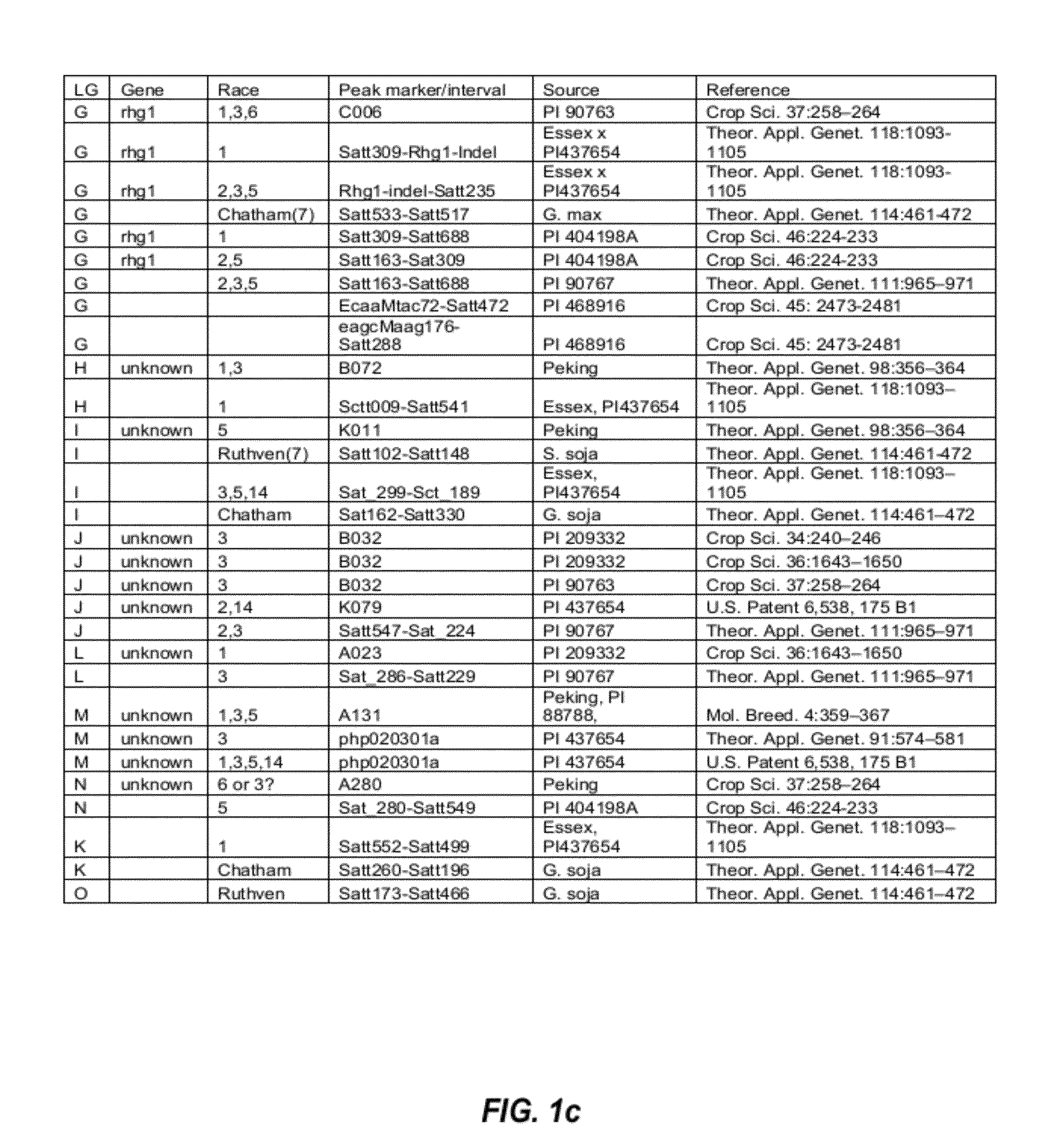
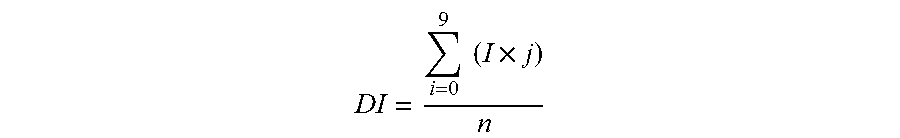Patents
Literature
72 results about "Resistant phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
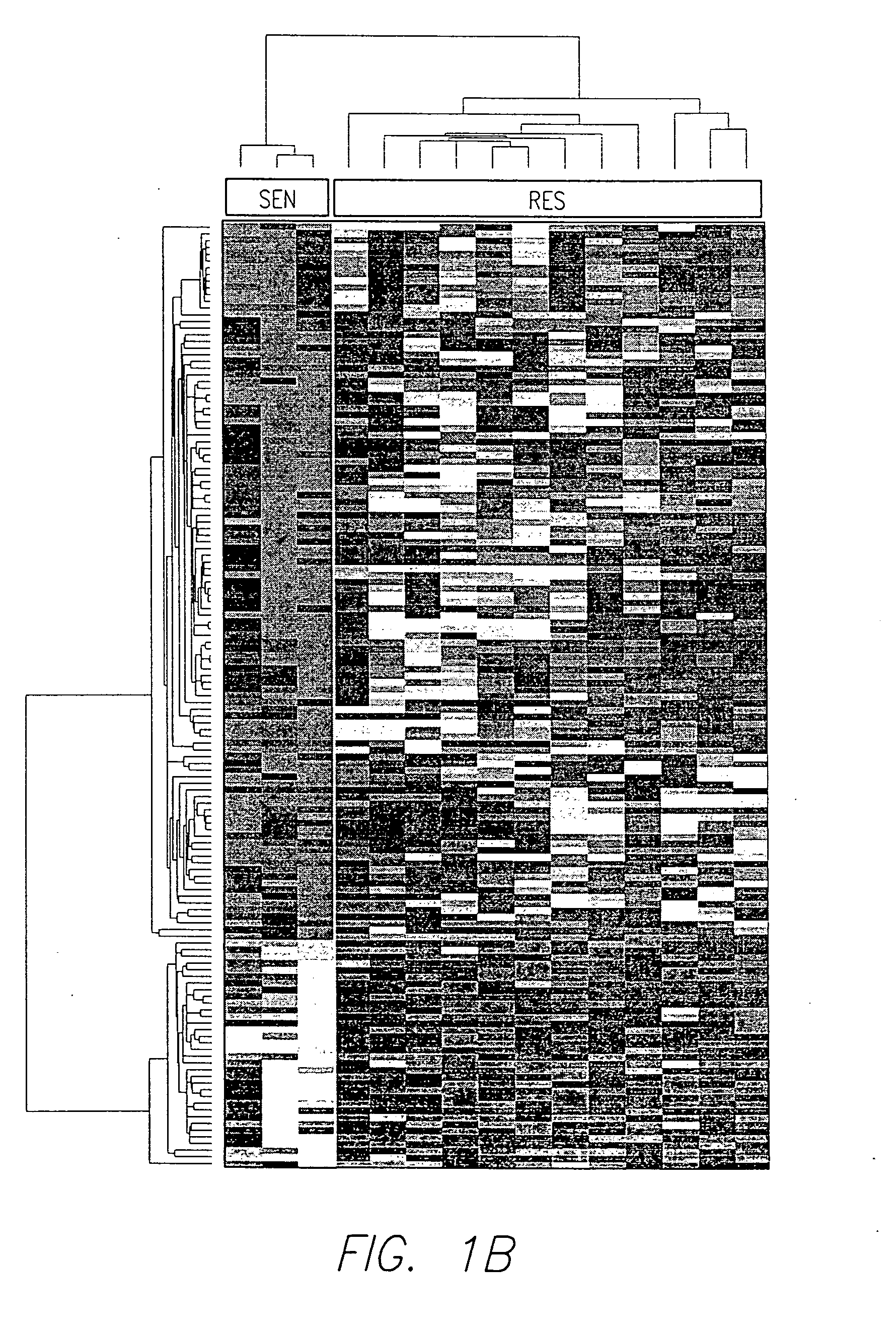
The phenotype is how the microbe responds to the antimicrobial in the laboratory setting, but would not pick up resistance potential, and in particular resistance genes that may code for “inducible” resistance.
Eukaryotic use of non-chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of Duplex Mutational Vector in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Non-Chimeric Mutational Vector, having no RNA:DNA hybrid-duplex is shown to be an effective substrate for eukaryotic enzymes. The invention concerns the use of Non-Chimeric Mutational Vectors protected from 3' exonuclease attack in eukaryotic cells. Such protection can be conferred by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the recombinagenic oligonucleobase.
Owner:VALIGEN US +1
Eukaryotic use of improved chimeric mutational vectors
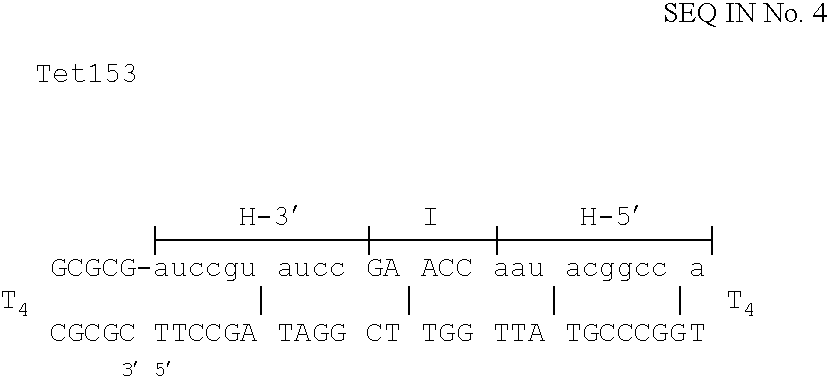
The invention is based on the reaction of recombinagenic oligonucleotides in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test duplex DNA on a plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria and allows for the rapid and quantitative comparison of recombinagenic oligonucleobases. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Heteroduplex Mutational Vector, was shown to be more active in than the types of mutational vectors heretofore tested. Further improvements in activity were obtained by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the Duplex Mutational Vector and removal of the DNA-containing intervening segment. The claims concern Duplex Mutational Vectors that contain the above improvements. In an alternative embodiment the claims concern a reaction mixture containing a recombinagenic oligonucleobase, a cell-free enzyme mixture and a duplex DNA containing a target sequence. In yet an alternative embodiment, the invention concerns the use of such mixture to test improvements in recombinagenic oligonucleobases, as well as to test the effects of compounds on the activity of the cell-free enzyme mixture and also to make specific changes in the target DNA sequence.
Owner:CIBUS
Vivo use of glutathione s-transferase activated nitric oxide donors
ActiveUS20050171066A1Increase delayReduce tumor volumeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsApoptosisNitric oxide
The present invention provides for a method of simultaneously treating both cancer and the Multidrug Resistance Phenotype via inhibition of cellular thiols, such as Glutathione S-Transferase (GST). This enzyme is overproduced in leukemia and solid tumor cells and is one of the main pathways involved in the Multidrug Resistance phenotype. The treatment provides for the administration of a chemically inert pro-drug, designed to be a specific substrate for the GST enzyme that, once cleaved, liberates the bioactive toxin Nitric Oxide (NO) intracellularly at the site of a malignant growth. NO then acts to inhibit the growth of the malignant cells and to induce cellular differentiation and apoptosis therein, effectively treating an existing cancerous condition. Additionally, once NO is liberated from the pro-drug, the remaining structure acts to inhibit further GST activity, providing a treatment for the Multidrug Resistant phenotype.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Human embryonic stem cells having genetic modifications
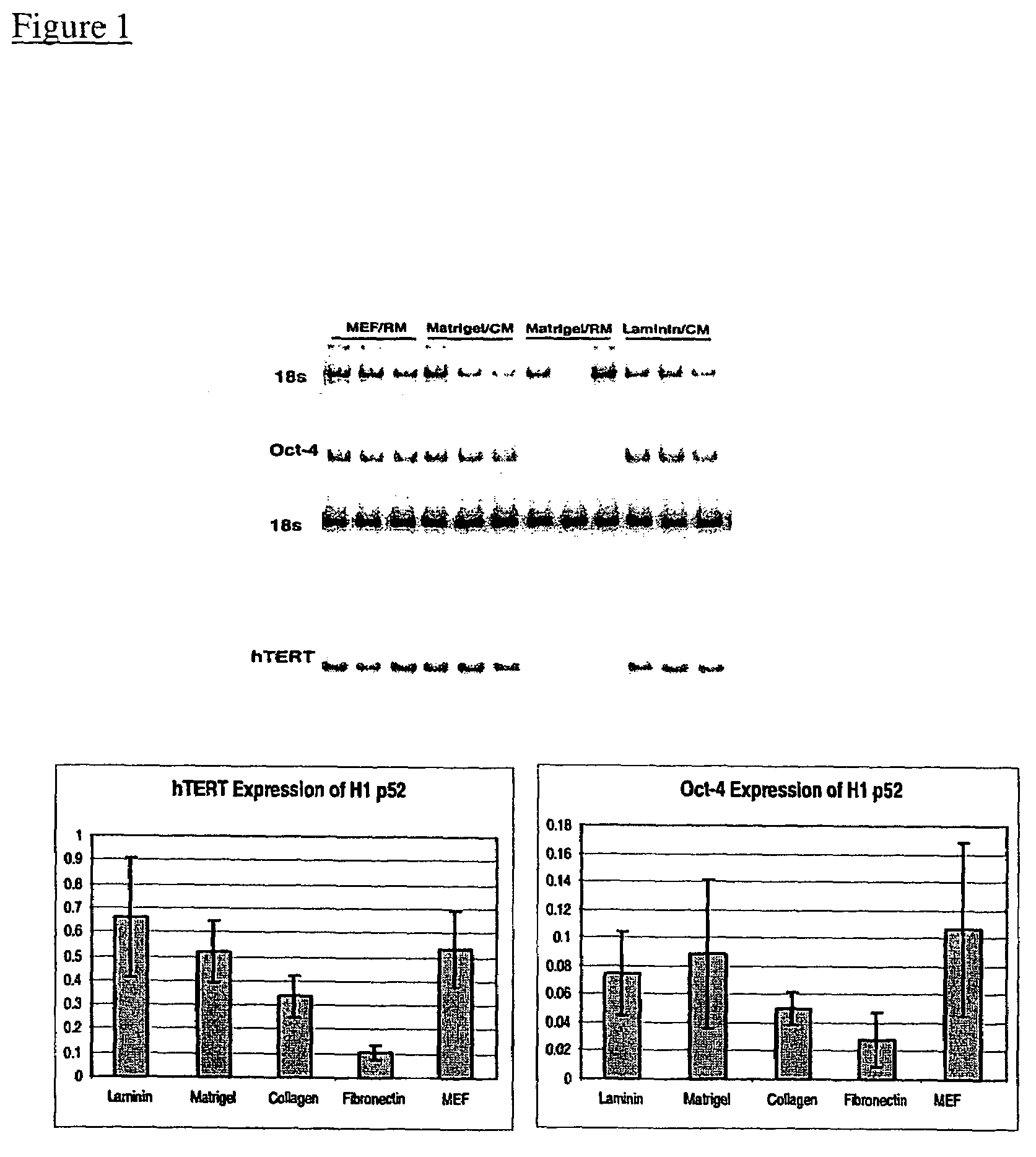
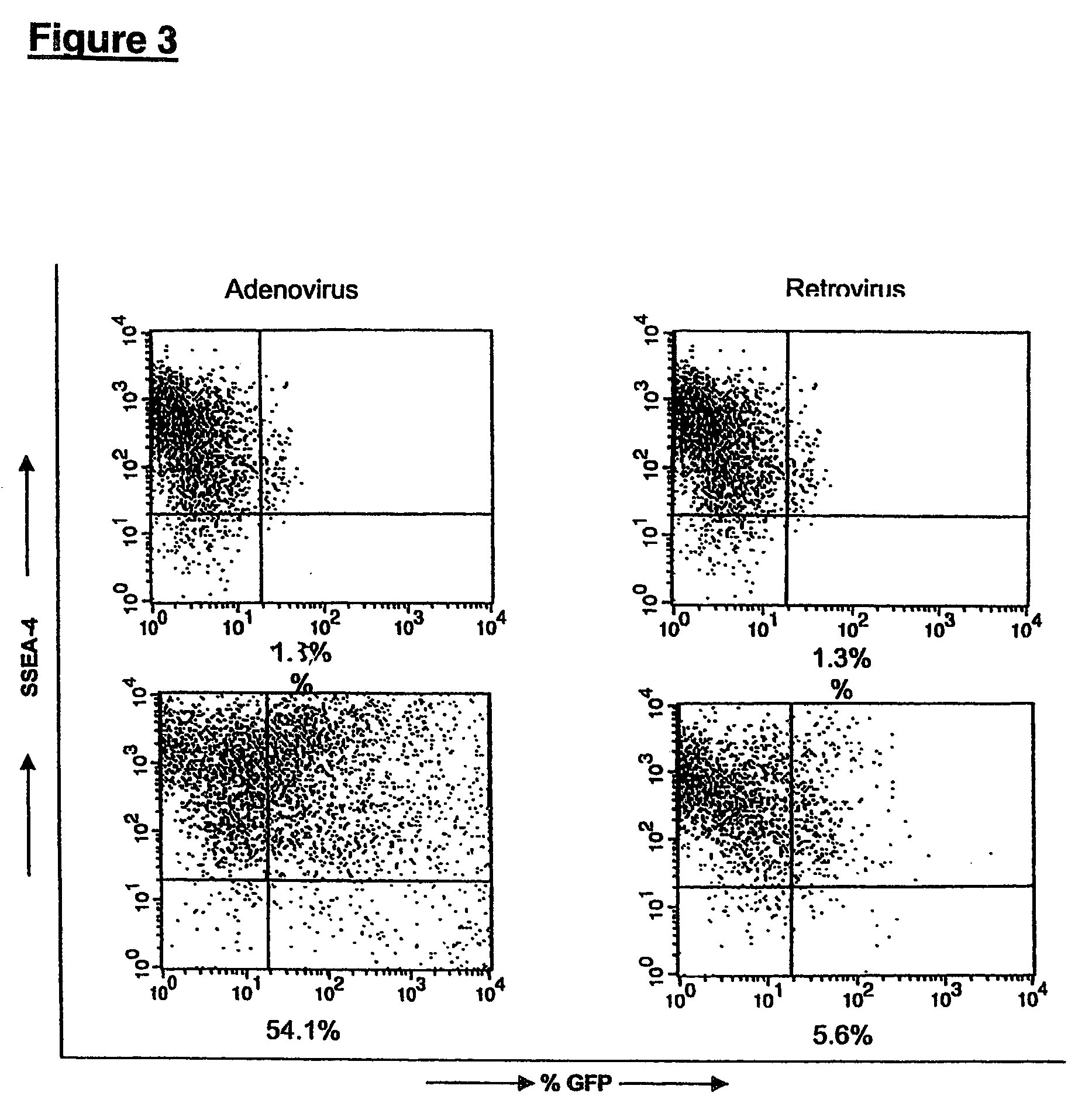
This disclosure provides a system for obtaining genetically altered primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cells. The role of the feeder cells is replaced by supporting the culture on an extracellular matrix, and culturing the cells in a conditioned medium. The cells can be genetically altered with a viral vector or DNA / lipid complex, and then selected for successful transfection by drug-resistant phenotype in the transfected cells. The system allows for bulk proliferation of genetically altered pPS cells as important products for use in human therapy or drug screening.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Preparation and application of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) chip for carbapenem antibiotic drug-resistant gene detection
InactiveCN104774941AImprove throughputStrong specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide chipA-DNA
The invention relates to preparation and application of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) chip for carbapenem antibiotic drug-resistant gene detection. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing nine carbapenem drug-resistant gene specific primers, preparing nine carbapenem antibiotic drug-resistant gene specific probes, preparing an oligonucleotide chip, establishing a multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system, and establishing a hybrid system. The gene chip can simultaneously detect nine common carbapenem drug-resistant genes, including KPC, NDM-1, OXA-23, OXA-48, OXA-51, IMP, VIM, SIM and DIM. The DNA chip has the advantages of high speed, high accuracy, high flux and high specificity, and can provide a new detection means for drug-resistant gene confirmation and molecular epidemiological survey of carbapenem antibiotic drug-resistant phenotypes.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance
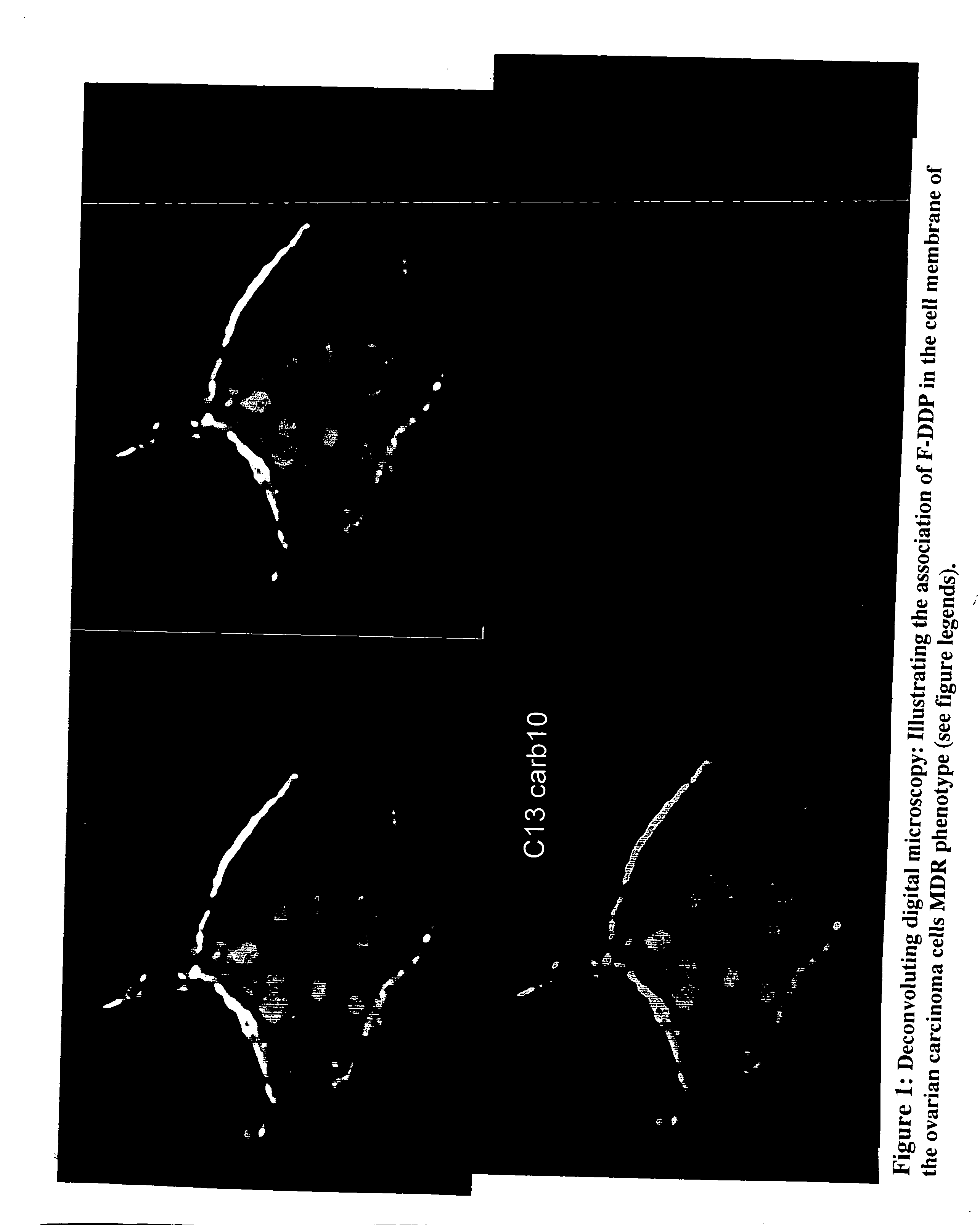
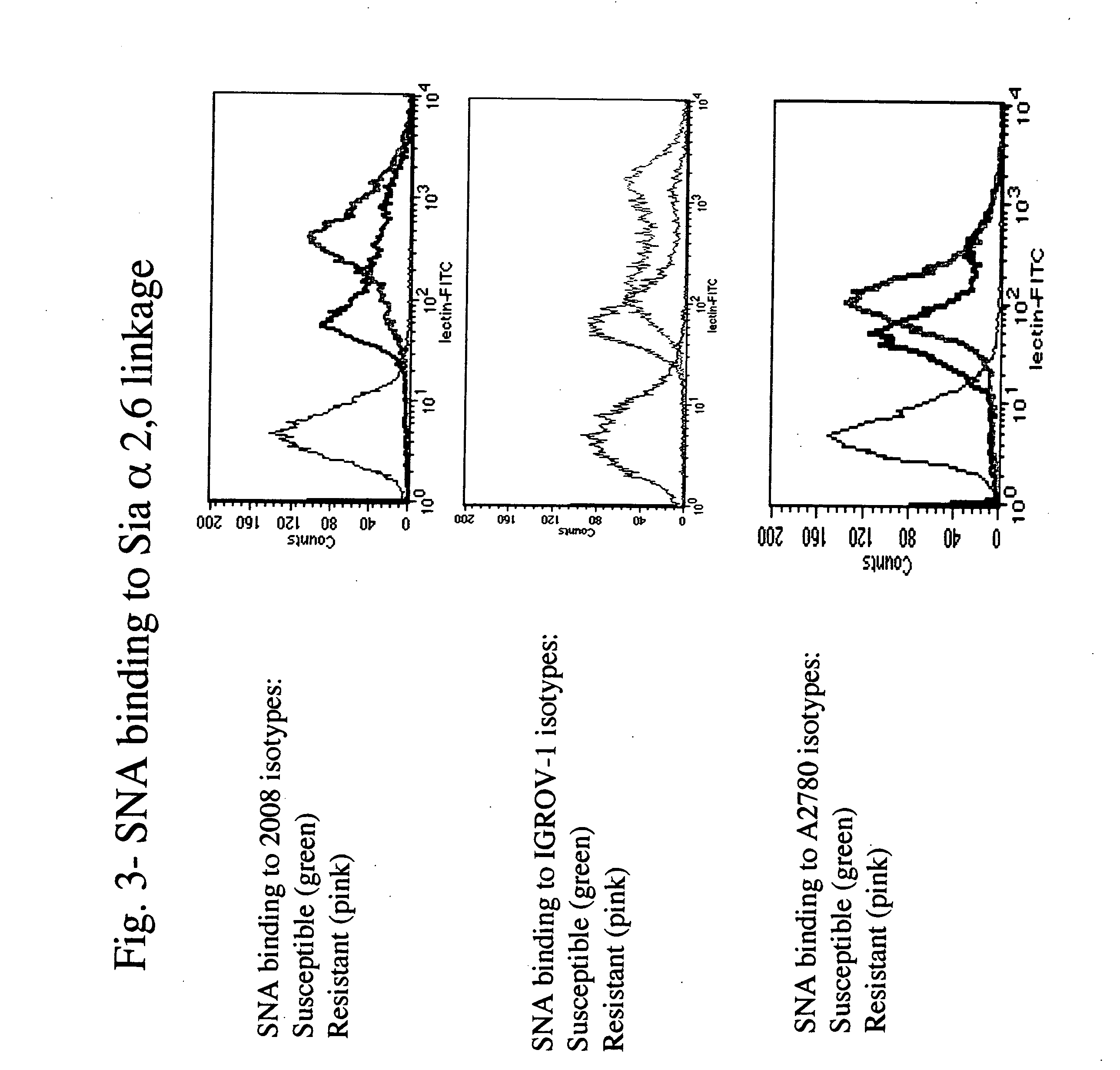
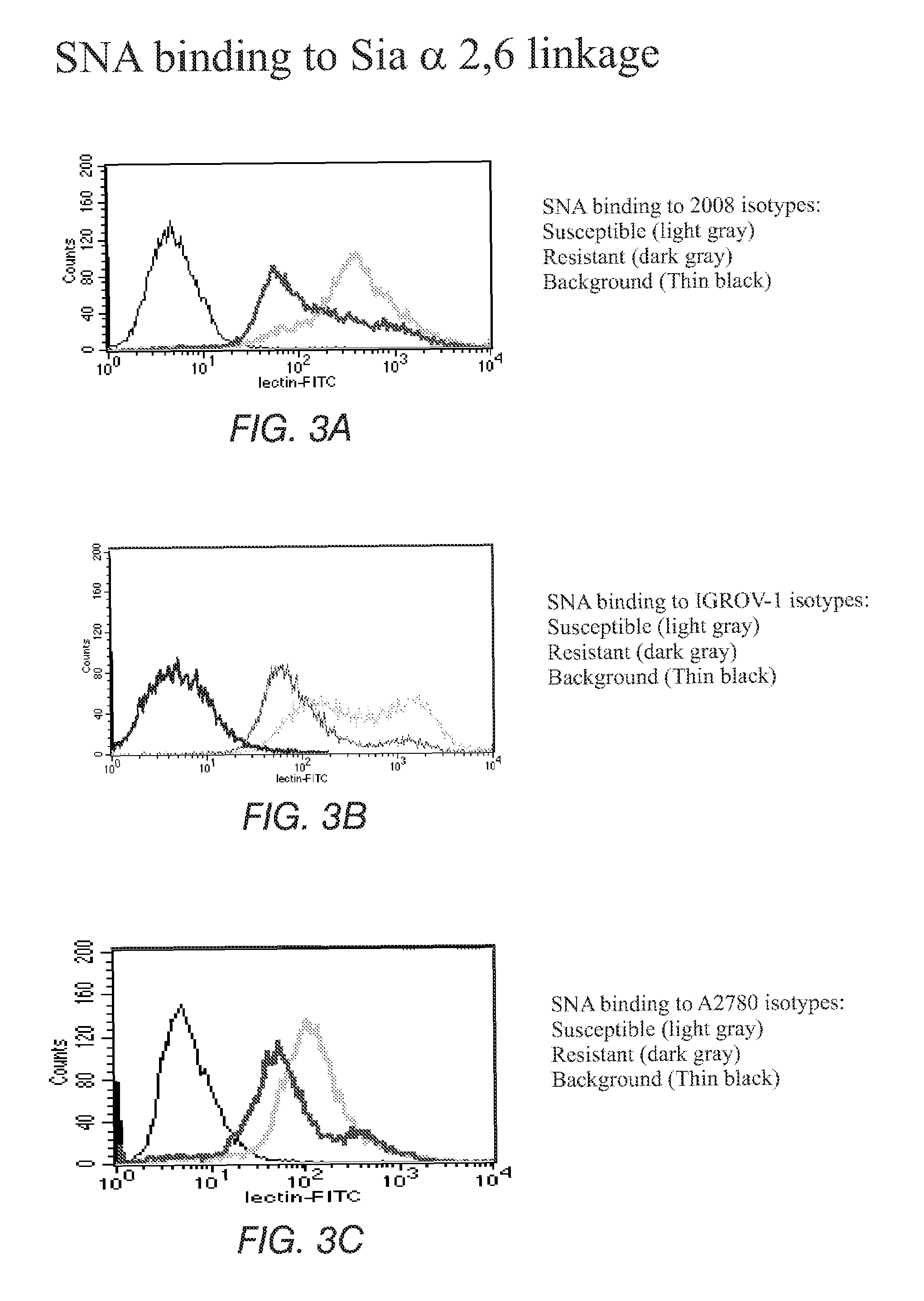
The present invention stems from the realization that the cell surface content of sialic acids is associated with drug susceptibility and resistance in neoplastic and damaged cells. A general decrease in the amounts of the α2-6 linked sialic acid has been confirmed in resistant phenotype compare to its corresponding sensitive parental cells. Treating the resistant phenotype with neuraminidase, an enzyme that removes the sialic acid from the sugar chain, facilitates the drug internalization and reinstalls the cell susceptibility to the drug. Based on these observations, methods for predicting the resistance to a number of drugs and detecting multi-drug resistanc in neoplastic and damaged cells have been invented.
Owner:RAZI NAHID
Method for screening important characteristic genes related to drug resistance phenotype of bacteria based on machine learning
ActiveCN114067912AFacilitate translational applied researchExpand Screening MiningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAntibiotic resistanceCorrelation analysis
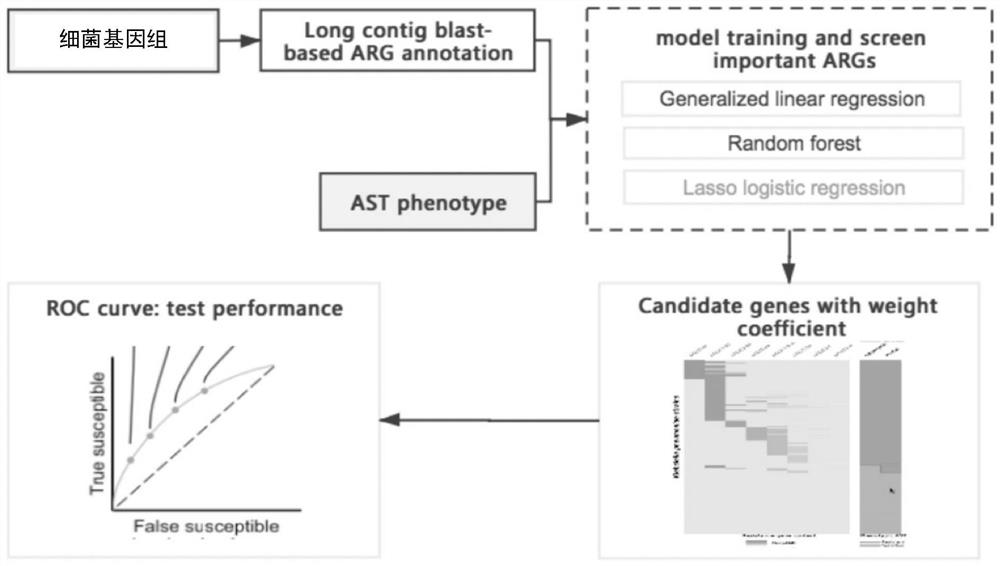
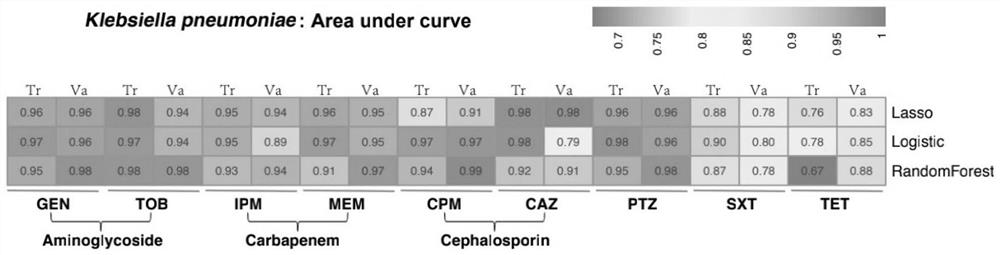
The invention relates to a method for screening important characteristic genes related to the drug resistance phenotype of bacterial based on a machine learning technology. According to the method, for the antibiotic resistance of the bacterial, on the basis of the BGWAS thought, target bacterial genomes on a public platform or large-sample-size bacterial strain genome data obtained after current collection, sequencing and assembly, and corresponding antibiotic drug susceptibility test results are collected, and correlation analysis between genotypes and drug resistance phenotypes is carried out by using the machine learning method, so that important characteristic genes (non-core drug-resistant genes) related to the drug resistance phenotypes are screened out, weight coefficients of the important characteristic genes are obtained;and finally the reliability of the drug-resistant genes related to drugs is determined by using ROC analysis.
Owner:天津金匙医学科技有限公司 +2
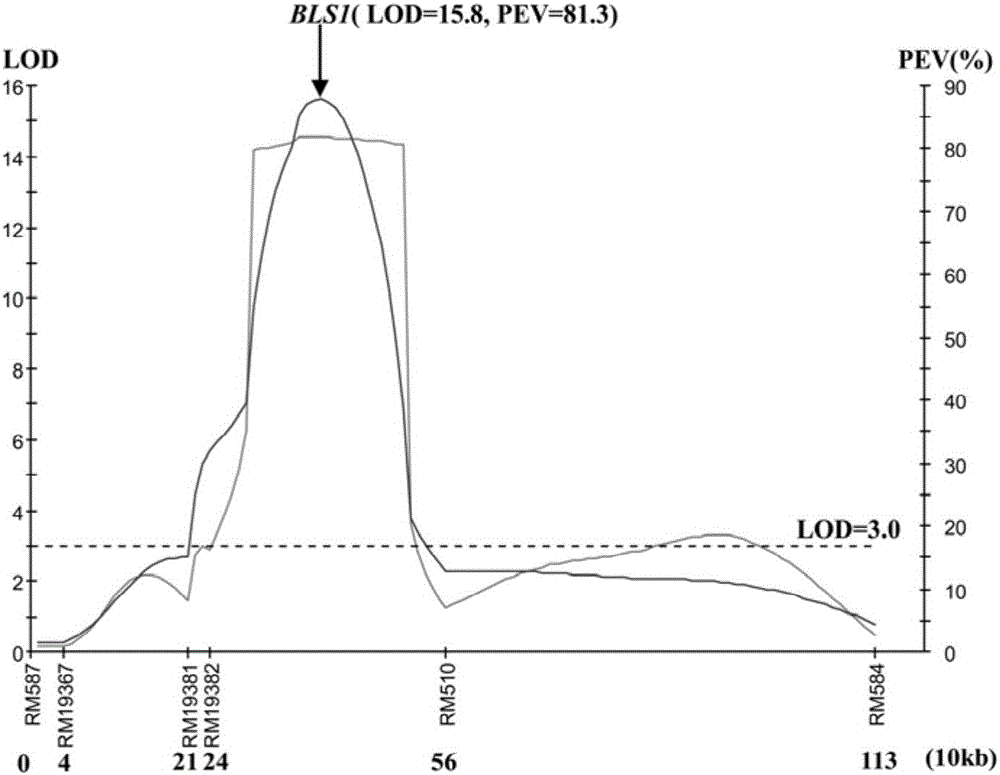
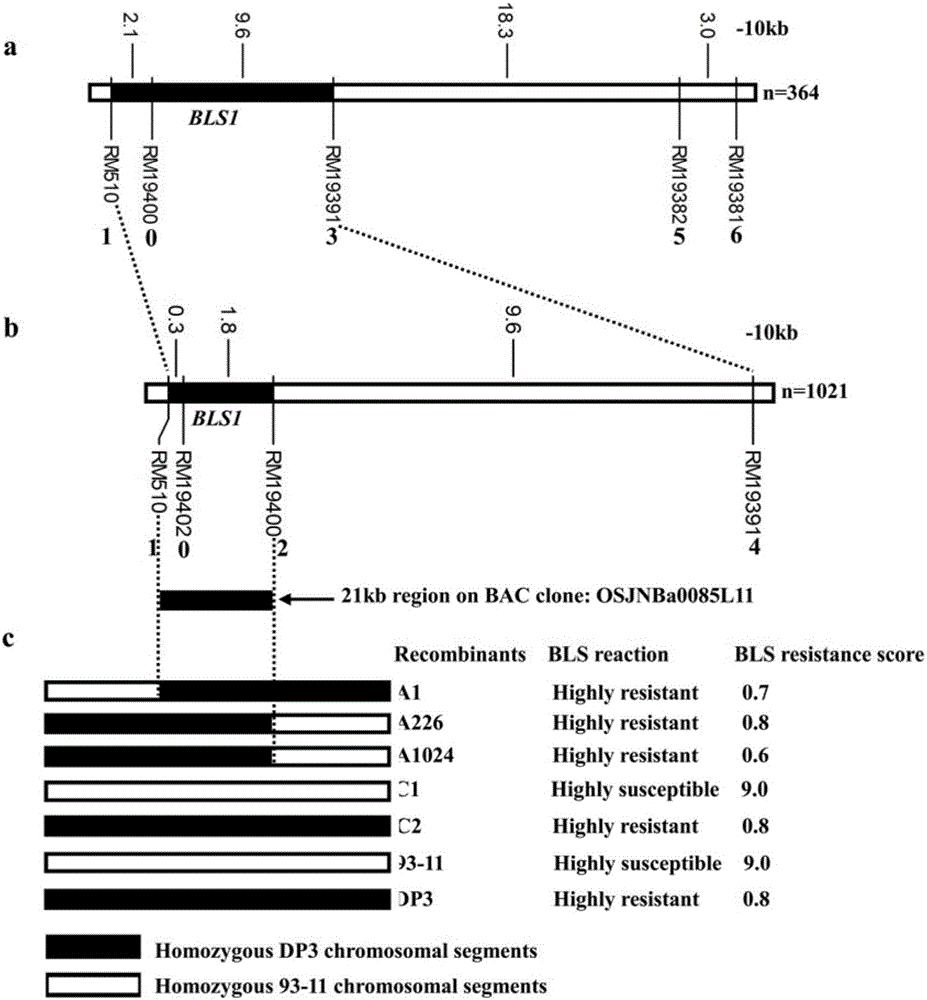
Molecular marker of main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN106244678AImprove selection efficiencyNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceOffspring F1
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and an application of the molecular marker. A bacterial streak resistant backcross inbred line obtained from deriving an ordinary wild paddy rice resistant source DP3 is crossed with a bacterial streak-infected nonglutinous rice variety 93-11 to obtain an offspring F1 hybrid and then the hybrid is self-fertilized to obtain F2 generation, genetic linkage analysis is performed for a gene type and corresponding resistant phenotype of each family of F2, and the bacterial streak-resistant main active gene BLS1 sourced from the ordinary wild paddy rice DP3 is detected. Molecular markers capable of being used for breeding such as RM19382, RM19391, RM19400, RM19402 and RM510 are obtained. The molecular markers can effectively detect whether the bacterial streak-resistant ordinary wild paddy rice DP3 and erivative varieties (lines) thereof contain a main active gene site, thereby greatly improving the selection efficiency of the bacterial streak resistant paddy rice, and obtaining the bacterial streak resistant paddy rice variety containing the BLS1 gene.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Rice brown planthopper resistant major gene Bph30 molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN107201395AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrown planthopperGenetics
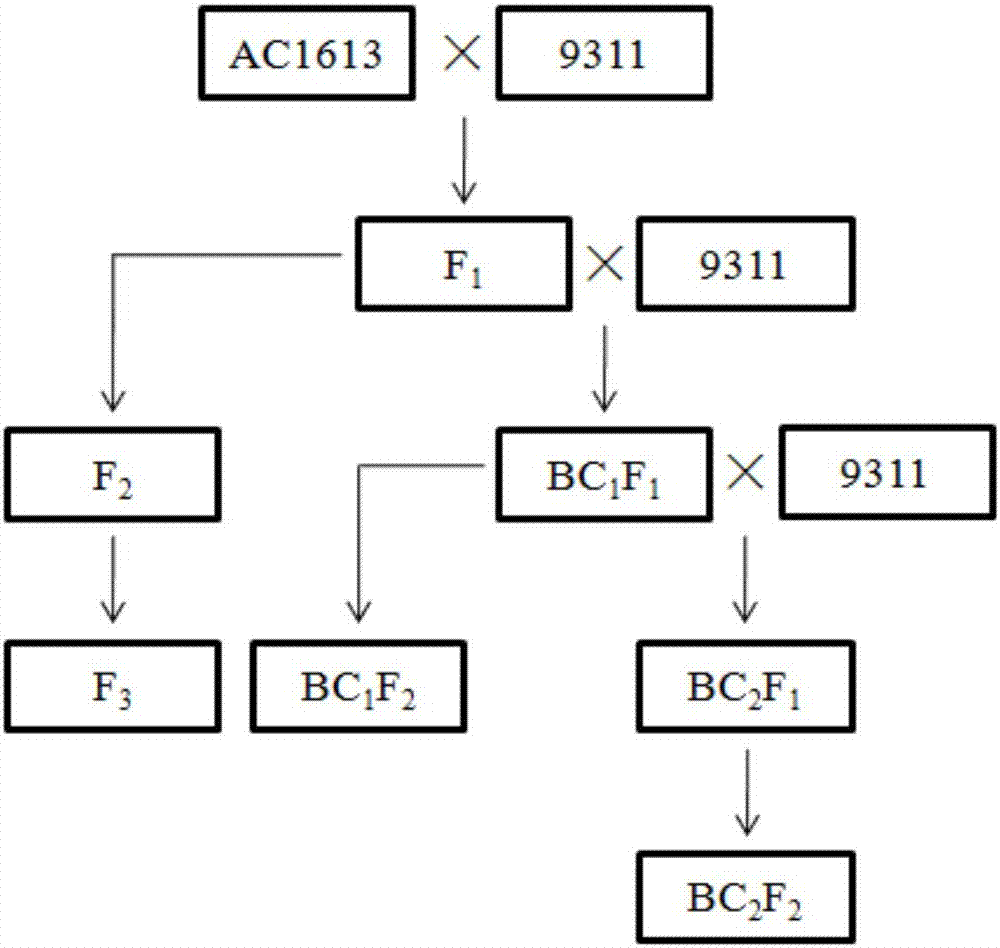
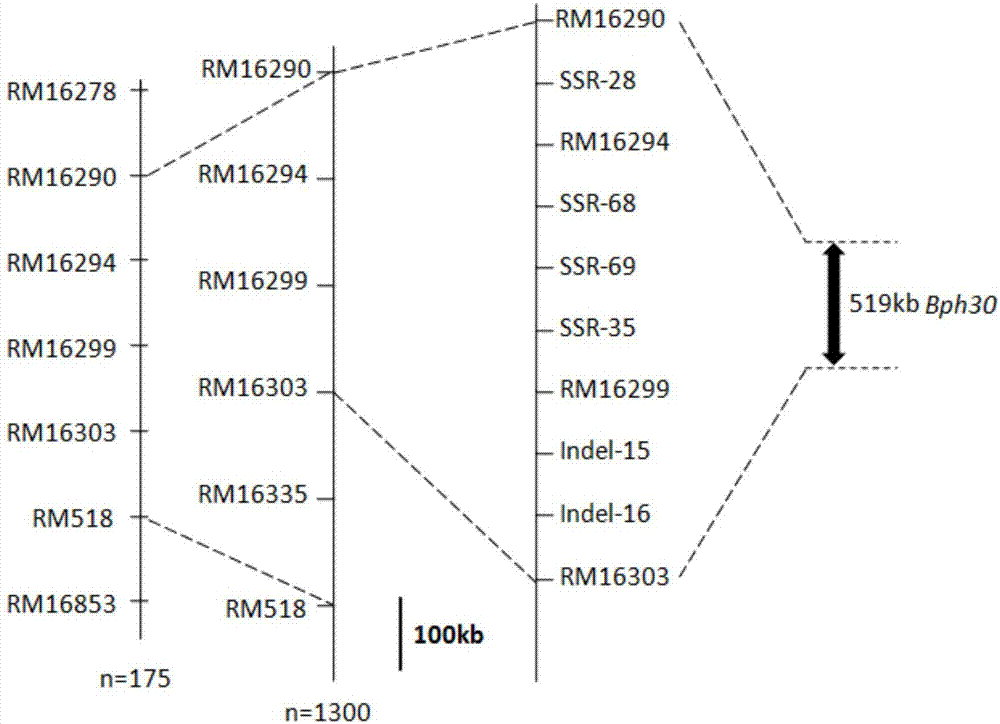
The invention provides a rice brown planthopper resistant major gene Bph30 molecular marker and application thereof. A genotype of each F2 single plant obtained by hybridization of a rice insect-resistant variety AC1613 (male parent ) and a susceptible variety 9311 (female parent ) and a brown planthopper resistant phenotype of each F2 single plant is combined for genetic linkage analysis to obtain an insect-resistant variety AC1613 resistance gene Bph30 positioned between molecular markers RM16290 and RM16303, and molecular markers in linkage with the gene also include SSR-28, RM16294, SSR-68, SSR-69, RM16299, Indel-15, Indel-16 and SSR-35. By the molecular marker, whether a locus of the major gene exists in rice or not can be effectively detected, and accordingly brown planthopper resistant rice selection efficiency is greatly improved, and brown planthopper resistant rice varieties with the gene Bph30 can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Protein modulators of resistance to alkylating agents
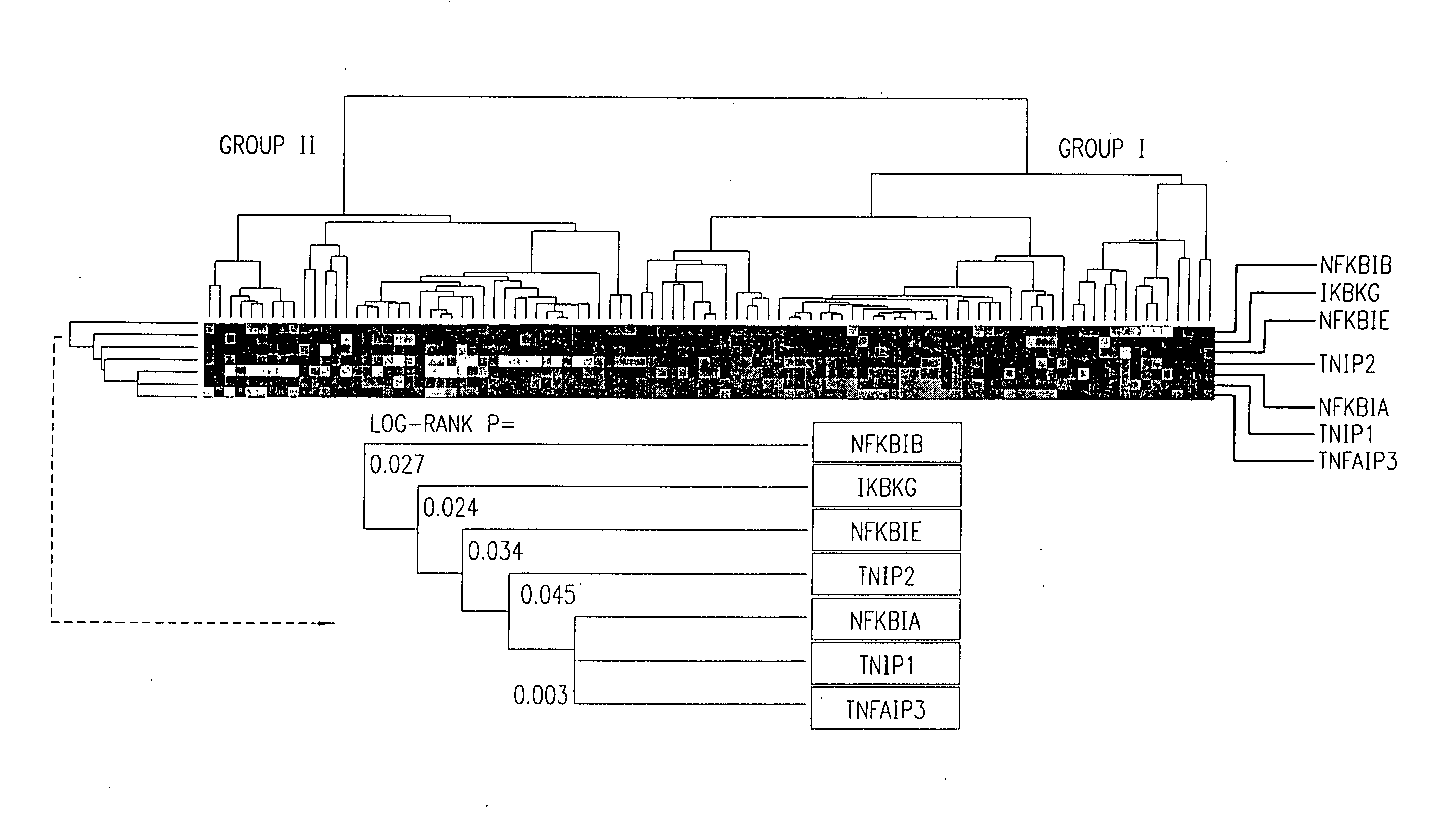
There is disclosed a method for identifying a therapeutically responsive phenotype, as distinguished, e.g. from an alkylating agent resistant phenotype in a cell, which method may be used to evaluate the likelihood of successful outcome of treating a tumor cell with an alkylating agent. The method is directed to the NF-κB activation in response to DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. It comprises the step of measuring a level of expression of a protein, which participates in the NF-κB pathway. Preferably it comprises measuring the expression of TNFAIP3 in the cell, wherein a resistant phenotype has less expression of TNFAIP3 than a sensitive phenotype. Another particularly significant gene, which predicts survival, is NFKBIA. Other genes whose altered expression level is associated with resistance or prognosis are TNIP1, TNIP2, RIP, NFKBIB, Beta4GalNAc-T4, NFKBIE, C8orf4, LIF, CD44, FBXO32, and SDC1, and these are also measured in certain embodiments.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
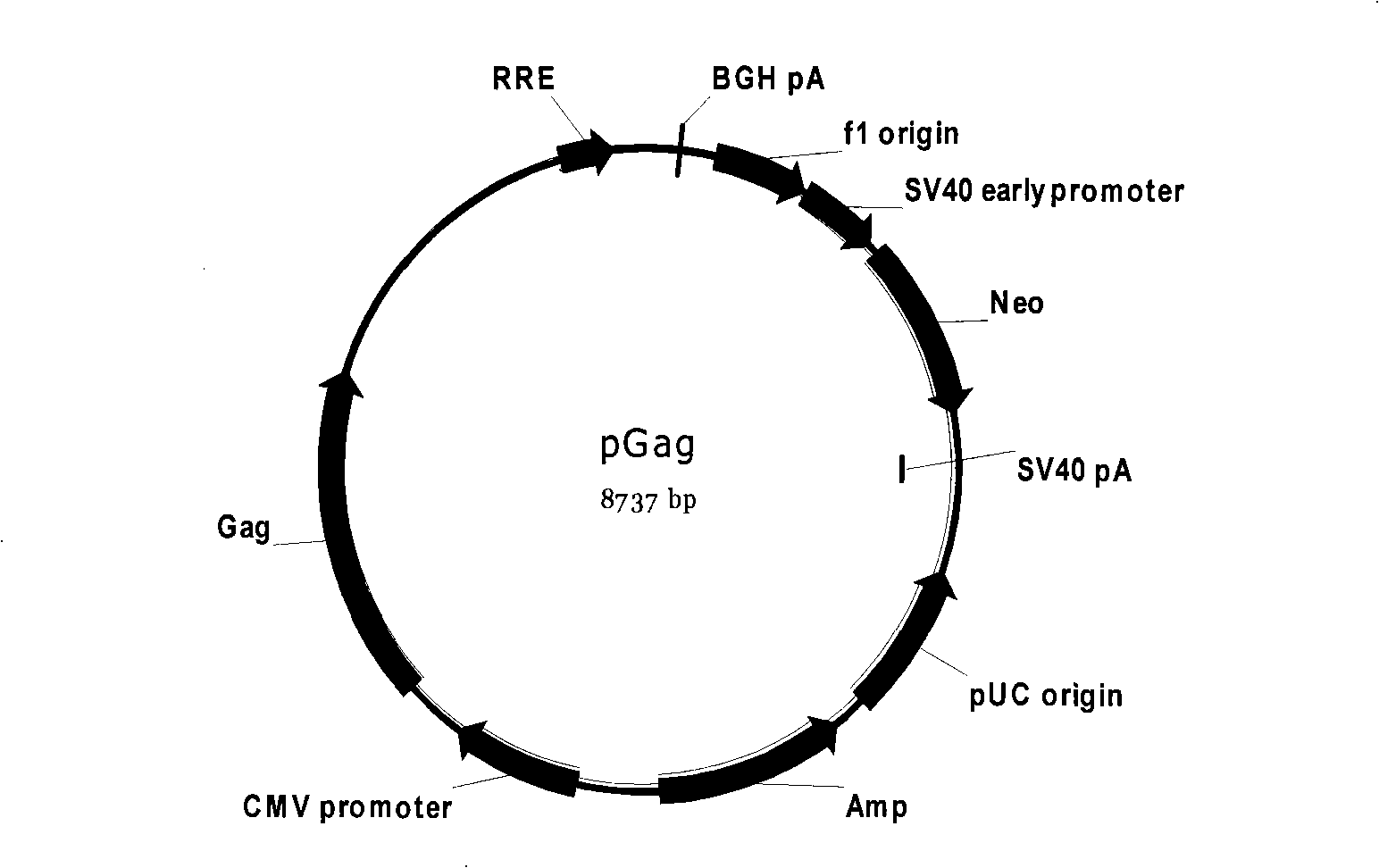
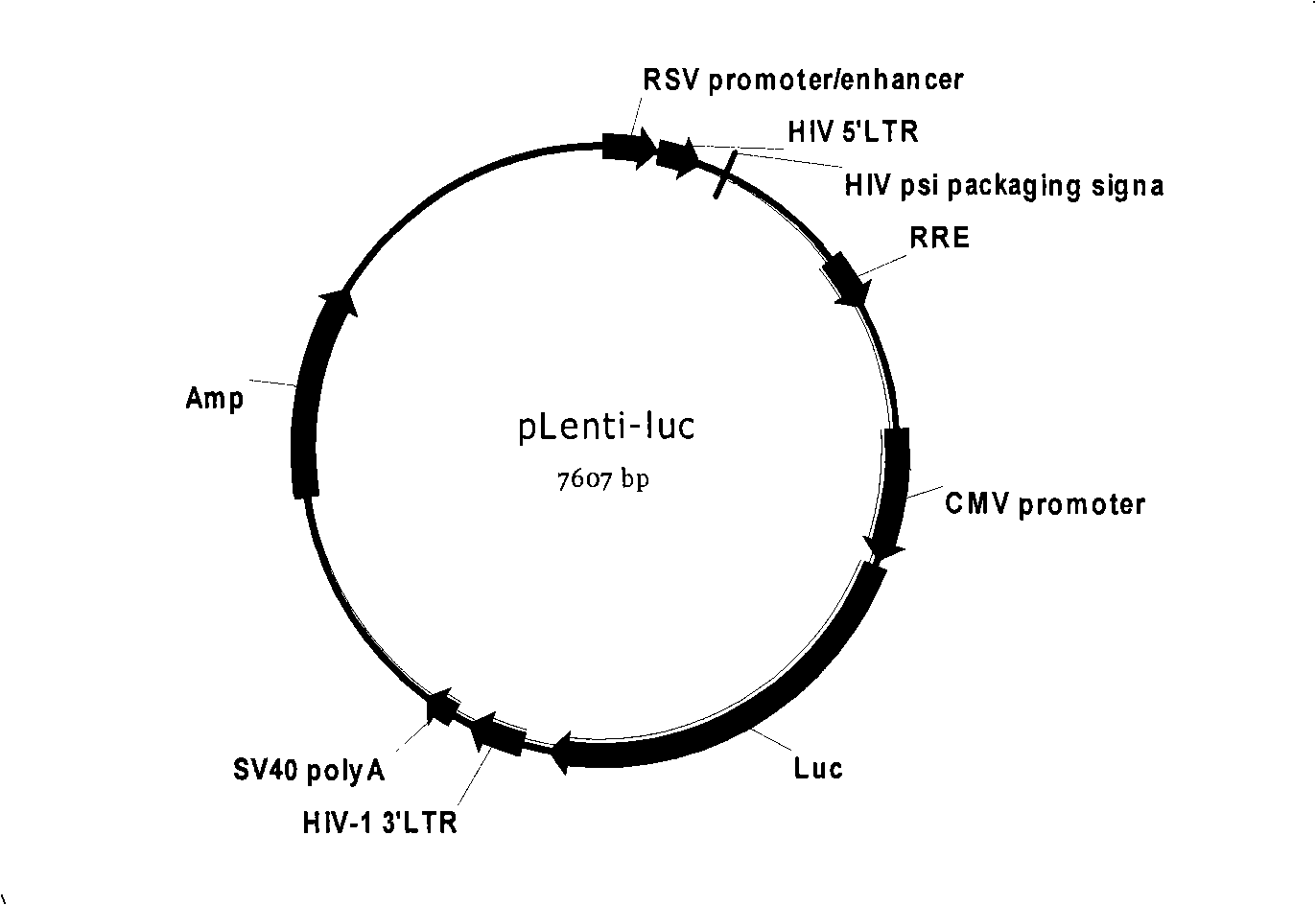
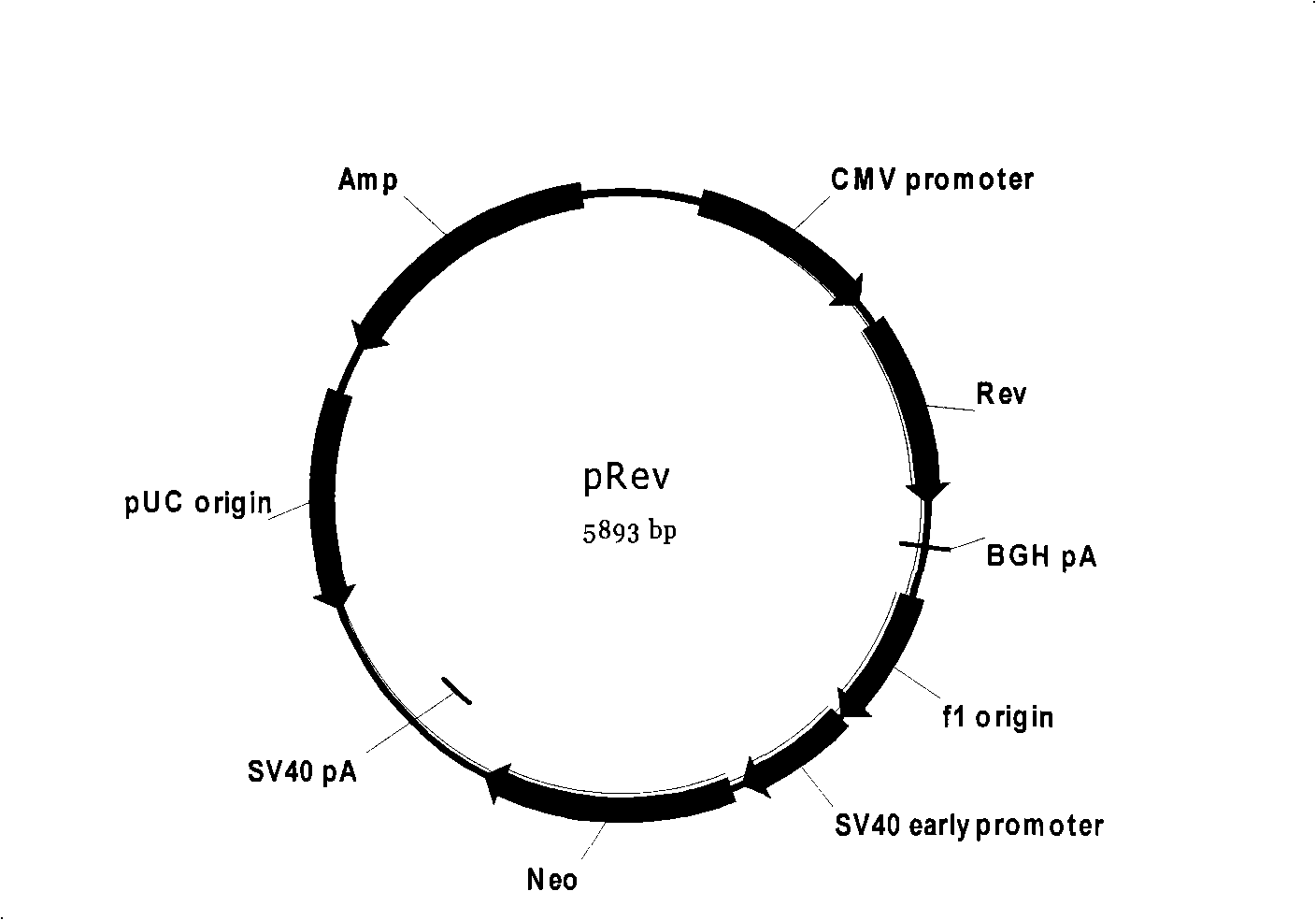
HIV stain drug-resistant phenotype analytical cell model and special pseudotype lentivirus therefor
InactiveCN101353667ARapid Phenotypic Resistance AnalysisSafety Phenotypic Resistance AnalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesPhenotypic resistanceReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a cell model of HIV strain phenotypic drug resistance analysis and special pseudotype slow virus thereof; the invention constructs plasmid for expressing Gag protein of HIV, recombinant slow-virus plasmid for expressing reporter gene and helper plasmid for expressing Rev protein of HIV; under the effect of the helper plasmid pVSV-G, the three plasmid and HIV reverse transcriptase and the gene fragment of protease which are amplified from strain can obtain the pseudotype slow virus of the HIV reverse transcriptase and protease gene containing strain. The pseudotype slow virus is used for infecting the cells of mammals, thus obtaining the strain phenotypic resistance cell model based on the reporter gene. The cell model of the invention can carry out phenotypic resistance analysis to the strain, the reporter gene leads the cell model to have super high sensitivity, and the cell model of HIV strain phenotypic drug resistance analysis is applicable to the phenotypic drug resistance analysis of HIV strain in Chinese population.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Genome selection method for breeding Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant improved variety
InactiveCN114015789AImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyZooid
The invention provides a genome selection method for breeding Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant improved variety. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant reference group by using Plectropomus leopardus young fishes from different geographical sources, and taking individuals which have disease-resistant phenotypes but are not included in the reference group as a verification group, wherein the Plectropomus leopardus young fishes used for constructing the disease-resistant reference group is obtained after disease resistance screening; and predicting a disease-resistant character genome estimation breeding value of the verification group by using the selected SNP sites and the constructed Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant reference group, and selecting alternative parents by using the disease-resistant character genome estimation breeding value to obtain individuals with strong disease resistance for disease-resistant improved variety cultivation. According to the invention, the method for breeding the Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant improved variety based on the whole-genome selection technology can be used for screening parents with high disease resistance, the selected parents can be directly used for breeding Plectropomus leopardus, and an efficient technical means is provided for improving the survival rate of Plectropomus leopardus breeding group.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI +1
Identification method for sulfur-resistant hybrid breeding progeny of saccharomyces bayanus
InactiveCN103740821AImprove accuracyAccurate distinctionMicrobiological testing/measurementYeastAgricultural science
The invention discloses an identification method for a sulfur-resistant hybrid breeding progeny of saccharomyces bayanus, belonging to an identification method for a novel saccharomyces bayanus breeding strain. The identification method comprises the following steps: saccharomyces bayanus hybridization; sulfur resistance measurement of a saccharomyces bayanus strain; saccharomyces bayanus DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction and purification, wherein a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system taking (i) FZF1 ( / i) as a primer and a procedure are adopted; PCR primer sequencing and identifying; and further ISSR (Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat) analysis for the sulfur-resistant hybrid breeding progeny. In the embodiment, 18 suspected hybrid progenies are obtained from 3 hybridized combinations. The PCR analysis results are as follows: the 18 suspected hybrid progenies contain 5 strains only containing sulfur-nonresistant parental characteristic bands, 2 strains containing sulfur-resistant parental characteristic bands and other 11 strains containing biparental characteristic bands. The ISSR analysis for 8 sulfur-resistant hybrid progenies proves that the same strain has two single colonies with the completely-consistent fingerprint spectrums. According to the invention, 6 sulfur-resistant hybrid breeding progeny strains of saccharomyces bayanus are obtained according to a DNA sequence and an ISSR atlas and through sulfur-resistant phenotype screening, so that the accuracy rate for identifying the hybrid breeding progeny strains is remarkably increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
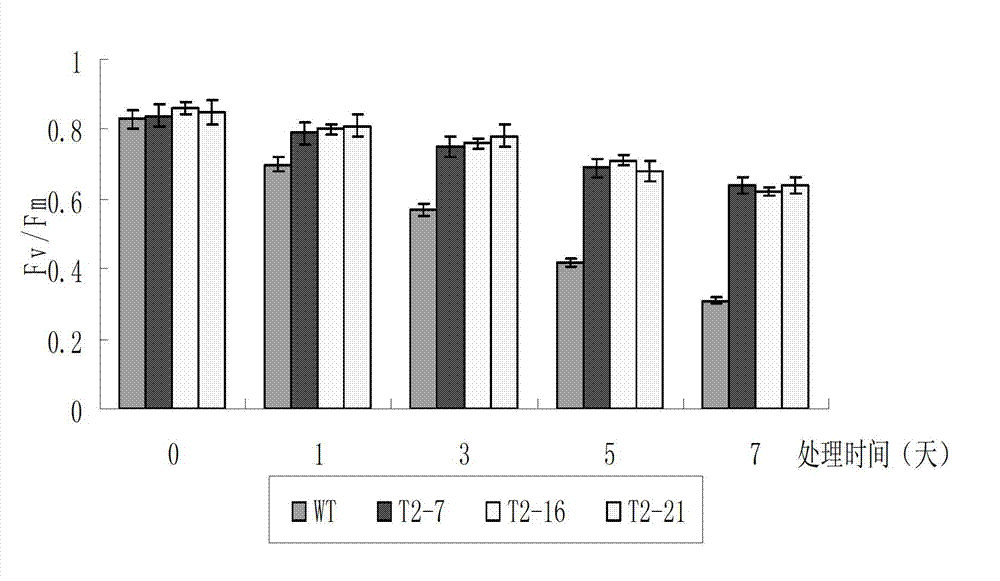
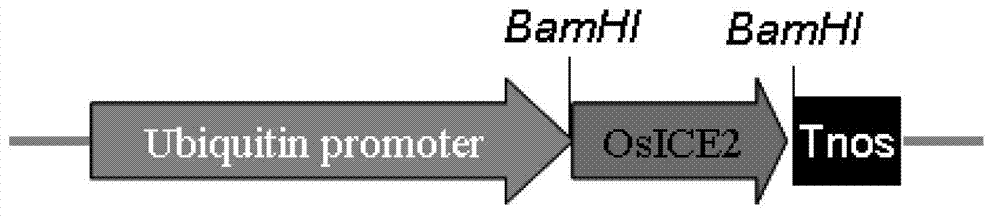
Cold-resistant gene engineering application method of rice OsICE2 gene
InactiveCN103290050AReduce expressionIncrease increaseFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
The invention discloses a cold-resistant gene engineering application method of rice OsICE2 gene. The method includes: (1) gene cloning, (2) vector construction, (3) transgenosis, (4) analysis of the cold-resistant phenotype of OsICE2 by a transgenic technology, and (5) comparative analysis of a transgenic plant and a control plant in the cold-resistant physiological aspect. By the steps, the method determines the influence of OsICE2 gene on protein expression quantity under low temperature stress, and finds that a transgenic rice strain can slow down the reduction of protein expression quantity of RuBi sCO subunit binding-protein alpha subunit, RuBi sCO activase small isoform precursor, Chlorophyll a-b binding protein and isocitrate dehydrogenase under low temperature stress, and improves the expression increase range of 70 kDa heat shock-related protein.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
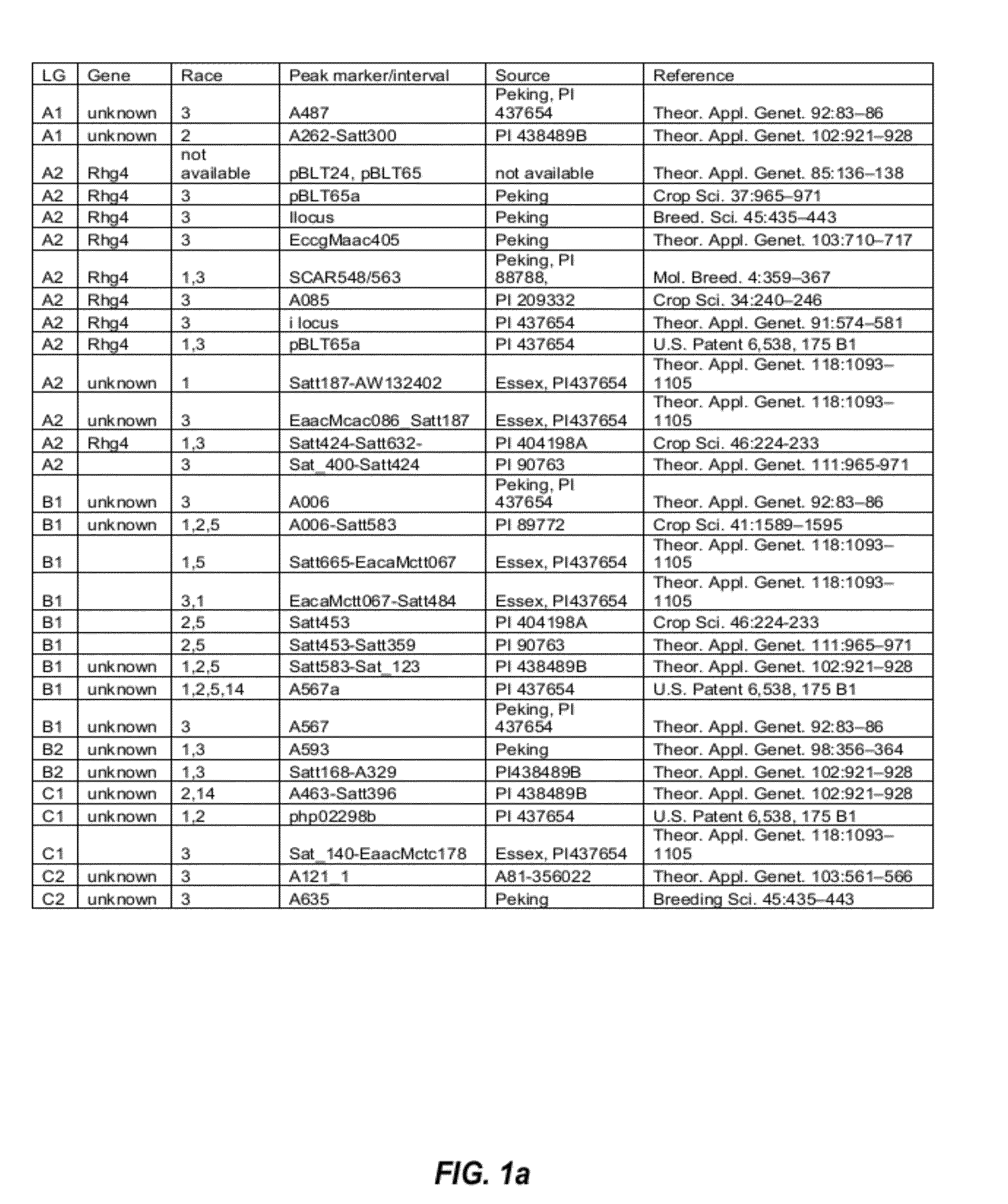
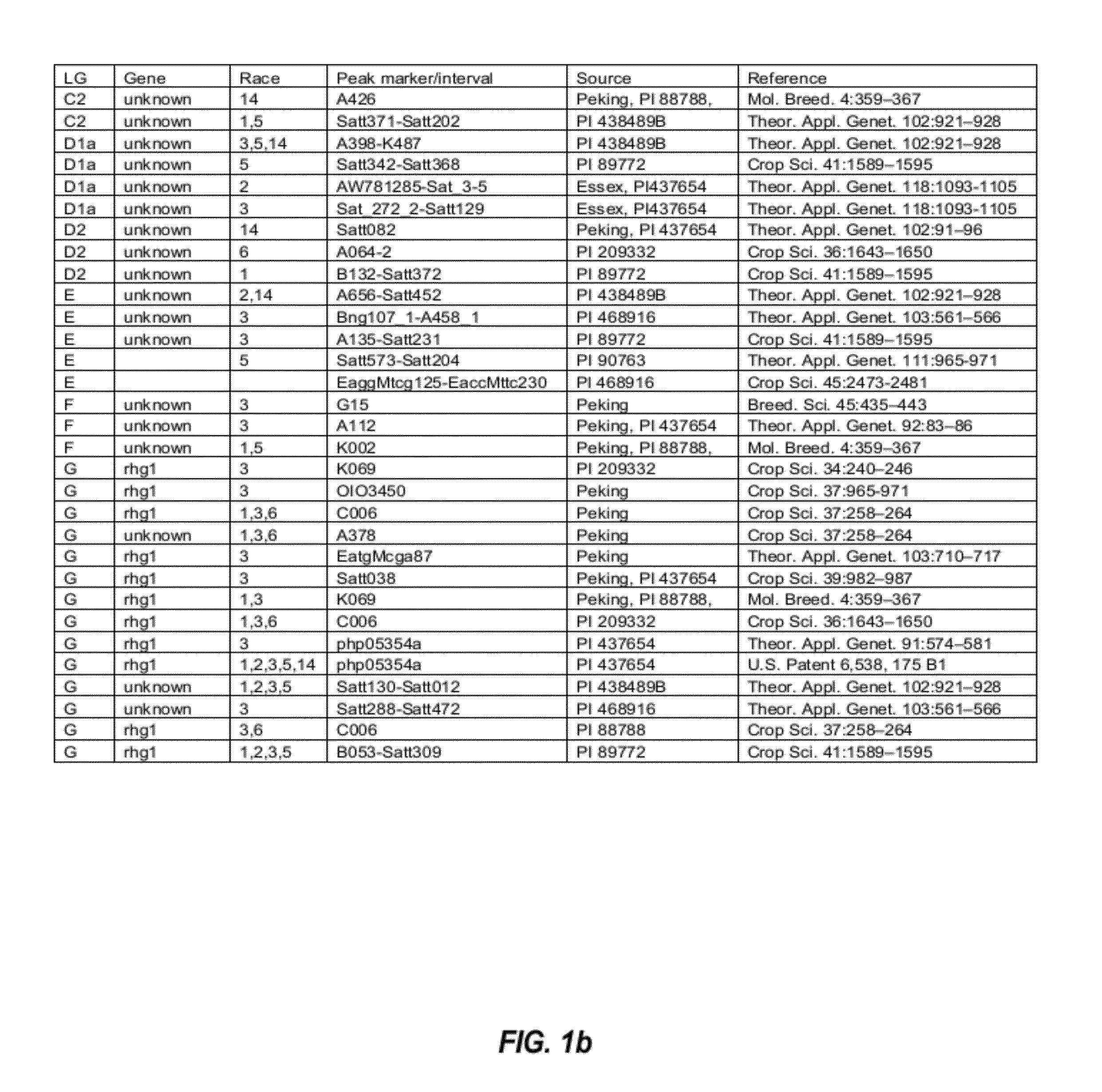
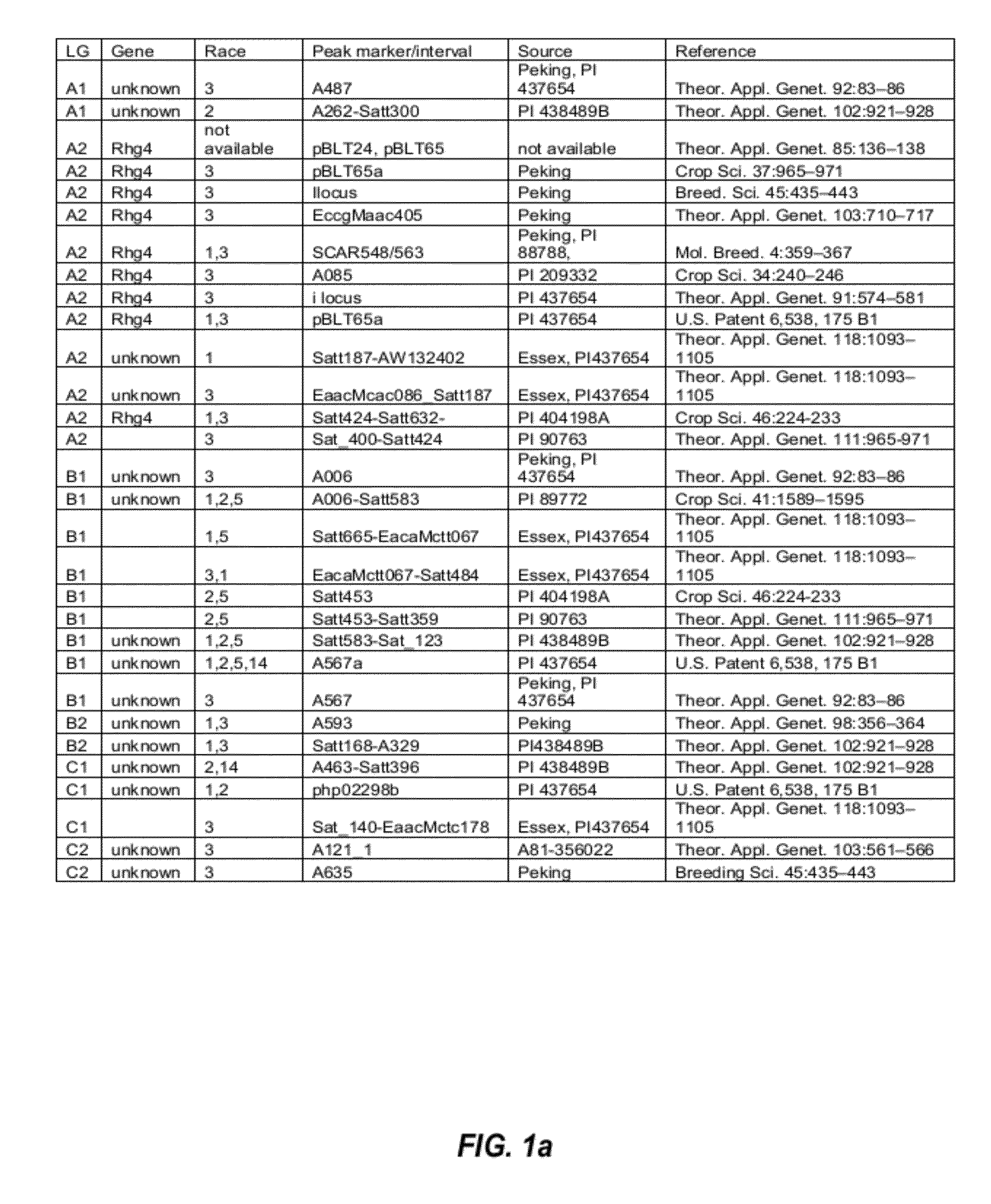
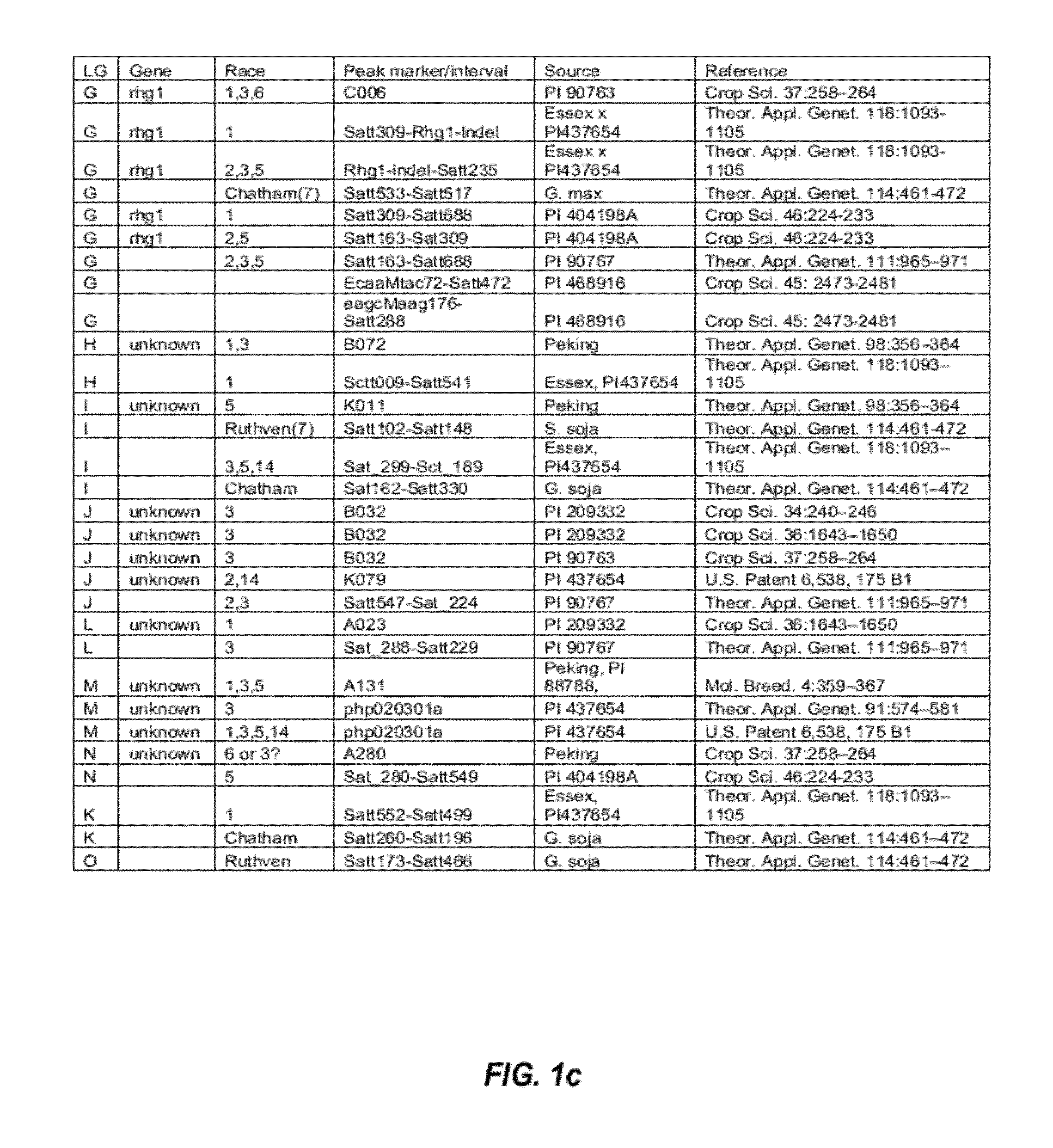
Soybean markers linked to scn resistance
ActiveUS20120131693A1Facilitate marker-assisted selectionImprove overall utilizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBiology
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for identifying the SCN resistant phenotype in soybean. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns methods for performing marker-assisted breeding and selection of plants carrying one or more determinants of SCN resistance in soybean.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Method used for simplified identification of tobacco brown spot resistance using artificial disease nursery
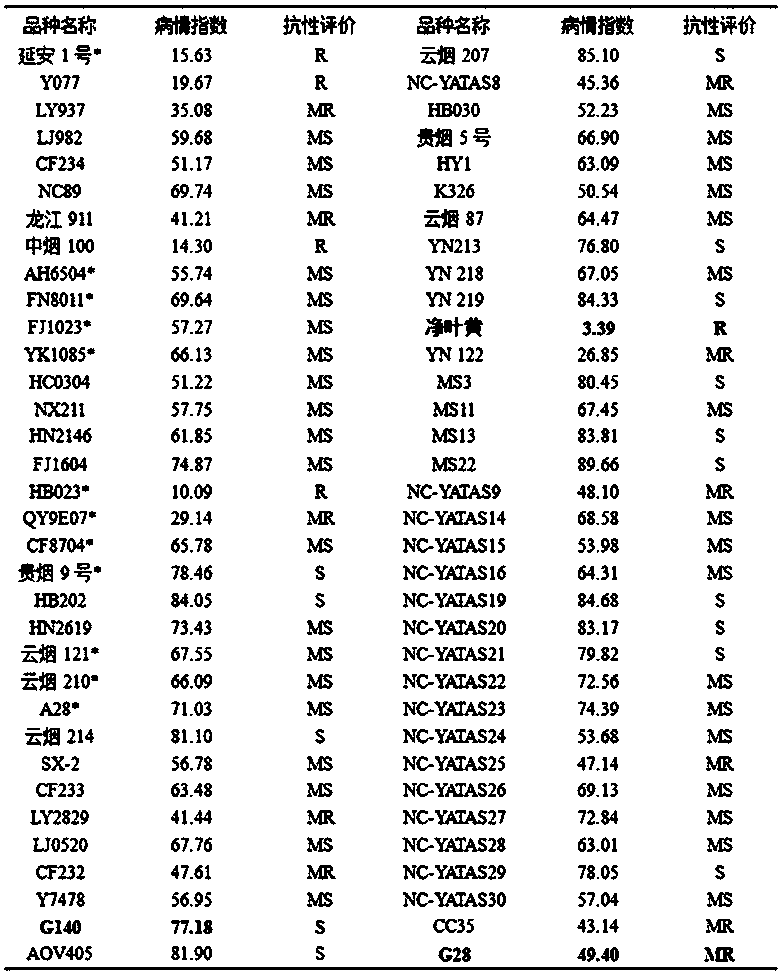
ActiveCN107821159AEffectively inducedImprove accuracyTobacco cultivationPlant genotype modificationDiseaseHigh humidity
The invention discloses a method used for simplified identification of tobacco brown spot resistance using artificial disease nursery. The method comprises following steps: disease nursery selection,intensive line-type field overall arrangement, fertilizer controlled cultivation, formation of artificial disease nursery via relatively low concentration large area spraying, moisture retention inducing, and resistance evaluation. According to the method, the characteristics of field tobacco plants, that leaves are susceptible to diseases at maturation stage, and tobacco brown spot is easily caused at an appropriate temperature and high humidity conditions, are taken into consideration, biological zones with appropriate temperature, high humidity, irrigation convenience, and excellent irrigation conditions at tobacco leaf maturation stage are taken as disease nursery; intensive line-type field overall arrangement, fertilizer controlled cultivation, and plant leaf disease susceptibility increasing are adopted, effective inducing of diseases is realized, the accuracy and the reproducibility of tobacco brown spot resistance identification are increased; follow up investigation on the disease infection process of resistant (resistance and moderate resistance) and susceptible reference varieties is taken as a key investigation. Operation is simple; labor intensity is low; both water and labor are saved; cost is reduced; efficiency is high; tobacco brown spot resistant phenotype identification is accurate; and the method is worthy of popularization.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
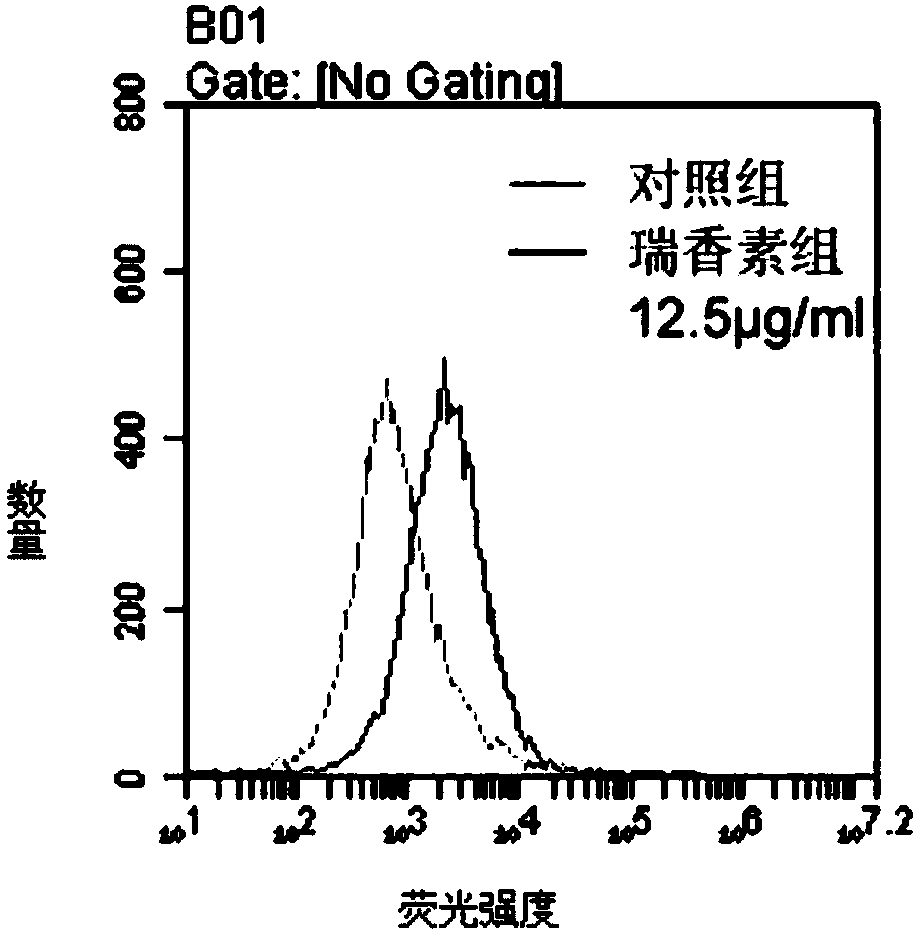
Applications of daphnetin in inhibition of Helicobacter pylori
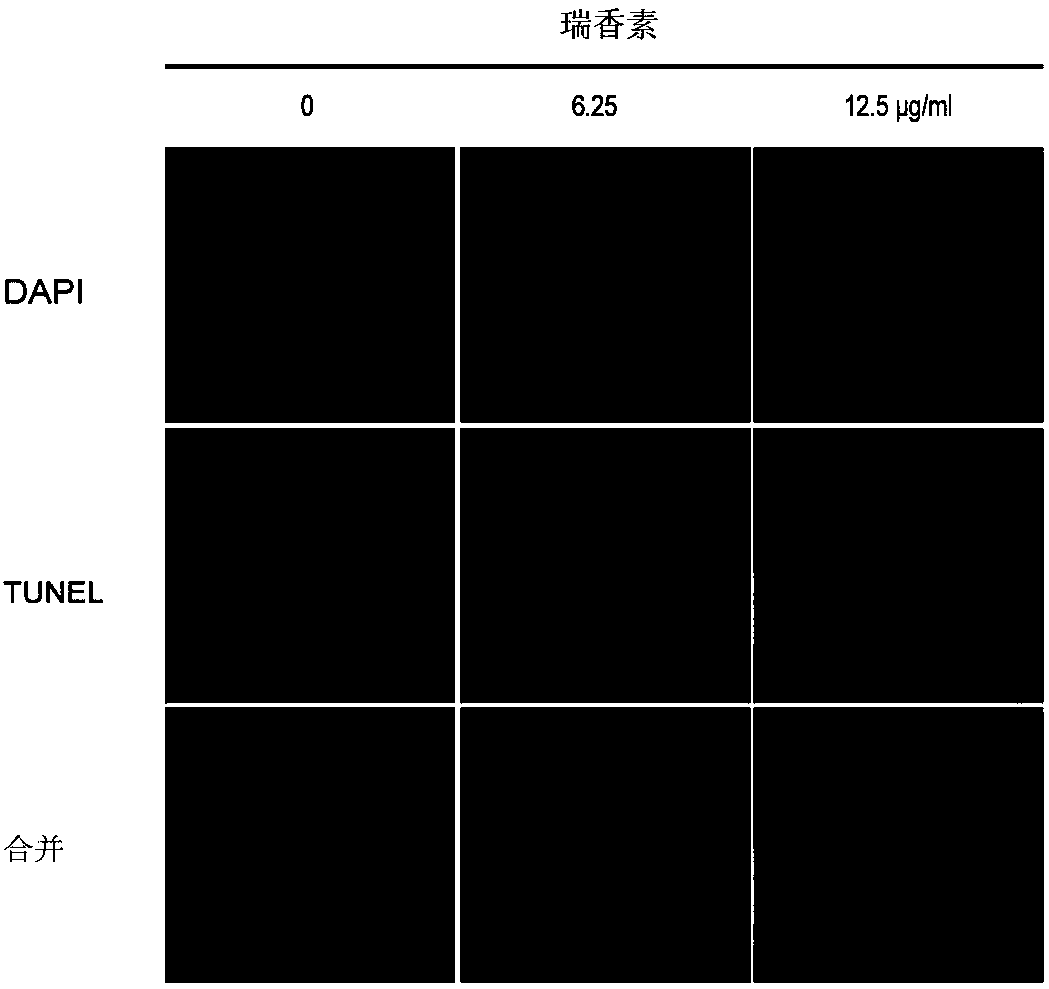
ActiveCN108379258AOpen up new usesAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemMinimum inhibitory concentrationHelicobacter pylori
The present invention relates to new uses of daphnetin in inhibition of Helicobacter pylori. According to the present invention, the daphnetin can well kill a variety of drug-resistant phenotype Helicobacter pylori; particularly the results show that the daphnetin can produce the zone-of-inhibition with a diameter of 39-53 mm at a concentration of 100 [mu]g / disc, and has the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 25-100 [mu]g / ml; and the new use of the daphnetin provide the new option for Helicobacter pylori inhibition drugs.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for identifying seedling-stage cold-resistant phenotypes of paddy rice
The invention discloses a method for identifying seedling-stage cold-resistant phenotypes of paddy rice. The method provided by the invention sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) culturing germination-accelerated paddy rice seeds to be identified, so as to obtain young seedlings of a three-leaf stage; (2) carrying out low-temperature stressing on stem growing points and parts below the same of the young seedlings obtained in the step (1); (3) carrying out recovery culture on the young seedlings obtained in the step (2); and (4) after the step (3) is completed, carrying out statistics on the survival rate of the young seedlings, and identifying the cold resistance of the paddy rice to be identified under low-temperature stress according to the survival rate. The low temperature is 18 DEG C or below. Through identifying cold resistance of indica rice, i.e., Guangluai 4# and japonica rice, i.e., Nipponbare by adopting the method, results are in full agreement with expected experimental results. Therefore, the method provided by the invention can be used for identifying the seedling stage cold resistance of paddy rice under low-temperature stress and has an important application value in screening cold-resistant varieties of plants.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
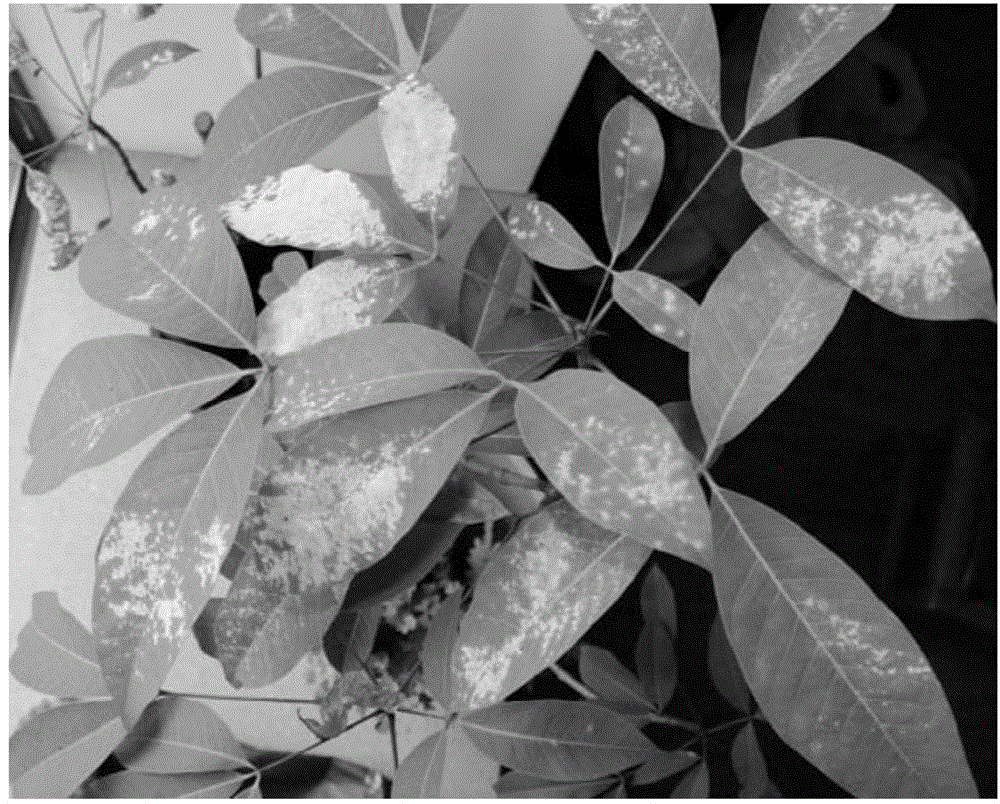
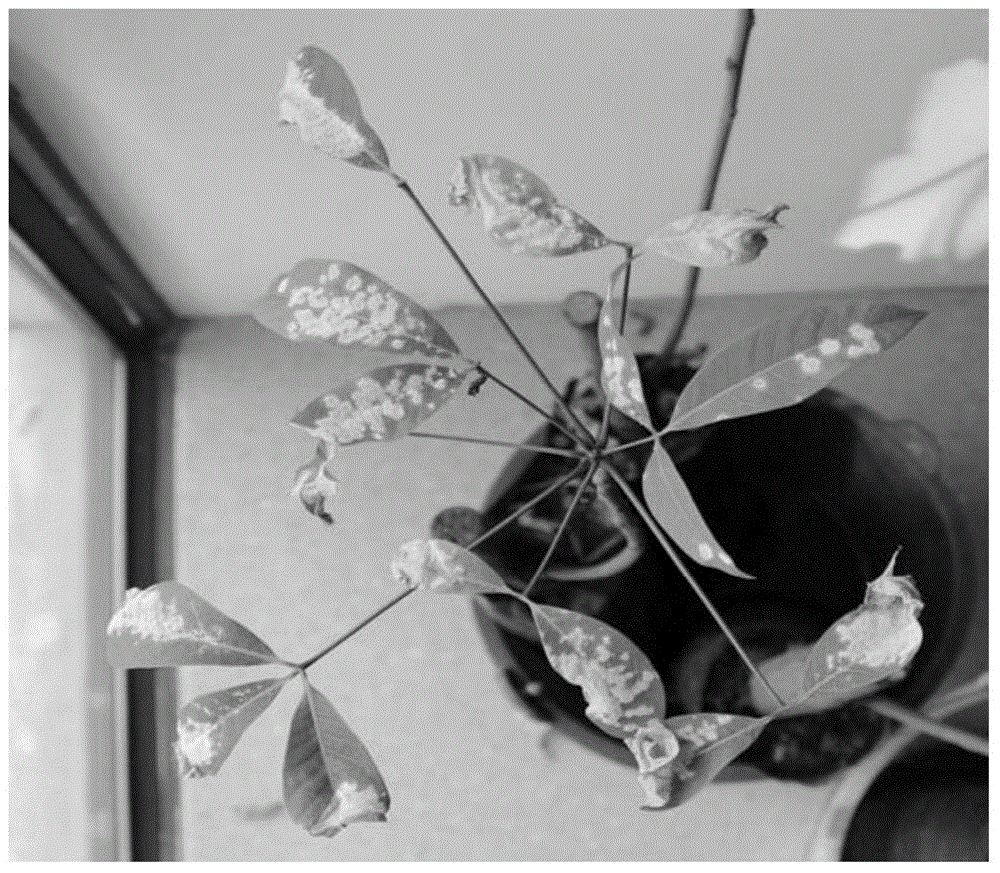
Application of oidium heveae-resistant gene ROH1 to arabidopsis
The invention discloses an application of an oidium heveae-resistant gene ROH1 to arabidopsis. The invention provides an application of ROH1 protein, a coding gene of the ROH1 protein or a recombinant vector containing the coding gene to the regulation and control of plant disease resistance; an amino acid sequence of the ROH1 protein is a sequence 2 in a sequence table. An arabidopsis mutant with ROH1 mutation is complemented with the gene ROH1, so that a transgenic plant is obtained and an oidium heveae-resistant phenotype of wild-type arabidopsis is recovered. Therefore, the fact proves that ROH1 is the oidium heveae-resistant gene and lays a very good foundation for breeding for disease resistance.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Glycerol-3- phosphoric desaturase gene relating with glycerol synthesis and uses thereof
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance
The present invention stems from the realization that the cell surface content of sialic acids is associated with drug susceptibility and resistance in neoplastic and damaged cells. A general decrease in the amounts of the α2-6 linked sialic acid has been confirmed in resistant phenotype compare to its corresponding sensitive parental cells. Treating the resistant phenotype with neuraminidase, an enzyme that removes the sialic acid from the sugar chain, facilitates the drug internalization and reinstalls the cell susceptibility to the drug. Based on these observations, methods for predicting the resistance to a number of drugs and detecting multi-drug resistanc in neoplastic and damaged cells have been invented.
Owner:RAZI NAHID
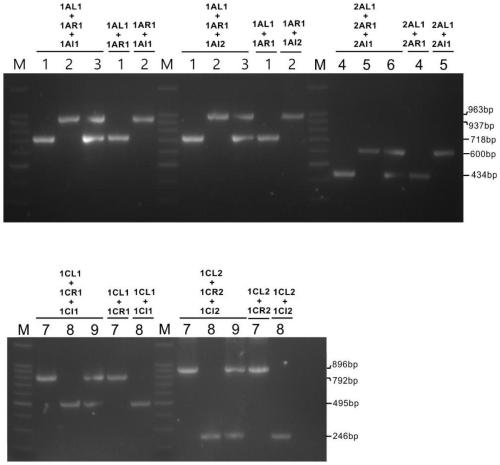
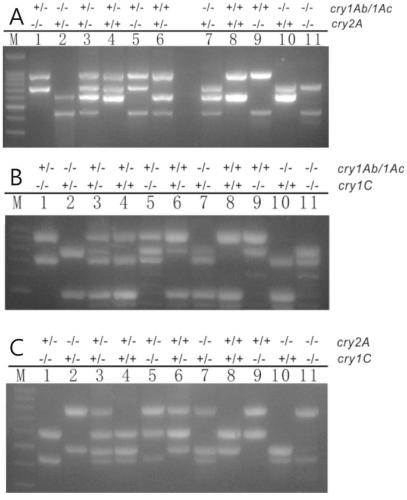
Multivalent transgenic insect-resistant rice genotype identification primer pair and method
ActiveCN109971881ASolve the problem that the identification cannot distinguish the unit priceSolve the problem of polyvalentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
The invention discloses a multivalent transgenic insect-resistant rice genotype identification primer pair and method. A series of multiplex primers are designed aiming at transgenic rice TT51-1 (trans-cry1Ab / cry1Ac fusion gene), T2A-1 (trans-cry2A gene) and T1C-19 (trans-cry1C gene) and used for detecting genotypes of univalent, divalent and trivalent trans-Bt genes in rice breeding material so as to confirm Bt gene homozygous or heterozygous states as soon as possible, and the problem of failure in distinguishing of univalence and multivalence in insect-resistant phenotype identification issolved. According to experiments, a detection method is high in specificity, expensive or high-time-consumption detection means are avoided, and an insect-resistant transgenic rice breeding process can be accelerated.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Single-cell Raman clinical drug resistance kit and detection method
PendingCN112080545AQuick checkRapid drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringStable Isotope LabelingMicroorganism
The invention discloses a single-cell Raman clinical drug resistance rapid detection kit and a detection method. The single-cell Raman clinical drug resistance rapid detection kit comprises an incubation solution, a stationary solution I and a stationary solution II, wherein the incubation solution contains heavy water; the stationary solution I contains normal saline or PBS; and the stationary solution II contains absolute ethyl alcohol. The kit is used for stable isotope labeled single-cell Raman drug resistance detection, can realize rapid detection of drug resistance phenotypes of trace microorganisms in a clinical sample without dependence on proliferation, and can solve the problem of slow detection of clinical drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria in the prior art.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Soybean markers linked to SCN resistance
ActiveUS9049822B2Facilitate marker-assisted selectionImprove overall utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationDeterminantBiotechnology
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for identifying the SCN resistant phenotype in soybean. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns methods for performing marker-assisted breeding and selection of plants carrying one or more determinants of SCN resistance in soybean.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Modified proteins, isolated novel peptides,and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040091964A1AmenableModulate transporter activityAntibacterial agentsFungiPolarized cellChemo therapy
The present invention provides several modified ABC transporter polypeptides that exhibit novel localization in the plasma membrane of polarized and non-polarized cells. The modified ABC transporter of the invention comprises the amino acid sequence of a native apically targeted ABC transporter, in particular cMOAT, MDR3 or MRP4, wherein the terminal tripeptide T-K-F motif of said native ABC transporter is mutated. The isolated modified ABC transporter polypeptide of the invention, and the nucleotide sequence encoding said polypeptide, have utility in the following applications: First, they are used to induce a drug resistant phenotype in a cell. Second, they are used to protect non-polarized cells during chemotherapy and other therapeutic applications. Third, they are used to produce novel cell lines that are used to screen for novel agonists or antagonists of the corresponding native ABC transporter polypeptides.
Owner:BOARD PHILLIP +1
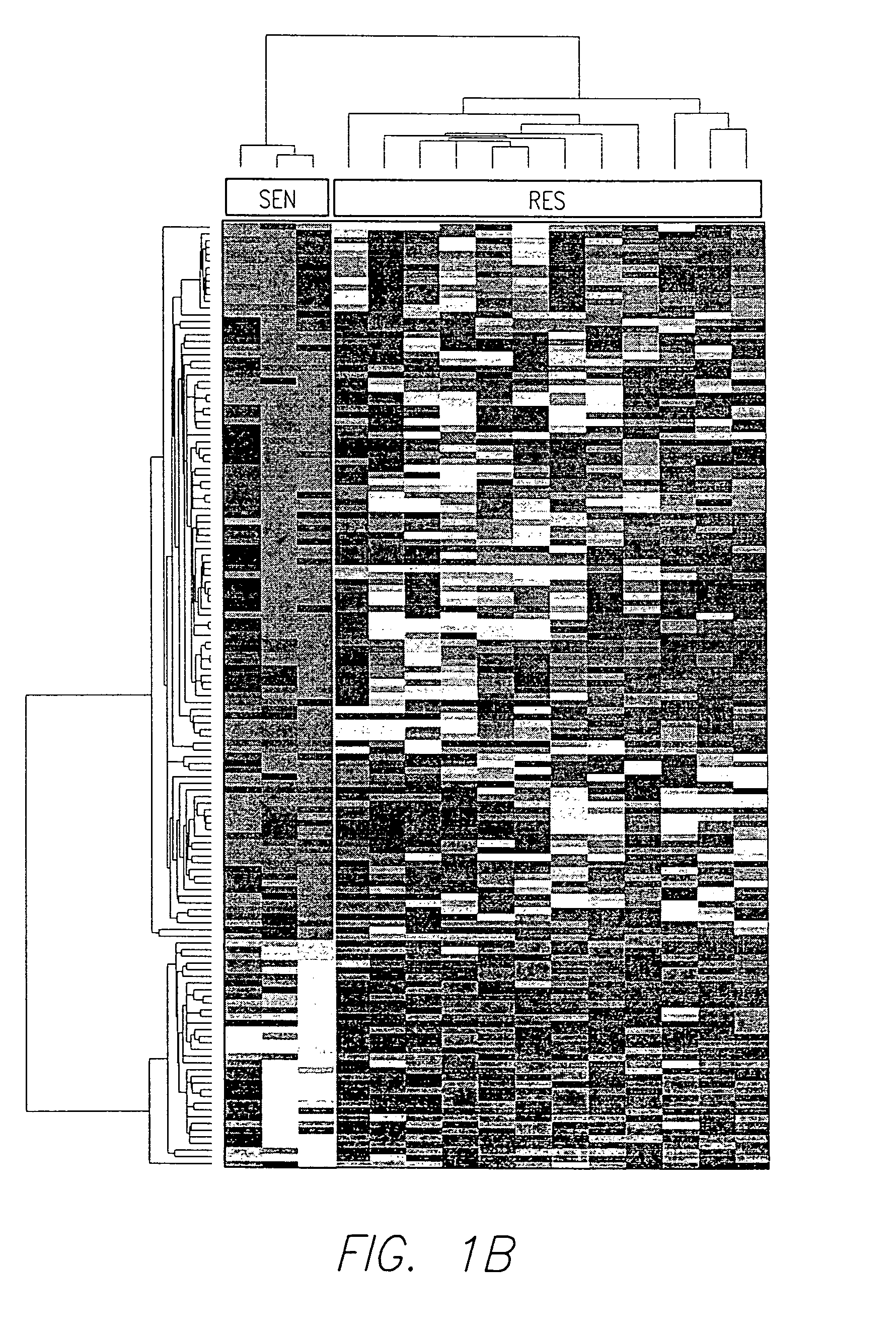
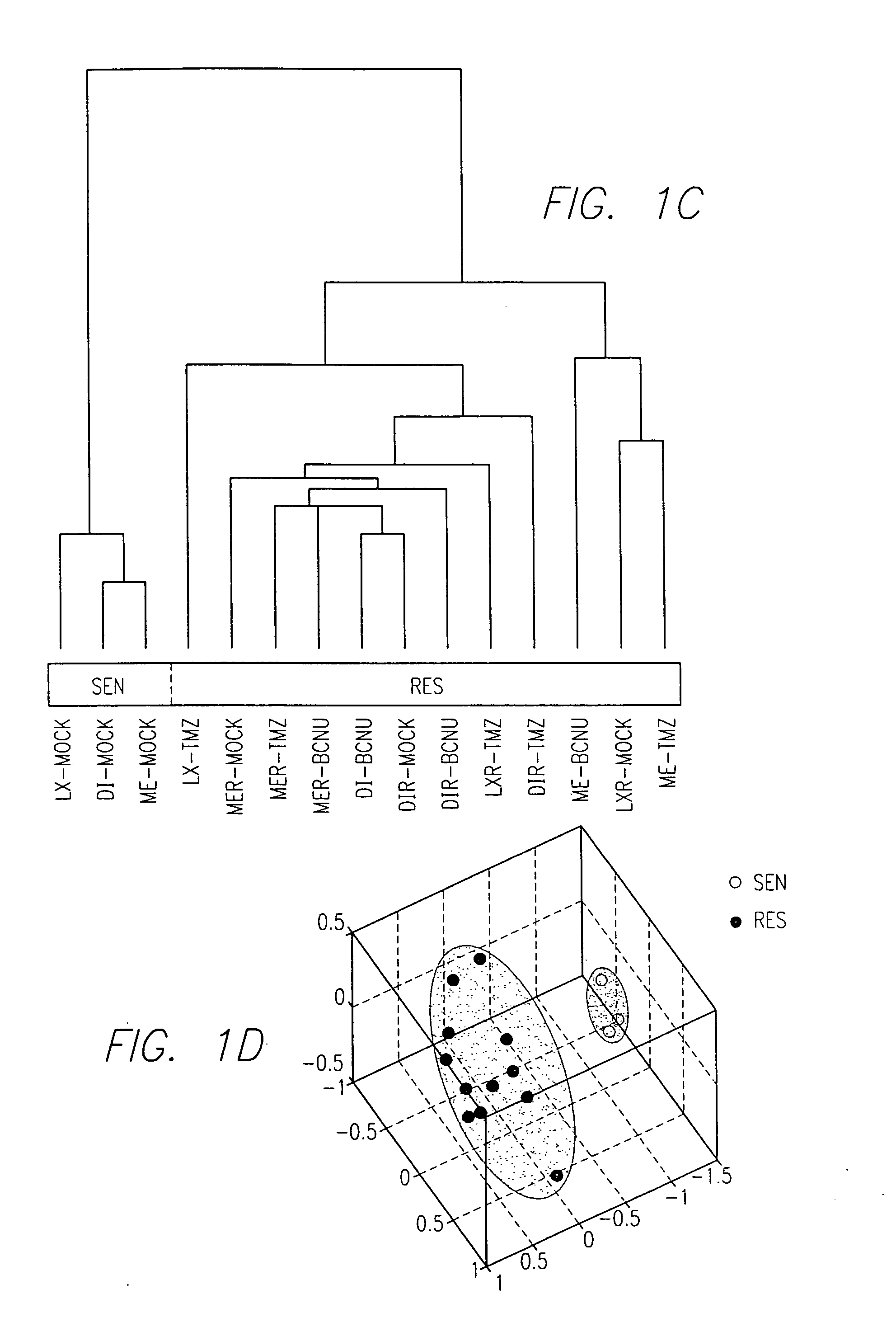
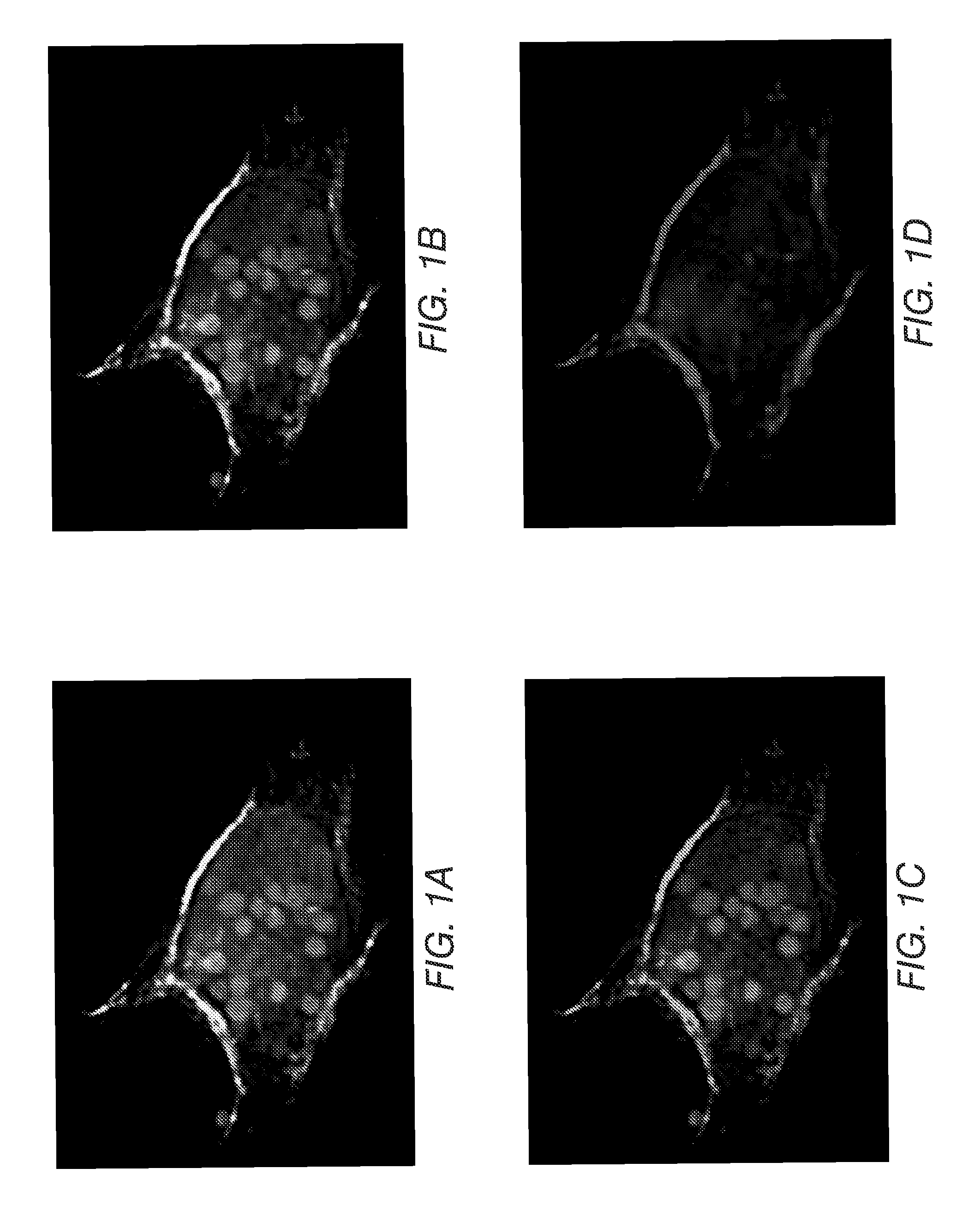
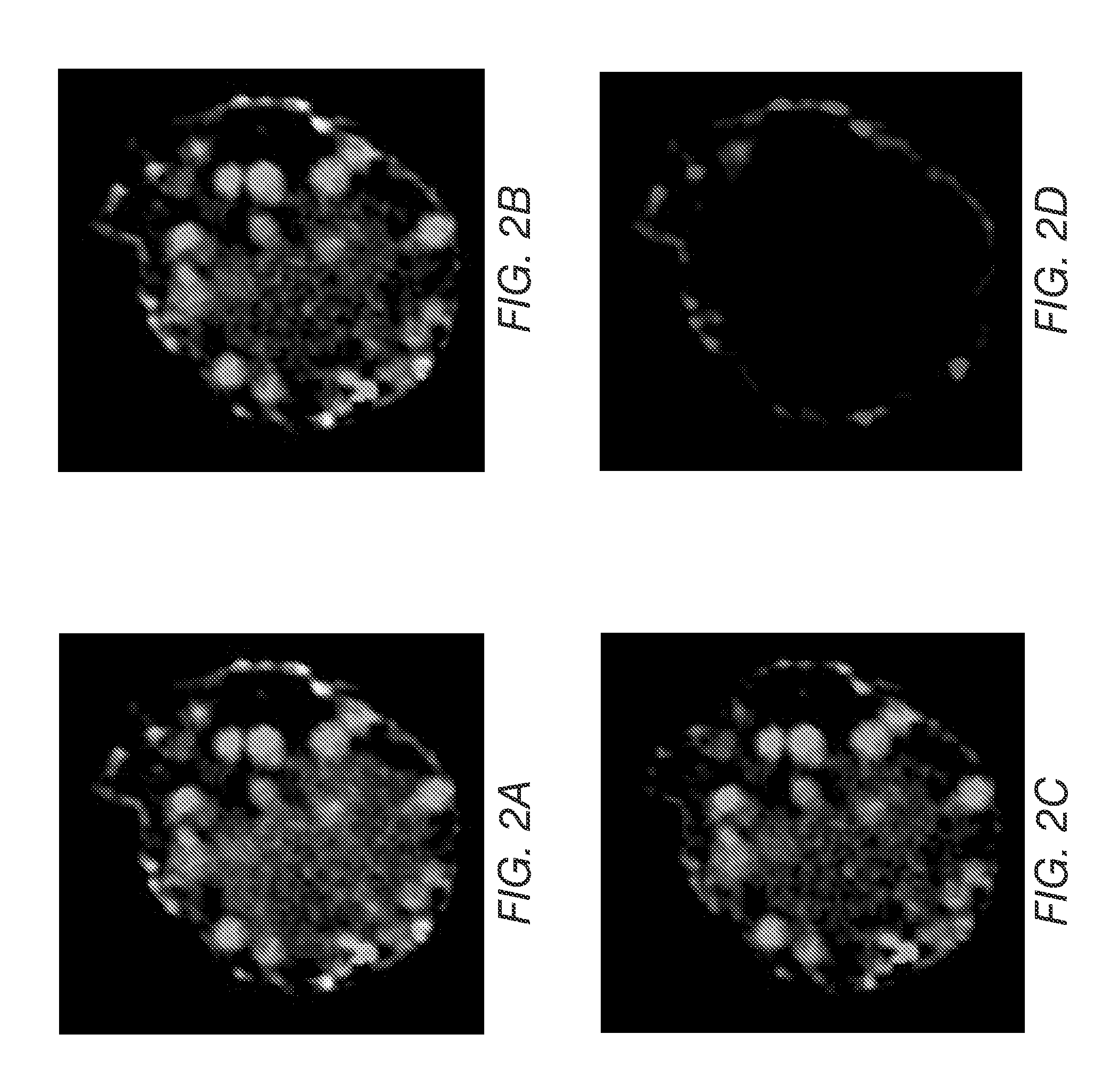
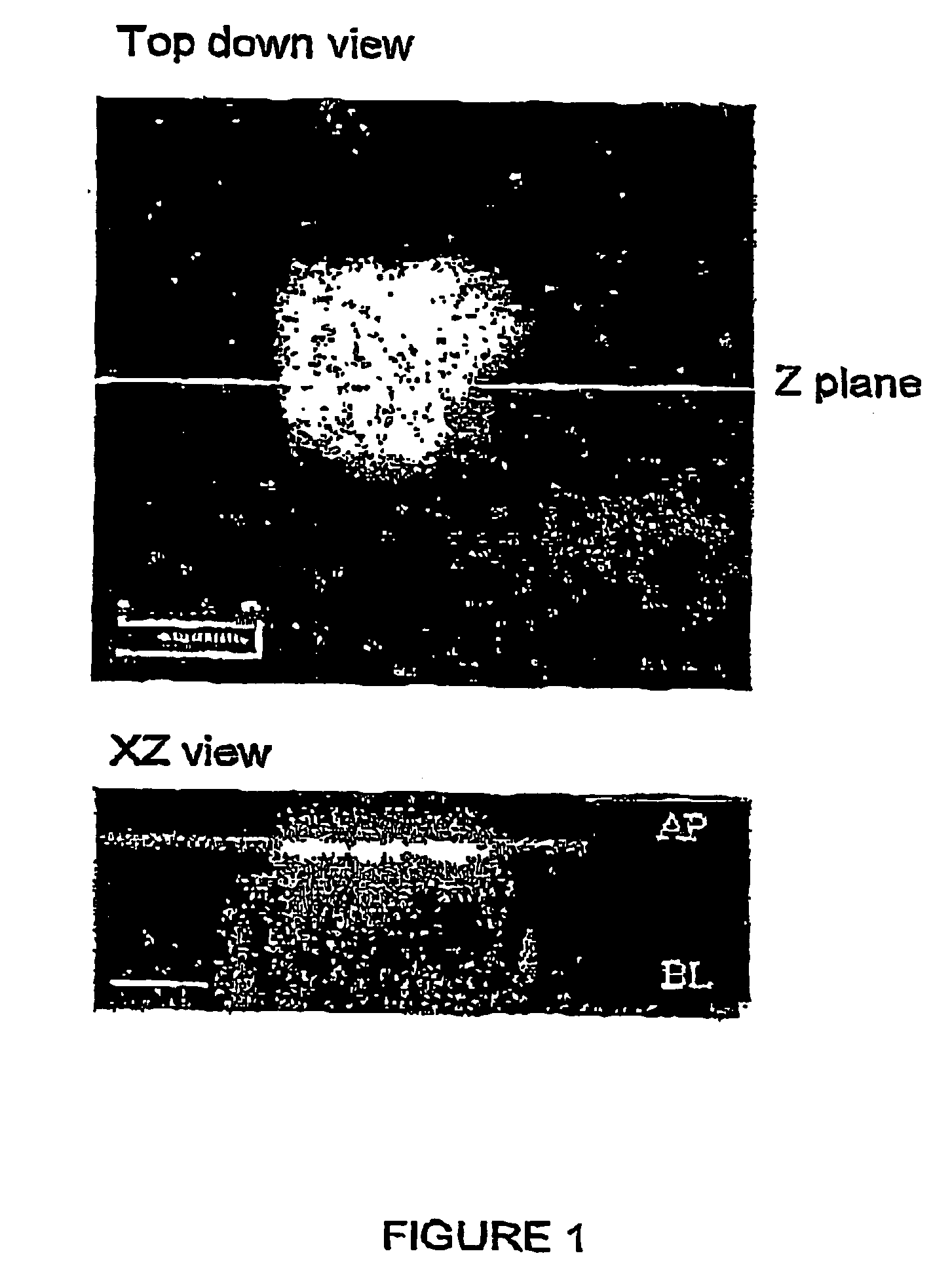
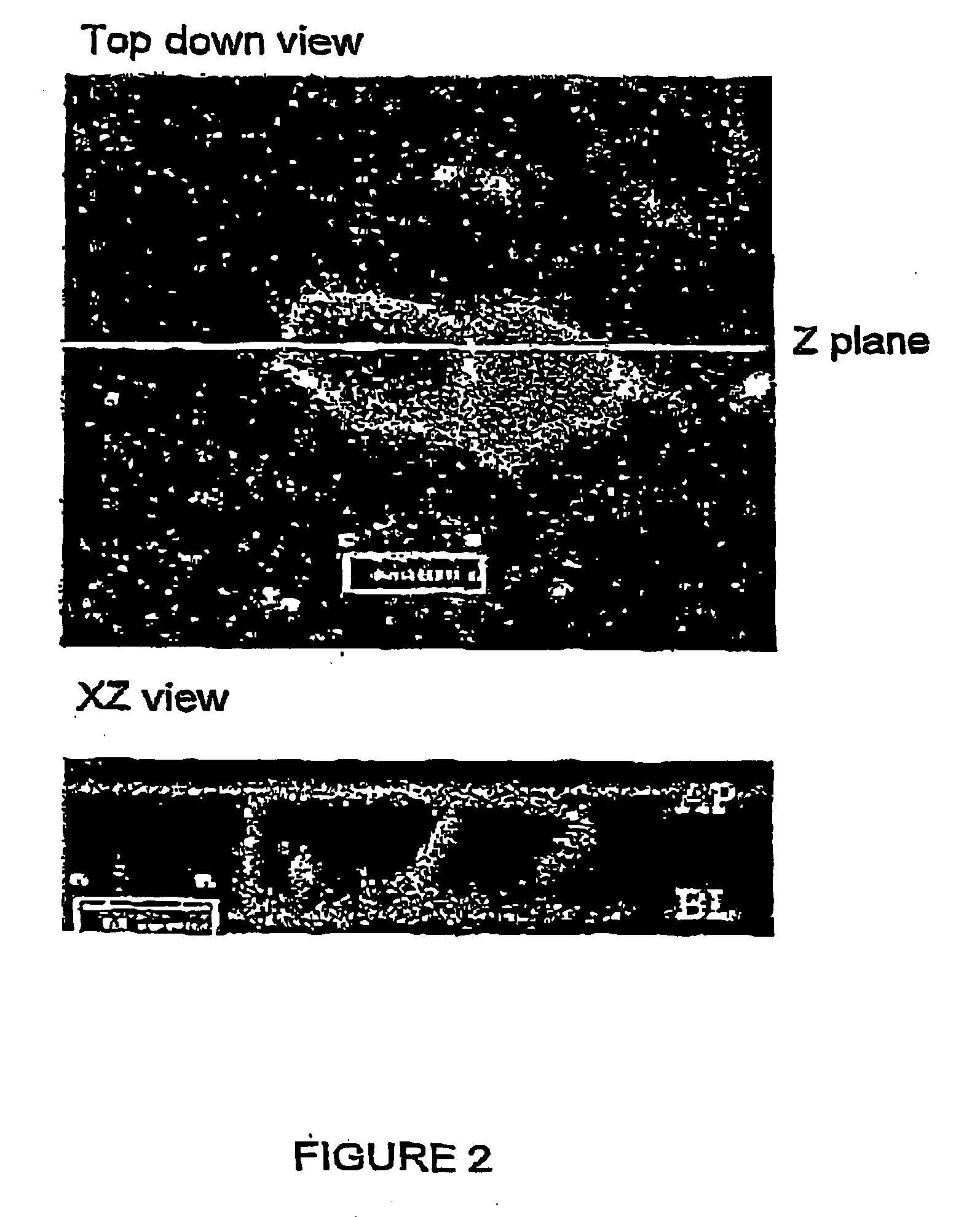
ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER
The present invention relates to a zinc-[Gamma]-PGA composition and a method for treating a cancer. The invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a zinc2+ salt and a [Gamma]-polyglutamic acid carrier, and optionally, an NF-kB inhibitor as a tumor-sensitizing agent, and methods for using such compositions to treat tumors in patients. The method comprises the steps of: administering a liquid dosage form or a solid dosage form of a therapeutically effective amount of a Zn(ll) salt and a [Gamma]-polyglutamic acid carrier to a patient in need thereof. The method of treating a broad spectrum of human tumors, including tumors with a drug-resistant phenotype, using the disclosed compositions are provided. Tumors that respond to the pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein include neuroendocrine (neuroblastoma), gastric, uterine, and lung tumors.
Owner:XYLONIX IP HLDG PTE LTD
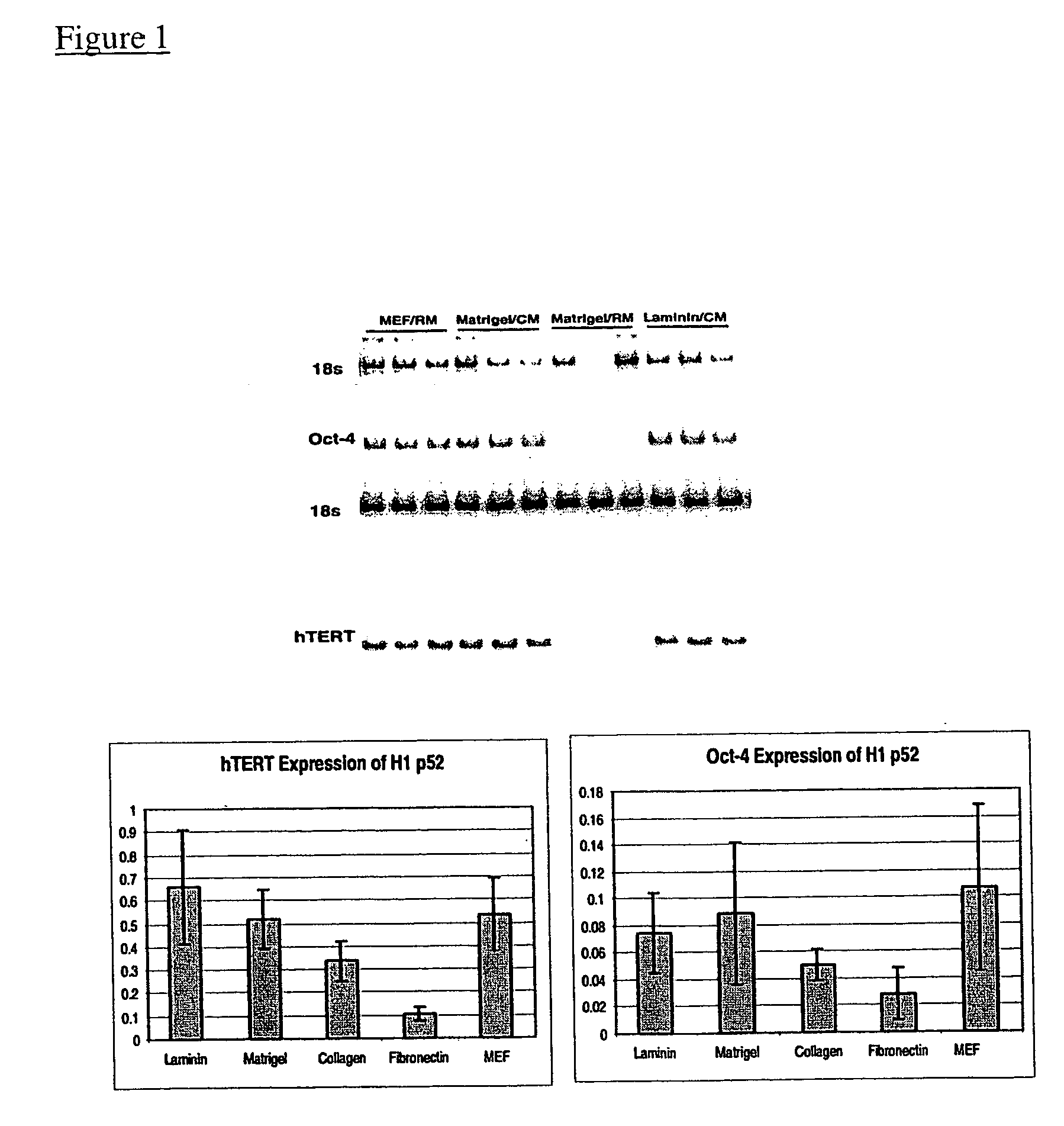
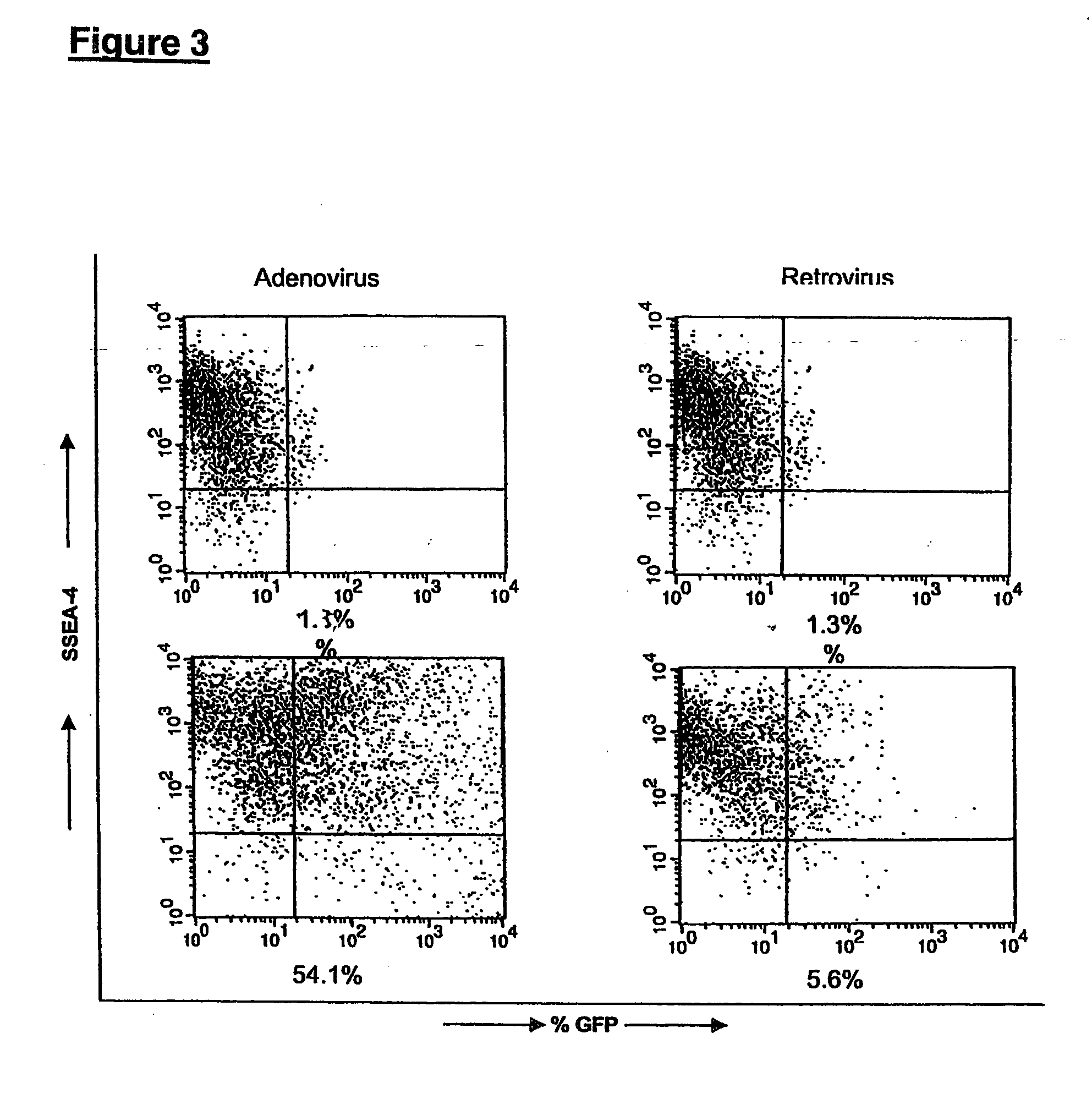
Embryonic stem cells having genetic modifications
InactiveUS20050164385A1Increase the challengeInhibition of differentiationGenetically modified cellsDrug screeningLipid formationPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides a system for obtaining genetically altered primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cells. The role of the feeder cells is replaced by supporting the culture on an extracellular matrix, and culturing the cells in a conditioned medium. The cells can be genetically altered with a viral vector or DNA / lipid complex, and then selected for successful transfection by drug-resistant phenotype in the transfected cells. The system allows for bulk proliferation of genetically altered pPS cells as important products for use in human therapy or drug screening.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
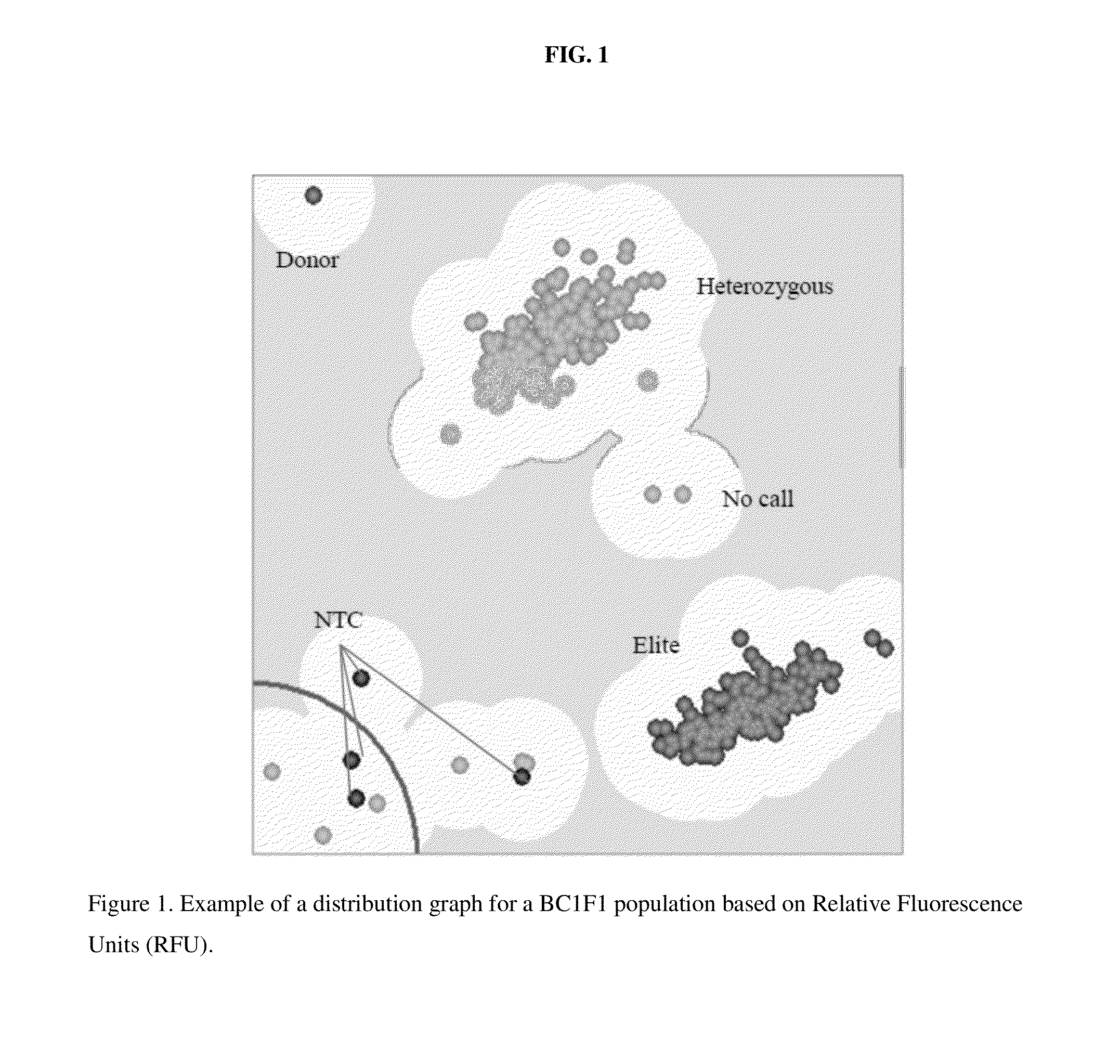
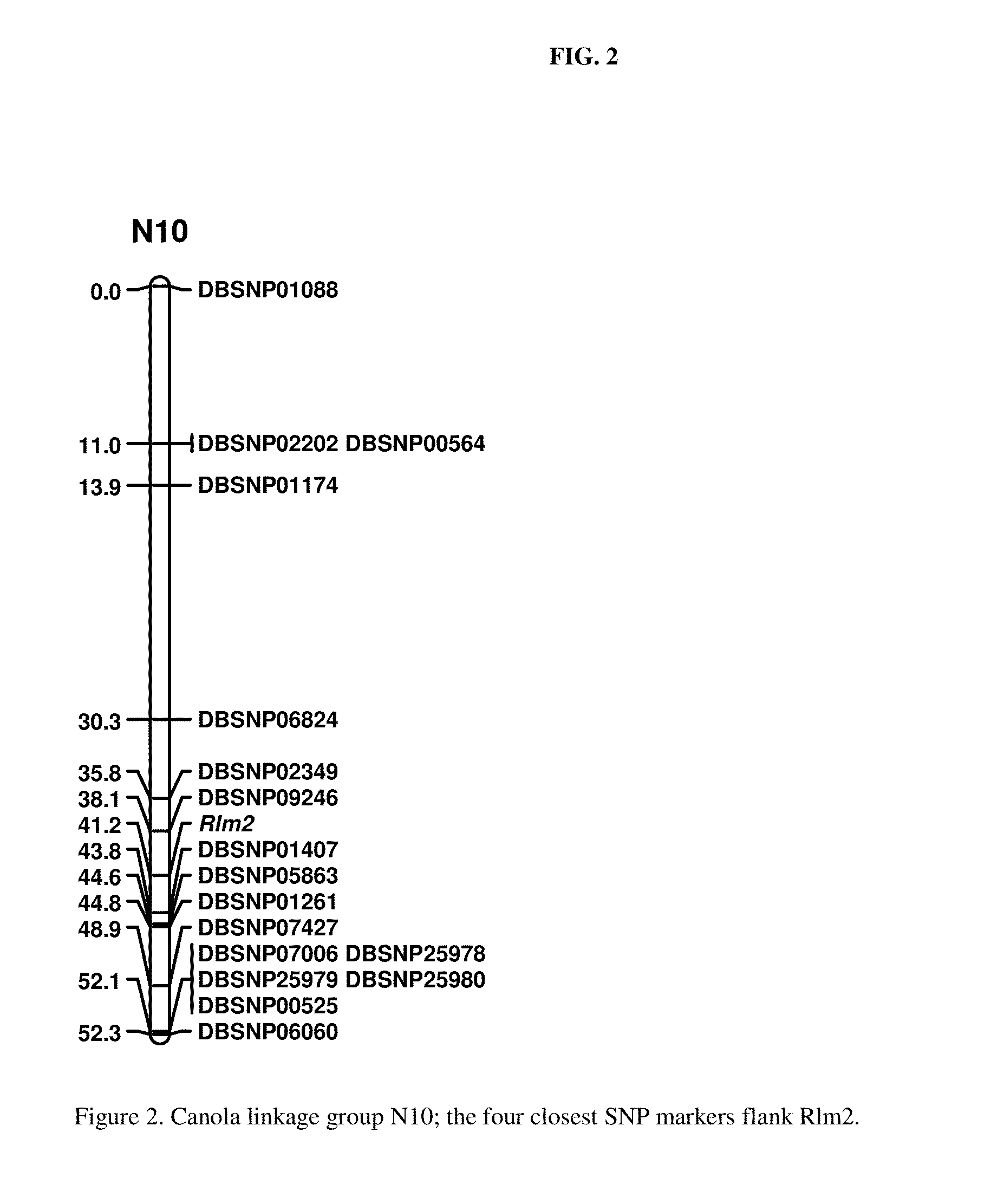
Molecular markers for blackleg resistance gene rlm2 in brassica napus and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20150074850A1Facilitate marker-assisted selectionImprove overall utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyGermplasm
This disclosure concerns methods and compositions for identifying canola plants that have a blackleg resistant phenotype. Some embodiments concern molecular markers to identify, select, and / or construct blackleg resistant plants and germplasm, or to identify and counter-select plants that are susceptible or have low resistance to blackleg disease. Some embodiments concern molecular markers to identify, select, and / or construct blackleg resistant plants that carry the rlm2 gene. This disclosure also concerns canola plants comprising a blackleg resistant phenotype that are generated by methods utilizing at least one marker described herein.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Protein modulators of resistance to alkylating agents
There is disclosed a method for identifying a therapeutically responsive phenotype, as distinguished, e.g. from an alkylating agent resistant phenotype in a cell, which method may be used to evaluate the likelihood of successful outcome of treating a tumor cell with an alkylating agent. The method is directed to the NF-κB activation in response to DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. It comprises the step of measuring a level of expression of a protein, which participates in the NF-κB pathway. Preferably it comprises measuring the expression of TNFAIP3 in the cell, wherein a resistant phenotype has less expression of TNFAIP3 than a sensitive phenotype. Another particularly significant gene, which predicts survival, is NFKBIA. Other genes whose altered expression level is associated with resistance or prognosis are TNIP1, TNIP2, RIP, NFKBIB, Beta4GalNAc-T4, NFKBIE, C8orf4, LIF, CD44, FBXO32, and SDC1, and these are also measured in certain embodiments.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
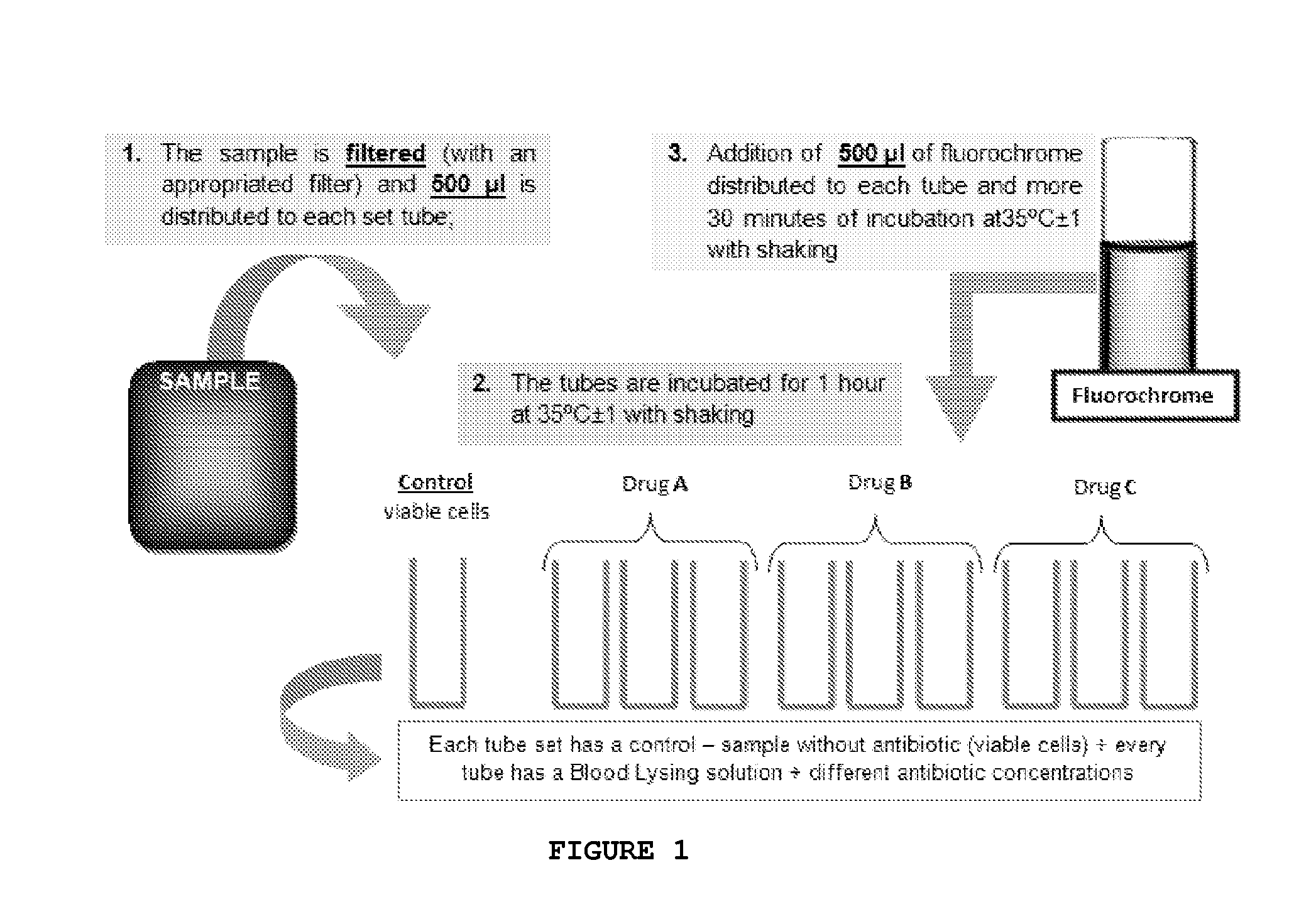
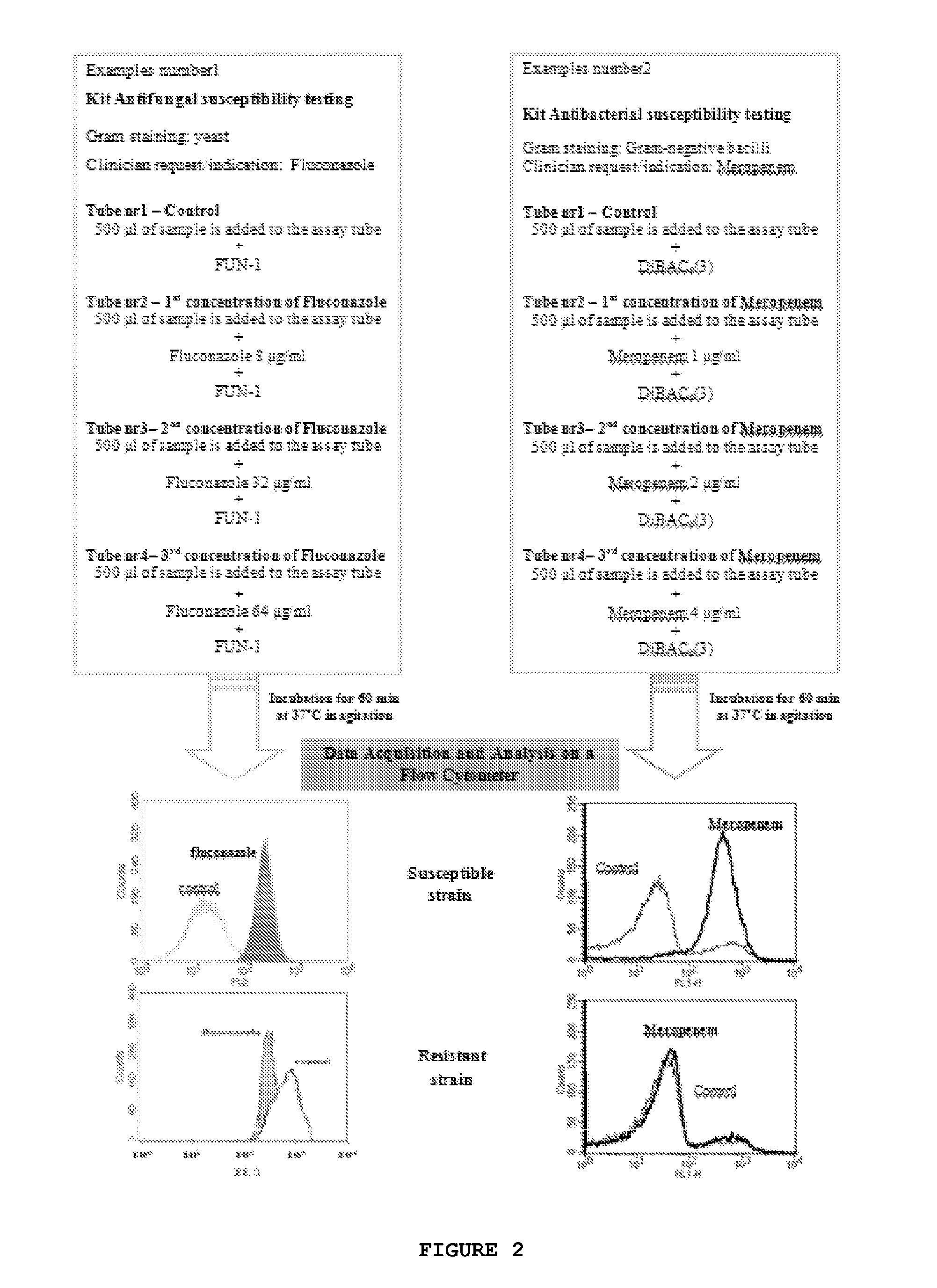
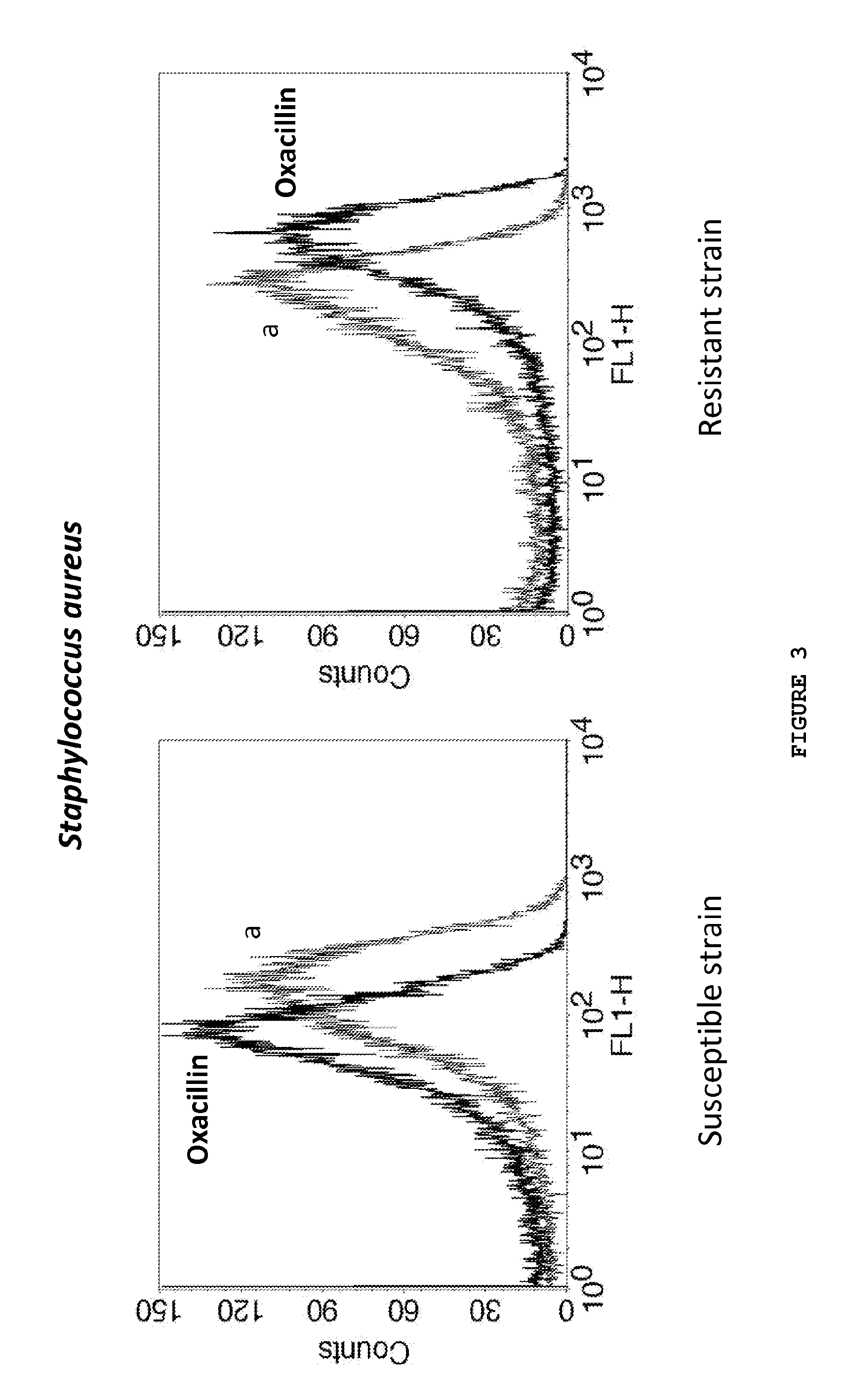
Kit and method of detecting the resistant microorganisms to a therapeutic agent
ActiveUS20140199703A1Improve drug activityActive drug is reducedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismAntimicrobial drug
The present invention relates to a method for detecting resistant microorganisms to a therapeutic agent in a biological sample, comprising the following steps:a. inoculate the said sample, uncultured, on a first tube with, and on a second tube without, at least one therapeutic agent; preferentially further including at least one lysing agent and / or a buffer, and / or a suitable culture medium, or put the sample on a separation serum tube; and incubated it;b. add to both tubes a fluorescent marker;c. perform a fluorescence analysis for obtaining one or more fluorescence or growth parameters for each of the two tubes;wherein the microorganisms resistant phenotype of the biological sample to said therapeutic agent is obtained by comparing the one or more fluorescence parameters between the two tubes.Therefore, the present invention is useful in laboratory procedures or routines for the detection of the susceptibility of different microorganisms to a therapeutic agent, to the determination of microorganisms resistance mechanisms or even to evaluate the amount of antimicrobial drug in the biological sample.
Owner:UNIV DO PORTO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
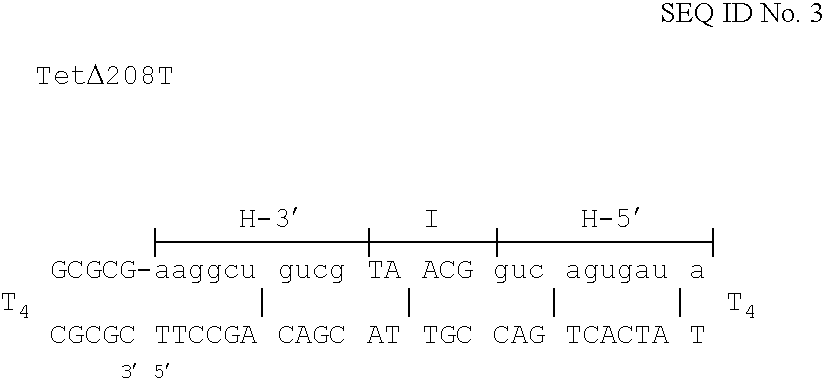














![ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6a766c61-50e6-478f-8cc7-d4fe3ea24b1e/HDA0001462210200000011.png)
![ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6a766c61-50e6-478f-8cc7-d4fe3ea24b1e/HDA0001462210200000021.png)
![ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER ZINC-[Gamma]-PGA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING CANCER](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6a766c61-50e6-478f-8cc7-d4fe3ea24b1e/HDA0001462210200000031.png)