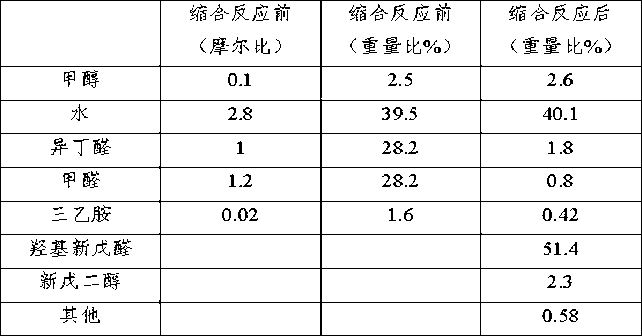
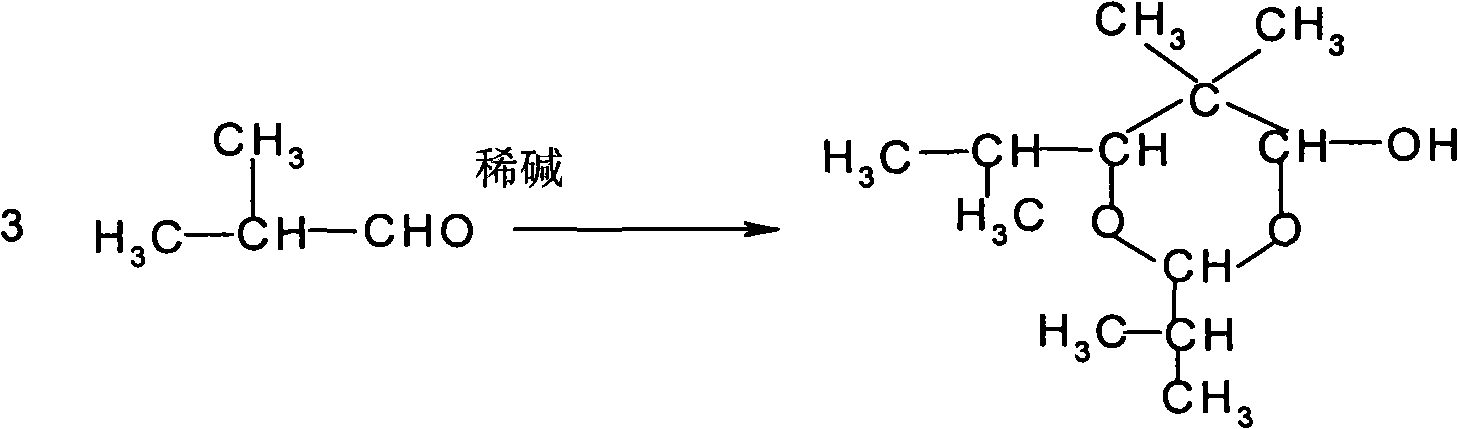
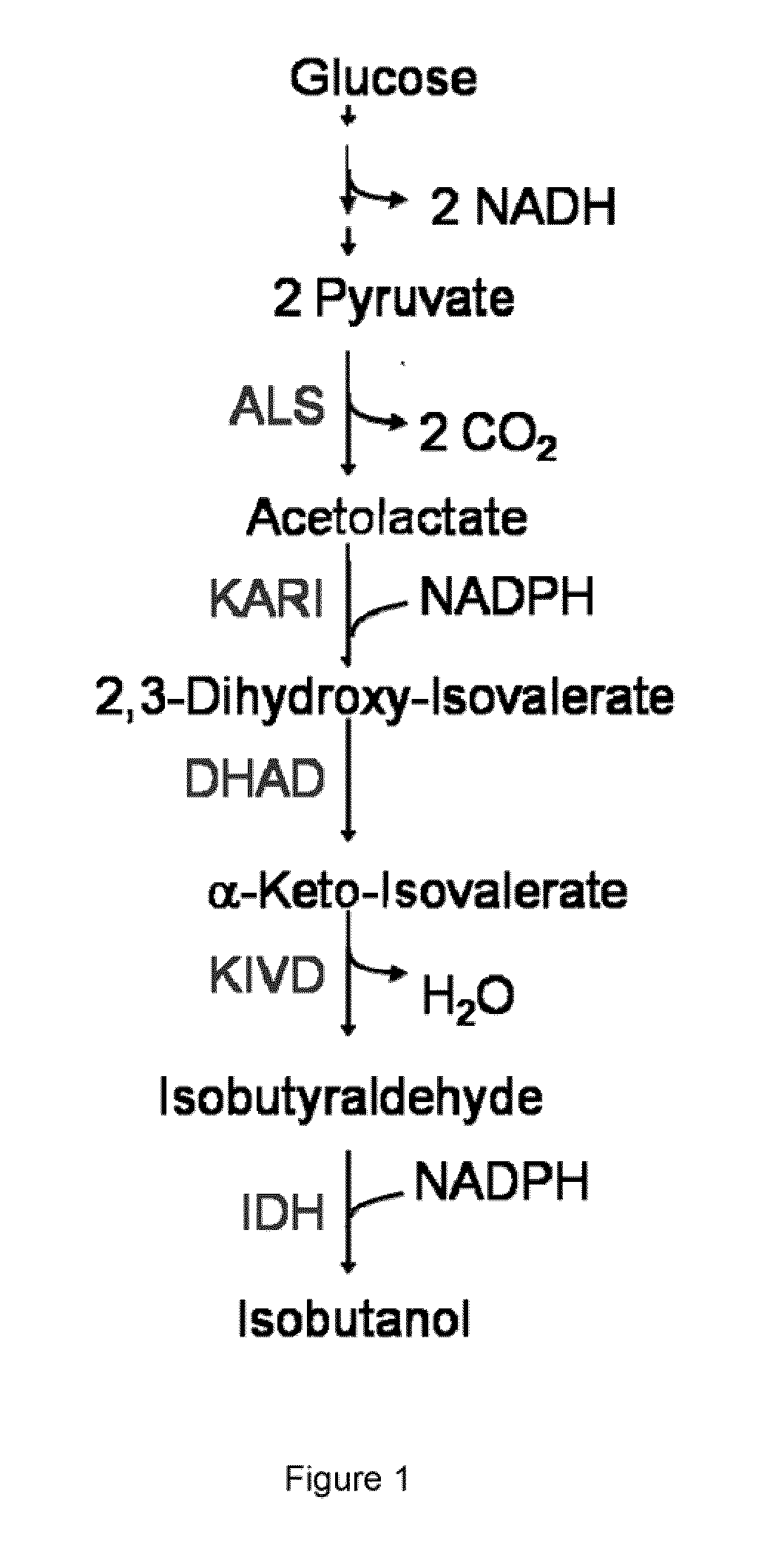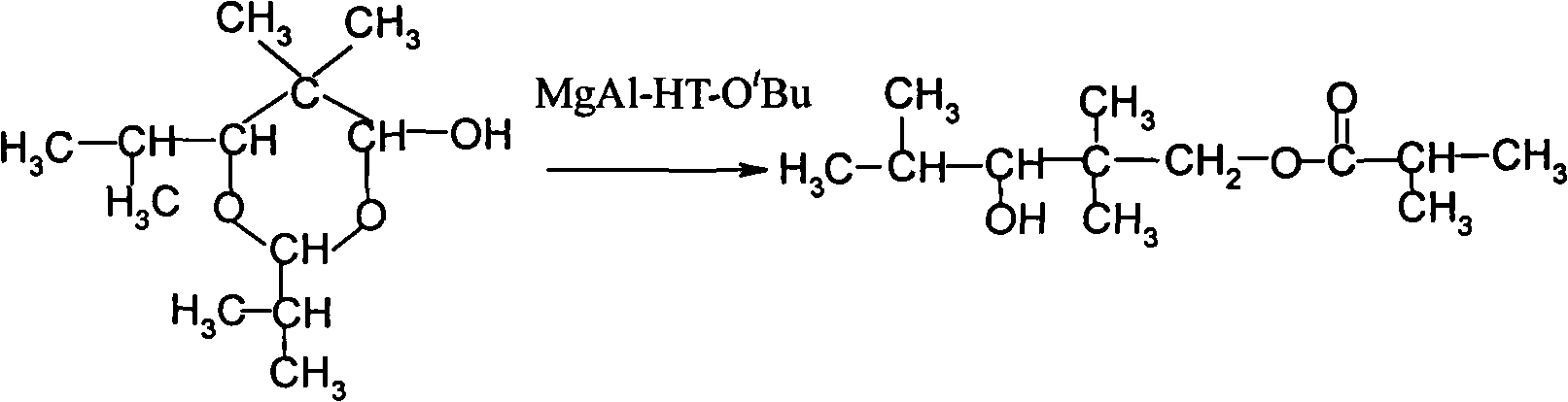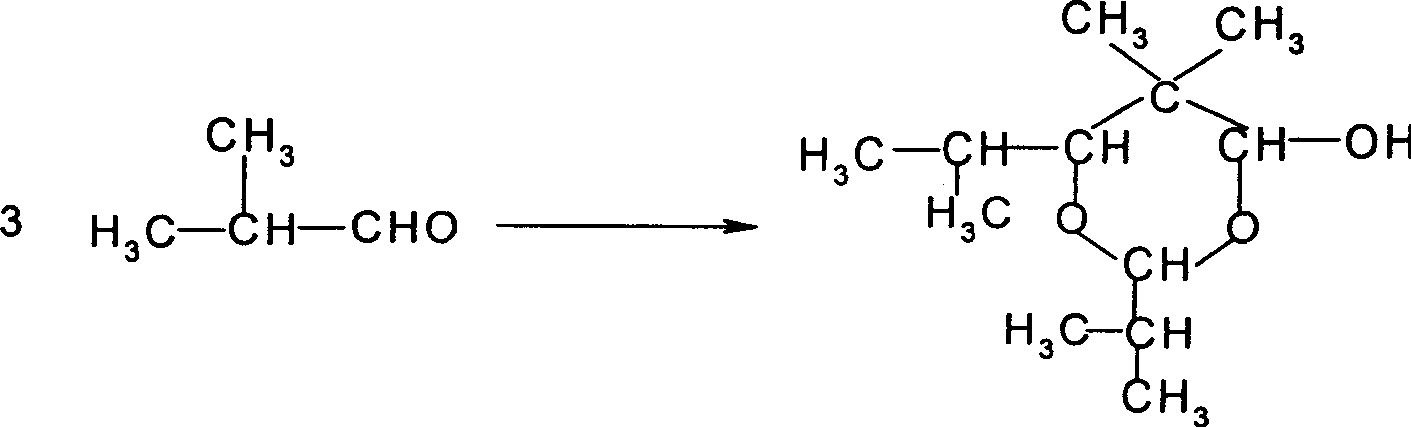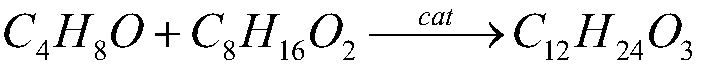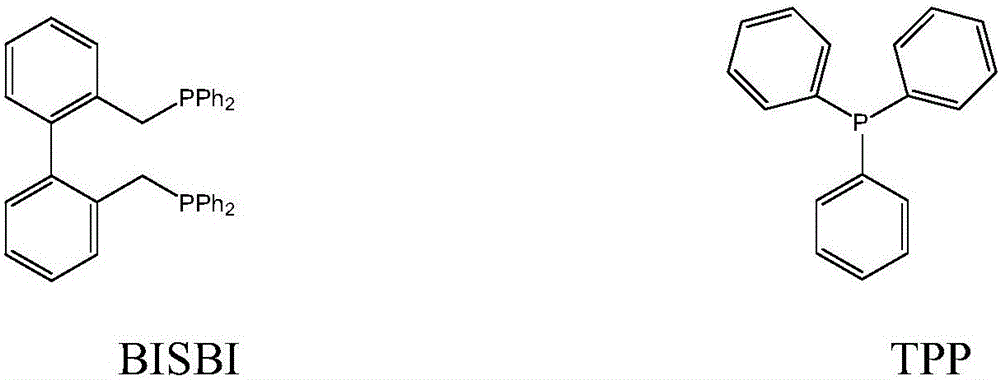Patents
Literature
295 results about "Isobutyraldehyde" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
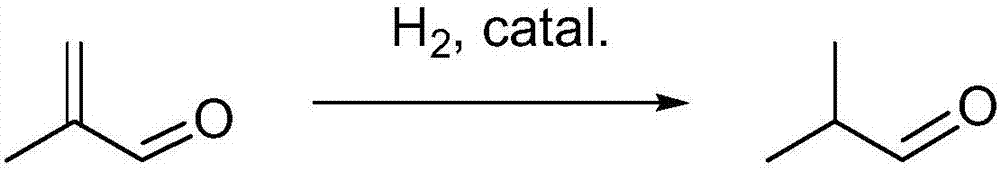
Isobutyraldehyde is the chemical compound with the formula (CH₃)₂CHCHO. It is an aldehyde, isomeric with n-butyraldehyde (butanal). Isobutyraldehyde is manufactured, often as a side-product, by the hydroformylation of propene. Its odour is described as that of wet cereal or straw. It undergoes the Cannizaro reaction even though it has alpha hydrogen atom.
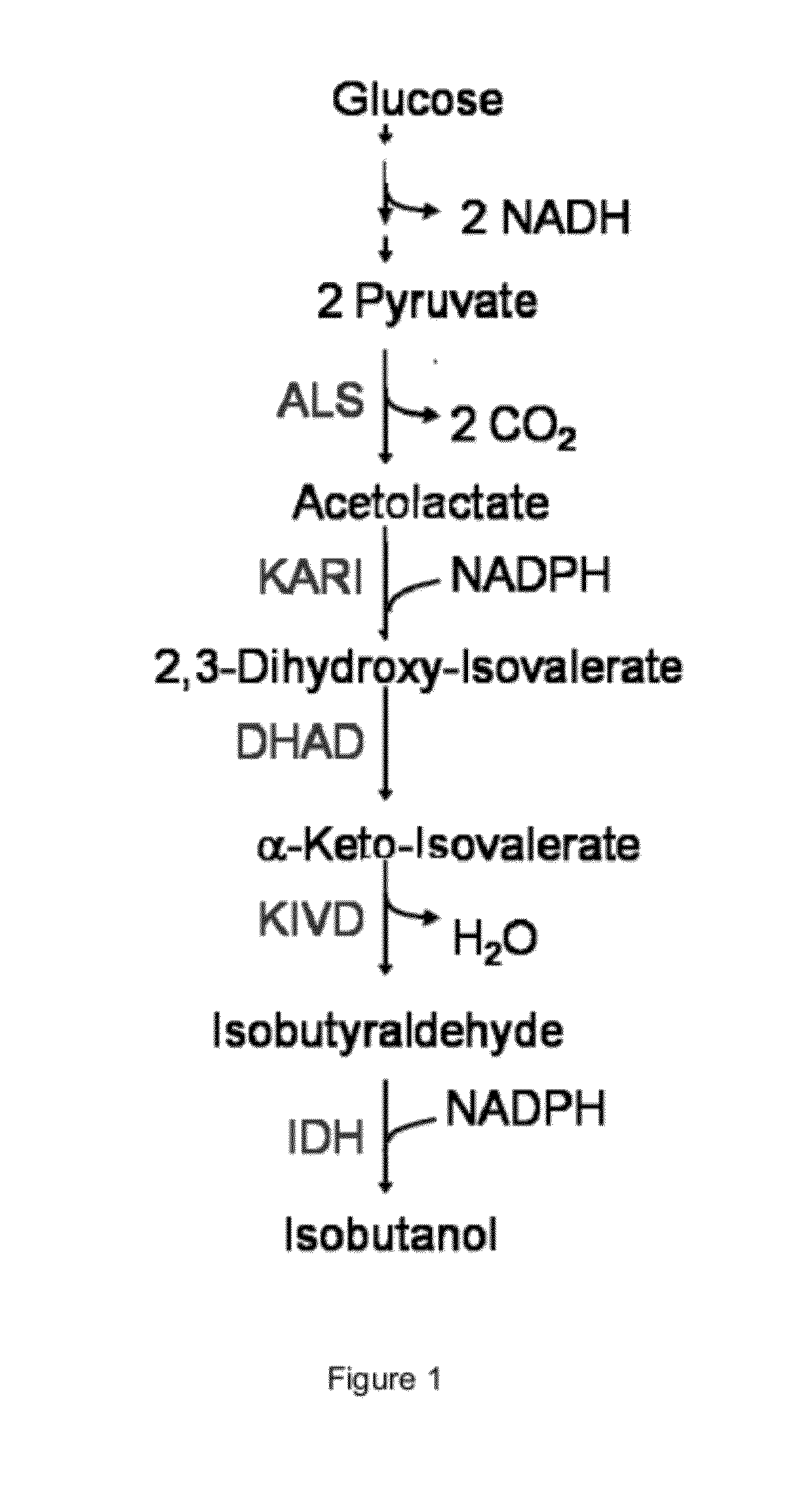
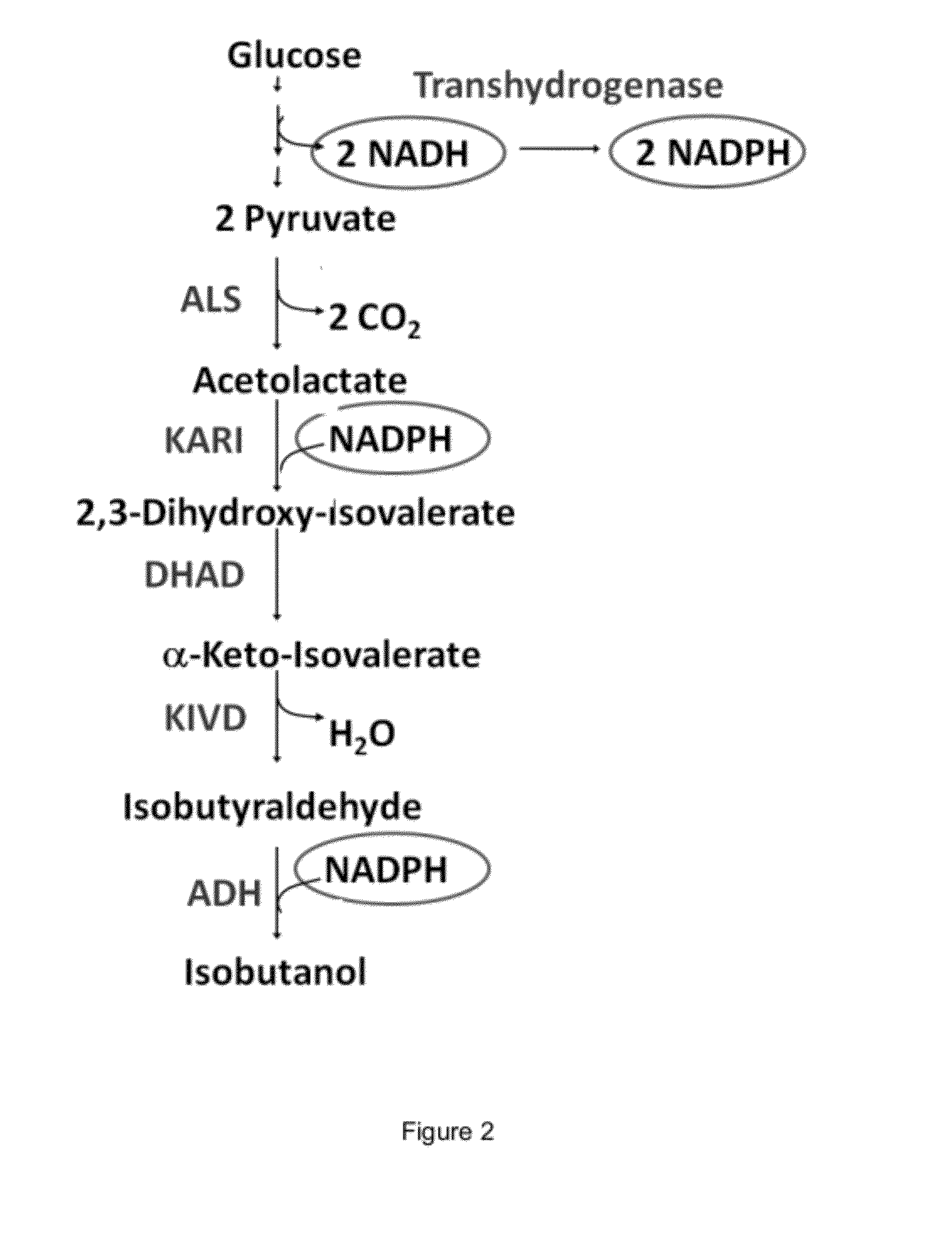
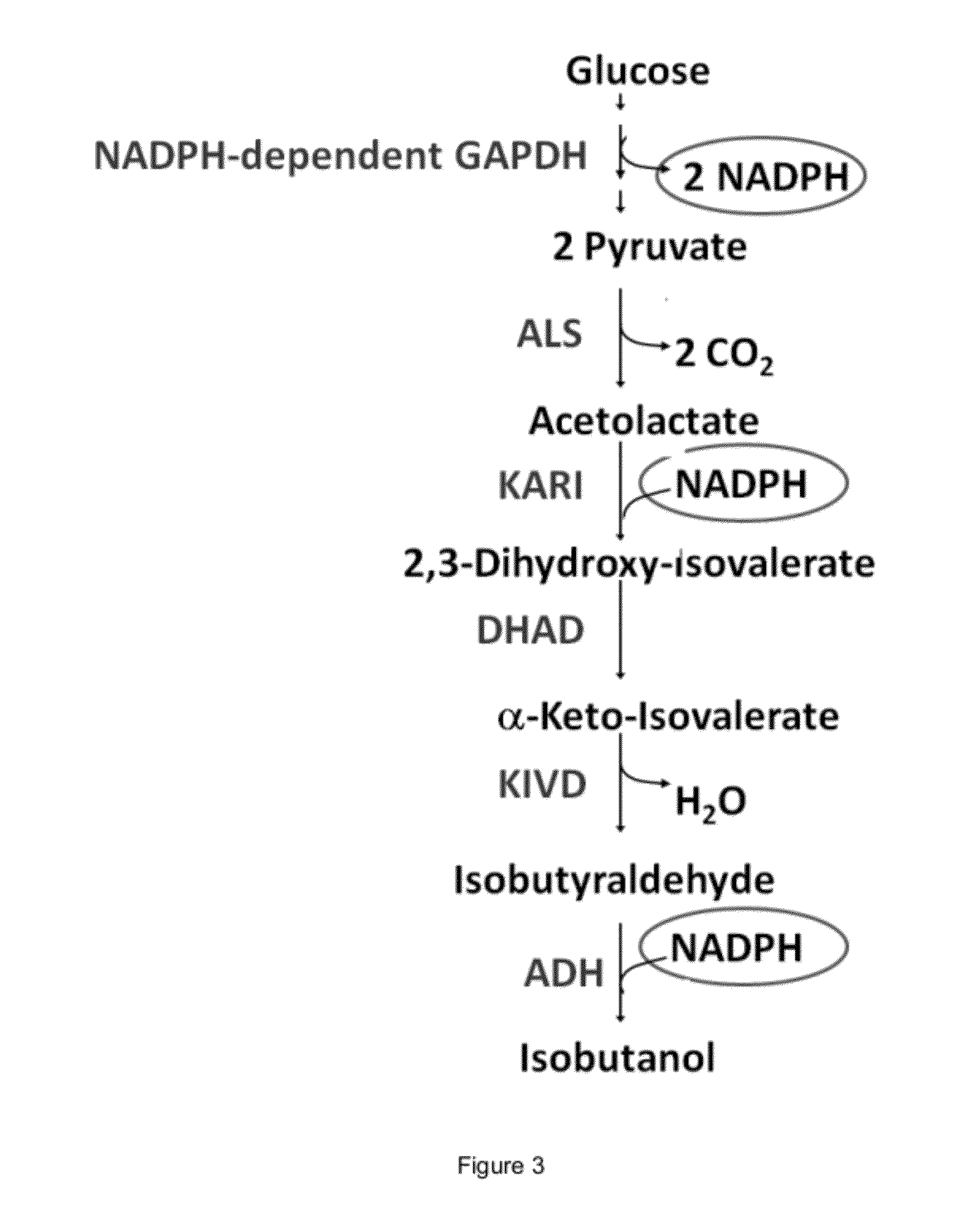
Engineered microorganisms capable of producing target compounds under anaerobic conditions
InactiveUS20100143997A1Improve abilitiesHigh catalytic efficiencyFungiBacteriaMicroorganismMetabolite
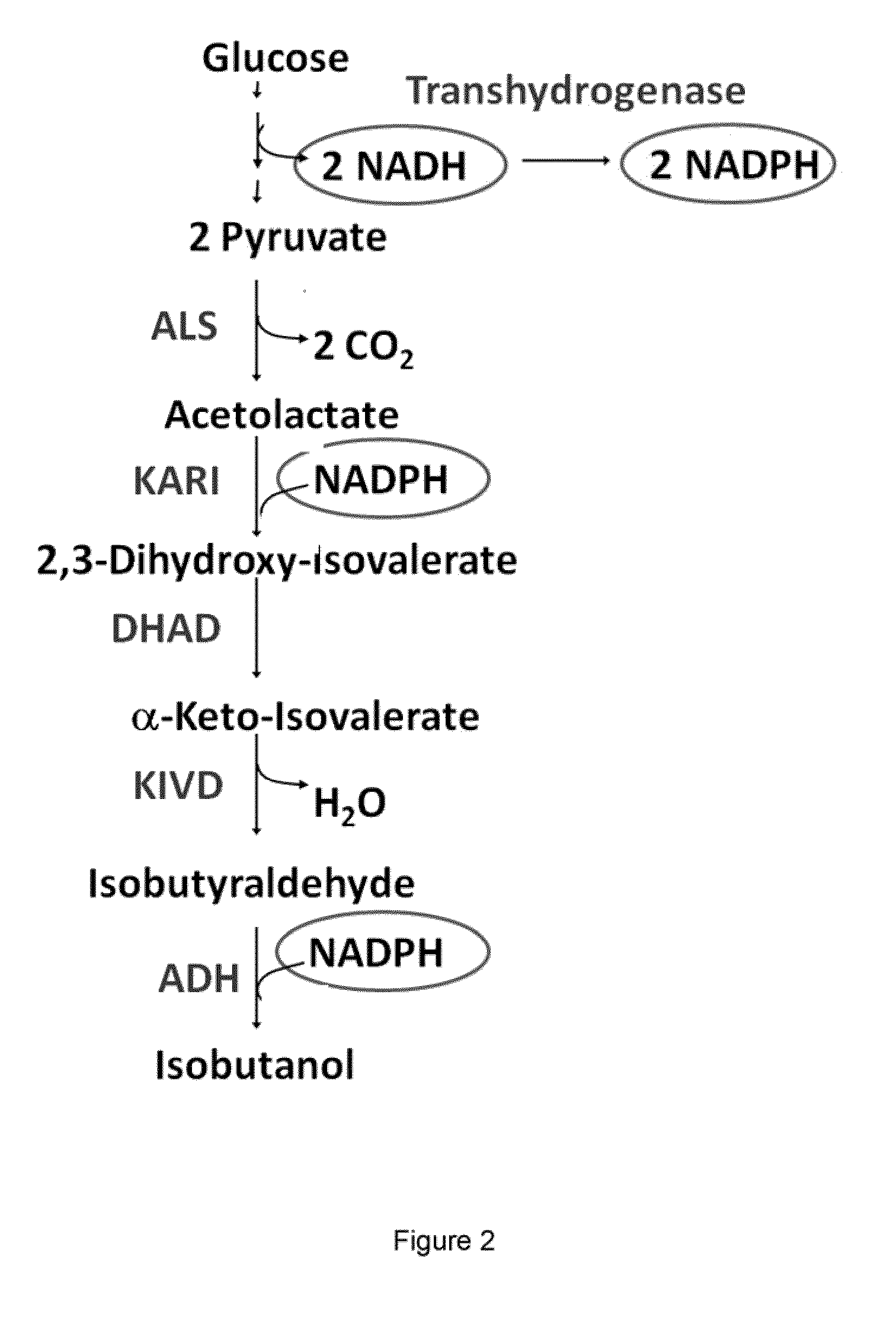
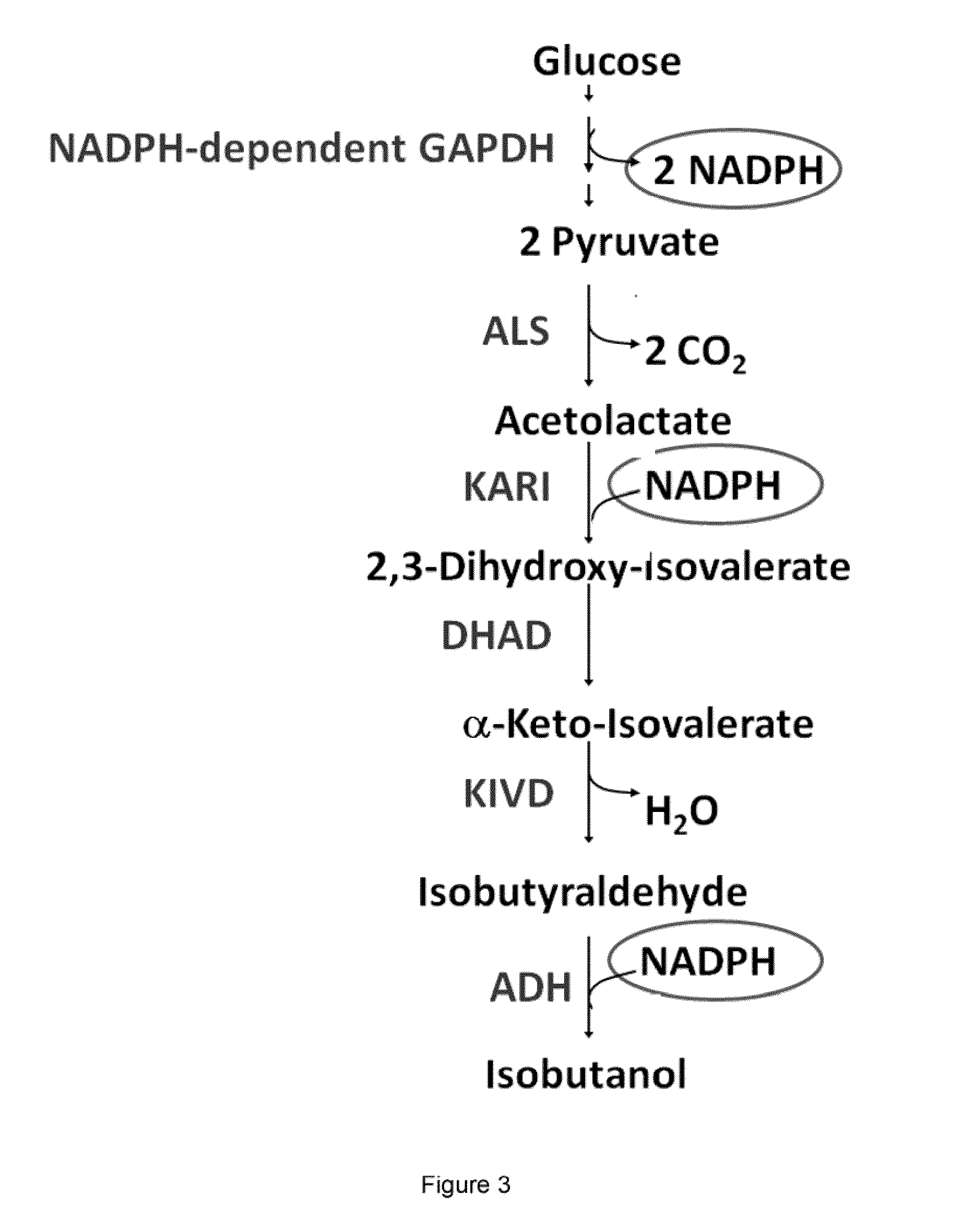
The present invention is generally provides recombinant microorganisms comprising engineered metabolic pathways capable of producing C3-C5 alcohols under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The invention further provides ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzymes which have been mutated or modified to increase their NADH-dependent activity or to switch the cofactor preference from NADPH to NADH and are expressed in the modified microorganisms. In addition, the invention provides isobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes expressed in modified microorganisms. Also provided are methods of producing beneficial metabolites under aerobic and anaerobic conditions by contacting a suitable substrate with the modified microorganisms of the present invention.
Owner:GEVO INC
A kind of propylene hydroformylation catalytic system and method
InactiveCN102266796AReduce dosageImprove stabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFormylation reactionTriphenylphosphine
The invention relates to a propylene hydroformylation catalyst system and a method for catalyzing synthesis of butyraldehyde. In the present invention, in the propylene hydroformylation reaction system catalyzed by triarylphosphine-Rh(I), by using appropriate types and quantities of additives, such as bisphosphite, the performance of the Rh(I) / triarylphosphine catalyst can be significantly improved The activity and the positive-iso ratio of butyraldehyde in the product (molar ratio of n-butyraldehyde / isobutyraldehyde>20), and significantly prolong the service life of the bisphosphite ligand, and significantly reduce the amount of triarylphosphine. This type of catalyst system is characterized by higher activity and selectivity than third-generation Rh(I) / triphenylphosphine catalysts and better stability than fourth-generation Rh(I) / bisphosphite catalysts, so The novel catalyst system provided by the present invention can overcome the shortcomings of the third and fourth generation catalysts, reduce the cost of industrialized production of propylene hydroformylation, and provide a new catalyst technology for its industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Process for preparing a catalyst for use in production of methacrylic acid and process of preparing methacrylic acid
InactiveUS6498270B1Lower performance requirementsHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsGas phaseDehydrogenation
The present invention provides a process for preparing a catalyst and the same for use in production of methacrylic acid, which is characterized by molding a raw material including a powder containing phosphorus and molybdenum at the specific pressure. The invention also provides a process for preparing methacrylic acid by gas phase oxidation and / or oxidative dehydrogenation of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of methacrolein, isobutyraldehyde and isobutyric acid in the presence of the catalyst.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
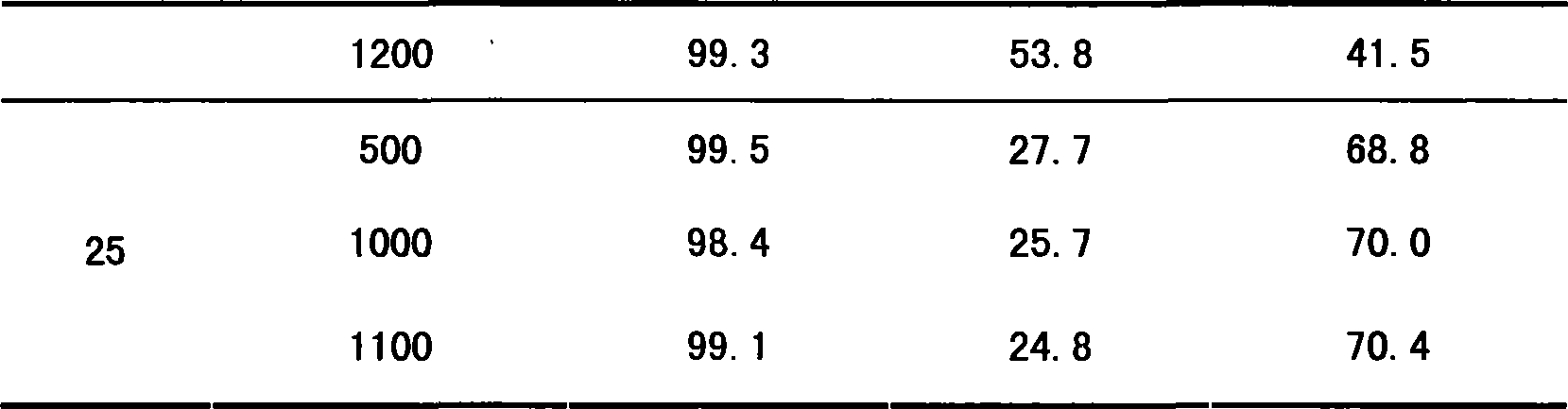
Method for processing cellulose by supercritical carbon dioxide, products and use thereof
The invention relates to a method for utilizing supercritical carbon dioxide to process cellulose; firstly, the cellulose and a cosolvent or an inorganic sol or a former body of the inorganic sol are arranged in a high pressure container; carbon dioxide is pumped by a pumping pressure; the reaction condition is 15 to 200 DEG C; the pressure is 4 to 40MPa; the reaction time is 0.5 to 24 hours; then the activated cellulose is manufactured; the cosolvent relates to carbinol, ethanol, normal butanol, isobutyl alcohol, acetone, tetrahydrofuran, formaldehyde, n-butyl aldehyde and isobutyraldehyde; the cellulose is a natural cellulose and a ramification thereof; the natural cellulose relates to chopped cotton fibers, cotton fabrics, bagasse, straws, paper products, bamboo, flax and wood. The method for utilizing the supercritical carbon dioxide to process the cellulose has the advantages that: the processing method is simply and easily operated; the supercritical carbon dioxide is adopted, thus having no burning, no pollution and no toxic action and being conveniently recycled and being repeatedly used; the content of the mixed inorganic oxide in a compound fiber material is high; the product is easily separated and purified; the characteristic is uniform and stable; the method for utilizing the supercritical carbon dioxide to process the cellulose has broad application prospects in the fields of catalyzing, chemical engineering, packaging, weaving, etc.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing iso-butyraldehyde and isobutyl alcohol by methylacrolein hydrogenation
ActiveCN101239892ALow costHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationIsobutanolMetal catalyst
The invention relates to a method for hydrogenation preparing isobutyraldehyde and isobutyl acohol from methacrolein. The method comprises using a supported metal catalyst, and hydrogenating methacrolein obtained by oxidating isobutene under gentle conditions. The invention provides a novel synthesis process for hydrogenation preparing isobutyraldehyde and isobutyl acohol from methacrolein which is obtained by air-oxidating low-utilization C4 material isobutene or tert-butanol. The methacrolein conversion rate is larger than 98%, the total selectivity of isobutyraldehyde and isobutyl acohol is larger than 95%, the performance of the catalyst is stable even the reaction lasts more than 1000 hours. The invention has the advantages of high activity and high selectivity of catalyst, good stability of catalyst, cheap material isobutene, low productin cost of isobutene, environment-protecting process, and suitability of industrialisation production. The process is flexible, can change the proportion of isobutyraldehyde and isobutyl acohol through adjusting the reaction process condition, thereby cogenerating isobutyraldehyde and isobutyl acohol, or only generating isobutyl acohol by cycling and hydrogenating isobutyraldehyde.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI NEW MATERIAL
Catalyst for the oxidation of a mixed aldehyde feedstock to methacrylic acid and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20070021296A1Improve distributionOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsIndiumCerium
A heteropolyacid catalyst for oxidation of isobutyraldehyde, methacrolein or mixtures or combinations thereof to methacrylic acid is disclosed where the heteropolyacid catalyst includes at least molybdenum (Mo), phosphorus (P), vanadium (V), and a first component including bismuth (Bi) and / or boron (B). The heteropolyacid catalyst can also optionally include a second component including potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and / or thallium (Tl) and optionally a third component including antimony (Sb), cerium (Ce), niobium (Nb), indium (In), iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), arsenic (As), silver (Ag), zinc (Zn), germanium (Ge), gallium (Ga), zirconium (Zr), magnesium (Mg), barium (Ba), lead (Pb), tin (Sn), titanium (Ti), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), and / or lanthanum (La). The heteropolyacid catalyst can also include an ammonium-containing compound designed to increase a value of medium pores in the final heteropolyacid catalyst. A method for oxidizing isobutanal to methacrylic acid using the heteropolyacid catalyst is also disclosed.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
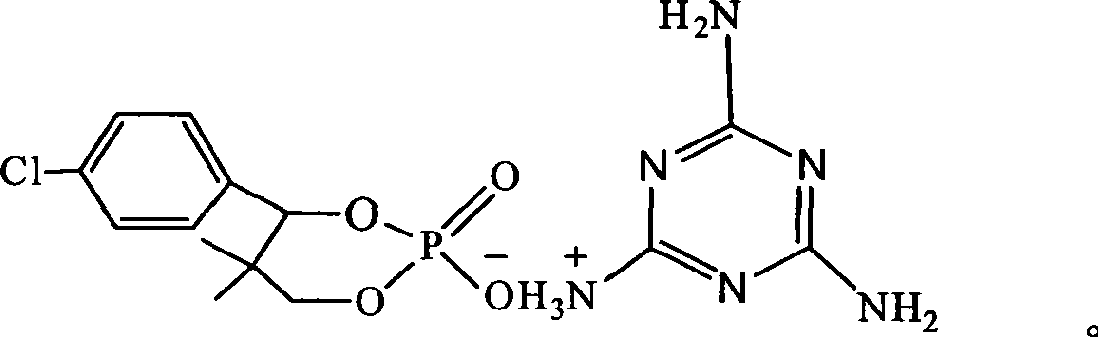
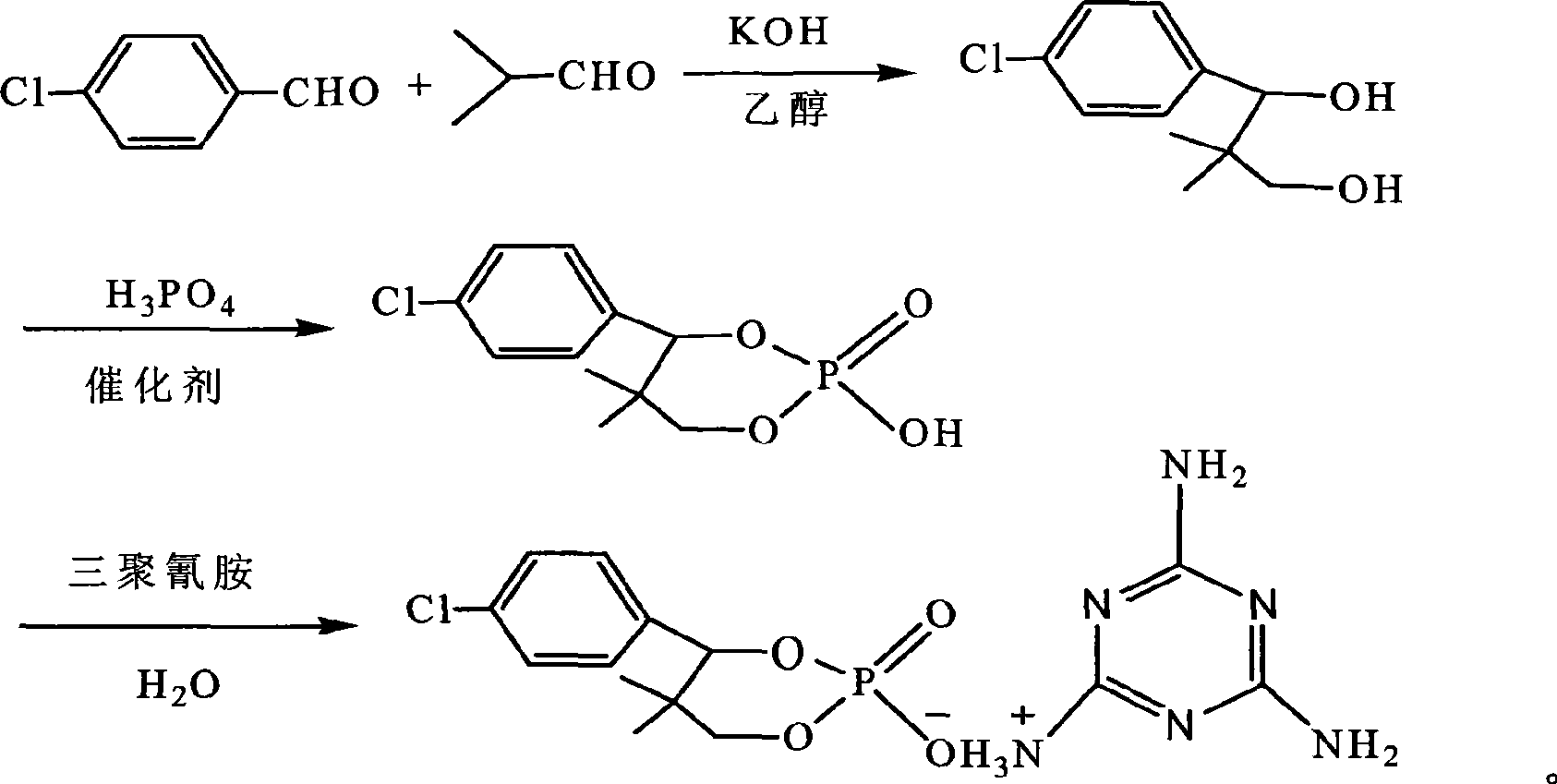
Phosphor-nitrogen expansion type combustion inhibitor and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101429438ALow viscosityReduce pollutionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBenzoic acidMelamine phosphate
The invention discloses a phosphorus-nitrogen swelling type fire retardant and a method for preparing the same. The chemical name of the fire retardant is 5, 5-dimethyl-4-p-chlorophenyl-1, 3, 2-dioxaphosphorinane phosphonate melamine salt. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) p-chlorobenzaldehyde and iso-butyraldehyde react with alkali ethanol solution, are cooled down and filtered to obtain an intermediate product (I); (2) the intermediate product (I) and phosphoric acid are added to solvent, and added with paratoluenesulfonic acid or benzoic acid or sodium salt of benzoic acid; and the mixing solution is distilled after reaction to reclaim the solvent to obtain an intermediate product(II); and (3) melamine and the intermediate product(II) are added to water for reaction, cooled down and filtered to obtain a filter cake; and the filter cake is dried to obtain phosphorus-nitrogen swelling type fire retardant. The phosphorus-nitrogen swelling type fire retardant has the advantages of high thermal stability, good compatibility, no halogen, less smoke and environmental protection. The preparation method has the advantages of materials available, simple process, mild reaction conditions, small viscosity of reaction liquid, low requirement on equipment and little environmental pollution.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANYI CHEM
Biofuel and chemical production by recombinant microorganisms via fermentation of proteinacious biomass
Provided herein are metabolically modified microorganisms characterized by having an increased keto-acid flux when compared with the wild-type organism and comprising at least one polynucleotide encoding an enzyme, and causing the production of a greater quantity of a chemical product when compared with the wild-type organism. The recombinant microorganisms are useful for producing a large number of chemical compositions from various nitrogen containing biomass compositions and other carbon sources. More specifically, provided herein are methods of producing alcohols, acetaldehyde, acetate, isobutyraldehyde, isobutyric acid, n- butyraldehyde, n-butyric acid, 2-methyl-l-butyraldehyde, 2-methyl-l -butyric acid, 3- methyl-l-butyraldehyde, 3 -methyl- 1 -butyric acid, ammonia, ammonium, amino acids, 2,3-butanediol, 1,4-butanediol, 2-methyl-l, 4-butanediol, 2-methyl- 1,4-butanediamine, isobutene, itaconate, acetoin, acetone, isobutene, 1,5-diaminopentane, L-lactic acid, D- lactic acid, shikimic acid, mevalonate, polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), isoprenoids, fatty acids, homoalanine, 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA), succinic acid, malic acid, citric acid, adipic acid, p-hydroxy-cinnamic acid, tetrahydrofuran, 3-methyl-tetrahydrofuran, gamma-butyrolactone, pyrrolidinone, n-methylpyrrolidone, aspartic acid, lysine, cadeverine, 2-ketoadipic acid, and / or S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM), from a suitable nitrogen rich biomass.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
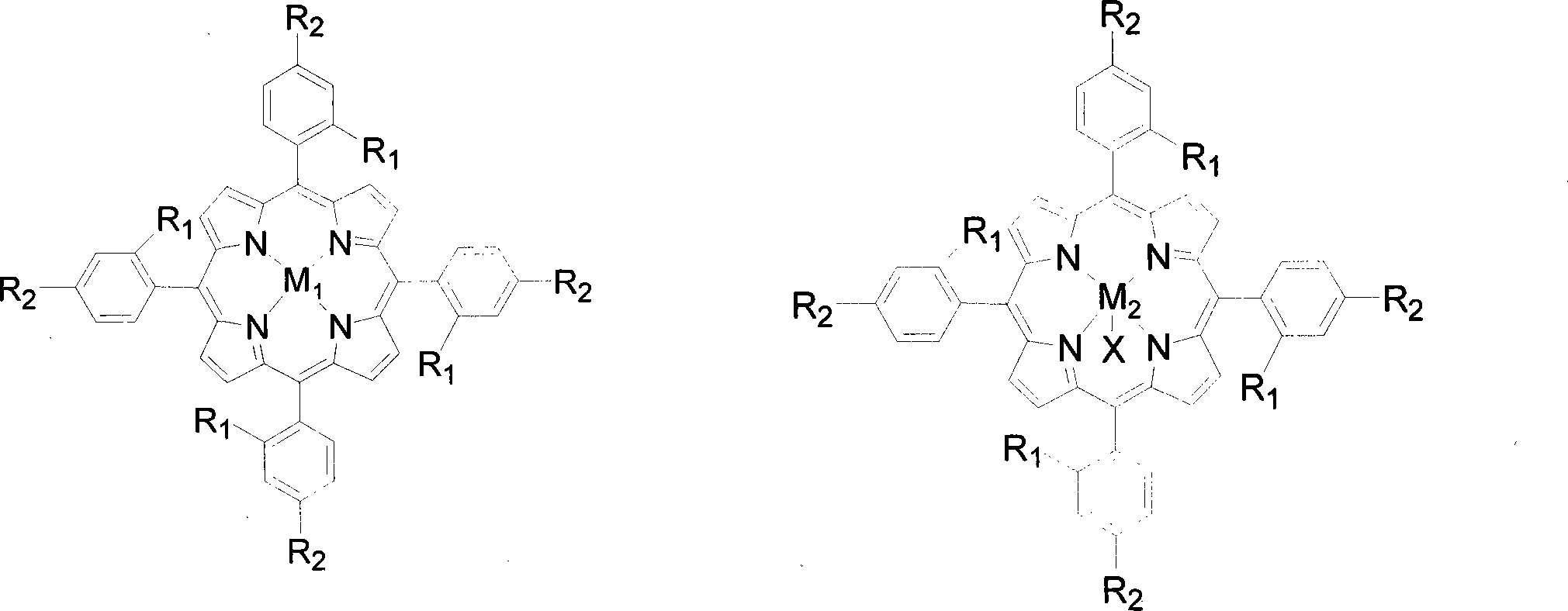
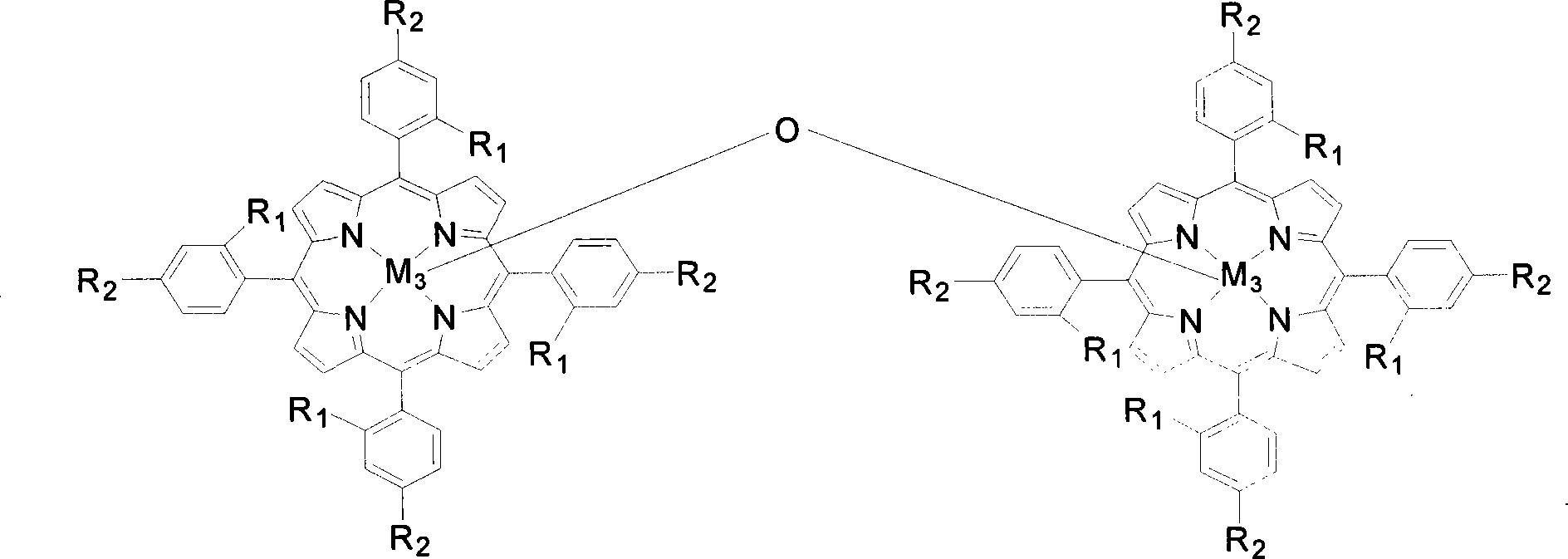
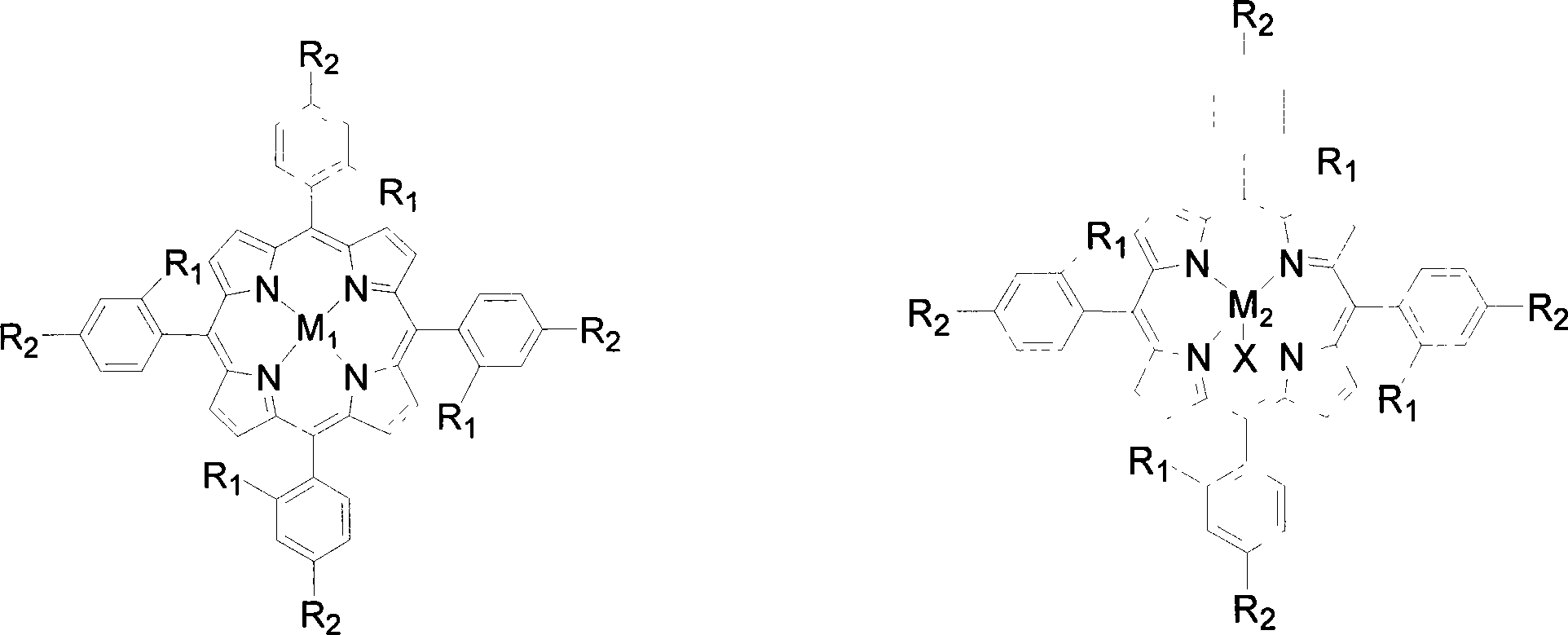
Method for preparing lactones by biomimetic catalytic oxidation of ketone compounds
InactiveCN101205225AMild reaction conditionsLow reaction temperatureOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBenzaldehydeReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for putting the oxydone compounds into the biomimetic catalysis to prepare the lactone. With the ketone compounds as the raw materials, the invention selects the mononuclear metalloporphyrins with structure in the general formulas (I) and (II) or Mu-oxygen-binuclear metalloporphyrins with structure in the general formula (III) as the catalysts; the concentration of the catalysts ranges from 2 multiplied by 10<-5>mol / L to 2 multiplied by 10<-2>mol / L and the concentration of the ketone compounds ranges from 0.02mol / L to 0.8mol / L; with the benzene, the toluene, the xylene, the benzotrifluoride or the cyclohexane as the solvents, the benzaldehyde, isobutyraldehyde or butyraldehyde with a molar ratio to the ketone compounds ranging from 0.5 to 1 to 20 to 1 is added in the mixtures; the oxygen with a pressure ranging from 0.1MPa to 1.6MPa is pumped in the mixtures; the reaction temperature is controlled to a range from 40 DEG C to 150 DEG C and the reaction time is controlled to a range from 1 to 10 hours. The invention has the advantages of gentile reaction conditions, a small dosage of catalysts, good catalytic effects, and high product selectivity, etc.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing hydroxypivalaldehyde through micro-channel reactor
InactiveCN105693491AShort residence time at high temperatureImprove conversion rateOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationProduct selectionReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydroxypivalaldehyde through a micro-channel reactor. The problems that in the prior art, reaction time is long, product selectivity is poor, and the raw material conversion rate is low are mainly solved. By means of the method for preparing hydroxypivalaldehyde through the micro-channel reactor, isobutyraldehyde, formaldehyde raw materials and a catalyst are mixed completely through a pre-mixer of the micro-channel reactor and then enter a constant-temperature reactor of the micro-channel reactor to react, and the product containing hydroxypivalaldehyde is obtained; the mass ratio of formaldehyde to isobutyraldehyde in the raw materials is (1-1.4) : 1; the using quantity of the catalyst is 0.5-5% of the total mass of a reaction solution; reaction temperature in the micro-channelconstant-temperature reactor is 100-140 DEG C, the pressure of a reaction meter is 0.5-1.5 MPa, and the reaction staying time of the reaction solution in the micro-channel reactor is 30-300 s; the technical scheme that after reaction, the conversation rate of the raw material isobutyraldehyde in the reaction solution after reaction is larger than 95%, the selectivity of the product hydroxypivalaldehyde is larger than 95% well solves the problems, and the method can be used for preparing hydroxypivalaldehyde.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
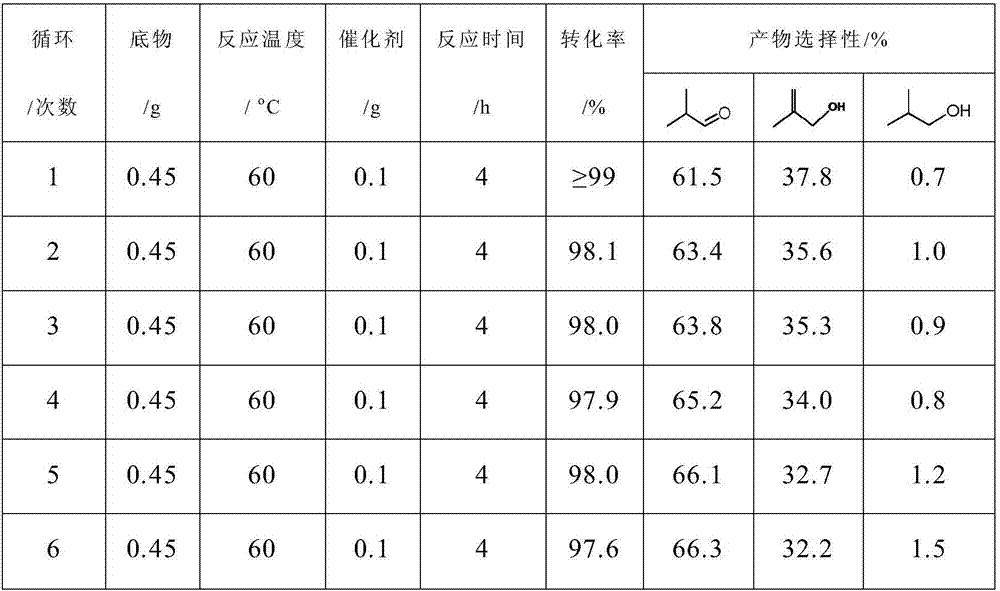
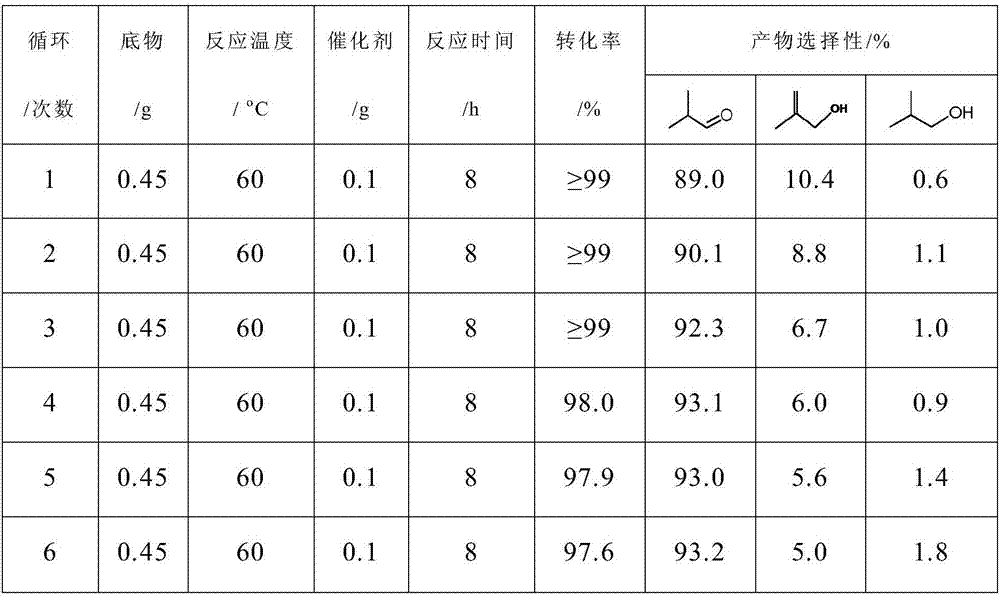
Selective hydrogenation catalyst, preparation method and catalyzing evaluation method on generation of isobutyraldehyde by the selective hydrogenation catalyst
InactiveCN106925267ALow costEasy to prepareOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationIridiumRhenium
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation catalyst, a preparation method and a catalyzing evaluation method for isobutyraldehyde by the selective hydrogenation catalyst. The selective hydrogenation catalyst comprises a carrier and active components, wherein the active components include a noble metal material and a non-noble metal material; the carrier is selected from one of fumed silica, precipitated silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, carbon nitride and titanium dioxide; the noble metal material is noble metal, namely Ir (iridium); the non-noble metal material is selected from one of non-noble metals, namely Mo (molybdenum), W (tungsten), Ni (nickel), Co (cobalt), Sm (samarium), Ce (cerium) and Re (rhenium); the atom ratio of non-noble metal material to noble metal material is 0.8 to 5. The selective hydrogenation catalyst has the advantage that the methylacrolein can be selectively hydrogenated to generate the isobutyraldehyde in environment-friendly green solvent water under the milder reaction condition.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
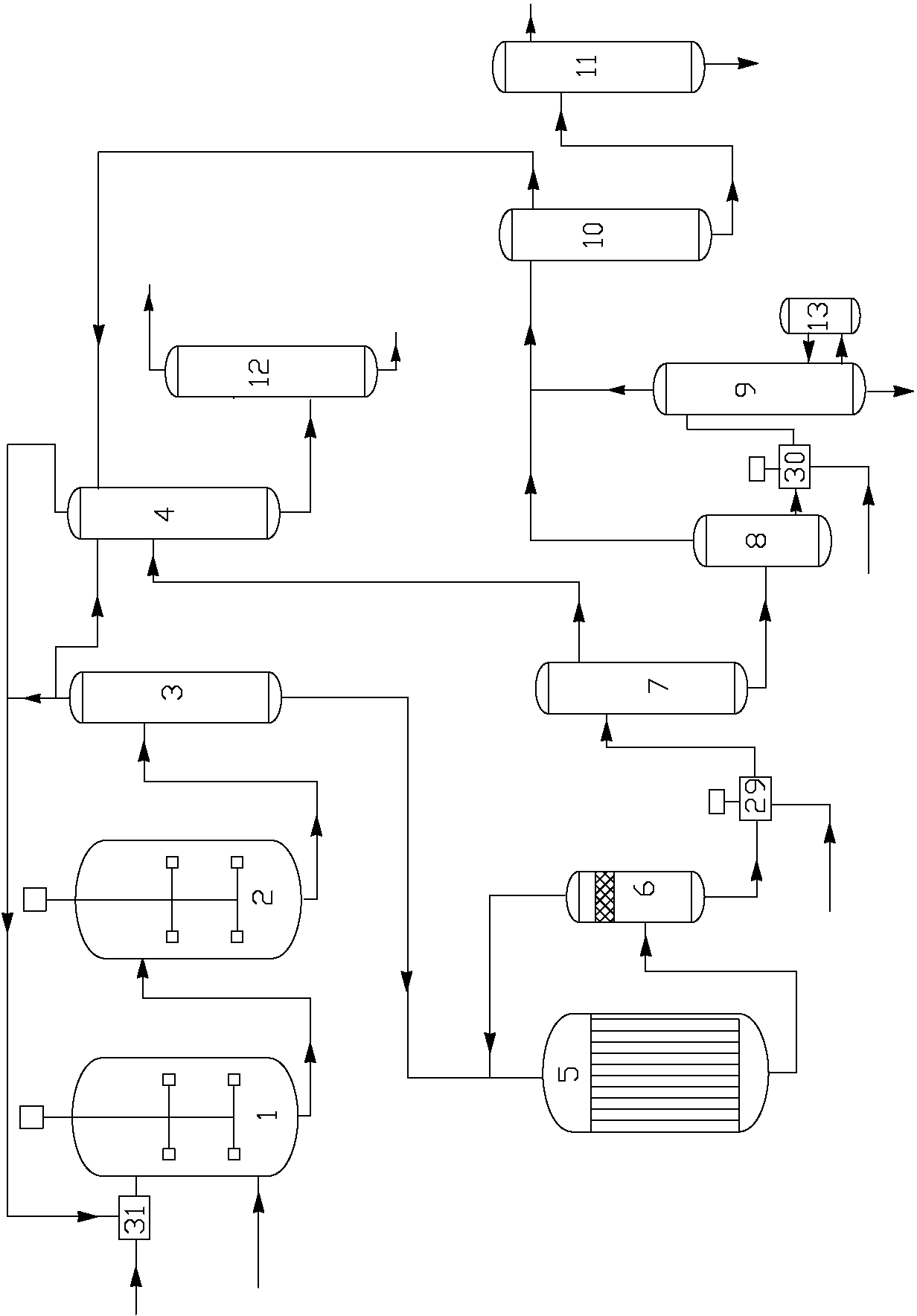
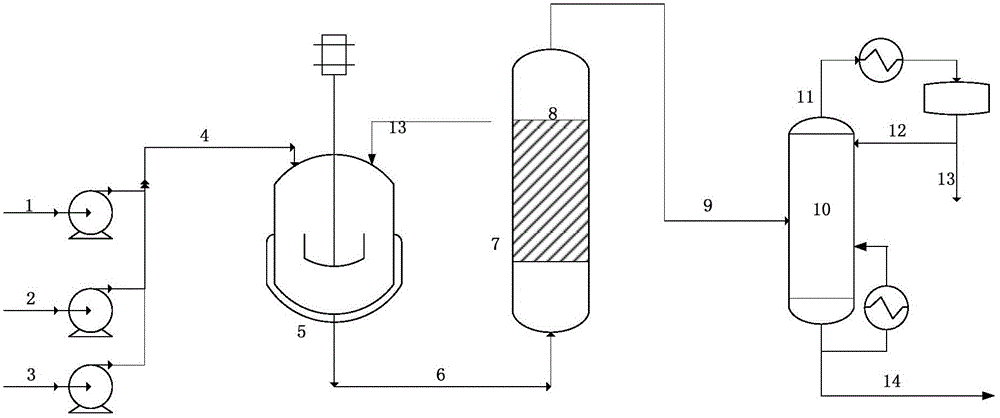
Neopentyl glycol condensation hydrogenation production process and device thereof
ActiveCN103130611AHigh yieldGood hydrogenation effectOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationGas phaseSaponification
The invention discloses a neopentyl glycol condensation hydrogenation production process which comprises the following steps of: 1) condensation, that is, performing a condensation reaction of isobutyraldehyde with a methanol aqueous solution of formaldehyde, delivering the mixed condensation products into a condensation circulation tower for separation, allowing hydroxypivalaldehyde to enter a hydrogenation reactor from the condensation circulation tower, allowing a gas-phase component to flow back to a raw material mixing zone for mixing, and to enter a condensation reactor; 2) hydrogenation, that is, performing a hydrogenation reaction of the hydroxypivalaldehyde with hydrogen, delivering the products into a gas-liquid separation tank, allowing a gas-phase component to flow back to the hydrogenation reactor, allowing the liquid-phase neopentyl glycol crude product to enter a saponification reactor; 3) refining, that is, performing a saponification reaction of the neopentyl glycol crude product, allowing the product to enter a low-boiling-point substance fractionating tower, allowing a liquid-phase component at the tower bottom to enter a flash tank, allowing a liquid-phase component at the flash tank bottom to enter a pH adjusting tank, adjusting the pH to 6.5-7, allowing the product to enter a falling film evaporator, allowing a gas-phase component at the top of the falling film evaporator to enter a drying tower, then to enter a rectifying tower for refining so as to obtain neopentyl glycol. The process of the invention is high in neopentyl glycol yield, and simple and effective in separation purification process.
Owner:SHANDONG HUALU HENGSHENG CHEM IND
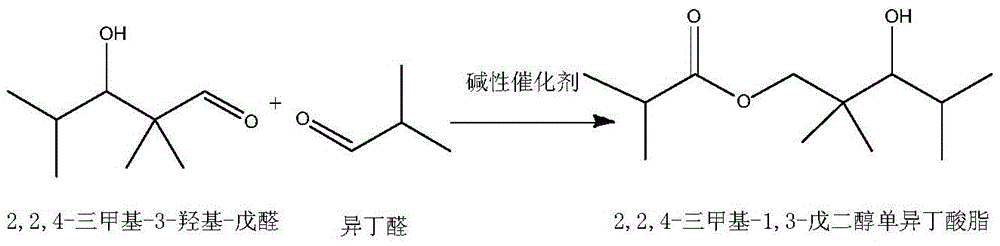
Method for preparing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate
InactiveCN101863762AImprove one-way yieldHigh selectivityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by aldehyde oxidation-reductionTert-butoxyTishchenko reaction
The invention provides an environmental-friendly method for preparing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate, which comprises a condensation reaction and a Tishchenko reaction of isobutyraldehyde, wherein condensation products of the isobutyraldehyde are subjected to the Tishchenko reaction under the catalytic action of tert-butoxy anion-pillared layered magnesium-aluminum anionic clay to generate 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate. The preparation method has the advantages of high single-pass yield, high selectivity of target products, a few by-products, mild reaction conditions, catalyst recycling and environmental-friendly synthetic process.
Owner:江苏天音化工有限公司 +1
Production of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,-3-pentadiol mono-isobutyric acid
InactiveCN1817850AImprove one-way yieldMild reaction conditionsPreparation by aldehyde oxidation-reductionHydrotalciteHomogeneous catalysis
Production of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoester isobutyrate is carried out by condensation pre-treating isobutyl aldehyde, and Knigcharlo reacting in molecule under the action of hydrotalcite-like solid catalyst to obtain the final product. It has high single-pass recovery rate, gentle reactive condition and no corrosion.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Catalyst for the oxidation of a mixed aldehyde feedstock to methacrylic acid and methods for making and using same
A heteropolyacid catalyst for oxidation of isobutyraldehyde, methacrolein or mixtures or combinations thereof to methacrylic acid is disclosed where the heteropolyacid catalyst includes at least molybdenum (Mo), phosphorus (P), vanadium (V), and a first component including bismuth (Bi) and / or boron (B). The heteropolyacid catalyst can also optionally include a second component including potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and / or thallium (Tl) and optionally a third component including antimony (Sb), cerium (Ce), niobium (Nb), indium (In), iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), arsenic (As), silver (Ag), zinc (Zn), germanium (Ge), gallium (Ga), zirconium (Zr), magnesium (Mg), barium (Ba), lead (Pb), tin (Sn), titanium (Ti), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), and / or lanthanum (La). The heteropolyacid catalyst can also include an ammonium-containing compound designed to increase a value of medium pores in the final heteropolyacid catalyst. A method for oxidizing isobutanal to methacrylic acid using the heteropolyacid catalyst is also disclosed.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Process for producing catalyst for methacrylic acid production
InactiveCN1795047AOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalytic oxidationMethacrolein
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing a catalyst for preparing methacrylic acid by gas-phase catalytic oxidation of methacrolein, isobutyraldehyde or isobutyric acid with high yield and high selectivity. The method comprises: (a) mixing compounds each containing any one of Mo, V, P, Cu, Cs or NH4 with water to prepare aqueous solutions or dispersions of these compounds (hereinafter, these two are referred to as slurries; ); (b) drying the slurry formed in step (a) to obtain a dry slurry; (c) calcining the dry slurry obtained in step (b) to obtain a calcined body; (d) filtering through mixing A step of separating the obtained mixture of the calcined body obtained in step (c) and water into an aqueous solution and a water-insoluble substance; (e) drying the water-insoluble substance obtained in step (d) to obtain a dry insoluble substance Water substance steps.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Engineered microogranisms capable of producing target compounds under anaerobic conditions
The present invention is generally provides recombinant microorganisms comprising engineered metabolic pathways capable of producing C3-C5 alcohols under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The invention further provides ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzymes which have been mutated or modified to increase their NADH-dependent activity or to switch the cofactor preference from NADPH to NADH and are expressed in the modified microorganisms. In addition, the invention provides isobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes expressed in modified microorganisms. Also provided are methods of producing beneficial metabolites under aerobic and anaerobic conditions by contacting a suitable substrate with the modified microorganisms of the present invention.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
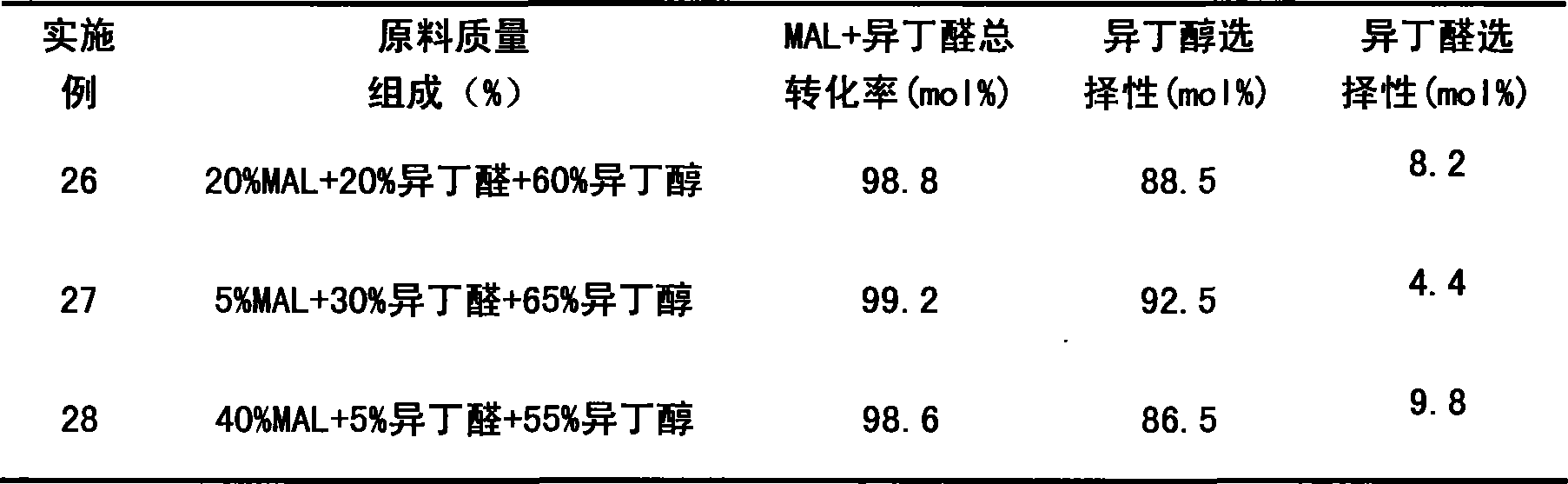
Method for preparing hydroxy neovaleraldehyde by condensing formaldehyde and isobutyraldehyde
InactiveCN105061167ALow selectivitySame dwell timeOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationBoiling pointTower
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydroxy neovaleraldehyde by condensing formaldehyde and isobutyraldehyde, which mainly solves the problems of lower conversion rate and lower selectivity in the prior art. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: mixing formaldehyde and isobutyraldehyde in a mixer, mixing with a condensation catalyst, sending into a tubular reactor with a reinforced liquid-liquid mixing internal component, reacting at 50-90 DEG C under the pressure of atmospheric pressure to 0.5 MPaG for 30-120 minutes to obtain a condensation product, sending the condensation product into a rectification tower to perform reduced pressure rectification, discharging low-boiling-point substances from the tower top, and sending the purified hydroxy neovaleraldehyde-water mixture obtained from the tower bottom into the subsequent section. The technical scheme well solves the problems, and can be used for preparing hydroxy neovaleraldehyde by condensing formaldehyde and isobutyraldehyde.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
Alcohol ester-12 production process
InactiveCN107698451AImprove performanceGood film formingOrganic compound preparationPreparation by aldehyde oxidation-reductionAlcoholBoiling point
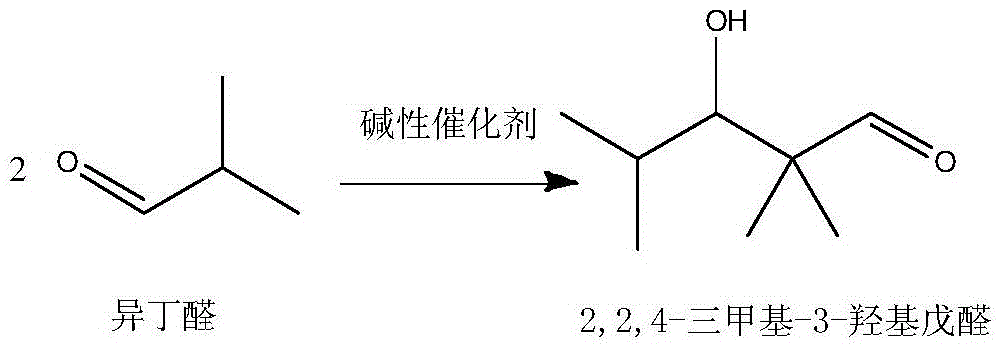
The invention discloses an alcohol ester-12 production process which includes the steps: condensing isobutyraldehyde under alkaline conditions to generate 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-hydroxyl-1-valeraldehyde; continuing to perform polycondensation reaction on the isobutyraldehyde and the 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-hydroxyl-1-valeraldehyde generated by reaction to generate the alcohol ester-12. The production processhas the advantages that the process is continuous and simple, convenient to operate, small in occupied area and leas in investment, and products prepared by the process are stable. The alcohol ester-12 prepared by the method is a dihydric alcohol ester solvent with high boiling point and poly-functional groups, a novel environmental-friendly green chemical and mainly used for special coalescing agents of waterborne architectural coatings, and the waterborne architectural coatings made of the coalescing agents cannot emit substances toxic for people into an atmospheric environment.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCE CHEM IND DESIGN INST
Method for preparing iso-butyl aldehyde by using isobutene or tert-butyl alcohol as raw material
ActiveCN101260028AHigh selectivityHigh space-time yieldOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationMethacroleinBismuth
The invention aims to provide a method of using isobutylene or tert-butyl alcohol as raw material to prepare isobutyraldehyde. The method prepares isobutyraldehyde through two steps as follows: (1) under the action of molybdenum-bismuth base composite oxide catalyst, isobutylene or tert-butyl alcohol selects oxidation to prepare methacrolein; (2) under the action of supported hydrogenation catalyst, methacrolein selects hydrogenation to prepare isobutyraldehyde. The raw material in the method is cheap and easy to get, which breaks the dependence of the prior isobutyraldehyde production on expensive C3 propylene raw material and opens up a brand new process route for preparing isobutyraldehyde through C4 raw material low in chemical utilization ratio. The method is high in the yield coefficient of isobutyraldehyde, simple in process, low in production cost and convenient for mass production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI NEW MATERIAL
Process for preparing a catalyst for use in production of methacrylic acid and process of preparing methacrylic acid
InactiveUS6333293B1Lower performance requirementsHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIsobutyraldehydeMethacrolein
The present invention provides a process for preparing a catalyst and the same for use in production of methacrylic acid, which is characterized by molding a raw material including a powder containing phosphorus and molybdenum at the specific pressure. The invention also provides a process for preparing methacrylic acid by gas phase oxidation and / or oxidative dehydrogenation of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of methacrolein, isobutyraldehyde and isobutyric acid in the presence of the catalyst
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Green preparation process for synthesizing 12-carbon alcohol ester by double catalytic system
InactiveCN106631776AOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlcoholWastewater
The invention relates to a preparation method of 12-carbon alcohol ester. The method is characterized in that the 12-carbon alcohol ester is directly prepared from isobutyraldehyde by one step under the action of a catalyst; the catalyst is a double catalytic system consisting of supported type solid alkali and alkaline ionic liquid. The process effectively overcome the defect that the catalyst which is sodium alcoholate or sodium hydroxide is removed from the reaction system difficultly, and has the advantages that the catalyst is easy to separate and recover, the selectivity is high, the yield is high and waste water is basically not generated in production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YINTIAN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
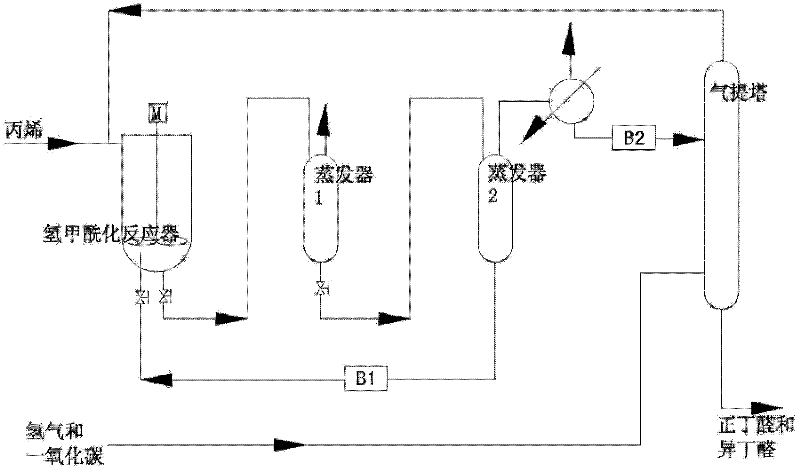
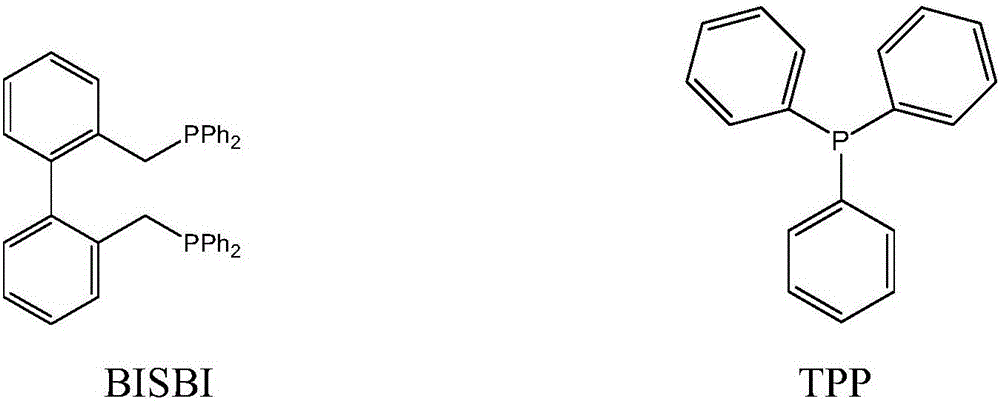
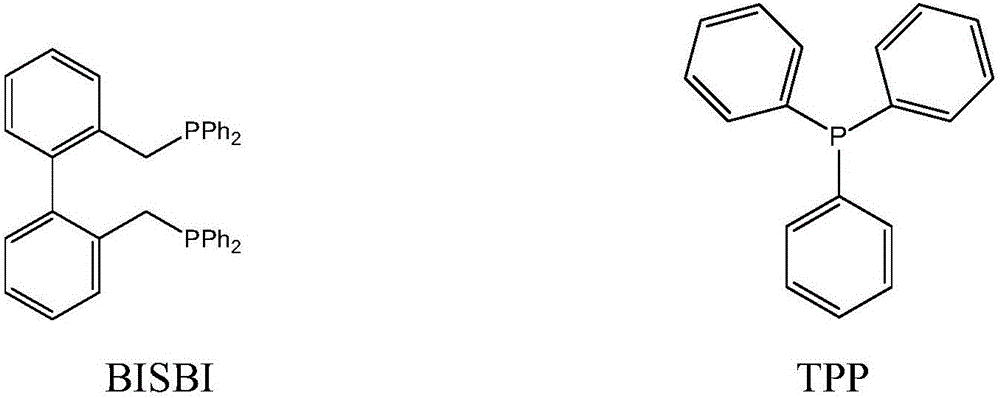
Method for preparing butyraldehyde through propylene hydroformylation
InactiveCN106083551AOvercome the disadvantages of prone to clogged pipesAdapt to market demandOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDistillationSolvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing butyraldehyde through propylene hydroformylation. The method is characterized in that a rhodium-phosphine complex, a composite catalyst system composed of bidentate phosphine 2,2'-bi(diphenylphosphinomethyl)-1,1'-biphenyl (BISBI) and triphenylphosphine (TPP) and a compound of methylbenzene or n-butyraldehyde or anisole are used as solvents, the solvents are added into a high-pressure reaction kettle, replacement is conducted 3-5 times with synthesis gas, then propylene and the synthesis gas (the molar ratio of H2 to CO is 1:1) are subjected to hydroformylation for preparing butyraldehyde under the stirring conditions that the total pressure ranges from 1 MPa to 3 MPa and the temperature ranges from 80 DEG C to 130 DEG C, the selectivity of generated butyraldehyde reaches 97% or above, the ratio of generated n-butyraldehyde to isobutyraldehyde can be regulated within the range of 9:1 to 30:1 by regulating the molar ratio of BISBI to TPP, the rhodium catalyst and the reaction product are subjected to reduced pressure distillation under the protection of the synthesis gas, and the rhodium catalyst is recovered and returned to the reaction kettle for recycling.
Owner:成都欣华源科技有限责任公司
Method for preparing hydroxy neovaleraldehyde
InactiveCN105061170AIncrease profitHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationBoiling pointAtmospheric pressure
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydroxy neovaleraldehyde, which mainly solves the problems of low raw material utilization ratio, lower product selectivity and lower yield in the prior art. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: mixing raw materials isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde with a catalyst, sending into a tank reactor, carrying out condensation reaction at 50-90 DEG C under the pressure of atmospheric pressure to 0.5 MPaG for 30-120 minutes at the rotating speed of 300-600 rpm, sending the discharged material of the tank reactor into a tubular reactor, reacting at 50-90 DEG C under the pressure of atmospheric pressure to 0.5 MPaG for 30-120 minutes to obtain a condensation product, sending the condensation product into a rectification tower to perform reduced pressure rectification, discharging low-boiling-point substances from the tower top, and sending the purified hydroxy neovaleraldehyde-water mixture obtained from the tower bottom into the subsequent section. The technical scheme well solves the problems, and can be used for preparing hydroxy neovaleraldehyde by condensing formaldehyde and isobutyraldehyde.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
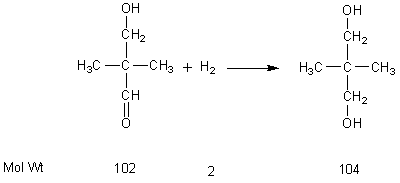
Method of producing neopentyl glycol
ActiveUS20110098515A1Easy to operateOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds purification/separationNickel catalystNeopentyl glycol
The present invention relates to a method of producing neopentyl glycol by addition of isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde in the presence of a tertiary alkylamine as catalyst to give the hydroxypivalinaldehyde with subsequent liquid phase hydrogenation in the presence of a nickel catalyst at a temperature of 80 to 180° C. and at a pressure of 6 to 18 MPa in the presence of an aliphatic alcohol and in the presence of water.
Owner:OQ CHEM GMBH
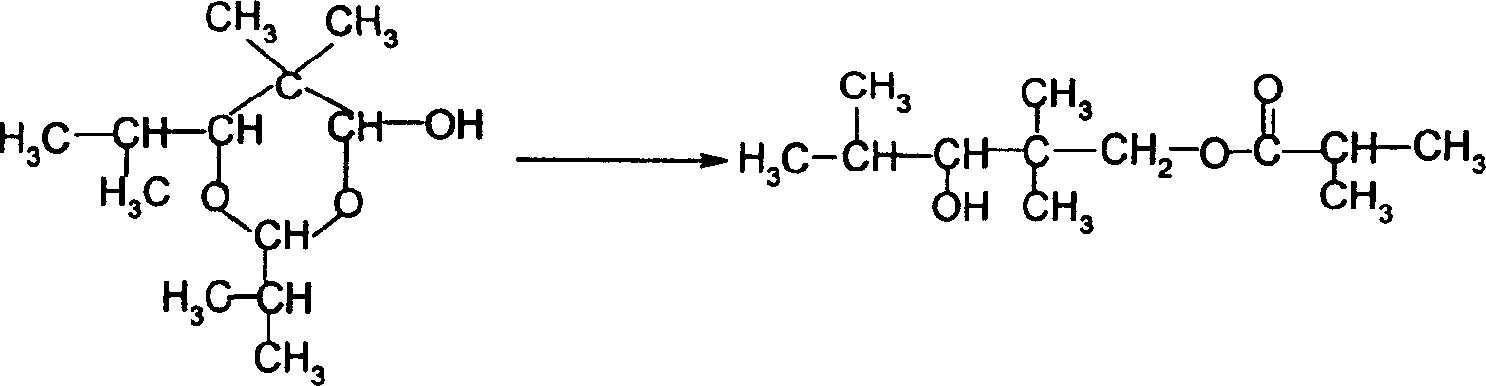
Method for directly synthesizing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate from isobutyraldehyde
ActiveCN105541583AImprove conversion rateEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationOctanolEsterification reaction
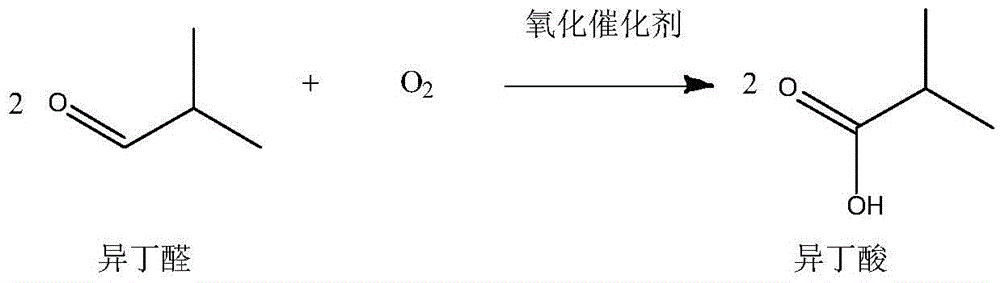
The invention belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for directly synthesizing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate from isobutyraldehyde. According to the method, isobutyraldehyde, as a by-product of an industrial butanol-octanol production process, is taken as a raw material, and 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate is directly synthesized. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, conducting aldol condensation and disproportionation-esterification on part of isobutyraldehyde to obtain 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol isobutyrate; then, conducting oxidization on the remaining unreacted isobutyraldehyde to generate isobutyric acid, wherein separation and purification are not needed; finally, carrying out an esterification reaction to obtain 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate. The method has the following advantages: the raw material is cheap and easy to obtain, and can be recycled for several times; the intermediate product needs not be separated and can be directly synthesized into the final product, so as to simplify the technical operation process for generation of the final product; and the raw material conversion rate is high, that is, the isobutyraldehyde conversion rate exceeds 92%.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Production method of neopentyl glycol
InactiveCN104672059AReduce energy consumptionLow investment costOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationDistillationEvaporation
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical production, and particularly relates to a production method of neopentyl glycol. The production method of the neopentyl glycol comprises the following three steps: condensation, evaporation and distillation, and specifically comprises the following steps: with isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde as raw materials, carrying out condensation reaction; adding alkali in the reaction process, warming for the second time, evaporating through an evaporator, and separating the neopentyl glycol from other substances; and finally obtaining a finished product neopentyl glycol by distillation. Compared with the methods disclosed by the prior art and background art, the method provided by the invention is low in energy consumption, and simple in technology; and the product is good in quality and low in investment cost.
Owner:ZHANHUA YUKAI NEW MATERIAL TECH
Method for preparing neopentyl glycol
InactiveCN101863738AReduce productionReduce dosageHydroxy compound separation/purificationPreparation by oxygen reductionWastewaterCopper
The invention discloses a method for preparing neopentyl glycol, which comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing aqueous solution of formaldehyde, isobutyraldehyde and a catalyst, and performing a condensation reaction on the isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde under the protection of inert gases to obtain solution in which hydroxypentanal is dissolved; (2) distilling the solution prepared by the step (1) under reduced pressure to obtain concentrated solution of the hydroxypentanal; (3) adding absolute methanol and a copper-based catalyst into the concentrated solution, and hydrogenating thehydroxypentanal to obtain a mixture containing neopentyl glycol; (4) purifying the mixture prepared by the step (3) to obtain neopentyl glycol solution; (5) distilling the neopentyl glycol solution prepared by the step (4) under the reduced pressure to obtain a neopentyl glycol crude product; and (6) heating the neopentyl glycol crude product to obtain gaseous neopentyl glycol, and condensing thegaseous neopentyl glycol to obtain the target product. The method has the advantages of small amount of waste water generated, high quality and yield of products, and low energy consumption.
Owner:ZIBO MINGXIN CHEM
Applying porous organic polymer to epoxidation of olefin on basis of Salen-Mn
ActiveCN104841486AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 7/17 element organic compoundsBenzeneOxygen
The invention relates to a porous organic polymer catalyst and a preparation method thereof, as well as application of porous organic polymer catalyst in epoxidation of olefin. The porous organic polymer catalyst consists of Salen-Mn ligand and 1, 3, 5-acetylenyl benzene, is prepared through Sonogashira-Hagihara coupled reaction, has the advantage of being simple to prepare, and can catalyze the olefin to react with oxygen and isobutyraldehyde to generate epoxidation reaction with relatively high activity and relatively high selectivity. The catalyst can be simply separated from a product, and can be repeatedly used for many times.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate
ActiveCN106008157AWide variety of sourcesEasy to getOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationMedicinal chemistryIsobutyraldehyde
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate. The preparation method includes the steps that isobutyraldehyde serves as the raw material and is converted into 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol with a base catalyst, and then, 2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol is converted into 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate with an acid catalyst. The preparation method of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate has the advantages that the material source is wide, the technological process is simple, the conversion rate is high, the product purity is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:谦信化工集团有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com