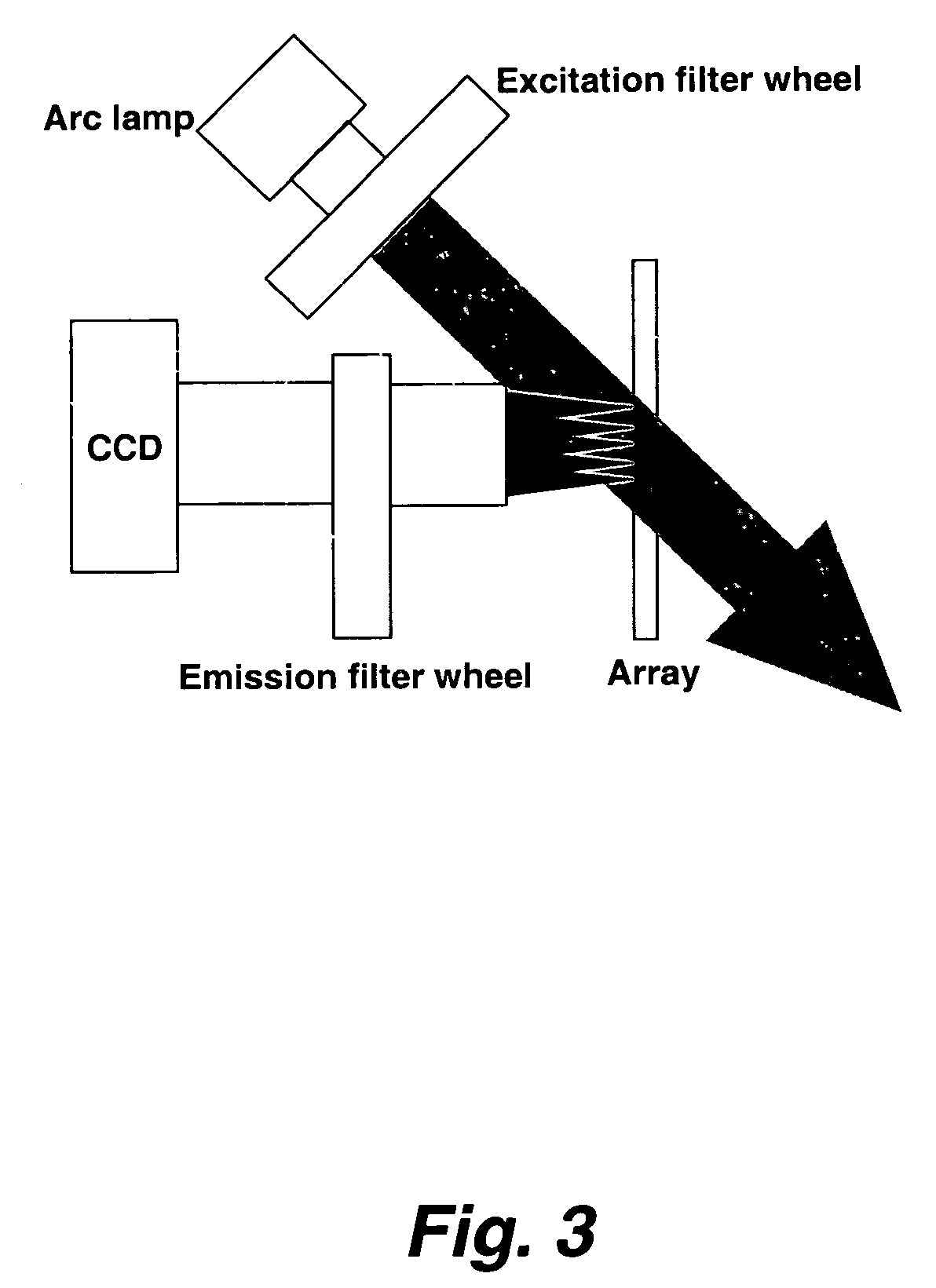
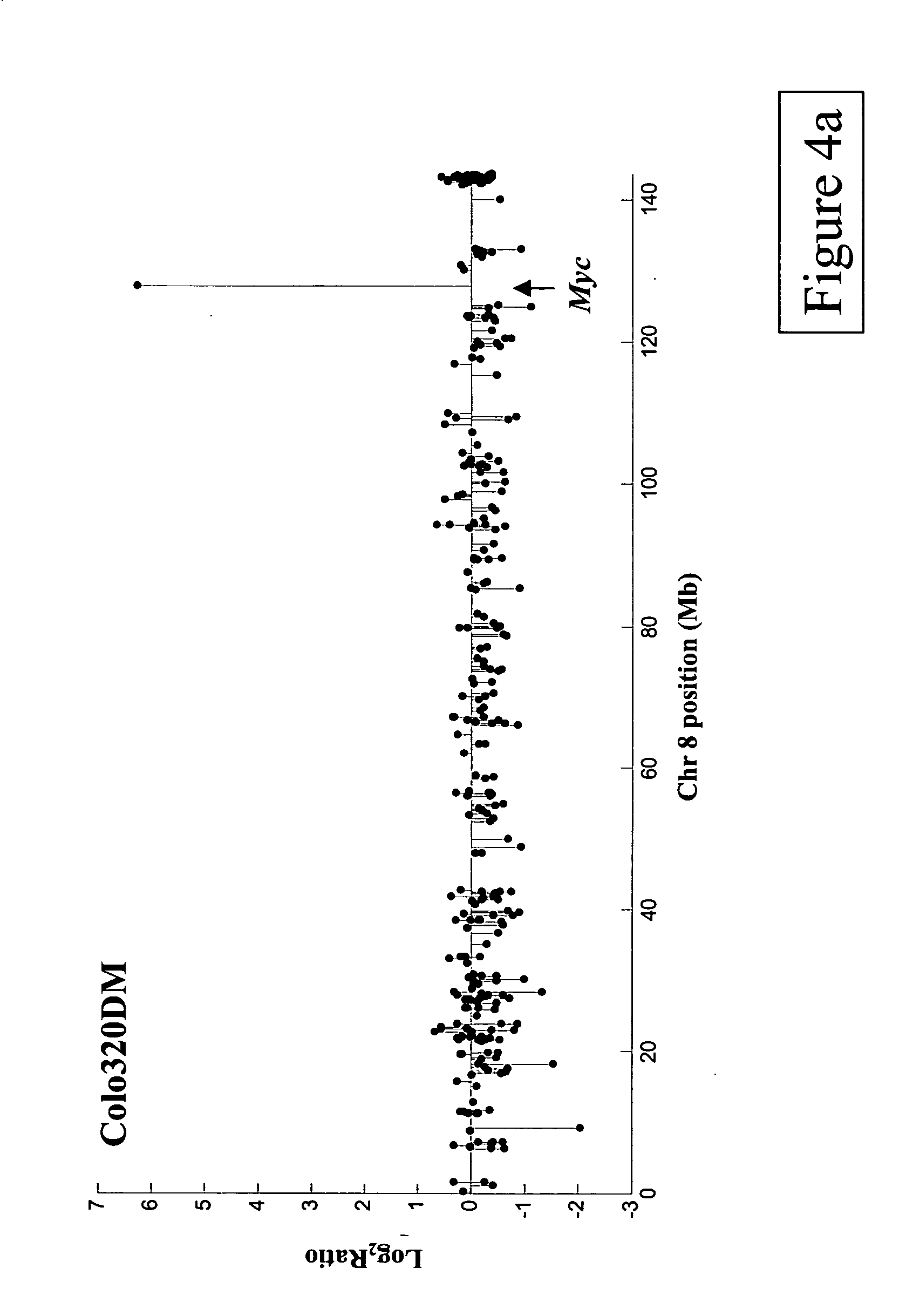
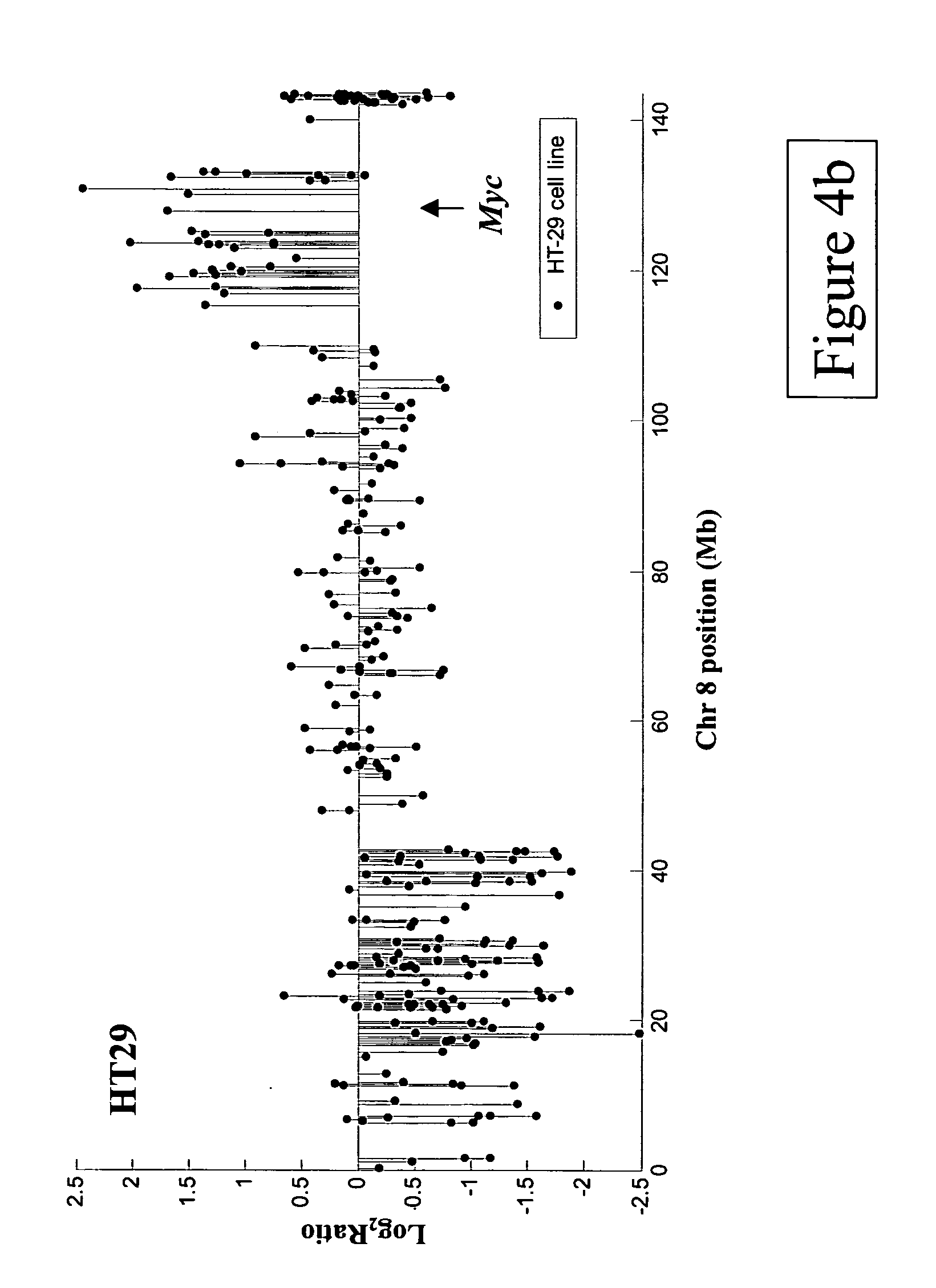
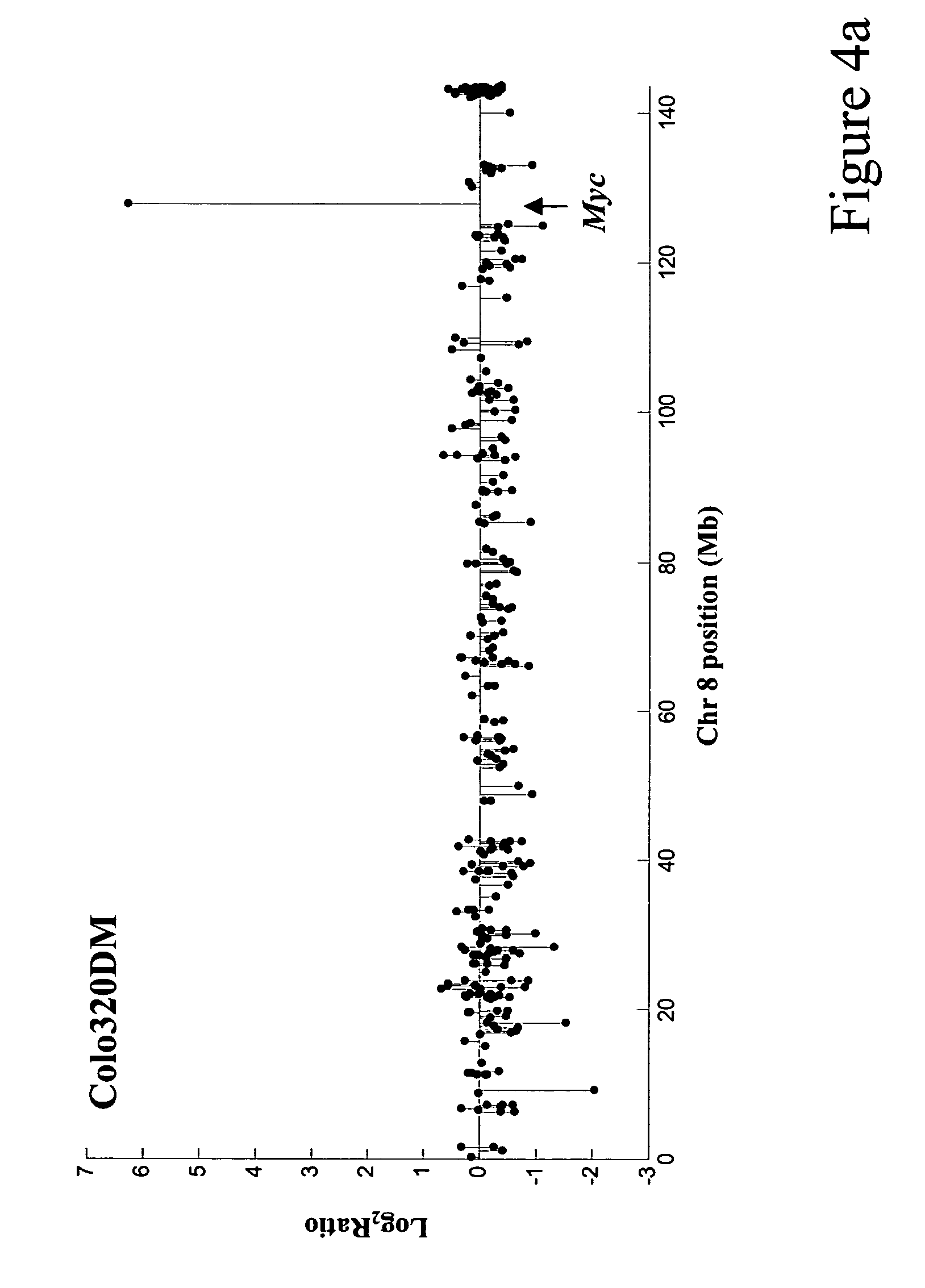
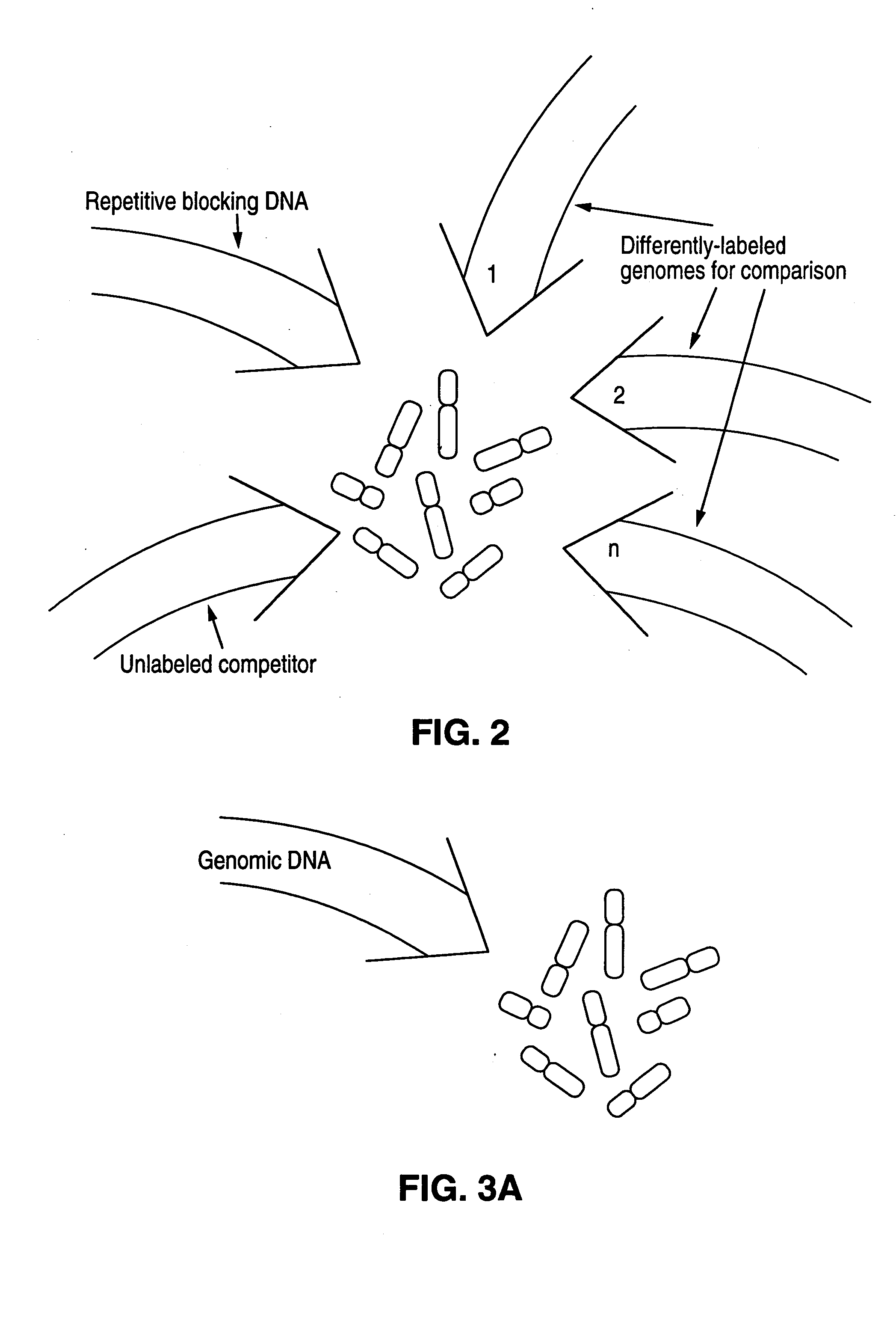
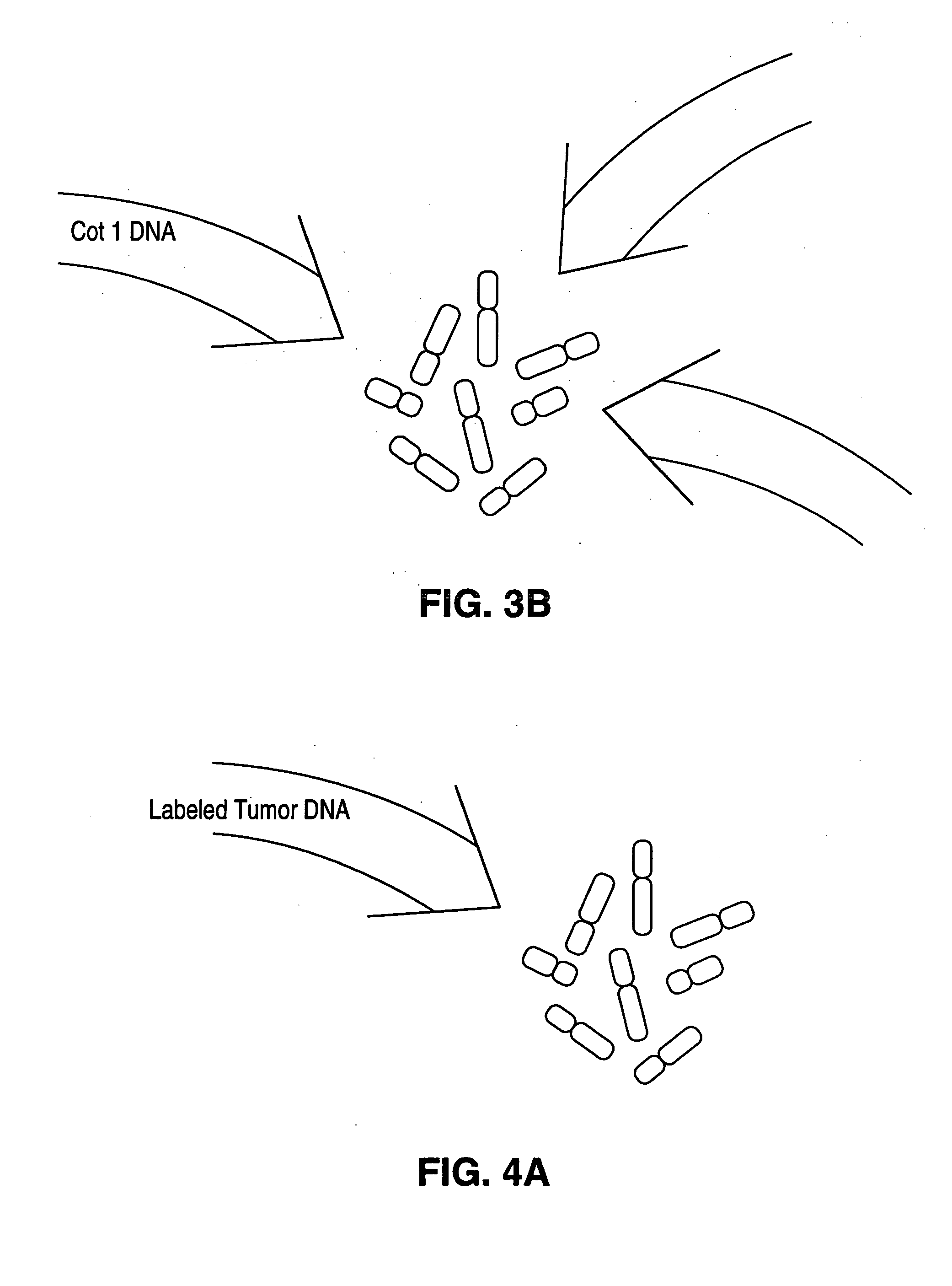
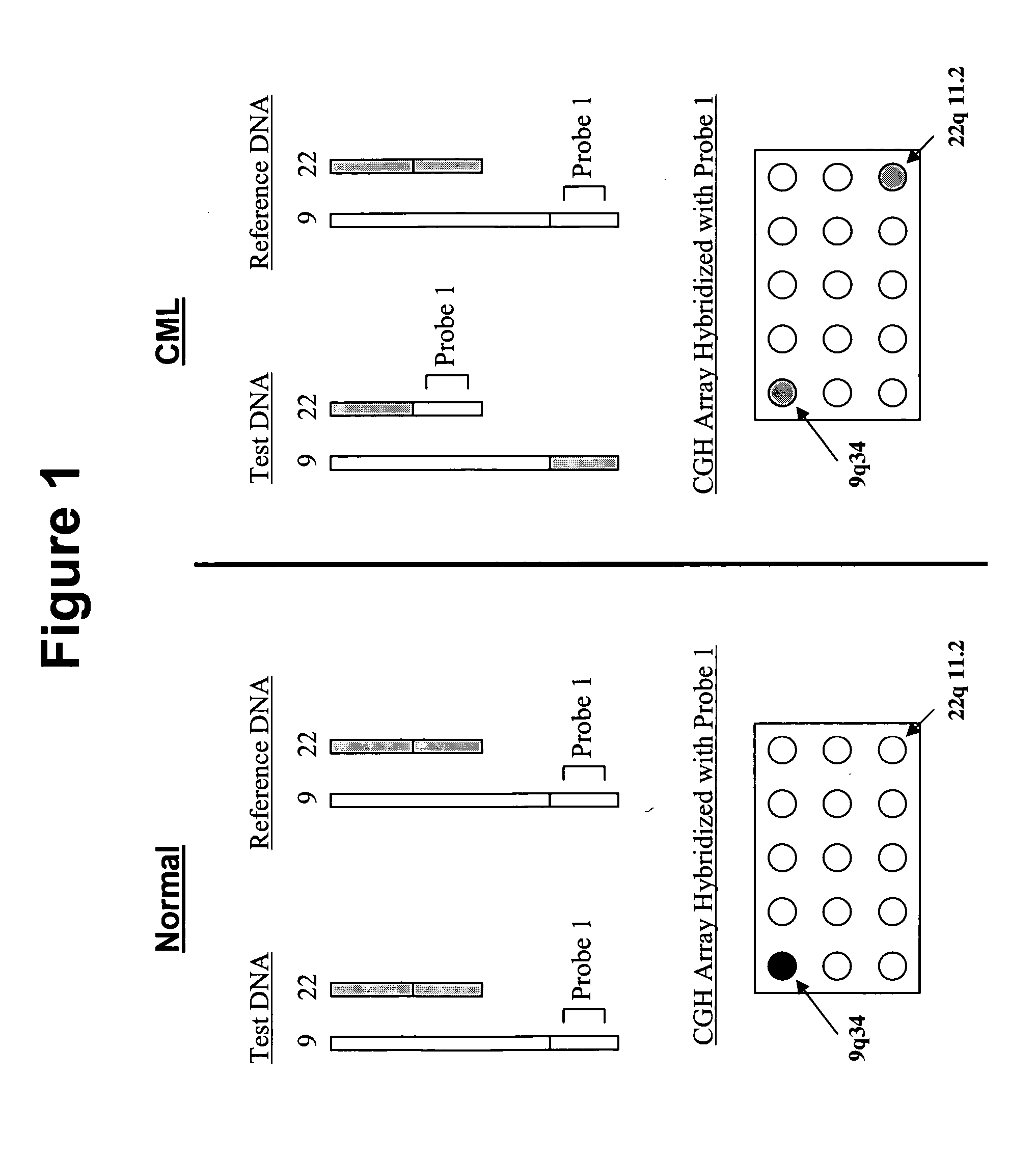
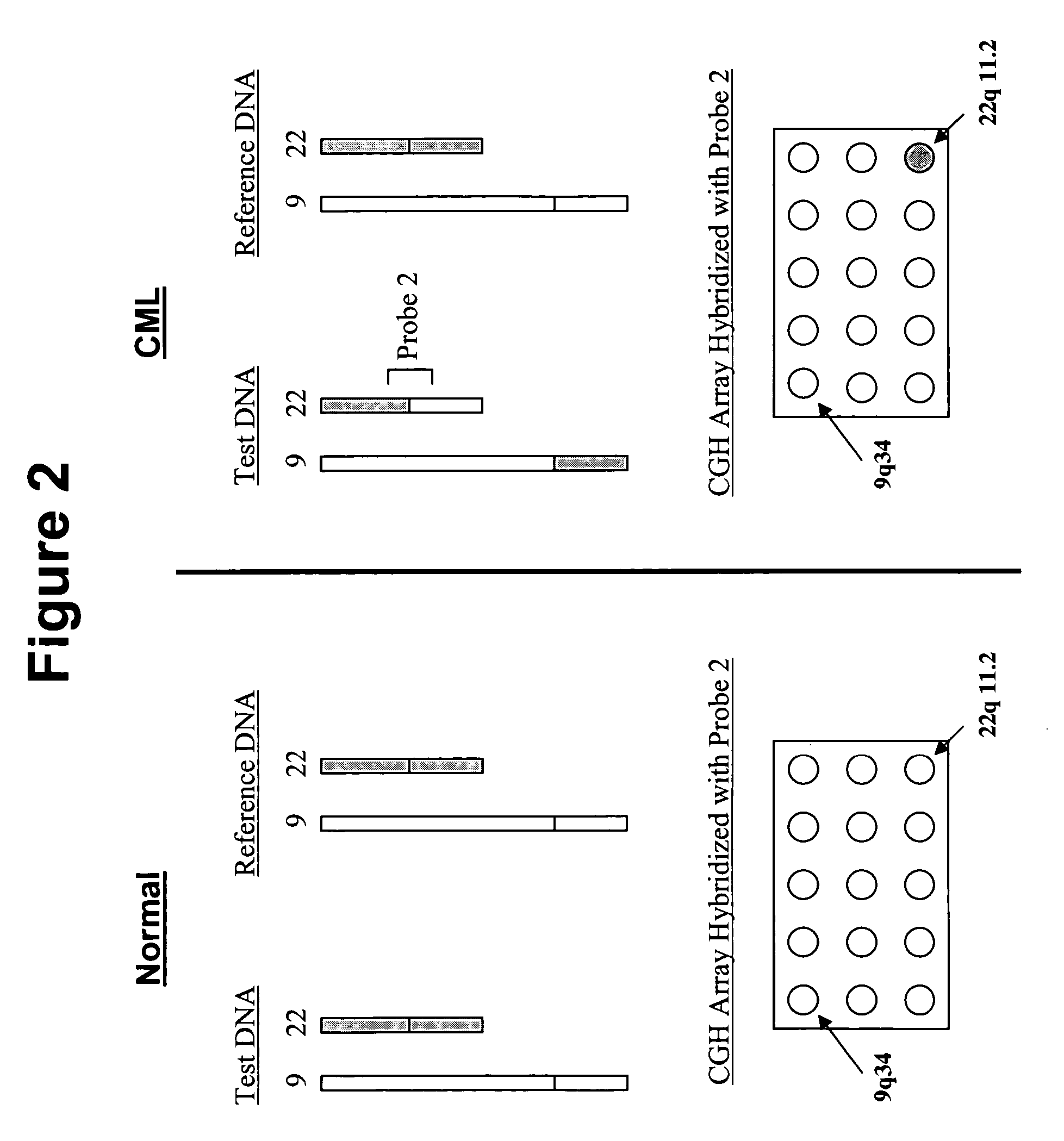
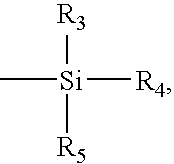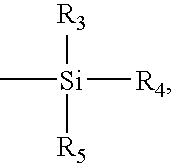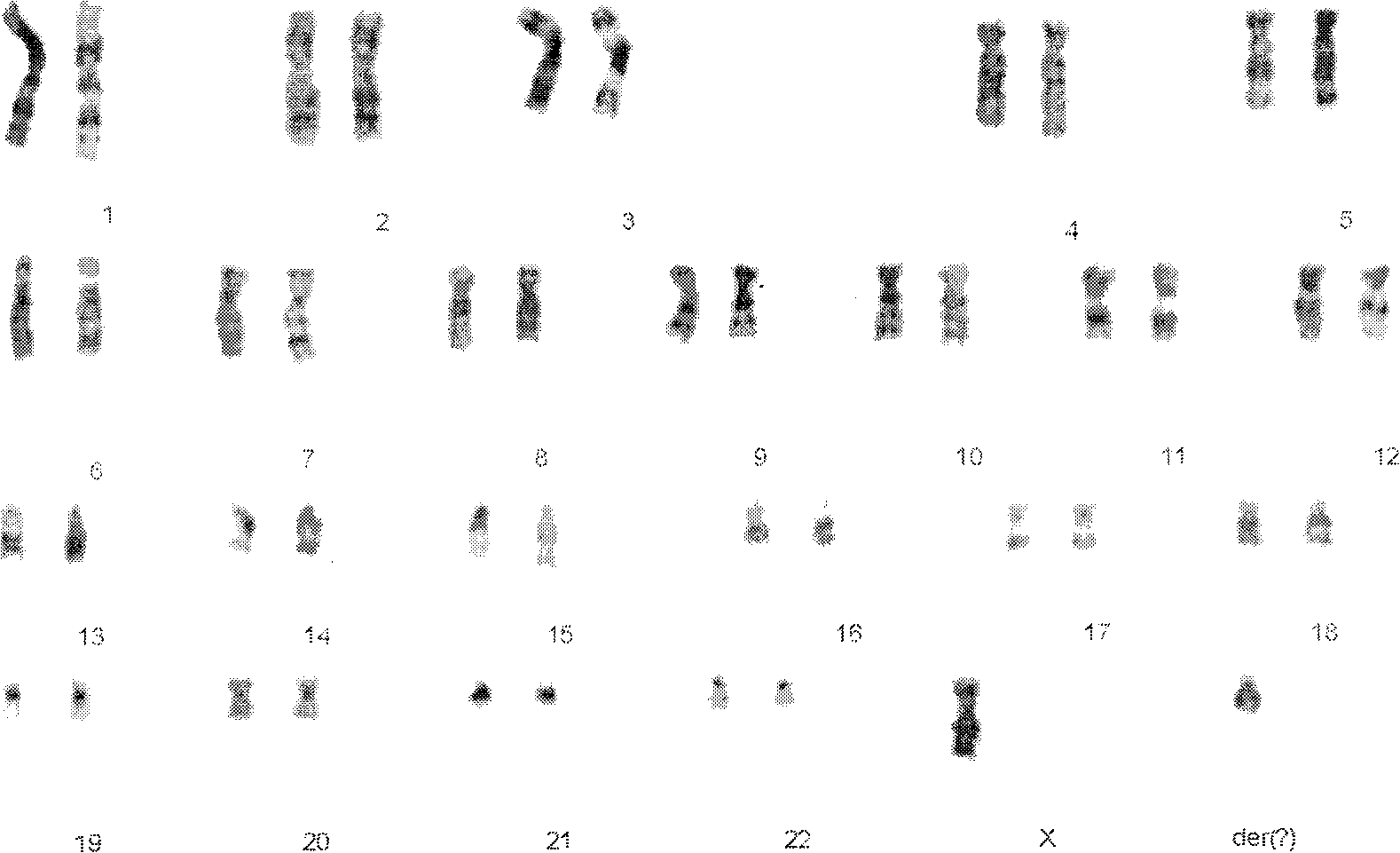Patents
Literature
36 results about "Comparative genomic hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
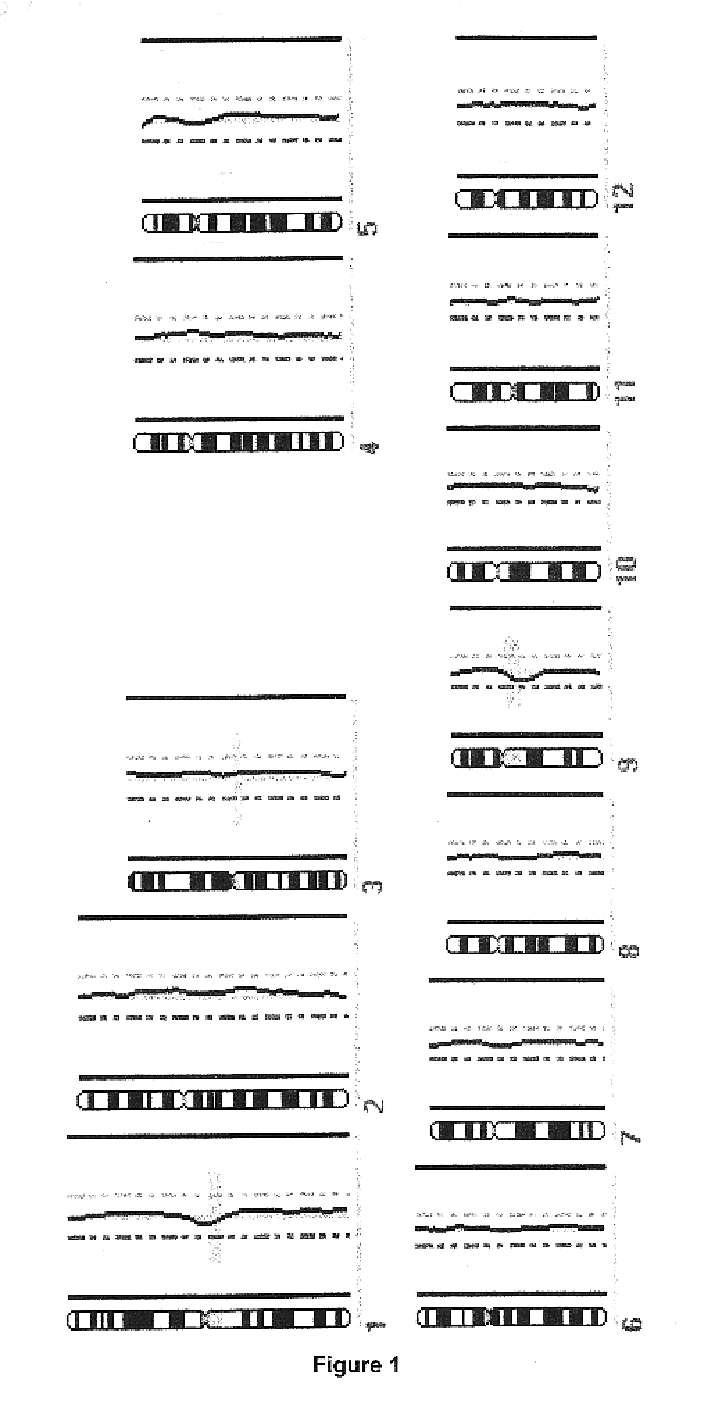
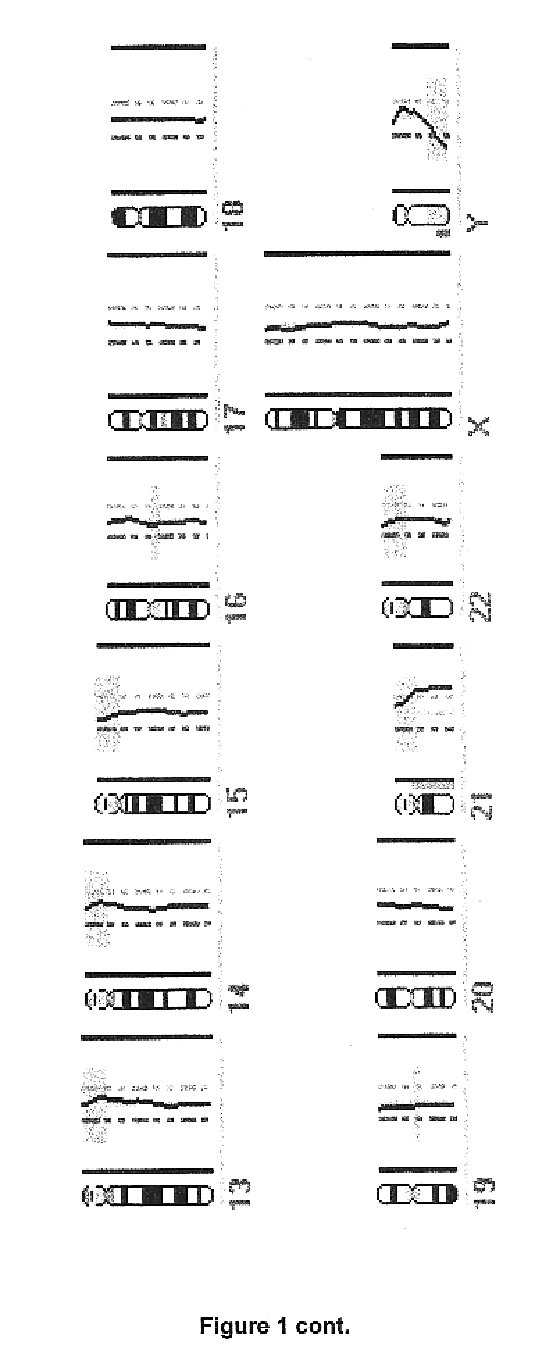
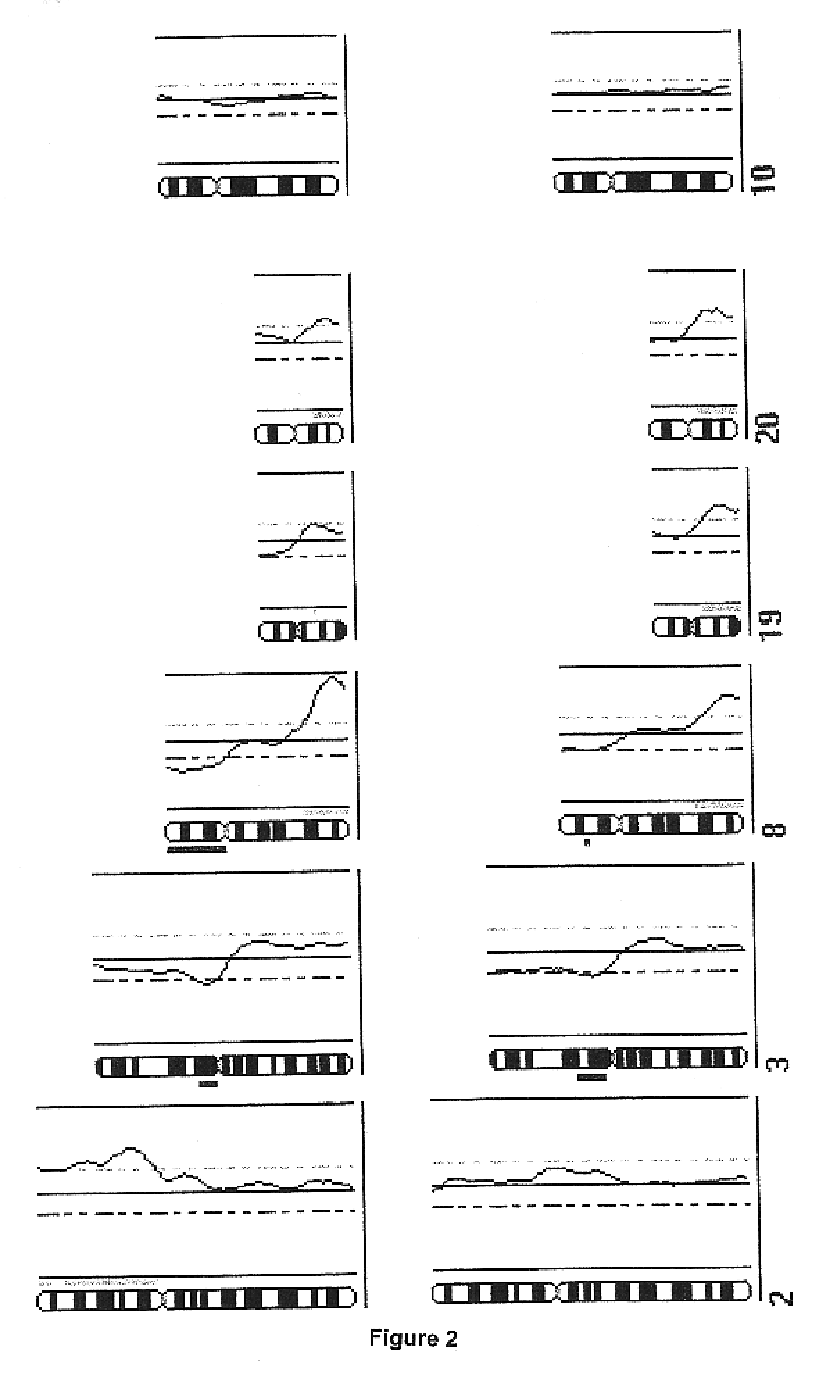
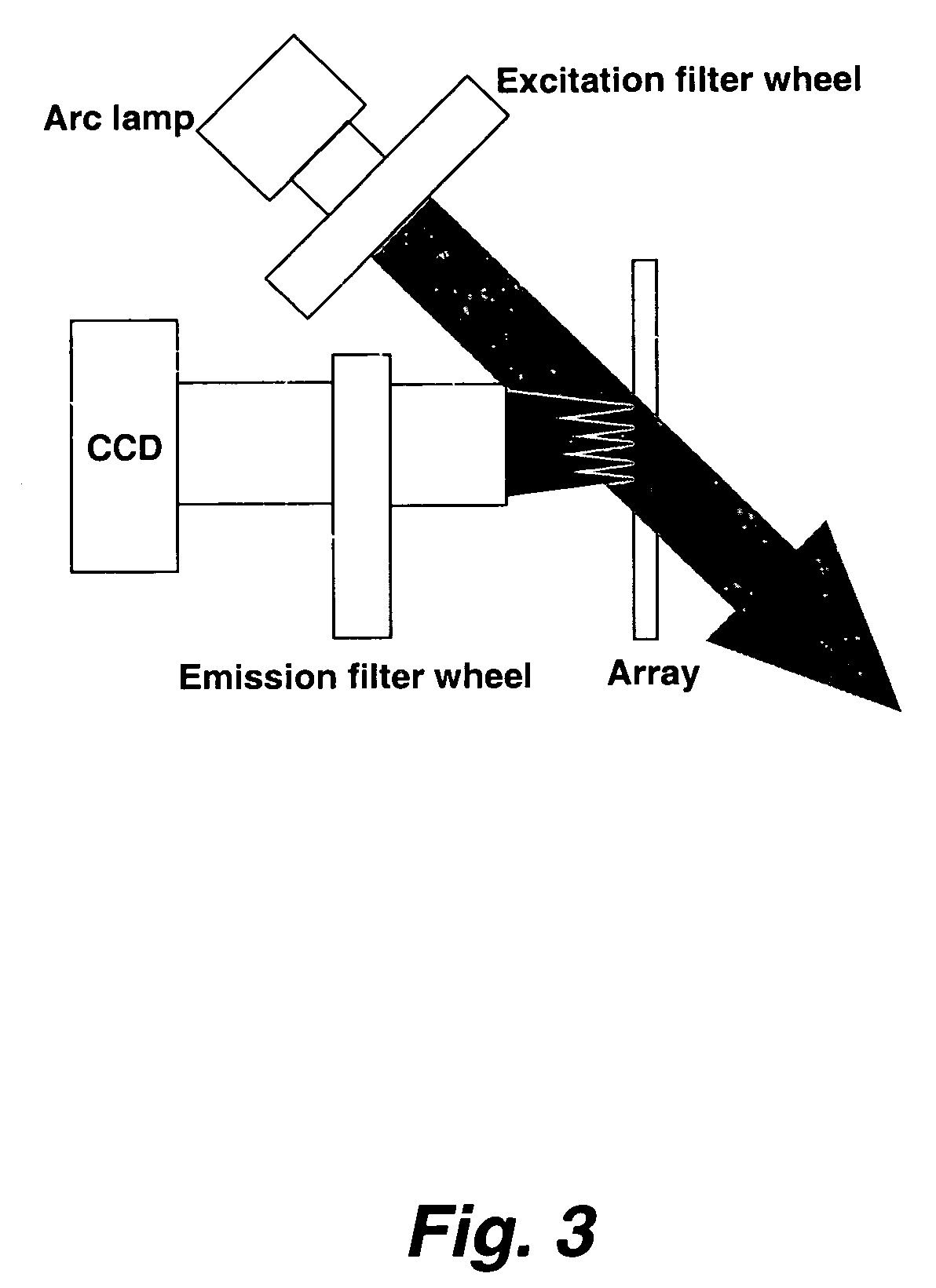
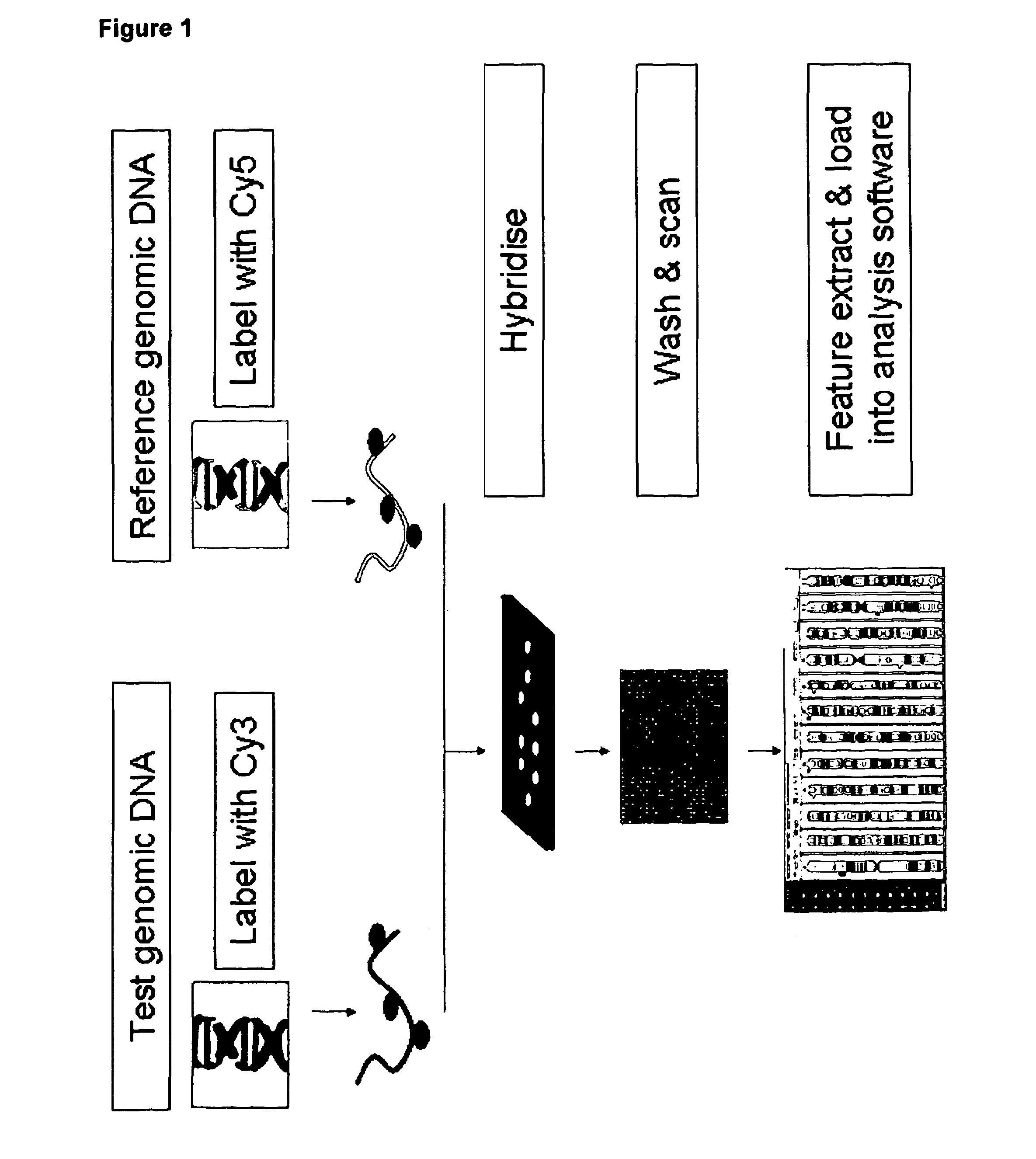
Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resolution of 5–10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
InactiveUS6335167B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
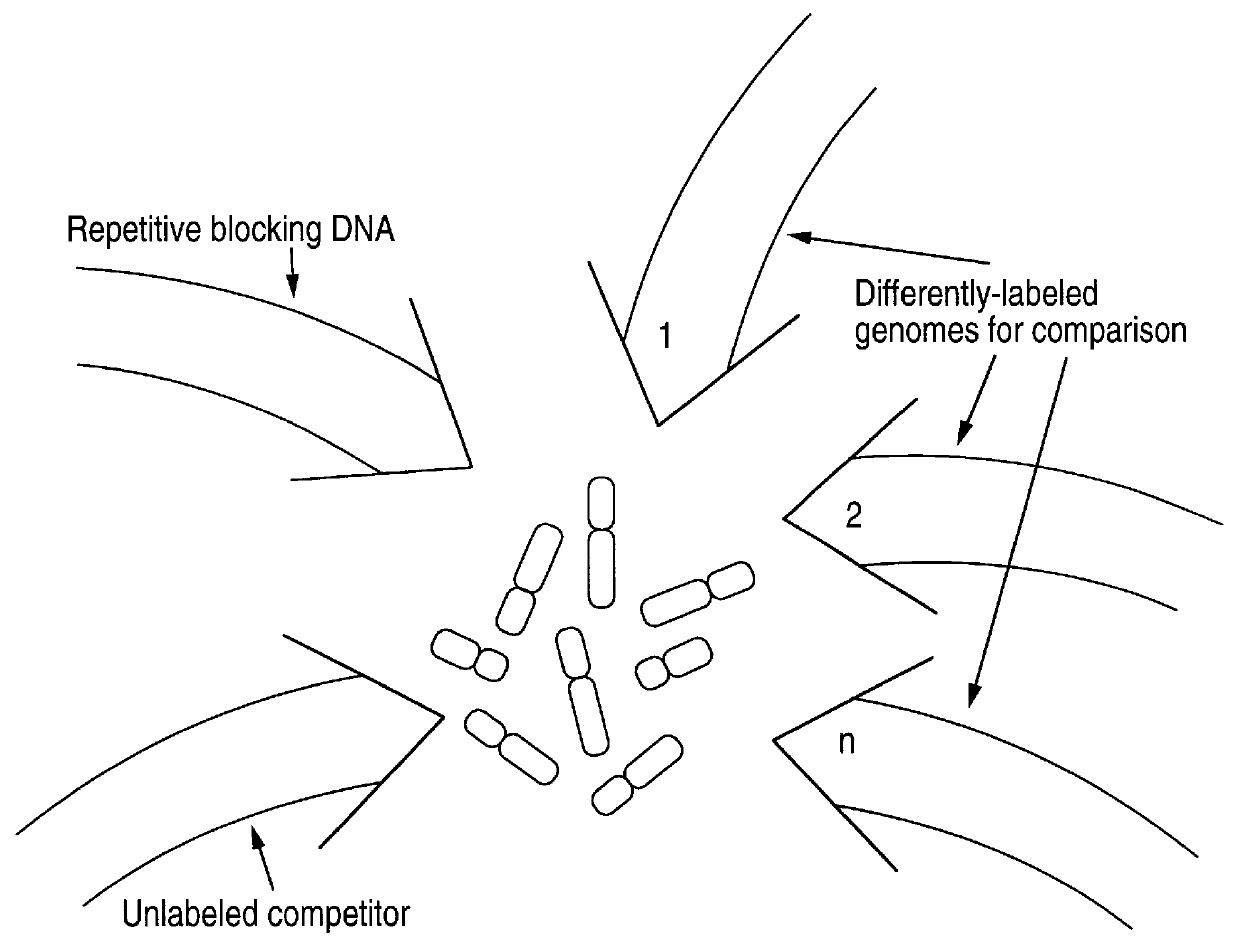
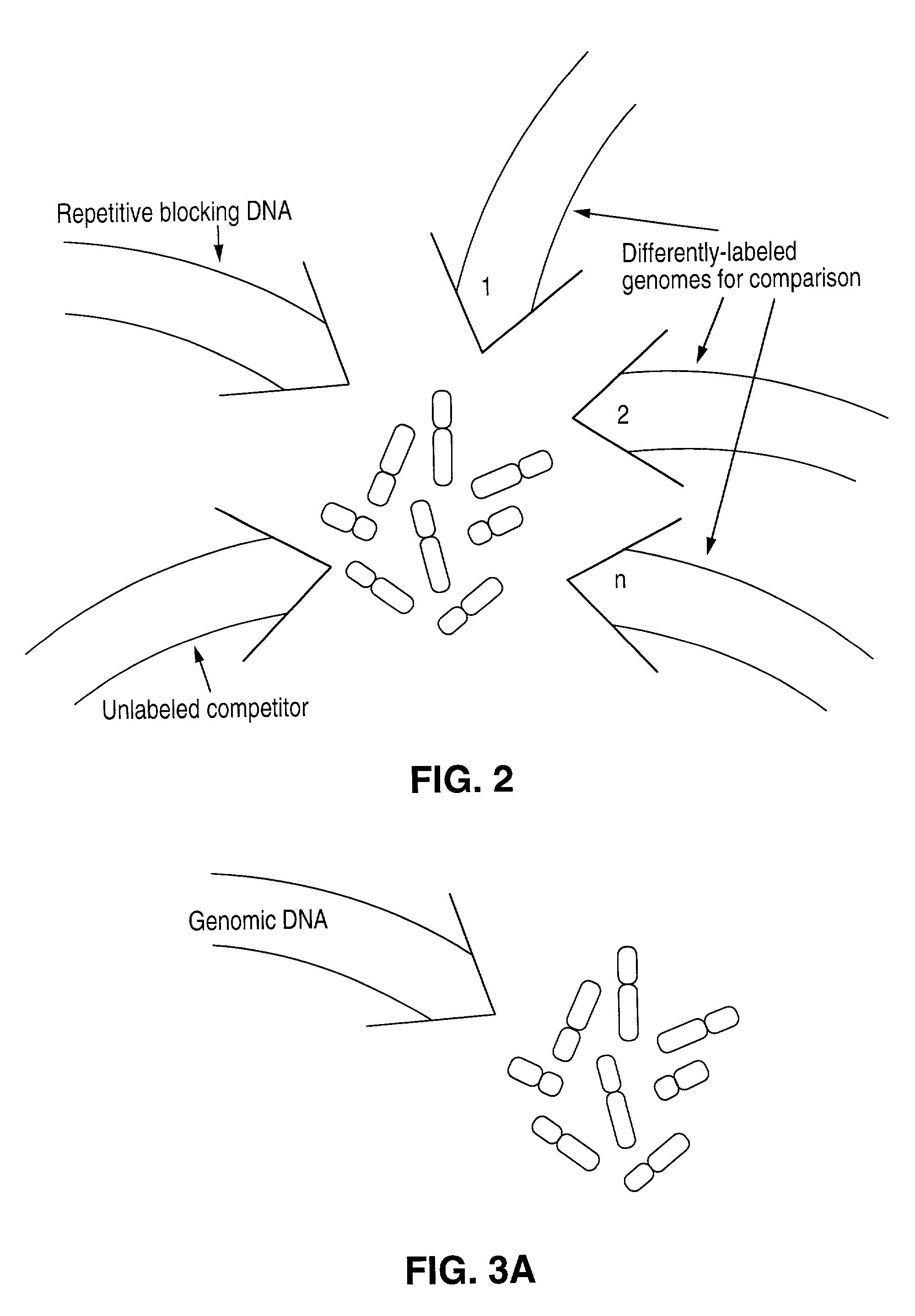
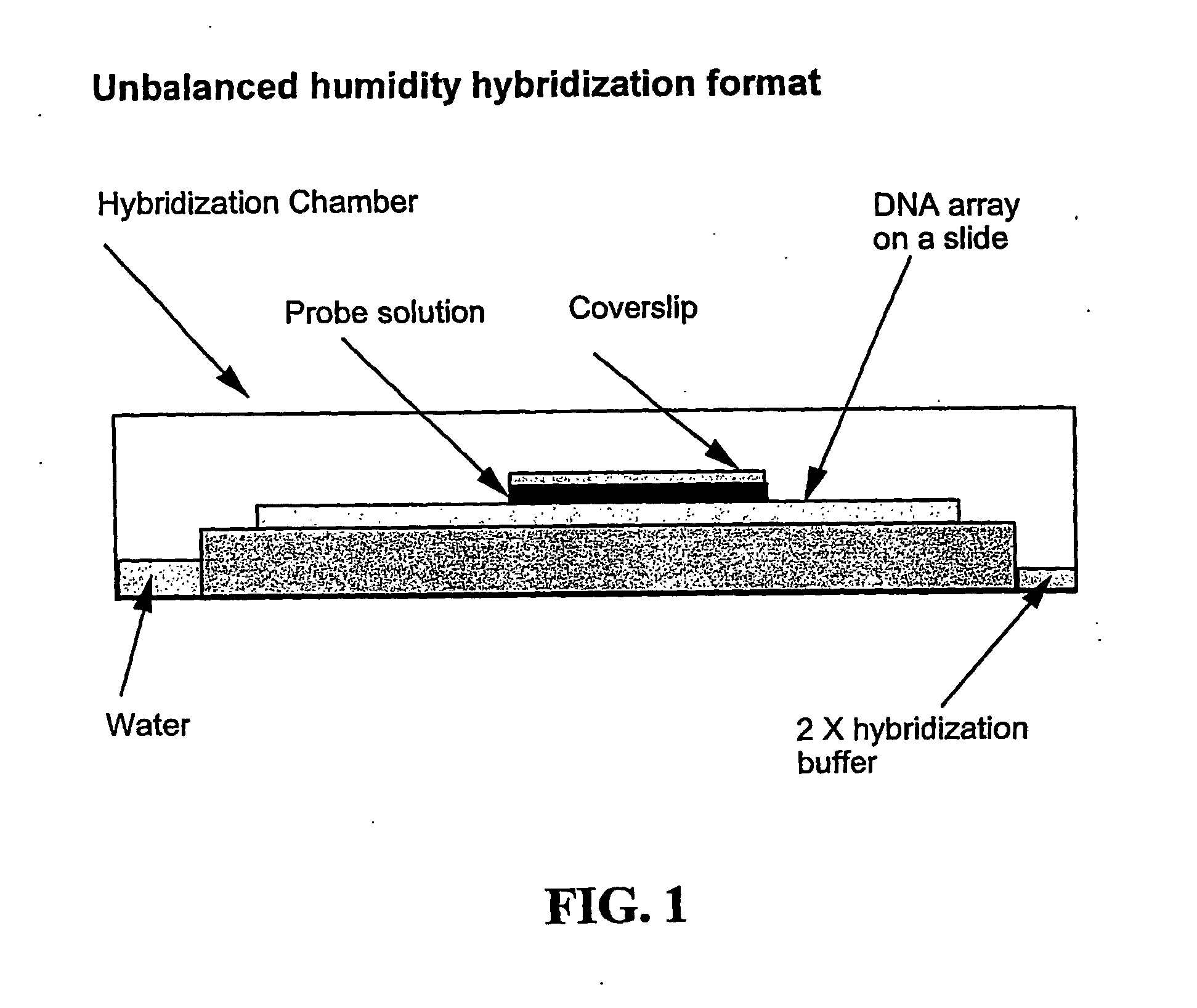
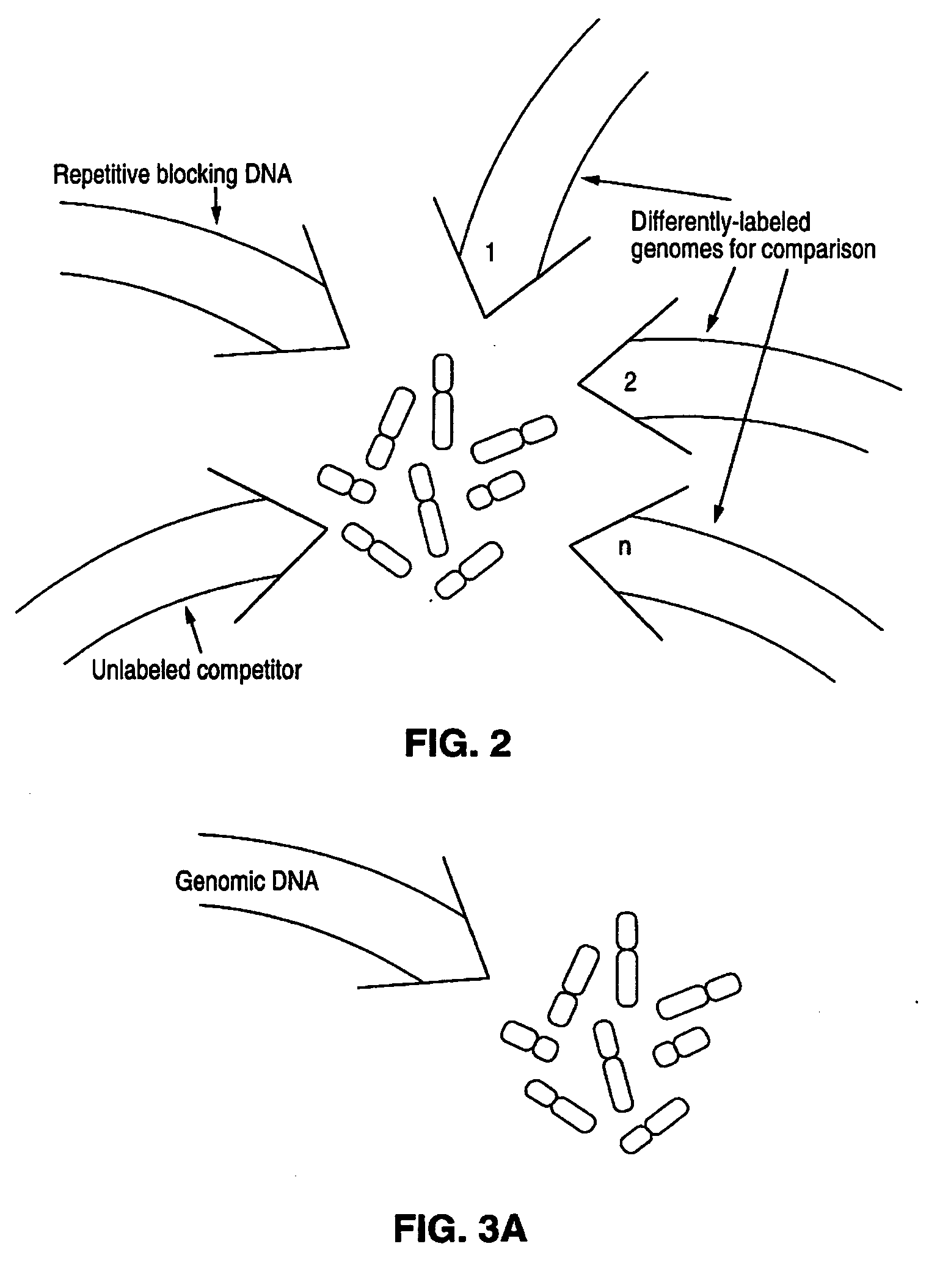
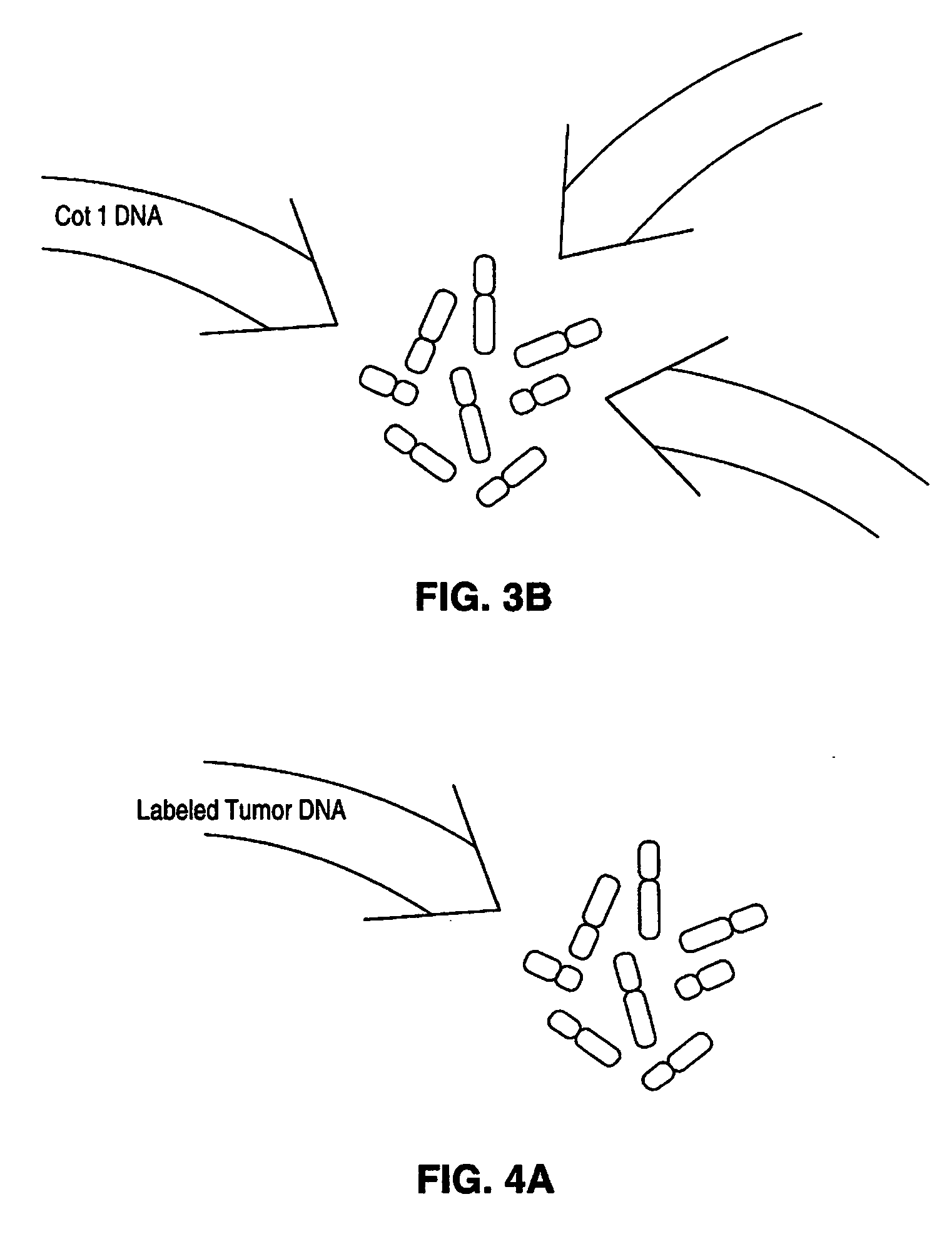
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
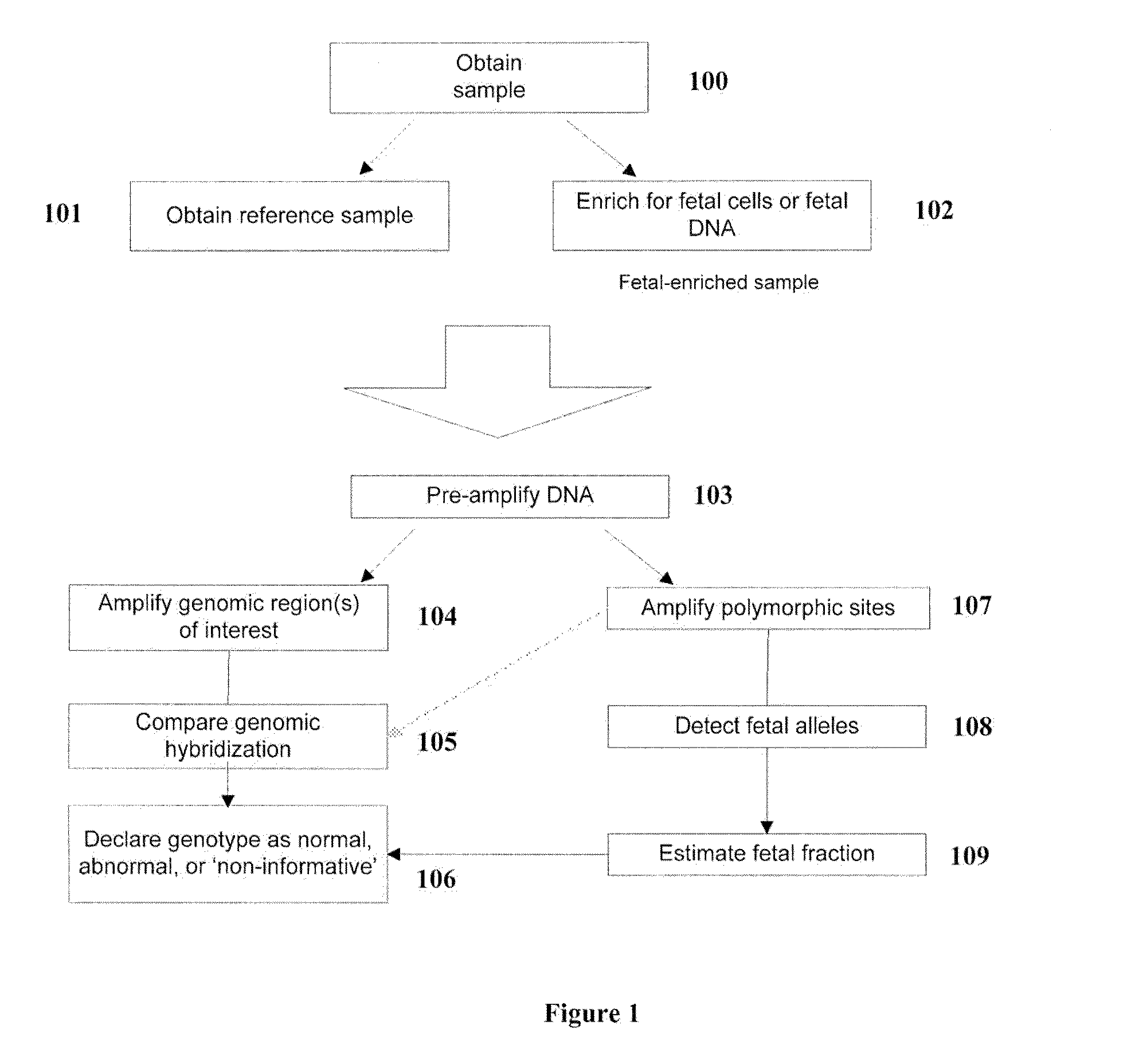
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities by comparative genomic hybridization analysis
InactiveUS20100112586A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +1
Validation of comparative genomic hybridization
InactiveUS20070238108A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingComparative genomic hybridizationGenome
The present invention generally relates to techniques involving comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and related techniques, including the validation of assay results. In one aspect, a region of interest of a genome or other target nucleic acid, identified using CGH or similar techniques, may be validated using a probe based on the CGH results. The oligonucleotides, in some embodiments, may bind the genome in some fashion (e.g., to the region of interest, and / or to other predetermined regions), and thus can be used for validation of CGH or other results.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Competitive oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20070238104A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingComparative genomic hybridizationGenomic DNA
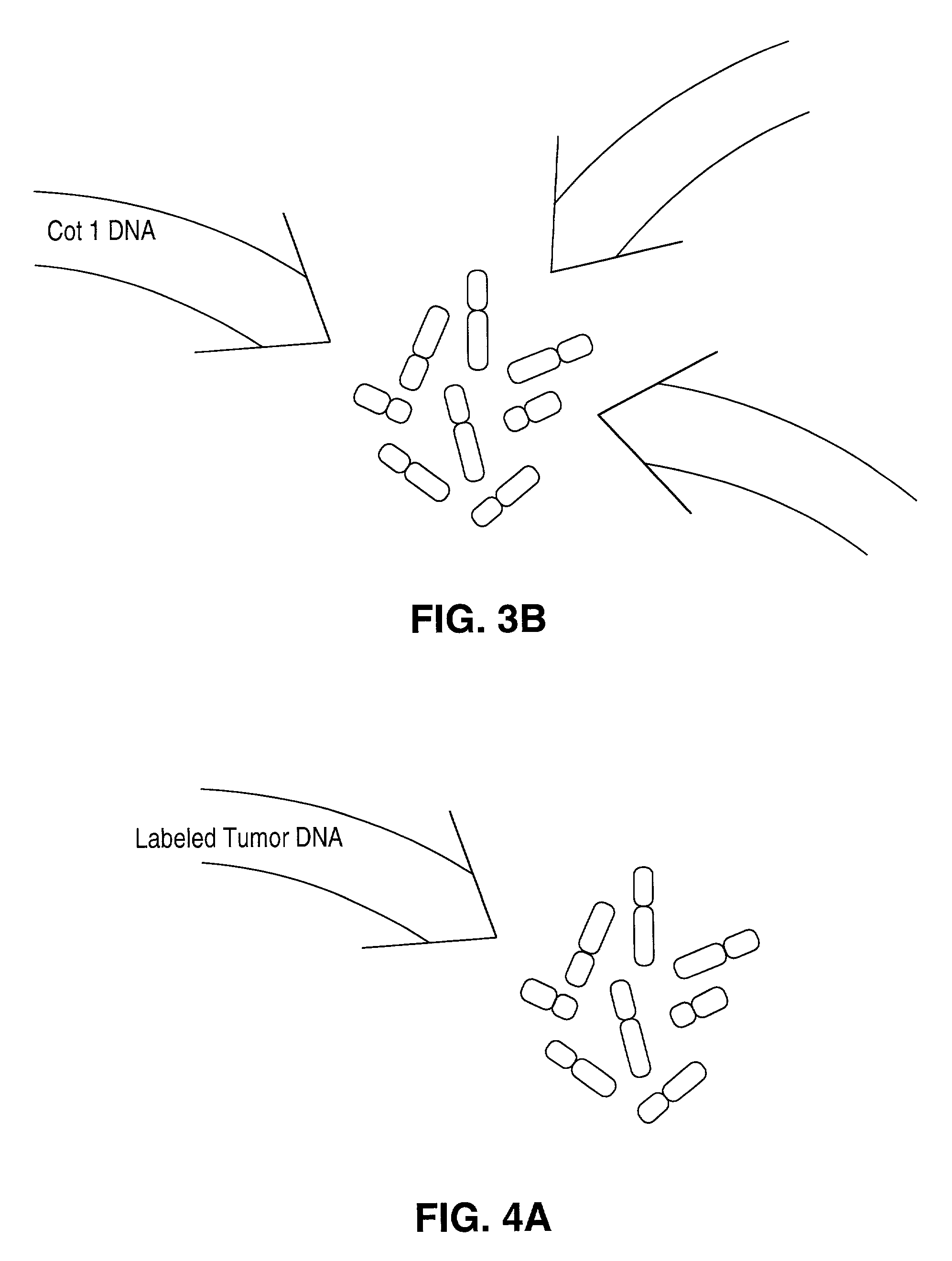
The present invention generally relates to competitive oligonucleotides and, in some embodiments, to competitive oligonucleotides for use in comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and related techniques. One aspect is generally directed to a blocking composition constructed and arranged to be used in an assay of a nucleic acid. The blocking composition may comprise oligonucleotides comprising sequences selected to hybridize to the nucleic acid used in the assay. Another aspect is generally directed to performing CGH assays and similar techniques on genomic DNA, in the absence of a Cot-1 fraction, such that the genomic DNA does not substantially cross-hybridize. Yet other aspects of the invention are directed to devices or kits for making or using competitive oligonucleotides, methods of promoting such competitive oligonucleotides, or the like.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Detection of nucleic acid sequence differences by comparative genomic hybridization
InactiveUS20060063168A1Microbiological testing/measurementComparative genomic hybridizationNucleotide
The present invention provides a method of detecting nucleotide sequence differences between two nucleic acid samples. The method employs a comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) technique to analyze the sequence differences between the samples. This method permits the identification of small sequence differences (e.g., sequence divergence of 1% or less) in nucleic acid samples of high complexity (e.g., an entire genome).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Comparative genomic hybridization assays using immobilized oligonucleotide features and compositions for practicing the same
ActiveUS20040191813A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingAssayComparative genomic hybridization
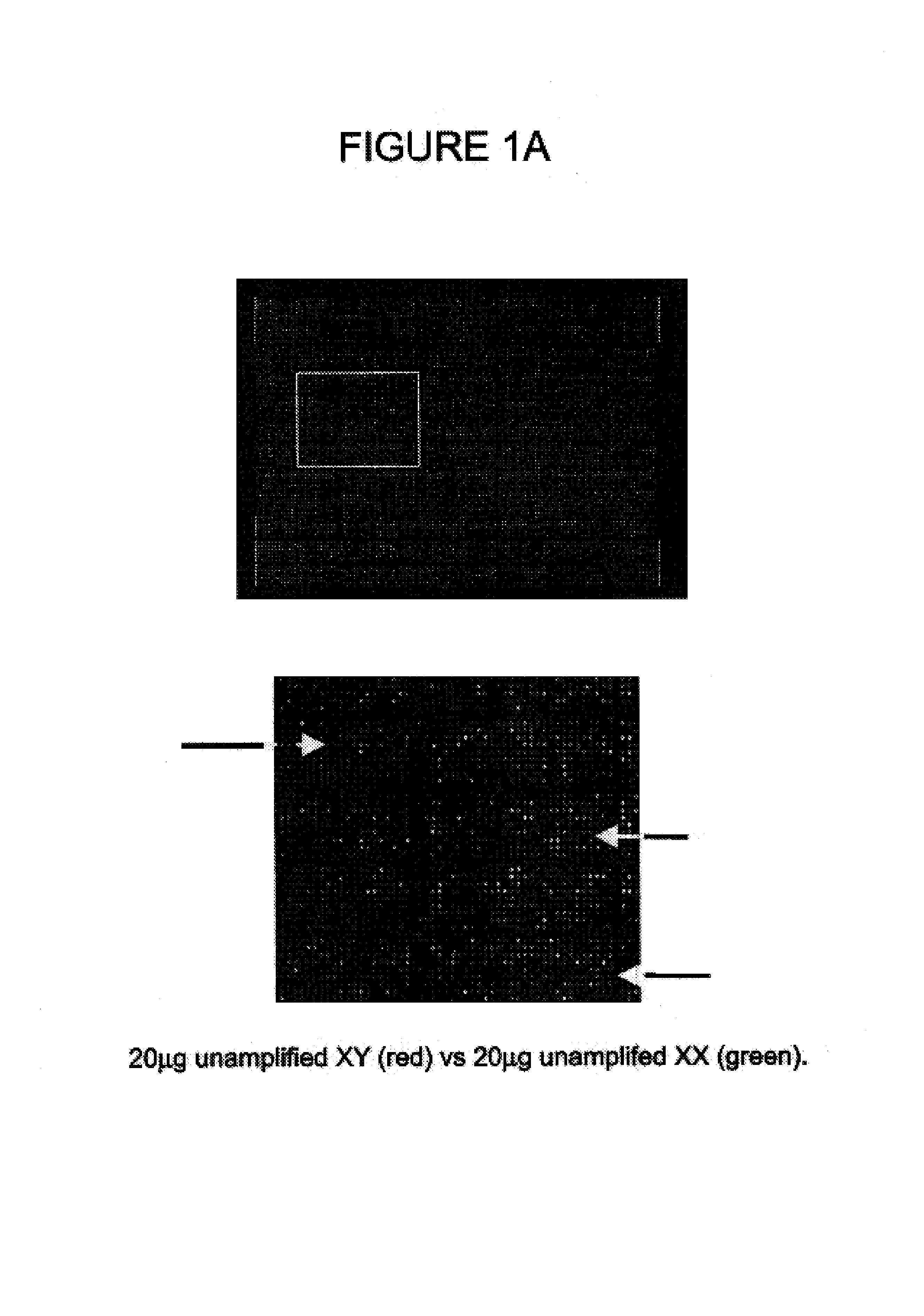
Comparative genomic hybridization assays and compositions for use in practicing the same are provided. A characteristic of the subject comparative genomic hybridization assays is that solid support immobilized oligonucleotide feature elements, e.g., in the form of an array, are employed. Specifically, at least first and second nucleic acid populations prepared from genomic templates are contacted with a plurality of distinct oligonucleotide feature elements immobilized on a solid support surface and the binding of the at least first and second populations is then evaluated. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
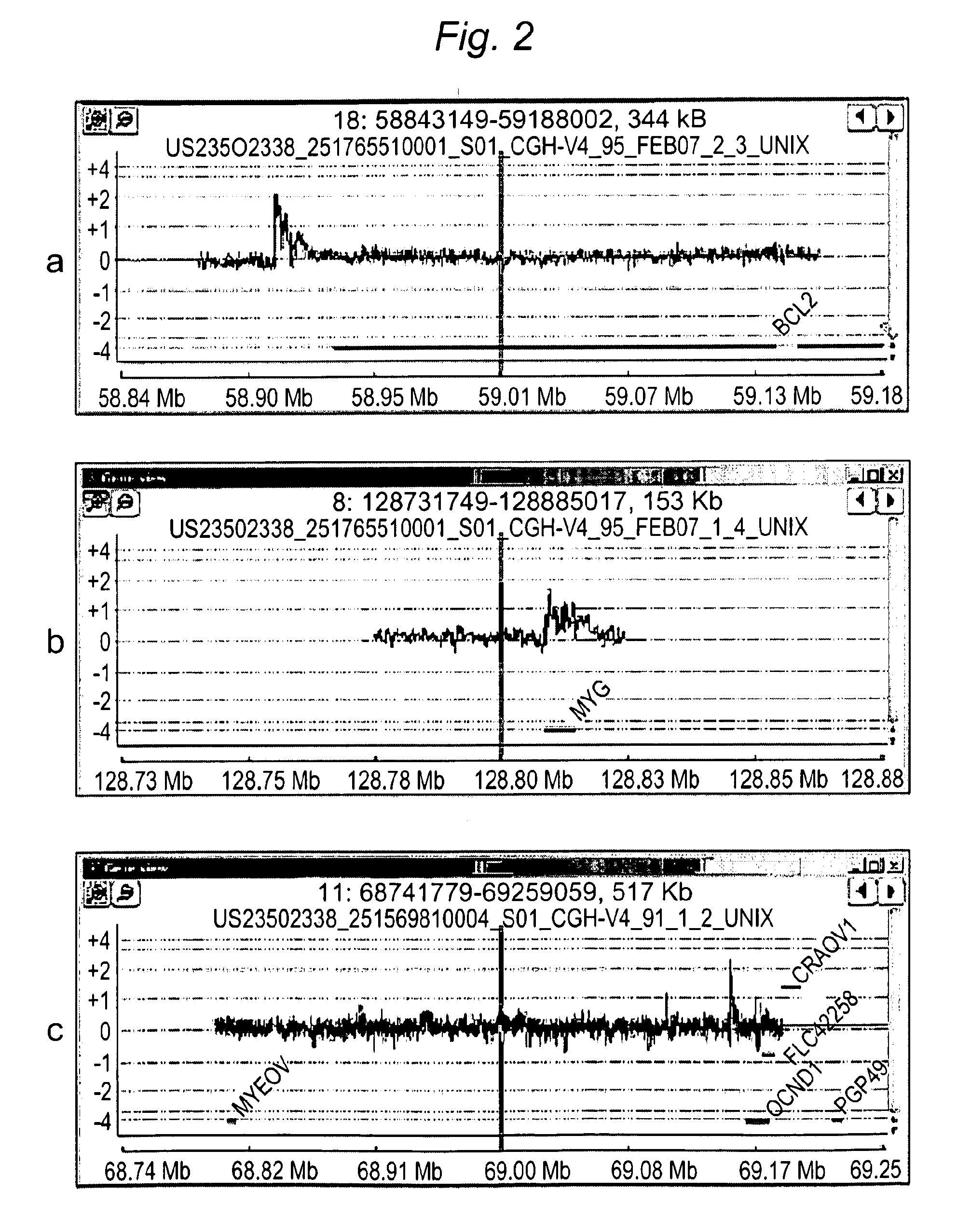
Detection of chromosoal abnormalities associated with breast cancer
InactiveUS7094534B2Avoid saturationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Arrays comprising pre-labeled biological molecules and methods for making and using these arrays
InactiveUS20050032060A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesMolecular arrayComparative genomic hybridization
The invention provides arrays comprising a plurality of biological molecules, wherein each biological molecule is immobilized to a discrete and known spot on a substrate surface to form an array of biological molecules, and each biological molecule comprises a detectable label. The invention provides a multiplexed system for performing comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) using an array of the invention. The invention also provides methods of making and using these arrays, including a method of comparing copy numbers of unique nucleic acid sequences in a sample.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Comparative genomic hybridization assays using immobilized oligonucleotide features and compositions for practicing the same
ActiveUS8232055B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingAssayComparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization assays and compositions for use in practicing the same are provided. A characteristic of the subject comparative genomic hybridization assays is that solid support immobilized oligonucleotide feature elements, e.g., in the form of an array, are employed. Specifically, at least first and second nucleic acid populations prepared from genomic templates are contacted with a plurality of distinct oligonucleotide feature elements immobilized on a solid support surface and the binding of the at least first and second populations is then evaluated. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Diagnostic methods and kits for hepatocellular carcinoma using comparative genomic hybridization
InactiveUS20090181394A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibraries apparatusComparative genomic hybridizationGenome
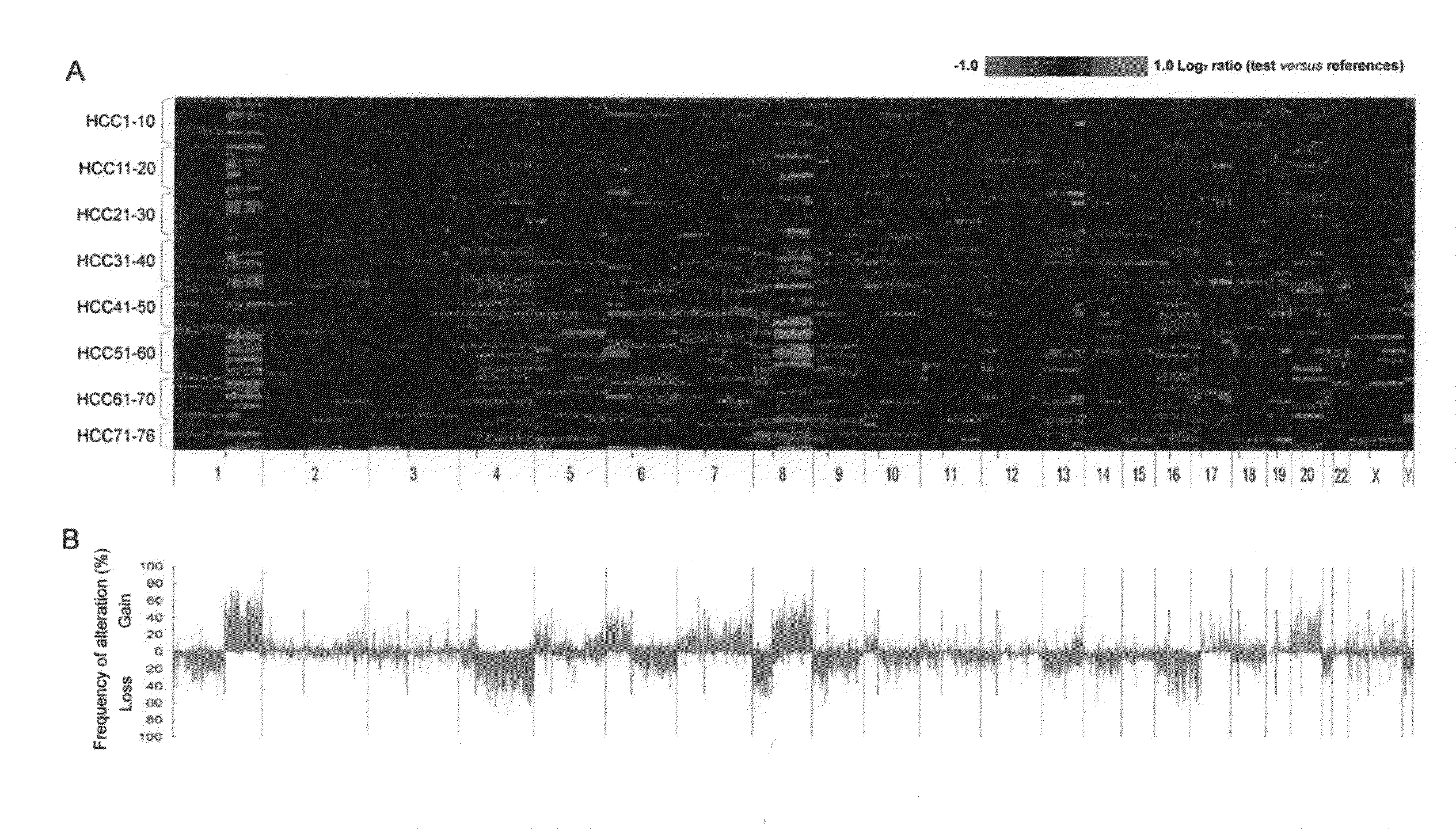
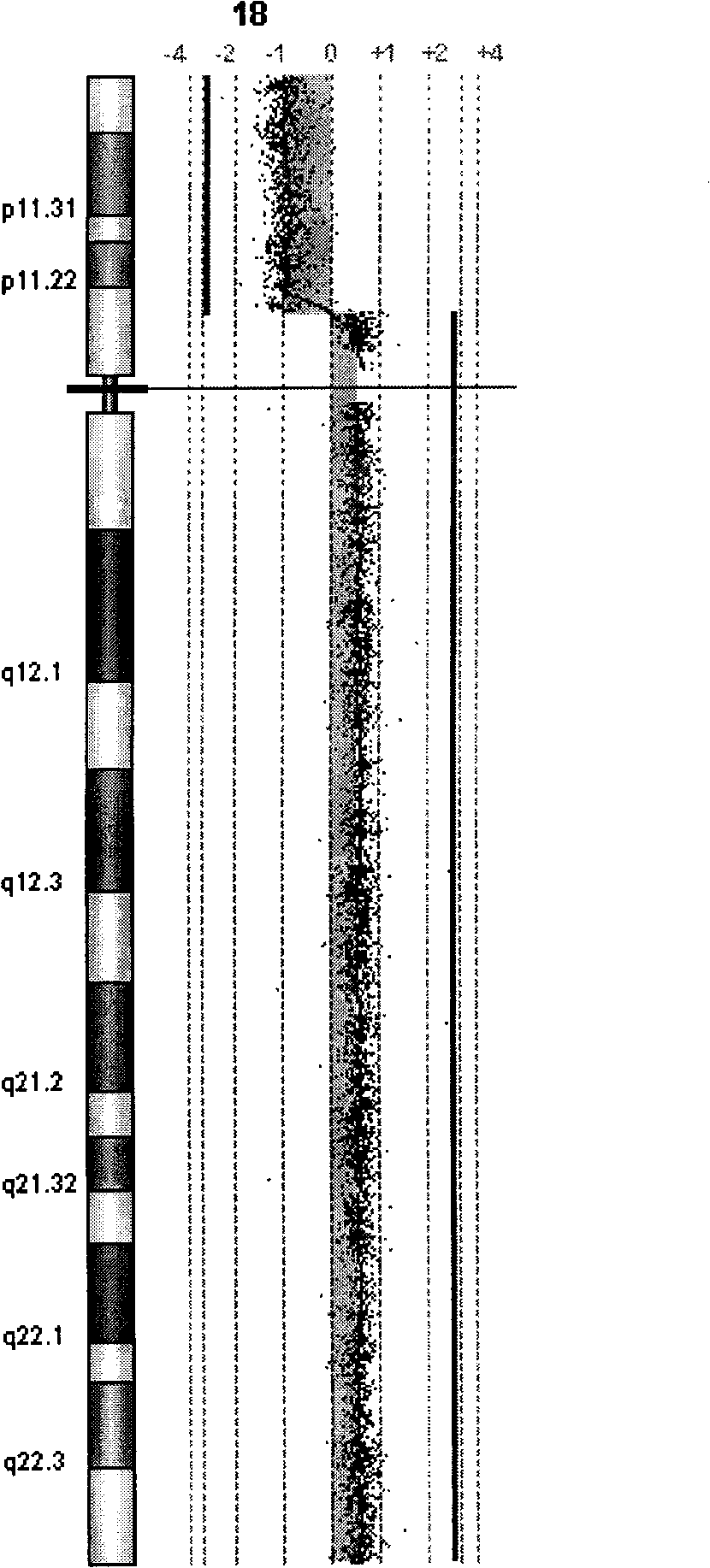
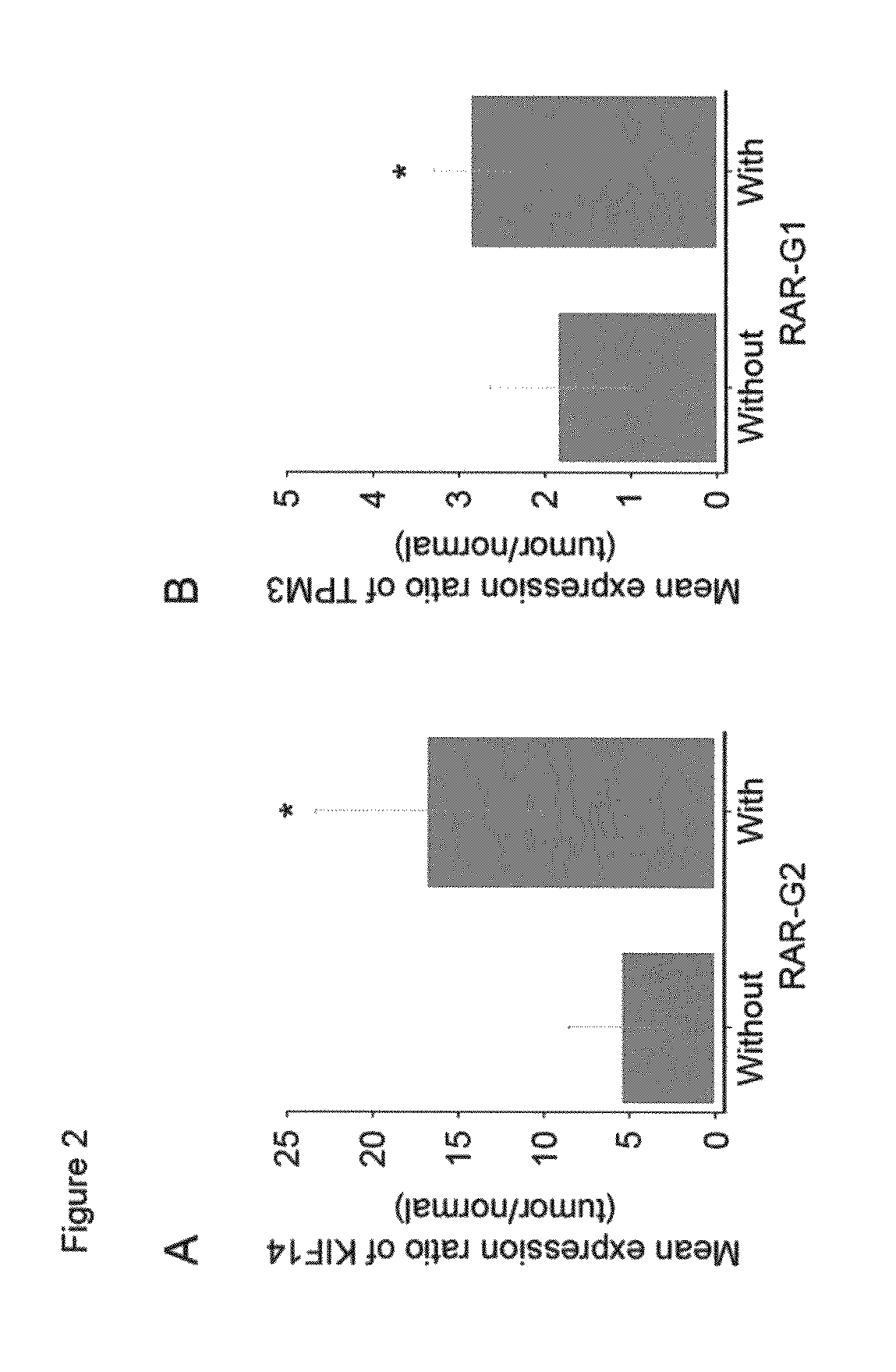
The invention provides diagnostic methods for determining the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) comprising the steps of (a) observing recurrently altered genomic region on a chromosome; (b) measuring variation of one or more of RAR expression variations selected from the RAR variation group consists of gains of RAR-G1 to RAR-G14 and losses of RAR-L1 to RAR-L18 as defined in table 1, a diagnostic kit, and genes for useful in diagnosis or prognosis of liver cancer.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Comparative genomic hybridization
InactiveUS20050118634A1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Balanced translocation in comparative hybridization
InactiveUS20070122820A1Quicker and more methodIncrease profitSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention provides comparative genomic hybridization methods for detecting and mapping chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases, or to detecting the phenomena of large scale copy number variants. The method includes hybridization with one or more probes for detecting balanced translocations. Such probes may be complementary to the moving genomic segment which is translocated or may be complementary to the translocation break point.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Gene expression profiling based identification of genomic signature of high-risk multiple myeloma and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080274911A1High-risk indexIncreased risk of deathMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNewly diagnosedComparative genomic hybridization
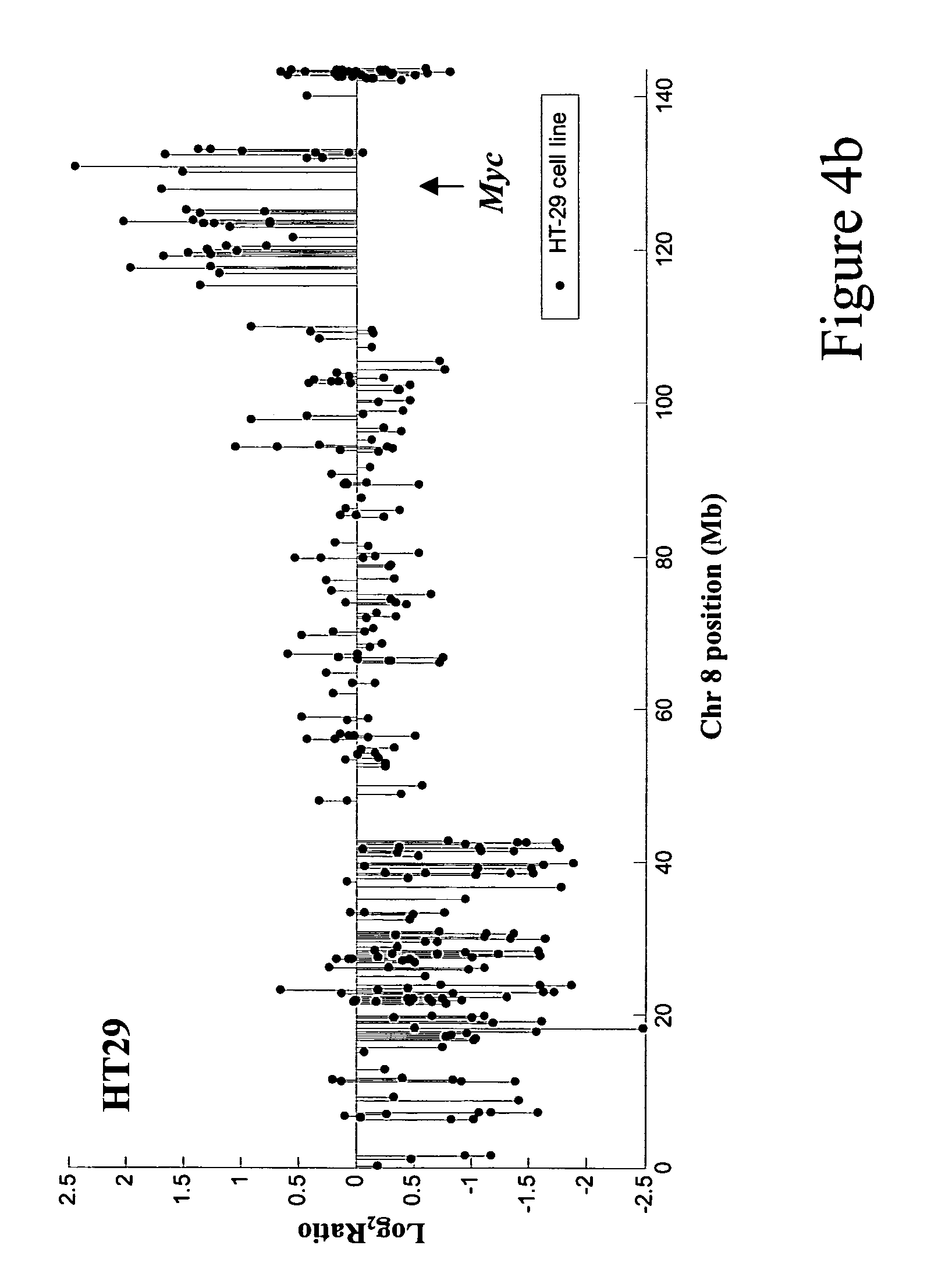
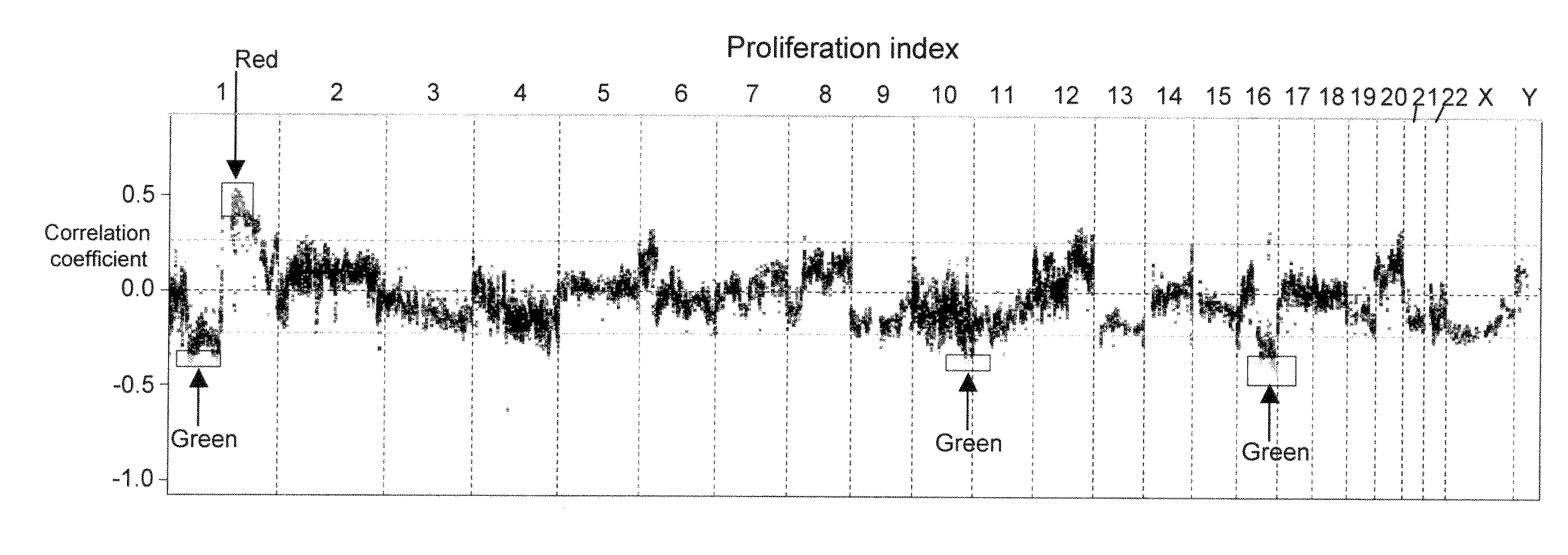
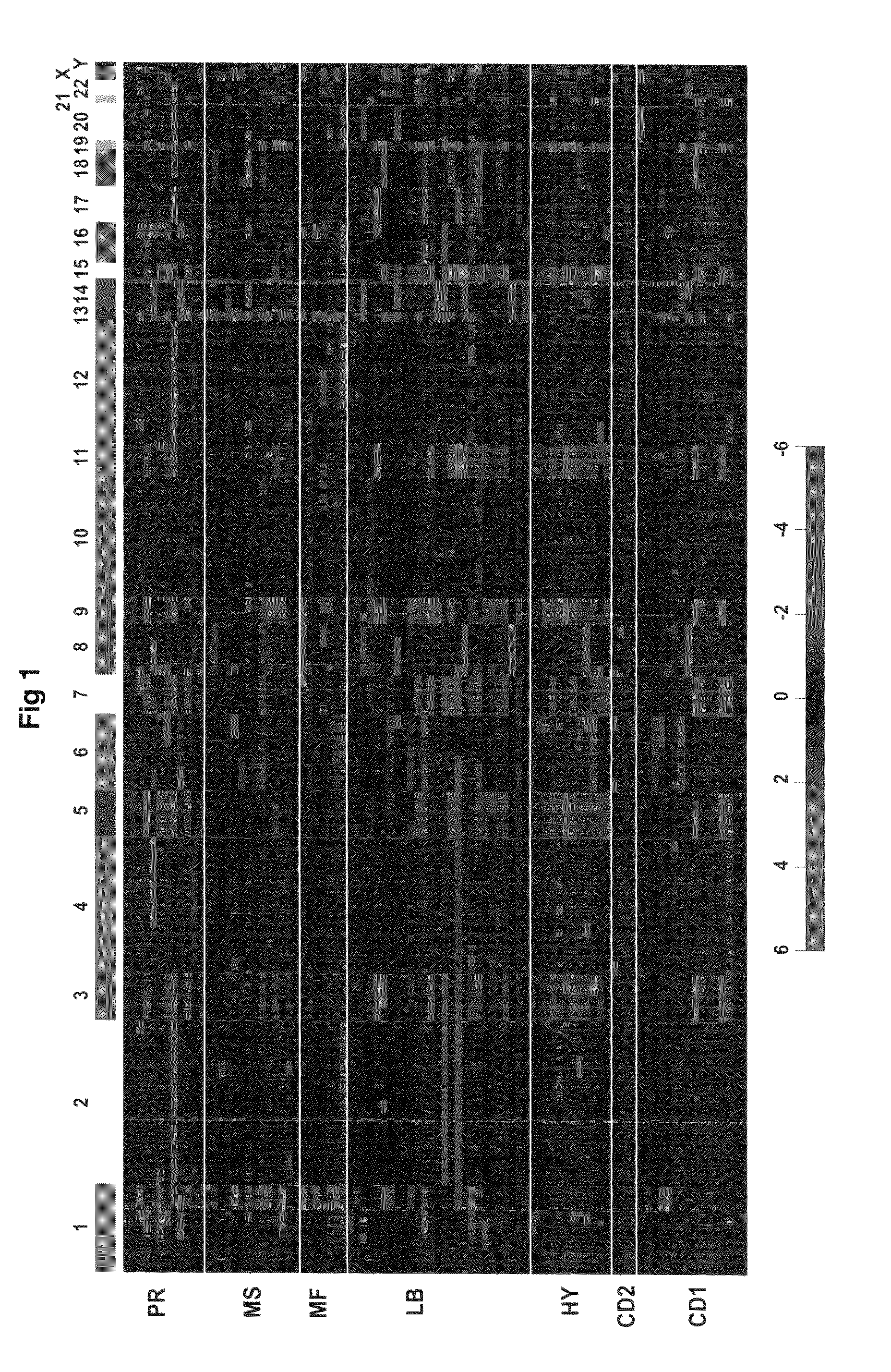
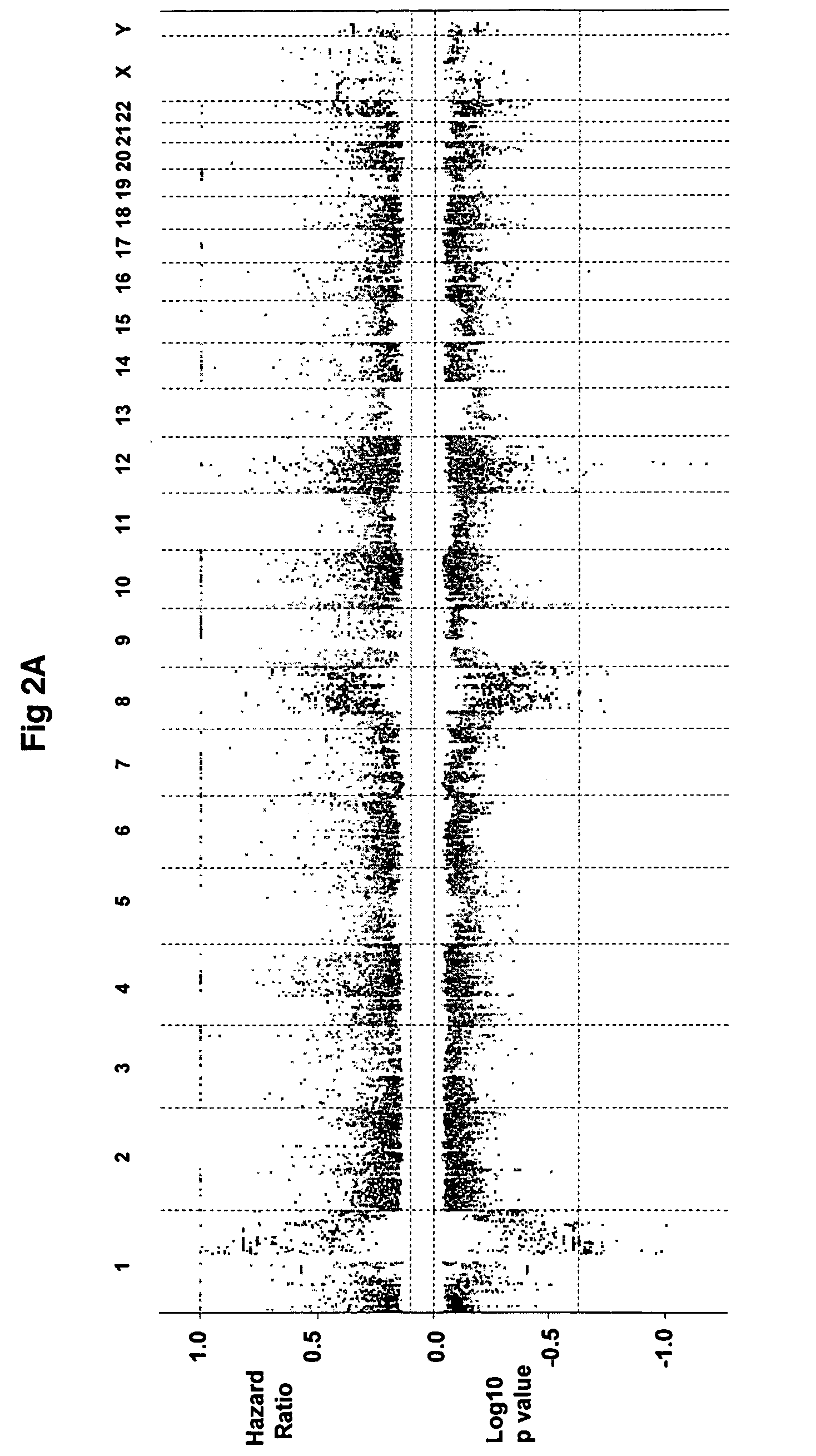
The present invention discloses a method of applying novel bioinformatics and computational methodologies to data generated by high-resolution genome-wide comparative genomic hybridization and gene expression profiling on CD138-sorted plasma cells from a cohort of 92 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients treated with high dose chemotherapy and stem cell rescue. The results revealed that gains the q arm and loss of the p arm of chromosome 1 were highly correlated with altered expression of resident genes in this chromosome, with these changes strongly correlated with 1) risk of death from disease progression, 2) a gene expression based proliferation index, and 3) a recently described gene expression-based high-risk index. Importantly, we also found a strong correlation between copy number gains of 8q24, and increased expression of Argonate 2 (AGO2) a gene coding for a master regulator of microRNA expression and maturation, also being significantly correlated with outcome. Our novel findings significantly improve our understanding of the genomic structure of multiple myeloma and its relationship to clinical outcome.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
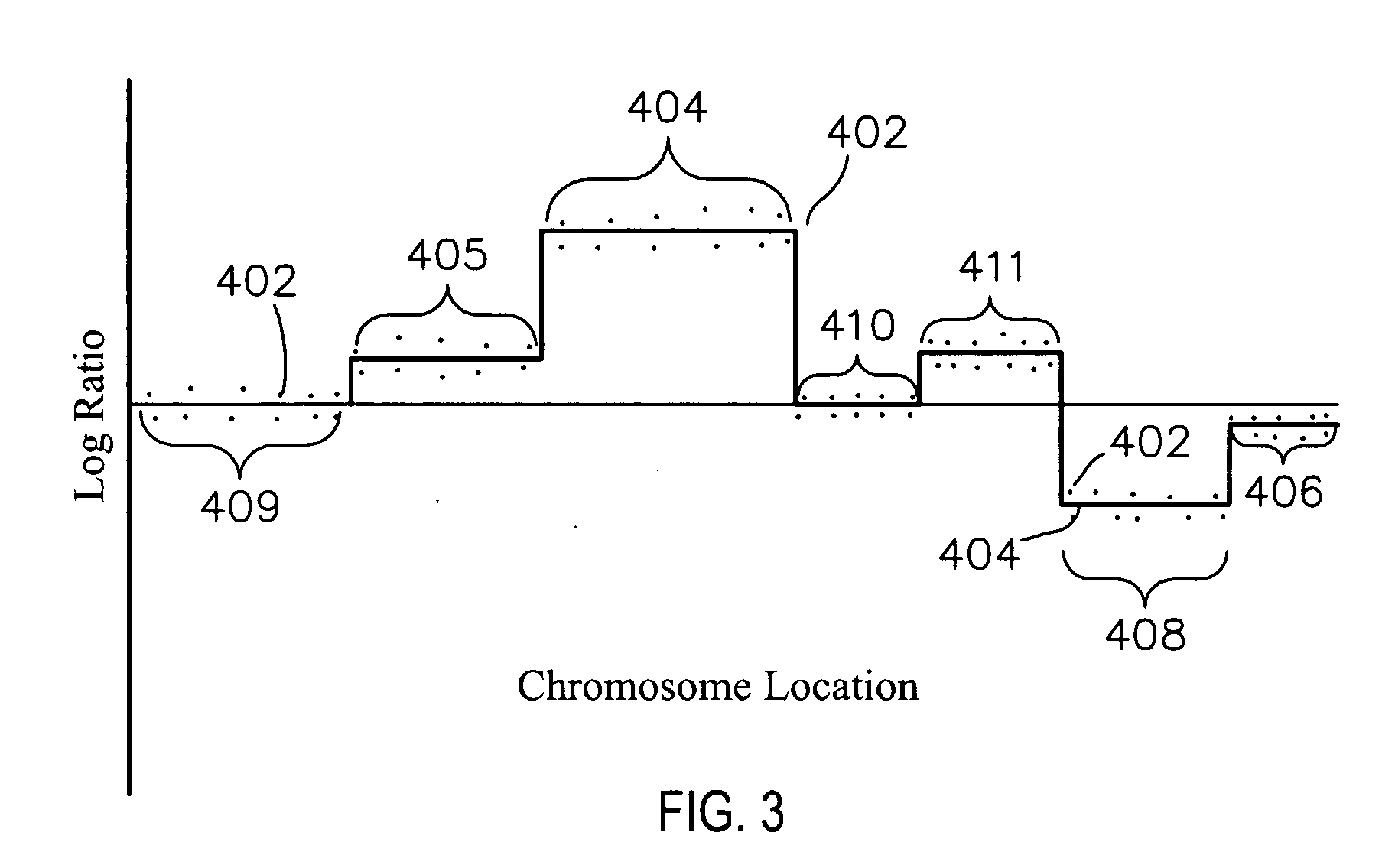
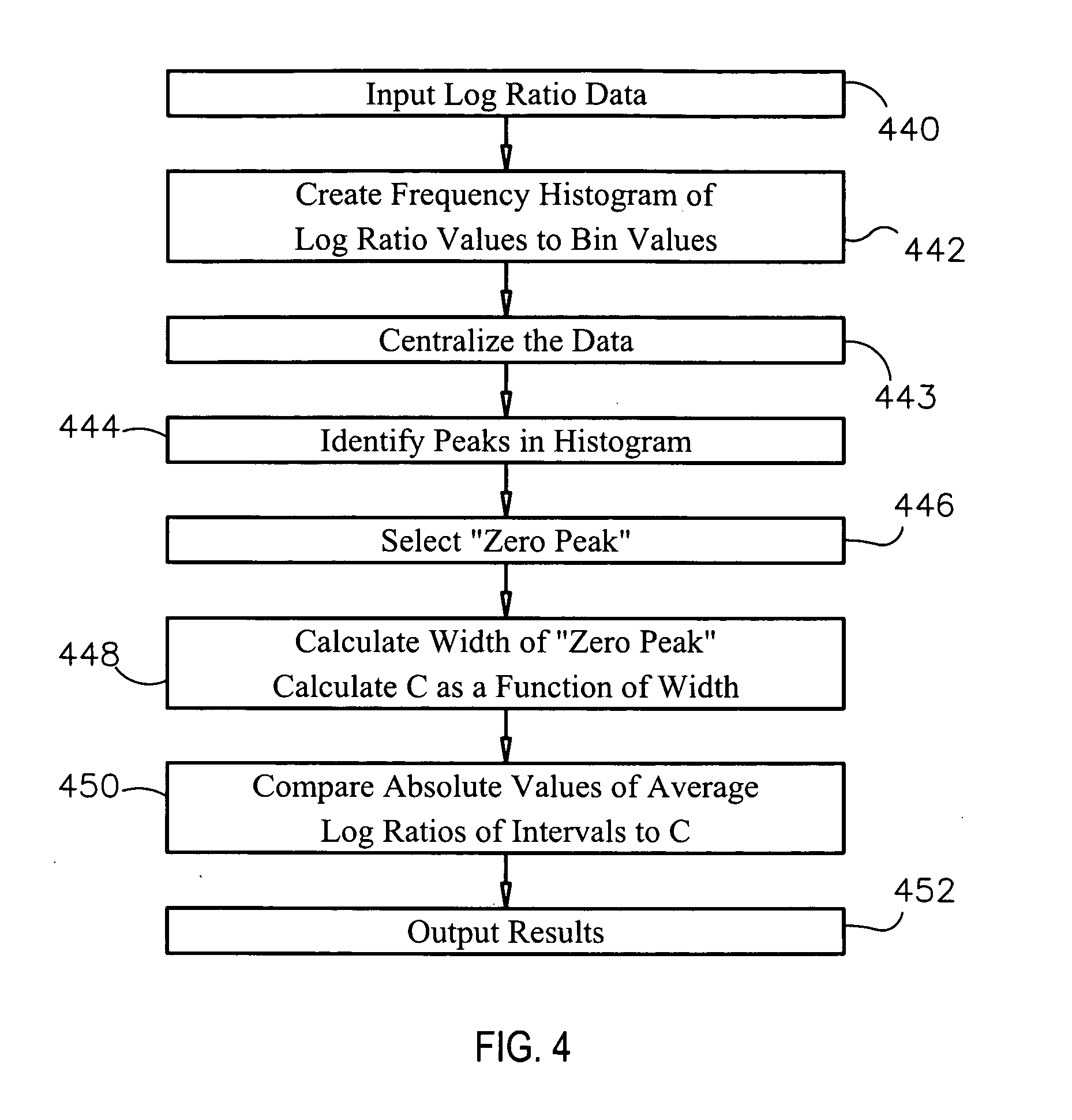
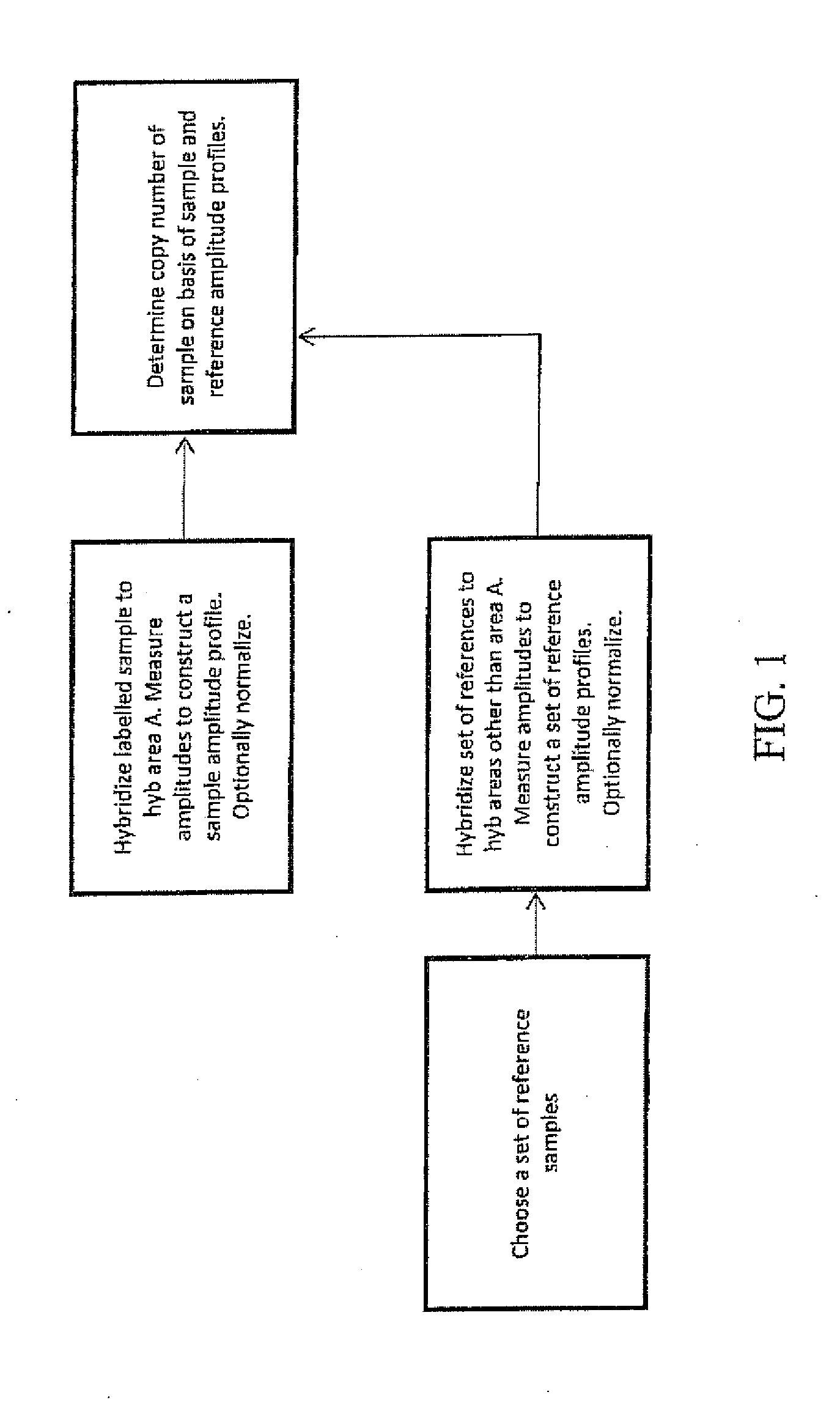
Methods and systems and analysis of CGH data
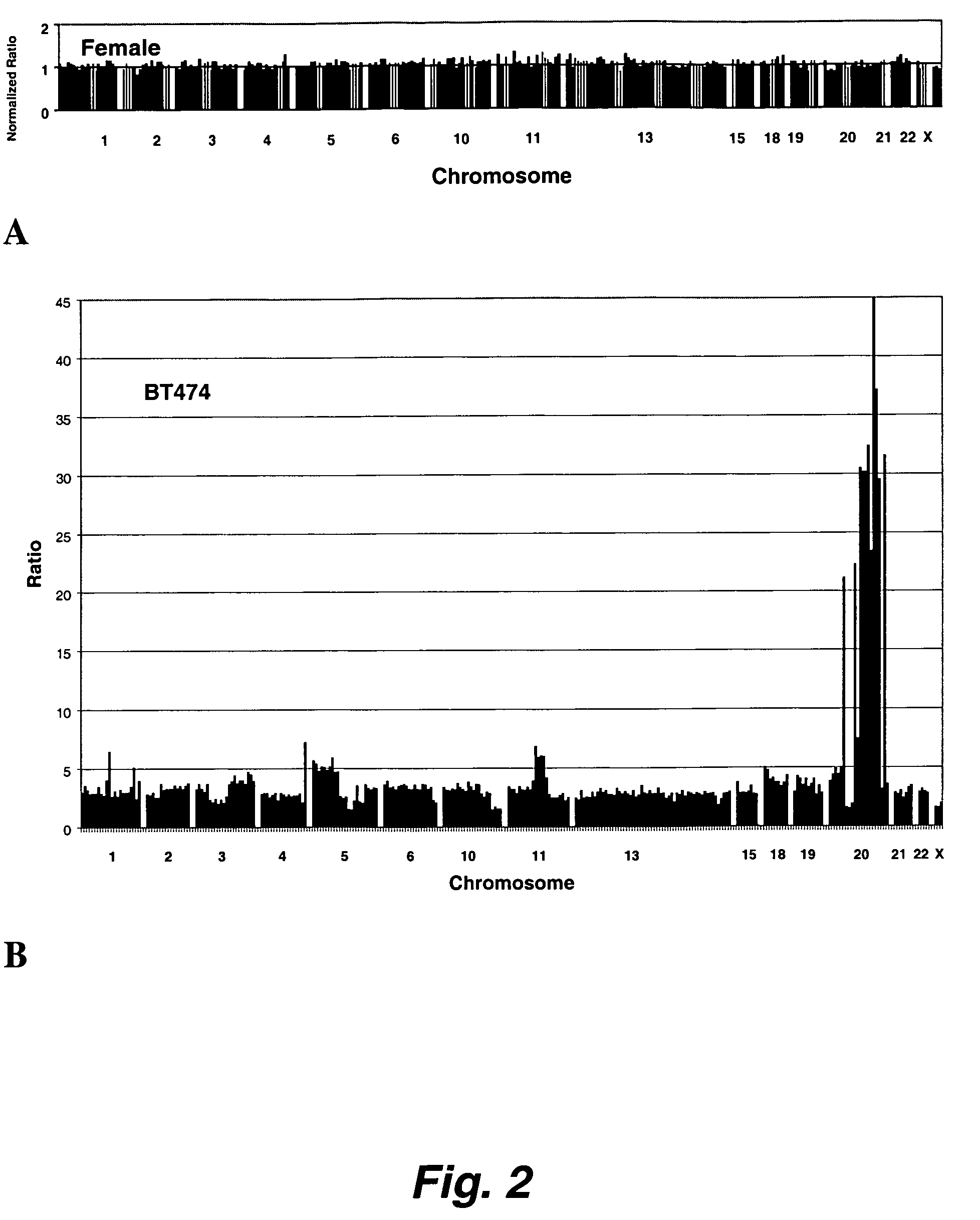
Methods, systems and computer readable media for analysis of comparative genomic hybridization data analysis, including creating a centralization curve from log ratio data values for DNA copy numbers of a genome of a test sample relative to a genome of a reference sample, wherein the reference sample has a known ploidy, and the test sample has a same copy number as the reference sample in normal, non-aberrant genomic regions; identifying a peak corresponding to regions of normal copy number in the centralization curve; centralizing the log ratio data so that the peak corresponding to regions of normal copy number is centered at a log ratio value of zero; calculating a mathematical measurement that is a function of the width of the peak corresponding to regions of normal copy number; calculating a tolerance value as a function of the mathematical measurement; and outputting the tolerance value. Methods, systems and computer readable media are provided to create a centralization curve from log ratio data values for DNA copy numbers of a genome of a test sample relative to a genome of a reference sample, wherein the reference sample has a known ploidy, and the test sample has a same copy number as the reference sample in normal, non-aberrant genomic regions; identify peaks in the centralization curve; assign copy numbers to the identified peaks; plot expected ratios, based on the assigned copy numbers, of the peaks versus observed ratios of the peaks calculated from the log ratio data values; conclude that the assigned copy numbers are correct if the plot of the expected ratios versus the observed ratios is substantially linear; and output at least one of the plot of expected ratios versus observed ratios, and a conclusion as to whether the plot is substantially linear.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Comparative genomic hybridization
InactiveUS20060292608A1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Comparative genomic hybridization assays and compositions for practicing the same
InactiveUS20070087355A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationComparative genomic hybridizationGenome
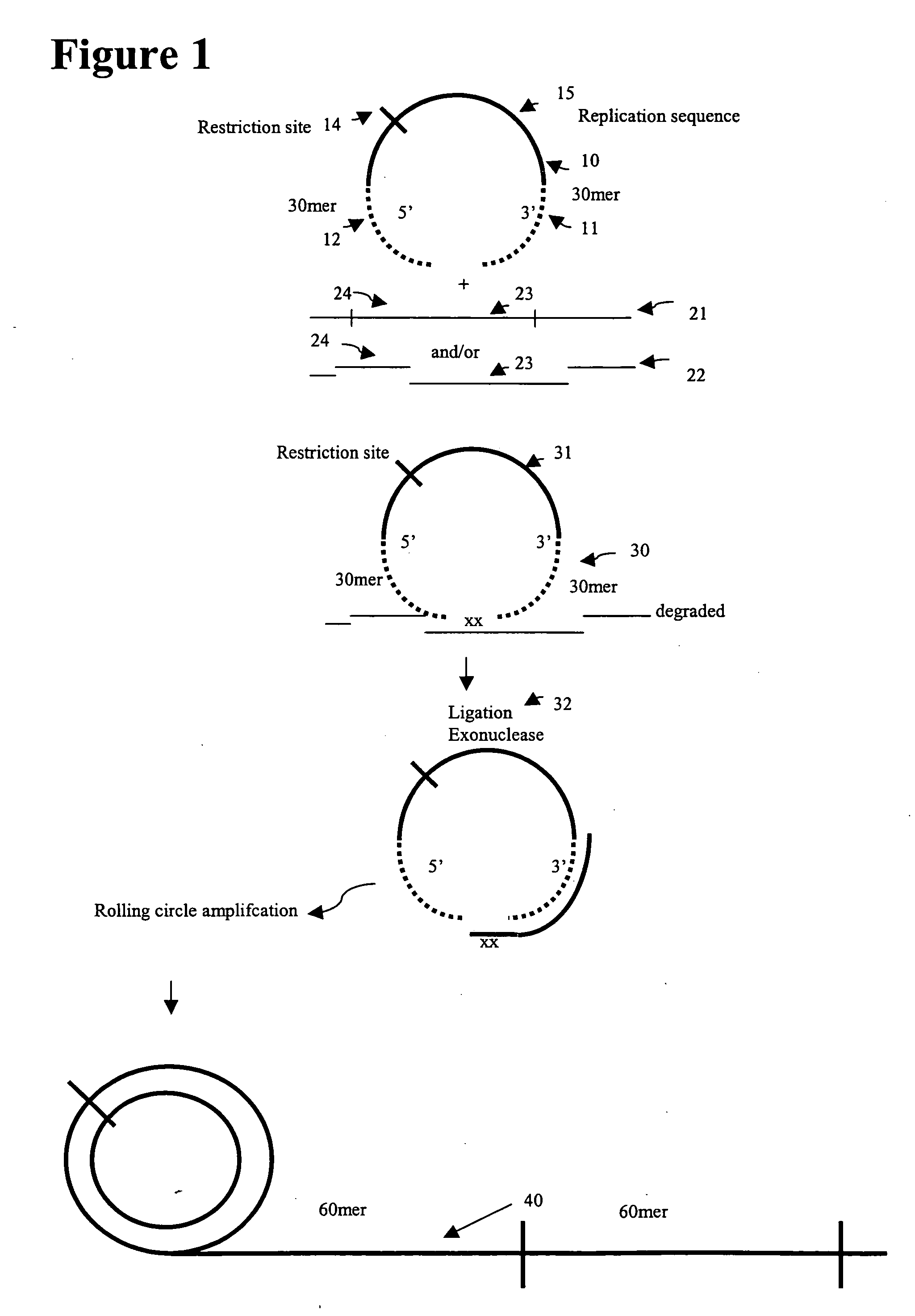
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) assays and compositions for use in practicing the same are provided. Aspects of the methods include first preparing genomic templates from an initial genomic source by using precursors of circular template nucleic acids, e.g., padlock probes. The precursors include first and second domains that are at least partially complementary to substantially neighboring regions of a genomic domain of interest. In certain embodiments, the methods include an isothermal amplification step, e.g., a rolling circle amplification step. The resultant templates may then be employed to produce target nucleic acid populations, e.g., for use in CGH applications. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and system for analysis of array-based, comparative-hybridization data
InactiveUS20060084067A1Quantization precision can be improvedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingComparative genomic hybridizationTissue sample
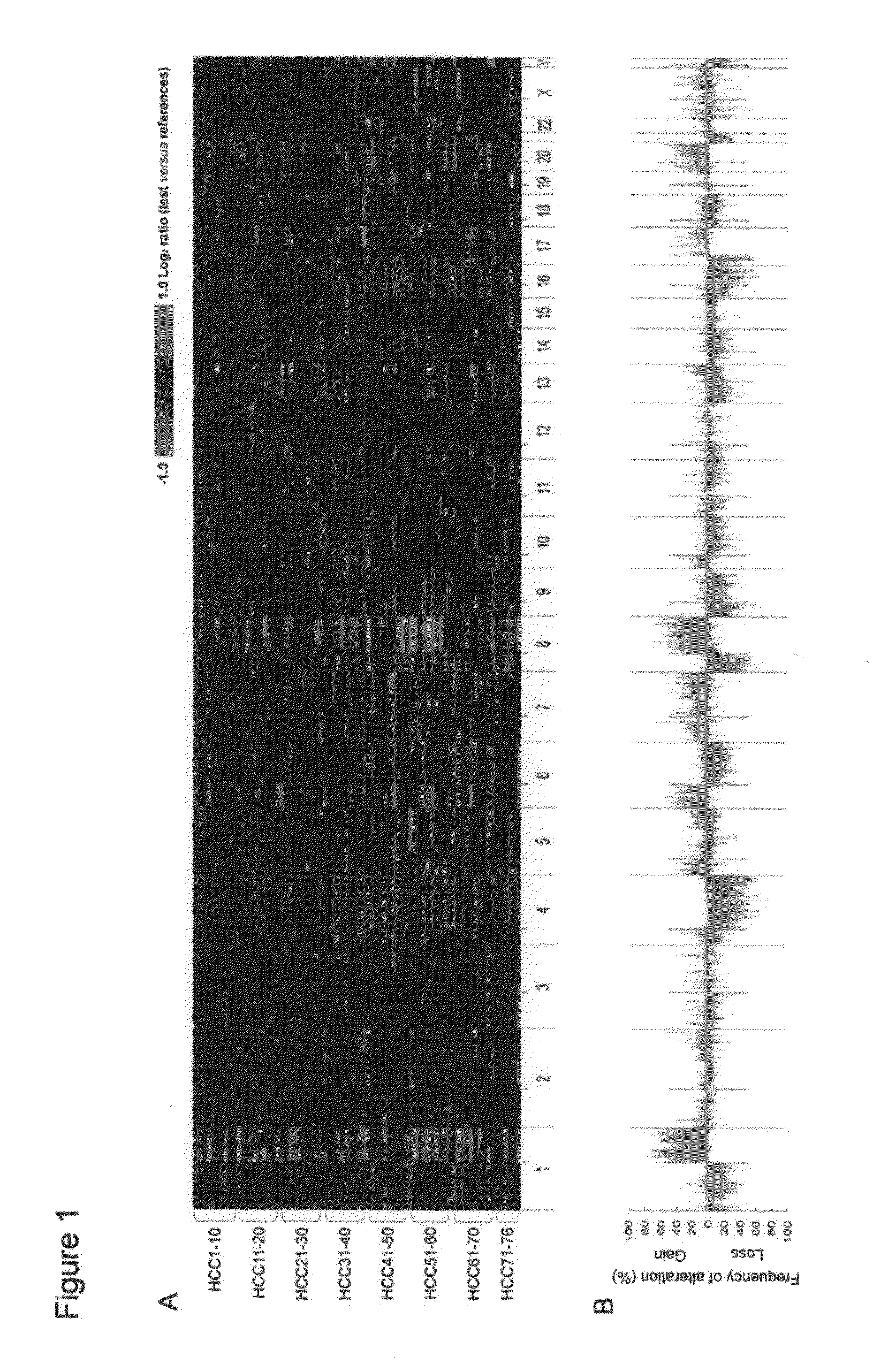
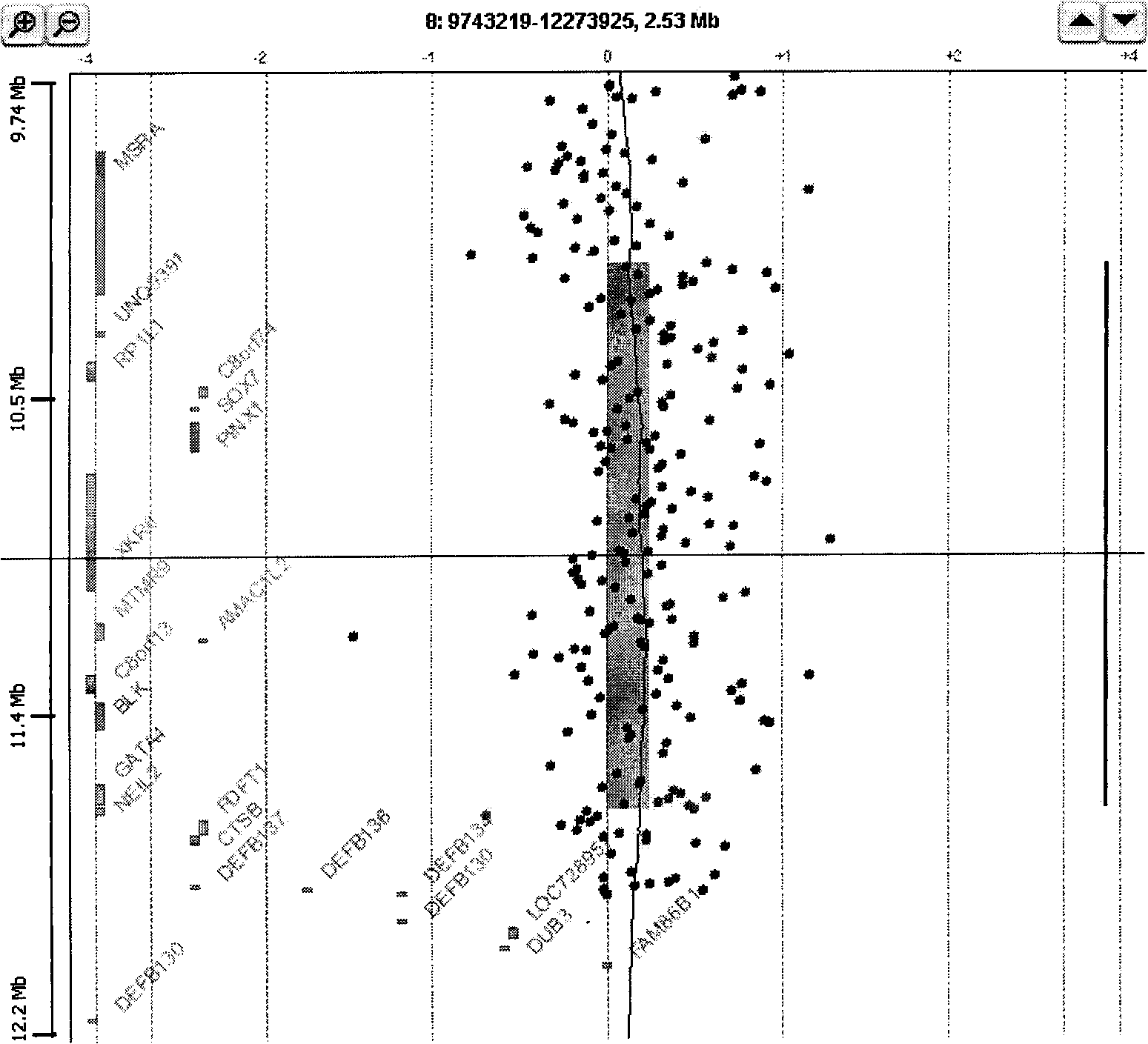
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and systems for analysis of comparative genomic hybridization (“CGH”) data, including CGH data obtained from microarray experiments. Various embodiments of the present invention include parametric and non-parametric normalization methods for CGH data, methods for identifying sets of one or more contiguous chromosomal DNA subsequences that are amplified or deleted in cells from particular tissue samples, and methods for determining amplifications and deletions common to a set of analyzed samples. When combined with well-designed microarray-based experimental systems, method embodiments of the present invention provide markedly increased quantitative precision in the identification of chromosomal abnormalities, including amplified and deleted DNA subsequences based on CGH data.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Balanced translocation in comparative hybridization
InactiveUS8076074B2Quicker and more methodIncrease profitSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention provides comparative genomic hybridization methods for detecting and mapping chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases, or to detecting the phenomena of large scale copy number variants. The method includes hybridization with one or more probes for detecting balanced translocations. Such probes may be complementary to the moving genomic segment which is translocated or may be complementary to the translocation break point.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Detection of nucleic acid sequence differences by comparative genomic hybridization
The present invention provides a method of detecting nucleotide sequence differences between two nucleic acid samples. The method employs a comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) technique to analyze the sequence differences between the samples. This method permits the identification of small sequence differences (e.g., sequence divergence of 1% or less) in nucleic acid samples of high complexity (e.g., an entire genome).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Probe Design Methods and Microarrays for Comparative Genomic Hybridization and Location Analysis
ActiveUS20100279883A1Shorten the timeReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningComparative genomic hybridizationNucleic Acid Probes
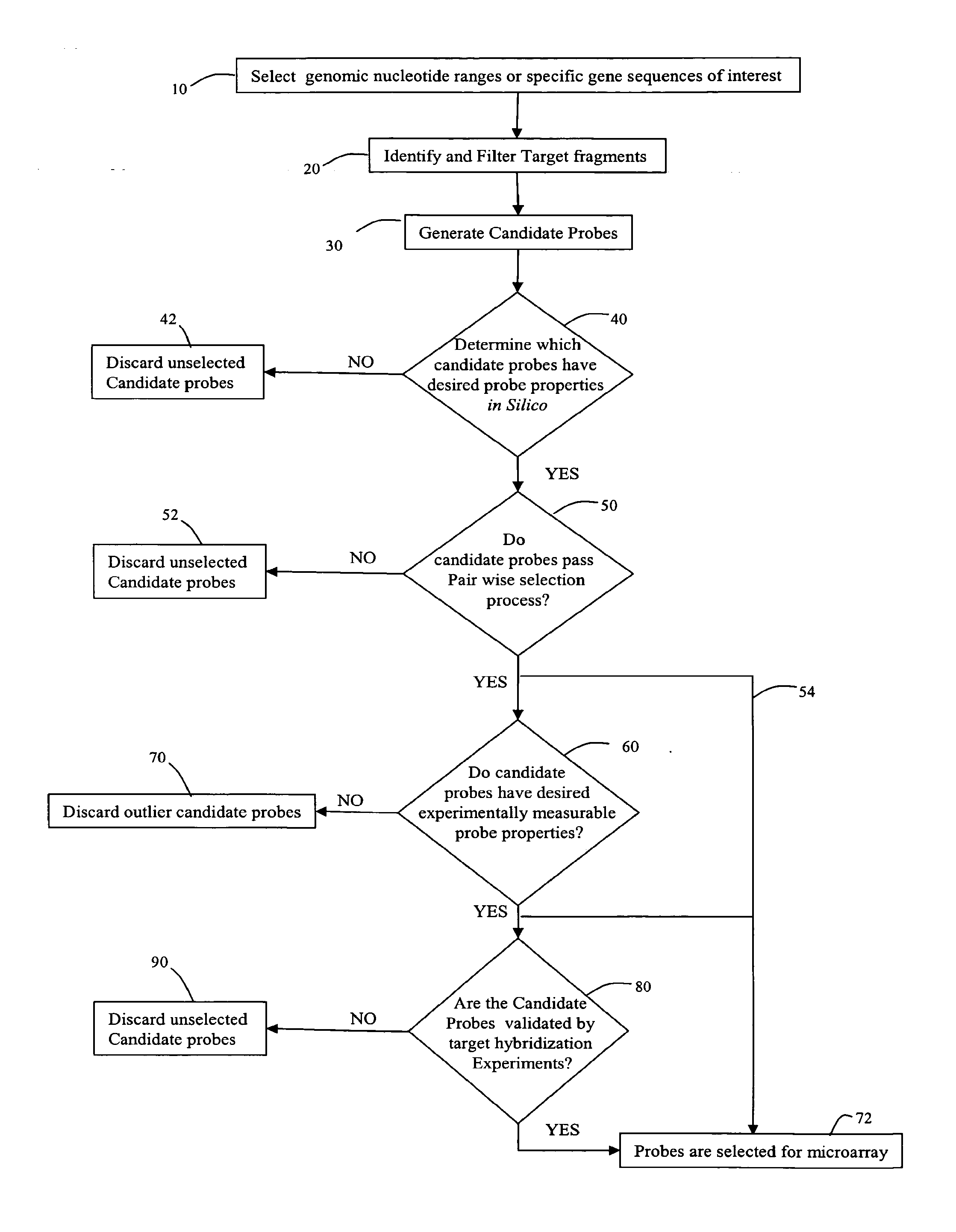
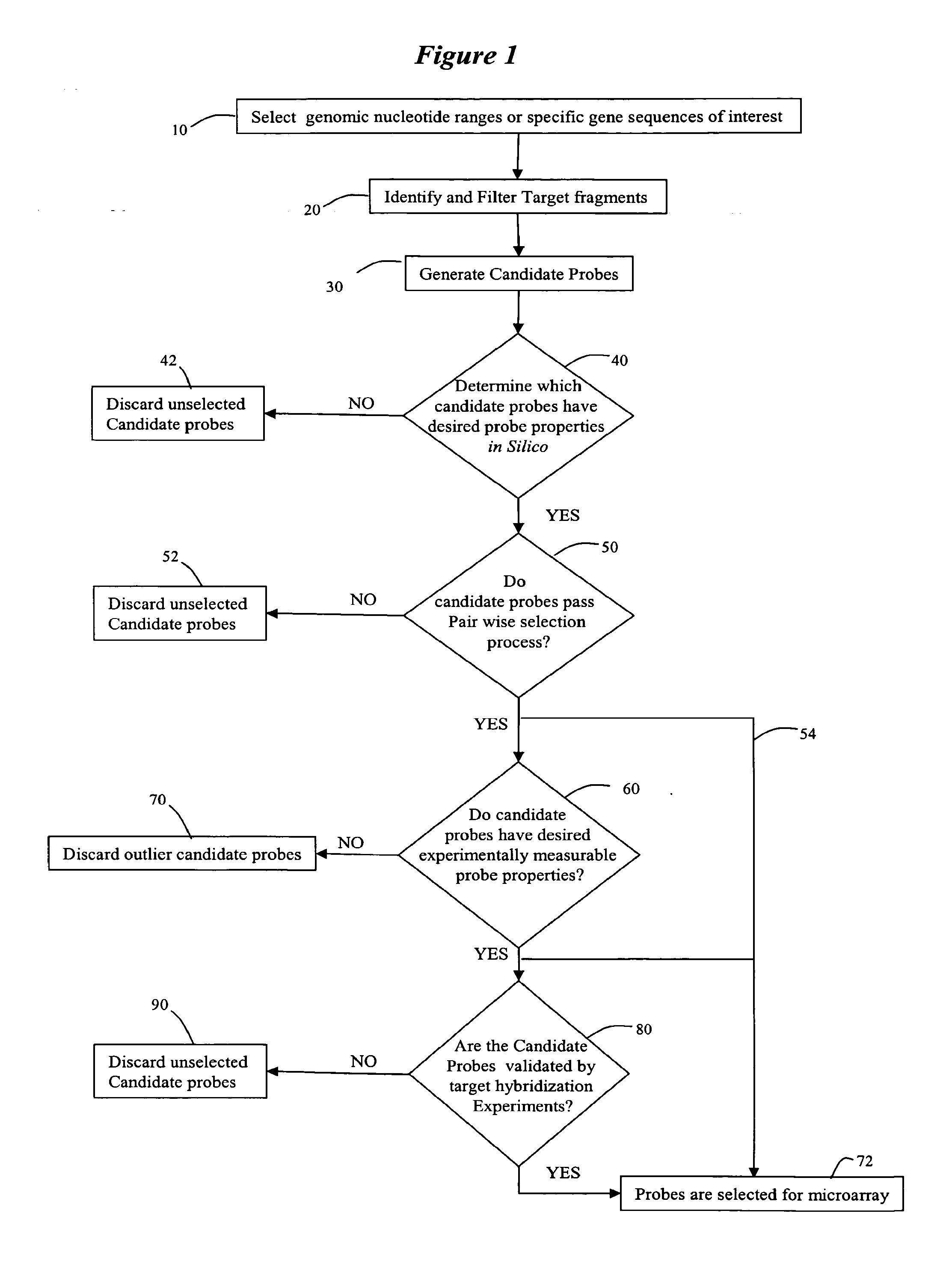
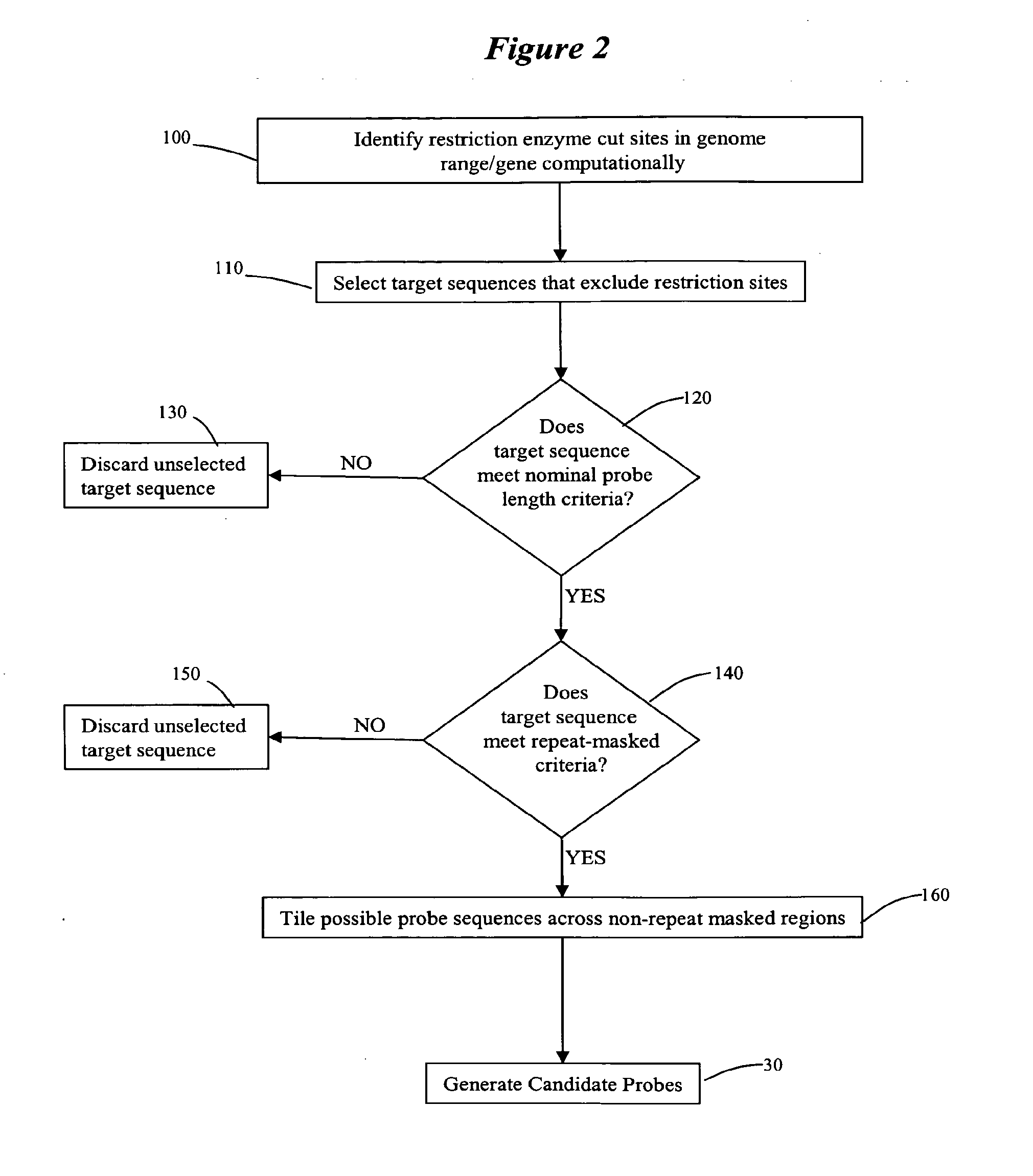
Methods and systems for identifying and selecting nucleic acid probes for detecting a target with a nucleic acid probe array or comparative genome hybridization microarray, comprising selecting a plurality of potential target sequences, generating a plurality of candidate probes from the target sequences, filtering the plurality of candidate probes by analyzing candidate probes for selected probe properties in silico. Microarrays comprising probes selected by the methods of the invention are particularly useful for comparative genome hybridization and location analysis.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for preparing birth defect target oligonucleotide microarray comparative genomic hybridization hybrid chip
InactiveCN101514372AGuaranteed check outReduce detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationComparative genomic hybridizationGenome
The present invention relates to the field of diagnostic reagent and provides a method for preparing birth defect target oligonucleotide microarray comparative genomic hybridization hybrid chip. The birth defect target oligonucleotide microarray comparative genomic hybridization hybrid chip prepared by the method of the invention is constructed by the probes of specifically targeted chromosome or chromosome area. Not only can the detection of pathological CNVs be guaranteed, but also the detection of CNVs which have indefinite clinical meaning can be greatly reduced.
Owner:戴勇
Comparative genomic hybridization assays using immobilized oligonucleotide targets with initially small sample sizes and compositions for practicing the same
ActiveUS7211384B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSmall sampleComparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization assays and compositions for use in practicing the same are provided. In the subject methods, at least first and second genomic templates are prepared from first and second genomic sources using an amplification reaction that employs a highly processive polymerase, where the amplification reaction produces amplification products having an average molecular size of at least about 10 kb with substantially no amplification bias. The resultant templates are then employed to produce at least first and second probe nucleic acid populations. The resultant probe nucleic acid populations are then contacted with a plurality of oligonucleotide target elements immobilized on a solid support surface and the binding of at least first and second populations is then evaluated. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Comparative genomic hybridization array method for preimplantation genetic screening
ActiveUS20110230362A1Reduce riskIncrease assay qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningReference sampleComparative genomic hybridization
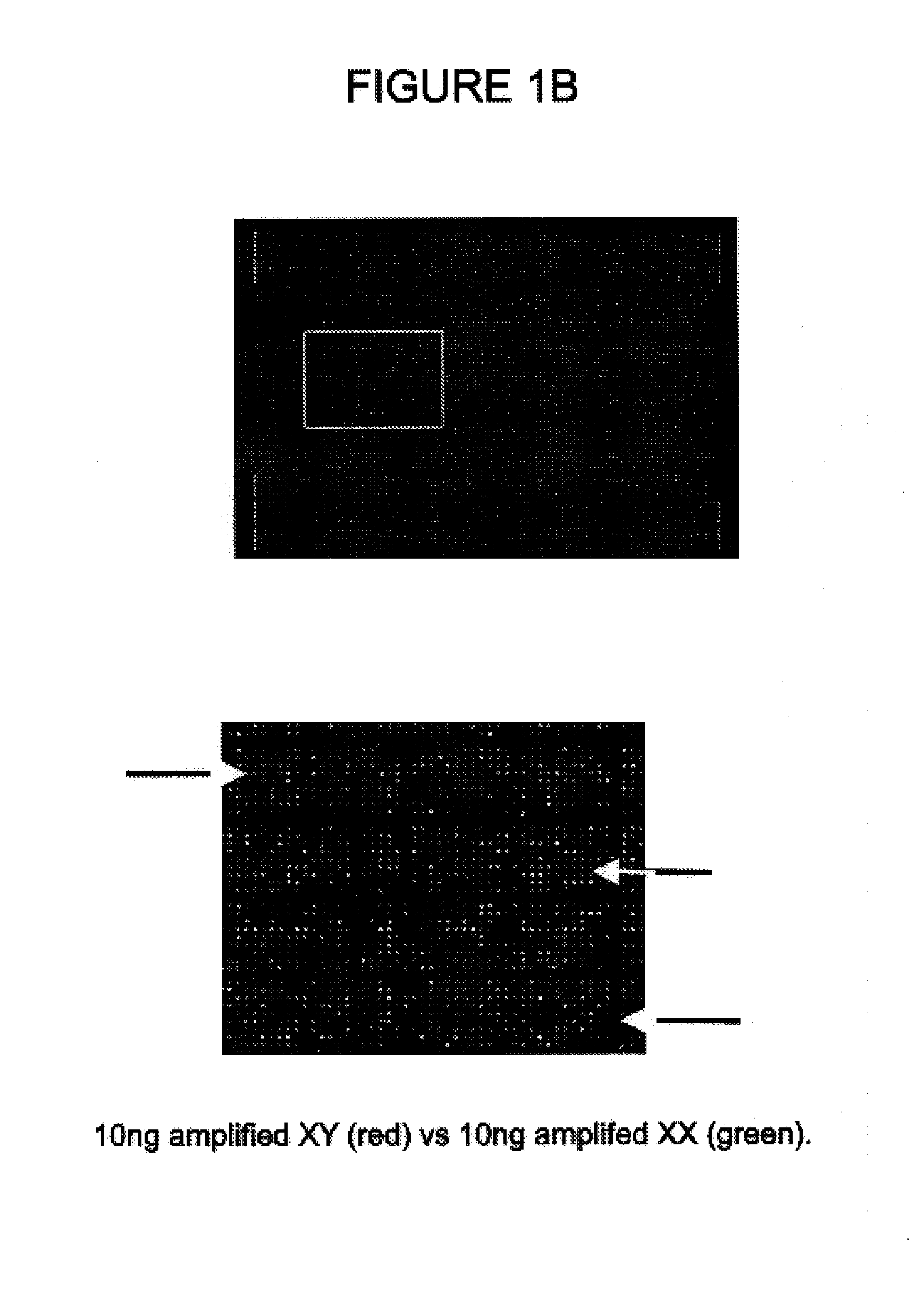
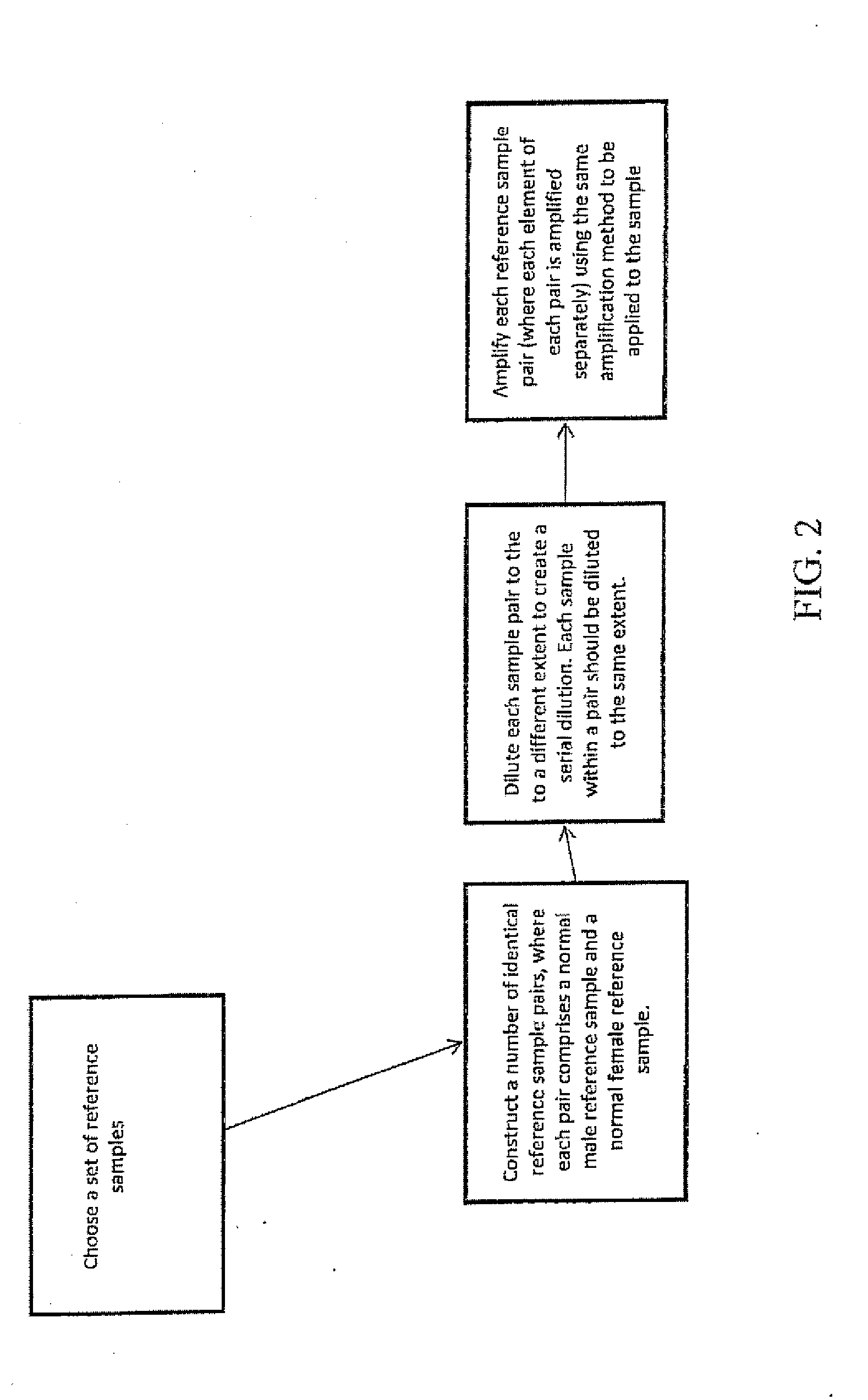
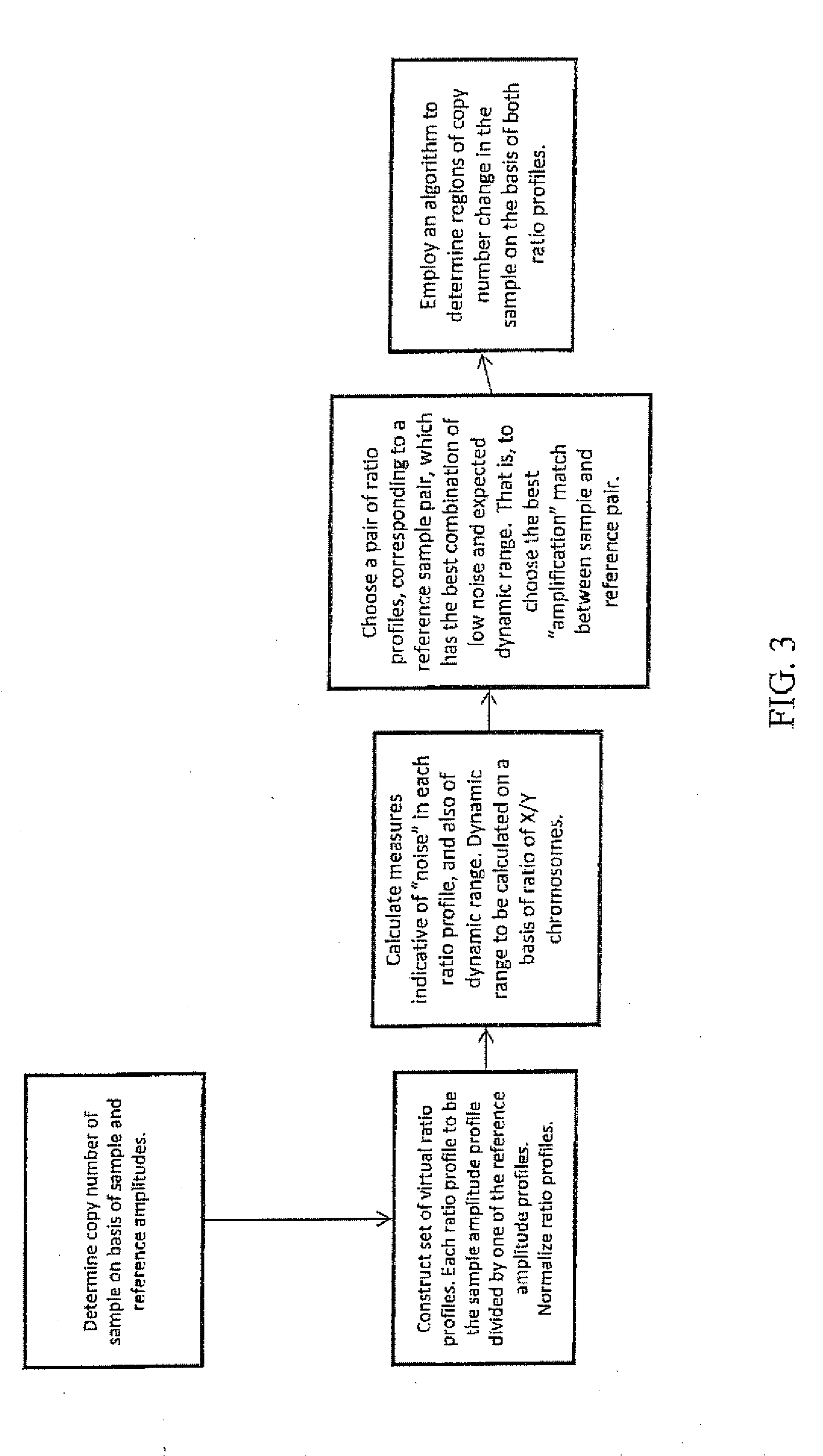
A method for determining the presence of a copy number imbalance in genomic DNA of a test sample is provided. The method can separately measure hybridization of a single test sample to a first hybridization array and hybridization of a plurality of reference samples to a plurality of other, respective test arrays. A determination of copy number can be based on the best fit reference array, relative to the test array. The best fit can be determined based on the closest or most similar signal-to-noise ratio of the measured signals.
Owner:BLUEGNOME
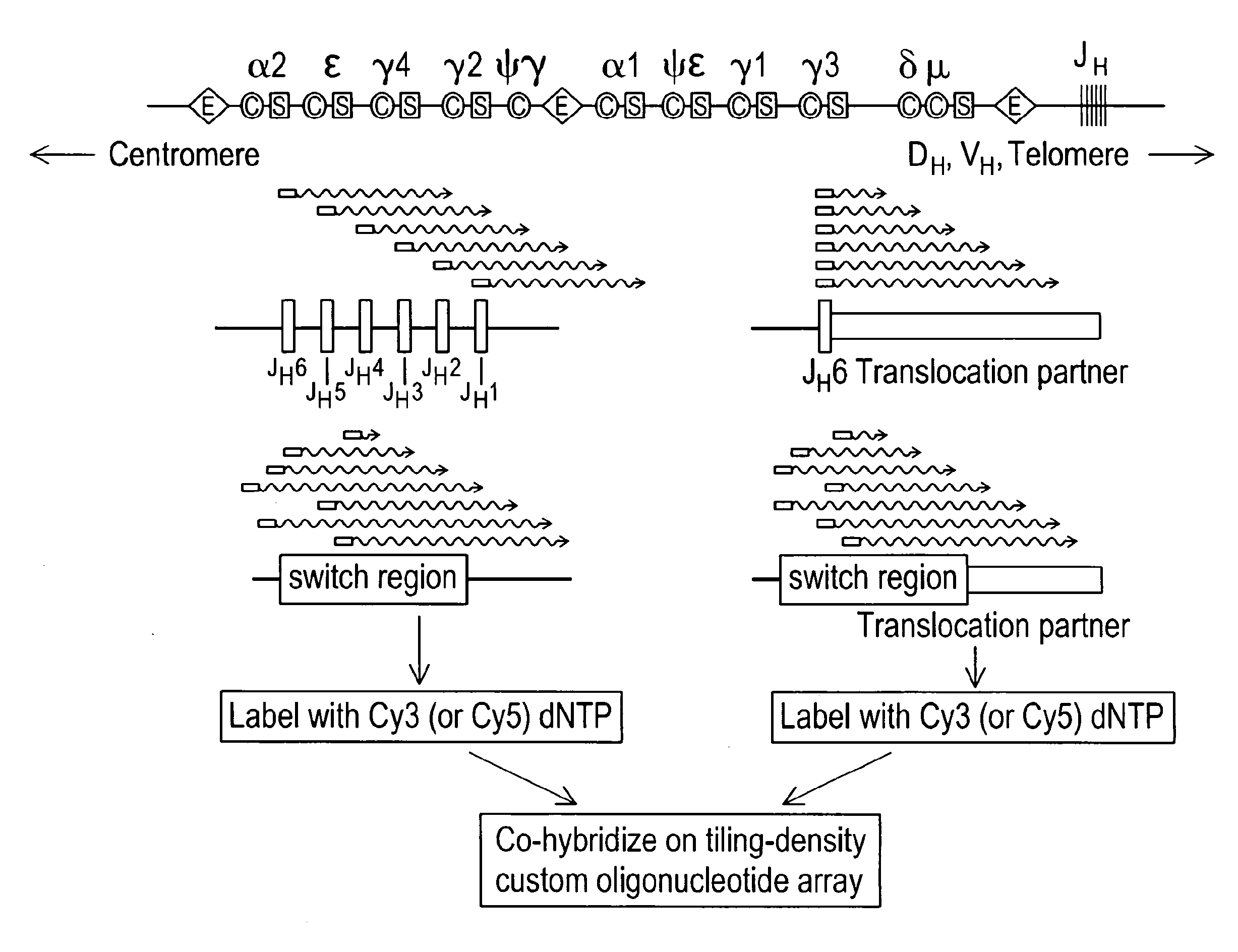
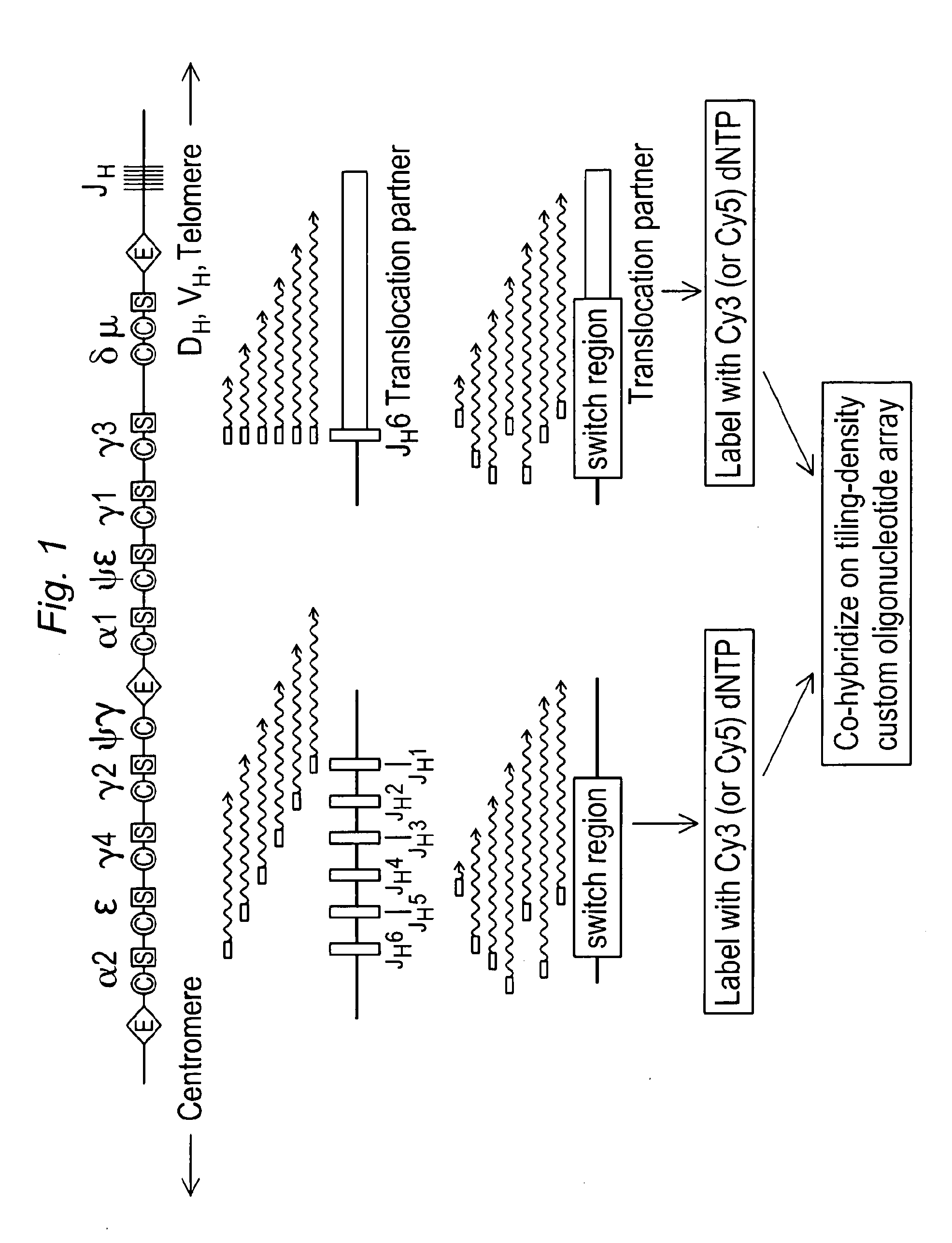
DNA microarray based identification and mapping of balanced translocation breakpoints
InactiveUS20110021371A1Increase rangeSuper high resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA microarrayComparative genomic hybridization
Methods for detecting and mapping chromosomal rearrangements associated with various diseases using comparative genomic hybridization are disclosed. Included are methods to identify translocation partners of known genomic loci and to determine translocation breakpoints. These methods may be used in the prognosis, diagnosis, and determination of predisposition to diseases that involve chromosomal rearrangements.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
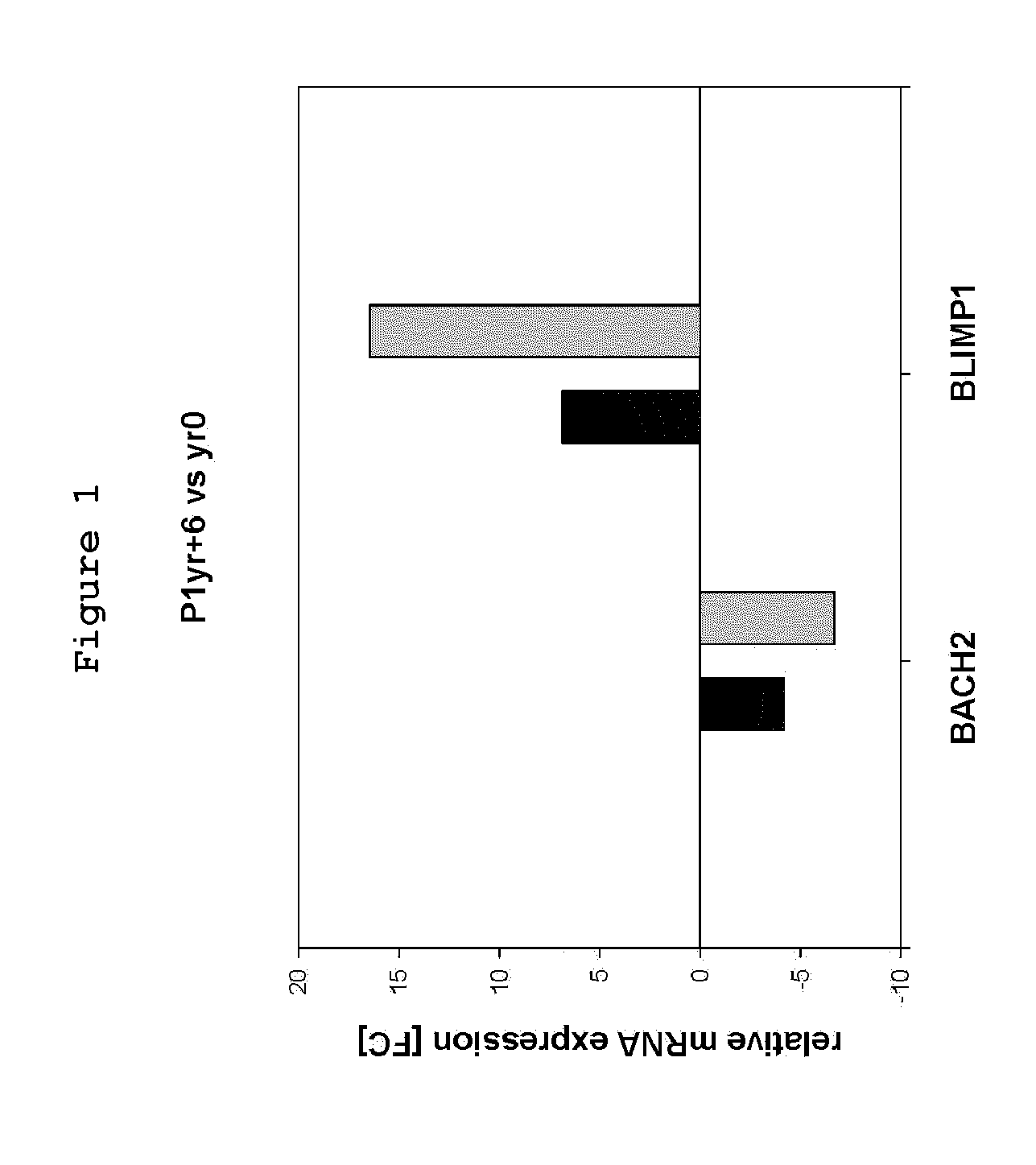
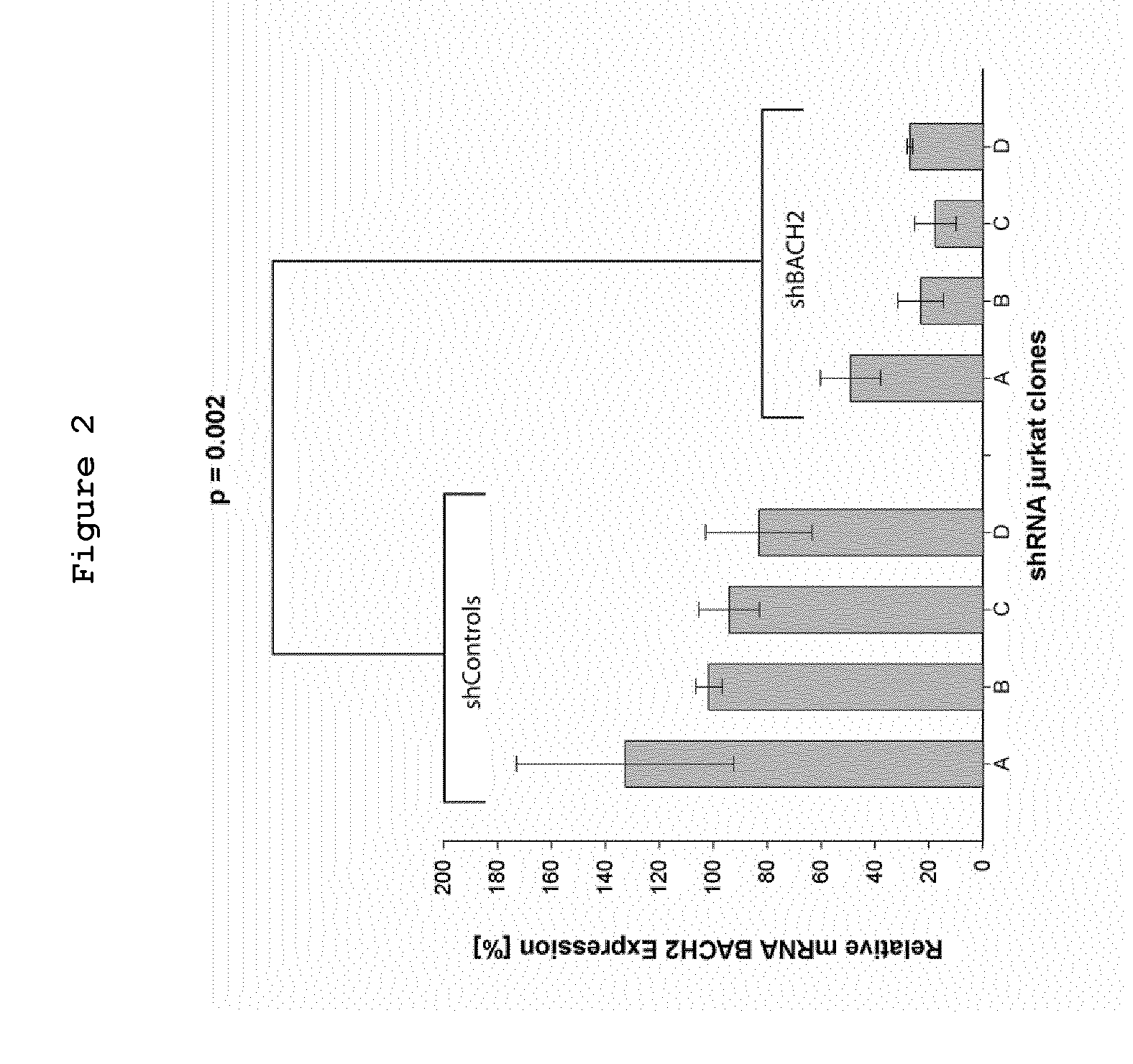
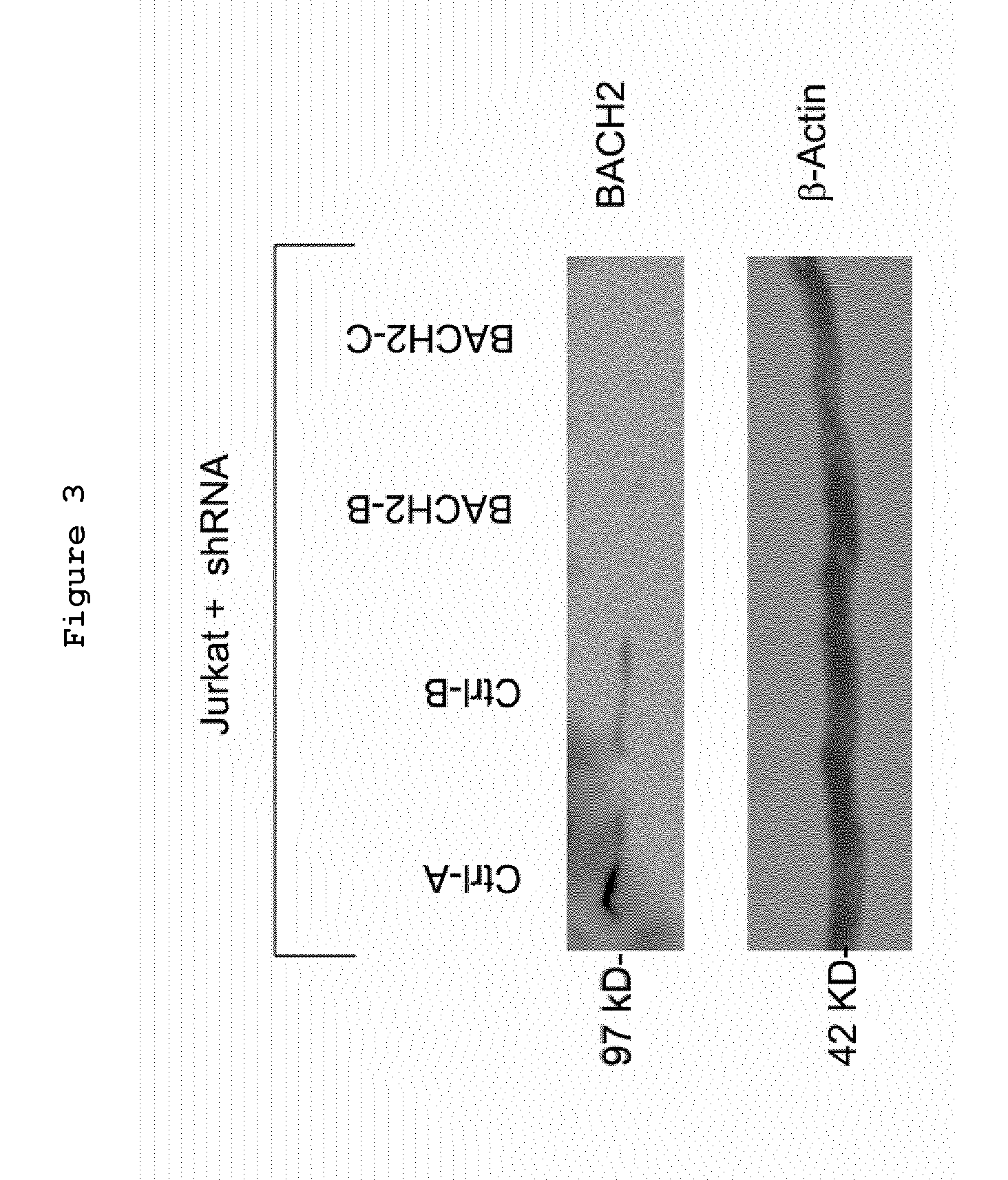
Bach2 repression in cells
ActiveUS20130338023A1Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementComparative genomic hybridizationFluorescence
A method for measuring the proliferation status of a cell present in a biological sample, comprising the step of measuring in the said cell the loss of BACH2 by Fluorescence after In Situ Hybridization (FISH) analysis and mRNA quantification or by Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) and corresponding kit and applications.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
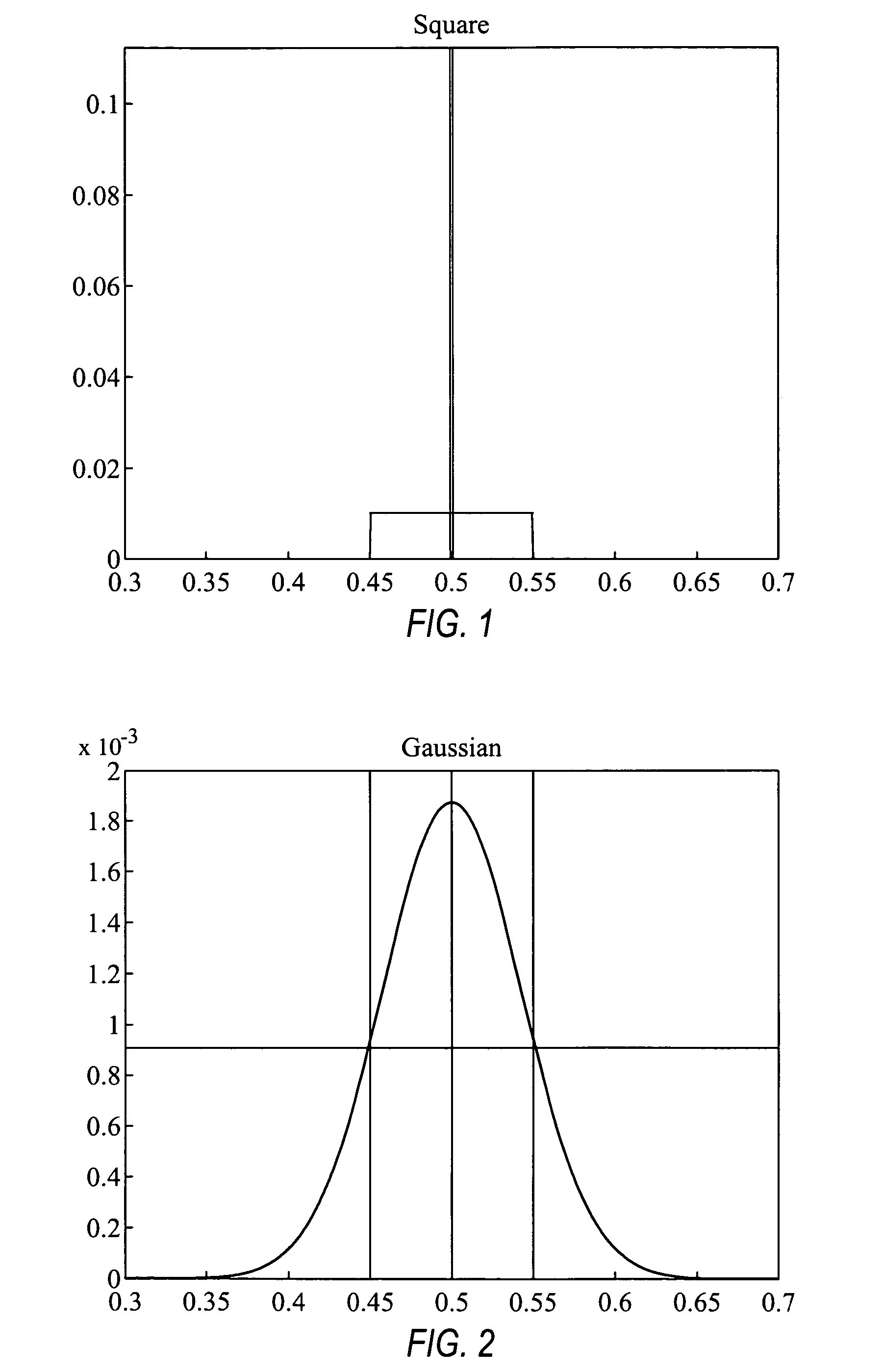
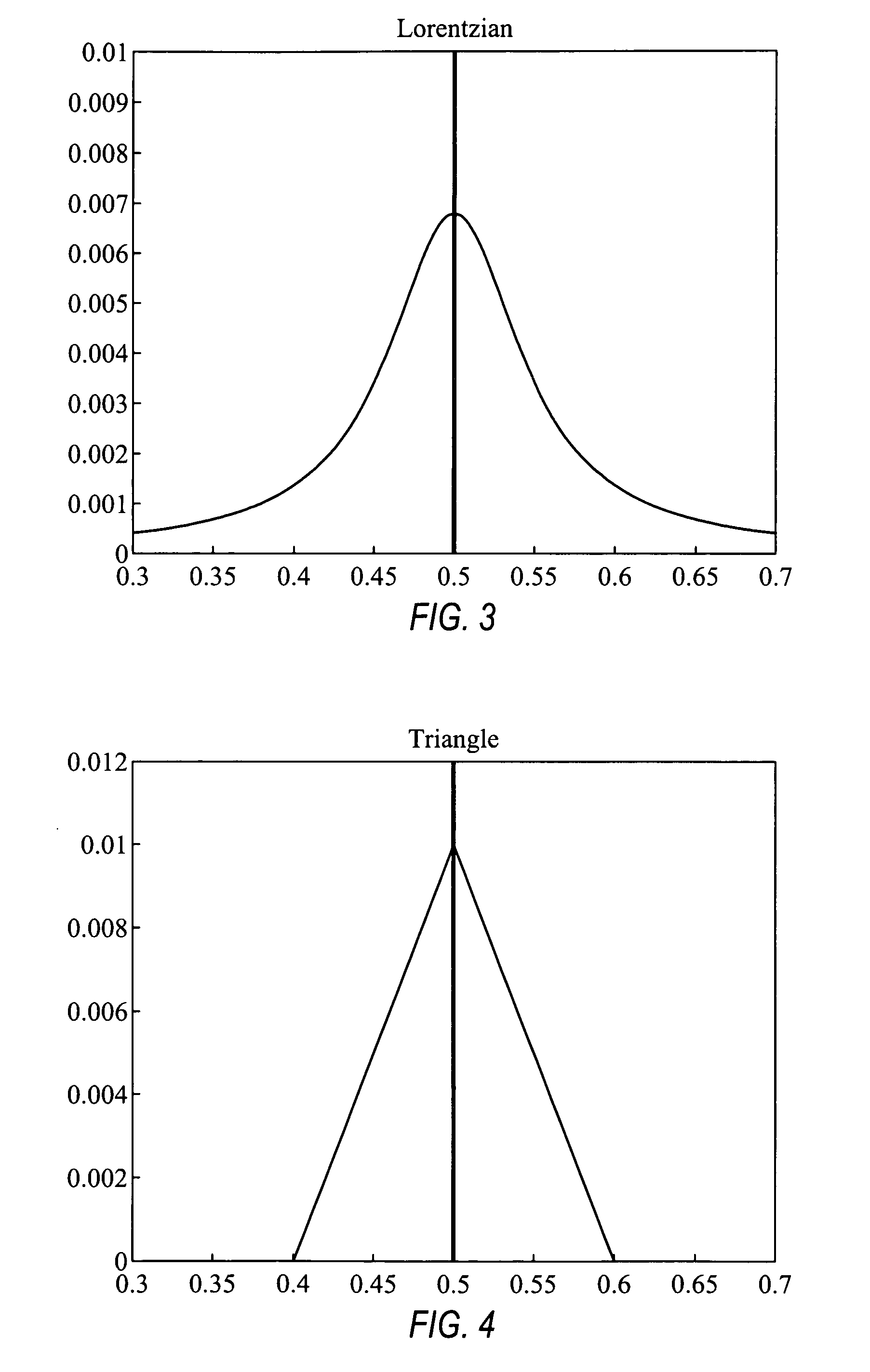
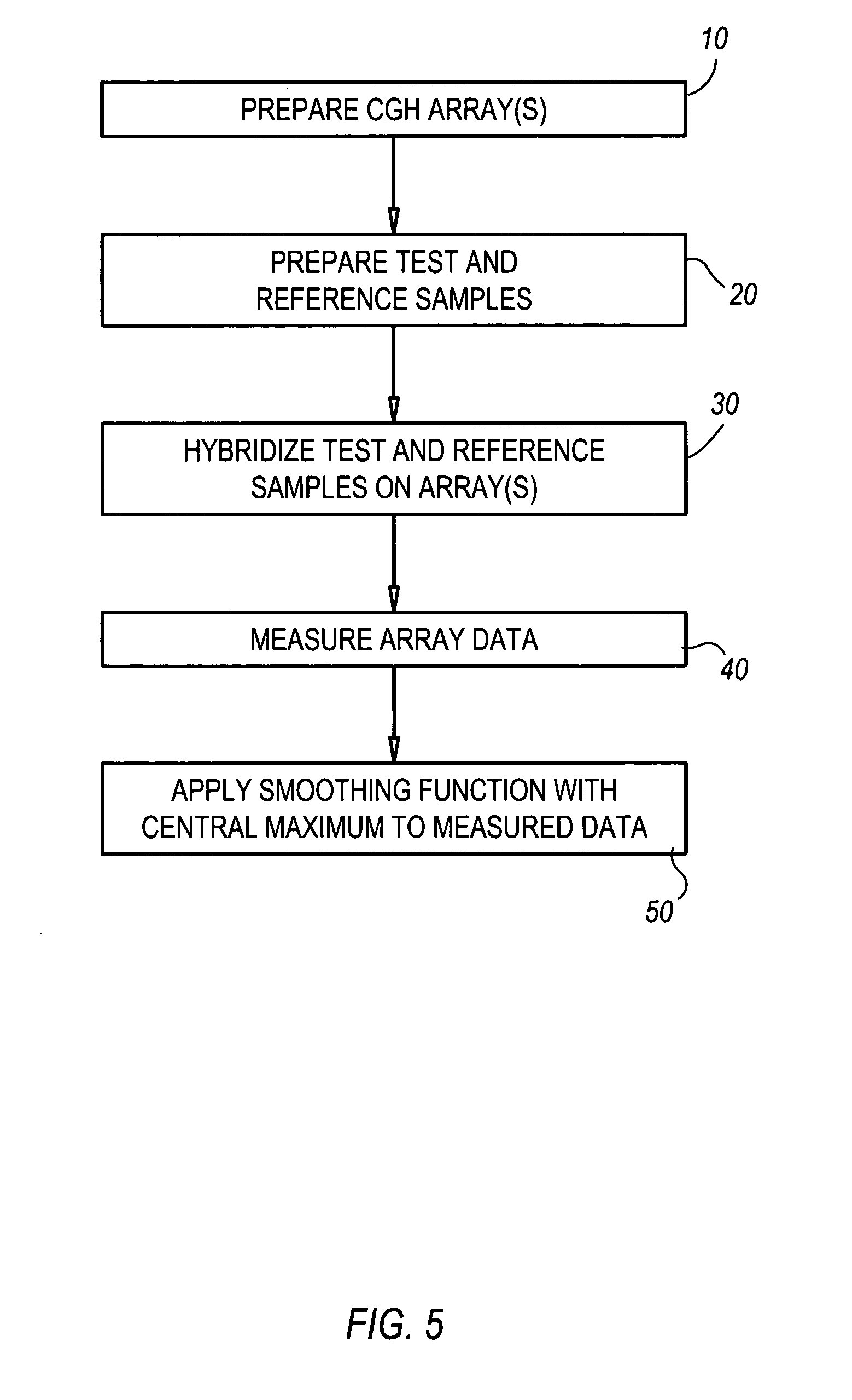
Comparative genomic hybridization significance analysis using data smoothing with shaped response functions
Methods and systems for analyzing comparative genomic hybridization data. The methods comprise measuring comparative genomic hybridization data, and applying a shaped response function to the comparative genomic hybridization data, wherein the shaped response function has a central maximum. The comparative genomic hybridization data may be obtained from a comparative genomic hybridization array. The shaped response function in many embodiments is symmetrical in shape tapers to zero on each side of said central maximum.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods and compositions for performing sample heterogeneity corrected comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
InactiveUS20070134676A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingComparative genomic hybridizationGenome
Methods and compositions for performing sample heterogeneity corrected comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) are provided. In the subject methods, an initial CGH result is processed to account for potential sample heterogeneity to obtain a sample-heterogeneity corrected CGH result. Also provided are methods for evaluating candidate surface-bound nucleic acids, e.g., candidate aCGH probe nucleic acids, to identify probes useful in assaying heterogeneous samples.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Combined CGH and allele specific hybridisation method
ActiveUS9587278B2Maximizing numberMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationReference sampleDisease
The invention combines the fields of comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) analysis and SNP array analysis. It relates to methods for detecting and mapping genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases. In particular the invention provides a method for simultaneously performing array CGH and SNP array analysis on a genomic DNA sample comprising contacting a nucleic acid array which comprises a first probe set and a second probe set with a genomic DNA sample, comprising a test and reference sample, under hybridization conditions, comparing the amount of test sample and reference sample hybridized to the hybridization probes of the first probe set, comparing the amount of test sample and reference sample hybridized to the hybridization probes of the second probe set; and using the data obtained to determine the copy number of at least one locus; and at least one SNP in the genomic DNA sample.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH OPERATIONS
Method for screening disease resistance breeding of animals
InactiveCN108841922ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseComparative genomic hybridization
The invention discloses a method for screening disease resistance breeding of animals and belongs to the technical field of disease resistance breeding of the animals. Genome copy number variation differences of affected animal individuals and disease-resistant animal individuals are detected by a comparative genomic hybridization chip, if the genome copy number of affected animals is more or lessthan that of disease-resistant animals, the condition that genes in genome copy number variation sections are related to disease resistance can be judged preliminarily, and the related animals havingrequired characteristics can be selected for breeding. The method for screening disease resistance breeding of the animals has the characteristics that the method is simple and convenient to operate,low in cost and high in efficiency, and the method is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com