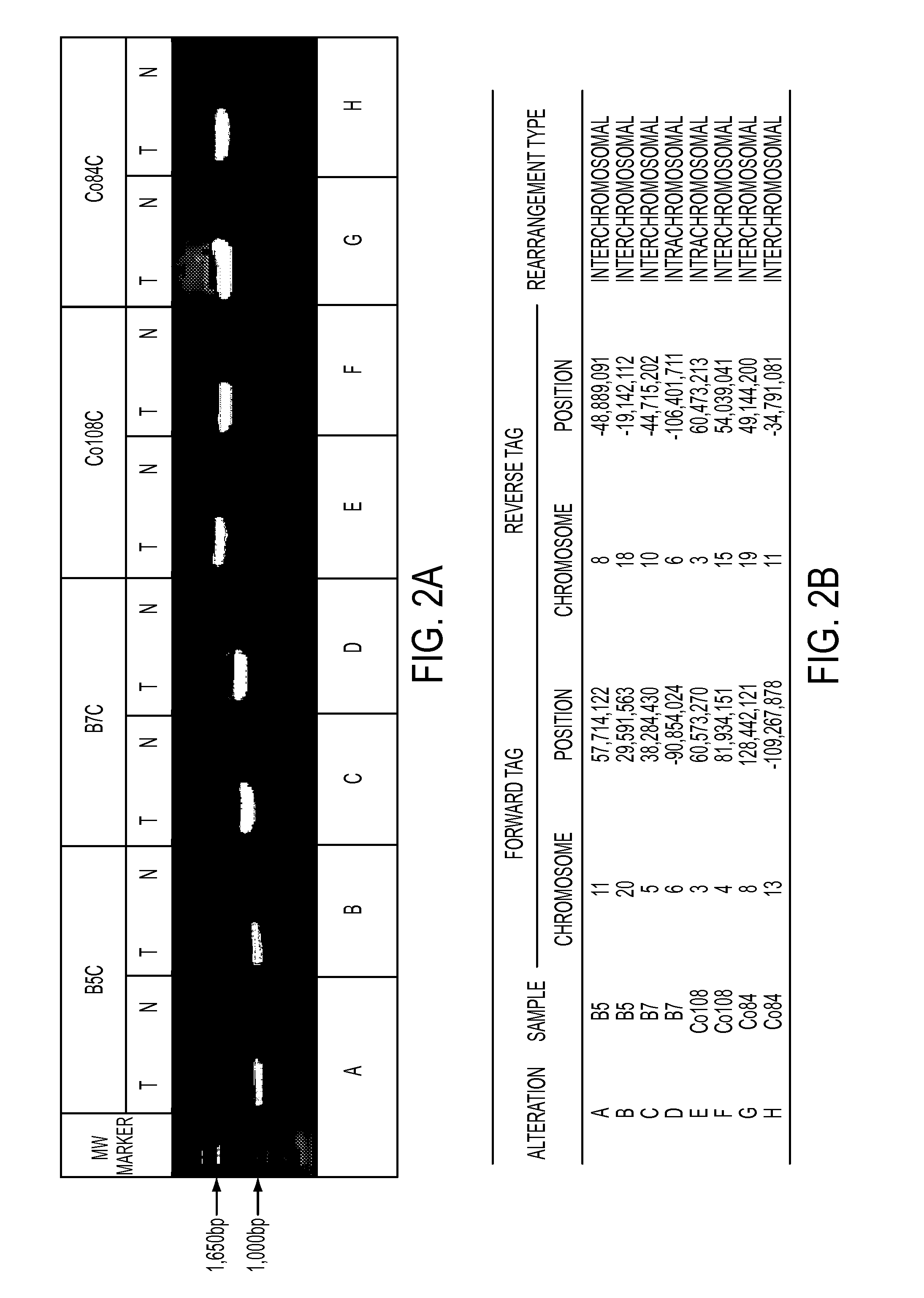
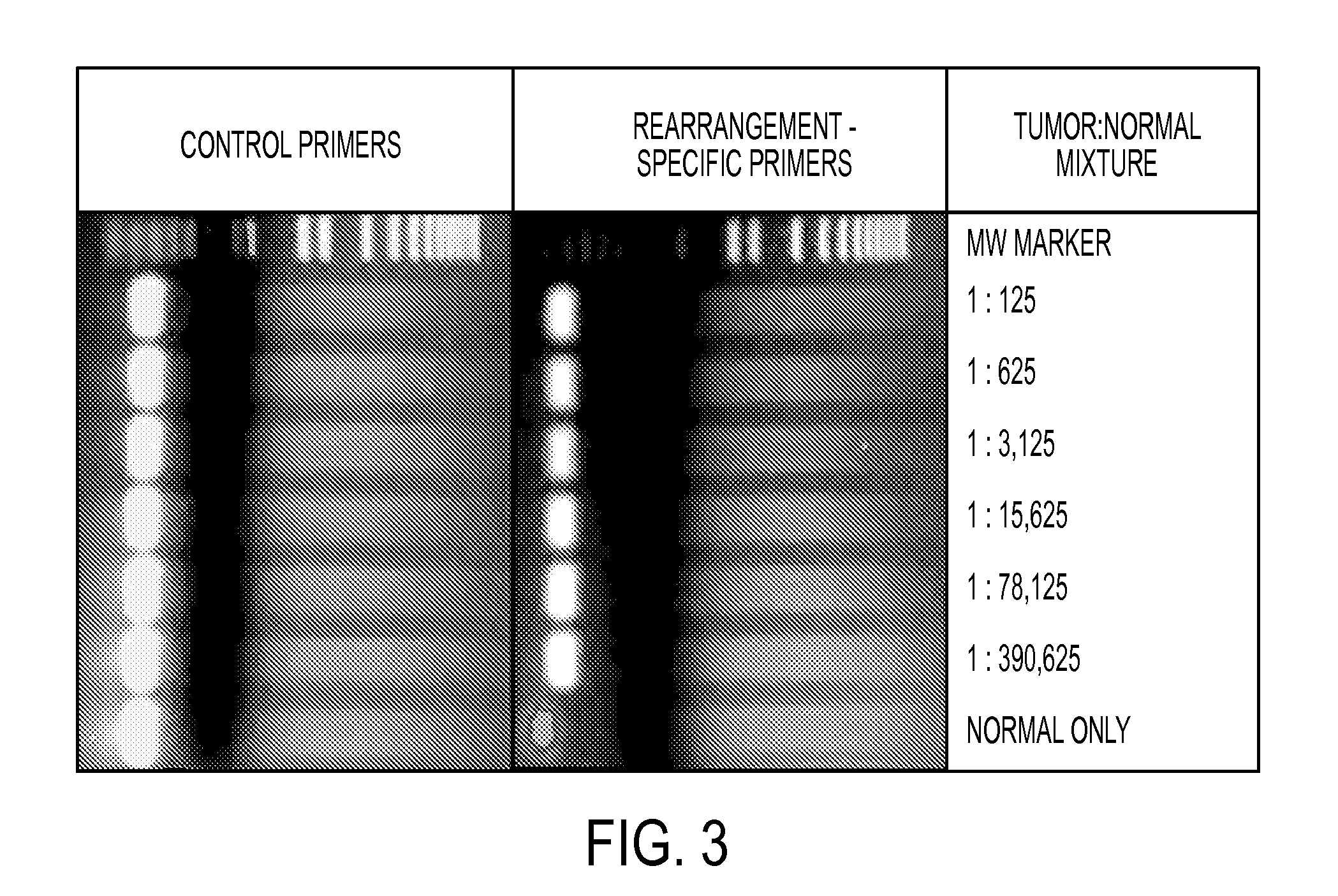
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints were able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Dual phase multiplex polymerase chain reaction
ActiveUS7432055B2Further amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomic DNASingle pair
Highly specific and sensitive methods were developed for multiplex amplification of nucleic acids on supports such as microarrays. Based on a specific primer design, methods include five types of amplification that proceed in a reaction chamber simultaneously. These relate to four types of multiplex amplification of a target DNA on a solid support, directed by forward and reverse complex primers immobilized to the support and a fifth type—pseudo-monoplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of multiple targets in solution, directed by a single pair of unbound universal primers. The addition of the universal primers in the reaction mixture increases the yield over the traditional “bridge” amplification on a solid support by approximately ten times. Methods that provide multitarget amplification and detection of as little as 0.45-4.5×10−12 g (equivalent to 102-103 genomes) of a bacterial genomic DNA are disclosed.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
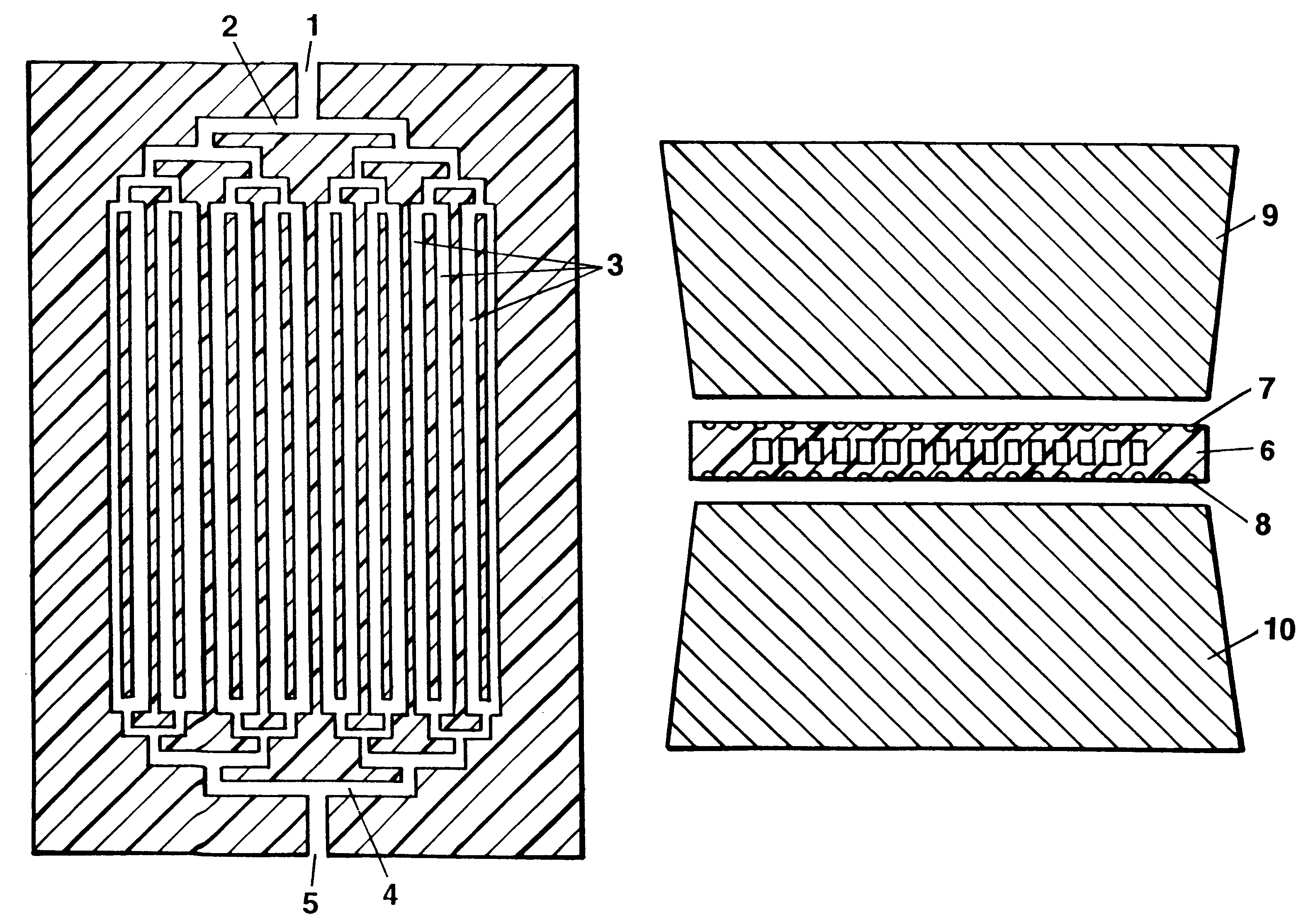
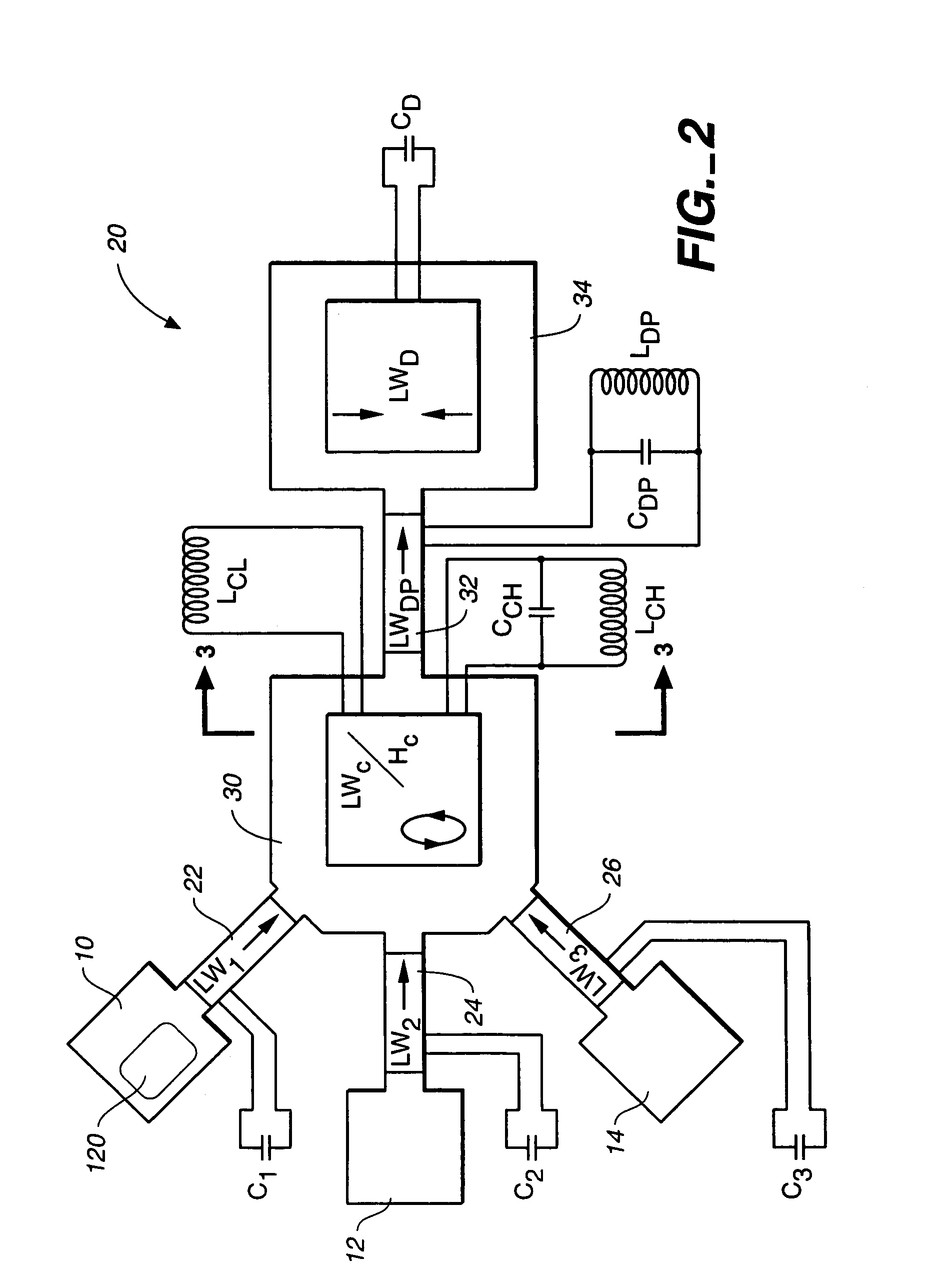
Microfabricated reactor
InactiveUS7169601B1Faster cycle timeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPolymerase chain reactionReal-time polymerase chain reaction
An integrated microfabricated instrument for manipulation, reaction and detection of microliter to picoliter samples. The instrument is suited for biochemical reactions, particularly DNA-based reactions such as the polymerase chain reaction, that require thermal cycling since the inherently small size of the instrument facilitates rapid cycle times. The integrated nature of the instrument provides accurate, contamination-free processing. The instrument may include reagent reservoirs, agitators and mixers, heaters, pumps, and optical or electromechanical sensors. Ultrasonic Lamb-wave devices may be used as sensors, pumps and agitators.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
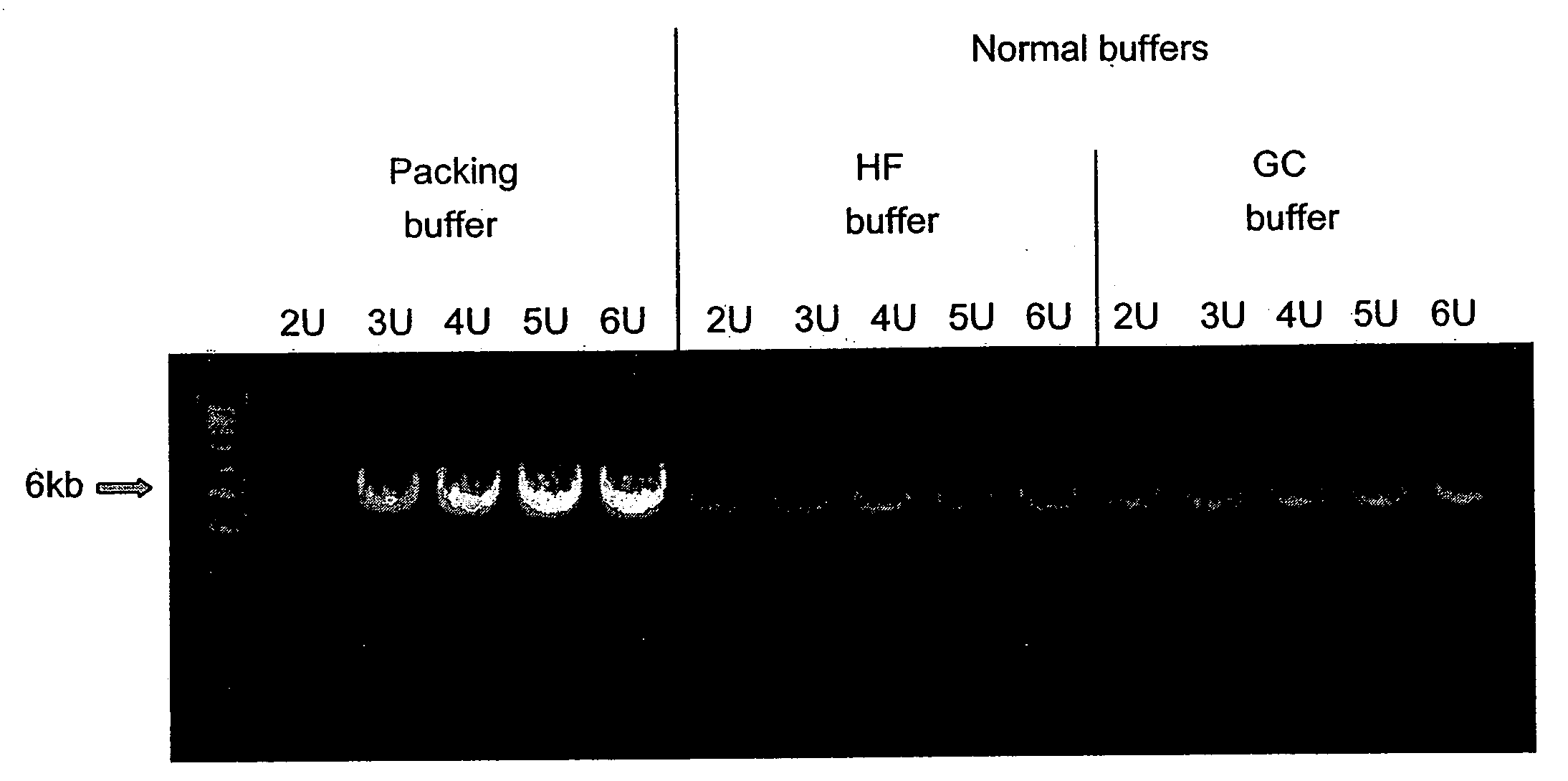
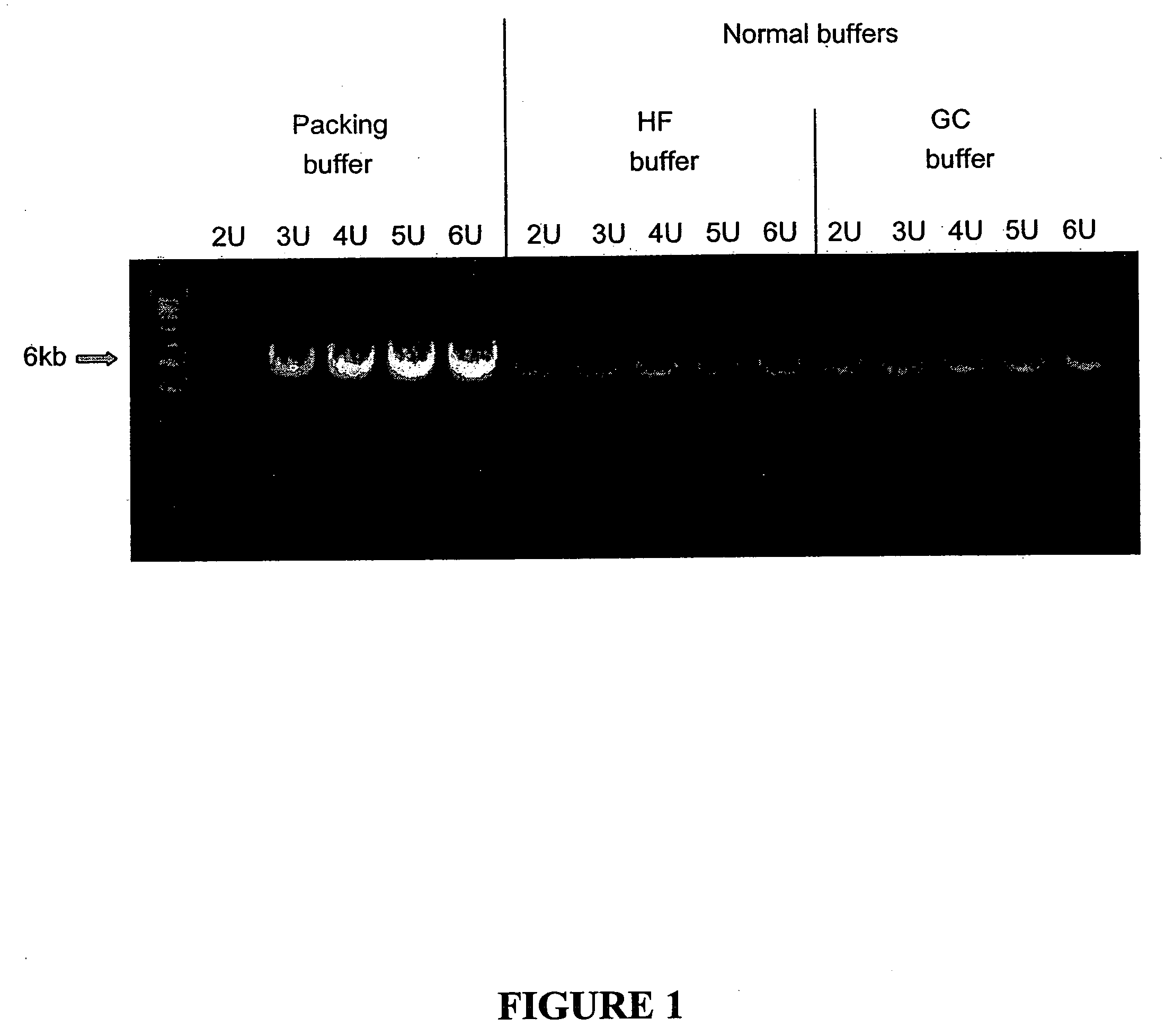
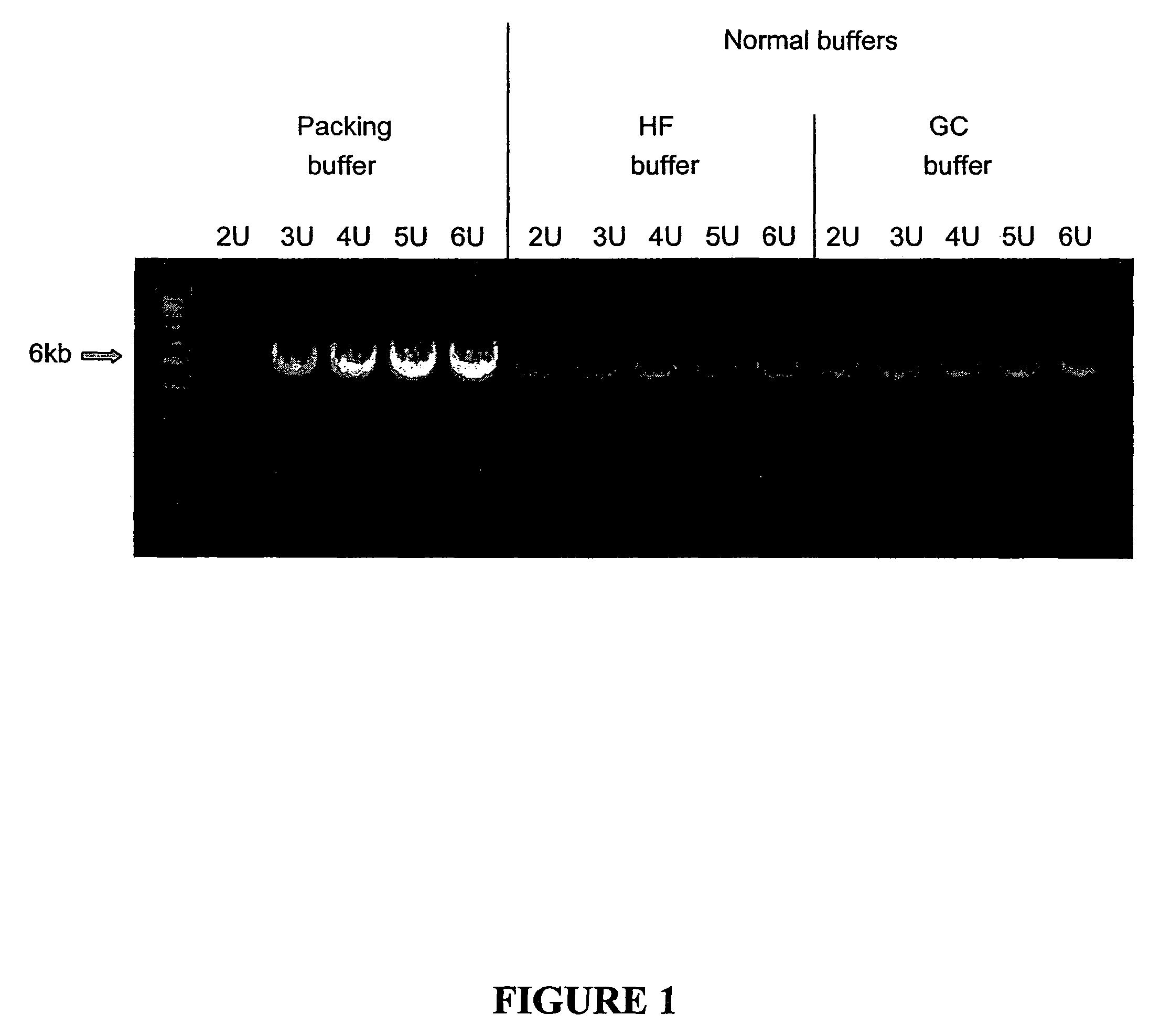
Reaction buffer composition for nucleic acid replication with packed DNA polymerases
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for nucleic acid replication, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and mutagenesis reactions. A buffer composition is provided which allows higher concentrations of DNA polymerase to be used, resulting in greater yield of amplified product and faster reaction kinetics.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
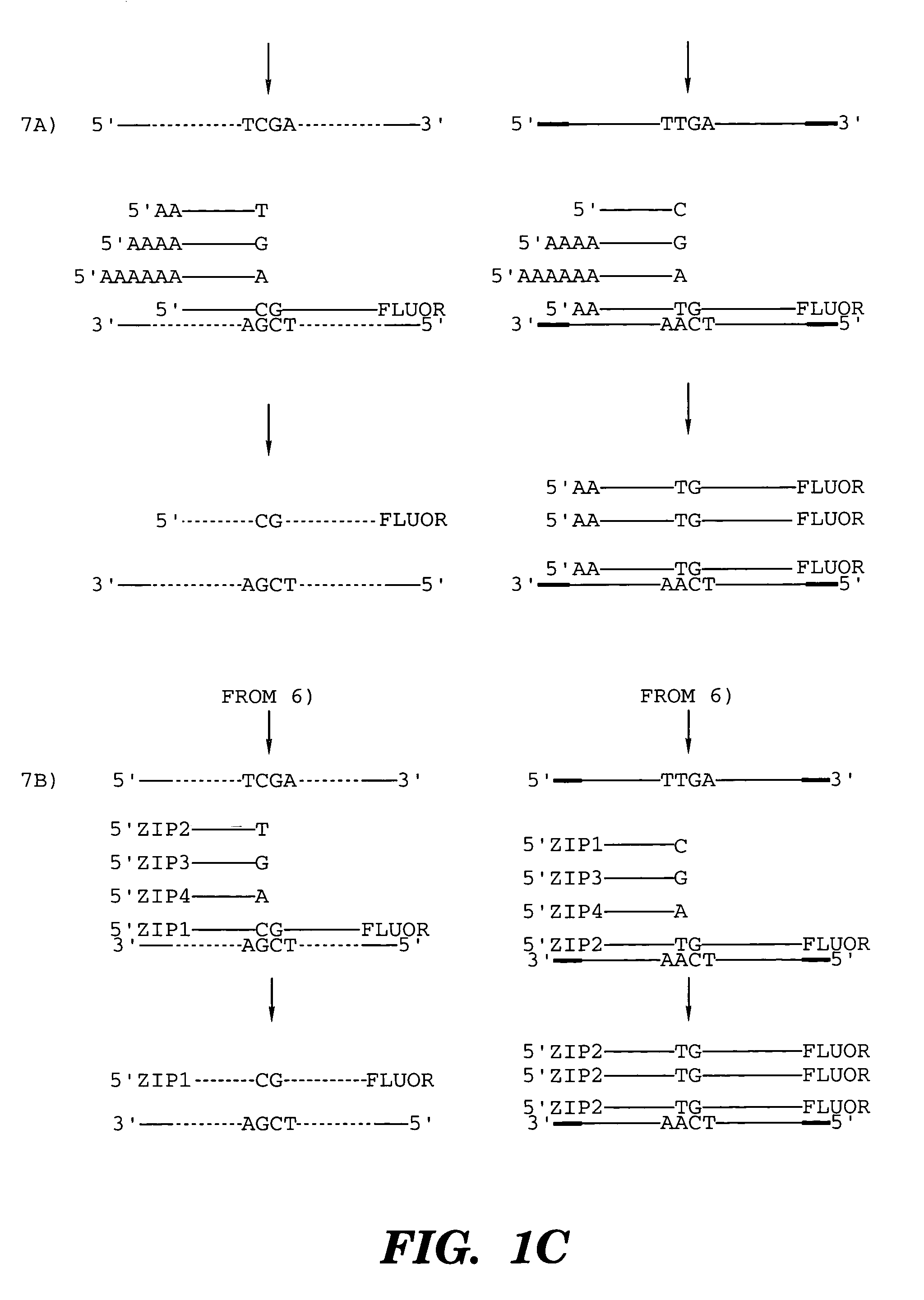
Method for carrying out high-throughput sequencing on TCR (T cell receptor) or BCR (B cell receptor) and method for correcting multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer deviation by utilizing tag sequences
InactiveCN103710454AFully functionalReduce sequencing errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationV regionPcr ctpp
The invention provides a method for carrying out high-throughput sequencing on a TCR (T cell receptor) or a BCR (B cell receptor). The method is characterized by designing upstream primers according to gene features of a V region of the TCR or the BCR and designing downstream primers according to gene features of a C region or a J region of the TCR or the BCR and obtaining sequences of the of the TCR or the BCR in combination with the multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology and high-throughput sequencing, thus analyzing the rearrangement information of the TCR or the BCR. Compared with 25-30 cycles of existing multiplex PCR, two cycles of the multiplex PCR technology provided by the invention can conduce to greatly reducing the sequencing errors caused by primer amplification preference. Besides, the invention also provides a method for correcting multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer deviation by utilizing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) tag sequences, thus further reducing the sequencing errors caused by primer amplification preference and intrinsic sequencing errors of high-throughput sequencing.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA +1
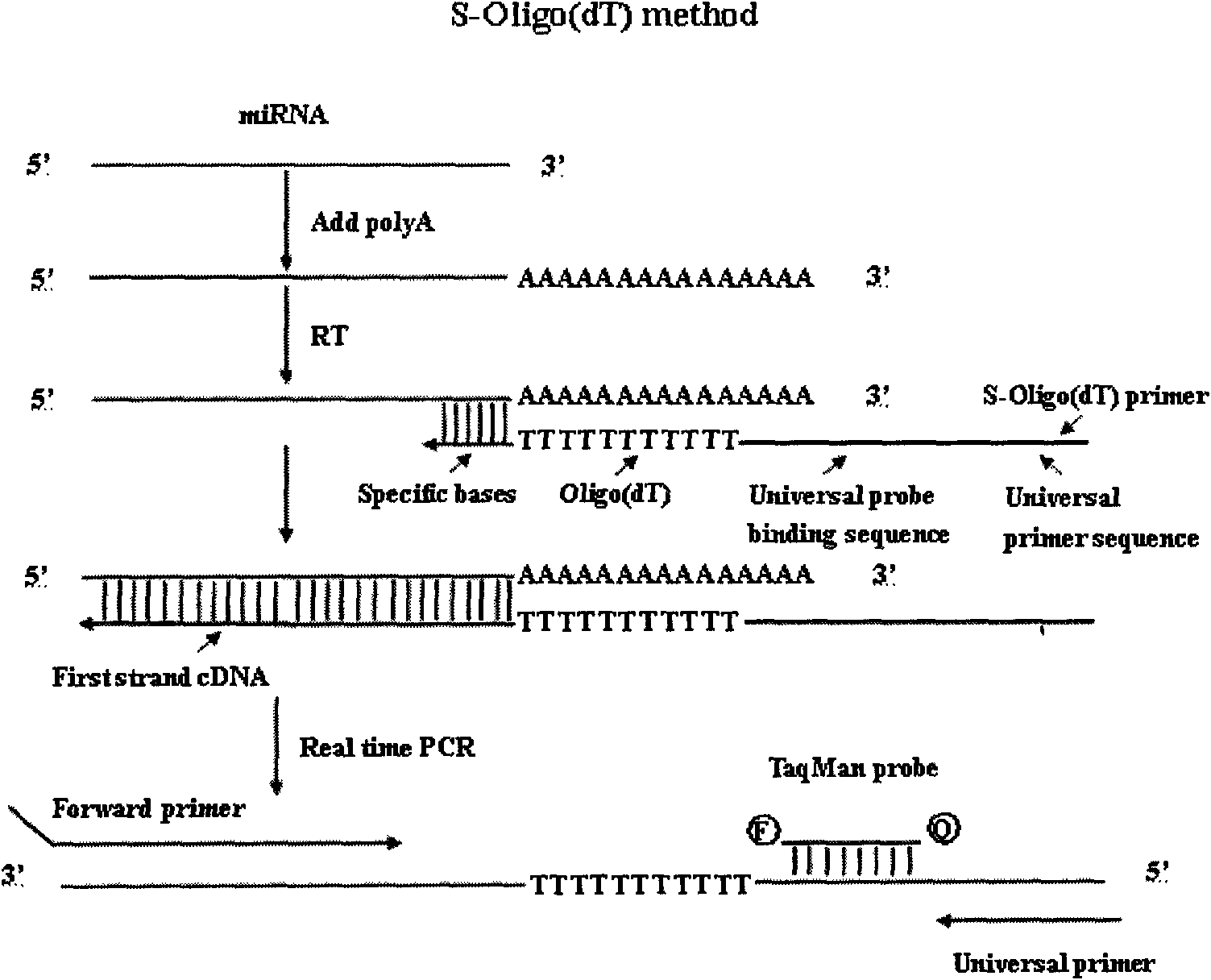
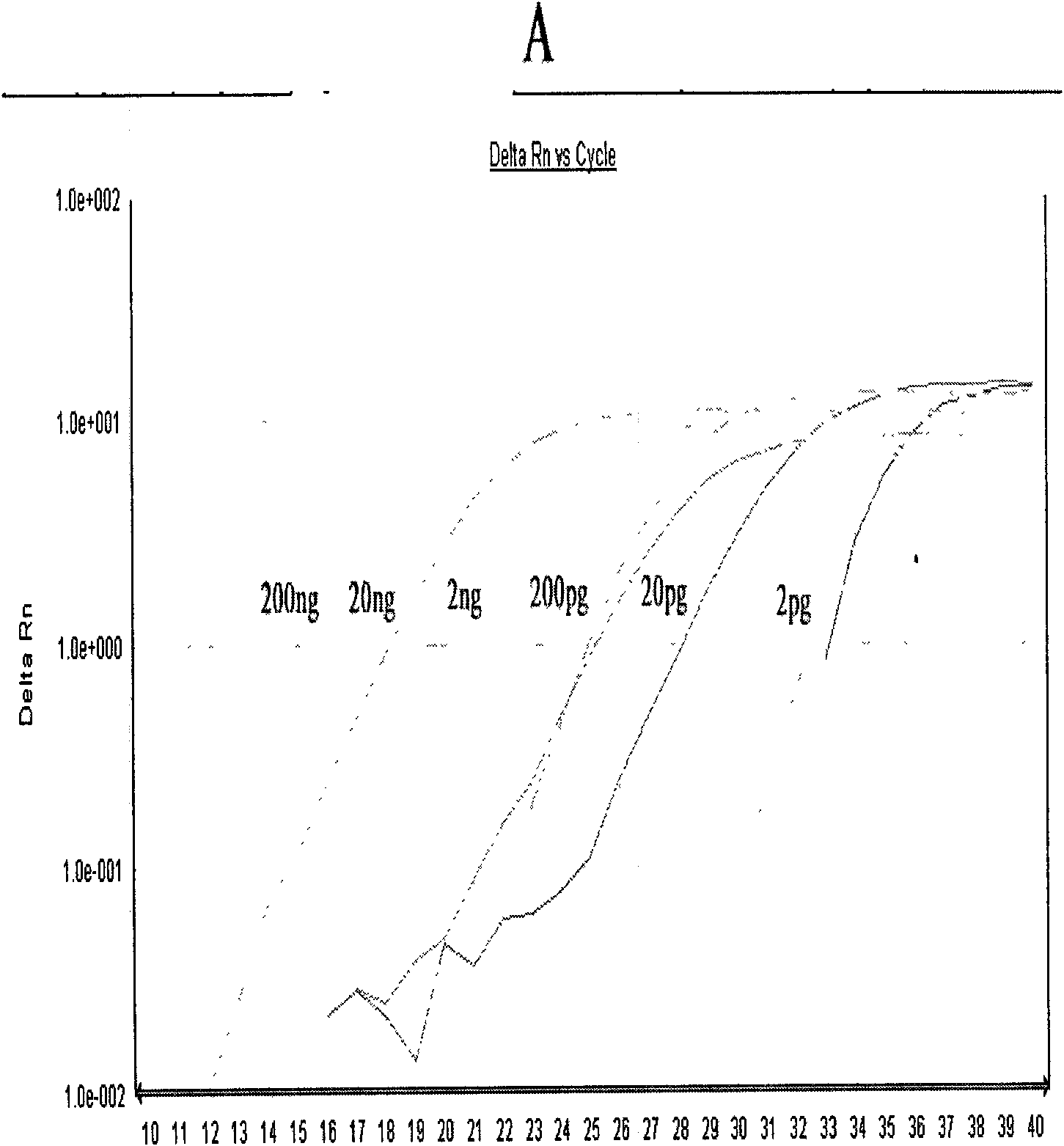
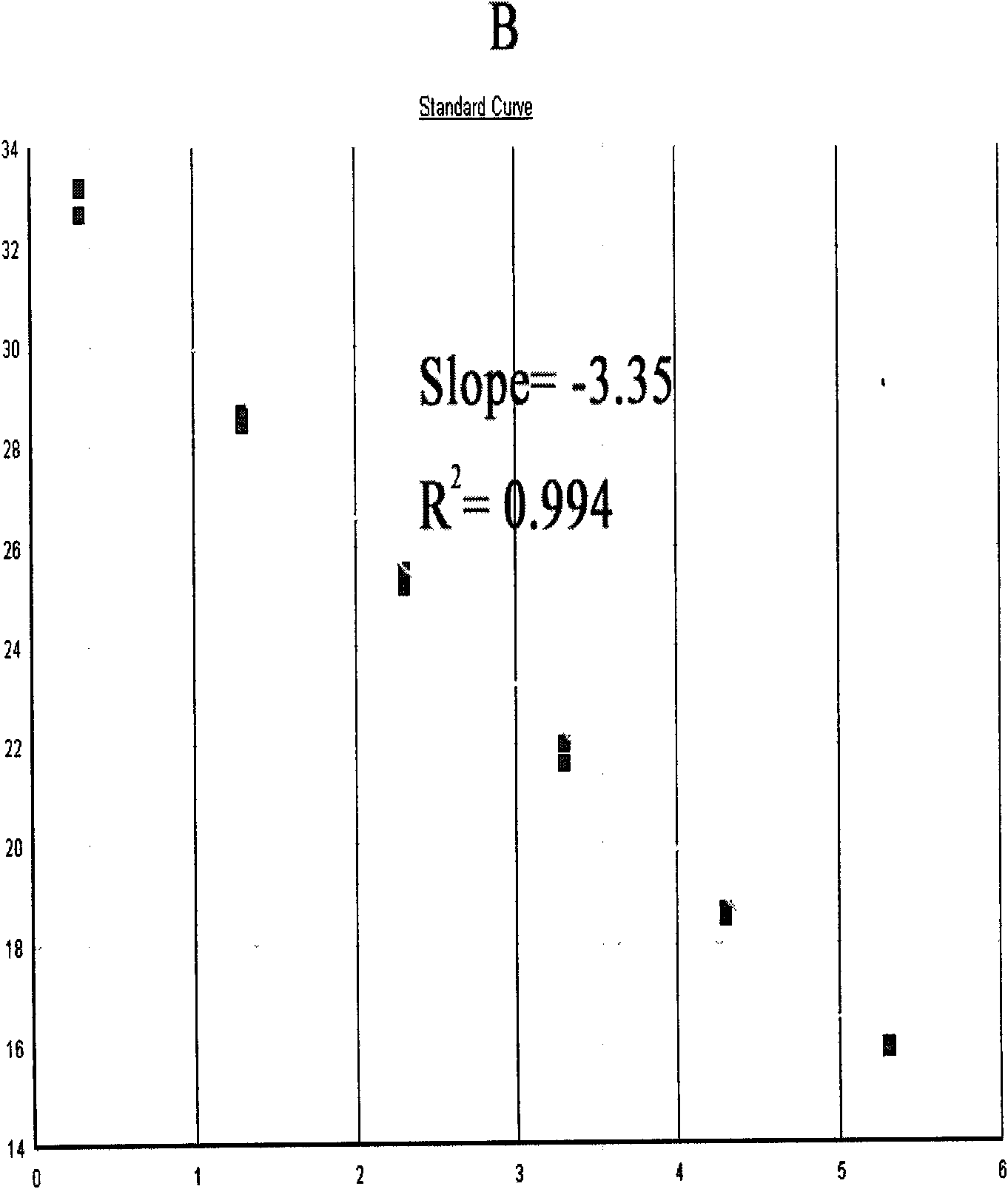
Method and primers for detecting mi ribonucleic acid (miRNA) and application of method
ActiveCN102154505AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerDisease
The invention discloses a method and primers for detecting mi ribonucleic acid (miRNA) and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing reverse transcription on the miRNA in a sample by using a reverse transcription primer formed by specific basic groups and Oligo (dT); and performing real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) quantitative detection on the miRNA by using a specific forward primer, a general reverse primer and a general probe. The invention has the characteristics that: the sensitivity and the specificity of the method are obviously higher than those of the conventional method; high-throughput analysis can be performed; and the method is simply and quickly operated, is low in cost, and can be widely used for early diagnosis and prediction of critical diseases such as tumors and the like.
Owner:苟德明 +1
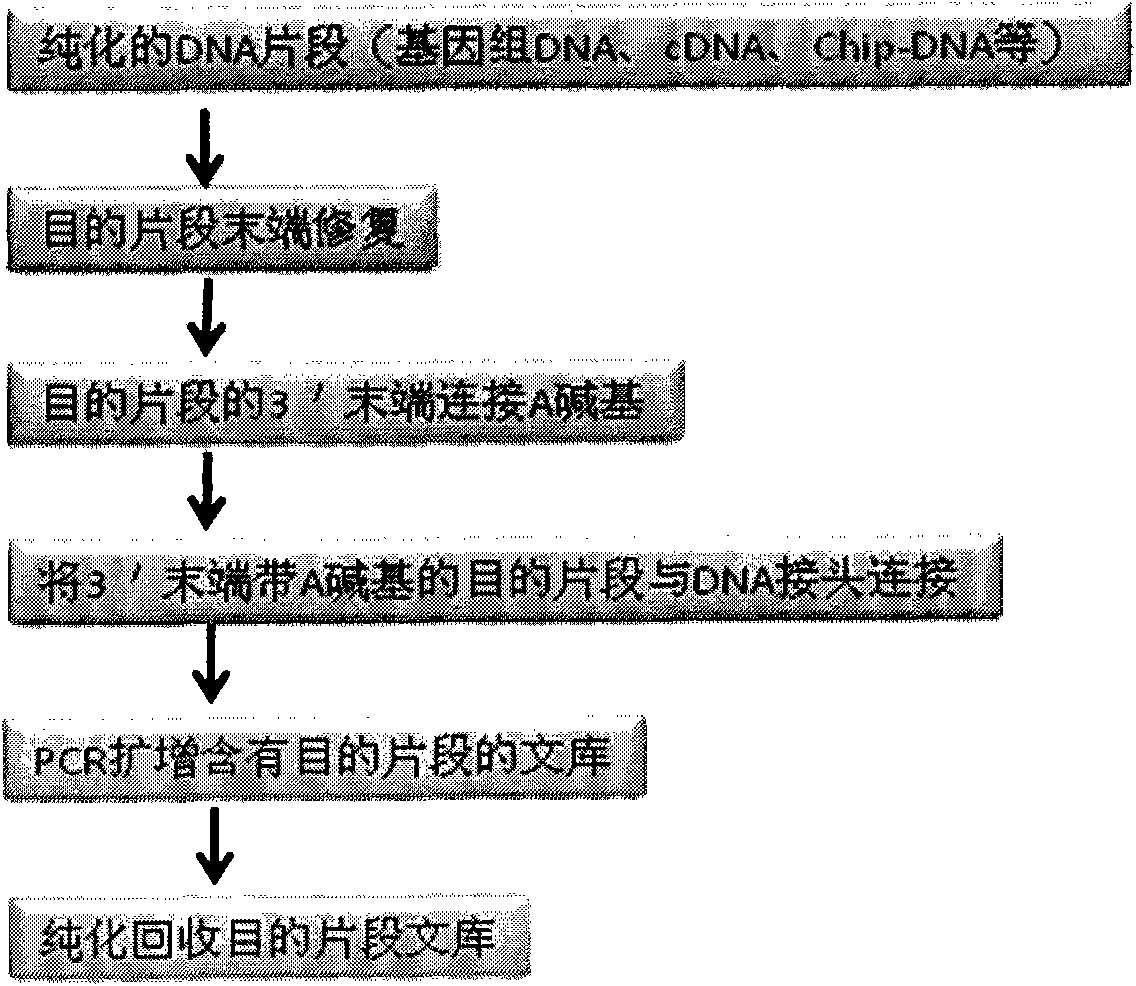
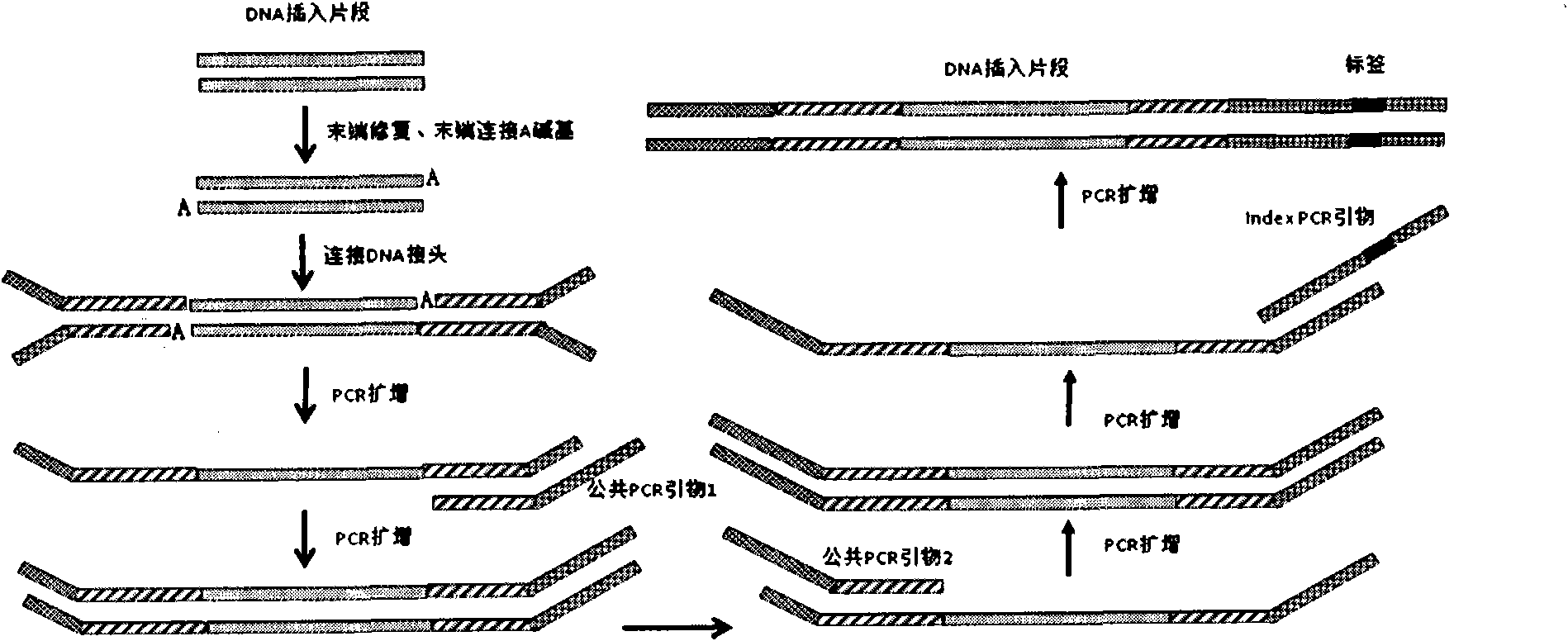
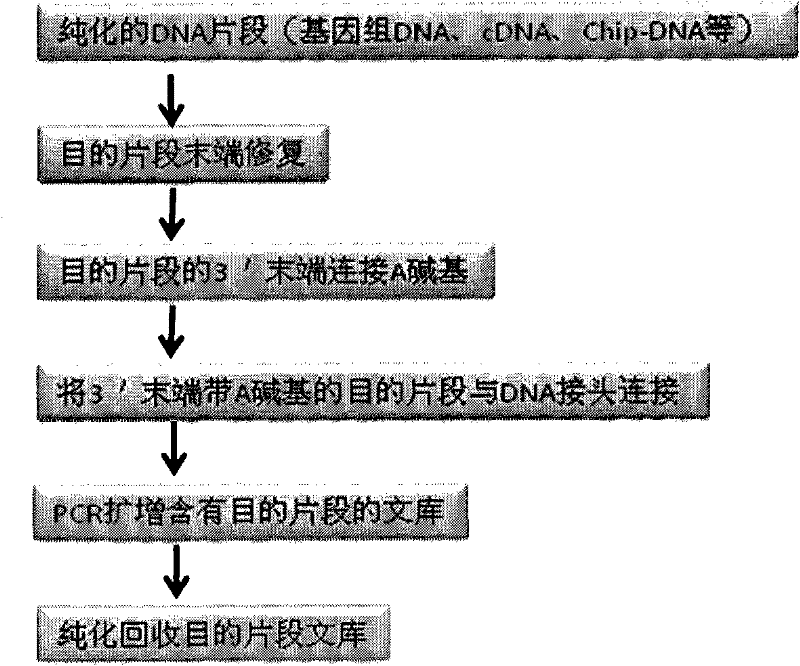
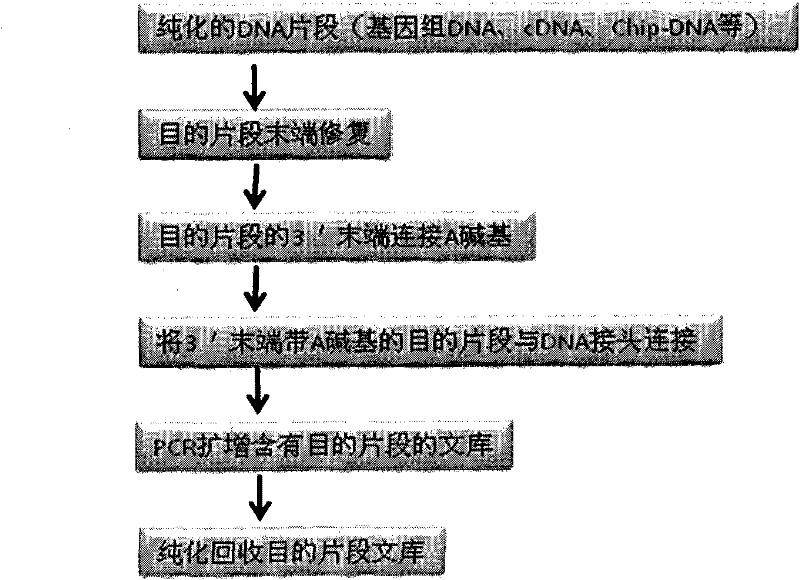
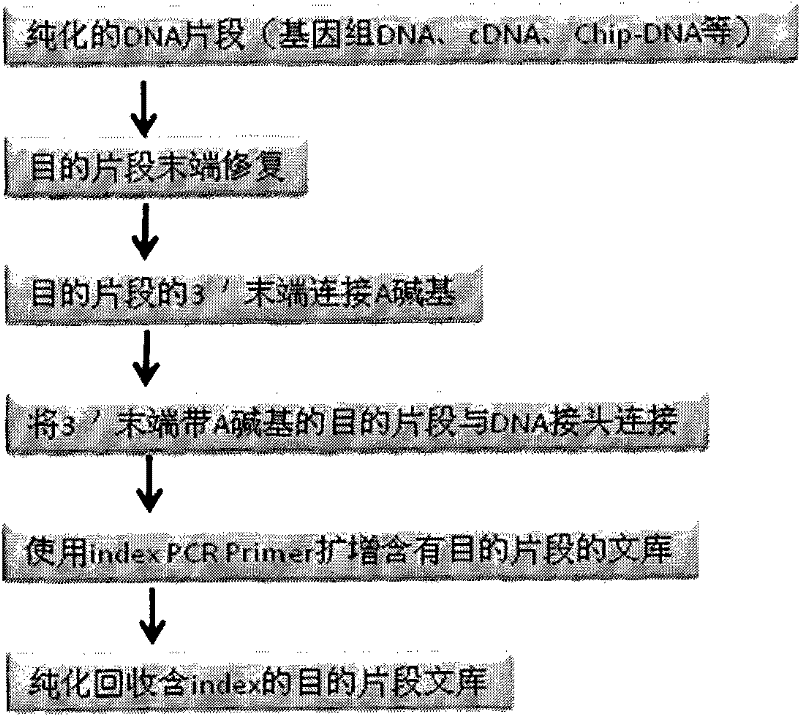
DNA index library building method based on high throughput sequencing
ActiveCN102409048AImprove production efficiencyHigh sequencing throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle sampleA-DNA
The invention provides unique index sequences with a length of 7bp. The index sequences can be respectively imported into a DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) index library through adapter link and PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The invention provides a method for building the DNA index library by using the index sequences based on a solexa sequencing platform of the current illumina company, and the method is applied to solexa DNA sequencing and has the effects on improving the preparation efficiency of the DNA index library, increasing the sequencing throughput of the DNA samples and lowering thesolexa sequencing cost of a single sample.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
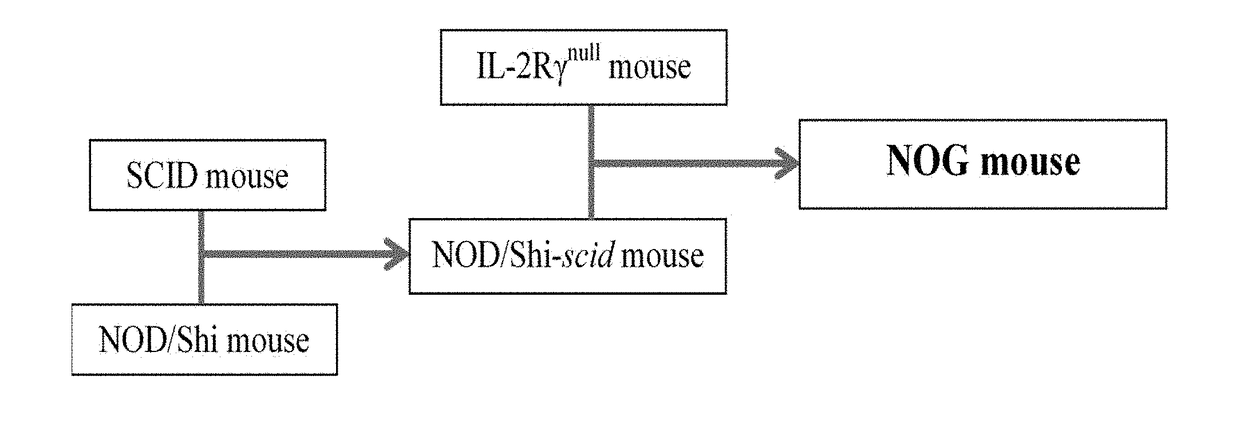
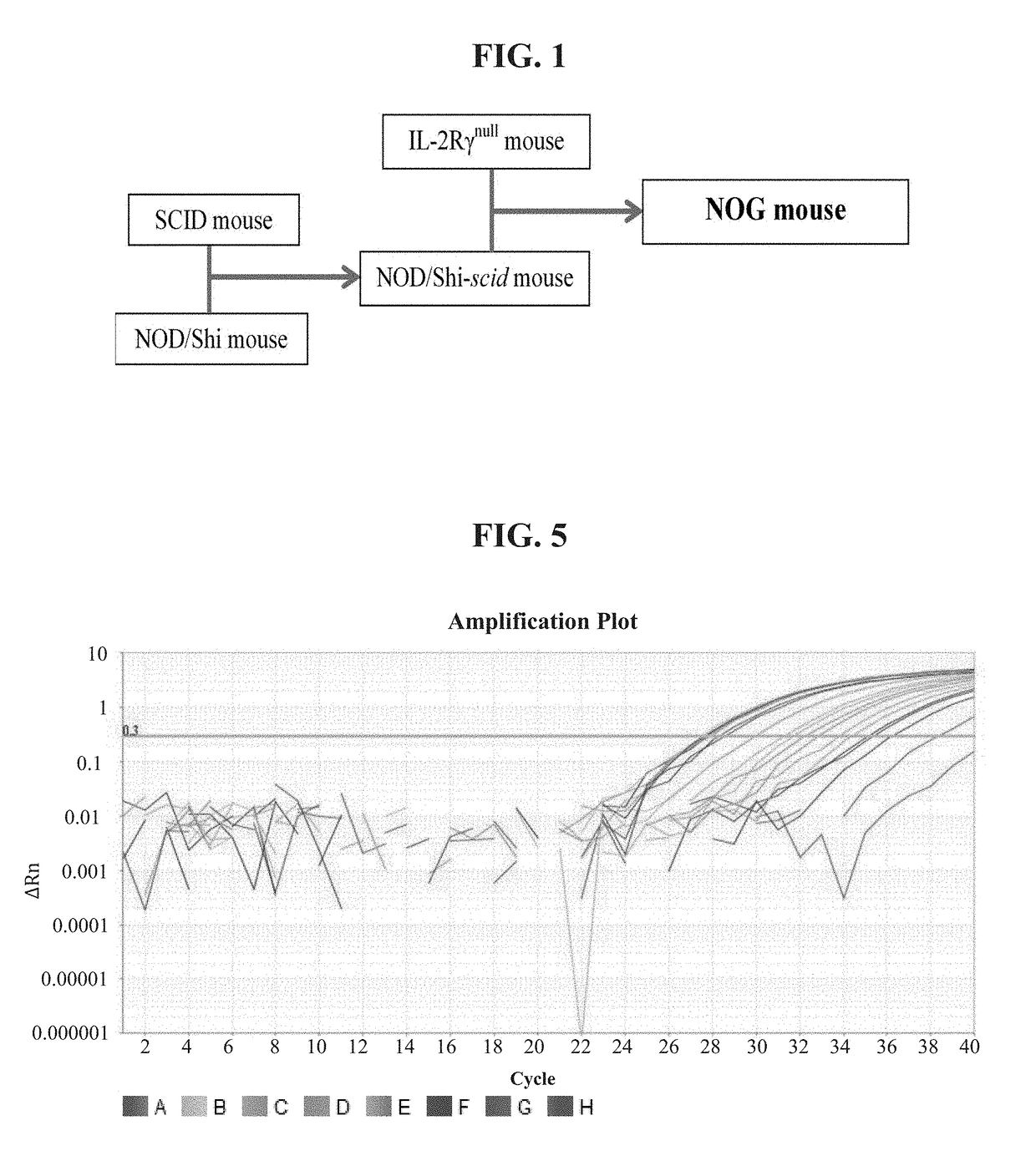
Method for measuring tumor burden in patient derived xenograft (PDX) mice
ActiveUS20180288982A1Easy to observeMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processCirculating tumor DNAHuman patient
Kits and methods providing measurement of tumor burden in a patient derived xenograft (PDX) mouse are described. Exemplary embodiments contemplate taking a sample, typically a blood sample, from a PDX mouse and using a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system to quantitate both human patient circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and mouse DNA. In preferred embodiments, both PCR amplifications are done simultaneously in a multiplex, and a highly polymorphic human DNA target sequence is amplified for high sensitivity, allowing for small volume samples, typically 50-100 μL, of mouse blood. Serial evaluations are possible because the mouse can survive withdrawal of these small volumes of blood. A related method allows for quantitation of ctDNA in the presence of human immune cells added to a “humanized” mouse. These relatively quick and easy methods of determining tumor burden in PDX mice can have predictive value for the efficacy of cancer treatments in human patients.
Owner:LIFE GENETICS LAB
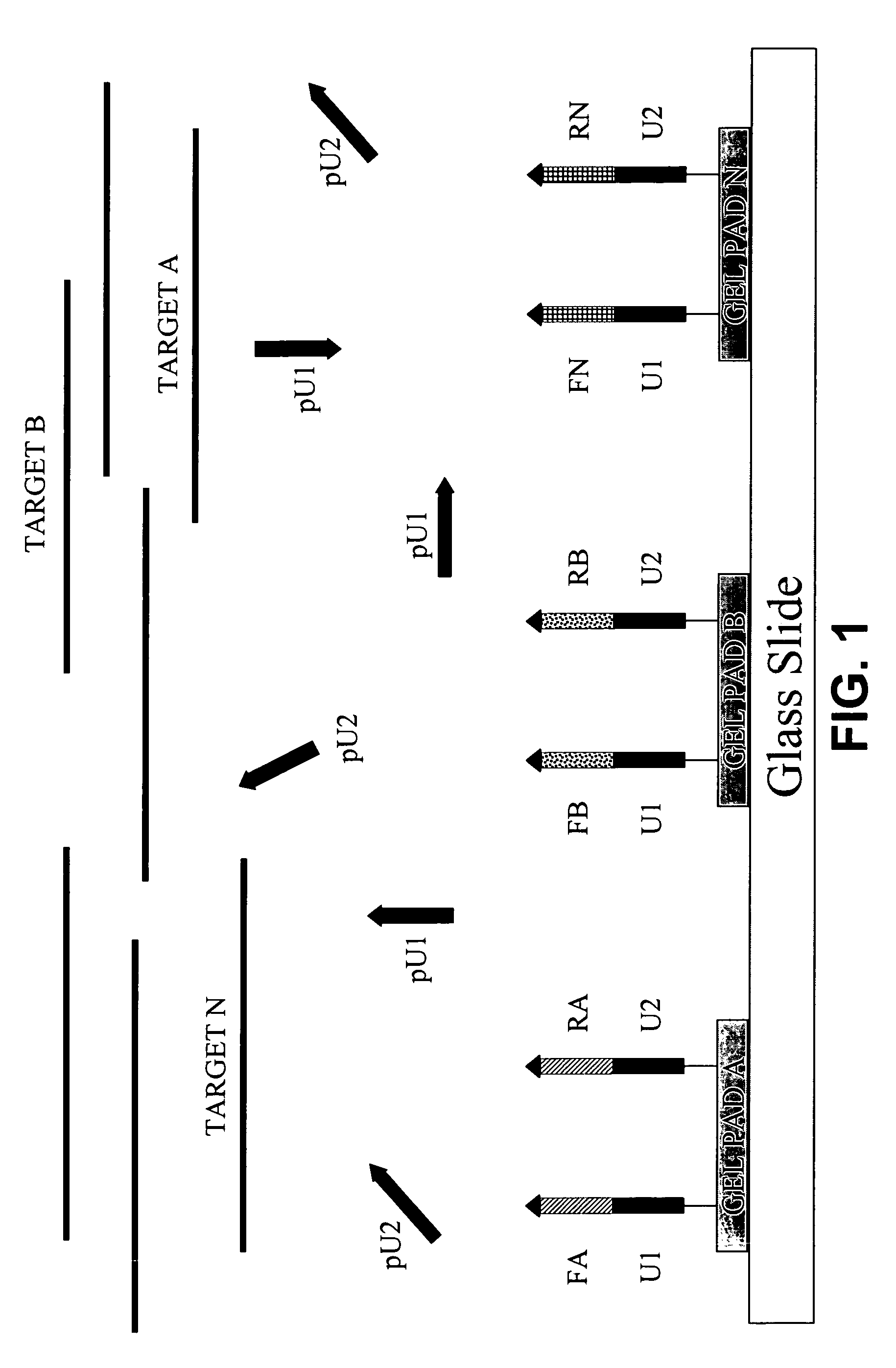
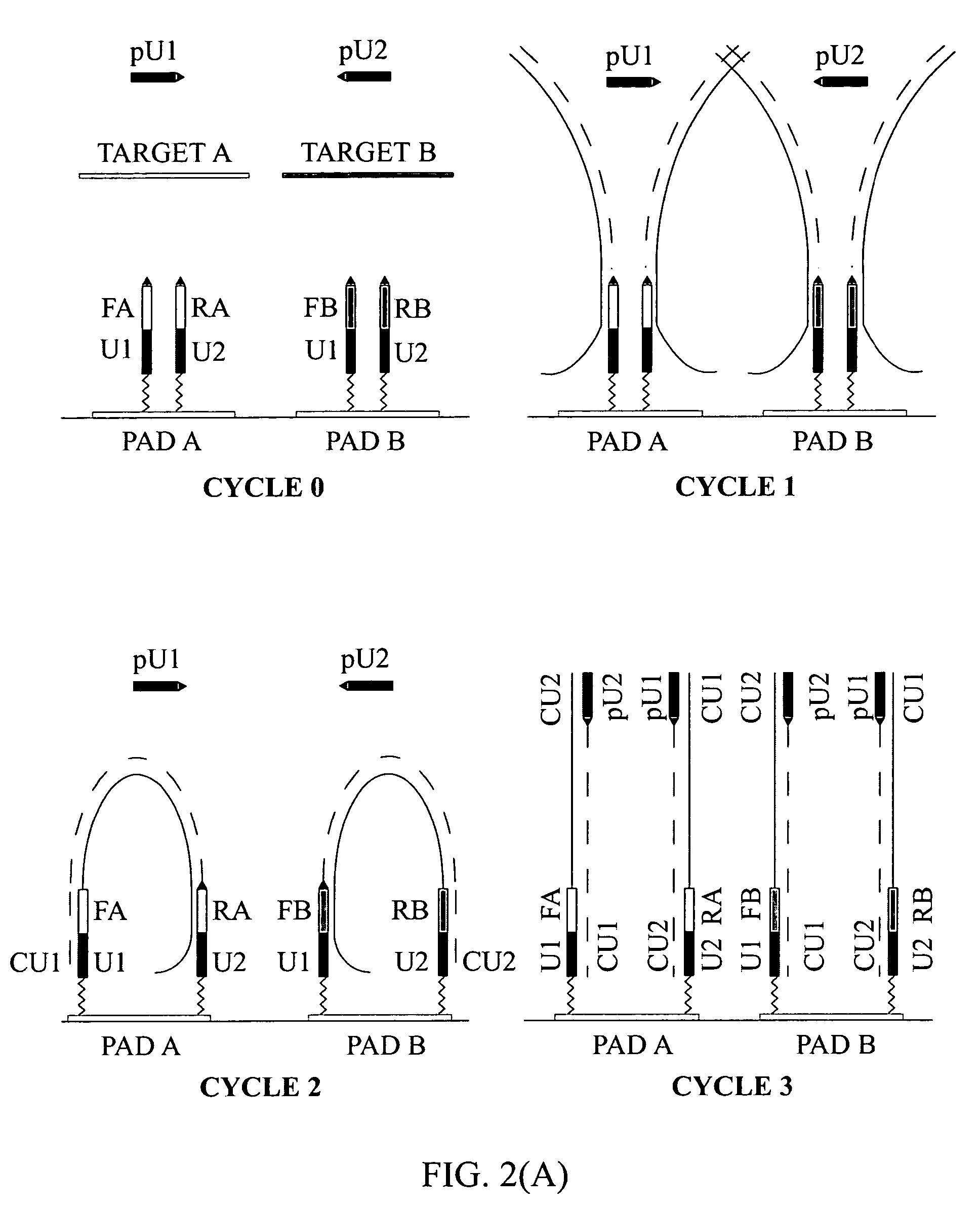
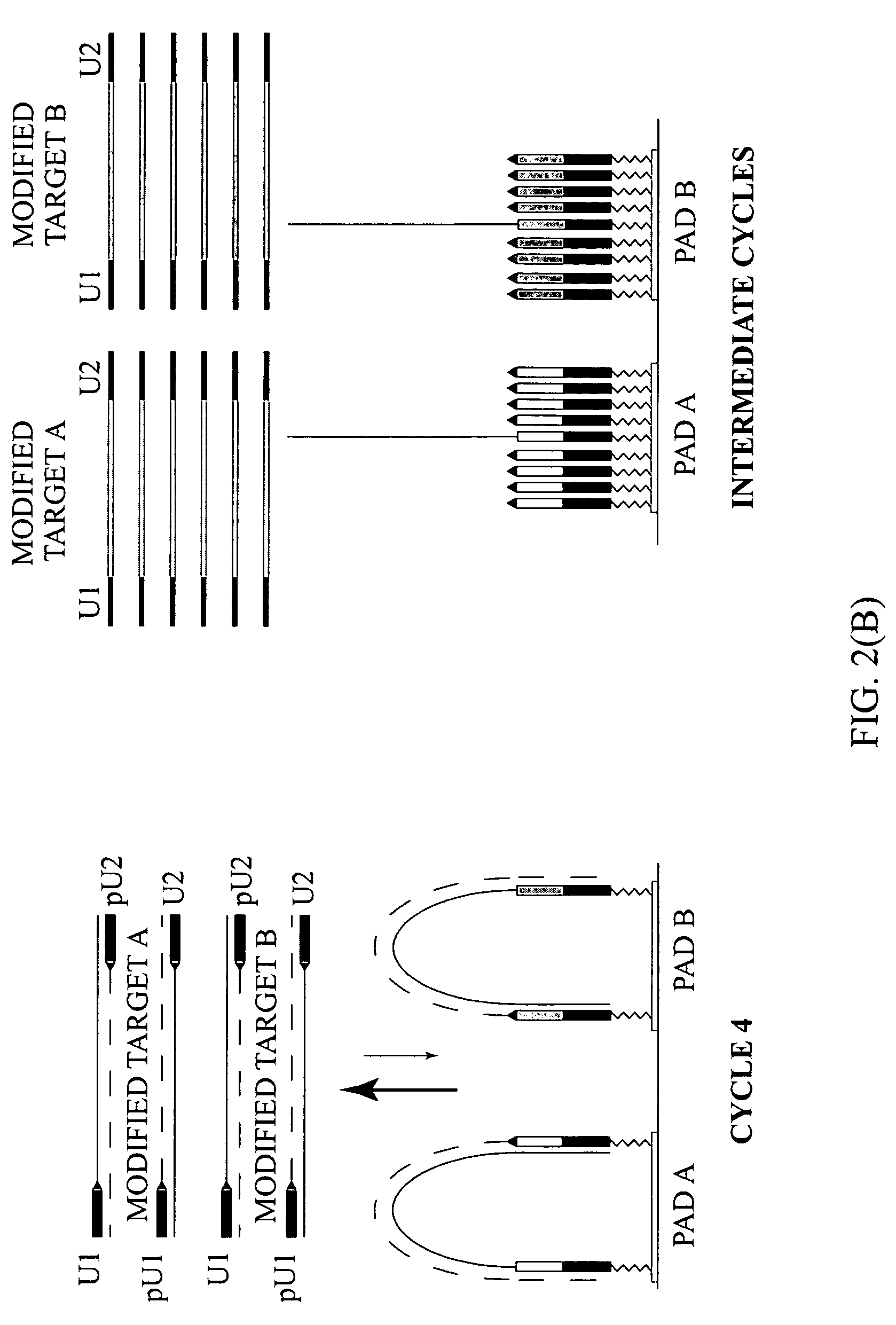
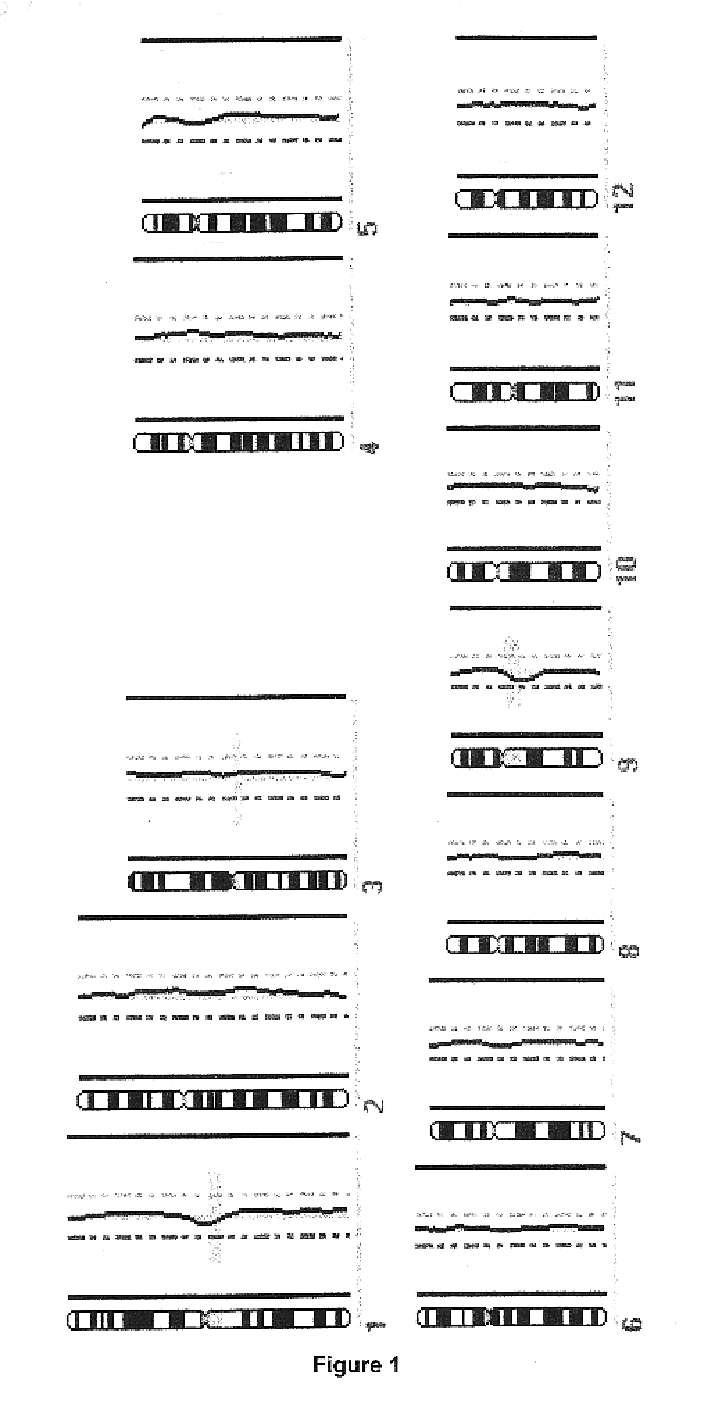
Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer
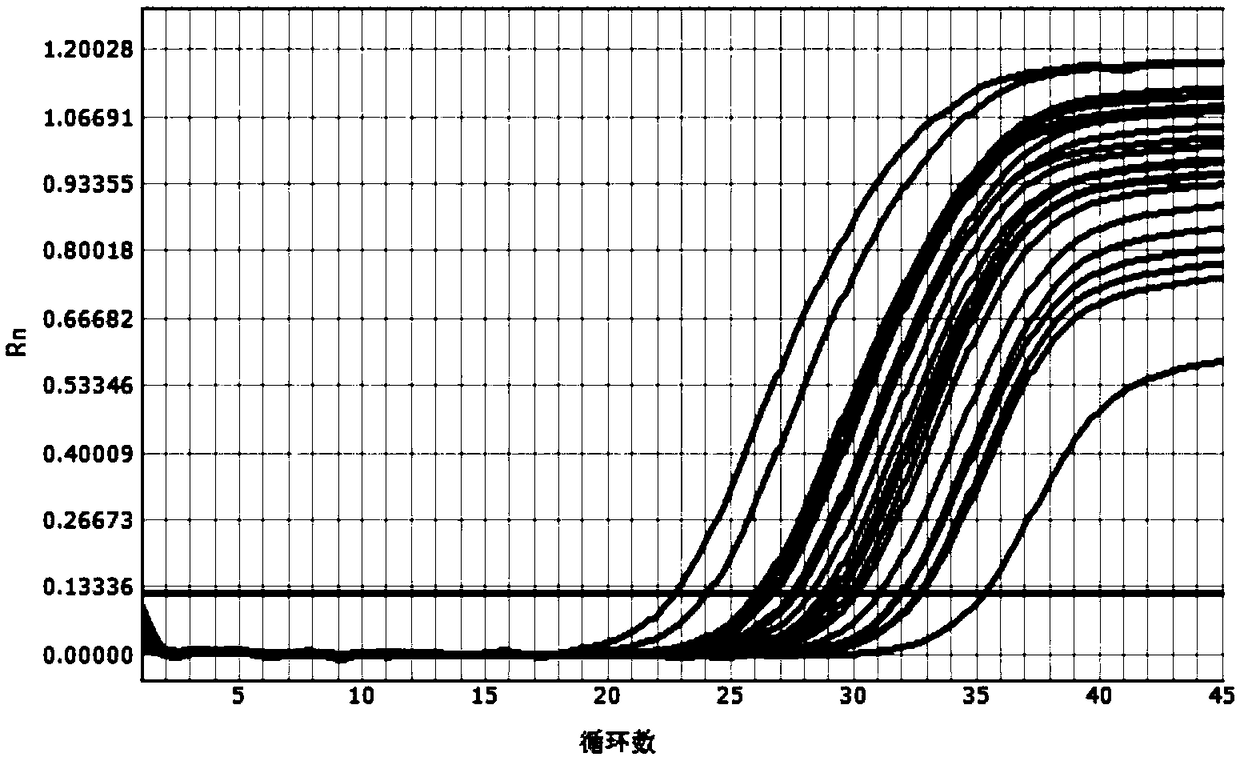
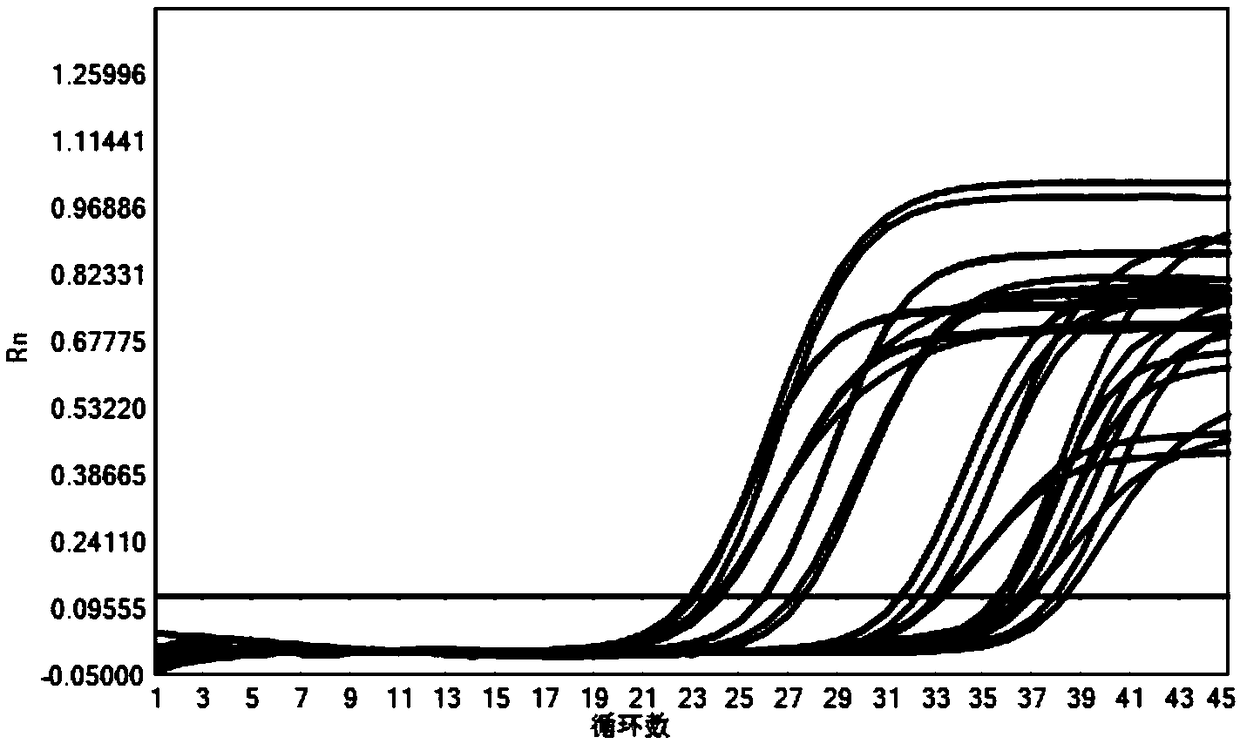
ActiveCN105112546AImprove throughputImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on the basis of a KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of the set primer. The primer set comprises totally 14 groups of KASP primers. The KASP primers are respectively designed for the 14 functional genes of the wheat, and particular nucleotide sequences of the KASP primers are sequences 1-42 in sequence tables. The primer set and the application have the advantages that the functional genes of different wheat varieties can be quickly detected by the aid of the KASP primer set, methods for detecting the functional genes of the wheat are simple, convenient and speedy, and detection results are accurate and reliable; the primer set has an important theoretical significance and important economic value in assistant selection of the wheat varieties by the aid of molecular markers.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Joint connection-based deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-free tag library construction method
The invention designs 161 unique tag sequences with the lengths of 8 bp. Tags are embedded into a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) joint so as to form a DNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-free tag joint. The invention also provides a DNA tag library which introduces the tag sequence by connecting the DNA PCR-free tag joint without a PCR and is applied to solexa DNA sequencing. After a library construction method is optimized, the DNA tag library is constructed without the PCR.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Reaction buffer composition for nucleic acid replication with packed DNA polymerases
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for nucleic acid replication, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and mutagenesis reactions. A buffer composition is provided which allows higher concentrations of DNA polymerase to be used, resulting in greater yield of amplified product and faster reaction kinetics.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
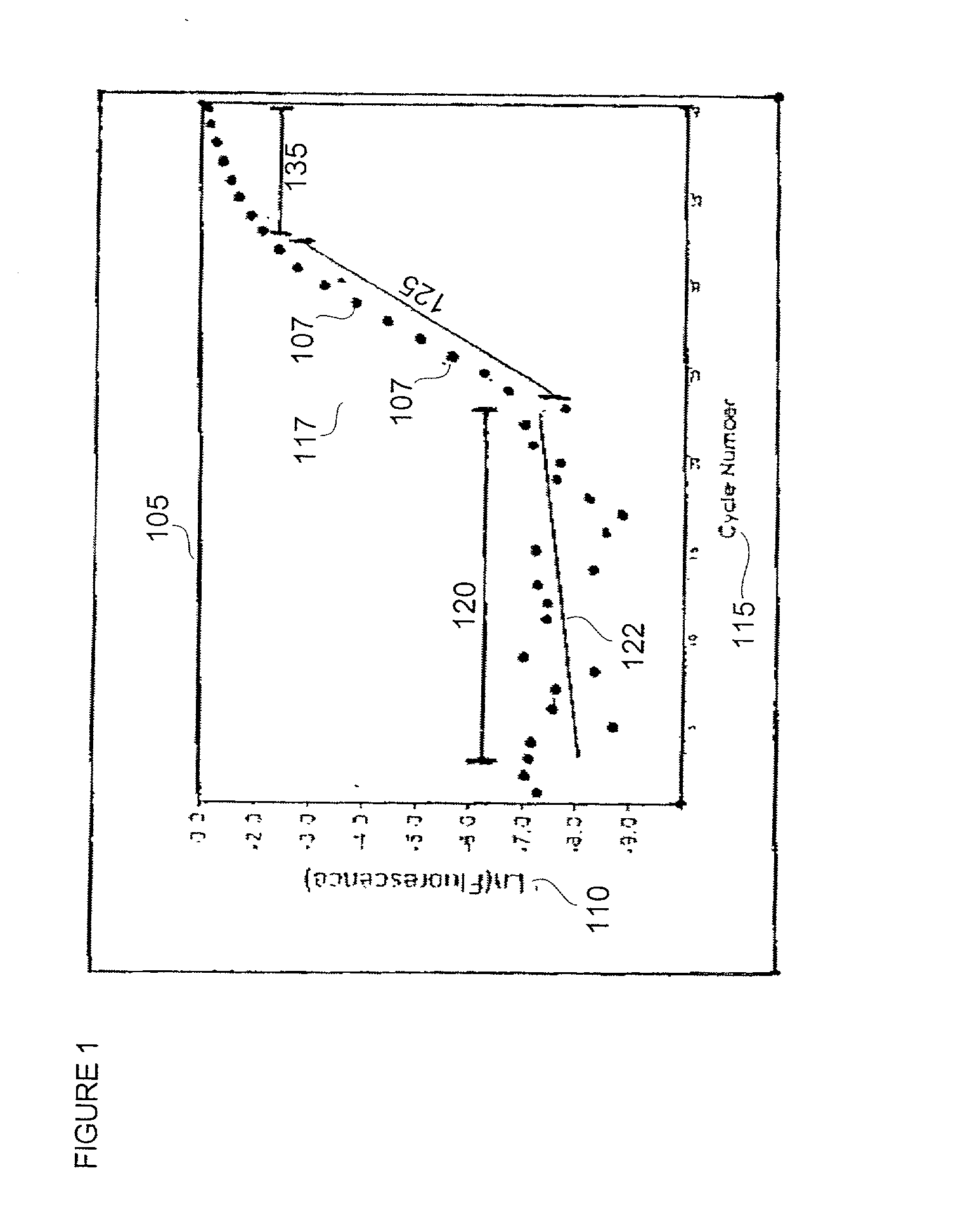
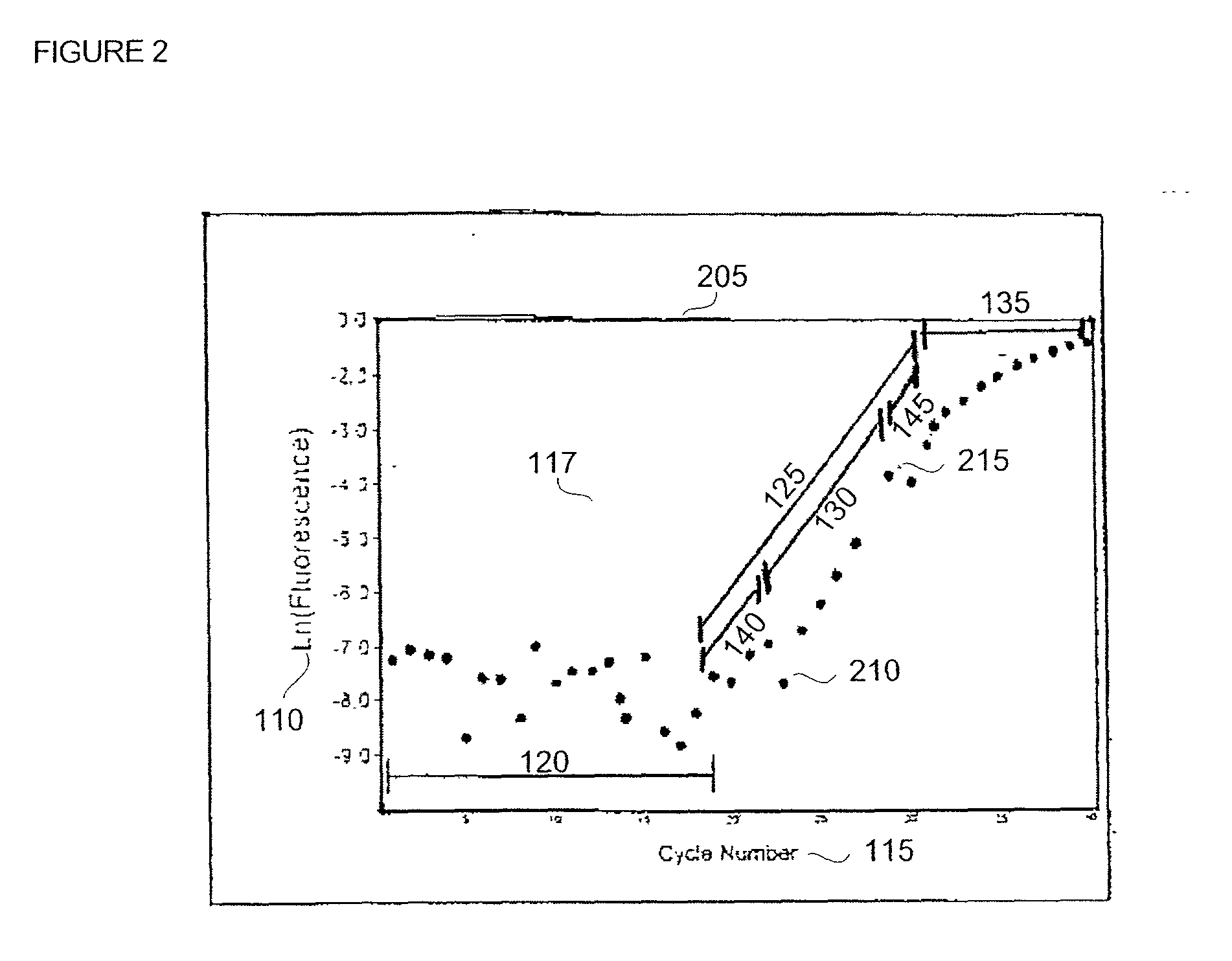
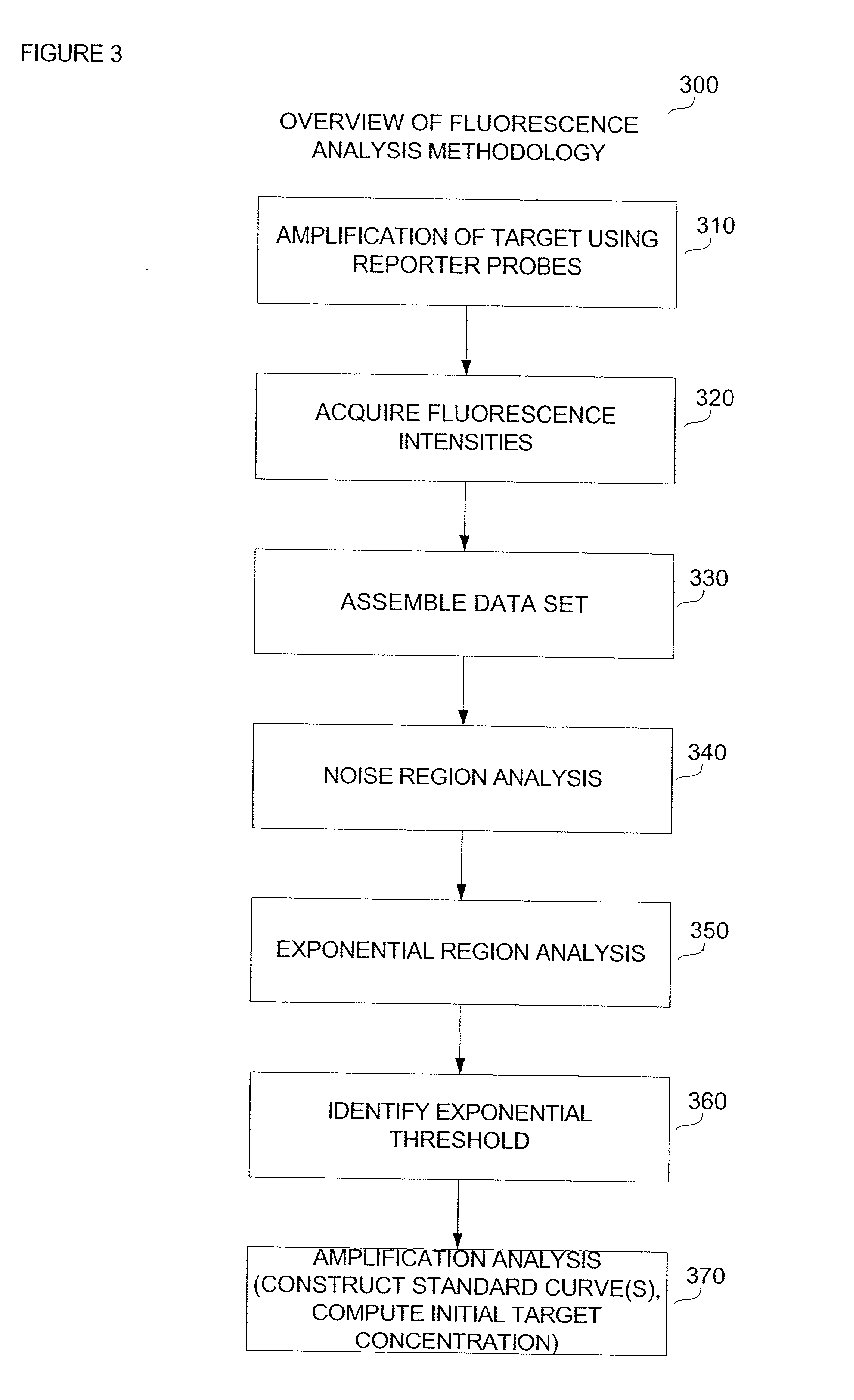
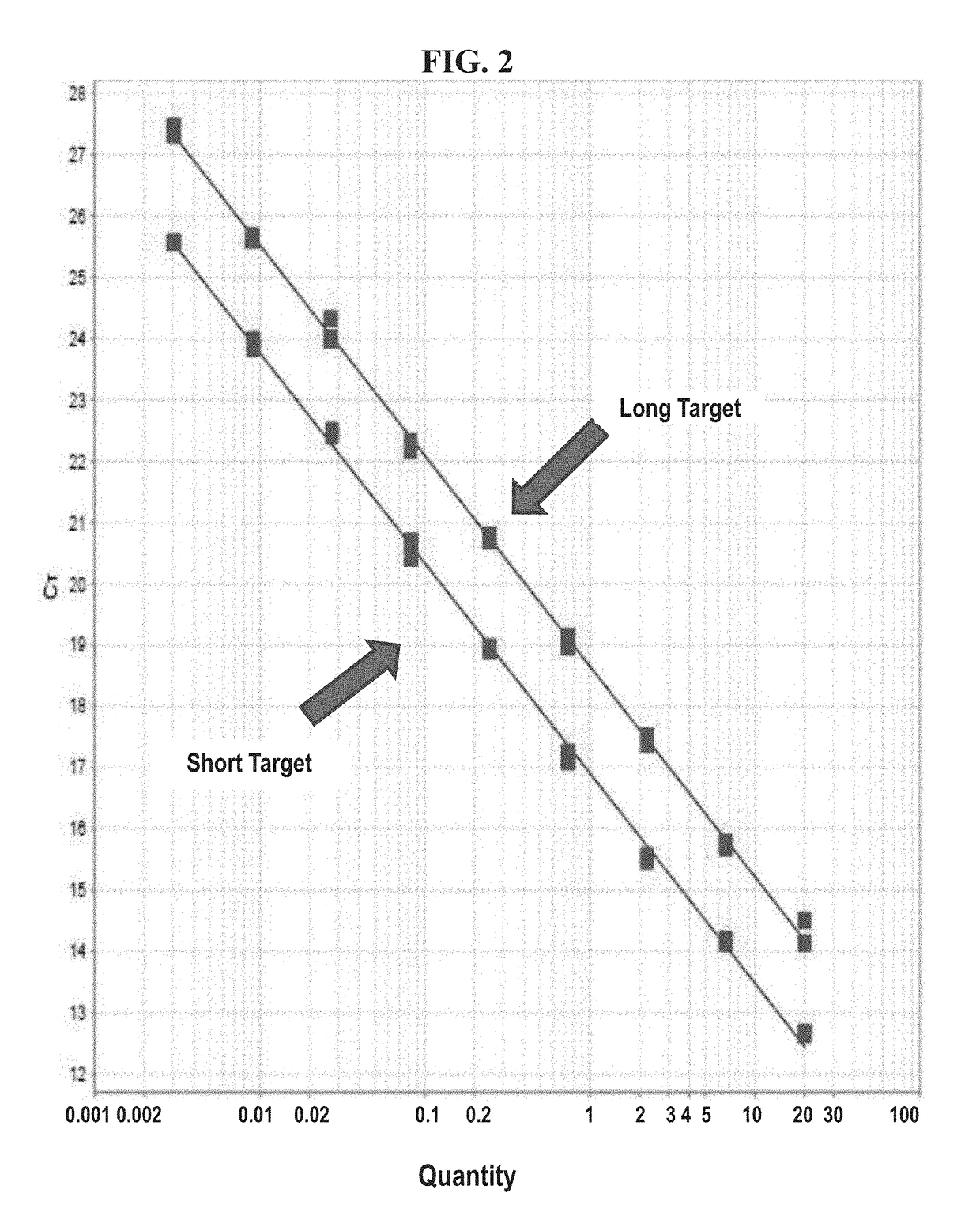
Automatic threshold setting for quantitative polymerase chain reaction
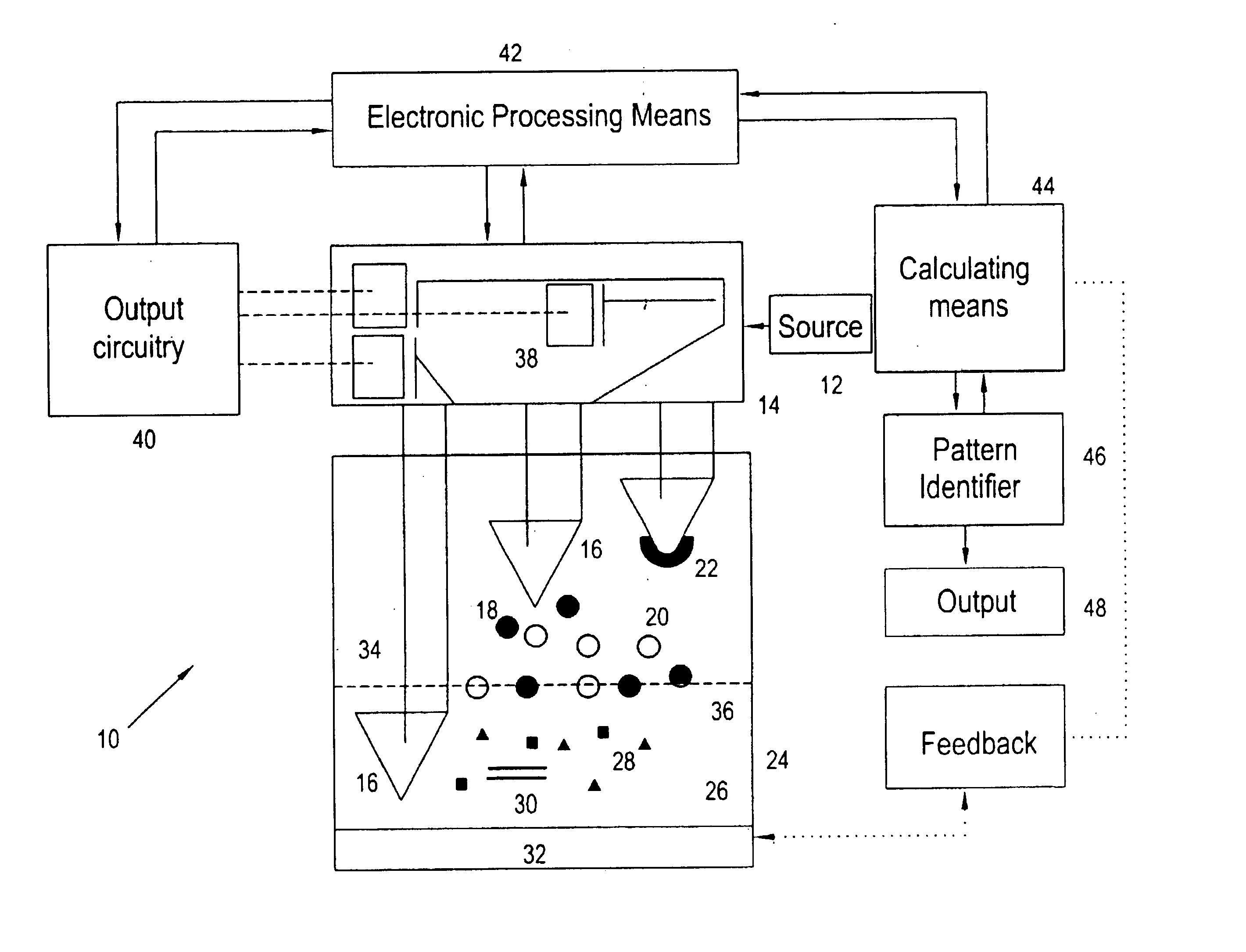
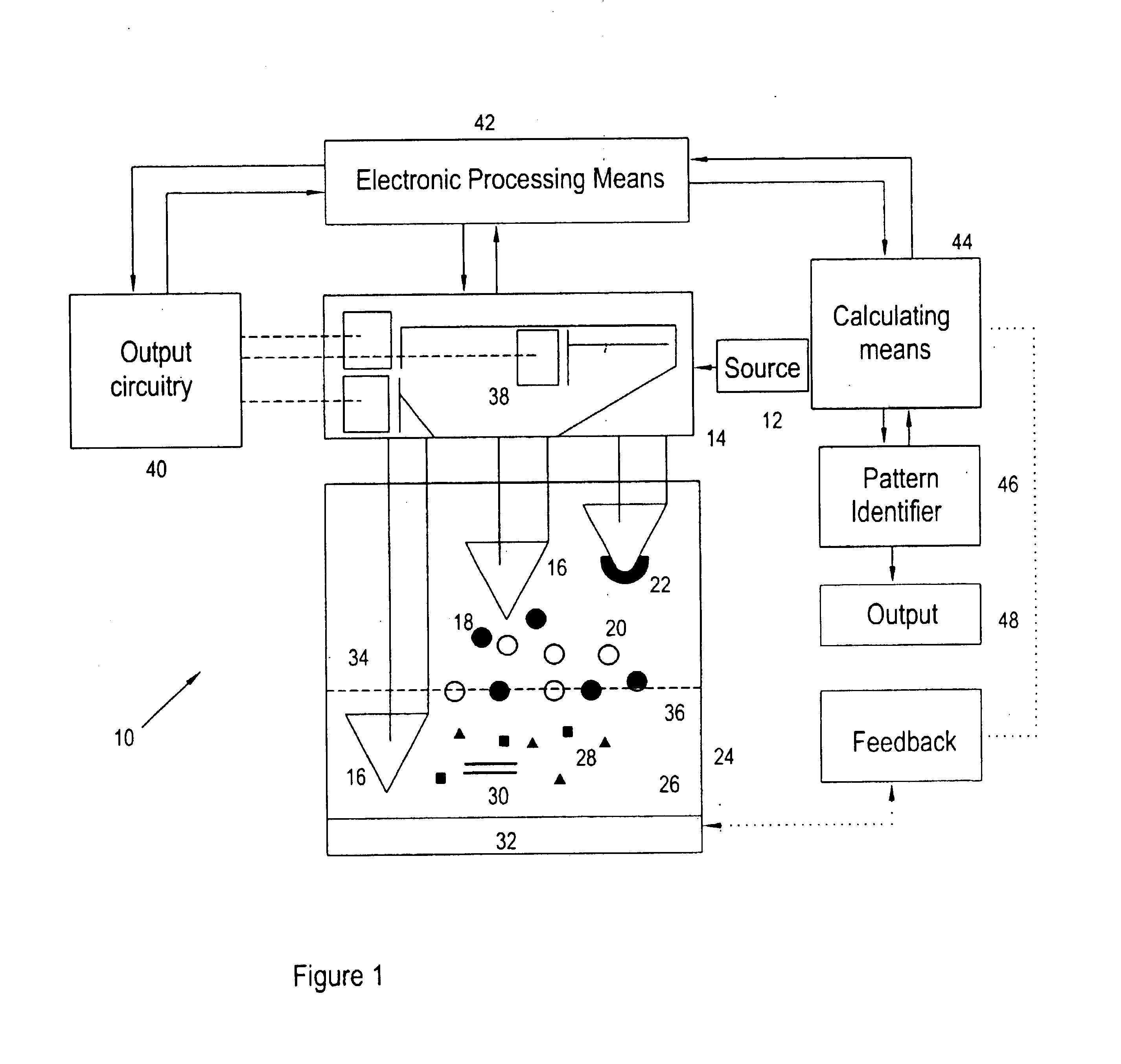
InactiveUS20030044826A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecognisation of pattern in signalsFluorescenceBiology
Disclosed are systems and methods for identifying and quantitating the presence of one or more DNA species in a sample population through PCR amplification. DNA species quantitation includes a determination of a threshold fluorescence value used in the assessment of the PCR amplification reaction. Various embodiments of the present invention incorporate an enhancement function useful in selecting appropriate threshold fluorescence values and facilitate the determination of DNA concentrations by quantitative PCR based methodologies.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
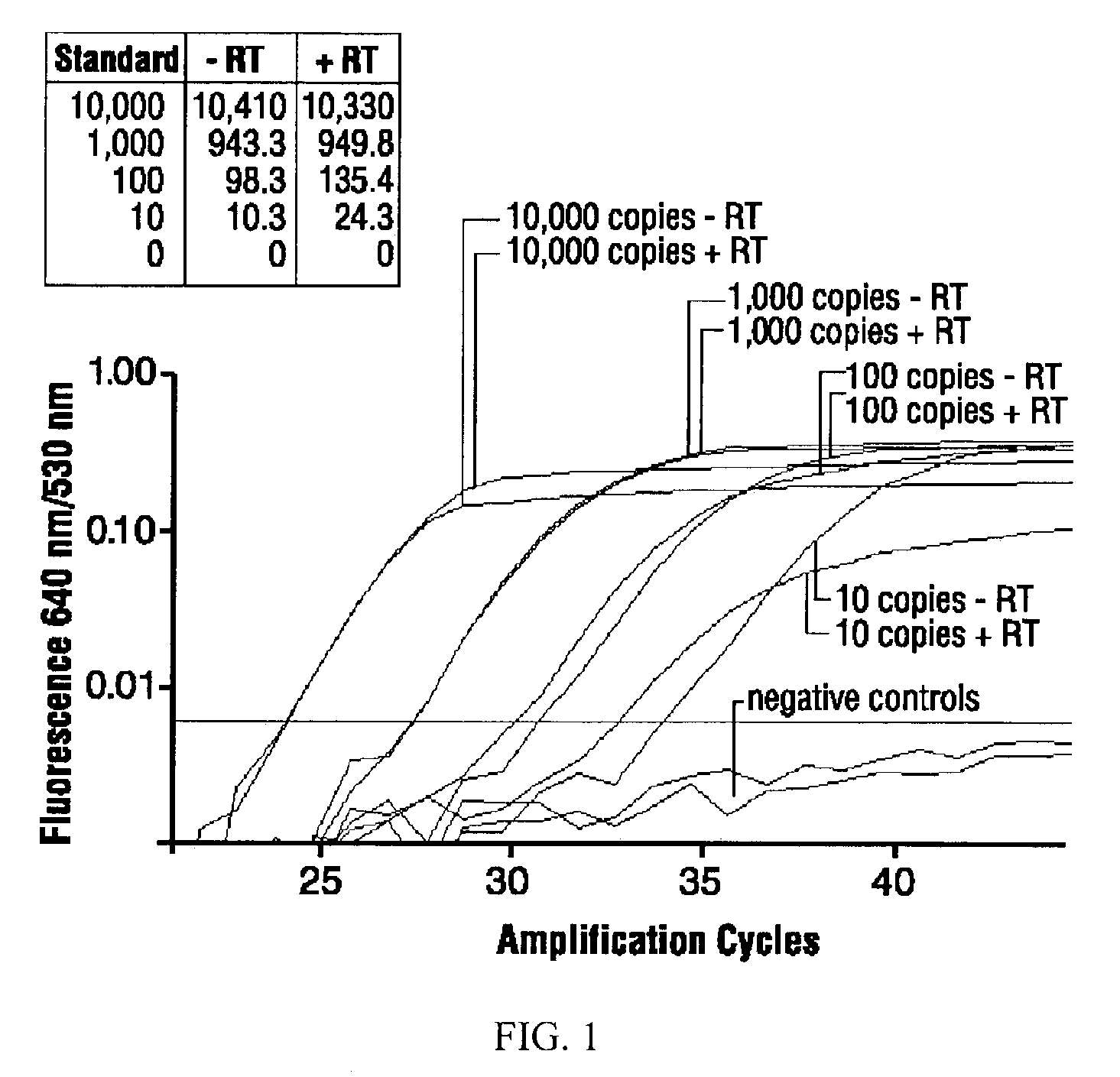
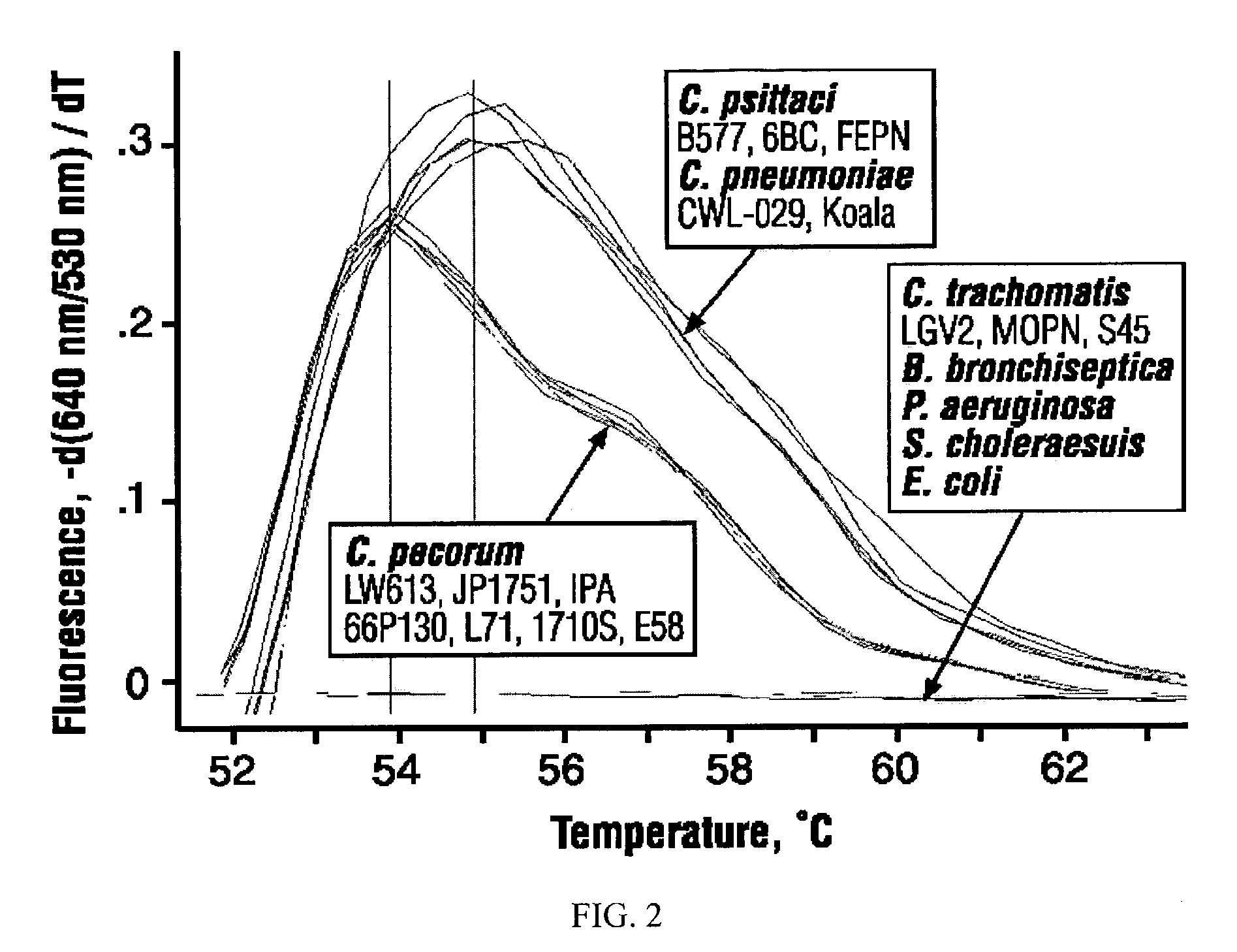
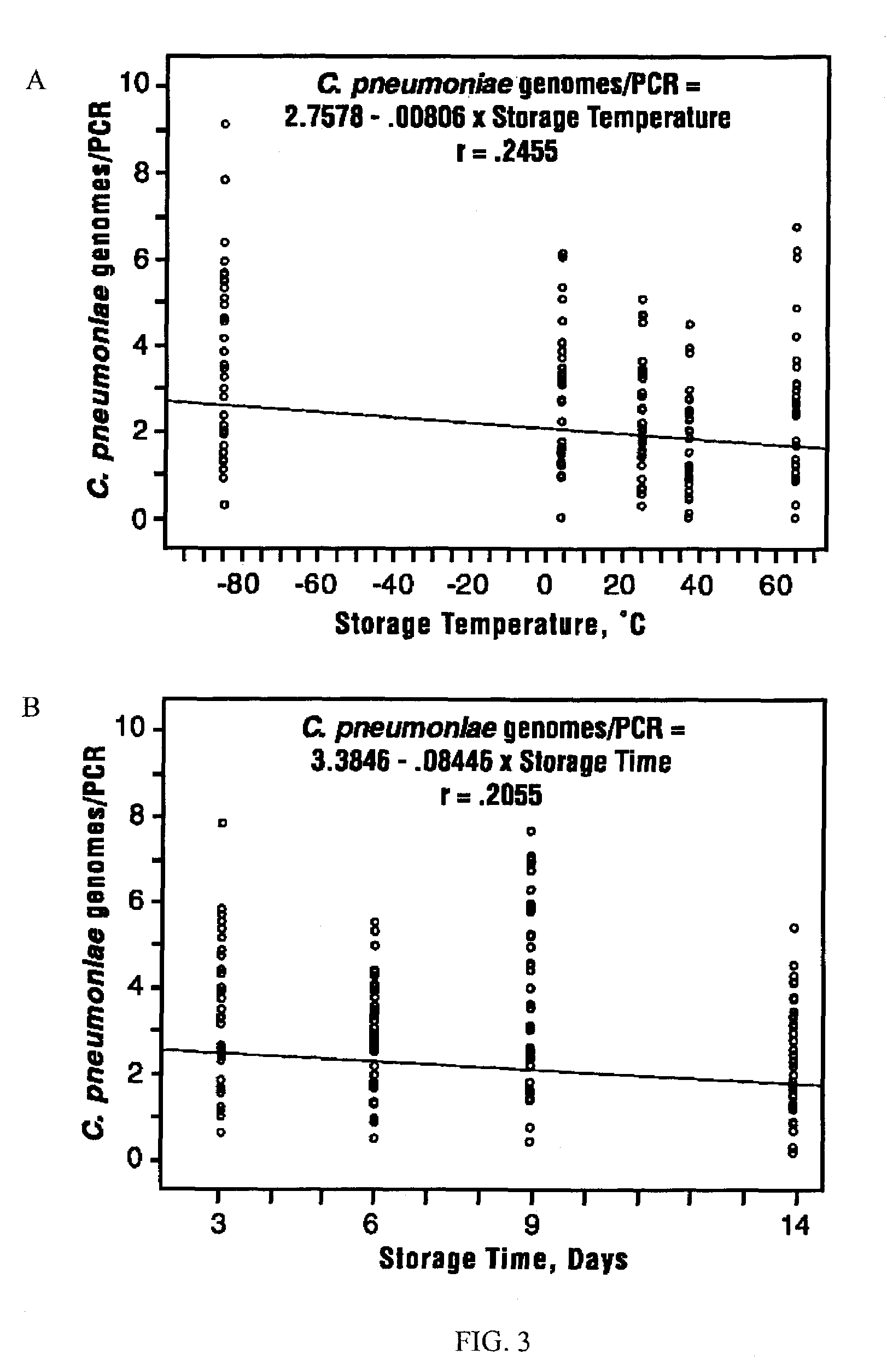
High-sensitivity real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7252937B2Easy extractionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical settingsHybridization probe
The invention features methods that are capable of detecting single target molecules in a sample input volume of, e.g., 5 μl, and of quantifying organismal, e.g., chiamydial, DNA. Desirably, these methods employ a single tube format coupled with fluorescent detection of amplicons. This approach facilitates the application of quantitative PCR (qPCR) to microbiological diagnosis in clinical settings. The invention also features primers and probes for the detection of Chlamydia. The use of specific hybridization probes with qPCR amplification provides the ability for identification of individual species or strains of microorganisms.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
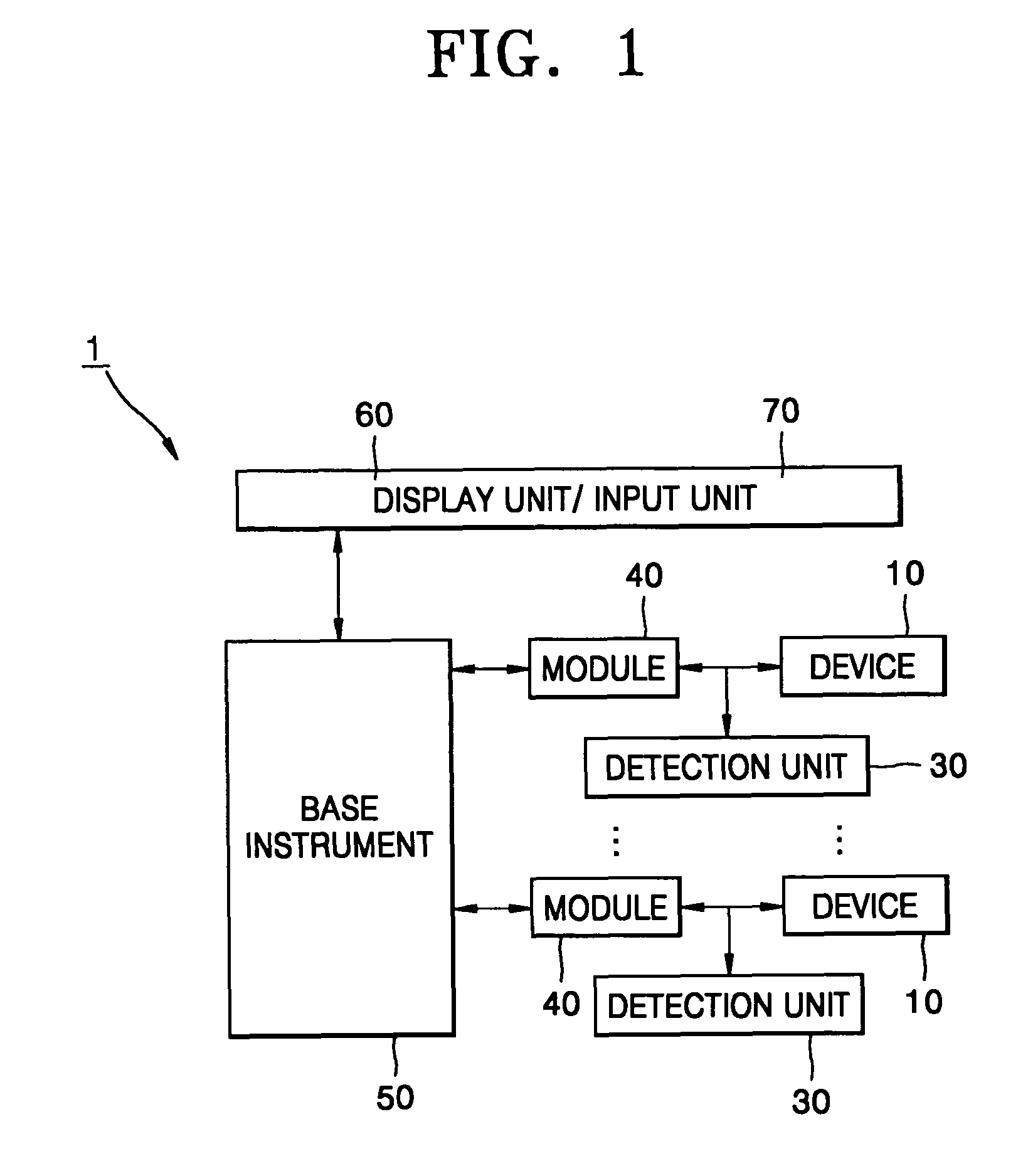
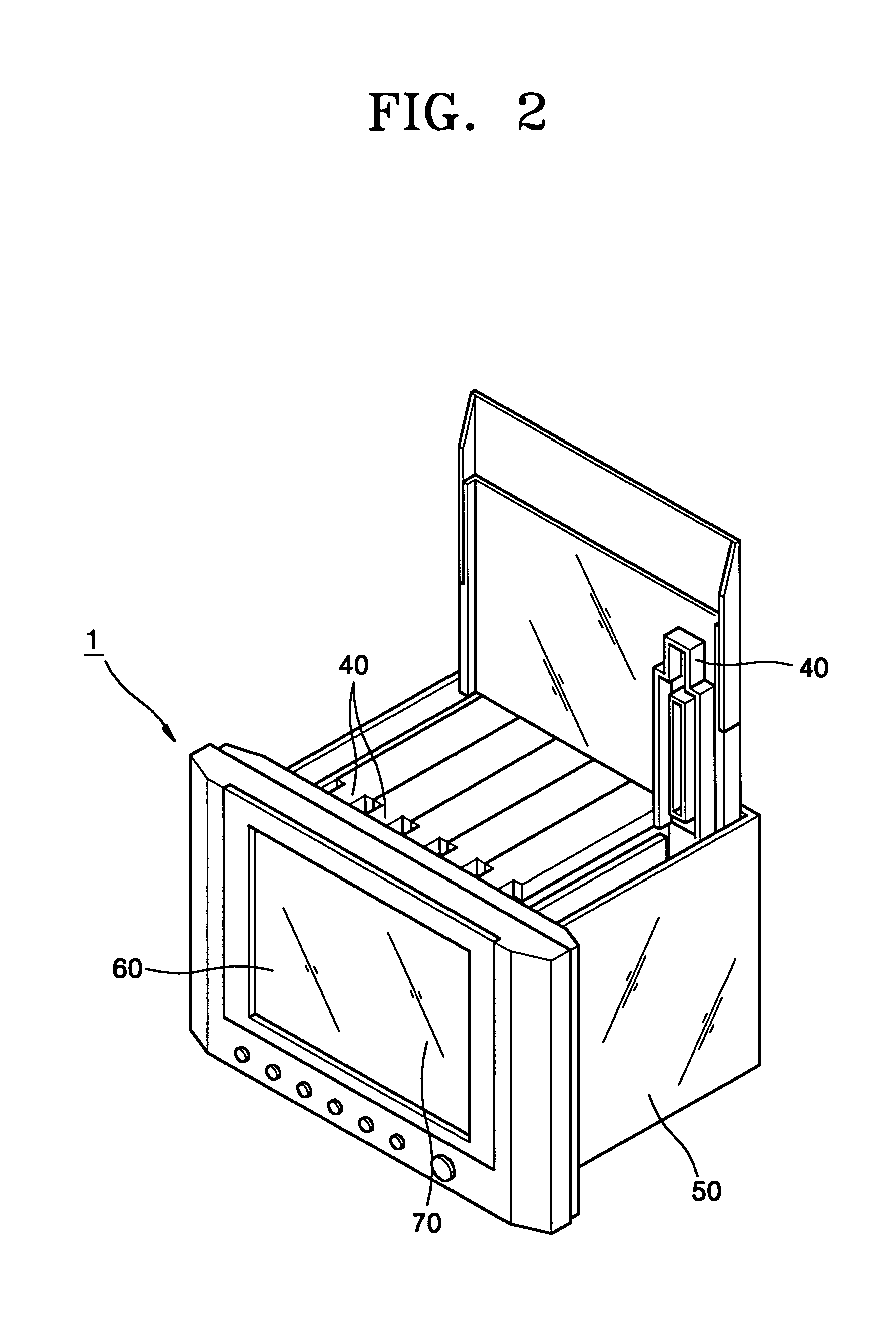
Real-time PCR monitoring apparatus and method
InactiveUS7767439B2Increase conversion rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCommunication unitComputer module
A real time polymerase chain reaction (“PCR”) monitoring apparatus includes, a microchip-type PCR tube that has a PCR solution-containing PCR chamber, a micro-heater, a detection unit detecting a PCR product signal based on the PCR solution, a plurality of modules, each of which includes the abovementioned elements in addition to a cooling fan and a control unit controlling the micro-heater and the cooling fan to adjust the temperature of the PCR chamber, a base instrument that comprises a power supply unit connected to the modules and a data communication unit connected to the control unit of each of the modules, and a display unit displaying data from the data communication unit, wherein the control unit of each of the modules independently controls at least one of both the detection unit and the temperature of the PCR chamber of the PCR tube in each of the modules.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for diagnosing human papillomavirus (HPV) and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101017141AEfficient, systematic, economical and simpleShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHuman bodyHuman papillomavirus
This invention relates to one polymer enzyme linkage reaction fluorescence test method to dialogue dangerous human body nipple shape virus and to isolate DNA sample HPV gene type to test one set of dangerous HPV infection from patient by the method, wherein, it belongs to life science and biological technique. This invention agent case comprises one fluorescence meter PCR technique as base of multi-layer polymer enzyme reaction composed of multiple HPV positive lead object, reaction lead object and fluorescence detector.
Owner:GENETEL PHARMA SHENZHEN
Multiplex quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for vibrio parahaemolyticus and detection method
InactiveCN102605055AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFood poisoningSaxitoxin
The invention provides a multiplex quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction detection kit for vibrio parahaemolyticus toxin gene and a detection method. The kit mainly comprises specific primers, probes and PCR reaction reagent, wherein the specific primers and the probes consist of specific primers and probes of vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin gene (tdh), thermolabile hemomysin gene (tlh), toxin expression regulating protein gene (toxR) and thermostable related hemolysin gene (trh). The invention provides the quick, sensitive and specific multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit and the detection method aiming at the vibrio parahaemolyticus toxin gene, and provides basis for controlling food poisoning caused by the vibrio parahaemolyticus in time and early diagnosis of the food poisoning caused by the vibrio parahaemolyticus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Integrated semiconductor microreactor for real-time monitoring of biological reactions
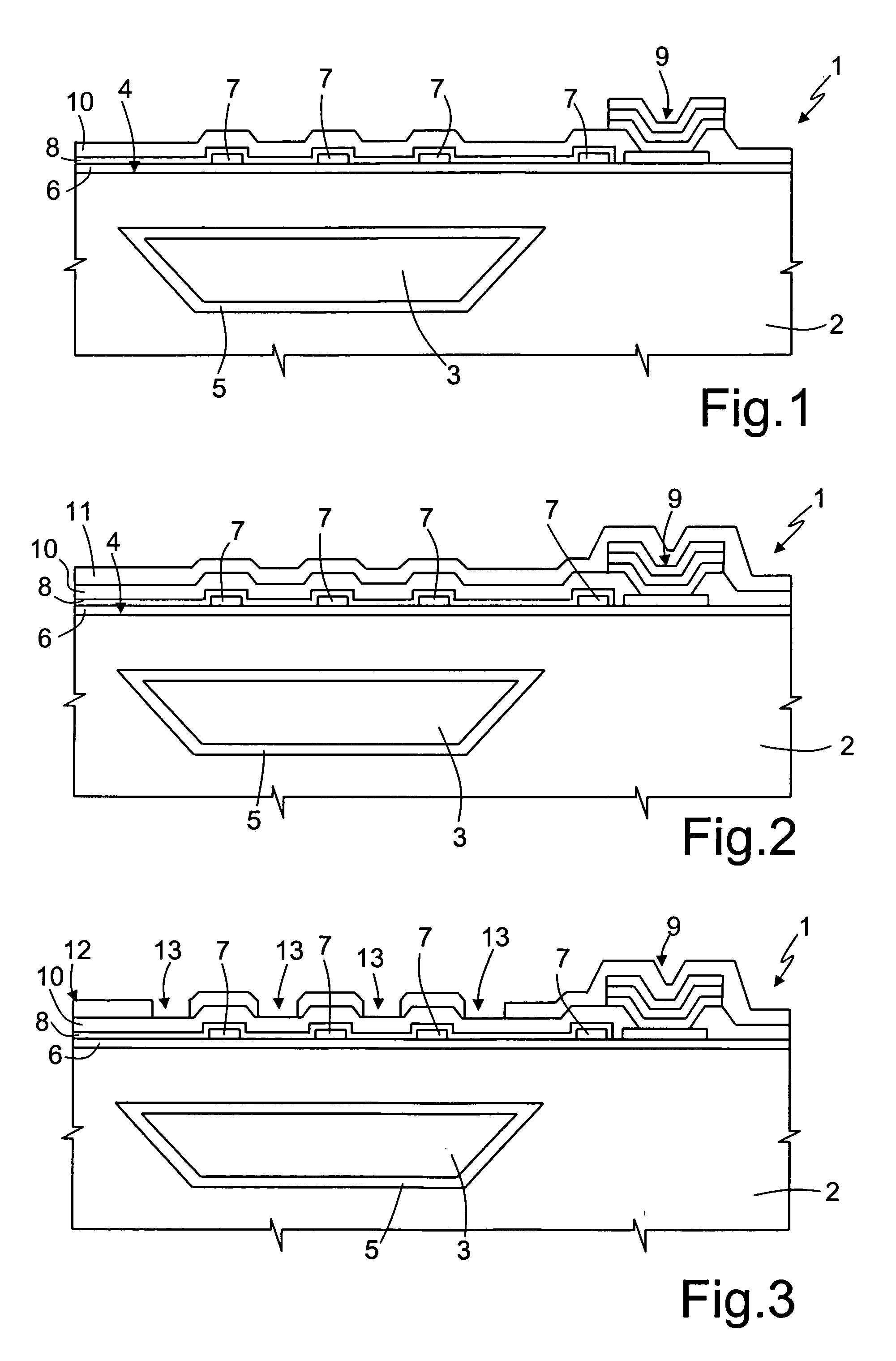
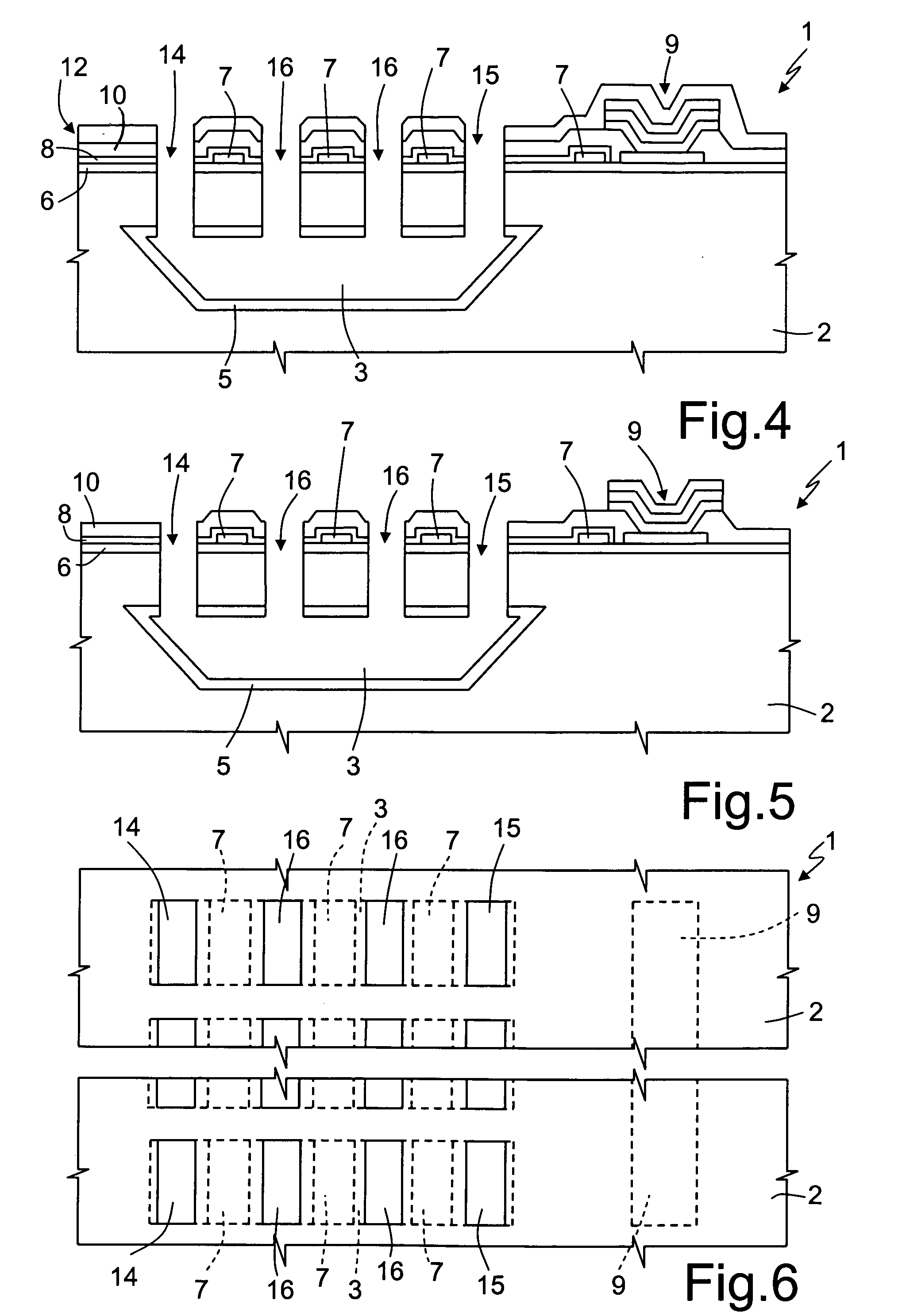
ActiveUS20050176037A1Loss and contaminationConvenient angleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroreactorComing out
An integrated semiconductor chemical microreactor for real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) monitoring, has a monolithic body of semiconductor material; a number of buried channels formed in the monolithic body; an inlet trench and an outlet trench for each buried channel; and a monitoring trench for each buried channel, extending between the inlet and outlet trenches thereof from the top surface of the monolithic body to the respective buried channel. Real-time PCR monitoring is carried out by channeling light beams into the buried channels, possibly through one of the inlet or outlet trenches, whereby the light beams impinge on the fluid therein and collecting the emergent light coming out from the monitoring trench.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Nucleic acid releasing agent, nucleic acid PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification method and PCR amplification kit
ActiveCN109402240AGuaranteed amplification efficiencyAvoid degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidasesPotassiumPolyethylene glycol
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Molecular identification method of atlantic salmon
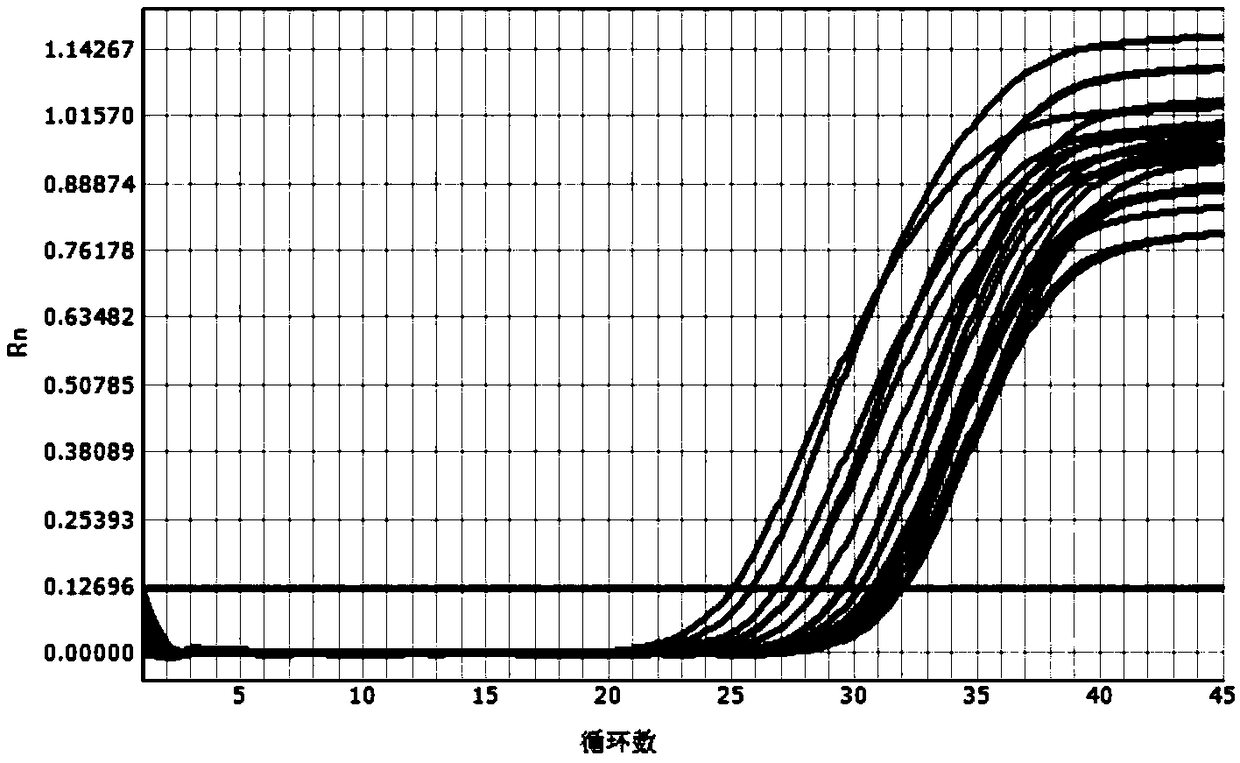
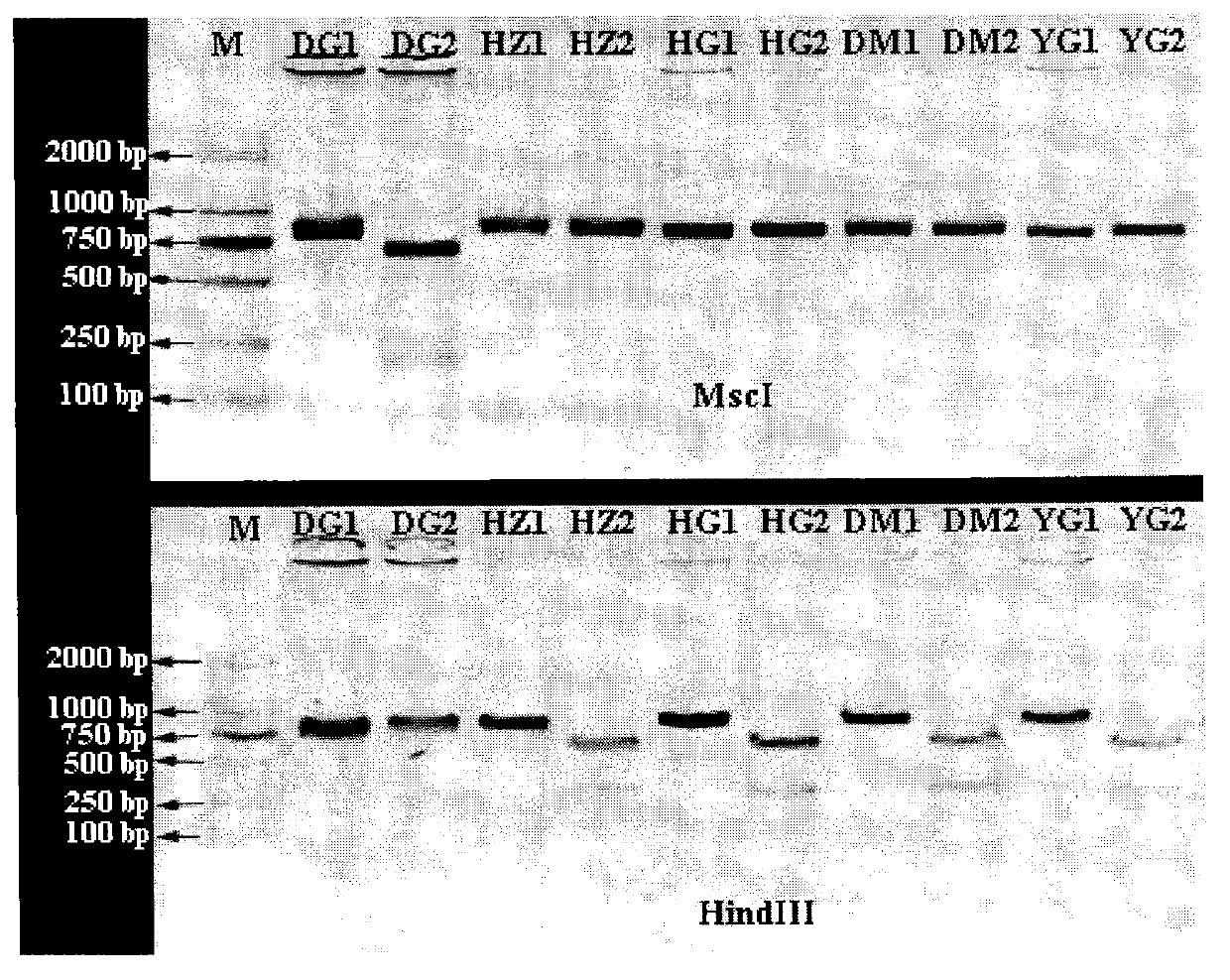
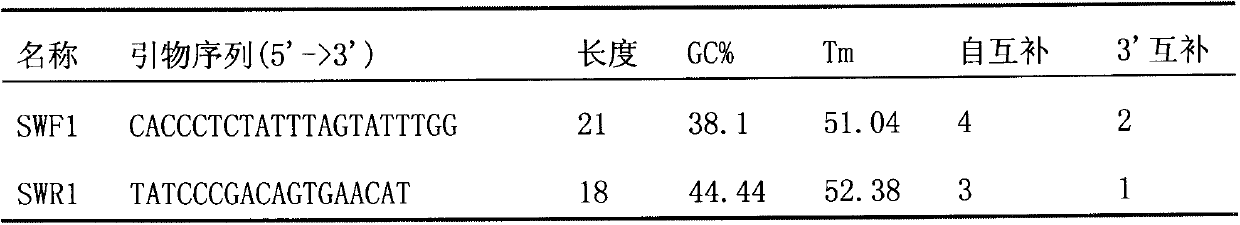
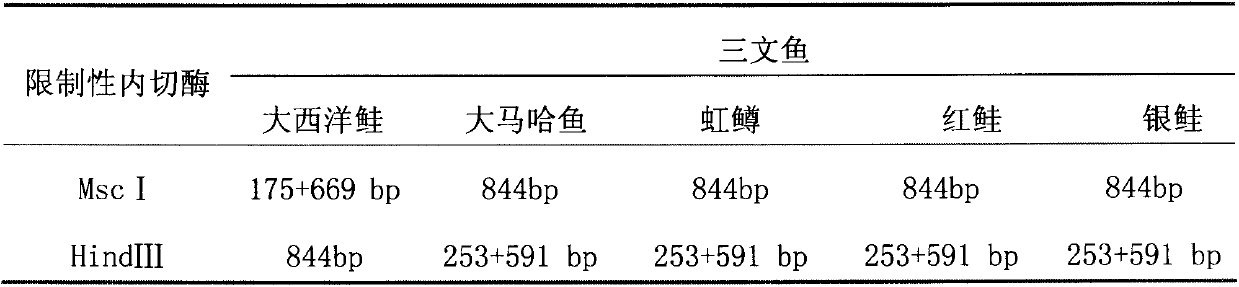
ActiveCN103122386ALower requirementEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a molecular identification method of an atlantic salmon. The molecular identification method comprises the following steps of 1, extraction of fish DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); 2, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) augmentation; 3, enzyme digestion and electrophoresis detection; and 4, identification. The atlantic salmon can be accurately determined in four steps. The molecular identification method of the atlantic salmon has the characteristics of being simple to operate, rapid and accurate, low in price, low in requirement on an instrument and equipment, and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
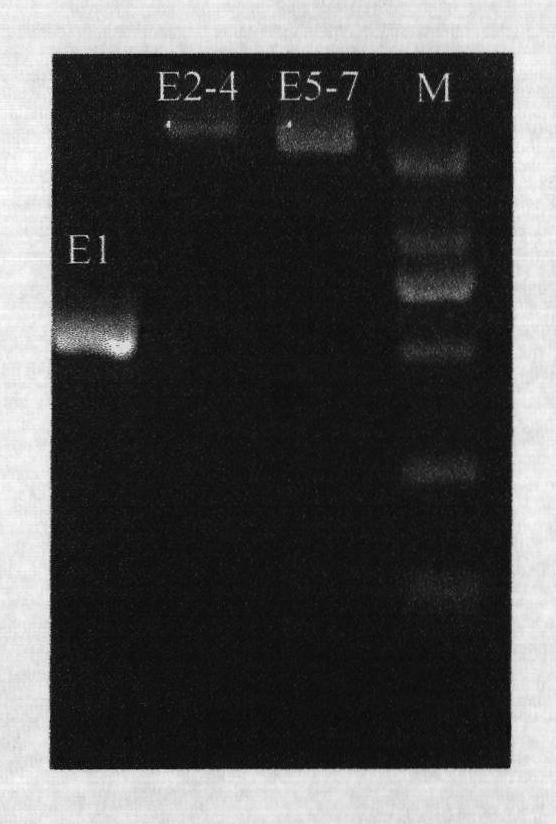
Polymerase chain reaction-sequence based typing (PCR-SBT) method for ABO blood type genotyping and reagent
ActiveCN101921834ASolve the recombination phenomenonThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium acetateHuman DNA sequencing
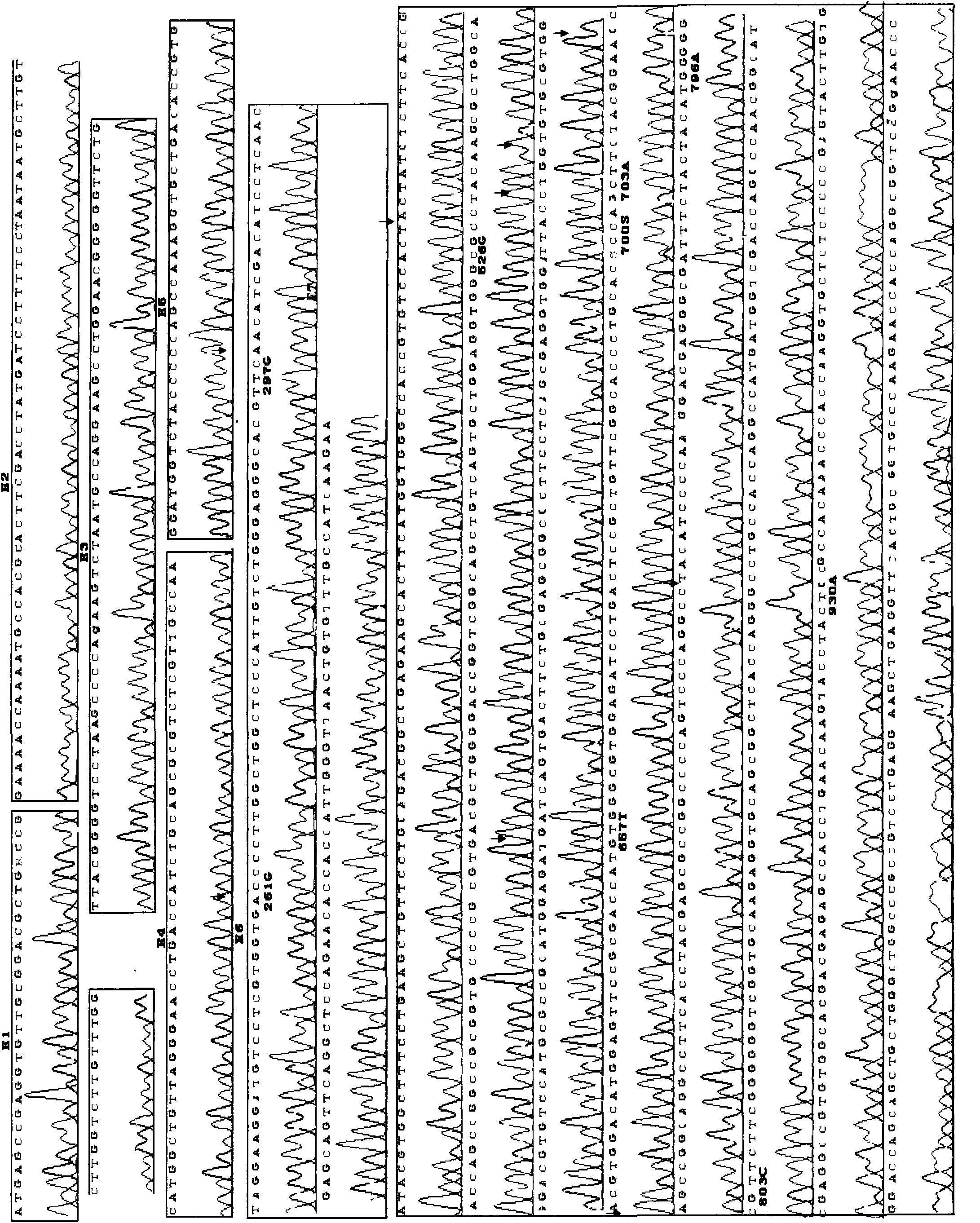
The invention provides a polymerase chain reaction-sequence based typing (PCR-SBT) method for ABO blood type genotyping. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing human genome DNA; amplifying segments of ABO gene exon 1, exons 2-4 and exons 5-7; performing double enzyme digestion purification on the obtained amplified products; performing a sequencing PCR reaction on the purified products; purifying the sequenced products by a sodium acetate-ethanol precipitation method and performing capillary electrophoresis sequencing; and analyzing the obtained sequences by using software to determine the genotype. The method has the advantages of solving the problems of identification of an ABO subtype, judgment of difficult blood types, discovery of a new mutational site, gene recombination among genes, genetic polymorphism detection and the like, exerting the characteristics of high flux and result accuracy of ABO genotyping operation by PCR-SBT, achieving great importance for the relative application in the fields of clinical transfusion medicinal research, genetics and the like and having important practical significance for medicinal research units, pharmic research and reagent development units.
Owner:浙江省血液中心
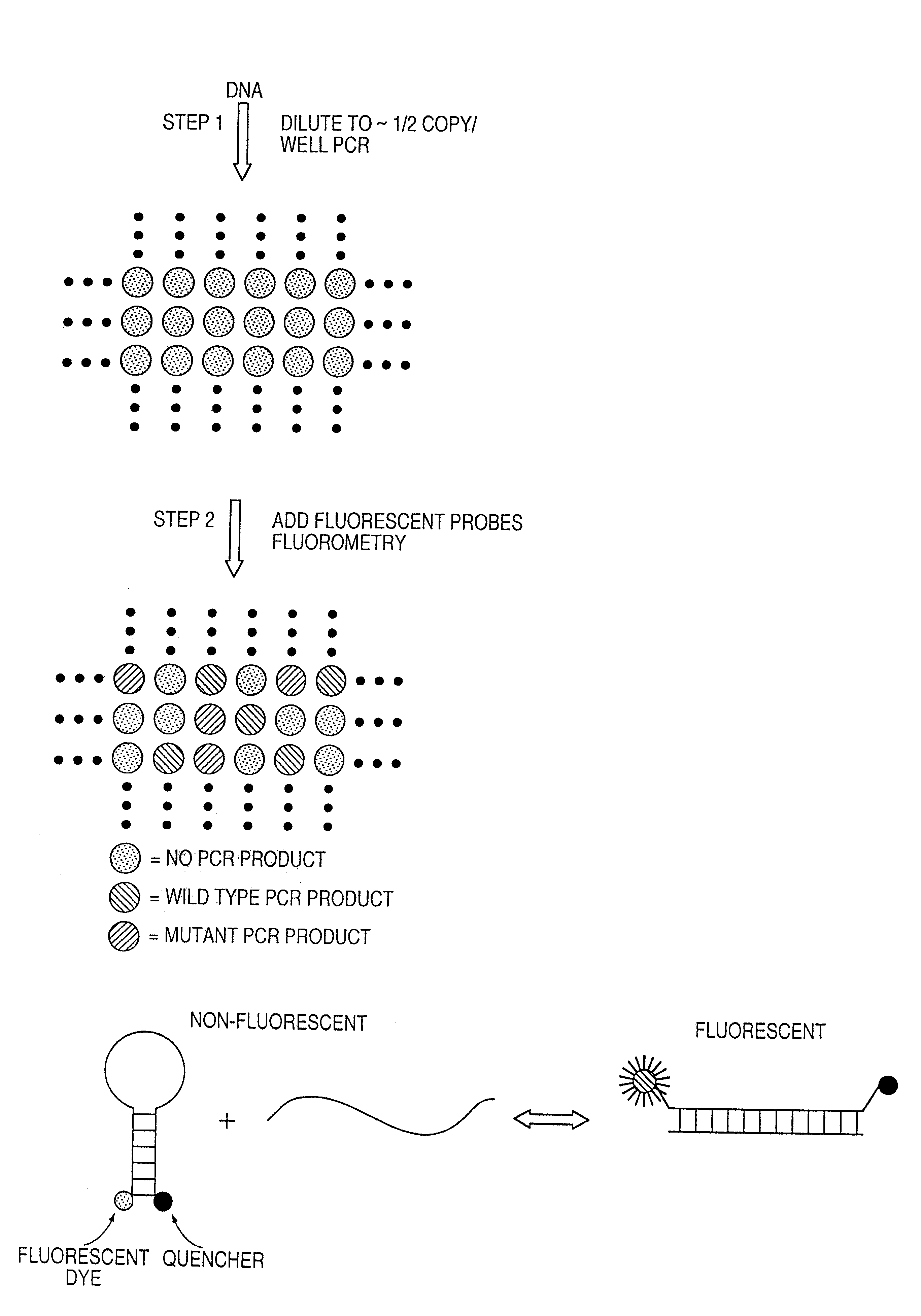
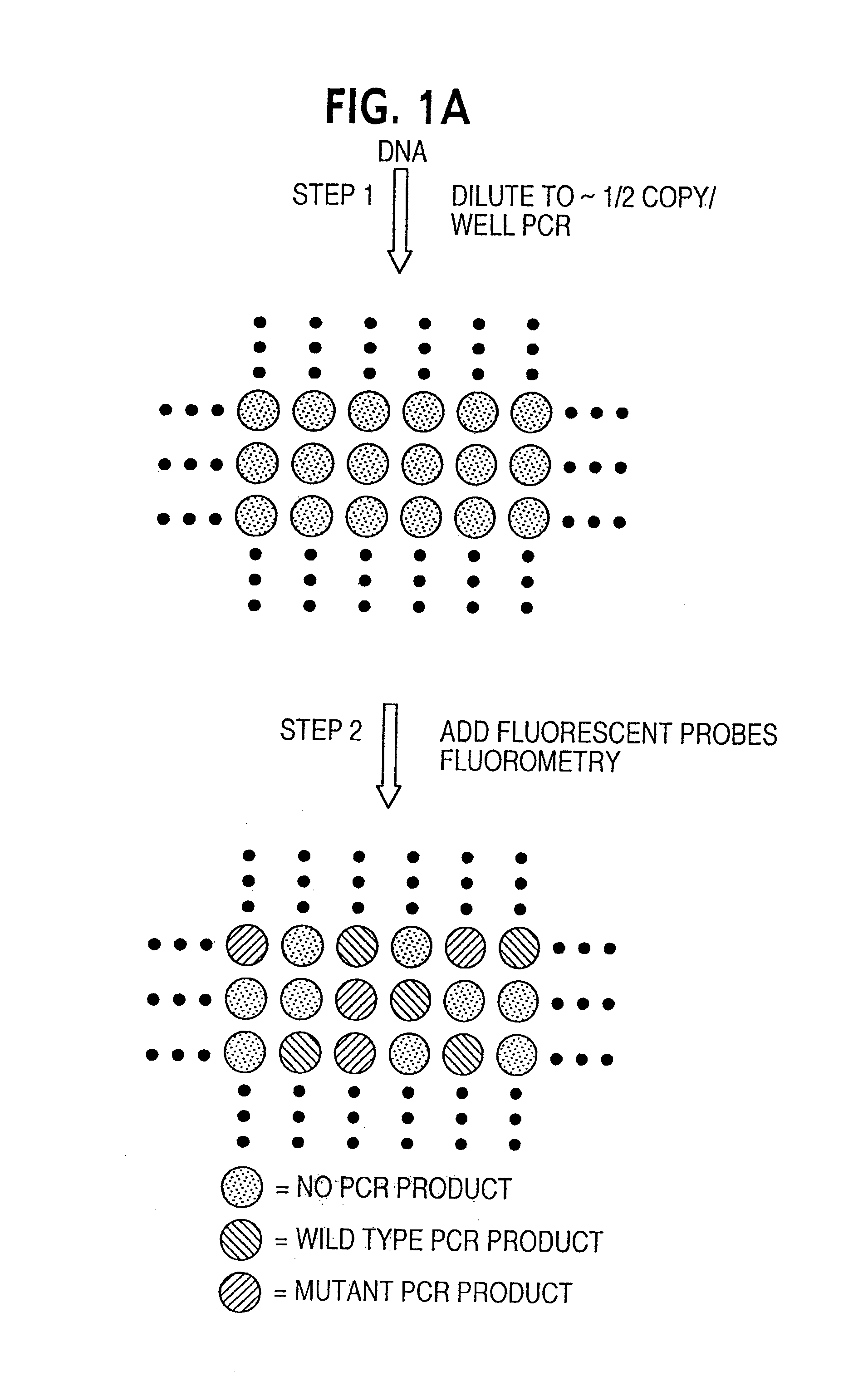
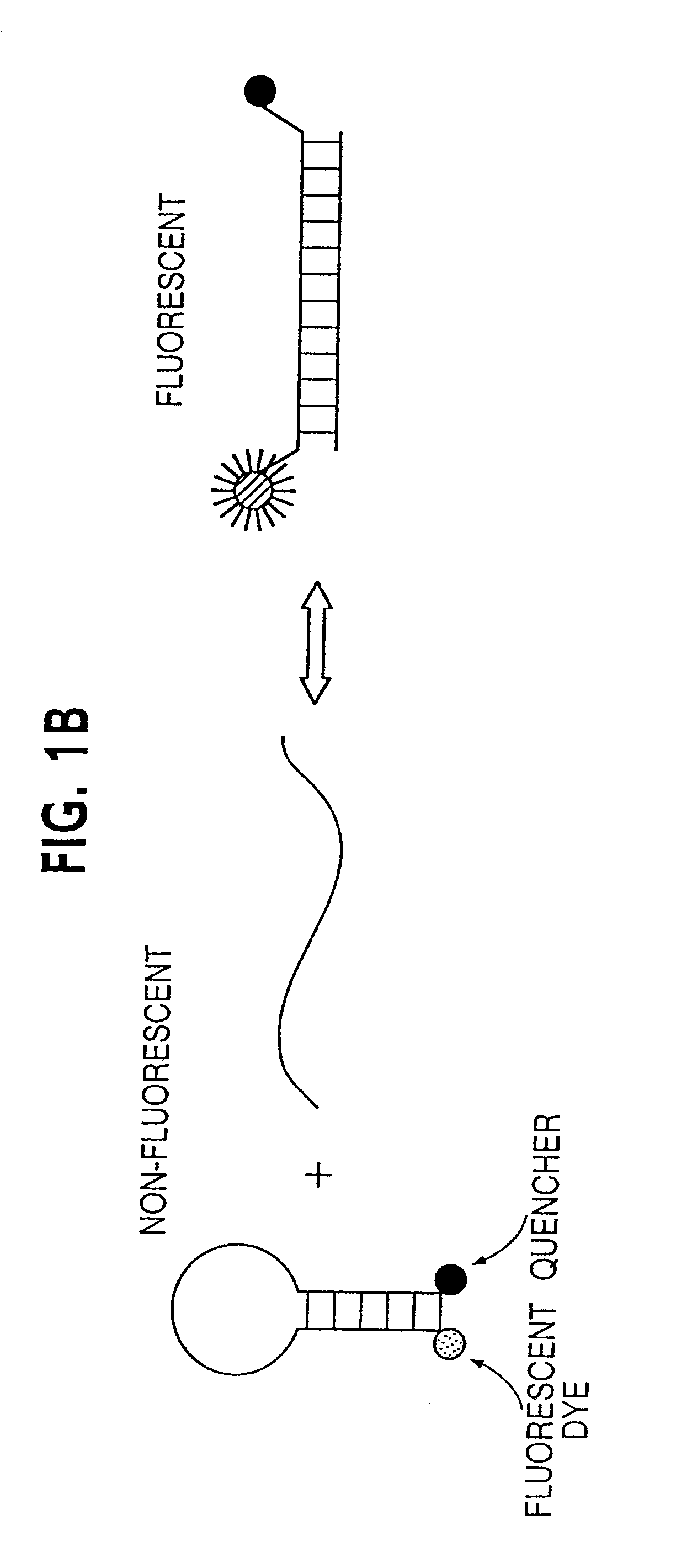
Digital amplification
The identification of pre-defined mutations expected to be present in a minor fraction of a cell population is important for a variety of basic research and clinical applications. The exponential, analog nature of the polymerase chain reaction is transformed into a linear, digital signal suitable for this purpose. Single molecules can be isolated by dilution and individually amplified; each product is then separately analyzed for the presence of pre-defined mutations. The process provides a reliable and quantitative measure of the proportion of variant sequences within a DNA sample.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Detection of Fusarium species infecting corn using the polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS6846631B2Detailed informationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFungal isolateMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
The present invention relates to the use of primers in polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of a Fusarium proliferatum, F. verticillioides and F. subglutinans. Specific primers are identified as being useful for the identification of fungal isolates using PCR based techniques.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
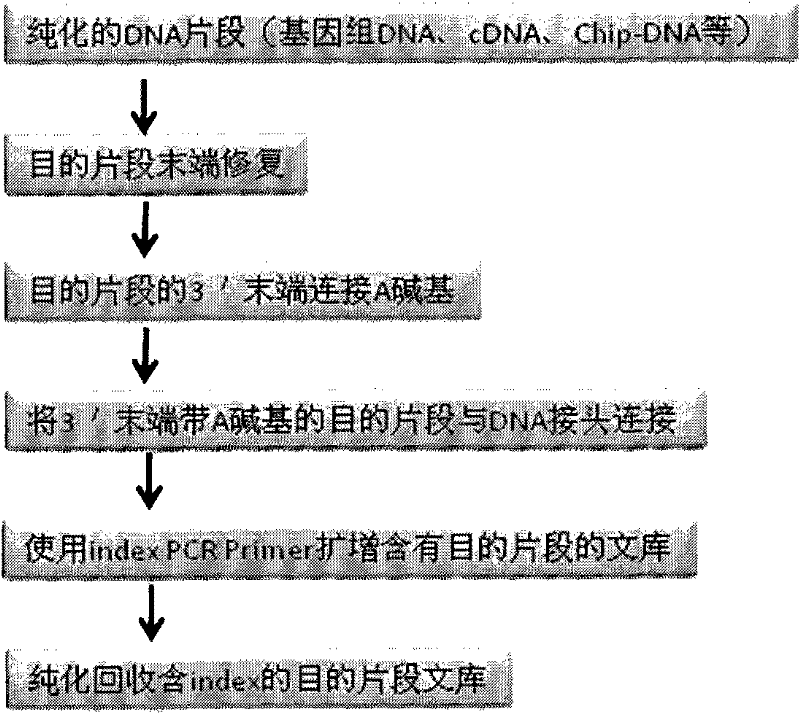
DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) index library building method based on PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
ActiveCN102409049AImprove production efficiencyHigh sequencing throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyInverse polymerase chain reaction
The invention designs 161 unique index sequences with a length of 8bp, and the indexes are embedded into DNA PCR (deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase chain reaction) primers to form DNA PCR index primers, thus being capable of importing the index sequences through PCR. The invention successfully establishes a method for building a DNA index library, and the method is applied to solexa DNA sequencing.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
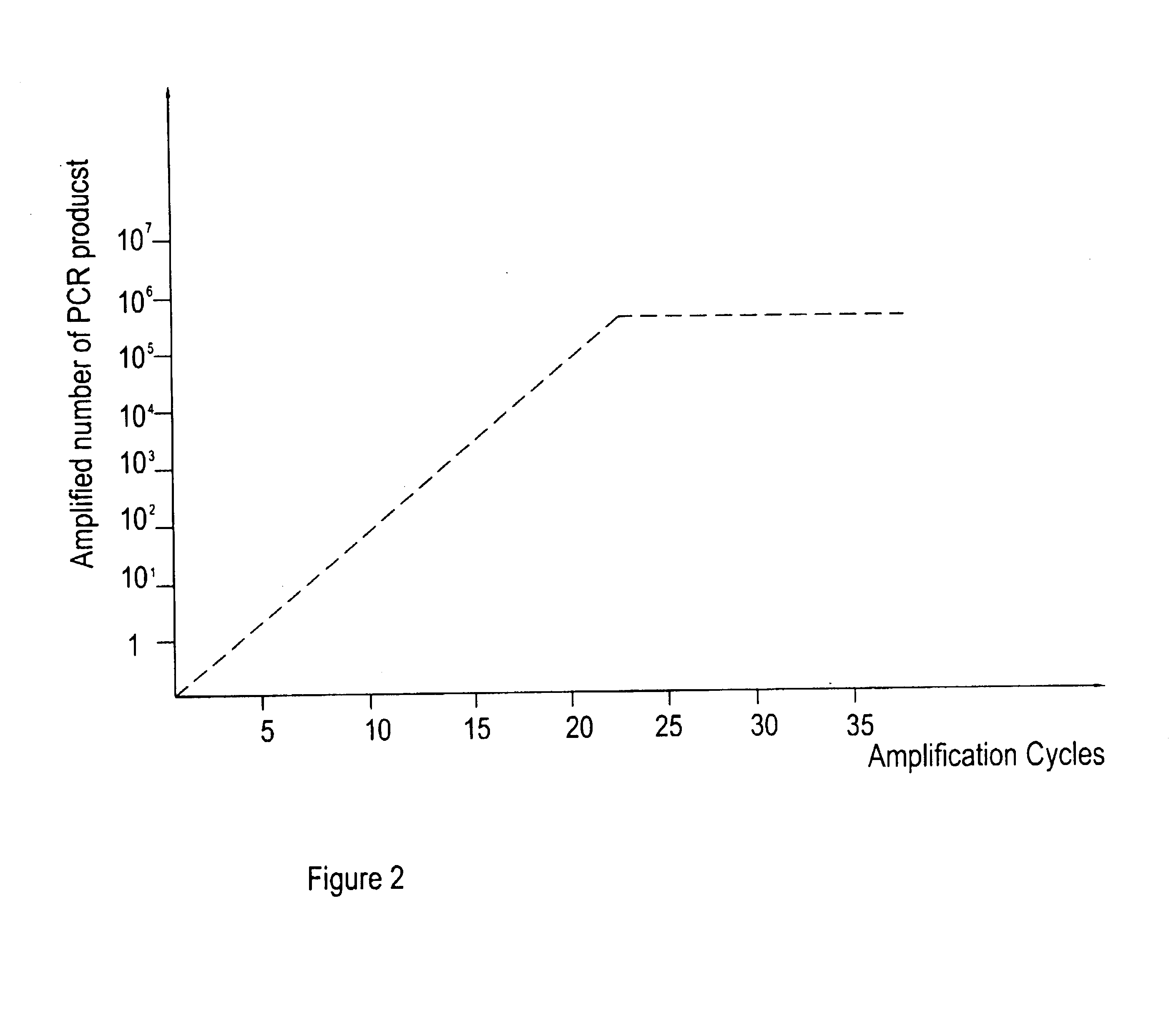





![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000011.PNG)
![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000012.PNG)
![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000013.PNG)