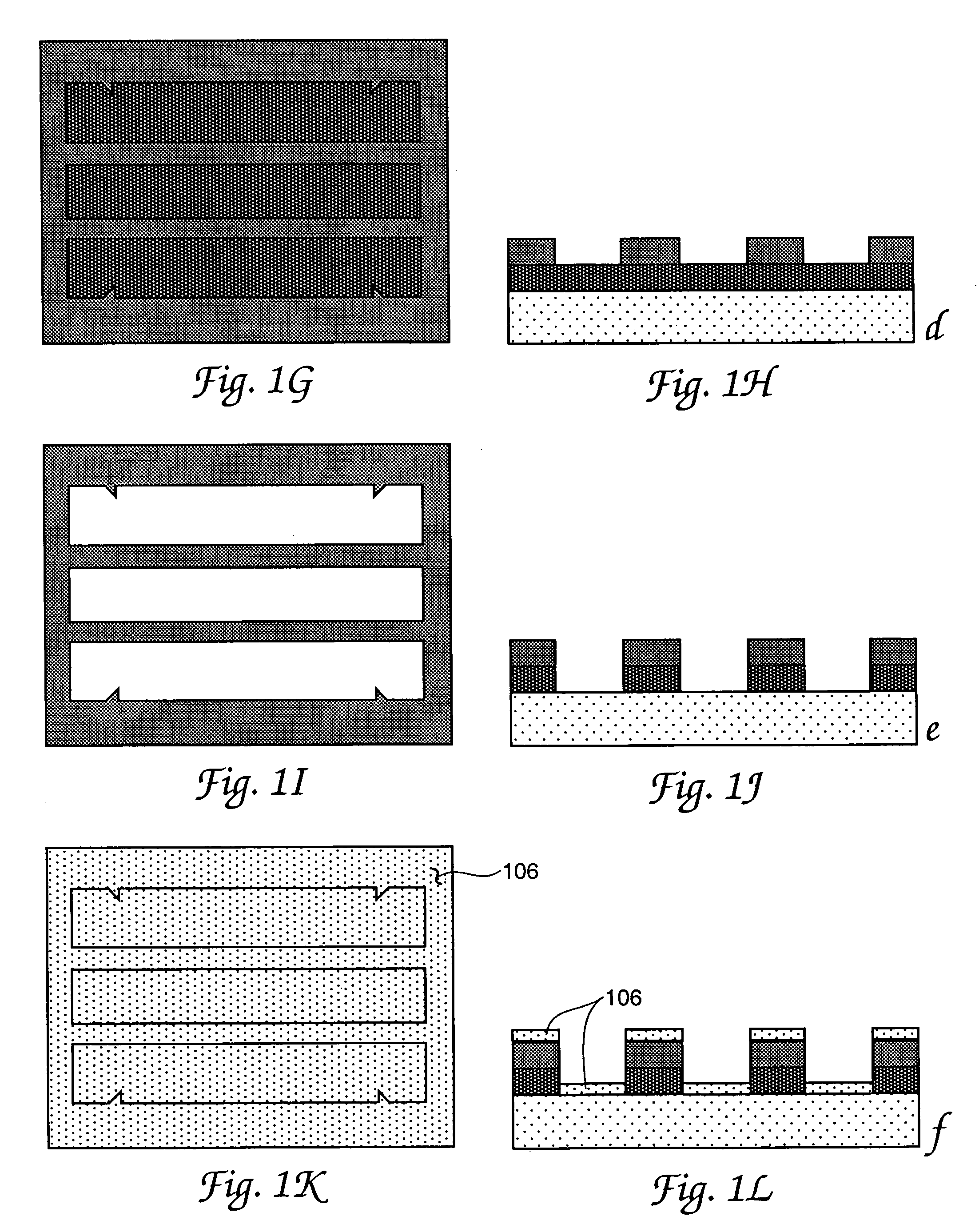
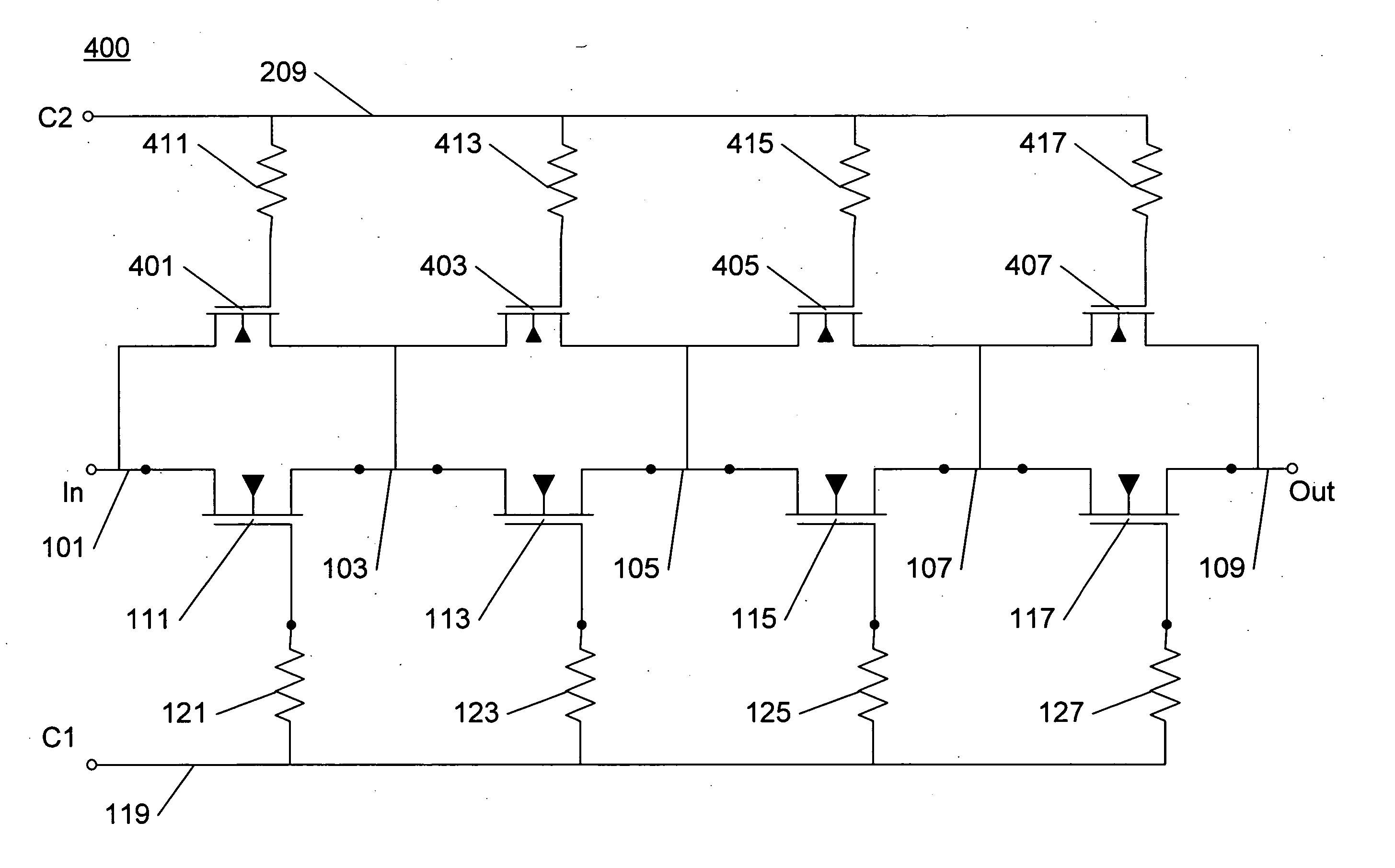
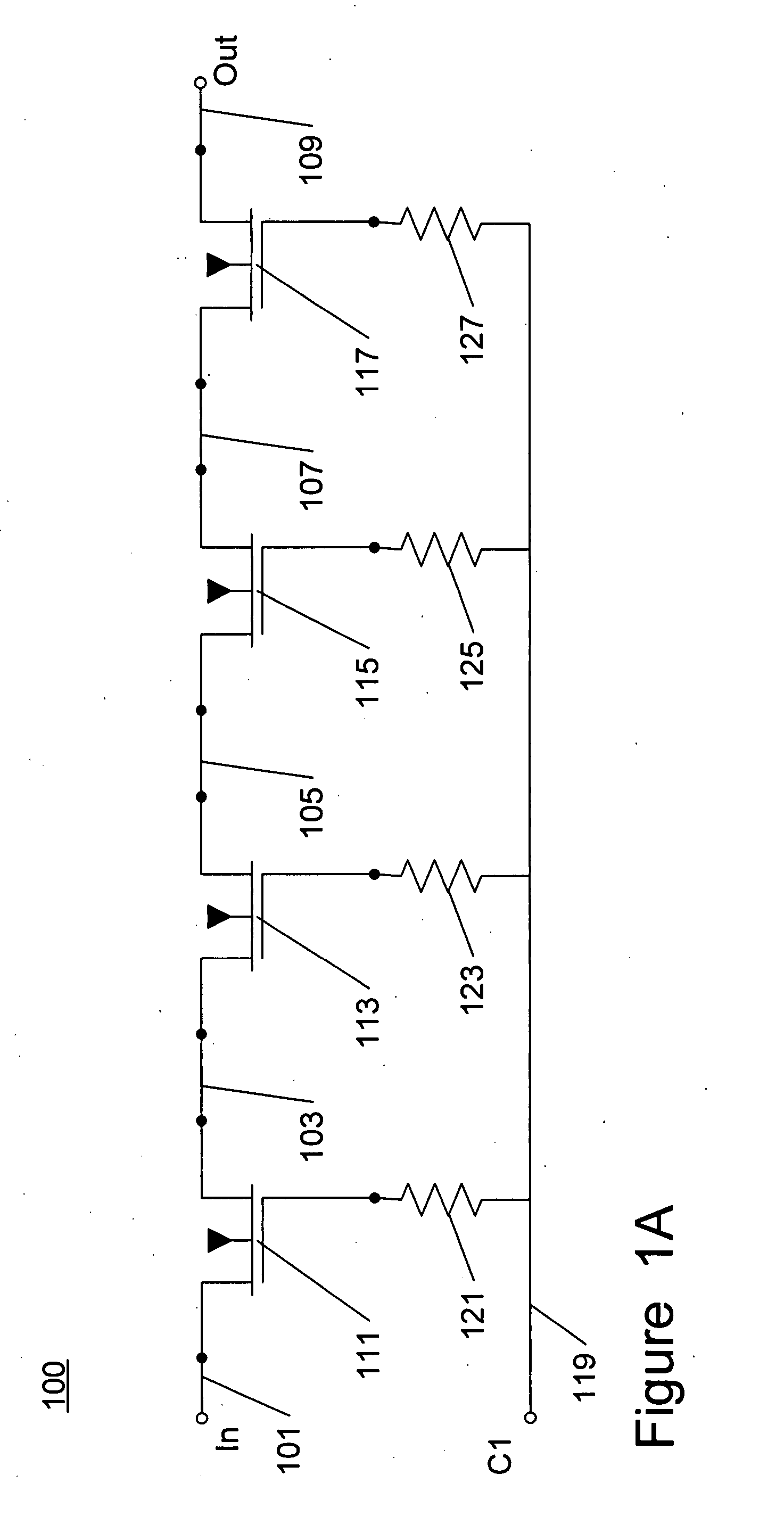
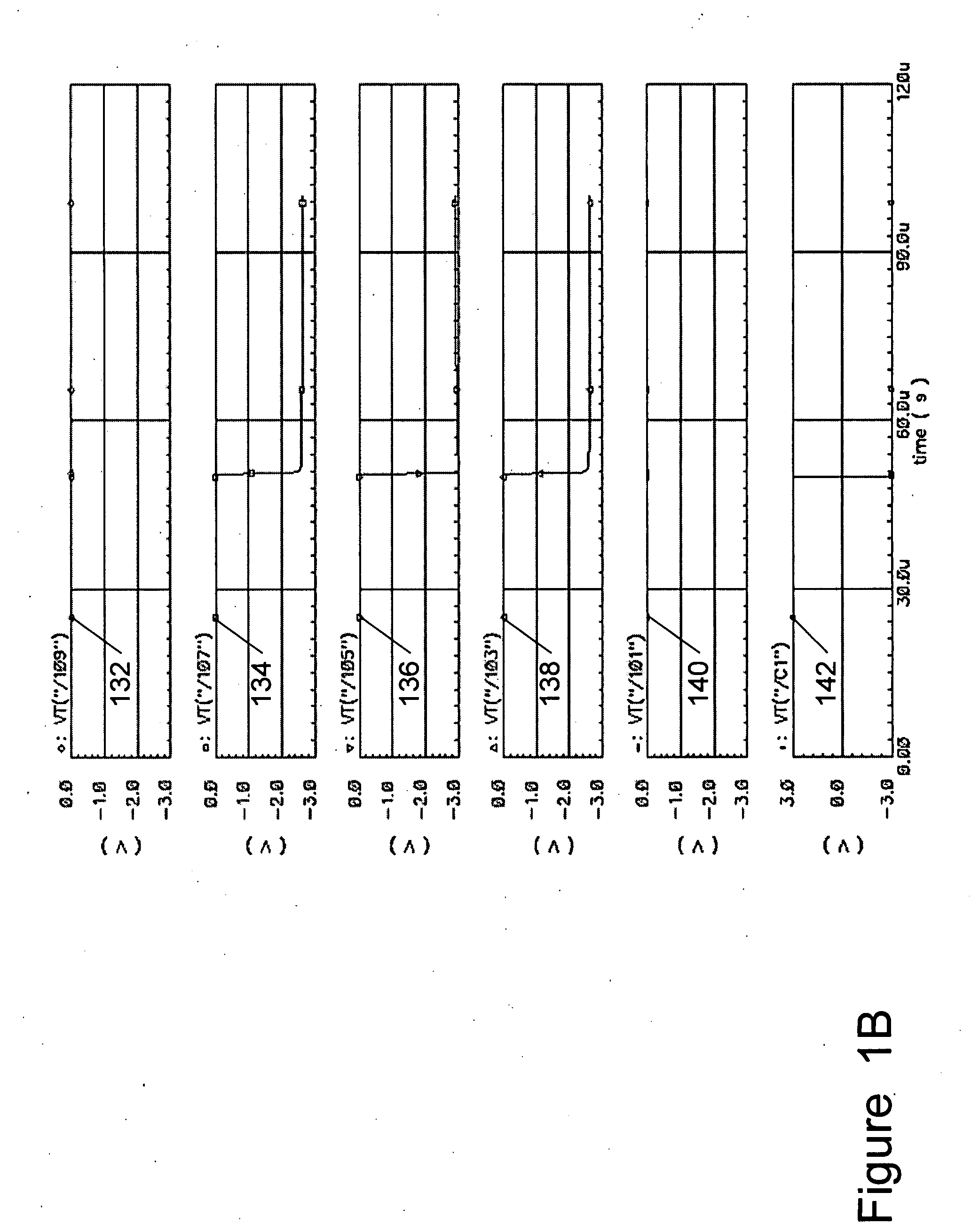
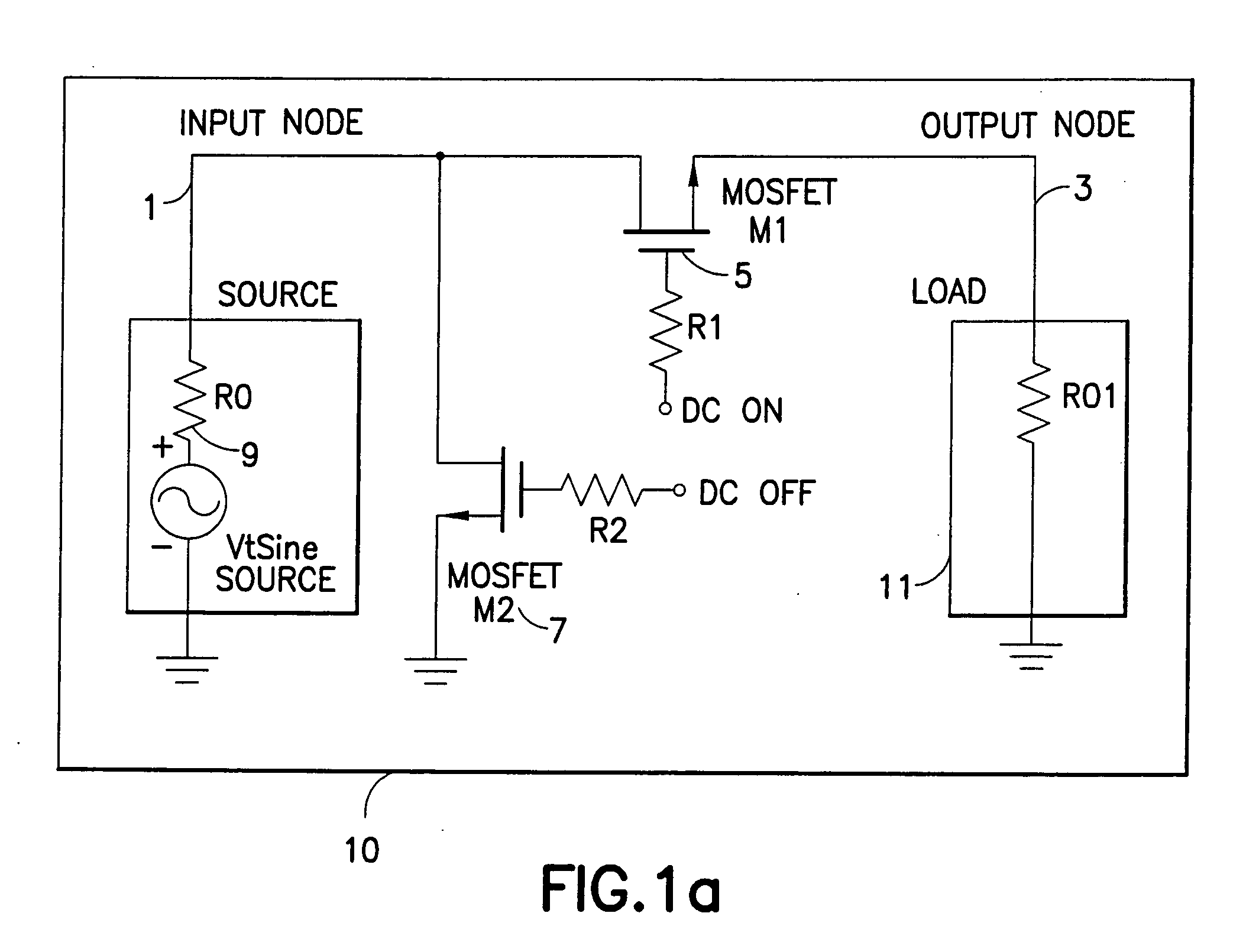
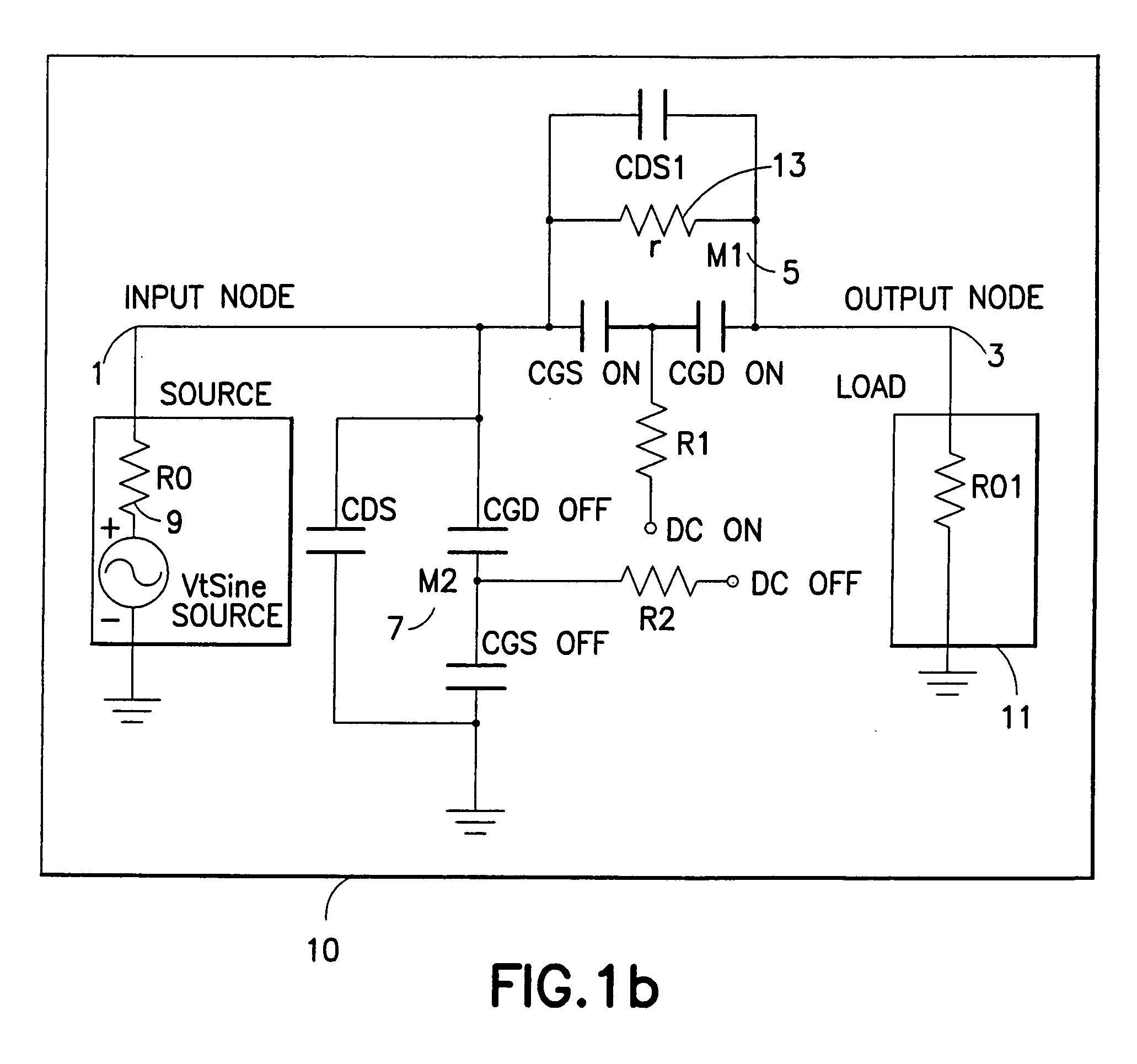
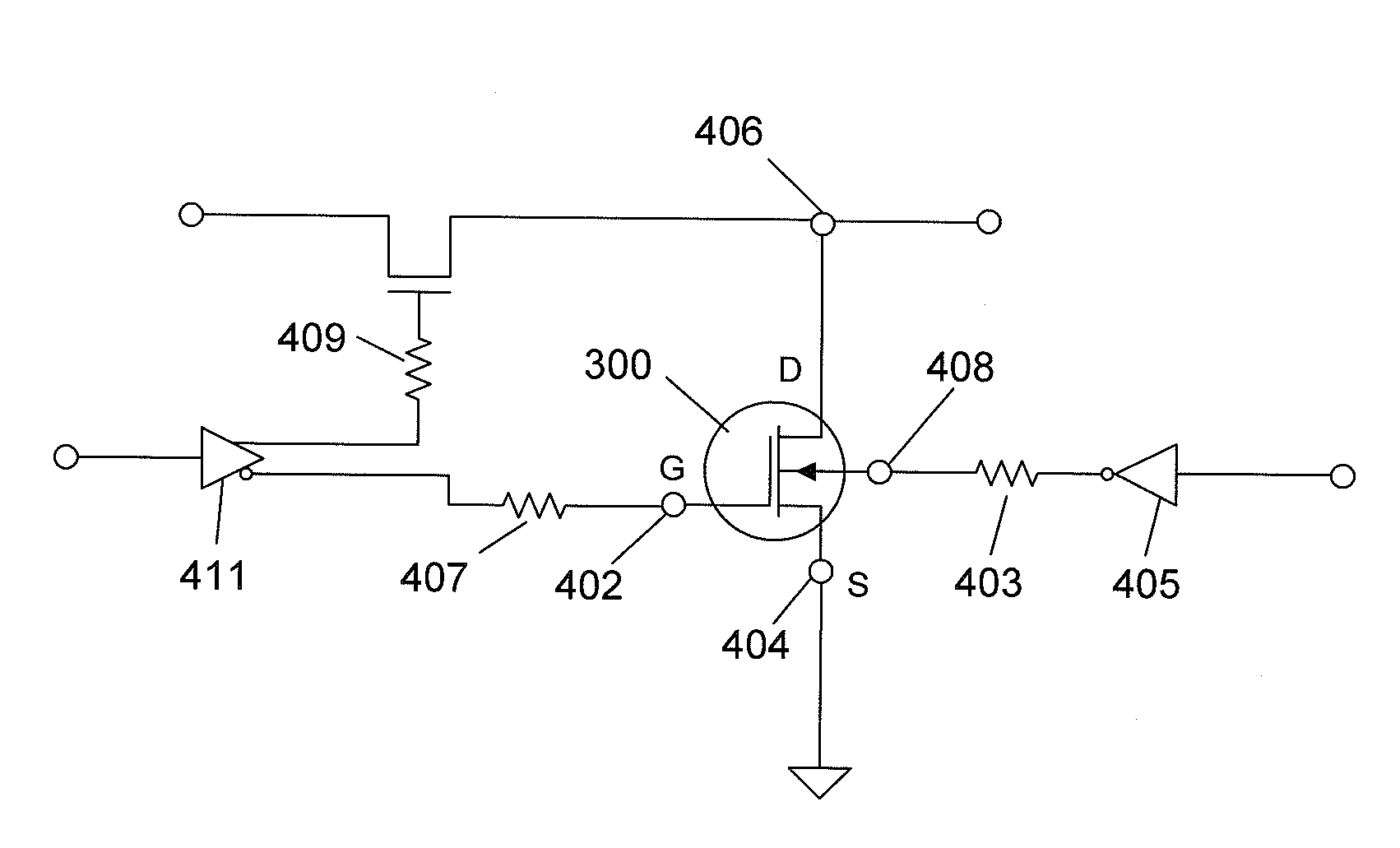
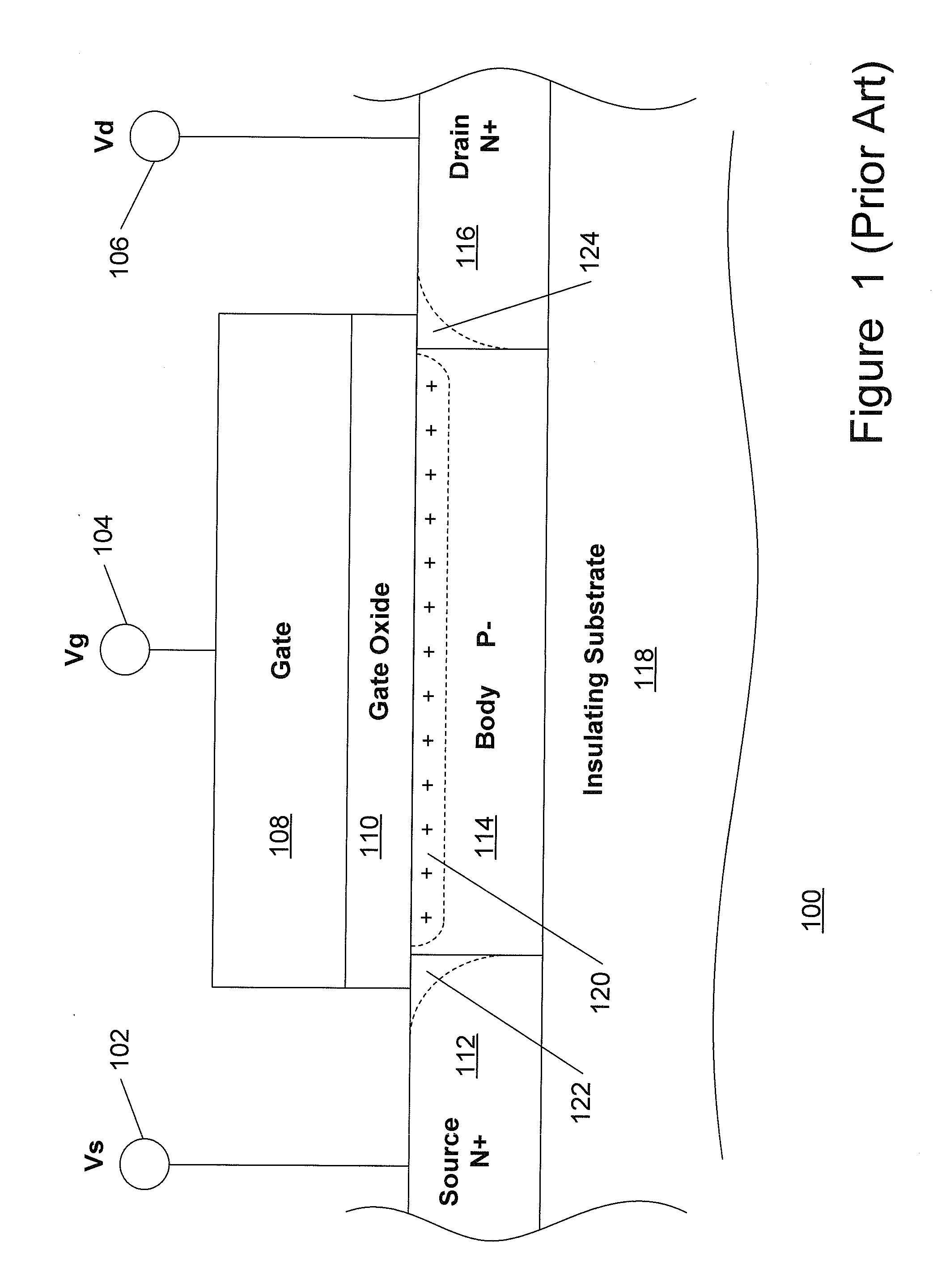
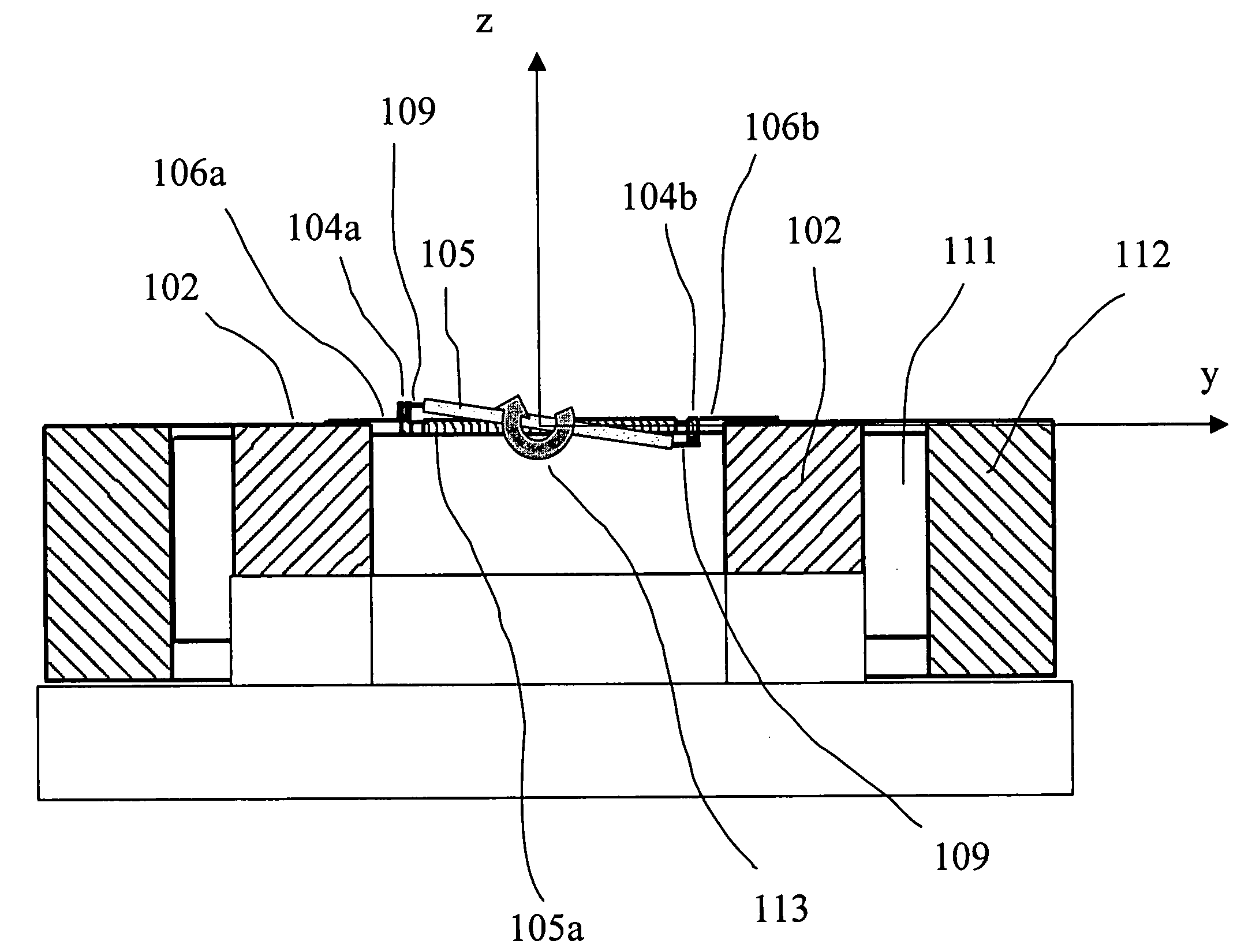
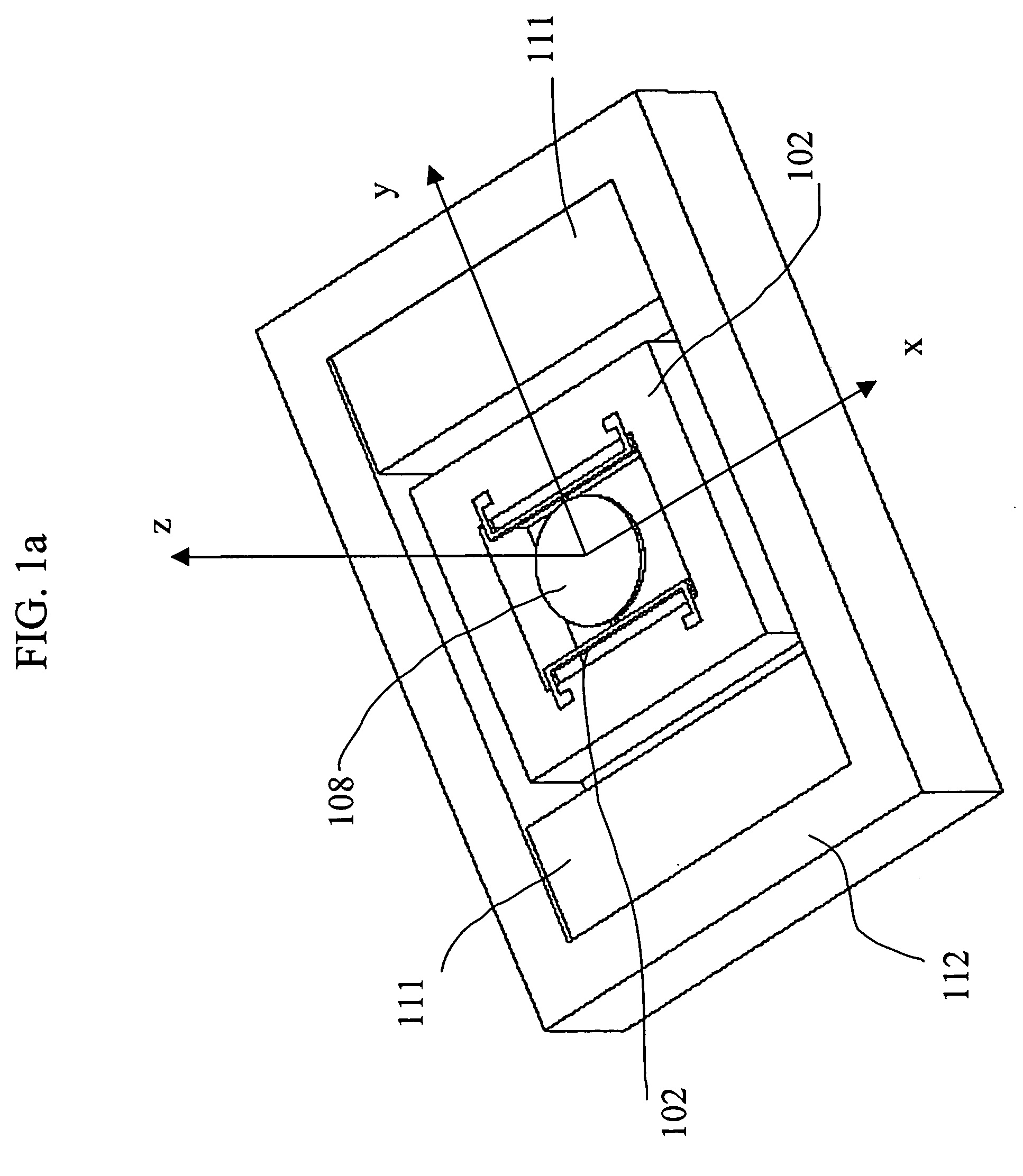
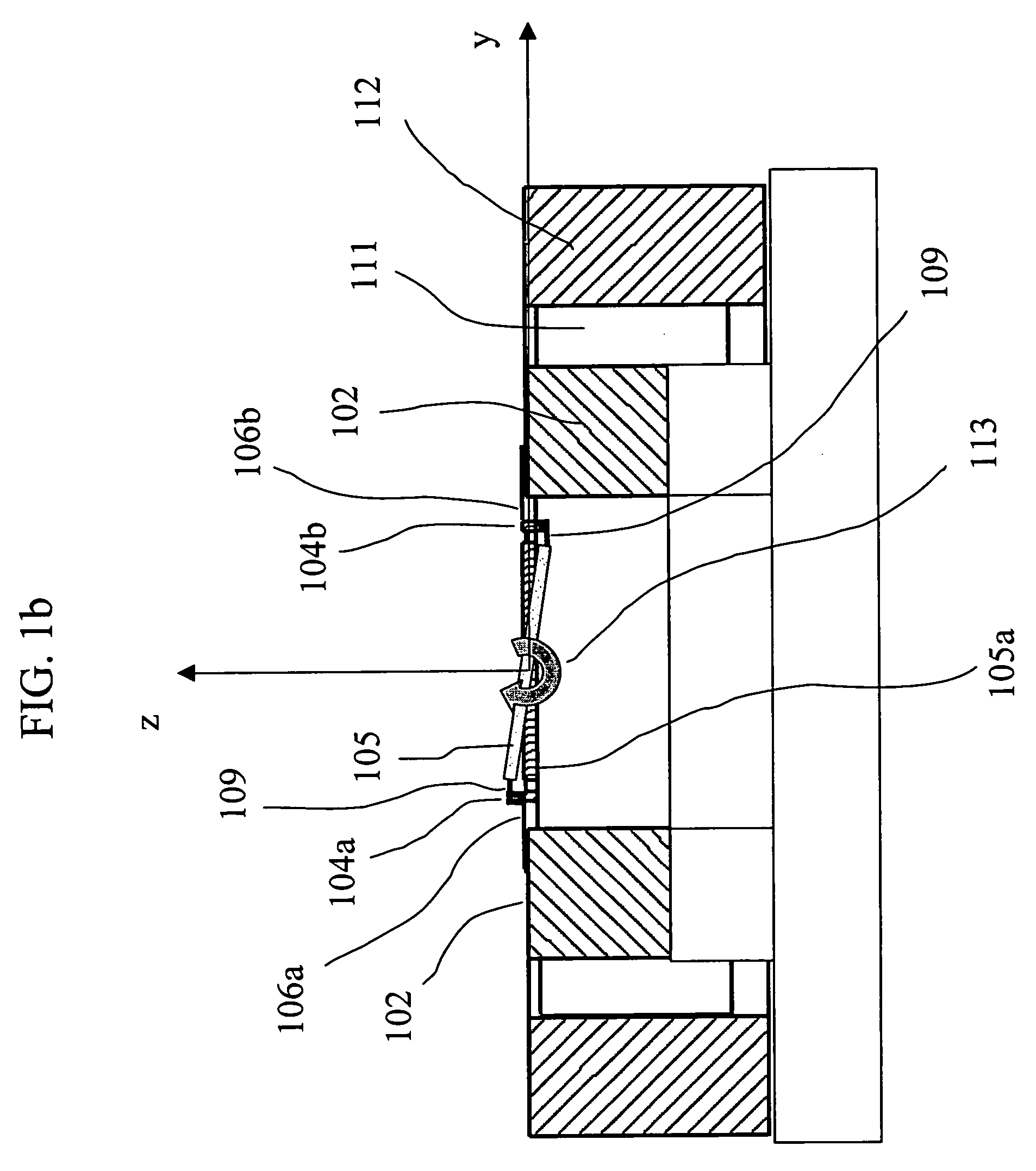
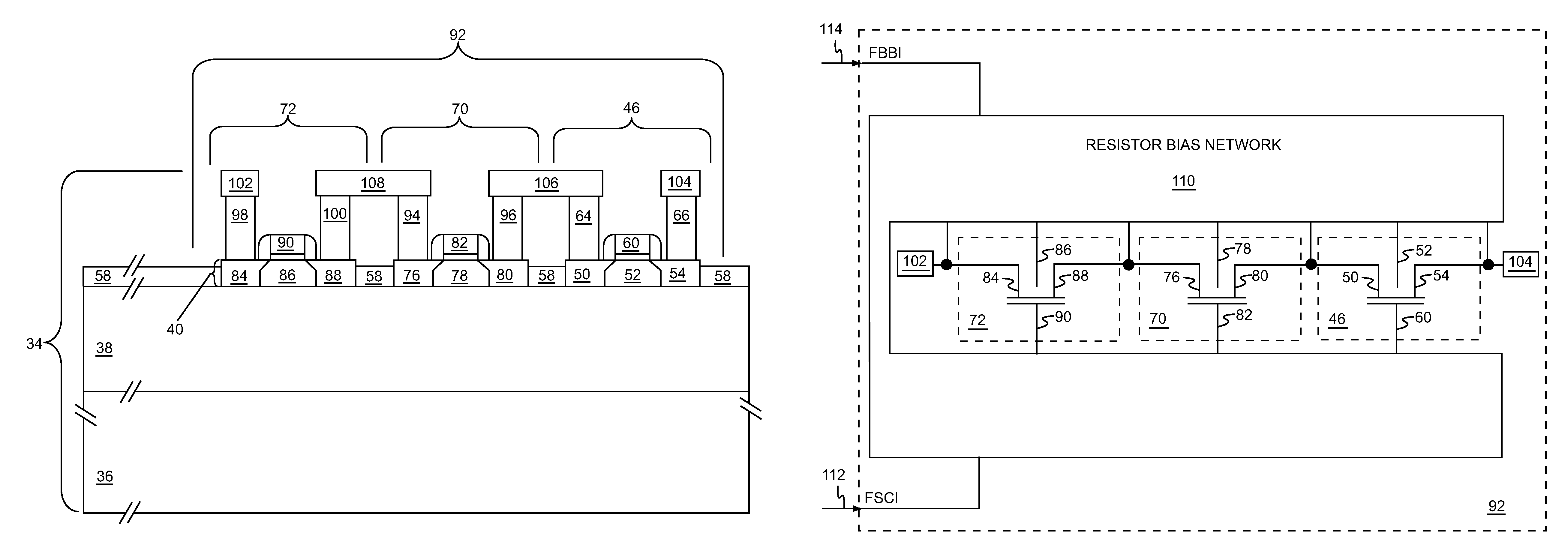
Patents
Literature
650 results about "RF switch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
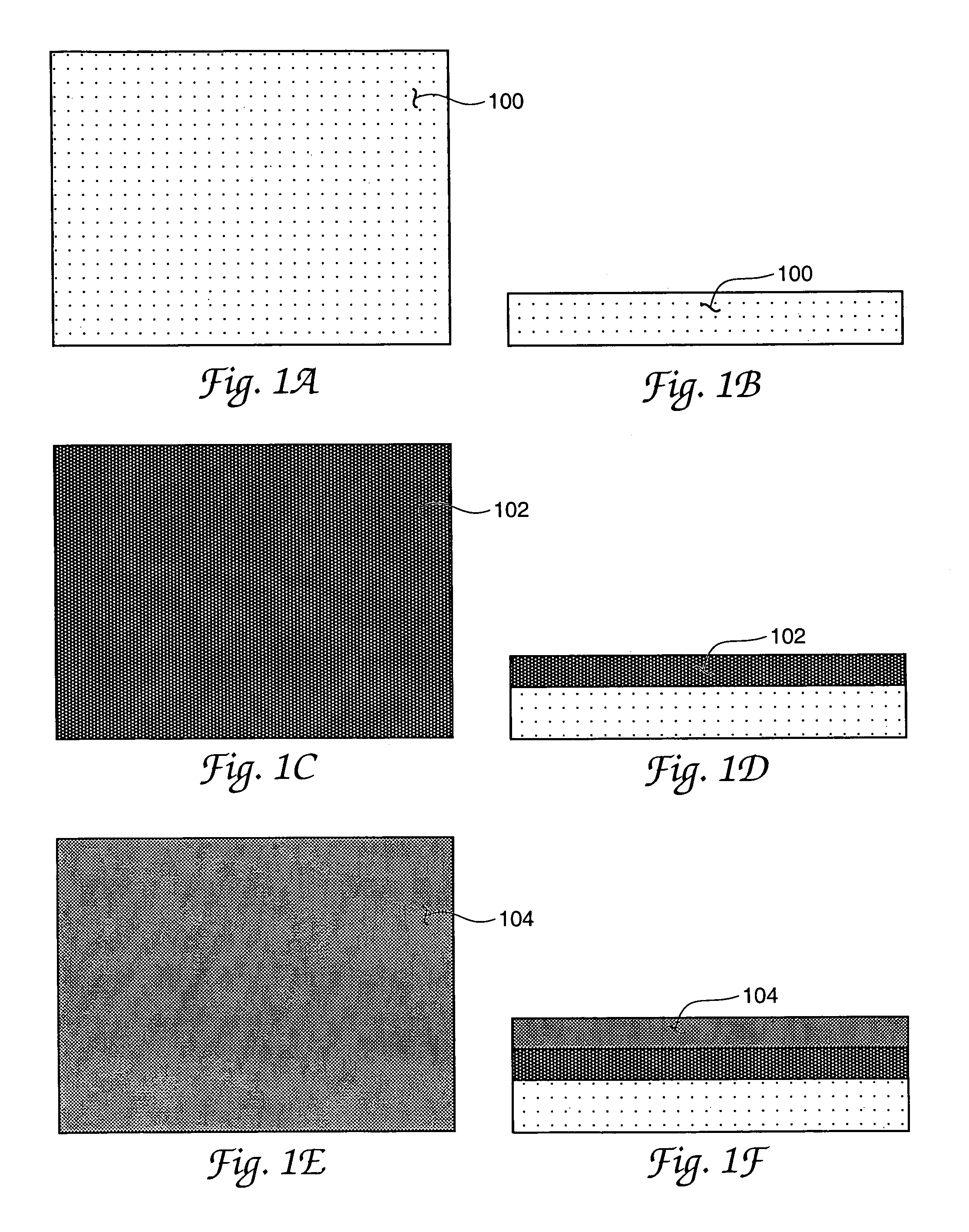
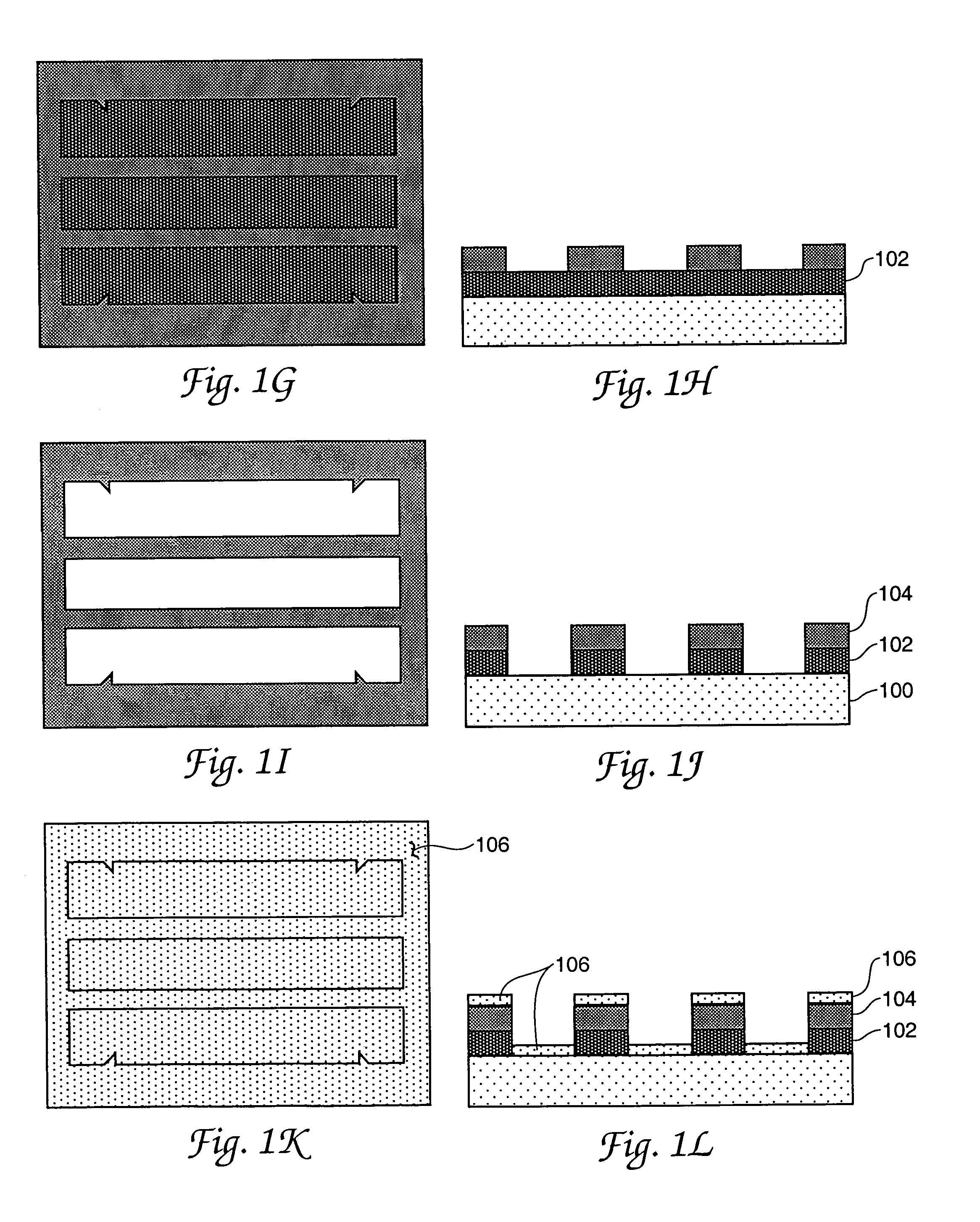
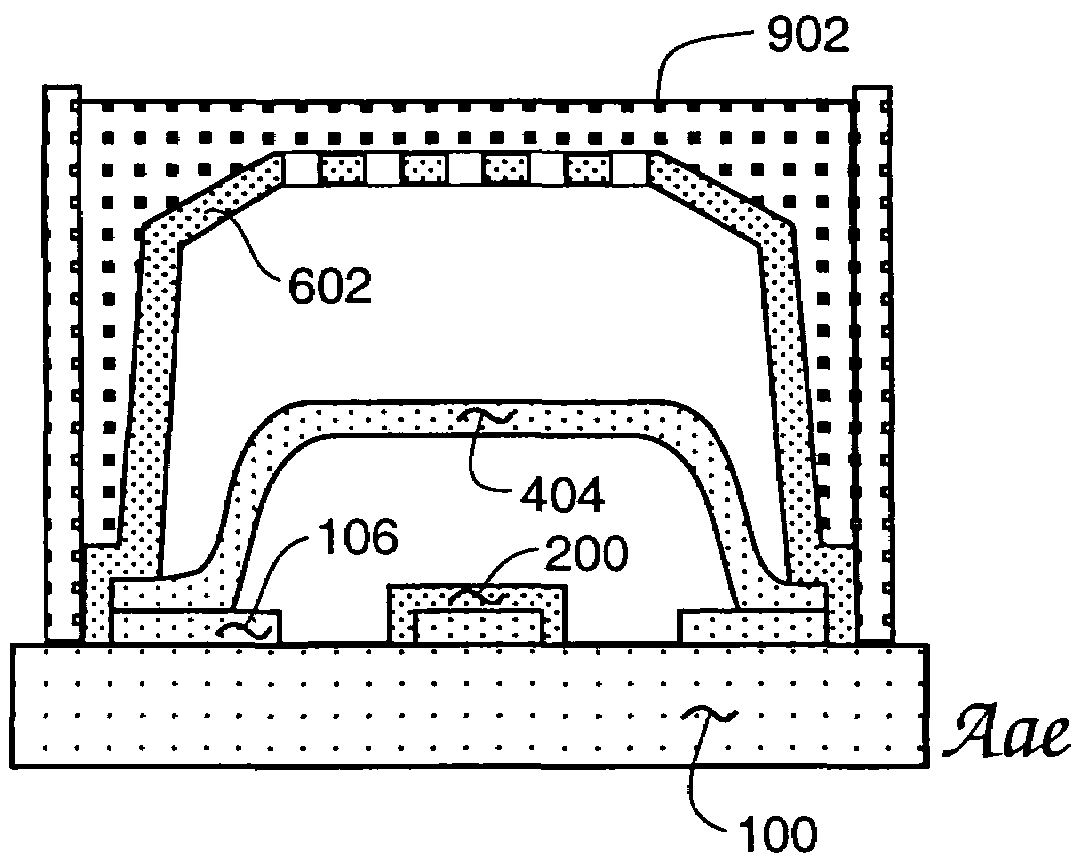
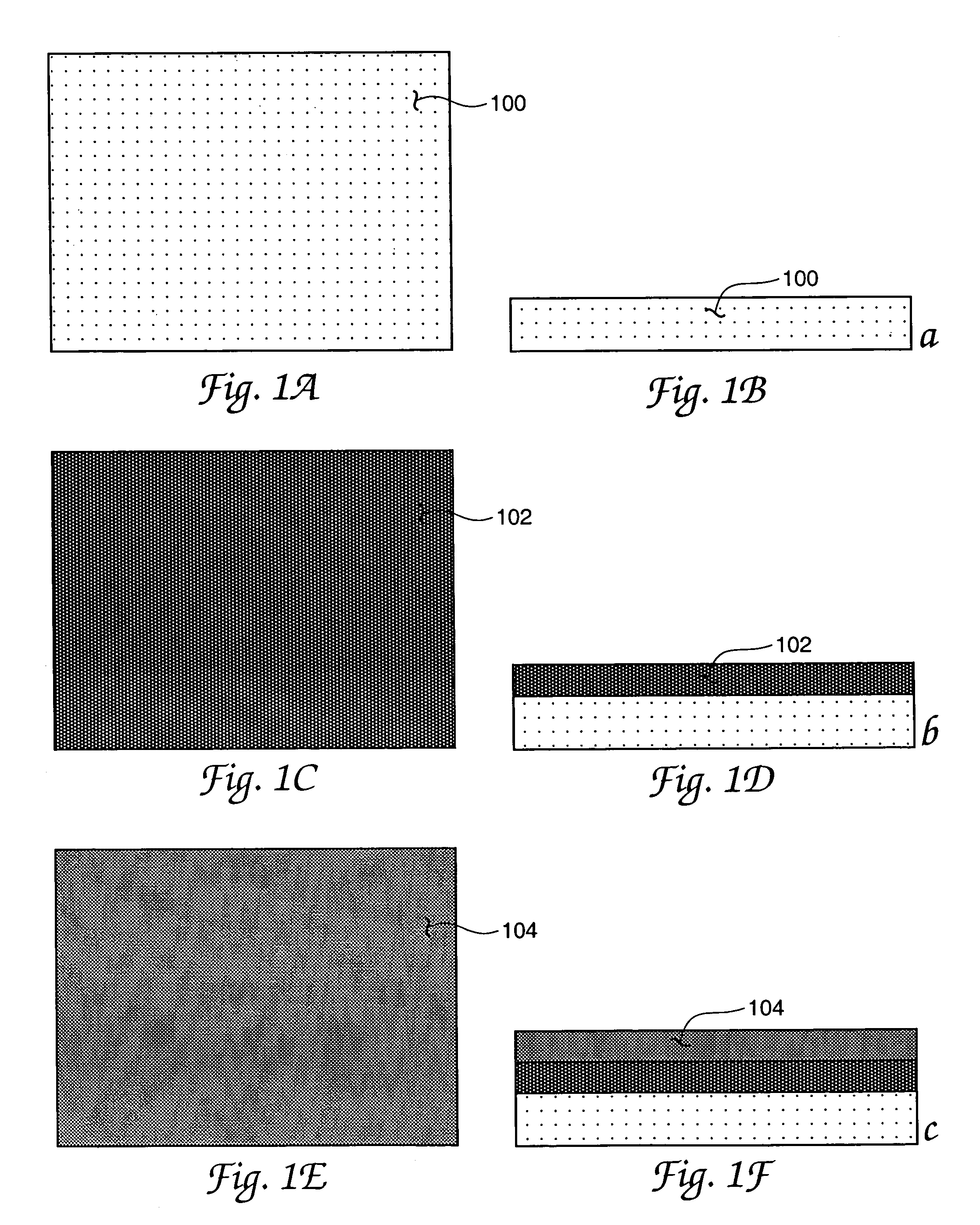
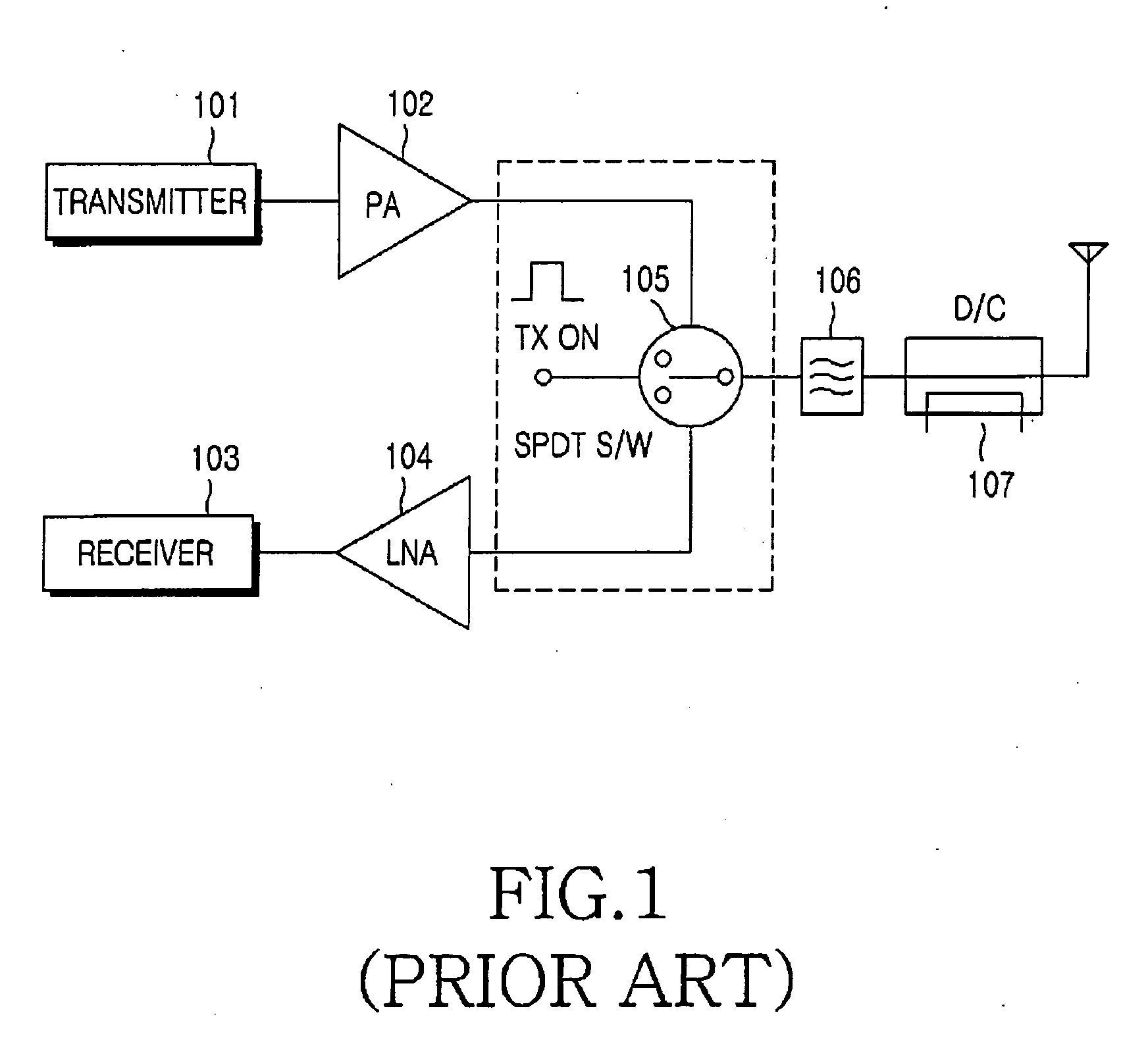
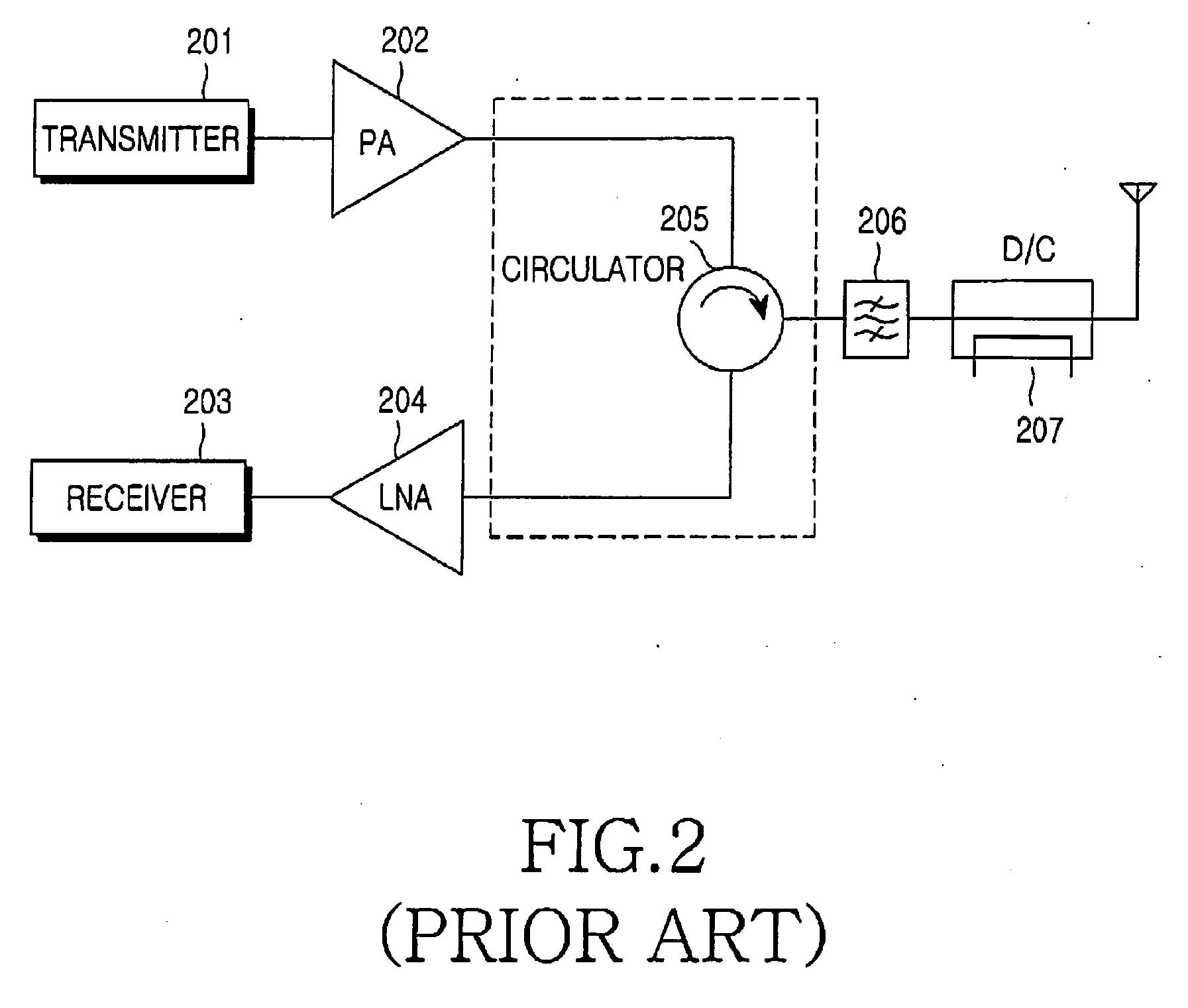
An RF Switch or Microwave Switch is a device to route high frequency signals through transmission paths. RF (radio frequency) and microwave switches are used extensively in microwave test systems for signal routing between instruments and devices under test (DUT). Incorporating a switch into a switch matrix system enables you to route signals from multiple instruments to single or multiple DUTs. This allows multiple tests to be performed with the same setup, eliminating the need for frequent connects and disconnects. The entire testing process can be automated, increasing the throughput in high-volume production environments.
Automated audio video messaging and answering system
ActiveUS7193644B2Weaken energyReduce energy consumptionTelephonic communicationTwo-way working systemsProximity sensorDatabase application
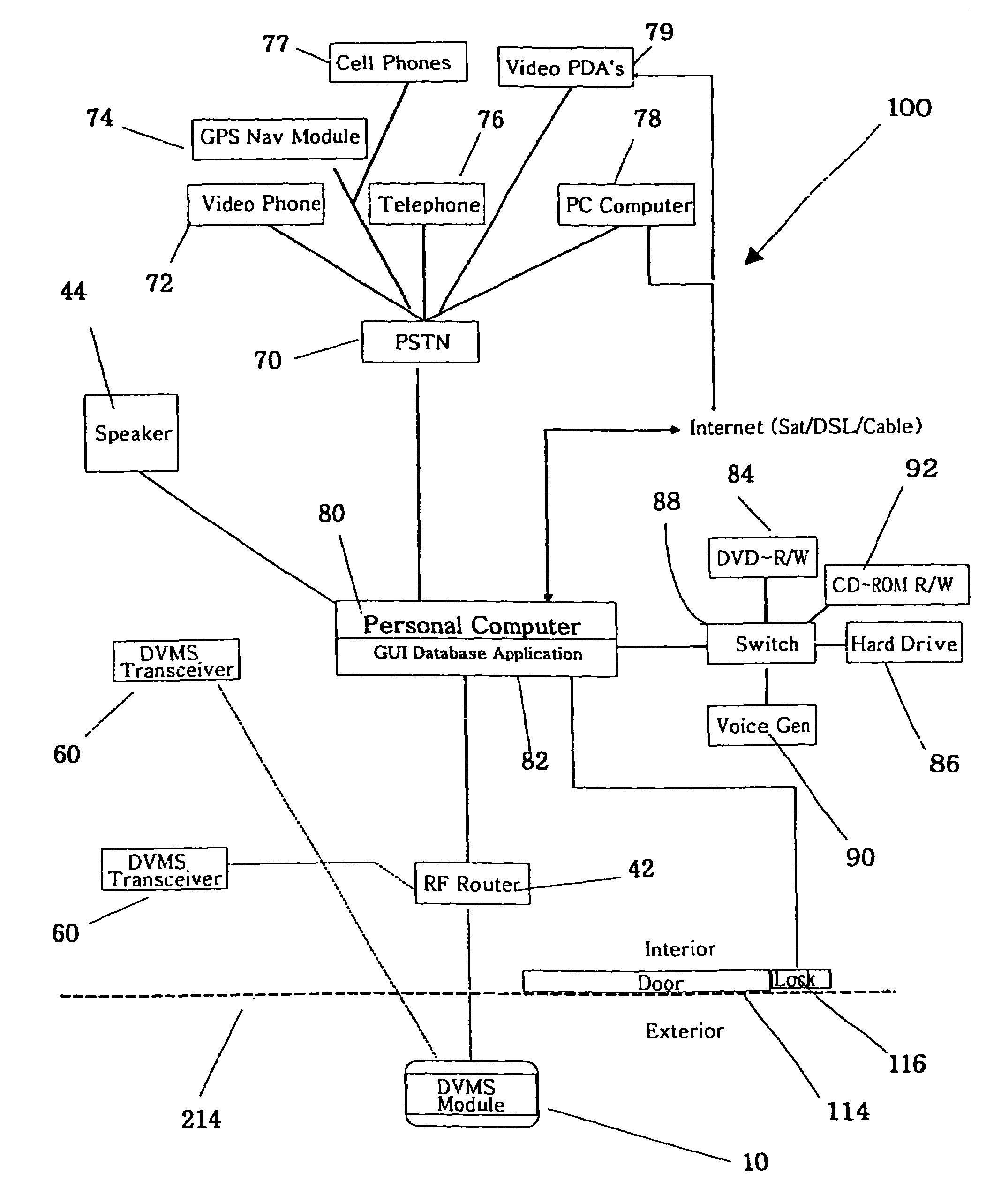
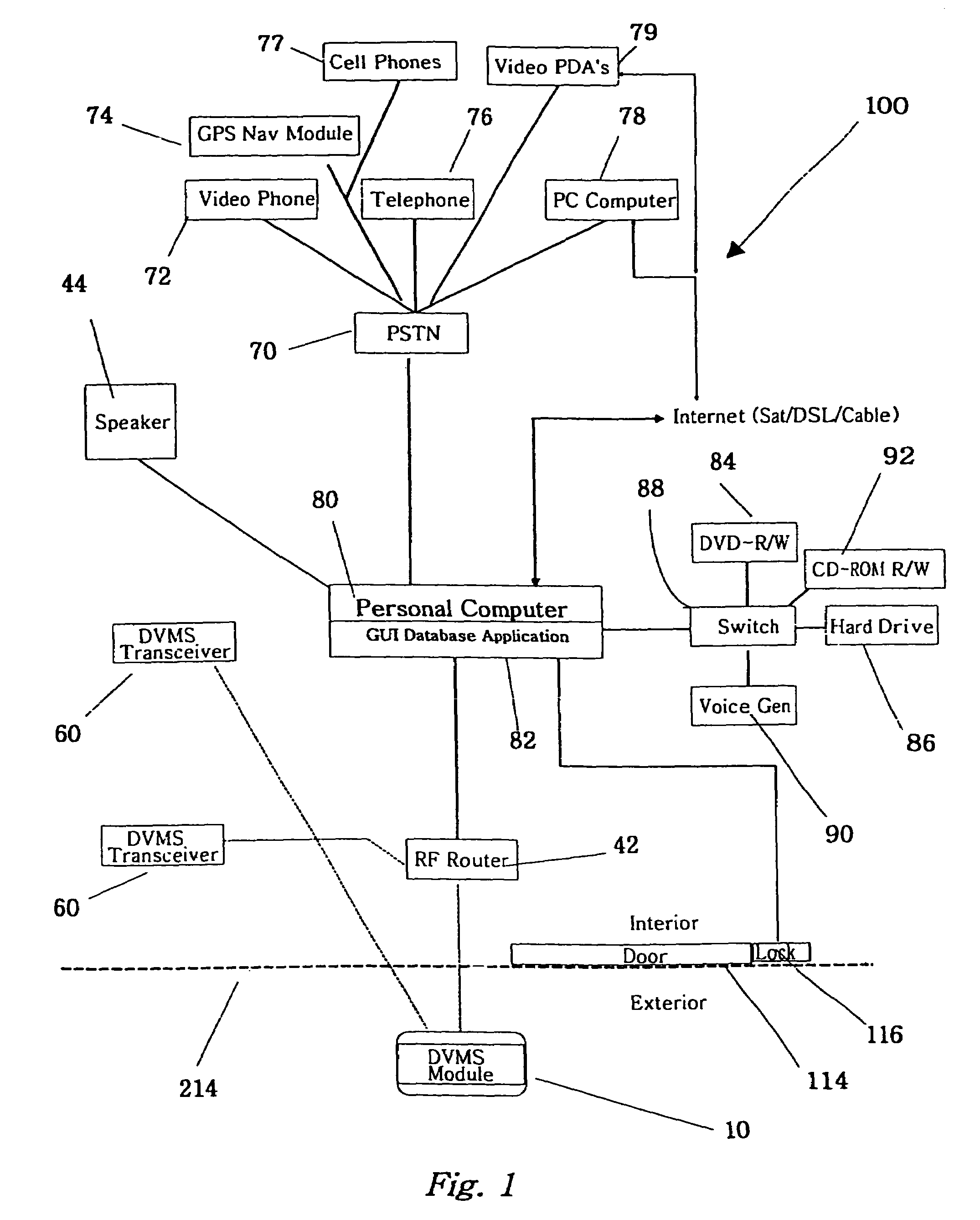
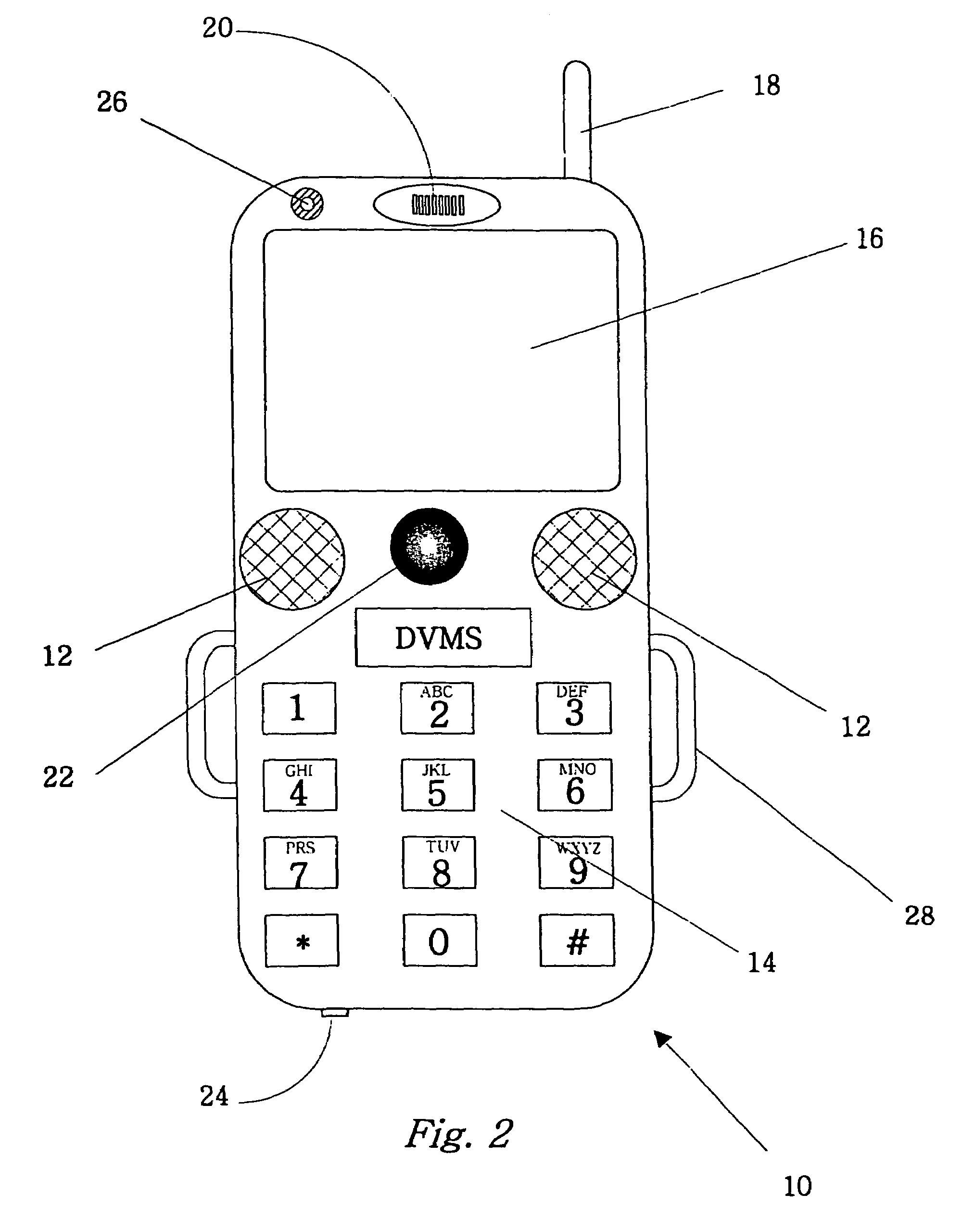
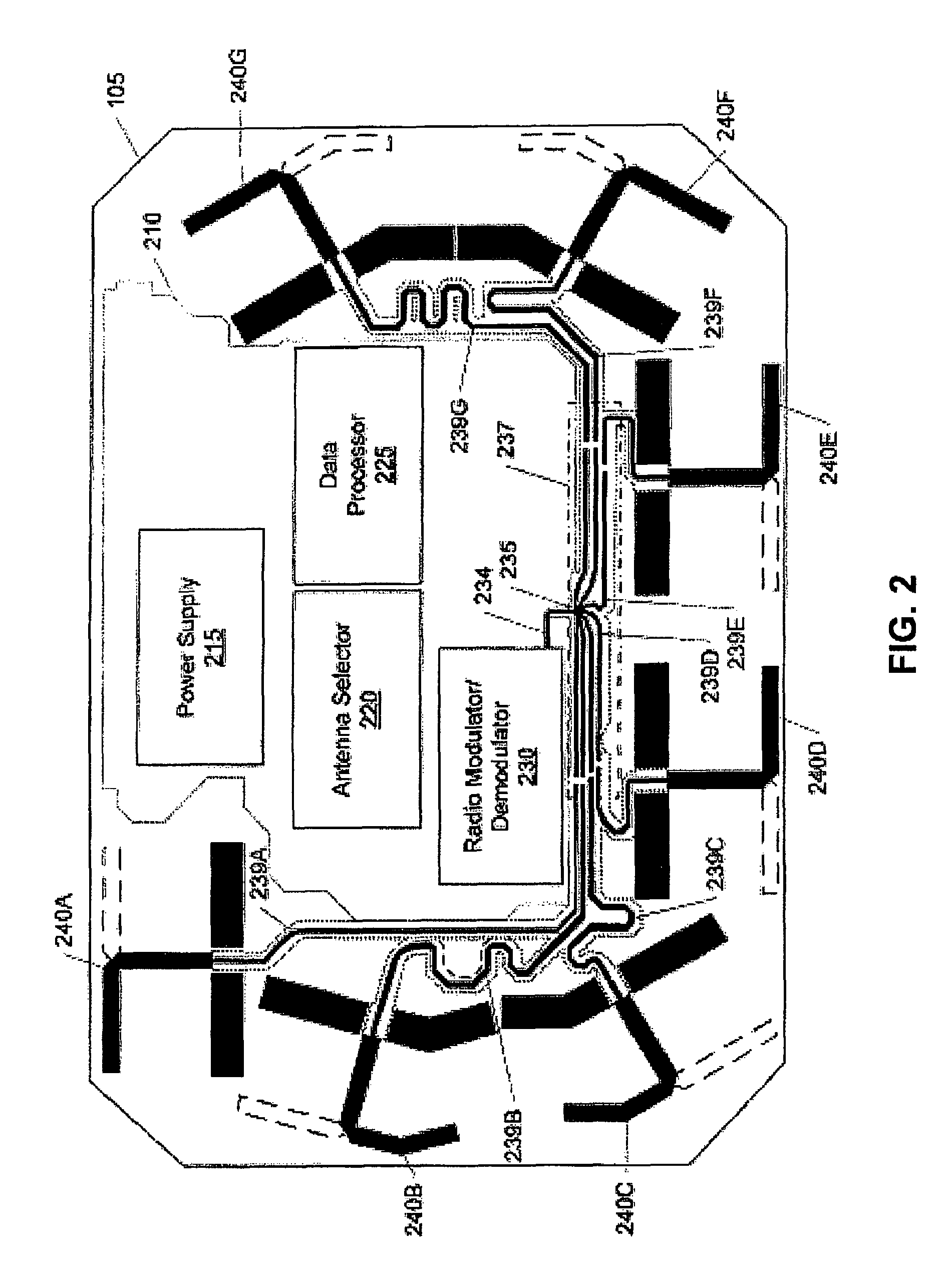
The invention is an audio-video communication and answering system that synergistically improves communication between an exterior and an interior of a business or residence and a remote location, enables messages to be stored and accessed from both locally and remotely, and enables viewing, listening, and recording from a remote location. The system's properties make it particularly suitable as a sophisticated door answering-messaging system. The system has a DVMS module on the exterior. The DVMS module has a proximity sensor, a video camera, a microphone, a speaker, an RF transmitter, and an RF receiver. The system also has a computerized controller with a graphic user interface DVMS database application. The computerized controller is in communication with a public switching telephone network, and an RF switching device. The RF switching device enables communication between the DVMS module and the computerized controller. The RF switching device can be in communication with other RF devices, such as a cell phone, PDA, or computer.
Owner:SB IP HLDG LLC
Programmable radio frequency sub-system with integrated antennas and filters and wireless communication device using same
InactiveUS20020183013A1Maximum flexibilityImprove user convenienceAntenna supports/mountingsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCapacitanceRF front end
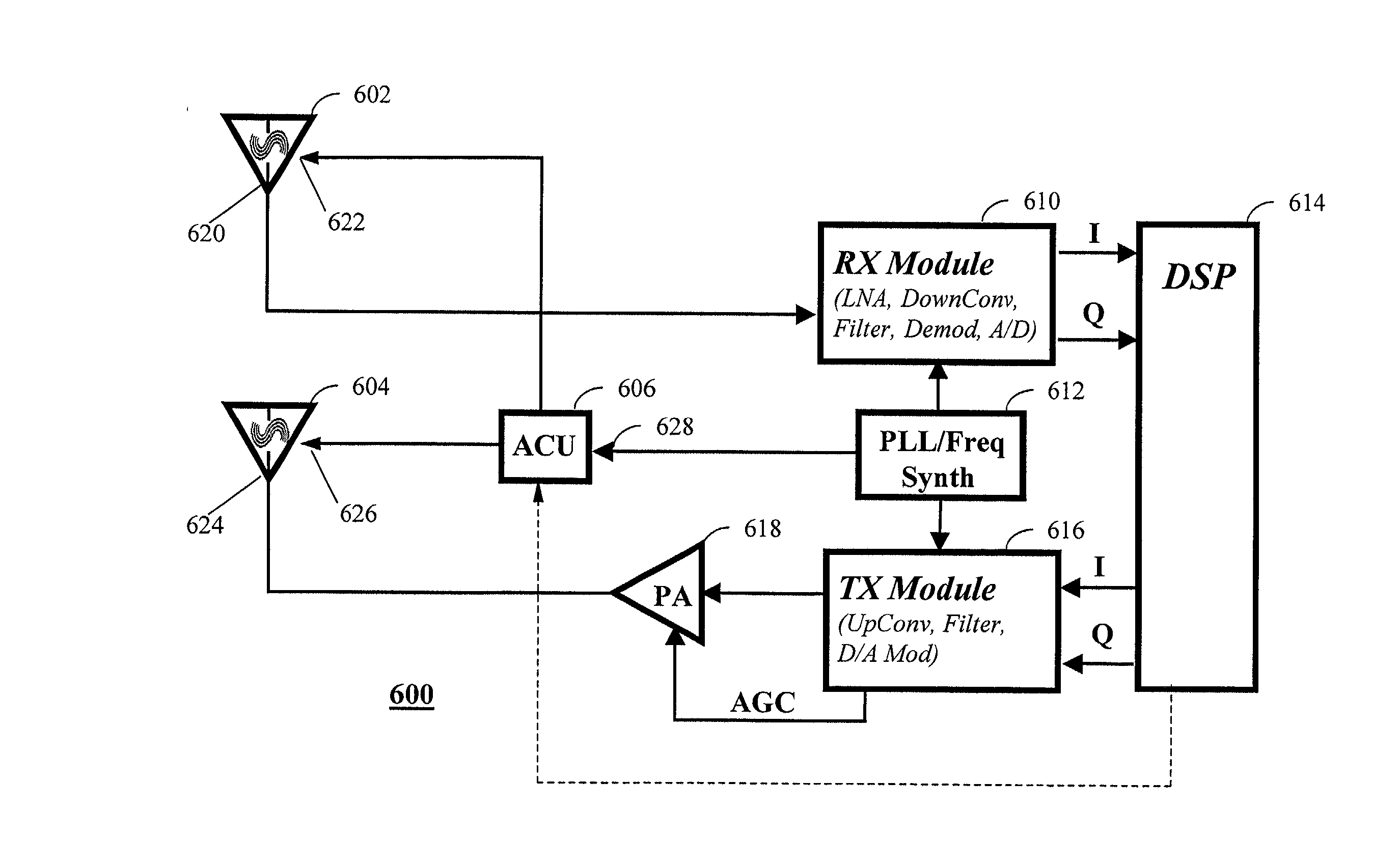
The present invention relates generally to radio communication devices. More particularly, the present invention relates to a programmable radio frequency (RF) sub-system and wireless communications devices using such an integrated antenna / filter sub-system. In one embodiment, the programmable RF front end subassembly includes two antennas, RF filter sections that are integral to each antenna, and a programmable logic device as an antenna control unit. Each antenna consists of a planar inverted "F" antenna (PIFA) that is tuned to operate over a range of frequencies using voltage variable capacitors or RF switches that connect various capacitive loads in order to achieve the desired resonant frequencies. The wireless communication device further includes a control circuit coupled to the antenna to provide the control signals.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
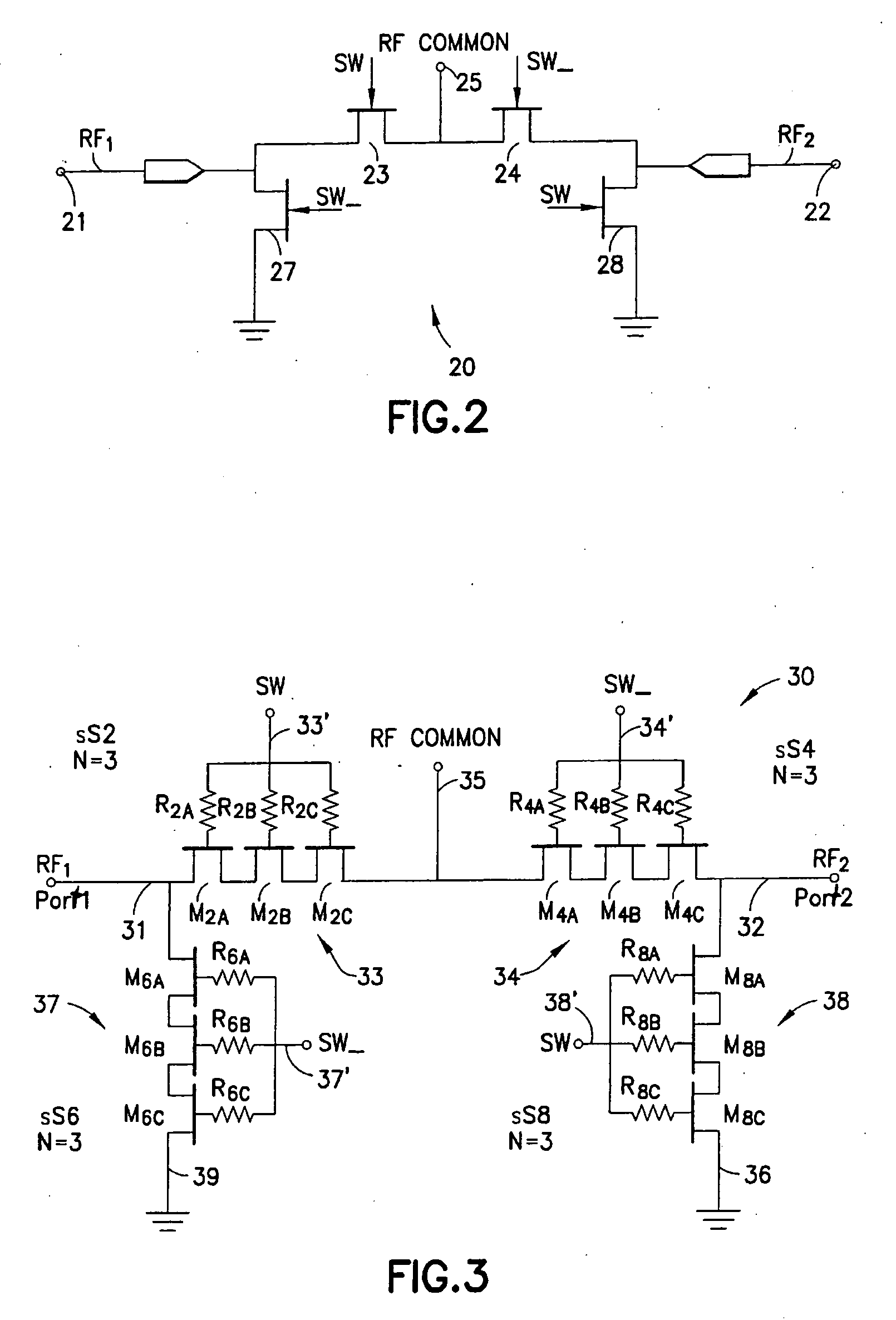
Symmetrically and asymmetrically stacked transistor group RF switch
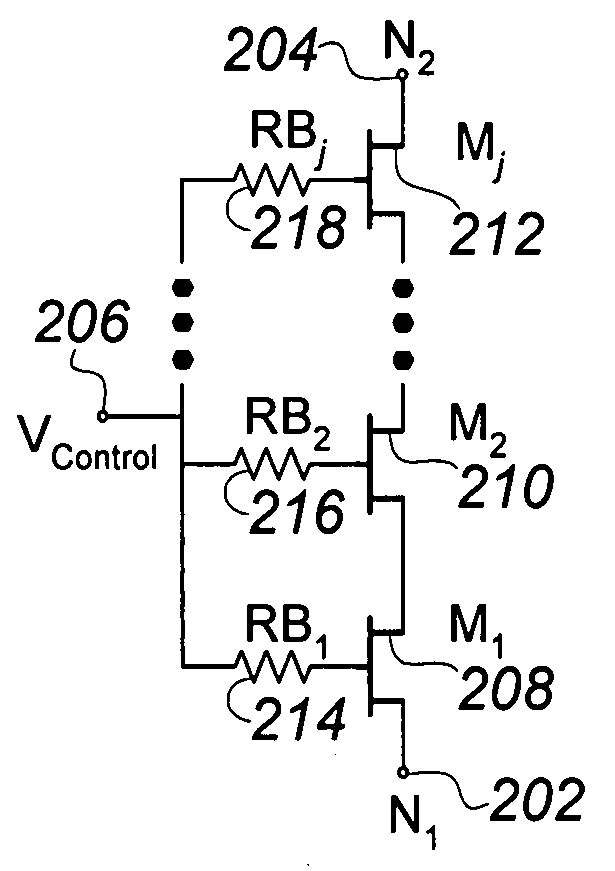
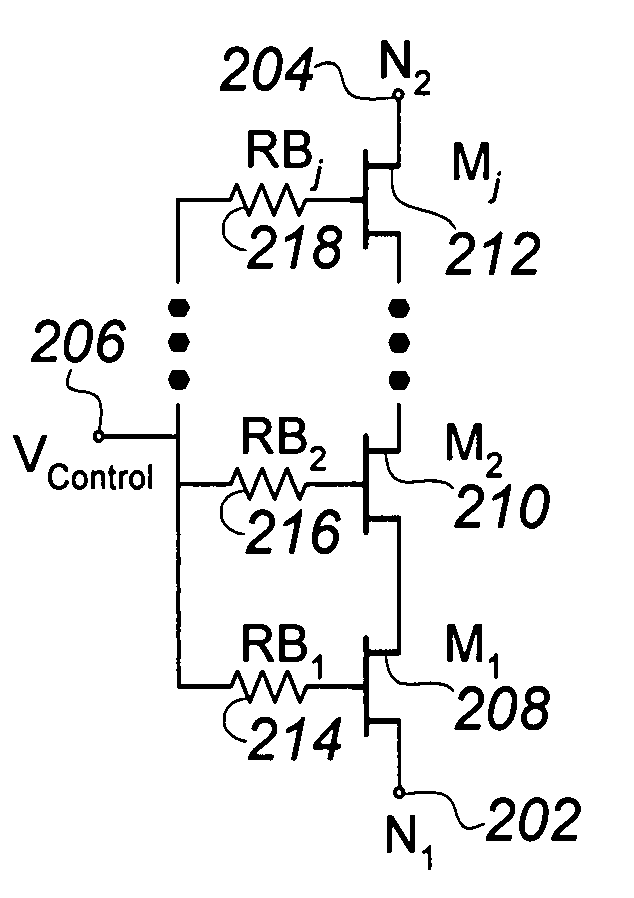
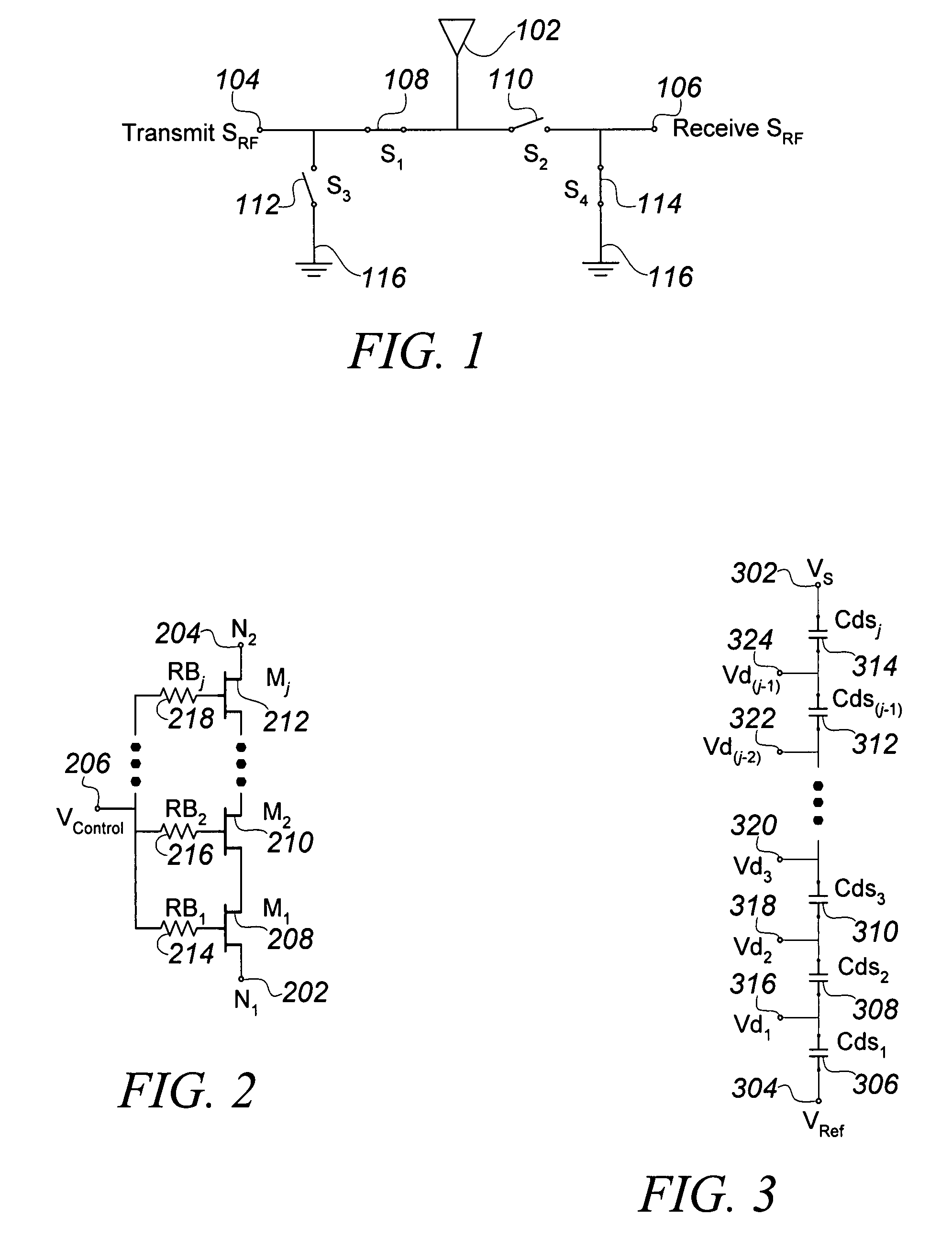
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI) RF switch adapted for improved power handling capability using a reduced number of transistors is described. In one embodiment, an RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting stacked transistor groupings to selectively couple RF signals between a plurality of input / output nodes and a common RF node. The switching and shunting stacked transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. In one embodiment, the transistor groupings are “symmetrically” stacked in the RF switch (i.e., the transistor groupings all comprise an identical number of transistors). In another embodiment, the transistor groupings are “asymmetrically” stacked in the RF switch (i.e., at least one transistor grouping comprises a number of transistors that is unequal to the number of transistors comprising at least one other transistor grouping). The stacked configuration of the transistor groupings enable the RF switch to withstand RF signals of varying and increased power levels. The asymmetrically stacked transistor grouping RF switch facilitates area-efficient implementation of the RF switch in an integrated circuit. Maximum input and output signal power levels can be withstood using a reduced number of stacked transistors.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Symmetrically and asymmetrically stacked transistor grouping RF switch
InactiveUS20060194567A1Reduce areaImprove area efficiencyTransistorDc-dc conversionMOSFETEngineering
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI) RF switch adapted for improved power handling capability using a reduced number of transistors is described. In one embodiment, an RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting stacked transistor groupings to selectively couple RF signals between a plurality of input / output nodes and a common RF node. The switching and shunting stacked transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. In one embodiment, the transistor groupings are “symmetrically” stacked in the RF switch (i.e., the transistor groupings all comprise an identical number of transistors). In another embodiment, the transistor groupings are “asymmetrically” stacked in the RF switch (i.e., at least one transistor grouping comprises a number of transistors that is unequal to the number of transistors comprising at least one other transistor grouping). The stacked configuration of the transistor groupings enable the RF switch to withstand RF signals of varying and increased power levels. The asymmetrically stacked transistor grouping RF switch facilitates area-efficient implementation of the RF switch in an integrated circuit. Maximum input and output signal power levels can be withstood using a reduced number of stacked transistors.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Tuning capacitance to enhance FET stack voltage withstand
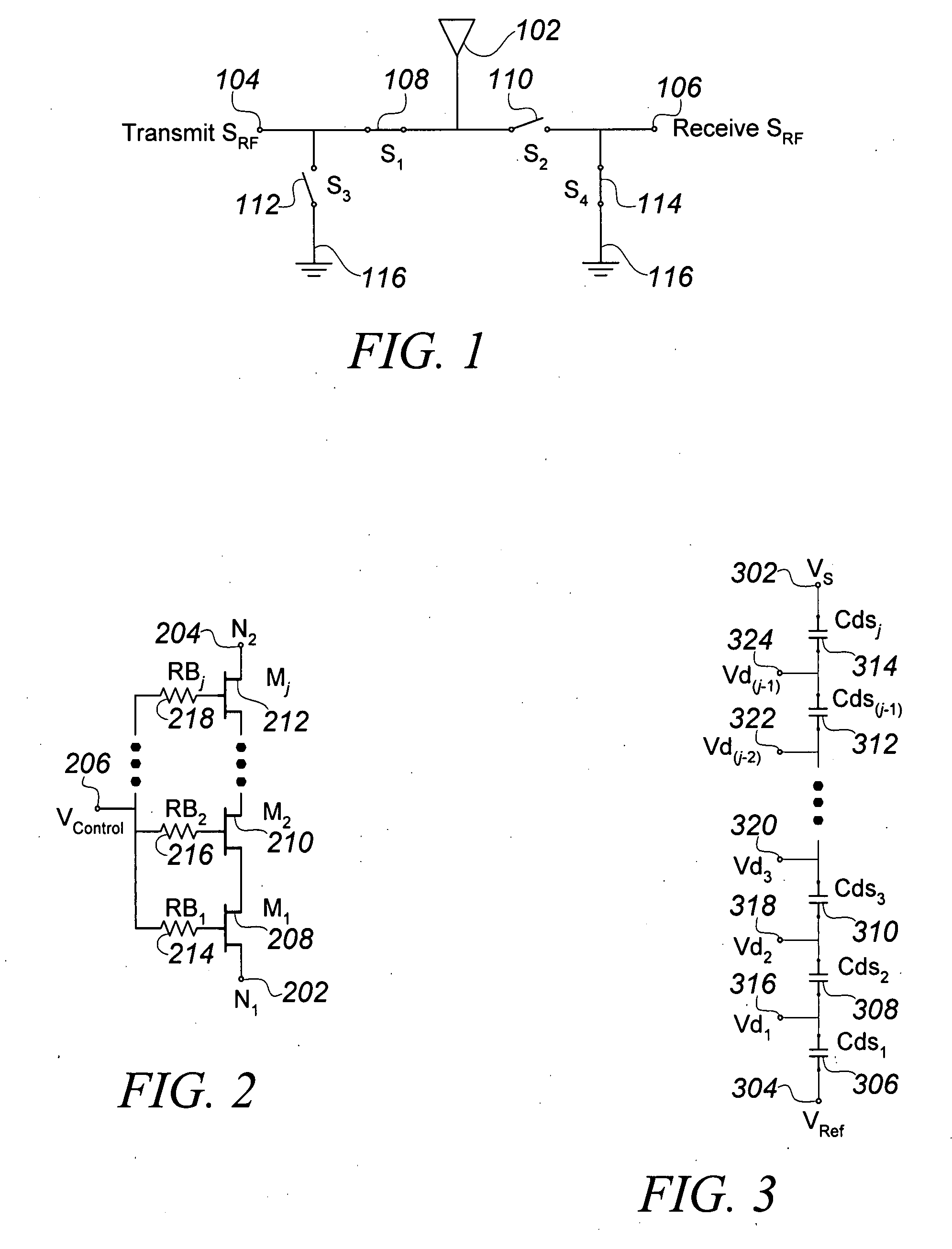
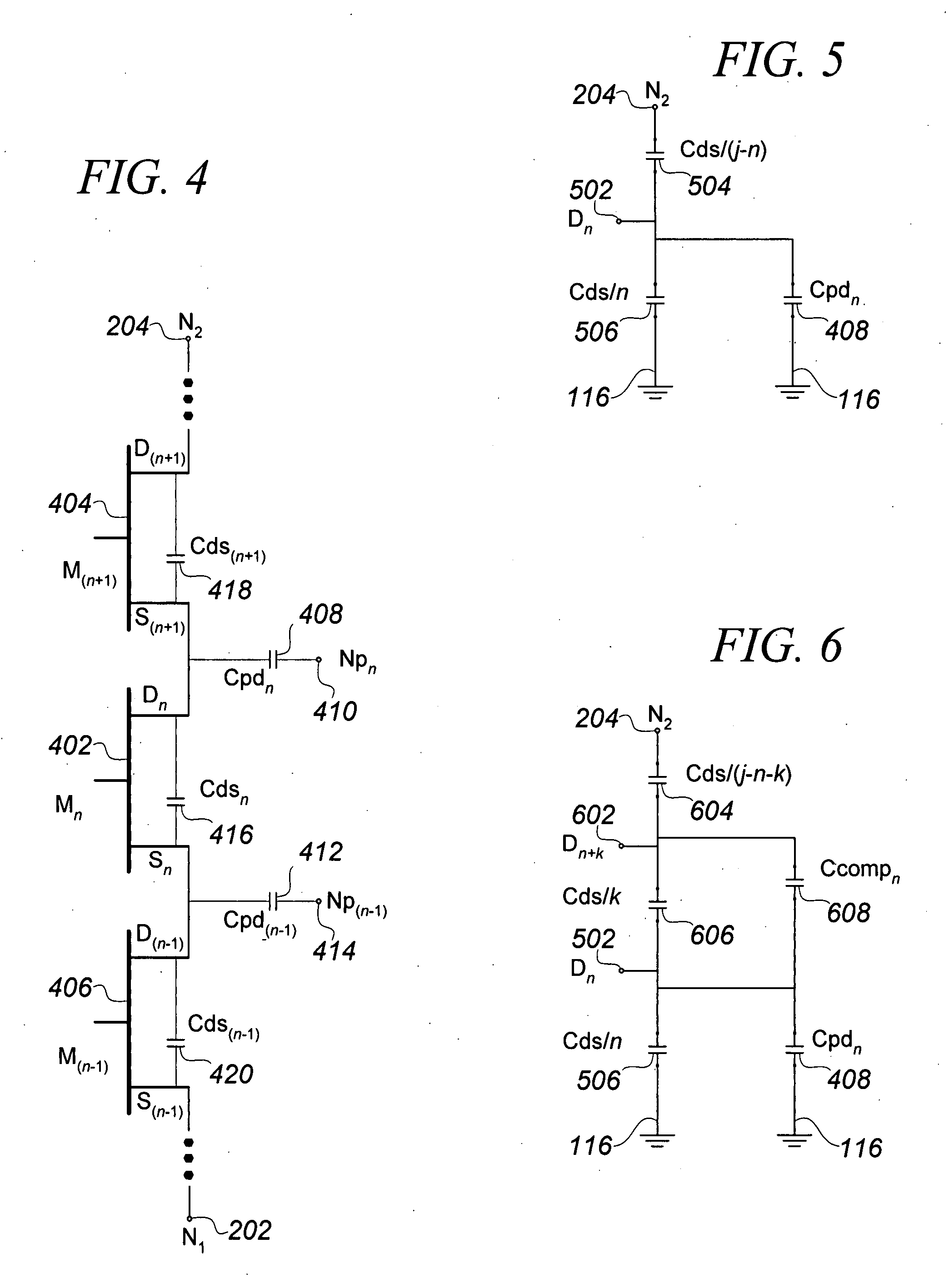
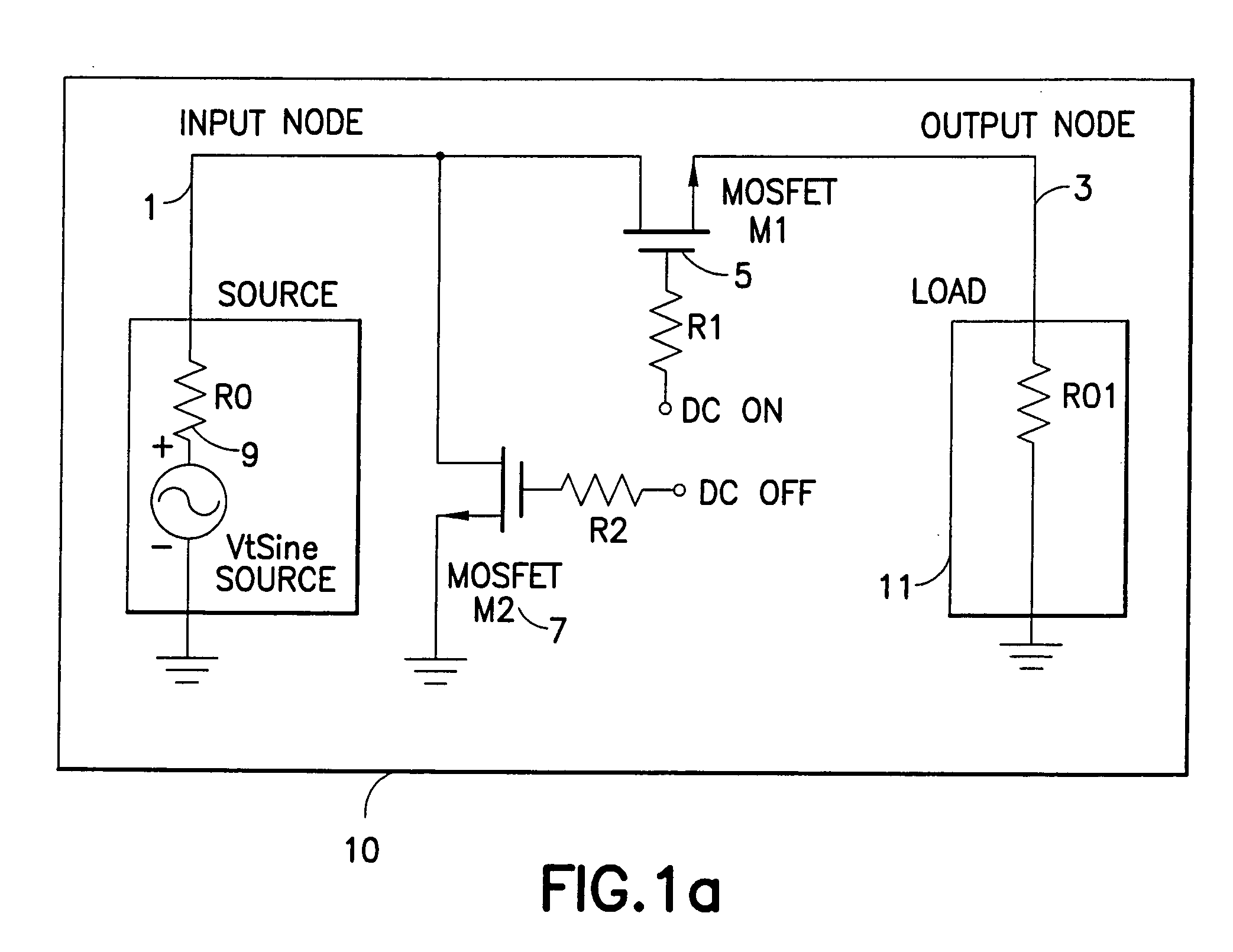
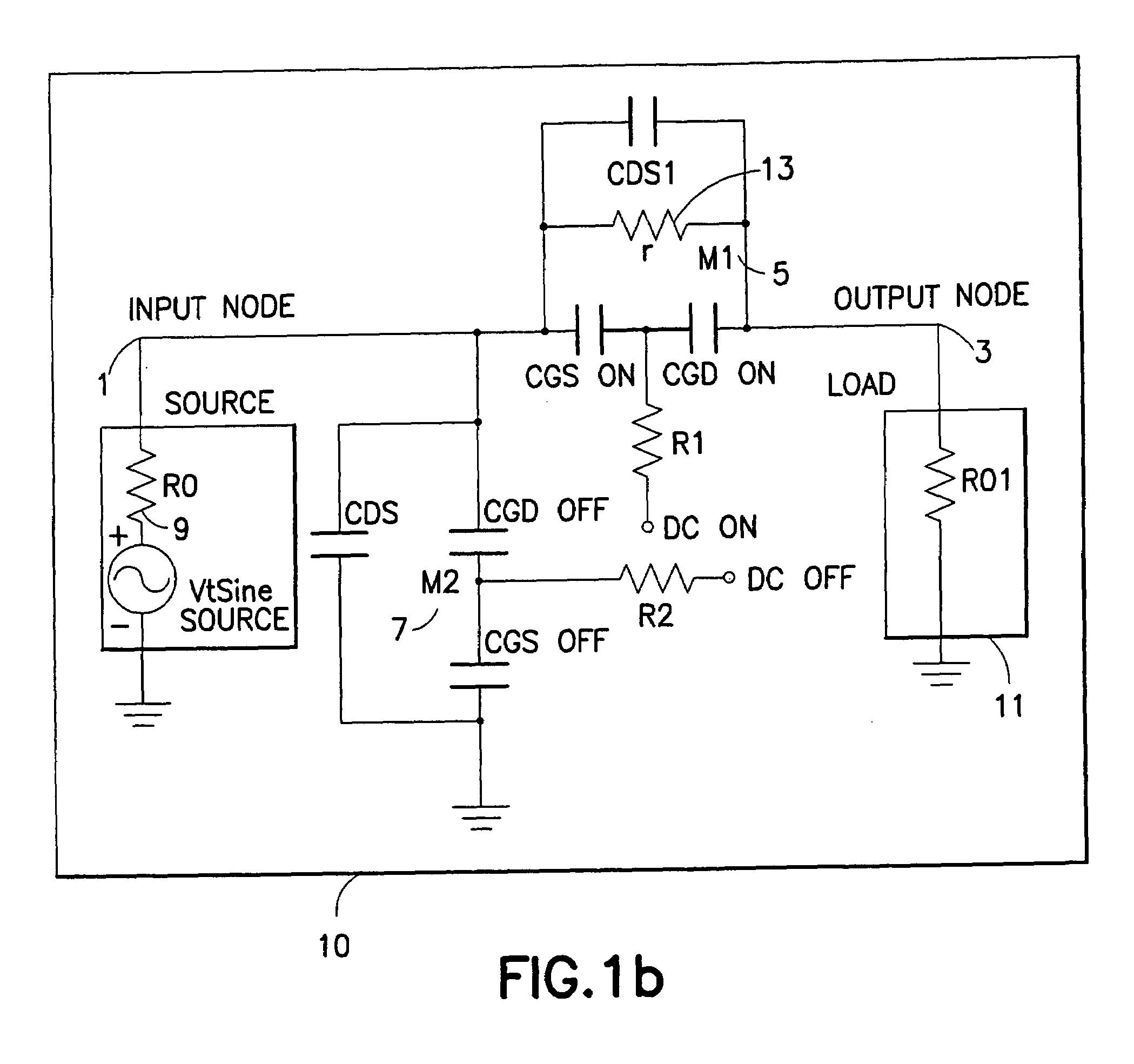
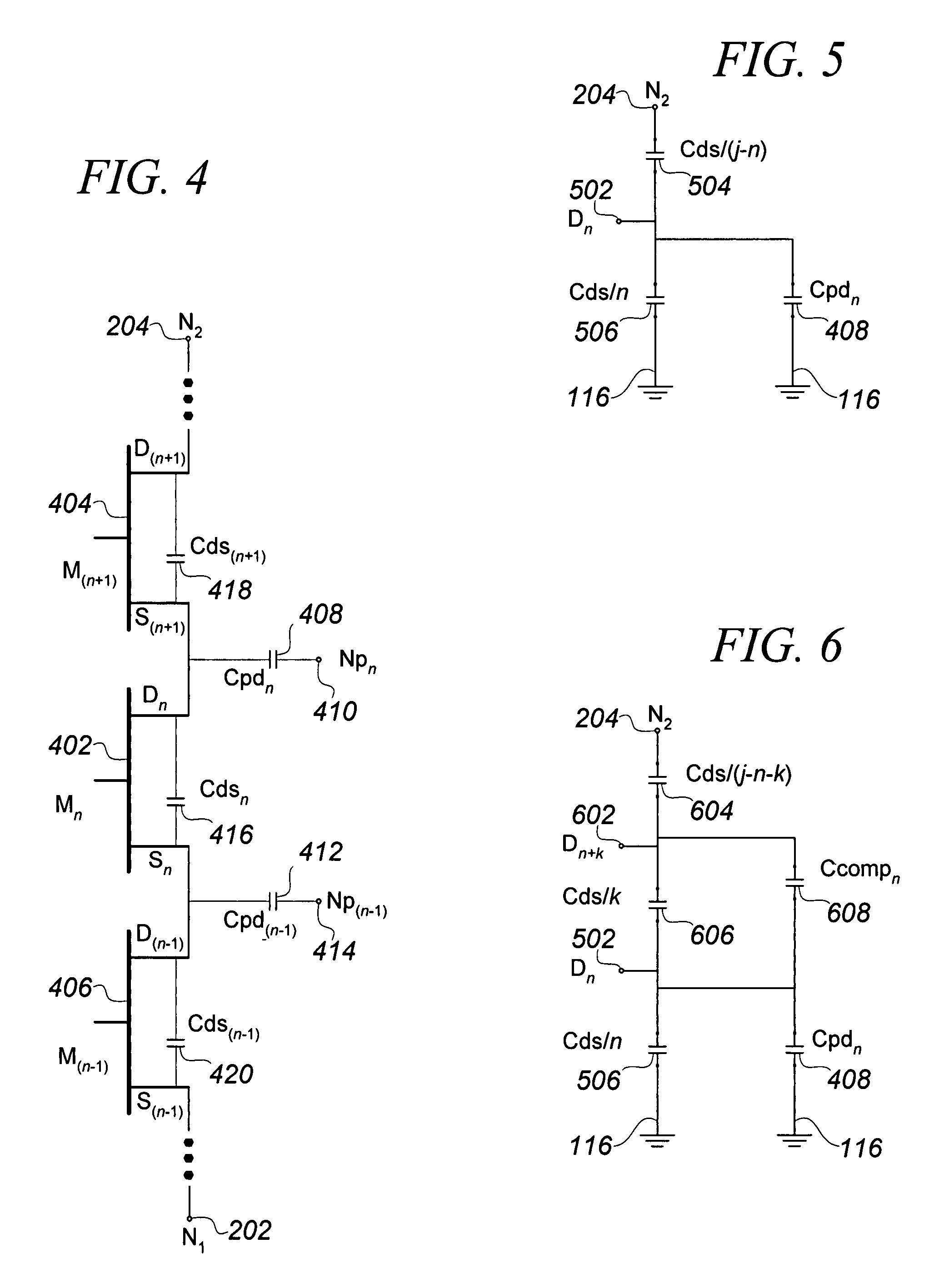
An RF switch to controllably withstand an applied RF voltage Vsw, or a method of fabricating such a switch, which includes a string of series-connected constituent FETs with a node of the string between each pair of adjacent FETs. The method includes controlling capacitances between different nodes of the string to effectively tune the string capacitively, which will reduce the variance in the RF switch voltage distributed across each constituent FET, thereby enhancing switch breakdown voltage. Capacitances are controlled, for example, by disposing capacitive features between nodes of the string, and / or by varying design parameters of different constituent FETs. For each node, a sum of products of each significant capacitor by a proportion of Vsw appearing across it may be controlled to approximately zero.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS7123898B2Easy to switchImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETDigital control
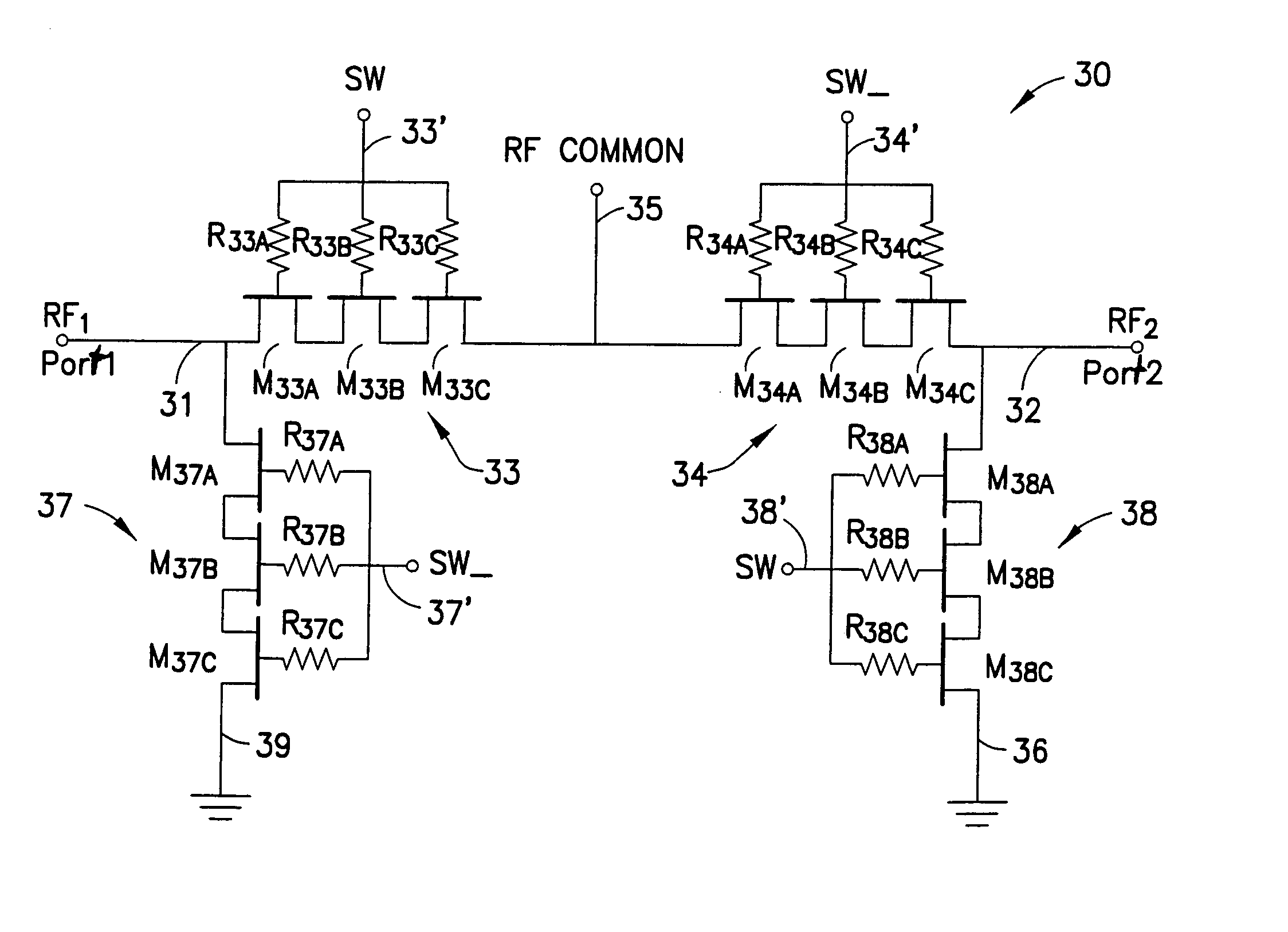
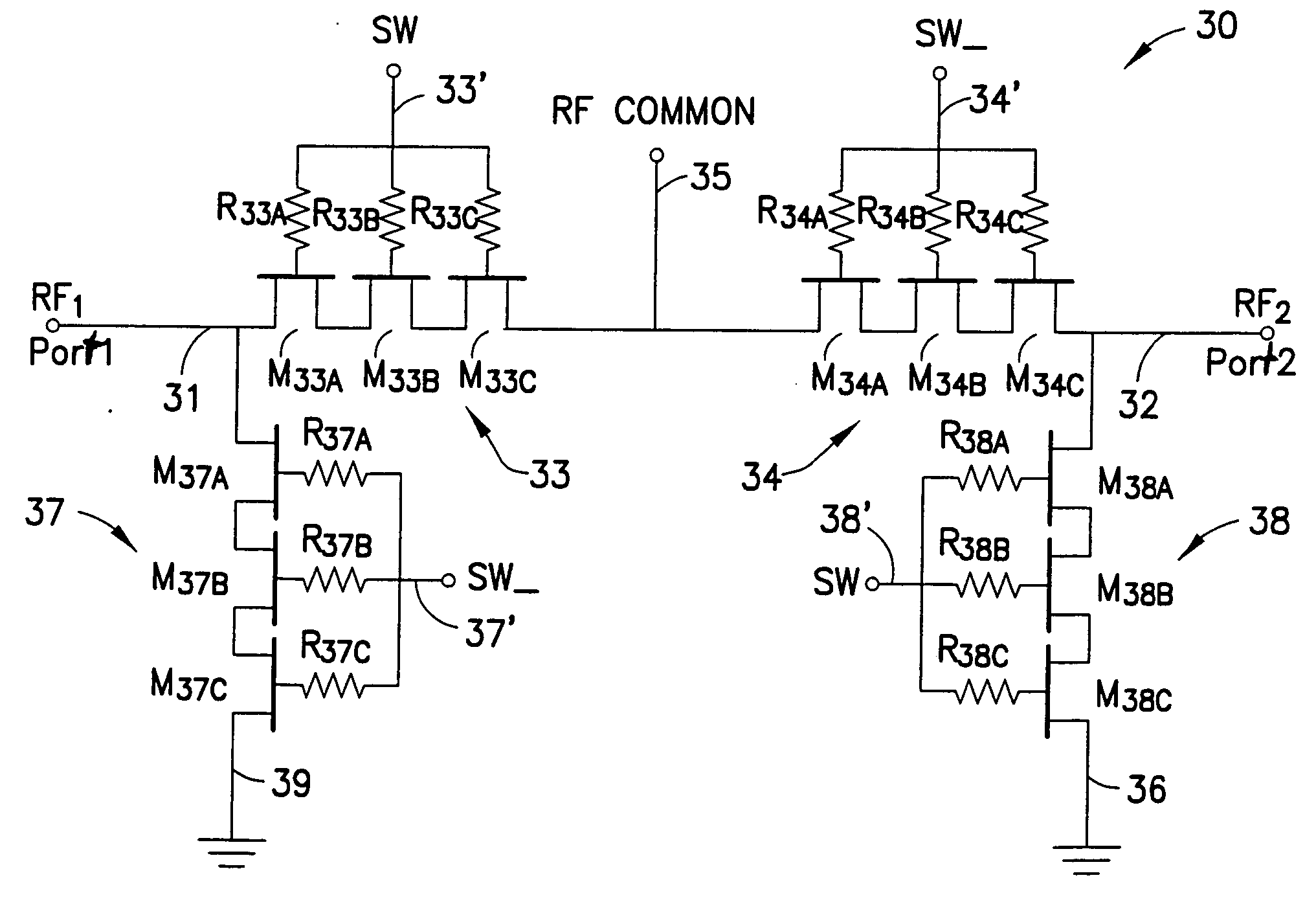
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
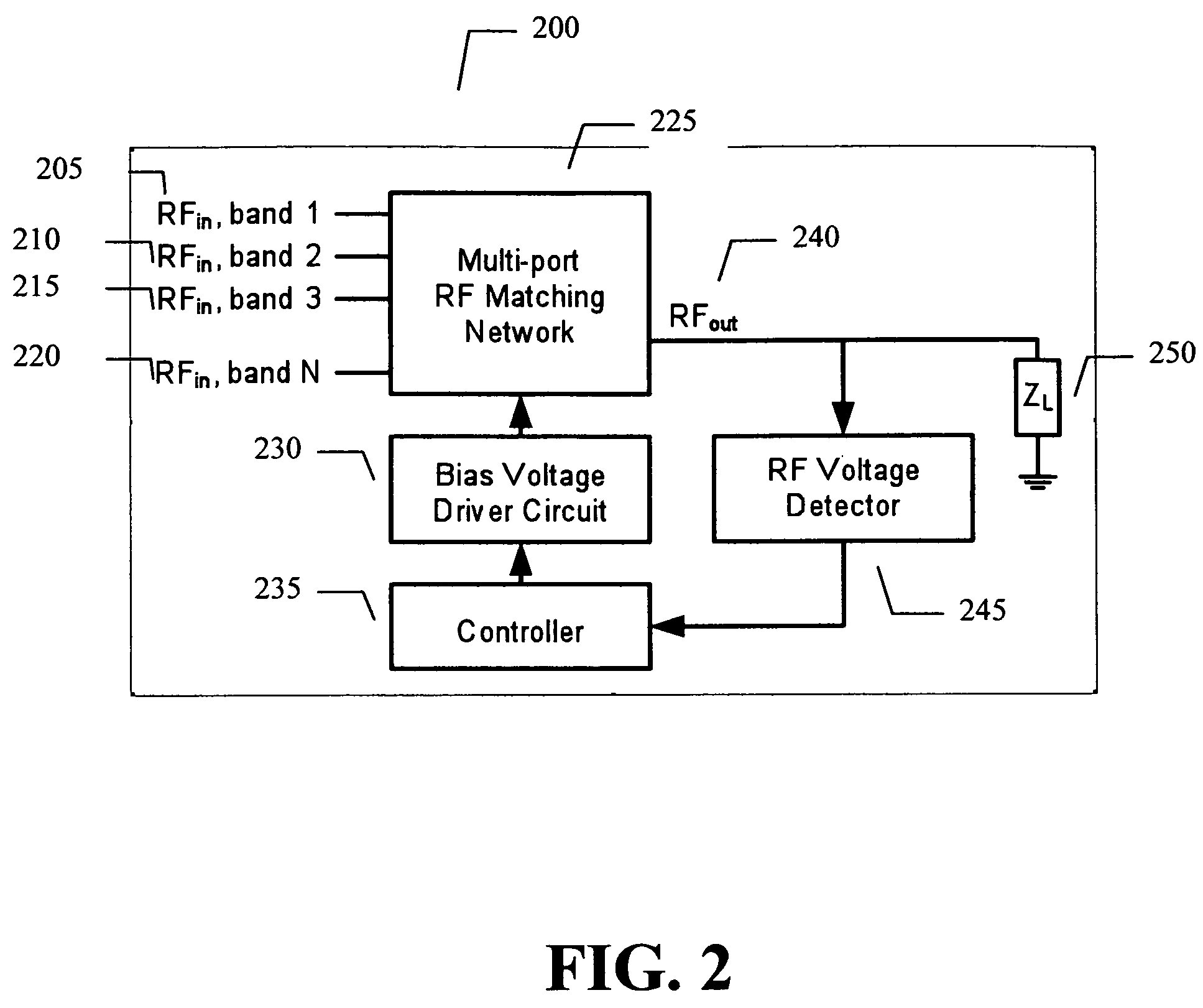
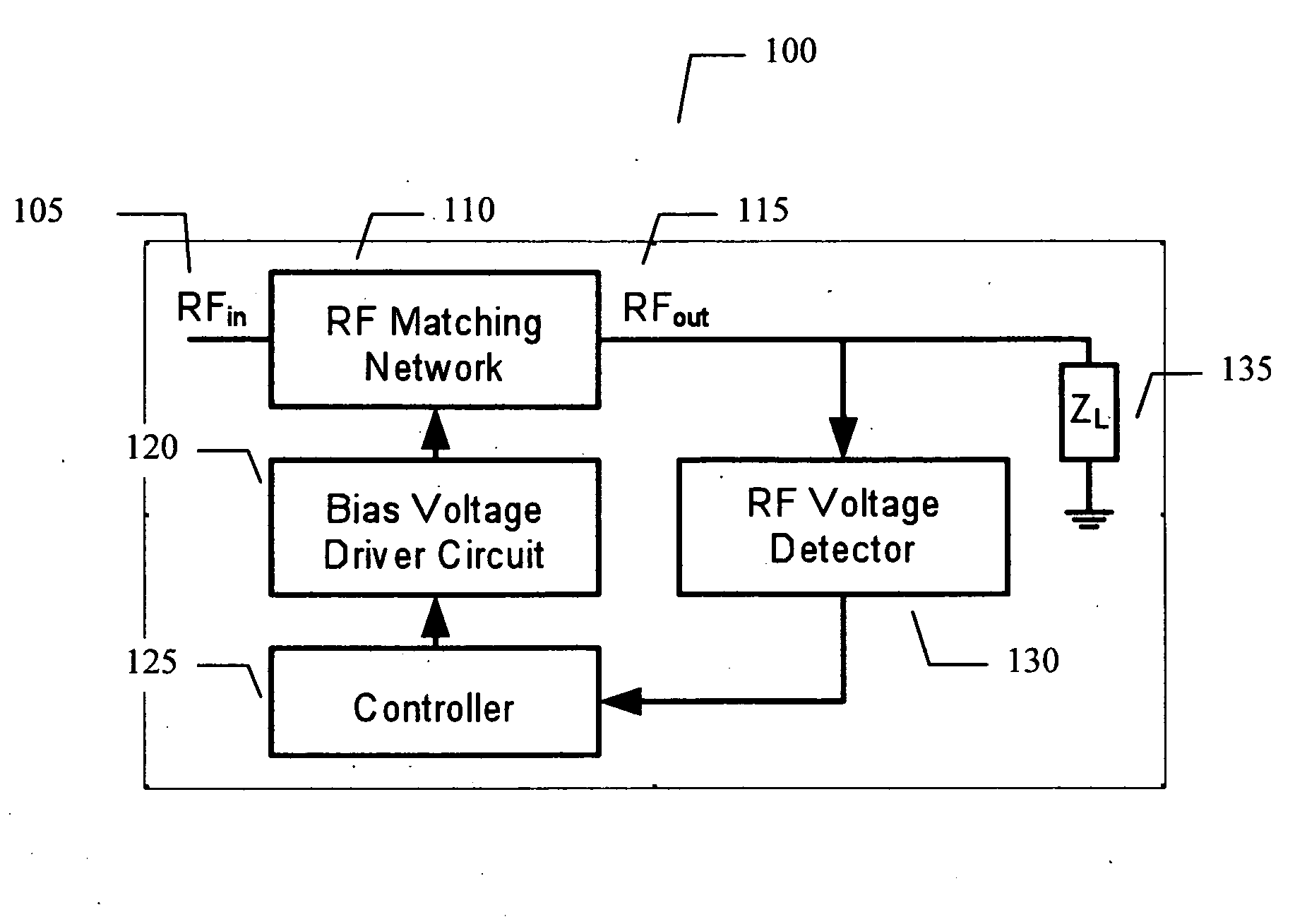
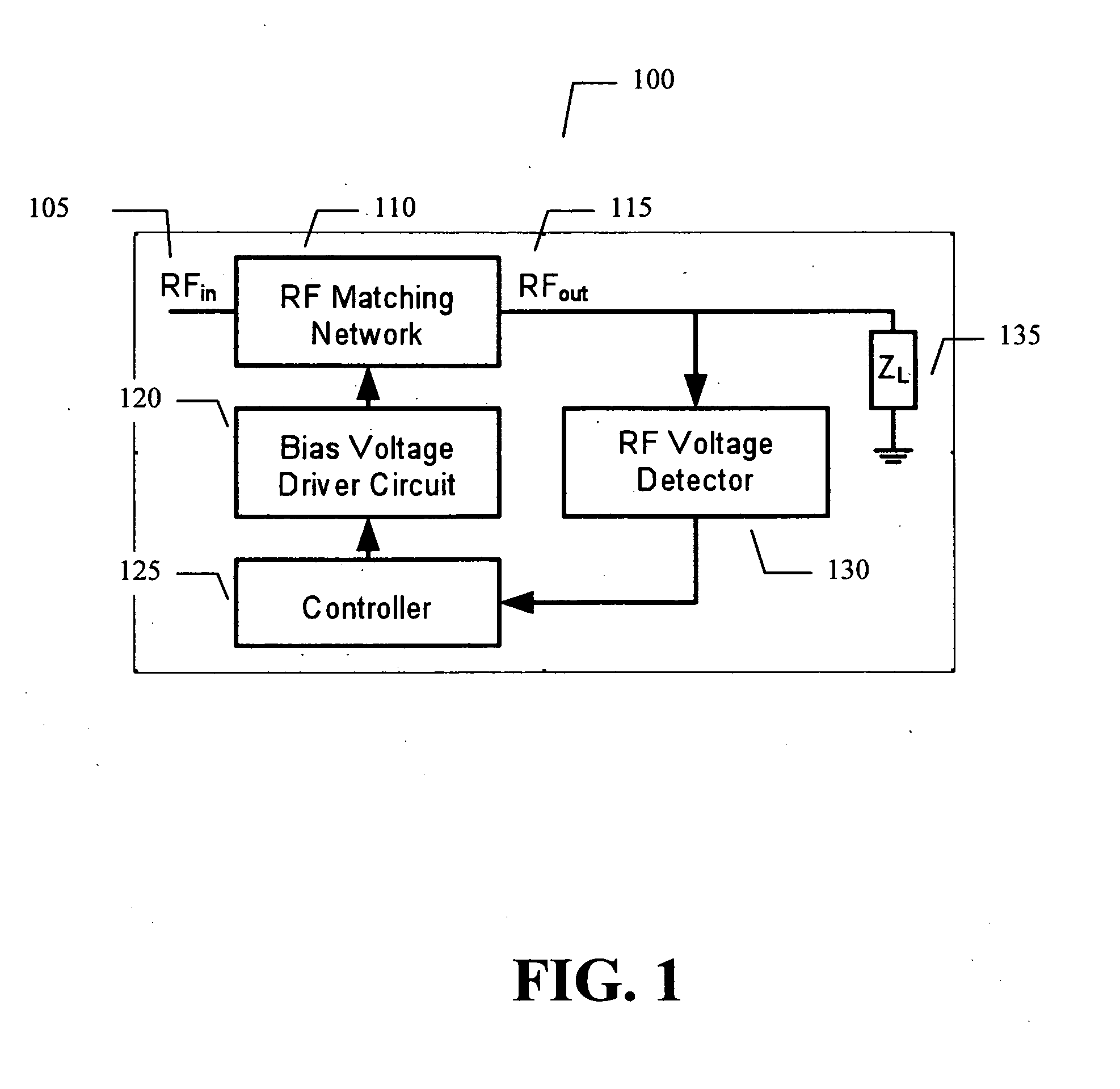
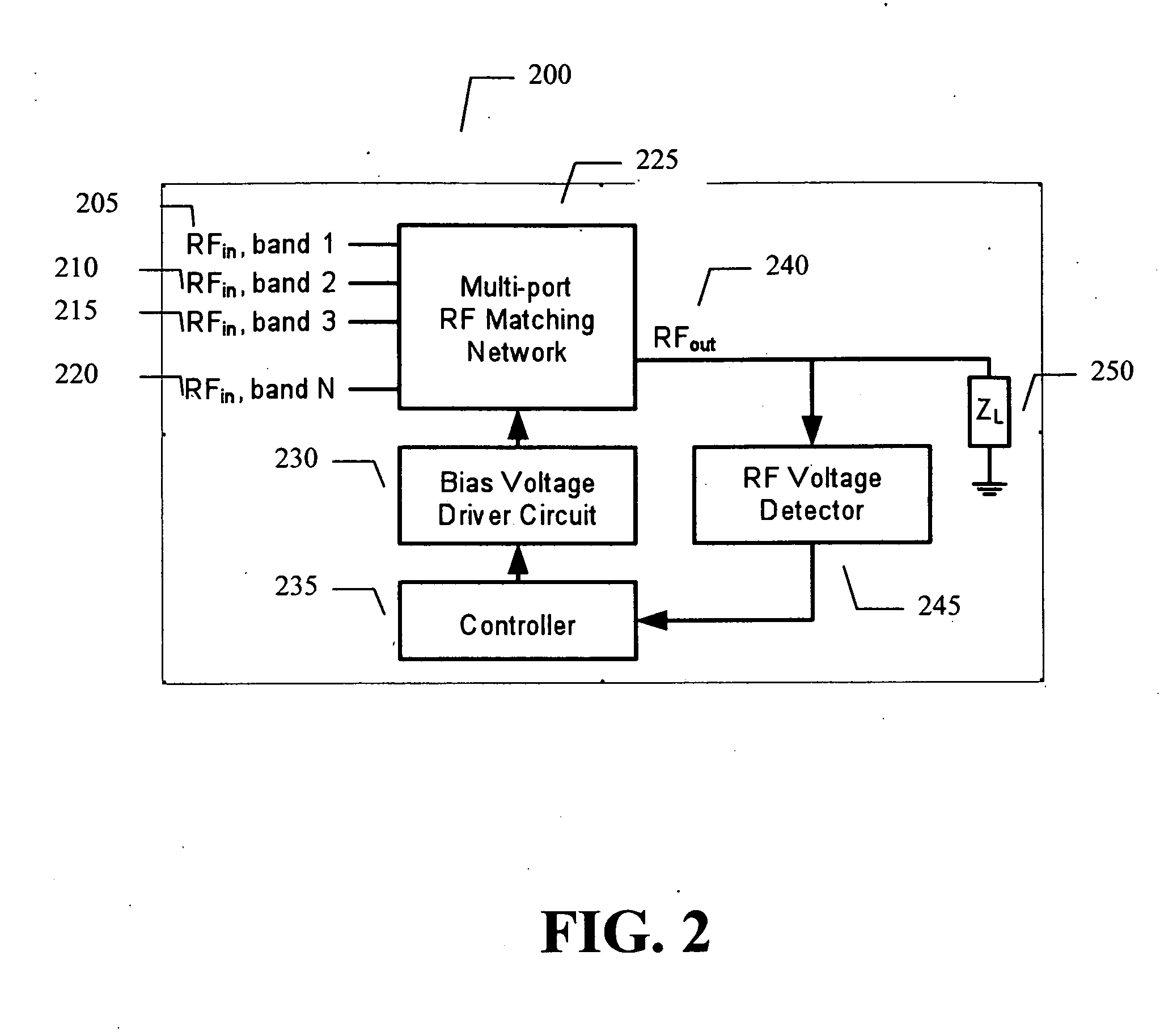
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus, system and method with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7852170B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityMultiple-port networksAntennas earthing switches associationElectrical resistance and conductanceNetwork connection
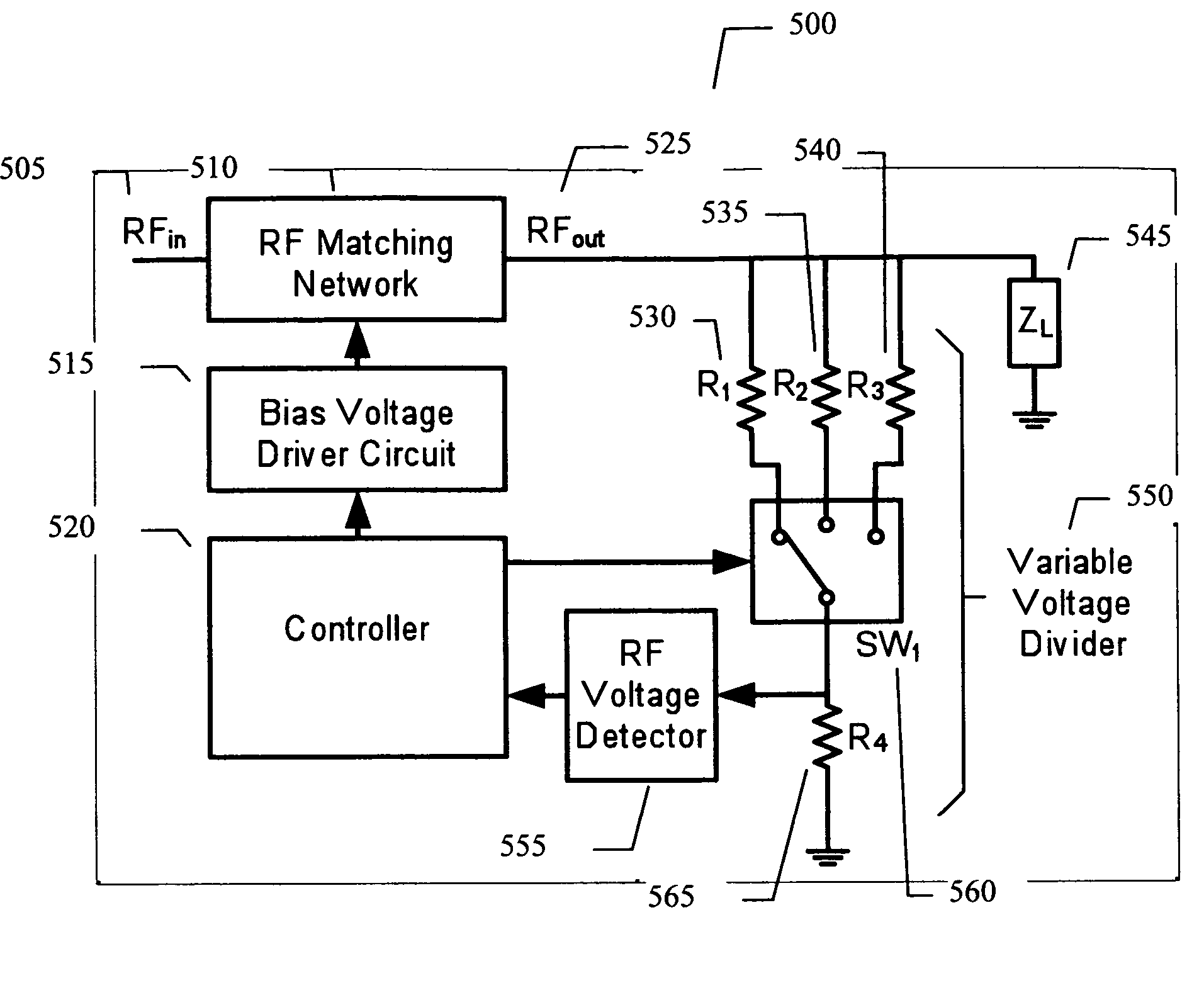
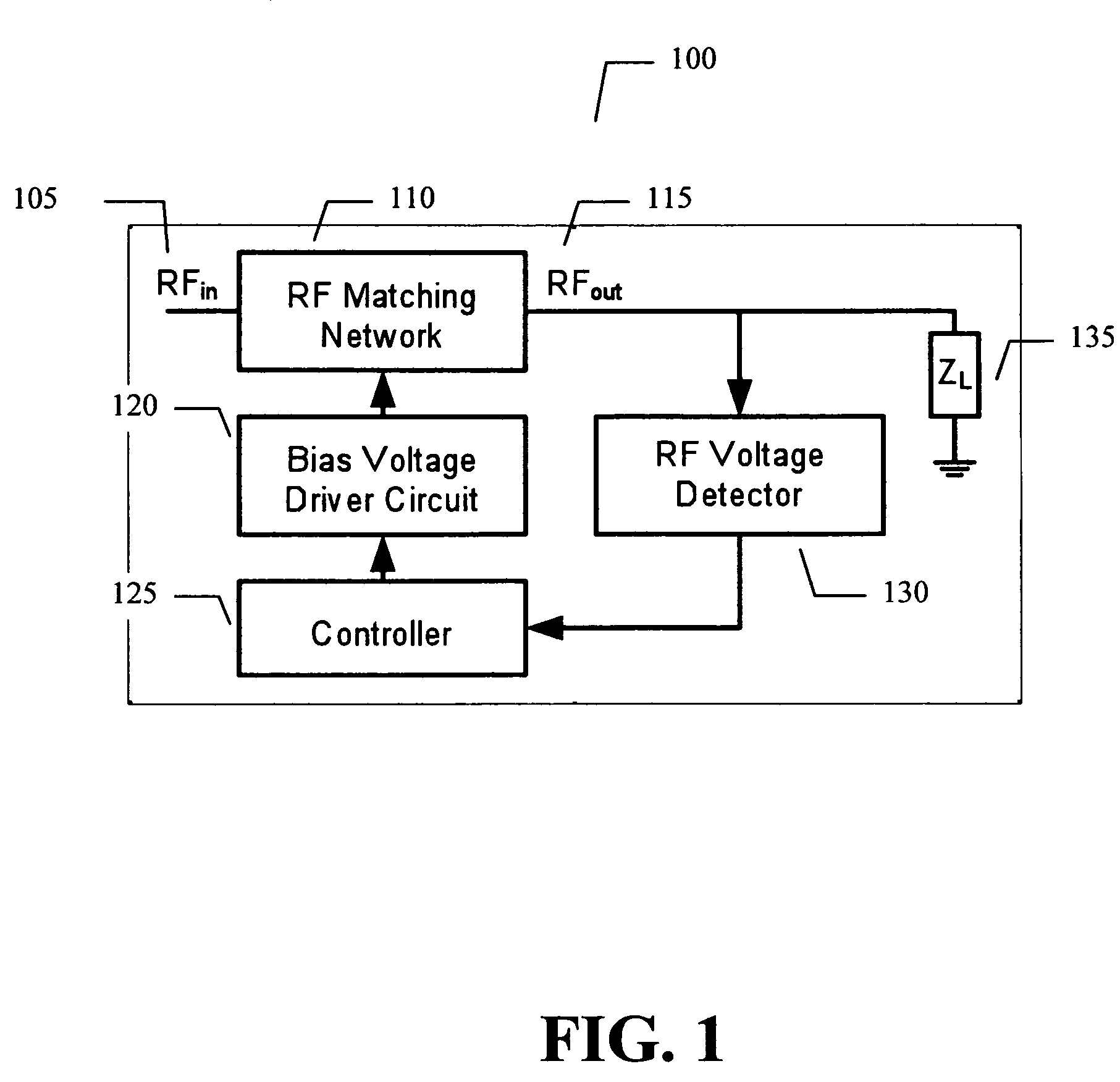
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements; a voltage detector connected to the at least one RF output port via a variable voltage divider to determine the voltage at the at least one RF output port and provide voltage information to a controller that controls a bias driving circuit which provides voltage or current bias to the RF matching network; a variable voltage divider connected to the voltage detector and implemented using a multi-pole RF switch to select one of a plurality of different resistance ratios to improve the dynamic range of the apparatus; and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Canceling harmonics in semiconductor RF switches
An RF switching circuit adapted to cancel selected harmonic signals. An unwanted harmonic signal Sh1 at a selected harmonic frequency Fsh of an operating frequency Fo exists in a signal Si conducted by the switching circuit, possibly produced by the switching circuit due to conduction through a first nonlinear impedance Znl(1). A compensating harmonic signal Sh2 is therefore generated by conduction via a nonlinear impedance Znl(2). Znl(1) may be due to parasitic conduction by “off” switching elements, while Znl(2) may be due to conduction by an “on” FET. The amplitude and / or phasing of Sh2 may be adjusted by selecting components for a network coupling Znl(2) to the conducted signal Si, such that Sh2 substantially cancels Sh1 across a target range of input power.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
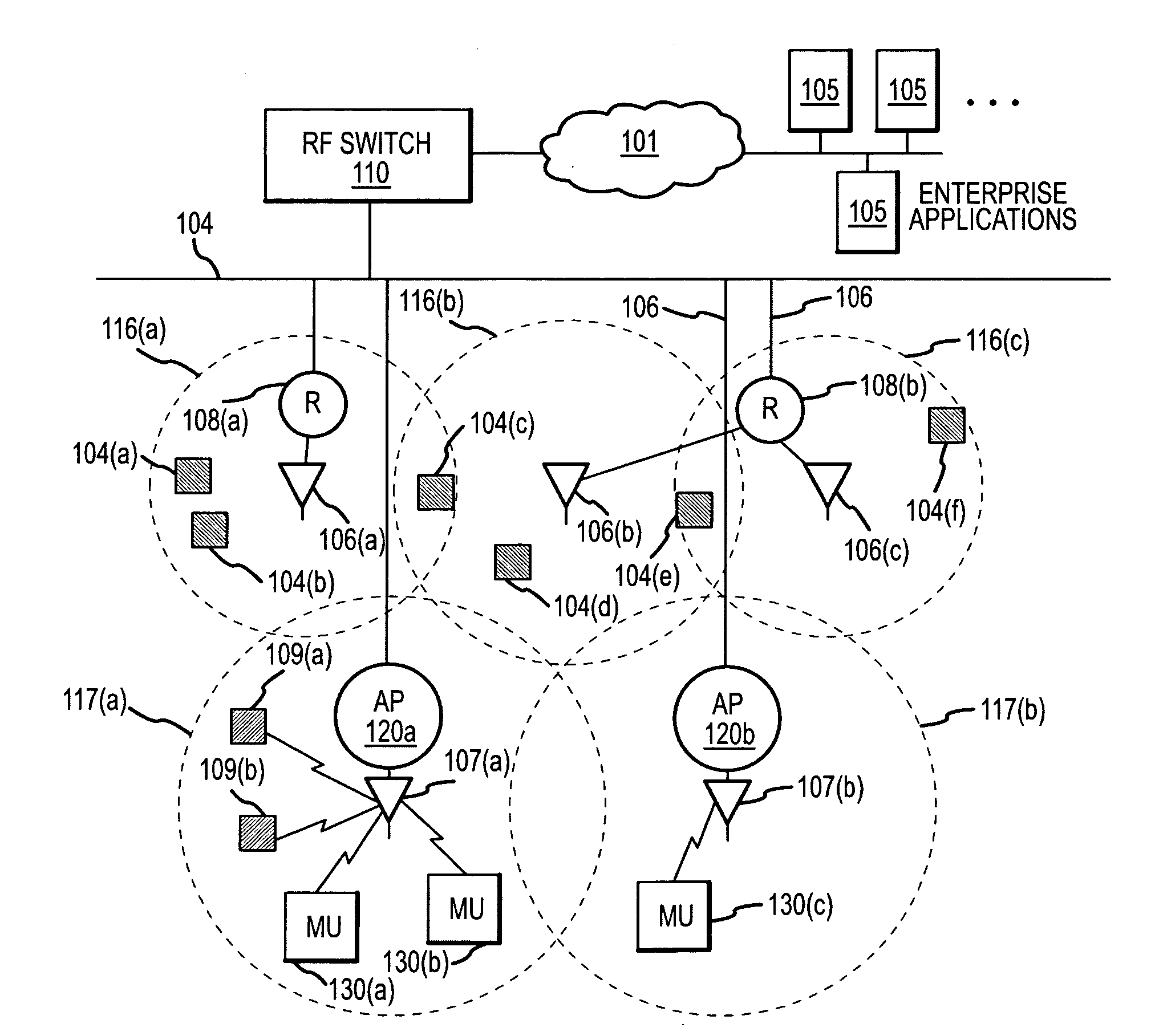
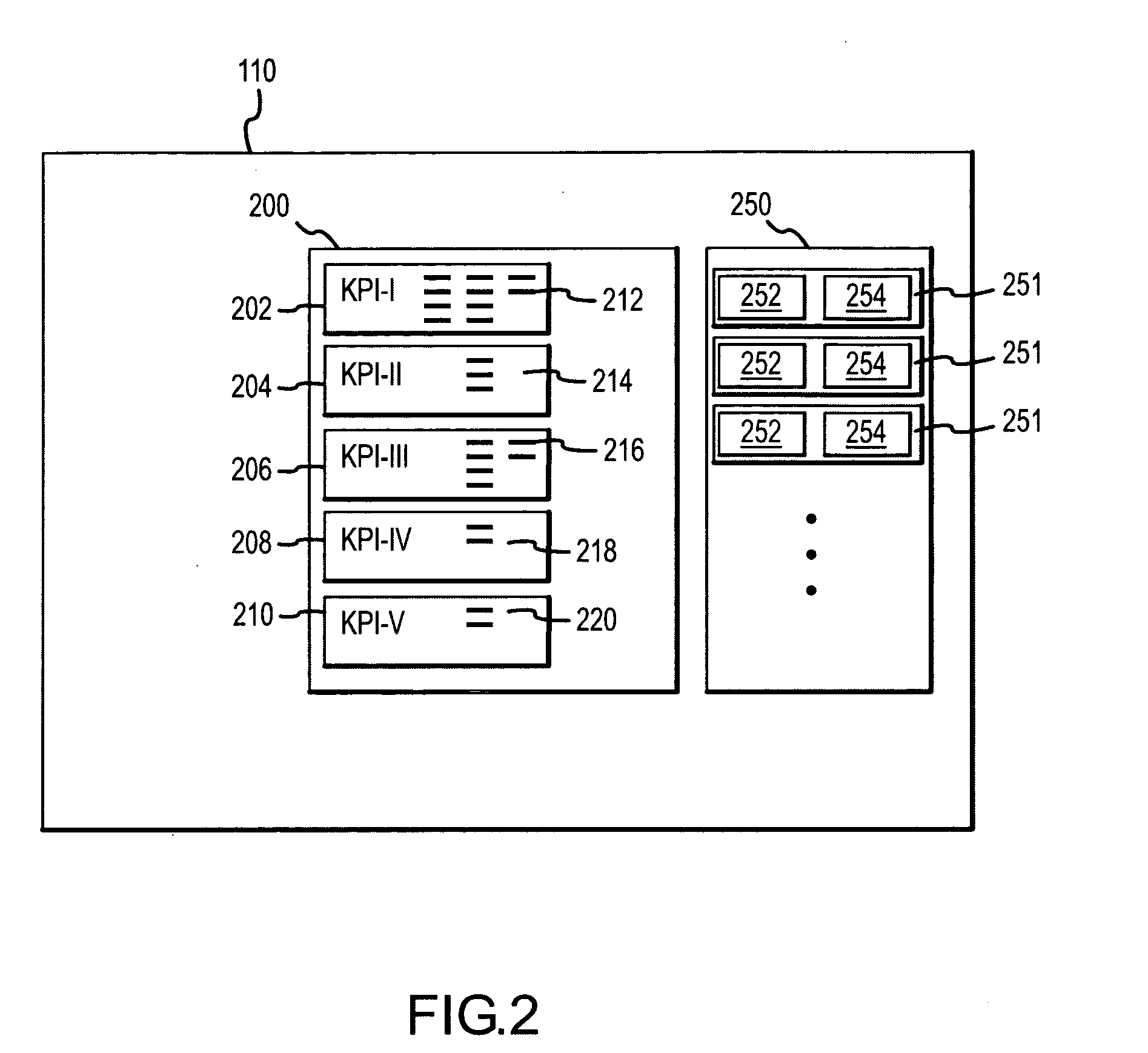
Methods and apparatus for defining, storing, and identifying key performance indicators associated with an RF network
InactiveUS20080081632A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationDisplay deviceSystem time
A system for assessing the state of an RF network includes a plurality of wireless devices coupled to the network and having one or more associated antennae, the wireless devices configured to process data received from a plurality of RF elements within range of the antennae. An RF switch is coupled to the network and configured to receive the data and transmit the data over the network. A first memory within the RF switch is configured to store a system state comprising a plurality of performance indicators, wherein each of the performance indicators is associated with an operational characteristic of one or more of the plurality of wireless devices. A second memory within the RF switch is configured to store a plurality of labeled data entries, the labeled data entries each including the system state and a user-entered identifier, wherein the user-entered identifier includes information related to the time at which the system state was selected. A display coupled to the network is configured to display a comparison of the system states.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
MEMS RF switch
A capacitance coupled, transmission line-fed, radio frequency MEMS switch and its fabrication process using photoresist and other low temperature processing steps are described. The achieved switch is disposed in a low cost dielectric housing free of undesired electrical effects on the switch and on the transmission line(s) coupling the switch to an electrical circuit. The dielectric housing is provided with an array of sealable apertures useful for wet, but hydrofluoric acid-free, removal of switch fabrication employed materials and also useful during processing for controlling the operating atmosphere surrounding the switch—e.g. at a pressure above the high vacuum level for enhanced switch damping during operation. Alternative arrangements for sealing an array of dielectric housing apertures are included. Processing details including plan and profile drawing views, specific equipment and materials identifications, temperatures and times are also disclosed.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
MEMS RF switch integrated process
InactiveUS7381583B1Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidCapacitance
A capacitance coupled, transmission line-fed, radio frequency MEMS switch and its fabrication process using photoresist and other low temperature processing steps are described. The achieved switch is disposed in a low cost dielectric housing free of undesired electrical effects on the switch and on the transmission line(s) coupling the switch to an electrical circuit. The dielectric housing is provided with an array of sealable apertures useful for wet, but hydrofluoric acid-free, removal of switch fabrication employed materials and also useful during processing for controlling the operating atmosphere surrounding the switch—e.g. at a pressure above the high vacuum level for enhanced switch damping during operation. Alternative arrangements for sealing an array of dielectric housing apertures are included. Processing details including plan and profile drawing views, specific equipment and materials identifications, temperatures and times are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
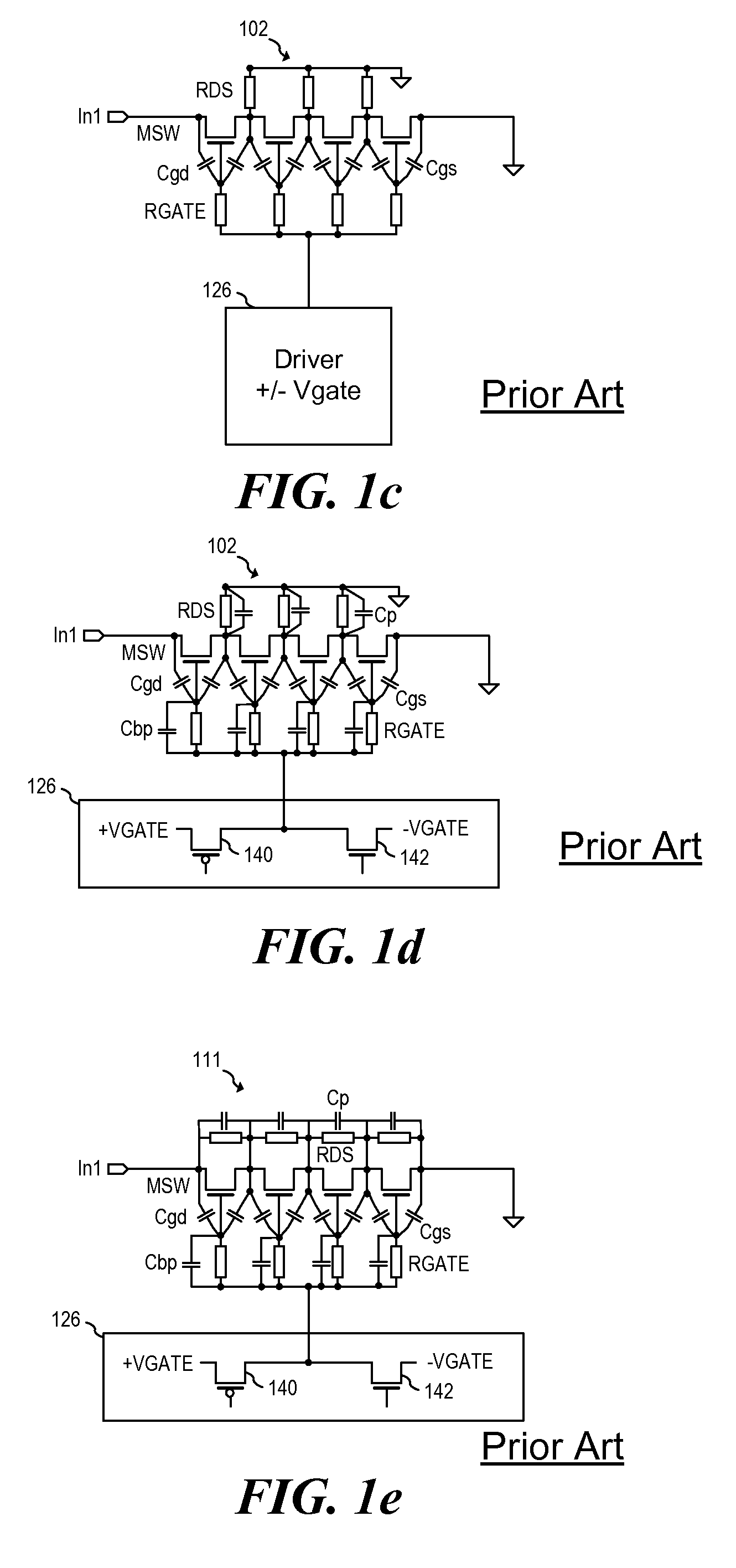
Circuit and method for controlling charge injection in radio frequency switches
A circuit and method for controlling charge injection in a circuit are disclosed. In one embodiment, the circuit and method are employed in a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) Radio Frequency (RF) switch. In one embodiment, an SOI RF switch comprises a plurality of switching transistors coupled in series, referred to as “stacked” transistors, and implemented as a monolithic integrated circuit on an SOI substrate. Charge injection control elements are coupled to receive injected charge from resistively-isolated nodes located between the switching transistors, and to convey the injected charge to at least one node that is not resistively-isolated. In one embodiment, the charge injection control elements comprise resistors. In another embodiment, the charge injection control elements comprise transistors. A method for controlling charge injection in a switch circuit is disclosed whereby injected charge is generated at resistively-isolated nodes between series coupled switching transistors, and the injected charge is conveyed to at least one node of the switch circuit that is not resistively-isolated.
Owner:PEREGRINE SEMICONDUCTOR
Signal processor for use with a power amplifier in a wireless circuit
InactiveUS20070123184A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
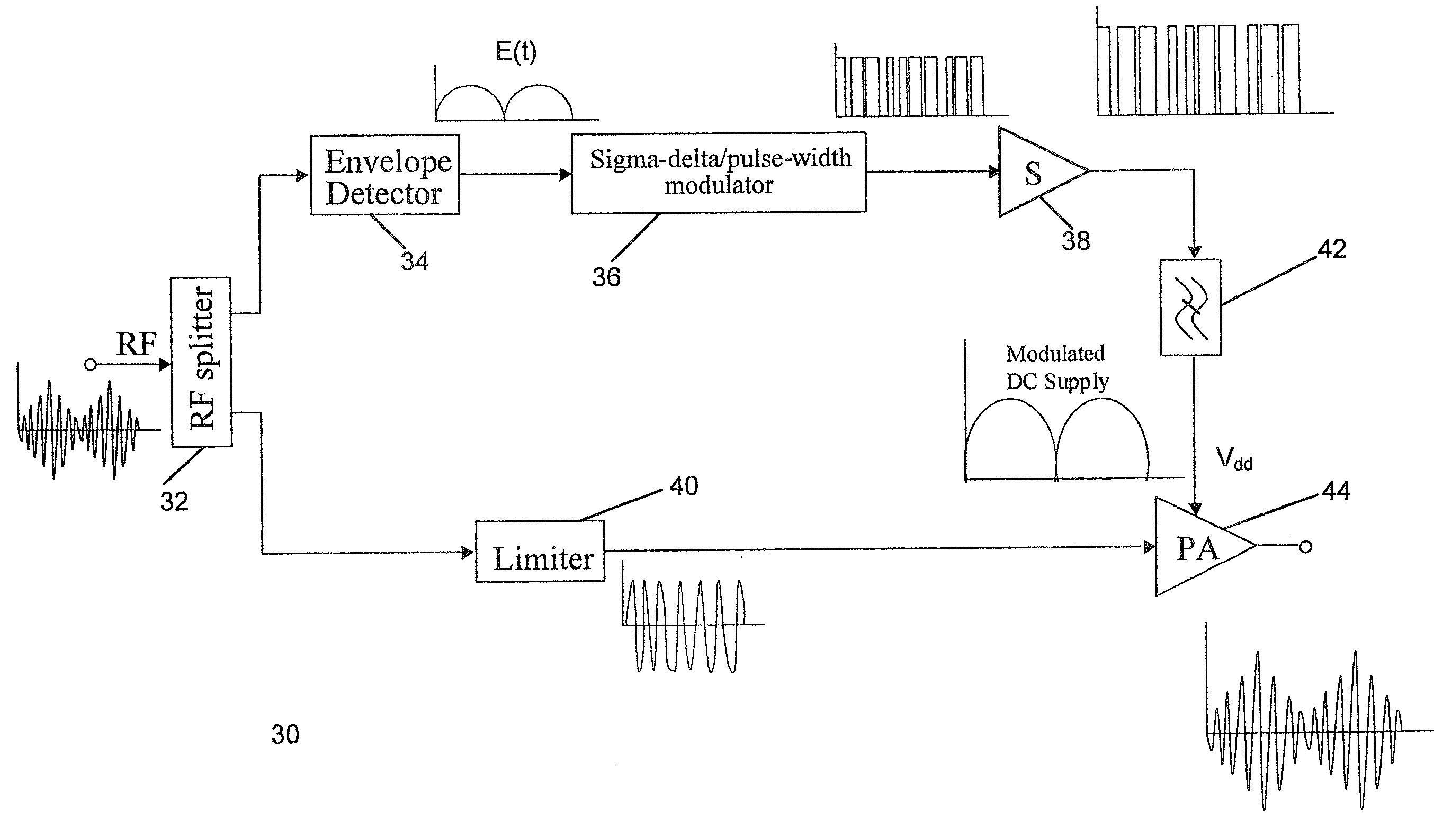
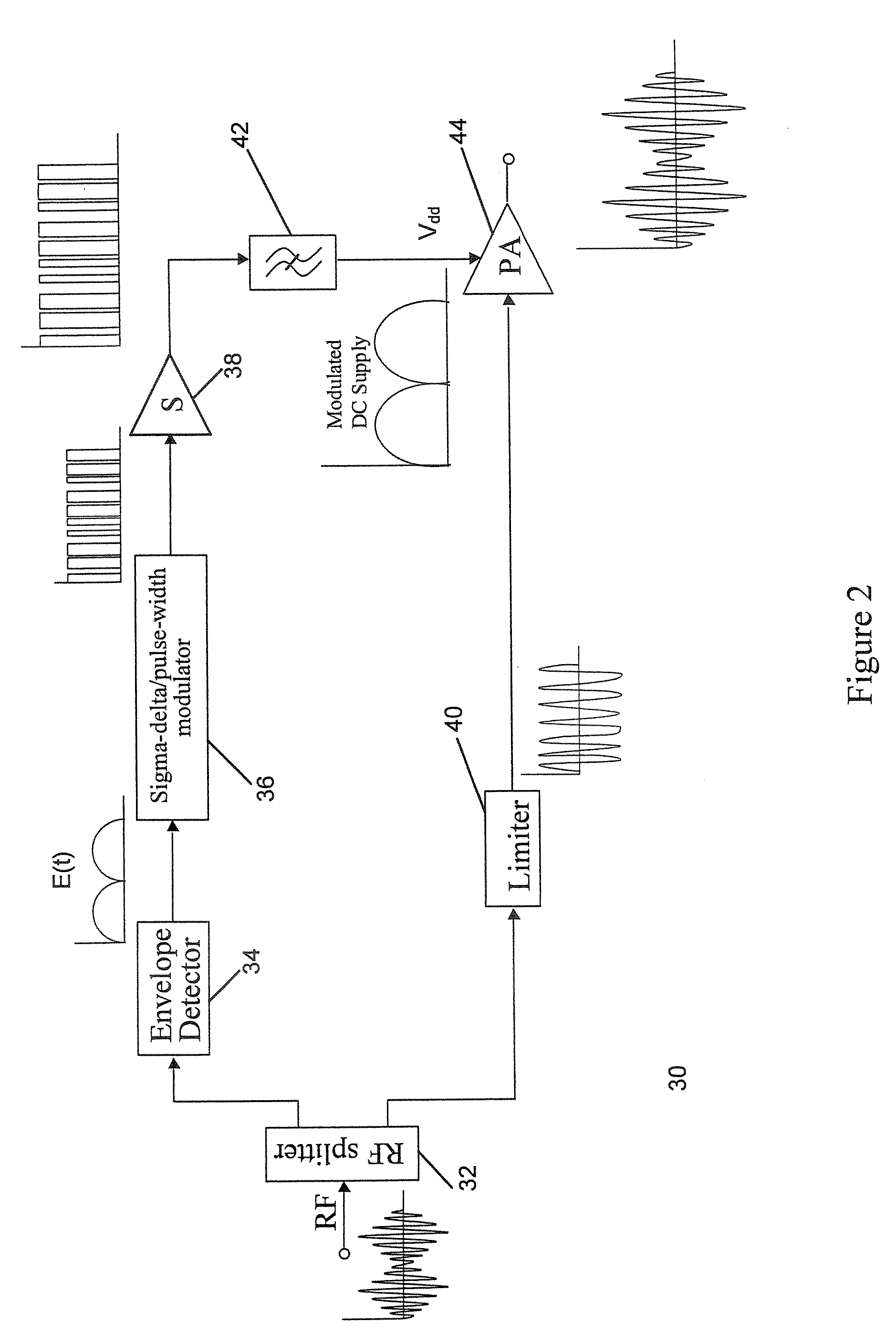
A signal processor has an input terminal and an output terminal for use in a wireless transmitter, for generating a radio frequency signal suitable for transmission, either with or without further power amplification. The signal processor separates an input signal into first and second processing paths, the first processing path generating a pulse train signal which is a digitised envelope signal, and the second processing path comprising phase processing means operable to generate a constant envelope phase signal. An RF switch is operable to switch the phase signal by means of the pulse train signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS20050017789A1Improving RF switch isolationRaise the compression pointTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETEngineering
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Method and Apparatus for Use in Improving Linearity of MOSFETs Using an Accumulated Charge Sink
ActiveUS20110169550A1Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceMOSFET
A method and apparatus for use in improving the linearity characteristics of MOSFET devices using an accumulated charge sink (ACS) are disclosed. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one exemplary embodiment, a circuit having at least one SOI MOSFET is configured to operate in an accumulated charge regime. An accumulated charge sink, operatively coupled to the body of the SOI MOSFET, eliminates, removes or otherwise controls accumulated charge when the FET is operated in the accumulated charge regime, thereby reducing the nonlinearity of the parasitic off-state source-to-drain capacitance of the SOI MOSFET. In RF switch circuits implemented with the improved SOI MOSFET devices, harmonic and intermodulation distortion is reduced by removing or otherwise controlling the accumulated charge when the SOI MOSFET operates in an accumulated charge regime.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
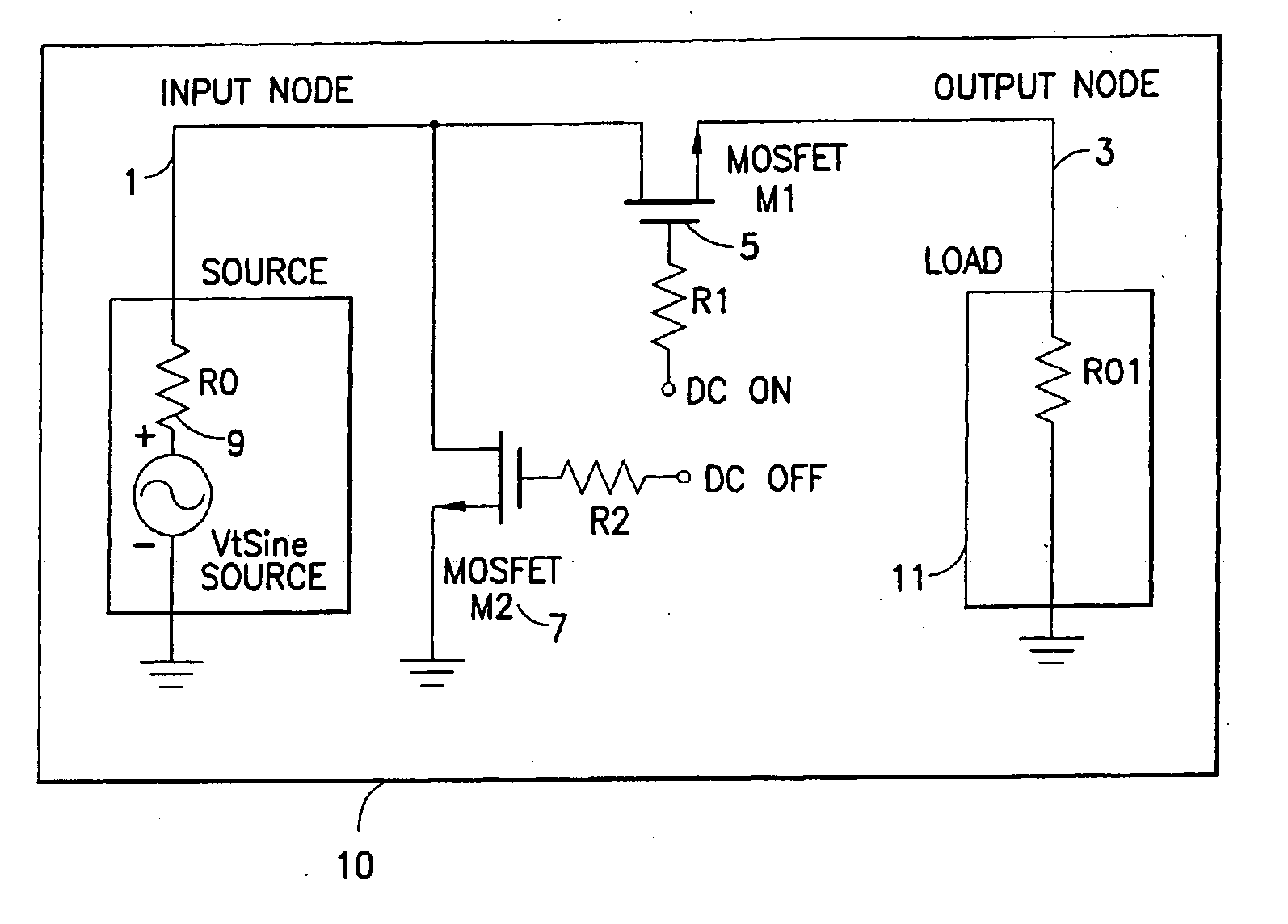
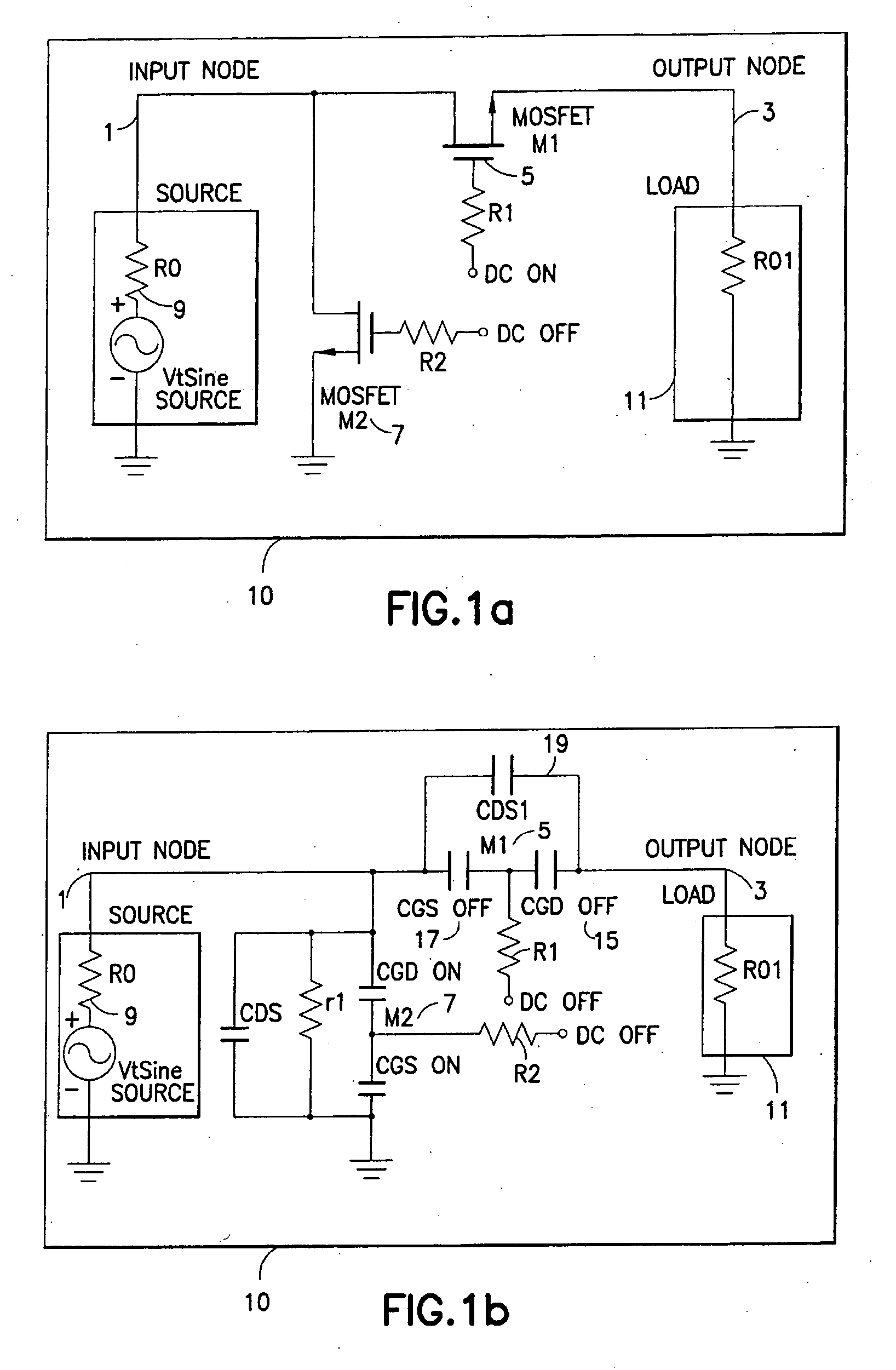
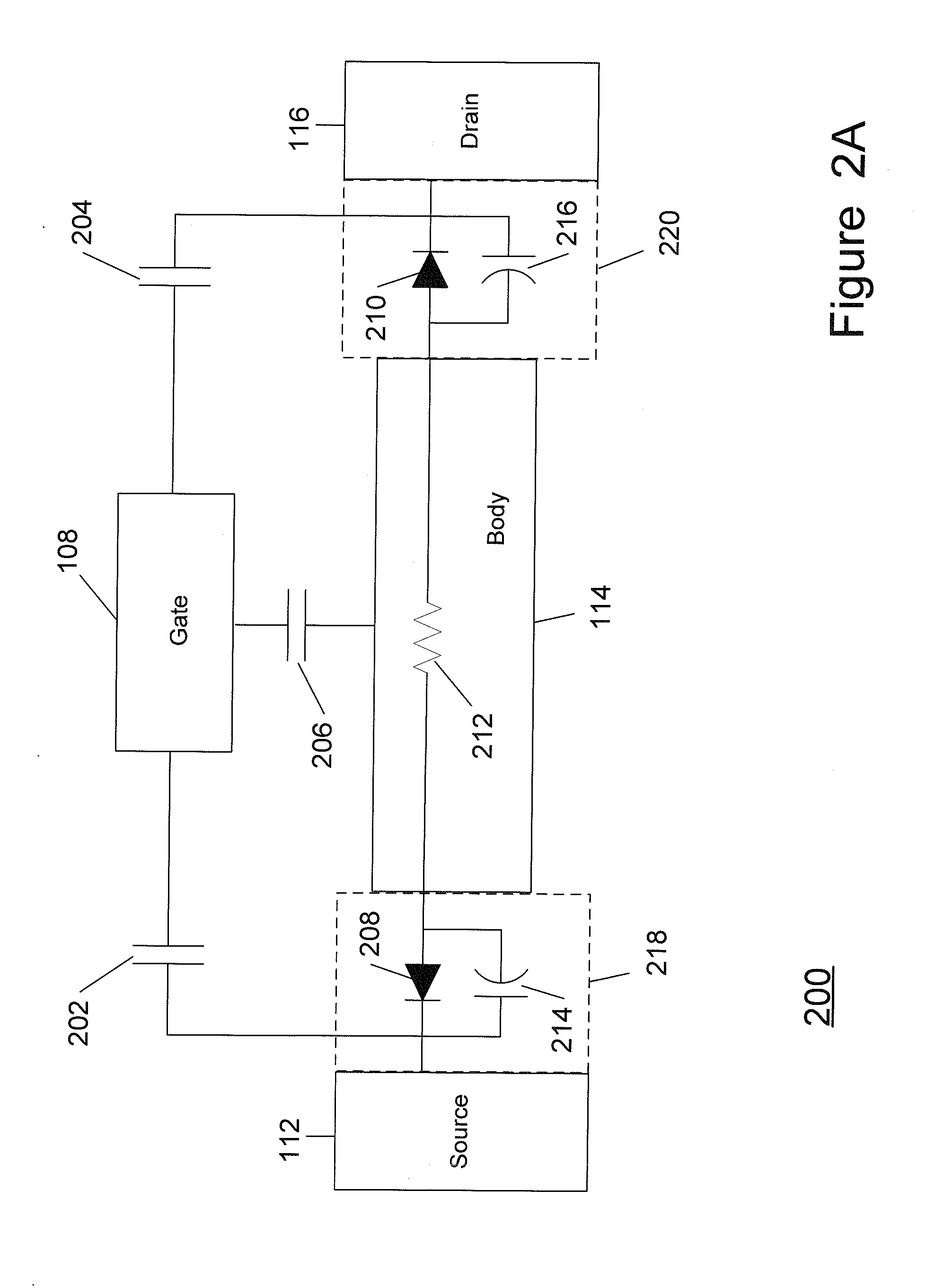
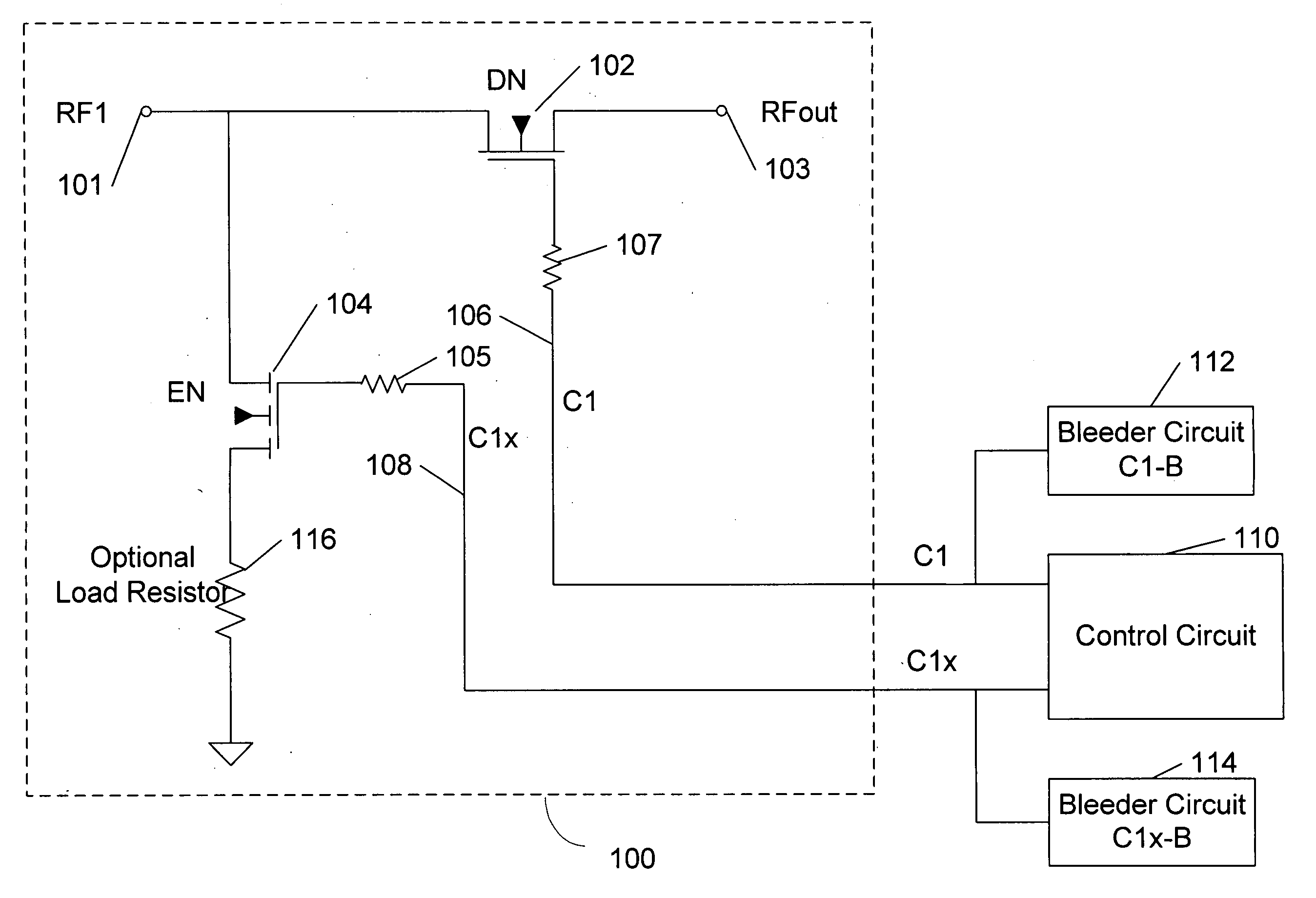
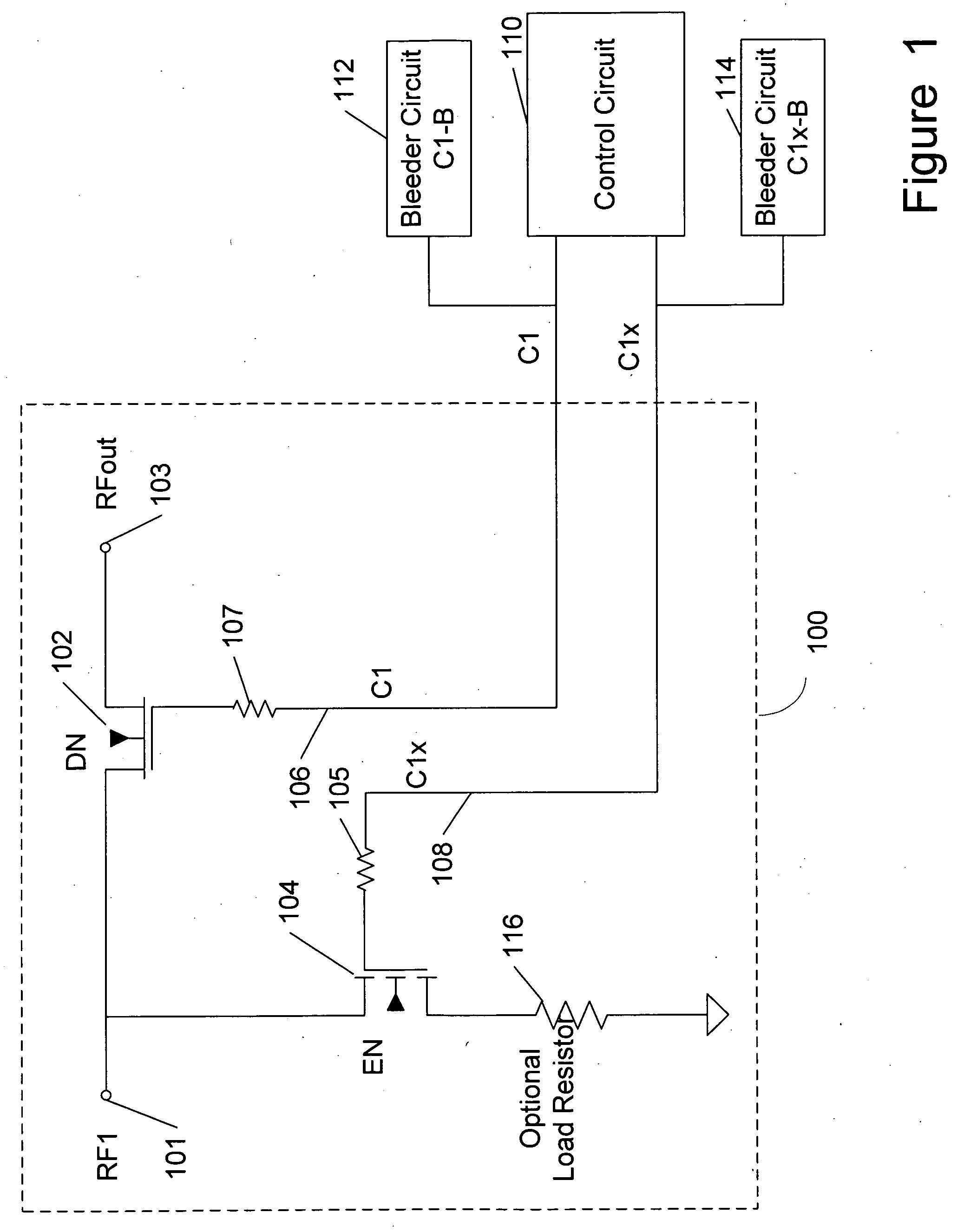
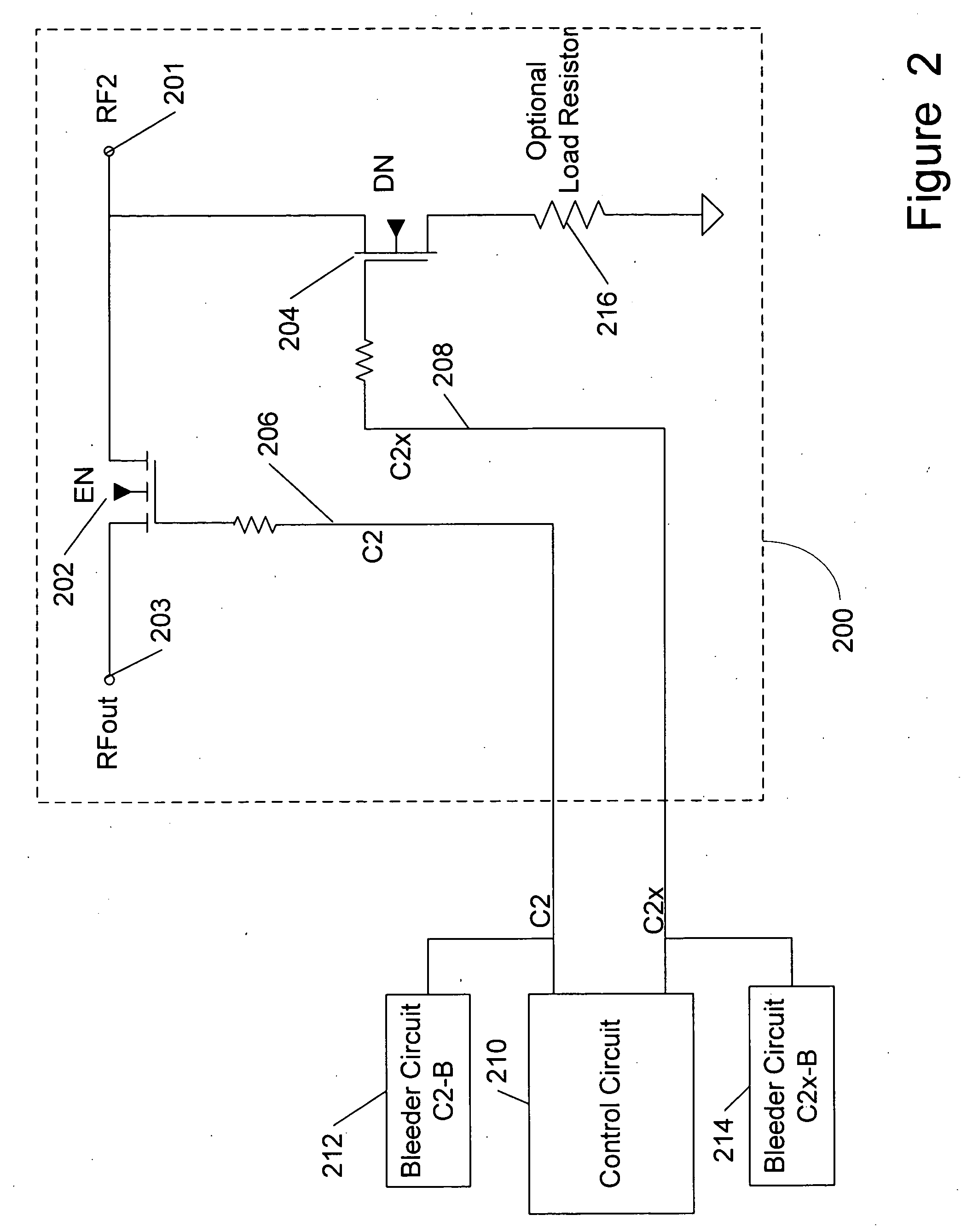
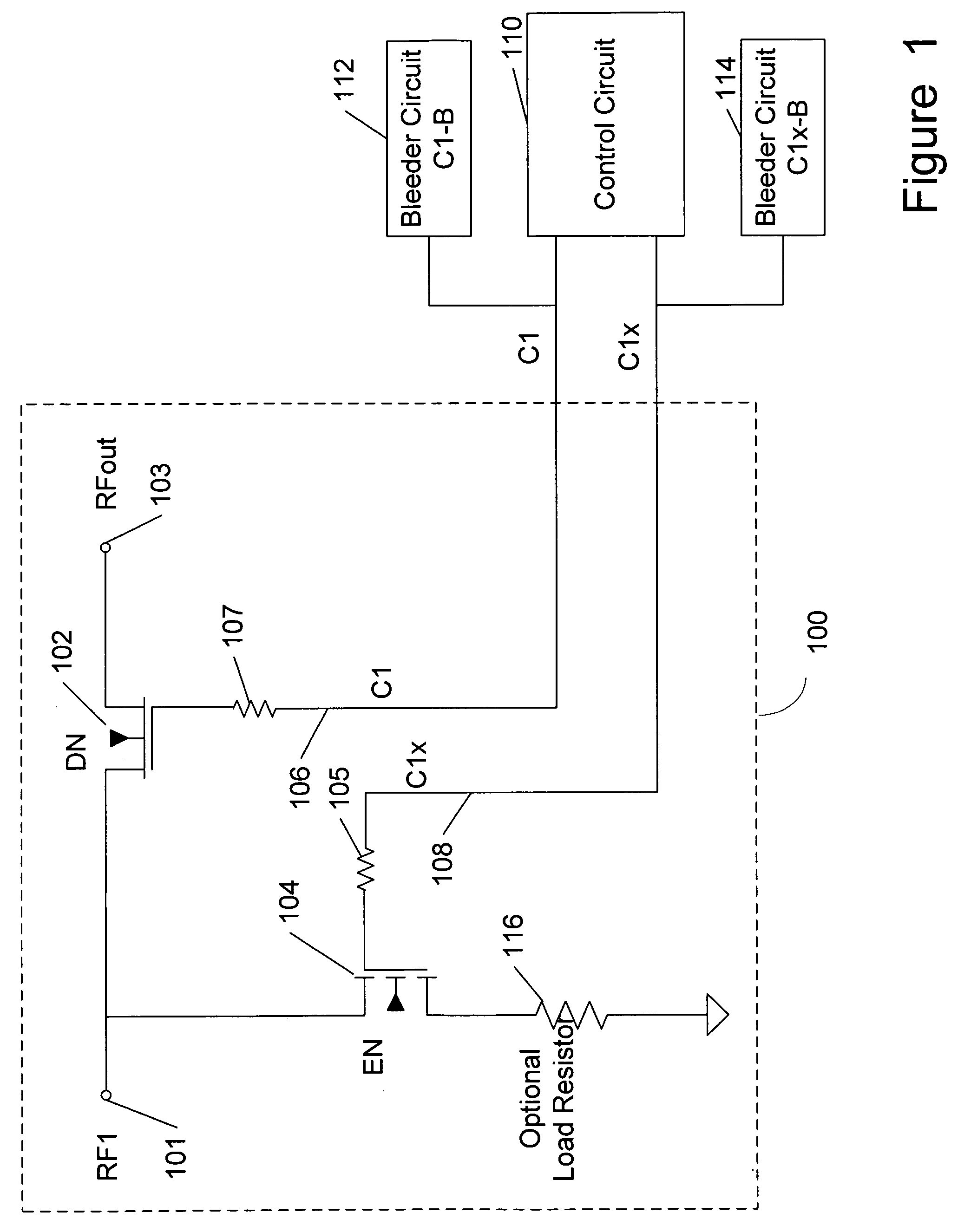
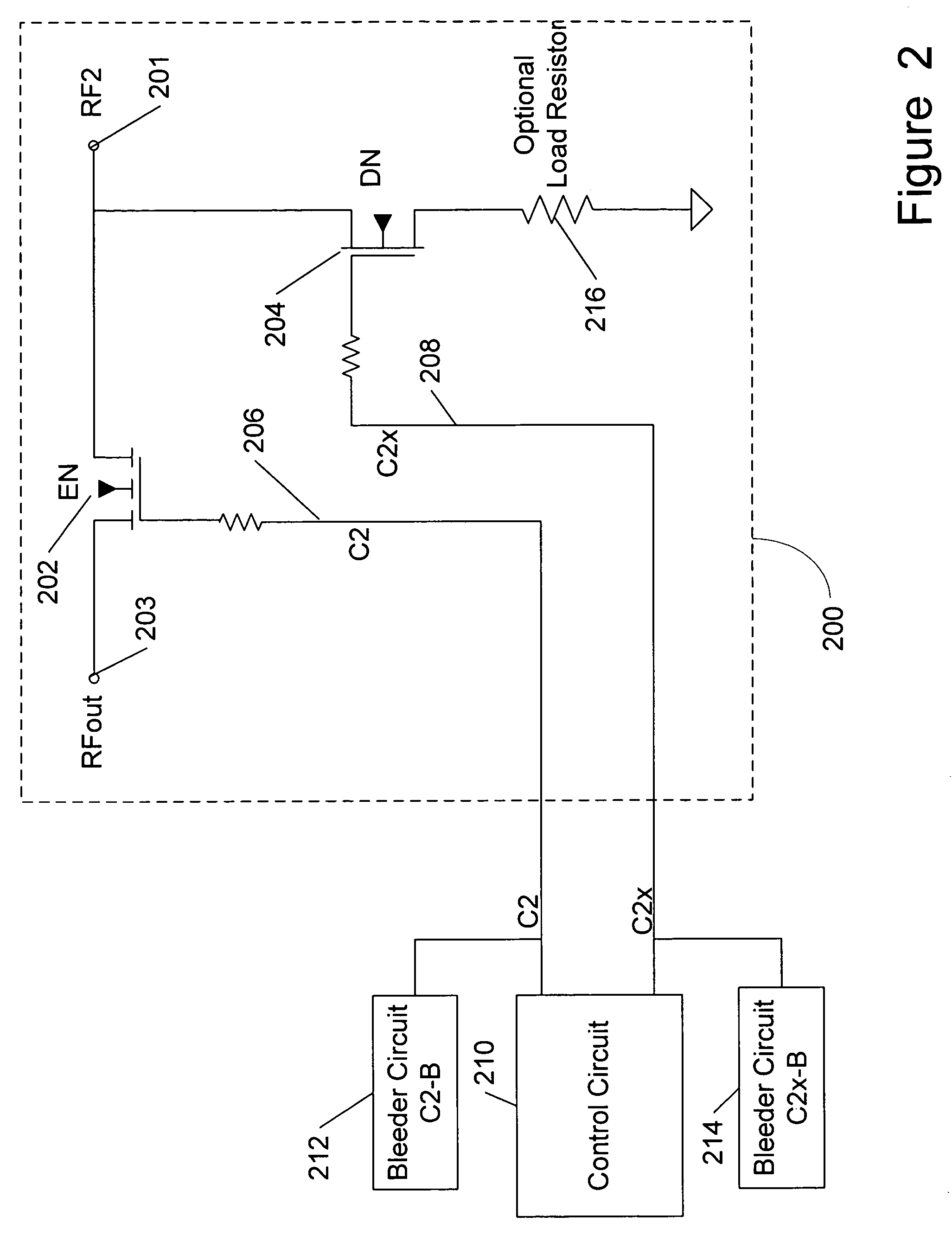
Unpowered switch and bleeder circuit
ActiveUS20060199563A1High voltageImprove performanceElectronic switchingTransmissionEngineeringField-effect transistor
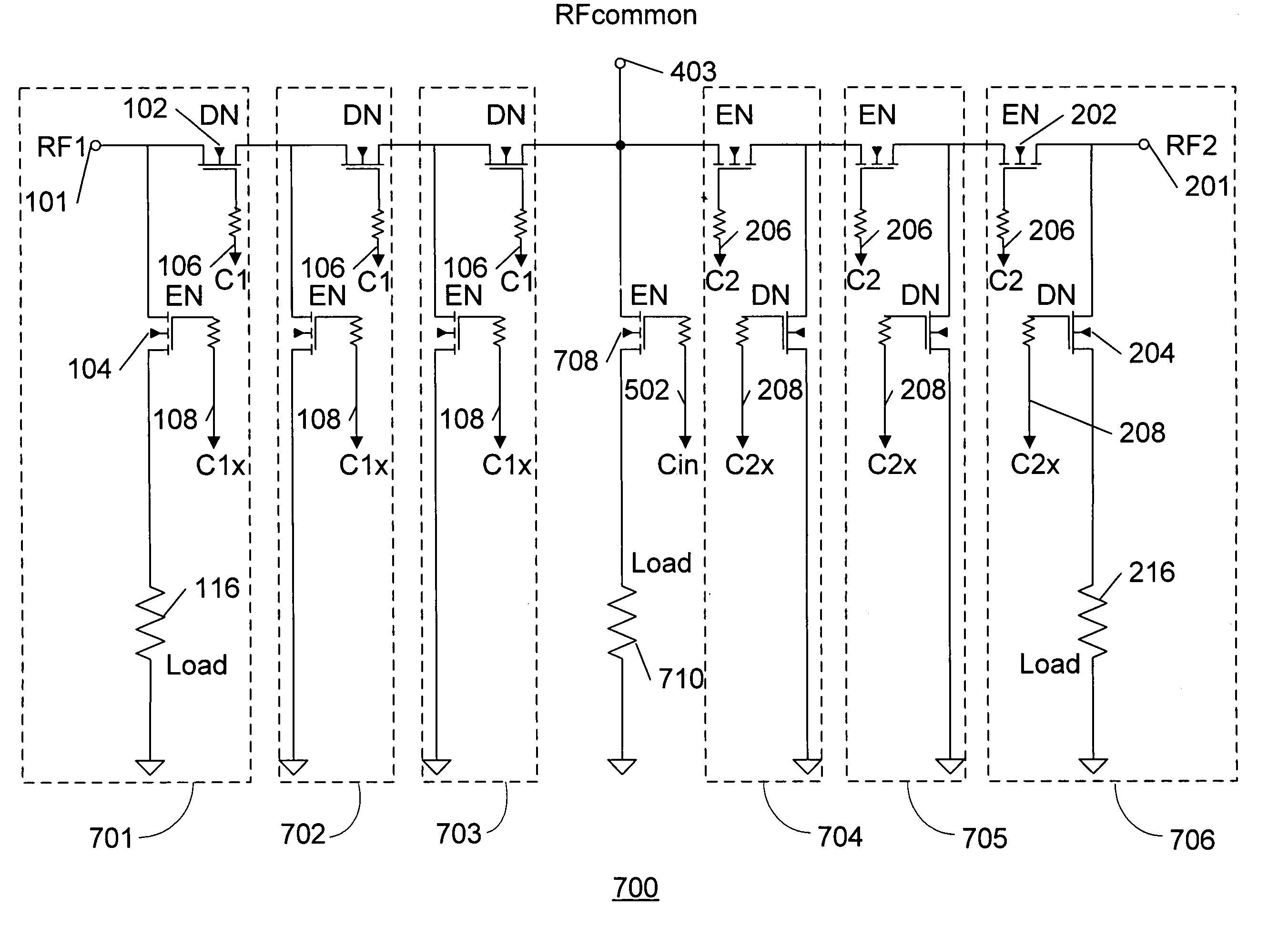
A novel RF switch for switching radio frequency (RF) signals is disclosed. The RF switch may comprise both enhancement and depletion mode field-effect transistors (E-FETs and D-FETs) implemented as a monolithic integrated circuit (IC) on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. The disclosed RF switch, with a novel bleeder circuit, may be used in RF applications wherein a selected switch state and performance are required when the switch and bleeder circuits are not provided with operating power (i.e., when the switch and bleeder circuits are “unpowered”).
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Tuning capacitance to enhance FET stack voltage withstand
An RF switch to controllably withstand an applied RF voltage Vsw, or a method of fabricating such a switch, which includes a string of series-connected constituent FETs with a node of the string between each pair of adjacent FETs. The method includes controlling capacitances between different nodes of the string to effectively tune the string capacitively, which will reduce the variance in the RF switch voltage distributed across each constituent FET, thereby enhancing switch breakdown voltage. Capacitances are controlled, for example, by disposing capacitive features between nodes of the string, and / or by varying design parameters of different constituent FETs. For each node, a sum of products of each significant capacitor by a proportion of Vsw appearing across it may be controlled to approximately zero.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
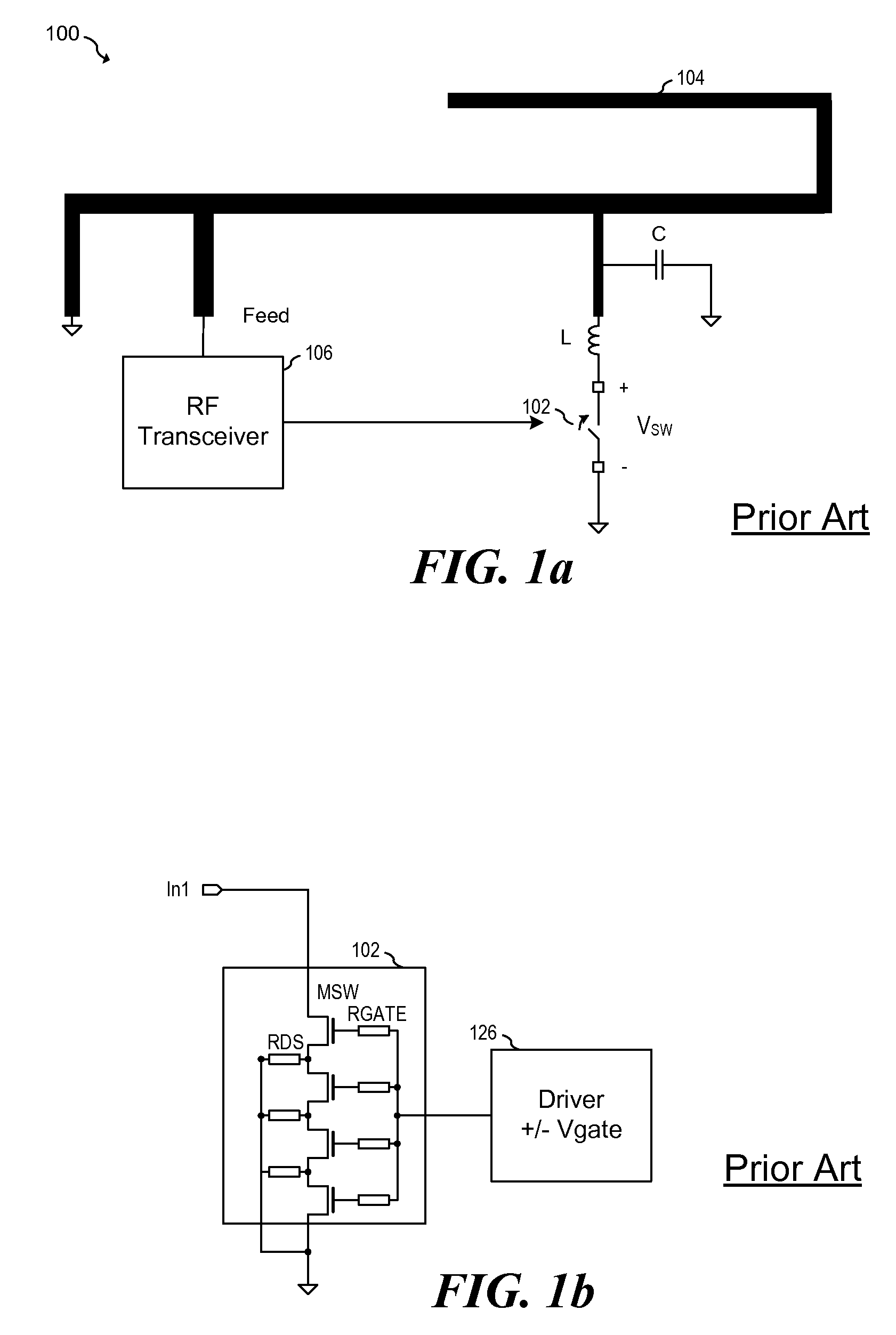
RF switching circuit for use in mobile communication systems
InactiveUS7161197B2Isolation is deterioratedImprove distortionTransistorThyristorElectricityElectrical connection
An RF switching circuit according to the present invention includes: a plurality of input / output terminals for inputting and outputting an RF signal; and a switch for opening and closing an electrical connection between the input / output terminals. The switch is constituted by a multi-gate field effect transistor including a plurality of gates located between source and drain spaced from each other on a semiconductor layer. A bias voltage is applied to an inter-gate region of the semiconductor layer between the gates. The bias voltage is equal to or lower than 90% of a high-level voltage, which is a voltage for turning the multi-gate field effect transistor ON, in a state where the multi-gate field effect transistor is ON, and is equal to or higher than 80% of the high-level voltage and equal to or lower than the high-level voltage in a state where the multi-gate field effect transistor is OFF.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
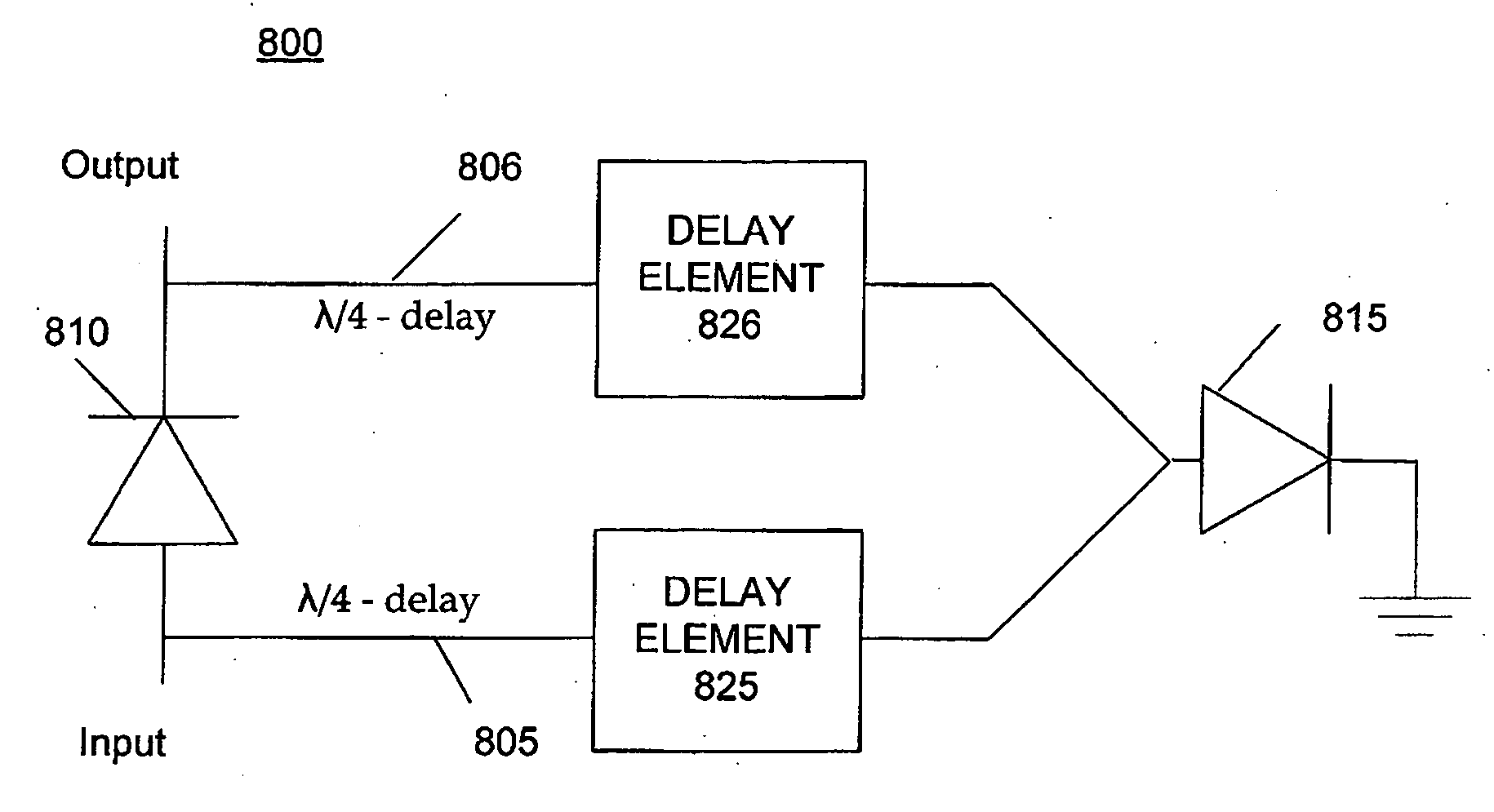
Circuit board having a peripheral antenna apparatus with selectable antenna elements and selectable phase shifting
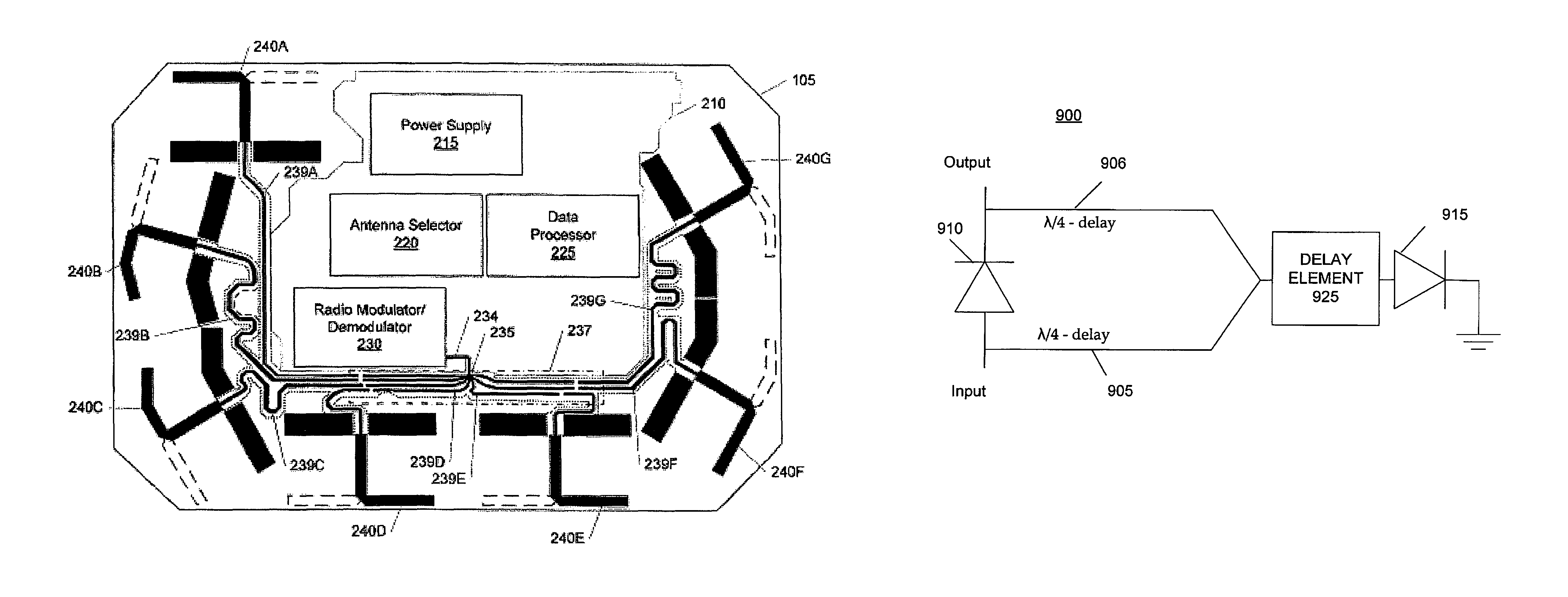
A circuit board for wireless communications includes communication circuitry for modulating and / or demodulating a radio frequency (RF) signal and an antenna apparatus for transmitting and receiving the RF signal, the antenna apparatus having selectable antenna elements located near one or more peripheries of the circuit board and selectable phase shifting. A switching network couples one or more of the selectable elements to the communication circuitry and provides impedance matching regardless of which or how many of the antenna elements are selected, and includes a selectable phase shifter to allow the phase of the antenna elements to be shifted by 180 degrees. The phase shifter includes a first RF switch and two ¼-wavelength delay lines of PCB traces or delay elements and a second RF switch. The phase shifter selectively provides a straight-through path, a 180 degree phase shift, a high impedance state, or a notch filter.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
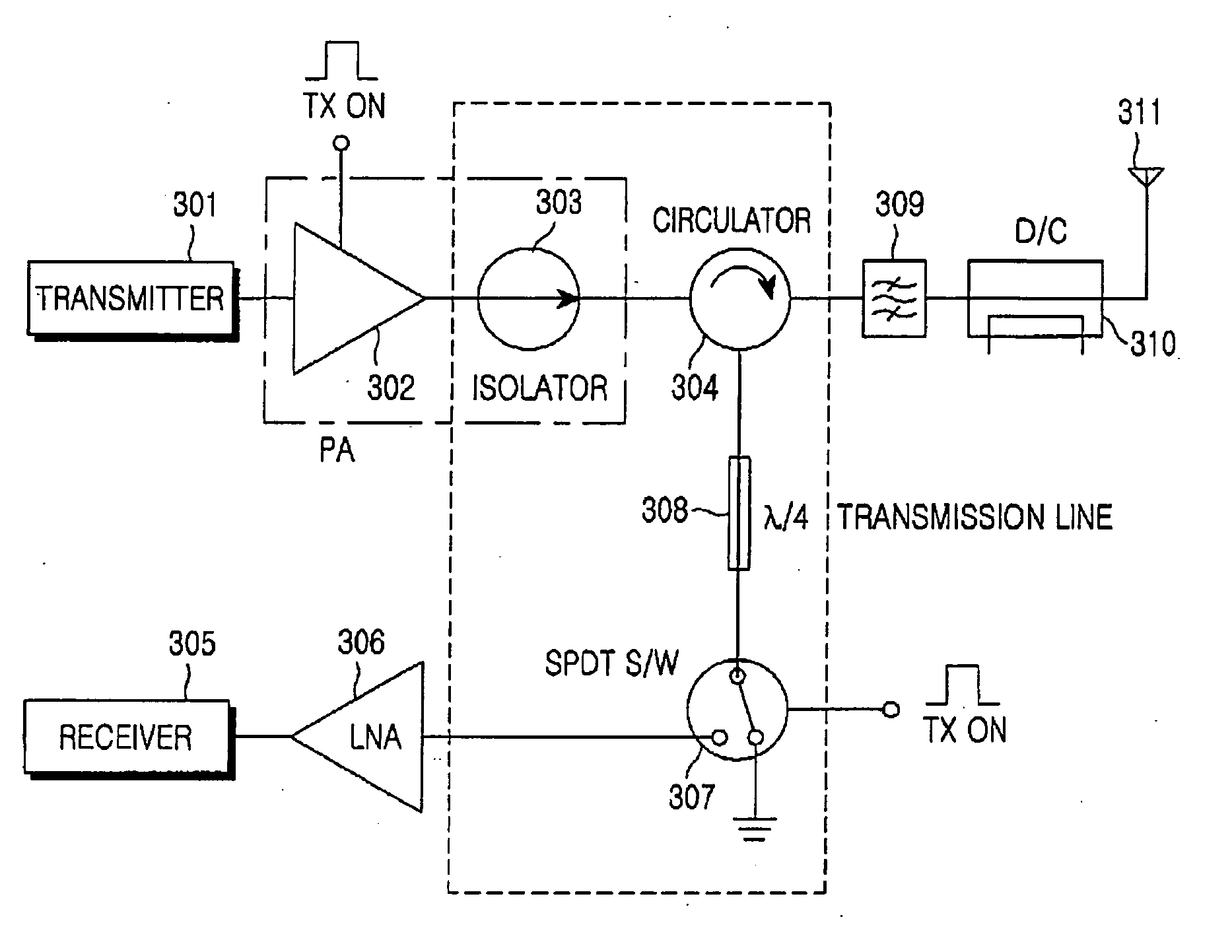
RF front-end apparatus in a TDD wireless communication system
A transmitting apparatus in a TDD wireless communication system is provided. In the transmitting apparatus, a circulator transmits a signal received from a power amplifier to an antenna feed line and transmits a signal received from the antenna feed line to a quarter-wave transmission line. The quarter-wave transmission line is installed in a reception path, for reception isolation in a transmission mode. An RF switch shorts the load of the quarter-wave transmission line to the ground or connects the load of the quarter-wave transmission line to an LNA according to a control signal. The LNA low-noise-amplifies a signal received from the RF switch.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetically actuated fast MEMS mirrors and microscanners
InactiveUS20050018322A1Quick scanImprove accuracyMirrorsDiffusing elementsMagnetic actuationEngineering
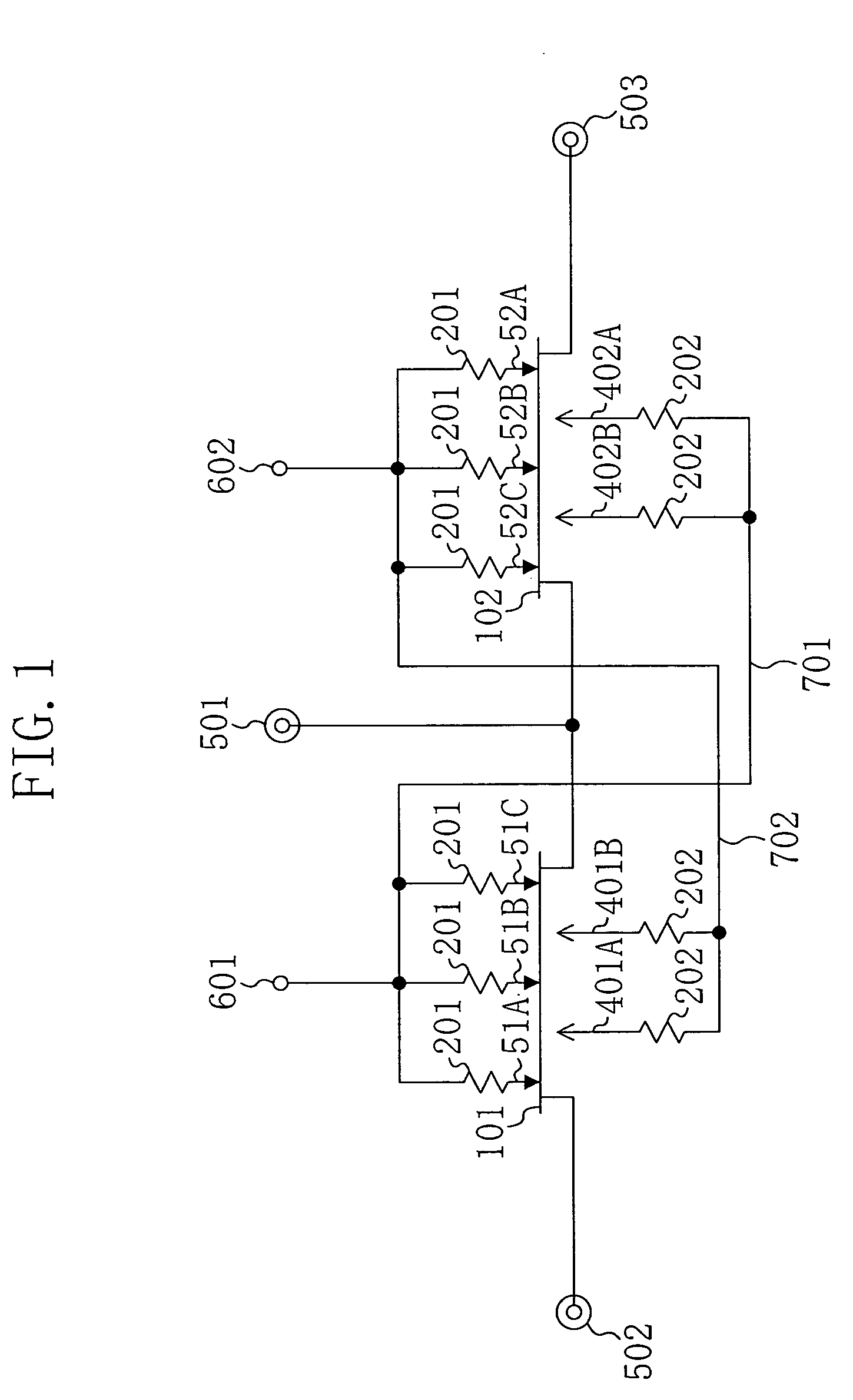
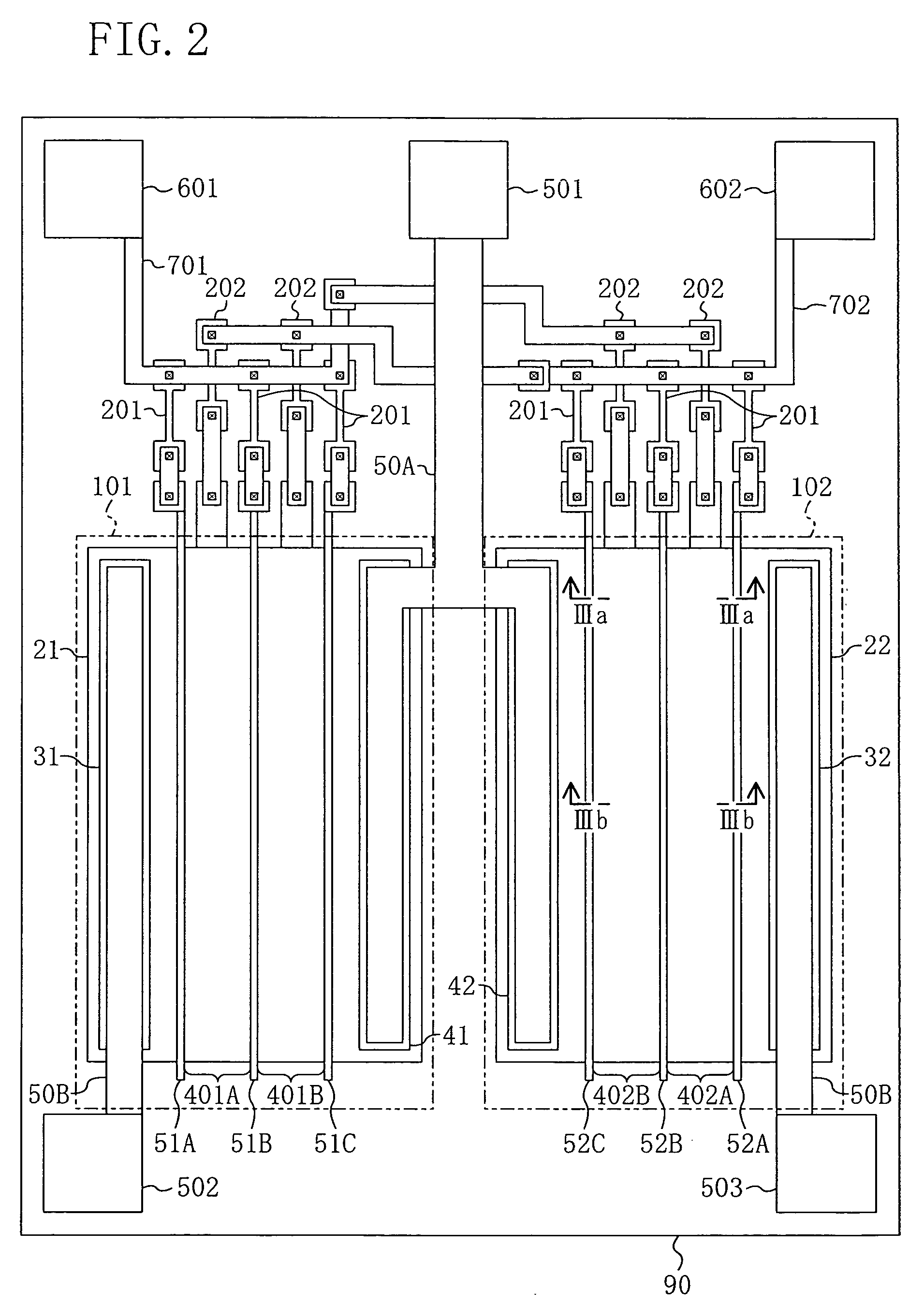
Magnetically and electromagnetically driven MEMS devices for reflecting light signals and for switching radio frequency (RF) signals are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a light reflecting device such as a mirror or micro-scanner comprises a plate operative to reflect light and at least two conductive flexural actuators connected to the plate and to a substrate and operative to impart a rotation or tilt motion to the plate under a force arising from the interaction of a current passing through the conductive flexural actuators and a magnetic field parallel to the substrate. An RF switch comprises a substrate and a membrane having a longitudinal dimension and a lateral dimension, the membrane positioned substantially parallel to and attached to the substrate and operative to provide at least two switching positions in response to actuation by a Lorenz force acting on it.
Owner:TERRAOP
Semiconductor radio frequency switch with body contact
ActiveUS8723260B1Improve balanceImprove linearityTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceReverse body bias
The present disclosure relates to a radio frequency (RF) switch that includes multiple body-contacted field effect transistor (FET) elements coupled in series. The FET elements may be formed using a thin-film semiconductor device layer, which is part of a thin-film semiconductor die. Conduction paths between the FET elements through the thin-film semiconductor device layer and through a substrate of the thin-film semiconductor die may be substantially eliminated by using insulating materials. Elimination of the conduction paths allows an RF signal across the RF switch to be divided across the series coupled FET elements, such that each FET element is subjected to only a portion of the RF signal. Further, each FET element is body-contacted and may receive reverse body biasing when the RF switch is in an OFF state, thereby reducing an OFF state drain-to-source capacitance of each FET element.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus,system and method with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS20090039976A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityMultiple-port networksAntennas earthing switches associationElectrical resistance and conductanceImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements; a voltage detector connected to the at least one RF output port via a variable voltage divider to determine the voltage at the at least one RF output port and provide voltage information to a controller that controls a bias driving circuit which provides voltage or current bias to the RF matching network; a variable voltage divider connected to the voltage detector and implemented using a multi-pole RF switch to select one of a plurality of different resistance ratios to improve the dynamic range of the apparatus; and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Circuit board having a pereipheral antenna apparatus with selectable antenna elements and selectable phase shifting
A circuit board for wireless communications includes communication circuitry for modulating and / or demodulating a radio frequency (RF) signal and an antenna apparatus for transmitting and receiving the RF signal, the antenna apparatus having selectable antenna elements located near one or more peripheries of the circuit board and selectable phase shifting. A switching network couples one or more of the selectable elements to the communication circuitry and provides impedance matching regardless of which or how many of the antenna elements are selected, and includes a selectable phase shifter to allow the phase of the antenna elements to be shifted by 180 degrees. The phase shifter includes a first RF switch and two ¼-wavelength delay lines of PCB traces or delay elements and a second RF switch. The phase shifter selectively provides a straight-through path, a 180 degree phase shift, a high impedance state, or a notch filter.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Repeater rise-over-thermal (ROT) value calibration
InactiveUS20070202826A1Receivers monitoringActive radio relay systemsAudio power amplifierEngineering
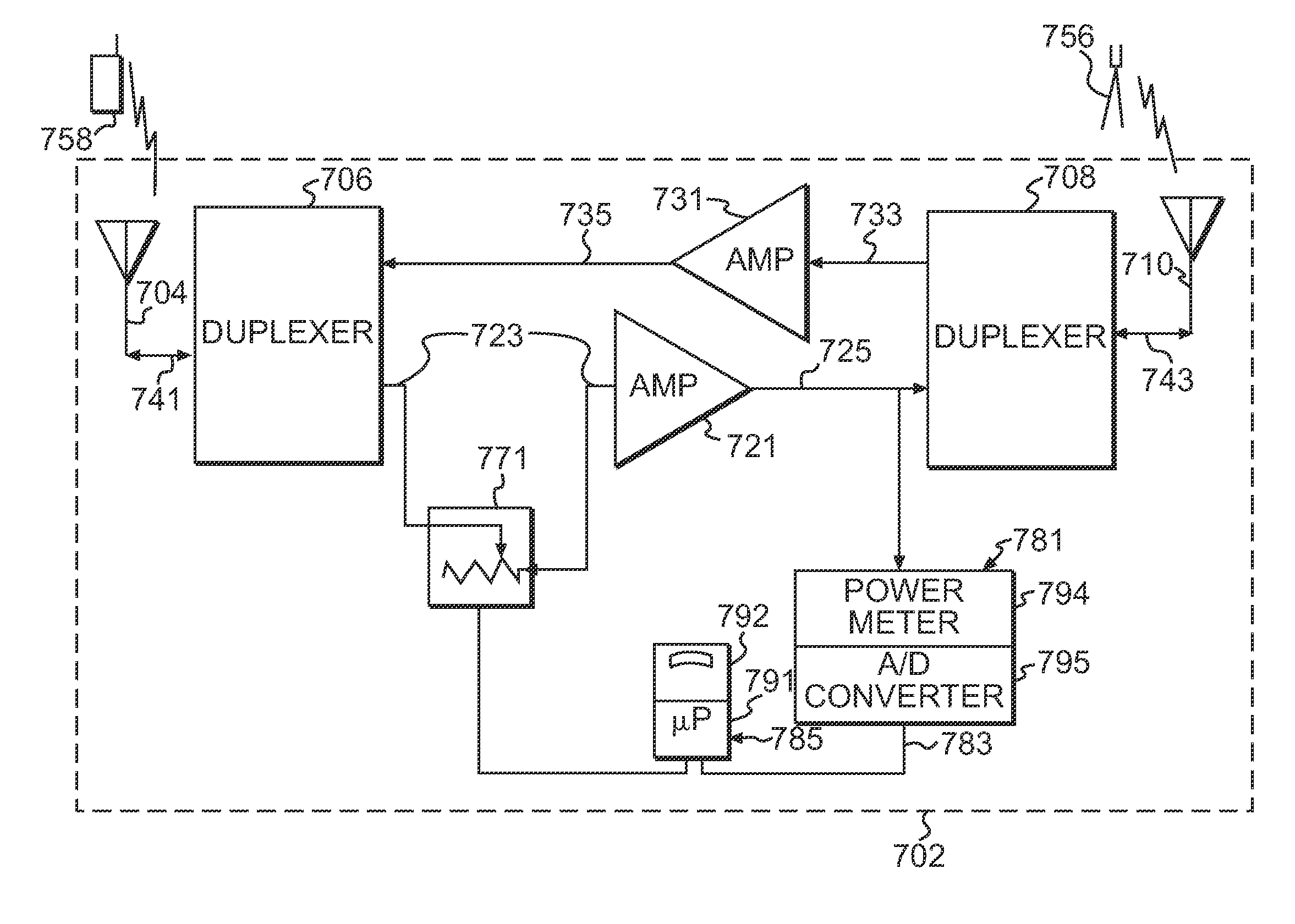
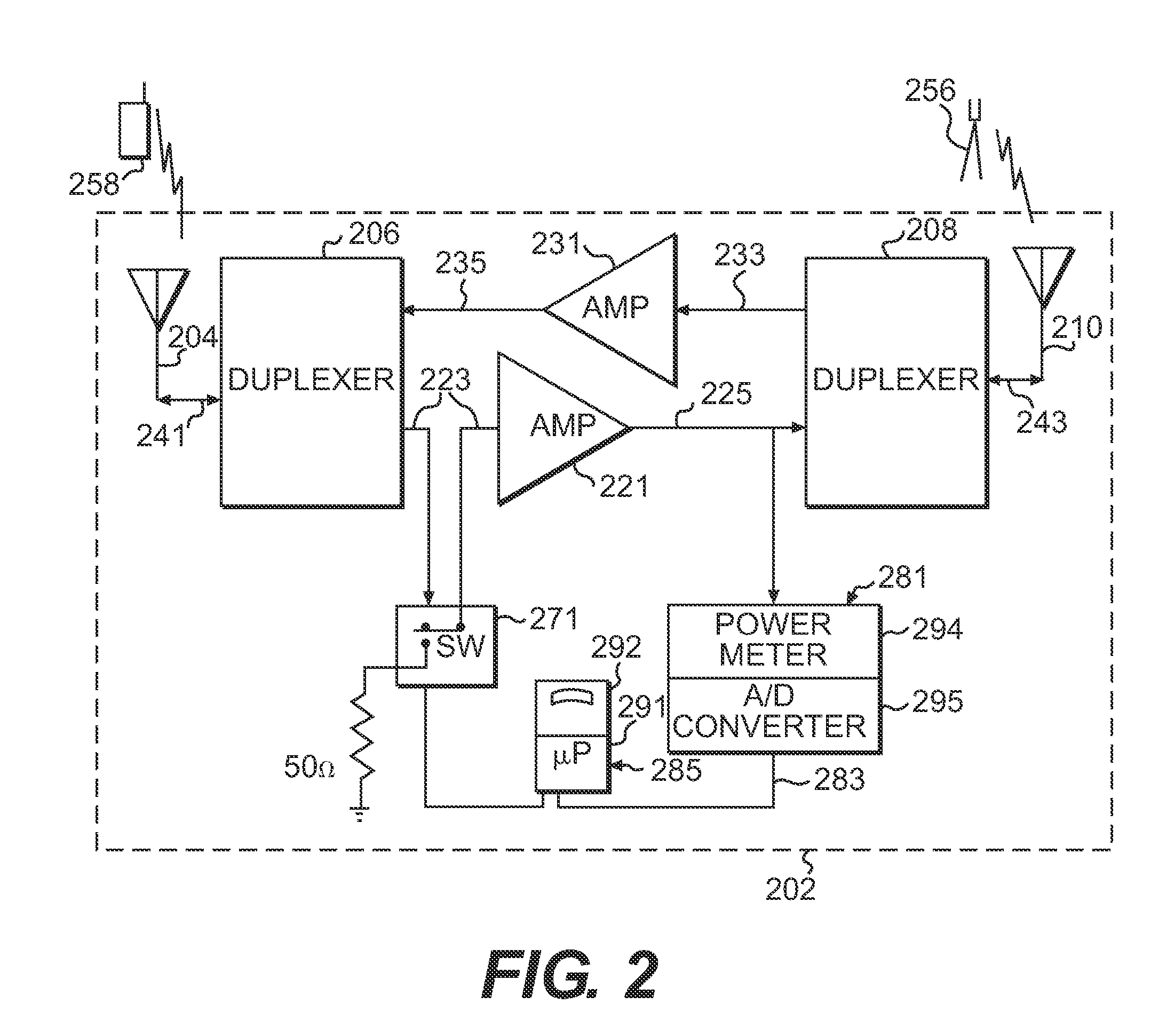
An RF switch is used in the signal path to an amplifier, for example between a receiving antenna and an amplifier. The switch is used to alternately connect the amplifier between a normal signal source for the amplifier and a fixed load for calibration. The power difference between the two switch states at the output of the amplifier would then yield a calibrated measurement of a signal value, such as rise over thermal (RoT). The amount of time spent in the calibration position is maintained at a minimized level so as to reduce impact on the normal operation of the amplifier. The invention provides an ability to estimate traffic load in a repeater system based on RoT measurements of repeater reverse-link output power by determining a reverse link gain.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Unpowered switch and bleeder circuit
ActiveUS7619462B2Accurate signalHigh voltageElectronic switchingTransmissionField-effect transistorSilicon on insulator
A novel RF switch for switching radio frequency (RF) signals is disclosed. The RF switch may comprise both enhancement and depletion mode field-effect transistors (E-FETs and D-FETs) implemented as a monolithic integrated circuit (IC) on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. The disclosed RF switch, with a novel bleeder circuit, may be used in RF applications wherein a selected switch state and performance are required when the switch and bleeder circuits are not provided with operating power (i.e., when the switch and bleeder circuits are “unpowered”).
Owner:PSEMI CORP
RF Switch with Integrated Tuning
ActiveUS20150249479A1Reduce complexityTransmitters monitoringEcho effect reductionTransceiverRF front end
Owner:PSEMI CORP
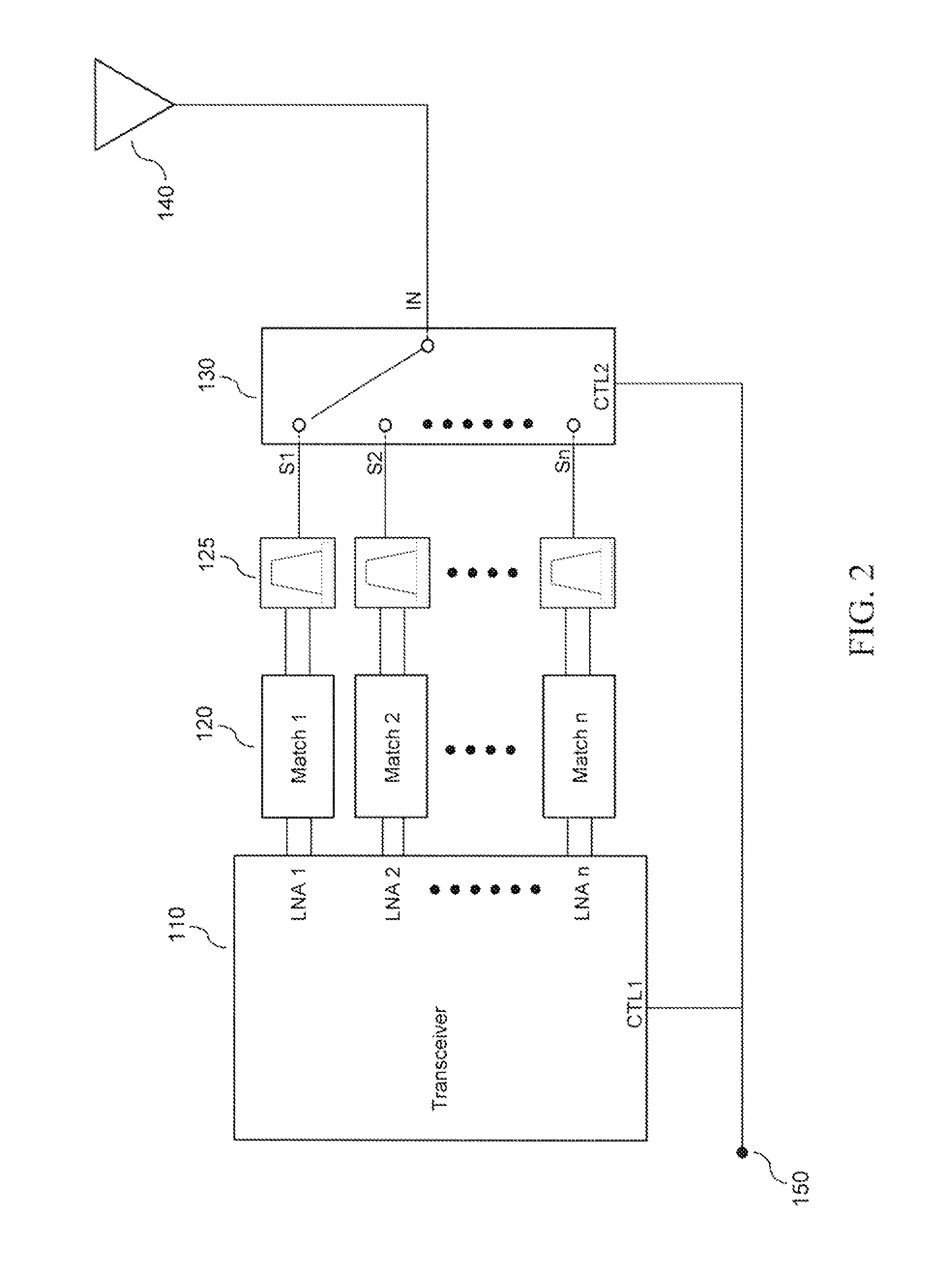
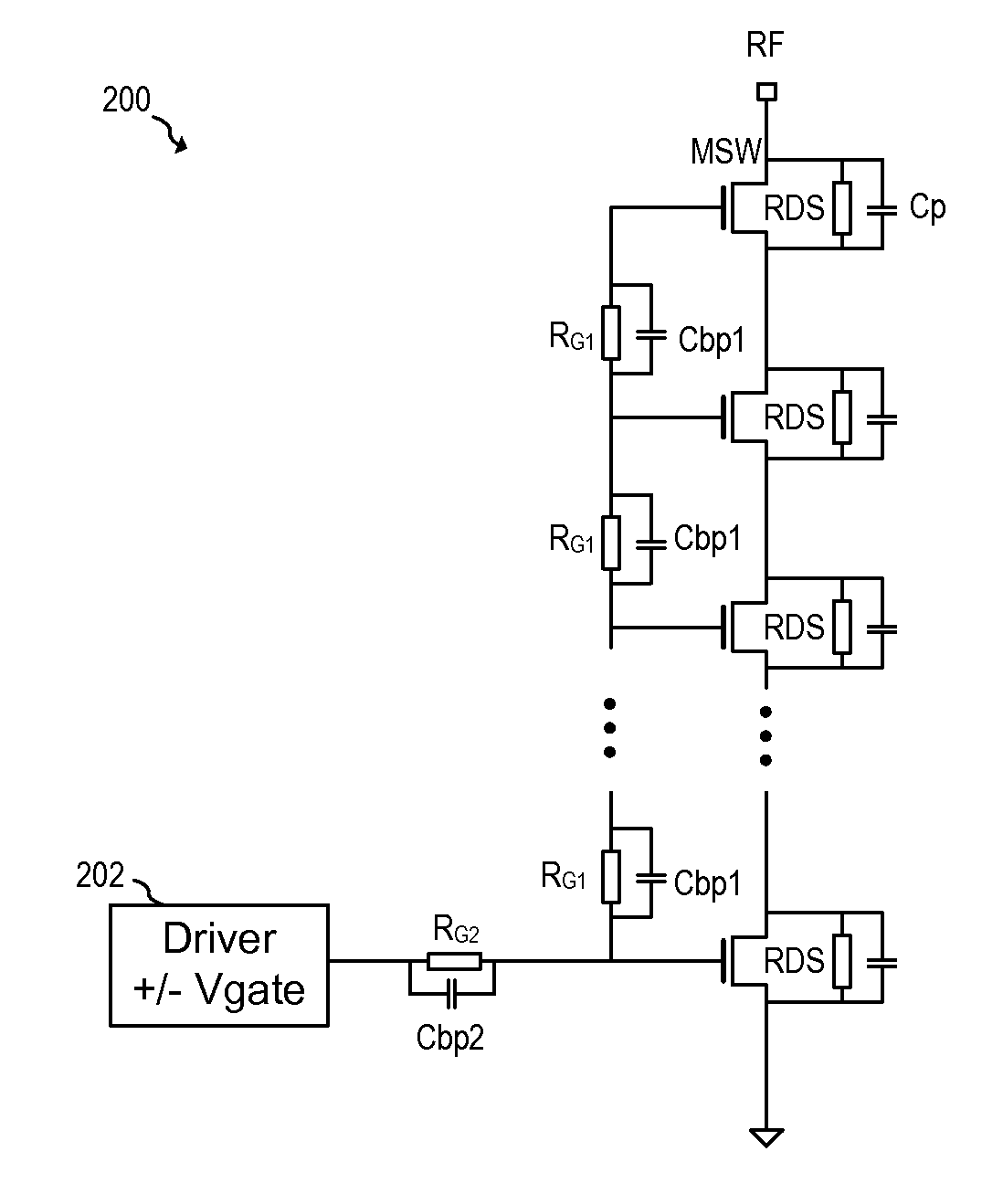
System and Method for a Driving a Radio Frequency Switch
In accordance with an embodiment, a radio frequency (RF) switching circuit includes a plurality of series connected RF switch cells comprising a load path and a control node, a plurality of first gate resistors coupled between control nodes of adjacent RF switch cells, and an input resistor having a first end coupled to a control node of one of the plurality of RF switch cells and a second end configured to an output of a switch driver. Each of the plurality of series connected RF switch cells includes a switch transistor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Beamformer configurable for connecting a variable number of antennas and radio circuits
InactiveUS20130324055A1Eliminate lossSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringUltrasound attenuationTransfer switch
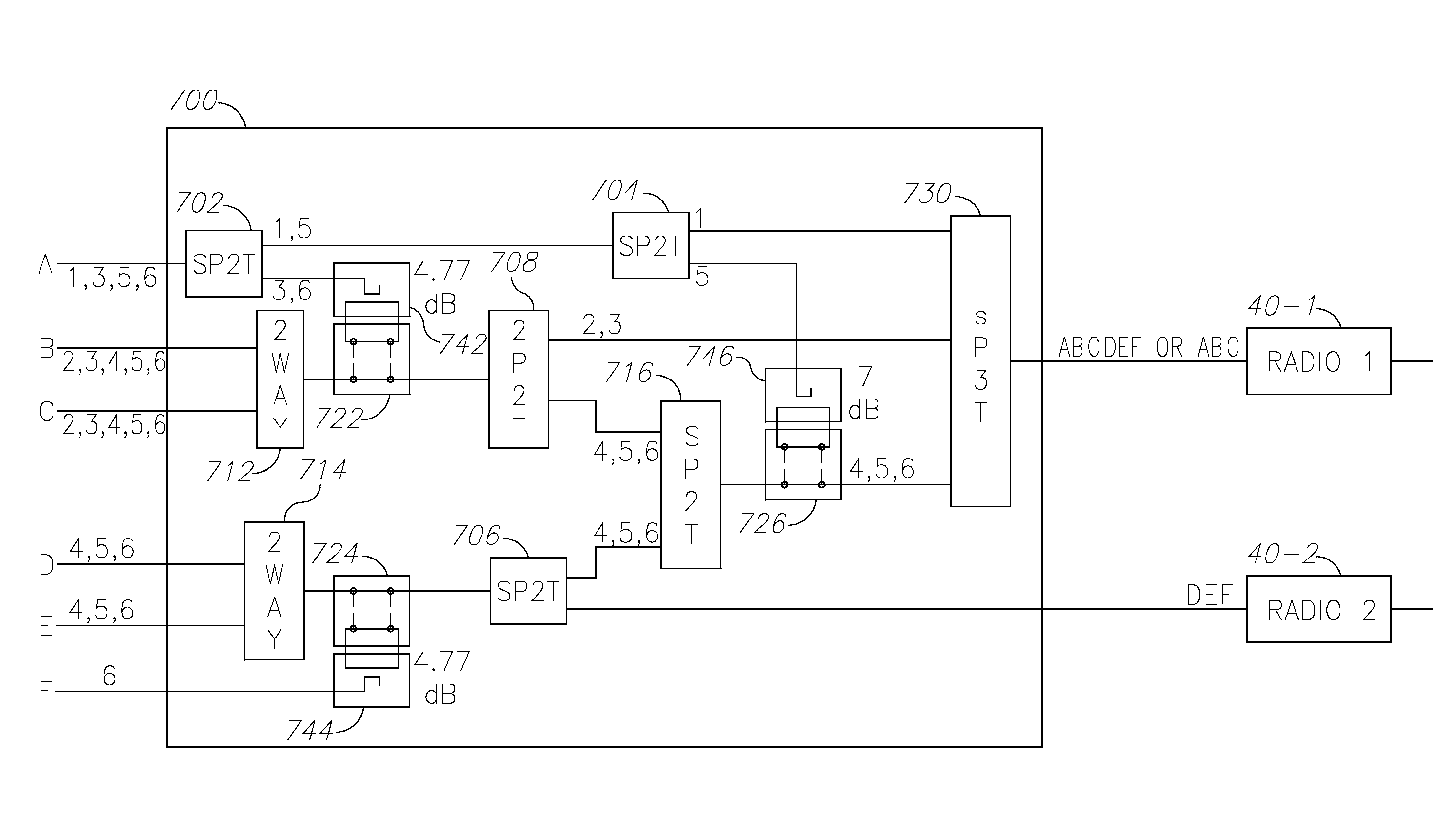
A reconfigurable RF routing module may include M RF inputs and N RF outputs, wherein M is greater than N; a plurality of RF switches arranged to select between incoming RF signals; a plurality of RF combiners arranged to combine RF signals to a single RF signal; and a plurality of RF couplers, each associated with a transfer switch and a specified attenuation, wherein the specified attenuation of each one of the plurality of RF couplers is selected so that the RF inputs of each one of the plurality of the RF combiners are combined in a balanced manner, wherein the switches, the combiners, and the RF couplers are configured to route any of 1 to M of the inputs into each of the N outputs.
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
Discrete spurious leakage cancellation for use in a cable modem
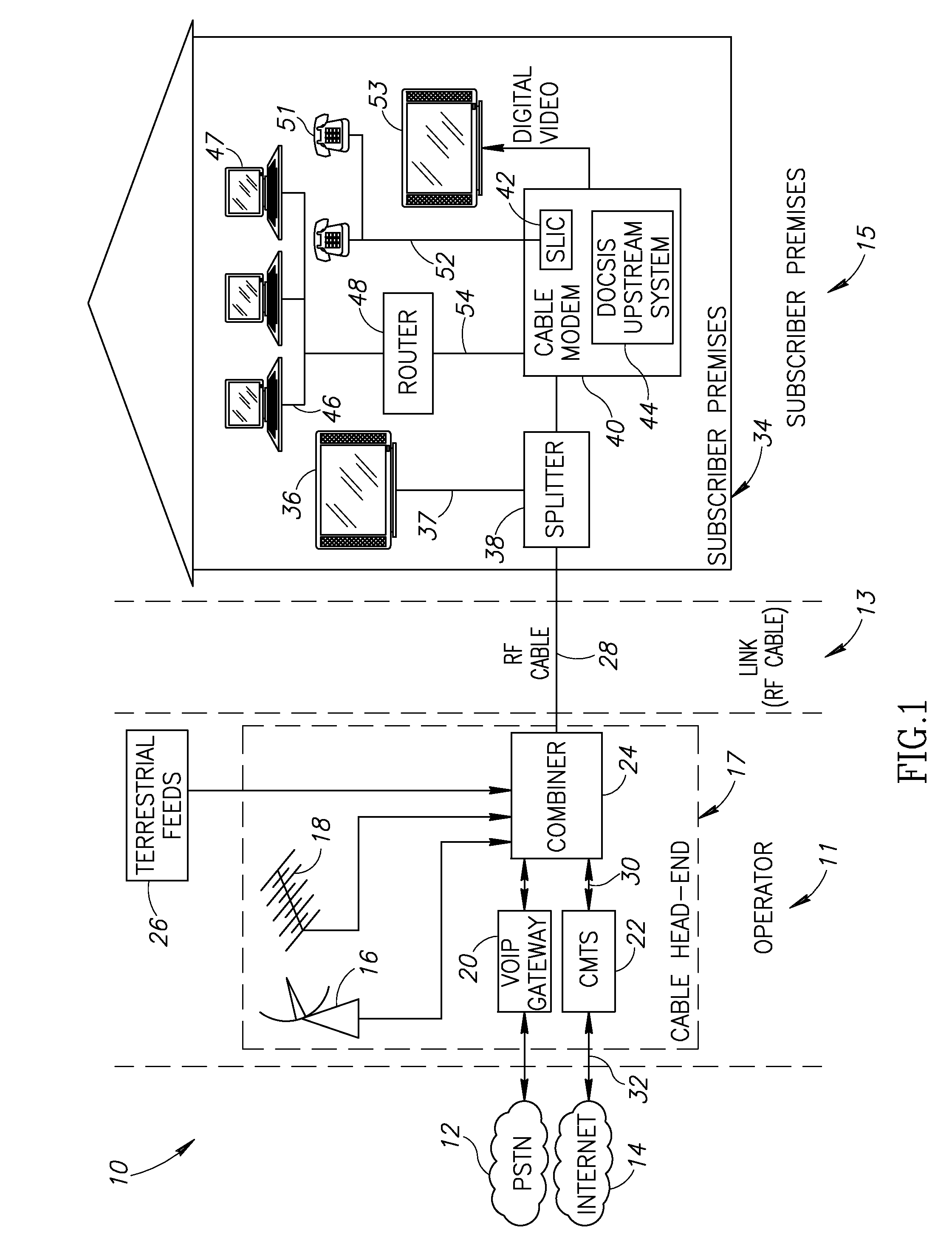
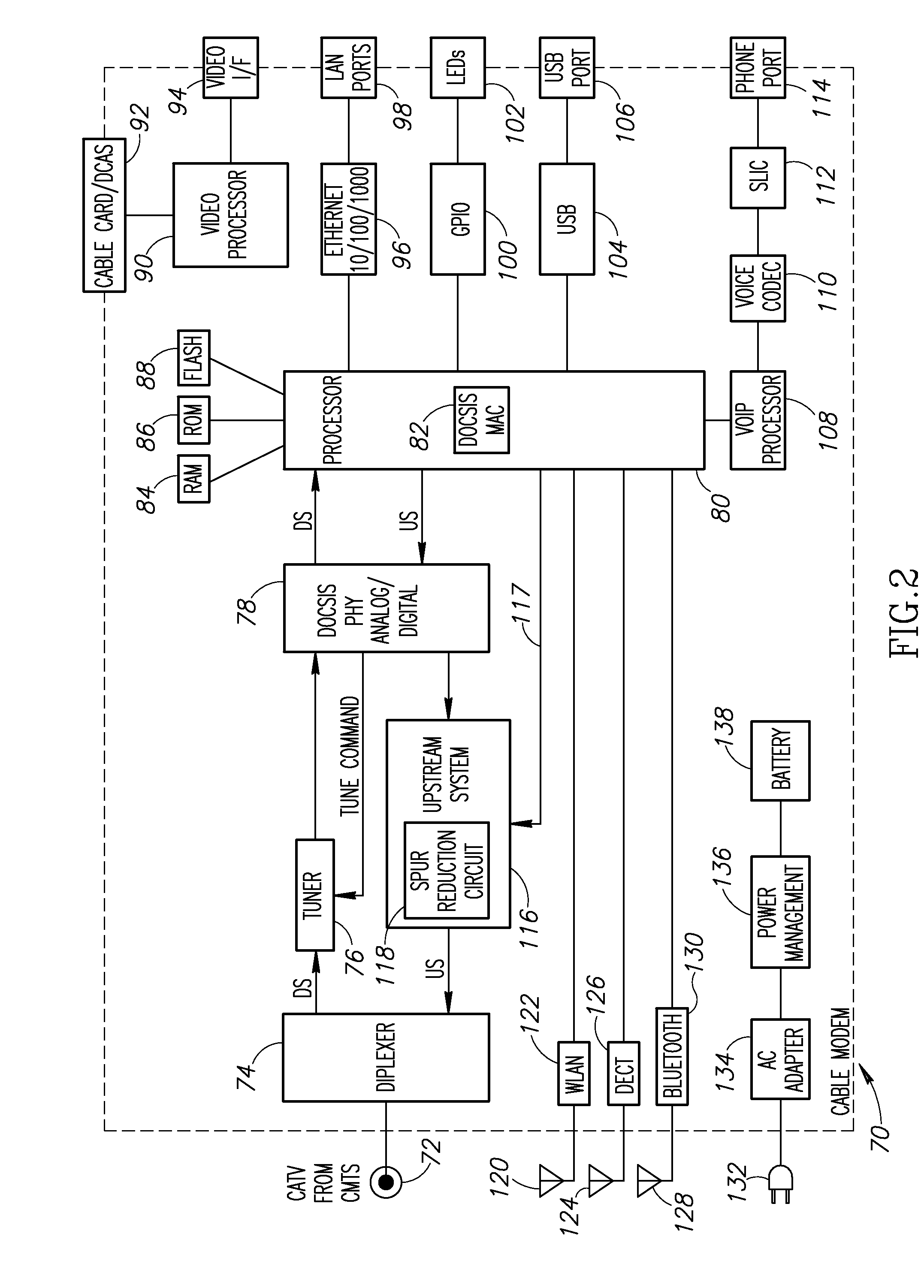
InactiveUS20100266000A1Reduced frequency spur energyLow costTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionPhase shiftedDOCSIS
A novel apparatus for and method of discrete spurious frequency leakage cancellation for use in a cable modem. The spurious leakage cancellation mechanism is particularly suitable for use in cable modem systems adapted to implement the DOCSIS 2.0 specification which specifies both downstream and upstream channels. In one embodiment, the spurious emission cancellation mechanism cancels the spurious emissions by first creating a replica of the aggressor clock signal having the same amplitude but 180 degree phase shift as the spurious signal. The phase shifted spurious replica is added to the original spurious signal thus cancelling the spurious signal. In another embodiment, an RF switch is used to couple the upstream path signal to the CATV cable only during transmission bursts. In between transmission bursts, the upstream signal is disconnected from the CATV cable. This embodiment takes advantage of the less stringent spurious requirements in the DOCSIS 2.0 specification for transmission bursts. In between transmission bursts, when stricter spurious requirements apply, the upstream signal is disconnected from the CATV cable.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com