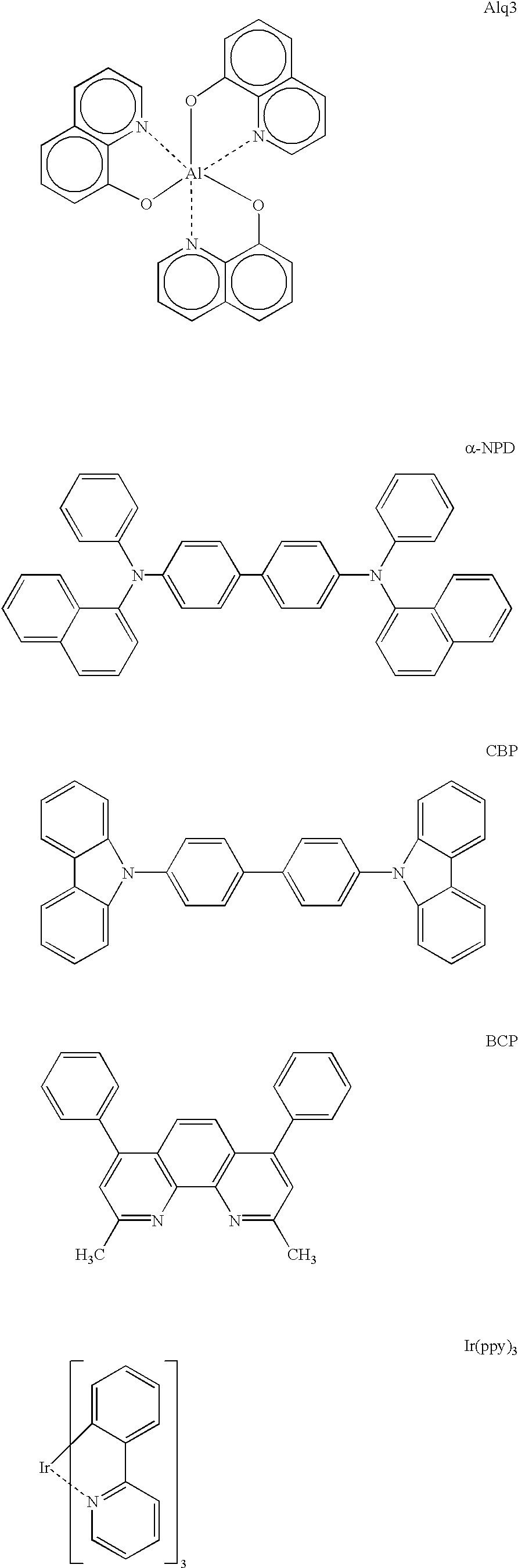
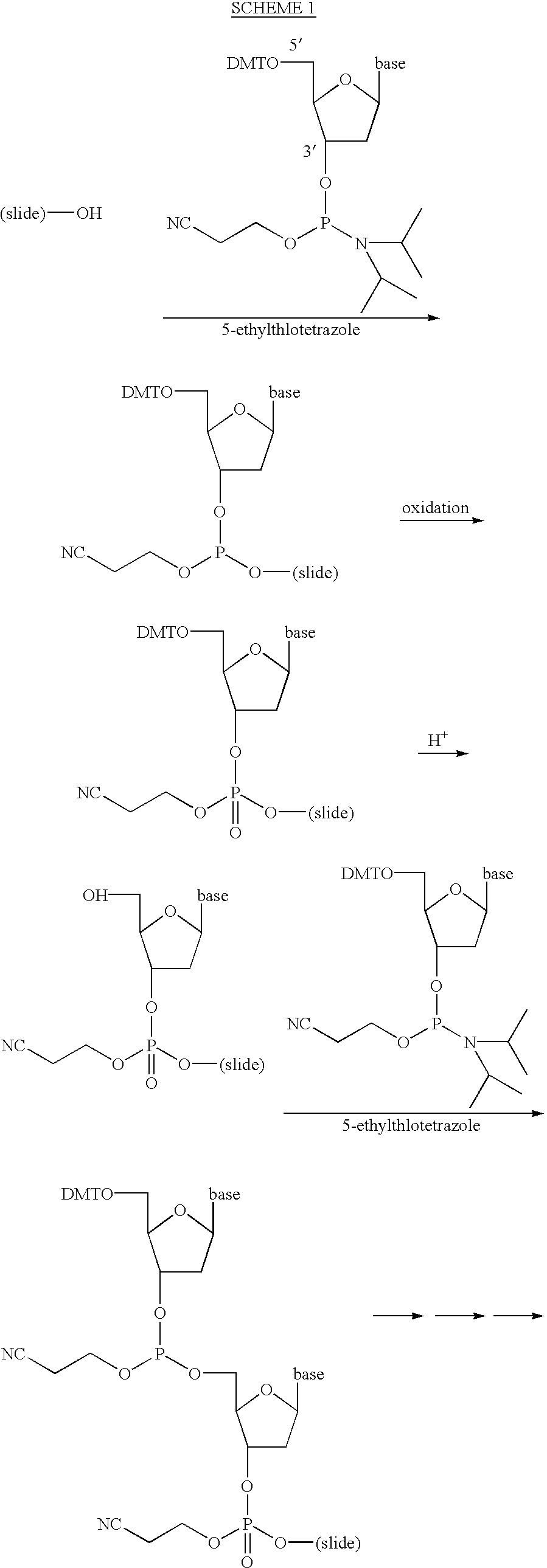
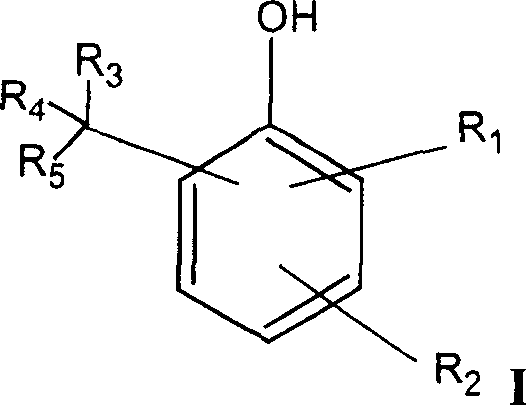
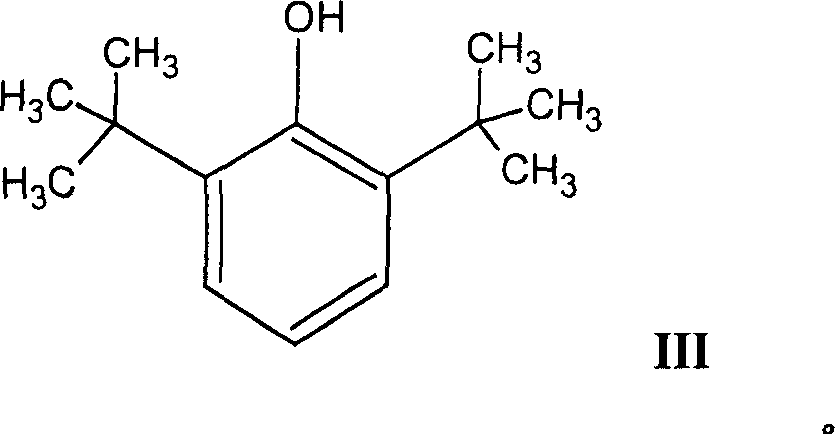
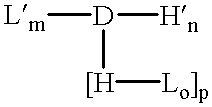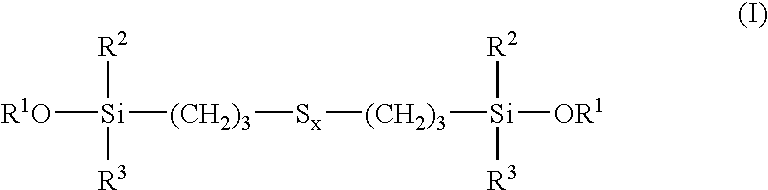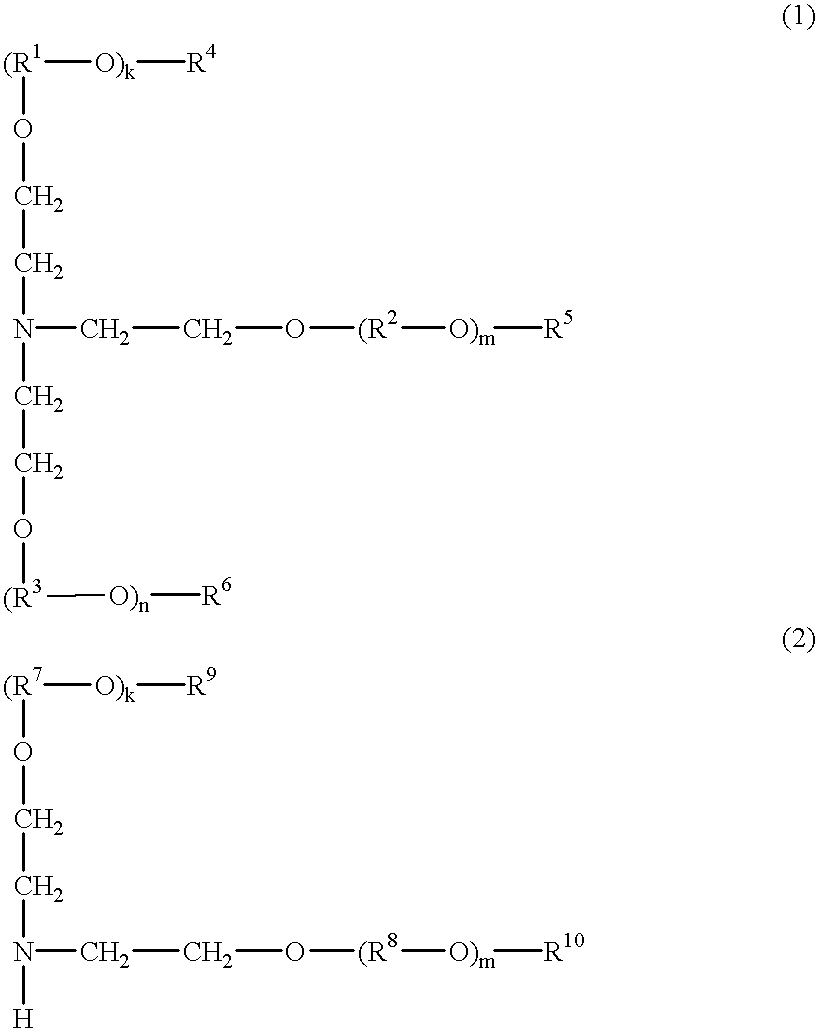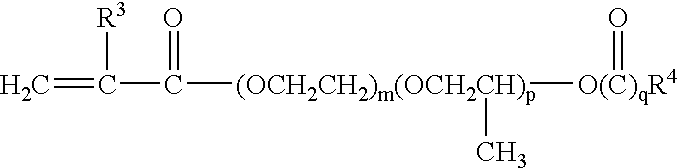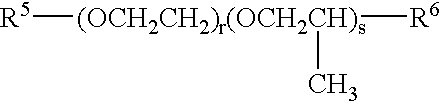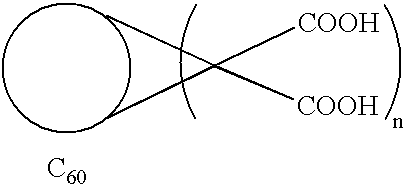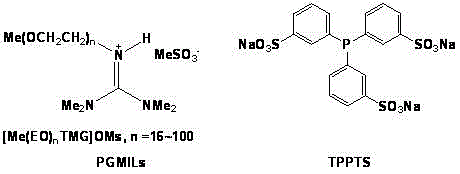Patents
Literature
6027 results about "Straight chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates with hydroyzable lipophile components and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS6309633B1Reduce deliveryExtended durationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinCholesterol
The invention provides a drug-oligomer conjugate having the following general formula:wherein D is a therapeutic drug moiety; H and H' are each a hydrophilic moiety, independently selected from the group consisting of straight or branched PEG polymers having from 2 to 130 PEG subunits, and sugars; L is a lipophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups having 2-26 carbon atoms, cholesterol, adamantane and fatty acids; o is a number from 1 to the maximum number of covalent bonding sites on H; m+n+p together have a value of at least one and not exceeding the total number of covalent bonding sites on D for the -H', -L and -H-L substituents; the H-L bond(s) are hydrolyzable and the D-L' bond(s), when present, are hydrolyzable; the conjugate being further characterized by one of the following: (i) m is 0 and p is at least 1; (ii) n is 0 and p is at least 1; (iii) m and n are each 0 and p is at least 1; (iv) p is 0 and m and n are each at least 1. The therapeutic drug moiety is preferably a therapeutic protein or peptide, preferably insulin or a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Catalyst for olefine polymerizing reaction and its components
The present invention provides one kind catalyst component for CH2=CHR olifine polymerization, where R is H or alkyl radical or aryl radical of C1-C6. The catalyst component contains Mg, Ti, halogenand electron donor.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
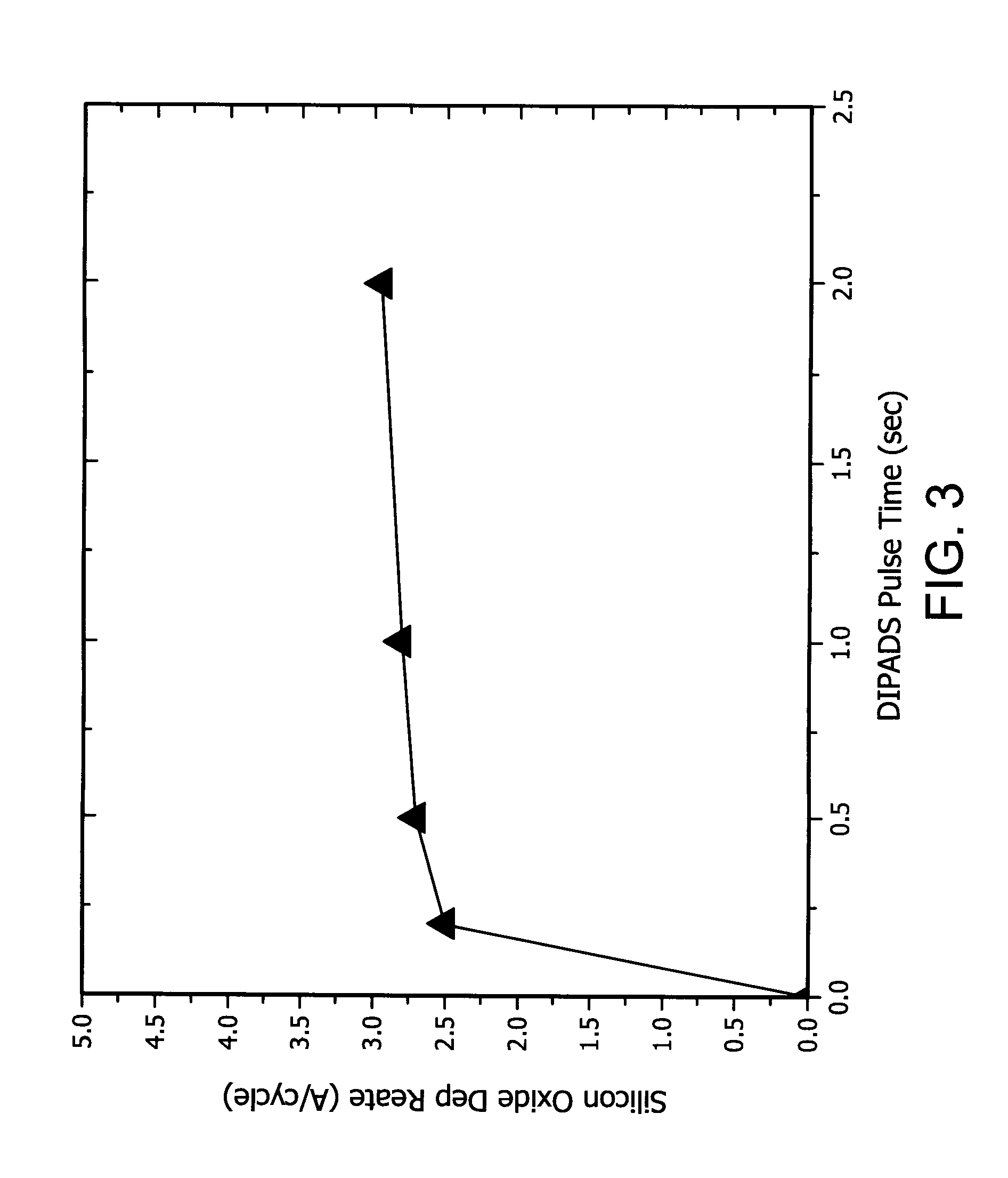
Organoaminodisilane precursors and methods for depositing films comprising same
Described herein are precursors and methods for forming silicon-containing films. In one aspect, there is provided a precursor of Formula I:wherein R1 is selected from linear or branched C3 to C10 alkyl group, linear or branched C3 to C10 alkenyl group, linear or branched C3 to C10 alkynyl group, C1 to C6 dialkylamino group, electron withdrawing group, and C6 to C10 aryl group; R2 is selected from hydrogen, linear or branched C1 to C10 alkyl group, linear or branched C3 to C6 alkenyl group, linear or branched C3 to C6 alkynyl group, C1 to C6 dialkylamino group, C6 to C10 aryl group, linear or branched C1 to C6 fluorinated alkyl group, electron withdrawing group, and C4 to C10 aryl group; optionally wherein R1 and R2 are linked together to form ring selected from substituted or unsubstituted aromatic ring or substituted or unsubstituted aliphatic ring; and n=1 or 2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Tire and tread comprising a bis-alkoxysilane tetrasulfide as coupling agent
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Low dielectric constant insulating film and method for forming the same
InactiveUS8828886B2Improve resistance to damageLow dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingArea ratioPolymer
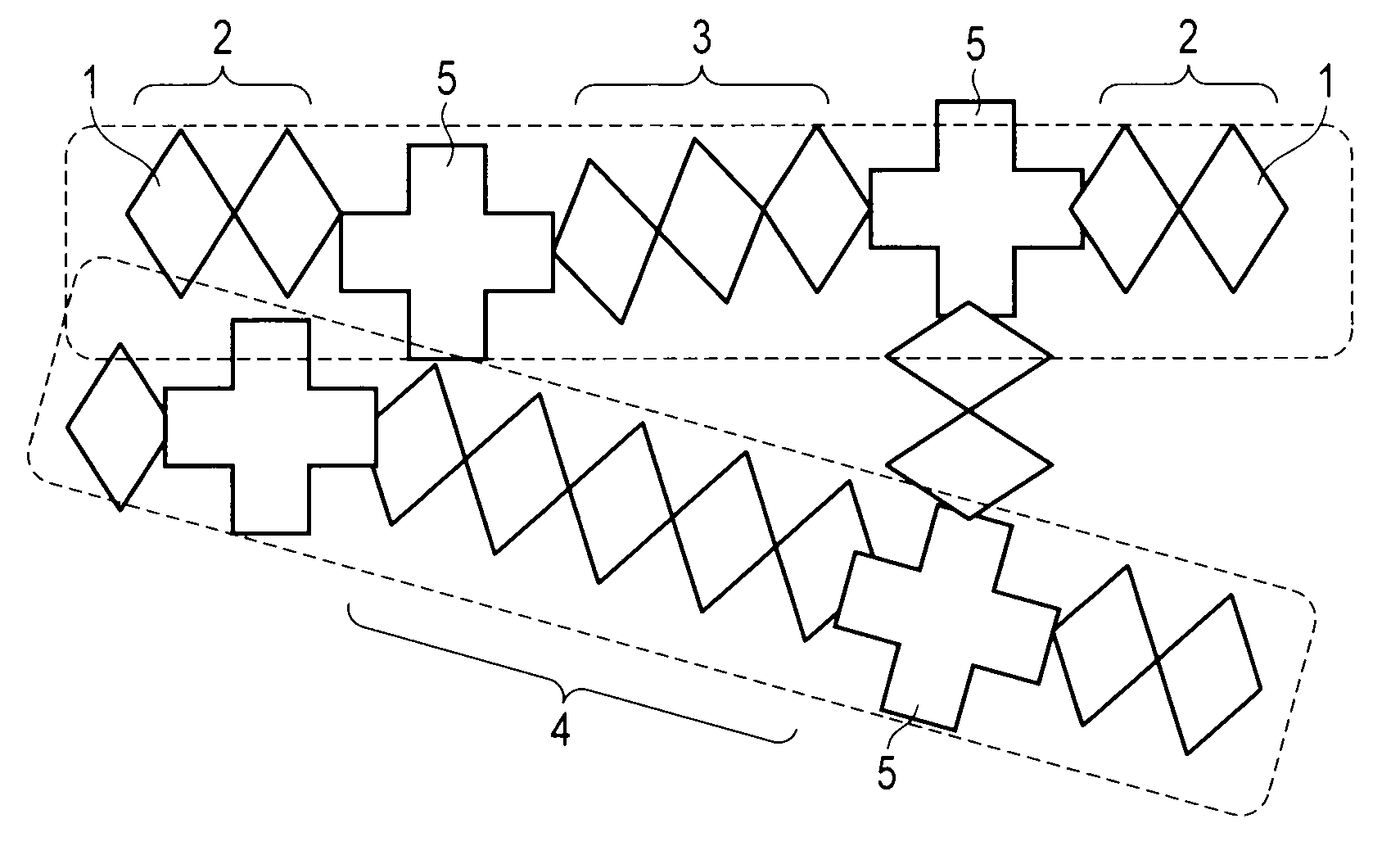
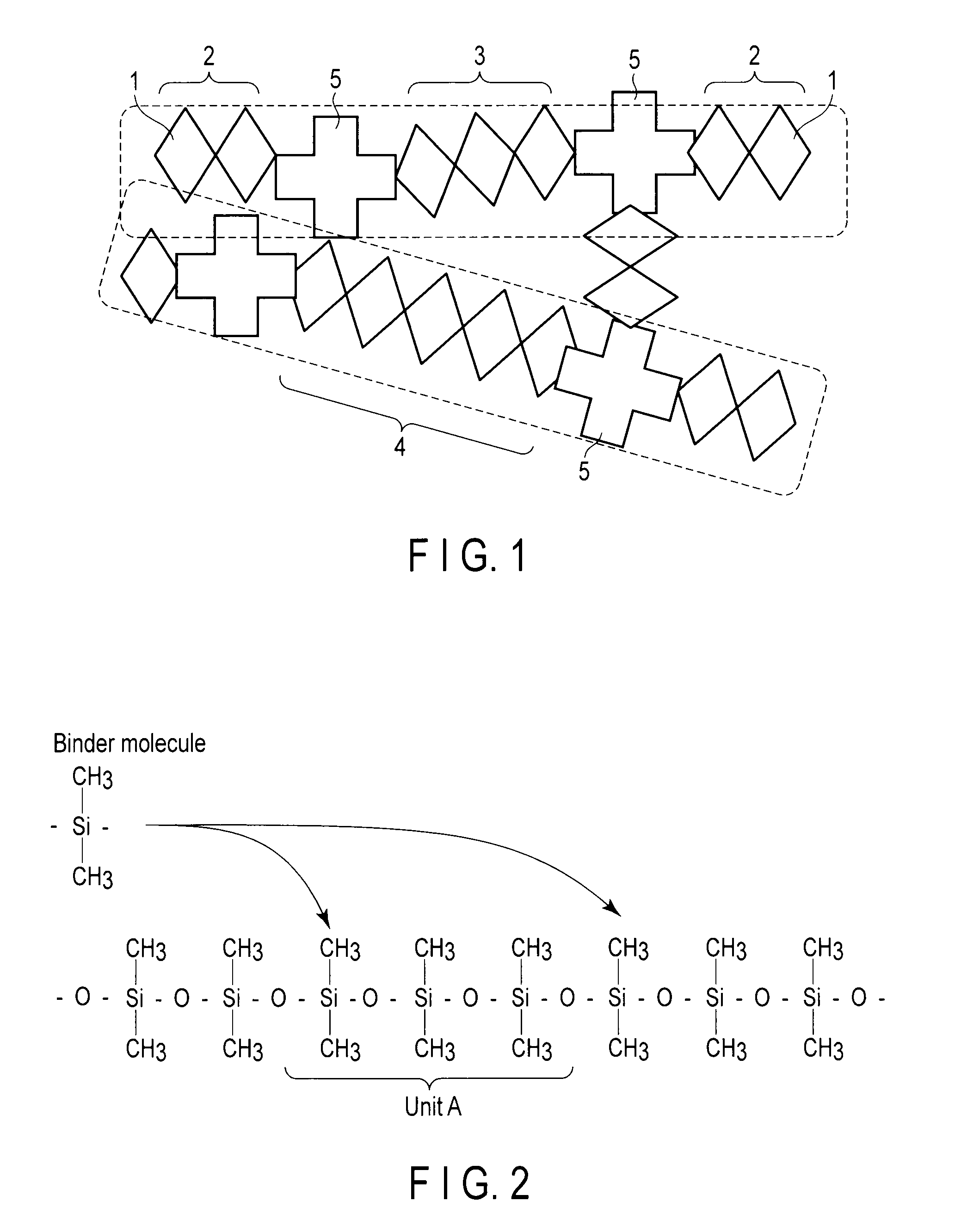
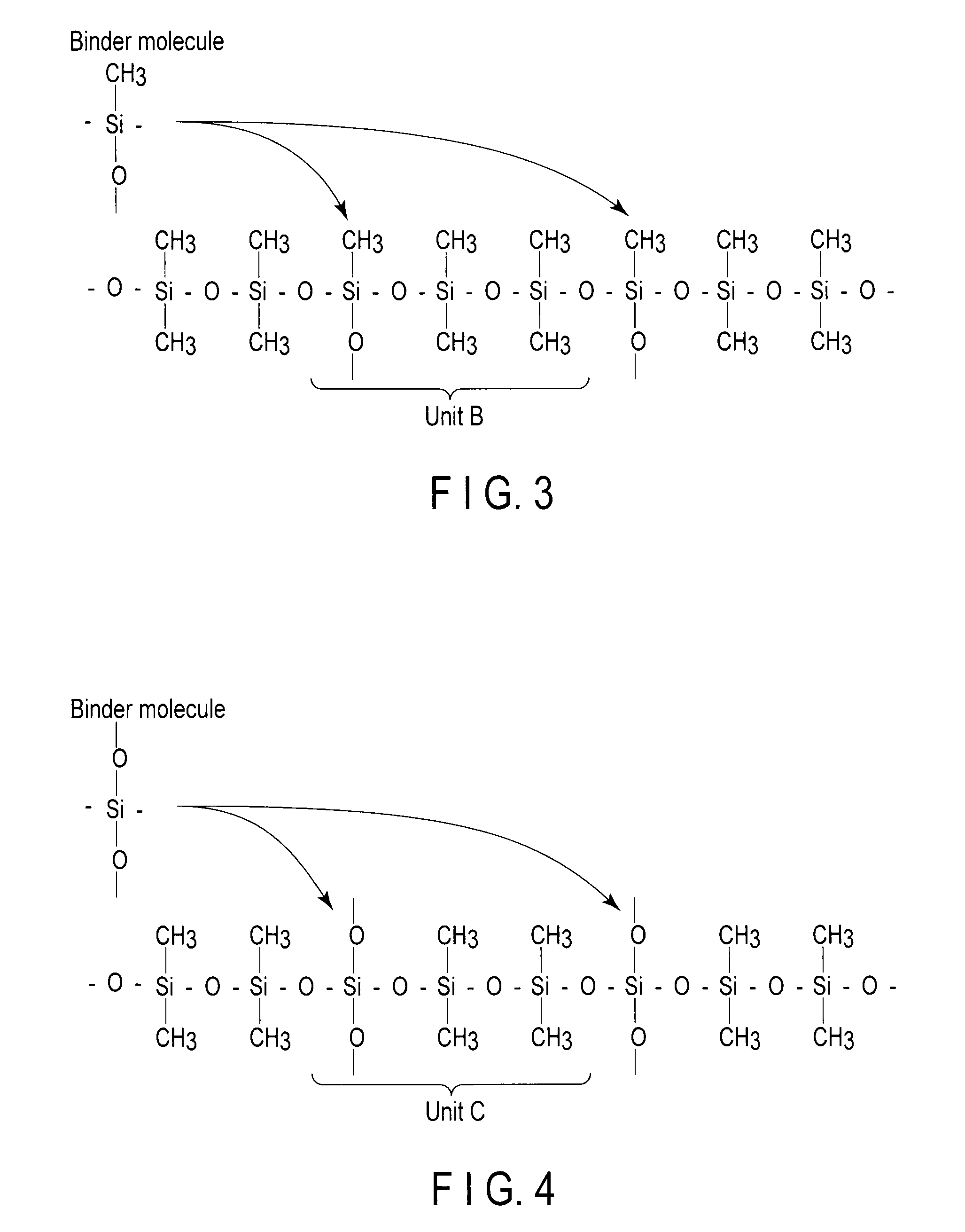
Disclosed is a low dielectric constant insulating film formed of a polymer containing Si atoms, O atoms, C atoms, and H atoms, which includes straight chain molecules in which a plurality of basic molecules with an SiO structure are linked in a straight chain, binder molecules with an SiO structure linking a plurality of the straight chain molecules. The area ratio of a signal indicating a linear type SiO structure is 49% or more, and the signal amount of the signal indicating Si(CH3) is 66% or more.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Luminescence device, display apparatus and metal coordination compound
InactiveUS20020064681A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic compoundLuminescence
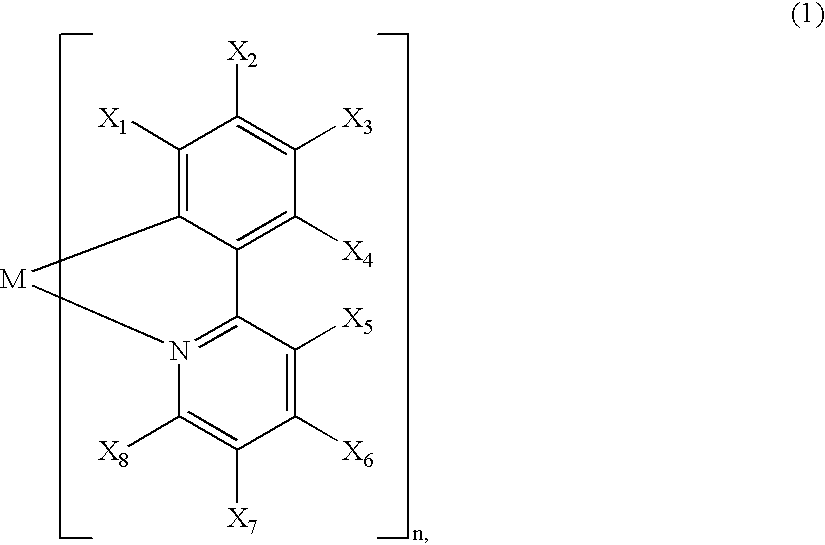
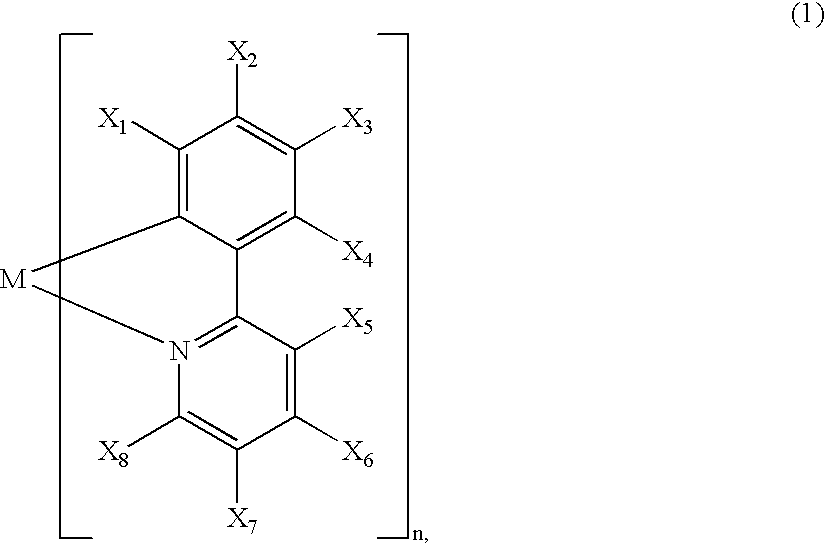
A luminescence device is principally constituted by a pair of electrodes and an organic compound layer disposed therebetween. The layer contains a metal coordination compound represented by the following formula (1): wherein M denotes Ir, Rh or Pd; n is 2 or 3; and X1 to X8 independently denote hydrogen atom or a substituent selected from the group consisting of halogen atom; nitro group; trifluoromethyl group trialkylsilyl group having three linear or branched alkyl groups each independently having 1-8 carbon atoms; and a linear or branched alkyl group having 2-20 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CO-O-, -O-CO-, -CH=CH- or -C=C- and capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with fluorine atom; with the proviso that at least one of X1 to X8 is a substituent other than hydrogen atom, and X2 and X3 cannot be fluorine atom at the same time.
Owner:CANON KK
Spherical carriers for olefin polymerization catalyst and preparation method
ActiveCN102040683ANarrow particle size distributionParticles in good shapeParticle-size distributionPhotochemistry
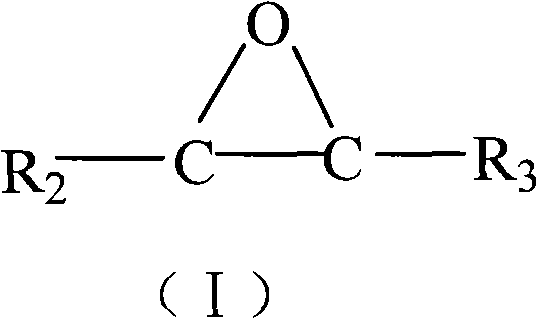
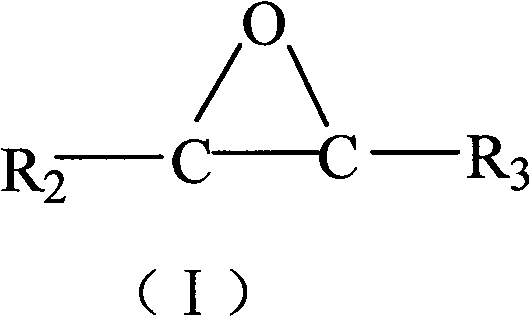
The invention relates to spherical carriers for an olefin polymerization catalyst and a preparation method. Each spherical carrier comprises reaction products of the following components: (1) magnesium halide which is shown as the general formula MgX2, (2) alcohol compounds which are shown as the general formula ROH, and (3) ethylene oxide compounds which are shown as the general formula (I), wherein in the general formula (I), R2 and R3 are alkyls with a C1-C5 straight chain or branched chain; and hydrogen on the alkyls can be randomly substituted by a halogen atom. The spherical carriers have good particle shapes, adjustable particle sizes and narrow particle size distribution, and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Metal coordination compound, luminescence device and display apparatus
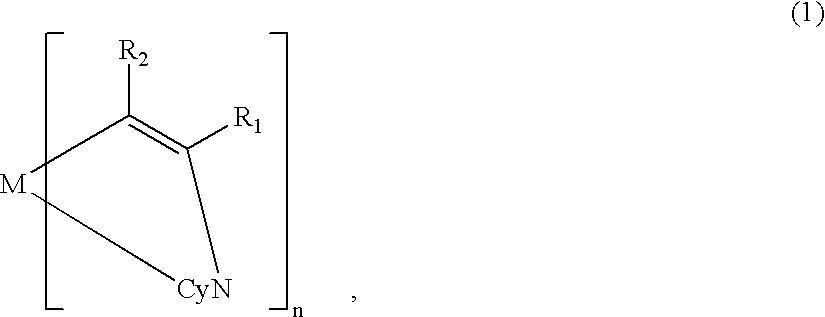
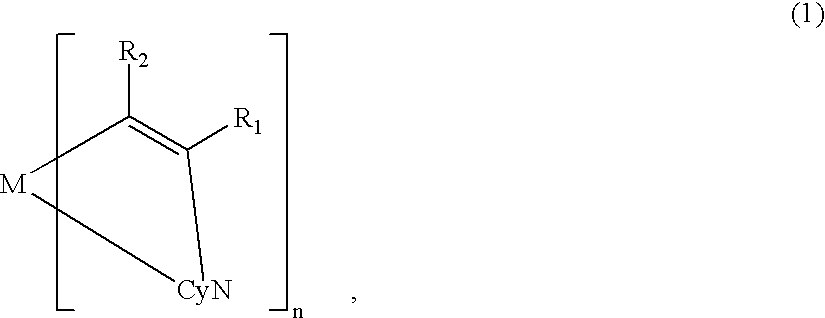
A metal coordination compound suitable as an organic material for a luminescent device is represented by the following formula (1): wherein M denotes Ir, Pt, Rh or Pd; n is 2 or 3; R1 and R2 independently denote a linear or branched alkyl group having 1-20 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CO-O-, -O-CO-, -CH=CH- or -C=C- and capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with fluorine atom; and CyN denotes a cyclic group containing nitrogen atom connected to M and capable of having a substituent selected from the group consisting of halogen atom; nitro group; phenyl group; trialkylsilyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms; and a linear or branched alkyl group having 1-20 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CO-O-, -O-CO-, -CH=CH- or -C=C- and capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with fluorine atom.
Owner:CANON KK
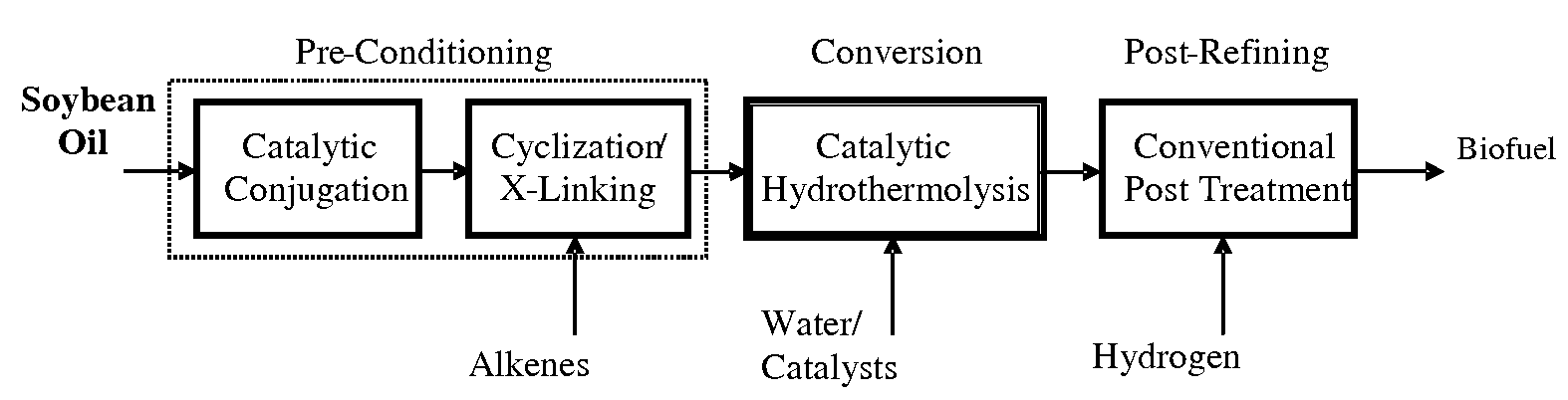
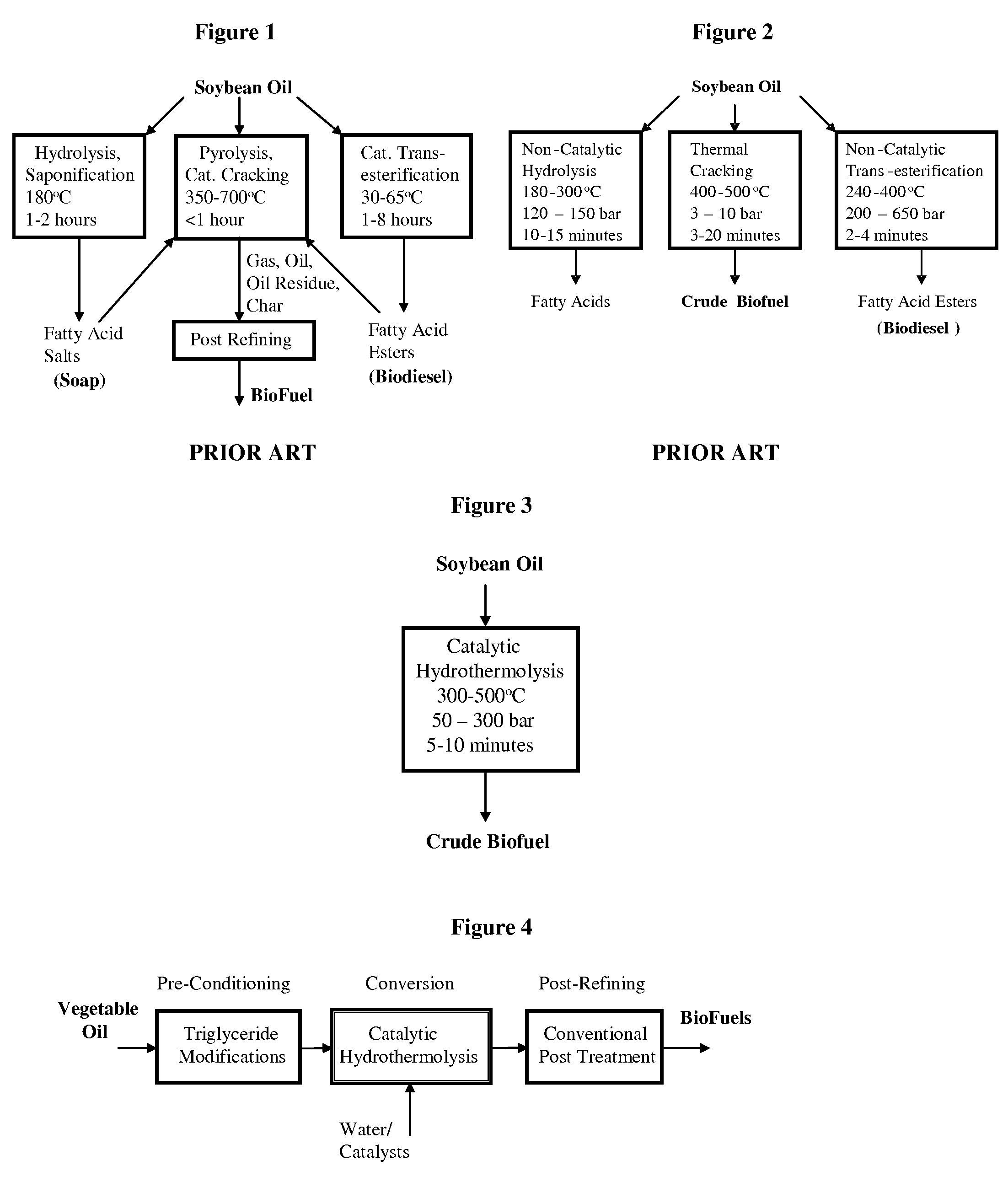
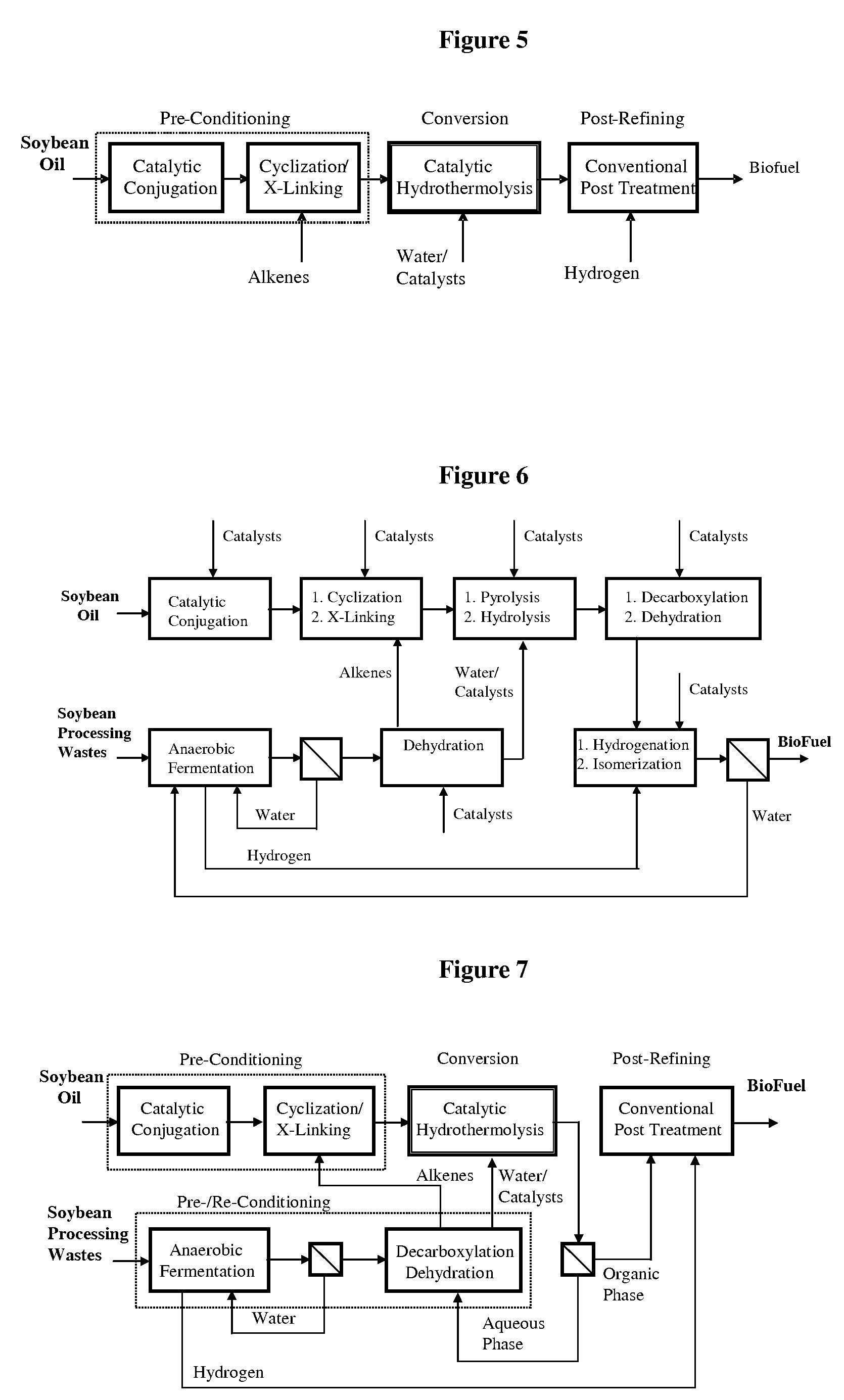
Method of converting triglycerides to biofuels
ActiveUS7691159B2Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkIsomerization
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Ionic liquid, lubricant, and magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20170058227A1Improve the lubrication effectMaintain good propertiesProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageConjugate acidIonic liquid
A lubricant including an ionic liquid, which includes a conjugate acid (B+) and a conjugate base (X−), and is protic, wherein the conjugate acid includes a straight-chain hydrocarbon group having 10 or more carbon atoms, and wherein the conjugate base is represented by the following general formula (1):where n is an integer of from 0 to 6 in the general formula (1).
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Ionic liquid, lubricant, and magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20170130156A1Improve the lubrication effectMaintain good propertiesOrganic chemistryProtective coatings for layersBenzeneHydrogen atom
A lubricant including: an ionic liquid, which includes a conjugate acid (B+) and a conjugate base (X−), and is protic, wherein the ionic liquid is represented by the following general formula (1), and wherein the conjugate base is a conjugate base of sulfonic acid, a conjugate base of sulfonimide, or a conjugate base of trisulfonylmethide:where R1 and R2 each represent a hydrogen atom or R1 and R2 form a benzene ring together with carbon atoms to which R1 and R2 are bonded, R3 represents a to straight-chain hydrocarbon group having 10 or more carbon atoms, and R4 represents a hydrogen atom or a hydrocarbon group in the general formula (1).
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS6268071B1Easy to useDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesBenzeneAliphatic hydrocarbon
An organic EL device comprises a substrate, an organic EL structure stacked on the substrate, a sealing plate located on the organic EL structure with a predetermined space therebetween, and a sealing adhesive agent for fixing the sealing plate on the substrate and thereby closing up the organic EL structure. The sealing adhesive agent is a photo-curing type adhesive agent which, upon photo-curing, generates gases under heating conditions of 85° C. and 60 minutes. In these gases, the total amount of a low-molecular straight-chain aliphatic hydrocarbon which may have a substituent, an aromatic hydrocarbon which may have a substituent, an alicyclic hydrocarbon which may have a substituent, and a heterocyclic compound and a siloxane which may have a substituent is 200 mug / g or lower calculated as benzene. The organic EL device of the invention is reduced as much as possible in terms of a deterioration with time, and can maintain its initial performance over a long period of time, so that it can have an ever longer service life.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Disinfecting composition and process for disinfecting surfaces
InactiveUS6841090B1Immediate and long lasting disinfectionBiocideOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydrogenEther
Liquid disinfecting compositions comprise an effective amount of a disinfecting material and a poly (alkylene glycol) ether having the following formula: R1—O—(CH2—CHR2O)n—R3, wherein R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched hydrocarbon chain having from 1 to 30 carbon atoms or a hydroxy bearing linear or branched hydrocarbon chain having from 1 to 30 carbon atoms. R3 is a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated, or unsaturated, linear or branched hydrocarbon chain having from 1 to 30 carbon atoms or a hydroxy bearing linear or branched hydrocarbon chain having from 1 to 30 carbon atoms, and n is greater than 2. Processes of disinfecting and hard-surface employ such a composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Chemical synthesis using solvent microdroplets
InactiveUS6419883B1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisChemical species
The present invention relates to microdroplets of a solution comprising a solvent having a boiling point of 150° C. or above, a surface tension of 30 dynes / cm or above, and a viscosity of 0.015 g / (cm)(sec). Such microdroplets are useful for the synthesis of chemical species, particularly biopolymers such as oligonucleotides and peptides, as well as arrays of chemical species. Preferably, the solvent has the formula (I):whereinA=O or S;X=O, S or N (C1-C4 alkyl)Y=O, S, N(C1-C4 alkyl) or CH2; andR=C1-C20 straight or branched chain alkyl.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Resist compositions
InactiveUS6274286B1Radiation applicationsDiazo compound compositionsPolymer scienceOrganic chemistry
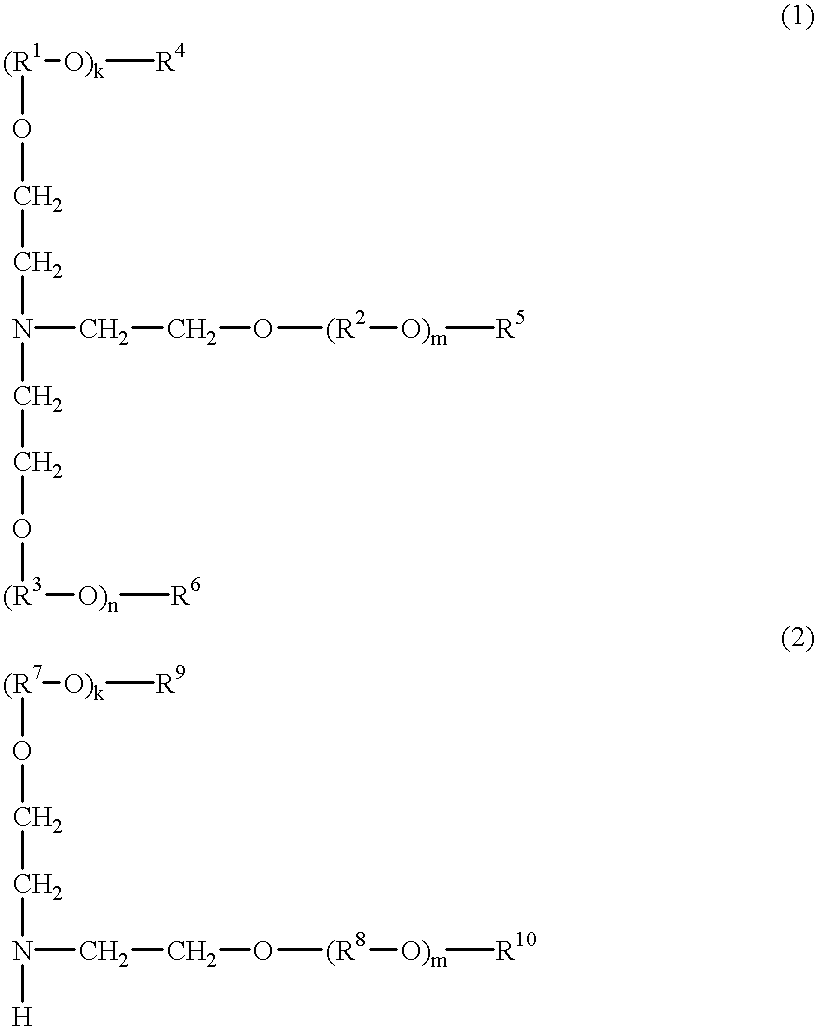
A chemically amplified positive resist composition comprising at least one basic compound of the following general formula (1) or (2):wherein R1, R2, R3, R7, and R8 are independently normal, branched or cyclic alkylene groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, R4, R5, R6, R9, and R10 are independently hydrogen, alkyl groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or amino groups, R4 and R5, R5 and R6, R4 and R6, or R8, R5 and R5, and R9 and R10, taken together, may form a ring, letters k, m and n are integers of 0 to 20, with the proviso that hydrogen is excluded from R4, R5, R6, R9 and R10 when k, m or n is equal to 0.The resist compositions of the present invention are effective for preventing resist films from thinning and for increasing the focus margin of an isolated pattern.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Compound and organic electroluminescense device using the same
InactiveUS20060003171A1High glass transition temperatureImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensHydrogen atomCompound (substance)
A compound represented by the following general formula (1). R3—(X)x-(A)a-(Y)y-(B)b-(Z)z-R12 (1) (A, B, X, Y, and Z represent the following general formulae, and CH on a phenylene ring of each of X, Y, and Z may be replaced with an N atom. a, b, x, y, and z each independently represent an integer of 0 to 5, and a≧1, y≧1, and a+b≧2. (R1 to R14 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, or a linear or branched alkyl group.)). The compound can be suitably used as a compound for an organic EL device.
Owner:CANON KK
Water-in-oil emulsions with ethylene oxide groups, compositions, and methods
Water-in-oil emulsions, compositions, and methods that include a vinyl polymer that includes ethylene oxide-containing side chains and alkyl-Y-containing side chains, wherein Y is O or NR, wherein R is H or CH3, and wherein the alkyl group of the alkyl-Y-containing side chain has at least 4 carbon atoms on average in a cyclic, branched-, or straight-chain configuration and optionally including one or more heteroatoms.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of increasing the oxidation stability of biodiesel
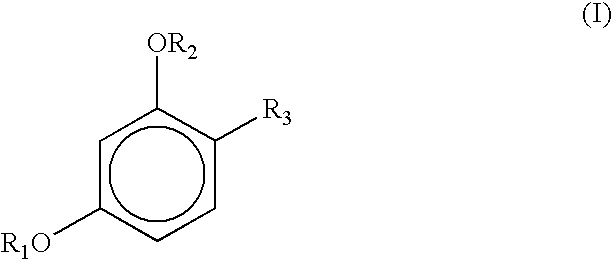
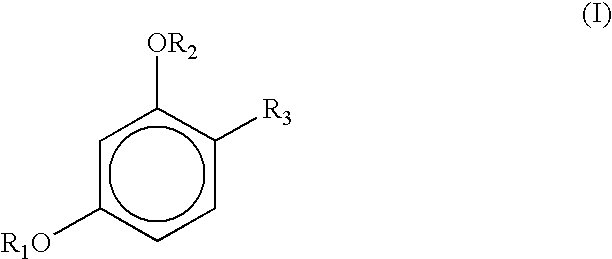
The present invention relates to a method for increasing the oxidation stability of biodiesel, which includes adding a main antioxidant with a melting point of less than or equal to 40°C in an amount of 10-20000 ppm (w / w) into the biodiesel to be stabilized, wherein the The primary antioxidant contains at least one compound of structure I, wherein R1, R2 = hydrogen, a linear alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or, where * is a carbon atom of an aromatic ring system, R3, R5 = hydrogen, straight-chain alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, R4 = hydrogen, straight-chain alkyl group having 1 to 40 carbon atoms, where the substituents of type R1 and R2 are the same as the substituents of type R3 and R5. Either the same or different in each case.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
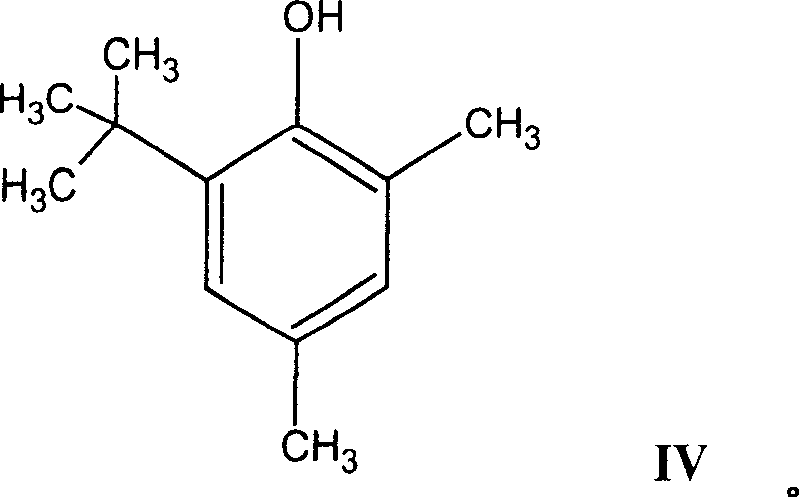
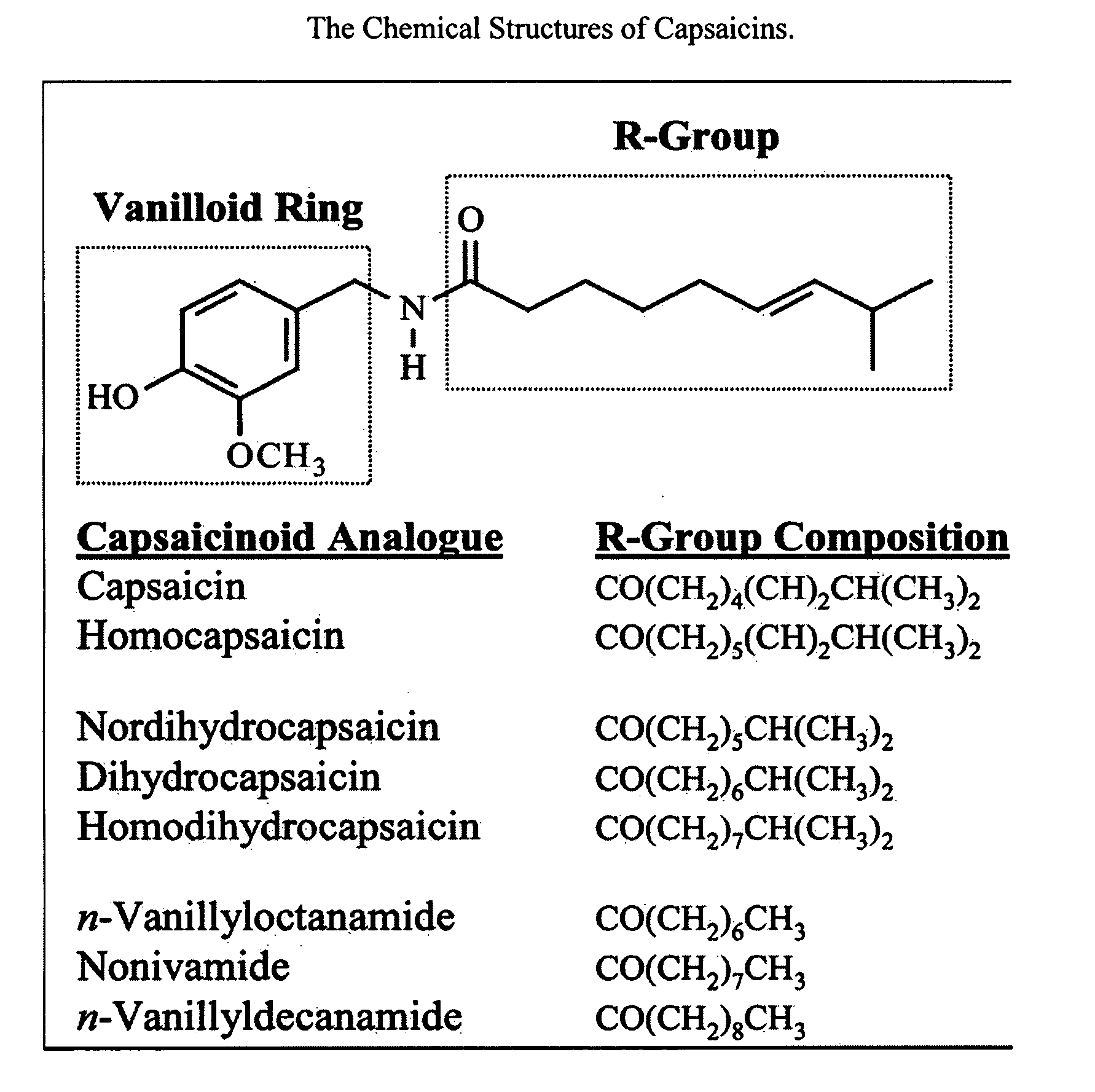
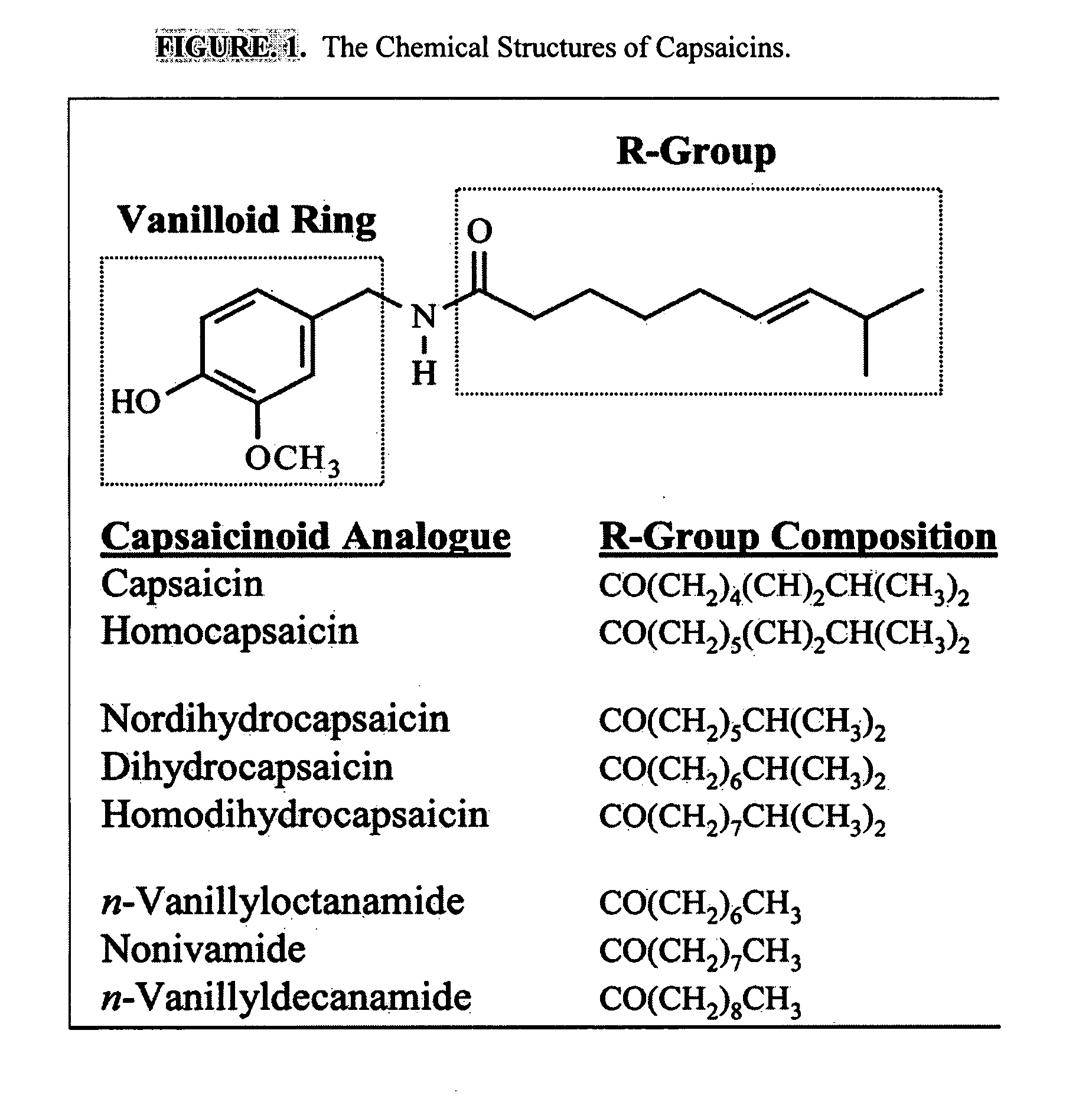
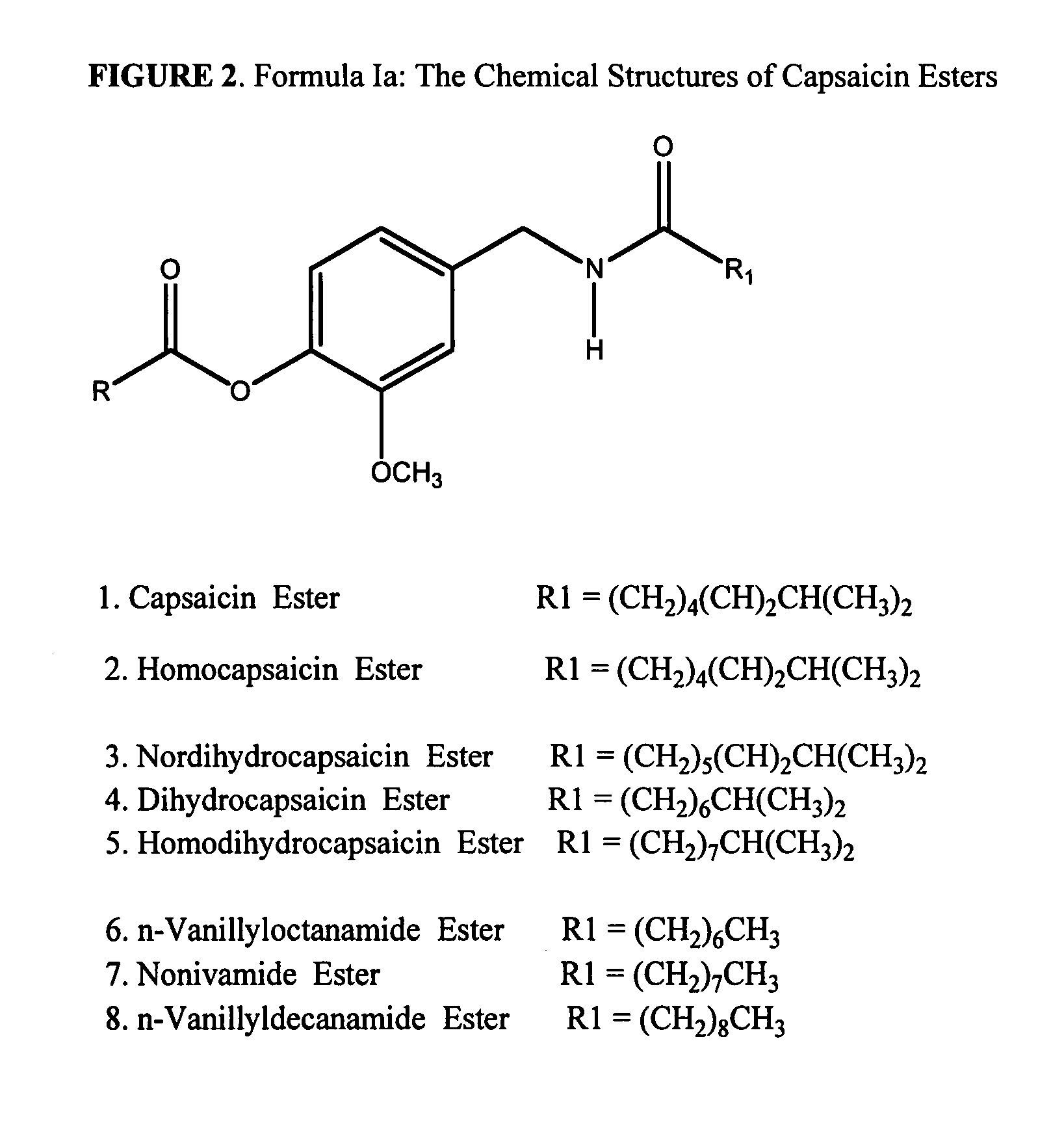
Esters of capsaicin for treating pain
ActiveUS20080020996A1Reduce generationImprove lipophilicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSolubilityIrritation
The present invention relates to the formulations of ester derivatives of capsaicin and ester derivatives of myristoleic acid. These derivatives are capable of reverting to the active parent compound following enzymatic or chemical hydrolysis. These derivatives have a higher lipophilicity, lipid solubility and less irritation to the skin than the parent compound, and hence are better able to be incorporated into certain pharmaceutical formulations, including cream and ointment pharmaceutical formulations. The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention contain a compound of following formula (Ia):R—CO-CAP (Ia)wherein CAP refers to collectively the capsaicins represented in FIG. 1 and a compound of formula (Ib):MCO-O—R (Ib)wherein MCO refers to myristoleic acid.In formulae Ia and Ib, R is selected from alkyl groups of up to about 18 carbon atoms and aryl groups of up to about 18 carbon atoms and alkylene group of up to about 18 carbon atoms and an arylene group of up to about 18 carbon atoms. The alkyl, aryl and alkylene groups may be substituted or un-substituted, branched or straight chains. In addition, R may contain heteroatoms and may be straight chained or branched.The pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of formulae Ia and Ib are useful for pain management in mammals in vivo and have been contemplated to be used in the treatment of various pains in humans.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Method of repairing process induced dielectric damage by the use of gcib surface treatment using gas clusters of organic molecular species
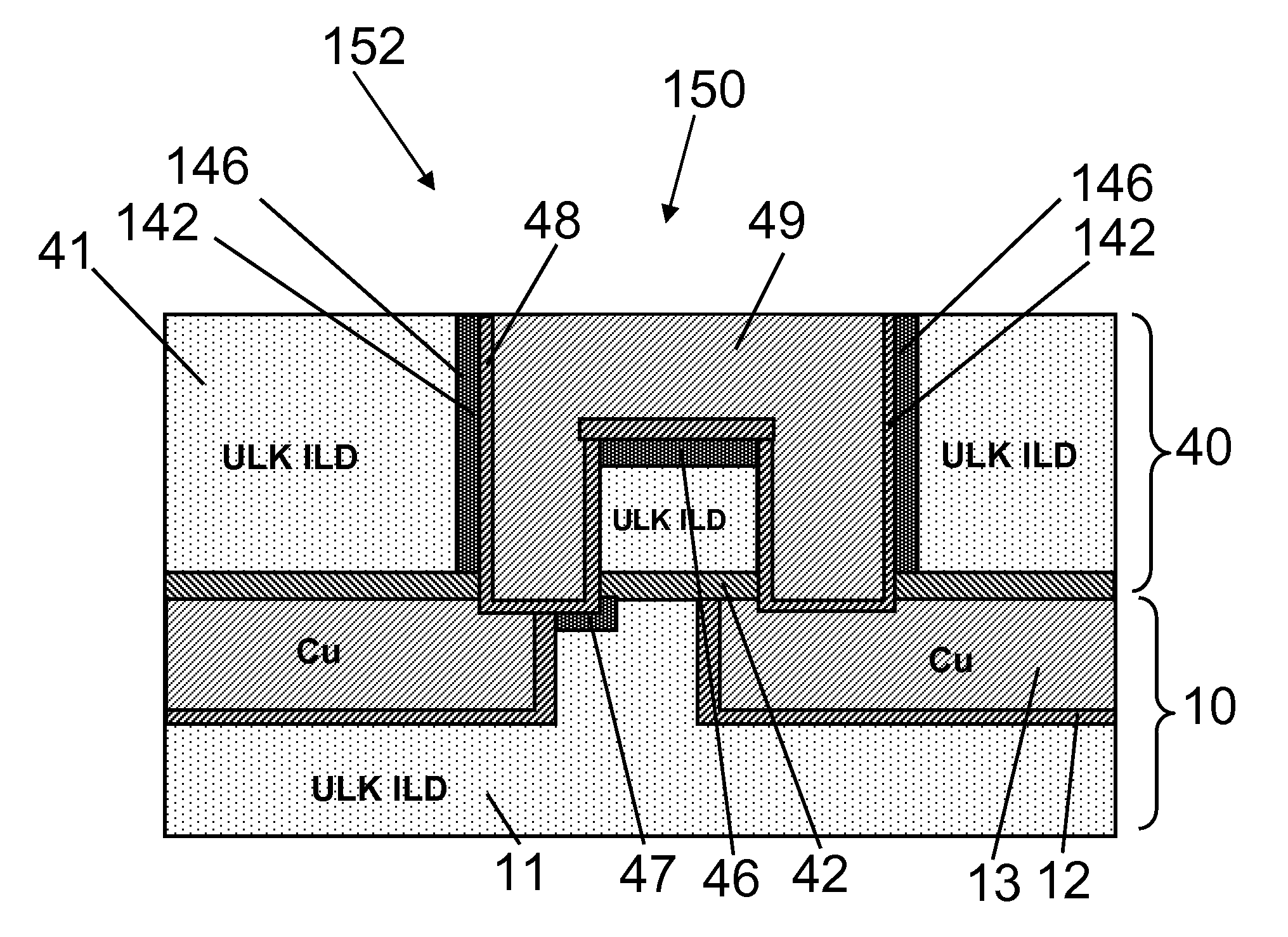
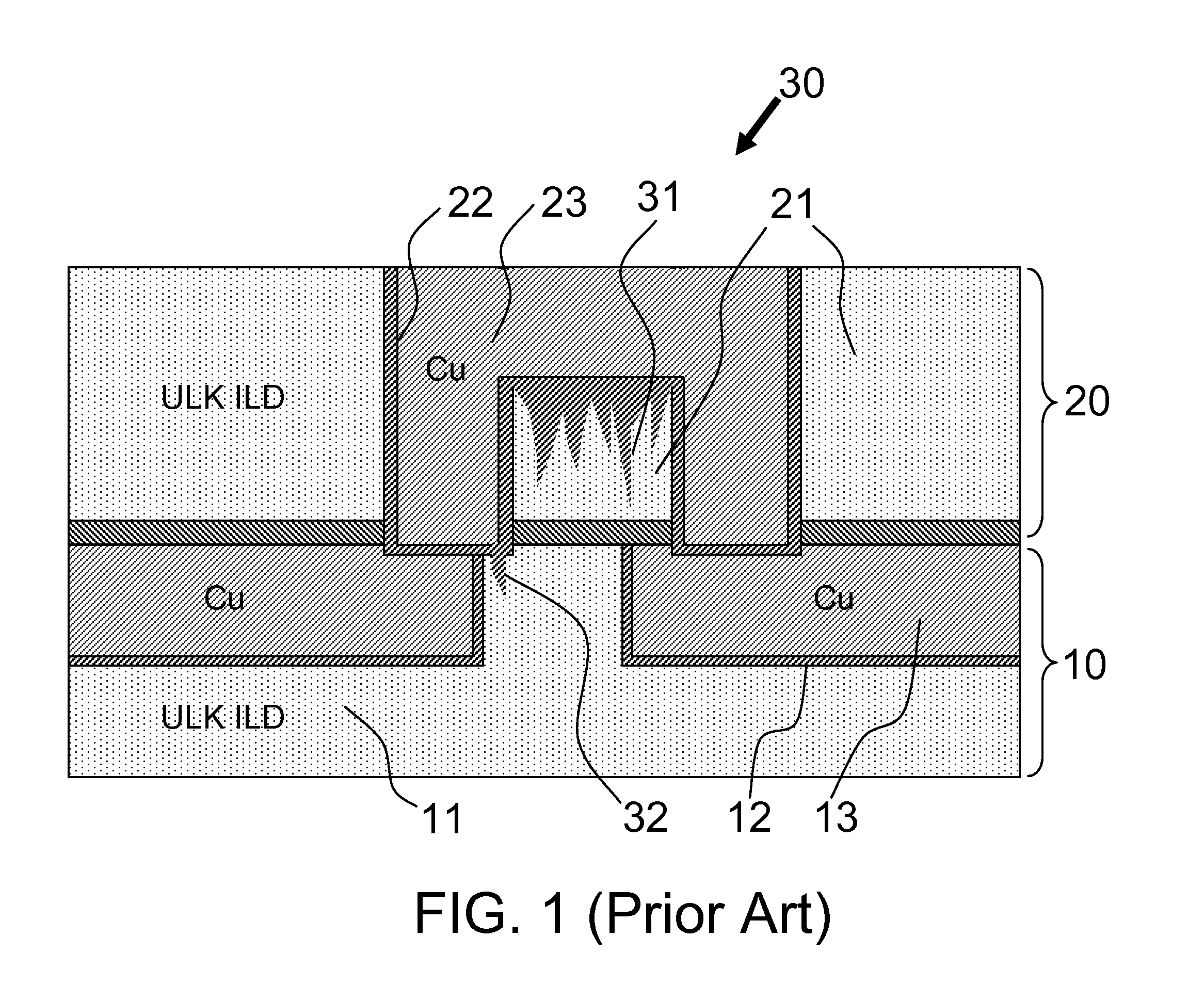
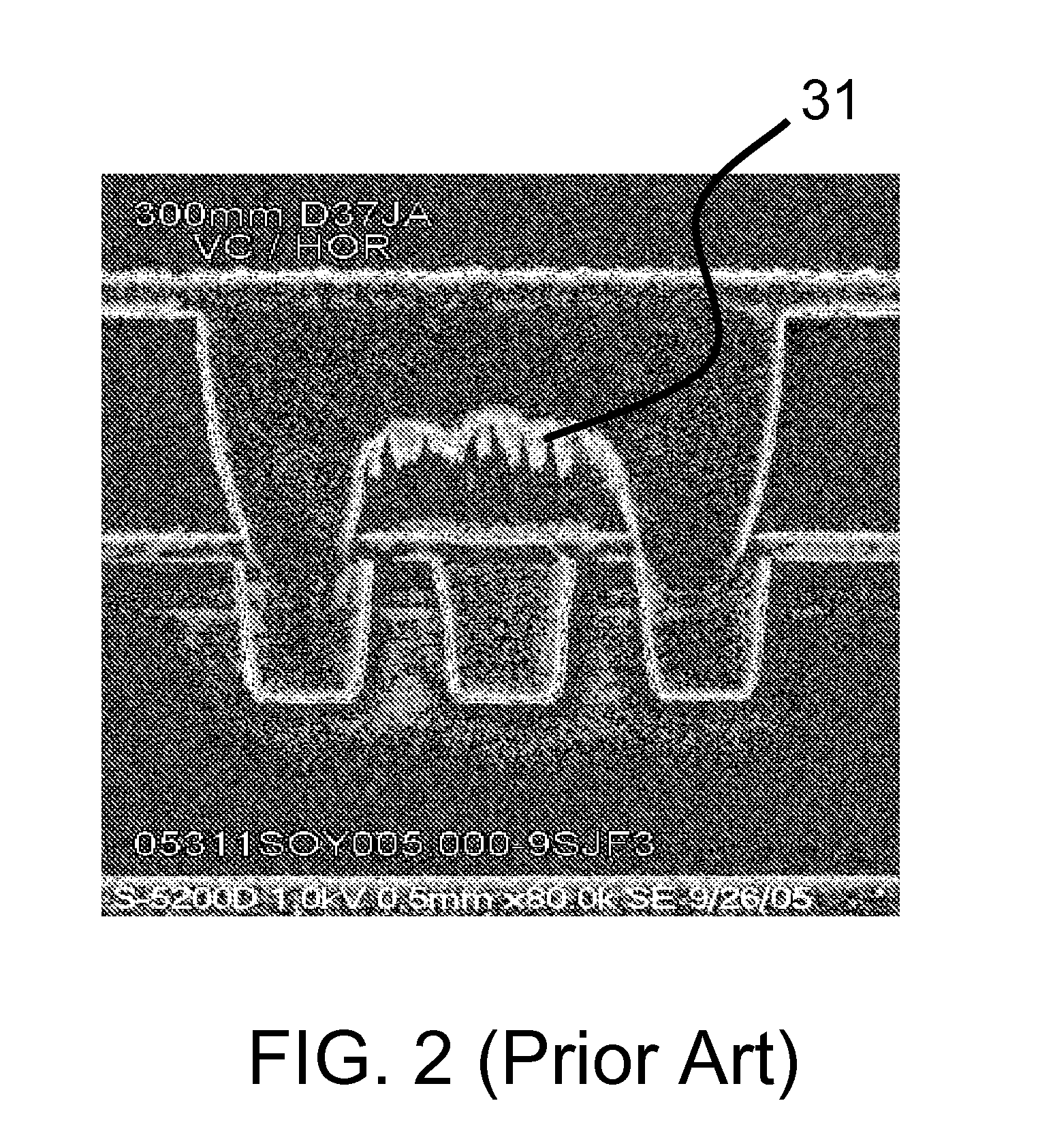
When an interconnect structure is built on porous ultra low k (ULK) material, the bottom and / or sidewall of the trench and / or via is usually damaged by a following metallization or cleaning process which may be suitable for dense higher dielectric materials. Embodiments of the present invention may provide a method of repairing process induced dielectric damage from forming an interconnect structure on an inter-layer dielectric (ILD) material. The method includes treating an exposed area of the ILD material to create a carbon-rich area, and metallizing the carbon-rich area. One embodiment includes providing treatment to an exposed sidewall area of the ILD material to create a carbon-rich area by irradiating the exposed area using a gas cluster ion beam (GCIB) generated through a gas including a straight chain or branched, aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon, and metallizing the carbon-rich area.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Image receptor medium containing ethylene vinyl acetate carbon monoxide terpolymer
An image receptor medium including an image reception layer having two major opposing surfaces. The image reception layer comprises a terpolymer of ethylene vinyl acetate carbon monoxide, optionally blended with at least one other polymer that can be wherein the image reception layer further comprises at least one other polymer blended with the terpolymer, wherein the other polymer is selected from the group consisting of ethylene vinyl acetate resins, ethylene (meth)acrylic acid copolymer resins, polyethylene resins, polypropylene resins, ionomers, acid-modified or acid / acrylate modified ethylene vinyl acetates and a polymer comprising at least two monoethylenically unsaturated monomeric units, wherein one monomeric unit comprises a substituted alkene where each branch comprises from 1 to about 8 carbon atoms and wherein one other monomeric unit comprises a (meth)acrylic acid ester of a nontertiary alkyl alcohol in which the alkyl group contains from 1 to about 12 carbon atoms and can include heteroatoms in the alkyl chain and in which the alcohol can be linear, branched, or cyclic in nature, and combinations of such other polymers thereof. Alternatively, the image receptor medium includes a substrate layer comprising a polymer substrate layer having two major opposing surfaces and an image reception layer on a first major surface of the substrate layer. The image reception layer has an outer surface for receiving images, and comprises a terpolymer identified above. Either embodiment of the image receptor medium may further include an optional prime layer, an optional adhesive layer, and an optional inkjet layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Stabilization of resorcinol derivatives in cosmetic compositions
InactiveUS6863897B2Improved storage/color stabilityImprove stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHydrogenEthyl group
Cosmetic compositions containing a micronized metal oxide along with a 4-substituted resorcinol derivatives of the general formula I exhibit improved storage stability: where each R1 and R2, independently, represents a hydrogen atom, —CO—R (acyl group), —COO—R, CONHR; where R represents saturated or unsaturated, linear, branched or cyclic C1-C18 hydrocarbon groups; andR3 represents (1) an alkyl group, having from 1 to 18 carbon atoms, preferably having from 2 to 12 carbon atoms, with or without substitution of one or more hydrogen atoms of a linear alkyl group with a methyl or ethyl group; e.g., R3 constitutes linear or branched chain alkyls, or (2) a group of the general formula formula (II) Where X is preferably H, n is 0 to 3 and the dashed lines represents an optional double bond.
Owner:UNILVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO
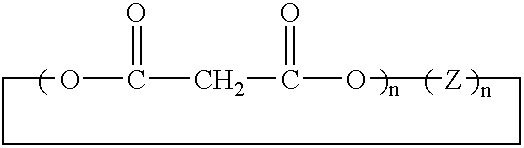
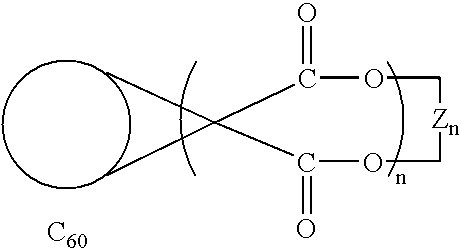
Method of synthesis of water soluble fullerene polyacids using a macrocyclic malonate reactant
InactiveUS6538153B1Increase productionInhibit productionNanotechPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesArylWater soluble
A method for synthesizing compounds of the formulawhere C60 is a C60 fullerene. The method comprises the steps of forming a macrocyclic malonate compound of the formulawhere each Z is the same or different and is a straight-chain or branched-chain aliphatic radical having from 1-30 carbon atoms which may be unsubstituted or monosubstituted or polysubstituted by identical or different substitutents, in which radicals up to every third CH2 unit can be replaced by O or NR where R is alkyl having 1-20 carbon atoms or a chain containing unsubstituted or substituted aryl or other cyclic groups and n is an integer from 2 to 10; reacting said macrocyclic malonate compound with C60 to form an adduct of the formulawhere the Z radicals are linked together to form said macrocycle adduct; and hydrolyzing said macrocycle adduct to form a compound of the formula
Owner:LUNA LABS USA LLC
Refrigerator oil and working fluid composition for refrigerator
The refrigerating machine oil of the invention is characterized by comprising an ester of a polyhydric alcohol and a fatty acid with a C5-C9 fatty acid content of 50-100 mol %, a C5-C9 branched fatty acid content of at least 30 mol % and a C5 or lower straight-chain fatty acid content of no greater than 40 mol %, and by being used with a fluoropropene refrigerant and / or a trifluoroiodomethane refrigerant. The working fluid composition for a refrigerating machine according to the invention comprises the ester and a fluoropropene refrigerant and / or a trifluoroiodomethane refrigerant.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
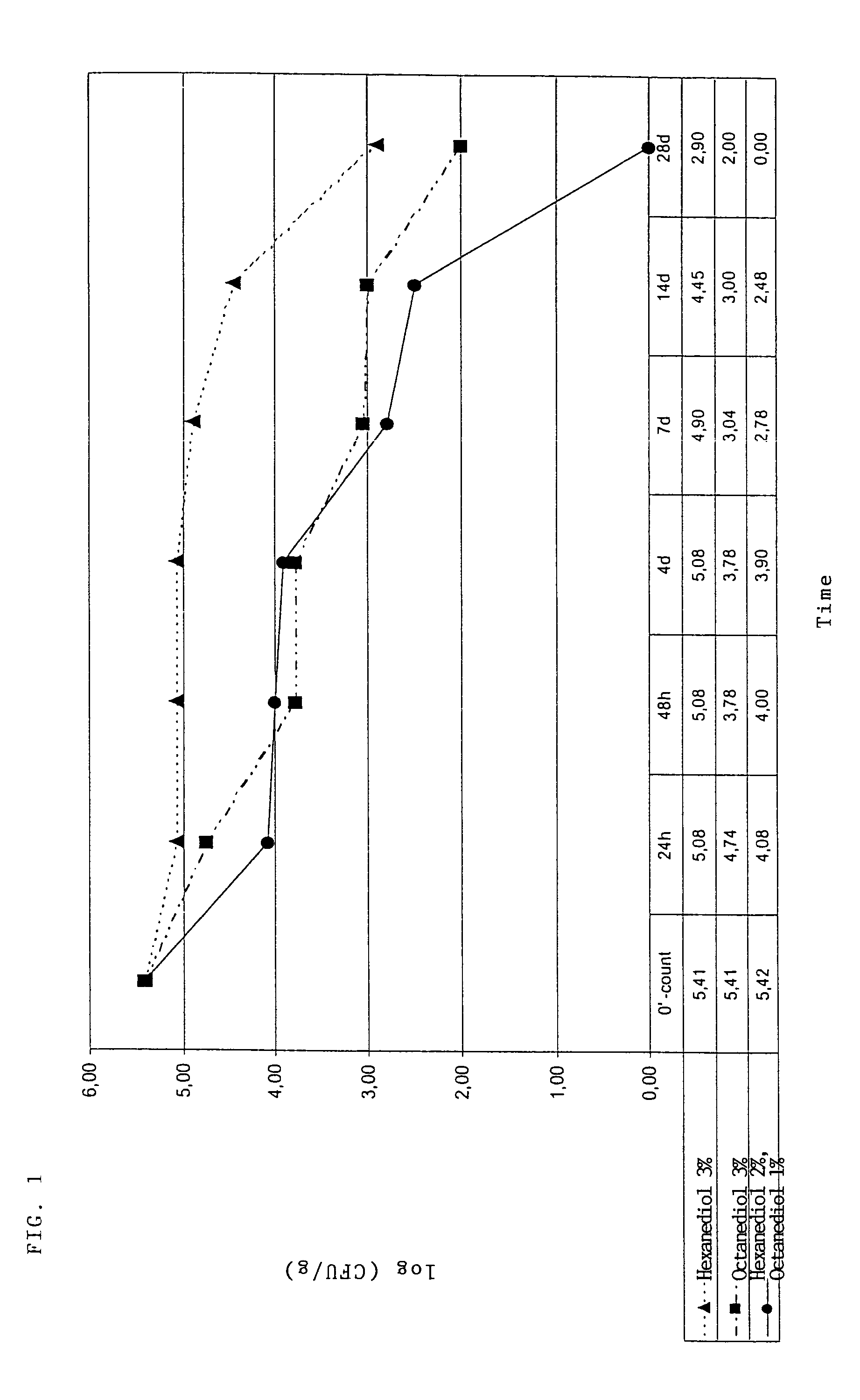
Synergistic mixtures of at least one 1,2 alkanediol such as 1,2-hexanediol and 1,2-octanediol with a further compound having antimicrobial properties
InactiveUS20070265352A1Antimicrobial effect is synergistically intensifiedBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsCompound (substance)Hexylene glycol
Antimicrobial active compositions and substances comprising at least one, preferably two, unbranched (straight-chain) 1,2-alkanediols and preferably a further preservative and also to products containing such mixtures in an antimicrobially effective quantity. One example of an antimicrobial mixture comprises: (a) 1,2-hexanediol and 1,2-octanediol and also optionally 1,2-pentanediol and / or 1,2-decanediol and (b) one, two or more substances selected from the group consisting of potassium sorbate, parabens and iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (IPBC).
Owner:SYMRISE GMBH & CO KG
Synergistic mixtures of 1,2-alkane diols
InactiveUS7582681B2Improve bindingImprove water retentionCosmetic preparationsBiocideAlkaneChain length
Owner:SYMRISE GMBH & CO KG
Diesters or polyesters of naphthalene dicarboxylic acid as solubilizer/stabilizer for retinoids
A topical composition for skin treatment comprising about 60.001% to 1% by weight of a retinoid solubilizer and / or stabilized with preferably about 0.1% to about 50% by weight of a diester or polyester of a naphthalene dicarboxylic acid having compound formula (I), (II), (III) or mixtures:wherein R1 is an alkyl group, straight chain or branched, having 1 to 22 carbon atoms;wherein each R1, same or different, is an alkyl group having 1 to 22 carbon atoms, a diol having the structure HO-R2-OH, or a polyglycol having the structure HO-R3-(-O-R2-)m-OH wherein R2 and R3, same or different, are each an alkylene group, straight chain or branched, having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and wherein m and n are each 1 to about 100, or a mixture thereof.
Owner:SYMRISE INC
Polyester DTY fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108385186AHigh molecular weightNarrow molecular weightSpinning head liquid feederFilament/thread formingFiberThermal insulation
The invention relates to polyester DTY fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: metering a modified polyester melt, extruding, cooling, oiling, and winding to preparethe polyester POY fiber. According to the present invention, during the cooling, the longitudinal height is maintained, and the cross section area of the slow cooling chamber is increased while the plate surface temperature of the spinning plate is maintained by using the thermal insulation method; the material of the fiber is the modified polyester, the molecular chain of the modified polyester comprises a terephthalic acid chain segment, an ethylene glycol chain segment and a diol chain segment having the branched chain, the structure formula of the diol chain segment having the branched chain is defined in the specification, R1 and R2 are respectively and independently selected from straight chain alkylidene with a carbon atom number of 1-3, R3 is selected from alkyl with a carbon atomnumber of 1-5, and R4 is selected from alkyl with a carbon atom number of 2-5; the chromatic aberration [delta]E of the prepared fiber is less than 0.200; and the preparation process is simple and reasonable, and the obtained fiber has excellent performance.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Olefin two-phase hydroformylation method
ActiveCN102617308AEffective fixed loadSeparation and easy handlingOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide reactionTPPTSPolymer science
The invention relates to an olefin two-phase hydroformylation method, which consists of three parts: polyether guanidine mesylate ionic liquid (PGMILs) with room temperature solidifiable characteristics, complex catalysts (Rh-TPPTS) formed by RhCl3.3H2O or dicarbonylacetylacetonato rhodium and triphenylphosphine sodium trithionate (TPPTS), and reactants of C6-C14 straight chain 1-olefin, wherein the Rh-TPPTS is dissolved in the PGMILs to form a lower layer catalyst phase, the C6-C14 straight chain 1-olefin or product aldehyde forms an upper layer organic phase, the selectivity of high-carbon aldehyde is 85 to 99 percent, the mol ratio of normal aldehyde to isomerism aldehyde is 2.0 to 2.4, the PGMILs phase containing Rh-TPPTS can be cyclically used for 35 times, the activity and the selectivity are unchanged, the accumulated conversion number (TON) reaches higher than 30000, rhodium flowing to the product phase is 0.04 percent to 0.07 percent, and ultra-long-period catalysis activity and selectivity can be realized.
Owner:山东聚强绿洲生物科技有限公司
Molding composition based on polyetheramides
InactiveUS6884485B2Increase melt viscosityEasy extrusionEnvelopes/bags making machineryBottlesPolymer scienceDicarboxylic acid
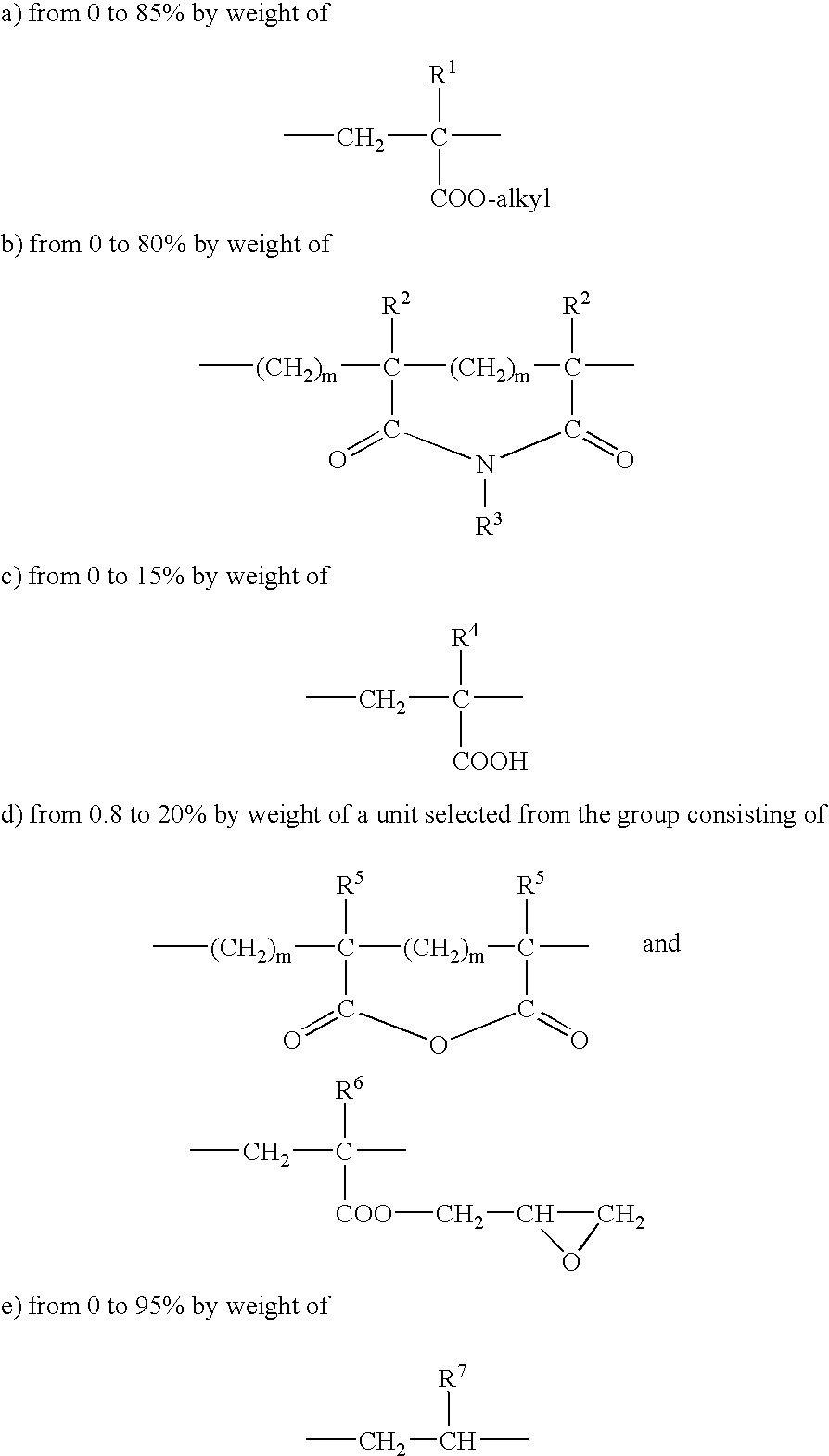
A molding composition containing the following components:I. from 99.9 to 95 parts by weight of a polyetheramide obtained from 1) a linear aliphatic diamine having from 6 to 12 carbon atoms, 2) a linear aliphatic or aromatic dicarboxylic acid having from 6 to 12 carbon atoms, and 3) a polyetherdiamine having at least 3 carbon atoms per ethereal oxygen atom and having a primary amino group at an end of the chain, andII. from 0.1 to 5 parts by weight of a copolymer which contains from 0.8 to 20% by weight of an anhydride or an epoxide in copolymerized form,wherein the total amount of I. and II. is 100 parts by weight, is suitable for the extrusion of flexible pipes, and also for the production of flexible blow-molded articles.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com