Patents
Literature
2341 results about "System time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science and computer programming, system time represents a computer system's notion of the passage of time. In this sense, time also includes the passing of days on the calendar. System time is measured by a system clock, which is typically implemented as a simple count of the number of ticks that have transpired since some arbitrary starting date, called the epoch. For example, Unix and POSIX-compliant systems encode system time ("Unix time") as the number of seconds elapsed since the start of the Unix epoch at 1 January 1970 00:00:00 UT, with exceptions for leap seconds. Systems that implement the 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the Windows API, such as Windows 9x and Windows NT, provide the system time as both SYSTEMTIME, represented as a year/month/day/hour/minute/second/milliseconds value, and FILETIME, represented as a count of the number of 100-nanosecond ticks since 1 January 1601 00:00:00 UT as reckoned in the proleptic Gregorian calendar.
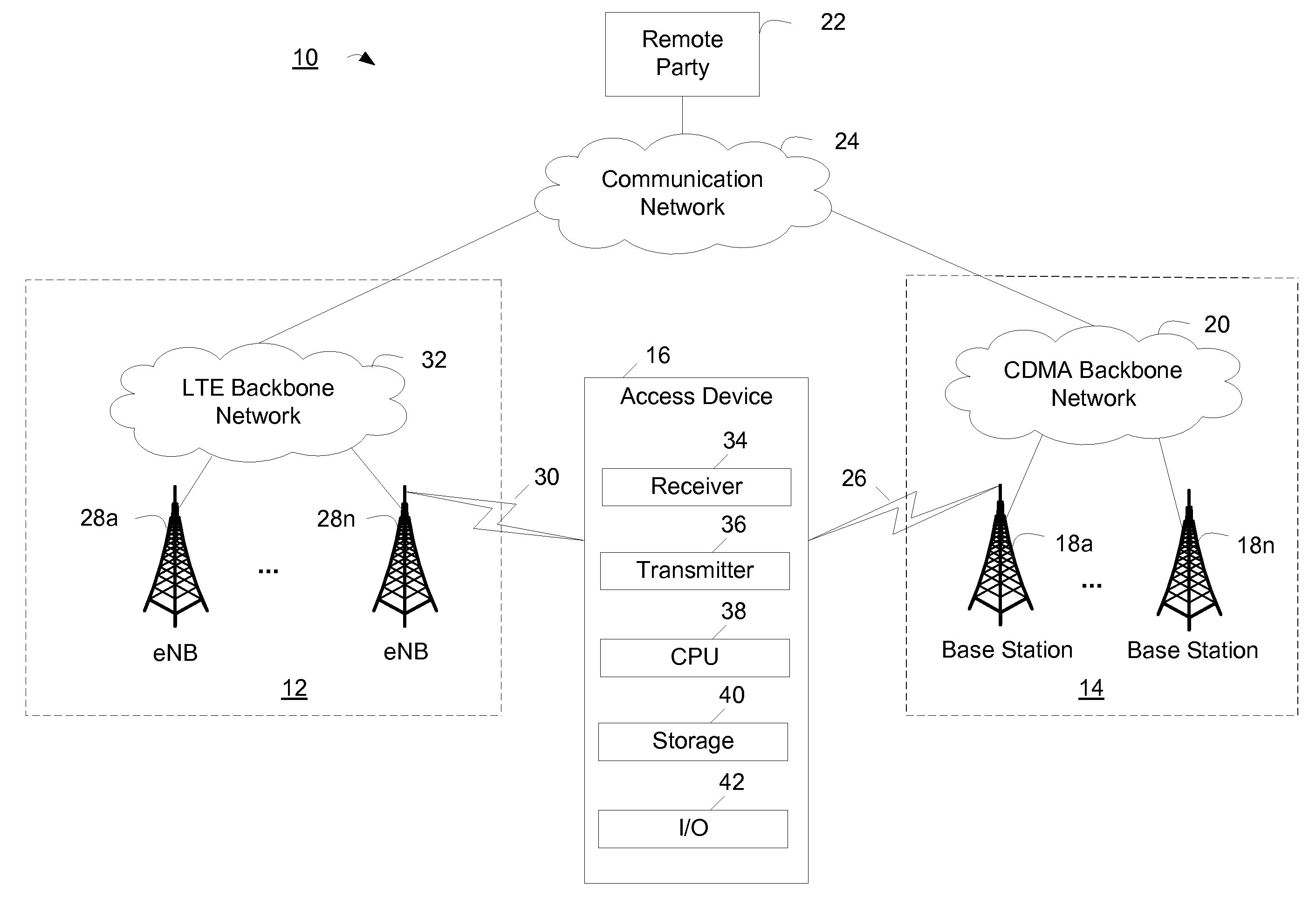
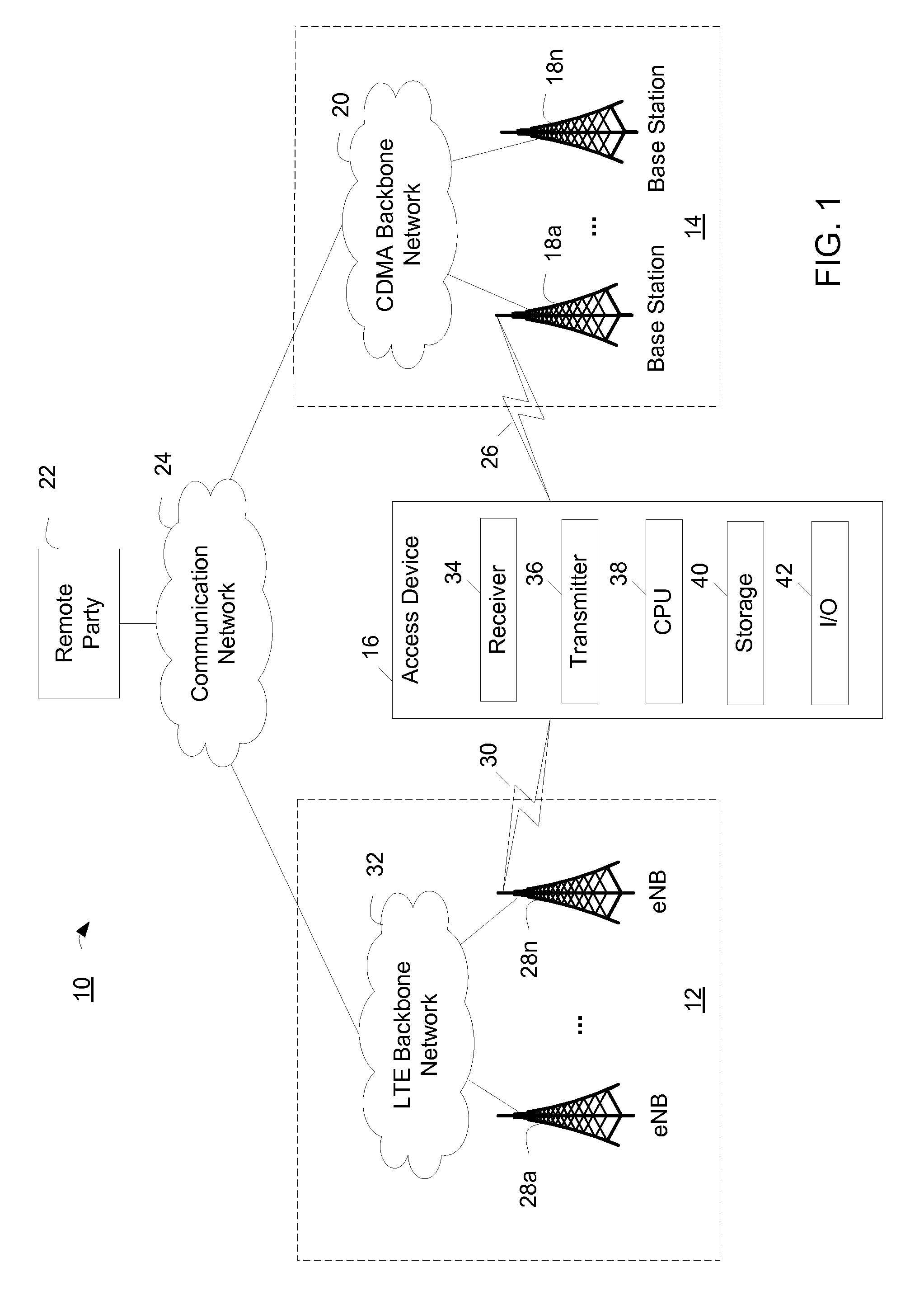
Method for transporting digital media
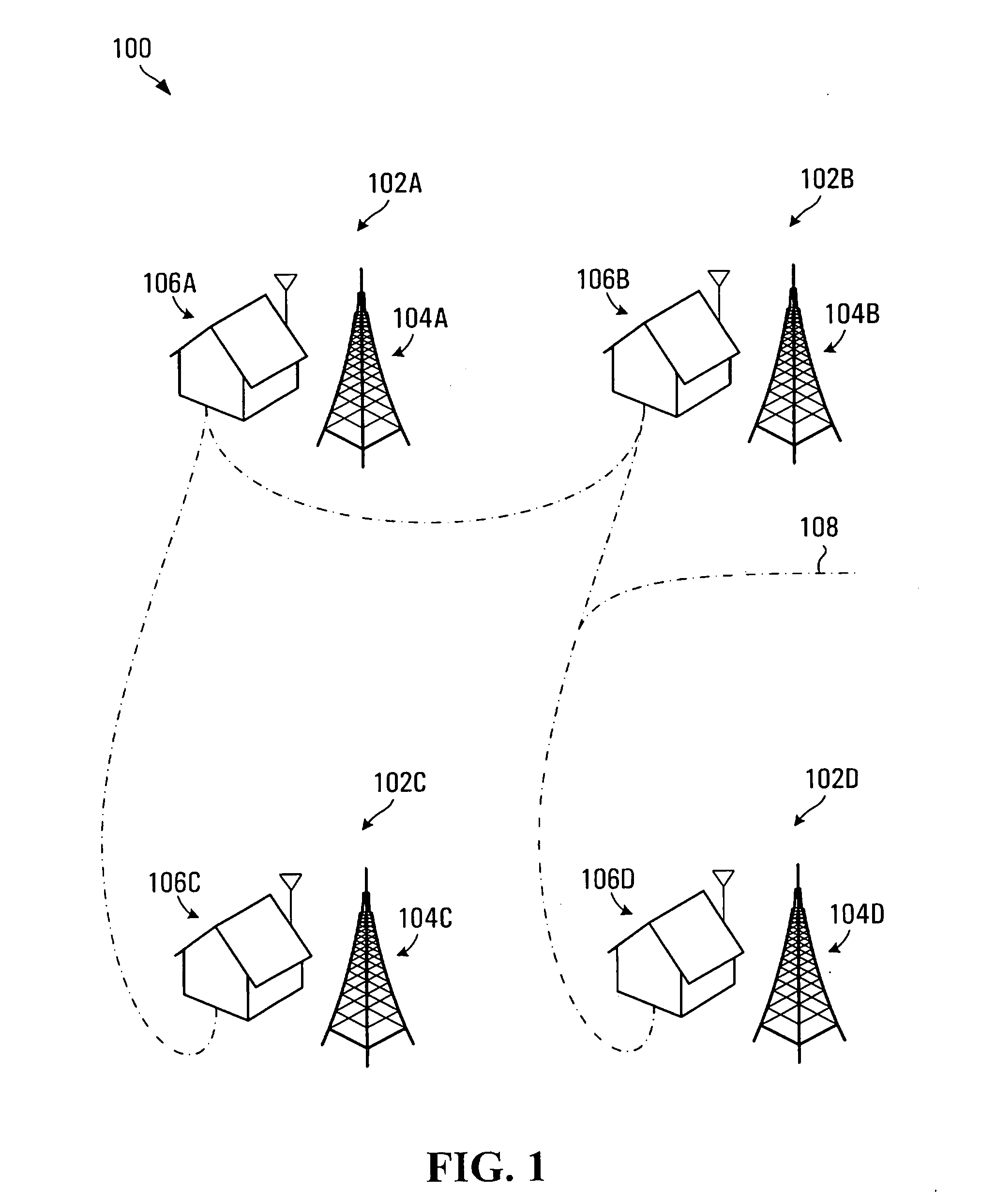
ActiveUS20060280182A1Low costSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesTime-division multiplexTime ProtocolNetworked system
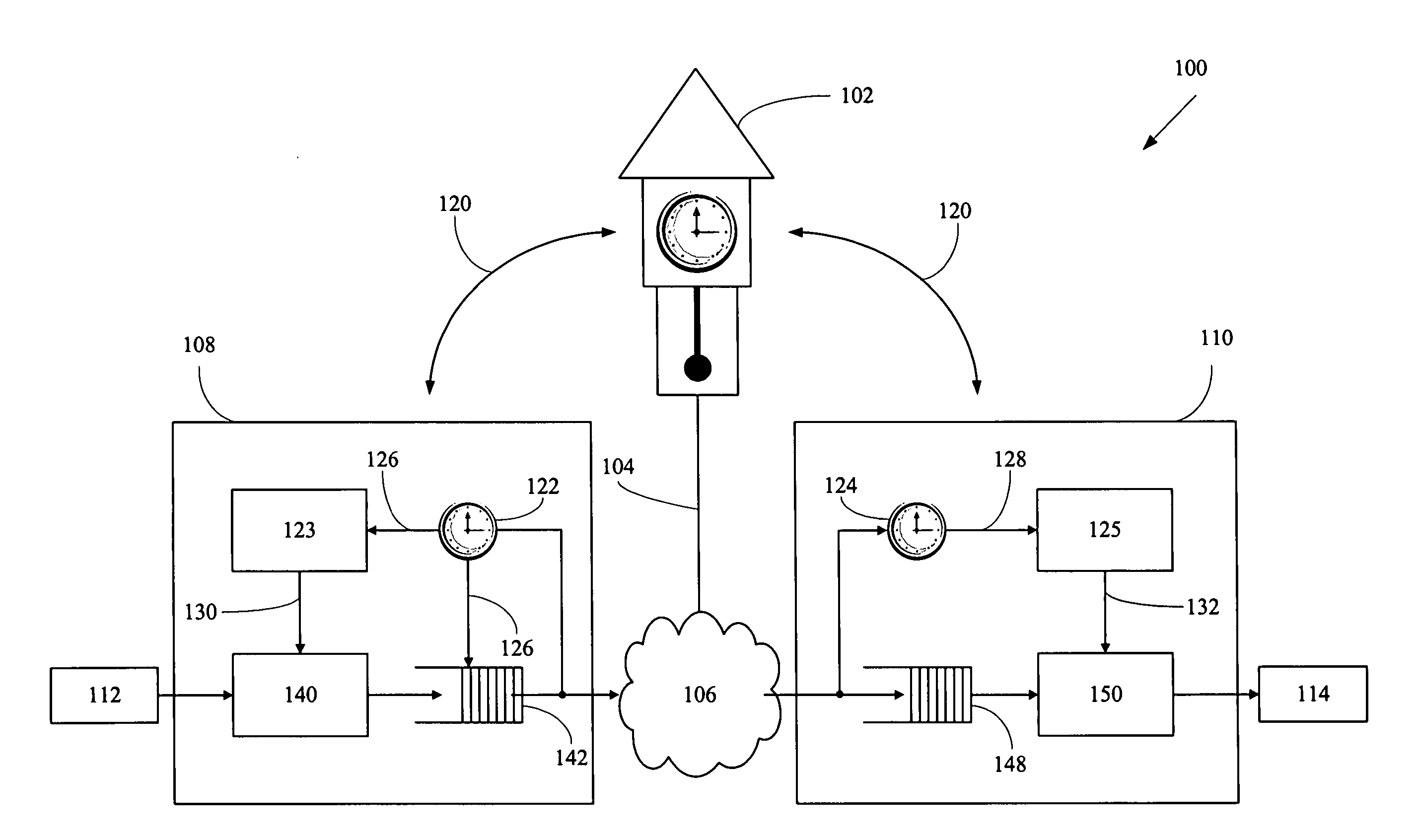
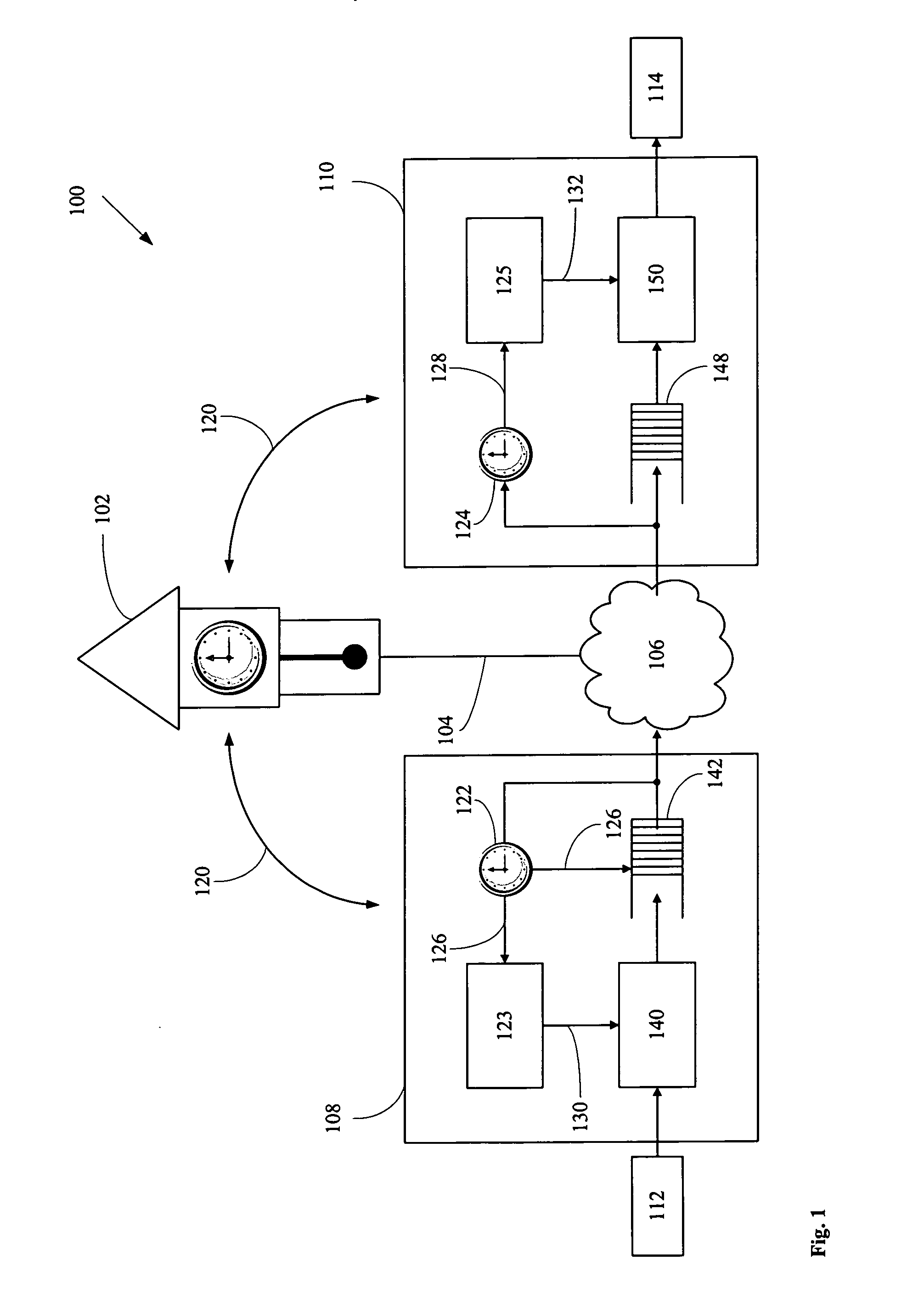
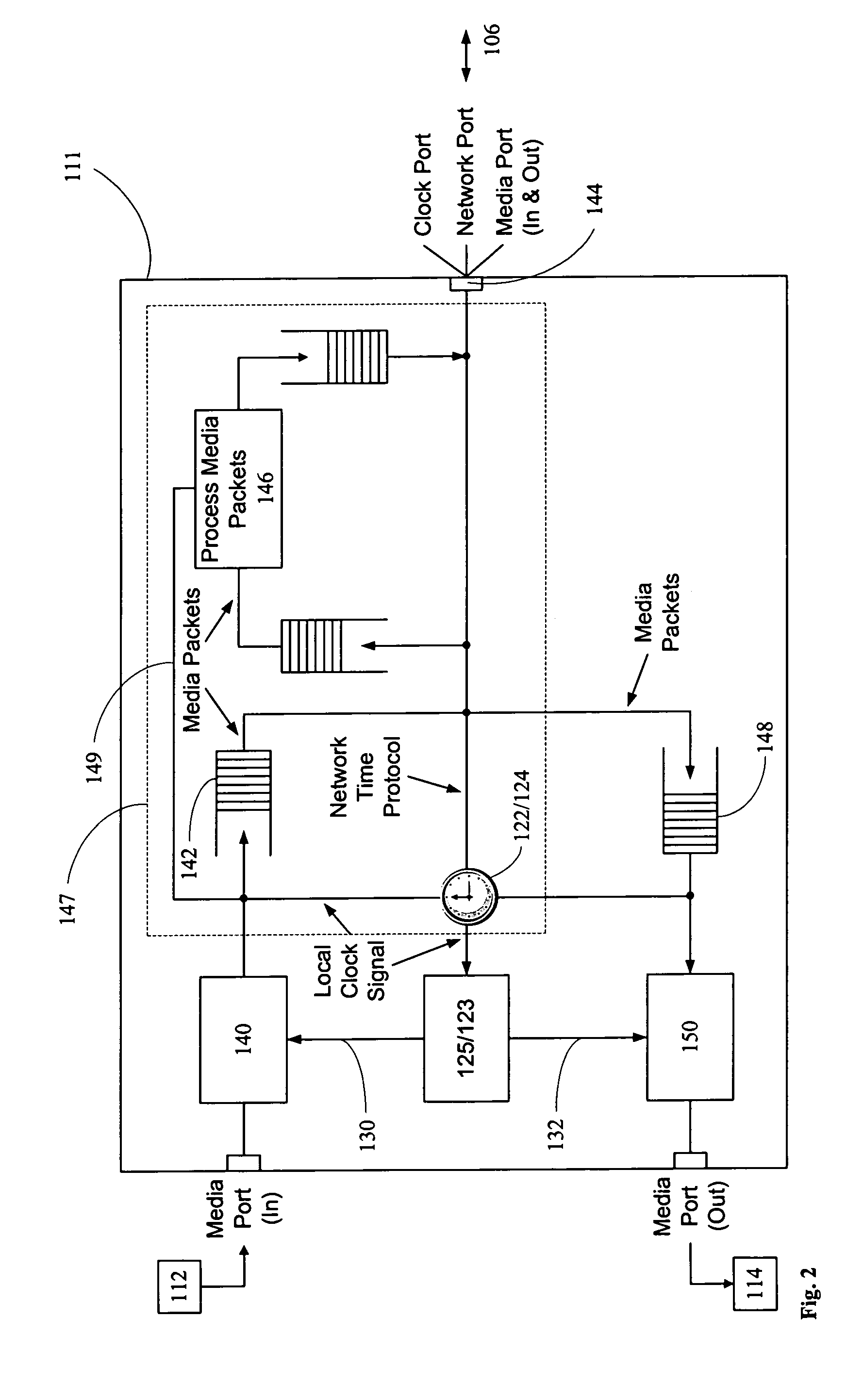
A networked system is provided for transporting digital media packets, such as audio and video. The network includes network devices interconnected to send and receive packets. Each network device can receive and transmit media signals from media devices. A master clock generates a system time signal that the network devices use, together with a network time protocol to generate a local clock signal synchronised to the system time signal for both rate and offset. The local clock signal governs both the rate and offset of the received or transmitted media signals. The system, which can be implemented using conventional network equipment enables media signals to be transported to meet quality and timing requirements for high quality audio and video reproduction.
Owner:AUDINATE HLDG PTY LTD
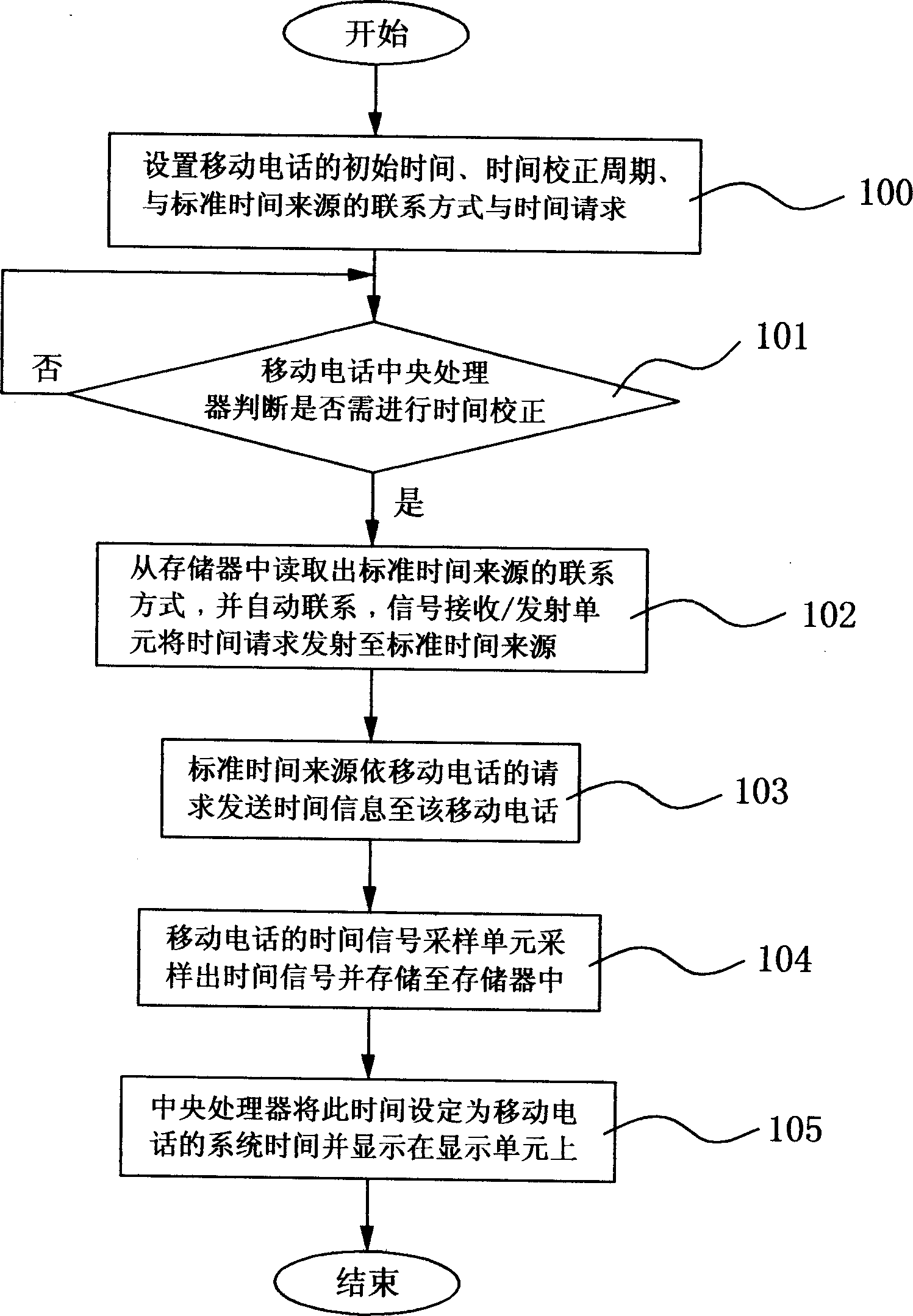
Mobile phone time automatic correction method
InactiveCN1801829ALow costMiniaturization hindranceSetting time indicationRadio-controlled time-piecesTemporal informationAutocorrection
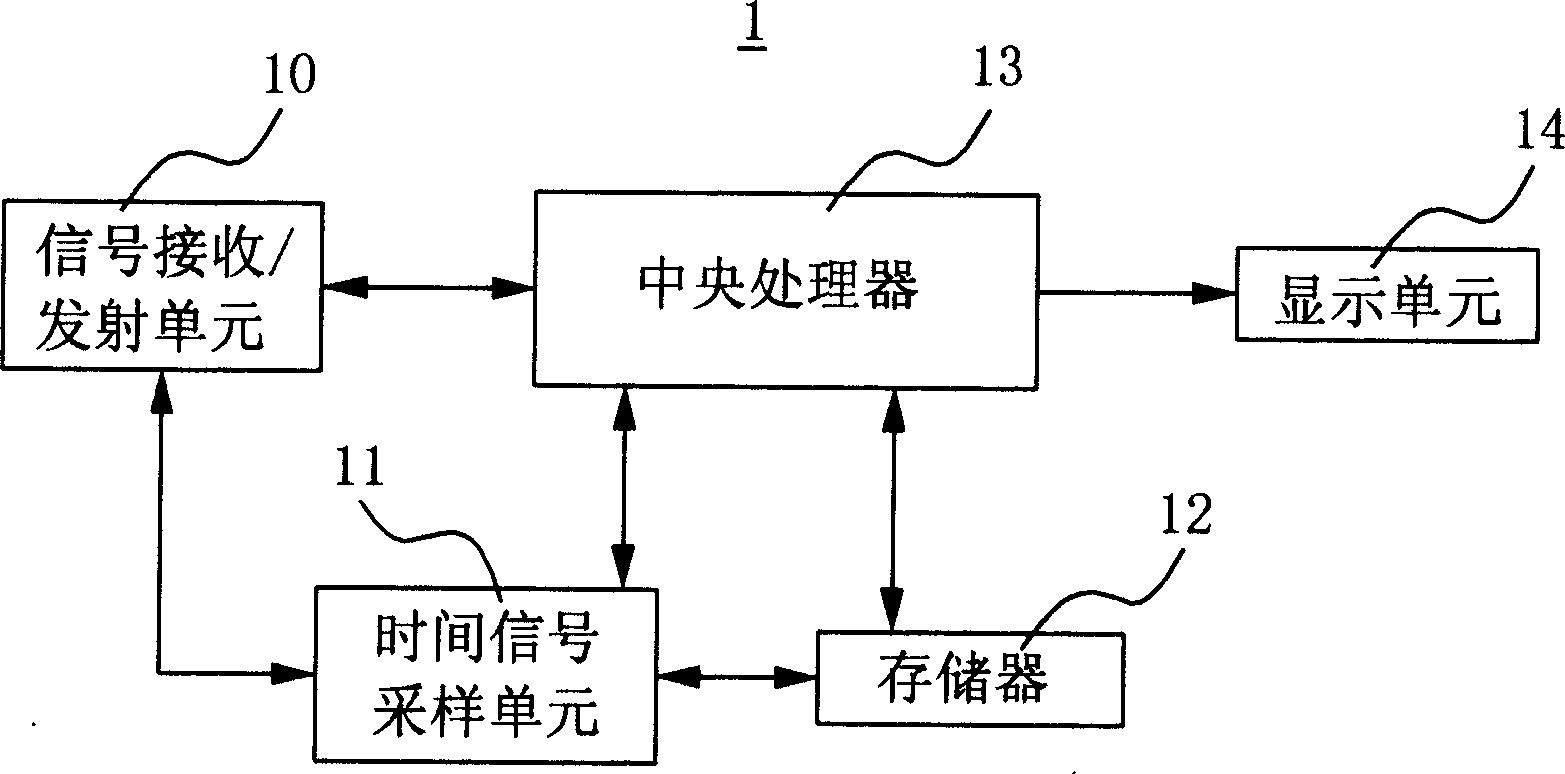
Said invention provides a mobile telephone time autocorrection method. It contains signal reception / transmitting unit, time signal sampling unit memory unit, central processing unit and display unit, said method mainly setting mobile telephone initial time, time adjustment cycle, and standard time source connection mode and time request , when need proceeding time correction, said mobile telephone automatically transmitting time request to standard time source and taking standard time then configuring said standard time as system time of mobile telephone to reach higher time precision by using normal quartz oscillator.
Owner:KUNDA COMP TECHKUSN
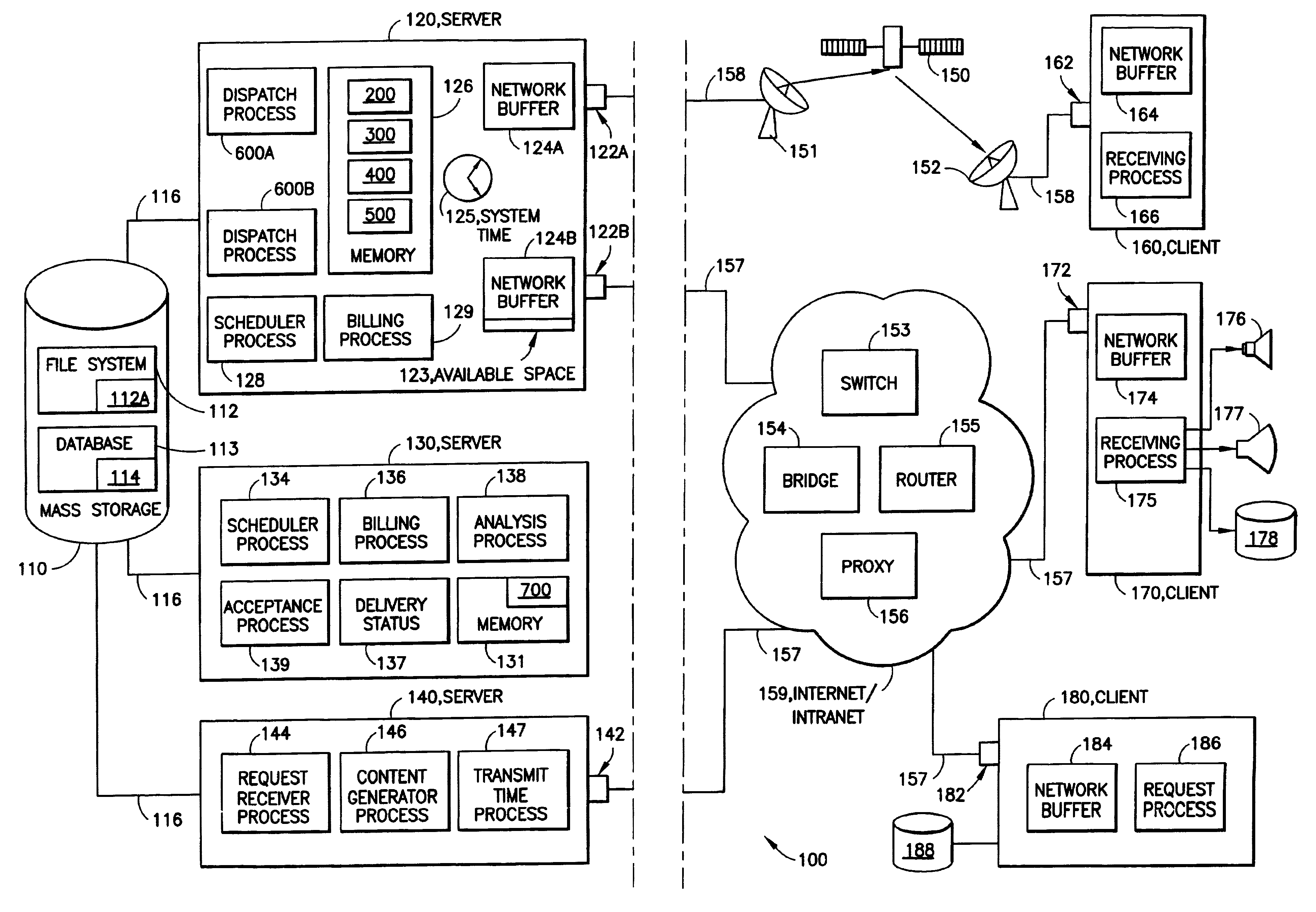
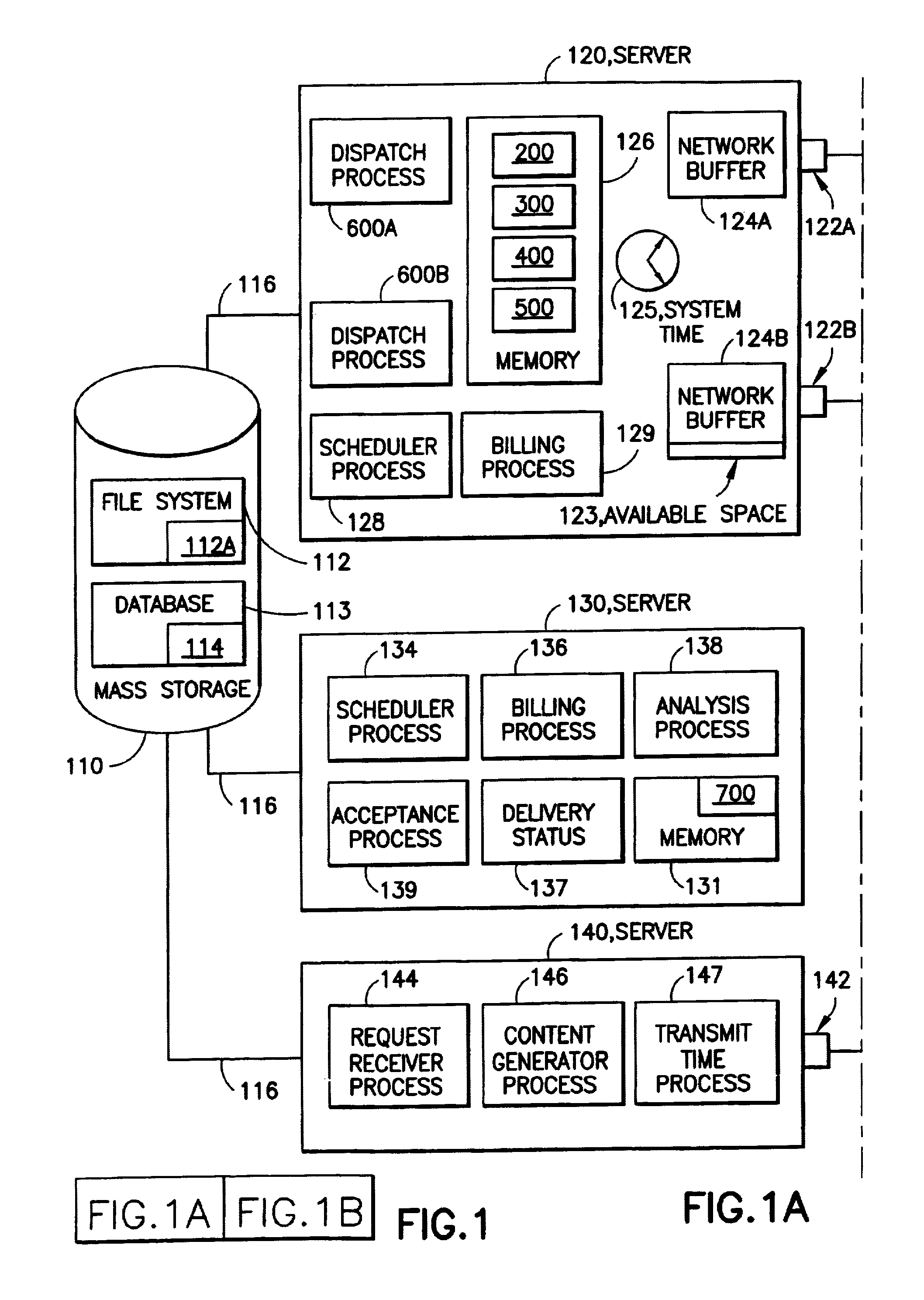
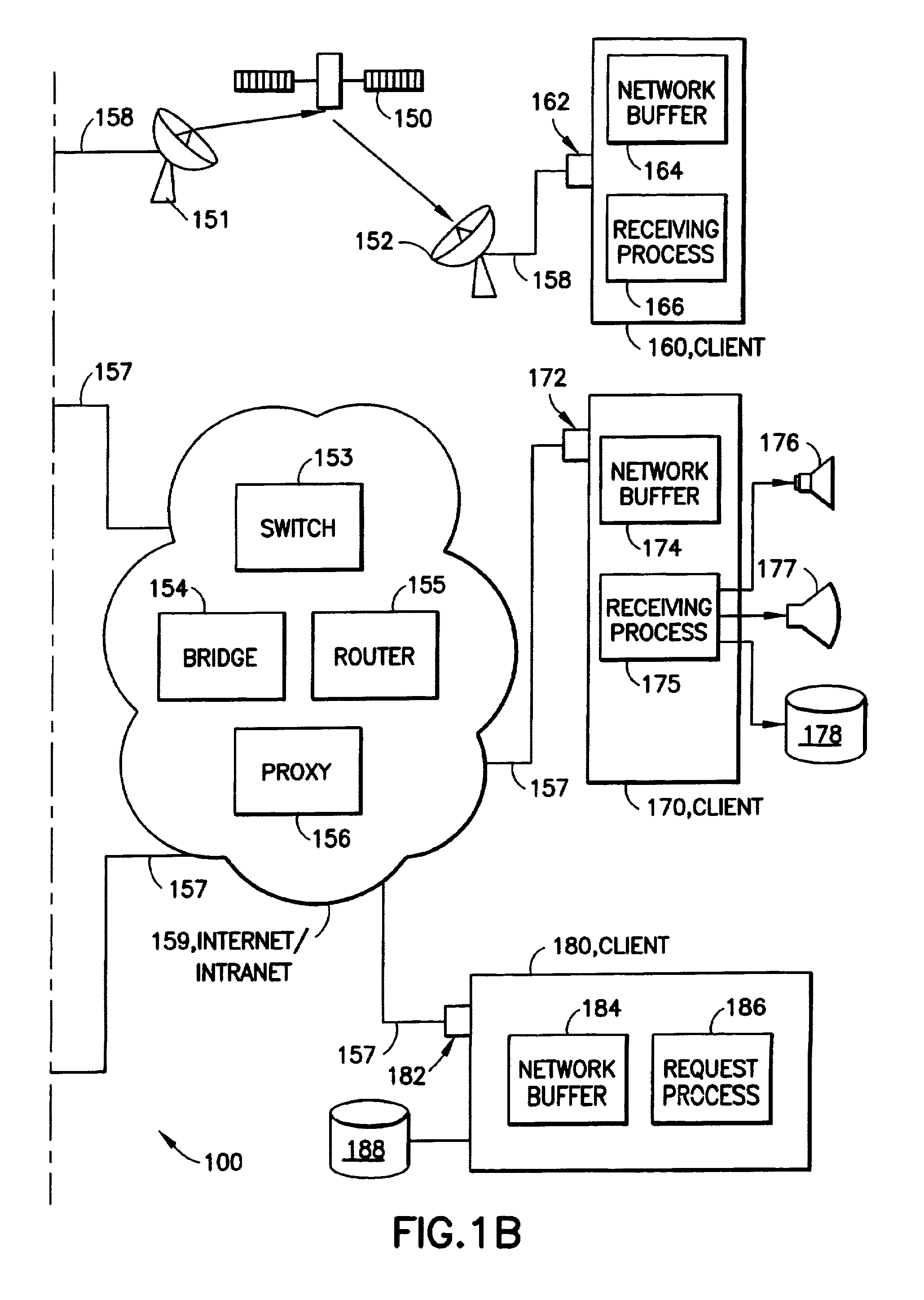
System and method for dispatching and scheduling network transmissions with feedback
InactiveUS6959327B1Efficient accurateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCompletion timeRelease time
A computer dispatcher connected to one or more respective network buffers has stored file lists that identify one or more of the files in the database that are to be transmitted over networks connected to the respective network buffer. A scheduler(s) schedule one or more portions of one or more of the files to be written to the respective network buffers by defining transmission criteria about each of the files in the file list. These transmission criteria include a quantity to transmit criteria, defining a quantity of one or more of the portions of the respective file to transmit, and one or more release times. The release times define the time at which the respective portion is to be written to the network buffer. The system includes a dispatching process that determines an available space on one or more of the network buffers and a current system time. The dispatching process determines if the system time is greater than or equal to one of the release times and further takes a minimum value of the available space and the quantity of the respective portion. The dispatching process then writes the minimum value of the respective portion to one or more of the network buffers. A feedback mechanism, e.g. a quantity completion measure, is used to estimate a completion time of the writing of the respective portion to the respective network buffer. The scheduler then reschedules one or more of the portions if one or more of the portions can not be scheduled to meet the respective transmission criteria.
Owner:IBM CORP
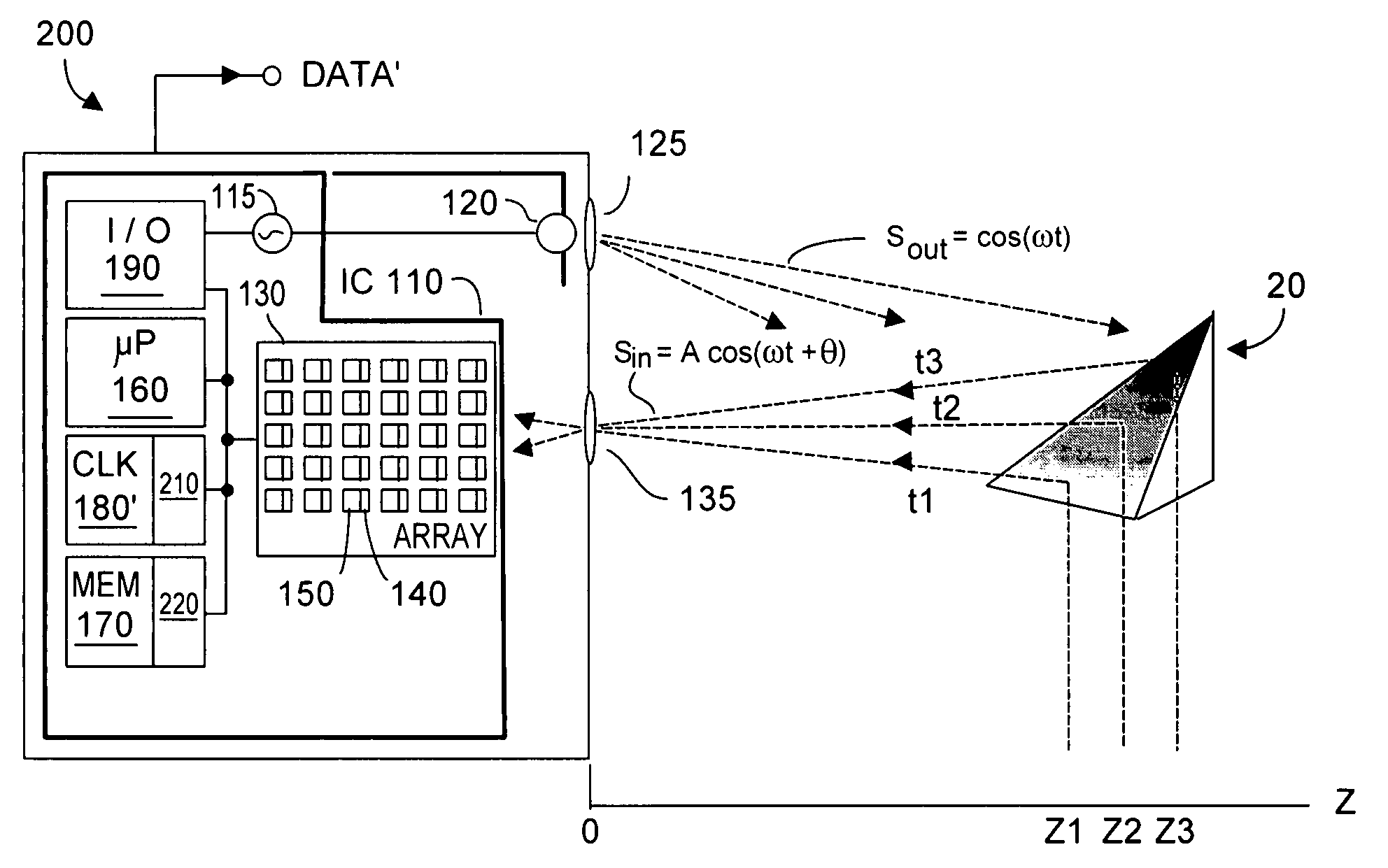
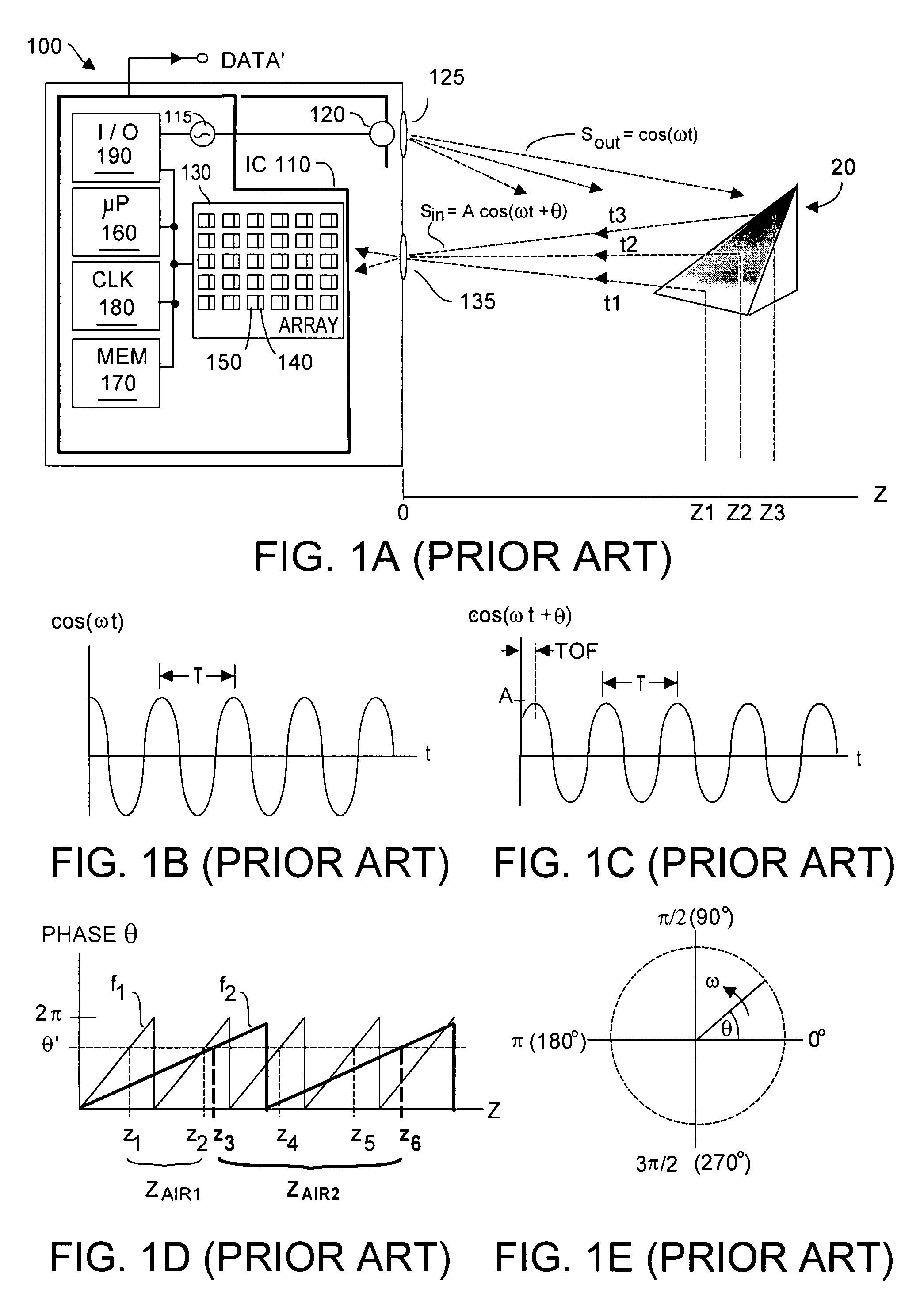
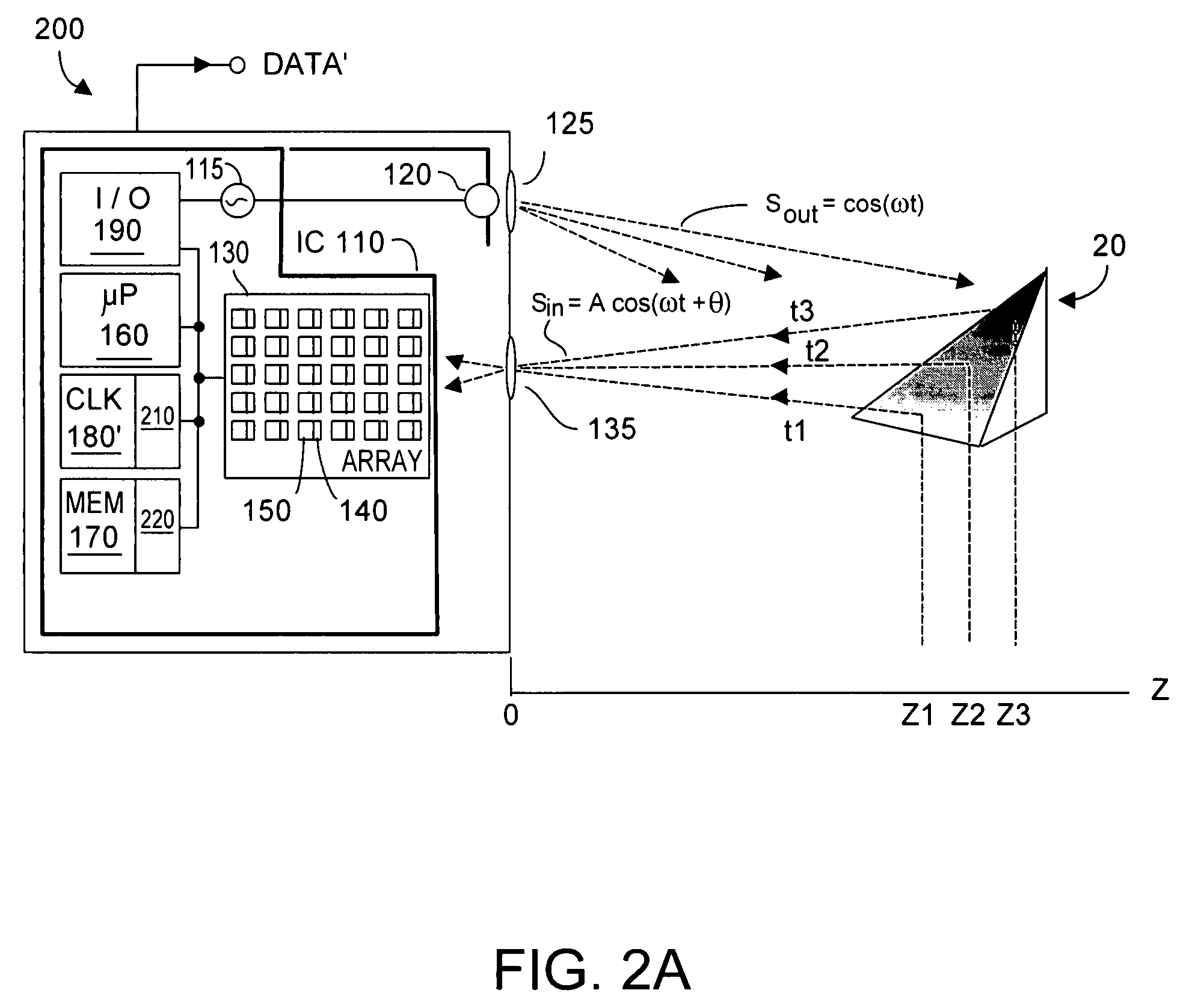
Method and system for lossless dealiasing in time-of-flight (TOF) systems
ActiveUS7791715B1Facilitates rapidly learning approximate valueEffective aliasingOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationSystem timeDerived Data
Time-of-flight (TOF) phase-derived data is dealiased by operating the TOF system using at least two close-together modulation frequencies f1 and f2 that are close to the TOF system maximum modulation frequency fm. On one hand, phase data acquired by the TOF is associated with a desirably long aliasing interval range ZAIR normally associated with a rather low modulation frequency. On the other hand, phase data acquired by the TOF system is also associated with the high precision certainty as to Z value normally associated with high modulation frequency. Preferably the TOF system operates always close to fm such that TOF operating efficiency is high, and system signal / noise ratio is not substantially degraded using the present invention.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
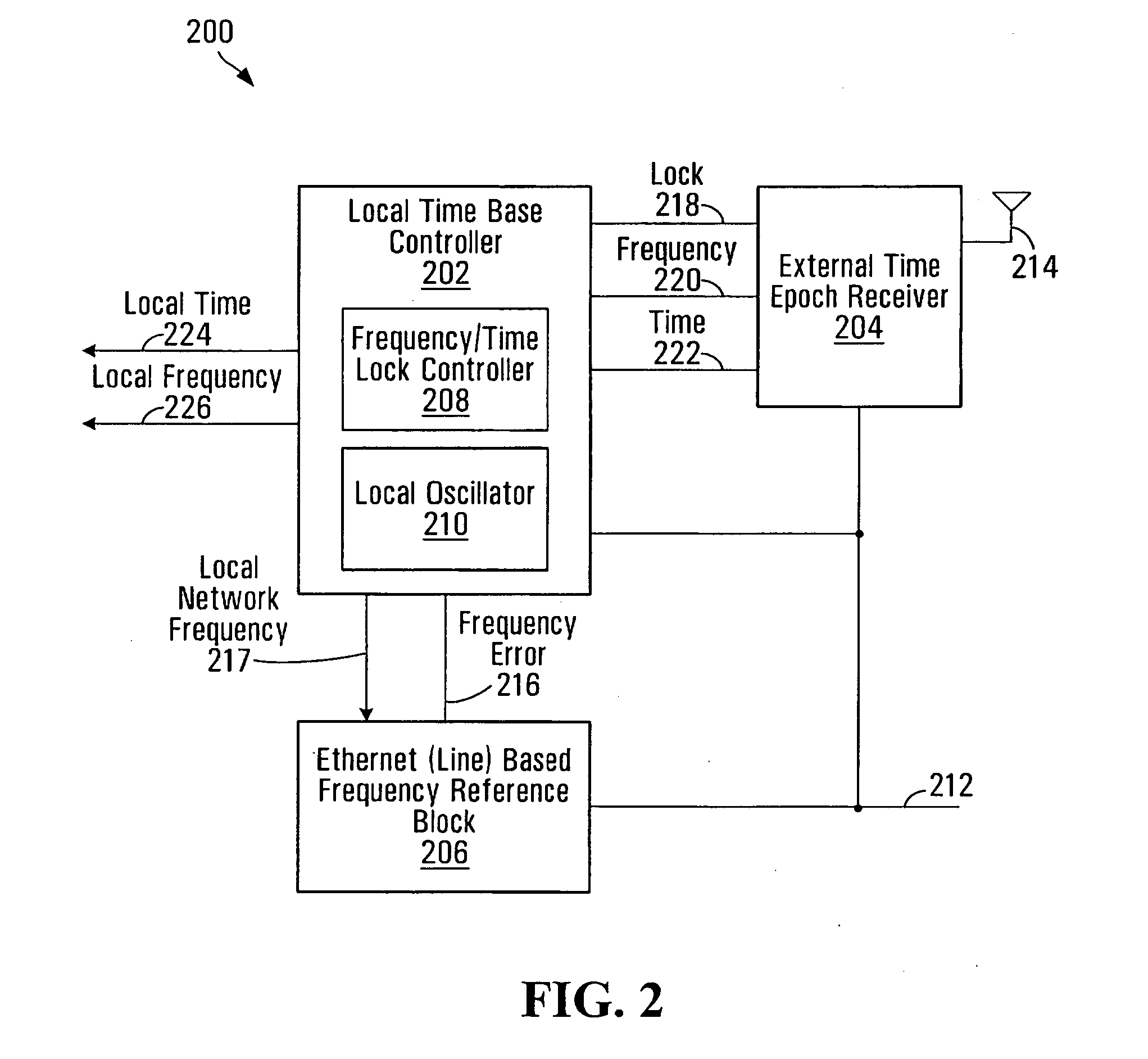
Using a network frequency reference to augment timing synchronization in a wireless base station
InactiveUS20090225743A1Maintenance frequencySynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesNetwork linkSystem time
A method and an apparatus for augmenting timing synchronization in a base station using backhaul network frequency synchronization are provided. When in a first mode an external time epoch reference synchronized with system time is used to synchronize the base station to system time. When in a second mode a network frequency reference recovered from a backhaul network link is used to maintain the timing synchronization.
Owner:APPLE INC
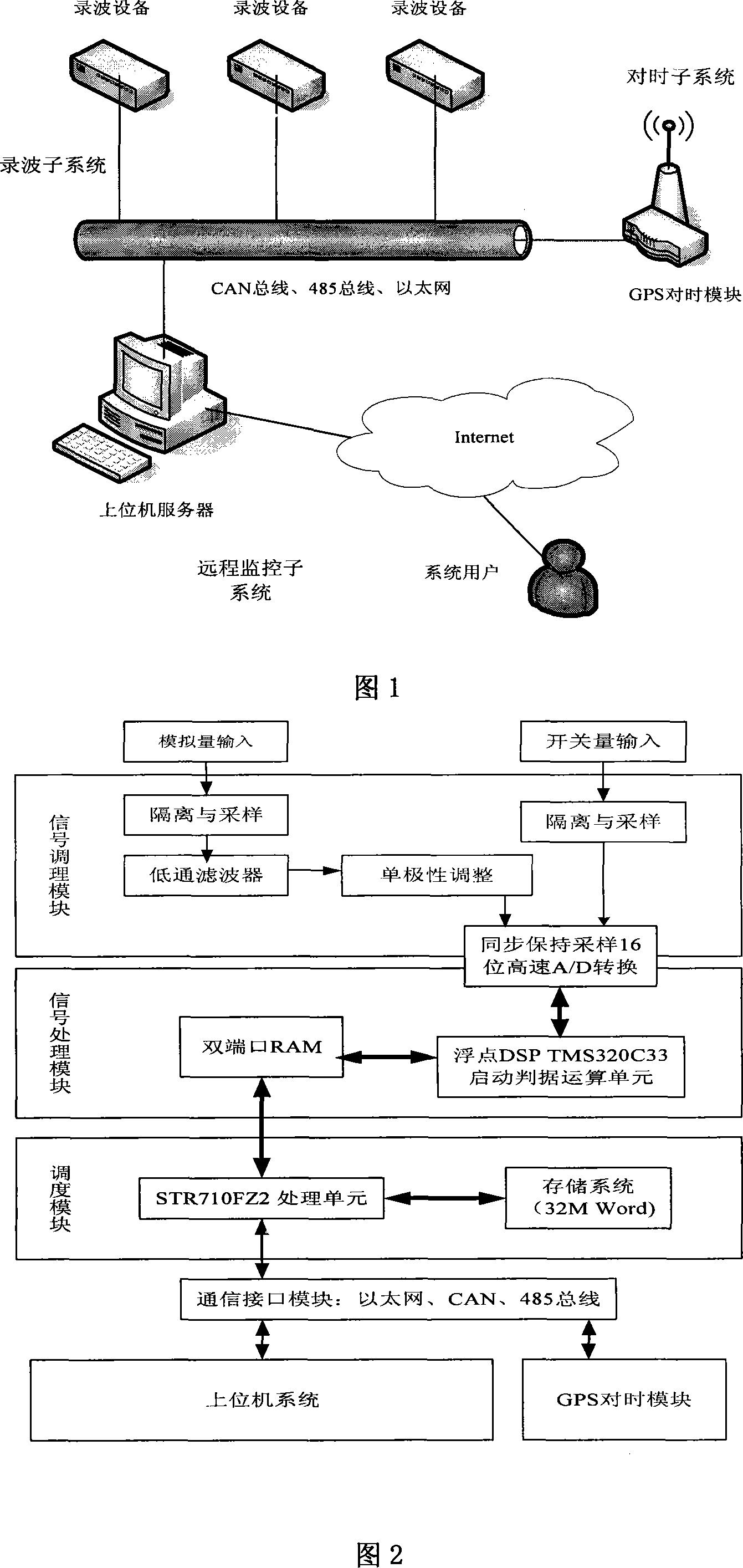
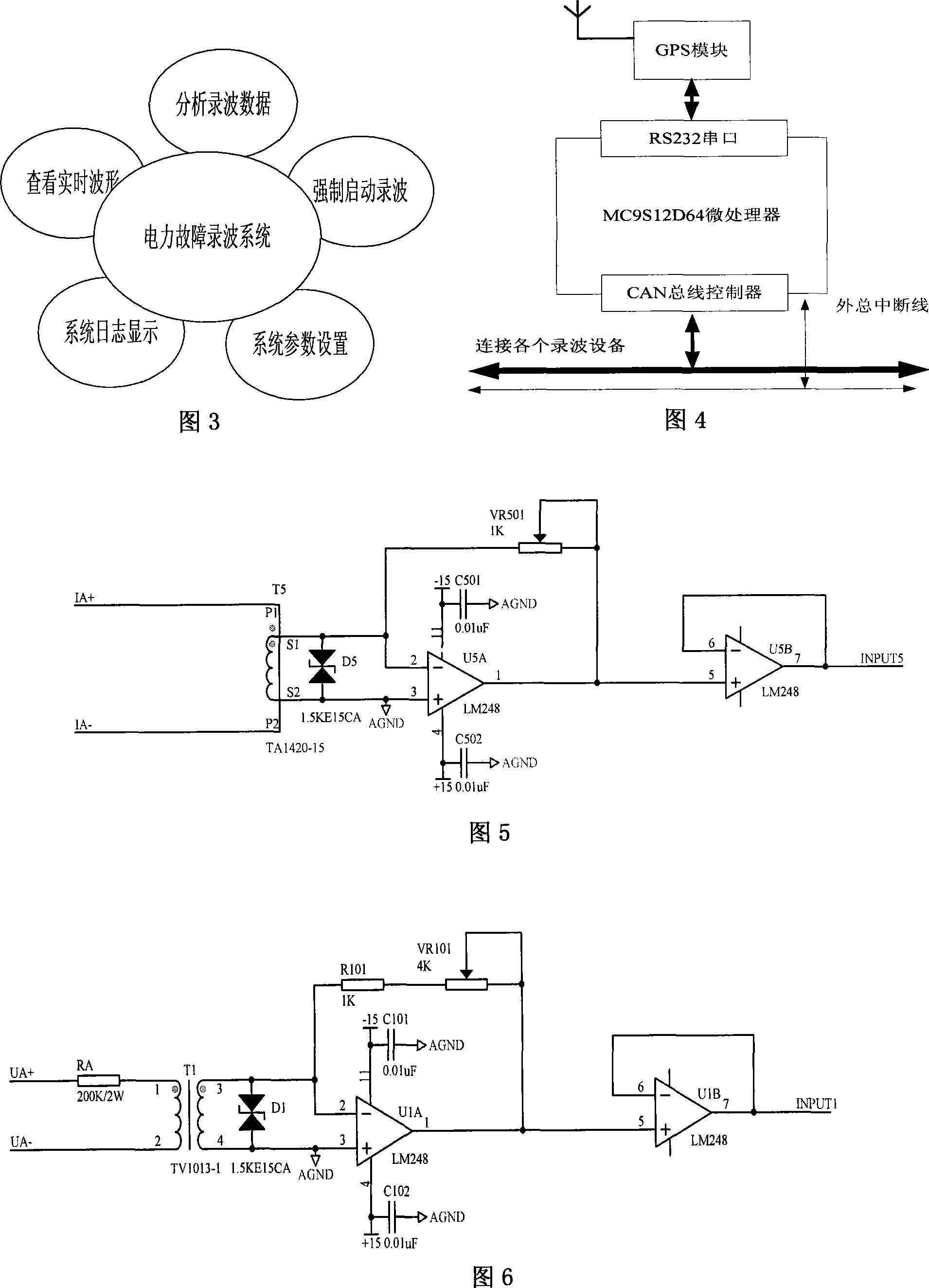
Electric energy quality and electrical power system malfunction detection wave recording device and method
InactiveCN101097653AElectric signal transmission systemsFault locationElectric power systemThe Internet
A kind of fault detection oscilloscope device and method for the quality of power and the electrical system are disclosed, which belongs to the field of detection technique of electric system, and it includes three subsystems: detection oscilloscope subsystem, remote-control monitor subsystem, and time setting subsystem; the oscilloscope subsystem can do multi-point diagnosis for electric system, and detects and records the quality parameters of power; the remote-control monitor subsystem consists of precedence sever and Internet client, and it can realize the double action that transmitting fault information and monitoring the daily running of protective and safe device; the time setting subsystem provides the system time and insures the time synchronization with system; the realizing method includes dynamic parameter measurement, fault time division; starting criterion, fault oscilloscope, uploading record, and remote-control command procession. The invention realizes the digitalization, network, intelligent, and integration of detection oscilloscope device, and it can improve the quality of power, ensure the equipment running safely and steadily.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and apparatus for background caching of encrypted programming data for later playback
InactiveUS6961430B1Improve distributionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoConditional access
A method and apparatus for enabling background caching of encrypted programming data on a storage medium for later playback in a digital video recorder (DVR) system. A set-top box (STB) equipped with a DVR searches a program guide for upcoming pay-per-view (PPV) events. When the PPV event begins, the STB tunes an appropriate transponder and begins receiving programming data packets containing audio, video, system time and conditional access data packets associated with the event, which are stored for playback on a storage medium. When the user turns the STB on and selects an option to playback a previously-recorded PPV event, the appropriate programming data is retrieved from the storage medium, and the STB recreates the original transmission timing of the data, to be displayed on a display device of the user.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
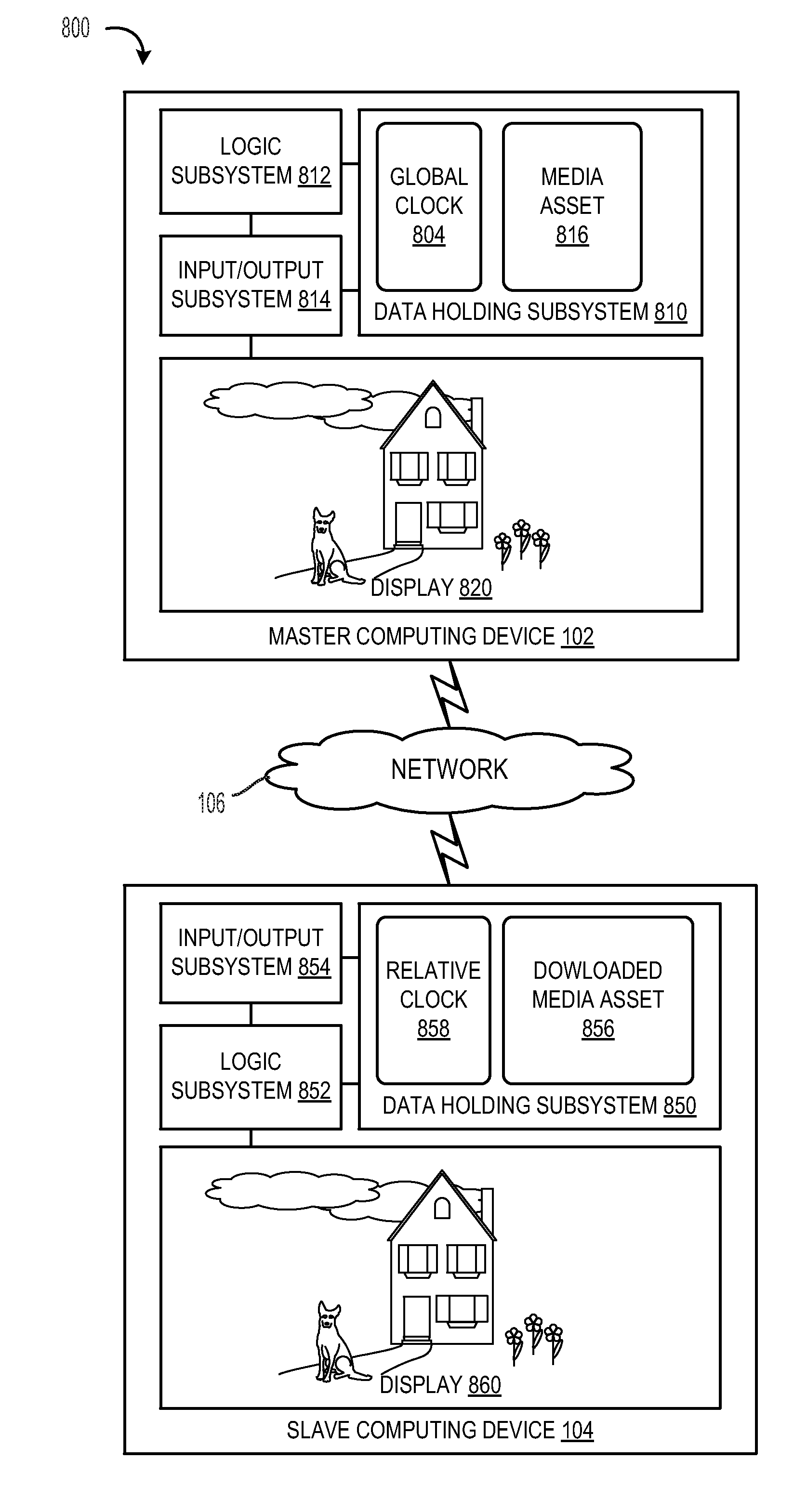
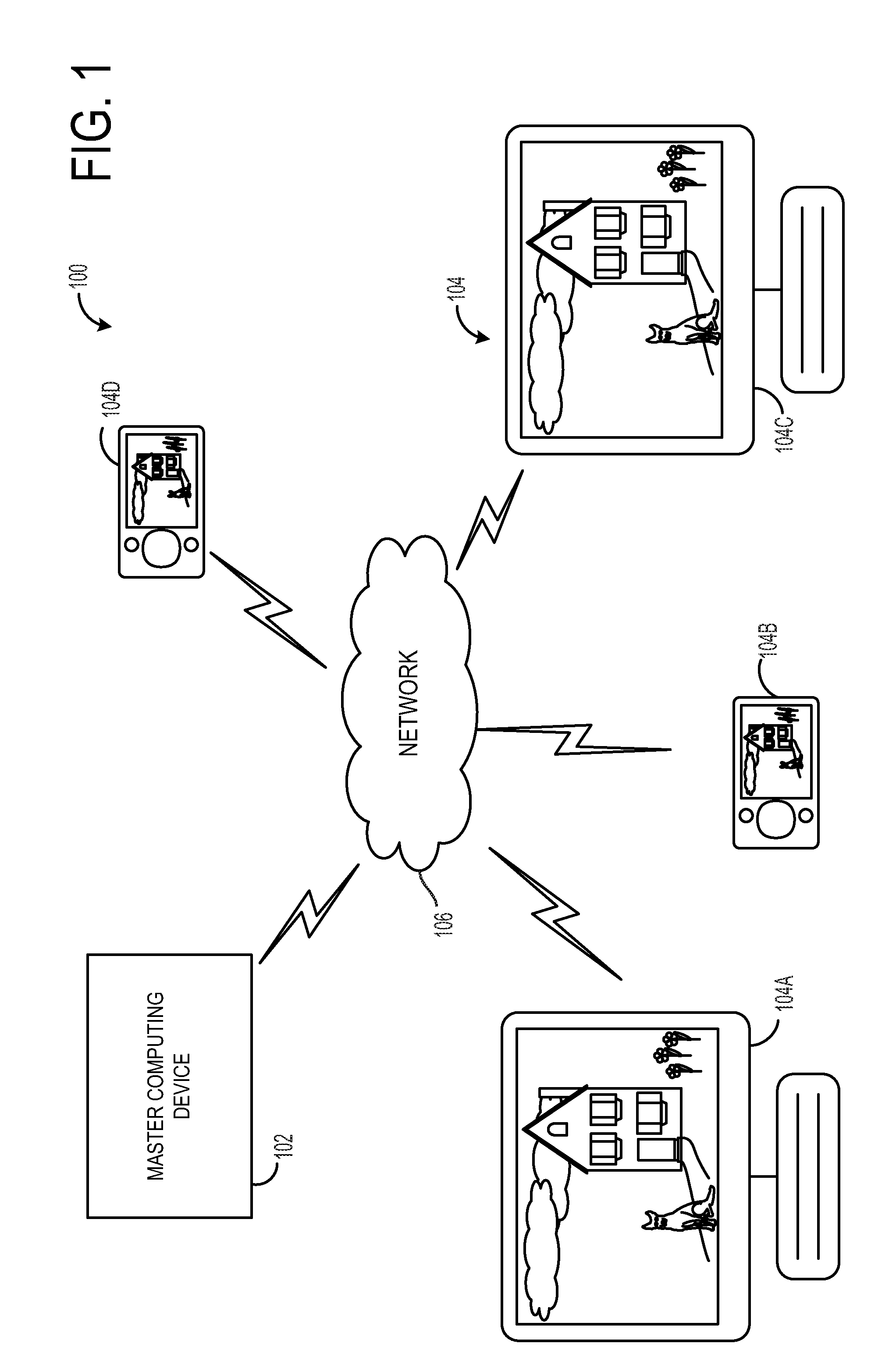
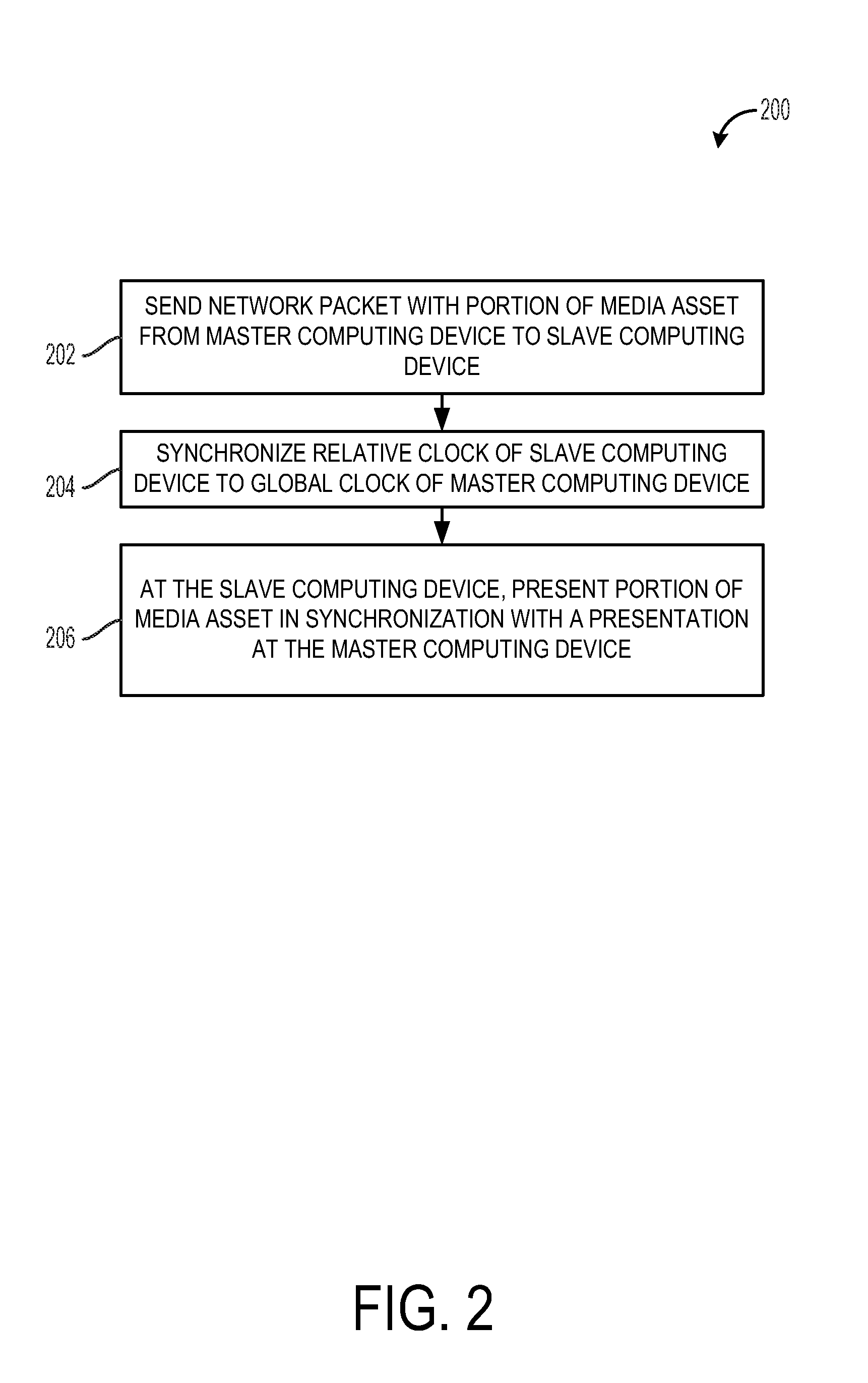
Clock synchronization for shared media playback
Various embodiments are provided that relate to clock synchronization. In one embodiment, a method for synchronizing a relative clock to a global clock comprises receiving a network packet from a master computing device, the network packet including a network packet time stamp indicating a system time of the global clock when the network packet was transmitted; determining a receipt time offset between a receipt time of the network packet and the network packet time stamp, the receipt time indicating a time at which the network packet is received as measured by the relative clock; and adjusting a system time of the relative clock toward the system time of the global clock by updating a system time offset to the receipt time offset if the receipt time offset is smaller than the system time offset.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
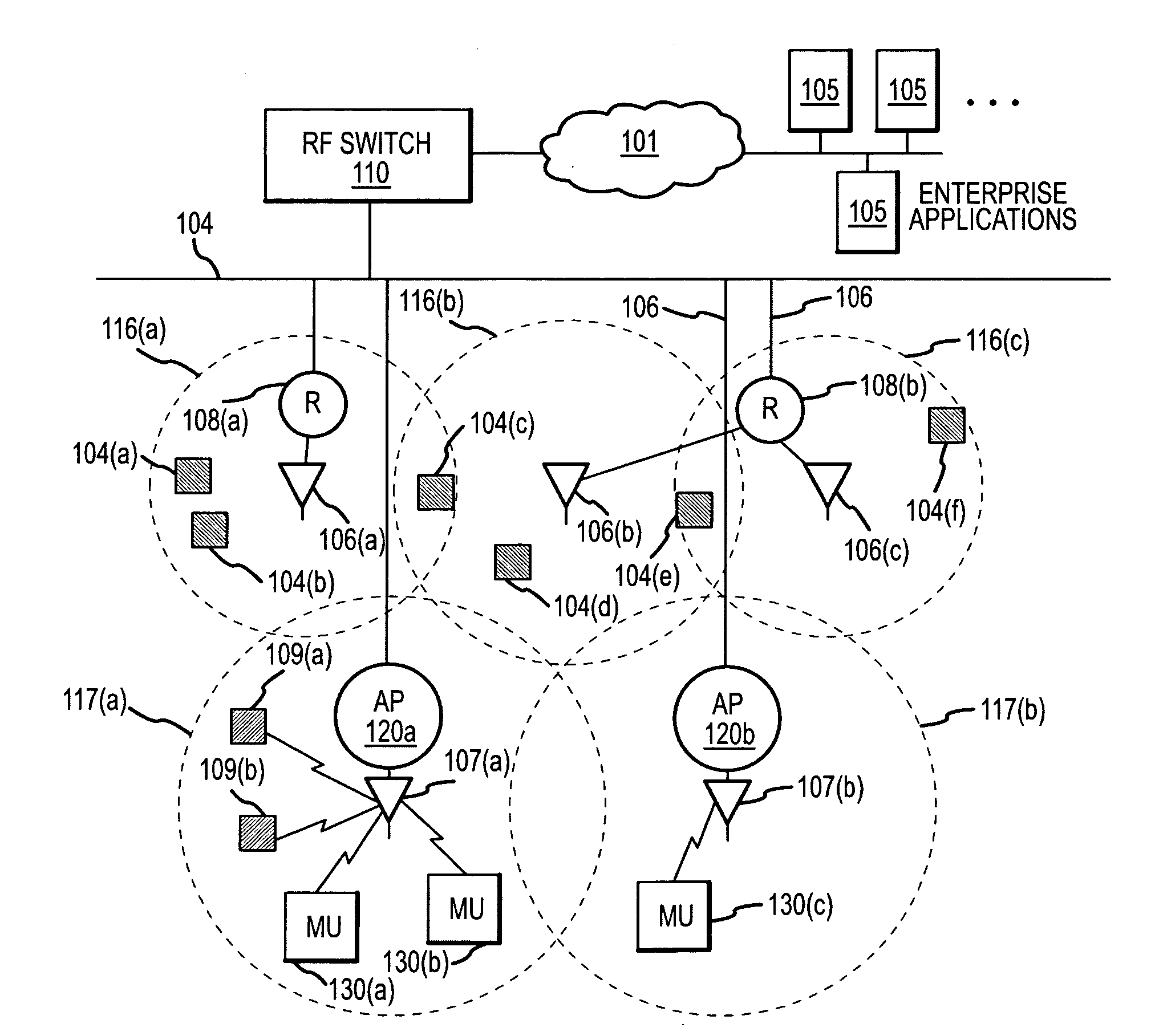
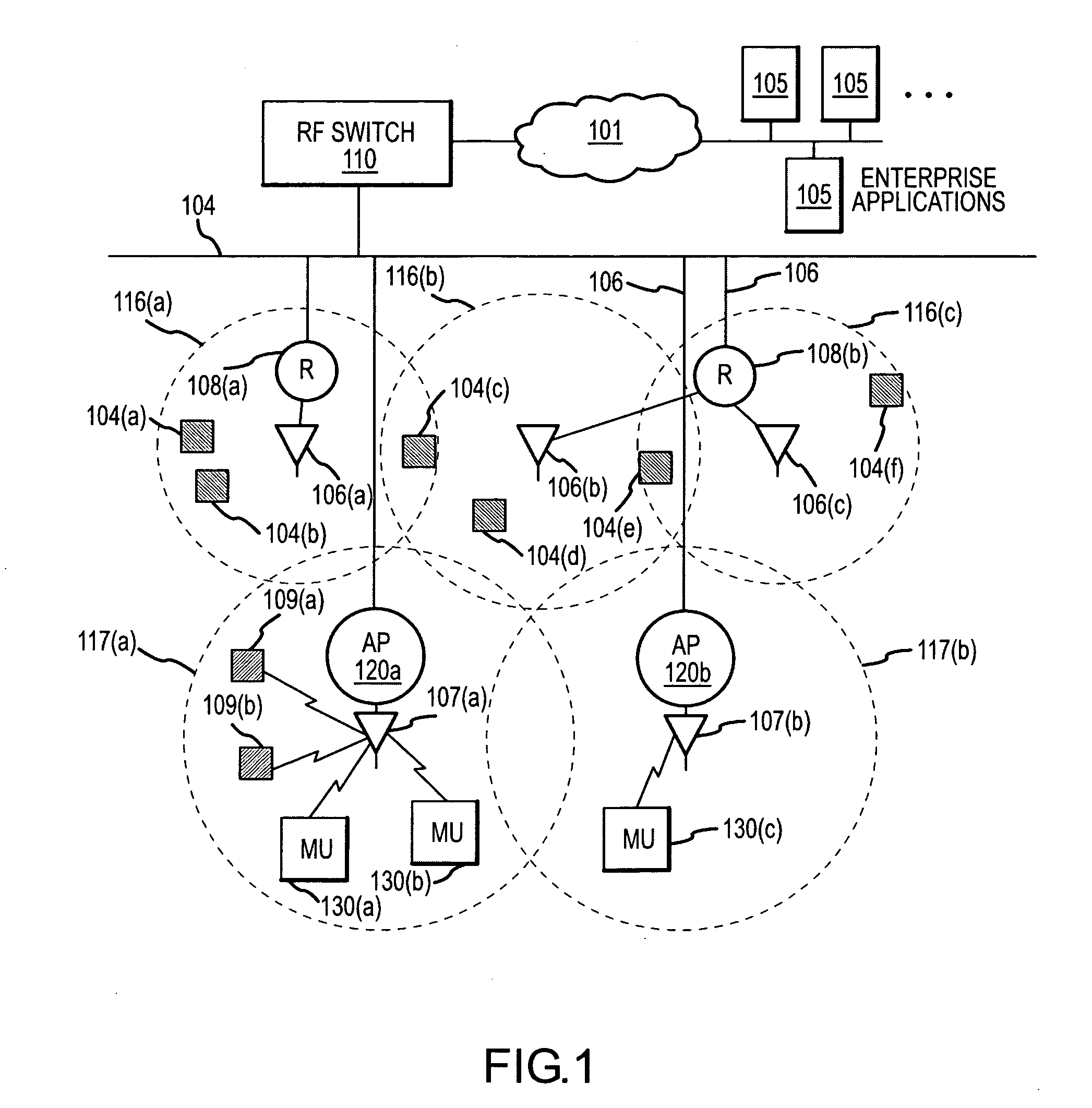
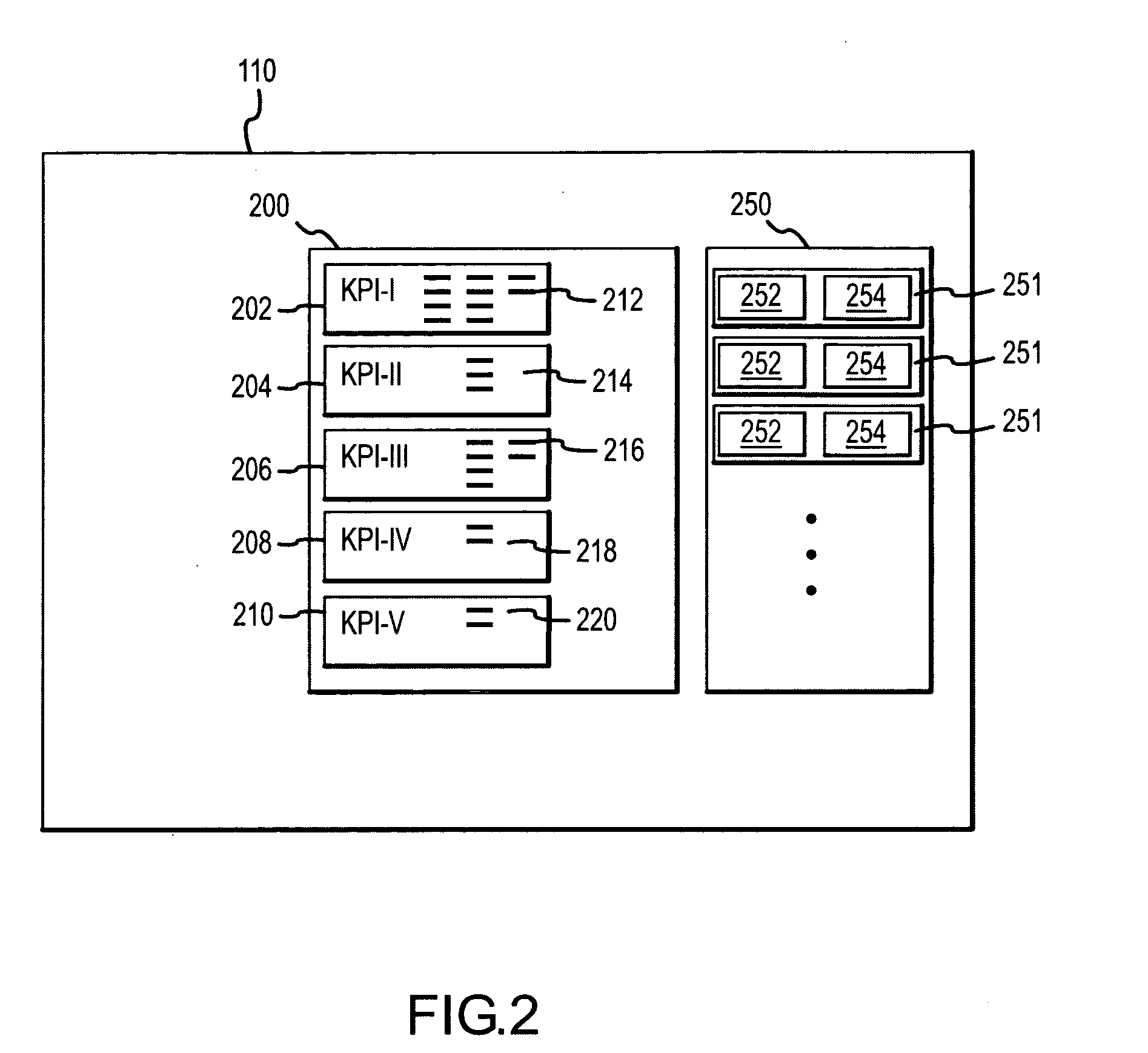
Methods and apparatus for defining, storing, and identifying key performance indicators associated with an RF network
InactiveUS20080081632A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationDisplay deviceSystem time
A system for assessing the state of an RF network includes a plurality of wireless devices coupled to the network and having one or more associated antennae, the wireless devices configured to process data received from a plurality of RF elements within range of the antennae. An RF switch is coupled to the network and configured to receive the data and transmit the data over the network. A first memory within the RF switch is configured to store a system state comprising a plurality of performance indicators, wherein each of the performance indicators is associated with an operational characteristic of one or more of the plurality of wireless devices. A second memory within the RF switch is configured to store a plurality of labeled data entries, the labeled data entries each including the system state and a user-entered identifier, wherein the user-entered identifier includes information related to the time at which the system state was selected. A display coupled to the network is configured to display a comparison of the system states.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
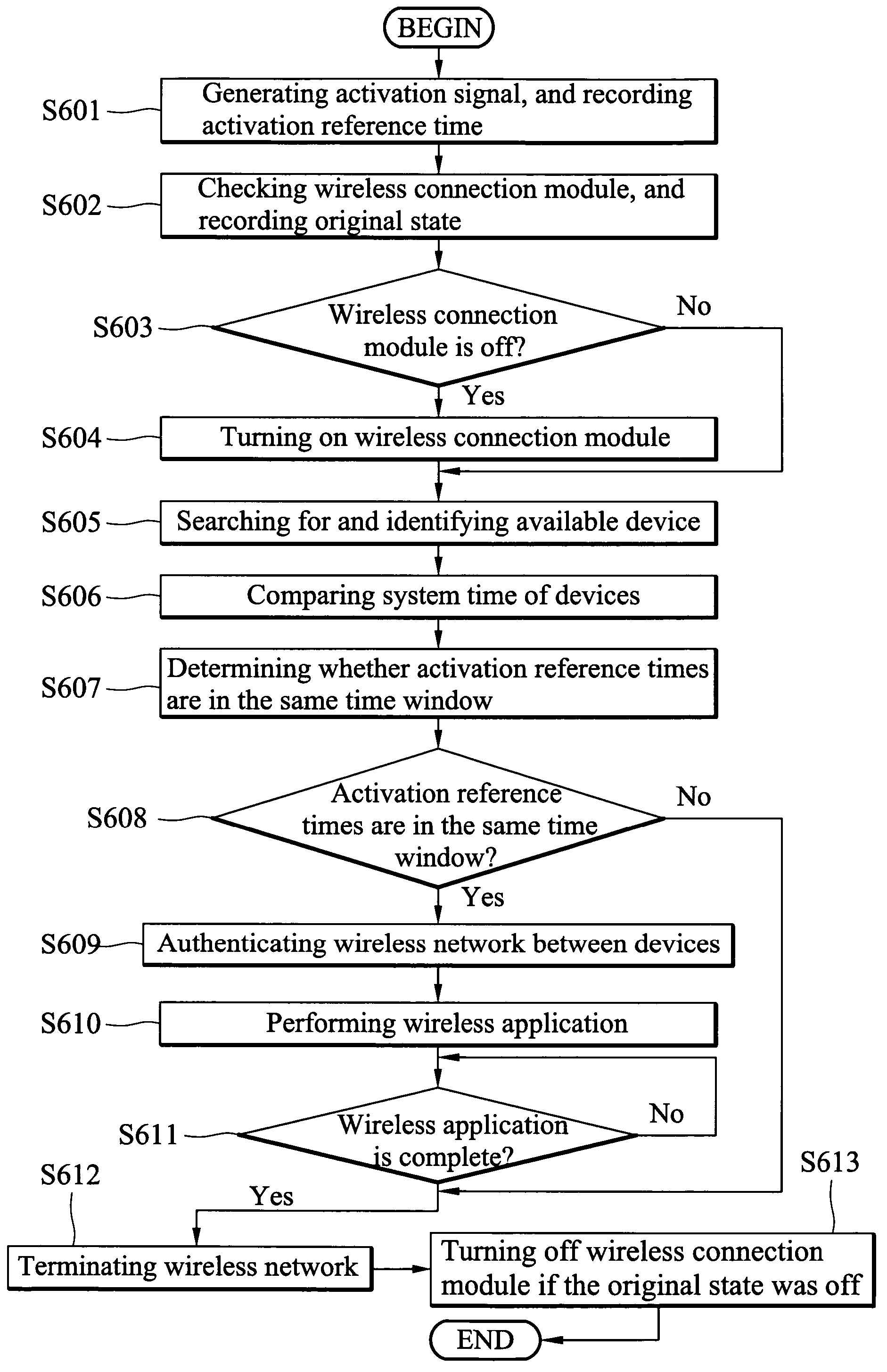
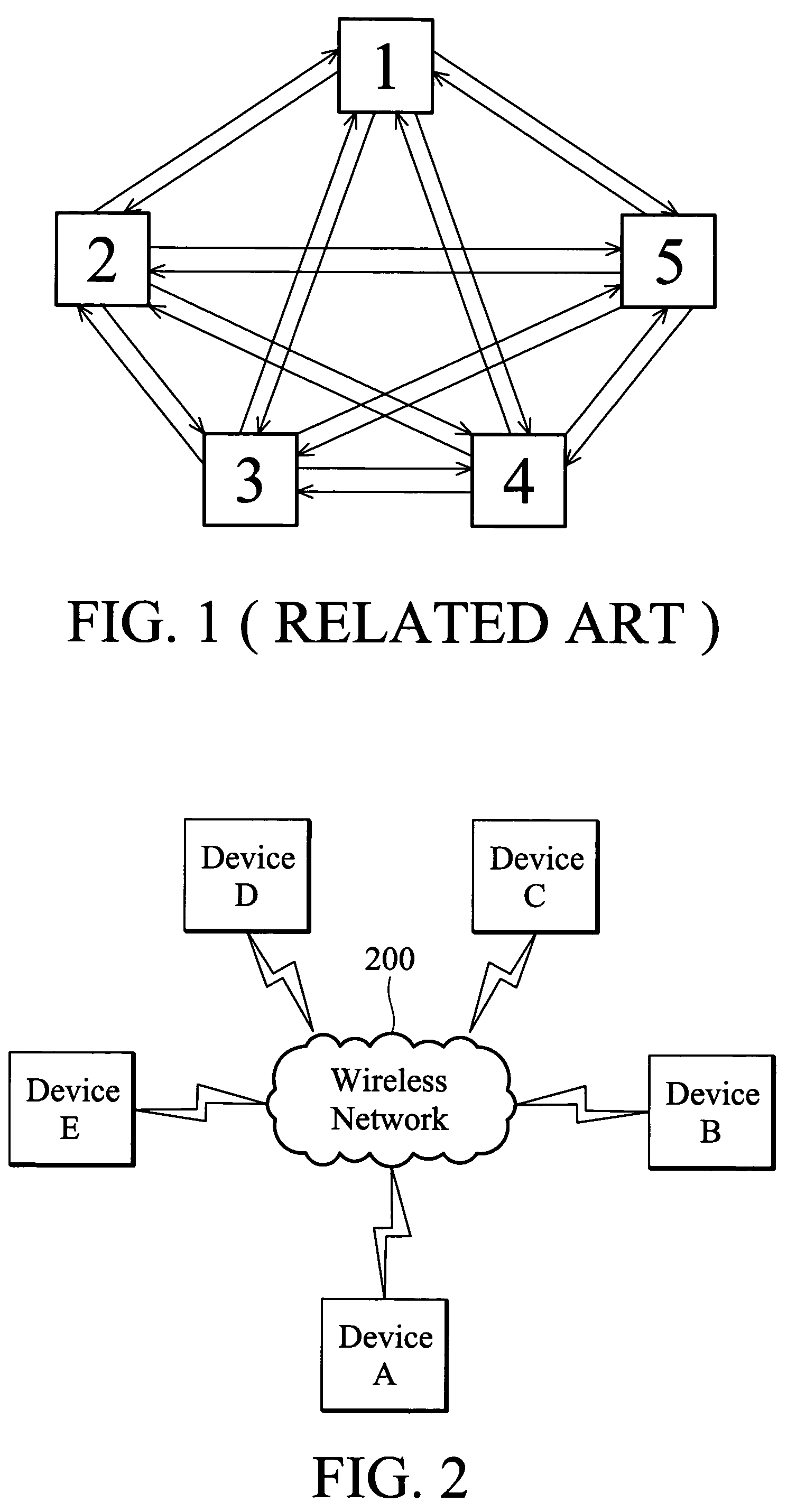
Methods for establishing wireless network communication and device utilizing same
ActiveUS7672291B2Improve accuracySynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexSystem timeBiological activation
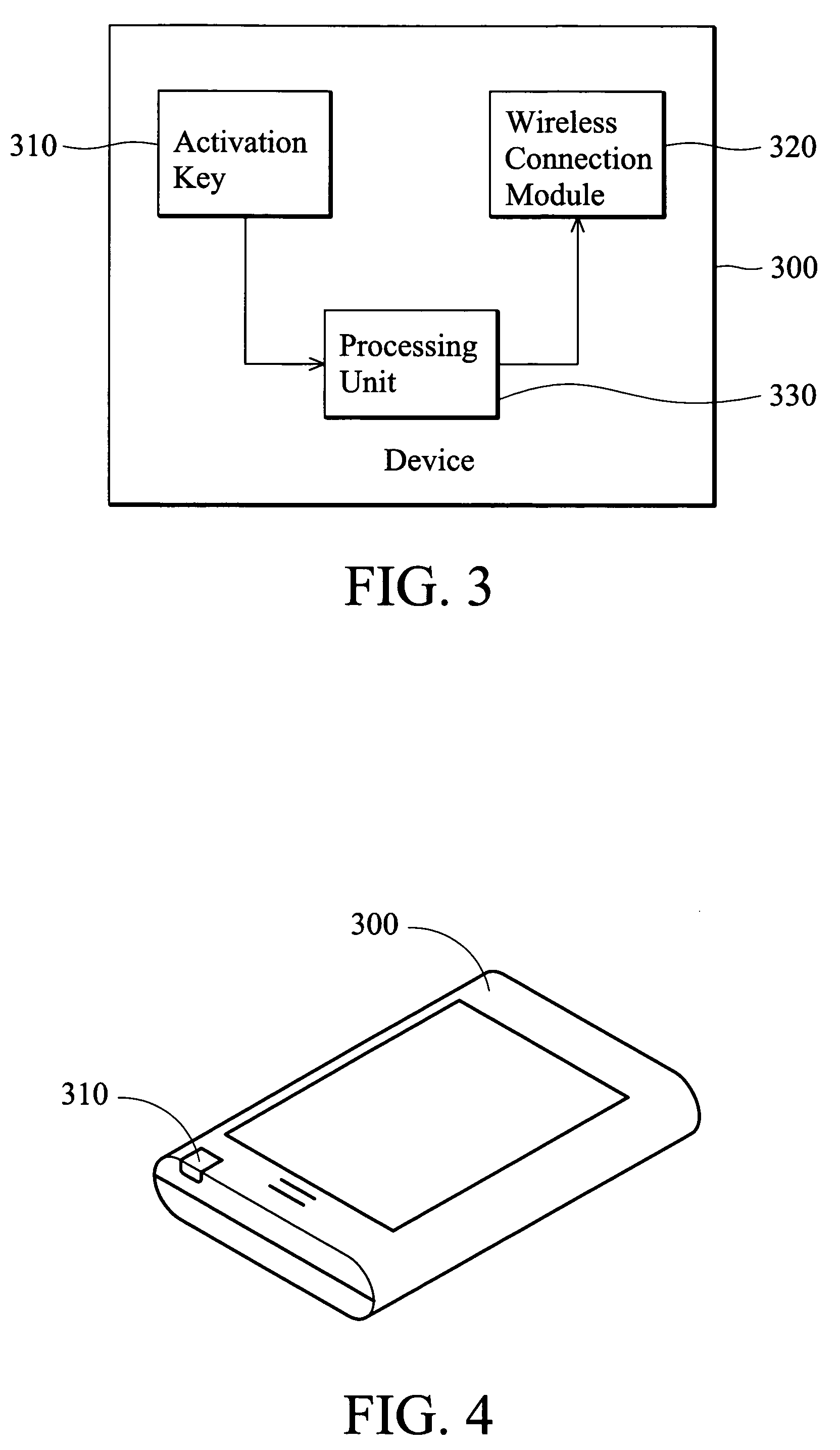
Method for establishing wireless networks between devices is disclosed. When a first device is activated to establish a wireless network with other devices, a first activation reference time is recorded. At least one second device that has at least one compatible networking capability is searched for and identified. When the second device is activated to establish wireless network with other devices, a second activation reference time also is recorded. The first and second activation reference times are compared to determine whether they fall into the same time window. The offset between the system time of the first device and that of the second may be factored into the calculation to further enhance the accuracy. If the first and second activation reference times are in the same time window, the authentication of wireless network is established between the devices.
Owner:HTC CORP
Method for measuring characteristics of path between nodes by using active testing packets based on priority
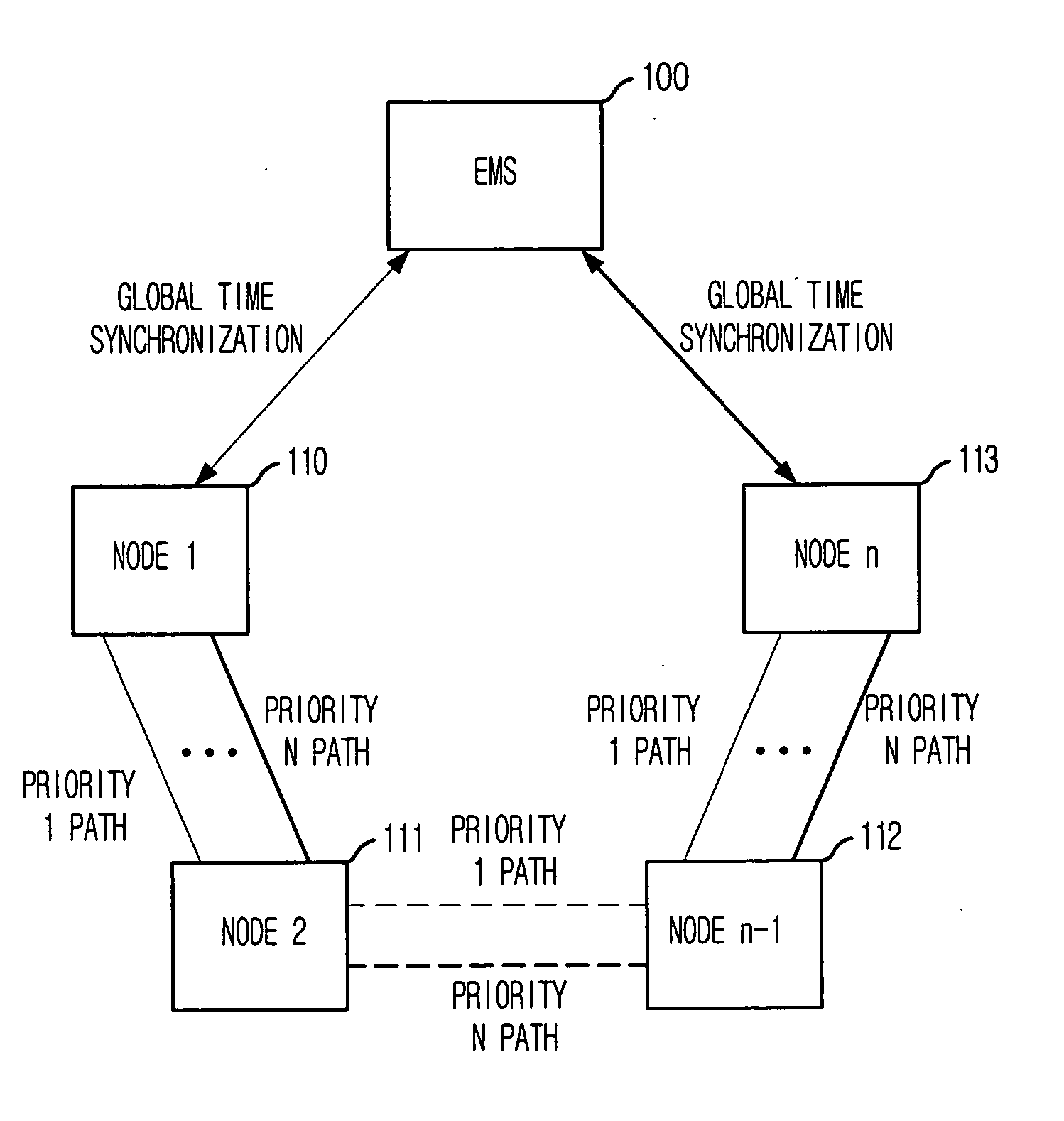
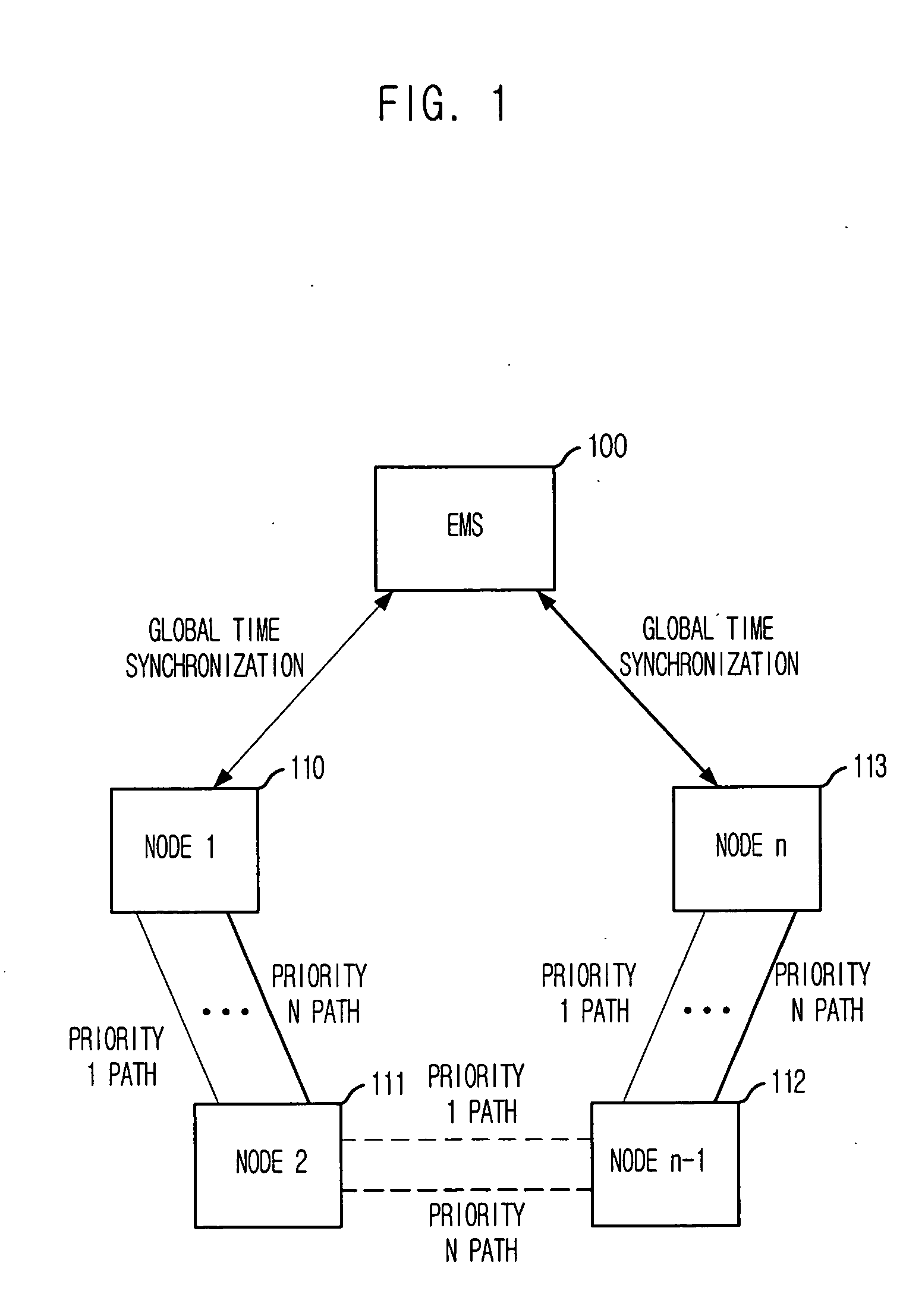
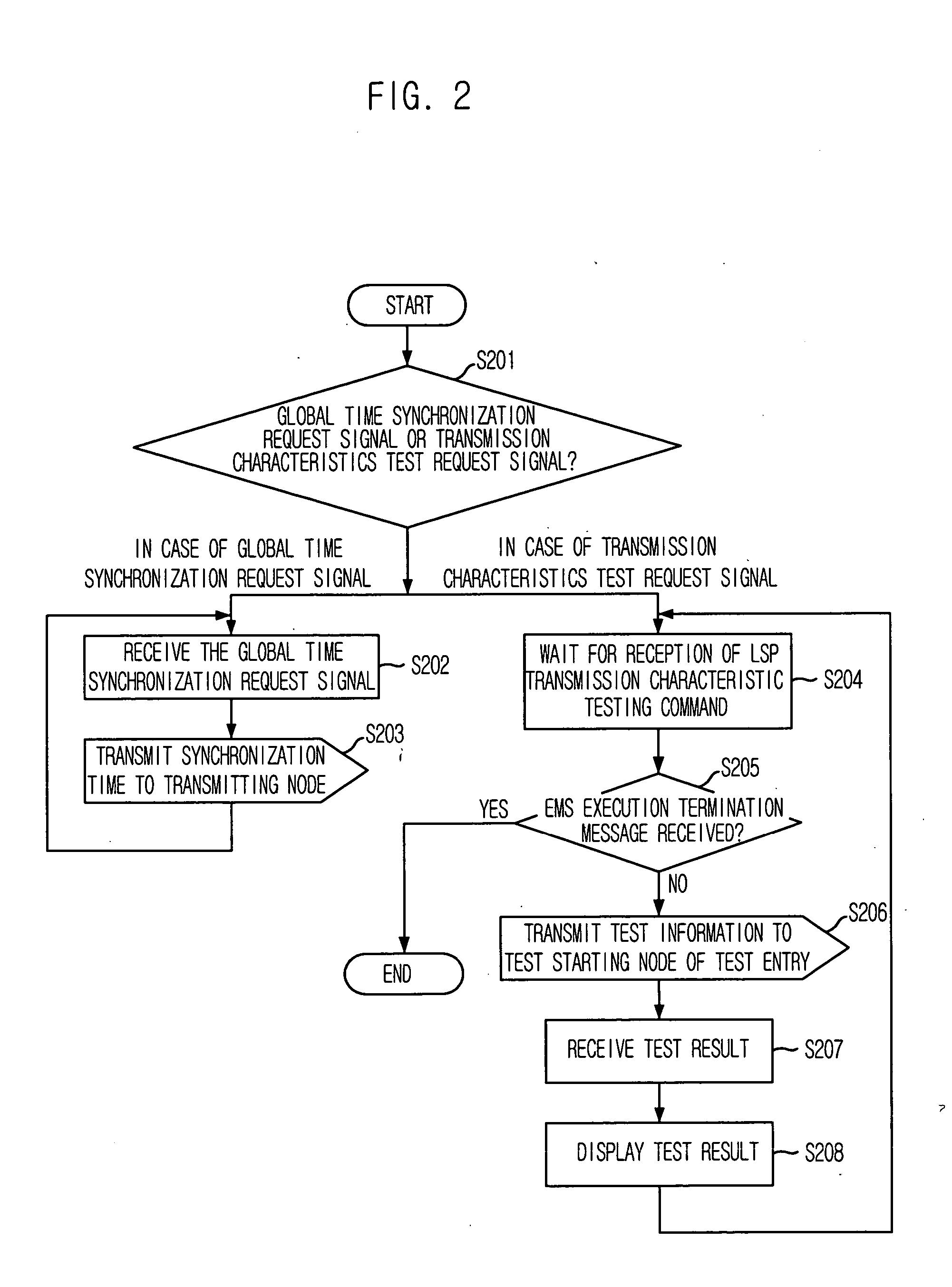
Provided are a method for measuring characteristics of a path between nodes by using active testing packets based on priority, i.e., an inter-node path characteristic measuring method, which can measure and provide characteristics of a generated node, when an inter-node data transmission path is generated based on Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) to provide a path with satisfactory transmission delay, jitter and packet loss that are required by a user, and to provide a computer-readable recording medium for recording a program that implement the method. The method includes the steps of: a) synchronizing system time of the nodes with a global standard time; b) forming each testing packet; c) registering frame sequence and the global standard time during transmission; and d) calculating transmission delay time, jitter and packet loss by using time stamp and packet sequence information of a frame received by the destination node and transmitting the result to the management system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
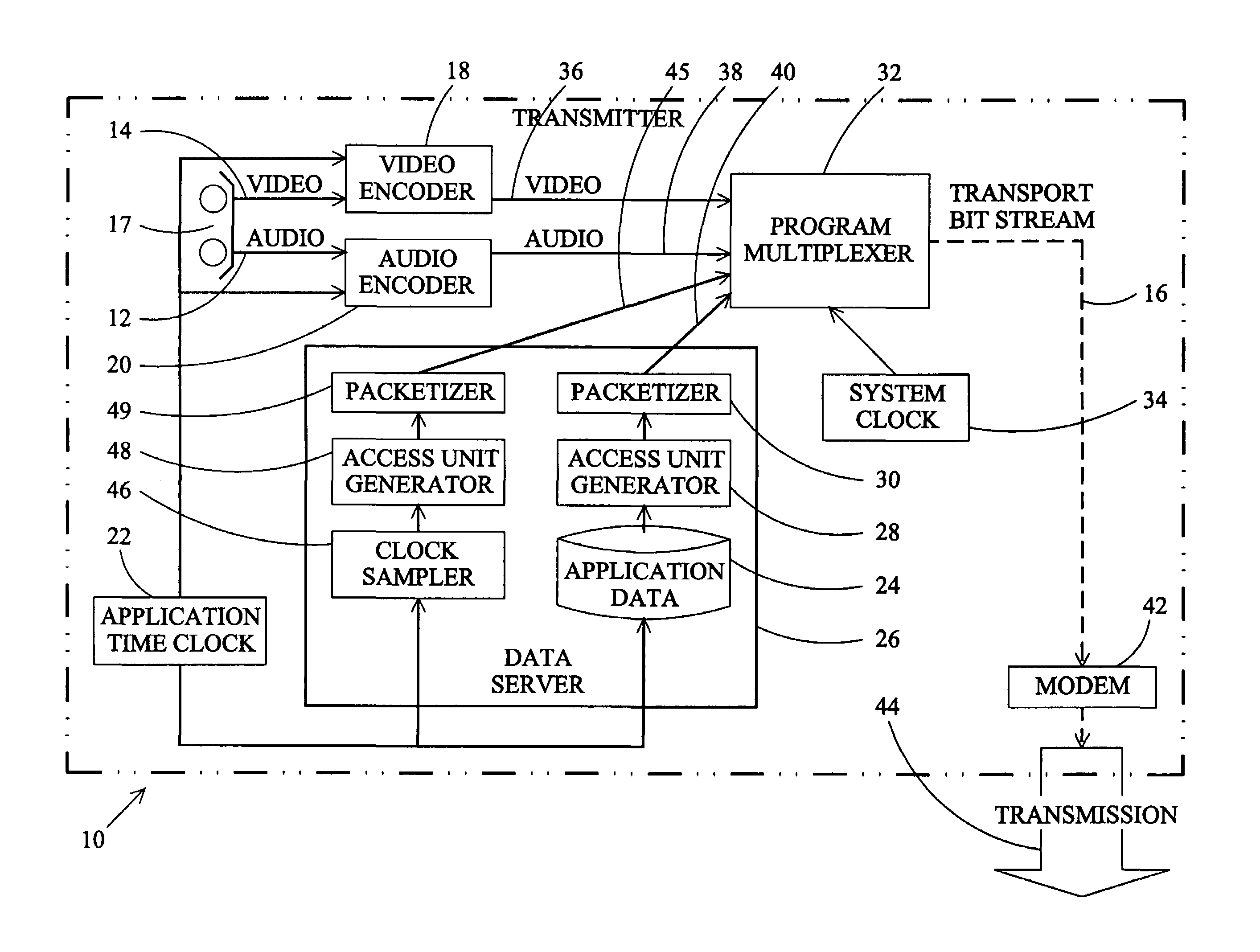
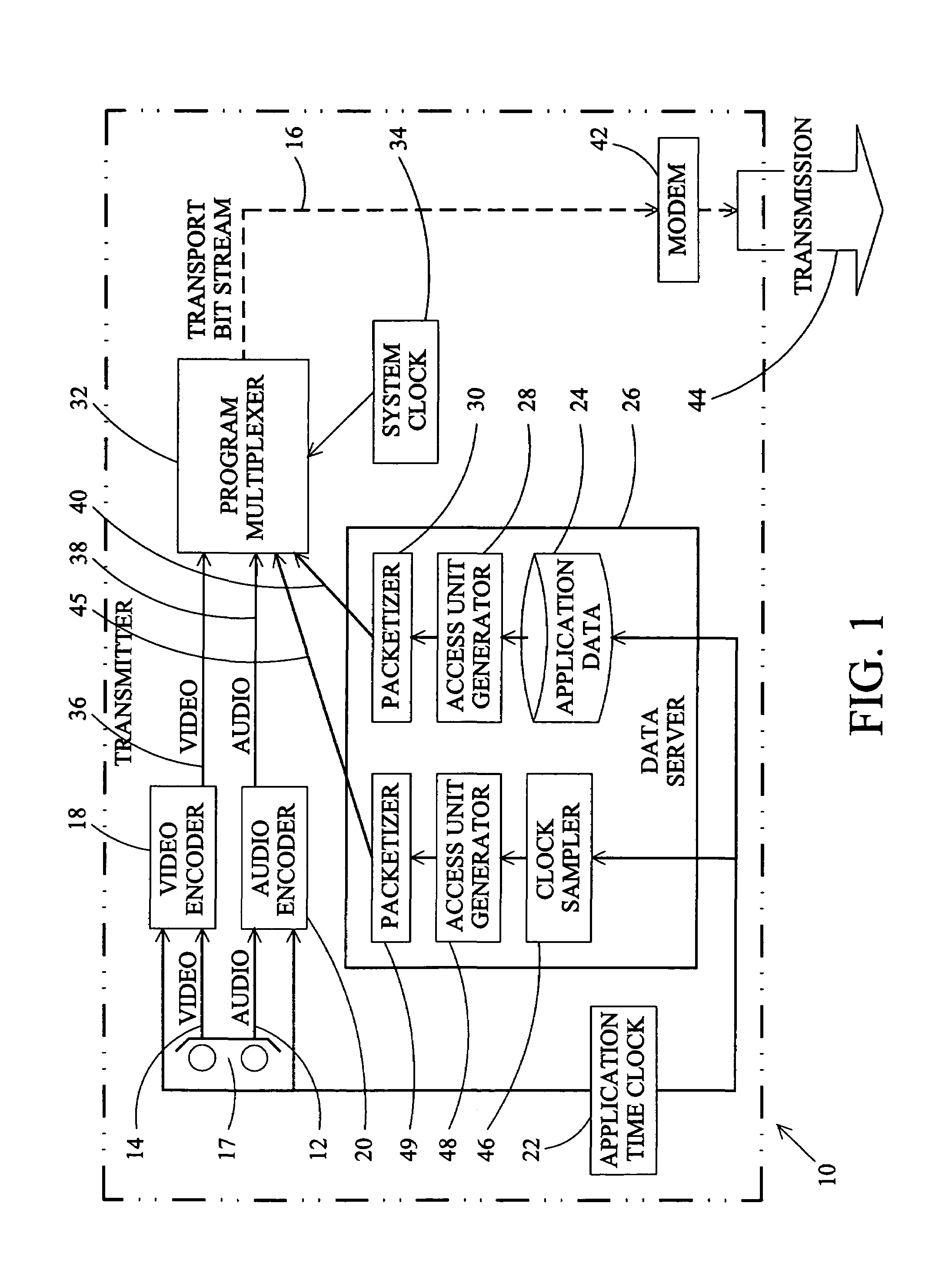
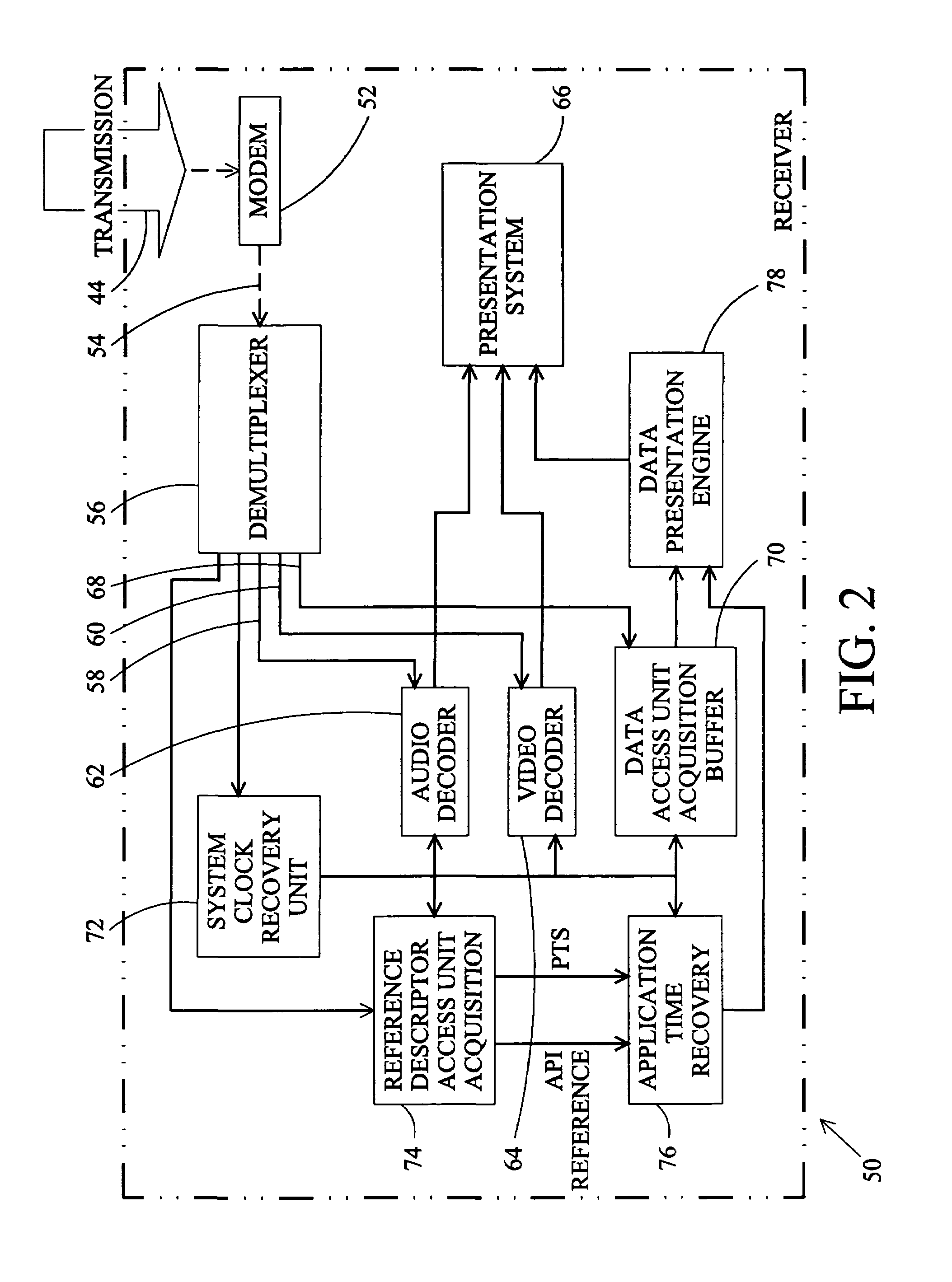
Method of synchronizing events with a digital television audio-visual program
InactiveUS7174560B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData accessAsynchronous data
A method and apparatus for synchronizing an event produced at a digital television receiver with an instant of a transmitted video, audio, or data element of a digital television program is disclosed. In a digital television system, a system time clock generates a timeline that is used to synchronize the presentation of the video, audio, and data elements of the television program. An application time is used in program production to synchronize instants of the several program elements. To synchronize a receiver generated event with an instant of a transmitted video, audio, or data program element, samples of the application time are transmitted to a receiver in a synchronized data service. A reconstructed application time is generated at the receiver as a function of the current system time, the application time sample, and the presentation time stamp of the data access unit in which the application time sample was transmitted. The presentation time of the program instant is associated with an application time correlating the event and the instant. The correlating application time is transmitted to the receiver as part of a synchronous or asynchronous data service and the event is instigated when the reconstructed application time corresponds to the correlating application time. A clock for generating a reconstructed application time synchronized to the system time is also disclosed.
Owner:SHARP KK
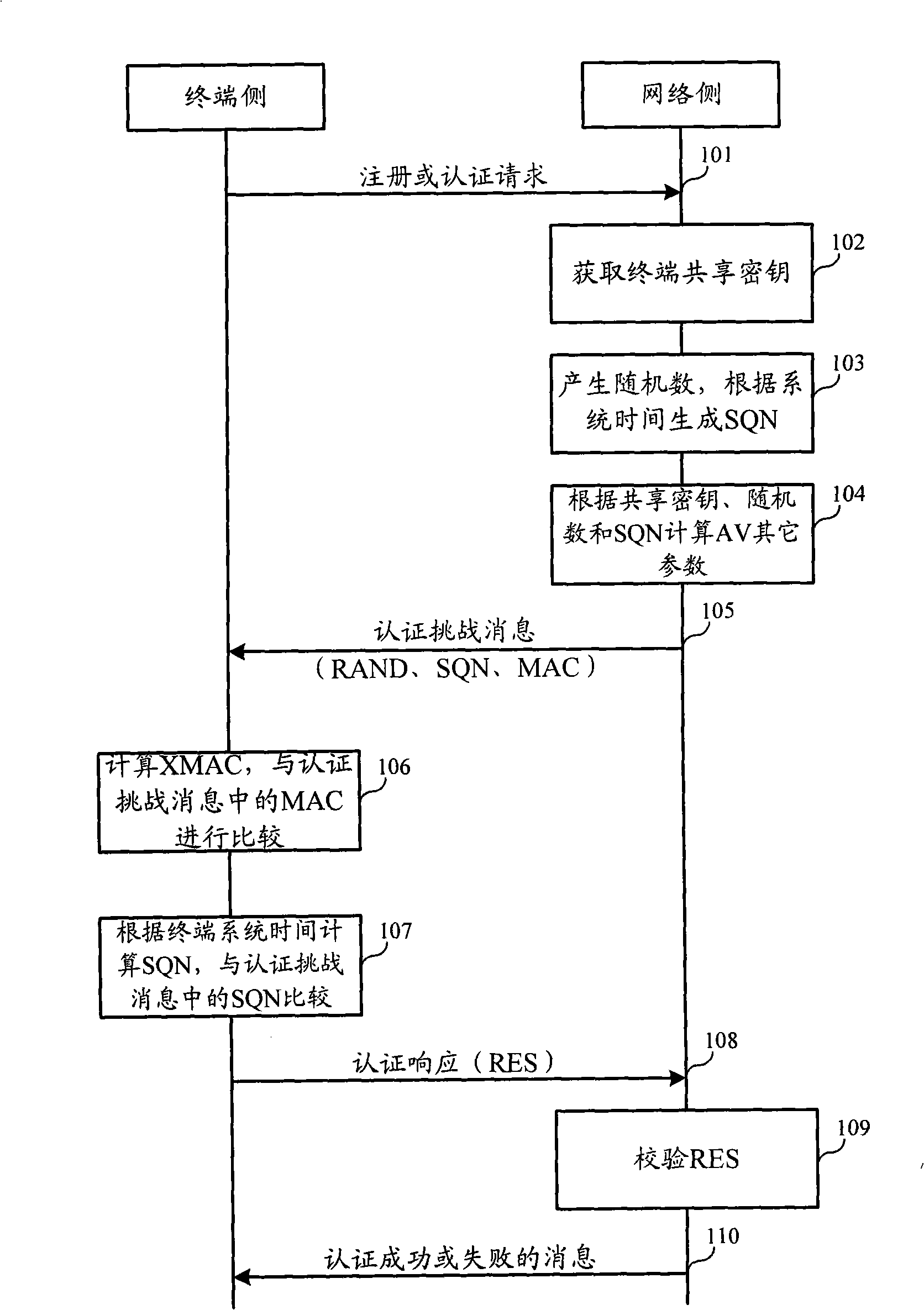
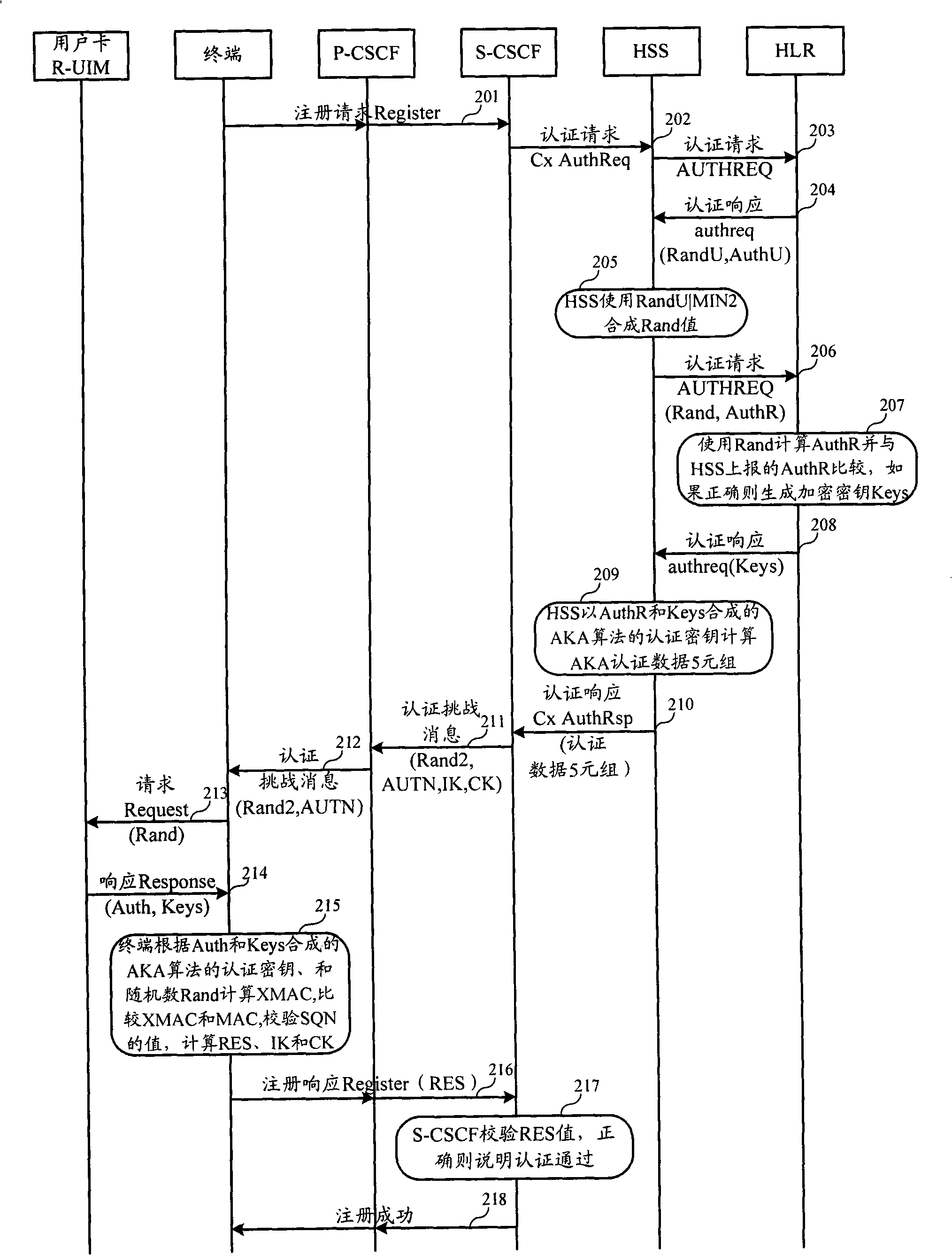
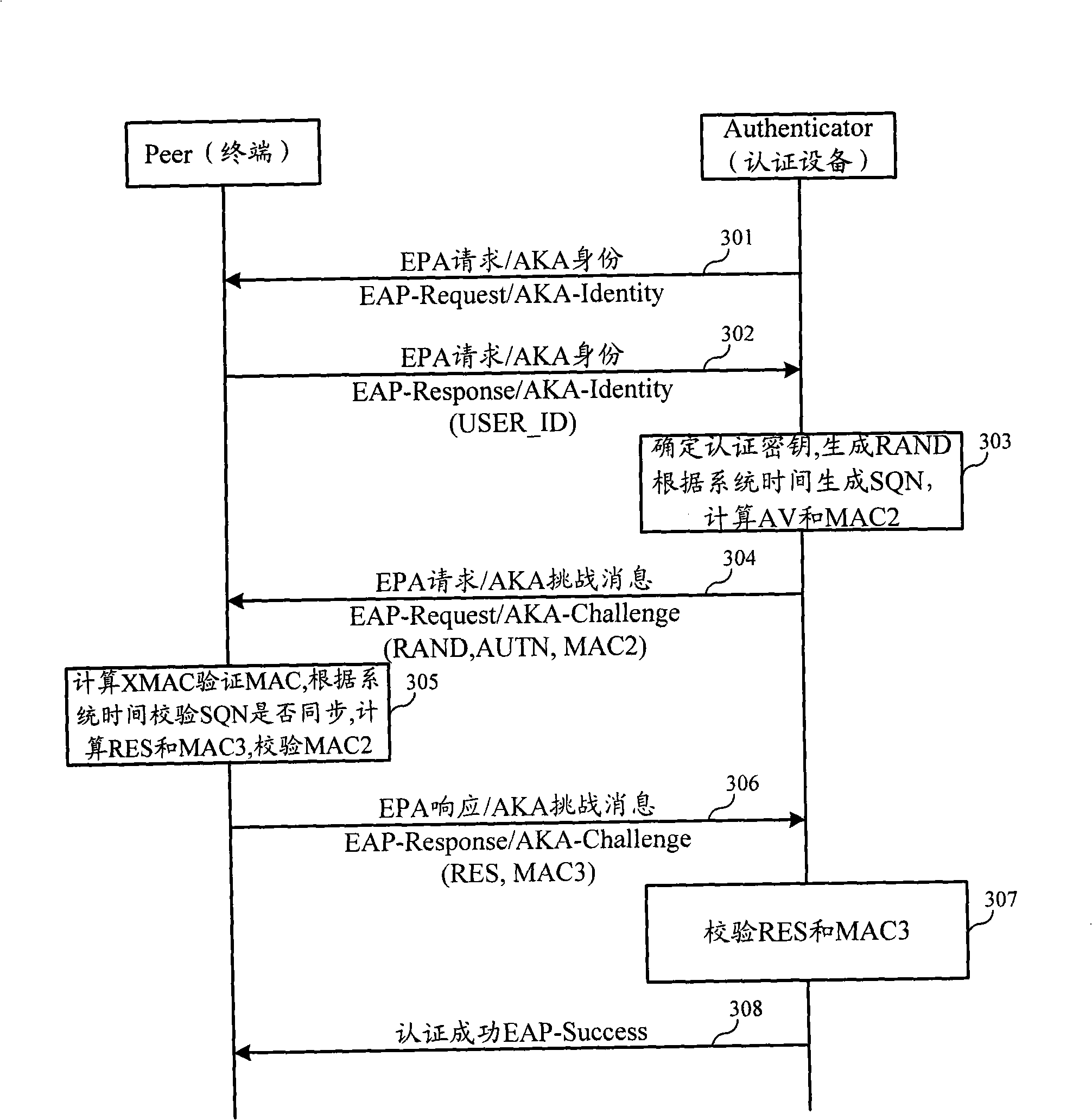
Authentication and cryptographic key negotiation method, authentication method, system and equipment
ActiveCN101272251AReplay is unique and accurateNo securitySynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUser identity/authority verificationSystem timeReplay attack
The invention relates to the field of commutation and discloses an authentication and key negotiation method, an authentication method, a system and a device, which leads a user card to be capable of resisting the playback attack during the process of an AKA under the situation of not supporting SQN storing. In the invention, when a network side receives the authentication request of a terminal, a random number, a first sequence number SQN1 and a first authentication code MAC are sent to the terminal according to the shared key, the random number and the first authentication code MAC generated by the first sequence number SQN1, the first authentication code MAC represents the current system time at the network side; if a second authentication code XMAC is the same as the first authentication code MAC, and the difference value of a second sequence number SQN2 representing the current system time at the terminal side and the first sequence number SQN1 meet a preset condition, the terminal determines the network side legal according to the key shared with the network side, the received random number and the first authentication code MAC generated by the first sequence number SQN1.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Synchronized audio/video decoding for network devices
InactiveUS20060233203A1Time-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTimestampClock rate
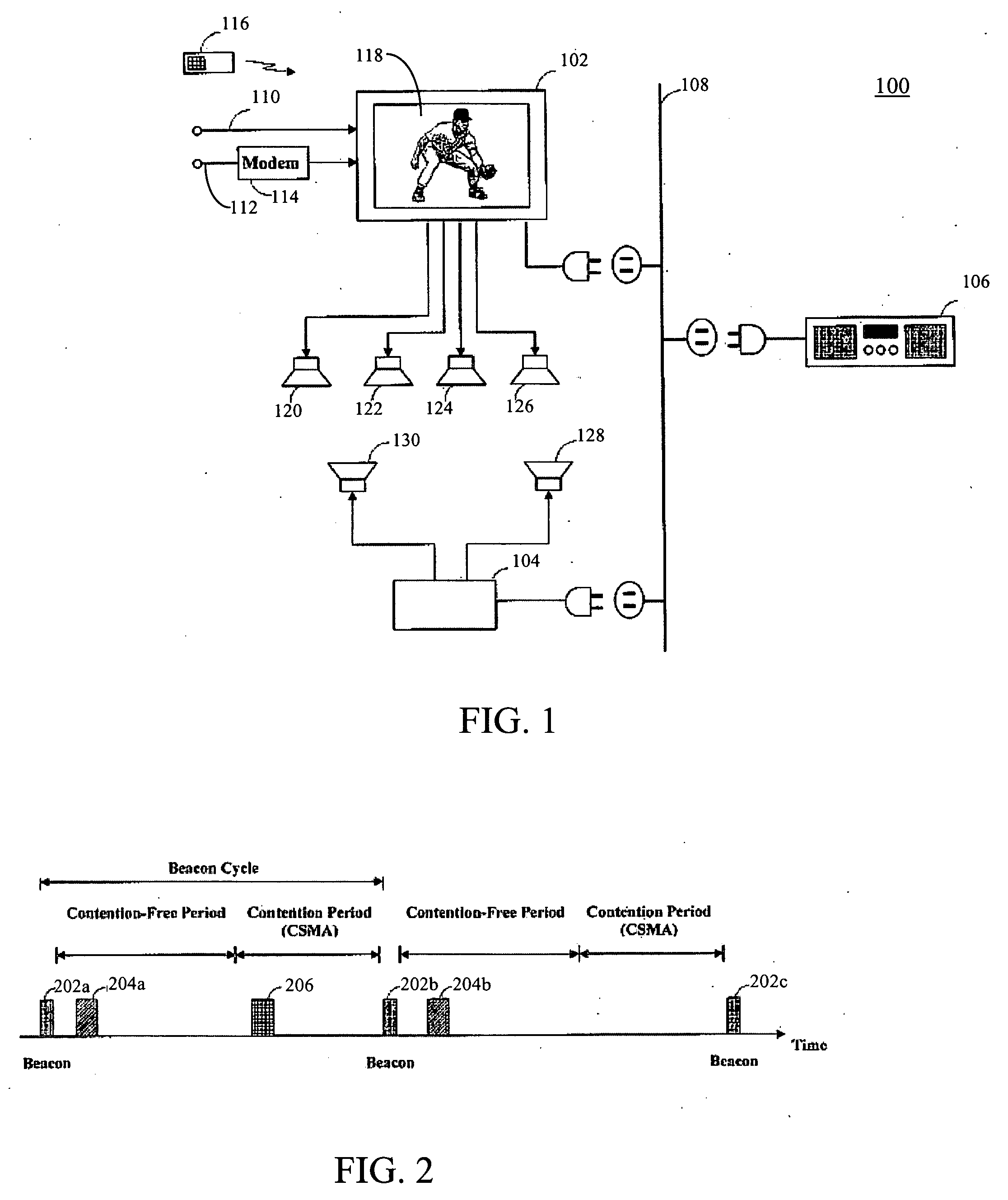
A method of synchronizing decoders within a network to a server includes receiving a set of timestamps and local clock signals upon receiving the beacon interrupt signal, computing differential timestamp and local clock values based on values of timestamp and local clock signals, respectively, within the sets of timestamp and local clock signals, determining whether the differential local clock value has a predetermined relationship with the differential timestamp value, and transmitting a clock rate adjustment command signal to the decoder when differential local clock value does not have the predetermined relationship with the differential timestamp value. The clock rate adjustment command signal adjusts the local system time clock of the decoder such that a subsequent differential clock value will have the predetermined relationship with the differential timestamp value. When this method is performed for each decoder within the network, the decoders are substantially synchronized and the decoding delay can be kept below humanly perceptible levels.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
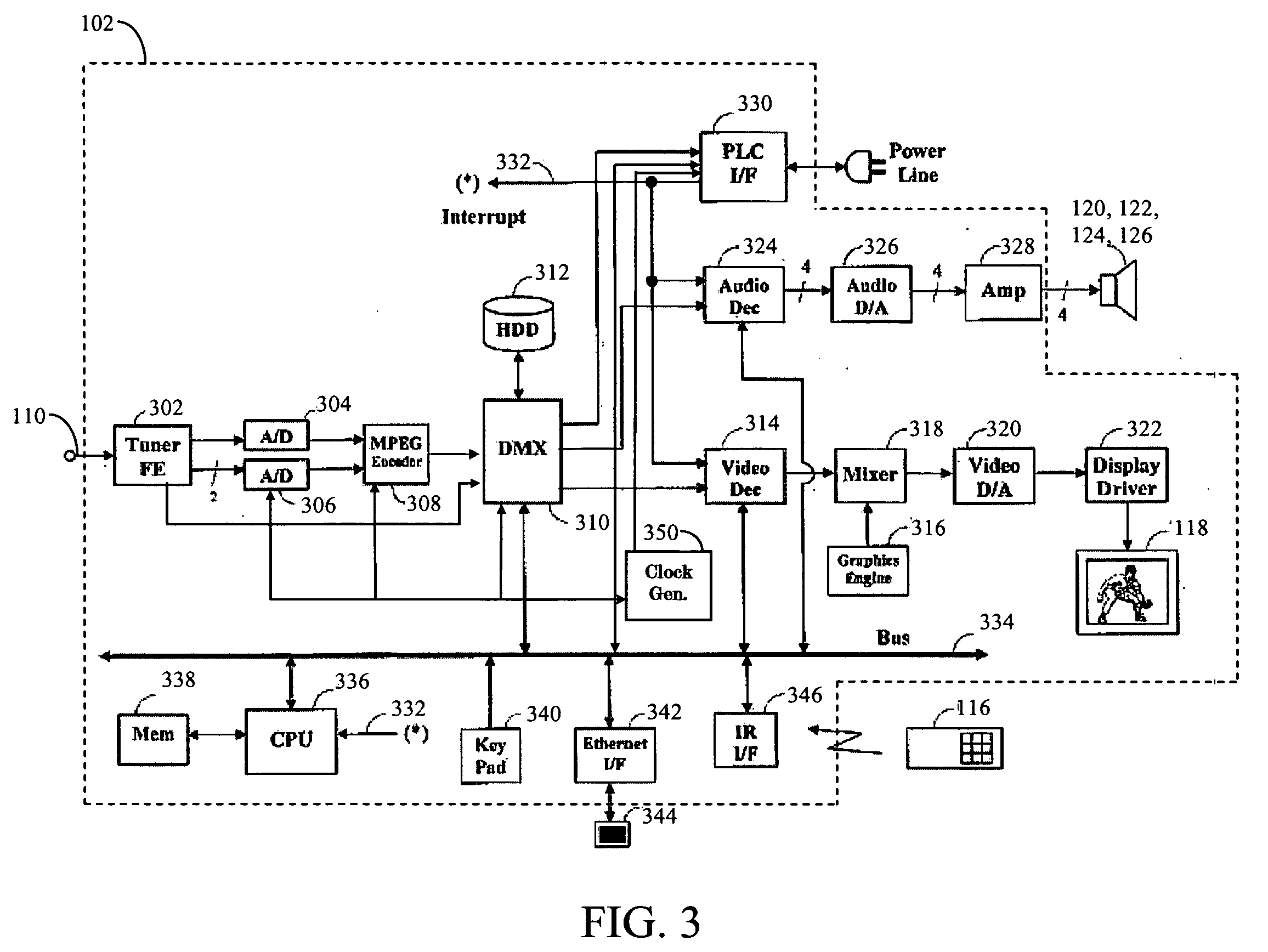
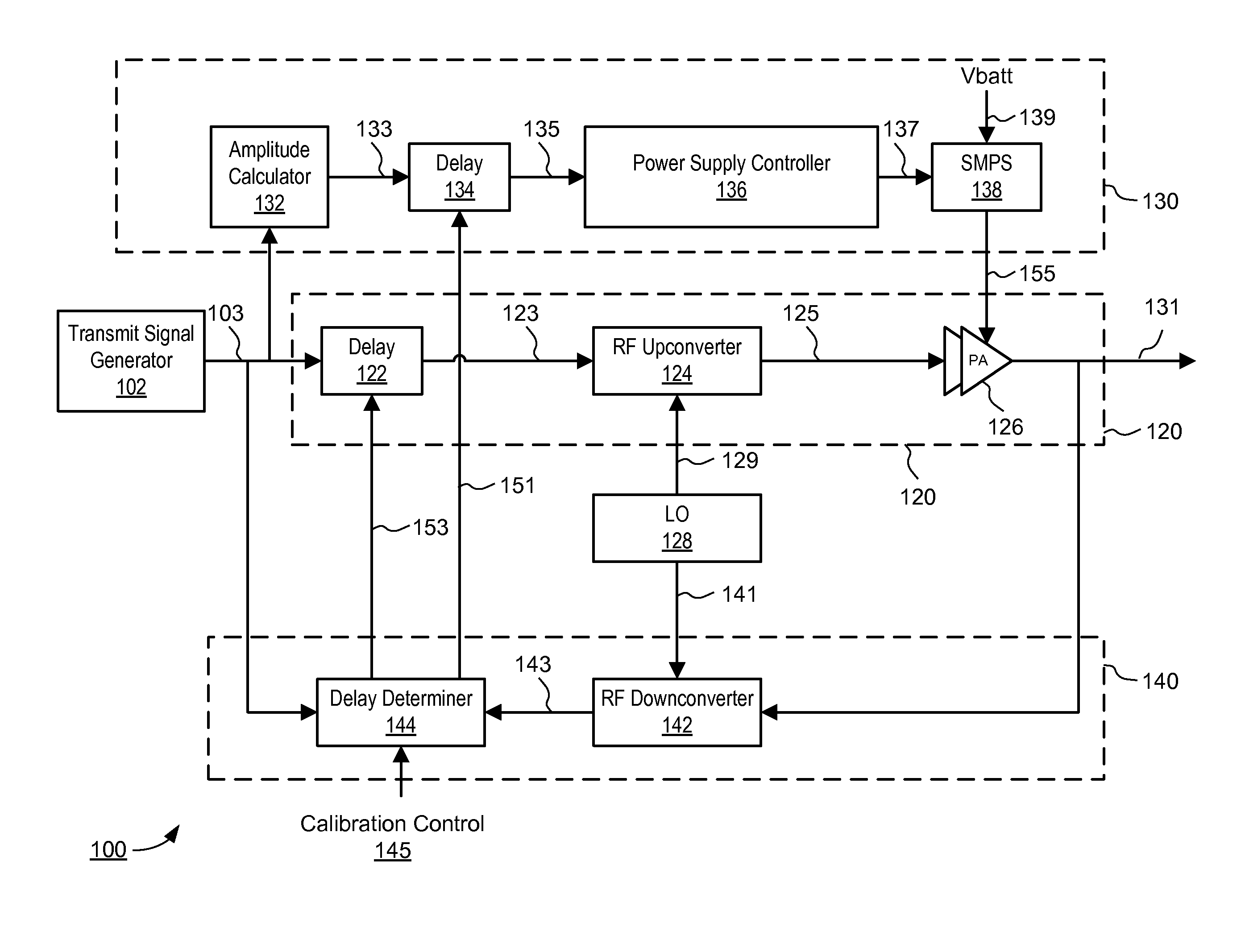
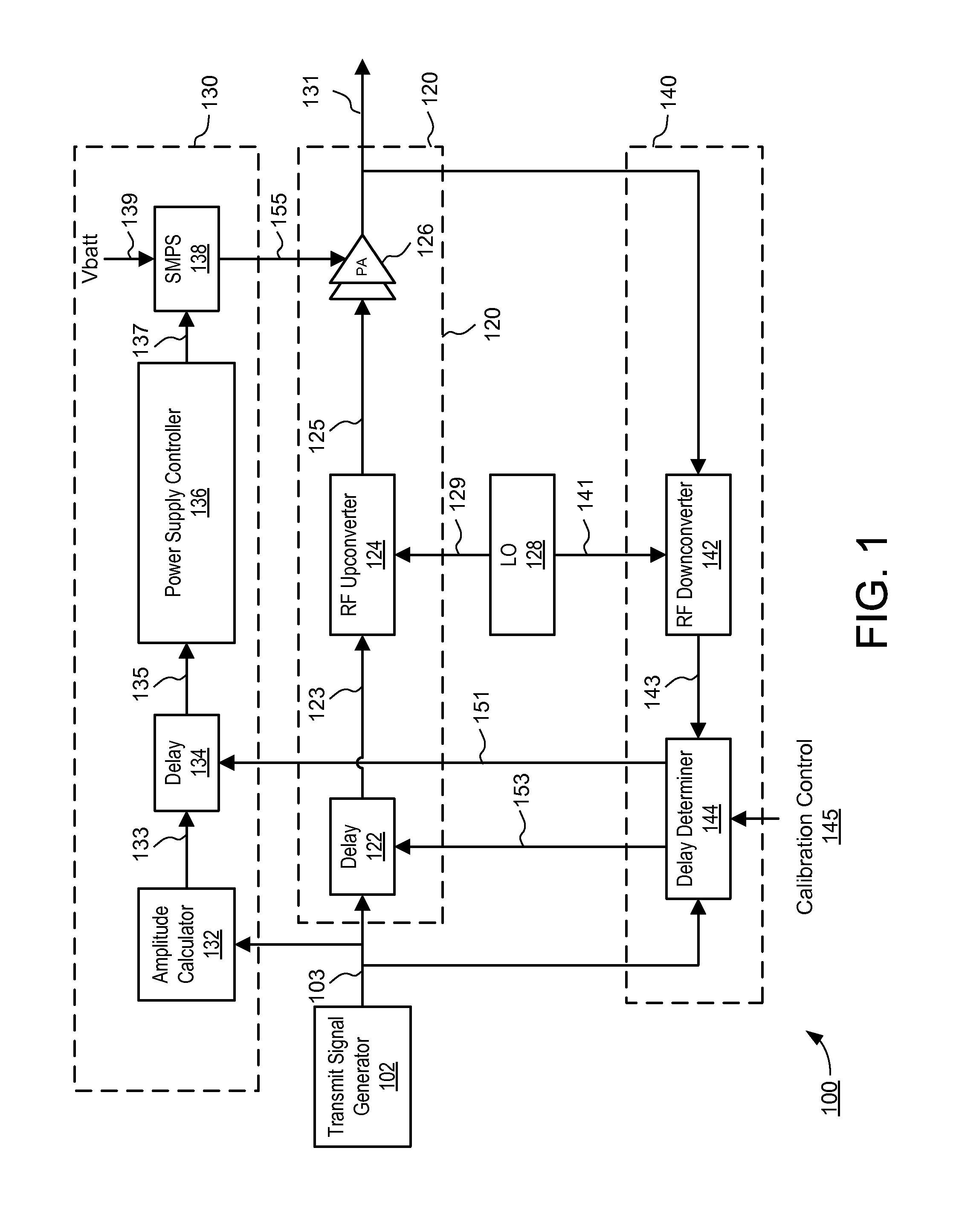
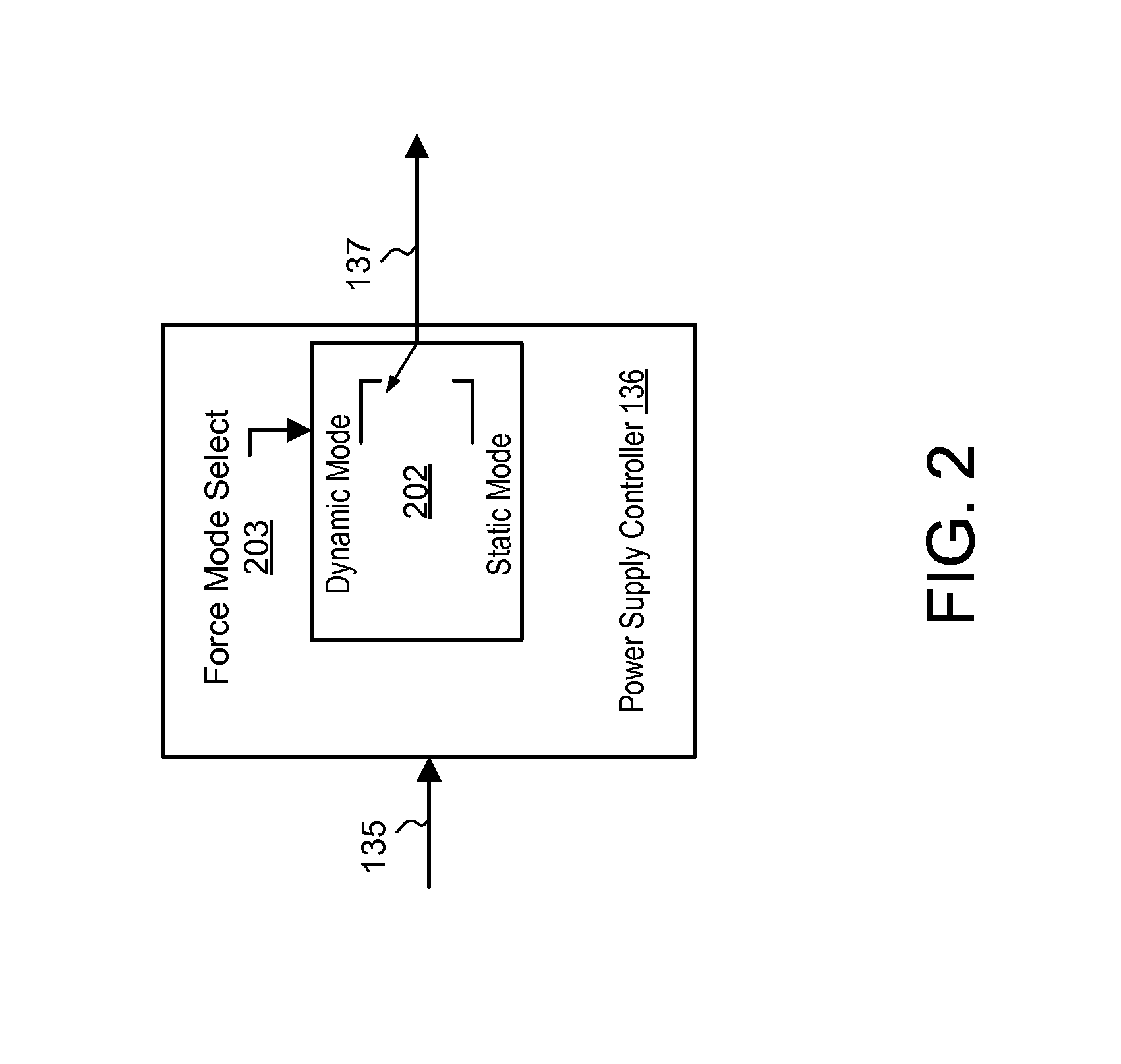
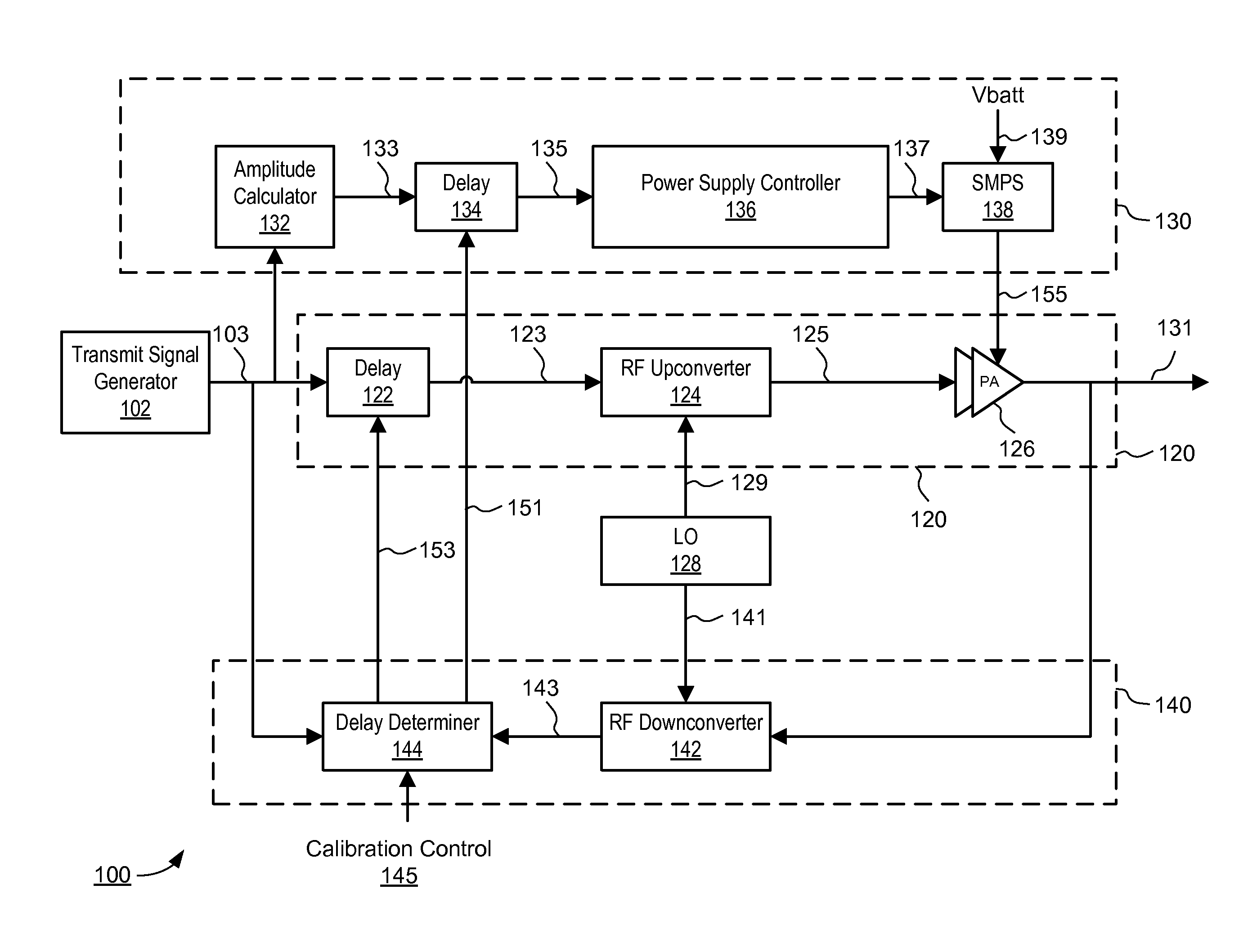
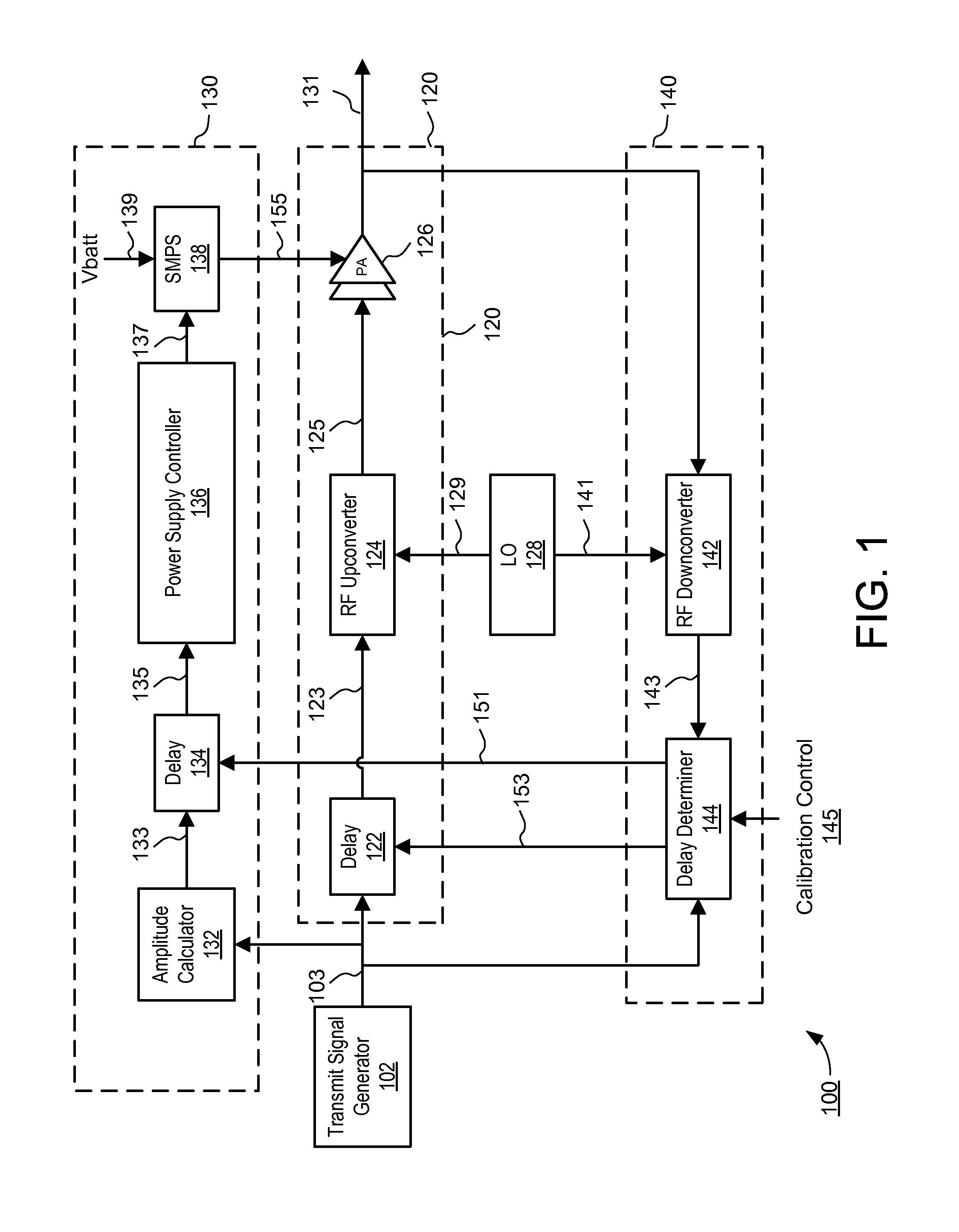
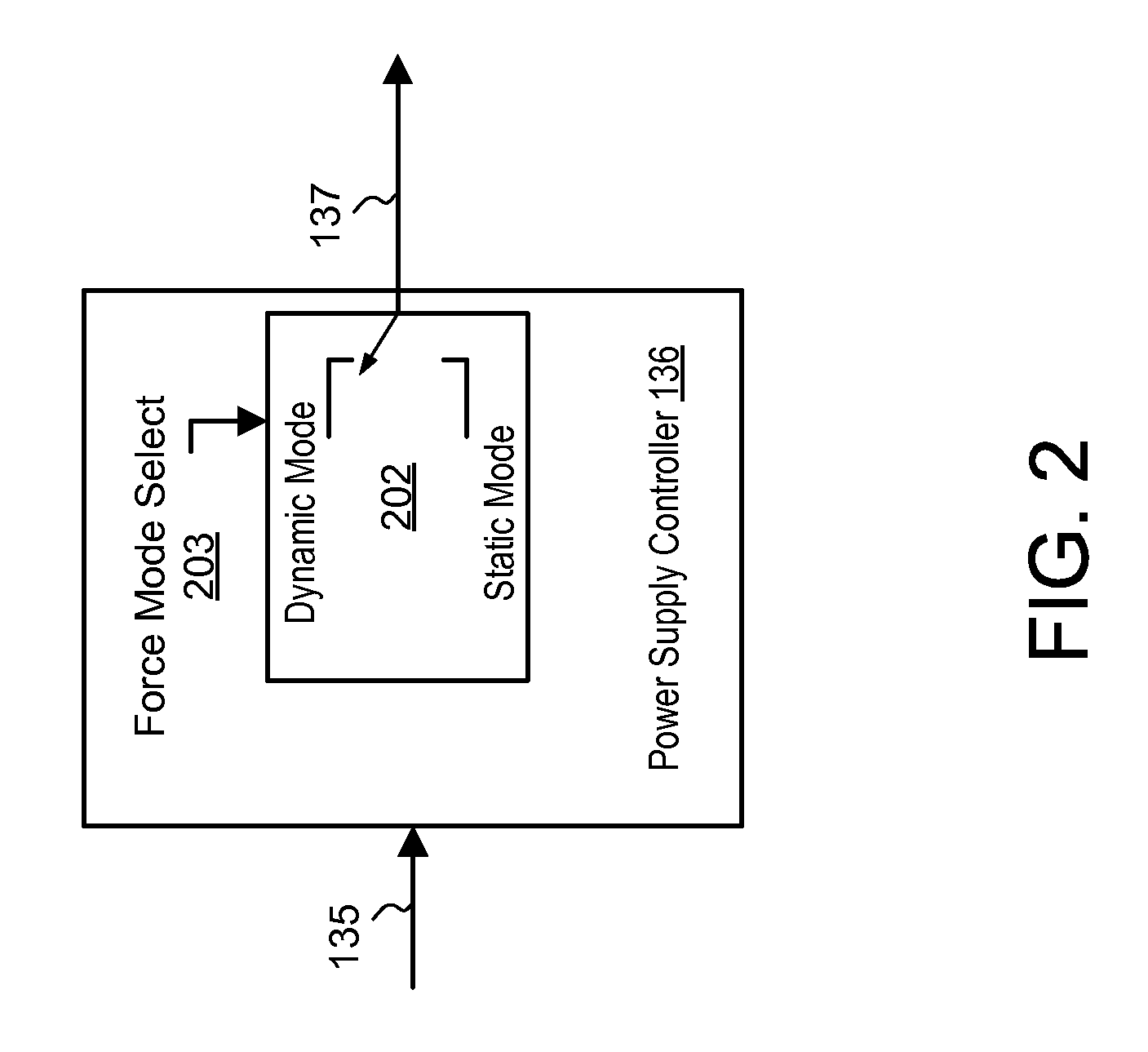
Envelope Tracking Power Amplifier System with Delay Calibration
An envelope tracking power amplifier system time-aligns a supply voltage to an input signal to a power amplifier. The power supply operates in a static mode for low amplitude input signals and operates in a dynamic mode for high amplitude input signals. In the static mode, the power supply produces a substantially constant supply voltage independent of the amplitude of the input signal. In the dynamic mode the power supply produces a dynamically varying envelope tracking supply voltage based on the amplitude of the input signal. A first delay is determined based on portions of the input and output signals captured during static operation of the power supply and a second delay is determined based on portions of the input and output signals captured during dynamic operation. A delay mismatch is estimated based on a difference between the first and second delays.
Owner:QUANTANCE
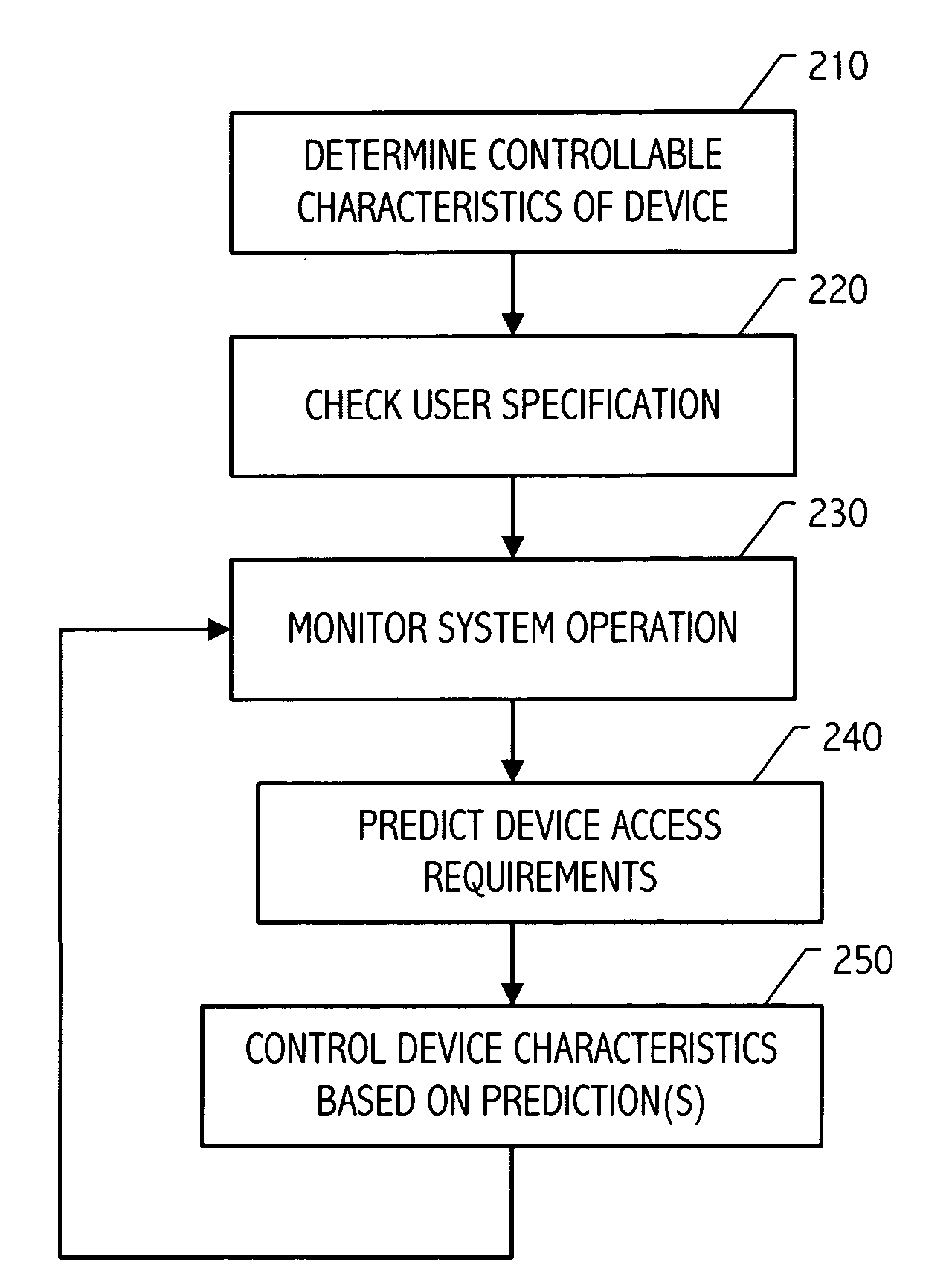
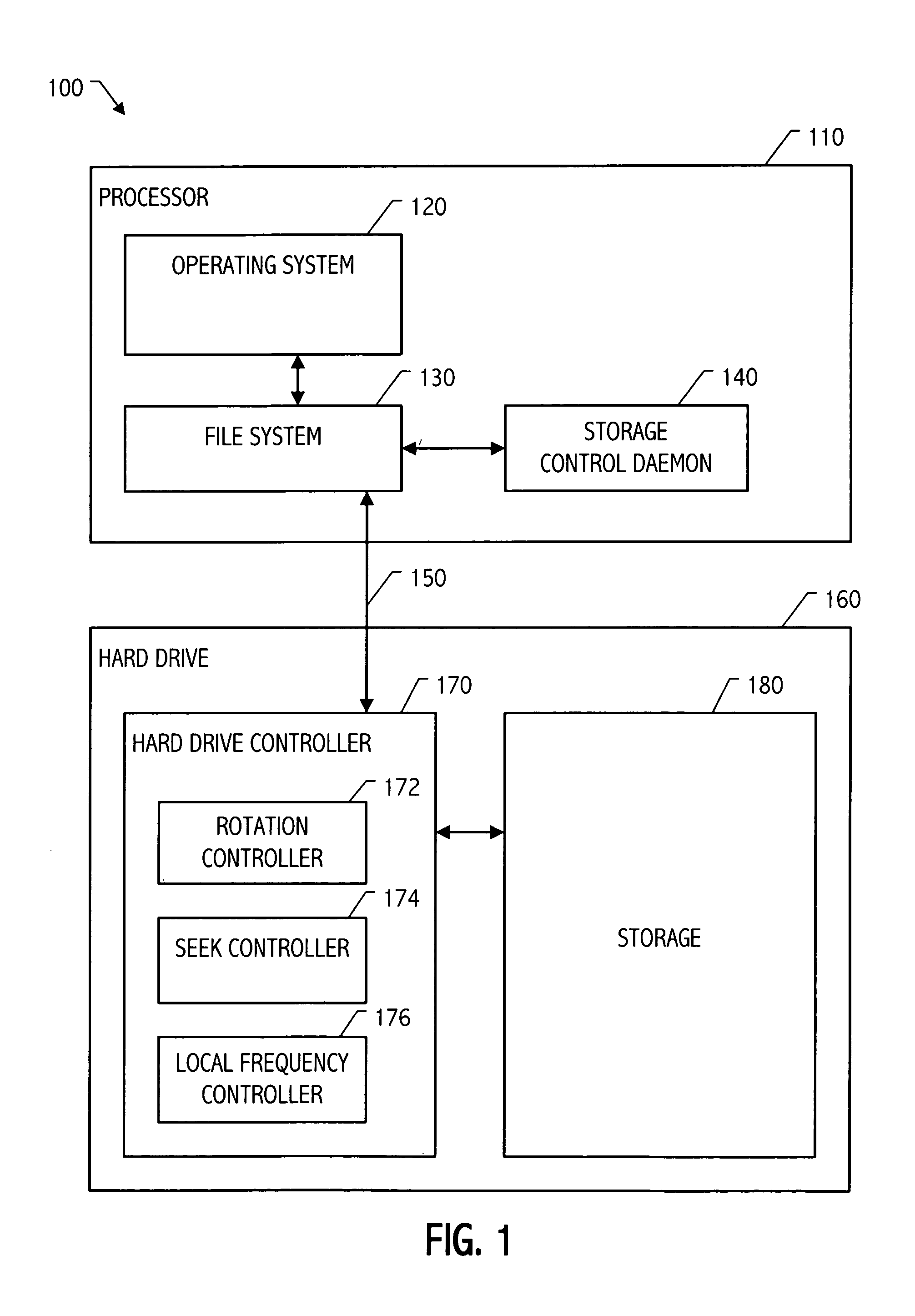
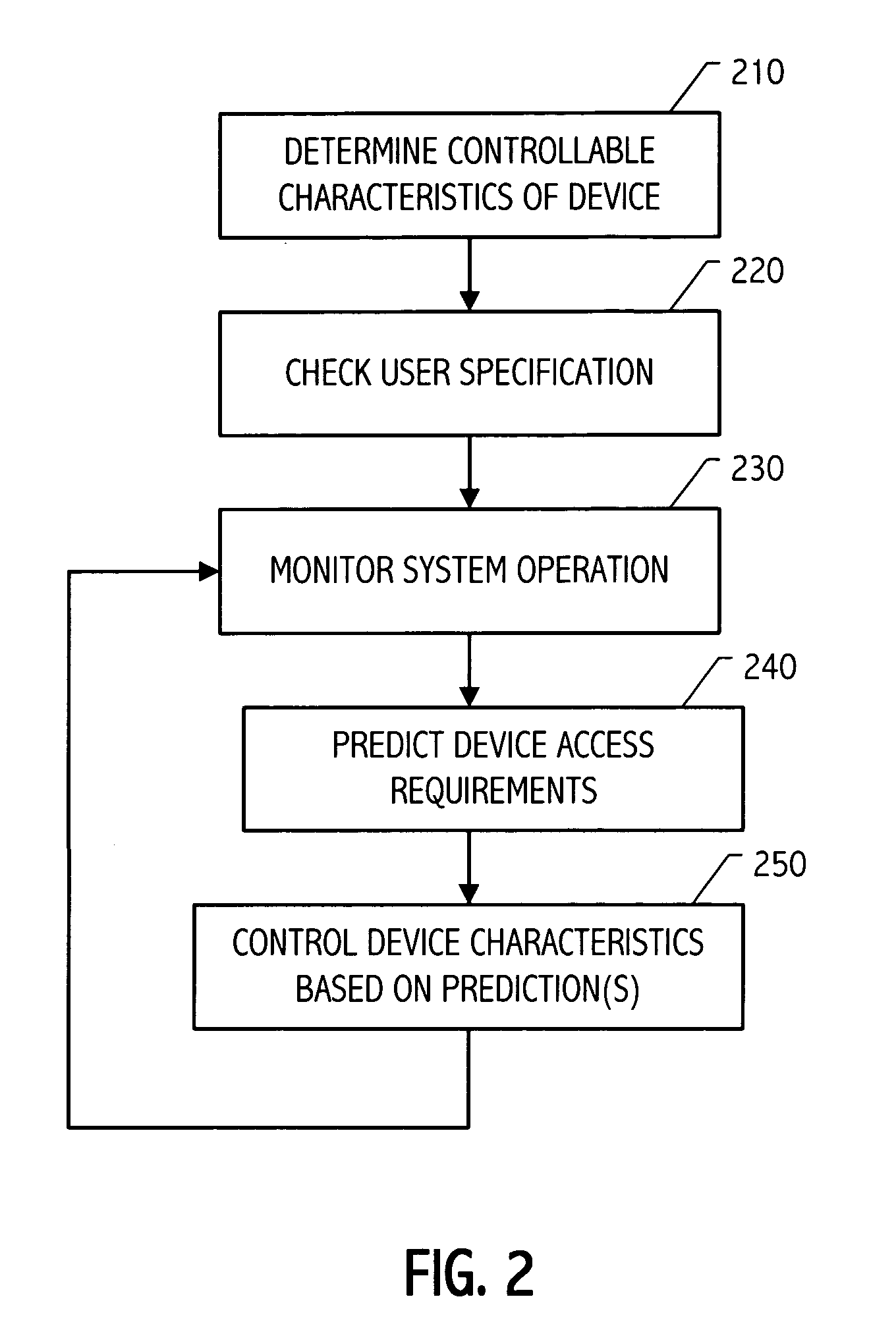
Storage device control responsive to operational characteristics of a system
It has been discovered that system operational characteristics (e.g., power level, clock frequency, processor utilization, operating system time slice utilization, size and age of queued jobs) may be used to predict storage access requirements for the system. By predicting the storage access requirements of a system, a storage subsystem may be advantageously controlled to anticipate storage accesses. A storage device or array of such devices can be configured to operate, for example, at selected speeds no greater than that required to process the predicted storage access requirements. The storage access prediction may be based, for example, on the frequency and voltage at which a processor is running or based on other system performance indicators such as job backlog and age and size thereof. Various controllable characteristics such as the speed of a hard drive's storage media, the current applied to a read / write head, etc., can be increased or decreased continuously or to discrete values in response to moving average indicators which provide advance warning of potential processing, and therefore potential storage access, swings.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
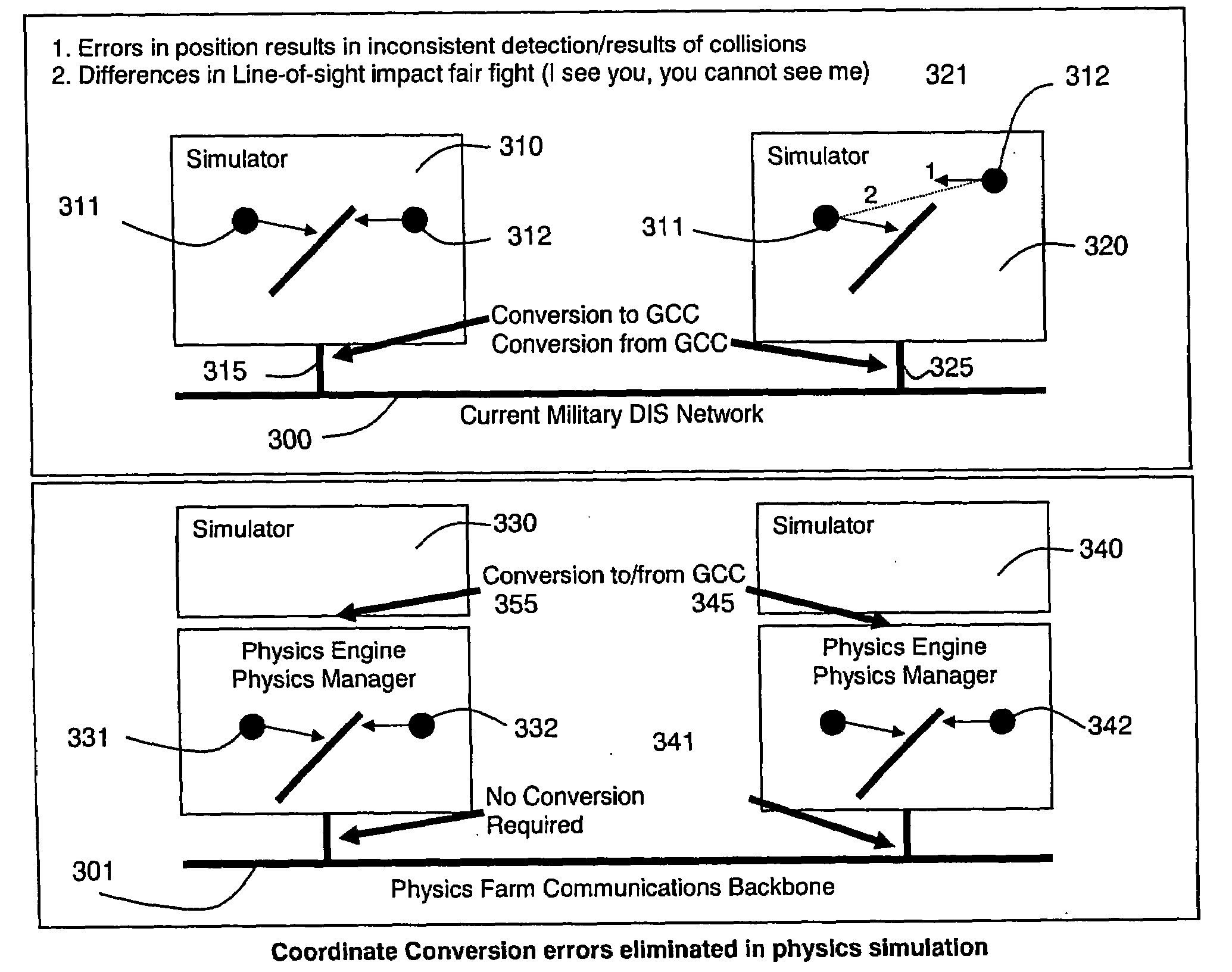
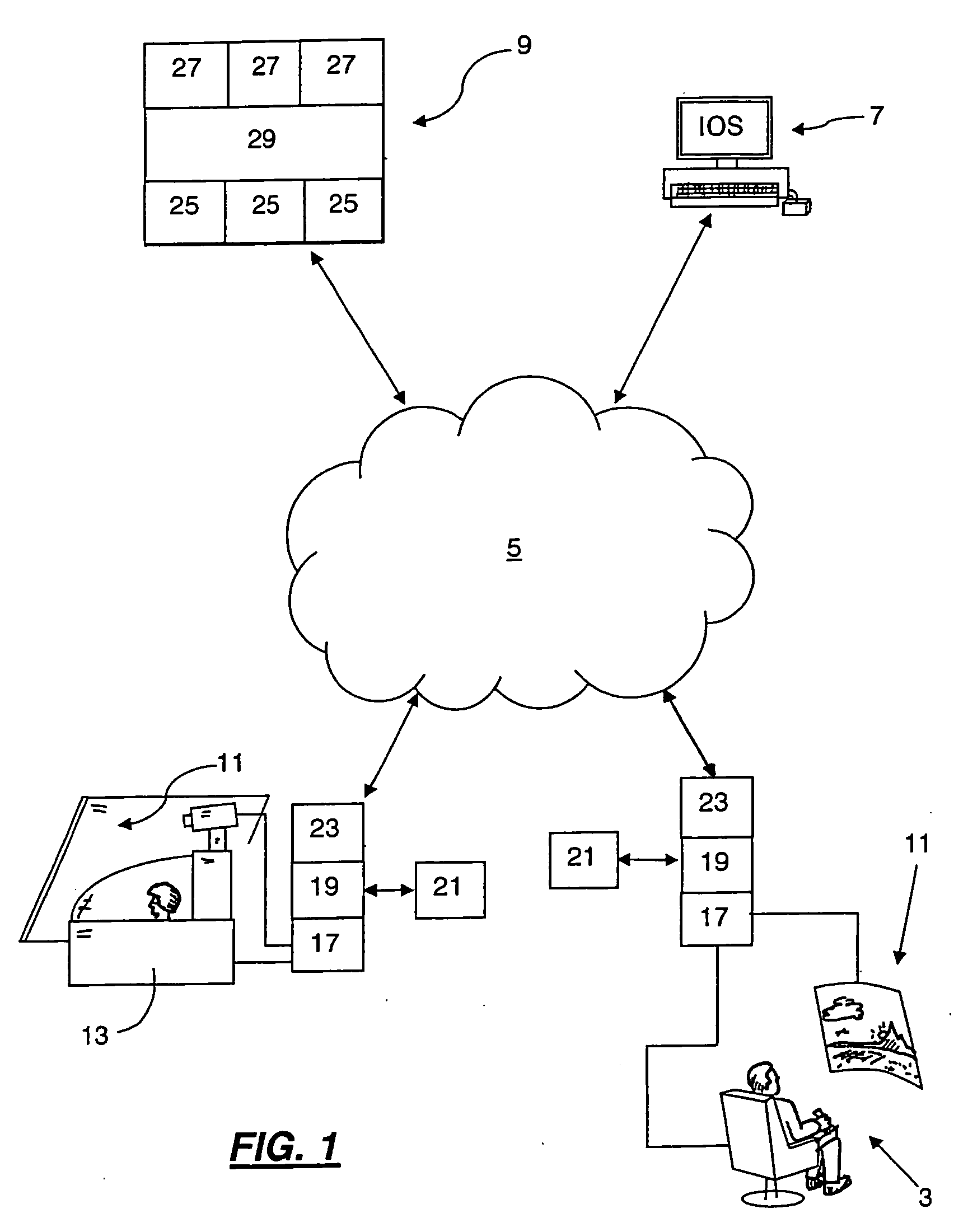
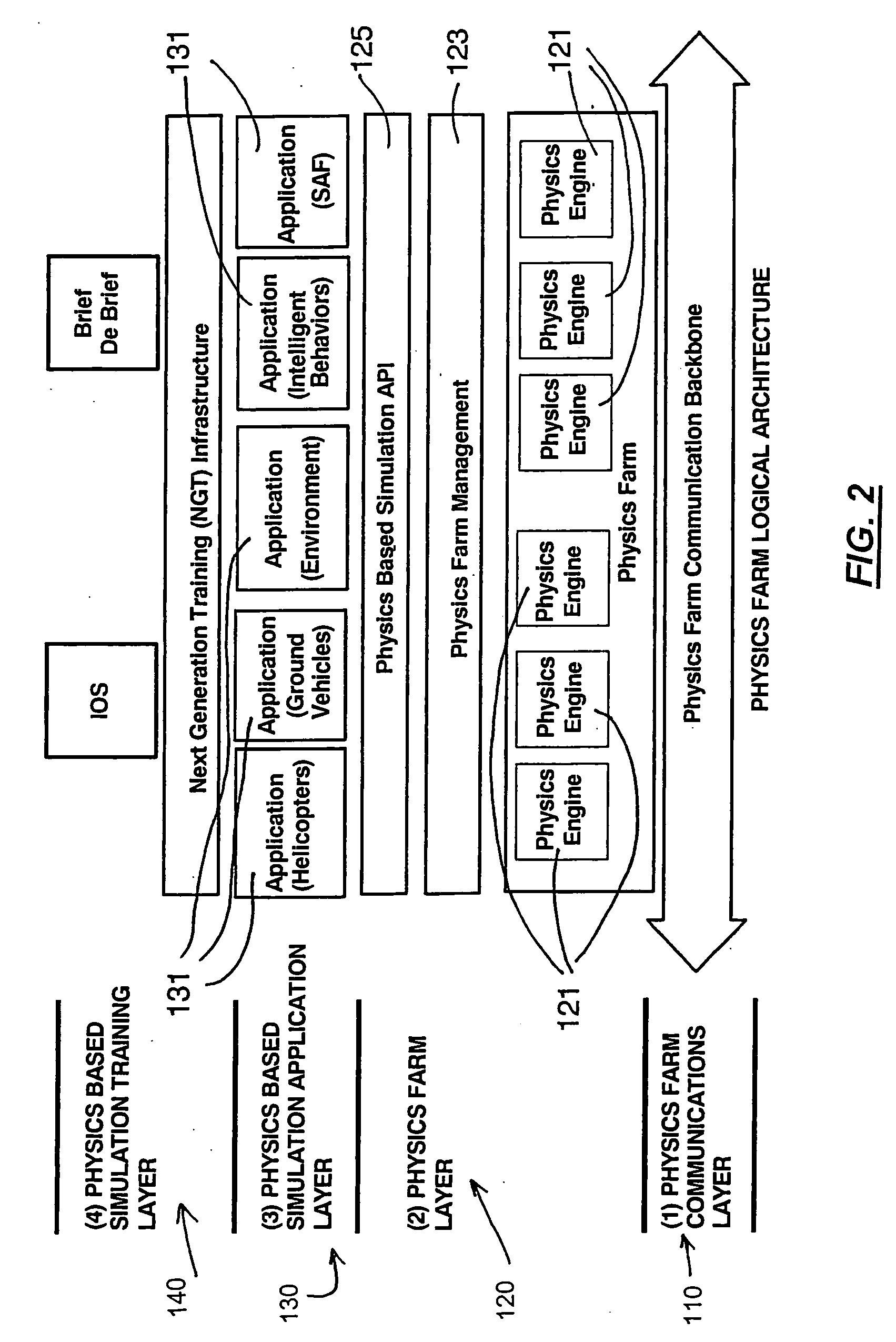
Distributed Physics Based Training System and Methods
ActiveUS20090099824A1Reduce realismReduce the valueAnalogue computers for vehiclesTransmissionPhysics basedPhysics engine
A distributed simulation system is composed of simulator stations linked over a network that each renders real-time video imagery for its user from scene data stored in its data storage. The simulation stations are each connected with a physics farm that manages the virtual objects in the shared virtual environment based on their physical attribute data using physics engines, including an engine at each simulation station. The physics engines of the physics farm are assigned virtual objects so as to reduce the effects of latency, to ensure fair fight requirements of the system, and, where the simulation is of a vehicle, to accurately model the ownship of the user at the station. A synchronizer system is also provided that allows for action of simulated entities relying on localized closed loop controls to cause the entities to meet specific goal points at specified system time points.
Owner:CAE USA INC +1
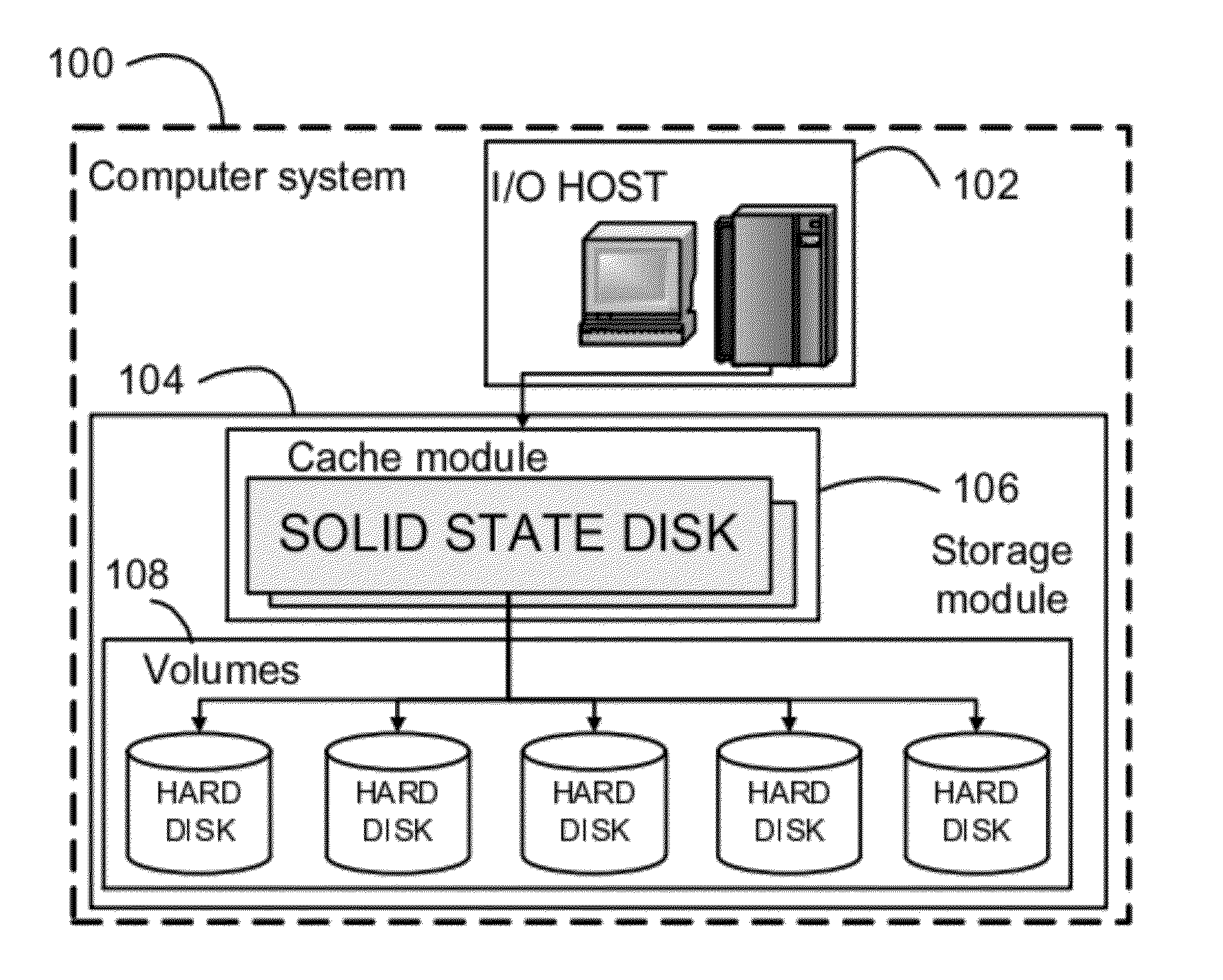
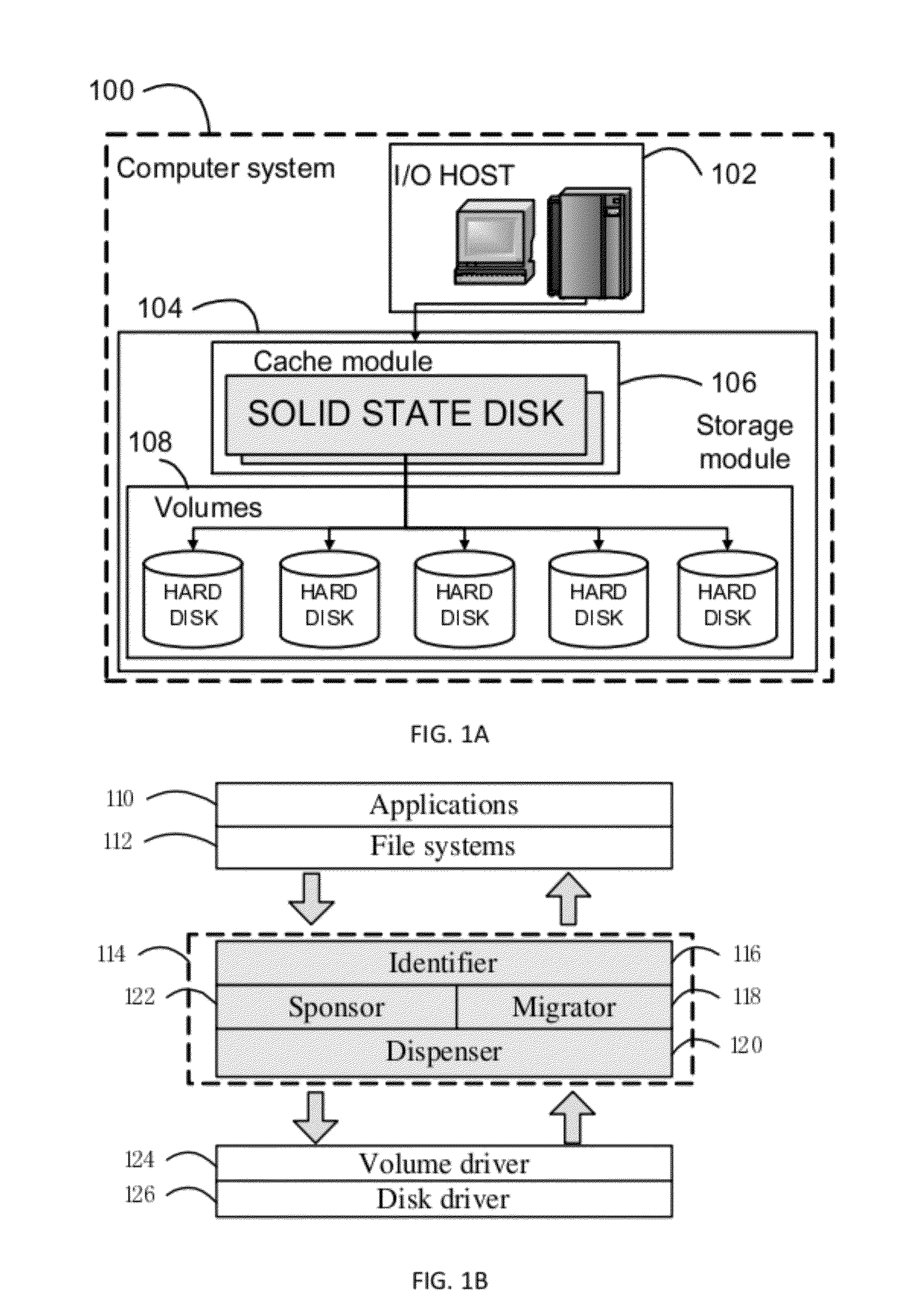
Solid-State Disk Caching the Top-K Hard-Disk Blocks Selected as a Function of Access Frequency and a Logarithmic System Time
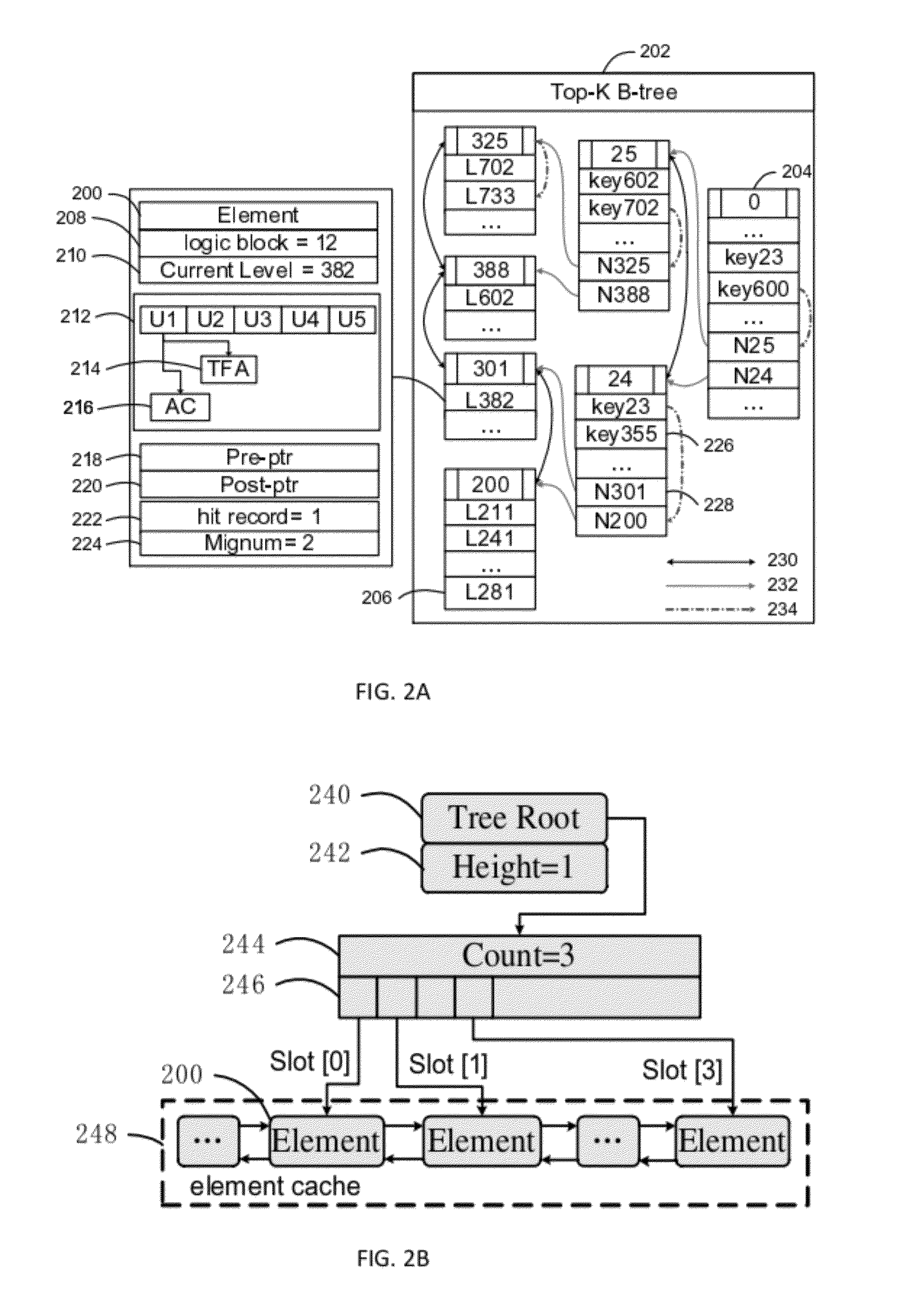
InactiveUS20120317338A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionAccess frequencySystem time
A solid state disk (SSD) caches disk-based volumes in a heterogeneous storage system, improving the overall storage-system performance. The hottest data blocks are identified based on two factors: the frequency of access, and temporal locality. Temporal locality is computed using a logarithmic system time. IO latency is reduced by migrating these hottest data blocks from hard-disk-based volumes to the solid-state flash-memory disks. Some dedicated mapping metadata and a novel top-K B-tree structure are used to index the blocks. Data blocks are ranked by awarding a higher current value for recent accesses, but also by the frequency of accesses. A non-trivial value for accesses in the past is retained by accumulating the two factors over many time spans expressed as a logarithmic system time. Having two factors, access frequency and the logarithmic system time, provides for a more balanced caching system.
Owner:21VIANET GRP INC
High-precision real-time synchronization method based on IEEE1588
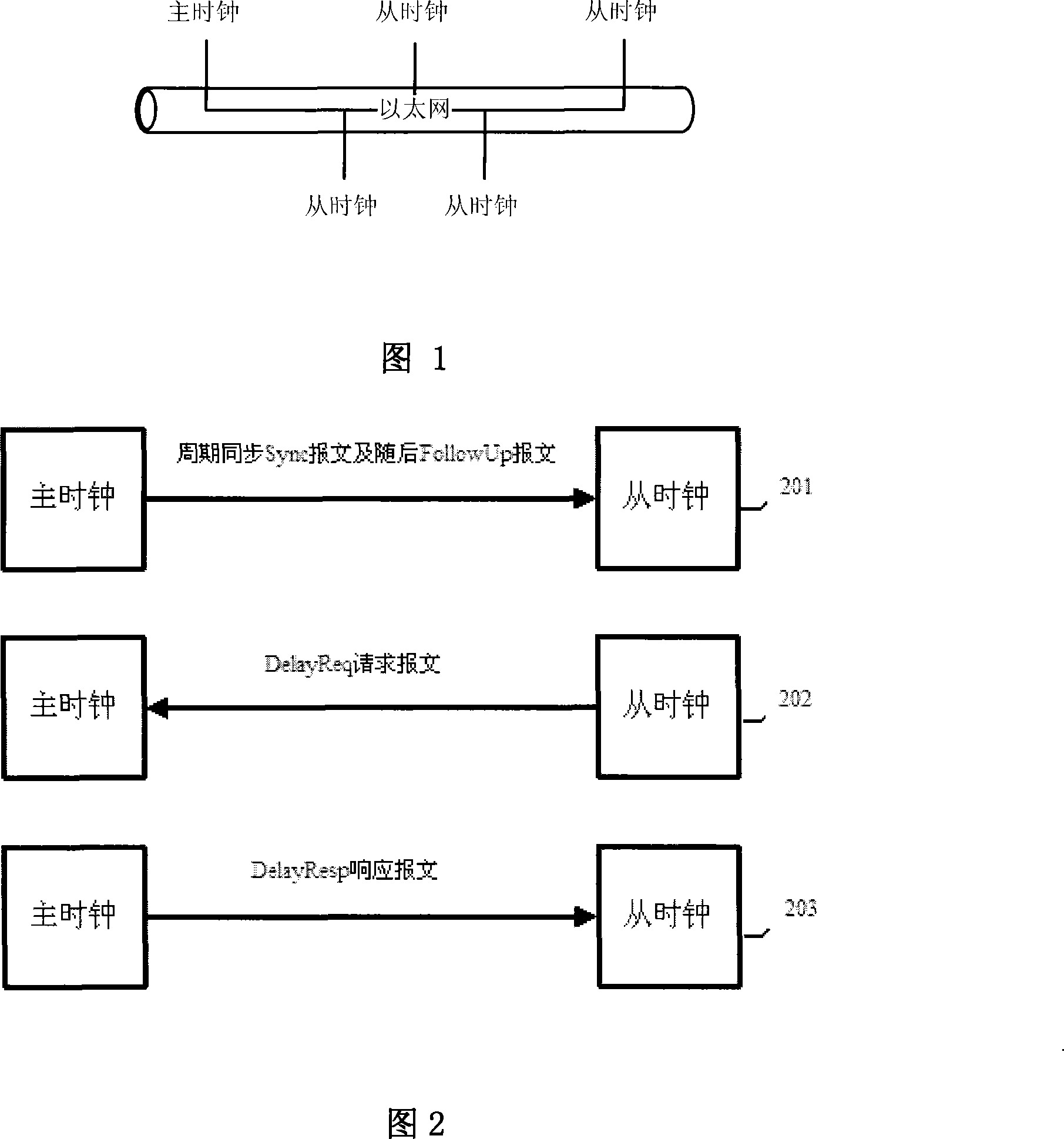
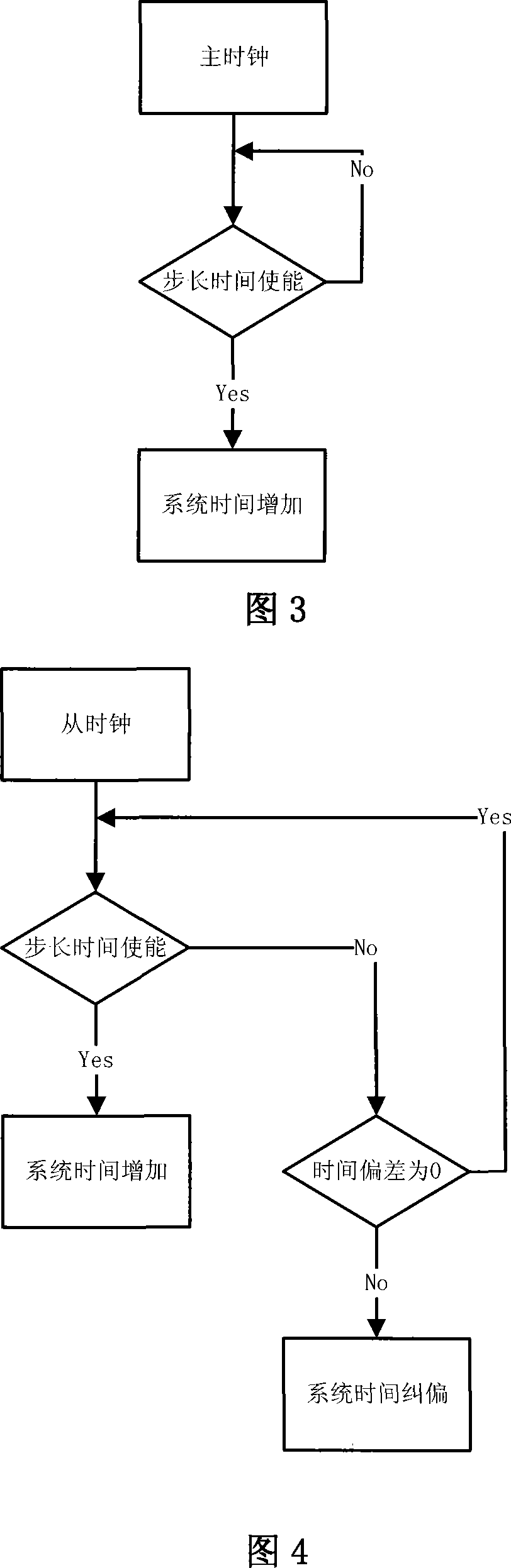
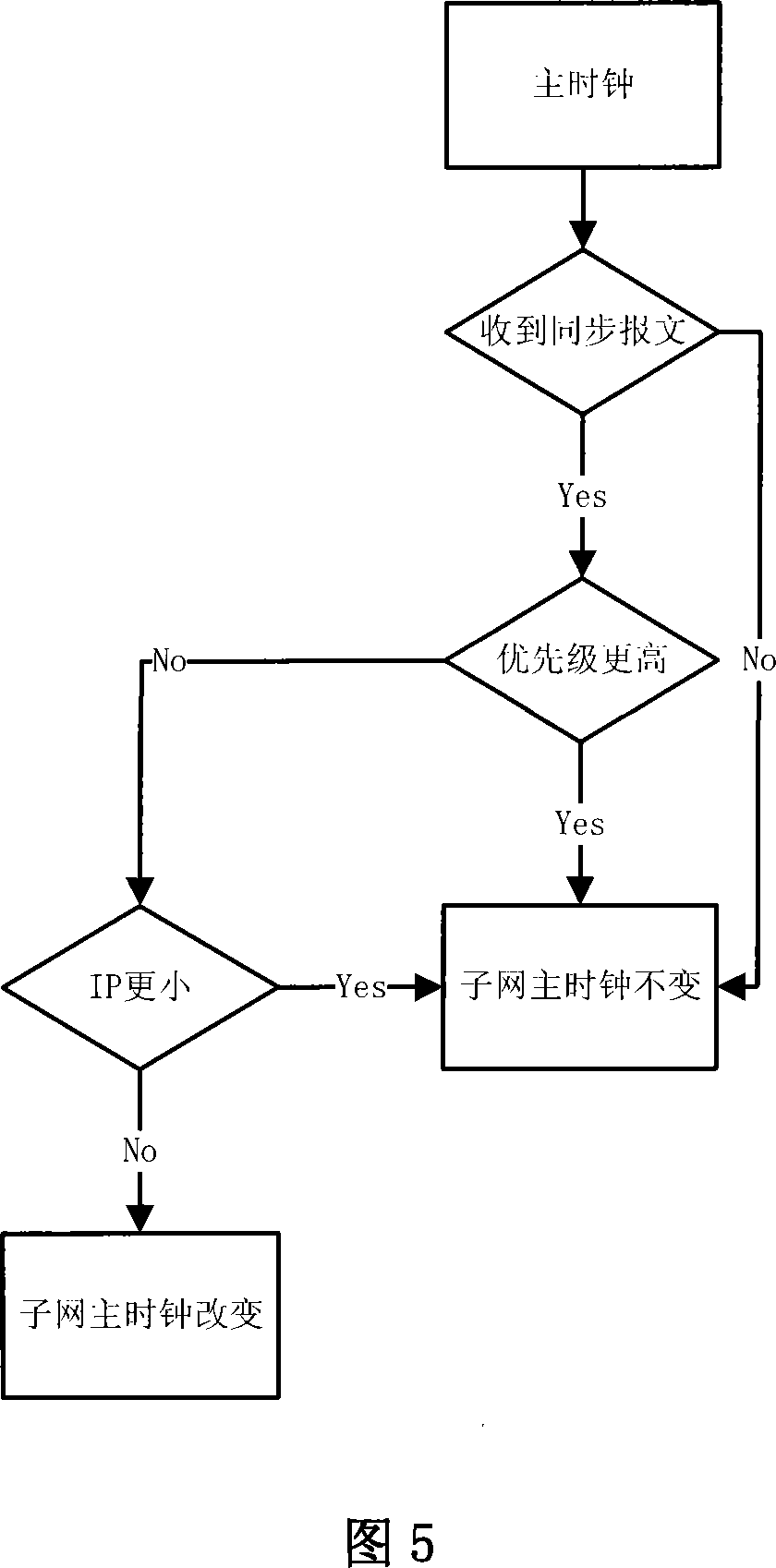
InactiveCN101232457ASolve the unity problemSolve the accuracy problemTime-division multiplexData switching networksSlave clockData transmission time
The invention relates to a real-time synchronization method based on PTP precision clock synchronization protocol of IEEE1588. The research on hardware of IEEE1588 protocol is still a blank at present. The method of the invention includes the following steps: sending messages; receiving messages; correcting the local system time; selecting the optimal master clock. And the synchronization action is different when the corresponding equipment is a master clock or a slave clock. The hardware method reduces the inherent fluctuation of data transmission time of internet technology, while not affecting the scope of precision control, thus resolving the problem of the clock uniformity and precision in a distributed network system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
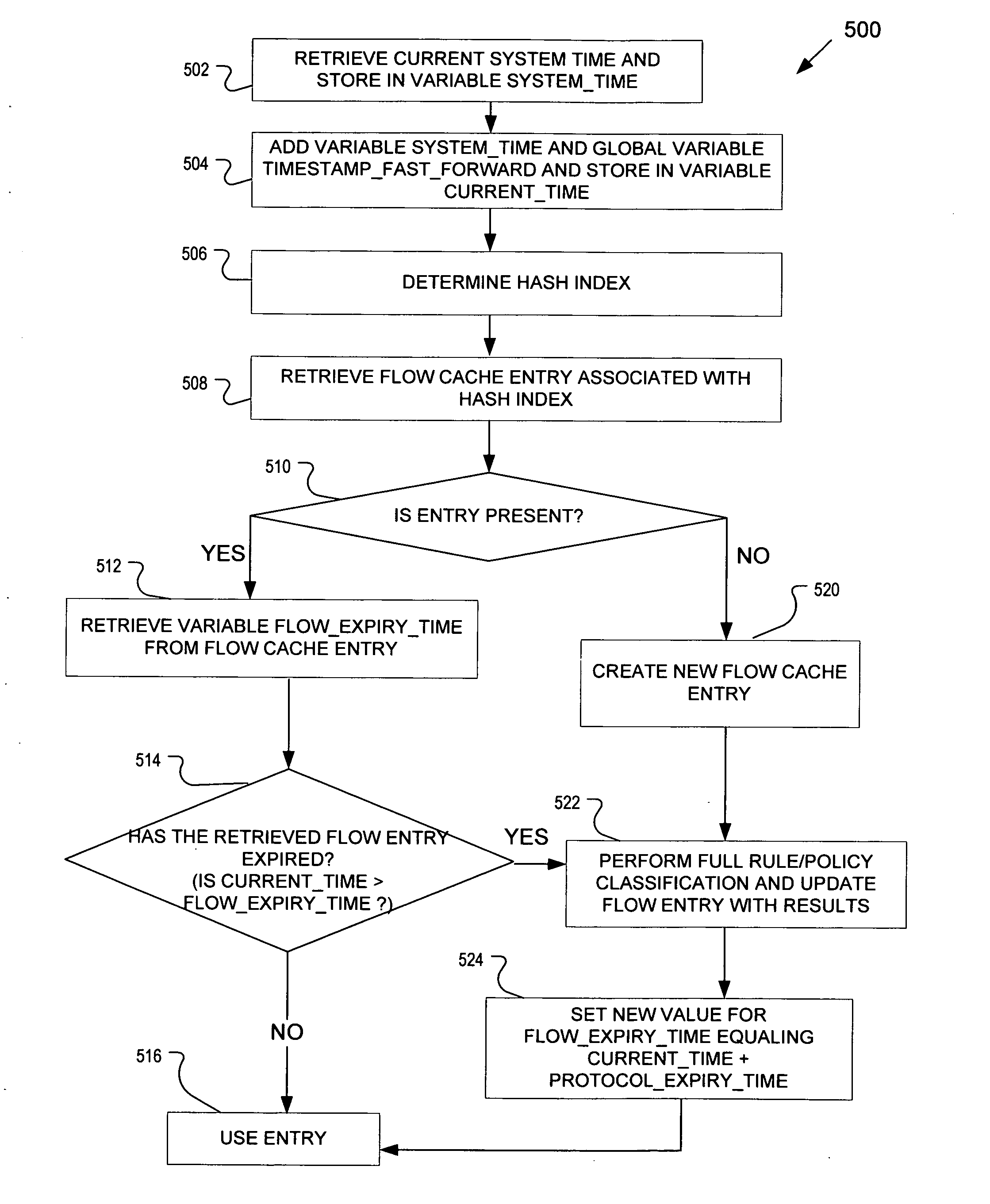
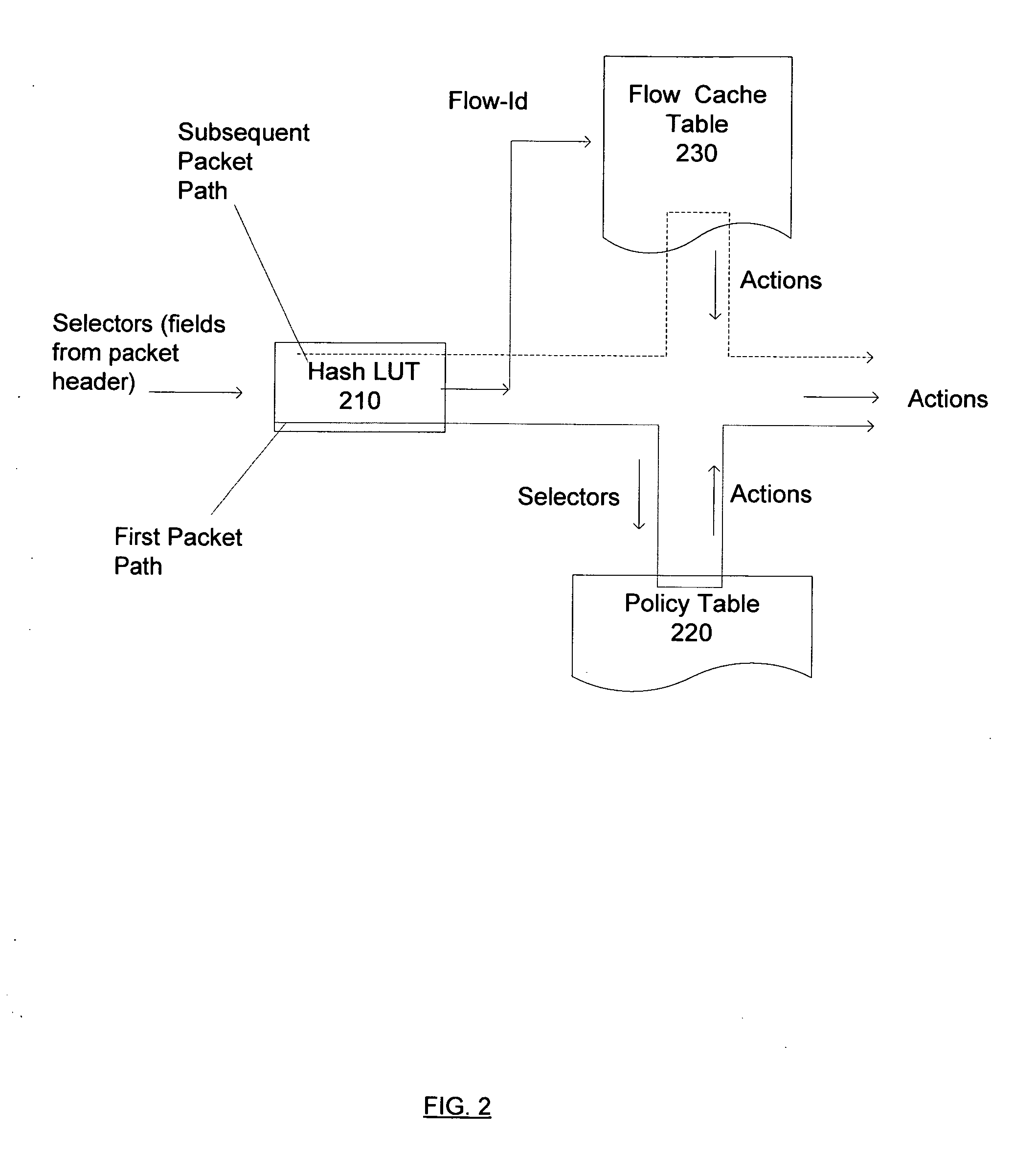
Techniques to manage a flow cache
Techniques are described herein that may be used to invalidate all entries in a table. For example, the table may be a flow cache. For example, an expiry time may be associated with one or more entries in the table. The expiry time of an entry may be initially set to the sum of the system time, the expiry time of the protocol associated with the entry, and a global time variable. To check if the entry is expired at any time, the current system time may be added to the global time variable and if the result is greater than the expiry time in the entry, then the entry is expired. To invalidate all the entries, the global time variable may be incremented by a large amount which may equal the maximum expiry time of all protocols. This may cause all entries to expire. New entries may be added using the new incremented value of the global time variable and will hence not expire.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Push message processing method and mobile terminal
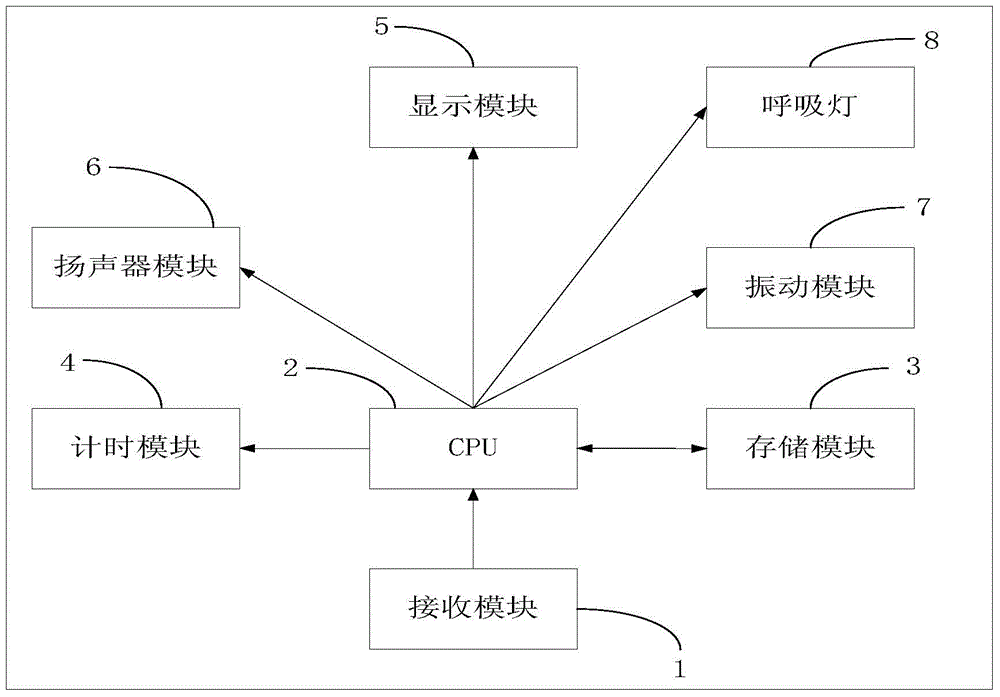
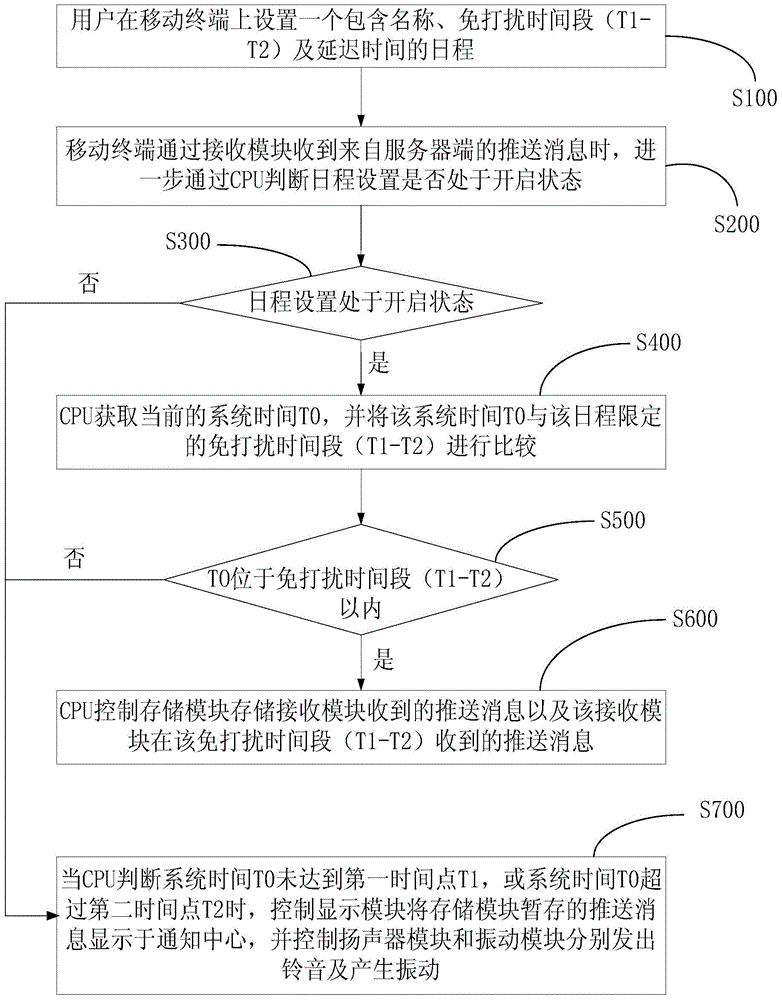
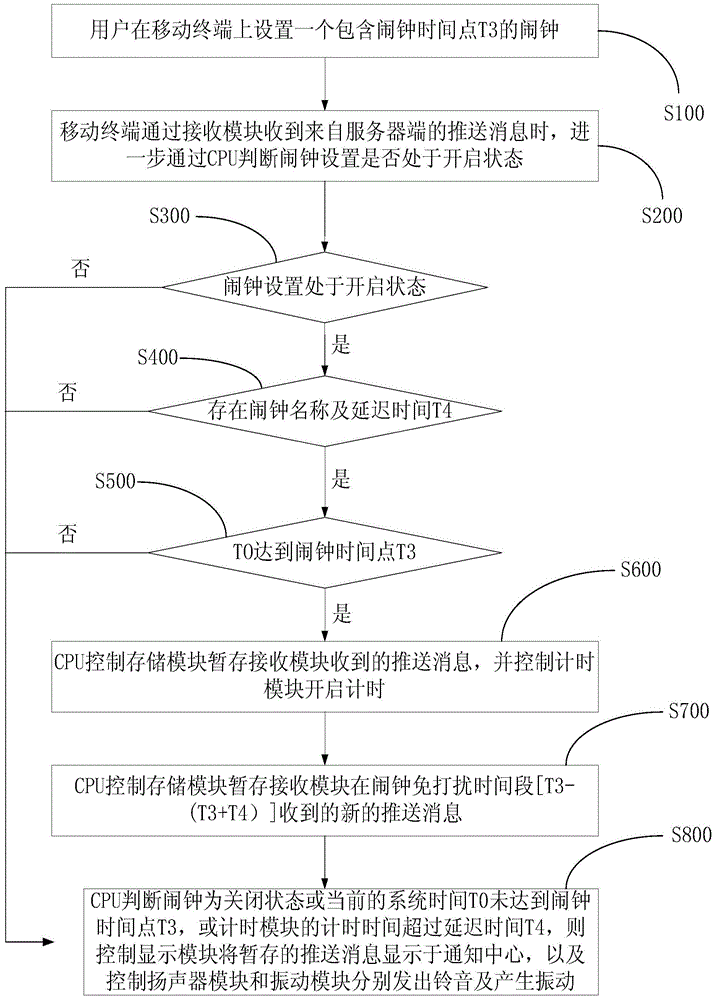
ActiveCN103561152AAvoid normal workInhibitory activityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsTime segmentSystem time
The invention discloses a push message processing method and a mobile terminal. The system comprises a receiving module (1), a CPU (2), a storage module (3) and a display module (5). The receiving module (1) is used for receiving push messages of a server terminal. The CPU is used for obtaining the current time (T0) of the system when no-disturbing of the system is determined to be in a started state, comparing the system time (T0) with a no-disturbing time segment (T1-T2) set by no-disturbing of the system and executing a corresponding order according to a comparison result. The storage module (3) is used for temporarily storing the push messages received by the receiving module (1) when the CPU (2) determines that the system time (T0) is within the no-disturbing time segment (T1-T2). The display module (5) is used for displaying the push messages received by the receiving module (1) when the CPU (2) determines that the system time (T0) is not within the no-disturbing time segment (T1-T2). By means of the push message processing method and the mobile terminal, a user is shielded from disturbance by a ring tone or vibration along with the push messages during the preset no-disturbing time segment.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Envelope tracking power amplifier system with delay calibration
An envelope tracking power amplifier system time-aligns a supply voltage to an input signal to a power amplifier. The power supply operates in a static mode for low amplitude input signals and operates in a dynamic mode for high amplitude input signals. In the static mode, the power supply produces a substantially constant supply voltage independent of the amplitude of the input signal. In the dynamic mode the power supply produces a dynamically varying envelope tracking supply voltage based on the amplitude of the input signal. A first delay is determined based on portions of the input and output signals captured during static operation of the power supply and a second delay is determined based on portions of the input and output signals captured during dynamic operation. A delay mismatch is estimated based on a difference between the first and second delays.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Method and apparatus for a virtual system time clock for digital audio/video processor
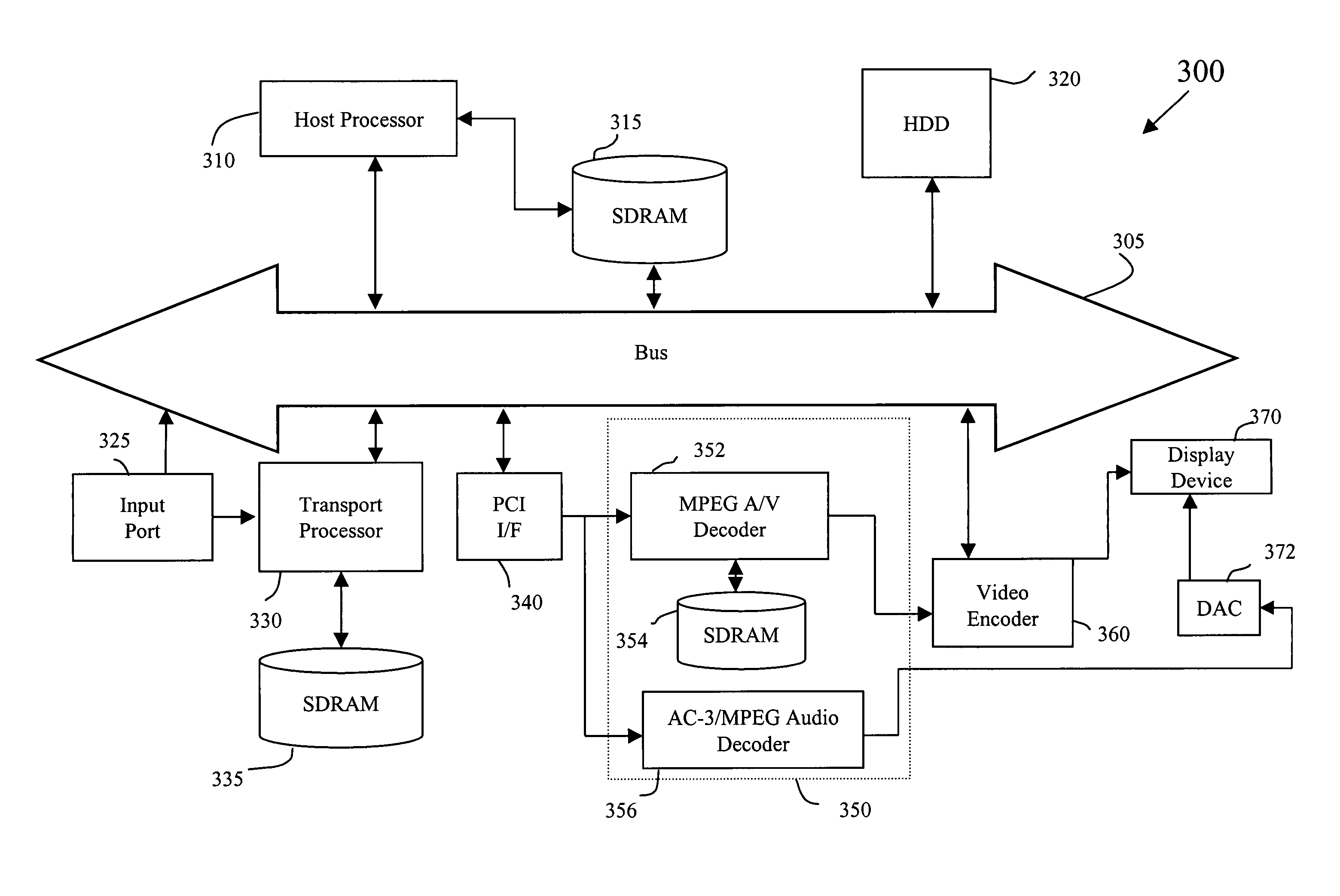
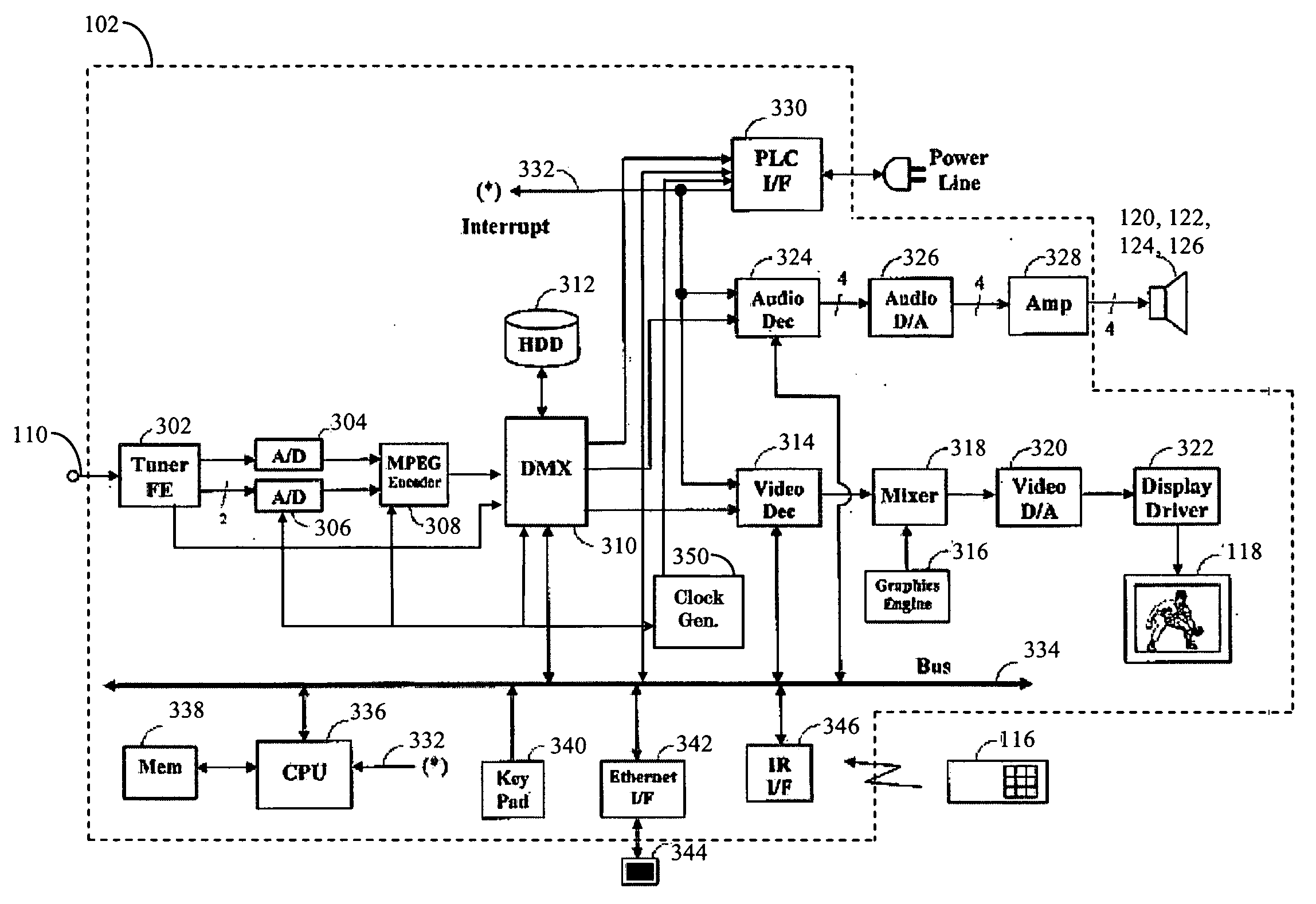
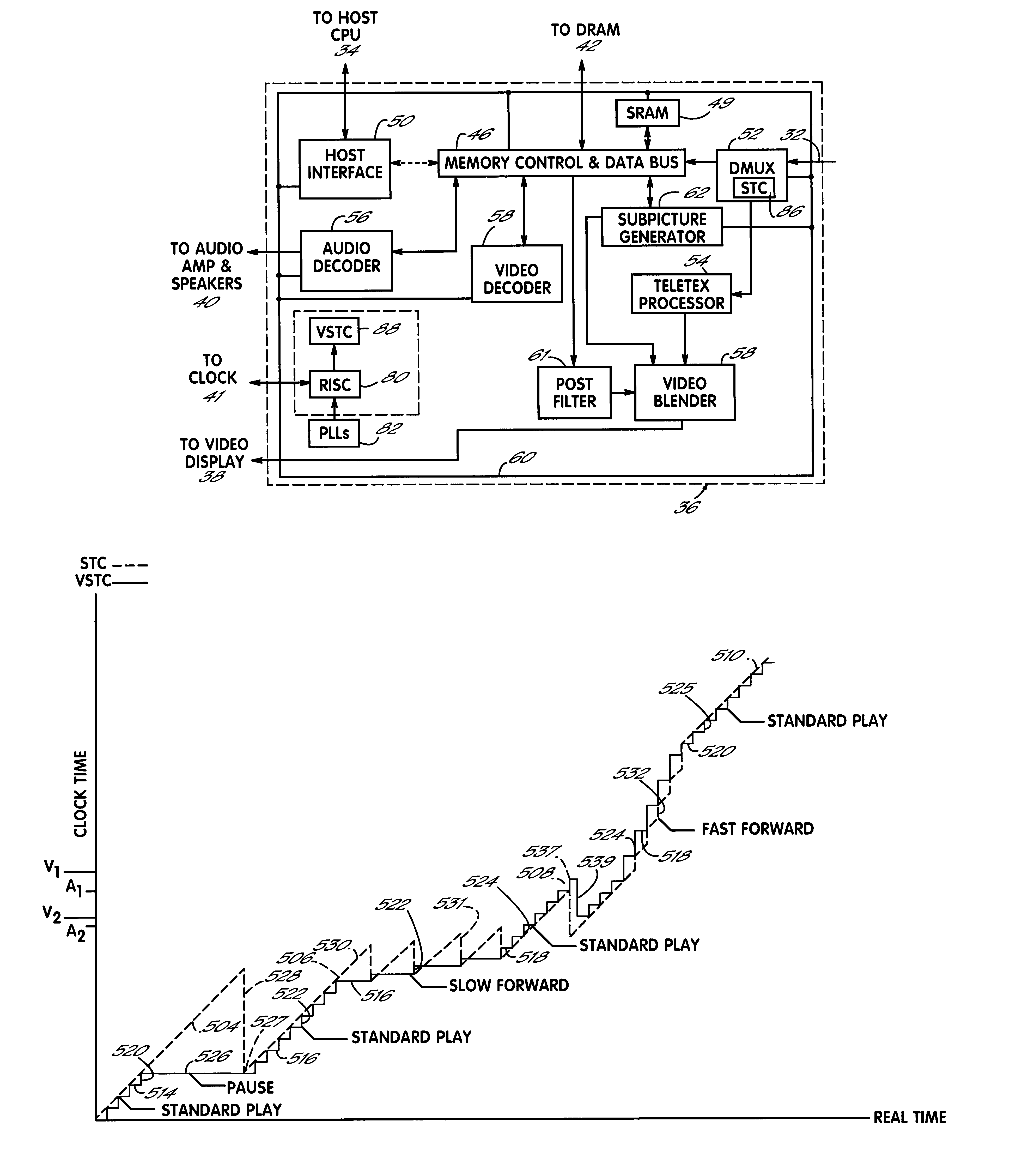
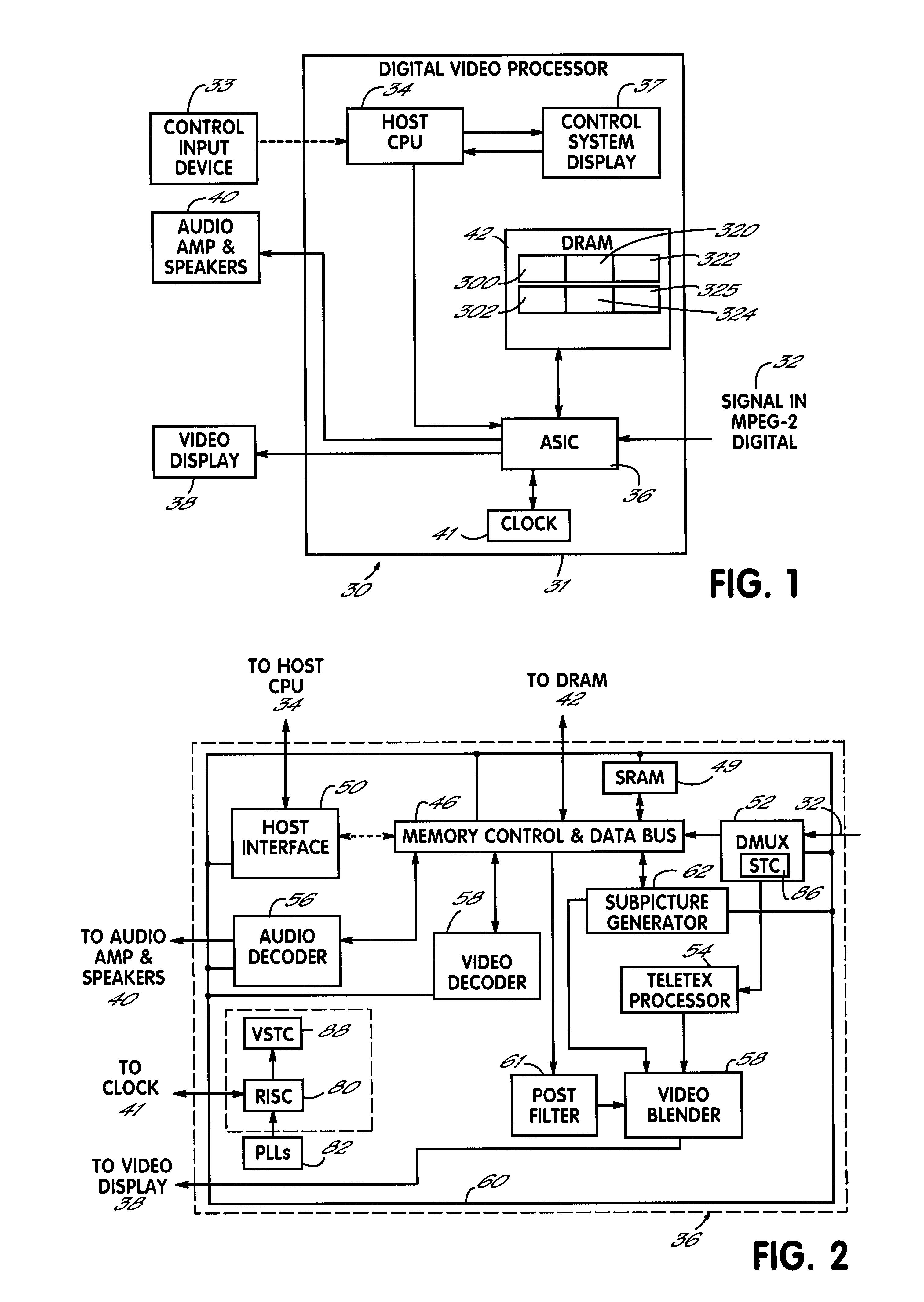
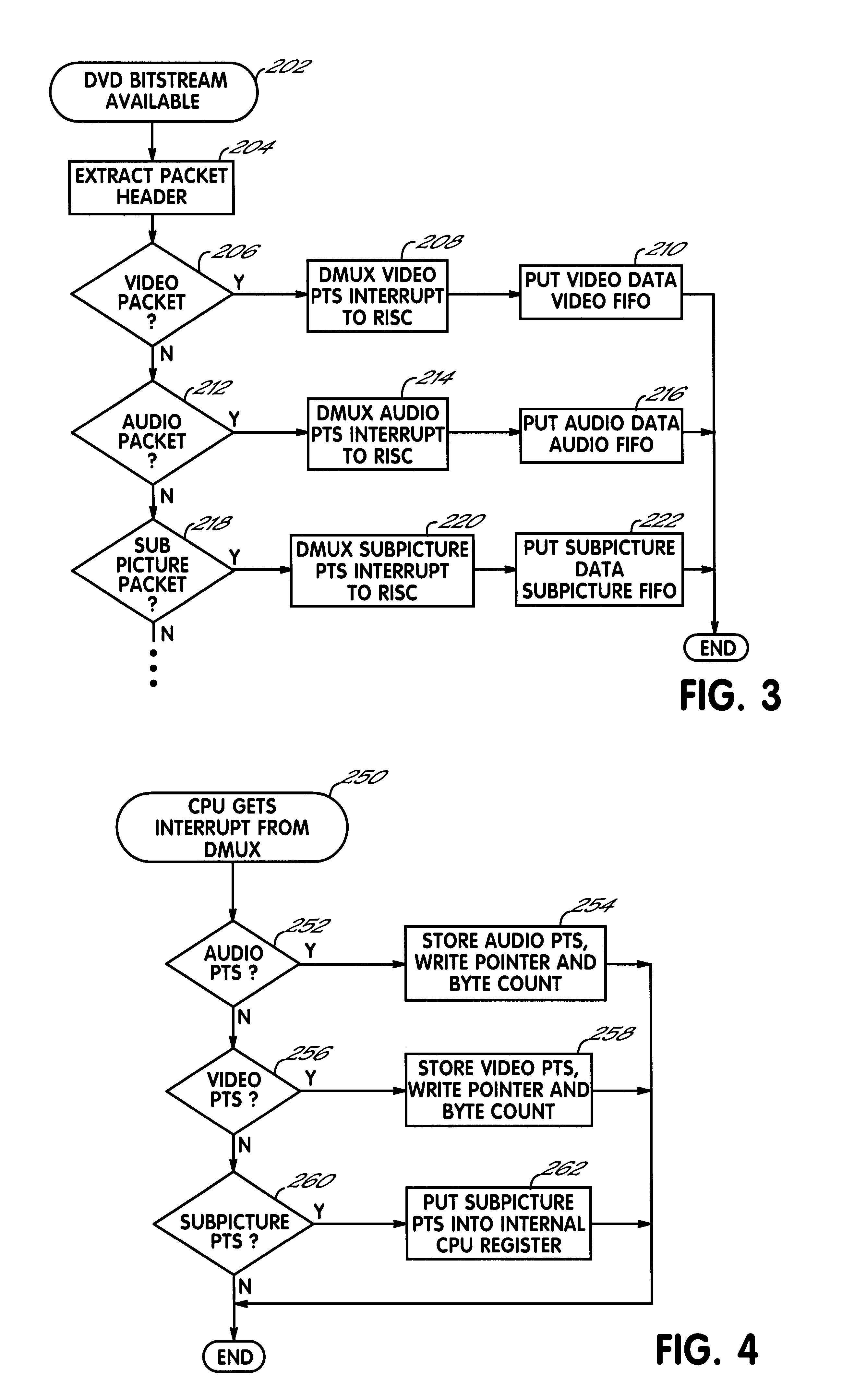
InactiveUS6363207B1Speed up the processSmooth and seamless play backTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital videoVideo processing
A digital video processor and operating method for a receiving raw audio and video data representing images and sound to be played. The processor includes a demultiplexer for receiving the raw audio and video data and providing demultiplexed audio and video data to a memory. A first system time clock provides first time values in response to being continuously clocked by the demultiplexer. A CPU decodes and plays back the audio and video data as a function of the audio and video PTS values. The processor further includes a second system time clock providing second time values in response to being periodically incremented by the CPU. The CPU periodically sets the second system time clock to a second time value equal to a current first time value of the first system time clock in response to a standard play mode, and the CPU periodically sets the first system time clock to a first time value equal to a current second time value of the second system time clock in response to a trick play mode.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
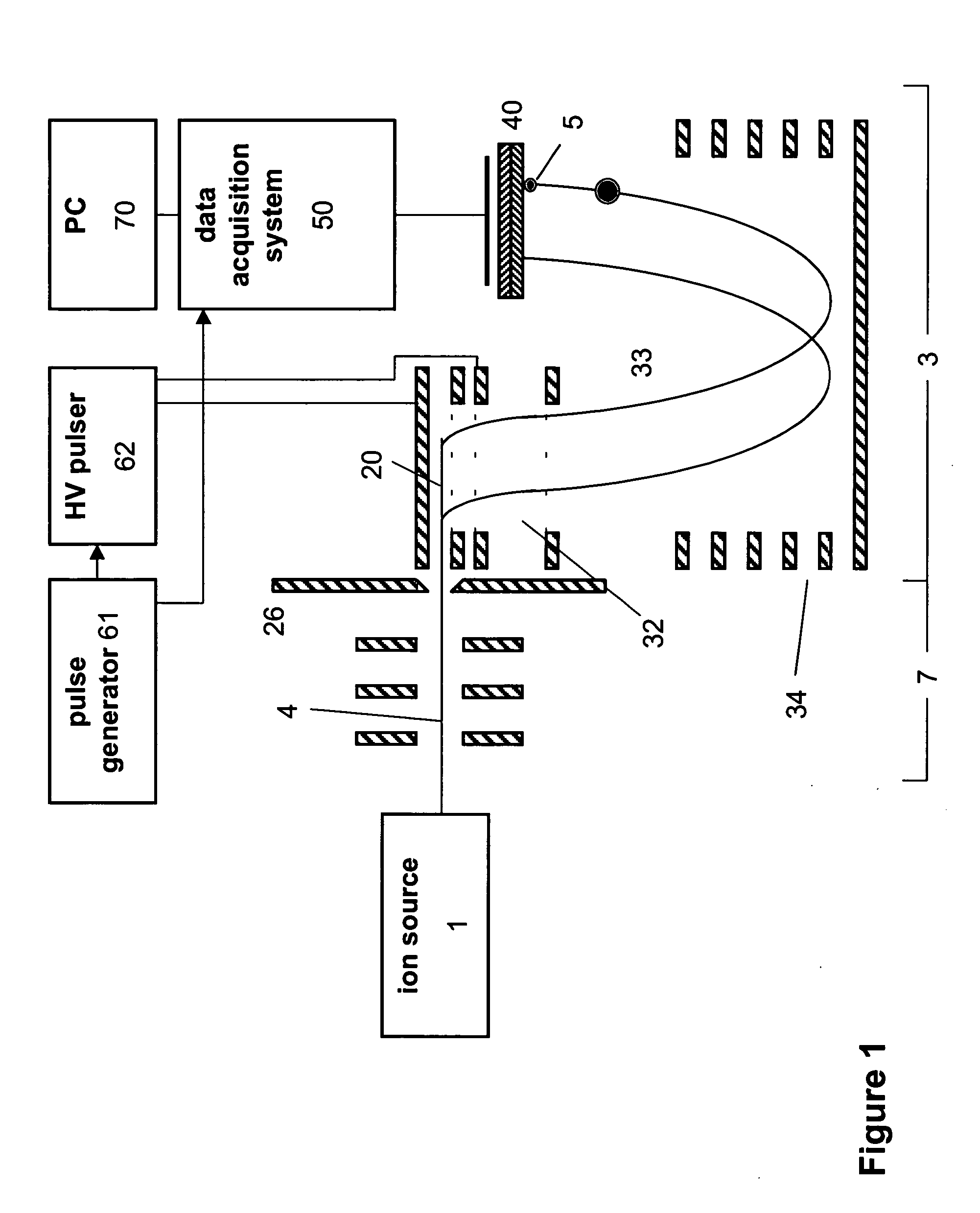
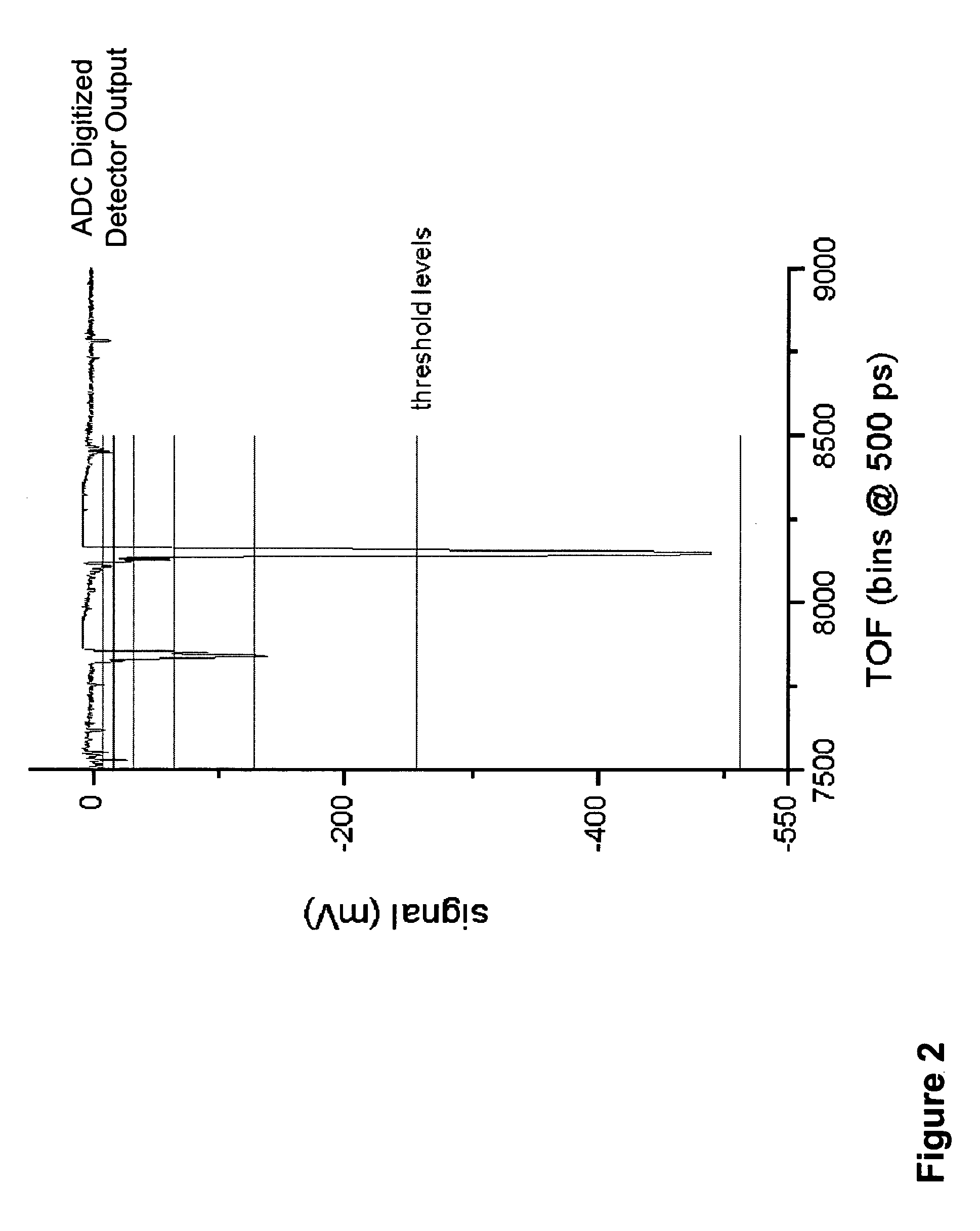
Fast time-of-flight mass spectrometer with improved data acquisition system
ActiveUS20050006577A1Reduce data volumeImprove dynamic rangeSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersData acquisitionSystem time
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer instruments are disclosed for monitoring fast processes with large dynamic range using a multi-threshold TDC data acquisition method or a threshold ADC data acquisition method. Embodiments using a combination of both methods are also disclosed.
Owner:IONWERKS
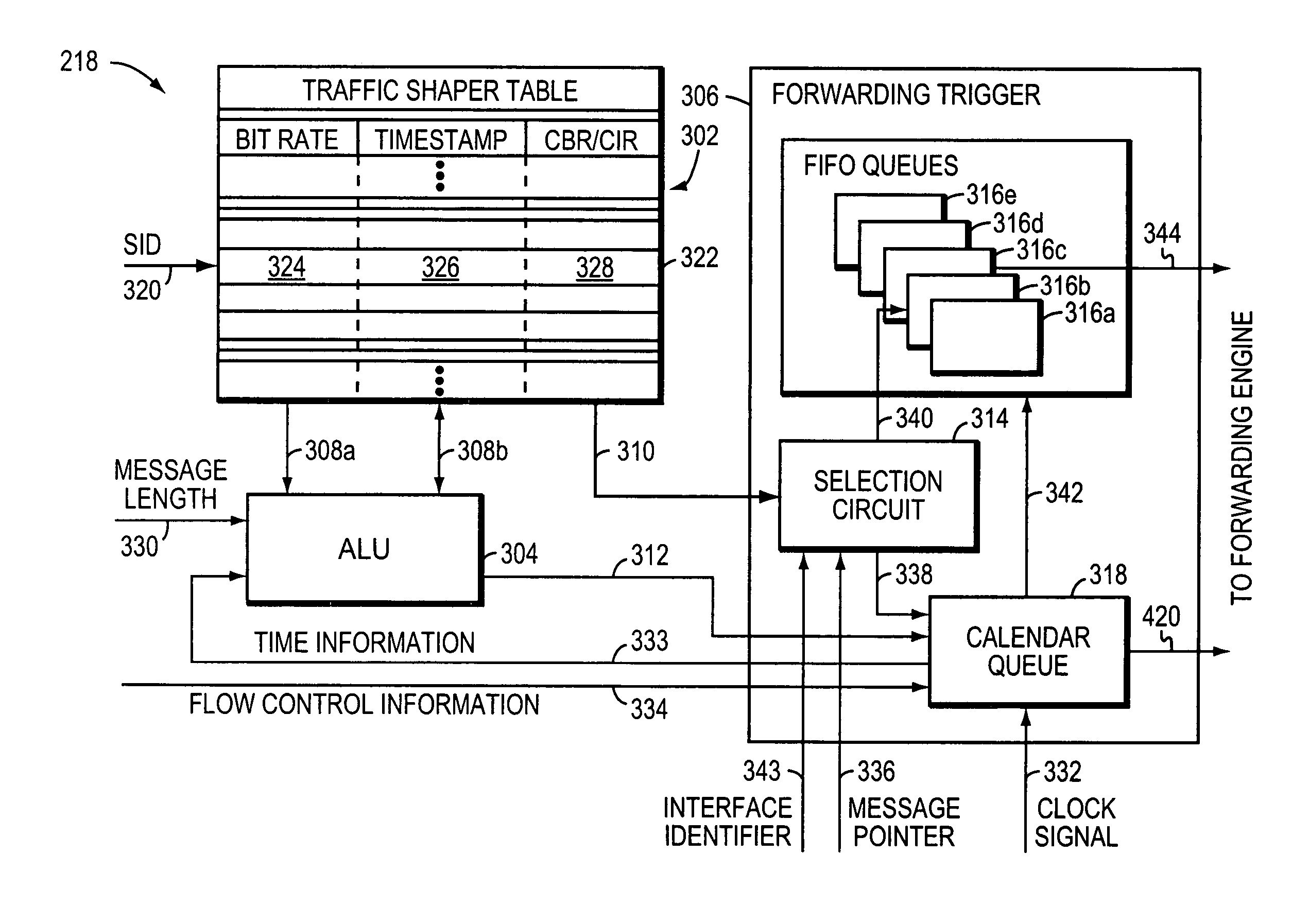
Method and apparatus for performing high-speed traffic shaping
A network traffic shaper for shapping transmission of network messages includes a system time generator for generating a system time, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for computing a transmission start time for each network message in response to the system time, and a retrieve time generator adapted to increment a retrieve time at a rate faster than the system time. As network messages are received, they are stored in a queue along with an associated transmission start time for each message. A forwarding trigger transmits a store network messages when its associated transmission start time matches the retrieve time. Alternately, a second transmission start time representing an excess bandwidth transmission start time may be computed for each network message. If excess bandwidth is detected, a message may be transmitted when its second transmission start time matches the retrieve time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
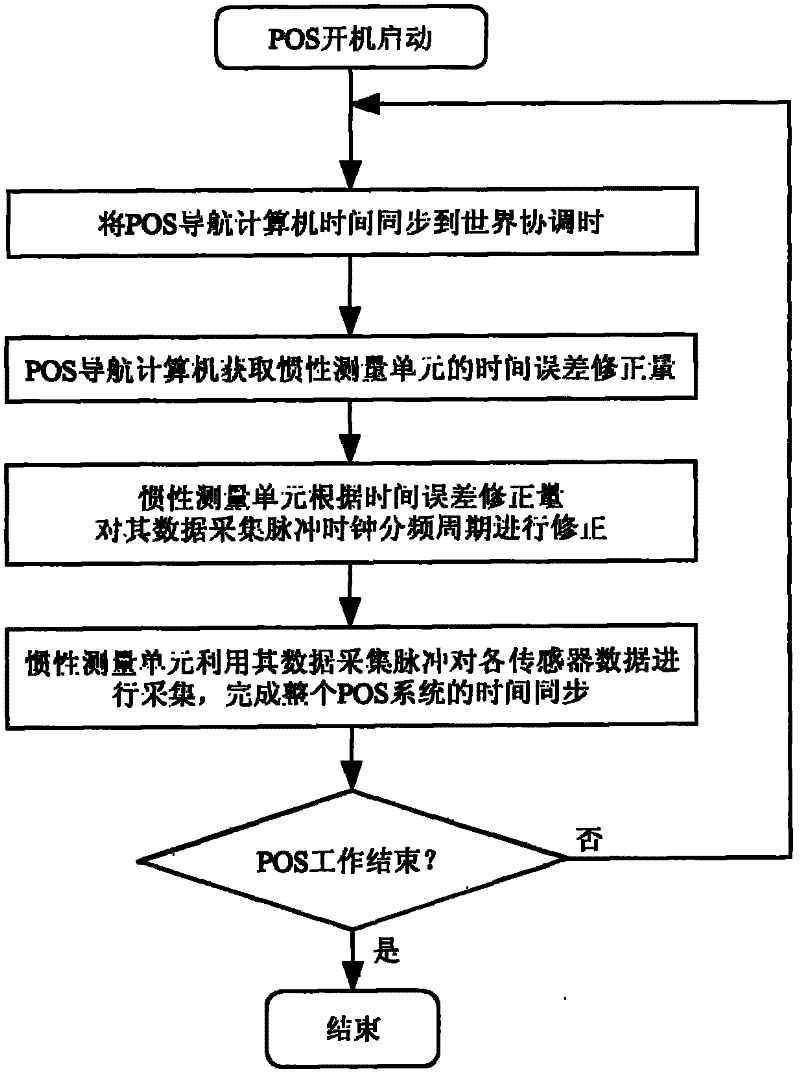
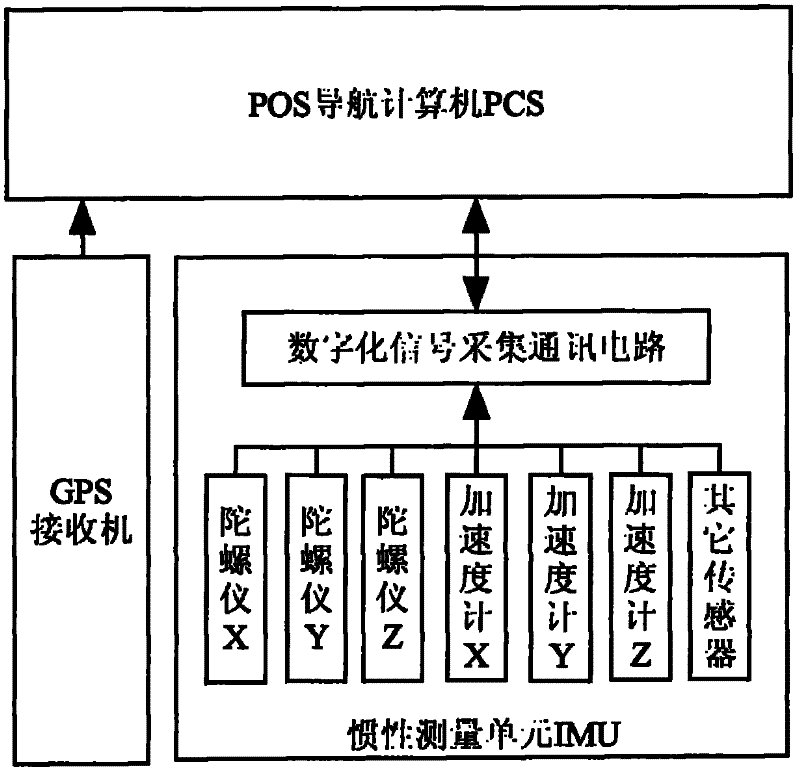
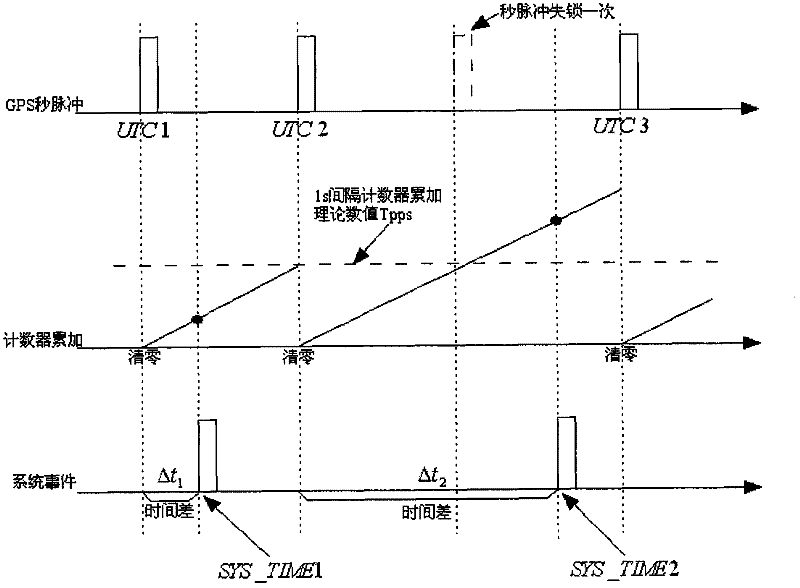
Software time synchronization method for position and orientation system
InactiveCN102183253AHigh precisionImprove time synchronization accuracySynchronous motors for clocksNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsClock driftCoordinate time
The invention provides a software time synchronization method for a position and orientation system (POS). The POS comprises an inertial measurement unit, a POS navigation computer, a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver and the like. The time synchronization method comprises the following steps of: firstly synchronizing system time of the POS navigation computer to world coordinated time by using a GPS second pulse sent by the GPS receiver and a time counter; and synchronizing the data acquisition time of the inertial measurement unit with the world coordinated time through a method of correcting a frequency division period of a data acquisition pulse clock of the inertial measurement unit so as to complete the time synchronization of the POS. In the invention, the problem of reducing of synchronization accuracy of the POS in a short time due to the clock drift is solved through the method of changing the frequency division period of the data acquisition pulse clock, and the software time synchronization method has the characteristics of high accuracy and high anti-interference capacity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Enhancement on radio link failure report to record necessary timing details for a dual-threshold handover trigger event
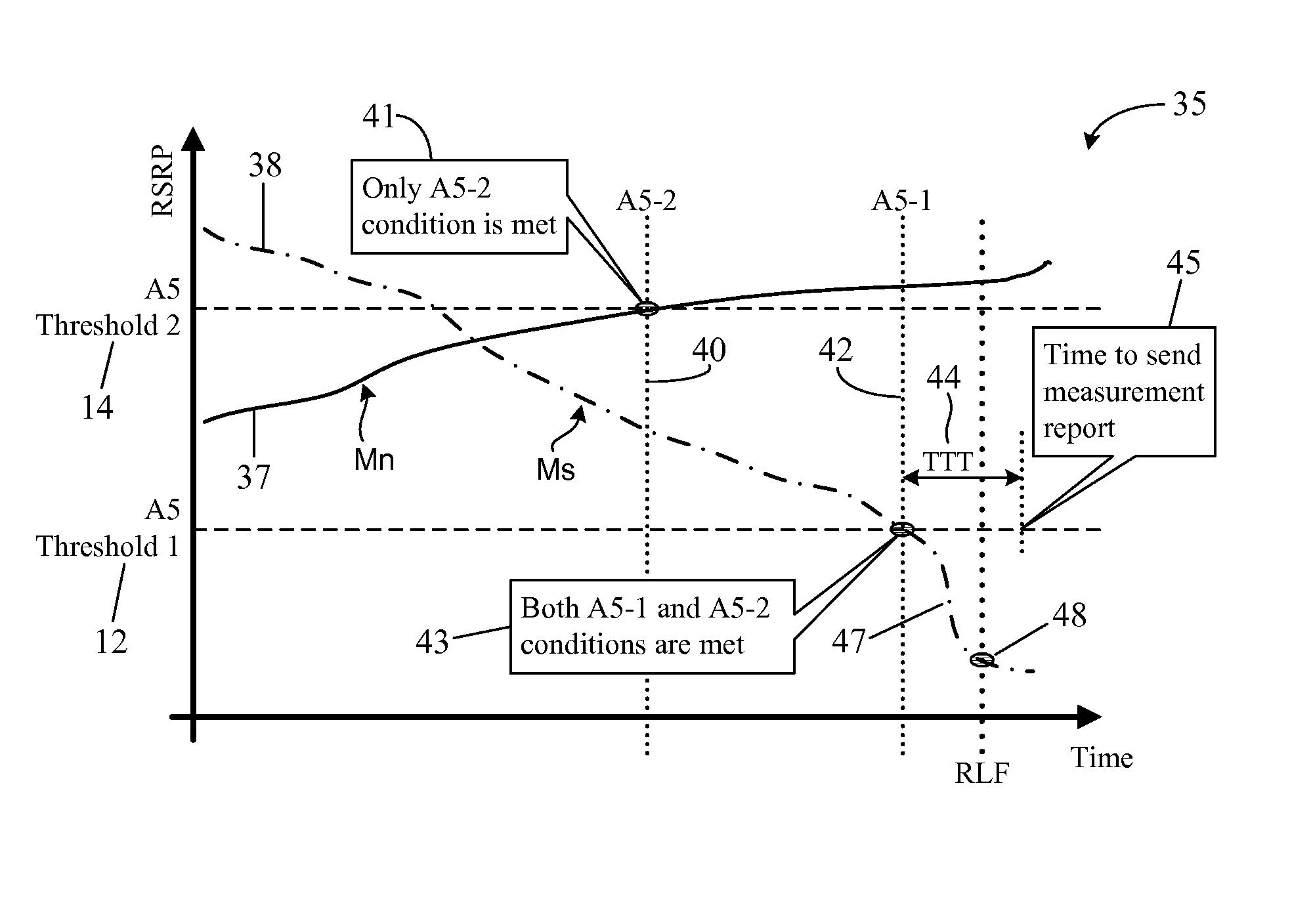
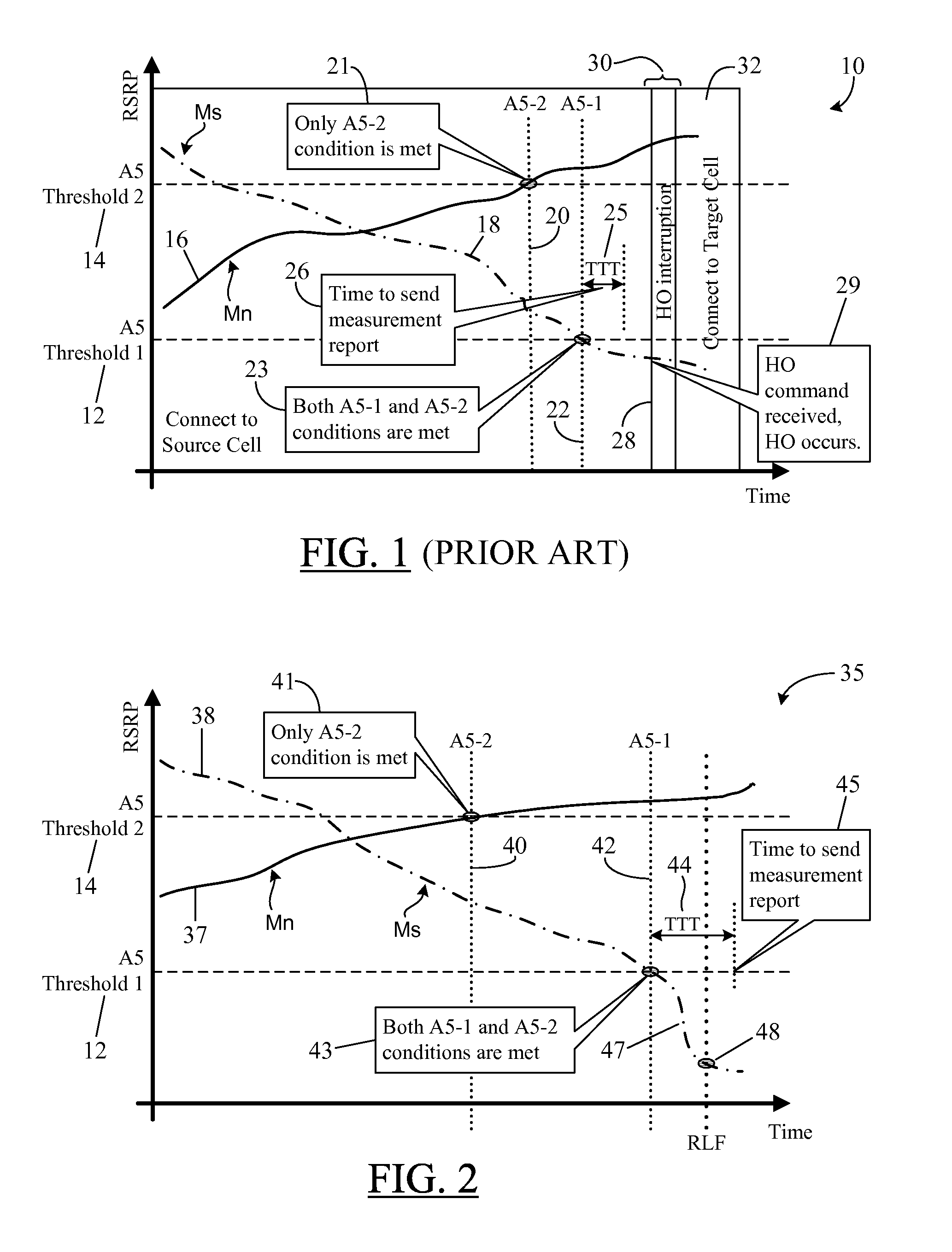
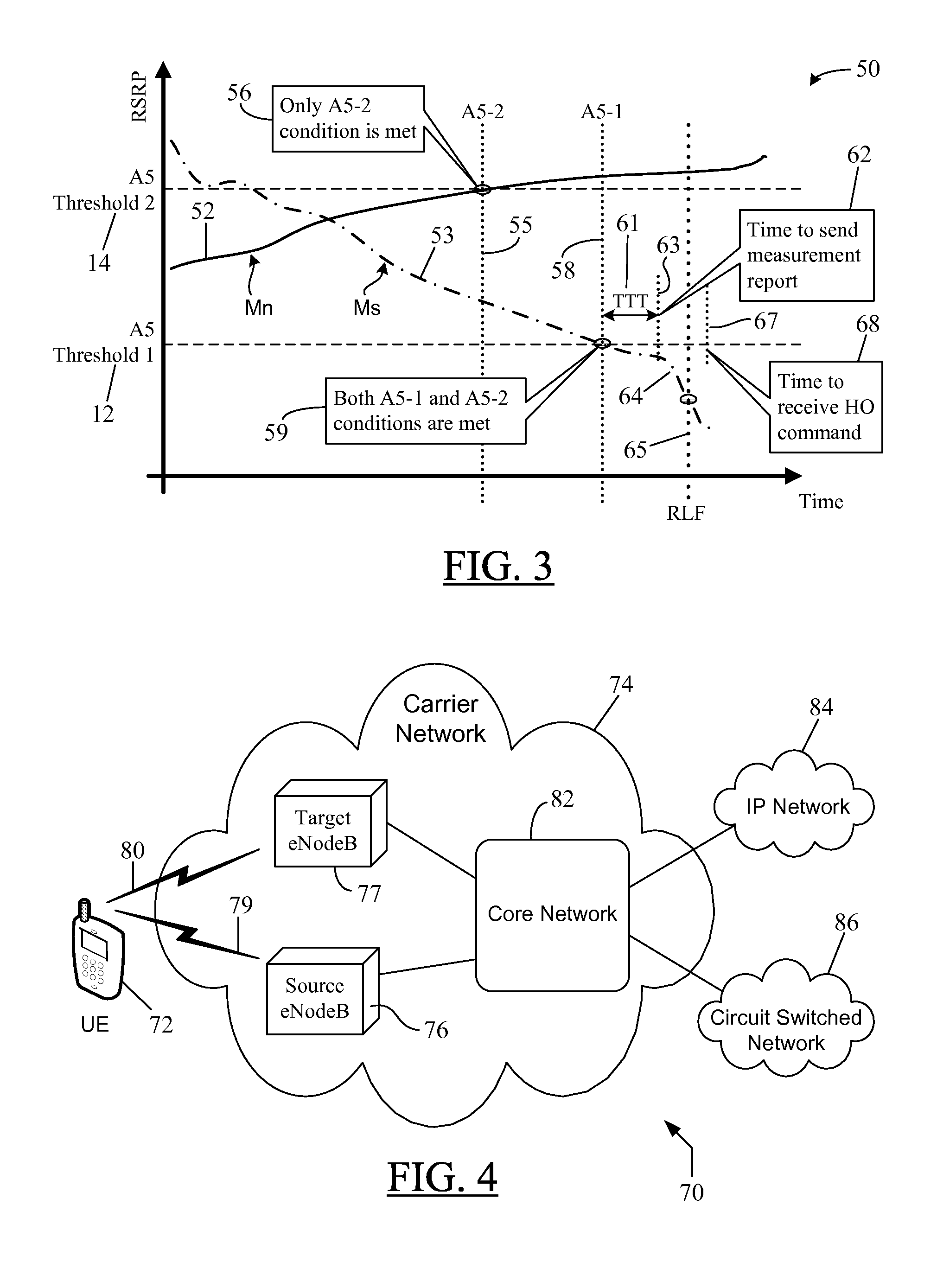
ActiveUS20150092746A1Fine picturePreventing unnecessary wastage of processing resourceWireless commuication servicesNODALTimestamp
A system and method in which a Radio Link Failure, RLF, report from a User Equipment, UE, provides system time-based timestamps to enable a source node to correctly analyze the real cause of an RLF associated with a handover. The timestamps are provided for the latest fulfillment of each event-specific entering condition associated with a handover-triggering event and for the occurrence of the RLF. The recorded timestamps are sent as part of RLF-reporting information to be forwarded to the source node to assist the source node in adjusting event-specific threshold(s) as well as other non-threshold related handover parameters such as the Time To Trigger, TTT, period, the time delay between a UE's transmission of its Measurement Report and the source node's transmission of the handover command, and the like, to reduce similar RLFs in the future. The generation of timestamps does not waste the UE's processing resources or battery power.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Synchronization process for mobile phone stream media audio and video
InactiveCN101271720ARealize synchronous playbackCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingSubstation equipmentData streamNetwork packet
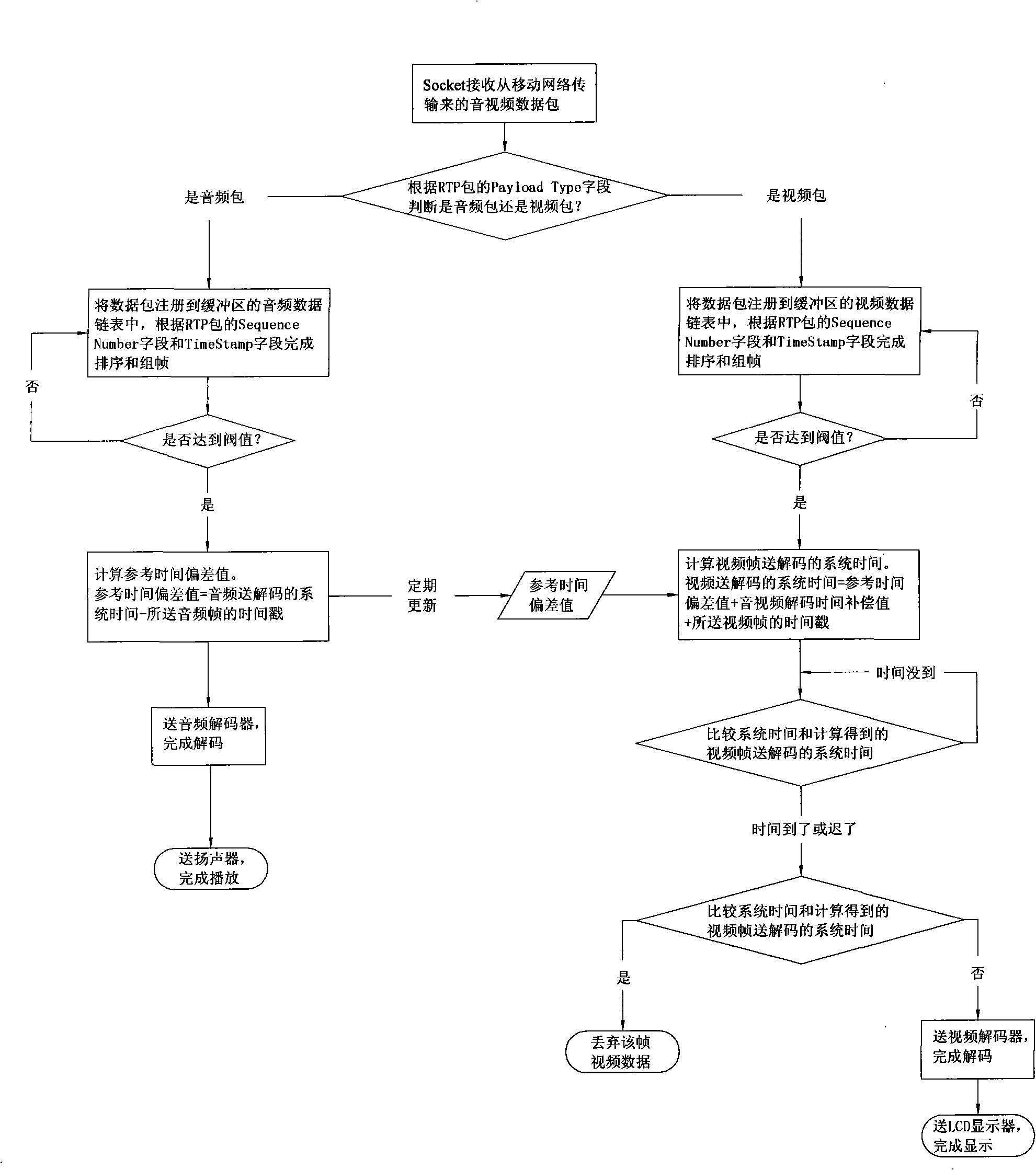
The invention discloses a synchronization method of a mobile phone streaming media audio and video, comprising the steps as follows: the received audio and video data packet is registered into the buffer area of a mobile phone terminal to carry out framing and sorting; when the audio data packet is decoded by a decoder, the difference value between system time when the audio data packet is sent to the decoder and time stamp of the audio frame of the audio data packet is recorded to be taken as a reference time offset value; the decoding and sending display time of the video data packet can be determined according to the reference offset value, so as to realize the synchronous playing. As the synchronization proposal before the audio and video decoding is adopted, more particularly, the reference time offset value is corrected by the audio and video decoding time compensation time, the time offset of the audio and video data flow caused by the equipment in the process before the transmission and decoding is effectively solved, the restriction that the decoded audio and video data flow can not be operated by certain techniques of the current mobile phone terminals and the used decoder is broken down, and the synchronous playing of the audio and video of the mobile phone is excellently realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
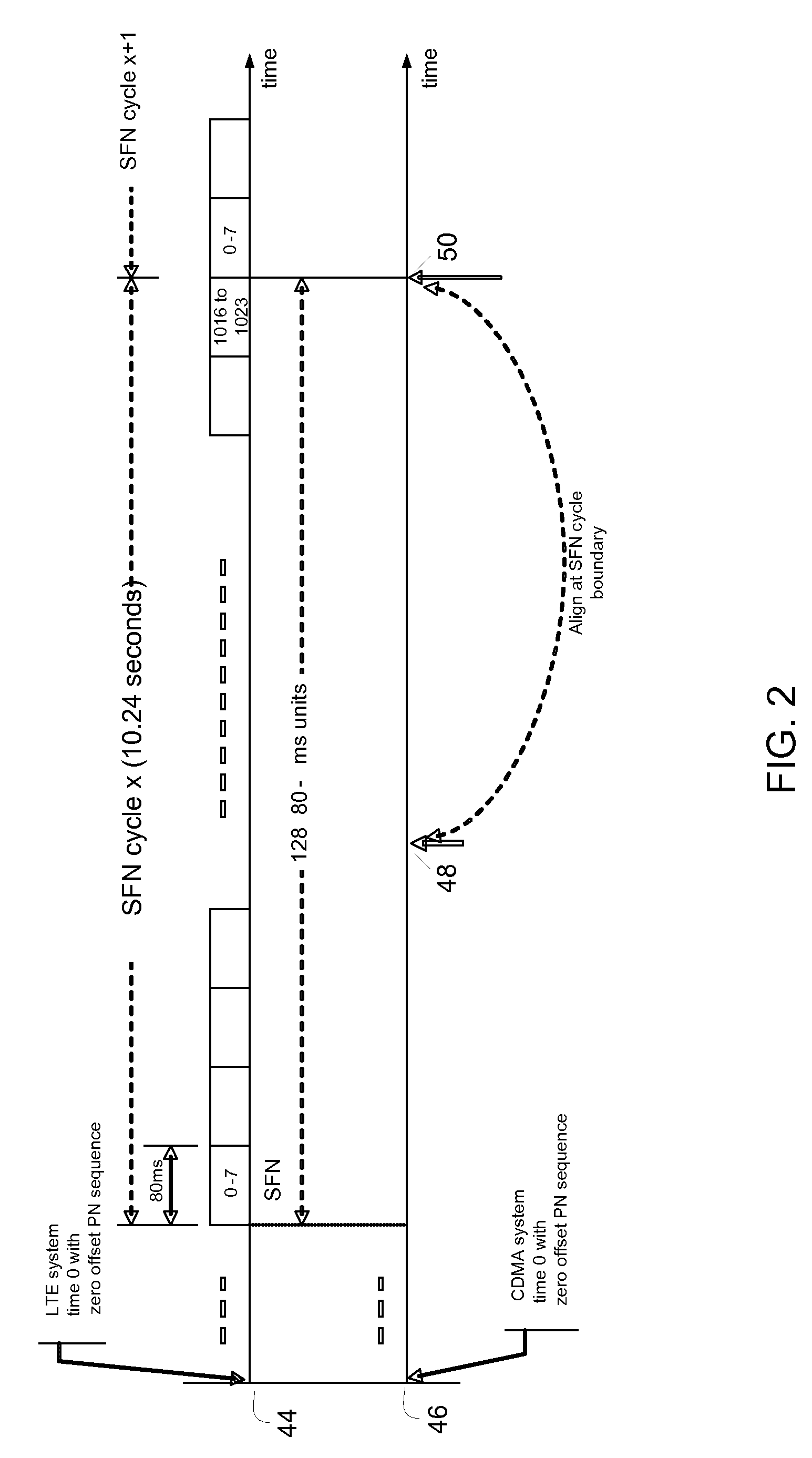
Method and system for reduced system-time overhead parameter length representation for inter-radio access technology communication
ActiveUS20110007856A1Minimizes overhead consumptionMinimize overheadSynchronisation arrangementSynchronising arrangementRadio access technologyCommunications system
A wireless access terminal, system and method for the wireless access terminal to synchronize to system times in a wireless communication system. A first timing hierarchy in a first wireless communication network is used to operate the wireless access terminal. The first wireless communication network has a first radio access technology. Operating with the first timing hierarchy includes determining a frame cycle for the first wireless communication network. The frame cycle has a frame cycle boundary. Broadcast parameters for a second wireless communication network having a second radio access technology different from the first radio access technology are received. The broadcast parameters include the system time of the second wireless communication network. The system time of second wireless communication network is aligned, from the perspective of the wireless access terminal, with the frame cycle boundary. The wireless access terminal engages in a communication session using the second wireless communication network.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com