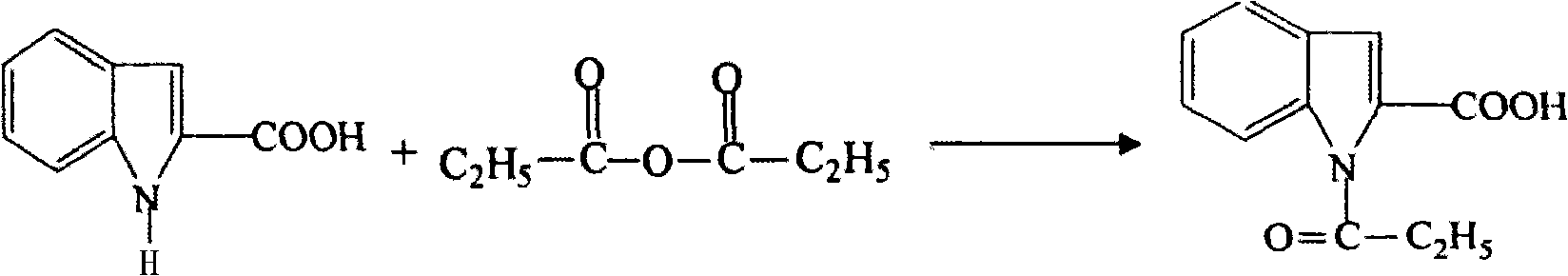Patents
Literature
241 results about "Diethyl oxalate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diethyl oxalate is a white solid compound synthesized from ethanol and carbon monoxide compounds, having molecular formulae C 6 H 10 O 4. Diethyl Oxalate is used as an intermediate/ raw material for the various manufacturing process.
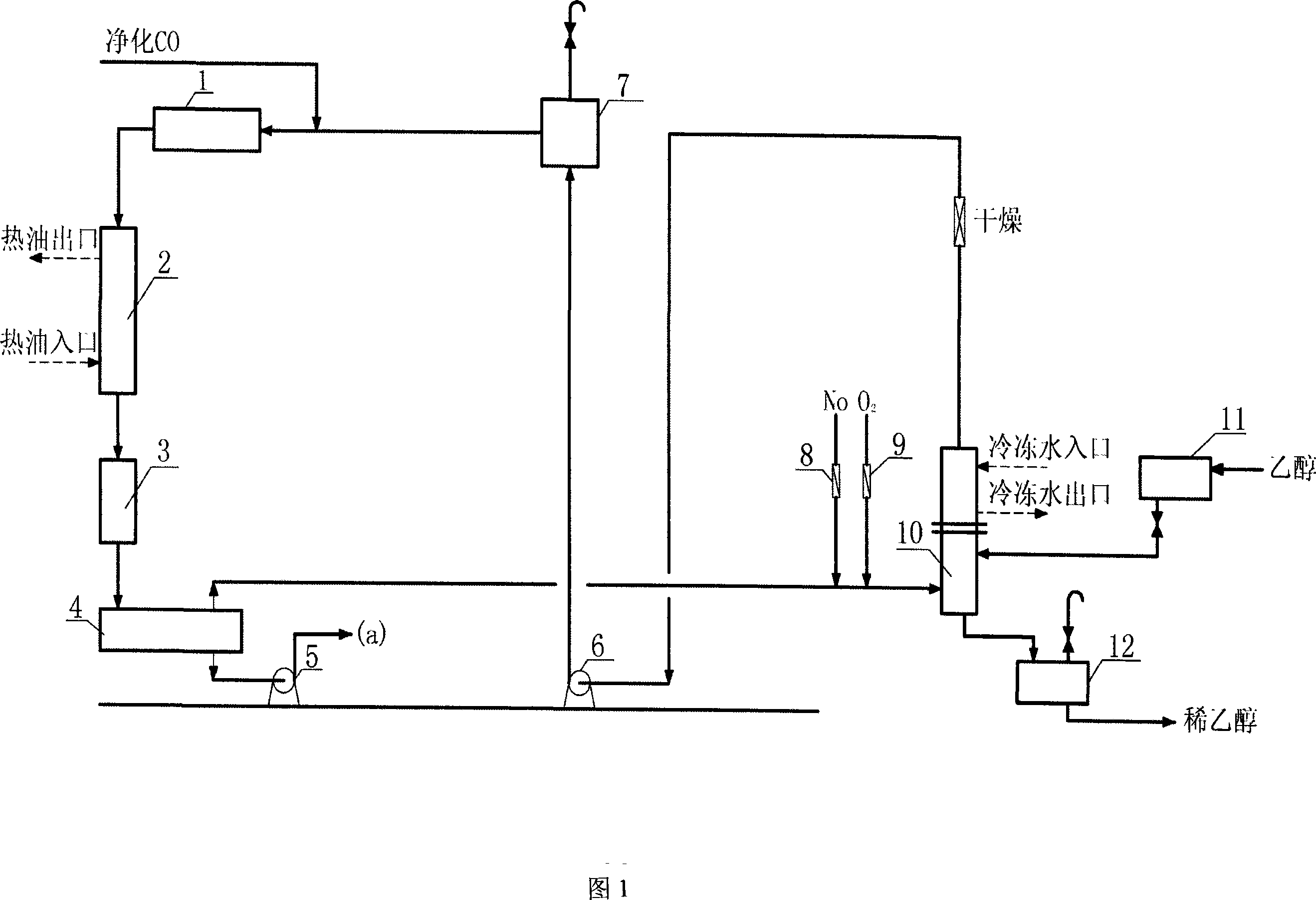
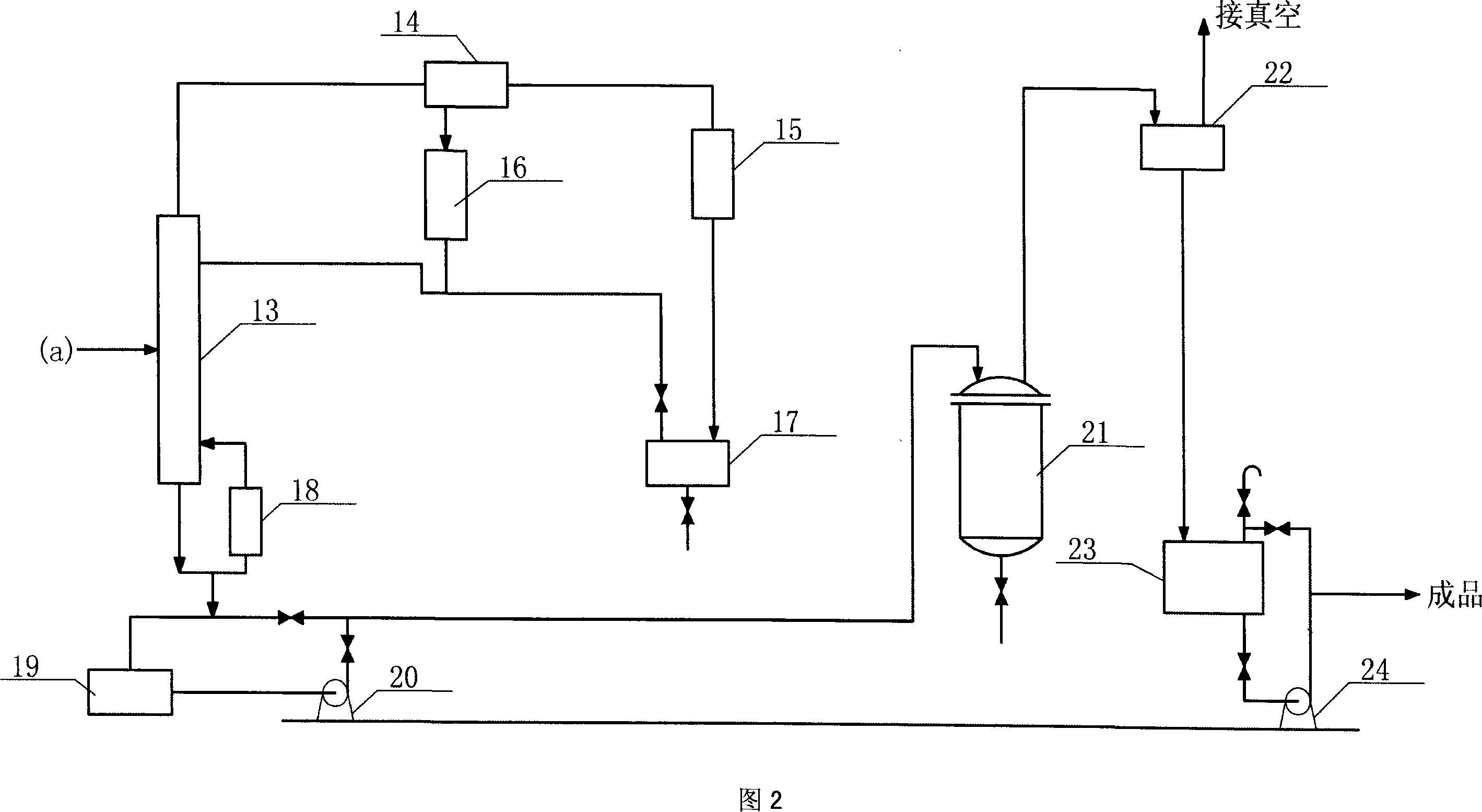
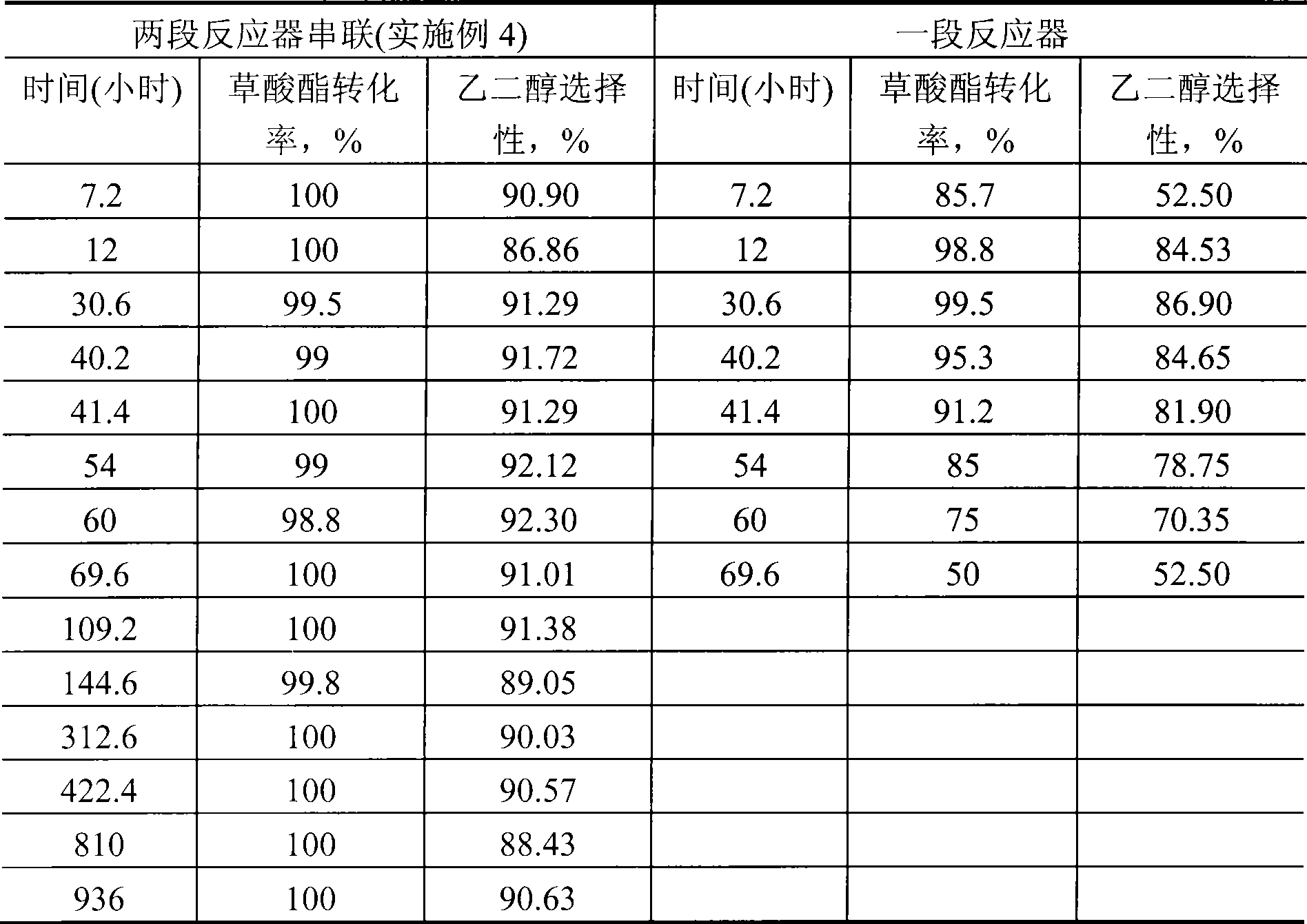
Method for preparing diethyl oxalate by coupling CO
ActiveCN101143821ANo pollution in the processImprove efficiencyPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCyclic processContinuous use
The invention discloses a method for preparing diethyl oxalate by CO coupling reaction. By applying a gas phase method, CO is coordinated with ethyl nitrite and is catalyzed by bimetallic supported catalyzer to couplingly generate crude diethyl oxalate, the reaction is a self-sealing circulation process, the CO gas mixed with the ethyl nitrite coming from a regeneration reactor is preheated and then enters into a coupling reactor, after the reaction, the gas is separated by condensation, so that the colorless and transparent condensed diethyl oxalate liquid is produced, and the uncondensed gas containing NO enters into the regeneration reactor to react with ethanol and oxygen in order to generate ethyl nitrite which is again circulated back to the coupling reactor for continuous use. The invention is carried out on the basis of previous laboratory research and under the background of industrial production and fulfils the continuous run examination of the bench scale test and pilot magnification under the condition of industrial operation, the temperature of the coupling reaction is low, and the concentration of products is increased. The method has the advantages of more energy saving, no pollution and high benefit. The total conversion rate of the CO generated by reaction is one hundred percent, and the selectivity of diethyl oxalate is over ninety six percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Catalyzer for CO low-voltage gas-phase synthesizing of oxalic ester and method of preparing the same
InactiveCN101138722AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTitanium metalGas phase
The present invention belongs to the oxalate preparation technical field and aims to provide a catalyst for synthesis of low pressure, high activity and high selectivity oxalate in a CO low-pressure gas phase, and a preparation method for the catalyst. The catalyst mainly uses the palladium metal as a main activated component, titanium and cerium as a promoter, and modified Alfa-Al2O3 as a carrier. The select content of palladium metal is 0.1 to 3.0 percent of the carrier weight, the content of the titanium metal is 0.02 to 1.5 percent of the carrier weight, and the content of the cerium metal is 0.01 to 0.75 percent of the carrier weight. The catalyst is manufactured with the method of immersion. The catalyst is manufactured with the method of immersion. Proven by experiments, the catalyst of the present invention is provided with the very high reaction activity and oxalate selectivity in the reaction to synthesize dimethyl oxalate or diethyl oxalate with carbon monoxide and nitrite. Moreover, the catalyst can resist affection by oxygen, hydrogen, water steam and other impurities. The catalyst is provided with the long usable life and the stable reaction performance, and can be easily controlled.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing ethylene glycol from oxalic ester
ActiveCN101475441AImprove technical effectOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationOxalateHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for producing glycol from oxalate, which mainly solves the problem that the prior art is low in the selectivity of target products and short in the regeneration period of catalysts. The method adopts oxalate as raw material, and comprises the following steps that: (a) hydrogen and a first stream of raw material enter a first reaction zone to be in contact with a copper-bearing catalyst I so as to form a first stream of glycol-containing reaction effluent; and (b) the first stream of reaction effluent and a second stream of raw material enter at least one second reaction zone to be in contact with a copper-bearing catalyst II so as to form a second stream of glycol-containing reaction effluent, wherein the molar ratio of the first stream of raw material to the second stream of raw material is 0.1-10:1; the molar ratio of the hydrogen to the sum of the first and second streams of raw material is 20-300:1; the first stream of raw material is selected from dimethyl oxalate, diethyl oxalate or a mixture thereof; and the second stream of raw material is selected from dimethyl oxalate, diethyl oxalate or a mixture thereof. The technical proposal well solves the problem, and the method can be used in the industrial production for increasing the yield of glycol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst for gas-phase synthesis of oxalate and its preparing process
InactiveCN1381310AHigh reactivityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitriteGas phase
A catalyst for gas-phase synthesis of dimethyl (or diethyl) oxalate from CO and nitrite is prepared from alpha-Al2O3 as carrier and Ce and Pd as active components through the dipping method. Its advantages are high reaction activity and selectivity, long service life and easy control of reaction.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Catalyst for preparing divalent alcohol by hydrogenating dibasic acid ester and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101590407ALow reaction temperatureHigh activityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationRare-earth elementDiethyl oxalate
The invention relates to a catalyst for preparing divalent alcohol by hydrogenating dibasic acid ester and a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of catalytic hydrogenation. The catalyst takes metal copper as a main active component, one or a few of rare earth elements or transitional metal elements as a cocatalyst, and SiO2 as a carrier, wherein the content of the metal copper is 5 to 50 percent of the weight of the catalyst, the content of the cocatalyst is 0.1 to 10 percent of the weight of the catalyst, and the balance of the carrier. The catalyst can be used for the reaction for preparing the divalent alcohol by hydrogenating the dibasic acid ester, such as the preparation of ethylene glycol by using diethyl oxalate; and the catalyst has better activity, selectivity and stability, high time space yield of products, simple flow and easiness for continuous operation.
Owner:HAO HUA CHENGDU TECH
Catalyst for synthesis of diethyl oxalate employing carbon monoxide gas-phase catalytic coupling and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101612580AHigh space-time yieldHigh reactivityPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGas phaseDiethyl oxalate
The invention discloses a catalyst for the synthesis of diethyl oxalate employing carbon monoxide gas-phase catalytic coupling and the catalyst adopts metal palladium as active component, alpha-Al2O3 as carrier and transition metal copper as promoter; wherein, the content of metal palladium is 0.1-5.0% of the carrier and the content of transition metal copper is 0.05-3.0%. The catalyst shows higher reactivity and higher time space yield of dimethyl oxalate in the reaction that carbon monoxide and ethyl nitrite are used to synthesize dimethyl oxalate. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the catalyst.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
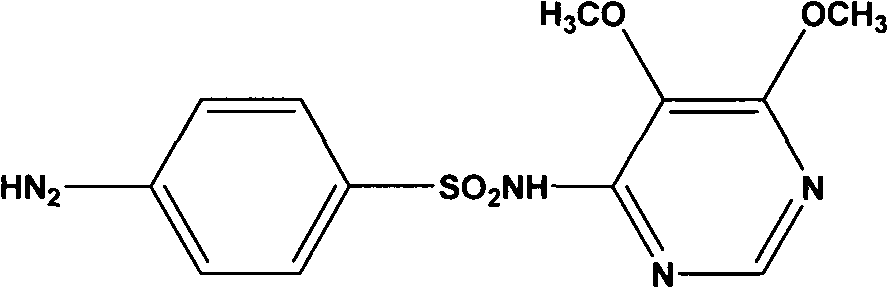
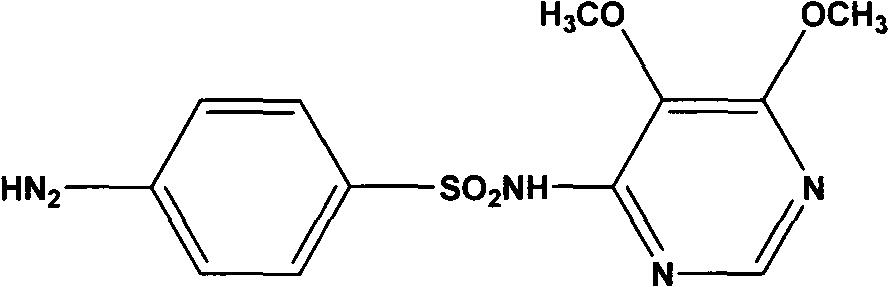
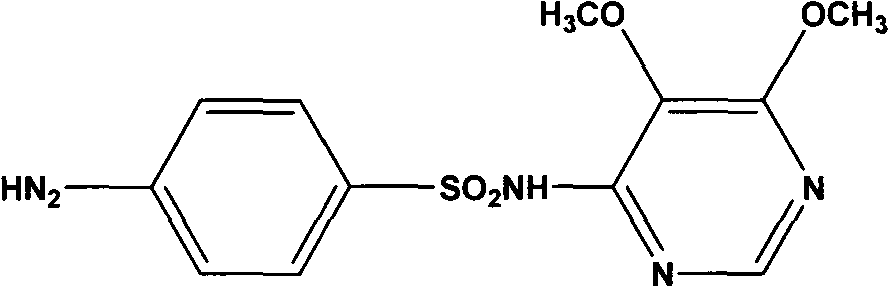
Preparation method of sulfadoxine and intermediate thereof
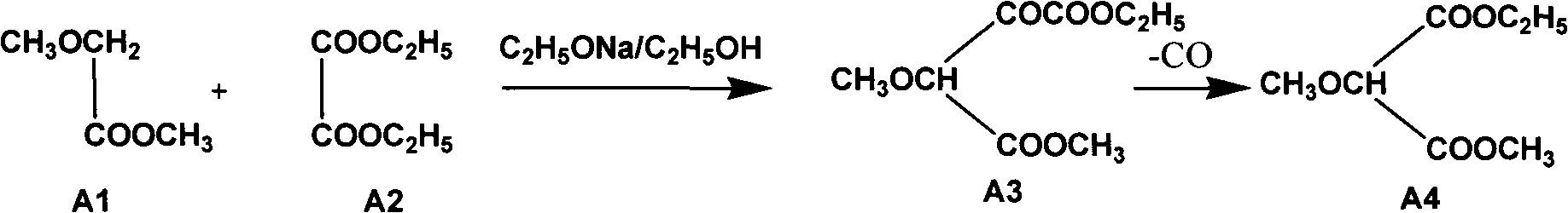
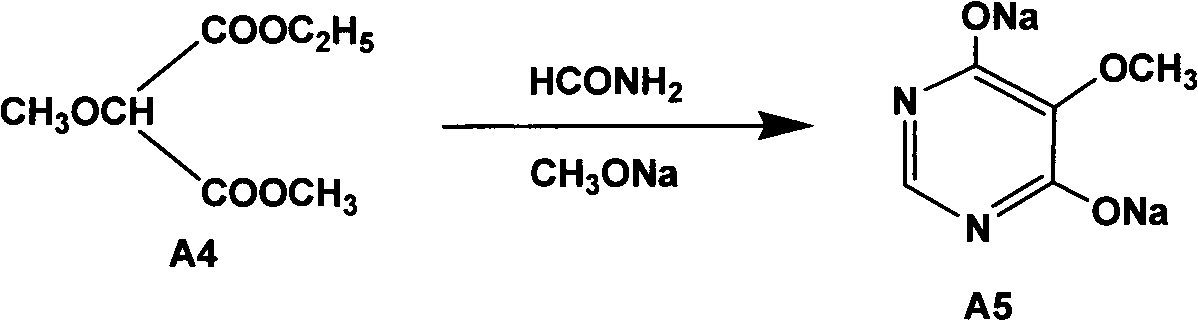
InactiveCN102304094AReduce manufacturing costHigh purityOrganic chemistryMethyl methoxyacetateMalonate
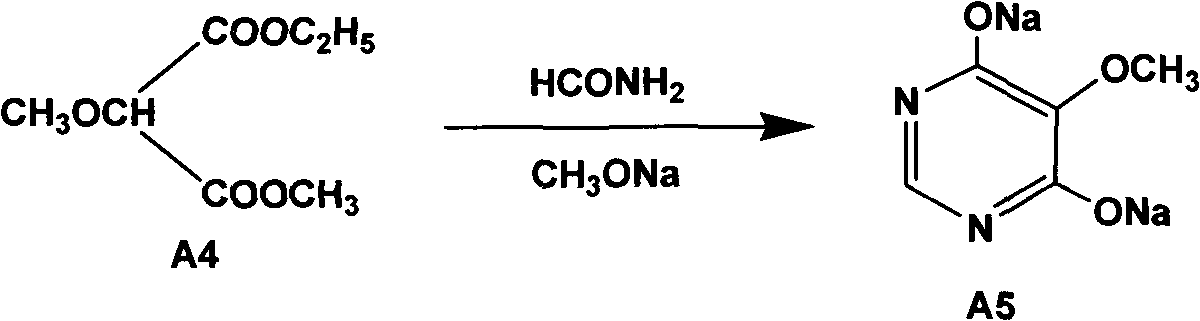
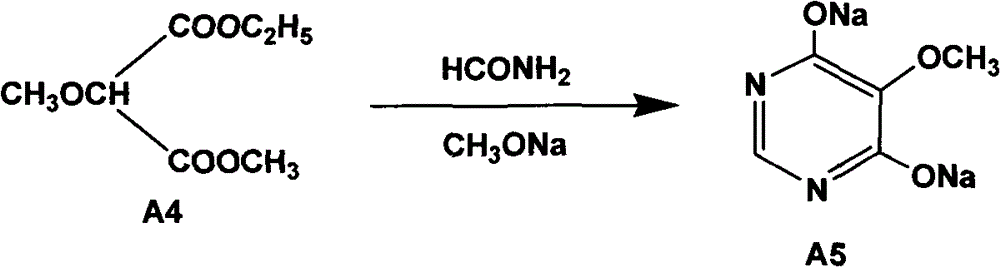
The invention relates to a preparation method of sulfadoxine and an intermediate thereof. The preparation method of sulfadoxine comprises the following steps: (1) reacting methyl methoxyacetate and excessive diethyl oxalate to generate 3-methoxy-2-oxo-methylethyl succinate, and decarbonylating to obtain 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate; (2) reacting the 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate and formamide to generate a cyclocompound; (3) reacting the cyclocompound and phosphorus oxychloride to generate chloride; (4) carrying out condensation reaction; and (5) carrying out methoxylation reaction. The obtained cyclocompound in the step (2) is controlled to exist in the form of anhydrous hydroxy sodium salt, so that N,N-dimethylaniline is not needed as a catalyst in the step (3), thereby lowering the cost, enhancing the quality of chloride and finally enhancing the quality of sulfadoxine.
Owner:CHANGSHU NANHU INDAL CHEM
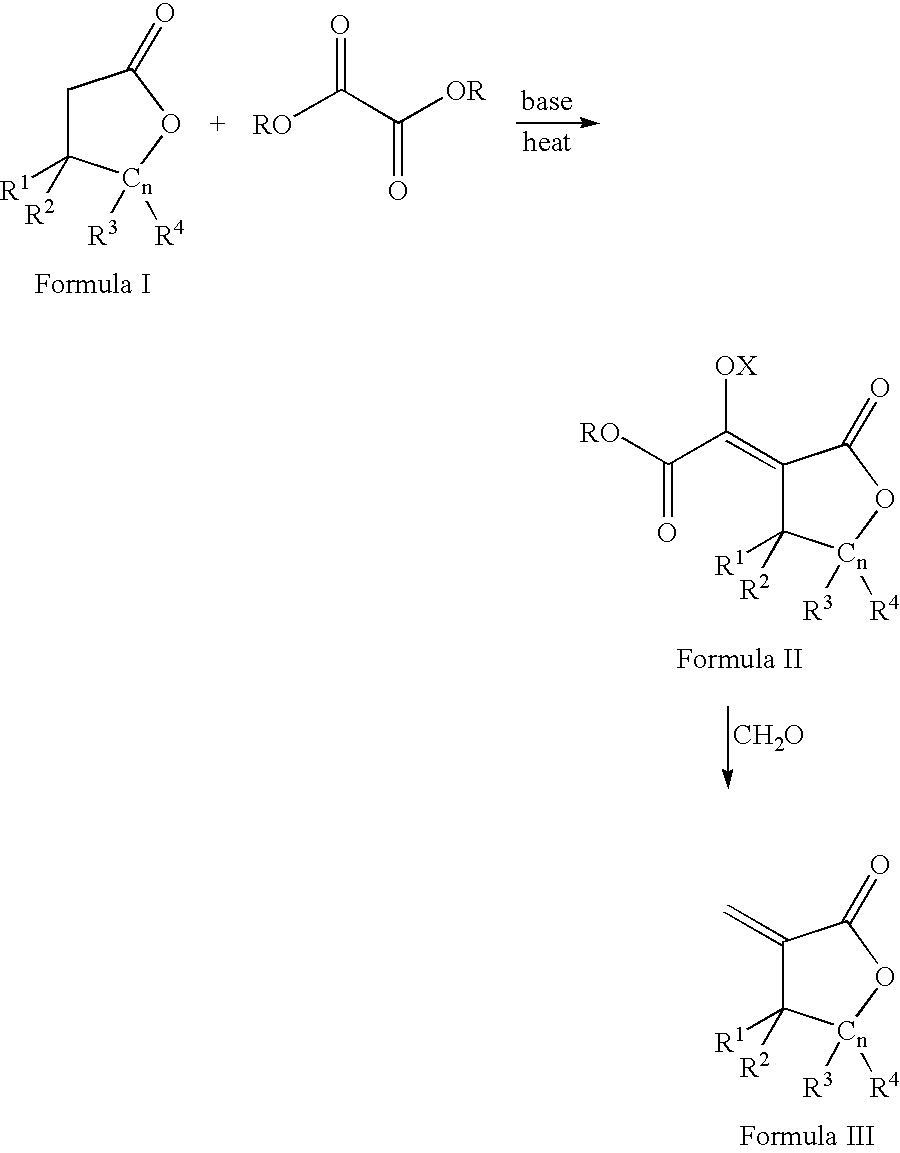
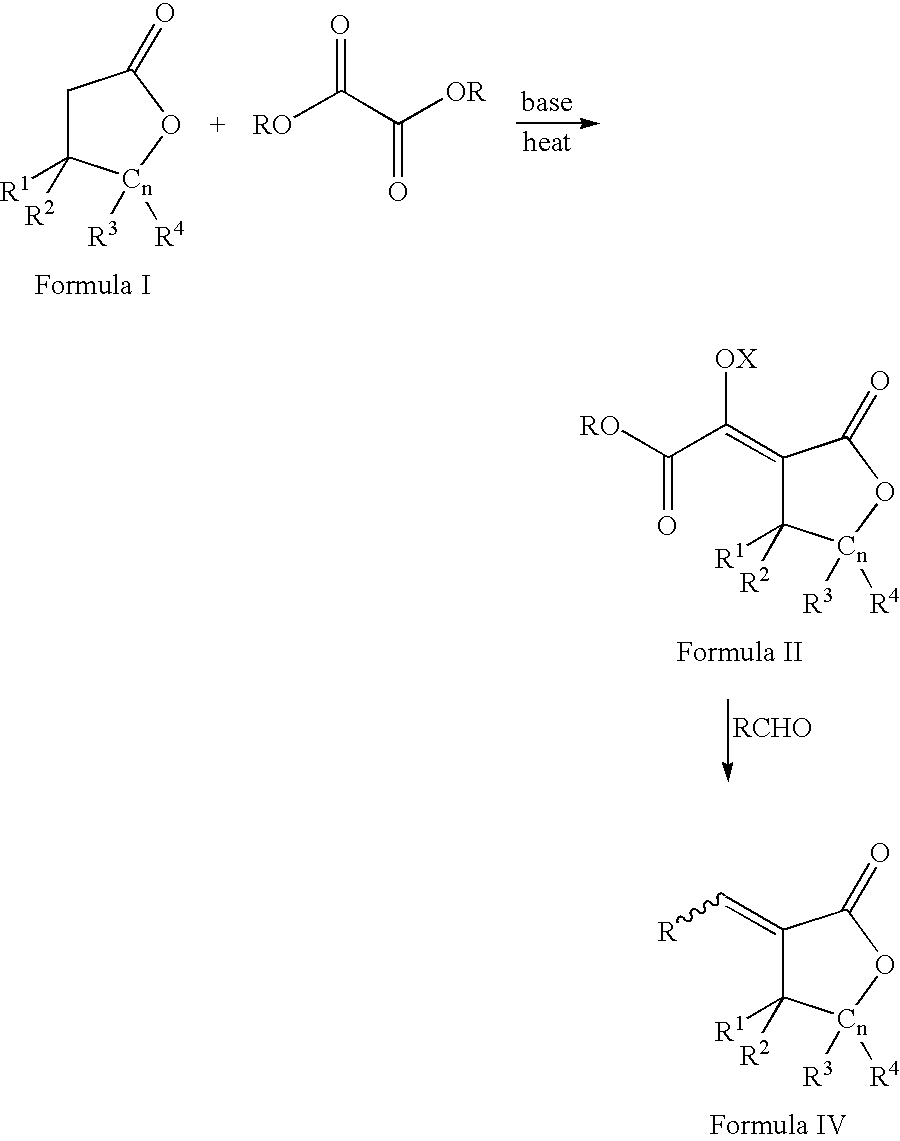
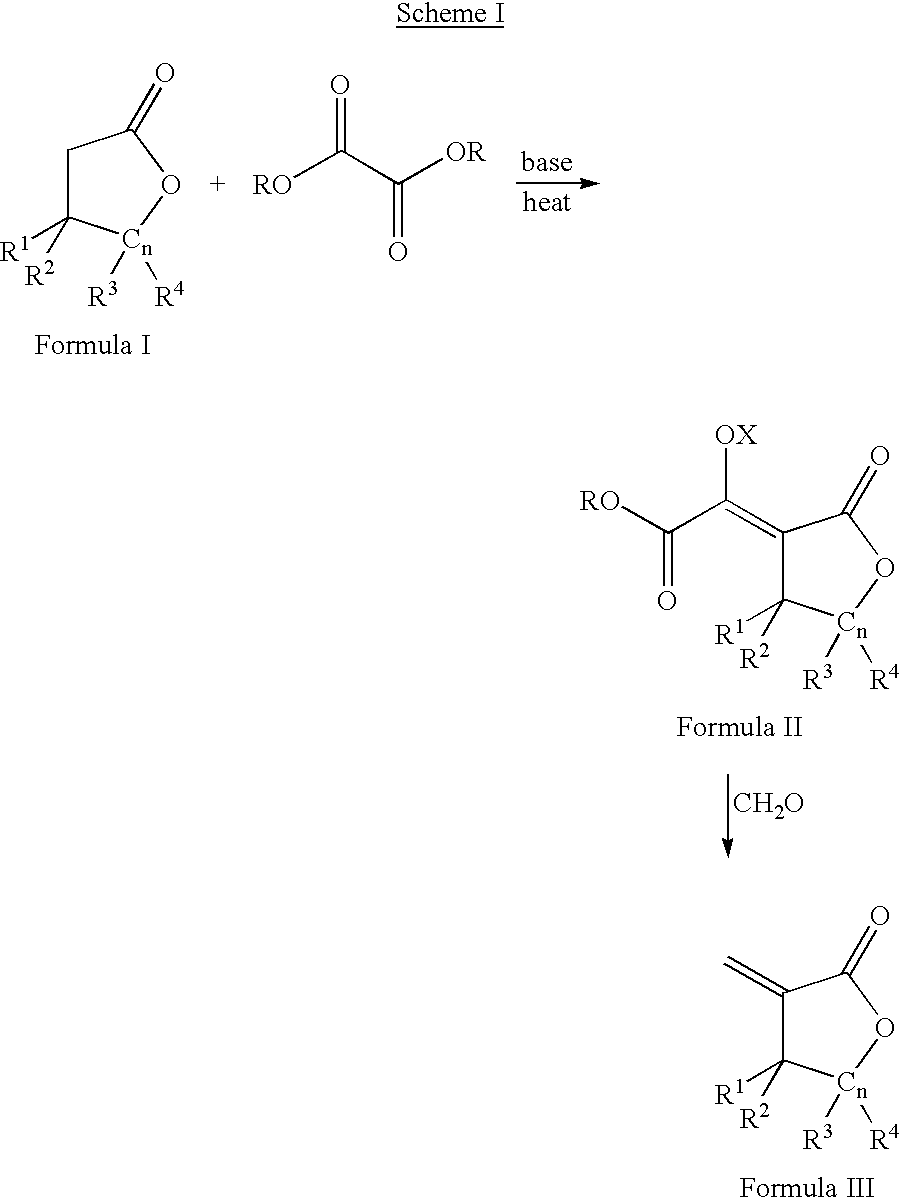
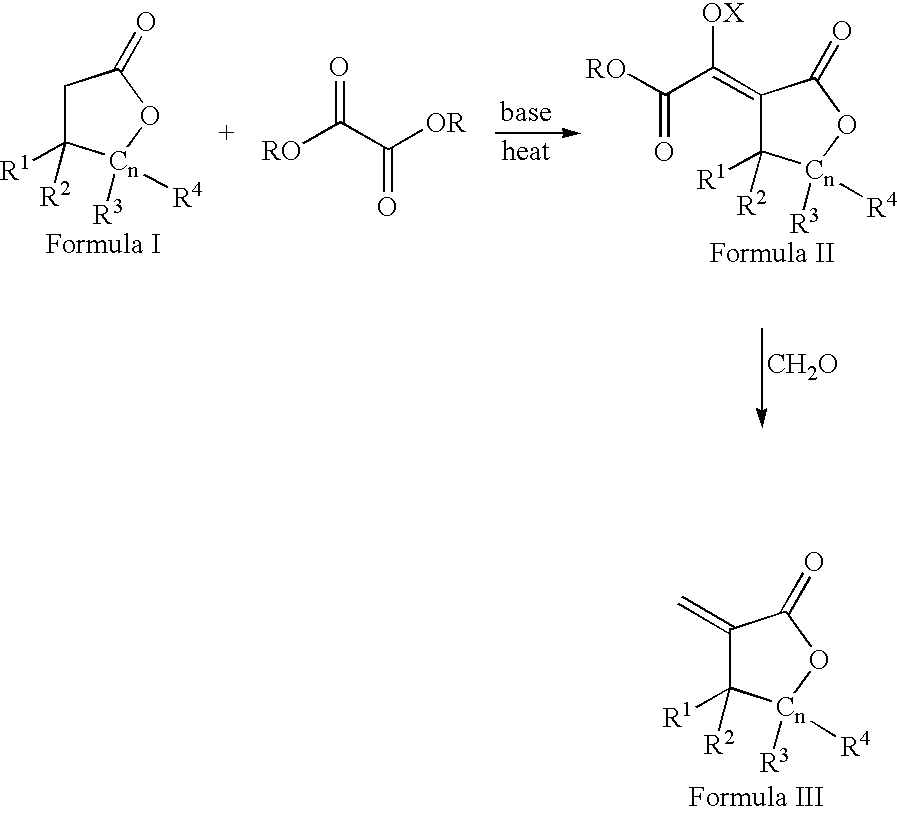
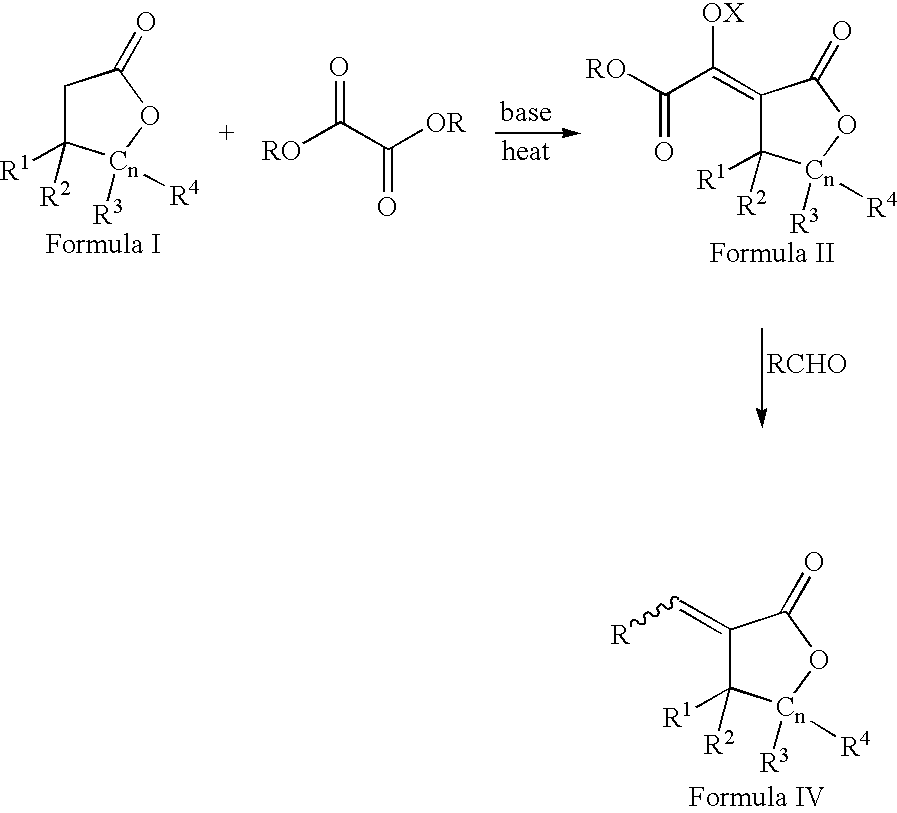
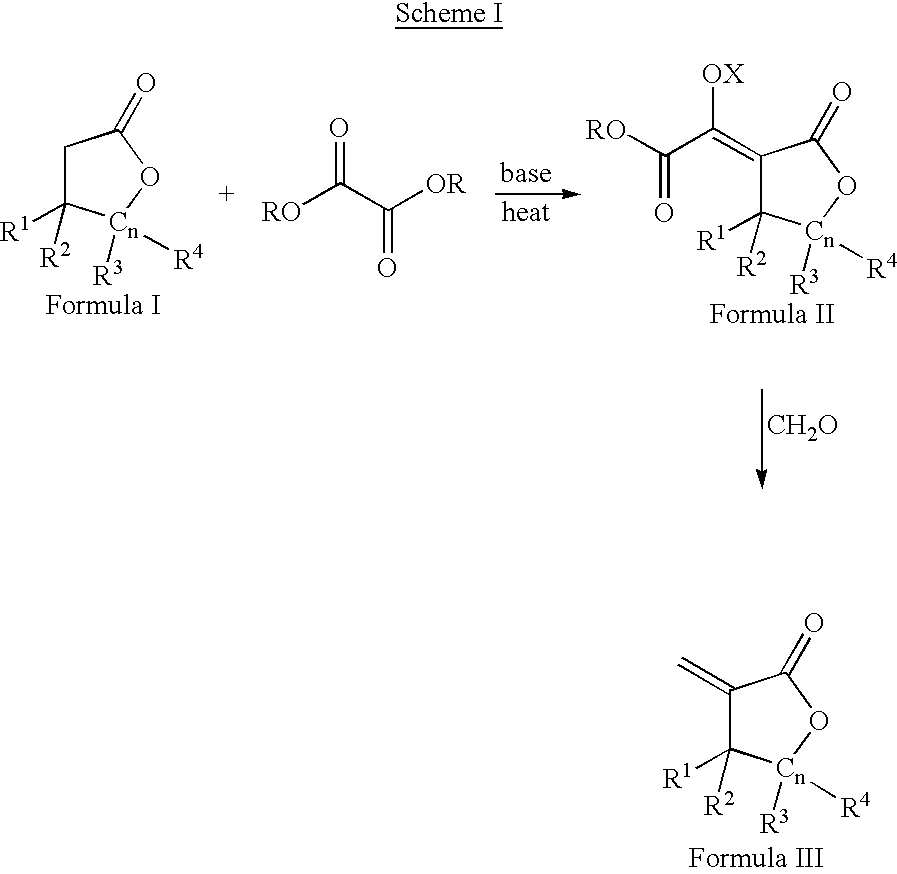
Process for the preparation of a-methylenelactones and a-substituted hydrocarbylidene lactones
This invention pertains to a process for making alpha-methylenelactones and alpha-substituted hydrocarbylidene lactones. More specifically, the present invention obtains high yields of alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone by heating gamma-butyrolactone and diethyl oxalate in the presence of a base. The second step comprises treatment of the alpha-oxalyl enolate salt with formaldehyde to afford the alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
D-calcium pantothenate synthesis method
InactiveCN1765877AReduce usageSolve environmental problemsCarboxylic acid amides optical isomer preparationSynthesis methodsDiethyl oxalate
The invention discloses a synthesis method for D-calcium pantothenate, which comprises: synthesizing keto lactone pantothenate with diethyl oxalate, isobutanal and formaldehyde, reducing said product, using carbamidine carbonate to resolution out D-pantothenic carbonate and L- pantothenic carbonate; preparing the product with D-pantoic lactone, beta-alanine both from D-pantothenic carbonate and calcium metal. This invention avoids the application of hypertoxic sodium cyanide, stabilizes product quality, and increases material utilization ratio.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Preparation method of sulfadoxine
InactiveCN102304095AReduce usageQuality improvementOrganic chemistrySodium methoxideDimethylaniline N-oxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of sulfadoxine, which comprises the following steps: (1) reacting methyl methoxyacetate and excessive diethyl oxalate to generate 3-methoxy-2-oxo-methylethyl succinate, and decarbonylating to obtain 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate; (2) reacting the 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate and formamide to generate a cyclocompound; (3) carrying out chlorination reaction; (4) carrying out condensation reaction; and (5) carrying out methoxylation reaction. The purity of the 2-methoxy-methylethyl malonate obtained in the step (1) is strictly controlled, and the cyclocompound in the step (2) is controlled to exist in the form of anhydrous hydroxy sodium salt; in the step (3), no catalyst, including N,N-dimethylaniline, is used; and in the step (5), solid sodium hydroxide is substituted for sodium methoxide solution. The invention is easy to operate, has the advantage of high product quality, greatly lowers the production cost, and has obvious economic benefit and environmental benefit.
Owner:CHANGSHU NANHU INDAL CHEM
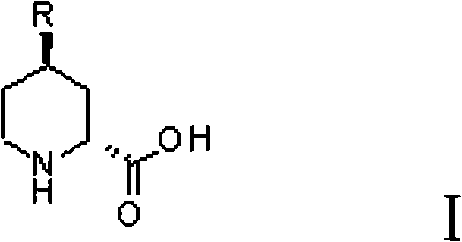
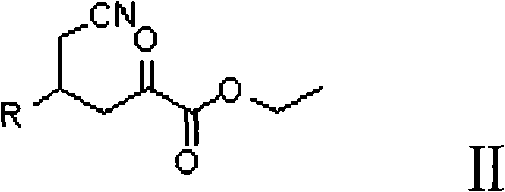
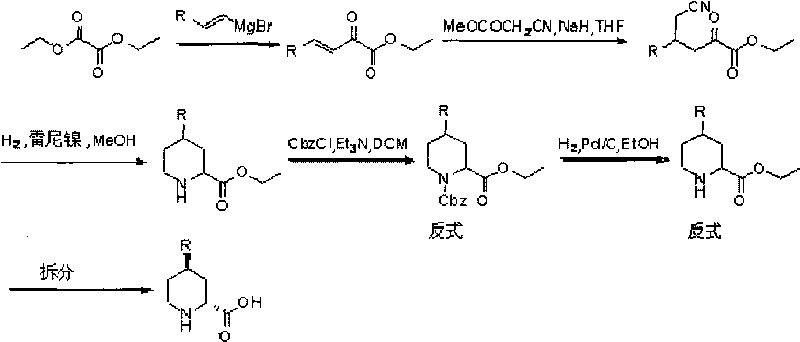
Preparation method for (2R, 4R)-4-substituted-2-piperidine carboxylic acid compound and intermediate thereof
InactiveCN101712645ARaw materials are easy to getSimple processAsymmetric synthesesSynthesis methodsOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to a synthesis method for preparing a (2R,4R)-4-methyl-2 -piperidine carboxylic acid compound taking diethyl oxalate as starting materials and an intermediate thereof, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The synthesis method comprises the following steps of: taking the diethyl oxalate and 1-bromo-substituted-propylene as the starting materials, performing a Grignard reaction and an addition reaction on the diethyl oxalate and 1-bromo-3-substituted-propylene to obtain intermediate 2-carbonyl-4-substituted-5 cyan ethyl valerate; and then performing a cyclization reaction, a benzyl ester protection reaction and a deprotection reaction on the intermediate 2-carbonyl-4-substituted-5 cyan ethyl valerate to obtain trans-4-substituted-2-piperidine ethyl formate; and finally, splitting the trans-4-substituted-2-piperidine carboxylic acid ethyl ester to obtain a chiral target product (2R,4R)-4-methyl-2-piperidine formic acid compound. The preparation method has the advantages of readily available raw materials, simple process, and mild reaction condition.
Owner:CHONGQING WORLD HAORUI PHARM CHEM
Preparation method of triazine ring
InactiveCN103224473AReduce manufacturing costSimple operation processOrganic chemistryThioureaNitrogen
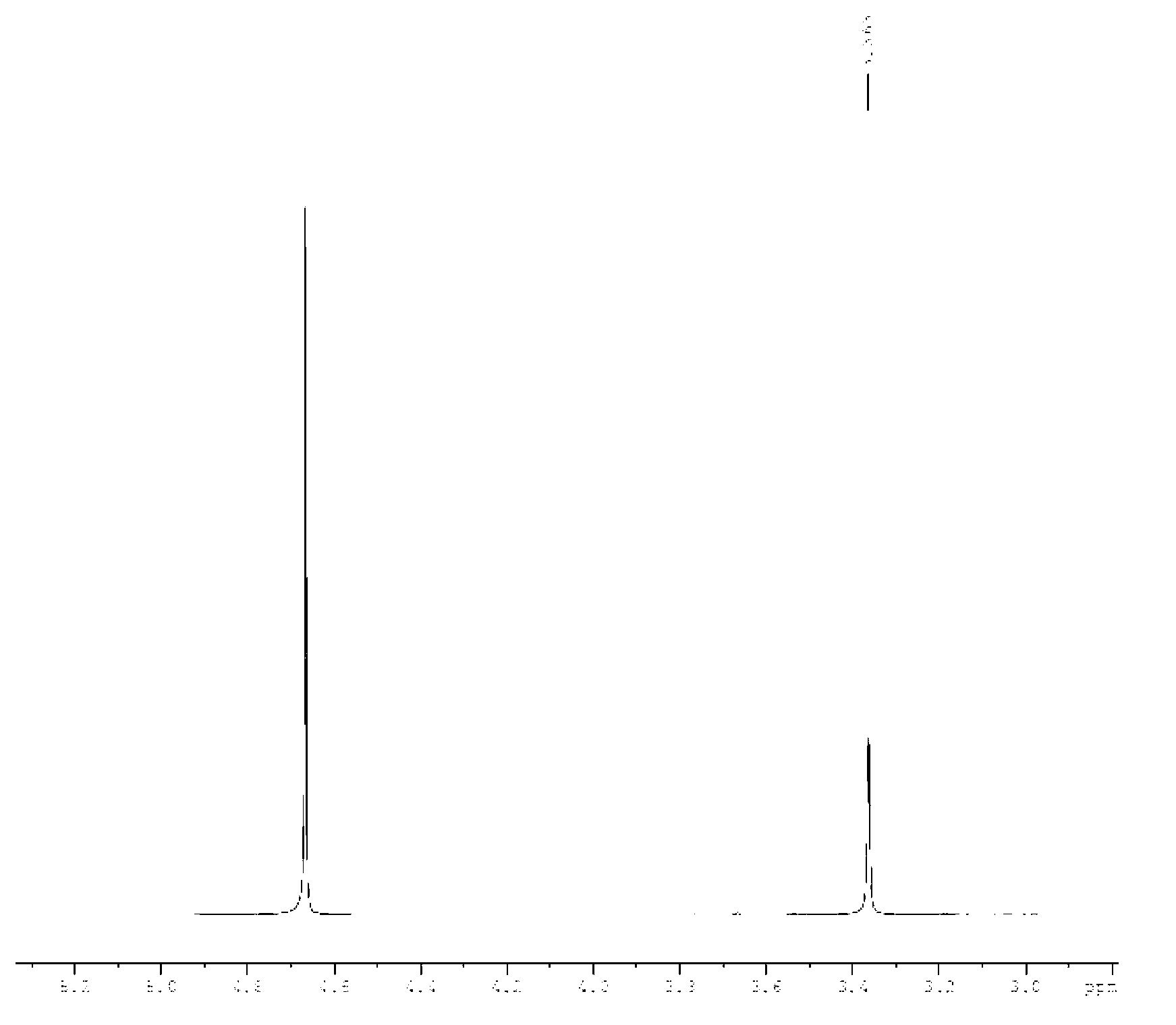
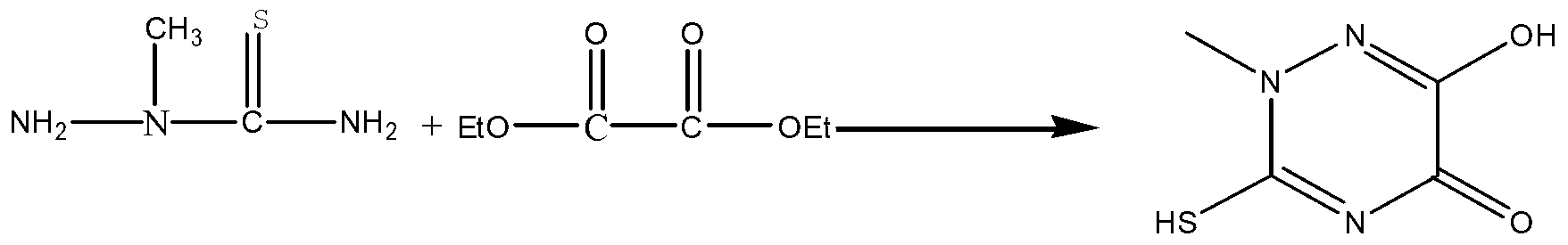
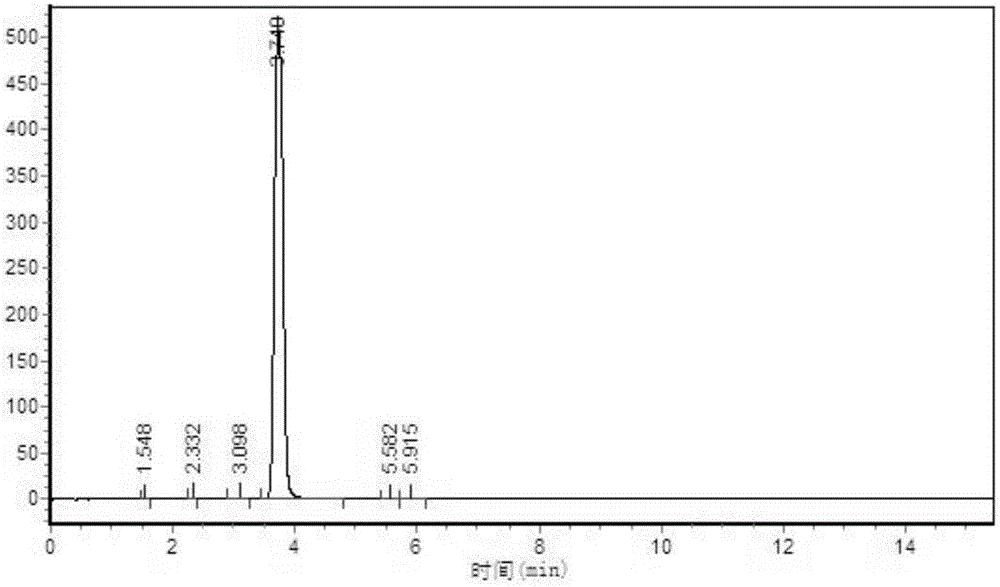
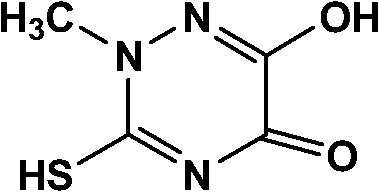
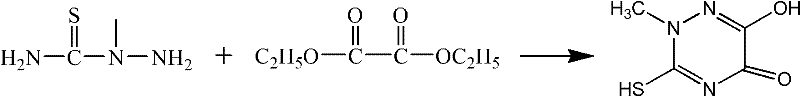
The invention relates to a preparation method of a triazine ring. The invention solves the problems that conventional preparation method of the triazine ring has the defects of many byproducts, high cost, low yield, inconvenient aftertreatment and unsuitability for large-scale production. The triazine ring is prepared from 2-methyl thiosemicarbazide and diethyl oxalate serving as starting raw materials through direct cyclization of a Lewis acid catalyst without any solvent system under the protection of nitrogen. The preparation method has the advantages of cheap and readily available raw materials, high yield, low cost and environment friendliness, and is suitable for industrial amplification. The preparation method is applied in the technical field of preparation of organic intermediates.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Method for synthesizing TTZ (thiotriazinone) by using self-made organic base catalyst taking graphene as carrier
InactiveCN106749063AReduce viscosityIncrease profitOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic baseFiltration
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing TTZ (thiotriazinone) by using a self-made organic base catalyst taking graphene as a carrier. The method comprises steps as follows: 2-methyl thiosemicarbazide, diethyl oxalate, the self-made base catalyst taking graphene as the carrier and methanol are subjected to a cyclization reaction at 0-60 DEG C to produce sodium TTZ, the graphene carrier is separated through decolorization and filtration, acidification with hydrochloric acid is performed, and TTZ is obtained. The self-made base catalyst taking graphene as the carrier is used, so that the reaction is conducted in a homogeneous reaction system, the reaction yield is increased, the cyclization yield of TTZ is increased to 85% (in terms of 2-methylthiourea) or above, meanwhile, the viscosity of the reaction system is reduced, and the reaction is easy to control; the content of byproduct 1-methyl-5-thiol-1,2,4-triazole-3-methyl carboxylate is controlled at 100 ppm or below, and the product quality is improved; due to increase of the yield, the utilization rate of raw materials is increased, environmental protection investment is reduced, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG HUIHAI PHARMA & CHEM
Process for producing 3,4-enedioxy thiophene
The invention provides a method for preparing 3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT for short). Firstly, thiodiglycolic acid and methanol generate dimethyl 2, 2'-thiobisacetate through an esterification reaction under the catalysis of an acid, and then the dimethyl 2, 2'-thiobisacetate is condensed with diethy-aceto oxalate under the catalysis of sodium methoxide to obtain 2, 5-dimethyl carboxylate-3, 4-dihydroxy-thiophene; then the 2, 5-dimethyl carboxylate-3, 4-dihydroxy-thiophene and a cyclic esterification reagent are cyclic-esterified to generate 2, 5-dimethyl carboxylate-3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene under the cocatalysis of copper powder or cuprous oxide and potassium carbonate, and 2, 5-dicarboxylic acid-3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene is obtained through alkaline saponification and acid regulation; and finally a copper catalyst remained in the cyclic esterification reaction is used for catalytic decarboxylation in specific pyridine solvents, and the high-purity EDOT is obtained through reduced pressure distillation. The method has higher yield in the preparation of the EDOT, has low impurity content, and meets the requirement of electronic chemicals.
Owner:APELOA PHARM CO LTD +1
Process for synthesizing 7-chloro-2-oxo-heptanoic acid
InactiveCN1587248ASimple processMild reaction conditionsPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesDiethyl oxalateHydrolysis
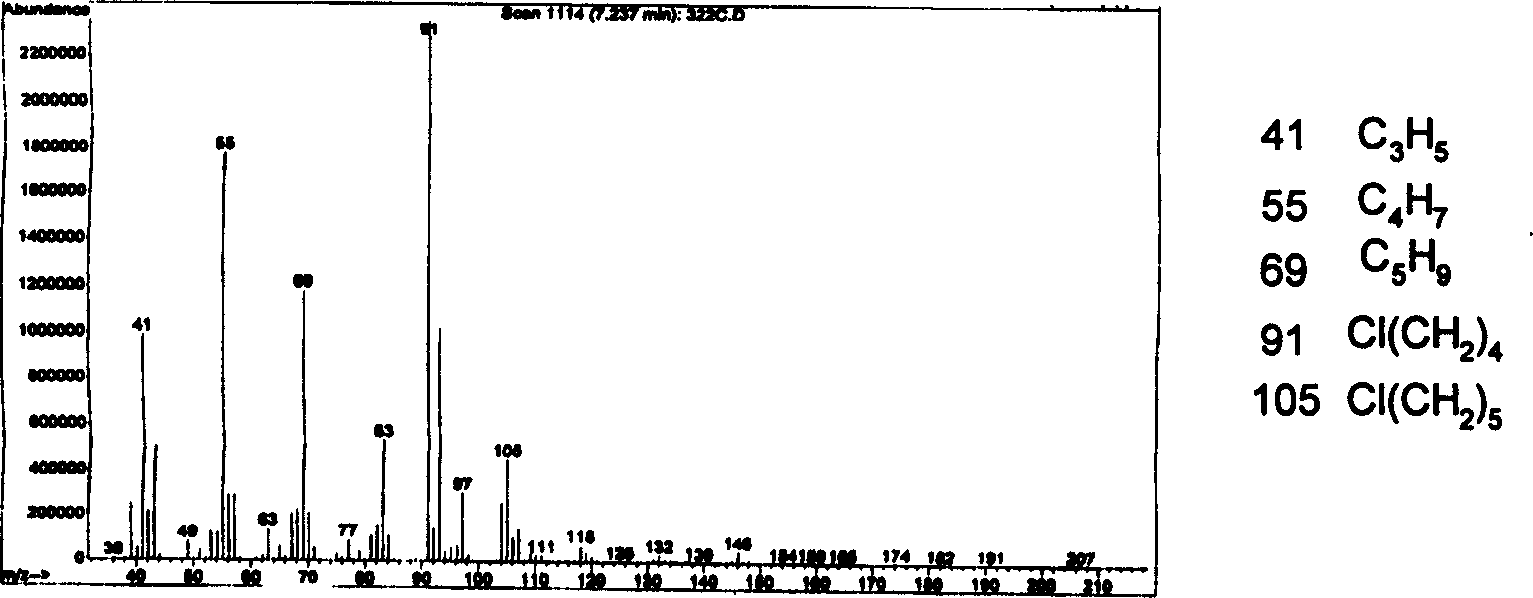
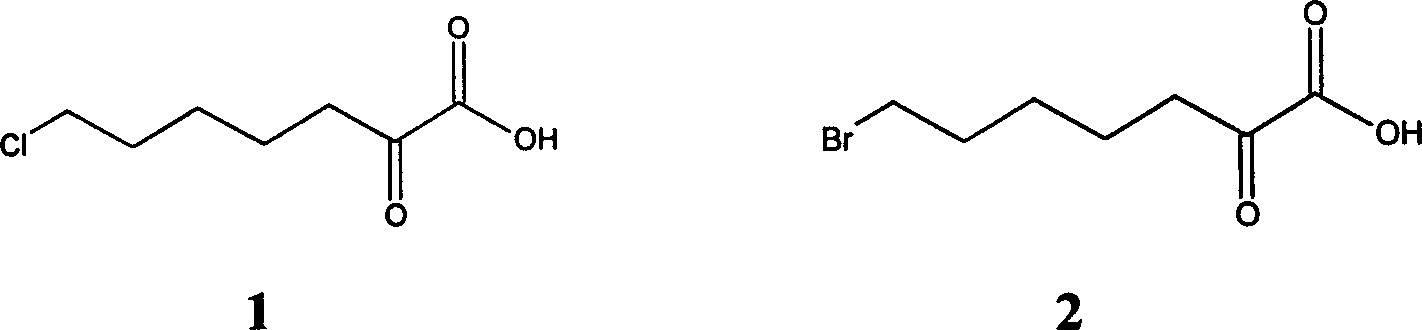
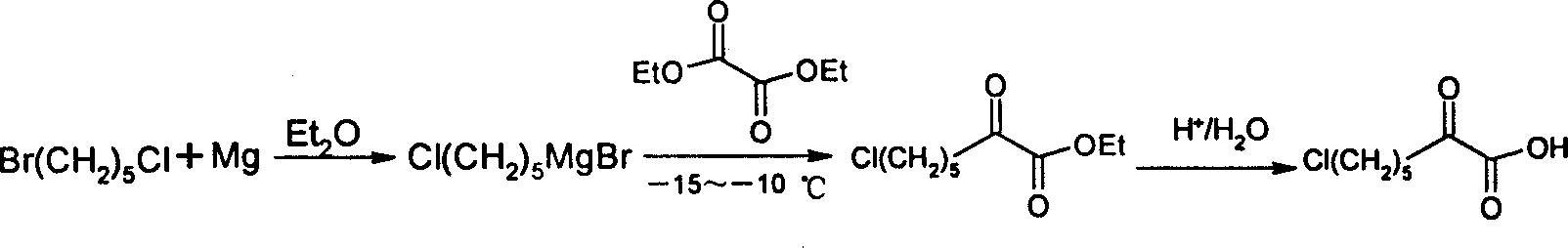
The process of synthesizing 7-chloro-2-oxo-heptanoic acid includes preparing 1-bromo-5-chloro-pentane into Dangler reagent, addition reaction of the Dangler reagent with diethyl oxalate, and hydrolysis to obtain 7-chloro-2-oxo-heptanoic acid. The present invention has simple technological process, mild reaction condition, low cost and total yield up to 43.0 %.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for synthesizing thiotriazinone
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a pharmaceutical intermediate, in particular to a method for synthesizing thiotriazinone. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting 2-methylaminothiourea and diethyl oxalate which are taken as raw materials and ethanol which is taken as a solvent to obtain crude thiotriazinone, and recrystallizing the crude thiotriazinone to obtain a final product, wherein a recrystallization solvent is water. The method is characterized in that: a catalyst is added in the reaction of the 2-methylaminothiourea and the diethyl oxalate, and is a mixture of ammonium chloride and a hydrochloric acid solution at the concentration of 10 weight percent. The method has the advantages that: the reaction yield is improved and the reaction time is shortened by selecting the appropriate catalyst; the cost of raw materials is reduced; operation steps are reduced; and the method is more suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:YIYUAN XINQUAN CHEM
Method for preparing N-ethoxy oxalyl-alanine ethyl ester
InactiveCN1470503ASimple processSave materialOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationBenzeneAlcohol
The preparation method of N-ethoxyoxalyl-alanine ethyl ester which is intermediate body for producing vitamin B6 is characterized by that it uses benzene as dewatering agent, and in the system of alpha-alanine, oxalic acid, ethyl alcohol, diethyl oxalate and benzene and under the condition of heating reaction it can continuously remove water content from said system, and can adopt one-step process to implement esterification and acylation of alpha-alanine to obtain the invented N-ethoxyoxalyl-alanine ethyl ester.
Owner:CHANGSHU CHEM JIANGSU
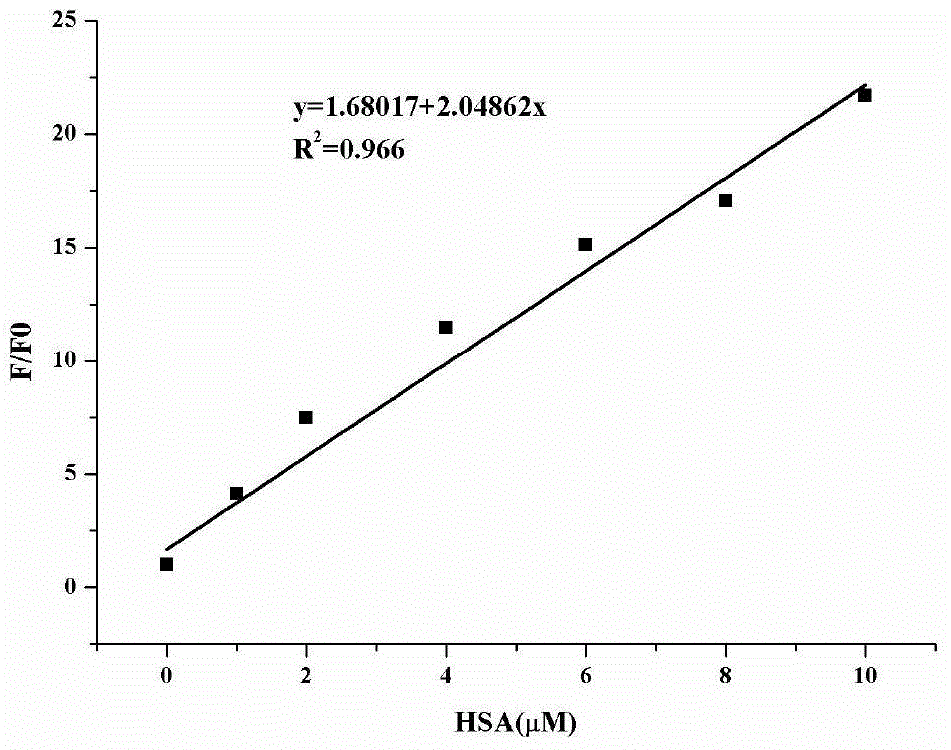
Fluorescence probe for detecting human serum albumin and preparation method therefor
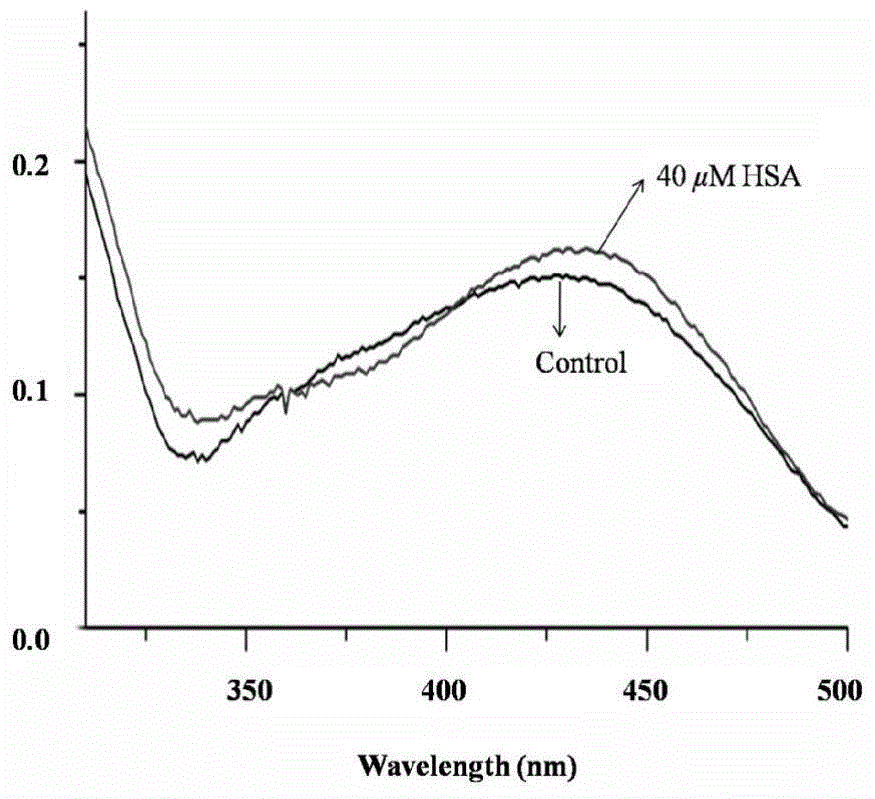
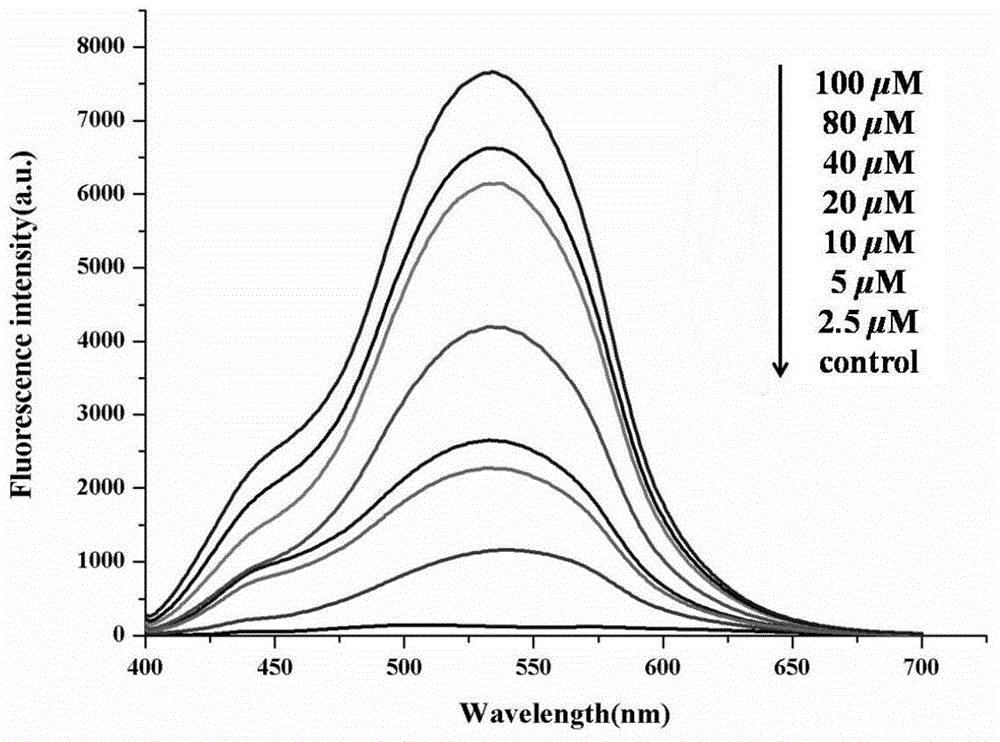
ActiveCN105018072AGood effectQuantitative concentrationOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuinolineDiethyl oxalate
The invention relates to a fluorescence probe, in particular to a fluorescence probe for detecting human serum albumin and a preparation method therefor. The molecular structural formula of the fluorescence probe is as shown in the specification. Quinoline fluorogen is used as a reporter group, a fluorescence ratio probe combined with diethyl oxalate has better effect in HSA detection; and the preparation method is simple in technology and easy to realize.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Catalyst for synthesizing diethyl oxalate with carbon monoxide, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101653731AGood effectHigh reactivityCatalyst activation/preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionOxalateActive component
The invention discloses a catalyst for synthesizing diethyl oxalate and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the oxalate preparation technical field. The catalyst includes the main active components of Pd, a carrier of alpha-Al2O3 and the auxiliary agent of the transition metal Ni. The catalyst is prepared by an immersion method. Test proves that Pd-Ni / alpha-Al2O3 catalyst has good reactionactivity and high selectivity. The diethyl oxalate space-time yield reaches more than 1000l[-1]h[-1] at the highest level.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Method for synthesizing phenyloxalate from dicthyl oxalate and phenol
ActiveCN1687003AEliminates separation processSave equipmentPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOxalateReaction temperature
The present invention discloses a method for catalytically synthesizing phenyloxalate by utilizing diethyl acetate and phenol as raw material. The mole ratio of diethyl acetaet and phenol is 1:20-20:1, its reaction time is 1-8 hr, reaction temperature is 160-240 deg.C and autogeneous reaction pressure is 0-1.0 MPa. Under the action of load metal oxide catalyst the above-mentioned raw material are undergone the process of ester-interchange reaction so as to obtain the invented phenyloxalate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for continuously preparing N-ethyloxyl oxalyl alanine ethyl ester
ActiveCN104725262ASuitable for industrial productionMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationBenzeneEthyl ester
The invention discloses a method for continuously preparing N-ethyloxyl oxalyl alanine ethyl ester. The method for continuously preparing the N-ethyloxyl oxalyl alanine ethyl ester concretely comprises the following steps: (1) providing reaction feed liquid, wherein the reaction feed liquid contains alanine, oxalate, ethanol and diethyl oxalate; (2) adding the reaction feed liquid into a reaction device as a reaction system, and carrying out reaction in the presence of a water carrying agent, so that product water and the water carrying agent form a water-water carrying agent dispersion system, wherein the water carrying agent is ethanol; and (3) distilling off the water-water carrying agent dispersion system and removing excessive diethyl oxalate, thus obtaining the N-ethyloxyl oxalyl alanine ethyl ester product. The method for continuously preparing the N-ethyloxyl oxalyl alanine ethyl ester has the advantages that continuous and automatic production can be realized, and hypertoxic benzene is not used, so that the method for continuously preparing the N-ethyloxyl oxalyl alanine ethyl ester is more environmental-friendly; meanwhile, reaction time is short and energy consumption is low.
Owner:DAFENG HEGNO PHARMA +1
Process for the preparation of a-methylenelactones and a-substituted hydrocarbylidene lactones
This invention pertains to a process for making alpha-methylenelactones and alpha-substitute hydrocarbylidene lactones. More specifically, the present invention obtains high yields of alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone by heating gamma-butyrolactone and diethyl oxalate in the presence of a base. The second step comprises treatment of the alpha-oxalyl enolate salt with formaldehyde to afford the alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Preparation method of sulfadoxine
InactiveCN102304095BHigh melting pointReduce usageOrganic chemistrySodium methoxideDimethylaniline N-oxide
Owner:CHANGSHU NANHU INDAL CHEM
Preparation method of TTZ (thiotriazinone)
The invention discloses a preparation method of TTZ (thiotriazinone), which comprises the following steps: 1) adding 5-10 kg of acetic acid and 50-150 kg of ammonium acetate into 1,800-2,200 kg of ethyl alcohol to prepare a buffer system with the pH value of 6-7; 2) adding 480-500 kg of 2-methyl-3-thiosemicarbazide, boron tribromide and diethyl oxalate, heating to 80-82 DEG C, and performing circulation reflux reaction for 4-6 hours, wherein the molar ratio of 2-methyl-3-thiosemicarbazide to diethyl oxalate is 1:(1.15-1.25), and the dosage of boron tribromide is 4-6% of the weight of 2-methyl-3-thiosemicarbazide; 3) cooling for crystallization, and separating to obtain a TTZ crude product and a mother liquor; 4) adding 1,800-2,200 kg of water in the TTZ crude product, heating to 70-80 DEG C, then adding 1,250-1,400 kg of hydrochloric acid with the concentration of 30%, cooling for crystallization, separating and drying to obtain the TTZ finished product. The preparation method has the advantages that the common problems of high cost, low yield, large yield variability, instability of product quality, difficulty in solvent recovery, large amount of waste water and the like in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SHANDONG HUIHAI PHARMA & CHEM
Amino molding plastic capable of solidifying quickly and being stored for long time
The invention relates to an amino molding plastic capable of solidifying quickly and being stored for a long time. The weight parts of amino sulfonated inorganic nano latent curing agent include 18-35 parts of sulfamic acid compound, 15-25 parts of triethanolamine, 0-7 parts of inorganic nano particles, and 40-50 parts of water. The weight parts of the amino molding plastic include 1500-3500 parts of urea, 4000-6000 parts of formaldehyde, 200-400 parts of tripolycyanamide, 10-120 parts of low shrink, 50-140 parts of 6- methyne-4-ammonia, 0-50 parts of amino sulfonated inorganic nano latent curing agent, 0-80 parts of diethyl oxalate, 50-150 parts of lubricant, 0-500 parts of dispersing agent, 100-500 parts of filler, 1000-2500 parts of cellulose, and 5-50 parts of pigment, wherein the curing time lasts 15-20 s / mm at the temperature of 135-140 DEG C, and the amino molding plastic can be stored at the temperature of 25 DEG C for more than 180 days.
Owner:JIANGSU SANJO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
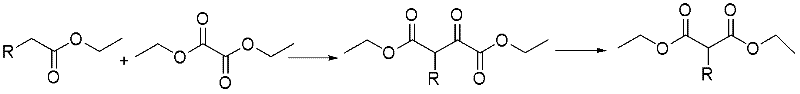
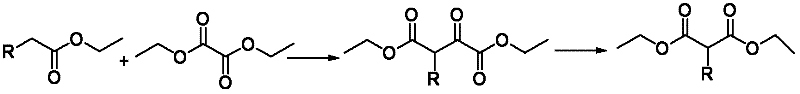
Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate
ActiveCN106008596AOvercoming the problem of instability and easy decompositionHigh feasibilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolubilityDecomposition
The invention discloses a preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as a glufosinate intermediate. The method comprises the following steps: 1) proper organic solvent, alkaline substance and phase-transfer catalyst are added to cyclic phosphoric anhydride at the temperature of subzero 30 DEG C, stirred, heated to 25-50 DEG C, subjected to a reaction with diethyl oxalate at the room temperature and stirred, and a product is obtained through direct precipitation and filtration from the solvent; 2) water is added to the product, hydrogen chloride is introduced slowly, the pH is controlled, heating is performed, water is removed through rotary evaporation after the reaction is performed for 16 h, and a final product is obtained through vacuum drying. The method has the advantages that the problems of poor solubility and high probability of precipitation of cyclic phosphoric anhydride at a low temperature as well as high probability of ring opening of anhydride and high probability of decomposition of phosphate groups of cyclic phosphoric anhydride under an alkaline condition due to temperature increasing are solved, and the feasibility for preparing 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as the glufosinate intermediate from cyclic phosphoric anhydride is realized successfully.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
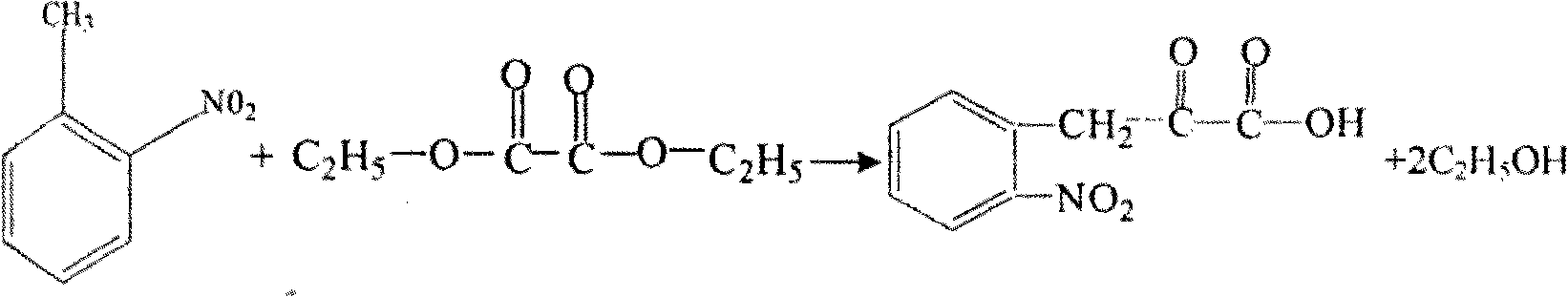
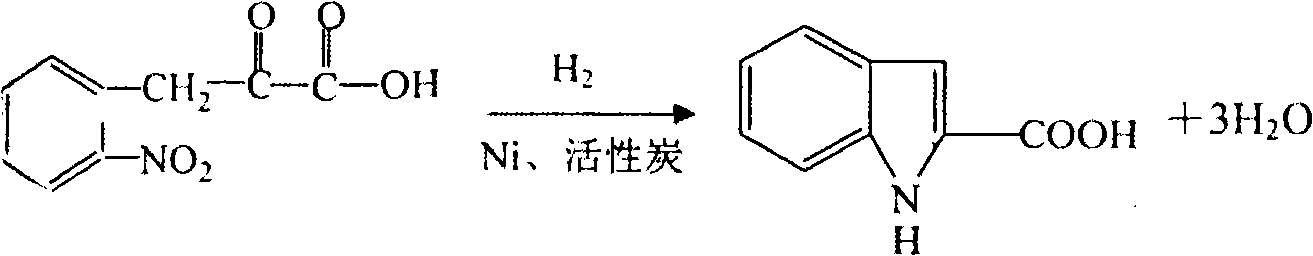
Preparation method of L-octohydroindoline-2-formic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of L-octohydroindoline-2-formic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing indole-2-formic acid through condensation and hydrogenation by using diethyl oxalate and ortho-nitrotoluene as raw materials; adding acetic anhydride and hydrochloric acid by using the indole-2-formic acid as a raw material to carry out acylation and hydrogenation working procedures to obtain a (R, S) indoline-2-formic acid mixture; splitting the (R, S) indoline-2-formic acid mixture to obtain R indoline-2-formic acid; treating the R indoline-2-formic acid, water and hydrochloric acid through racemizing, cooling, regulating the pH value, centrifuging and drying to obtain S indoline-2-formic acid; and reacting the S indoline-2-formic acid, methanol and a catalyst to obtain the L-octohydroindoline-2-formic acid. The invention has the advantages of low cost, clean and environmentally-friendly hydrogenation route, less generated waste water and high yield of the final finished product L-octohydroindoline-2-formic acid.
Owner:安徽世华化工有限公司
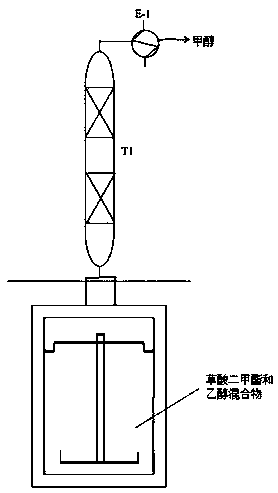
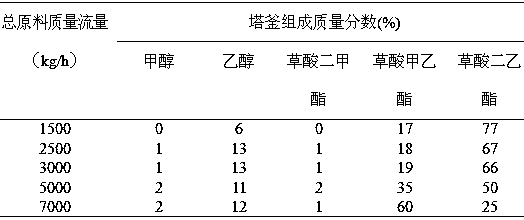
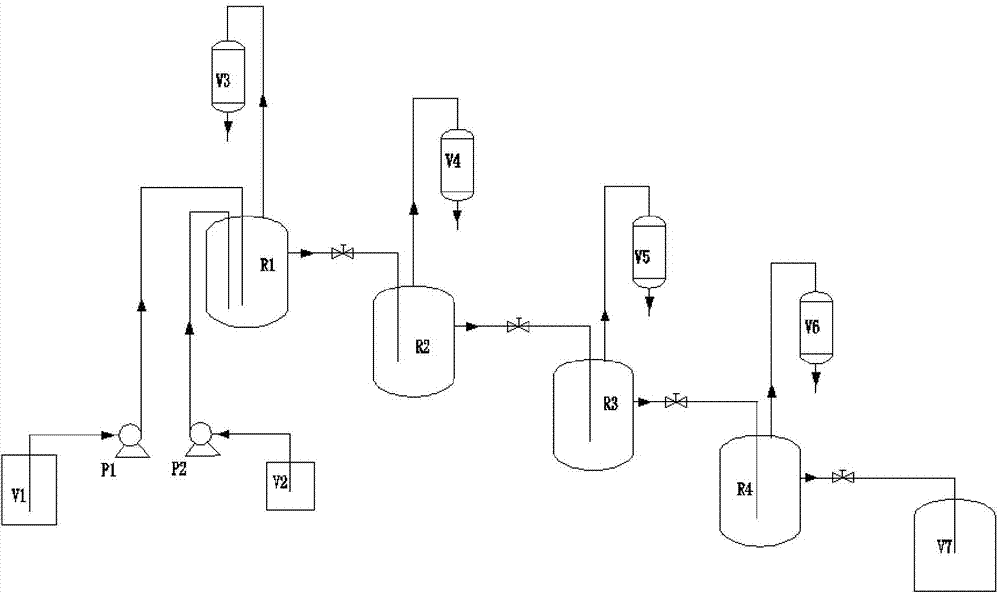
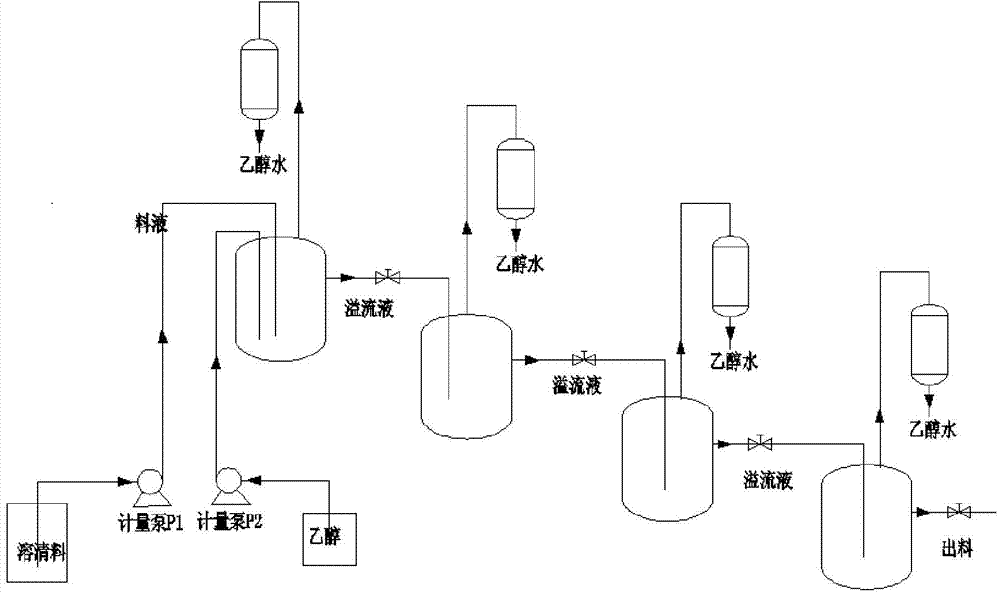
Process for synthesizing symmetric oxalate through ester exchange path
The invention relates to a process for synthesizing symmetric oxalate, in particular to a process for synthesizing symmetric oxalate through an ester exchange path. A process route for synthesizing oxalate through ester exchange of dimethyl oxalate and various alcohols (high-carbon alcohol like alcohol, propanol and butanol) is created. Rectifying simple separation technology is realized in a fixed bed catalytic rectifying tower and a reaction kettle by using a multifunctional composite alkaline material to directly catalyze dimethyl oxalate and various alcohols. Taking preparing of diethyl pure oxalate as an example, a product-diethyl oxalate and methanol or alcohol are not be azeotropic, methanol is separated out through simple distillation to continuously push reaction to go forwards, ahigh-purity diethyl oxalate alcohol solution is obtained in tower kettle liquid finally, and high-purity diethyl oxalate is crystallized out after alcohol is separated out through decompression rectifying.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
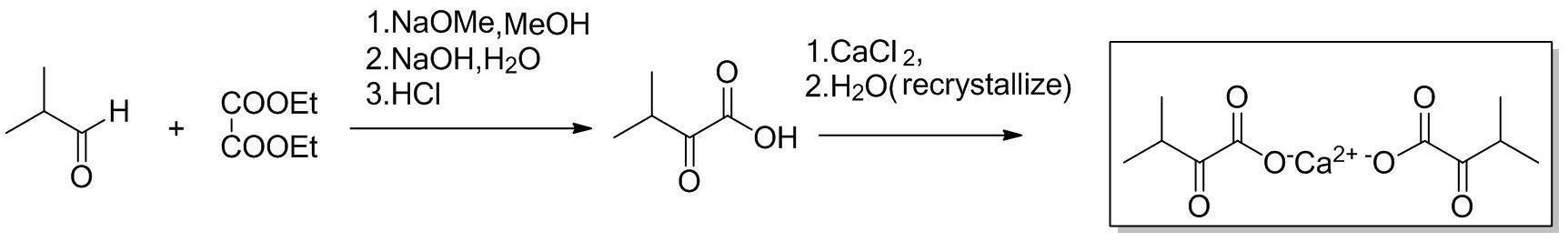
Preparation method of novel alpha-ketovaline calcium
ActiveCN102675087AAvoid pollutionMild conditionsCarboxylic acid salt preparationDiethyl oxalateSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of novel alpha-ketovaline calcium, which comprises the steps of: dropping diethyl oxalate into alcoholic solution of metal alkoxide, then dropping isobutyraldehyde, preserving heat and agitating, adding alkali solution, regulating pH after heat preservation, extracting, adding a certain amount of water into the extract, adding alkali liquor for regulating the pH, dropping calcium chloride water solution for salification to obtain crude alpha-ketovaline calcium and then refining the crude alpha-ketovaline calcium in mixed solvent of purified water and organic solvent to obtain refined alpha-ketovaline calcium. The preparation method has the advantages that the reaction conditions are moderate, the operation is simple to conduct, the steps are fewer, the yield is high, the quality is high, the price of the used raw materials is low, no pollution is caused, waste gas and a great quantity of waste residues are not produced and the method is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:SHAOXING MINSHENG PHARMA
Method for preparing alpha-replacing malonic acid diacetoxyiodo derivative
ActiveCN102531897AReduce usageMeet the needs of large-scale productionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidMalonic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing an alpha-a replacing malonic acid diacetoxyiodo derivative. Replacing ethyl acetate and oxalic acid diacetoxyiodo which are already commercialized raw materials on the market or easy to produce are selected as initial raw materials, and after the two steps of condensation and oxidation, target products are synthesized. The method for preparing alpha-the replacing malonic acid diacetoxyiodo derivative is easy in obtaining raw materials, high in conversion rate of raw materials, high in purity yield, stable in process condition, simple in operation and suitable for large-scale production, and provides a novel idea and method for preparing alpha-the replacing malonic acid diacetoxyiodo derivative.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN +4
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
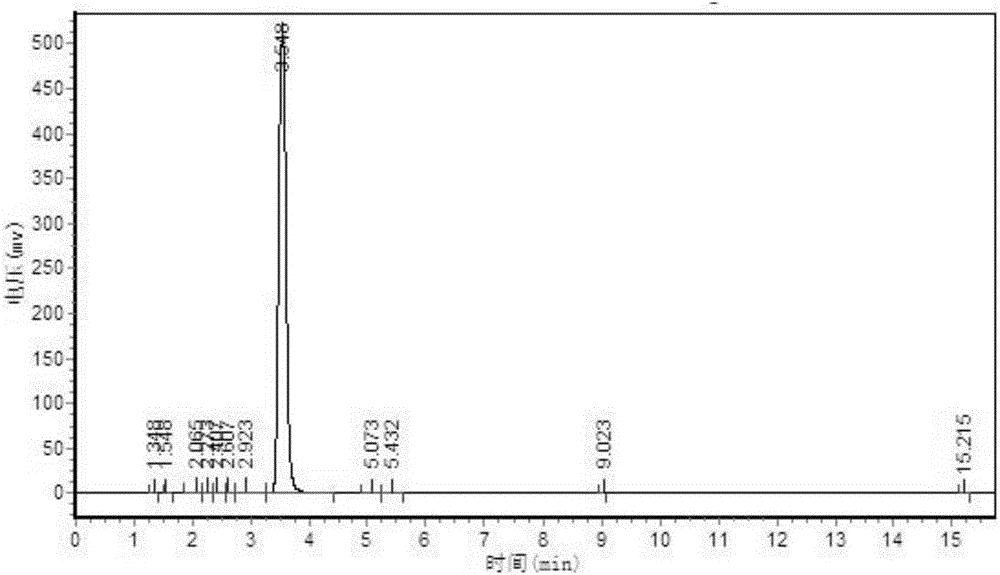
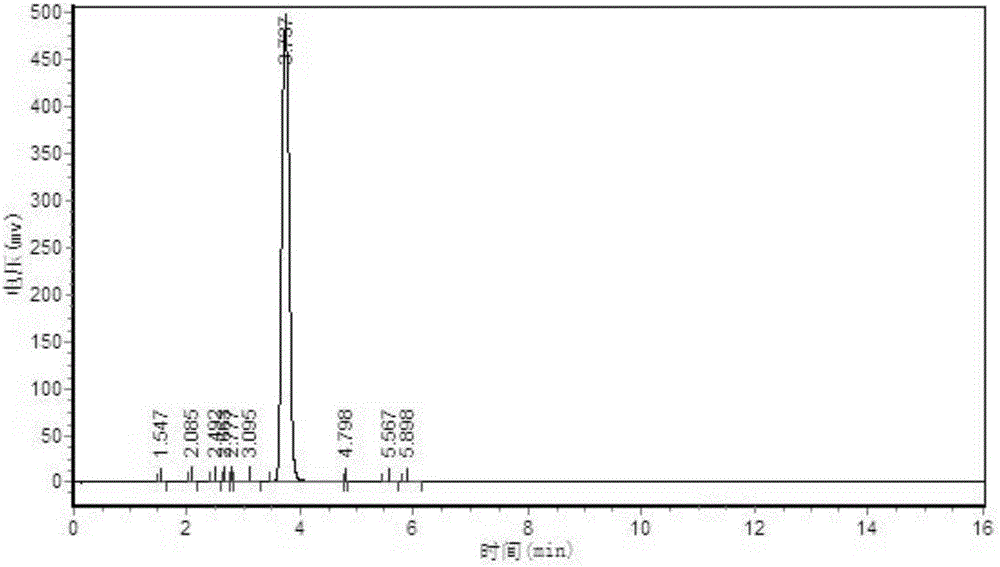
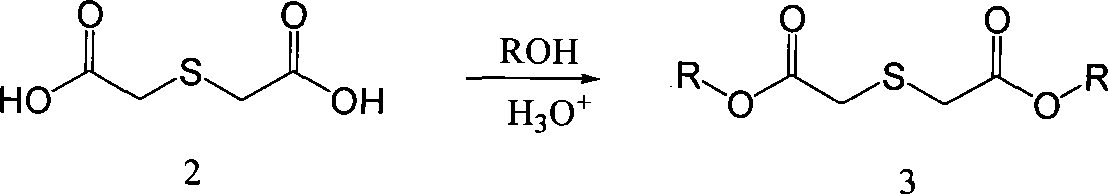
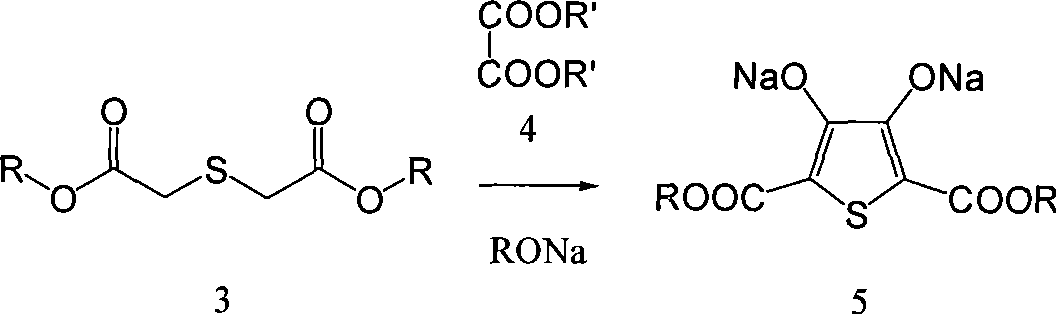
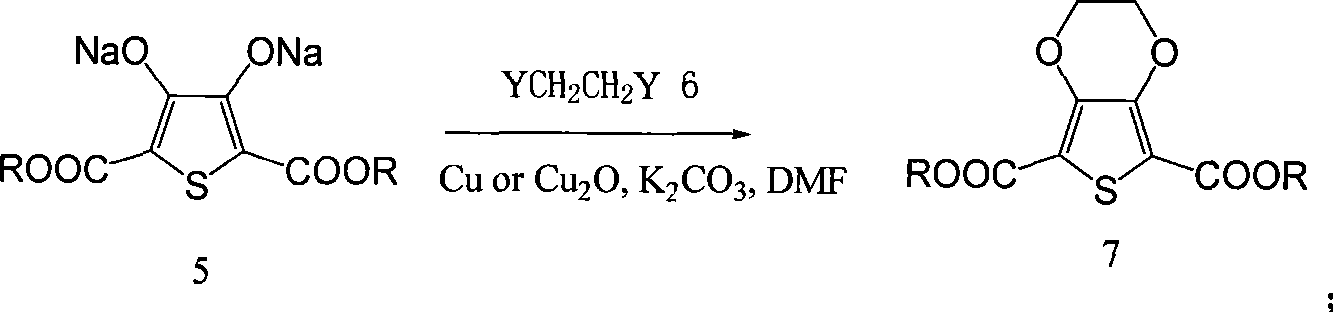
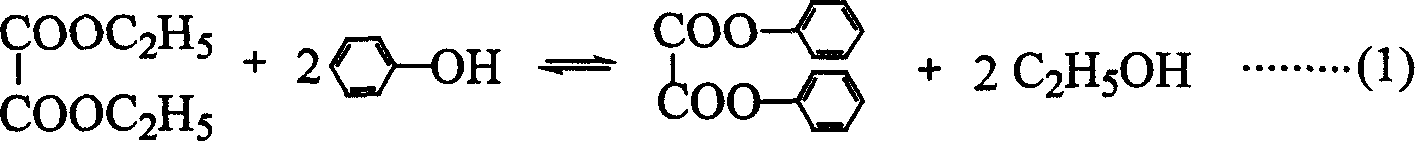


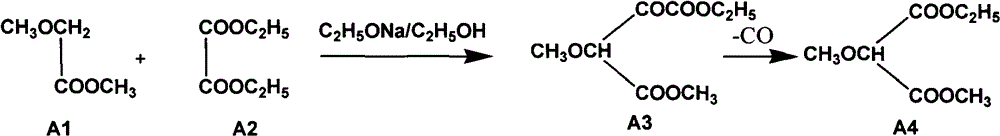

![Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/612c6417-1bb1-4030-911a-20a36fce8964/BDA0000992003570000021.PNG)
![Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/612c6417-1bb1-4030-911a-20a36fce8964/BDA0000992003570000022.PNG)
![Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate Preparation method of 4-[hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-2-oxobutanoic acid as glufosinate intermediate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/612c6417-1bb1-4030-911a-20a36fce8964/FDA0000992003560000011.PNG)