Patents
Literature
56 results about "Electrical mobility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrical mobility is the ability of charged particles (such as electrons or protons) to move through a medium in response to an electric field that is pulling them. The separation of ions according to their mobility in gas phase is called ion mobility spectrometry, in liquid phase it is called electrophoresis.
Measuring Analyte Concentrations in Liquids
InactiveUS20080137065A1Higher kinetic energy mixingSmall dropletSamplingComponent separationElectrical mobilityDroplet size
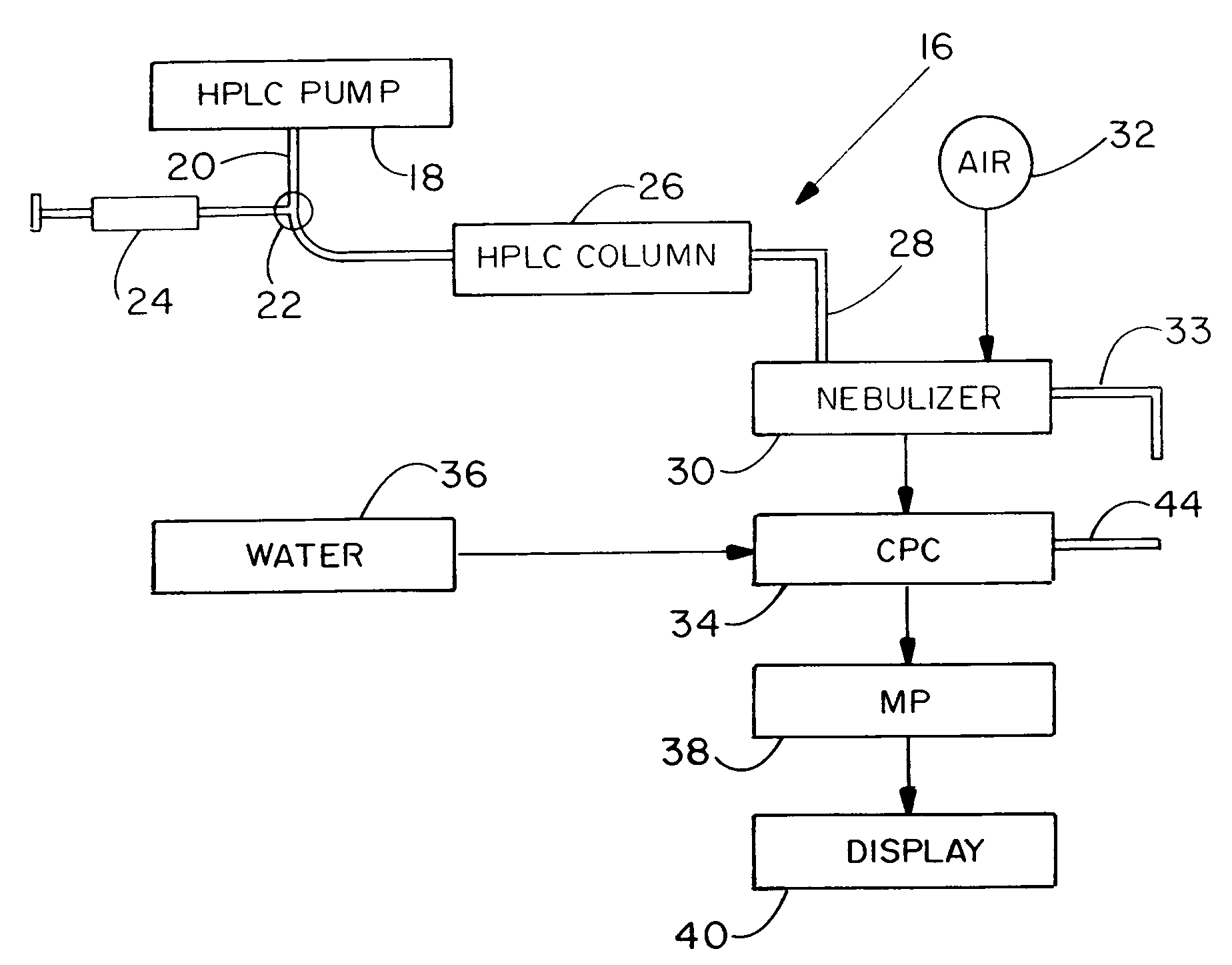
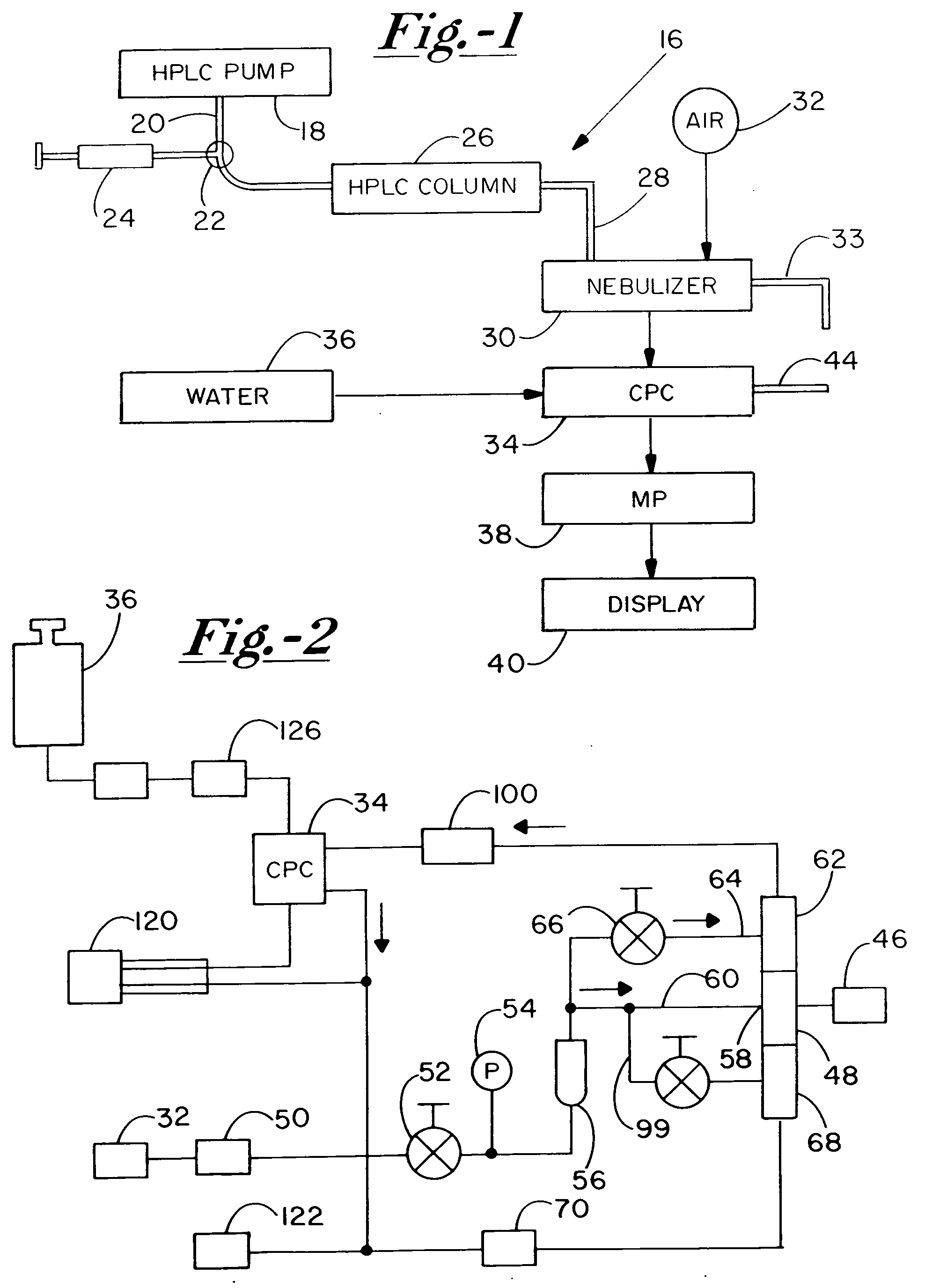
A high performance liquid chromatography system employs a nebulizer with a flow restriction at the exit of its mixing chamber to produce finer droplets, and an adjustable impactor for increased control over droplet sizes. Downstream of the mixing chamber, the nebulizer can incorporate tubing that is permeable to the sample liquid, to promote aerosol drying through perevaporation. A condensation particle counter downstream of the nebulizer uses water as the working medium, and is adjustable to control threshold nucleation sizes and droplet growth rates. A particle size selector employing diffusion, electrostatic attraction or selection based on electrical mobility, is advantageously positioned between the nebulizer and the CPC.
Owner:TSI INC
Stackable differential mobility analyzer for aerosol measurement
InactiveUS20060266132A1High resolution sizing measurementEvenly distributedMaterial analysisElectrical mobilityDifferential mobility analyzer
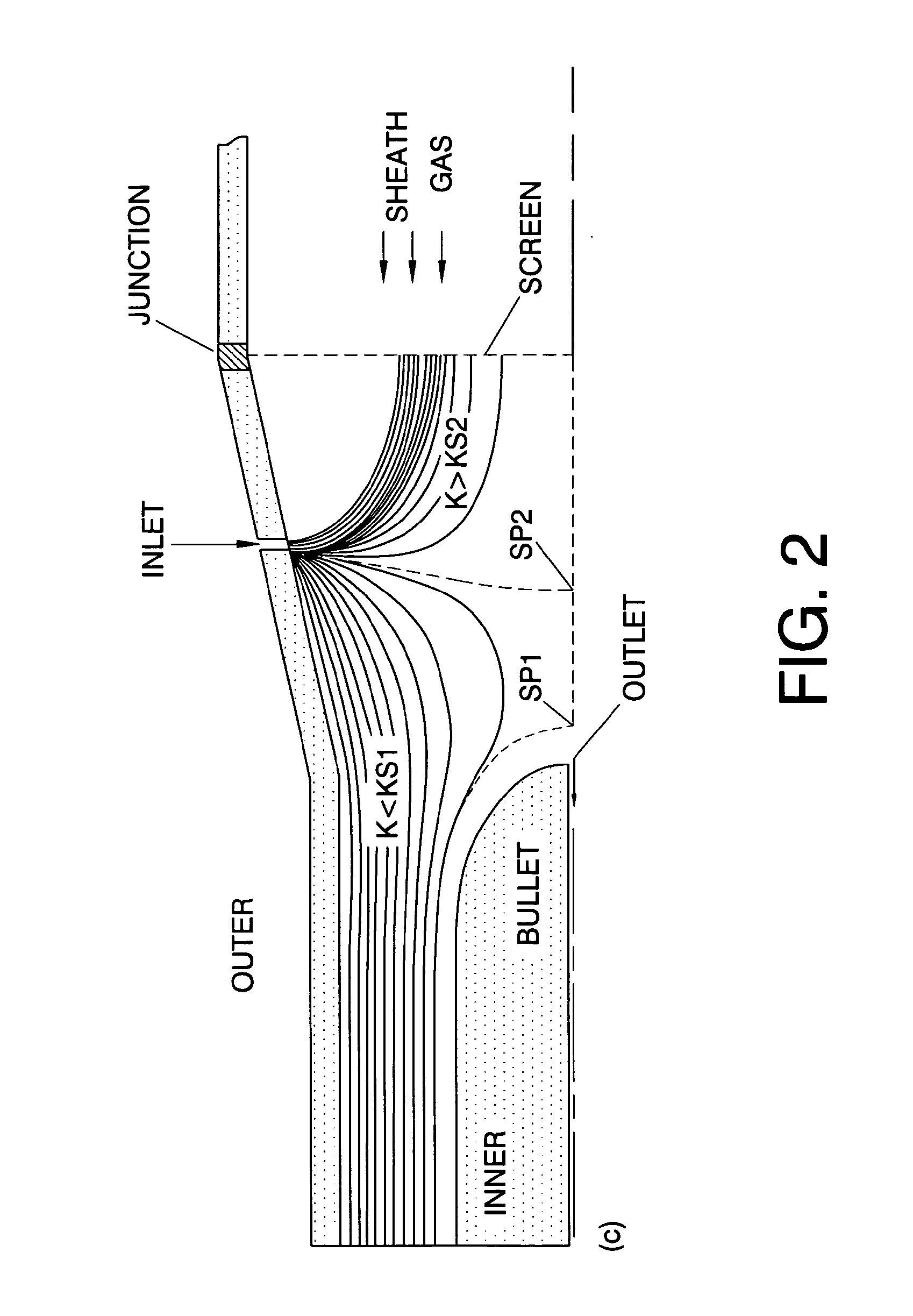
A multi-stage differential mobility analyzer (MDMA) for aerosol measurements includes a first electrode or grid including at least one inlet or injection slit for receiving an aerosol including charged particles for analysis. A second electrode or grid is spaced apart from the first electrode. The second electrode has at least one sampling outlet disposed at a plurality different distances along its length. A volume between the first and the second electrode or grid between the inlet or injection slit and a distal one of the plurality of sampling outlets forms a classifying region, the first and second electrodes for charging to suitable potentials to create an electric field within the classifying region. At least one inlet or injection slit in the second electrode receives a sheath gas flow into an upstream end of the classifying region, wherein each sampling outlet functions as an independent DMA stage and classifies different size ranges of charged particles based on electric mobility simultaneously.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Material for conductor tracks made of copper alloy
ActiveCN1985014AMeet a wide range of requirementsLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceLanthanide
The invention relates to a material for conductor tracks made of copper alloy containing Cu > 90 At. %, whereby said material contains 0.5 to 10 At. % of one or more elements from the group consisting of Ca, Sr, Ba, Sc, Y, lanthanide, Cr, Ti, Zr, Hf, Si; and 0 to 5 At. % of one or more elements from the group consisting of Mg, V, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, Ag, Au, Fe, B. Said material has a low electrical resistance, good adhesion to the glass substrate, excellent oxidation resistance, and a low electromigration rate.
Owner:PLANSEE SE
Method and apparatus to produce steady beams of mobility selected ions via time-dependent electric fields
InactiveUS20100243883A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansContinuous flowElectrical mobility
A method is described to select ions based on their electrical mobility. Ions are subjected to at least one full cycle of a time-dependent electric field. Ions are separated in space, and a continuous flow of filtered ions with a narrow range of selected mobility ions is produced at the outlet of the device, as in Differential Mobility Analyzers (DMAs). Yet, no high fluid velocity field is required, avoiding limitations associated in DMAs to flow unsteadiness, compressibility and turbulent transition. Instead, separation relies on the use of time-dependent ion trajectories generated by the time-dependent electric fields. Unlike FAIMS, full separation according to the mobility takes place within one or a few characteristic times for field variation, rather than via many tiny separation steps over many periods of field variation producing separation according to the mobility non-linearities in the mobility. Unlike conventional pulsating ion mobility spectrometry, a steady ion flow is produced with high duty cycle. Different embodiments of the apparatus using the method of the present invention are also described comprising different geometrical configurations and different time-dependent electric profiles, each of them having specific advantages. In a first configuration proposed, a rotary electric field is combined with an axial steady field achieving high resolution and a continuous output throughout all the selected and undesired ions. In a second two-dimensional configuration, an oscillating field is combined with a perpendicular steady field. Much higher sample flow rates can be achieved, though the undesired ions will periodically be transferred. Configurations using more than one stage allow minimizing the undesired pulsed signal of non selected ions. In all those configurations, the trajectories of ions are time dependent and the selected ions are subjected to at least one full cycle of the variable electric field. Separation is based on synchronizing the period of the field with the flight time of an ion from an inlet to an outlet for a particular electrical mobility.
Owner:VIDAL DE MIGUEL GUILLERMO
Charged particle selector as a function of particle electrical mobility and relaxation time
A charged particle selector having first and second circular electrical mobility selector portions is shown to include directing portions for directing particles selected by the first circular electrical mobility selector to the input of the second circular electrical mobility selector. These selectors may be combined to be in parallel instead of in series. The charged particle selector can be used to make in-line measurement of the mass and / or density of aerosol particles, to make measurements of the size of the particles and / or their distribution as well as the distribution of aerosol electrical charges.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Stackable differential mobility analyzer for aerosol measurement
InactiveUS7213476B2Easy to measureEvenly distributedMaterial analysisElectrical mobilityDifferential mobility analyzer
A multi-stage differential mobility analyzer (MDMA) for aerosol measurements includes a first electrode or grid including at least one inlet or injection slit for receiving an aerosol including charged particles for analysis. A second electrode or grid is spaced apart from the first electrode. The second electrode has at least one sampling outlet disposed at a plurality different distances along its length. A volume between the first and the second electrode or grid between the inlet or injection slit and a distal one of the plurality of sampling outlets forms a classifying region, the first and second electrodes for charging to suitable potentials to create an electric field within the classifying region. At least one inlet or injection slit in the second electrode receives a sheath gas flow into an upstream end of the classifying region, wherein each sampling outlet functions as an independent DMA stage and classifies different size ranges of charged particles based on electric mobility simultaneously.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Differential mobility analyzer, particle measuring system, and particle sorting system
ActiveCN102192949AIncrease the upper limit of the particle sizeOptimizing the upper limit of the particle sizeSamplingNanoparticle analysisVoltage generatorParticle sorting
In order to provide a differential mobility analyzer and the like that allows (i) easy increase of an upper limit of particle size of charged particle which can be classified and (ii) analysis of charged particles whose particle size is variable, a DMA (Differential Mobility Analyzer) includes: a classification tank in which an inlet electrode having an inlet slit, an intermediate electrode having a slit, and an outlet electrode having an outlet slit are arranged in sequence in such a manner that adjacent electrodes are disposed opposing each other at predetermined intervals; a gas supply section supplying the classification tank with sheath gas; and a voltage generator applying a predetermined voltage between the electrodes disposed opposing each other, the classification tank including a first classification section and a second classification section each formed by the electrodes disposed opposing each other, and the gas supply section controlling a flow rate of the sheath gas to be supplied to the classification tank individually per first classification section and second classification section.
Owner:折井孝彰
Determination of particle properties
ActiveUS20110036719A1Accurate measurementAccuracy is reachedSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementParticle propertiesElectrical mobility
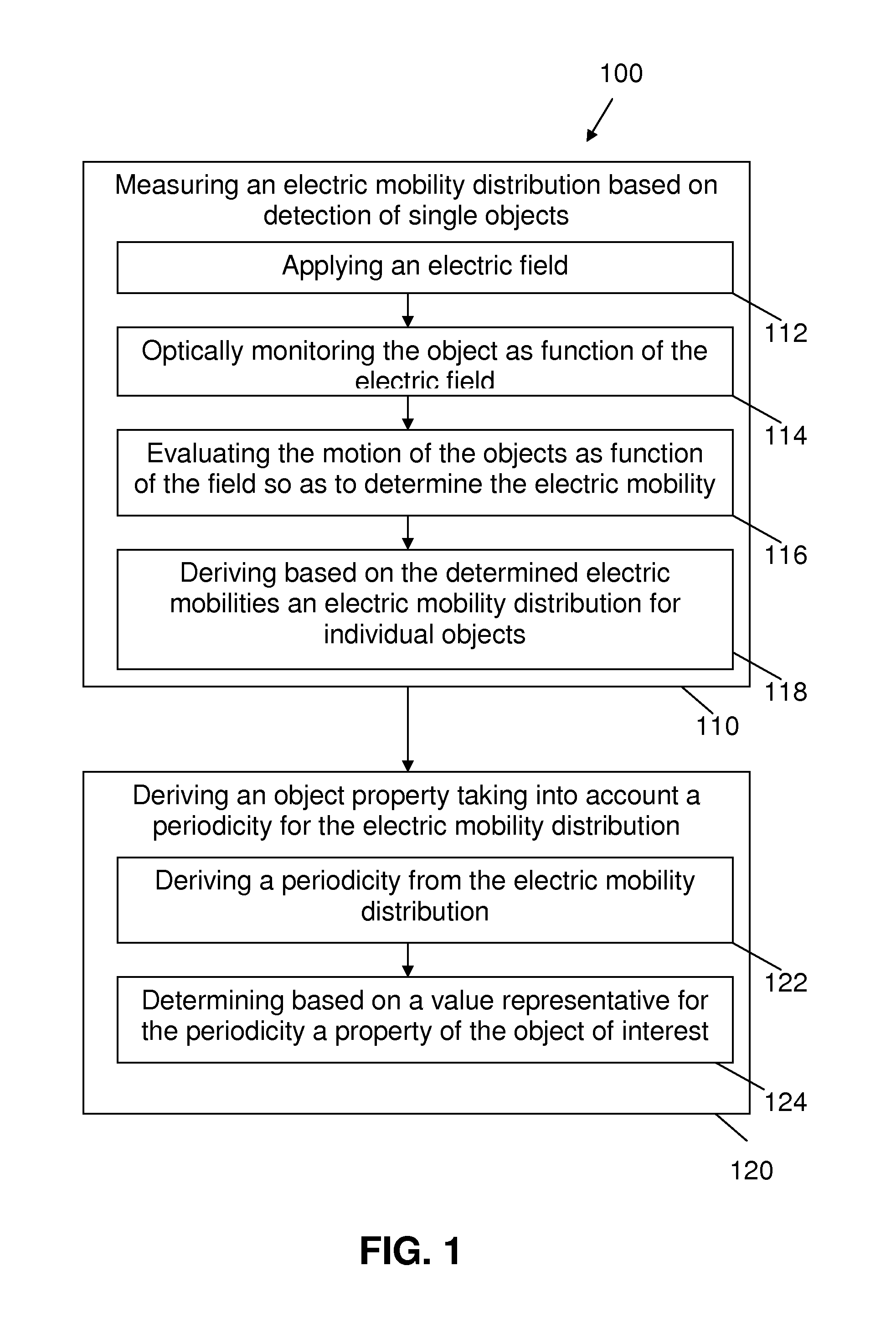
The present invention relates to a method and system for determining particle properties. Such properties may for example be charge, size, drift, etc. The method comprises determining (110) an electric mobility distribution based on detection of individual particles. The latter may be performed for a single particle over time, for a plurality of particles at the same time or in a combination thereof. The method also comprises deriving a particle property based on a periodicity in the electric mobility distribution.
Owner:UNIV GENT
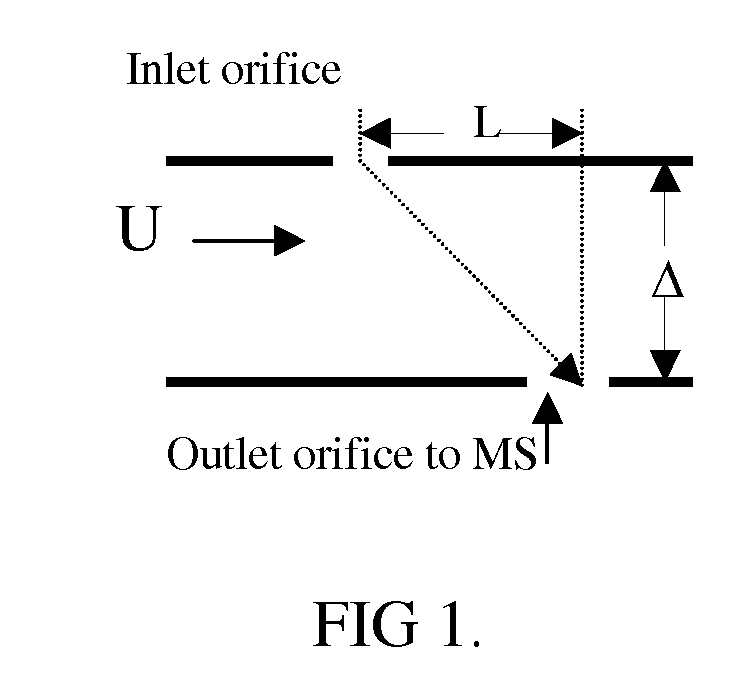
Coupling between axisymmetric differential mobility analyzers and mass spectrometers or other analyzers and detectors
ActiveUS20100213366A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSmall sampleMass analyzer
Prior work on differential mobility analysis (DMA) combined with mass spectrometry (MS) has shown how to couple the output of a planar DMA with the atmospheric pressure inlet of an atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometer (APCI-MS). However, because the ion inlet to APCI-MS instruments is a round orifice, while conventional DMA geometries make use of elongated slits, the coupling of both has attained less resolving power or tolerated a smaller sample flow rate than a DMA alone. The present invention overcomes these limitations with an axial DMA of cylindrical symmetry using more than two electrodes. The configuration is related to that previously proposed by Labowsky and Fernández de la. Mora (2004, 2006), where ions with a critical electrical mobility are brought into the symmetry axis of the DMA. Ions with this critical mobility are now optimally transmitted into the MS, with much higher resolution than possible in planar DMAs. In a preferred embodiment of this DMA facilitating DMA-MS coupling, one DMA electrode intersecting the symmetry axis is relatively planar.
Owner:NANOENG +1
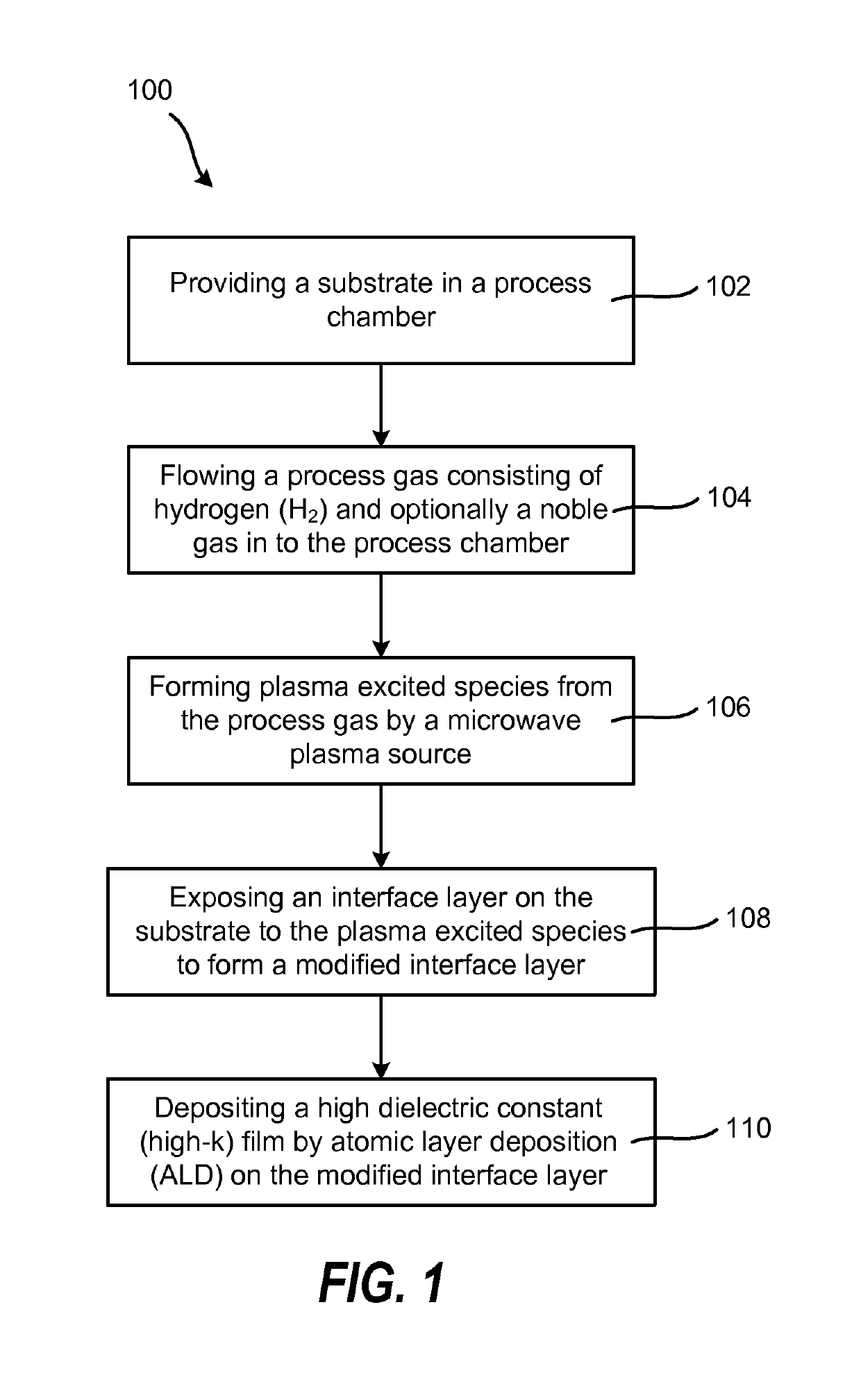
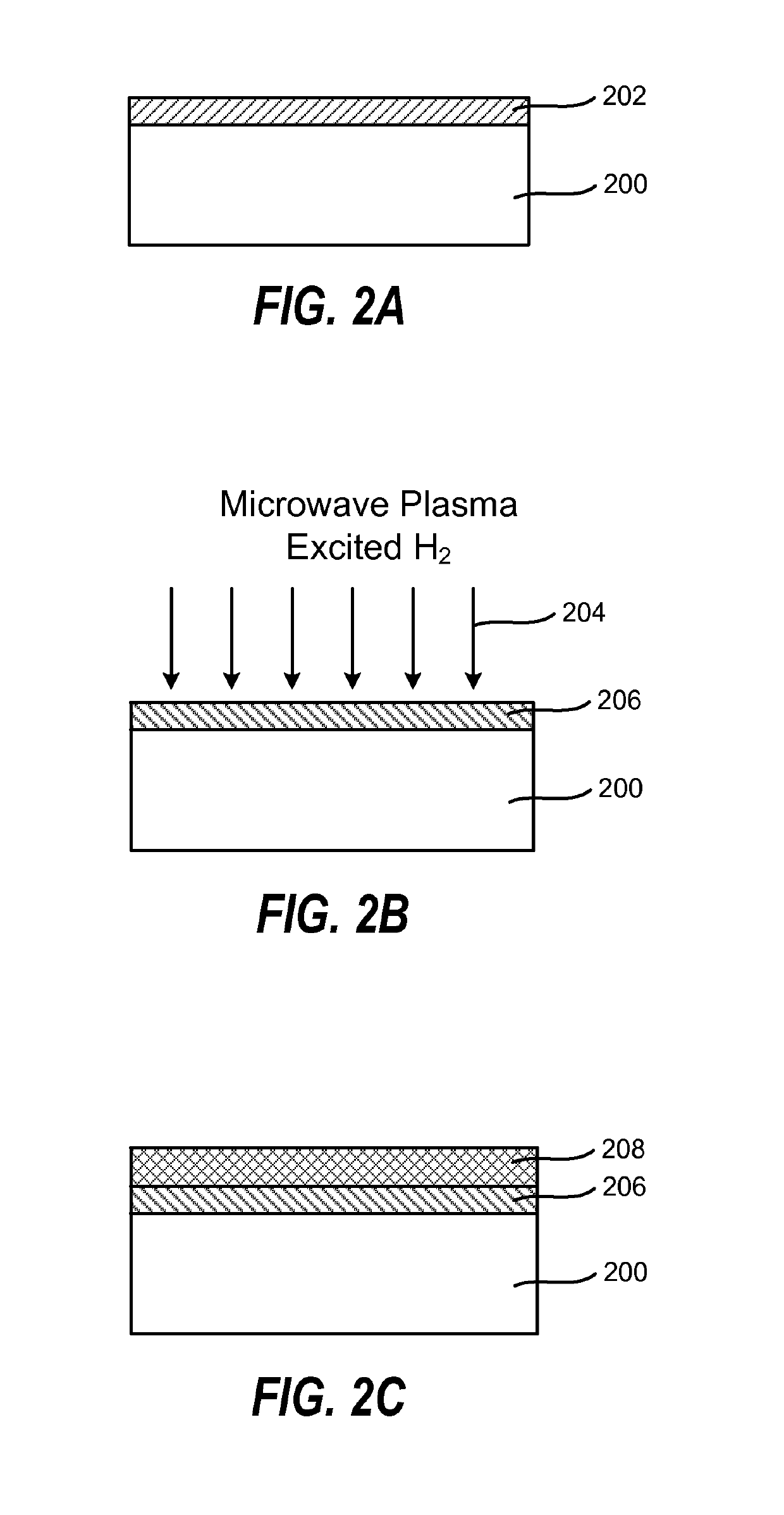
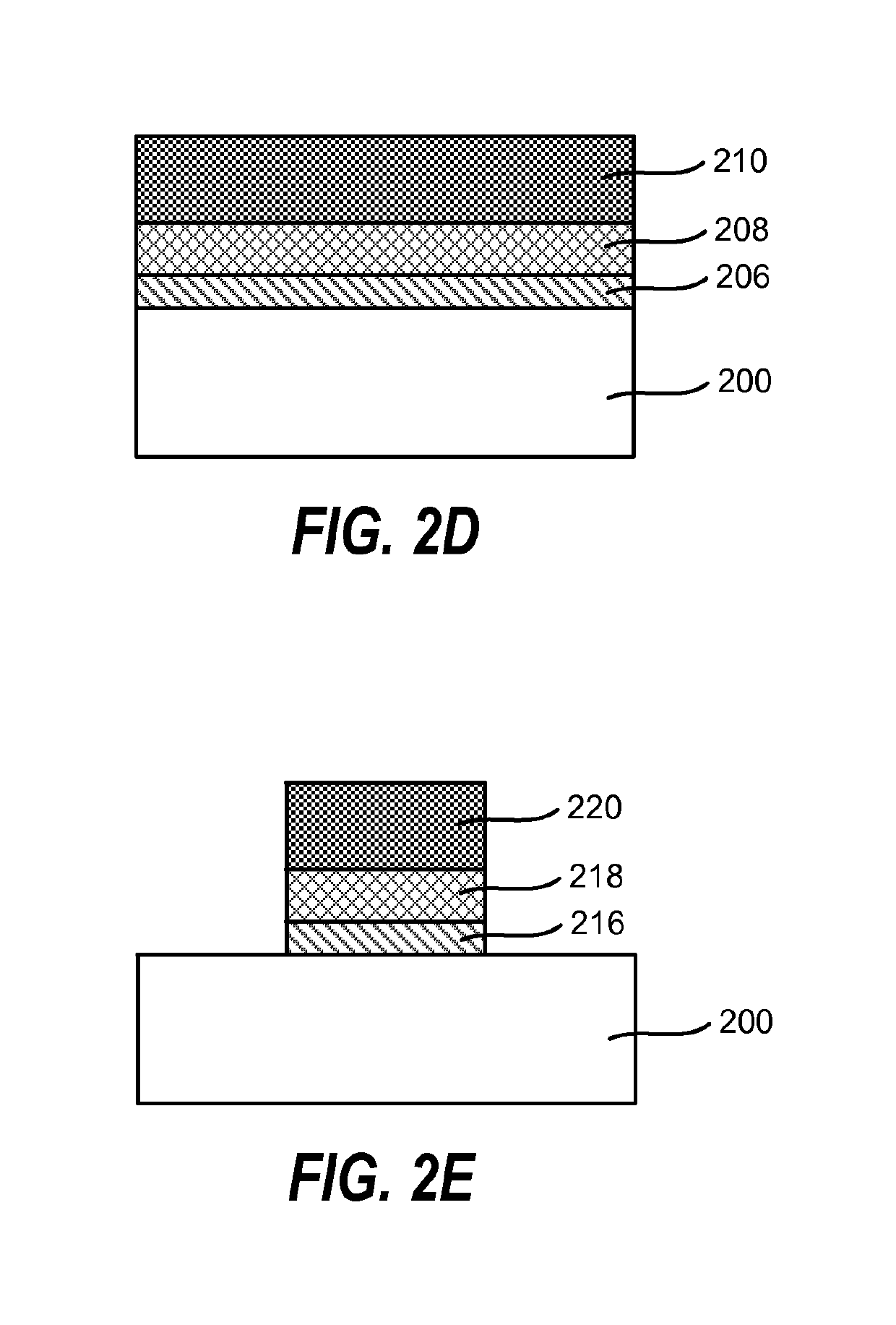
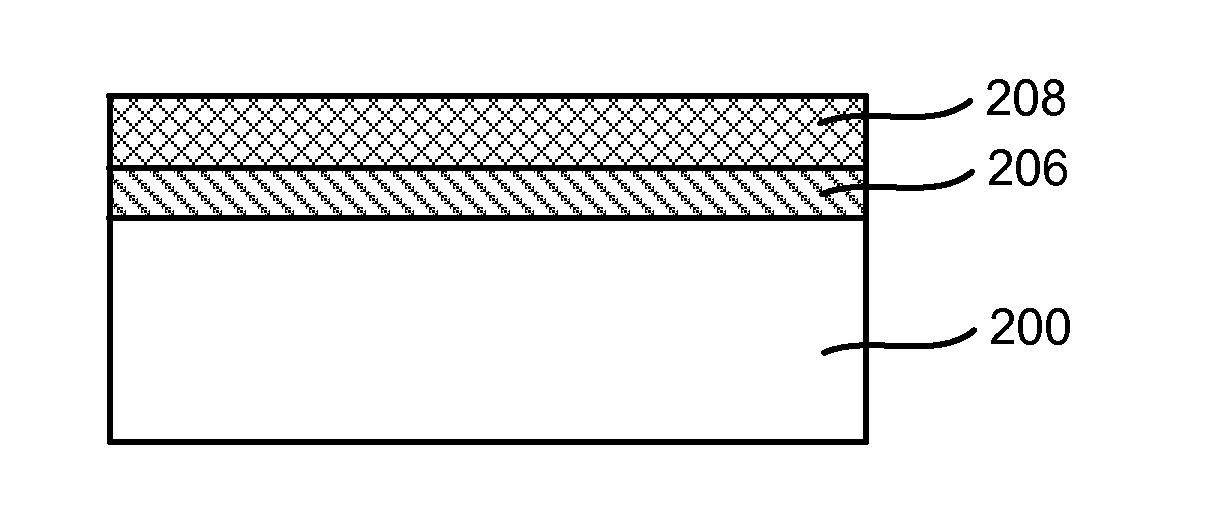
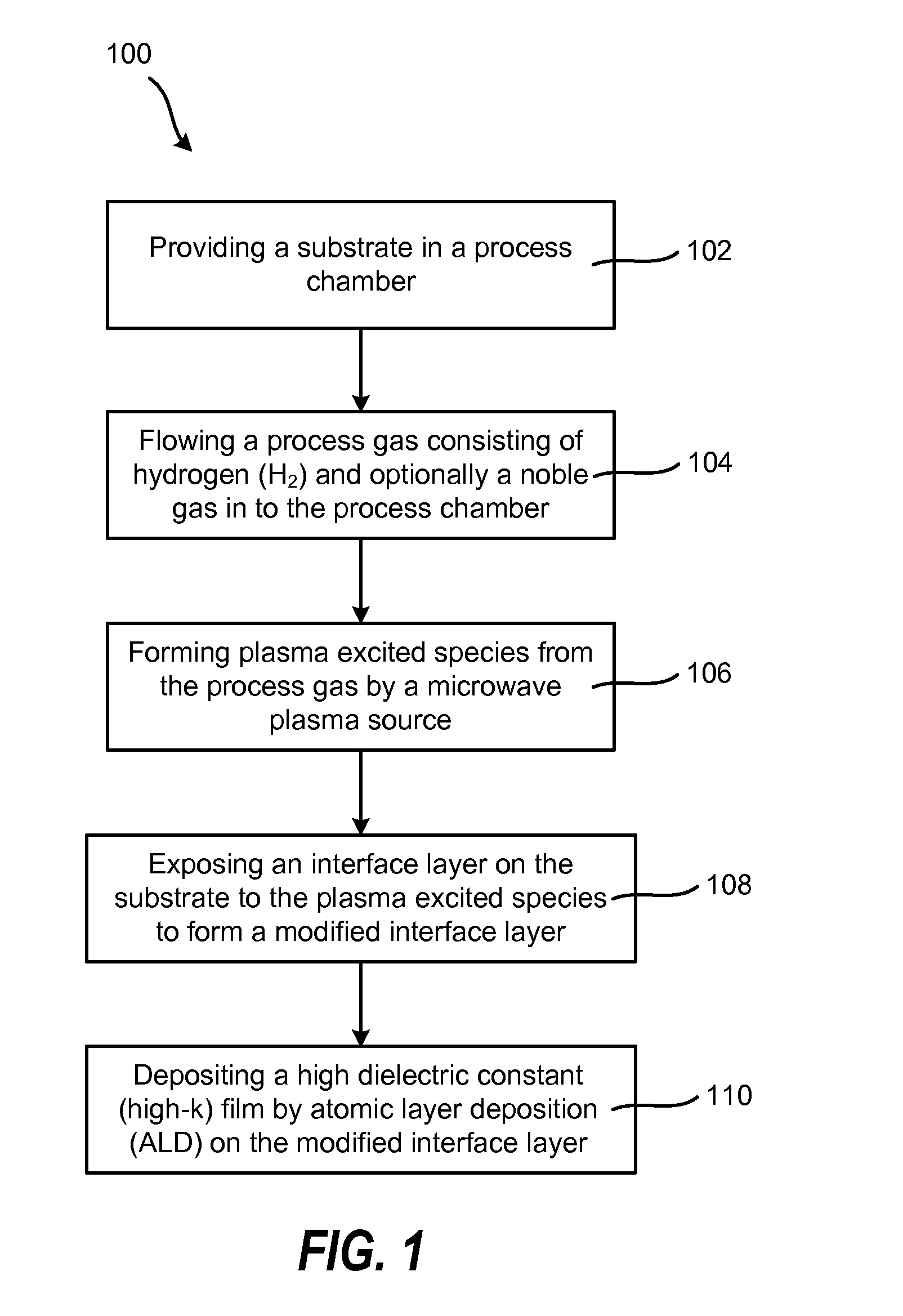
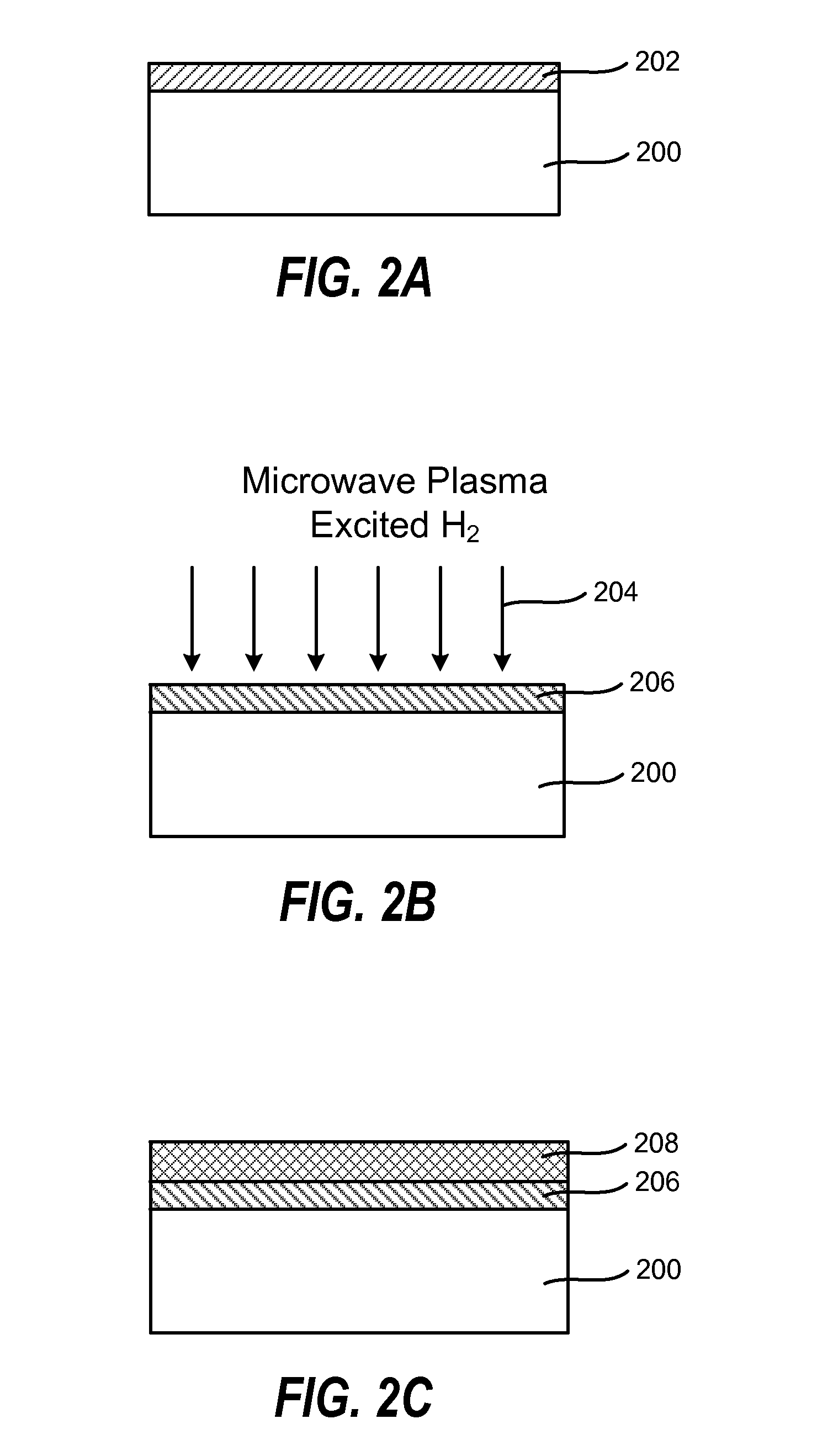
Method of enhancing high-k film nucleation rate and electrical mobility in a semiconductor device by microwave plasma treatment
ActiveUS10522343B2Increased electrical mobilityReduce thicknessElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNoble gasHigh rate
A method for forming a semiconductor device is provided in several embodiments. According to one embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate in a process chamber, flowing a process gas consisting of hydrogen (H2) and optionally a noble gas into the process chamber, forming plasma excited species from the process gas by a microwave plasma source. The method further includes exposing an interface layer on the substrate to the plasma excited species to form a modified interface layer, and depositing a high dielectric constant (high-k) film by atomic layer deposition (ALD) on the modified interface layer. In some embodiments, the modified interface layer has higher electrical mobility than the interface layer, and the high-k film nucleates at a higher rate on the modified interface layer rate than on the interface layer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
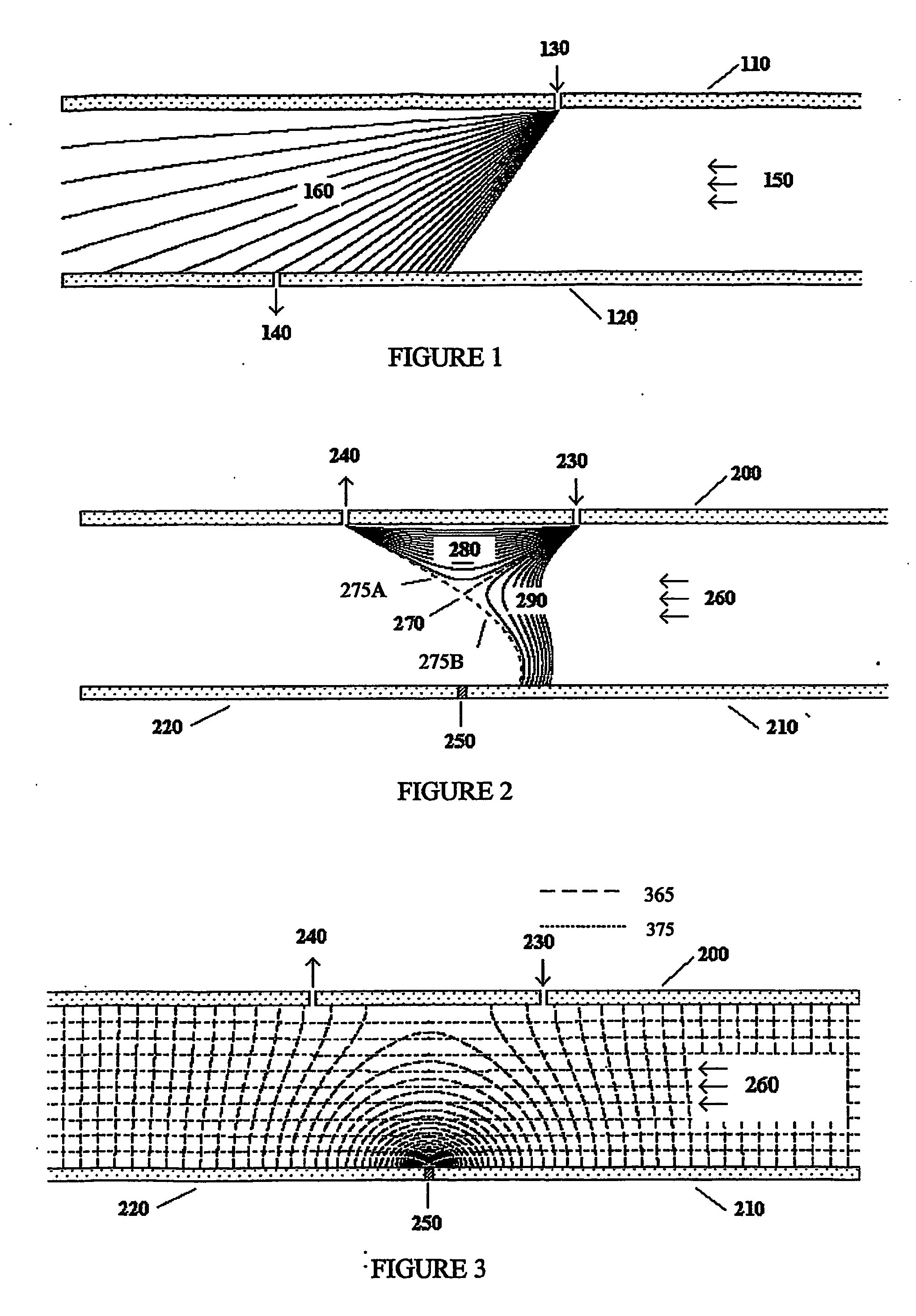
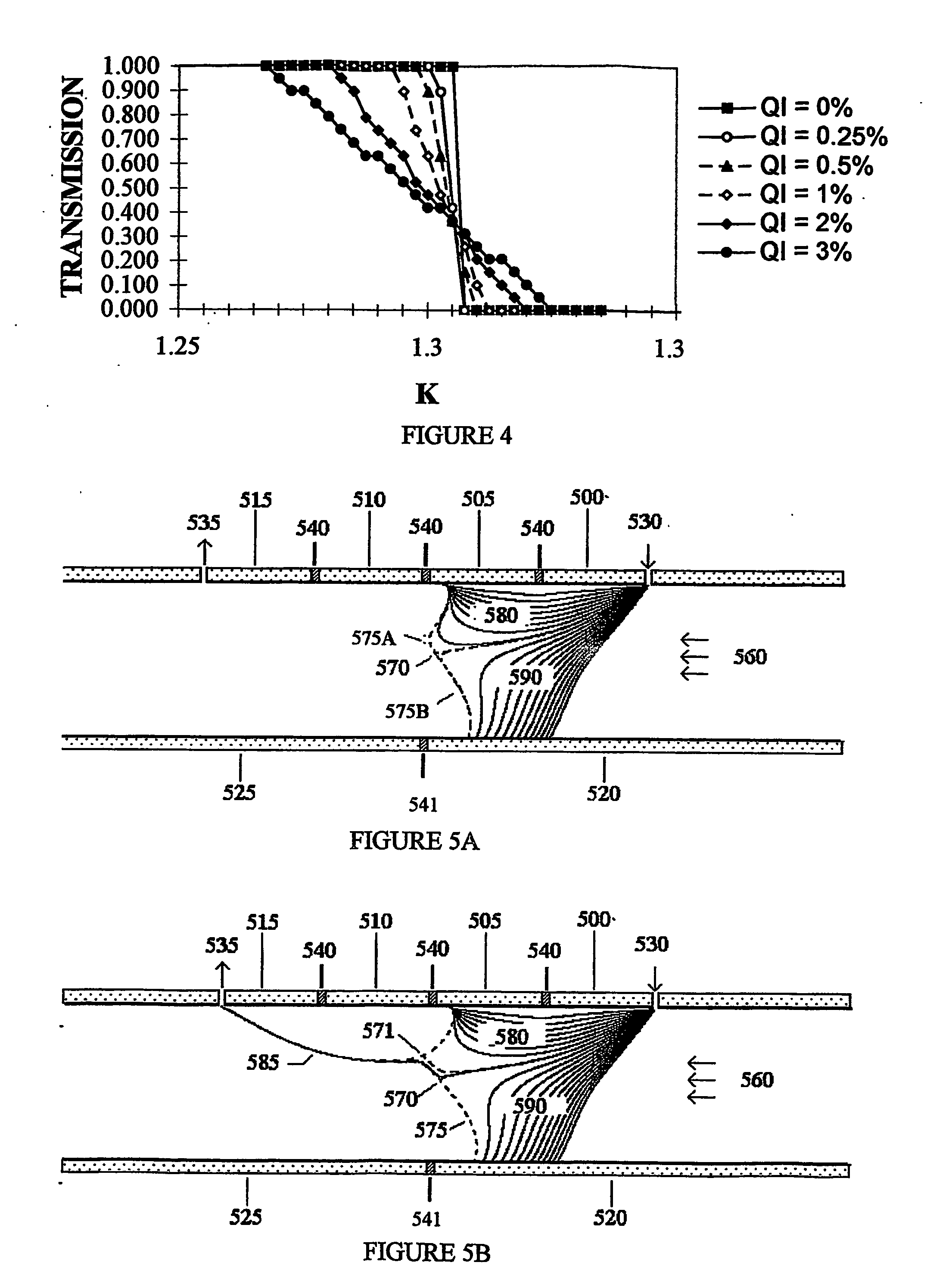
Ion Mobility Separation Devices
ActiveUS20070272847A1Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionParallel plateLow mobility
Owner:LABOWSKY MICHAEL J +1
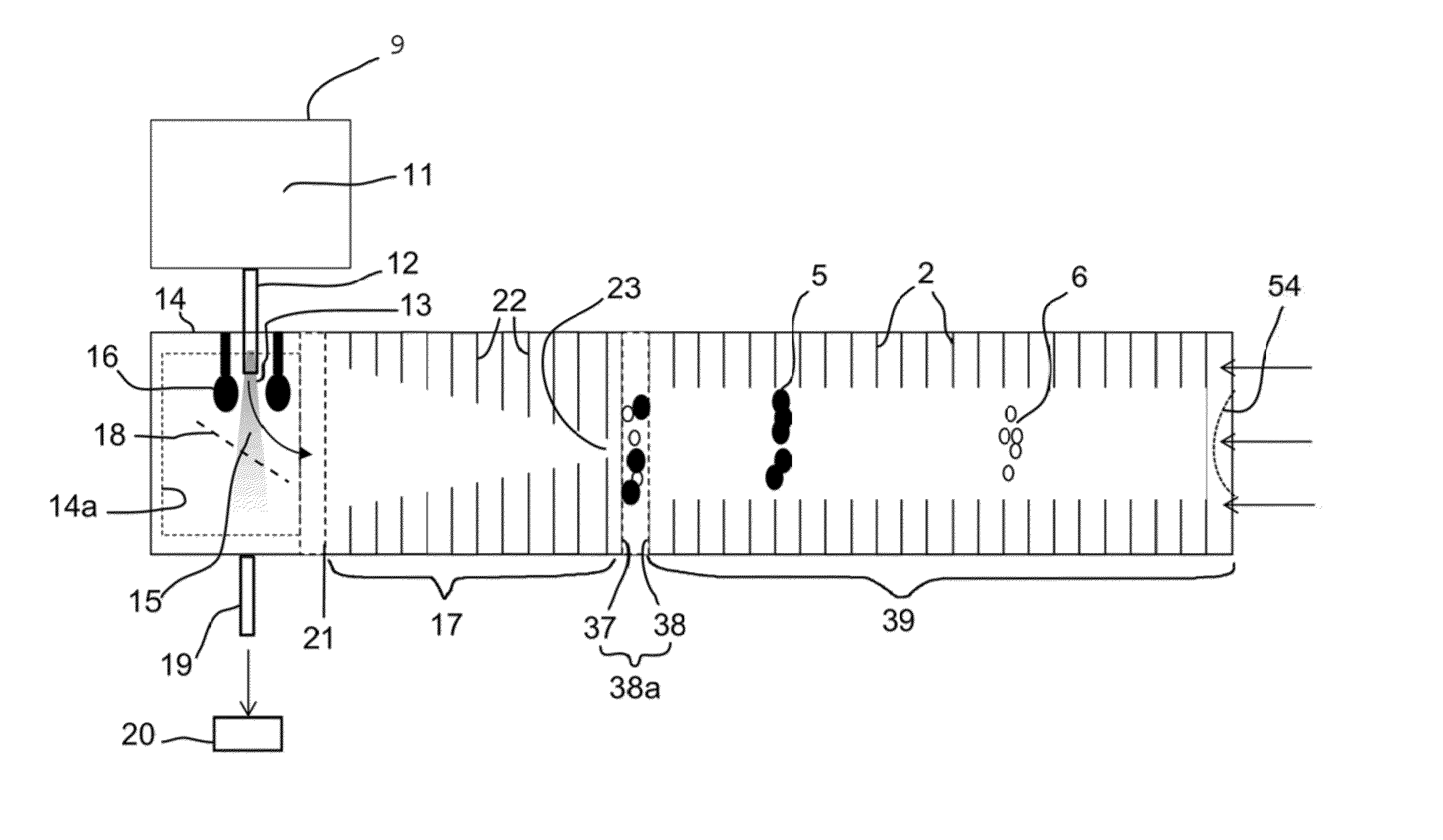
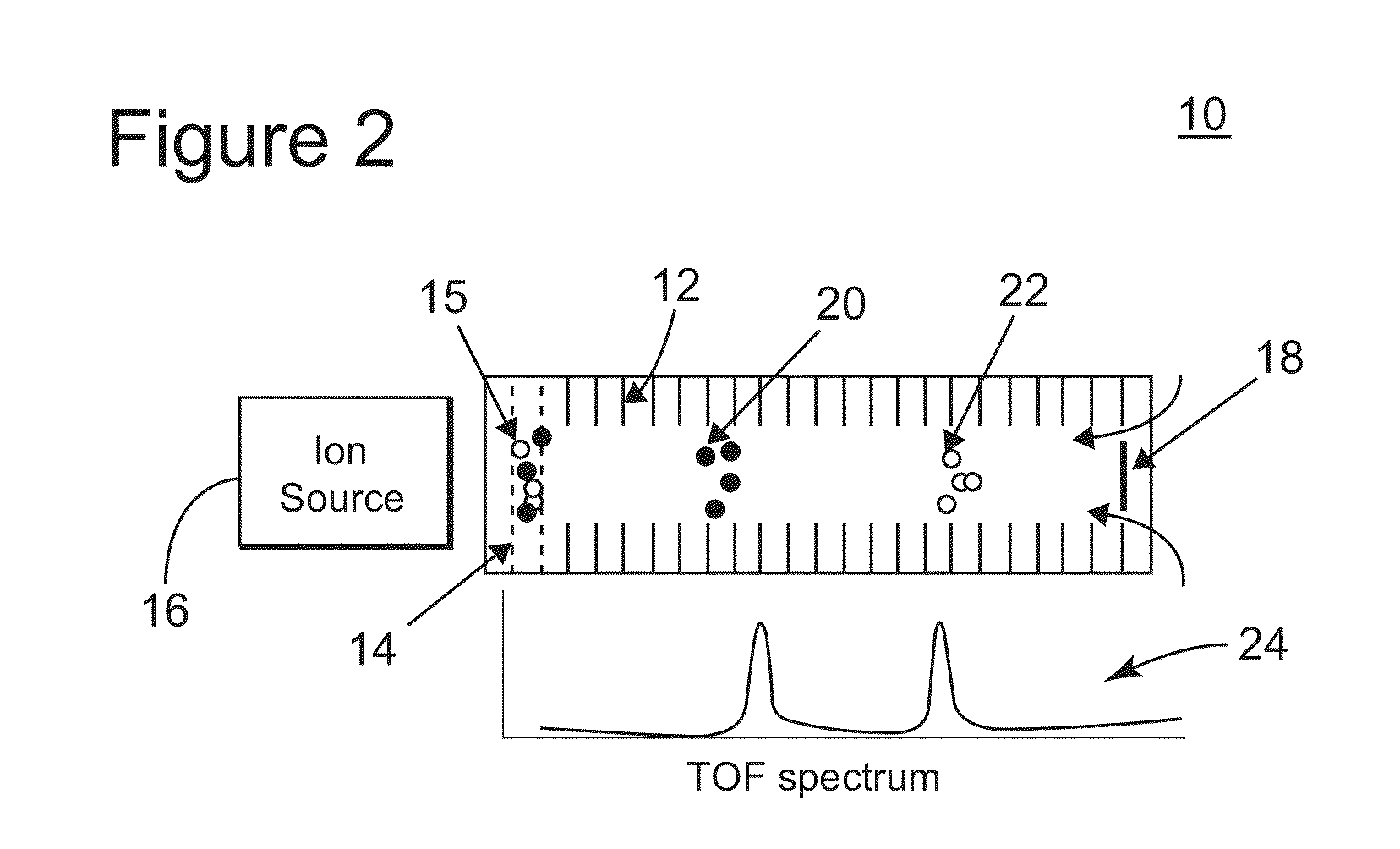
Instruments for measuring ion size distribution and concentration
ActiveUS20150340221A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical mobilityElectron
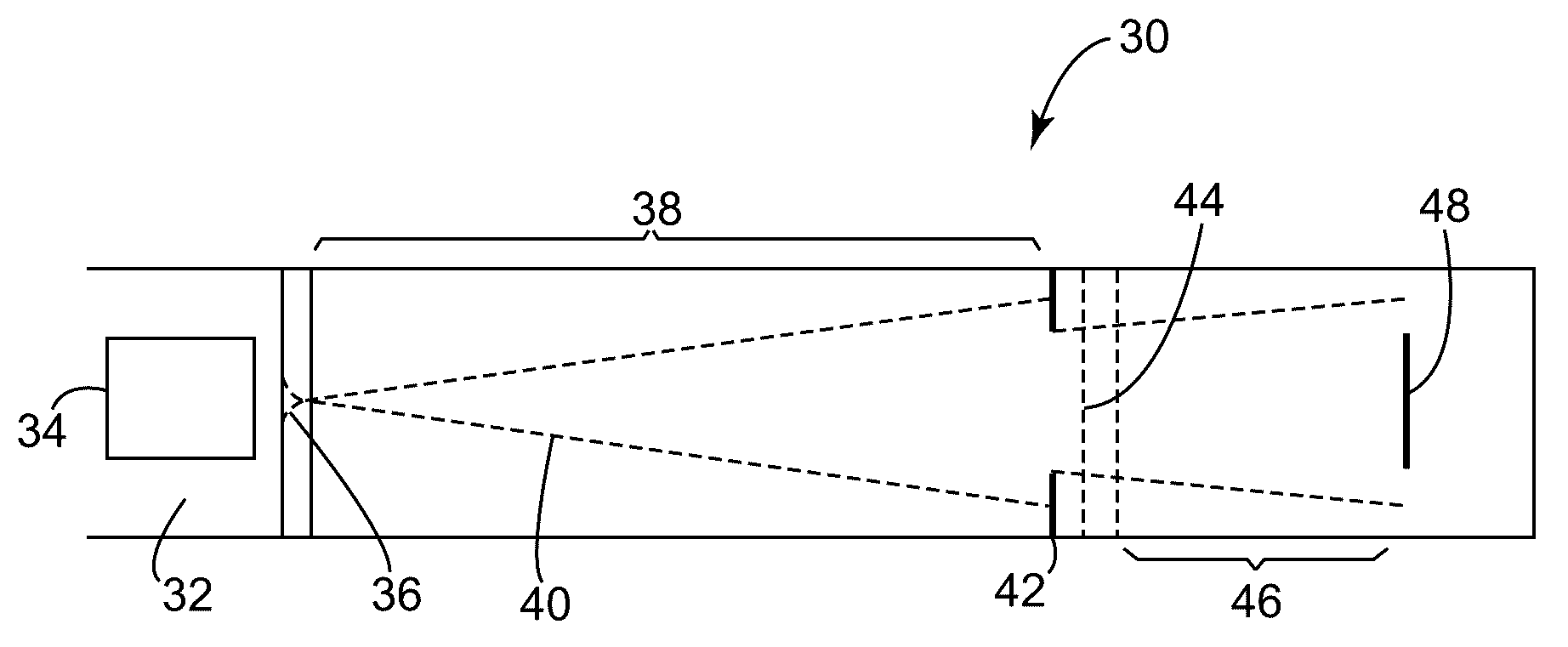
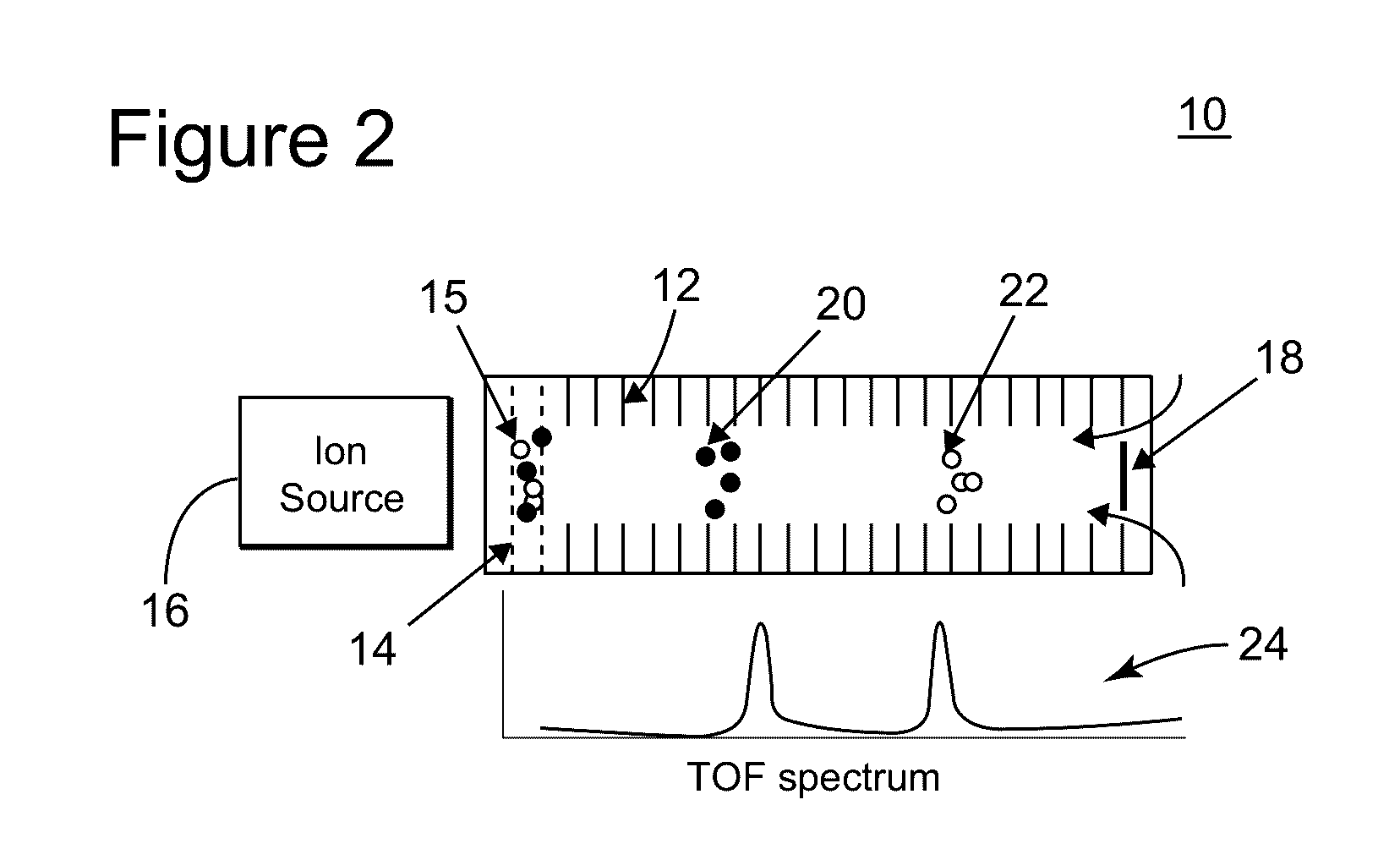
Instruments are disclosed for analyzing ions from about 1000 to 10,000,000 Daltons by controlling a gaseous medium through which the ions travel under the influence of an electric field so that properties of the ions, such as diameter, electrical mobility, and charge, are measured. One embodiment of the disclosed instruments include an ion source, a nozzle, a jet relaxation region, an ion accumulation region, an electronic gate, a flow chamber and an ion detector.
Owner:BENNER W HENRY
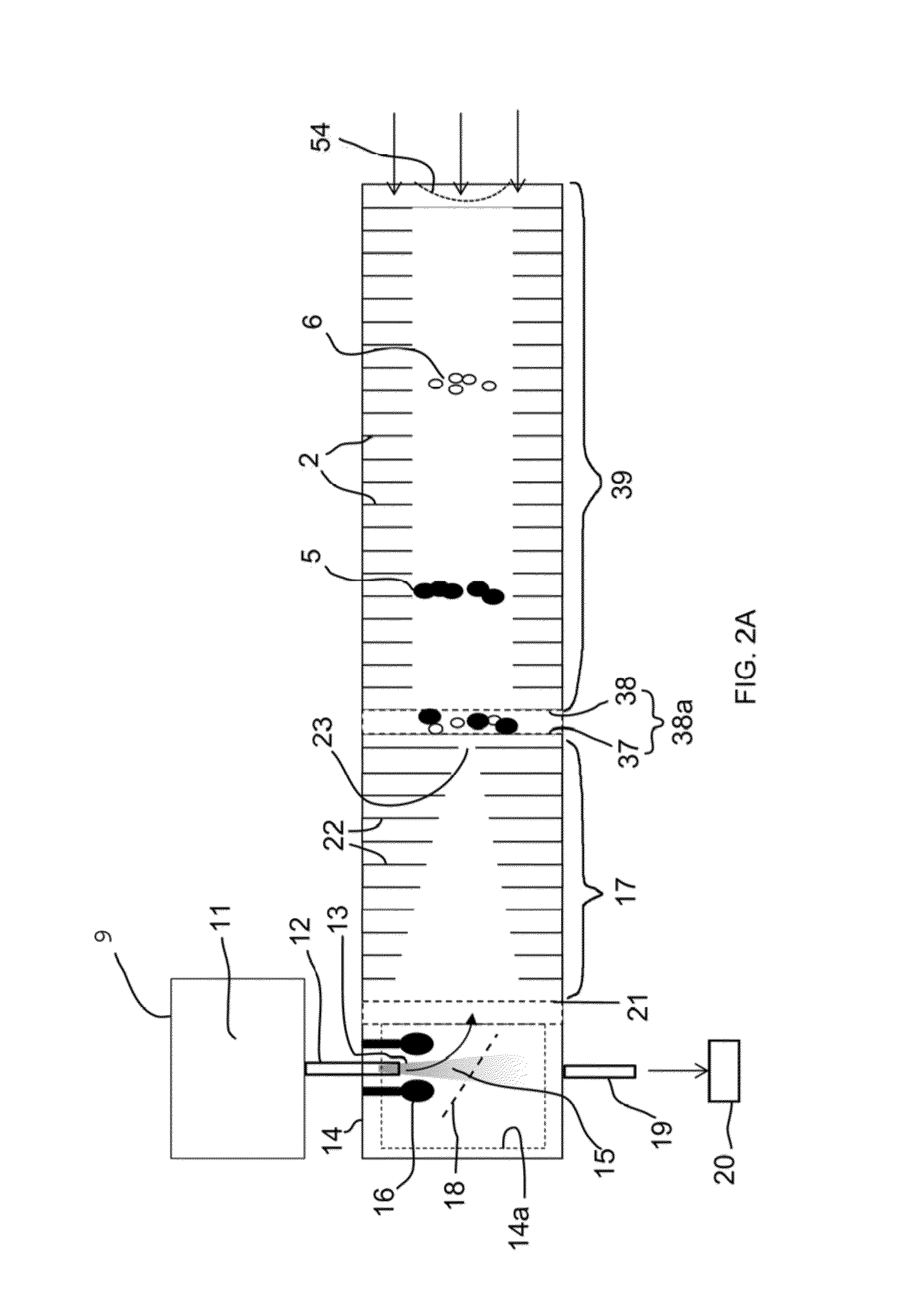
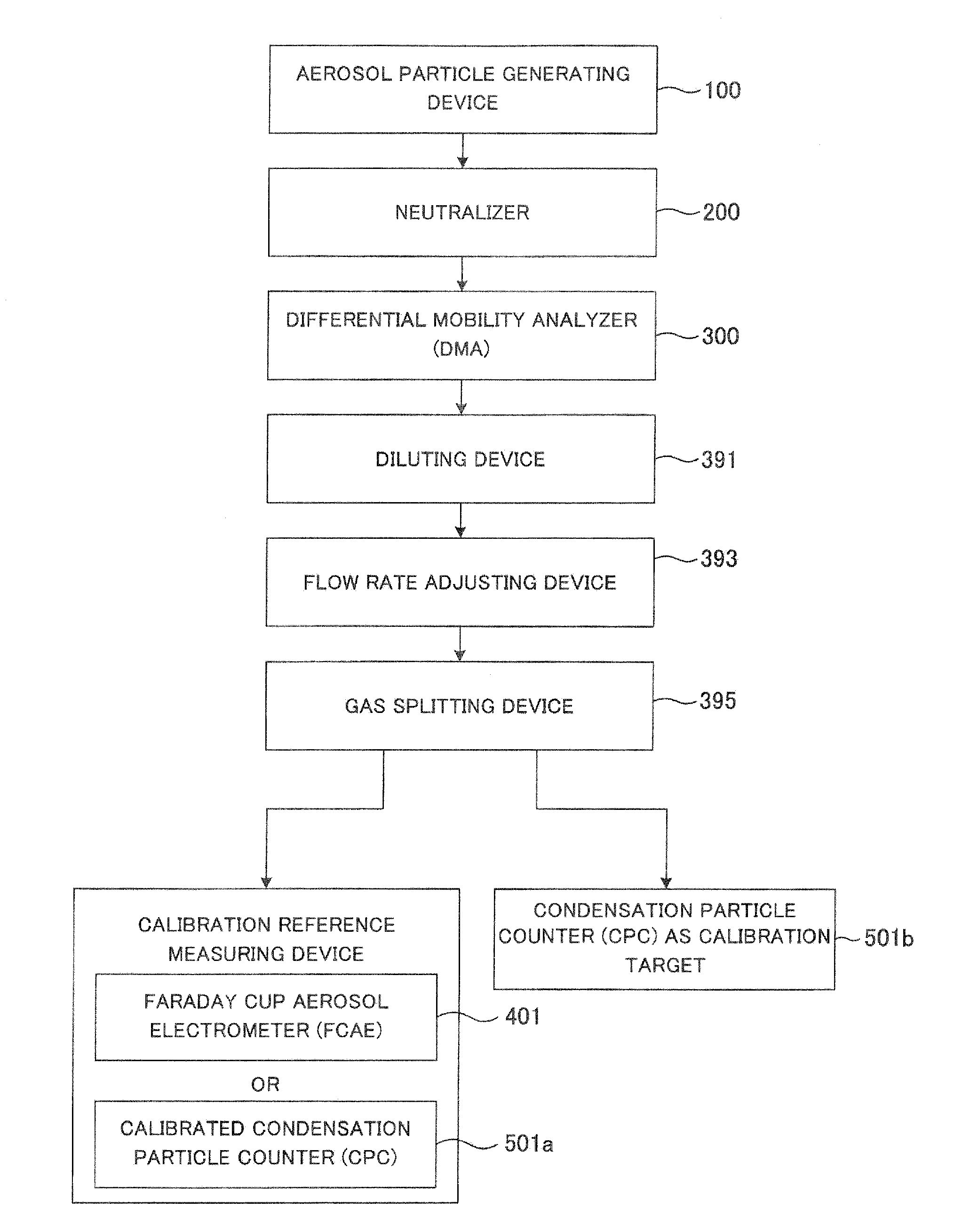
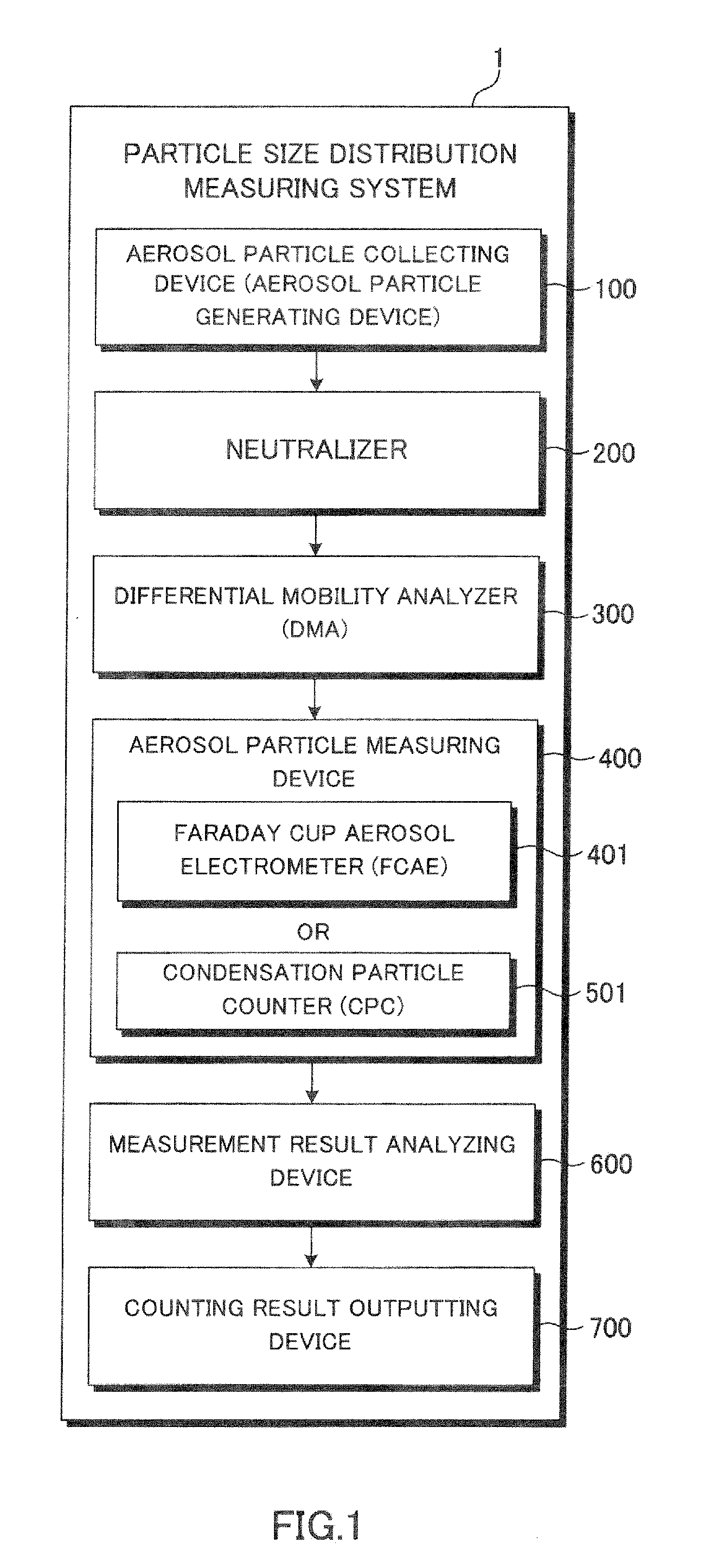
System and method for detecting aerosol particles in atmosphere and counting aerosol particles with respect to each particle size
ActiveUS20130060509A1Electrostatic separationDigital computer detailsComputational physicsElectrical mobility
A particle size distribution measuring system 1 sets a reference voltage in a DMA 300 to a voltage value U, and executes the classifying of aerosol particles based on electrical mobility, in an electric field to which the voltage value U is supplied. When a predetermined condition is not satisfied, an analyzing device 600 causes a sum of the voltage value for the previous classifying (previous value) and the voltage value U to be re-set in the DMA 300 and causes the classifying of the aerosol particles to be executed again. A particle measuring device 400 defines a first measurement result as a measurement result M1, and defines a result of the re-measurement as a new measurement result Mx every time the measurement is thereafter repeated. An analyzing device 600 calculates a ratio of the measurement result Mx to the measurement result M1, and confirms that the condition is satisfied when the calculation result is a prescribed value or smaller, while confirming that the condition is not satisfied when the calculation result is larger than the prescribed value.
Owner:RION COMPANY
Method and apparatus to produce steady beams of mobility selected ions via time-dependent electric fields
InactiveUS8378297B2Stability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionIon beamContinuous flow
Owner:VIDAL DE MIGUEL GUILLERMO
Instruments for measuring nanoparticle exposure
ActiveUS7812306B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesHEPAAudio power amplifier
An instrument for non-invasively measuring nanoparticle exposure includes a corona discharge element generating ions to effect unipolar diffusion charging of an aerosol, followed by an ion trap for removing excess ions and a portion of the charged particles with electrical mobilities above a threshold. Downstream, an electrically conductive HEPA filter or other collecting element accumulates the charged particles and provides the resultant current to an electrometer amplifier. The instrument is tunable to alter the electrometer amplifier output toward closer correspondence with a selected function describing particle behavior, e.g. nanoparticle deposition in a selected region of the respiratory system. Tuning entails adjusting voltages applied to one or more of the ion trap, the corona discharge element and the collecting element. Alternatively, tuning involves adjusting the aerosol flow rate, either directly or in comparison to the flow rate of a gas conducting the ions toward merger with the aerosol.
Owner:TSI INC
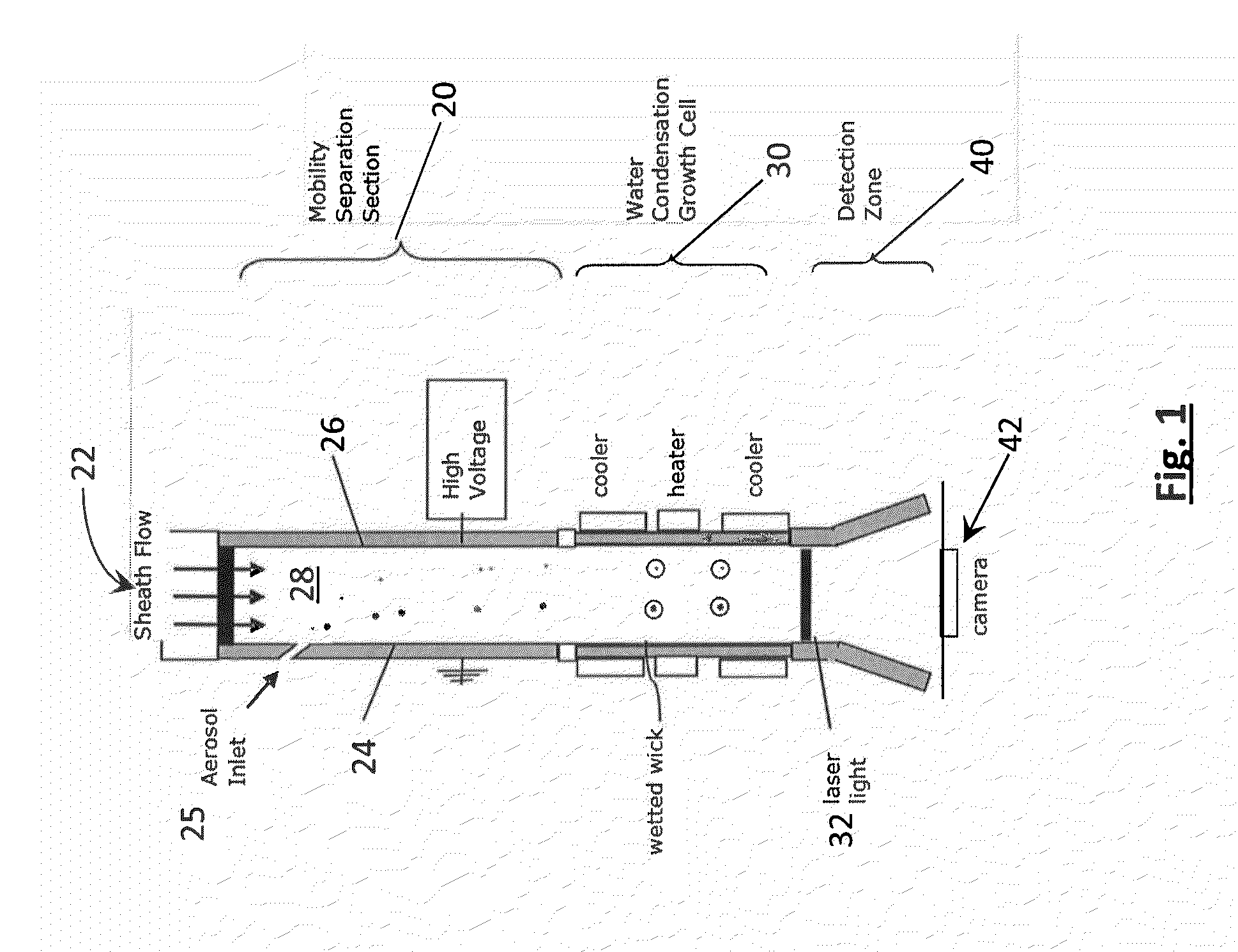
Aerosol mobility imaging for rapid size distribution measurements
ActiveUS20150268140A1Preparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansChemical physicsParallel plate
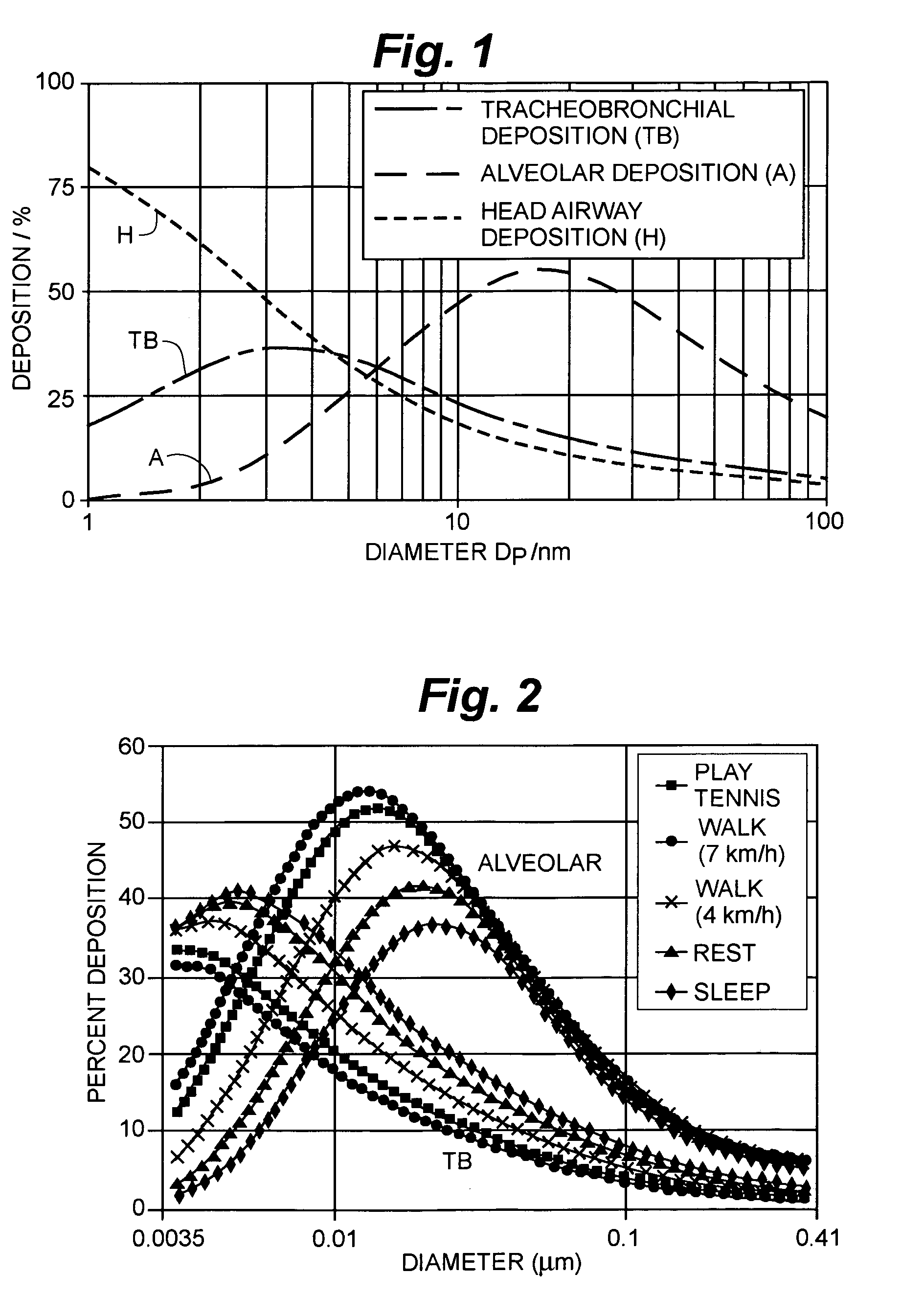
A parallel plate dimensional electrical mobility separator and laminar flow water condensation provide rapid, mobility-based particle sizing at concentrations typical of the remote atmosphere. Particles are separated spatially within the electrical mobility separator, enlarged through water condensation, and imaged onto a CCD array. The mobility separation distributes particles in accordance with their size. The condensation enlarges size-separated particles by water condensation while they are still within the gap of the mobility drift tube. Once enlarged the particles are illuminated by a laser. At a pre-selected frequency, typically 10 Hz, the position of all of the individual particles illuminated by the laser are captured by CCD camera. This instantly records the particle number concentration at each position. Because the position is directly related to the particle size (or mobility), the particle size spectra is derived from the images recorded by the CCD.
Owner:AEROSOL DYNAMICS INC +1
Aerosol mass spectrometer for measuring chemical components of nanoparticles
ActiveCN107946165AEasy to detectGuaranteed normal transmissionSamples introduction/extractionNanotechnologyParticulatesNanoparticle
The invention discloses an aerosol mass spectrometer for measuring chemical components of nanoparticles. The aerosol mass spectrometer comprises a nano-scan electromobility particle size spectrometer,a first differential chamber, a second differential chamber, a photo ionization chamber and a reflective type time-of-flight mass spectrum apparatus, wherein the aerosol outlet of the nano-scan electromobility particle size spectrometer is connected with the inlet of the first differential chamber; the outlet of the first differential chamber is connected with the inlet of the second differentialchamber; the outlet of the second differential chamber is connected with the inlet of the photo ionization chamber; and the outlet of the photo ionization chamber is connected with the reflective type time-of-flight mass spectrum apparatus. By virtue of the nano-scan electromobility particle size spectrometer, charge, particle size selection and particle spectrum analysis of the nanoparticles arerealized by the aerosol mass spectrometer, so as to perform real-time and online measurement and acquisition of the chemical component information of the nanoparticles with particle sizes of smallerthan 60nm; and the detection process is simple, and quick and high-efficiency transmission of the nanoparticles are realized.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
1-3nm monodisperse aerosol generating system
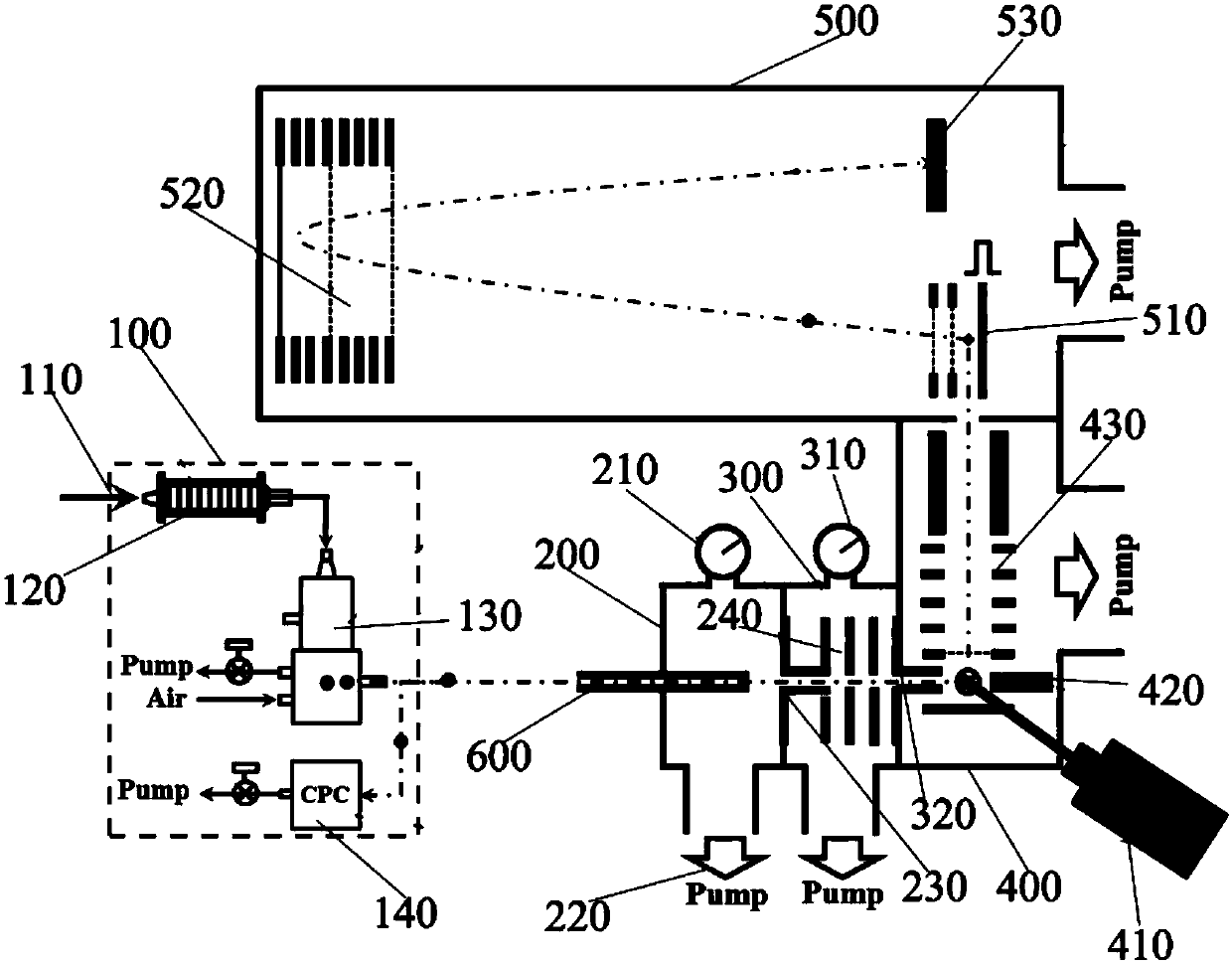
ActiveCN103933901AGuaranteed air tightnessComponent separationElectrostatic spraying apparatusElectricityImage resolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment aerosol, and particularly relates to a 1-3nm monodisperse aerosol generating system. The 1-3nm monodisperse aerosol generating system mainly comprises an electrospray generator, a high-resolution difference electromobility analyzer and an aerosol electrometer. A series of standard ions are screened by the high-resolution difference electromobility analyzer so as to obtain the required monodisperse aerosol; the aerosol is measured by the aerosol electrometer with the efficiency no less than 99%, and the measurement accuracy is ensured; the monodisperse nano aerosol is obtained by the system; aerosol with severe monodispersity at the geometric particle size range of 0.7-3nm can be obtained by utilizing an organic solution of tera alkyl ammonium halide and a water solution of ammonium acetate, and the obtained standard positive and negative ion aerosol concentrations are respectively within the concentration ranges of 10<6>-10<7> piece / cm<3> and 10<5>-10<6> piece / cm<3>.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ion mobility separation devices
ActiveUS7626161B2Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionParallel plateLow mobility
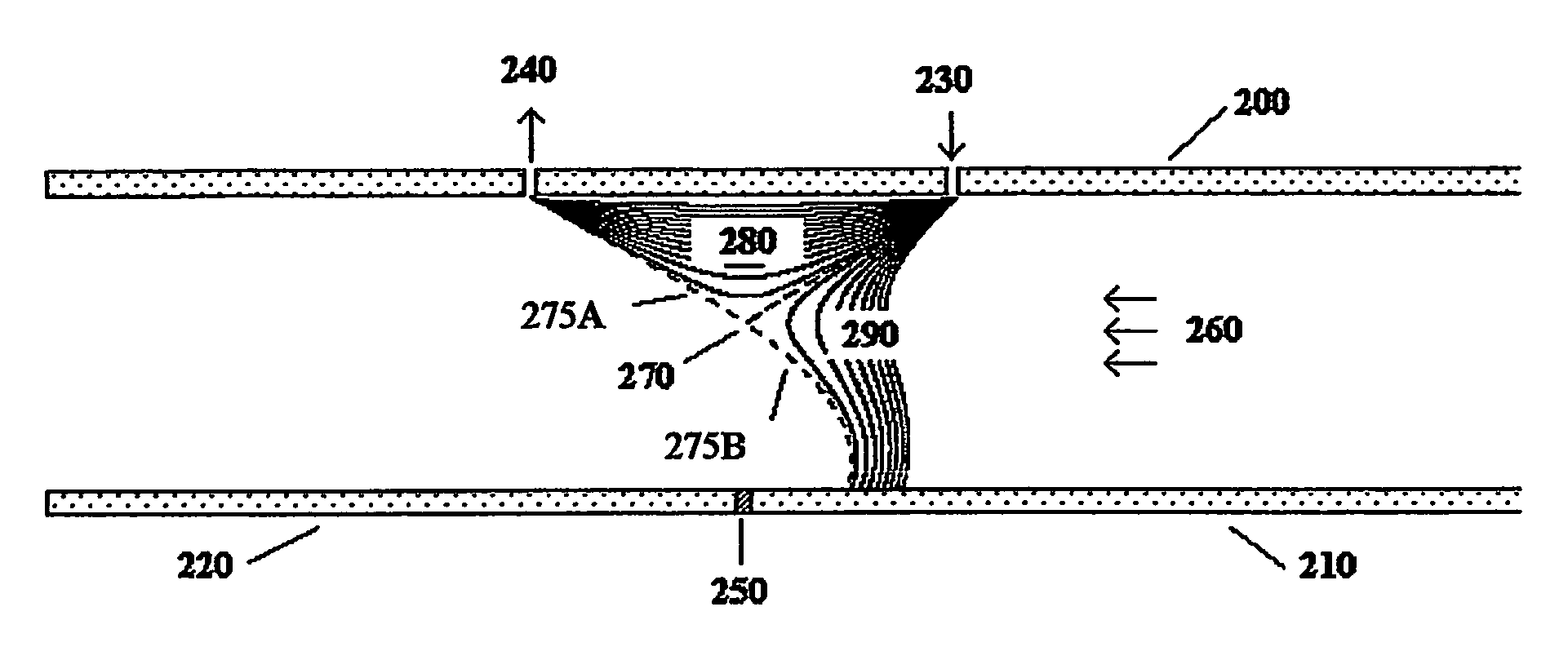
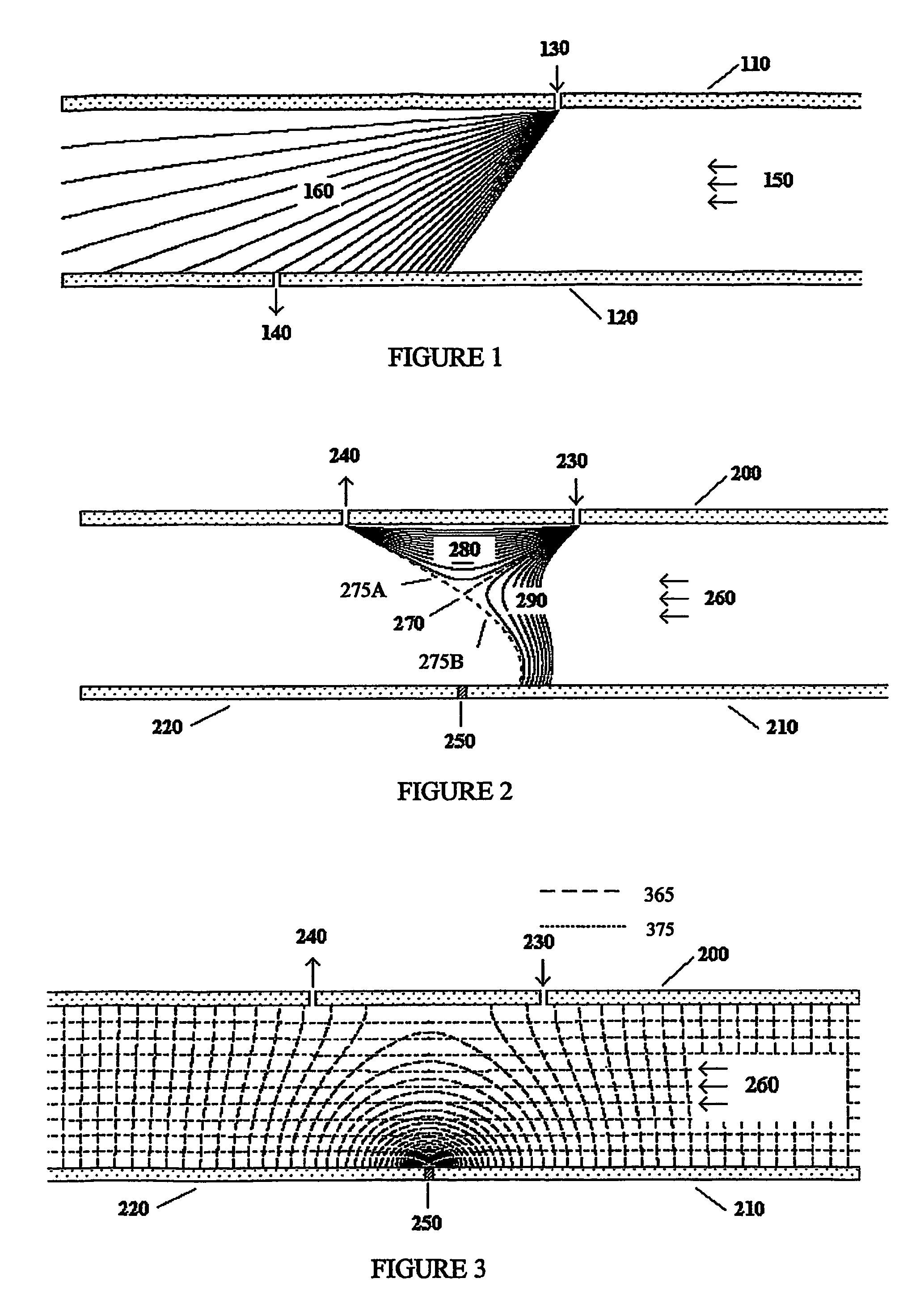
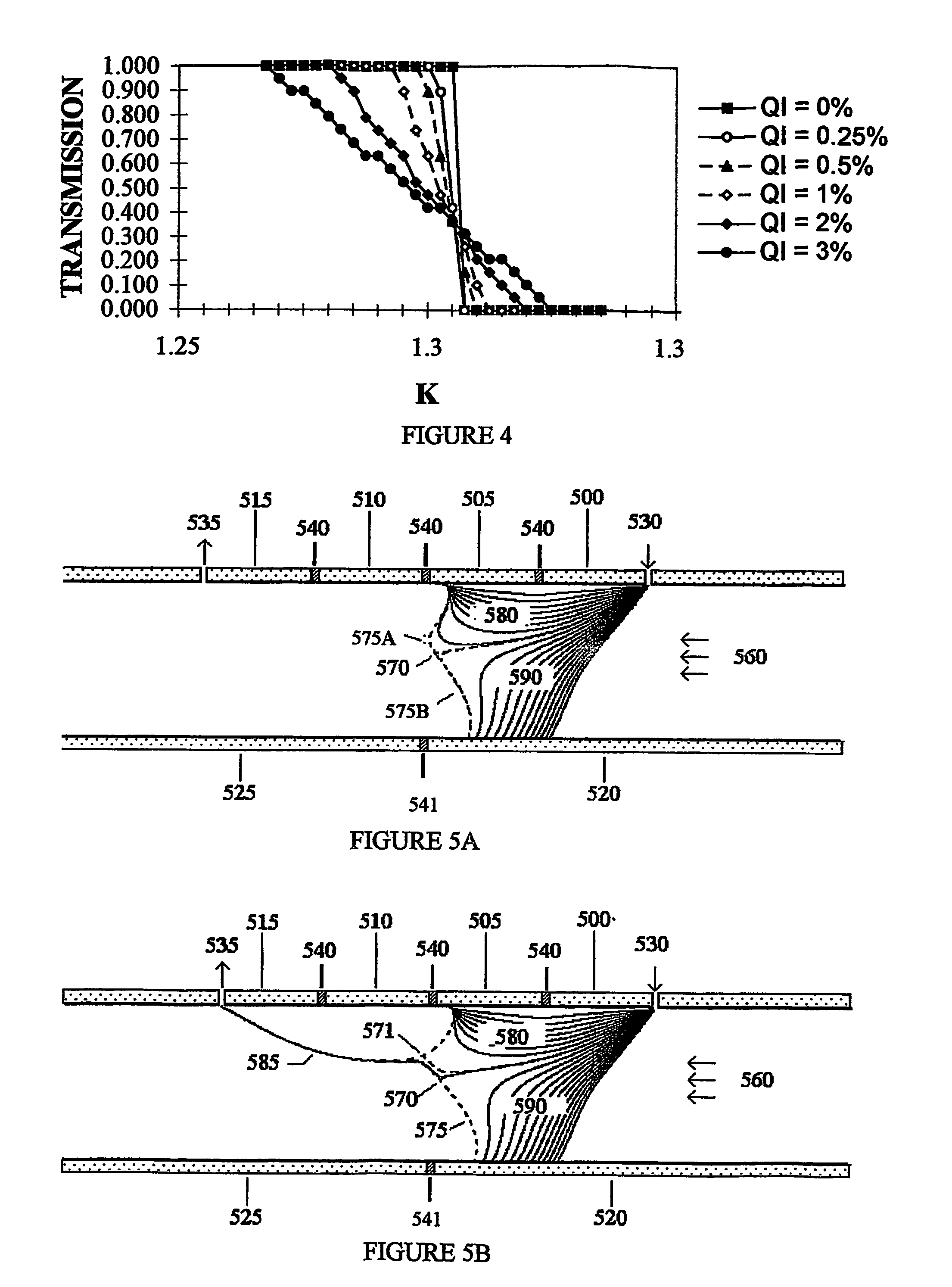
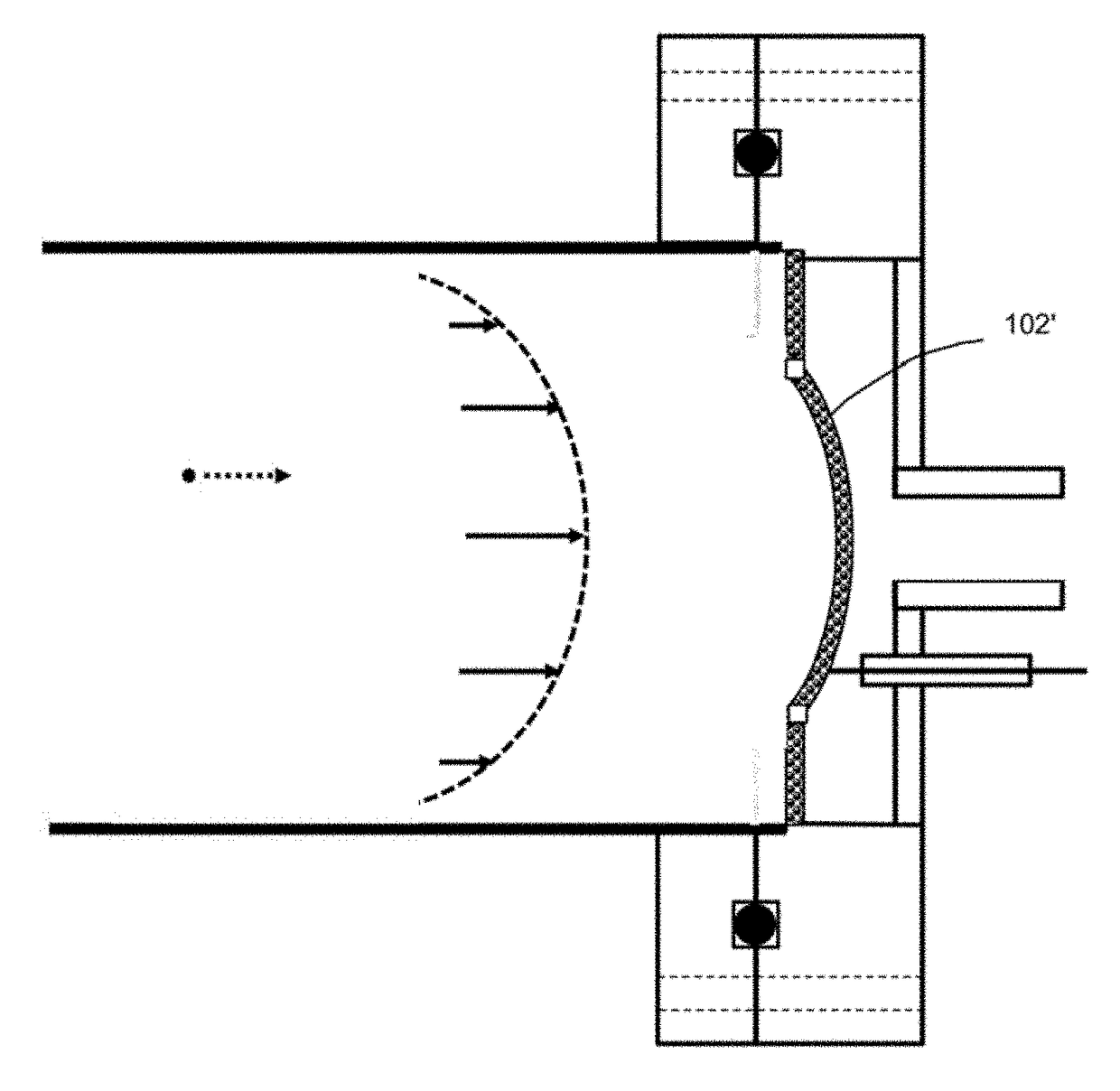
The invention describes a system and method to separate ions (and charged particles) suspended in gas based on their ion electrical mobility. Most common ion mobility analyzers involve two parallel plate (or concentric cylinder) elements (electrodes) between which is imposed an electrical field perpendicular to a sheath gas flow field between the cylinders. Separation occurs because high mobility ions tend to follow the electrical field while low mobility ions tend to follow the flow field. This invention describes various configurations of electrical elements and sheath gas flow fields for ion mobility separation devices with unique performance characteristics. These characteristics include devices in which: the ion inlet and outlet are on the same element; the inlet and outlet are at the same voltage; the outlet is upstream from the inlet; the outlet is on the axis; the inlet is on the axis; and the ions are focused on the outlet.
Owner:LABOWSKY MICHAEL J +1
High-flow dual-channel differential mobility analyzer
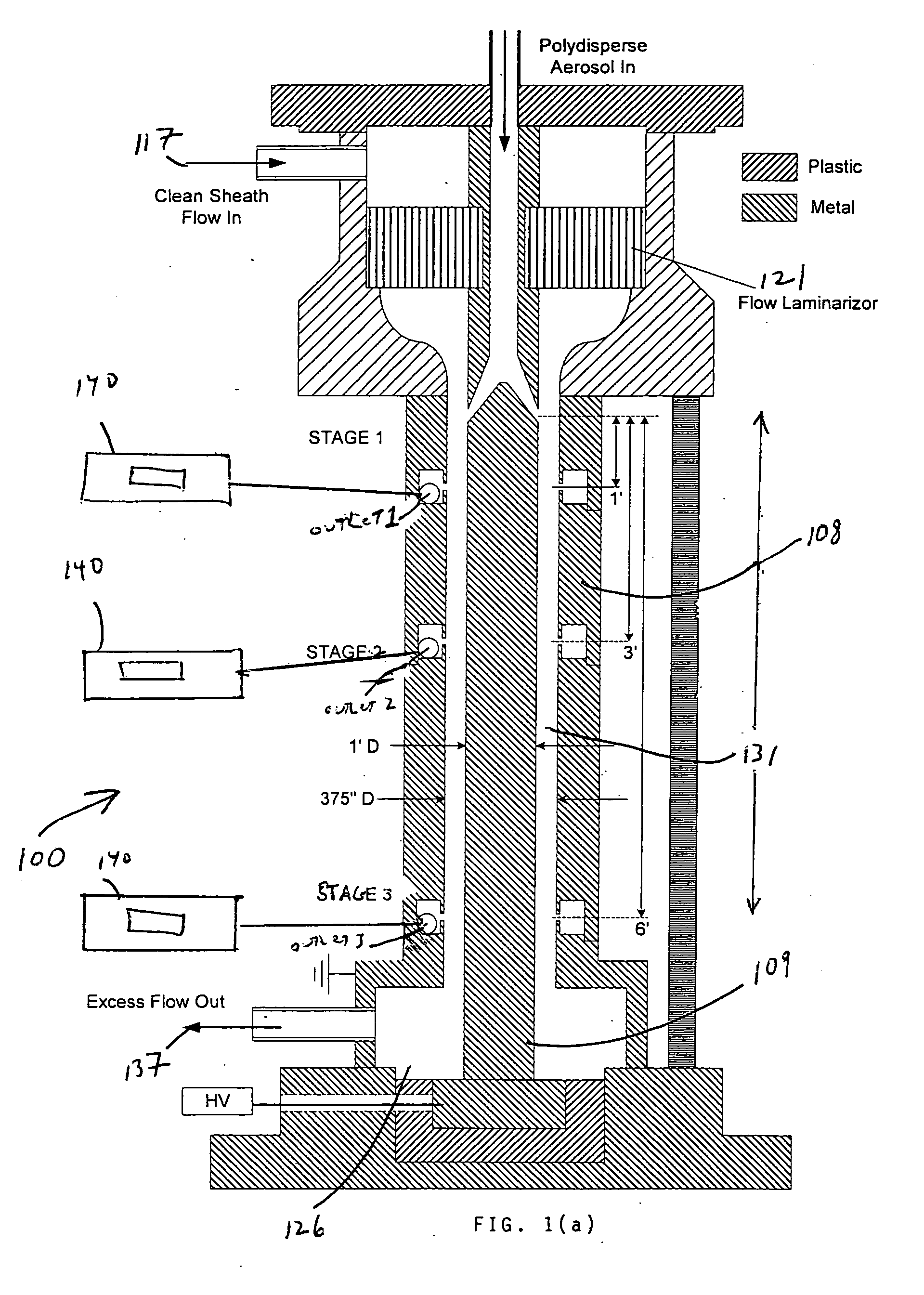
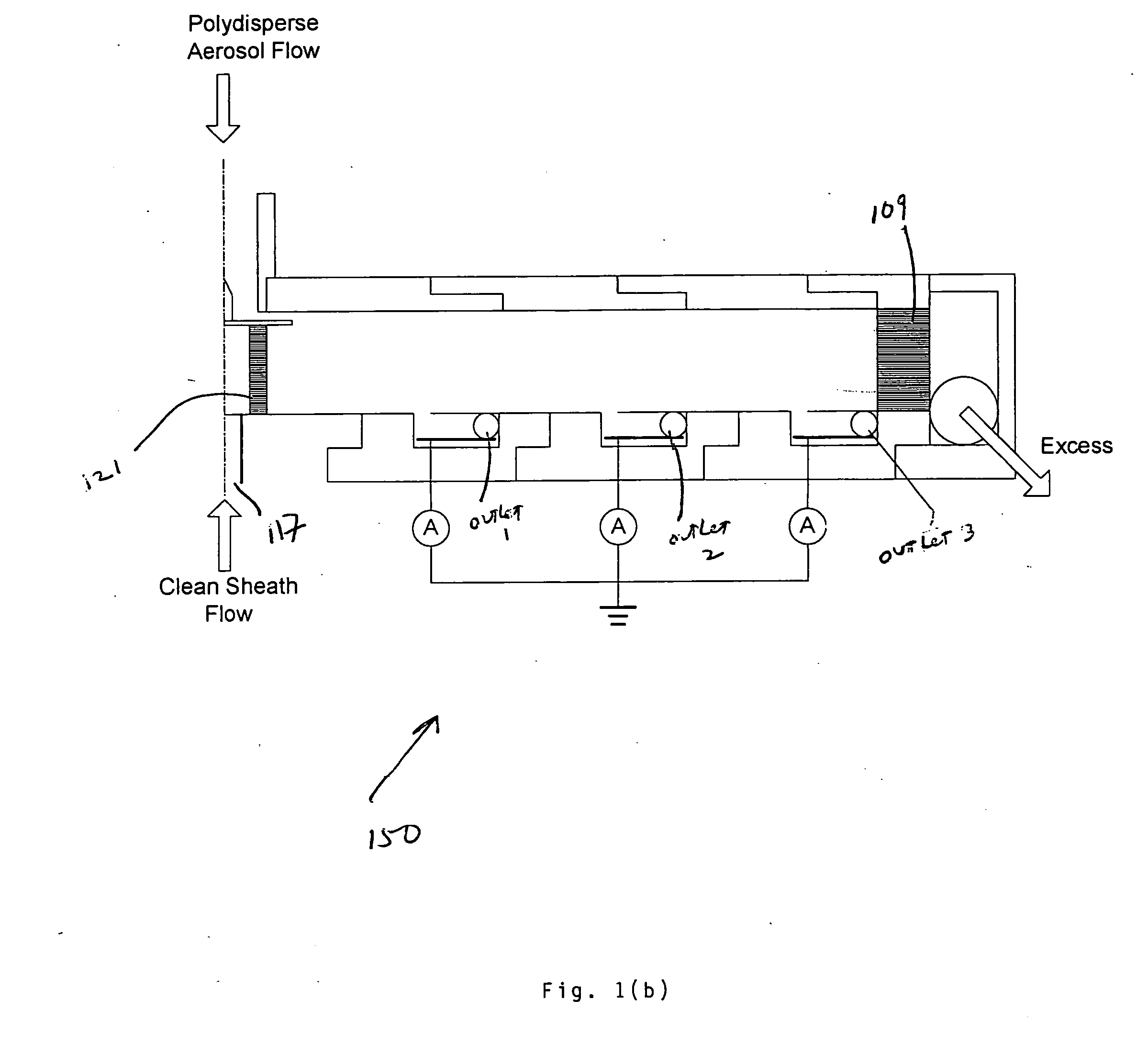
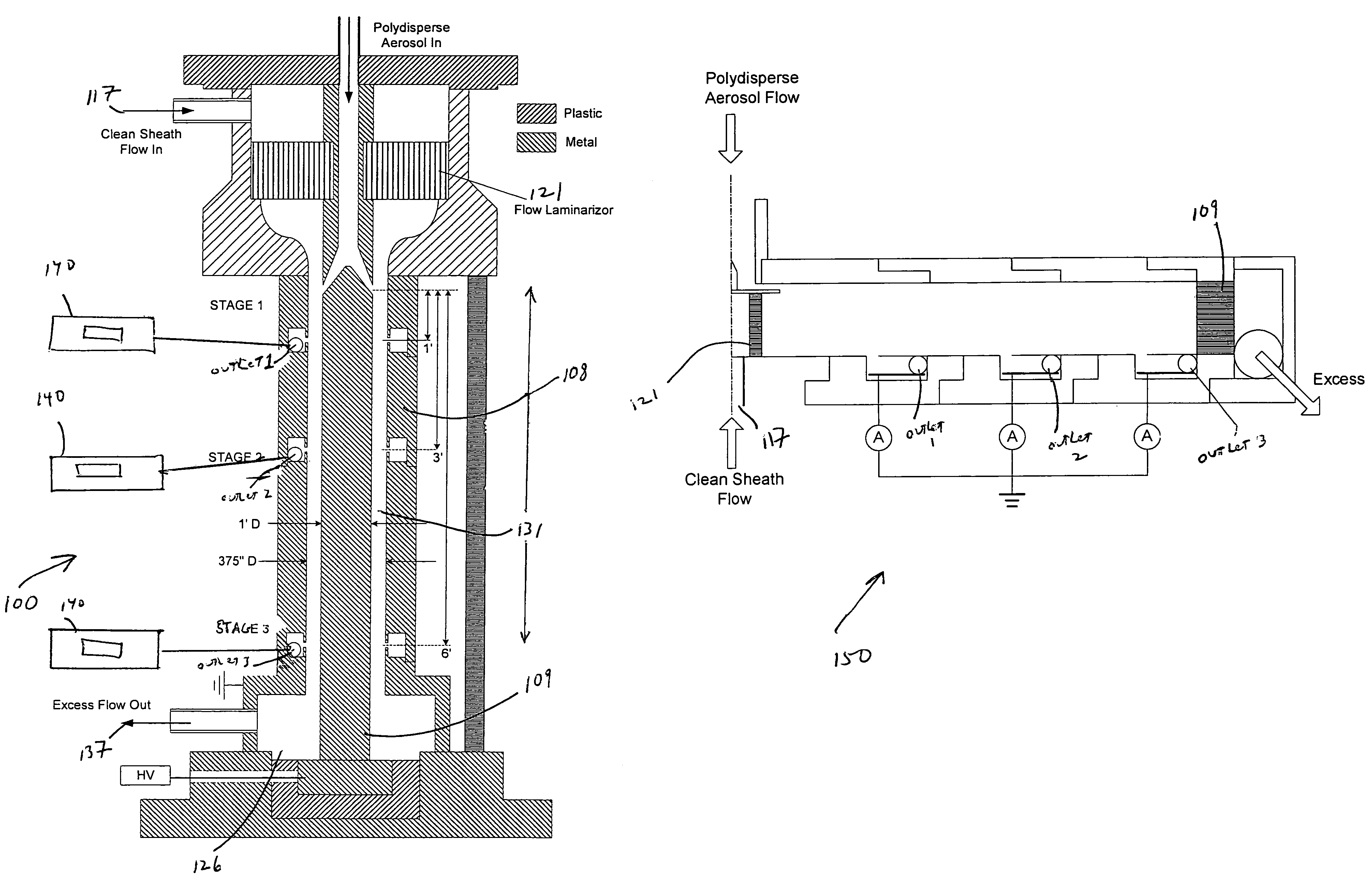
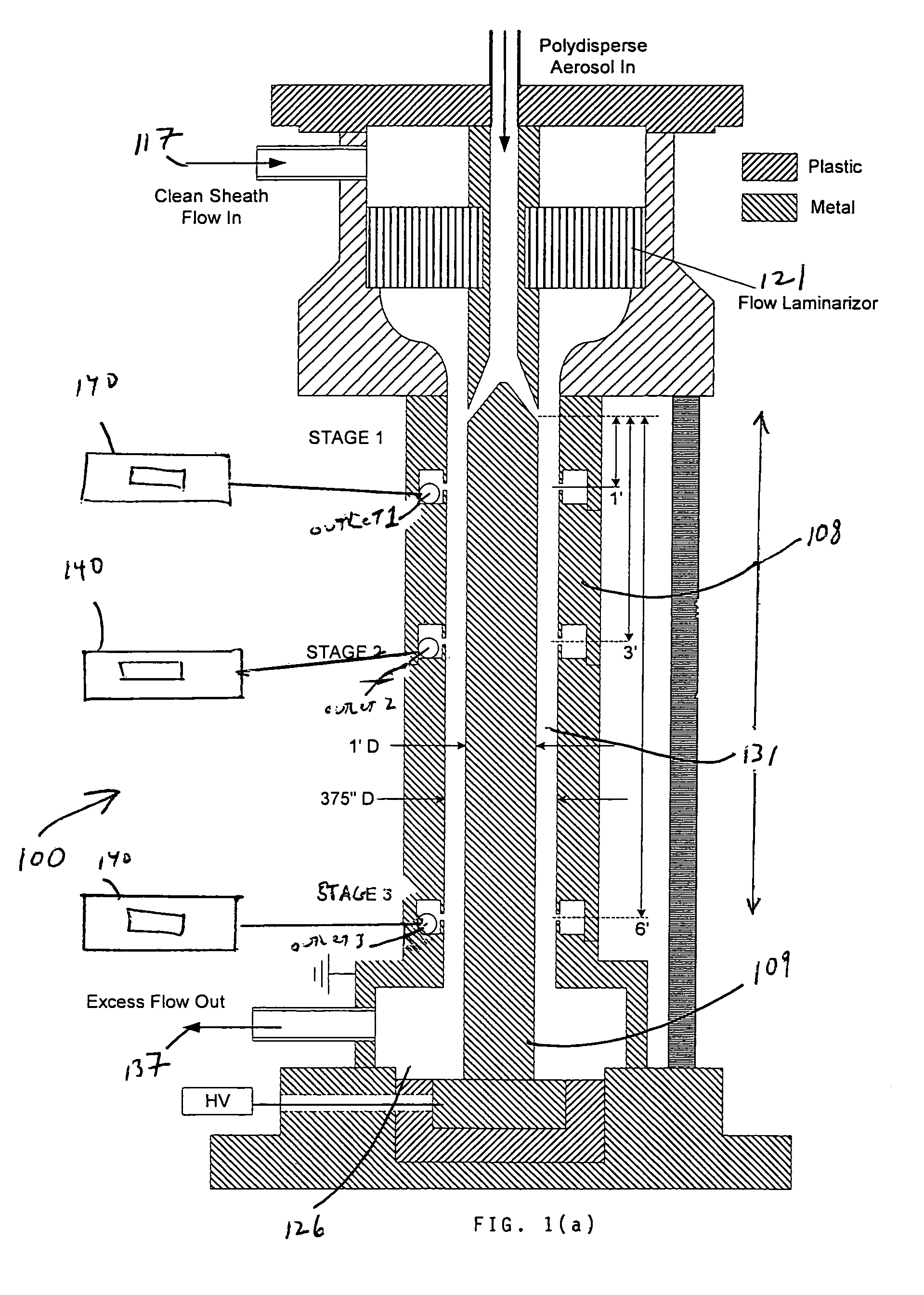
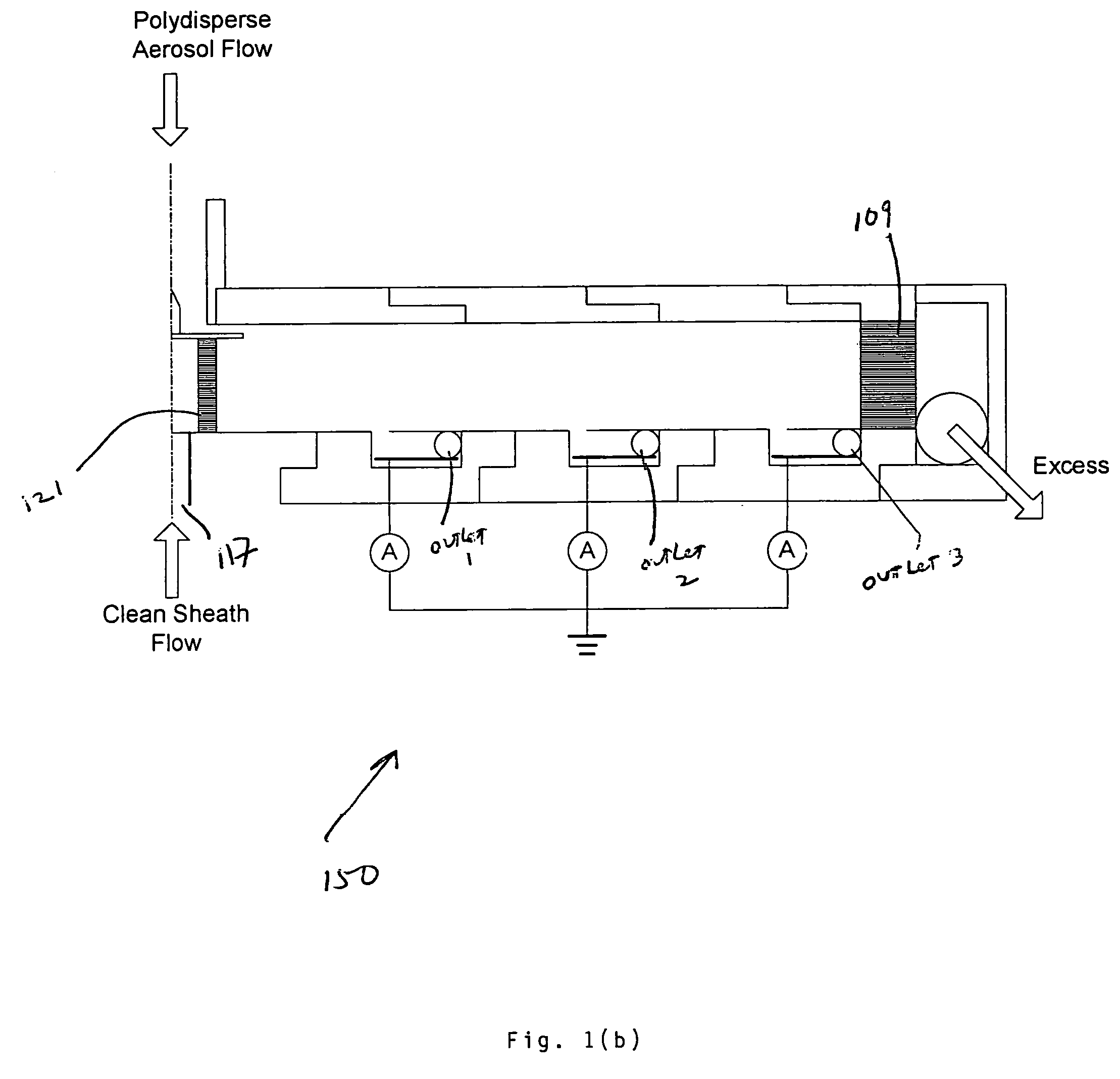
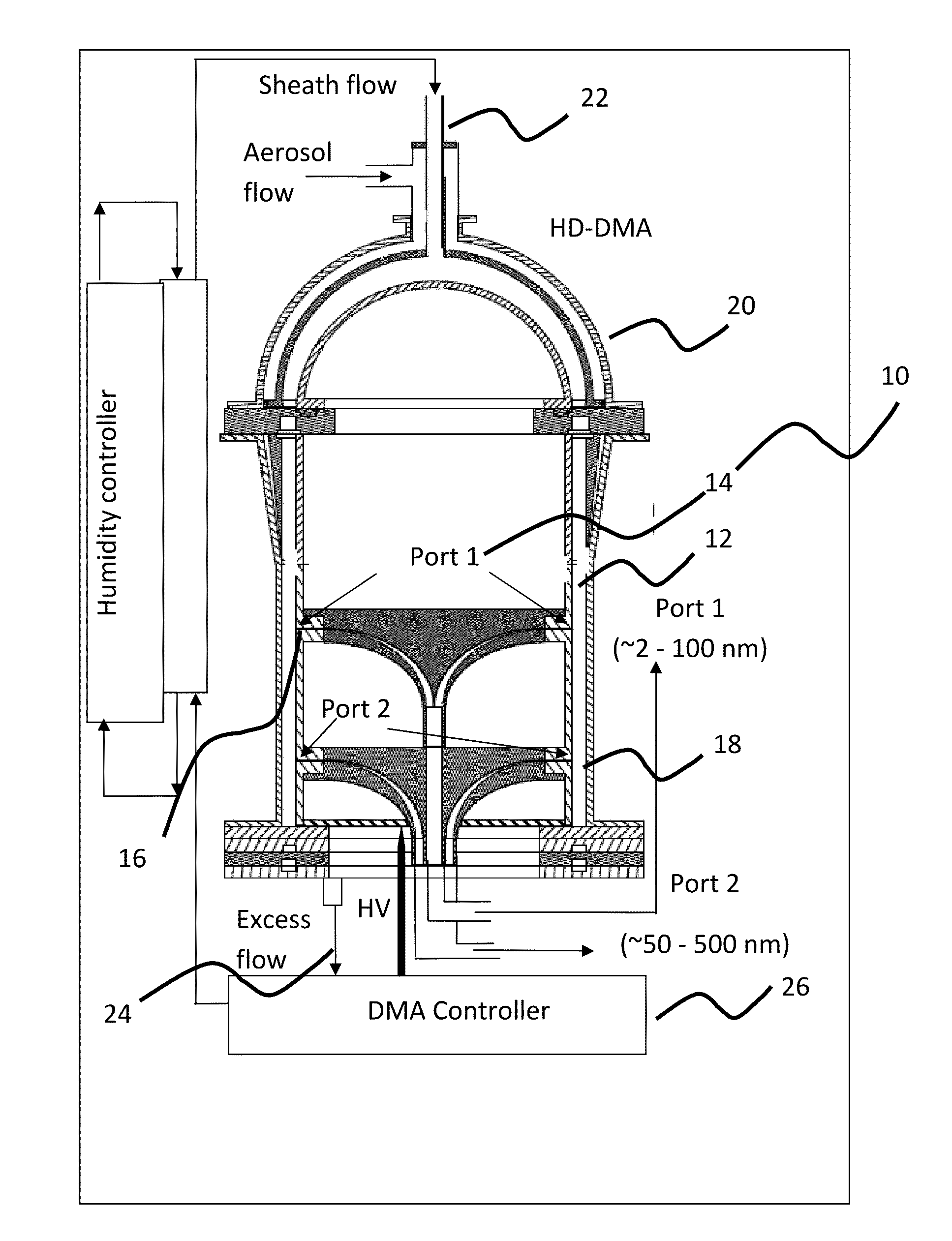
InactiveUS8919183B1High resolutionAvoid instrument performance degradationSamplingStream flowElectrical mobility
A new instrument for electrical-mobility based size segregation of particles at high resolution is described. The instrument called the high-flow dual-channel differential mobility analyzer (HD-DMA) comprises of five flows: a polydisperse aerosol flow, a clean sheath flow, two monodisperse sample flows and a residual excess flow. High resolution measurements are possible because of the large sheath flowrates that are permissible in this instrument.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
Miniature ultrafine particle sensor
ActiveUS8301396B1Easy to operateExternal electric electrostatic seperatorSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringElectrical mobility
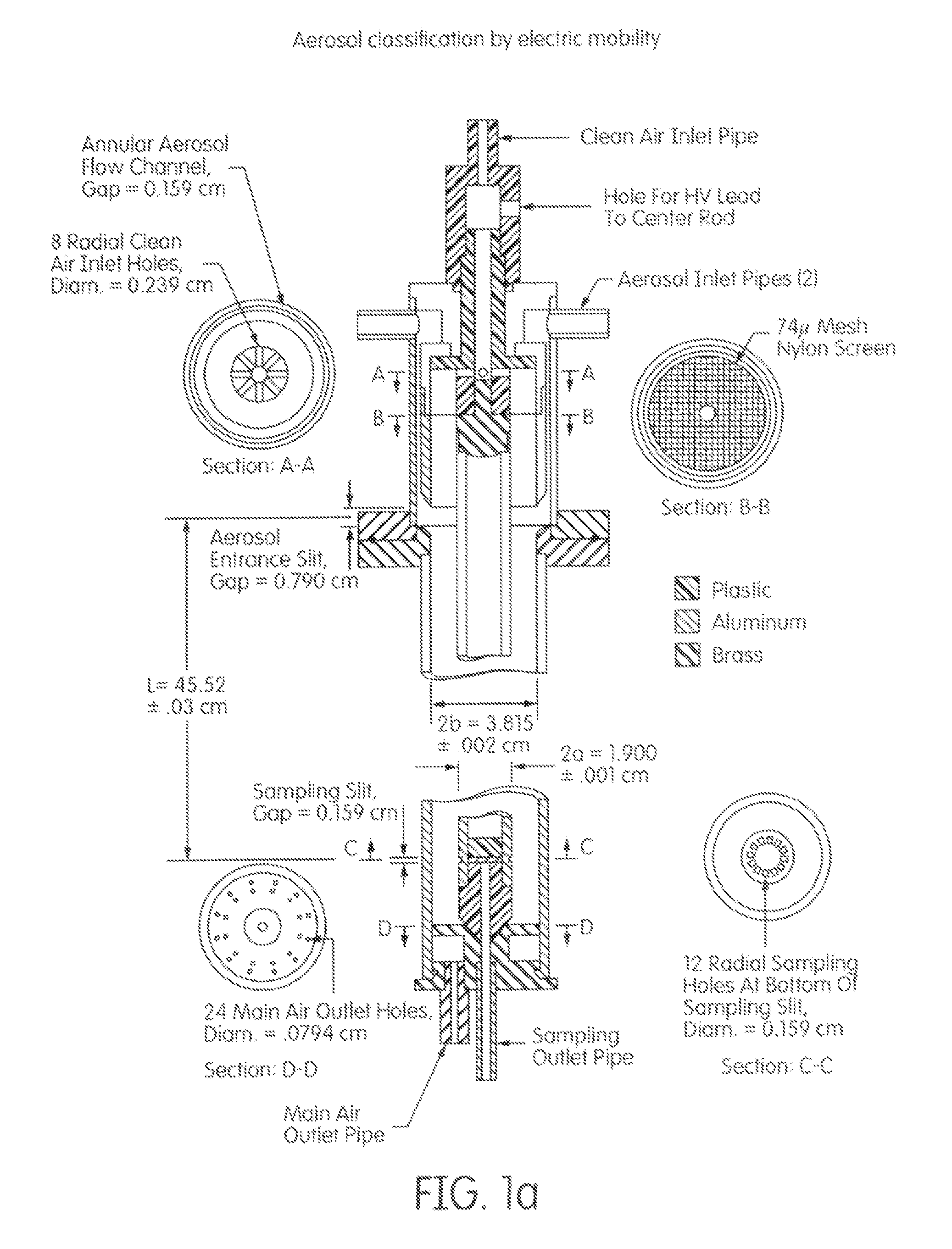
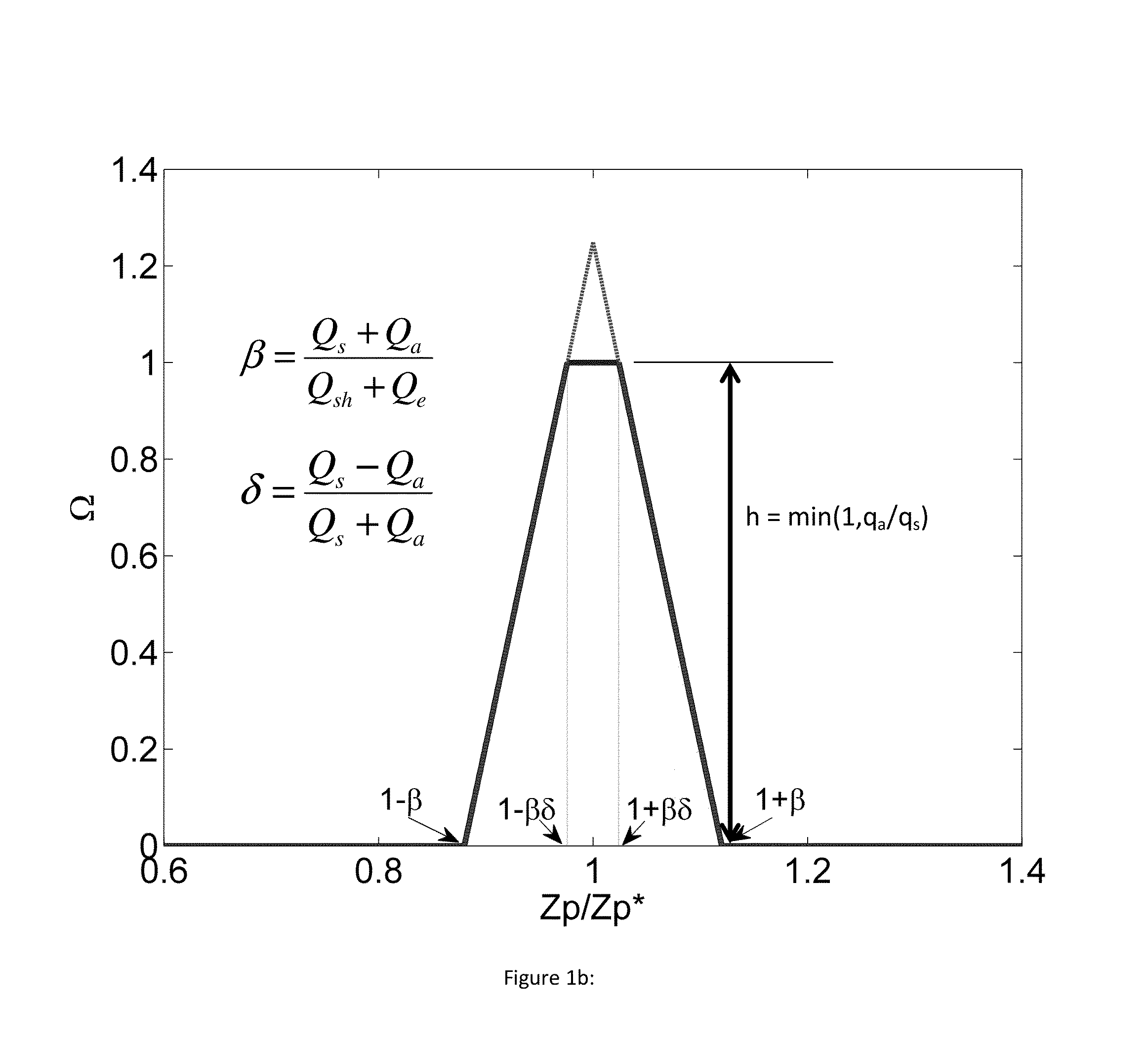
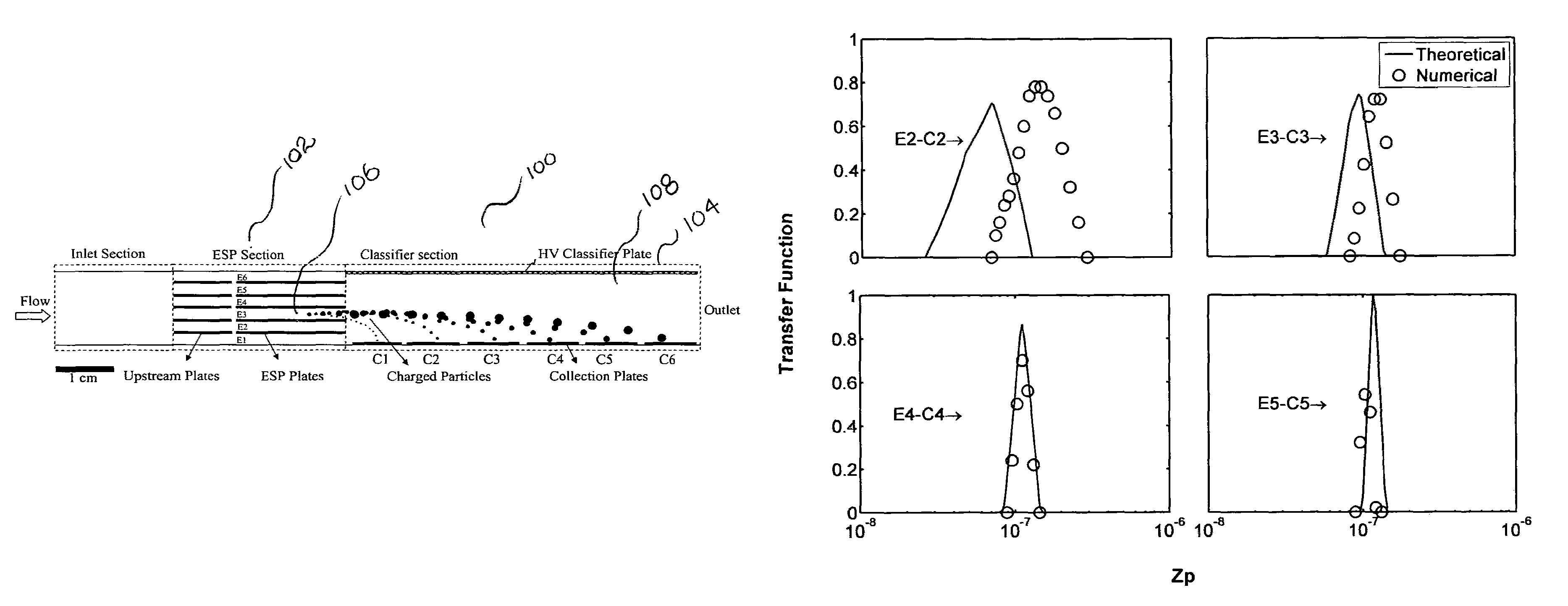
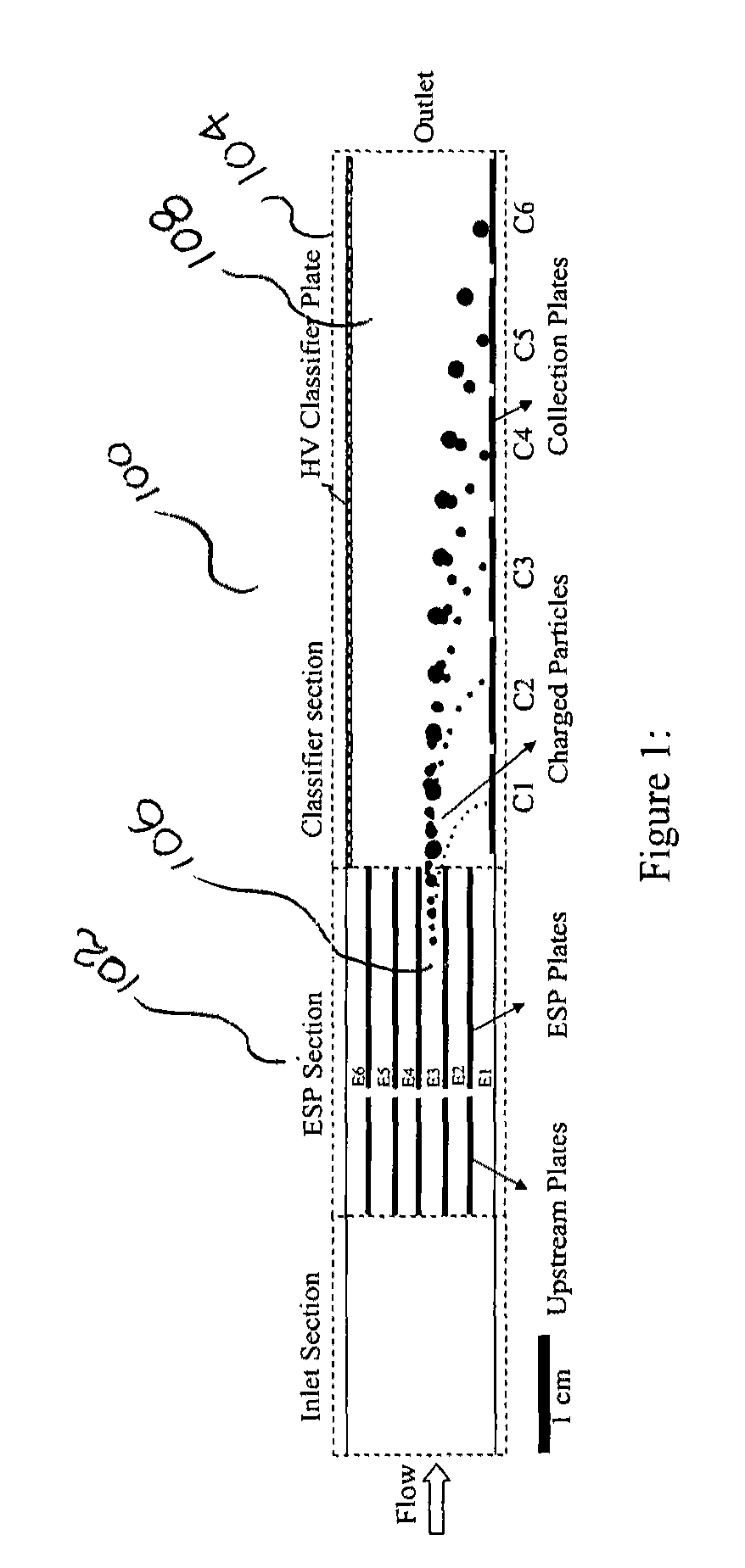
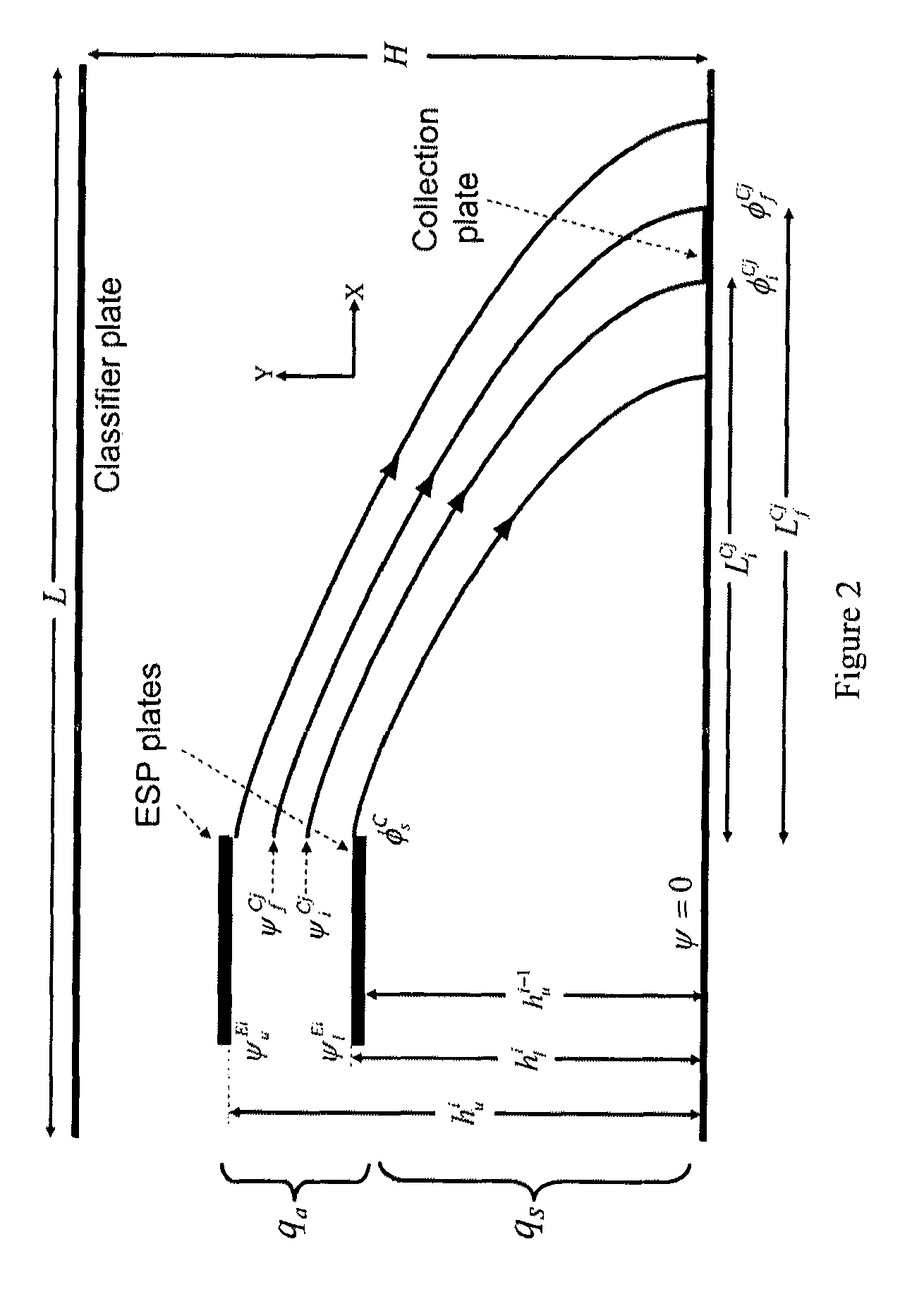
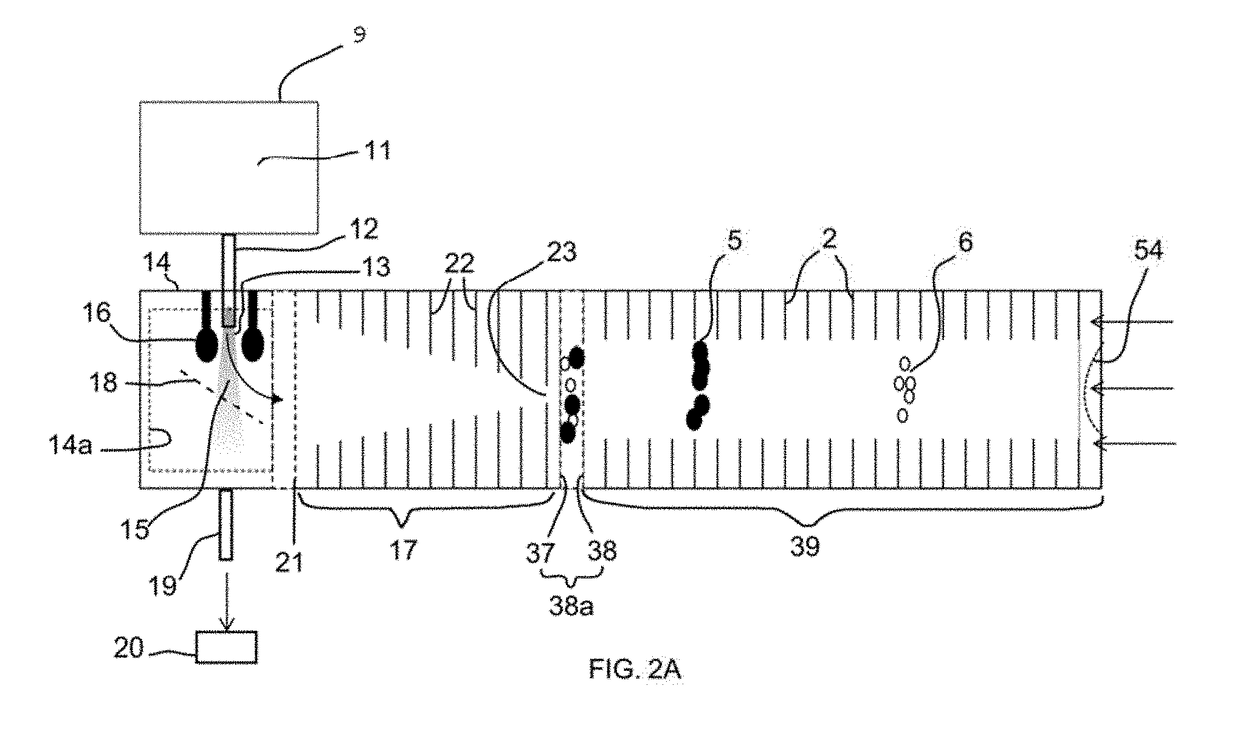
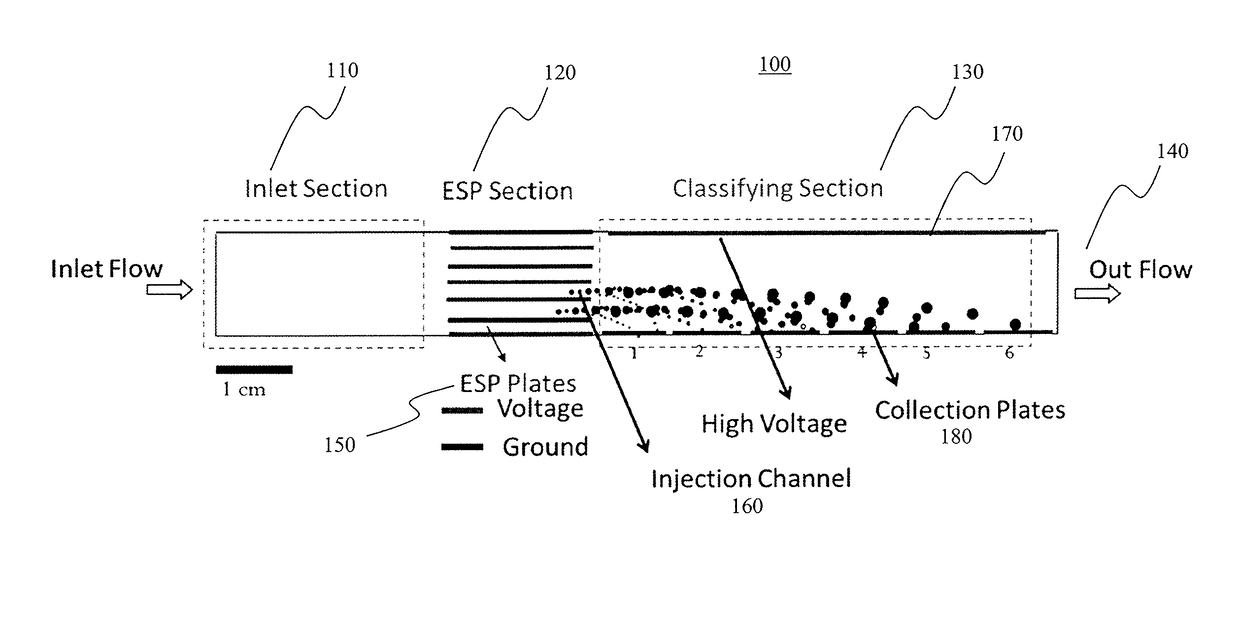
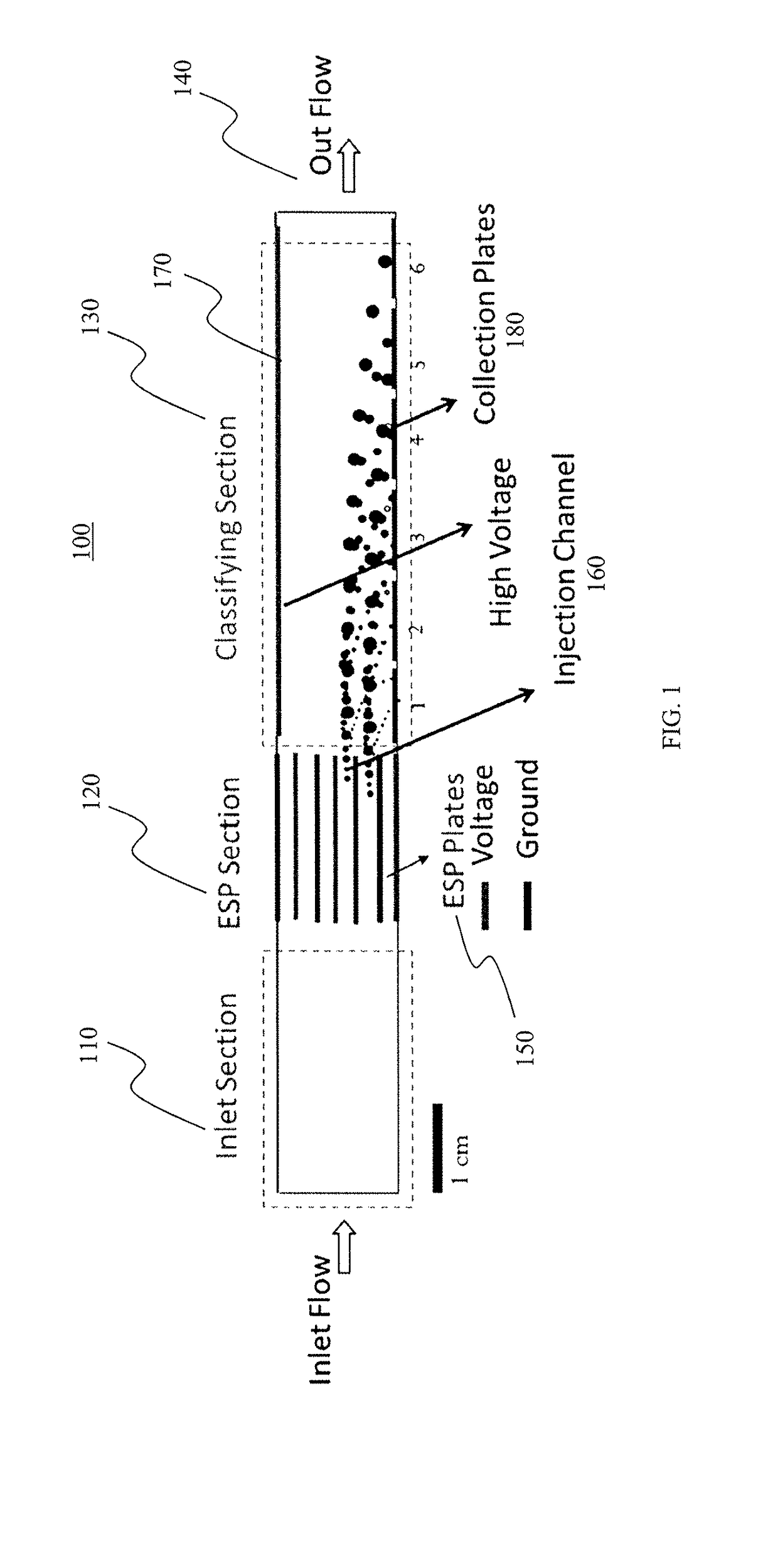
Theory and design of a new electrical-mobility based instrument for measurement of aerosol particle size distributions in real time is presented. Miniature Electrical Aerosol Spectrometer has a rectangular cross-section with two main regions: the Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) and Classifier sections. The ESP section enables charged particle injection into the classifier section in a narrow range of streamlines at the desired location. The injected charged particles are then segregated based on their electrical mobility in the classifier section and collected on a series of plates that are connected to electrometers. Real-time particle size distribution measurements can be inferred from the electrometer signal strengths with the knowledge of the instrument transfer function. A theoretical approach is developed to calculate Miniature Electrical Aerosol Spectrometer transfer function considering the non-uniformity in the electric and flow fields inside the instrument, and accounting for the instrument dimensions and its operating conditions. The theoretical predictions of size classification characteristics are seen to compare well with numerical results. The modeling results suggest that an optimal operational domain exists for Miniature Electrical Aerosol Spectrometer.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
Apparatuses, Processes, and Systems for Measuring Particle Size Distribution and Concentration
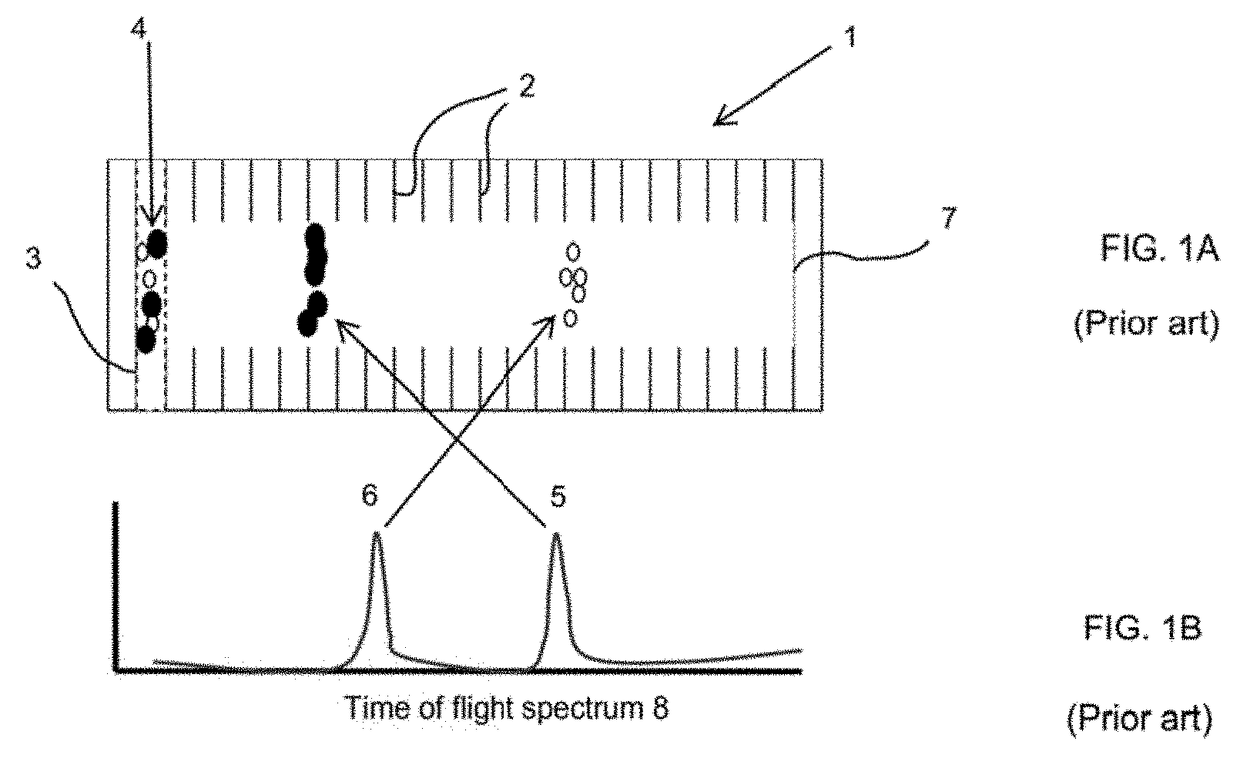
Apparatuses, methods, and systems are disclosed for analyzing particles from about 0.001 to about 1 μm in diameter by controlling a gaseous medium through which the particles travel so that properties of the particles, such as diameter, electrical mobility, and charge, are measured. One embodiment of the disclosed apparatuses includes a particle source generator, a nozzle, a chamber, an electronic gate, and a detector. Resolution of the measurements made by the disclosed apparatuses is improved by use of a mathematical deconvolution of a spread in arrival times generated by particles of different sizes and charge levels and non-ideal background flow velocity variations.
Owner:CARDIO METRIX
METHOD OF ENHANCING HIGH-k FILM NUCLEATION RATE AND ELECTRICAL MOBILITY IN A SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE BY MICROWAVE PLASMA TREATMENT
ActiveUS20150249009A1Increased electrical mobilityReduce thicknessElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh rateNoble gas
A method for forming a semiconductor device is provided in several embodiments. According to one embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate in a process chamber, flowing a process gas consisting of hydrogen (H2) and optionally a noble gas into the process chamber, forming plasma excited species from the process gas by a microwave plasma source. The method further includes exposing an interface layer on the substrate to the plasma excited species to form a modified interface layer, and depositing a high dielectric constant (high-k) film by atomic layer deposition (ALD) on the modified interface layer. In some embodiments, the modified interface layer has higher electrical mobility than the interface layer, and the high-k film nucleates at a higher rate on the modified interface layer rate than on the interface layer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Flowing reaction device allowing forming and growing of new particles of atmospheric aerosol
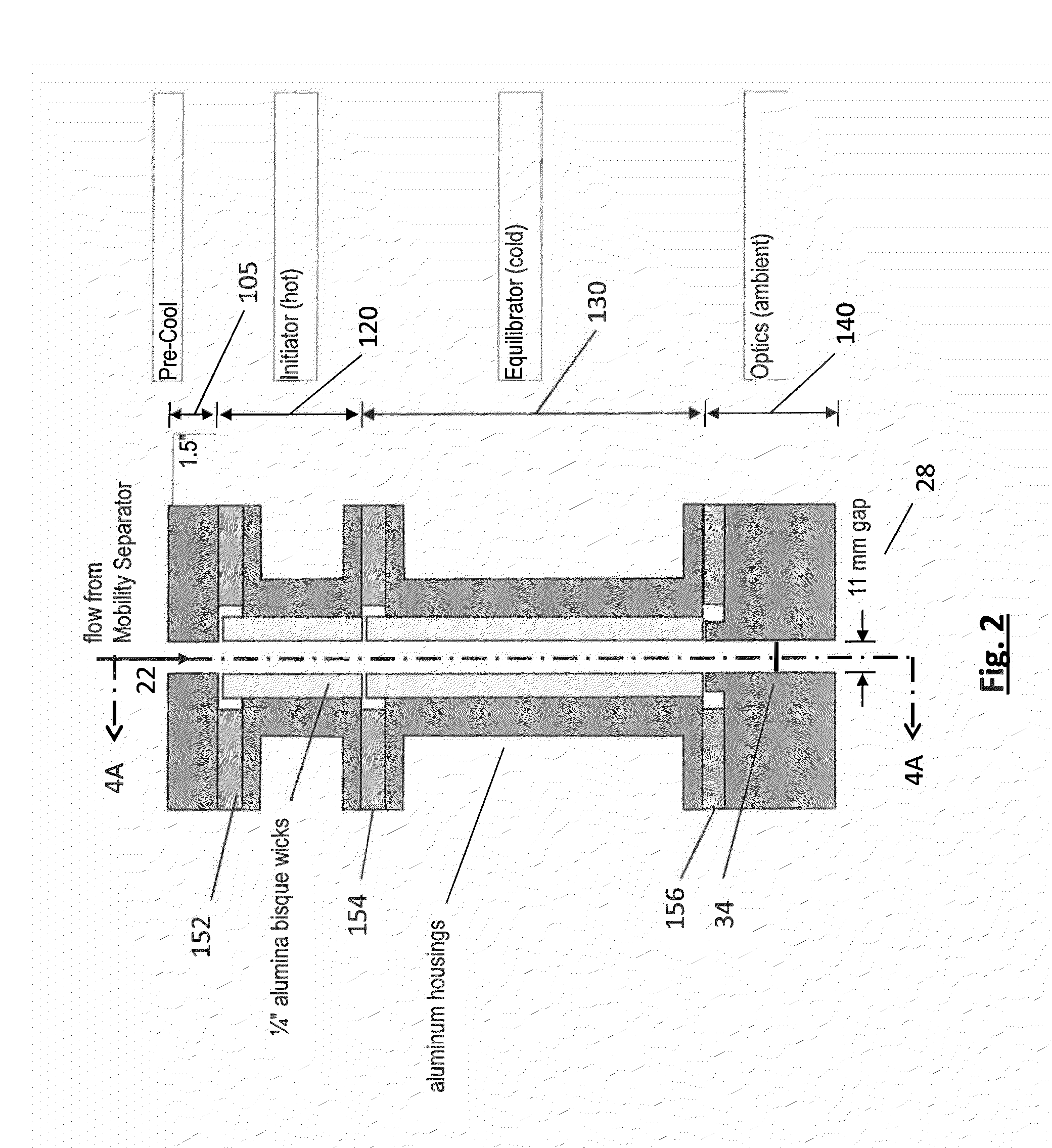
ActiveCN106644850AIncrease the lengthExtended reaction timeParticle size analysisWater bathsElectrical mobility
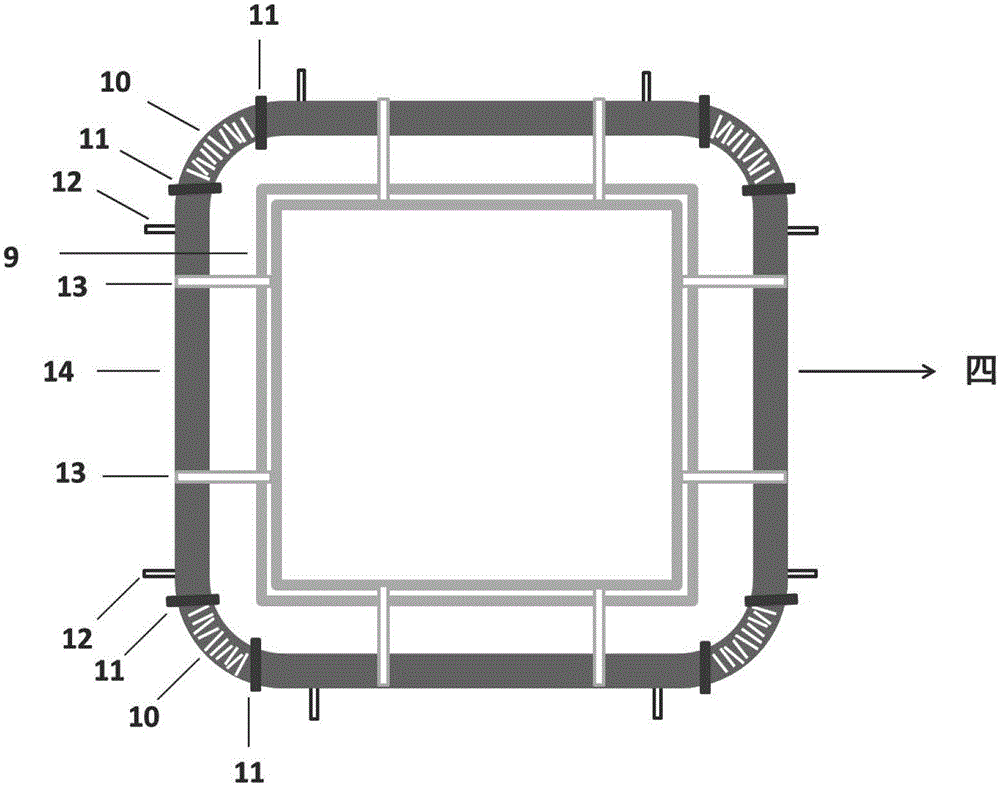
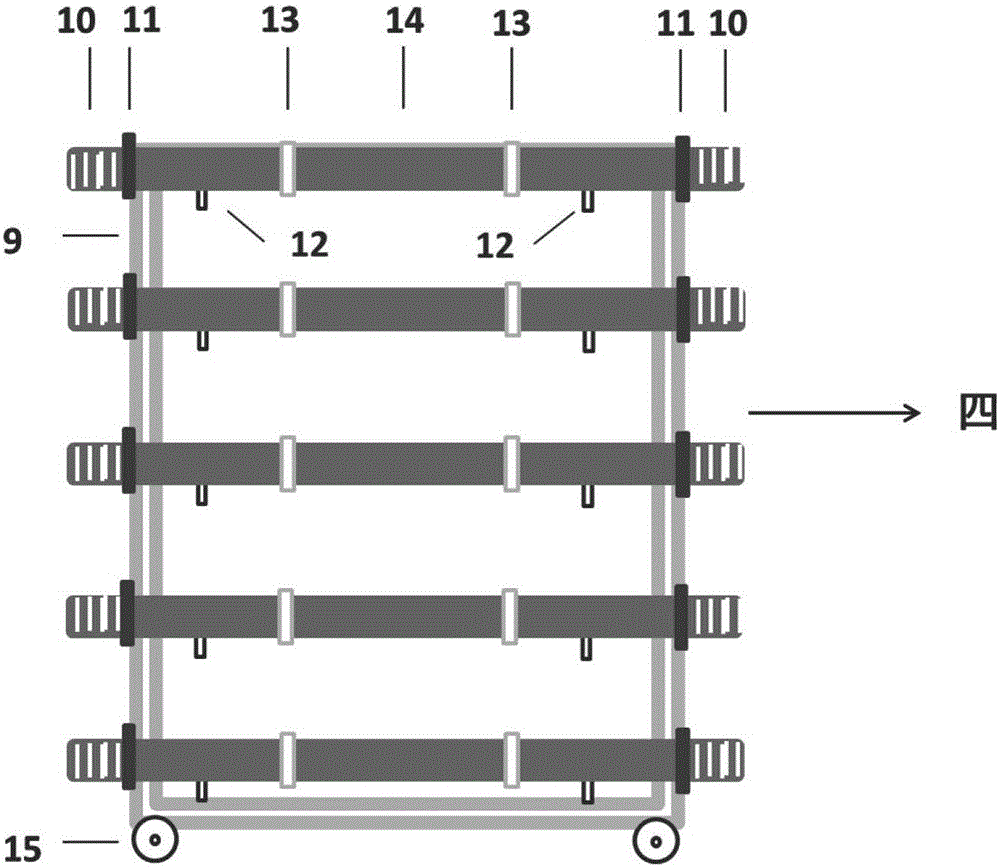
The invention discloses a flowing reaction device allowing forming and growing of new particles of atmospheric aerosol. The length of the flowing reaction device is about 22 meters. The flowing reaction device comprises four parts of a sample injection region (I), a transition region (II), a nucleation region (III) and a growing region (IV), wherein the sample injection region comprises three sample inlets and a set of water bath heating water inlets and outlets; the transition region comprises a temperature humidity detecting opening, a low-volatility substance sample inlet and a primary sampling opening; the nucleation region comprises a set of water inlets and outlets for controlling temperature of water bath, a plurality of intermediate sampling openings and a temperature humidity detecting opening formed in the upper part of the nucleation region; the growing region comprises a plurality of growing region sampling openings; the change of the particle number concentration and the change of the particle diameter of each sampling opening are detected through scanning an electrical mobility particle diameter spectrometer. The flowing reaction device disclosed by the invention can be used for researching the generative mechanism and the rising characteristic of the new particles in the atmosphere, so that the dynamics of the nucleation of the aerosol is further researched, and the flowing reaction device has the characteristics of being high in precision, good in stability, simple and convenient to operate, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Instruments for measuring ion size distribution and concentration
Instruments are disclosed for analyzing ions from about 1000 to 10,000,000 Daltons by controlling a gaseous medium through which the ions travel under the influence of an electric field so that properties of the ions, such as diameter, electrical mobility, and charge, are measured. One embodiment of the disclosed instruments includes an ion source, a nozzle, a jet relaxation region, an ion accumulation region, an electronic gate, a flow chamber and an ion detector.
Owner:BENNER W HENRY
Miniature electrical aerosol spectrometer
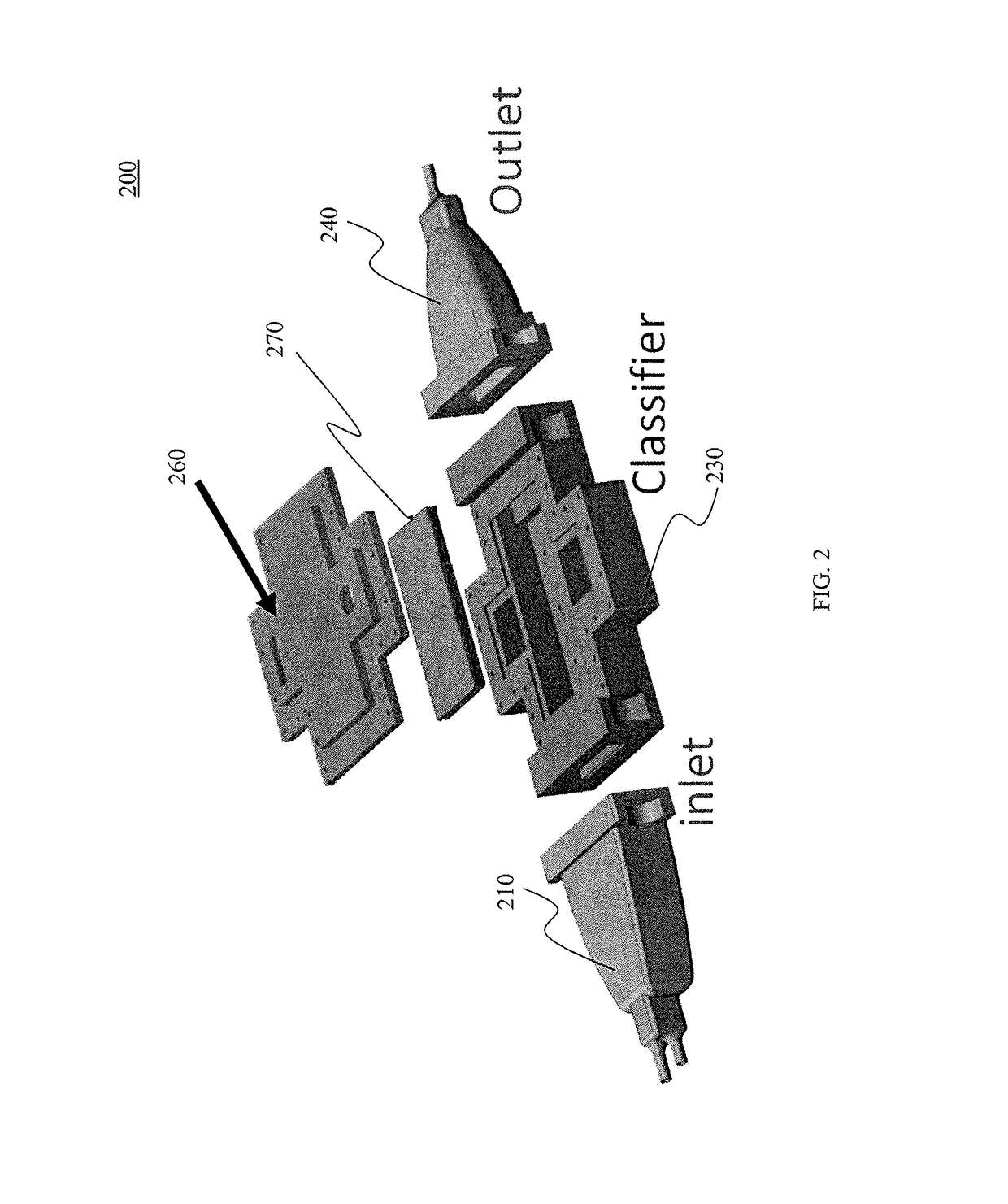
A miniature electrical-mobility aerosol spectrometer comprising a 3D-printed body comprising: (i) a single inlet section configured to receive particles to be evaluated by the spectrometer; (ii) an electrostatic precipitator section coupled to the electrostatic precipitator section; (iii) a classifier section, wherein the electrostatic precipitator section is coupled to the classifier section; and (iv) an outlet, wherein the classifier section is coupled to the outlet; a high voltage classifier plate positioned within the classifier section; and a classifier component positioned within the classifier section opposite the high voltage classifier plate, wherein the classifier component comprises sensing circuitry configured to detect particles in the classifier section, and wherein the classifier section comprises a two-sided printed circuit board, wherein the two-sided printed circuit board comprises the sensing circuitry, and wherein a first side of the two-sided printed circuit board comprises a plurality of printed collection plates.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
Host Material for Blue Phosphor, and Organic Thin Film and Organic Light-Emitting Device Including Same
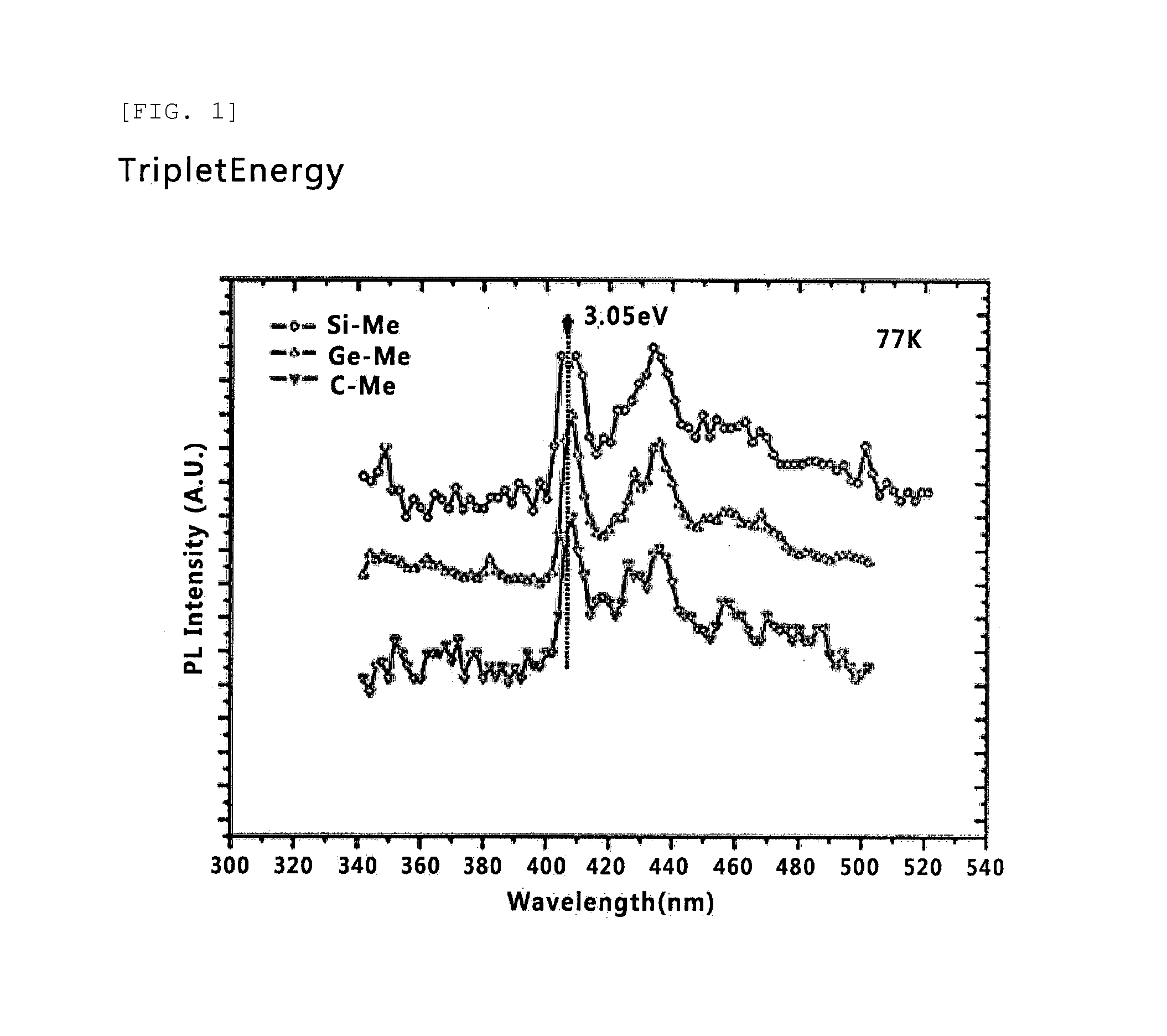
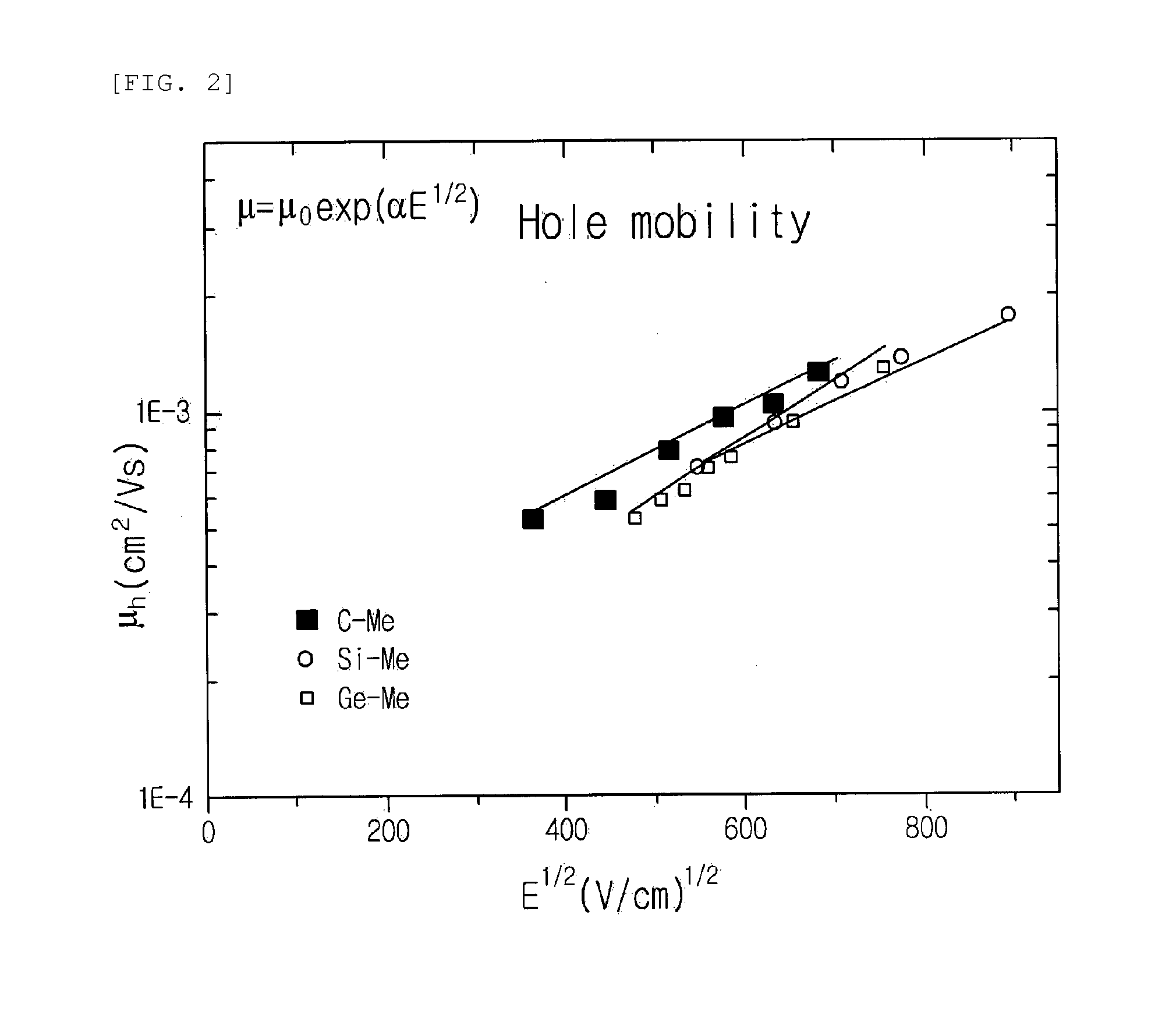
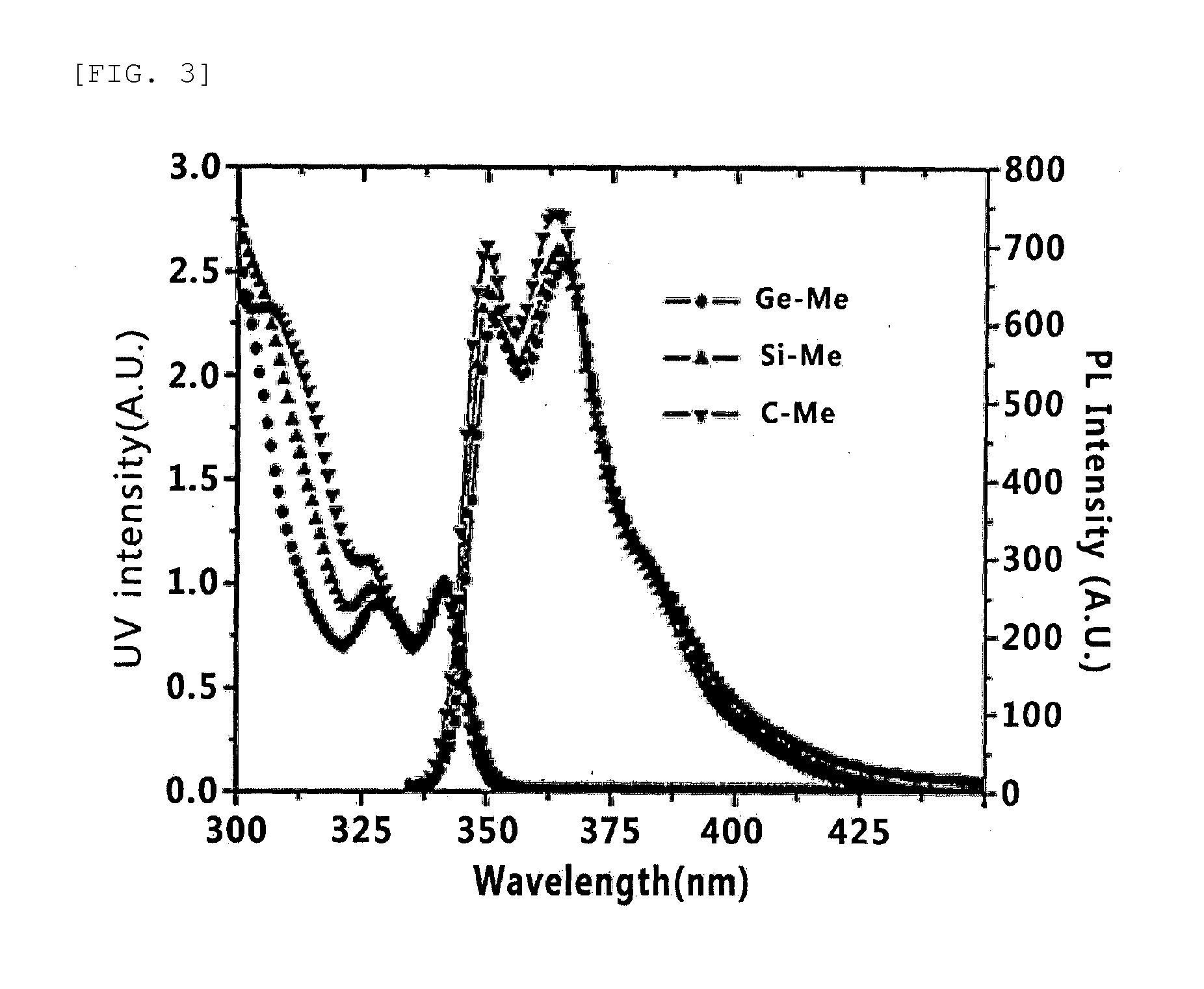
ActiveUS20140159027A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh triplet energySilicon organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsElectrical mobilityHost material
Provided are a host material for a blue phosphor, and an organic thin film and an organic light-emitting device including the same. The host material for a blue phosphor is such that a carbazole compound is bonded around a central atom, wherein the central atom is a Group 14 element, and the carbazole compound bonded around the central atom is 3 or 4, wherein the carbazole compound includes carbazole in which an alkyl group is substituted. The host material for a blue phosphor has high triplet energy (ET) and excellent electrical mobility and thermal stability. As a result, the organic thin film, which includes the host material, and the organic light-emitting device, which includes the organic thin film, implement a deep blue color and have excellent luminous efficiency.
Owner:YOULCHON CHEM
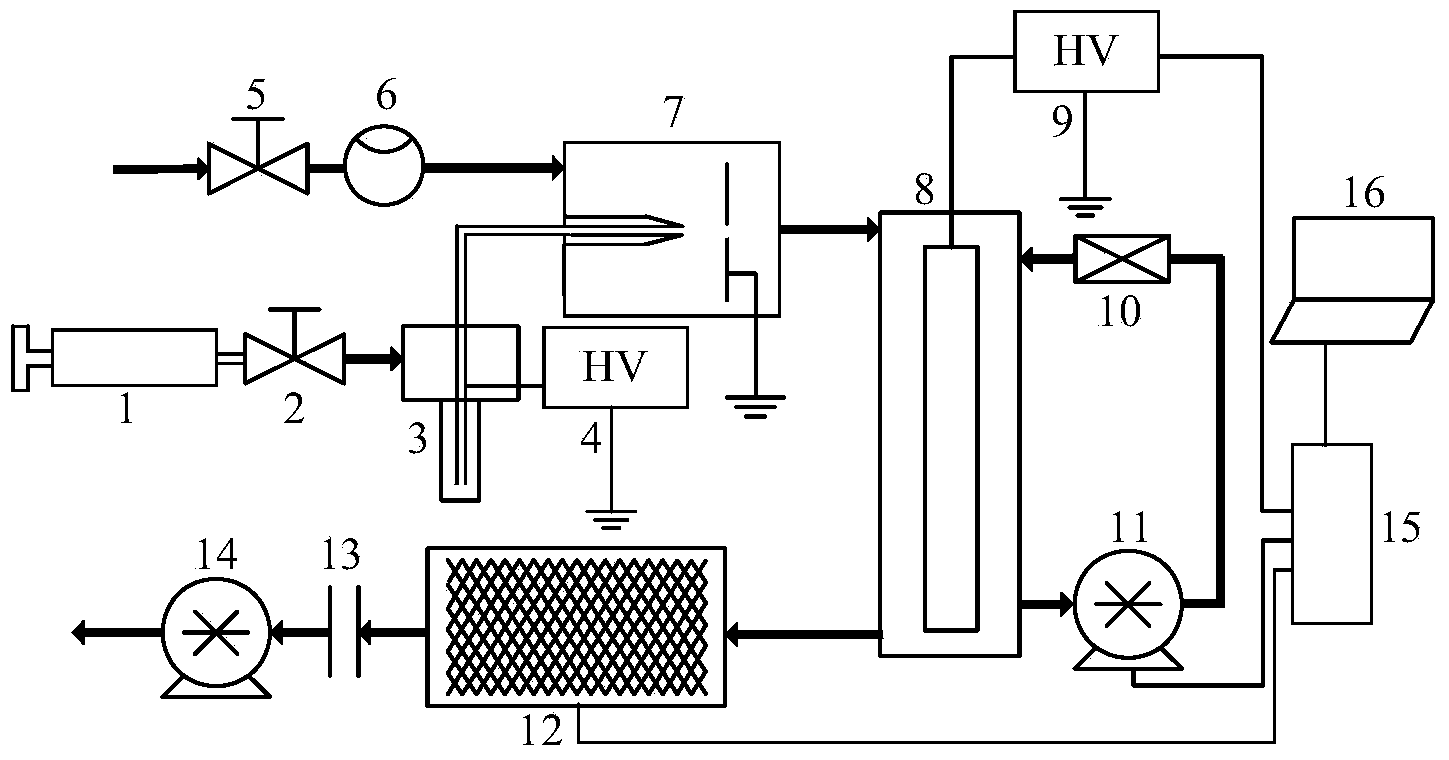
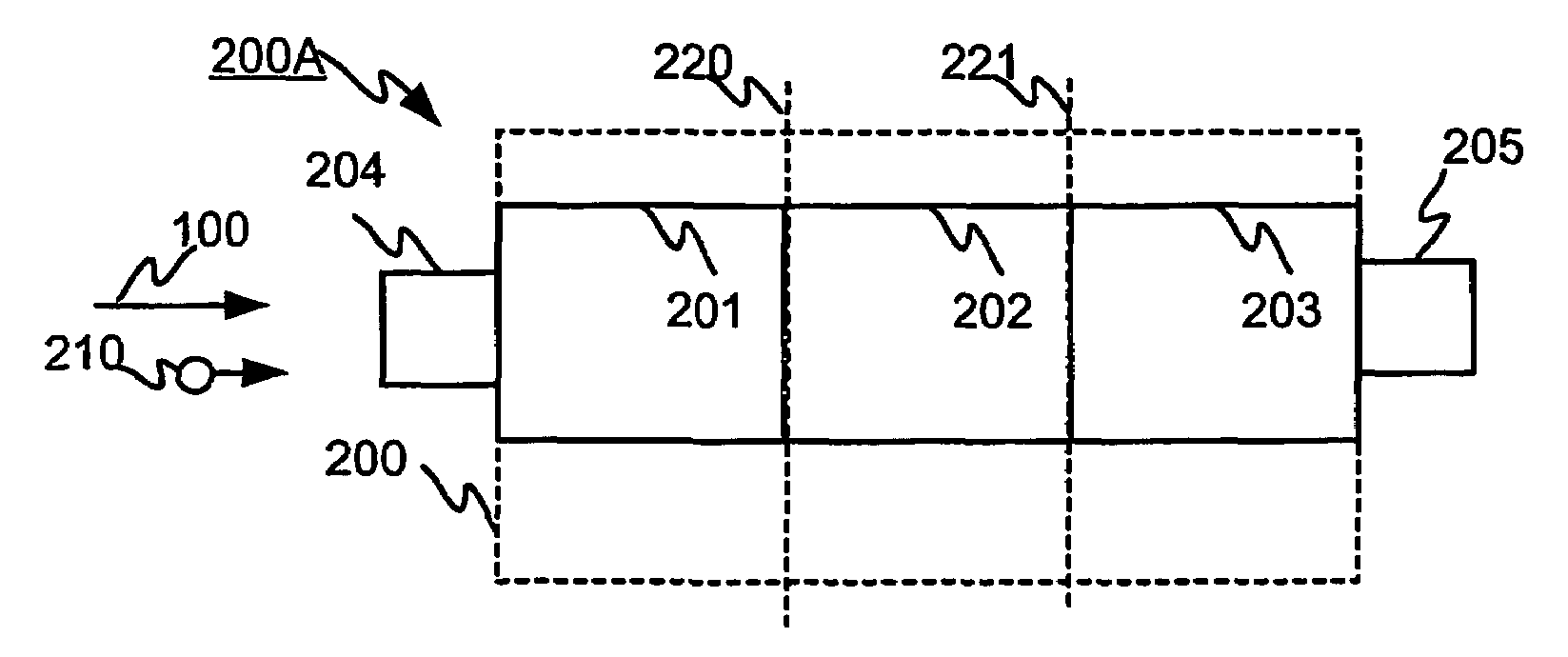
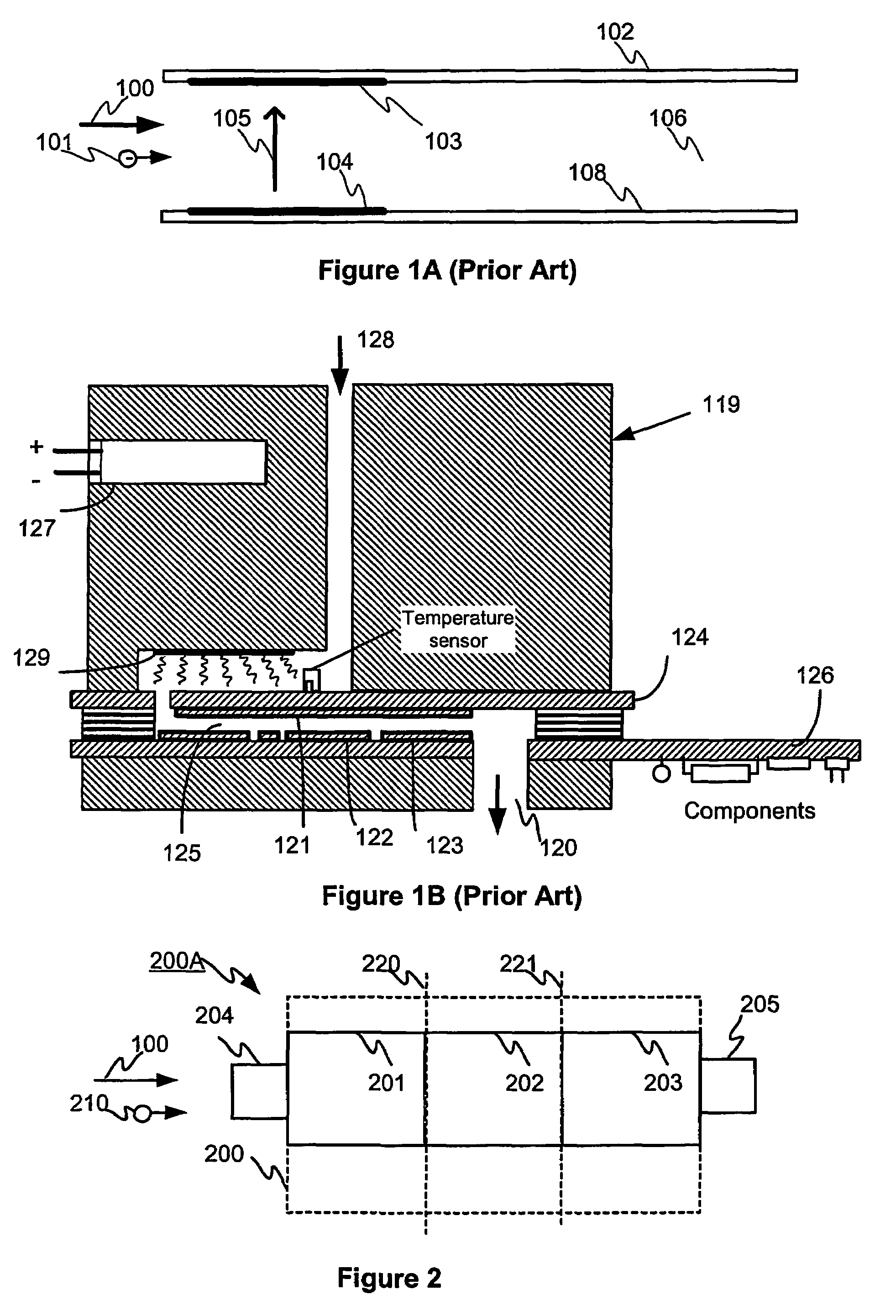
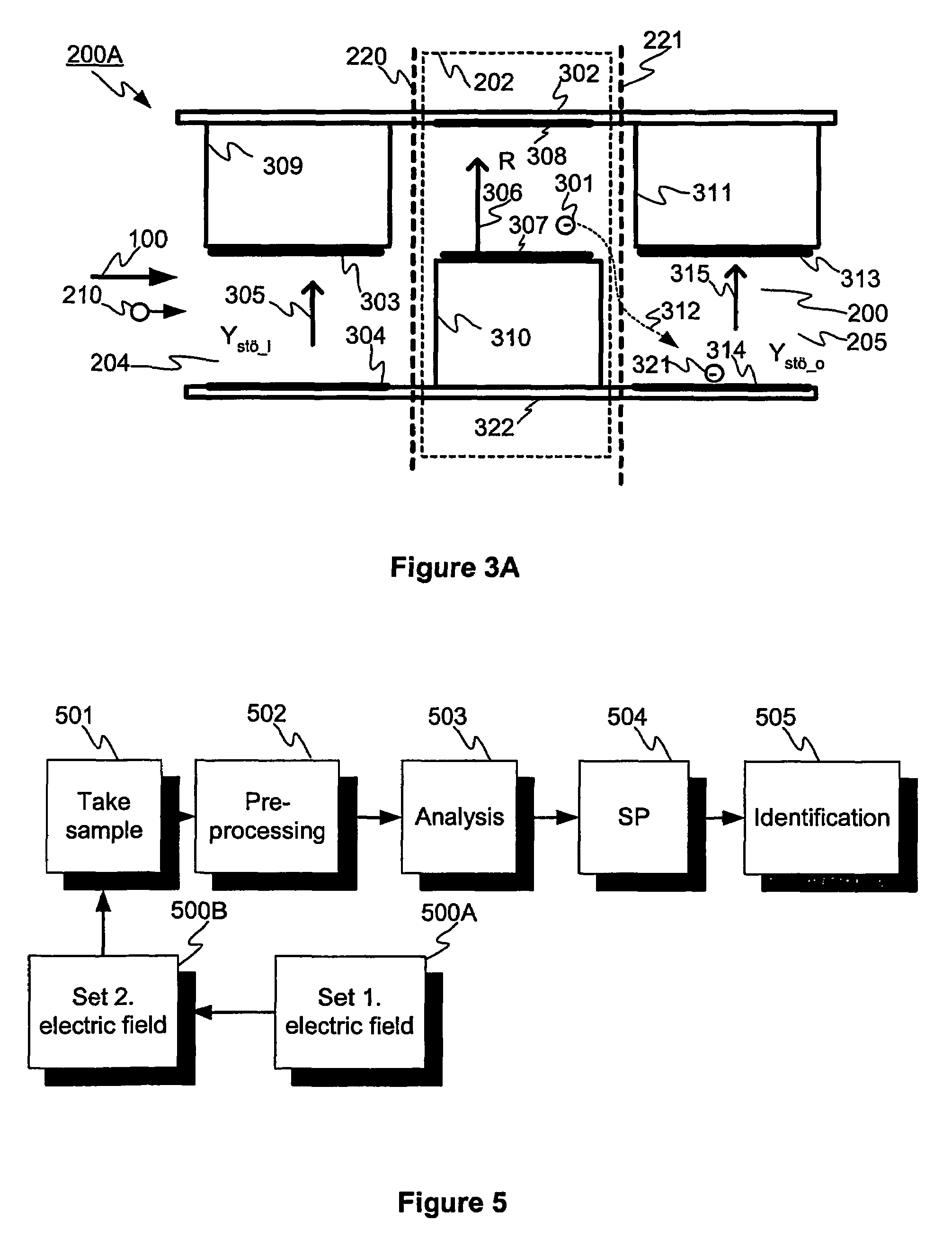
Cell structure, device and method for gas analysis
The invention relates to a gas analysis based on the mobility of ions. The invention relates to a cell structure of an analysis device, the cell structure comprising the reference cell (201), the ionisation section (202) and the analysis cell (203) for identifying the electric mobility of ions. The invention also relates to a method for identifying the ions. Further, the invention relates to a system for identifying the ions.
Owner:ENVIRONICS
Coupling between axisymmetric differential mobility analyzers and mass spectrometers or other analyzers and detectors
ActiveUS8232519B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSmall sampleElectrical mobility
Prior work on differential mobility analysis (DMA) combined with mass spectrometry (MS) has shown how to couple the output of a planar DMA with the atmospheric pressure inlet of an atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometer (APCI-MS). However, because the ion inlet to APCI-MS instruments is a round orifice, while conventional DMA geometries make use of elongated slits, the coupling of both has attained less resolving power or tolerated a smaller sample flow rate than a DMA alone. The present invention overcomes these limitations with an axial DMA of cylindrical symmetry using more than two electrodes. The configuration is related to that previously proposed by Labowsky and Fernández de la Mora (2004, 2006), where ions with a critical electrical mobility are brought into the symmetry axis of the DMA. Ions with this critical mobility are now optimally transmitted into the MS, with much higher resolution than possible in planar DMAs. In a preferred embodiment of this DMA facilitating DMA-MS coupling, one DMA electrode intersecting the symmetry axis is relatively planar.
Owner:NANOENG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com