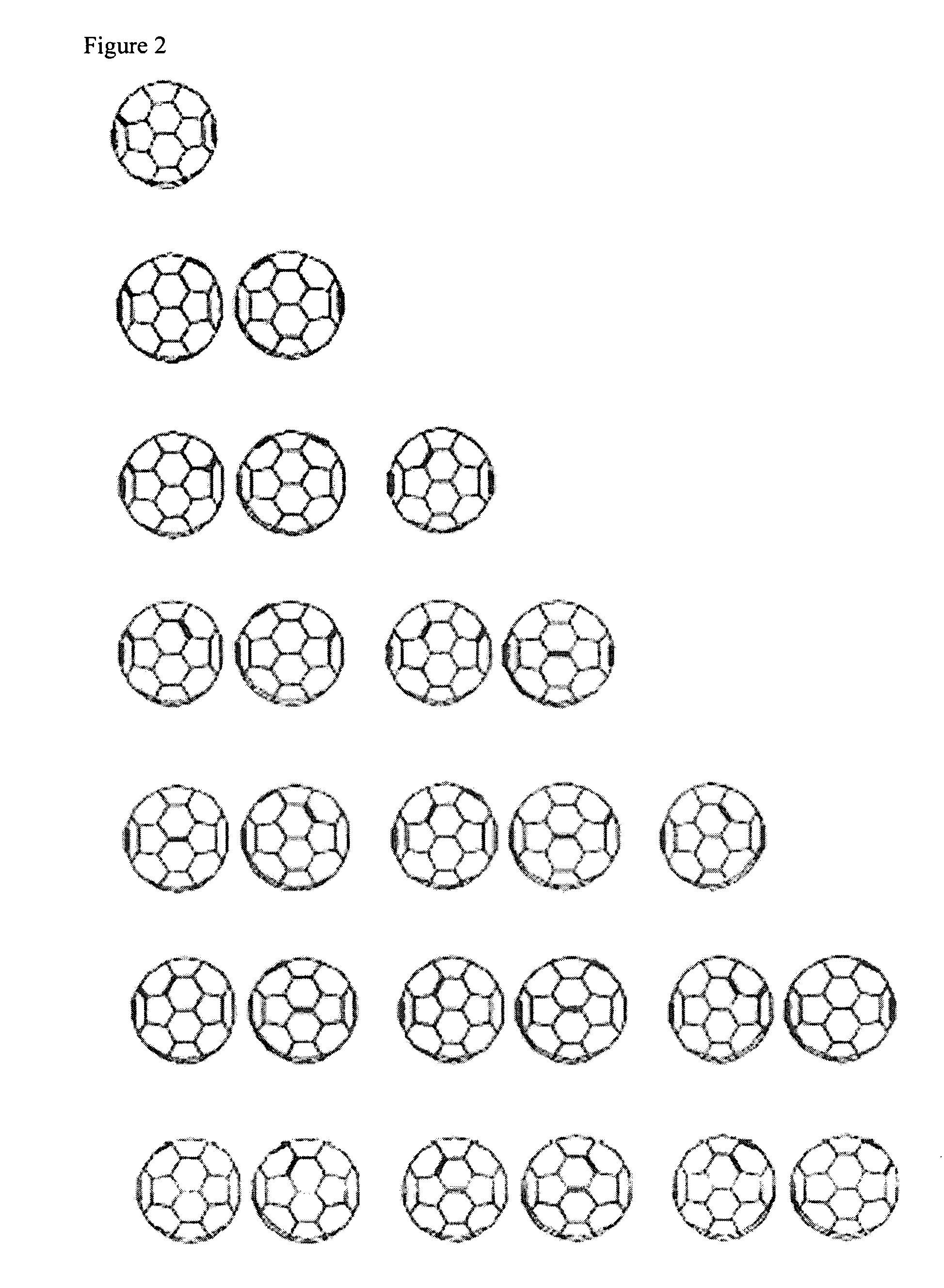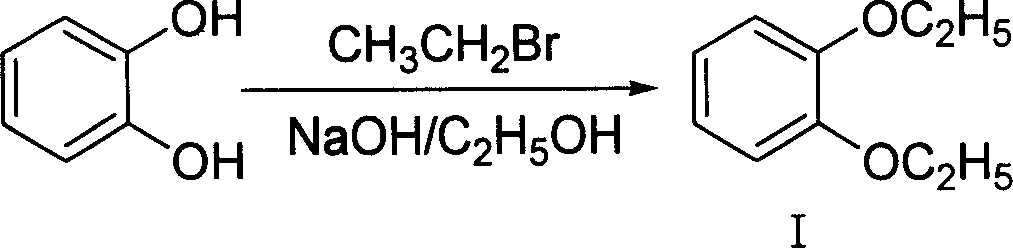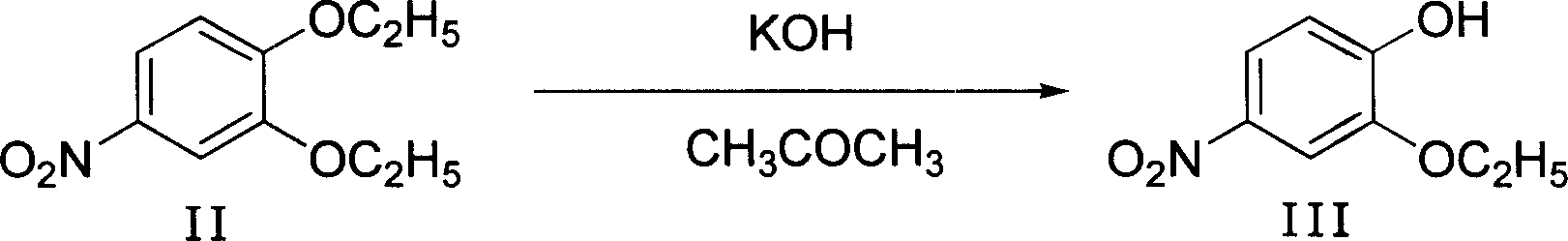Patents
Literature
530 results about "Malonate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
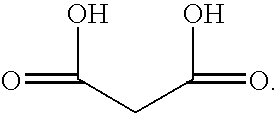
The malonate or propanedioate ion is CH2(COO)2−2 (malonic acid minus two hydrogen ions). Malonate compounds include salts and esters of malonic acid, such as...
Method of synthesis of water soluble fullerene polyacids using a macrocyclic malonate reactant
InactiveUS6538153B1Increase productionInhibit productionNanotechPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesArylWater soluble
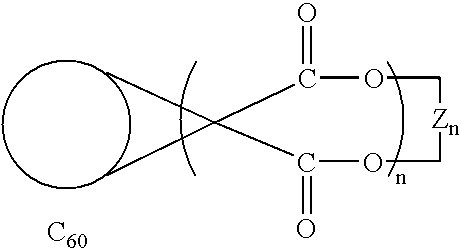
A method for synthesizing compounds of the formulawhere C60 is a C60 fullerene. The method comprises the steps of forming a macrocyclic malonate compound of the formulawhere each Z is the same or different and is a straight-chain or branched-chain aliphatic radical having from 1-30 carbon atoms which may be unsubstituted or monosubstituted or polysubstituted by identical or different substitutents, in which radicals up to every third CH2 unit can be replaced by O or NR where R is alkyl having 1-20 carbon atoms or a chain containing unsubstituted or substituted aryl or other cyclic groups and n is an integer from 2 to 10; reacting said macrocyclic malonate compound with C60 to form an adduct of the formulawhere the Z radicals are linked together to form said macrocycle adduct; and hydrolyzing said macrocycle adduct to form a compound of the formula
Owner:LUNA LABS USA LLC
Methylidene malonate process
ActiveUS20100286438A1High purityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMalonatePolymerization
An improvement in the production of methylidene malonates is attained by use of specific reaction phase and / or separation phase polymerization inhibitors and combinations thereof.
Owner:HB FULLER CO
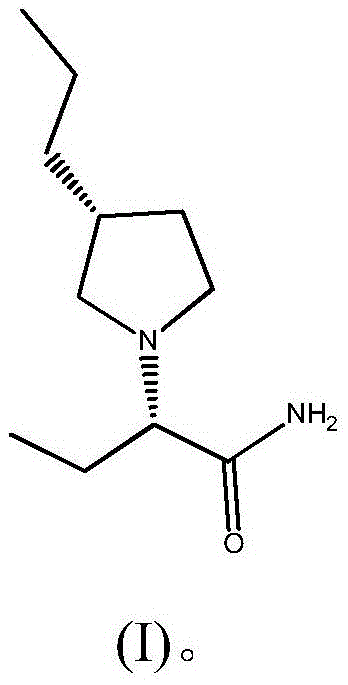
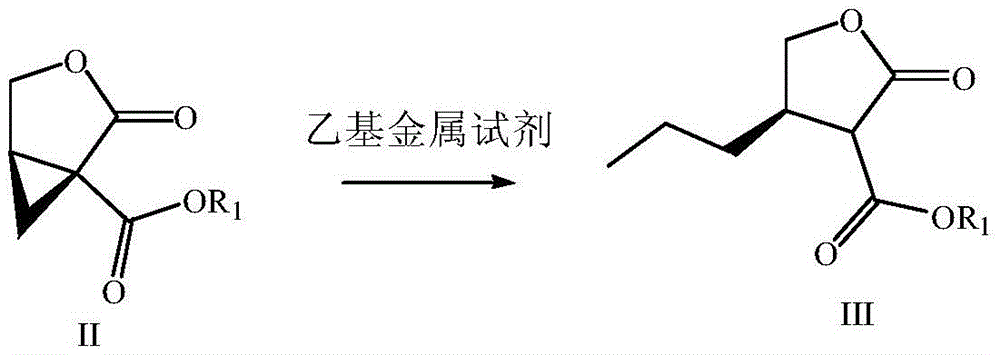
Preparation method of brivaracetam
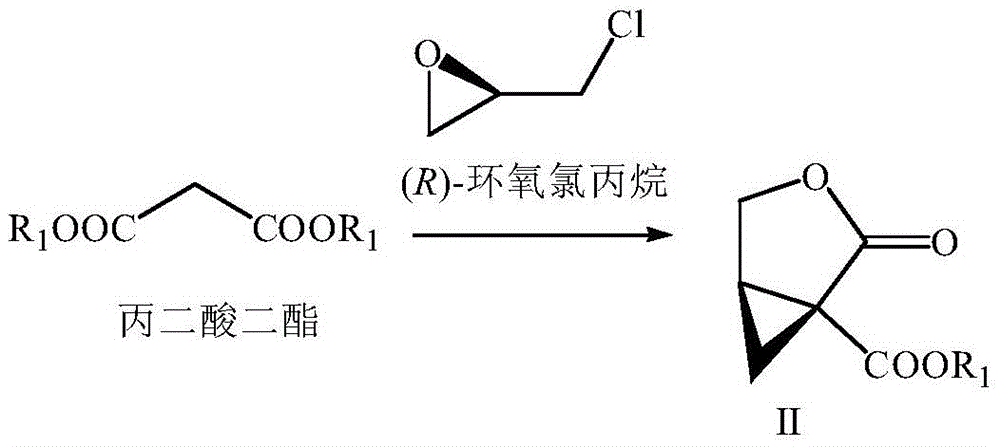
The invention provides a preparation method of brivaracetam. The preparation method of brivaracetam comprises the following steps of in an alkaline reagent, reacting malonate ester and (R)-epichlorohydrin to obtain lactone (II), reacting the lactone (II) and an ethyl metal-based reagent to obtain an intermediate (III), removing carboxylase to obtain (R)-4-propyl-dihydrofuran-2-ketone (IV), performing ring-opening reaction under the action of a halogenated ring-opening reagent to obtain (R)-3-halogenarated methyl hexanoate or (R)-3- halogenarated methyl hexyl acetate (V), and reacting with (S)-2-aminobutanamide or an acceptable salt, so as to obtain the brivaracetam. The preparation method has the advantages that the high-purity brivaracetam (HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography: greater than 96%) and stereo rotary brivaracetam (chirality HPLC: greater than 98%) can be directly prepared; the silicagel column separation and purification or the chirality preparation column separation and purification is not used, so that the complicated separation and purification step is not performed, the cost is saved, and the preparation method is more suitable for industrial production.
Owner:佛山市隆信医药科技有限公司
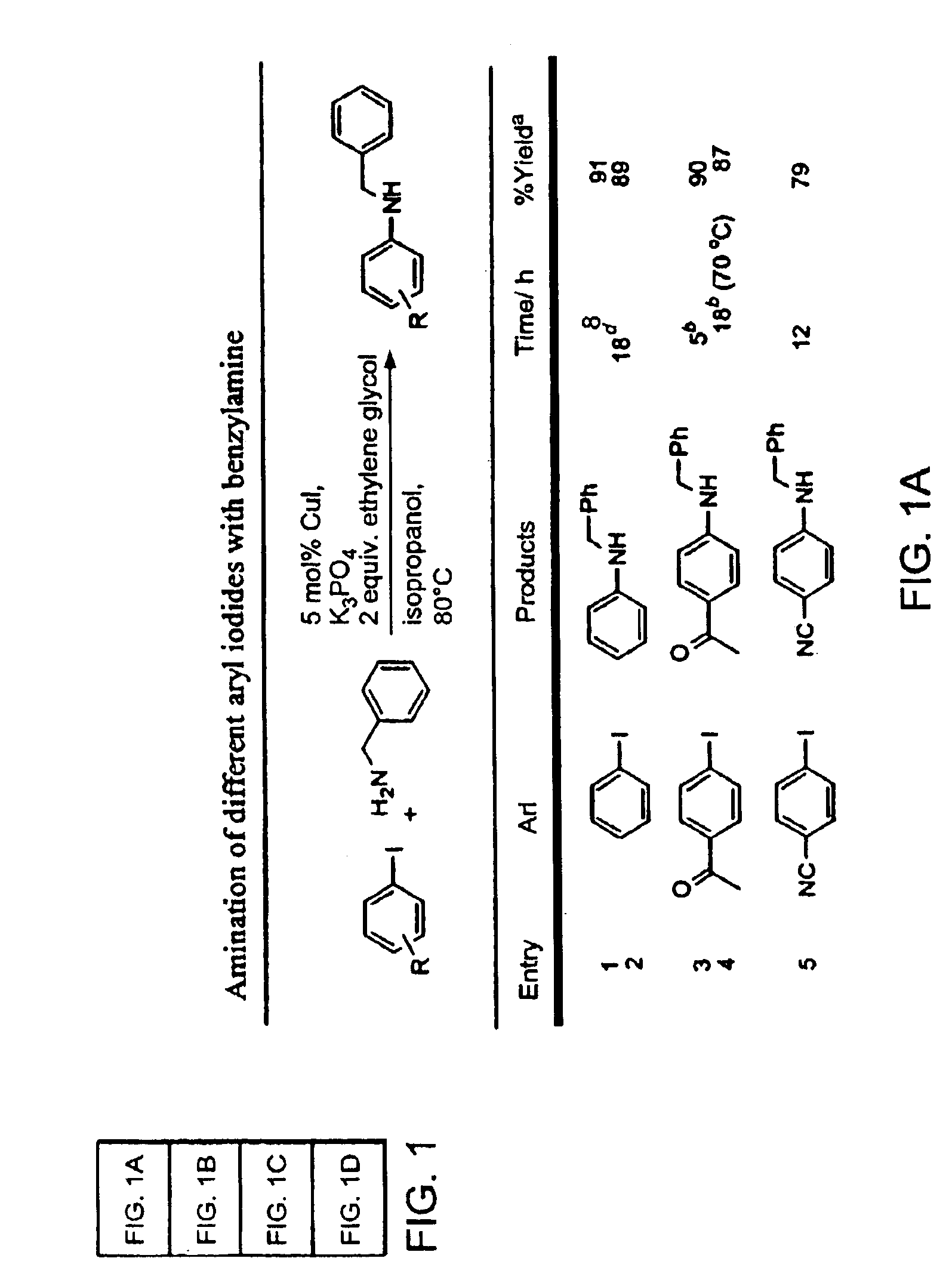
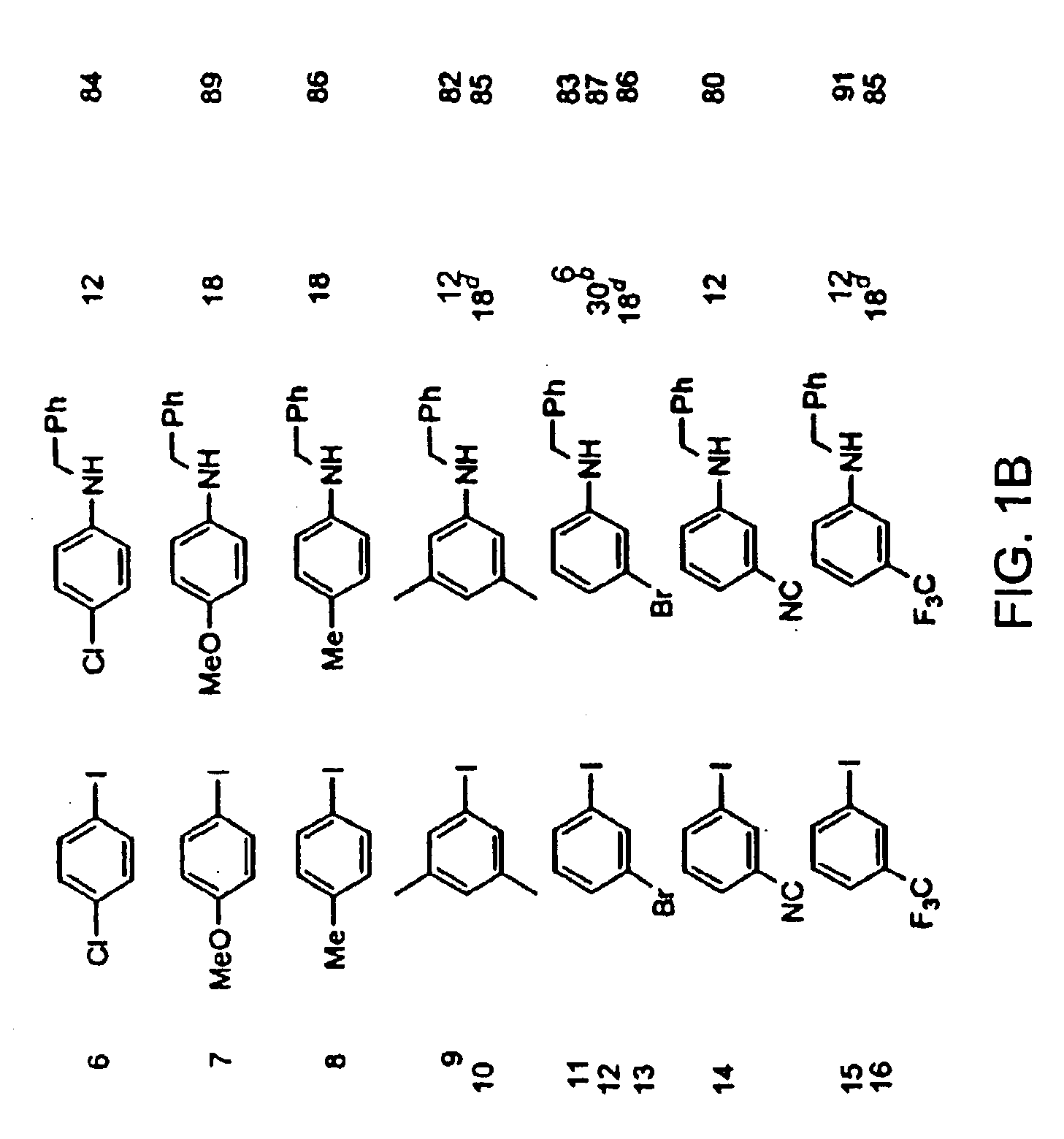
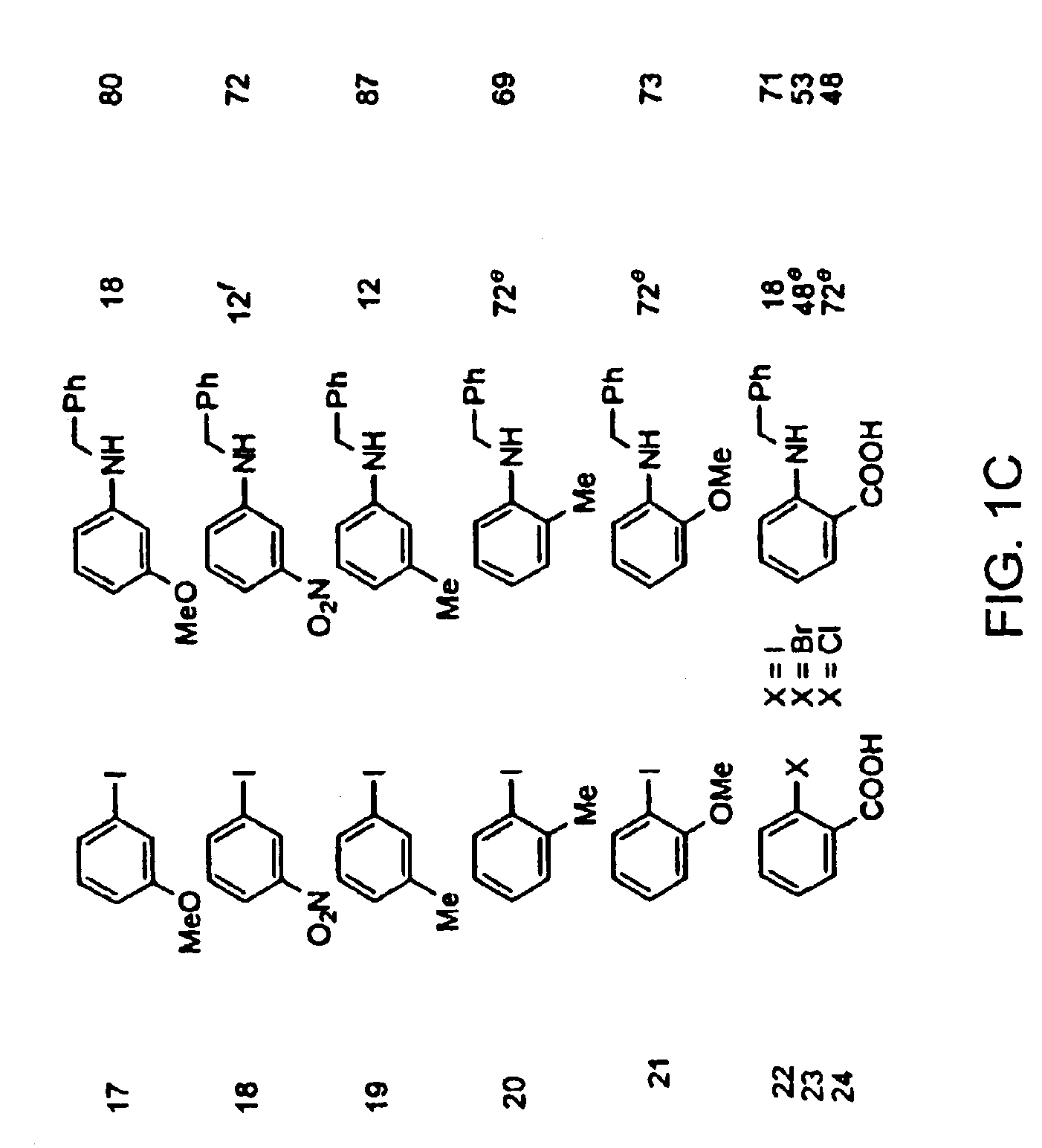
Copper-catalyzed formation of carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bonds
InactiveUS6867298B2Cheap and practicalLow costUrea derivatives preparationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarbon–oxygen bondHydrazine compound
The present invention relates to copper-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming methods. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of an amide or amine moiety and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In additional embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between a nitrogen atom of an acyl hydrazine and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In other embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of a nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic, e.g., indole, pyrazole, and indazole, and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-oxygen bond between the oxygen atom of an alcohol and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. The present invention also relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-carbon bond between a reactant comprising a nucleophilic carbon atom, e.g., an enolate or malonate anion, and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. Importantly, all the methods of the present invention are relatively inexpensive to practice due to the low cost of the copper comprised by the catalysts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methylidene malonate process
ActiveUS20100286433A1Speed up the processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationMalonateChemistry
Novel improved processes for the production and isolation of methylidene malonates via direct and indirect adduct processes.
Owner:HB FULLER CO
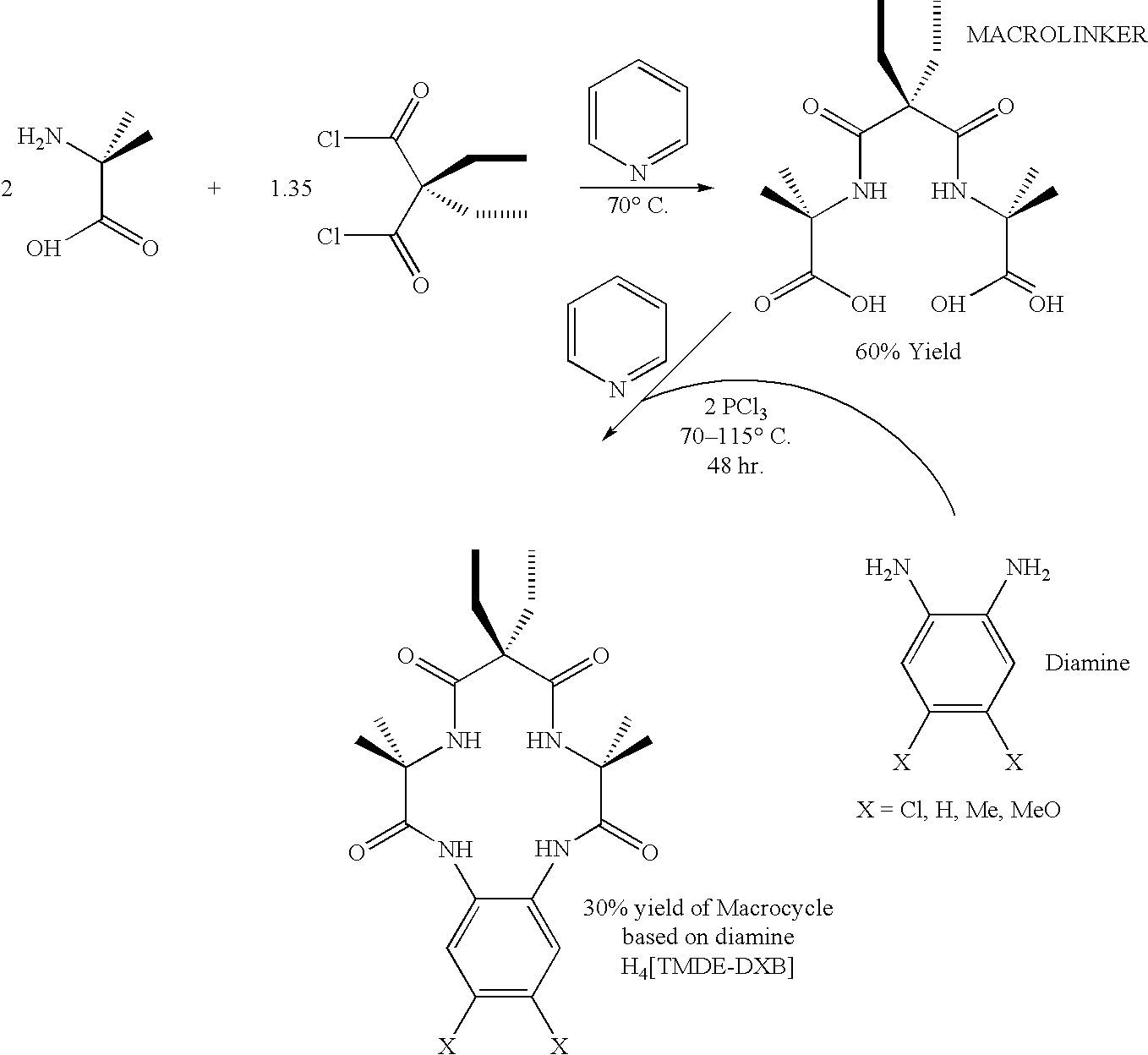
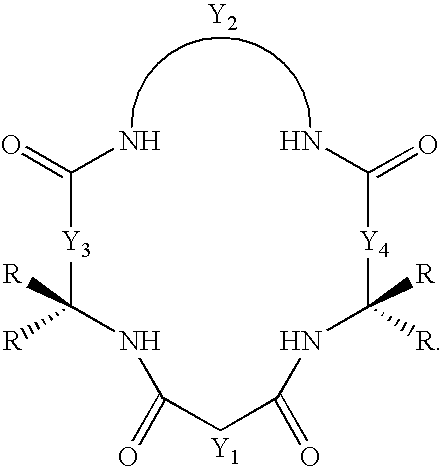
Synthesis of macrocyclic tetraamido-N ligands
InactiveUS6011152AIncrease productionLow costOrganic compound preparationIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesArylCatalytic oxidation
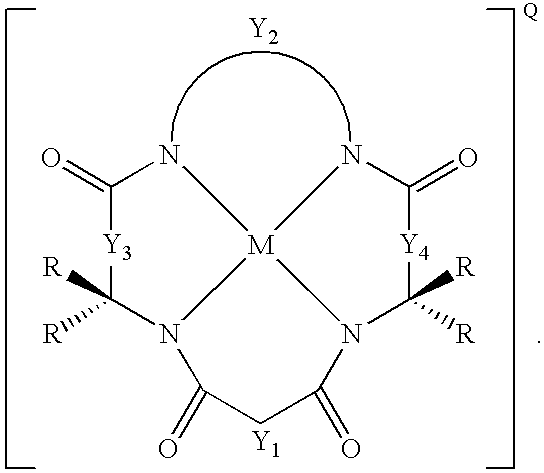
New synthetic methods for the preparation of macrocyclic amido-N donor ligands are provided. The primary method of the present invention involves in general only two synthetic steps. In the first step, an alpha or beta amino carboxylic acid is allowed to react with an optimal (approximately stoichiometric) amount of an activated malonate or oxalate derivative with mild heating. Upon completion of the double coupling reaction, hydrolysis of the reaction mixture yields a diamide containing intermediate (a macro linker). In the second step, stoichiometric amounts of a diamine, preferably an orthophenylene diamine, are added to the macro linker intermediate in the presence of a coupling agent and heat. This second double coupling reaction, is allowed to proceed for a period of time sufficient to produce a macrocyclic tetraamido compound. The substituent groups on the alpha or beta amino carboxylic acid, the malonate, and the aryl diamine may all be selectively varied so that the resulting tetraamido macrocycle can be tailored to specific desired end uses. The macrocyclic tetraamide ligand may then be complexed with a metal, such as a transition metal, and preferably the middle and later transition metals, to form a robust chelate complex suitable for catalyzing oxidation reactions.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Precursors for cvd/ald of metal-containing films
InactiveUS20100018439A1Improve coordinationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGas phaseElectron donor
Precursors useful for vapor phase deposition processes, e.g., CVD / ALD, to form metal-containing films on substrates. The precursors include, in one class, a central metal atom M to which is coordinated at least one ligand of formula (I):wherein:R1, R2 and R3 are each independently H or ogano moieties; andG1 is an electron donor arm substituent that increases the coordination of the ligand to the central metal atom M;wherein when Ga is aminoalkyl, the substituents on the amino nitrogen are not alkyl, fluoroalkyl, cycloaliphatic, or aryl, and are not connected to form a ring structure containing carbon, oxygen or nitrogen atoms. Also disclosed are ketoester, malonate and other precursors adapted for forming metal-containing films on substrates, suitable for use in the manufacture of microelectronic device products such as semiconductor devices and flat panel displays.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Polycarbonate compositions
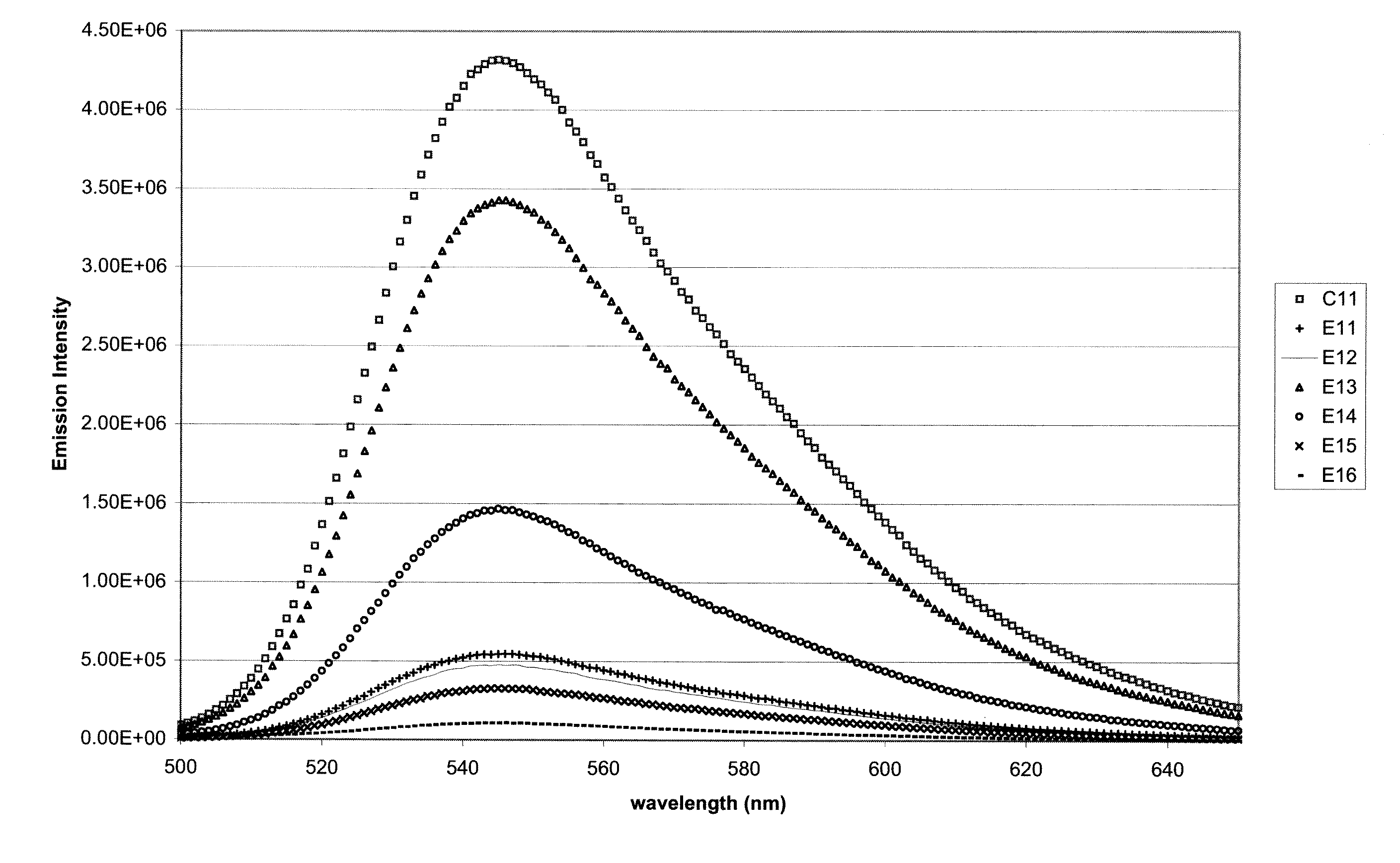
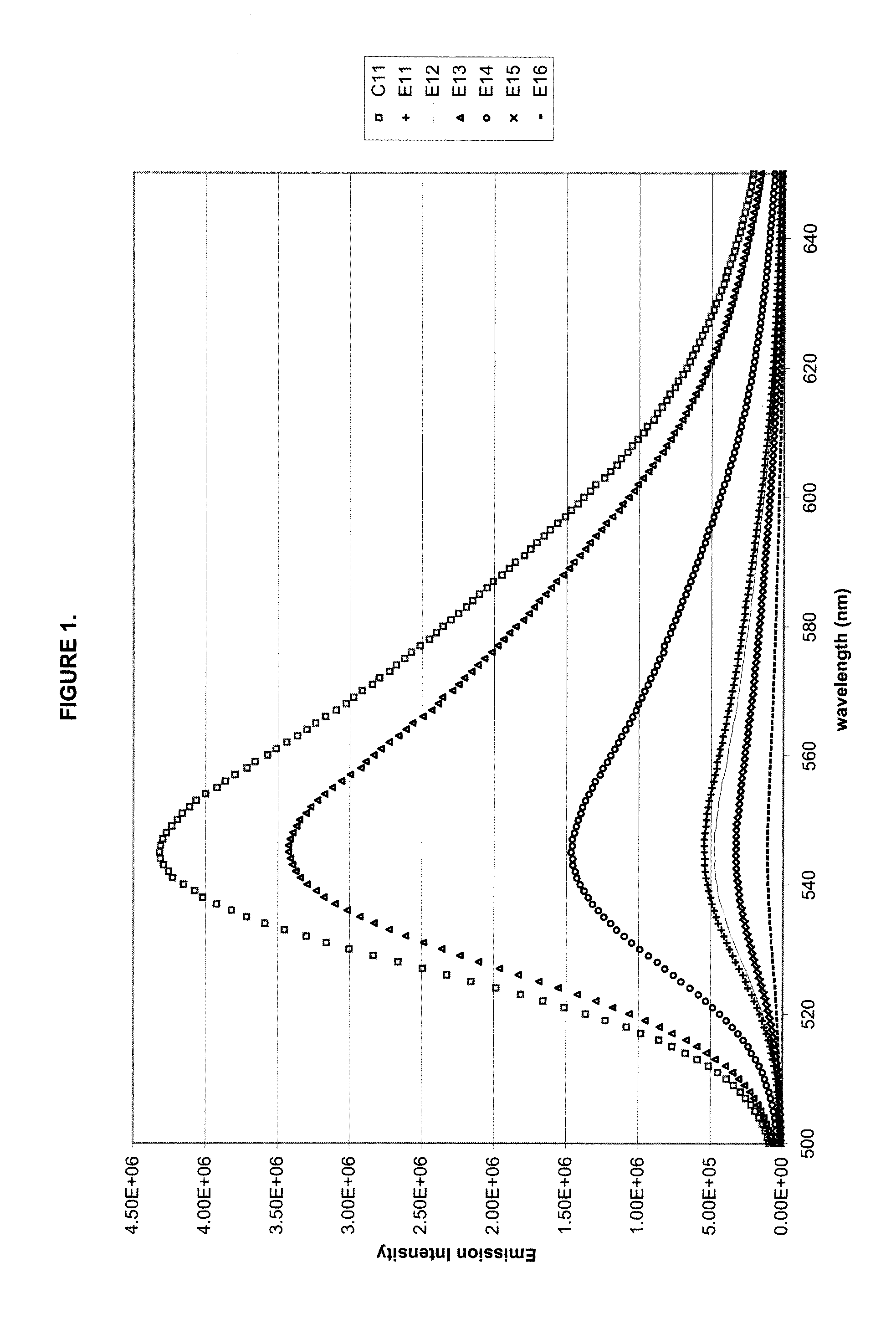
ActiveUS20090054586A1Good color retentionStrong initial fluorescence emission intensityOrganic dyesLuminescent compositionsCyanoacrylateUltraviolet
A polycarbonate composition is disclosed comprising a polycarbonate resin, a 3-hydroxychromone dye, and an ultraviolet absorber selected from the group consisting of cyanoacrylates, malonates, and oxanilides. The combination of the 3-hydroxychromone dye and ultraviolet absorber results in a composition with good color retention and strong initial fluorescent emission intensity.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Stable salts of olanzapine
InactiveUS20050272721A1Improve stabilityGood water solubilityBiocideNervous disorderMalonatePharmacology
Several salts of olanzapine, including olanzapine malonate, olanzapine glycolate, olanzapine maleate, and olanzapine benzoate, have been found to have favorable solid state characteristics.
Owner:SYNTHON IP
Personal Care Compositions Comprising Alpha-Glucans and/or Beta-Glucans
Personal care compositions containing at an alpha-glucan and / or beta-glucan; at least one additional skin and / or hair care active selected from the group consisting of sugar amine, vitamin B3, retinoids, peptides, phytosterol, dialkanoyl hydroxyproline, hexamidine, salicylic acid, n-acyl amino acid compounds, sunscreen actives, water soluble vitamins, oil soluble vitamins, hesperedin, mustard seed extract, glycyrrhizic acid, glycyrrhetinic acid, carnosine, Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) and Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA), menthyl anthranilate, cetyl pyridinium chloride, ergothioneine, vanillin or its derivatives, diethylhexyl syrinylidene malonate, melanostatine, sterol esters, tetrahydrocurcumin, their derivatives, their precursors, and combinations thereof; and a dermatologically acceptable carrier.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
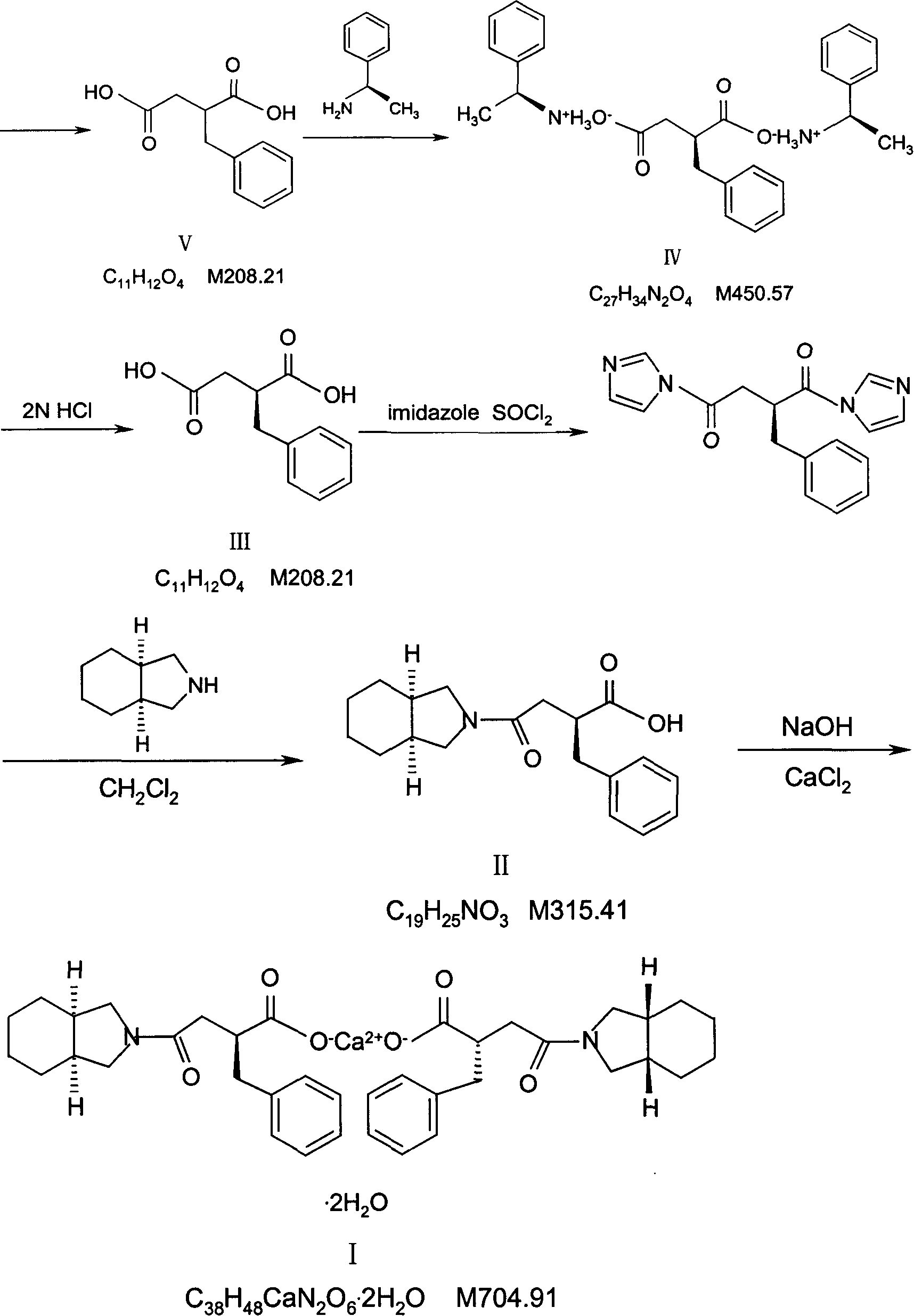
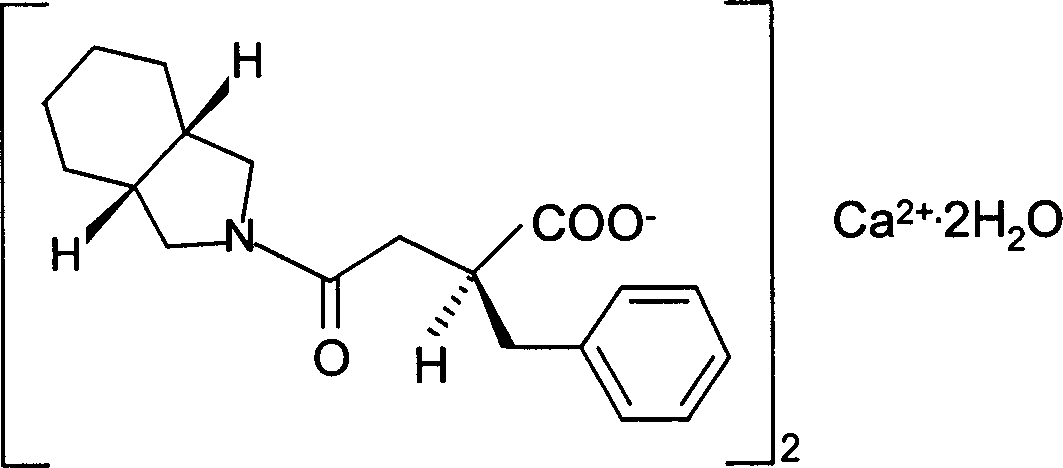
Preparation of mitiglinide calcium and its quality control method
InactiveCN1844096AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPropanoic acidMalonate
The invention relates to a preparation and quality control method of Mitiglinide Calcium comprising steps: 1,synthesis of cis- cyclohexyl-1,2-dimethylacid imide; 2,synthesis of cis-hexa-hydrogen isoindole; 3,synthesis of alpha-benzyldiethyl malonate; 4,synthesis of benzylsuccinic acid; 5,S- benzylsuccinic acid methylbenzylamine salt; 6,synthesis of s- benzylsuccinic acid; 7,synthesis of (2S)-2- benzyl-3-(cis-hexa-hydrogen isoindole-2- carbonyl) propanoic acid; 8,synthesis of Mitiglinide Calcium; 9,purity of Mitiglinide Calcium. This invention also contains the method for quality control of Mitiglinide Calcium comprising steps: watching deseription, messureing specific rotation, authenticating, checking, content messureing for Mitiglinide Calcium.
Owner:天津汉康医药生物技术有限公司
Synthesis of macrocyclic tetraamido compounds and new metal insertion process
An improved method of synthesizing a macrocyclic tetraamido compound includes protecting the amino portion of an amino carboxylic acid to form a protected amino carboxylic acid; exposing the protected amino carboxylic acid to a first solvent, preferably a hydrocarbon solvent, such as toluene or 1,2-dichloroethane, dichloromethane, dibromomethane and 1,2-dibromoethane. The carboxylic acid portion of the protected amino carboxylic acid is then converted to an activated carboxylic acid by one of esterification or acid halide formation, to form a protected amino activated carboxylic acid derivative. The protected amino activated carboxylic acid derivative is reacted with a diamine in the presence of a second solvent, such as THF or ,2-dichloroethane, dichloromethane, dibromomethane and 1,2-dibromoethane, to form a protected diamide diamine intermediate. Following deprotection, the diamide diamine intermediate is reacted with an activated diacid, such as an activated malonate, oxalate or succinate derivative to form the macrocyclic tetraamido compound. The macrocyclic tetraamido compound may further be complexed with a transition metal.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Method for synthesizing 4-dihydroxyborane-2-fluorophenylalanine
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a 4-dihydroxyborane-2-fluorophenylalanine, wherein the method comprises the following steps of taking p-iodotoluene as a raw material, carrying out nitratlon reaction and bromination reaction in sequence on the raw material to obtain p-iodo-o-nitrobenzyl bromine, firstly substituting the p-iodo-o-nitrobenzyl bromine with diethyl sodium acetamidomalonate to obtain diethyl 2-acetamido-2-(4-iodo-2-nitrobenzyl) malonate, and then reacting with ammonium tetrabutyl fluoride to obtain fluorinated diethyl 2-acetamido-2-(4-iodo-2-fluorobenzyl) malonate, carrying out Suzuki coupling reaction on the obtained fluorinated product and bisdiboron under an inert atmosphere, hydrolyzing the obtained diethyl 2-acetamido-2-(4-valerylboron-2-fluorobenzyl) malonate to obtain the 4-dihydroxyborane-2-fluorophenylalanine. The method provided by the invention is not necessary to use fluorine gas; the method provided by the invention has low requirement to production equipment; the reaction is carried out under common experimental conditions; the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple synthesis step, high yield, high product purity and easy purification.
Owner:NANJING PET TRACER +1
Processing aids and polymer formulations containing the same and method for producing the same
A multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer comprising one or more functionalized ethylenically unsaturated monomer into the emulsion polymerization reactor, wherein the functionality is selected from the group consisting of β-keto esters, β-keto amides, β-diketones, cyanoacetic esters, malonates, nitroalkanes, β-nitro esters, sulfonazides, thiols, thiol-s-triazines, and amine, where the functionality is incorporated into polymers by polymerizing, ethylenically unsaturated monomers containing these functionalities or by post functionalization of a polymer with additional reactions after polymerization in one of the first or second stages. Foamable halogenated polymers comprising the multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer is also provided. Also provided are methods for making the multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer and foamable halogenated polymers.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Benzoin oxime derivative and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104447396AComplex structureBroad use prospectsImino compound preparationChemical industryMalonate
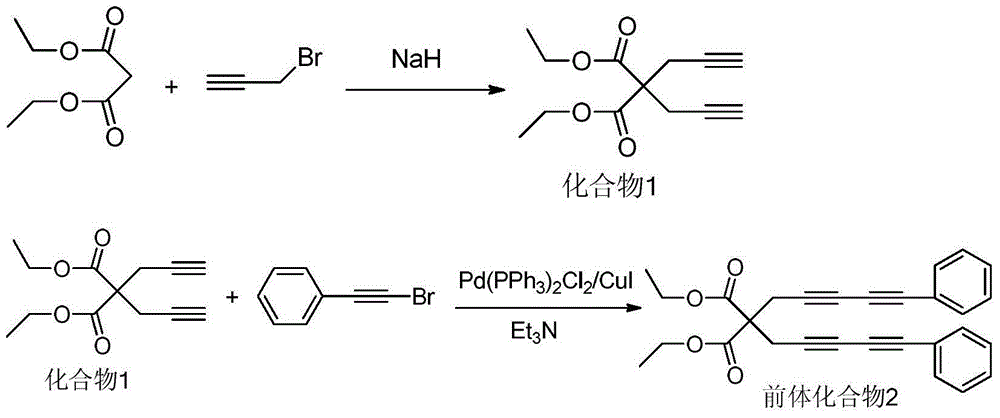
The invention relates to a benzoin oxime derivative and a preparation method thereof. A structural formula of the benzoin oxime derivative is shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: reacting malonate with propargyl bromide in anhydrous acetonitrile under the catalysis of sodium hydride to obtain a white solid product; by taking triethylamine as alkali, reacting the white solid product with phenylethynyl bromine or substituted phenylethynyl bromine in anhydrous acetonitrile under the catalysis of Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 / CuI to obtain a light brown solid product; reacting the light brown solid product with benzoin oxime in toluene at 95-105 DEG C to obtain the benzoin oxime derivative. A brand new synthetic method of polysubstituted benzoin oxime is provided, and a series of new benzoin oxime derivatives are generated. Compared with normal benzoin oxime derivatives, the benzoin oxime derivative prepared by virtue of the preparation method has relatively complex and diverse structures by virtue of multiple cycles, and presents relatively wide application prospects in chemical industry production and clinic medicines.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Cytarabine 5'-O-amino-acid ester, salts thereof and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101812105AGood membrane permeabilityIncrease Absolute BioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCytarabineSodium bicarbonate
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and discloses cytarabine 5'-O-amino-acid ester, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: slowly dropping carbobenzoxy chloride into a solution formed by cytarabine, sodium bicarbonate and N,N-dimethylacetylamide, and obtaining a compound A after reacting at room temperature; using the compound A and N-butyloxy formoxyl-amino acid as raw materials; adding a reagent to the solution to carry out an esterification reaction to obtain the cytarabine 5'-O-amino-acid ester; and then adding acid to obtain a finished product. The pharmaceutically acceptable salts comprise hydrochlorides, sulfates, formates, acetates, mesylates, propionates, butyrates, p-toluene sulphonates, phosphates, bisulfates, maleates, lactates, carbonates, bicarbonates, malonates, and salts formed with acidic amino acids, and the like. The invention can obviously improve the membrane permeability of the cytarabine so as to improve the bioavailability of the cytarabine.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
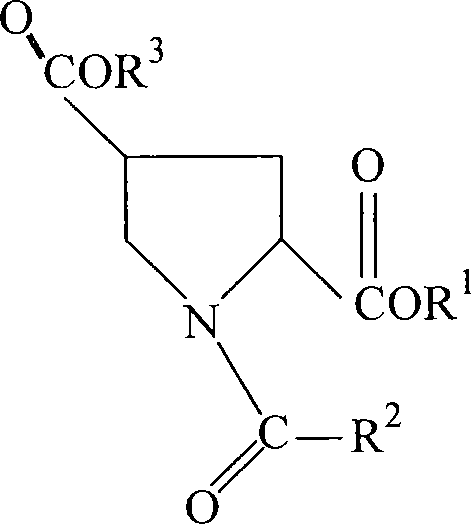
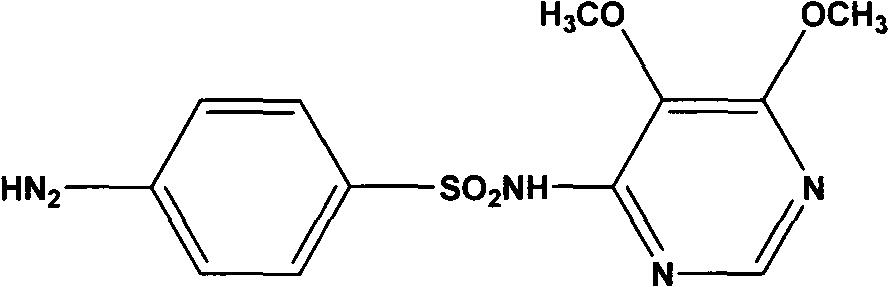
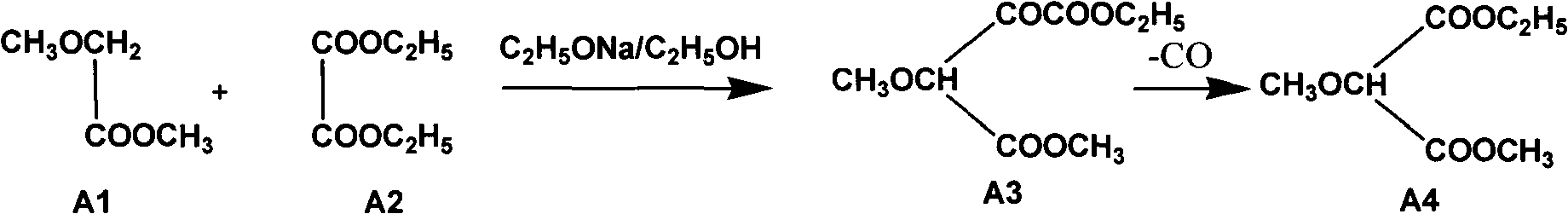
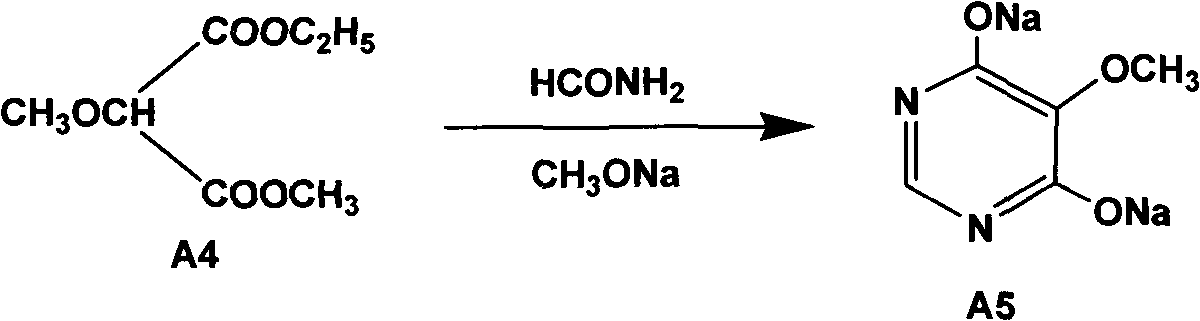
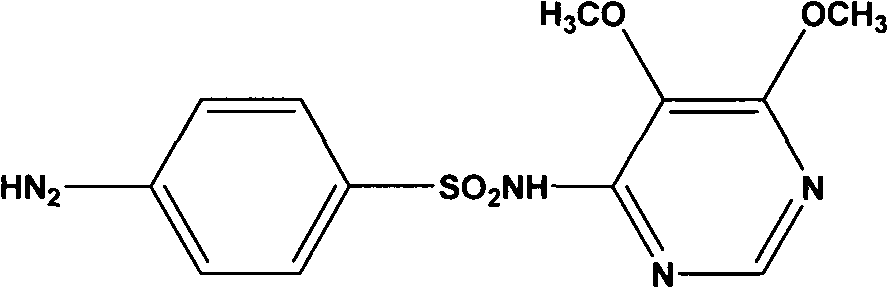
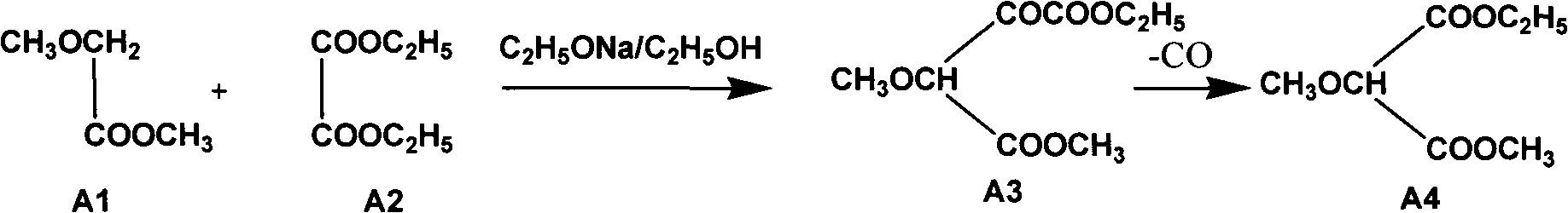
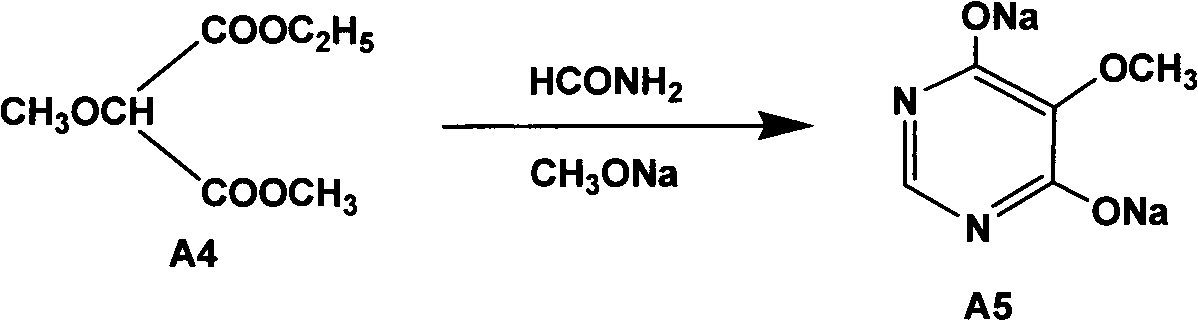
Preparation method of sulfadoxine and intermediate thereof
InactiveCN102304094AReduce manufacturing costHigh purityOrganic chemistryMethyl methoxyacetateMalonate
The invention relates to a preparation method of sulfadoxine and an intermediate thereof. The preparation method of sulfadoxine comprises the following steps: (1) reacting methyl methoxyacetate and excessive diethyl oxalate to generate 3-methoxy-2-oxo-methylethyl succinate, and decarbonylating to obtain 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate; (2) reacting the 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate and formamide to generate a cyclocompound; (3) reacting the cyclocompound and phosphorus oxychloride to generate chloride; (4) carrying out condensation reaction; and (5) carrying out methoxylation reaction. The obtained cyclocompound in the step (2) is controlled to exist in the form of anhydrous hydroxy sodium salt, so that N,N-dimethylaniline is not needed as a catalyst in the step (3), thereby lowering the cost, enhancing the quality of chloride and finally enhancing the quality of sulfadoxine.
Owner:CHANGSHU NANHU INDAL CHEM
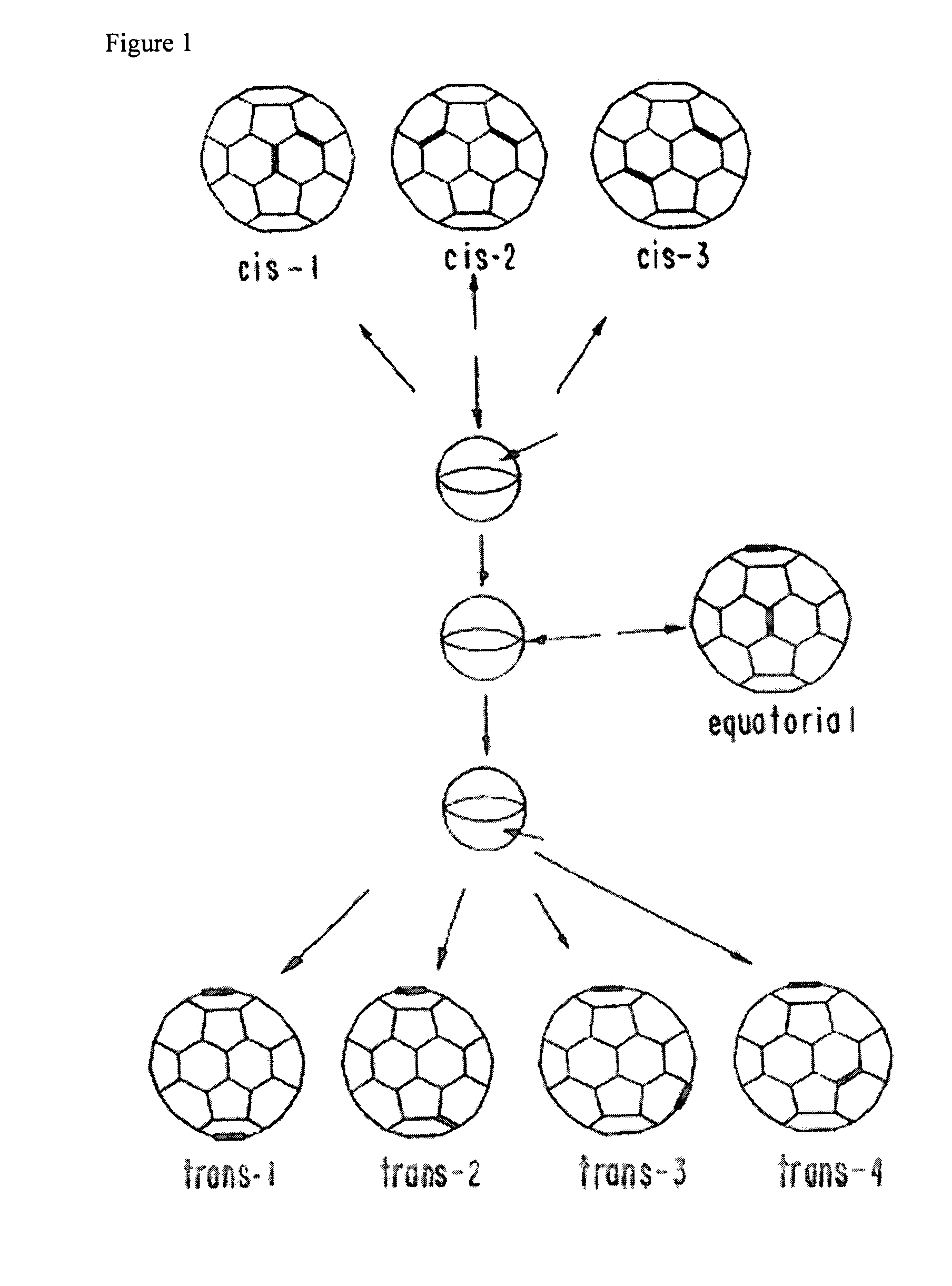
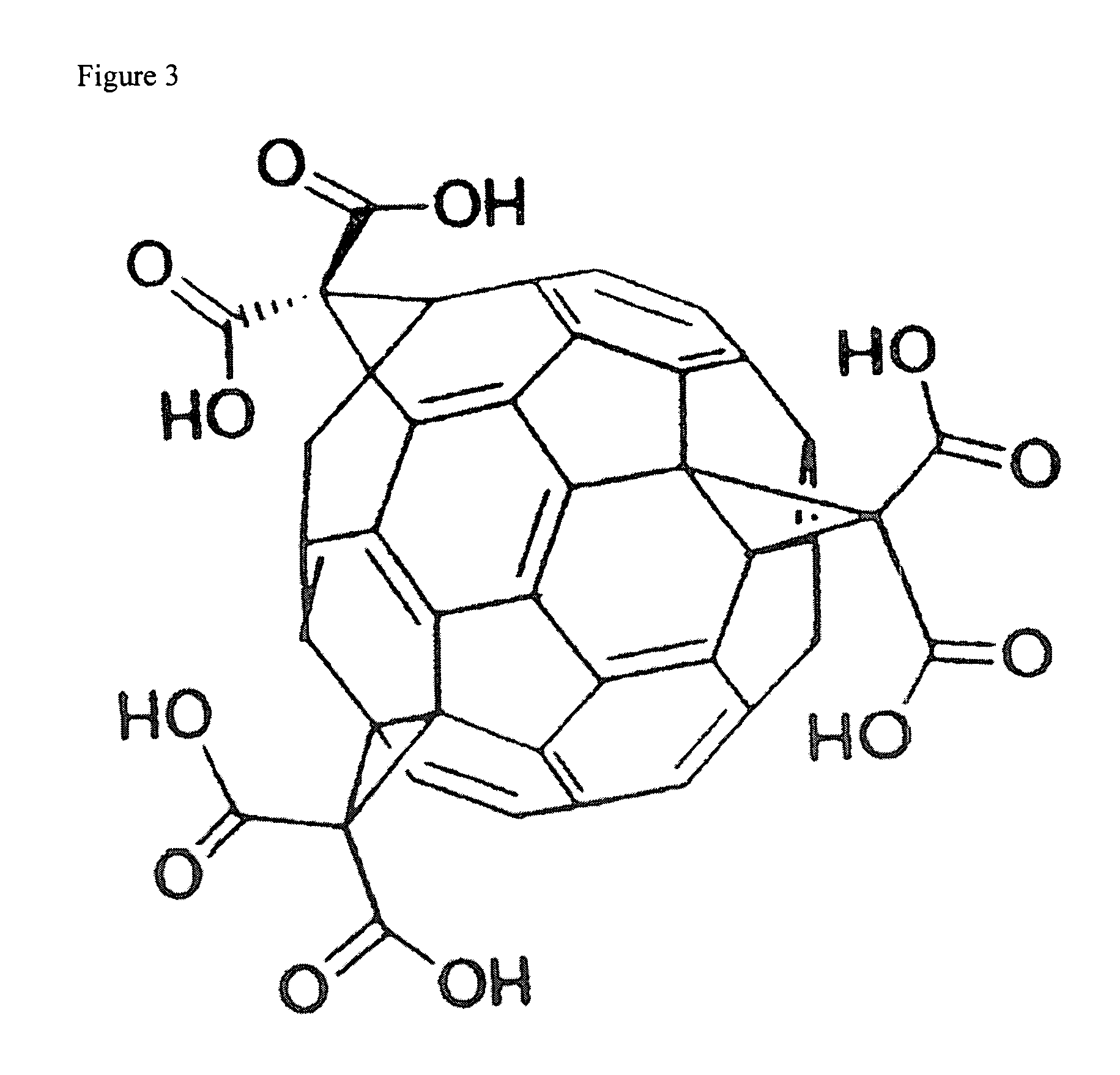
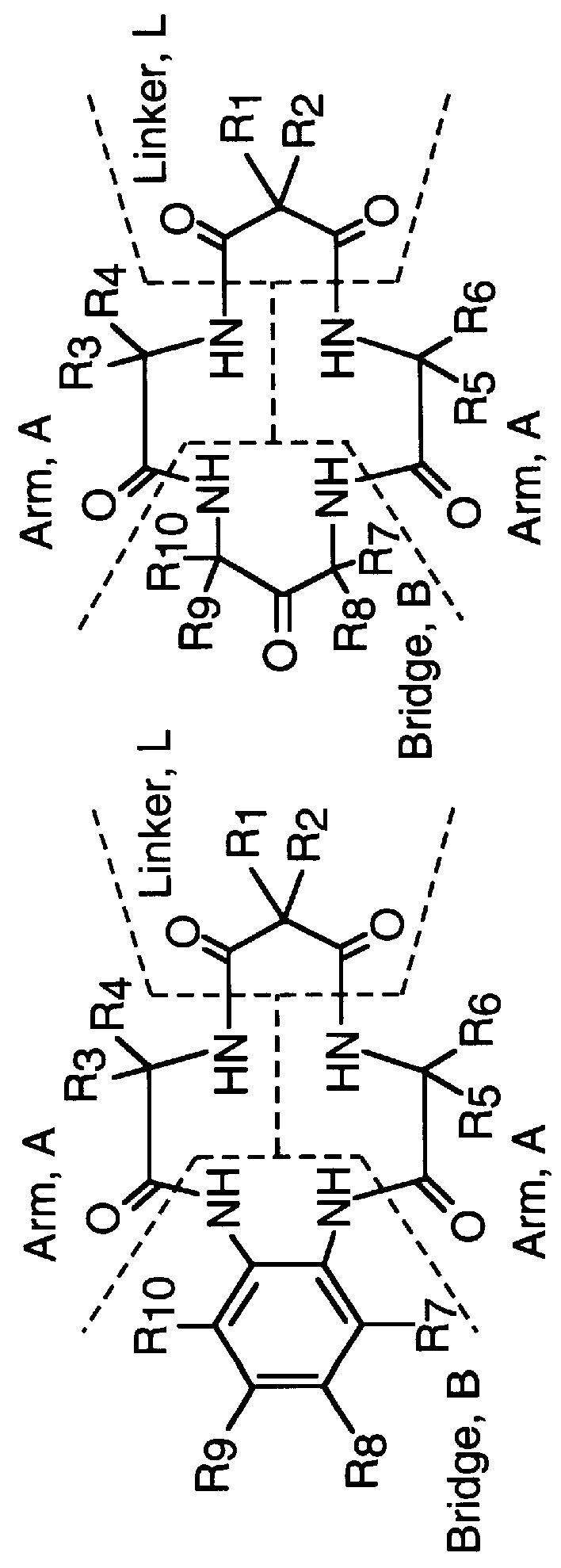
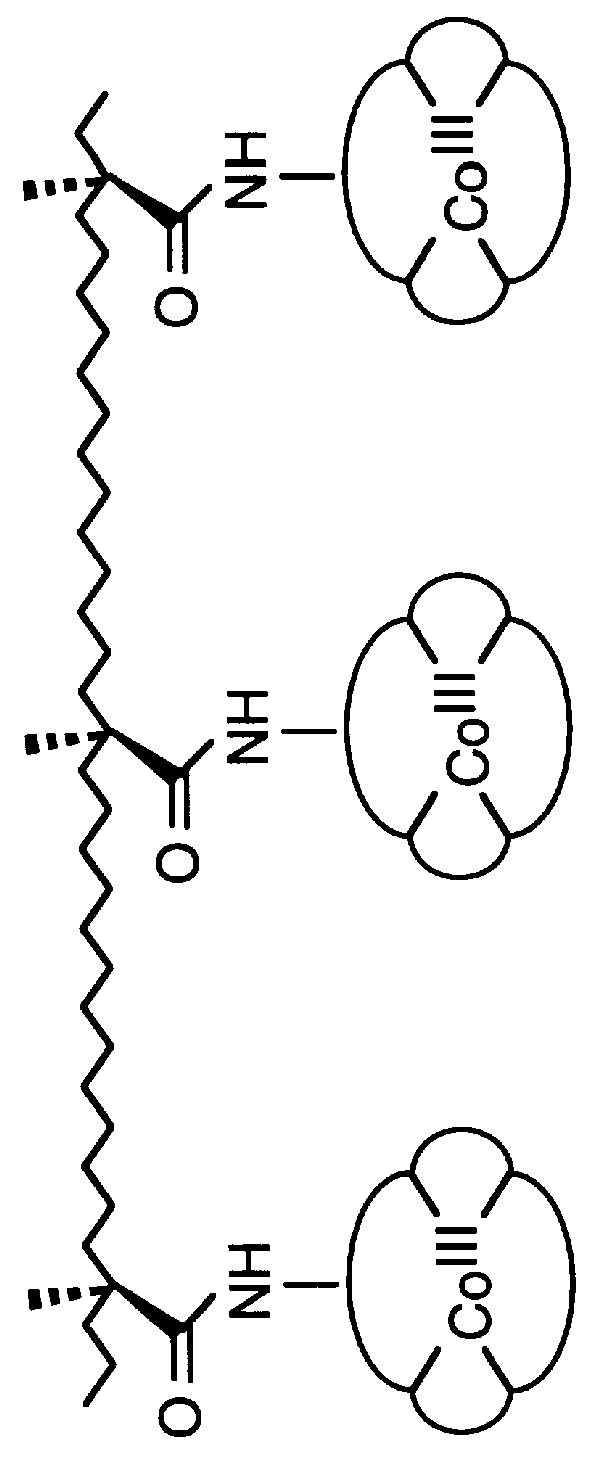
Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes
ActiveUS20050143327A1Ameliorating damage to tissues for transplantationAmeliorating spoilage of foodBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer scienceMalonic acid
Herein are disclosed substituted fullerenes, comprising a fullerene core (Cn), wherein n is an even integer greater than or equal to 60; 3 or 5 dihydrocarbylmalonate (>C(COOR1)(COOR2)) groups bonded to the fullerene core; and 1 or 3 polar extended malonate groups (>C(COOR3)(COOR4)) bonded to the fullerene core. The substituted fullerenes can form micelles, and can be used to ameliorate oxidative stress diseases.
Owner:LUNA LABS USA LLC
Chemical compositions and methods of making them
ActiveUS20070191620A1Copper organic compoundsGroup 2/12 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesChemical compositionMalonate
Metal complex salts of the coordination elements listed in Groups IIIA to VIIIA, Groups IB to IIIB, of periods 4 and 5 and aluminum in Group IIIB, period 3 of The Periodic Table of the Elements, obtained as the reaction products of polyfunctional acids with two or more of such elements are described. Copper-zinc malonates and a process for their preparation are disclosed.
Owner:OBAGI COSMECEUTICALS LLC
Method of synthesis of water soluble fullerene polyacids using a malonate reactant
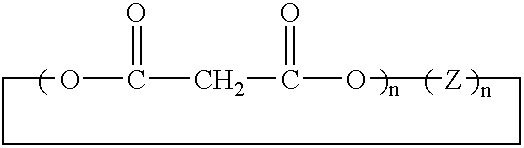
In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to a method for synthesizing compounds of the formula where Cm is a fullerene having m carbon atoms, the method comprising the steps of forming a linear malonate compound of the formula where each Z is the same or different and is a straight-chain or branched-chain aliphatic radical having from 1-30 carbon atoms which may be unsubstituted or monosubstituted or polysubstituted by identical or different substitutents, in which radicals up to every third —CH2— unit can be replaced by O or NR″, n is an integer from 2 to 10, and the unfilled valences of the first and nth malonate groups are filled with bonds to hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group or substituted hydrocarbon group having 1-20 carbon atoms, or a chain containing unsubstituted or substituted aryl or other cyclic groups; or (ii) a branched malonate compound of the formula where Z′ is an aliphatic radical having from 1-30 carbon atoms which may be unsubstituted or monosubstituted or polysubstituted by identical or different substitutents, in which radicals up to every third —CH2— unit can be replaced by O or NR″; and n is an integer from 2 to 10; reacting said malonate compound with Cm to form an adduct of the formula each Z is bonded to both one carboxylate group of a first malonate moiety and one carboxylate group of a second malonate moiety and the unfilled valences of the first and nth malonate groups are filled with bonds to hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group or substituted hydrocarbon group having 1-20 carbon atoms, or a chain containing unsubstituted or substituted aryl or other cyclic groups; and hydrolyzing said adduct to form the compound.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
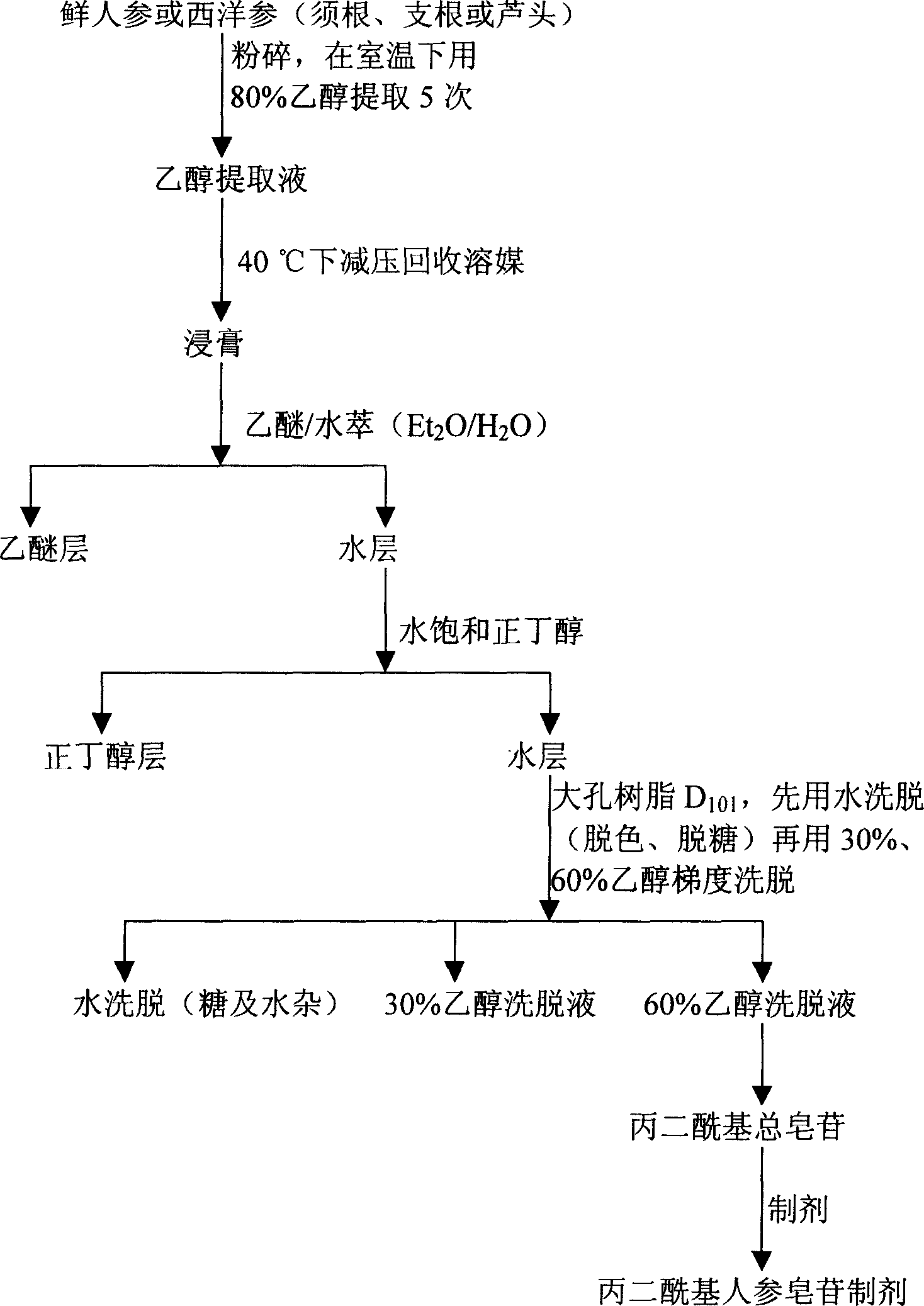
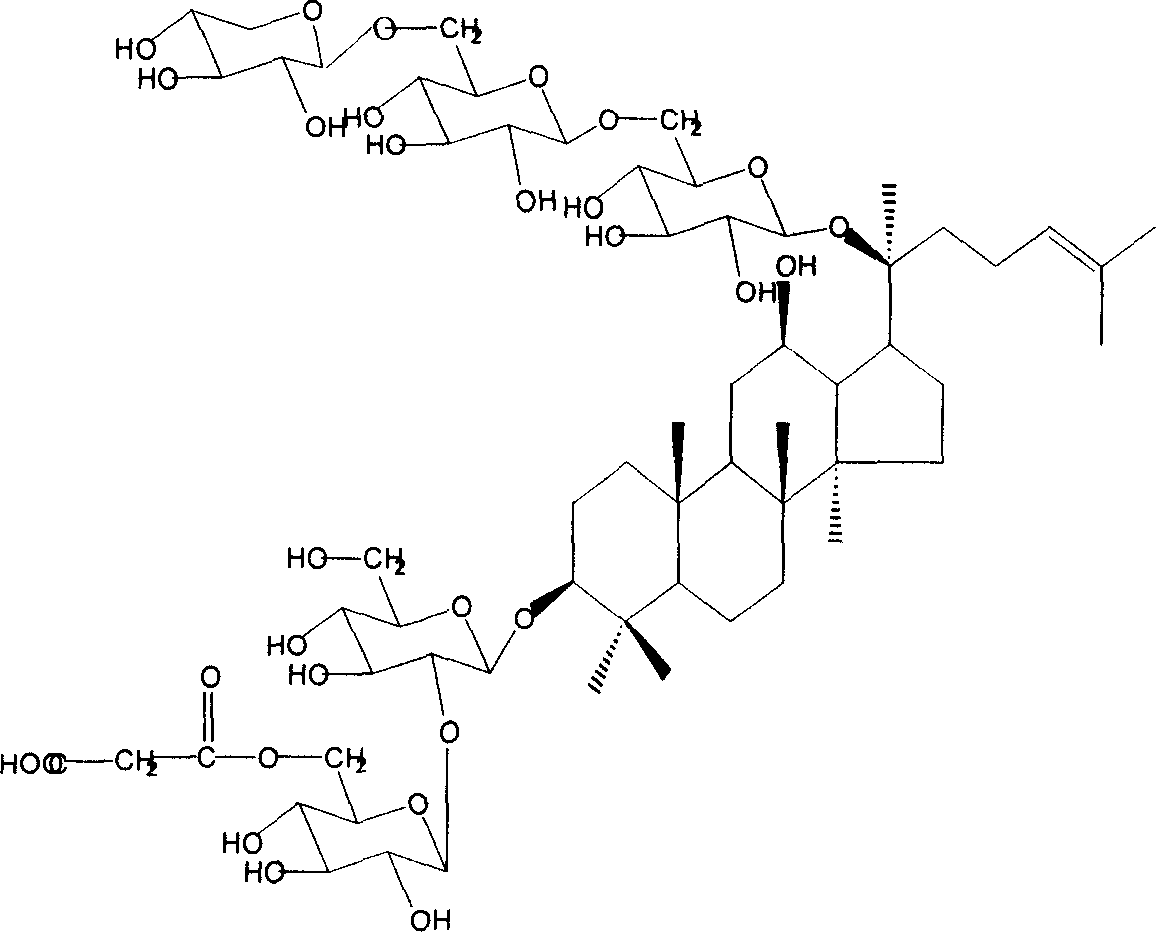
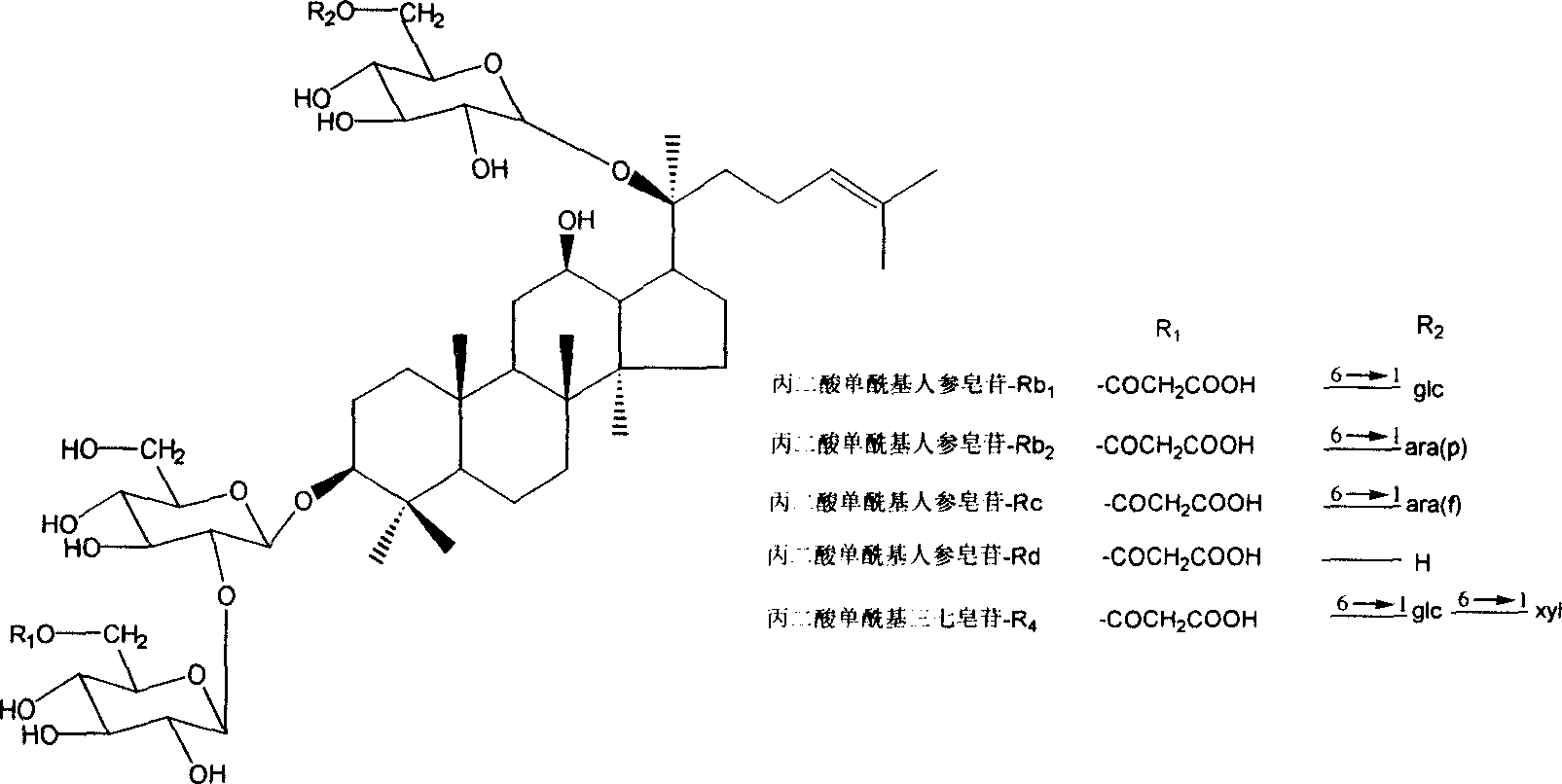
Technique for preparing malonyl ginsenoside, and application of medication in treating diabetes
A process for preparing the malonyl ginsenoside used to prepare the medicine for treating diabetes includes pulverizing fresh ginseng, immersing in alcohol for extracting, vacuum recovering of solvent, concentrating to become aqueous solution, repeated extraction by n-butanol and water, concentrating, adsorbing by macroreticular resin column, eluting with alcohol, and recovering alcohol. A monoacyl arasaponin-R4 malonate and its medical application are also disclosed.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Processing Aids and Polymer Formulations Containing the Same and Method for Producing the Same
ActiveUS20140371396A1Increase profitHigh molecular weightTransportation and packagingMixingProcedure AgentsThiol
A multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer comprising one or more functionalized ethylenically unsaturated monomer into the emulsion polymerization reactor, wherein the functionality is selected from the group consisting of β-keto esters, β-keto amides, β-diketones, cyanoacetic esters, malonates, nitroalkanes, β-nitro esters, sulfonazides, thiols, thiol-s-triazines, and amine, where the functionality is incorporated into polymers by polymerizing, ethylenically unsaturated monomers containing these functionalities or by post functionalization of a polymer with additional reactions after polymerization in one of the first or second stages. Foamable halogenated polymers comprising the multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer is also provided. Also provided are methods for making the multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer and foamable halogenated polymers.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
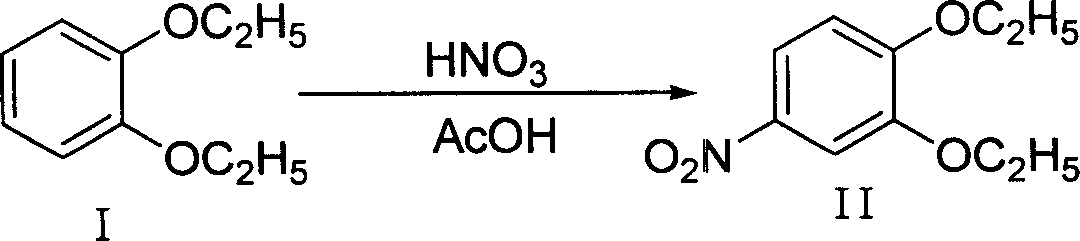
Method of preparing 4-hydroxy-6-decyloxy-7-ethoxy-3-quinoline carboxylic acid ethyl ester
InactiveCN101012195AAvoid the disadvantages of greater pollutionWide variety of sourcesOrganic chemistryNitrobenzeneQuinoline
The invention discloses a making method of 4-hydroxy-6-oxy-7-ethoxy-3-quinoline carboxylic acid carbethoxy in the coccidiostat domain, which comprises the following steps: A. preparing catechol diethyl ether; B. making .3, 4-diethyloxy nitrobenzene; C. making 2-ethoxy-4-nitrophenol; D. making 3-ethoxy-4-oxynitrobenzene; E. making 3-ethoxy-4-oxyphenylamine; F. preparing N-methylene ethyl malonate-3-ethoxy-4-oxyphenylamine; G obtaining the product.
Owner:CHANGSHU OUYAJI BIOMEDICINE INST
Regulation of mammalian keratinous tissue using personal care compositions comprising diethylhexyl syringylidene malonate
The present invention provides personal care compositions, containing tetrahydrocurcumin alone, or in combination with tetrahydromethoxycurcumin and / or tetrahydrobisdemethoxycurcumin are provided. Methods for regulating the condition of mammalian keratinous tissue by topically applying the personal care compositions are also provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Preparation method of sulfadoxine
InactiveCN102304095AReduce usageQuality improvementOrganic chemistrySodium methoxideDimethylaniline N-oxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of sulfadoxine, which comprises the following steps: (1) reacting methyl methoxyacetate and excessive diethyl oxalate to generate 3-methoxy-2-oxo-methylethyl succinate, and decarbonylating to obtain 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate; (2) reacting the 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate and formamide to generate a cyclocompound; (3) carrying out chlorination reaction; (4) carrying out condensation reaction; and (5) carrying out methoxylation reaction. The purity of the 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate obtained in the step (1) is strictly controlled, and the cyclocompound in the step (2) is controlled to exist in the form of anhydrous hydroxy sodium salt; in the step (3), no catalyst, including N,N-dimethylaniline, is used; and in the step (5), solid sodium hydroxide is substituted for sodium methoxide solution. The invention is easy to operate, has the advantage of high product quality, greatly lowers the production cost, and has obvious economic benefit and environmental benefit.
Owner:CHANGSHU NANHU INDAL CHEM
Temperature-resistant jelly
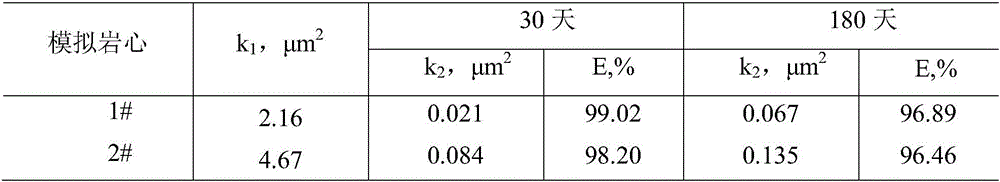
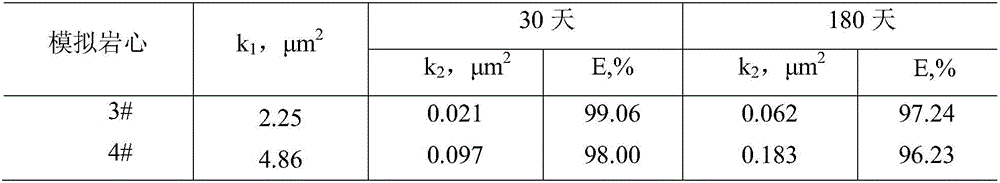
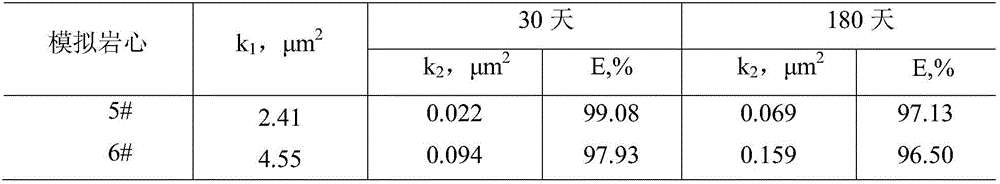
The invention provides a temperature-resistant jelly comprising the following components in percentage by mass: 0.3-0.5% of an acrylamide / acryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride copolymer, 0.1-0.5% of sodium tripolyphosphate or / and amino methenesodium phosphate, 0.05-0.15% of phenol, 0.05-0.1% of paraformaldehyde, 0.2-0.4% of thiourea, 0.05-0.2% of sodium malonate or / and D-sodium erythorbate and the balance of water, wherein the total mass percentages of each component are 100%, the relative molecular mass of the acrylamide / acryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride copolymer is 200*10<4> to 500*10<4>, and the mass content of an acryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride monomer is 10-30%. According to the jelly provided by the invention, the gelling time of the jelly can be adjusted in a range of 15-54 hours, the jelly is excellent in temperature-resistant performance, and a water loss shrinkage phenomenon cannot be caused after the jelly is aged for 180 days at 160 DEG C; and the jelly can be used as a plugging agent applied to near borehole zones and oil well deep parts, and can also be used for sealing steam channeling in a thermal exploitation process of viscous oil.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Process of preparing malonic ester
InactiveCN1834081AReduce consumptionCause a lot of decompositionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidMalonic acid
This invention relates to a method to synthesize malonate from chloroacetic acid, which includes neutralization, cyanidation, acidification, dehydration and esterification. It has the characteristics that dilute sulphuric acid is added after dehydration so that cyanoacetic acid is hydrolyzed into malonic acid which is then esterified to obtain malonate. This invention has the advantages of low cost, easily-controlled technique and high yield.
Owner:CHONGQING UNISPLENDOUR CHEM
New oxaliplatin derivate
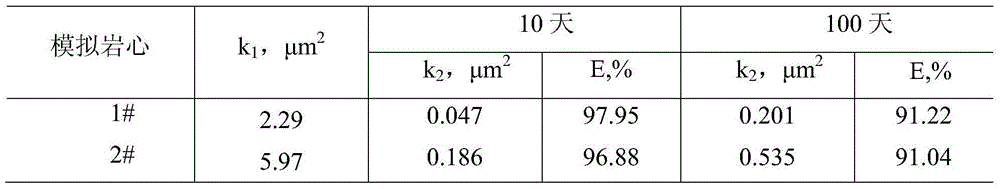
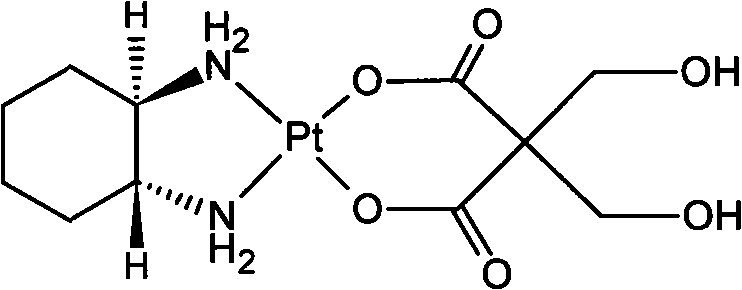
InactiveCN101289468AGood inhibitory effectHigh activityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a novel oxaliplatin derivative of (1R, 2R-cyclohexanediamine.2, 2-Bis (hydroxymethyl)-1, 3-malonato-platinum (II)) and ((1R, 2R-cyclohexanediamine).2, 2-Bis (hydroxymethyl)malonato-platinum (II)). The derivative is prepared with the steps that the cis-(PtA2I2) (A2 is equal to 1R, 2R-cyclohexanediamine) is adopted as the raw material and quantitatively reacts with the 2, 2-Bis (hydroxymethyl)-1, 3-malonate silver, and a crude product then is obtained through the mother liquor concentration and freeze-drying after the AgI is filtered and separated; a pure product is obtained by recrystallizing the crude product in a system that the ratio of water to ethanol is 1:1. The anti-caner activity of the complex of the derivative is obviously higher than the oxaliplatin and the toxic side effect is obviously less than the oxaliplatin, and can be prepared into freeze-dried powders or injections and used for treating the cancer clinically.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS +1
Profile modification agent for amphion jelly
InactiveCN102153999AImprove gelation performanceHigh strengthDrilling compositionSodium acetateThiourea
The invention provides a profile modification agent for amphion jelly. The profile modification agent comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.1%-0.3% of amphion polymer, 0.1%-0.3% of compound cross-linking agent and the balance of water, wherein the molecule weight of the amphion polymer is above 1500 ten thousand. The compound cross-linking agent is prepared by a method comprising the following steps: firstly, adding phenol and formaldehyde in an enamel reaction kettle with a stirrer at a mass ratio of 1:1, heating and raising the temperature to 60 DEG C, then adding triethanolamine so that the phenol and formaldehyde are reacted to generate a mixture of monohydroxymethyl phenol, dihydroxymethyl phenol and trihydroxymethyl phenol for later use; next, adding sodium dichromate and thiourea in the reaction kettle with the stirrer at a weight ratio of 1:1, adding hydrochloric acid and a mixture of sodium acetate and sodium malonate which are at a weight ratio of 1:1 to react for 12 hours for later use; and mixing the products obtained from the former two steps at an isovolumetric ratio, and adding absolute ethyl alcohol for evenly stirring so as to obtain the compound cross-linking agent. According to the invention, the glue-forming property and glue-forming strength of the jelly profile modification agent in high-hypersalinity oil field water are improved, and the validity of the profile modification of the oil field is prolonged.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Slow-crosslinked high-strength jelly profile control water-plugging agent
The invention discloses a slow-crosslinked high-strength jelly profile control water-plugging agent. The slow-crosslinked high-strength jelly profile control water-plugging agent comprises, by mass, 0.3% to 0.6% of a hydrophobic associating polymer, 0. 3% to 0.6% of a melamine resin crosslinking agent, 0.03% to 0.05% of a phenol crosslinking agent, 0.2% to 0.4% of an oxygen scavenger, 0.1% to 0.3% of a delayed crosslinking agent, 0.1% to 0.2% of a water loss inhibitor and the balance water. The phenol crosslinking agent comprises one or two of resorcinol and hydroquinone. The oxygen scavenger comprises one or more of thiourea, sodium sulfite and sodium bisulfate. The delayed crosslinking agent comprises one or two of ammonium chloride and sodium trimetaphosphate. The water loss inhibitor comprises one or two of sodium malonate and sodium salicylate. The gelatinization time of the jelly provided by the invention is adjustable and is 6 days or more. After gelatinization, the jelly strength at least reach to level H based on visual inspection. The water-plugging agent has excellent thermal stability, does not lose water after hot treatment at a temperature of 60-90 DEG C for 270 days and can satisfy the requirements on most of deep oil reservoir displacement.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
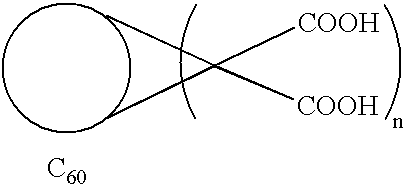






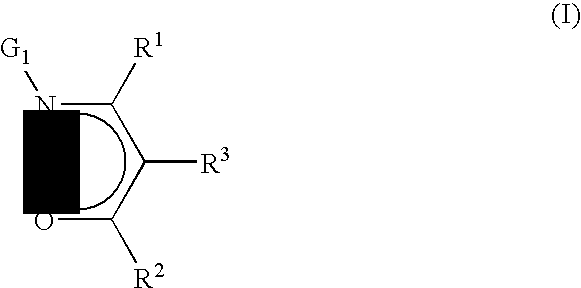
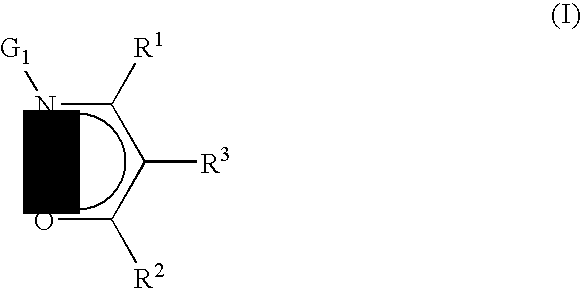
![Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1a2f6665-a551-442d-a298-41ccefc1f89a/US20050143327A1-20050630-D00001.png)
![Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1a2f6665-a551-442d-a298-41ccefc1f89a/US20050143327A1-20050630-D00002.png)
![Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1a2f6665-a551-442d-a298-41ccefc1f89a/US20050143327A1-20050630-D00003.png)