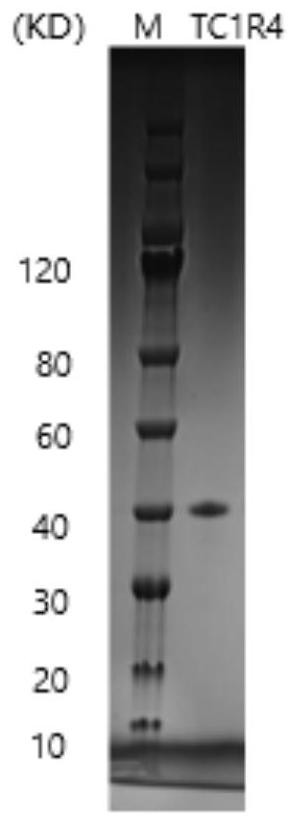
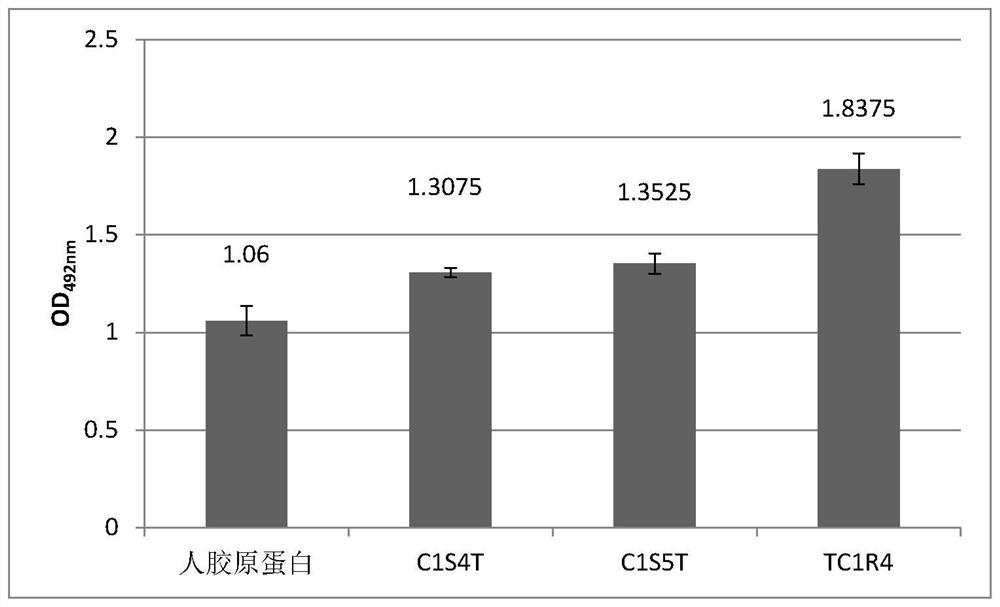
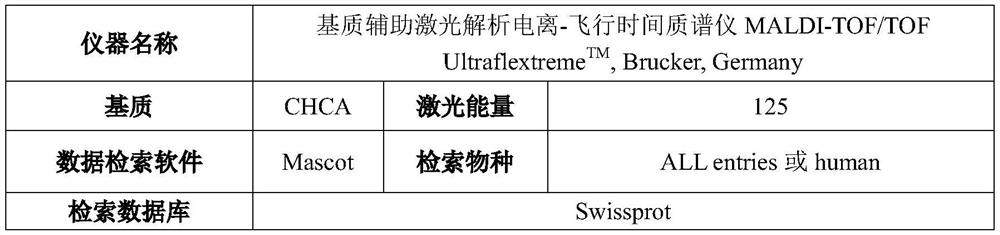
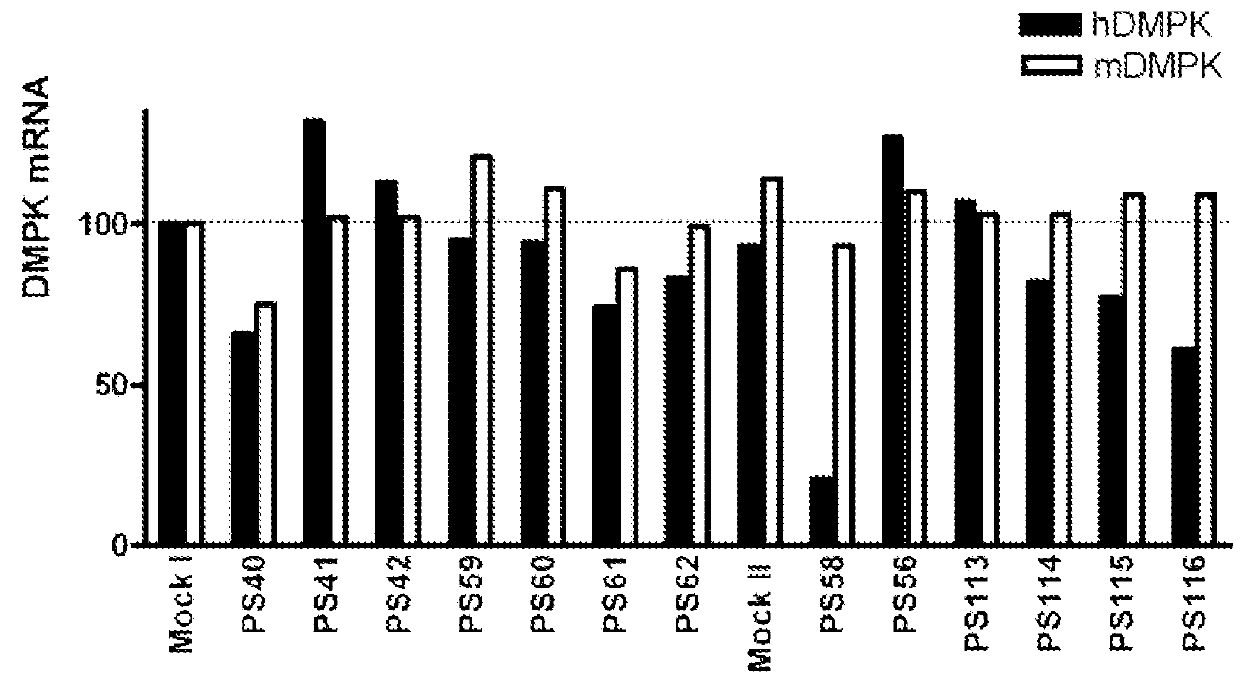
Patents
Literature
268 results about "Repetitive sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
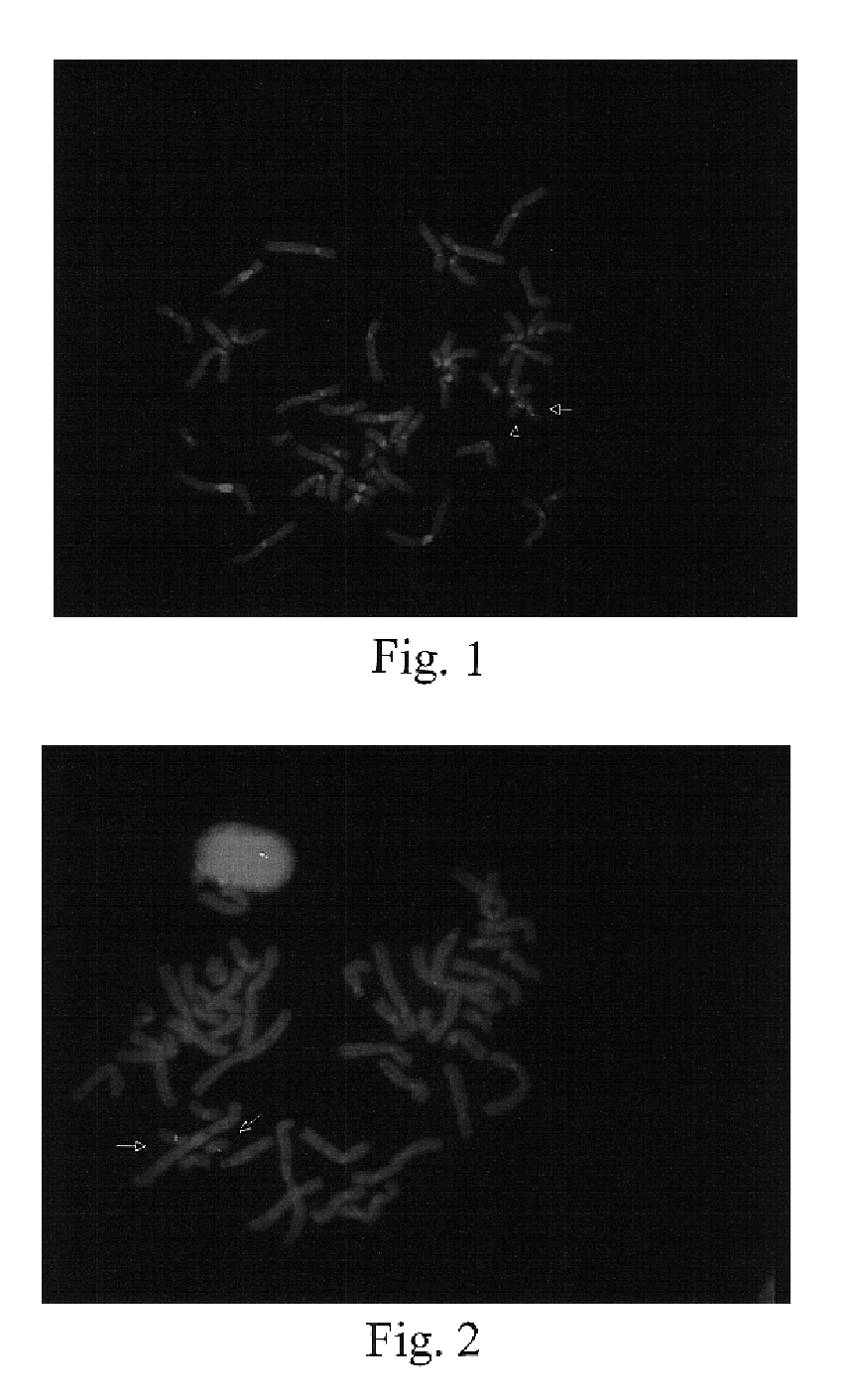
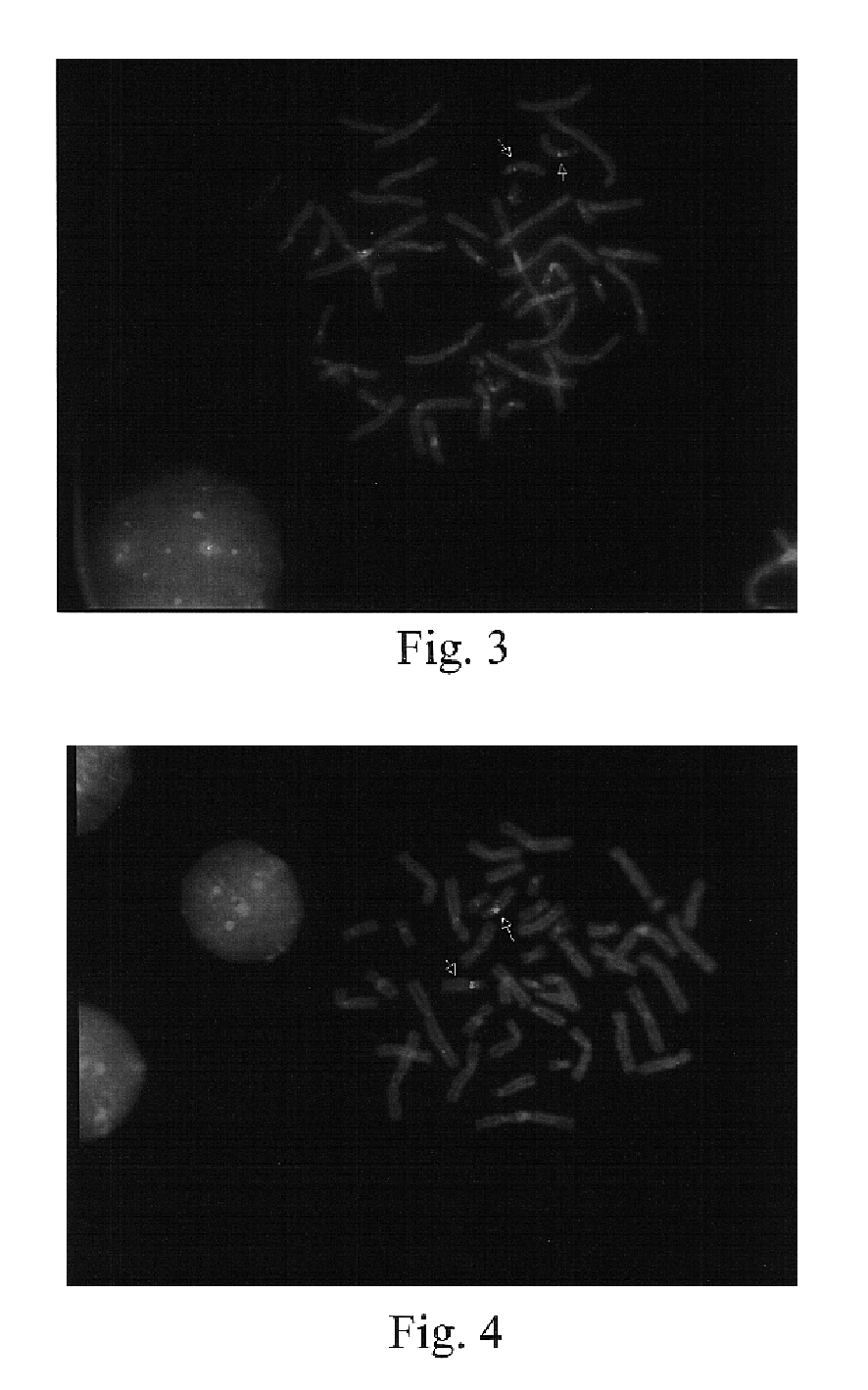
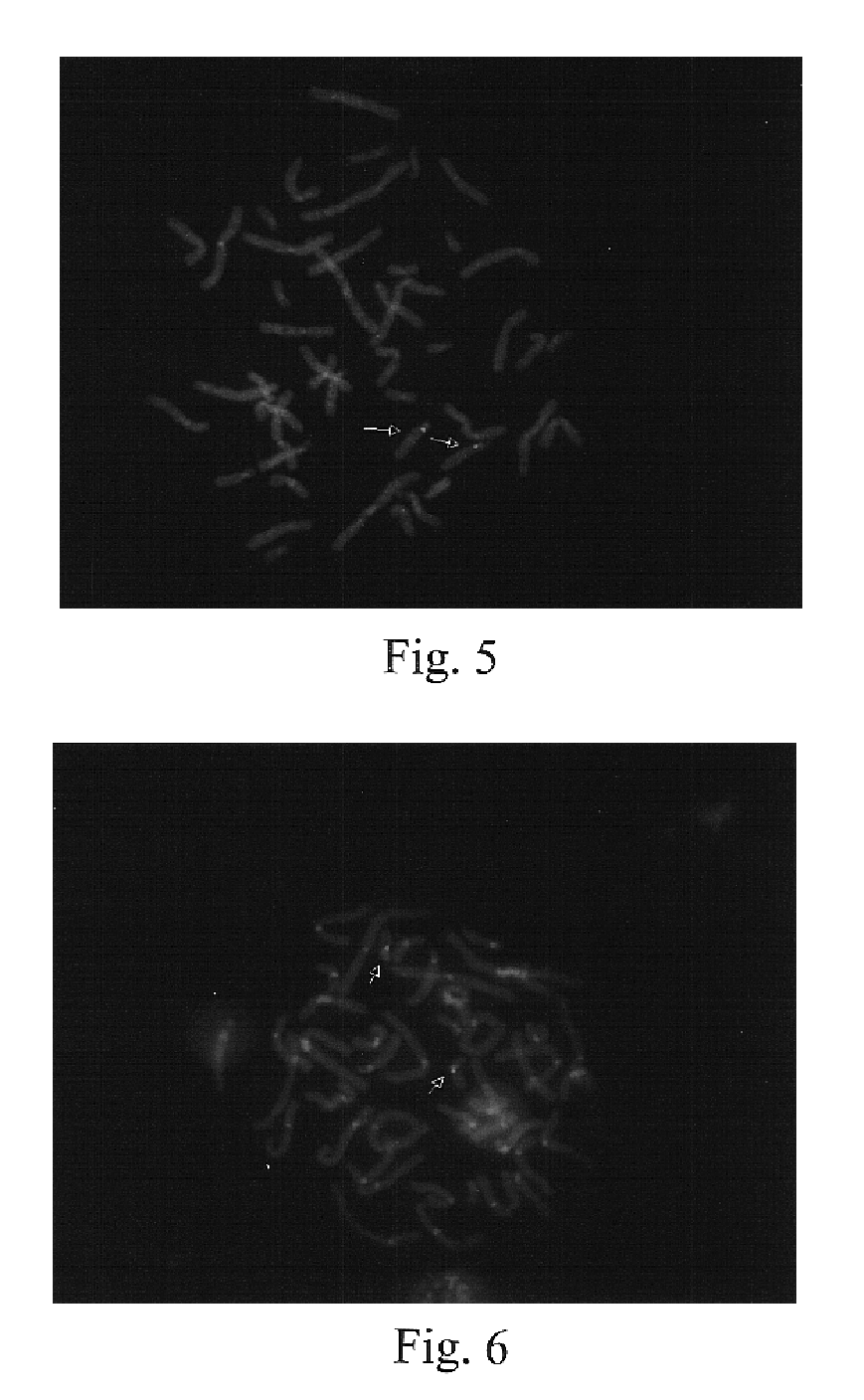
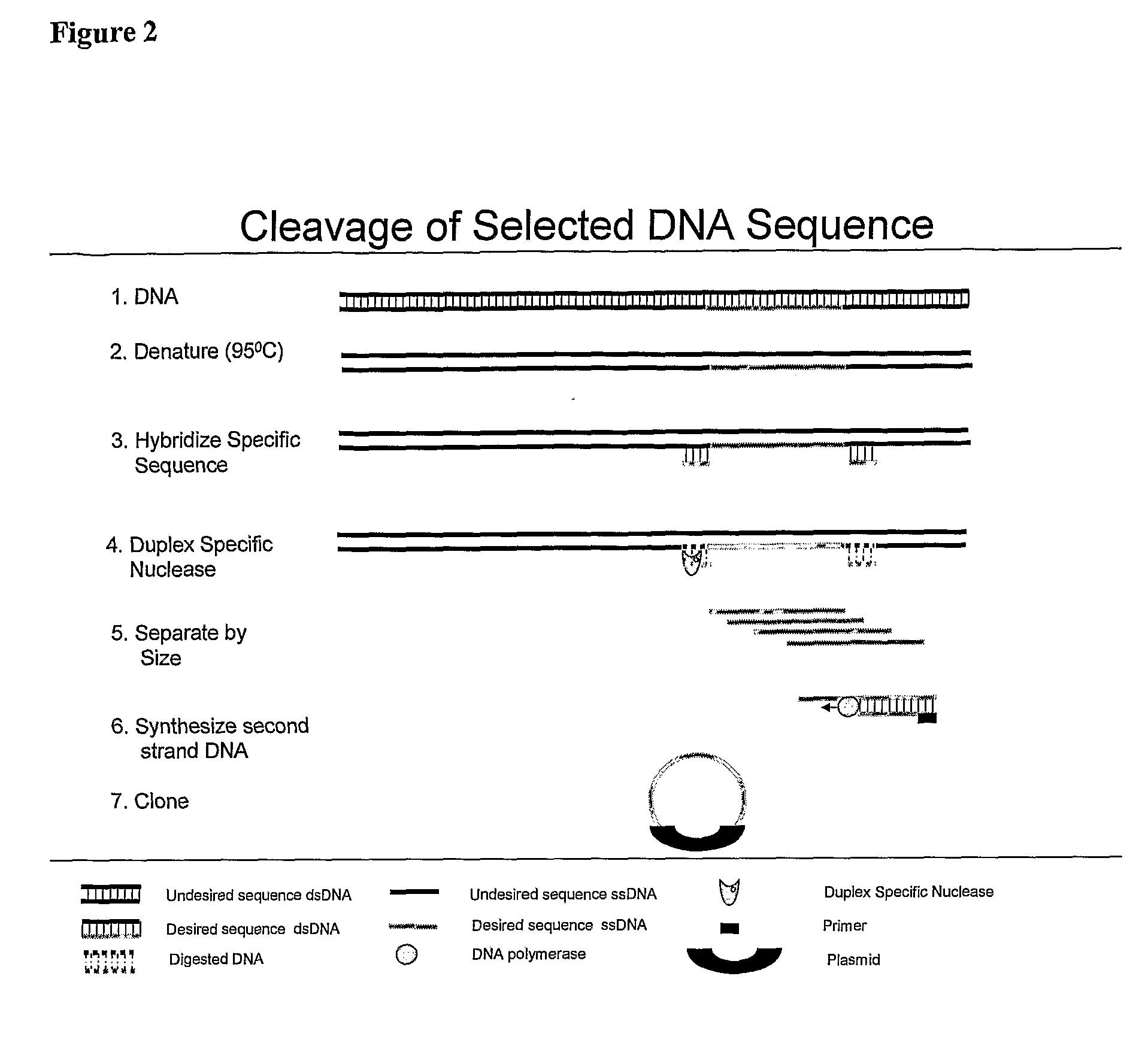
Repetitive DNA: DNA sequences that are repeated in the genome. These sequences do not code for protein. One class termed highly repetitive DNA consists of short sequences, 5-100 nucleotides, repeated thousands of times in a single stretch and includes satellite DNA.
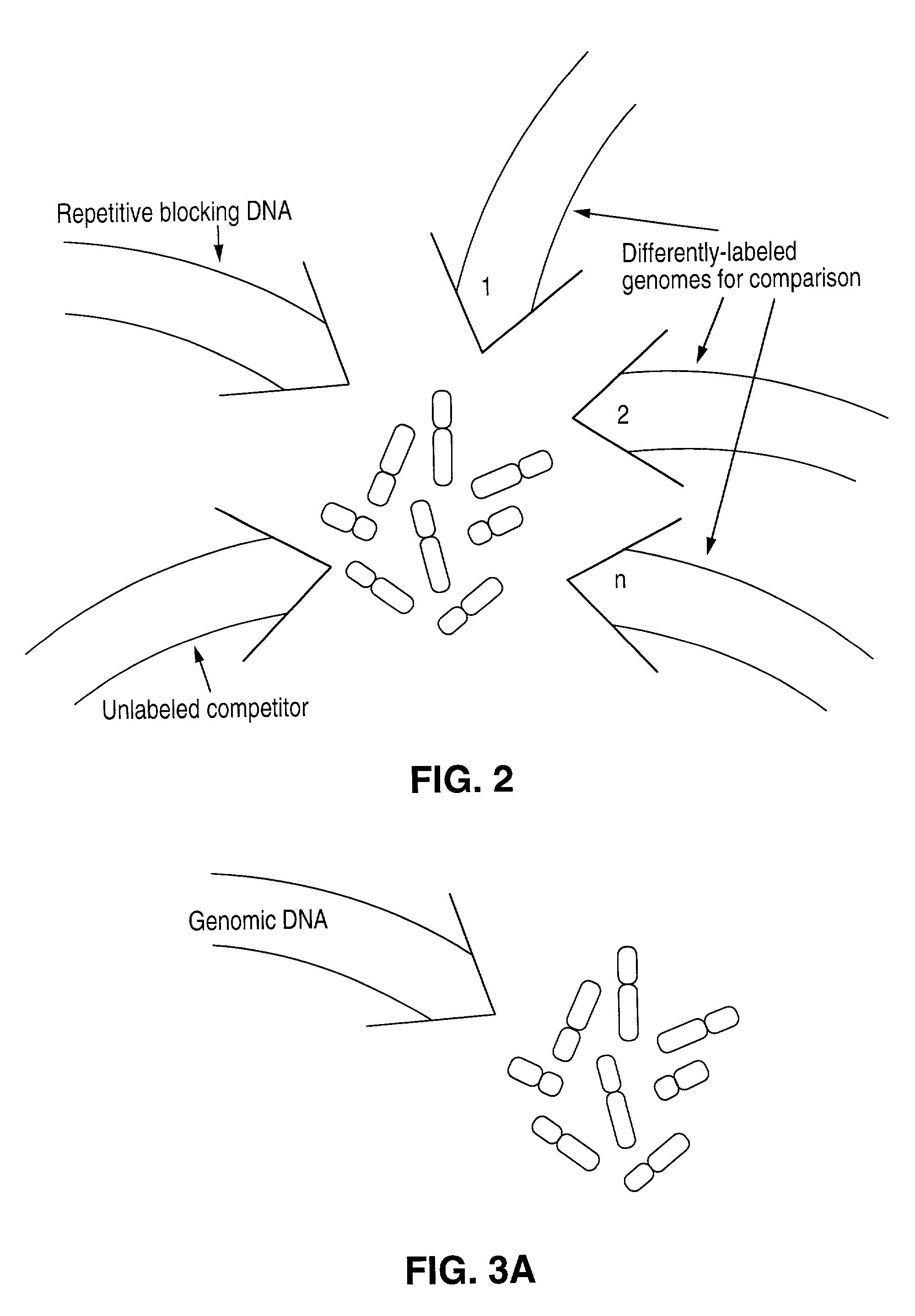
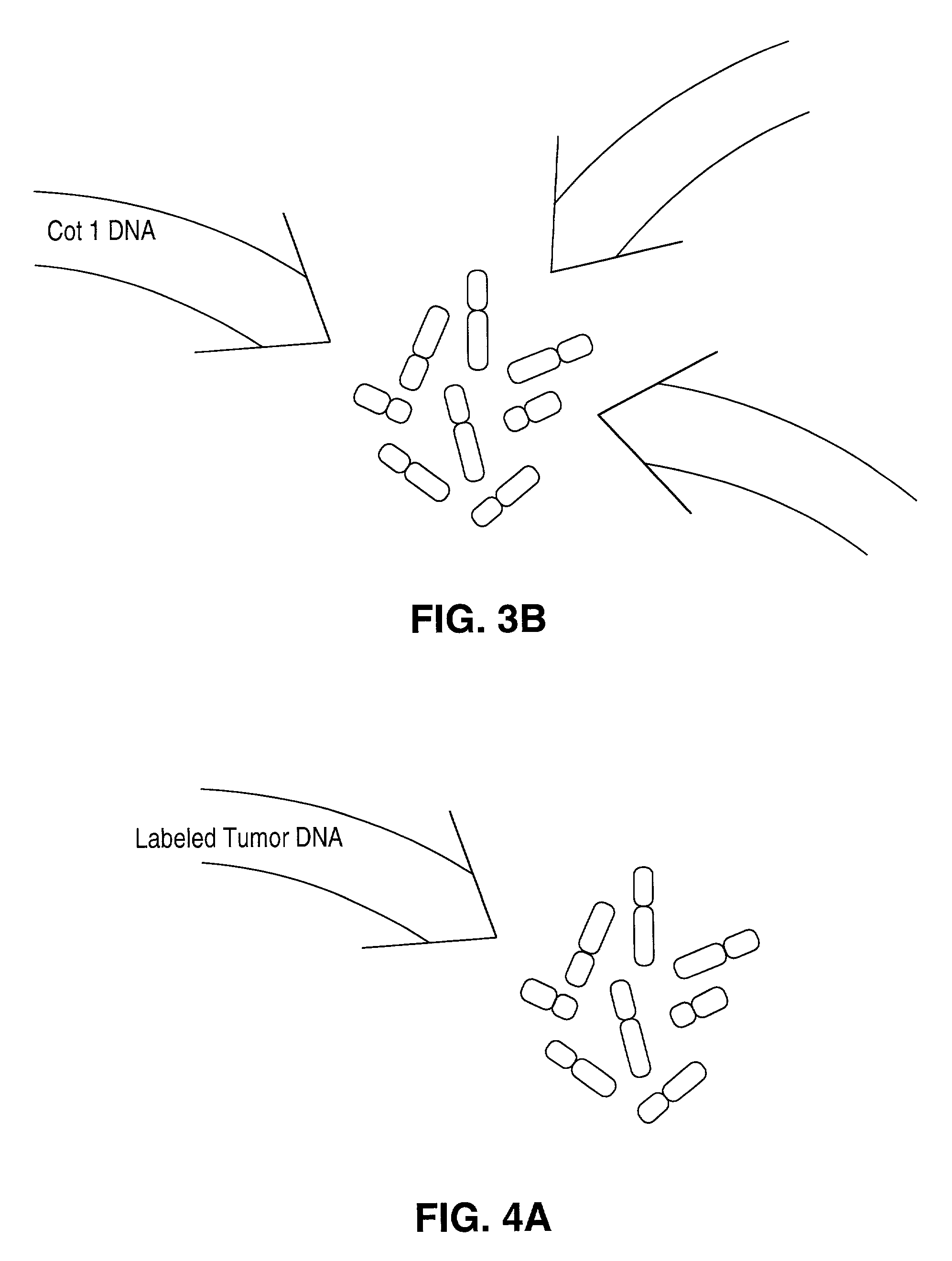
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
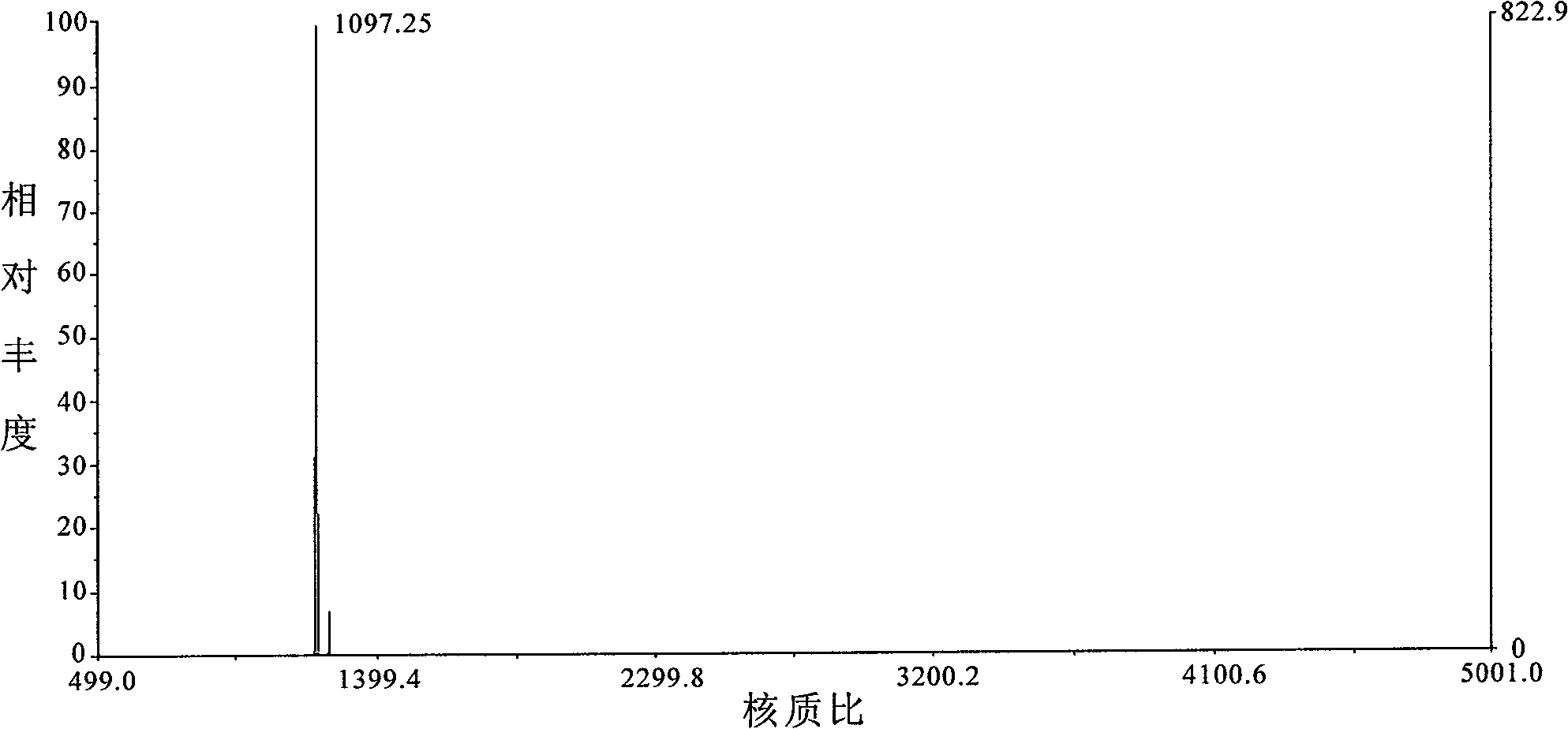
InactiveUS6335167B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
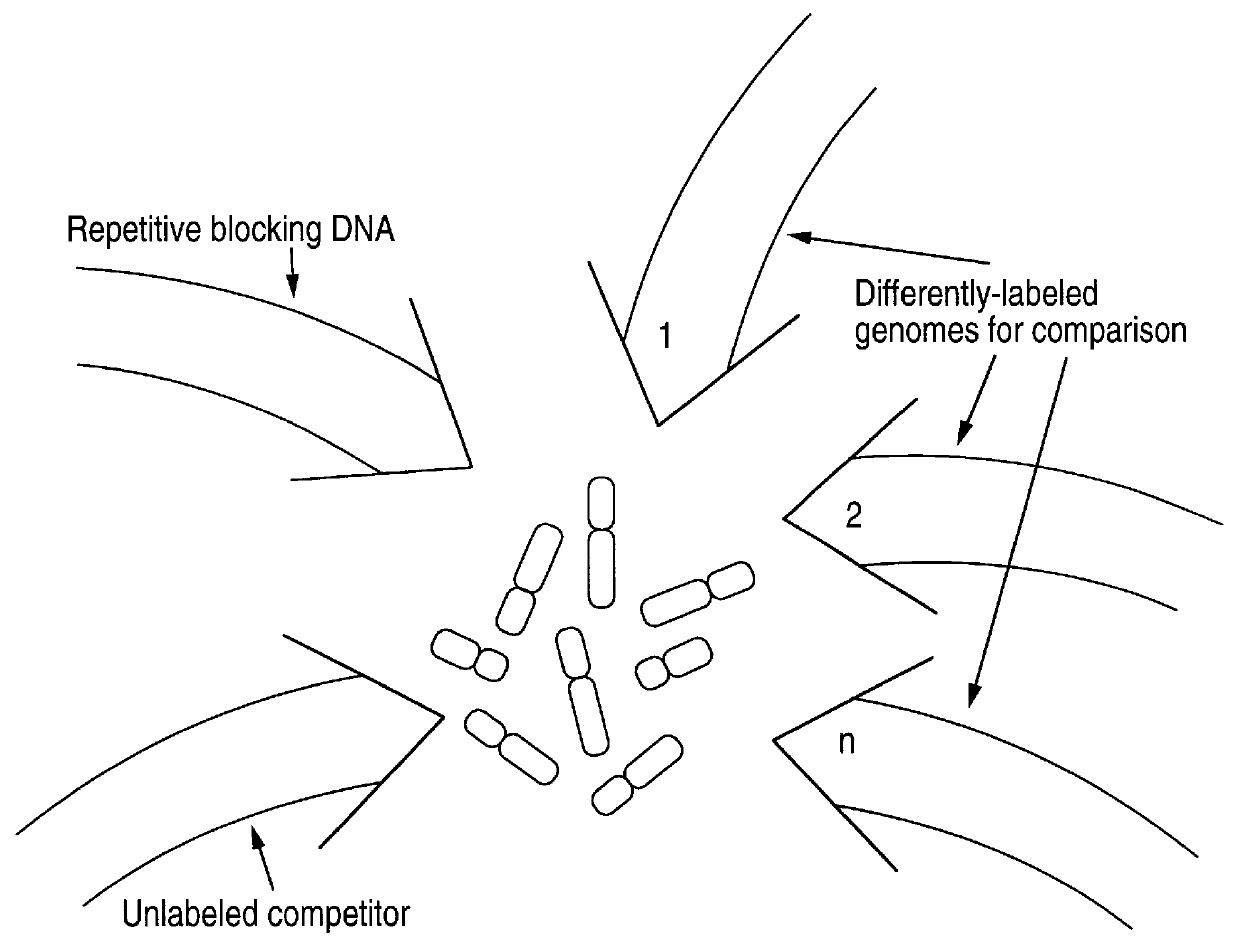
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Duplexed parvovirus vectors
InactiveUS7465583B2High transduction efficiencyRapid onsetBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral vector
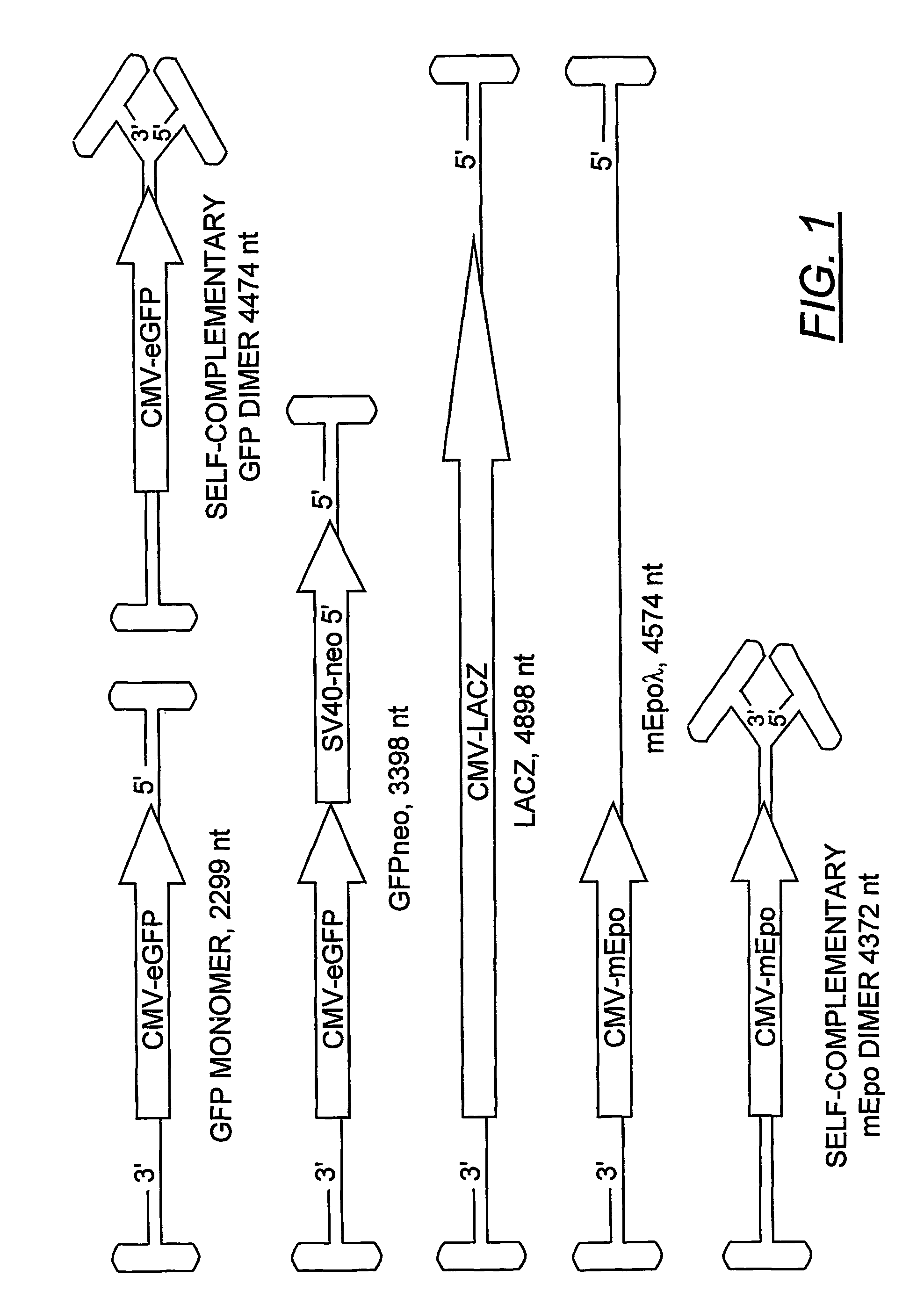
The present invention provides duplexed parvovirus vector genomes that are capable under appropriate conditions of forming a double-stranded molecule by intrastrand base-pairing. Also provided are duplexed parvovirus particles comprising the vector genome. Further disclosed are templates and methods for producing the duplexed vector genomes and duplexed parvovirus particles of the invention. Methods of administering these reagents to a cell or subject are also described. Preferably, the parvovirus capsid is an AAV capsid. It is further preferred that the vector genome comprises AAV terminal repeat sequences.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
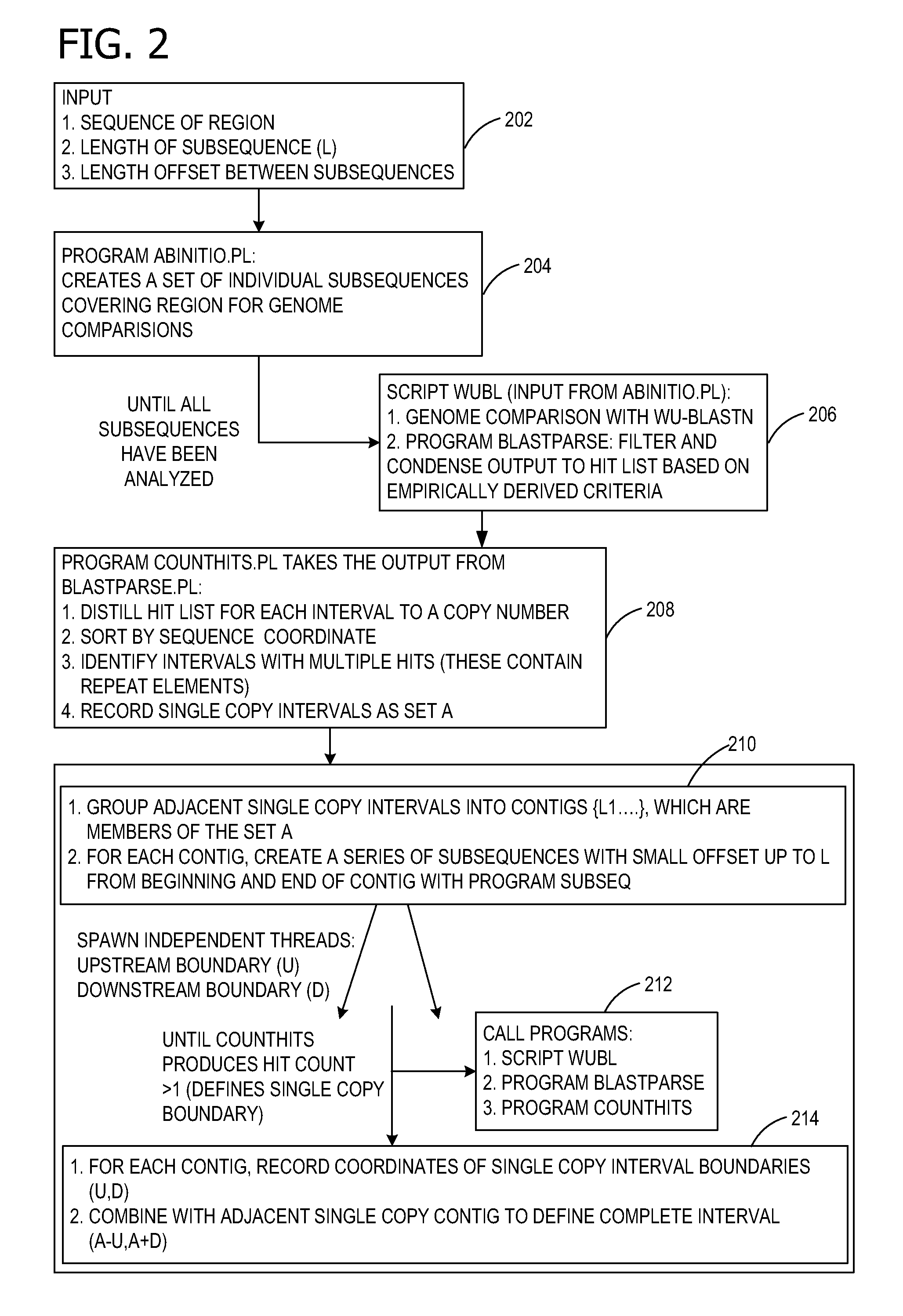
Ab initio generation of single copy genomic probes
Single copy sequences suitable for use as DNA probes can be defined by computational analysis of genomic sequences. The present invention provides an ab initio method for identification of single copy sequences for use as probes which obviates the need to compare genomic sequences with existing catalogs of repetitive sequences. By dividing a target reference sequence into a series of shorter contiguous sequence windows and comparing these sequences with the reference genome sequence, one can identify single copy sequences in a genome. Probes can then be designed and produced from these single copy intervals.
Owner:ROGAN PETER K
LIDAR Based 3-D Imaging With Varying Illumination Intensity
ActiveUS20170269197A1Reduce energy consumptionReduce consumptionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadarPulse sequence
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with different illumination intensity patterns are described herein. Repetitive sequences of measurement pulses each having different illumination intensity patterns are emitted from a LIDAR system. One or more pulses of each repetitive sequence have a different illumination intensity than another pulse within the sequence. The illumination intensity patterns are varied to reduce total energy consumption and heat generated by the LIDAR system. In some examples, the illumination intensity pattern is varied based on the orientation of the LIDAR device. In some examples, the illumination intensity pattern is varied based on the distance between a detected object and the LIDAR device. In some examples, the illumination intensity pattern is varied based on the presence of an object detected by the LIDAR device or another imaging system.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Chromosome structural abnormality localization with single copy probes
InactiveUS7014997B2Eliminates spurious hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
Nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) hybridization probes are described which comprise a labeled, single copy nucleic acid which hybridizes to a deduced single copy sequence interval in target nucleic acid of known sequence. The probes, which are essentially free of repetitive sequences, can be used in hybridization analyses without adding repetitive sequence-blocking nucleic acids. This allows rapid and accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The probes are preferably designed by first determining the sequence of at least one single copy interval in a target nucleic acid sequence, and developing corresponding hybridization probes which hybridize to at least a part of the deduced single copy sequence. In practice, the sequences of the target and of known genomic repetitive sequence representatives are compared in order to deduce locations of the single copy sequence intervals. The single copy probes can be developed by any variety of methods, such as PCR amplification, restriction or exonuclease digestion of purified genomic fragments, or direct synthesis of DNA sequences. This is followed by labeling of the probes and hybridization to a target sequence.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
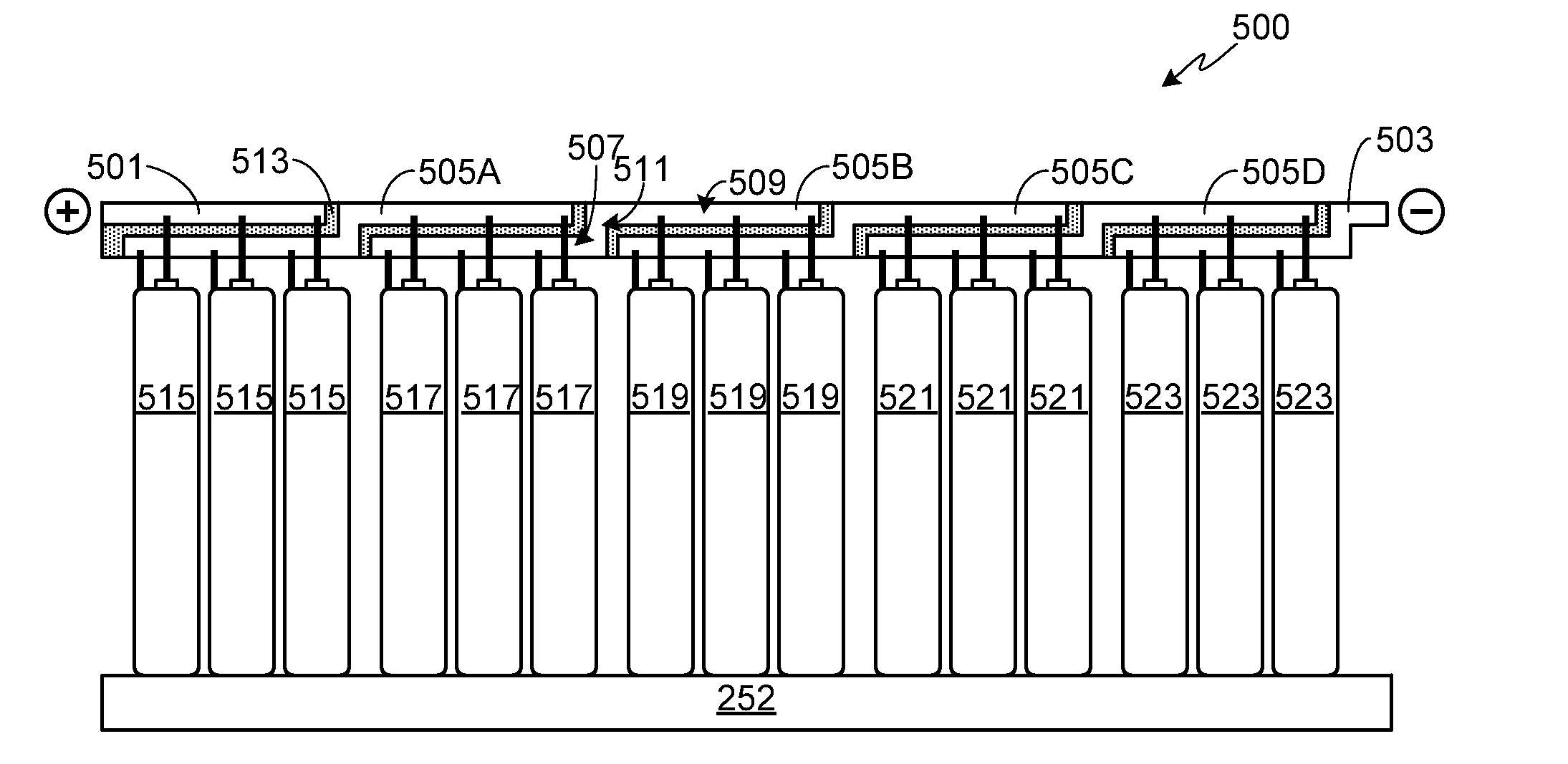
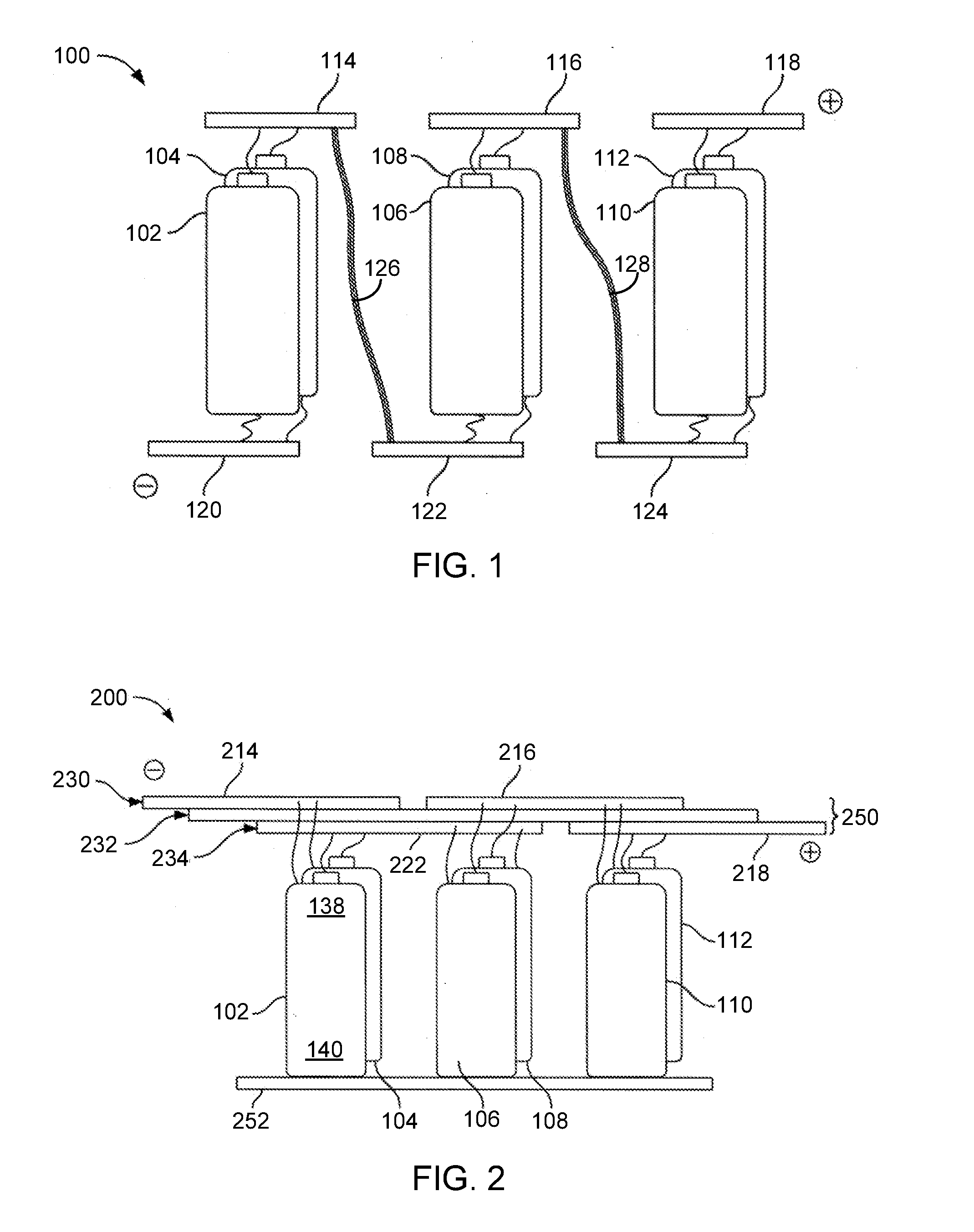
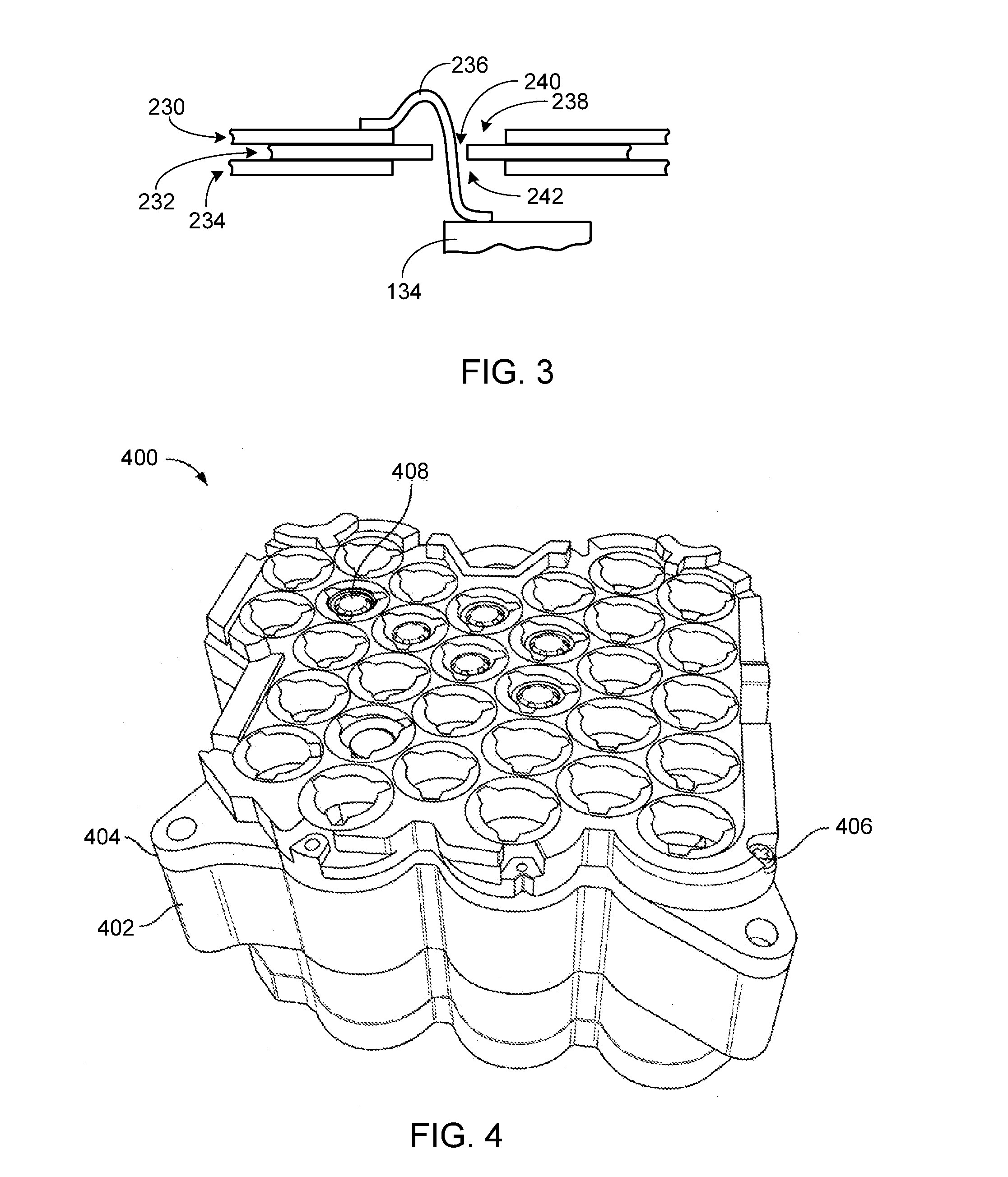
Z-Shaped Bus Bar for a Battery Pack
ActiveUS20140255750A1Primary cell to battery groupingCell temperature controlEngineeringBattery pack
A battery pack with a compact and robust bus bar assembly is provided. The batteries within the pack are divided into groups, where the batteries within each battery group are connected in parallel and the groups are connected in series. A repetitive sequence of overlapping bus bars is used, with each bus bar comprised of upper and lower segments coupled together via a step segment. The overlapping design allows the upper surface of the upper segment of each of the repetitive bus bars to be aligned within an upper plane, and the lower surface of the lower segment of each of the repetitive bus bars to be aligned within a lower plane.
Owner:ATIEVA USA INC
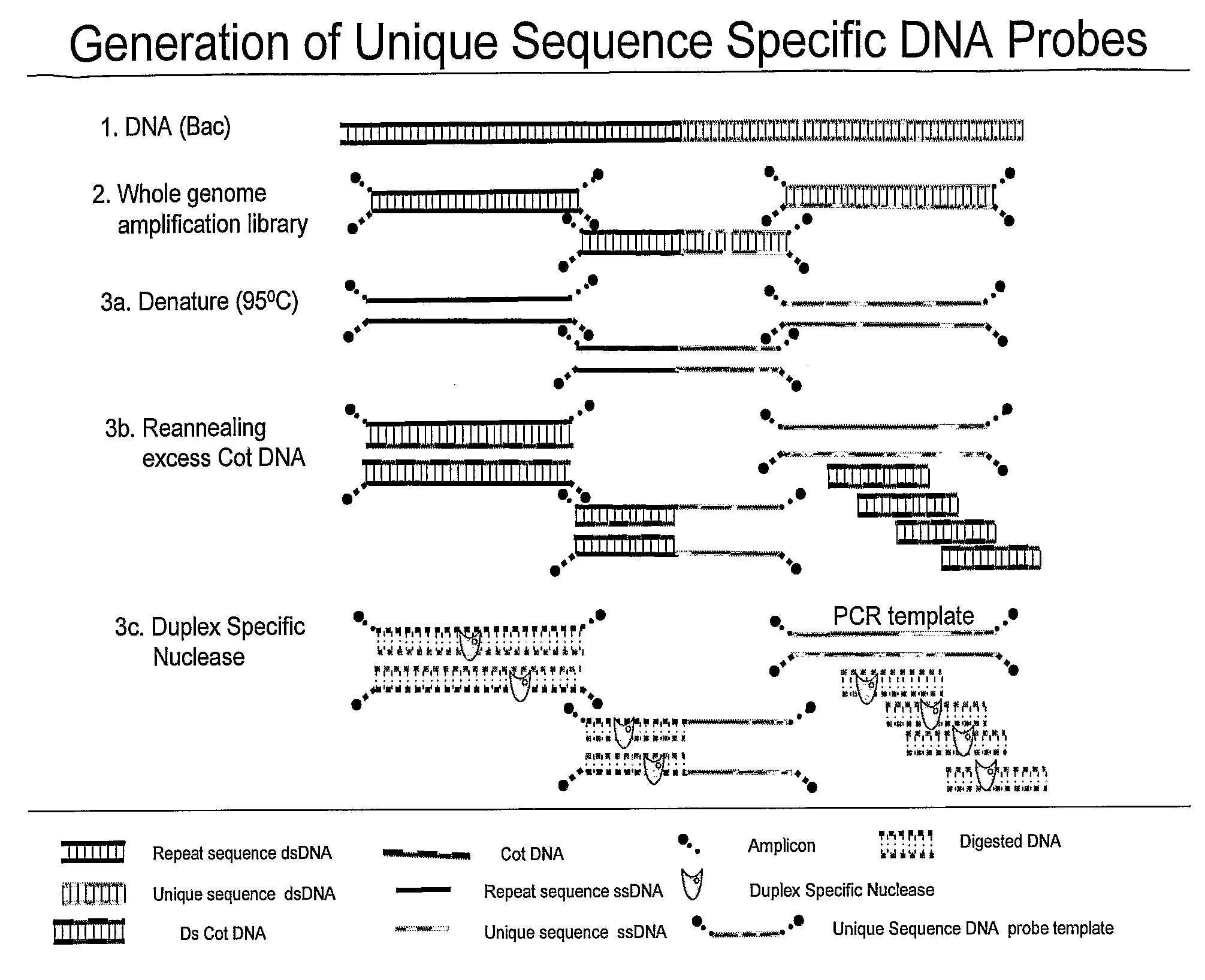
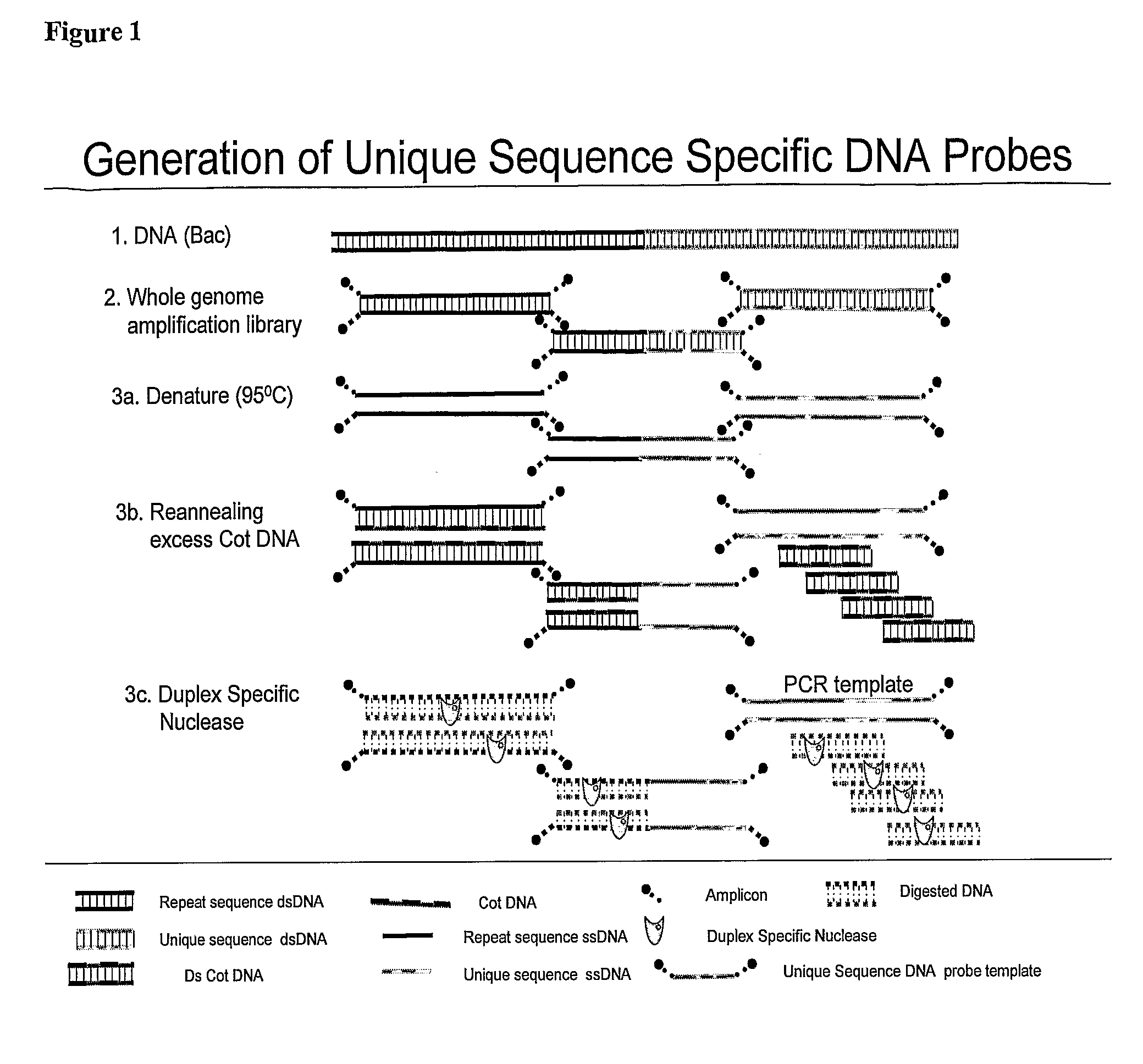
Methods and composition to generate unique sequence DNA probes labeling of DNA probes and the use of these probes
ActiveUS20090220955A1Strong specificityIncreased riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceDouble stranded
The invention relates generally to the field of identification of DNA sequences, genes or chromosomes. Methods and composition to obtain Unique Sequence DNA probes are provided. Composition comprises of any double stranded DNA containing Unique Sequences from which the repetitive sequences are eliminated according to the method described in this invention. The invention also relates to the preservation of cells that have been identified after immunuomagnetic selection and fluorescent labeling in order to further interrogate the cells of interest. Furthermore the invention relates to genetic analysis of cells that have been identified after immunomagnetic selection and fluorescent labeling.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
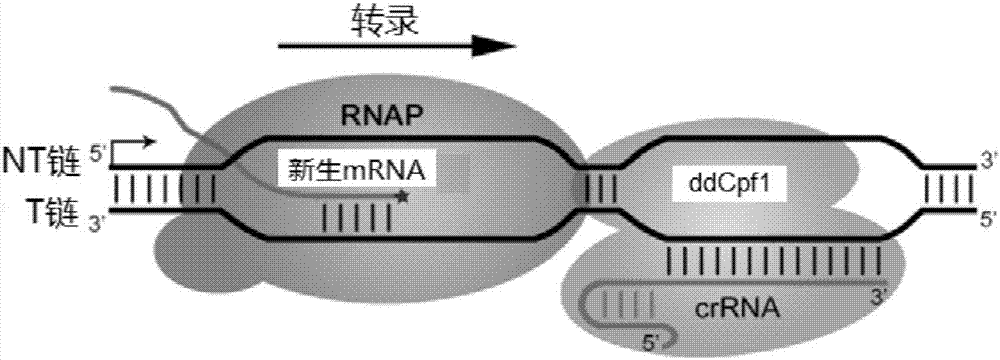
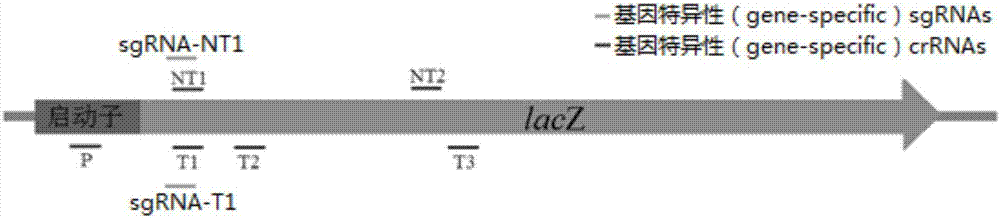
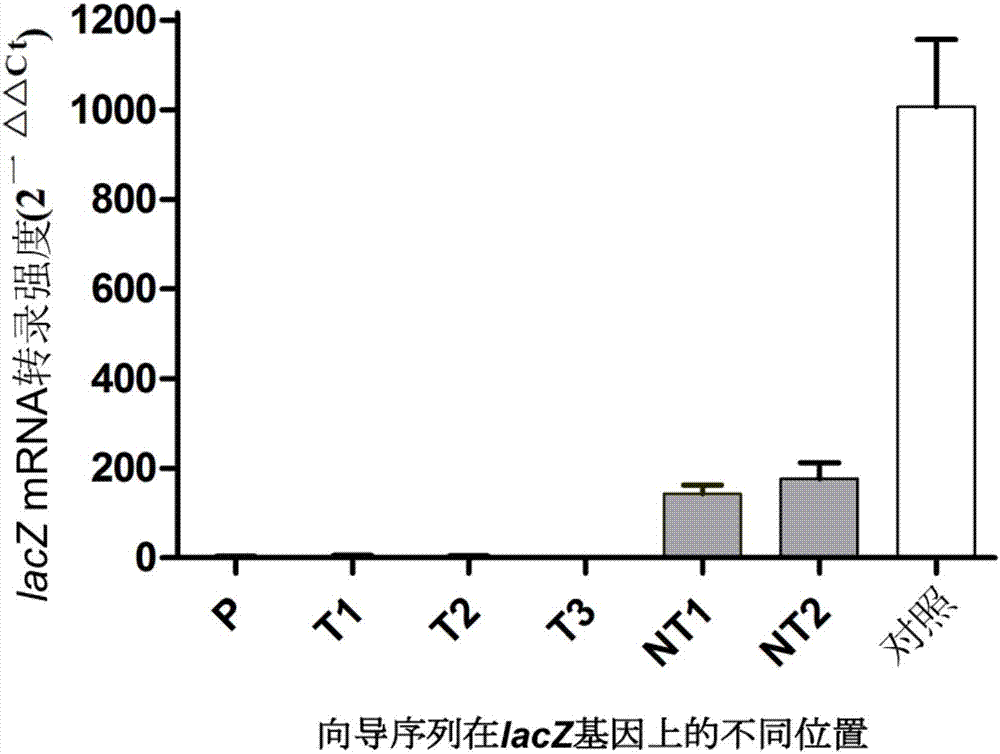
Cas protein specific binding target DNA, method for regulating and controlling target gene transcription and kit
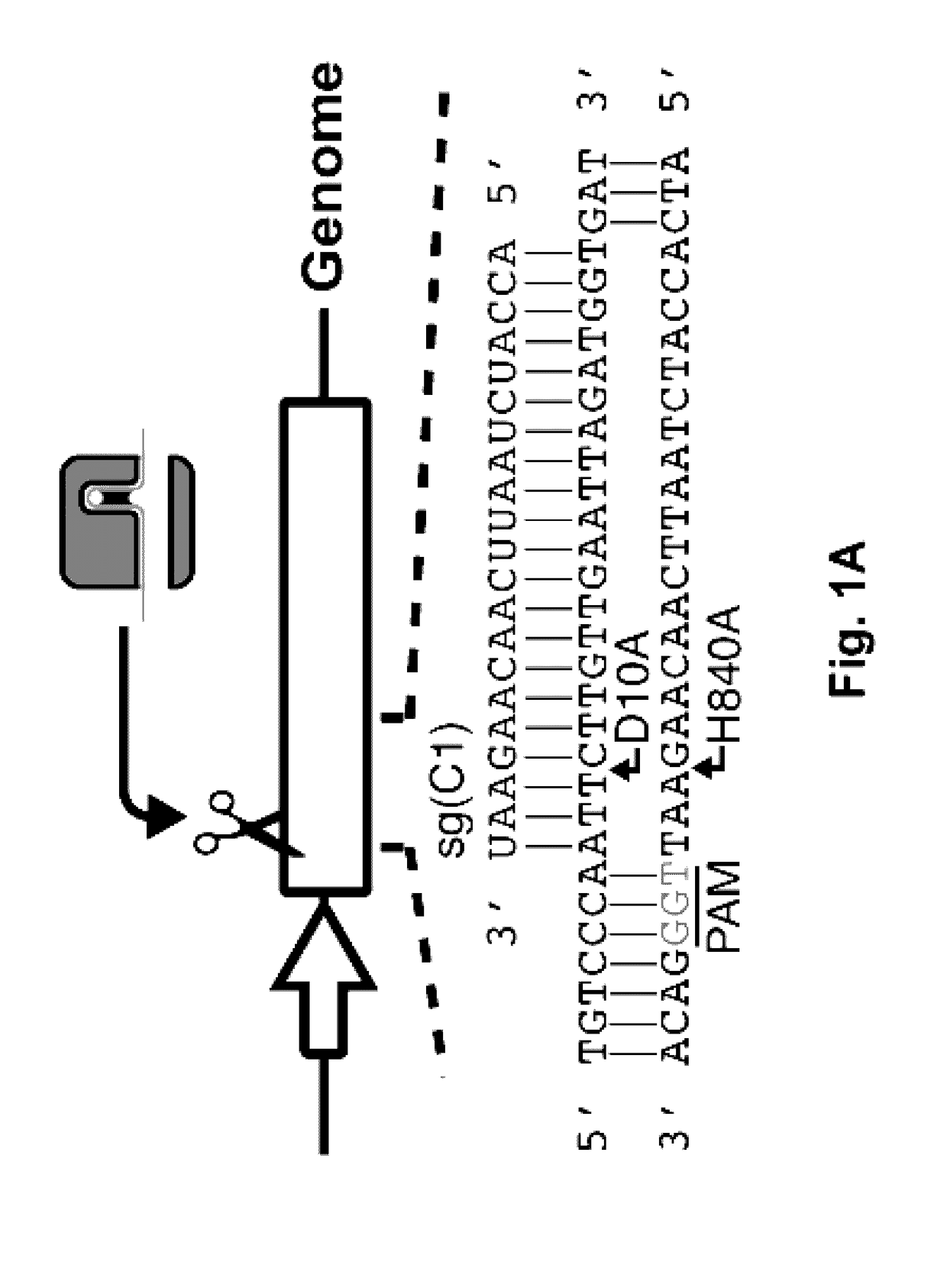
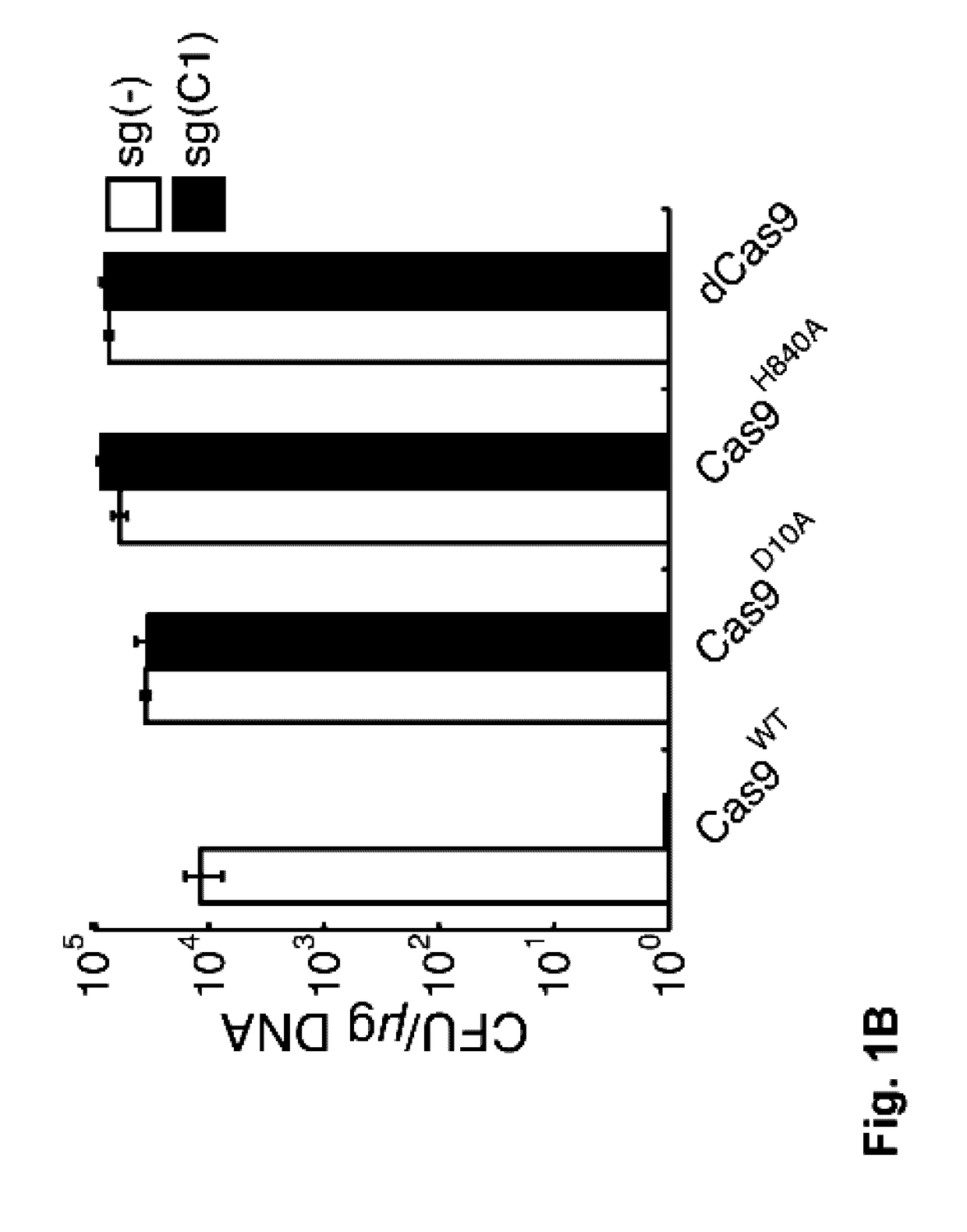
The invention relates to a method for binding Cas protein to DNA, and in particular to a method which is capable of conveniently, rapidly and efficiently regulating and controlling gene transcription for one or more targets as well as a kit applicable to the method. The method comprises the following steps: determining a target on genome, finding out a PAM site required by binding of the Cas protein (the Cas protein is a Cas protein mutant having an RNA enzymatic activity and in lack of a DNA enzymatic activity) within left and right regions of the target, designing a go-ahead sequence in accordance with the PAM site, determining direct repeat of the Cas protein and constructing crRNA plasmid for transcribing a crRNA sequence, connected to the go-ahead sequence, of the direct repeat; and promoting co-expression of an encoding gene of the Cas protein and the transcription crRNA plasmid in cells, so that the specific binding of the Cas protein to the target is achieved. With the application of the method provided by the invention, transcription of one or more target genes can be inhibited; and the method, in comparison with CRISPR / dCas9, is quite simple in entire operating process and is equivalent to dCas9 in editing efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI TOLO BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Method for melting curve analysis of repetitive PCR products
InactiveUS6664064B1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probePolynucleotide
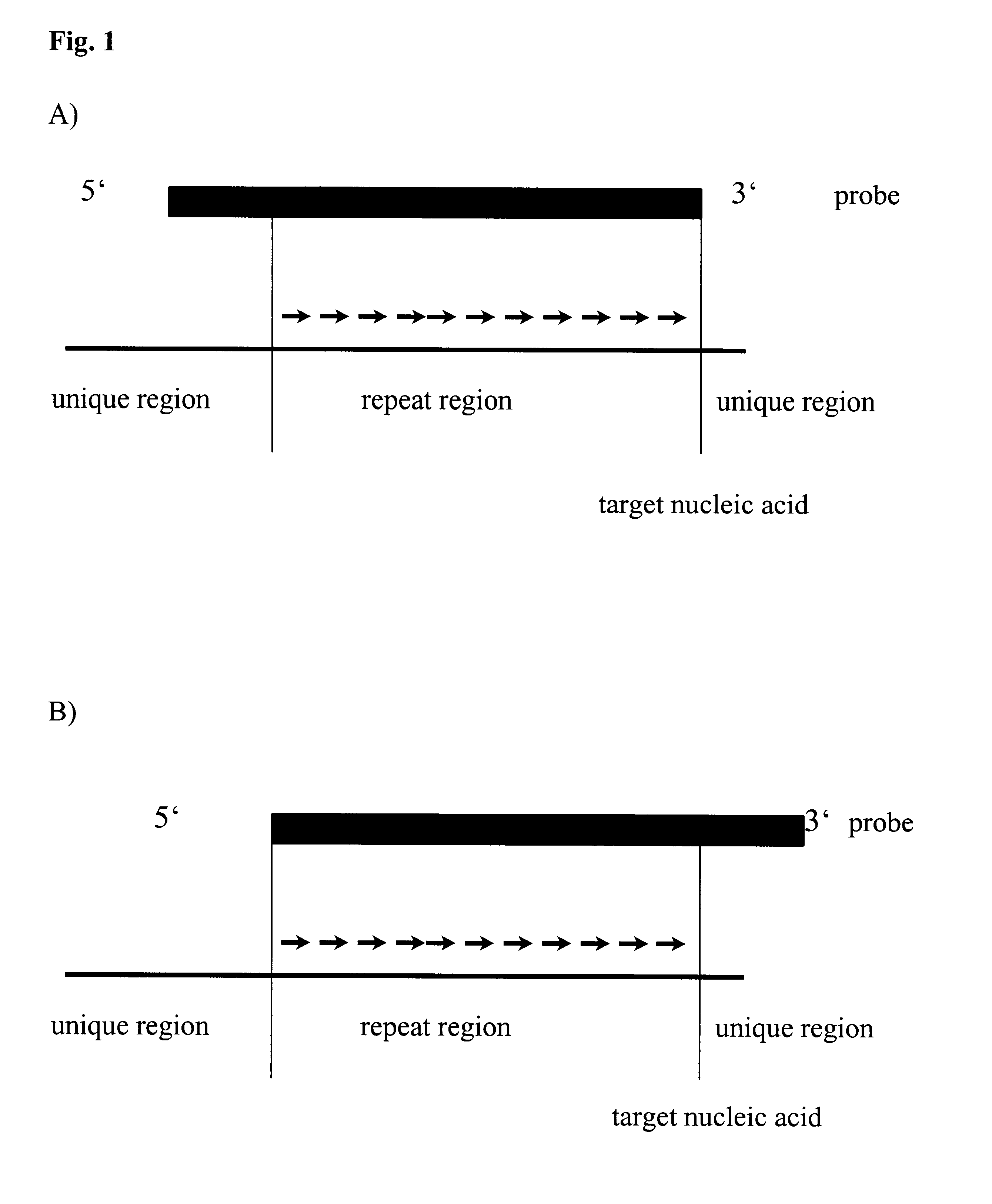
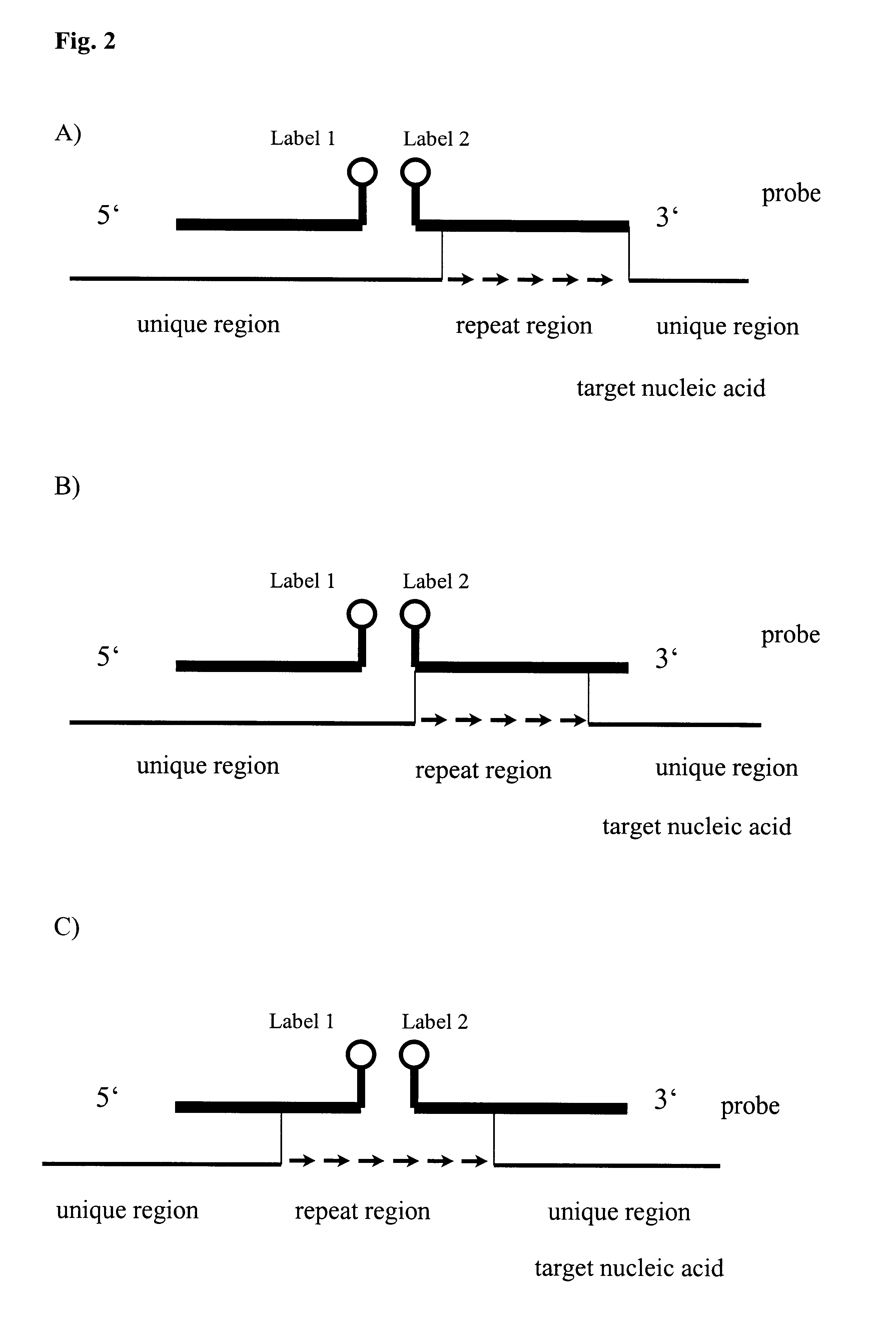
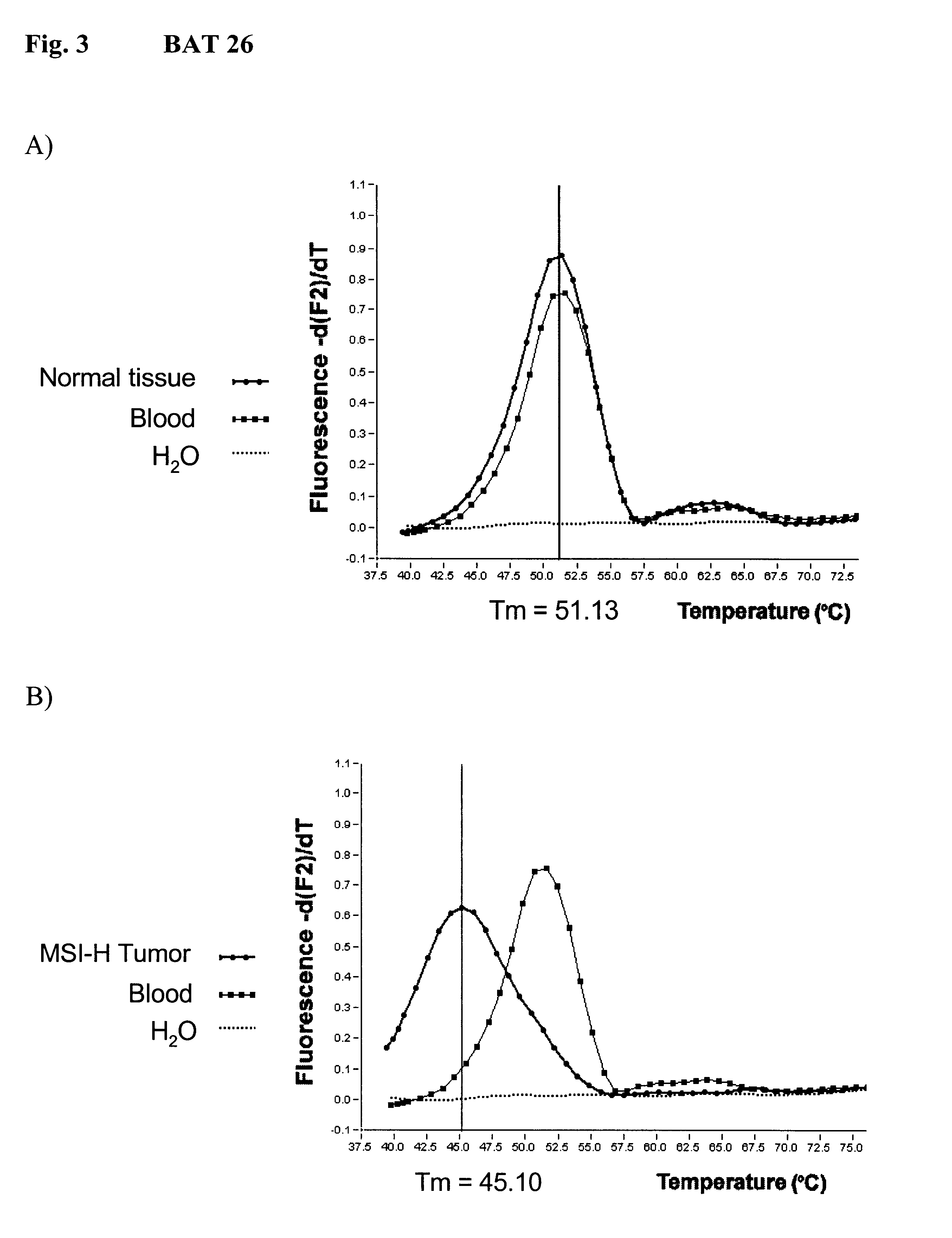
The invention relates to method, wherein the number of repeat sequences which are present in a sample is detemined by means of melting temperature analysis. More precisely, the invention relates to a method for analysis of a target nucleic acid consisting of repetitive and non repetitive sequences comprising (i) hybridization of at least one polynucleotide hybridization probe comprising a first segment which is complementary to a non repetitive region and a second segment which is compementary to an adjacent repetitive region, said second segment consisting of a defined number of repeats and (ii) determination of the melting point temperature of the hybrid which has been formed between the target nucleic acid and the at least one hybridization probe.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
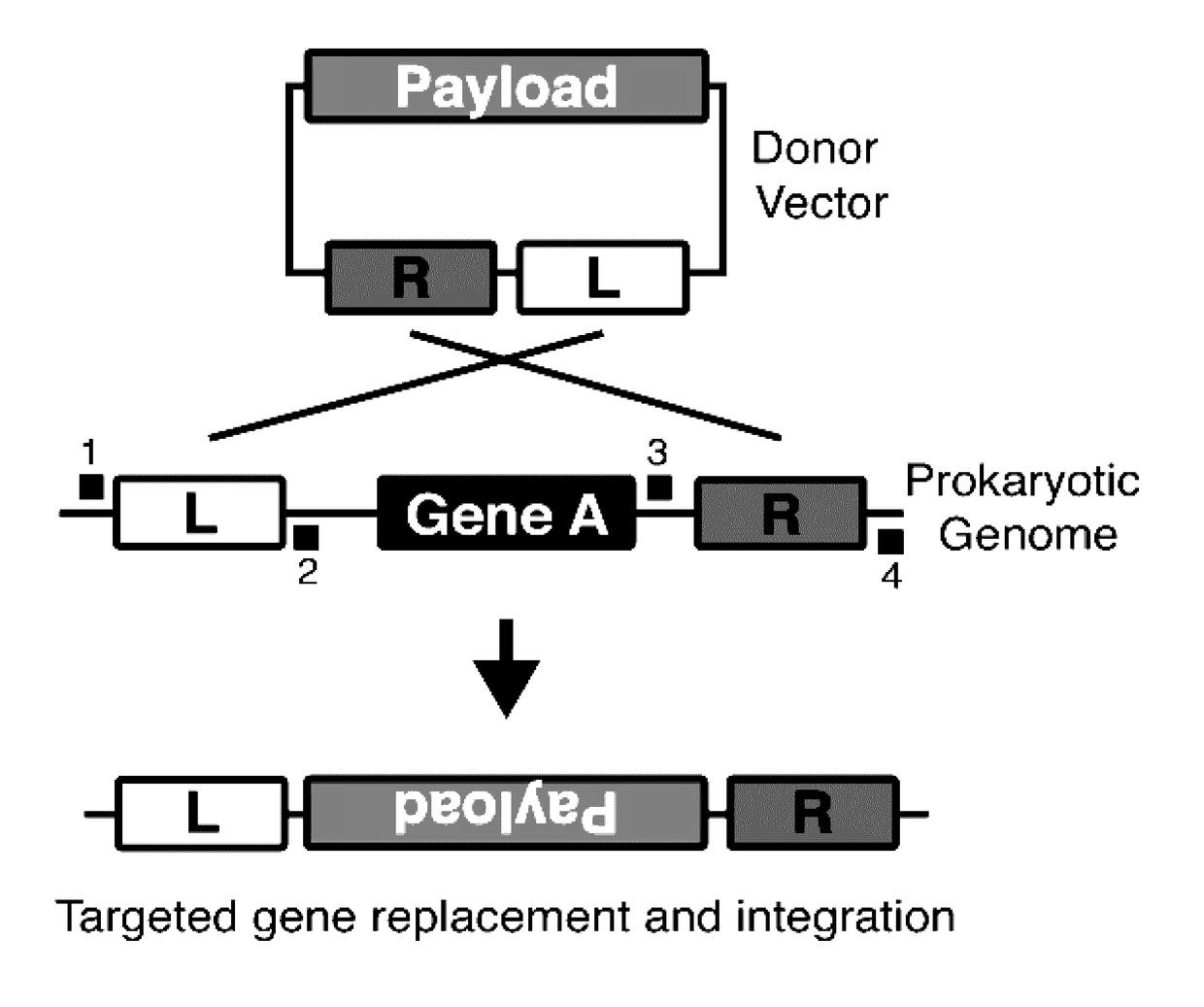
Targeted remodeling of prokaryotic genomes using crispr-nickases
The present invention relates to kits and methods of modifying the prokaryotic genome a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas system that utilized one nicking Cas nuclease and crRNAs. The kid and methods delete or replace portions of the prokaryotic genome. In some embodiments, an entire gene or multiple genes may be deleted or replaced.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
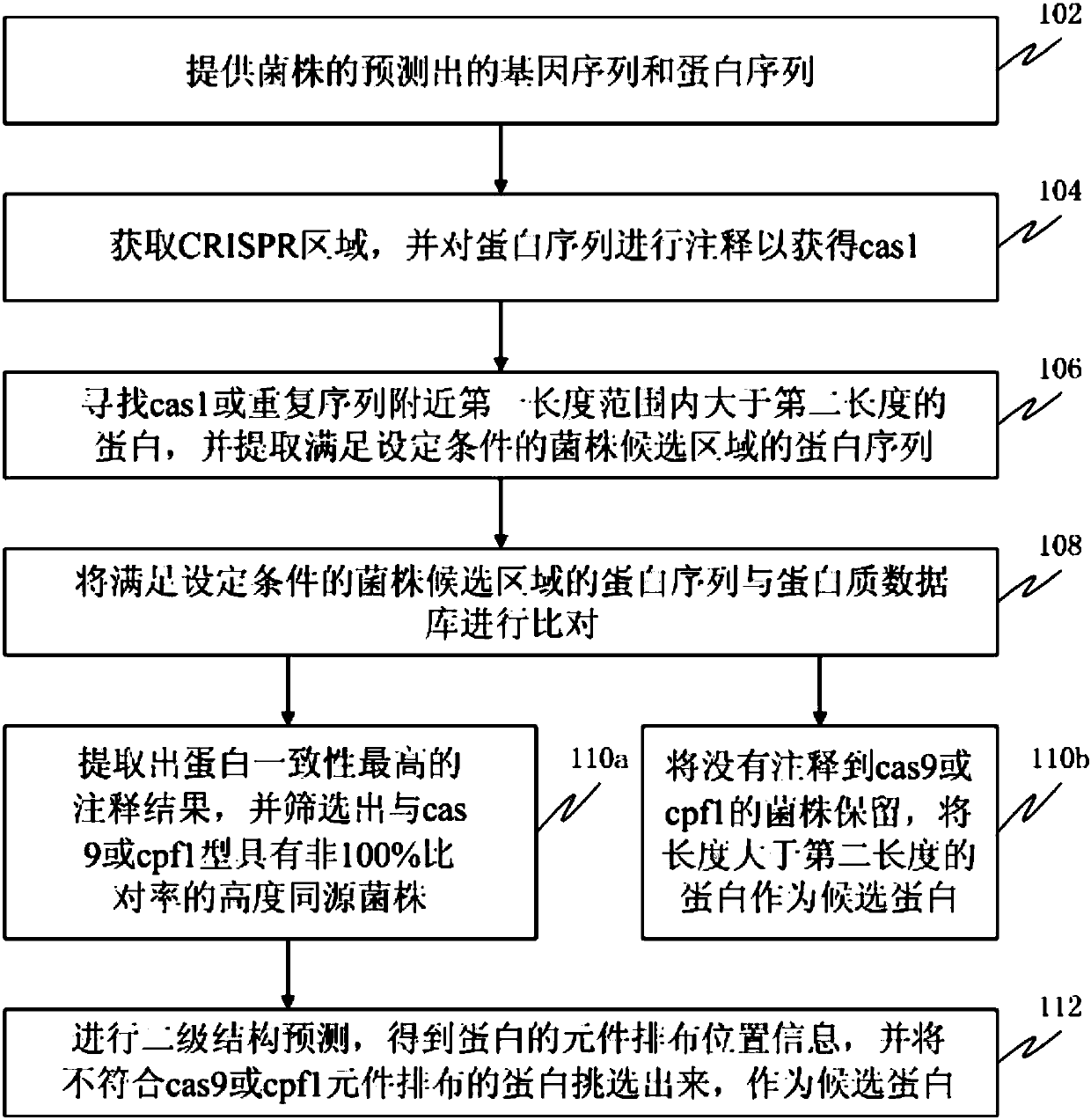
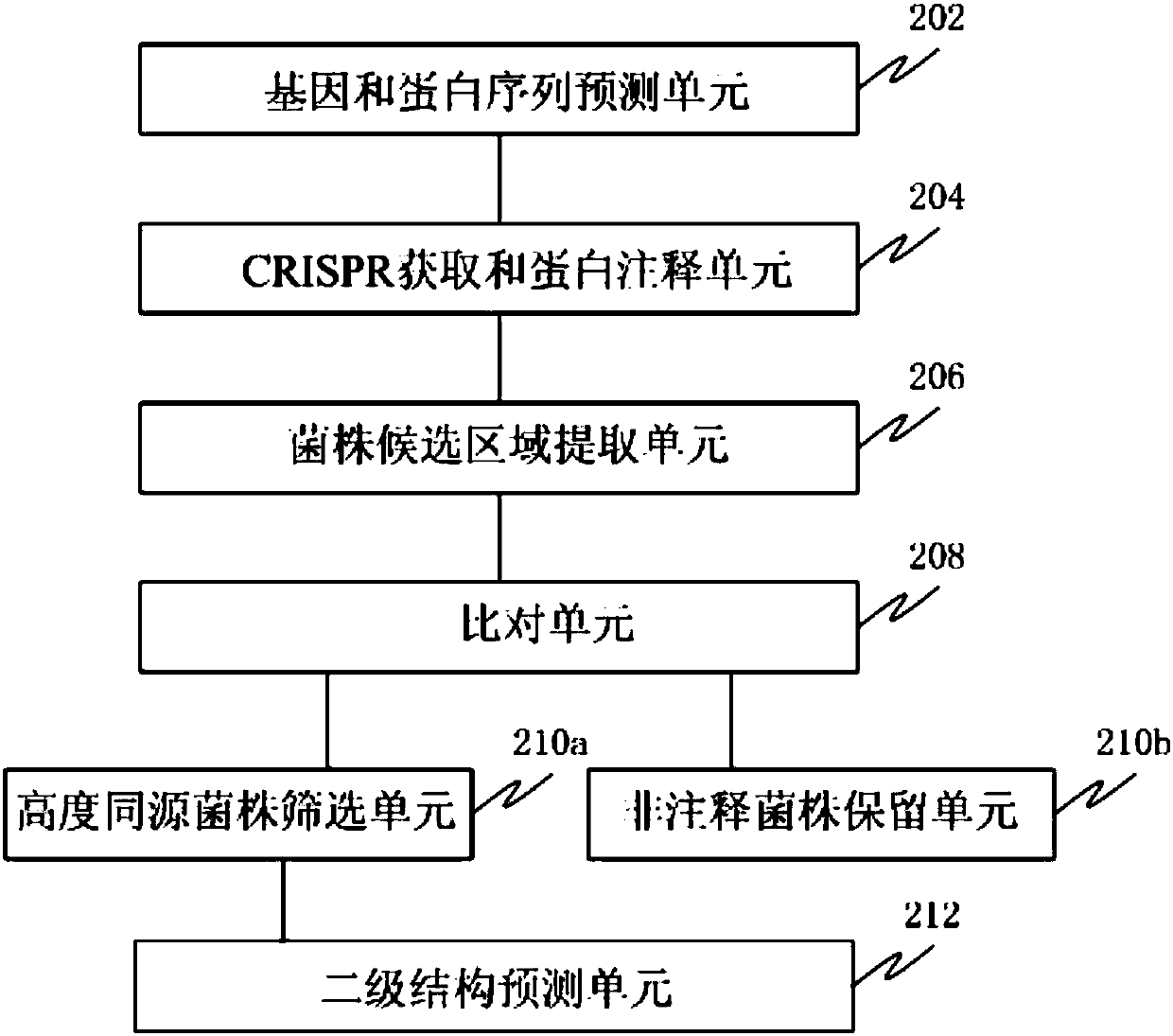
Screening method and device for novel CRISPR-Cas system
ActiveCN107784200AEffective positioningProteomicsGenomicsScreening methodProtein secondary structure
The invention discloses a screening method and device for a novel CRISPR-Cas system. The method comprises the following steps that the predicted gene sequences and protein sequences of strains are provided; CRISPR regions and proteins with cas1 annotation information are acquired; proteins larger than second length near cas1 or repetitive sequences in the range of first length are searched for, and protein sequences in candidate regions of the strains are extracted; a comparison is conducted; annotation result of the highest protein consistency is extracted, highly homologous strains of non 100% comparison ratio with cas9 or cpf1 type are screened out, a secondary structure prediction is conducted, arrangement position information of components of the proteins are acquired, proteins whichare not conformed to cas9 or cpf1 component arrangements are selected to serve as candidate proteins. The method can be used for analyzing single strain genome data so as to select strain proteins which may belong to the novel CRISPR-Cas system.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Method of and composite for in situ fluorescent hybridization
InactiveUS6043039AMaximize denaturationReduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHybridization probeSingle strand
A fluorescent in situ hybridization method including the steps of (a) obtaining a chromosome spread of a species; (b) preparing a hybridization composite containing a plurality of chromosomal paints each of the plurality of chromosomal paints being labeled with a different fluorophore-or-combination-of-fluorophores, such that an averaged specific activity of highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite substantially equals an averaged specific activity of unique sequences in the hybridization composite; (c) denaturing the hybridization composite and subjecting the hybridization composite to conditions for allowing at least a part of the highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite to reanneal while at least a part of the unique sequences in the hybridization composite remaining single stranded; (d) contacting under hybridization conditions the hybridization composite with the chromosome spread; (e) washing away excess of the hybridization composite; and (d) analyzing and presenting images of the now hybridized chromosome spread.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Nucleic acid size detection method
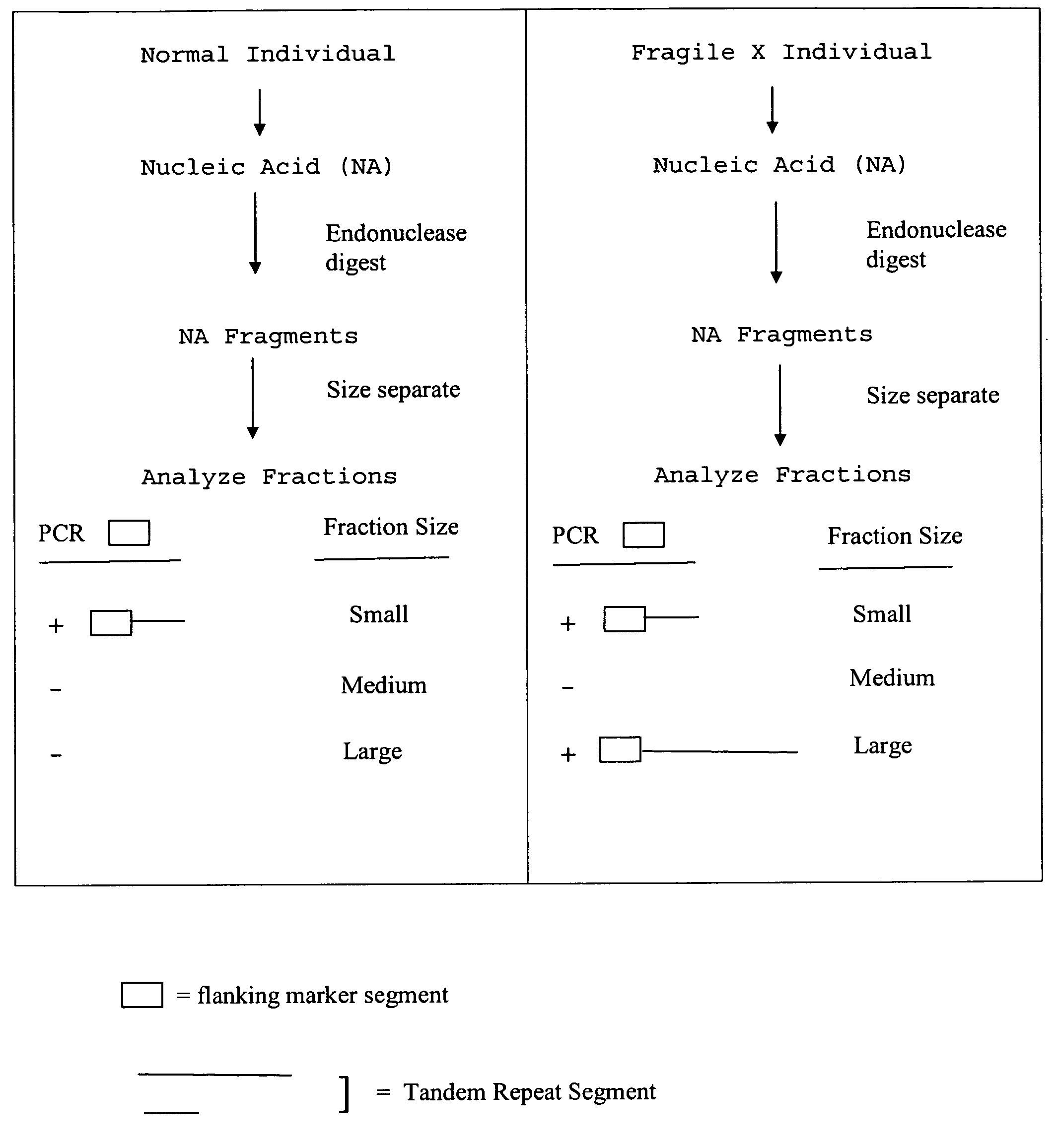
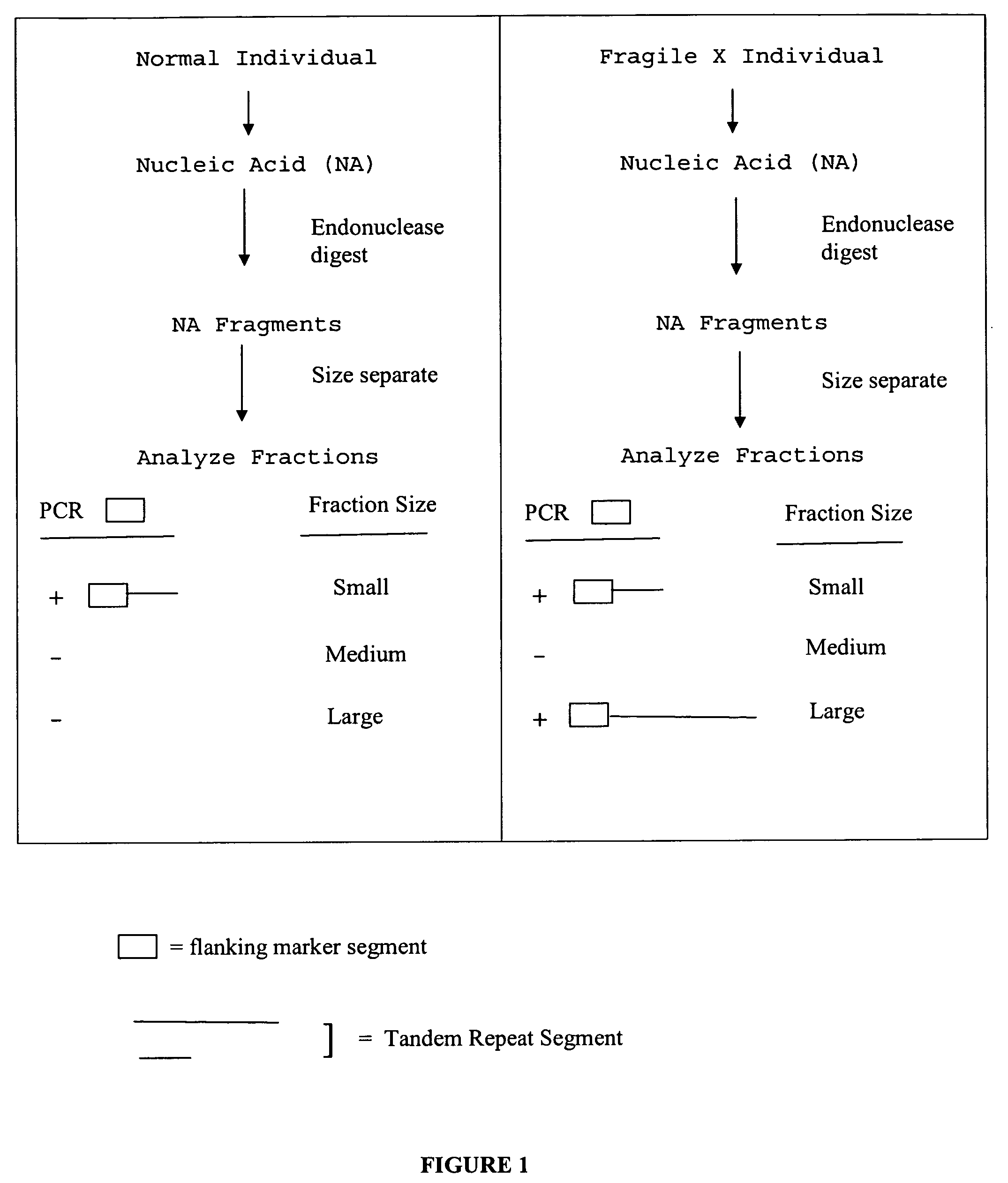
InactiveUS20080124709A1Finer of numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFragile X chromosomeFractionation
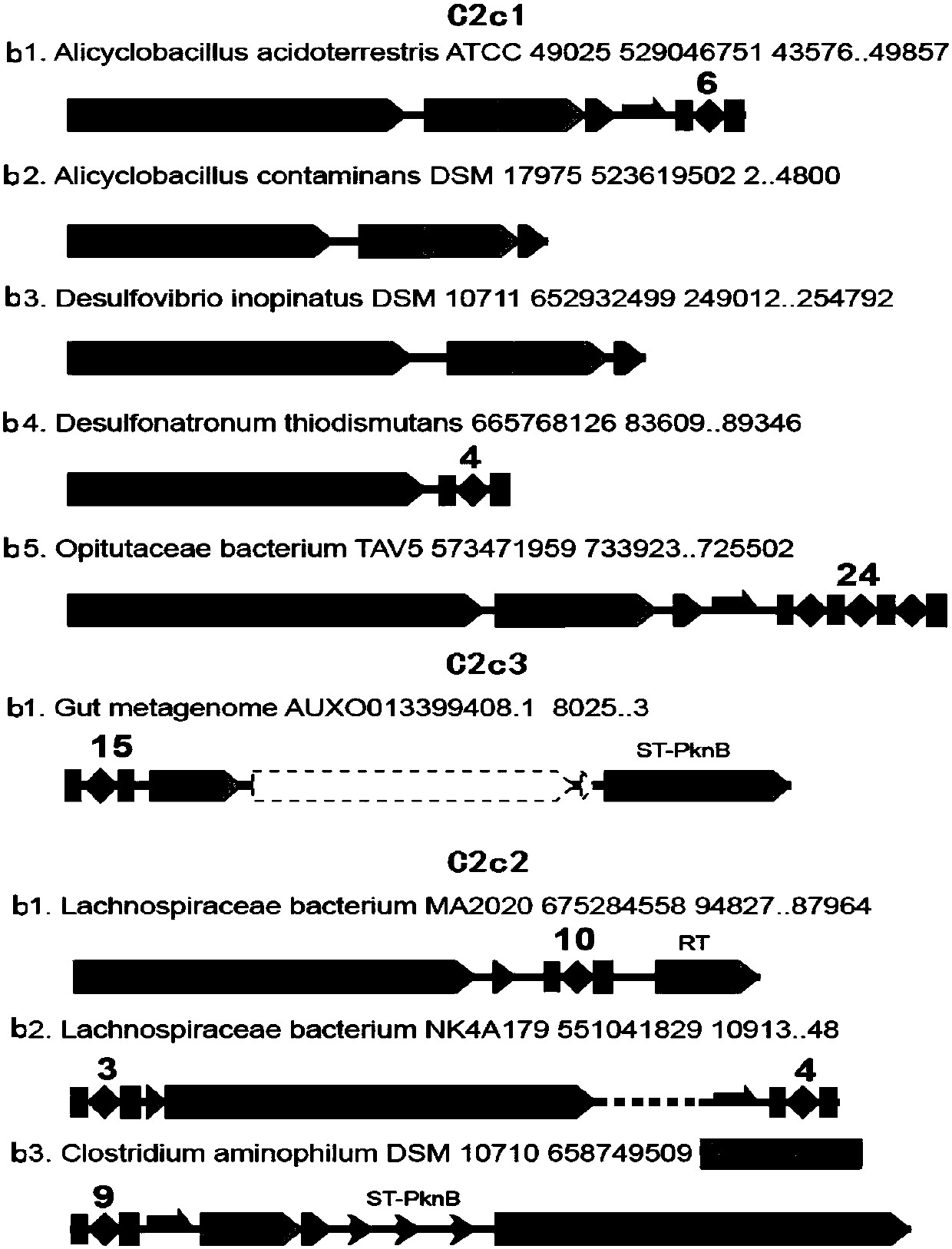
The present invention provides methods of determining the size of a particular nucleic acid segment of interest in a sample of nucleic acids through fragmentation of DNA, size fractionation, an optional second fragmentation, and identification using a marker sequence. In particular aspects, an expansion or reduction of tandem repeat sequences can be detected. In further aspects, carriers and individuals afflicted with fragile X syndrome or other diseases associated with tandem repeats can be distinguished from normal individuals.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC +1
Self-polymerization polypeptide and preparation method and application thereof
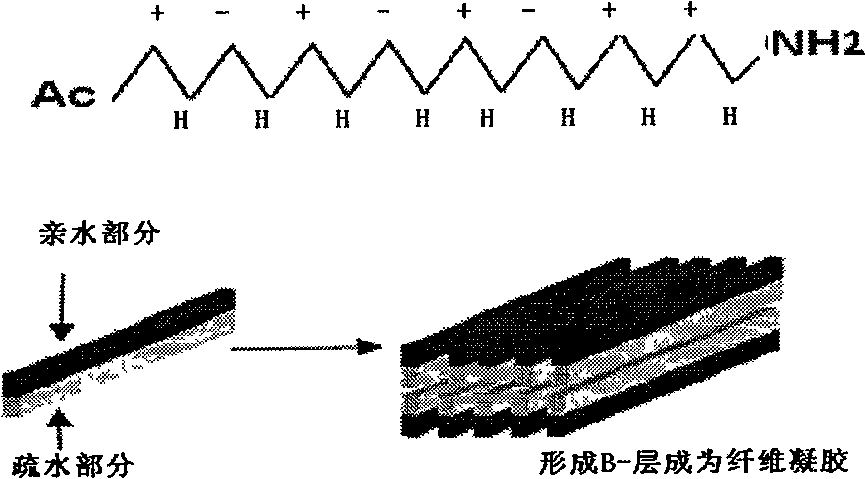
InactiveCN101514225AWide range of usesEasy to degradePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFiberIn vivo
The invention discloses a synthetic polypeptide, the amino acid sequence of the synthetic polypeptide meets the following general formula: Ac-X0-(X1-X2-X3-X4)n-NH2, wherein Ac is an acetylized N-terminal; X0 is an L-amino acid, and the type of the amino acid is Ala, Val or Gly; X1, X2, X3 and X4 are all L-amino acids or D-amino acids, X1 is a positive charge amino acid Arg, Lys or His, X3 is a negative charge amino acid Asp or Glu, and X2 and X4 are amino acids Ala, Val or Gly without charge; X1-X2-X3-X4 is a repeated sequence; and n is repeated times of amino acid arrangement in the sequence, and is equal to 2, 3 and 4. The polypeptide has the characteristics of forming a nano fiber screen through self-assembly, and can form a gel-like fiber screen in the particle environment in vitro or in vivo for hemostasis or wound nursing.
Owner:西安蓝晶生物科技有限公司
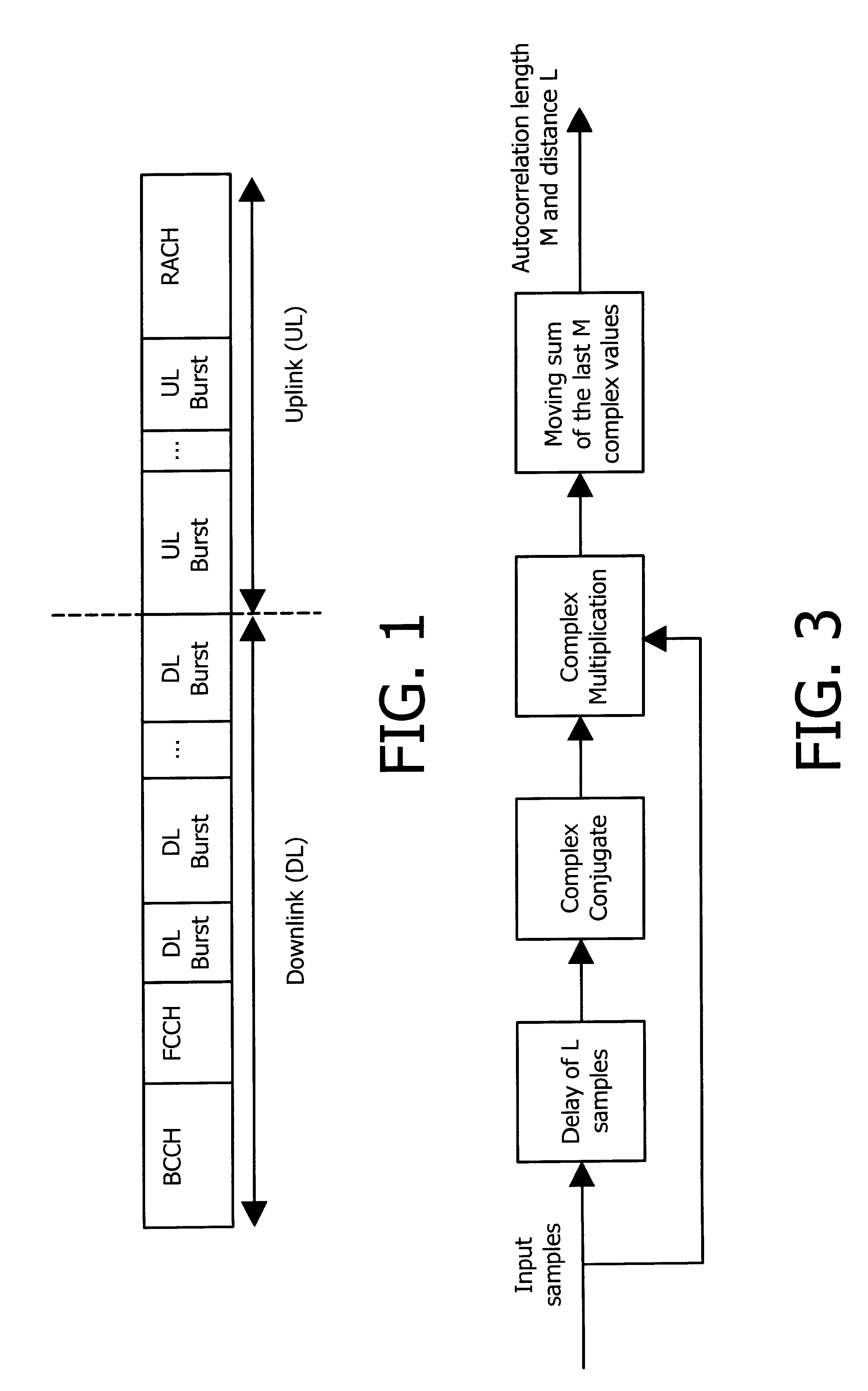
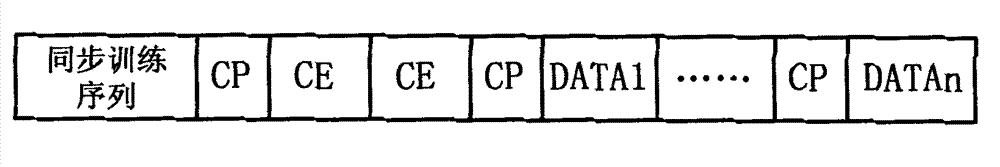
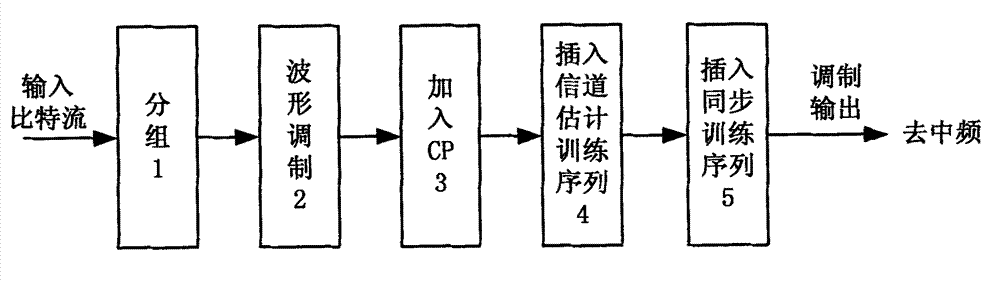
Method for efficient synchronization in a communication system
InactiveUS6442220B1Improve discriminationImprove robustnessSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemComputer science
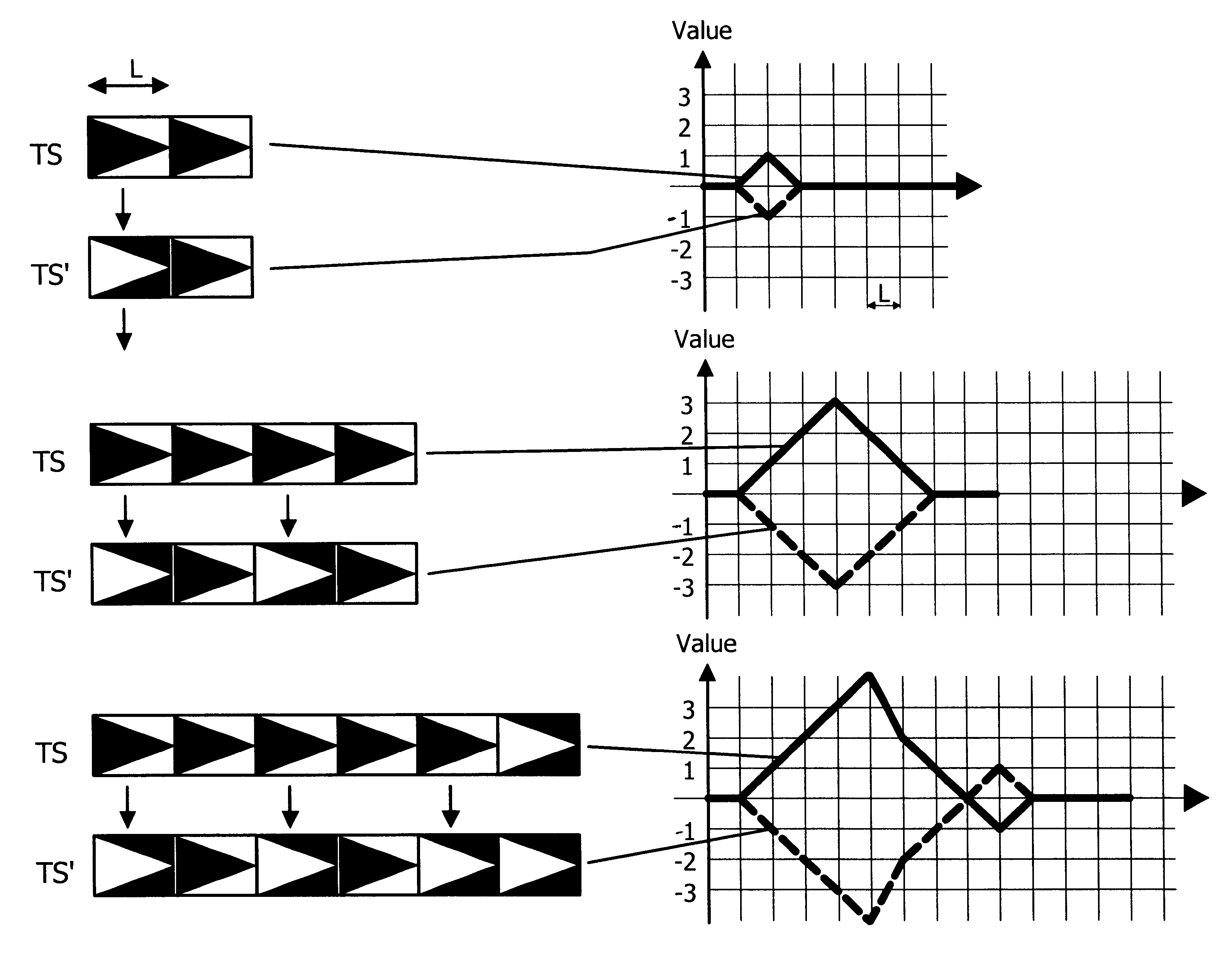
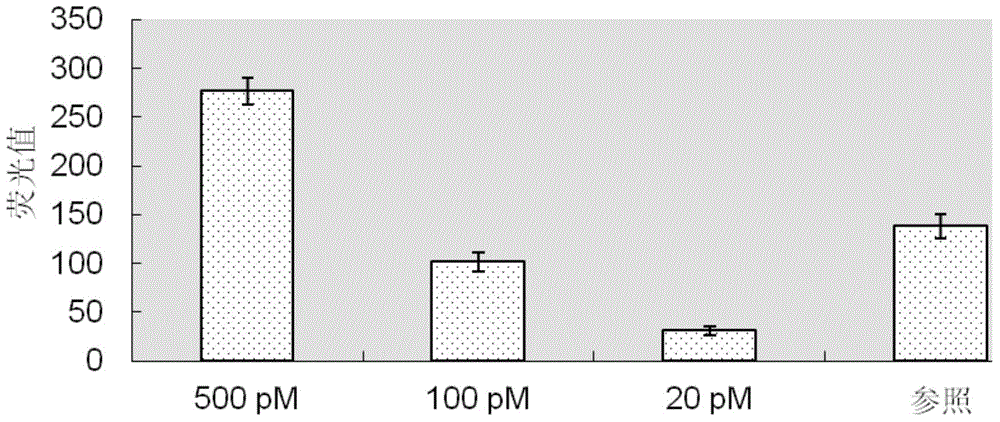
A method for discrimination of repetitive sequences in a wireless communication system in which the repetitive sequences have the same repetition length. For the discrimination the repetitive sequences are modified by changing the phase of at least one of the sequences. The auto-correlation values of the repetition sequences and of the modified repetitive sequences are calculated and the auto-correlation signs of the repetition sequences and of the modified sequences are compared.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
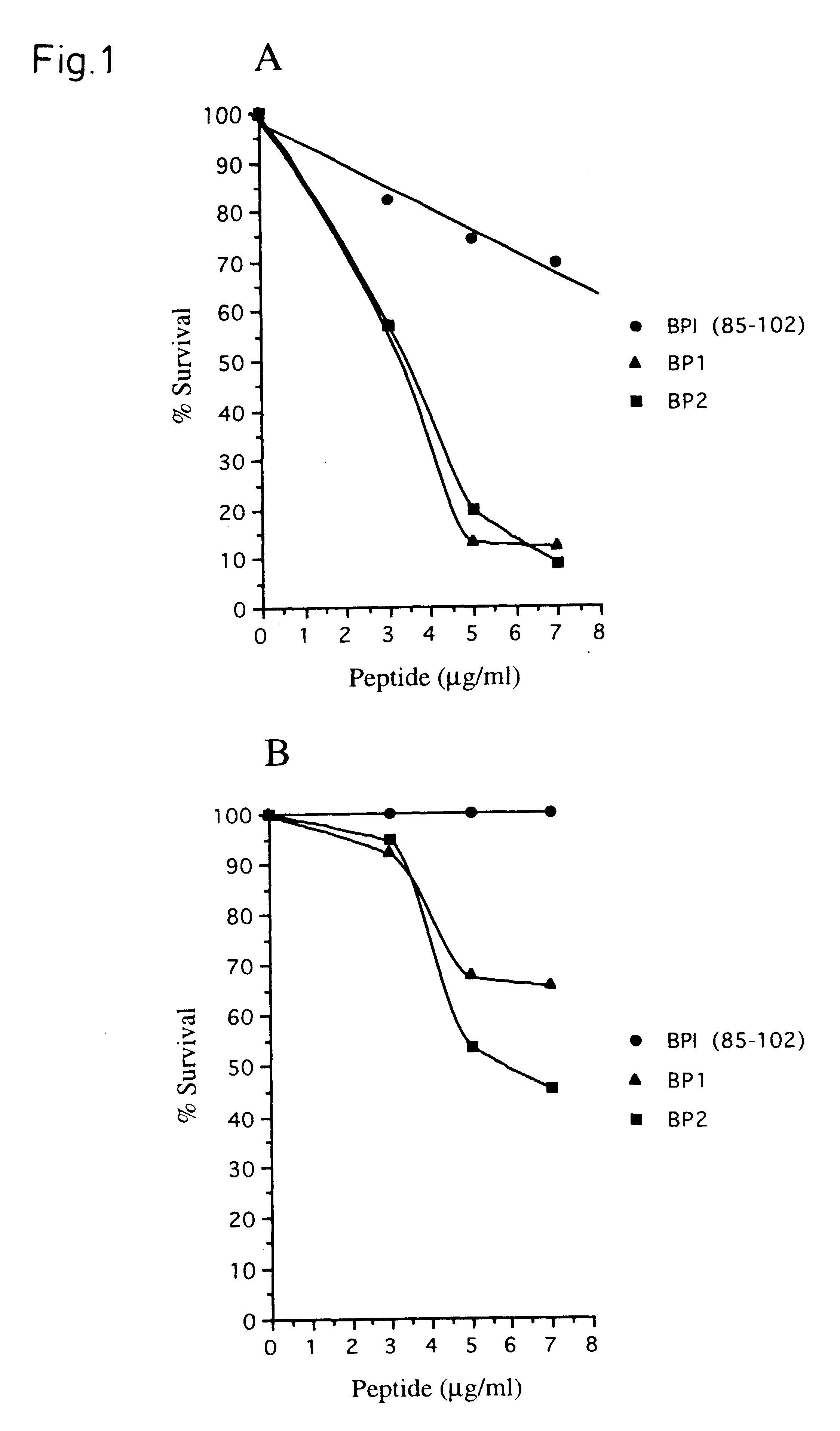
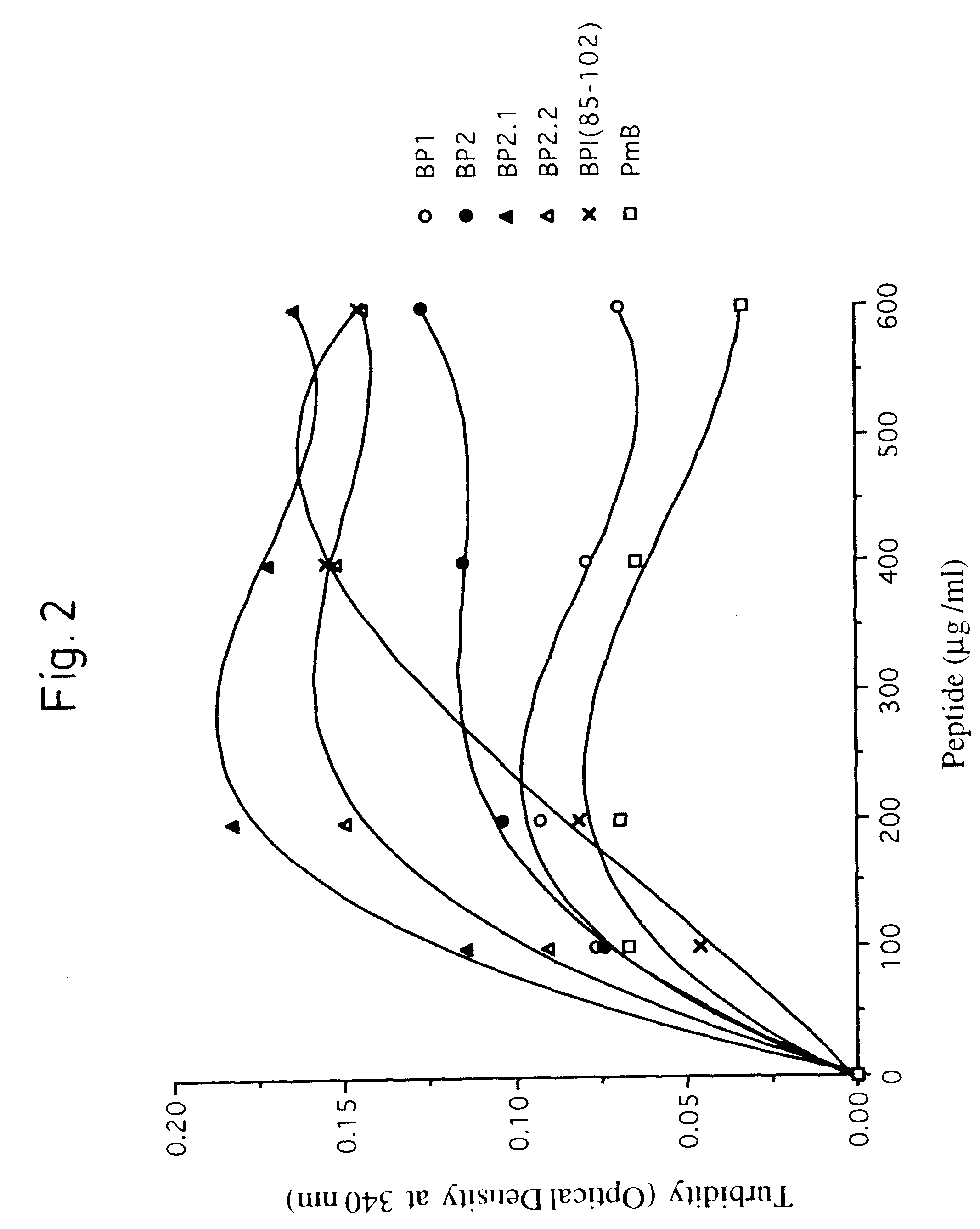
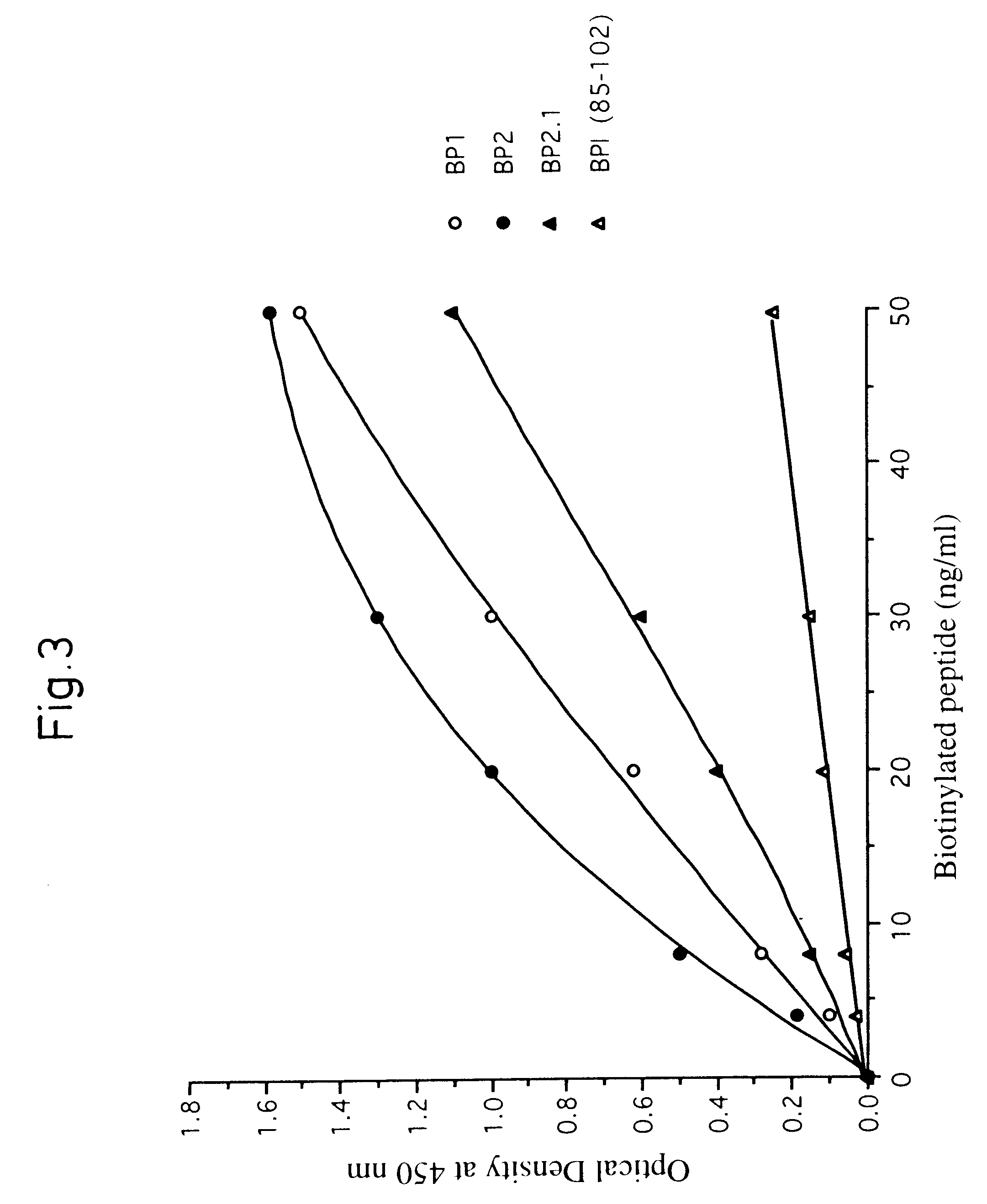
Synthetic peptides with antimicrobial and endotoxin neutralizing properties for management of the sepsis syndrome
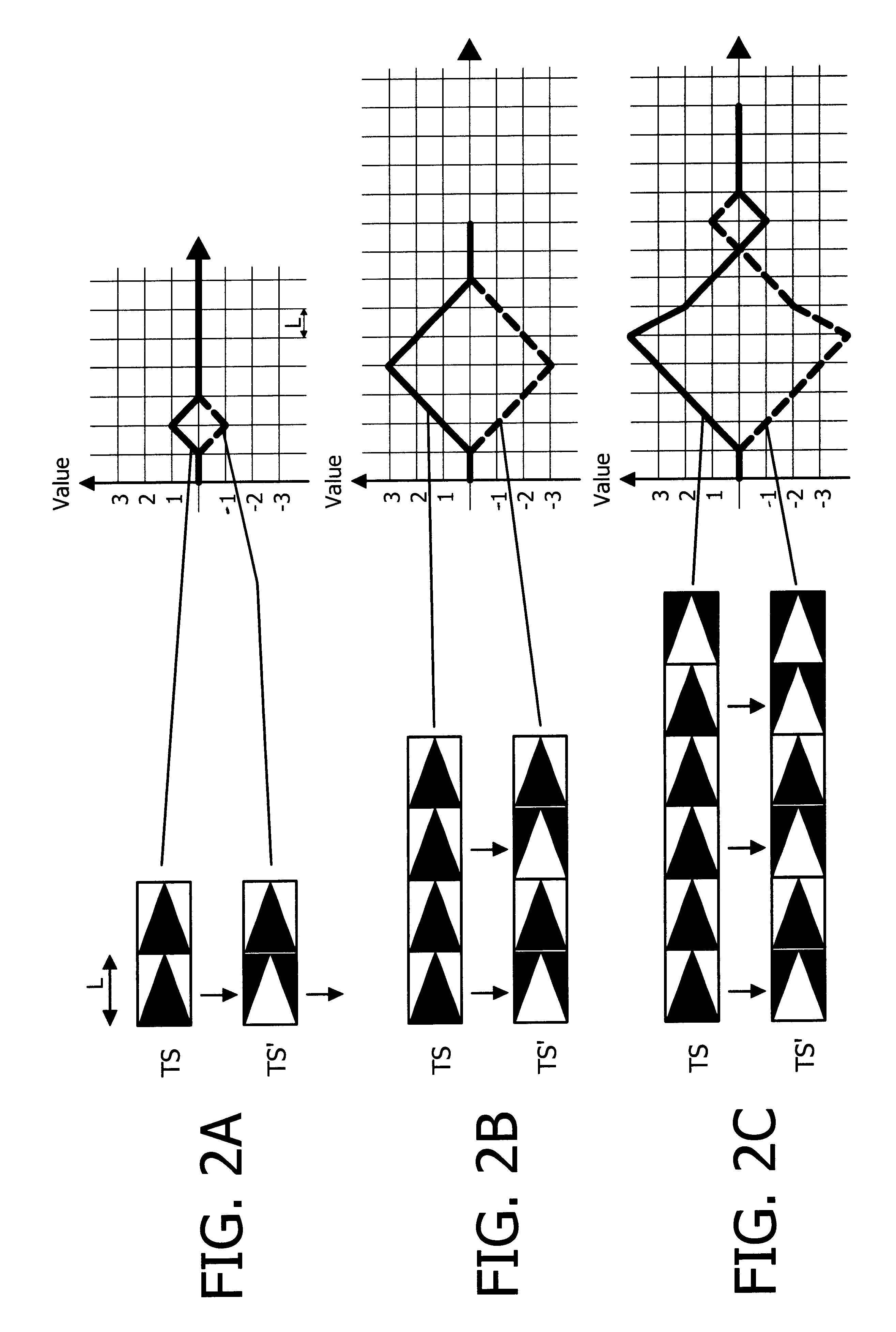
A peptide with an amino acid composition such that the peptide is amphipathic, cationic and forms a stable alpha-helix and has the following structure comprising at least 12 amino acidsA=an amino acid selected from the basic amino acids Lys,Arg or HisB=an amino acid selected from the aromatic amino acids Phe, Trp or TyrC=an amino acid selected from the group comprising the hydrophobic amino acids Leu, Ile, Val or Ala, andsaid peptide has either the orientation according to the formula or the retro orientation thereof, wherein at least 0-m of the repetitive sequence motifs (A2-B2-C1-A3) have the retro orientation and the remaining repetitive motifs (A2-B2-C1-A3) have the orientation as presented in the formula and wherein,R1-R2- and R3 are a number of amino acids, and whereinm=1-10, preferably 2-8, more preferably 2-5 andn=1-3, a pharmaceutical composition comprising such a peptide application thereof in treatment or diagnosis related to i.a. parasite infection topical and systemic tumors and septic shock.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT +1
Detection of chromosoal abnormalities associated with breast cancer
InactiveUS7094534B2Avoid saturationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
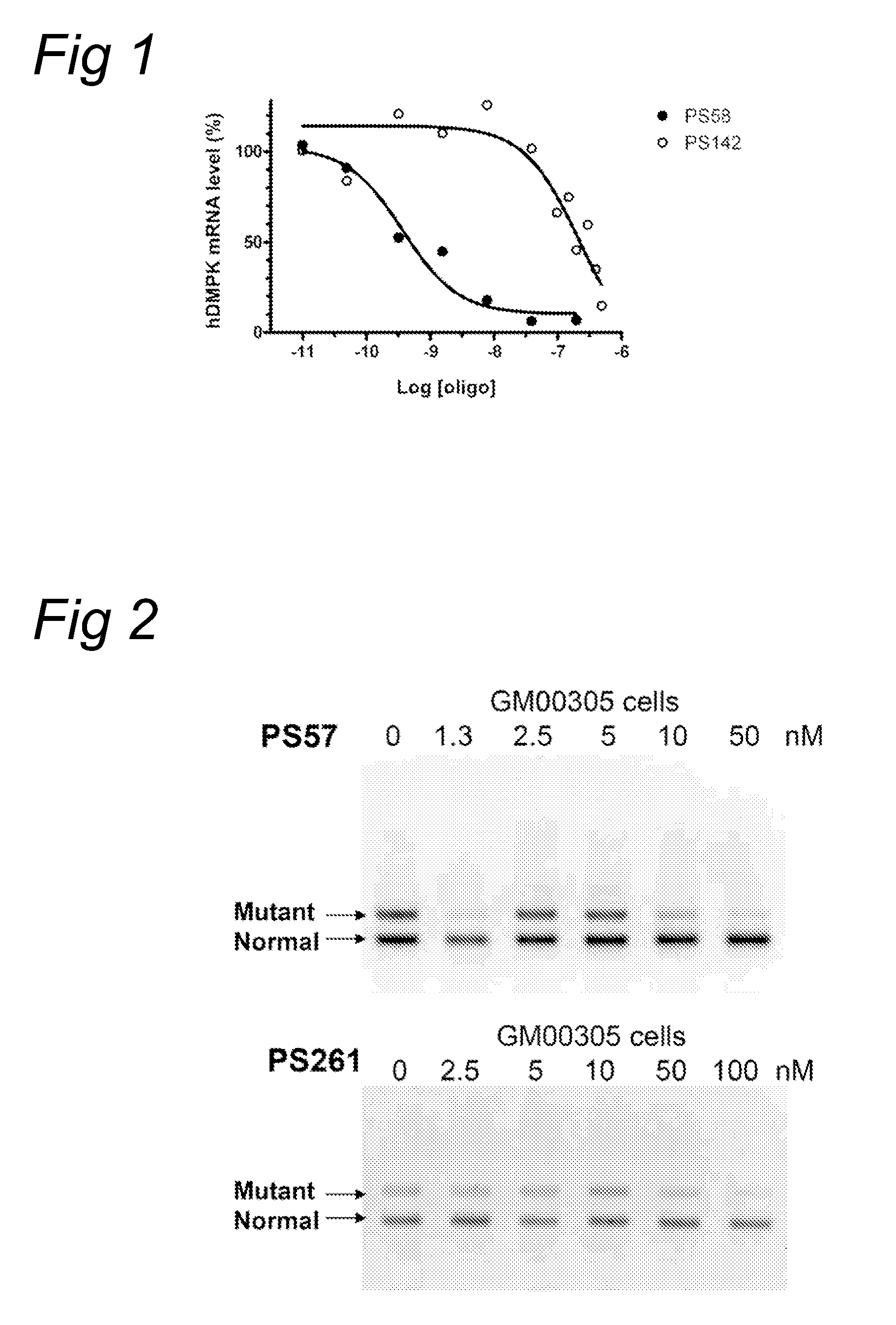
Methods and means for treating DNA repeat instability associated genetic disorders
InactiveUS8263760B2Lower Level RequirementsReduced stabilityNervous disorderSugar derivativesUracilInstability
The current invention provides for methods and medicaments that apply an oligonucleotide comprising aninosine and / or an uracile and / or a nucleotide containing a base able to form a wobble base pair, said oligonucleotide being preferably RNAse H substantially independent and being complementary only to a repetitive sequence in a human gene transcript, for the manufacture of a medicament for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders in humans. The invention hence provides a method of treatment for cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders. The invention also pertains to a modified oligonucleotide which can be applied in a method of the invention to prevent the accumulation and / or translation of repeat expanded transcripts in cells.
Owner:PROSENSA HLDG BV +1
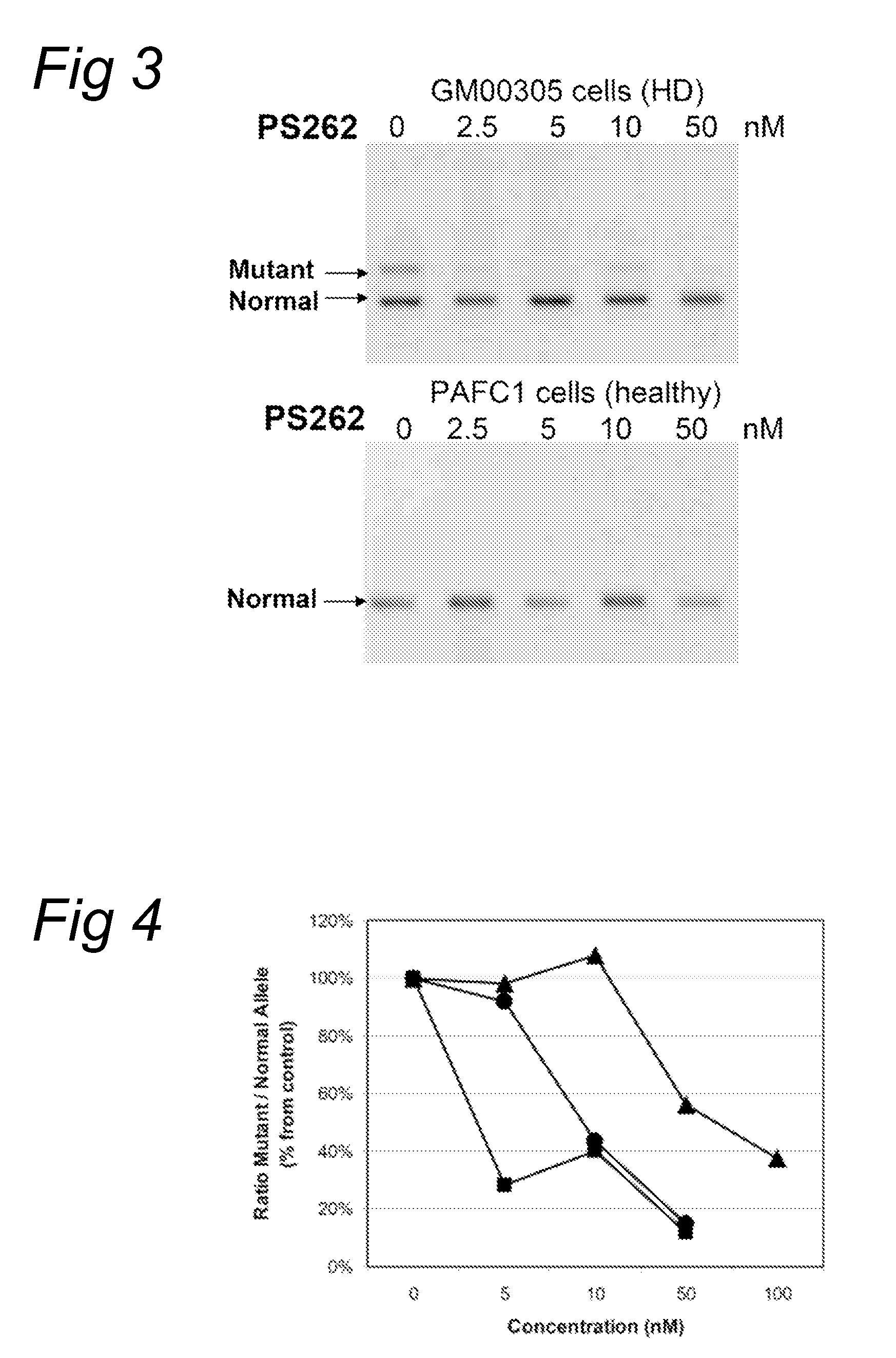
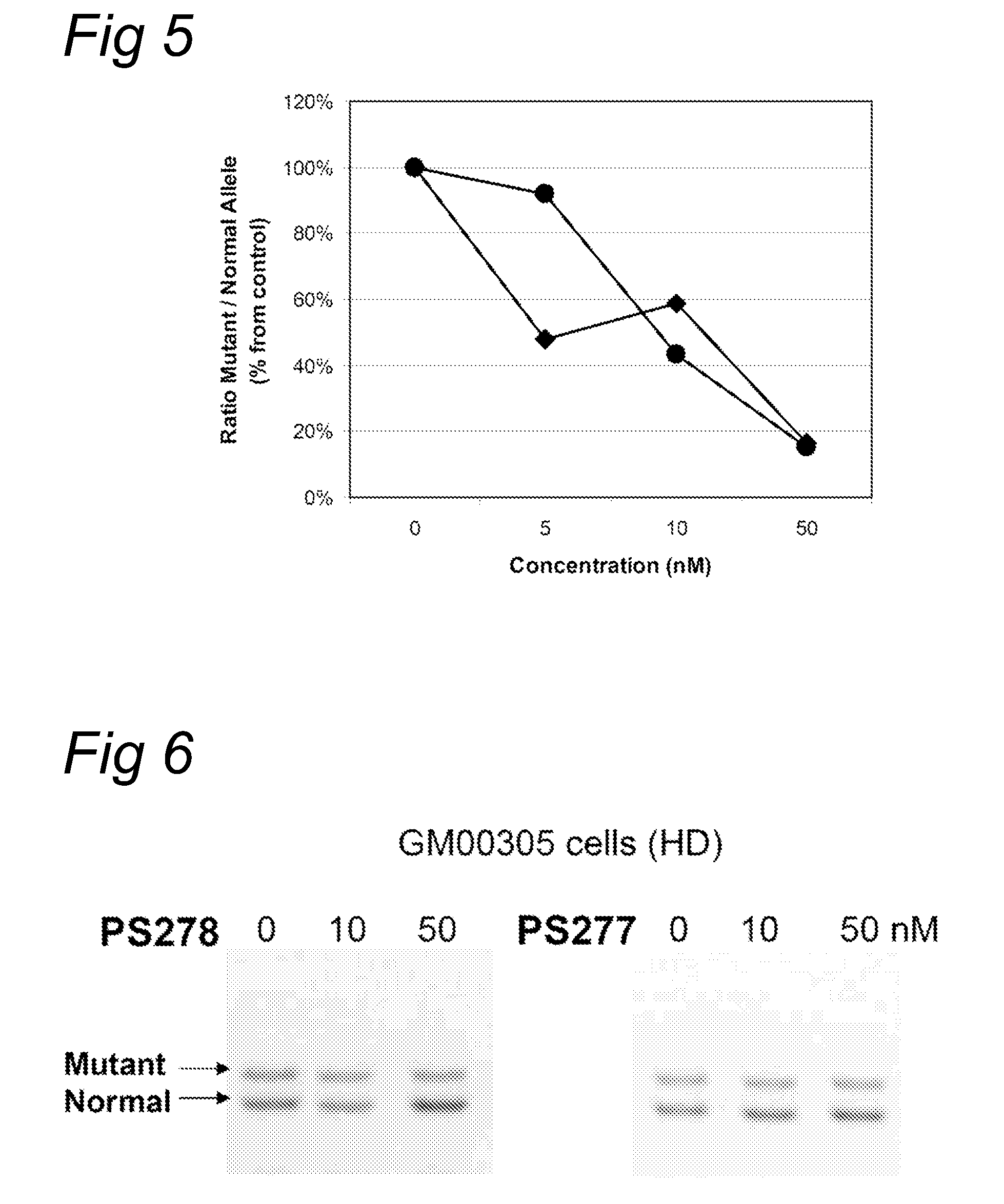
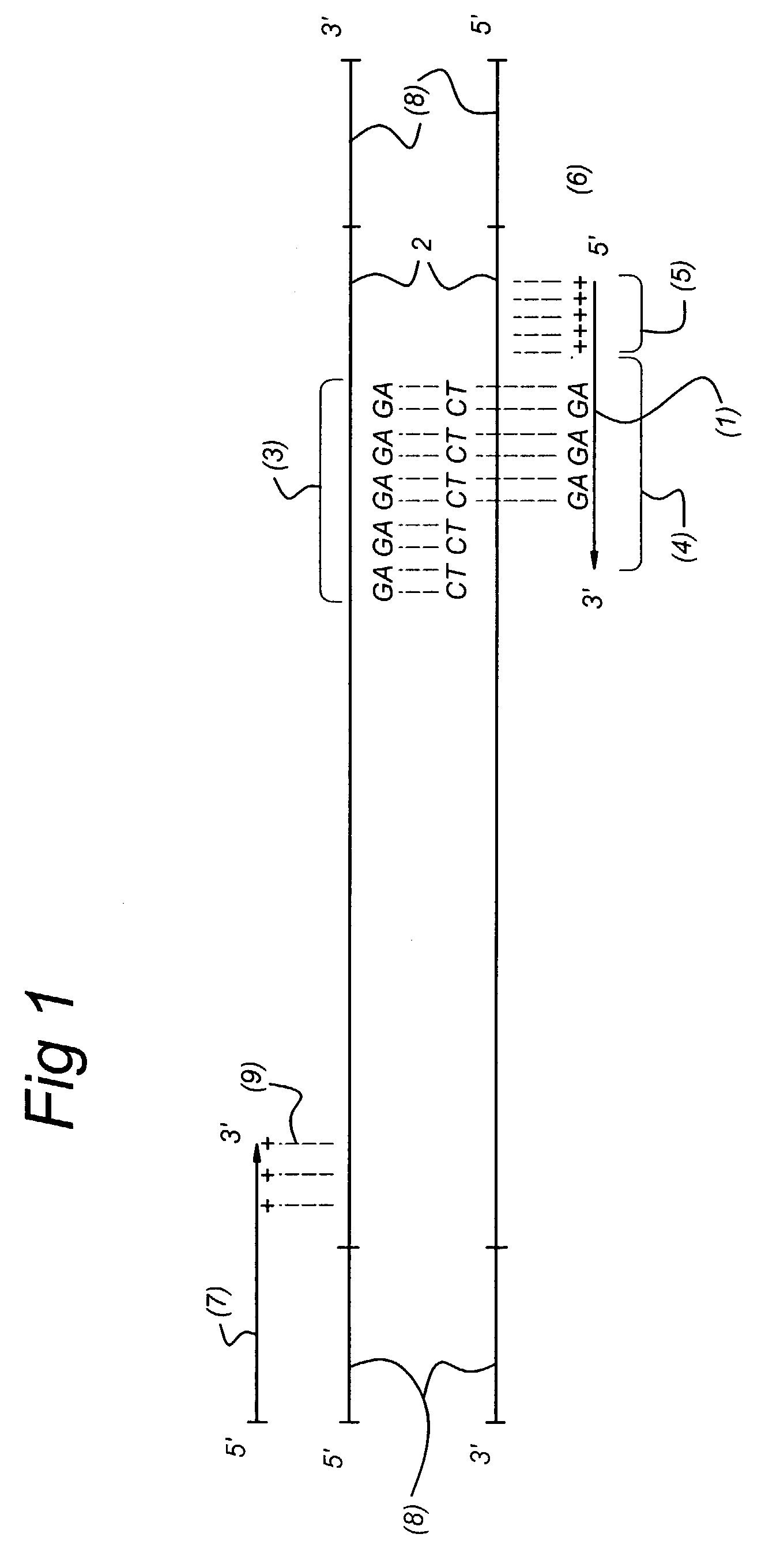
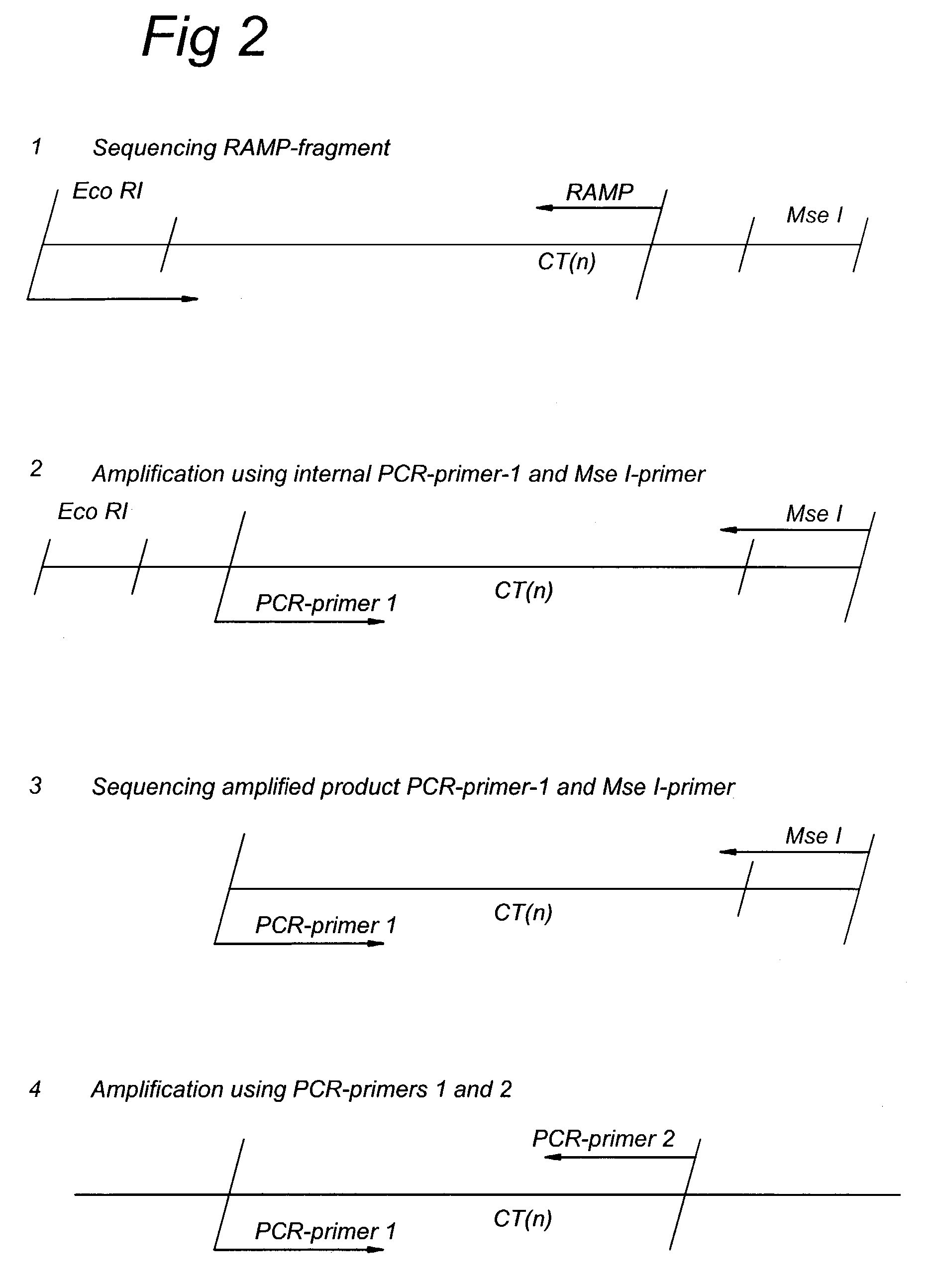
Methods and kits comprising AFLP primers, and ramp primers with a part complementary to a compound microsatellite repeat and an anchor part complementary to nucleotides adjacent to the repeat
InactiveUS7217516B2Quick identificationReliable and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleotide
The present invention discloses methods for identifying and analysing microsatellite-associated polymorphisms between different DNA samples. Different DNA samples, e.g. from different individuals, are analysed using a PCR based on the combination of a RAMP-primer and an AFLP-primer and polymorphisms between the different DNA samples are identified. The polymorphisms thus identified may be isolated and further analysed by e.g. DNA sequence analysis both upstream and downstream from the microsatellite-associated polymorphism. These sequences may subsequently be used to devise and synthesise new means for analysis of the polymorphic locus, such as e.g. PCR-primer pairs or oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Methods for Detecting The Presence of Expanded CGG Repeats in the FMR1 Gene 5' Untranslated Region
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
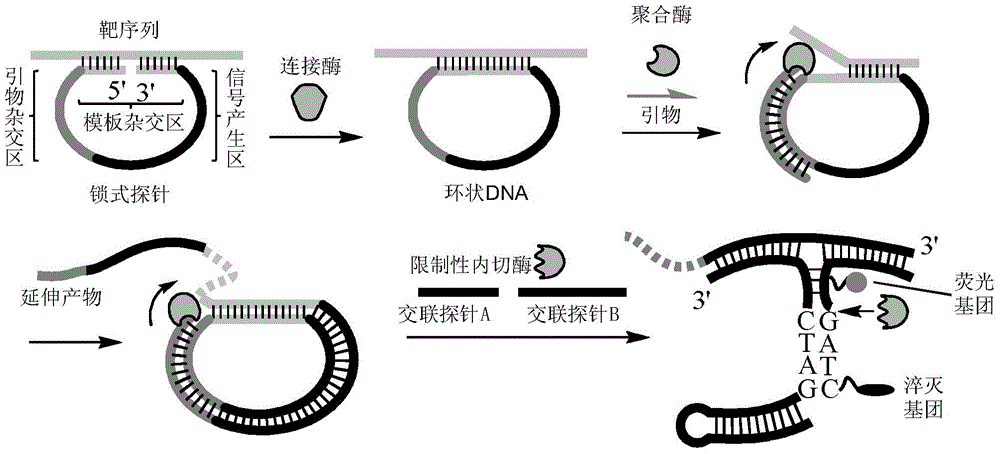
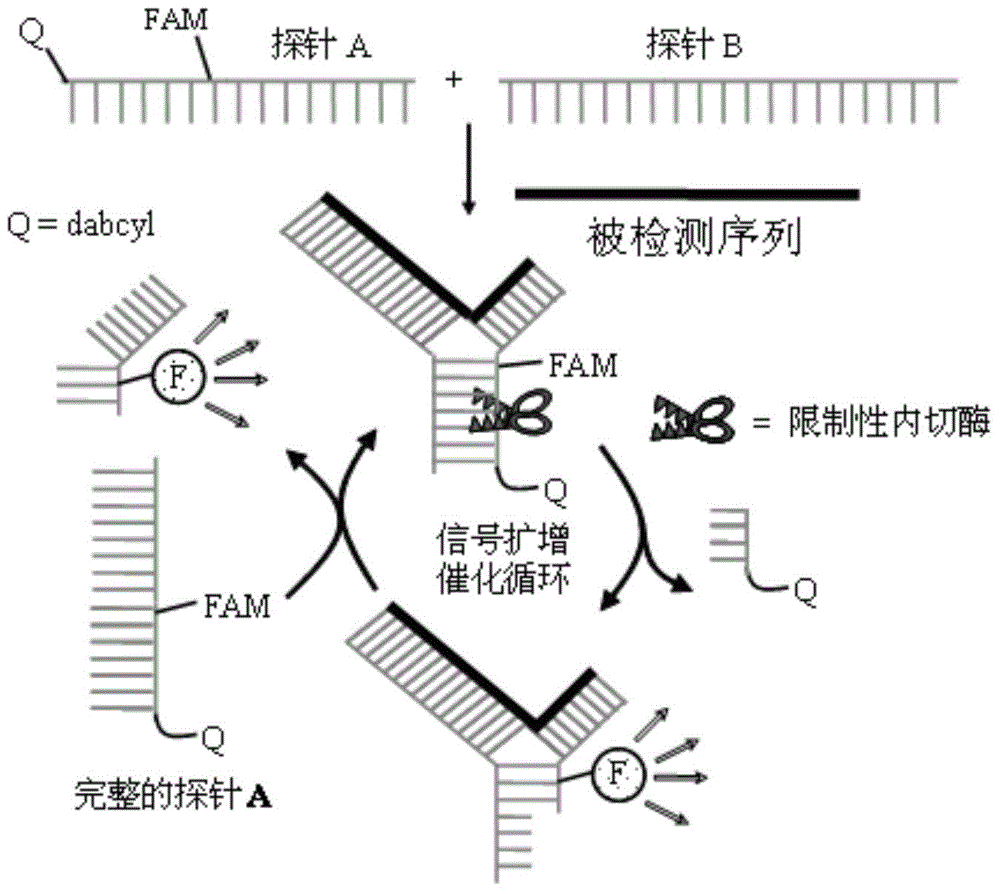
Nucleic acid detection method
ActiveCN104017861ASensitive highEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The invention discloses a nucleic acid detection method comprising the following steps of determining an objective sequence to be detected and a target sequence to be detected; designing and synthesizing a padlock probe according to the objective sequence; preparing a rolling circle amplification primer; preparing a crosslinking probe; carrying out coupled reaction, and carrying out rolling circle amplification by utilizing the amplification primer through taking a coupled product as a template; after the rolling circle amplification is ended, detecting a rolling circle amplification product by using the crosslinking probe, and proving that the objective target sequence exists if a fluorescent signal is remarkably enhanced. A DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) which can be detected by using a crosslinking probe detecting technology is amplified through the padlock probe and the rolling circle amplification reaction under the condition that a target to be detected exists, and no long-chain products can be detected by using the crosslinking probe detecting technology if no targets to be detected exist. One unit of sequence to be detected can be amplified to form hundreds of units of repetitive sequences through rolling circle amplification, and hundreds of times of signal amplification can be obtained on the basis of one unit of repetitive sequence by using the crosslinking probe detecting technology. The flexibility of the method disclosed by the invention is greatly enhanced.
Owner:CHANGZHOU FANGYUAN PHARMA +1
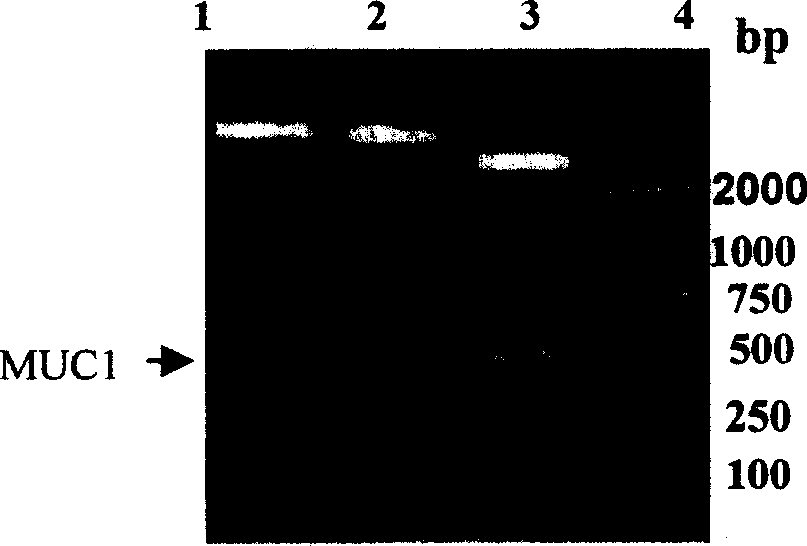
Recombination human Mucl-MBP fusion protein antitumour vaccine and production technology
InactiveCN1513556ATo achieve the purpose of anti-tumorLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
An anticancer vaccine of recombinant human MOC1-MBP fusion protein is disclosed, in which MBP is used as its adjuvant. The MBP gene and MUC1 gene are fused together. The MBP substituted for other fusion protein to induce CTL reaction. The pMAL-P2 is the carrier for effectively expressing maltose fusion protein. The serial repetitive sequence of MUC1 is inserted to downstream of malE gene.
Owner:台桂香
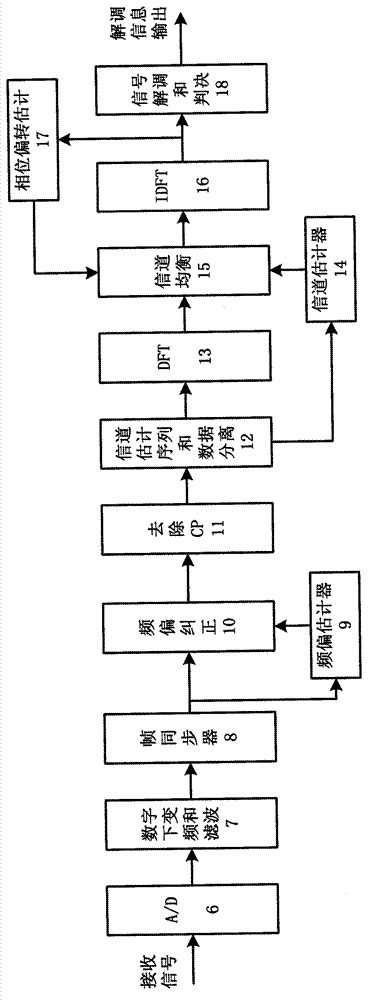
Carrier frequency deviation estimation and compensation method of single-carrier frequency domain balance system in great-frequency deviation condition
InactiveCN102821079AWide Range Frequency Offset EstimationHigh Frequency Offset CompensationMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCommunications systemCarrier signal
The invention discloses a carrier frequency deviation estimation and compensation method of a single-carrier frequency domain balance system in great-frequency deviation condition. The method comprises the following steps of: performing related operation of the received frame header repetitive sequence to obtain a rough frequency deviation estimated value, and performing open-loop compensation processing on the signal by use of the frequency deviation estimated value; after frequency deviation compensation, processing the signal through balance and the like to obtain a demodulated constellation diagram; calculating the rotary phase of the constellation diagram to obtain a fine frequency deviation estimated value; and feeding the estimated value back to a balancer part, and performing closed-loop compensation to finish the estimation and compensation of the signal frequency deviation. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of large range of estimated frequency deviation, high precision of frequency deviation compensation, moderate algorithm complexity and the like, and is particularly suitable for the single-carrier frequency domain balance communication system in great-frequency deviation environment.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, kit and detection method for detecting Her2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) gene free from repetitive sequence
ActiveCN103409504AHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationFluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, a kit and a detection method for detecting Her2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) gene free from repetitive sequence. The Her2 gene is used as a template to perform polymerase chain reaction on non-repetitive sequence in the Her2 gene, the amplification product is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments with 350-800 different base pairs, the repetitive sequence in the Her2 gene is eliminated so as to form the product free from repetitive sequence; after the product is in fluorescence labeling, the Her2 gene free from repetitive FISH is obtained for the Her2 gene FISH detection. The Her2 gene FISH probe obtained by the invention can eliminate the repetitive sequence, the non-specific background signal of the Her2 gene FISH probe can be obviously reduced, and the specificity of the FISH probe is improved.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
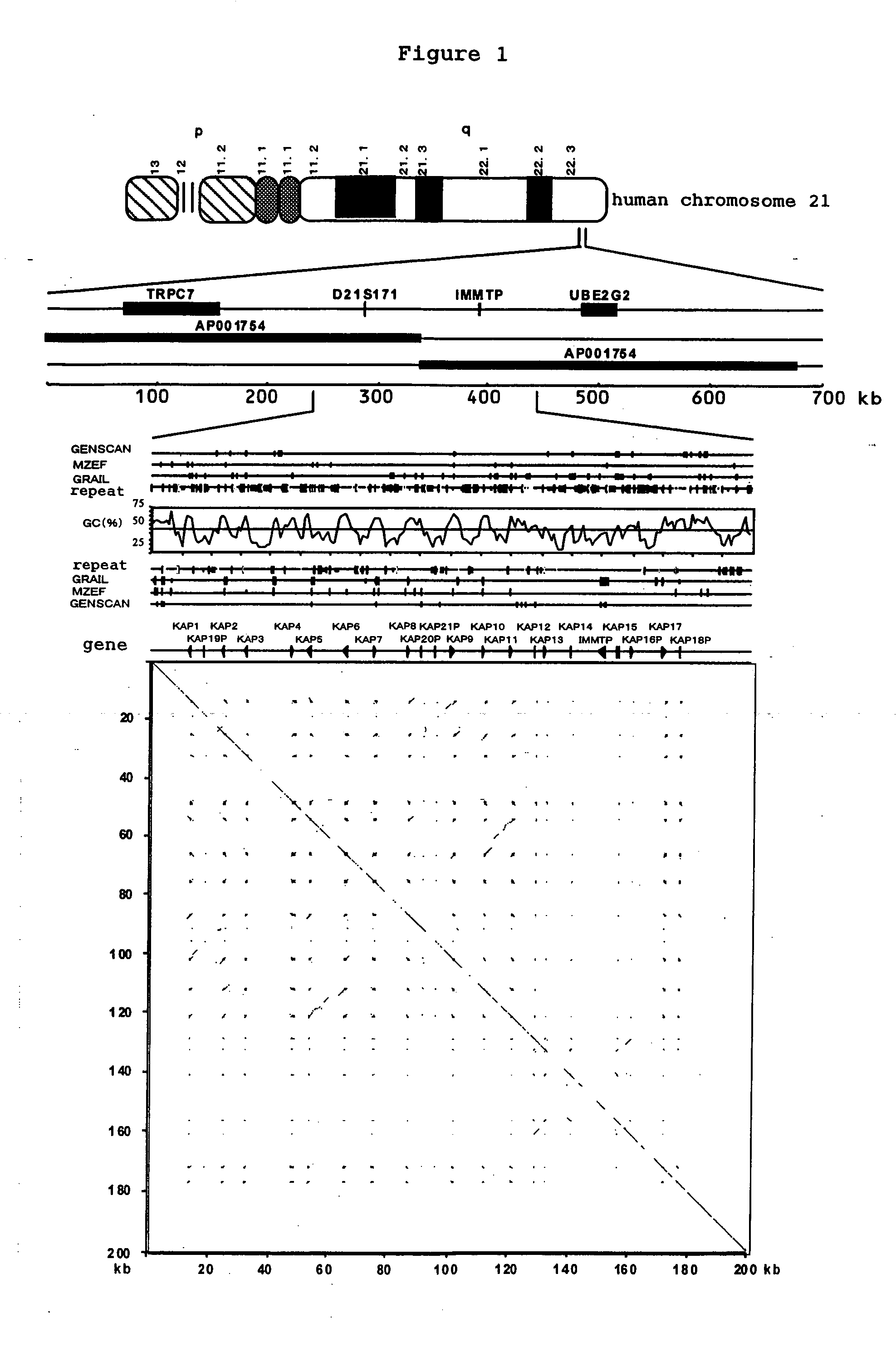
Novel hair keratin-associated proteins
InactiveUS20050170366A1Promoting and suppressing expressionPromoting and suppressing expression of proteinCosmetic preparationsBacteriaKeratin-Associated ProteinsProteome
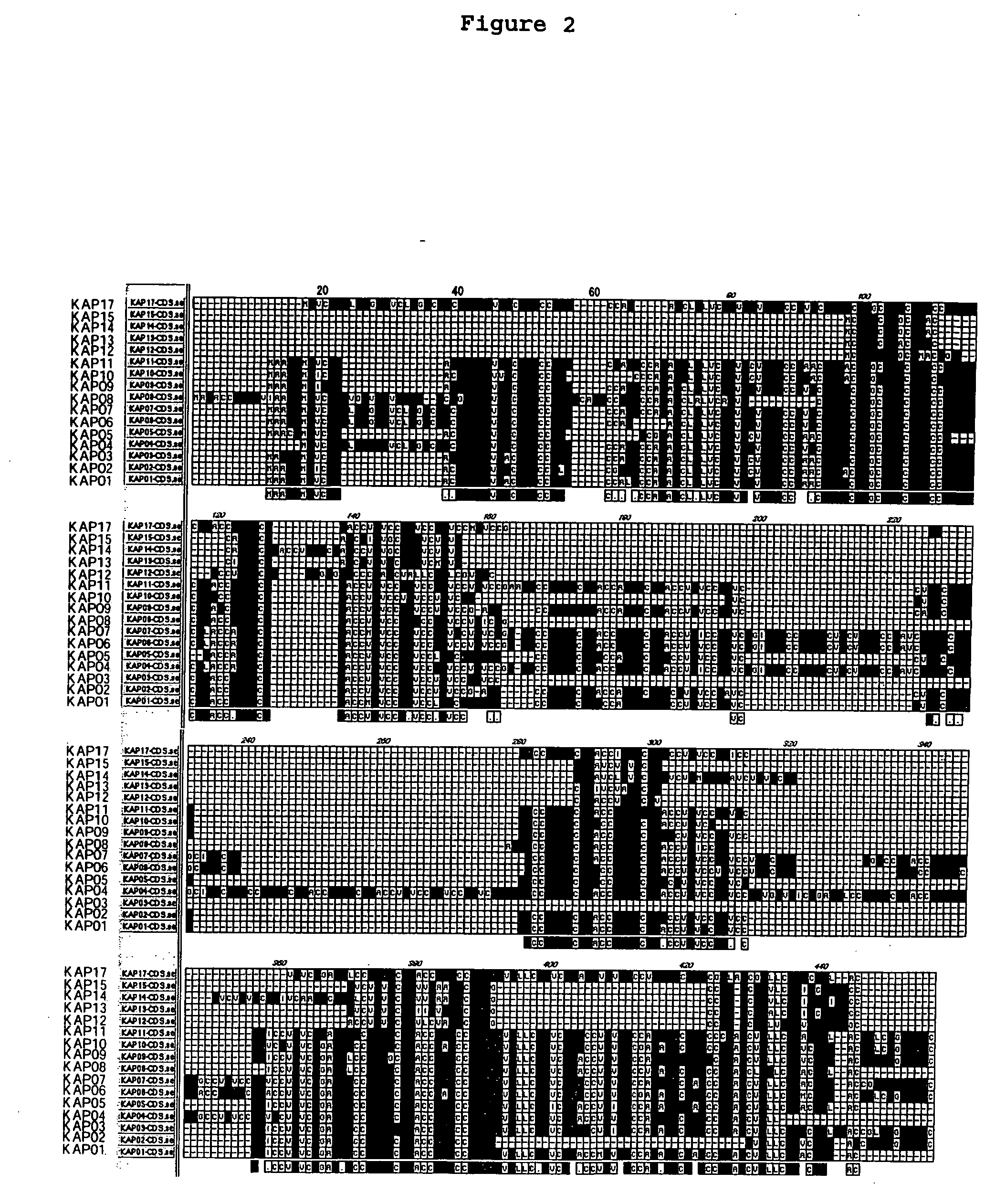
The present invention relates to provide a protein group binding to keratin which is the major component of body hair, or genes encoding the same, particularly to keratin-associated proteins (KAP) which bind specifically and strongly to hair keratin or genes encoding the same. The base sequence of eurochromtic region of approximately 33.5 Mb of human chromosome 21 was determined, a dot-matrix analysis of the base sequence of the long arm region of chromosome 21 (21q22.3) was carried out, homology search was made to low frequency repetitive sequences and 16 KAP genes being expressed only in hair root cells were found. Moreover, the high frequency repetitive sequences present in the sequence spanning for approximately 1 Mb between CLDN8 gene and TIAM1 gene in the long arm region of chromosome 21 (21q22.11) were masked, the presence or absence of short low frequency repetitive sequence was searched, and 22 KAP genes were found. Moreover, a group of functional peptide was designed from the above mentioned KAPs.
Owner:SHIMIZU NOBUYOSHI
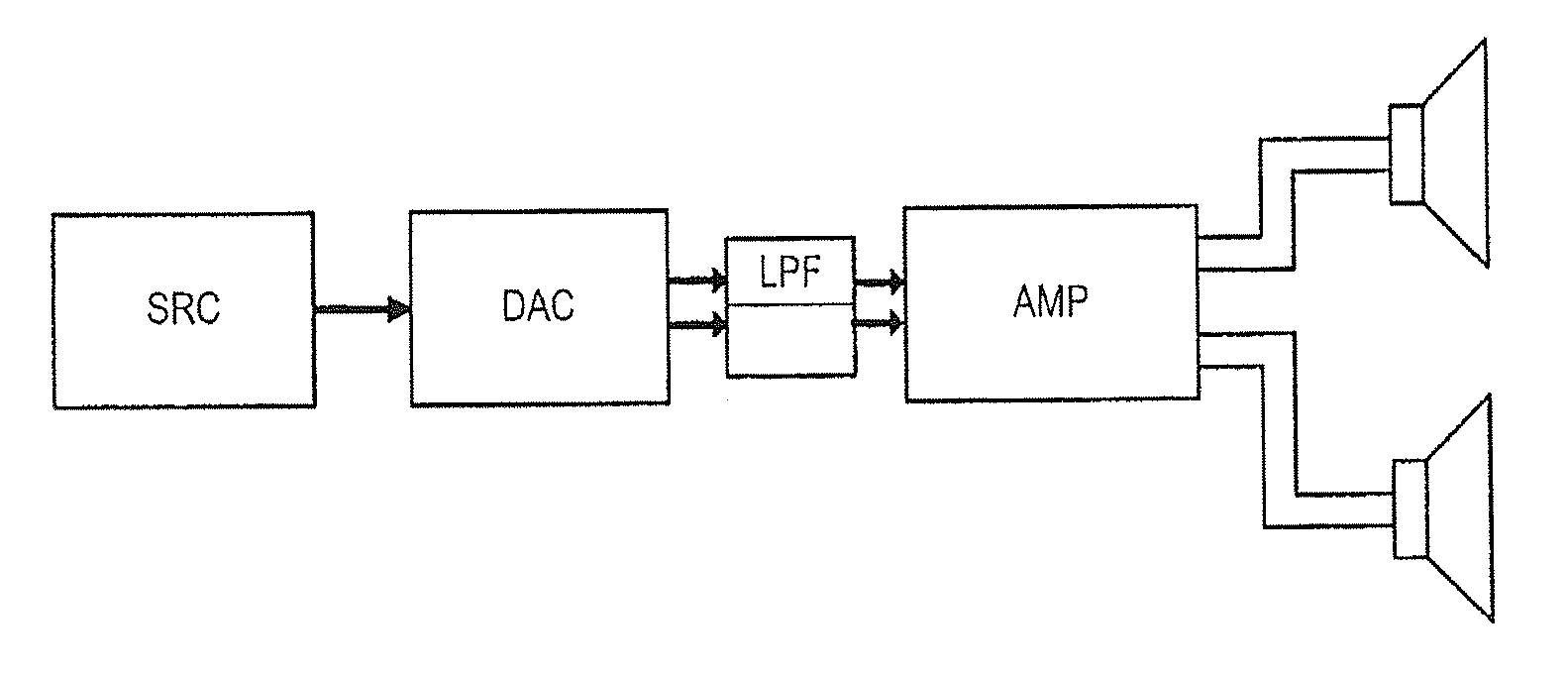
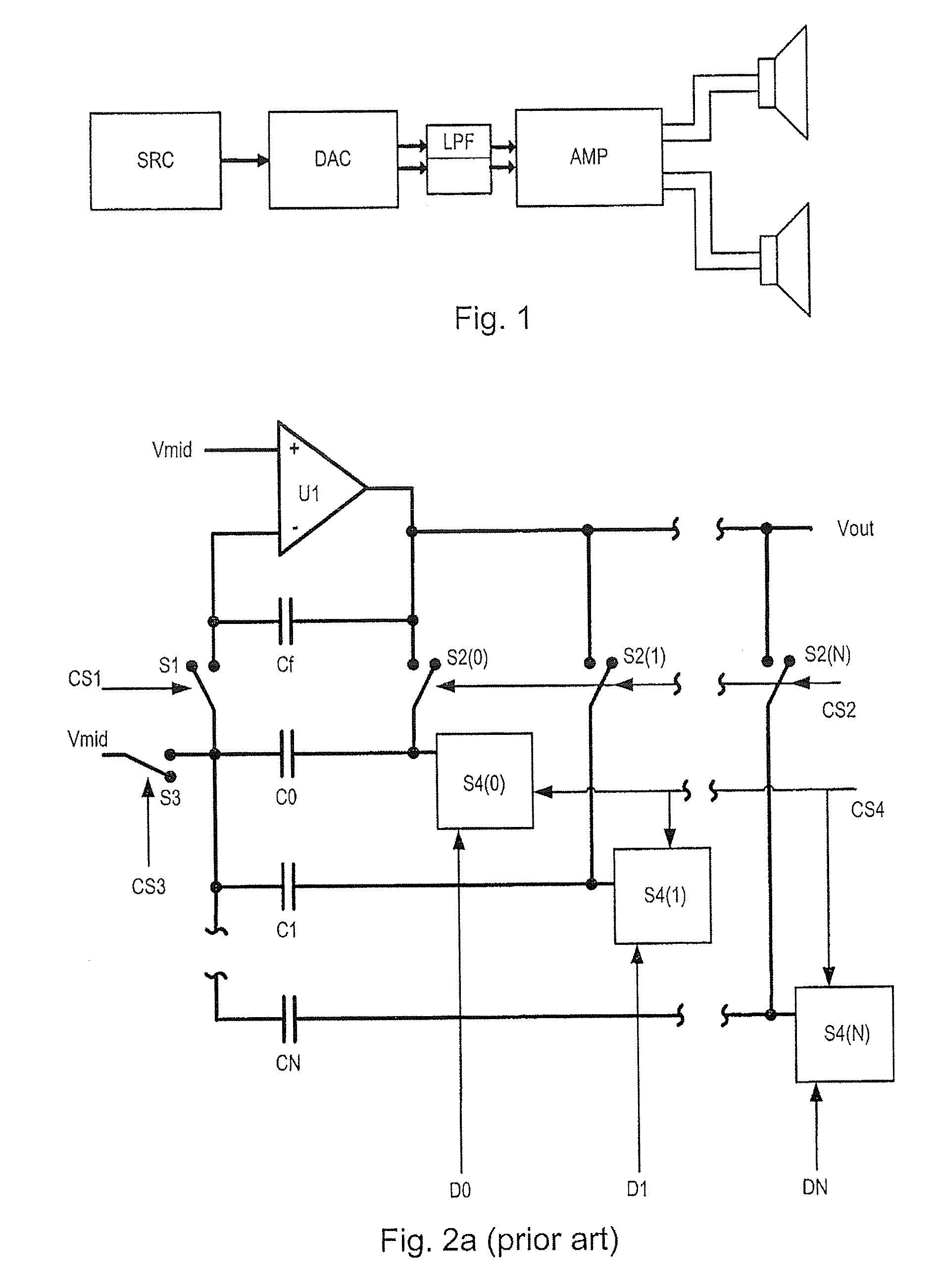
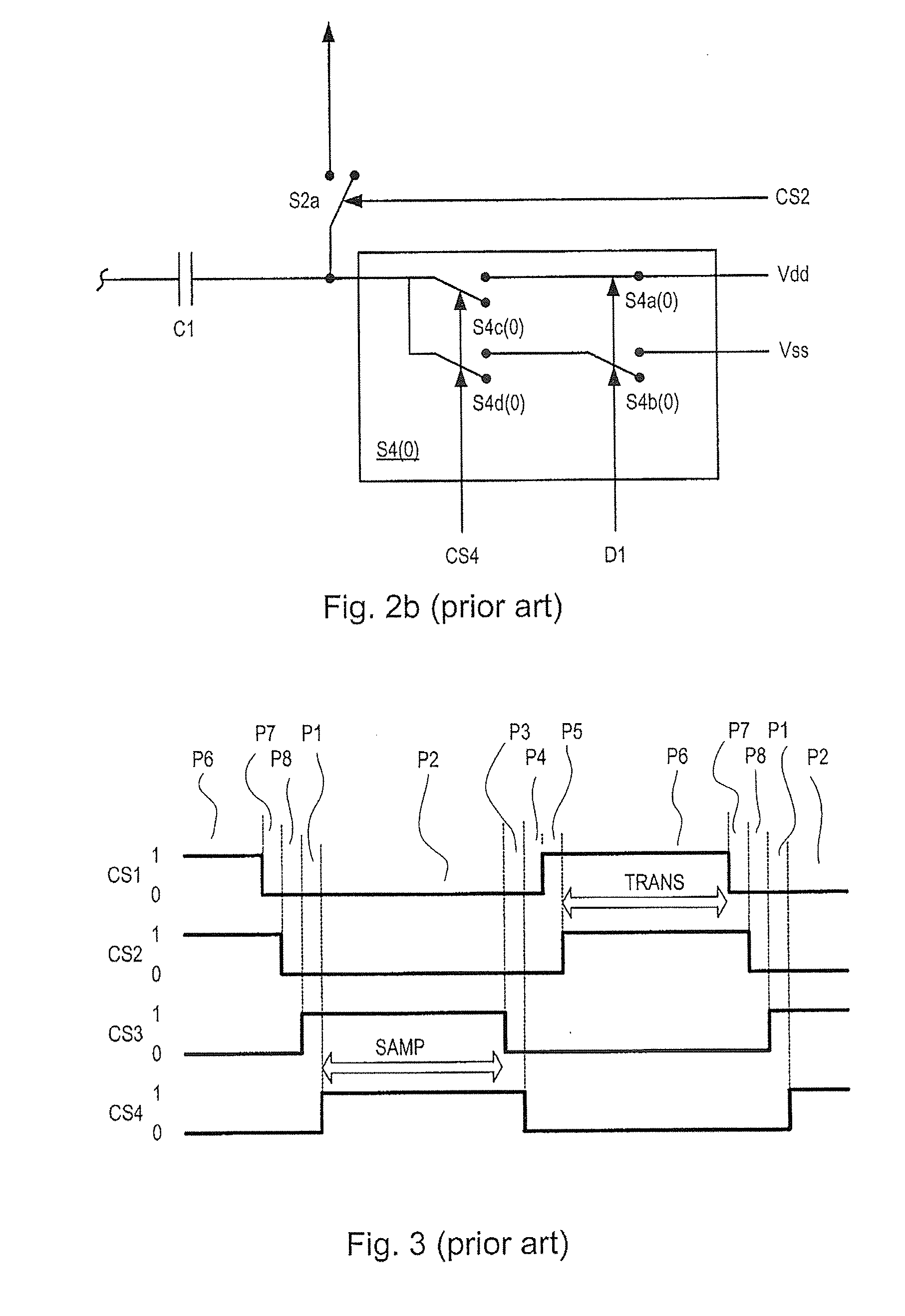
Digital to analog converter circuits and methods of operation thereof
InactiveUS20090066552A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionIncrease in other type of errorElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationDigital analog converterEngineering
A multi-bit digital to analog converter is implemented by a switched-capacitor arrangement in which a reservoir capacitor (Cf) accumulates charge representing the desired analog output signal (Vout+ / Vout−). An array of further capacitors (C0-CN) correspond in number at least to the number of data bits (D0-DN) to be converted. The capacitors (Cf, C0-CN) are selectively interconnected with one another and with reference voltage sources (Vmid, Vdd, Vss) in a repetitive sequence of phases including (i) a sampling phase (P2) in which the further capacitors are connected (S3, S4) to reference voltages selected in accordance with the values of the data bits, (ii) an equalization phase (P6a) in which the further capacitors are connected (S2) in parallel with one another without connecting them in parallel with the first capacitor, followed by (iii) a transfer phase (P6b) in which the parallel connected further capacitors are connected (S1, S5) in parallel with the first capacitor. The equalization phase masks nonlinearities arising in switches (S2) and thereby improves harmonic distortion.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Recombinant I-type humanized collagen polypeptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113621052AIncrease productionPromote cell adhesionCosmetic preparationsBacteriaCell adhesionProteinogenic amino acid
The invention discloses a recombinant I-type humanized collagen polypeptide as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The recombinant I-type humanized collagen polypeptide provided by the invention comprises n repeats of a sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1, wherein n is an integer greater than or equal to 1, and when n is an integer greater than or equal to 2, the repeat sequences are directly connected; and optionally, the N tail end of the recombinant I-type humanized collagen polypeptide comprises an amino acid sequence which can be excised by TEV protease. The recombinant I-type humanized collagen polypeptide provided by the invention has the activity of promoting cell adhesion, the amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is selected from a natural collagen amino acid sequence, and the recombinant protein does not generate an immune response when being applied to a human body; and moreover, the preparation method is simple, and high-yield collagen can be obtained at low cost.
Owner:SHANXI JINBO BIO PHARMA CO LTD
Treatment of genetic disorders associated with DNA repeat instability
ActiveUS20160053254A1Lower Level RequirementsAltered RNA processing and/or splicingNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsInstabilityGene transcript
The current invention provides for methods and medicaments that apply oligonucleotide molecules complementary only to a repetitive sequence in a human gene transcript, for the manufacture of a medicament for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders in humans. The invention hence provides a method of treatment for cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders. The invention also pertains to modified oligonucleotides which can be applied in method of the invention to prevent the accumulation and / or translation of repeat expanded transcripts in cells.
Owner:VICO THERAPEUTICS BV
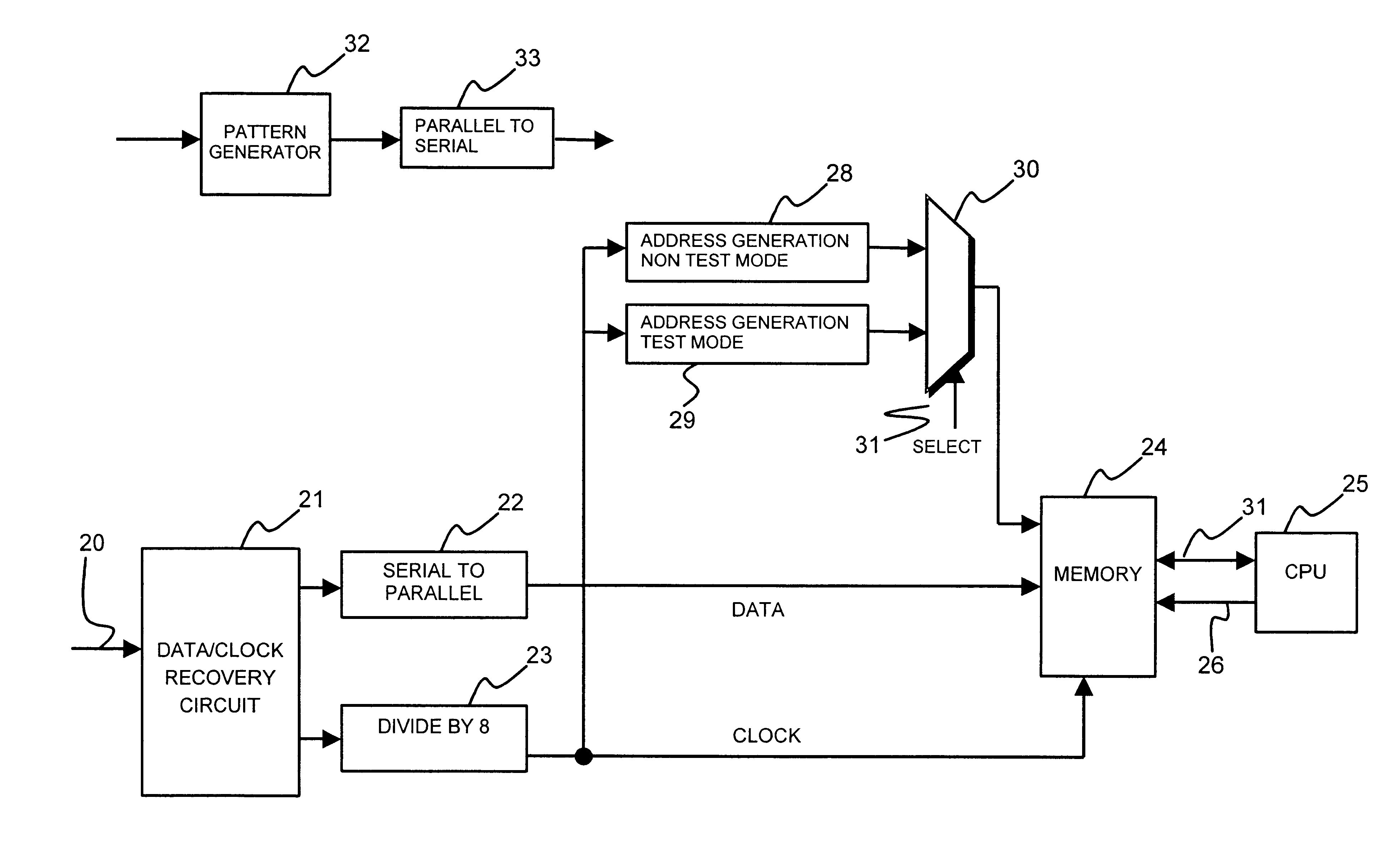
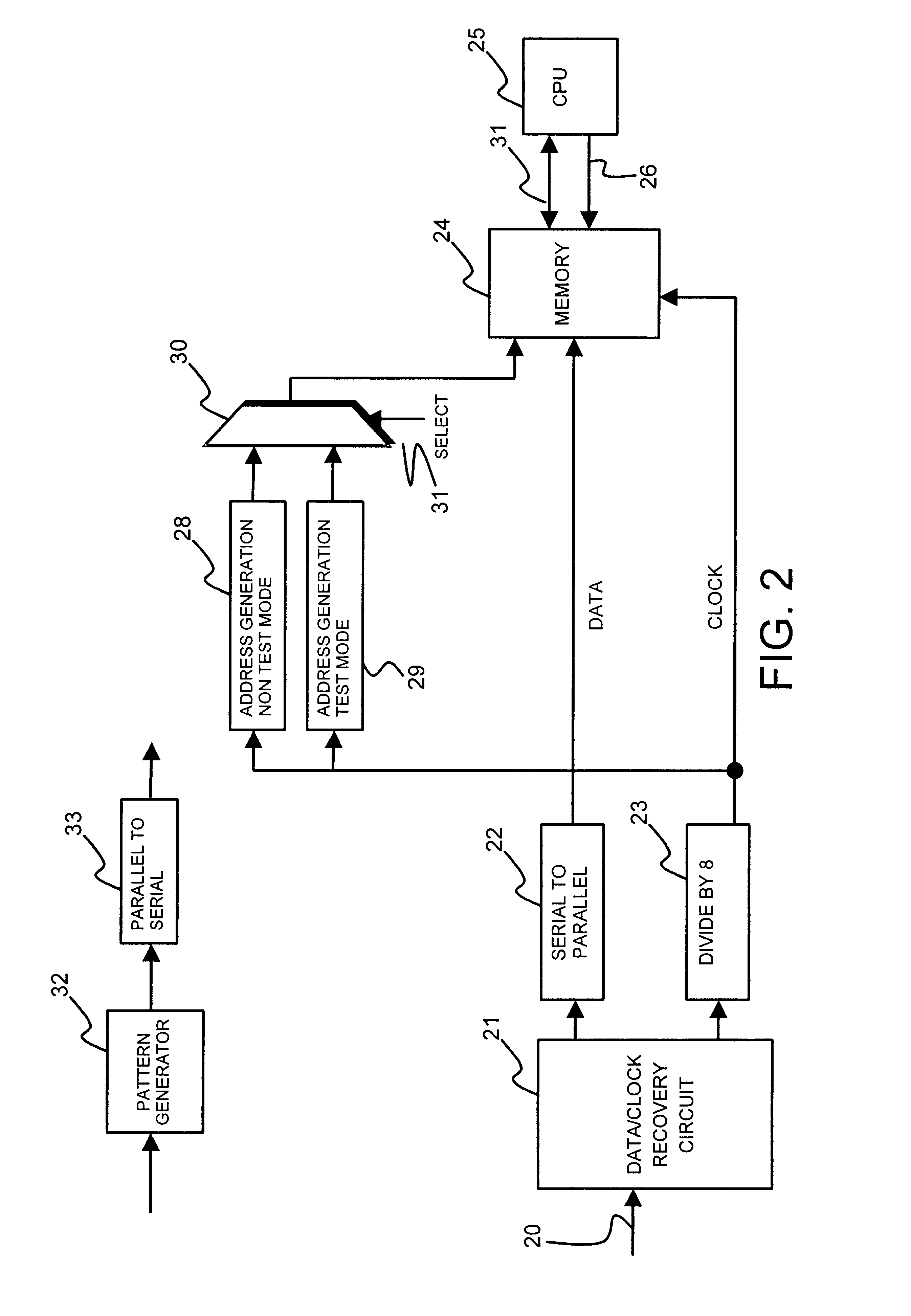
On-chip detection of clock gitches by examination of consecutive data
An application specific integrated circuit includes a clock recovery circuit which recovers from an input signal a repetitive sequence of data values wherein no two consecutive values are the same and a recovered clock. An address generator responds to the recovered clock to cause storage of the data values in said memory in a set of locations having addresses generated by the address generator, so that the address generated by the generator increments in response to a repetitive transition in the recovered clock. The existence of a clock glitch is found by reading the data values from the set of locations to determine whether any two consecutive locations contain the same data value.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Preparation method of developing Phaseolus vulgaris SSR primers by magnetic bead enrichment
InactiveCN102533727AImprove efficiencyDecline in clone sequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural scienceStreptolydigin
The invention discloses a preparation method of developing Phaseolus vulgaris SSR primers by magnetic bead enrichment. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) digesting Phaseolus vulgaris genome DNA with Msel, and establishing a library by AFLP; (2) hybridizing the genome PCR library with a biotin-labeled repetitive sequence probe; (3) adding the hybridization mixed liquid into streptavidin-coated magnetic beads; (4) amplifying micro-satellite DNA fragments by PCR using eluent-purified micro-satellite DNA as DNA template; (5) linking the purified PCR amplification product on a T vector for cloning to obtain a DNA sequence with inserted fragments; and (6) repeating on the two sides of the core area to design primers, and screening primers to obtain effective microsatellite loci. The method is simple and feasible, increases efficiency of the primers, screens 20 pairs of effective primers from 48 pairs of primers, and provides guarantee for large-batch development of SSR primers.
Owner:WUHAN VEGETABLE RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com