Patents
Literature
1578results about How to "Improve diffusivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
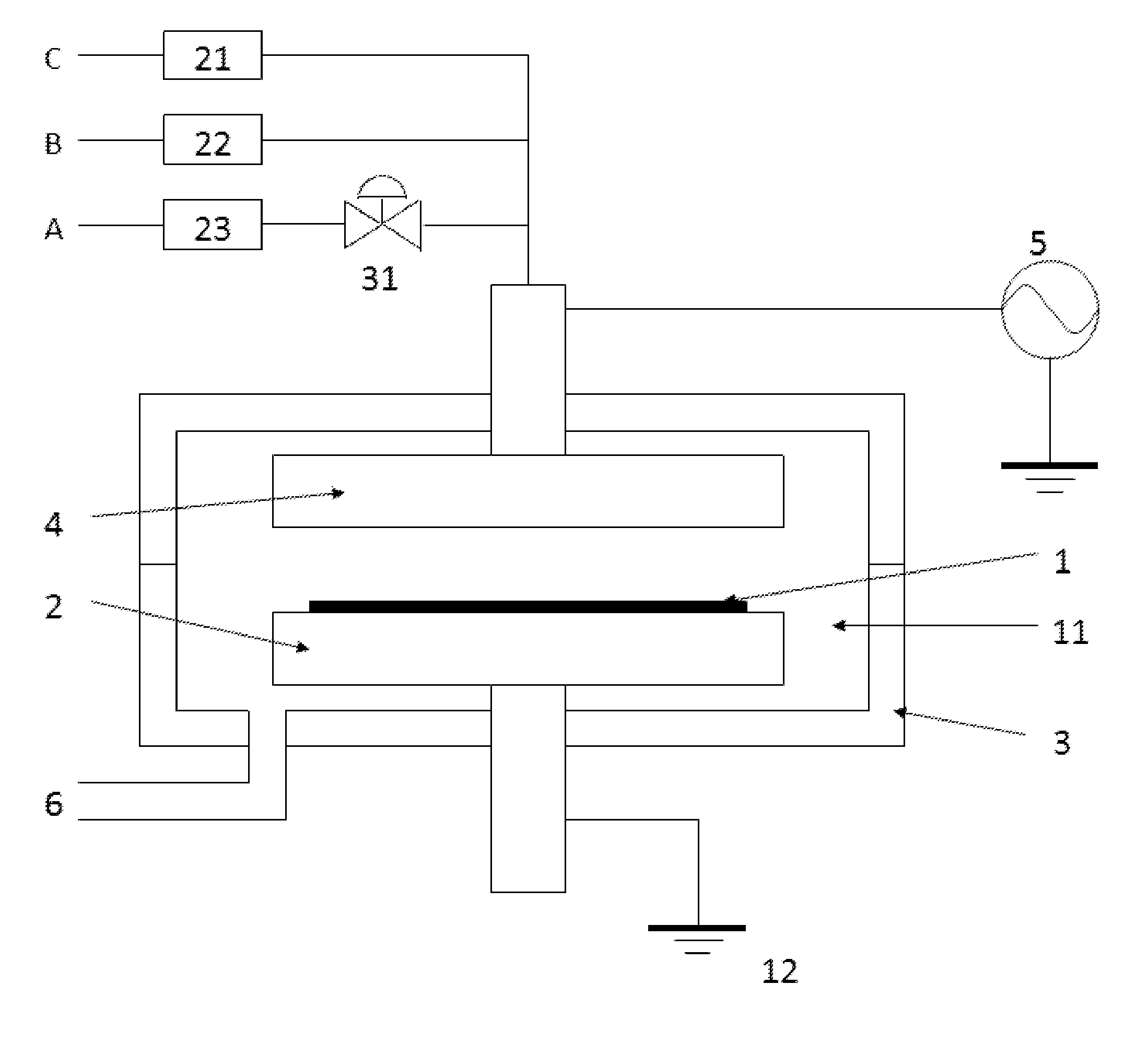
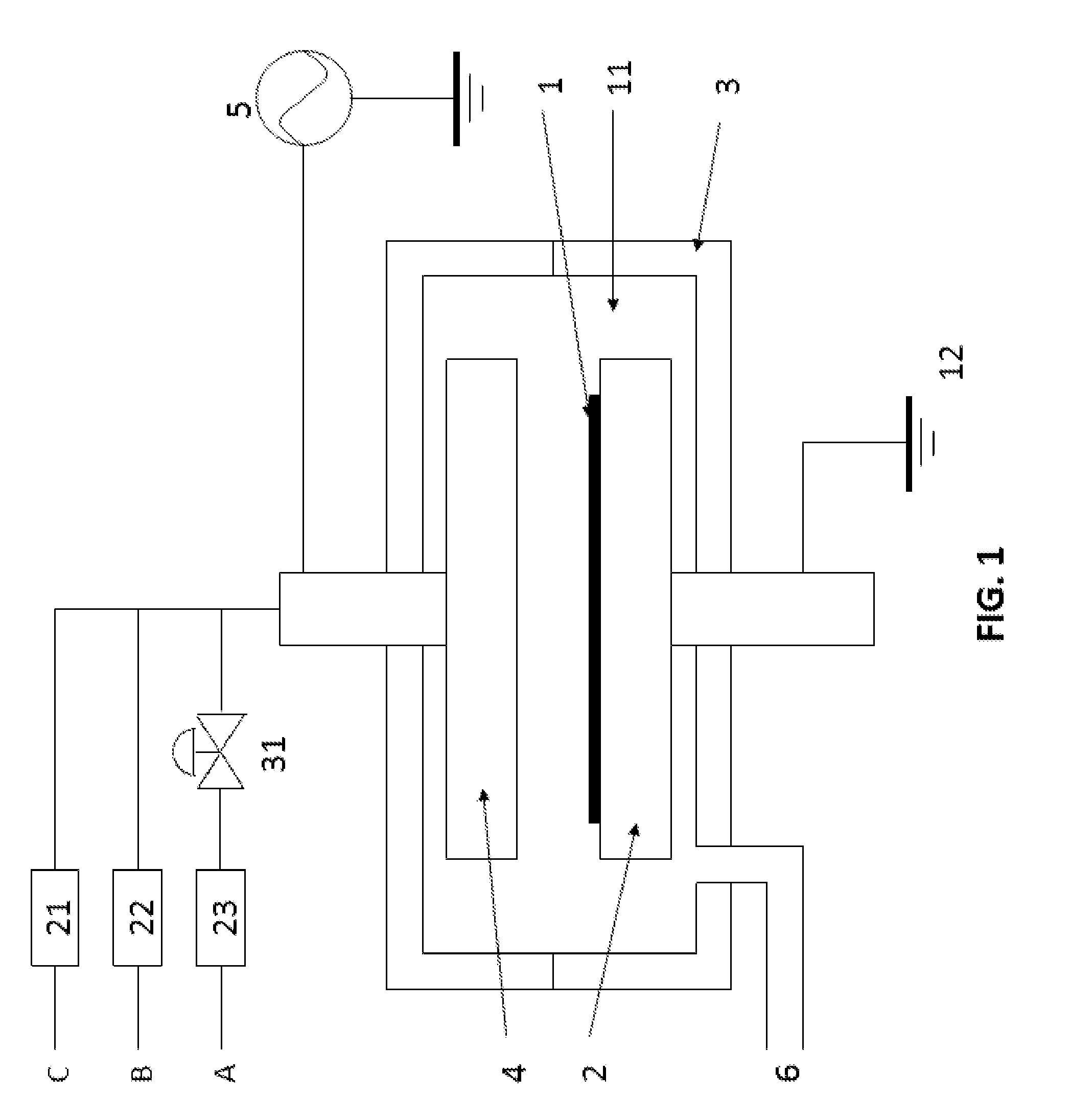
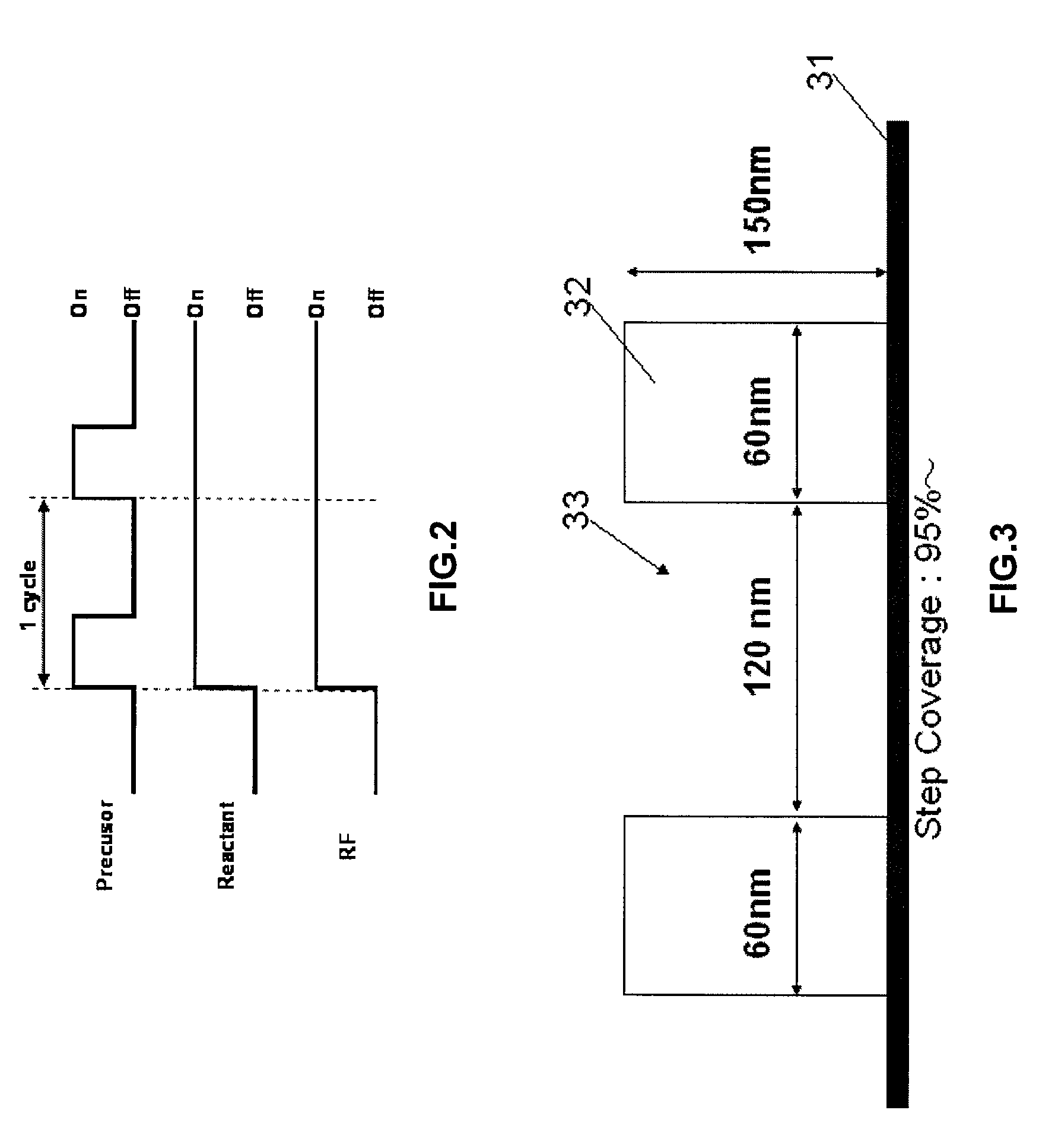
Method of forming conformal film having si-N bonds on high-aspect ratio pattern
ActiveUS8394466B2Increasing mobilityIncreasing diffusivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSiliconConformal map
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070027370A1Increase liquid volumeLarge flowMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteBiointerface
Biointerface membranes are provided which can be utilized with implantable devices, such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample. More particularly, methods for monitoring glucose levels in a biological fluid sample using an implantable analyte detection device incorporating such membranes are provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
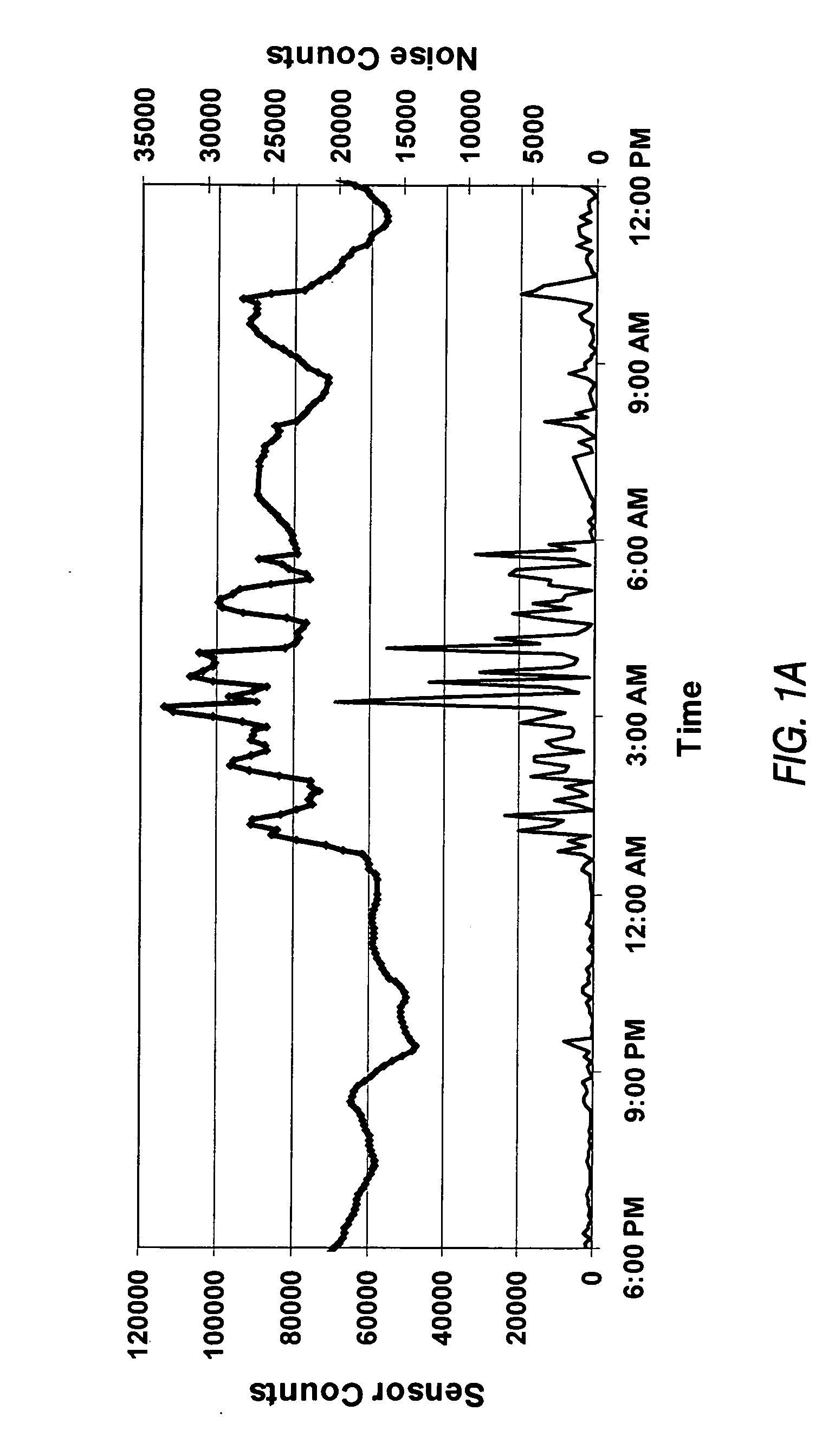
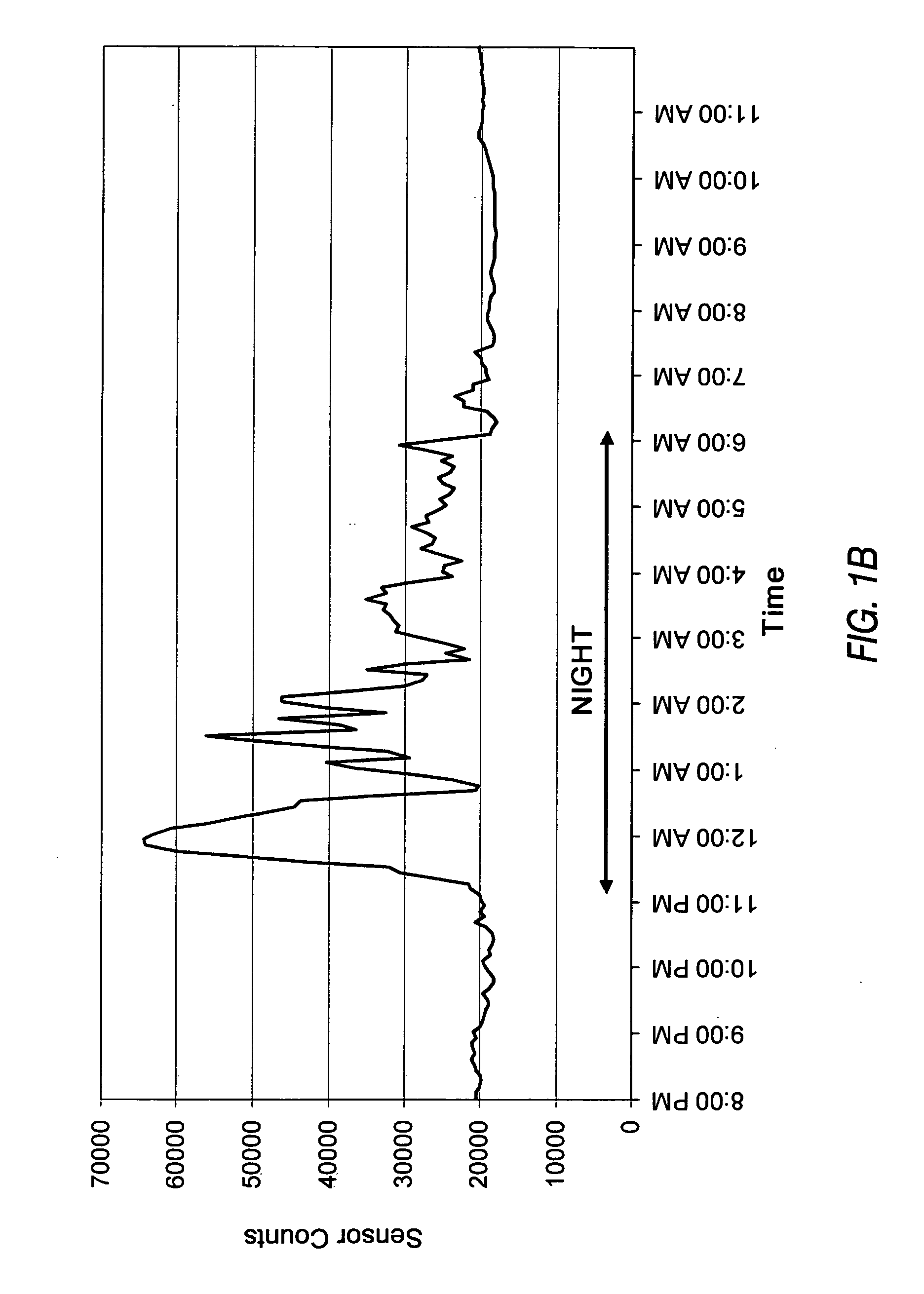
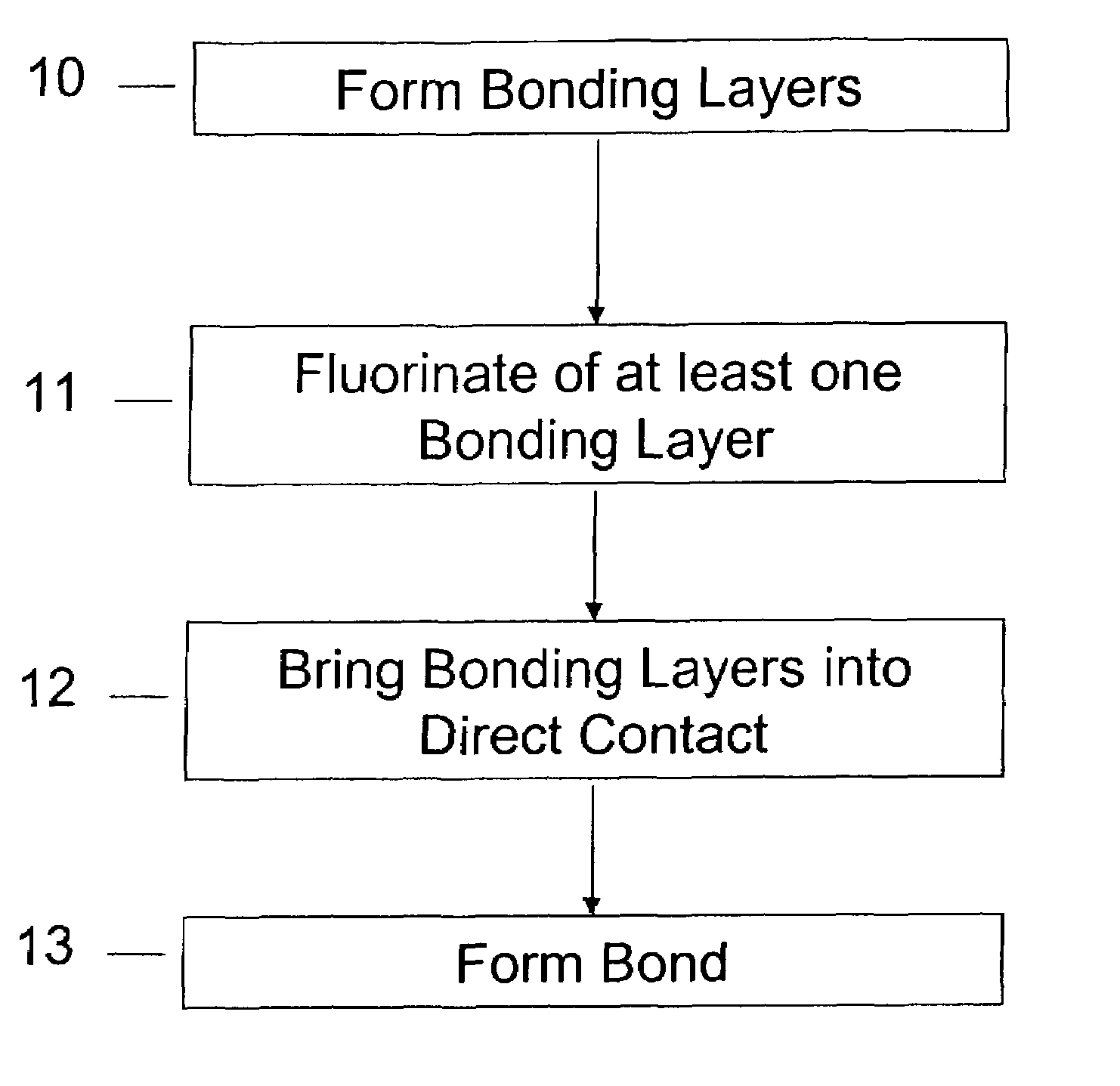
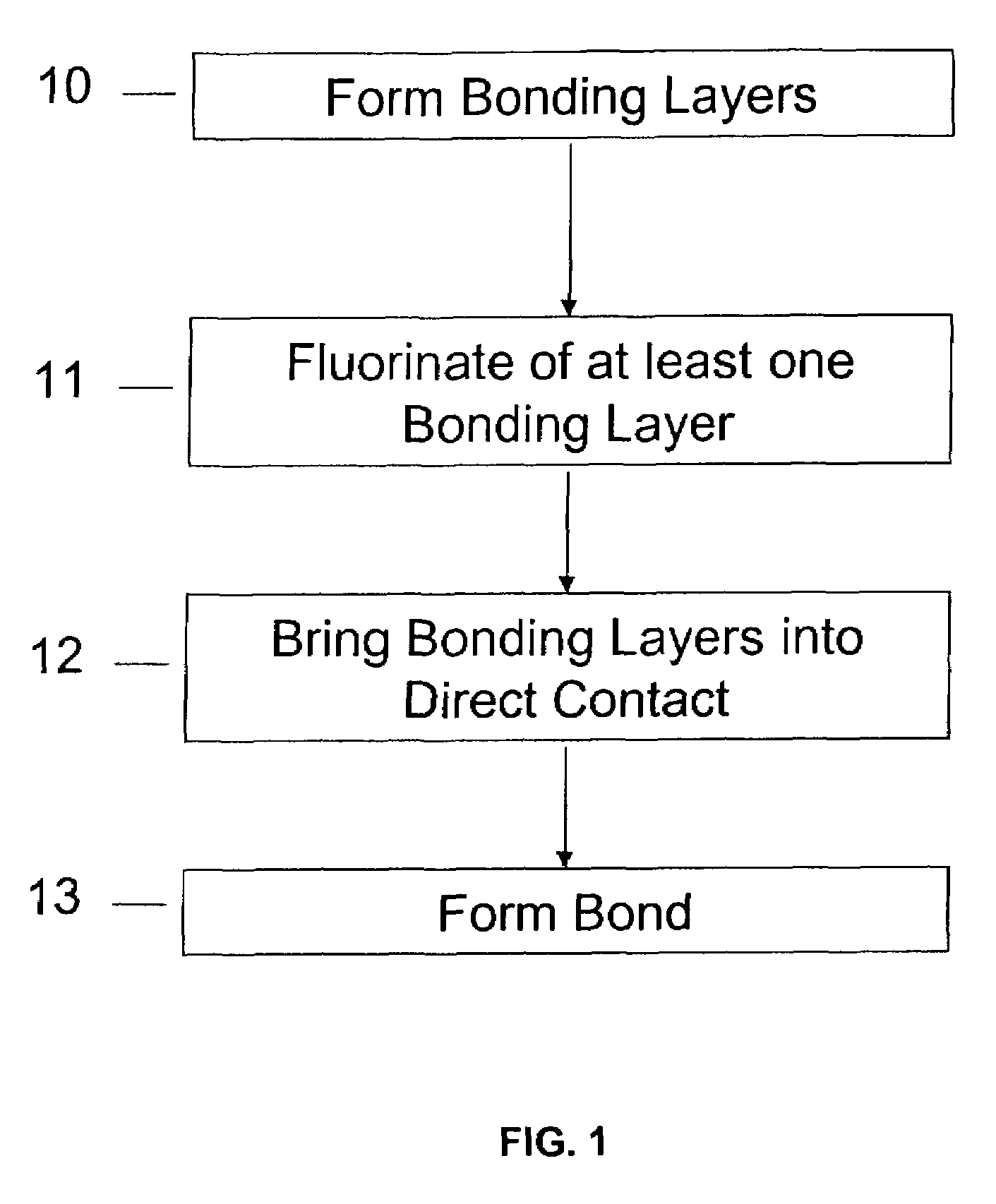
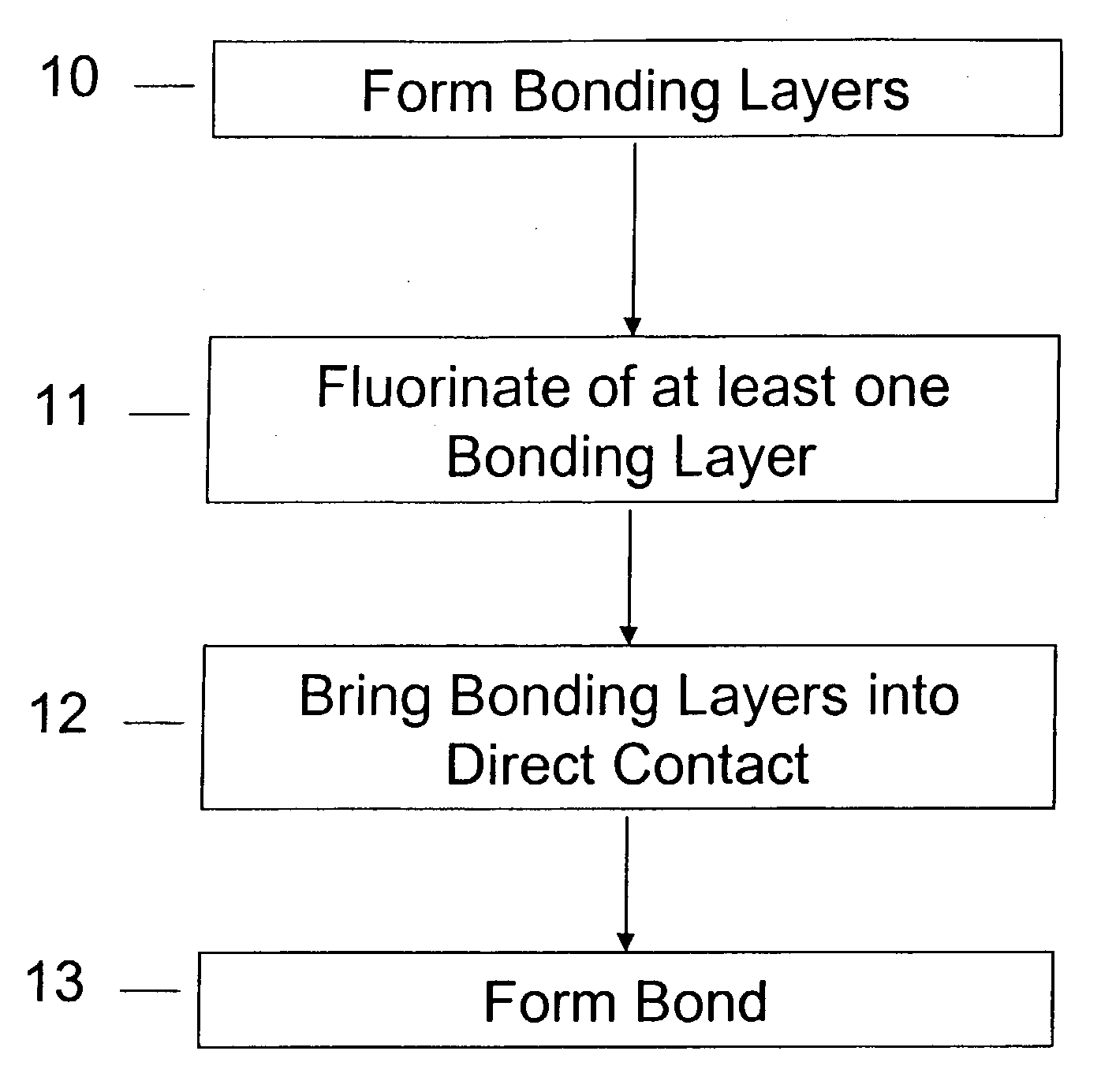
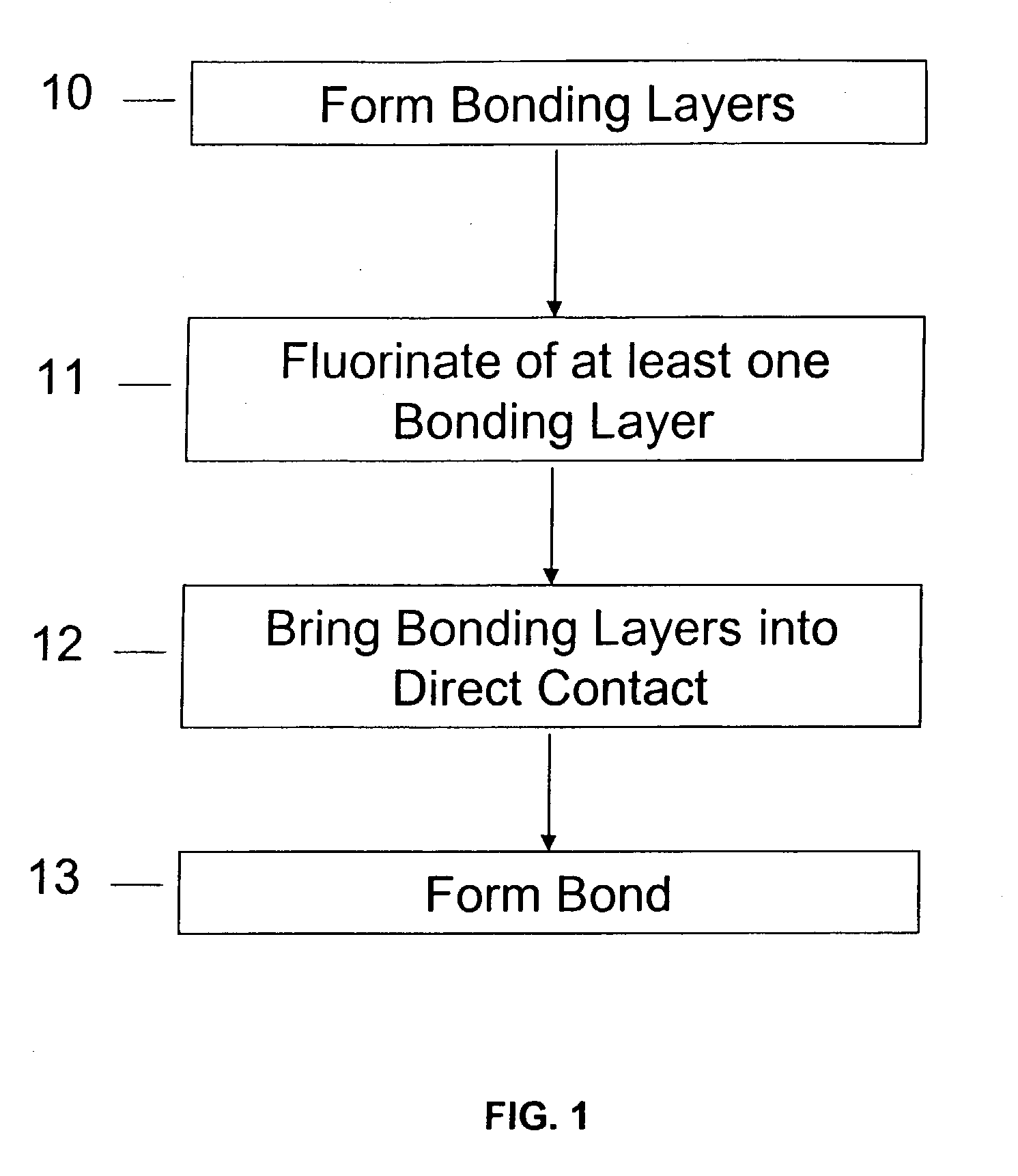
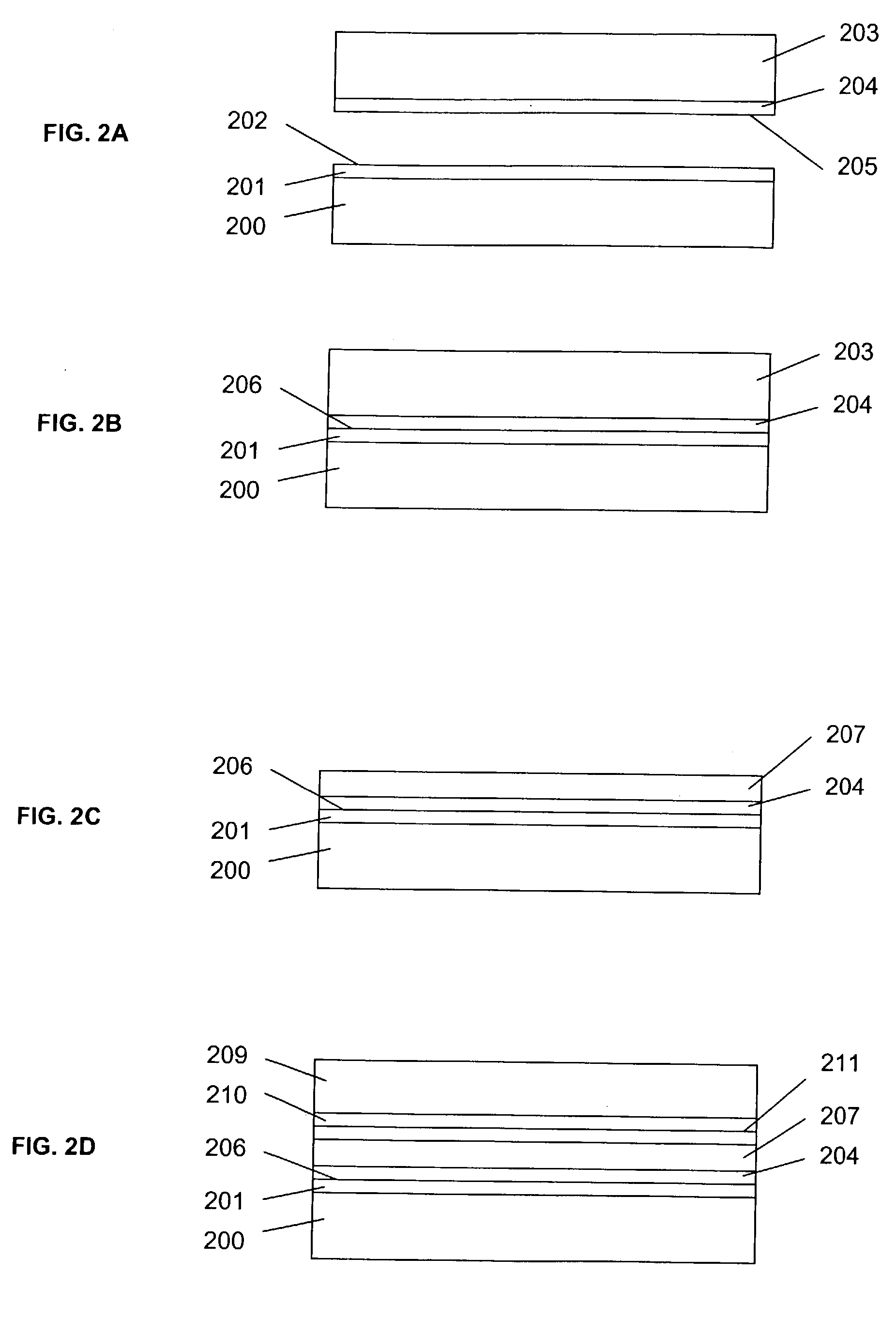
Method of room temperature covalent bonding
InactiveUS7109092B2High densityLow densityLayered productsDecorative surface effectsRoom temperatureFluorine containing
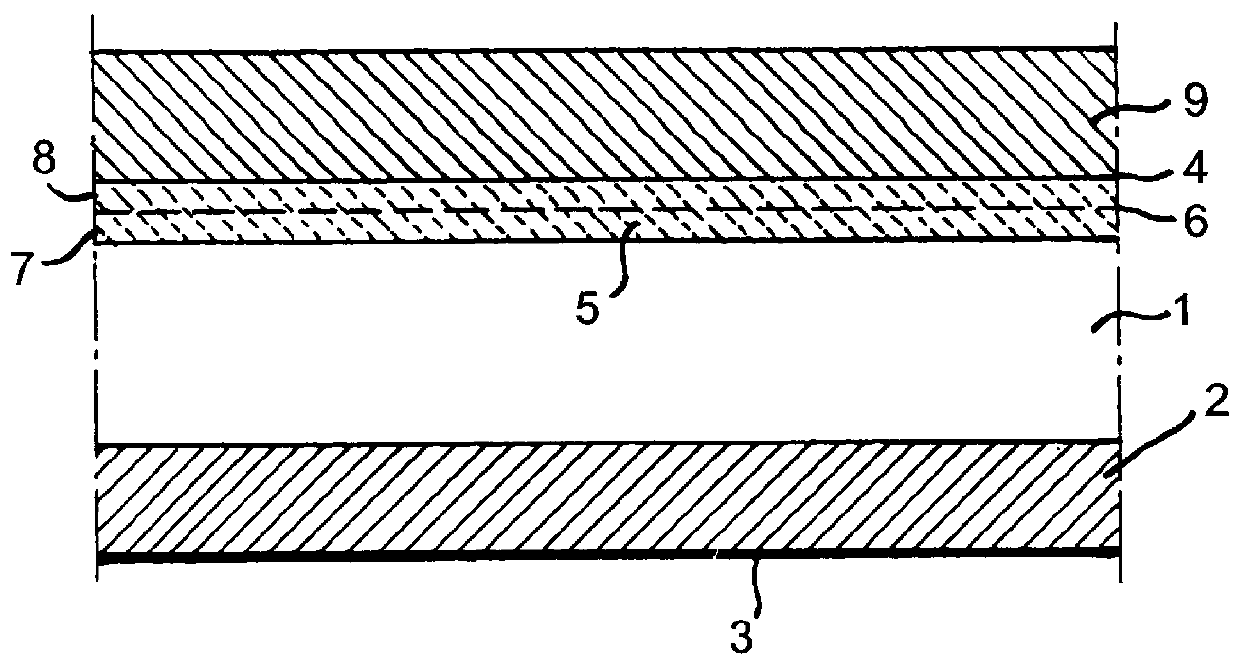
A method of bonding includes using a bonding layer having a fluorinated oxide. Fluorine may be introduced into the bonding layer by exposure to a fluorine-containing solution, vapor or gas or by implantation. The bonding layer may also be formed using a method where fluorine is introduced into the layer during its formation. The surface of the bonding layer is terminated with a desired species, preferably an NH2 species. This may be accomplished by exposing the bonding layer to an NH4OH solution. High bonding strength is obtained at room temperature. The method may also include bonding two bonding layers together and creating a fluorine distribution having a peak in the vicinity of the interface between the bonding layers. One of the bonding layers may include two oxide layers formed on each other. The fluorine concentration may also have a second peak at the interface between the two oxide layers.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Selective area epitaxy growth method and structure
InactiveUS20090309127A1Improve the level ofSmall sizePolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsIndiumPhotoluminescence
A gallium containing crystalline material. The material comprises a bulk semi-polar gallium indium containing crystalline material having a thickness of about 20 nanometers to about 1000 nanometers. The material includes a spatial width dimension of no greater than about 10 microns characterizing the thickness of the bulk semi-polar gallium indium containing crystalline material. The material includes a photoluminescent characteristic of the crystalline material having a first wavelength, which is at least five nanometers greater than a second wavelength, which is derived from an indium gallium containing crystalline material grown on a growth region of greater than about 15 microns.
Owner:SORAA +1
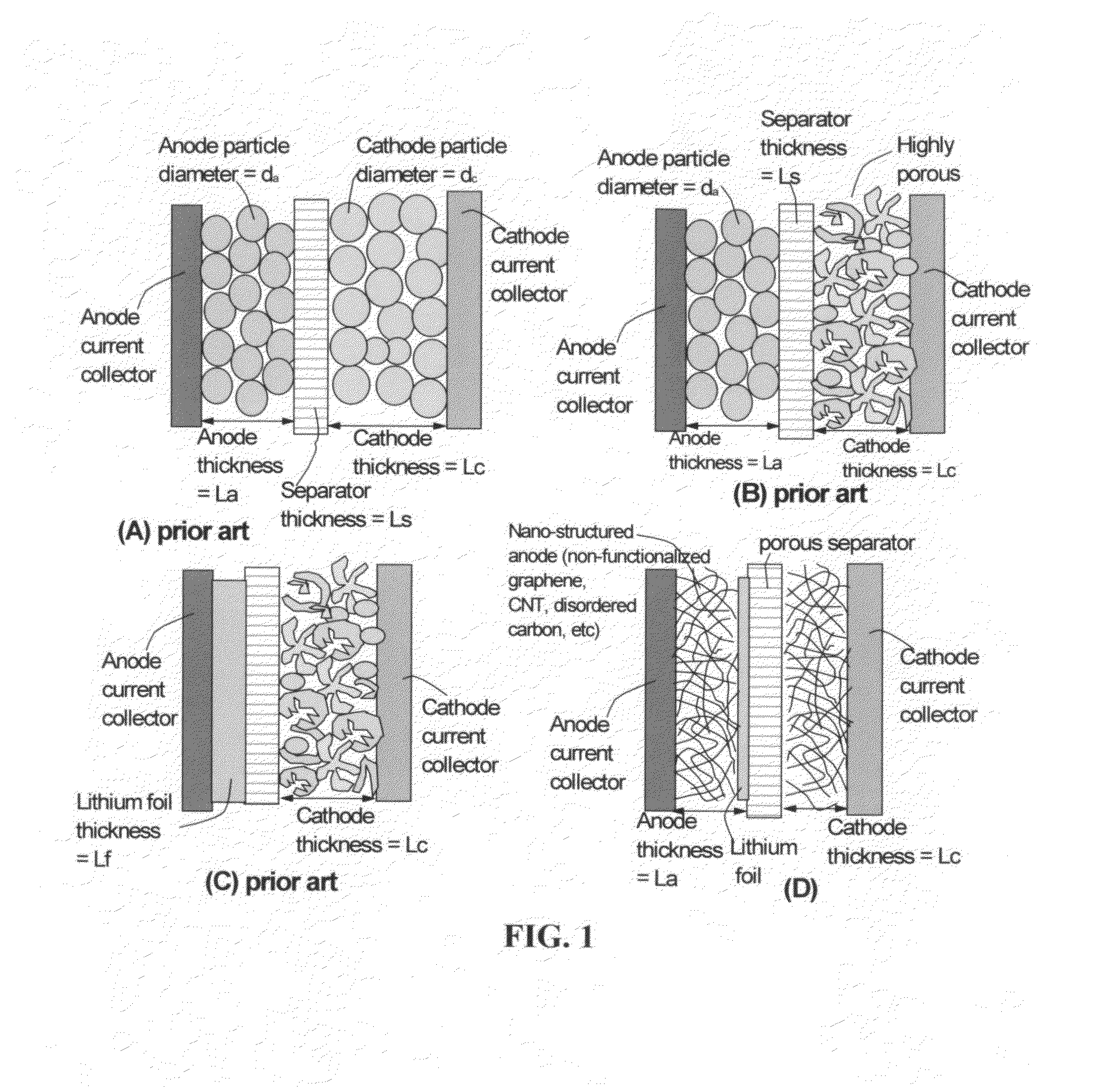
Lithium-ion cell having a high-capacity anode and a high-capacity cathode
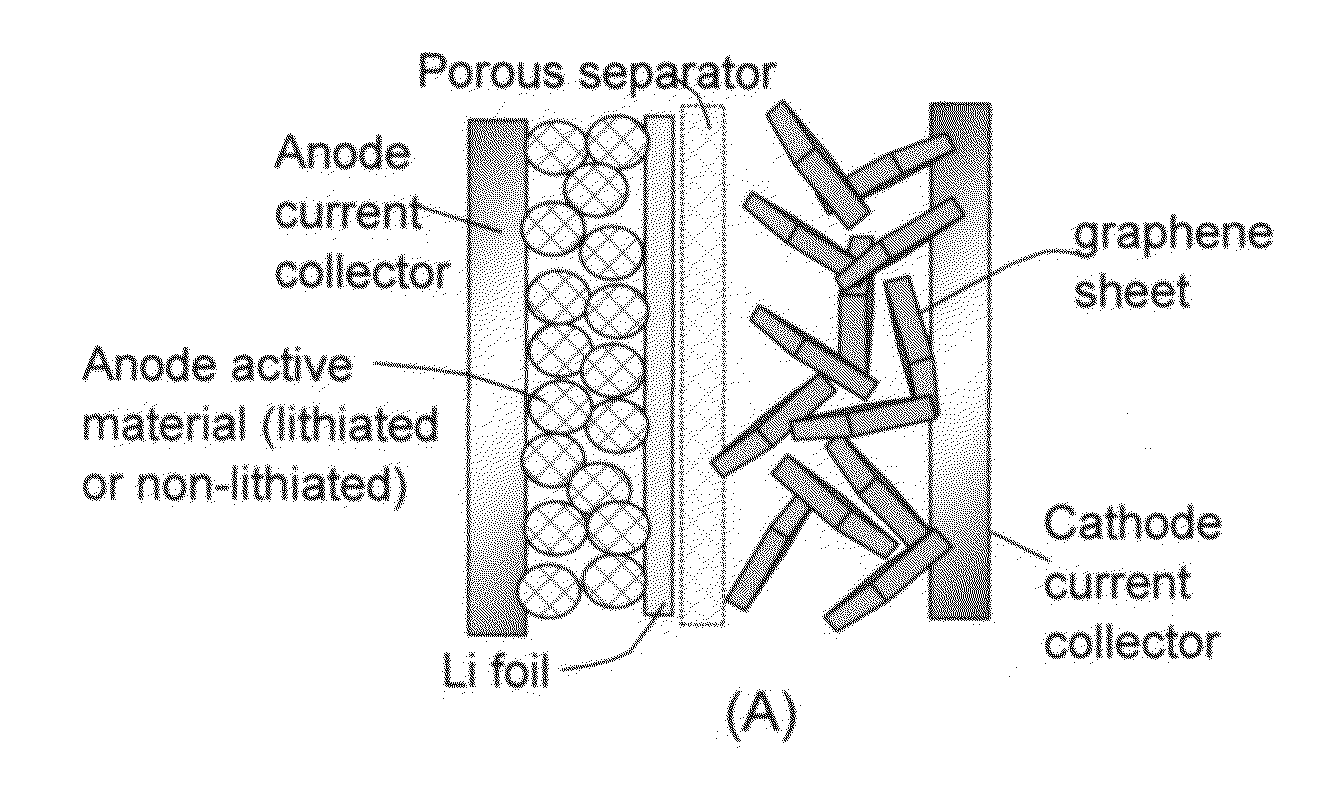
ActiveUS20130224603A1Easy dischargeImprove power densityMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesLithiumHigh energy
A lithium-ion cell comprising: (A) a cathode comprising graphene as the cathode active material having a surface area to capture and store lithium thereon and wherein said graphene cathode is meso-porous having a specific surface area greater than 100 m2 / g; (B) an anode comprising an anode active material for inserting and extracting lithium, wherein the anode active material is mixed with a conductive additive and / or a resin binder to form a porous electrode structure, or coated onto a current collector in a coating or thin film form; (C) a porous separator disposed between the anode and the cathode; (D) a lithium-containing electrolyte in physical contact with the two electrodes; and (E) a lithium source disposed in at least one of the two electrodes when the cell is made. This new Li-ion cell exhibits an unprecedentedly high energy density.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
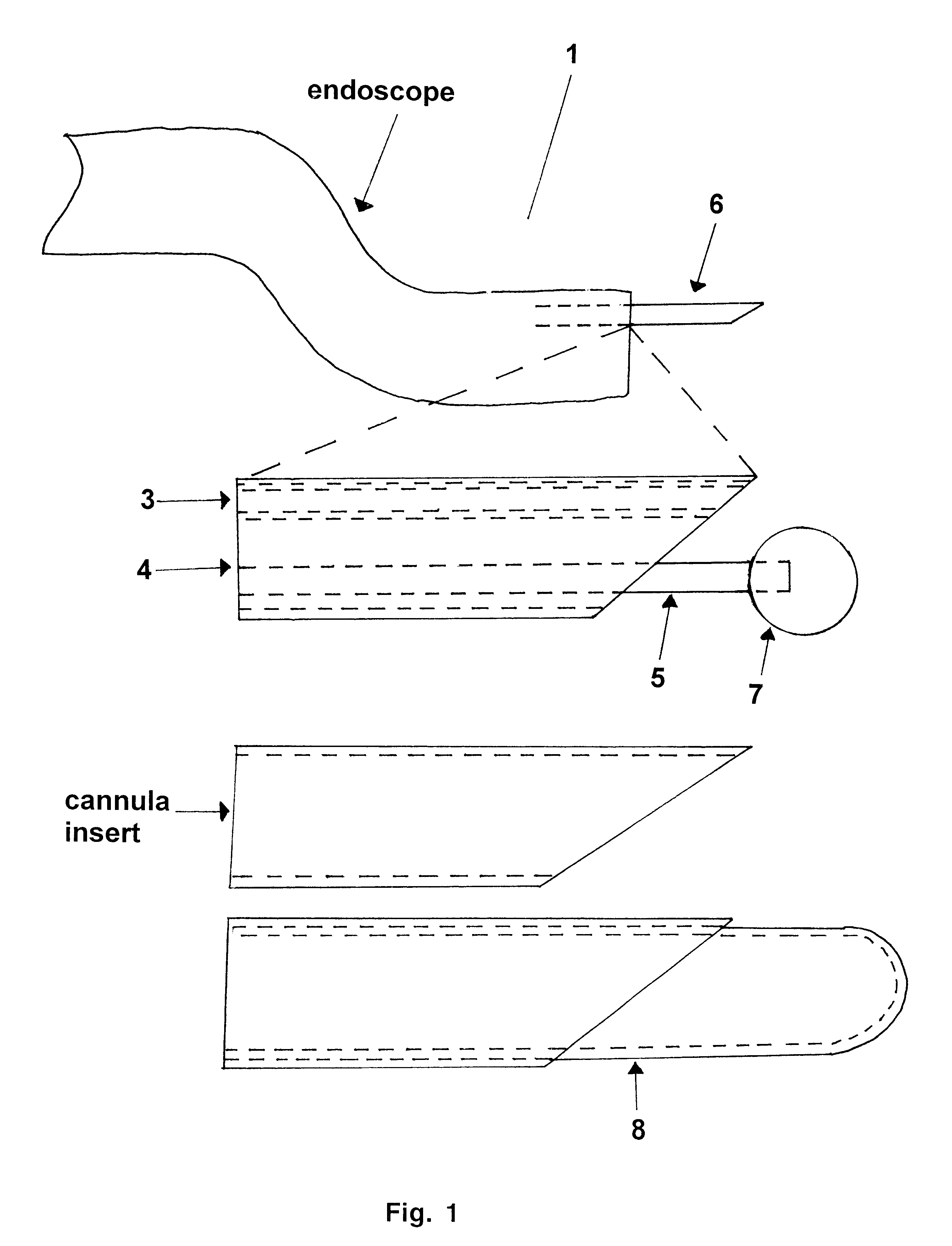
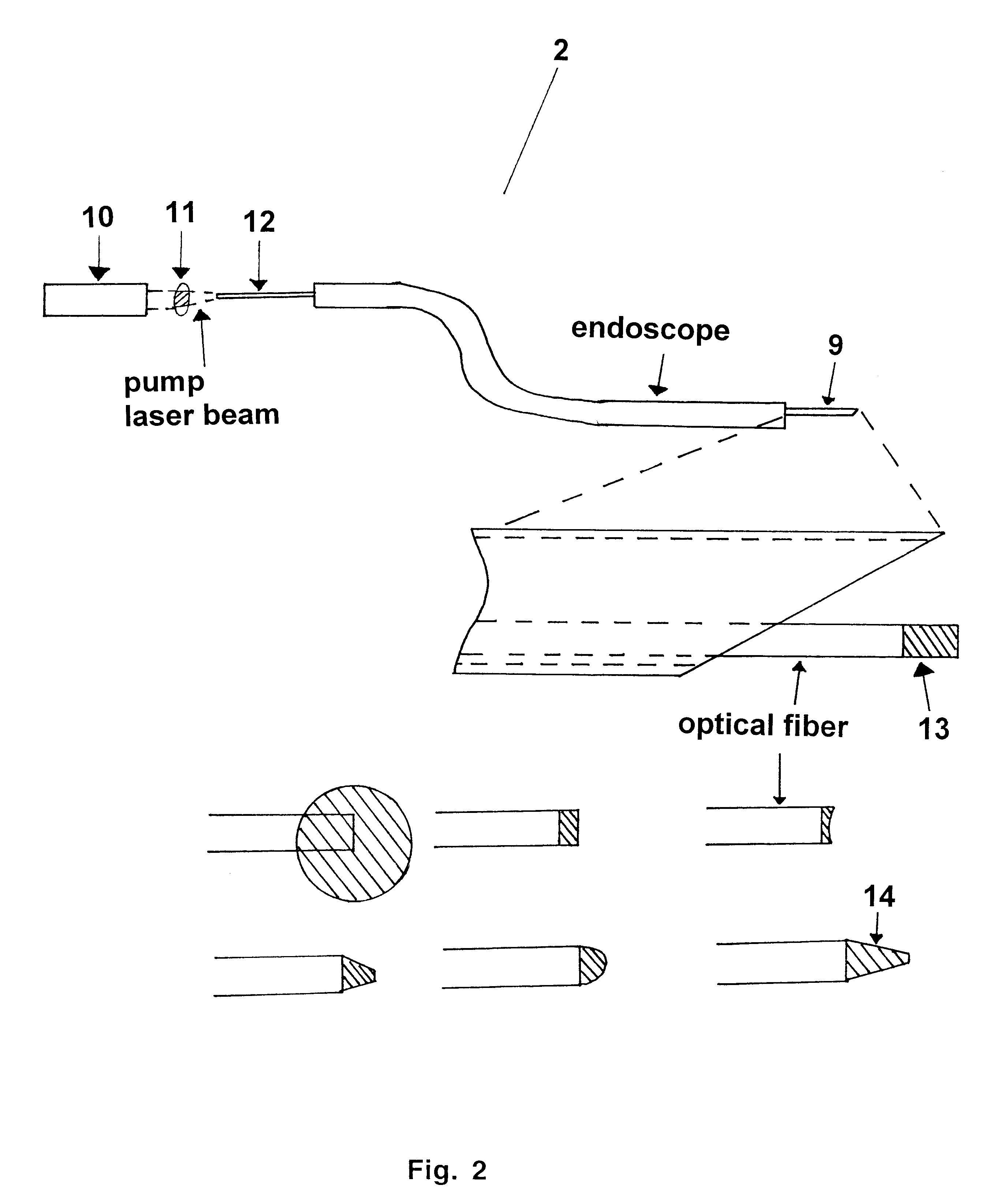
Laser probes for drug permeation
InactiveUS6389313B1Improve diffusivityImprove permeabilityElectrotherapyEar treatmentHigh concentrationLaser probe
Owner:SPECTRAL BIOSYST
High modulus crosslinked polyethylene with reduced residual free radical concentration prepared below the melt
InactiveUS6852772B2Improve diffusivityHigh-frequency sonicationImpression capsAnkle jointsPolymer scienceCross-linked polyethylene
The present invention provides an irradiated crosslinked polyethylene containing reduced free radicals, preferably containing substantially no residual free radical. Disclosed is a process of making irradiated crosslinked polyethylene by irradiating the polyethylene in contact with a sensitizing environment at an elevated temperature that is below the melting point, in order to reduce the concentration of residual free radicals to an undetectable level. A process of making irradiated crosslinked polyethylene composition having reduced free radical content, preferably containing substantially no residual free radicals, by mechanically deforming the polyethylene at a temperature that is below the melting point of the polyethylene, optionally in a sensitizing environment, is also disclosed herein.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Water-absorbent agent and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6187872B1Improve securityStable pHOther chemical processesAbsorbent padsPolymer scienceCross linker
A hydrogel polymer obtained by polymerizing a monomer component including acrylic acid (salt) is post-neutralized so that each of polymer particles derived from a polymer produced by neutralizing the hydrogel polymer has an allowable neutralization ratio. The polymer as obtained by neutralizing the hydrogel polymer is reacted with a crosslinking agent reactive to a functional group of the polymer. The allowable neutralization ratio, for example, is a neutralization ratio which is not lower, by not less than 20 mole percent, or more than, at least 55 mole percent, than an average neutralization ratio of a mass of the polymer particles, and the post-neutralization is carried out so that a number of polymer particles having a non-allowable neutralization ratio outside the allowable neutralization range is not more than 10 in 200 polymer particles, thus obtaining a water-absorbent agent having high absorbency under no applied pressure and high pressure wherein the amount of water soluble component is lower compared with the conventional water-absorbent agent and a change in pH of a swollen gel is small.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Method of operating a lithium-ion cell having a high-capacity cathode
ActiveUS20130271085A1Improvement factorImprove diffusivityMaterial nanotechnologyBatteries circuit arrangementsLithiumLow voltage
A method of operating a lithium-ion cell comprising (a) a cathode comprising a carbon or graphitic material having a surface area to capture and store lithium thereon; (b) an anode comprising an anode active material; (c) a porous separator disposed between the two electrodes; (d) an electrolyte in ionic contact with the two electrodes; and (e) a lithium source disposed in at least one of the two electrodes to obtain an open circuit voltage (OCV) from 0.5 volts to 2.8 volts when the cell is made; wherein the method comprises: (A) electrochemically forming the cell from the OCV to either a first lower voltage limit (LVL) or a first upper voltage limit (UVL), wherein the first LVL is no lower than 0.1 volts and the first UVL is no higher than 4.6 volts; and (B) cycling the cell between a second LVL and a second UVL.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Diamond composite heat spreaders having low thermal mismatch stress and associated methods
InactiveUS20060113546A1Present inventionImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal conductivityThermal transmittance
A diamond composite heat spreader having a low thermal mismatch stress can improve reliability and cost of diamond-based heat spreaders. A diamond composite heat spreader can have a thermally conductive base and a diamond film in thermal contact with the thermally conductive base. The diamond film and the thermally conductive base can have a residual thermal mismatch stress which is less than about 75% of a residual thermal mismatch stress which would result from forming the diamond film on the thermally conductive base using a high temperature deposition process at 700° C. The diamond film can be formed on the thermally conductive base using a low temperature vapor deposition process performed at a temperature from about 10° C to less than 700° C, and typically lower than about 450° C. The diamond films further have high thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity which allow for dramatic improvements in heat transfer away from a heat source without the need for growing a thick diamond film. By providing a low temperature deposition of the diamond film, residual thermal mismatch stress can be significantly reduced, while allowing for use of well known heat spreaders such as standard copper heat spreaders and associated technologies.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Sustained-release liposomal anesthetic compositions
InactiveUS8182835B2High acceptabilityImprove encapsulationInorganic non-active ingredientsAnaestheticsHalf-lifeMaximum tolerated dose
Owner:PACIRA PHARMA INC
Inducing hypothermia and rewarming using a helium-oxygen mixture
ActiveUS6983749B2Mitigate warmingReduce coolingLighting and heating apparatusInorganic active ingredientsREFLEX DECREASEInspired gas temperature
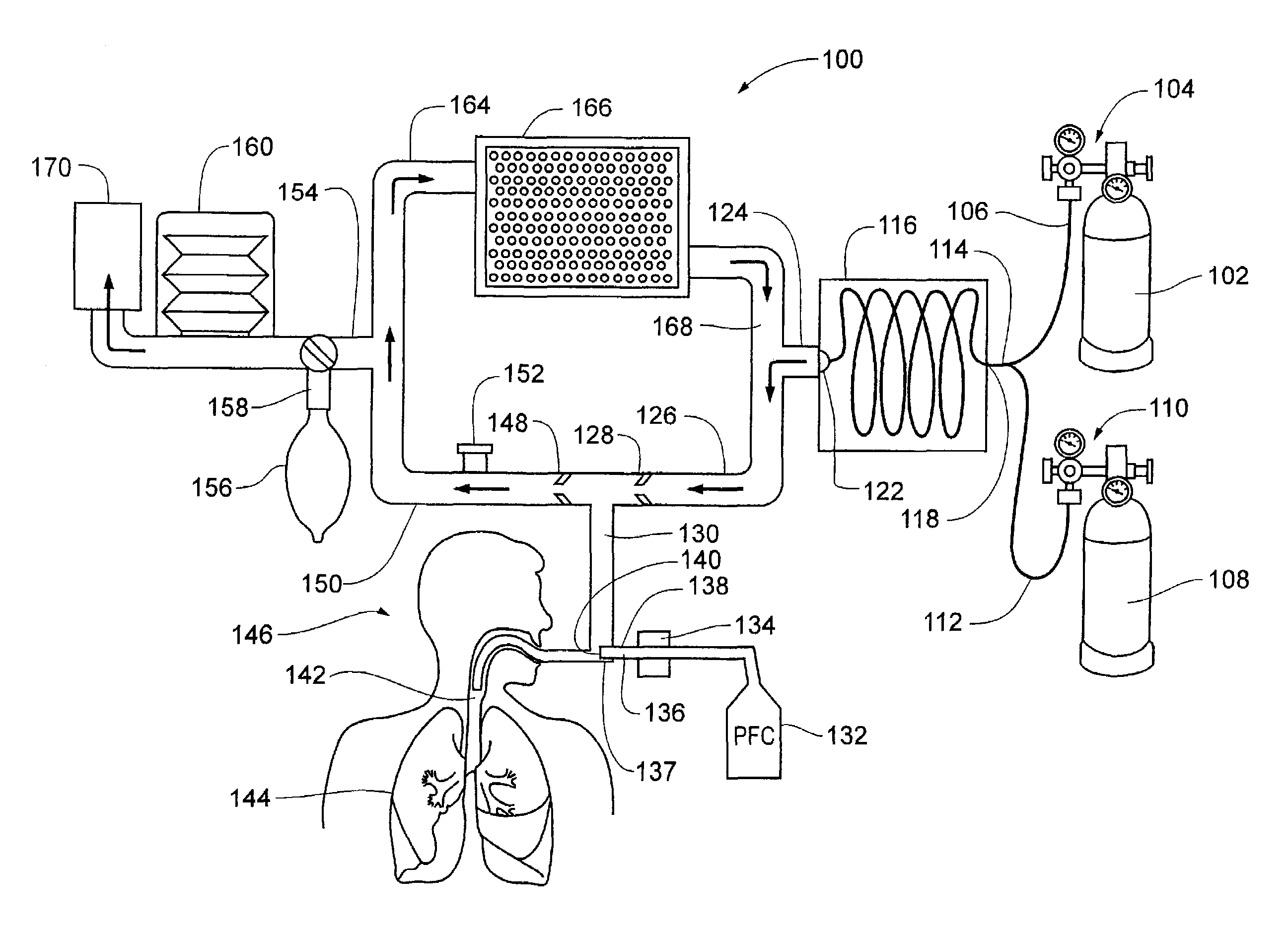
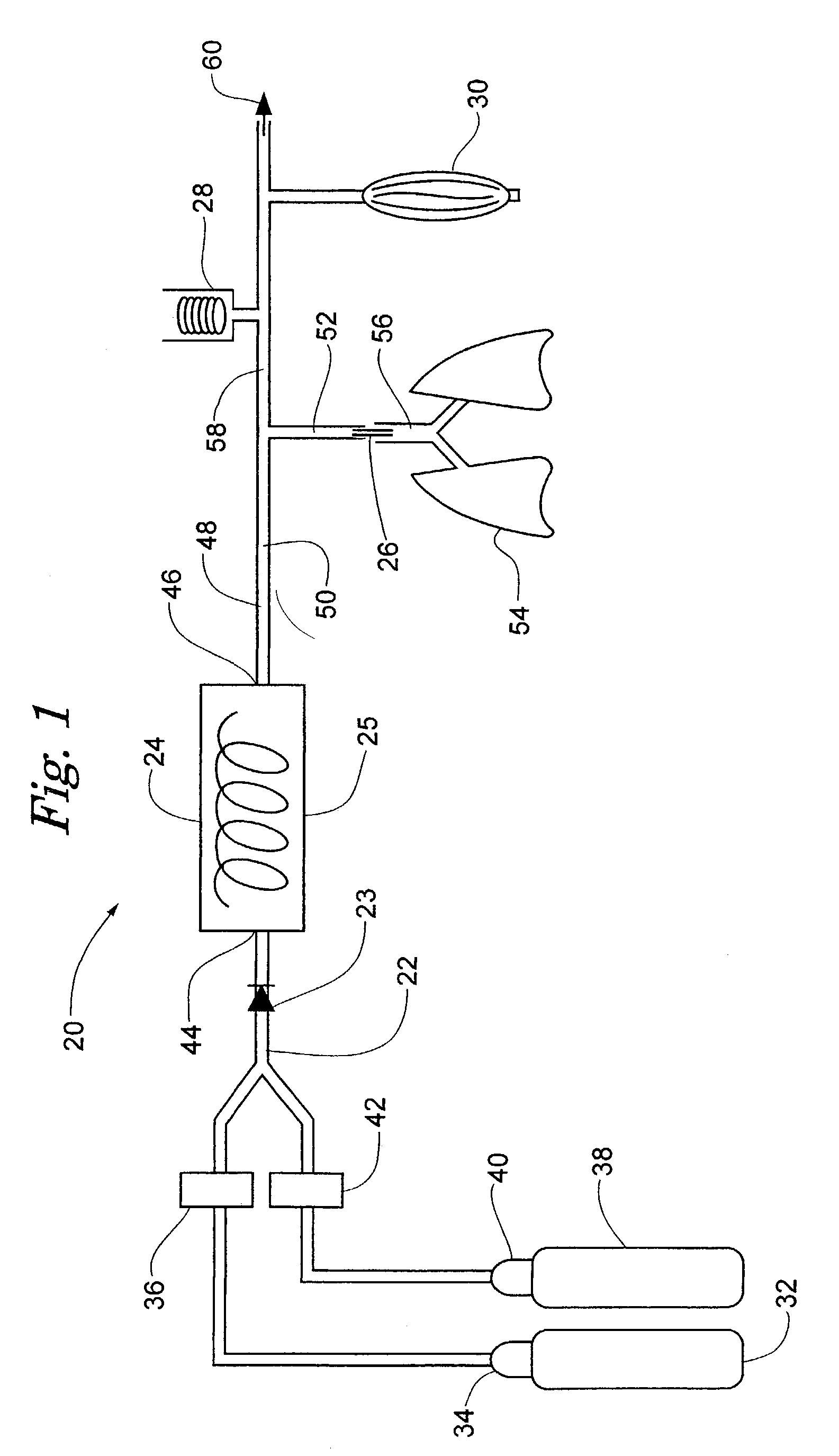
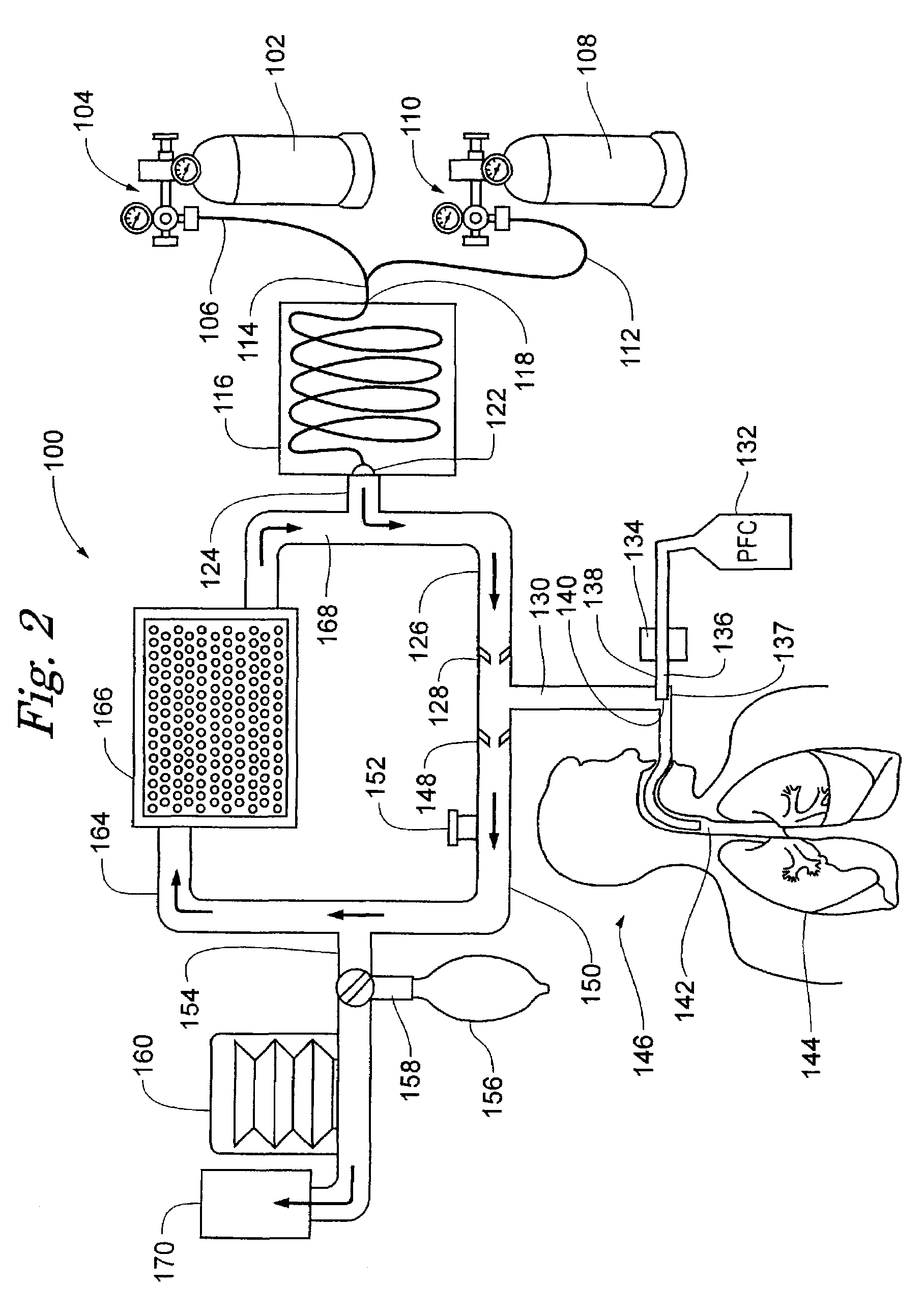
Devices and methods to heat and cool human beings, including inducing and maintaining hypothermia in human patients. Methods include inducing hypothermia to treat ischemic events, including heart attack and stroke, to limit damage caused by the ischemic event. Methods can include: using the lungs for heat exchange; using cooled gases for ventilation; using helium in the ventilation gas mixture, using medications to control reflex heat production; and injecting a perfluorocarbon mist into the gas stream to increase the cooling rate. The high thermal conductivity and diffusivity of helium results in greater inspired gas temperature equalization toward body temperature. Due to the latent heat of vaporization, addition of even small quantity of phase-change perfluorocarbon dramatically increases the heat carrying capacity of the respiratory gases. Hypothermia may be terminated by discontinuing the medications and warming the patient using a warmed helium-oxygen mixture.
Owner:MINNESOTA HIGH TECH RESOURCES
Method for producing a pn-junction for a semiconductor device of SiC
InactiveUS6083814AShort timeNumber of processing stepSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactEngineering
A method for producing a pn-junction for a semiconductor device of SiC intended to have at least one lateral zone of junction termination with a lower doping concentration of a first conductivity type than a main zone for smearing out the electrical field at said junction comprising at least the step of applying a first layer of SiC over the entire surface and on top of a second layer of SiC. A mask is applied on the first layer over a portion thereof where said main zone and an ohmic contact are to be formed. It is after that etched through the first layer to the second layer while leaving a main zone of said first layer and a contact layer thereof under said mask.
Owner:CREE INC
Programmable resistor, switch or vertical memory cell
InactiveUS20080173975A1Decrease resistivity and hence resistanceSimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMetal electrodes
Disclosed are embodiments of a device and method of forming the device that utilize metal ion migration under controllable conditions. The device embodiments comprise two metal electrodes separated by one or more different dielectric materials. One electrode is sealed from the dielectric material, the other is not. The device is adapted to allow controlled migration of embedded metal ions from the unsealed electrode into dielectric material to form a conductive path under field between the electrodes and, thereby, to decrease the resistance of the dielectric material. Reversing the field causes the metal ions to reverse their migration, to break the conductive metallic path between the electrodes and, thereby, to increase the resistance of the dielectric material. Thus, the device can comprise a simple switch or programmable resistor. Additionally, by monitoring the resistance change, a two-state, two-terminal, silicon technology-compatible, flash memory device with a very simple tuning process can be created.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Topical composition
ActiveUS20080234239A1Improve solubilityImprove permeabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideChemical compositionDermatology
A composition suitable for topical application comprising a continuous phase and at least one discontinuous phase, said composition comprising at least one polyaphron dispersion, at least one vitamin D or vitamin D analogue and at least one corticosteroid.
Owner:MC2 THERAPEUTICS LTD
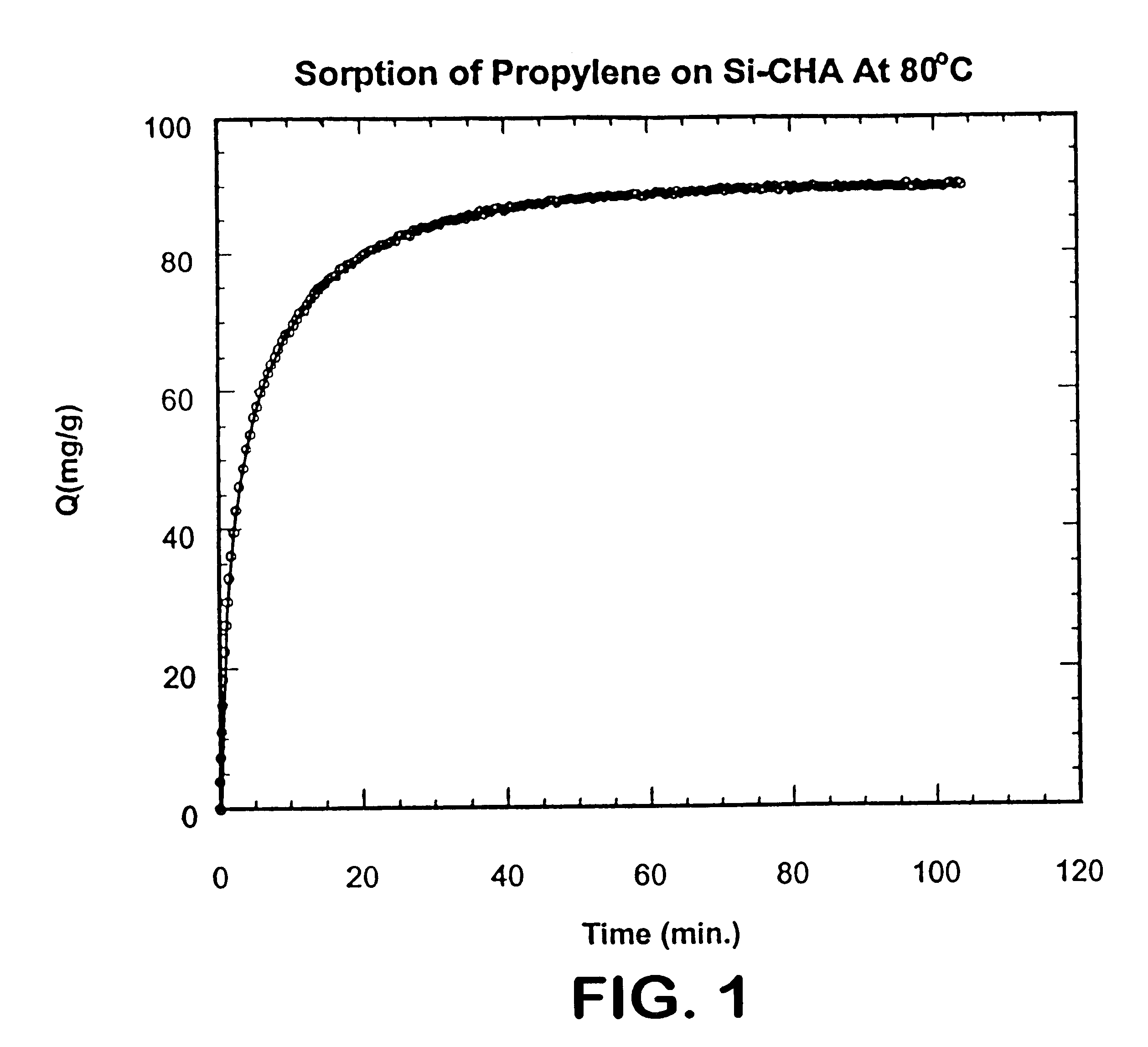
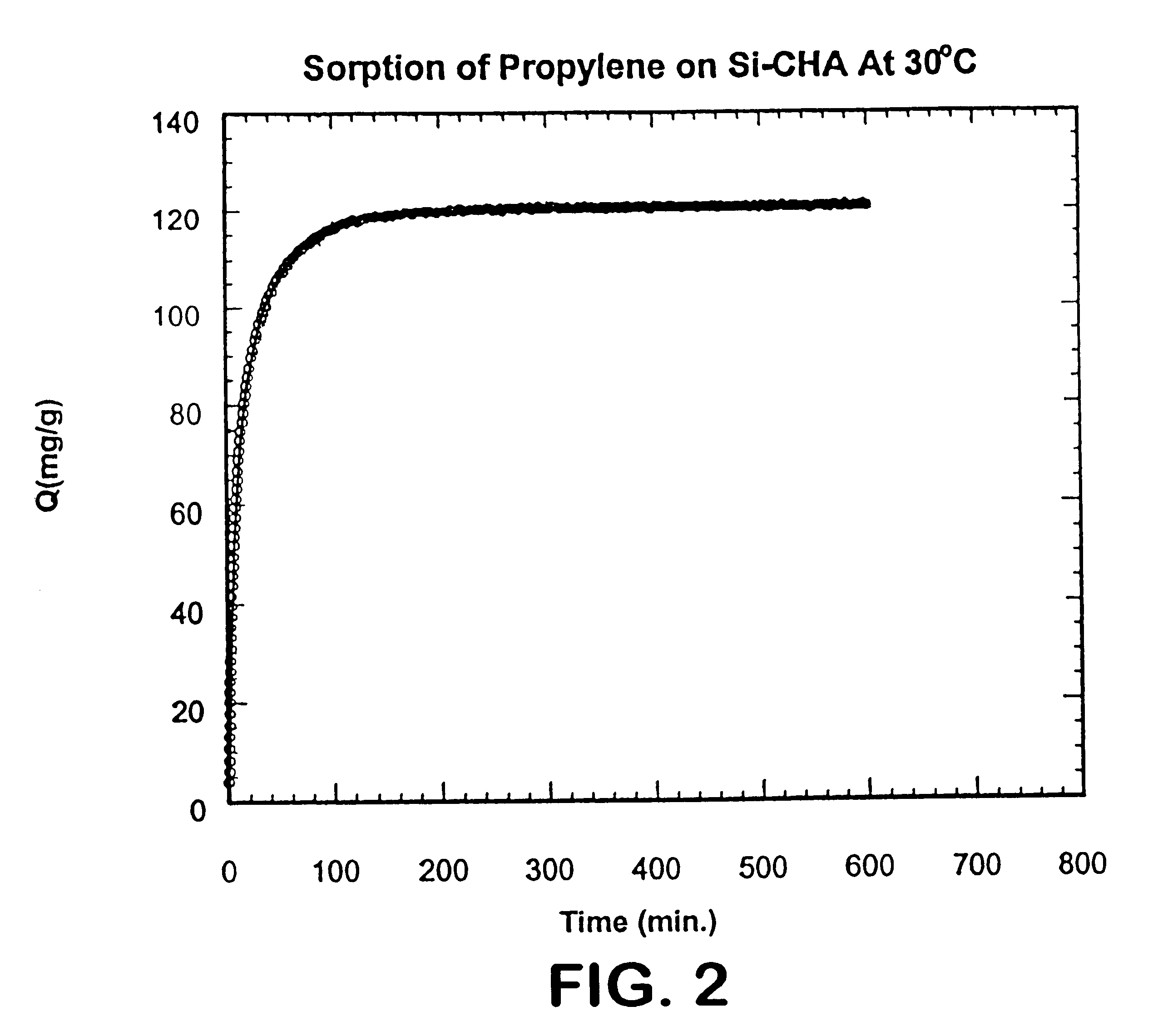
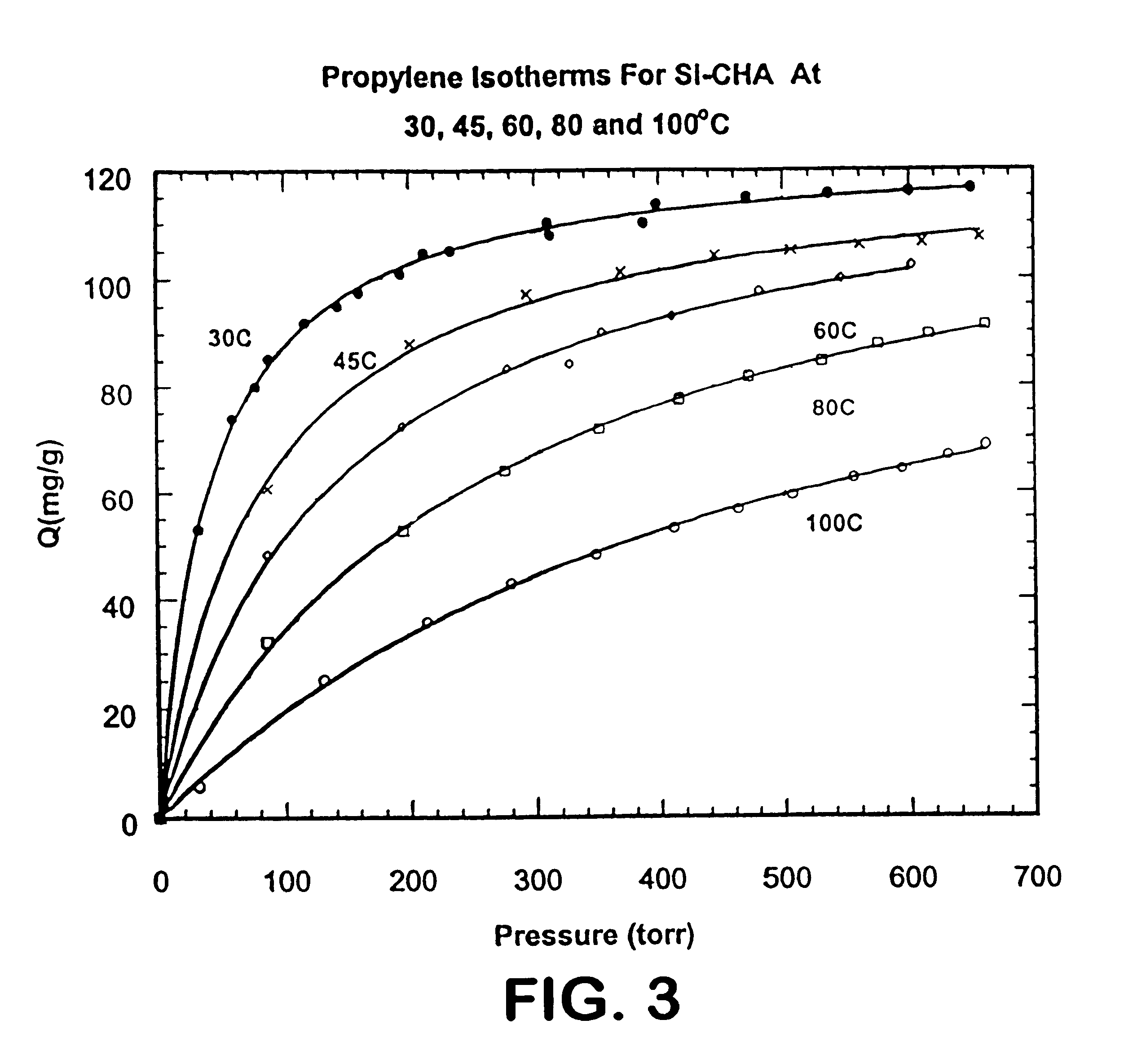
Light hydrocarbon separation using 8-member ring zeolites
InactiveUS6488741B2Improve efficiencyImprove diffusivityGas treatmentIsotope separationSorbentPropane
A method of selectively adsorbing propylene in mixtures of propylene / propane and propylene / olefins through the use of zeolites having structures with a maximum of 8-member rings of tetraheda controlling the diffusion rate. Suitable zeolite adsorbents are those having the CHA and ITE structure types. Other 8-member ring zeolites, including aluminosilicates, with a Si:Al molar ratio of at least about 200 and having substantially no free acid are also suitable adsorbents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
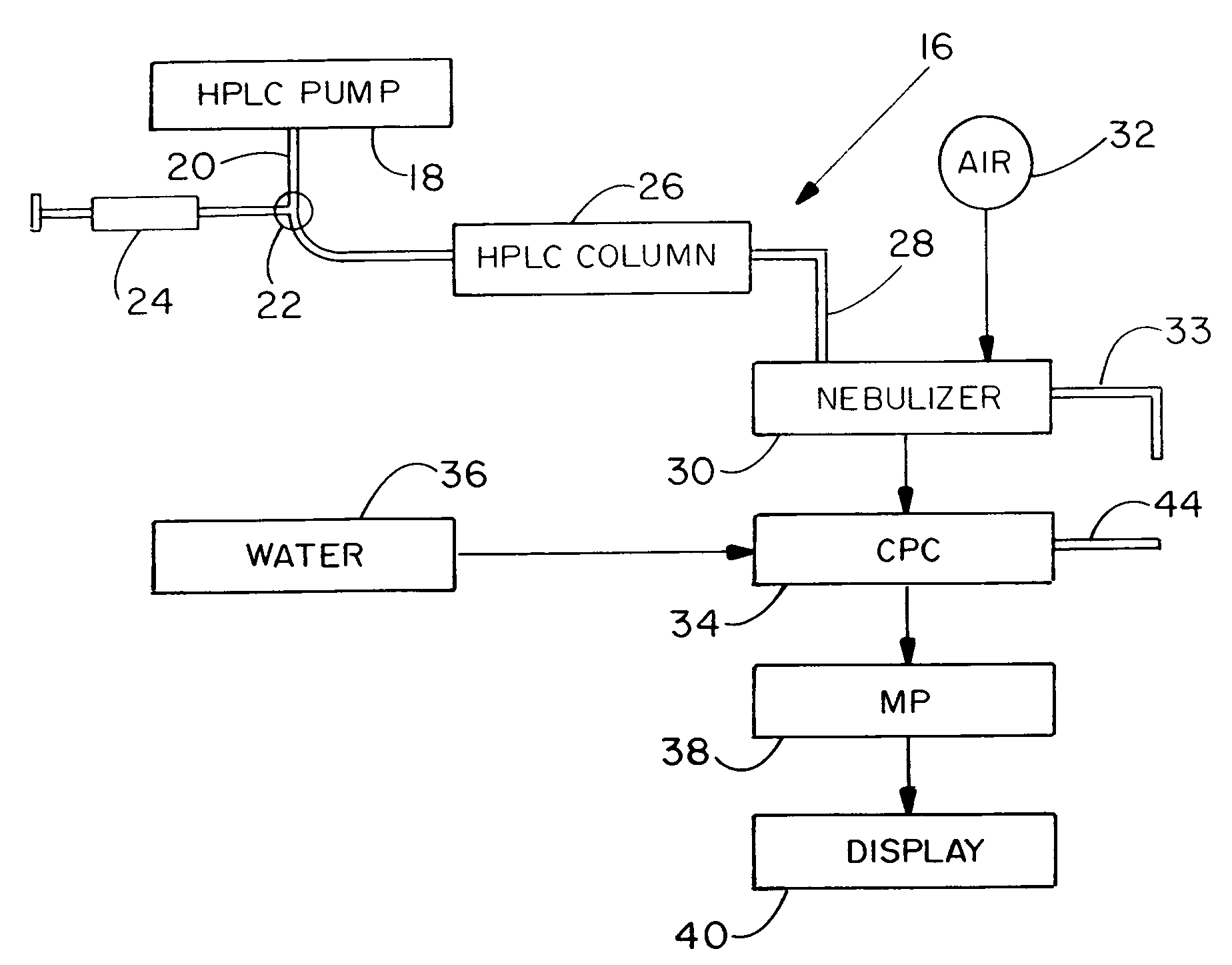
Measuring Analyte Concentrations in Liquids
InactiveUS20080137065A1Higher kinetic energy mixingSmall dropletSamplingComponent separationElectrical mobilityDroplet size
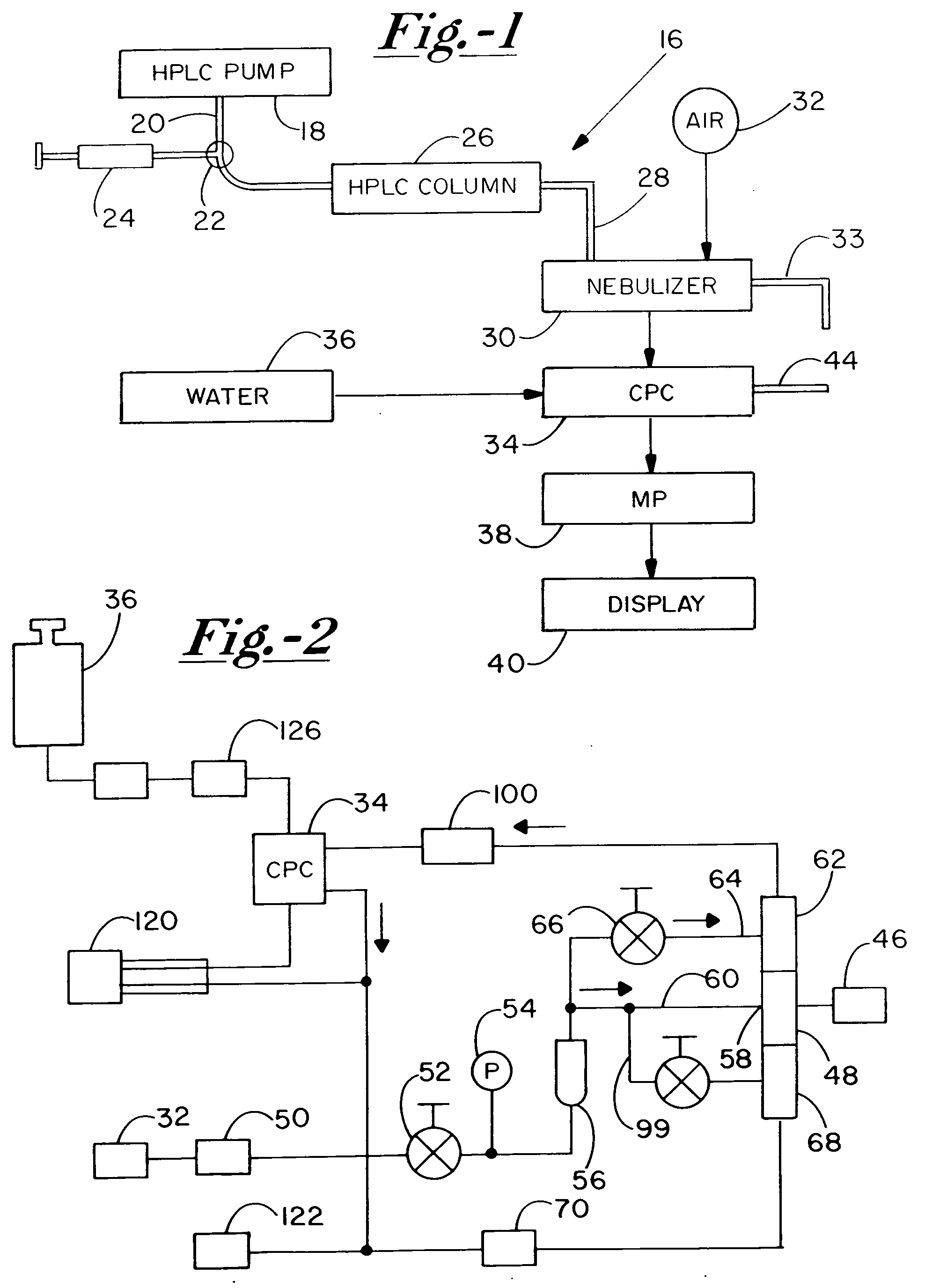
A high performance liquid chromatography system employs a nebulizer with a flow restriction at the exit of its mixing chamber to produce finer droplets, and an adjustable impactor for increased control over droplet sizes. Downstream of the mixing chamber, the nebulizer can incorporate tubing that is permeable to the sample liquid, to promote aerosol drying through perevaporation. A condensation particle counter downstream of the nebulizer uses water as the working medium, and is adjustable to control threshold nucleation sizes and droplet growth rates. A particle size selector employing diffusion, electrostatic attraction or selection based on electrical mobility, is advantageously positioned between the nebulizer and the CPC.
Owner:TSI INC
Mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material
ActiveCN101723403AImprove diffusivityImprove anti-coking performancePentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteTolueneAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material and mainly aims to solve the problem that the ZSM-5 zeolite material cannot contain mesopores and micropores at the same time, the problem that inactivation speed is high when the ZSM-5 zeolite material is used in the reactions such as toluene disproportionation and the like in the prior art. To solve the problems existing in the prior art, the invention adopts a technical scheme that: in the mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material, the molar ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is 15 to 500, and the material has 0.5 to 0.6 nanometer micropores and 5 to 100 nanometer mesopores, and the pore volume of the mesopores is 1 to 10 times that of the micropores. The mesopore and micropore compound ZSM-5 zeolite material can be applied to the industrial production of conversion and treatment of aromatic hydrocarbons, such as toluene disproportionation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
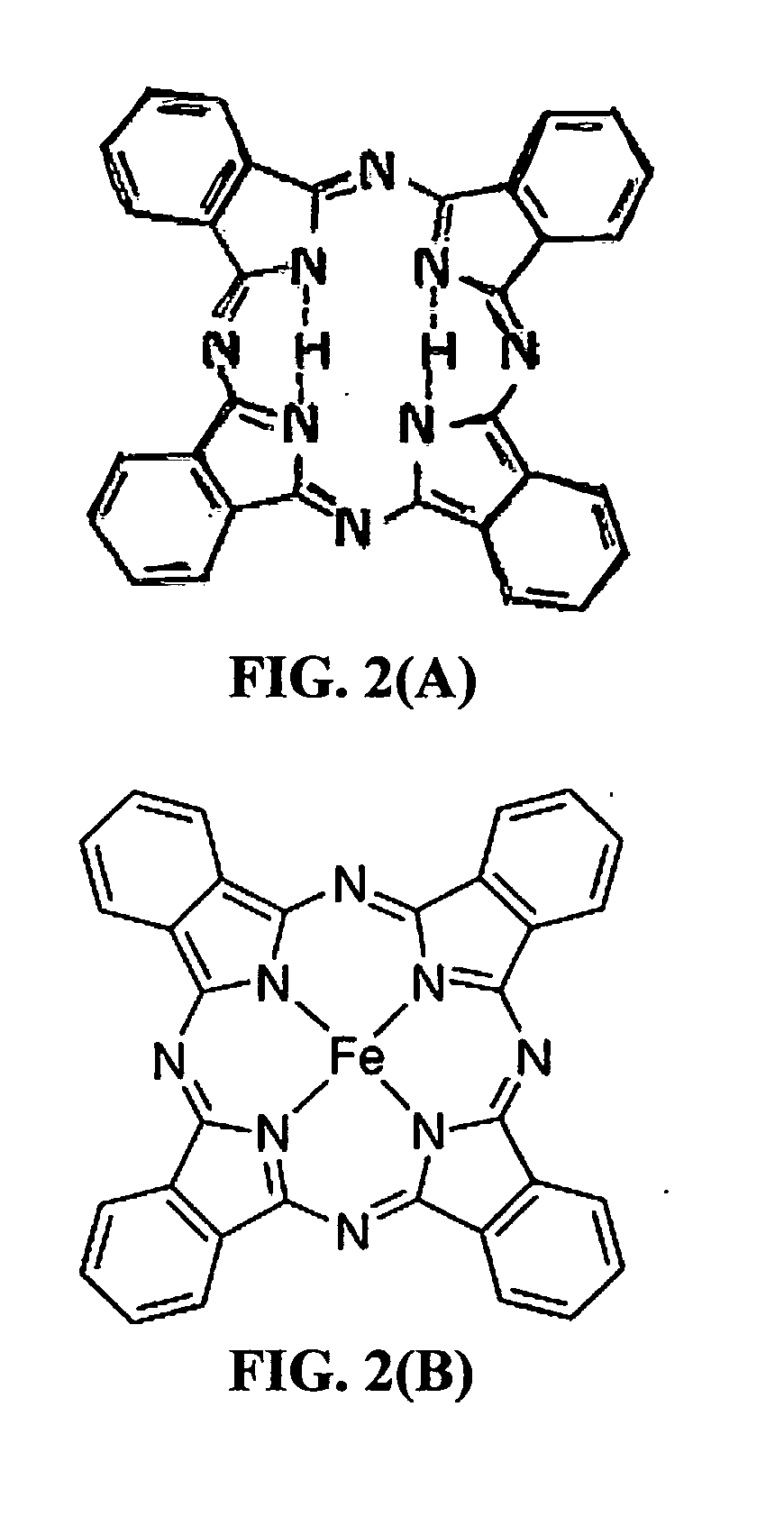
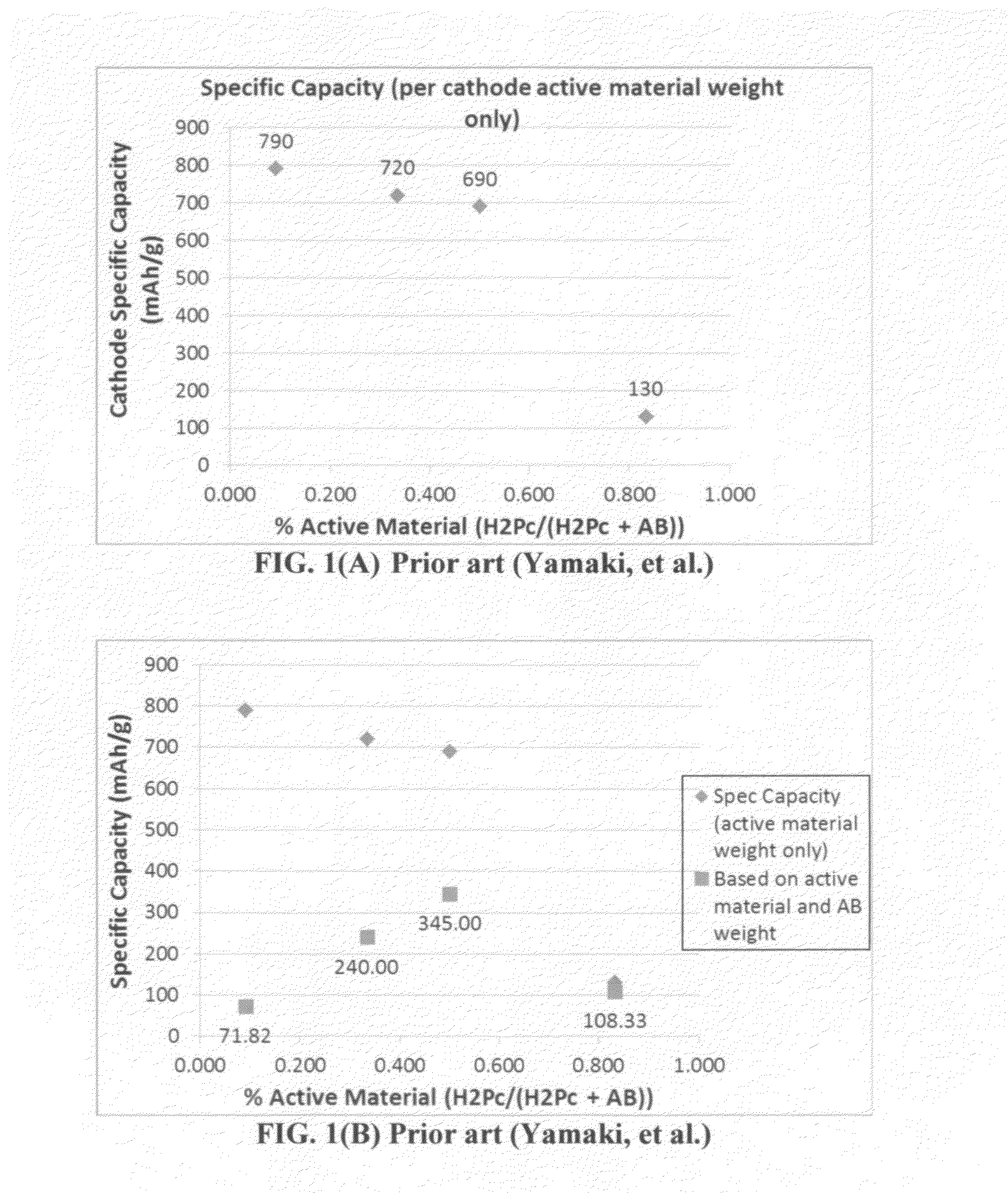
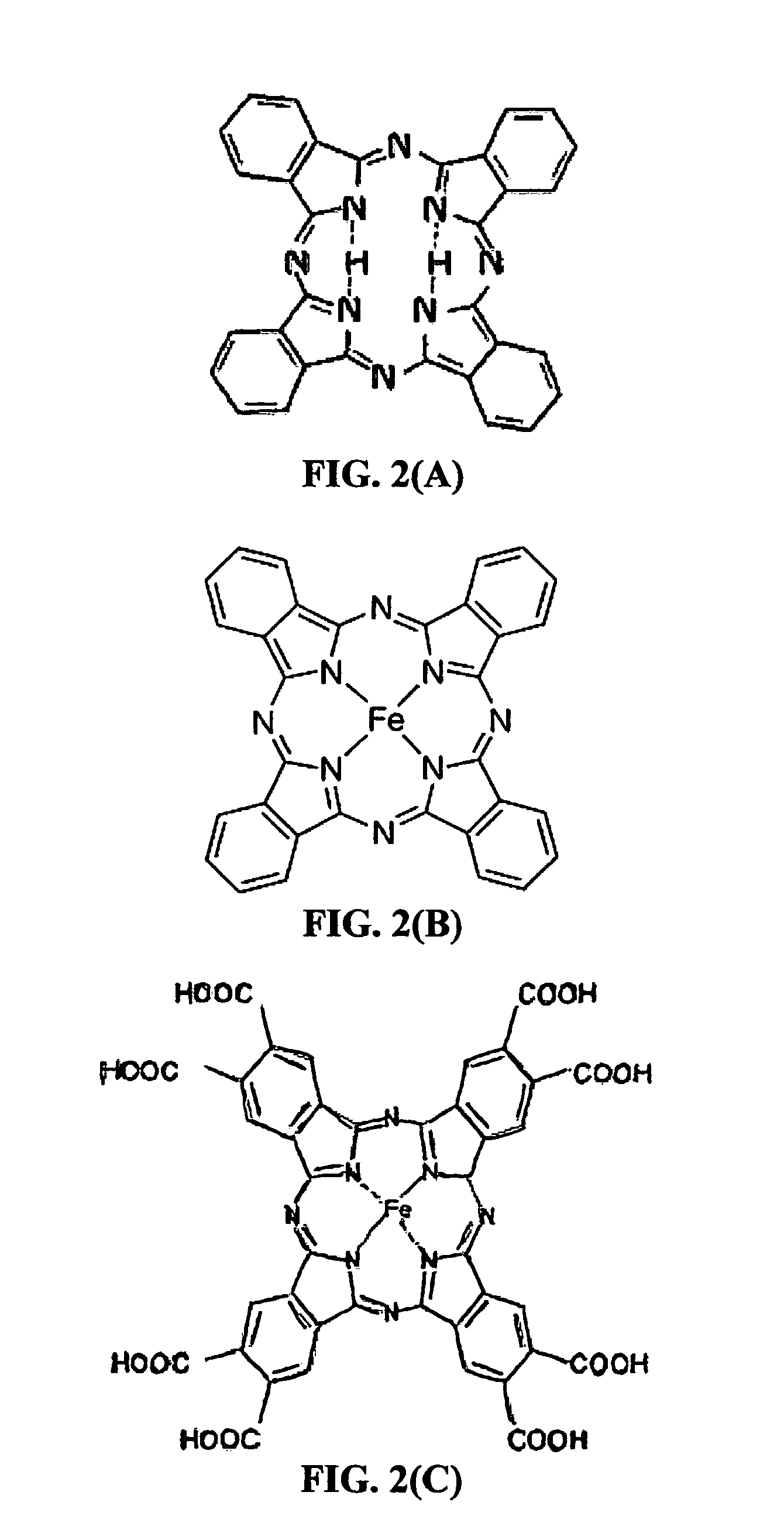
Rechargeable lithium cell having a meso-porous conductive material structure-supported phthalocyanine compound cathode
ActiveUS20130330611A1High oxygen contentIncreased riskMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode carriers/collectorsConductive polymerConductive materials
A rechargeable lithium cell comprising: (a) an anode comprising a prelithiated lithium storage material or a combination of a lithium storage material and a lithium ion source; (b) a hybrid cathode active material composed of a meso-porous structure of a carbon, graphite, metal, or conductive polymer and a phthalocyanine compound, wherein the meso-porous structure is in an amount of from 1% to 99% by weight based on the total weight of the meso-porous structure and the phthalocyanine combined, and wherein the meso-porous structure has a pore with a size from 2 nm to 50 nm to accommodate phthalocyanine compound therein; and (c) an electrolyte or electrolyte / separator assembly. This secondary cell exhibits a long cycle life and the best cathode specific capacity and best cell-level specific energy of all rechargeable lithium-ion cells ever reported.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method of room temperature covalent bonding
InactiveUS20040235266A1High densityLow densityLayered productsDecorative surface effectsChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
A method of bonding includes using a bonding layer having a fluorinated oxide. Fluorine may be introduced into the bonding layer by exposure to a fluorine-containing solution, vapor or gas or by implantation. The bonding layer may also be formed using a method where fluorine is introduced into the layer during its formation. The surface of the bonding layer is terminated with a desired species, preferably an NH2 species. This may be accomplished by exposing the bonding layer to an NH4OH solution. High bonding strength is obtained at room temperature. The method may also include bonding two bonding layers together and creating a fluorine distribution having a peak in the vicinity of the interface between the bonding layers. One of the bonding layers may include two oxide layers formed on each other. The fluorine concentration may also have a second peak at the interface between the two oxide layers.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
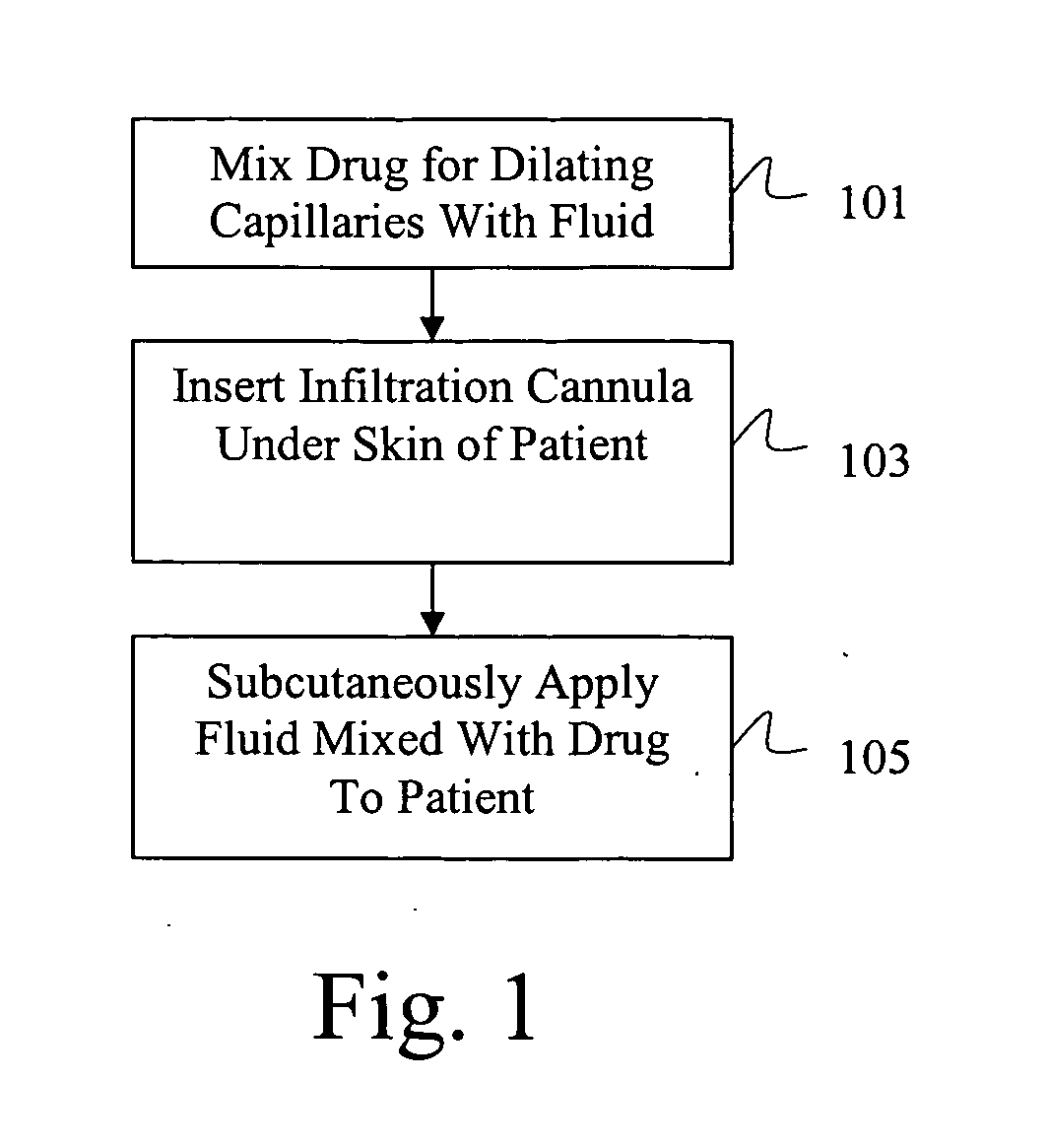
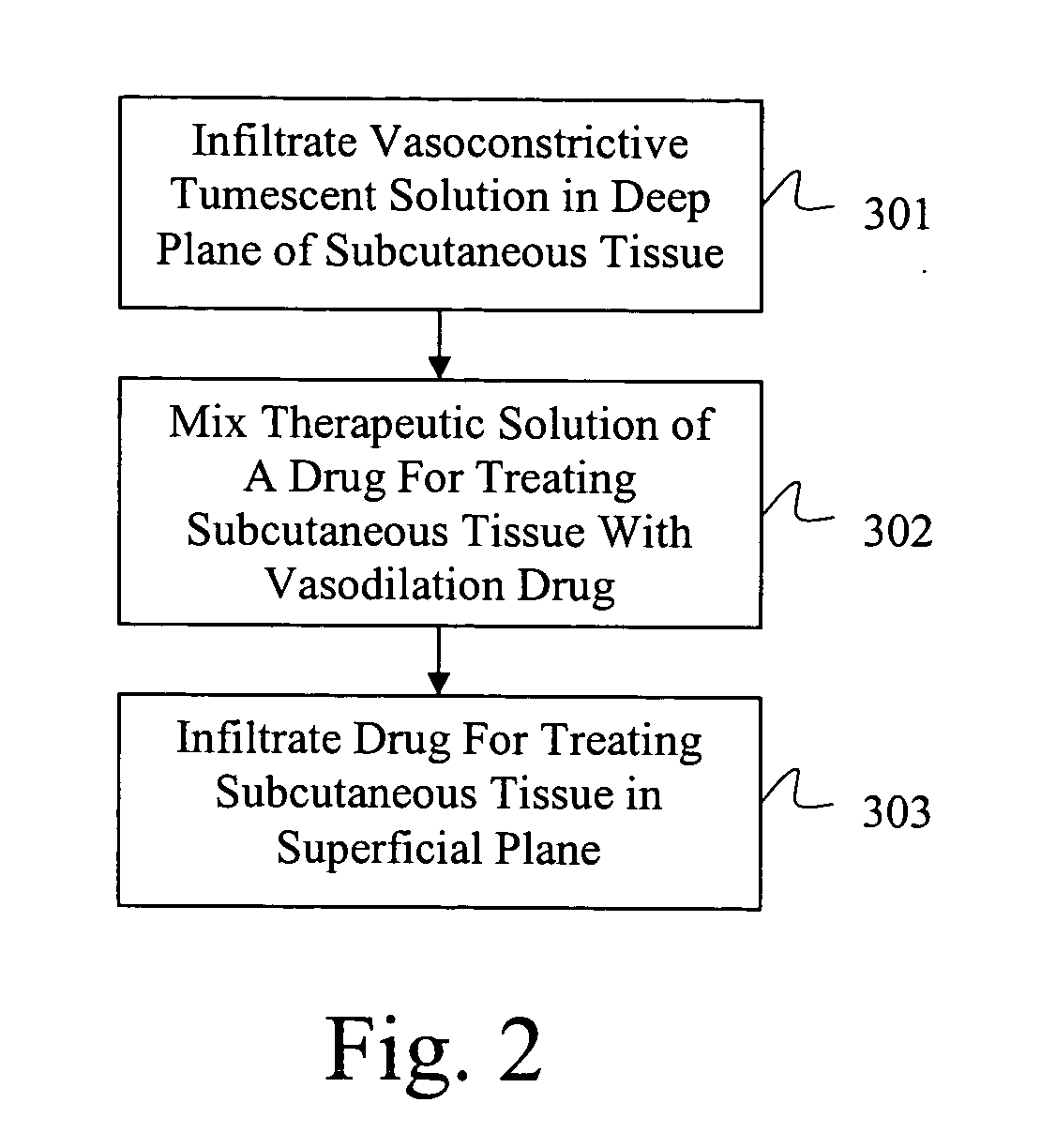
Drug delivery system for accelerated subcutaneous absorption
ActiveUS20050287134A1Prevent and delay absorptionImprove absorption rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyVascular dilation
A method for accelerating subcutaneous absorption of a fluid or drug into the systemic circulation of a specific targeted tissue. A first drug operative to produce local capillary vasodilatation and / or increase the rate of bulk flow of solution through the interstitial space is mixed with a fluid. The fluid may contain a crystalloid solution or a dilute solution of a pharmacologic drug required for a routine or emergency therapeutic treatment for a patient. The first drug is substantially non-toxic to the patient. The fluid mixed with the first drug is then delivered subcutaneously or into deeper tissues of the patient, by use of a hyperdermic needle or infiltration cannula. As the capillaries are dilated, the fluid is efficiently absorbed and circulated systemically.
Owner:KLEIN JEFFREY A
LiFePO4 FLAKES FOR Li-ION BATTERY AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME
ActiveUS20120328947A1Charge-discharge efficiency can be improvedShort diffusion pathMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphatesCharge dischargeEngineering
LiFePO4 flakes for a Li-ion battery and a method for manufacturing the same are disclosed. The LiFePO4 flakes of the present invention have a thickness of 5 nm-200 nm, and the angle between the flat surface normal of the flake and the Li-ion diffusion channel is 0°-80°. In addition, according to the present invention, the LiFePO4 flakes with short Li ion diffusion path can be prepared through a simple process. Hence, not only the charge-discharge efficiency of the Li-ion battery can be improved by use of the LiFePO4 flakes of the present invention, but also the cost of the Li-ion battery can be further reduced.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Devices and methods to immobilize analytes of interest
InactiveUS20050254995A1Rapid and efficient immobilizationSimple processAnalysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationTarget analysisDiffusion
The invention provides devices and methods using assemblies of shaped inserts coated with diverse binder materials optionally positioned inside conformal housings. The devices are capable of immobilizing target analytes of interest (e.g., specific or groups of biomolecules) and are optionally usable as single units, linear strips or array formats. The coatings on the inserts and, optionally also on the inside walls of the housings, create variable gaps with narrow fluid paths resulting in enhanced diffusion and absorption of target analytes from transiting fluid samples while exhibiting minimal resistance to flow or back pressure commonly seen in conventional plug-type packings. The devices are intended for sample preparations requiring: filtering, enriching, separating, purifying of target analytes by selective absorption / elution as part of desalting, buffer exchange and / or enrichment applications in analyses by mass spectrometry and / or electrophoresis; purifying biomolecules; culturing cells; analytical separation processes, and general chemical, biological and / or biochemical separations in manual or automated systems.
Owner:HARVARD APPARATUS
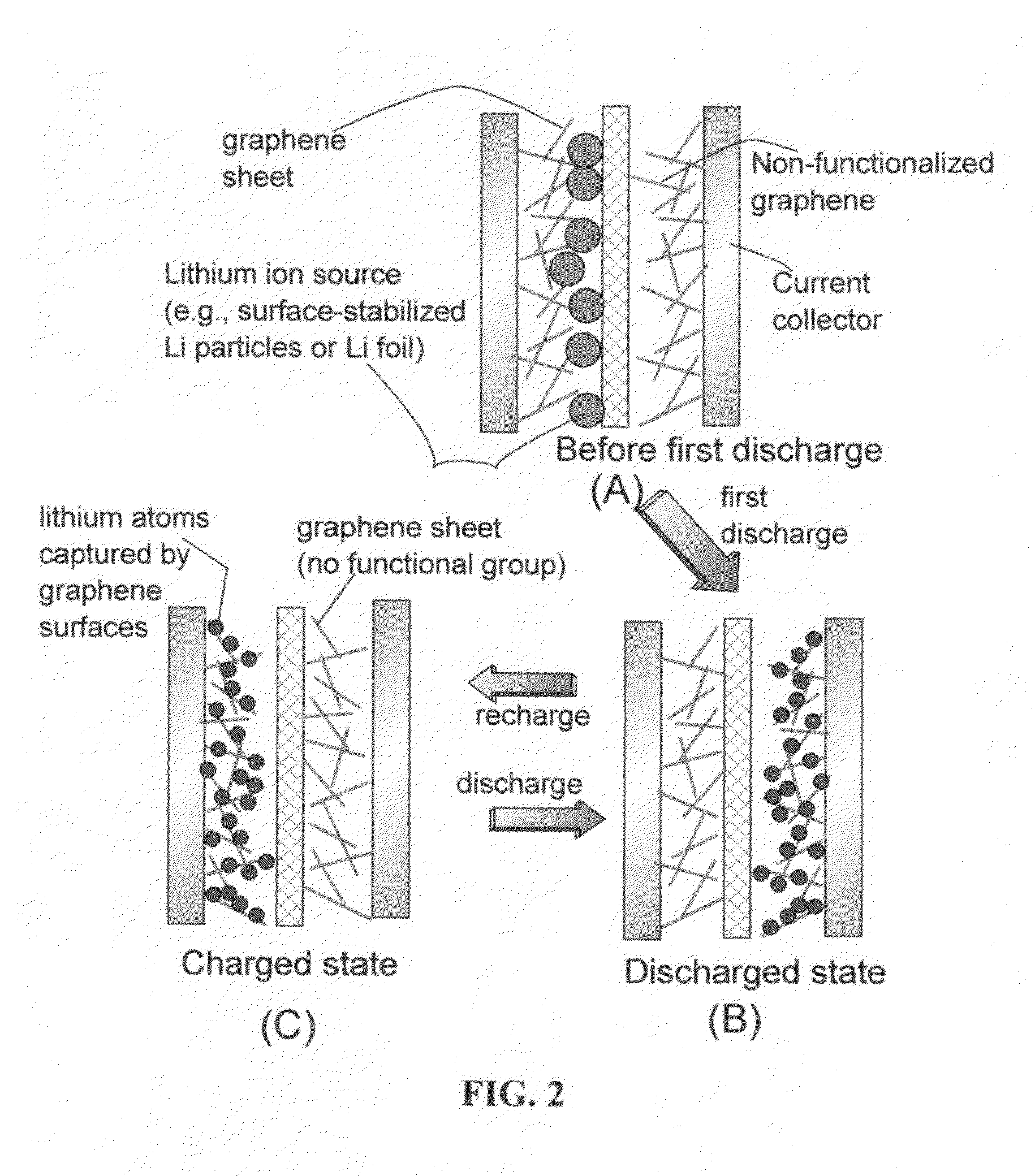
Surface-mediated cells with high power density and high energy density
ActiveUS20130202945A1Improvement factorImprove diffusivityPrimary cell to battery groupingMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical batteryHigh energy
A surface-mediated cell (SMC) comprising: (a) a cathode comprising a carbon-based cathode active material having a surface area to capture or store lithium thereon; (b) an anode comprising an anode current collector alone, or combined anode current collector and anode active material; (c) a porous separator disposed between the anode and the cathode; (d) a lithium-containing electrolyte, wherein the anode and / or cathode active material has a specific surface area no less than 100 m2 / g in direct physical contact with the electrolyte to receive lithium ions therefrom or to provide lithium ions thereto; and (e) a lithium source disposed in at least one of the two electrodes when the cell is made, and the cell has an open-circuit voltage (OCV) of at least 0.8 volts; wherein the cell operates between a lower voltage limit lower than the OCV and an upper limit of between 3.8 and 4.5 volts.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC +1
Rechargeable lithium cell having a chemically bonded phthalocyanine compound cathode
ActiveUS20140072871A1High oxygen contentIncreased riskMaterial nanotechnologyNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesPhthalocyanineLongest cycle
A rechargeable lithium cell comprising: (a) an anode comprising an anode active material; (b) a cathode comprising a hybrid cathode active material composed of an electrically conductive substrate and a phthalocyanine compound chemically bonded to or immobilized by the conductive substrate, wherein the phthalocyanine compound is in an amount of from 1% to 99% by weight based on the total weight of the conductive substrate and the phthalocyanine compound combined; and (c) electrolyte or a combination of electrolyte and a porous separator, wherein the separator is disposed between the anode and the cathode and the electrolyte is in ionic contact with the anode and the cathode. This secondary cell exhibits a long cycle life, the best cathode specific capacity, and best cell-level specific energy of all rechargeable lithium-ion cells ever reported.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
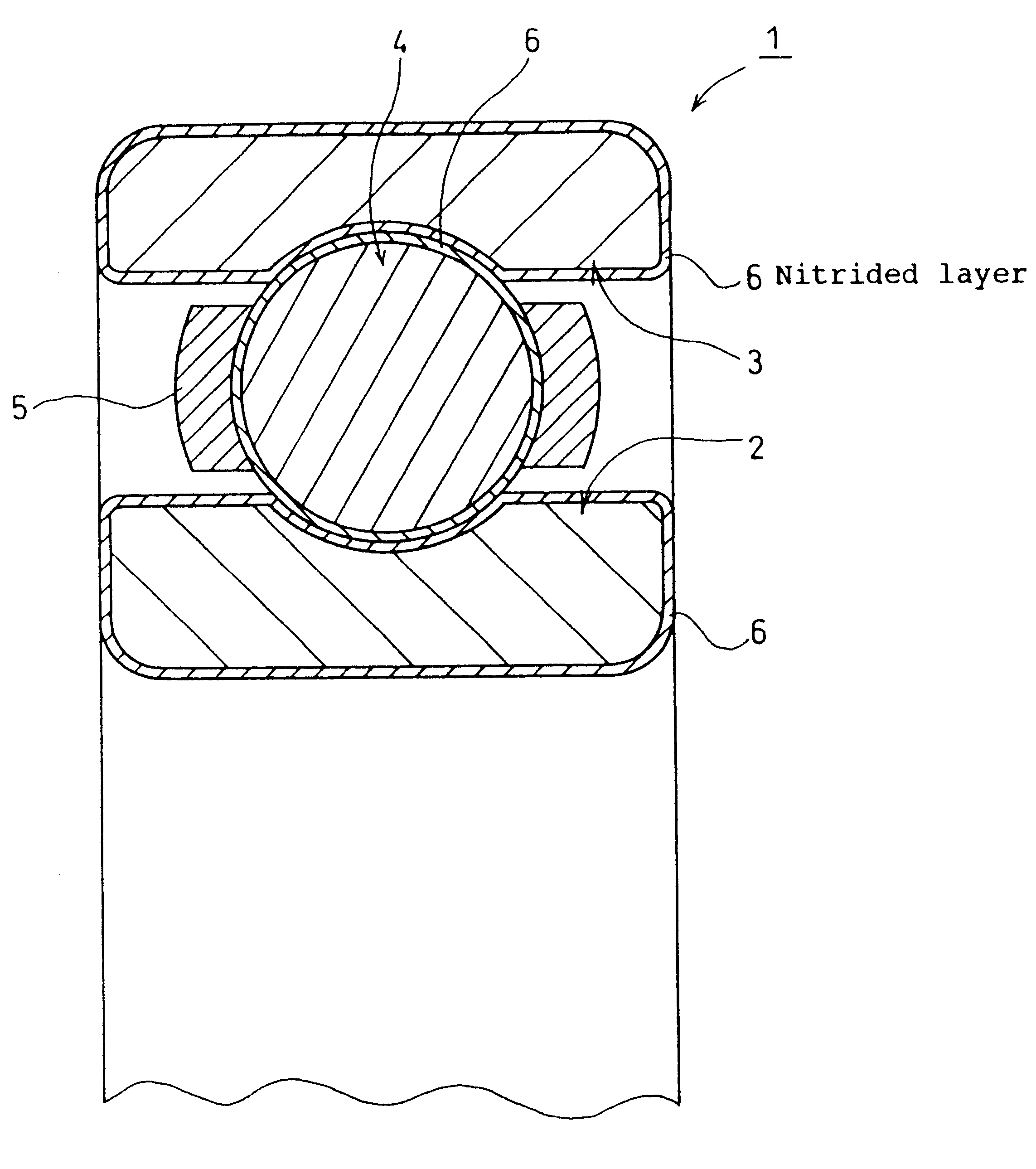
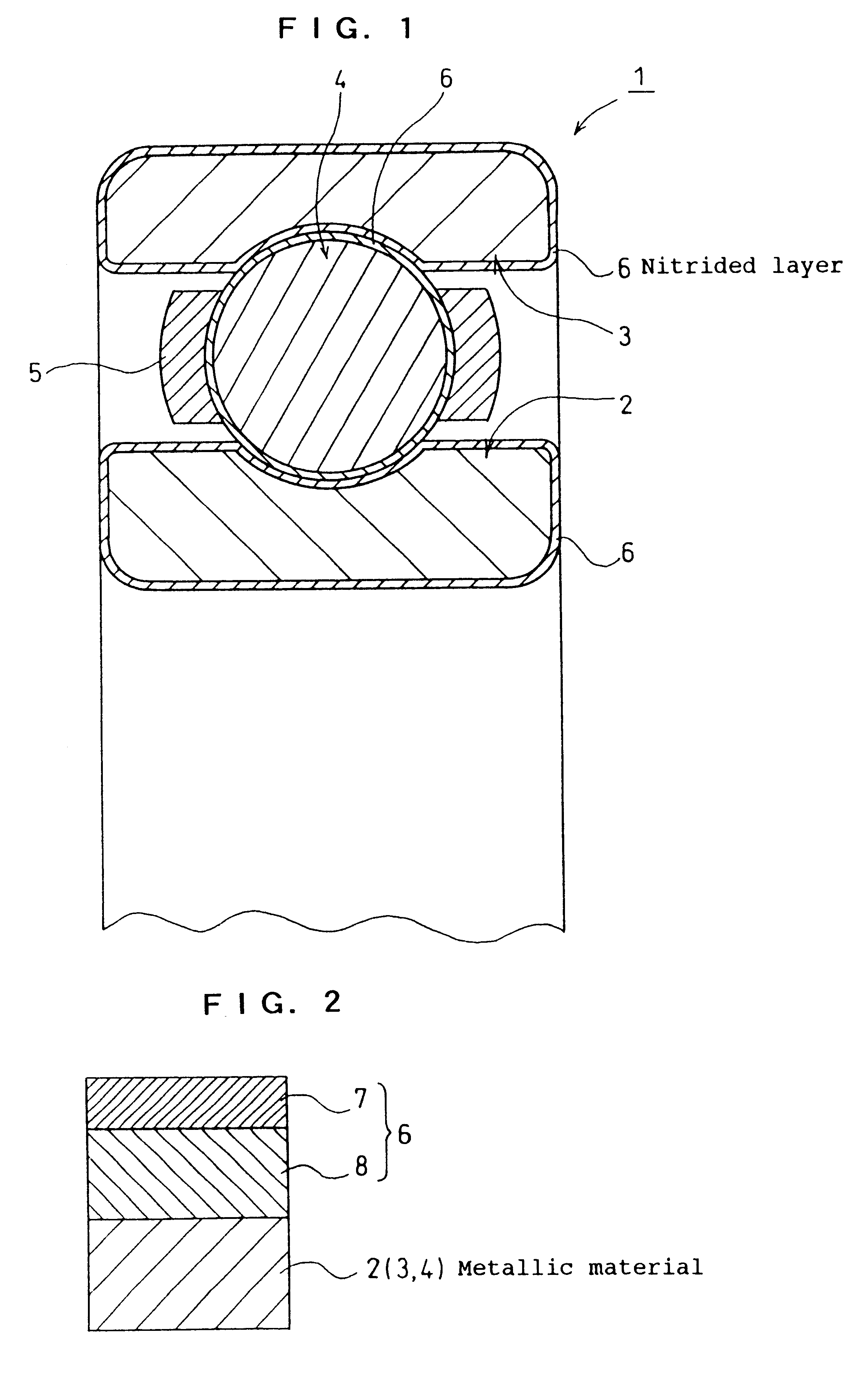
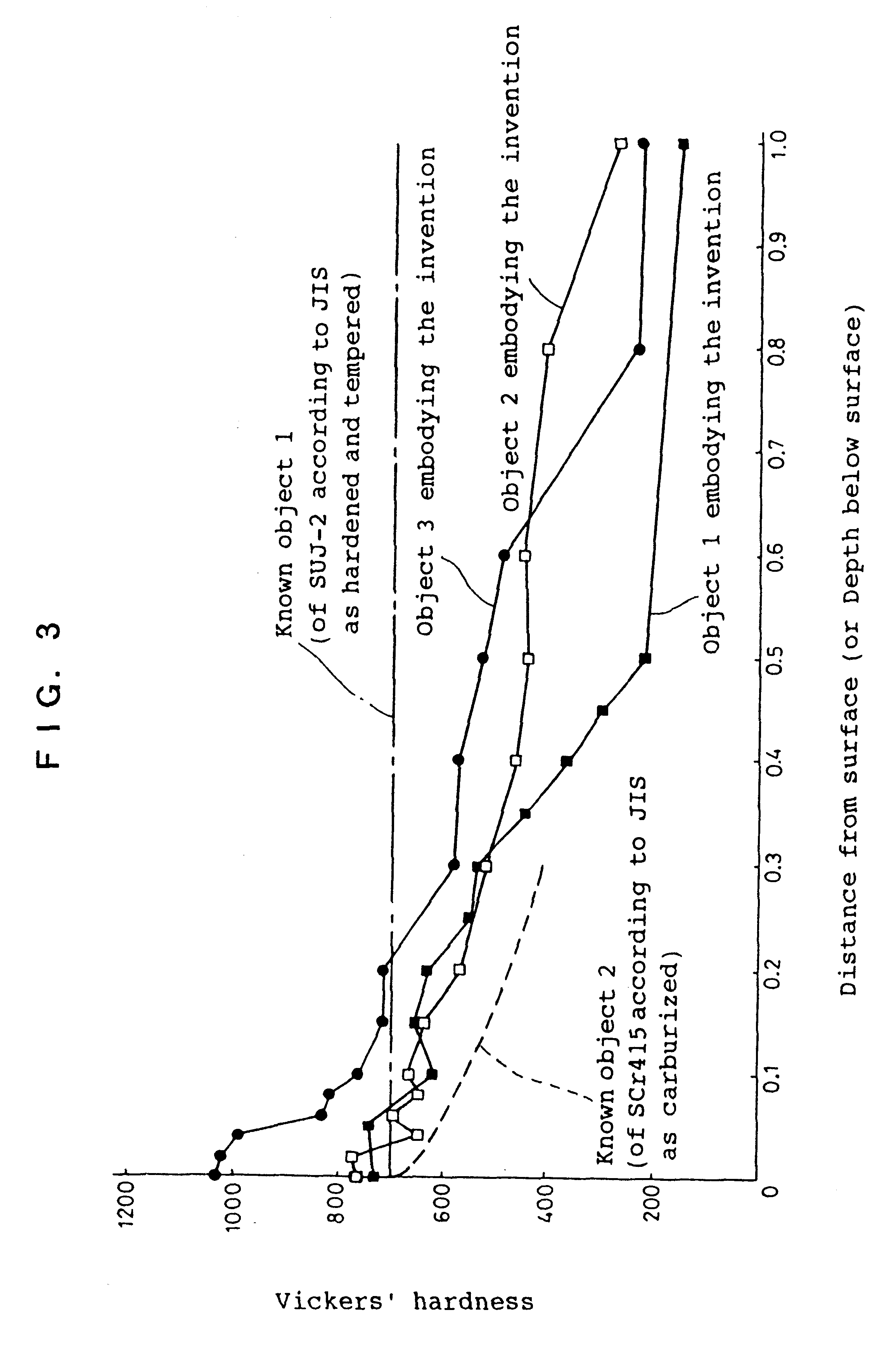
Rolling bearing
InactiveUS6290398B1Short timeImprove diffusivityBearing componentsSolid state diffusion coatingAlloy elementMetallic materials
At least one of constituent elements of a rolling bearing is formed of a metallic material which contains an alloy element having a strong affinity for nitrogen while being of low grade in terms of cost and characteristics, and has a nitriding layer formed on surfaces thereof to be hardened. Accordingly, it is possible to use such rolling bearing as a substitute for conventional rolling bearings or rolling bearings of high grade which are known as general rolling bearings.
Owner:KOYO SEIKO CO LTD
Method and apparatus for electrowinning copper using the ferrous/ferric anode reaction
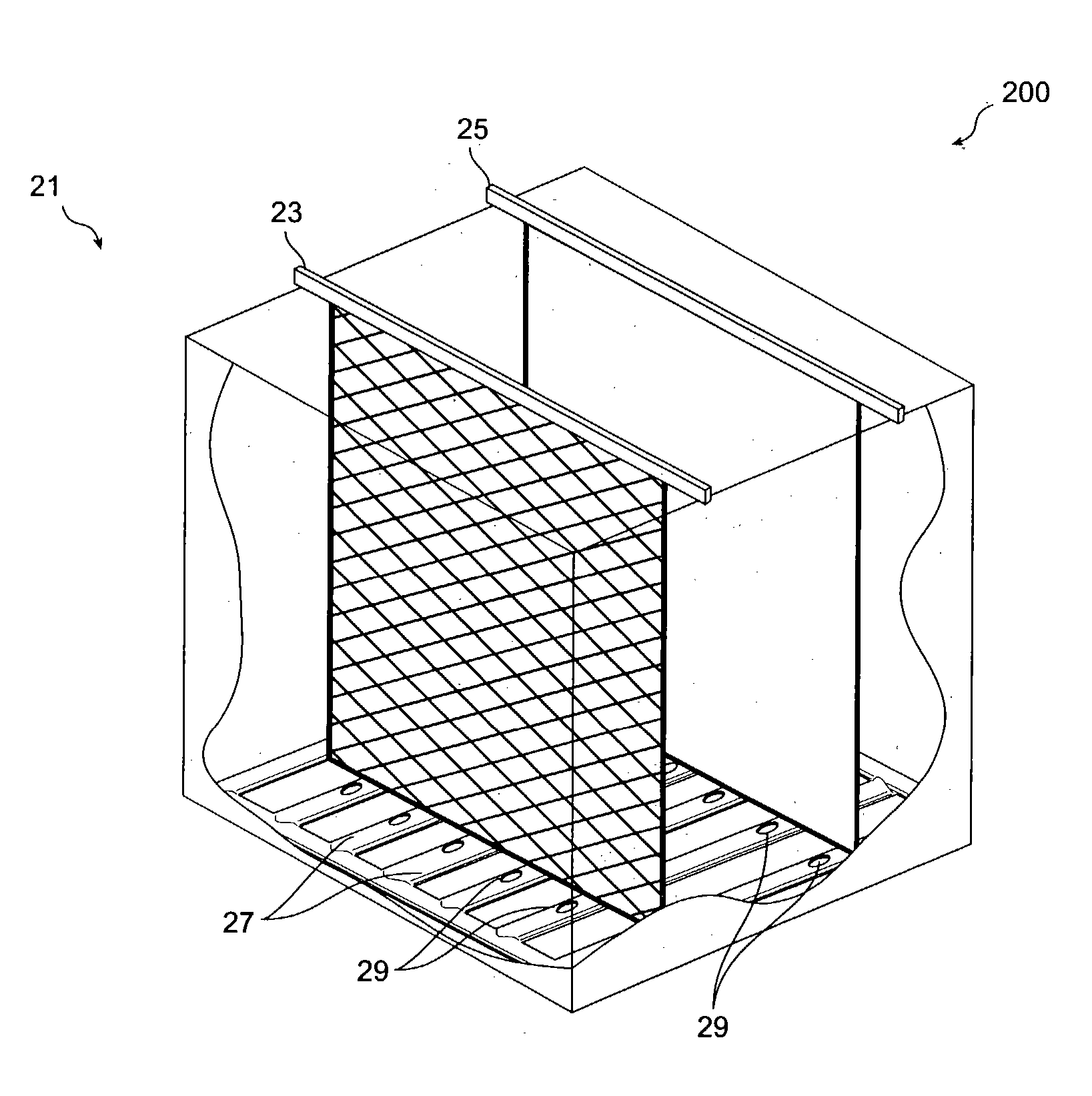
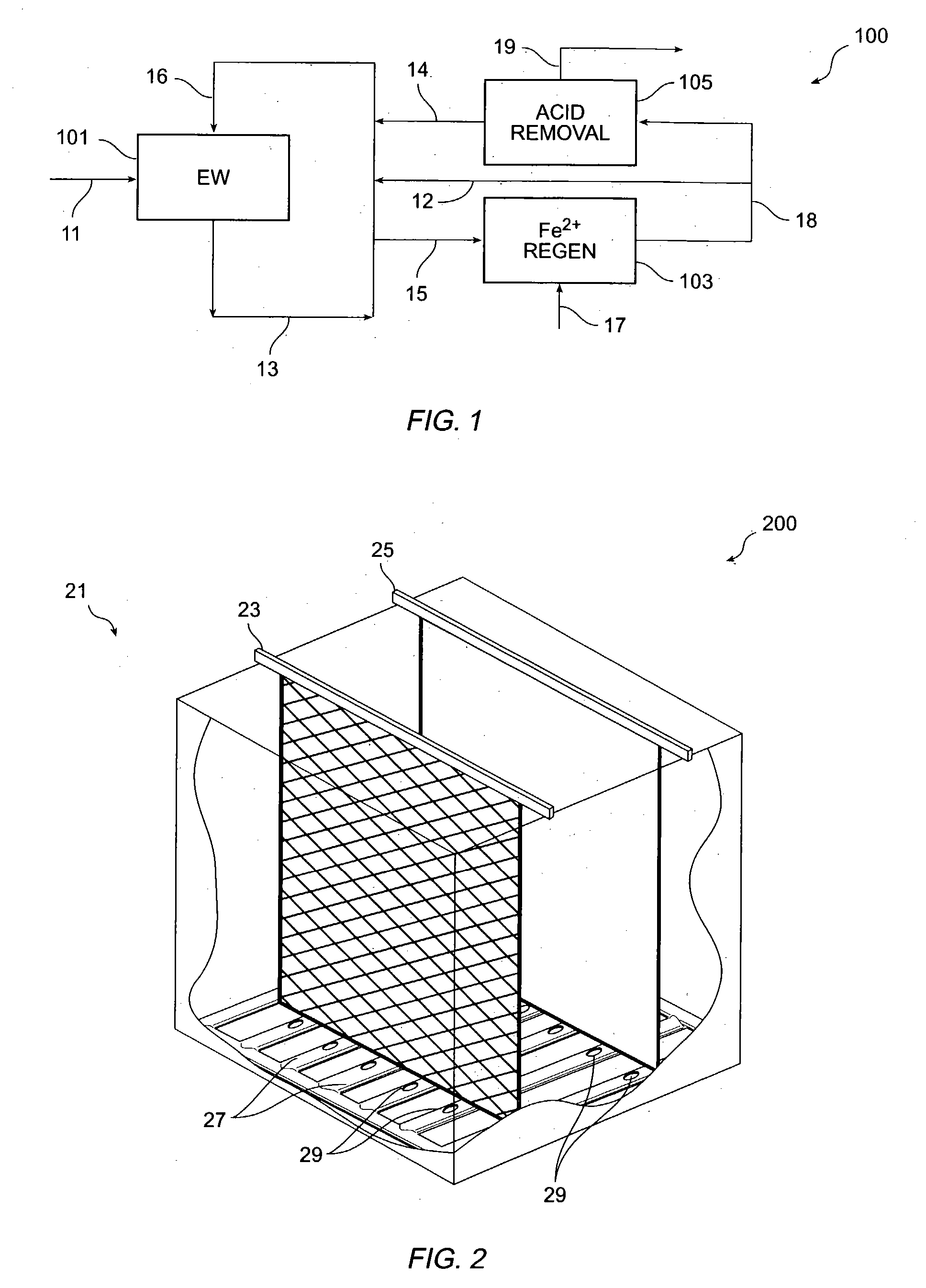
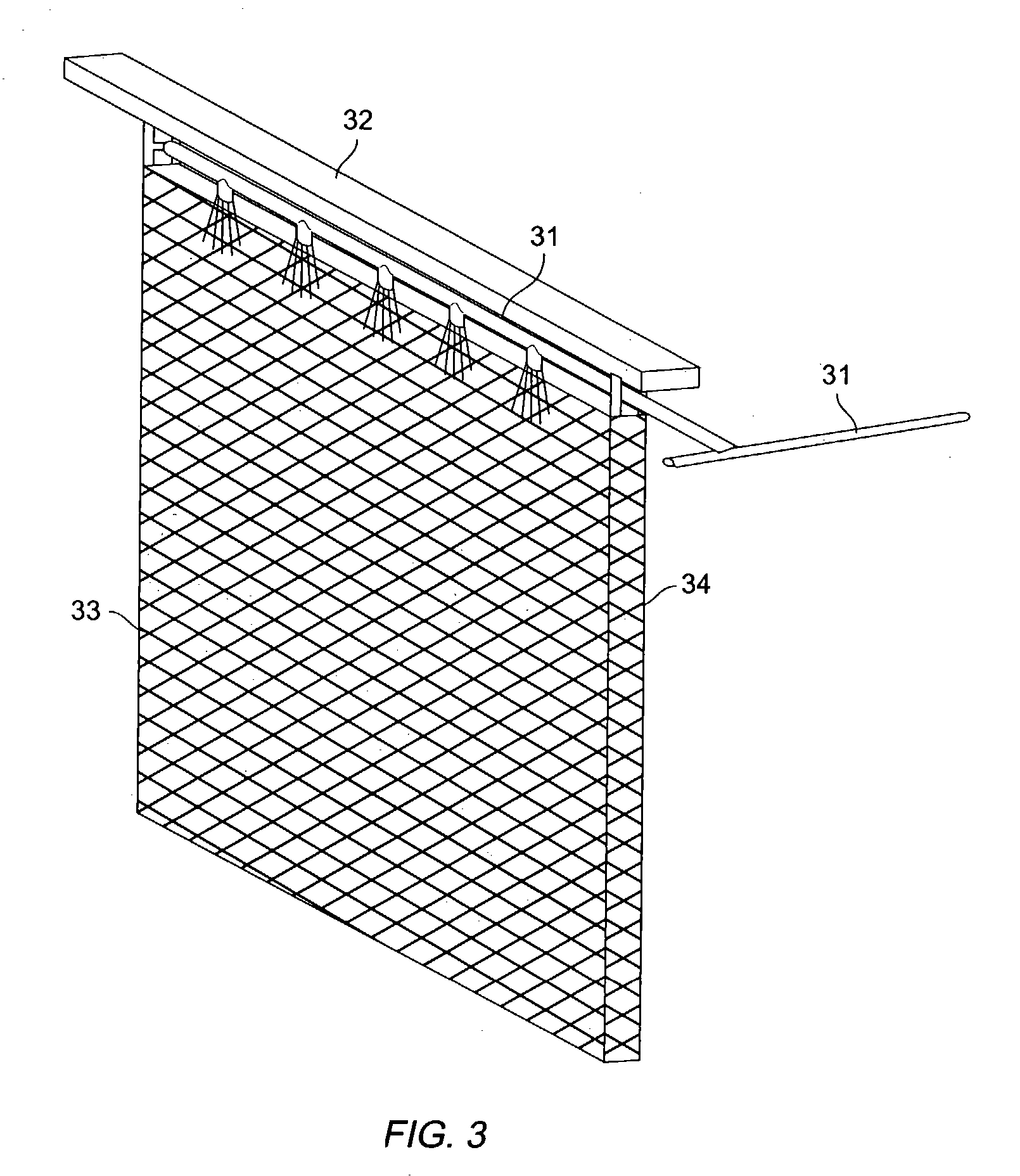
InactiveUS20050023151A1Reduce generationIncrease consumptionCellsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisCopper
The present invention relates, generally, to a method and apparatus for electrowinning metals, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for copper electrowinning using the ferrous / ferric anode reaction. In general, the use of a flow-through anode—coupled with an effective electrolyte circulation system—enables the efficient and cost-effective operation of a copper electrowinning system employing the ferrous / ferric anode reaction at a total cell voltage of less than about 1.5 V and at current densities of greater than about 26 Amps per square foot (about 280 A / m2), and reduces acid mist generation. Furthermore, the use of such a system permits the use of low ferrous iron concentrations and optimized electrolyte flow rates as compared to prior art systems while producing high quality, commercially saleable product (i.e., LME Grade A copper cathode or equivalent), which is advantageous.
Owner:FREEPORT MCMORAN COPPER & GOLD INC
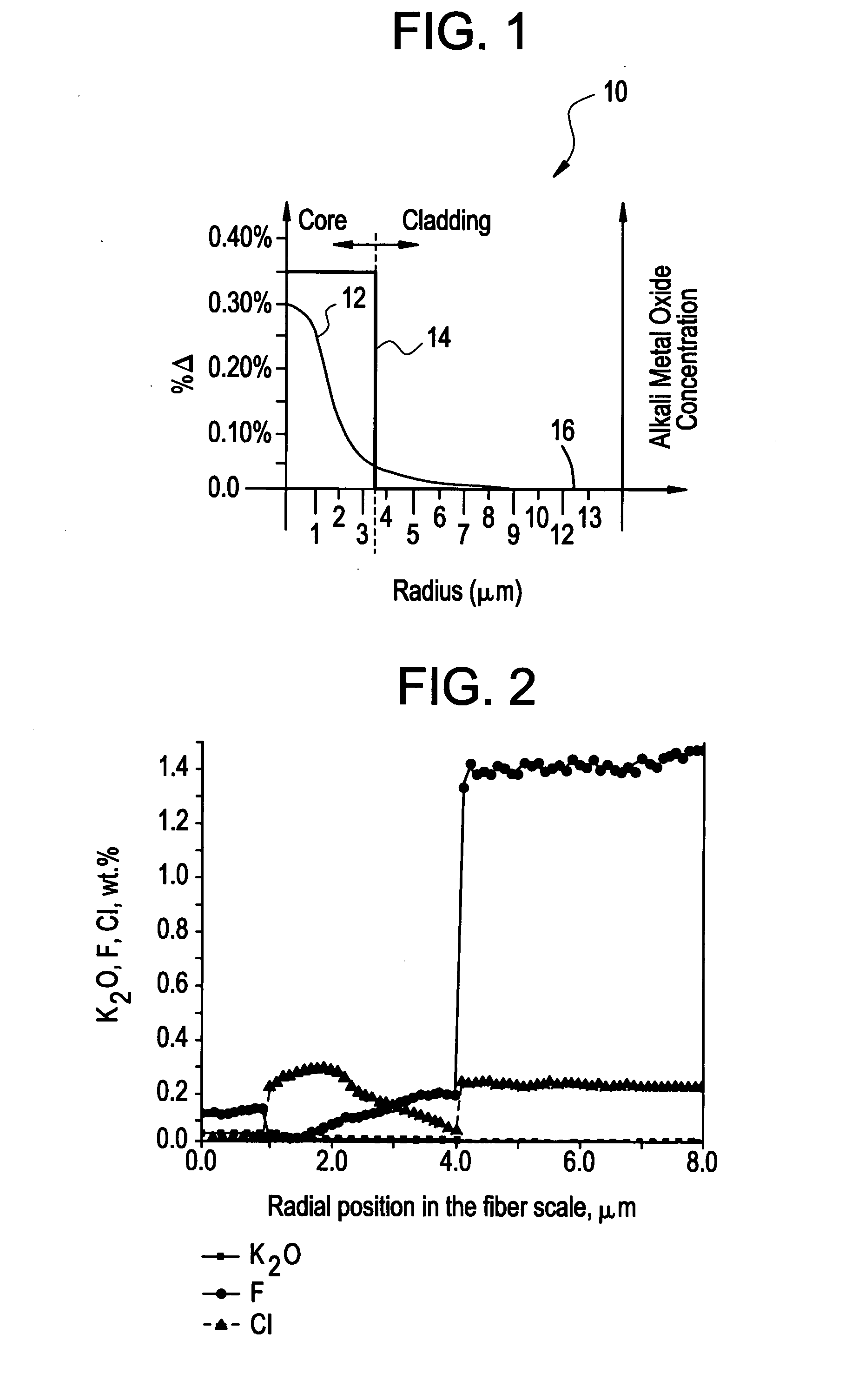
Optical fiber containing alkali metal oxide
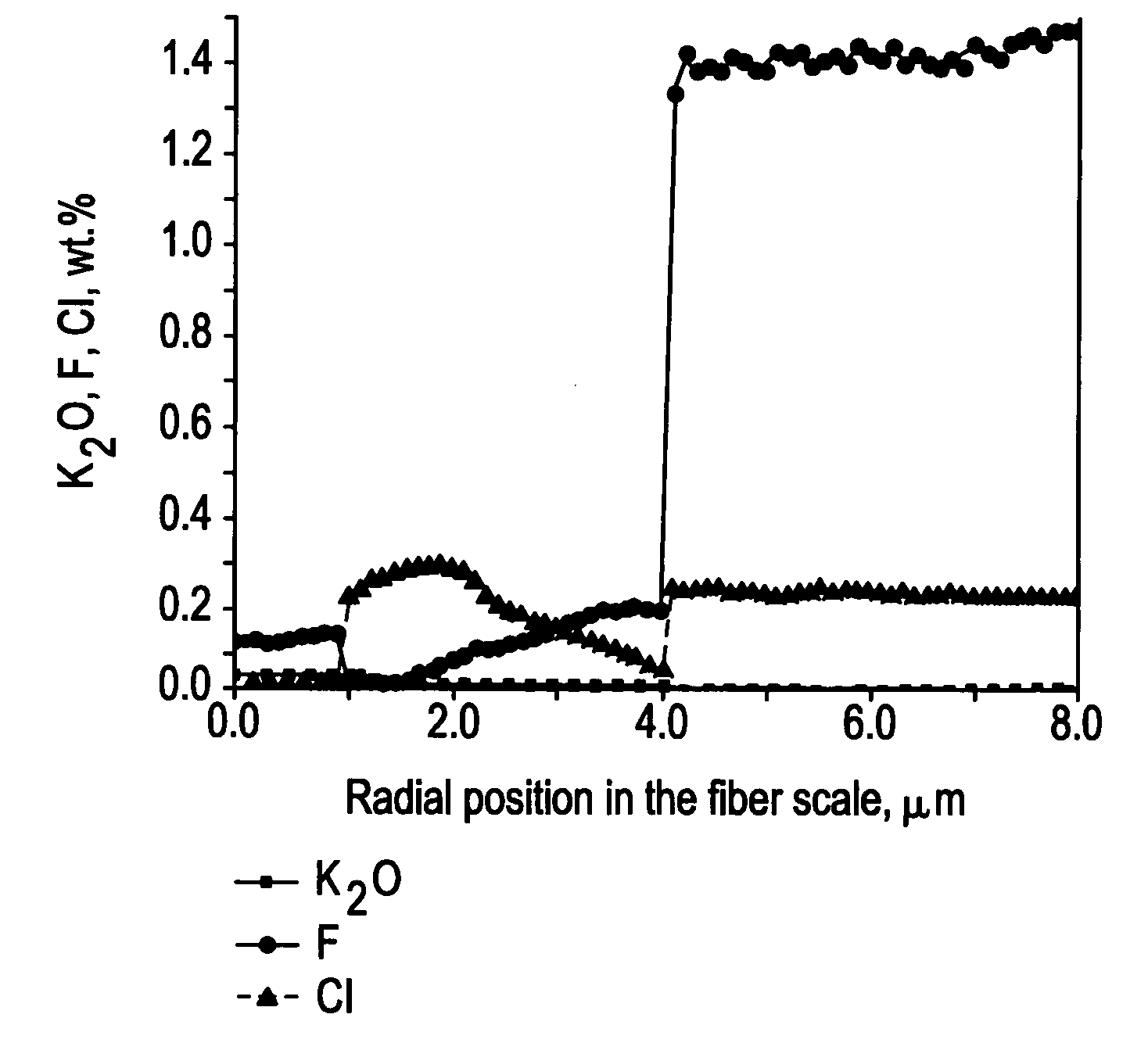
ActiveUS20070297735A1Reduce lossReduce concentrationGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantAlkali metal oxide
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a silica-based core comprising an alkali metal oxide selected from the group consisting of K2O, Na2O, LiO2, Rb2O, Cs2O and mixtures thereof in an average concentration in said core between about 50 and 500 ppm by weight, said core further comprising chlorine and fluorine, wherein the average concentration of fluorine in said core is greater than the average concentration of alkali metal oxide in said core and the average concentration of chlorine in said core is greater than the average concentration of alkali metal oxide in said core; and a silica-based cladding surrounding and directly adjacent the core. By appropriately selecting the concentration of alkali metal oxide dopant in the core and the cladding, a low loss optical fiber may be obtained.
Owner:CORNING INC
Lithium-ion cell having a high energy density and high power density
ActiveUS20130260246A1Low lithium ion contentReduce the amount of solutionMaterial nanotechnologySecondary cellsElectrical batteryHigh energy
A lithium-ion cell comprising: (A) a cathode comprising graphene as the cathode active material having a surface area to capture and store lithium thereon and wherein said graphene cathode is meso-porous having a specific surface area greater than 100 m2 / g; (B) an anode comprising an anode active material for inserting and extracting lithium, wherein the anode active material is mixed with a conductive additive and / or a resin binder to form a porous electrode structure, or coated onto a current collector in a coating or thin film form; (C) a porous separator disposed between the anode and the cathode; (D) a lithium-containing electrolyte in physical contact with the two electrodes; and (E) a lithium source disposed in at least one of the two electrodes when the cell is made. This new Li-ion cell exhibits an unprecedentedly high energy density.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC +1
Diffuse reflector comprising nonwoven sheet with binder layer comprising binder and scatterer of visible light
InactiveUS20080080055A1Improve reflectivityLess non-uniformityMirrorsDiffusing elementsMaterials scienceCable television
This invention relates to diffuse reflectors of visible light comprising a nonwoven sheet having on at least one face thereof a binder layer comprising a binder and a scatterer of visible light dispersed in the binder. These diffuse reflectors have utility in light management in optical displays such as backlit LCD displays for lap top computers and televisions.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com