Application of perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride amidation compound in anti-staphylococcus aureus
A technology of tetracarboxylic dianhydride amide and perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride, which is applied in the fields of antibacterial drugs and organic chemistry, can solve the problems of limited antibacterial effect, achieve compound stability, simple preparation, and the effect of inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] This example proposes a compound against Staphylococcus aureus: PDI-ACI, which has the following molecular structural formula:
[0063]
[0064] The preparation method of this compound is as follows:
[0065] Dissolve tetrachloroperylene anhydride and N,N-dimethylethylenediamine at a ratio of 1:16 (tetrachloroperylene anhydride 1 mmol, N,N-dimethylethylenediamine 16 mmol) in N-methylpyrrolidone (30 ml) and glacial acetic acid (15 ml) were reacted at 120 °C, followed by argon for 10 min and heated for 24 h. After the completion, add 60 ml of 2 mol / L hydrochloric acid and 60 ml of absolute ethanol, stir vigorously, put it in the refrigerator to stand still, suction filter after 24 h, wash with ethanol, and dry in vacuum to obtain the product and methyl iodide in a ratio of 1:8 ( The former (0.15 mmol, the latter 1.2 mmol) was dissolved in 8 ml of toluene, argon was passed through for 10 min at 85°C, and then heated to reflux for 12 h. After the reaction was completed,...
Embodiment 2
[0069] This embodiment proposes a compound against Staphylococcus aureus: PDI-I, which has the following molecular structural formula:
[0070] .
[0071] PDI-I preparation method is as follows:
[0072] 3,4,9,10-Perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride (1 mmol; compared with tetrachloroperylene anhydride, which has 4 more chlorine atoms in the alkyl position), N,N-dimethylethylene di Amine (10 mmol)) and glacial acetic acid (10 ml) were sequentially added to N,N-dimethylpyrrolidone (NMP, 20 ml) and reacted at 120 °C for 24 h under the protection of argon. Cool the reacted mixture to room temperature, add 50 ml each of absolute ethanol and 2M HCl, stir with a glass rod, let it stand, filter, dry in vacuo, and refine by column chromatography (mobile phase: trichloromethane (CHCl 3 )), to obtain red solid PDI-I. Then PDI-I (0.188 mmol) and iodomethane (CH 3 I, 1.502 mmol) was added to toluene (8 ml), heated to reflux at 85°C for 9h. Then add diethyl ether to precipitate, filte...
Embodiment 3
[0074] This example proposes a compound against Staphylococcus aureus: PDI-2Br, which has the following molecular structural formula: ,
[0075] The preparation method of PDI-2Br is as follows:
[0076] Dissolve 1 mmol of dibromoic anhydride and 1.8 ml of N,N-dimethylethylenediamine in quinoline (10 ml), react at 160 °C, first pass argon for 10 min, and heat for 24 h. Cool and suction filter, wash with methanol, and dry in vacuo to obtain the product N,N-dimethyl-dibromoperyleneimide. Take N,N-dimethyl-dibromoperyleneimide and methyl iodide at a ratio of 1:8 (for example, the former is 0.1 mmol, the latter is 0.8 mmol) and dissolved in 40 ml of toluene, first pass argon for 10 min, and then heat at 85°C Reflux for 12 h. After the reaction, cool, filter with suction, wash with ether three times, and dry in vacuum to obtain PDI-2Br.
[0077] application
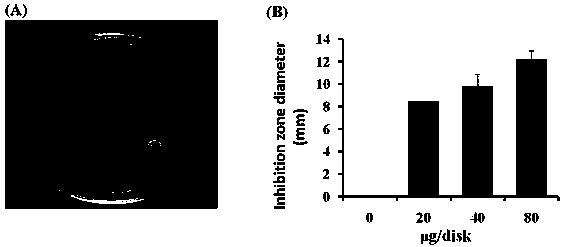
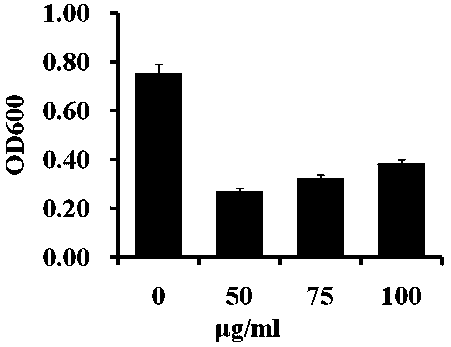
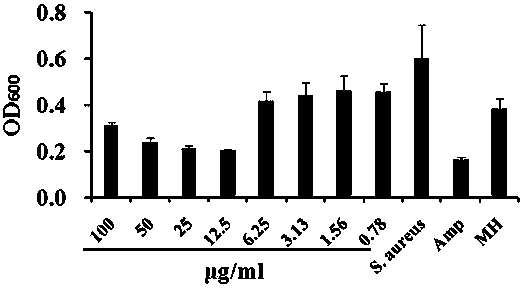
[0078] Anti-Staphylococcus aureus application based on the compound described in Example 1:
[0079] 1) Prepare strains...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com