Patents
Literature
549results about "Spectrometer detectors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
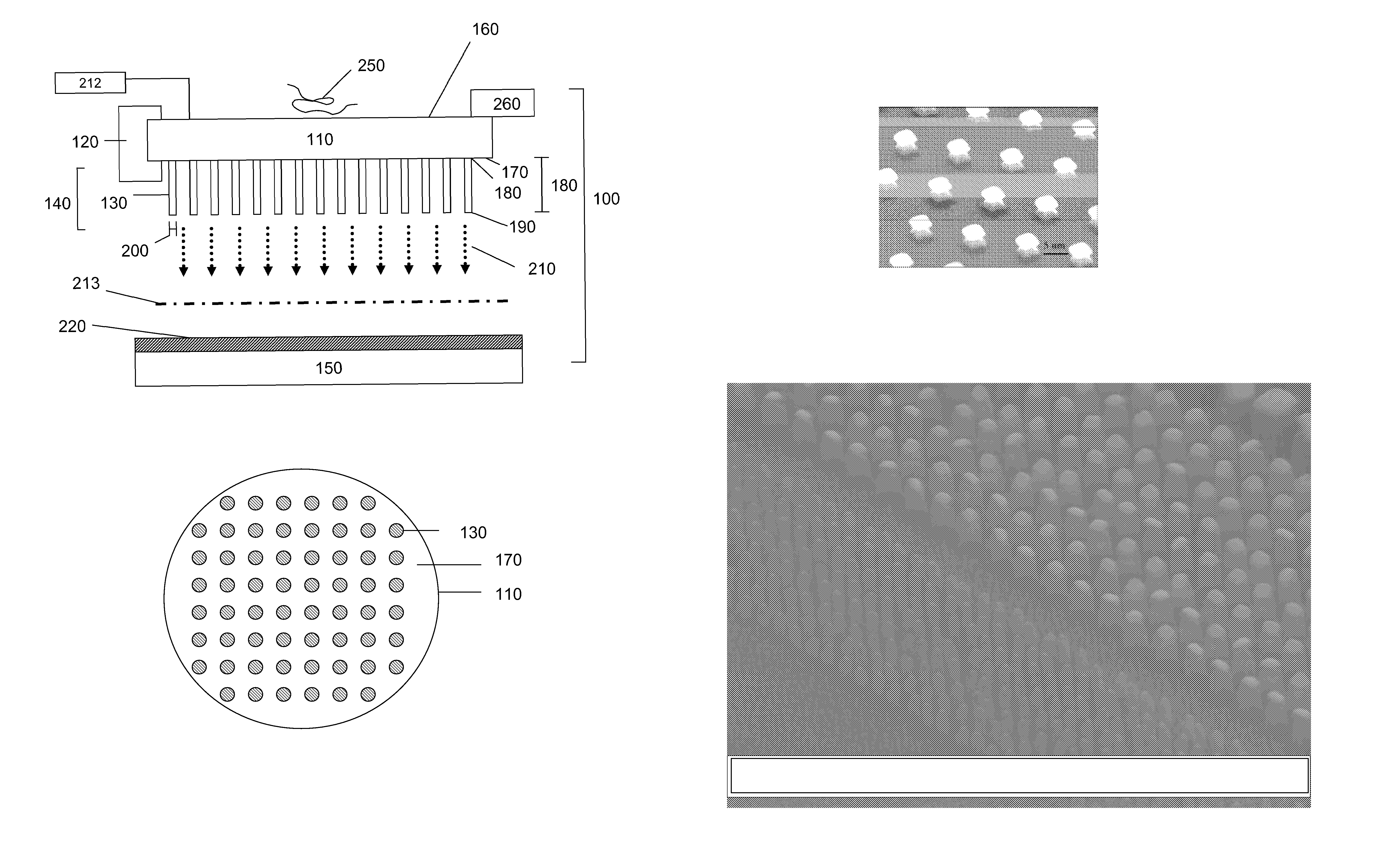
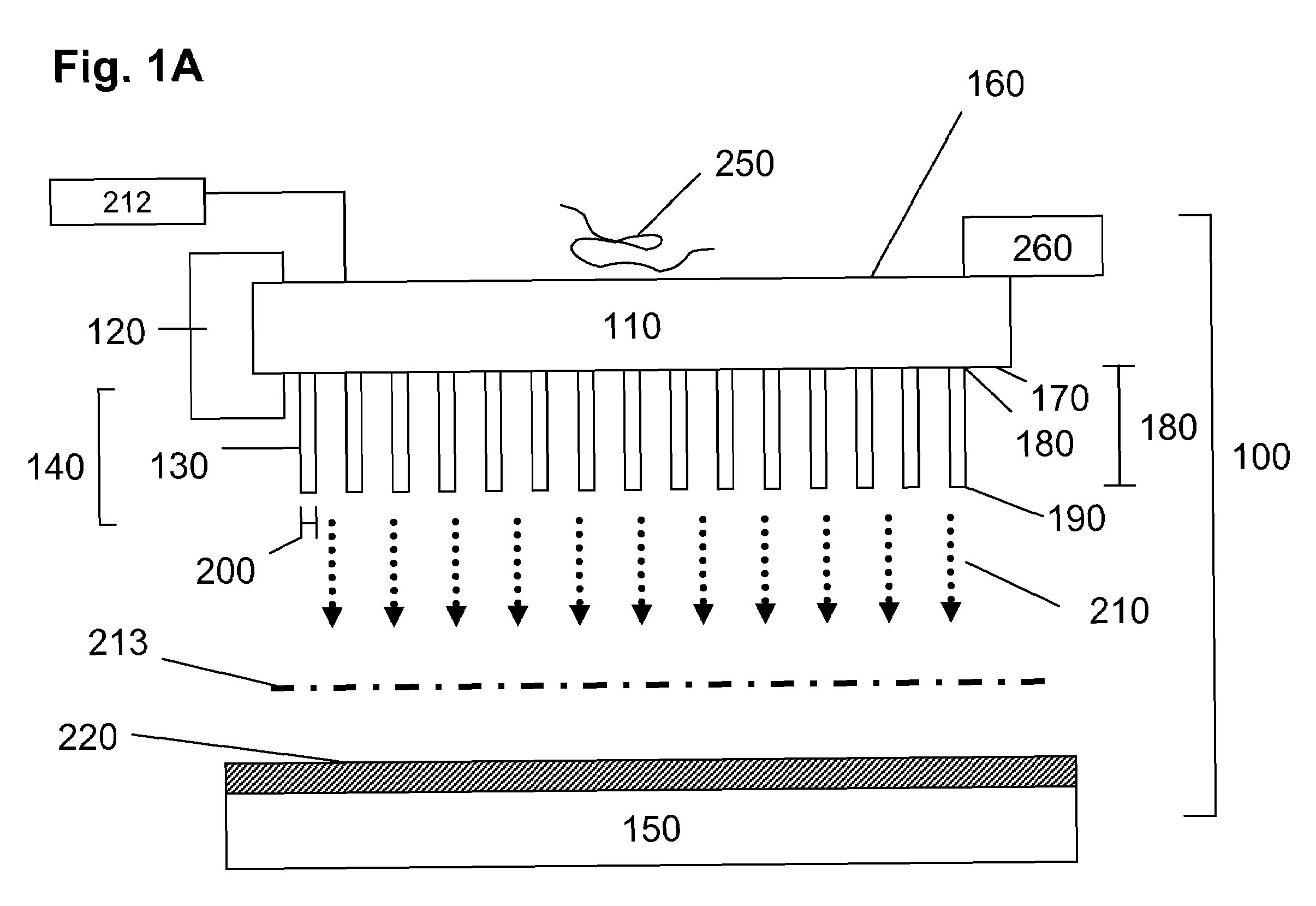
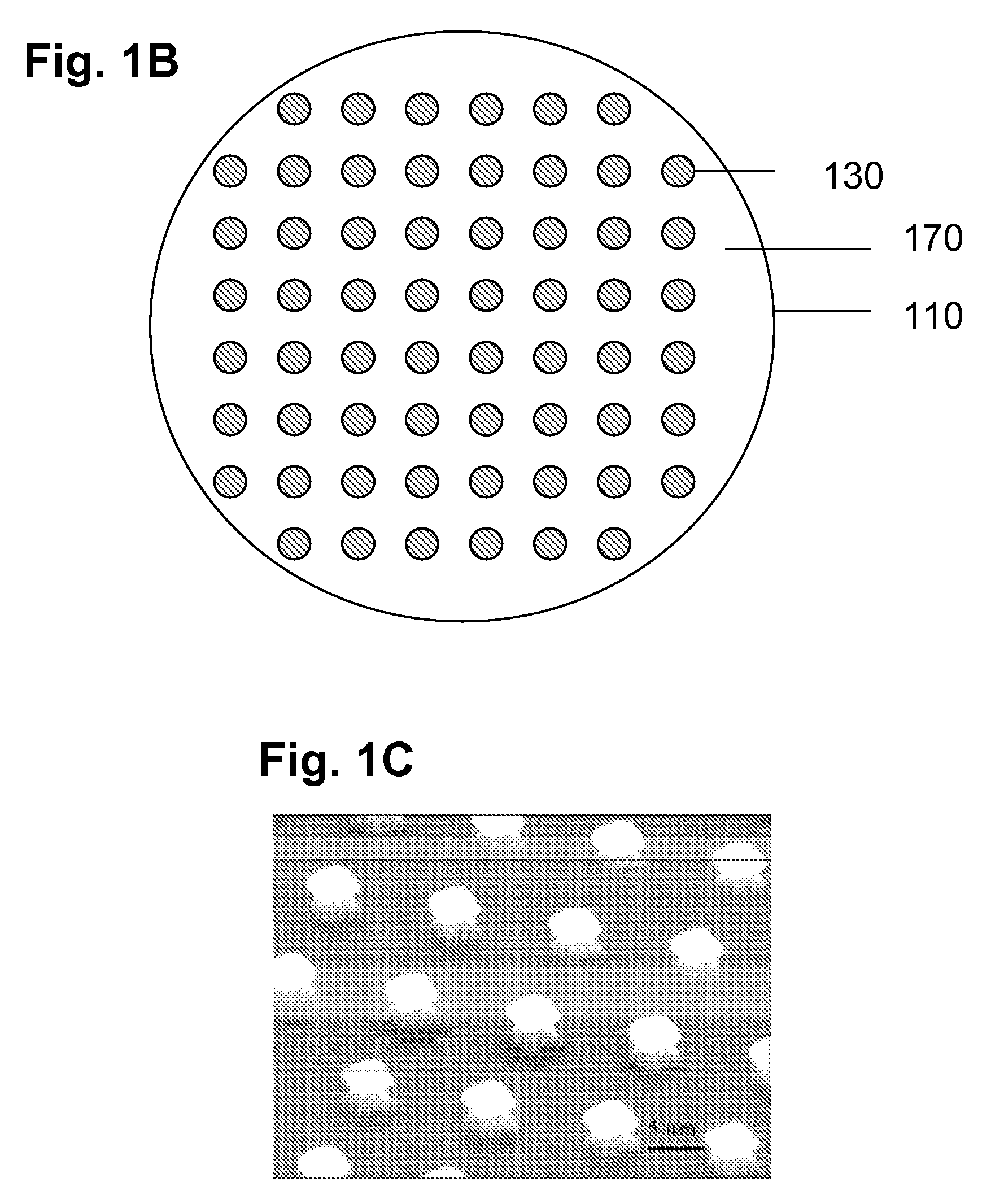
Linear quadrupole mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6403955B1Minimize feedbackLarge useful ion trapping volumeStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsTrappingLinear element
A quadrupole ion trap mass analyzer in which the trapping volume is defined by spaced linear rods in which linear elements located between the spaced linear rods produce image currents produced by motion of ions in the trapping volume.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
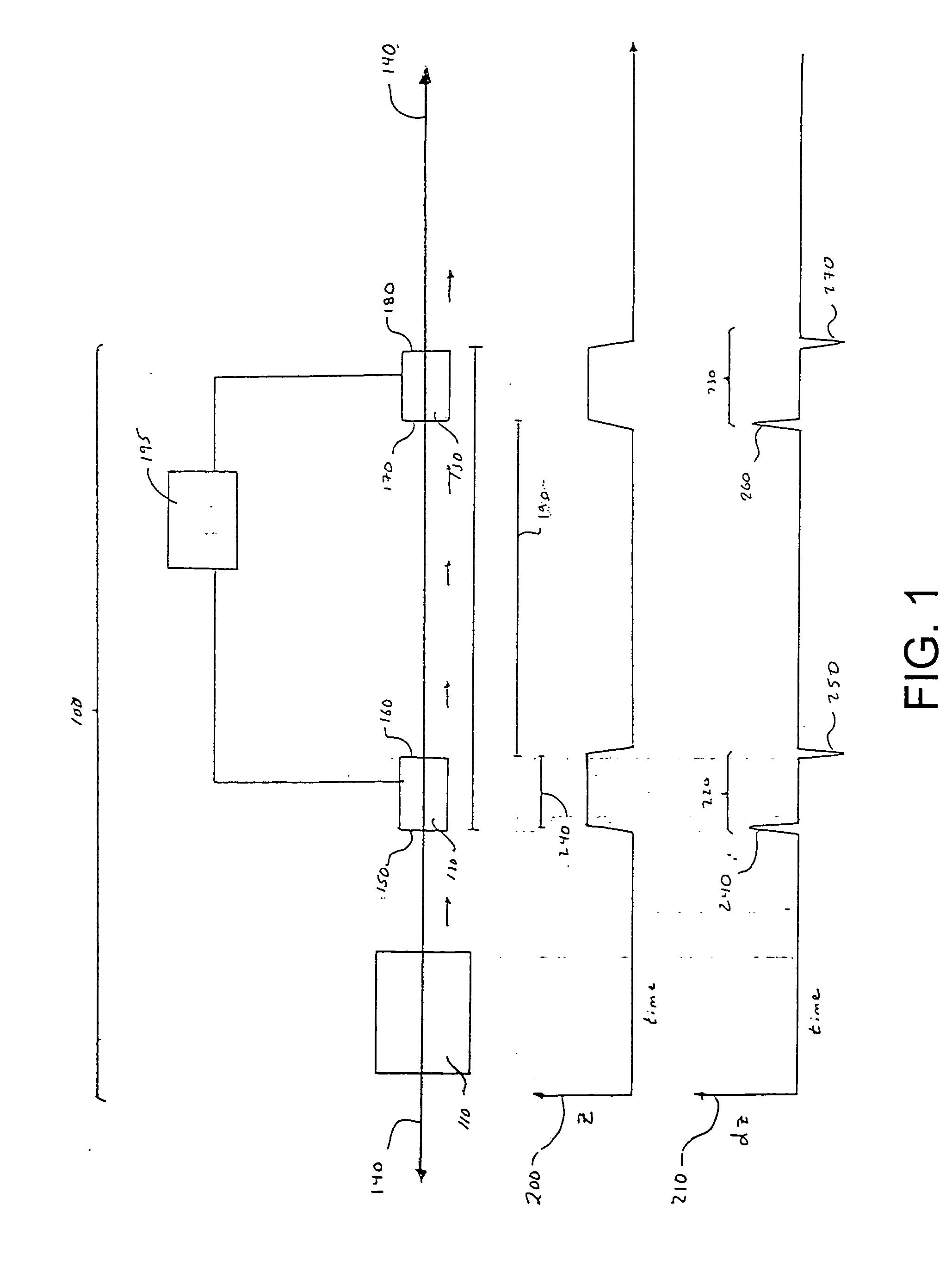
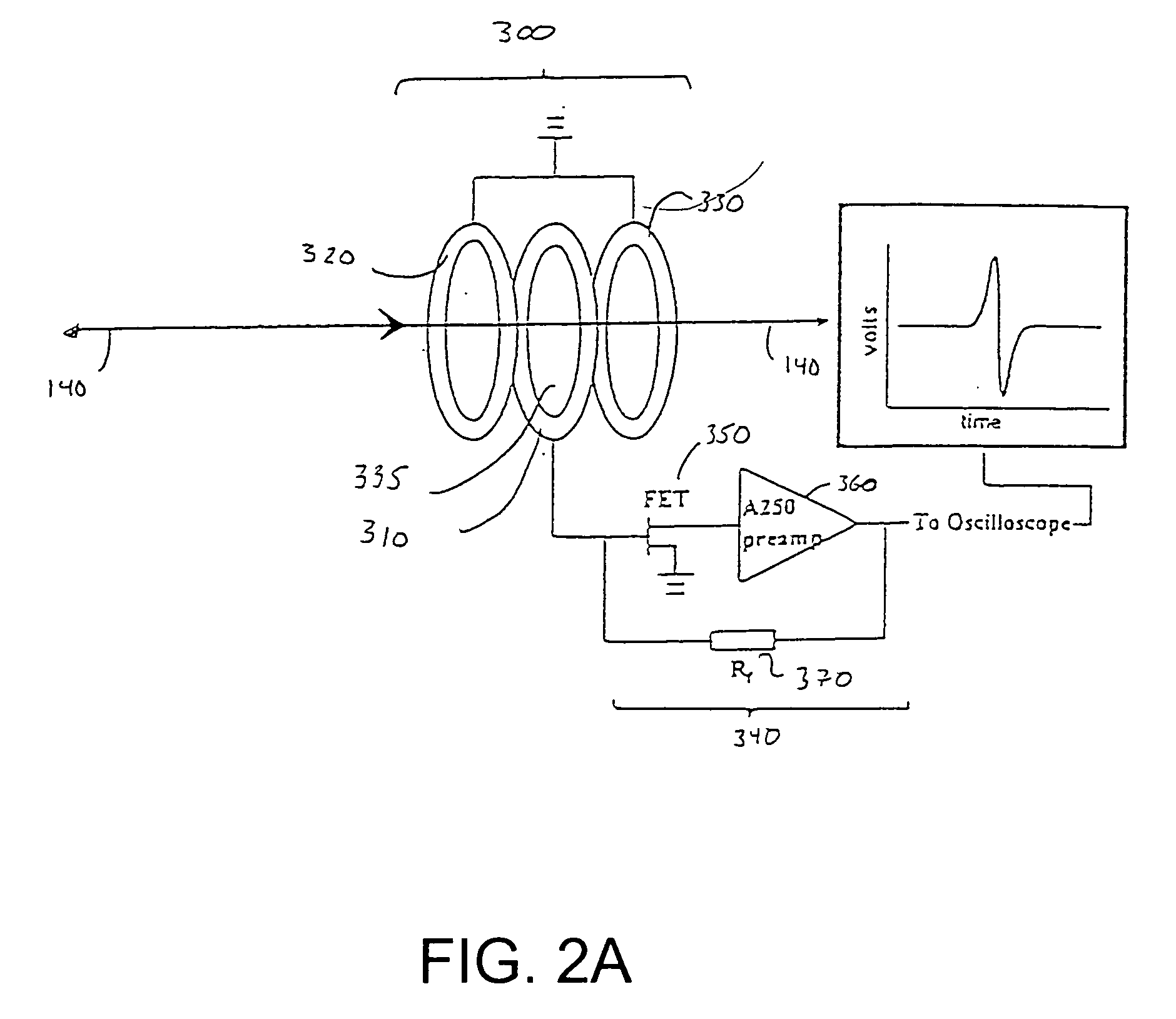
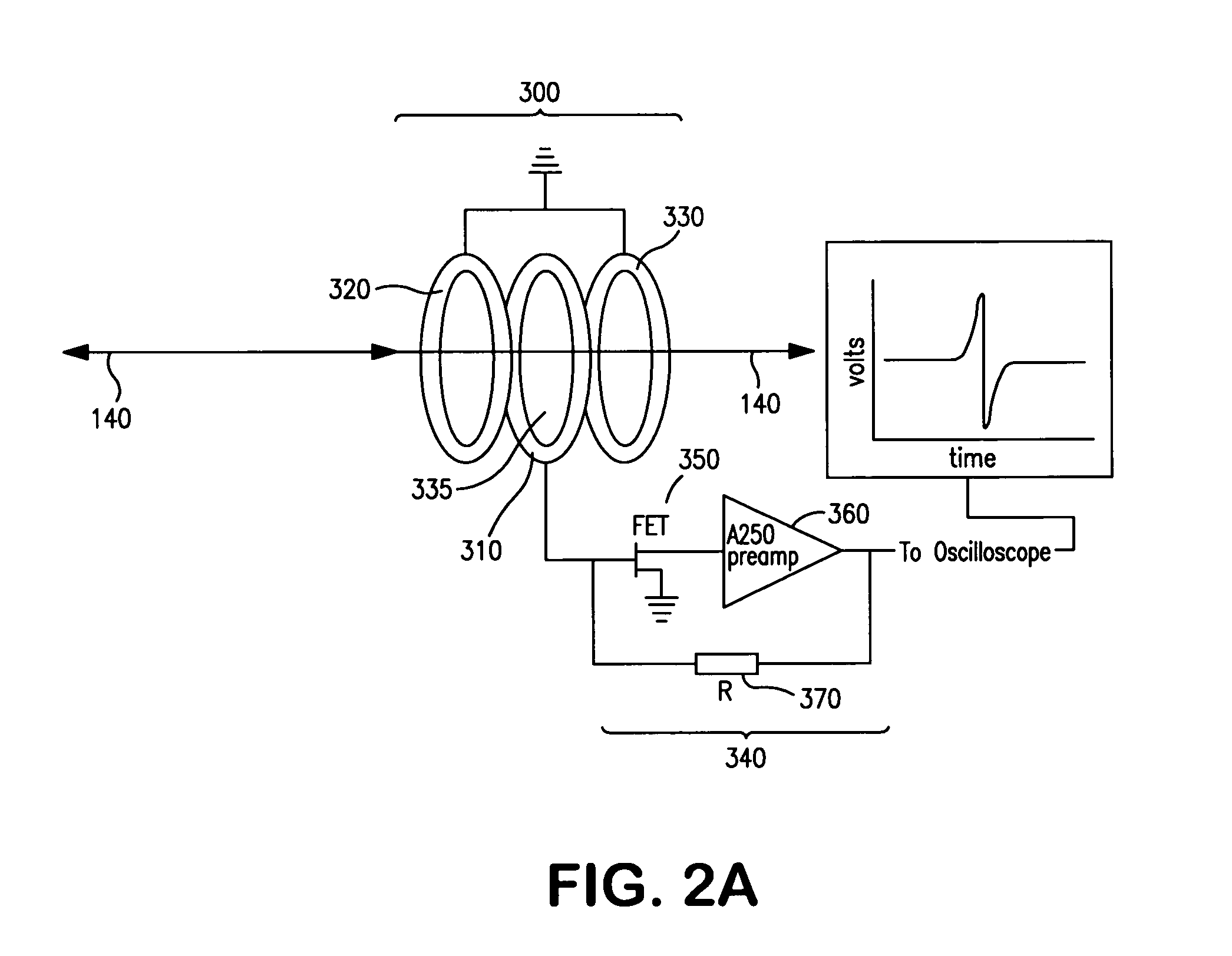
Inductive detection for mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20040169137A1Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsGas phaseBiopolymer
The invention provides devices, device configurations and methods for improved sensitivity, resolution and efficiency in mass spectrometry, particularly as applied to biological molecules, including biological polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention provides methods and devices for analyzing and detecting electrically charged particles, especially suitable for gas phase ions generated from high molecular weight compounds. In one aspect, the invention provides devices and methods for determining the velocity, charged state or both of electrically charged particles and packets of electrically charged particles. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and devices for the time-of-flight analysis of electrically charged particles comprising spatially collimated sources. In another aspect, the invention relates to multiple detection using inductive detectors, improved methods of signal averaging and charged particle detection in coincidence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
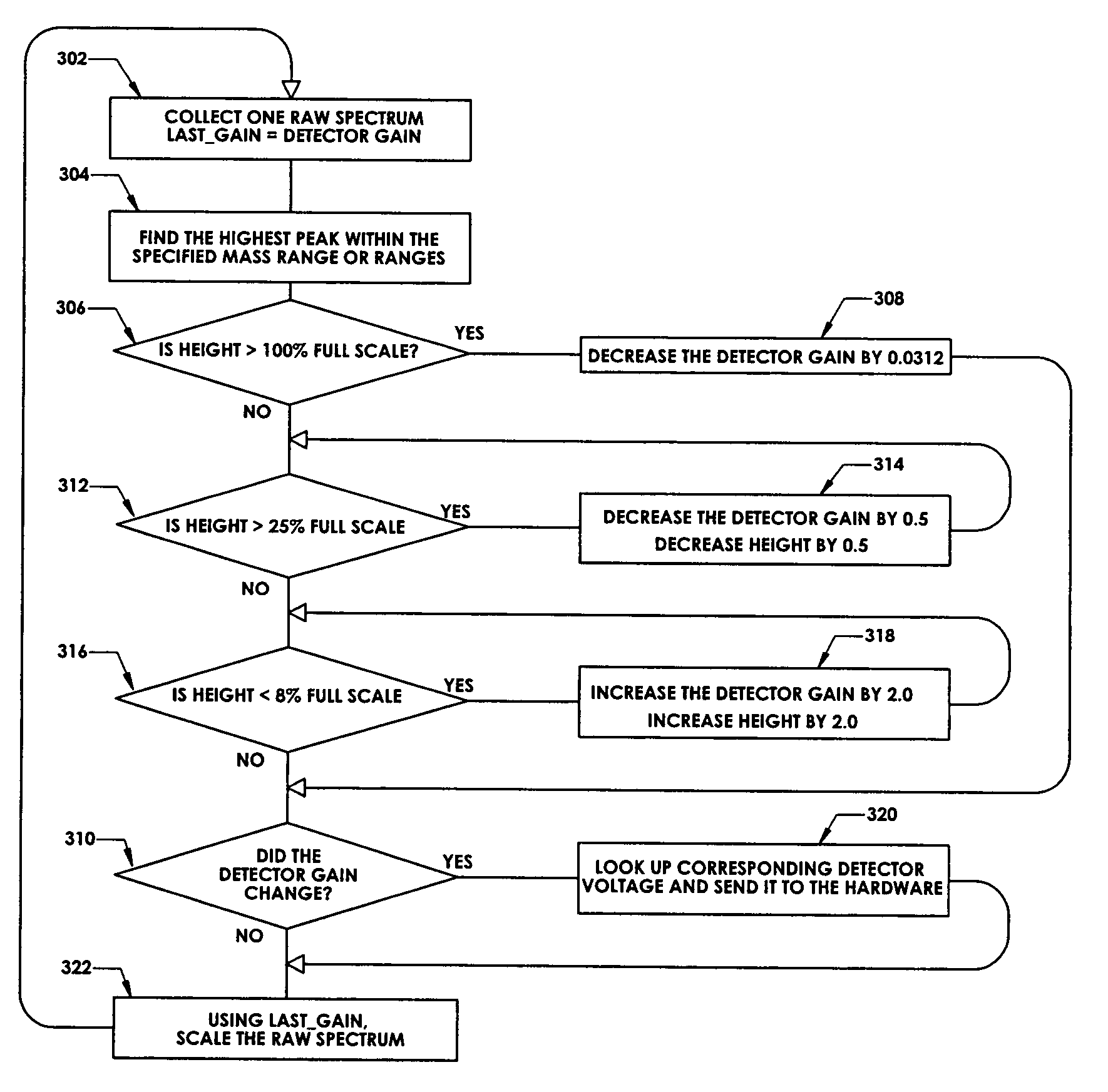
Ion detection in mass spectrometry with extended dynamic range
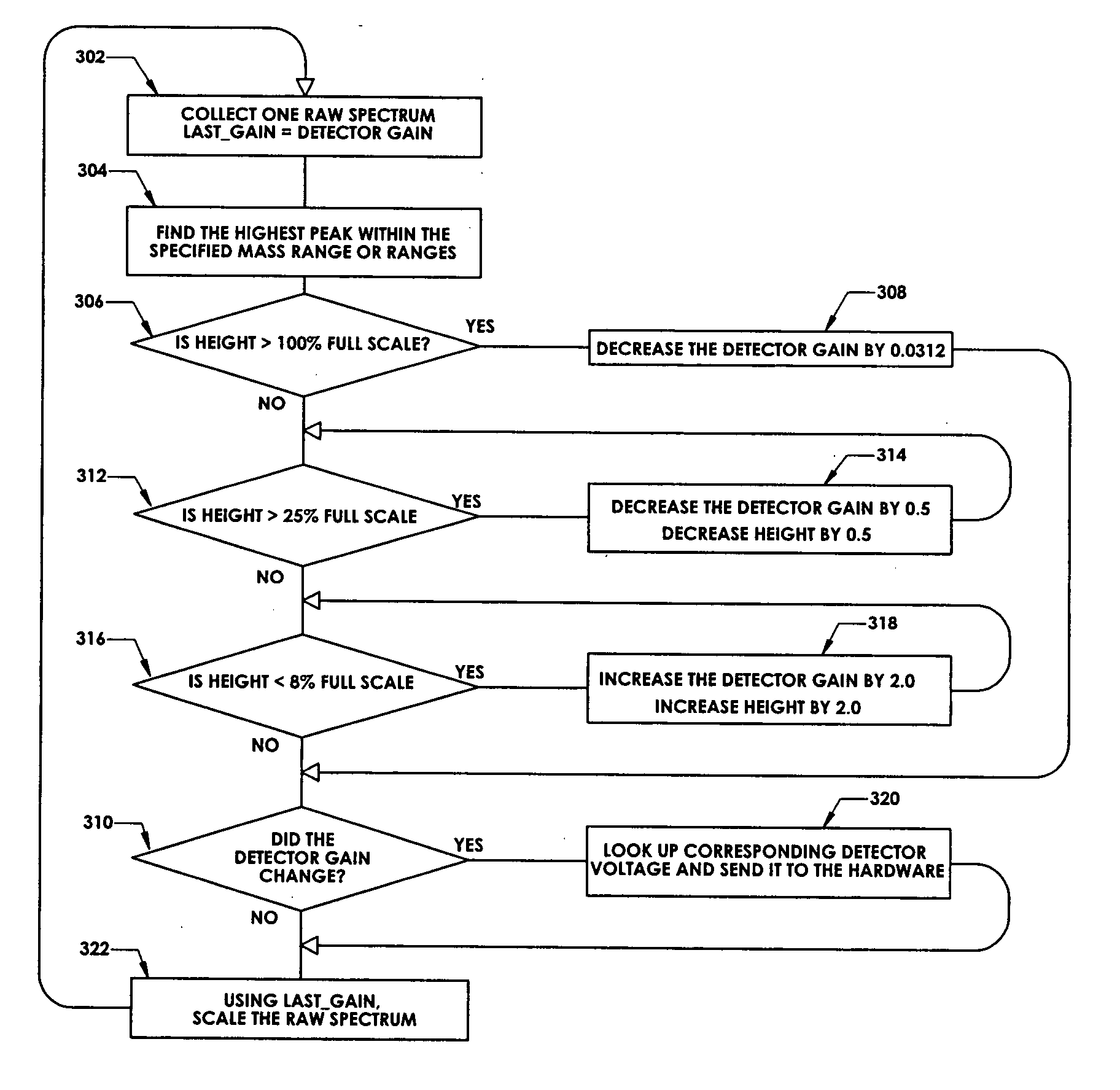
ActiveUS7047144B2Spectrometer detectorsResistance/reactance/impedenceMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPeak value
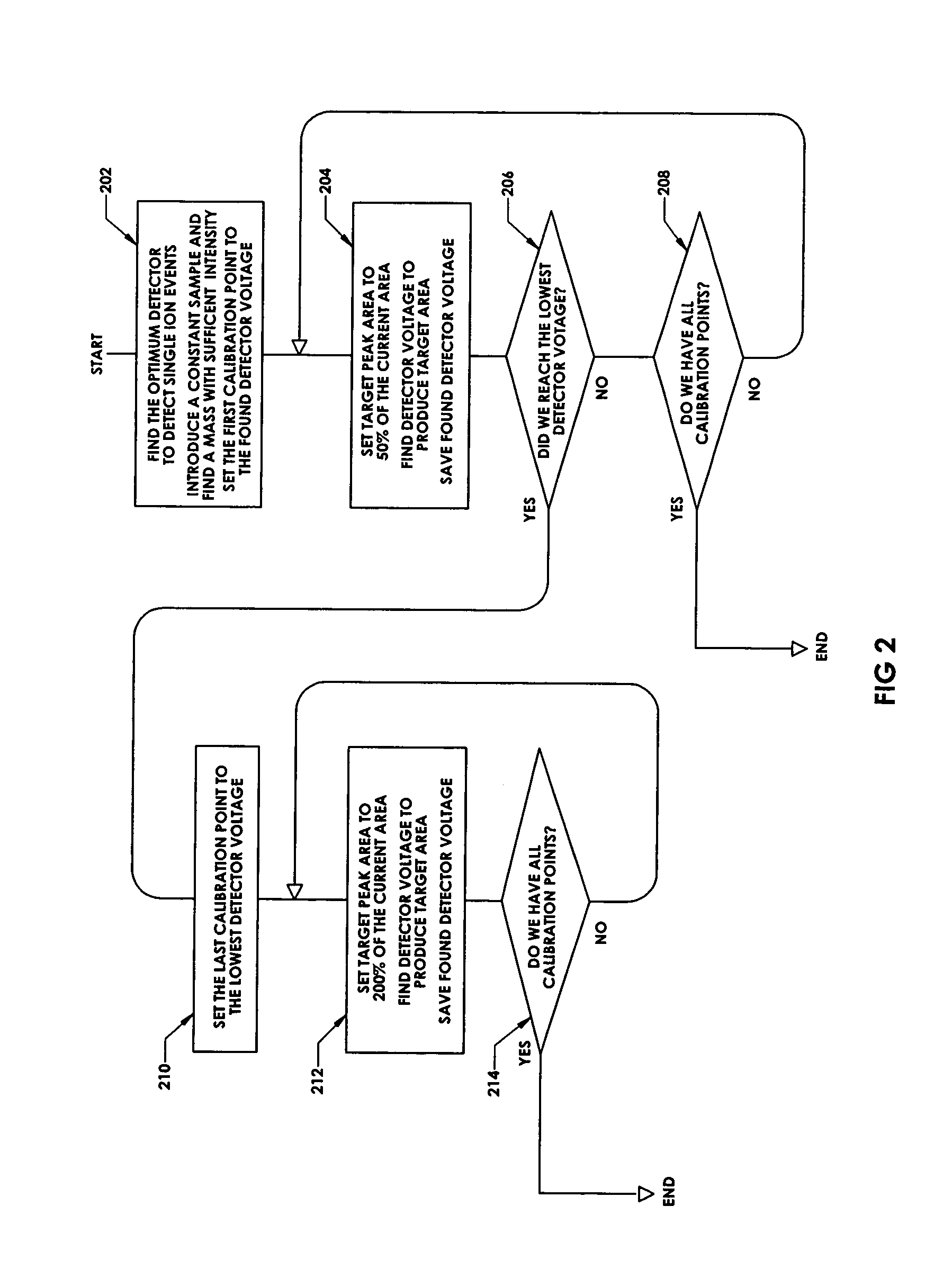
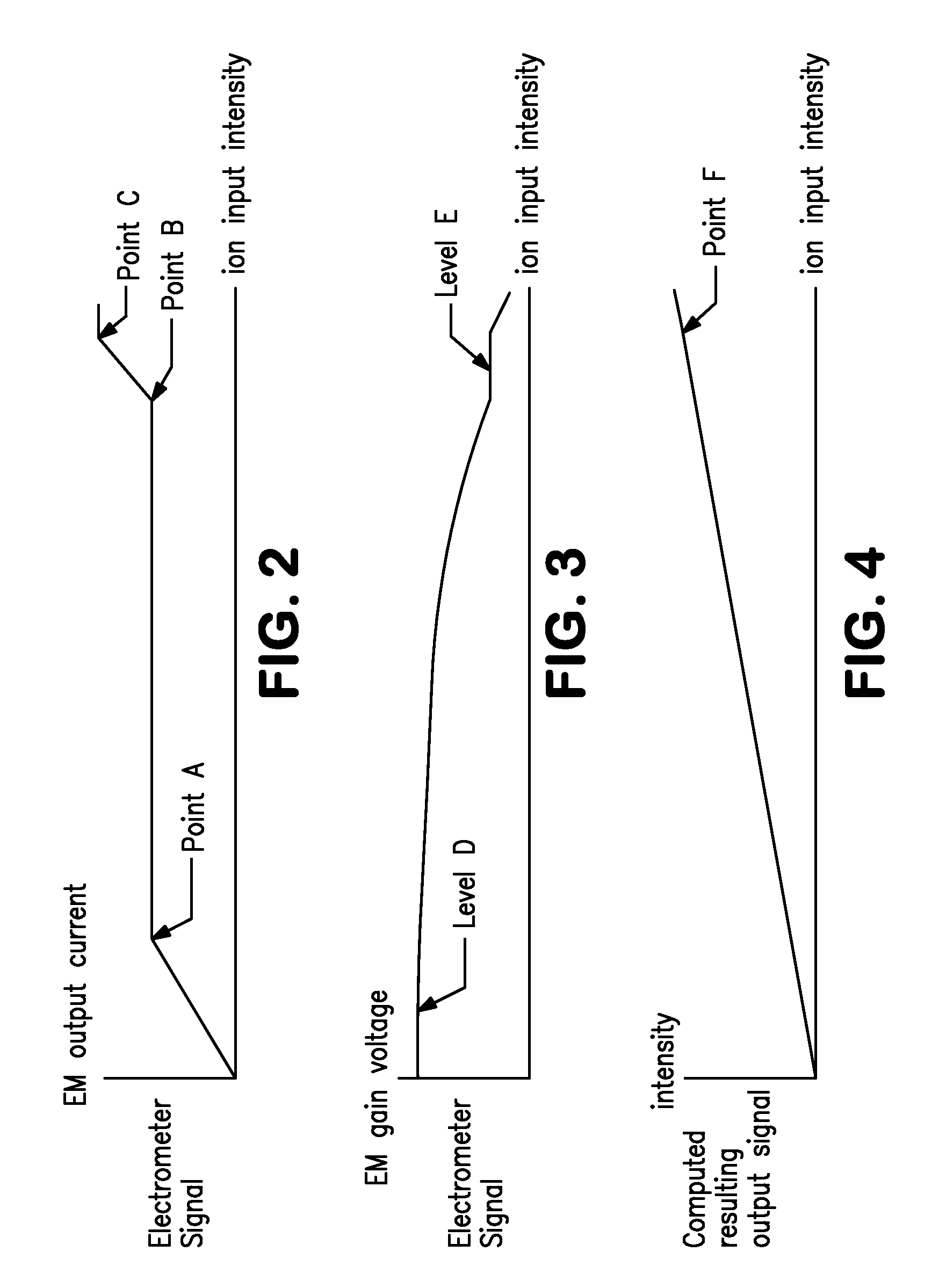
In a method for optimizing an ion detector a control voltage, such as in a mass spectrometry system, an array of mass scan data is acquired. Based on the size of the largest peak in the array or part of the array, a determination is made as to whether the current detector gain should be changed to a new detector gain. If the current detector gain should be changed, the control voltage for the subsequent mass scan is adjusted to a new control voltage corresponding to the new detector gain. The data are scaled based on the current detector gain. In another method, a gain versus control voltage curve is generated for calibration. These methods may be implemented by hardware, software, analog or digital circuitry, and / or computer-readable or signal-bearing media.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer for monitoring of fast processes
InactiveUS20050127289A1Easily be turnedGive flexibilitySpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersTime-of-flight mass spectrometryMass analyzer
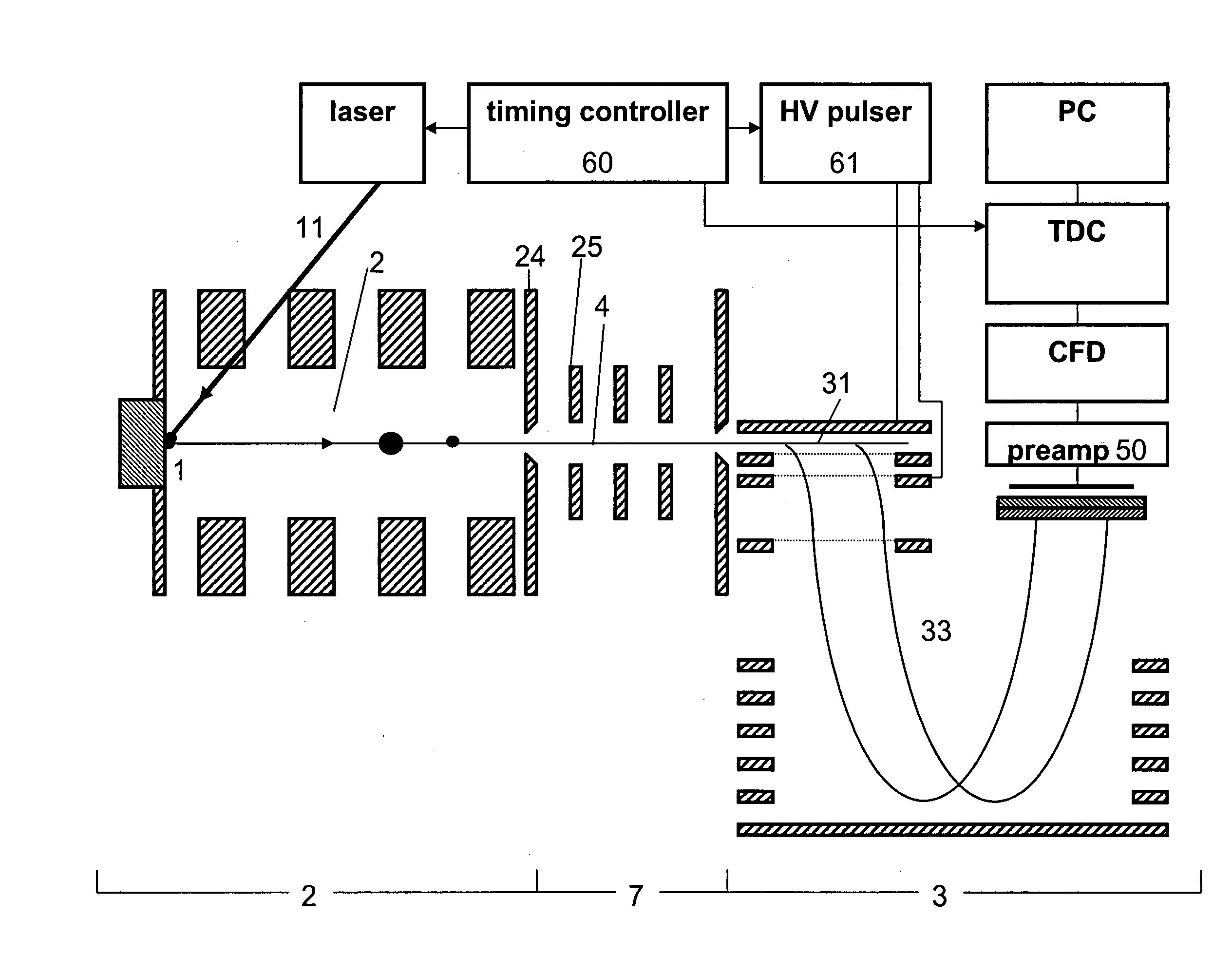
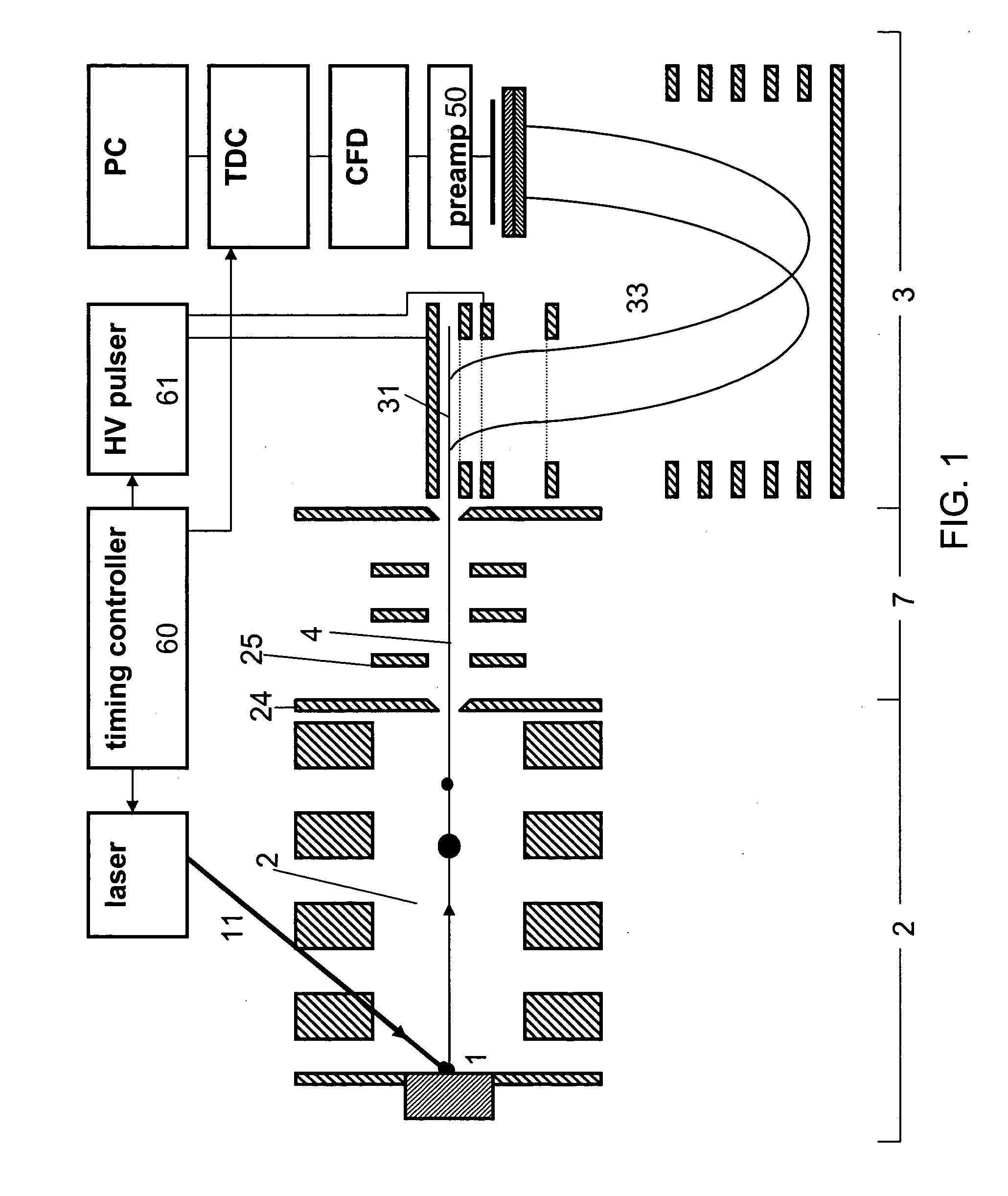
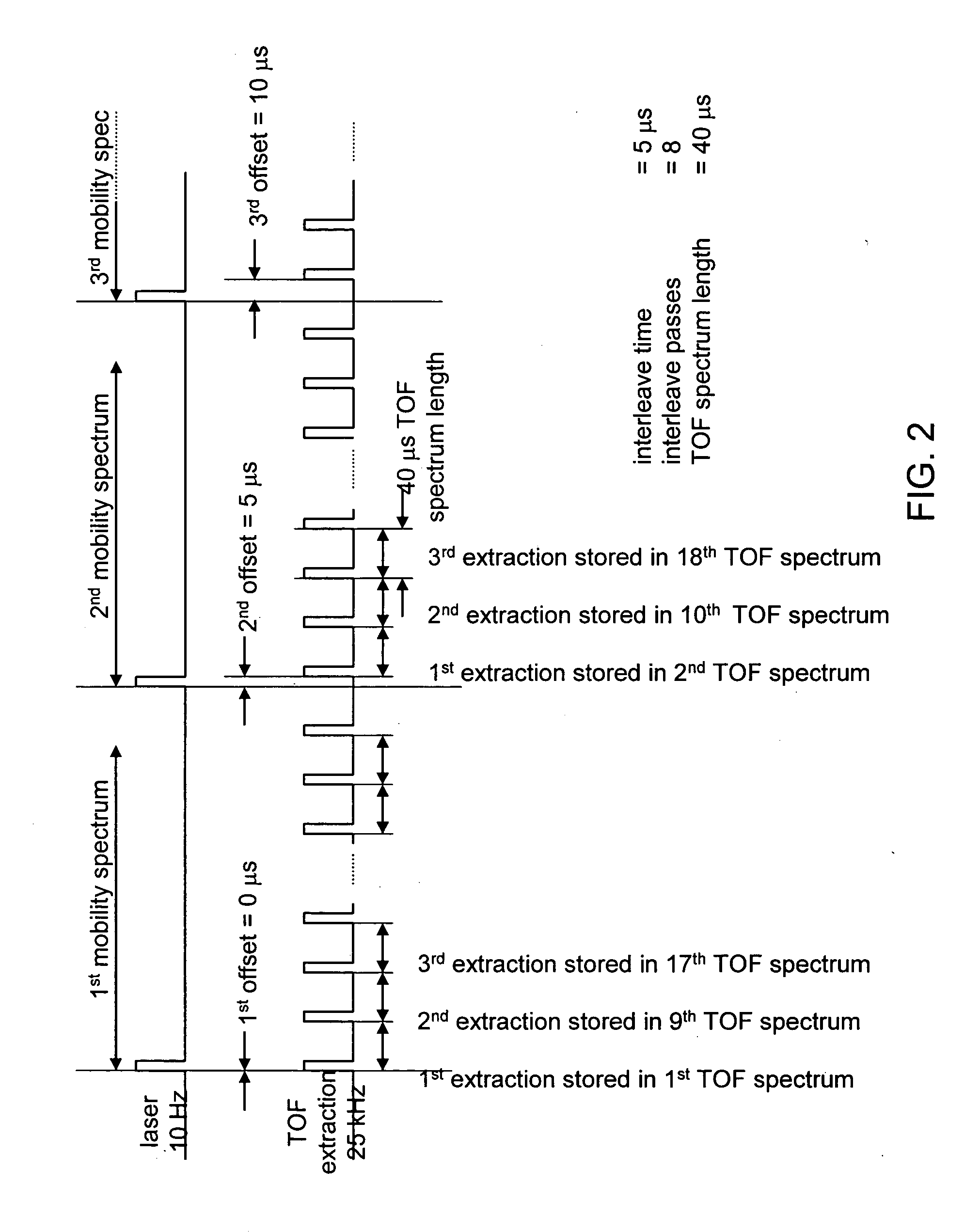
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer instruments for monitoring fast processes using an interleaved timing scheme and a position sensitive detector are described. The combination of both methods is also described.
Owner:IONWERKS
Fast time-of-flight mass spectrometer with improved data acquisition system
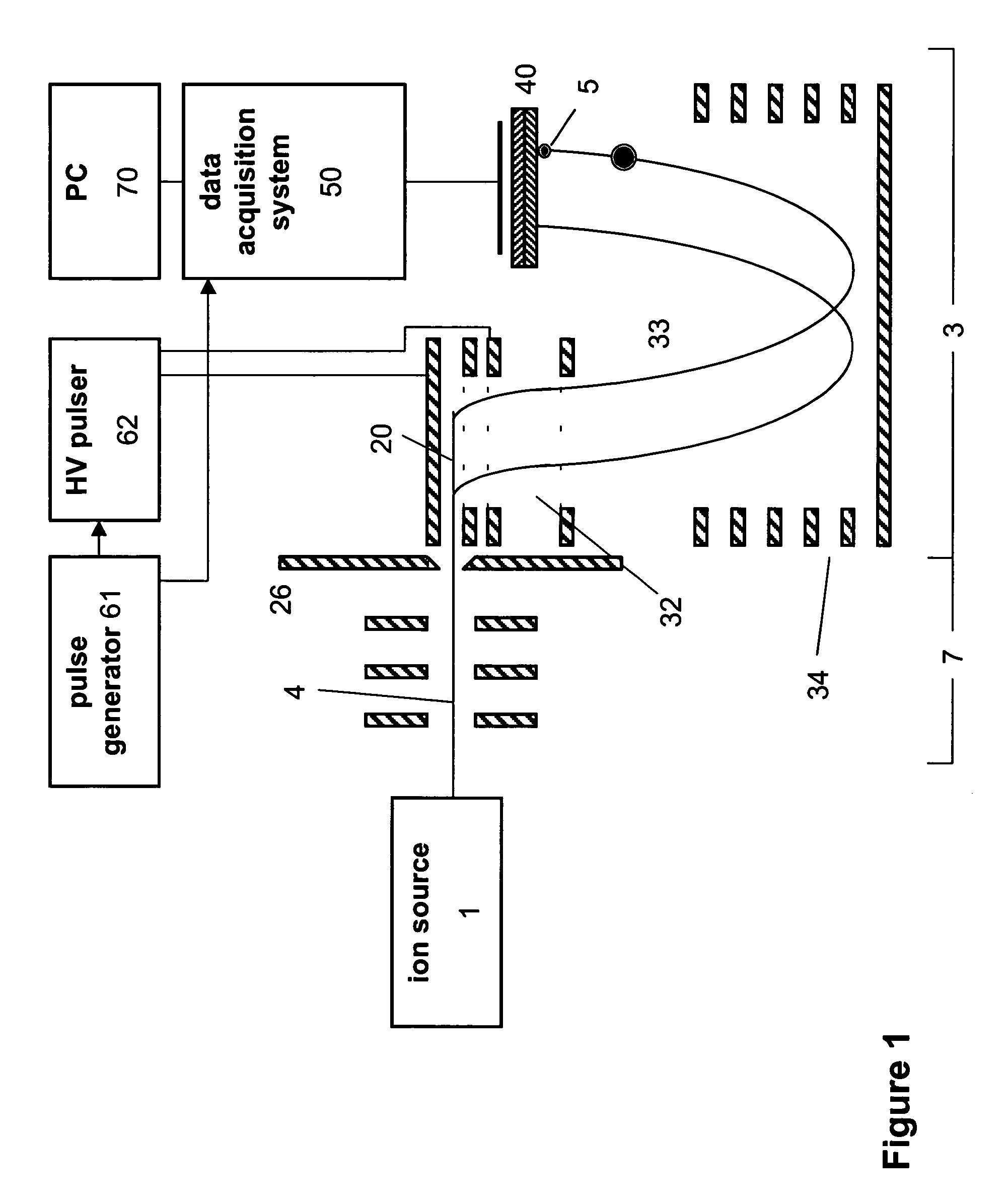
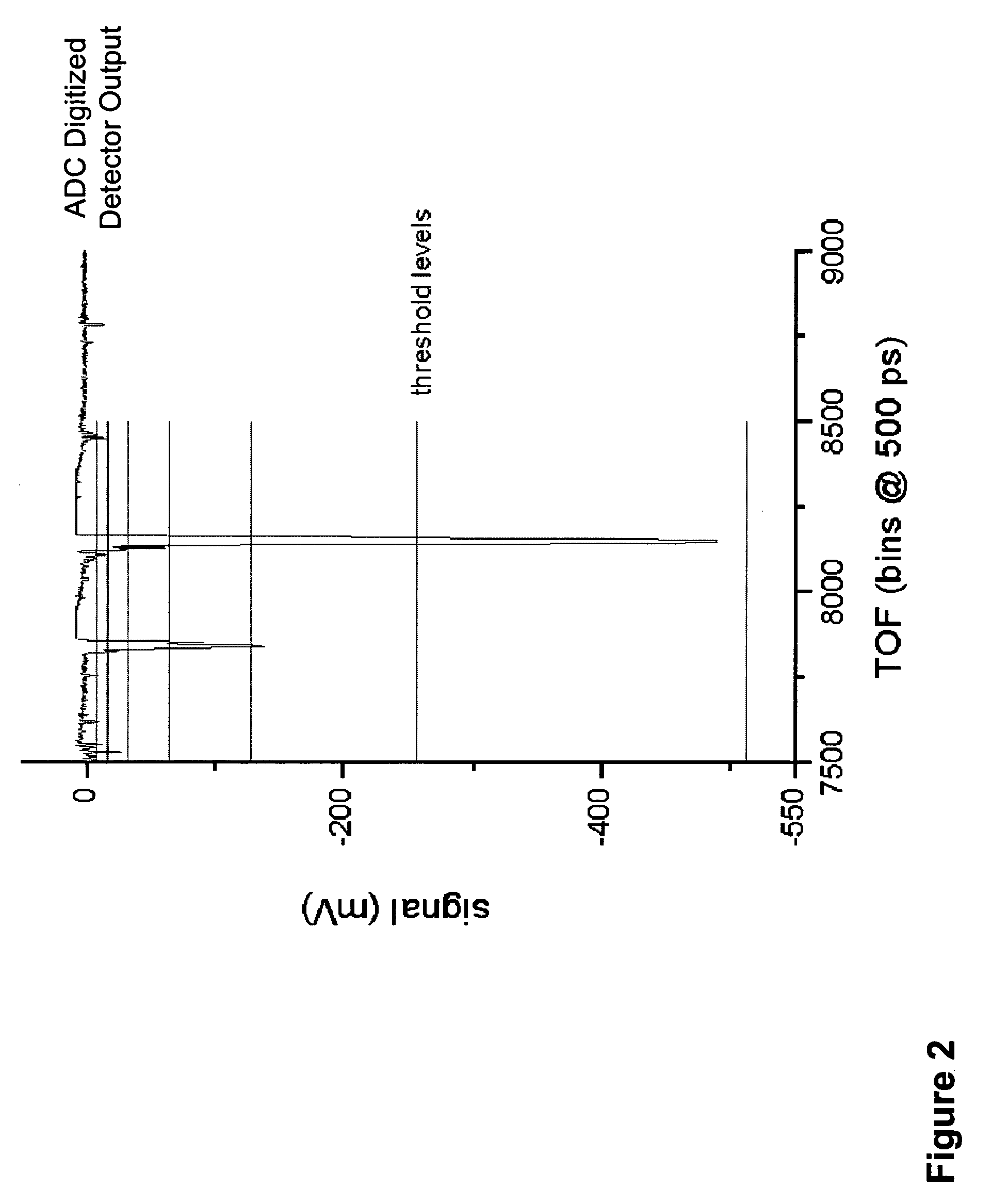
ActiveUS20050006577A1Reduce data volumeImprove dynamic rangeSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersData acquisitionSystem time
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer instruments are disclosed for monitoring fast processes with large dynamic range using a multi-threshold TDC data acquisition method or a threshold ADC data acquisition method. Embodiments using a combination of both methods are also disclosed.
Owner:IONWERKS
Detection Apparatus for Detecting Charged Particles, Methods for Detecting Charged Particles and Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20110095177A1Improve dynamic rangeProlong lifeTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsPhoton detectionCharged particle detectors
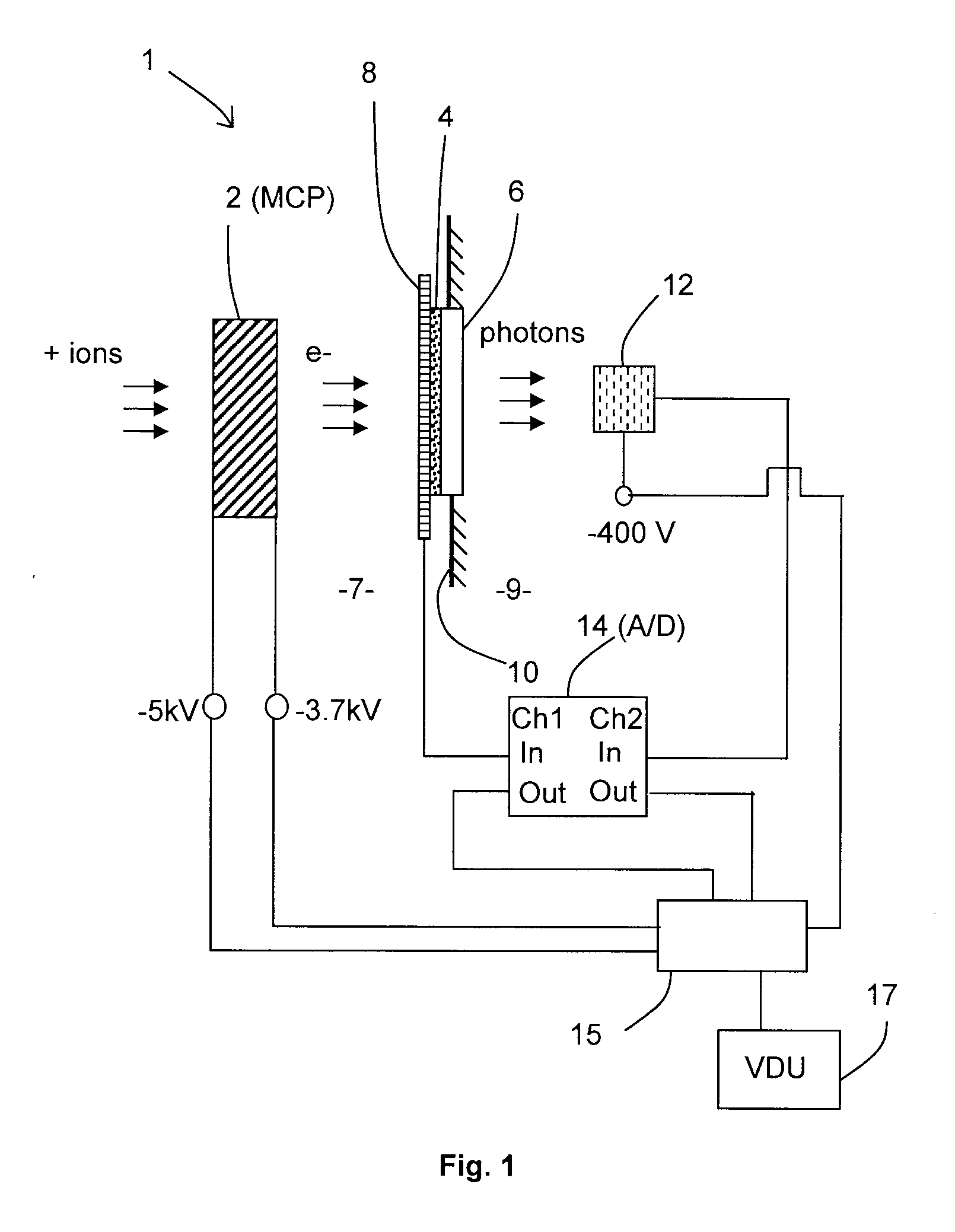
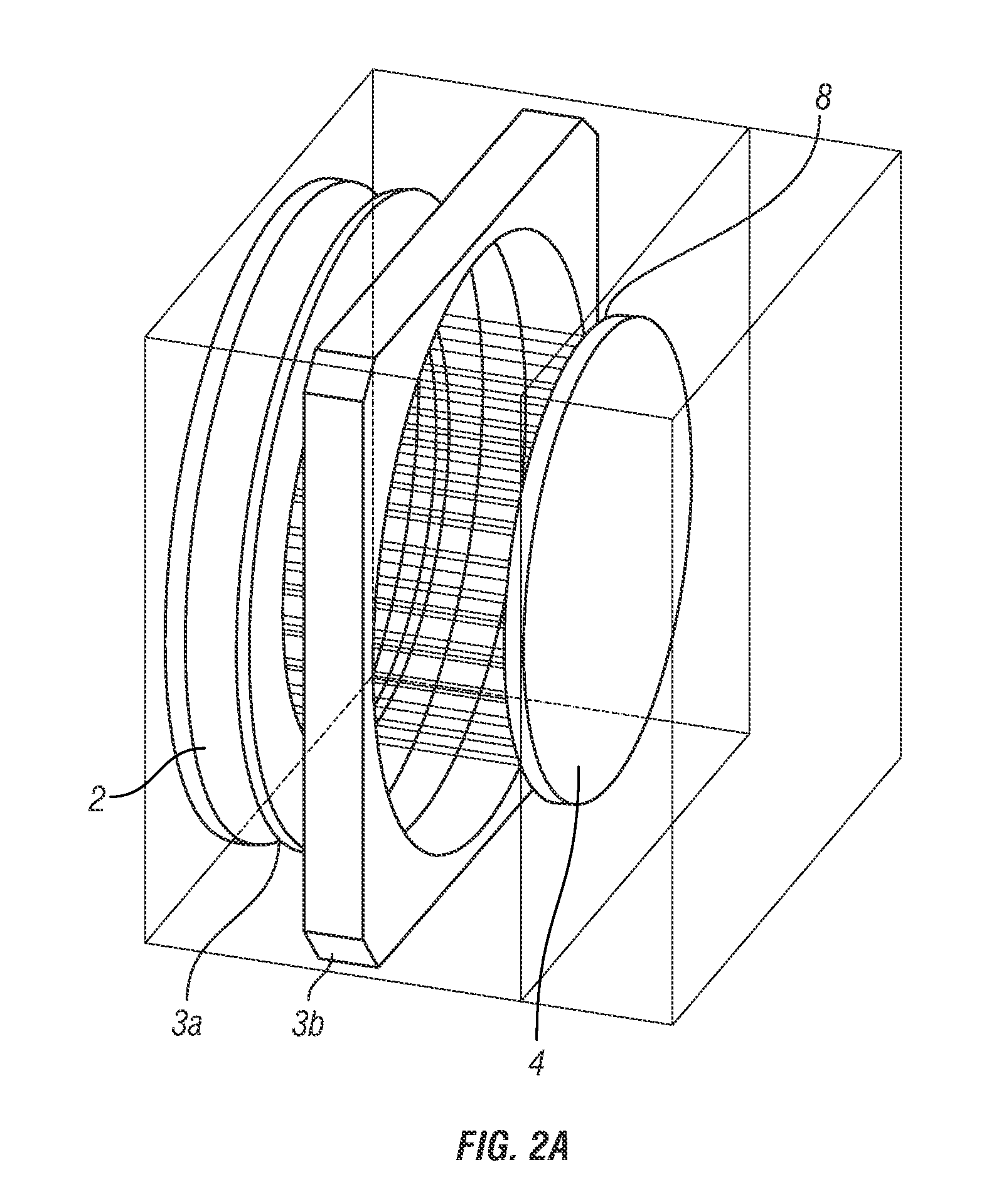
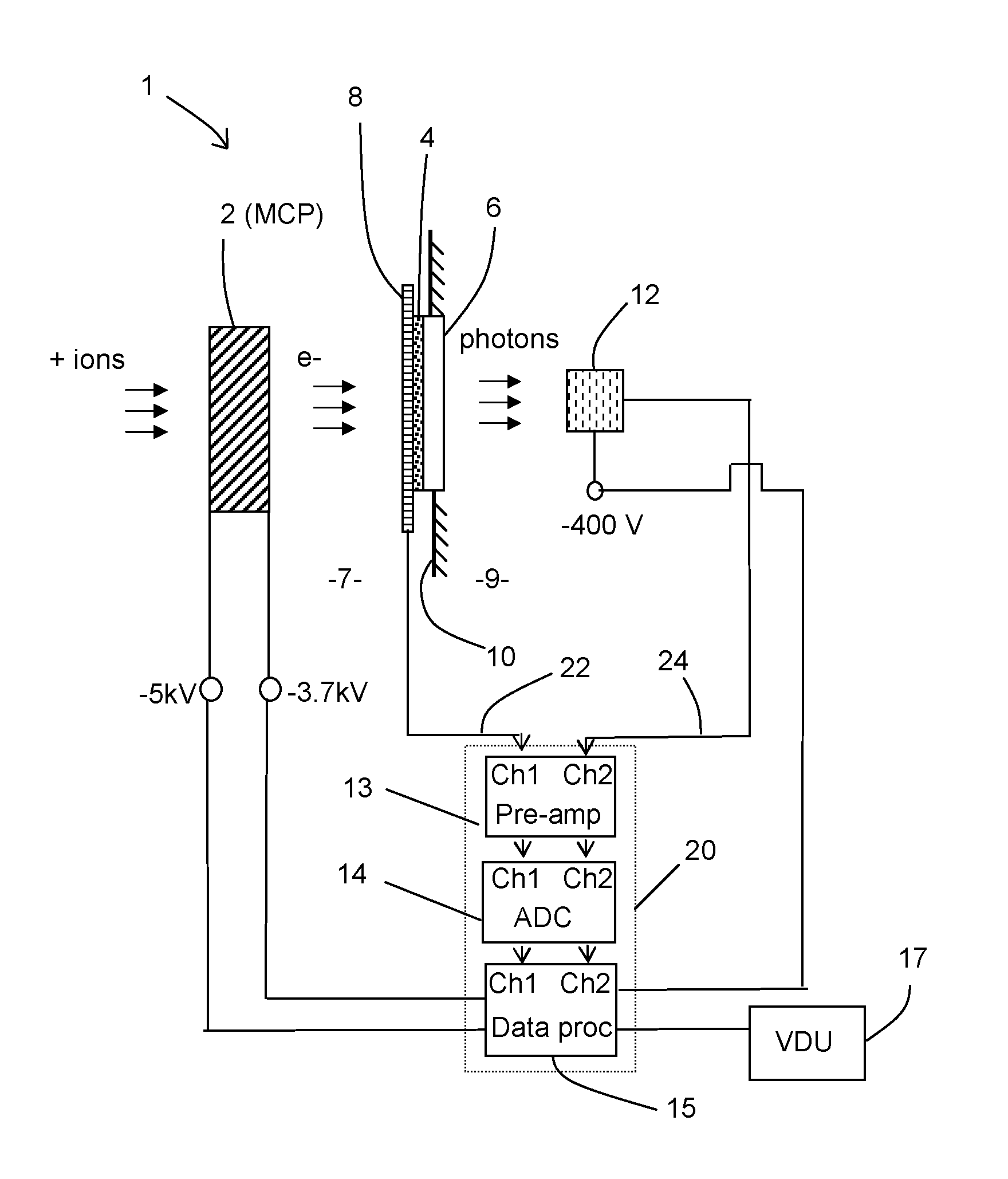
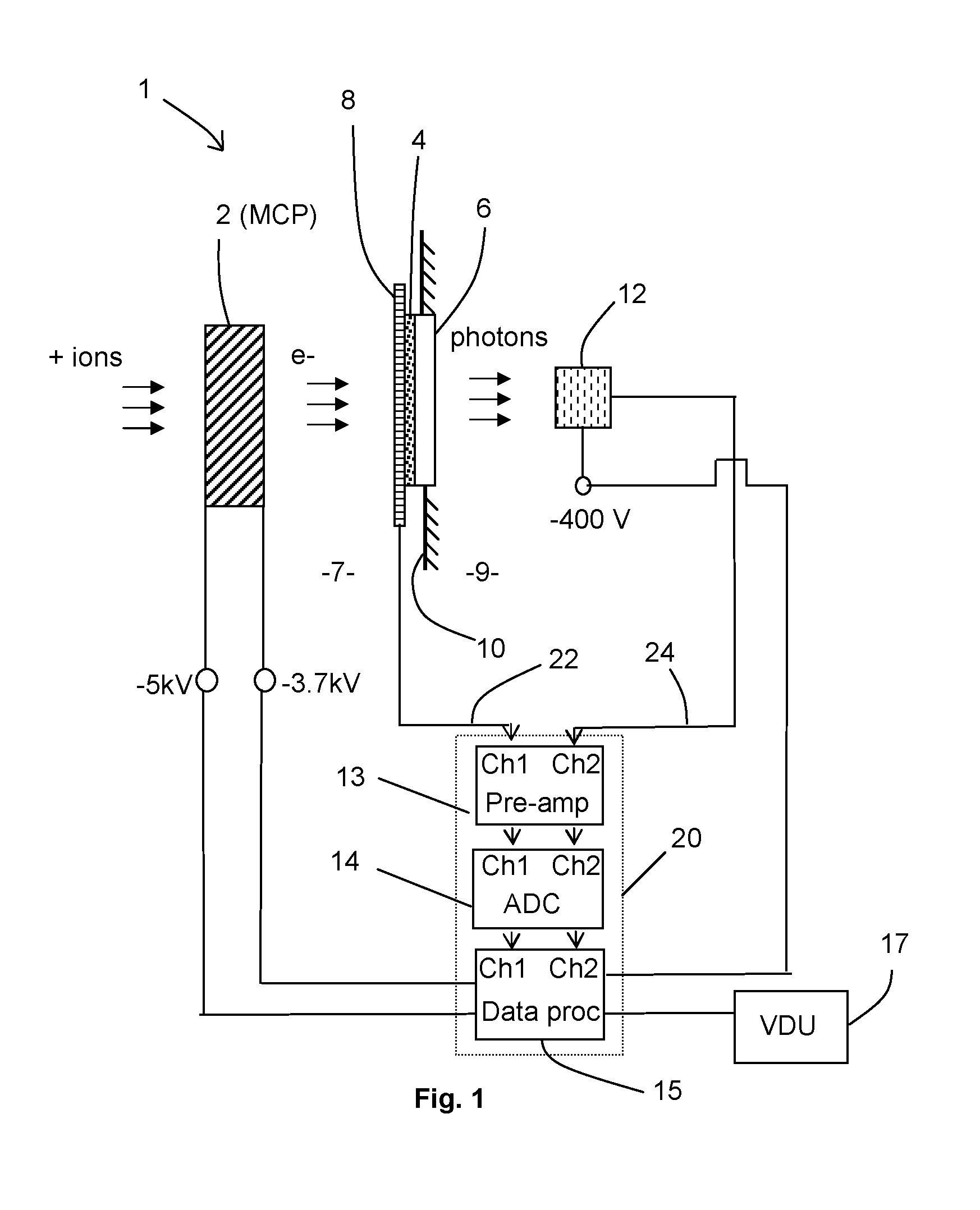
Embodiments of the invention provide a detection apparatus for detecting charged particles having a secondary particle generator for generating secondary charged particles in response to receiving incoming charged particles, a charged particle detector for receiving and detecting secondary charged particles generated by the secondary particle generator, a photon generator for generating photons in response to receiving secondary charged particles generated by the secondary particle generator, and a photon detector for detecting the photons generated by the photon generator.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
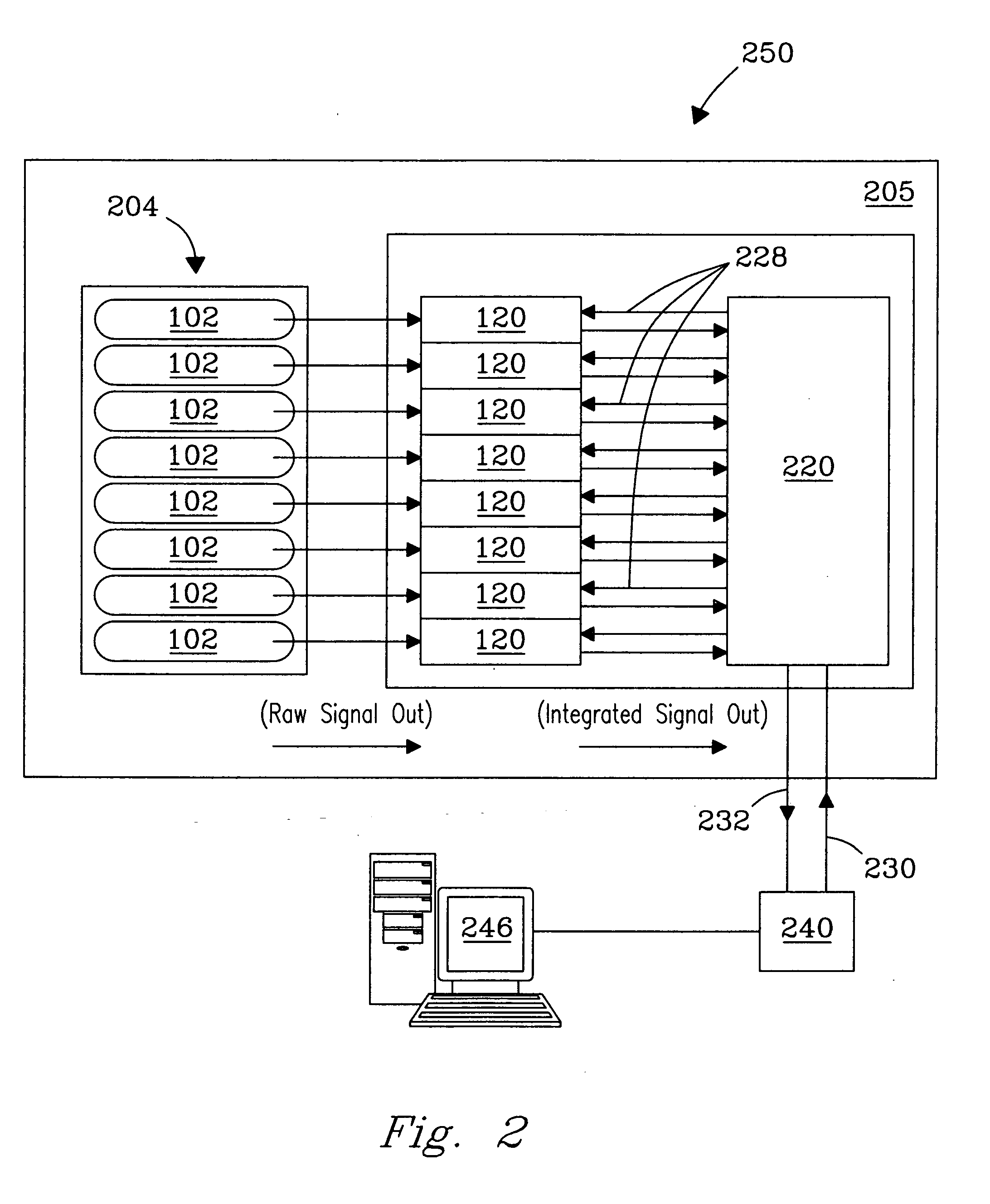
Data Acquisition System and Method for Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20130268212A1Easy to handleEfficient executionSpectrometer detectorsSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemData acquisition
The invention provides a data acquisition system and method for detecting ions in a mass spectrometer, comprising: a detection system for detecting ions comprising two or more detectors for outputting two or more detection signals in separate channels in response to ions arriving at the detection system; and a data processing system for receiving and processing the detection signals in separate channels of the data processing system and for merging the processed detection signals to construct a mass spectrum; wherein the processing in separate channels comprises removing noise from the detection signals by applying a threshold to the detection signals. The detection signals are preferably produced in response to the same ions, the signals being shifted in time relative to each other. The invention is suitable for a TOF mass spectrometer.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Quadrupole mass spectrometer with enhanced sensitivity and mass resolving power
ActiveUS8389929B2Low costImprove robustnessStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerQuadrupole
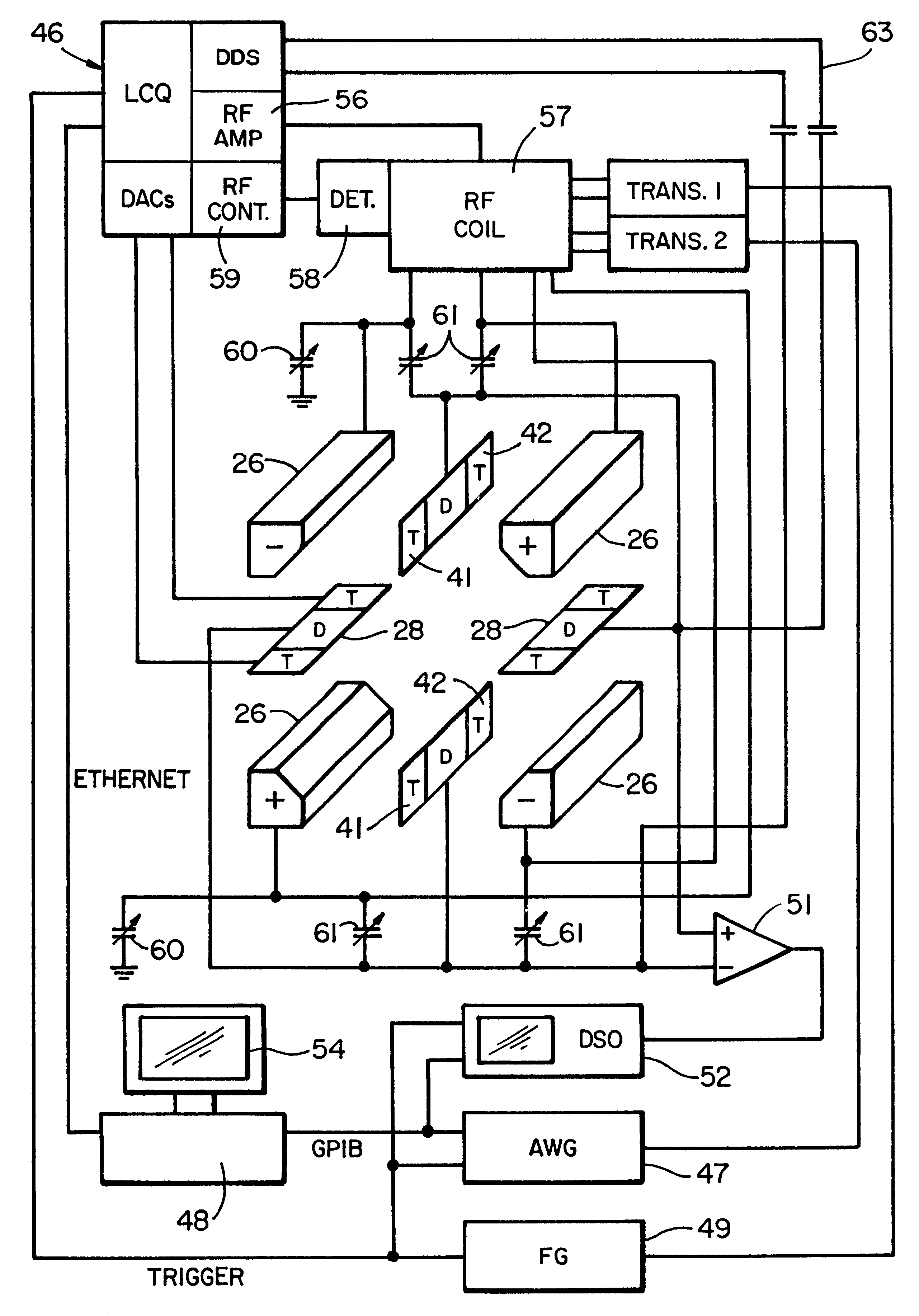
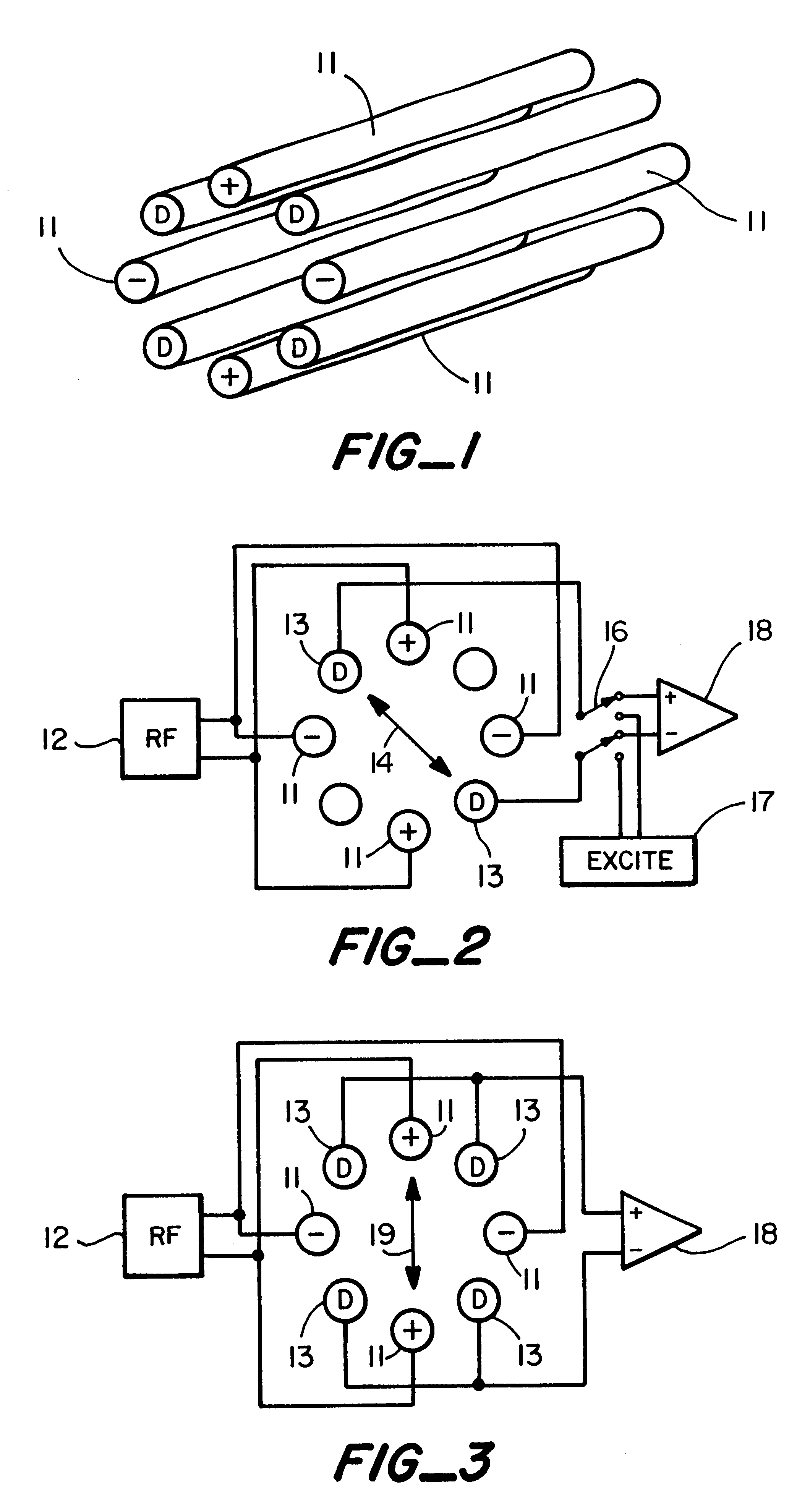
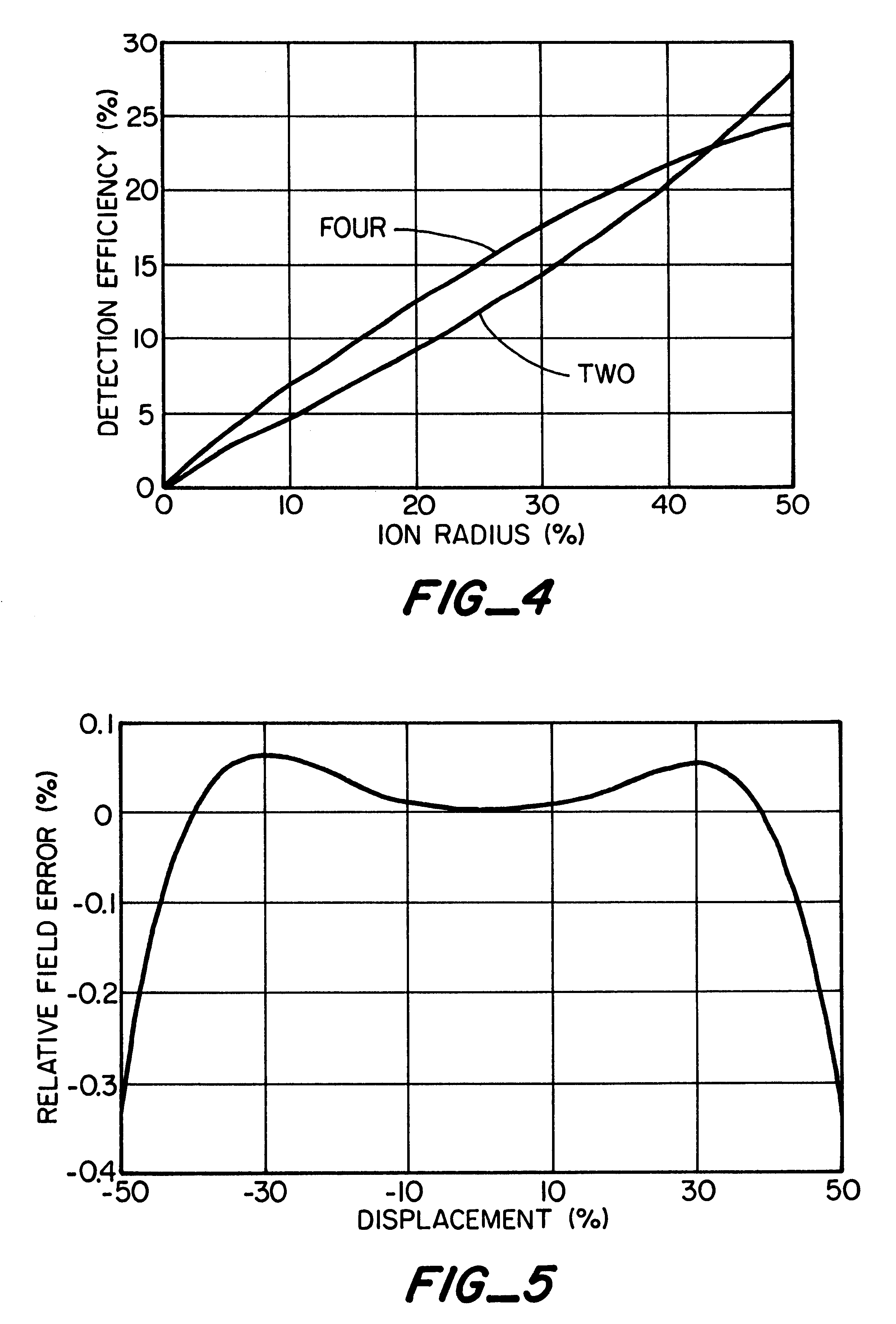
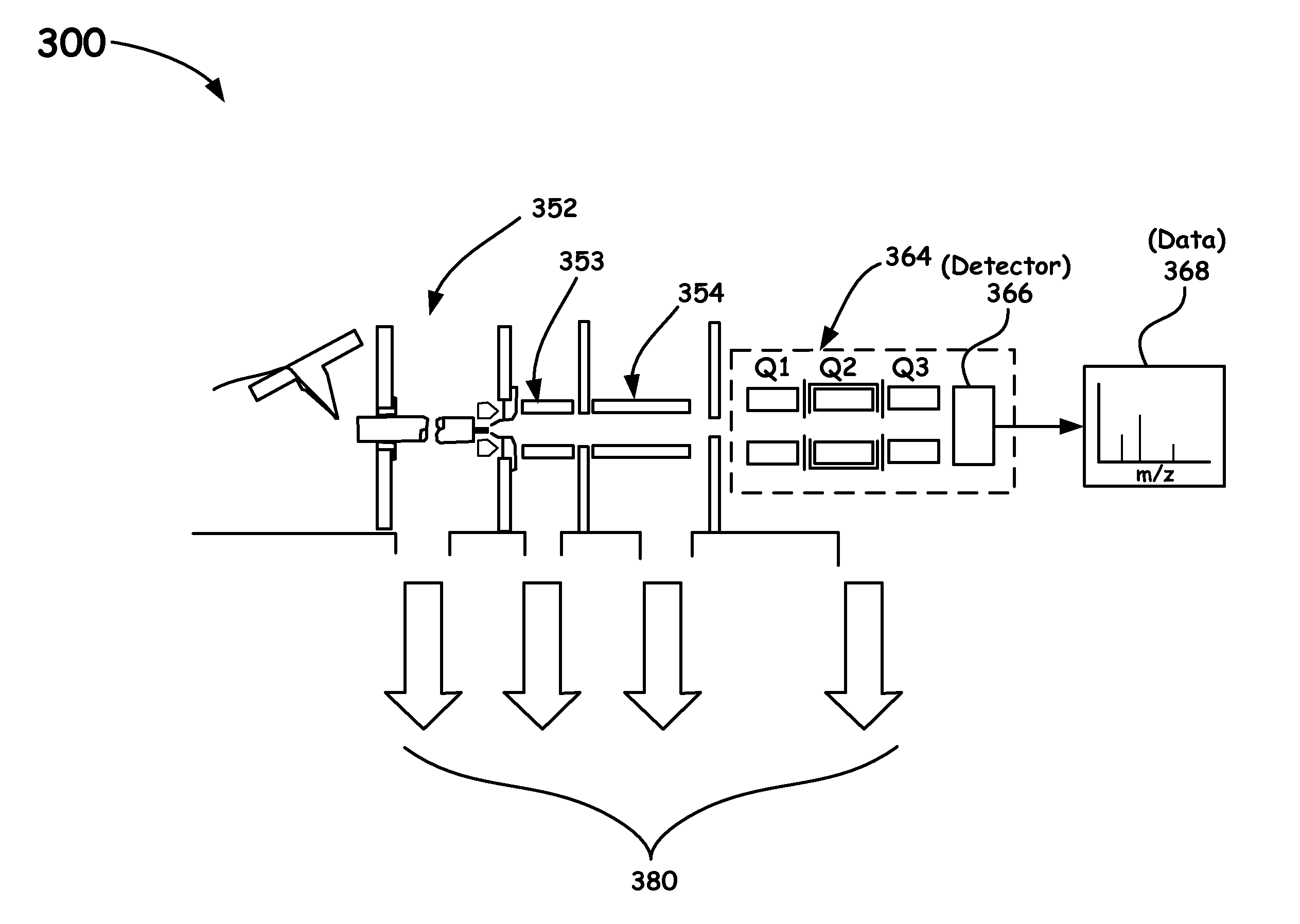
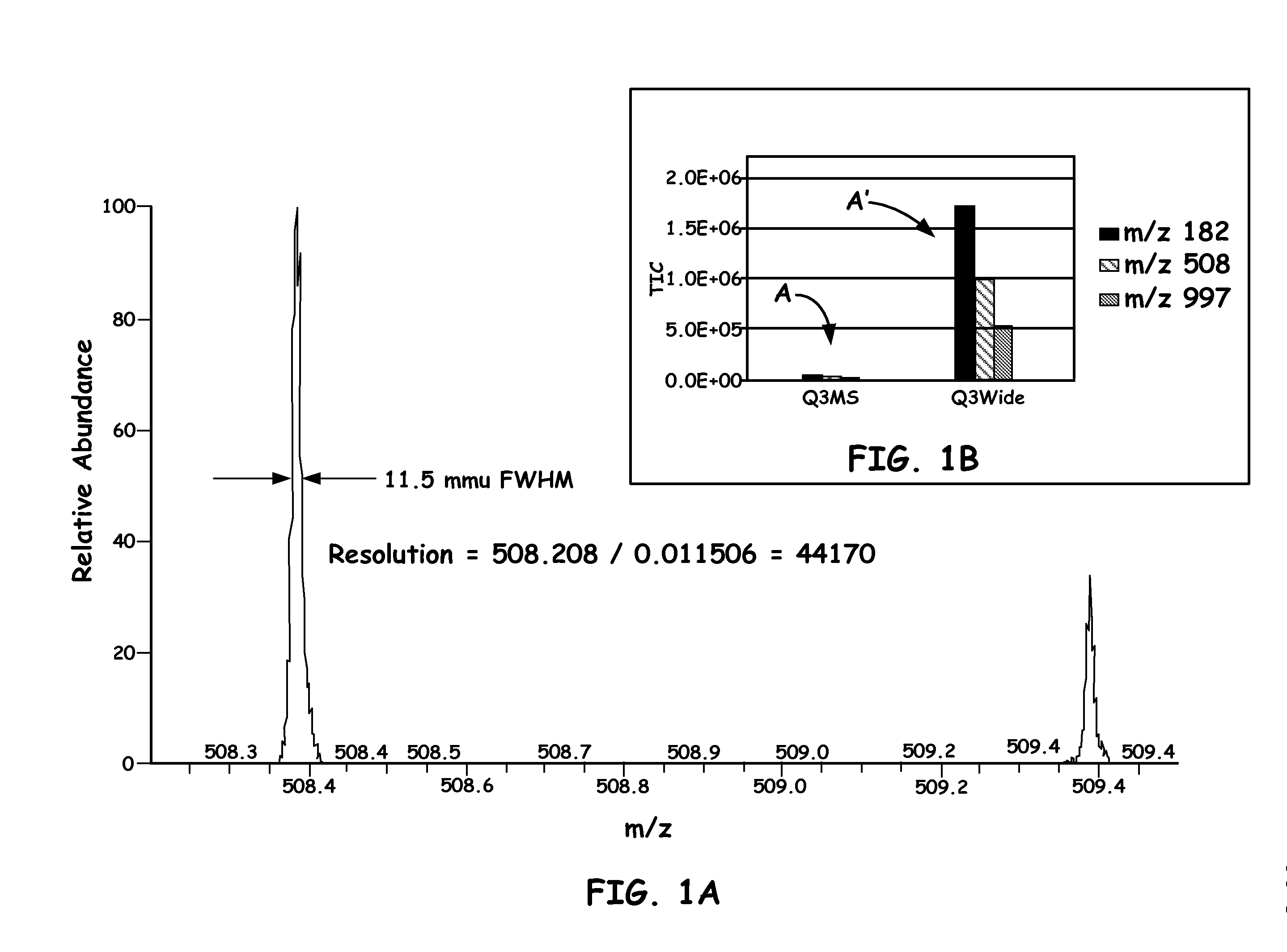
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to spatially and temporally resolve images of one or more ion exit patterns of a multipole instrument. In particular, the methods and structures of the present invention measures the ion current as a function of time and spatial displacement in the beam cross-section of a quadrupole mass filter via an arrayed detector. The linearity of the detected quadrupole ion current in combination with it reproducible spatial-temporal structure enables the deconvolution of the contributions of signals from individual ion species in complex mixtures where both sensitivity and mass resolving power are essential.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
MCP unit, MCP detector and time of flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7564043B2Reduce widthShortened fall timeThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight mass spectrometryTime response
The present invention relates to an MCP unit or the like having a structure intended to achieve a desired time response characteristic, without depending on a limitation imposed by a channel diameter of MCP. The MCP unit comprises the MCP for releasing secondary electrons internally multiplied in response to incidence of charged particles, an anode arranged in a position where the secondary electrons reach, and an acceleration electrode arranged between the MCP and the anode. In particular, the acceleration electrode includes a plurality of openings which permit passing of the secondary electrons migrating from the MCP toward the anode. Further, the acceleration electrode is arranged such that the shortest distance B between the acceleration electrode and the anode is longer than the shortest distance A between the MCP and the acceleration electrode. Thus, an FWHM of a detected peak appearing in response to the incidence of the charged particles is remarkably shortened.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Fast time-of-flight mass spectrometer with improved data acquisition system
ActiveUS7084393B2Reduce data volumeImprove dynamic rangeSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersTime-of-flight mass spectrometryData acquisition
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer instruments are disclosed for monitoring fast processes with large dynamic range using a multi-threshold TDC data acquisition method or a threshold ADC data acquisition method. Embodiments using a combination of both methods are also disclosed.
Owner:IONWERKS
High resolution detection for time-of-flight mass spectrometers
InactiveUS6870156B2High resolutionInhibit transferSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersEngineeringMass analyzer
The invention covers a method for detecting ions in high resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometers which operate with secondary electron multiplier multichannel plates and in which many single spectra are acquired and added to produce a sum spectrum. The invention involves (a) using an analog digital converter (ADC) for converting electron currents from secondary electron multipliers, instead of a time-to-digital converter (TDC) which was previously used for highest possible signal resolution, (b) performing a separate rapid peak recognition procedure for the ion signals of each spectrum by a fast calculation method, thereby collecting flight time and intensity value pairs for the ion peaks, and (c) constructing a time-of-flight / intensity histogram, which is further processed as a composite time-of-flight spectrum. The invention retains the significantly higher measurement dynamics of an ADC and achieves the improved resolution capability of a TDC, but without showing the latter's known signal distortion due to dead times.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
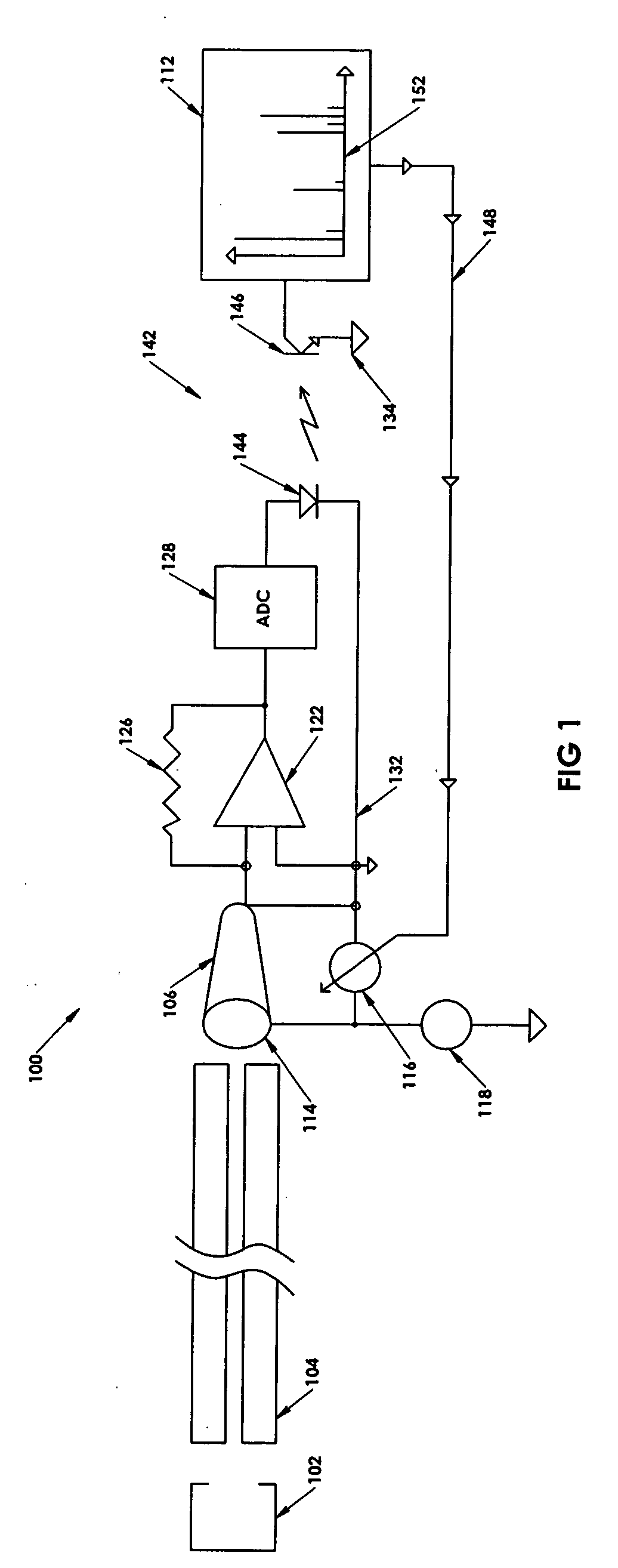
High dynamic range mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6969847B2Reduce the numberImprove dynamic rangeThermometer detailsTime-of-flight spectrometersUltrasound attenuationA d converter
A mass spectrometer comprises an ion source which produces an ion beam from a substance to be analysed and a detector to detect a quantity of ions incident thereon. The detector includes two elements (16, 18) each of which detect a part of the quantity of ions and an attenuation device attenuates the quantity of ions reaching one of the detector elements. At least one of the detector elements (16, 18) is connected to a time to digital converter (TDC) to allow counting of the ions and at least one of the detector elements is connected in parallel to both a time to digital converter (TDC) and an analogue to digital converter (ADC).
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer With Enhanced Sensitivity And Mass Resolving Power
ActiveUS20110215235A1Low costImprove robustnessStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerQuadrupole
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to spatially and temporally resolve images of one or more ion exit patterns of a multipole instrument. In particular, the methods and structures of the present invention measures the ion current as a function of time and spatial displacement in the beam cross-section of a quadrupole mass filter via an arrayed detector. The linearity of the detected quadrupole ion current in combination with it reproducible spatial-temporal structure enables the deconvolution of the contributions of signals from individual ion species in complex mixtures where both sensitivity and mass resolving power are essential.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
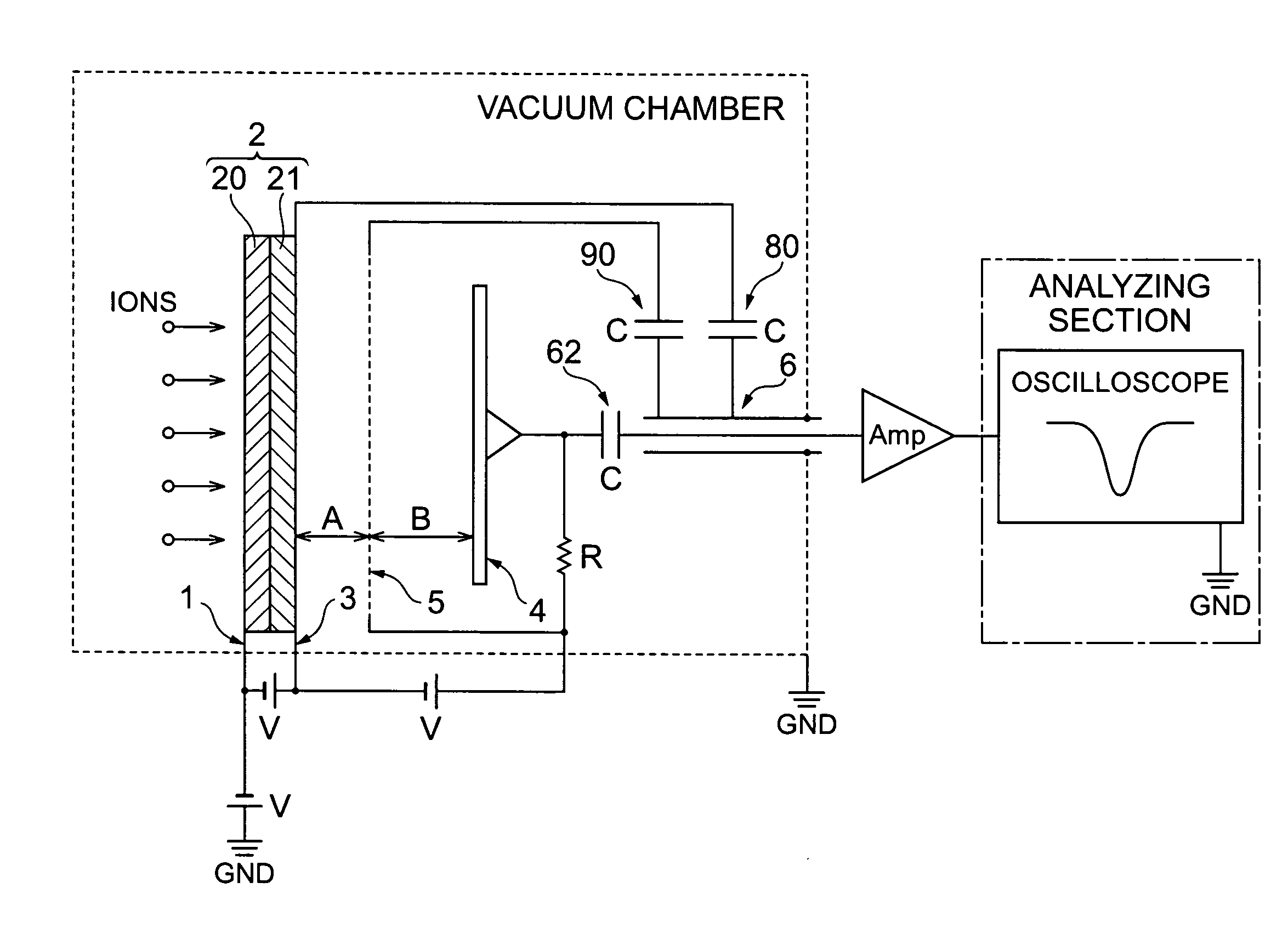
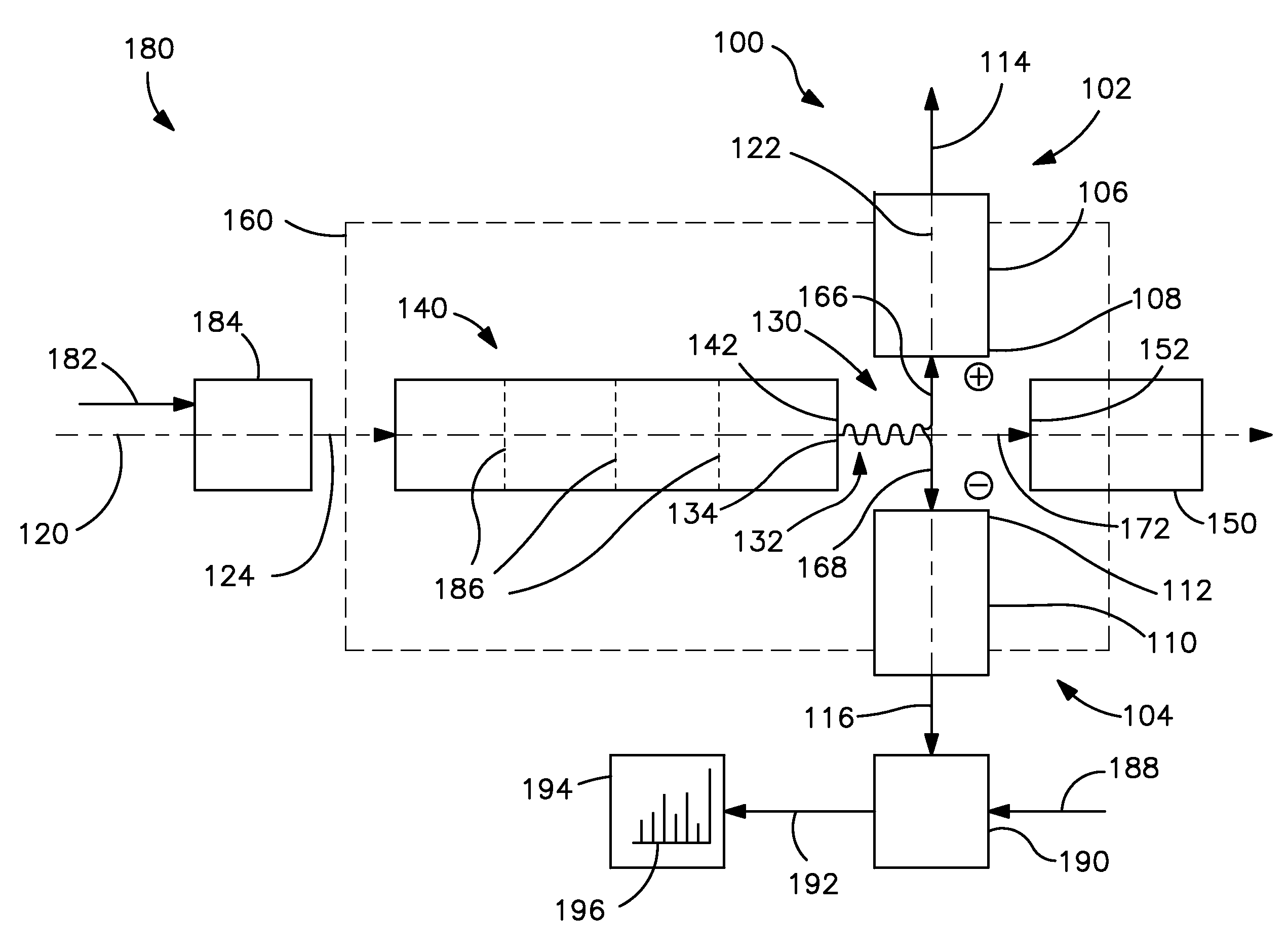
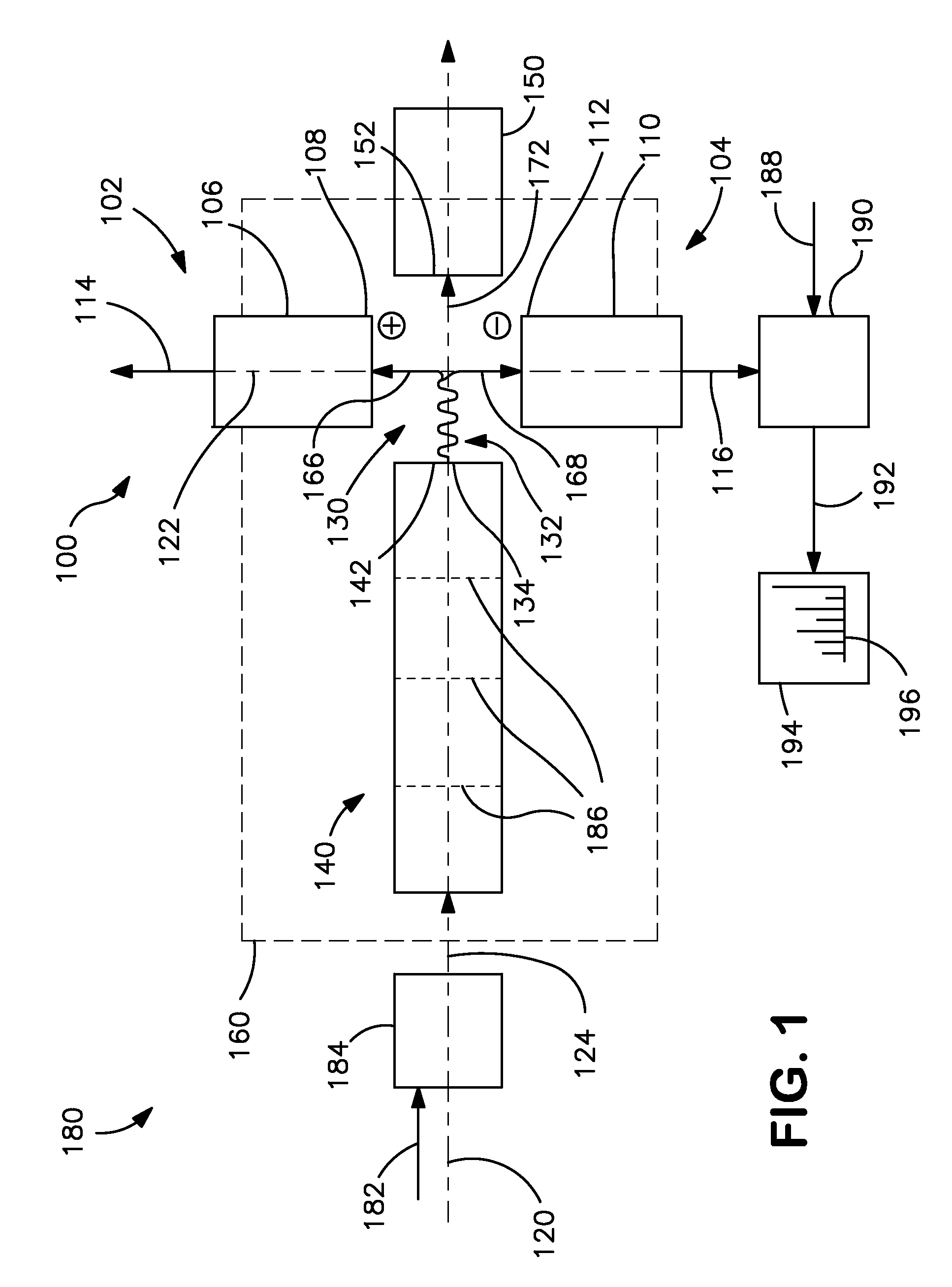
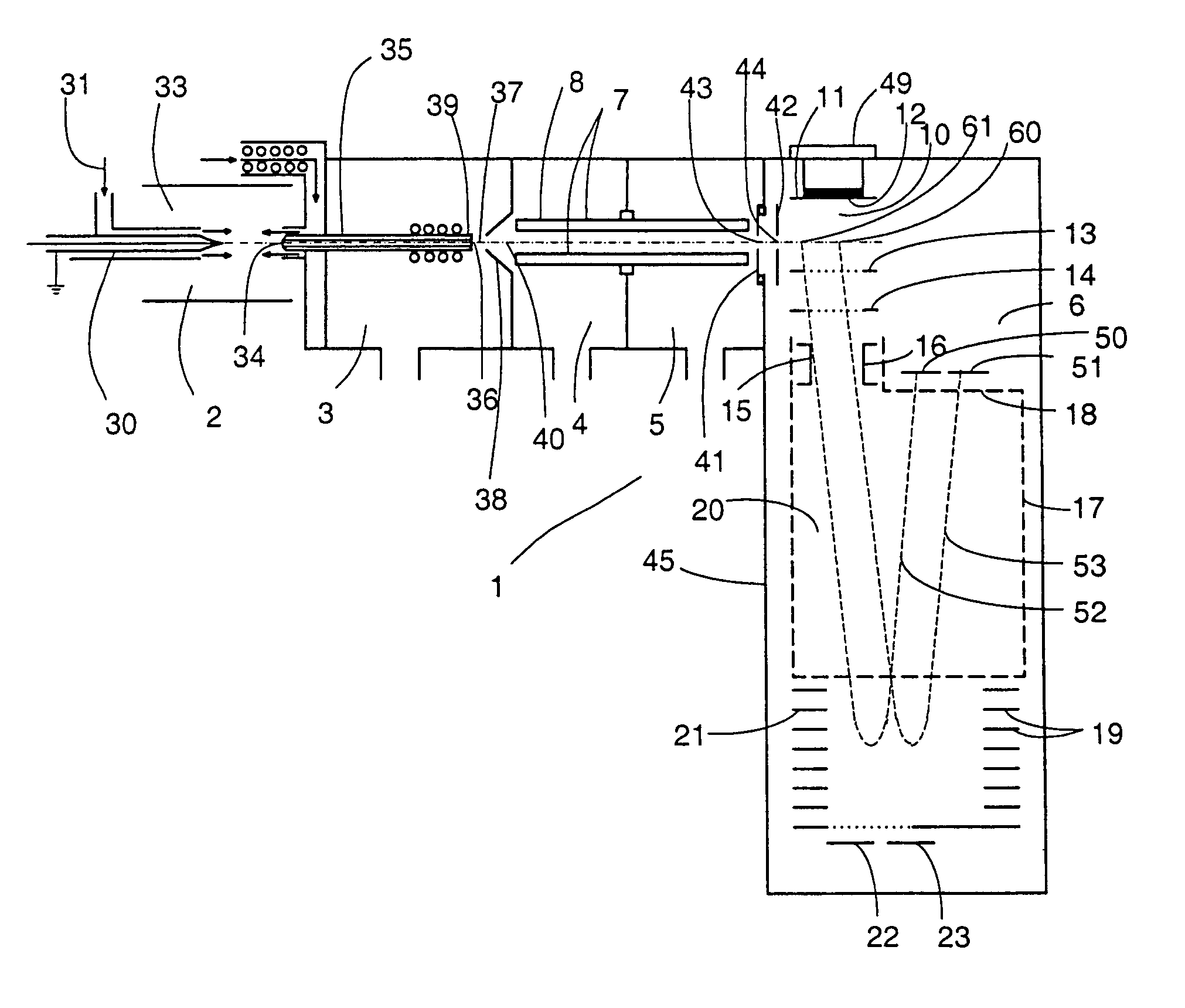
Detection of positive and negative ions
An ion detector comprises an ion guide with electrodes arranged about a first axis; a positive ion detection device with an ion inlet at a first side of the ion output section offset from and at an angle to the first axis; and a negative ion detection device with an ion inlet at a second side opposite the first side, offset from and at an angle to the first axis. A negative voltage bias applied to the positive ion device accelerates positive ions toward the inlet along a path including a component along a second axis orthogonal to the first axis. A positive voltage bias applied to the negative ion detection device accelerates negative ions toward the inlet along a path that includes a component along the second axis orthogonal to the first axis in a direction generally opposite to the path of the positive ions.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method and apparatus for simultaneous detection and measurement of charged particles at one or more levels of particle flux for analysis of same
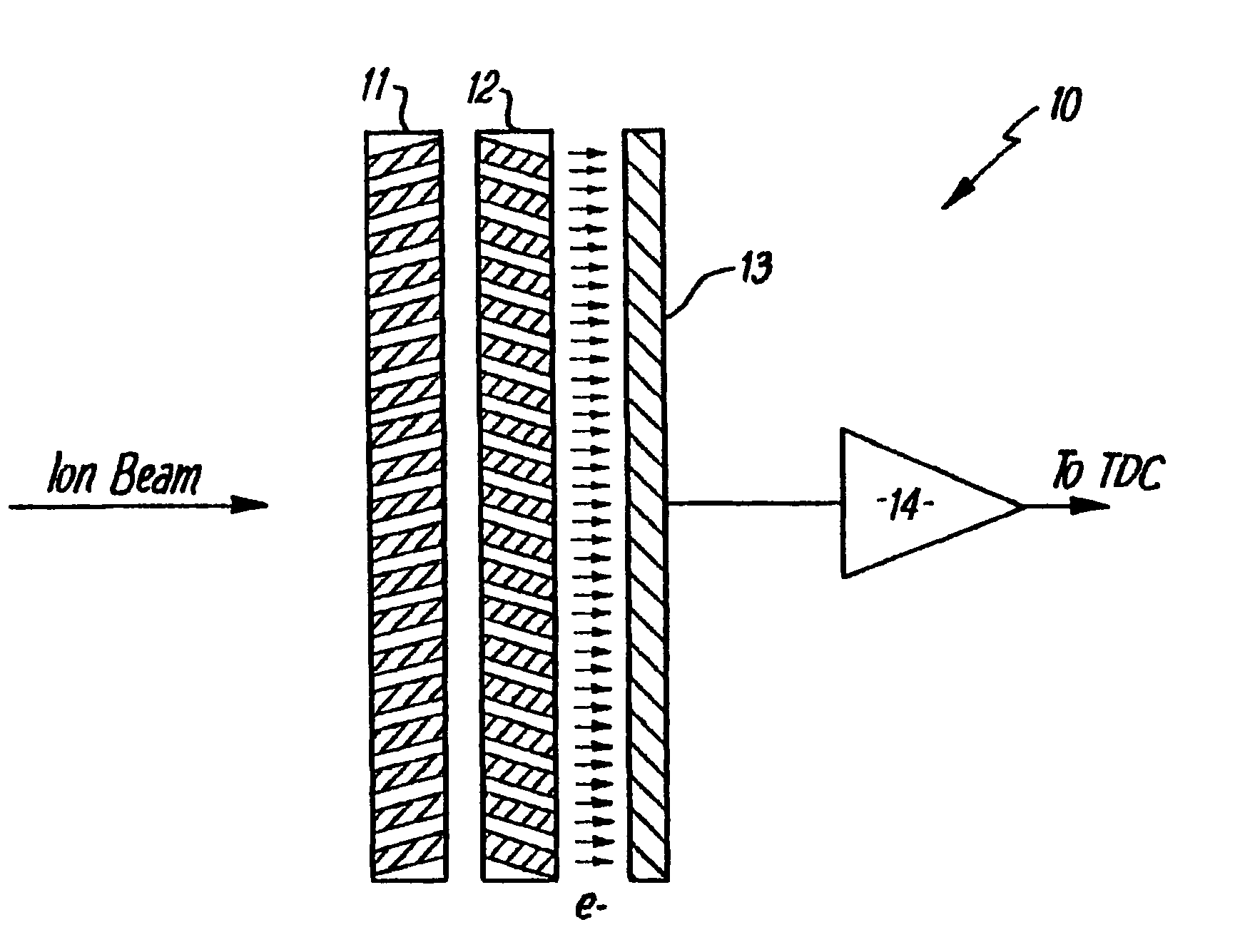
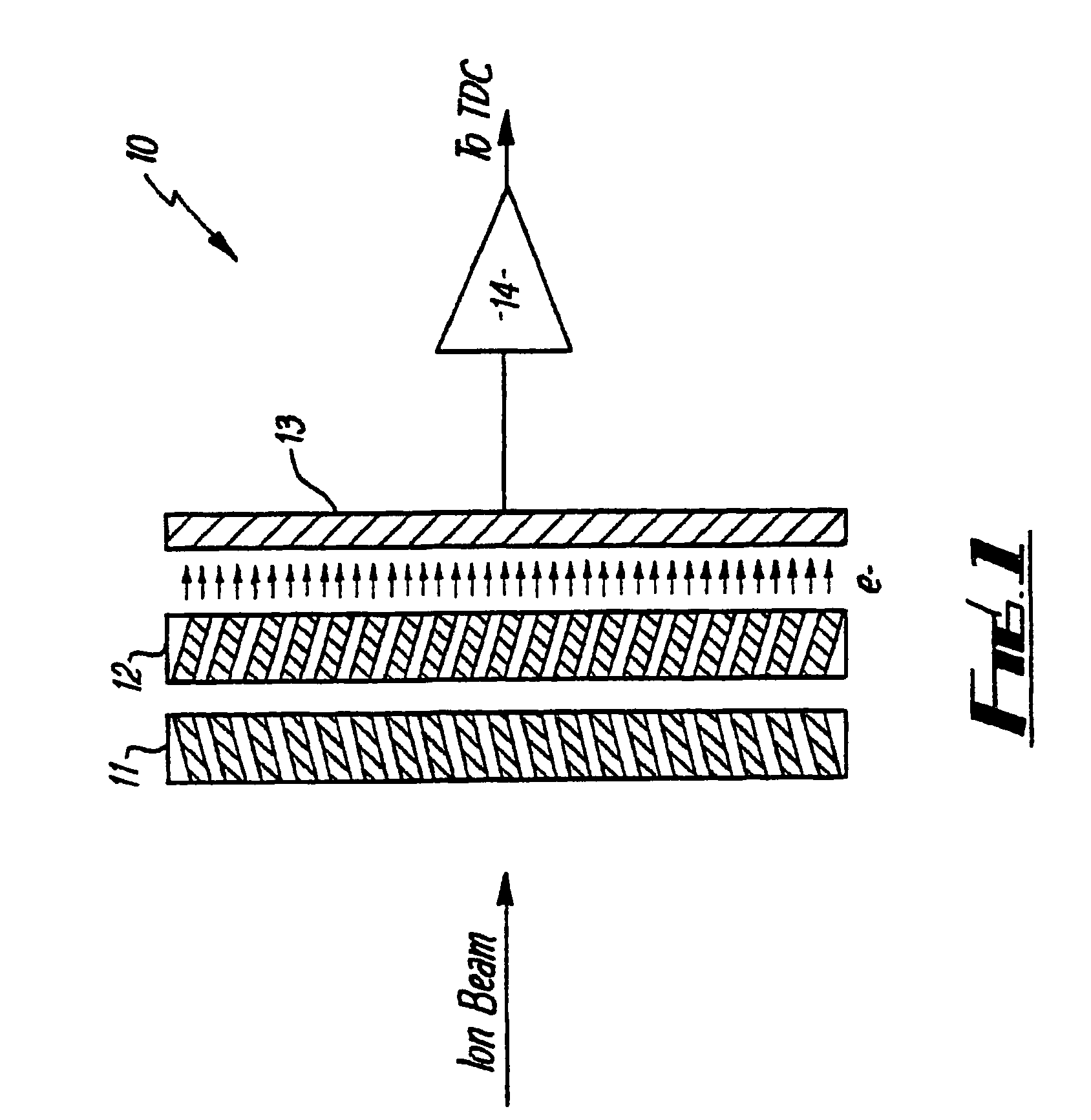
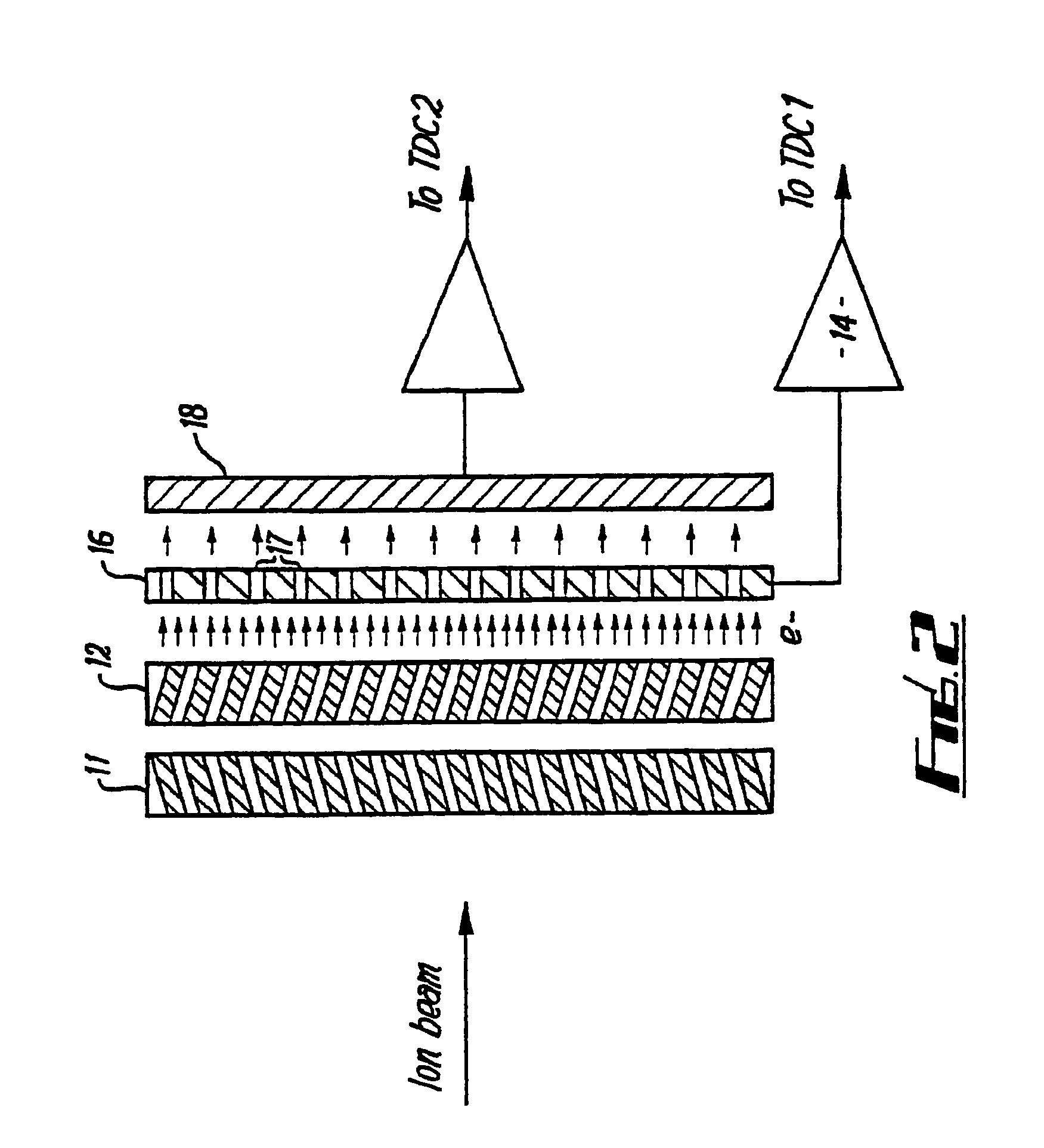
InactiveUS20080073548A1Solve the low detection efficiencyVariation can be minimizedThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsCharged particle detectorsParticle physics
A charged particle detector and method are disclosed providing for simultaneous detection and measurement of charged particles at one or more levels of particle flux in a measurement cycle. The detector provides multiple and independently selectable levels of integration and / or gain in a fully addressable readout manner.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP +2
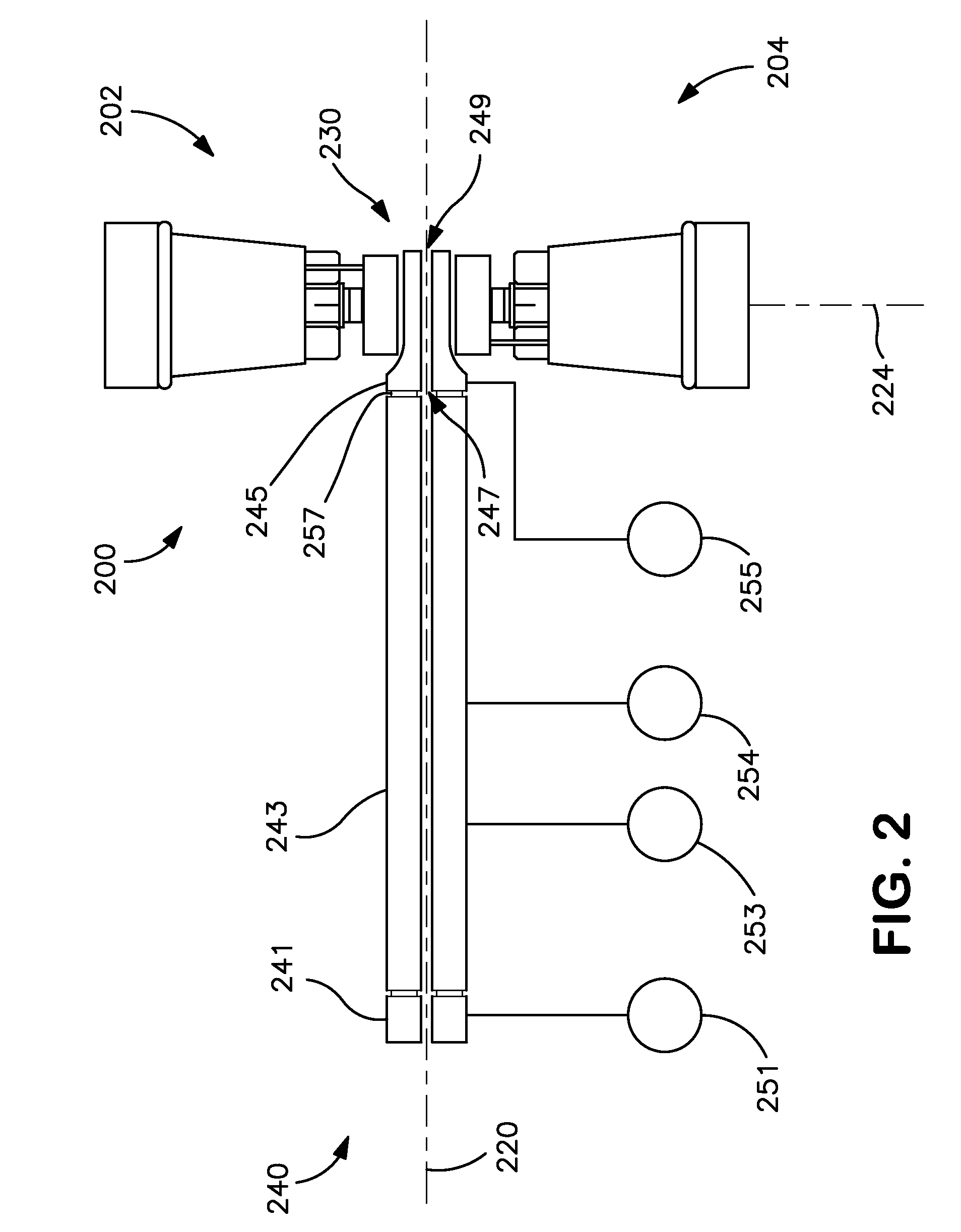
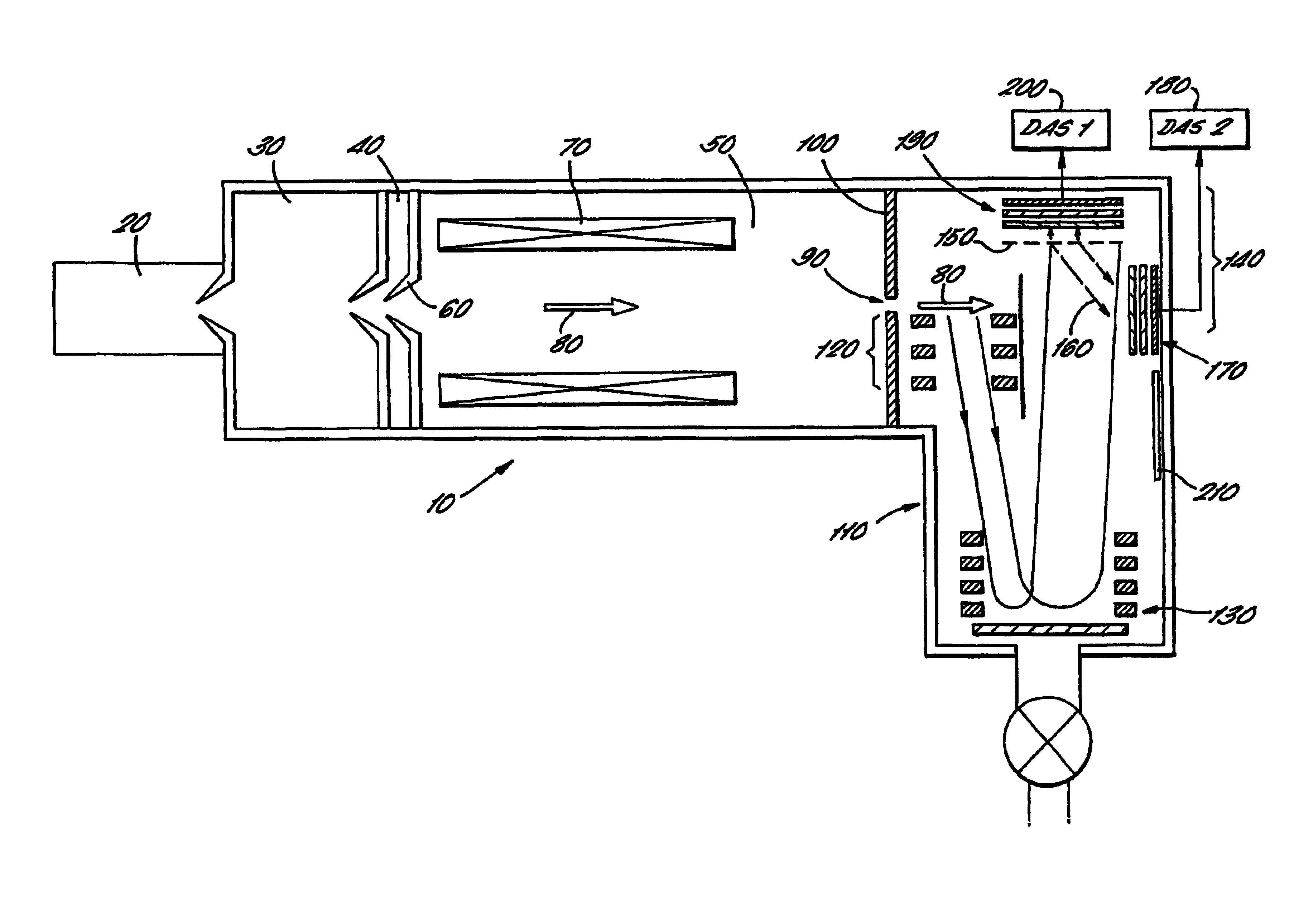
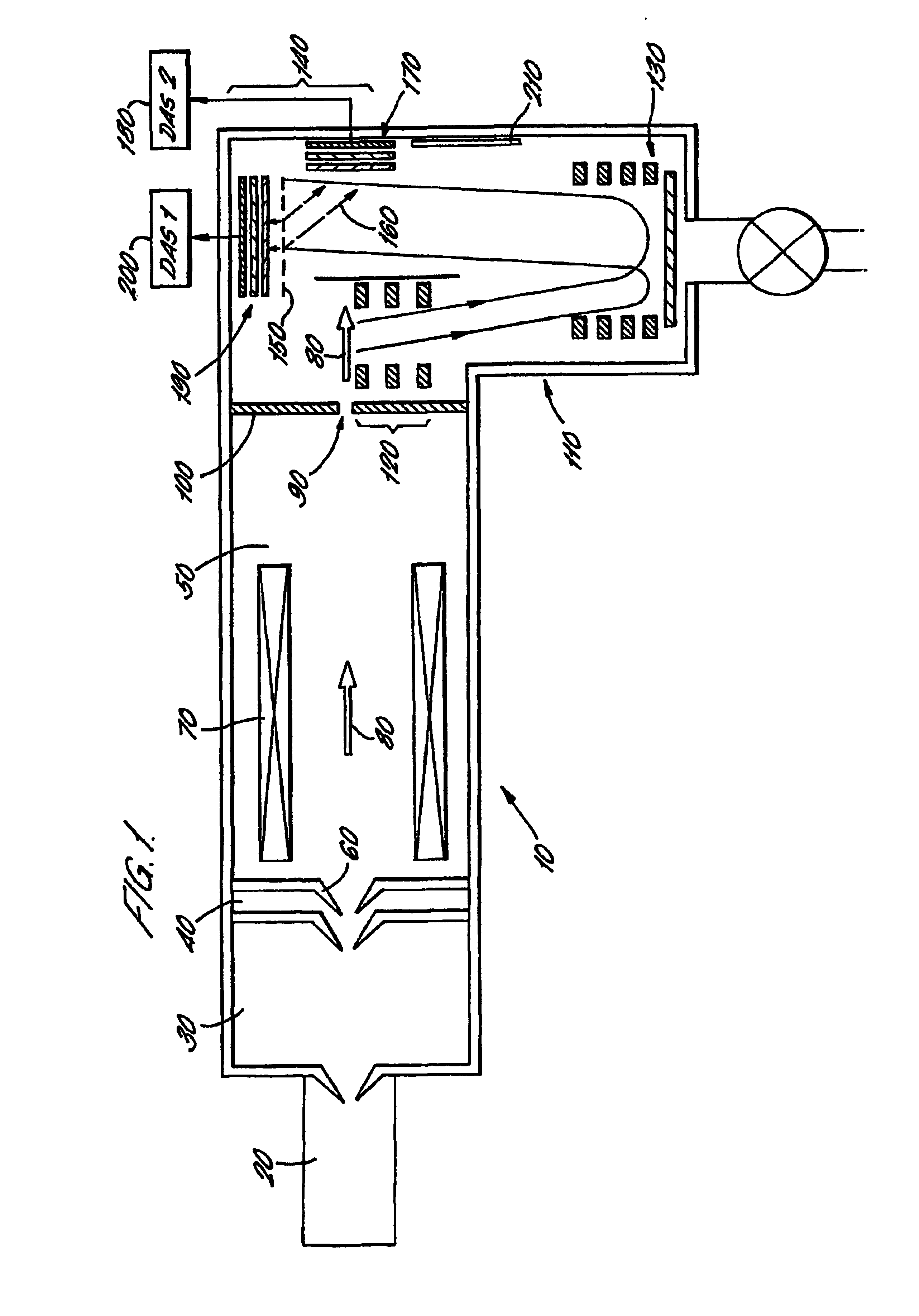
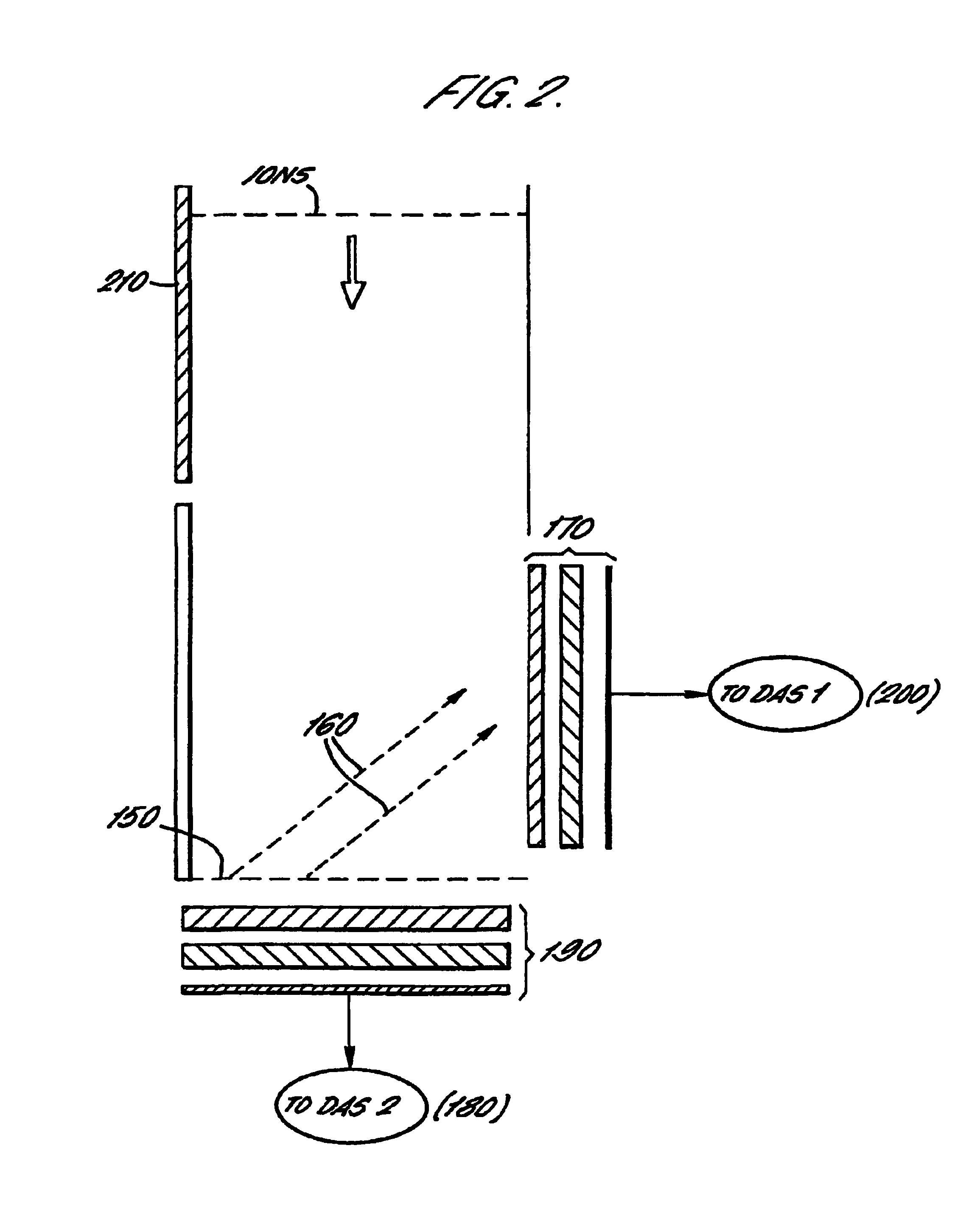
Time of flight mass spectrometer and multiple detector therefor
InactiveUS6940066B2Reduced electronic and physical cross-talkImprove dynamic rangeThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsMass spectrum analysisData combination
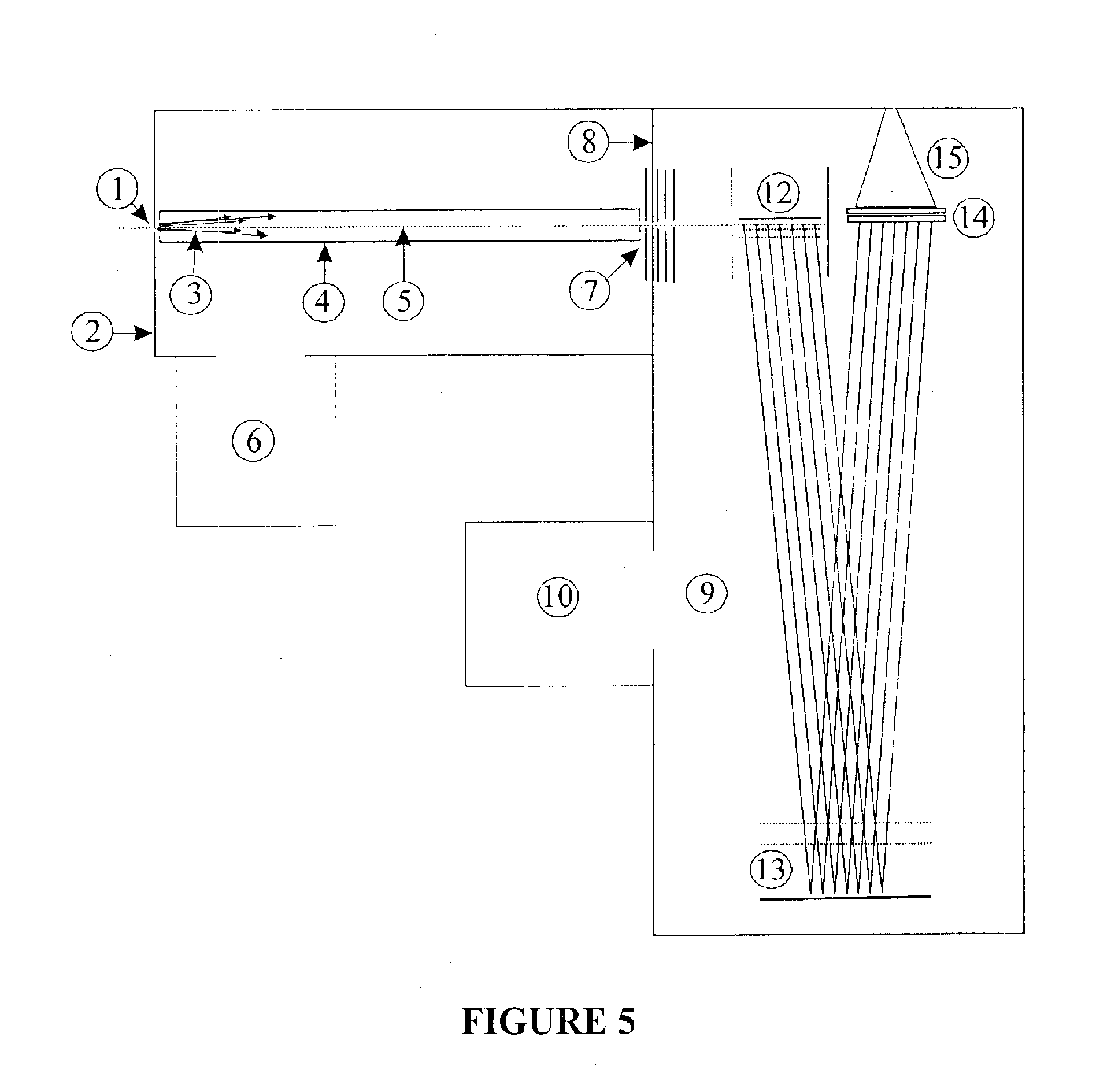
An ion detection arrangement 140 for a time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer 10 includes a beam splitter formed as a mesh 150 at the end of the TOF acceleration and detection chamber 110. Ions enter the detection arrangement through a common entrance window and are then divided by the beam splitter. Those ions striking the mesh 150 generate secondary electrons 160 which are detected by a microchannel plate forming a first detector 170. Those ions passing through the ion beam splitter are detected directly by a second detector 190 also formed from a microchannel plate.The two detectors are each connected to a corresponding data acquisition system 180, 200 and the data obtained by each are combined to generate a mass spectrum. The problems of detector saturation are thus avoided.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Ion detection in mass spectrometry with extended dynamic range
ActiveUS20060080045A1Small sizeIncrease in sizeSpectrometer detectorsResistance/reactance/impedenceMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPeak value
In a method for optimizing an ion detector a control voltage, such as in a mass spectrometry system, an array of mass scan data is acquired. Based on the size of the largest peak in the array or part of the array, a determination is made as to whether the current detector gain should be changed to a new detector gain. If the current detector gain should be changed, the control voltage for the subsequent mass scan is adjusted to a new control voltage corresponding to the new detector gain. The data are scaled based on the current detector gain. In another method, a gain versus control voltage curve is generated for calibration. These methods may be implemented by hardware, software, analog or digital circuitry, and / or computer-readable or signal-bearing media.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
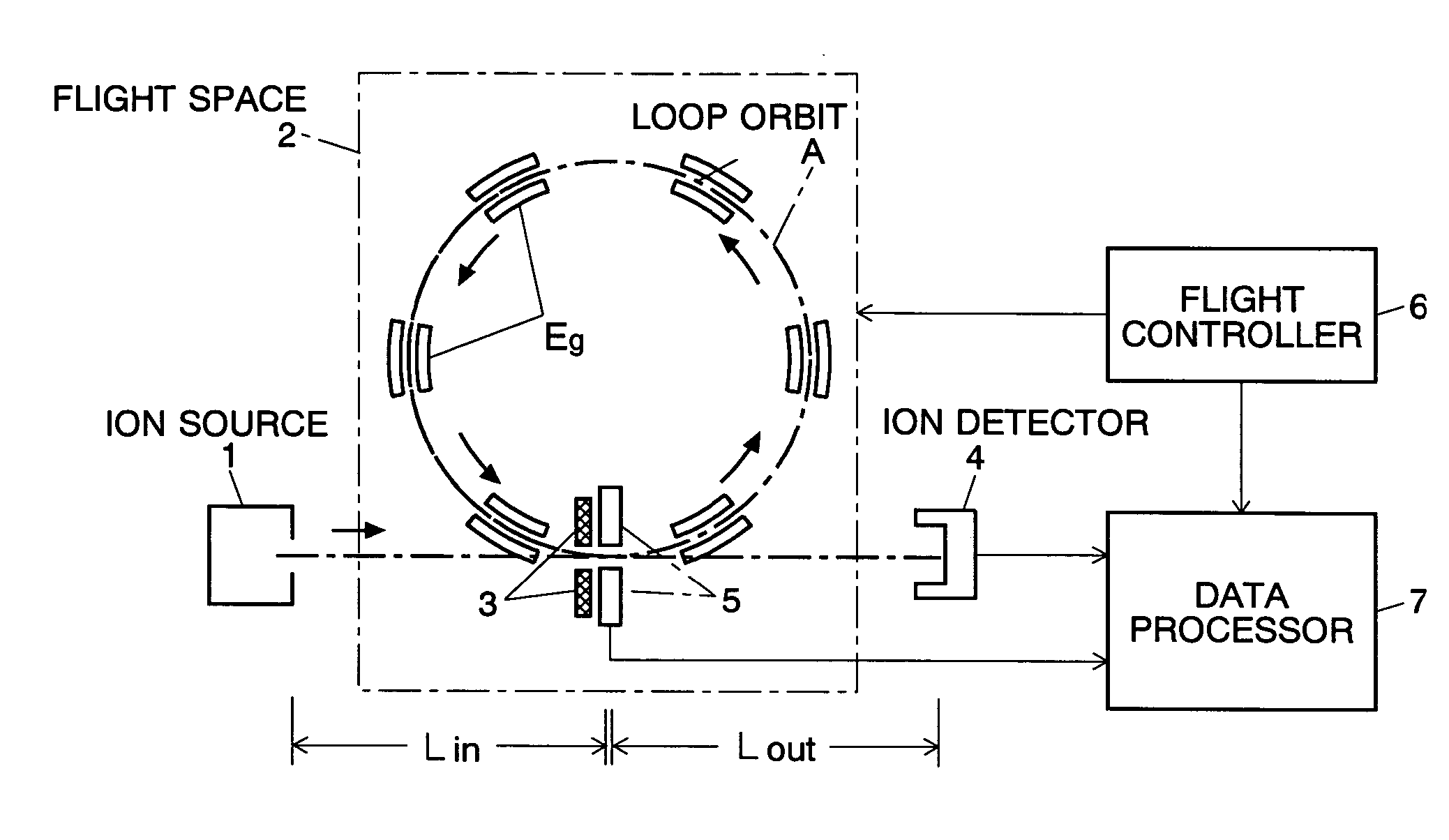
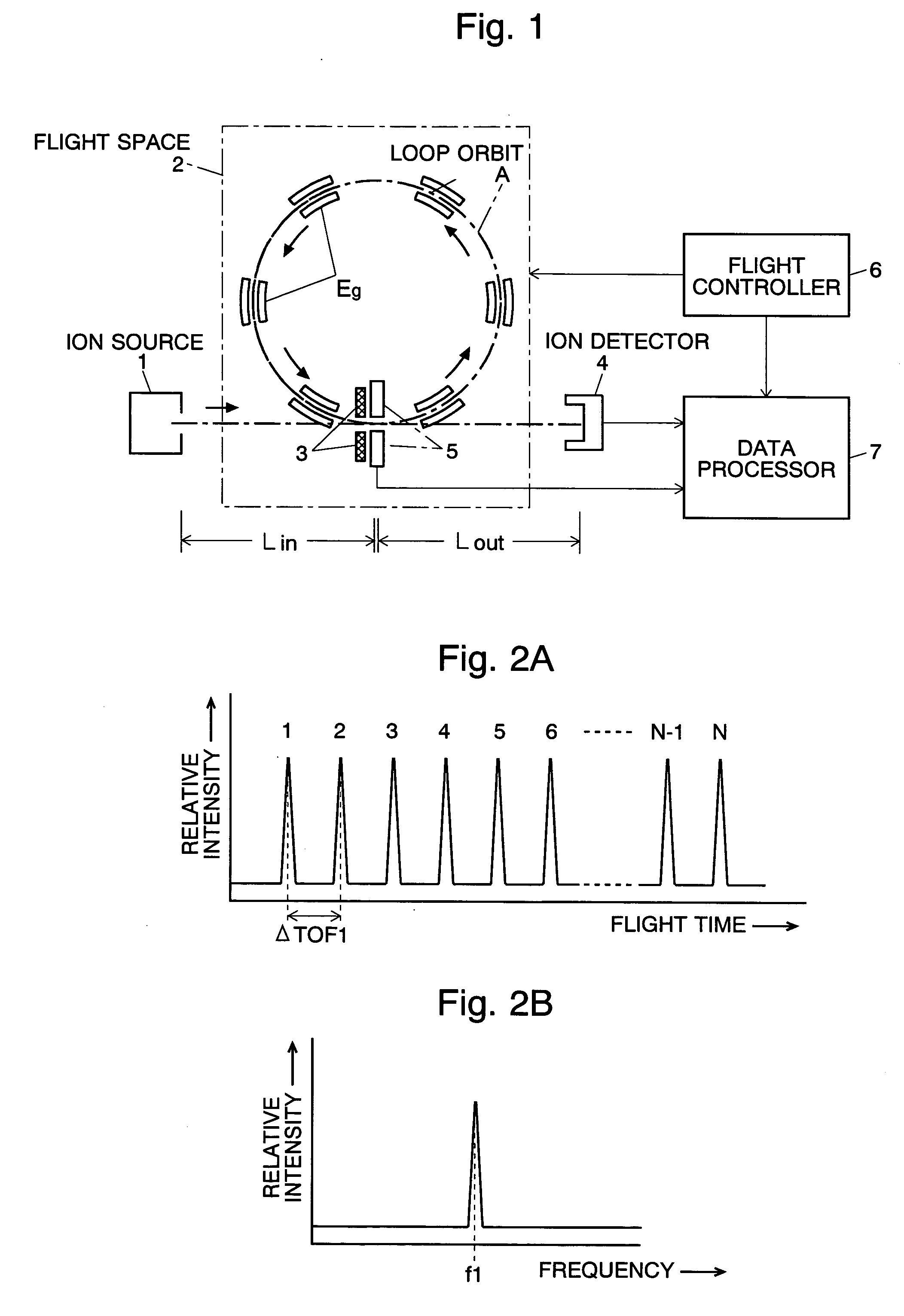
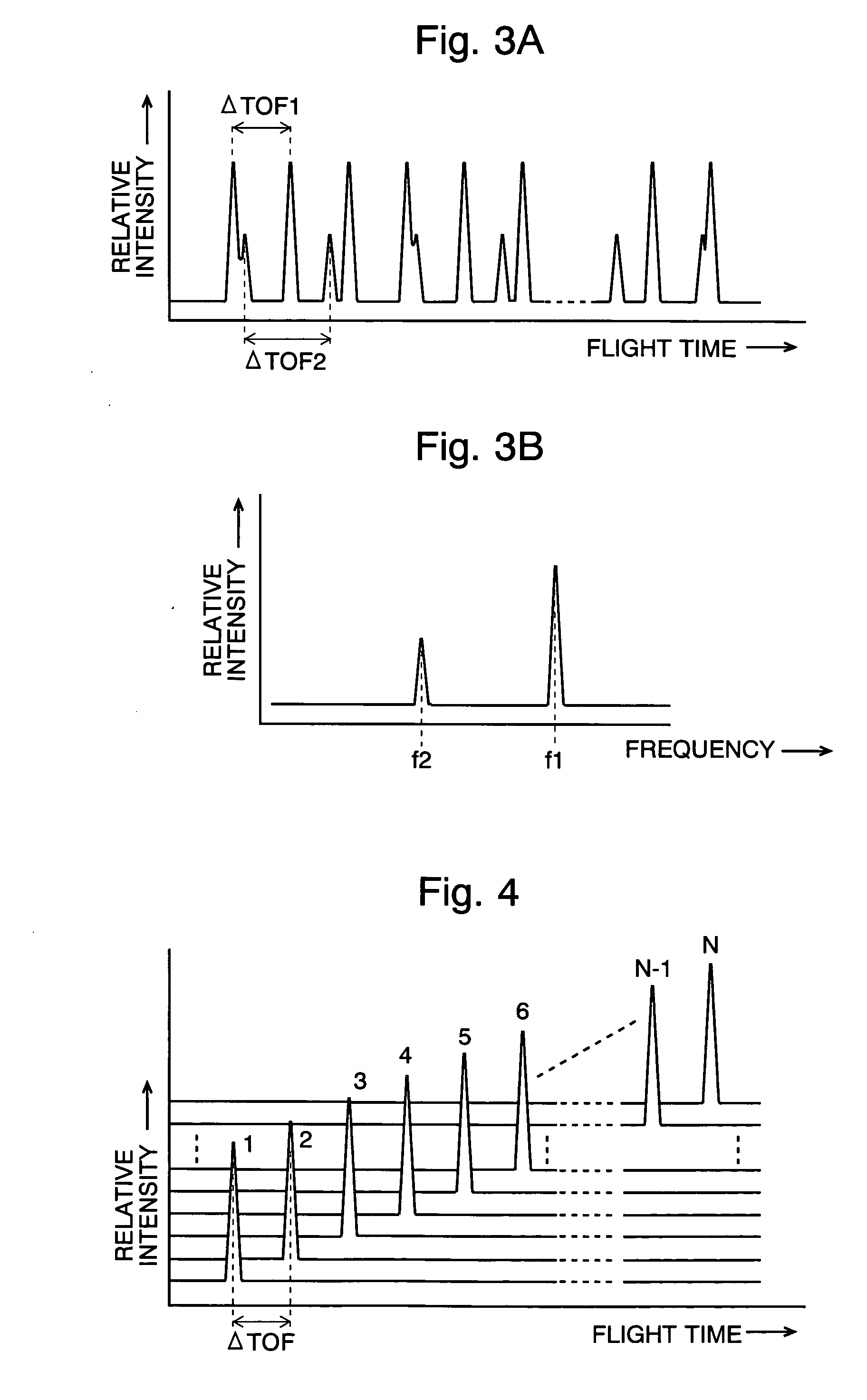
Time of flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20050045817A1Improve accuracyReduce errorsSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersFrequency spectrumPeak value
In a time of flight mass spectrometer (TOF-MS) of the present invention, a flight controller makes ions fly a loop orbit a predetermined number of turns, and an ion detector detects the ions at each turn of the flight. A flight time measurer measures the length of flight time of ions of a same mass to charge ratio at every turn, and a data processor constructs a spectrum of flight time. The data processor further computes the Fourier transformation of the spectrum, and determines the mass to charge ratio of the ions based on a frequency peak appearing in the Fourier transformation.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
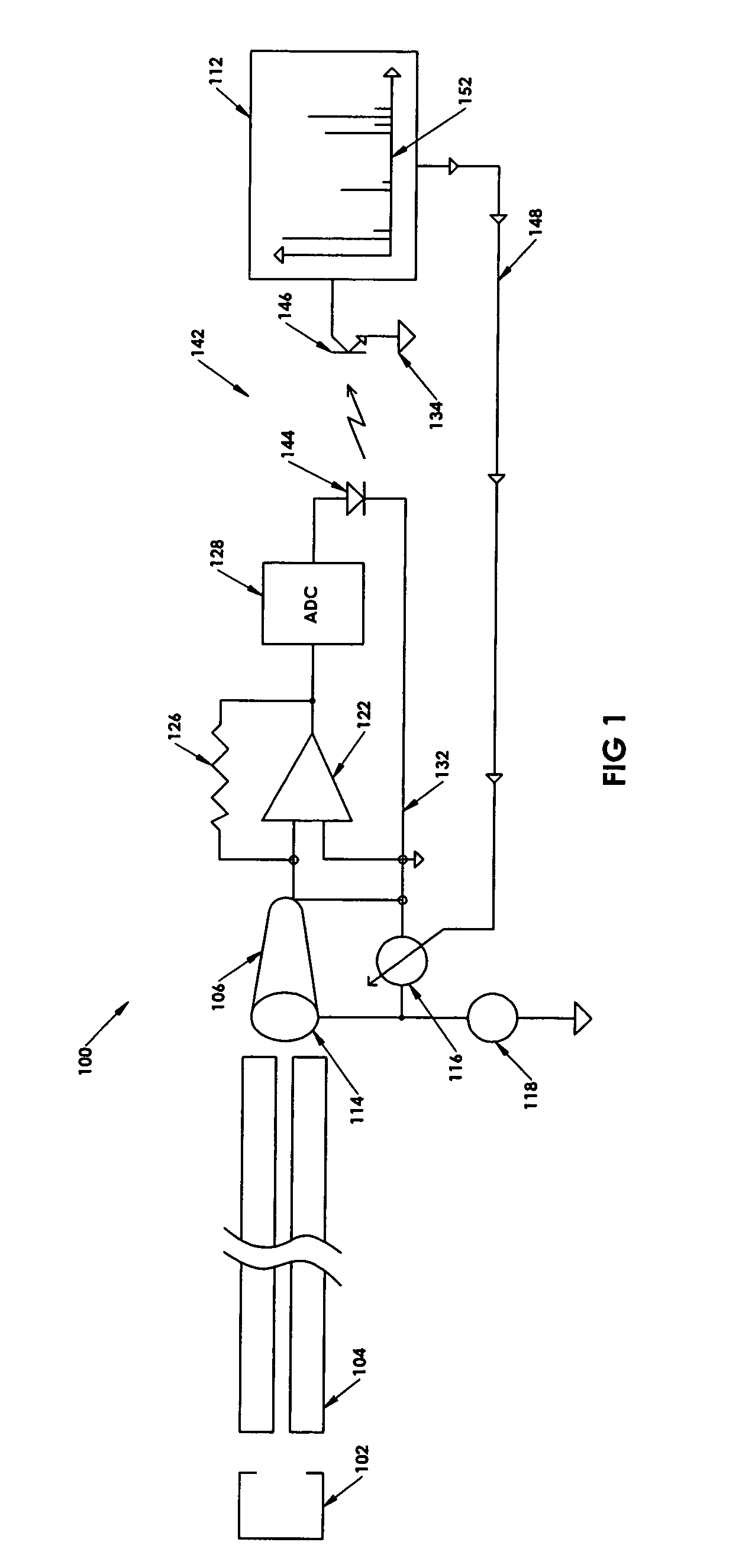
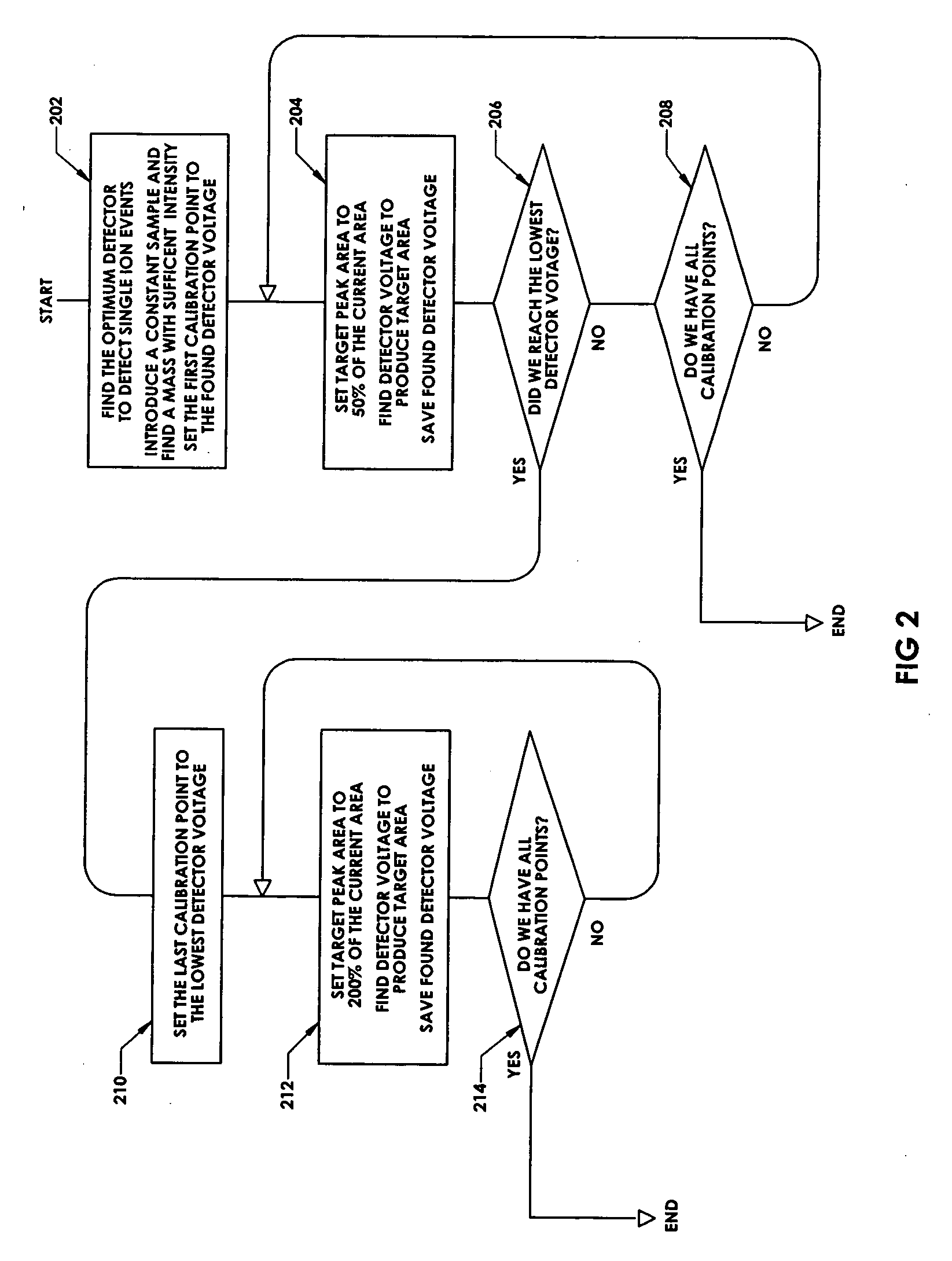
Real-time control of ion detection with extended dynamic range
In a method controlling an ion detector, one or more ion input signals are received at the ion detector. A data point indicative of an intensity of at least one of the received ion input signals is acquired. Asynchronously with acquiring the data point, a drive voltage applied to the ion detector is regulated to operate the ion detector at a gain optimal for the intensity of at least one of the received ion input signals. An ion detector for implementing the method is also provided.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
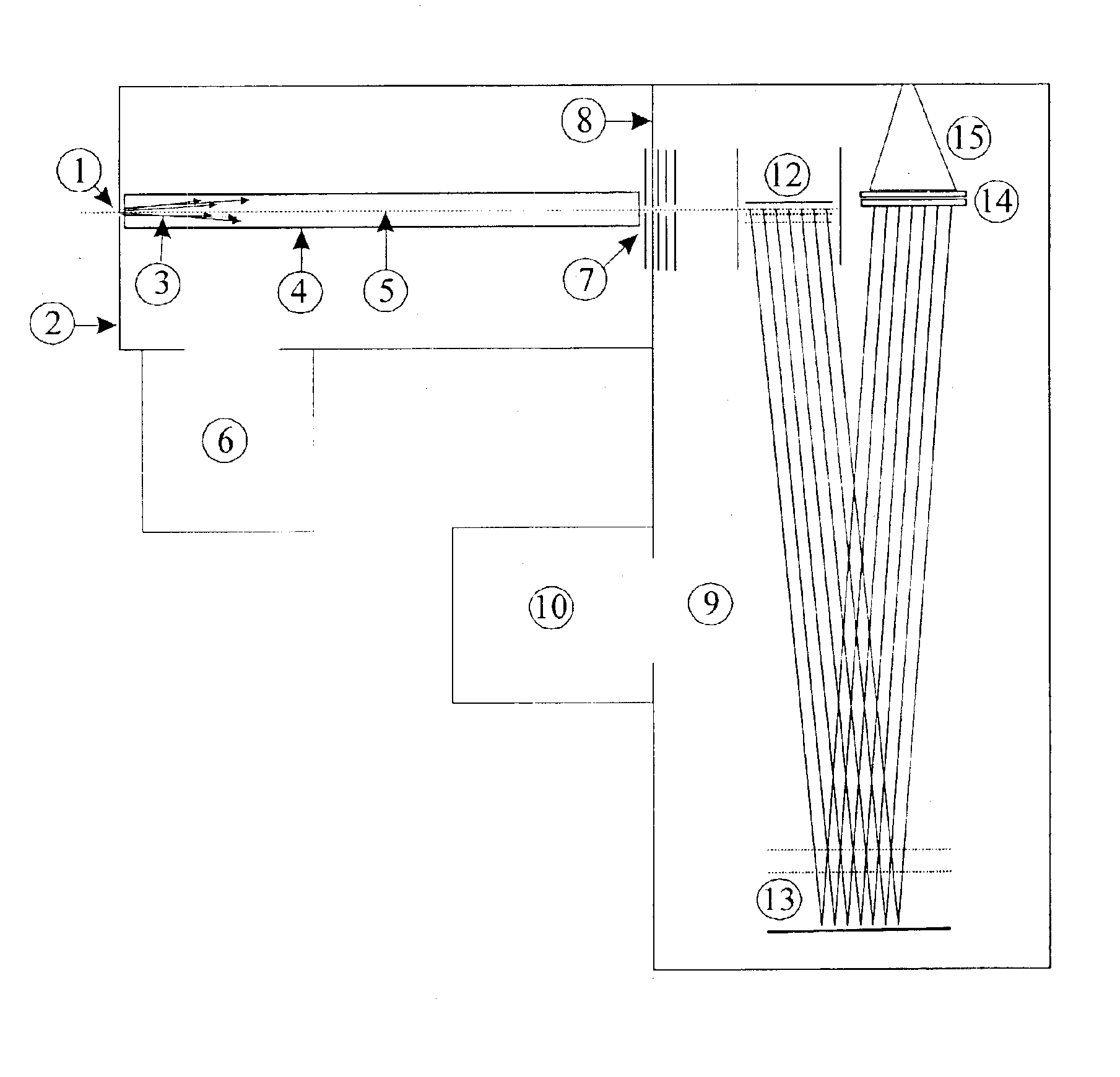
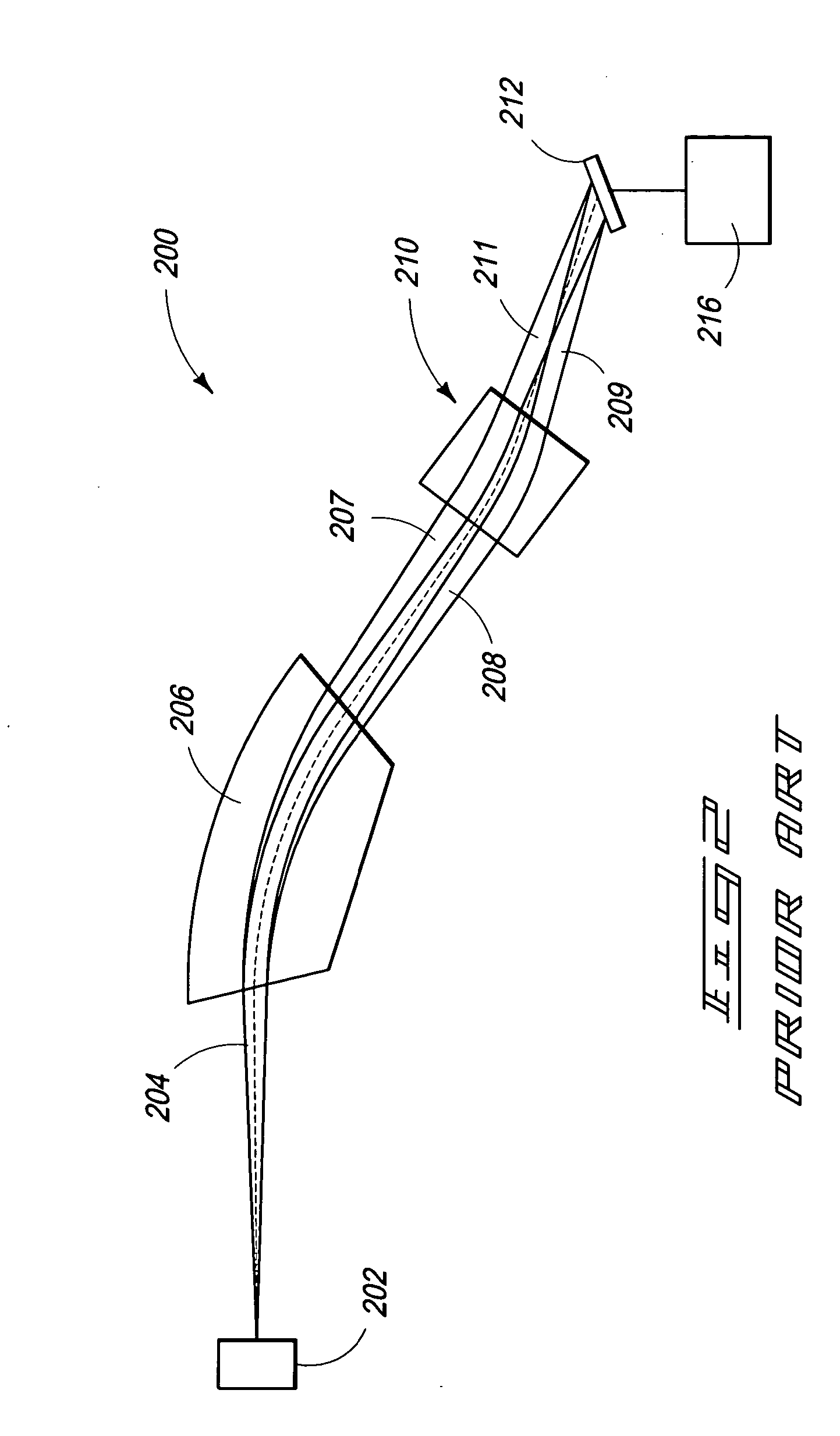
Time-of-flight mass analyzer with multiple flight paths
InactiveUS6933497B2Less-expensive to manufactureMore efficientSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersMass analyzerMass-to-charge ratio
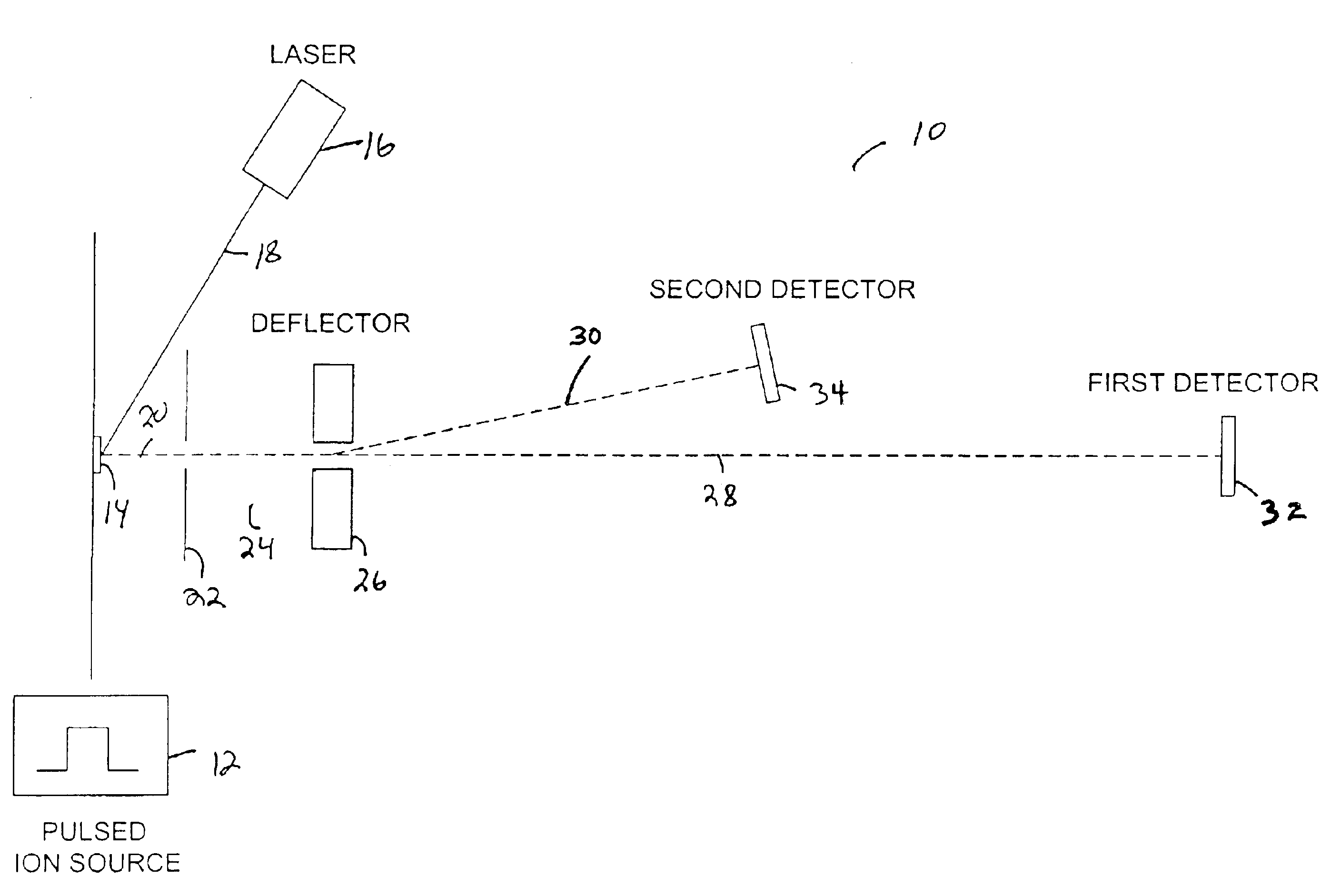
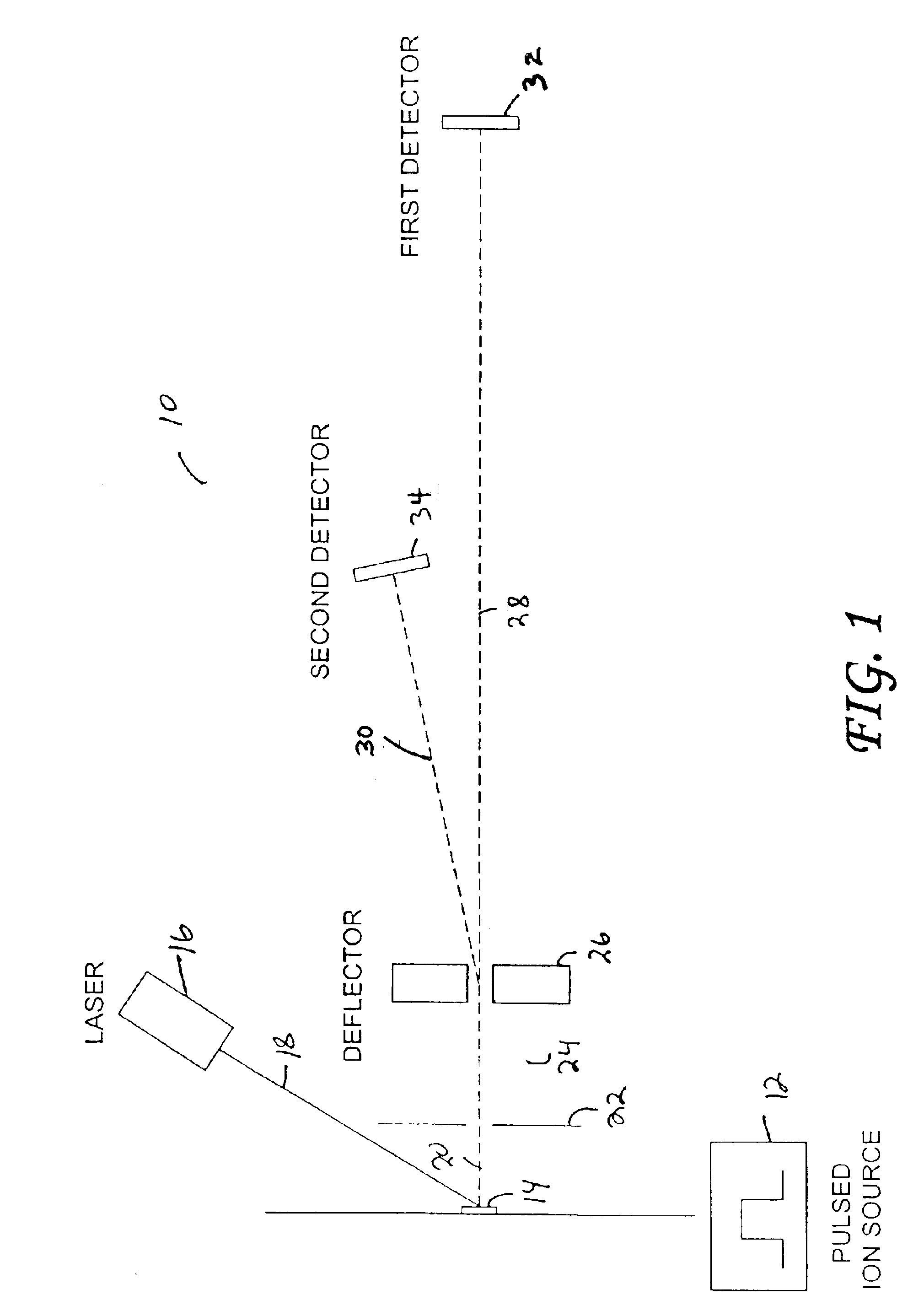
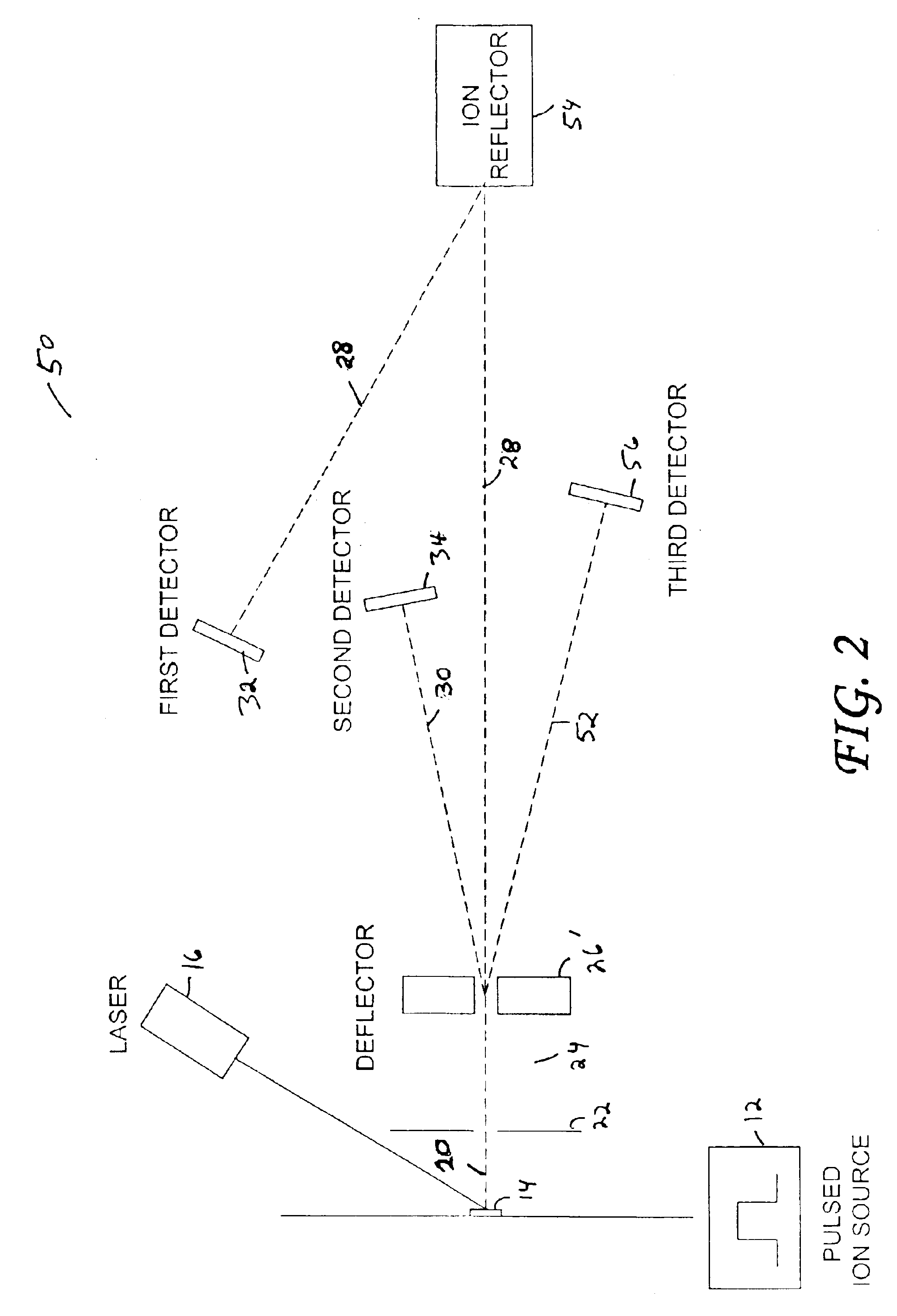
A TOF mass analyzer having multiple flight paths is described. The TOF mass analyzer includes a pulsed ion source that generates a packet of ions and that accelerates the packet of ions. An ion deflector directs a first group of ions from the packet of ions to a first ion path, and a second group of ions to a second ion path for each of a first and second predetermined time interval after the pulsed ion source generates the packet of ions. A first TOF mass separator separates the first group of ions according to their mass to-charge ratio and a first detector is positioned to receive the first group of ions A second TOF mass separator separates a second group of ions according to their mass to-charge ratio and a second detector is positioned to receive the second group of ions. Additional ion paths may be employed, and any type of TOF mass separator may be used in each ion path.
Owner:MDS INC THROUGH ITS MDS SCIEX DIV +2
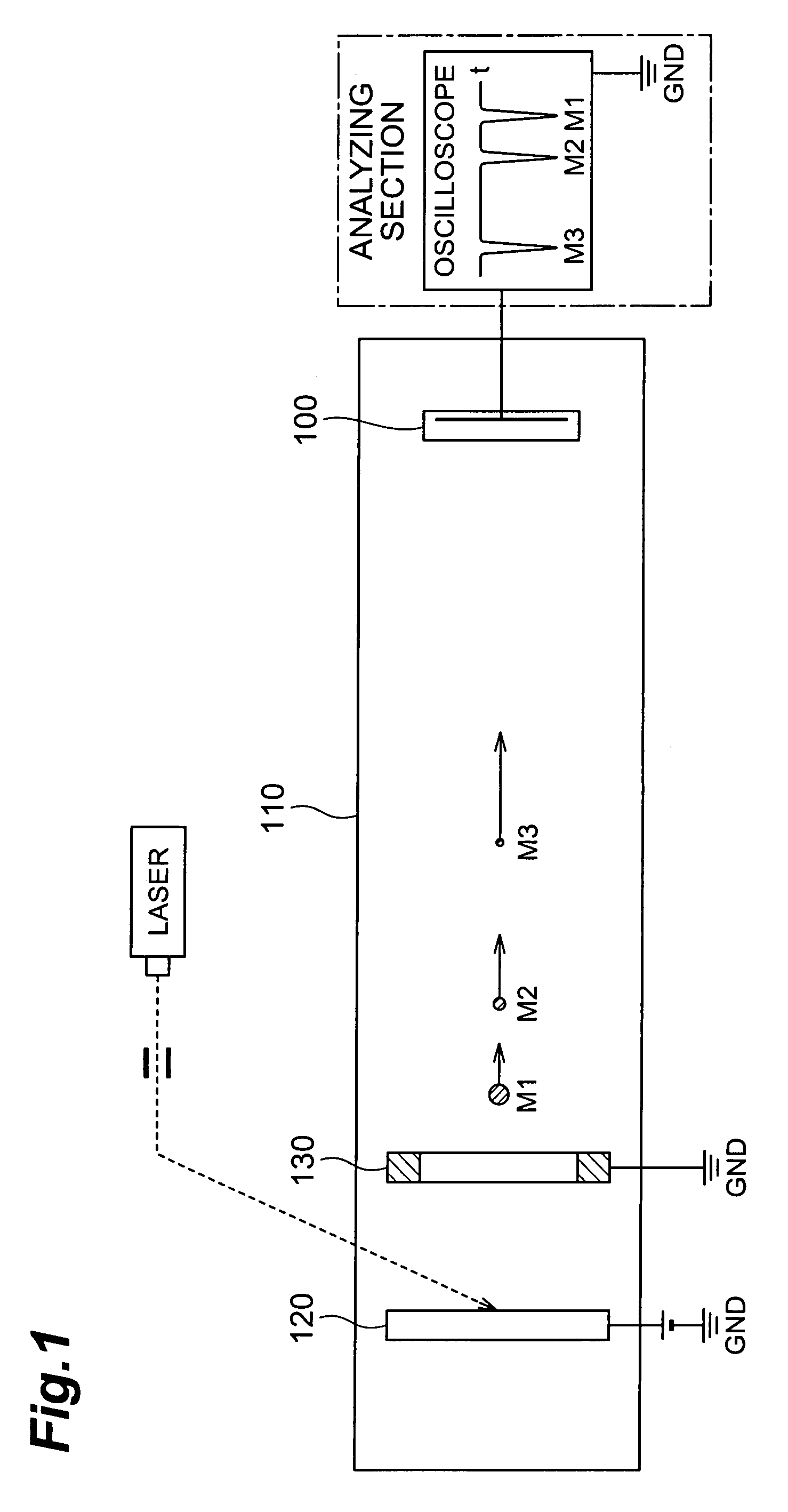
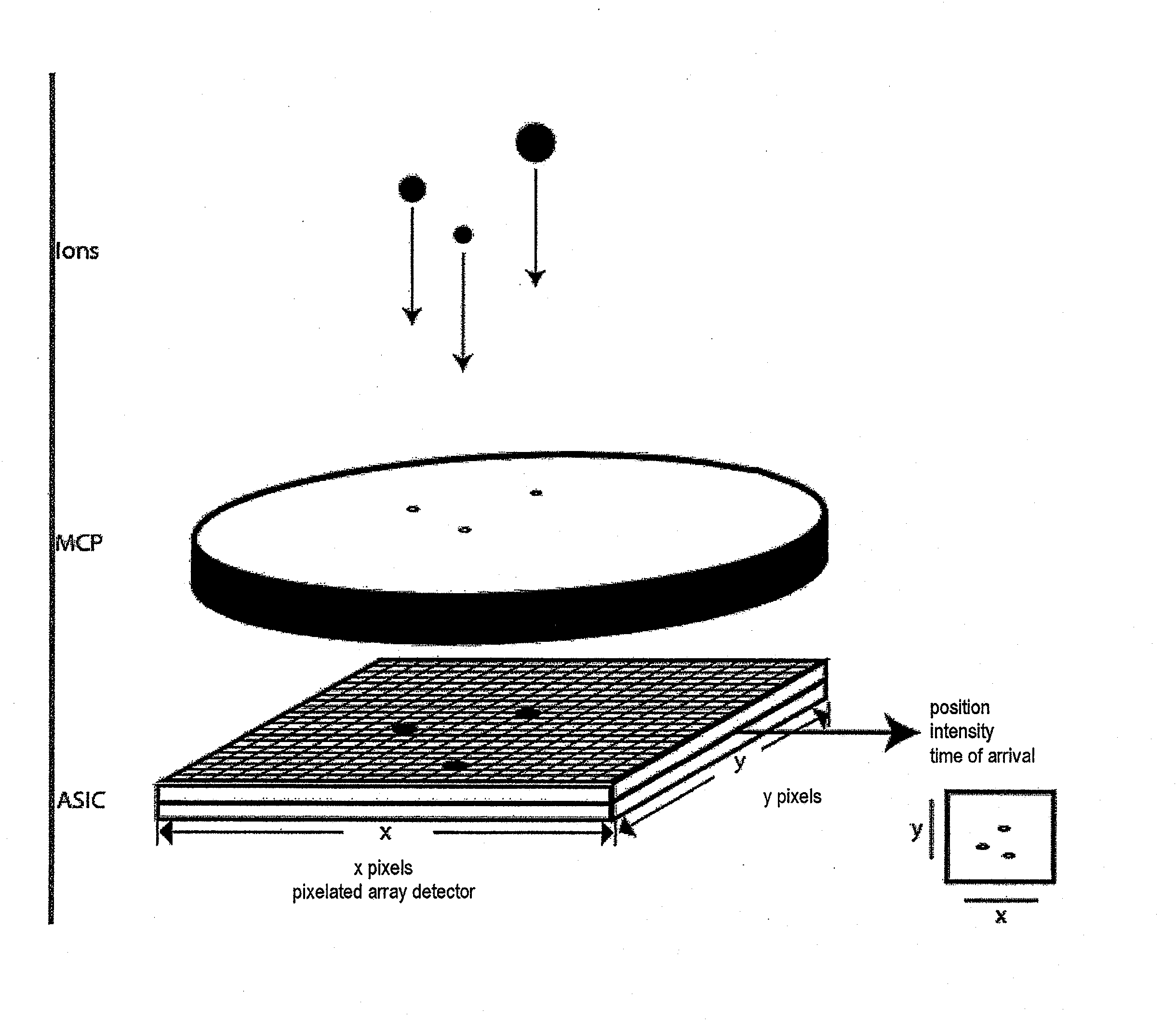
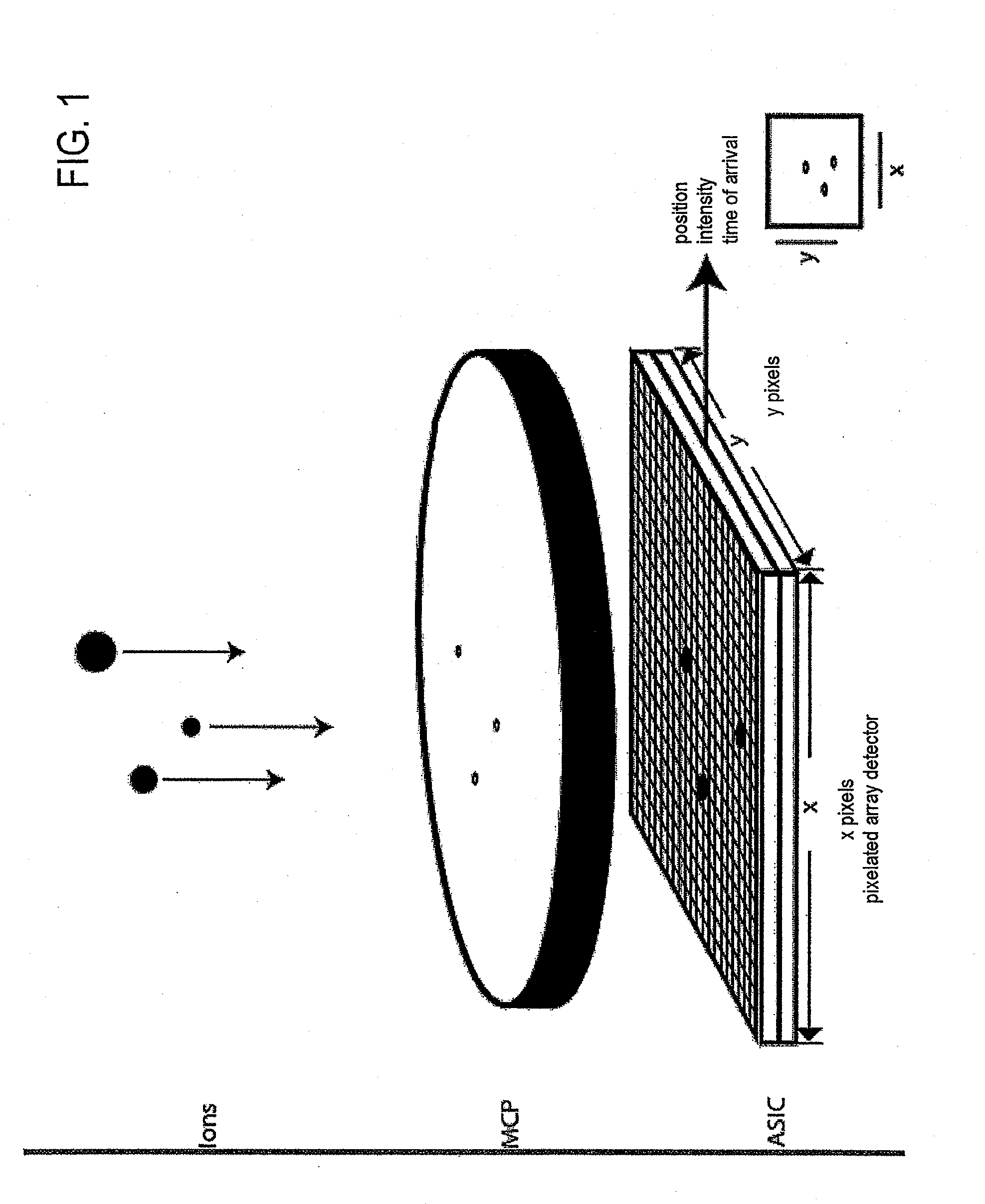
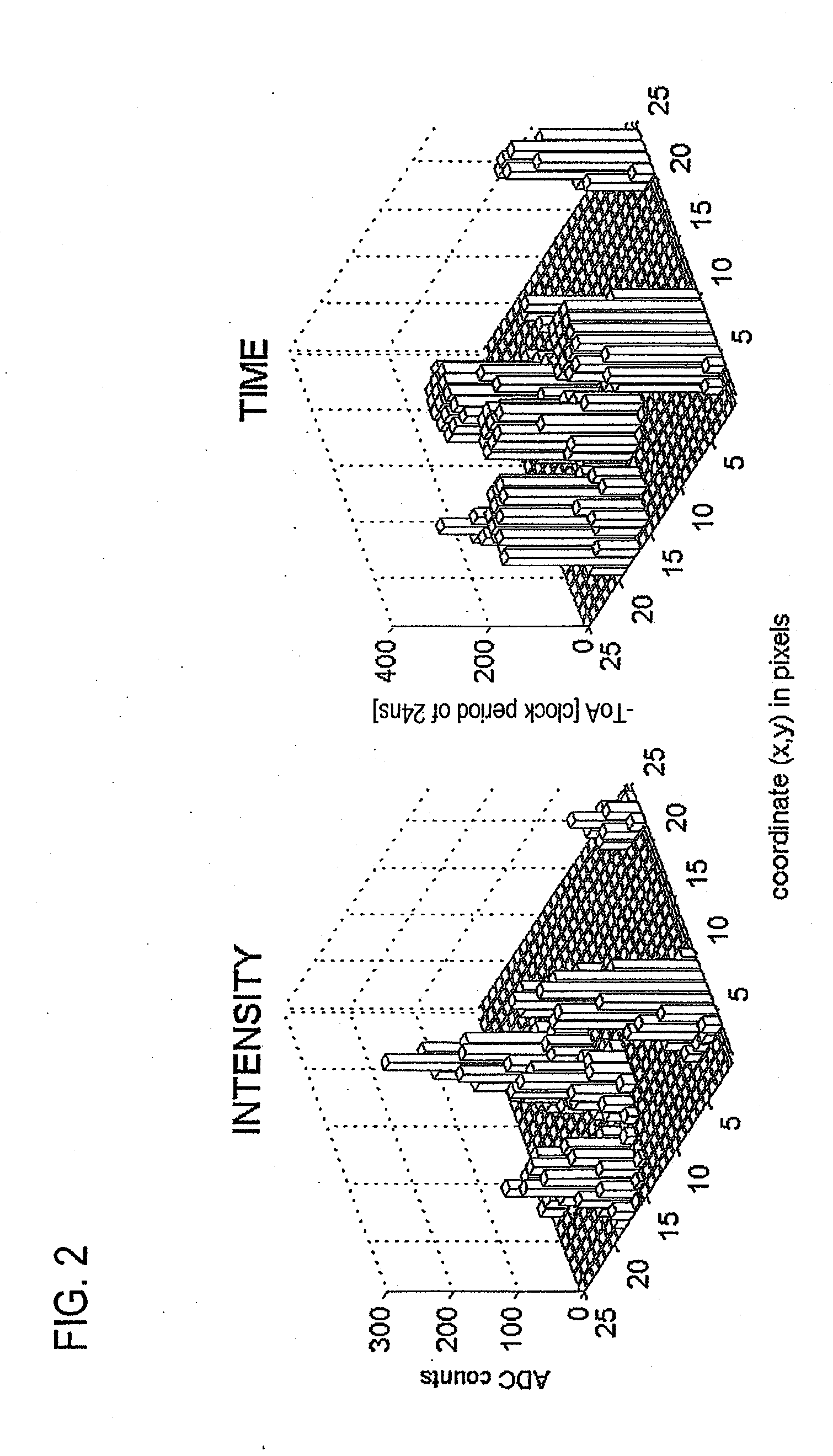
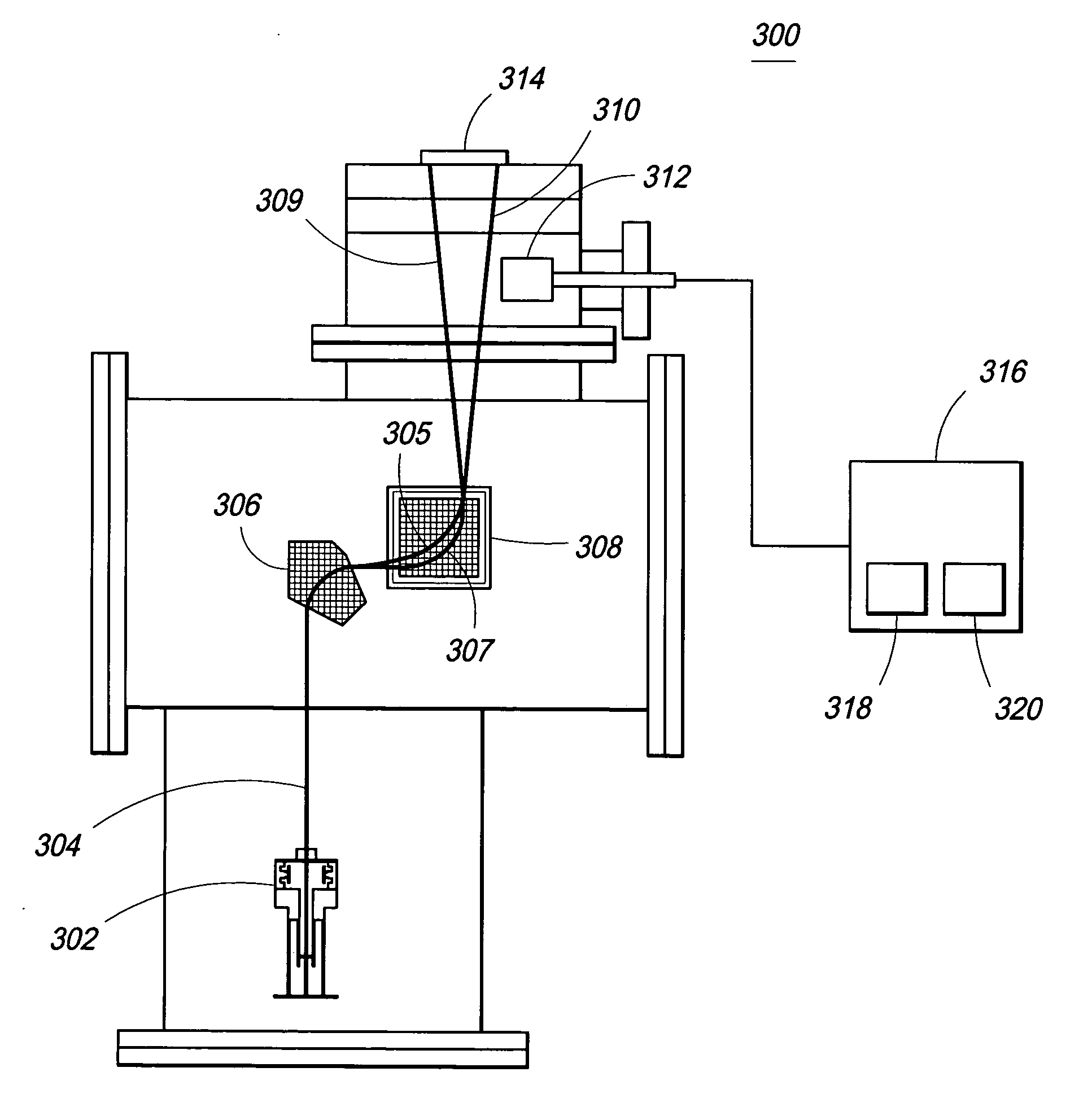
Imaging mass spectrometry principle and its application in a device
InactiveUS20090261243A1Shorten the timeFast constructionSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectroscopyMethod of images
A method of imaging mass spectroscopy and a corresponding apparatus are provided, wherein the m / z-ratio of ions as well as the location of said ions on a sample surface are detected simultaneously in a time of flight mass spectrometer. The detector is a semiconductor array detector comprising pixels, that each can be arranged to measure a signal intensity of a signal induced by the ions or their time of arrival. A four-dimensional image consisting of the two lateral dimensions on the sample surface, the m / z-ratio representing the ion type and the abundance of an ion type on the surface can be reconstructed from repeated measurements for which a correspondingly adapted computer program product can be involved.
Owner:BAMBERGER
MCP unit, MCP detector and time of flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20080290267A1Reduce widthShortened fall timeThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsTime responseTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
The present invention relates to an MCP unit or the like having a structure intended to achieve a desired time response characteristic, without depending on a limitation imposed by a channel diameter of MCP. The MCP unit comprises the MCP for releasing secondary electrons internally multiplied in response to incidence of charged particles, an anode arranged in a position where the secondary electrons reach, and an acceleration electrode arranged between the MCP and the anode. In particular, the acceleration electrode includes a plurality of openings which permit passing of the secondary electrons migrating from the MCP toward the anode. Further, the acceleration electrode is arranged such that the shortest distance B between the acceleration electrode and the anode is longer than the shortest distance A between the MCP and the acceleration electrode. Thus, an FWHM of a detected peak appearing in response to the incidence of the charged particles is remarkably shortened.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
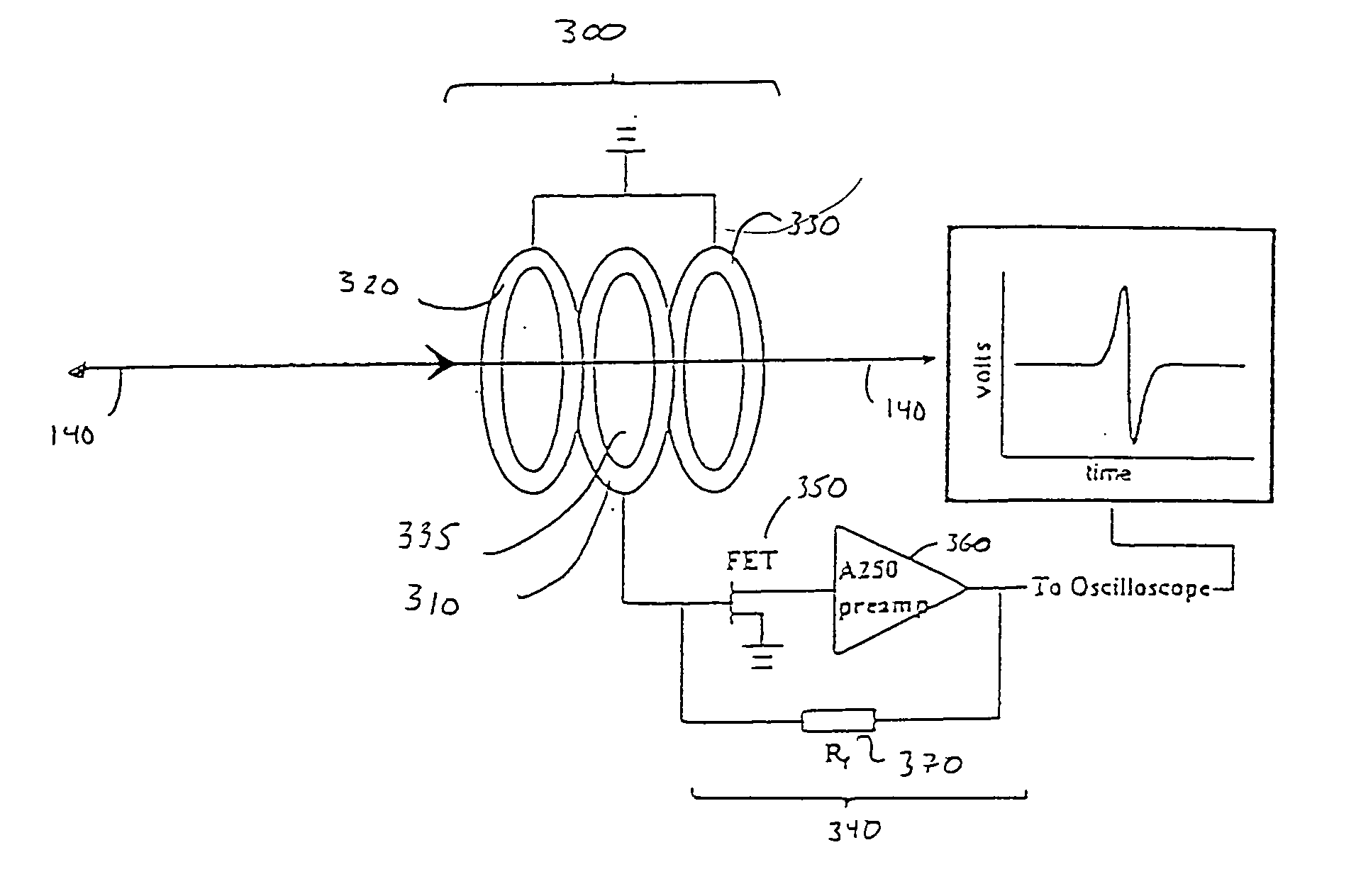
Inductive detection for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7078679B2Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsGas phaseBiopolymer
The invention provides devices, device configurations and methods for improved sensitivity, resolution and efficiency in mass spectrometry, particularly as applied to biological molecules, including biological polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention provides methods and devices for analyzing and detecting electrically charged particles, especially suitable for gas phase ions generated from high molecular weight compounds. In one aspect, the invention provides devices and methods for determining the velocity, charged state or both of electrically charged particles and packets of electrically charged particles. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and devices for the time-of-flight analysis of electrically charged particles comprising spatially collimated sources. In another aspect, the invention relates to multiple detection using inductive detectors, improved methods of signal averaging and charged particle detection in coincidence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
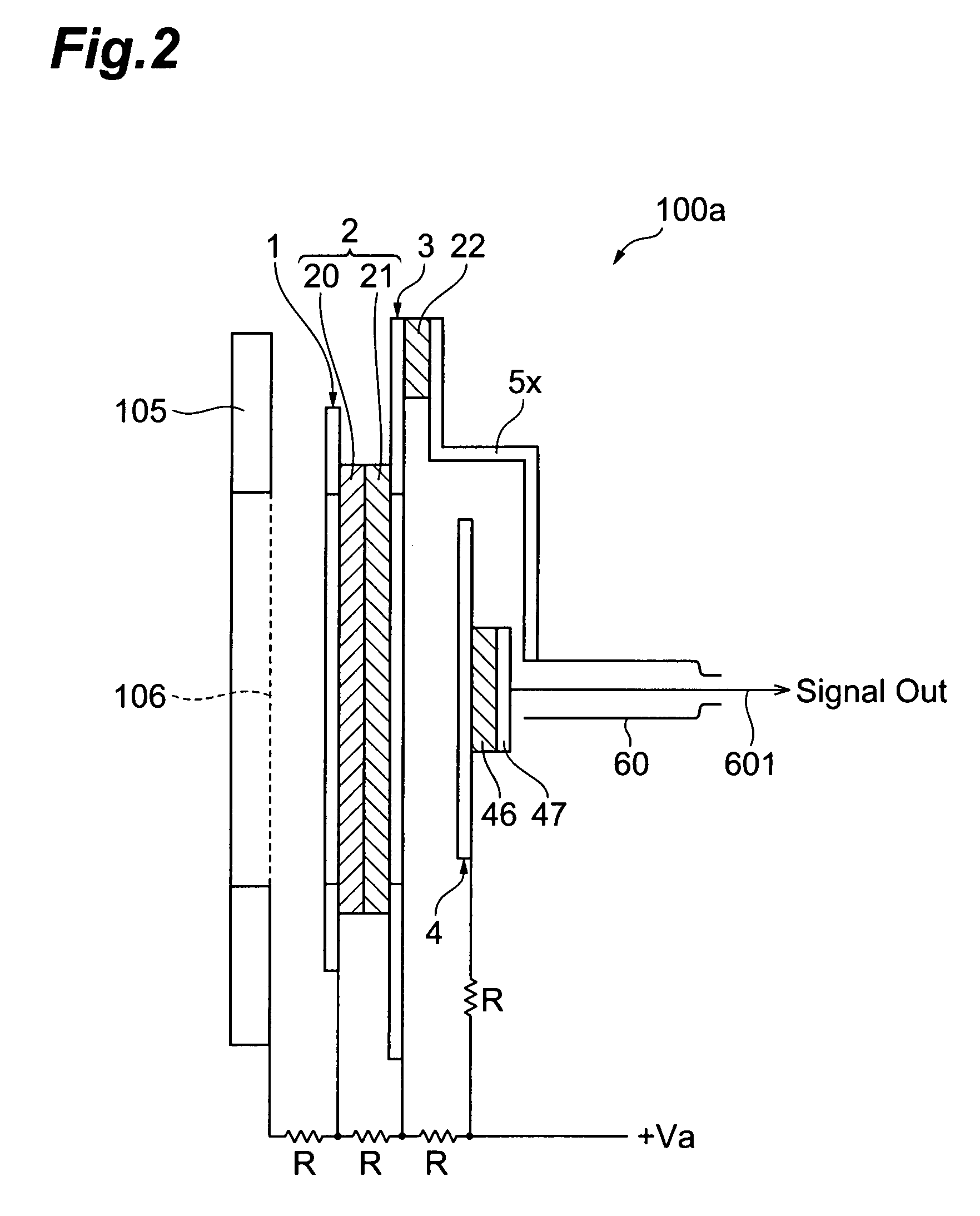
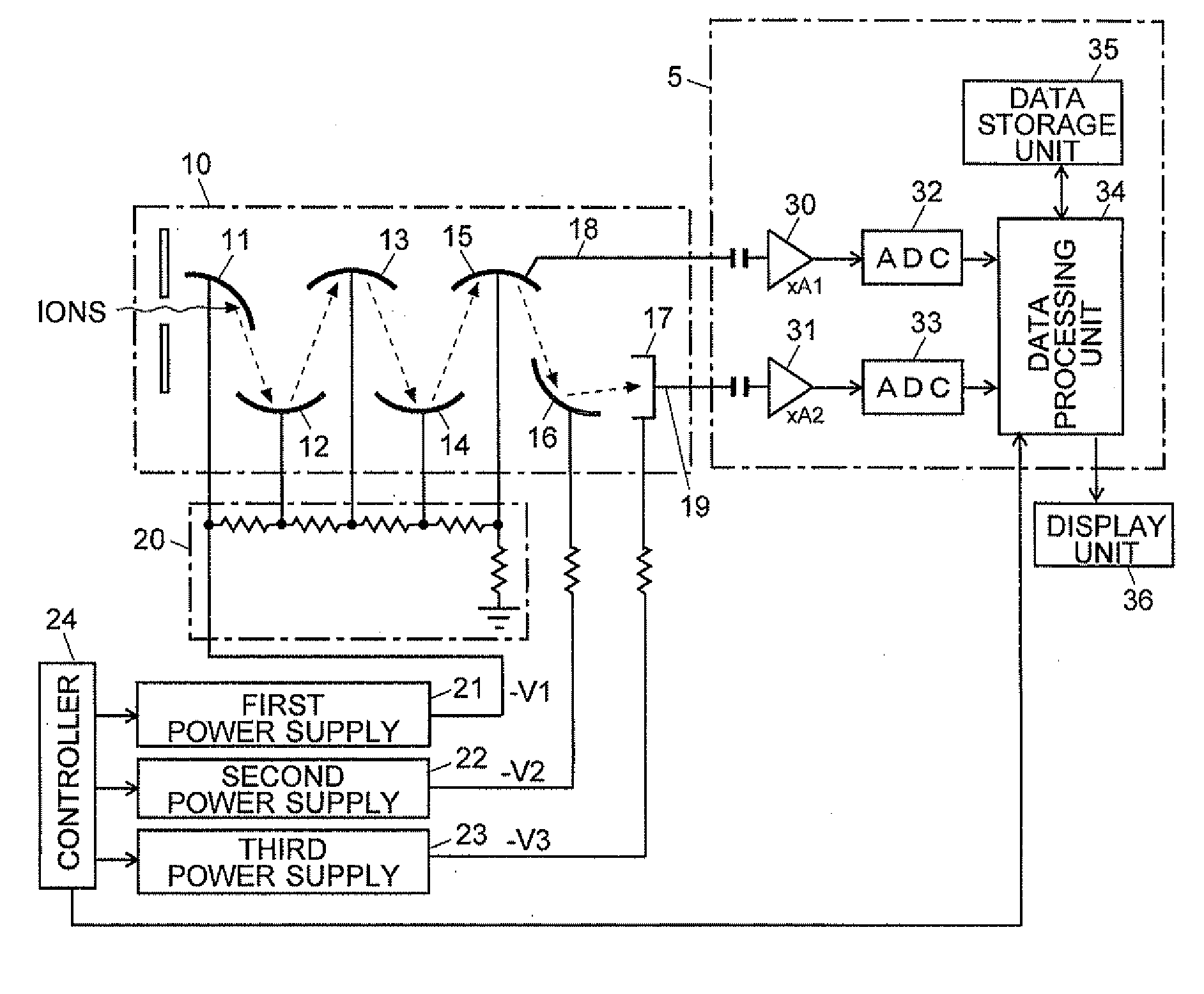
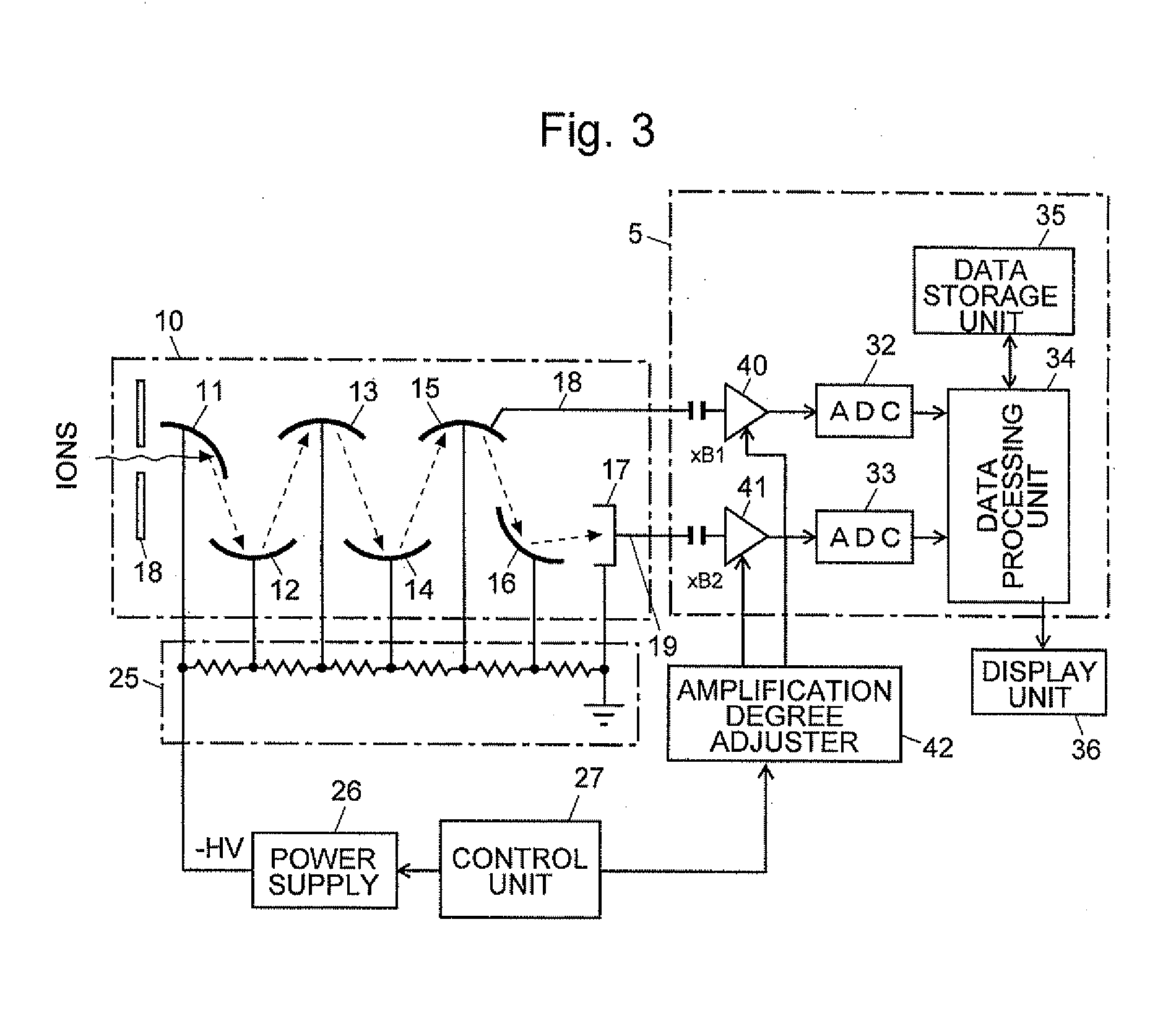
Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20120175514A1Improve dynamic rangeMultiplication factor can be restoredThermometer detailsTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron multiplicationHigh probability
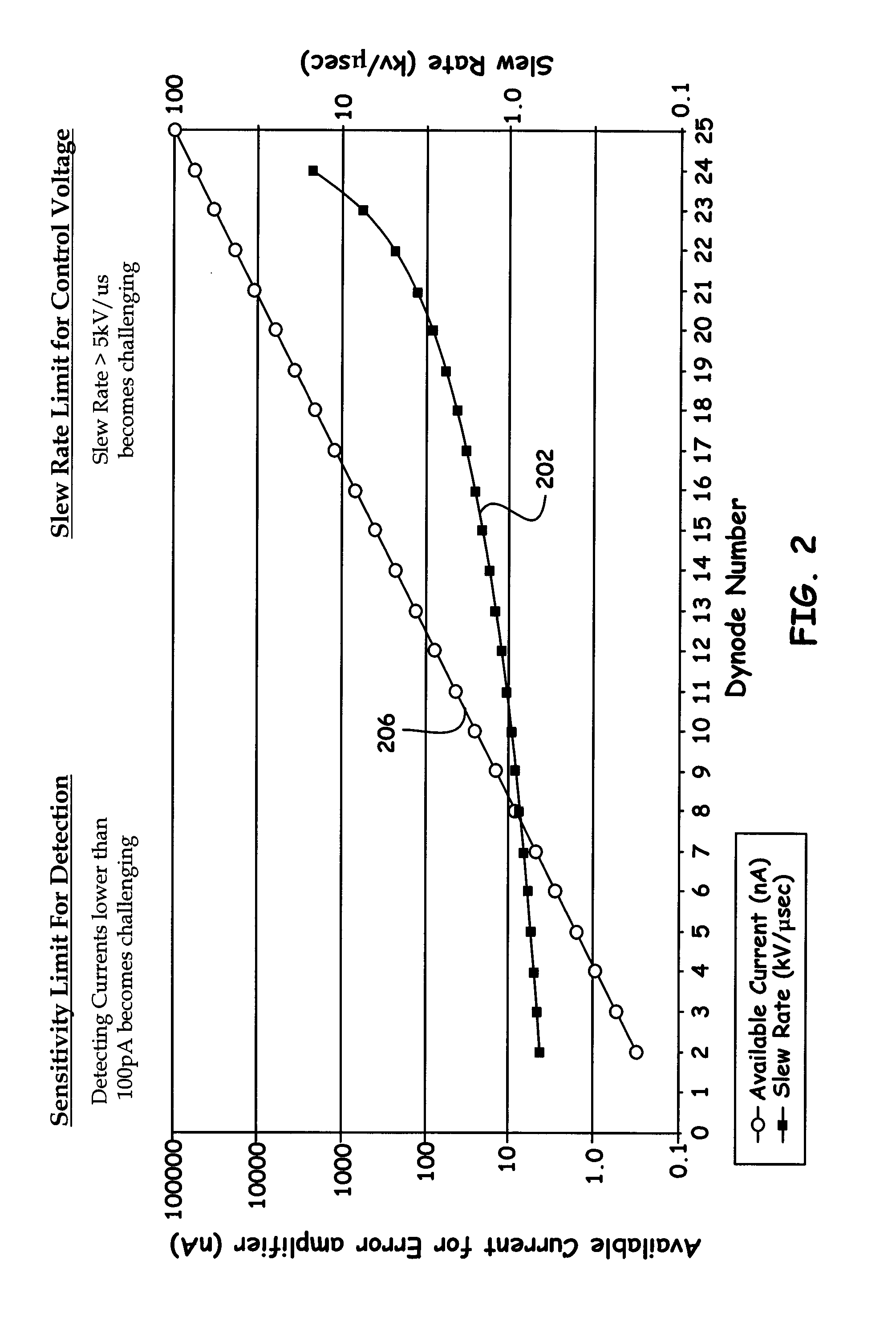
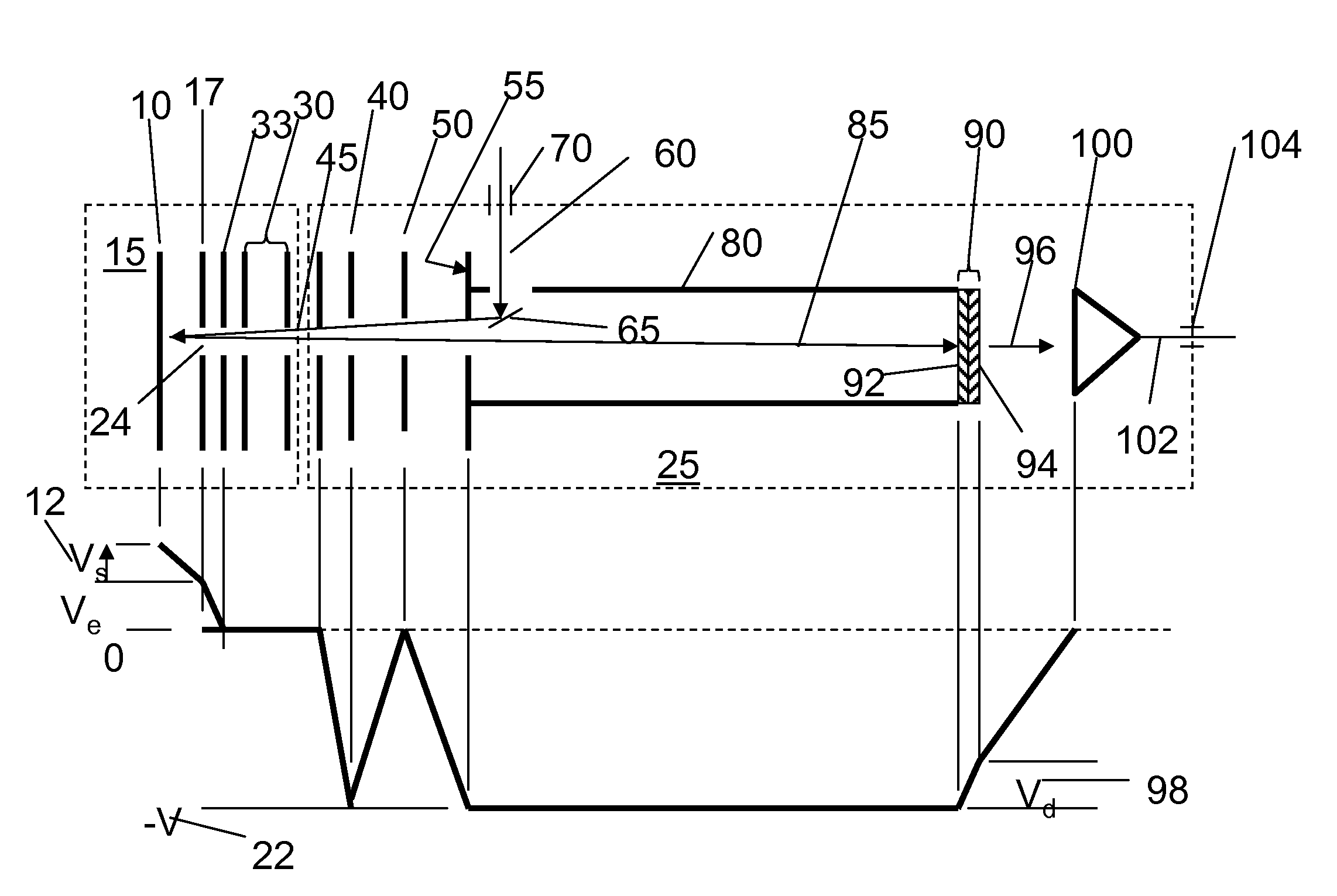
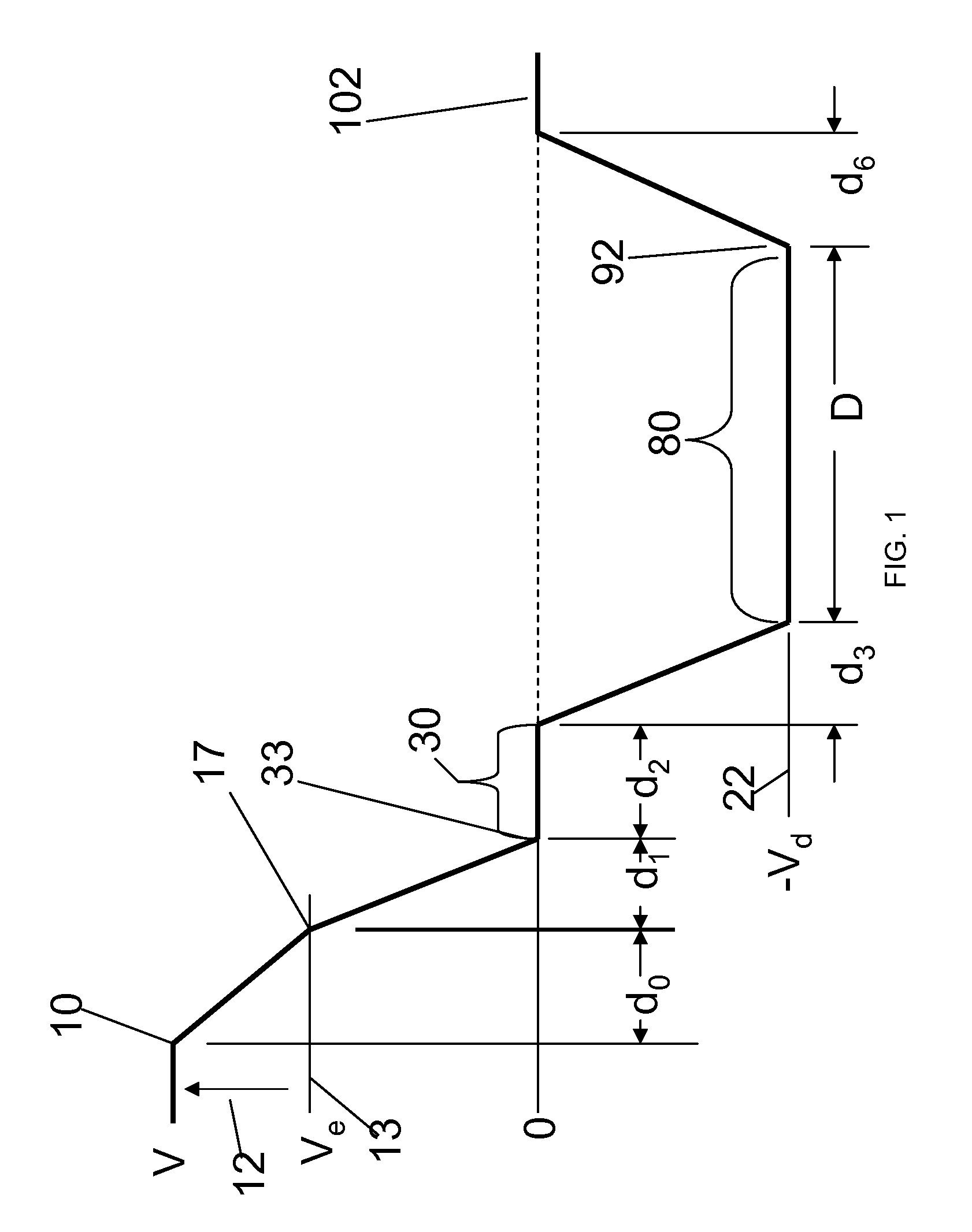
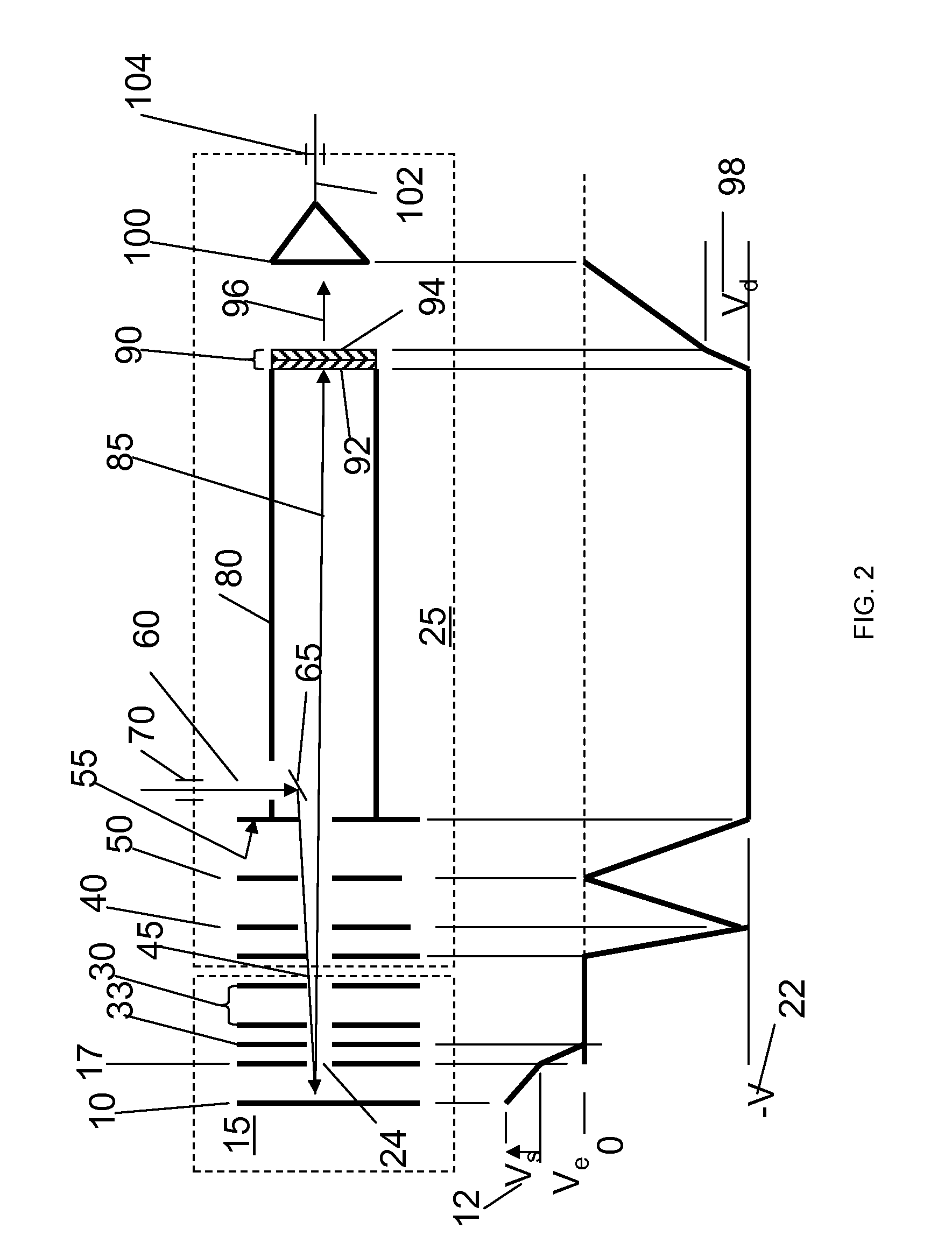
In an ion detector, power supplies (21 through 23) generating independently controllable voltages are provided to respectively apply voltages to first to fifth dynodes (11 through 15), a final dynode (16), and an anode (17) in a secondary electron multiplier (10). Furthermore, the signal from the anode (17) is extracted, and the signal from the fifth dynode (15), which has a low electron multiplication rate, is extracted. These two signals are concurrently converted into digital values, taken in by a data processing unit (34), and stored in a data storage unit (35). When a mass spectrum is created in the data processing unit (34), the two detected data for the same time are read out and the presence or absence of signal saturation or waveform deformation is determined from the values of one of the detection data. If there is a high probability of signal saturation, the detection data based on the signals in the intermediate stages are selected, and the level of the selected data is corrected. The application of independent voltages to the secondary electron multiplier (10) makes the signal saturation less likely to occur. Even if saturation temporarily occurs, an unsaturated signal can be reflected in the mass spectrum.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
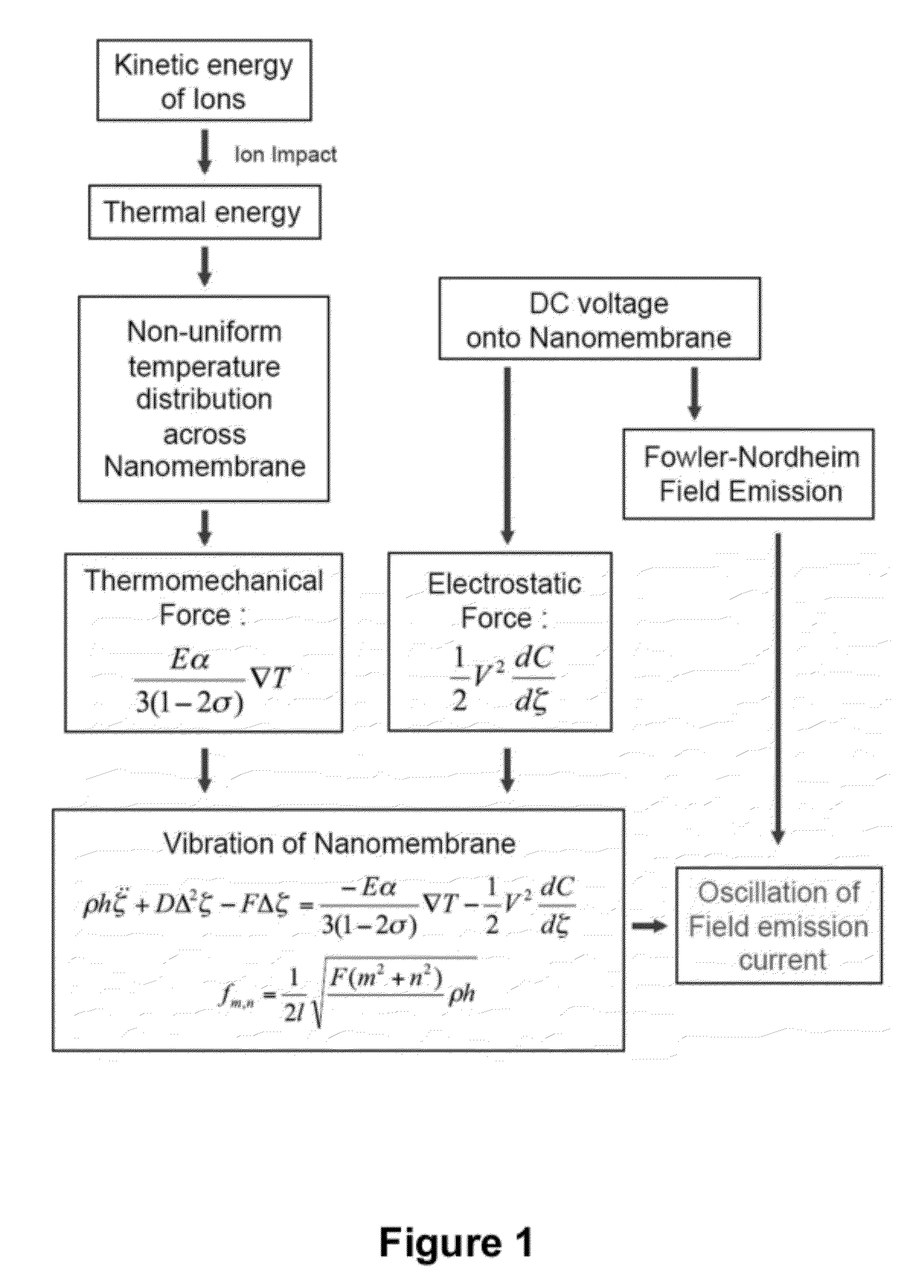
Nanoelectromechanical and microelectromechanical sensors and analyzers
ActiveUS7408147B2High detection sensitivityHigh resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectricityImage resolution
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for detecting, sensing and analyzing molecules. Detectors of the present invention provide good detection sensitivity over a wide range of molecular masses ranging from a few Daltons up to 10s of megadaltons, which does not decrease as function of molecular mass. Sensors and analyzers of the present invention detect emission from an array of resonators to determine the molecular masses and / or electric charges of molecules which impact or contact an external surface of a membrane that is used to mount and excite the resonators in the array. Resonators in the array are excited via piezoelectric and / or magnetic excitation of the mounting membrane and, optionally, grid electrodes are used in certain configurations for electrically biasing for the resonator array, and for amplification or suppression of emission from the resonators so as to provide detection and mass / electric charge analysis with good sensitivity and resolution.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
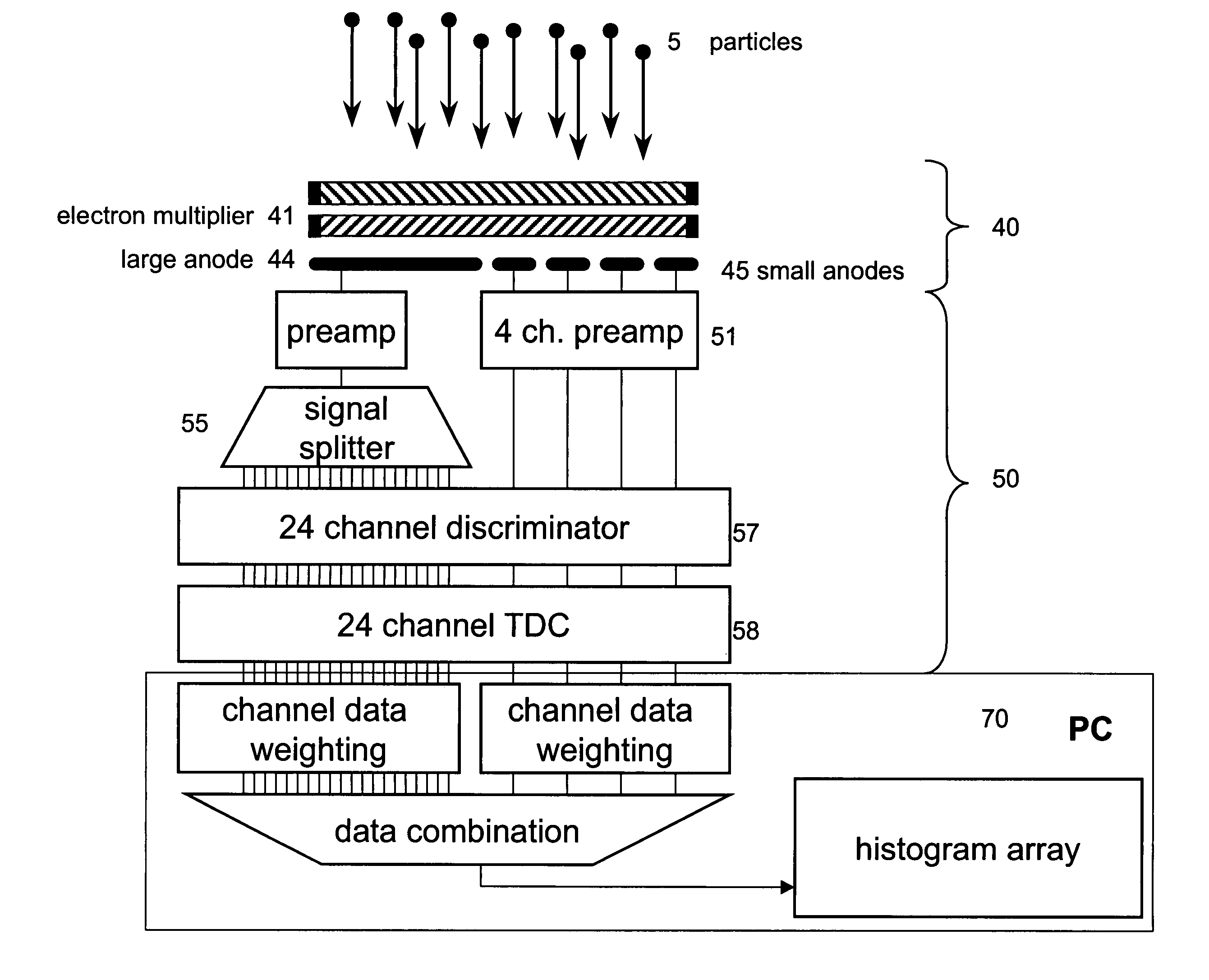
Multiple detection systems
InactiveUS7928361B1Improve accuracyIncrease powerTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsTemporal resolutionData set
A particle detection system is configured and operated as two or more separate and completely independent detection systems. The detection systems may be of the same or different design, may be operated in the same or different modes, and may be operated with the same or different operating parameters. Each detection system may record signals simultaneously, or alternately; the measurements obtained from each of the detection systems may either be combined into a single unified data set, or recorded separately. Means are provided to direct particles to impinge on one of the detectors or any of the other detectors. Alternatively, a population of particles can be dispersed in a manner that allows a population of particles to be distributed among two or more detectors simultaneously. The implementation of completely independent detection systems, for example, in a Time-of-Flight mass spectrometer, allows the design and operation of each detection system to be optimized independently, while being employed simultaneously. The flexibility afforded by the apparatus and methods in the invention allows signals to be recorded with enhanced signal dynamic range, signal-to-noise, and / or temporal resolution, relative to other presently available detection systems.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Discrete Dynode Detector with Dynamic Gain Control
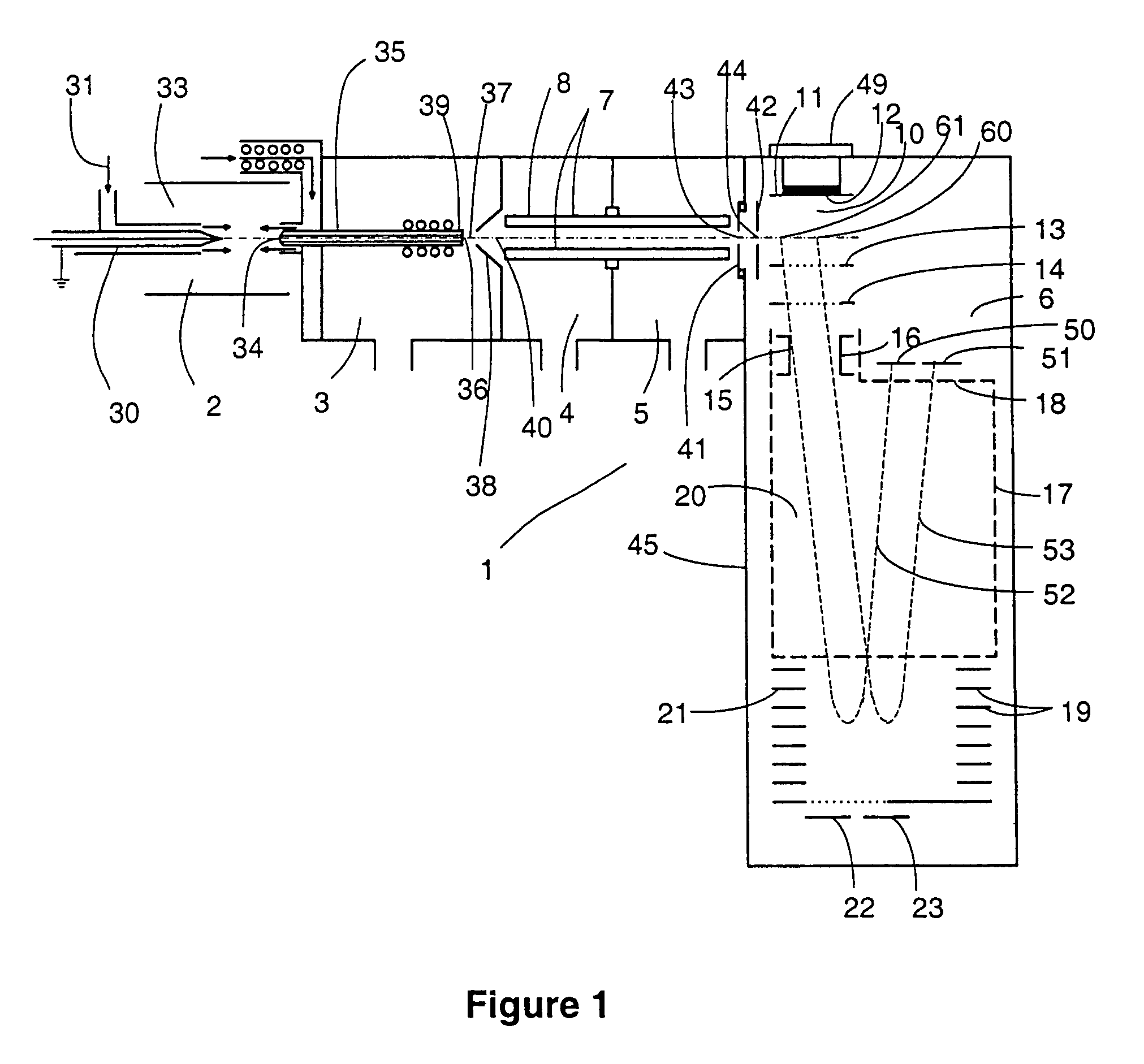
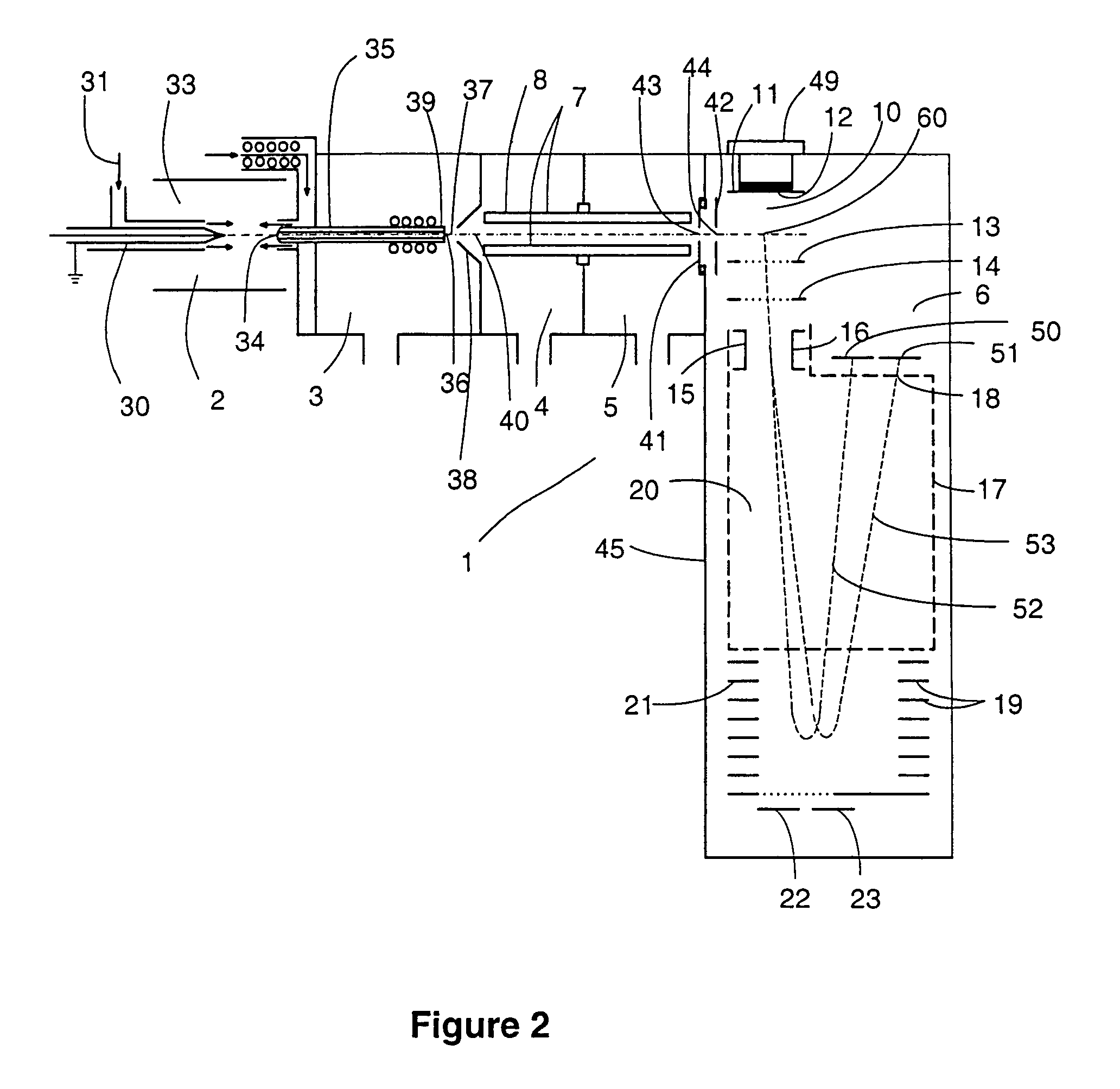
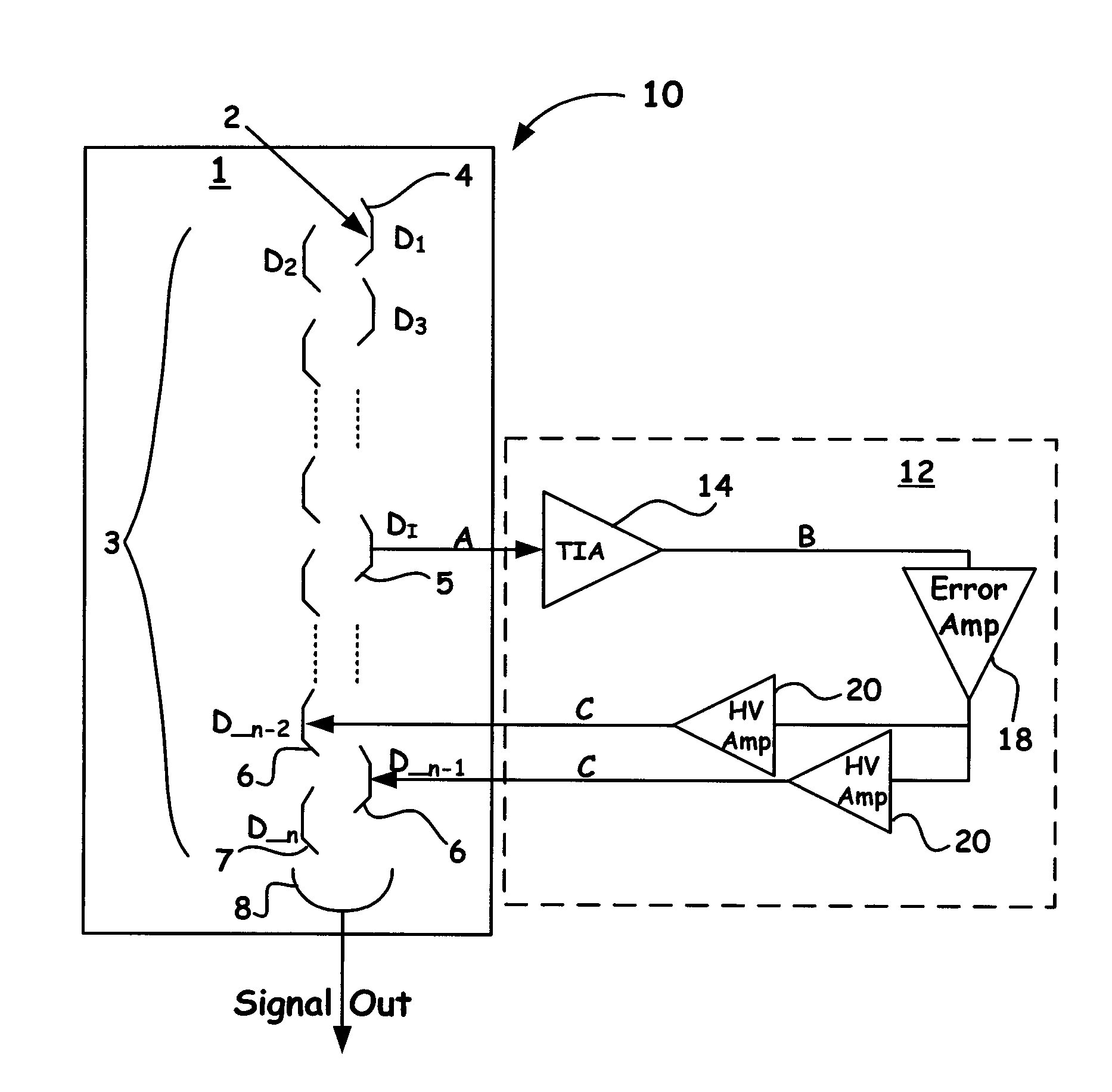
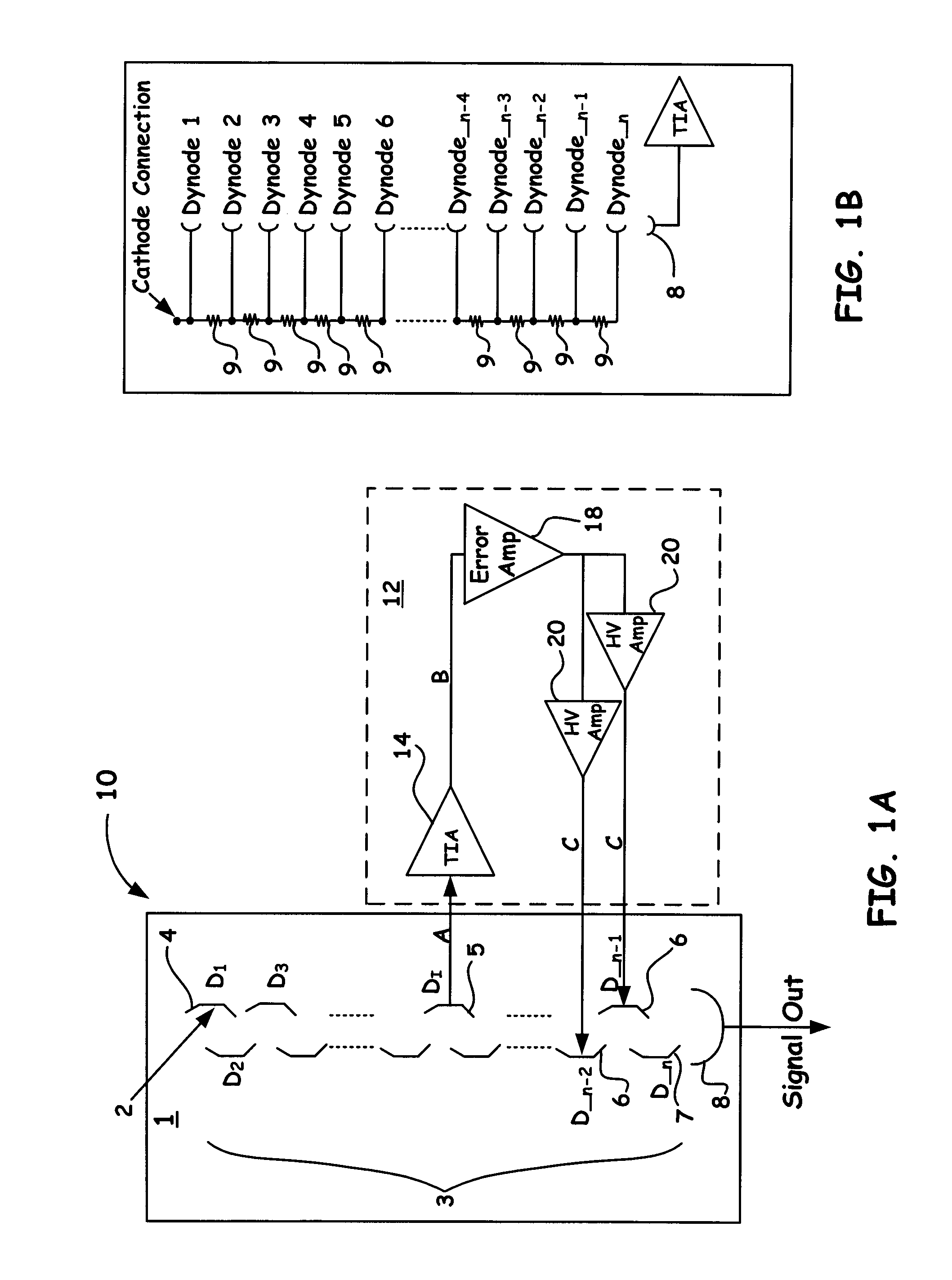
A novel electron multiplier that regulates in real time the gain of downstream dynodes as the instrument receives input signals is introduced. In particular, the methods, electron multiplier structures, and coupled control circuits of the present invention enable a resultant on the fly control signal to be generated upon receiving a predetermined threshold detection signal so as to enable the voltage regulation of one or more downstream dynodes near the output of the device. Accordingly, such a novel design, as presented herein, prevents the dynodes near the output of the instrument from being exposed to deleterious current pulses that can accelerate the aging process of the dynode structures that are essential to the device.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Linear tof geometry for high sensitivity at high mass
InactiveUS20080272289A1Improve performanceIncrease the lengthSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersElectrical polarityMass analyzer
The present invention provides a time-of-flight (TOF) mass analyzer. The system includes an analyzer vacuum housing isolated from the evacuated ion source vacuum housing by a gate valve maintained at ground potential. A pulsed ion source is located within the ion source housing, and the gate valve is located in a first field-free region at ground potential. A second field-free drift space within the analyzer housing is biased at high voltage with opposite polarity to the voltage applied to the pulsed ion source. Novel ion detectors are provided with input surfaces in electrical contact with the second field-free drift space with output connected to an external digitizer at ground potential.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
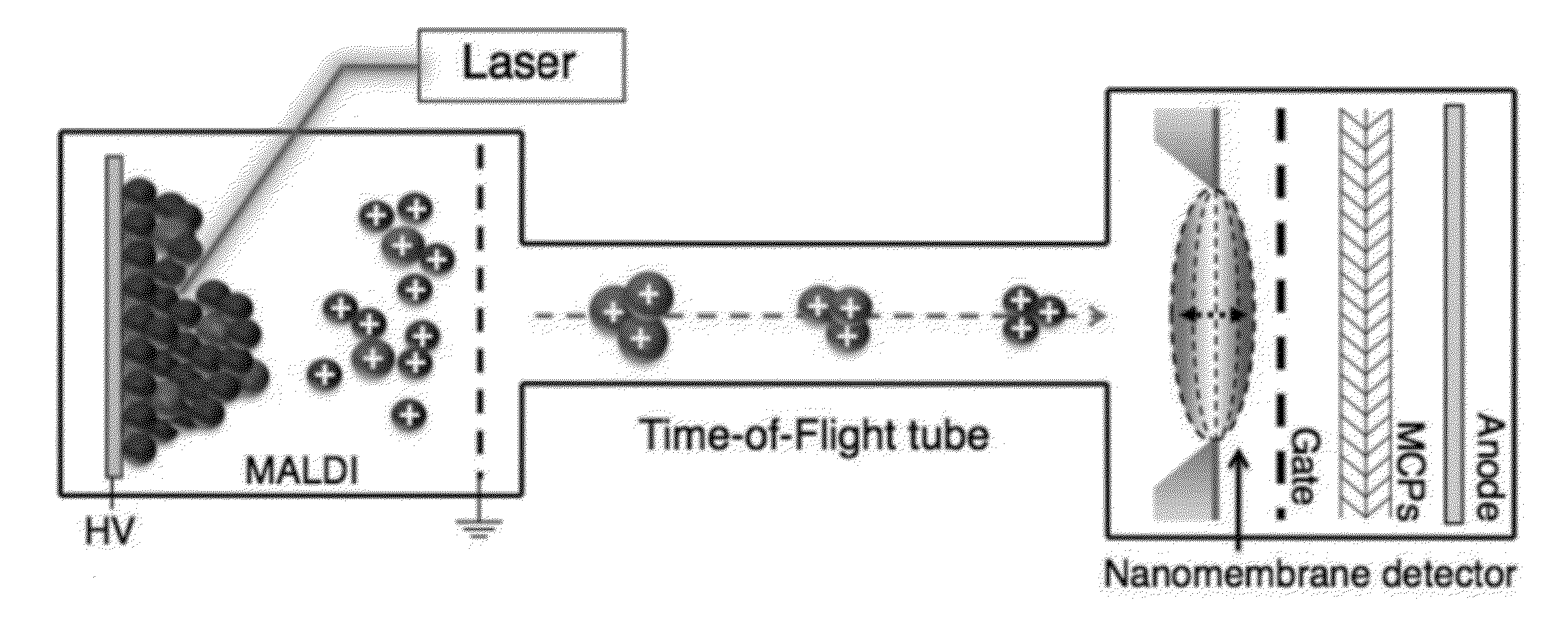
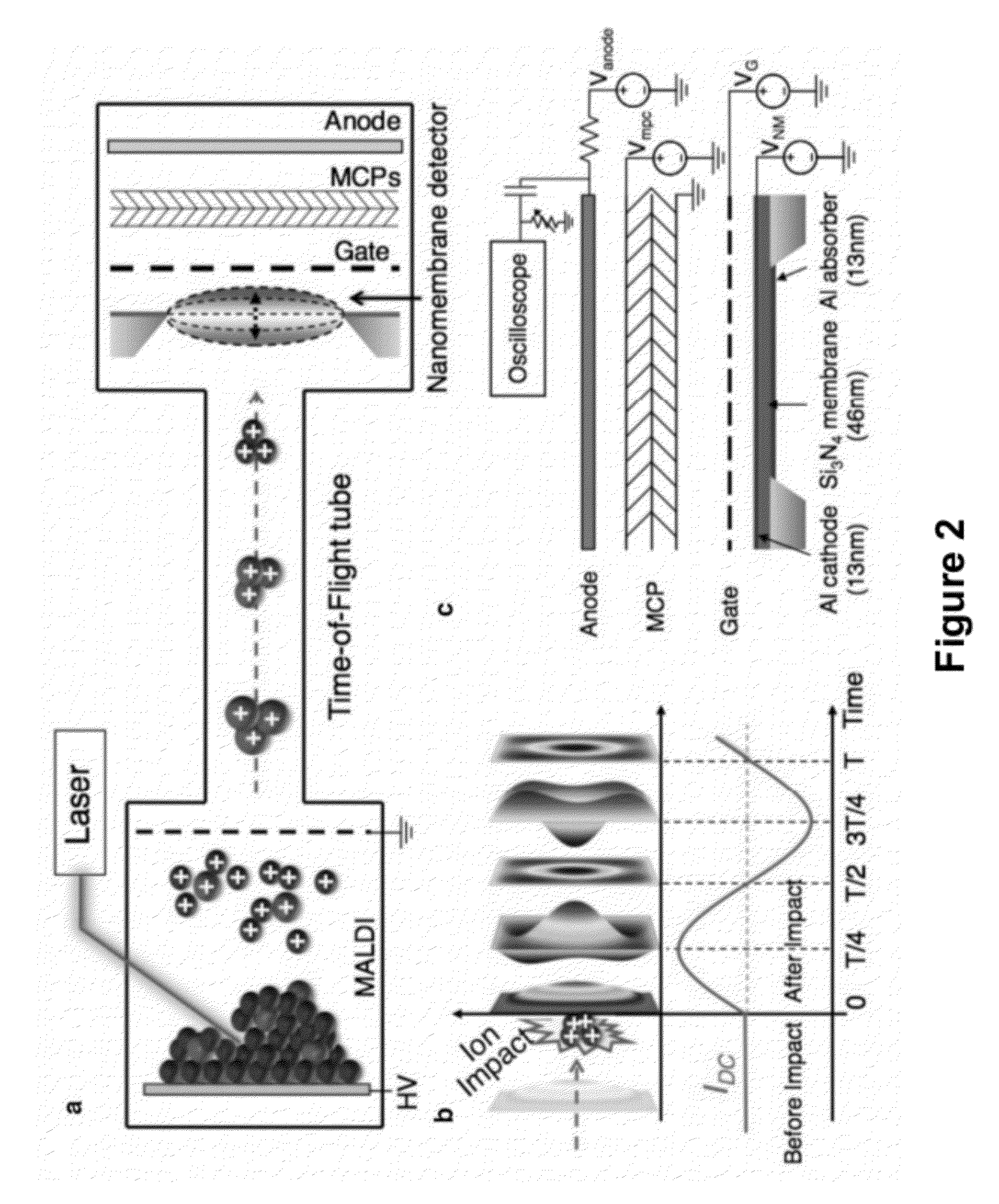
Membrane Detector for Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20120305760A1High detection sensitivityGood temporal resolution and sensitivityThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerCell lysates
The invention provides methods, and related devices and device components, for detecting, sensing and analyzing analytes in samples. In some aspects, the invention provides methods, and related devices and device components, useful in combination with a mass analyzer for the mass spectrometric analysis of analytes derived from biomolecules in biological samples including biological fluids cell extracts, and cell lysates. Methods of some aspects of the invention utilize a thin membrane-based detector as a transducer for converting the kinetic energies of analytes into a field emission signal via excitation of mechanical vibrations in an electromechanically biased membrane by generation of a thermal gradient.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
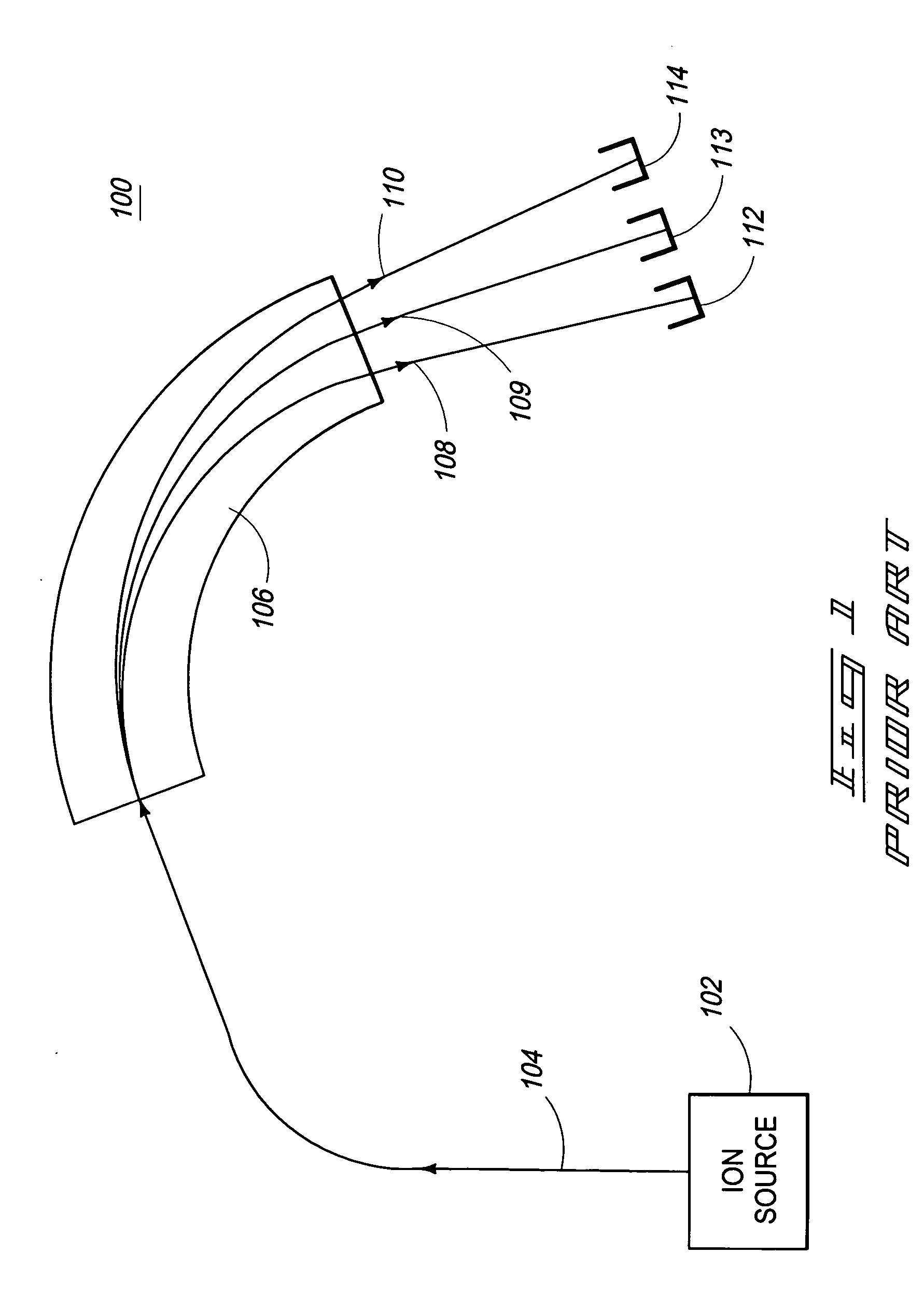
Mass spectrometer and methods of increasing dispersion between ion beams
InactiveUS20050279933A1Good dispersionSufficiently dispersedStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsIon beamMass spectrometric
A mass spectrometer includes a magnetic sector configured to separate a plurality of ion beams, and an electrostatic sector configured to receive the plurality of ion beams from the magnetic sector and increase separation between the ion beams, the electrostatic sector being used as a dispersive element following magnetic separation of the plurality of ion beams. Other apparatus and methods are provided.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com