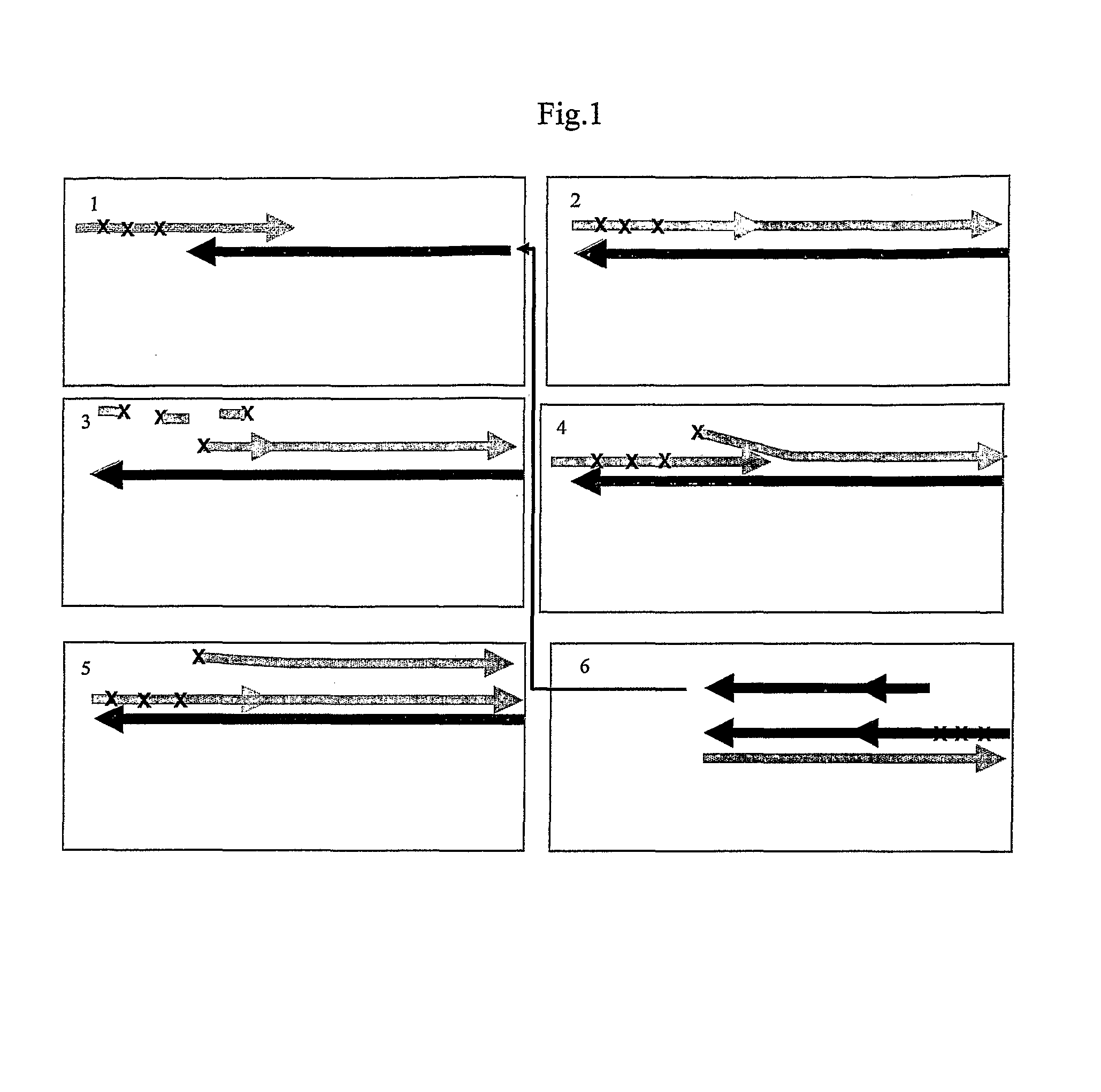
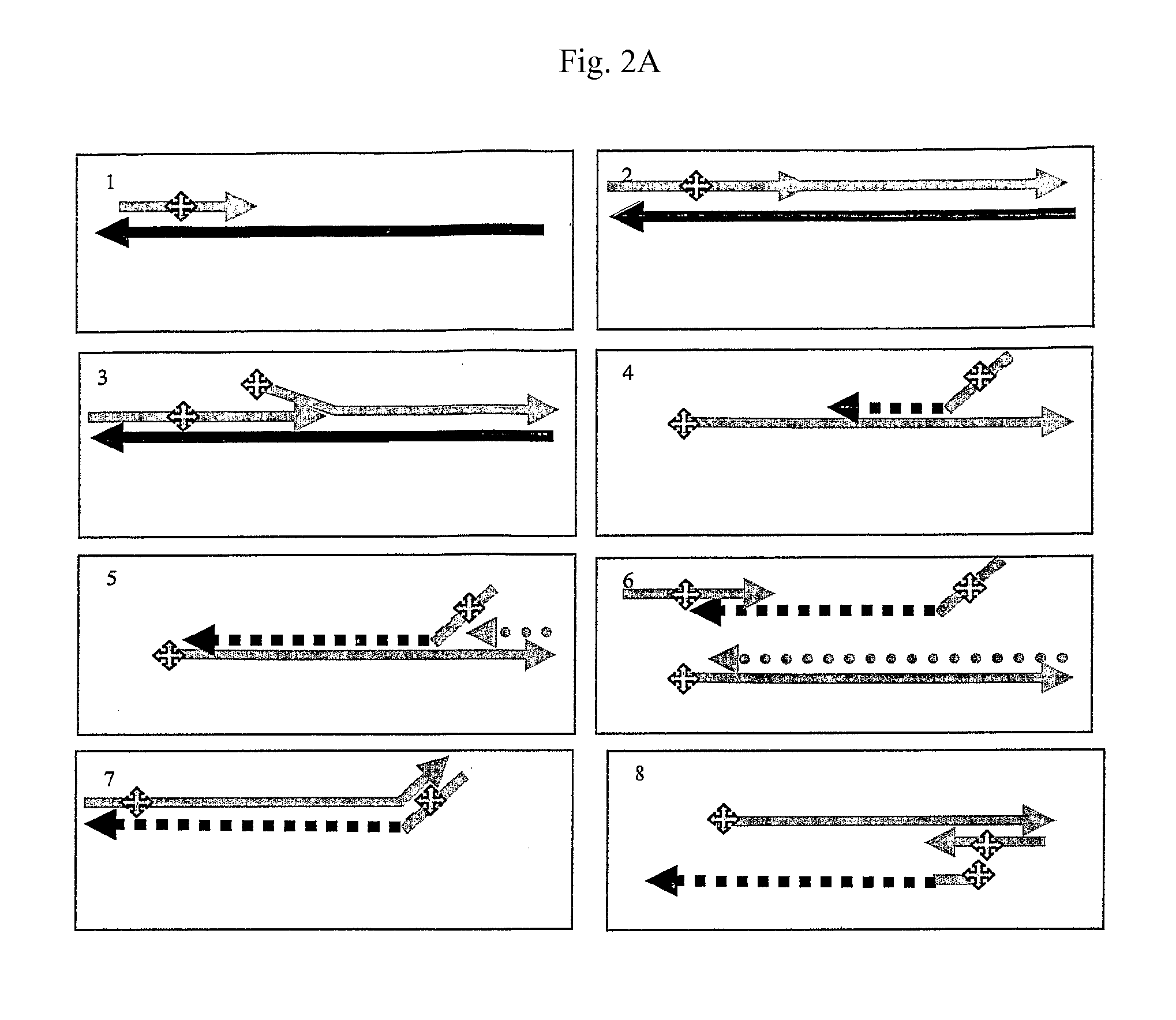
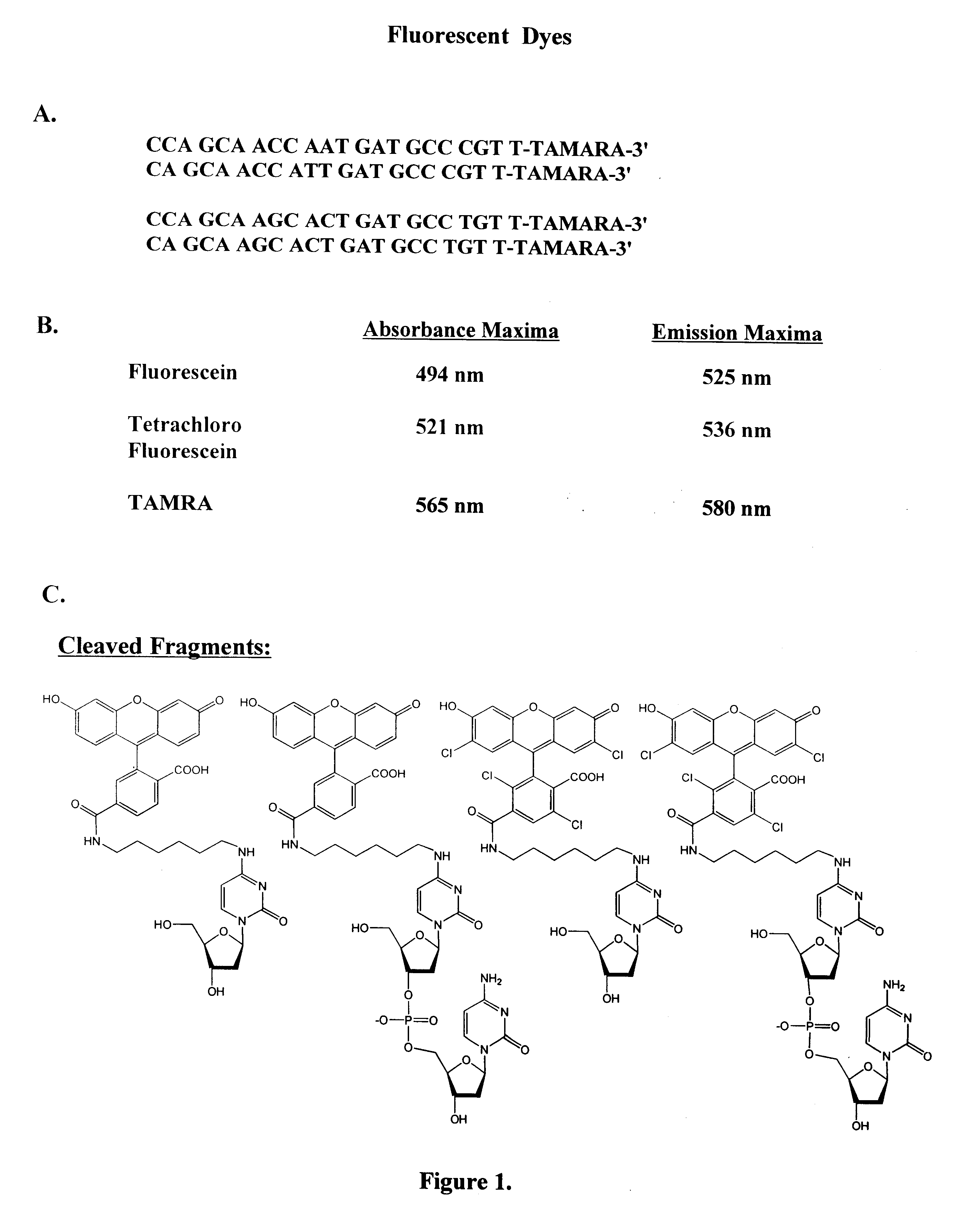
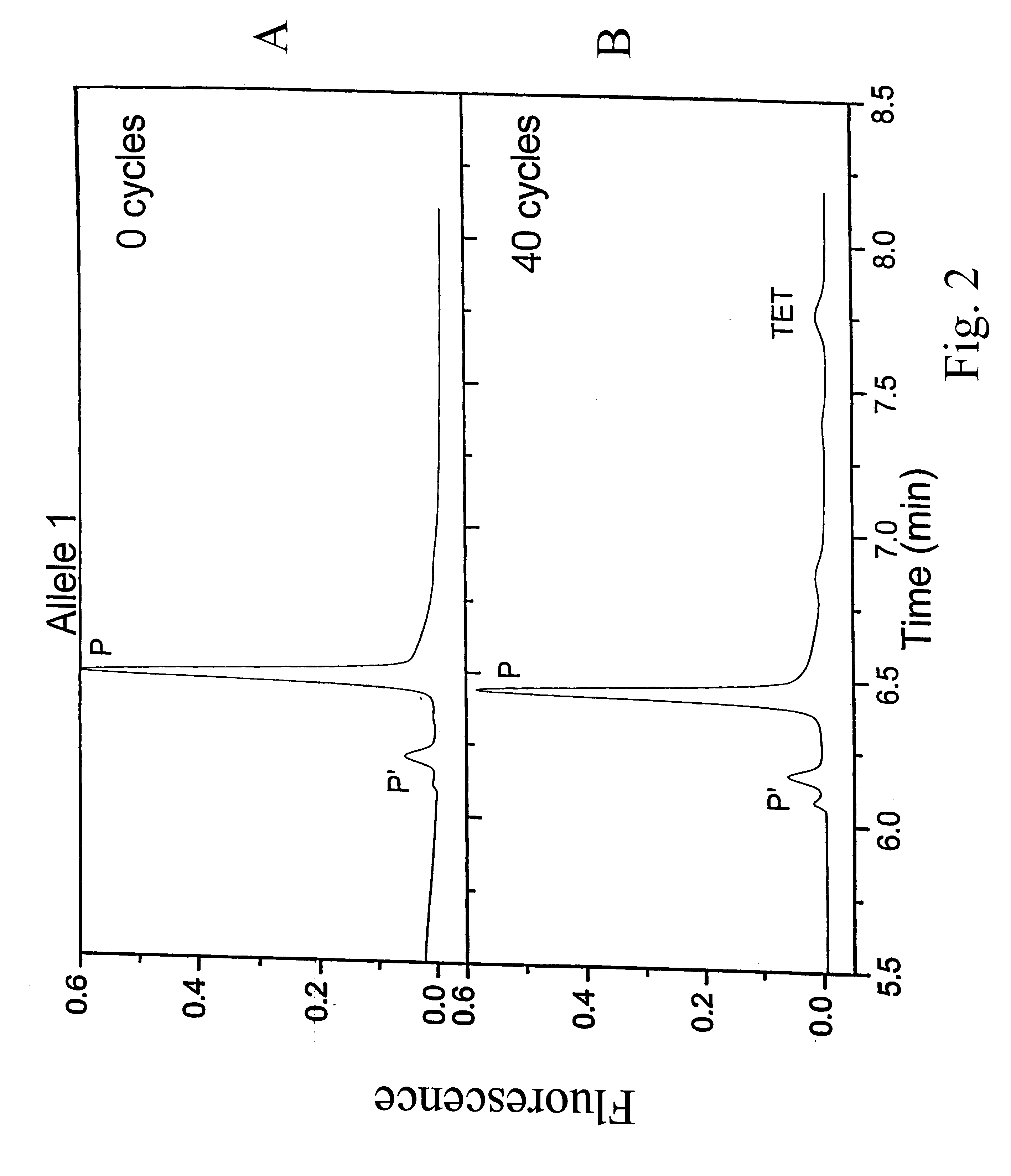
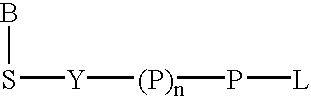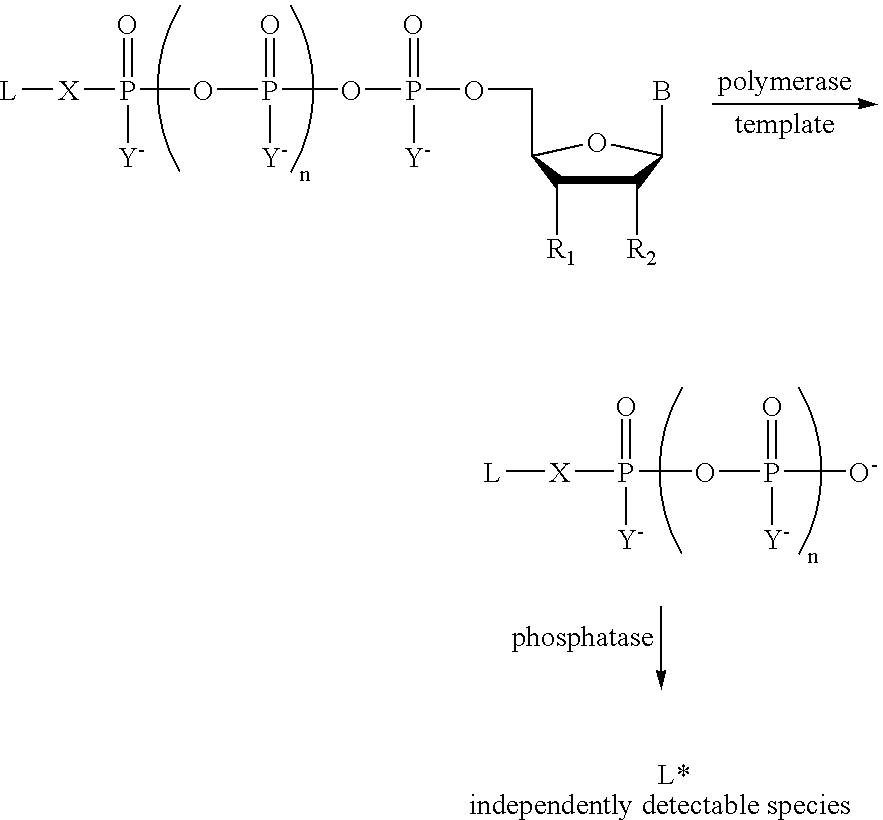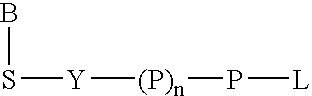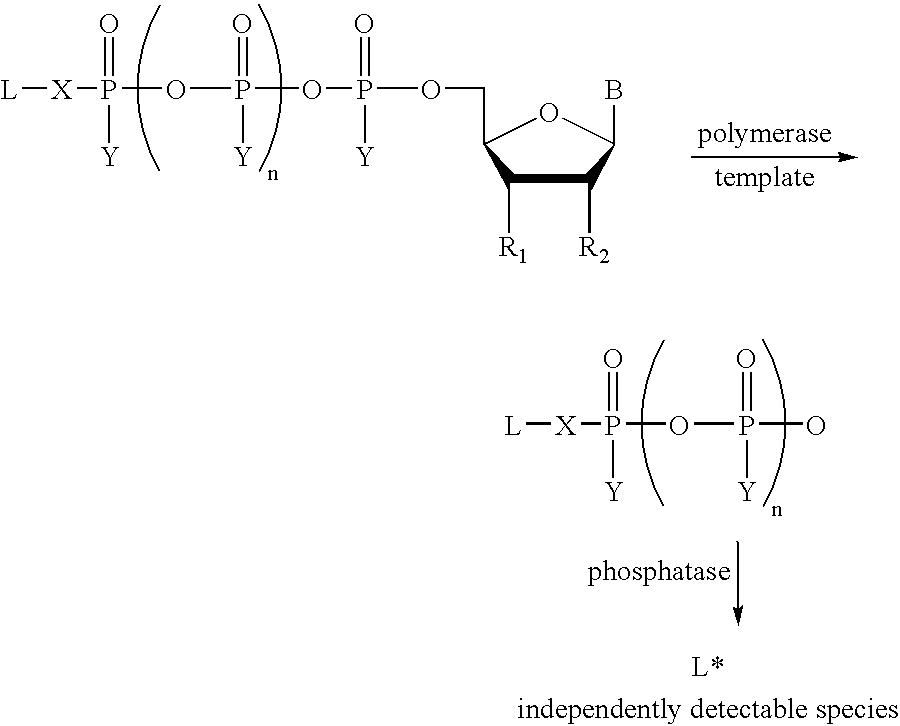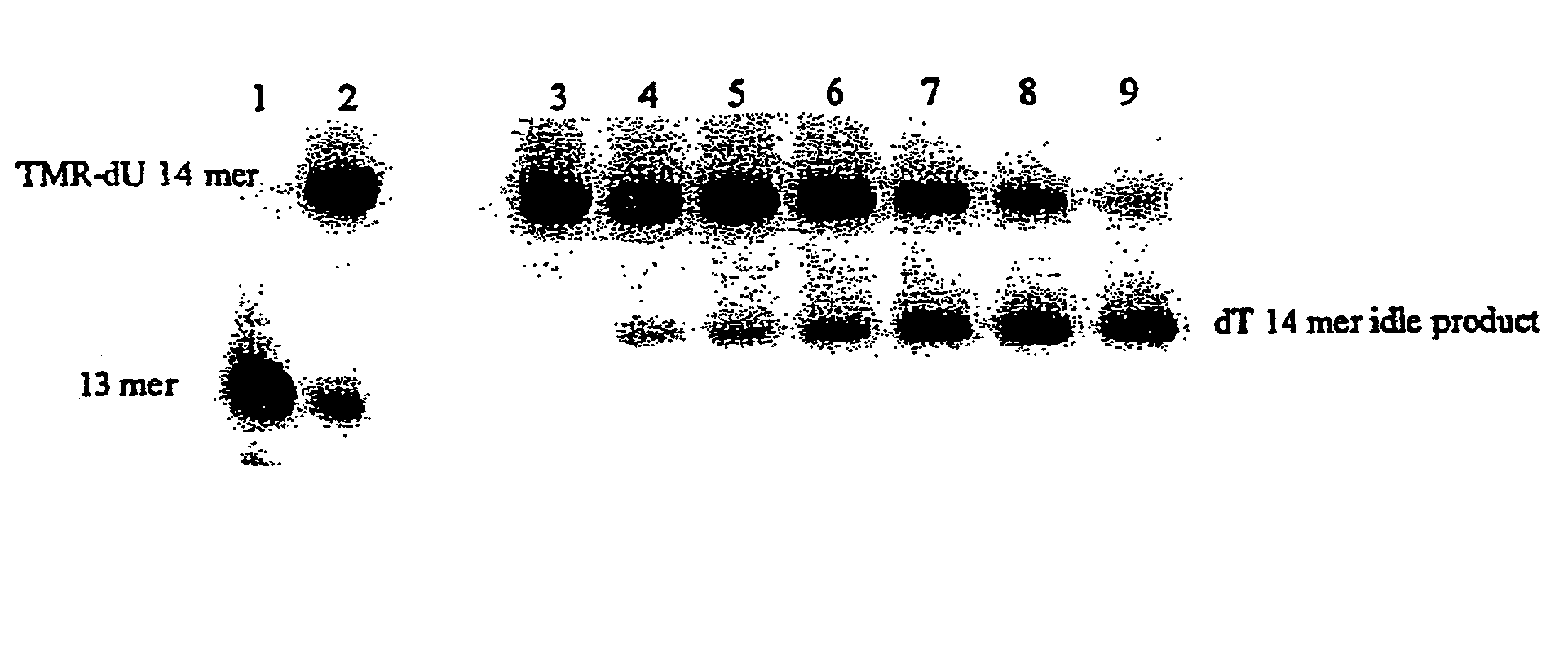Patents
Literature
479 results about "Exonuclease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
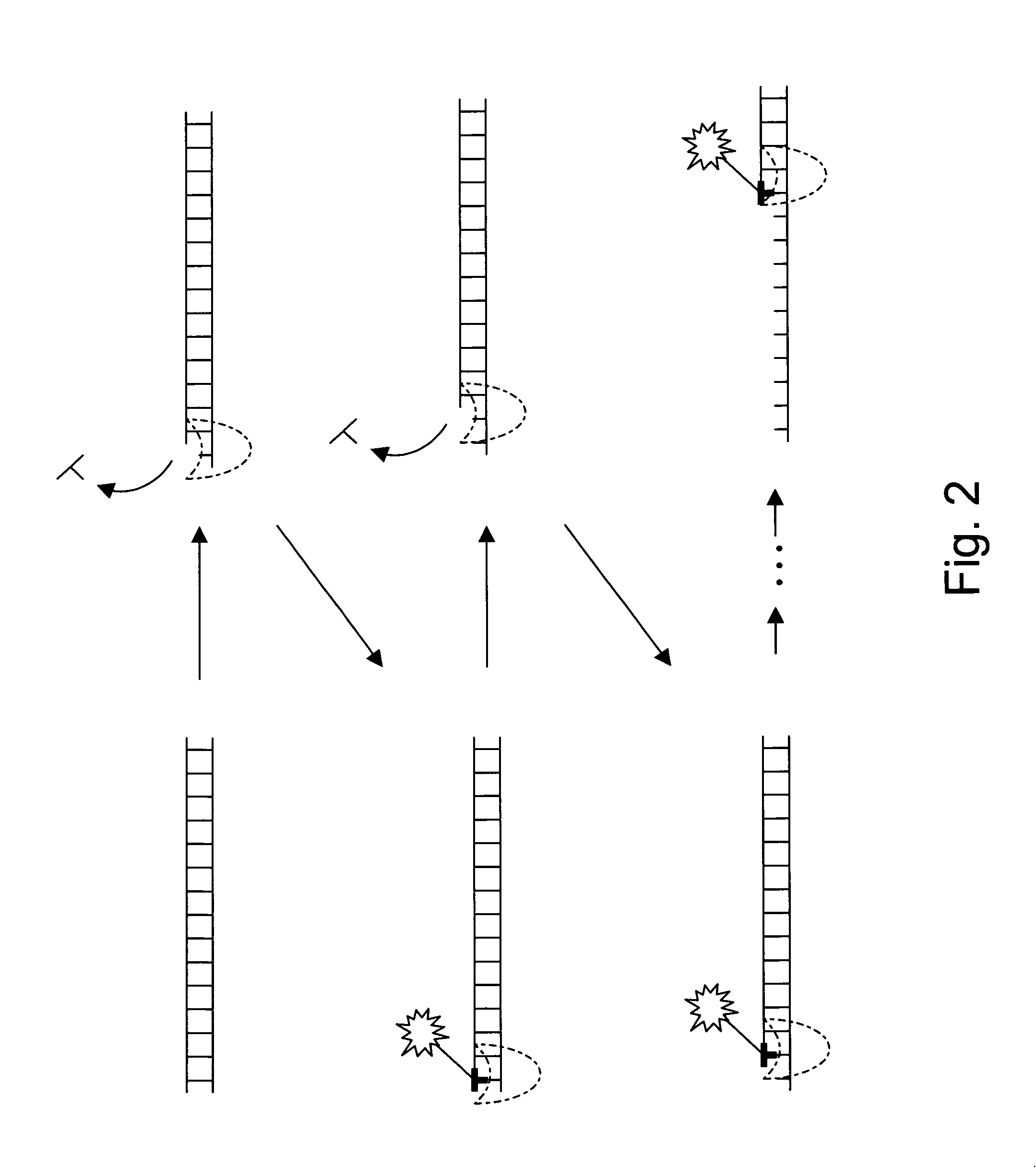
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3' or the 5' end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5' to 3' exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3' to 5' exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3' to 5' exonuclease.
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
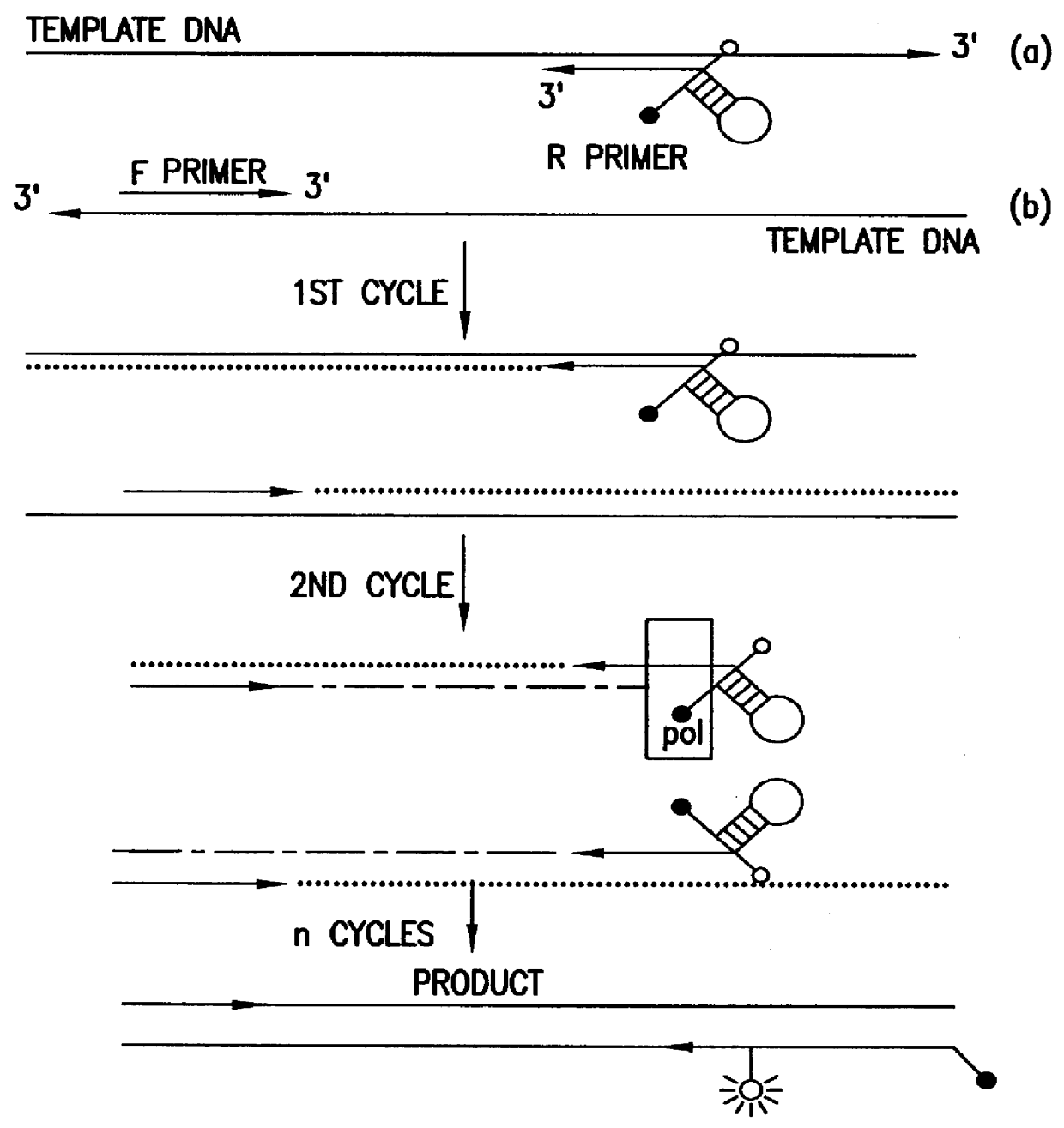
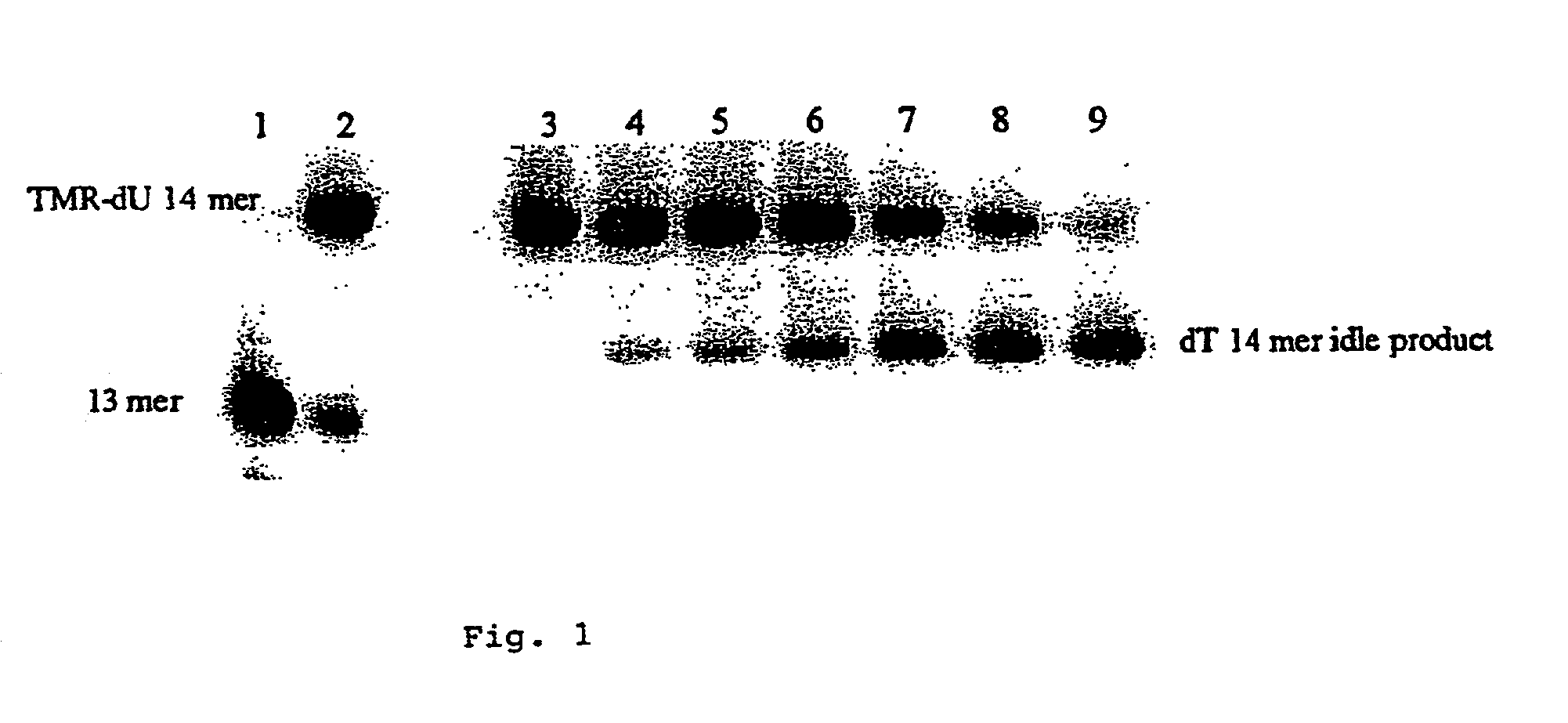
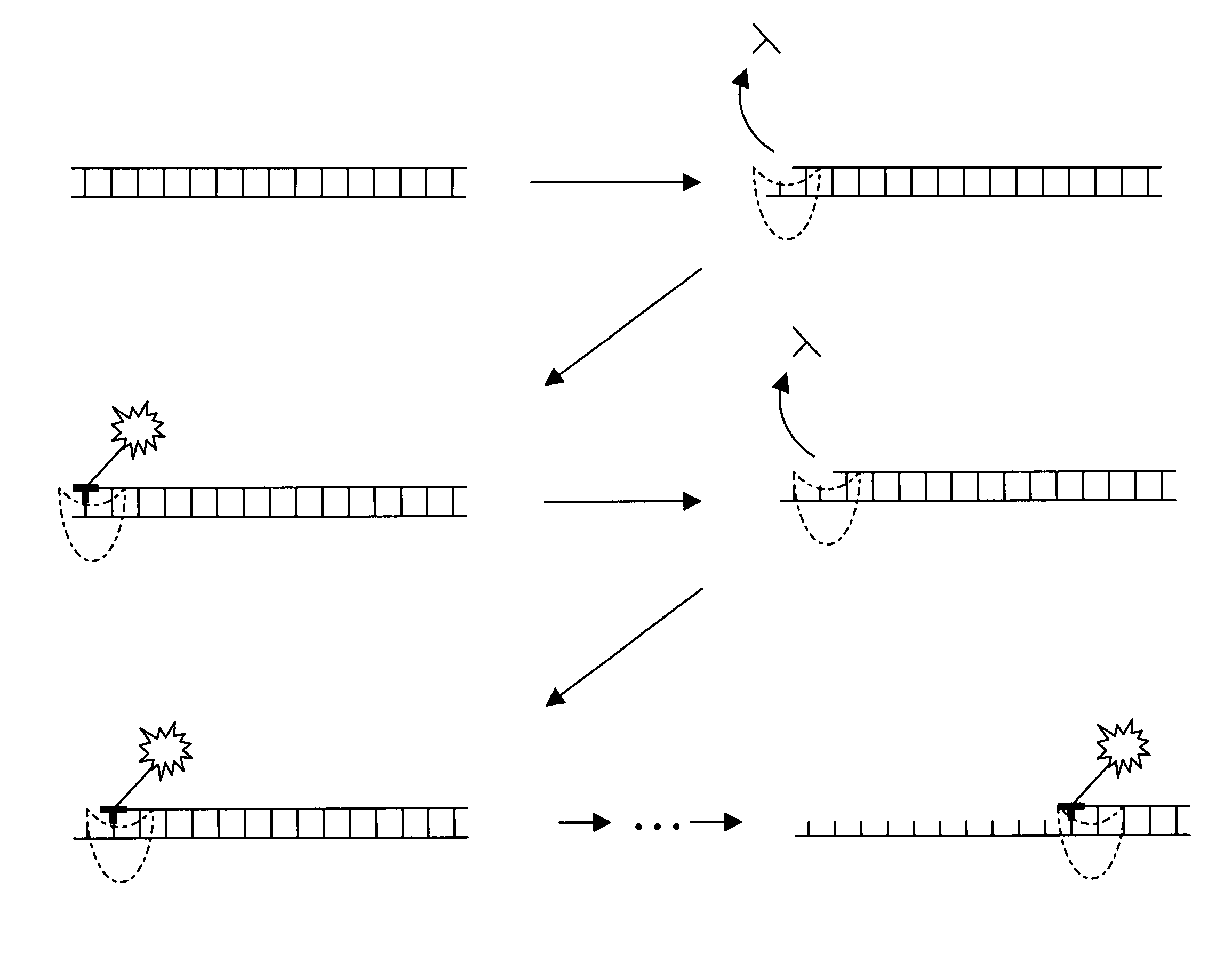
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Nucleic acid amplification oligonucleotides with molecular energy transfer labels and methods based thereon
InactiveUS6117635AReduce the possibilityRapid and sensitive and reliableSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferFluorophore
The present invention provides labeled nucleic acid amplification oligonucleotides, which can be linear or hairpin primers or blocking oligonucleotides. The oligonucleotides of the invention are labeled with donor and / or acceptor moieties of molecular energy transfer pairs. The moieties can be fluorophores, such that fluorescent energy emitted by the donor is absorbed by the acceptor. The acceptor may be a fluorophore that fluoresces at a wavelength different from the donor moiety, or it may be a quencher. The oligonucleotides of the invention are configured so that a donor moiety and an acceptor moiety are incorporated into the amplification product. The invention also provides methods and kits for directly detecting amplification products employing the nucleic acid amplification primers. When labeled linear primers are used, treatment with exonuclease or by using specific temperature eliminates the need for separation of unincorporated primers. This "closed-tube" format greatly reduces the possibility of carryover contamination with amplification products, provides for high throughput of samples, and may be totally automated.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Modified nucleotide compounds
ActiveUS7495088B1Increased nuclease resistanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyModified nucleosides
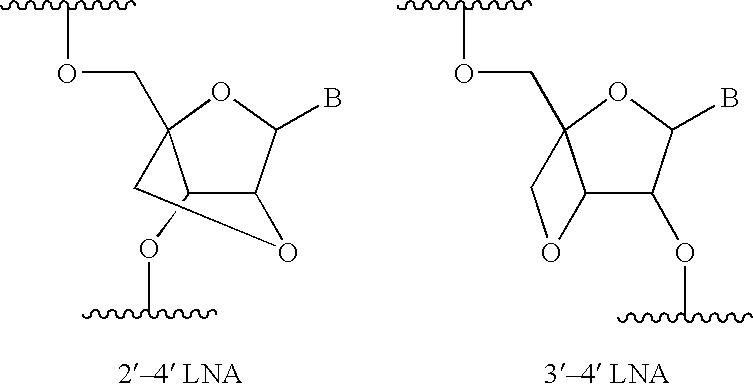
Disclosed is a nuclease resistant nucleotide compound capable of hybridizing with a complementary RNA in a manner which inhibits the function thereof, which modified nucleotide compound includes at least one component selected from the group consisting of MN3M, B(N)xM and M(N)xB wherein N is a phosphodiester-linked modified 2′-deoxynucleoside moiety; M is a moiety that confers endonuclease resistance on said component and that contains at least one modified or unmodified nucleic acid base; B is a moiety that confers exonuclease resistance to the terminus to which it is attached; and x is an integer of at least 2.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Single nucleotide amplification and detection by polymerase
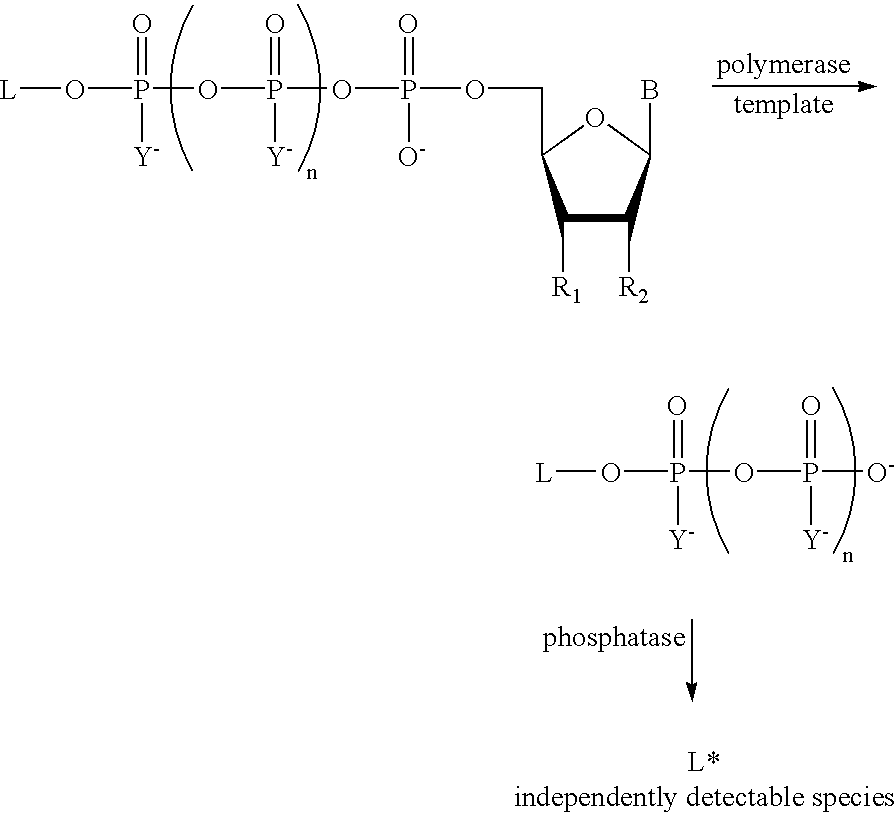
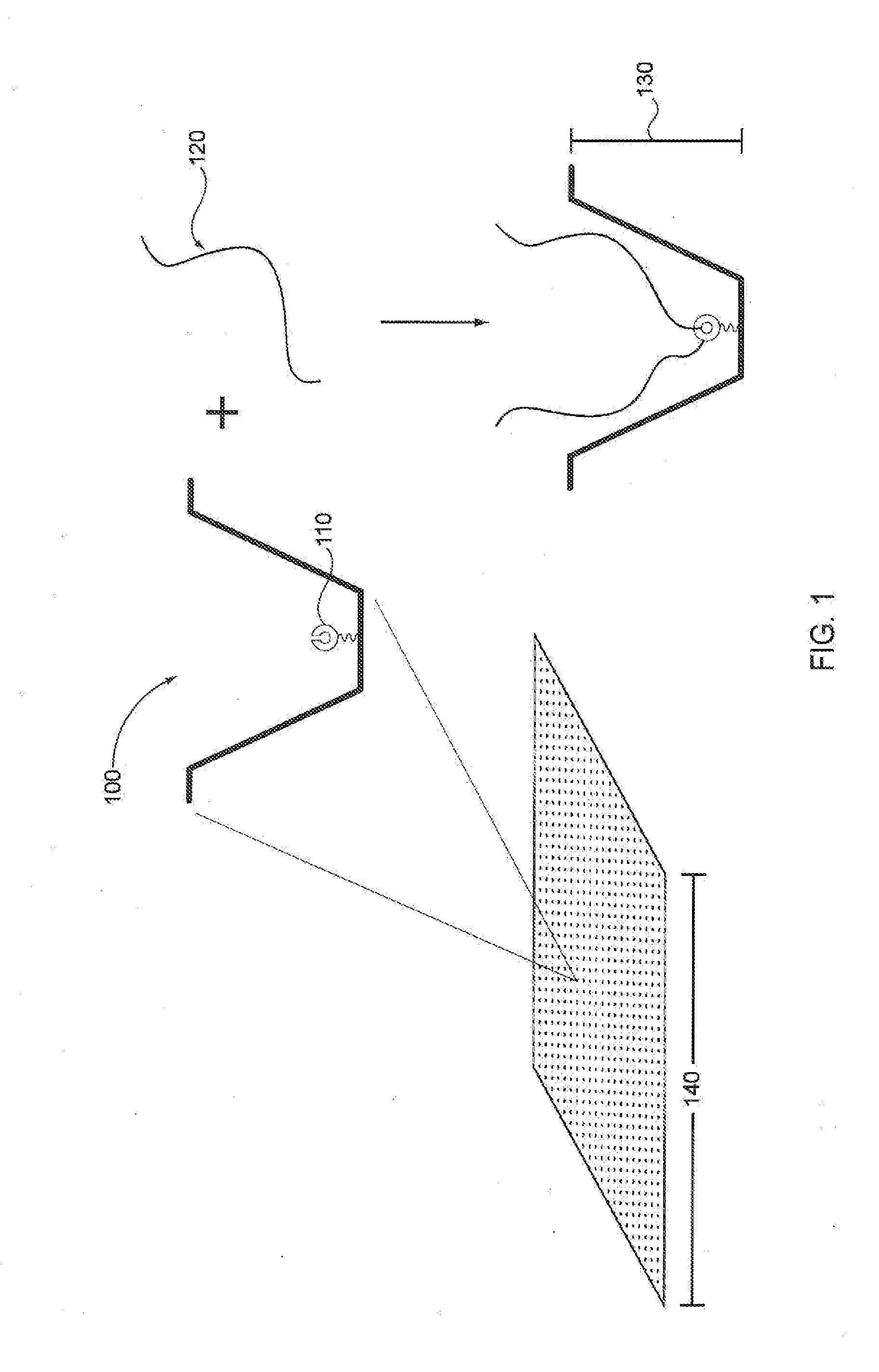
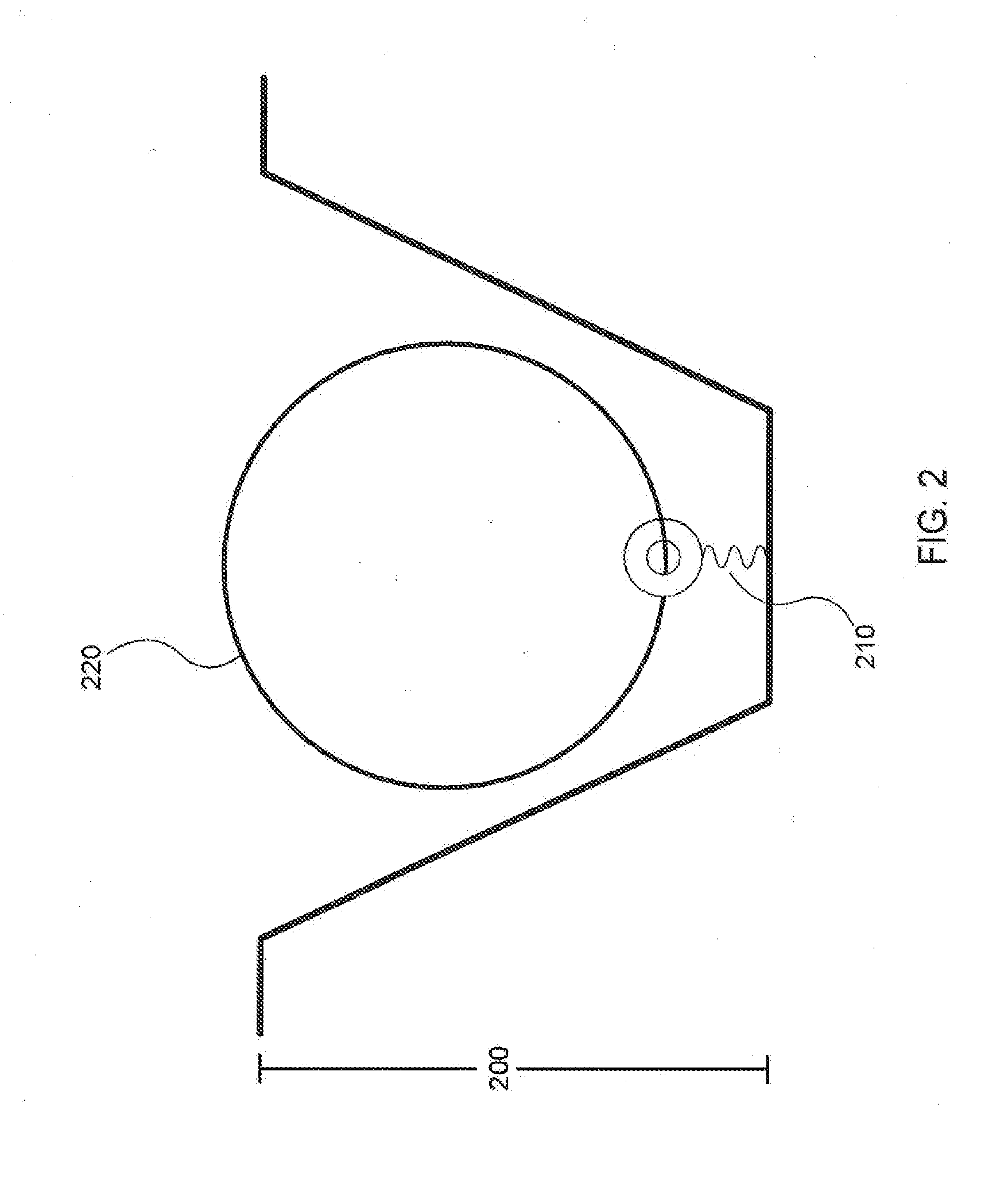
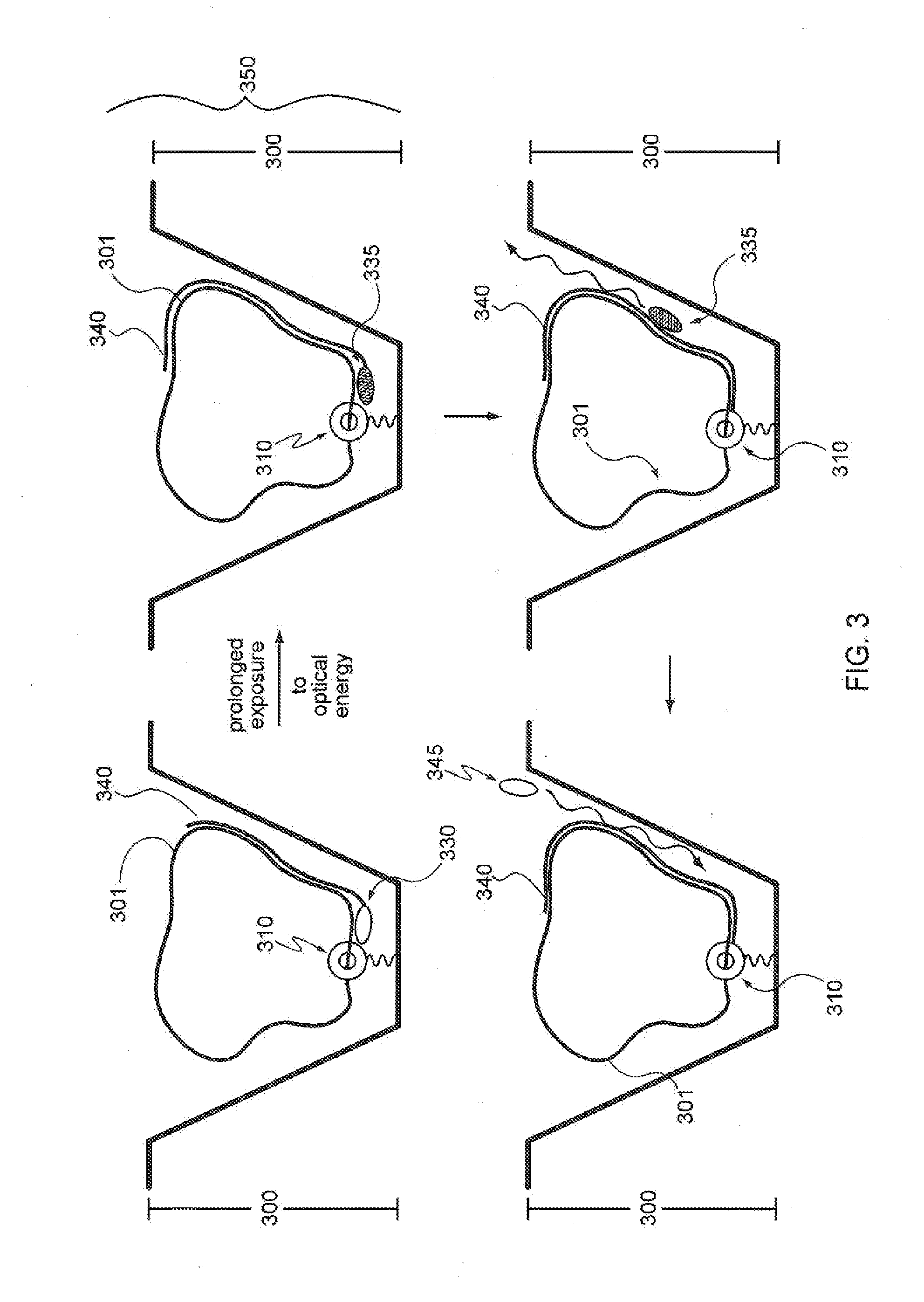
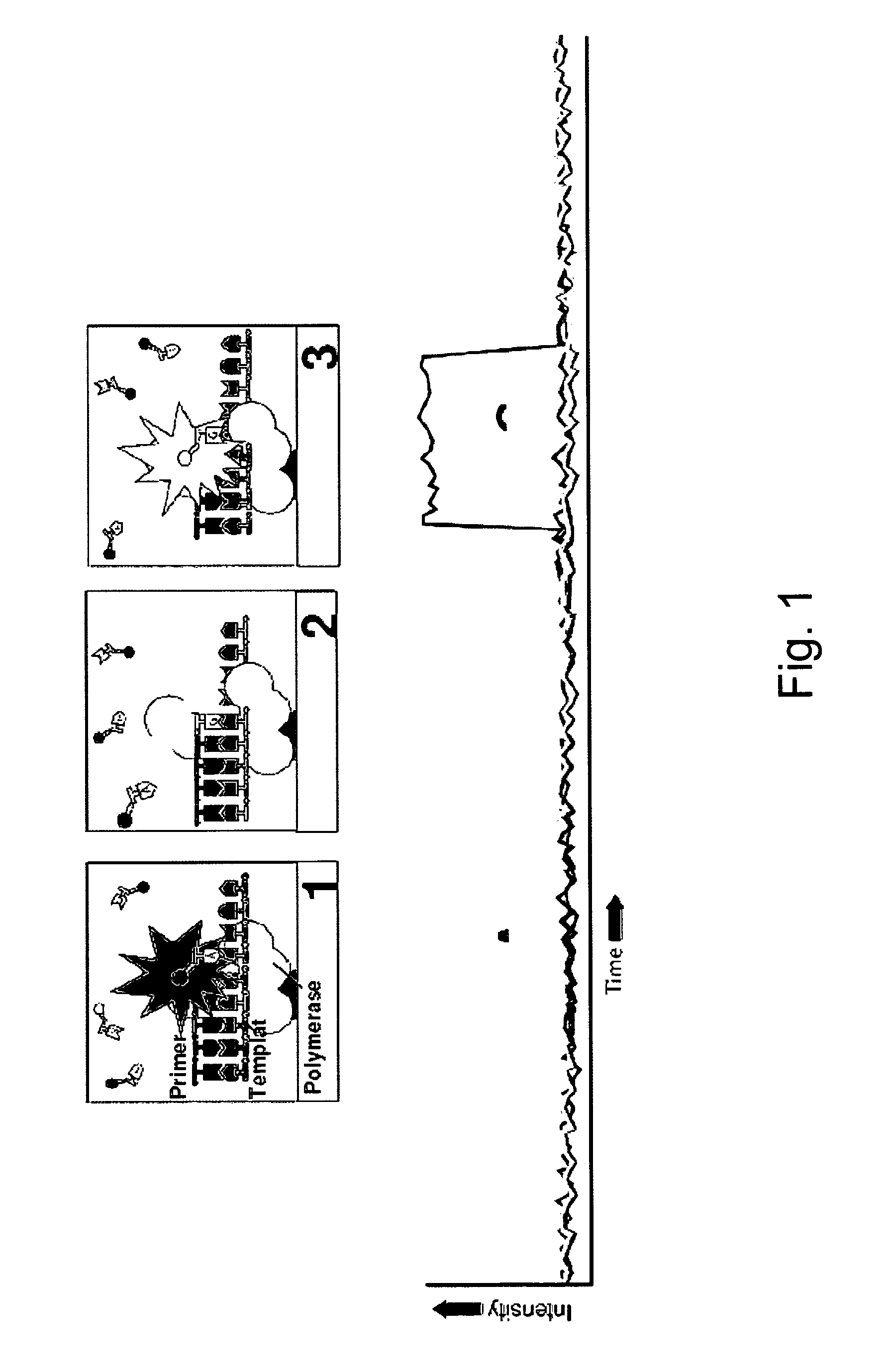
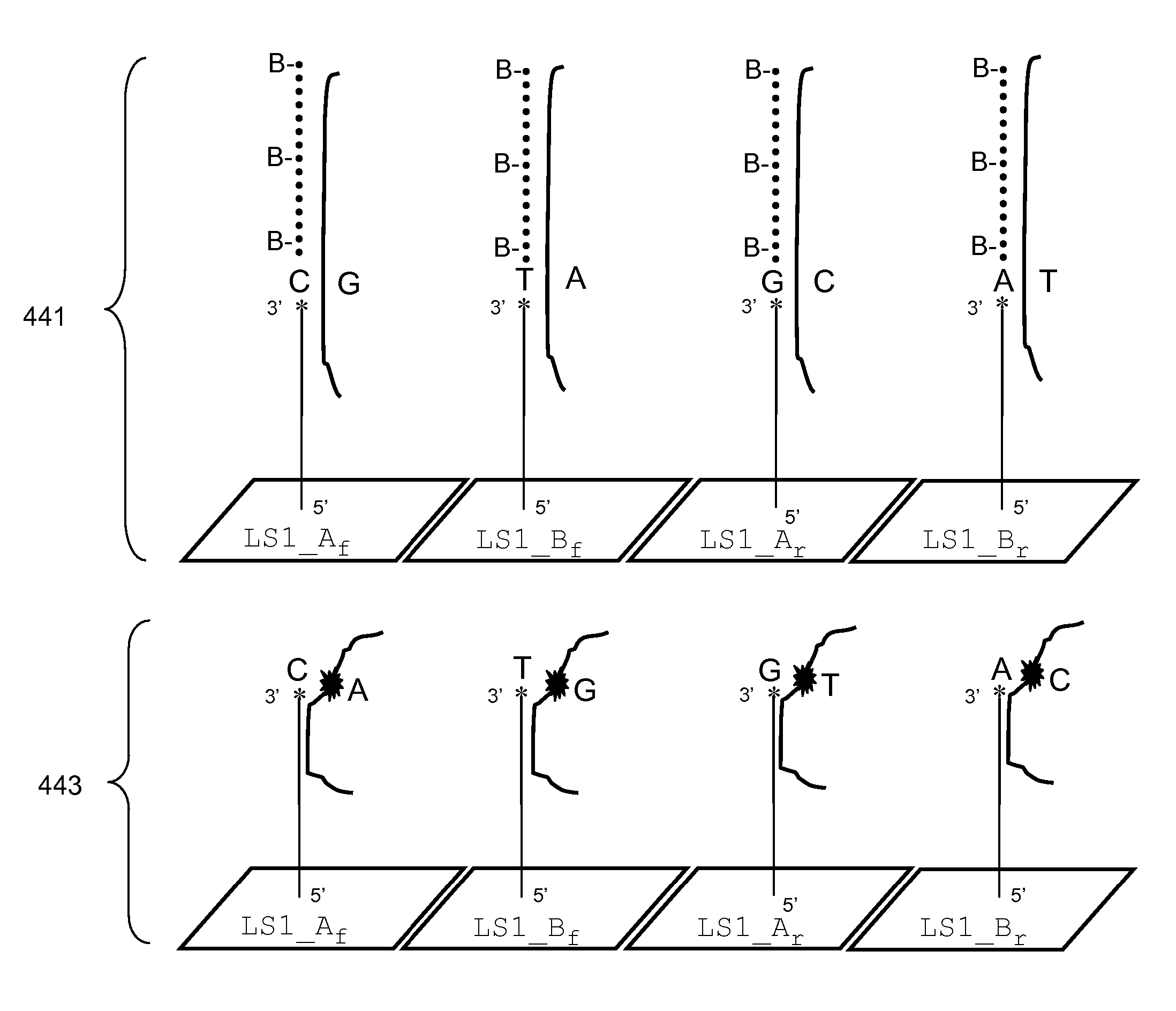
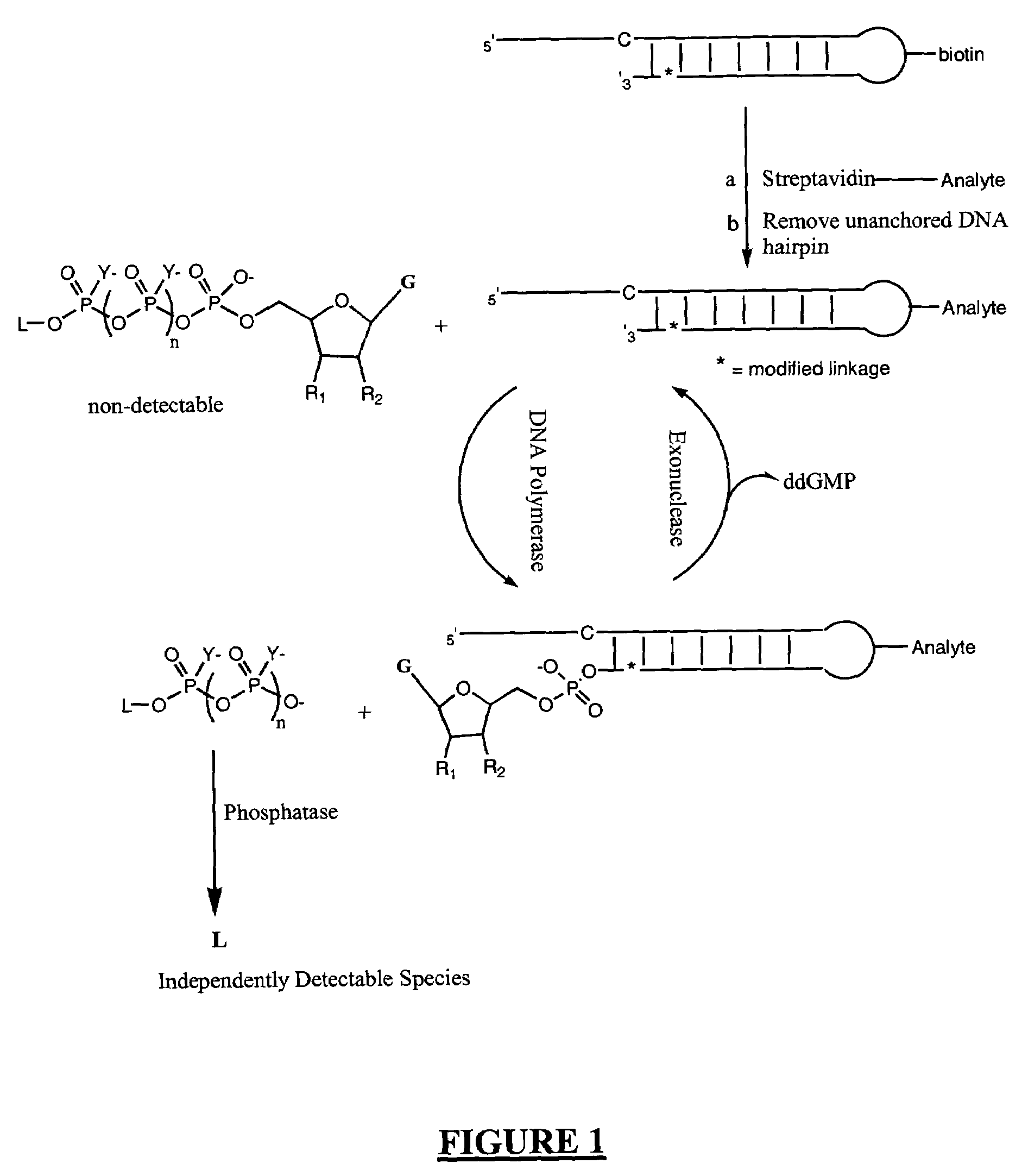
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Nucleic acid amplification oligonucleotides with molecular energy transfer labels and methods based thereon
InactiveUS6090552AReduce the possibilityRapid and sensitive and reliableSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferFluorophore
The present invention provides labeled nucleic acid amplification oligonucleotides, which can be linear or hairpin primers or blocking oligonucleotides. The oligonucleotides of the invention are labeled with donor and / or acceptor moieties of molecular energy transfer pairs. The moieties can be fluorophores, such that fluorescent energy emitted by the donor is absorbed by the acceptor. The acceptor may be a fluorophore that fluoresces at a wavelength different from the donor moiety, or it may be a quencher. The oligonucleotides of the invention are configured so that a donor moiety and an acceptor moiety are incorporated into the amplification product. The invention also provides methods and kits for directly detecting amplification products employing the nucleic acid amplification primers. When labeled linear primers are used, treatment with exonuclease or by using specific temperature eliminates the need for separation of unincorporated primers. This "closed-tube" format greatly reduces the possibility of carryover contamination with amplification products, provides for high throughput of samples, and may be totally automated.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Eukaryotic use of non-chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of Duplex Mutational Vector in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Non-Chimeric Mutational Vector, having no RNA:DNA hybrid-duplex is shown to be an effective substrate for eukaryotic enzymes. The invention concerns the use of Non-Chimeric Mutational Vectors protected from 3' exonuclease attack in eukaryotic cells. Such protection can be conferred by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the recombinagenic oligonucleobase.
Owner:VALIGEN US +1
Analyte detection
A method of characterizing an analyte sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) anchoring the analyte to a nucleic acid template of known sequence; (b) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (c) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (d) detecting the detectable species. The method may include the step of characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection. Also provided are methods of analyzing multiple analytes in a sample, and kits for characterizing analyte samples.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7824890B2Fluorescence enhancementEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStrand invasionEndonuclease
A process of amplifying a nucleic acid template dependent on partial destruction of primer molecules which have extended onto the template molecule followed by strand invasion of the partially destroyed primer template by a replacement primer. The destruction of the primer molecule may be performed by either endonuclease or exonuclease digestion. A signal generation from the amplified products may be obtained by the use of adaptors capable of binding probe molecules as well as the amplified product.
Owner:AVACTA GROUP
Single nucleotide detection using degradation of a fluorescent sequence
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms using a pair of oligonucleotides, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence hybridizes to the target DNA downstream from the primer and in the direction of primer extension. The snp detection sequence is characterized by having a nucleotide complementary to the snp and adjacent nucleotide complementary to adjacent nucleotides in the target and an electophoretic tag bonded to the 5'-nucleotide. The pair of oligonucleotides is combined with the target DNA under primer extension conditions, where the polymerase has 5'-3' exonuclease activity. When the snp is present, the electophoretic tag is released from the snp detection sequence, and can be detected by electrophoresis as indicative of the presence of the snp in the target DNA.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Method for making linear, covalently closed DNA constructs
InactiveUS6451563B1Bulking digestionHigh processivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructGenomic DNA
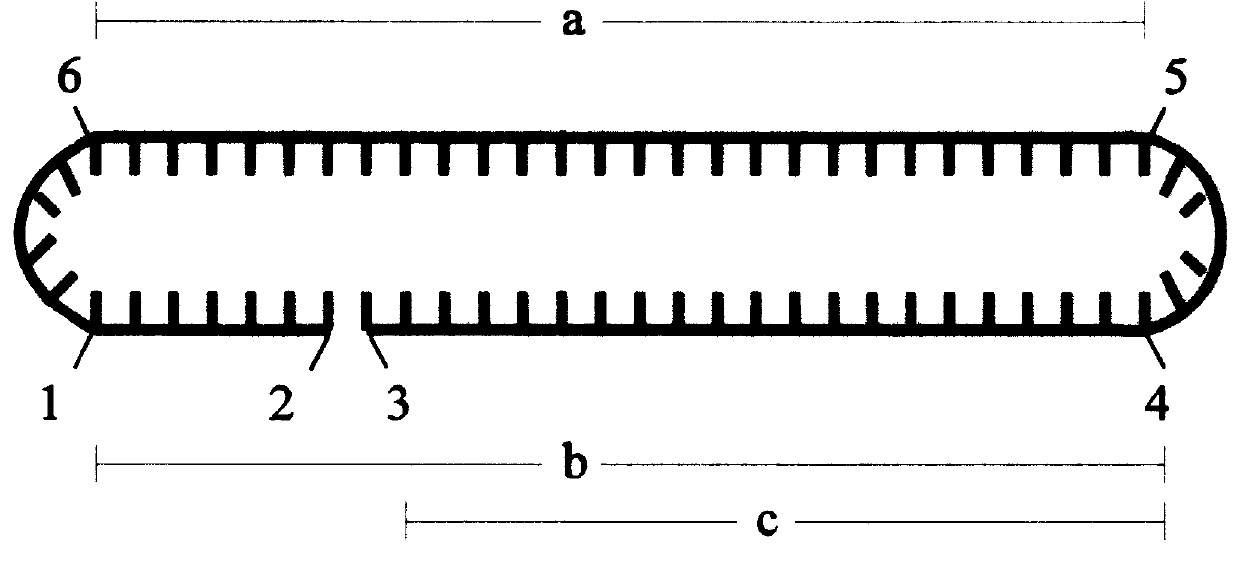
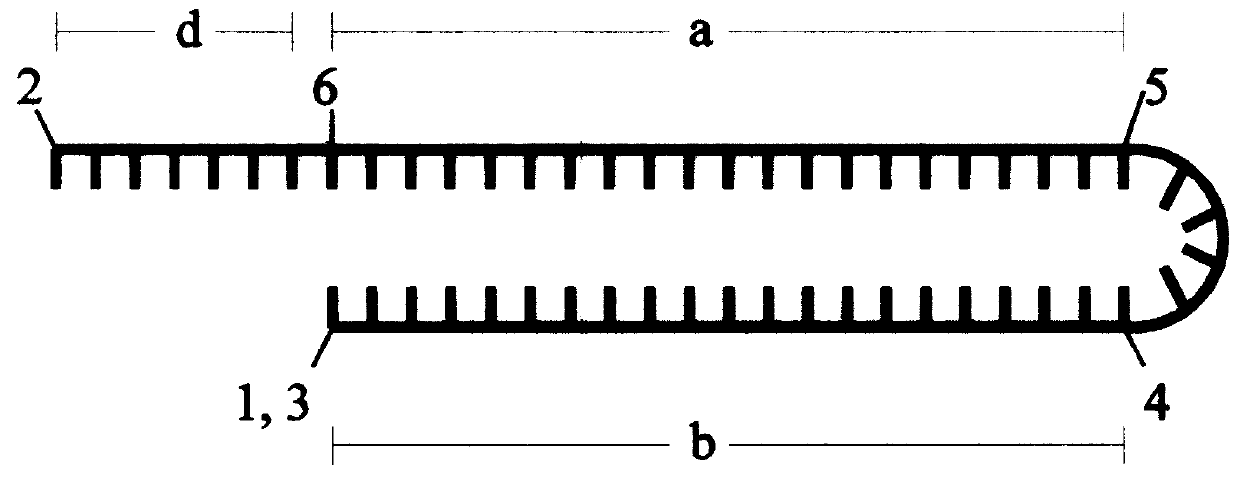
A process to obtain linear double-stranded covalently closed DNA "dumbbell" constructs from plasmids by restriction digest, subsequent ligation with hairpin oligodesoxyribonucleotides, optionally in the presence of restriction enzyme, and a final digestion with endo- and exonucleolytic enzymes that degrade all contaminating polymeric DNA molecules but the desired construct. The invention also provides a process to obtain said dumbbell constructs employing endonuclease class II enzymes. Furthermore, the invention provides a process to obtain linear, covalently closed DNA molecules, such as plasmids, free from contamination by genomic DNA, by submitting the DNA preparation to a facultative endonucleolytic degradation step and an obligatory exonucleolytic degradation step.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG +1
Immobilized nucleic acid complexes for sequence analysis
ActiveUS20100075328A1Use performanceImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPolymerase L
Provided are methods for sequencing a nucleic acid that include fixing a template to a surface through a template localizing moiety and sequencing the nucleic acid with a sequencing enzyme, e.g. a polymerase or exonuclease. The sequencing enzyme can optionally be exchanged with a second sequencing enzyme, which continues the sequencing of the nucleic acid. The template localizing moiety can optionally anneal with the nucleic acid and / or associate with the sequencing enzyme. Also provided are compositions comprising a nucleic acid fixed to a surface via a template localizing moiety, and a first sequencing enzyme, which can sequence the nucleic acid and optionally exchange with a second sequencing enzyme present in the composition. Compositions in which a template localizing moiety is immobilized on a surface are provided. Compositions for sequencing reactions are provided. Also provided are sequencing systems comprising reaction regions in which or near which template localizing moieties are immobilized.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Nucleic acid sequence analysis
ActiveUS20120115736A1Improve accuracyImprove processivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesNucleic acid detectionPolymerase L
Provided are methods for sequencing a nucleic acid with a sequencing enzyme, e.g., a polymerase or exonuclease. The sequencing enzyme can optionally be exchanged with a second sequencing enzyme, which continues the sequencing of the nucleic acid. In certain embodiments, a template is fixed to a surface through a template localizing moiety. The template localizing moiety can optionally anneal with the nucleic acid and / or associate with the sequencing enzyme. Also provided are compositions comprising a nucleic acid and a first sequencing enzyme, which can sequence the nucleic acid and optionally exchange with a second sequencing enzyme present in the composition. Compositions in which a template localizing moiety is immobilized on a surface are provided. Also provided are methods for using data from analytical reactions wherein two different enzymes are employed, e.g., at a same or different reaction regions.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Allele specific primer extension
InactiveUS20040048301A1Rapid rise in fluorescenceEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, an allele specific primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and optionally an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity when the primer is non-hydrolyzable, which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on such detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Composition and method for hot start nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS20030119150A1Good choiceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyPolymerase L
The present invention is directed to a new composition for performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction comprising (i) a thermostable DNA-Polymerase, (ii) a thermostable 3'-5' Exonuclease, and (iii) at least one primer for nucleic acid amplification with a modified 3' terminal residue which is not elongated by said thermostable DNA-Polymerase as well as methods for performing a PCR reaction using this composition. Furthermore, the method is directed to kits comprising such a composition.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS20030013101A1Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
Owner:SOLEXA
Nucleic acid sequencing methods and systems
ActiveUS7960116B2Reduced activityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleobase bindingExonuclease I
Sequencing methods that use an exonuclease that comprises template dependent nucleobase binding activity are provided. Related compositions and sequencing systems are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Compositions and methods utilizing DNA polymerases
The invention features a novel isolated Family B DNA polymerase, a Thermococcus polymerase JDF-3, and mutant recombinant forms thereof. Mutant polymerases of the invention are deficient in 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity and / or exhibit reduced discrimination against non-conventional nucleotides relative to the wild-type form of the polymerase.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Compositions and methods utilizing DNA polymerases
InactiveUS6946273B1Reduced discriminationImprove signal uniformitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideWild type
The invention features a novel isolated Family B DNA polymerase, a Thermococcus polymerase JDF-3, and mutant recombinant forms thereof. Mutant polymerases of the invention are deficient in 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity and / or exhibit reduced discrimination against non-conventional nucleotides relative to the wild-type form of the polymerase.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Thermostable or thermoactive DNA polymerase molecules with attenuated 3′-5′ exonuclease activity
The present invention provides thermostable or thermoactive DNA polymerases with attenuated 3′-5′ exonuclease activity, methods for their synthesis, methods for their use, kits comprising the polymerases, nucleic acids encoding the polymerases and cells comprising such a nucleic acid. The DNA polymerases of the invention are useful in many recombinant DNA techniques, such as nucleic acid amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. The DNA polymerases of the invention allow higher fidelity replication and amplification of a template DNA sequence, allow less degradation of primers and / or more efficient use of deoxynucleotide triphosphates and are in general more efficient and less costly to make and use.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Asynchronous primed PCR
InactiveUS20030207266A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferFluorescence
An asynchronous thermal cycling protocol for nucleic acid amplification uses two primers with thermal melting temperatures different by about 10 to 30° C. After the higher melting primer has annealed and polymerase mediated extension, the uncopied, single-stranded target sequence may be hybridized and detected by a probe. DNA probes may be cleaved by the exonuclease activity of a polymerase. The probe may be a non-cleaving analog such as PNA. When a probe is labelled with a reporter dye and a quencher selected to undergo energy transfer, e.g. FRET, fluorescence from the reporter dye may be effectively quenched when the probe is unbound. Upon hybridization of the probe to complementary target or upon cleavage while bound to target, the reporter dye is no longer quenched, resulting in a detectable amount of fluorescence. The second, lower-melting primer may be annealed and extended to generate a double-stranded nucleic acid. Amplification may be monitored in real time, including each cycle, or at the end point. The asynchronous PCR thermal cycling protocol can generate a preponderance of the PCR amplicon in single-stranded form by repetition at the end of the protocol of annealing and extension of the higher melting primer.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
High fidelity DNA polymerase compositions and uses therefor
The subject invention relates to compositions comprising an enzyme mixture which comprises a first enzyme and a second enzyme, where the first enzyme comprises a DNA polymerization activity and the second enzyme comprises an 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and a reduced DNA polymerization activity. The invention also relates to the above compositions in kit format and methods for high fidelity DNA synthesis using the subject compositions of the invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
DNA polymerase compositions for quantitative PCR and methods thereof
ActiveUS8283148B2Increased reverse transcriptase activitySugar derivativesBacteriaReverse transcriptase activityMutant
The invention relates to the generation and characterization of Archaeal DNA polymerase mutants with deficient 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and reduced base analog detection activity. The invention further provides for Archaeal DNA polymerase mutants with deficient 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and reduced base analog detection activity containing additional mutations that modulate other DNA polymerase activities including DNA polymerization or reverse transcriptase activity. The invention also discloses methods and applications of DNA polymerases with deficient 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and reduced base analog detection activity.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods for Genotyping
InactiveUS20070269817A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotidePolymerase L
The present invention provides for methods for discriminating between alleles at polymorphic positions in a genome. In general the methods employ allele specific extension of oligonucleotides that are complementary to one of the alleles at the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. The allele specific oligonucleotides are resistant to proof reading activity from a polymerase and may be extended in an allele specific manner by a DNA polymerase with a functional 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. The allele specific oligonucleotides may be attached to a solid support such as a chip or a bead.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Analyte detection
A method of characterizing an analyte sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) anchoring the analyte to a nucleic acid template of known sequence; (b) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (c) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (d) detecting the detectable species. The method may include the step of characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection. Also provided are methods of analyzing multiple analytes in a sample, and kits for characterizing analyte samples.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Methods of using FET labeled oligonucleotides that include a 3'->5' exonuclease resistant quencher domain and compositions for practicing the same
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting a primer extension product in a reaction mixture. In the subject methods, a primer extension reaction is conducted in the presence of a polymerase having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity and at least one FET labeled oligonucleotide probe that includes a 3′→5′ exonuclease resistant quencher domain. Also provided are systems and kits for practicing the subject methods. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, and are particularly suited for use in high fidelity PCR based reactions, including SNP detection applications, allelic variation detection applications, and the like.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for long range allele-specific PCR
InactiveUS20070184457A1Enhanced hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LA-DNA
The present invention is directed to a method and kit for determining the molecular haplotype of a gene in a diploid DNA sample. The method discriminates between two haplotypes on the basis of a difference of one or more nucleotides using allele-specific PCR amplification in combination with long range PCR, using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, using annealing temperature conditions sufficiently greater than the predicted annealing temperature (Tm) to effect selective hybridization and extension of an allele-specific extension primer to the target allele relative to the variant allele. The present invention is particularly useful, for example, to determine the haplotype of a gene having multi-allelic genetic loci separated by a distance in which accurate PCR amplification of a single fragment containing the multiple genetic loci cannot be performed without using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, generally about 5 kilobases or more.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Compositions and methods employing 5' phosphate-dependent nucleic acid exonucleases
InactiveUS20060240451A1Increase heightImprove representationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementP phosphateNuclease
The present invention relates to compositions and methods employing 5′-phosphate-dependent nucleic acid exonucleases. In particular, the present invention provides kits and methods employing 5′-phosphate-dependent nucleic acid exonucleases for selective enrichment, isolation and amplification of a particular set of desired nucleic acid molecules from samples that also contain undesired nucleic acid molecules for a variety of uses. In preferred embodiments, the desired nucleic acid molecules comprise prokaryotic and / or eukaryotic mRNA.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Circular RNA for inhibition of microrna
InactiveUS20150299702A1Avoid interactionControl degradationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDecoyCircular RNA
The present invention relates to inhibition of microRNAs (miRNA), other types of RNA and RNA-binding proteins. In particular the present invention relates to nucleic acid sequences that are circular and allow inhibition of the interactions between microRNAs and their RNA target and being resistant to degradation by exonucleases. Also, the present invention relates to nucleic acid sequence that are circular and acts as an RNA blocker or protein decoy.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
DNA joining method
InactiveUS7575860B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzymeExonuclease
The present invention provides a method to directionally clone any linear template DNA molecule into any linearized vector. The vector ends may be generated from any restriction enzyme cleavage. The method does not require a ligation step nor the use of carefully controlled conditions as is required with methods involving specific exonucleases alone. It has been determined that specific DNA polymerases are able to efficiently join one or more linear DNA molecules sharing ends with appropriate complementation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
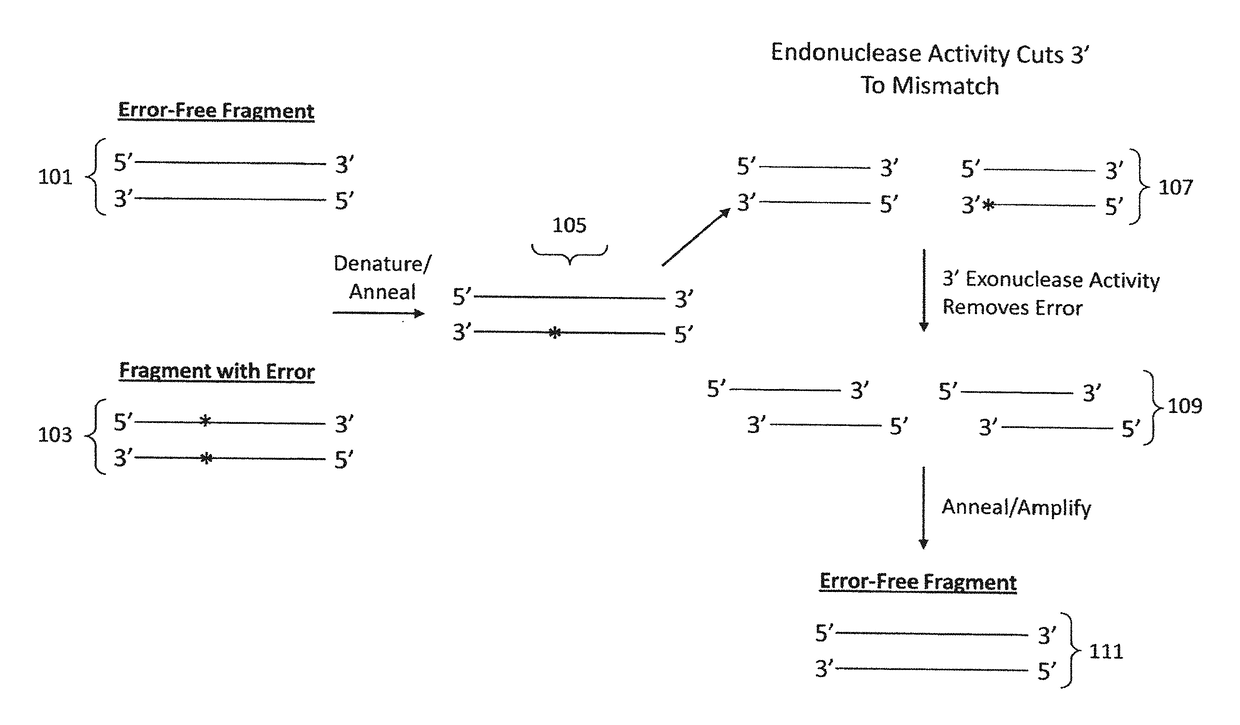
Materials and methods for the synthesis of error-minimized nucleic acid molecules
ActiveUS20180051280A1Reduce frequencyCorrection errorHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideProviding material
The present invention provides materials and methods useful for error correction of nucleic acid molecules. In one embodiment of the invention, a first plurality of double-stranded nucleic acid molecules having a nucleotide mismatch are fragmented by exposure to a molecule having unidirectional mismatch endonuclease activity. The nucleic acid molecules are cut at the mismatch site or near the mismatch site, leaving a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule having a mismatch at the end or near end of the molecule. The nucleic acid molecule is then exposed to a molecule having unidirectional exonuclease activity to remove the mismatched nucleotide. The missing nucleotides can then be filled in by the action of, e.g., a molecule having DNA polymerase activity. The result is double-stranded nucleic acid molecules with a decreased frequency of nucleotide mismatches. Also provided are novel nucleic acid sequences encoding mismatch endonucleases, polypeptides encoded thereby, as well as nucleic acid constructs, transgenic cells, and various compositions thereof.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com