Patents
Literature
554results about "Master clocks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
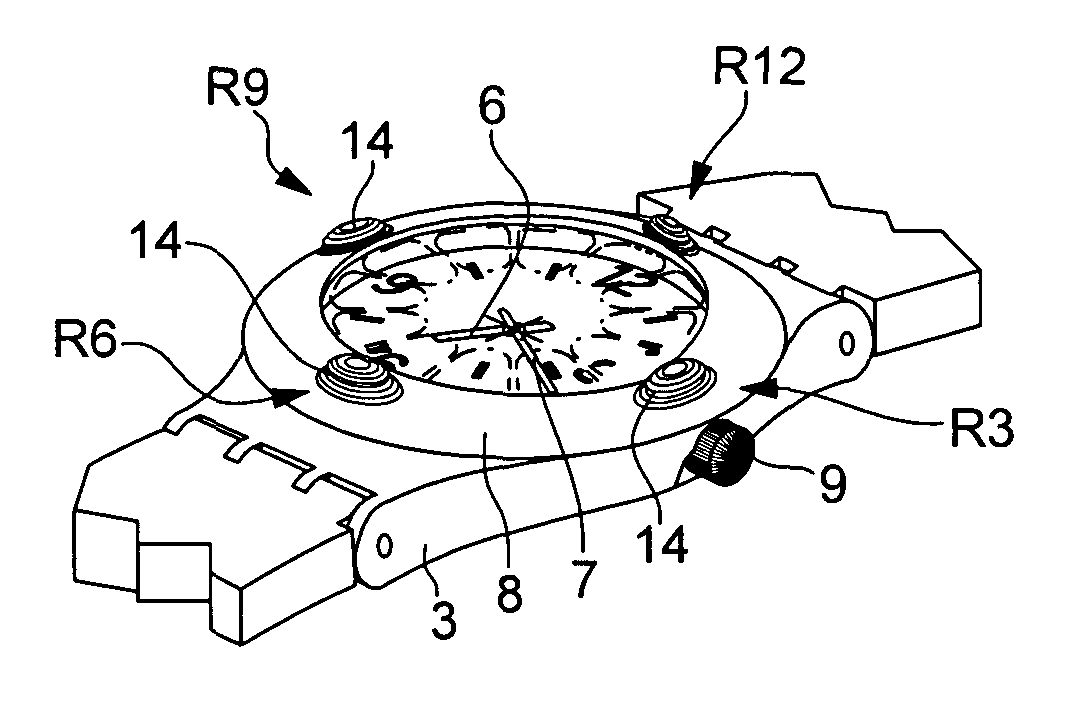
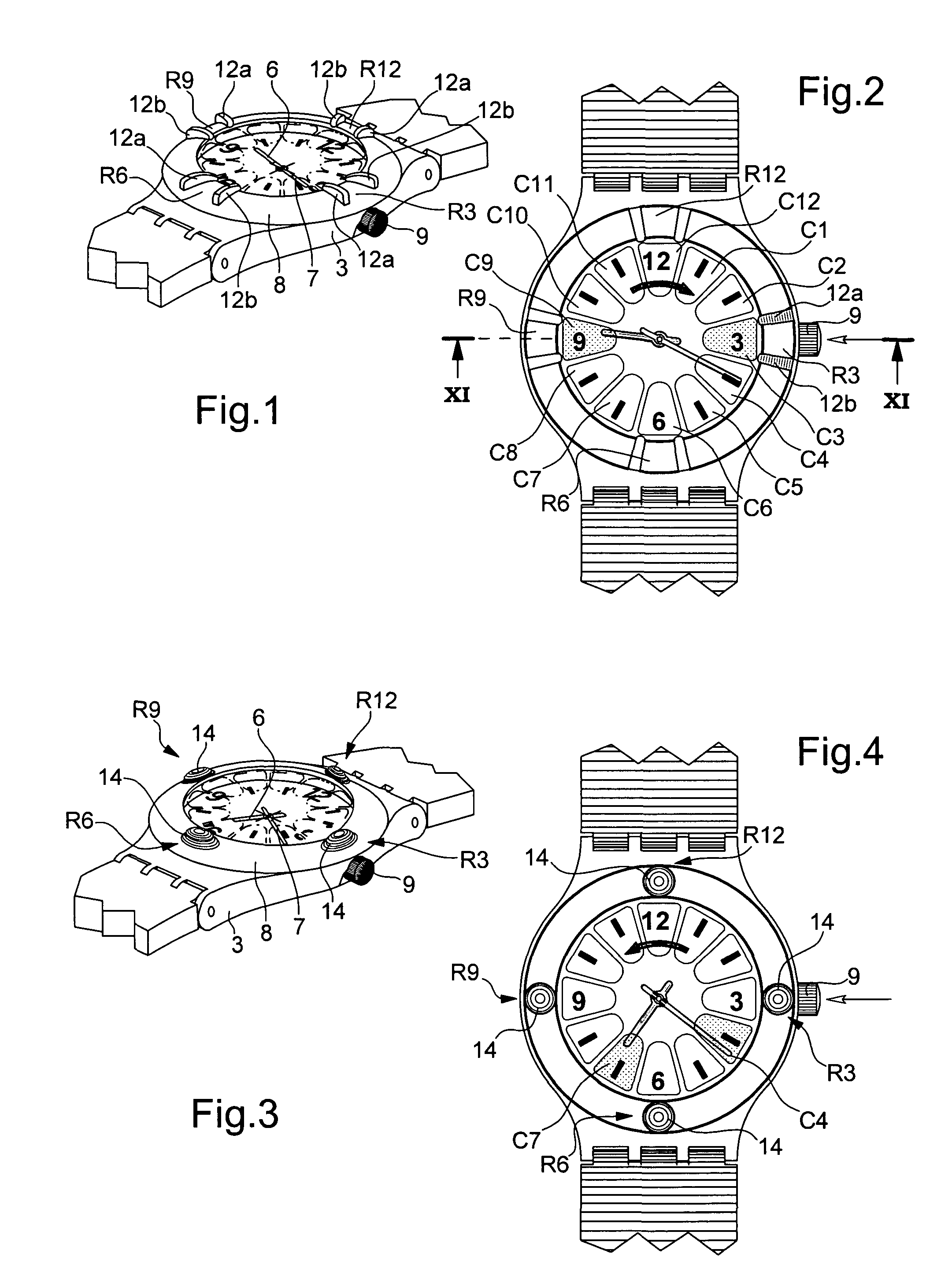
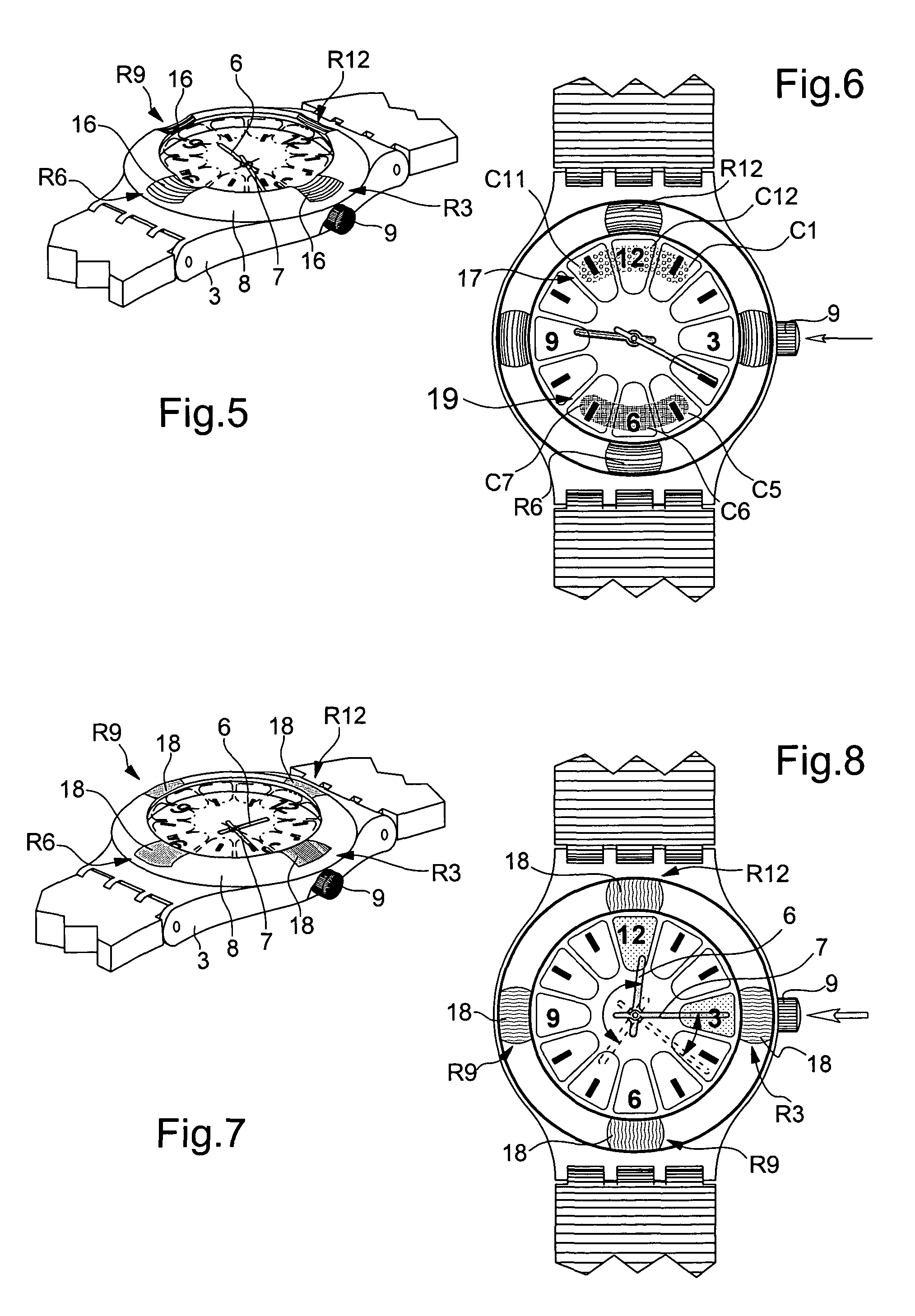
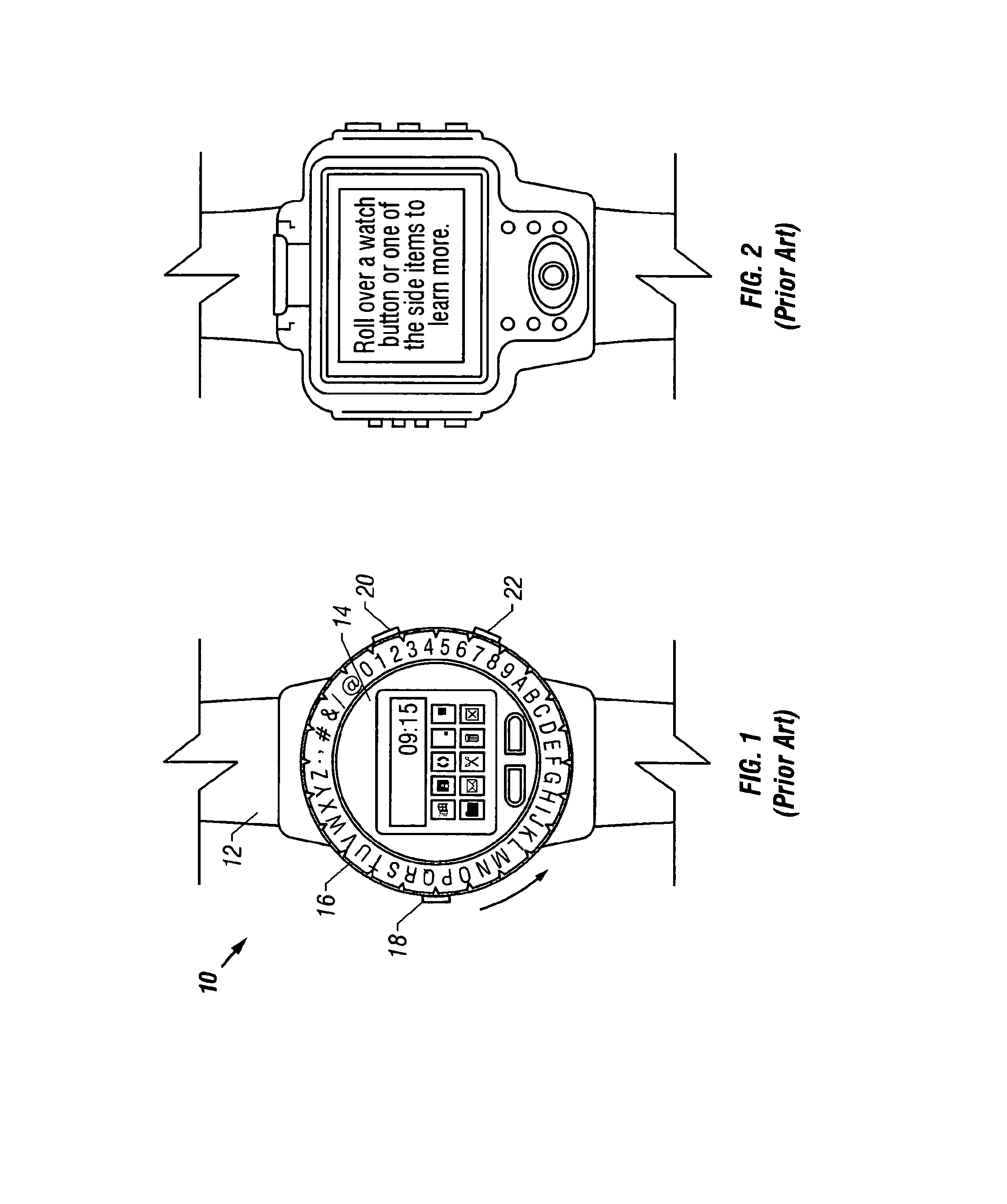
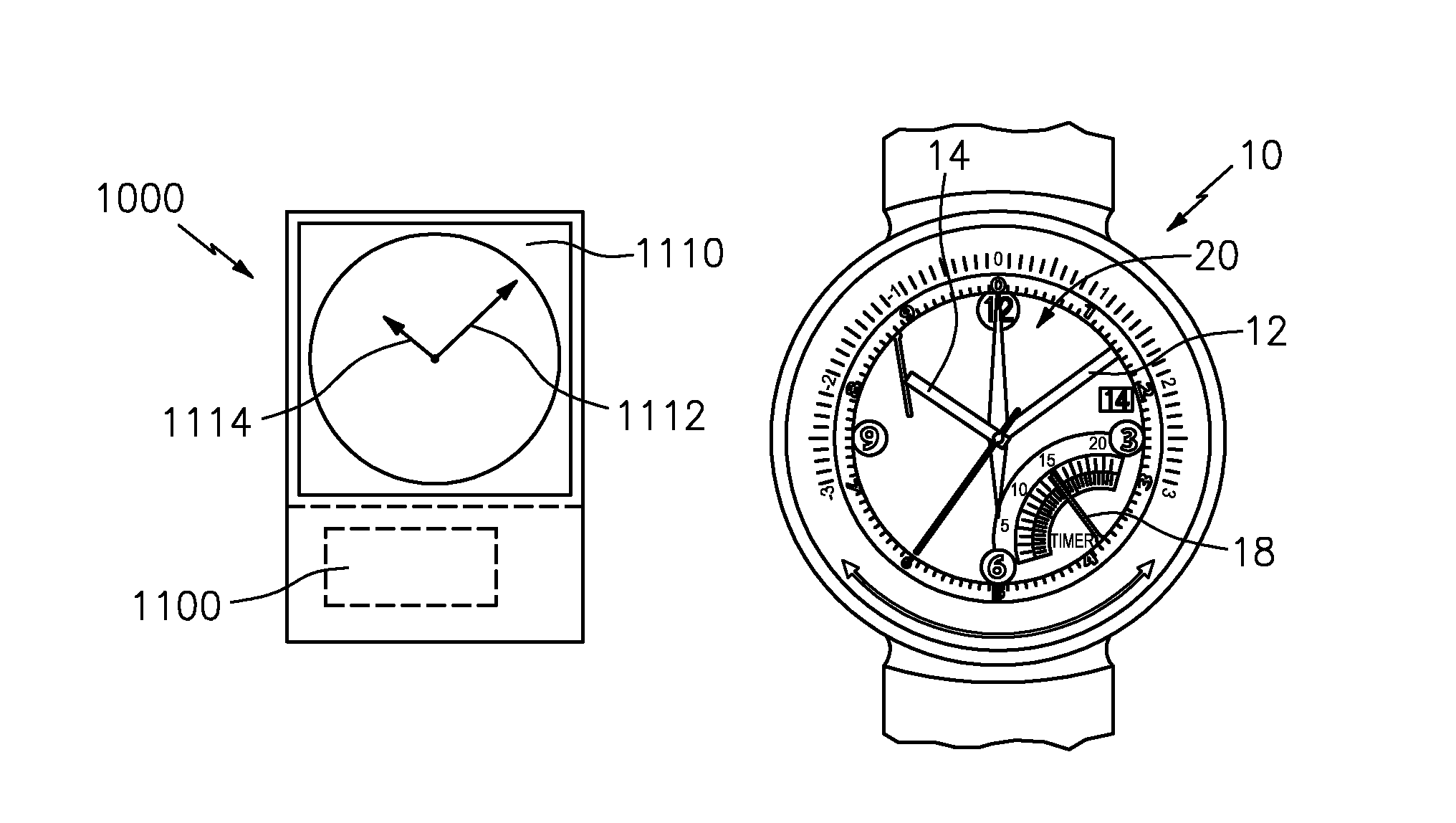
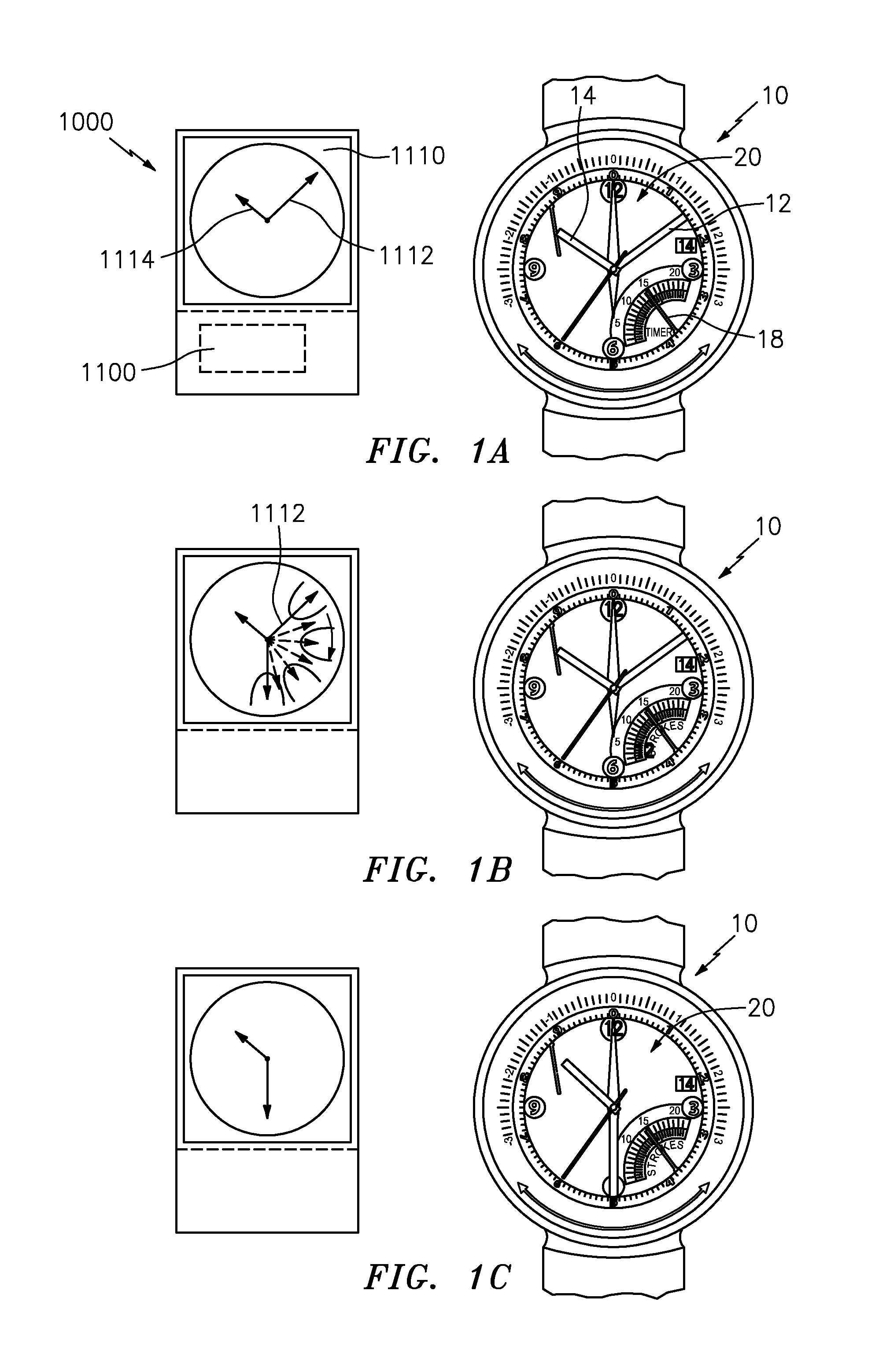
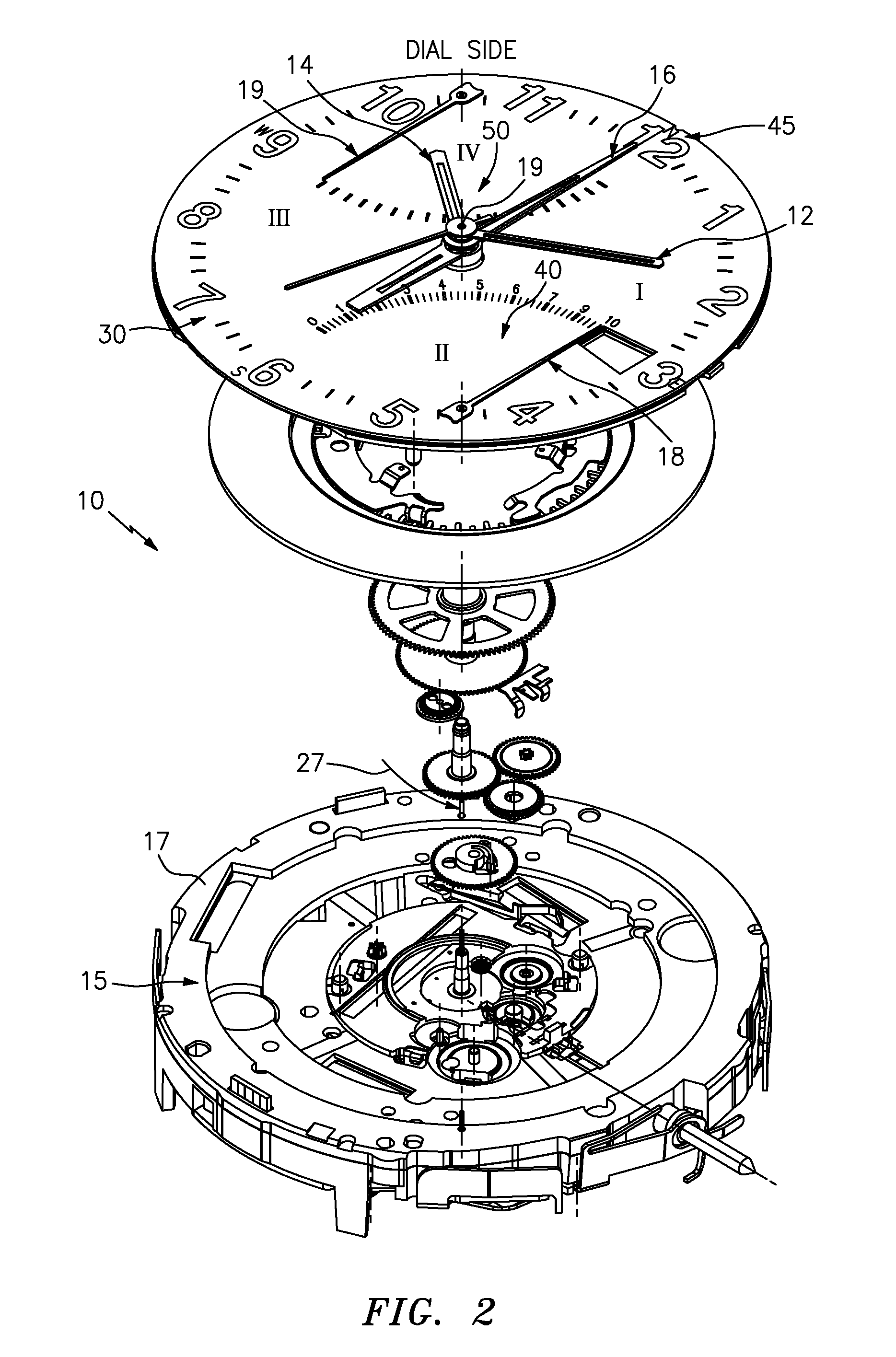
Timepiece with touch-type reading and control of time data
The timepiece, which is preferably a wristwatch, includes for each time position a capacitive sensor (C1 to C12), on a fixed bezel, including only four markings (R3, R6, R9, R12) at 3 o'clock, 6 o'clock, 9 o'clock and 12 o'clock, and a single crown-push-button (9). The case contains, in particular, a non-acoustic vibration generator (20) and an electronic interpretation and coding circuit (15), associated with a time-keeper circuit (10), with the sensors and with the crown to control the vibration device, said circuit (15) being designed to identify the manipulations on the crown (brief, long application of pressure or pull) and on the sensors (positioning or movement).
Owner:ASULAB SA
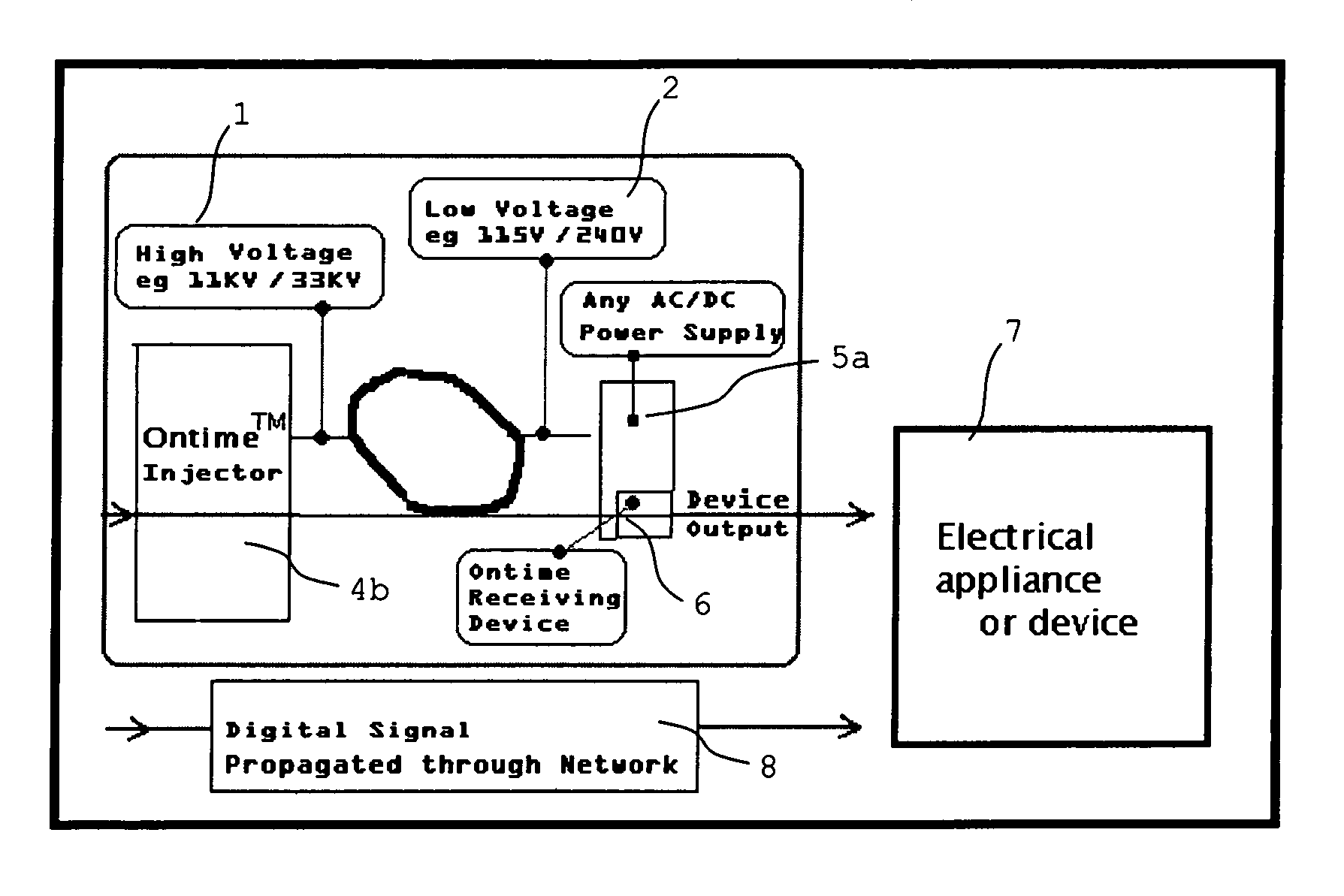
System and method for transmitting control information over an AC power network
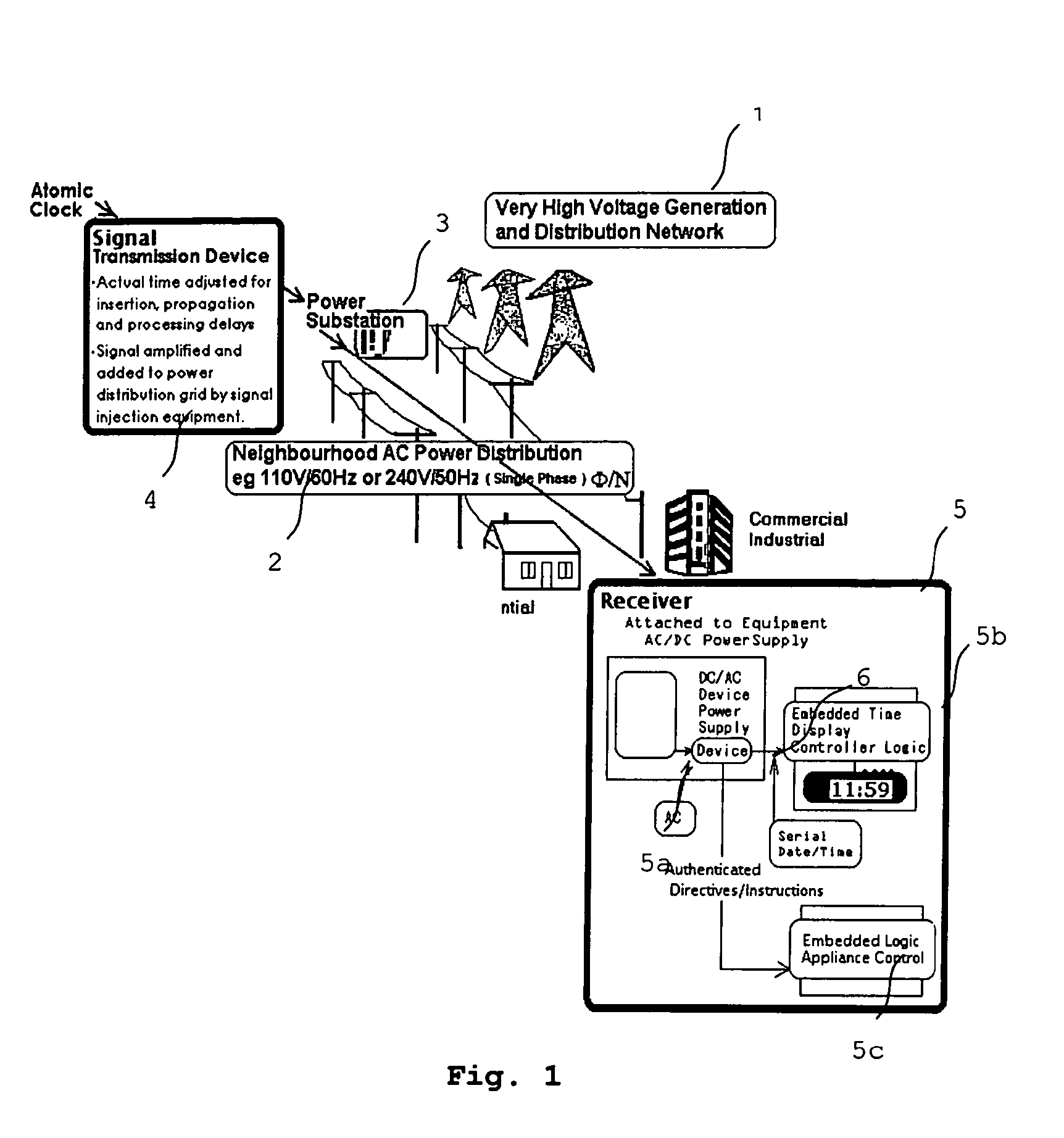
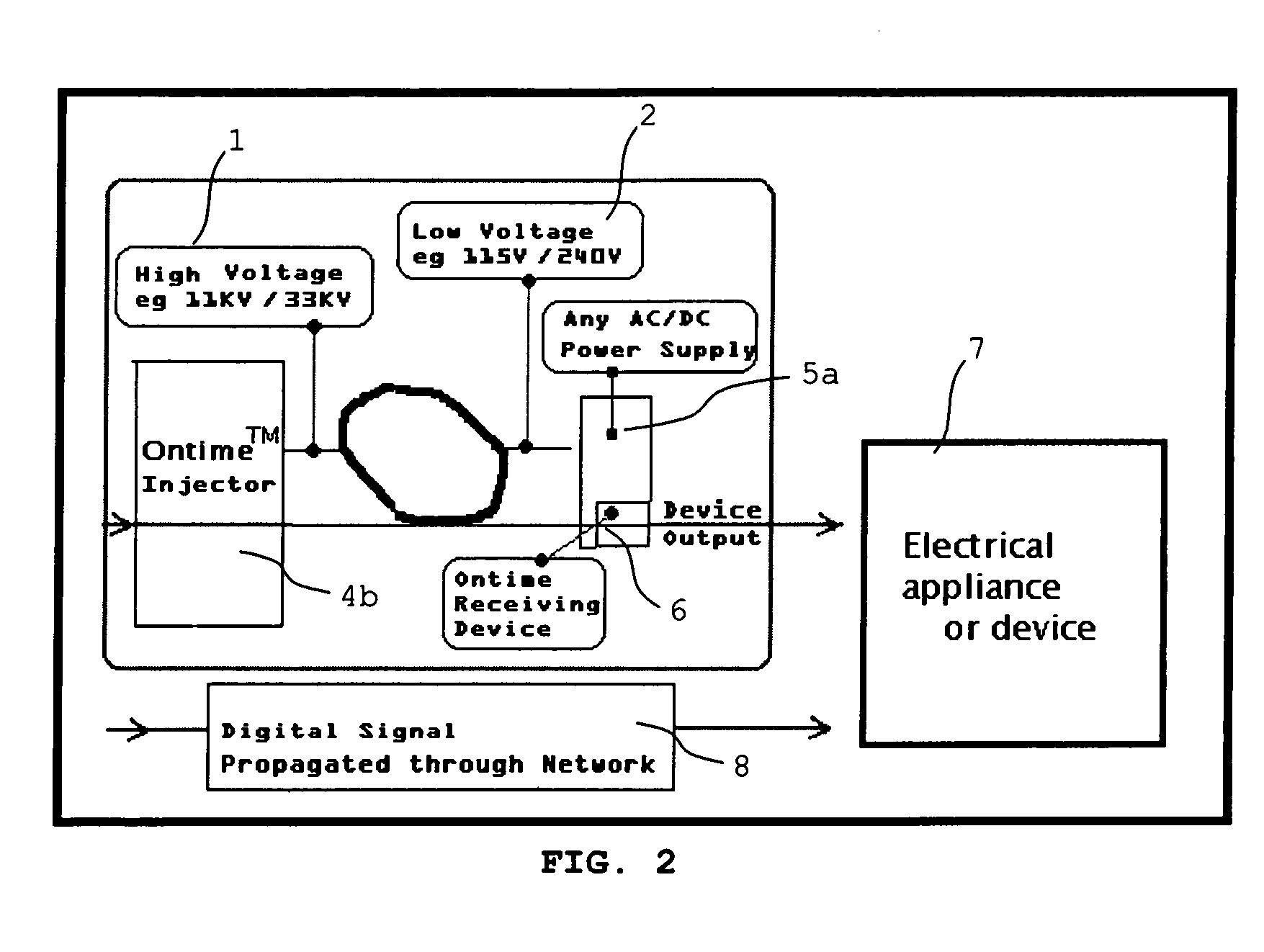
Disclosed is a transmission system for transmitting digital information via a power supply network. In one embodiment, there is a transmission device which comprises a generator for generating a simulated digital wave-form carrying the digital information to be transmitted, and a high-voltage injector to inject the generated simulated digital wave-form carrying the digital information into the power supply network. A receiving device is also disclosed, which comprises an analog detector for detecting predetermined harmonic frequencies of a signal frequency, and a logic device to output a logic signal corresponding to the output of the analog detector as said digital information.
Owner:ADS ENTERPRISES NZ
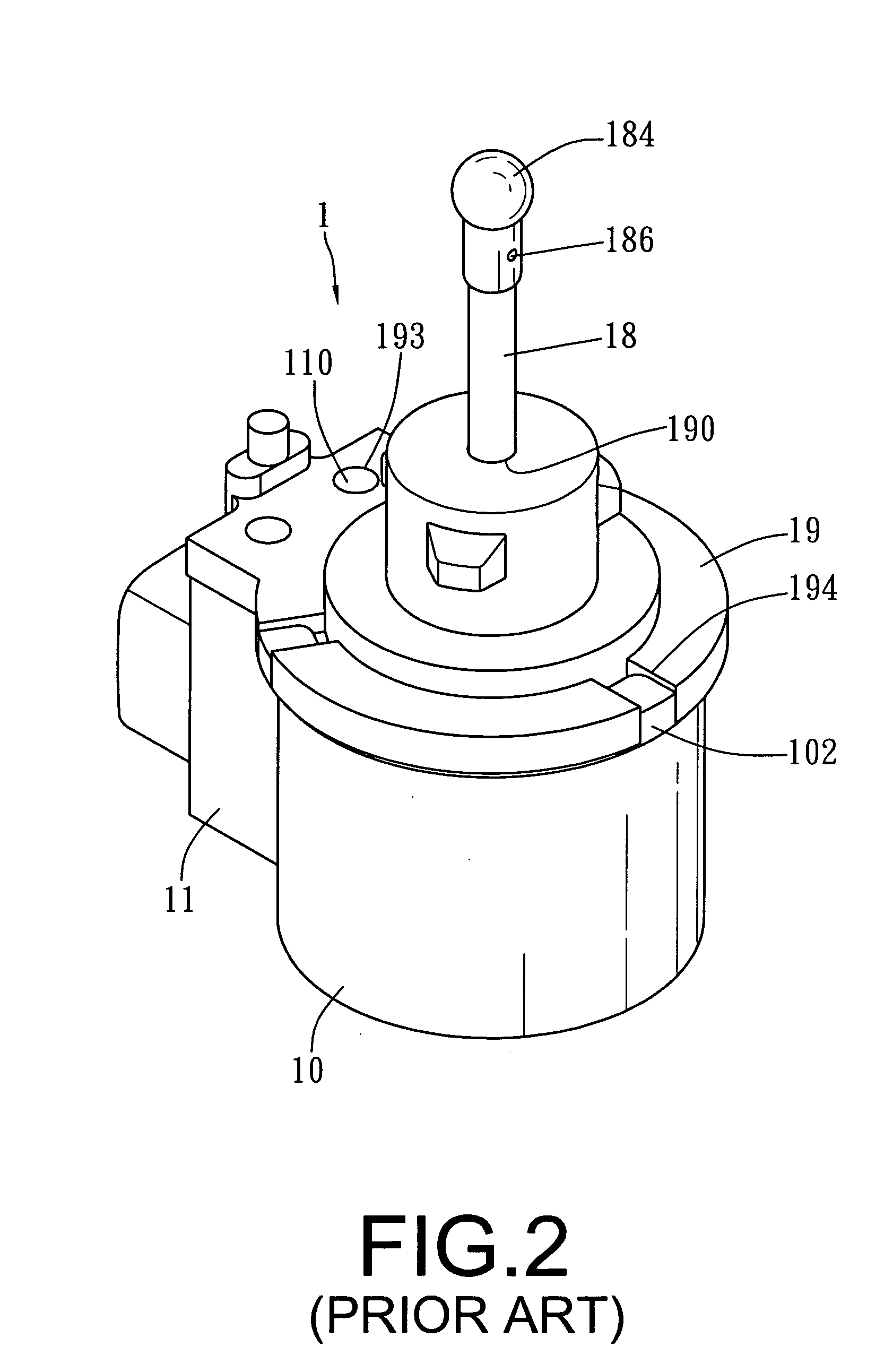
Reluctance motor with improved stator structure
InactiveUS20100123426A1Reduce efficiency of motorHigh cost of controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlReluctance motorEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
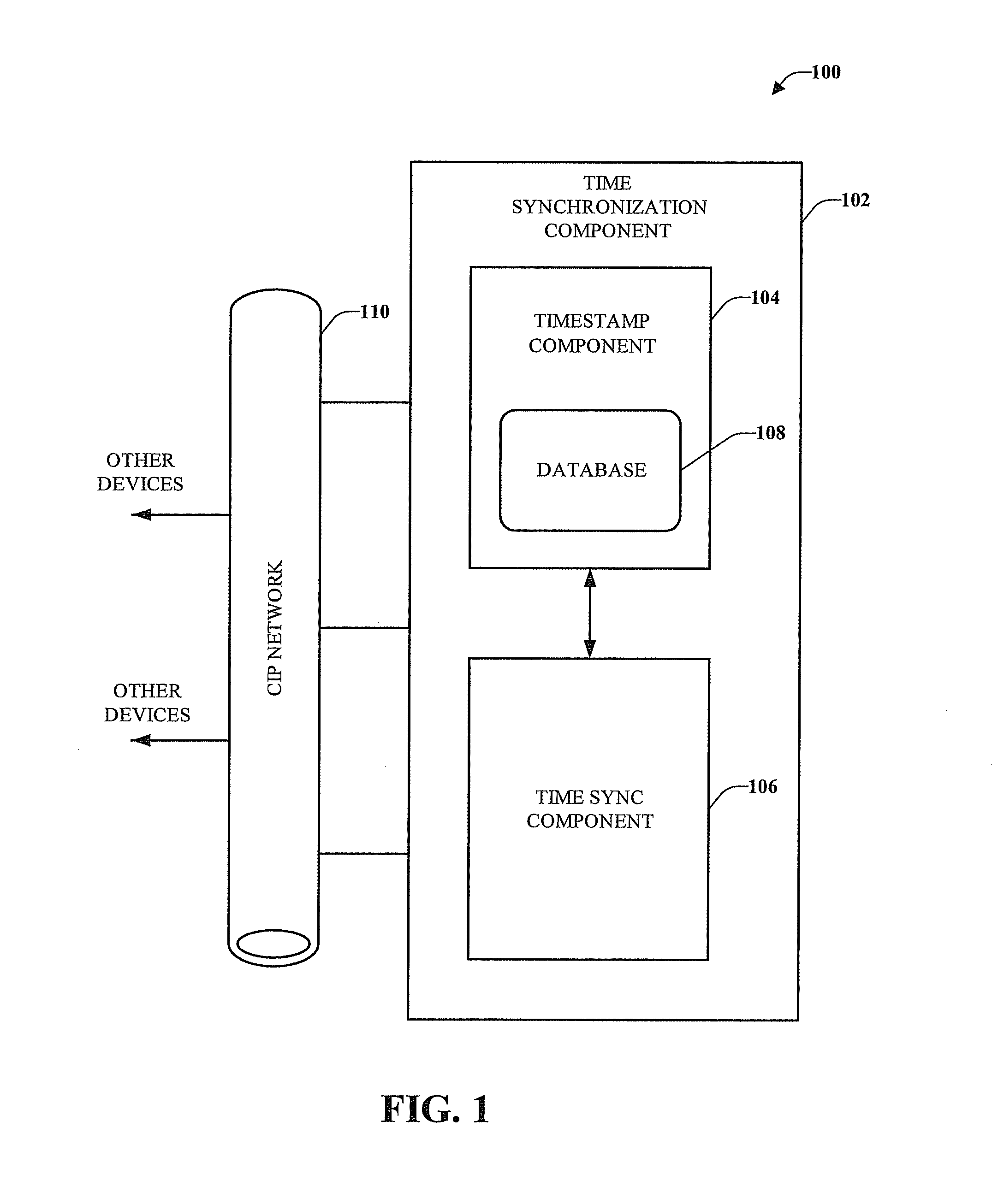
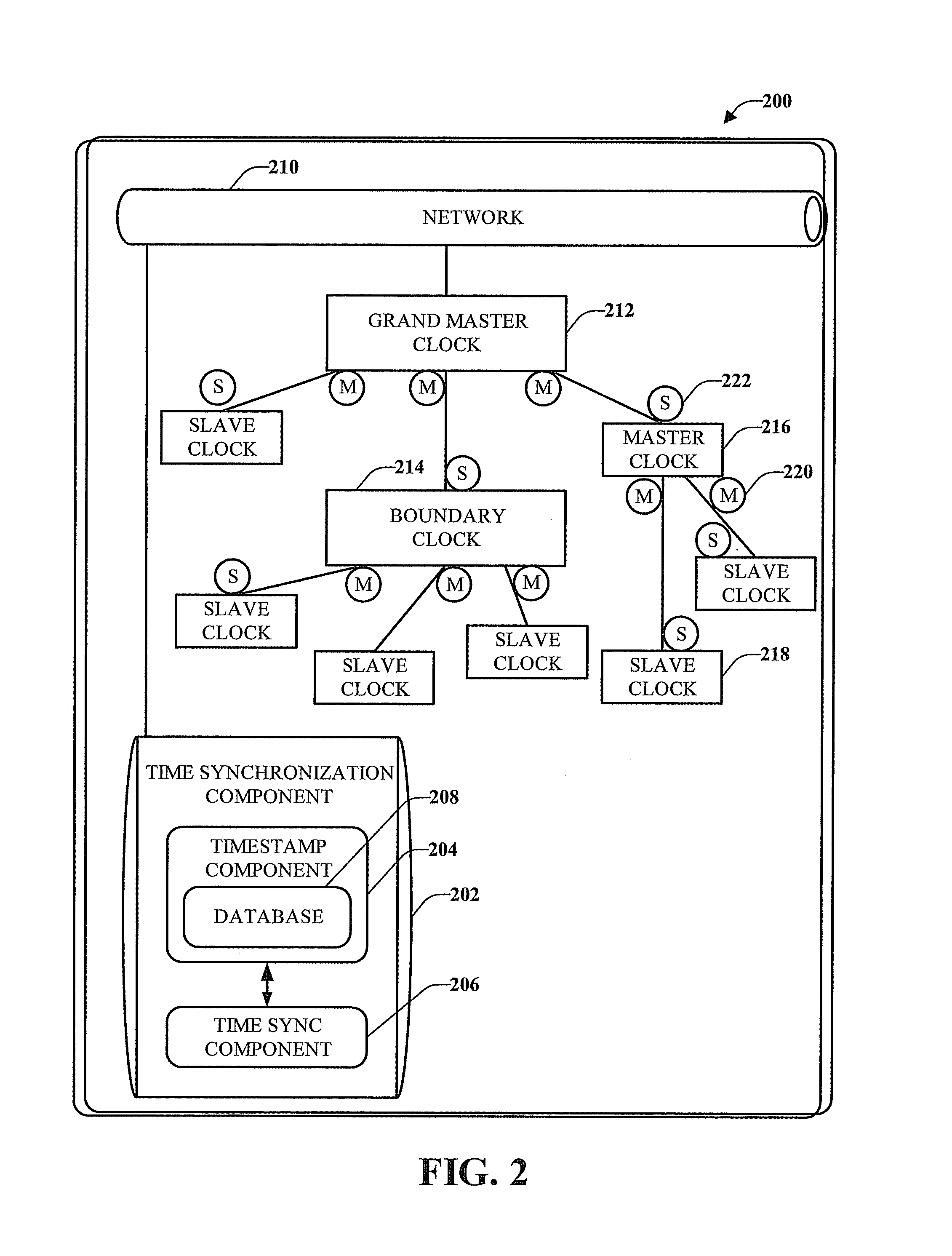
Step time change compensation in an industrial automation network
ActiveUS7447931B1Easy to handleEfficient transferSynchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexTime changesComputer science
One or more embodiments provide Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) based time synchronization systems and methods. The CIP Sync solution can be part of Ethernet / IP and can be based on standard UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and / or IEEE 1588 (Time Synchronization) Ethernet technology. According to an embodiment is a system that compensates for step changes in a master clock.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
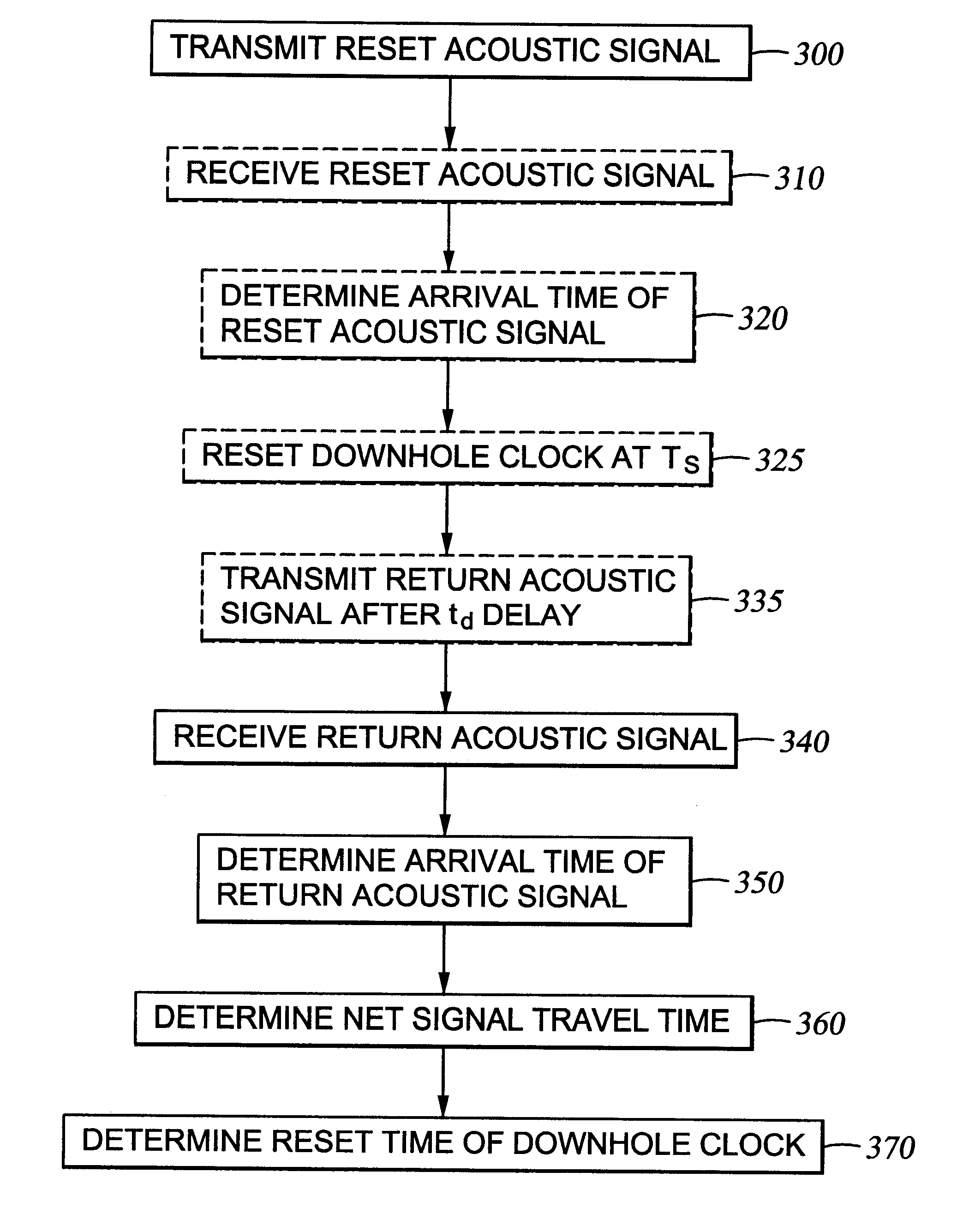
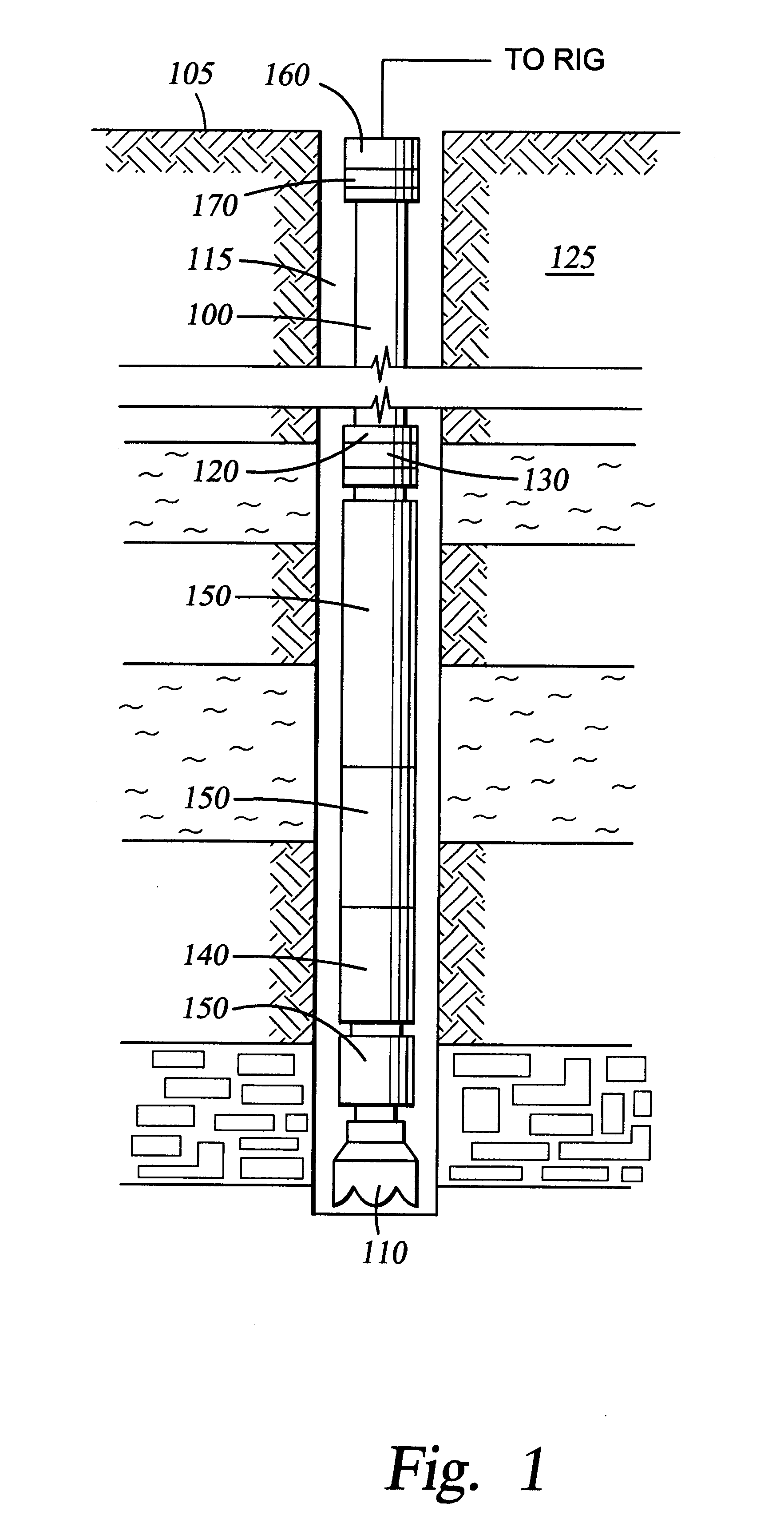
Method for compensating for remote clock offset
A system is disclosed for synchronizing a clock in a well containing a drill string with a clock located near the surface of the well. The system includes devices for transmitting and receiving a pair of acoustic signals between locations associated with each clock and processing those signals. The system determines the time of arrival of each acoustic signal by analyzing the shape of a function of the acoustic signal chosen from a group of functions suitable to determine a clock offset with millisecond accuracy.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
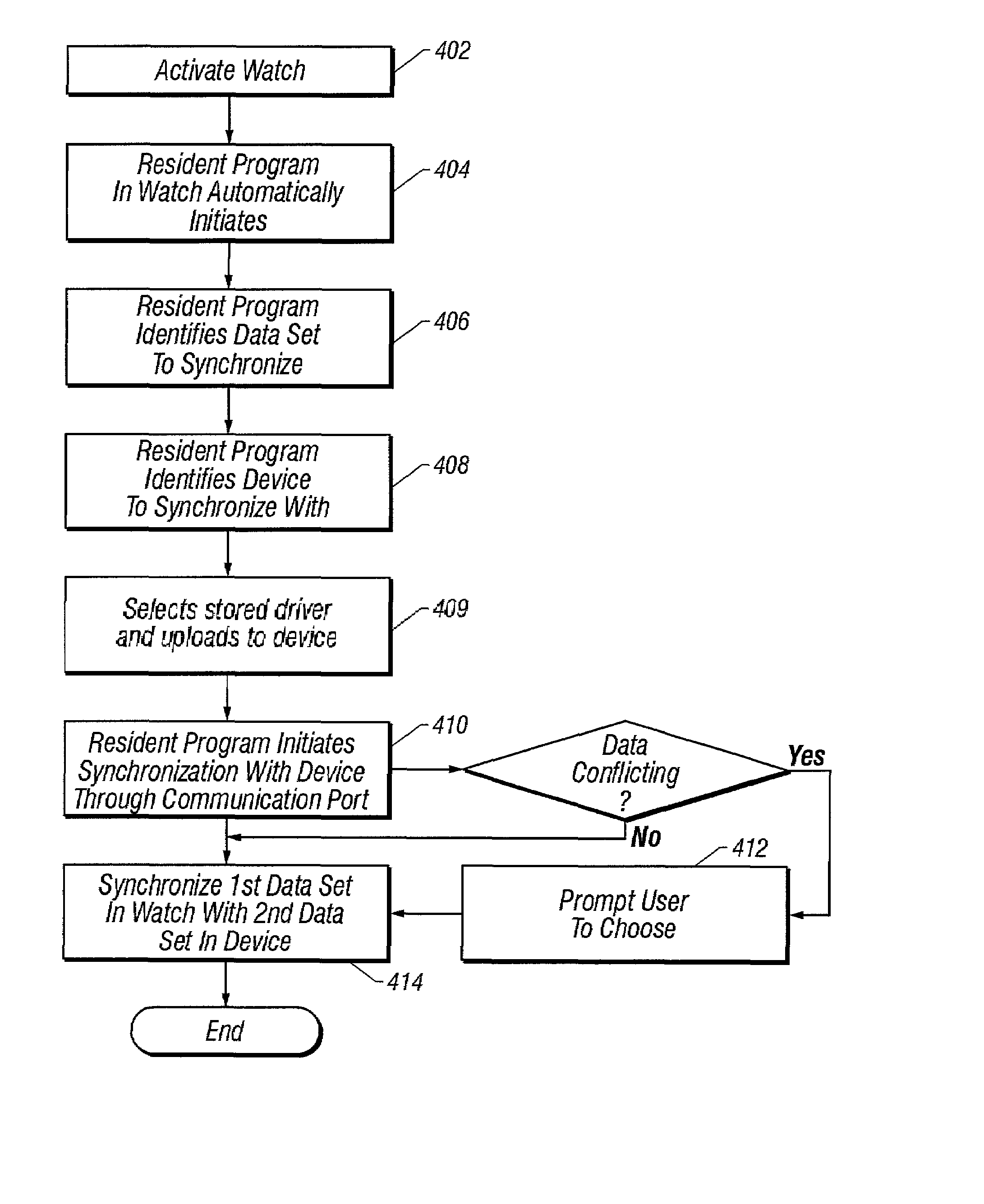
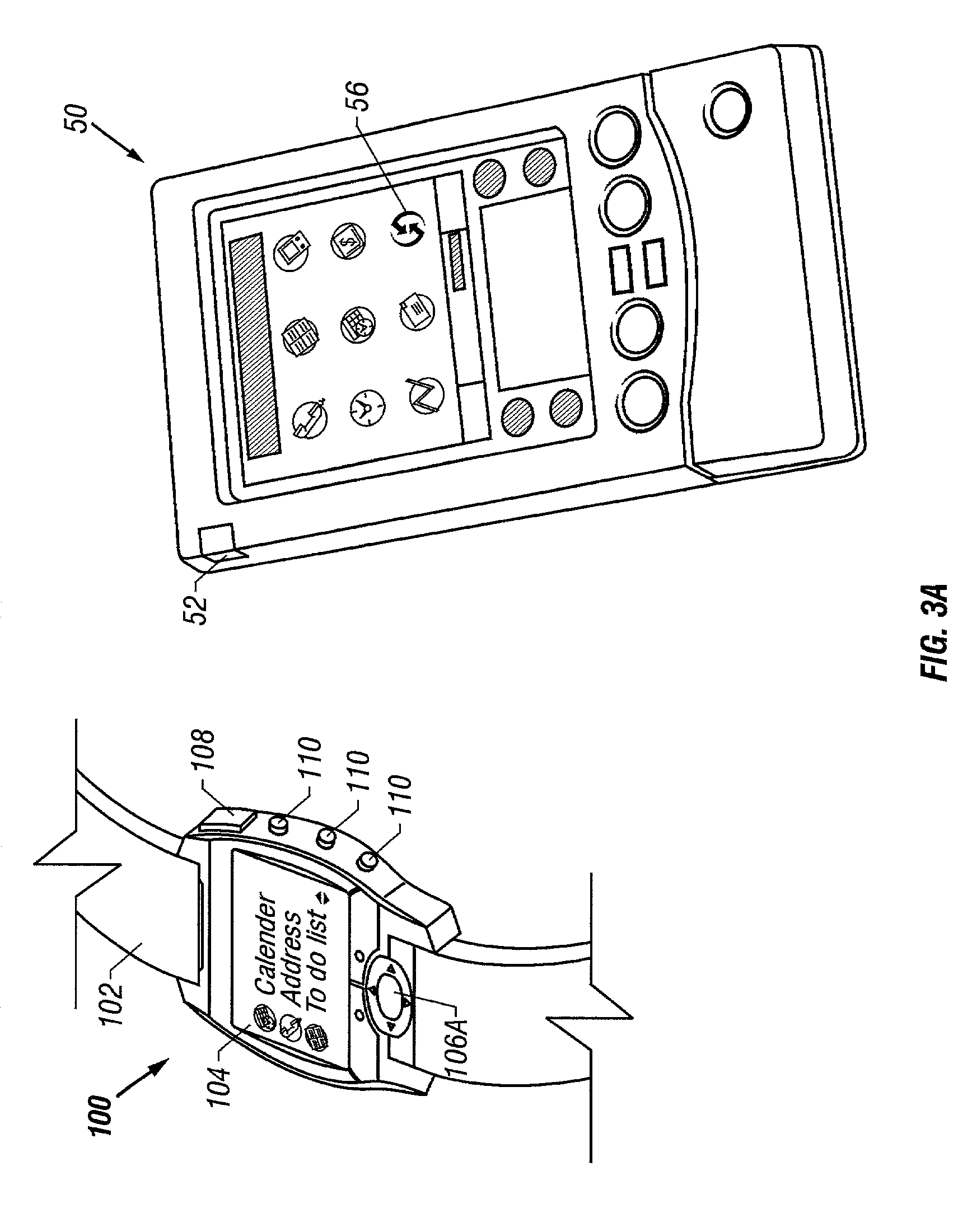
Method and apparatus for synchronizing data between a watch and external digital device
InactiveUS6977868B2Save battery powerSynchronous motors for clocksElectric windingData synchronizationDevices fixation
The present invention is an apparatus and method for synchronizing and updating the memory of an external digital device, such as a personal digital assistant, and the memory of a watch via a two way communication link providing for the synchronous transfer of data between the devices. The data transfer is accomplished by placing the external digital device and watch into an alignment device which secures and positions each device in an appropriate spatial relationship allowing data to be transferred between devices. A separate integrated display controller provides for operation of the watch display thereby conserving power required to operate the device.
Owner:FOSSIL GRP INC
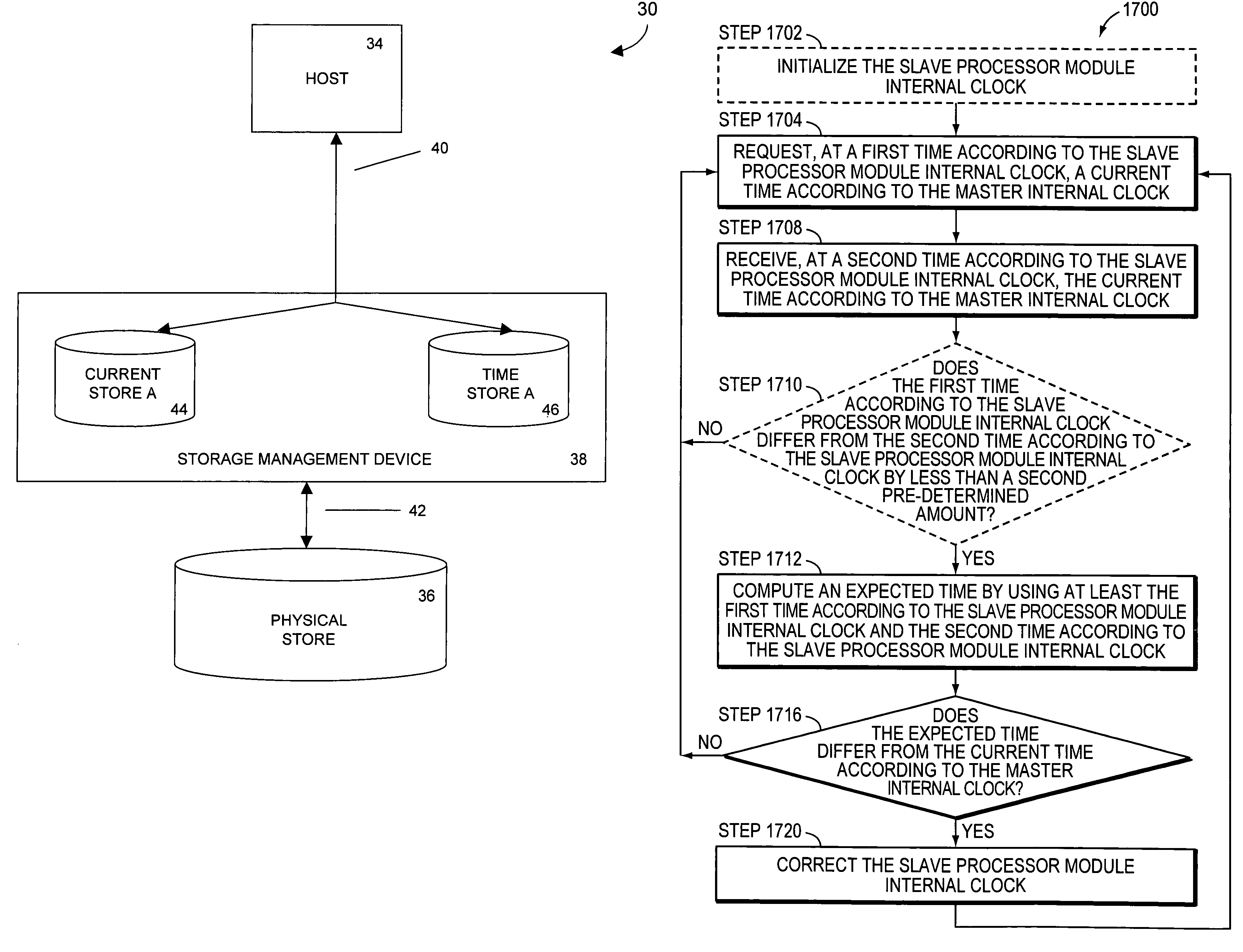
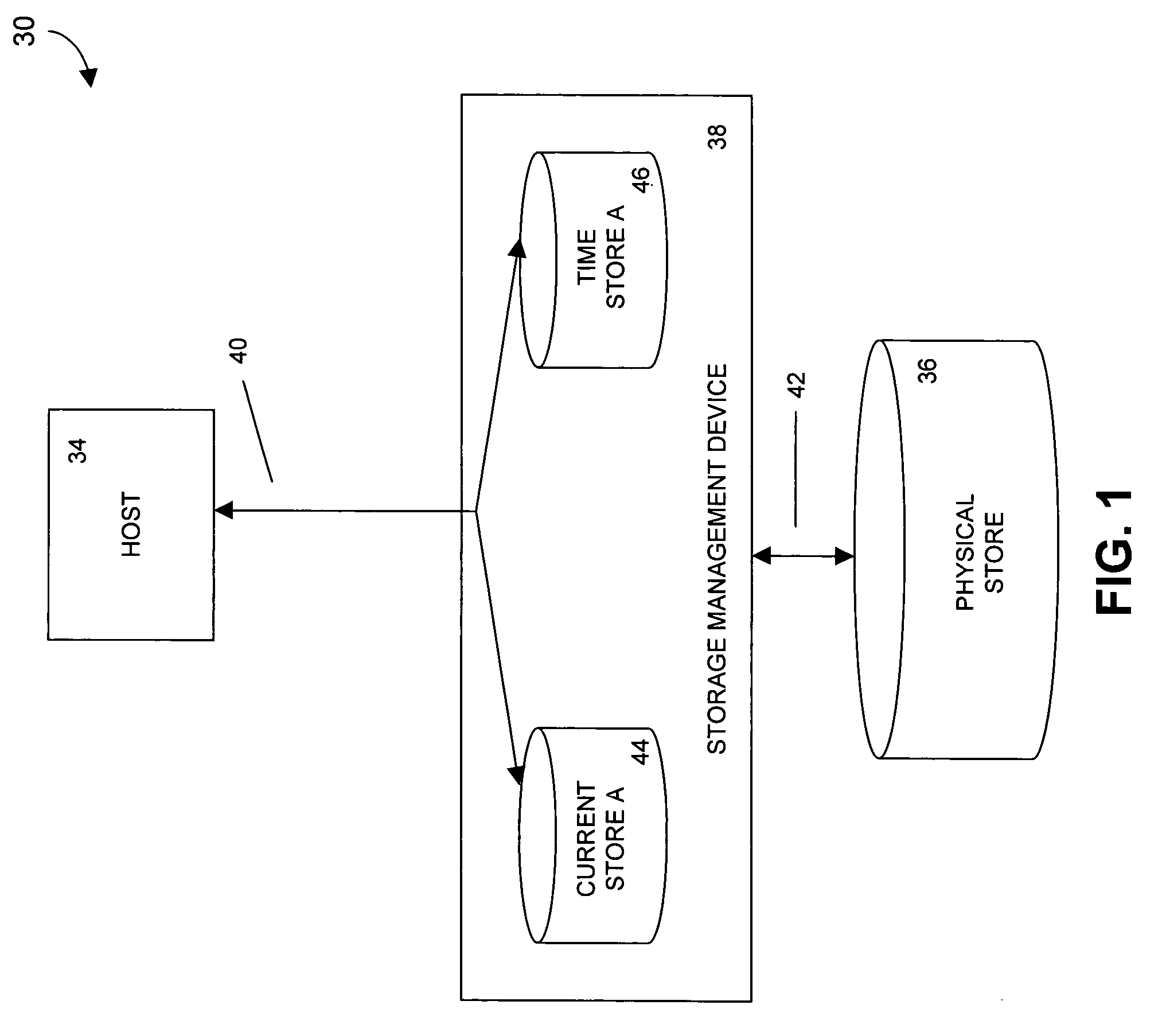
Systems and methods for synchronizing the internal clocks of a plurality of processor modules
ActiveUS20060047989A1Promote recoveryData storage is convenientMechanical clocksSynchronous motors for clocksComputer architectureMulti processor
In a multiprocessor system that includes a plurality of processor modules, each one of which includes its own internal clock, one of the plurality of processor modules is designated as a master processor module having a master internal clock. Each other processor module is designated as a slave processor module having a slave processor module internal clock. Each slave processor module synchronizes its internal clock with the master internal clock.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
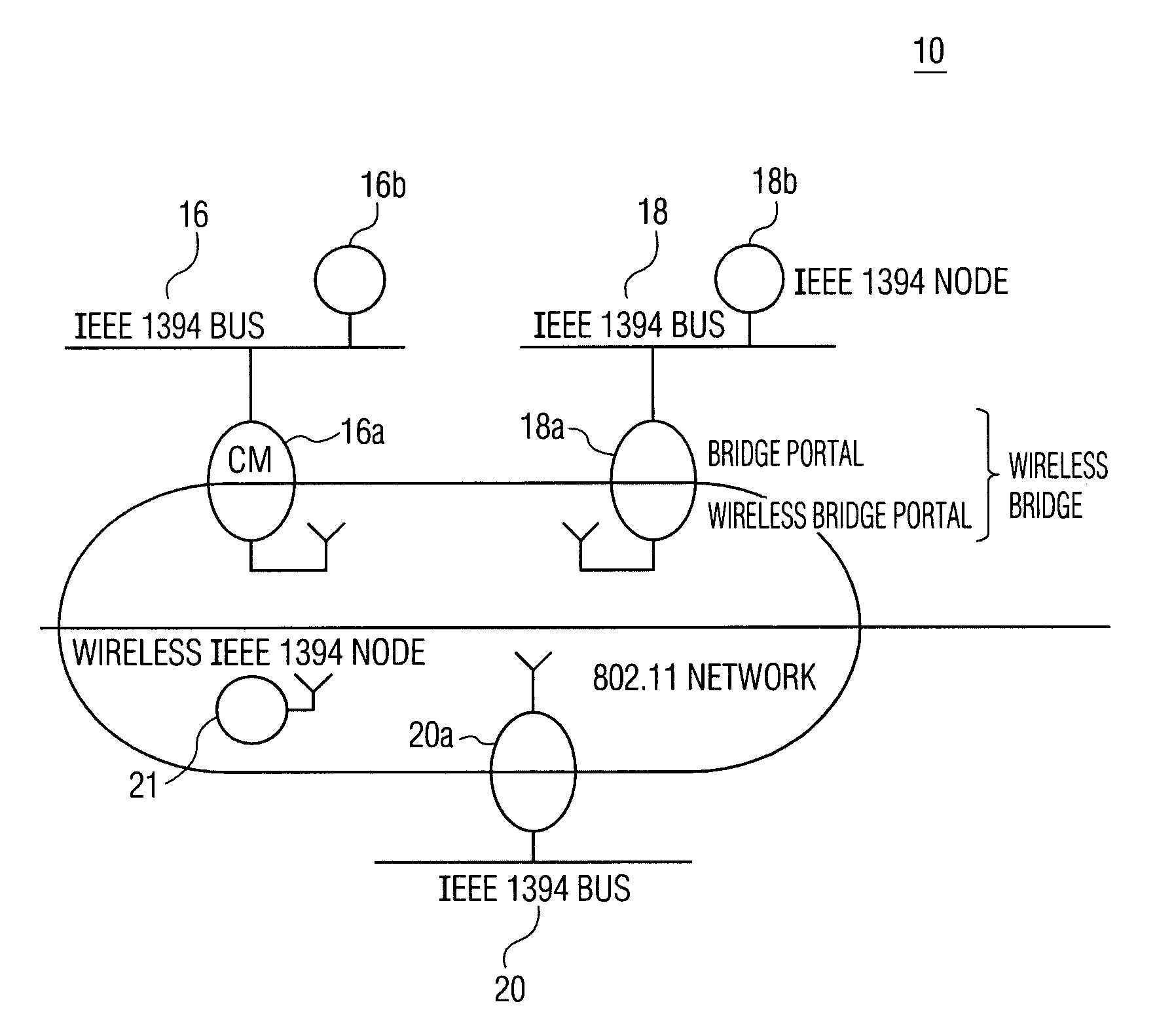
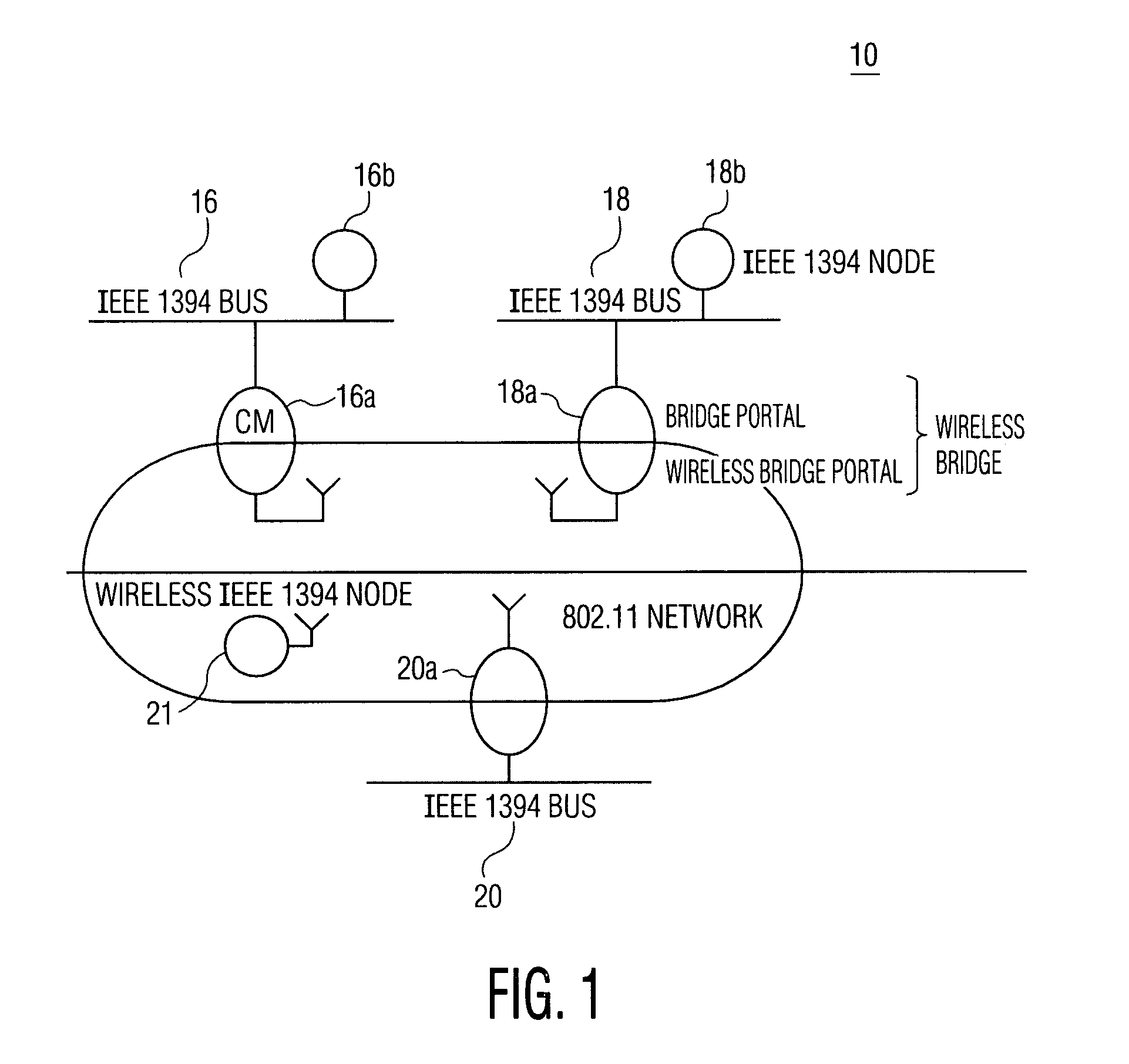
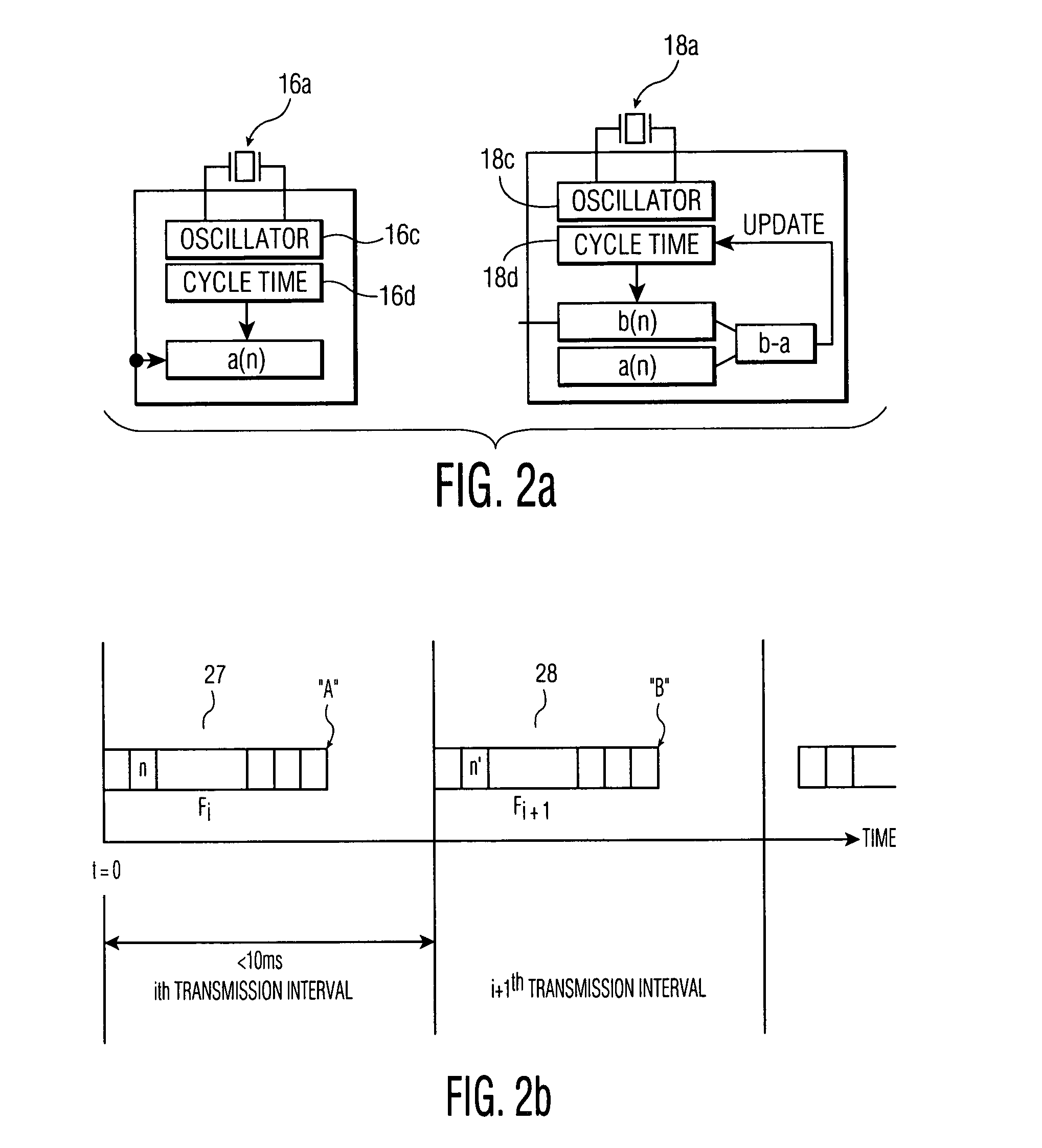
System and method for performing clock synchronization of nodes connected via a wireless local area network
ActiveUS7120092B2Synchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSlave clock
A clock synchronization method and apparatus is disclosed for use in a communication system including a plurality of wireless nodes communicatively coupled via a wireless network, each of the plurality of wireless nodes having a local time base, and one of the plurality of wireless nodes being designated as a master node having a master time base which serves as a master clock against which the local time bases are synchronized. The clock synchronization method includes the steps of periodically transmitting synchronization frames to the plurality of non-master nodes so as to adjust the slave clocks associated with the respective non-master nodes. The synchronization frames are distributed from the master node at near-periodic intervals and includes a cycle time value that corresponds to the end of the previously transmitted synchronization frame. The slave clocks (i.e., non-master nodes) receiving the synchronization frame determine the cycle time value at the point of reception of the synchronization frame and adjusts their clocks by calculating a difference value between the received cycle time and a previously saved local cycle time value.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
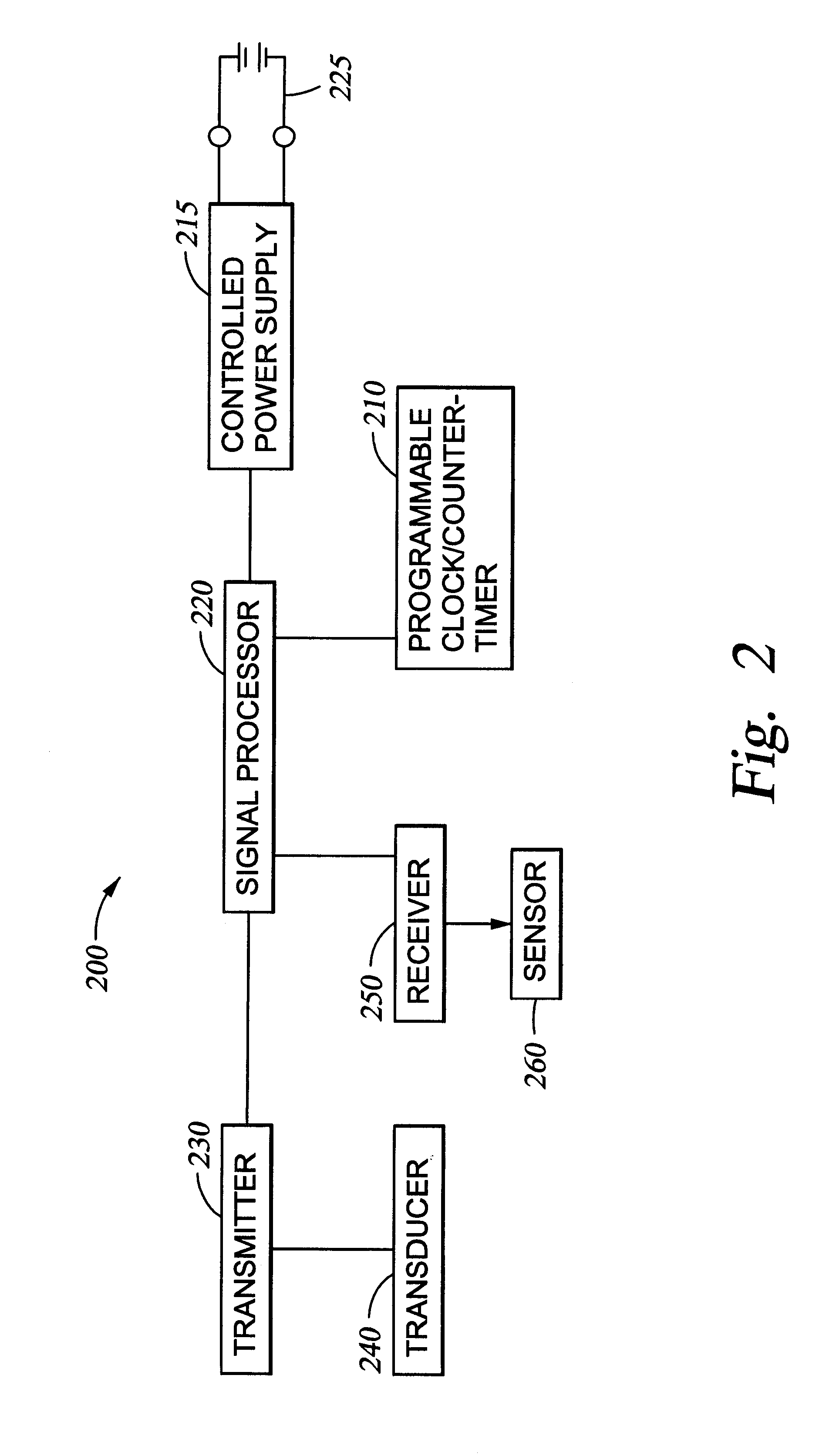
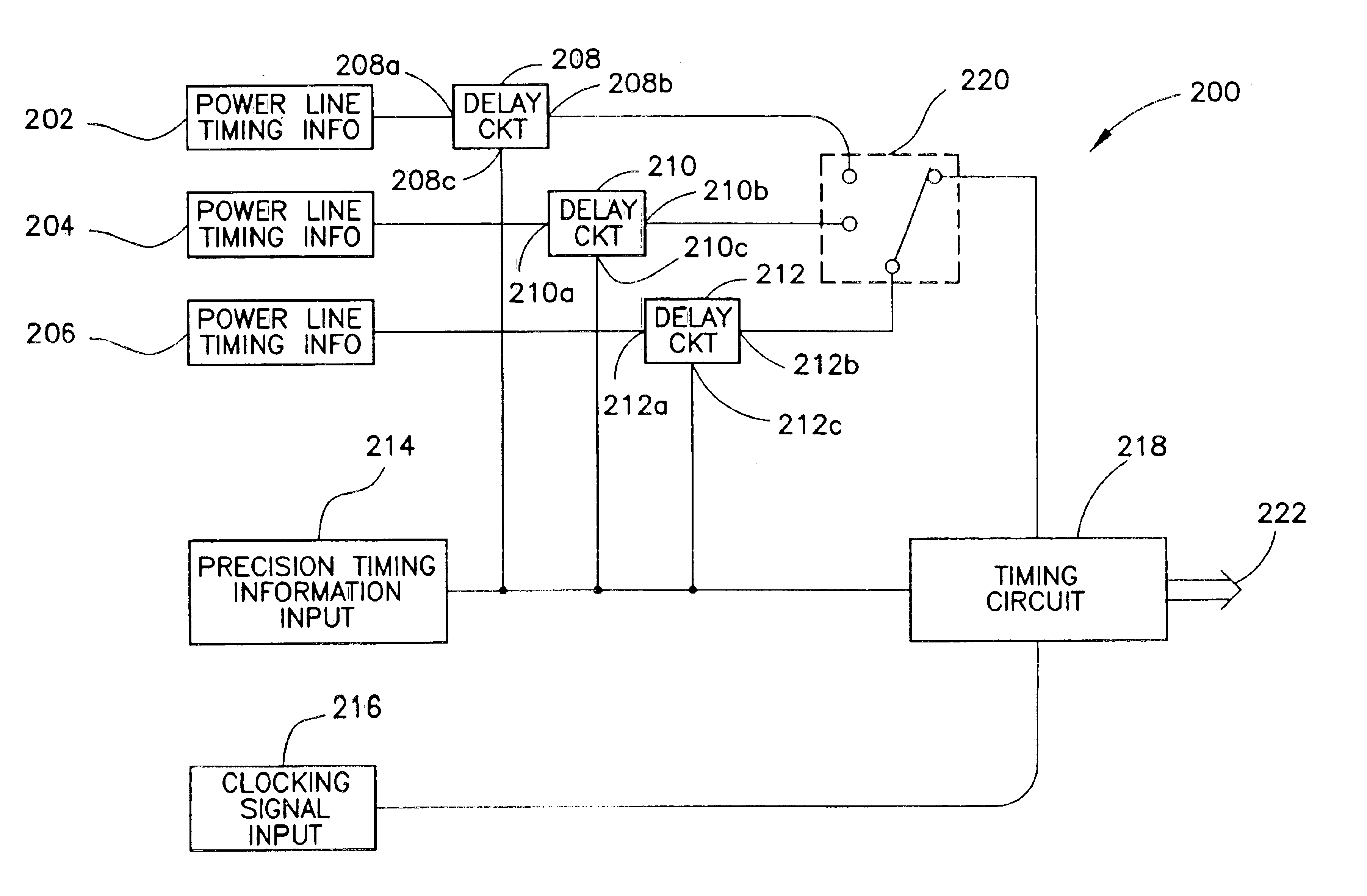
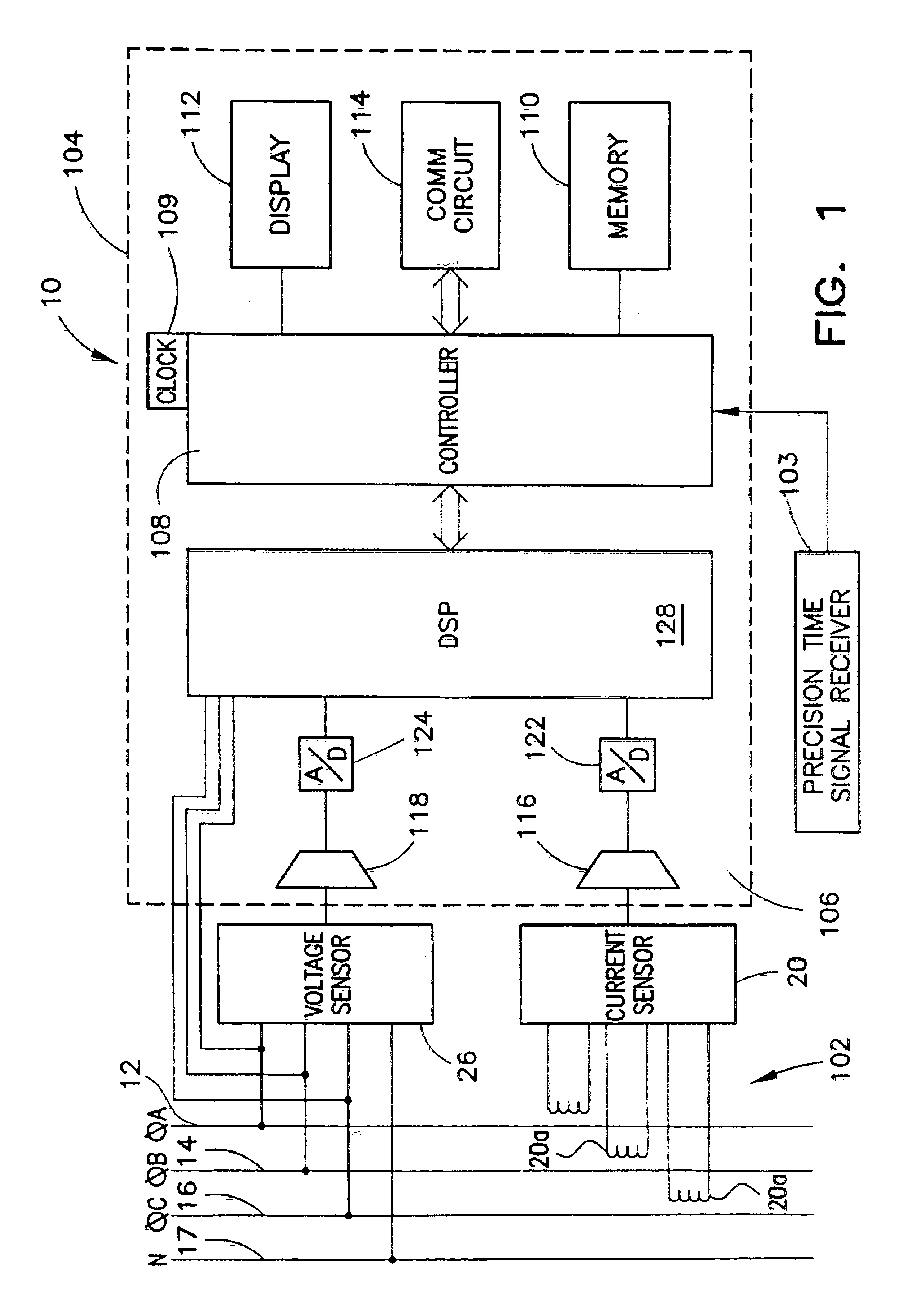
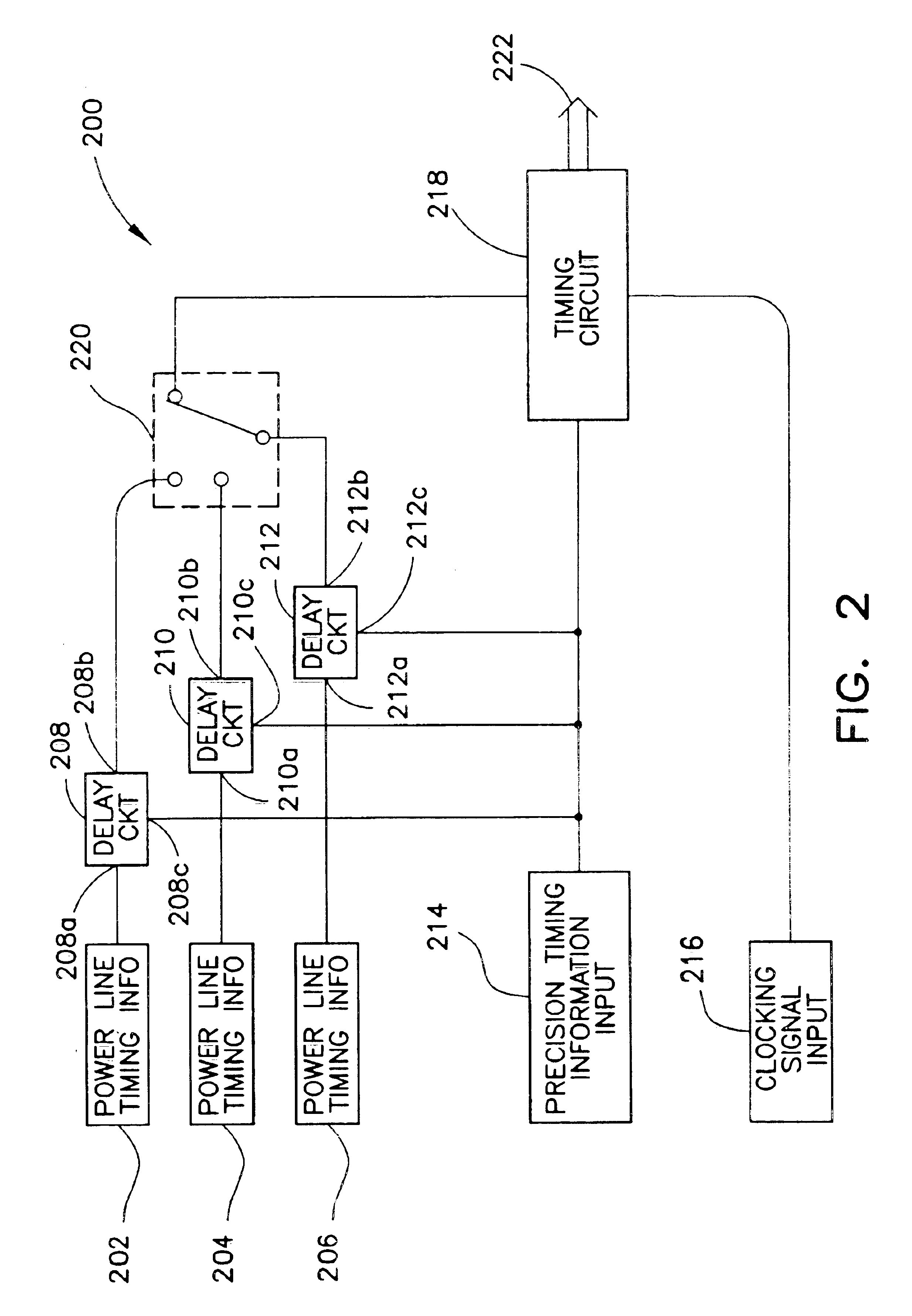
Redundant precision time keeping for utility meters
InactiveUS6859742B2Smooth transitionAccurate pictureElectric devicesDynamo-electric motor metersSignal sourceTime signal
An apparatus for generating precision time signals includes a source of power line timing information, a source of precision time signals, and a timing circuit. The timing circuit is coupled to the source of precision time signals to receive a precision time signal there from, and is operable to generate clock information based on the precision time signal. The timing circuit is further operable to generate clock information based on the power line timing information.
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
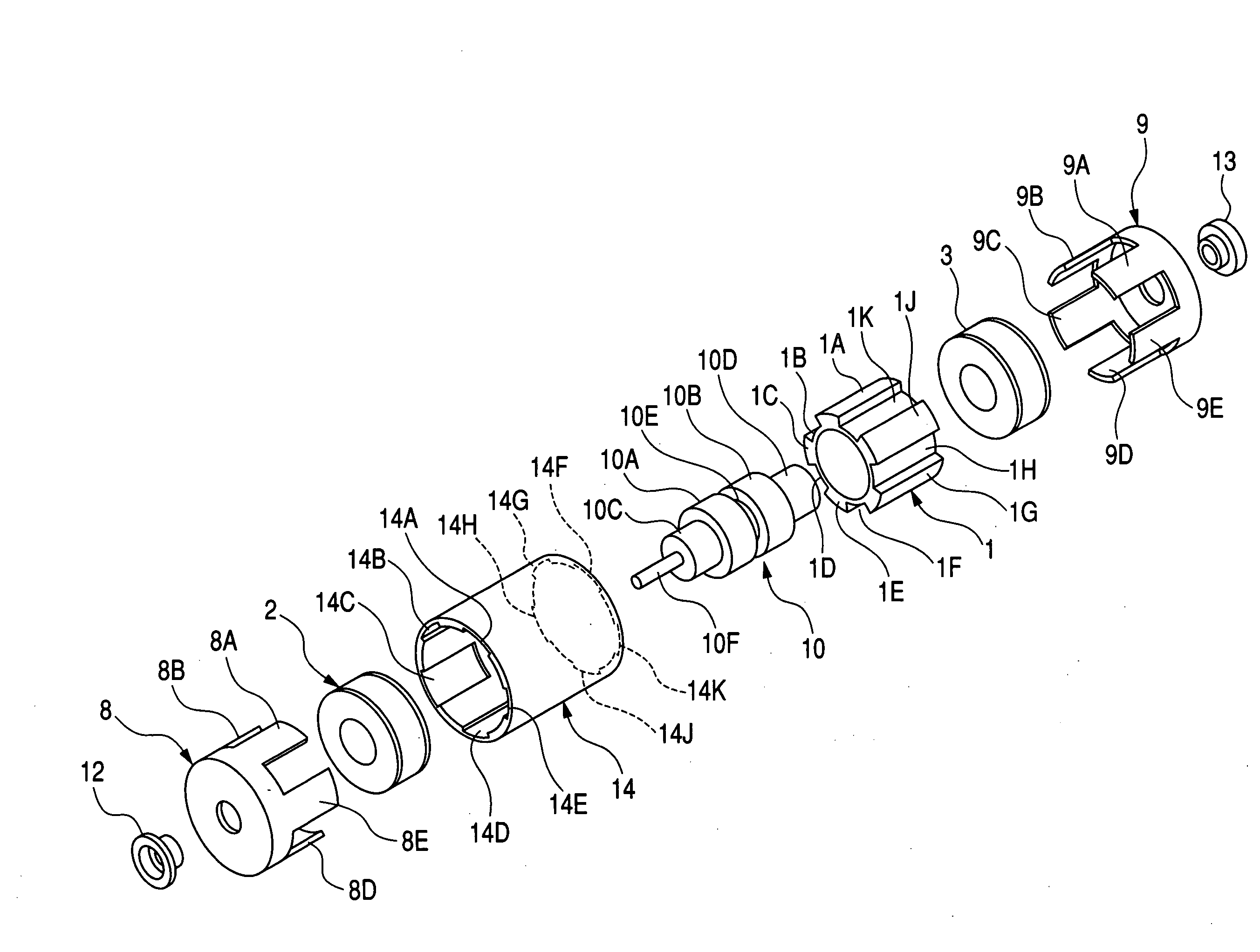
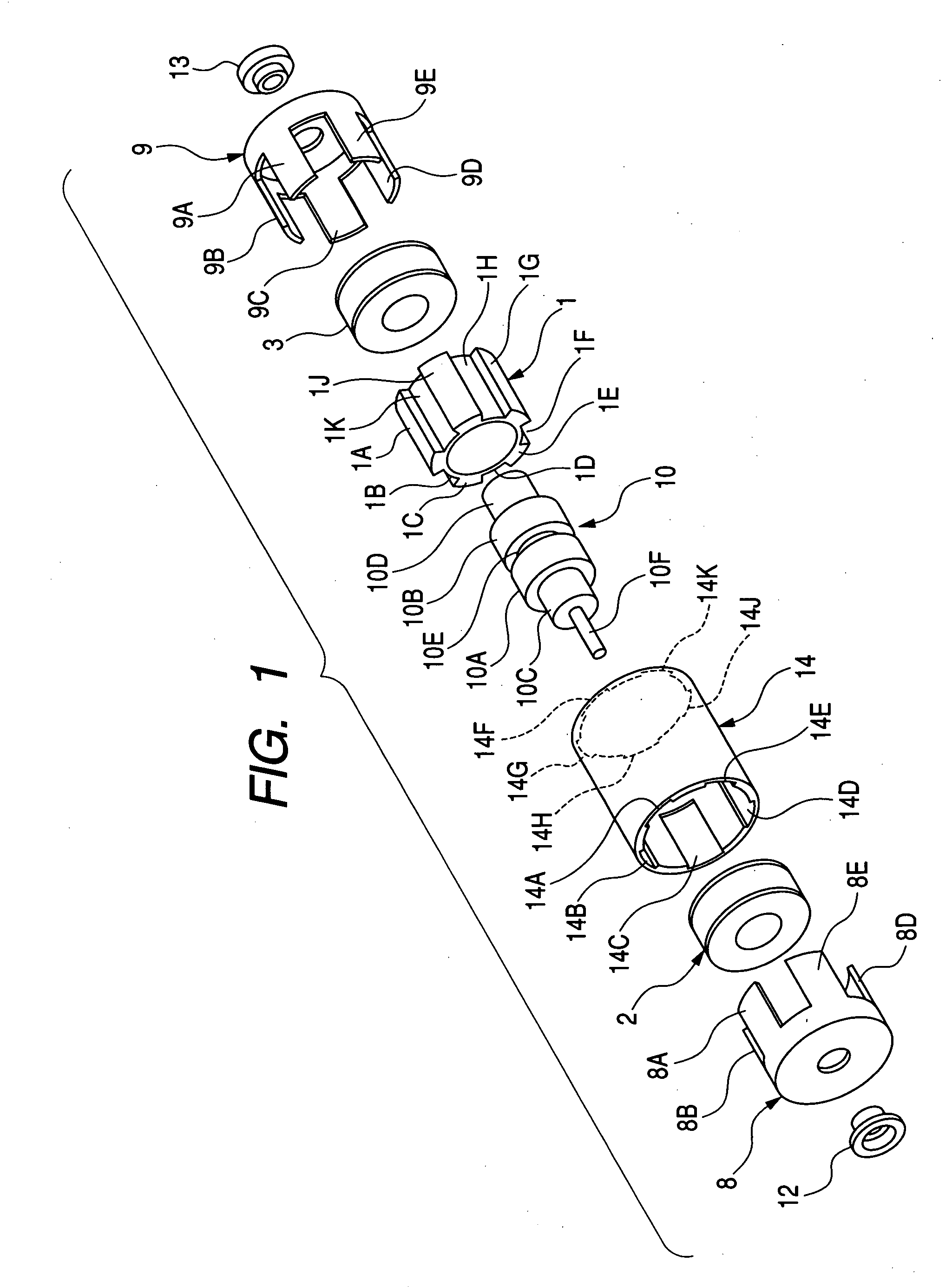
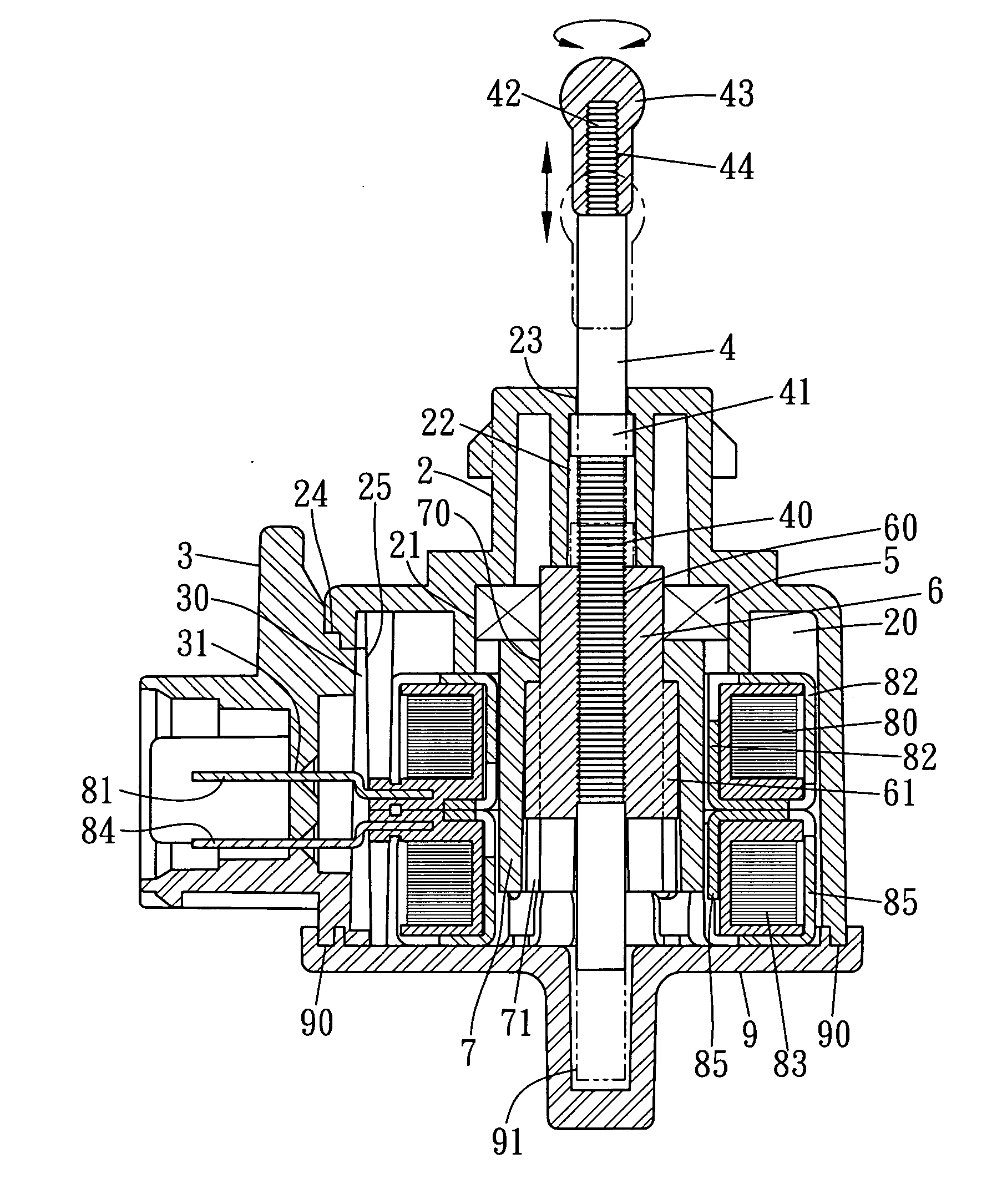
Stepping motor
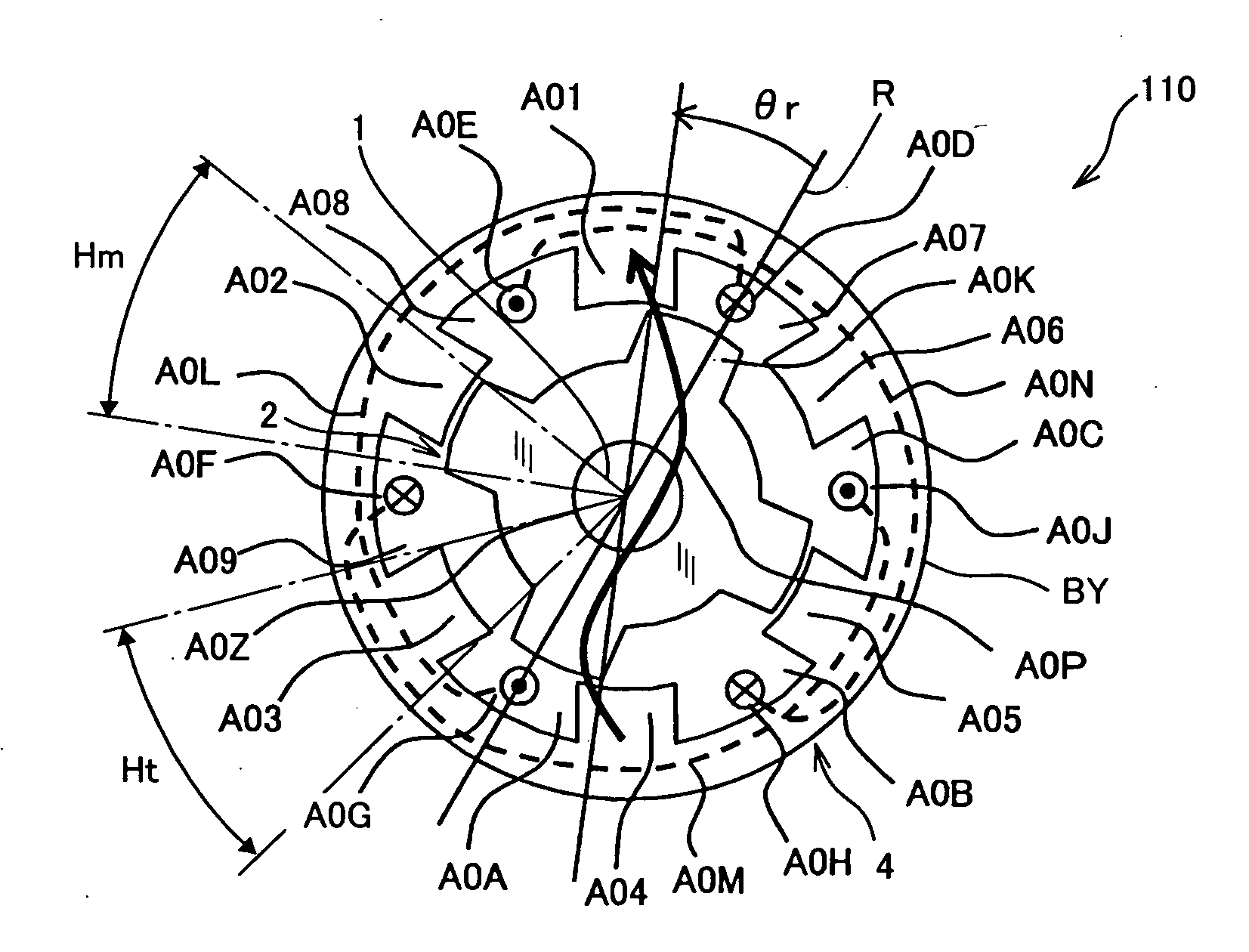
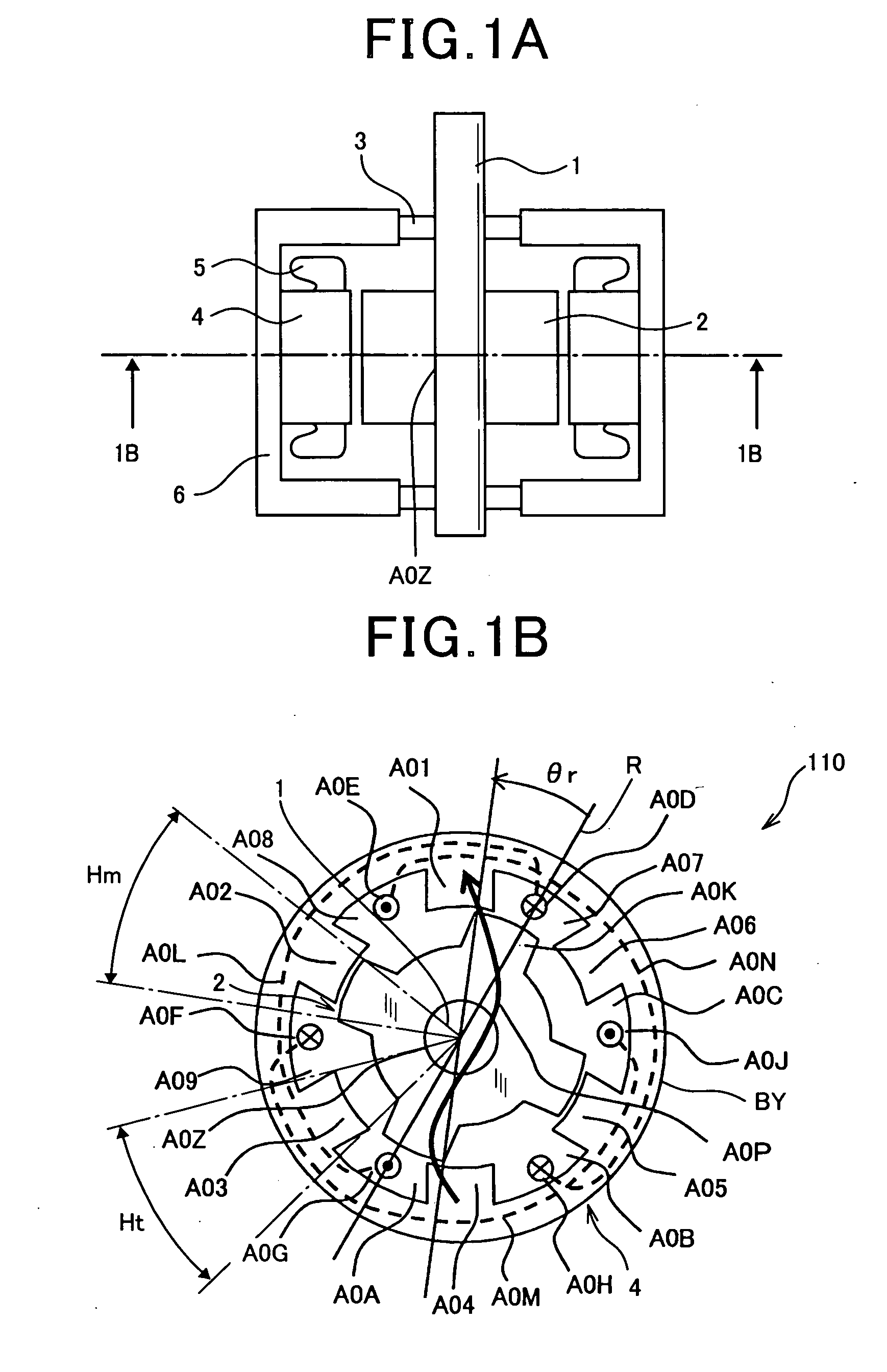
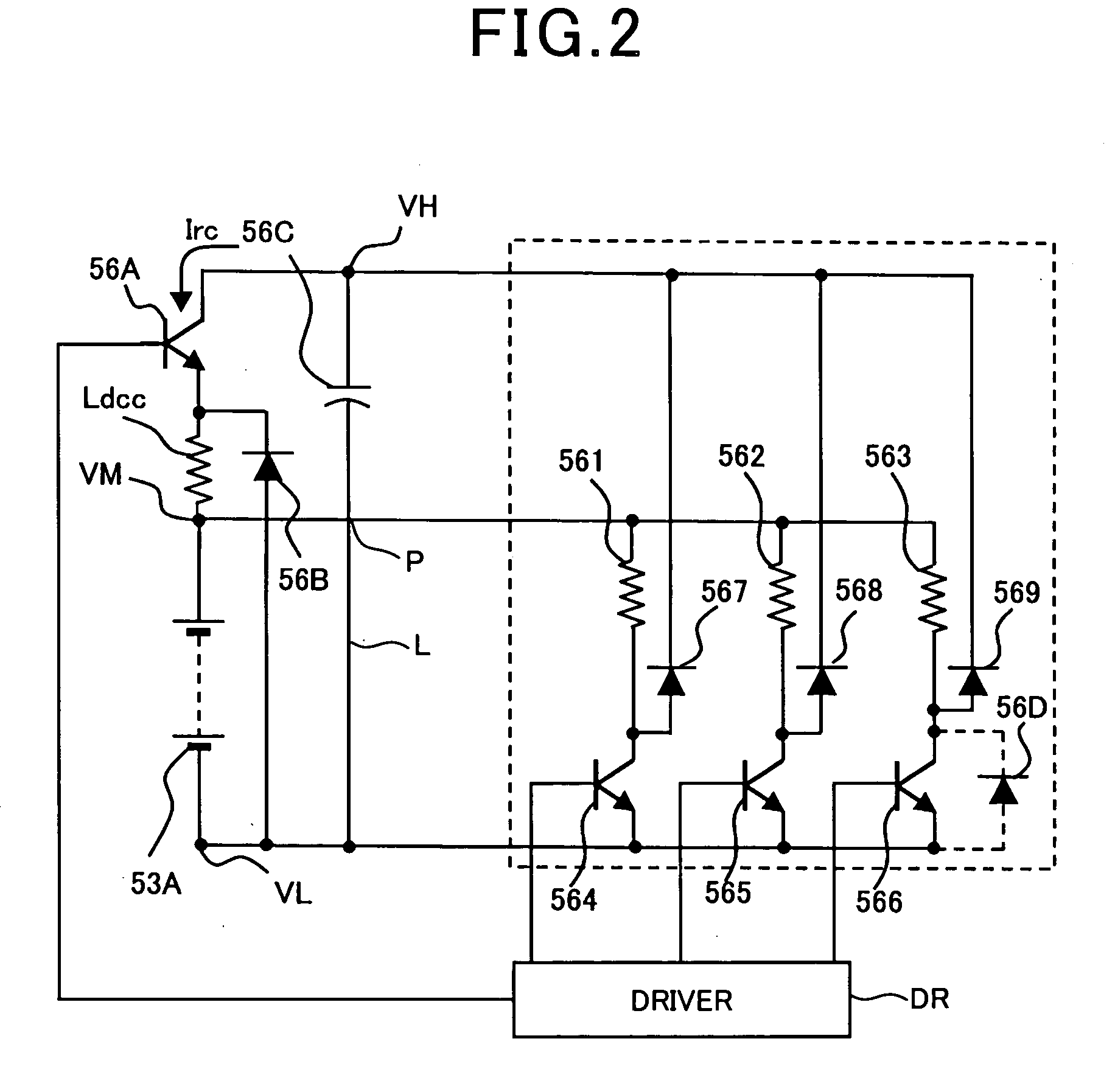
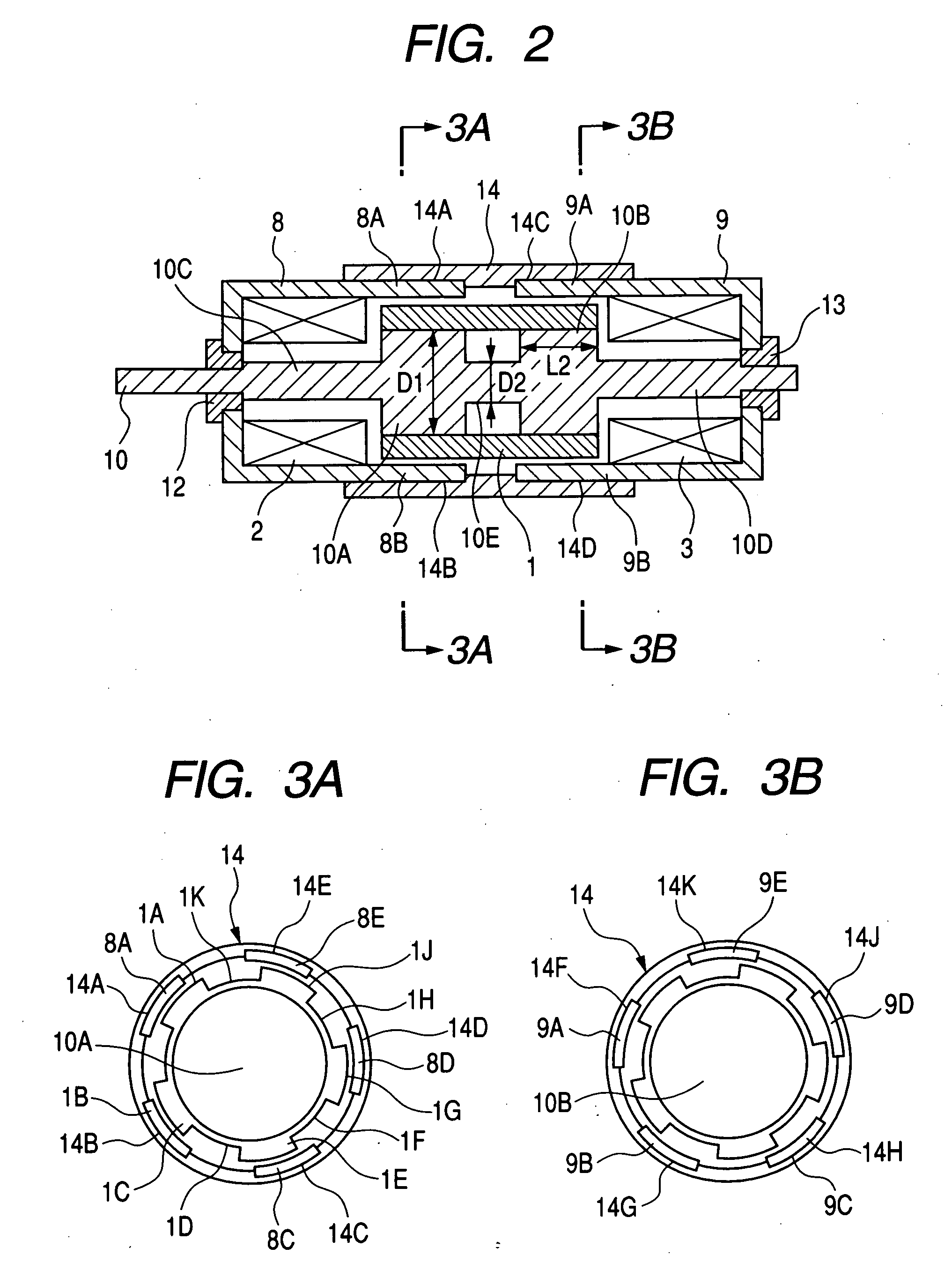
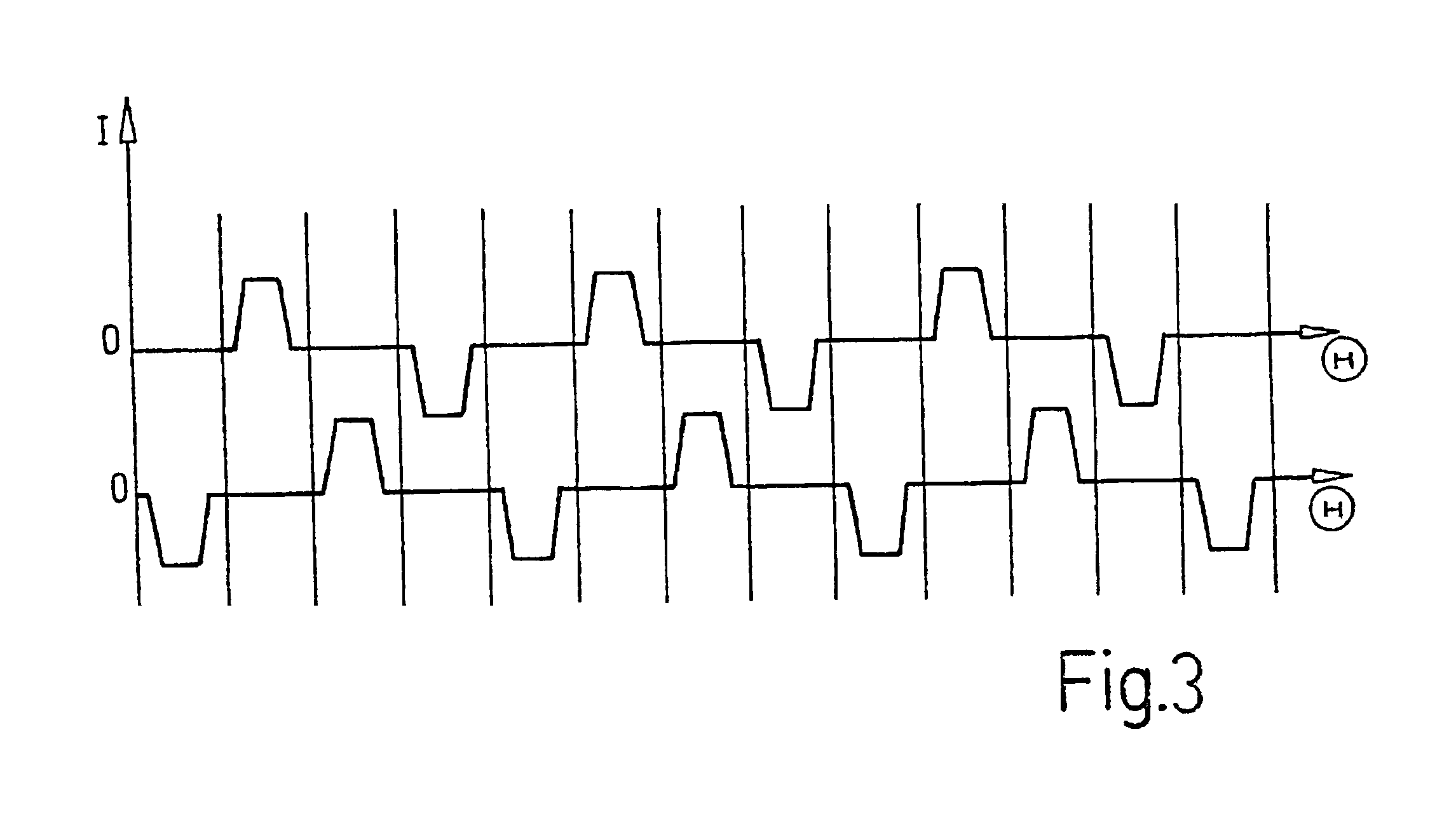
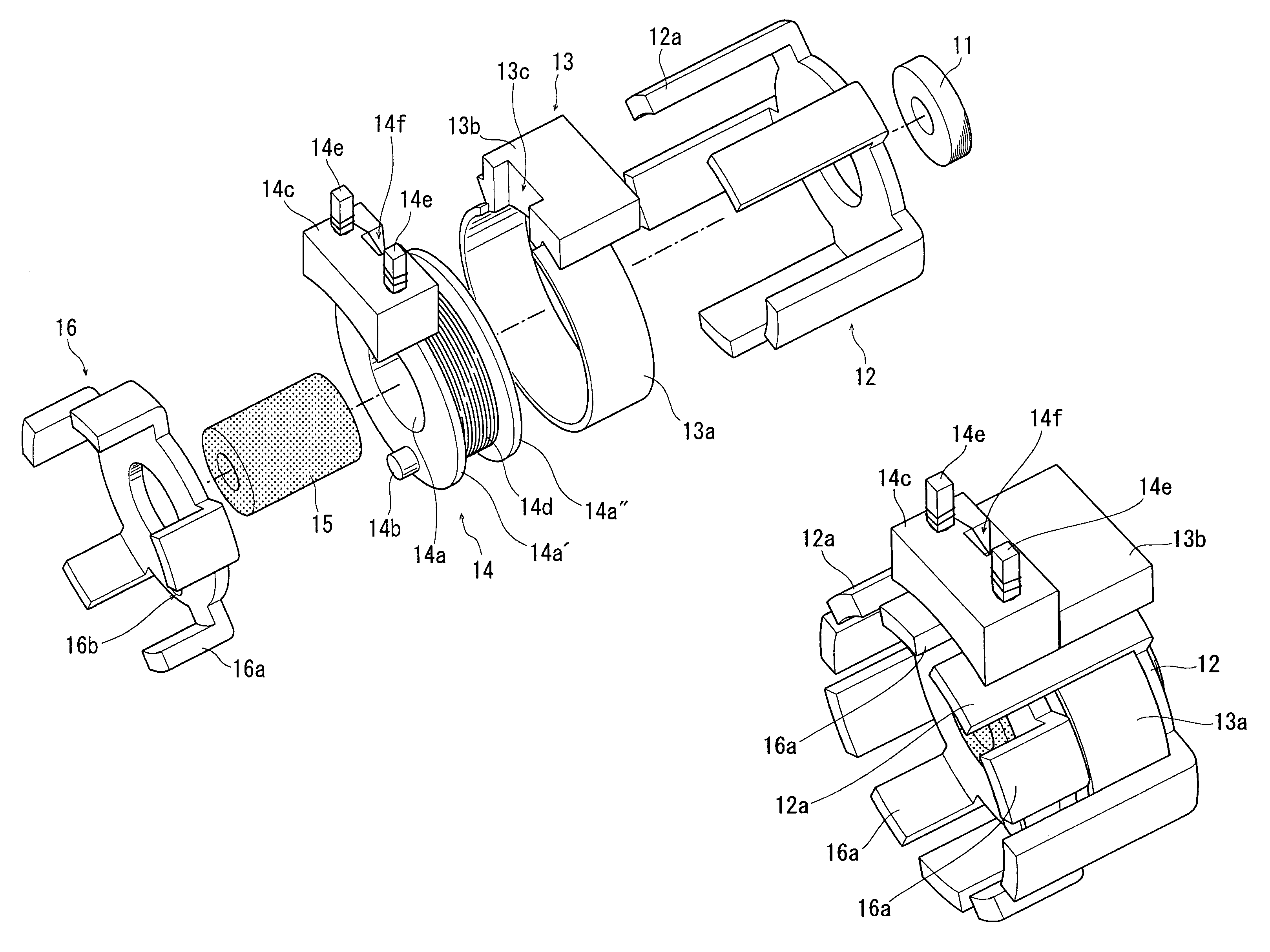
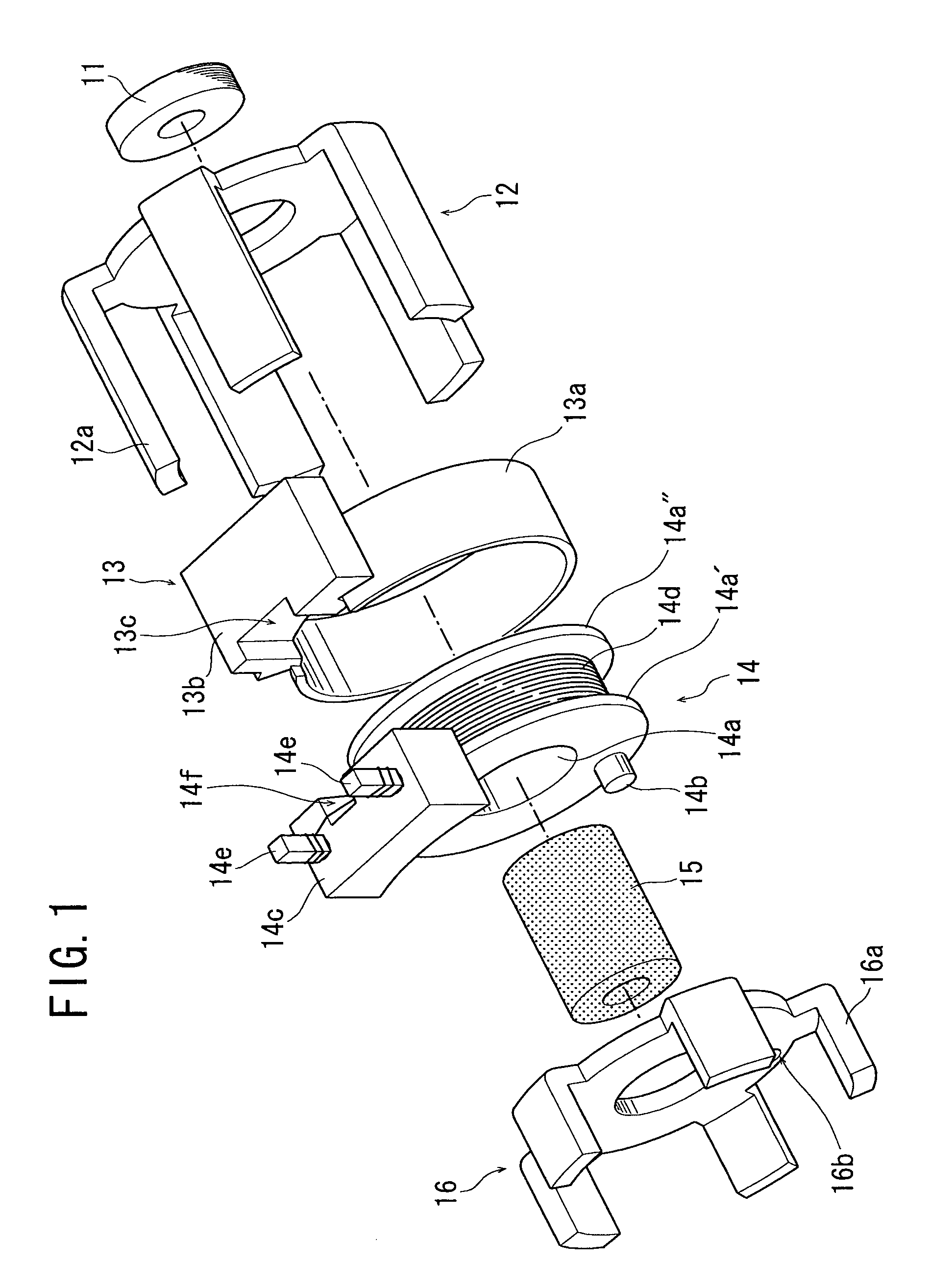
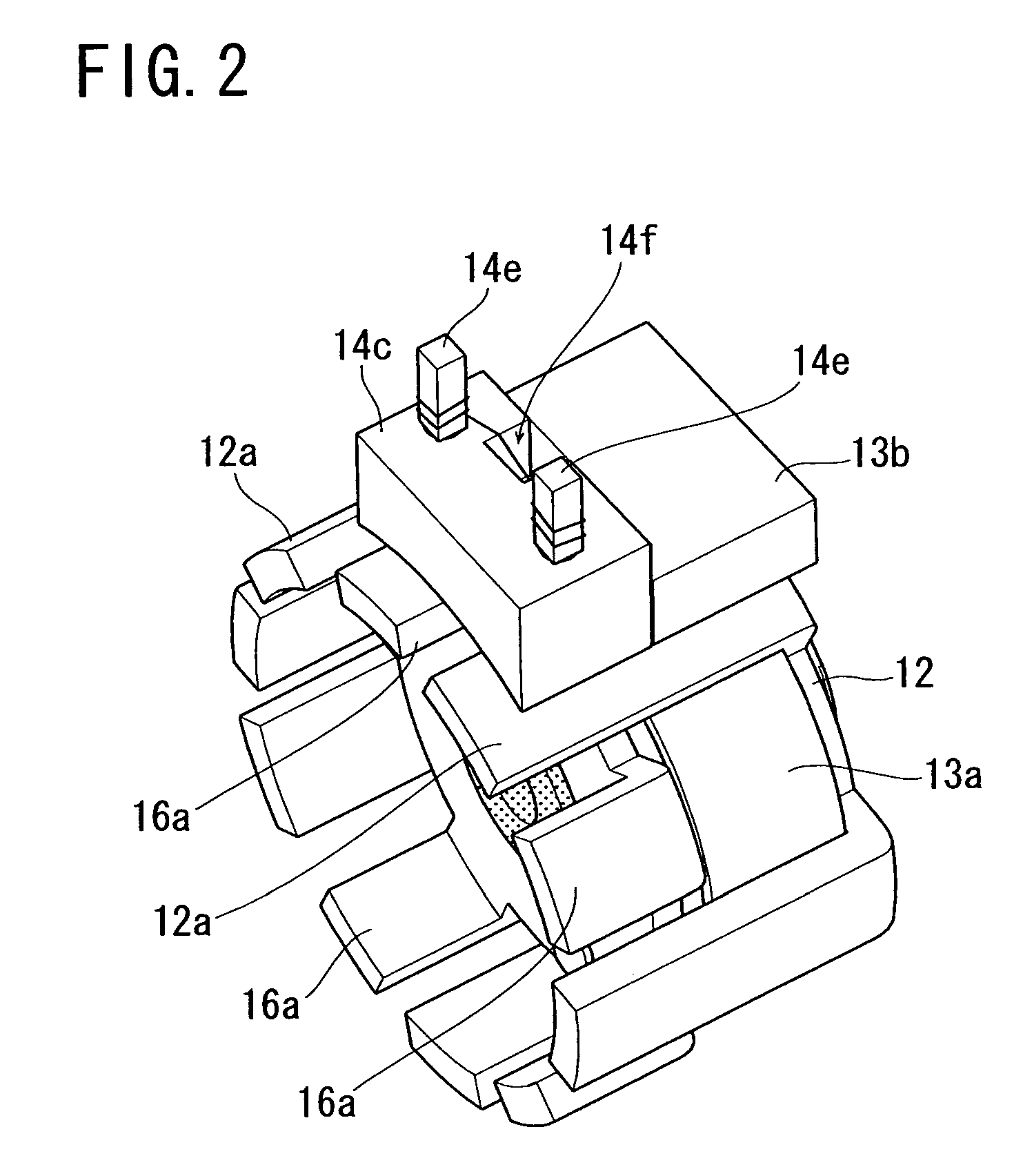
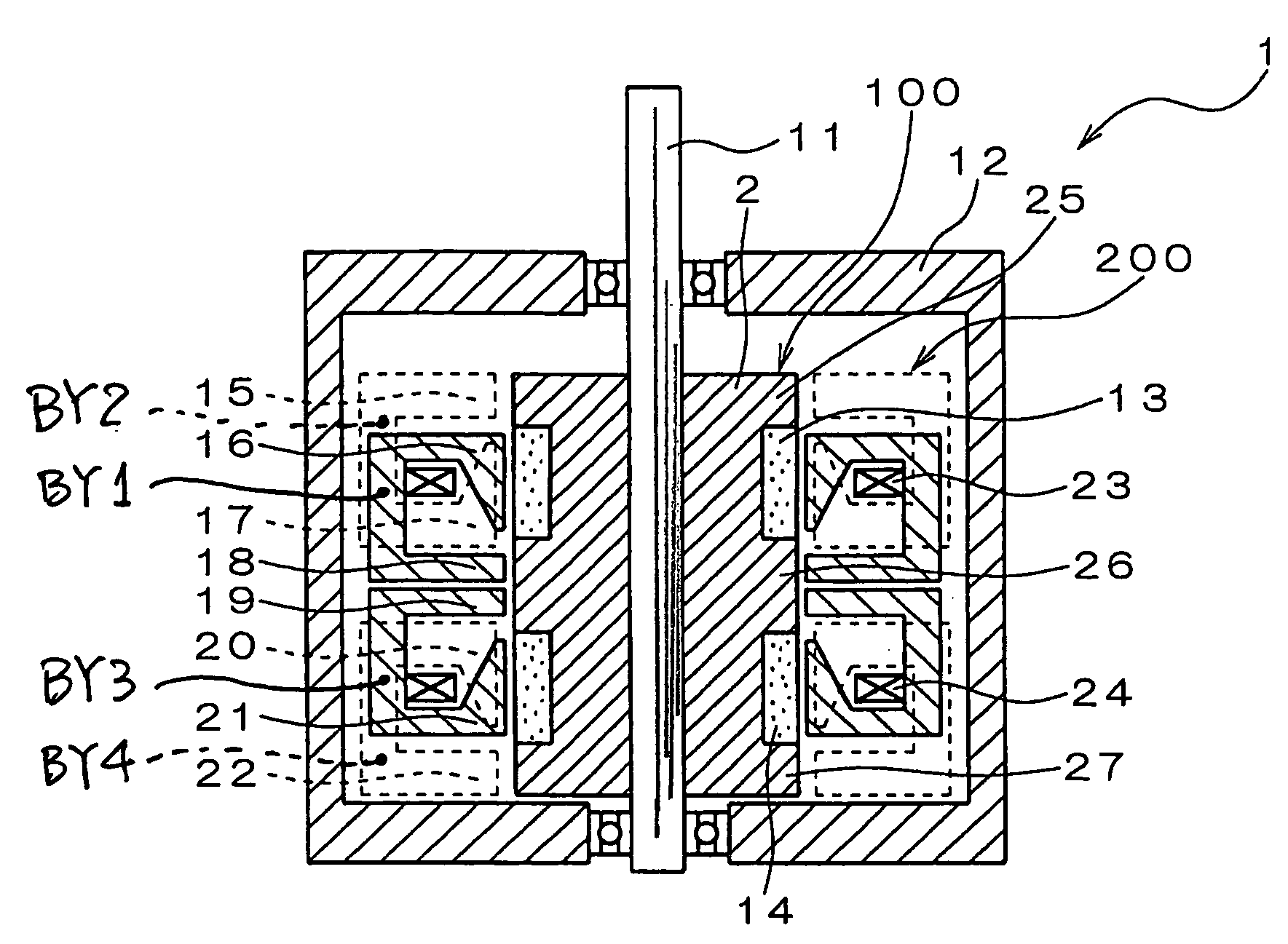
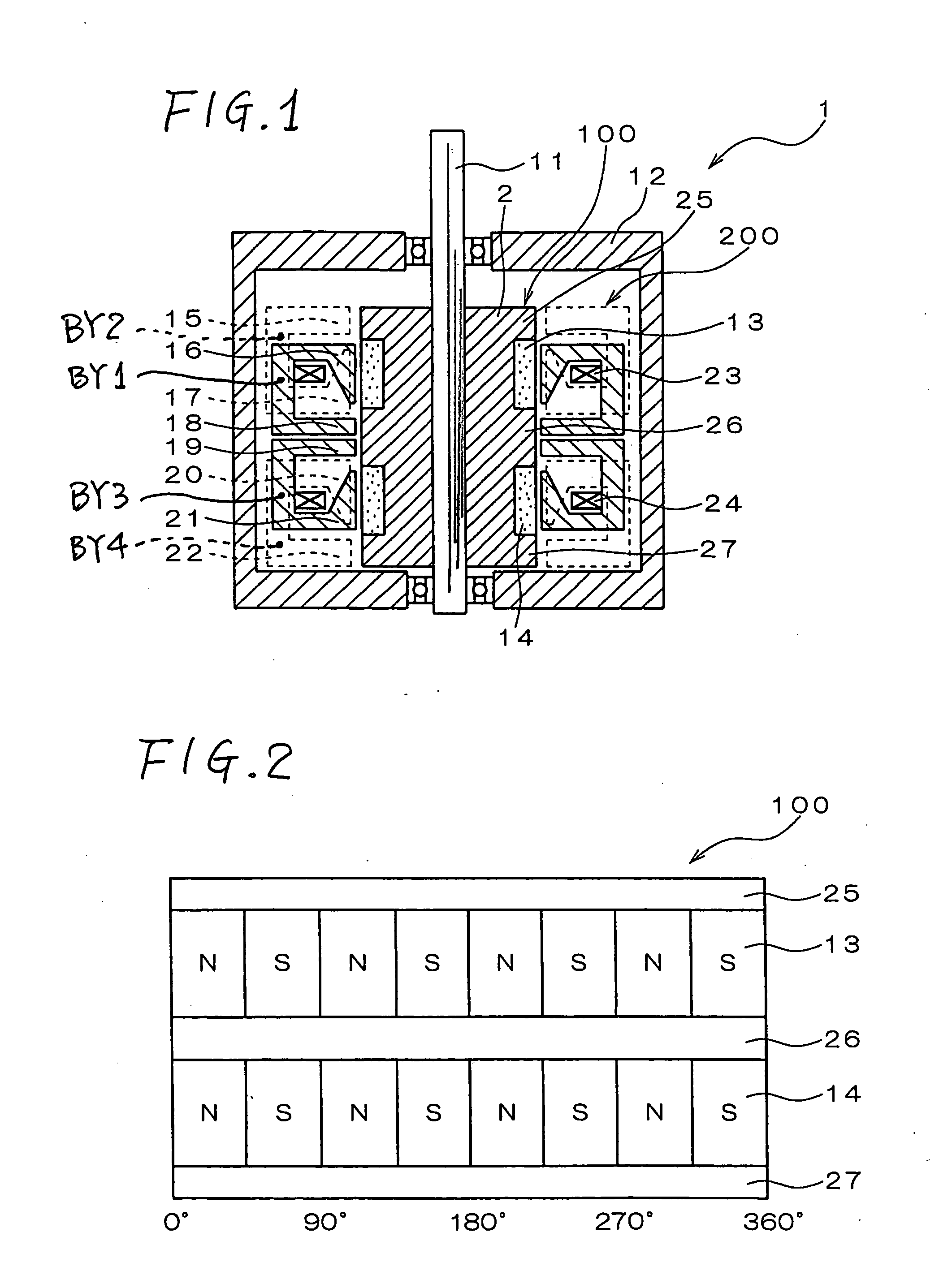
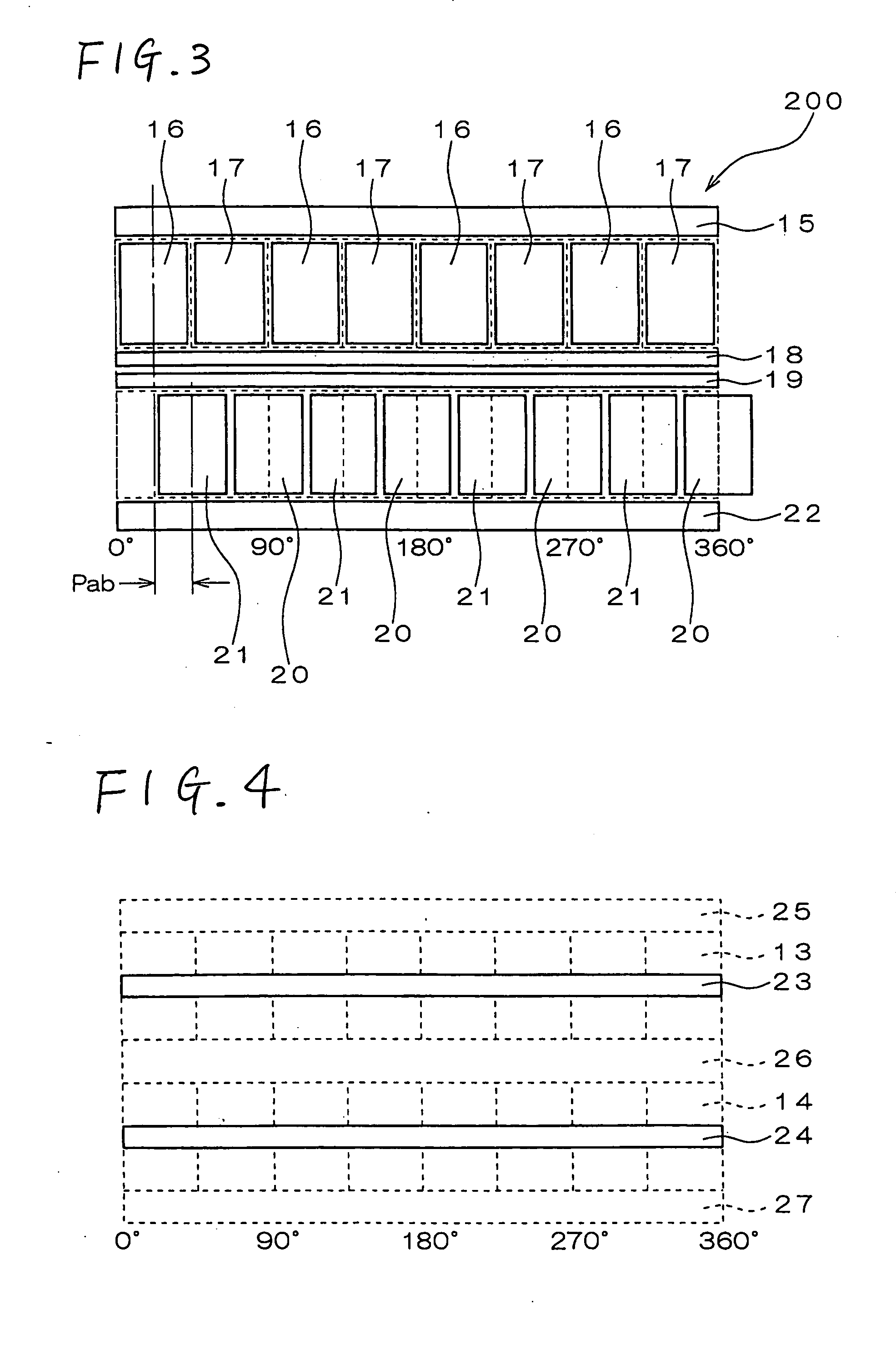
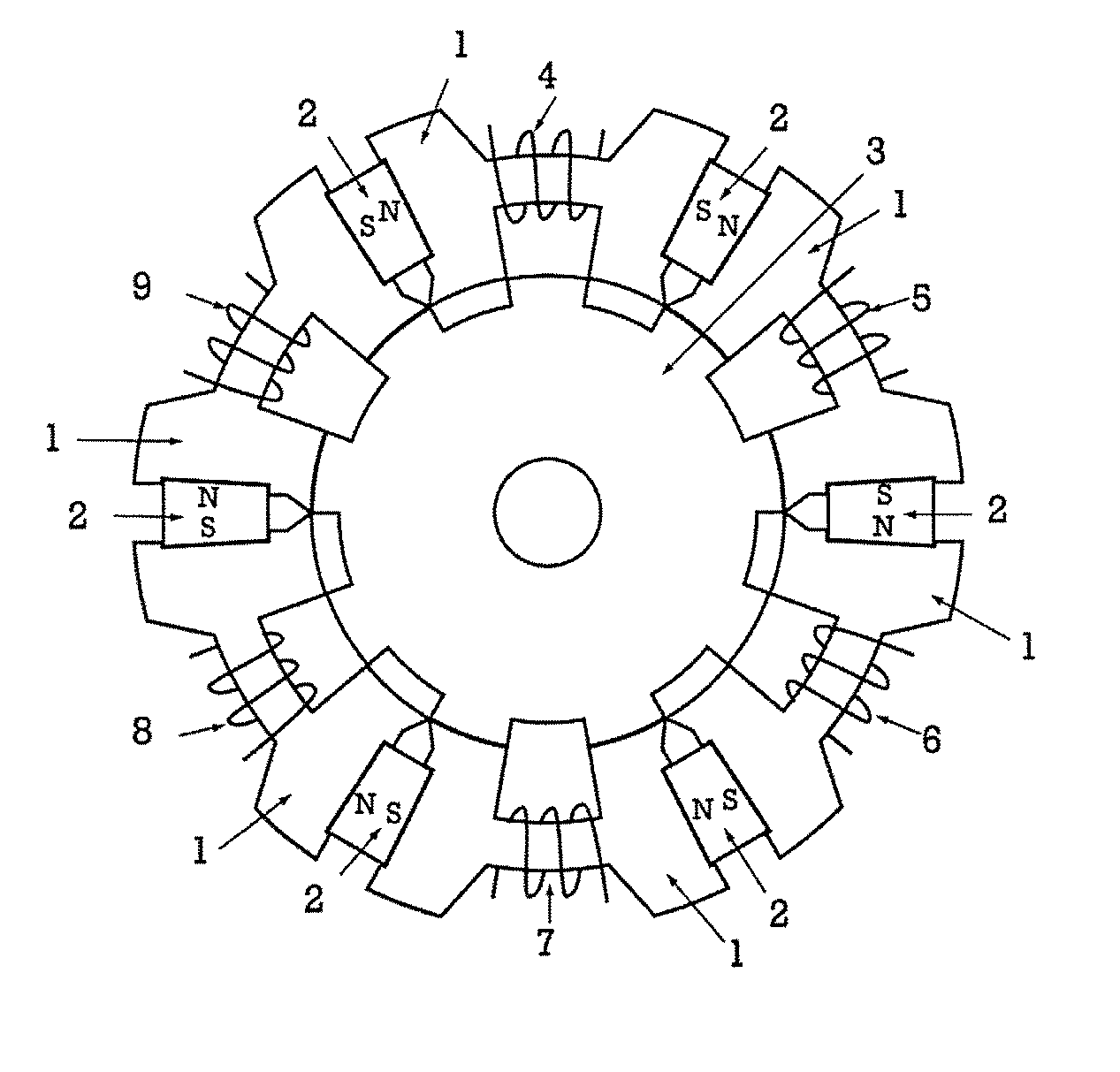
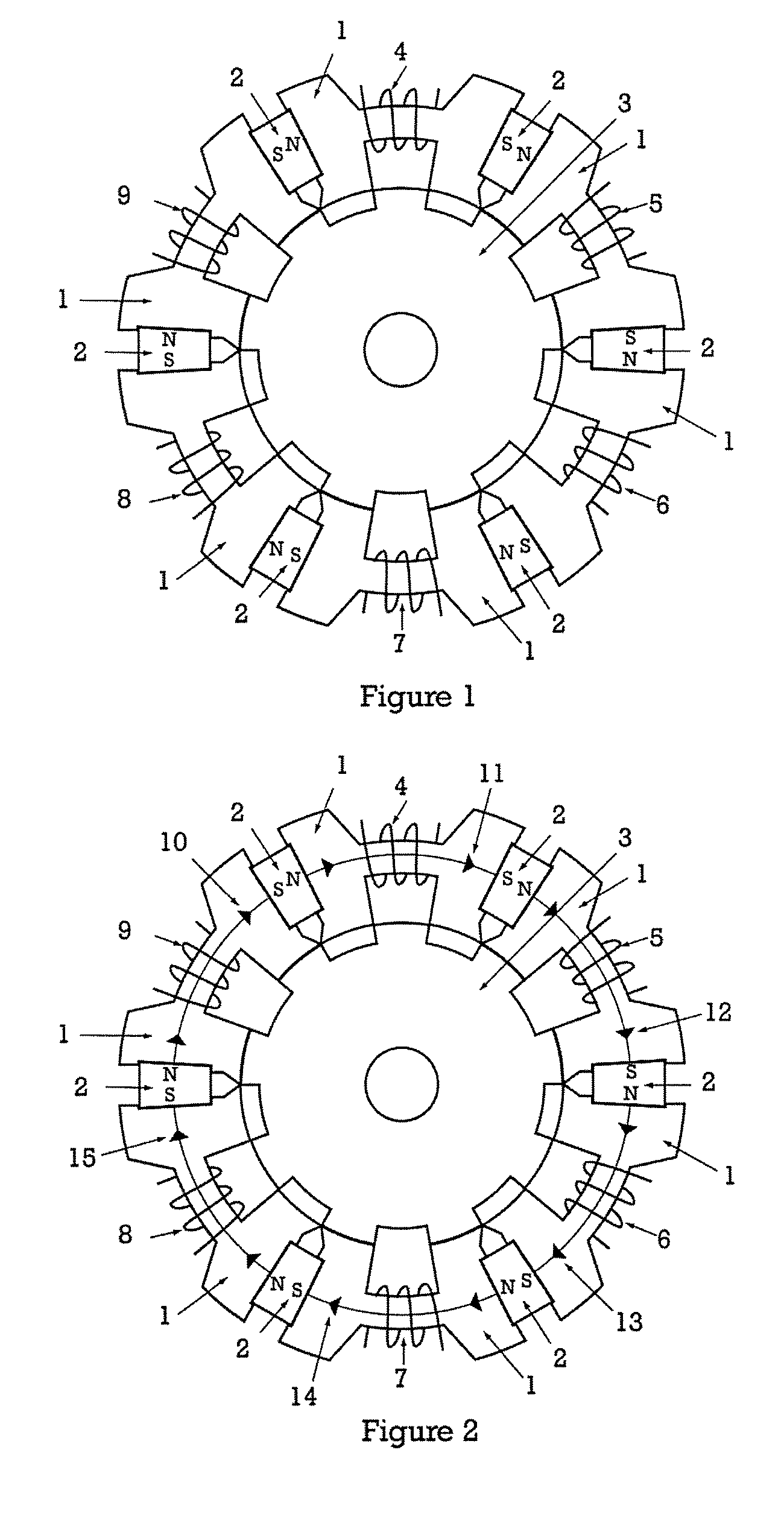
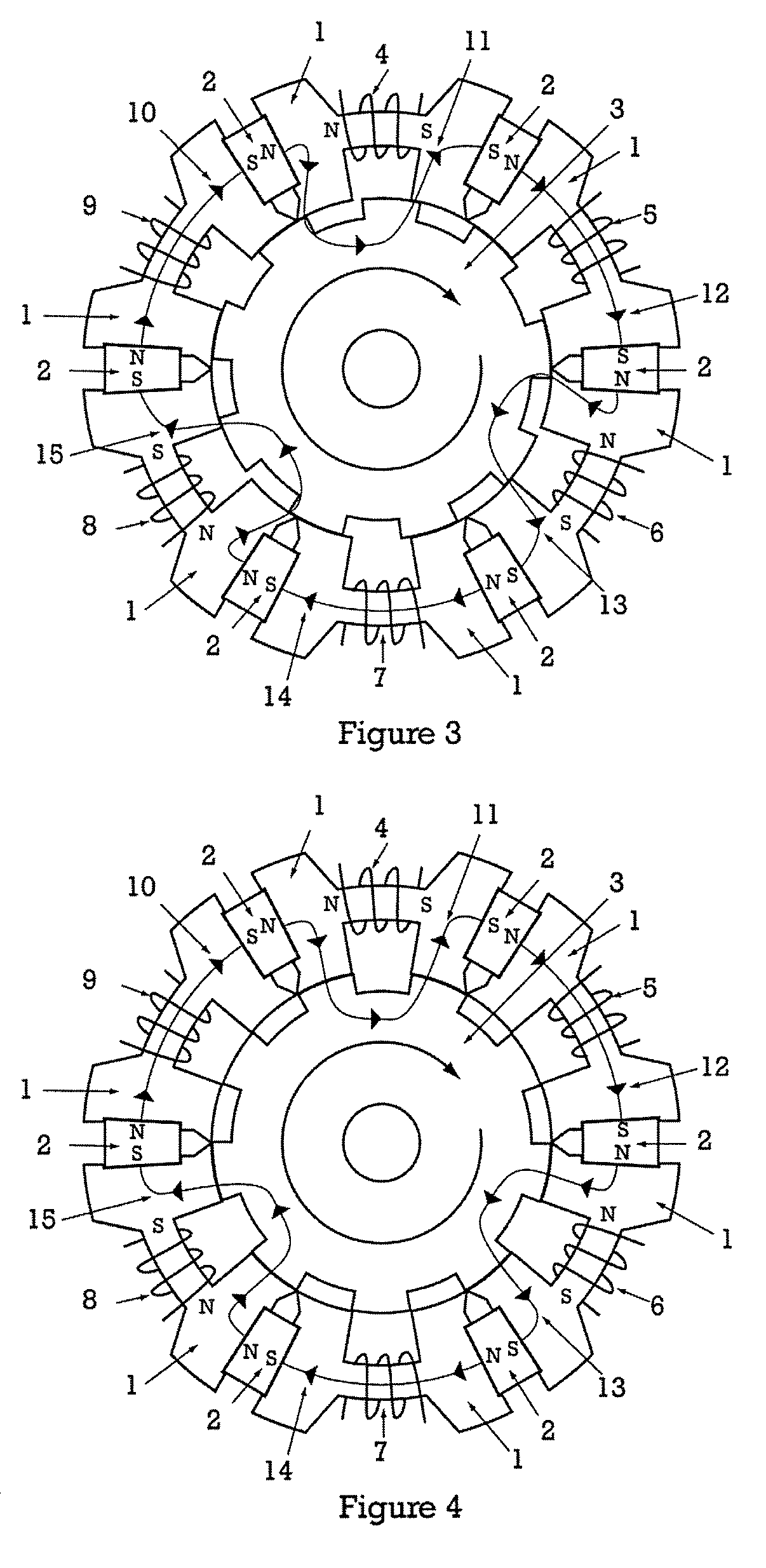
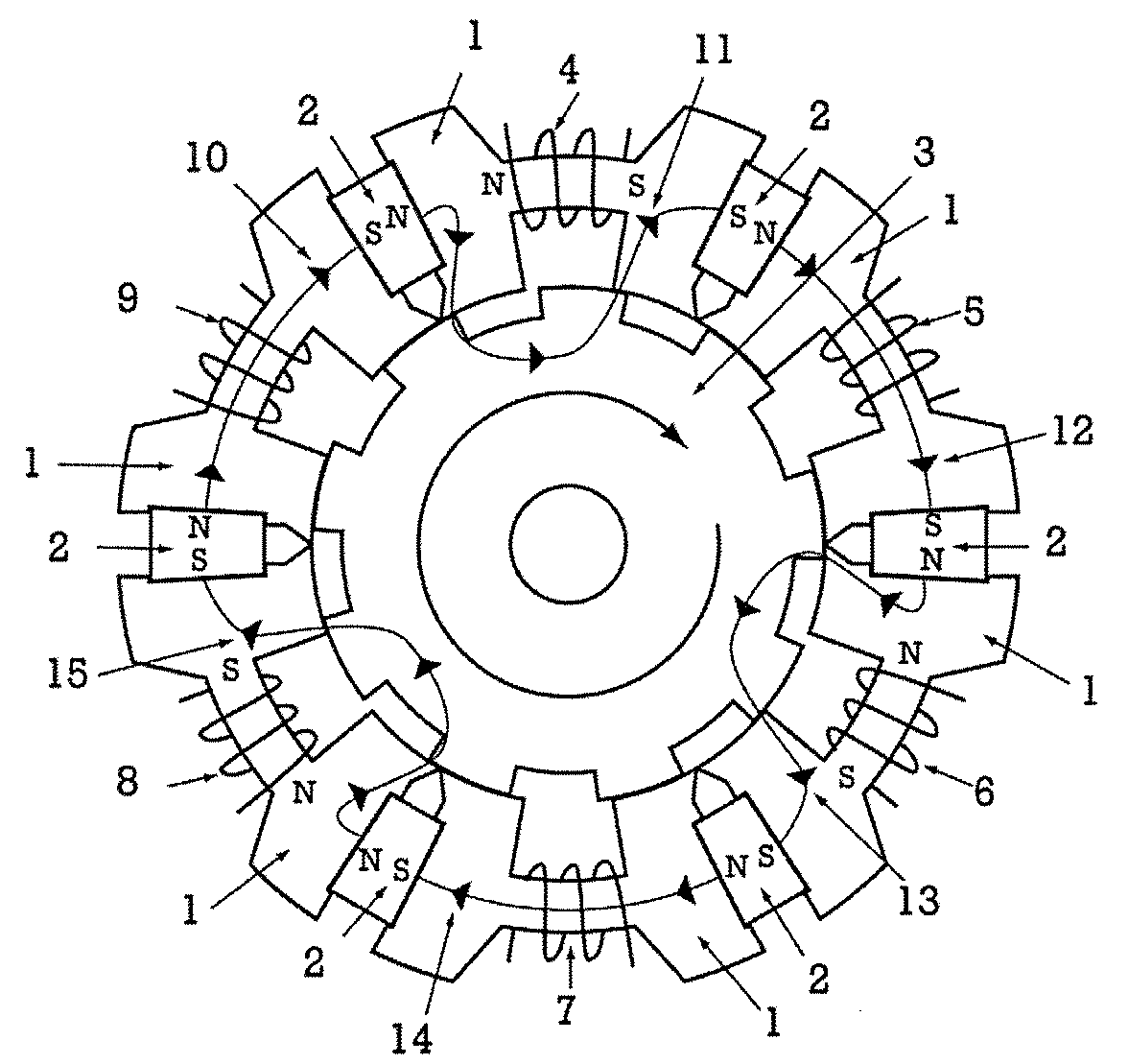
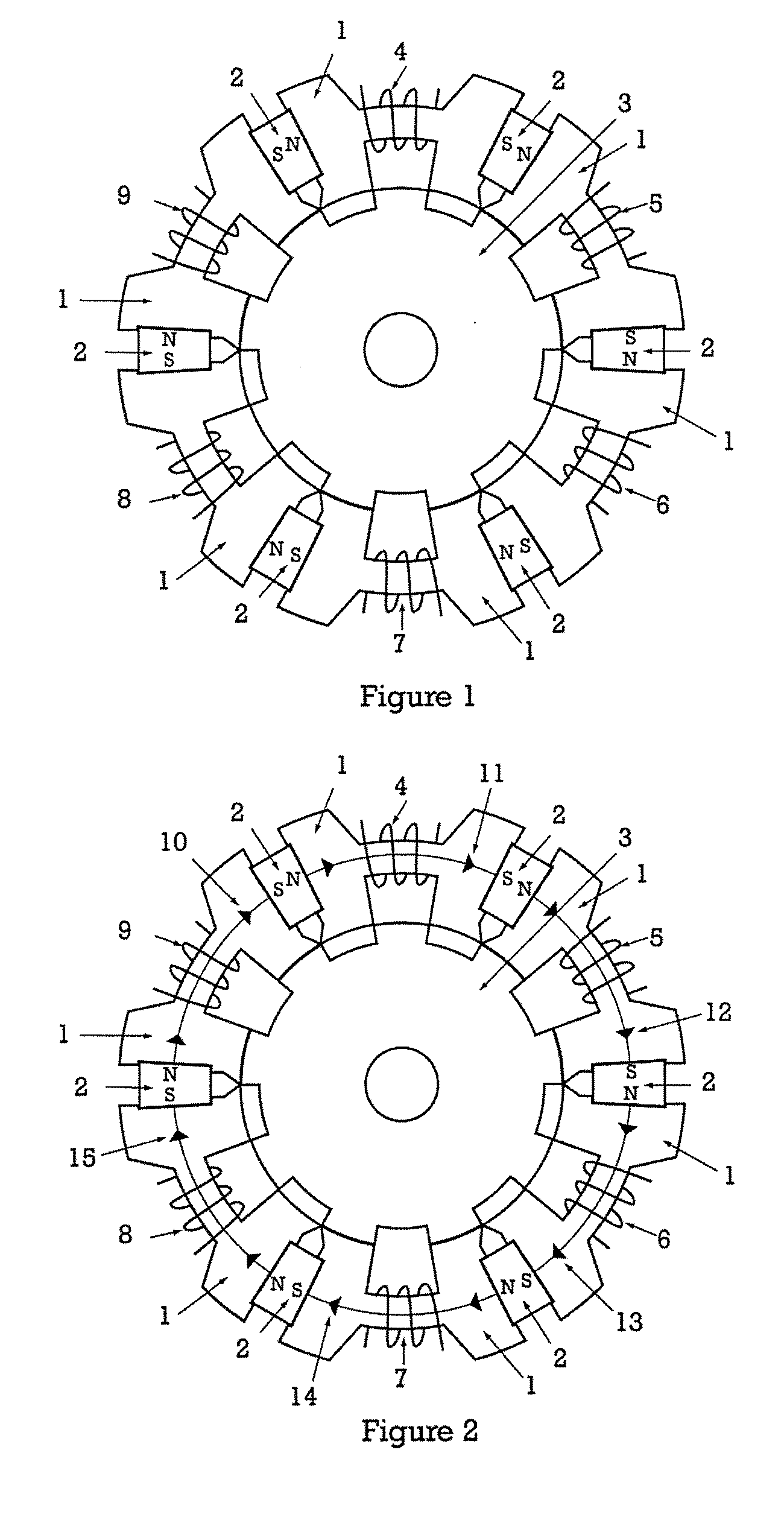
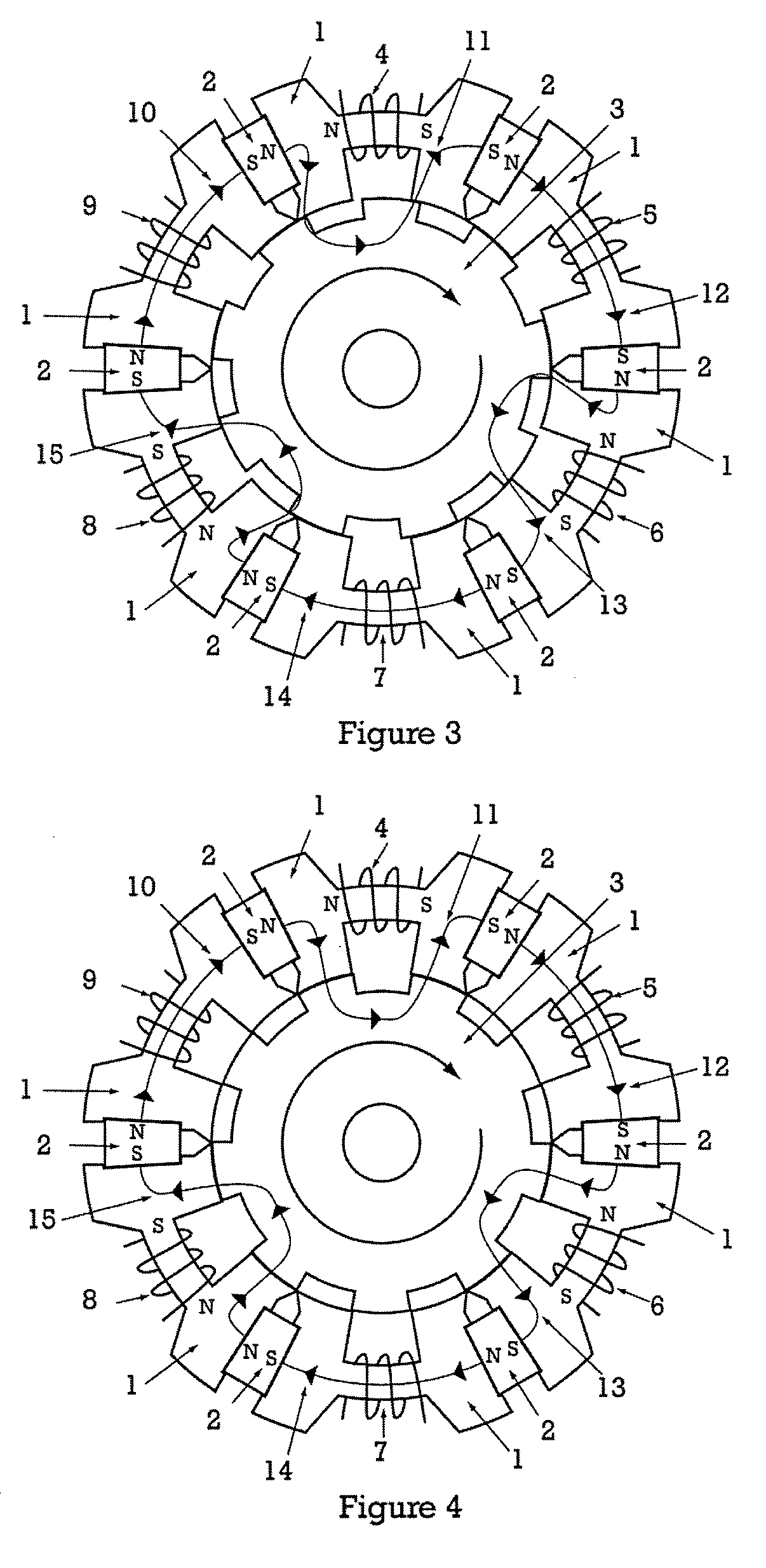
InactiveUS20050231046A1Increase productionHigh resolutionMaster clocksDynamo-electric machinesMagnetic polesElectrical polarity
A stepping motor includes a magnet ring 1 whose outer peripheral surface is circumferentially divided to form radial protrusions and recesses and whose outer peripheral surface consists of a cylindrical permanent magnet magnetized to the same polarity, first and second cylindrical coils 2 and 3, a first outer magnetic pole portion 8 excited by the first coil, a second outer magnetic pole portion 9 excited by the second coil, and an output shaft 10 formed of a soft magnetic material and fixed to the inner peripheral portion of the magnet ring, the output shaft 10 being opposed to at least one of the first outer magnetic pole portion and the second outer magnetic pole portion in a predetermined axial range and equipped with an inner magnetic pole portion excited by at least one of the first coil and the second coil. Accordingly, a low-cost, high output, and high resolution stepping motor can be provided without hindering miniaturization.
Owner:CANON KK
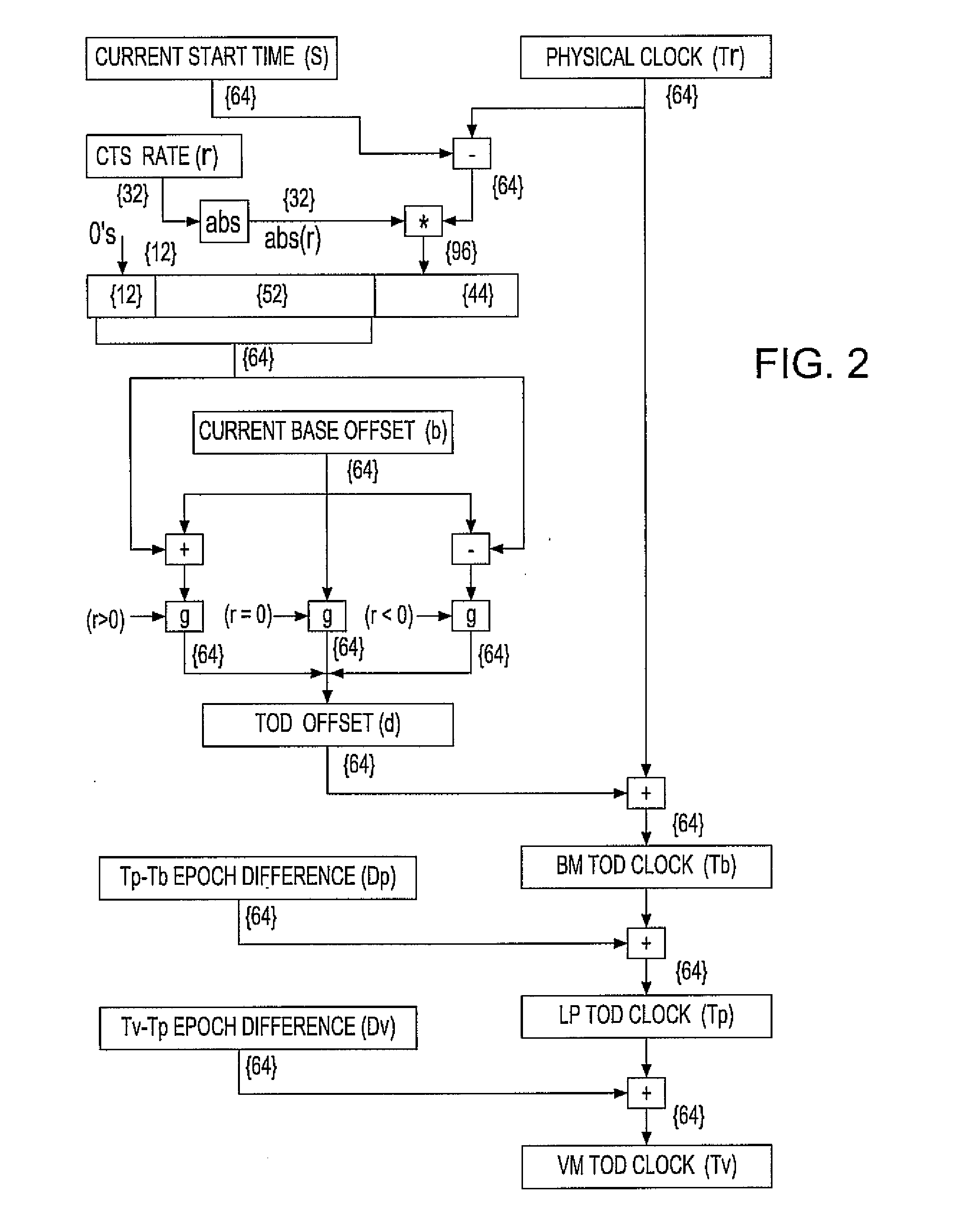
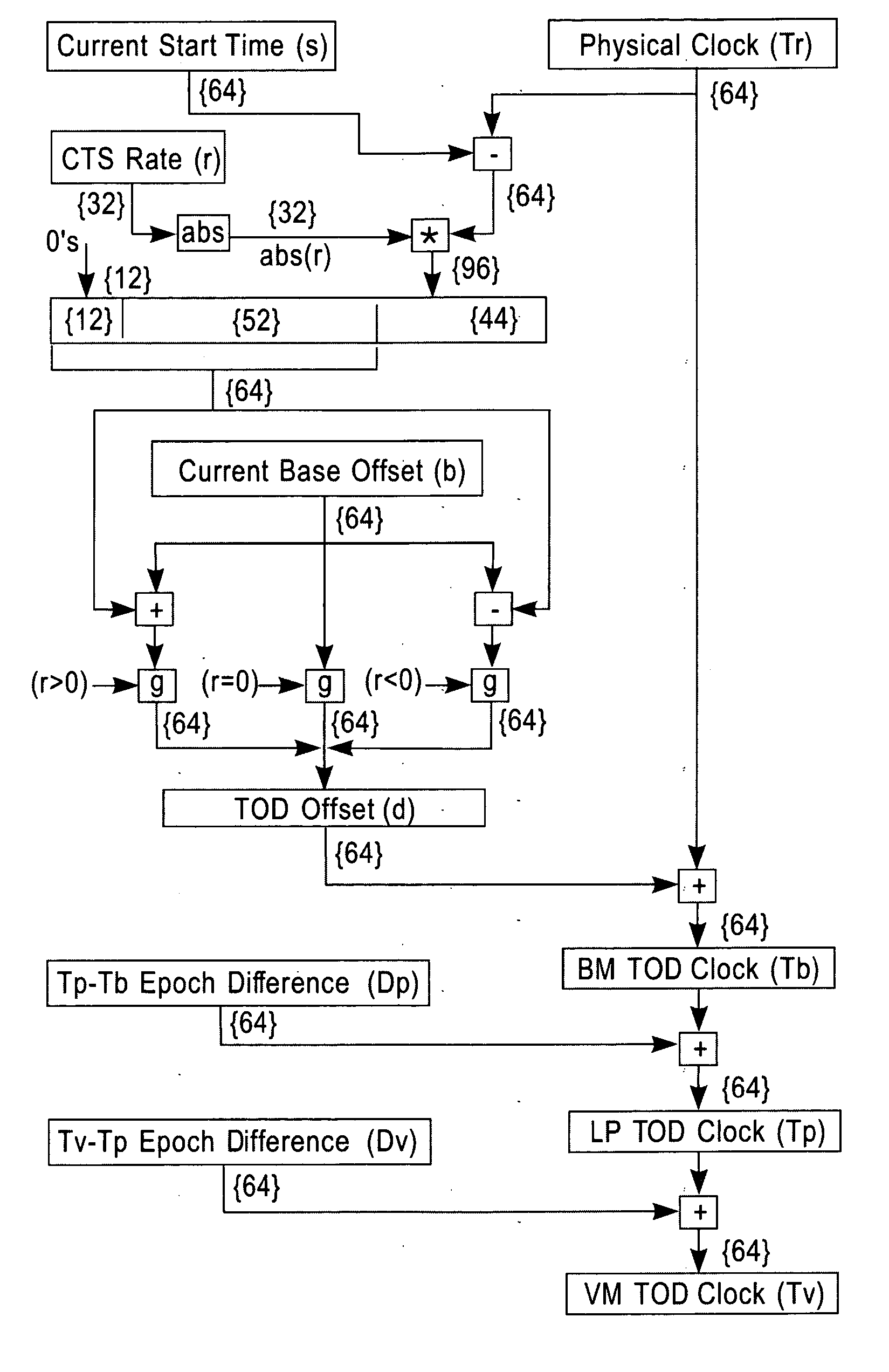
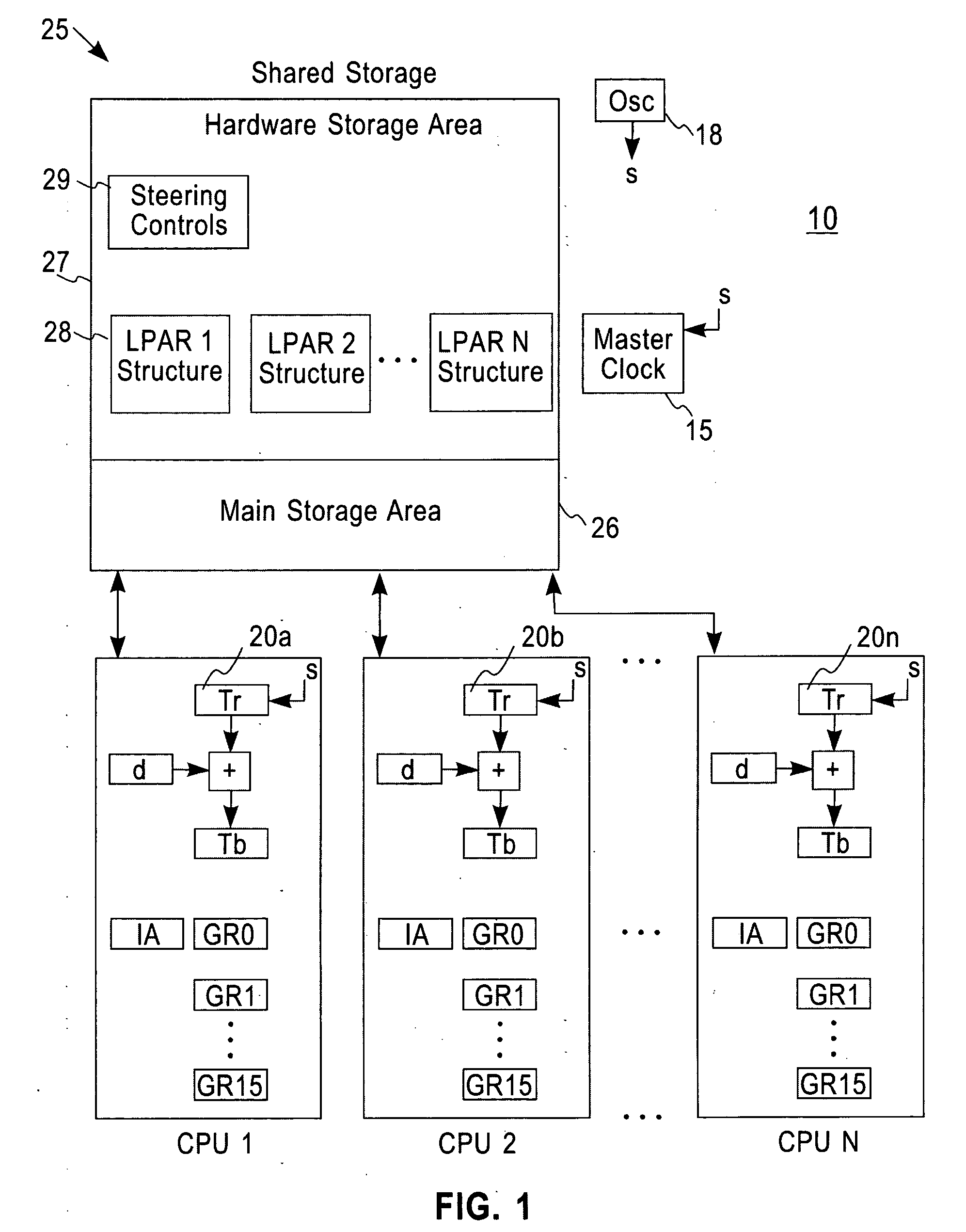
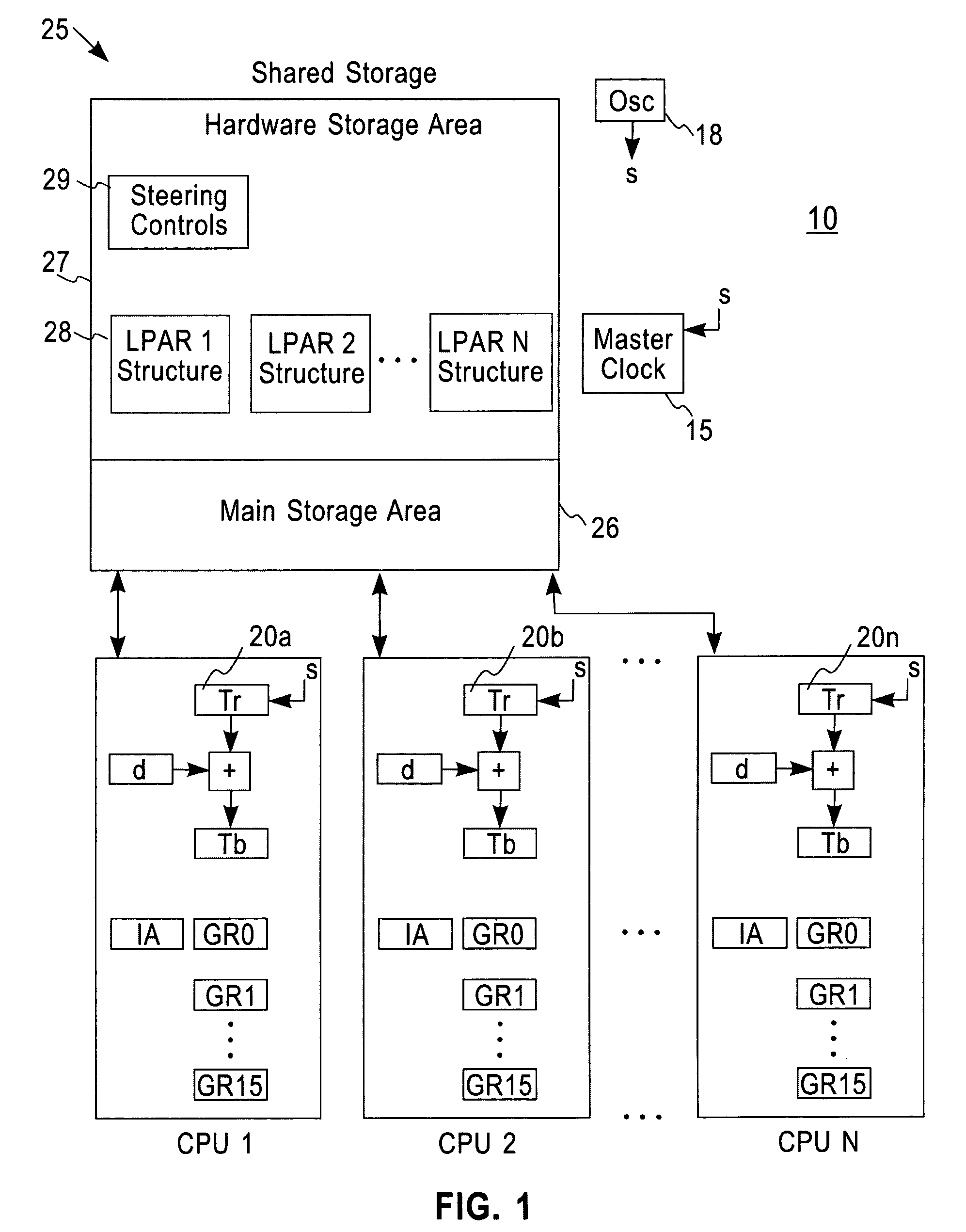
System and method for calibrating a tod clock
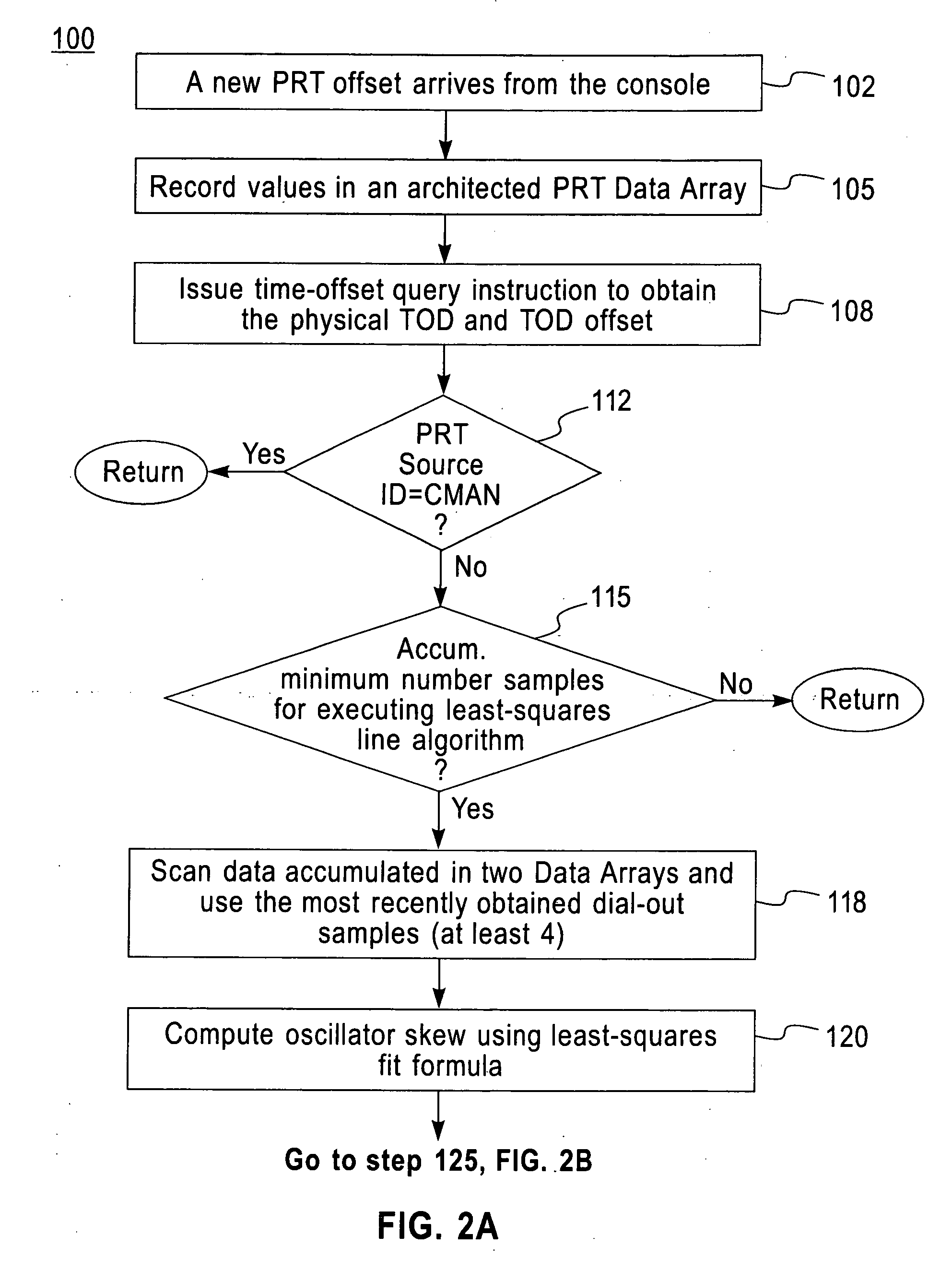
ActiveUS20070058491A1Improve accuracyReducing the PRT offsets receivedSynchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexComputer scienceComputing systems
A system, method and computer program product for calibrating a Time Of Day (TOD)-clock in a computing system node provided in a multi-node network. The network comprises an infrastructure of computing devices each having a physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepped to a common oscillator. The system implements steps for obtaining samples of timing values of a computing device in the network, the values including a physical clock value maintained at that device and a TOD-offset value; computing an oscillator skew value from the samples; setting a fine steering rate value as equal to the opposite of the computed oscillator skew value; and, utilizing the fine steering rate value to adjust the physical clock value and correct for potential oscillator skew errors occurring in the oscillator crystal at the computing device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wearable electronic device
ActiveUS9001625B2Visual indicationsSynchronous motors for clocksComputer hardwareInformation control
An analog wearable electronic device that is operationally coupleable to a transmitting device. The transmitting device includes means for viewing a simulation of a display provided on the wearable electronic device, changing information displayable on the simulated display and transmitting the changed information and / or information from which the changed information is derivable to the wearable electronic device. The wearable electronic device includes a receiver for receiving from the transmitting device the changed information and / or the information from which the changed information is derivable. A controller assembly processes the changed information and / or derives the changed information, and an actuation mechanism moves a display indicator based at least in part on the changed information. The changed information is thereafter reflected on the display of the wearable electronic device by the display indicator.
Owner:TIMEX CORP
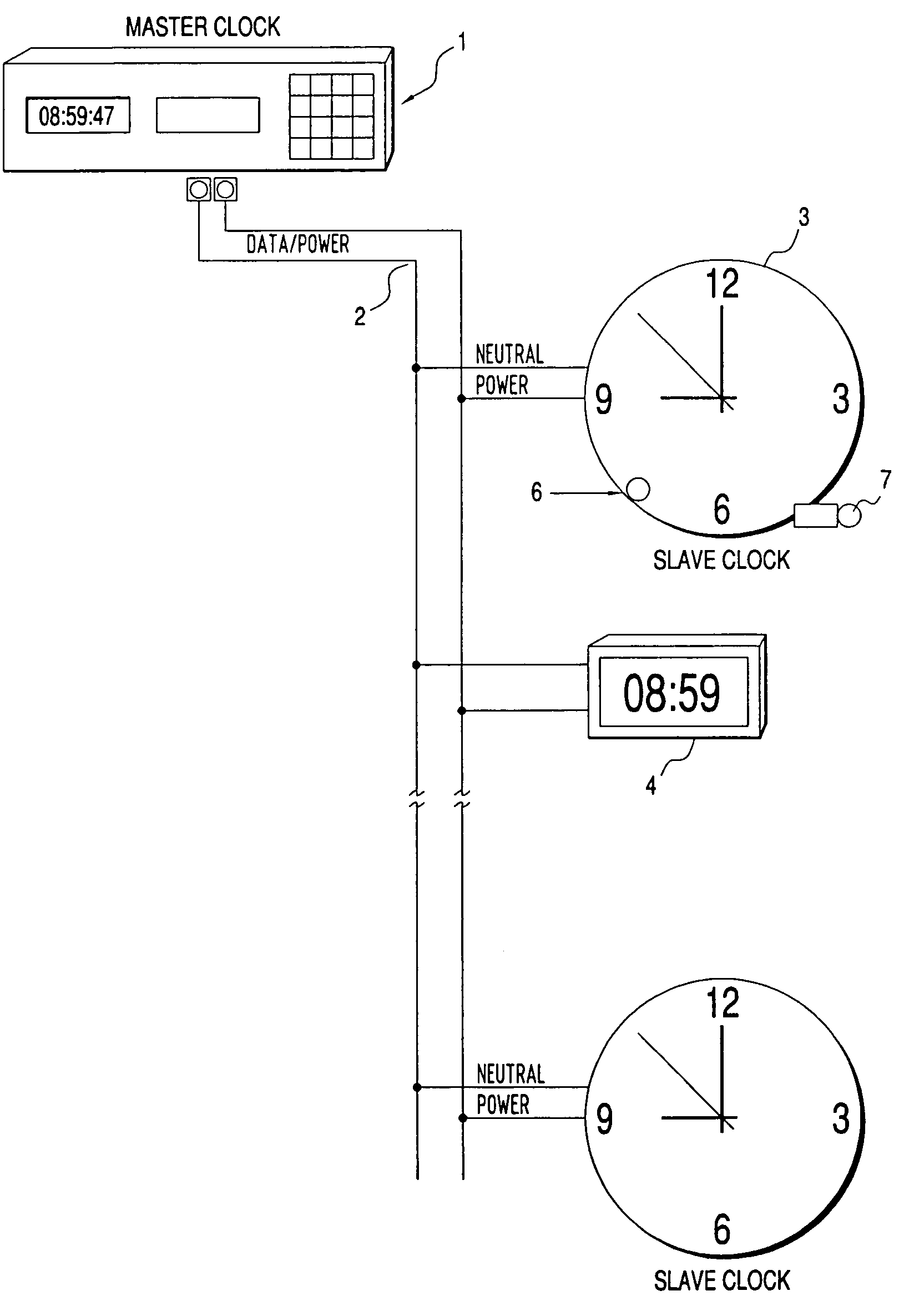
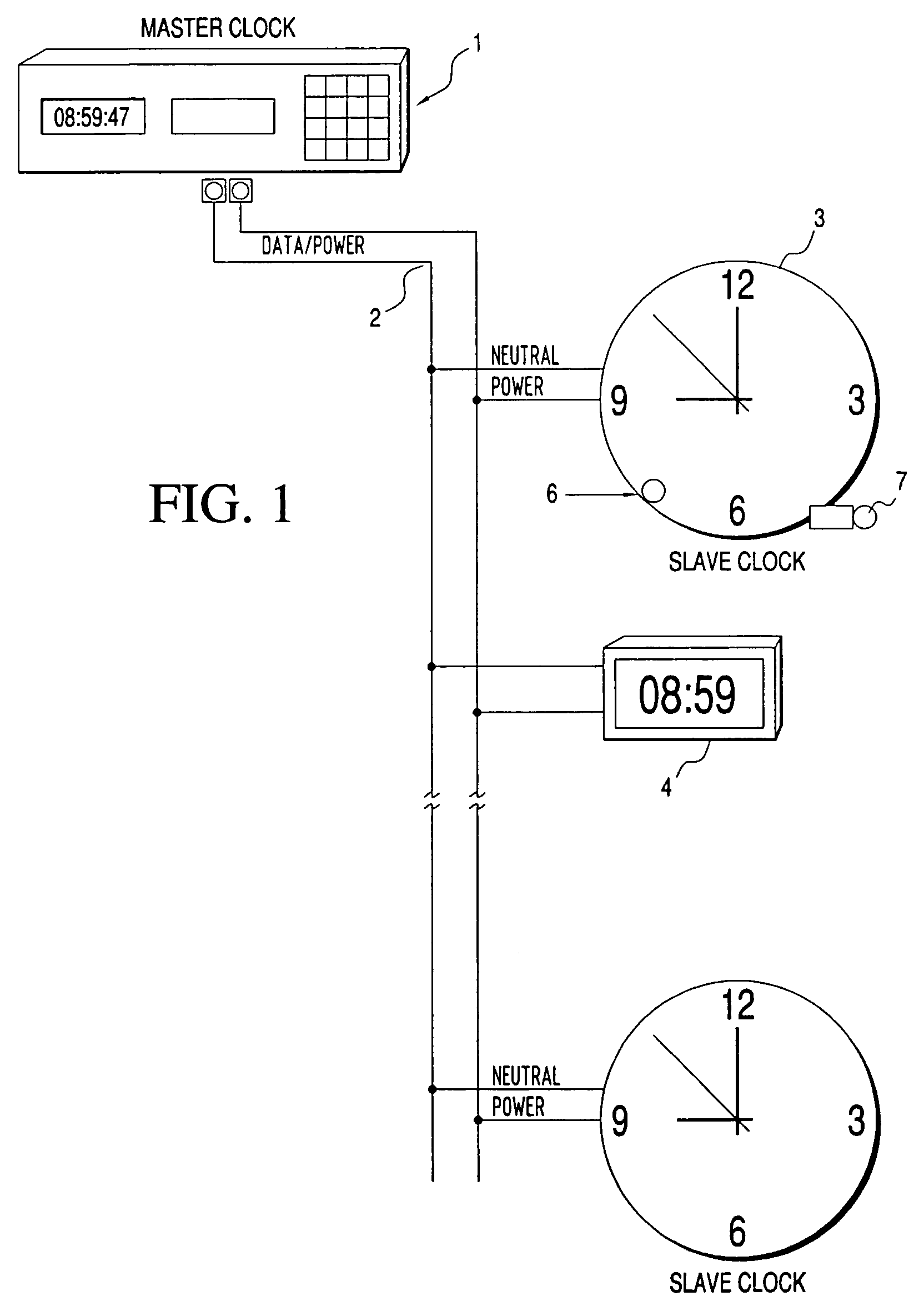
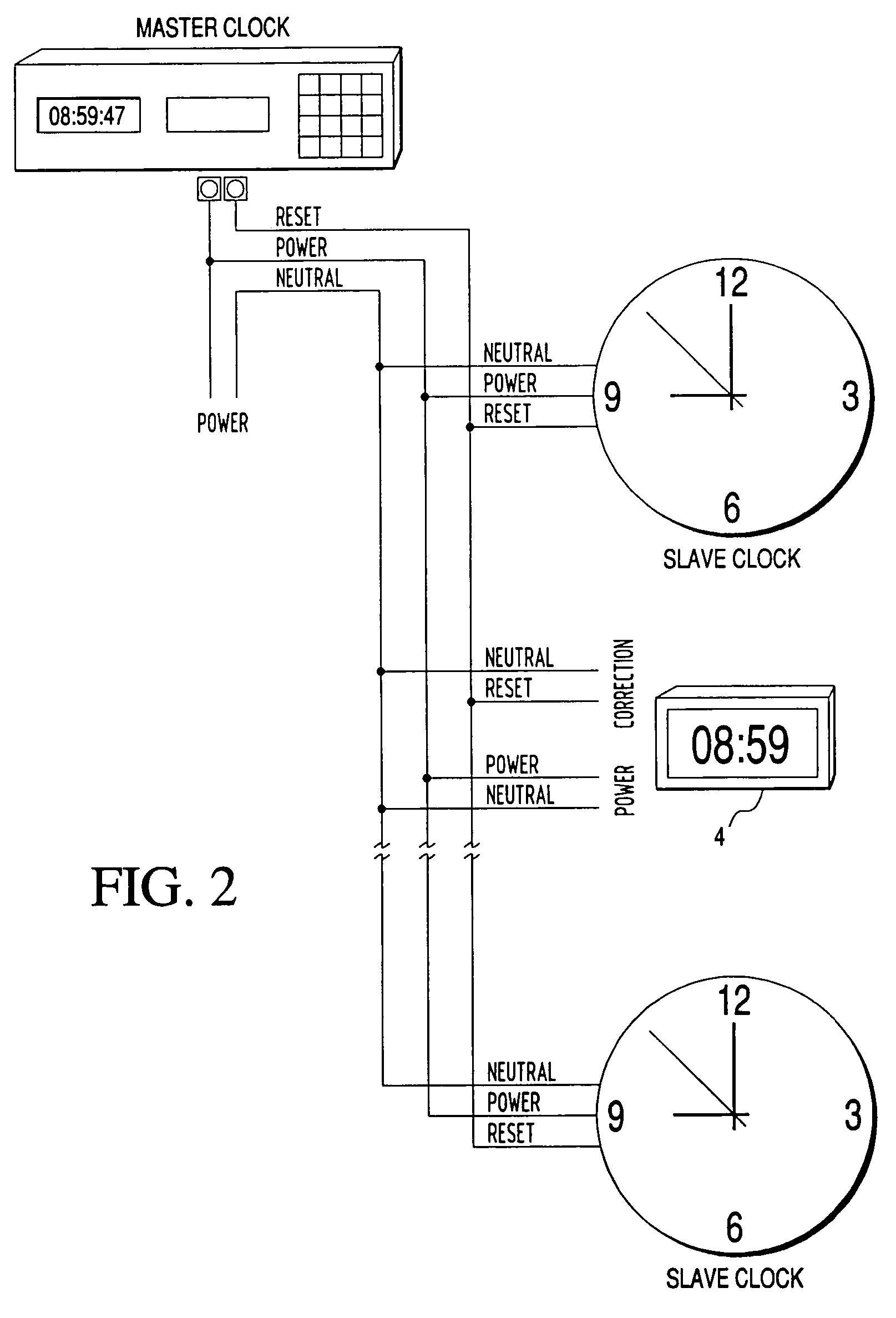
Clock diagnostics
ActiveUS7230884B2Accurate readingResistance/reactance/impedenceSynchronous motors for clocksSemi automaticOperability
Disclosed is a clock for use in a master / slave clock system, including a system and method for semi-automatically performing diagnostic self-tests on the status and operability of a plurality of components of one or more secondary clocks. The invention addresses a multitude of diagnostic and problem detection issues, including “no fault found.”
Owner:SAPLING
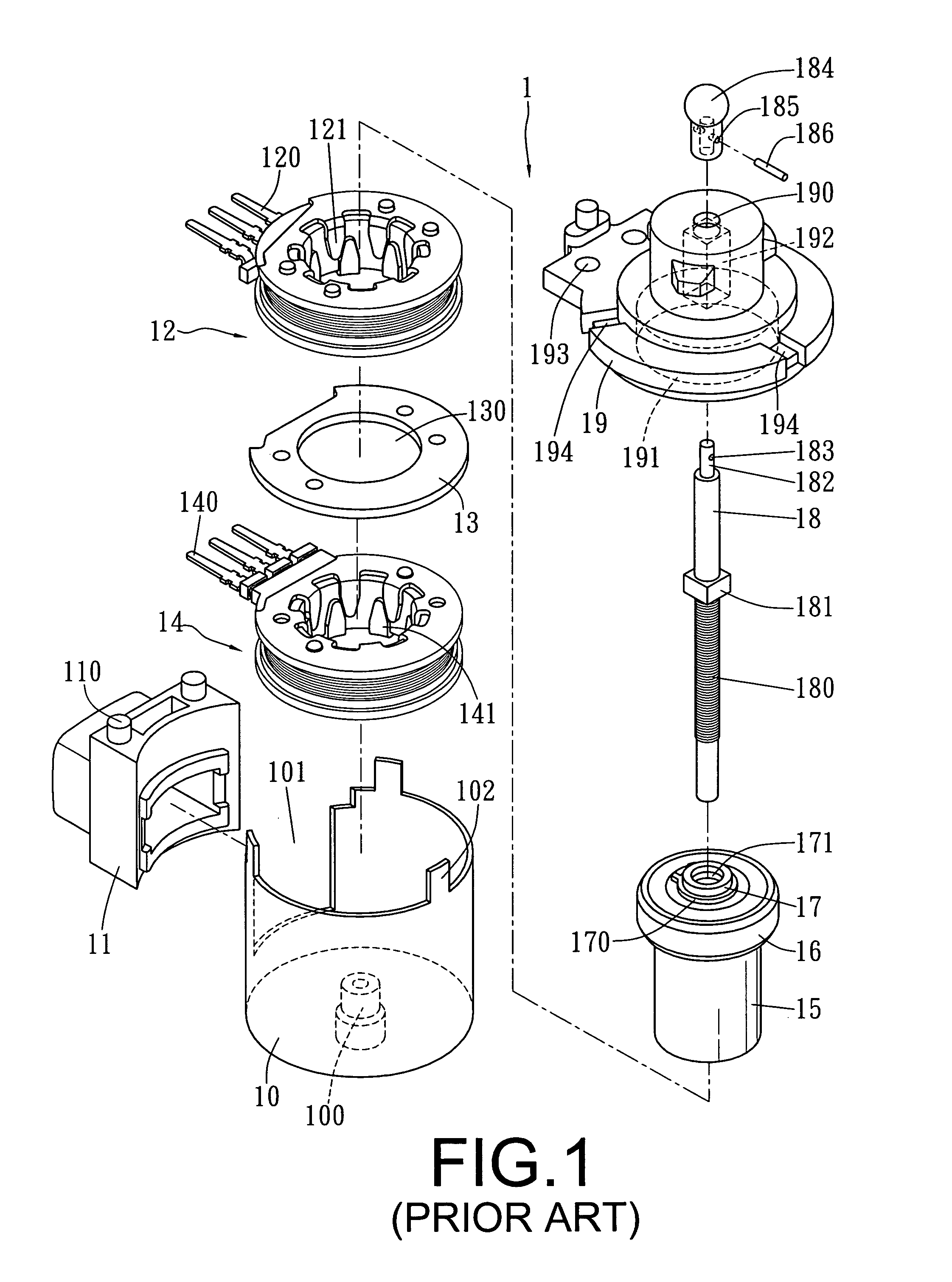
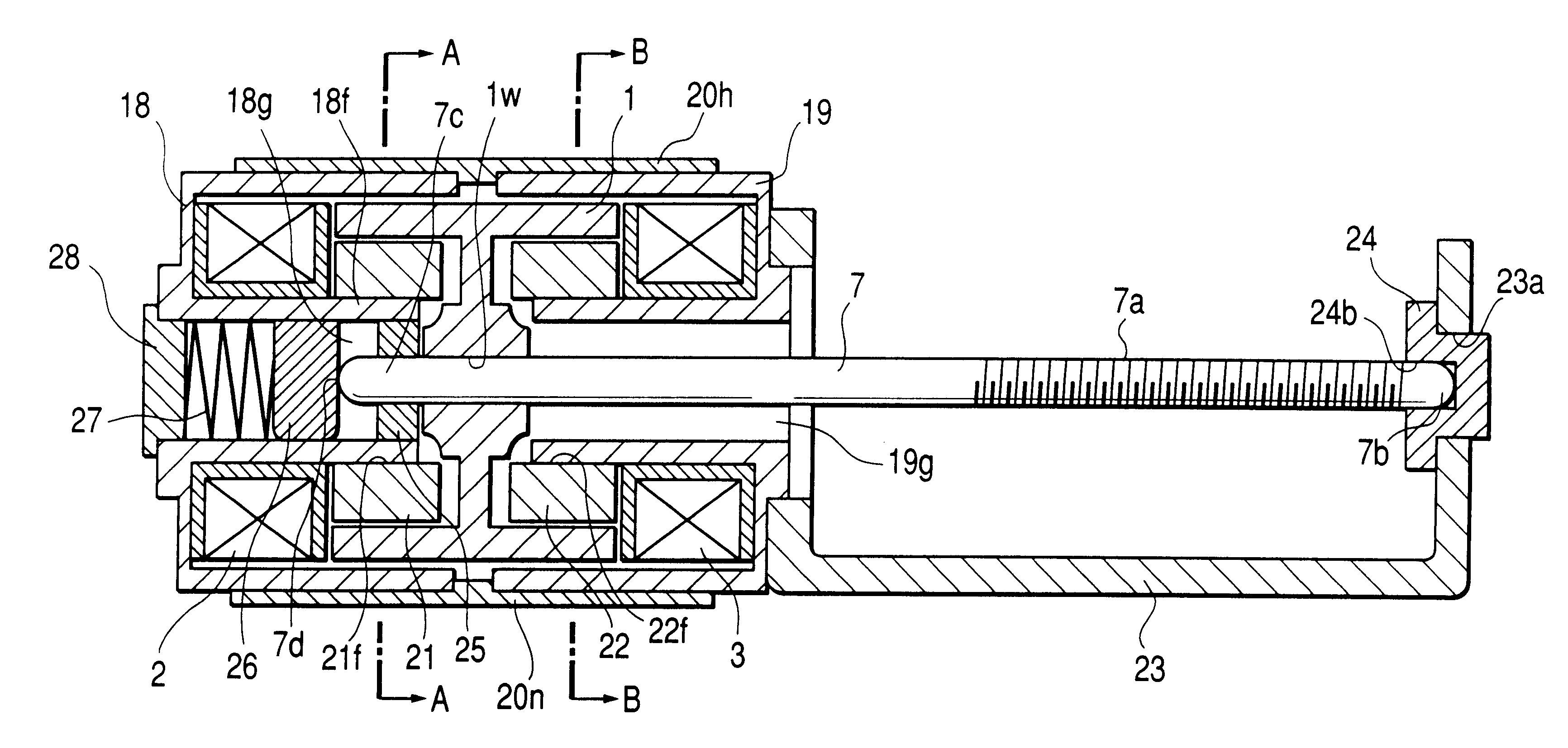
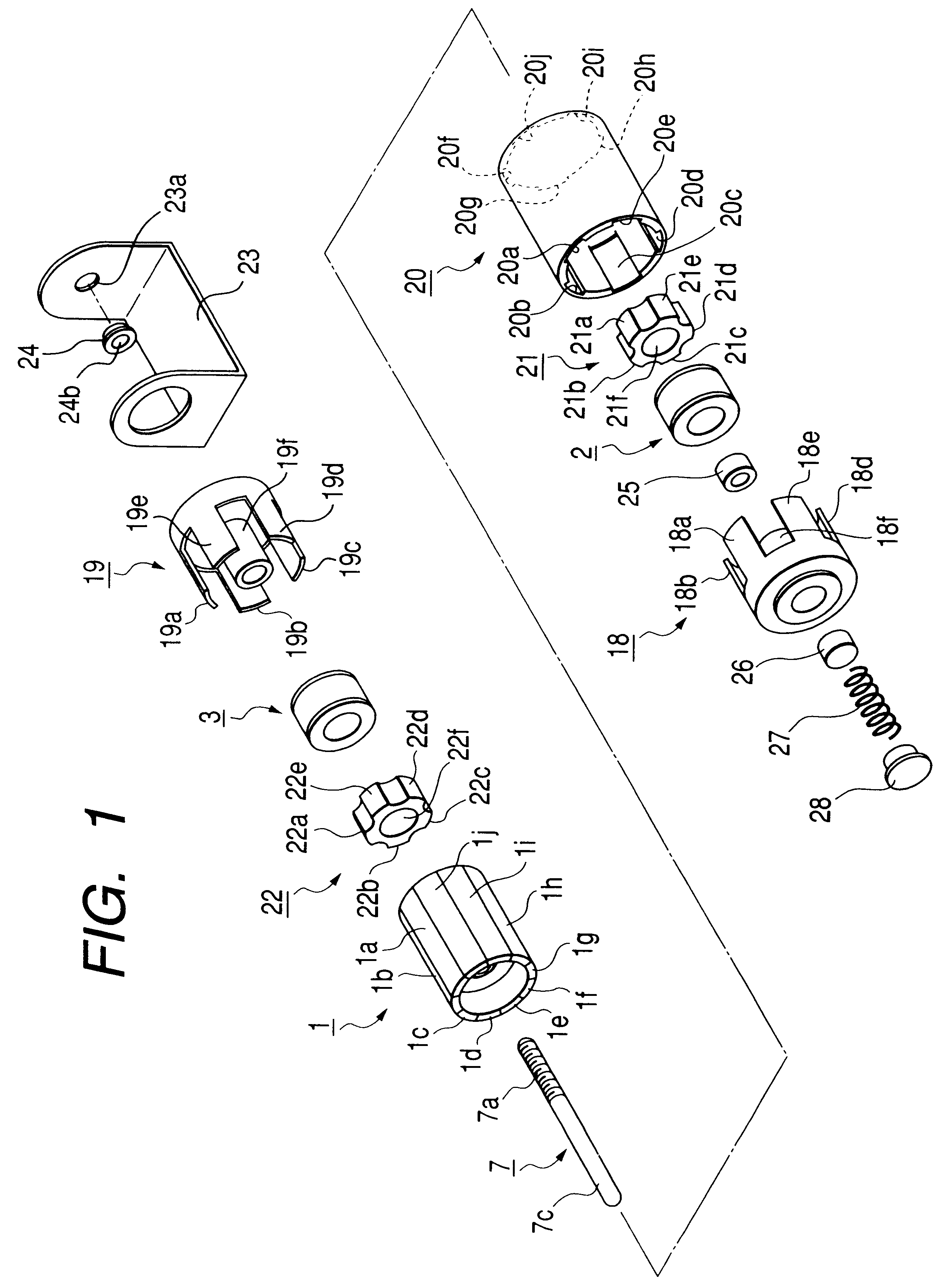
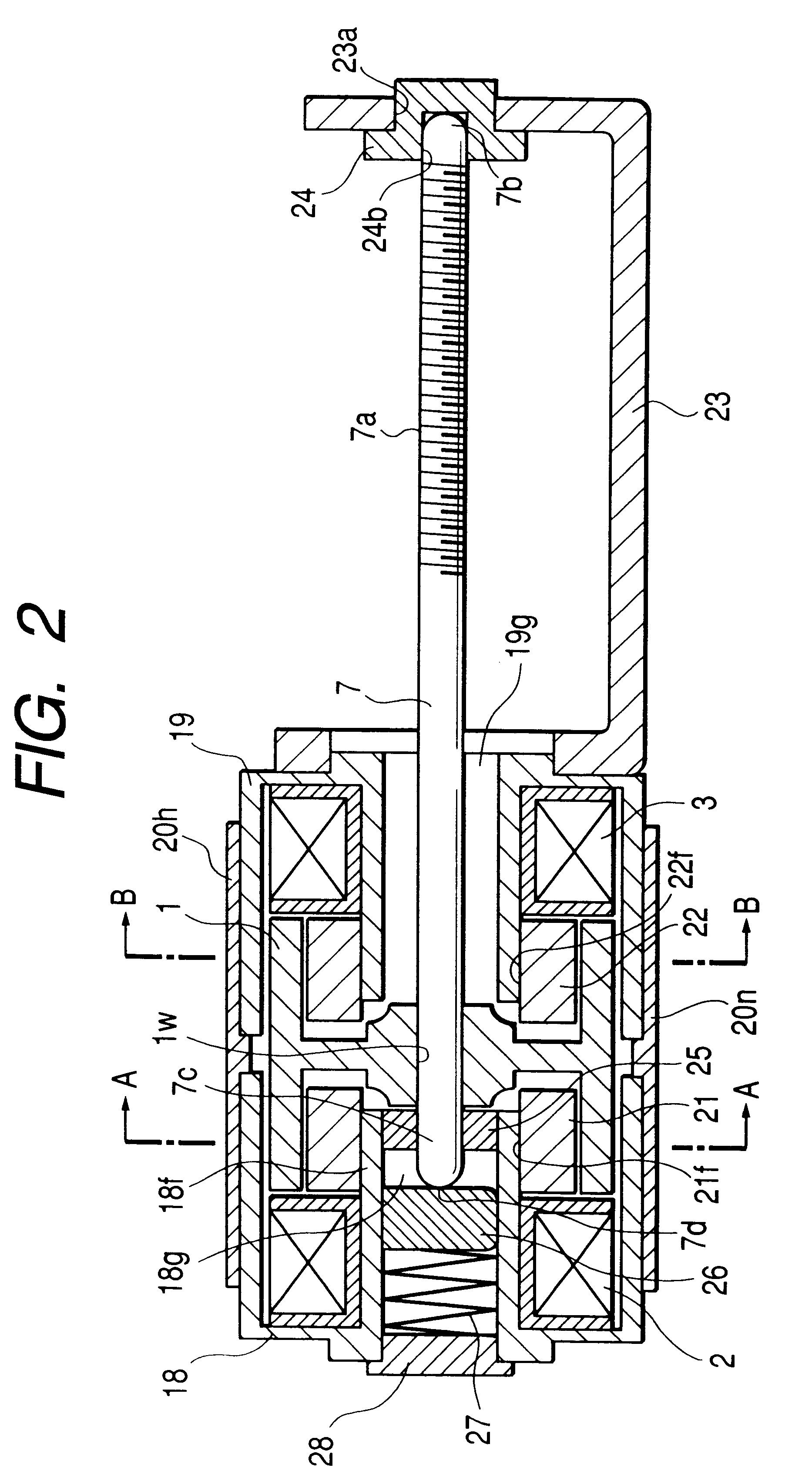
Step-by-step motor able to carry out up-and-down motion
A step-by-step motor able to carry out up-and-down motion includes a housing, a connecting base, a top rod, a bearing, a connecting member, a magnet, a right-handed coil, a reverse coil and a bottom cover combined together. The housing has one side bored with an opening and its inner wall bored with a slide groove, and the connecting base has one outer wall formed with a slide rail for combining the connecting base on the outer wall of the housing. The bottom cover is provided with an annular recess for engaging the bottom edge of the housing, and then the bottom cover and the housing are firmly combined together by supersonic welding. By so designing, the step-by-step motor can be assembled conveniently, quickly and stably.
Owner:HUANG HSIU MING
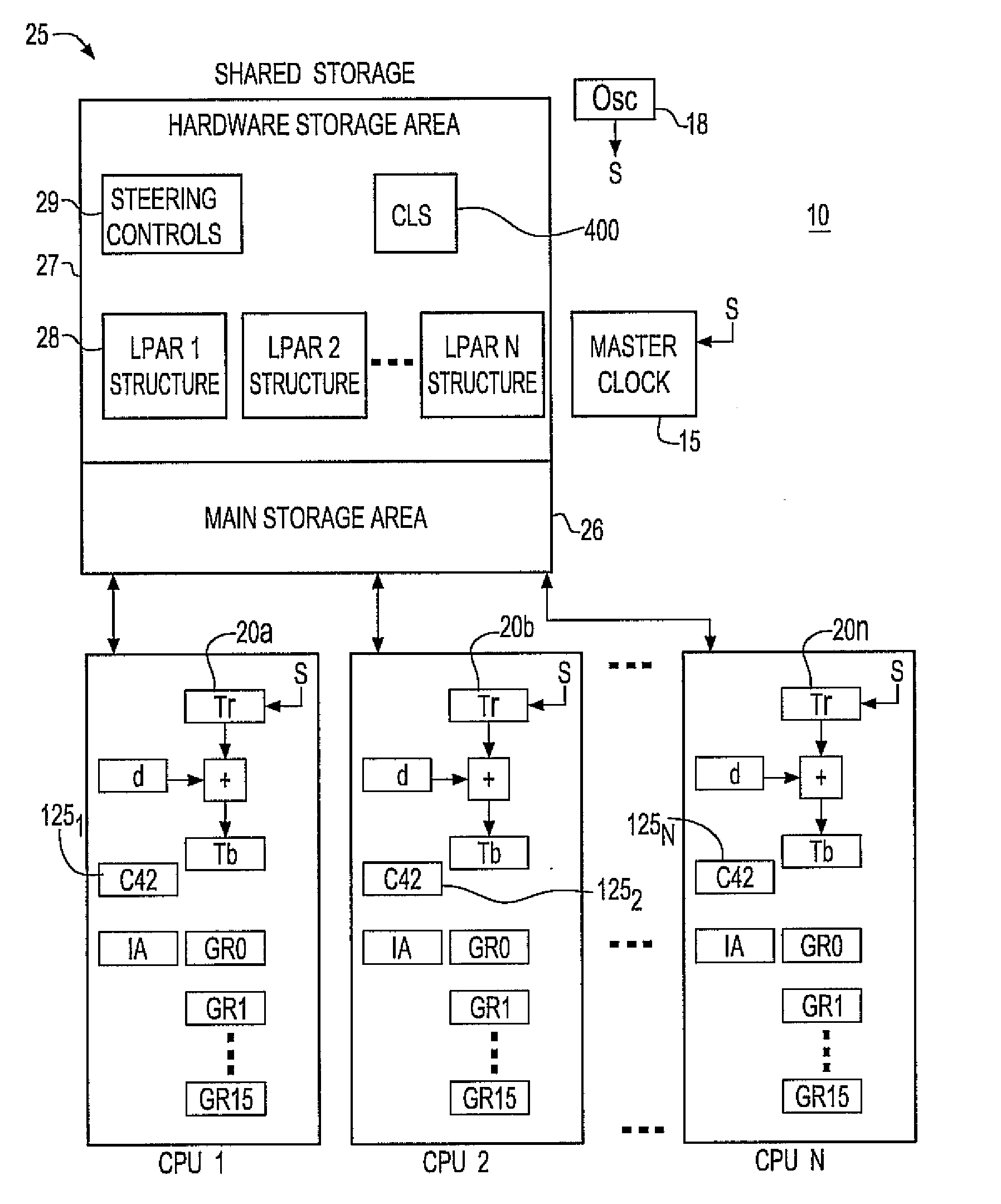
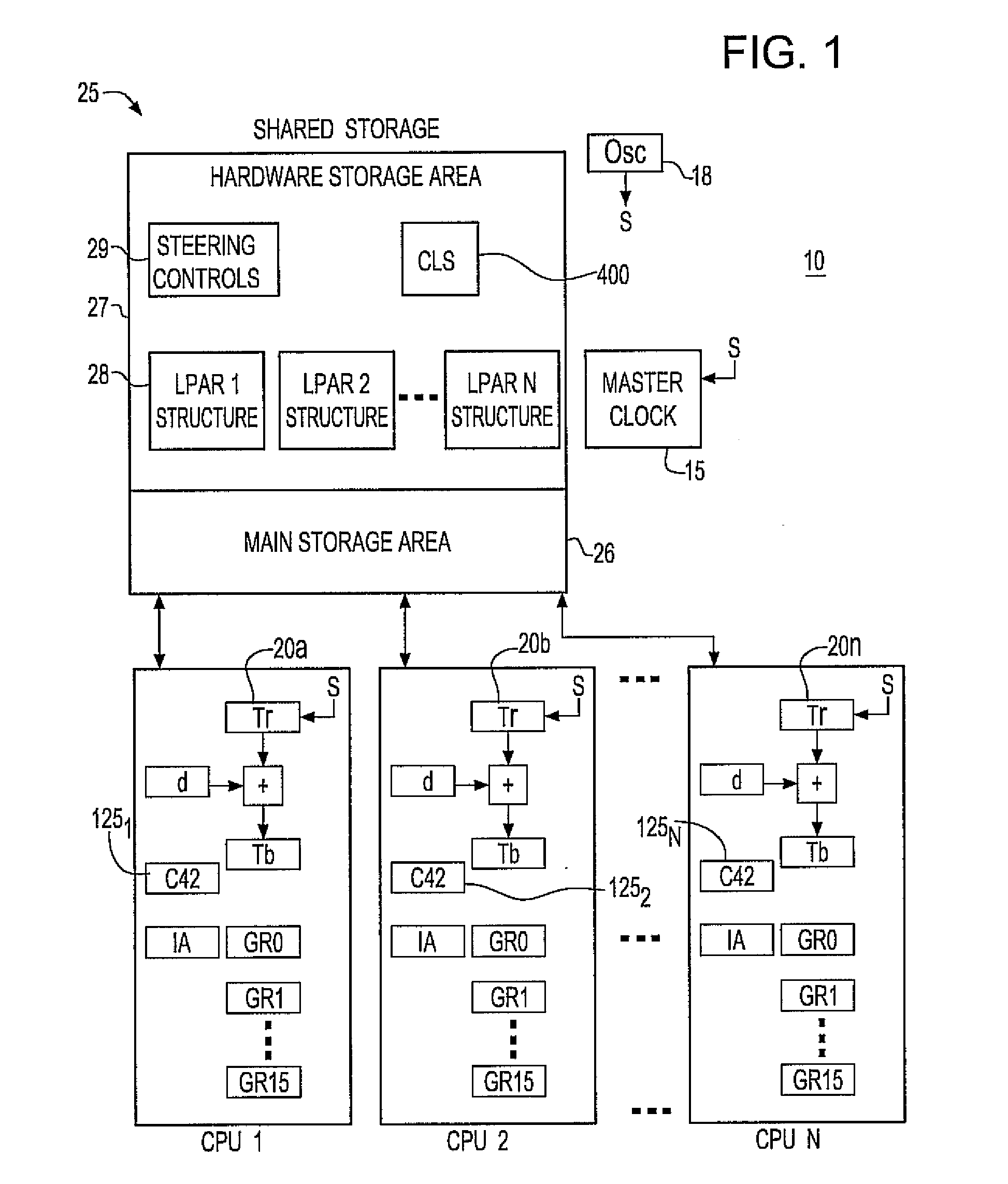
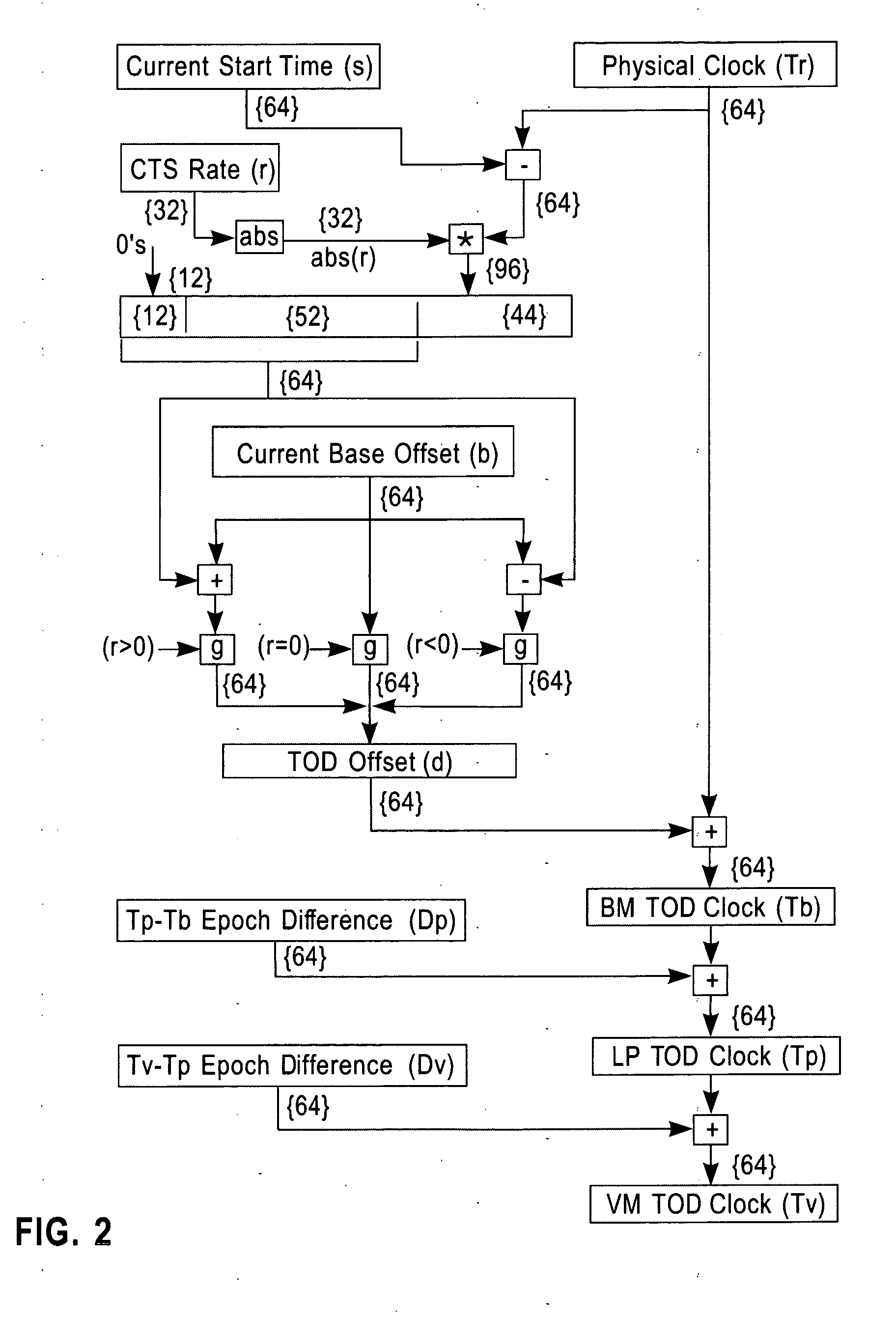
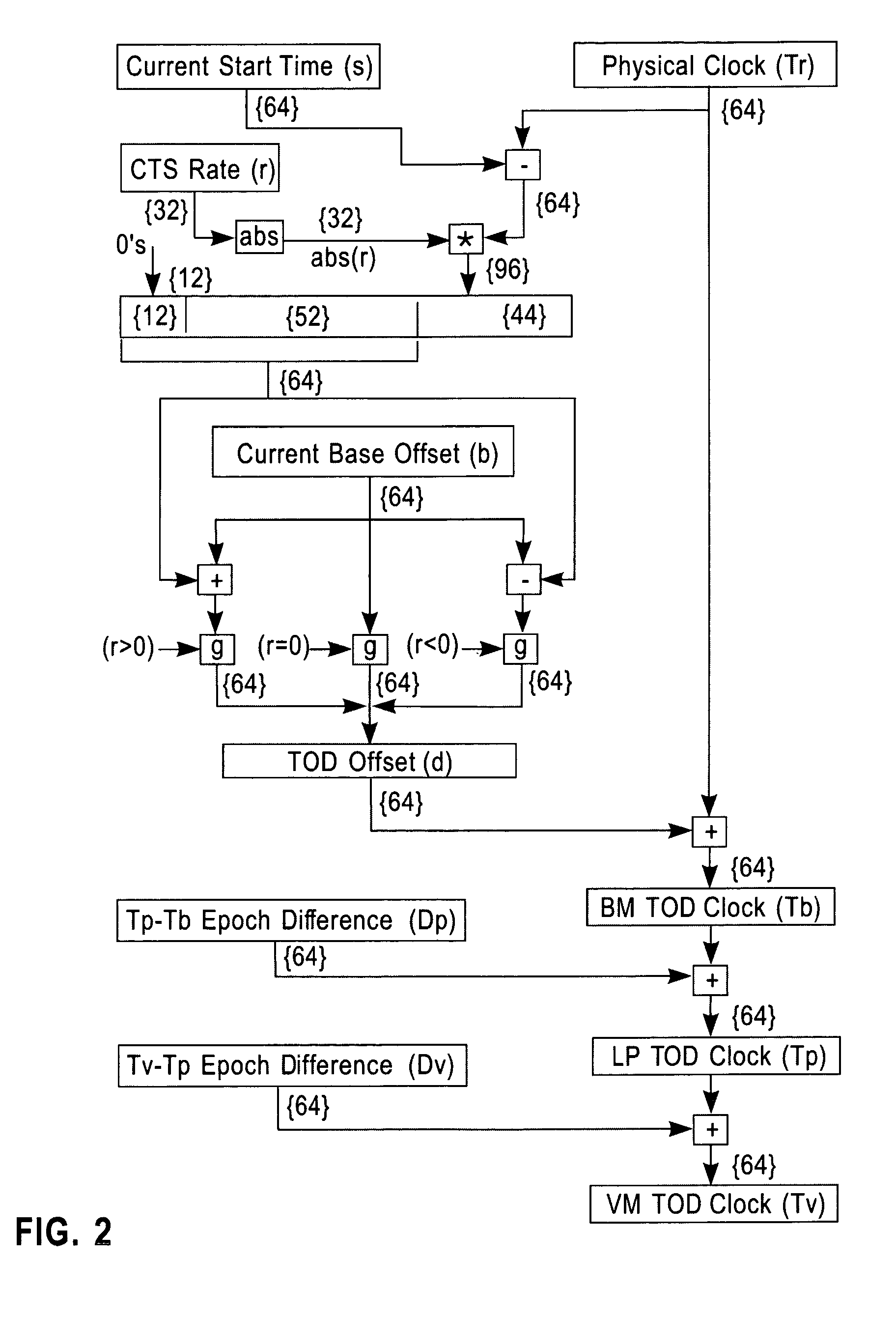
Synchronization signal for tod-clock steering adjusment
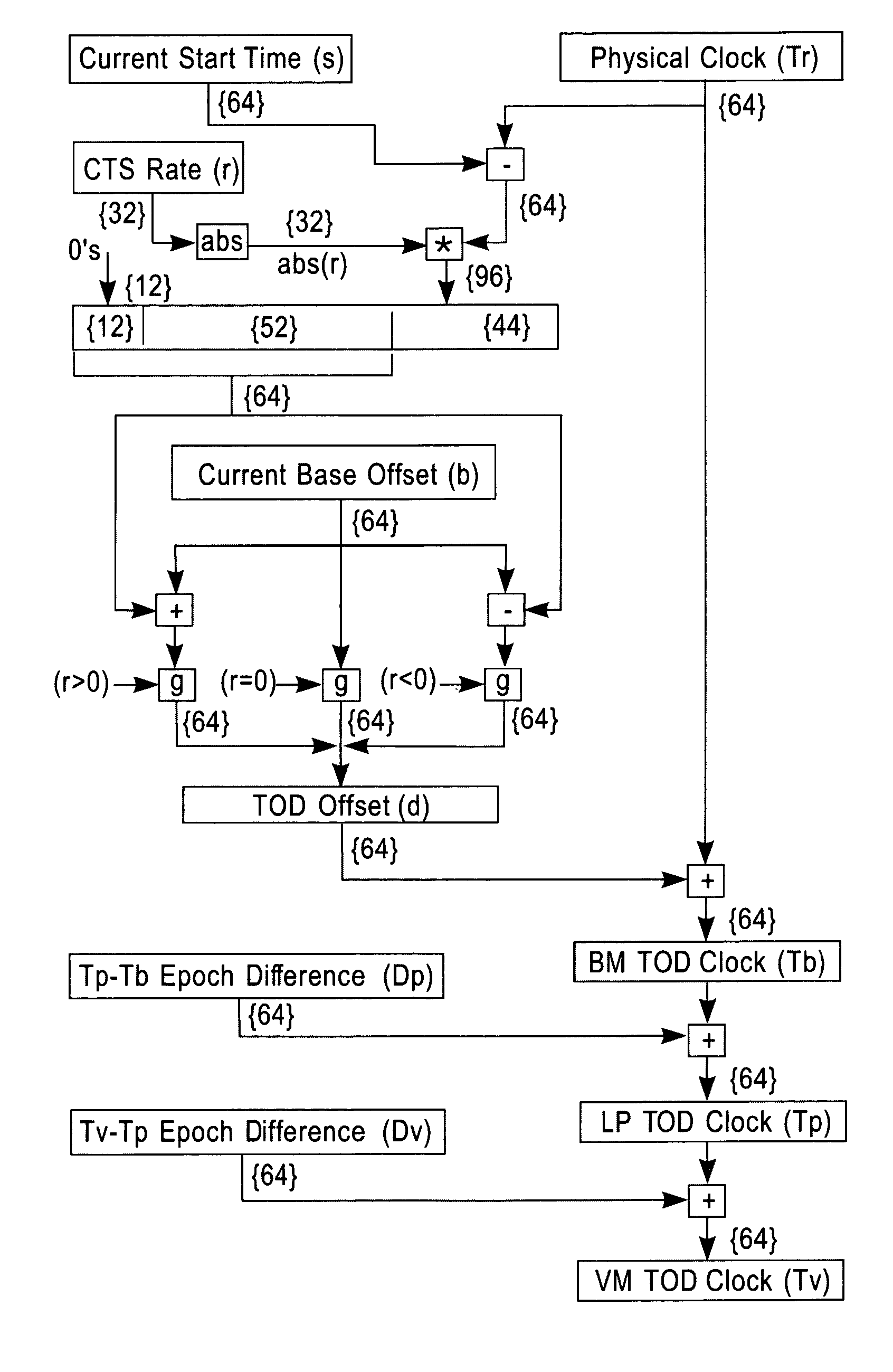
InactiveUS20080072097A1Minimize overheadAvoids a further carry propagatingError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksComputer hardwareClock offset
A system, method and computer program product for synchronizing adjustment of a time of day (TOD) clock for a computer system having multiple CPUs, each CPU having an associated physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepping to a common oscillator, and an associated logical TOD clock. The method includes detecting propagation of a carry at a pre-determined bit position of the physical clock associated with a CPU in the computer system; and, updating, in response to the detecting of the pre-determined bit position carry, a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD clock value (Tb) for use by a CPU in the system. In this manner, each CPU computes a new logical TOD clock value in synchronization—the new logical TOD clock value taking effect simultaneously for the multiple CPUs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for synchronizing the internal clocks of a plurality of processor modules
ActiveUS7239581B2Data storage is convenientMechanical clocksSynchronous motors for clocksComputer architectureMulti processor
In a multiprocessor system that includes a plurality of processor modules, each one of which includes its own internal clock, one of the plurality of processor modules is designated as a master processor module having a master internal clock. Each other processor module is designated as a slave processor module having a slave processor module internal clock. Each slave processor module synchronizes its internal clock with the master internal clock.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
System and method for TOD-clock steering
ActiveUS20070061605A1Minimize overheadError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksClock offsetTime of day
A system, method and computer program product for steering a time-of-day (TOD) clock for a computer system having a physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepped to a common oscillator. The method includes computing a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical-clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD-clock value (Tb), where the logical TOD-clock value is adjustable without adjusting a stepping rate of the oscillator.
Owner:IBM CORP
Unipolar transverse flux machine
InactiveUS6882066B2Flat designMagnetic circuit stationary partsMaster clocksTransverse fluxMagnetic poles
In a unipolar transverse flux machine, in particular a motor, having a rotor, which is comprised of two coaxial, ferromagnetic, toothed rotor rings, and a permanent magnet ring, which is magnetized in an axially unipolar fashion and is clamped axially between these rotor rings, and having a stator, which is concentric to the rotor shaft and has U-shaped stator yokes that represent the magnet poles, yoke elements, and a stator winding, in order to achieve an extremely flat design and to assure a definite start in a particular direction, the stator winding is embodied with two coils, whose one coil side extends respectively over a group of stator yokes and yoke elements arranged in succession in the circumference direction, along the side of the yoke elements remote from the rotor shaft, between the yoke legs, where the group spanned by the coil side of the one coil is disposed spatially offset on the stator circumference and electrically offset by 90° in relation to the group spanned by the coil side of the other coil.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Claw-pole type stepping motor
InactiveUS7071593B2Reduce radial sizeMaintain mechanical strengthSynchronous generatorsWindingsBobbinSolid structure
A claw-pole type stepping motor comprises: a rotor assembly shaped substantially cylindrical, and having a center shaft; and a stator assembly composed of two cup-shaped stator units which are coupled to each other coaxially so as to axially sandwich the rotor assembly, and which each include a bobbin having a magnet wire wound therearound, and two pole tooth arrays magnetically connected to each other and shifted in phase from each other by an electrical angle of 180 degrees. In the motor, each stator unit further includes a cover ring which protects the magnet wire wound around the bobbin against resin injected when the stator unit is resin-molded for an integrated solid structure. The motor structured as described above can be successfully resin-molded so as to enable elimination of a motor case, thus achieving downsizing for the dimension of the eliminated motor case while maintaining a sufficient mechanical strength.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
AC motor and control device therefor
InactiveUS20060006744A1Small sizeLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsDynamo-electric converter controlConductor CoilAC motor
A rotor, which is rotatable about a rotor shaft, comprises N poles and S poles alternately disposed in the circumferential direction, and rotor-side neutral poles disposed adjacent to the N poles and the S poles along the axial direction of the rotor, being magnetically connected to their back yoke. A stator comprises two modules which are adjacently disposed in the axial direction of the rotor. Each of these two modules comprises a winding wound, in a loop shape, around the rotor shaft, stator-side neutral poles disposed at positions opposed to the rotor-side neutral poles, stator poles each of which is disposed at a position opposed to either the N pole or the S pole, and a back yoke which connects the stator-side neutral poles and the stator poles to surround the winding.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for adjusting a time of day clock without adjusting the stepping rate of an oscillator
ActiveUS7356725B2Minimize overheadError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksClock offsetComputerized system
A system, method and computer program product for steering a time-of-day (TOD) clock for a computer system having a physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepped to a common oscillator. The method includes computing a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical-clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD-clock value (Tb), where the logical TOD-clock value is adjustable without adjusting a stepping rate of the oscillator.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
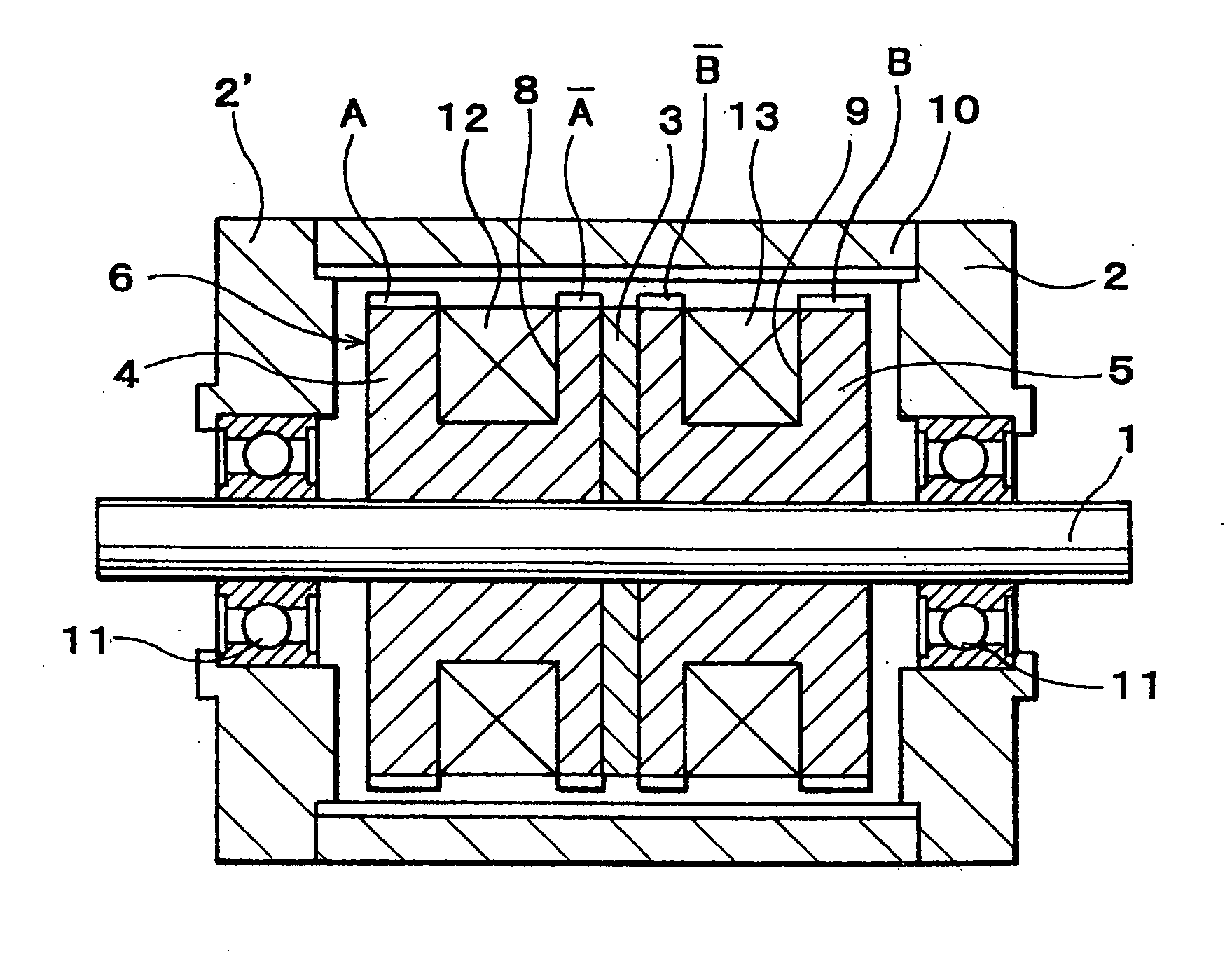
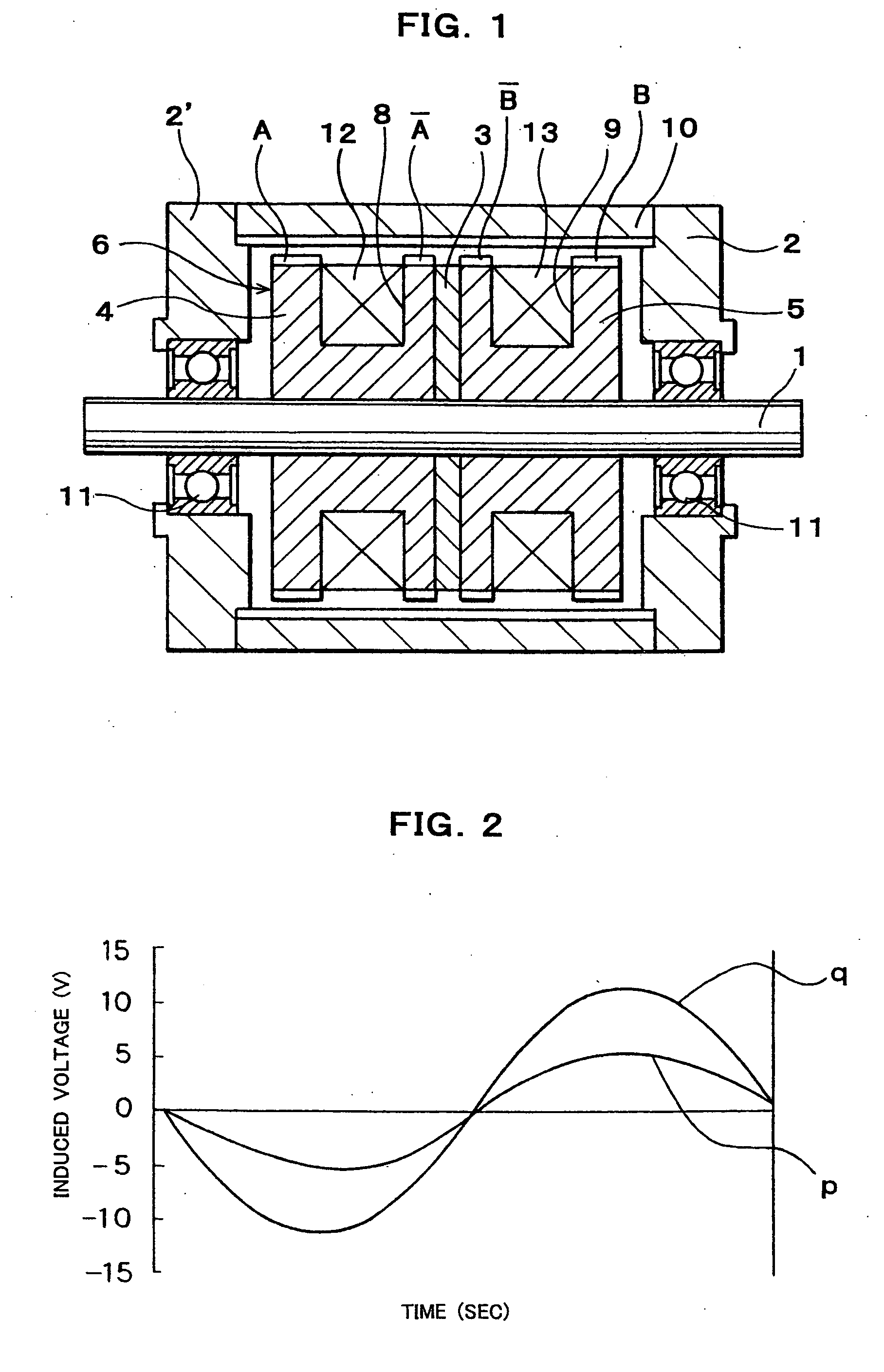
Multi-polar rotary machine
InactiveUS20050062348A1Reducing the magnetic reluctanceMagnetic flux interlinkaging the winding is increasedSynchronous generatorsWindingsInorganic materialsMagnet
A multi-polar rotary machine comprises a and a cylindrical outer rotor arranged concentrically with the stator and with an air gap therebetween. The stator has two splitted stator elements and a ring shaped permanent magnet held between the stator elements and magnetized so as to form N and S poles in the axial direction of the stator. Small axially separated stator teeth A and {overscore (A)} and {overscore (B)} and B are formed on the outer peripheral surface of the splitted stator elements. Stator windings for A phase and B phase are wound around the respective stator elements. The small stator teeth A, {overscore (A)}, {overscore (B)} and B are circumferentially shifted from corresponding small rotor teeth by a ¼ pitch of the small stator teeth, respectively. Each of the stator and rotor is formed of pressed powder consisting of soft magnetic material, and of resin and / or inorganic material. A ratio of a thickness of the small stator teeth {overscore (A)} in the axial direction of the stator to a thickness of the small stator teeth A in the axial direction of the stator or a ratio of a thickness of the small stator teeth {overscore (B)} in the axial direction of the stator to a thickness of the small stator teeth B in the axial direction of the stator is set to a value smaller than 1 so as to equalize substantially in mean permeance both small stator teeth A and {overscore (A)} or {overscore (B)} and B to each other.
Owner:JAPAN SERVO CO LTD
System and method for maintaining a common sense of time on a network segment
ActiveUS20050180466A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexFrequency ratioEngineering
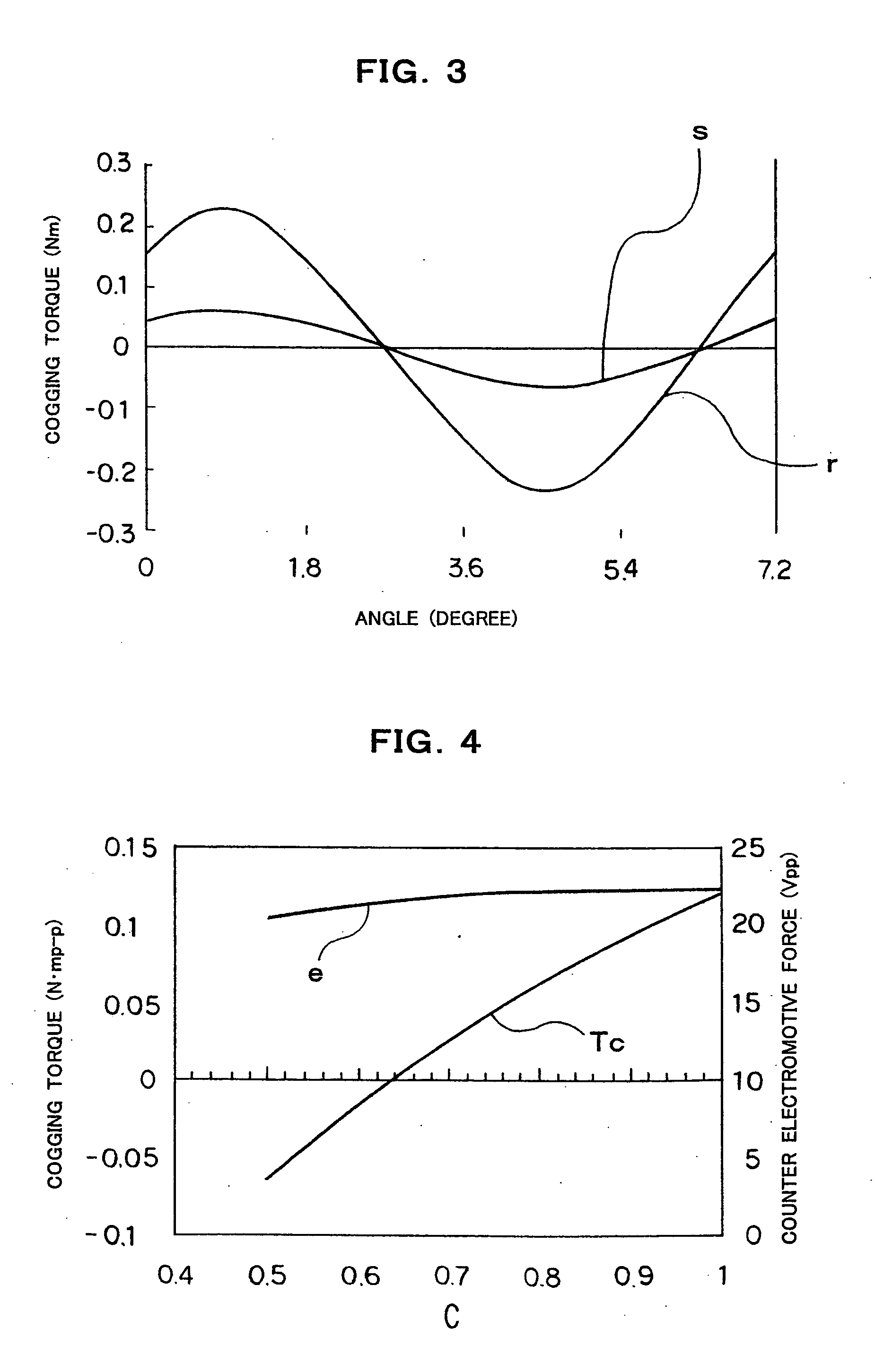
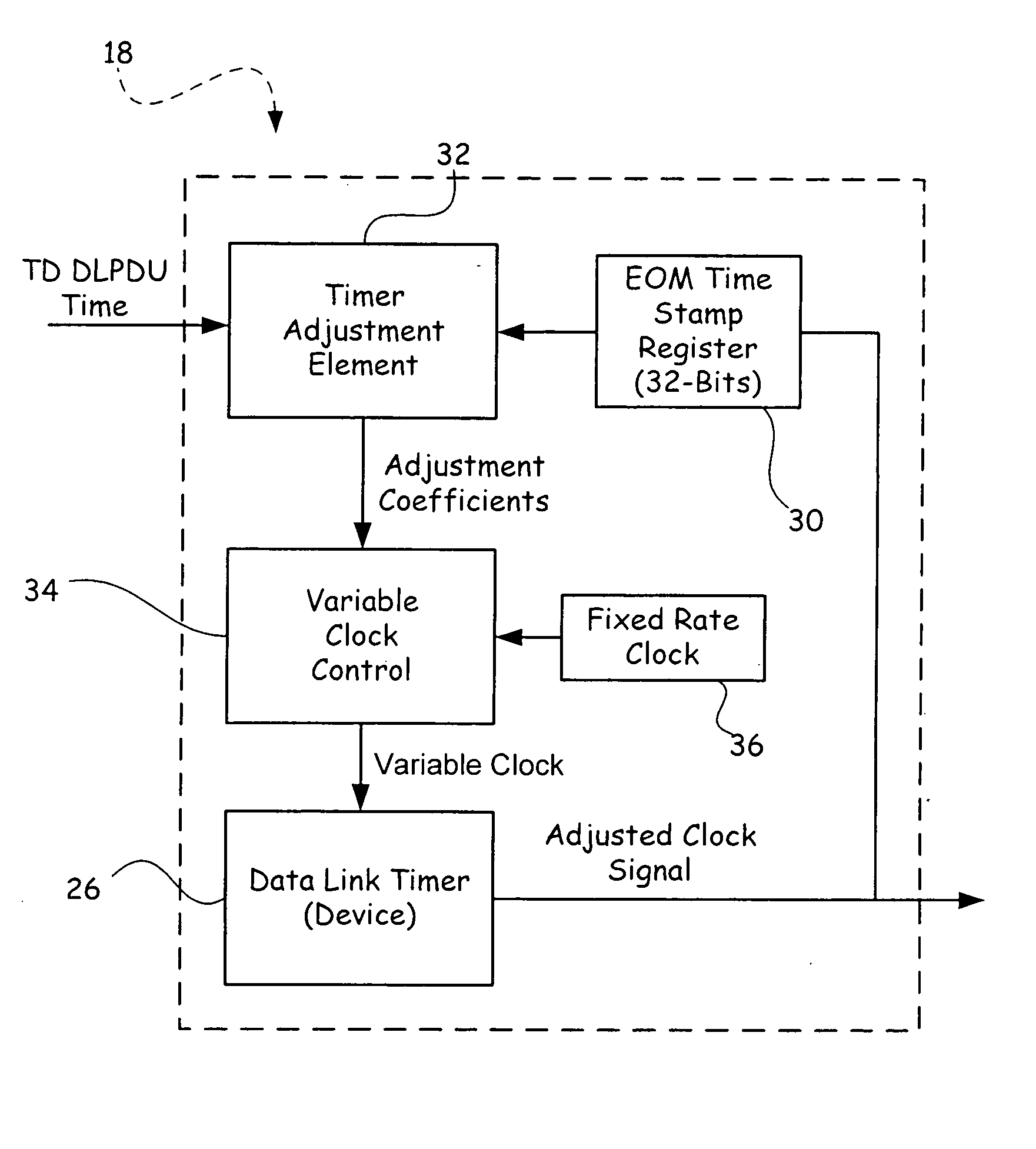
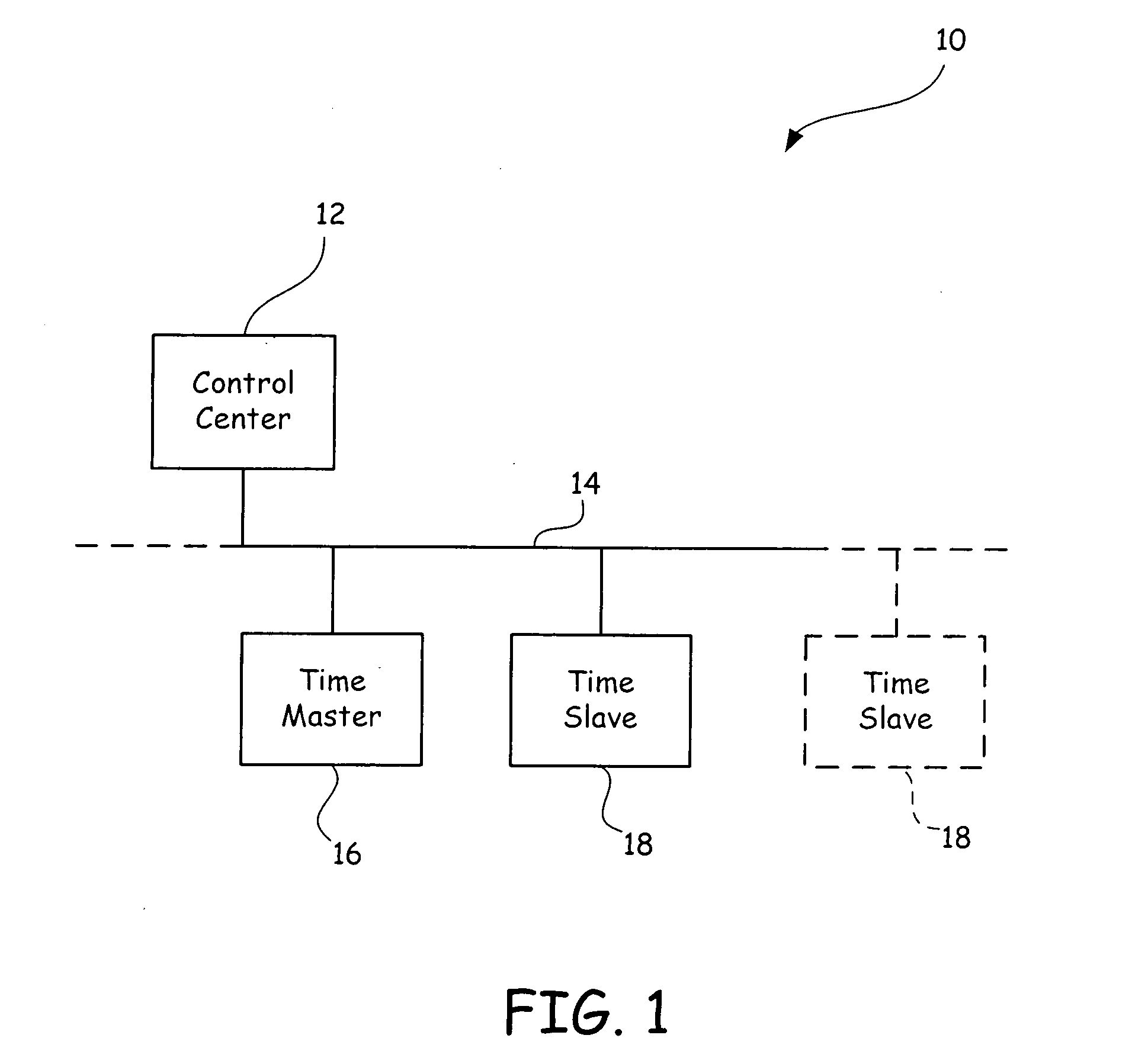
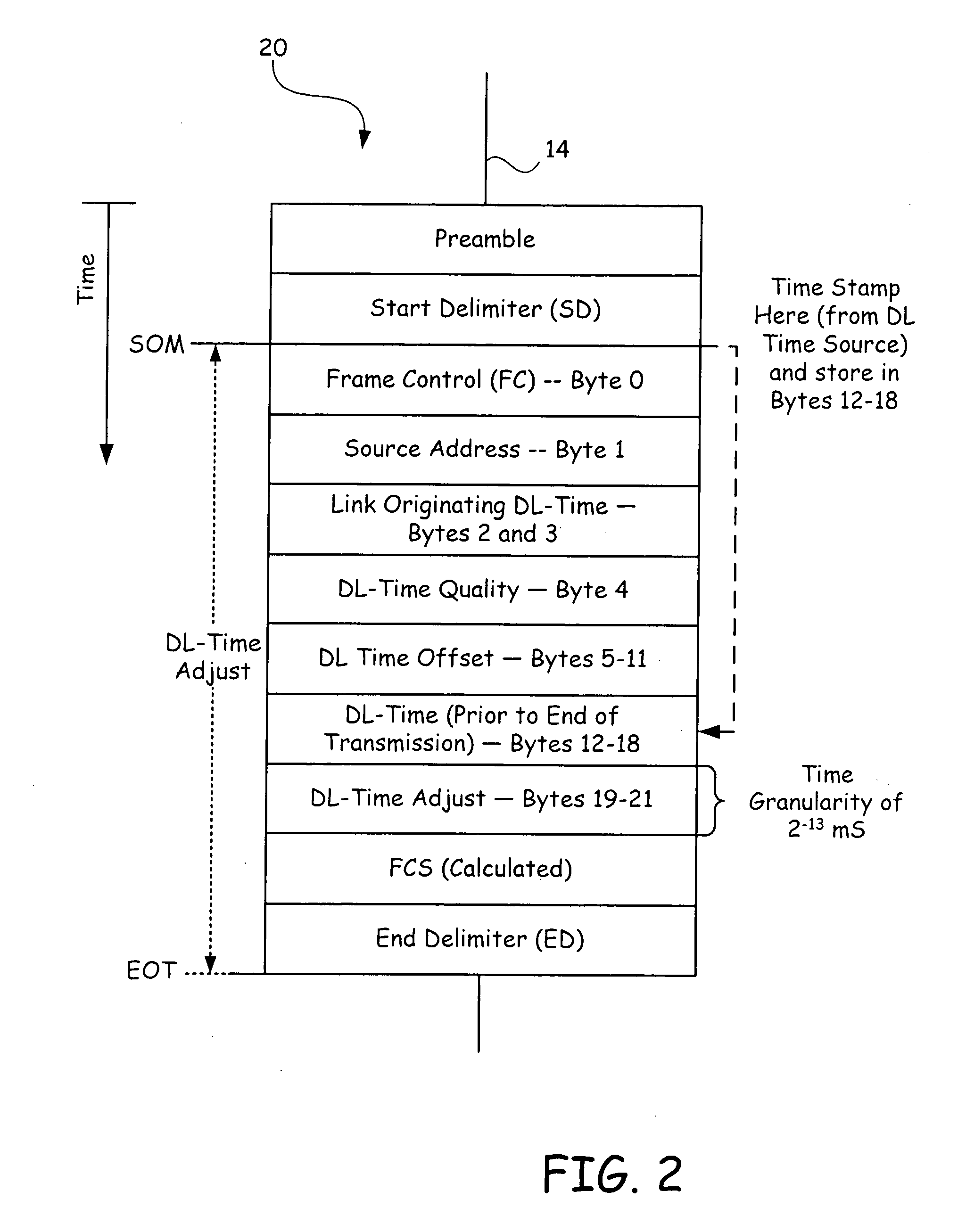
The system has a control center, a time master device and a plurality of distributed, time slave field devices in synchronization with a master clock of the time master device. The time master device periodically transmits a time distribution data unit. Each time slave field device has a timer adjustment element, a fixed rate clock and a variable clock. The timer adjustment element calculates a frequency ratio between the master clock and the fixed rate clock and uses the frequency ratio to calculate adjustment coefficients to adjust a local sense of time for each field device, such that a time stamp of each field device is synchronized to the master clock.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Hybrid permanent magnet motor
ActiveUS7898135B2Synchronous generatorsElectronic commutation motor controlStable statePermanent magnet motor
An electro-mechanical device that functions as a motor or a generator and methods for constructing and using such electro-mechanical device are provided. The electro-mechanical device features permanent magnets placed in a magnetically attracting manner and inter-dispersed between control coils. The control coils are energized to create a flux opposing the flux of the permanent magnets and to create a rotational torque on the poles of a salient pole rotor before those poles align with the poles of the energized control coil stator segment. Power can be generated by placing the flux of the control coils in a steady state and mechanically rotating the salient pole rotor. The electro-mechanical device provides little or no cogging forces, high-efficiency operation, and a high power density.
Owner:QM POWER
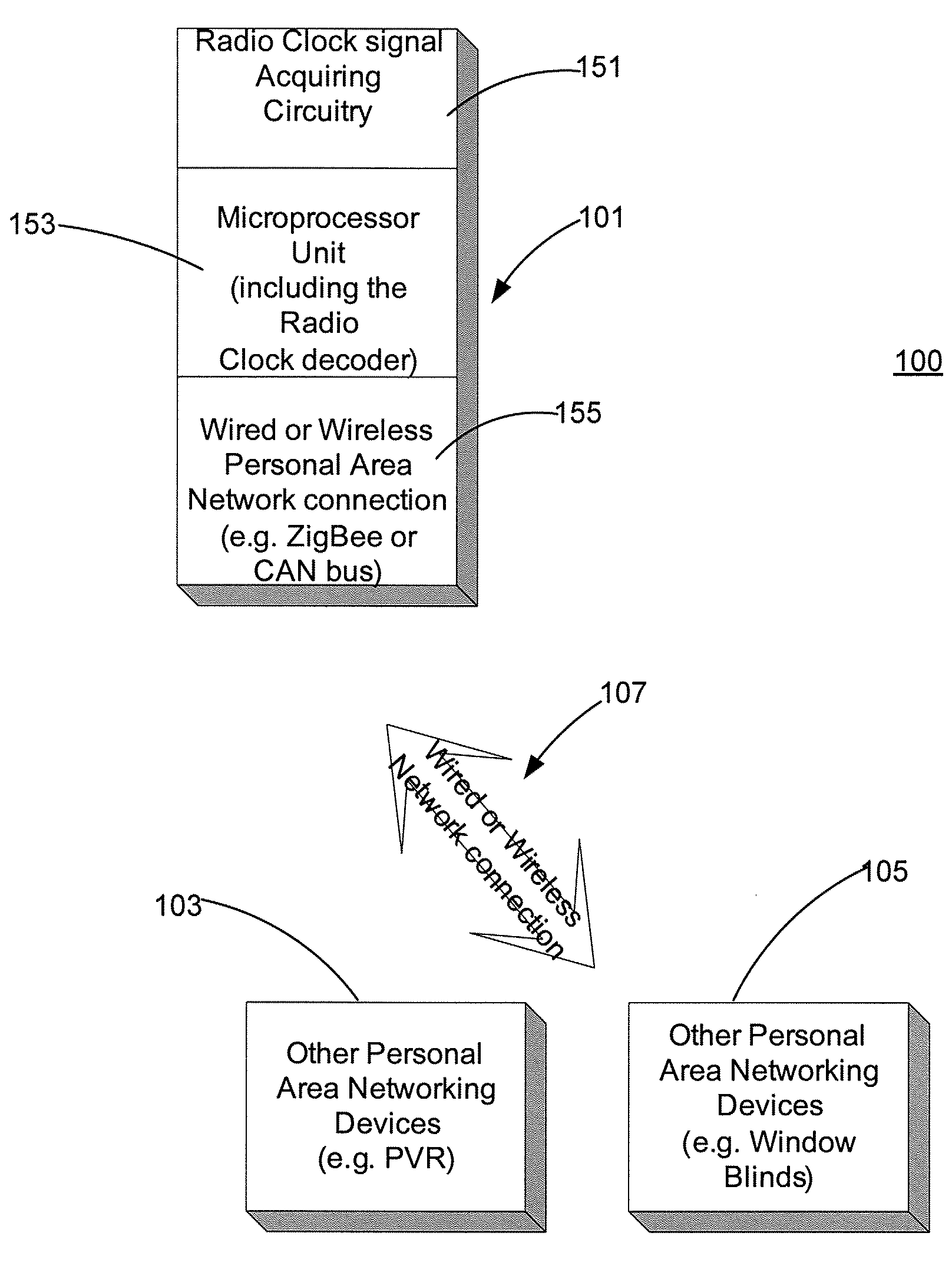
Clock Setup Over a Network
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for updating a target device from a clock device through a network. The clock device obtains a time value from a clock source and sends the time value to a target device. A node within the network determines a time delay, adjusts the time value in accordance with the time delay, and sends the adjusted time value to the target device. The node may determine a time delay from an internal timer or from a measurement message when adjusting the time value. The clock device may send a subsequent time update message to the target device if the target device does not acknowledge reception of a time update. The clock device may also send a time update message to a target device when a status change of daylight savings time occurs and obtain a subsequent time value from a clock source.
Owner:COMPUTIME LIMITED
Hybrid permanent magnet motor
ActiveUS20090160391A1Reduce cogging forceImprove efficiencySynchronous generatorsElectronic commutation motor controlStable statePermanent magnet motor
An electro-mechanical device that functions as a motor or a generator and methods for constructing and using such electro-mechanical device are provided. The electro-mechanical device features permanent magnets placed in a magnetically attracting manner and inter-dispersed between control coils. The control coils are energized to create a flux opposing the flux of the permanent magnets and to create a rotational torque on the poles of a salient pole rotor before those poles align with the poles of the energized control coil stator segment. Power can be generated by placing the flux of the control coils in a steady state and mechanically rotating the salient pole rotor. The electro-mechanical device provides little or no cogging forces, high-efficiency operation, and a high power density.
Owner:QM POWER
Motor
InactiveUS6255749B1Magnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesElectric motor
A motor includes a magnet formed in a cylindrical shape and divided in the circumferential direction in at least the outer periphery and alternately polarized to different poles, a first coil, a magnet and a second coil placed in the axial direction of the magnet, a first outer magnetic pole opposed to the outer periphery of the magnet and a hollow-shaped first inner magnetic pole opposed to the inner periphery of the magnet, excited by the first coil respectively, a second outer magnetic pole opposed to the outer periphery of the magnet and a hollow-shaped second inner magnetic pole opposed to the inner periphery of the magnet, excited by the second coil respectively, a rotatable rotary shaft integral with the magnet, and a pressurizing device for pressurizing the rotary shaft in the axial direction, the pressurizing device being placed in the hollow cylindrical portion of the first inner magnetic pole. A motor having a high output, a compact shape and small working noises is provided.
Owner:CANON KK +1
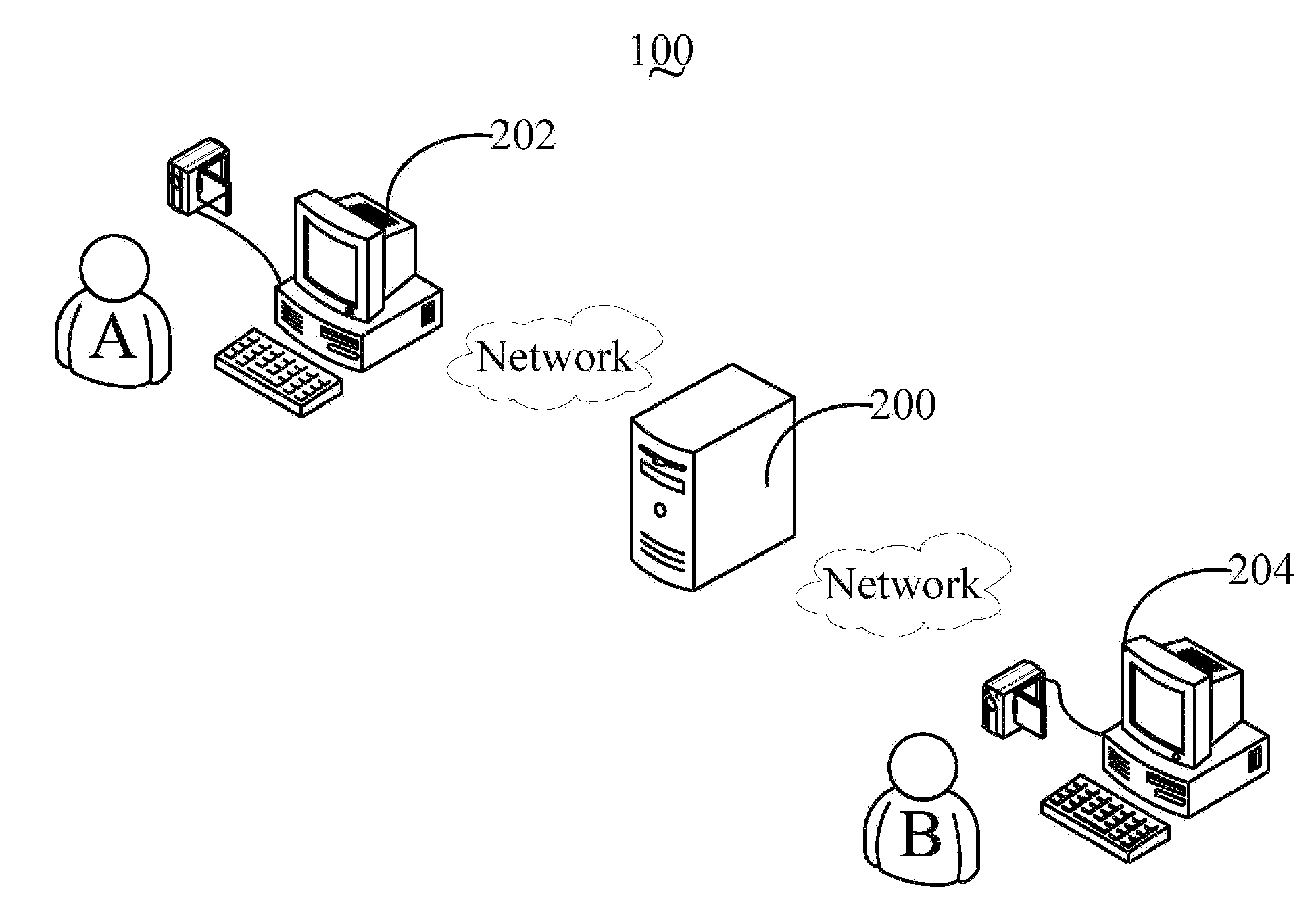
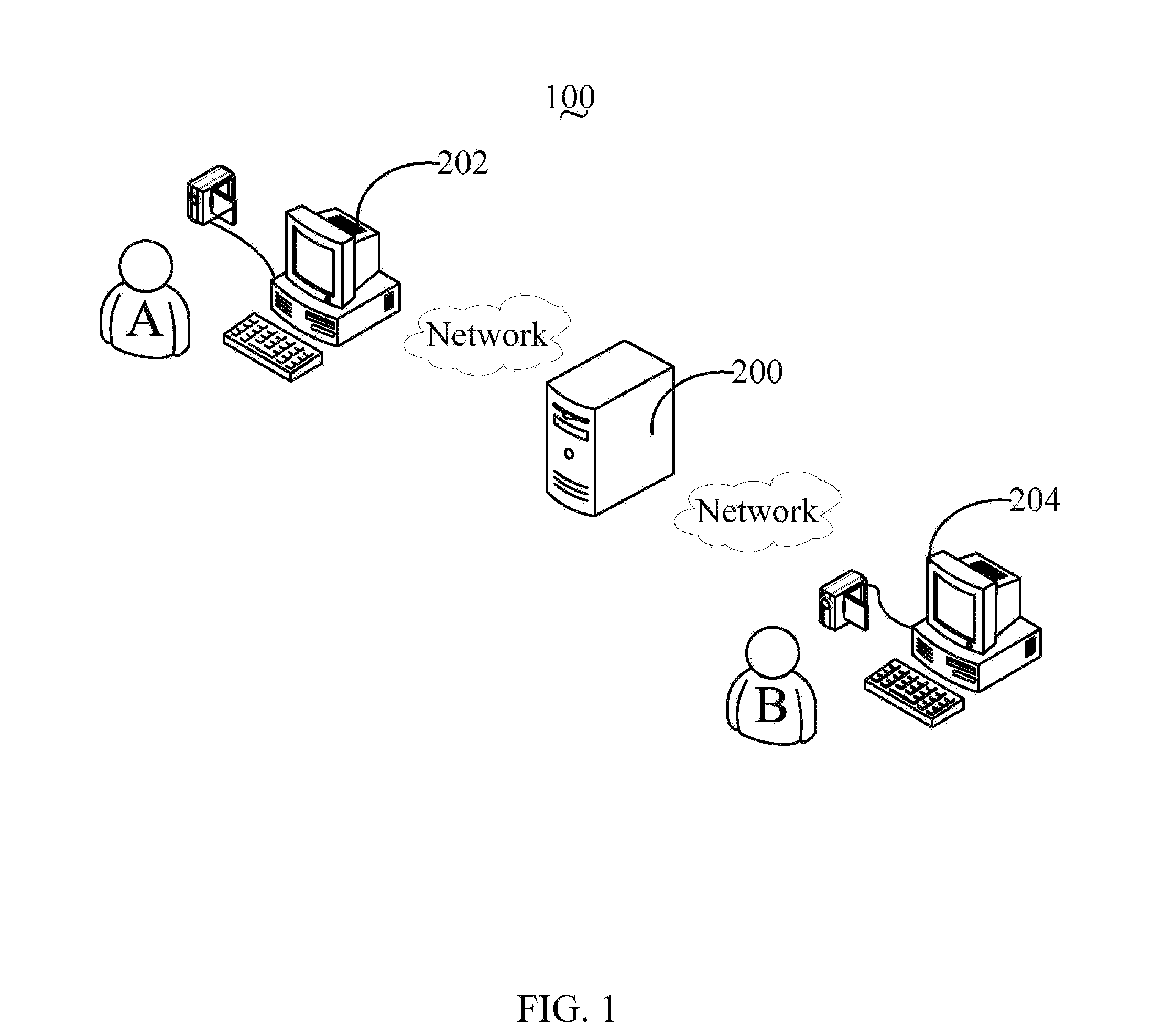
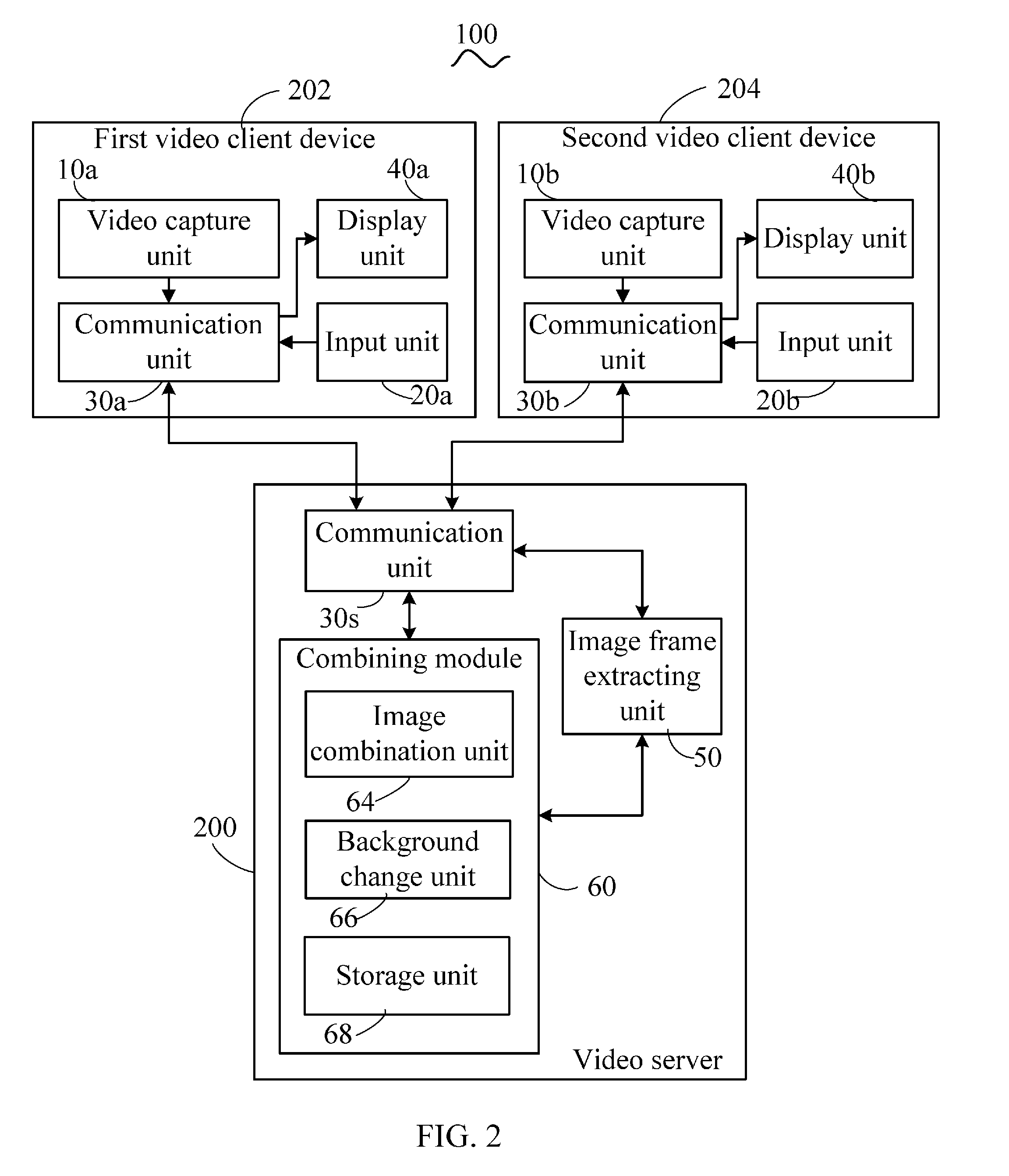
Video server, video client device and video processing method thereof
InactiveUS20090257730A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsCommunication unitComputer graphics (images)
A video server includes a communication unit for receiving a first video signal from a first video client device and a second video signal from a second video client device, an image combination unit for combining the first video signal and the second video signal to generate a combined video signal, and an image frame extracting unit for extracting a combined image frame from the combined video signal in response to a grab command received from one of the first video client device and the second video client device, and sending the extracted combined image frame to the one of the first video client device and the second video client device via the communication unit. A related client device and a video processing method are also provided.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
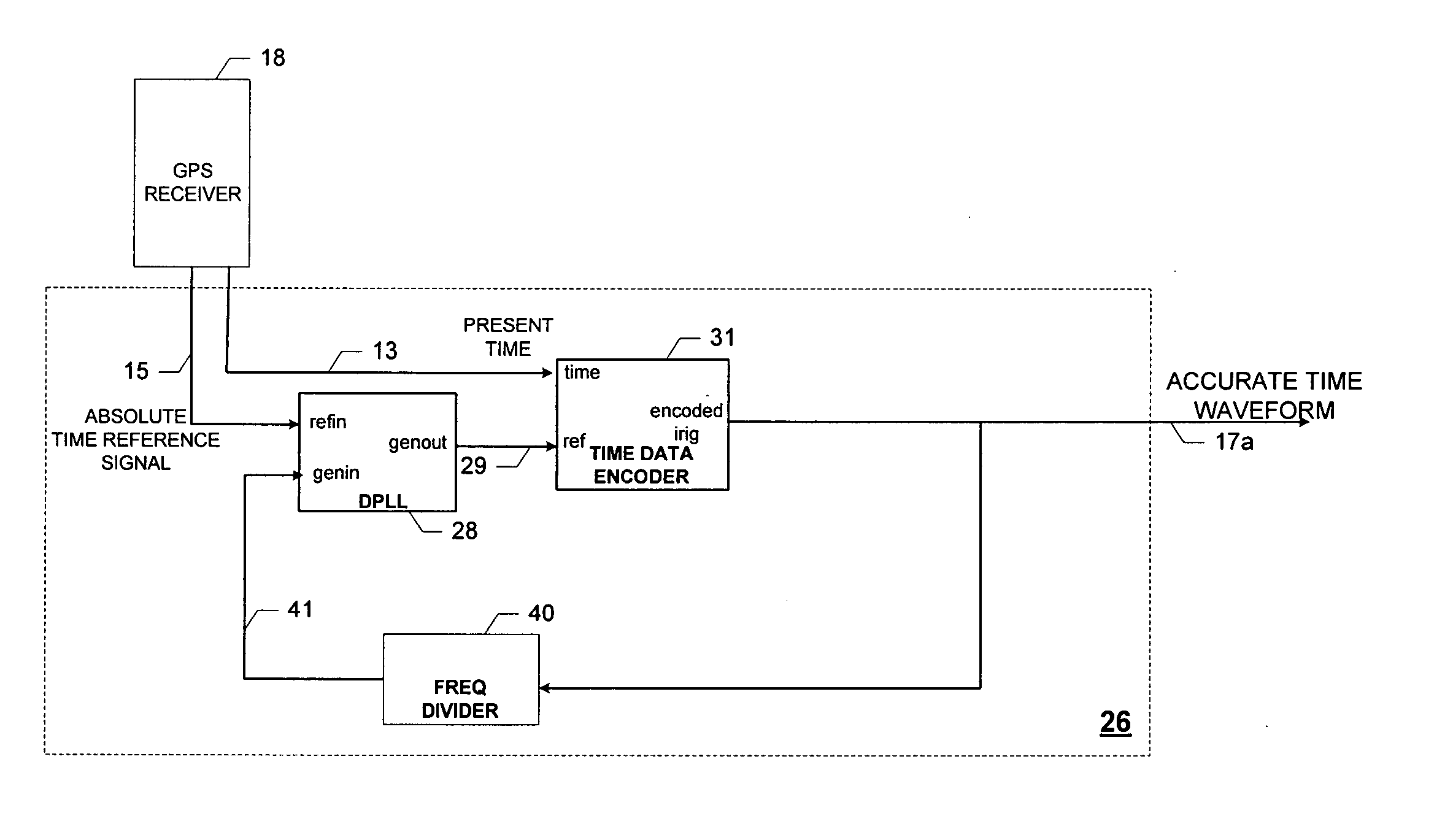
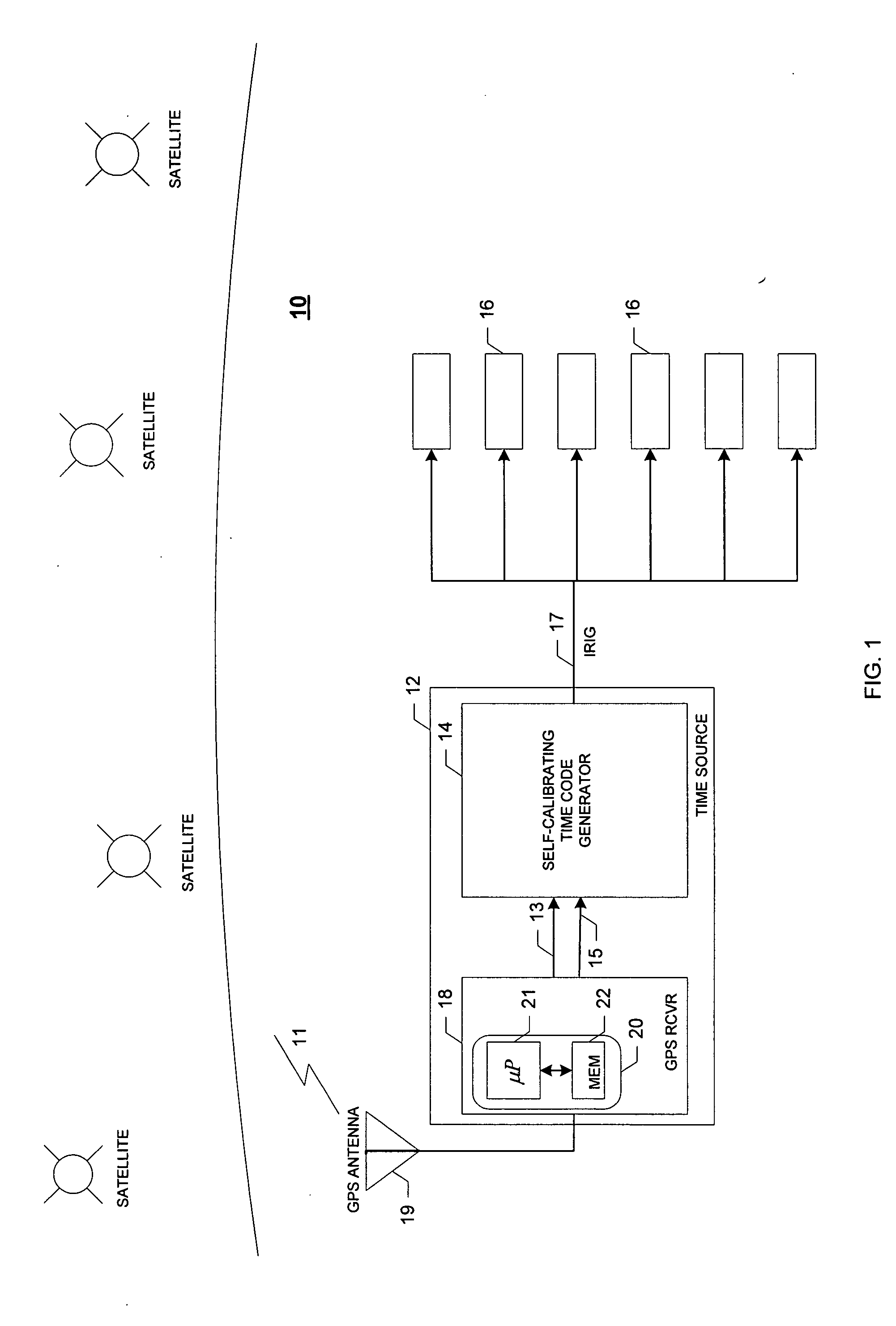
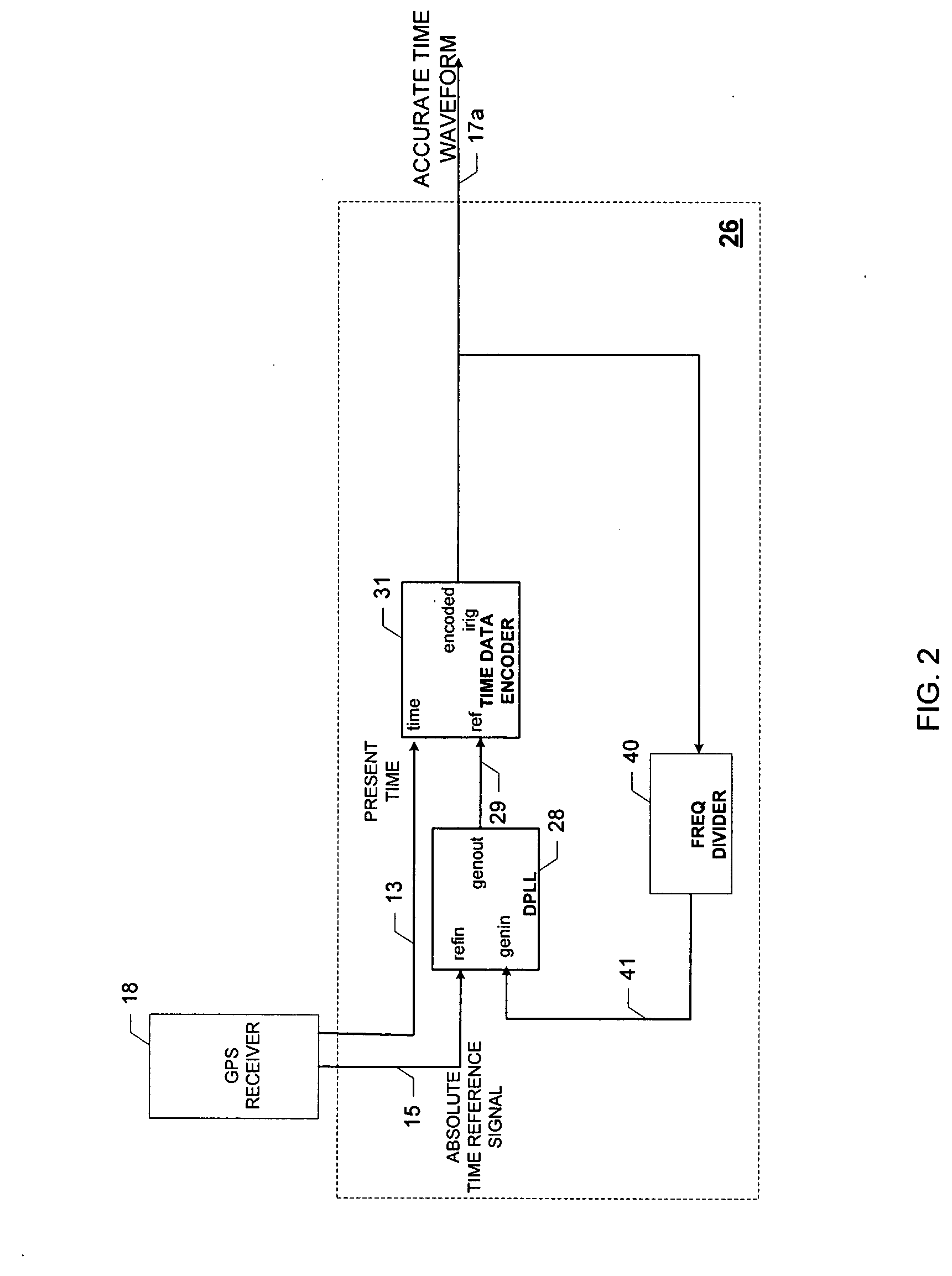
Self-calibrating time code generator
ActiveUS20060259806A1Accurate timingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementMaster clocksPhase differenceTime alignment
Provided is a self-calibrating time code generator and method for generating an accurate time code (e.g., an accurate IRIG waveform). The self-calibrating time code generator includes a phase-locked loop configured to provide a generated output signal based on a phase difference between an absolute time reference signal and a compensated generated input signal, an IRIG encoder configured to couple a present time value with the generated output signal to form an IRIG waveform, a delay difference indicator configured to provide a time interval value based on a comparison of corresponding pulse edges of the generated output signal and the IRIG waveform, and a numerical delay component configured to delay the generated output signal by the time interval value to form the compensated generated input signal used to time-align the IRIG waveform with the absolute time reference signal to form the accurate IRIG waveform.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
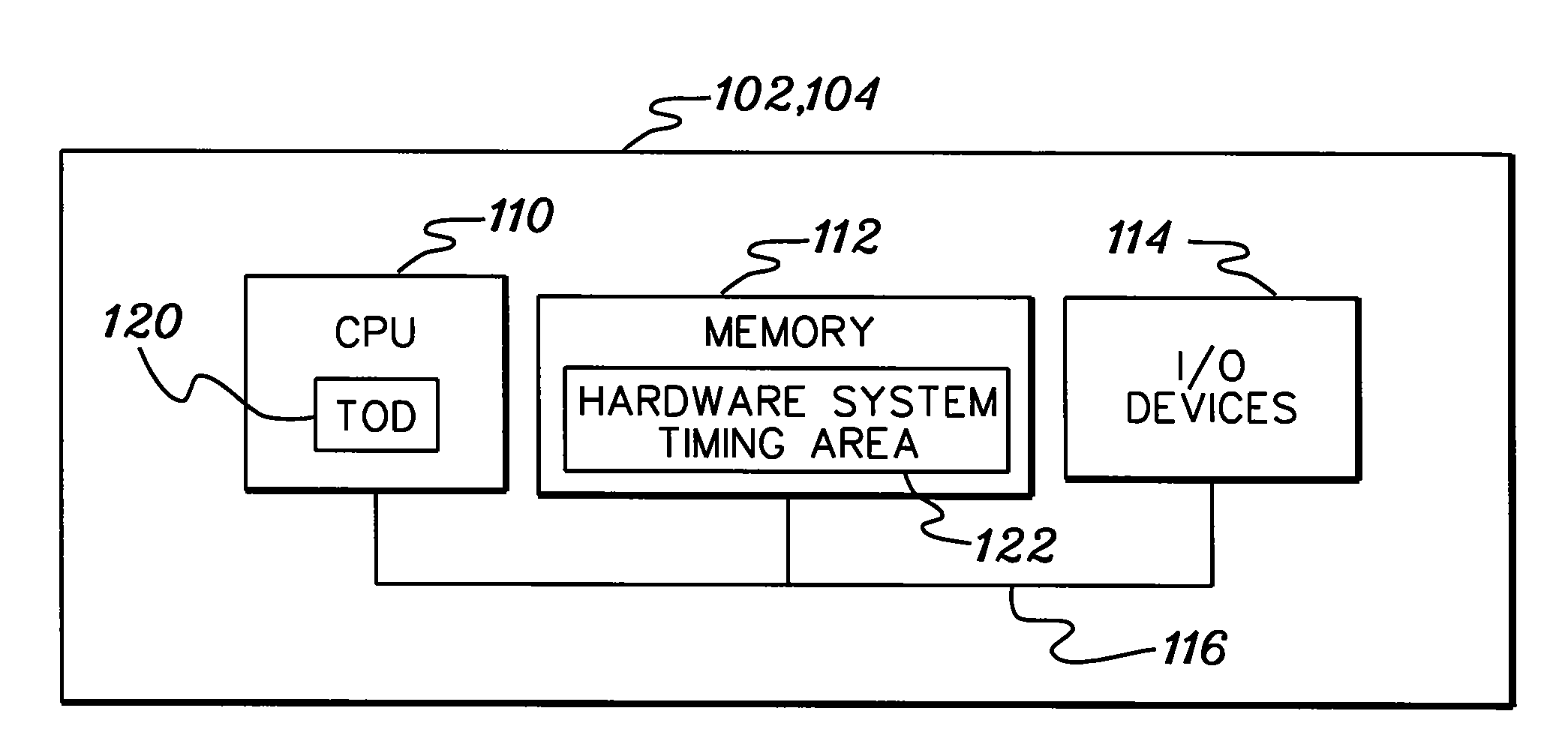
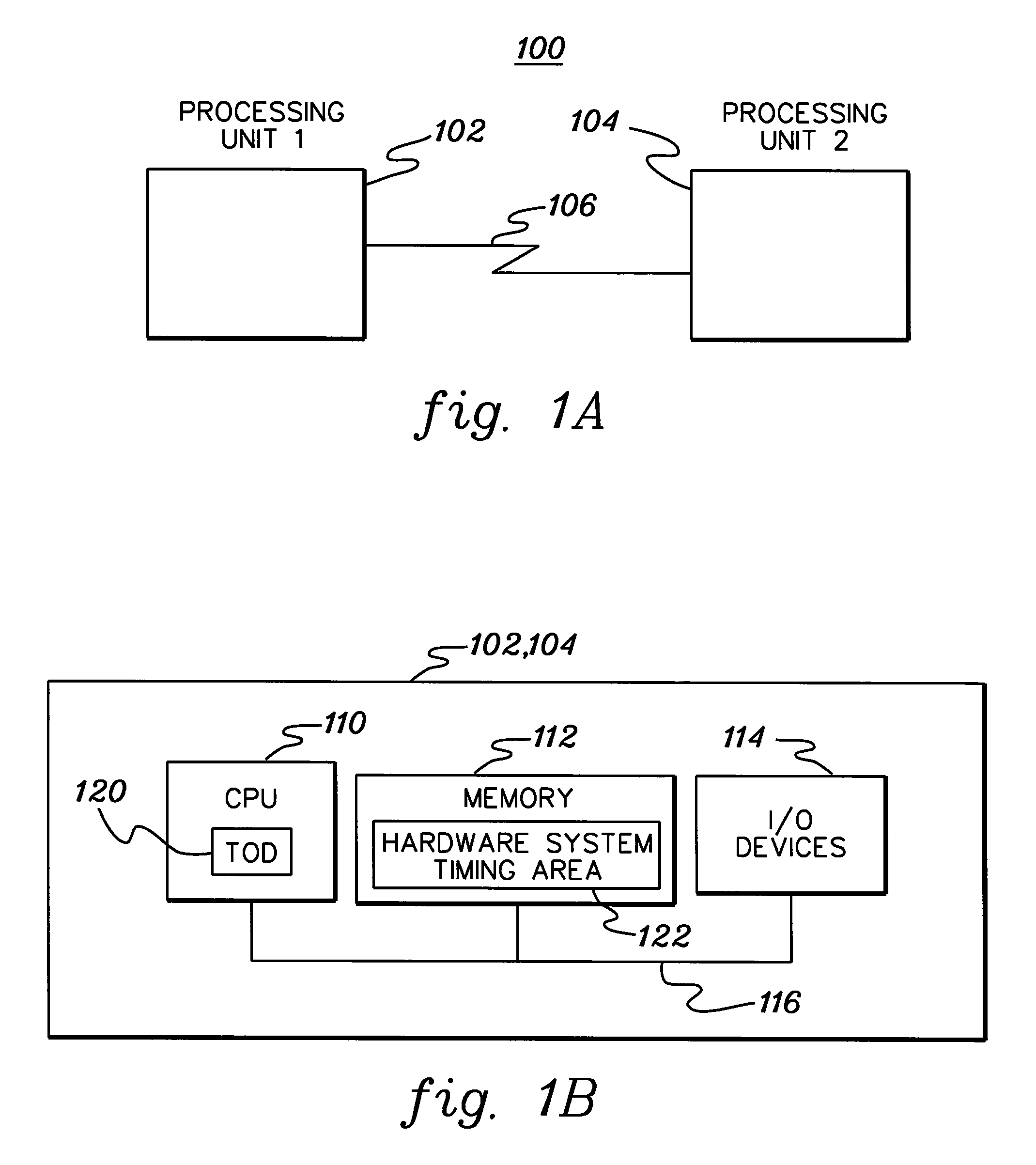
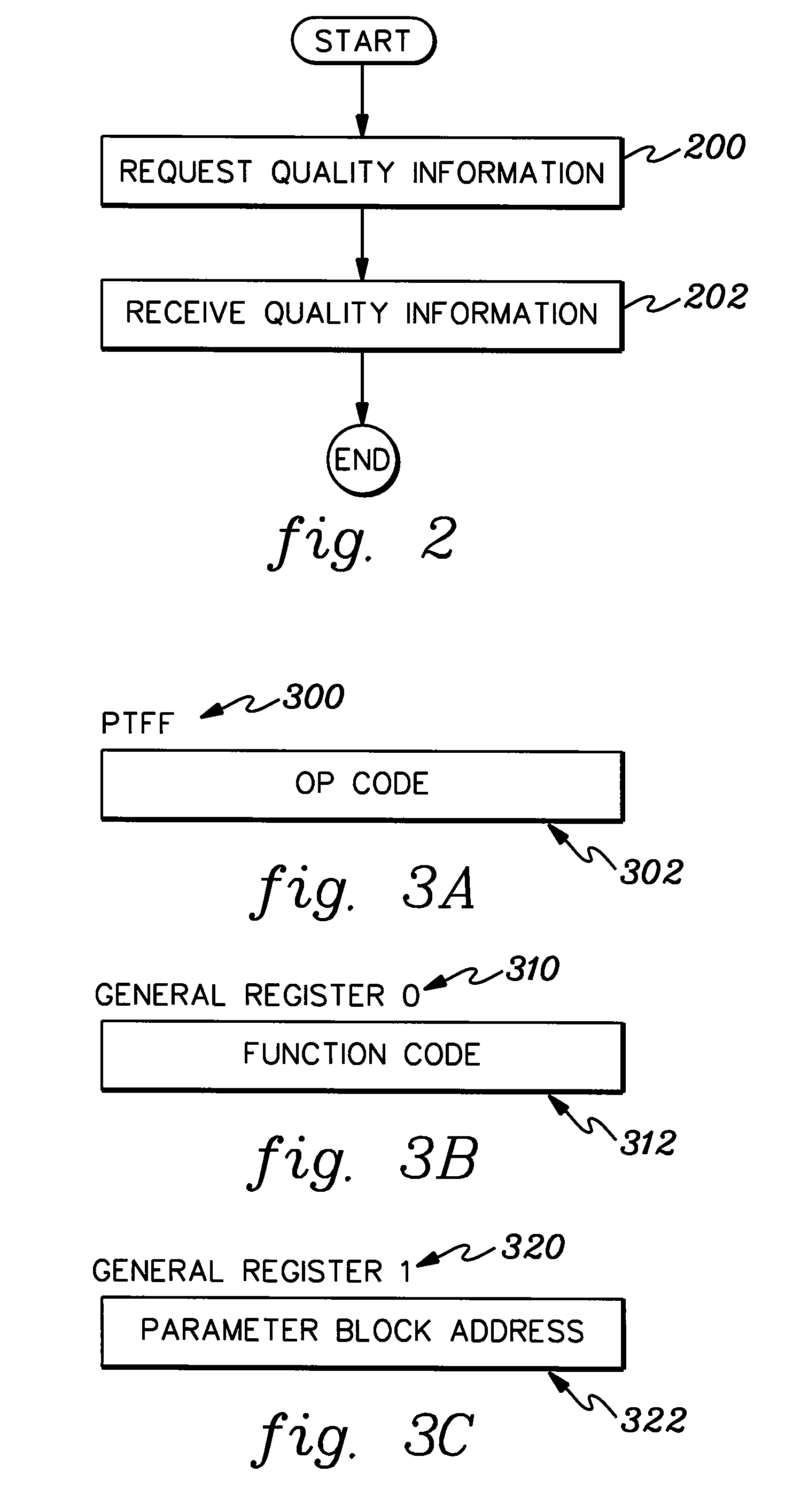
Directly obtaining by application programs information usable in determining clock accuracy
ActiveUS20080028254A1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageMaster clocksGenerating/distributing signalsOperational systemApplication software
Information usable in determining the quality of time produced by a clock of a processing environment is obtained. The information is obtained directly by an application program absent use of a supervisor service, such as an operating system or operating system service. The application program invokes an instruction that returns a parameter block that includes the information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com