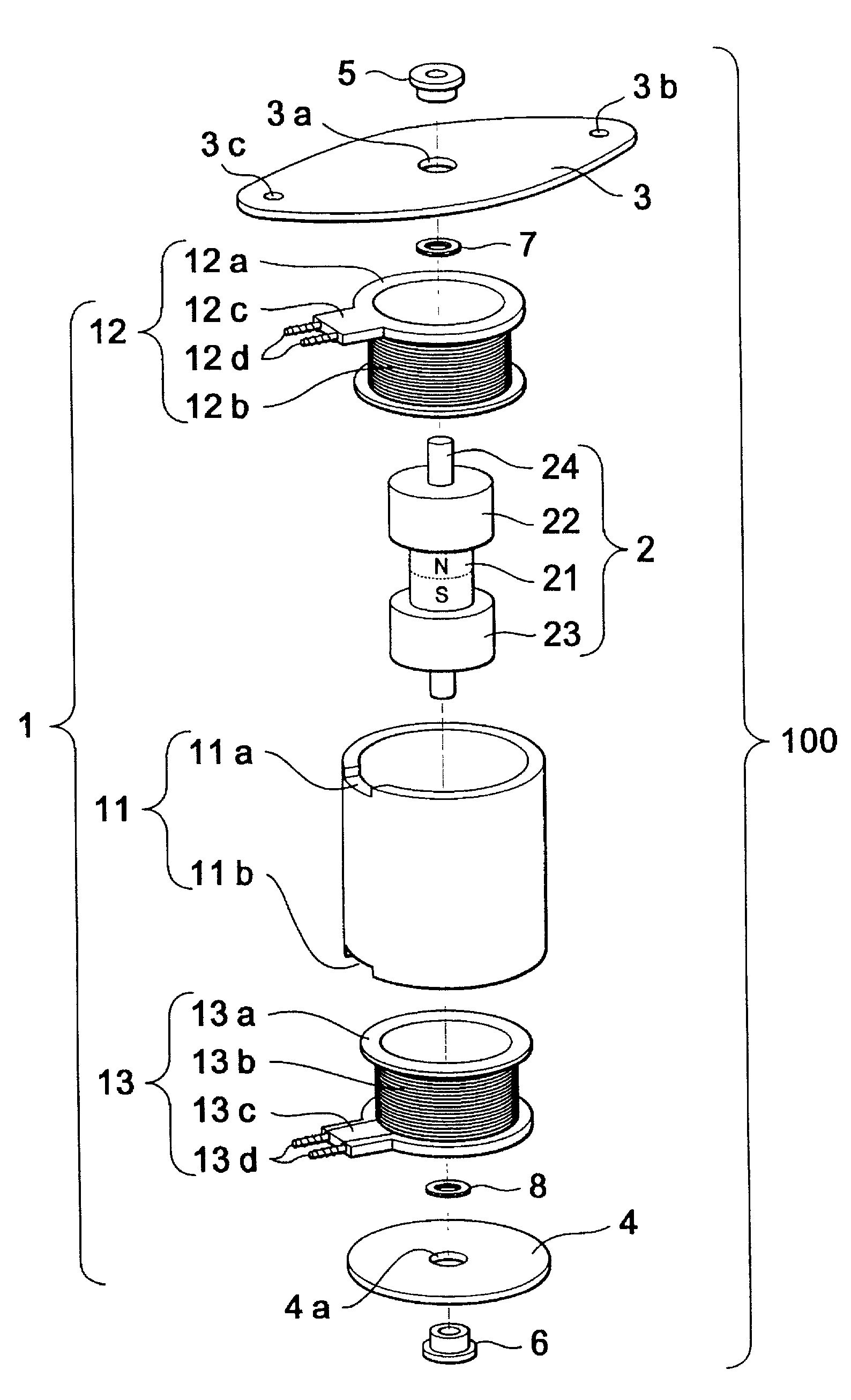
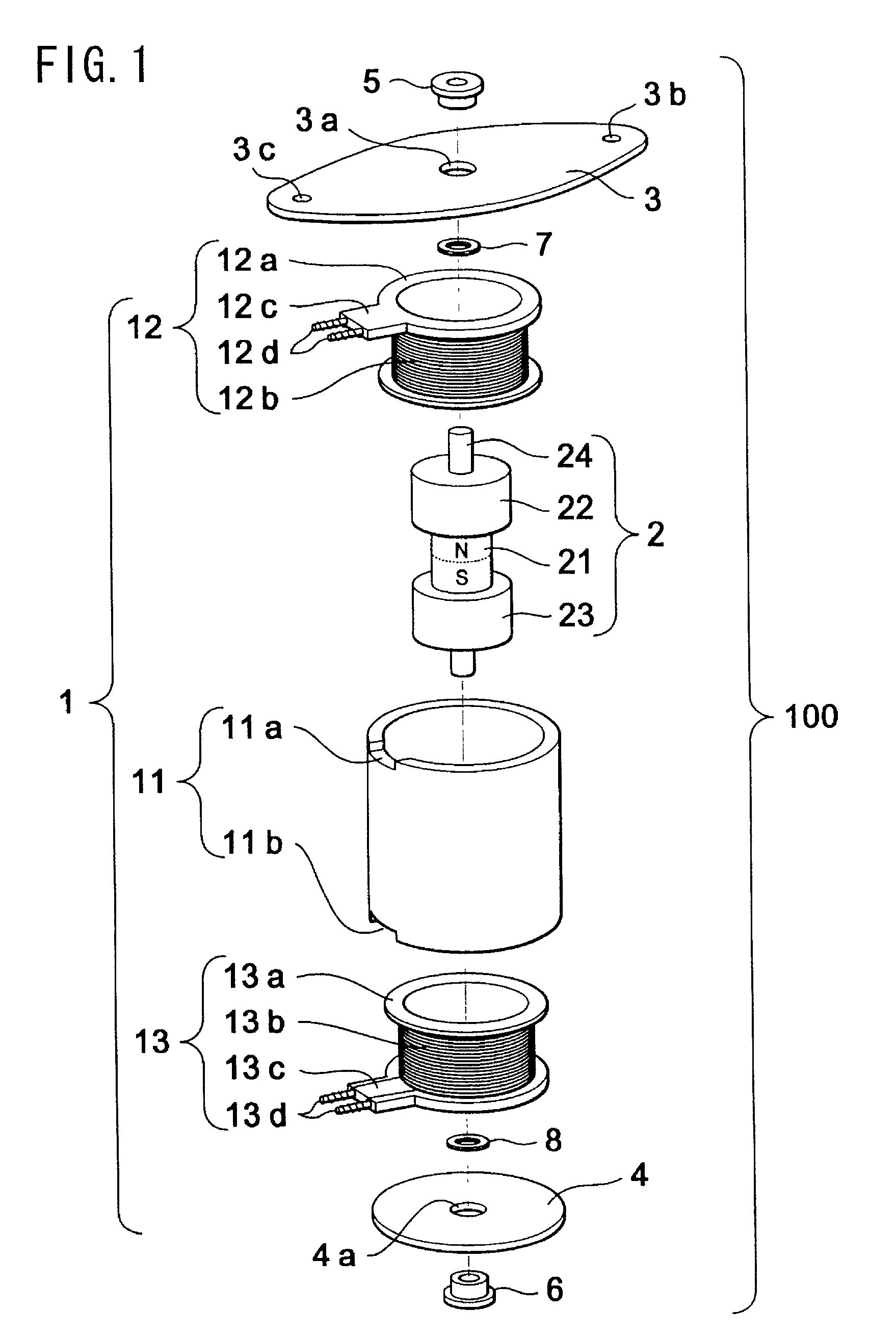
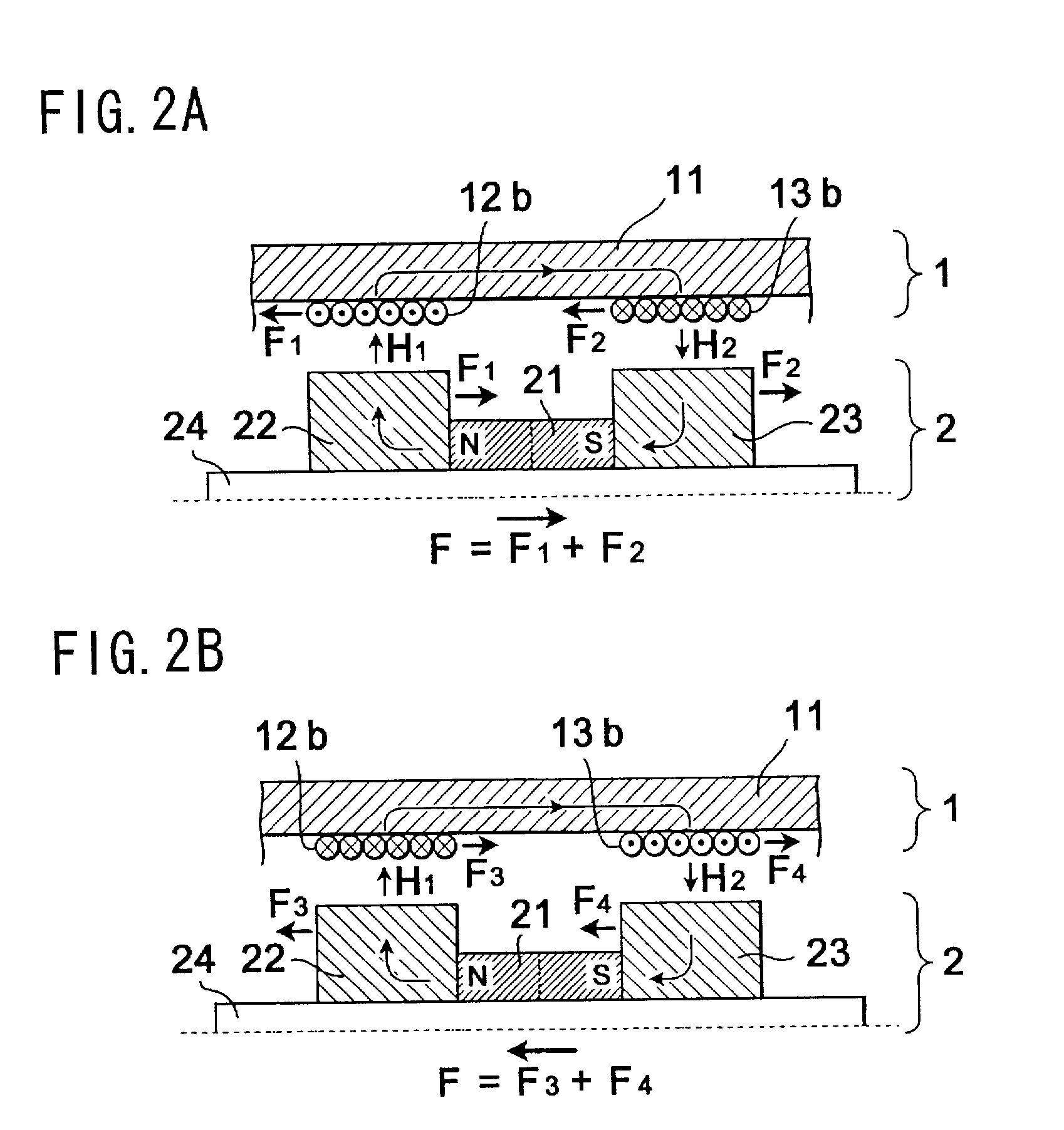
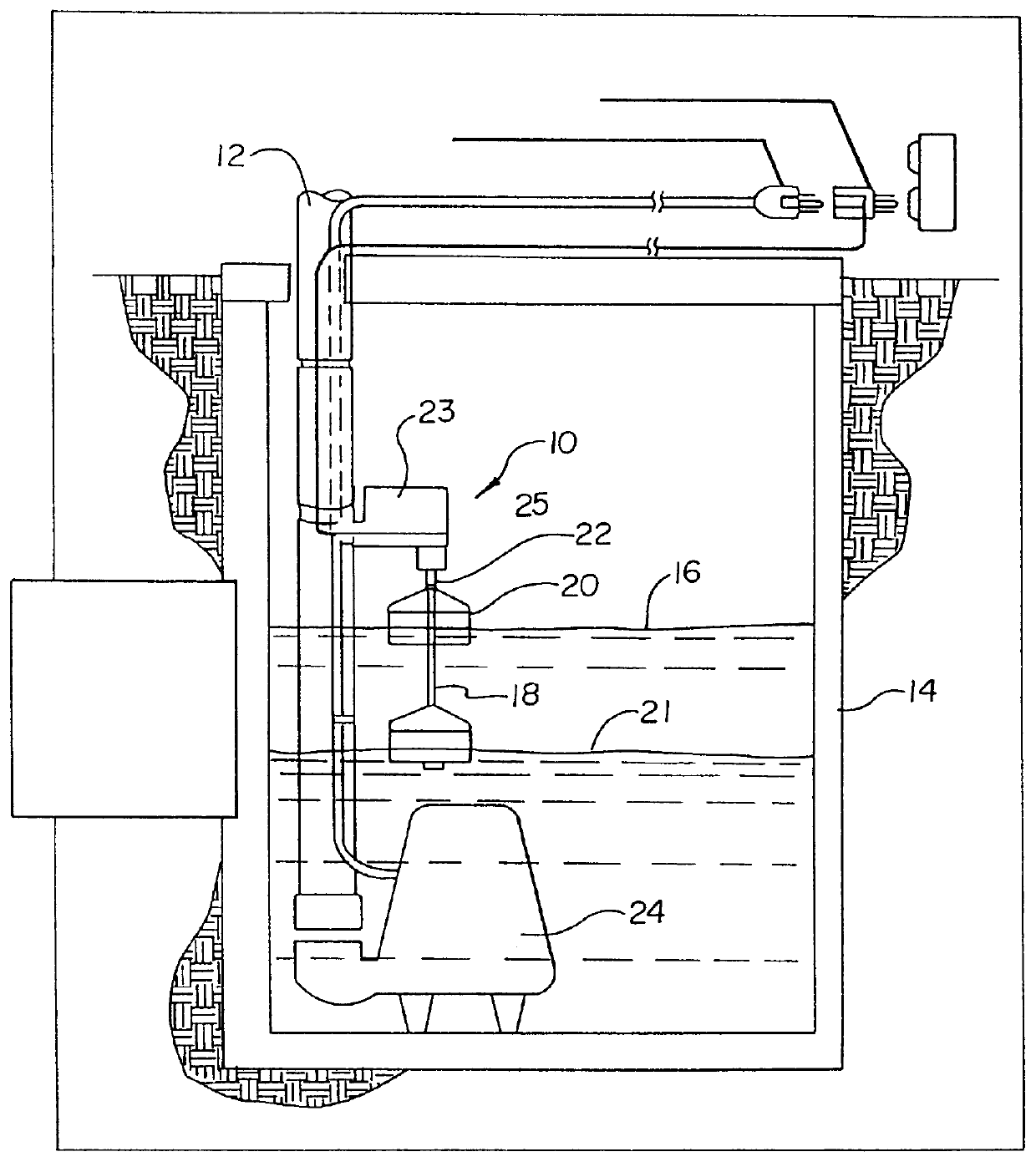
Patents
Literature
193 results about "Magnetic actuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
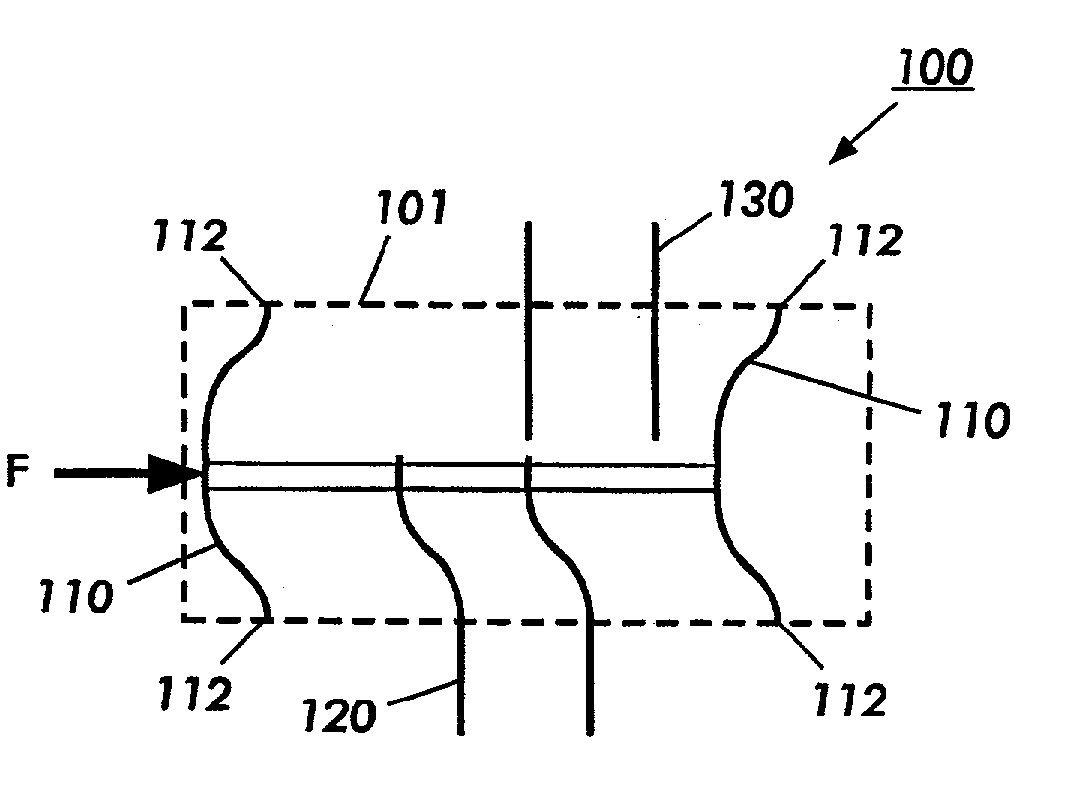
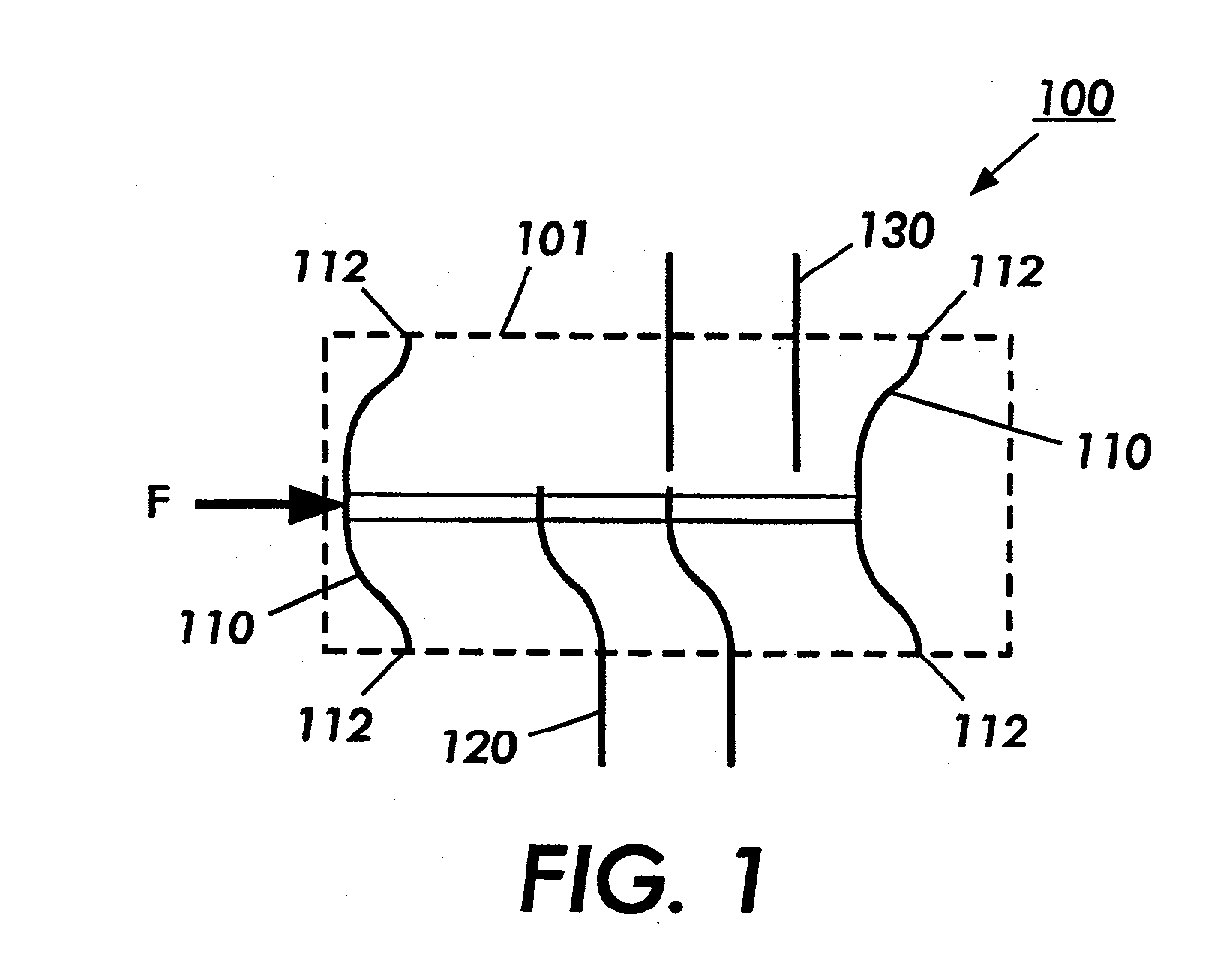
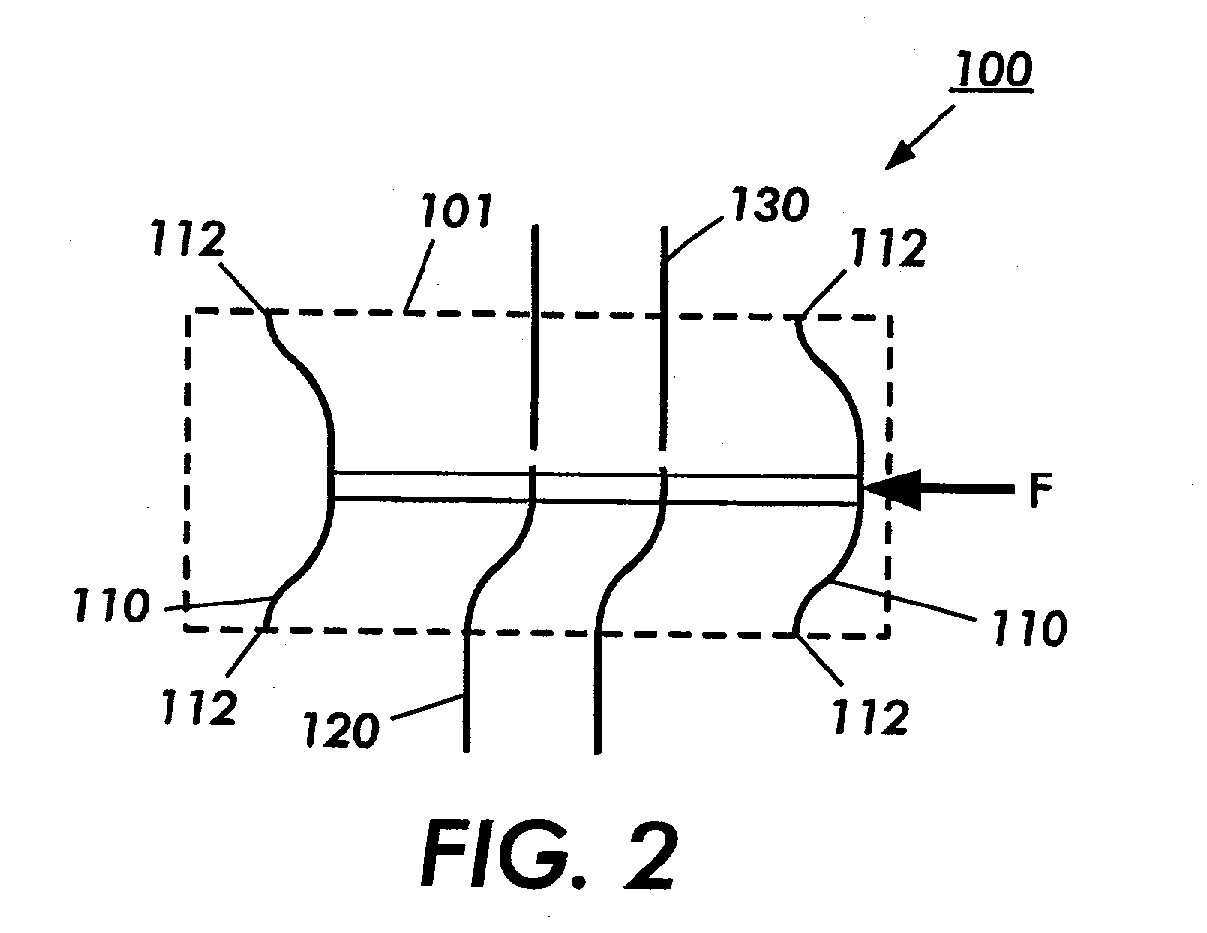
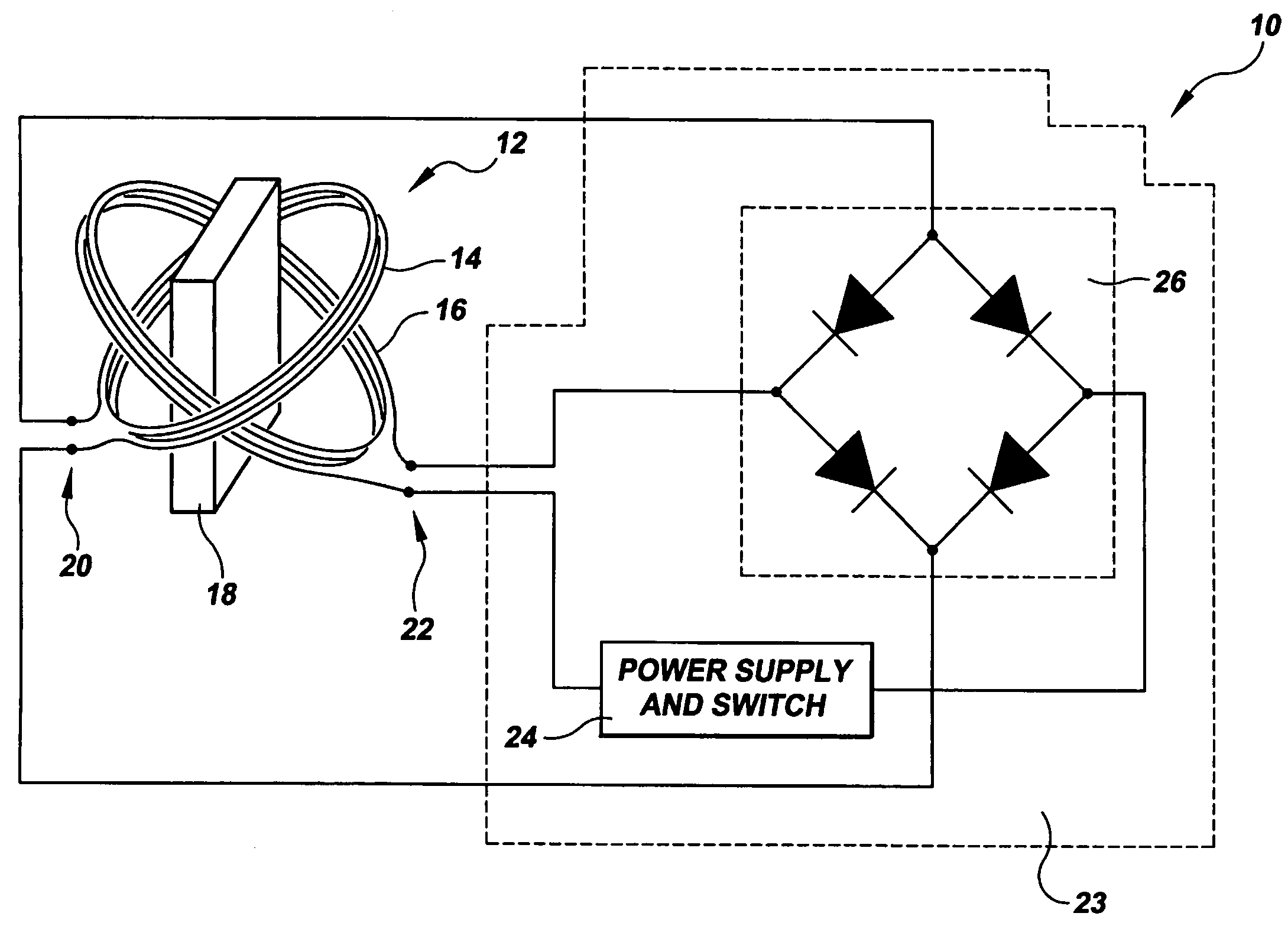
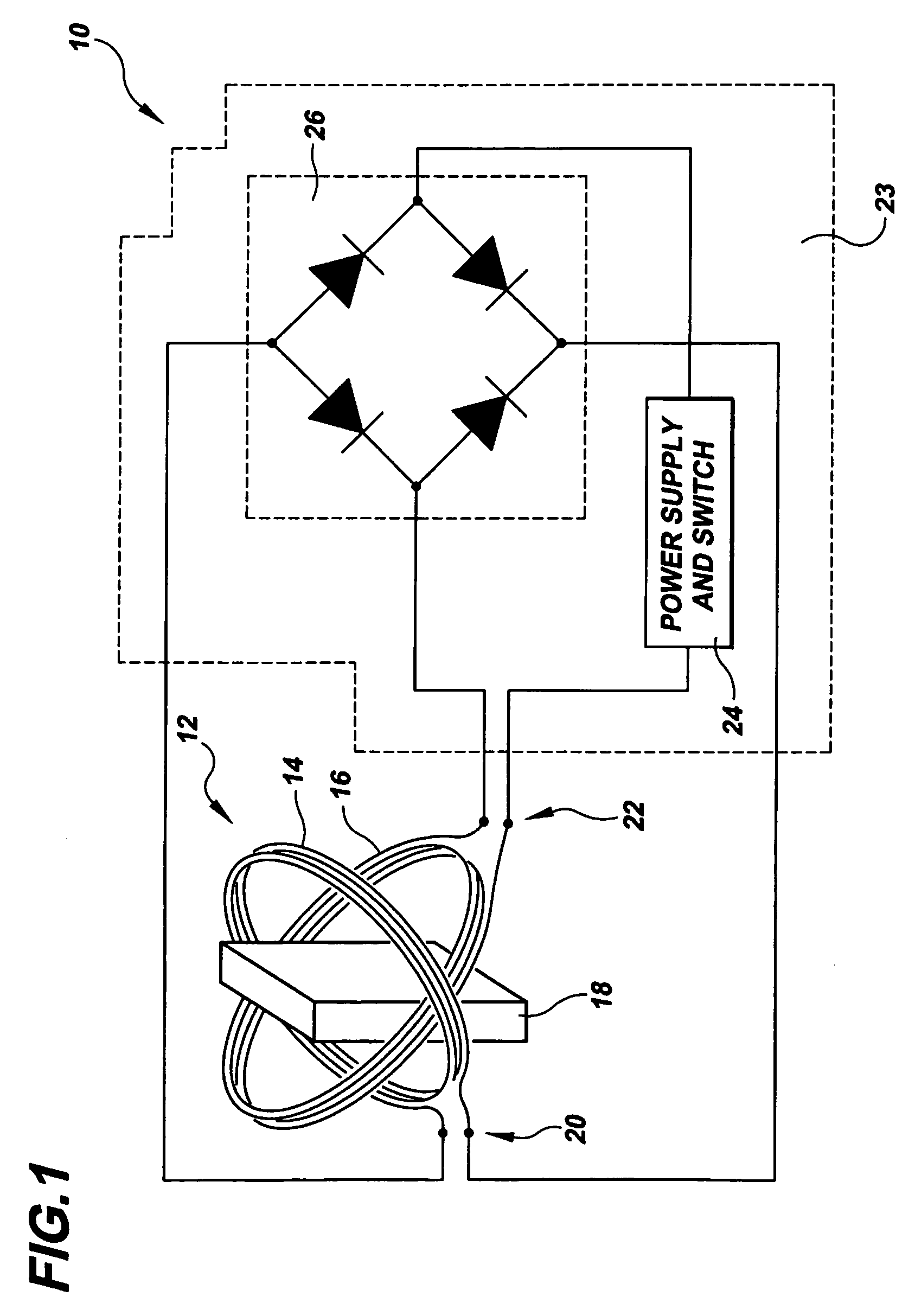
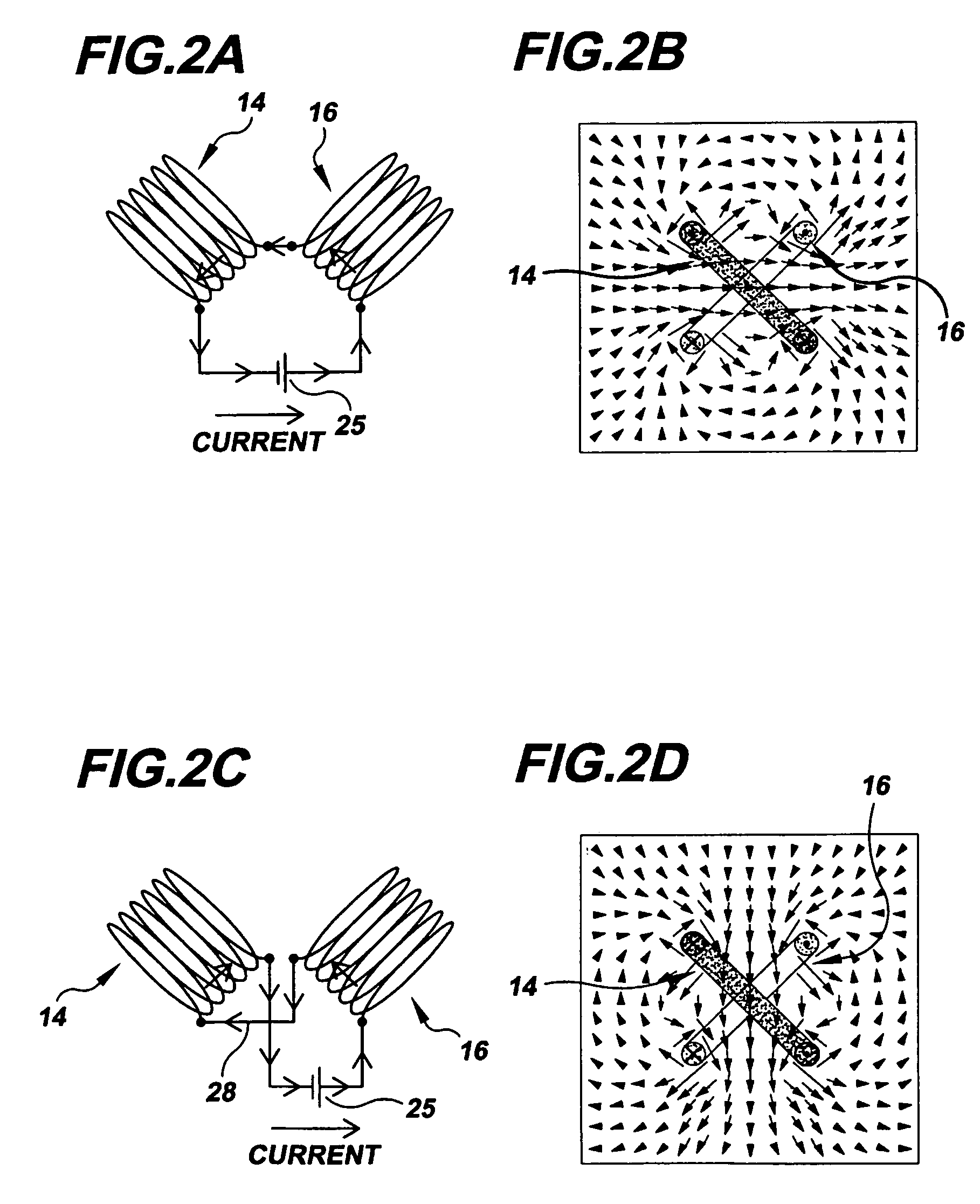
Magnetic Actuation: Forces and Torques. The principle of magnetic actuation is to propel microrobots with magnetic forces and/or torques. A quasi-static and low-frequency magnetic field is an approach to apply forces and torques directly to magnetic materials without the need for any tethers or direct contact [4].
Apparatus for performing an electrosurgical procedure
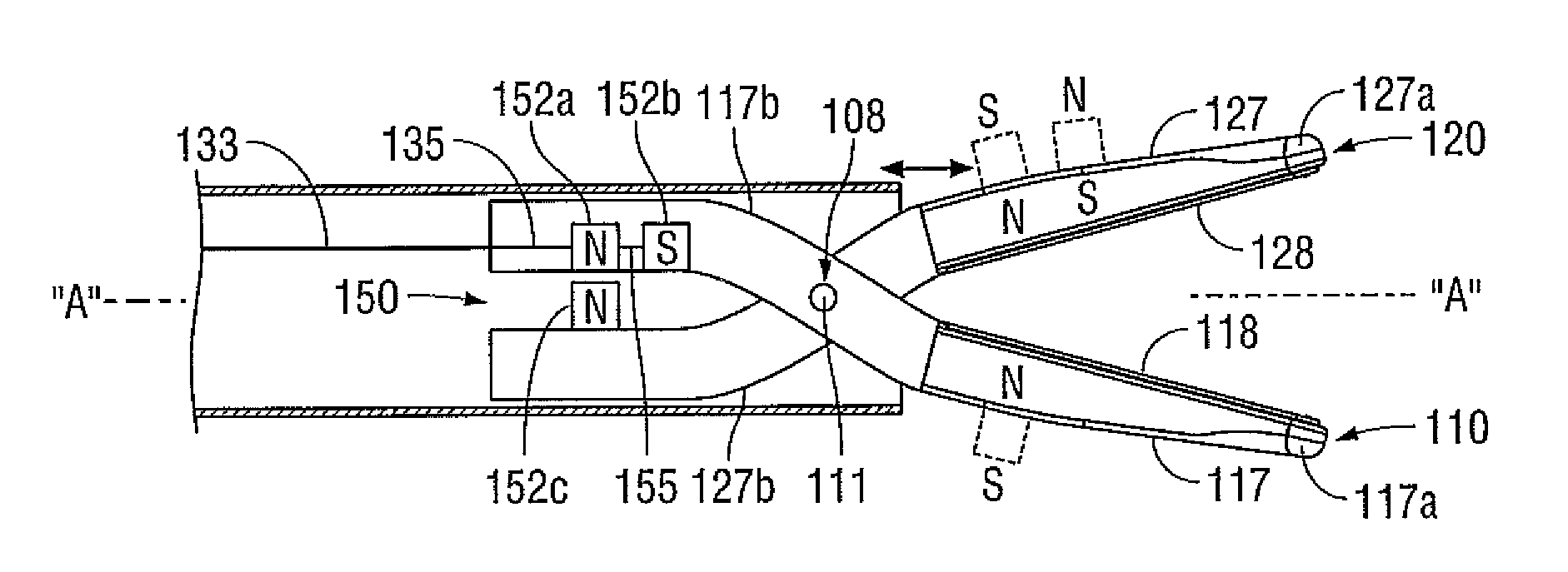
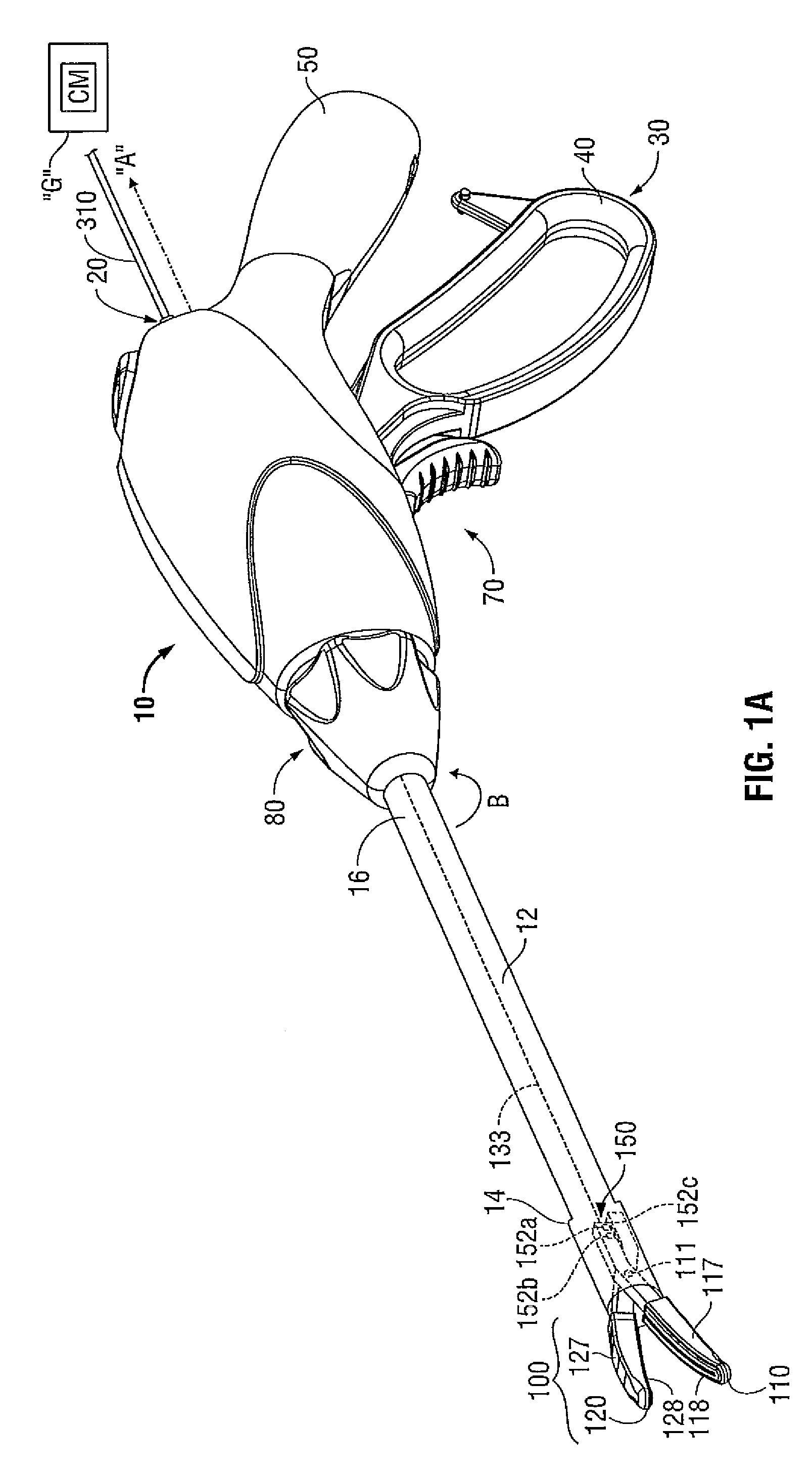
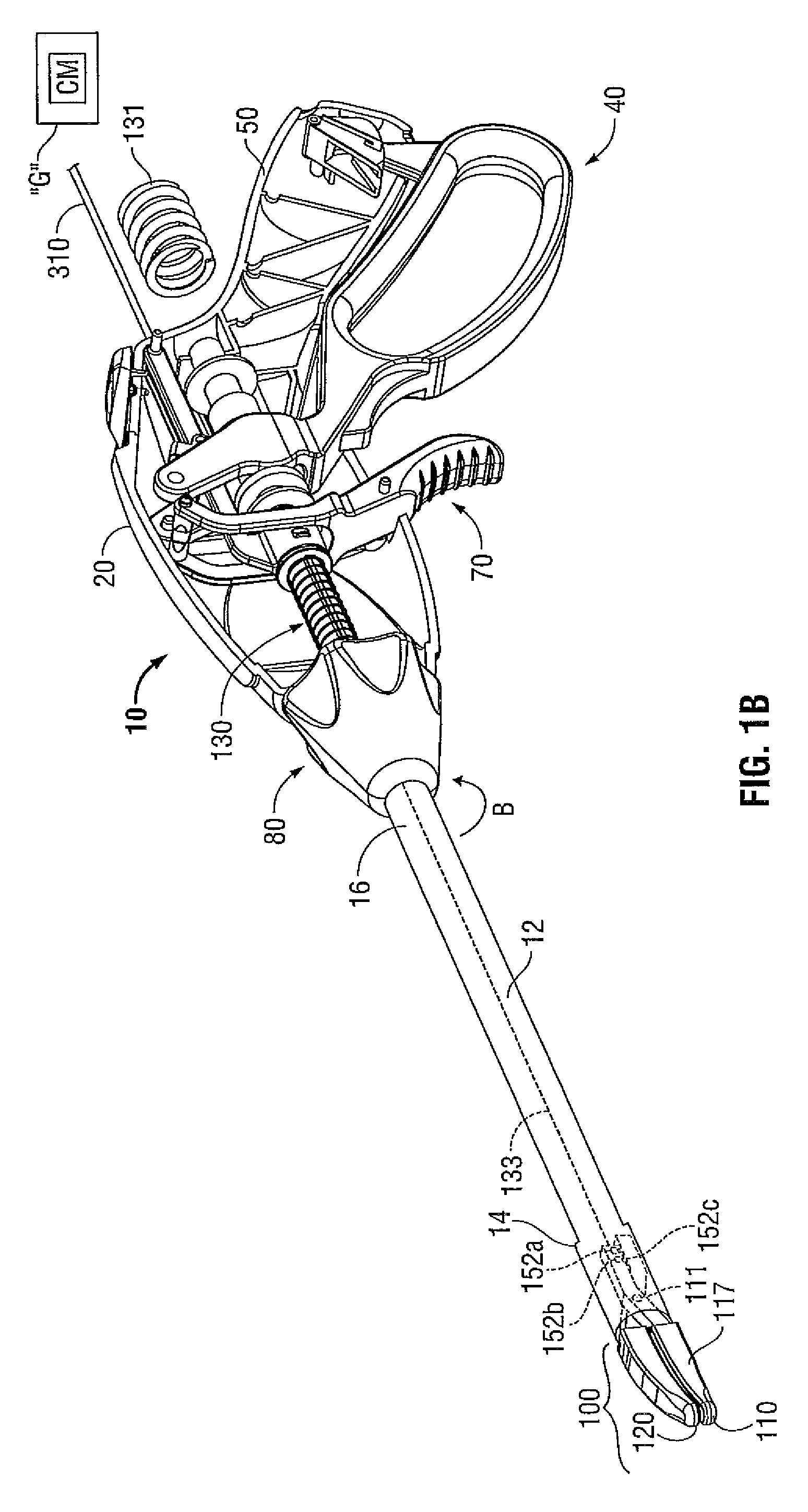
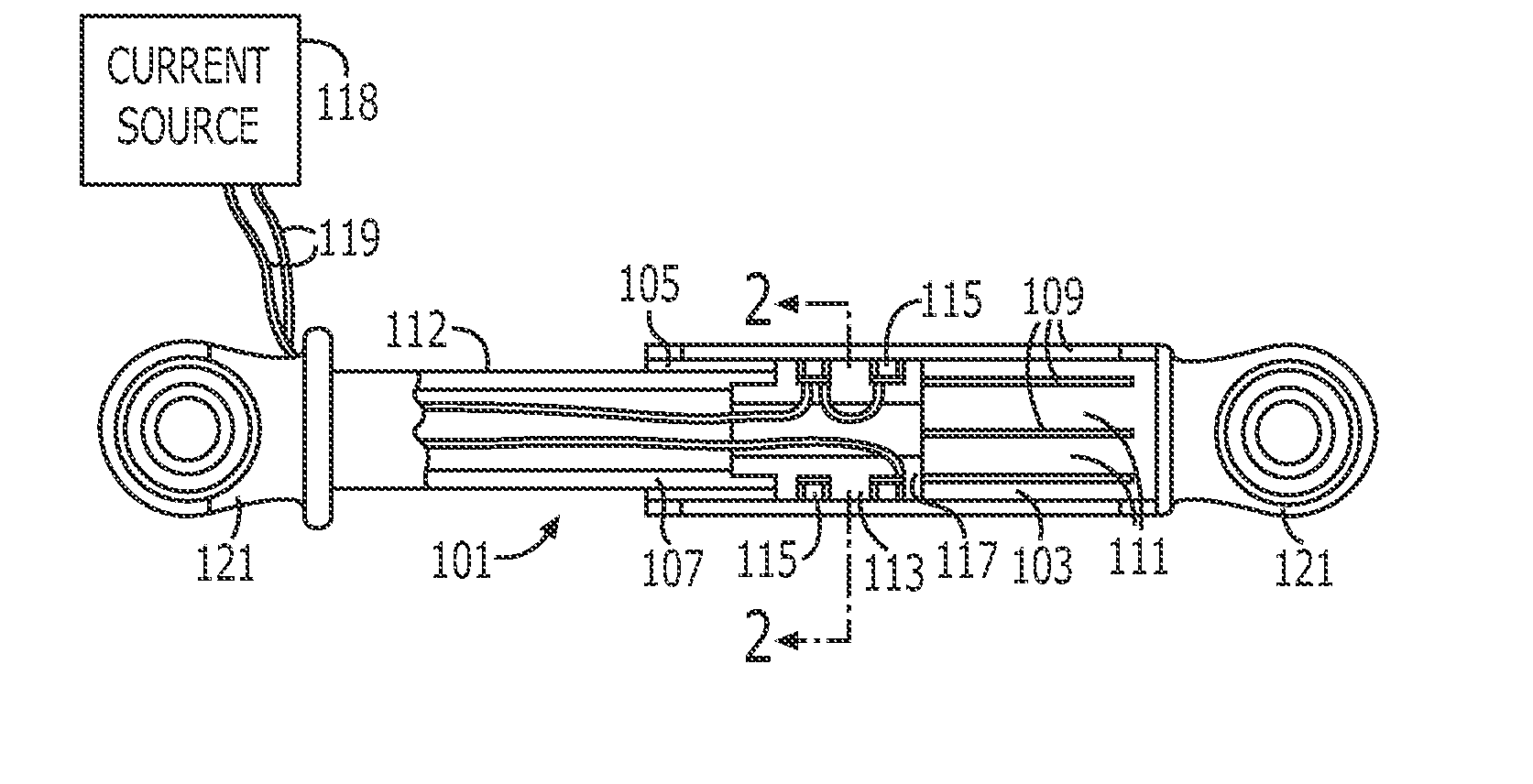
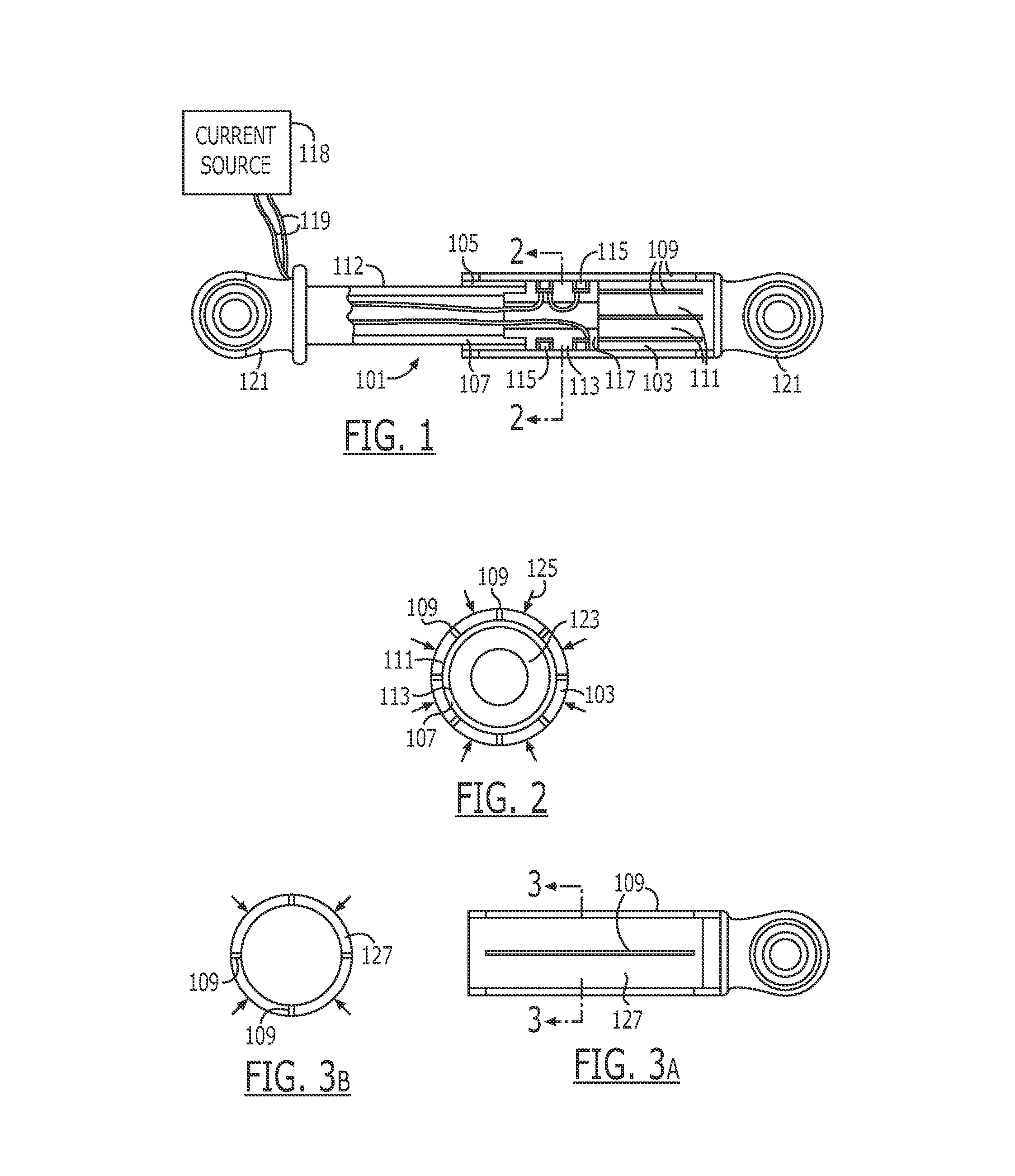
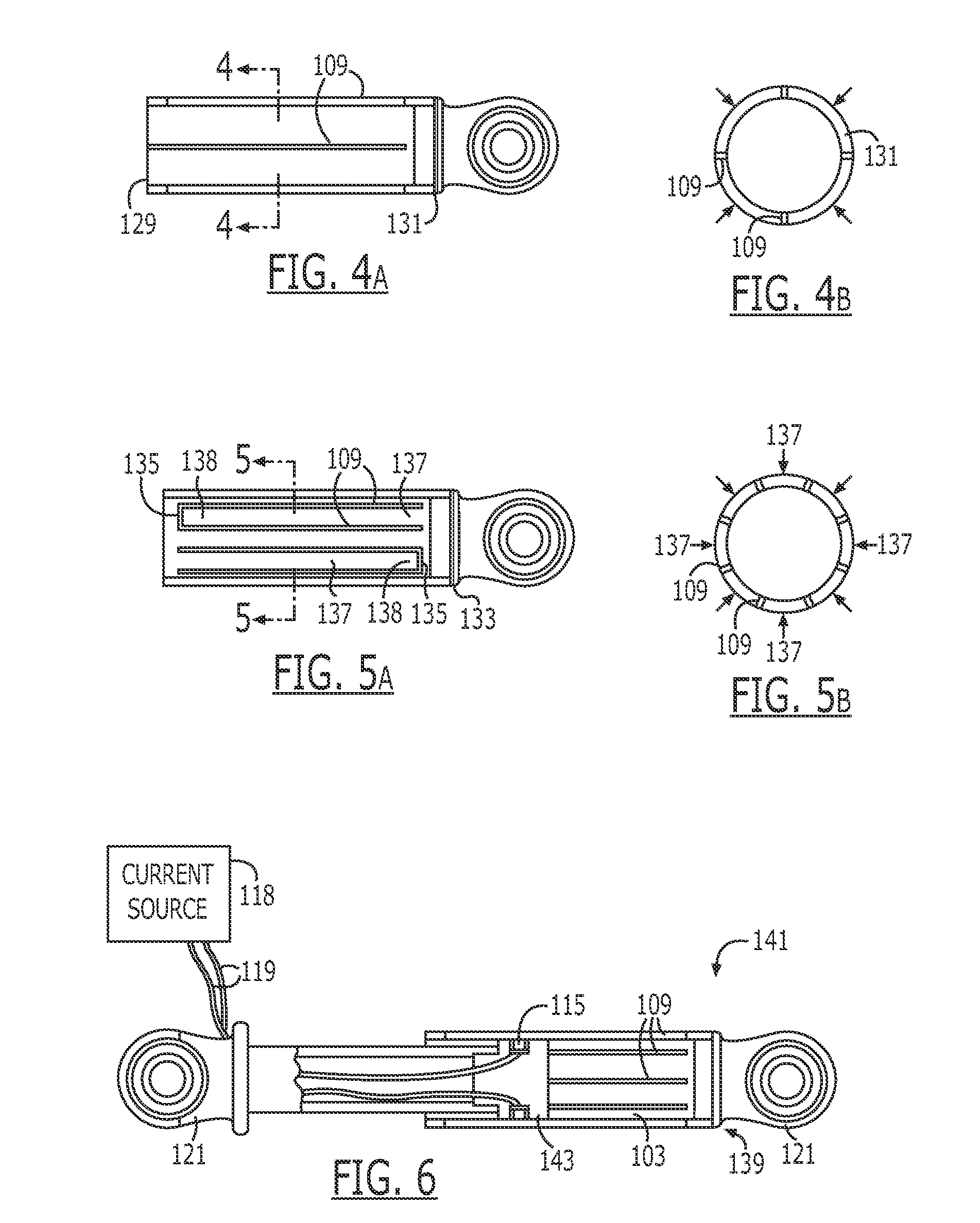
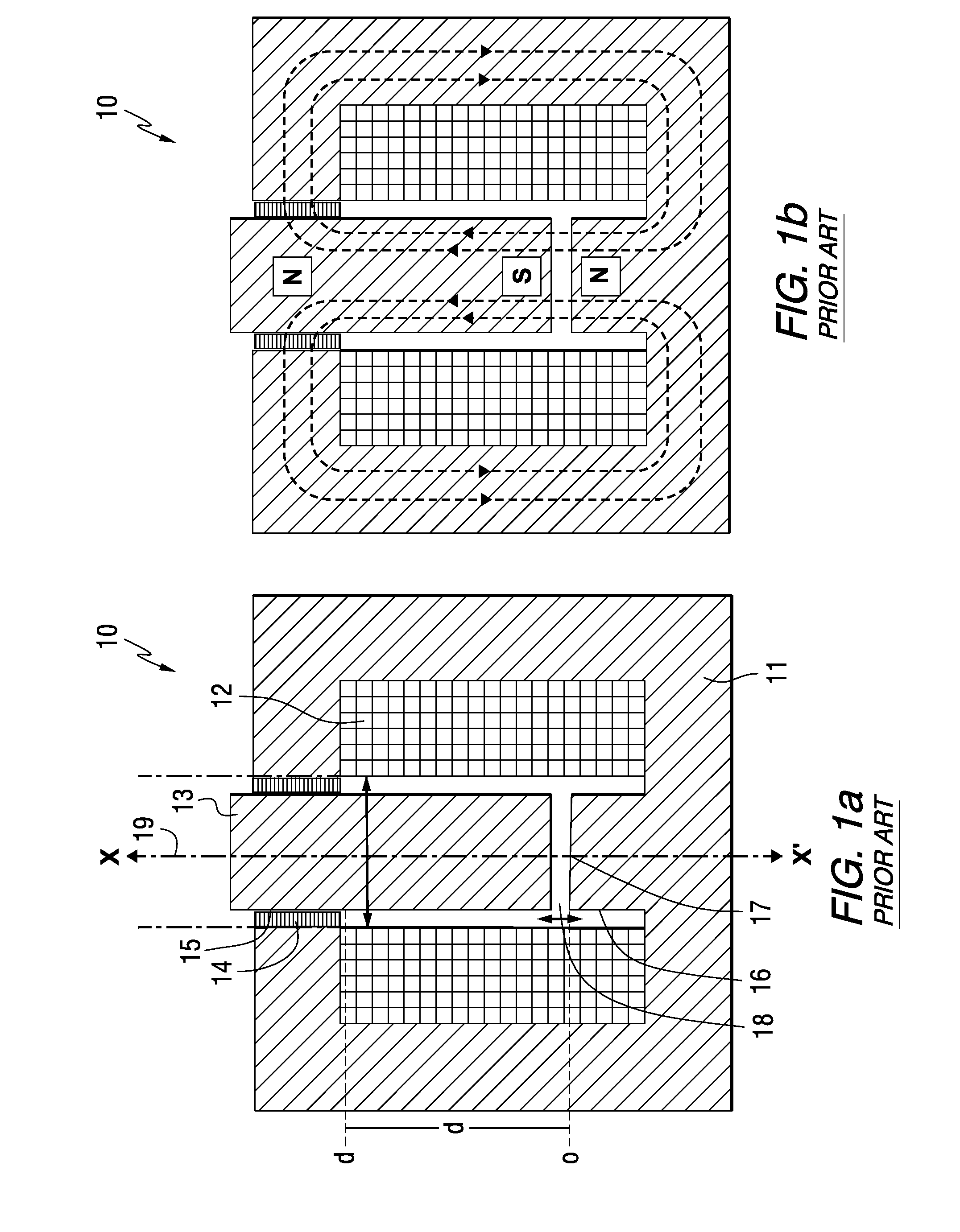
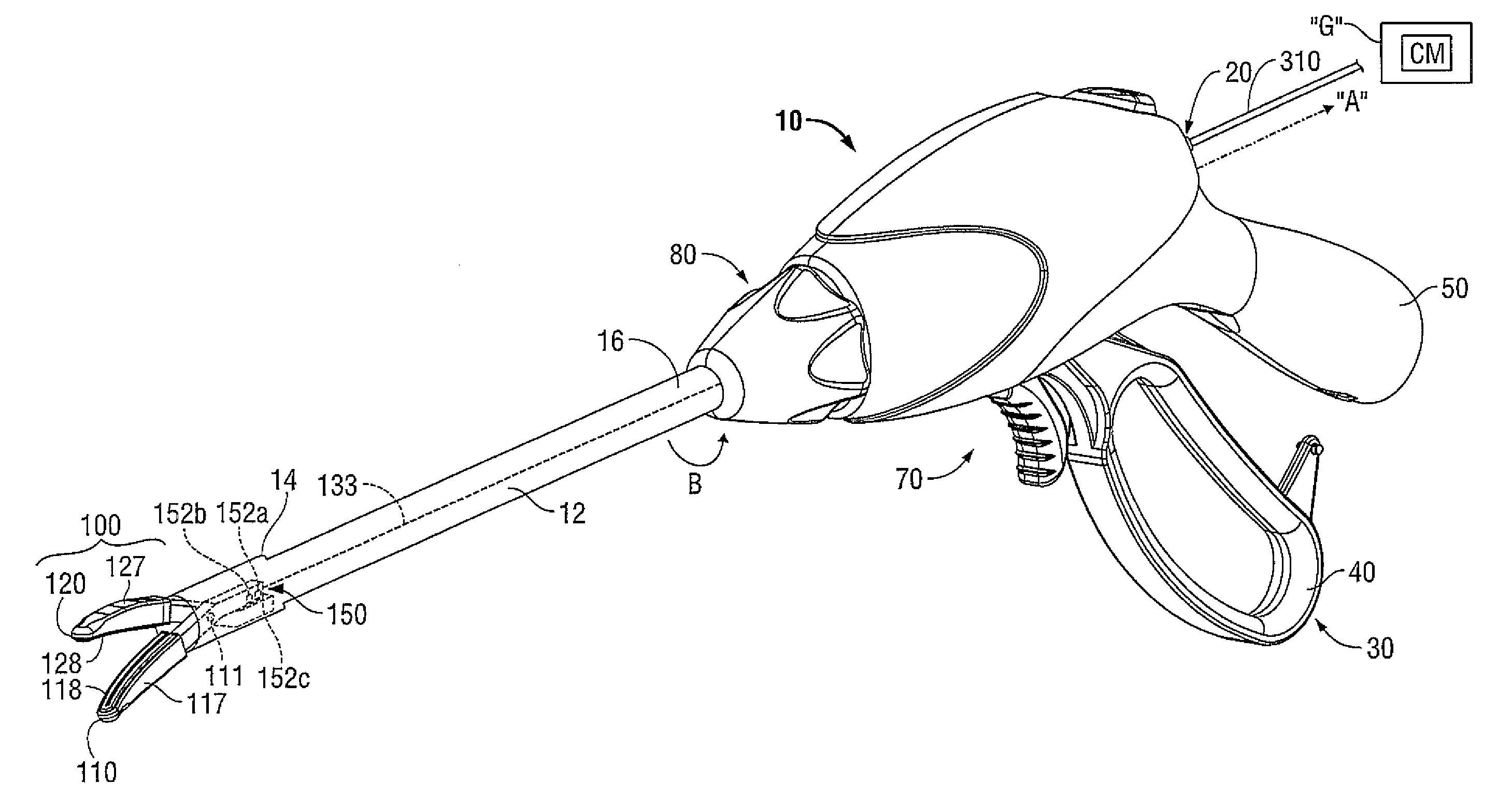
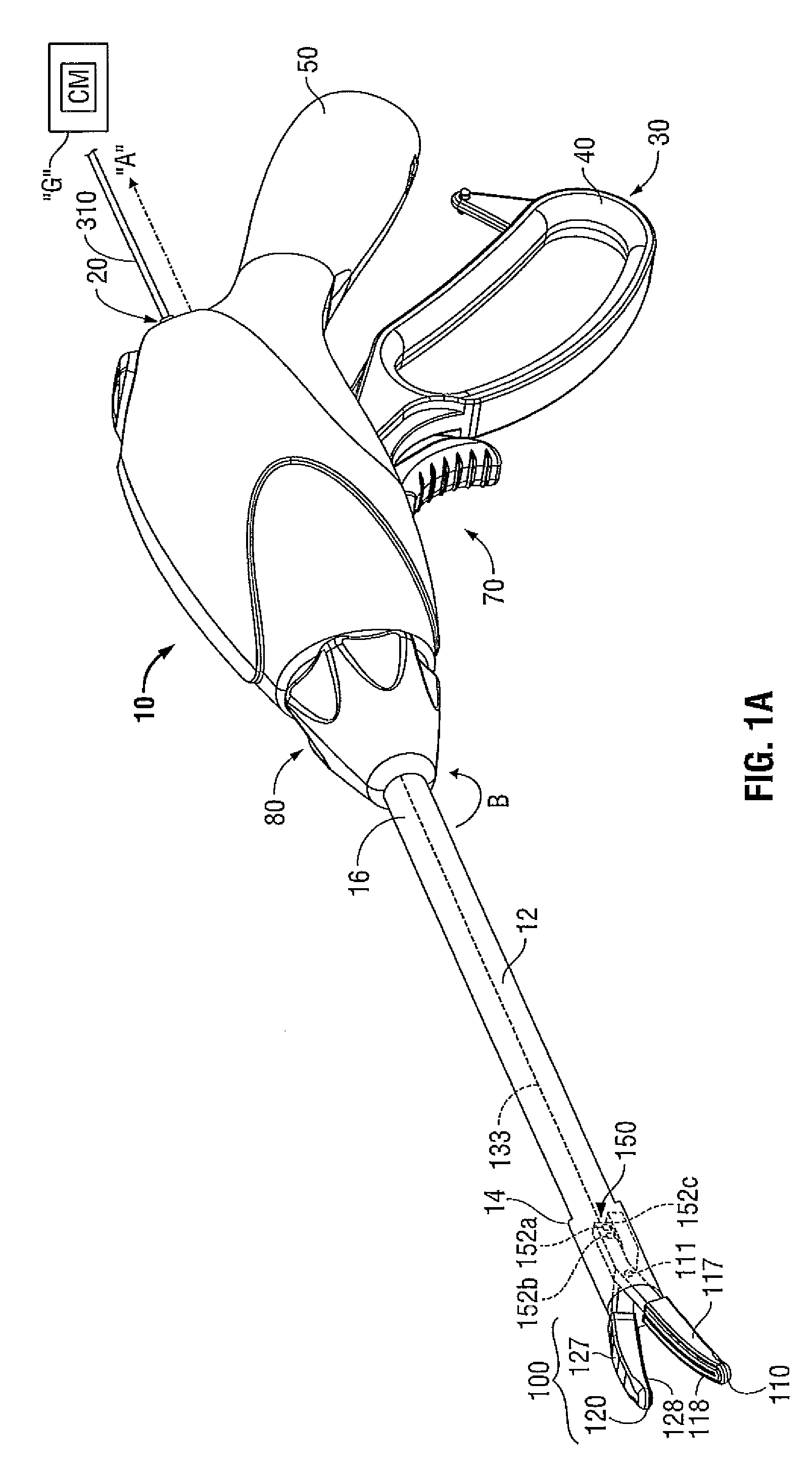
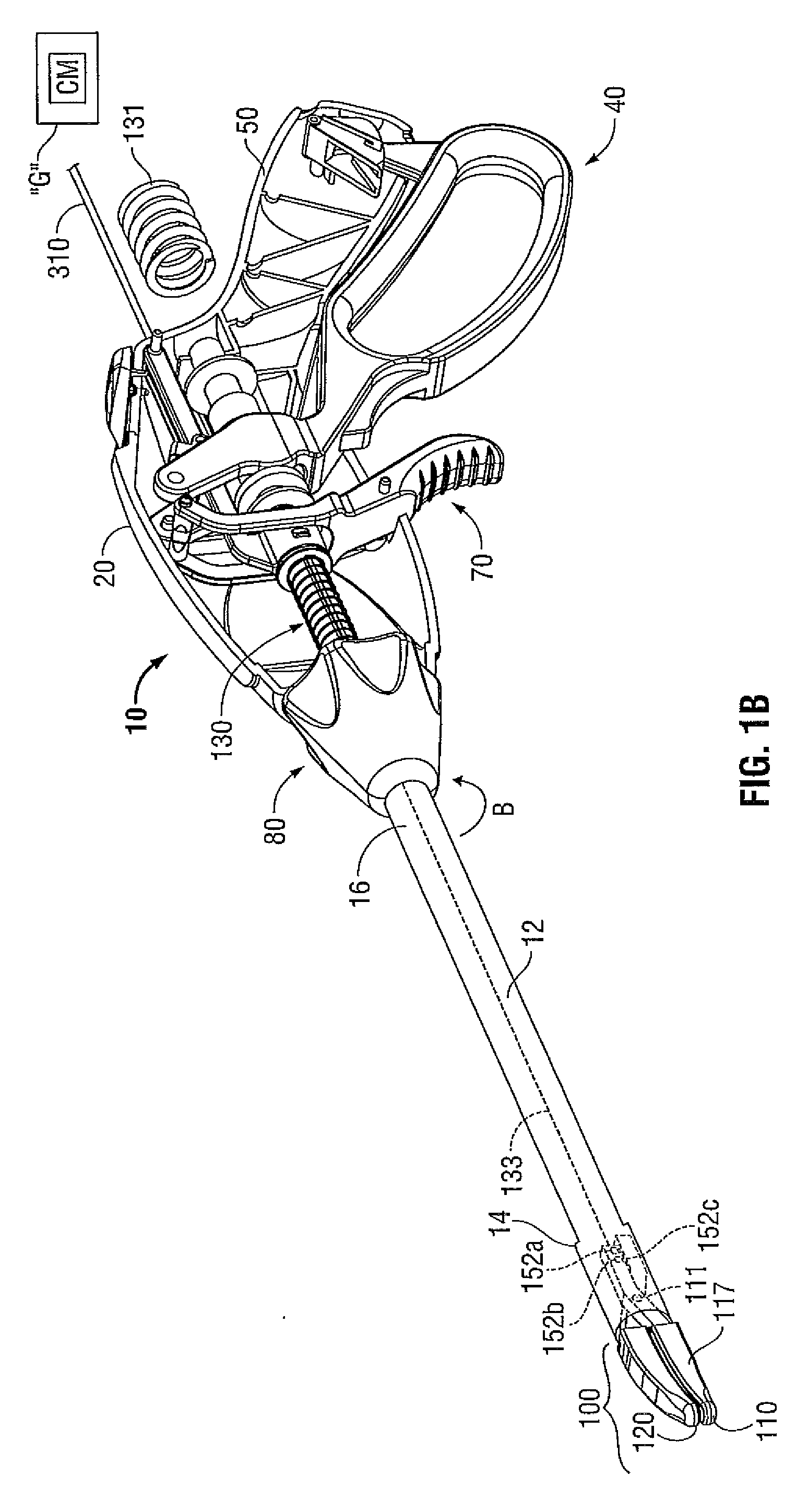
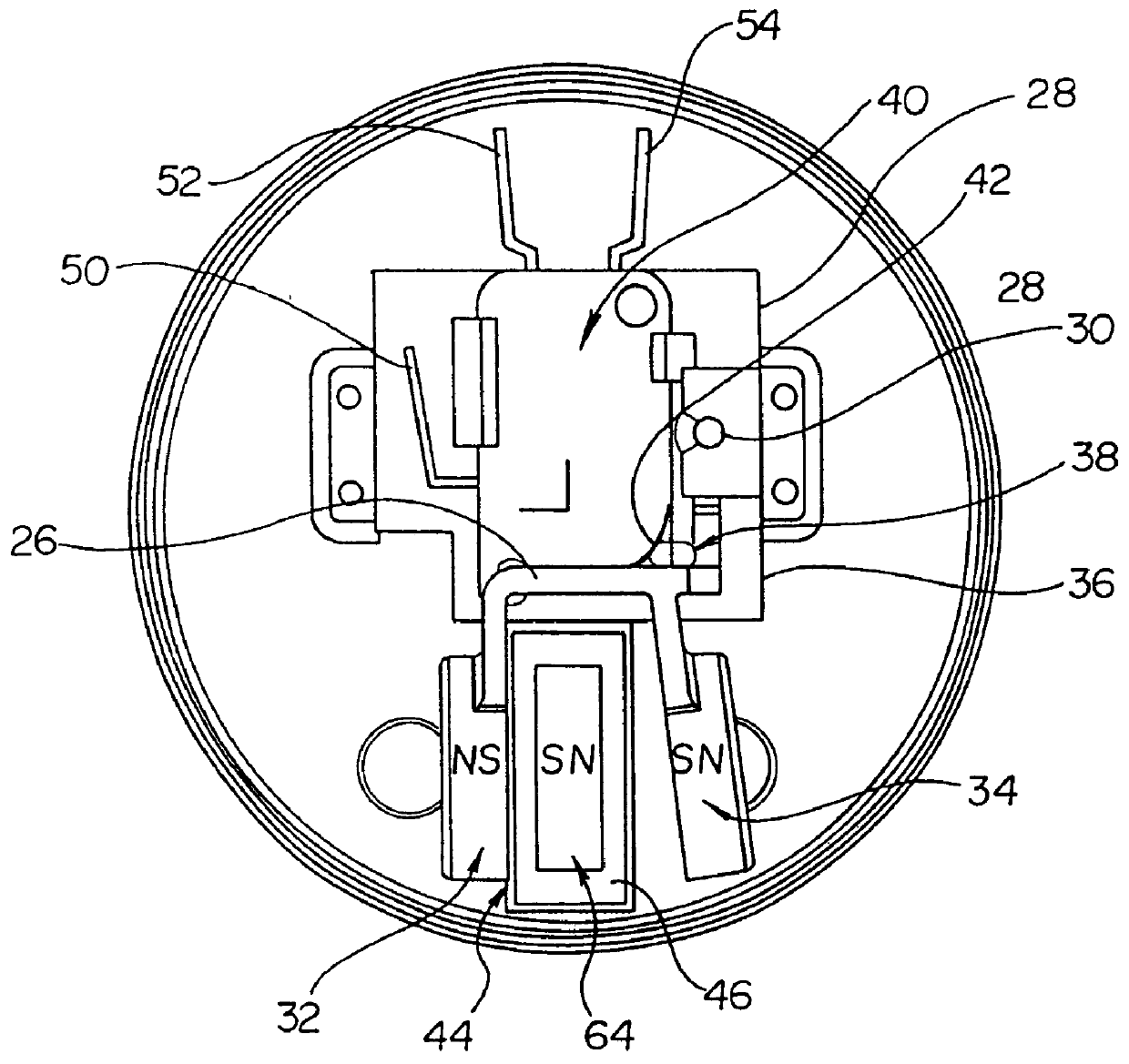
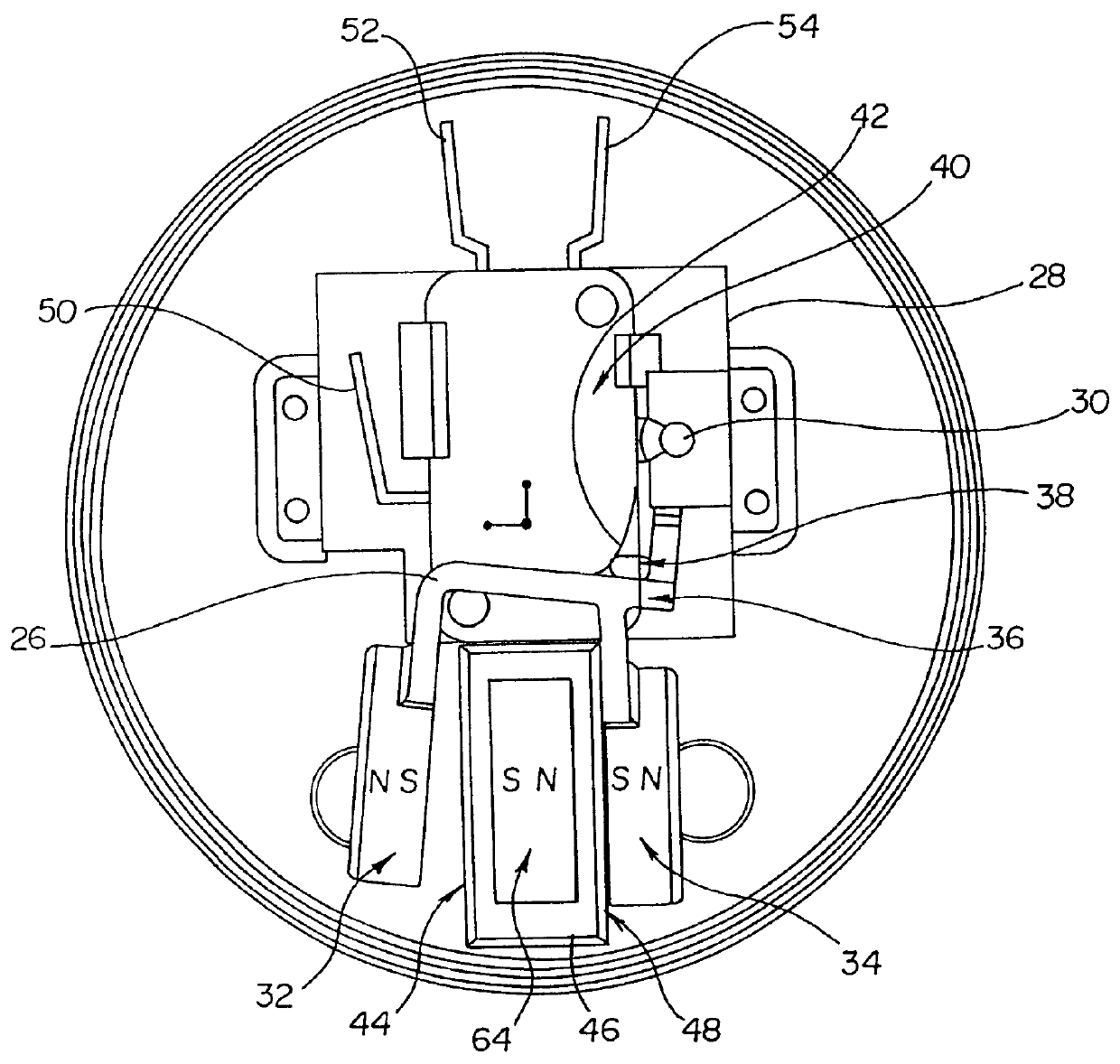
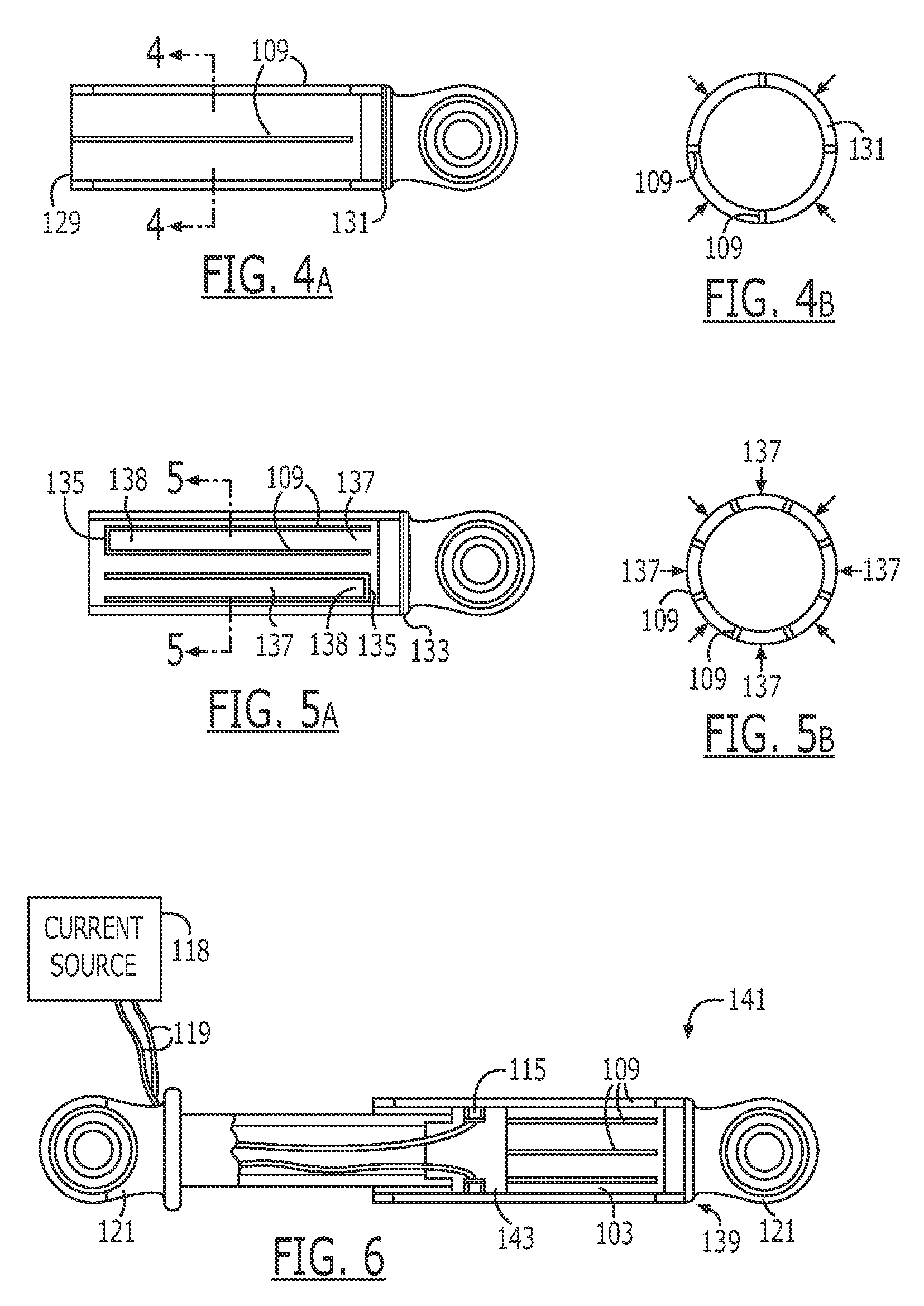
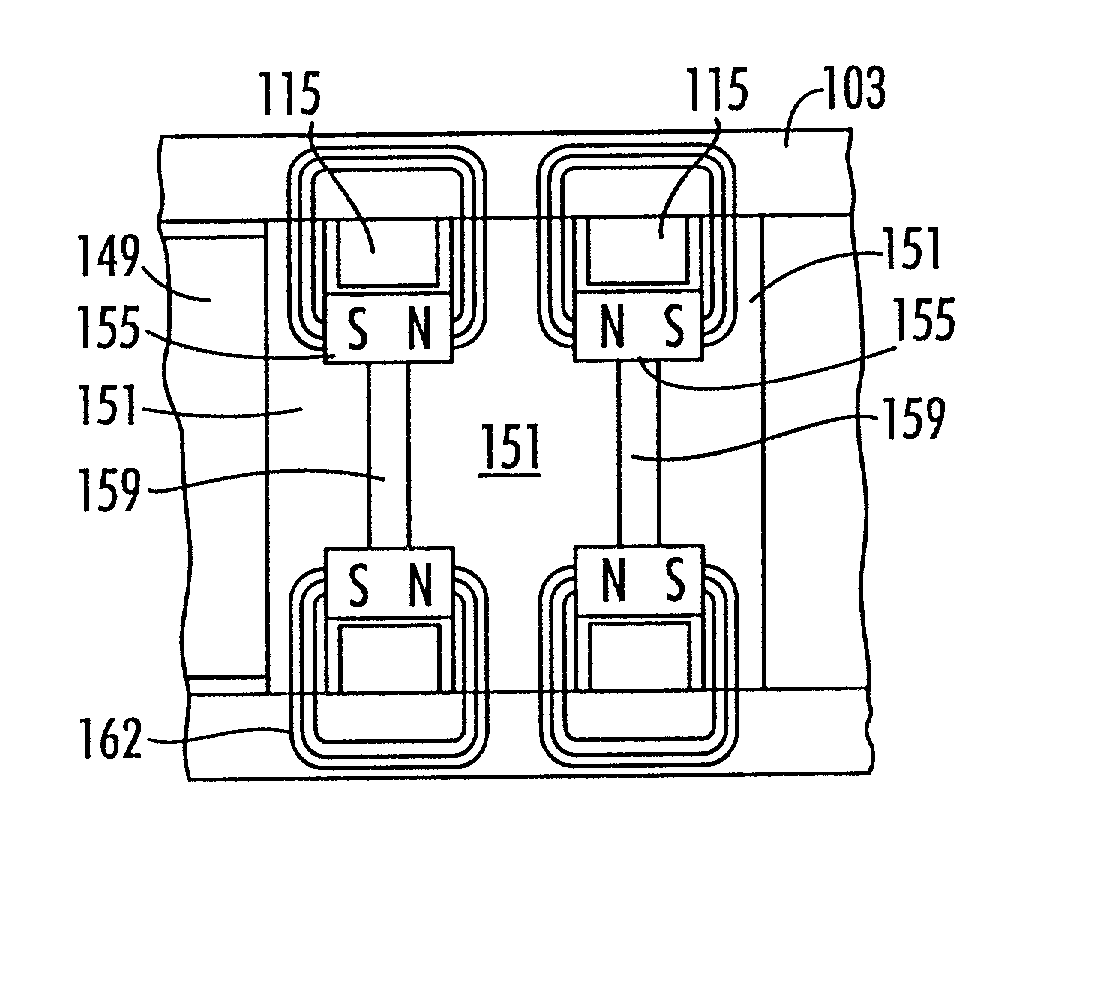
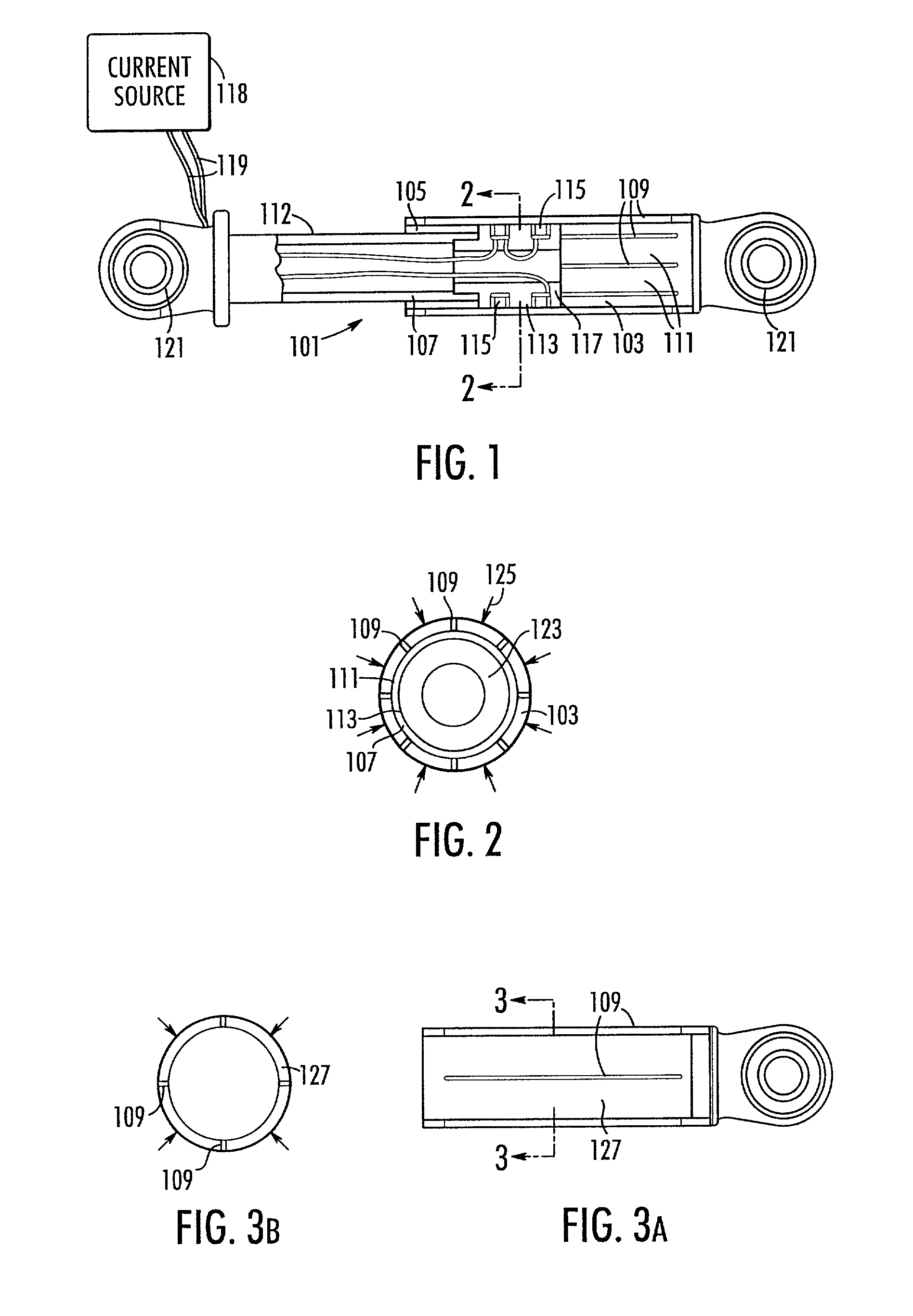
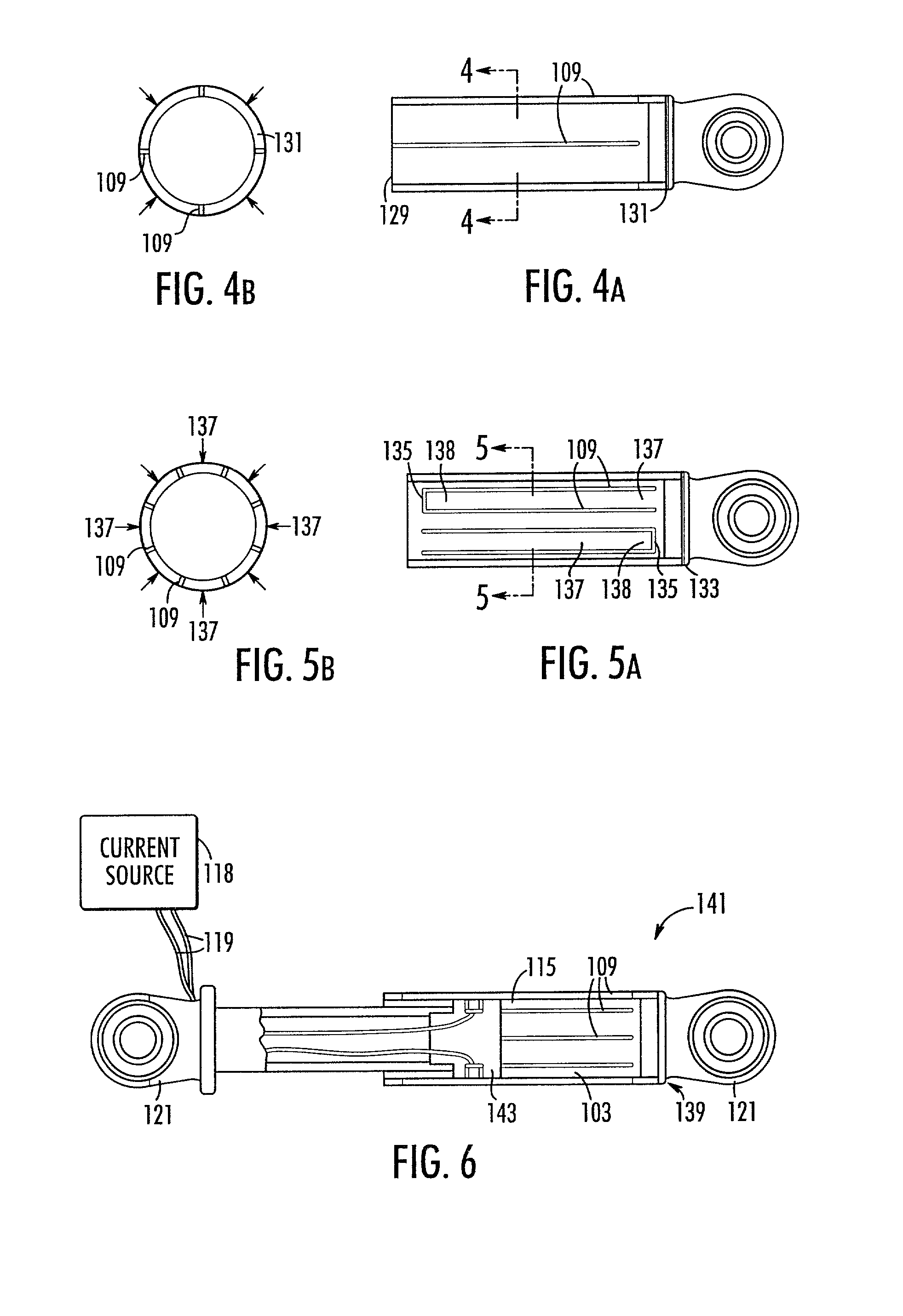
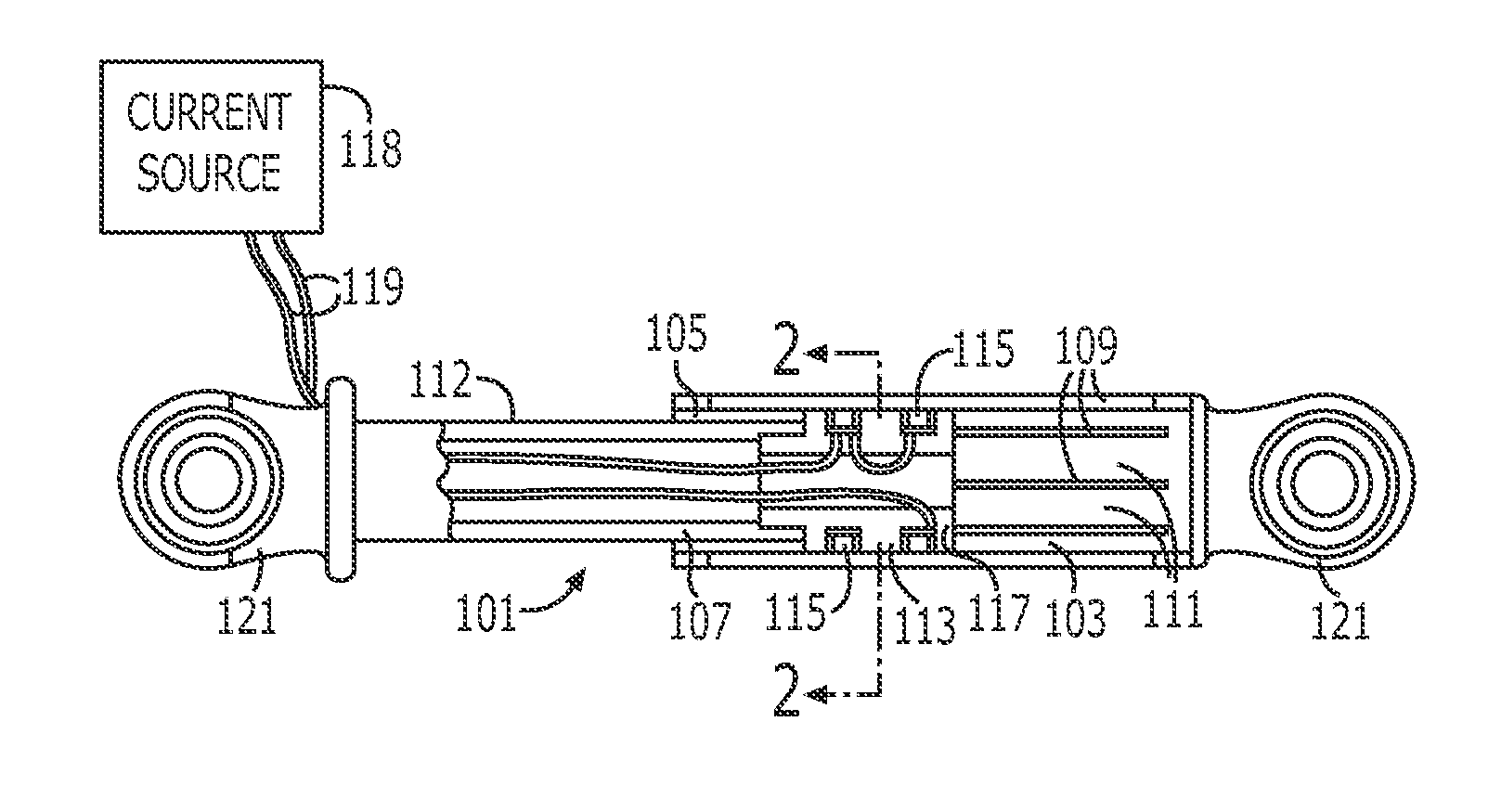
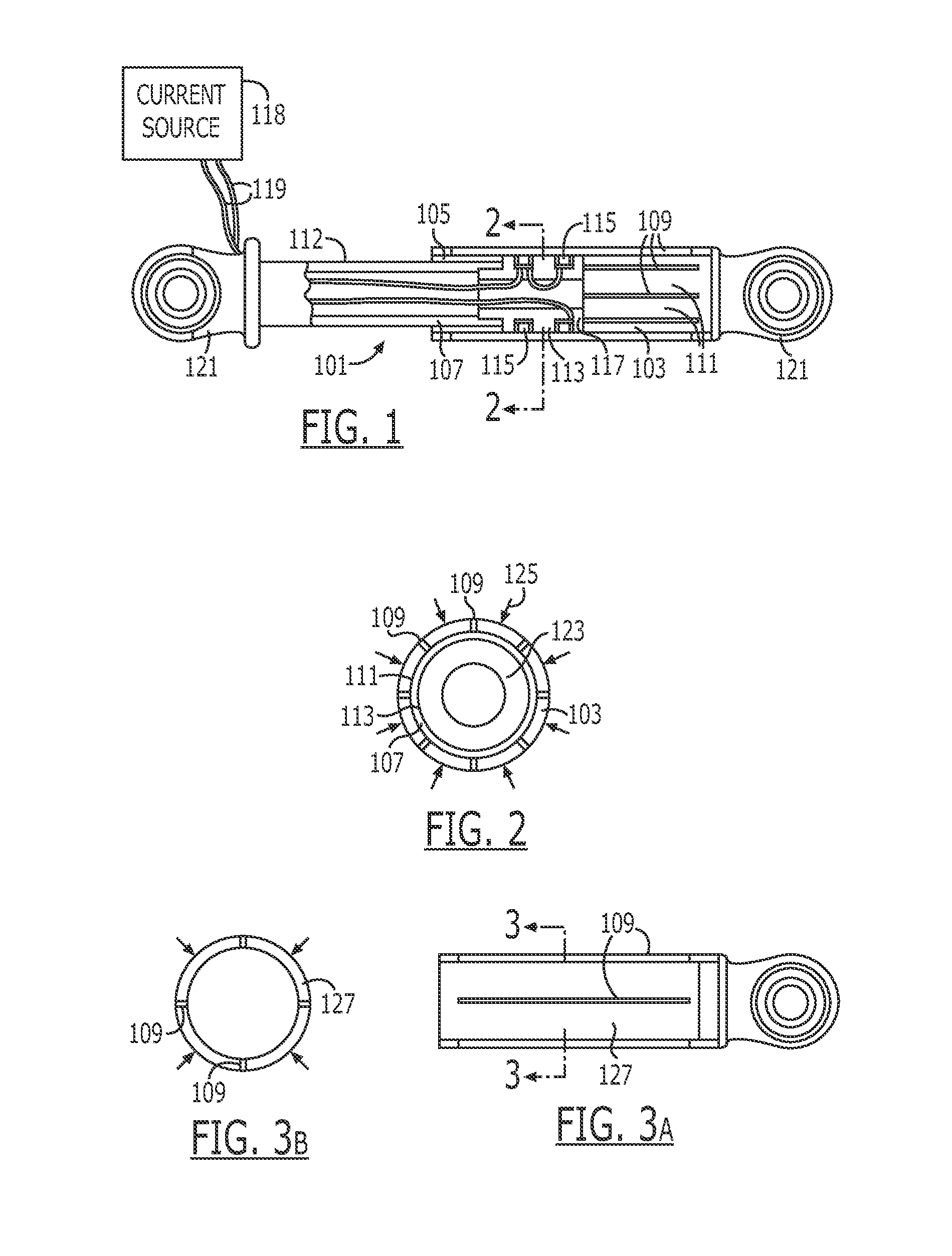
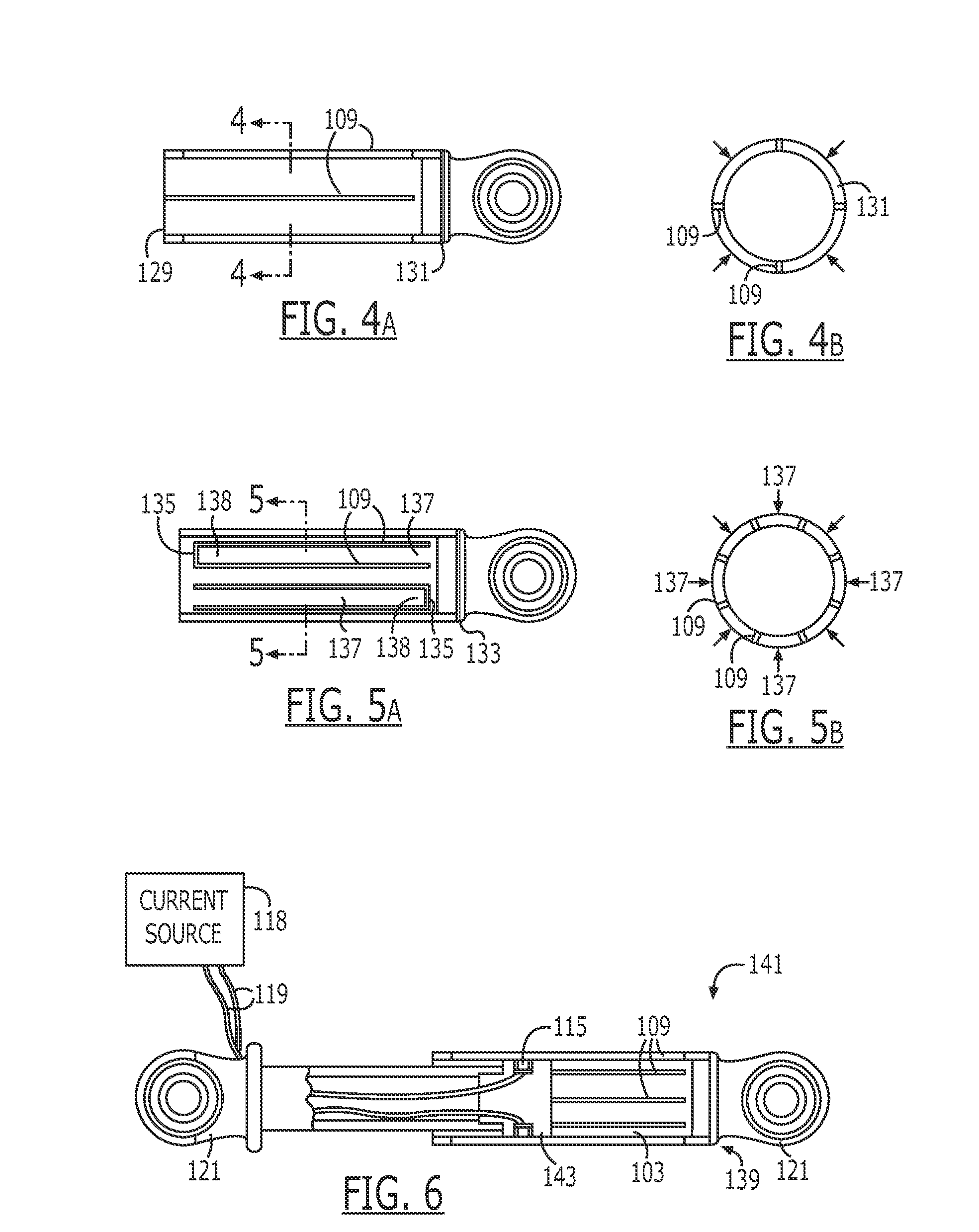
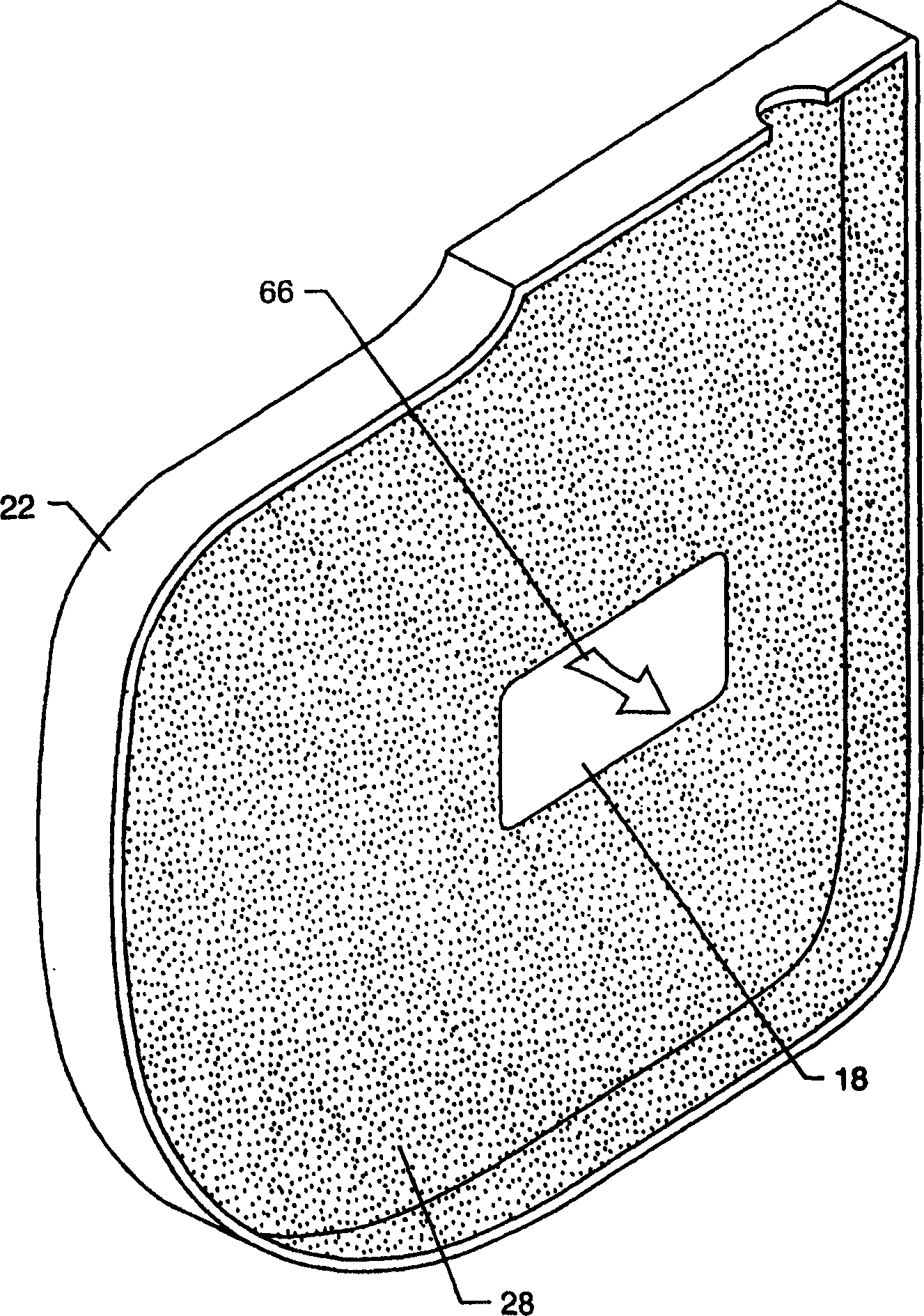
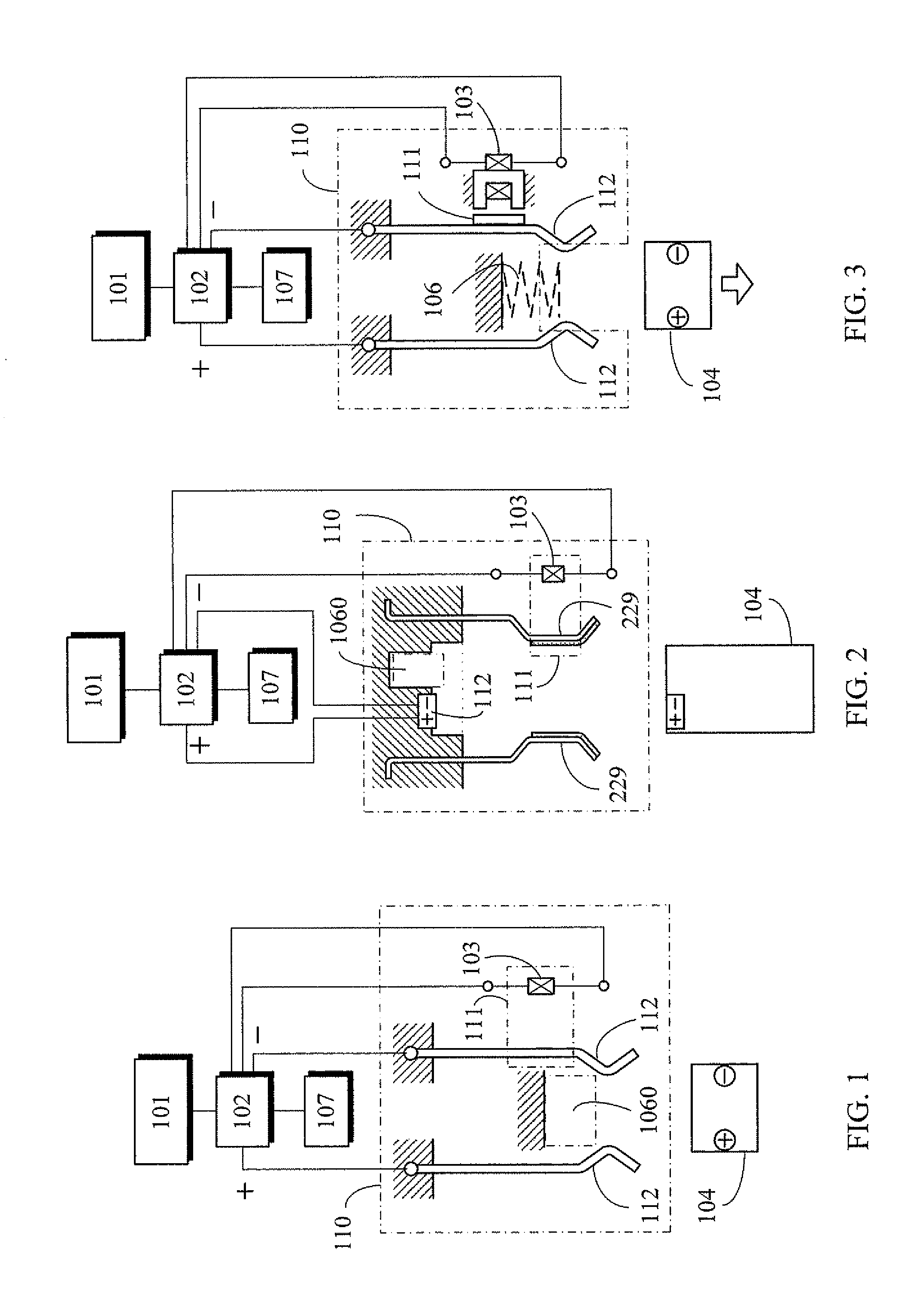
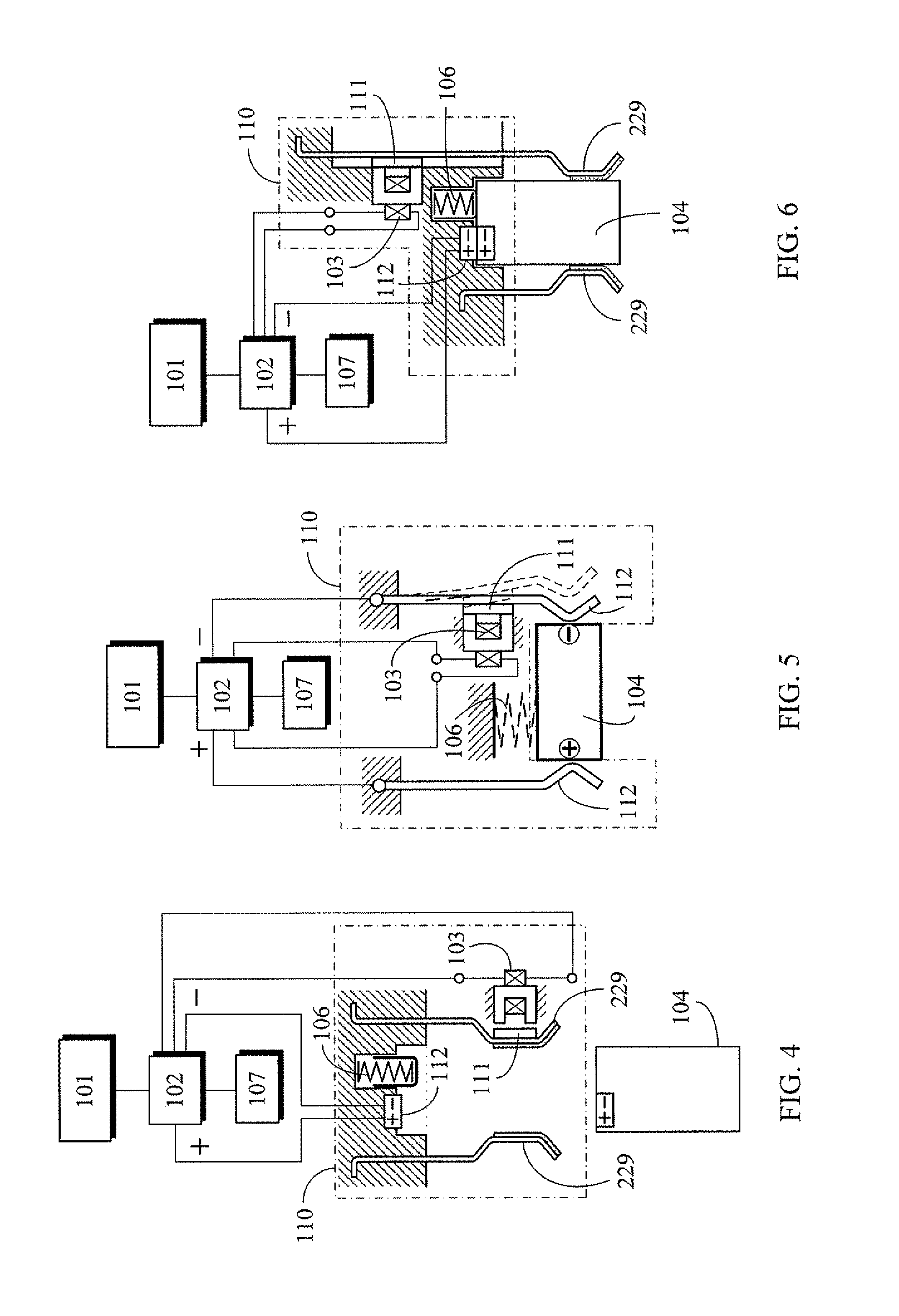
An endoscopic forceps is provided and includes a housing having a shaft that extends therefrom. An end effector assembly is operatively connected to a distal end of the shaft and includes a pair of first and second jaw members that are pivotably coupled to one another and movable relative to one another. The first and second jaw members are disposed in a first configuration, wherein the first and second jaw members are disposed in spaced relation relative to one another, to a second configuration, wherein the first and second jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. A magnetic actuation mechanism is operably coupled to one or both of the first and second jaw members and configured to generate opposing magnetic fields on each of the first jaw and second jaw members to actuate the first and second jaw members between the first and second configurations.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
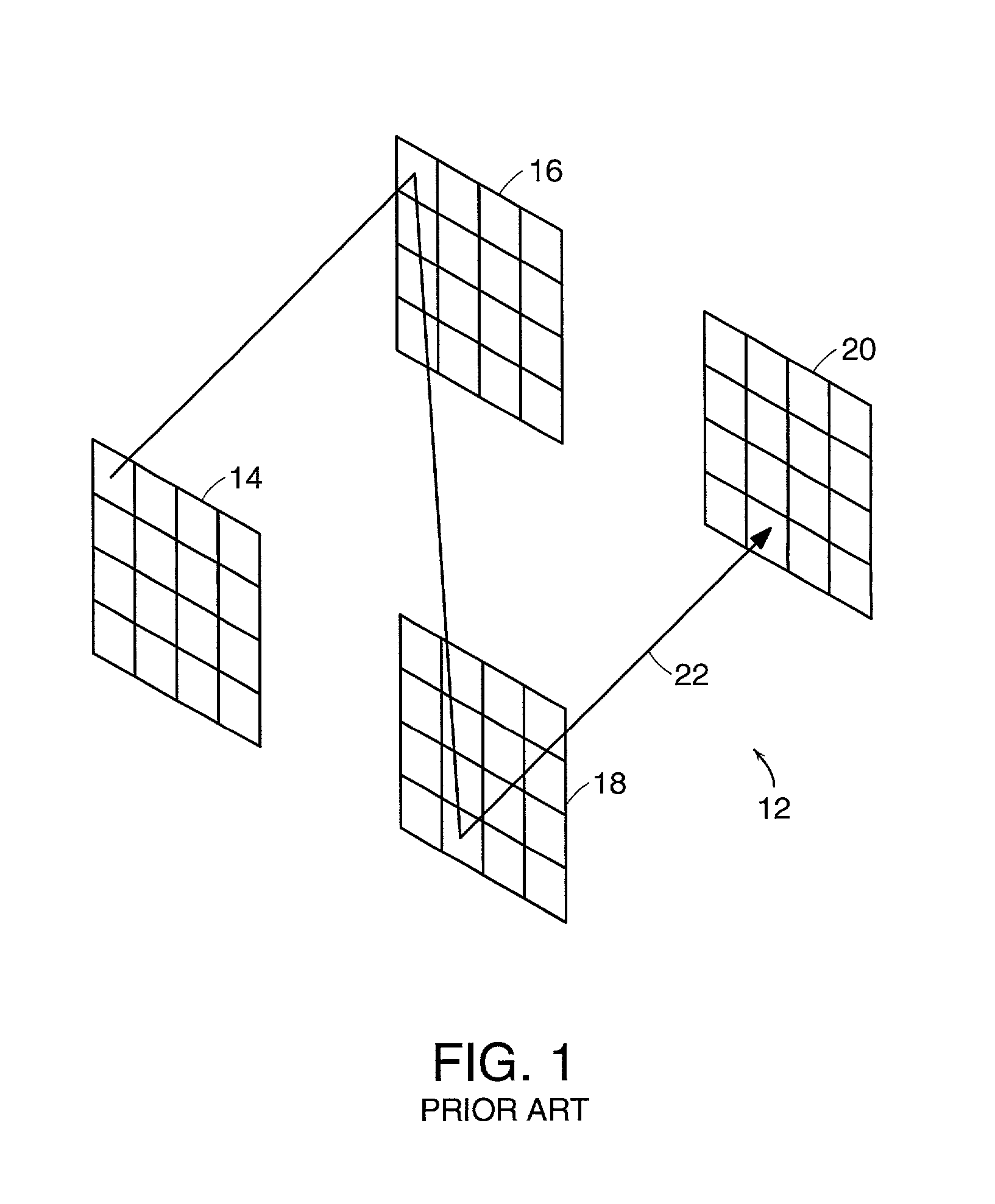
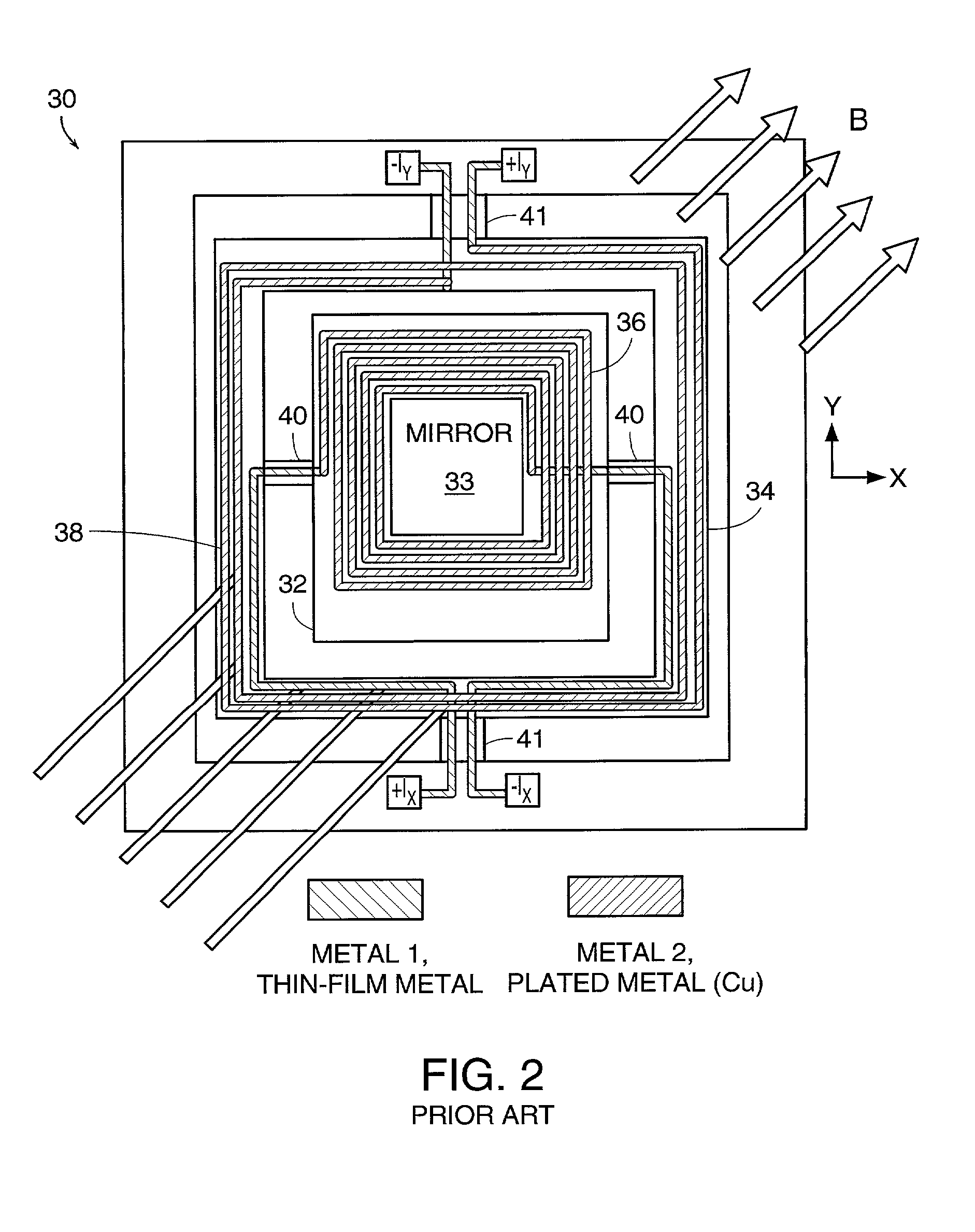
Magnetically actuated micro-electro-mechanical apparatus and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20020050744A1Increase torqueReduce the numberForming microstructural systemsElectrostatic generators/motorsEngineeringMagnet
An array of magnetically actuated MEMS mirror devices is provided having stationary magnets configured to provide strong magnetic fields in the plane of the mirrors without any magnets or magnet-system components in the plane of the mirrors. Also, a magnetically actuated mirror device is provided that includes an improved actuation coil configuration that provides greater torque during mirror actuation. In addition, a mechanism is provided to detect the angular deflection of a moveable mirror. Also, an improved process is provided for manufacturing MEMS mirror devices.
Owner:CORNING INC
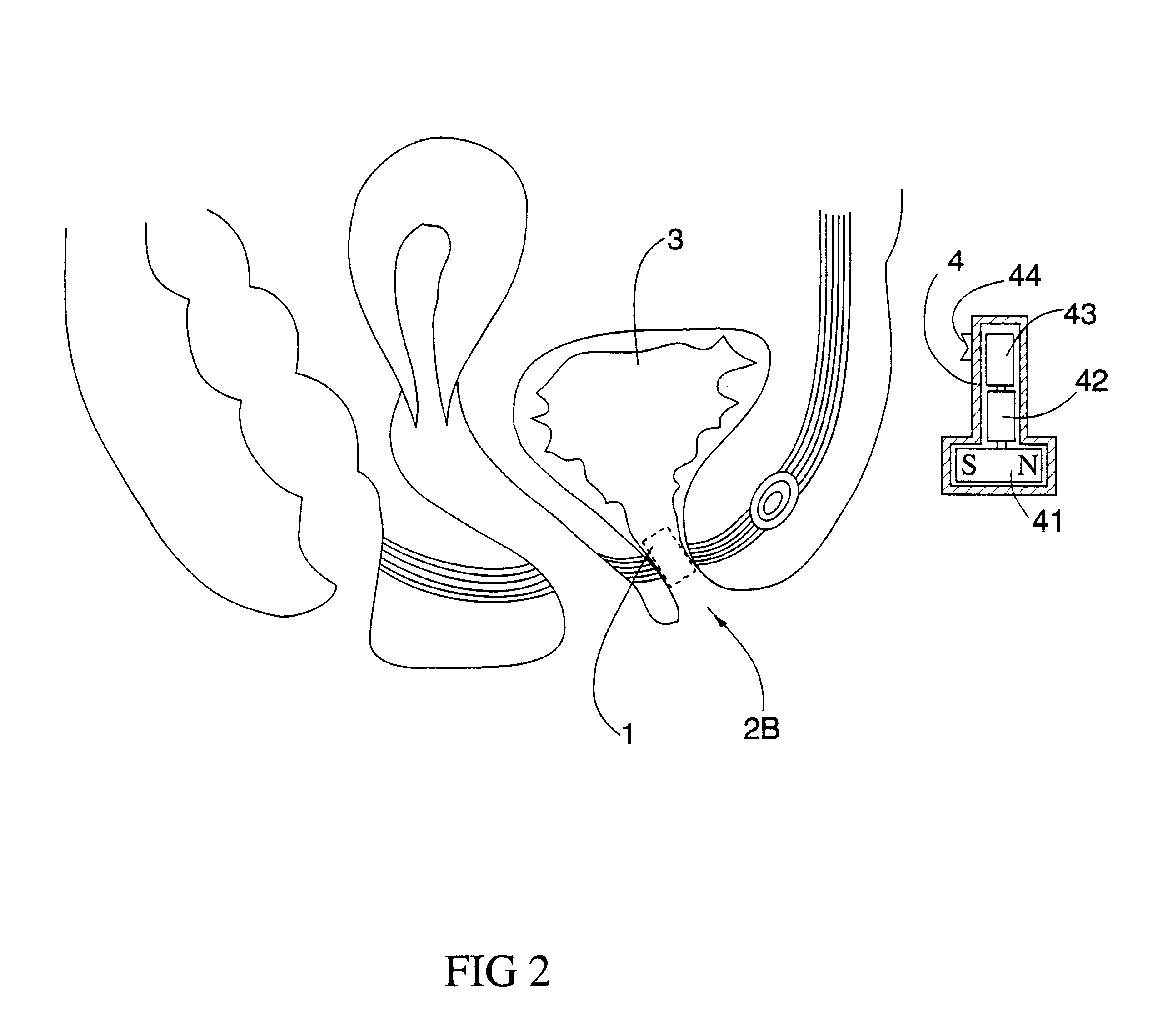
Magnetic actuation urethral valve
InactiveUS6234956B1Easy to installEasy to removeAnti-incontinence devicesMagnetic actuationEngineering
A magnetic actuation urethral valve is adapted for inserting into the urethra of a patient who suffering from urinary incontinence in order to recover control of urine flow. The valve member is driven by a magnet rotor which is magnetically actuated by a rotating magnetic field generated from a controller outside the body. There is also an actuation device for the user to discharge by inserting an indwelling catheter into the valve in case the valve does not work for any reason.
Owner:HE HONGPING +1
Magnetically actuated fast MEMS mirrors and microscanners
InactiveUS20050018322A1Quick scanImprove accuracyMirrorsDiffusing elementsMagnetic actuationEngineering
Magnetically and electromagnetically driven MEMS devices for reflecting light signals and for switching radio frequency (RF) signals are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a light reflecting device such as a mirror or micro-scanner comprises a plate operative to reflect light and at least two conductive flexural actuators connected to the plate and to a substrate and operative to impart a rotation or tilt motion to the plate under a force arising from the interaction of a current passing through the conductive flexural actuators and a magnetic field parallel to the substrate. An RF switch comprises a substrate and a membrane having a longitudinal dimension and a lateral dimension, the membrane positioned substantially parallel to and attached to the substrate and operative to provide at least two switching positions in response to actuation by a Lorenz force acting on it.
Owner:TERRAOP
System comprising magnetically actuated motion control device
InactiveUS20070023244A1Damping frictionSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic actuationMovement control
A system that includes a magnetically actuated motion control device comprising a housing defining a cavity and including a slot therethrough. A movable member is located within the cavity and is movable relative to the housing. A magnetic field generator located on either the housing or the movable member causes the housing to press against the movable member to develop a friction force.
Owner:LORD CORP
Electromagnetic opposing field actuators
ActiveUS20140354381A1Even by forceReduce in quantityPermanent magnetsElectric switchesMagnetic actuationEngineering
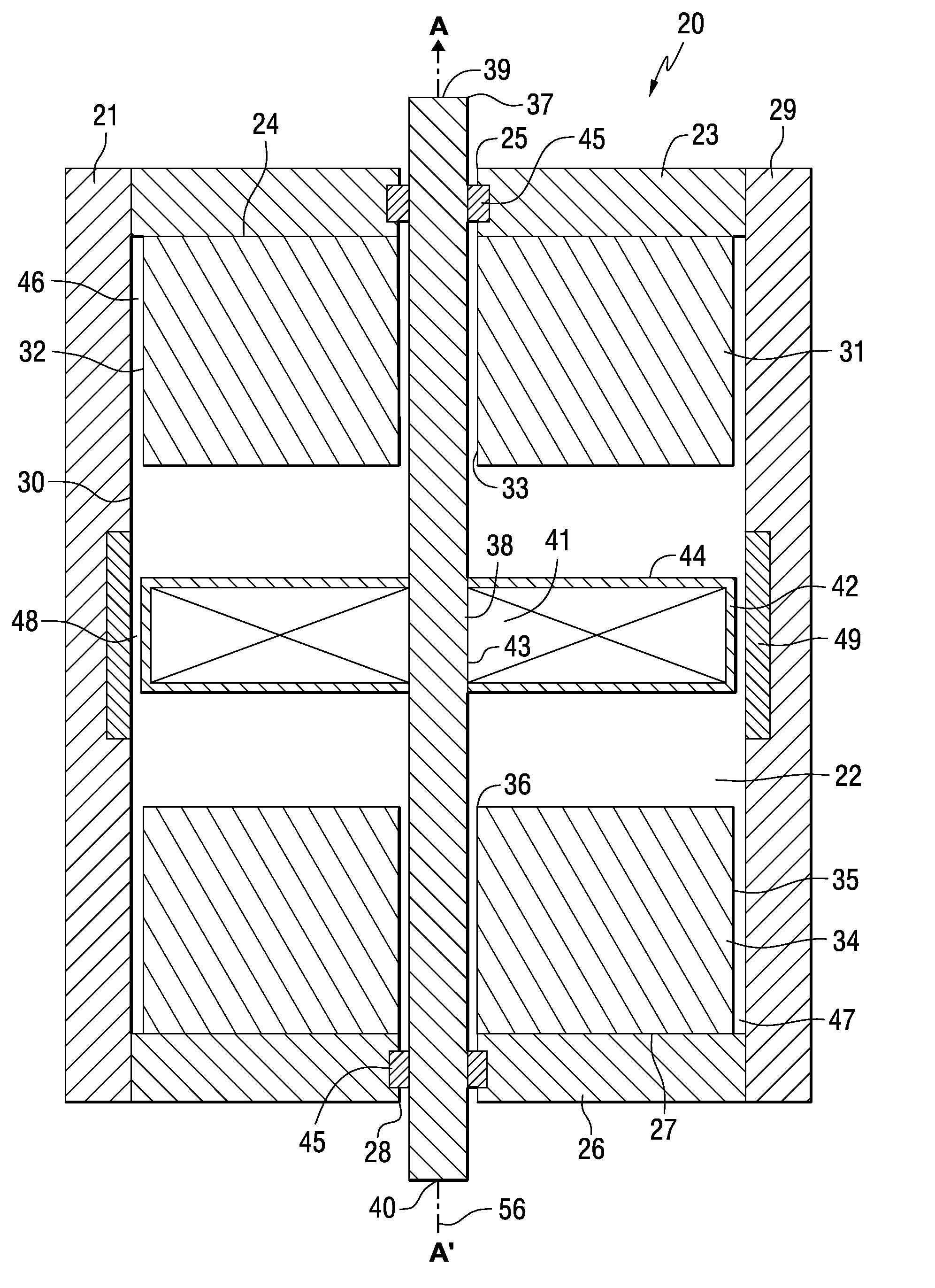
Electromagnetic actuators capable of generating a symmetrical bidirectional force are disclosed. The electromagnetic actuators include a housing made of a ferromagnetic material and a shaft made of a magnetically inert material movable along an axis within the housing. In one type of actuator, captive permanent magnets are arranged on opposite interior end walls of the housing and an electromagnetic coil is mounted on a central portion of the shaft. The electromagnetic coil is capable of generating a force when energized that causes linear displacement of the shaft in either direction along its axis depending on the direction of current through the electromagnetic coil. In another type of actuator, captive electromagnetic coils are arranged on opposing inner end walls of the housing, and a permanent magnet is mounted on a central portion of the shaft. The electromagnetic coils are capable of generating a force when energized that causes linear displacement of the shaft in either direction along its axis depending on a direction of current through the electromagnetic coils.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
Apparatus for Performing an Electrosurgical Procedure
ActiveUS20110301602A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsMagnetic actuationElectrosurgery
An endoscopic forceps is provided and includes a housing having a shaft that extends therefrom. An end effector assembly is operatively connected to a distal end of the shaft and includes a pair of first and second jaw members that are pivotably coupled to one another and movable relative to one another. The first and second jaw members are disposed in a first configuration, wherein the first and second jaw members are disposed in spaced relation relative to one another, to a second configuration, wherein the first and second jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. A magnetic actuation mechanism is operably coupled to one or both of the first and second jaw members and configured to generate opposing magnetic fields on each of the first jaw and second jaw members to actuate the first and second jaw members between the first and second configurations.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Bistable microelectromechanical system based structures, systems and methods
InactiveUS20030210115A1Increase flexibilityReduce complexityElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCoupling light guidesStable stateThermal impact
A bistable microelectromechanical system (MEMS) based system comprises a micromachined beam having a first stable state, in which the beam is substantially stress-free and has a specified non-linear shape, and a second stable state. The curved shape may comprises a simple curve or a compound curve. In embodiments, the boundary conditions for the beam are fixed boundary conditions, bearing boundary conditions, spring boundary conditions, or a combination thereof. The system may further comprise an actuator arranged to move the beam between the first and second stable states and a movable element that is moved between a first position and a second position in accordance with the movement of the beam between the first and second stable states. The actuator may comprise one of a thermal actuator, an electrostatic actuator, a piezoelectric actuator and a magnetic actuator. The actuator may further comprise a thermal impact actuator or a zippering electrostatic actuator.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Electromagnetic actuator and composite electromagnetic actuator apparatus
InactiveUS6960847B2Low priceImprove performanceTrack finding/aligningMaster clocksMagnetic actuationClassical mechanics
An electromagnetic actuator with high performance such as high speed and high resolution is inexpensively provided with solutions to problems associated with power supply and leakage flux, which have been involved in the structure of a moving coil type and have been shortcomings of a VCM type actuator. A composite electromagnetic actuator apparatus employs the foregoing electromagnetic actuator. The electromagnetic actuator is equipped with a stationary assembly that includes two coils disposed coaxially with each other inside a hollow stator yoke composed of a soft magnetic material, and a movable assembly composed of a movable magnet unit and a movable yoke unit both disposed inside the coils with a very small clearance therefrom so as to be movable in the axial direction, wherein the movable assembly travels in the axial direction by the interaction between a magnetic field generated by the movable magnet unit and a current passing through the coils.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Magnetically actuated float switch
InactiveUS6140925AUniform and consistent forceIncrease attractivenessMachines/enginesAlarmsFloat switchMagnet
A magnetically actuated float switch for turning on and off an electrical load device which includes a mounting member, a moveable bracket member which is attached to the mounting member and which is moveable between a first bracket position and a second bracket position by an external force. The moveable bracket member further has a first magnetic end and a second magnetic end which define a space therebetween. The first magnetic end and second magnetic end are oriented in a repelling arrangement. Insertion of a magnet in the space between the magnetic ends of the bracket results in the moveable bracket being moved from the first position to the second position. The moveable bracket member is operatively arranged to change the state of a switch between a first and second state. The switch is in turn operably arranged to change the state of an electrical load device between an on state and an off state.
Owner:S J ELECTRO SYST INC
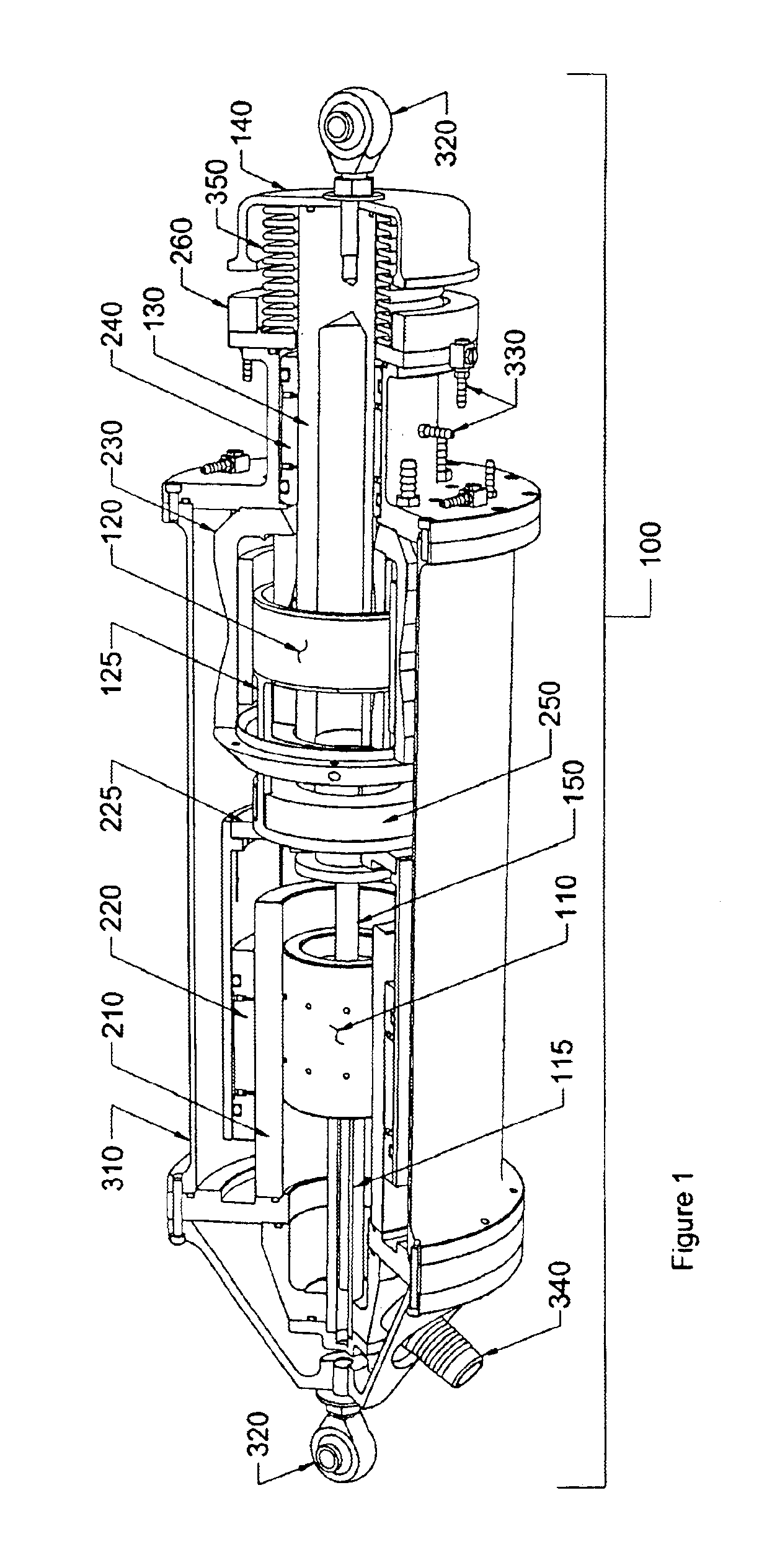
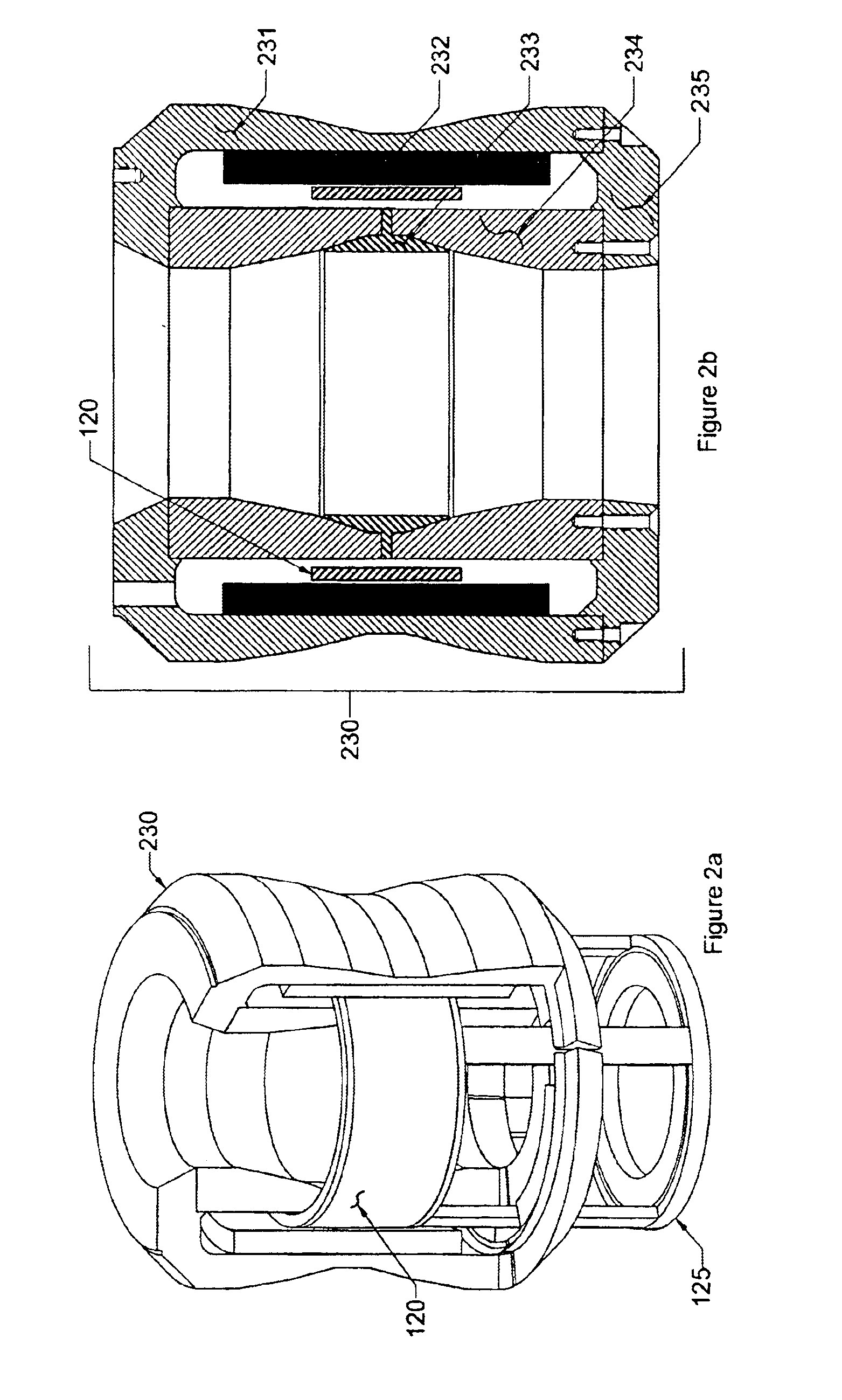
Permanent-magnet magnetic actuator of reduced volume
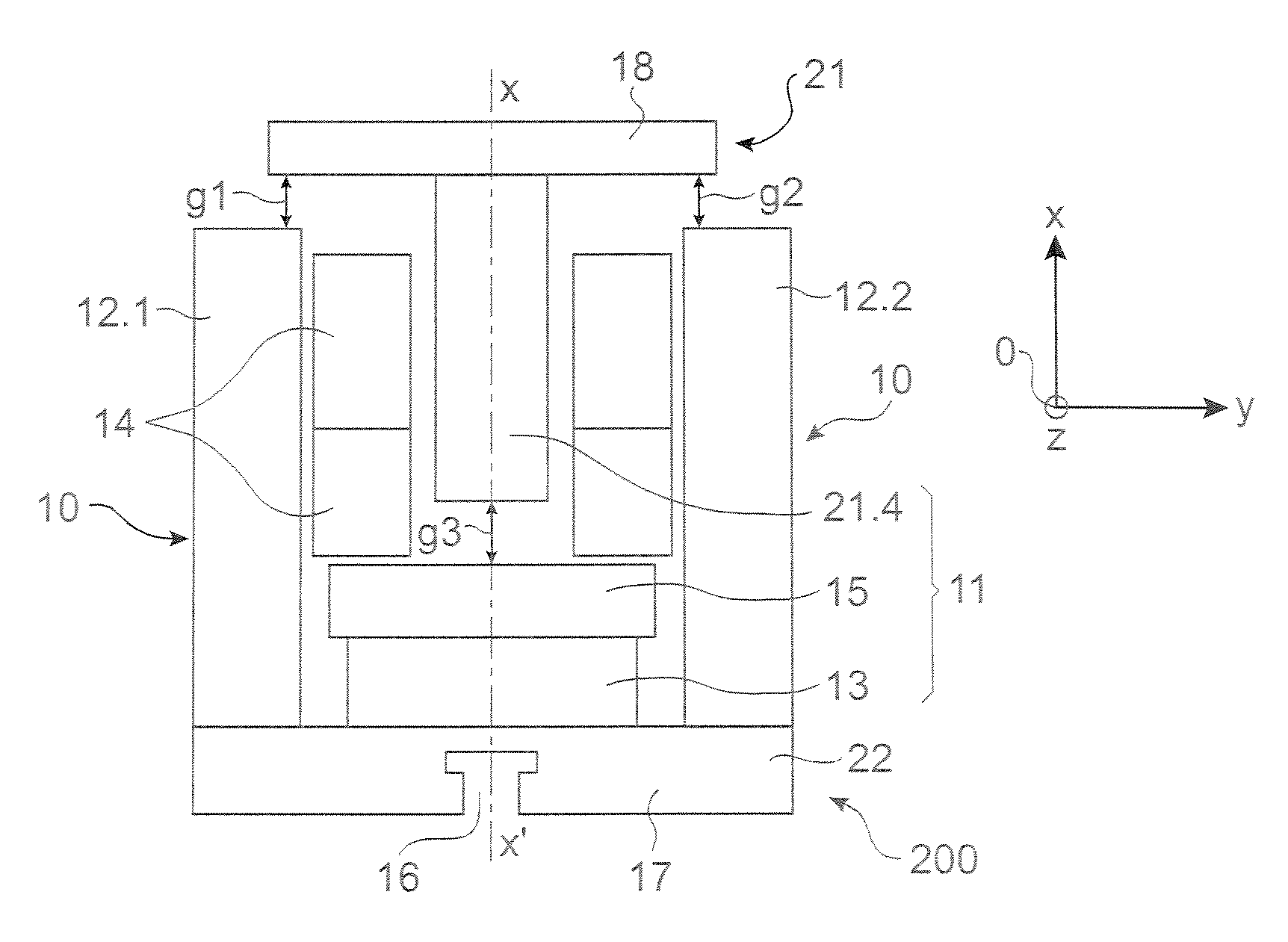
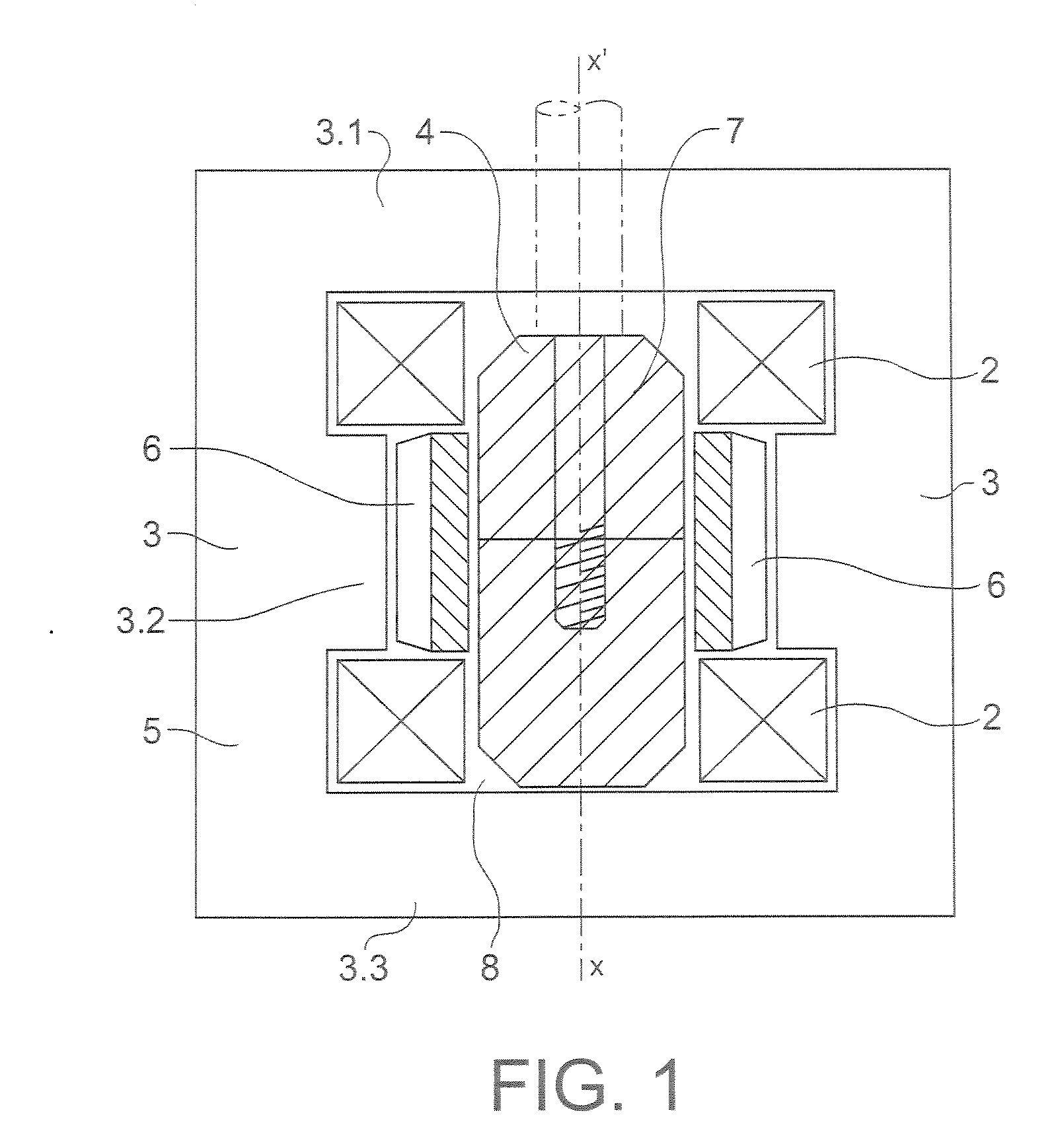
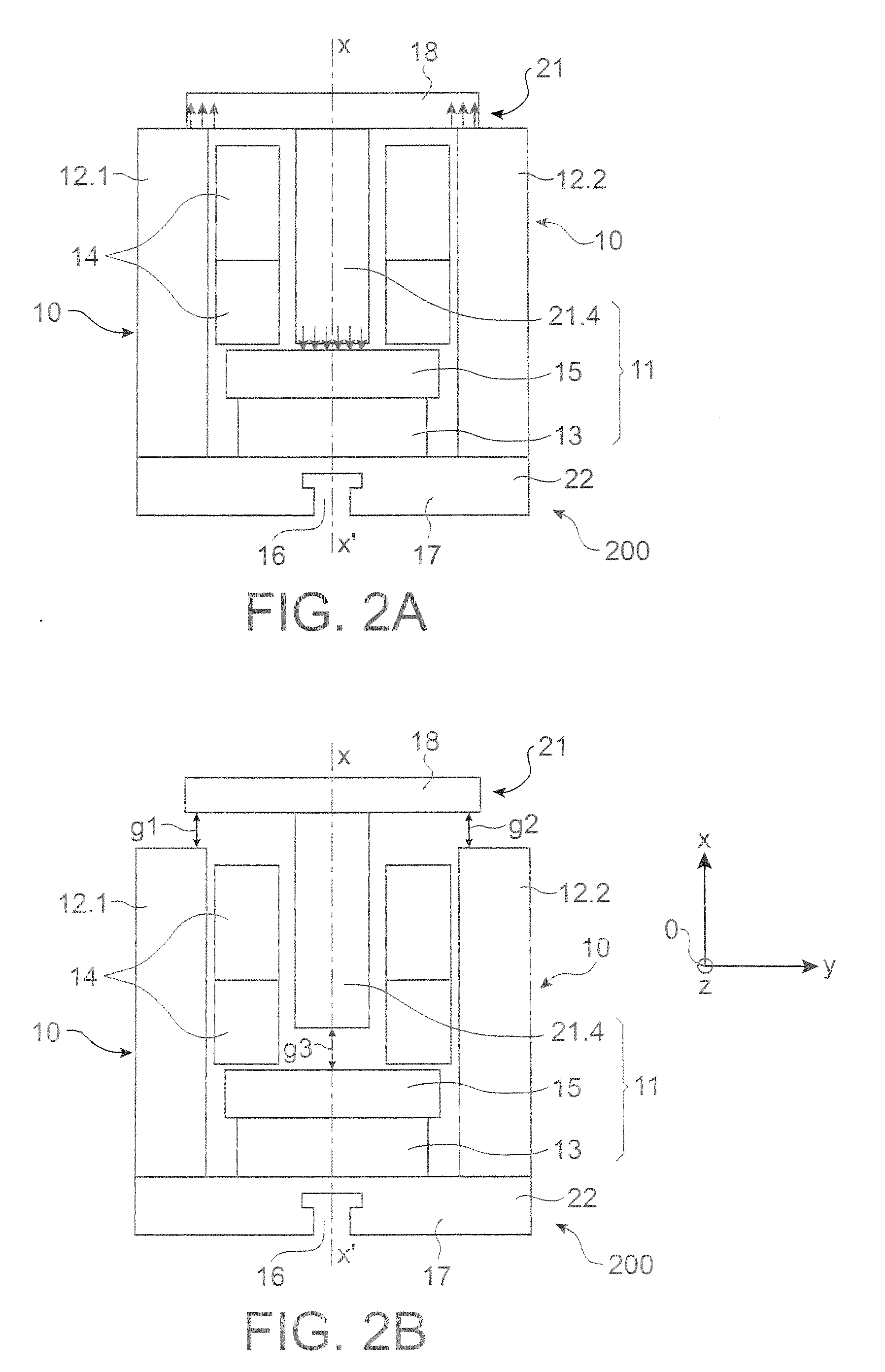
InactiveUS20070171016A1Easy to fixEasy can be made in modularHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectromagnets with armaturesMagnetic actuationEngineering
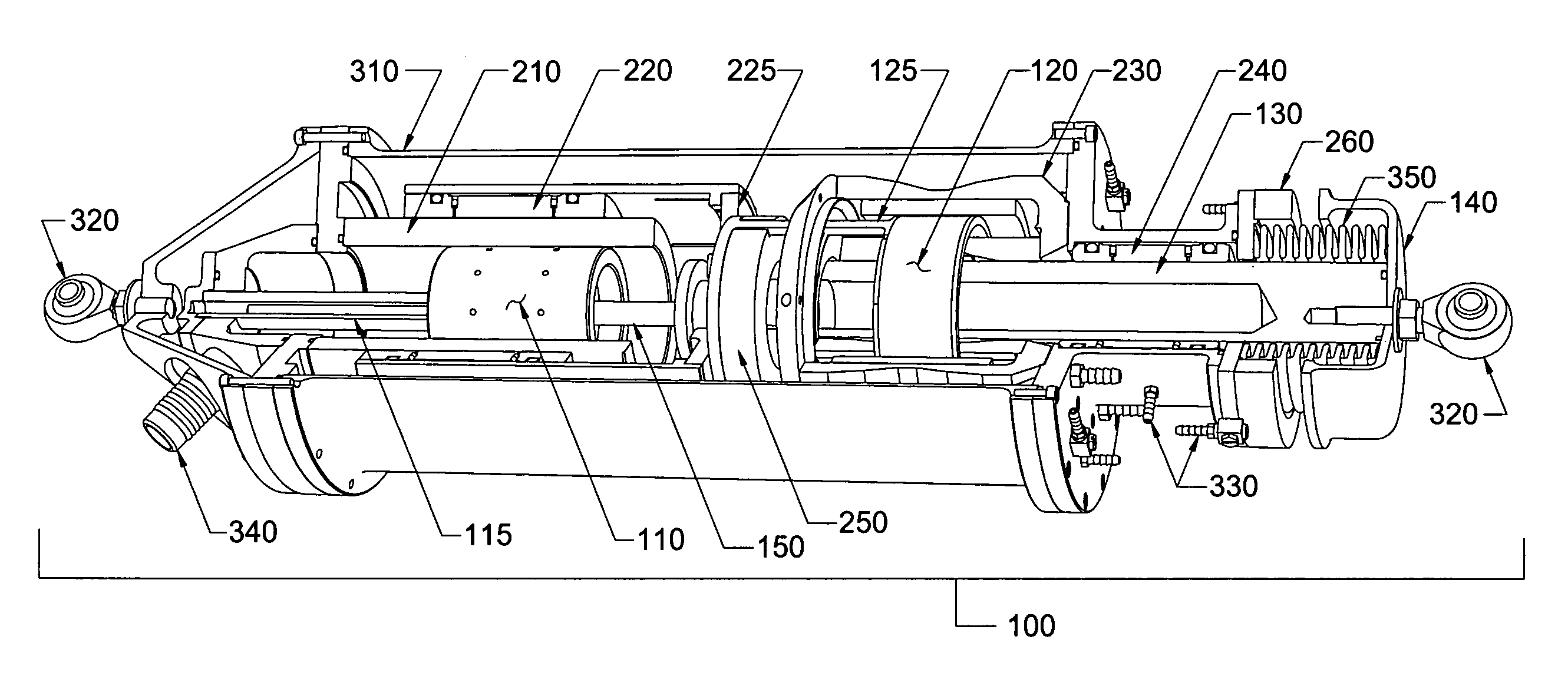
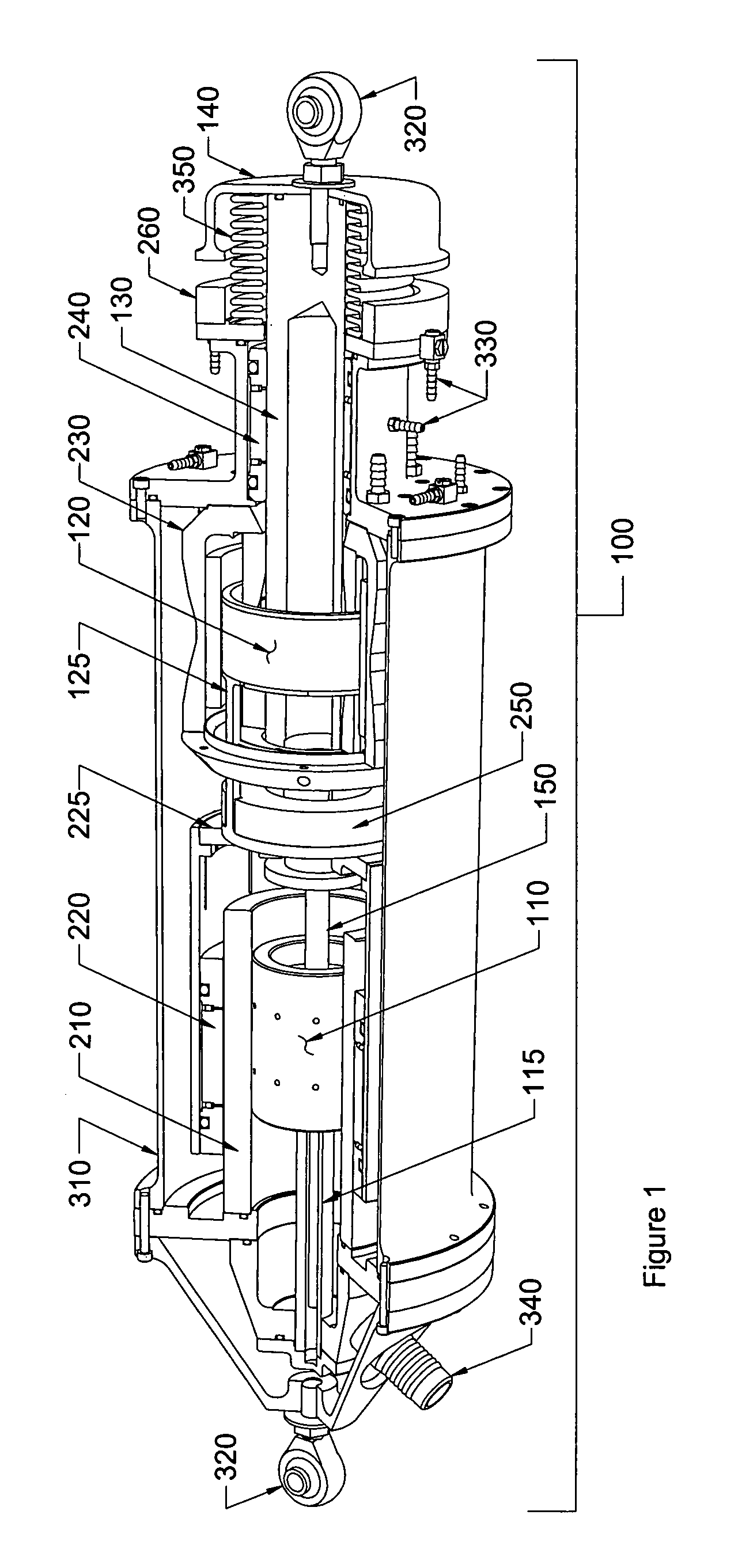
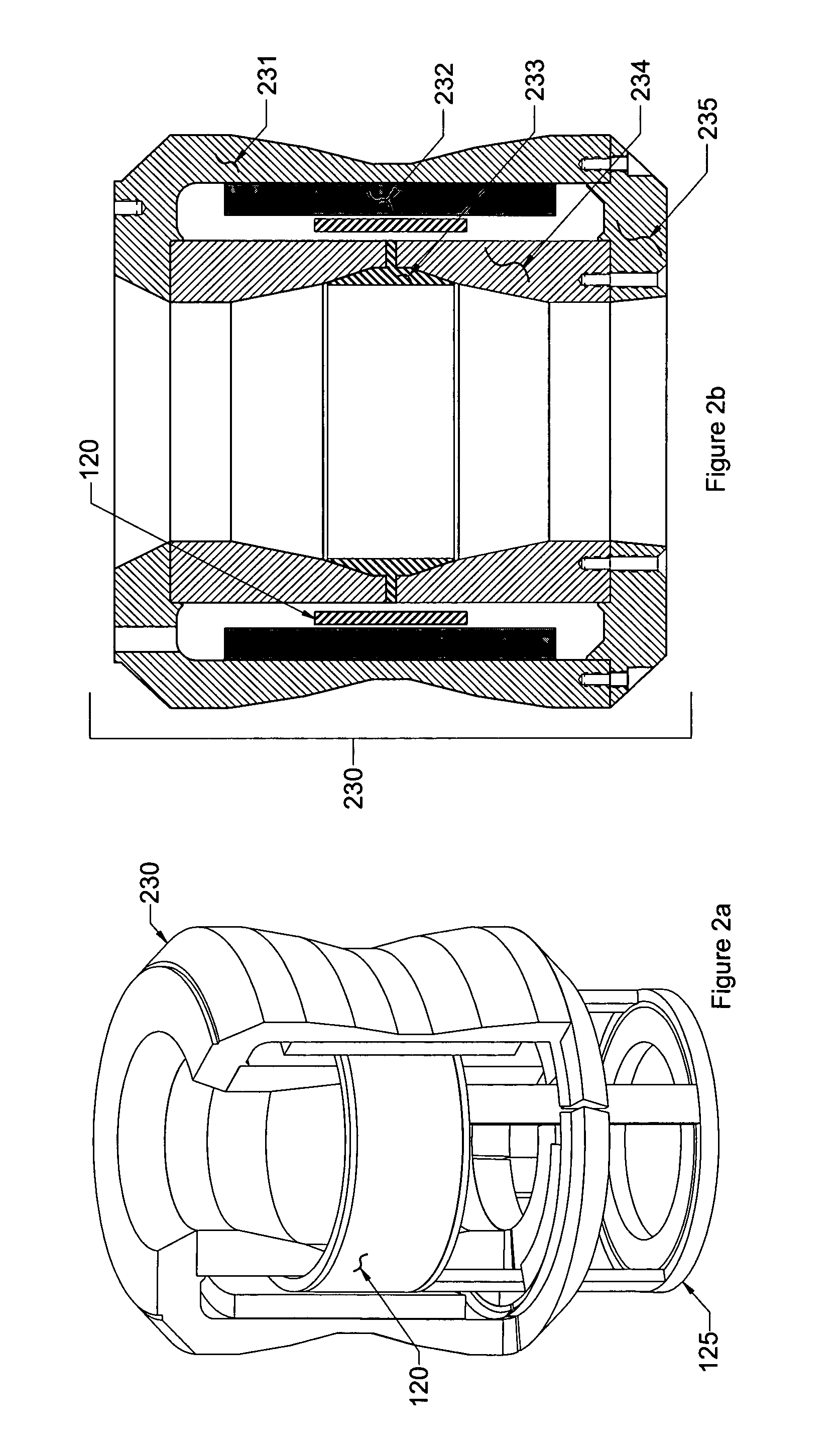
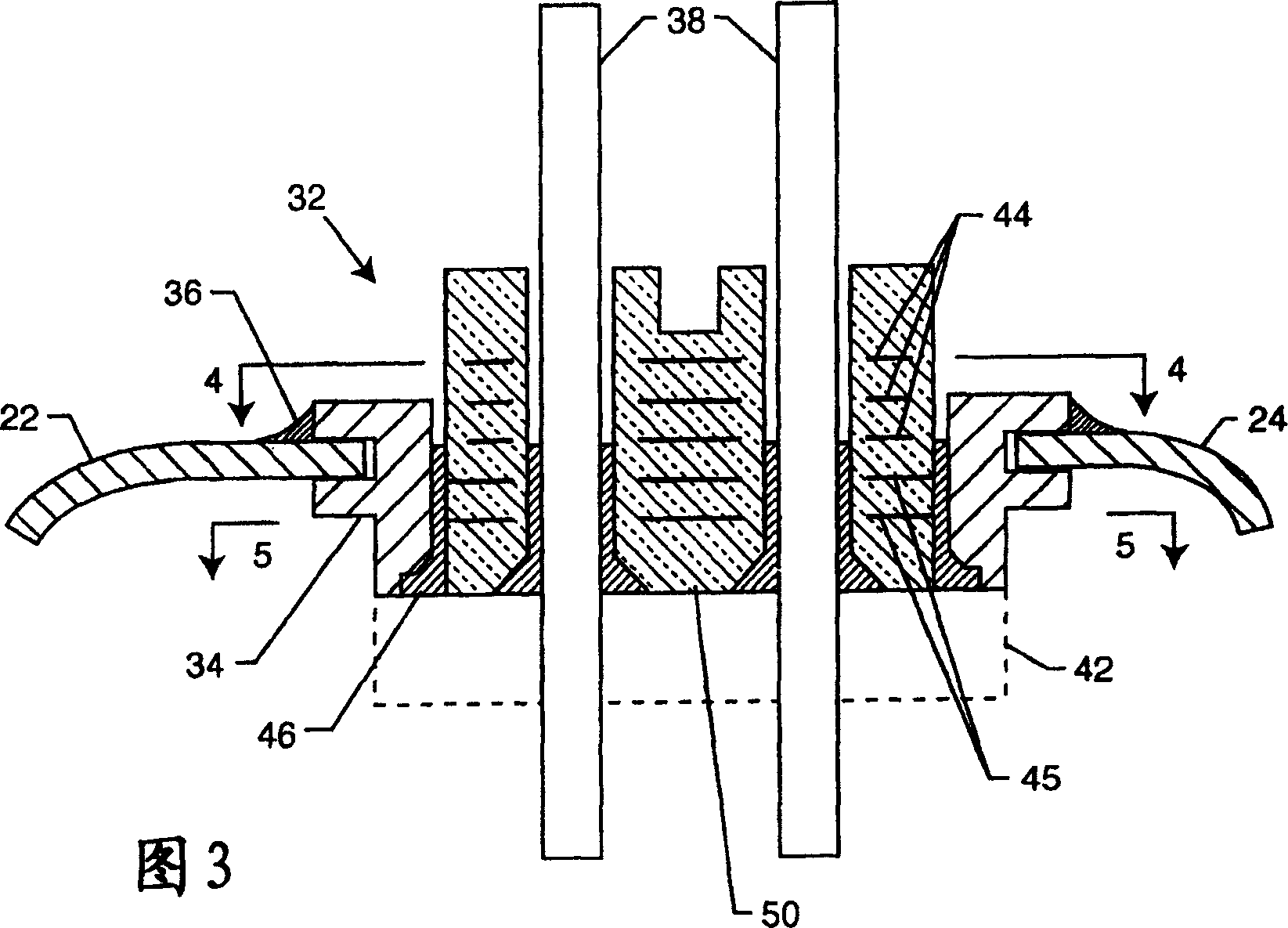
The invention relates to a magnetic actuator comprising at least one coil (14) surrounded by a magnetic circuit (10), the magnetic circuit possessing: three legs (12.1, 12.2, 11), comprising two outer legs on either side of the coil (14) and an intermediate leg passing through the coil, these legs having no direct mechanical contact with one another; and two facing end plates (17, 18) magnetically interconnecting the three legs (12.1, 12.2, 11). The magnetic circuit comprises a moving armature (21) comprising at least one of the end plates (18), and a stationary portion (200) including a yoke (22) having at least the other one of the end plates (17) and at least one permanent magnet (13), the permanent magnet (13) being placed at one end of the intermediate leg (11) beside the end plate (17) of the yoke (22). The invention is applicable to controlling medium-voltage and high-voltage circuit breaker vacuum chambers.
Owner:AREVA T&D
Hybrid pneumatic-magnetic isolator-actuator
InactiveUS6942202B2Large forceLarge strokeNon-rotating vibration suppressionStands/trestlesMagnetic actuationAir bearing
The invention disclosed is a compact and lightweight hybrid pneumatic-magnetic isolator-actuator capable of large force, substantial stroke and bandwidth actuation with near frictionless operation and vibration isolation with very low break frequency. Pneumatic and magnetic forces are applied to a single carriage comprised primarily of a coaxially arranged air piston and coil. The carriage is driven relative to a frame or housing including an internally mounted cylindrical piston sleeve and magnetic actuator body. A combination of air bearings and air bearing piston construction provide for frictionless motion of the carriage relative to the frame. The pneumatic piston provides the actuation force for both static loads and low frequency dynamic loads. An integrally mounted sensor and control unit determine the pressure error resulting at the pneumatic piston. The control unit utilizes the pressure error to drive a high bandwidth magnetic actuation capability in parallel with the pneumatic actuation capability. An air tank of prescribed volume may be connected to the pneumatic piston for effecting a desired air-spring stiffness upon the isolator-actuator.
Owner:MOOG INC
Electromagnetic actuator
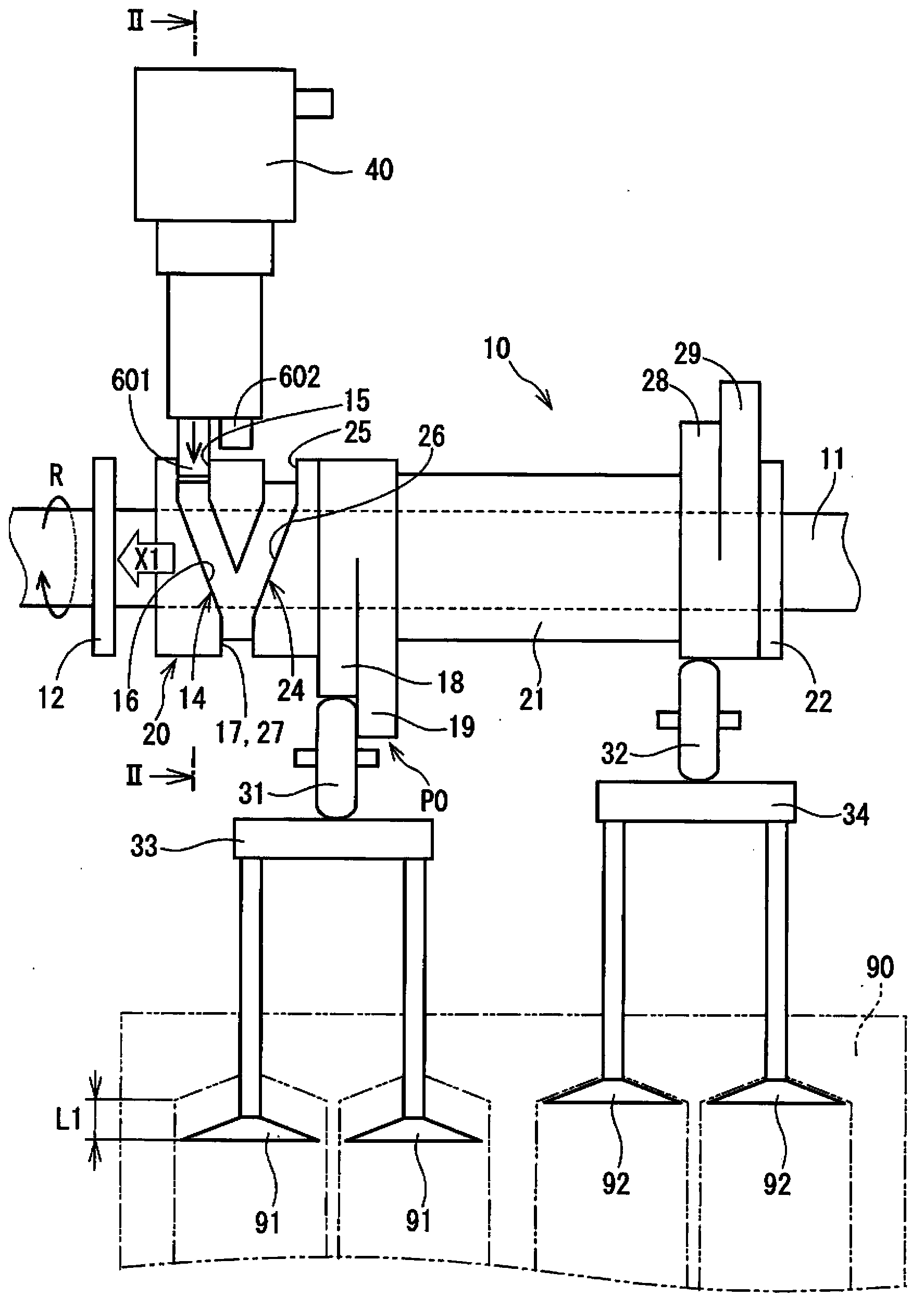
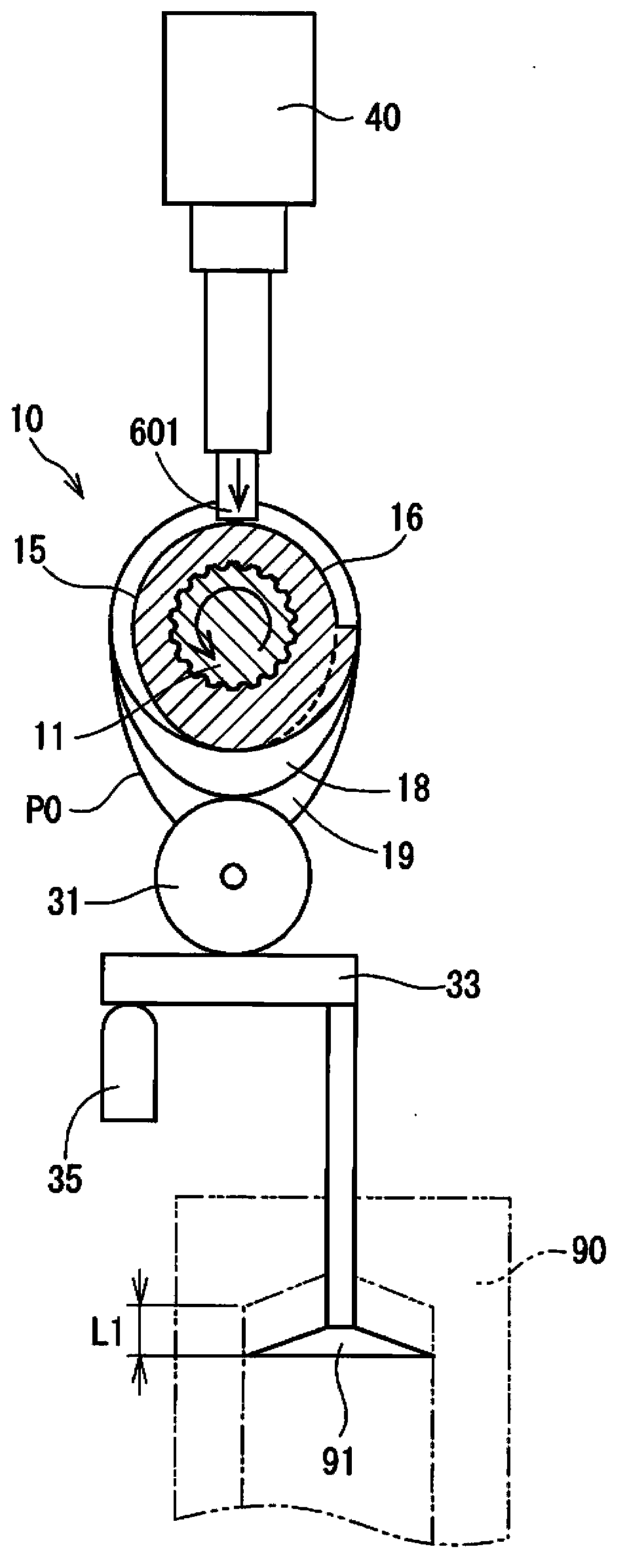
InactiveCN103423503AOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesEngineeringMagnetic flux
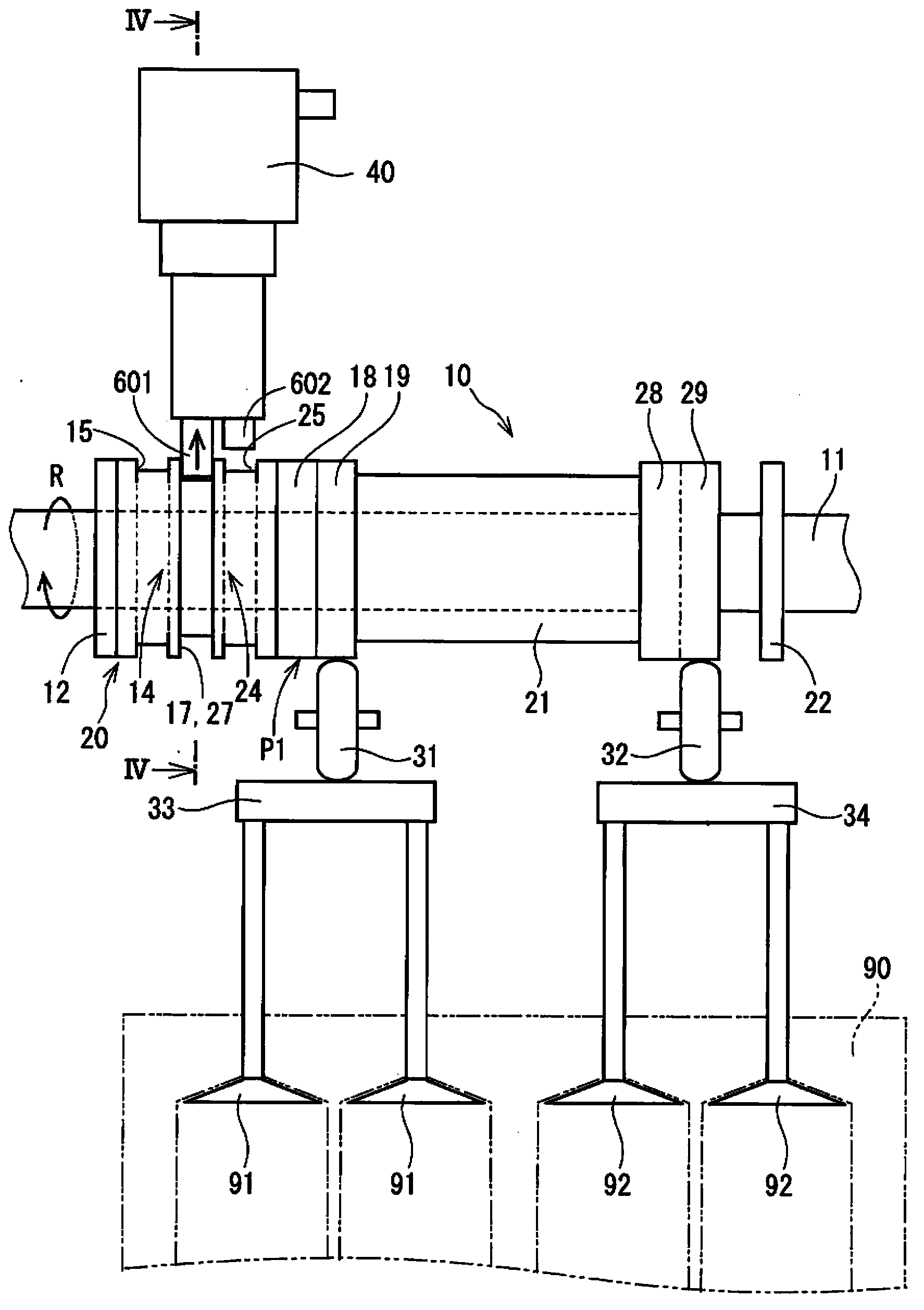
The actuator (40) has two permanent magnets located in two pistons, respectively, and a coil for producing a coil magnetic flux. One of the selected permanent magnets produces a magnetic force such that such that a magnet attractive force produced by the selected permanent magnet is reduced. Two springs pretension two control pins (601, 602) in a forward direction, respectively, where the pins move towards engaging grooves (14, 24) in the forward direction. The coil is alternately energized in two directions such that the direction of the flux is changed in the two directions.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Hybrid pneumatic-magnetic isolator-actuator
InactiveUS6959795B2Large forceLarge strokeNon-rotating vibration suppressionStands/trestlesMagnetic actuationAir bearing
The invention disclosed is a compact and lightweight hybrid pneumatic-magnetic isolator-actuator capable of large force, substantial stroke and bandwidth actuation with near frictionless operation and vibration isolation with very low break frequency. Pneumatic and magnetic forces are applied to a single carriage comprised primarily of a coaxially arranged air piston and coil. The carriage is driven relative to a frame or housing including an internally mounted cylindrical piston sleeve and magnetic actuator body. A combination of air bearings and air bearing piston construction provide for frictionless motion of the carriage relative to the frame. The pneumatic piston provides the actuation force for both static loads and low frequency dynamic loads. An integrally mounted sensor and control unit determine the pressure error resulting at the pneumatic piston. The control unit utilizes the pressure error to drive a high bandwidth magnetic actuation capability in parallel with the pneumatic actuation capability. An air tank of prescribed volume may be connected to the pneumatic piston for effecting a desired air-spring stiffness upon the isolator-actuator.
Owner:MOOG INC
System comprising magnetically actuated motion control device
A system that includes a magnetically actuated motion control device comprising a housing defining a cavity and including a slot therethrough. A movable member is located within the cavity and is movable relative to the housing. A magnetic field generator located on either the housing or the movable member causes the housing to press against the movable member to develop a friction force.
Owner:CARLSON J DAVID +1
Magnetic assembly for magnetically actuated control devices
ActiveUS20050077989A1Increase distanceElectromagnetic relaysMagnetic/electric field switchesMagnetic actuationState of art
A magnetically actuated apparatus, which enlarges, extends and makes continuous magnetic fields used by magnetically controlled devices, such as a magnetic reed switch for use in physical security monitoring systems is shown. Apparatus includes a sensor and a magnetic actuator for use with a movable closure member. The sensor is mounted into to a fixed support member that is arranged for displacement relative to a second movable support member. The sensor has a pair of contacts that are connectable to an electronic circuit. The contacts form a switch that is actuated by the magnetic actuator. The magnetic actuator comprises a unique elongated magnet with specific polarity or a plurality of aligned, alike permanent magnets that are mountable to the second support member. The aligned magnets have like magnetic fields that align one another and combine to form an effective magnetic actuation field that has a given magnitude and a given direction that is greater that the magnitude and direction than any one of the magnets. The elongated magnet has a specific pole for a given distance as its controlling means. The effective magnetic actuation field increases the distance in which the movable support member is displaceable relative to the fixed support member without changing the electric condition of the sensor. The present invention creates a magnetic apparatus, having a wider and controllable gap and break point distance not found in the present art.
Owner:EDMONSON JR MAHLON WILLIAM
Medical Devices, Apparatuses, Systems, and Methods for Magnetic Transmural and/or Transdermal Activation of Medical Tools
Systems, methods, apparatuses, and medical devices configured for transmural and / or transdermal magnetic actuation of a tool of a medical device (e.g., without translation of the medical device and / or relative to a platform of the medical device).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
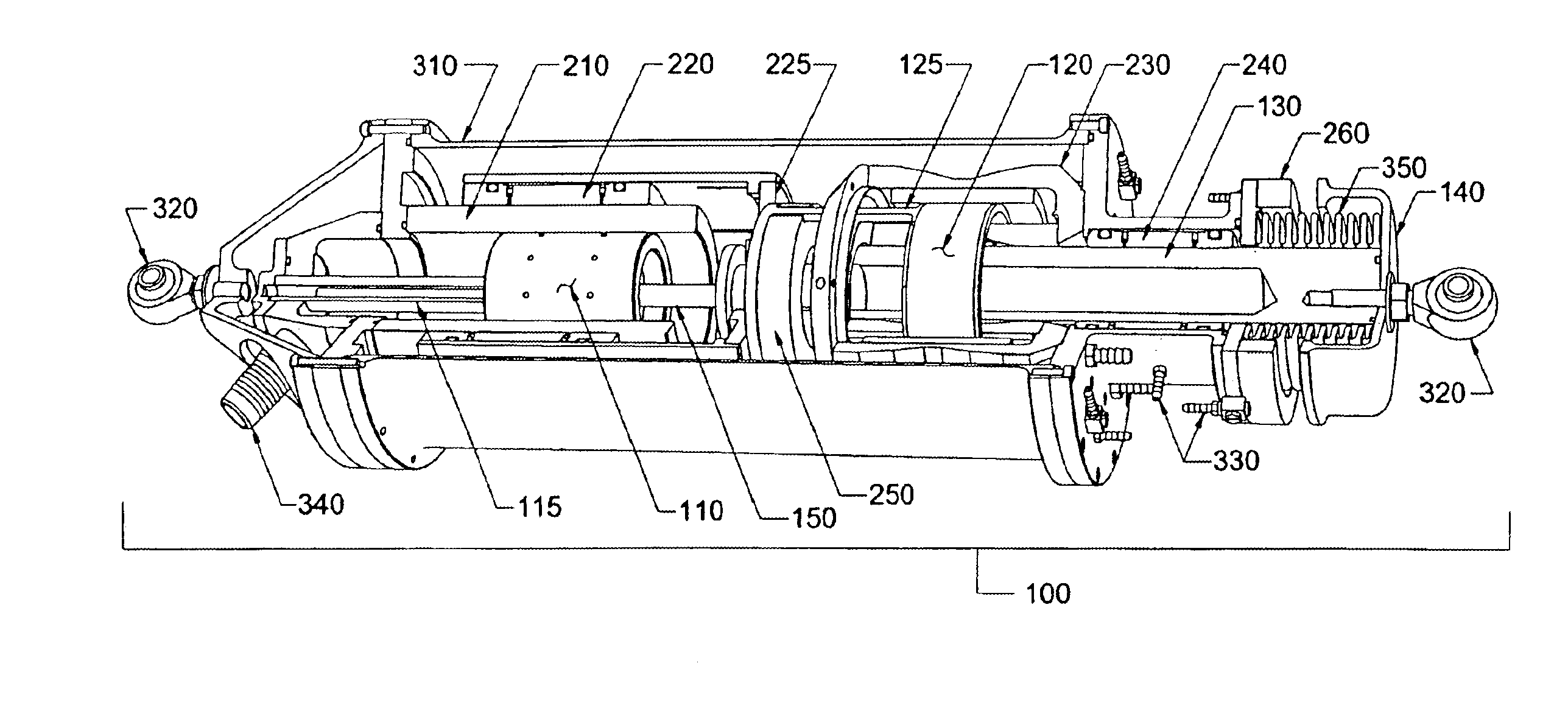
Method and apparatus for magnetic actuation of variable pitch impeller blades
An integrated propulsion and guidance system for a vehicle includes an engine coupled to an impeller via a driveshaft to produce propulsive force. The impeller includes a hub and a plurality of blades, including at least one control blade pivotably mounted to the hub. A control system provides a control signal to a magnetic actuator to adjust the blade pitch of the control blades as the blades rotate about the hub. The change in blade pitch produces a torque on the driveshaft that can be used to control the heading of the vehicle.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
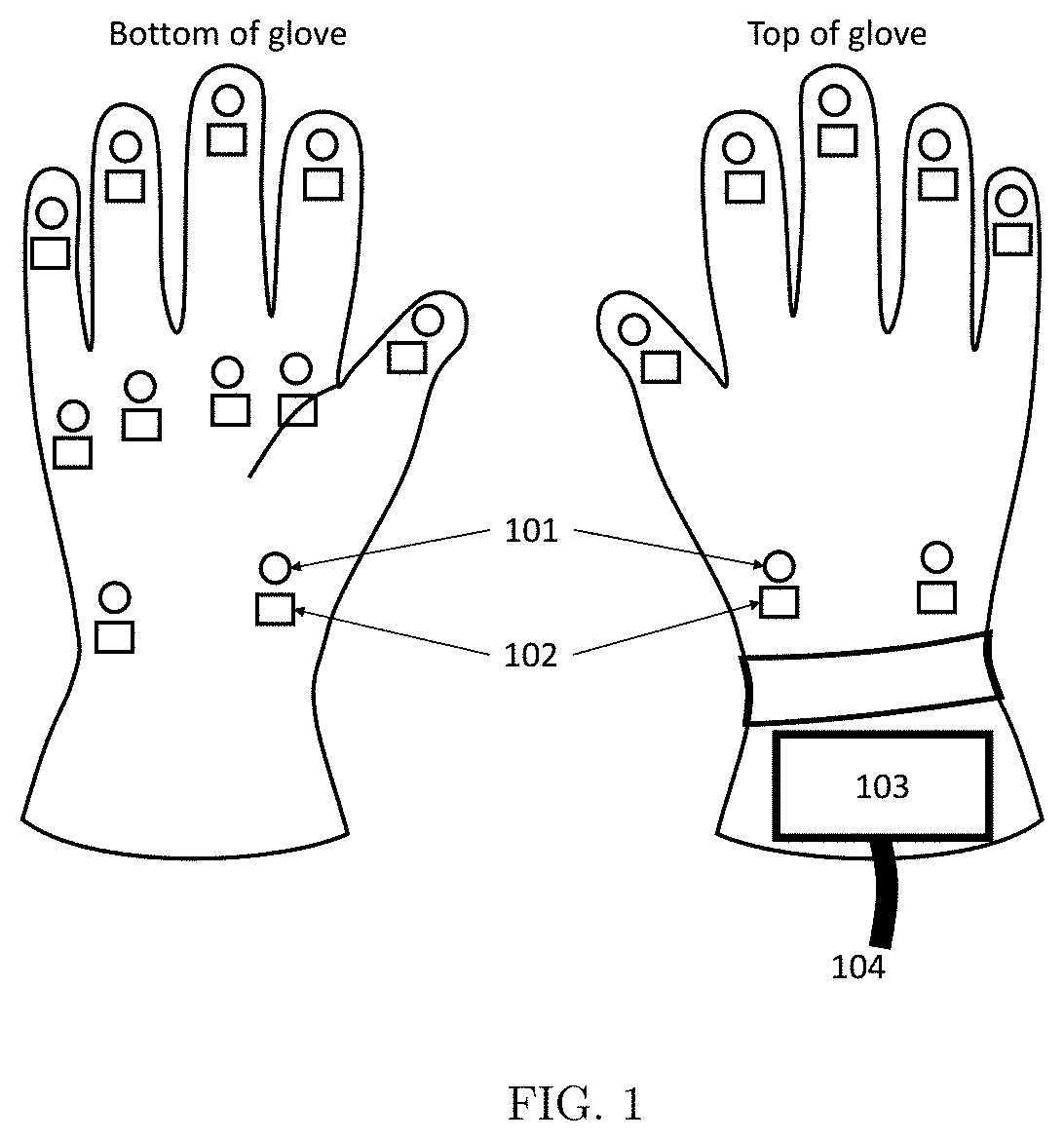
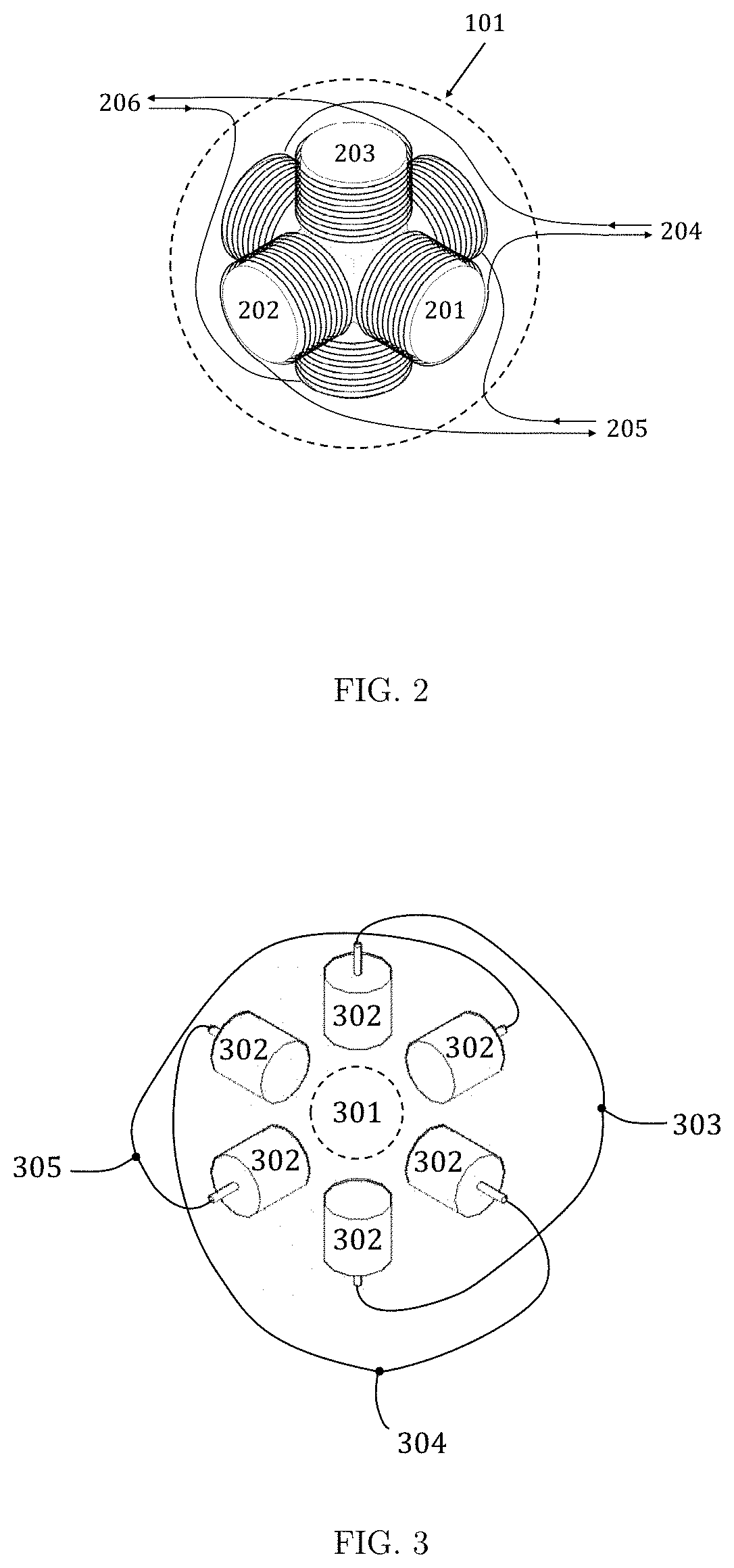
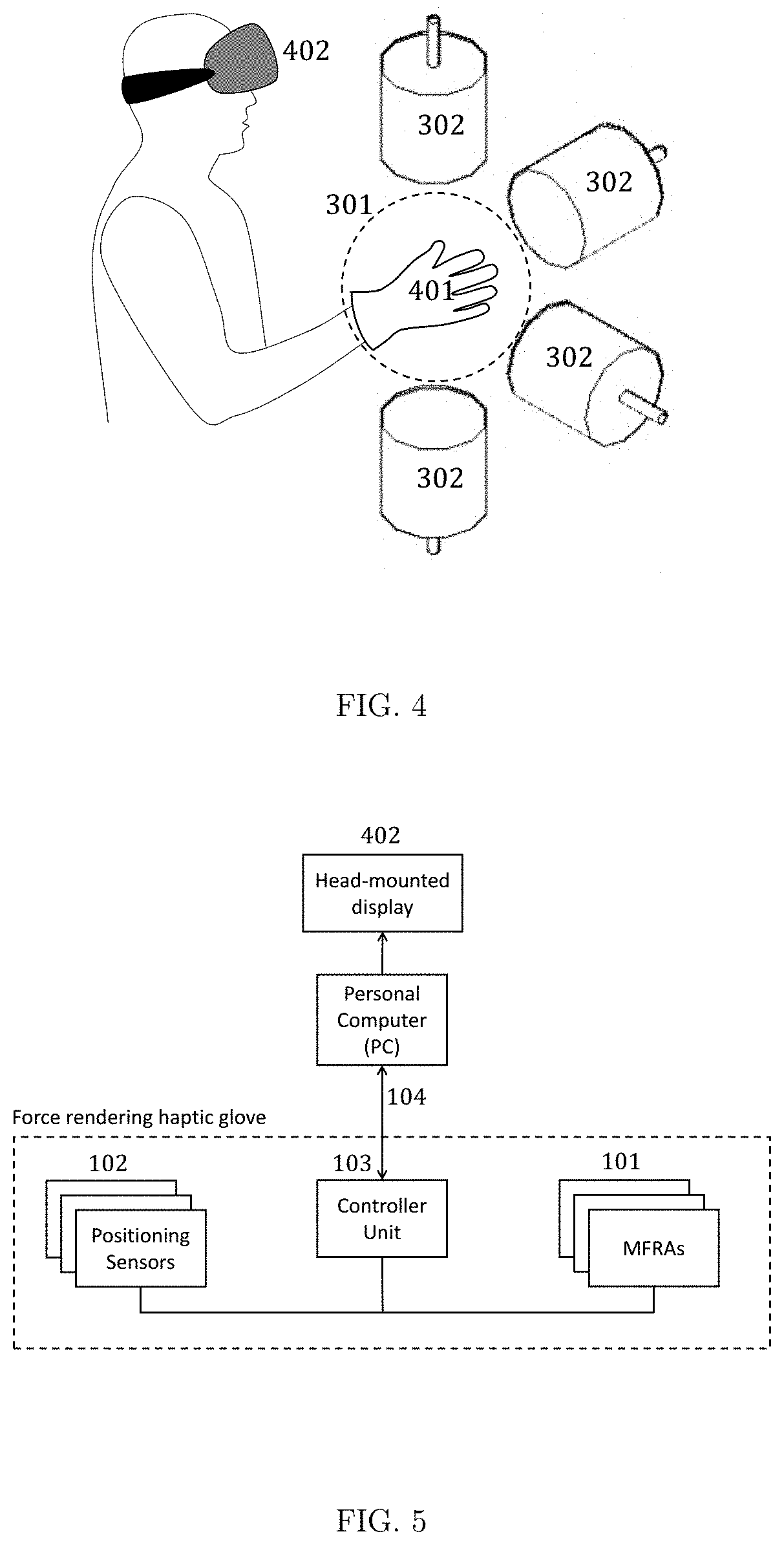
Force Rendering Haptic Glove
InactiveUS20190377412A1Adding sense of touchInput/output for user-computer interactionVideo gamesHaptic gloveEngineering
A force rendering haptic glove interface is presented that has multiple magnetic actuators positioned on the glove. Each magnetic actuator includes multiple small electromagnetic coils. Multiple positioning sensors are placed on the glove. An external magnetic field generation setup is provided that consists of multiple stationary electromagnetic coils. A controller unit is placed on the glove cuff that receives the position of the sensors and controls the electrical current of electromagnetic coils in the actuators on the glove based on received force feedback data.
Owner:PARASTEGARI MOHAMMAD SINA +1
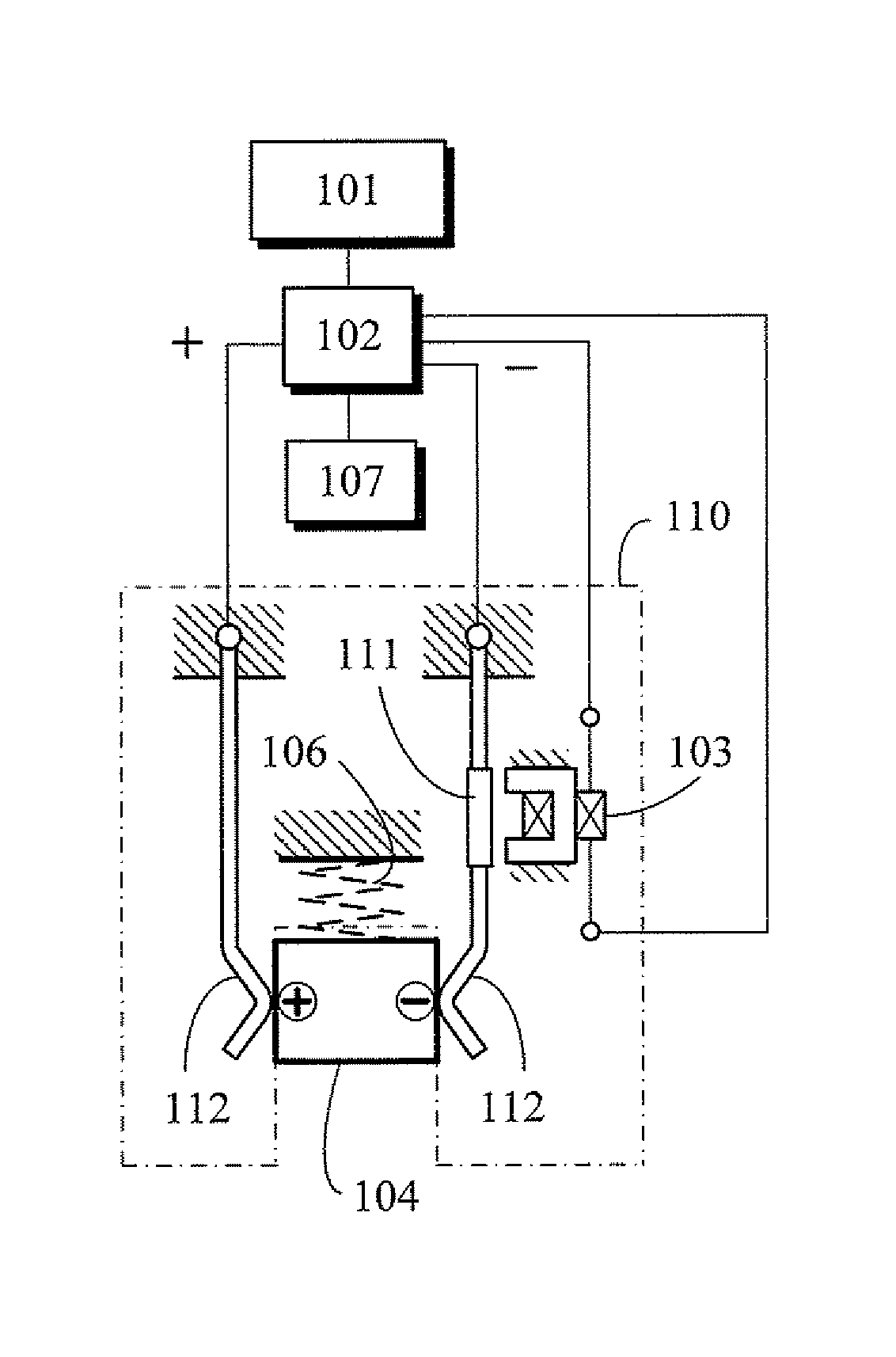
Magnetic shielding aimd housing equipped with window for magnetic actuation type switch
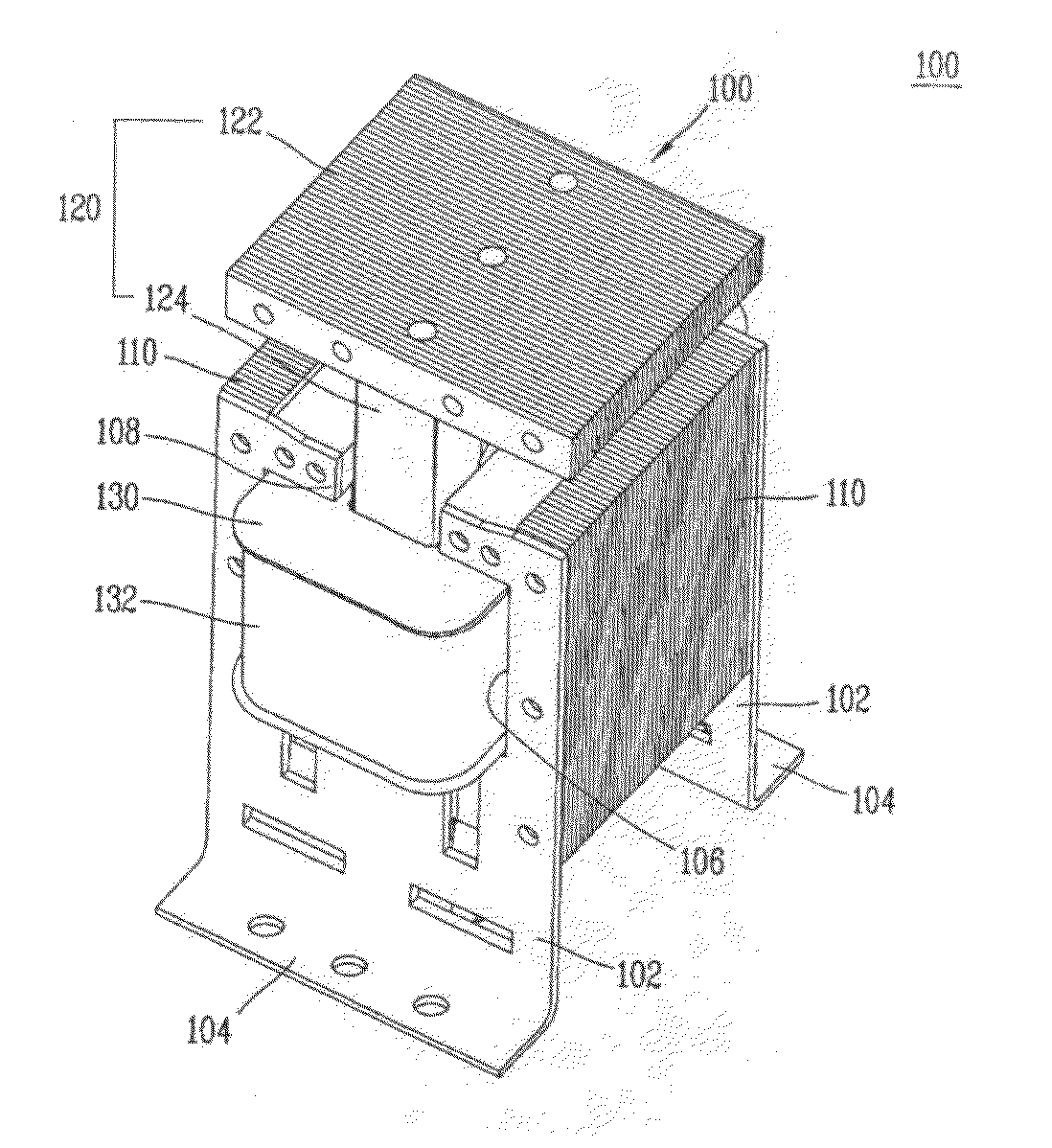
An active implantable medical device (AIMD) having a magnetic shield on its housing for shielding the interior of the device from magnetic fields generated outside the housing. Magnetic shielding is created using a magnetically absorbing coating on the inner surface of the housing. The AIMD includes the remaining enclosure area without magnetic shielding, ie the magnetic window, adjacent to the magnetic actuating device located within the enclosure. This magnetic window allows actuation of the magnetic starting device.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
Monostable permanent magnetic actuator using laminated steel core
ActiveUS20100164662A1Total current dropReduce manufacturing costHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesCores/yokesMagnetic tension forceMetal sheet
A monostable permanent magnetic actuator using a laminated steel core, comprises: lamination cores formed as a plurality of metallic thin plates are laminated to each other; a coil disposed to be adjacent to the lamination cores, and configured to apply a magnetic force to the lamination cores by an external power; a mover mounted in the lamination cores so as to be movable in upper and lower directions; permanent magnets installed at the lamination cores, and configured to apply an upward and downward magnetic force to the mover; and an elastic means configured to apply an elastic force to the mover in an opposite direction to the permanent magnets.
Owner:LS IND SYETEMS CO LTD
Magnetic assembly for magnetically actuated control devices
ActiveUS7199688B2Increase distanceElectromagnetic relaysMagnetic/electric field switchesMagnetic actuationMagnetic tension force
A magnetically actuated apparatus, which enlarges, extends and makes continuous magnetic fields used by magnetically controlled devices, such as a magnetic reed switch for use in physical security monitoring systems is shown. Apparatus includes a sensor and a magnetic actuator for use with a movable closure member. The sensor is mounted into to a fixed support member that is arranged for displacement relative to a second movable support member. The sensor has a pair of contacts that are connectable to an electronic circuit. The contacts form a switch that is actuated by the magnetic actuator. The magnetic actuator comprises a unique elongated magnet with specific polarity or a plurality of aligned, alike permanent magnets that are mountable to the second support member. The aligned magnets have like magnetic fields that align one another and combine to form an effective magnetic actuation field that has a given magnitude and a given direction that is greater that the magnitude and direction than any one of the magnets. The elongated magnet has a specific pole for a given distance as its controlling means. The effective magnetic actuation field increases the distance in which the movable support member is displaceable relative to the fixed support member without changing the electric condition of the sensor. The present invention creates a magnetic apparatus, having a wider and controllable gap and break point distance not found in the present art.
Owner:EDMONSON JR MAHLON WILLIAM
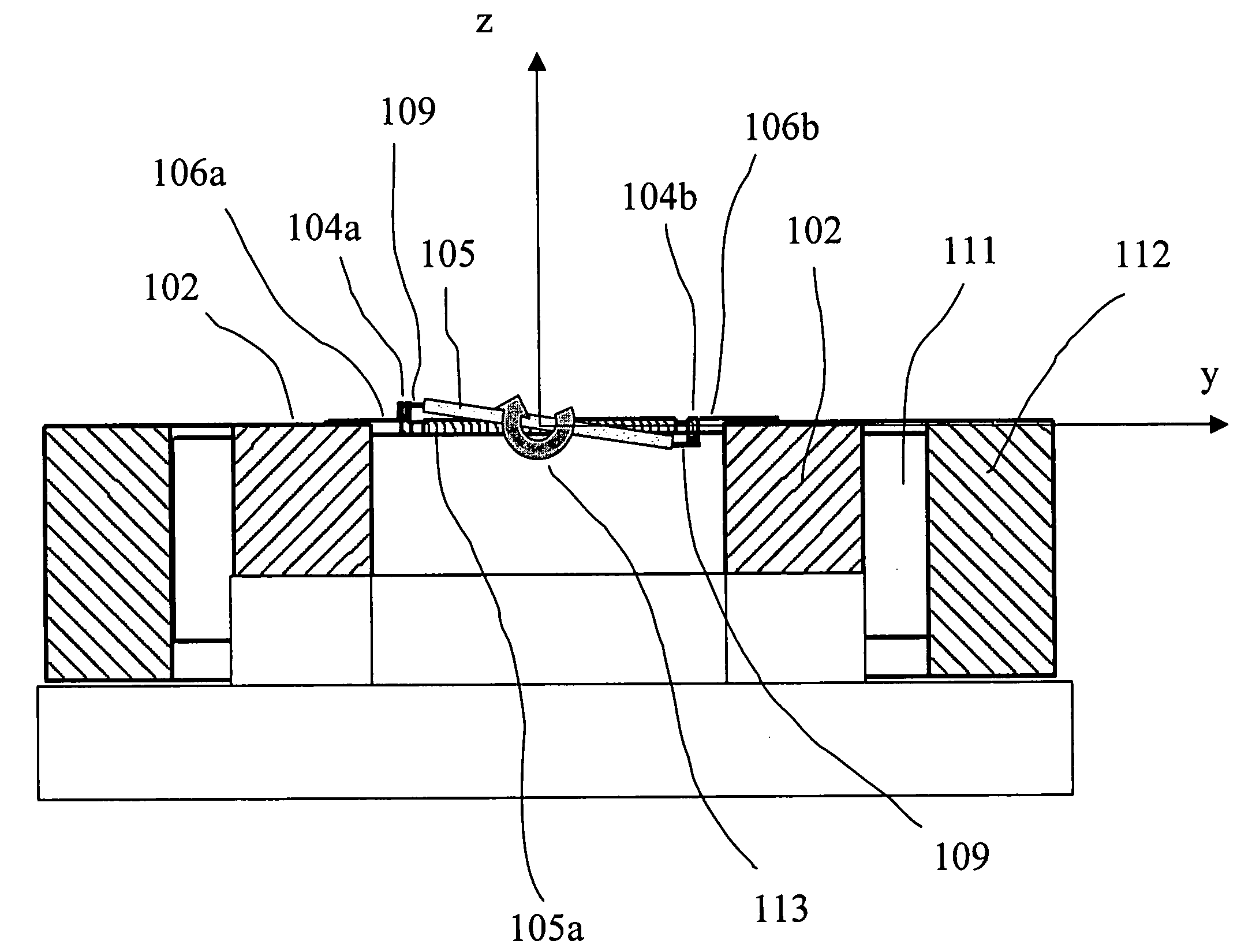
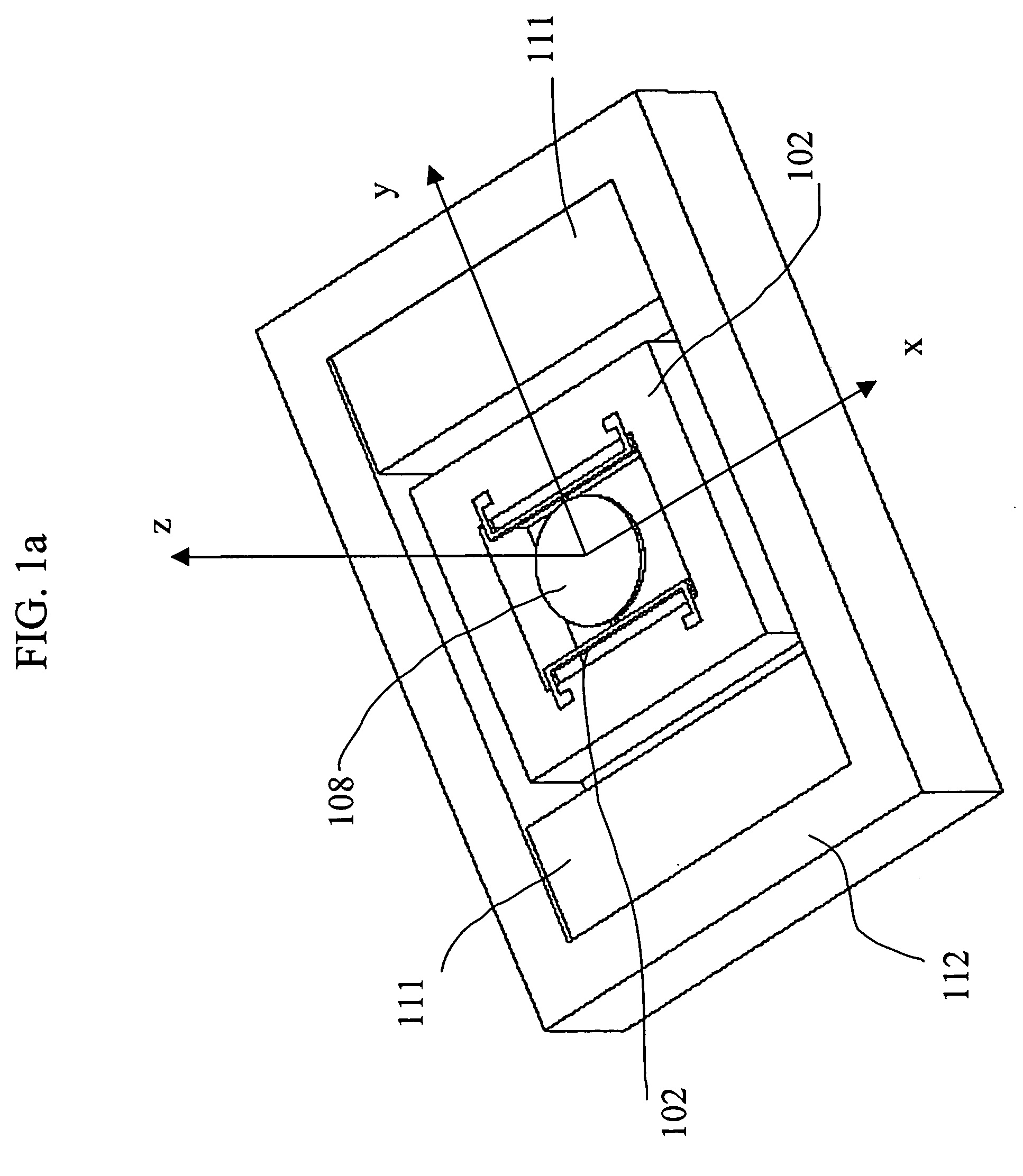
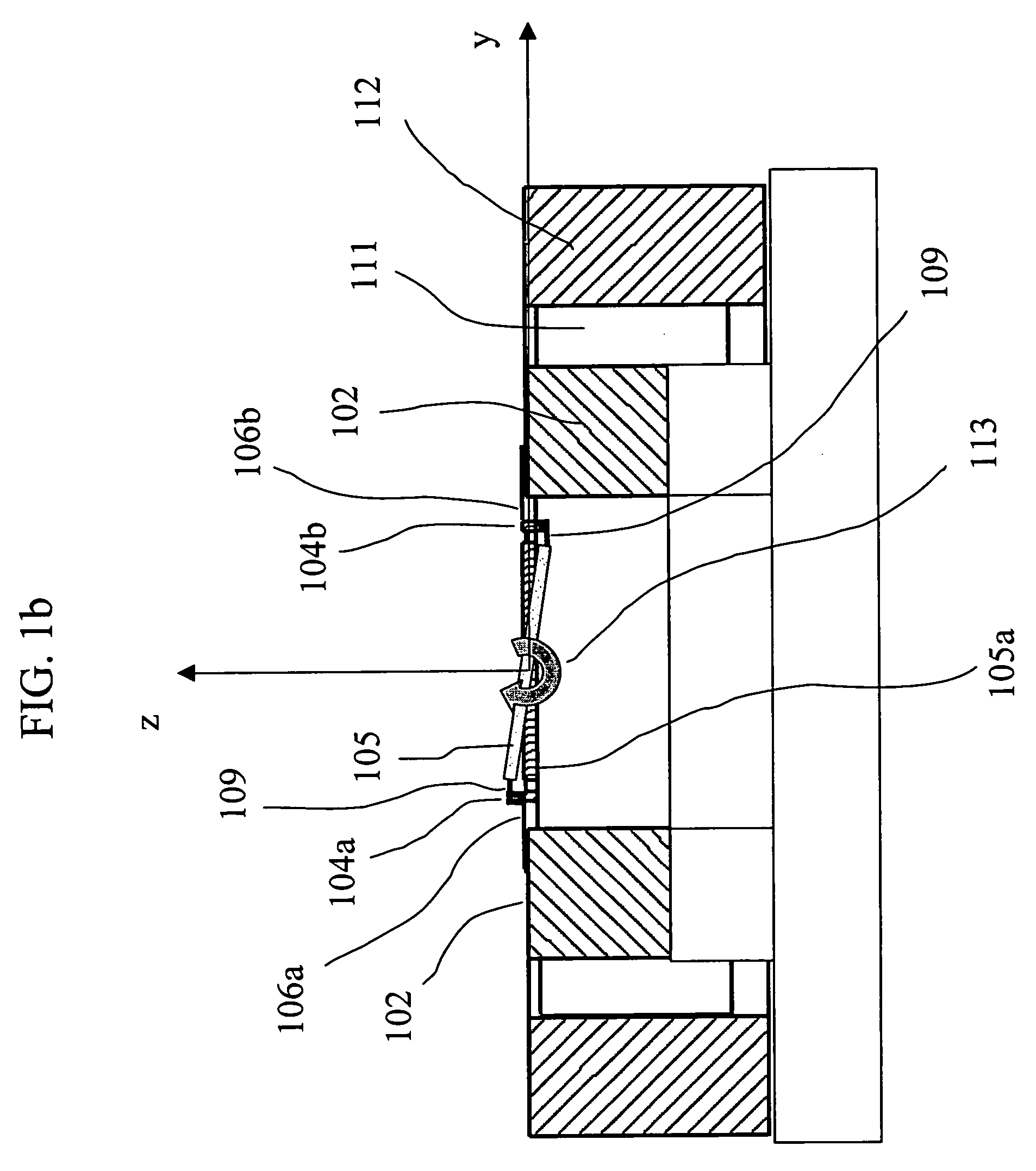
Magnetic actuator drive for actuation and resetting of magnetic actuation materials
InactiveUS7218067B2Small power sourceHighly controllablePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesInorganic material magnetismMagnetic actuationEngineering
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Enhanced drop mixing using magnetic actuation
InactiveUS20110263464A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic actuationEngineering
A method and device for merging and mixing at least two separate and distinct fluid drops on a substrate, includes a drop merging area on the surface, where a first magnetic material is placed at a first location. A first drop of fluid is then placed at the first location on the surface, resulting in the first magnetic material being at least partially positioned within the first drop of fluid. A second drop of fluid is then placed at a second location on the surface of the drop merging area. A magnetic field is applied by a varying magnetic field generator to at least a portion of the drop merge area of the substrate, which includes at least the first location on the substrate. The varying magnetic field will act on the first magnetic material to move the first magnetic material within the first drop of fluid, causing a stirring of the fluid. A drop merging force from a drop merging mechanism is applied to at least one of the first drop of fluid and the second drop of fluid within the drop merge area. This causes at least one of the first drop of fluid and the second drop of fluid to move toward the other and make contact. The internal stirring of the fluid in the first drop of fluid by the movement of the magnetic material enhances the mixing of the constituents of the first drop of fluid and the constituents of the second drop of fluid.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Enhanced drop mixing using magnetic actuation
InactiveUS8617899B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic actuationEngineering
A method and device for merging and mixing at least two separate and distinct fluid drops on a substrate, includes a drop merging area on the surface, where a first magnetic material is placed at a first location. A first drop of fluid is then placed at the first location on the surface, resulting in the first magnetic material being at least partially positioned within the first drop of fluid. A second drop of fluid is then placed at a second location on the surface of the drop merging area. A magnetic field is applied by a varying magnetic field generator to at least a portion of the drop merge area of the substrate, which includes at least the first location on the substrate. The varying magnetic field will act on the first magnetic material to move the first magnetic material within the first drop of fluid, causing a stirring of the fluid. A drop merging force from a drop merging mechanism is applied to at least one of the first drop of fluid and the second drop of fluid within the drop merge area. This causes at least one of the first drop of fluid and the second drop of fluid to move toward the other and make contact. The internal stirring of the fluid in the first drop of fluid by the movement of the magnetic material enhances the mixing of the constituents of the first drop of fluid and the constituents of the second drop of fluid.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Electromagnetic actuator and method for adjusting said electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS6838965B1Minimizing overall energy requiredMinimization requirementsElectric switchesMachines/enginesMagnetic tension forceCombustion
An electromagnetic actuator includes two electromagnets spaced apart from one another, an armature that is movable back and forth by magnetic force between the electromagnets against the force of two respectively counteracting springs, and setting means for adjusting the actuator to have a low energy requirement. To this end, the springs are pre-stressed such that the same energy is stored in both springs in connection with a maximum compression of the springs corresponding to the maximum stroke travel distance of the armature. The actuator is useful for actuating a valve to control the gas exchange in an internal combustion machine.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
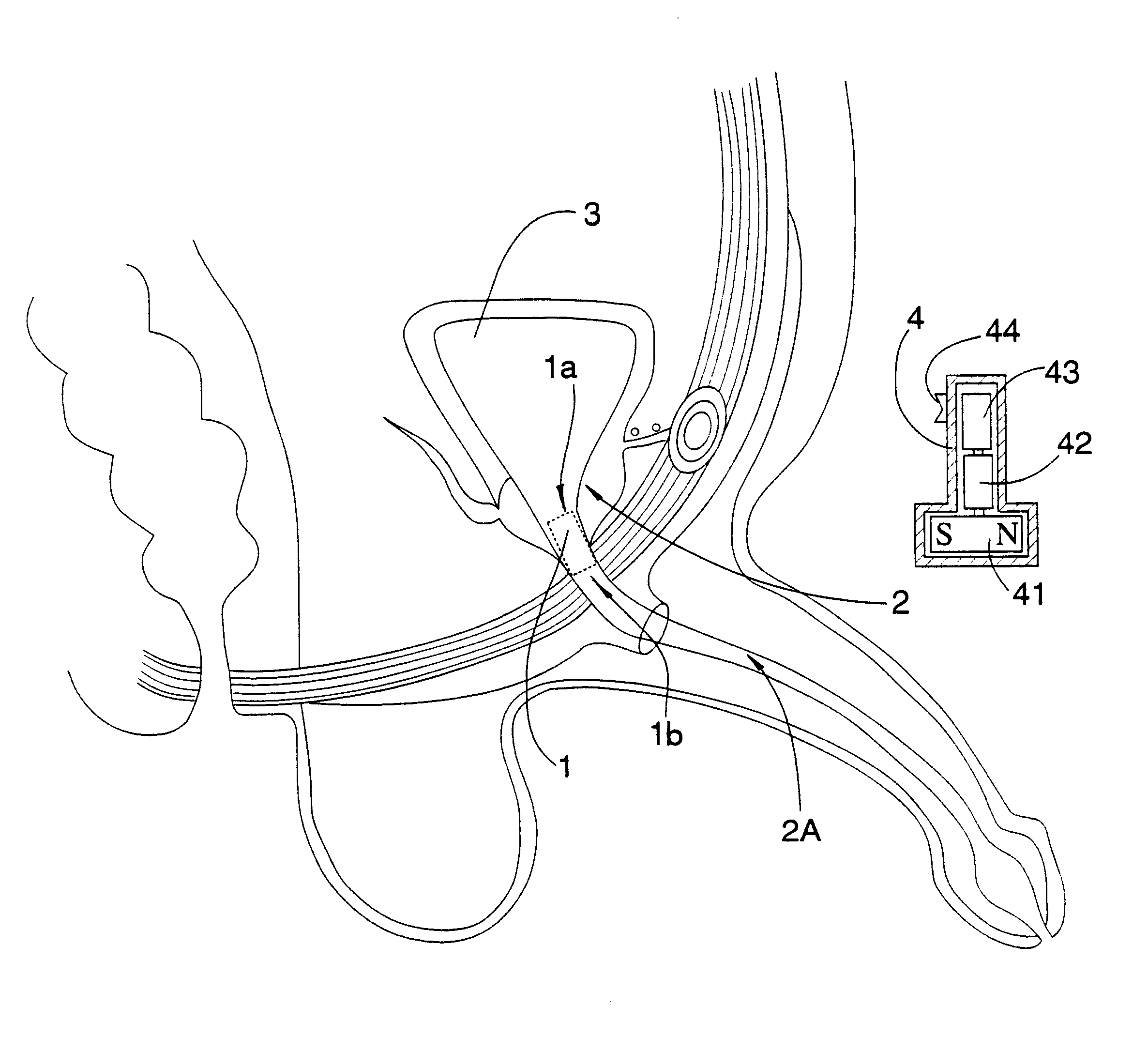
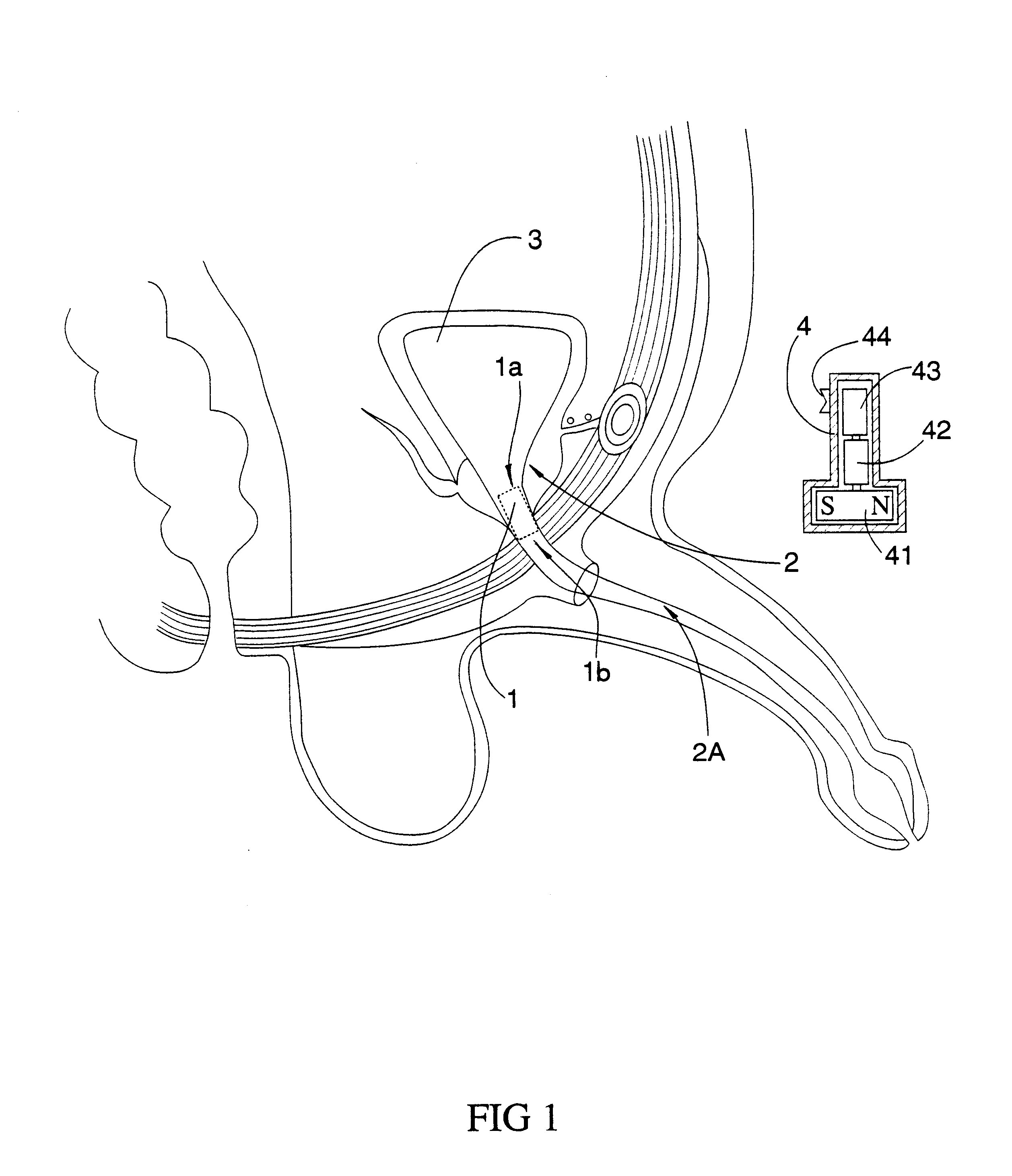
External magnetic actuation valve for intraurethral artificial urinary sphincter
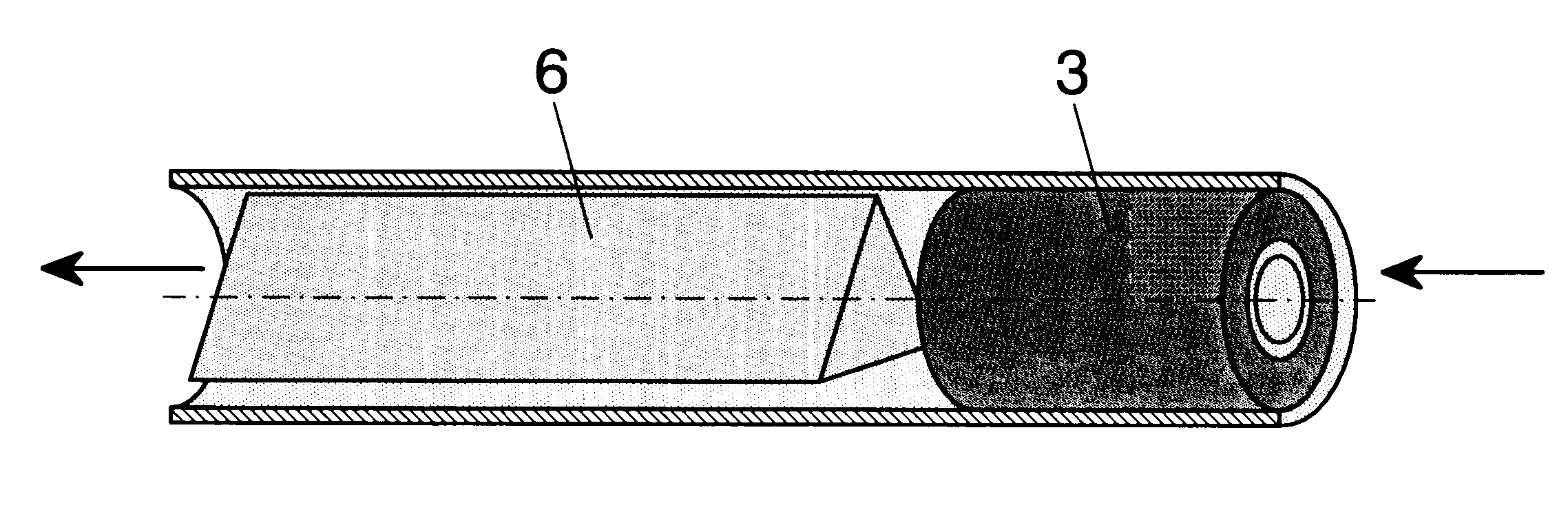
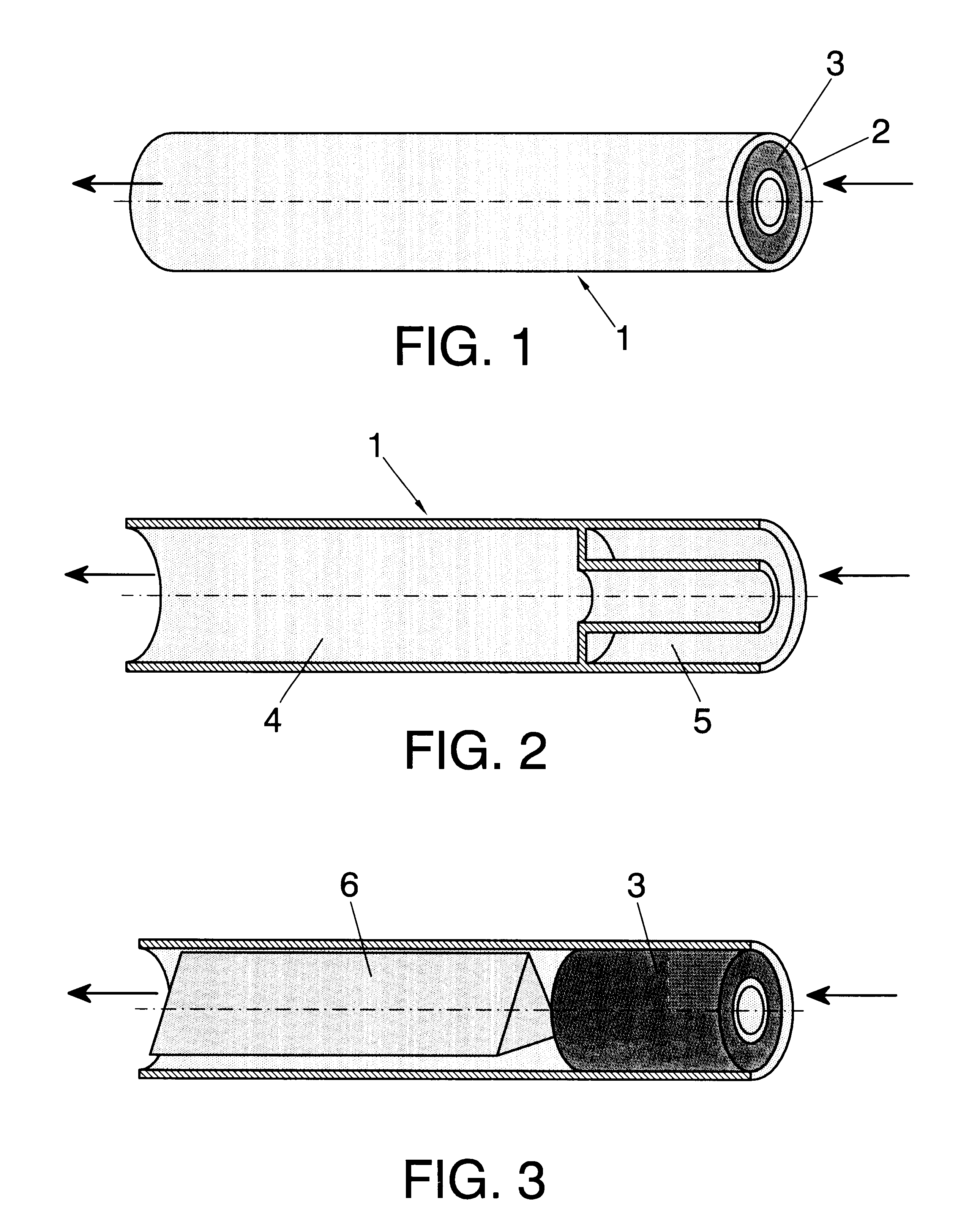
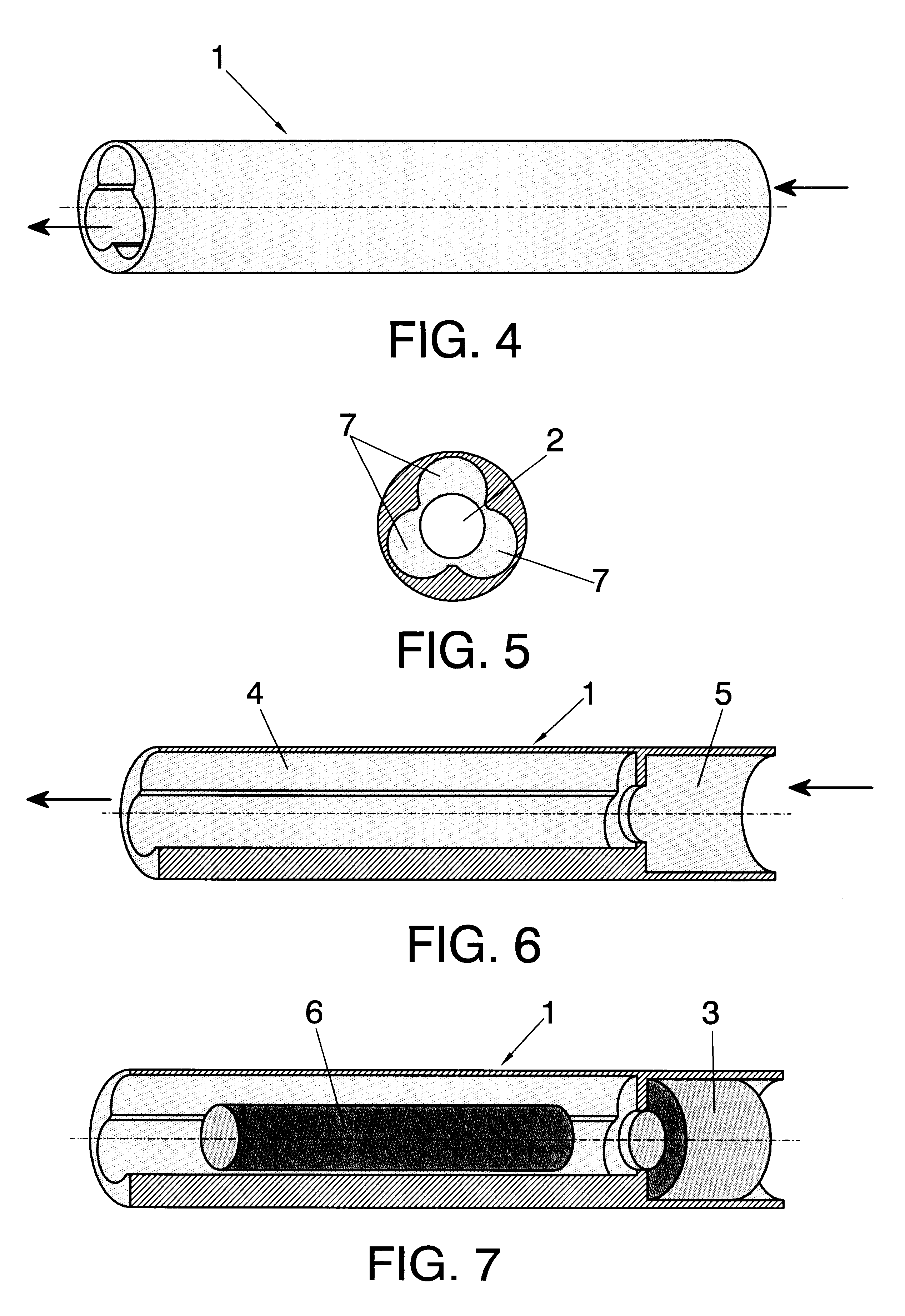
InactiveUS6623421B1Avoid damageGreat wall thicknessAnti-incontinence devicesTubular organ implantsMagnetic actuationUrethra
External magnetically actuated valve for an artificial intraurethral urinary sphincter. External magnetically actuated valve for an artificial intraurethral urinary sphincter, allowing urine control for people suffering from urinary incontinence or retention, by the application of an external magnetic field. After valve (1), object of the present invention, is placed in the patient's urethra (9), said patient may control urination. Urine is evacuated when a permanent magnet (3) is approached to the body of the patient. Closing is automatic. The system is provided with a safety system to prevent over pressures in bladder (8).
Owner:UNIV COMPLUTENSE DE MADRID
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com