Patents
Literature
312 results about "Minimum inhibitory concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible growth of a bacterium or bacteria. MIC depends on the microorganism, the affected human being (in vivo only), and the antibiotic itself.
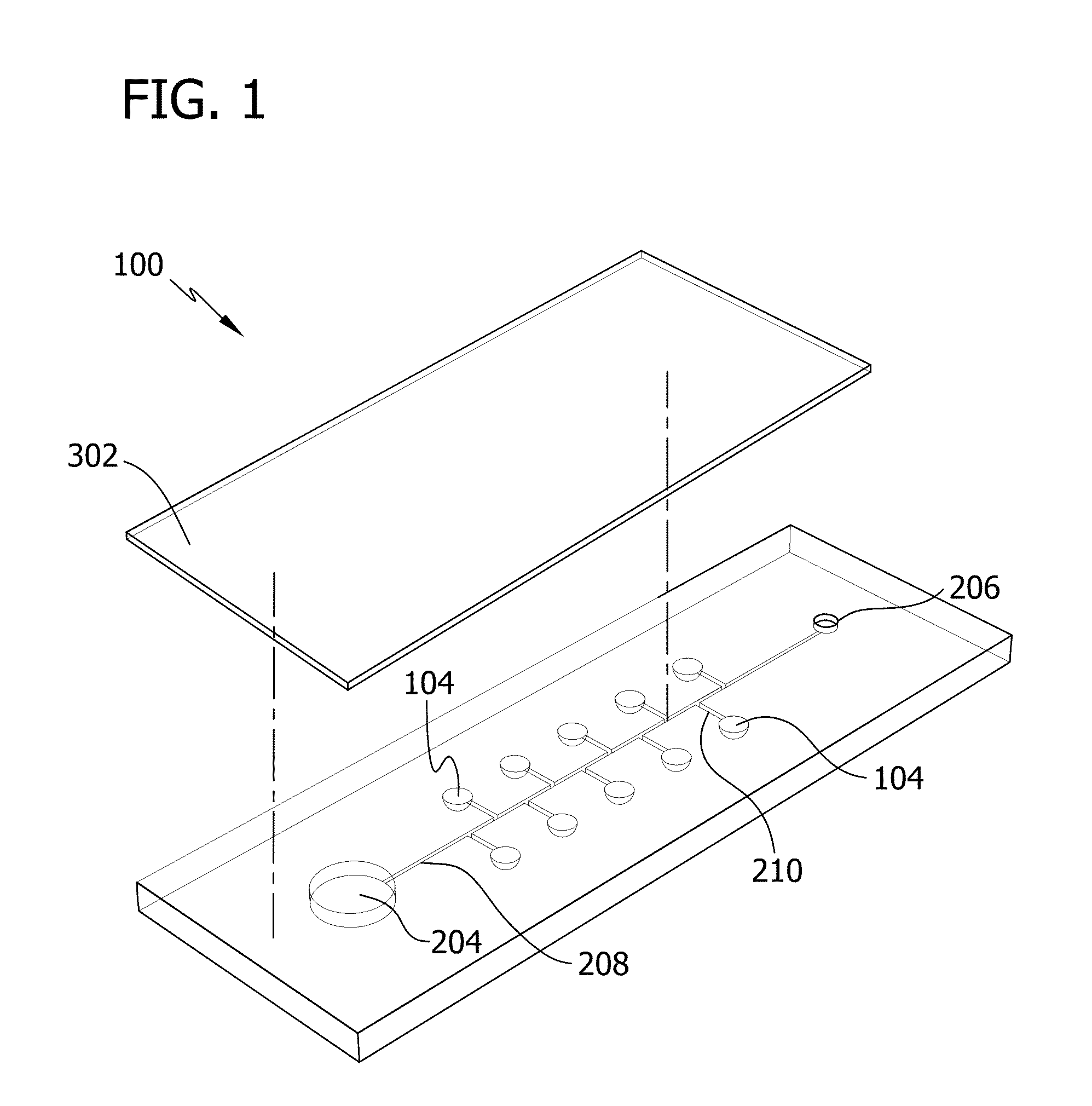
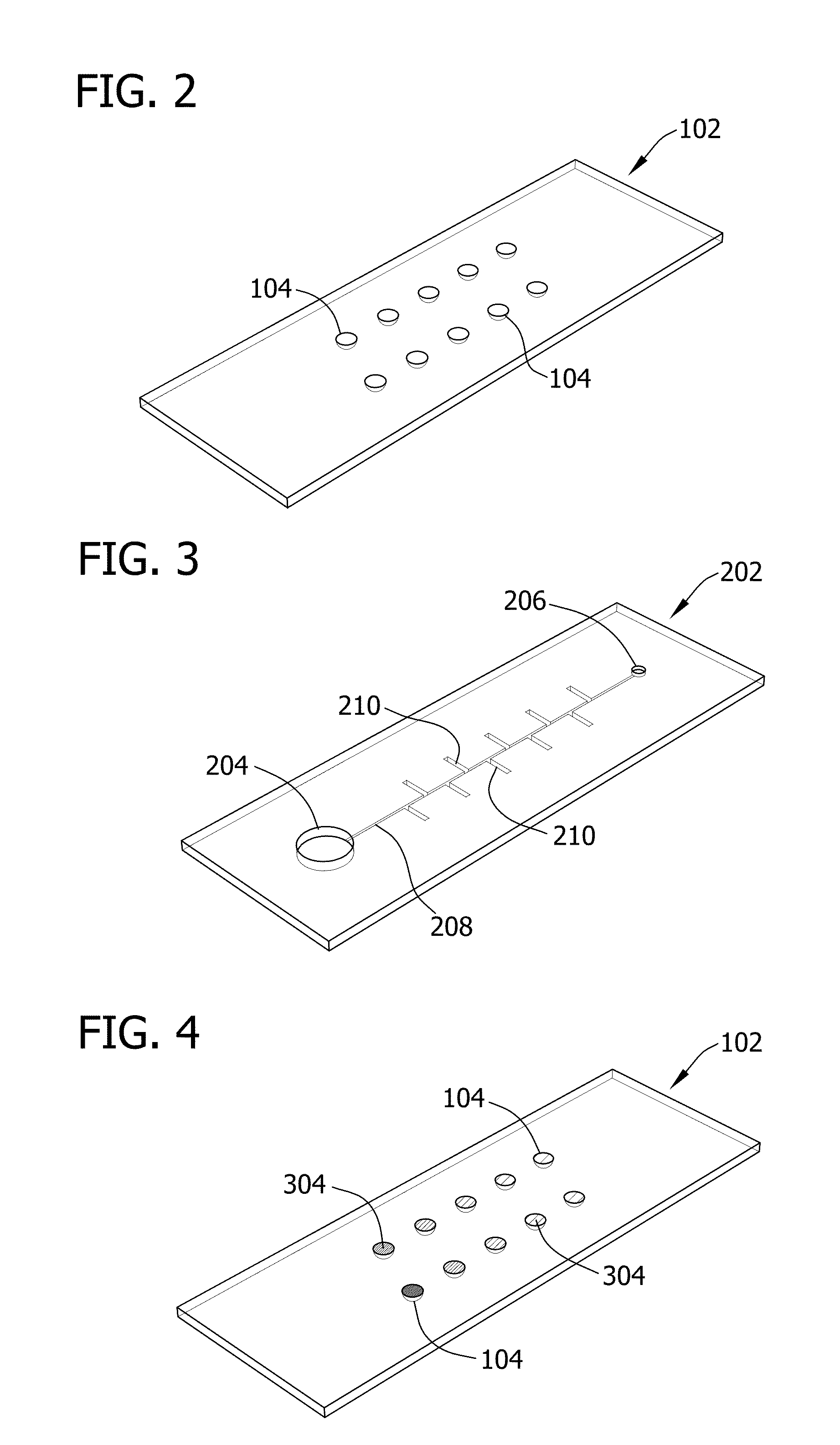
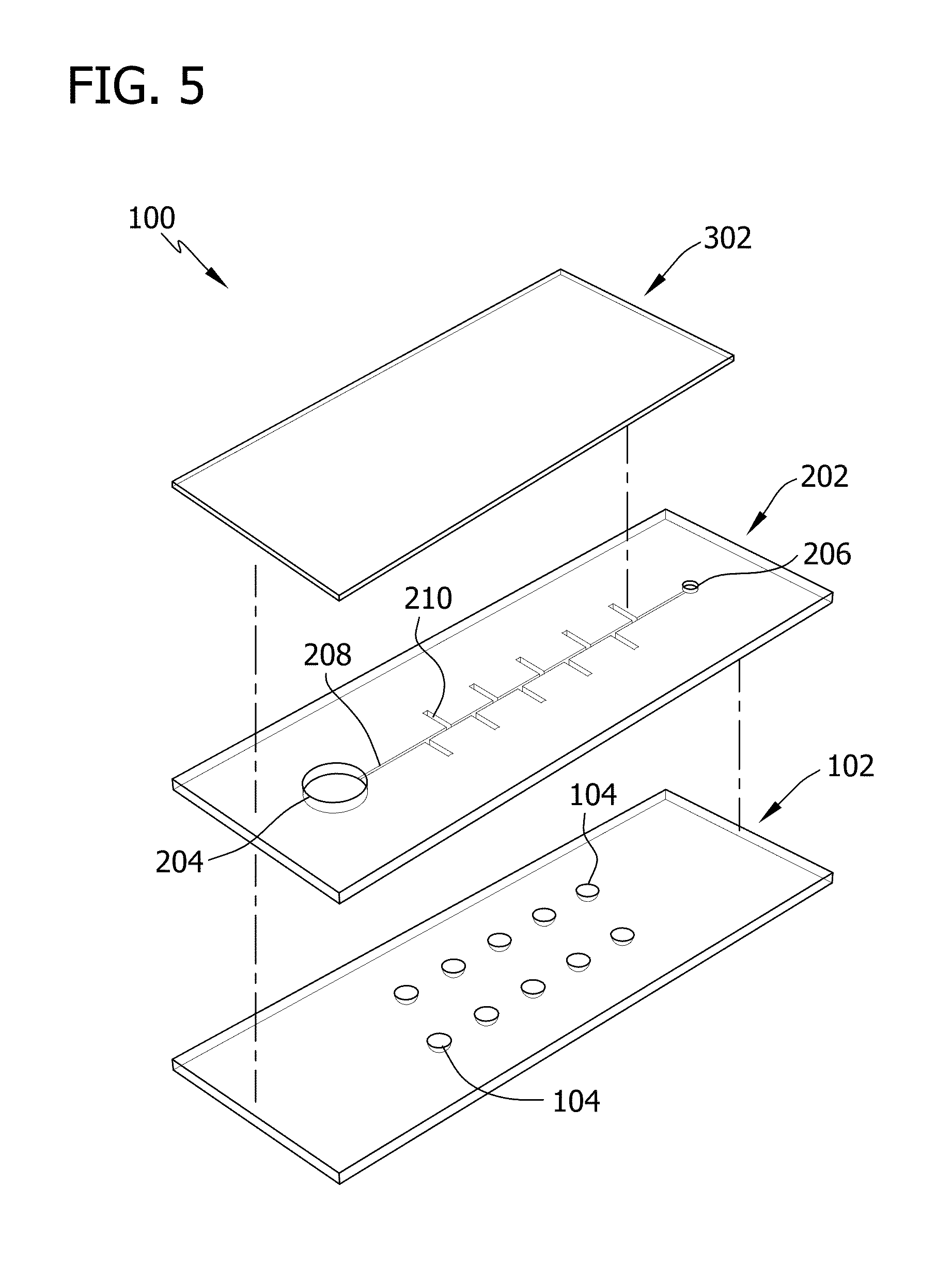
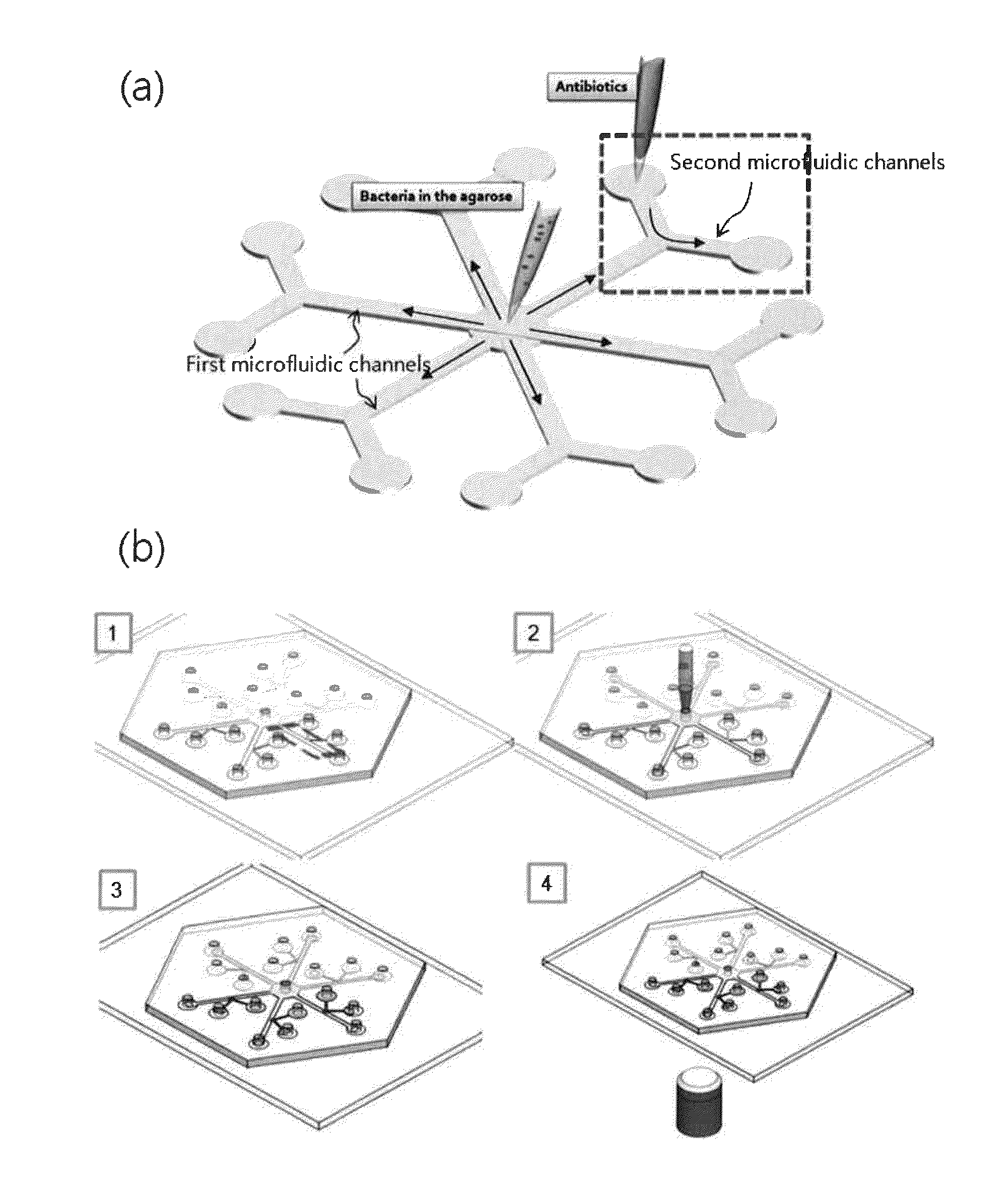
Self-loading microfluidic device and methods of use
ActiveUS20130130232A1SamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementMinimum inhibitory concentrationSubstrate Interaction
Microfluidic devices and methods for conducting chemical assays and biological assays using microfluidic devices are disclosed. The microfluidic devices do not require external connections, tethers, tubing, valves and actuators. The microfluidic devices are useful in methods for analyzing a wide variety of chemical and biological assays such as, for example, molecule-molecule interactions, enzyme-substrate interactions, molecule identification, minimum inhibitory concentrations, therapeutically effective amounts, and toxic amounts.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
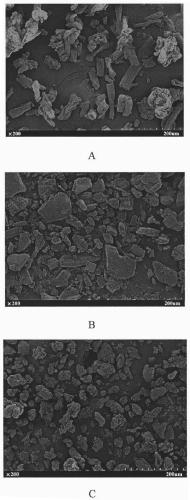
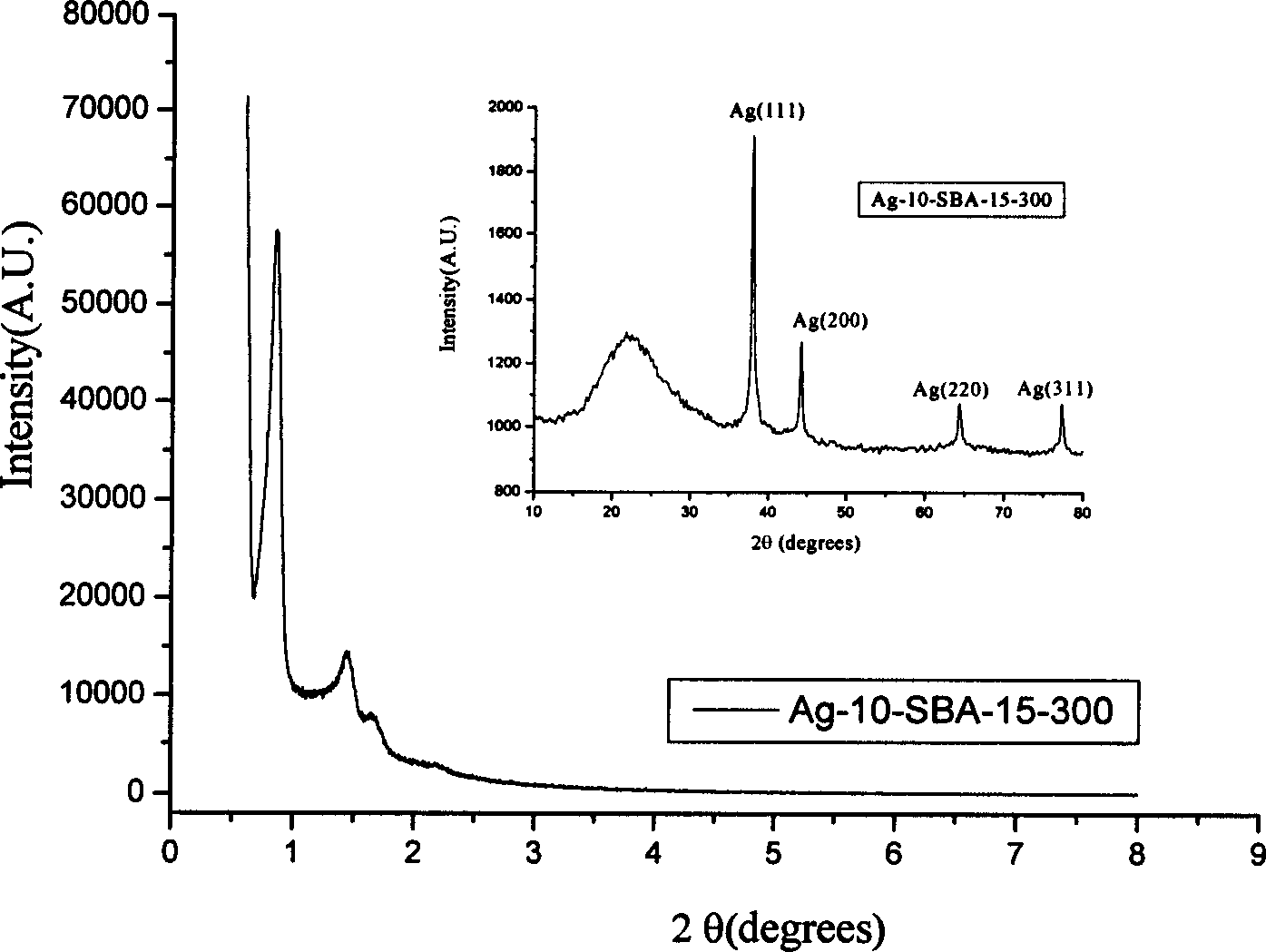
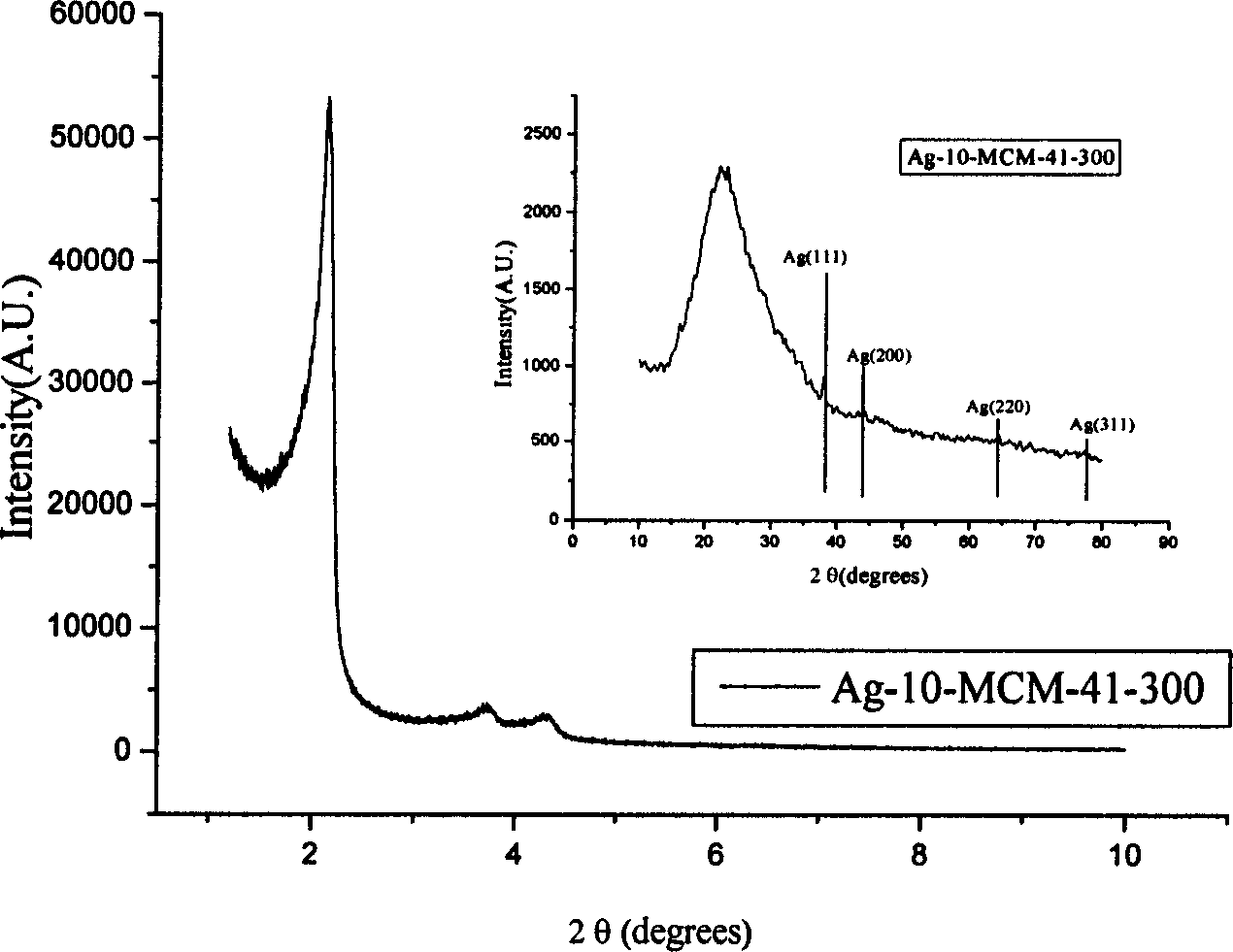
Silver-carried antibacterial agent with nanometer porous and making method thereof
InactiveCN1817138AEasy to operateNo pollution in the processBiocideDisinfectantsMinimum inhibitory concentrationAntibacterial activity
A nano-class mesoporous Ag-carried antibacterial agent used for detergent, cosmetics, water treating, textile, etc contains inorganic oxide as carrier with orderly mesopore structure and Ag as active antibacterial component. Its advantages are large specific surface area, broad spectrum, high effect and durability, and no damage to people.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Antifungal effects of Morinda citrifolia
InactiveUS20030225005A1Relieve inflammationCalming feelings of anxietyAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesAcetic acid
The present invention relates to antifungal and antibacterial activity of processed Morinda citrifolia products, as well as from various fractions of extracts from these processed products and the Morinda citrifolia L. plant, and related methods to determine mean inhibitory concentrations. In particular, the present invention relates to ethanol, methanol and ethyl acetate extracts from Morinda citrifolia L. and their inhibitory activities on common fungi and bacteria and the identification of mean inhibitory concentrations.
Owner:TAHITIAN NONI INT INC
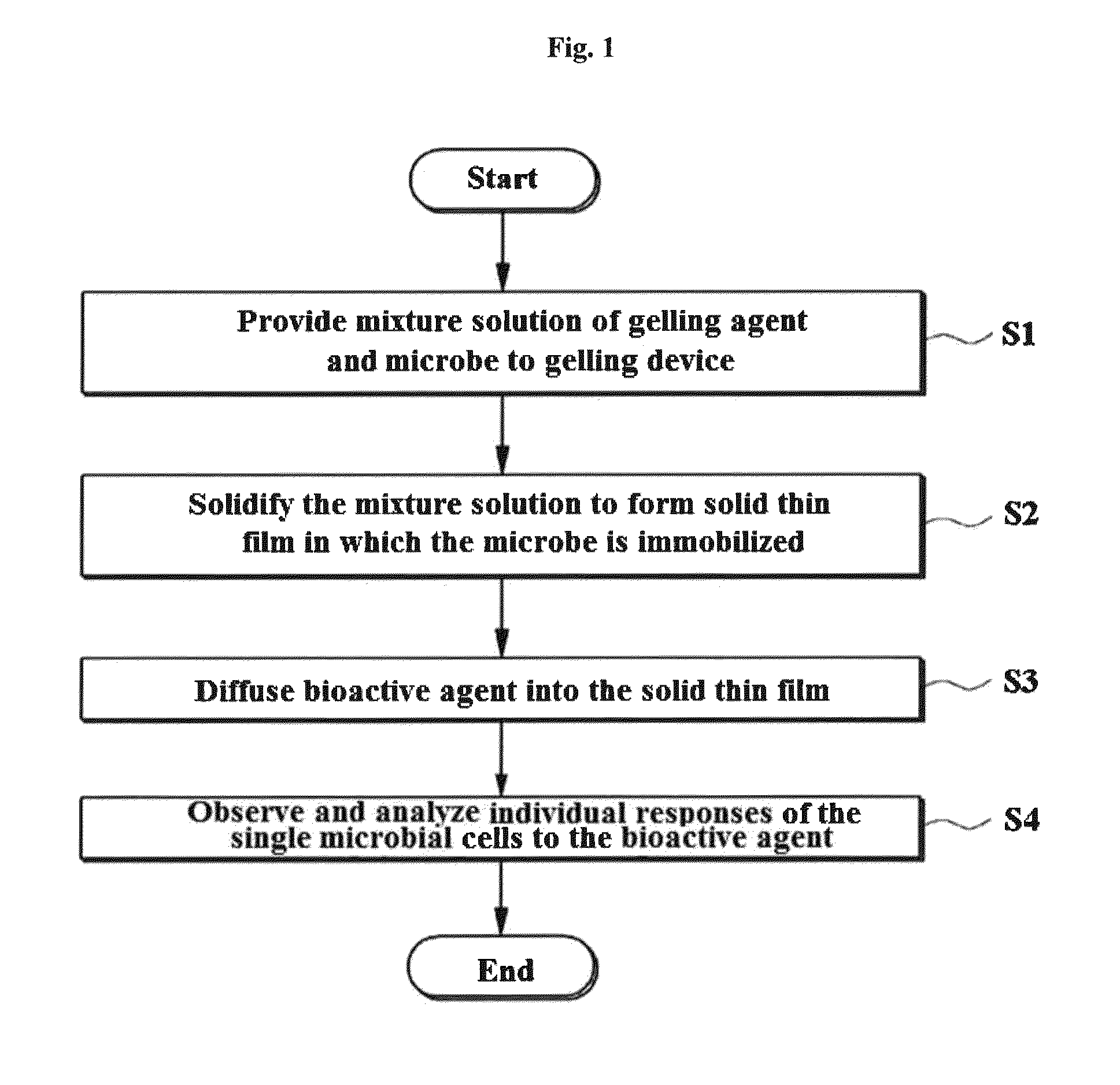
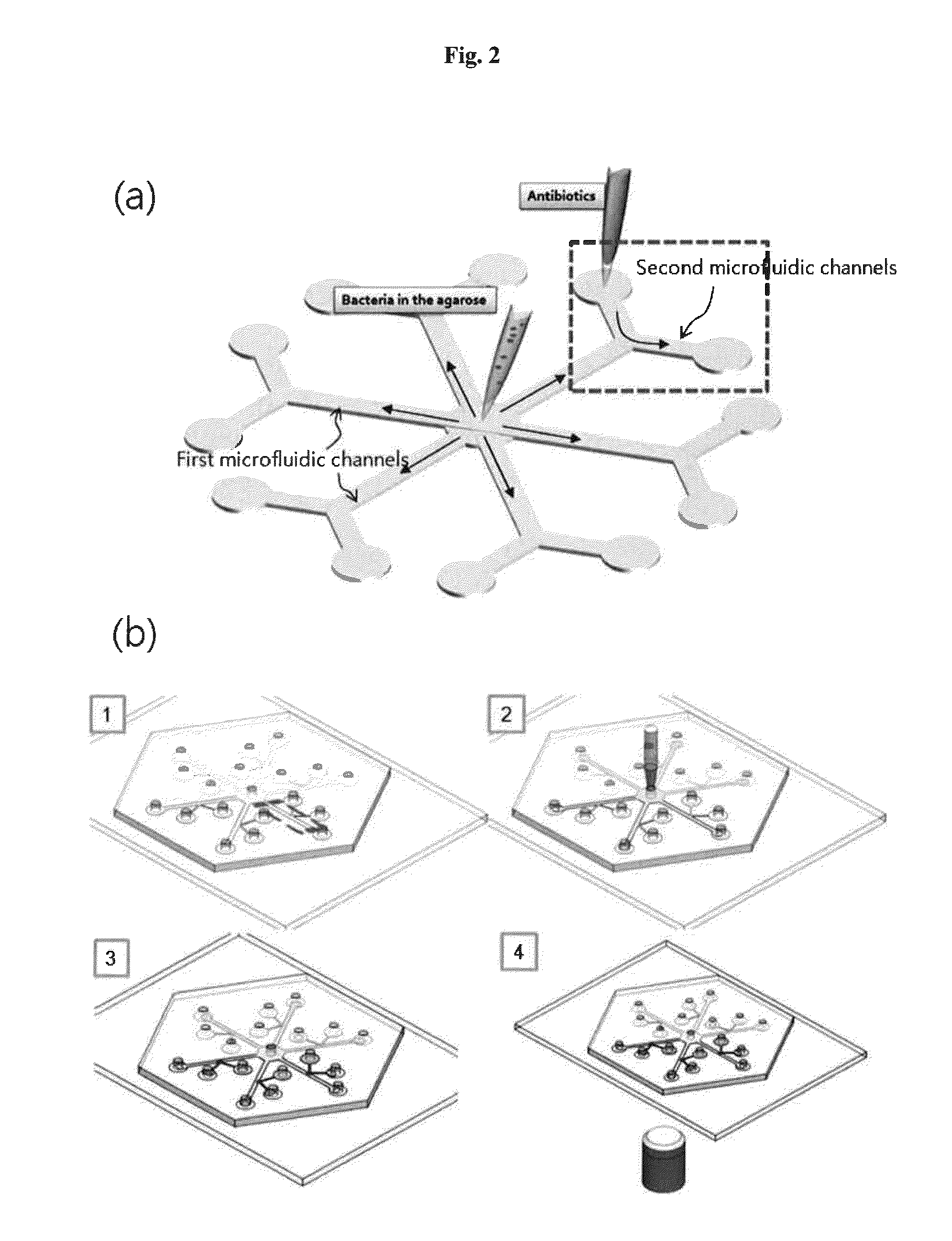
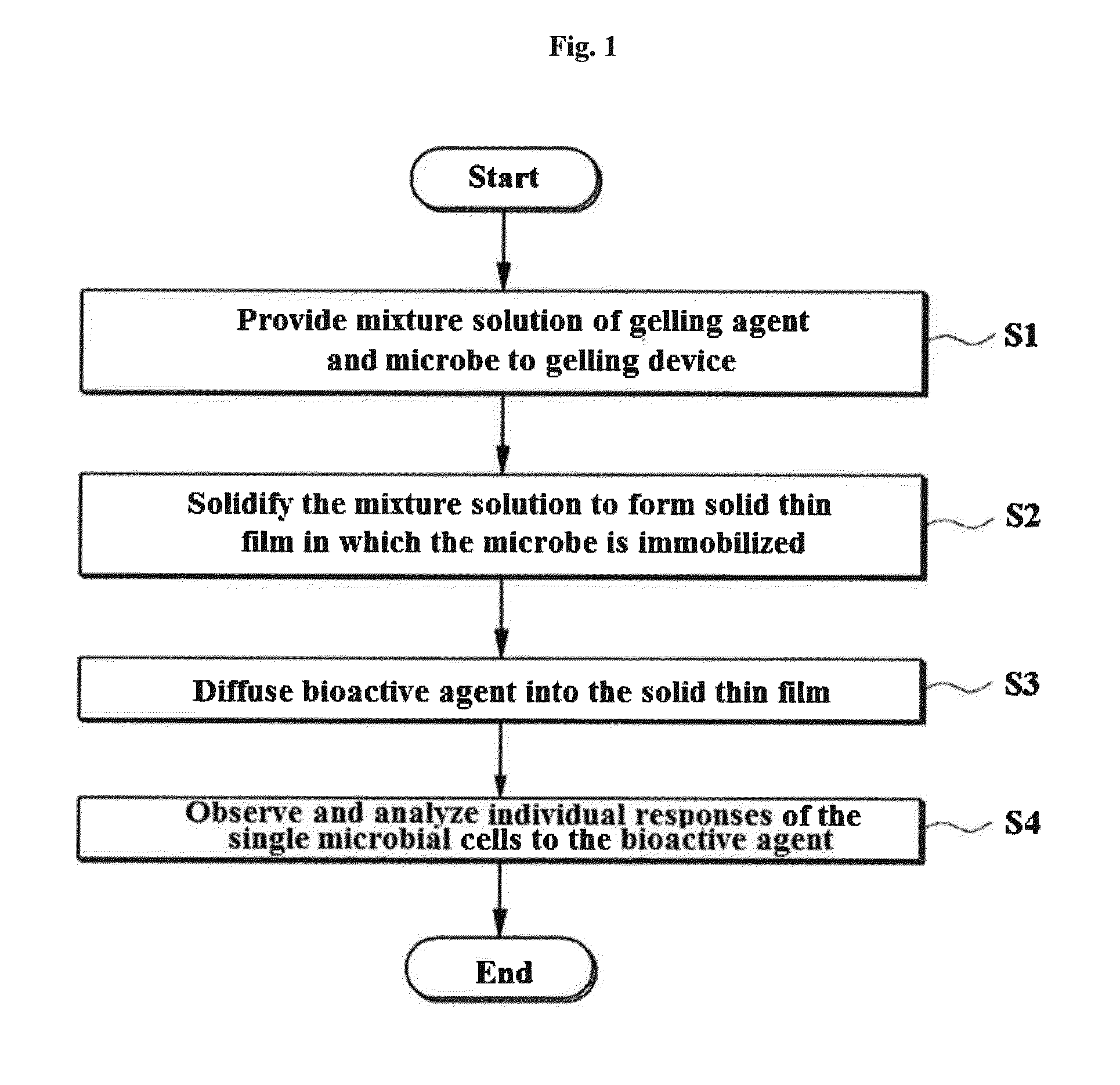
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing system based on bacterial immobilization using gelling agent, antibiotic diffusion and tracking of single bacterial cells
ActiveUS9133498B2Prevent burstBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage analysisDiffusionMinimum inhibitory concentration
A testing method is disclosed. The testing method includes: providing a mixture solution of a gelling agent and a microbe to a gelling device; solidifying the mixture solution to form a solid thin film in which the microbe is immobilized; supplying a bioactive agent to the solid thin film and allowing the bioactive agent to diffuse into the solid thin film; and imaging the individual responses of the single microbial cells to the bioactive agent, and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the bioactive agent based on the analysis of the images to obtain AST results.
Owner:QUANTA MATRIX
Nano silver copper bimetal colloid/liquid with high antibacterial performance and preparation method thereof
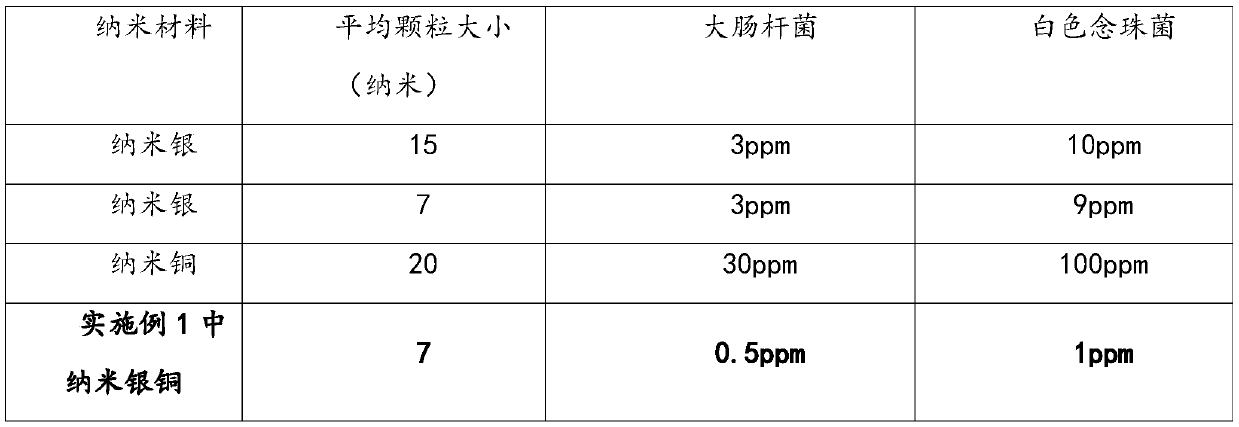
InactiveCN109819979AImprove antibacterial propertiesReduce usageBiocideFungicidesChemical synthesisMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention discloses nano silver copper bimetallic colloid / liquid with high antibacterial performance.A preparation method of the nano silver copper bimetallic colloid / liquid with high antibacterial performancecomprises the following steps of: adding an aqueous solution or an absolute ethyl alcohol solution of a stabilizing agent into the aqueous solution or the absolute ethyl alcohol solutionof silver nitrate and copper nitrate, stirring uniformly, adding the aqueous solution or the absolute ethyl alcohol solution of a reducing agent, and stirring for 30-60minutes to obtain the nano silver copper bimetallic colloid / liquid.According to the preparation method of the nano silver copper bimetallic colloid / liquid with high antibacterial performance,a chemical synthesis method is utilized to obtain the nano silver copper bimetallic colloid / liquid, and prepared nano particles are within 10 nanometers.The minimum bacteriostatic concentration of the composite nano silver copper bimetal toescherichia coli and candida albicans reaches 0.5ppm and 1ppm respectively.The minimum bacteriostatic concentration of nano silver synthesized by the conventional method is 3ppm and 10ppm respectively.The antibacterial capacity of anano silver copper dispersion is improved by 6 times and 10 times.The use of the nano silver copper bimetal saves the use amount of silver and has high practical value.
Owner:尚蒙科技无锡有限公司
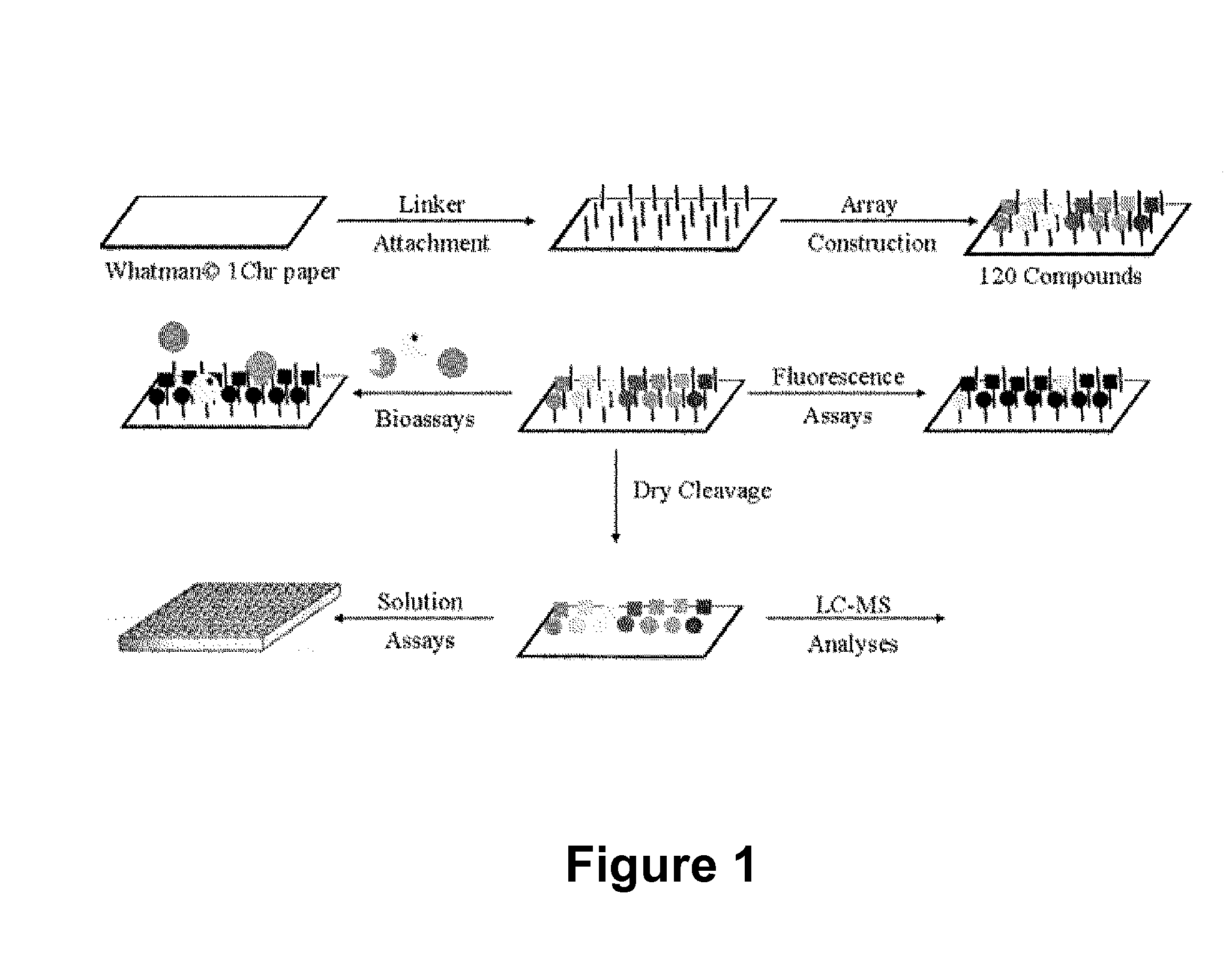
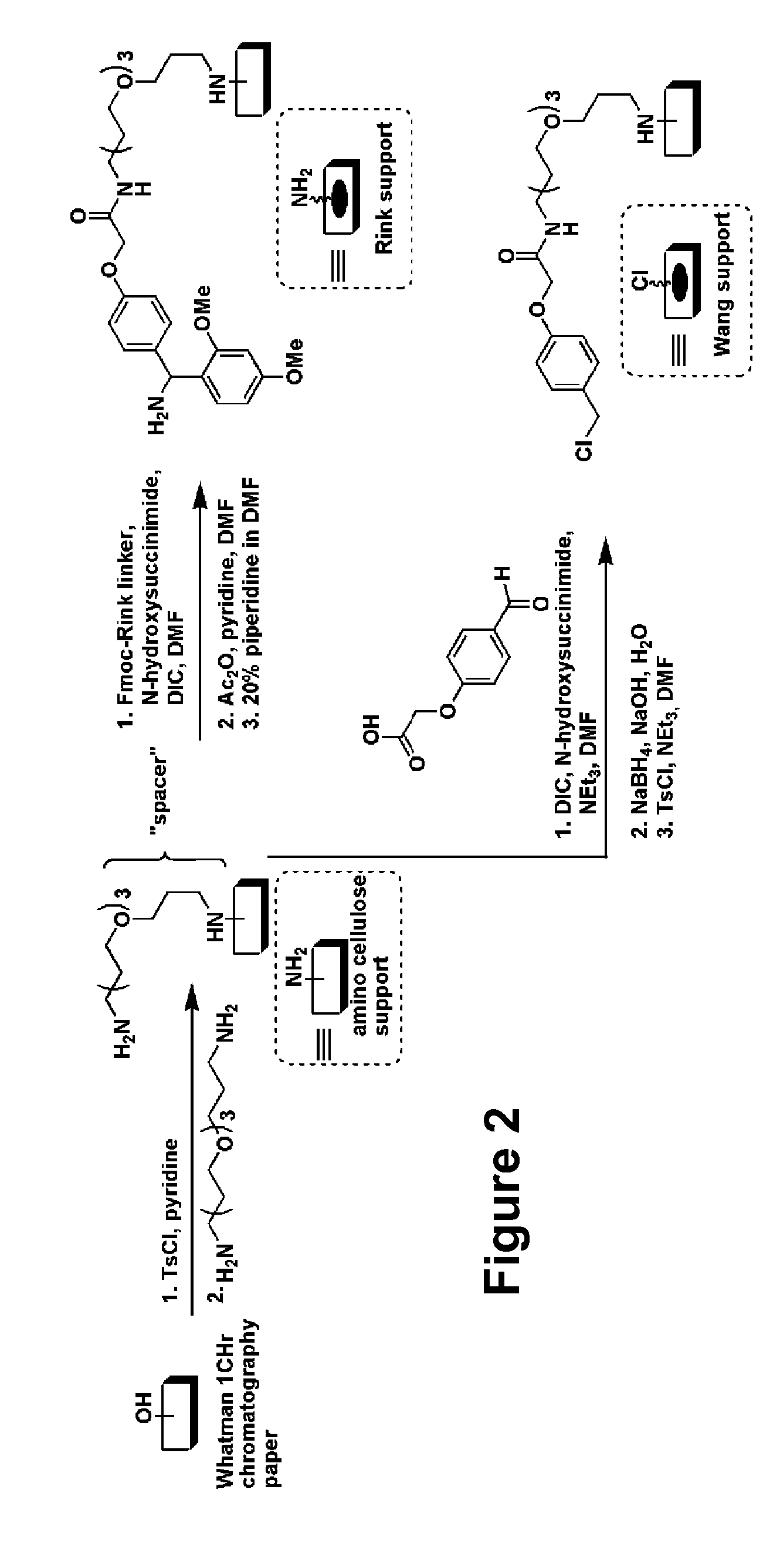
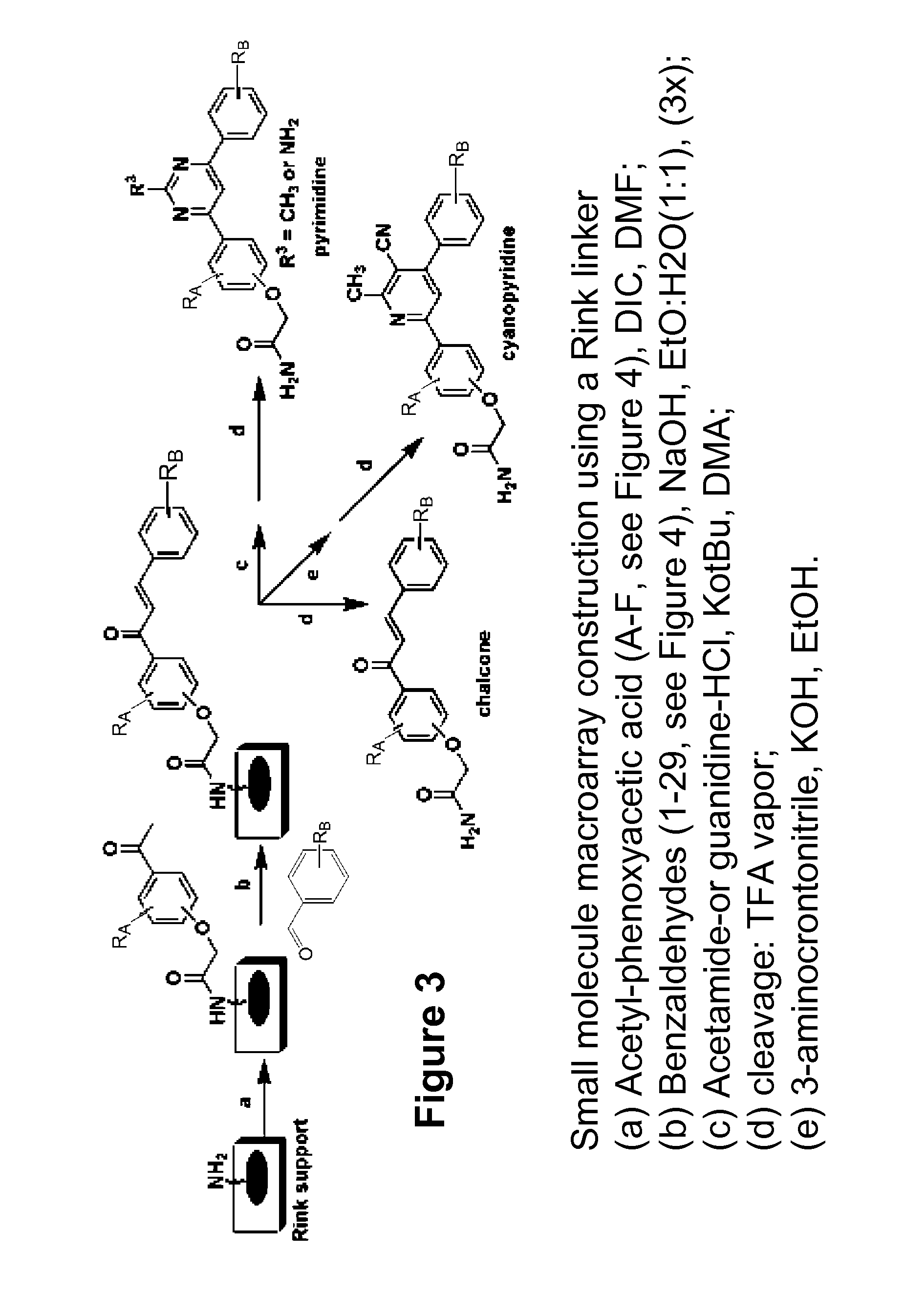
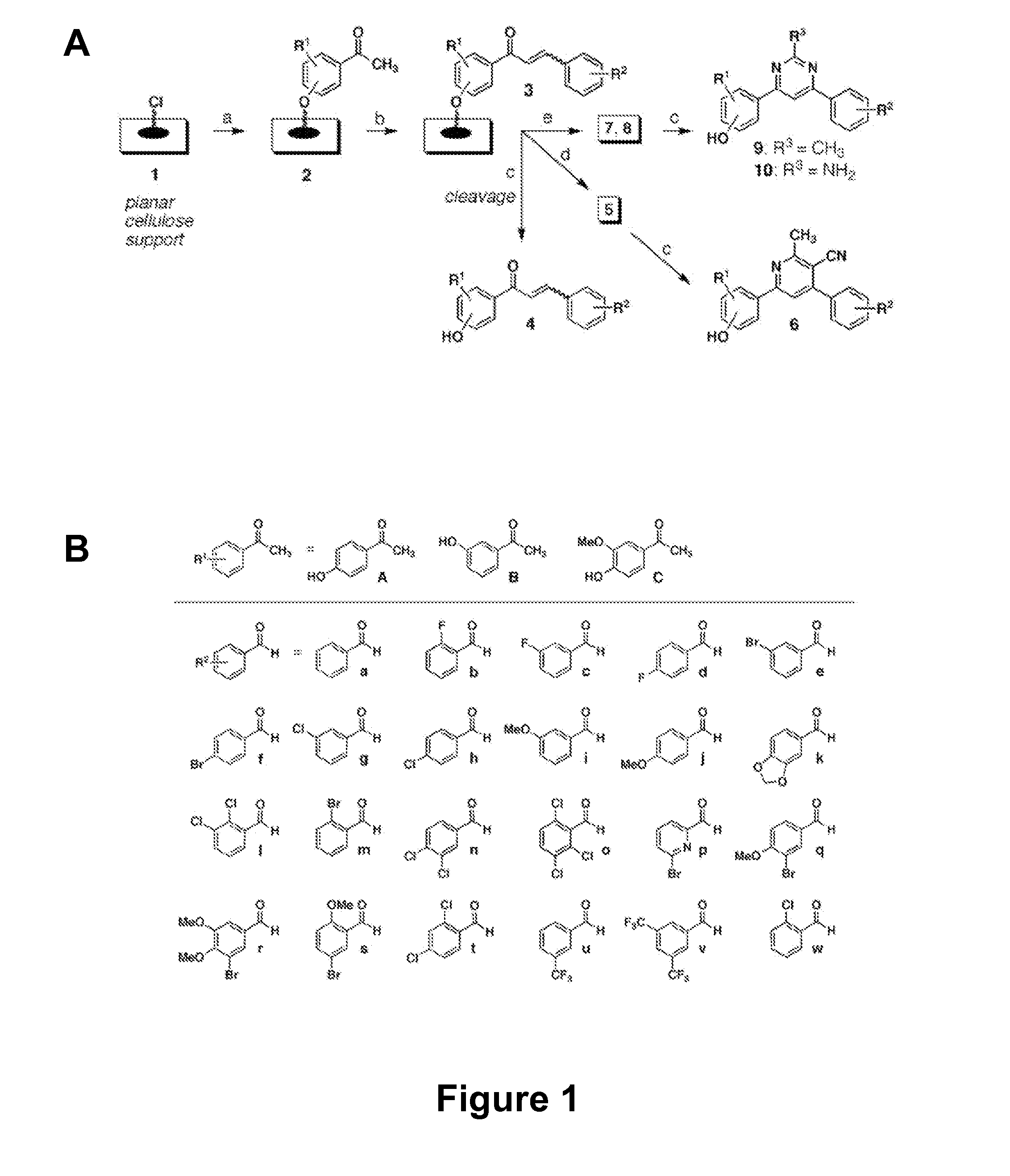
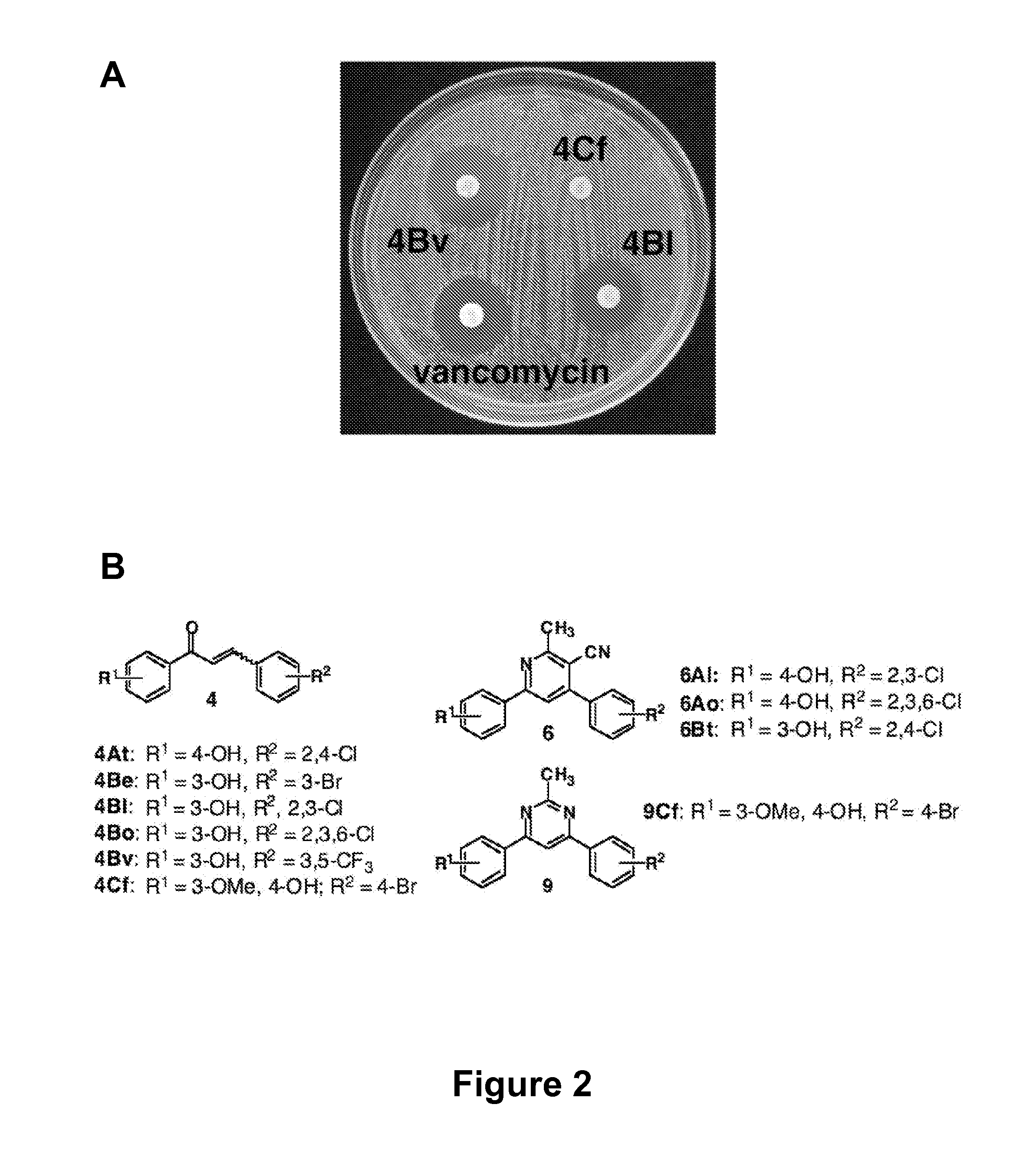
Antibacterial small molecules and methods for their synthesis
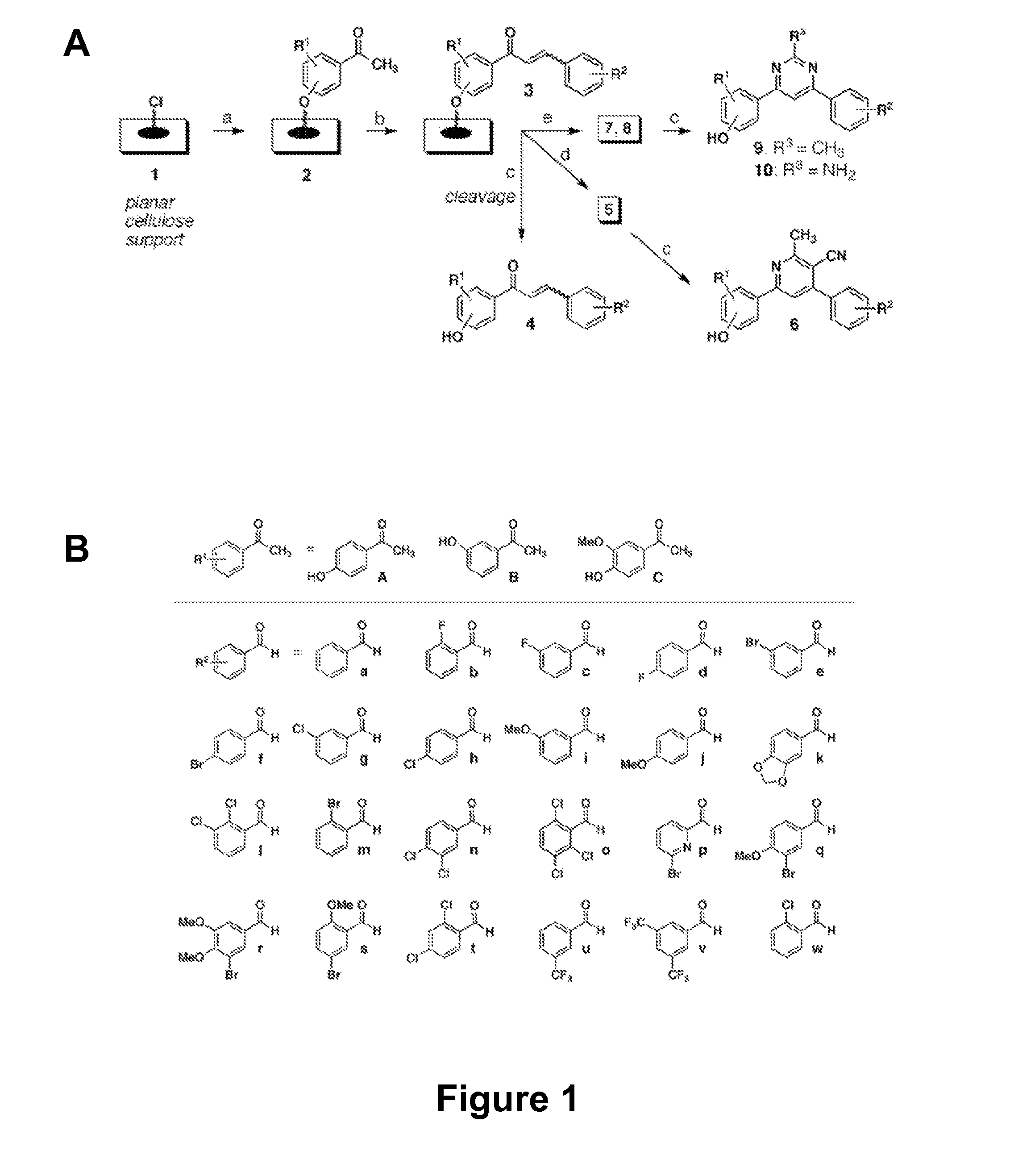
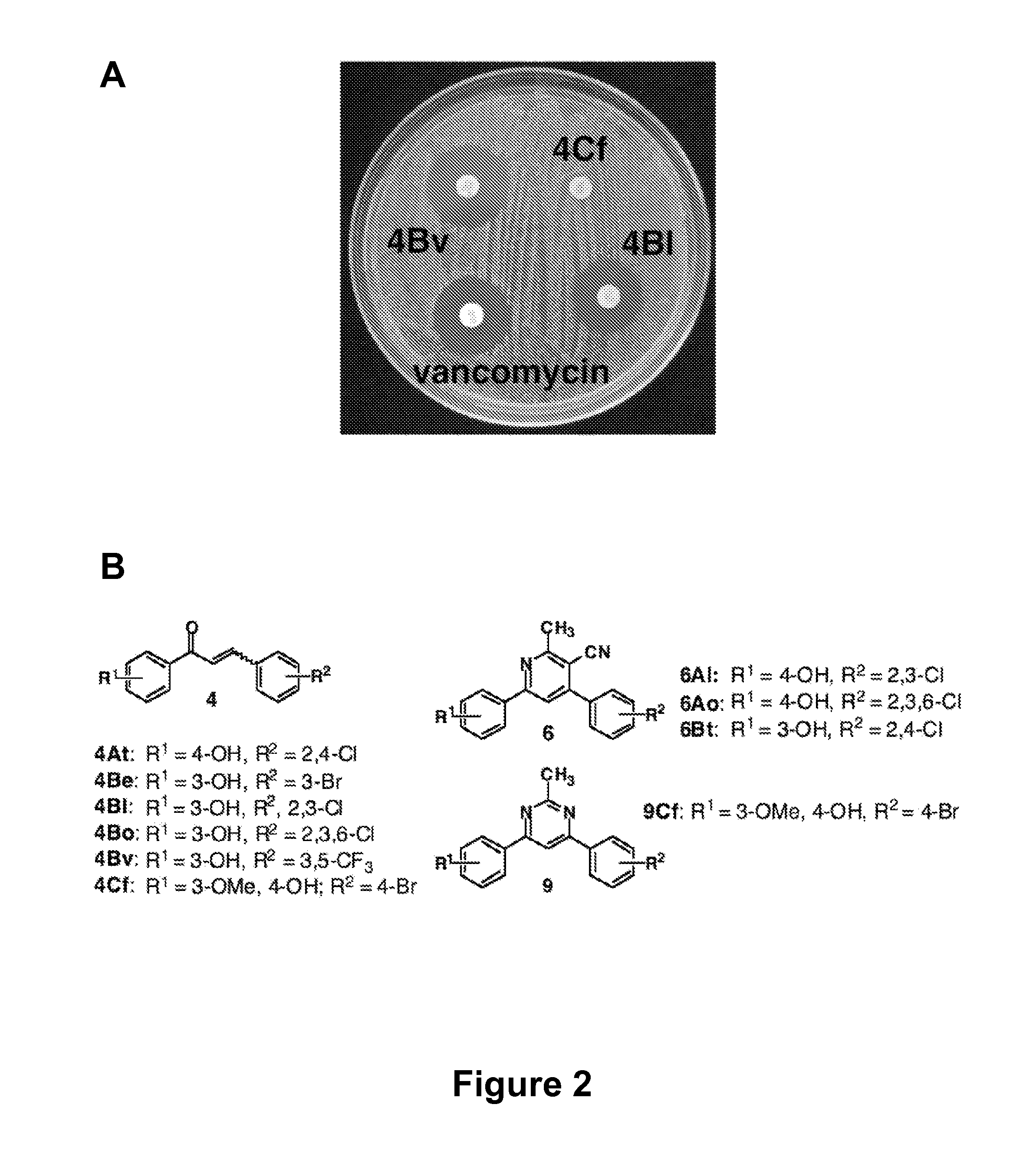
ActiveUS20090270423A1Good water solubilityEnhance and expand biological activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSynthesis methodsMinimum inhibitory concentration
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Kernel-shell structured rare-earth nanometer antibiotic agent, prepn. method and application thereof
InactiveCN100998335AGood antibacterial effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideDisinfectantsMinimum inhibitory concentrationRare earth
A nano-class RE antibacterial agent with core-shell structure for plastics, paine and ceramics is prepared from binary RE-heterocyclic compound match composed of RE ions chosen from La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Er, Eu, Y, Dy and Gd and the heterocyclic compound (imidazole or benzimidazole), and the carrier chosen from spherical SiO2 or spherical meta-porous SiO2. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of nano-silver composite antibacterial agent
ActiveCN104126611AIngenious ideaExperiment operation is simpleBiocideFungicidesEscherichia coliMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano-silver composite antibacterial agent. The invention is characterized in that the nano-silver composite antibacterial agent is formed by combining a nano-silver solution and an organic antibacterial agent which have synergistic effect and adduction effect according to a certain ratio. The structure and performance of the antibacterial agent after combination are stable, and the antibacterial agent has more rapid, efficient and broad-spectrum antibacterial performance. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the antibacterial agent for inhibiting escherichia coli, Enterobacter hormaechei, staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa, penicillium and Aspergillus niger is only 1-10 microgram / ml. The preparation method of the nano-silver composite antibacterial agent is characterized in that the nano-silver in the nano-silver composite antibacterial agent has monodispersity and there is no agglomeration phenomenon. The preparation method has advantages of ingenious conception, simple experimental operation, high operationality and short period, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method and compositions for transdermal administration of antimicrobial medications
InactiveUS20060222692A1Avoid gastrointestinal side effectsReduce the possibilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSerum concentrationMedicine
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved efficacy and delivery of time-dependent antimicrobial drug compositions to a patient. Transdermal dosage forms and methods for steady-state delivery of drug to produce and maintain a serum concentration of drug above the minimum inhibitory concentration or minimum microbicidal concentration are provided.
Owner:FAIRFIELD CLINICAL TRIALS
3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN101613362ANovel structureSimple manufacturing methodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMinimum inhibitory concentrationSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a 3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound and a synthesis method and application thereof. The compound has a right structure formula. The 3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound serving as an inhibiting agent of YyCG histidine kinase protein for a staphylococcus epidermidis signal transduction system has a novel structure, and the adopted method for preparing the compound is simple and easy to implement. The test results of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) show that the compound has excellent inhibitory action on the formation of a staphylococcal biological film and can effectively kill and wound the bacteria in the staphylococcal biological film.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Antibacterial agents and related screening methods using small molecule macroarrays
ActiveUS20080009528A1Common methodFacilitates effectiveAntibacterial agentsBiocideHalogenMinimum inhibitory concentration
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use. For example, the present invention provides chalcone and cyanopyridine compounds, and derivatives thereof, exhibiting high antibacterial activities having multiple electron withdrawing group substituents, such as halogens and fluorinated alky groups, and optionally having hydroxyl and / or alkoxyl groups substituents.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Application of perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride amidation compound in anti-staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN110156781AEasy to makeGood water solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
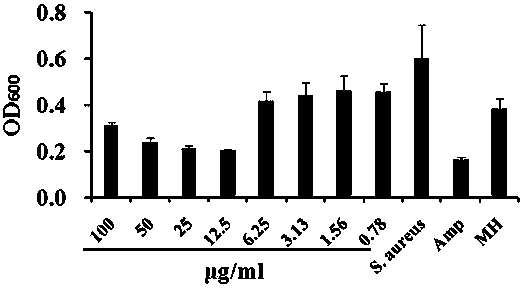
The invention provides an application of a perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride amidation compound in anti-staphylococcus aureus. The compound is simple to prepare, a perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride compound and N,N-dimethylethylenediamine are used as raw materials, multiple steps are carried out, the compound can inhibit the growth of staphylococcus aureus, and the bacteriostasis circle of the compound is up to about 10 mm measured by the K-B method. The compound is subjected to 2-fold gradient dilution, and the measured minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against staphylococcus aureus is up to 6.25 mg / mL. The growth curve inhibition test shows that when a growth curve of the bacteria in the non-drug treatment group enters the logarithmic phase, a growth curve of the bacteria in the compound treatment group is still in the lag phase, and indicates that the compound can inhibit the division of staphylococcus aureus. The discovered compound in the future can be used for the control of staphylococcus aureus infection, can also be applied in the preparation of antibacterial biomaterials, and has certain application value.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Antibiotice Susceptibility Profiling Methods
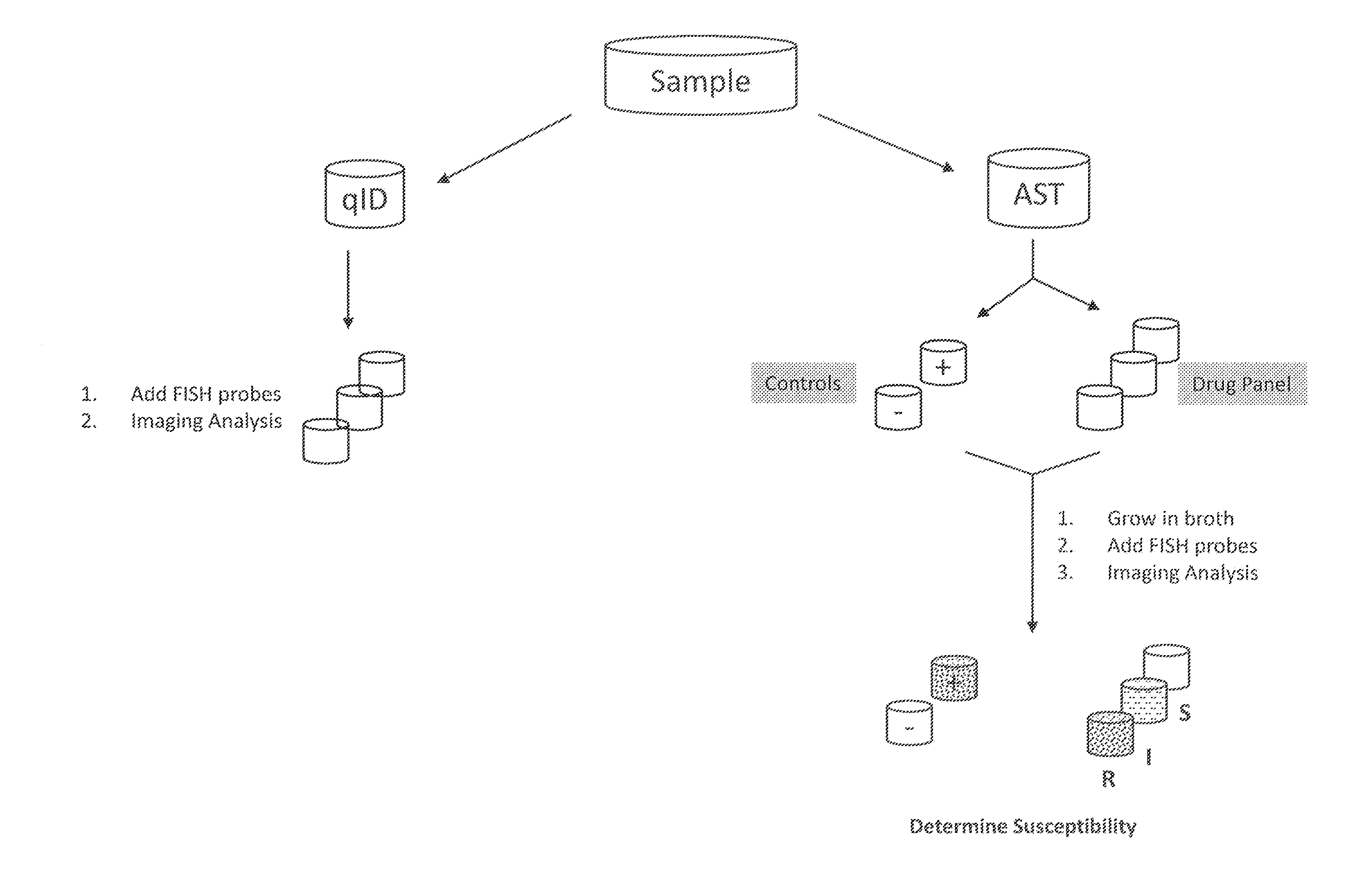
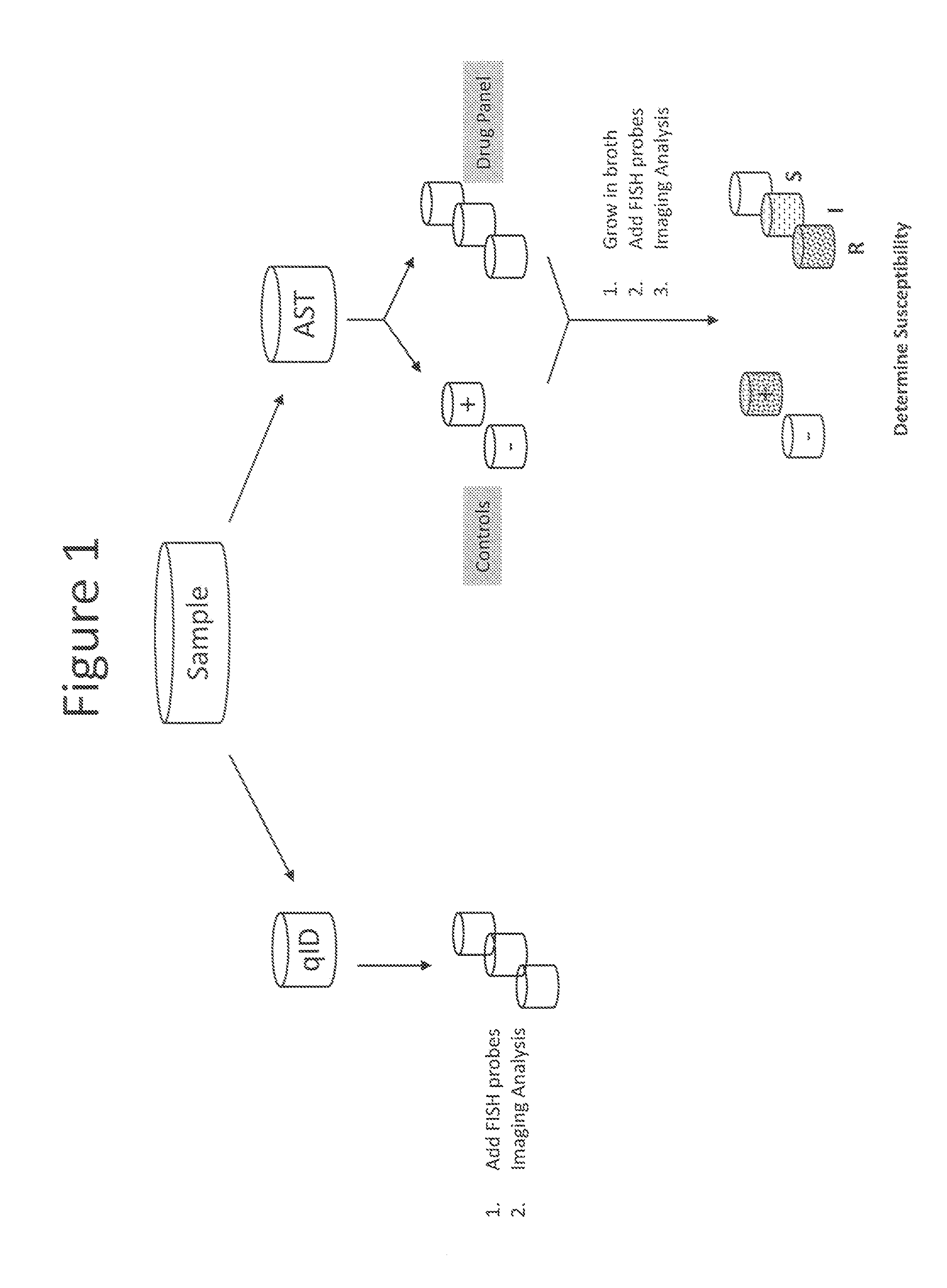
InactiveUS20110269130A1Low costReduce the necessary timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMinimum inhibitory concentrationRapid identification
The invention provides methods for the rapid determination of the antibiotic susceptibility of a microorganism, such as, an infectious microorganism in a biological sample, using fluorescence in situ hybridization (“FISH”). Methods of the invention may be applied to the rapid identification, typing, antibiotic susceptibility determination, and / or antibiotic minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination for any infectious microorganism, such as a Gram positive bacteria, a Gram negative bacteria, or a yeast.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Use of hop acids in fuel ethanol production
InactiveUS20060263484A1Accurate doseEffective controlMilk preparationBeer fermentationBacteroidesMinimum inhibitory concentration
Six hop acids are common to hops and beer: alpha acid, beta acids, isoalpha acids, rho-isoalpha acids, tetrahydro-isoalpha acids, and hexahydro-isoalpha acids. The six hop acids were tested to determine which were the most effective in inhibiting the growth of bacteria common to fuel ethanol production. The bacteria used in the tests were Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus fermentum. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of the hop acids were determined using MRS-broth. Molasses mash and wheat mashes were used as the growth media for the fermentations. In all cases the hop acids controlled the growth of these two lactobacillus bacteria with tetrahydroisoalpha acid, hexahydroisoalpha acid, and isoalpha acid killing the most bacteria at the lowest MIC. Treating yeast propagators, steep tanks, and fermenters with a minimum inhibitory concentration of hop acids will stop bacteria growth, increase ethanol yields and avoid the need for antibiotics.
Owner:JOHN I HAAS
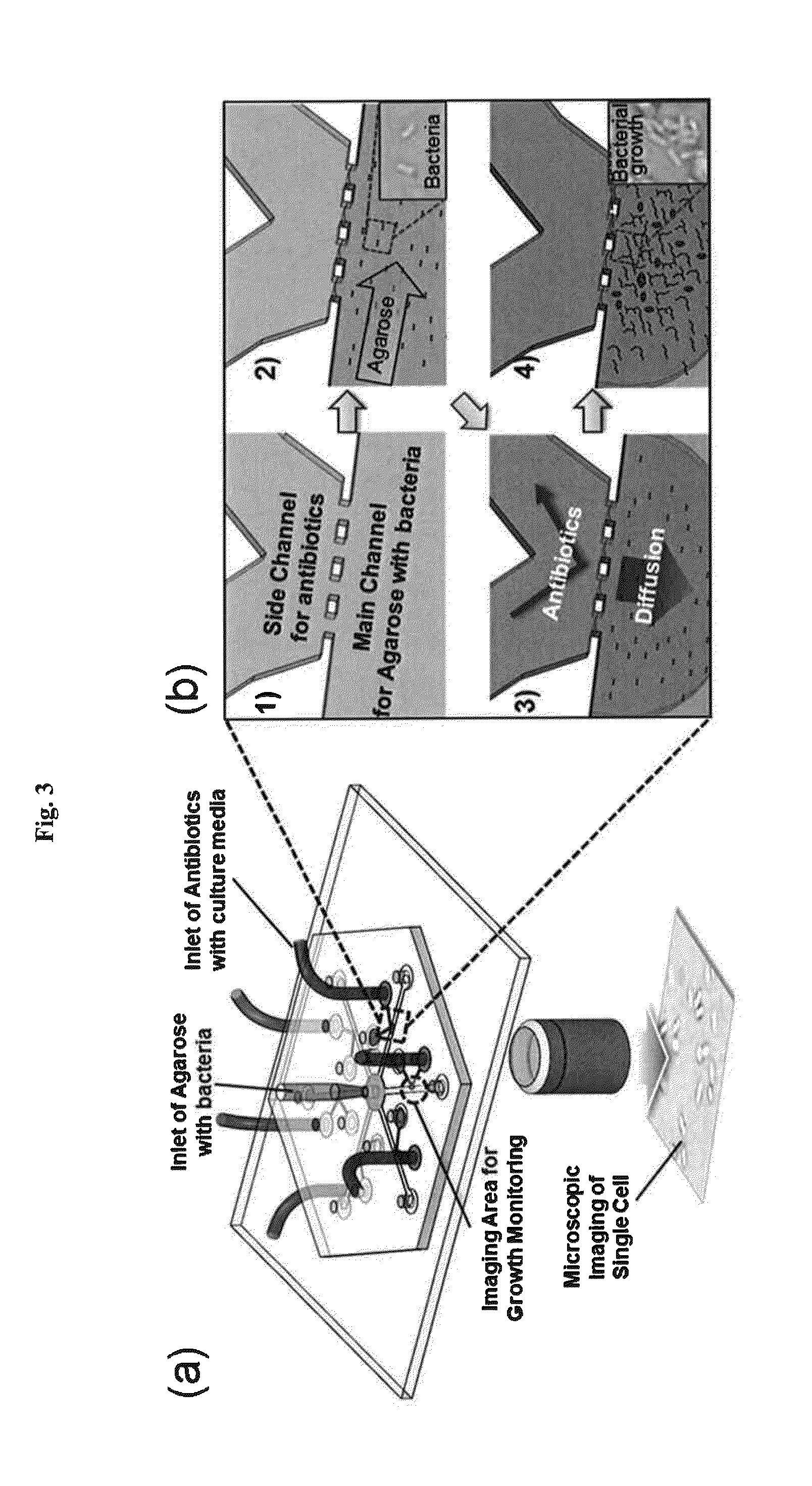
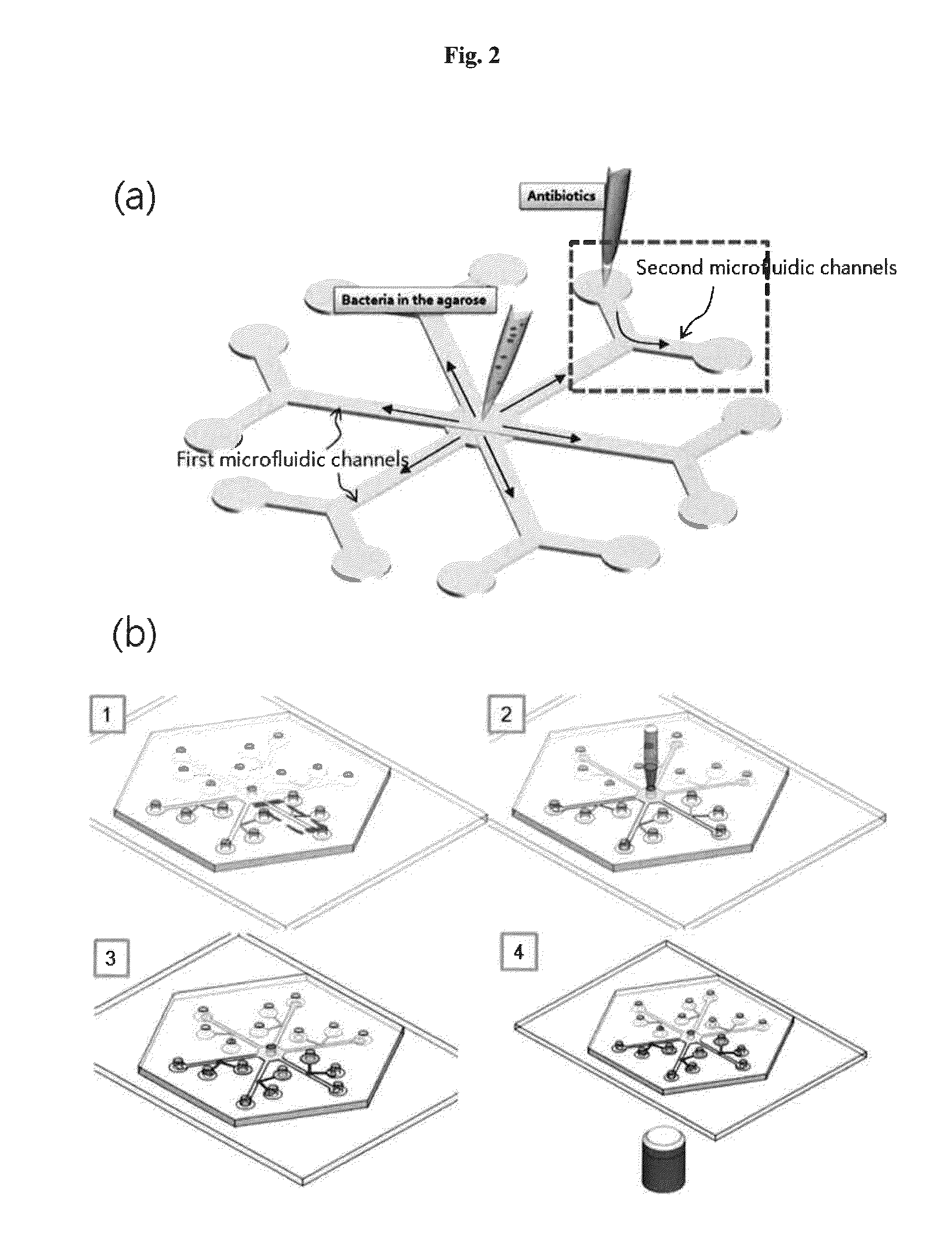
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing system based on bacterial immobilization using gelling agent, antibiotic diffusion and tracking of single bacterial cells
ActiveUS20130196364A1Prevent burstBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMinimum inhibitory concentrationDrug biological activity
A testing method is disclosed. The testing method includes: providing a mixture solution of a gelling agent and a microbe to a gelling device; solidifying the mixture solution to form a solid thin film in which the microbe is immobilized; supplying a bioactive agent to the solid thin film and allowing the bioactive agent to diffuse into the solid thin film; and imaging the individual responses of the single microbial cells to the bioactive agent, and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the bioactive agent based on the analysis of the images to obtain AST results.
Owner:QUANTA MATRIX
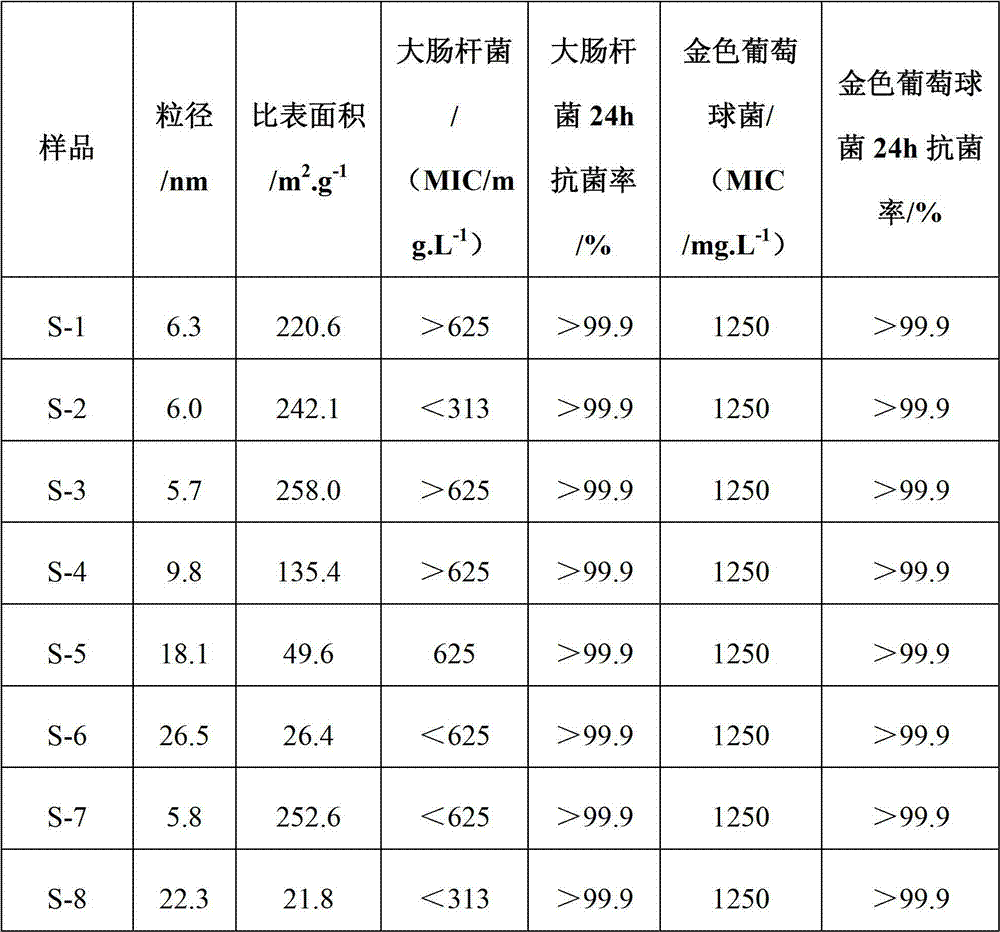
Nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent, preparation method and applications of nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent
ActiveCN102885087ASimple processEase of industrial productionBiocideDisinfectantsAir atmosphereMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention relates to a nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent, a preparation method and applications of the nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent. The method comprises the steps of mixing magnesium salt alcoholic solution containing copper ions and oxalic acid alcoholic solution at room temperature, and reacting to obtain precursor gel containing copper ions; ageing, separating and drying the gel, then conducting high-temperature calcination on the gel under air atmosphere to obtain ion-doped nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent. The diameters of the antibacterial agent particles are controlled to be 5-30nm, the specific surface area is 26.4-258.0m2 / g, the antibacterial rate of the antibacterial agent to representative gram-negative colon bacillus and gram-positive staphylococcus aureus in 24 hours can be more than 99.9%, and along with the increasing of the diameters of the particles, the minimal inhibitory concentration is lower and lower gradually, and the good antibacterial capability can be displayed. The nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent and the preparation method have the advantages that the antibacterial capability can be controlled by utilizing the doped ions, the requirement on the diameter range of the particles is low, the requirement on the preparation process and equipment can be lowered greatly, raw materials are easy to obtain, the operation is easy, the yield is high, the nanometer magnesium oxide inorganic antibacterial agent is suitable for large-batch preparation.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antimicrobial peptide Cm-CATH2, gene thereof, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106188265AStrong broad-spectrum antibacterial activityGood killing effectAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsChemical synthesisHemolysis
The invention relates to an antimicrobial peptide Cm-CATH2, a preparation method thereof and an application. The Cm-CATH2 is a straight chain polypeptide containing 33 amino acid residues, the theoretical isoelectric point is 12.96, molecular weight is 4089.97Da, and net charge is +12. A gene of a precursor cathelicidin of the encoding antimicrobial peptide Cm-CATH2 comprises 486 nucleotides. The Cm-CATH2 has high antibacterial activity for Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria and fungi, comprises various clinical drug-resistant bacteria, is low in minimal inhibitory concentration and rapid and lasting in sterilizing effect, does not contain disulfide bonds and cyclic structures, has the advantages of low hemolysis, cell toxicity, difficulty in generating drug resistance and the like, can replace an antibiotic for preparing clinical drugs resisting pathogenic microorganism infection, diminishing inflammation and the like, is applied to additives in daily chemicals such as cosmetics, health care products, food and feed, and has an excellent application prospect. Chemical synthesis and gene engineering preparation are facilitated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
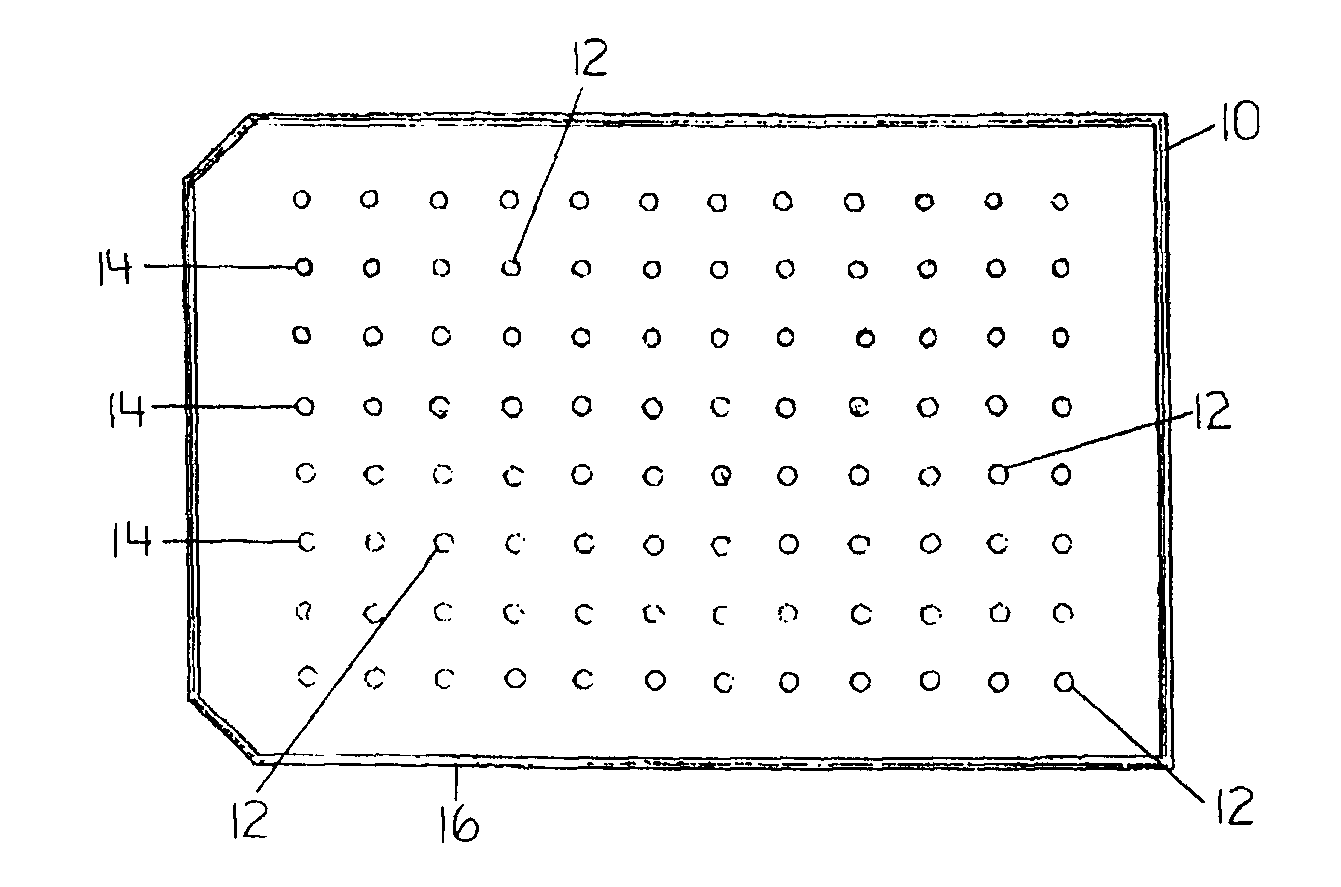
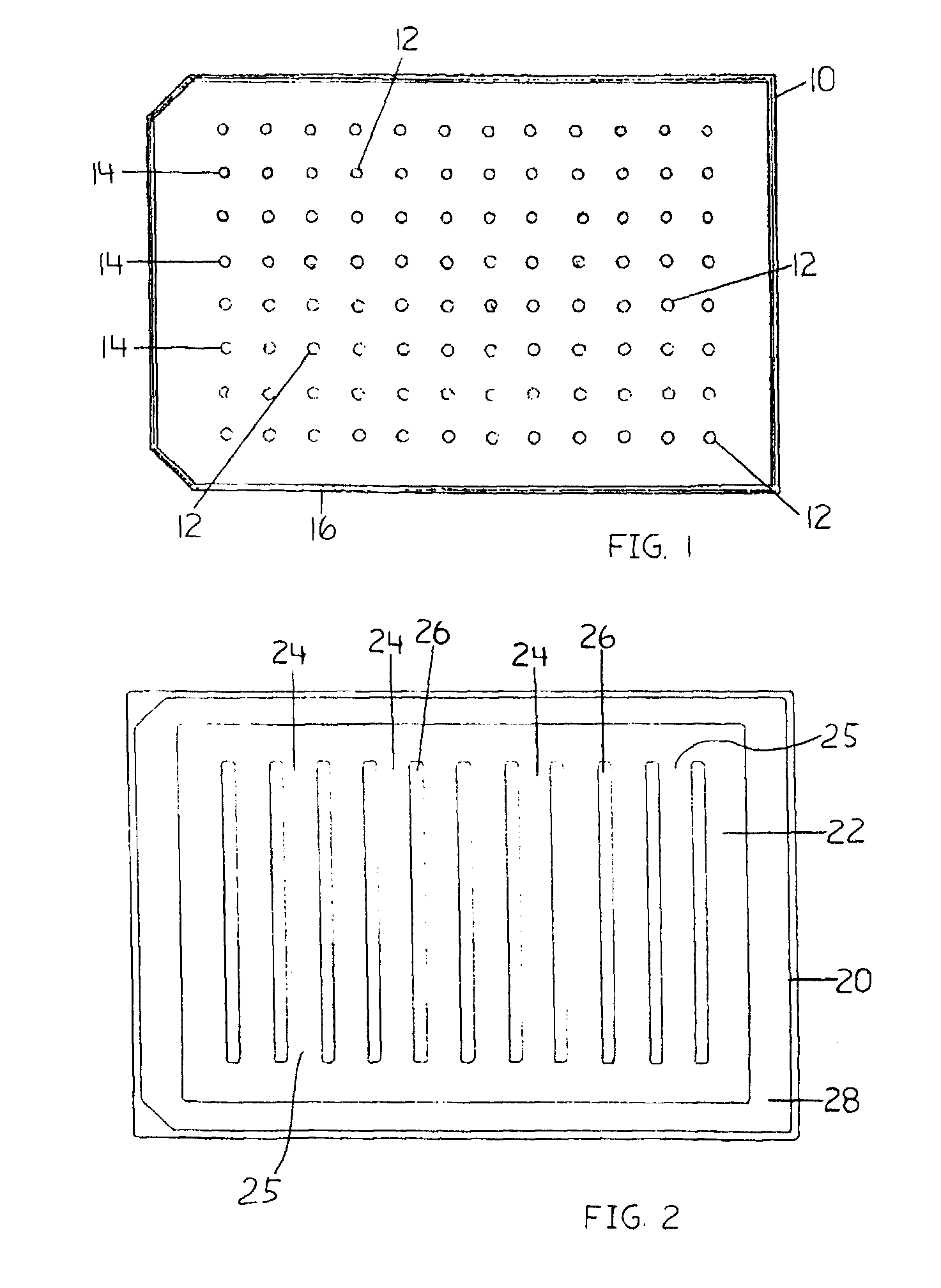
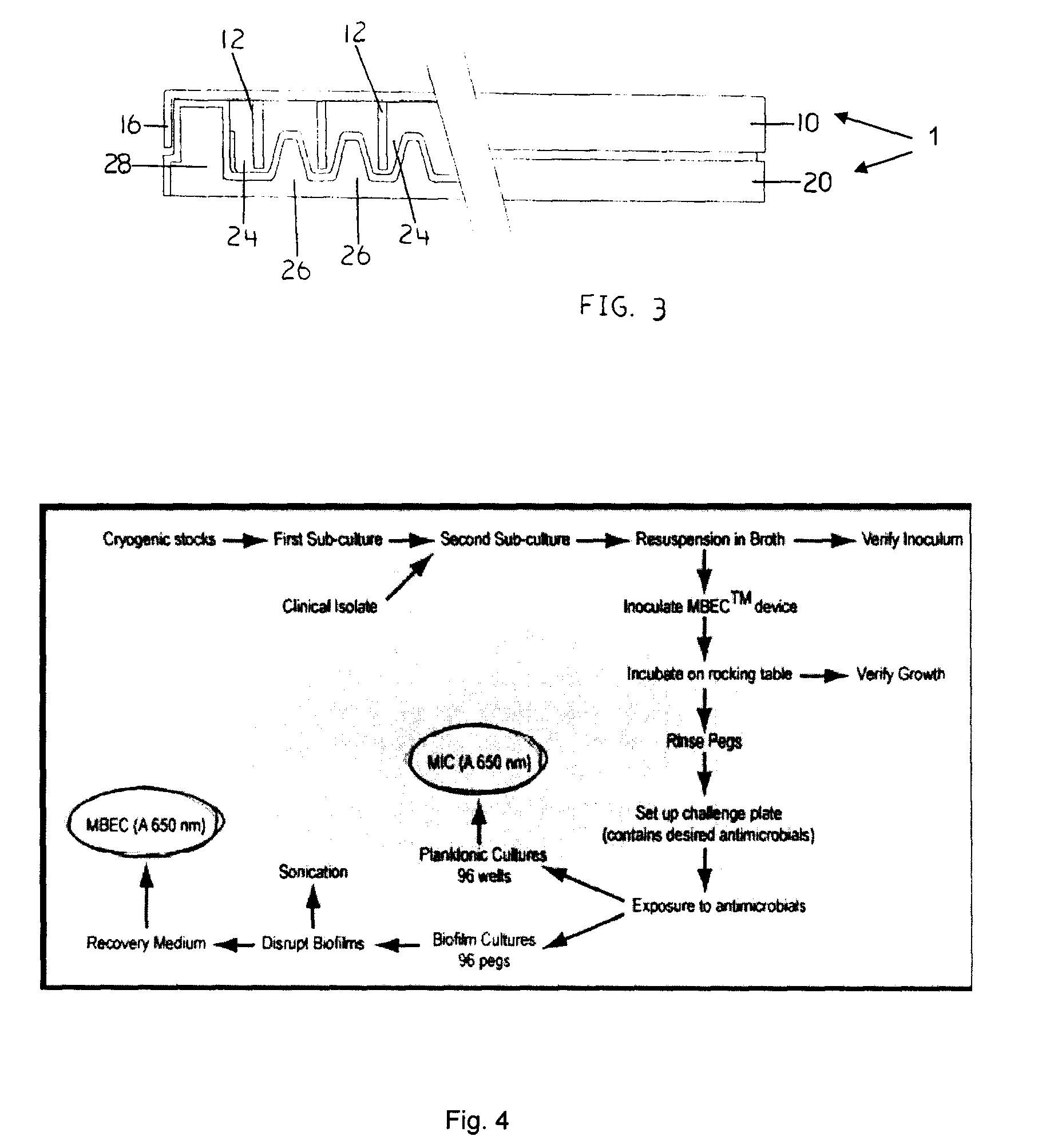
Devices and Methods for the Selection of Agents with Efficacy Against Biofilm
InactiveUS20080318268A1Efficient and cost-effectiveBroaden applicationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityMinimum inhibitory concentration
This invention is a diagnostic plate that can be used to select antibiotic combinations with efficacy against microorganisms growing as a biofilm. The plate allows growth of biofilm on a plurality of projections, and the subsequent simultaneous challenge of biofilms on all projections of the plate to independent concentrations and combinations of anti-biofilm agents. Resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics is higher when they grow as a biofilm, as compared to when they grow in a planktonic state which is usually used to determine their level of antibiotic sensitivity. Growth of microorganisms that slough off the biofilm in the anti-biofilm agent challenge determines the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) which relates to sensitivity of the microorganisms in a planktonic state. Growth of any surviving microorganisms from the biofilm in a subsequent recovery step determines the Minimal Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) which relates to the sensitivity of the microorganisms growing as a biofilm. Enumeration of the surviving microorganisms in the recovery step determines the Minimum Biocidal Concentration (MBC).
Owner:OLSON MERLE E +1
Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof
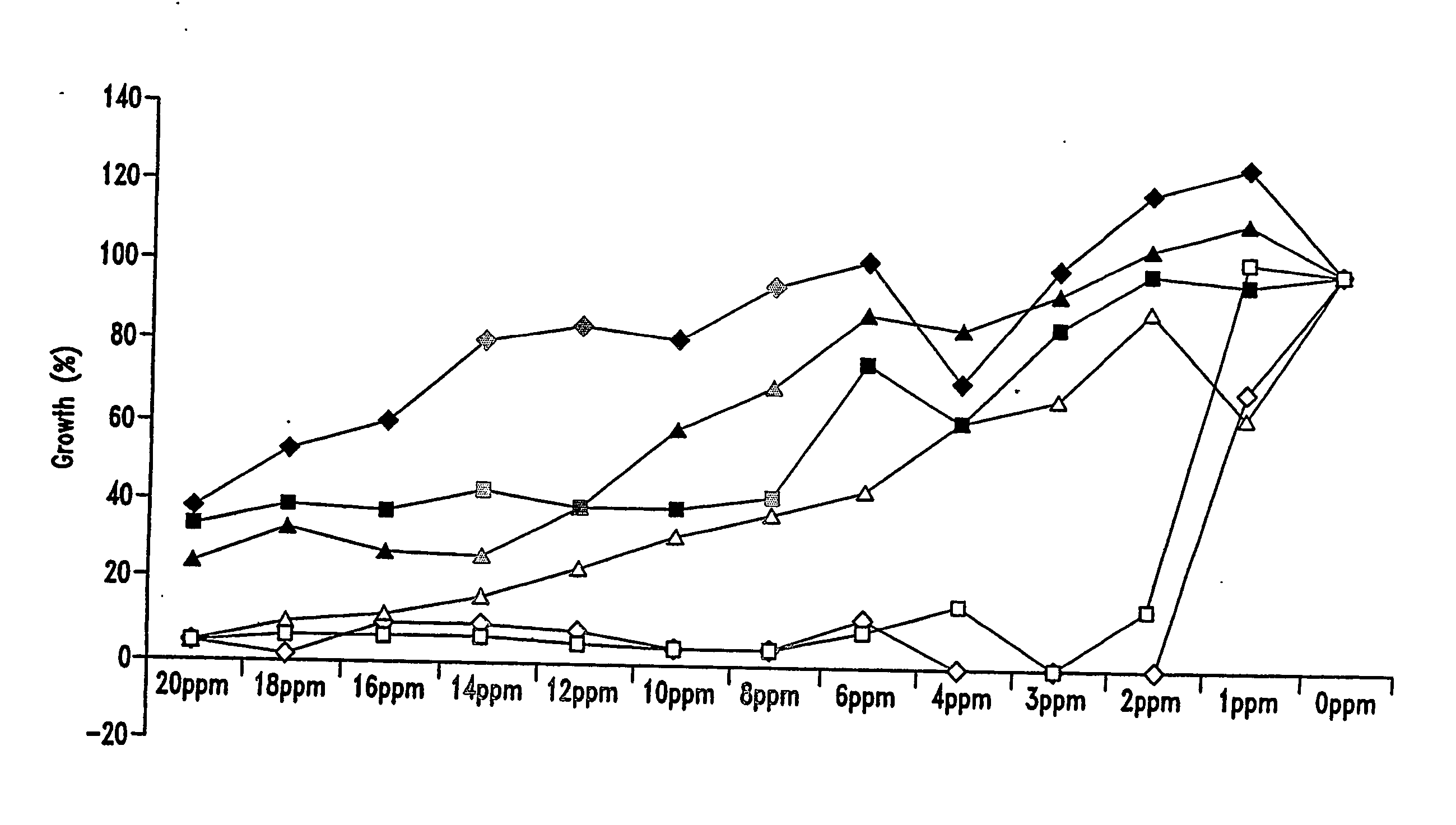
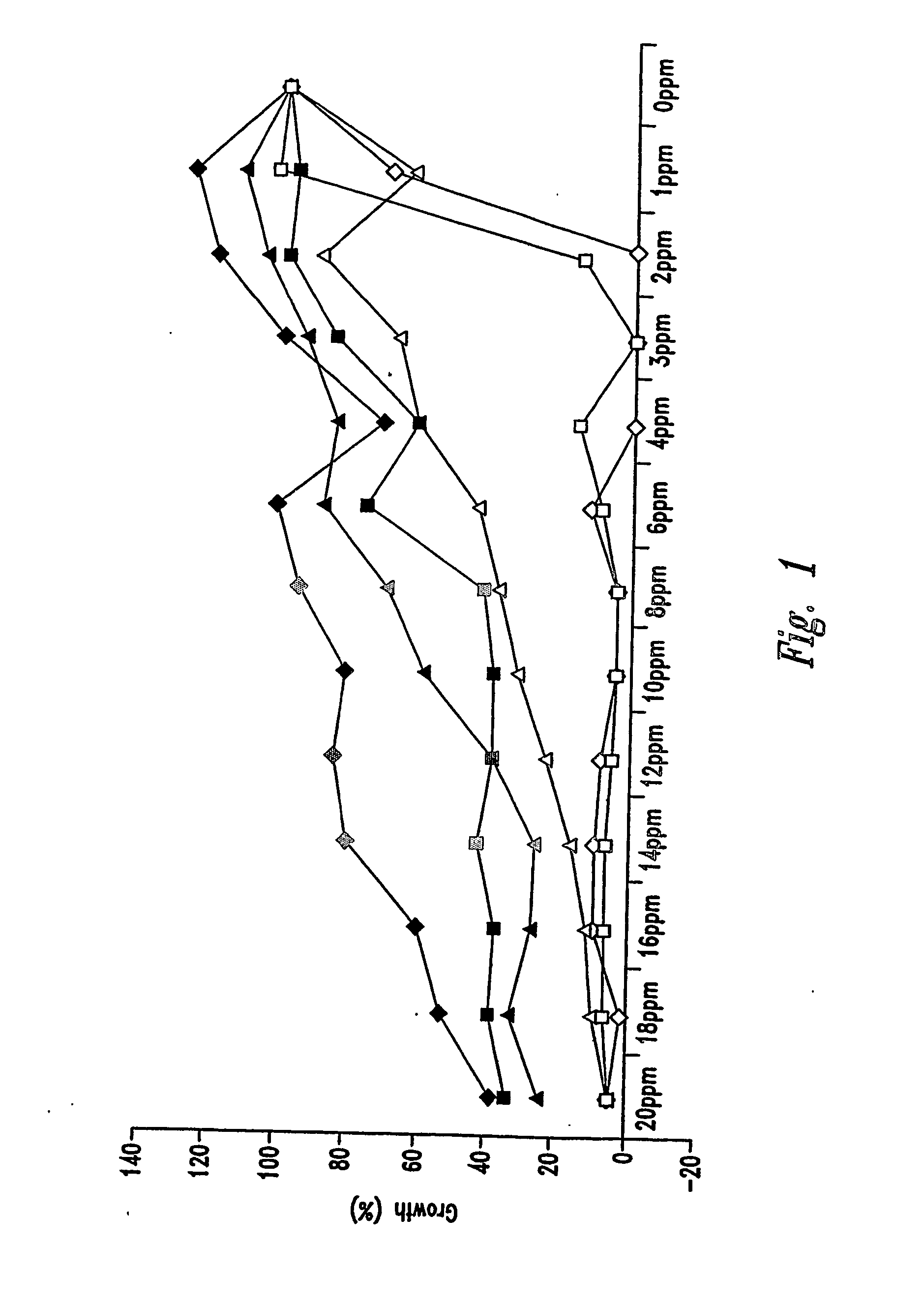
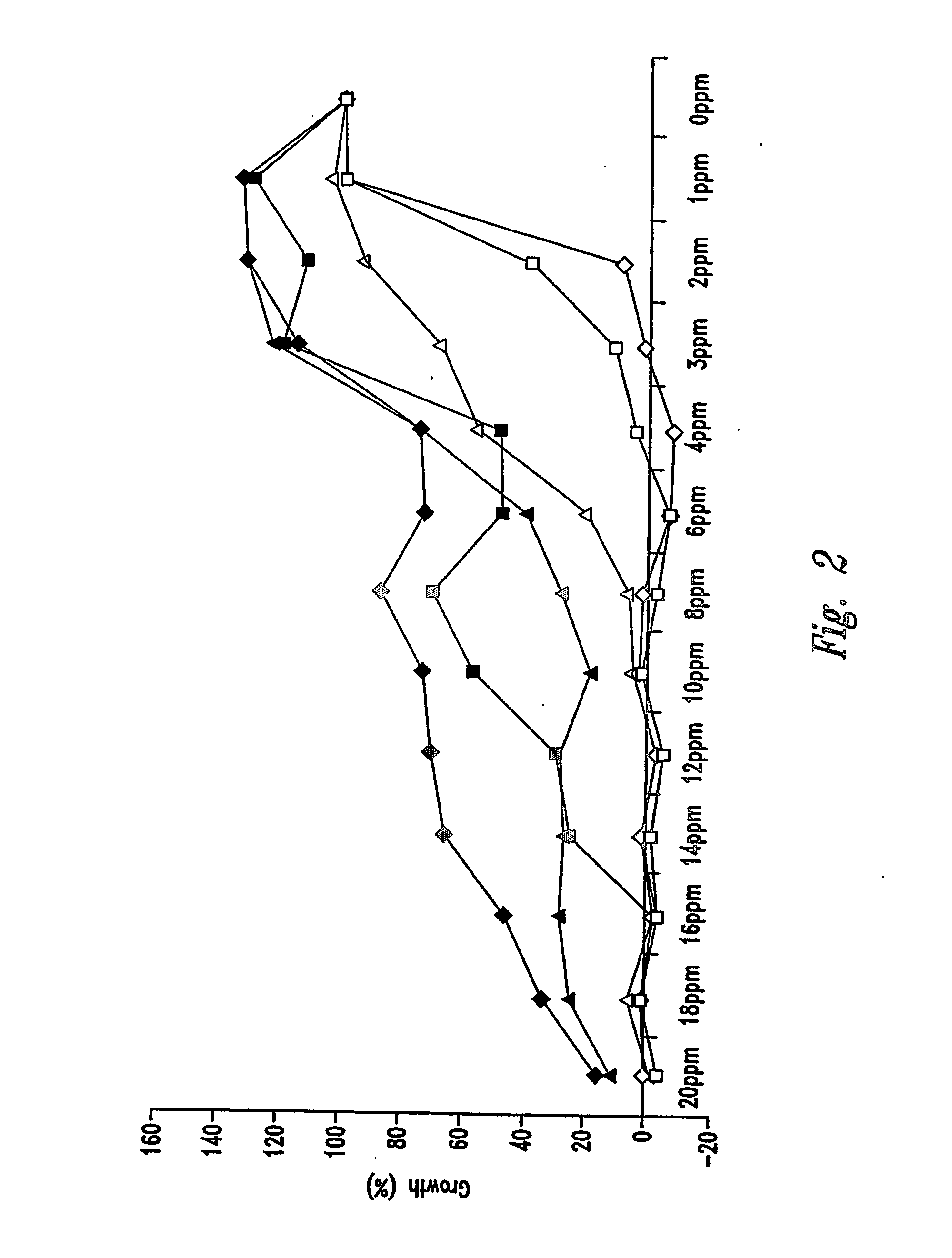
ActiveCN105524058AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood in vitro anti-tuberculosis activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMulti-drug-resistant tuberculosisMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention discloses a pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound with the structure characteristic shown in the formula (I) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, stereoisomer or prodrug molecule and a use thereof. The compound has good in-vitro anti-tubercle bacillus activity, has the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than 0.1 micrograms per milliliter and partial MIC of 0.01 micrograms per milliliter and has strong inhibition effects on a clinically sorted multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) strain. In an in-vivo experiment, at a dosage of 20mg / kg / d, the pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound can effectively eliminate H37Ra infection in a mouse and is a novel anti-tuberculosis compound.
Owner:GUANGDONG GOOD MEDICINE & HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of silver-loaded shell powder antibacterial agent
InactiveCN106172386AAbundant resourcesIncrease storage capacityBiocideDead animal preservationMinimum inhibitory concentrationSodium borohydride
The invention records a preparation method of a silver-loaded shell powder antibacterial agent. By preparing the shell powder, mixing the obtained shell powder with a sodium citrate solution and a silver nitrate solution, and dissolving and reducing it with sodium borohydride, the silver-loaded shell powder is obtained. After centrifugal drying, the silver-loaded shell powder antibacterial agent product is obtained. The method of the invention is simple, the sources of raw materials are wide, and the minimum inhibitory concentration of the obtained antibacterial product reaches 4-8 μg / ml, which shows strong antibacterial effect and has wide application value.
Owner:赵雪芹
Cyanopyridine antibacterial agents
ActiveUS7737164B2Common methodFacilitates effectiveAntibacterial agentsBiocideHalogenMinimum inhibitory concentration
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use. For example, the present invention provides chalcone and cyanopyridine compounds, and derivatives thereof, exhibiting high antibacterial activities having multiple electron withdrawing group substituents, such as halogens and fluorinated alky groups, and optionally having hydroxyl and / or alkoxyl groups substituents.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Antibacterial small molecules and methods for their synthesis
ActiveUS8367680B2Good water solubilityIncrease diversityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMinimum inhibitory concentrationSynthesis methods
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
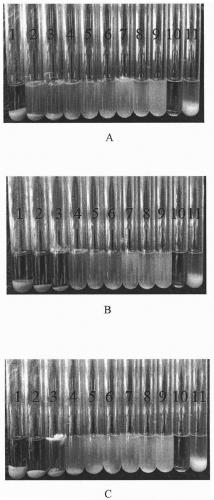
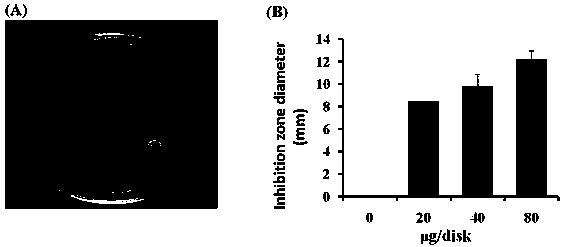
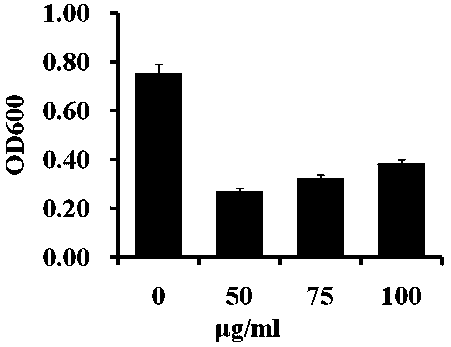
Method for Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Drugs
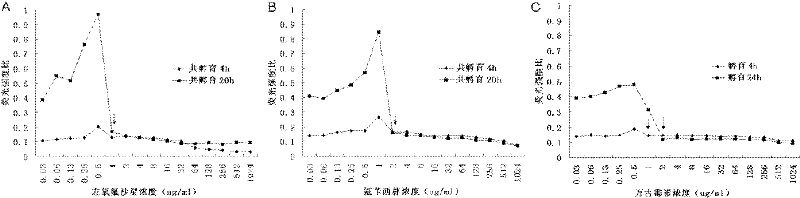
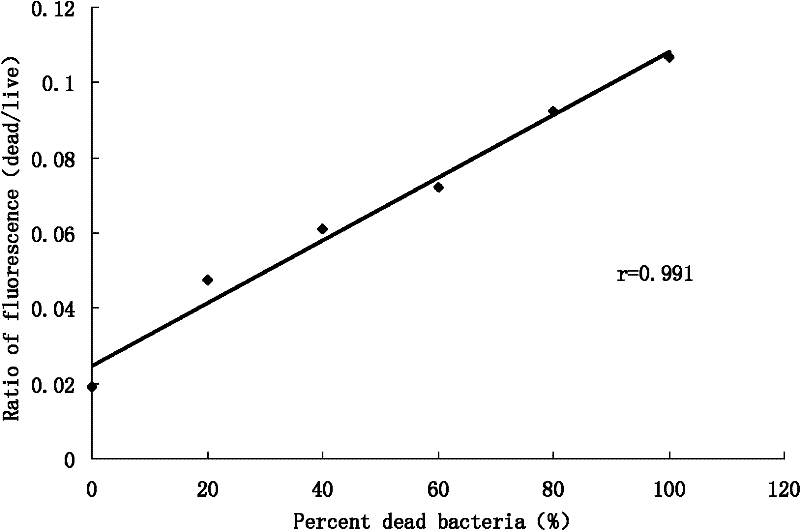
ActiveCN102288586AMIC value is accurateLow costFluorescence/phosphorescenceMinimum inhibitory concentrationConcentration gradient
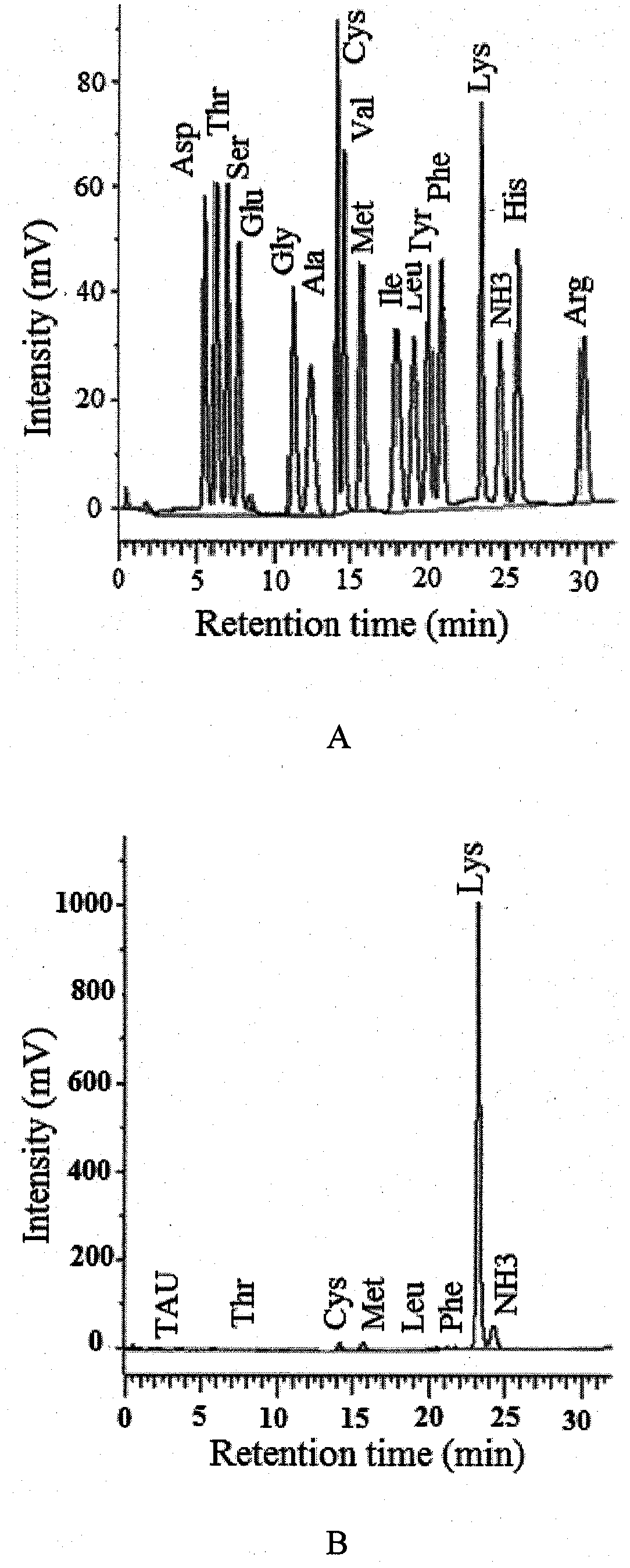
The invention discloses a method capable of rapidly, simply, conveniently and quantitatively detecting minimal inhibitory concentration, and the method comprises the following steps of: in accordance with the standard of CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) (Version 2010), adding a fresh enterococcus suspension of a certain concentration into a sterile 96-well plate containing concentration gradient antibacterials for co-incubation; upon the ending of the 4-hour incubation, adding a fixed amount of fluorescent dyes SYTOX Green and DAPI (4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole) to all the wells, protecting the wells from light for 15 minutes at room temperature, reading the fluorescent intensity of the two dyes in the wells by use of a fluorescent microplate reader respectively; after relevant background fluorescence is deducted, drawing a corresponding curve between bacterial fluorescence intensity ratio (Pdead / livel) and concentration of drug (CDrug), and determining the minimal concentration of drug corresponding to the moment the Pdead / livel is no longer fluctuated as the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) of the antibiotic to the bacterium. The detection method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being simple, convenient, rapid and objective and being capable of performing mathematic statistics and analysis directly on detected data, becomes a new detection method for determining the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibacterials, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of cellulose-based antibacterial material dialdehyde cellulose-lysine
The invention relates to a novel cellulose-based antibacterial material, which is mainly produced via the steps of: controlling reaction temperature, time, pH value and oxidization ratio of dialdehydecellulose in order to perform a reaction to the dialdehyde cellulose and lysine, and when the reaction is finished, performing centrifugal separation and drying and grinding the product. The antibacterial material has excellent antibacterial activity, and can reach 30 mg / ml in minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Gram negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, and 7.5 mg / ml in MIC against Gram positive bacteria, such as staphylococcus aureus, with penicillin as a positive control and an LB liquid culture medium as a negative control; under special conditions, the antibacterial material can completely growth of bacteria. The antibacterial material has simple process and is free of toxic and side effect. The raw material, cellulose, has abundant sources and is environment friendly. The invention supplies a new idea for researching and developing novel antibacterial materials.
Owner:江苏灵源沂岸科技股份有限公司
Method for quickly detecting drug resistance of bacteria
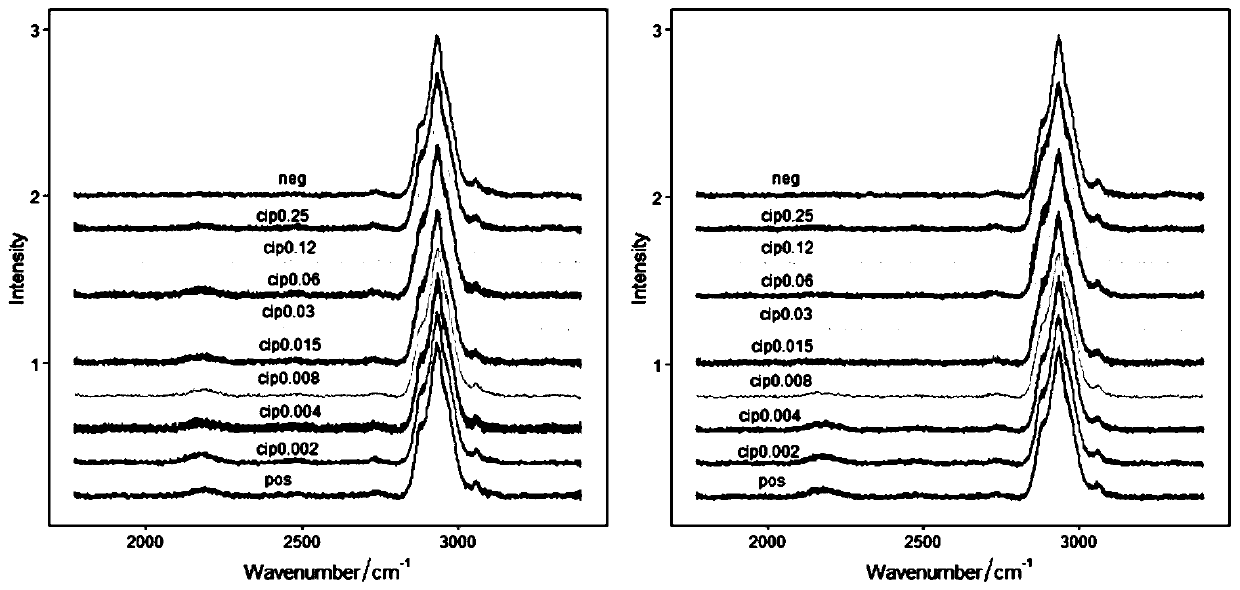
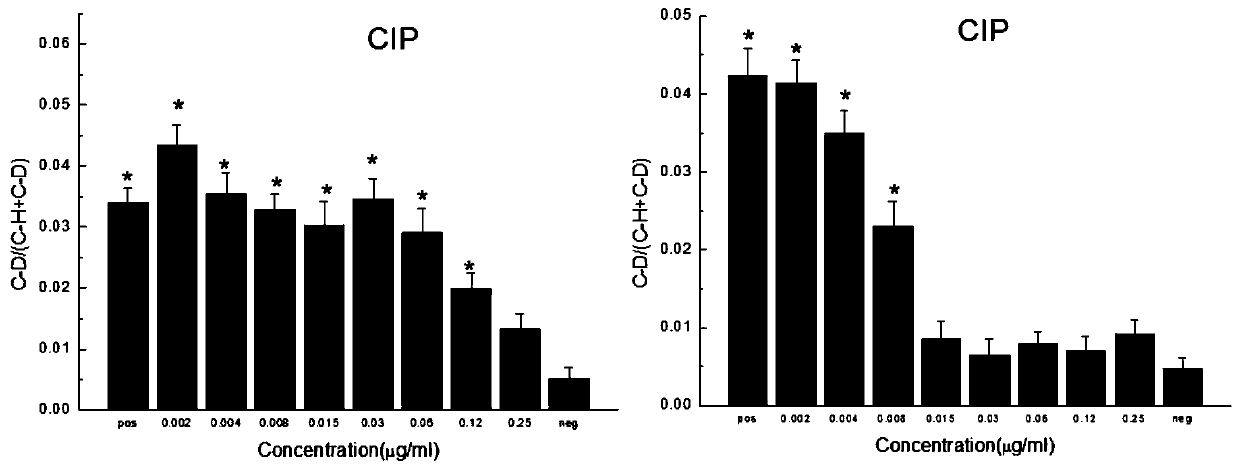
PendingCN110643675AStrong metabolic activityExactly give the sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringMinimum inhibitory concentrationDrug resistance
The invention relates to a method for quickly detecting drug resistance of bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: experimental groups of antibiotics with different concentrations, a positive control group and a negative control group are set, wherein the experimental groups of the antibiotics with the different concentrations refer to experimental groups of adding the antibiotics withthe different concentrations into culture mediums and adding heavy water in subsequent steps, the positive control group refers to the experimental group of adding antibiotics with a concentration of0 into a culture medium and adding heavy water in subsequent steps, and the negative control group refers to the experimental group of adding antibiotics with a concentration of 0 intp a culture medium without adding heavy water in subsequent steps, after incubation is performed, centrifugal washing is performed, samples are subjected to Raman detection, values of C-D / (C-D + C-H) are calculated respectively according to the obtained Raman spectra, a turning point of value decrease of C-D / (C-D + C-H) of the experimental groups of the antibiotics with different concentrations relative to the control groups is taken as a minimum inhibitory concentration of the antibiotics on the bacteria, and the minimum inhibitory concentration is compared with a breakpoint given in a CLSI susceptibility test standard to determine the bacterial sensitivity, intermediation or drug resistance. The method introduces a breakpoint comparison to more accurately give the sensitivity of the bacteria to the antibiotics.
Owner:上海氘峰医疗科技有限公司
Broiler feed additive and preparation method thereof
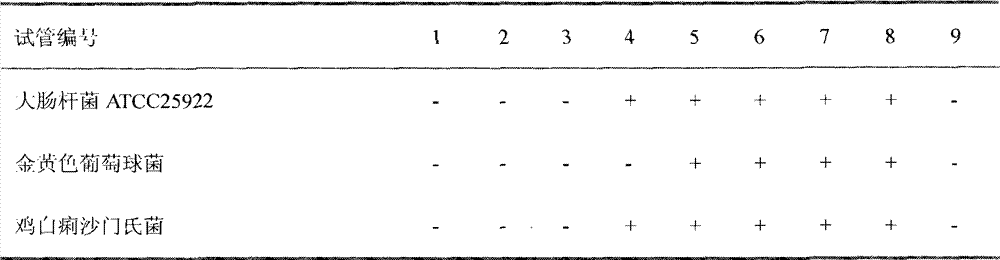
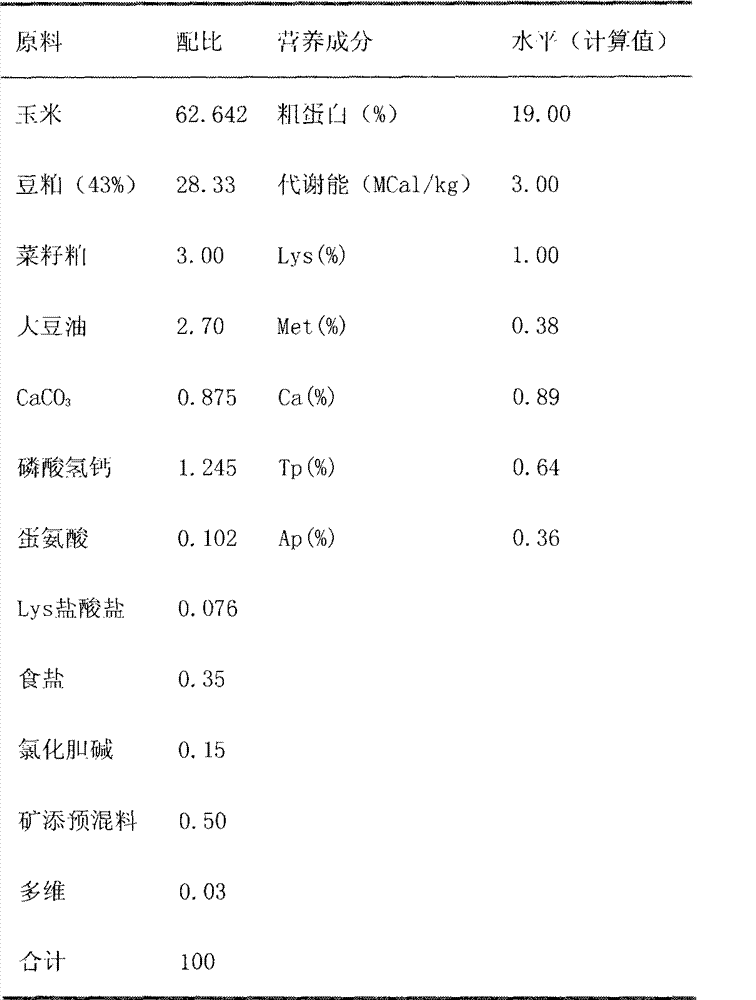
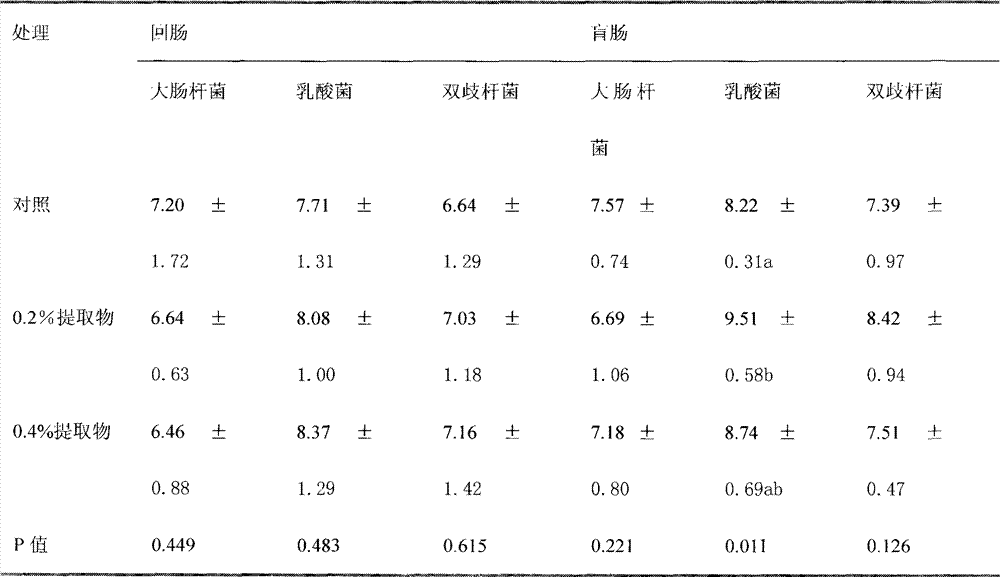
InactiveCN103039723AReduce mortalityReduce in quantityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBifidobacteriumEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a broiler feed additive and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking whole red-knees herb, cutting into 0.2-0.5cm long, adding water according to the ratio of 1:5(g / ml), immersing for 30min, boiling, decocting for 15min by soft fire, and filtering liquid medicine by four layers of gauze; adding water into remaining slag according to the ratio of 1: (2-3) (g / ml), boiling, decocting for 15min by soft fire, and filtering; adding water into filter residue according to the ratio of 1: (2-3) (g / ml), boiling, decocting for 15min by soft fire, and filtering; and combining the liquid medicine of the three times, concentrating to be paste by soft fire, and drying the paste by a freezer drier, thereby obtaining the extract. Through broiler raising tests, two adding levels are set according to the minimal inhibitory concentration obtained by an in-vitro method. The results show that the adding level is 0.2wt% to 0.4wt%. By adoption of the preparation method, the death rate of the broiler can be reduced, the amount of beneficial bacteria (represented as lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacterium) in ileum and caecum is improved, and meanwhile, the amount of harmful bacteria (represented as escherichia coli) is reduced.
Owner:彭焕伟
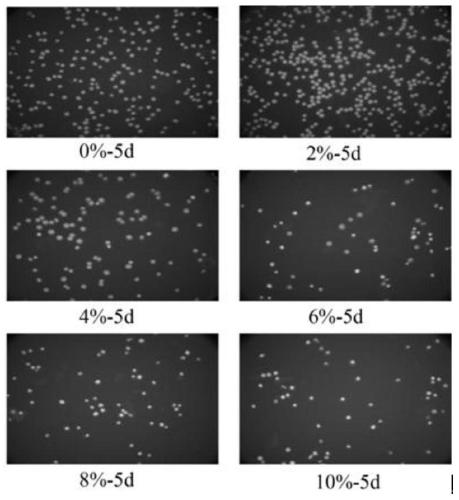
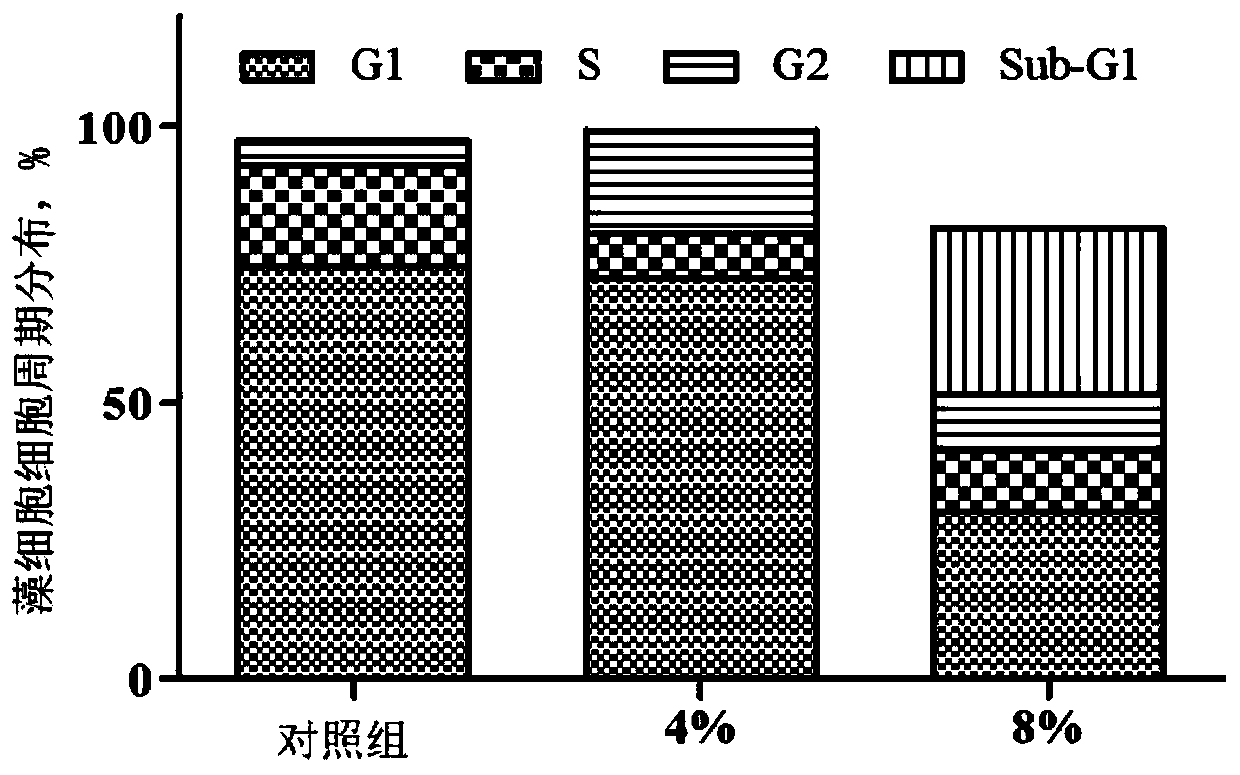
Method for preventing and controlling red tide resulting from Karenia mikimotoi by pseudoalteromonas
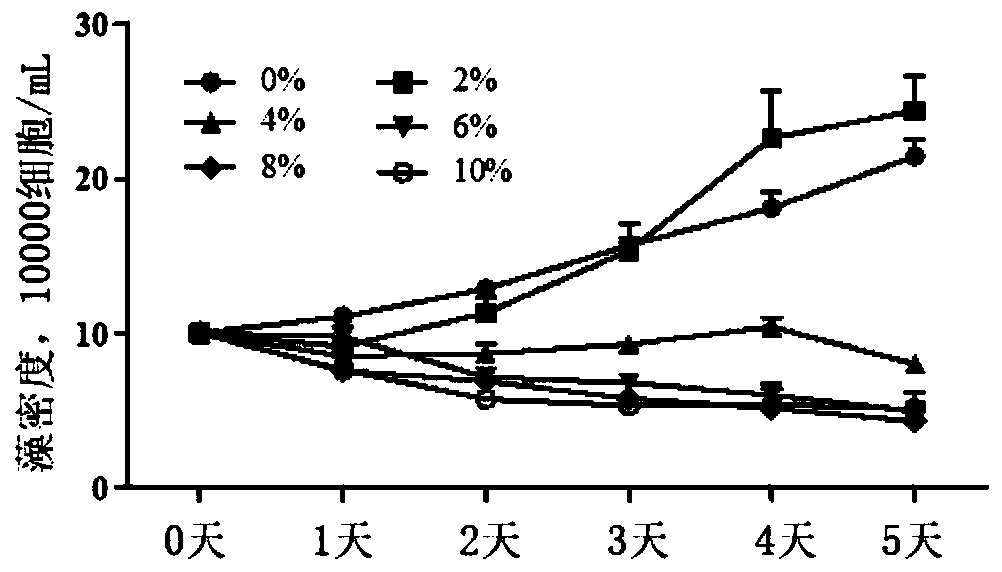
InactiveCN110255719ARealize red tide prevention and controlBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMinimum inhibitory concentrationFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for preventing and controlling a red tide resulting from Karenia mikimotoi by pseudoalteromonas. According to the method, a pseudoalteromonas strain capable of remarkably inhibiting growth of red-tide Karenia mikimotoi is separated from a soil environment of a river estuary through a co-culture experiment; pseudoalteromonas fermentation liquor, thalli, filtrate and a fermentation culture medium are separately added into Karenia mikimotoi liquor for co-culture; 4% pseudoalteromonas fermentation liquor filtrate is a minimum inhibitory concentration; through 12h of treatment by the 4% pseudoalteromonas fermentation liquor filtrate, an algae cell cycle of the Karenia mikimotoi can be retarded at a G2 phase, and thus, the Karenia mikimotoi cannot enter a division stage; through 3h of action by 8% filtrate, the level of active oxygen in algae cells reaches the maximum, and it is observed by a fluorescent microscope that the algae cells completely present red; and through 6h of action, the level of active oxygen in the algae cells is lowered, and then, the algae cells rupture and present green yellow. The method has the beneficial effect that the red tide resulting from red-tide microalgae Karenia mikimotoi can be prevented and treated.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
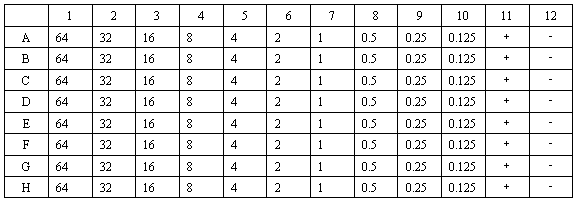
Microdetermination method for measuring minimum inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration of cationic antimicrobial peptide
ActiveCN103173517AMeet measurement needsEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention discloses a microdetermination method for measuring minimum inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration of cationic antimicrobial peptide. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a reagent, namely preparing an MHB culture medium; 2) preparing bacterial suspension, namely reviving the bacteria to logarithmic phase, and preparing bacterial suspension with a certain concentration; 3) counting the bacterial suspension, namely performing coubling dilution on the bacterial suspension in the step 2), dripping and counting; 4) diluting the agent, namely performing coubling dilution on the agent to different testing concentration gradient; 4) measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration, namely mixing and culturing the diluted agent in the step 4) with the bacterial suspension prepared in the step 2), and observing whether macroscopic bacterial precipitation exists; and 6) measuring the minimal bactericidal concentration, namely culturing the testing dripping plate with the antibacterial effect in the step 5), and observing whether colony growth exists. The method for measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration of cationic antimicrobial peptide has the characteristics of low interference, trace, convenience and rapidness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor and antibacterial application thereof
InactiveCN104784160AImprove securitySeparation and purification are simple and easy to controlAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention relates to antibacterial application of small molecular bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor Falcarindiol in the condition of no inhibition on bacteria growth concentration (subinhibitory concentration). The active compound has a broad-spectrum bacterial quorum sensing resistant activity, can inhibit bacterial virulence in subinhibitory concentration, reduces the harm of bacteria to the host, and can prevent and treat quorum sensing bacterial infections. The compound can play the role of inhibition of bacterial virulence in subinhibitory concentration, so that pressure for survival of pathogenic bacteria is not brought, drug resistance is not easy to produce, the antibacterial application of the small molecular bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor Falcarindiol in the condition of no inhibition on bacteria growth concentration (subinhibitory concentration) is different from application of killing bacteria and bacteria growth inhibition of other antibacterial agent, is also is different from the antibacterial application of bacteria growth inhibition of Falcarindiol with the bacteria concentration (the use final concentration is greater than the minimum bacteriostasis concentration), and is a new antibacterial application. The antibacterial application of the small molecular bacterial quorum sensing inhibitor Falcarindiol in the condition of no inhibition on bacteria growth concentration (subinhibitory concentration) has the advantages that: raw materials are easy to get, compound separation and purification are simple and easy to control, security is high, use concentration is low, and drug resistance is easy to produce, and the like, so that the Falcarindiol can be used in preparation of a new antibacterial agent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method of dialdehyde cellulose grafted epsilon-polylysine antibacterial material
The invention relates to dialdehyde cellulose grafted epsilon-polylysine antibacterial material, prepared by oxidizing cellulose into dialdehyde cellulose, and using the dialdehyde cellulose as a supporter to modify with epsilon-polylysine under a certain aldehyde group molar ratio through grafting reaction so that epsilon-polylysine is grafted to dialdehyde microcrystalline cellulose. The processto prepare the dialdehyde cellulose grafted epsilon-polylysine antibacterial material is simple; the dialdehyde cellulose grafted epsilon-polylysine antibacterial material has no toxic and side effects and has good antibacterial activity; with penicillin acting as a positive control and LB (lysogeny broth) liquid medium as a negative control, the material herein has minimum inhibitory concentrations of 7.5 mg / mL, 15 mg / mL and 30 mg / mL respectively for E. coli and S. aureus, S. typhimurium, and S. lutea and B. subtilis. A new idea is provided for the research and development of novel antibacterial materials.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/909a5abe-a2d3-4ecd-9adb-643e3707a5fe/HDA0000770441560000011.PNG)
![Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/909a5abe-a2d3-4ecd-9adb-643e3707a5fe/HDA0000770441560000012.PNG)
![Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof Pyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyridine compound and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/909a5abe-a2d3-4ecd-9adb-643e3707a5fe/HDA0000770441560000021.PNG)