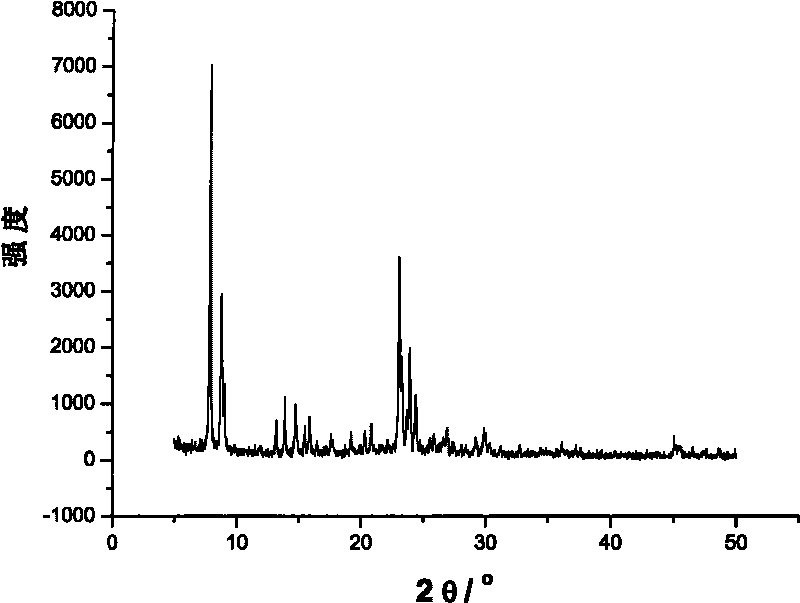
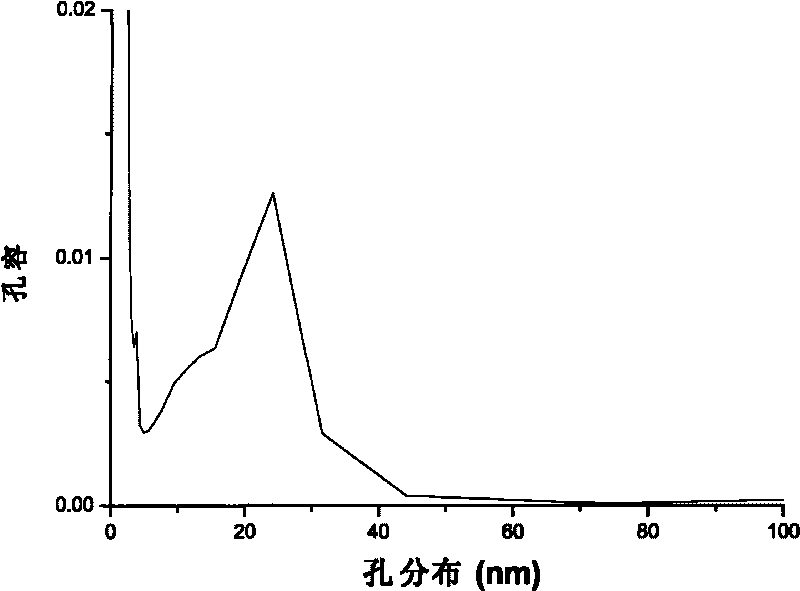
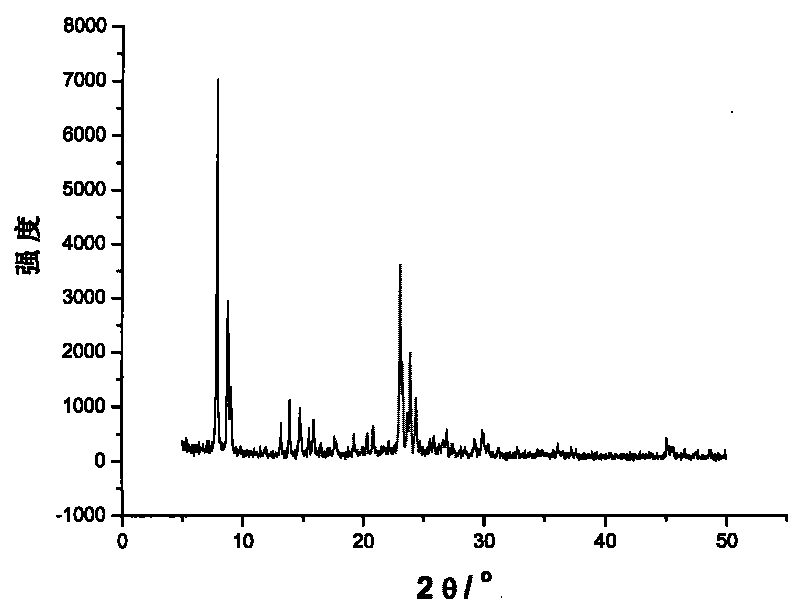
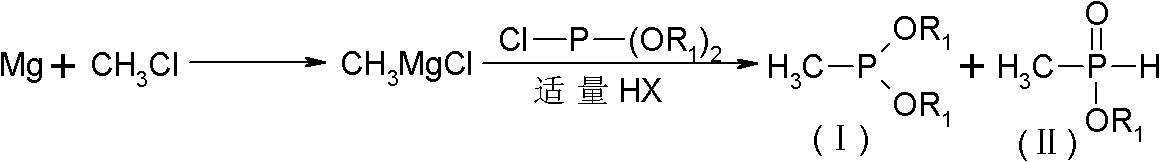
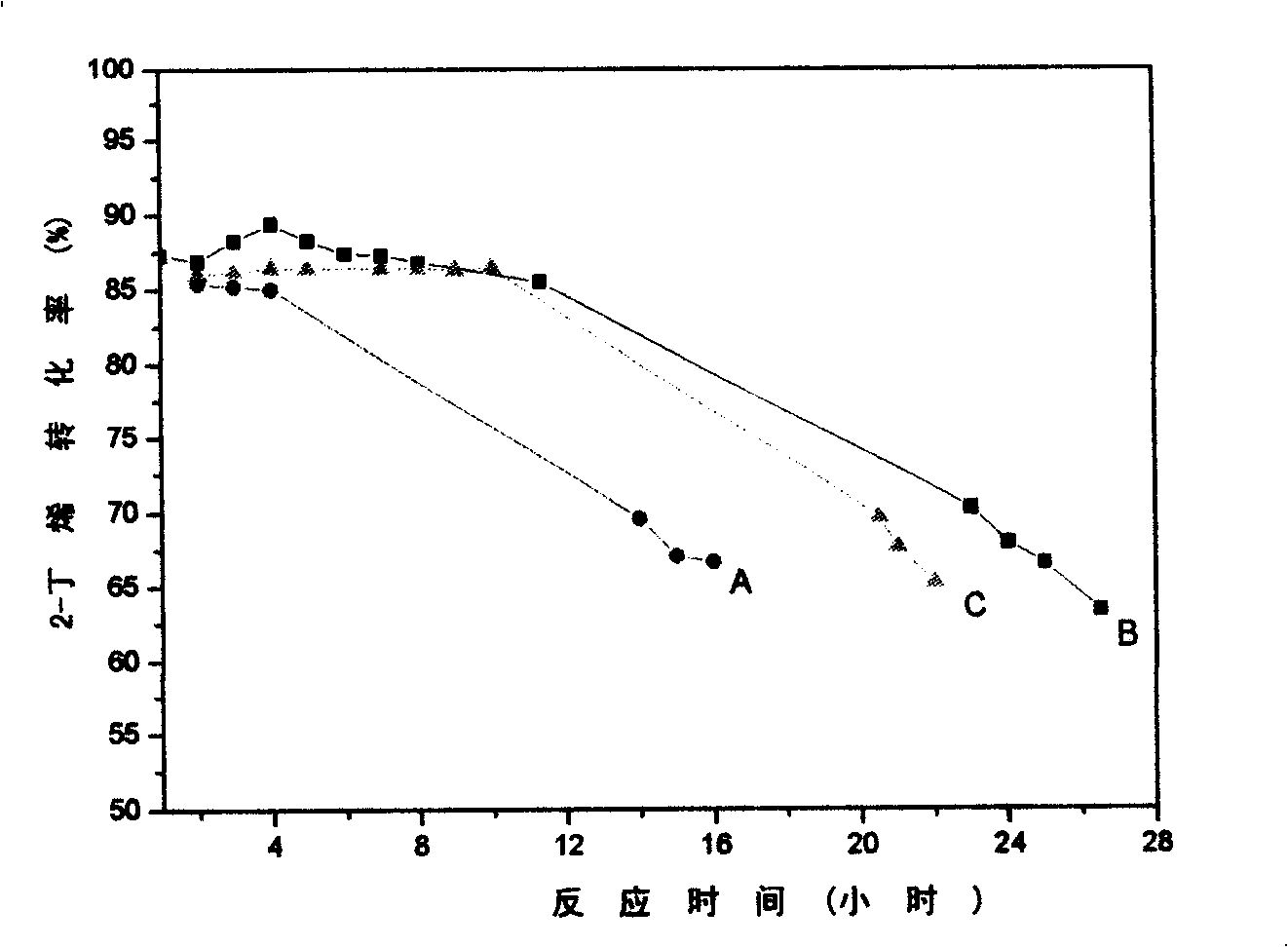
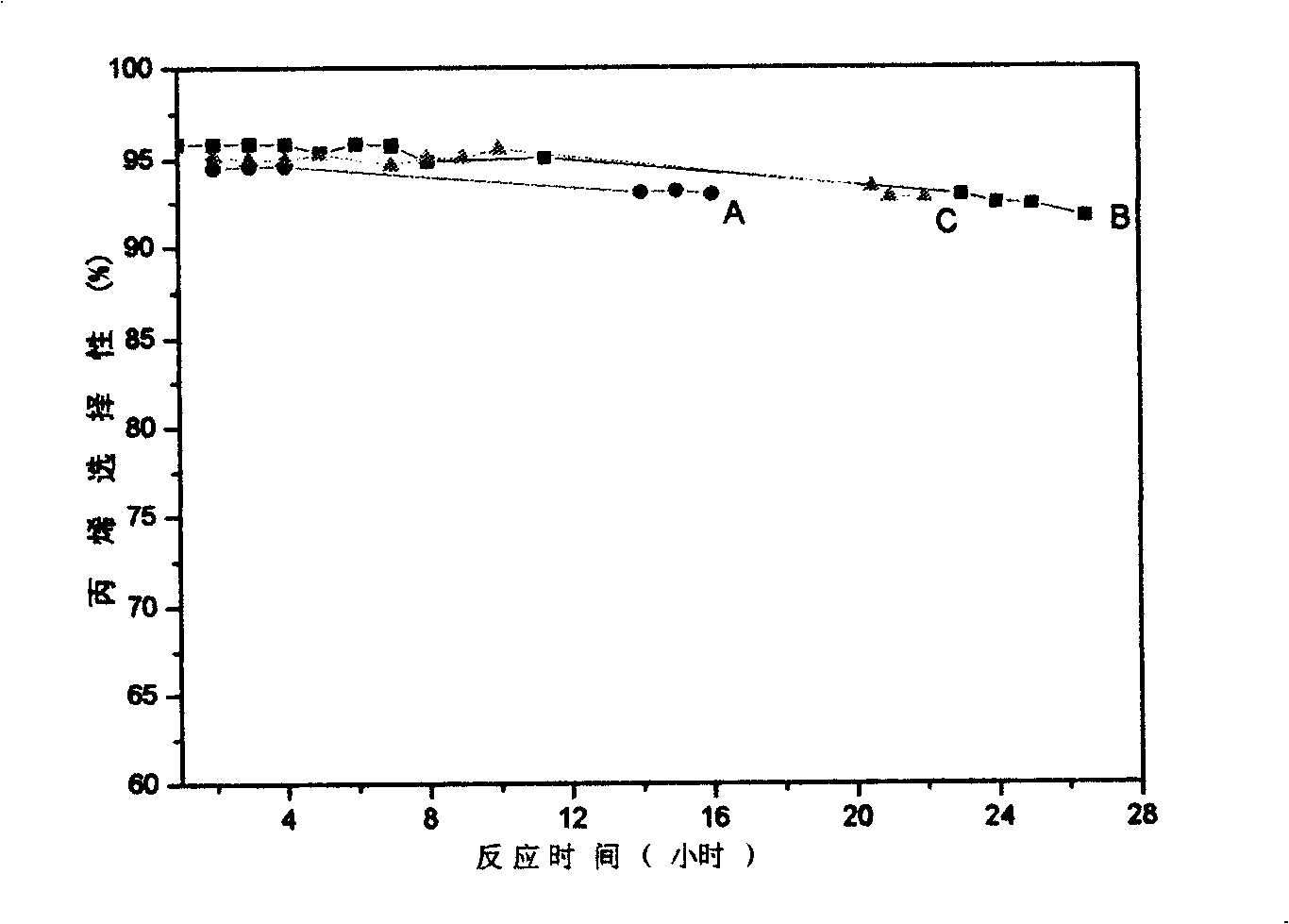
Patents
Literature
1157 results about "Disproportionation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
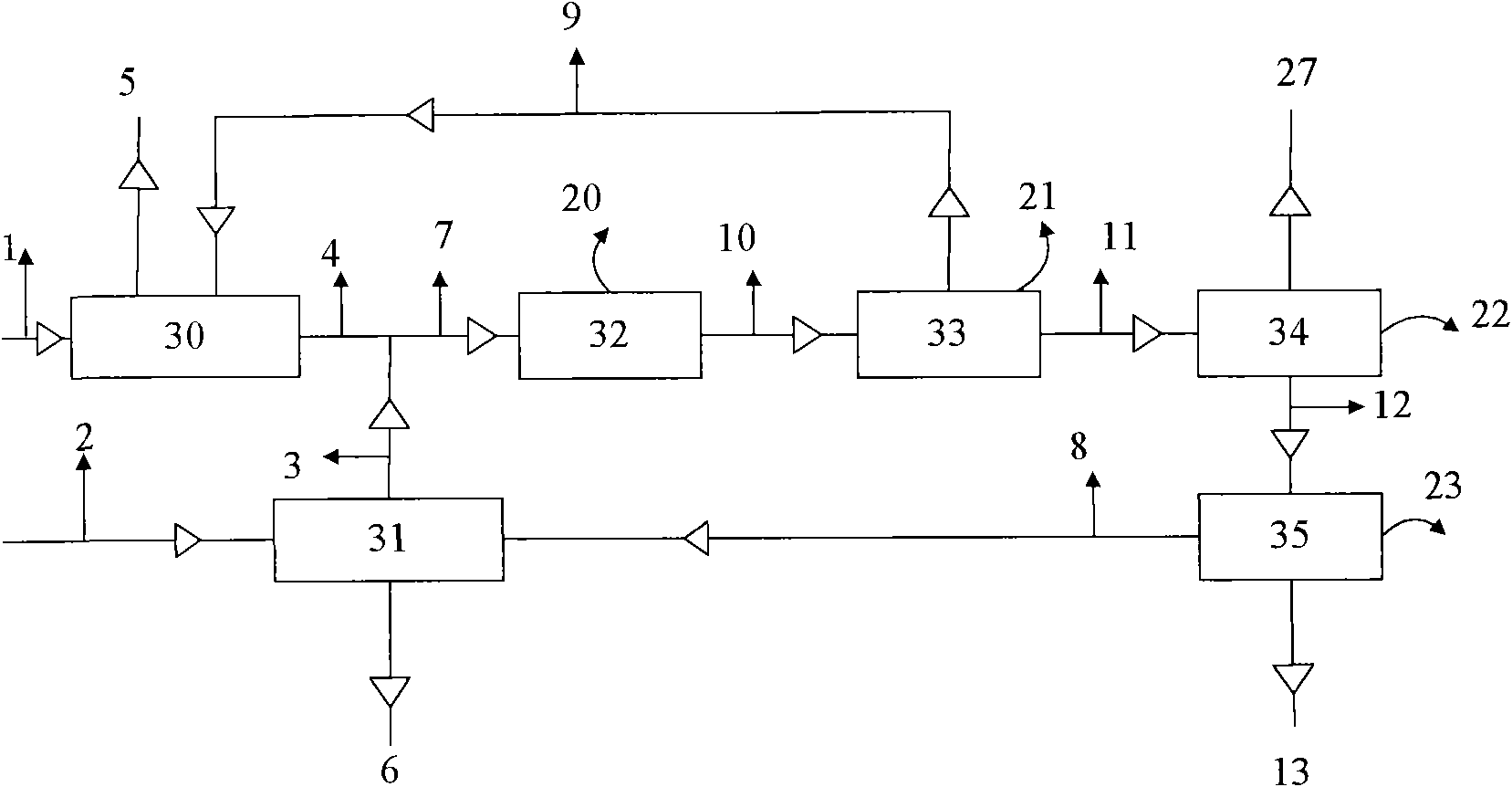
Disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which a compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two different compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. Although not widely accepted, disproportionation is sometimes used to describe any desymmetrizing reaction of the following type: 2 A → A' + A", regardless of any redox process.
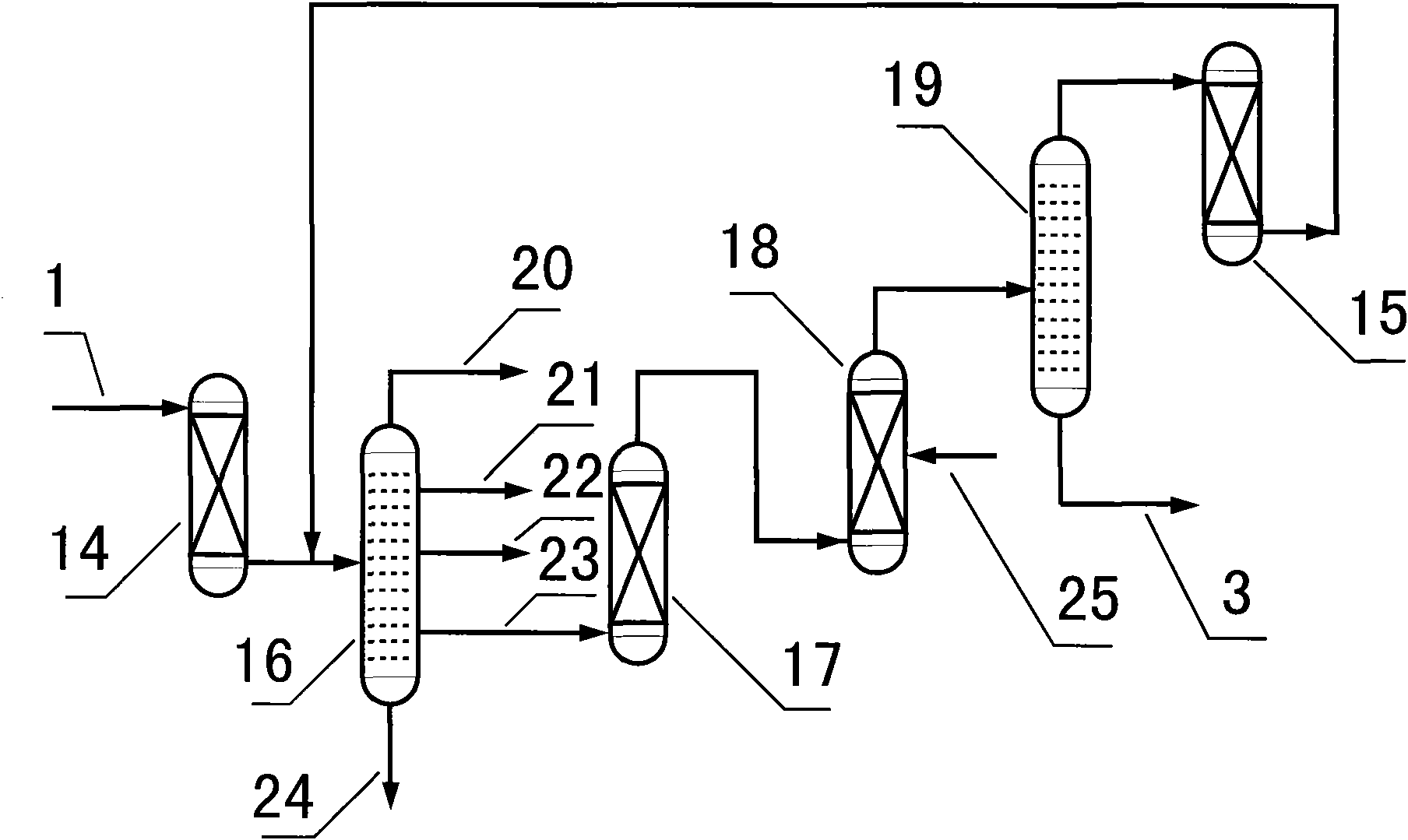
Mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material
ActiveCN101723403AImprove diffusivityImprove anti-coking performancePentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteTolueneAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material and mainly aims to solve the problem that the ZSM-5 zeolite material cannot contain mesopores and micropores at the same time, the problem that inactivation speed is high when the ZSM-5 zeolite material is used in the reactions such as toluene disproportionation and the like in the prior art. To solve the problems existing in the prior art, the invention adopts a technical scheme that: in the mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material, the molar ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is 15 to 500, and the material has 0.5 to 0.6 nanometer micropores and 5 to 100 nanometer mesopores, and the pore volume of the mesopores is 1 to 10 times that of the micropores. The mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material can be applied to the industrial production of conversion and treatment of aromatic hydrocarbons, such as toluene disproportionation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for manufacturing polycrystalline silicon used for solar battery
InactiveCN101122047ASolve environmental problemsPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureSilicon monoxideElectrical battery
A method of preparing a polycrystalline silicon for solar batteries adopts combined means of silicon monoxide disproportionation, acid dipping separation and vacuum melting and processes by the following procedures: (1) the silicon monoxide is made from chemical pure industrial silicon and high purity sand quartz. (2) the high purity silicon is obtained by disproportionation of the silicon monoxide. (3)impurities boron and phosphorus in the silicon are removed by soaking with aquafortis. (4) the high purity silicon is further purified by melting of a vacuum electro beam furnace, and parts with impurities heavily gathered in a cast ingot are cut. (5) nitrogen or nitrogen plus hydrogen is fed into a plasma furnace for melting, so as to further remove the rest boron, phosphorus and other impurities, and conduct directional solidification. (6)the outer skin and parts with impurities heavily gathered of the cast ingot are cut, and finally the high purity silicon which is above 6N pure and applicable to solar batteries is obtained. The invention rejects the technical route of the Siemens method, prevents environment pollution, improves safety of production, and is good for promotion and application in China.
Owner:李绍光
Improved synthesis method for glufosinate and analogue thereof
InactiveCN102399240AReduce generationReduce processing costsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiethyl phosphateHydrogen halide
The invention discloses a comprehensive method for synthesizing glufosinate and analogue thereof by using phosphorus trichloride, triethyl phosphate and chloromethane as initiative raw materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing Grignard, disproportionation and coupling; introducing a proper amount of hydrogen halide; and synthesizing to obtain two intermediates, namely methyl diethyl phosphate (intermediate I) and methyl phosphinate (intermediate II), wherein the two intermediates can synthesize the glufosinate and the analogue thereof. By the method, the glufosinate and the analogue thereof are synthesized by completely utilizing the methyl diethyl phosphate and the methyl phosphinate synthesized by a Grignard route; yield is increased; production cost is reduced; and three wastes are reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU YOUTH CHEM +1
Stabilization of transition metal complexes for catalysis in diverse environments
This present invention is directed towards the identification or design, preparation, and use of suitable transition metal complexes for use as catalysts. The transition metal complexes may comprise heterodonor ligands. The present invention is also directed toward a method of determining the suitability of a transition metal complex for use in a catalytic reaction, such as, but not limited to, atom transfer radical polymerization (“ATRP”), atom transfer radical addition (“ATRA”), atom transfer radical cyclization (“ATRC”), and other catalytic redox reactions. The method assists in the approximate determination of the fundamental properties of the transition metal complex in a reaction media, such as, but not limited to, solubility, redox potential, stability towards acidic, basic, or ionic species, conditional radically transferable atom phylicity, and propensity toward disproportionation and therefore, the suitability of the complex to be used as a catalyst in the reaction media. The method provides a basis for prediction and evaluation of the properties of a transition metal complex for a particular selective catalytic reaction in a broad range of reaction environments. An understanding of the principles of the disclosed method allows a transition metal complex to be tuned to specific reaction medium by selecting a transition metal complex and ligand combination having the desired qualities.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Olefin disproportionation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102614867AExtend your lifeHigh selectivityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAlkene
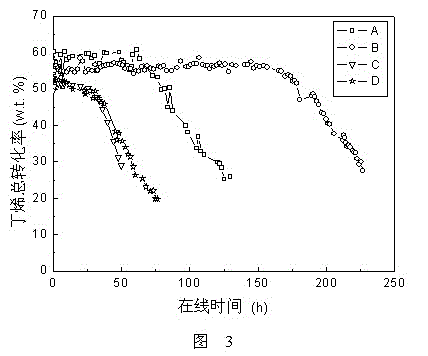
The invention discloses an olefin disproportionation catalyst having a mesoporous and macroporous composite pore structure. The catalyst comprises at least one catalytic activity metal from oxides of rhenium, molybdenum and tungsten, and a catalyst carrier, wherein the catalyst carrier is alumina having the mesoporous / macroporous composite pore structure, pore diameters of mesopores are 2-25nm, pore diameters of macropores are 50-5000nm, the specific surface area is greater than 200m<2> / g, the pore volume is 0.6-1.8cm<3> / g, mesopores account for 40-90% of the total pore volume, macropores account for 10-60% of the total pore volume, and the macropores are communicated through pores or the mesopores. The catalyst carrier is prepared by mixing and roasting an aluminum-containing compound, a mesoporous template and a macroporous particle template. The catalyst solves problems of low activity and fast inactivation of low carbon olefin disproportionation catalysts prepared through previous technologies. A preparation method of the olefin disproportionation catalyst is also disclosed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method for preparing propylene by butene disproportionation
InactiveCN1490289ALow costLow reaction temperatureHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionActive componentReaction temperature
A process for preparing propylene features that under existance of catalyst the butylene is disproportioned at 250-450 deg.C and 0.1-1.0 / hr of space speed under 0-10 MPa to obtain propylene. Said catalyst is composed of SiO2 as carrier and tungsten oxide as active component. Its advantages are cheaper catalyst and low reaction temp.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Supported ionic liquid and the use thereof in the disproportionation of isopentane
InactiveUS20050033102A1Increased product formationIncreased formationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalysts2-methylbutaneAlkane
A catalyst system containing an ionic liquid dispersed on a support having an average pore diameter greater than about 225 Å is disclosed. The catalyst system is employed in a process to disproportionate a C5 paraffin.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Process for producing organic carbonates
ActiveUS20070093672A1Speed up the conversion processCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCatalyst activation/preparationBenzeneTransesterification
A process for producing various organic carbonates by performing transesterification and disproportionation reactions in dual vapor / liquid phase mode preferably in the presence of solid catalyst composition selected from the group consisting of oxides, hydroxides, oxyhydroxides or alkoxides of two to four elements from Group IV, V and VI of the Periodic Table supported on porous material which has surface hydroxyl groups and the method of reactivating catalyst deactivated by polymer deposition by contacting the deactivated catalyst with a solution of hydroxy containing compound in a solvent such as benzene or THF.
Owner:CHEM RES & LICENSING CO
Catalyst for toluene disproportionation and alkyl transfer
ActiveCN1721069AEffectively modulate acid distributionAdjust acid distributionMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsRheniumLanthanum
The present invention relates to catalyst for toluene disproportionation and transalkylation to solve problems in past that catalyst active is low, yield of benzene and particular xylol is on the low side. It uses the scheme to achieve purpose well that loads IA and / or IIA group metal or oxide and at least one metal or oxide selected from bismuth, molybdenum, argentums, copper, zirconium, lanthanum or rhenium on big-hole zeolite with SiO2 / Al2O3 of 12~50 mole rate, and can be used in practical industry.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing propylene and coproducing ethylene from C4 olefins
ActiveCN104370676AHigh yieldPromote lysisHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon crackingDisproportionationCracking reaction
The invention provides a method for producing propylene and coproducing ethylene from C4 olefins, which comprises the following steps: filling the mixture of an olefin disproportionation catalyst and a catalytic cracking catalyst in one reactor or sectionally filling the olefin disproportionation catalyst and catalytic cracking catalyst in differential reactors which are connected in series, and passing a C4 olefin raw material through the olefin disproportionation catalyst and catalytic cracking catalyst to carry out C4 olefin disproportionation reaction and low-carbon olefin cracking reaction, thereby generating the propylene and ethylene. The method couples a low-carbon olefin disproportionation technique with a low-carbon olefin deep catalytic cracking technique, and adopts an appropriate combination mode for the olefin disproportionation catalyst and olefin cracking catalyst, thereby achieving the goal of enhancing the yields of the propylene and ethylene.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Core-shell type aromatic conversion catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101722033AGuaranteed to be completely wrappedDecrease the external area char rateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionAlcoholCore shell
The invention relates to a core-shell type aromatic conversion catalyst, a preparation method and application thereof, mainly solving the problems of strong acidity of an outside surface, rapid inactivation speed and low selectivity of aromatic shape selective catalysis in previous molecular sieve based catalysts. The invention adopts the following technical scheme: the preparation method that ZSM-5 crystal grain is taken as a core and a high silicon MF1 molecular sieve shell layer is formed on the outside surface of the core crystal by secondary growth is used for synthesizing the core-shell type zeolite molecular sieve with tightly-bonded core and shell and communicated pore canals, then the catalyst is prepared by shaping and baking 10-100% of core-shell type zeolite molecular sieves and the balance binder in terms of weight percent to better solve the above problems. The invention can be used in industrial production of aromatic conversion reactions of toluene disproportionation, toluene methylation, xylene isomerisation, trimethylbenzene cracking, cumin cracking and styralyl alcohol alkylating.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
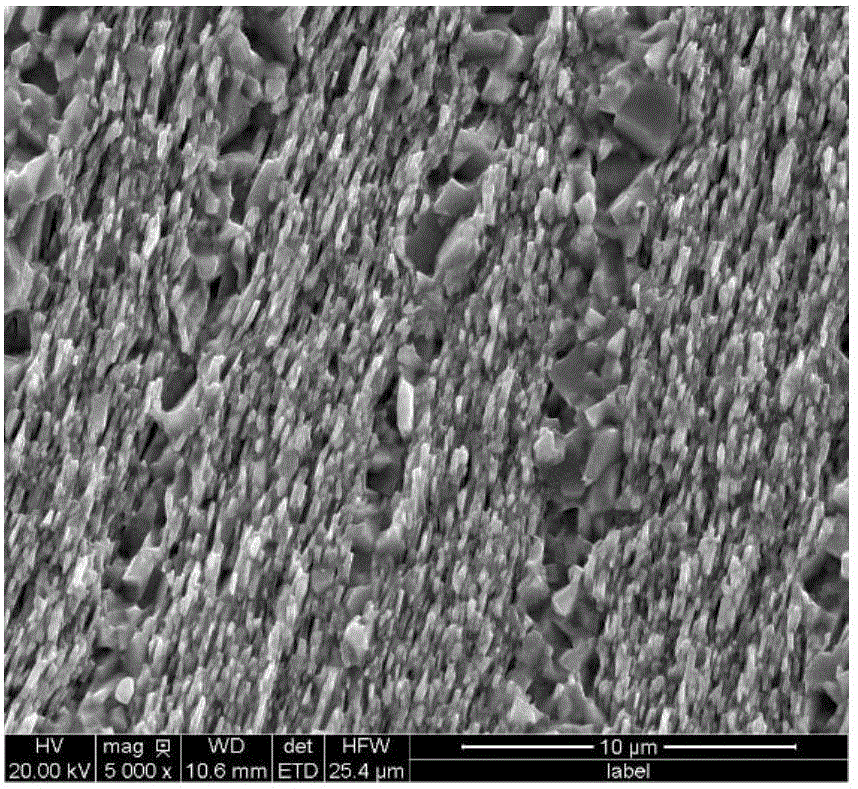
R-Fe-B MICROCRYSTALLINE HIGH-DENSITY MAGNET AND PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION THEREOF
ActiveUS20090032147A1Produced easily and cost-effectivelyDone more uniformlyInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureDesorptionRare earth
An R—Fe—B based rare-earth alloy powder with a mean particle size of less than about 20 μm is provided and compacted to make a powder compact. Next, the powder compact is subjected to a heat treatment at a temperature of about 550° C. to less than about 1,000° C. within hydrogen gas, thereby producing hydrogenation and disproportionation reactions (HD processes). Then, the powder compact is subjected to another heat treatment at a temperature of about 550° C. to less than about 1,000° C. within either a vacuum or an inert atmosphere, thereby producing desorption and recombination reactions and obtaining a porous material including fine crystal grains, of which the density is about 60% to about 90% of their true density and which have an average crystal grain size of about 0.01 μm to about 2 μm (DR processes). Thereafter, the porous material is subjected to yet another heat treatment at a temperature of about 750° C. to less than about 1,000° C. within either the vacuum or the inert atmosphere, thereby further increasing its density to about 93% or more of their true density and making an R—Fe—B based microcrystalline high-density magnet.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Method for improving mixed C4 chemical industry exploitation value
ActiveCN101492334AIncrease valueChemical added value is highHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon purification/separationChemical industryDisproportionation
The invention relates to a method for improving the chemical industrial utilization value of mixed C4. The method mainly solves the problem that the chemical industrial utilization value and the comprehensive utilization rate of a byproduct of the mixed C4 of a steam cracking device and the byproduct of the mixed C4 of an FCC device in the prior art are low. The invention solves the problem well by the technical proposal which comprises the steps as follows: 1) a selective hydrogenation technology is adopted to ensure that butadiene and acetylene in the mixed C4 are hydrogenated into monoolefine; 2) a hydroisomerization technology is adopted to ensure that butylene-1which is a product in step 1 is isomerized into butylene-2; 3) the product of step 2 is separated by rectifying technology to obtain a product of isobutene; 4) olefin disproportionation technology is used for disproportionating the butylene-2 in the rest of the mixed C4 in step 3 and ethane to produce propylene; and 5) the remained mixed C4 in step 4 is recycled as a cracking raw material. The invention can be used in the industrial production for increasing the production of the propylene and improving the chemical industrial utilization value of the mixed C4.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing pale disproportionated rosin with high content dehydroabietic acid and P-camphogen simultinuously
InactiveCN1616570APrevent browningPrevent oxidationNatural resin purificationNickel catalystDistillation
The process of producing pale disproportionated rosin with high dehydroabietic acid content and paracymene simultaneously includes the following steps: rinsing turpentine to eliminate impurity, dissolving turpentine in turpentine oil to form turpentine solution, catalytic disproportionating turpentine in solution in the presence of Pd / C catalyst, filtering and decompression distillation to obtain pale disproportionated rosin with high dehydroabietic acid content and disproportionated turpentine oil containing paracymene in 20-60 %, and distilling disproportionated turpentine oil to obtain paracymene and pinane. Or, the rinsed turpentine as material may be re-crystallized to purify and catalytically disproportionated to prepare pale disproportionated rosin containing high dehydroabietic acid in 72-82 %. The Pd / C catalyst may be replaced with skeletal nickel catalyst.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
SIOx-based compound cathode material for lithium ion batteries and preparation method of material
InactiveCN108493438AImprove the first Coulombic efficiencySmall volume changeCell electrodesSilicon oxideSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses a SIOx-based compound cathode material for lithium ion batteries and a preparation method of the material. Firstly, silicon oxide raw materials are subjected to ball-milling treatment, uniformly blended with metal salts and then subjected to spray drying, roasting is conducted at an inert atmosphere to trigger high-temperature disproportionation, and the surfaces of particles are coated with a layer of silicate; then, the surfaces of the particles are coated with a layer of amorphous-type conductive carbon to enhance the conductivity, and a finished product of the SIOx-based compound cathode material is obtained at last. The synthetic process is simple, the process conditions are easy to control, and industrialization is easily achieved. The prepared SIOx-based compound cathode material is high in efficacy and great in circulating performance and can serve as a lithium ion power battery cathode material of a new generation.
Owner:TIANJIN B&M SCI & TECH
Hydrogen generator and fuel cell system
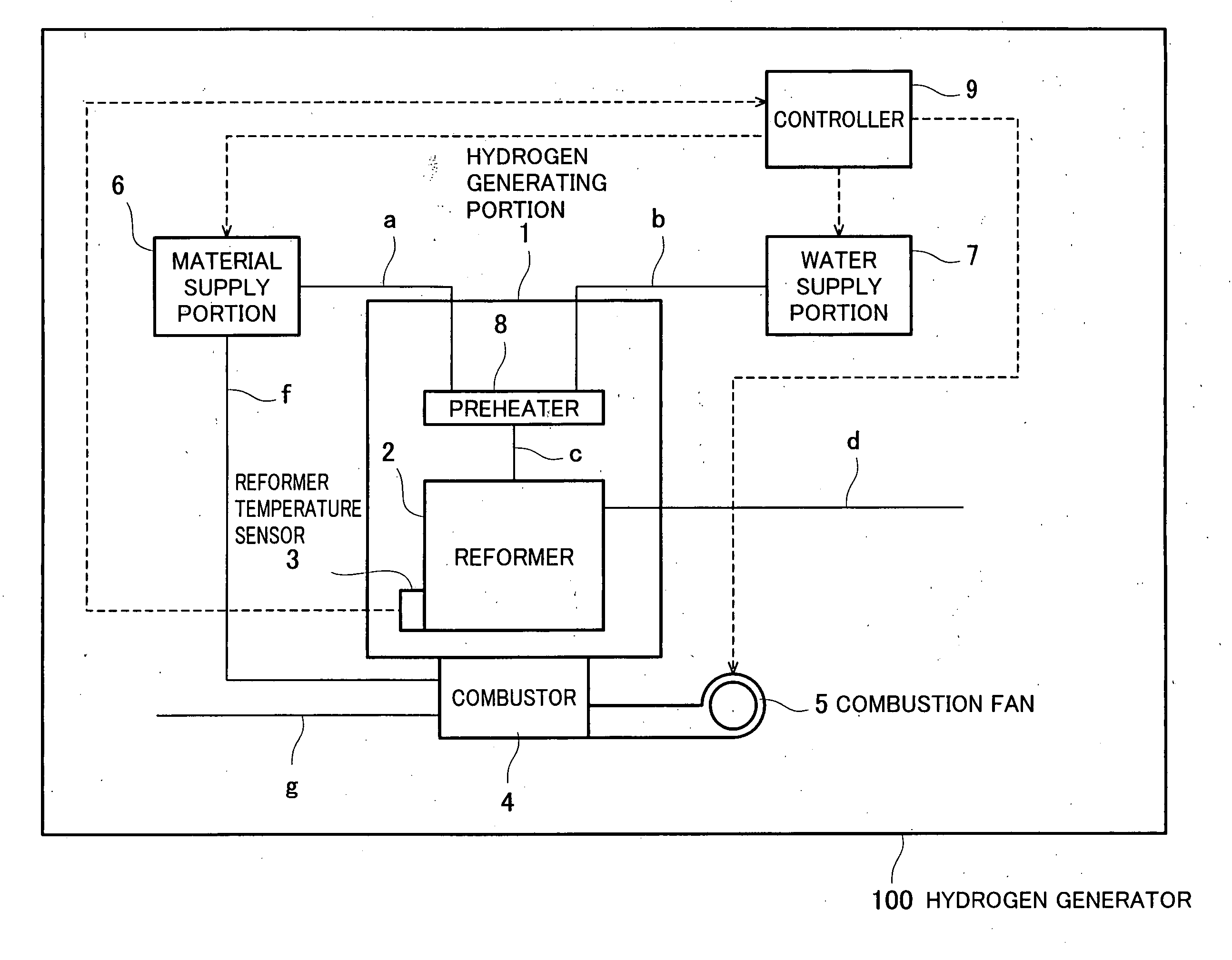
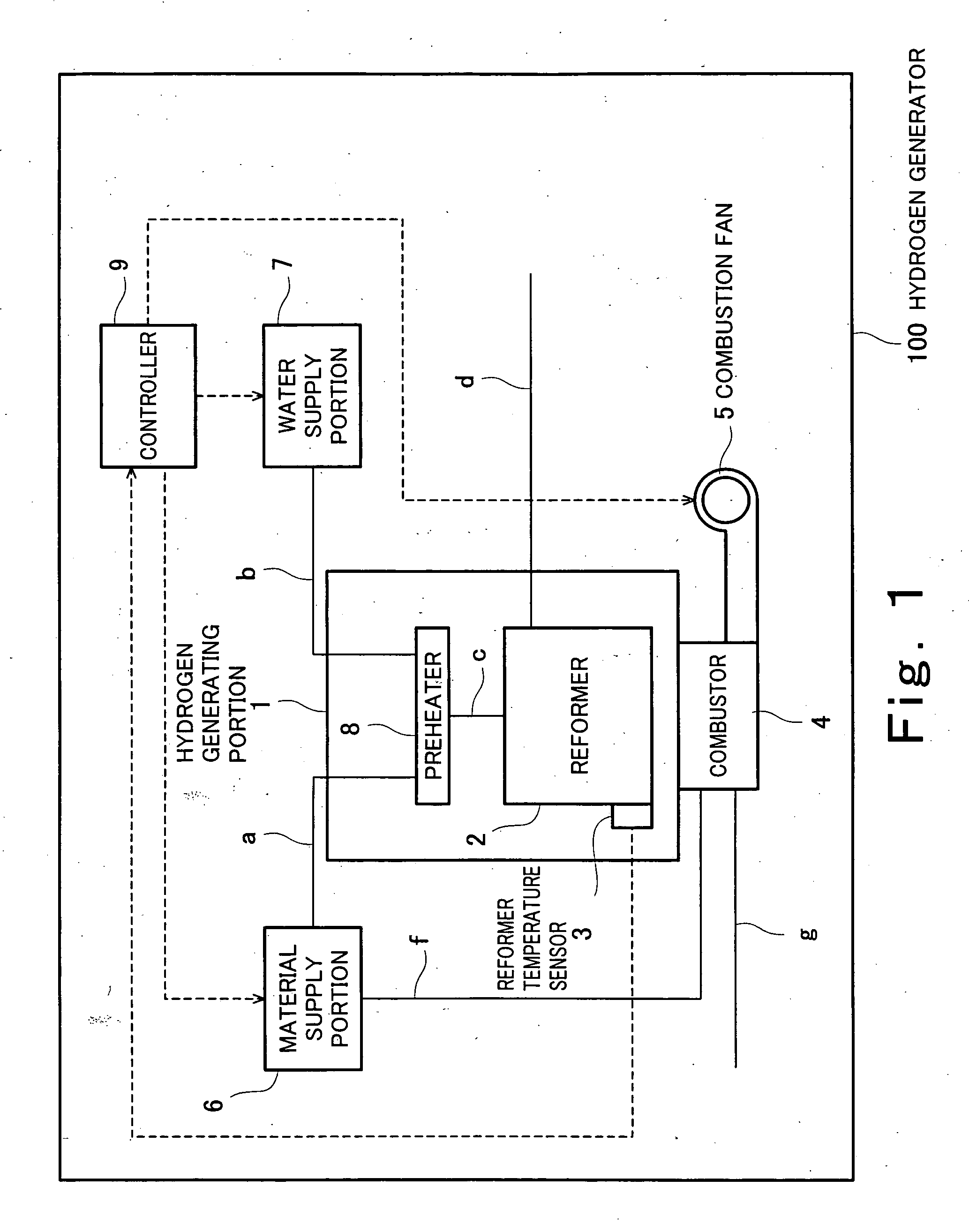
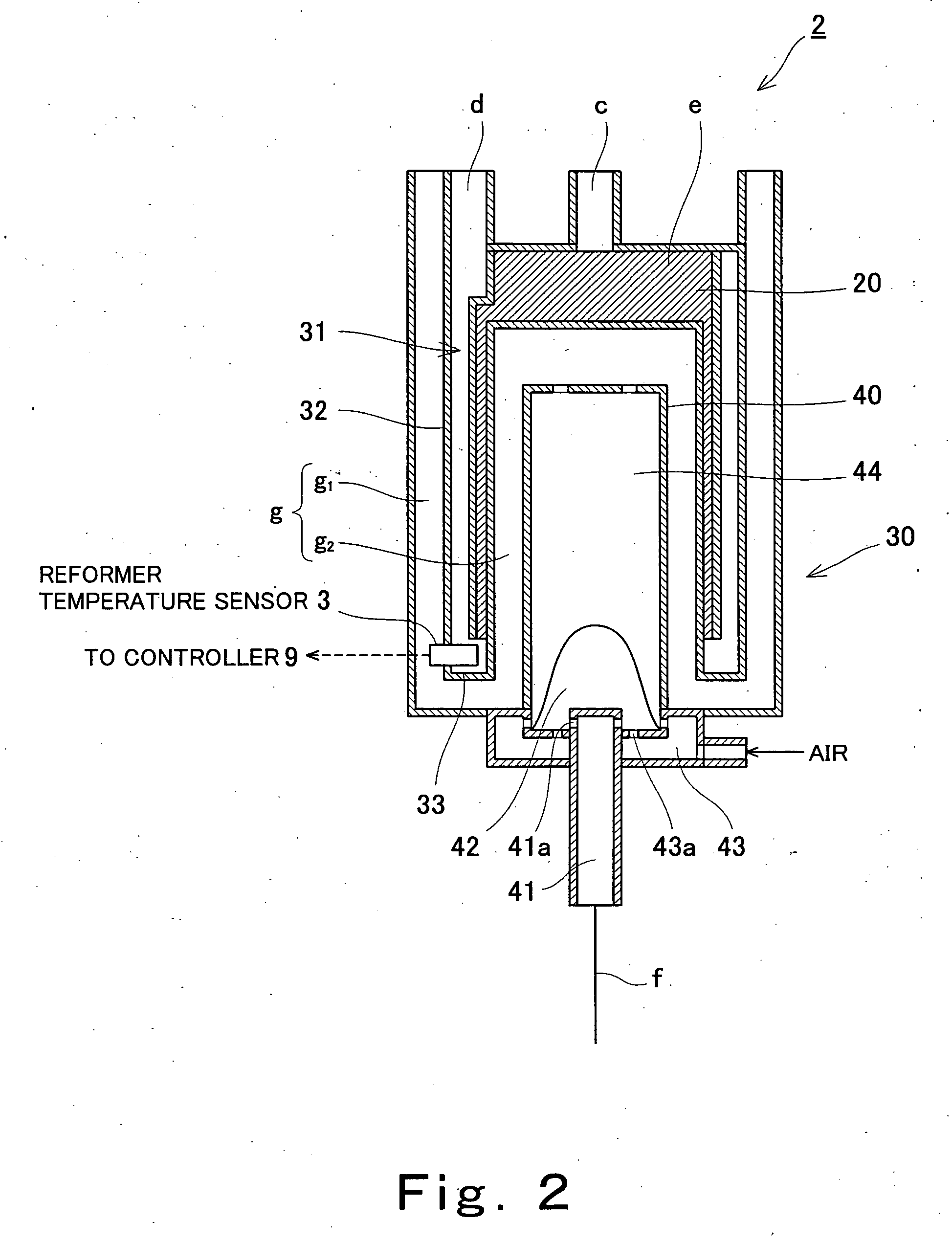
ActiveUS20060083956A1Reduce catalytic activityImprove accuracyProcess control/regulationHydrogenFuel cellsHydrogen
In a hydrogen generator according to the invention, a reformer temperature sensor detects the temperature of a reformer at a start of a stop operation of a hydrogen generator. In a controller, a processing and controlling portion compares the detected temperature with first to fourth reference temperatures pre-stored in a storage portion, and determines which of the following conditions is the temperature condition of the hydrogen generator at the stop; a first condition in which water condensation occurs, a second condition in which water condensation and carbon deposition are avoidable, a third condition in which carbon deposition occurs, a fourth condition in which disproportionation reaction occurs, and a fifth condition in which oxidization of catalyst occurs. According to the determination result, an appropriate setting is selected among first to fifth replacement settings pre-stored in the controller corresponding to the first to fifth conditions, and an internal gas replacement operation is performed according to the selected setting.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Comprehensive use method of mixed C-4
ActiveCN101555197AIncrease valueImprove technical effectHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionEther preparation by compound additionAlcoholBiochemical engineering
The invention relates to a comprehensive use method of mixed C-4, which mainly aims at solving the problem that the comprehensive utilization ratio of mixed C-4 by-products generated by a steam cracking device and an FCC device is low in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adopting an extract technology to obtain butadiene through separation; (2) adopting an etherificationtechnology to synthesize MTBE by using isobutene remained in the C-4 undergoing the extraction in the first step; (3) separating water, ether and alcohol in the C-4 undergoing the etherification in the second step by adopting a refining and separating technology; (4) producing propylene through the disproportionating reaction between the mixed C-4 which is purified in the third step and ethyleneby adopting an olefine disproportionation technology; and (5) cyclically taking the mixed C-4 which is left after the reaction in the fourth step as the raw material of a cracking furnace. Such a technical scheme better solves the problem and can be used in the industrial production for increasing the propylene production and the comprehensive value of the mixed C-4.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
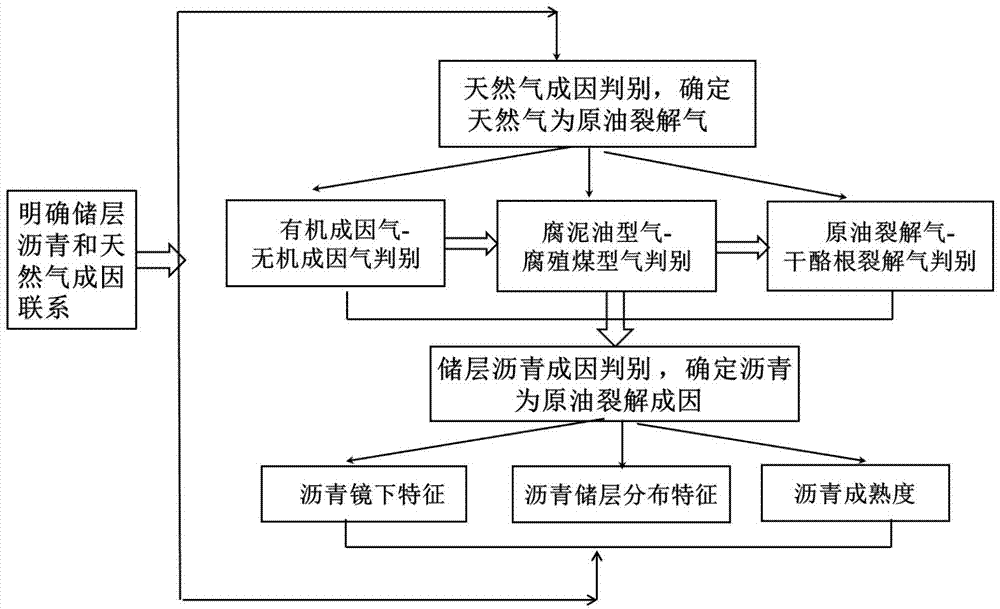
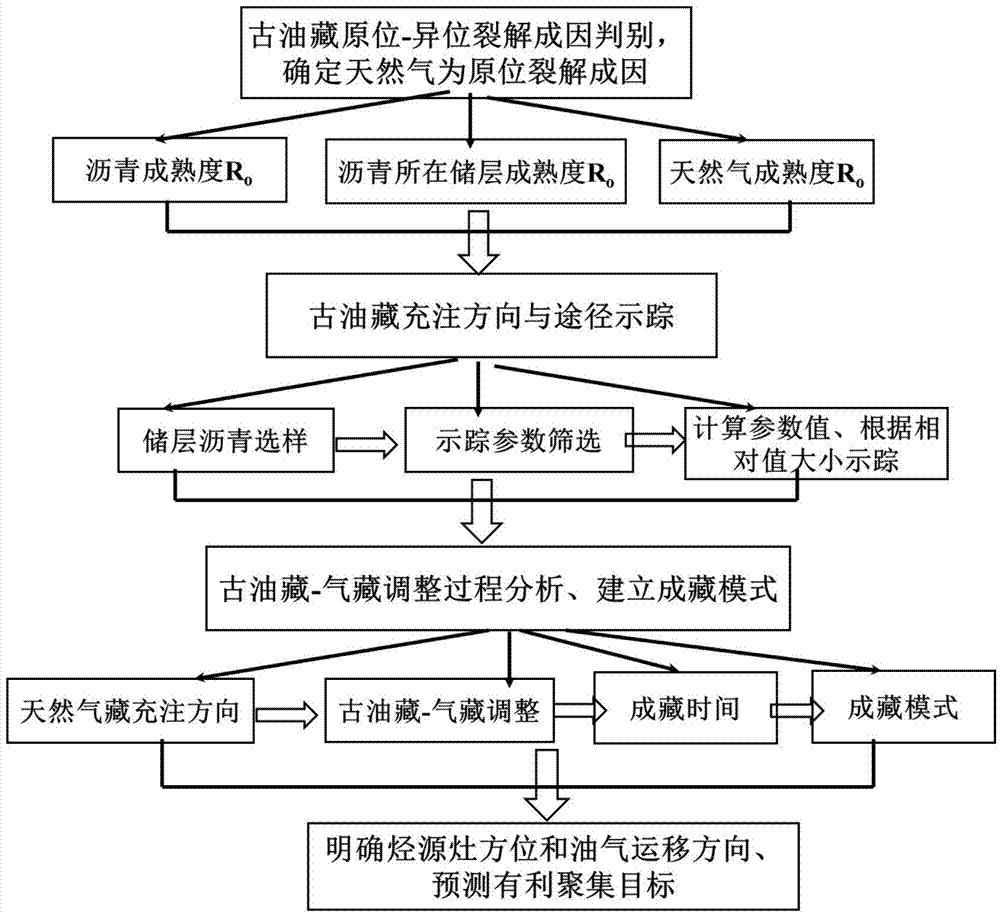
Method for tracing filling directions and paths of deep fossil oil reservoirs
InactiveCN104730595AGood effectExploration service is goodGeological measurementsPaleontologyDecomposition
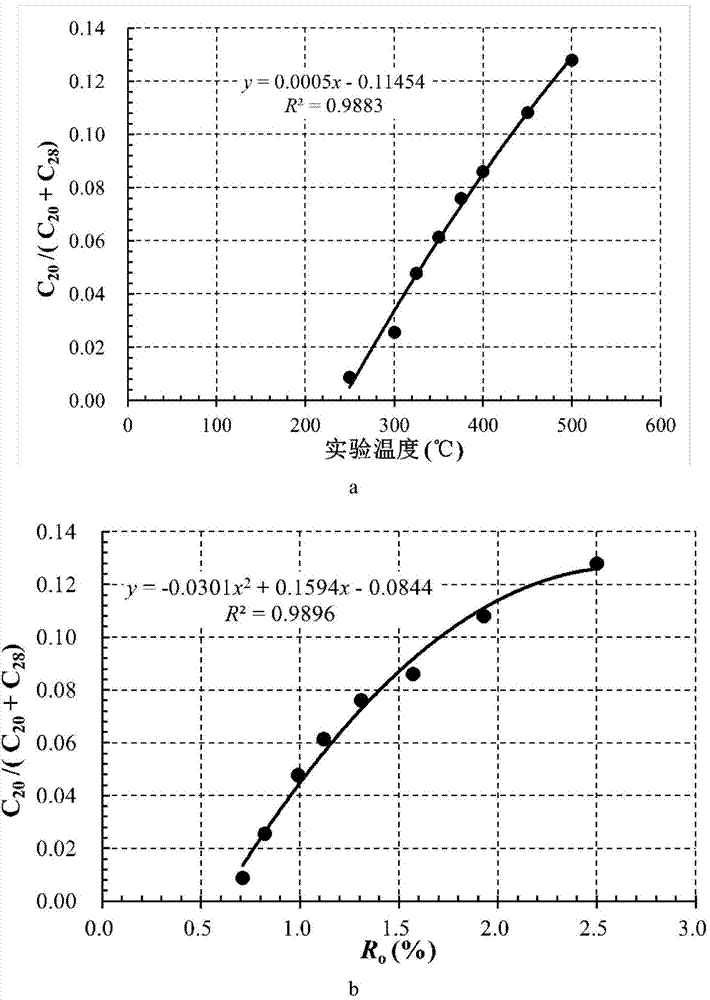
The invention relates to a method for tracing filling directions and paths of deep fossil oil reservoirs. The method includes steps of determining that reservoir bitumen and natural gas are factors for decomposition and disproportionation reaction of crude oil and have genesis relationship with each other; judging in-situ decomposition factors of the fossil oil reservoirs; tracking the filling directions and paths of the fossil oil reservoirs. The method has the advantages that the filling directions and paths of the fossil oil reservoirs are traced by the aid of the reservoir bitumen according to genesis relationships between the reservoir bitumen and the fossil oil reservoirs, and accordingly the method is applicable to completely decomposed deep high-mature and post-mature fossil oil reservoirs where natural gas is formed; study on processes in which the fossil oil reservoir are developed into natural gas reservoirs can be implemented; relationships between the reservoir bitumen and the natural gas can be determined according to relationships among reservoir bitumen R<o>, the natural gas R<o> and reservoir stratums R<o>, and whether the natural gas is an in-situ decomposition factor of the fossil oil reservoirs or not can be judged; study on reservoir formation mechanisms of the deep high-mature and post-mature natural gas reservoirs can be deepened and improved, study results are reliable, and the method can effectively serve for deep natural gas exploration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
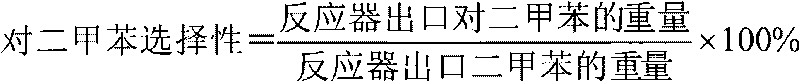
Manufacture of high purity benzene and para-rich xylenes by combining aromatization and selective disproportionation of impure toluene
InactiveUS6323381B1Reduce acidityEasy to crackHydrocarbon by isomerisationRefining with metal oxidesNaphthaAromatization
A process is set forth for reacting impure toluene to obtain benzene, toluene and a para-rich xylene stream, which are substantially free of close-boiling non-aromatics. The impure toluene comprises at least 70 wt % toluene and between about 0.2 wt % and about 5 wt % close-boiling non-aromatics. The process may also comprise aromatizing a naphtha over a non-acidic catalyst. The impure toluene from the aromatization step is passed over an acidic intermediate pore zeolite to produce a para-rich xylene stream and chemically pure benzene.
Owner:CHEVRON CHEM
Conversion of waste plastic to propylene and cumene
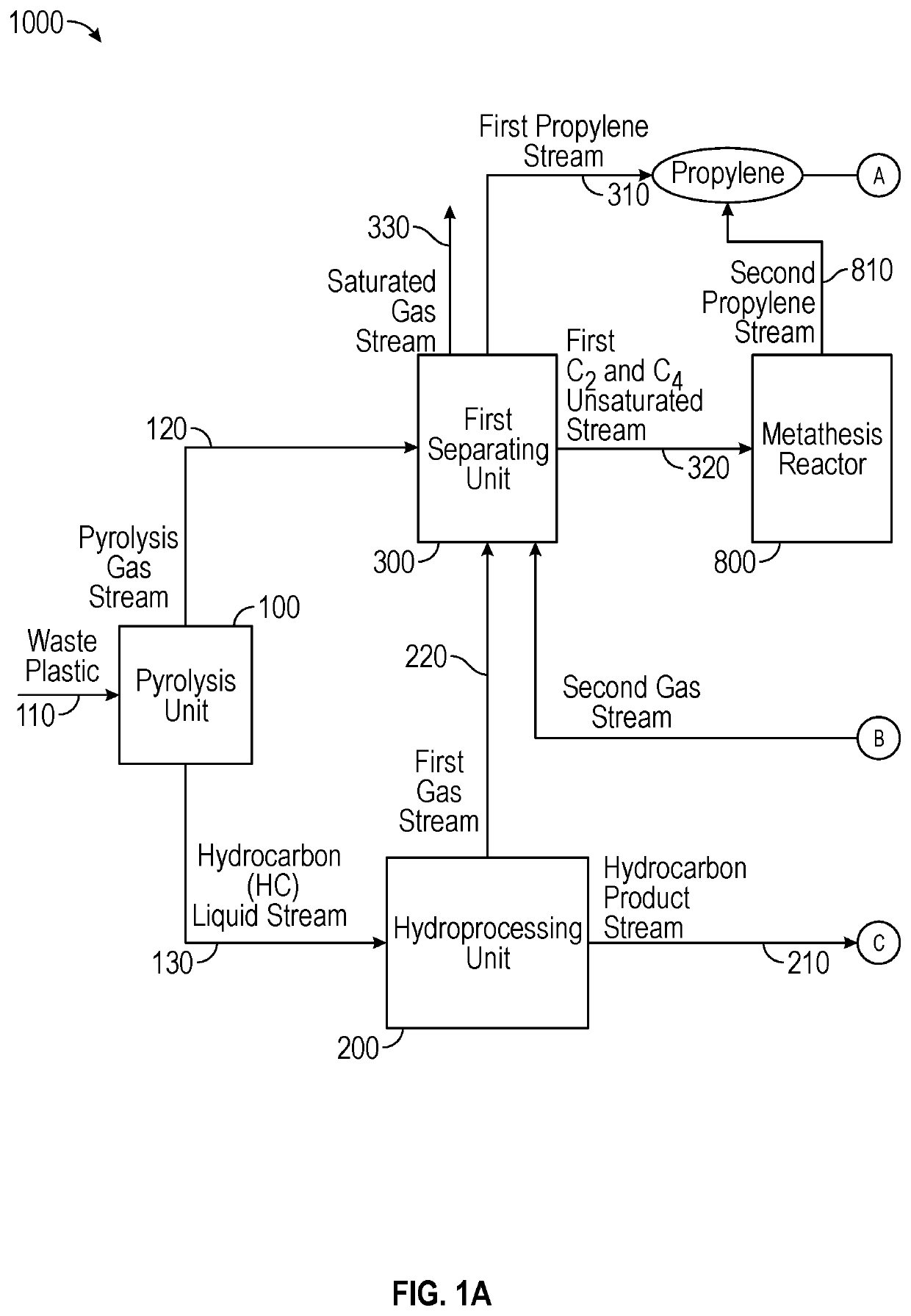
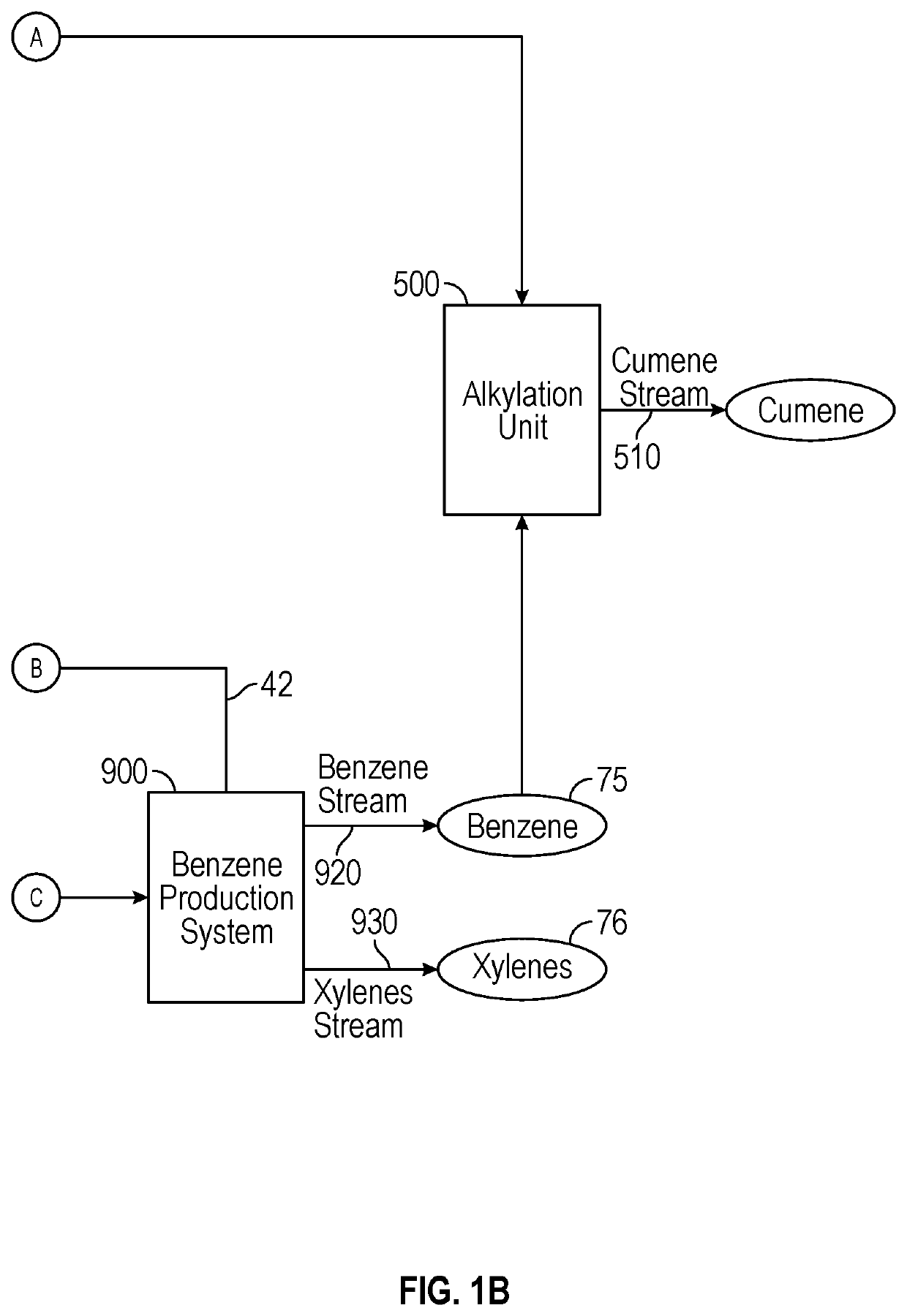
A process for producing cumene comprising converting plastics to hydrocarbon liquid and pyrolysis gas; feeding hydrocarbon liquid to hydroprocessor to yield hydrocarbon product and first gas stream; feeding hydrocarbon product to reforming unit to produce reforming product, second gas stream, and hydrogen; separating reforming product into non-aromatics recycle stream and second aromatics stream (C6+ aromatics); recycling non-aromatics recycle stream to reforming unit; separating second aromatics stream into benzene, C7, C8, C9, C10, and C11+ aromatics; contacting C7, C9, and / or C10 aromatics with a disproportionation&transalkylation catalyst / H2 to yield benzene&xylenes; conveying C11+ aromatics to hydroprocessor; introducing pyrolysis gas, first and / or second gas stream to first separator to produce first propylene stream, first C2&C4 unsaturated stream, and saturated gas (H2 and C1-4 saturated hydrocarbons); introducing first C2&C4 unsaturated stream to metathesis reactor to produce second propylene stream; and feeding benzene, and first and / or second propylene stream to alkylation unit to produce cumene.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Method for sulfidizing heavy metal waste and recovering valuable metals in heavy metal waste
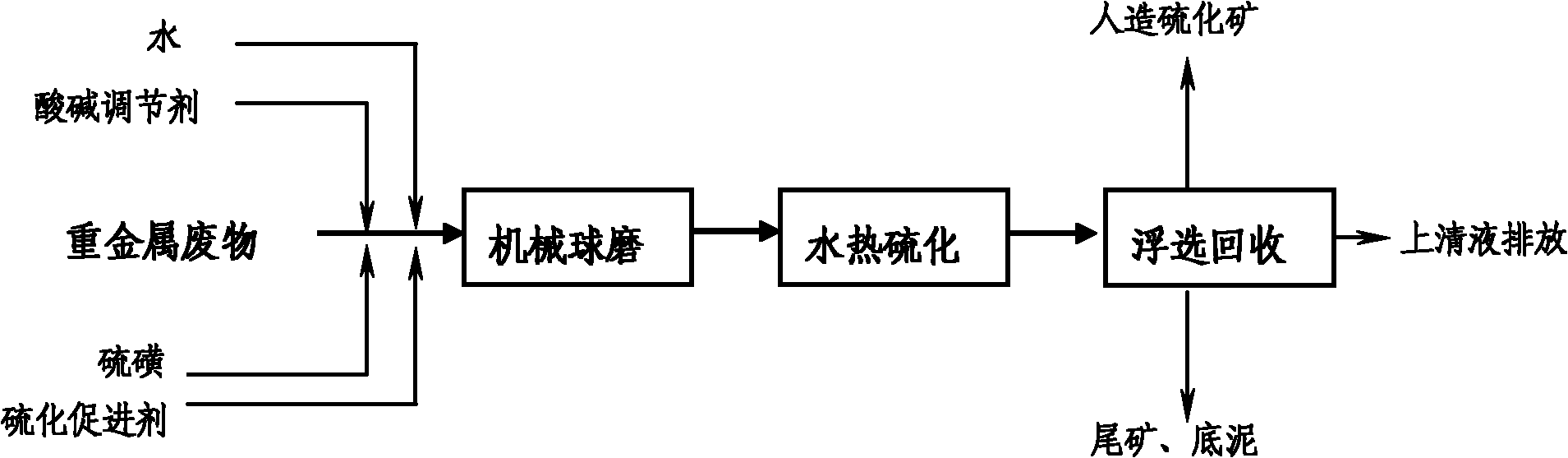
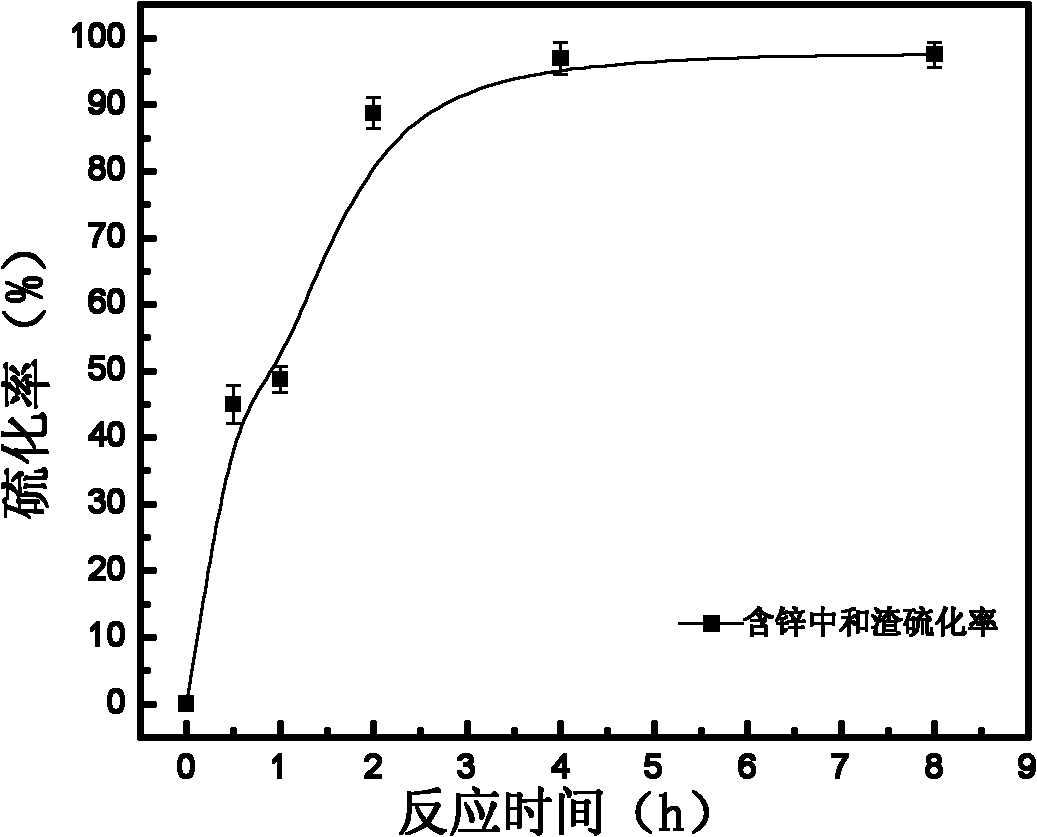
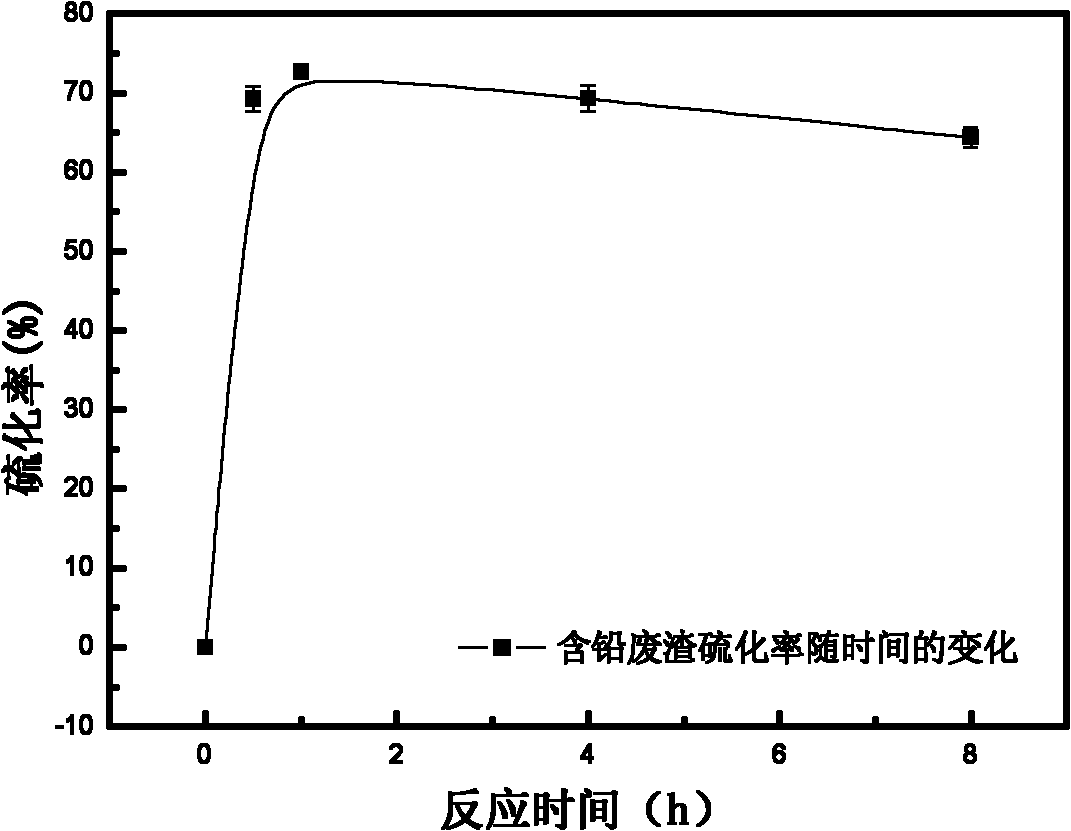
ActiveCN101824543ASave raw materialsHigh crystallinityProcess efficiency improvementVulcanizationMetallic sulfide
The invention discloses a method for sulfidizing heavy metal waste and recovering valuable metals in the heavy metal waste, comprising the following steps of: crushing the heavy metal waste, and ball-milling mixing the crushed heavy metal waste with sulphur simple substance and corresponding vulcanizing accelerator; after further fine grinding and activating, putting activated fine residue into a reaction kettle, and using sulphur disproportionation reaction to lead heavy metal in the waste into stable metal sulfide under the condition that the temperature is 160-240 DEG C, and the pressure is 1.8-2.2MPa; completing the process of hydrothermal vulcanization reaction; and then, recovering metals in a way of sulphide ore flotation. By adopting the hydrothermal vulcanization way, the method leads the sulphuration rate of the heavy metal in the residue to reach more than 90%, and secondary pollution is not caused in the sulphuration process. The method is not only used for sulfidizing and recovering the valuable metals in the waste residue, but also used for sulfidizing and stabilizing treatment of heavy metal waste residue.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
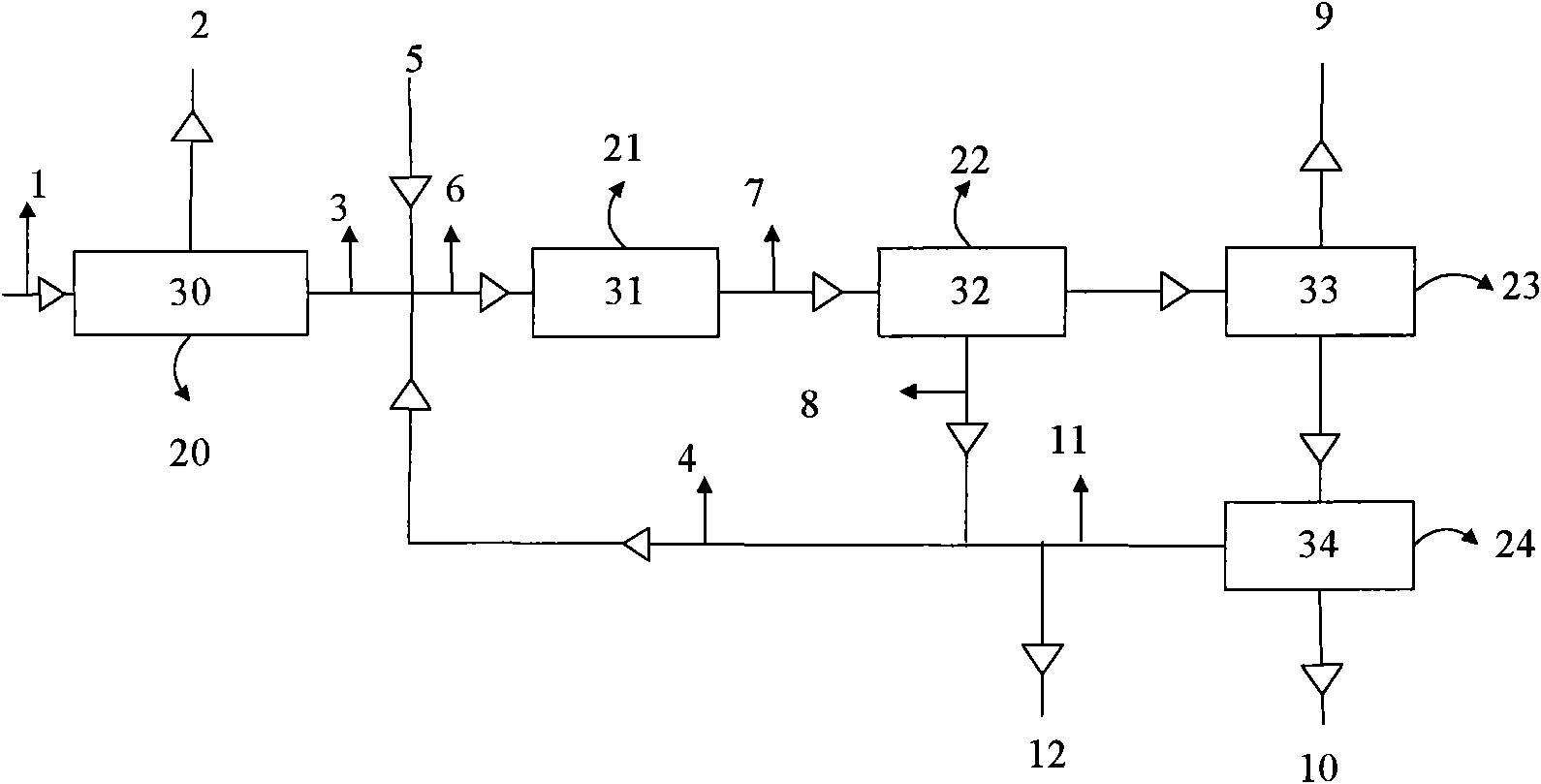
Integrated Process for the Production of P-Xylene
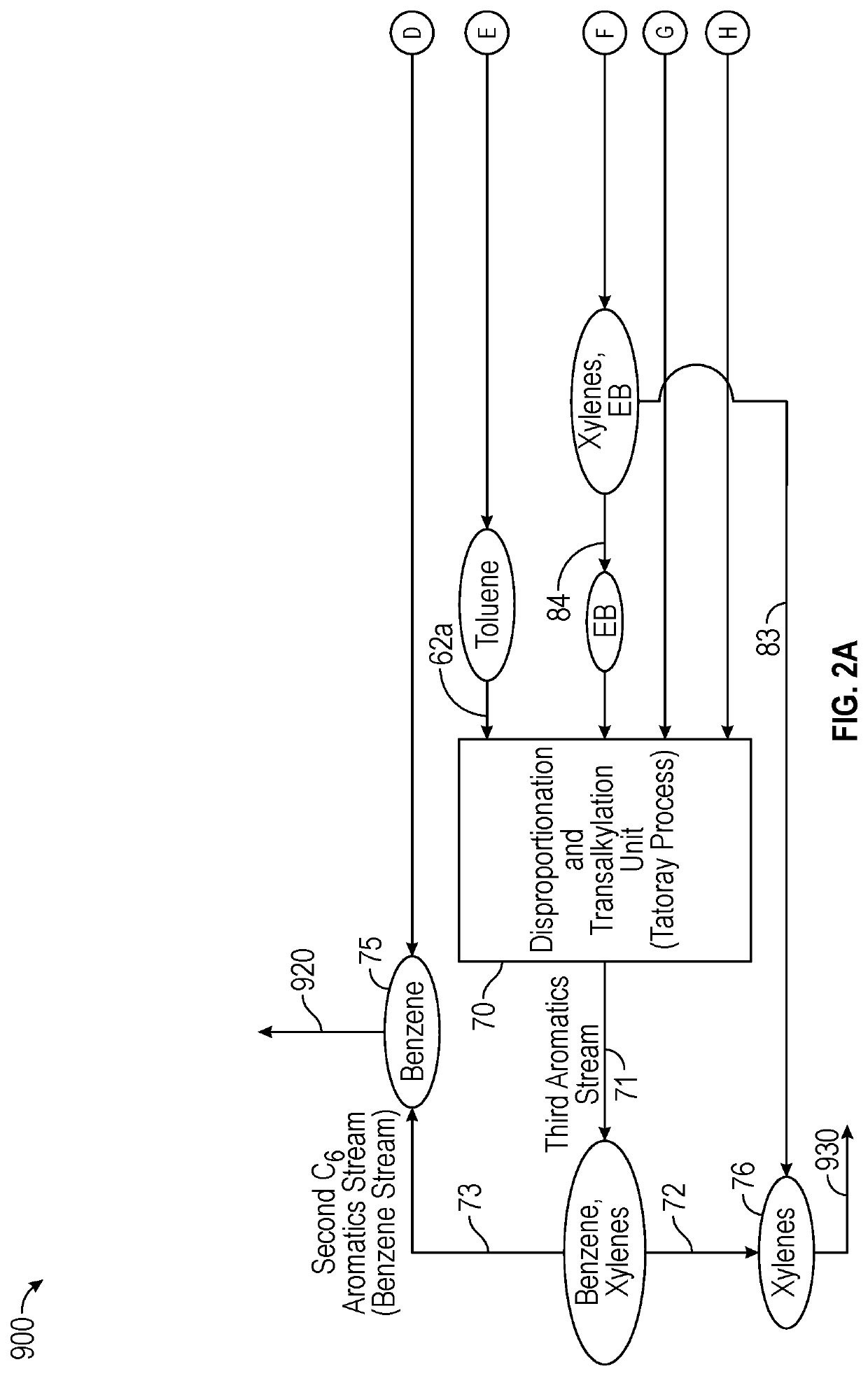
ActiveUS20100228066A1High energy consumptionImprove concentrationHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationHydrogen
The present invention provides an integrated process for the production of p-xylene, comprising the steps of A) separating a mixed feedstock containing benzene, toluene, C8 aromatic hydrocarbons, C9 and higher aromatic hydrocarbons, and non-aromatic hydrocarbons from a reforming unit, to obtain a first benzene stream, a first toluene stream, a first C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream, a stream of C9 and higher aromatic hydrocarbons, and a stream of non-aromatic hydrocarbons; B) feeding the stream of C9 and higher aromatic hydrocarbons from step A) to a C9 and higher aromatic hydrocarbon dealkylation unit, where dealkylation reaction occurs in the presence of hydrogen, and separating the reaction effluent to obtain a second benzene stream, a second toluene stream, and a second C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream; C) feeding both the first toluene stream and the second toluene stream to a toluene selective disproportionation unit, where toluene selective disproportionation reaction occurs in the presence of hydrogen to produce a stream containing C8 aromatic hydrocarbons including p-xylene and benzene, which stream is separated to obtain a third C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream, a third toluene stream, and a third benzene stream, with the third toluene stream being returned to an inlet of this unit; D) feeding both the first C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream and the second C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream to an adsorption separation unit, to obtain a first p-xylene product stream and a fifth C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream, with the fifth C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream being passed to an isomerization unit; E) feeding the third C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream to a crystallization separation unit, to obtain a fourth C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream and a second p-xylene product stream, with the fourth C8 aromatic hydrocarbon stream being passed to the adsorption separation unit or the isomerization unit; and F) feeding an effluent of the isomerization unit to an inlet of the adsorption separation unit.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101797508AEvenly distributedIncrease profitGas purification by catalytic conversionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrodesulfurizationMethanation
The invention discloses coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst and a method for preparing the same. The coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst is prepared by loading active components on the carrier of Gamma-Al2O3 with the immersion method. The active components comprises iron oxide, molybdenum oxide and cobalt oxide, wherein the weight of the iron oxide is 2-10 percent of the totalweight of the coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst, the weight of the molybdenum oxide is 5-20 percent of the total weight of the coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst, the weight ofthe cobalt oxide is 0.1-5 percent of the total weight of the coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst, and the balance is Gamma-Al2O3. The coking oven gas hydrodesulfurization catalyst has the characteristic of high hydrodesulfurization activity, less methanation reaction and CO disproportionation reaction and good thermal stability, etc.
Owner:WUHAN KELIN FINE CHEM
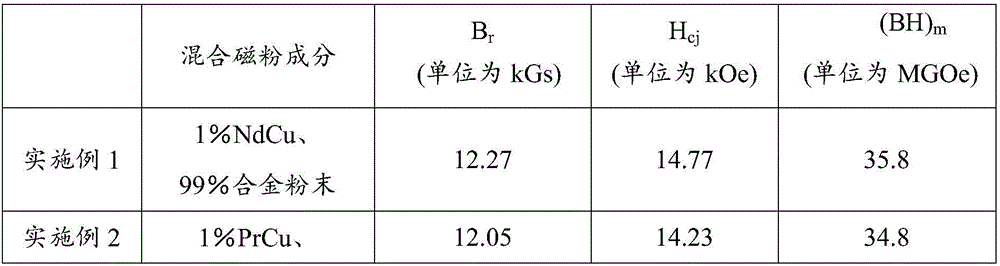
Thermal deformation rare-earth permanent magnet material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106548844APromote formationEasy to optimizeInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMass ratioRare earth
The invention relates to a preparation method of a thermal deformation rare-earth permanent magnet material. The method comprises the following steps of (1) providing main magnetic powder and low-melting-point alloy powder separately, wherein a chemical formula of the main magnetic powder is Re<x>Fe<100-x-y-z>M<y>B<z> according to the mass percent, the chemical formula of the low-melting-point alloy powder is ReCu<100-a>, Re is one or more of Nd, Pr, Dy, Tb, La and Ce and a is smaller than or equal to 90 and greater than or equal to 60; (2) mixing the main magnetic powder with the low-melting-point alloy powder evenly to obtain mixed magnetic powder, wherein the mass ratio of the low-melting-point alloy powder in the mixed magnetic powder is greater than 0 and smaller than or equal to 10%; (3) carrying out hydrogenation-disproportionation-dehydrogenation-recombination treatment on the mixed magnetic powder and diffusing a low-melting-point alloy in the treatment process to obtain HDDR magnetic powder; and (4) sequentially carrying out hot-press molding and deformation molding on the HDDR magnetic powder to obtain the thermal deformation rare-earth permanent magnet material. The invention further provides the thermal deformation rare-earth permanent magnet material.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Catalyst with shape selecting function
The invention relates to a catalyst with shape selecting function, which mainly solves the problems that the shape selecting function of the conventional shape selective catalyst is difficult to realize, the molecular sieve has the shape selecting function after modifying and the modified catalyst has lower activity. The catalyst with the shape selecting function comprises the following components in part by weight: a) 5 to 95 parts of core-shell molecular sieve material and b) 5 to 95 parts of adhesive, wherein the core phase of the core-shell molecular sieve is selected from ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-35, ZSM-48, beta, mordenite, MCM-22 and phosphorus-aluminum molecular sieve; and the technical scheme that the core-shell molecular sieve is continuous and compact ZSM-5 crystalline grains well solves the problems. The catalyst can be used in industrial production of methylbenzene selective disproportionation and methylbenzene methylation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing propylene by using etherified C4 and ethylene
ActiveCN102372573AIncrease profitGood choiceHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionIsomerizationSulfur containing
The invention relates to a method for preparing propylene by using etherified C4 and ethylene, and mainly solves the problems of low selectivity of target products and low utilization rate of raw materials existing in the prior art. The invention has the technical scheme that the etherified C4 and the ethylene are taken as raw materials and the method sequentially comprises the following steps that: (1) a raw material I obtained by removing water, alcohol, ether and sulfur-containing impurities in the raw materials and ethylene material flow II are mixed and then treated by using an isomerization catalyst to obtain material flow III containing butene-2 with the weight content of more than 80 percent; (2) the material flow III reacts to generate reaction product material flow IV containing ethylene, propylene, butene and a trace amount of C5 component under the action of a disproportionation catalyst and the isomerization catalyst; (3) the material flow IV is subjected to ethylene removal through an ethylene removal tower so as to obtain material flow V containing propylene, butane and a trace amount of C5; (4) the material flow V is separated by using a depropenizer so as to obtain a propylene product and material flow VI containing butane and a trace amount of C5; and (5) a trace amount of hydrocarbon above C5 in the material flow VI is removed through a debutanizer so as to obtain material flow VII containing the butane. The method can be used for the industrial production of the propylene by using the etherified C4 and the ethylene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
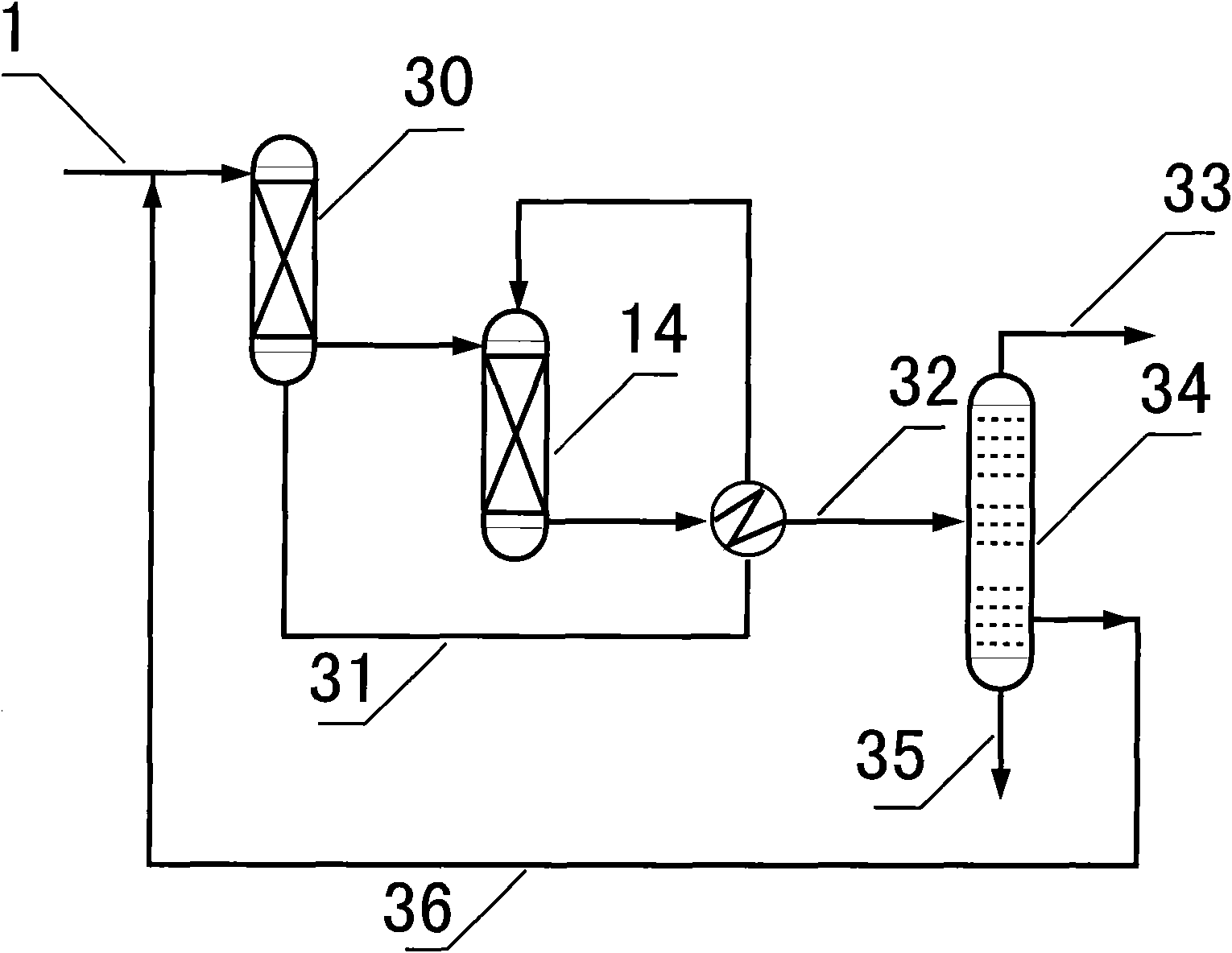
Production method of silane
The invention discloses a production method of silane. The production method comprises the following steps of: heating trichlorosilane to 70-90 DEG C by using a preheater; feeding heated trichlorosilane into a first reaction region of a reaction rectifying tower, and performing a first step catalytic disproportionation reaction of trichlorosilane in the first reaction region to generate dichlorosilane and silicon tetrachloride; feeding silicon tetrachloride generated in the first reaction region into the stripping section of the reaction rectifying tower, separating, purifying and discharging from a tower kettle; raising dichlorosilane generated in the first reaction region to a second reaction region of the reaction rectifying tower, and performing a second step catalytic disproportionation reaction to generate trichlorosilane and silane; refluxing the trichlorosilane generated in the second reaction region into the first reaction region, mixing with trichlorosilane heated by using the preheater, and continually performing the first step catalytic disproportionation reaction; and raising silane generated in the second reaction region into the rectifying section of the reaction rectifying tower, separating, purifying and discharging from the tower top of the reaction rectifying tower to obtain silane.
Owner:覃攀
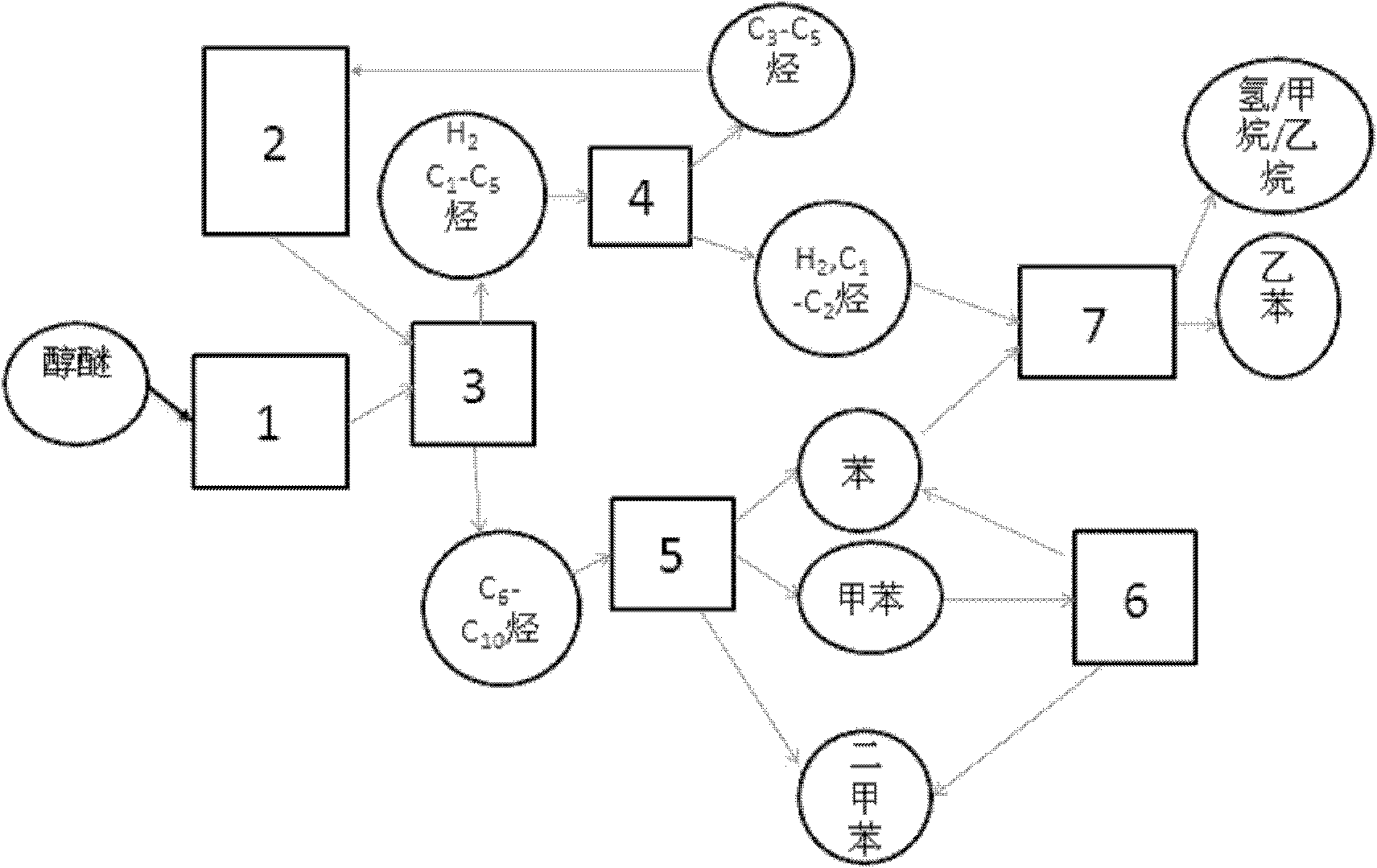
Device and method for preparing ethylbenzene by catalytic conversion of alcohol ether
ActiveCN102134178AEasy to separateDifferent operating temperaturesMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsChemical industryAlkyl transfer
The invention discloses a device and method for preparing ethylbenzene by catalytic conversion of alcohol ether, belonging to the field of chemical industry. The device comprises two aromatization reaction subsystems, a toluene disproportionation subsystem, an alkylation subsystem of ethylene and benzene and three separation subsystems. By using the device, alcohol ether raw materials can be converted to the greatest extent into the benzene and ethylene which are in a match magnitude, the confluence of the same materials among different subsystems is effectively achieved, simultaneously, a dried gas at the outlet of the alkylation subsystem is directly used as a process gas of the toluene disproportionation subsystem, and the separation of ethylene and ethane is realized. Compared with the existing device and technique for independently producing the ethylene and benzene, the device and method disclosed by the invention have the characteristics of wide raw material adaptability, short separation flow, no rigorous separation condition and low energy consumption; and the yield and purity of the product are high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Aromatic conversion process employing low surface area zeolite Y
InactiveUS6897346B1Reduced polyalkylbenzene contentEnhanced monoalkylbenzene contentHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystPorosityMolecular sieve
A process for the transalkylation of polyalkylated aromatic compounds over a high porosity zeolite-Y molecular sieve having a surface area of no more than 500 m2 / g. A feedstock comprising a polyalkylated aromatic component, including polyalkylbenzenes in which the predominant alkyl substituents contain from 2 to 4 carbon atoms, is supplied to a transalkylation reaction zone containing the high porosity zeolite-Y catalyst. Benzene is also supplied to the transalkylation zone, and the reaction zone is operated under temperature and pressure conditions to maintain the polyalkylated aromatic component in the liquid phase and which are effective to cause disproportionation of the polyalkylated aromatic component to arrive a disproportionation product having a reduced polyalkylbenzene content and an enhanced monoalkylbenzene content. An alkylation reaction zone is provided which contains a molecular sieve aromatic alkylation catalyst having an average pore size which is less than the average pore size of the average pore size of the high porosity zeolite-Y. A feedstock comprising benzene in a C2-C4 alkylating agent is supplied to the alkylation reaction zone which is operated under conditions to produce alkylation of the benzene by the alkylating agent in the presence of the molecular sieve alkylation catalyst. The alkylation product from the alkylation reaction zone is supplied to an intermediate recovery zone for the separation and recovery of a monoalkylbenzene, e.g. ethylbenzene, from the alkylation product; together with the recovery of a polyalkylated aromatic component employing a dialkylbenzene, e.g. diethylbenzene. The polyalkylated aromatic component is employed in at least a portion of the feedstream supplied to the transalkylation reactor.
Owner:FINA TECH
Catalyst for preparing propylene with ethylene and butene inverse-disproportionation and method of preparing the same
InactiveCN101254470AEasy to prepareImprove stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionMolecular sieveActive component
The invention discloses a Mo-based catalyst for inverse disproportionate synthesis of propylene from ethylene and butylene and the preparation method thereof. The Mo-based catalyst is characterized in that: the catalyst is composed of A / S, wherein A as major active component is an oxide of molybdenum and S as carrier is a mixture. The preparation method of the catalyst includes the following steps: removing a mesoporous molecular sieve with a templating agent, preparing the carrier mixture S of a certain particle size by using aluminum oxide or a precursor thereof by different methods, immersing the resulting product in a Mo-containing solution, drying, and calcining at 500-800 DEG C for 1-4 hours to obtain the required catalyst. The invention utilizes the composite carrier composed of mesoporous molecular sieve and aluminum oxide. The catalyst has the advantages of simple preparation and excellent stability. Therefore, the catalyst prepared in the invention can be used for the production of propylene with high conversion rate, high selectivity and high stability.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com