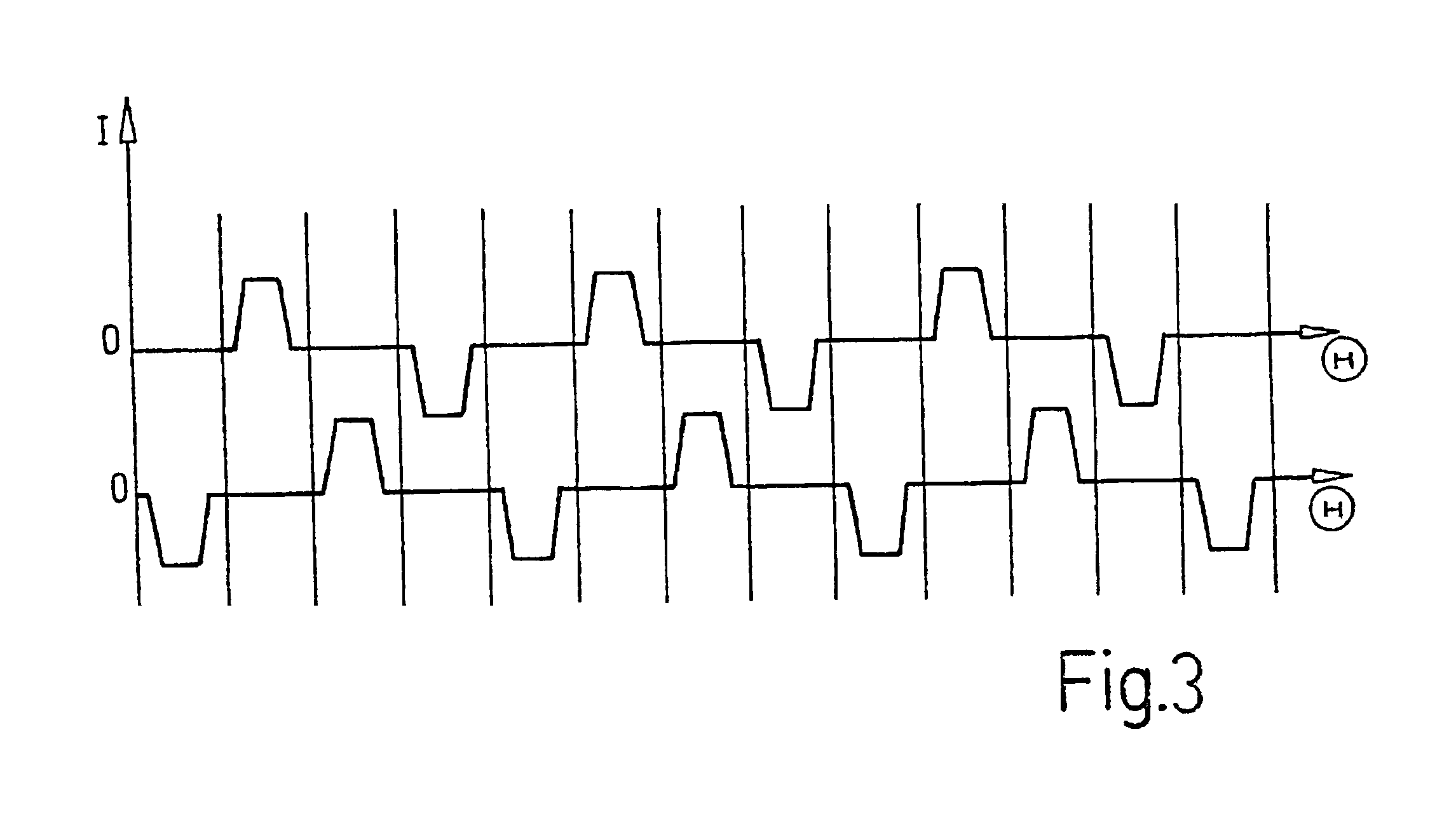
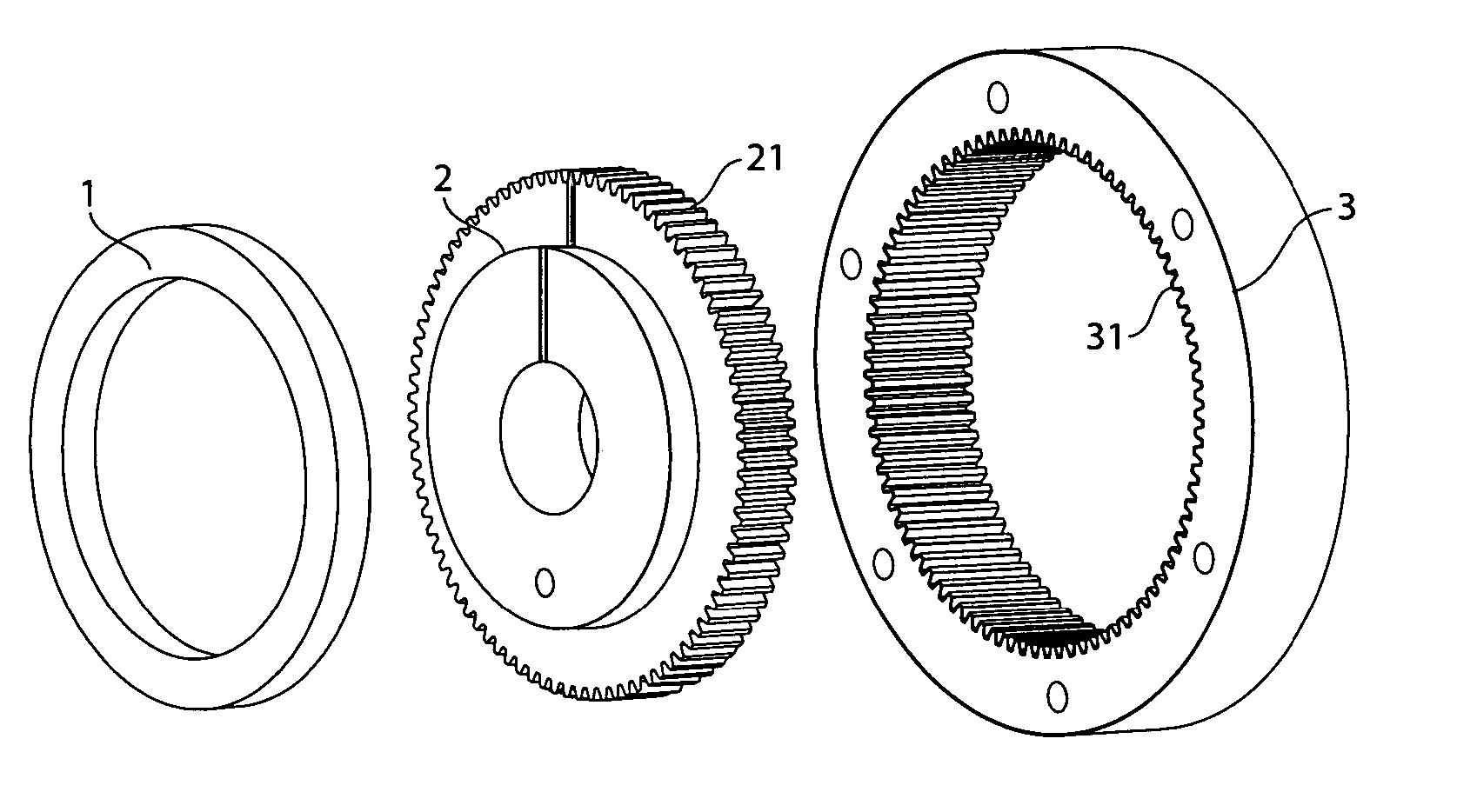
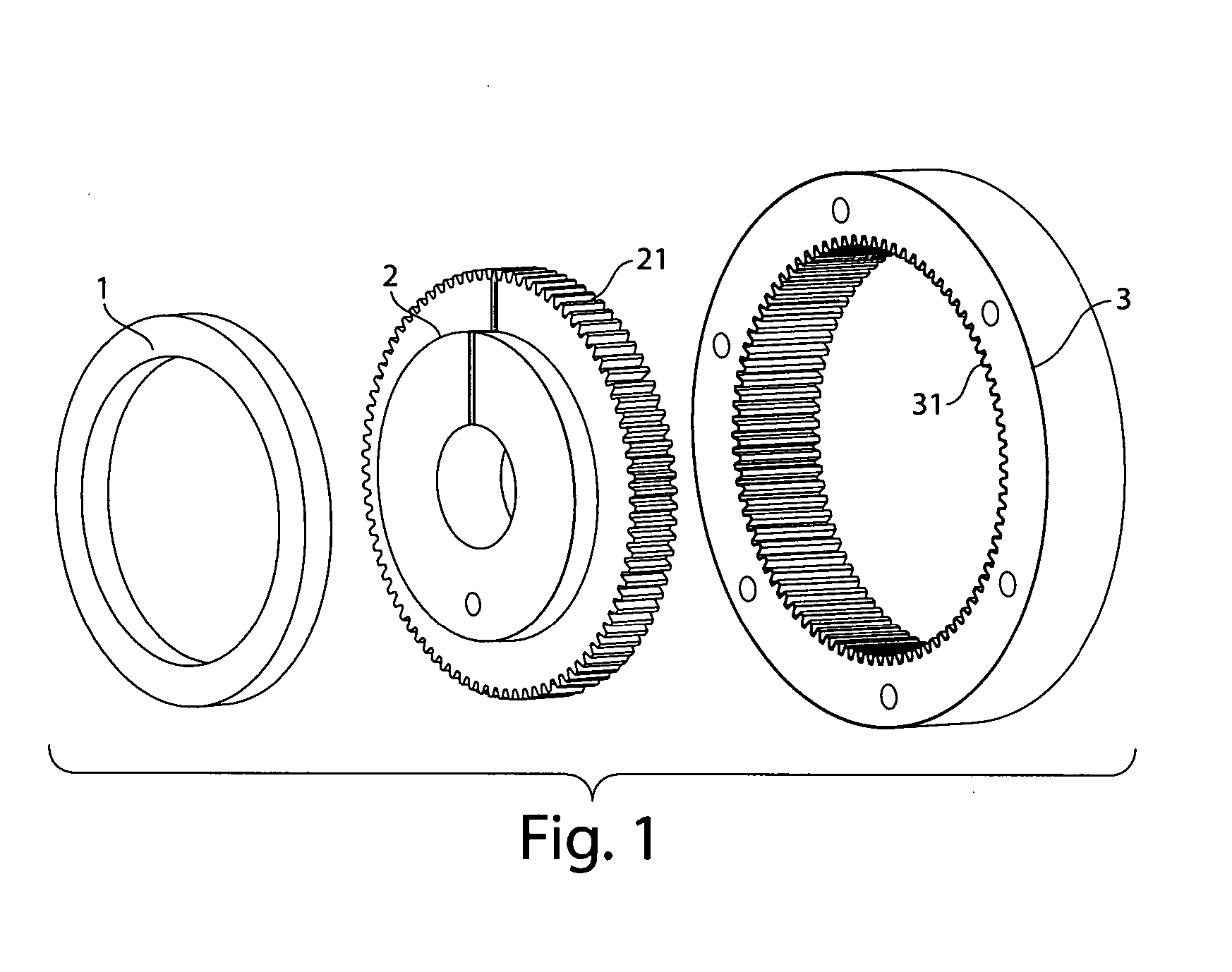
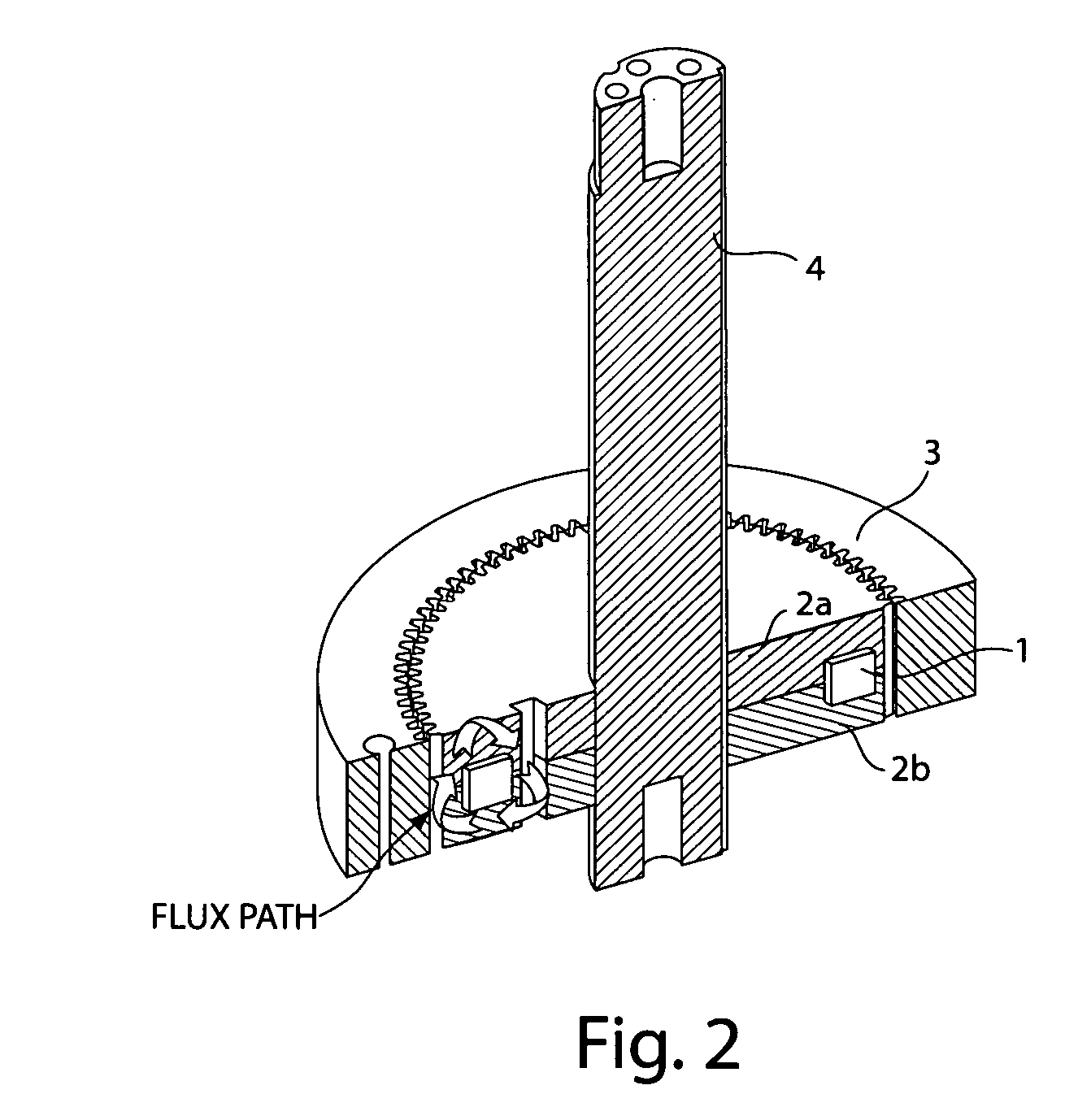
Patents
Literature
265 results about "Transverse flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
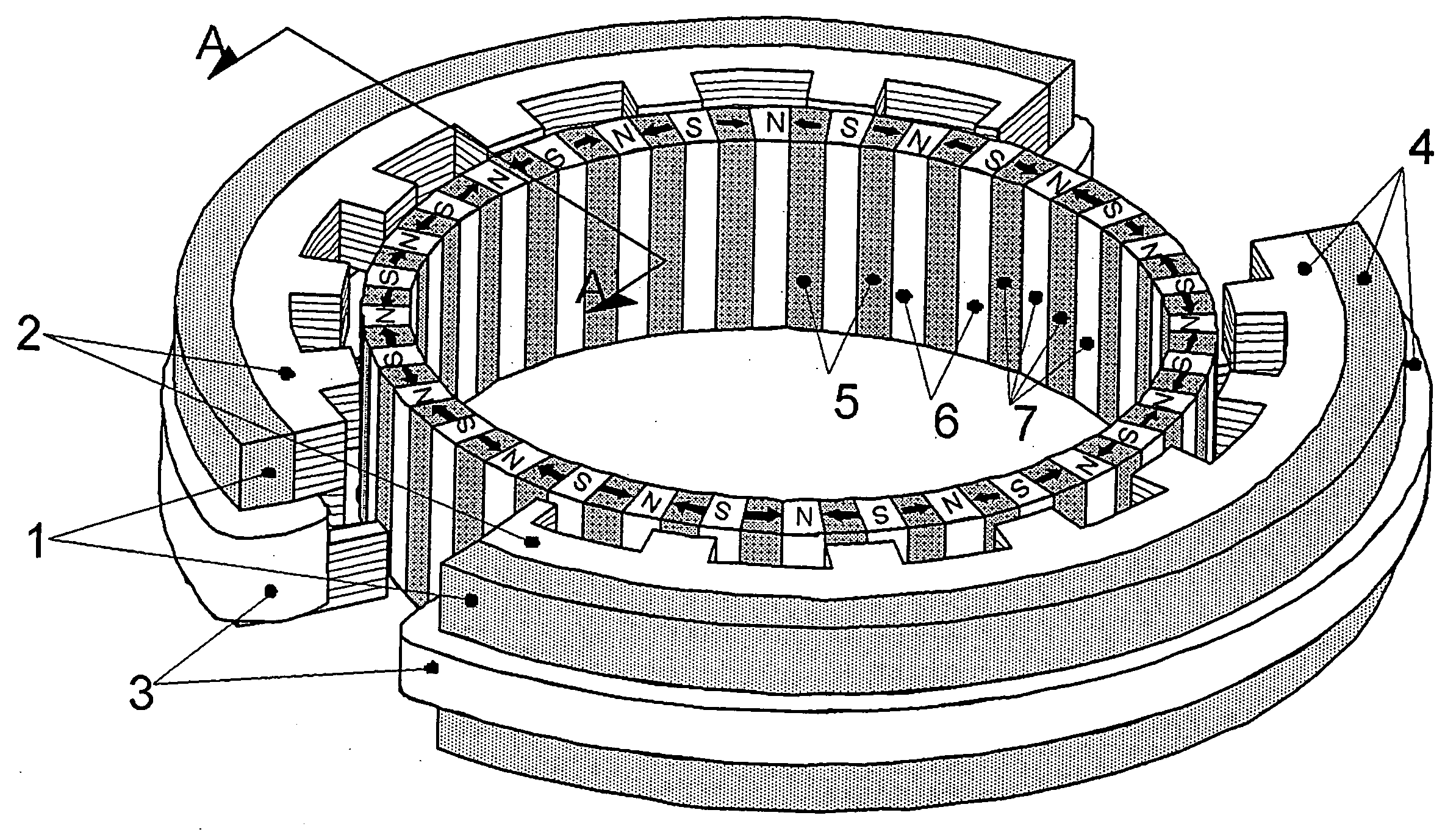
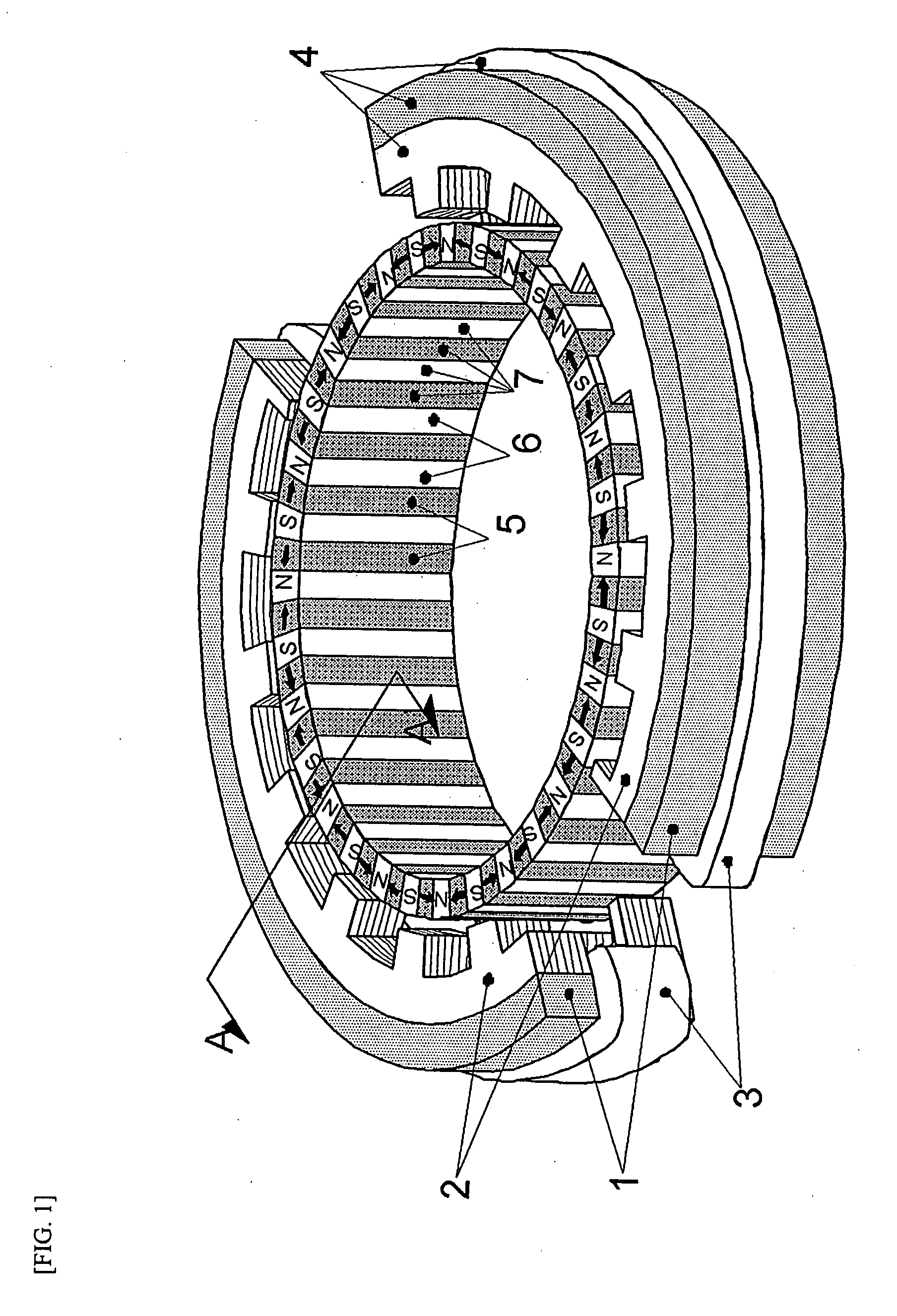
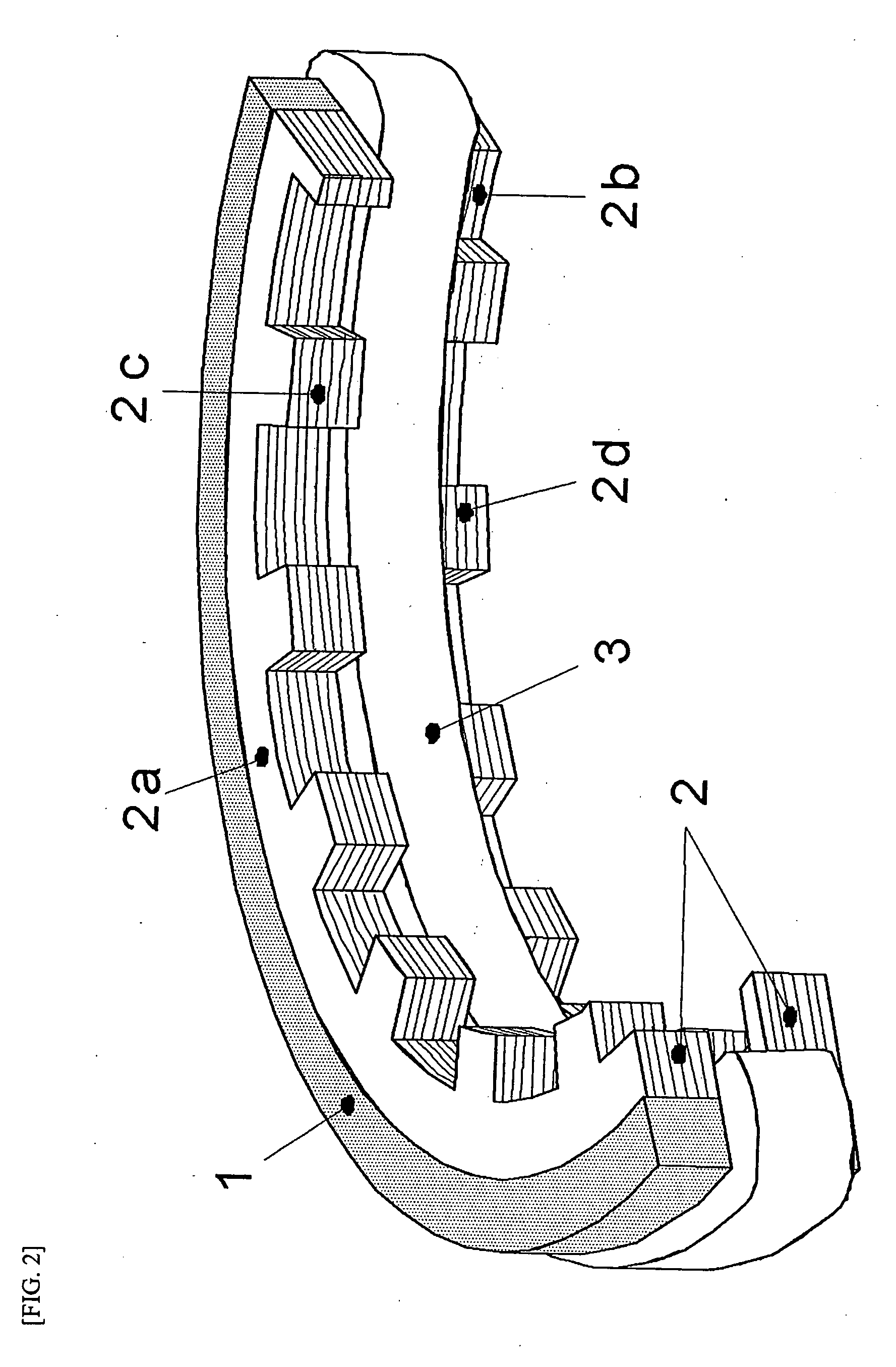
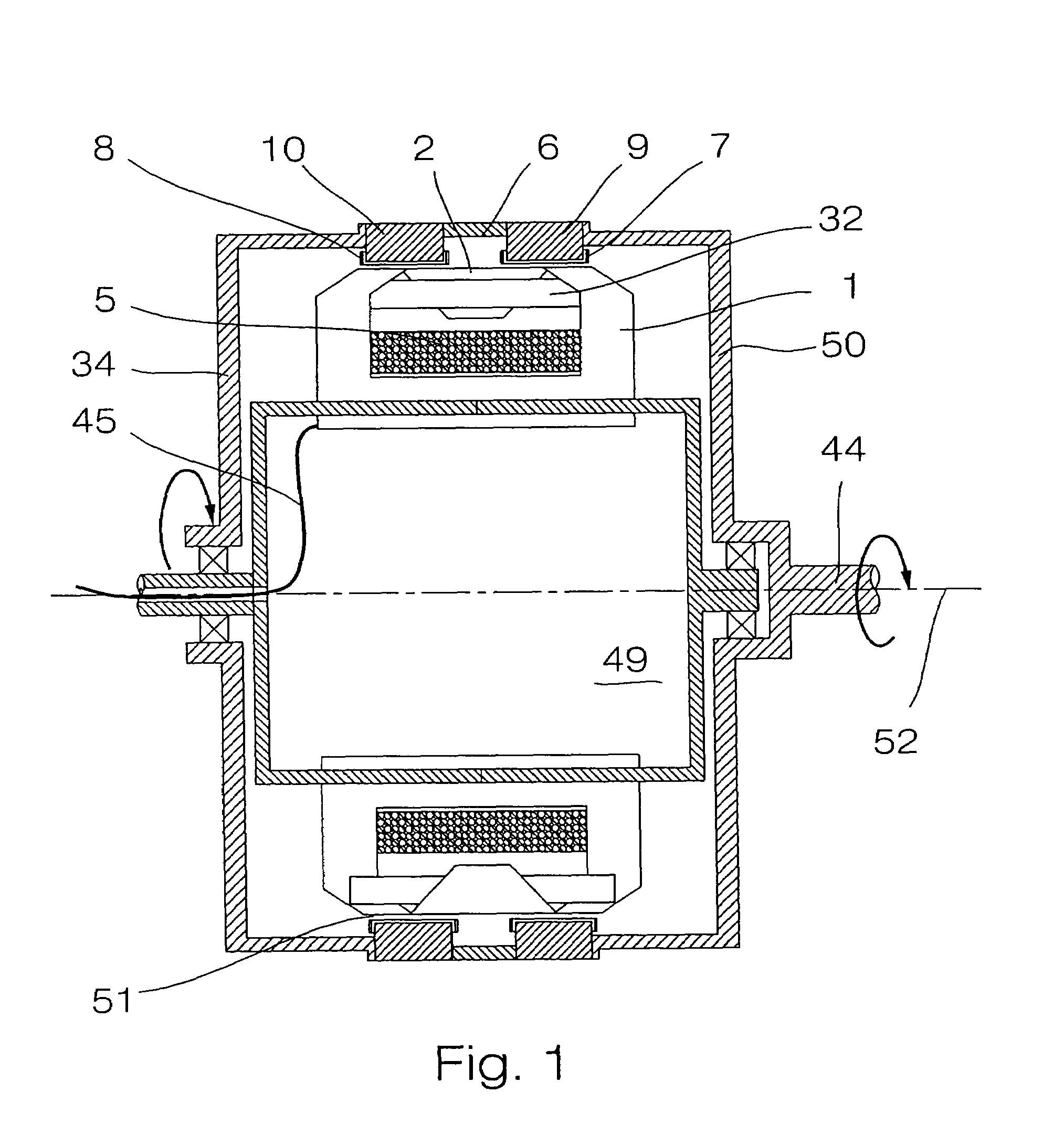
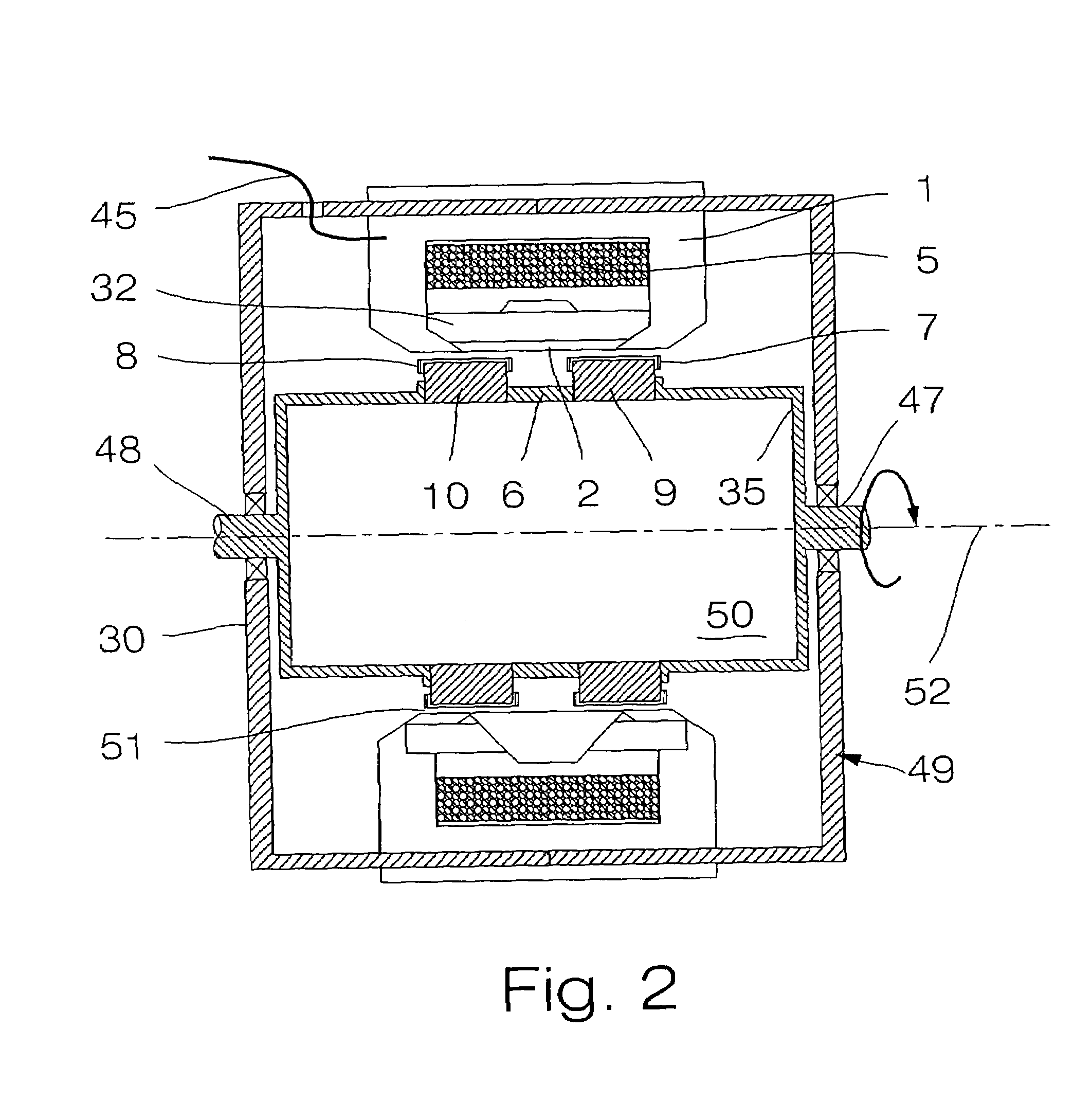
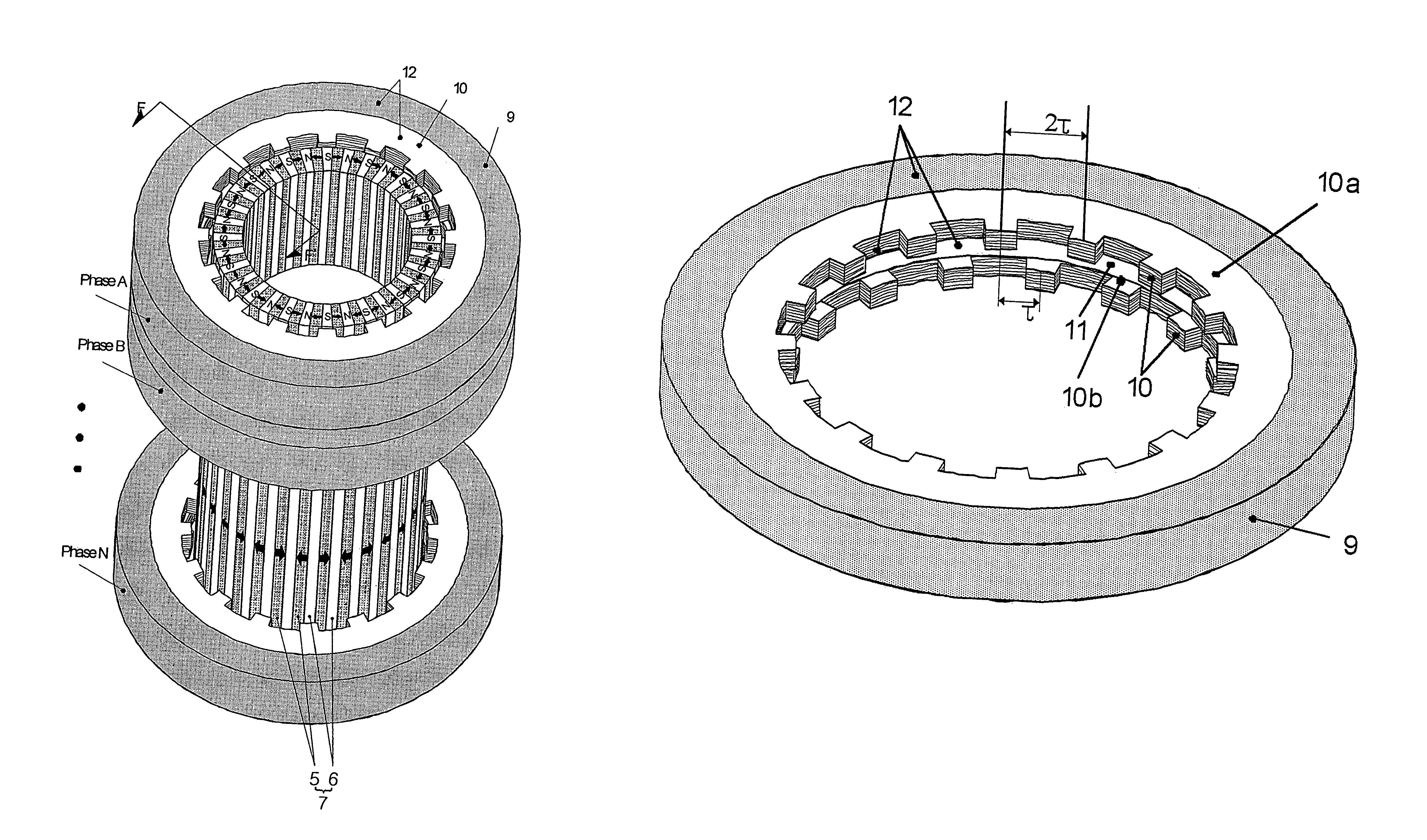
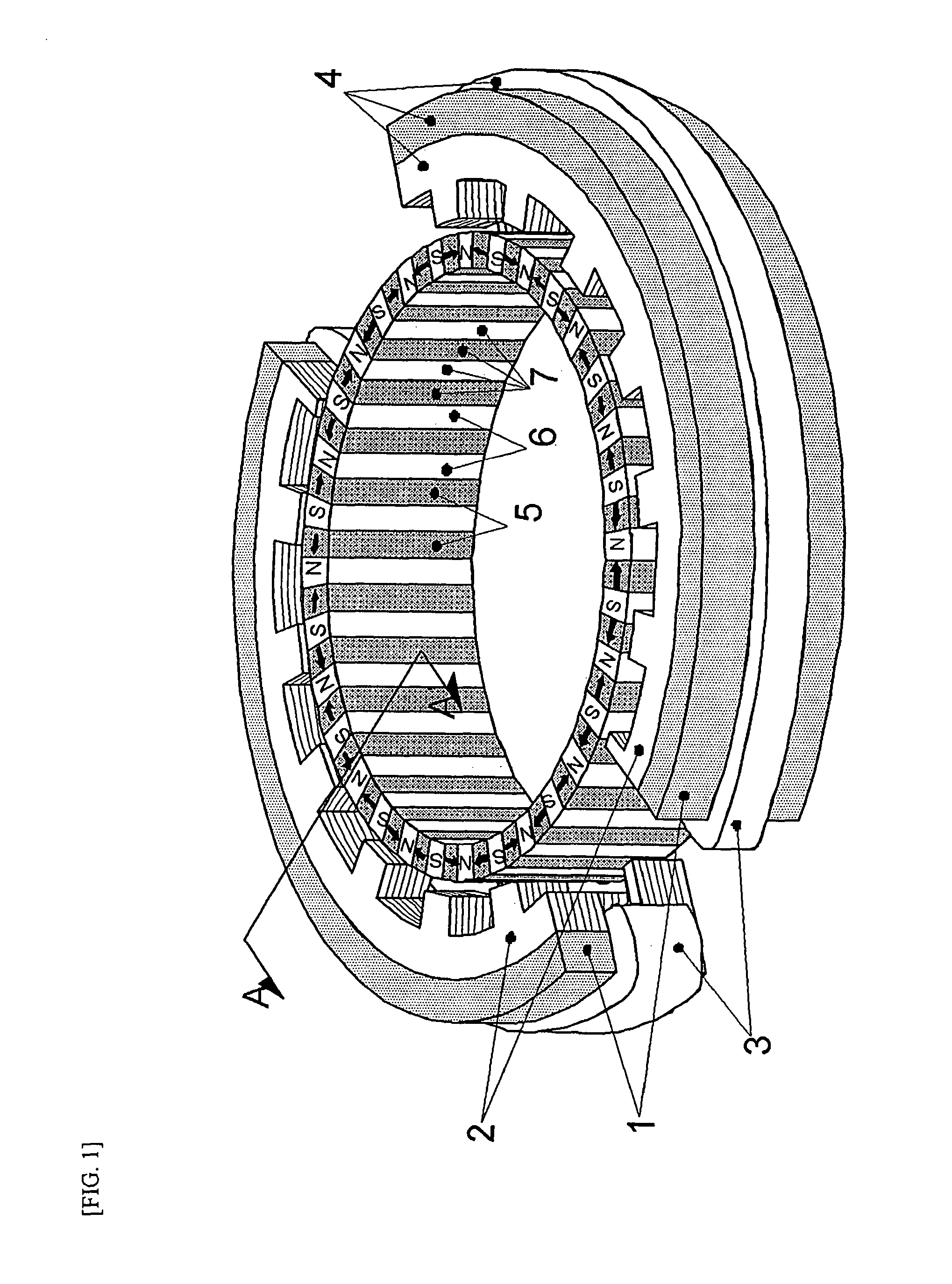
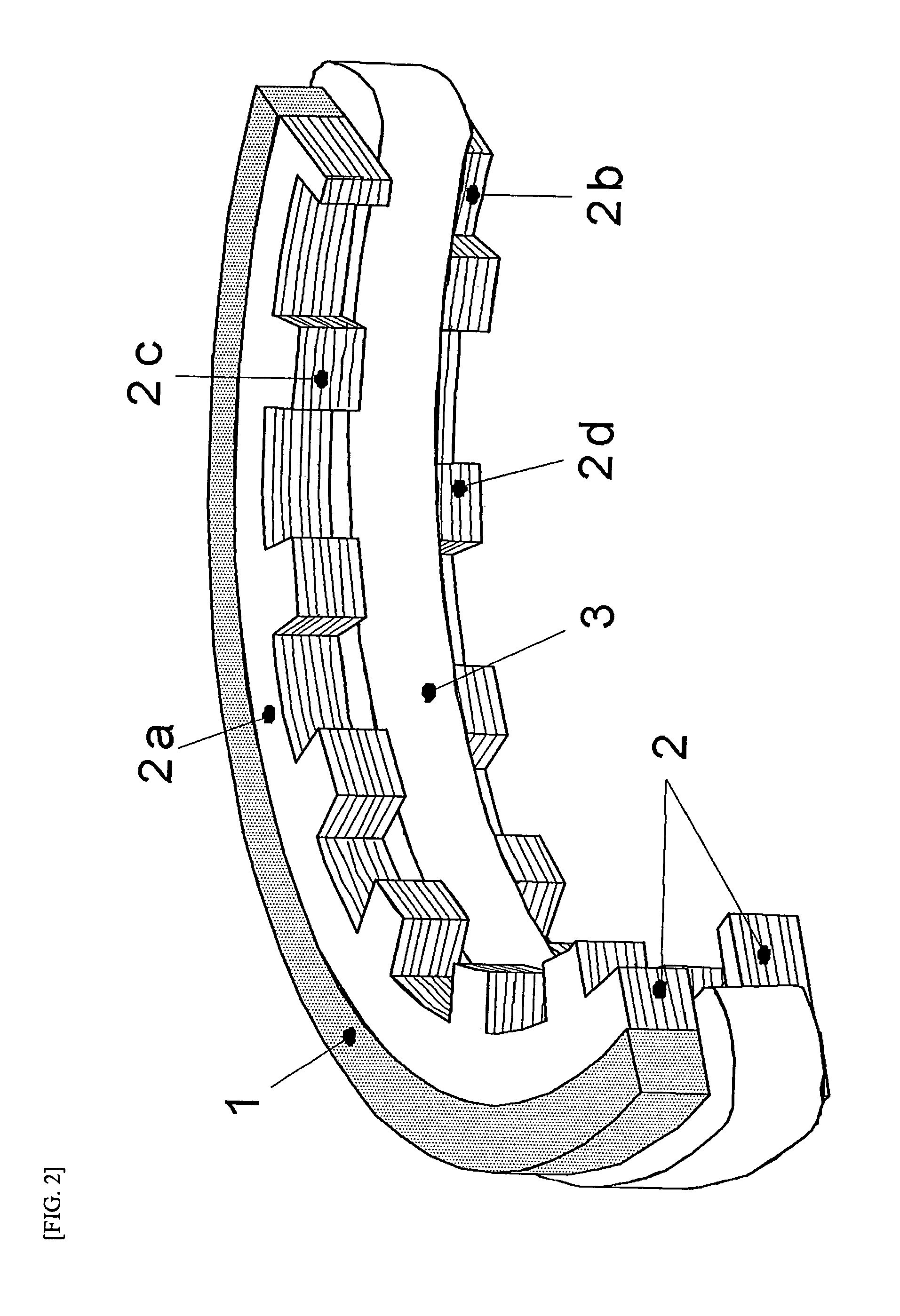
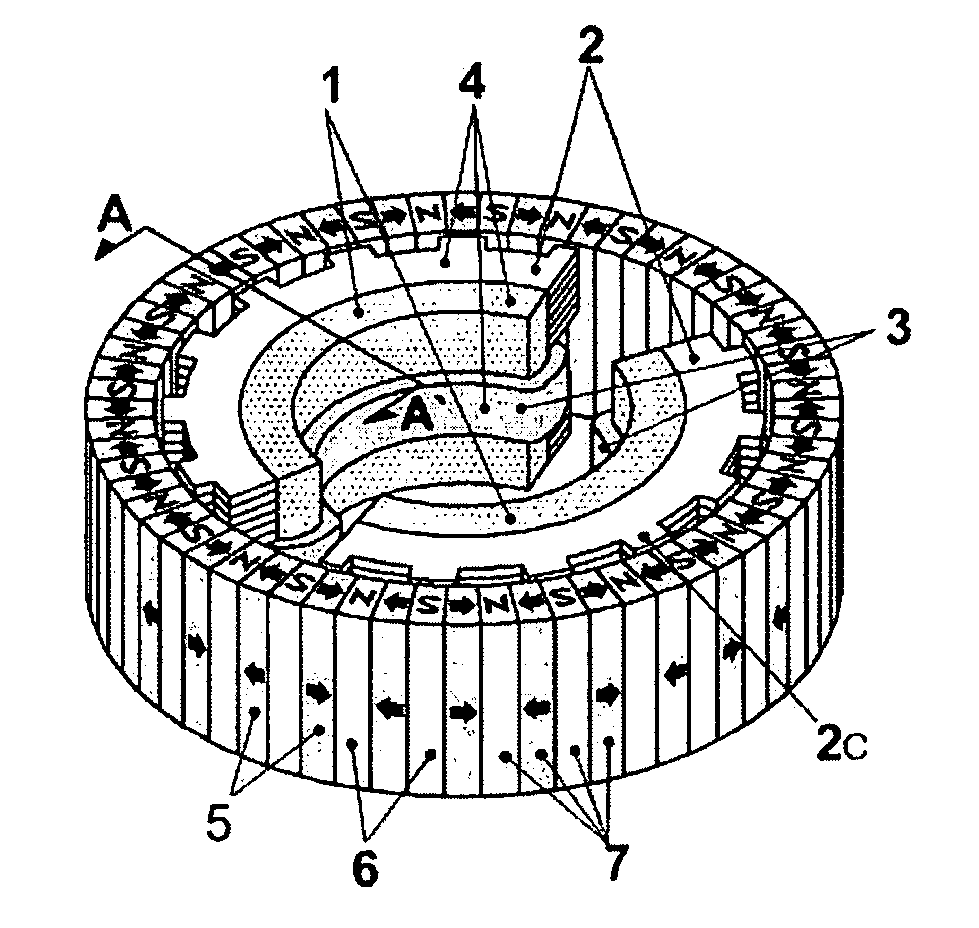
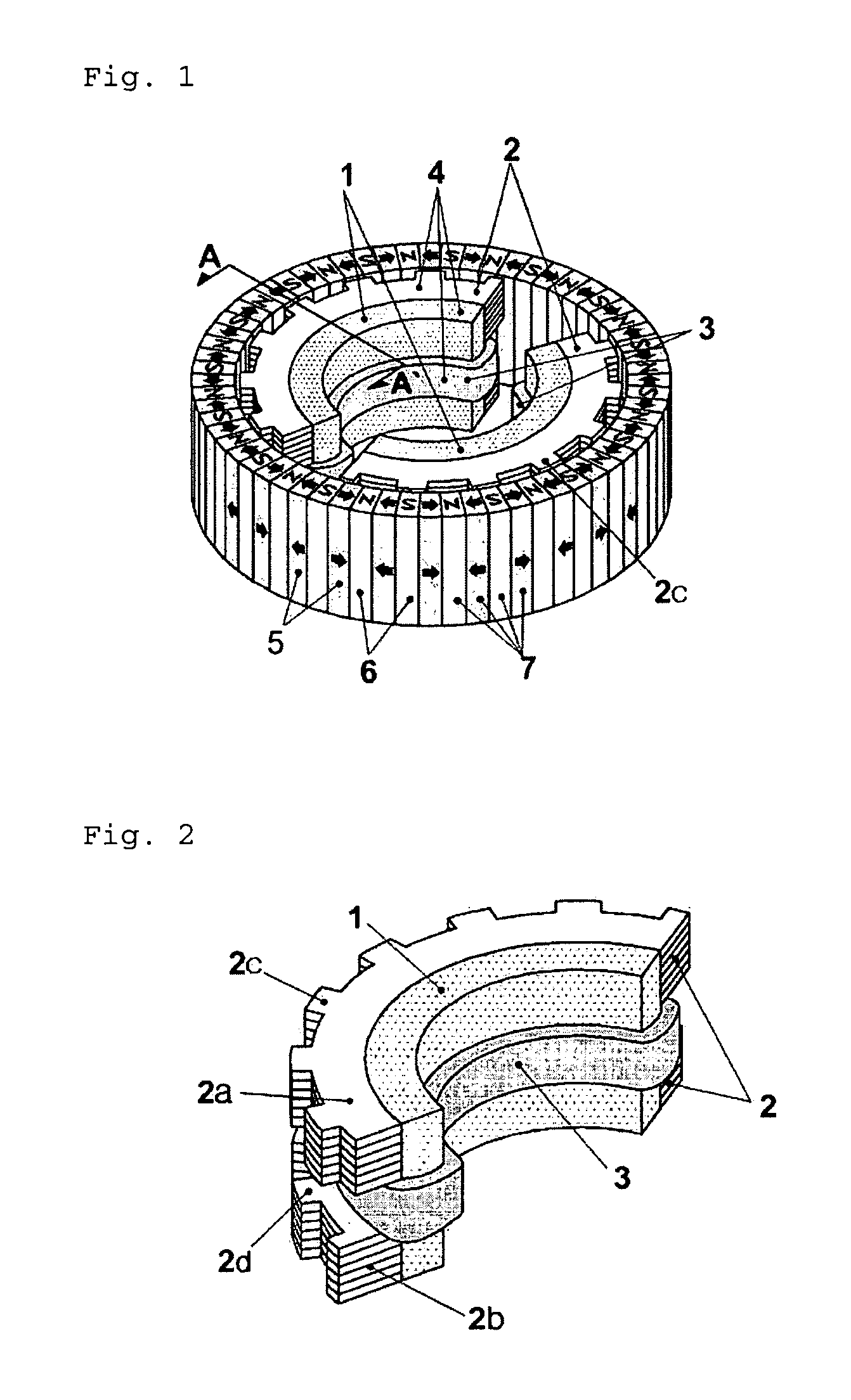
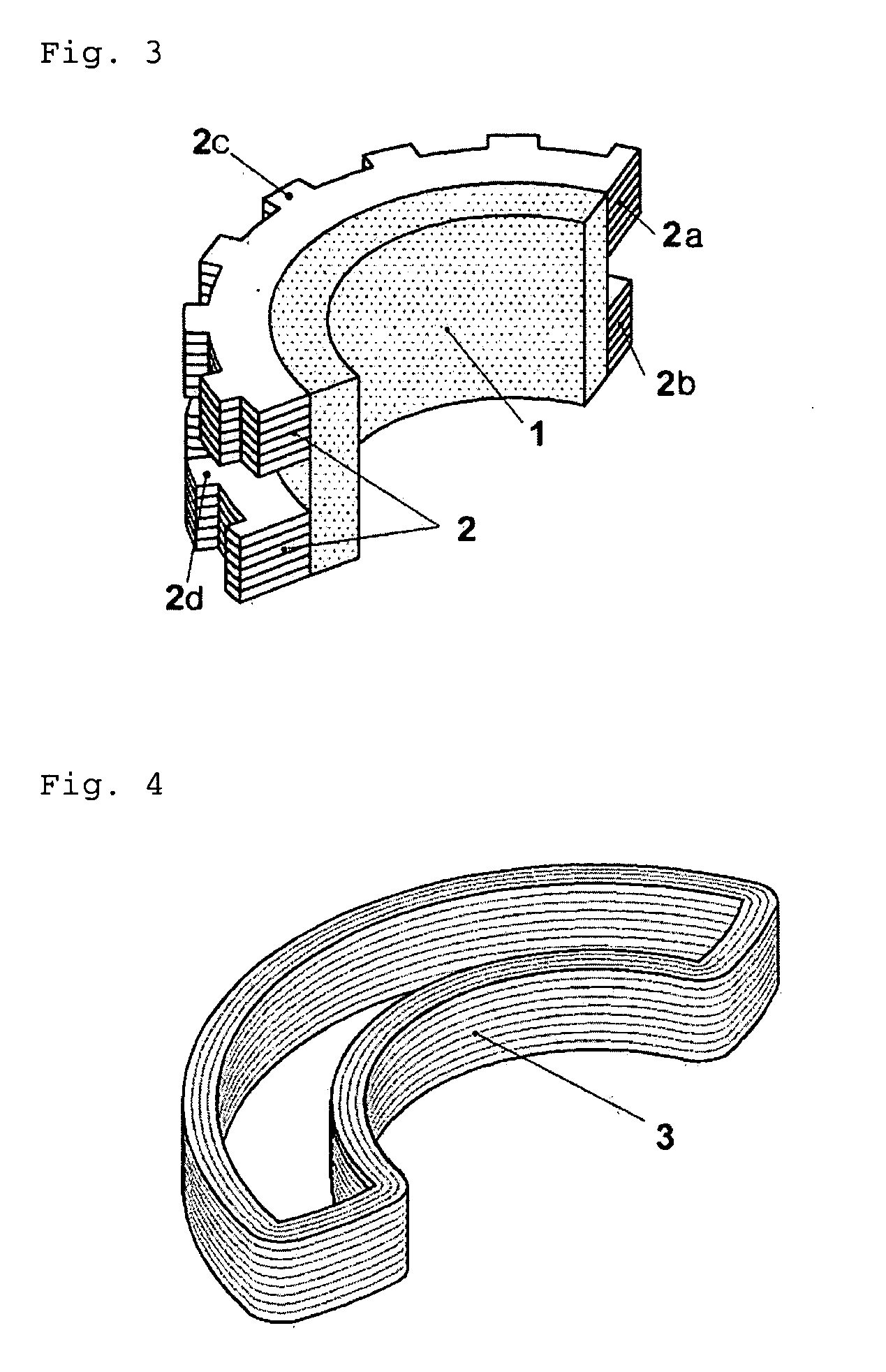
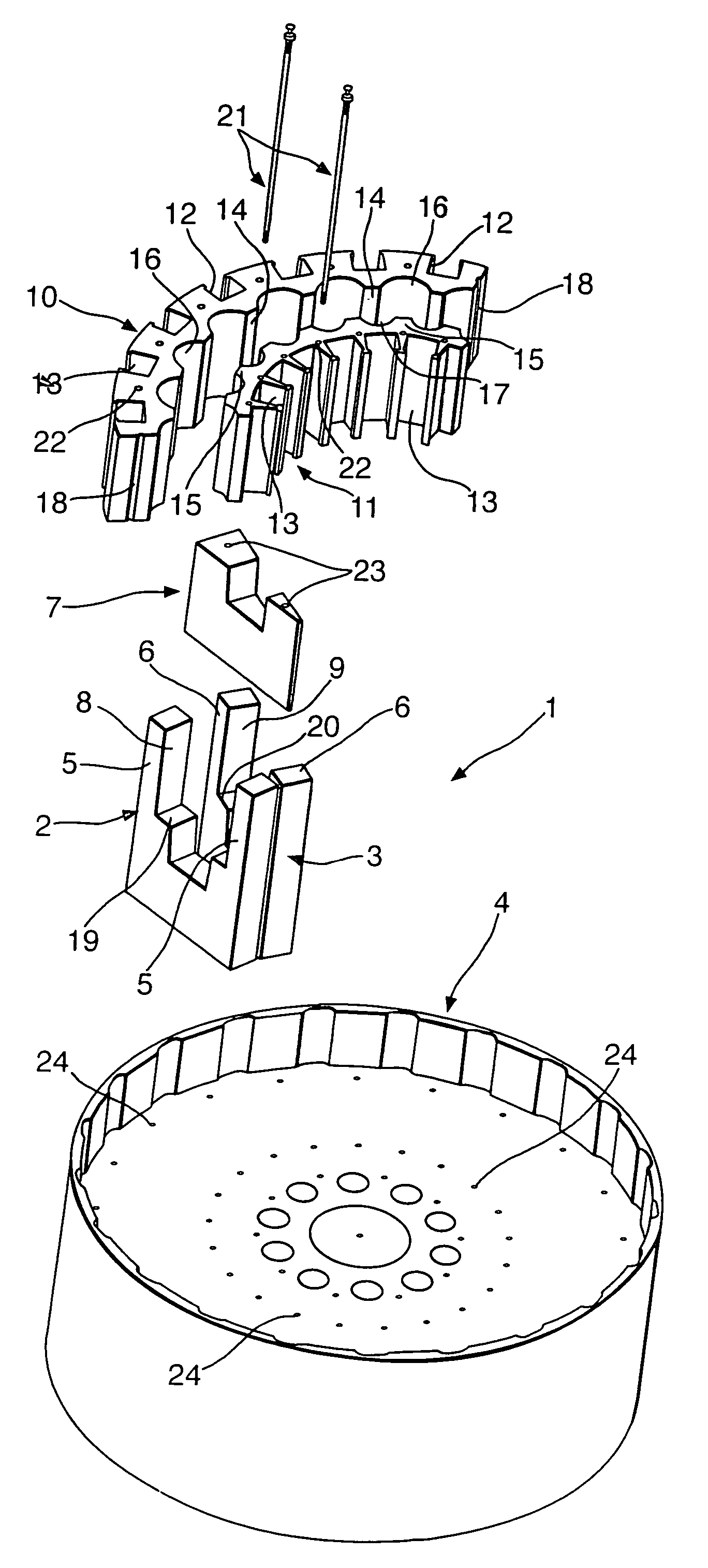
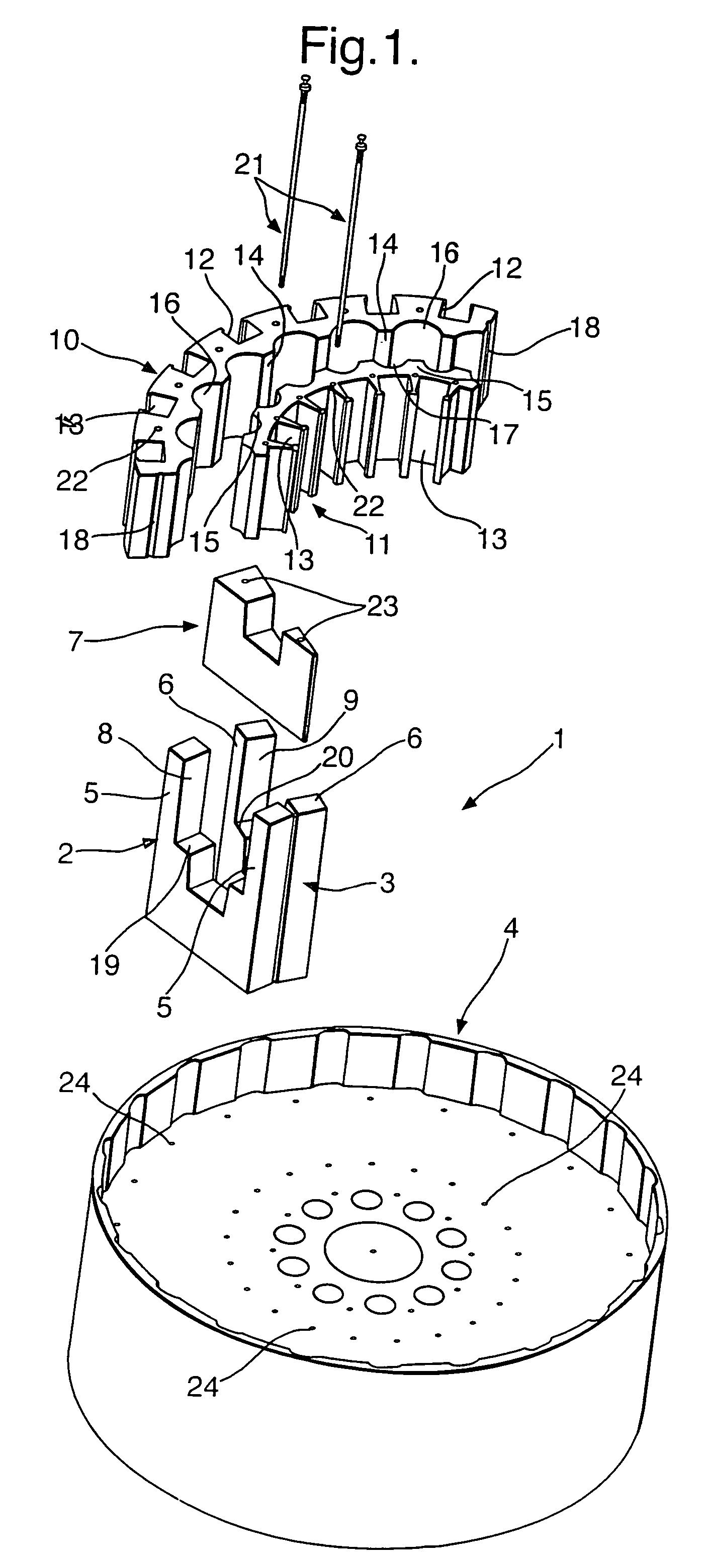
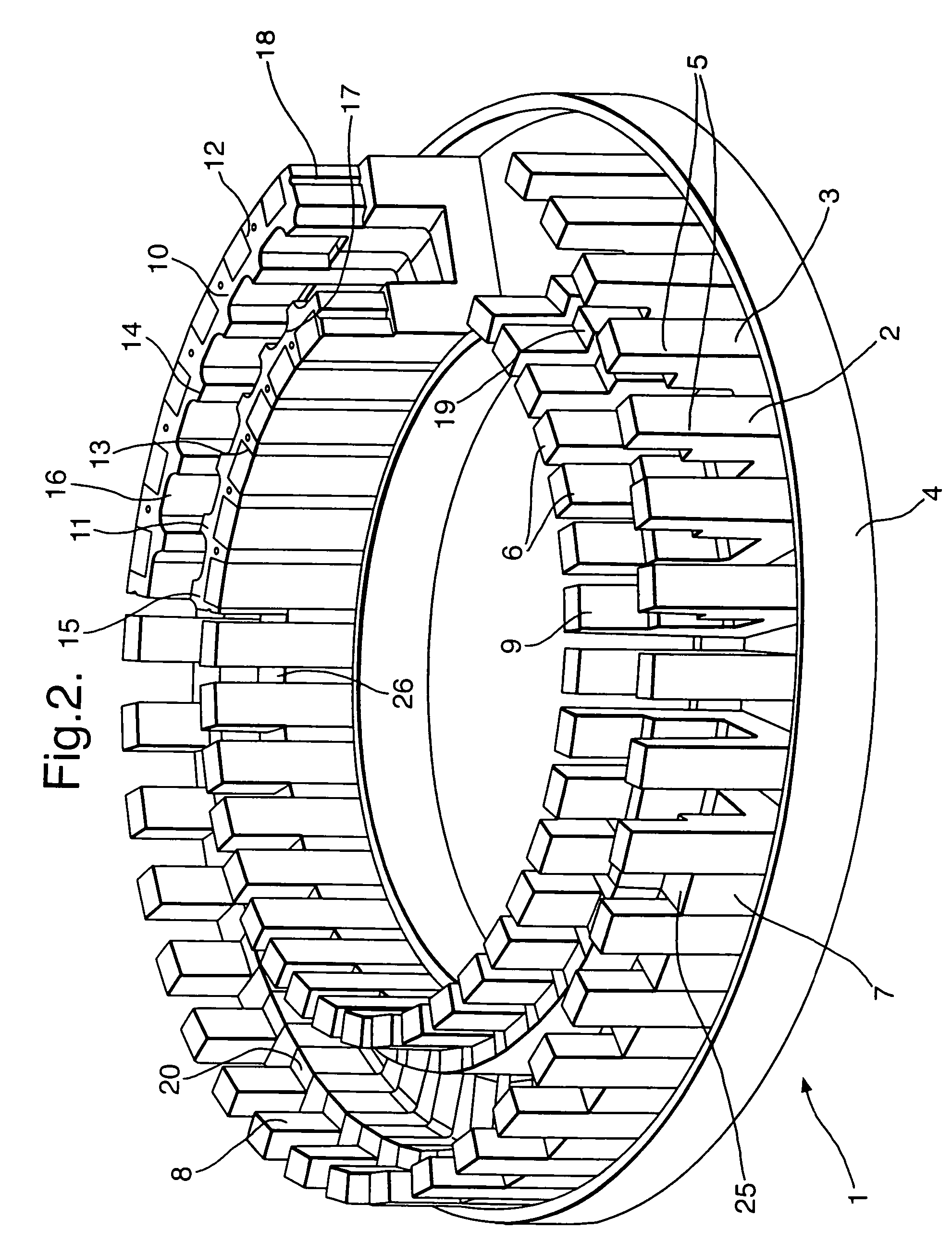
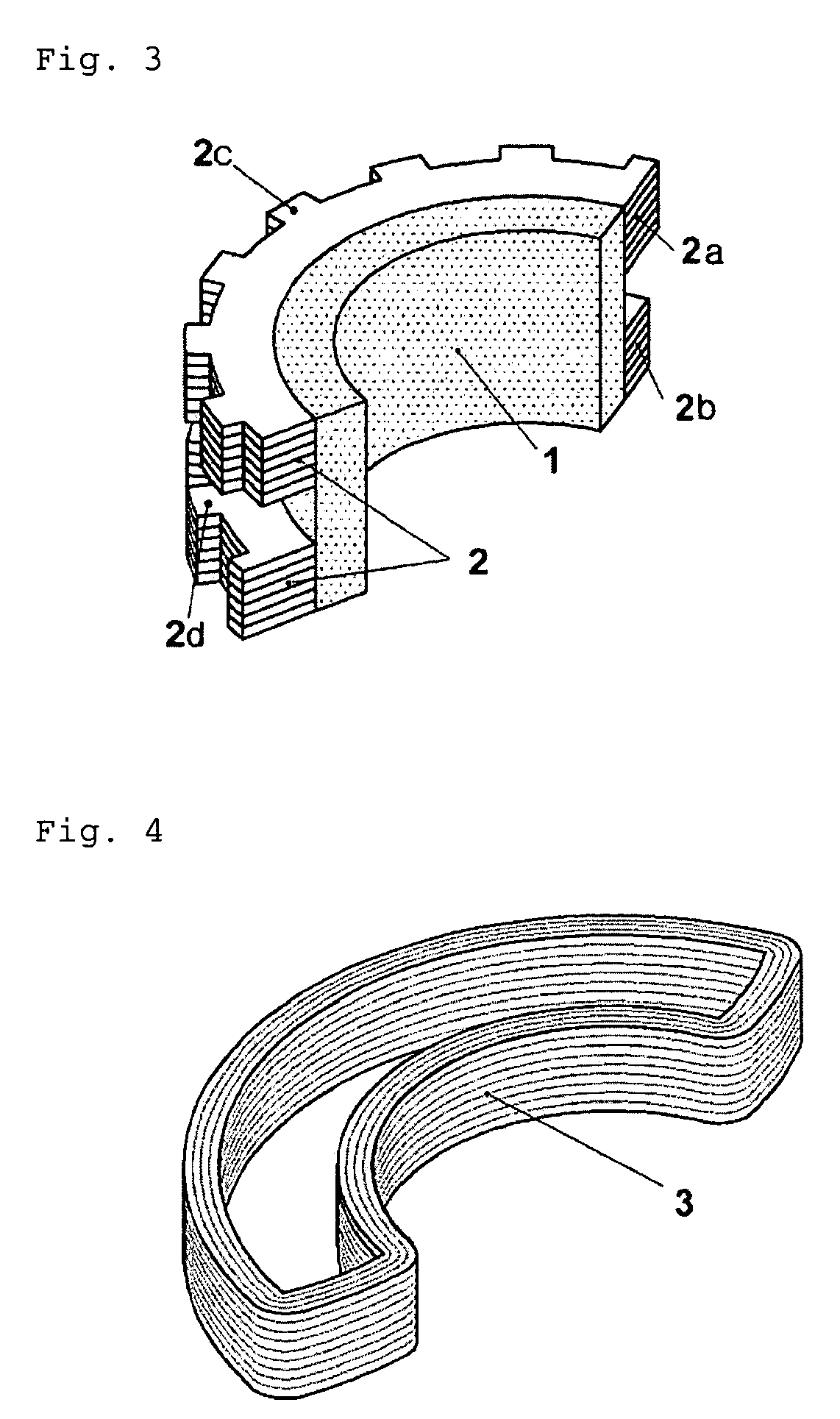
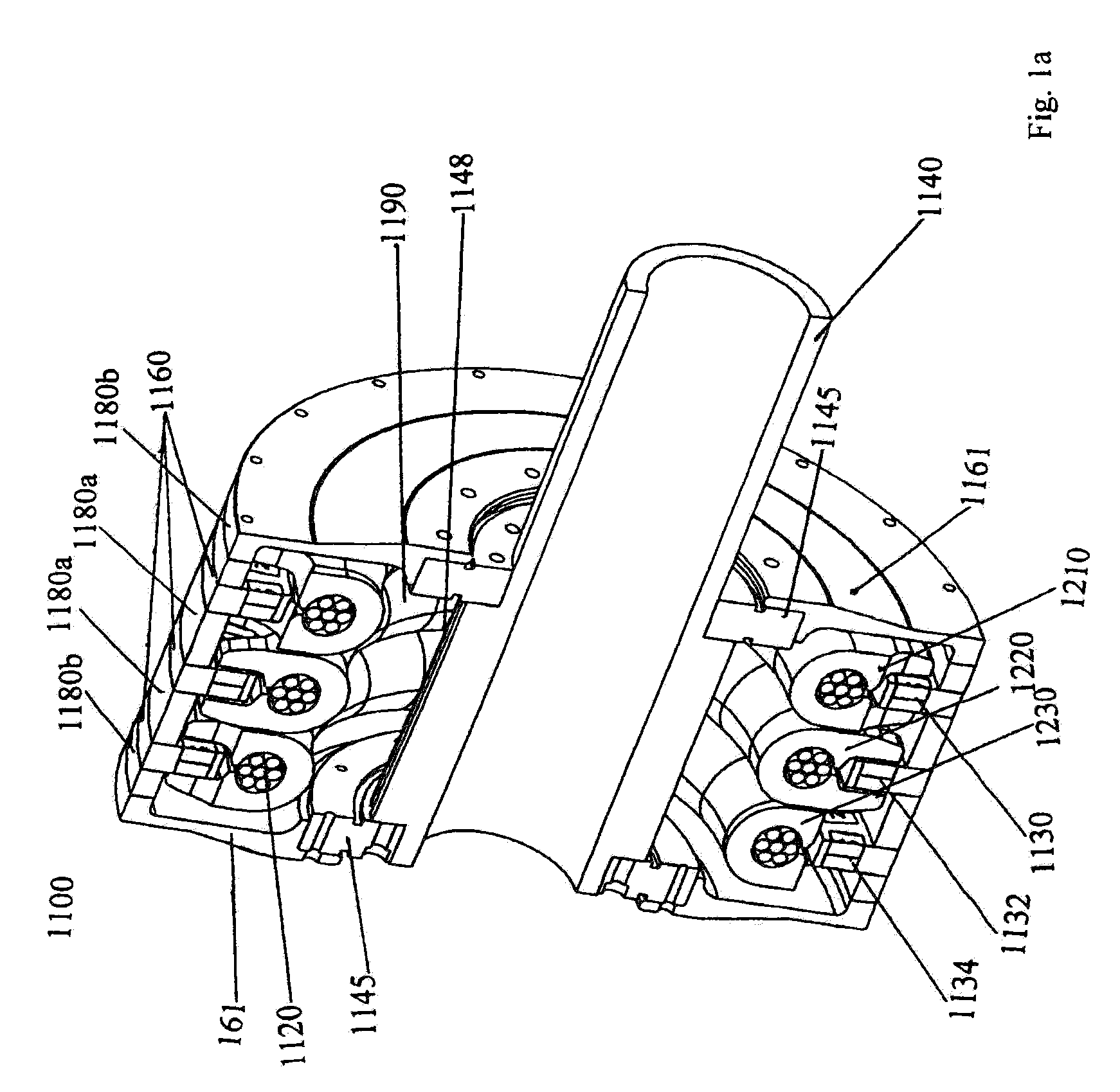
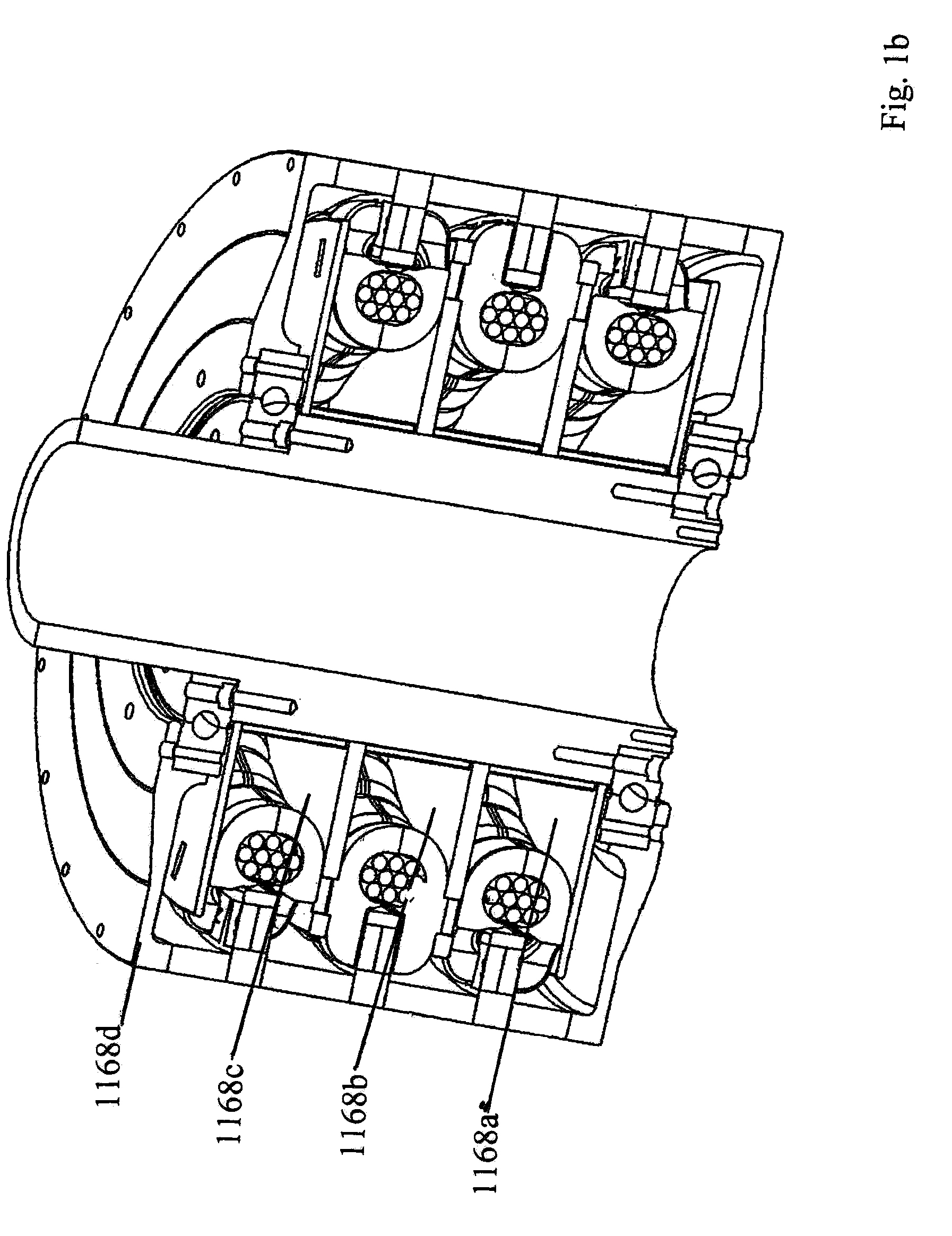
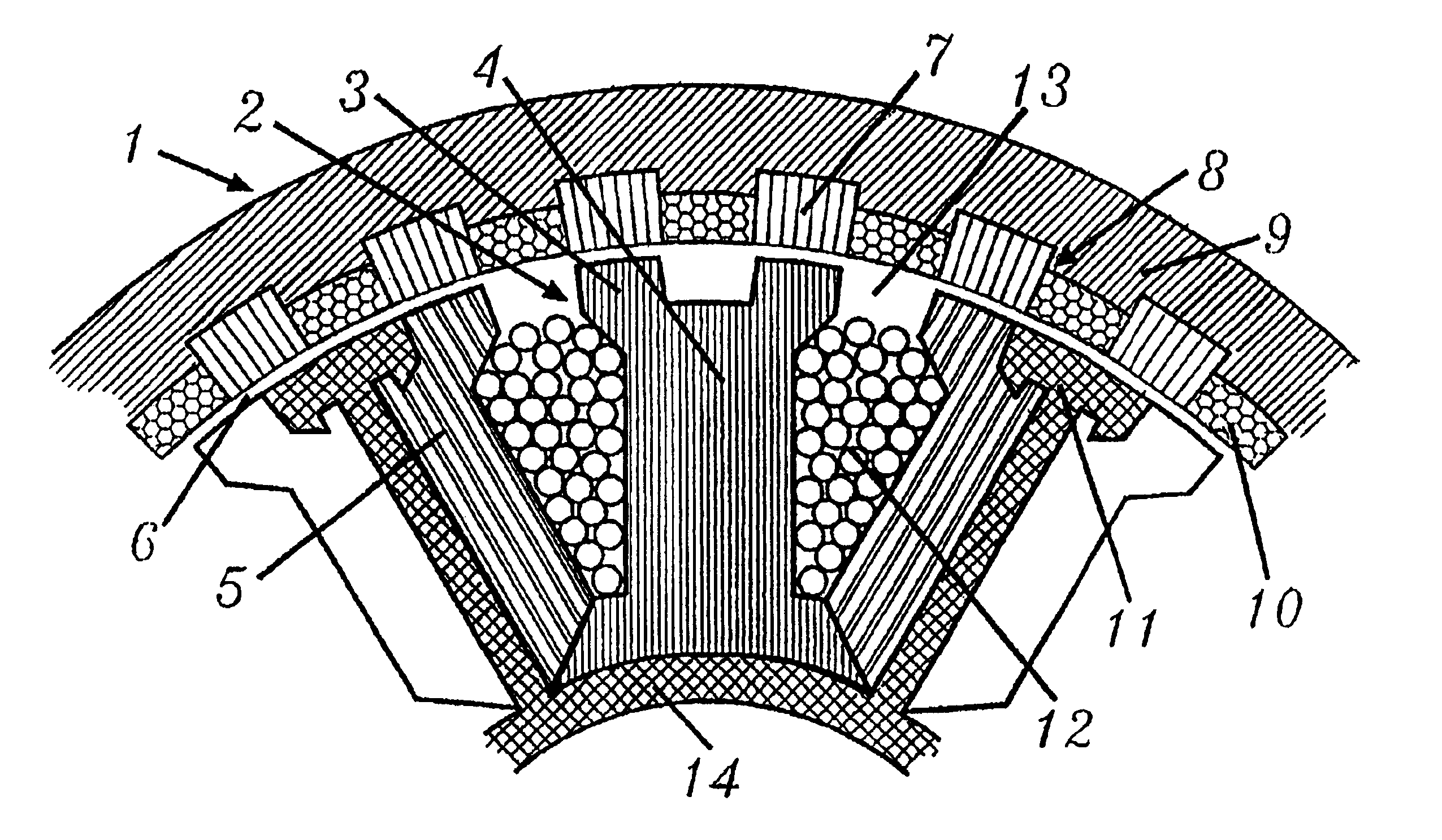
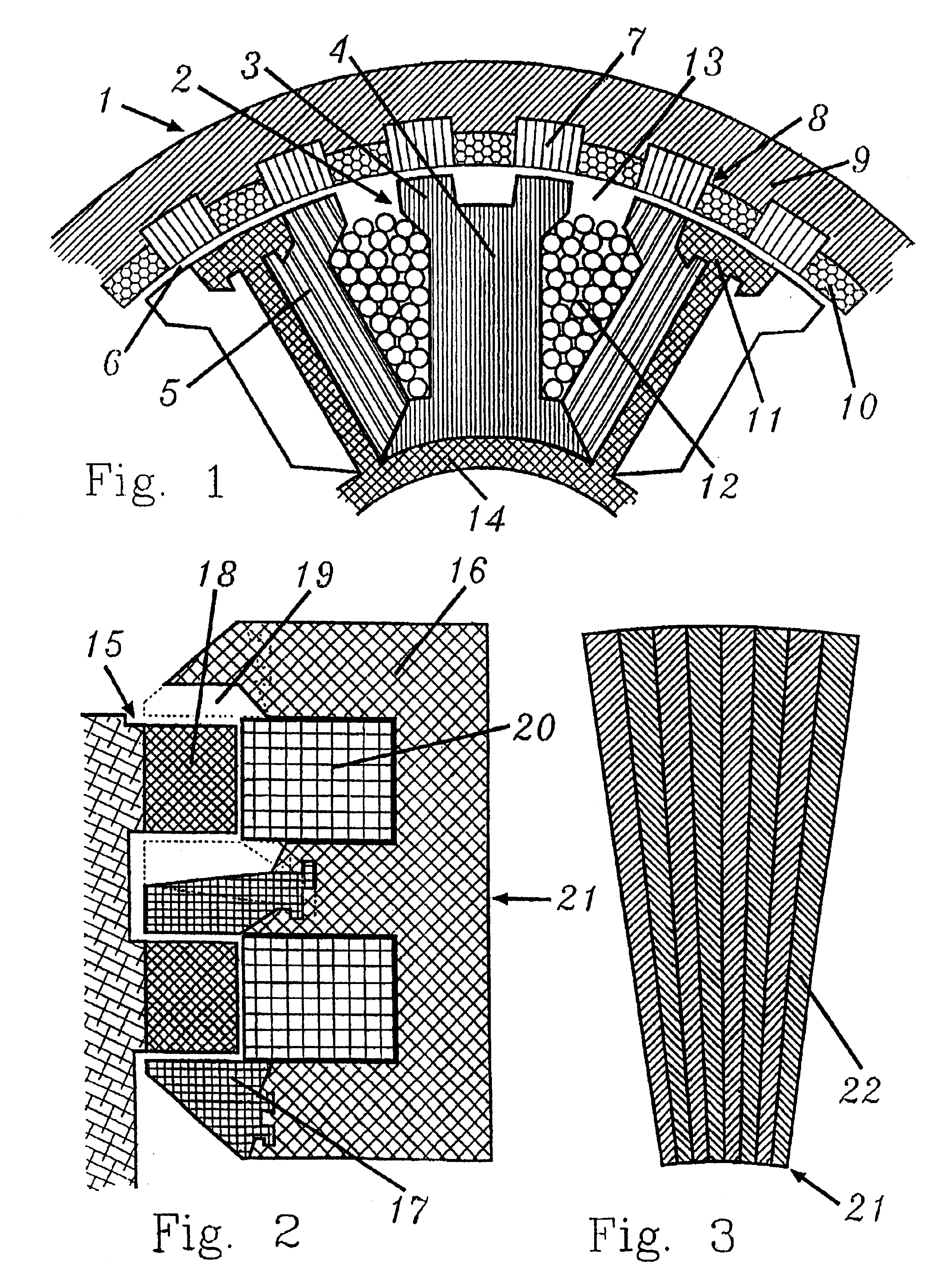
Inner rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor
ActiveUS20080211326A1Improve efficiencyIncrease output powerMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxConductor Coil
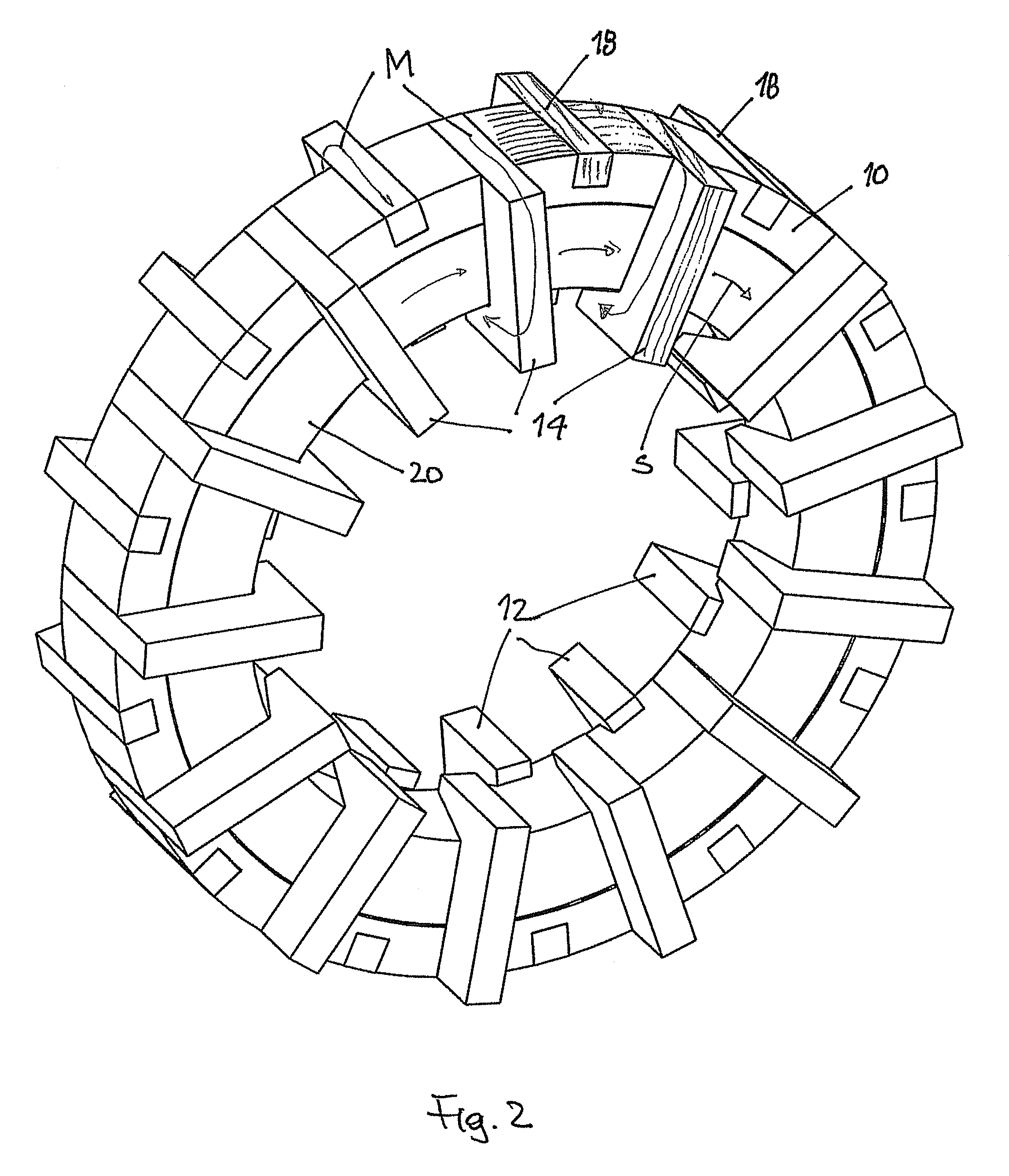
Disclosed herein is an inner rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor, in which a laminated structure in an axial direction or in a radial shape is applied to a stator iron core so as to employ a small amount of permanent magnets compared with a conventional outer rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor, thus providing high output power, increasing the efficiency of power generation, and reducing noise and vibration.For this, the present invention provides an inner rotor type permanent magnetic excited transverse flux motor comprising: a stator including a stator powdered iron core press-molded using a mold, a stator laminated iron core laminated on upper and lower layer portions of the circumference of the stator powdered iron core at regular intervals, and a stator winding which winds the segmented stator powdered iron core in which a current flows is wound between the intervals; and a rotor in which a rotor permanent magnet and a rotor powdered iron core are arranged alternately to face each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Polyphase transverse flux motor
InactiveUS6492758B1Synchronous motorsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet rotorTransverse flux
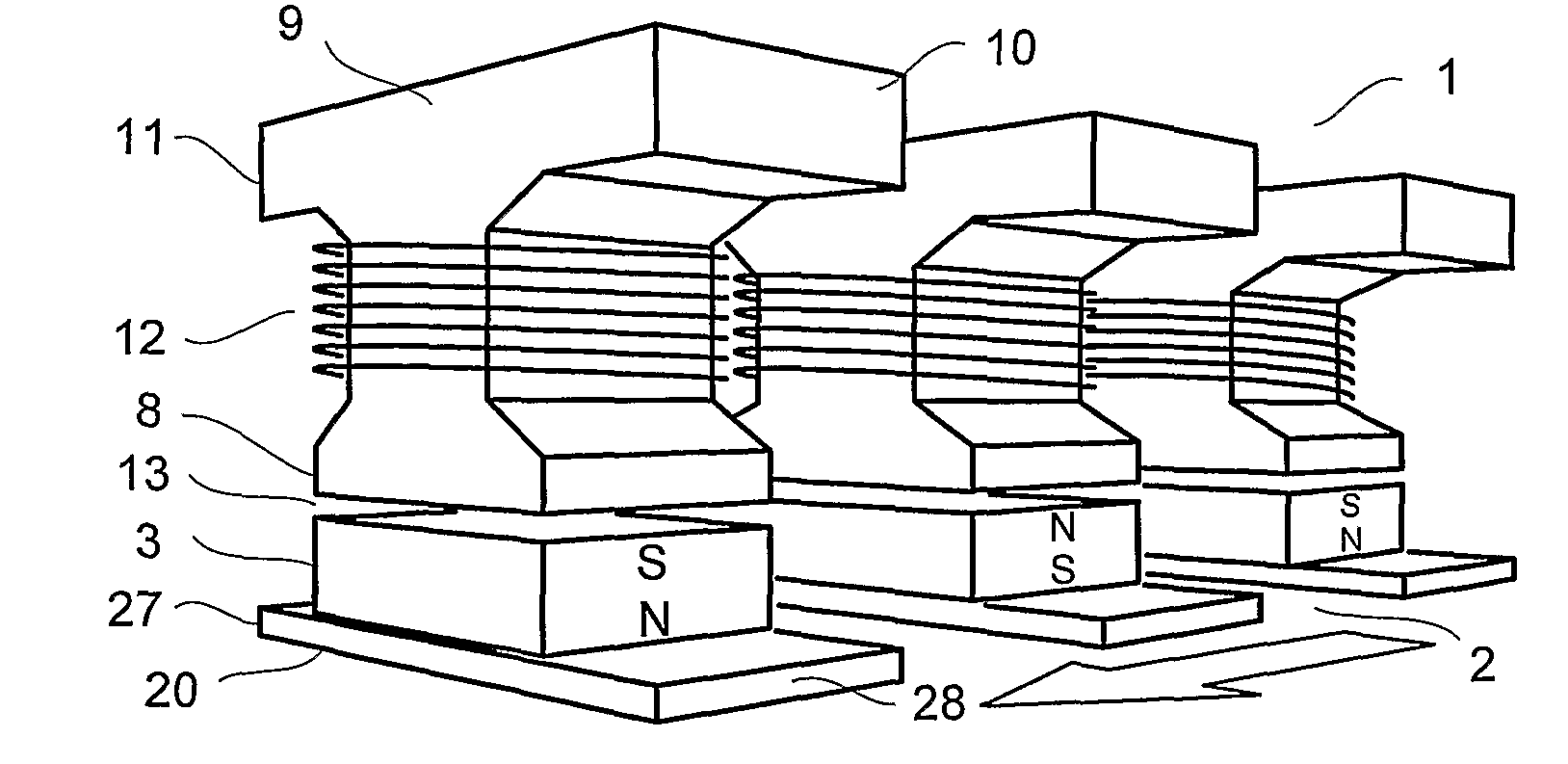
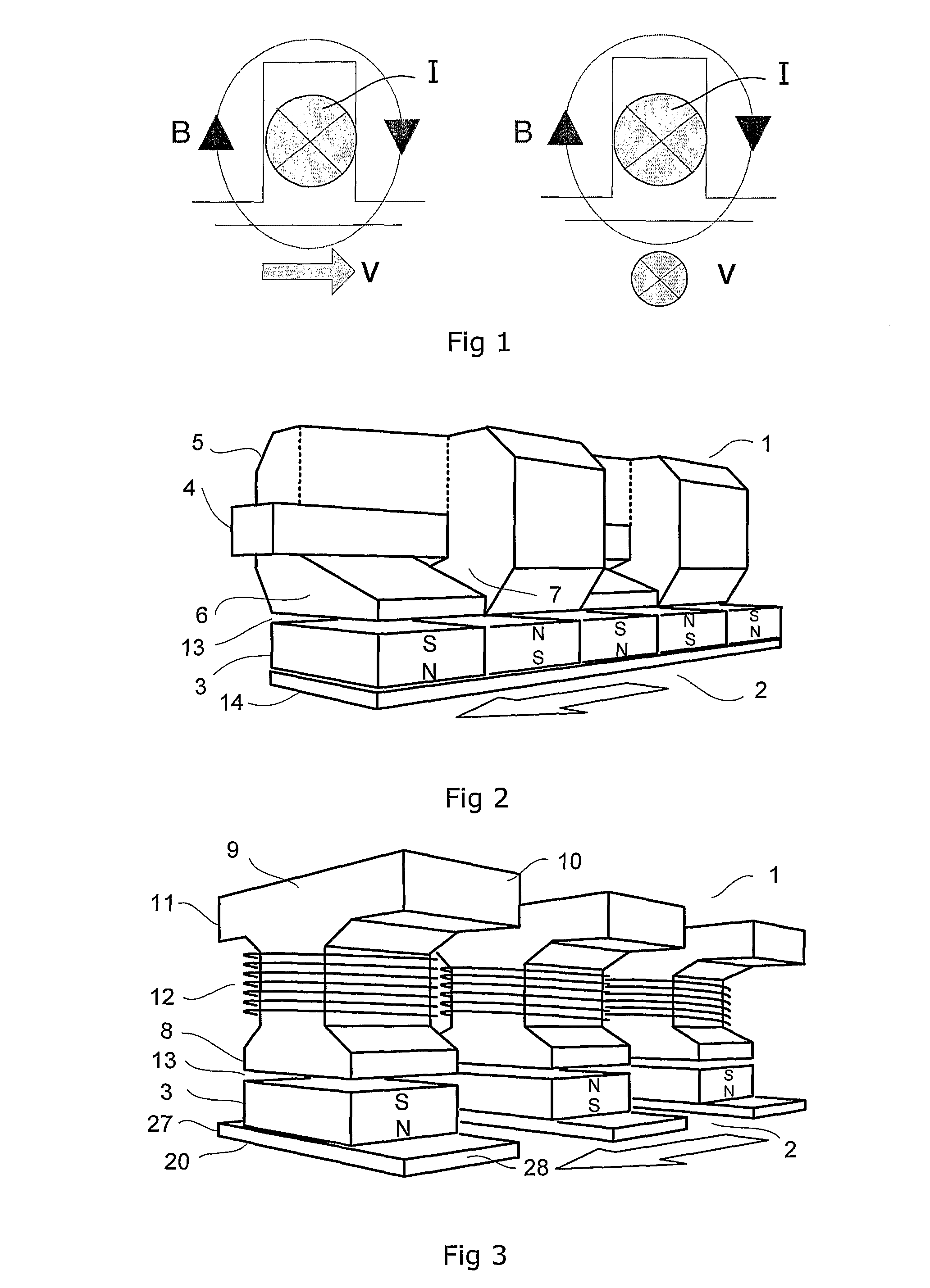
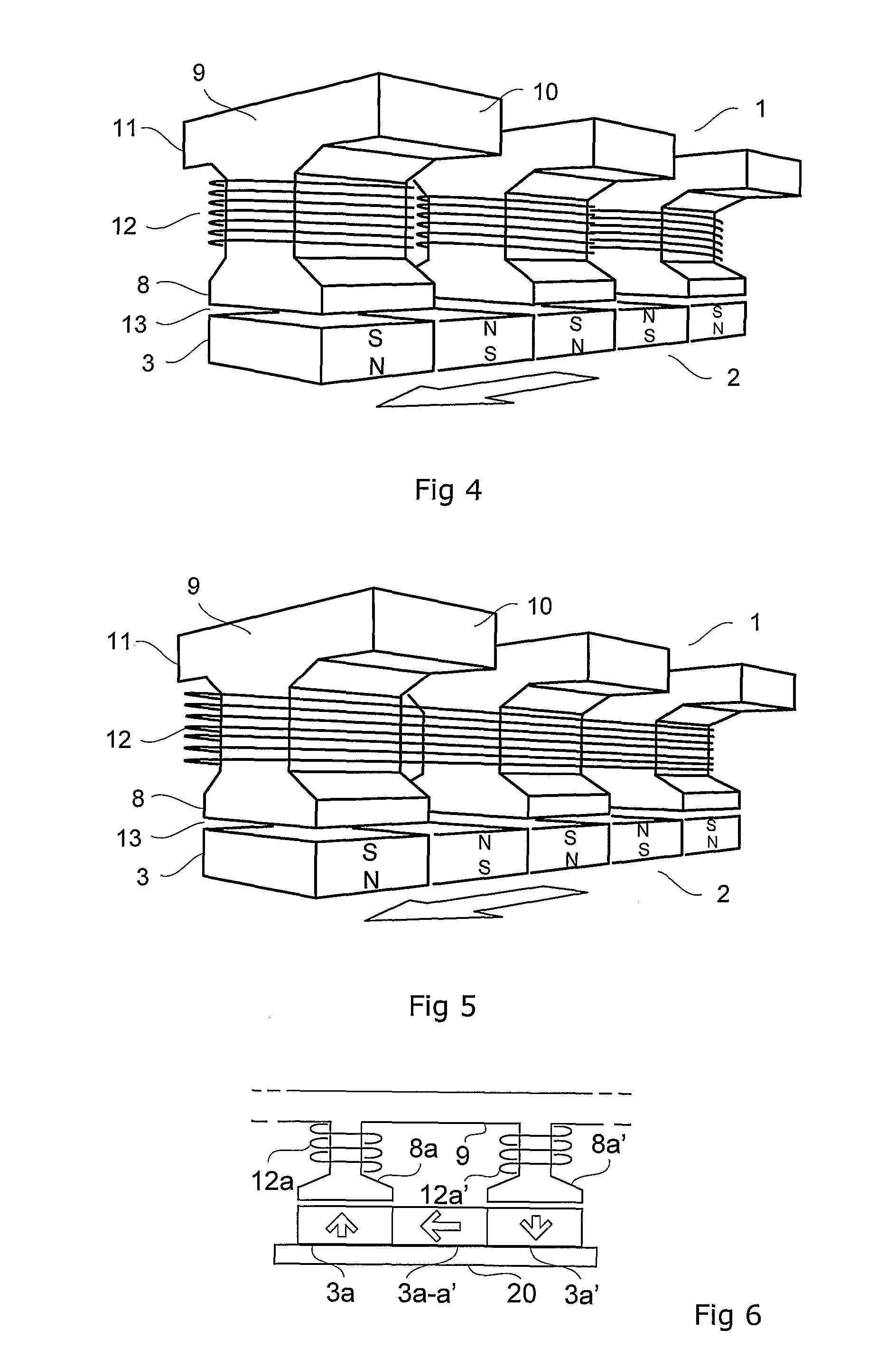
A tranverse flux motor having multiple stator phase windings which are electronically commutated to produce a rotating flux to drive a permanent magnet rotor located externally of the stator. The stator is formed by two complementary facing pieces each carrying half the stator poles, the latter preferably being of claw pole configuration. The stator windings are sandwiched between the stator pieces and wound about cores which magnetically couple the stator pieces. Preferably the number of motor phases (P) is selected from the series 2, 3, . . . , N, the number of windings per phase (W) is selected from the series 1, 2, . . . , M, the number of poles per winding (PW) is selected from the series 2, 4, . . . , L, and the number of stator poles (SP) is equal to the product P*WP*PW and the number of rotor poles is SP±W.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
High-Efficiency Wheel-Motor Utilizing Molded Magnetic Flux Channels with Transverse-Flux Stator
InactiveUS20090322165A1Reducing hysteresis lossIncrease torqueMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor control for very low speedsTransverse fluxEngineering
A motor including an outside rotor having a rotor disc with plural magnets alternating polarities flush mounted in the disc, an inside stator assembly with a ring of pole pieces forming a channel to house a transversely wound stator windings, and a controller coupled with feedback electronics for monitoring a timing, speed and direction and coupling a signal to a processing unit for adjusting the drive electronics driving the phase windings. A u-shaped gap above the channel to receive the rotor disc and focus the captured magnetic flux in the pole pieces toward the magnets. In an embodiment the molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces of the inside stator are sets of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces, each set forming a channel and corresponding to one phase of the motor; and a section of each one of the transverse windings passing through one channel, the remaining section folding back outside the set in close proximity to the outer base of the set of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces.
Owner:RITTENHOUSE NORMAN P
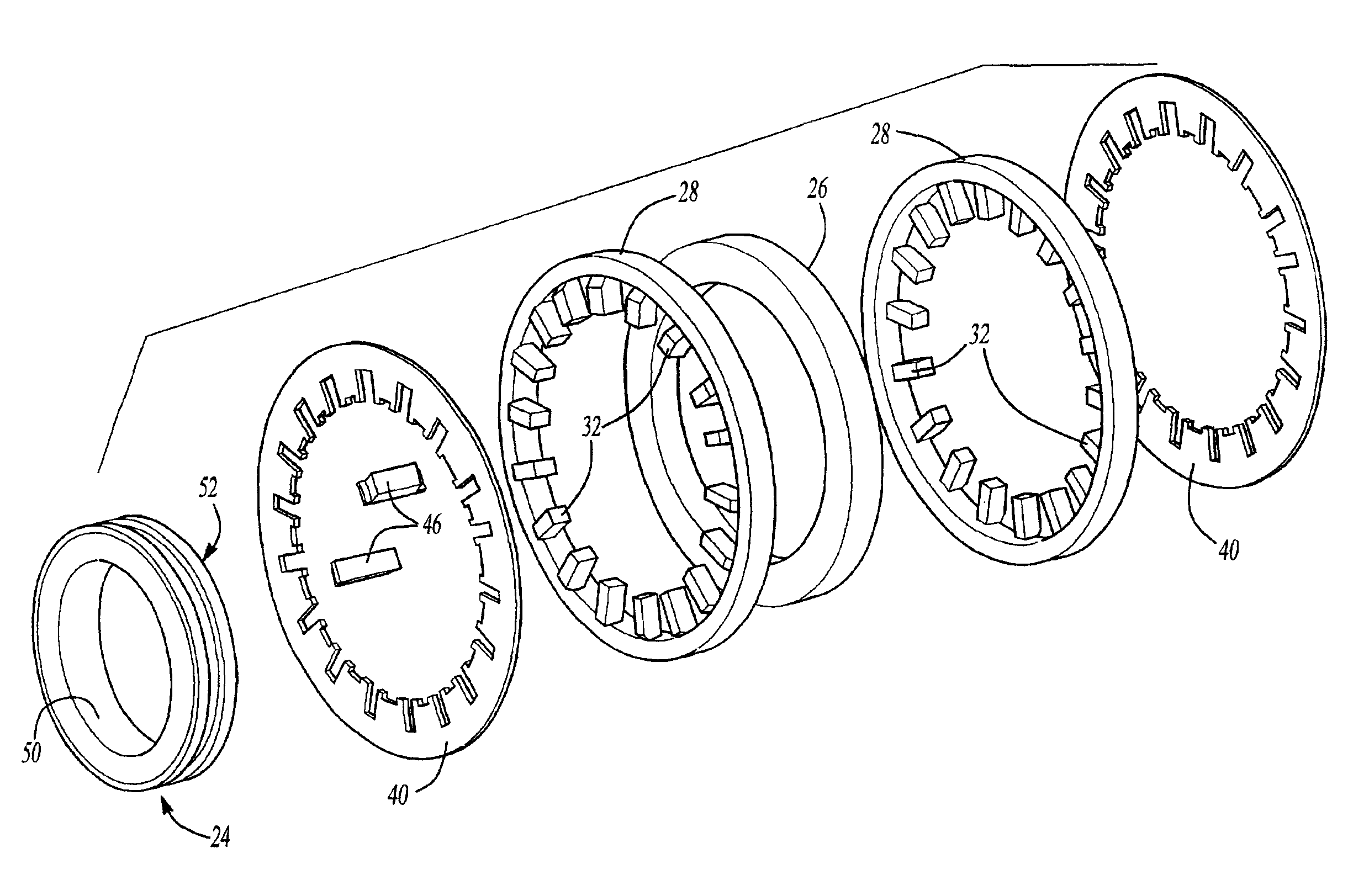
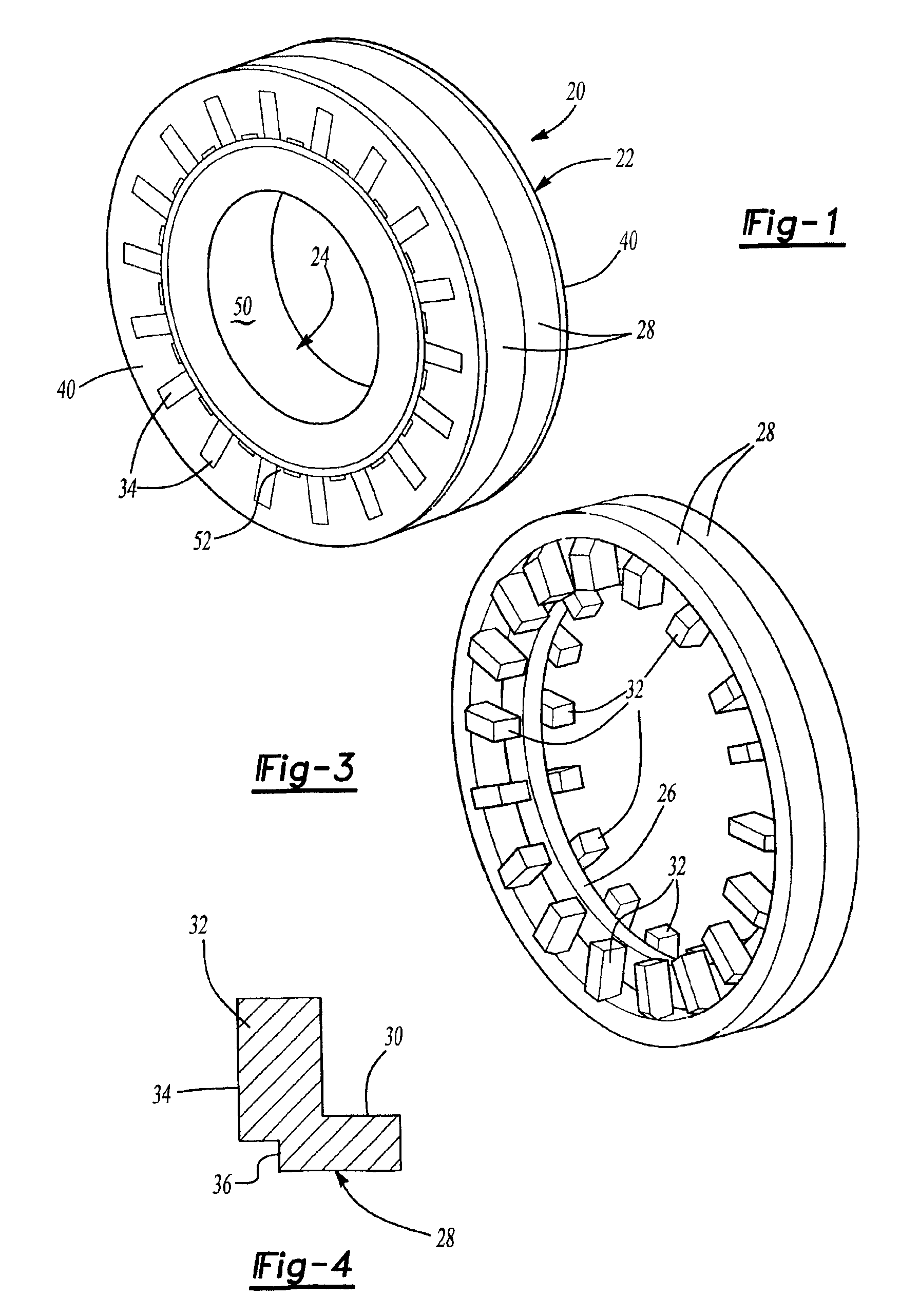
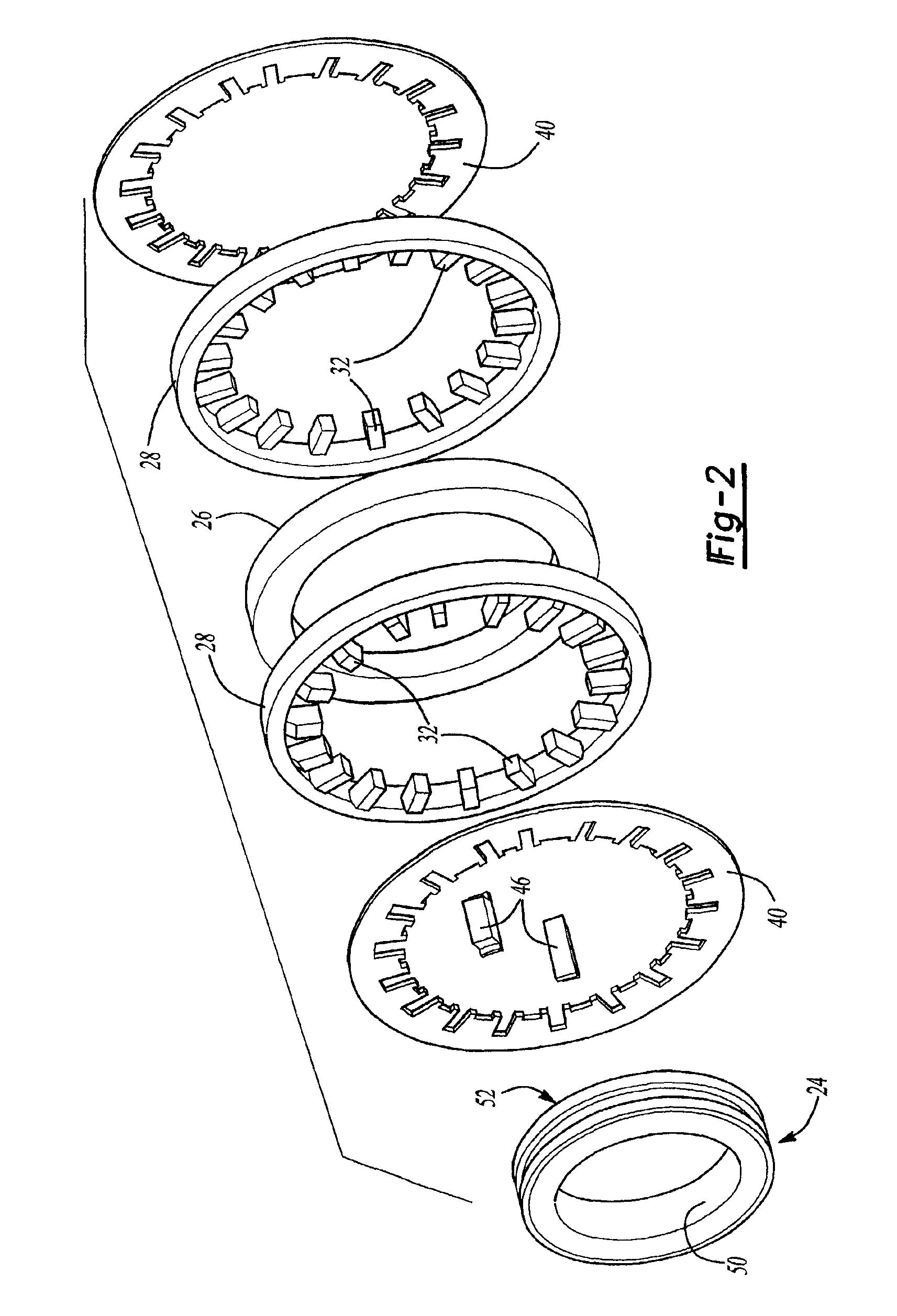
Modular transverse flux motor with integrated brake
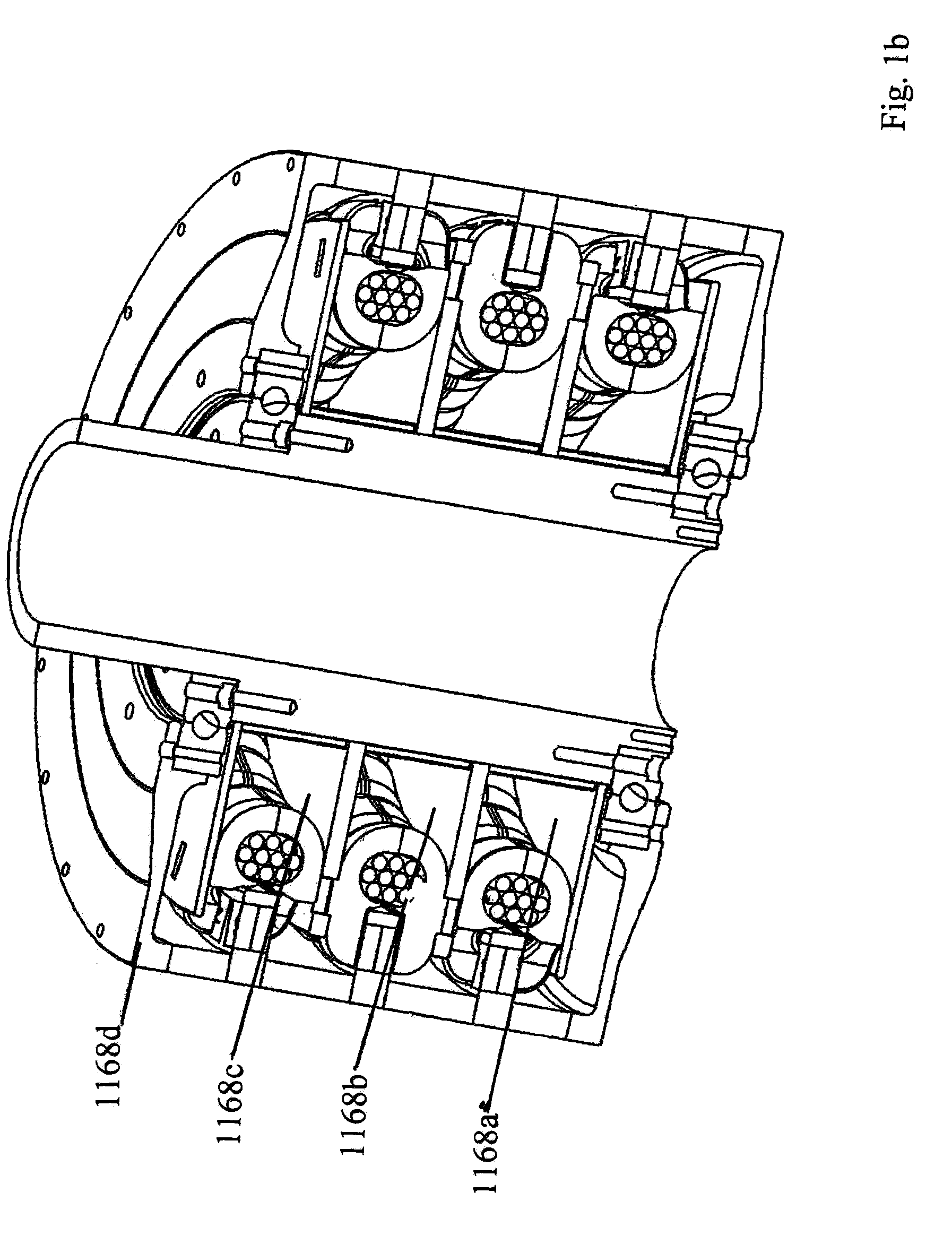
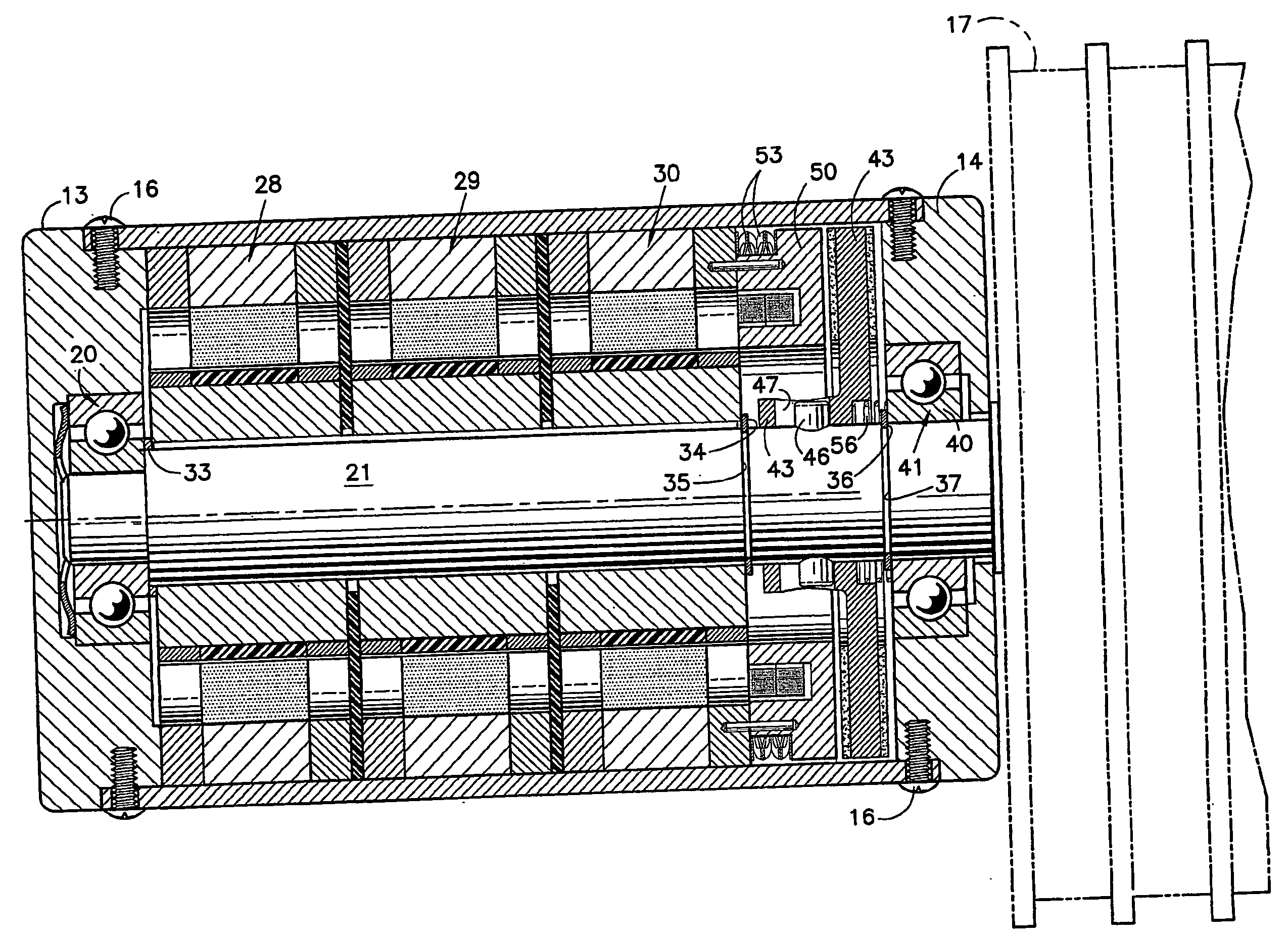
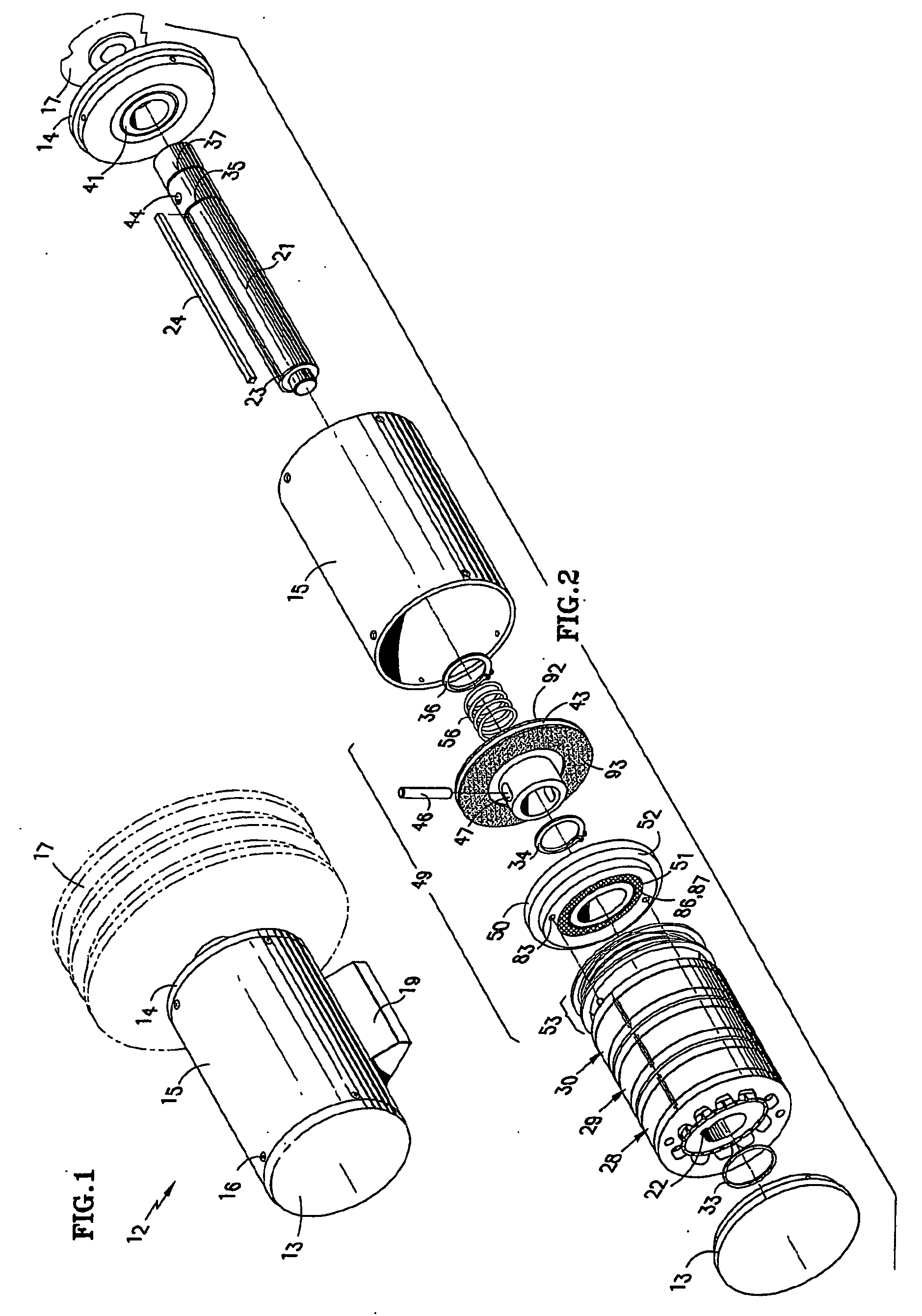
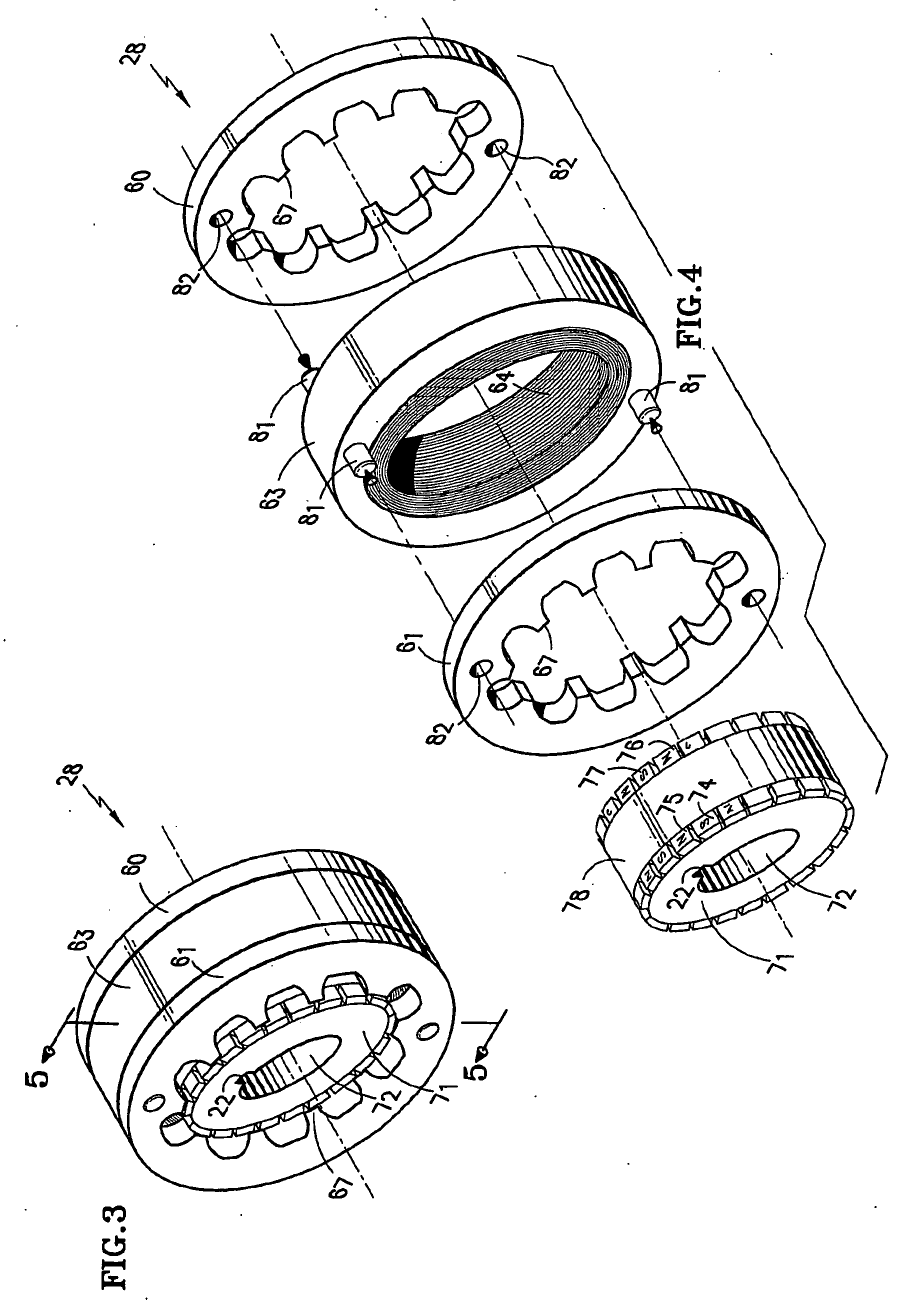
InactiveUS20060192453A1Increased torque densityImprove efficiencySynchronous generatorsDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesTransverse fluxMotor end plates
An elevator machine (12) has a plurality of identical transverse flux rotor / stator modules (28-30) of a generally cylindrical configuration arranged contiguously on a common shaft (21) to provide torque to the shaft equal to the torque capability of the modules times the number of modules. A disc brake (49) is integrated with the motor; a two-sided brake disc (49) has friction pads (92, 93) on both sides, braking force being applied to motor end plate (14) and through the brake disc to a stator (60) of one phase (30) of the motor. A process (113) forms variously-sized motors from identically sized modular components, in various configurations (12, 100, 110).
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Fabricated components of transverse flux electric motors
InactiveUS6952068B2Improve performanceRaise transfer toSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxEngineering
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Transverse flux electrical machine with toothed rotor
InactiveUS6949855B2Easy to produceEasy to insertMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsTransverse fluxElectrical conductor
The invention concerns a transverse flux electrical machine operating with alternating current, having a first element having an alternate arrangement of excitation cores and of flux return cores and a winding of electrical conductors, the winding of electrical conductors being wound as a toroid, inside all said excitation cores; a second element having an exciter section comprising two toothed magnetic structures, each toothed magnetic structure comprising a number of slots equal in number to the total number of excitation cores and of flux return cores, the corresponding slots of each magnetic structure being toothed by being aligned; a magnetized sub-assembly is inserted inside each indentation so that an alternating arrangement of magnetic north poles and south poles is produced in each of these magnetic toothed structures of said exciter section; an air gap between the first element and the second element; at least one of the first element and of the second element being capable of rotating around a rotation axis that is common to the first element and to the second element.
Owner:EOCYCLE TECH
Unipolar transverse flux machine
InactiveUS6882066B2Flat designMagnetic circuit stationary partsMaster clocksTransverse fluxMagnetic poles
In a unipolar transverse flux machine, in particular a motor, having a rotor, which is comprised of two coaxial, ferromagnetic, toothed rotor rings, and a permanent magnet ring, which is magnetized in an axially unipolar fashion and is clamped axially between these rotor rings, and having a stator, which is concentric to the rotor shaft and has U-shaped stator yokes that represent the magnet poles, yoke elements, and a stator winding, in order to achieve an extremely flat design and to assure a definite start in a particular direction, the stator winding is embodied with two coils, whose one coil side extends respectively over a group of stator yokes and yoke elements arranged in succession in the circumference direction, along the side of the yoke elements remote from the rotor shaft, between the yoke legs, where the group spanned by the coil side of the one coil is disposed spatially offset on the stator circumference and electrically offset by 90° in relation to the group spanned by the coil side of the other coil.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Transverse flux switched reluctance motor and control methods
InactiveUS20060091755A1Eliminate end turn lossHigh densitySynchronous generatorsElectronic commutation motor controlTransverse fluxElectric machine
A variable reluctance motor and methods for control. The motor may include N motor phases, where N equals three or more. Each motor phase may include a coil to generate a magnetic flux, a stator and a rotor. A flux-carrying element for the rotor and / or stator may be made entirely of SMC. The stators and rotors of the N motor phases may be arranged relative to each other so that when the stator and rotor teeth of a selected phase are aligned, the stator and rotor teeth in each of the other motor phases are offset from each other, e.g., by an integer multiple of 1 / N of a pitch of the stator or rotor teeth. A fill factor of the coil relative to the space in which it is housed may be at least 60%, and up to 90% or more. The stator and rotor flux-carrying elements together may include at most three separable parts.
Owner:PRECISE AUTOMATION
Inner rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor
ActiveUS7952252B2Reducing iron lossImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesTransverse fluxPower flow
Disclosed herein is an inner rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor, in which a laminated structure in an axial direction or in a radial shape is applied to a stator iron core so as to employ a small amount of permanent magnets compared with a conventional outer rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor, thus providing high output power, increasing the efficiency of power generation, and reducing noise and vibration. For this, the present invention provides an inner rotor type permanent magnetic excited transverse flux motor comprising: a stator including a stator powdered iron core press-molded using a mold, a stator laminated iron core laminated on upper and lower layer portions of the circumference of the stator powdered iron core at regular intervals, and a stator winding which winds the segmented stator powdered iron core in which a current flows is wound between the intervals; and a rotor in which a rotor permanent magnet and a rotor powdered iron core are arranged alternately to face each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
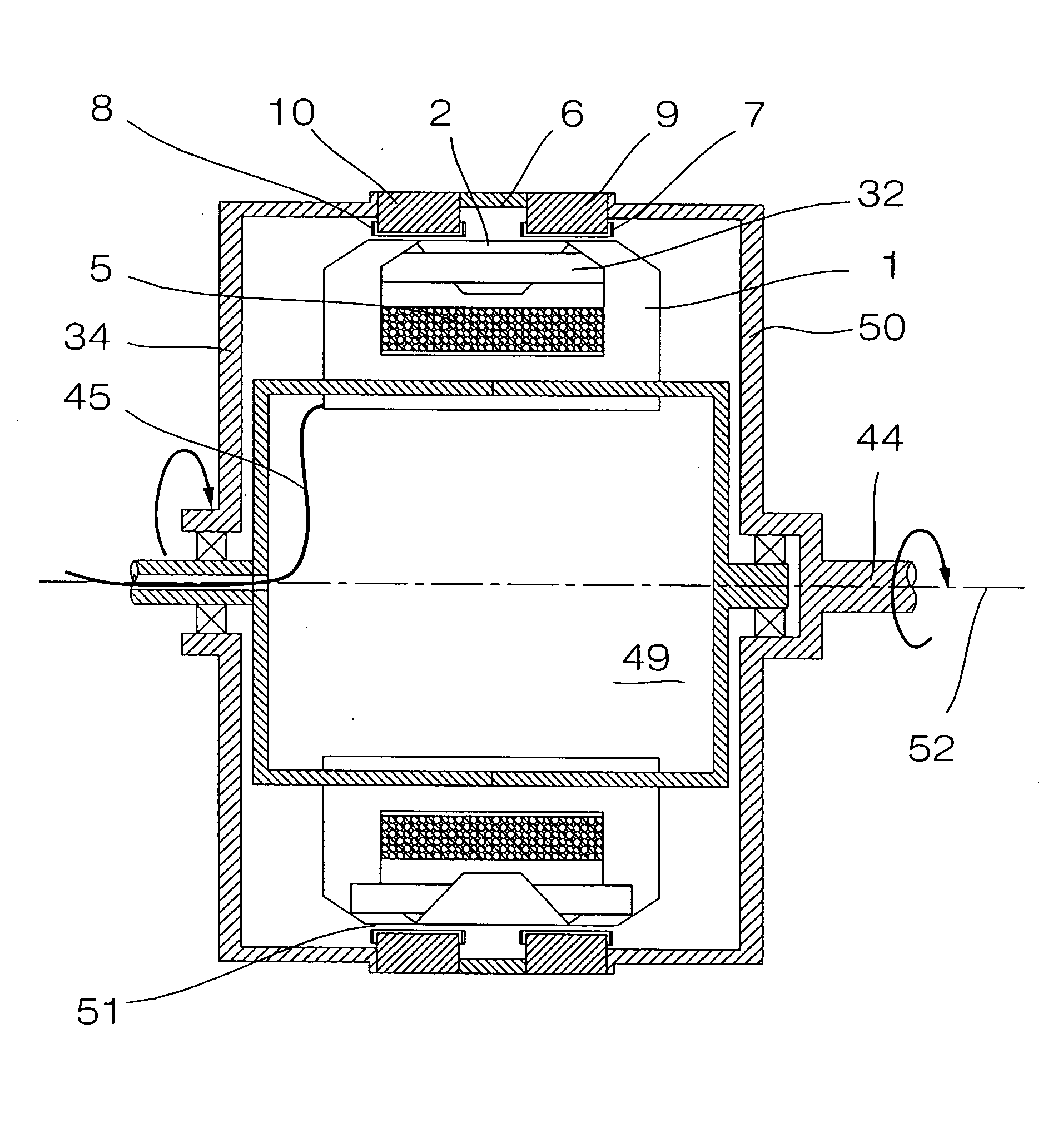
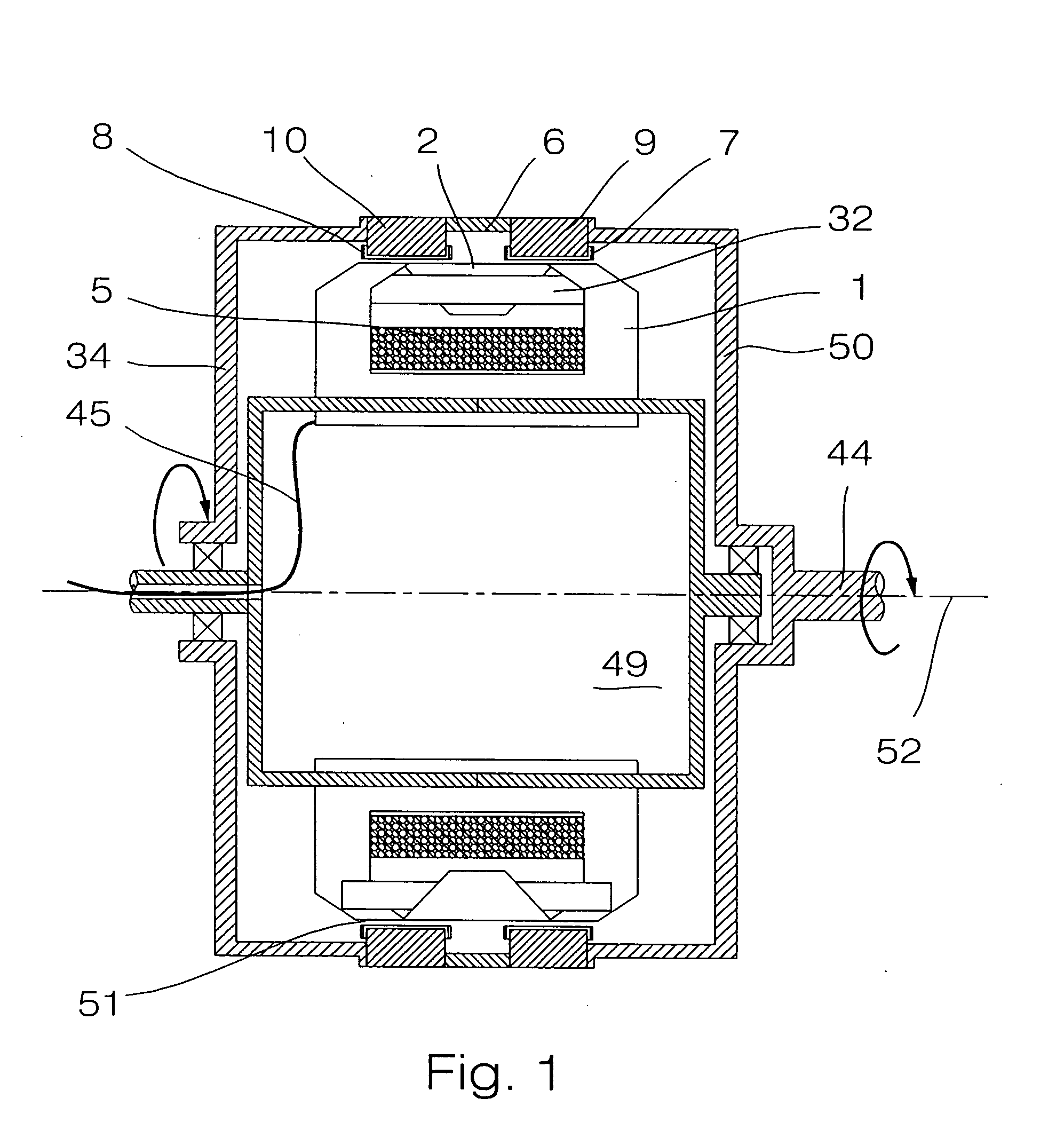
Permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor with outer rotor
ActiveUS20070152528A1Improve output power densityReduce noiseMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesTransverse fluxConductor Coil
Disclosed herein is a permanent magnet-excited transverse flux motor with an outer rotor. The permanent magnet-excited transverse flux motor comprises: a stator including a stator powdered iron core formed by an extruded molding through a mold, a pair of stator laminated iron cores stacked respectively at an upper layer portion and a lower layer portion of an outer circumference of the stator powdered iron core in such fashion as to be spaced apart from each other by a certain interval, and a stator winding interposed between the upper layer portion and the lower layer portion in such fashion as to be wound around the stator powdered iron core to form a multiple coil through which current flows; and a rotor including a plurality of rotor permanent magnets and a plurality of rotor powdered iron cores disposed on the outer circumference of the stator in such a fashion as to be are alternately arranged adjacent to one another.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
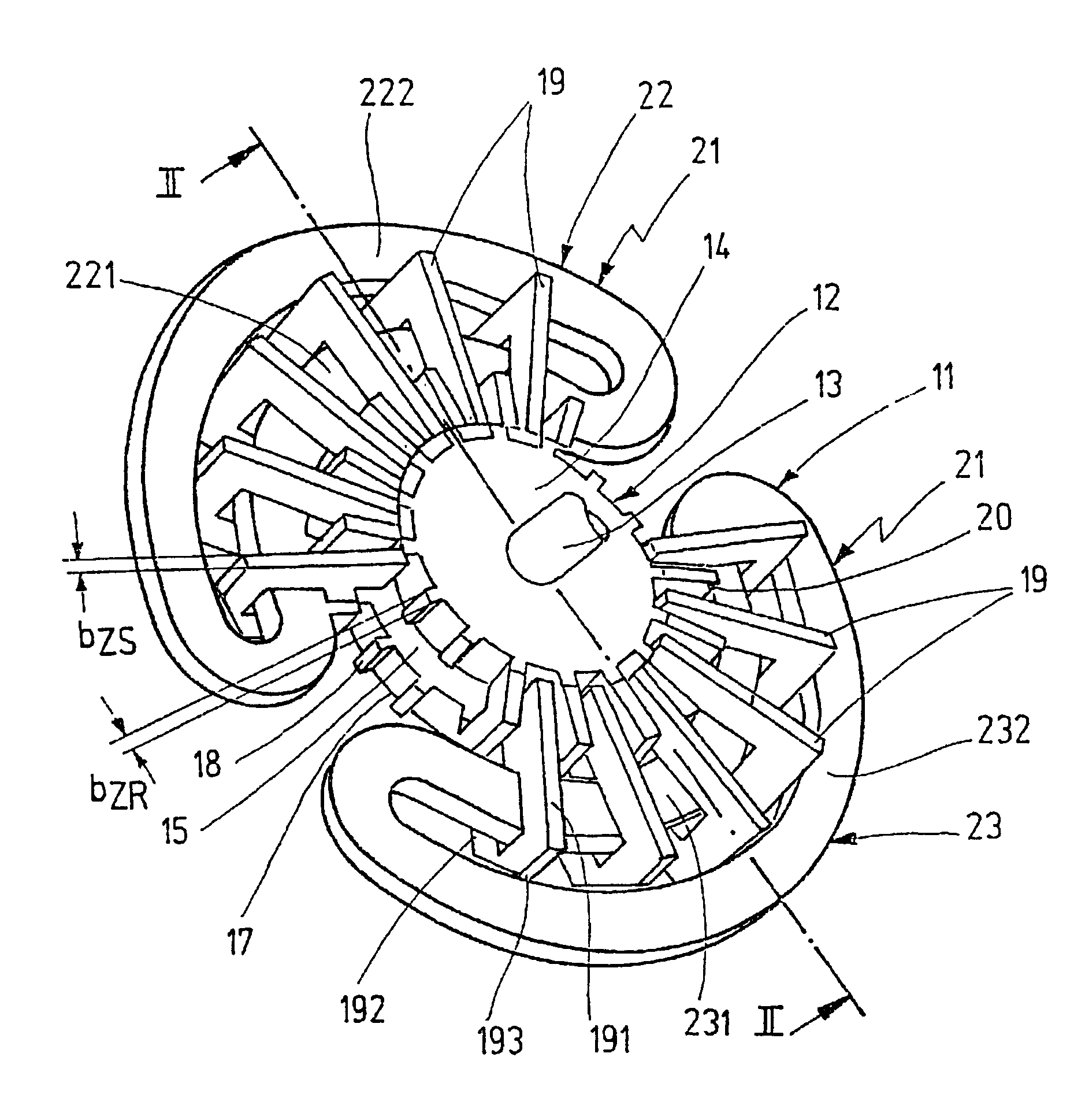
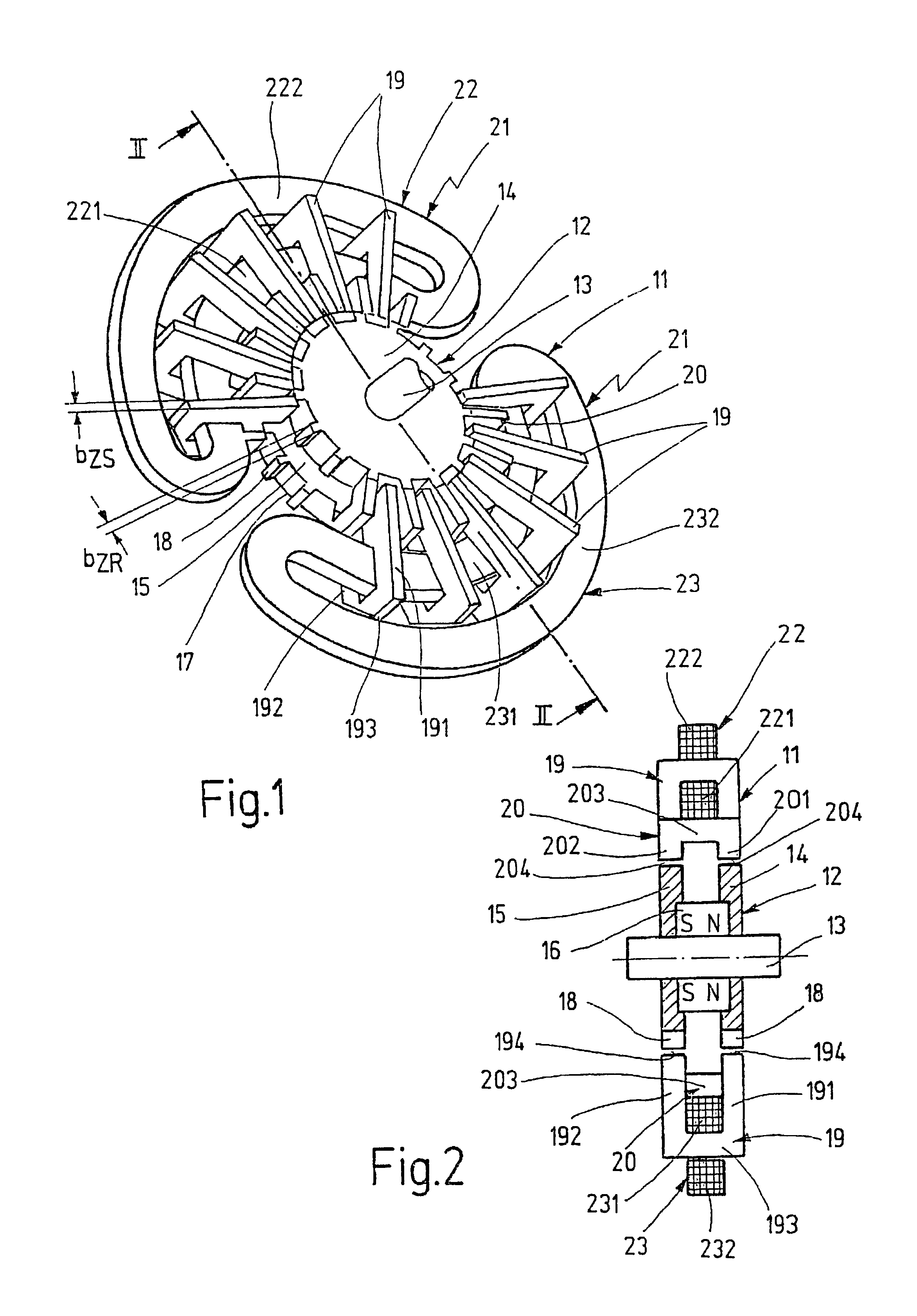
Stator arrangement and rotor arrangement for a transverse flux machine
InactiveUS7638919B2Easily magnetized unipolarGreat magnet volumeMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxMetal sheet
A stator arrangement and a rotor arrangement for a transverse flux machine. The stator arrangement comprises an annular stator back yoke having a number of stator poles designed in the manner of claw poles. The rotor arrangement includes number of rotor poles designed in the manner of claw poles and connected to each other to form an annular rotor body enclosing a unipolar ring magnet magnetized in an axial direction. In the stator arrangement, the stator back yoke includes a first laminated stack of metal sheets whose laminations are stacked in an axial direction, and the stator poles include a second laminated stack of metal sheets whose laminations are stacked in a tangential direction. In the rotor arrangement, the rotor poles include laminated stacks of metal sheets whose laminations are stacked in a tangential direction.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Transverse flux electrical machine with segmented core stator
InactiveUS20070013253A1Prevent removalMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsTransverse fluxElectrical conductor
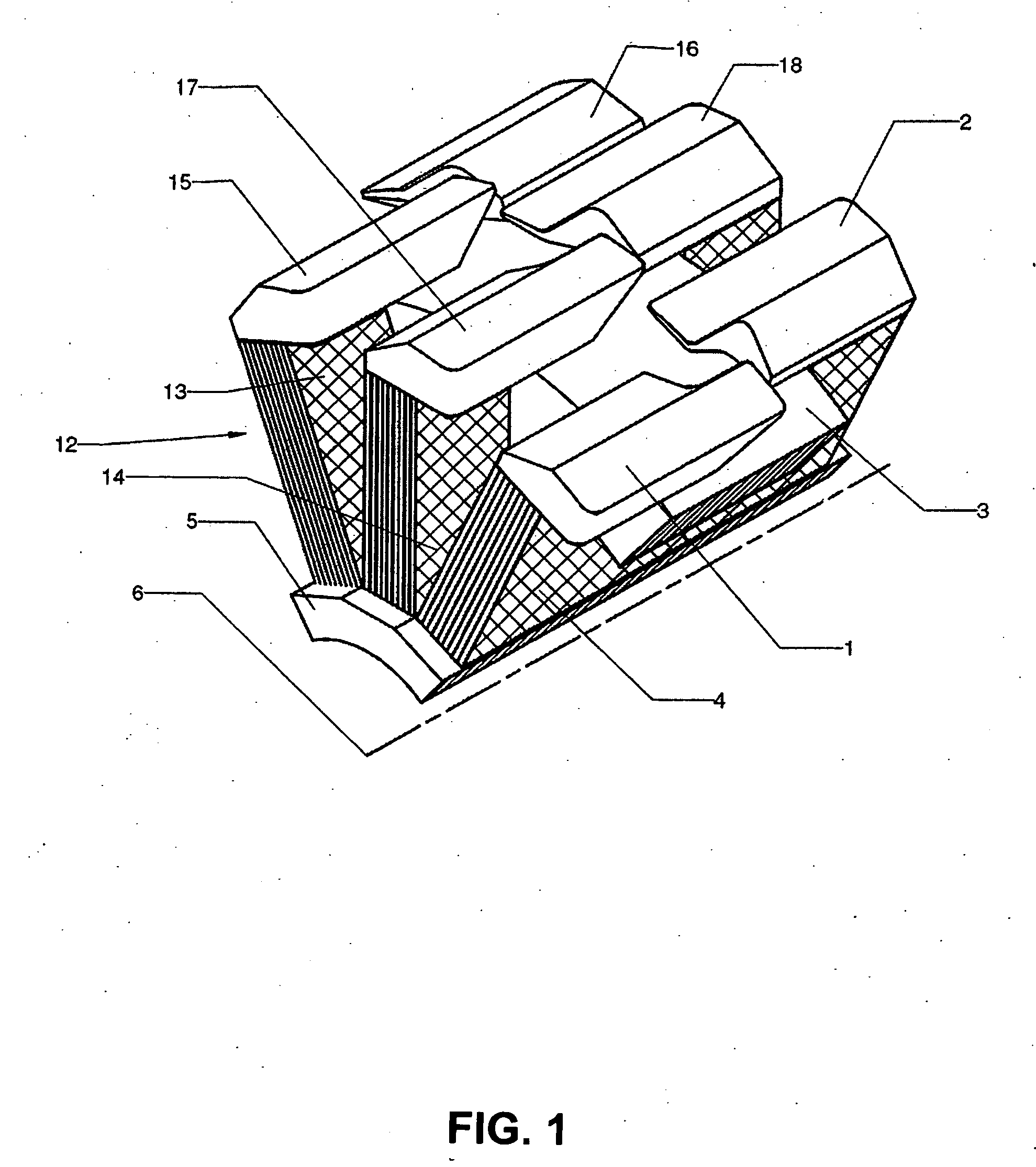
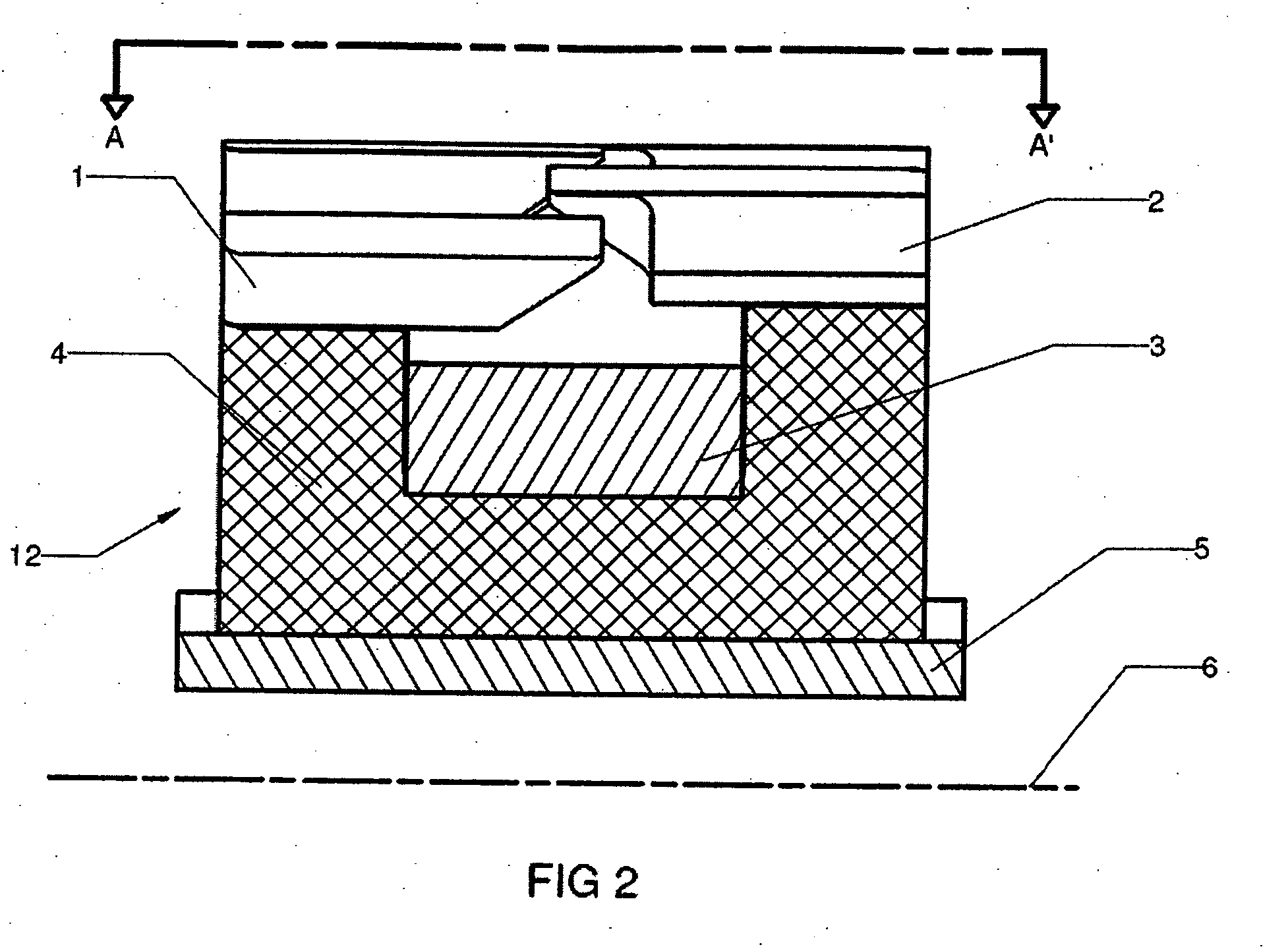
The invention relates to a transverse flux electrical machine, comprising a rotor and a stator. The rotor has magnets, angularly adjacent magnets having magnetic polarizations of opposite directions. The stator has a plurality of magnetic cores annularly disposed along the stator. Each core comprises a U-shaped part and a magnetic foot. The U-shaped part is disposed such that its open side faces the air gap between the rotor and the stator and that a segment of a magnetic flux circulating in the U-shaped part is substantially parallel to the rotation axis. The magnetic foot is assembled to the U-shaped part such that it is contiguous to the air gap. The magnetic foot provides a magnetic pole. An electrical conductor coil is disposed in the interior area of all of the U-shaped parts.
Owner:EOCYCLE TECH
High-efficiency wheel-motor utilizing molded magnetic flux channels with transverse-flux stator
InactiveUS7492074B1Improve efficiencyTotal current dropMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesTransverse fluxPole piece
A motor including a mounting shaft having a hollow channel and a bearing attached to each end, a cylindrical hub having a hollow core for the mounting shaft, and plural rows of plural Molded Magnetic Flux Channels with a hollow core and a channel forming a U-shaped recess and mounted the surface of the hub, each row corresponding to a motor phase. Each magnetic flux channel forms two pole pieces divided by the channel. The motor also includes plural phase windings, one passing through each row of plural Molded Magnetic Flux Channels, a rotating drum having plural rows of permanent magnets on an inner surface, each row pair corresponding to and aligned with one of the plural rows of Molded Magnetic Flux Channels. The rotating drum connected with the bearing, and drive electronics for driving the plural phase windings, wherein the plural Molded Magnetic Flux Channels increases torque and motor efficiency.
Owner:RITTENHOUSE NORMAN
Elevator with transverse flux drive
InactiveUS7261186B2Improve power performanceLow production costMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlTransverse fluxDrive motor
An elevator, particularly for transporting passengers, has an elevator car guided in an elevator shaft a direct drive motor. The drive motor includes an active primary part at the elevator car and a passive secondary part that is fixed in the elevator shaft and is spaced from the primary part by an air gap. In order to achieve a high power capability, the drive motor is configured as a transverse flux motor that moves the primary part linearly relative to the secondary part under the influence of an electromagnetic propulsive force. The secondary part has at least one rail made of a soft magnetic material and subdivided into a plurality of segments having a predetermined length. The segments are fixed to a wall of the elevator shaft by intermediate elements.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Stator module for an electric motor
InactiveUS6365999B1Simple structural designCost-favorable productionMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsTransverse fluxAxis of symmetry
The invention relates to a stator module for an electric motor, especially an electric motor with transverse flux, comprising at least one stator unit that consists of at least one armature winding and which, when mounted, is associated with a rotor, whereby an interferric space is created in a radial direction in relation to the axis of symmetry of the electric motor. The invention is characterized by the following features: the stator unit comprises at least one return element that is made of a pressed material produced by means of powder metallurgy and which comprises a peripheral surface extending in a peripheral direction; two soft iron units which can be formed from tooth elements are associated with the return element, whereby substantially U-shaped cross-sectional surfaces, when seen from an axial viewpoint, are formed and the tooth elements of the individual soft iron units form the limbs of the cross-sectional surfaces; the position of the armature winding is defined by the peripheral surface of the return element, oriented towards the rotor and the self-oriented front faces of the soft iron units.
Owner:VOITH TURBO GMBH & CO KG
Transverse flux electrical machine with segmented core stator
InactiveUS7466058B2Prevent removalMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsTransverse fluxElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a transverse flux electrical machine, comprising a rotor and a stator. The rotor has magnets, angularly adjacent magnets having magnetic polarizations of opposite directions. The stator has a plurality of magnetic cores annularly disposed along the stator. Each core comprises a U-shaped part and a magnetic foot. The U-shaped part is disposed such that its open side faces the air gap between the rotor and the stator and that a segment of a magnetic flux circulating in the U-shaped part is substantially parallel to the rotation axis. The magnetic foot is assembled to the U-shaped part such that it is contiguous to the air gap. The magnetic foot provides a magnetic pole. An electrical conductor coil is disposed in the interior area of all of the U-shaped parts.
Owner:EOCYCLE TECH
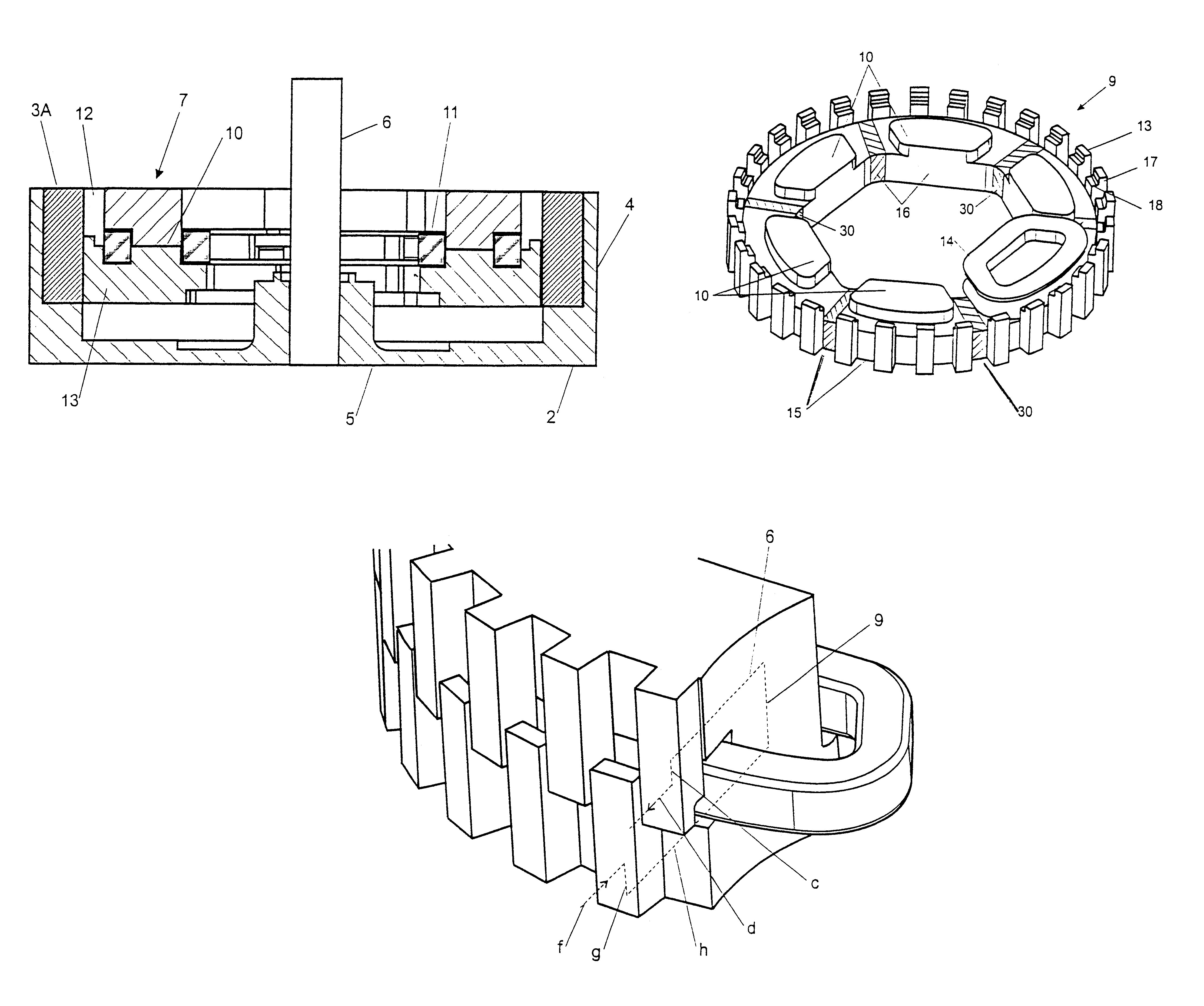
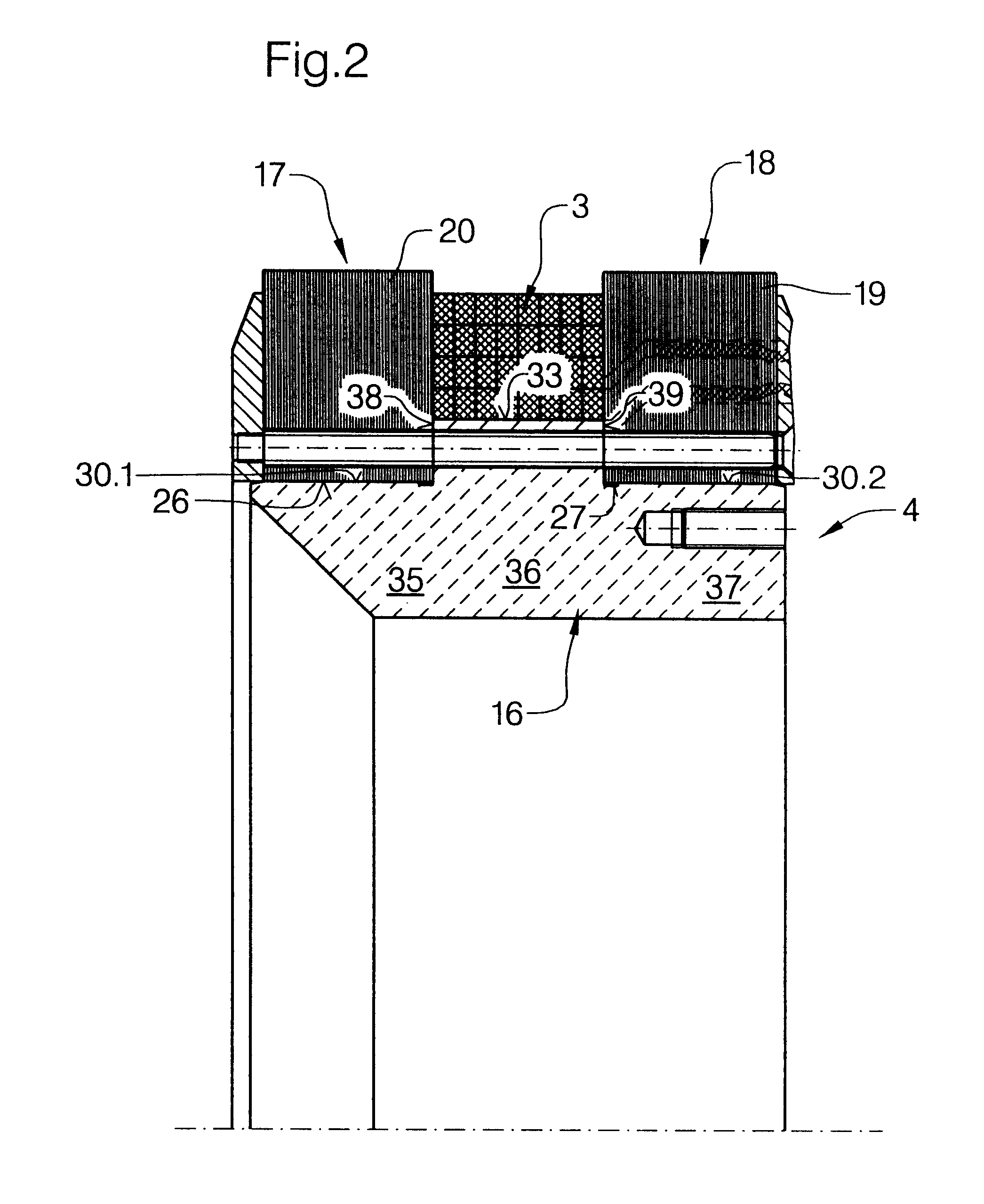
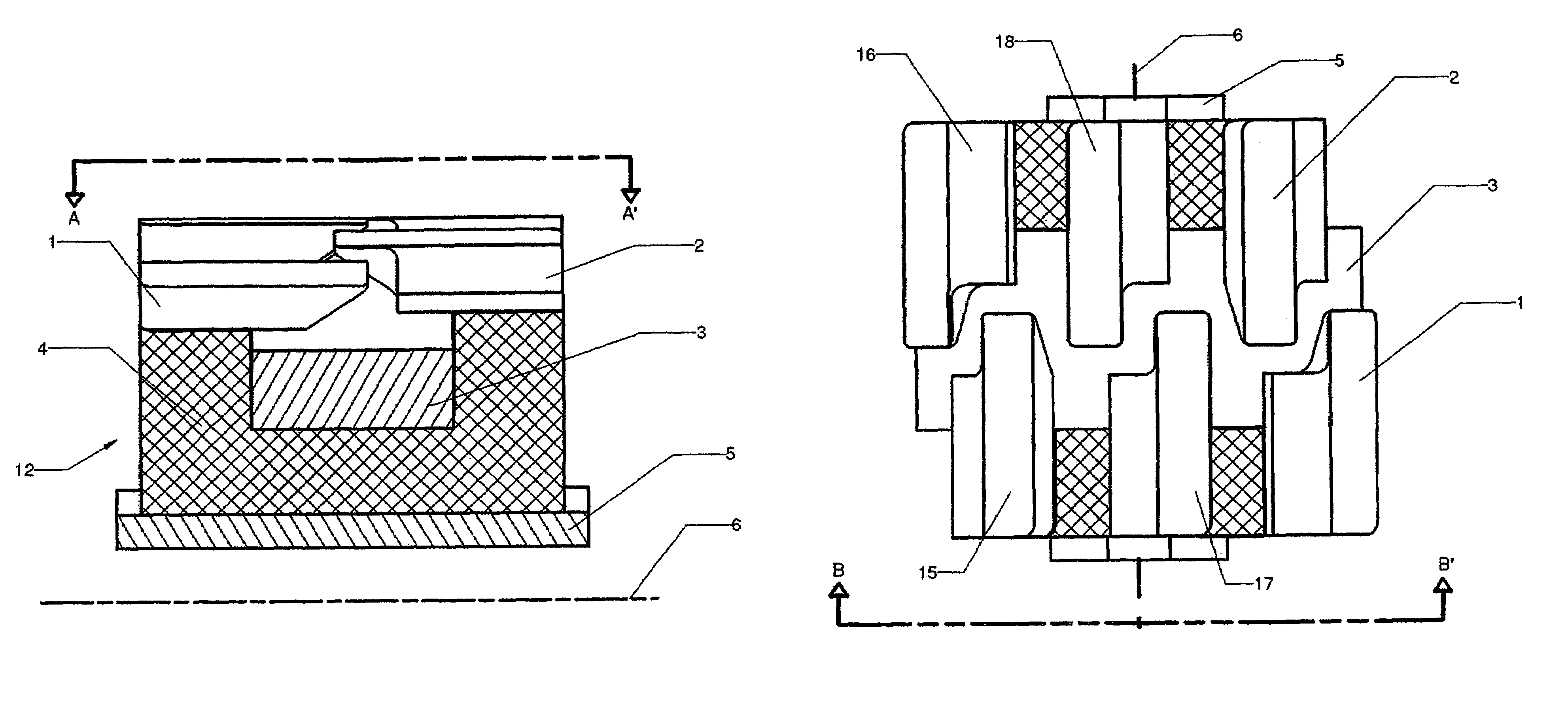
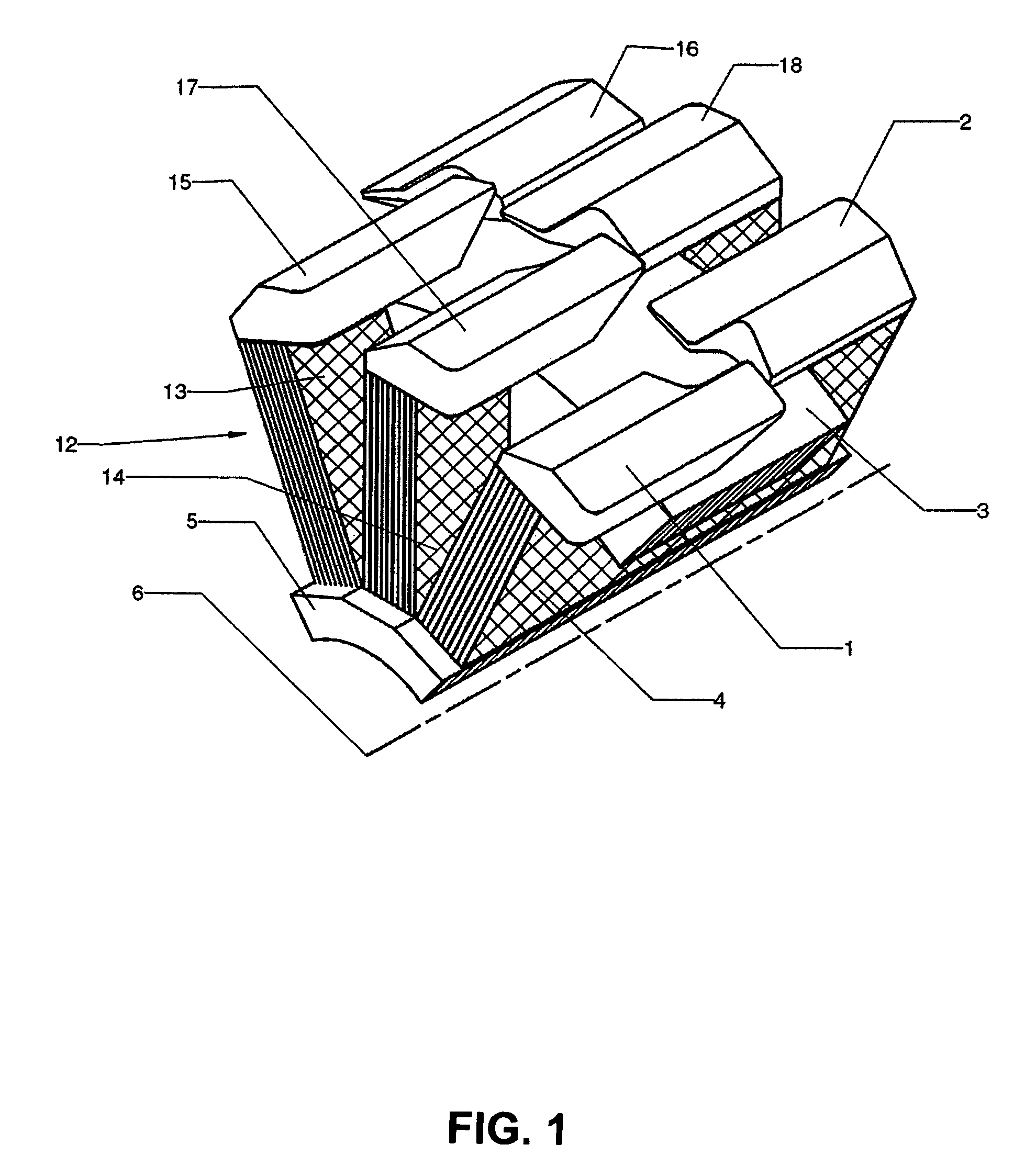
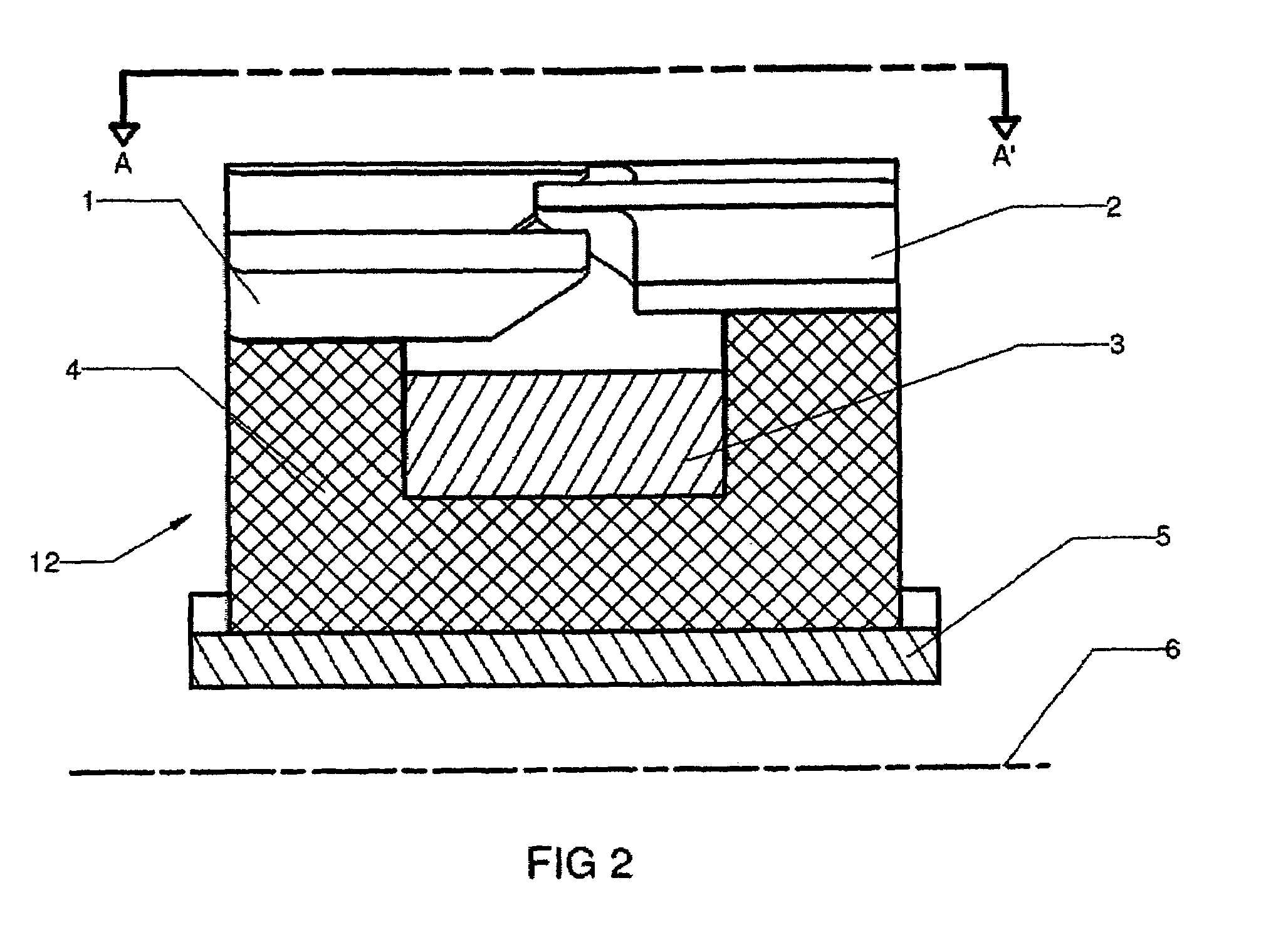
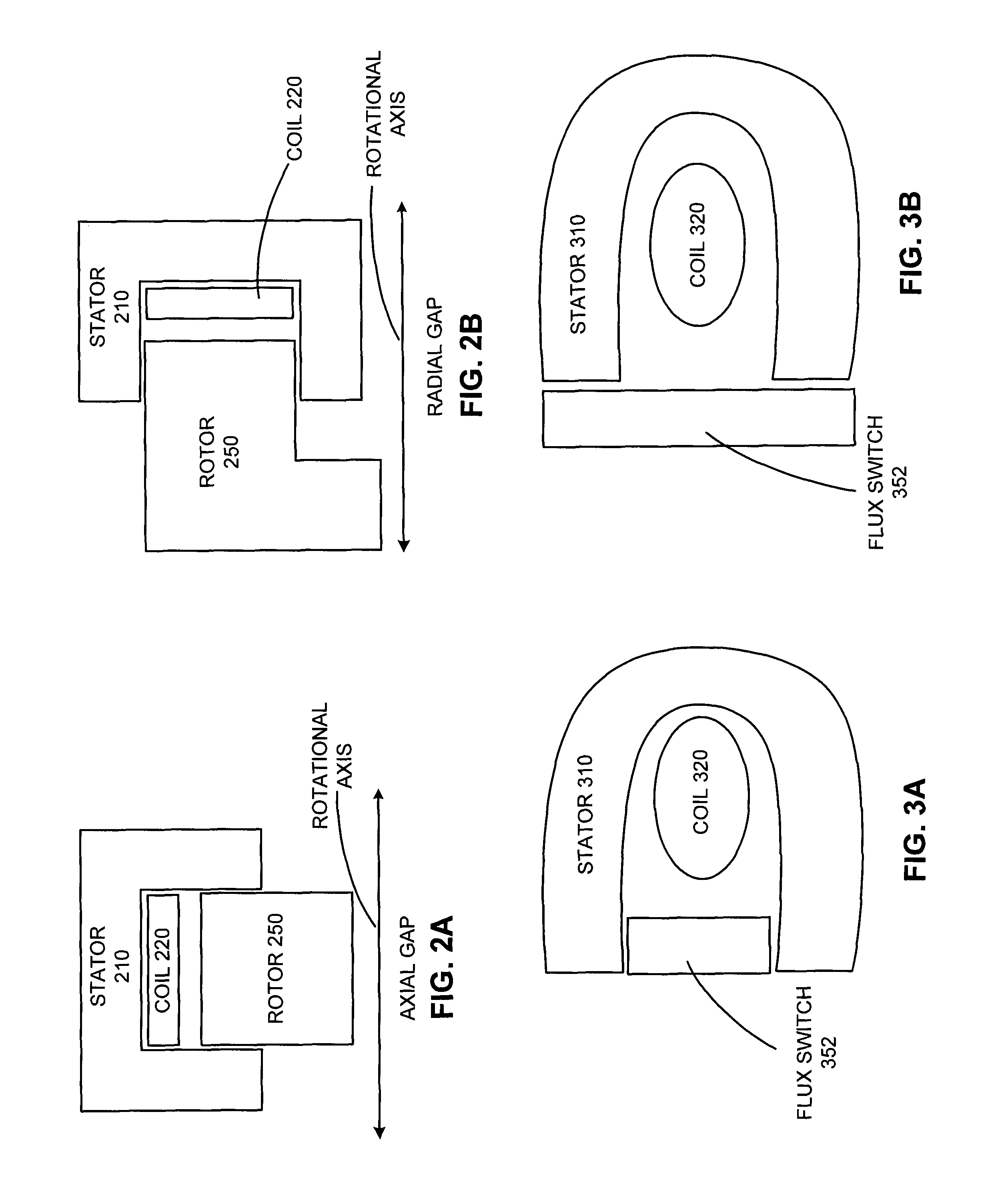
Stator pole structure for an electrical machine
InactiveUS7164220B2Provides structural stabilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxEngineering
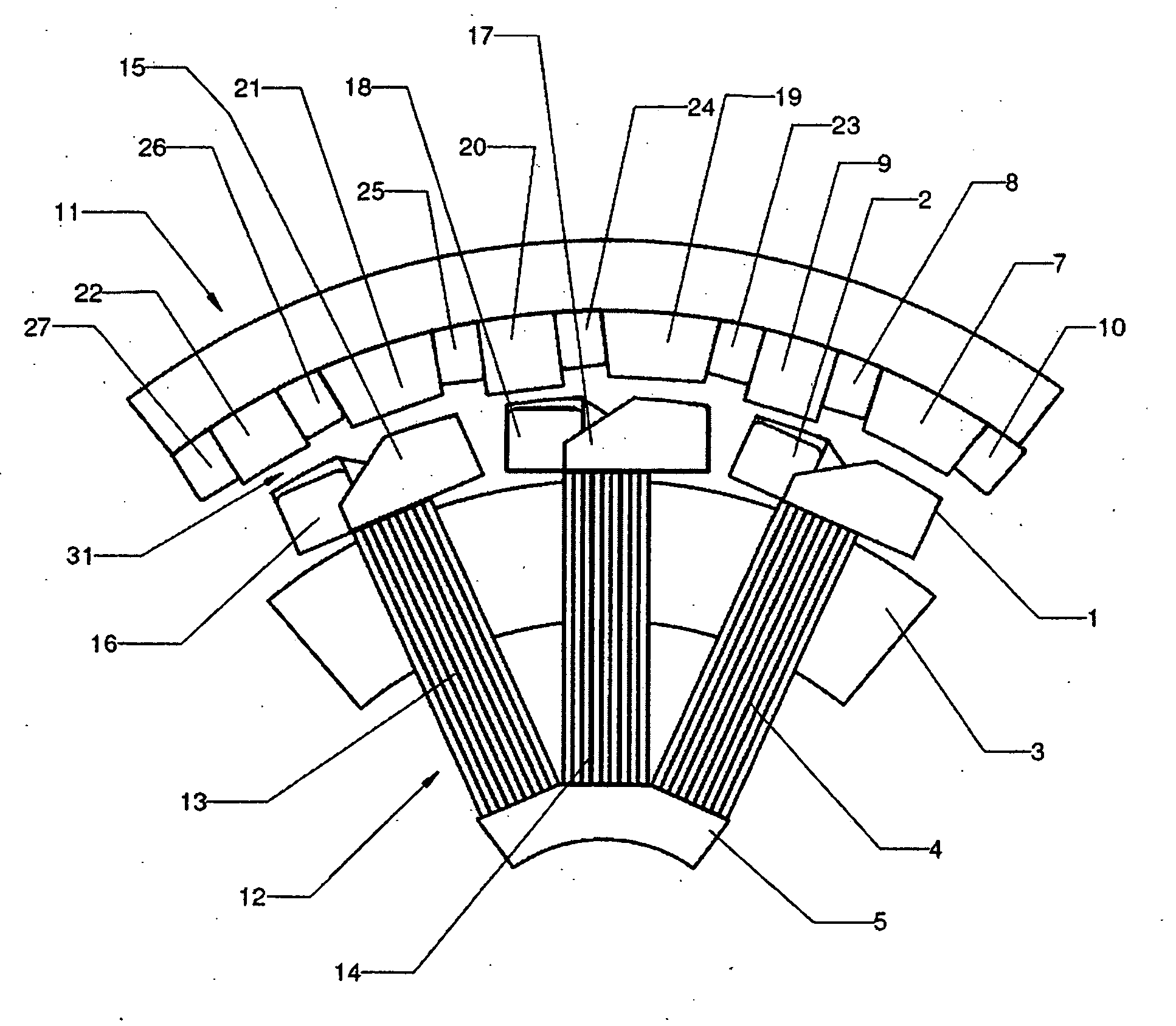
An electrical machine, such as a transverse flux motor, incorporates a stator core assembly 1. The stator core assembly 1 comprises a stator frame 4 upon which stator cores 2,3 are located with spacer elements 7 therebetween. A number of stator pole members 10,11 are located such that channels 13 in these members 10,11 accommodate limbs 5,6 of the cores 2,3. The stator pole members 10,11 straddle more than two limbs 5,6 in order to provide greater structural stability for the assembly 1 despite magnetic flux cycling and other distortion effects. By such greater structural stability more accurate control of a gap between the stator core assembly 1 and a rotor in the machine can be maintained.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Transverse flux, switched reluctance, traction motor with bobbin wound coil, with integral liquid cooling loop
InactiveUS20080179982A1Light weightIncrease torqueAsynchronous induction motorsMechanical energy handlingTransverse fluxBobbin
The present invention deals with a transverse flux machine of the switched reluctance variety. The transverse flux machine consists of multiple phases where each phase is spaced axially along the shaft. Axial spacing provides many benefits including a decreased weight and a capability to use simple wound bobbin coils for the windings. An embedded cooling loop is provided within the coils themselves. This cooling loop provides internal temperature regulation for the windings and allows for a higher efficiency among other benefits.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
Permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor with outer rotor
ActiveUS7626308B2Core lossHigh densityMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesTransverse fluxConductor Coil
Disclosed herein is a permanent magnet-excited transverse flux motor with an outer rotor. The permanent magnet-excited transverse flux motor comprises: a stator including a stator powdered iron core formed by an extruded molding through a mold, a pair of stator laminated iron cores stacked respectively at an upper layer portion and a lower layer portion of an outer circumference of the stator powdered iron core in such fashion as to be spaced apart from each other by a certain interval, and a stator winding interposed between the upper layer portion and the lower layer portion in such fashion as to be wound around the stator powdered iron core to form a multiple coil through which current flows; and a rotor including a plurality of rotor permanent magnets and a plurality of rotor powdered iron cores disposed on the outer circumference of the stator in such a fashion as to be are alternately arranged adjacent to one another.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
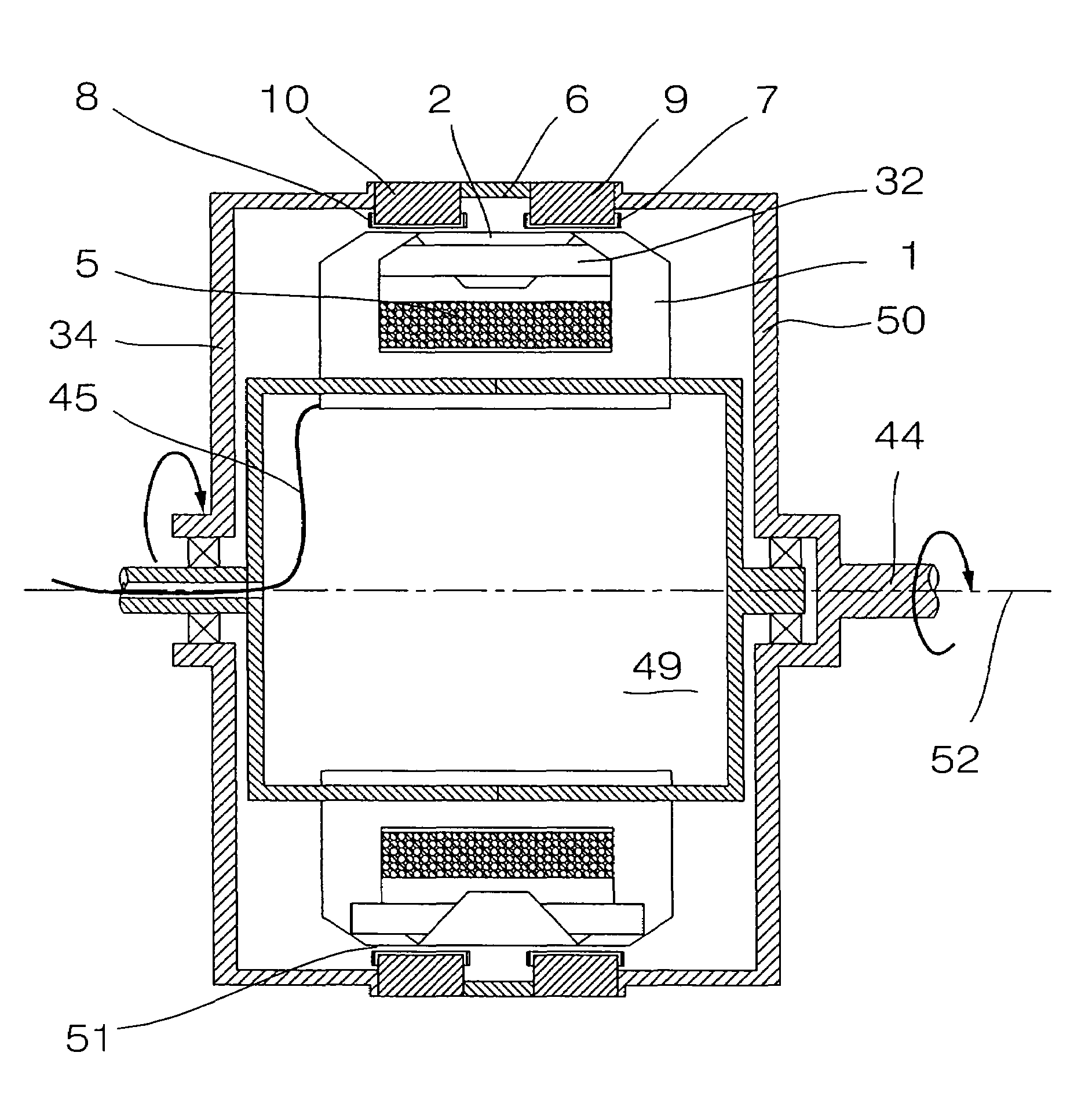
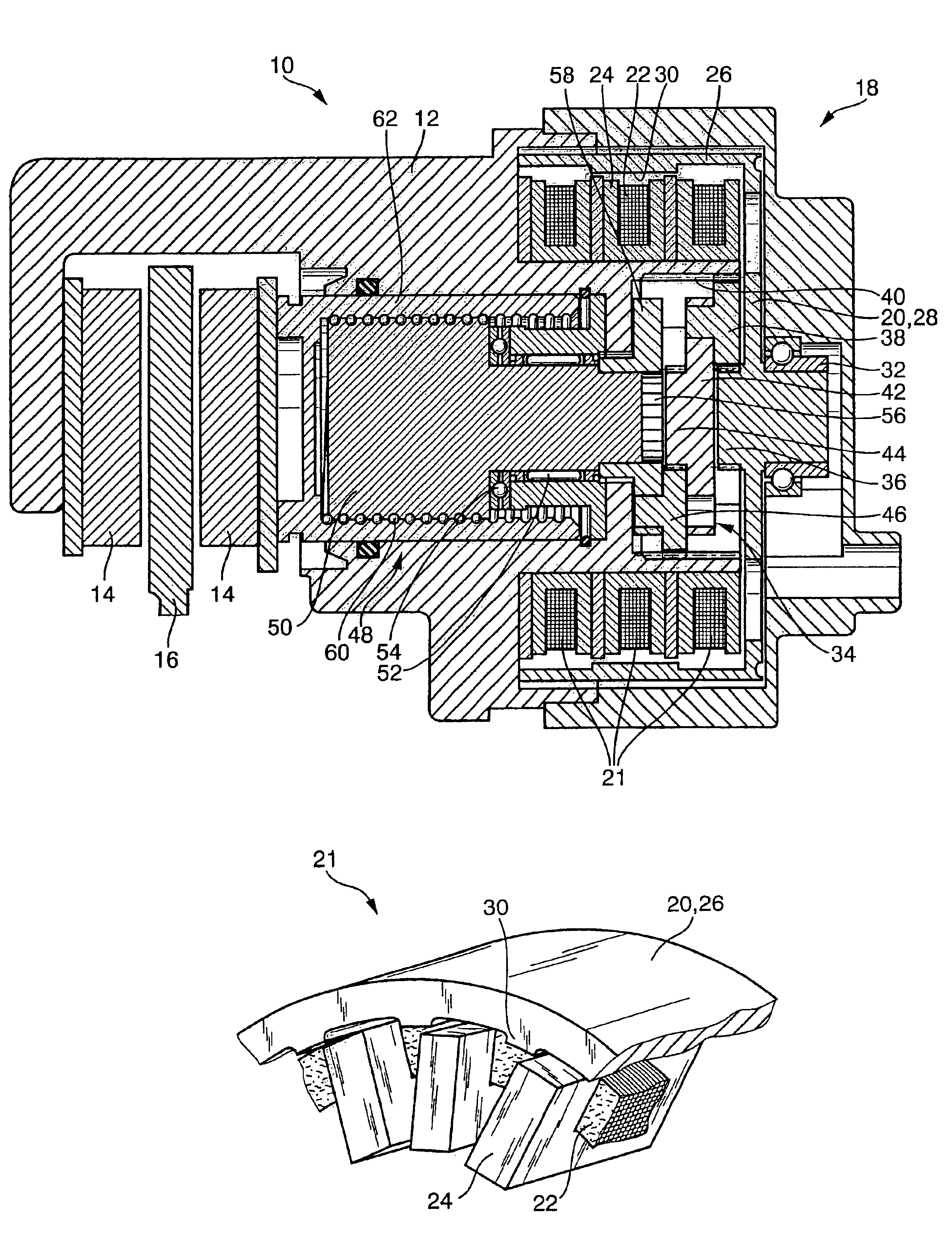
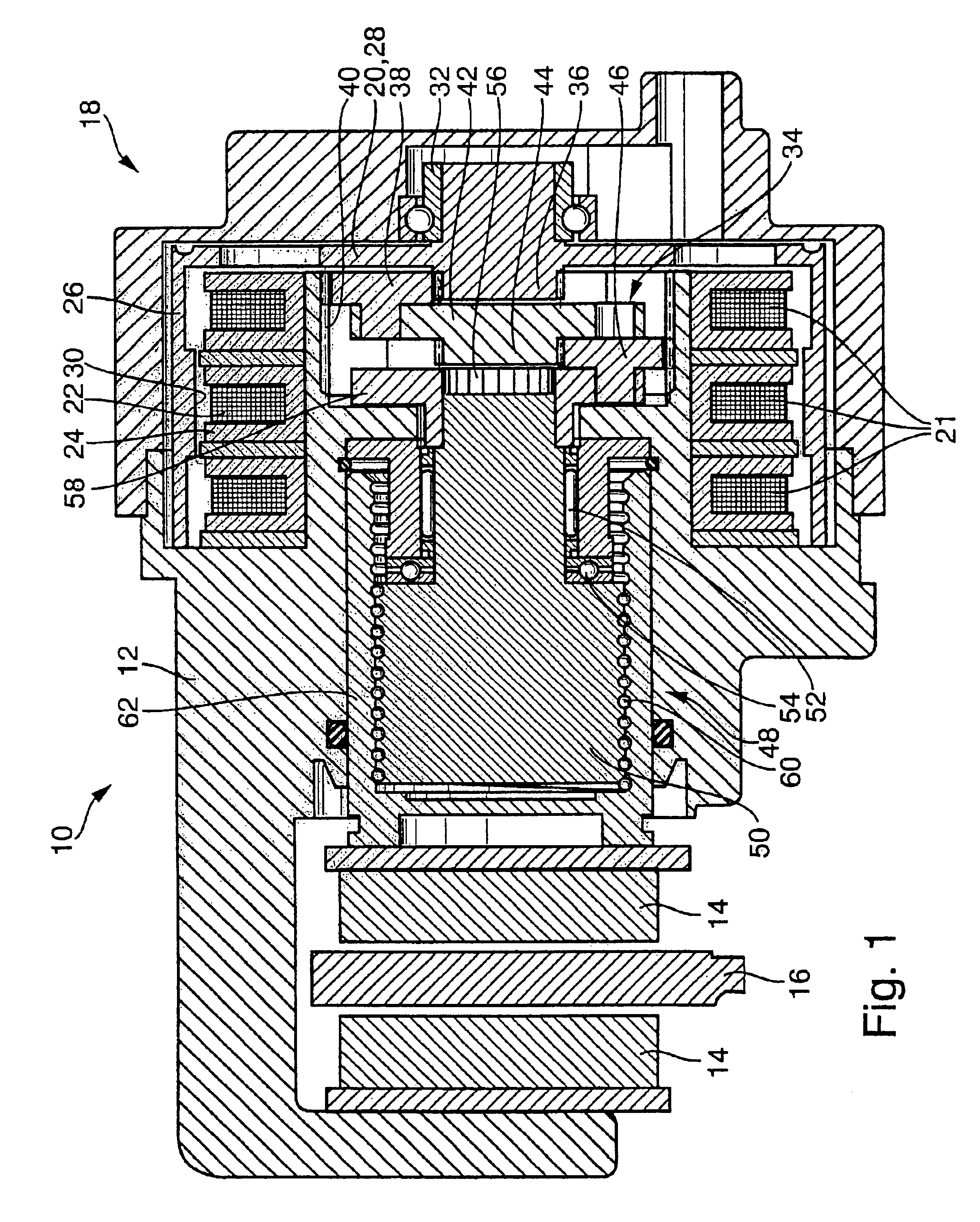
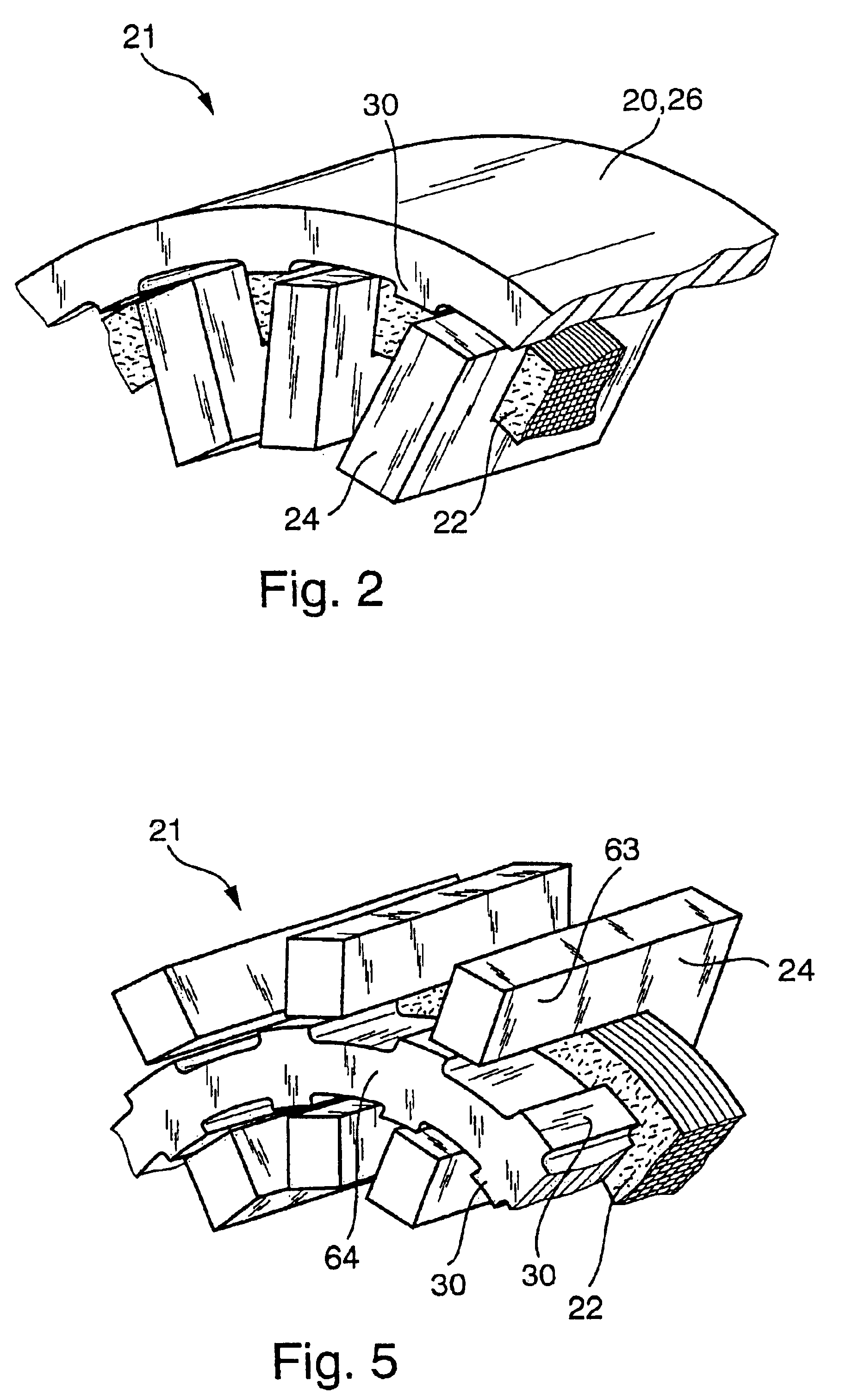
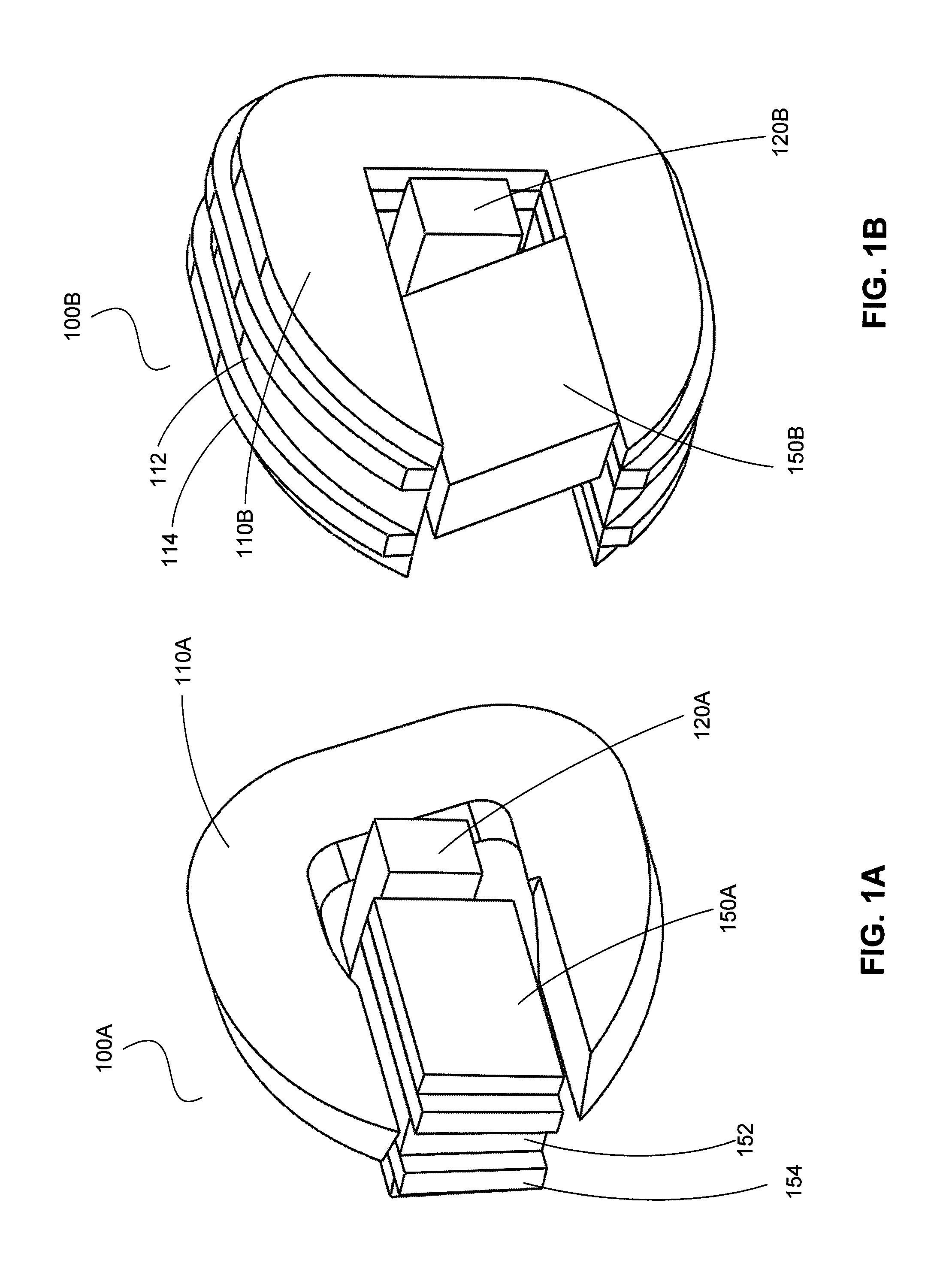
Electromechanical wheel brake device
InactiveUS6806602B2Improve power densityInterrupt supplyDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesBraking action transmissionTransverse fluxBall screw
The invention relates to an electromechanical wheel brake device, with an electric motor that can press a frictional brake lining against a brake body (brake disk) by a reduction gear (planetary gear) and a rotation / translation conversion gear (ball screw). The invention proposes embodying the electric motor as a transverse flux motor with three phase windings; each phrase winding has a circular, annular excitation winding that is disposed inside U-shaped yokes, which are distributed over the circumference of the excitation winding. This embodiment of the electric motor permits a compact design of the electric motor in an annular, hollow shaft design so that the reduction gear and the rotation / translation conversion gear can be disposed at least partially inside the electric motor.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Rotating Transverse Flux Machine
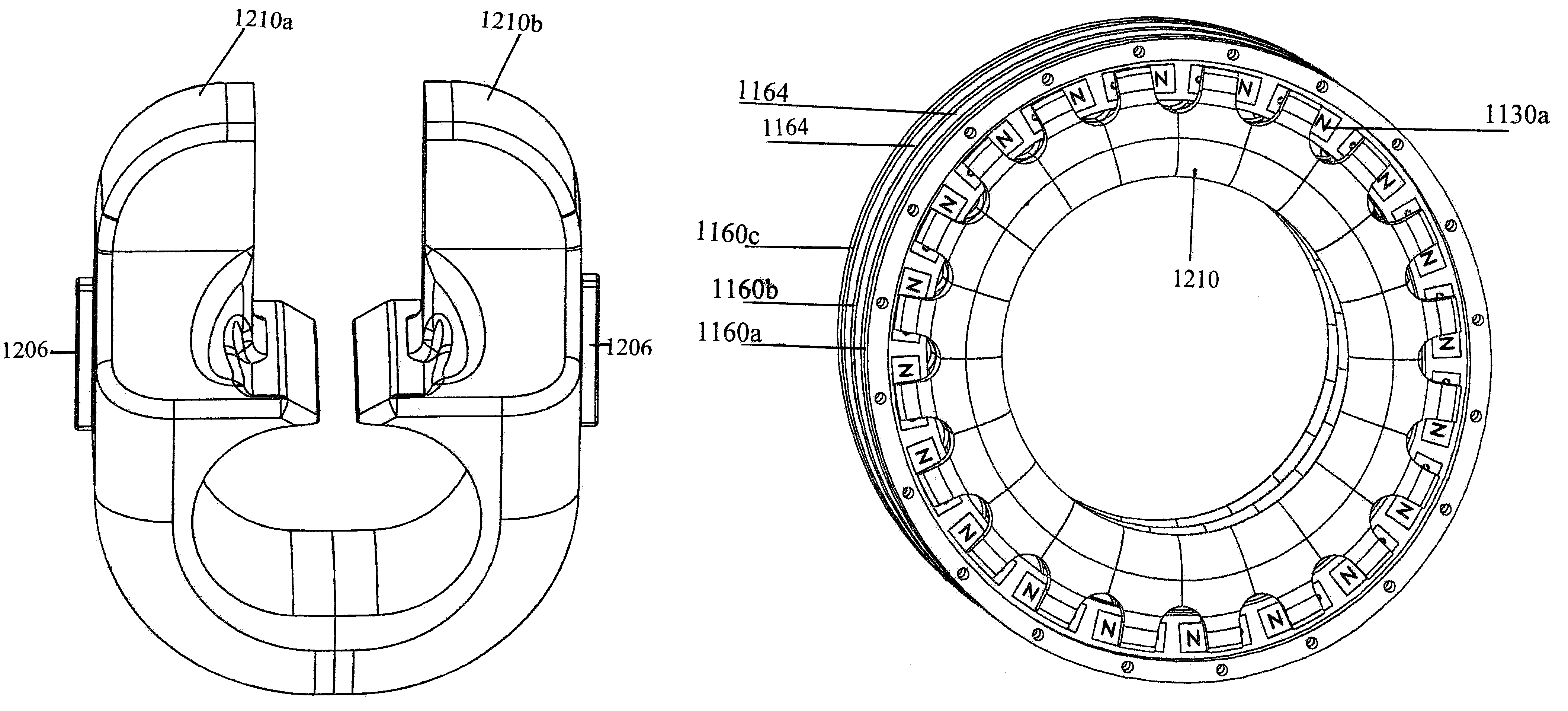
InactiveUS20080211336A1Increased torque densitySimple designMagnetic circuitManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesTransverse fluxMagnetic poles
A transverse flux rotating machine including a first interacting part including an electric winding and a second interacting part including a plurality of magnetic poles. The first and second interacting parts are movable relative to each other and defining between them an airgap.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
High-efficiency wheel-motor utilizing molded magnetic flux channels with transverse-flux stator
InactiveUS7868510B2Improve efficiencyImprove magnetismMotor control for very low speedsMagnetic circuit rotating partsTransverse fluxElectric machine
A motor including an outside rotor having a rotor disc with plural magnets alternating polarities flush mounted in the disc, an inside stator assembly with a ring of pole pieces forming a channel to house a transversely wound stator windings, and a controller coupled with feedback electronics for monitoring a timing, speed and direction and coupling a signal to a processing unit for adjusting the drive electronics driving the phase windings. A u-shaped gap above the channel to receive the rotor disc and focus the captured magnetic flux in the pole pieces toward the magnets. In an embodiment the molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces of the inside stator are sets of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces, each set forming a channel and corresponding to one phase of the motor; and a section of each one of the transverse windings passing through one channel, the remaining section folding back outside the set in close proximity to the outer base of the set of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces.
Owner:RITTENHOUSE NORMAN P
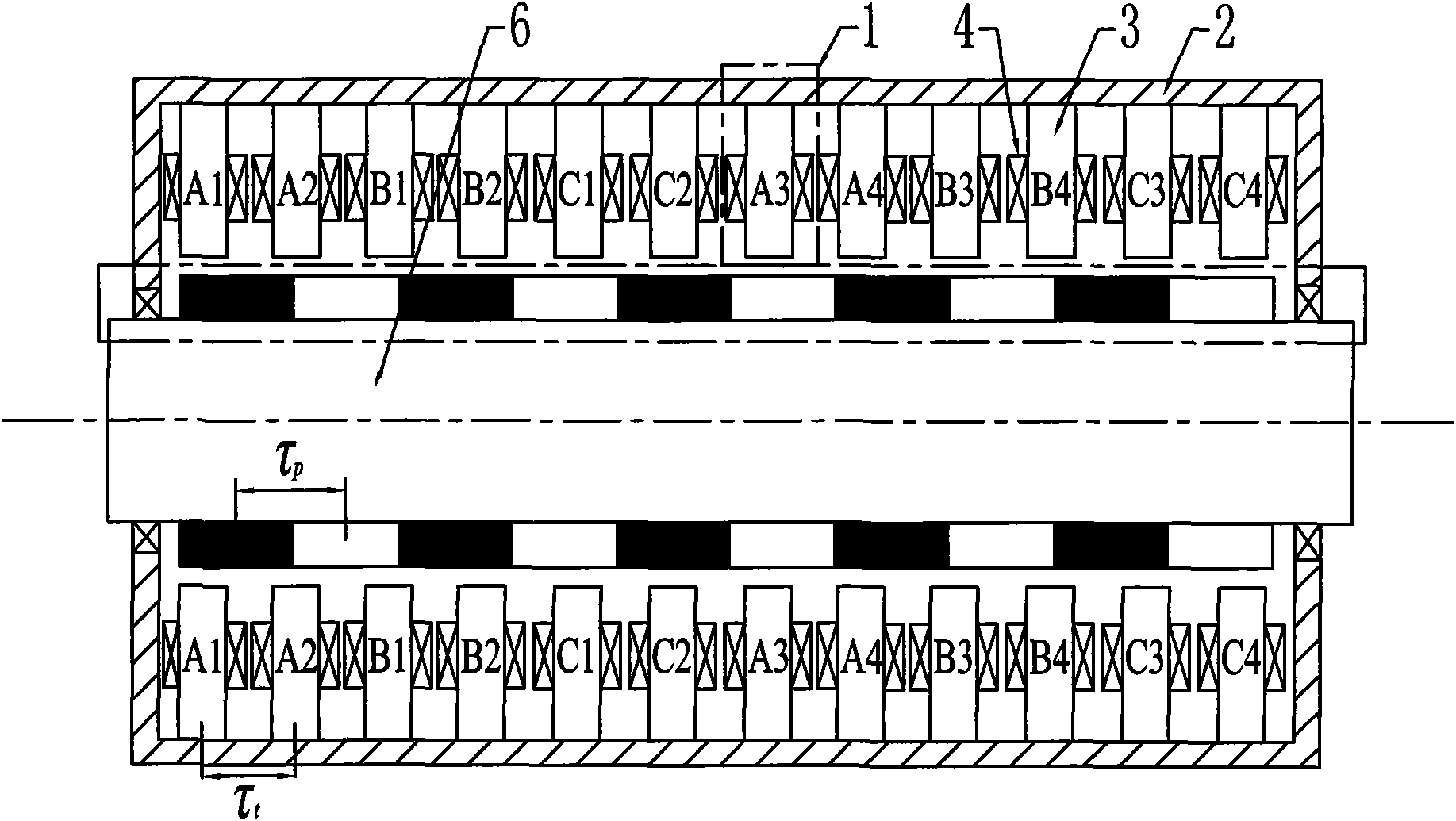
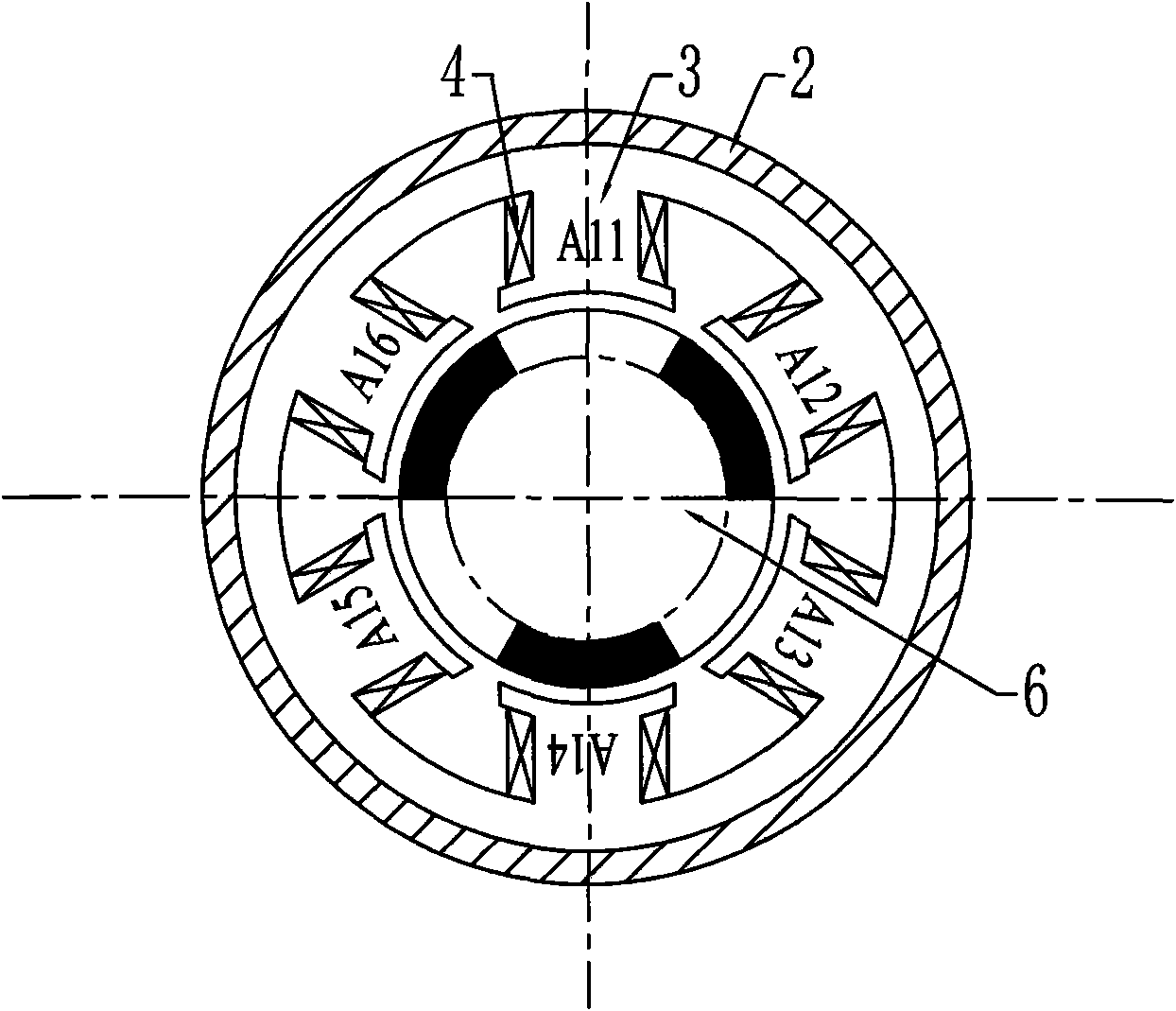
Transverse flux cylinder type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
A transverse flux cylinder type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor relates to the field of motor, and settles the problems of low efficiency, large eddy current loss, complex technique and effect to the control precision and dynamic characteristic. The transverse flux cylinder type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor of the invention comprises a primary stage, a secondary stage and an air gap. The number of phase armature units is S=nm, wherein n is a natural number. The number of axial magnetic poles formed by secondary permanent magnets is P=2i, wherein is a natural number. When no common divisor exists between S and P, the S phase armature units are equally divided to m groups along the axial direction, and each n adjacent phase armature units belong to one phase. When a highest common divisor j exists between S and P, the S phase armature units are equally divided into mj parts along the axial direction, and windings on each adjacent n / j phase armature units belong to one phase. The phase unit armature core tooth pitch taut between two adjacent phase armature units along the axial direction and the pole distance taup along the axial permanent magnet satisfy a relationship mktaut=(mk+ / -1)taup, wherein m and k are natural numbers, and m is the phase number of motor. The motor not only can be used as an electric motor, but also can be used as a generator.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
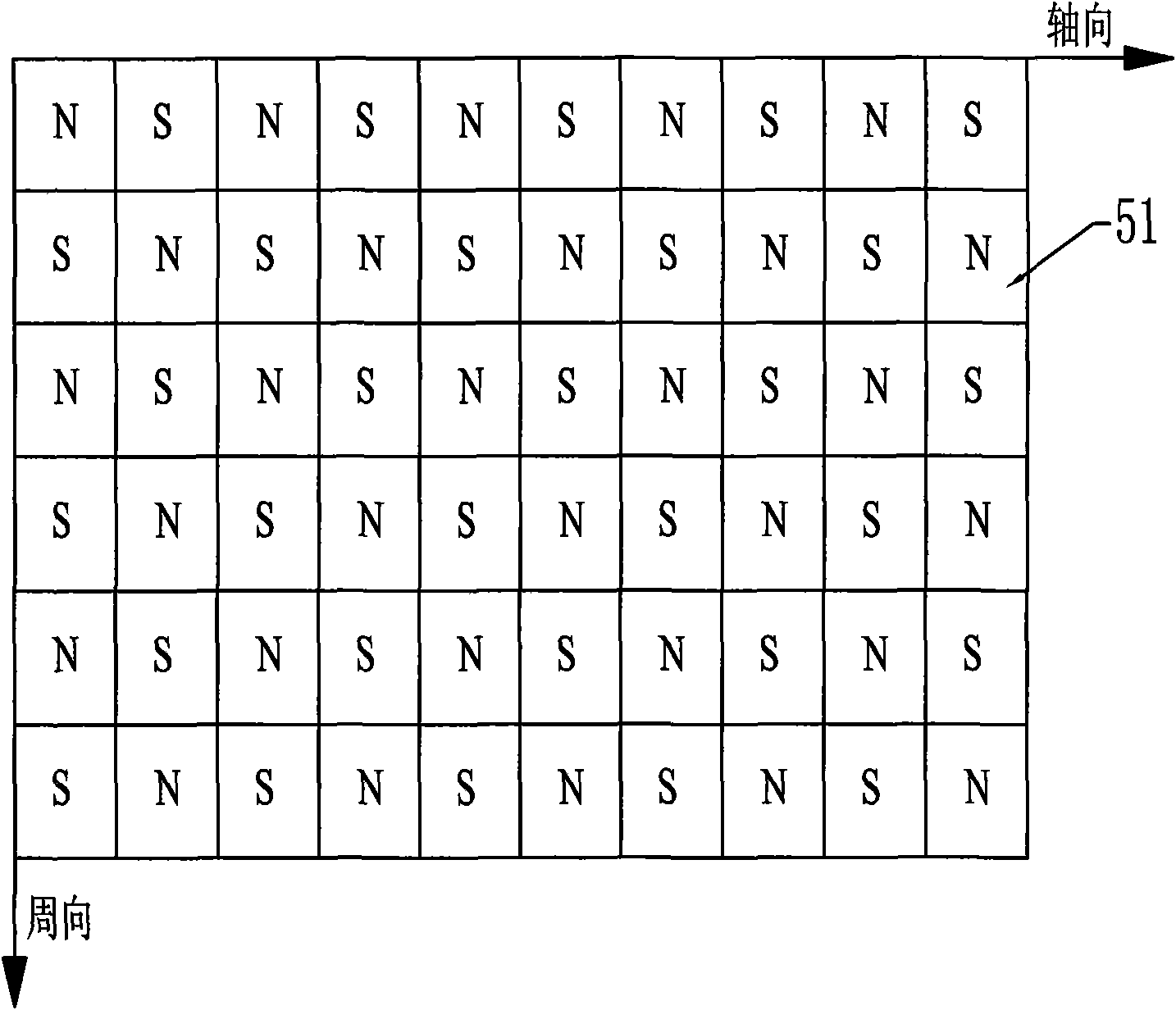
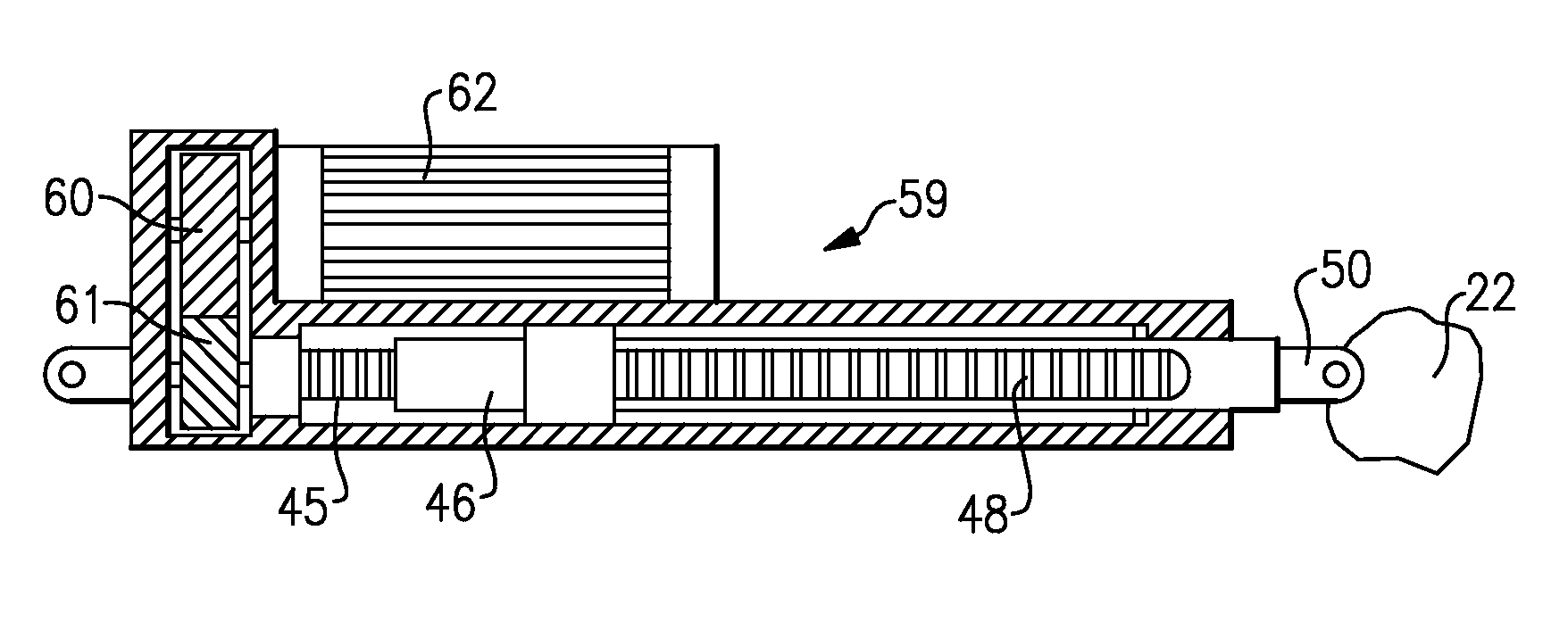
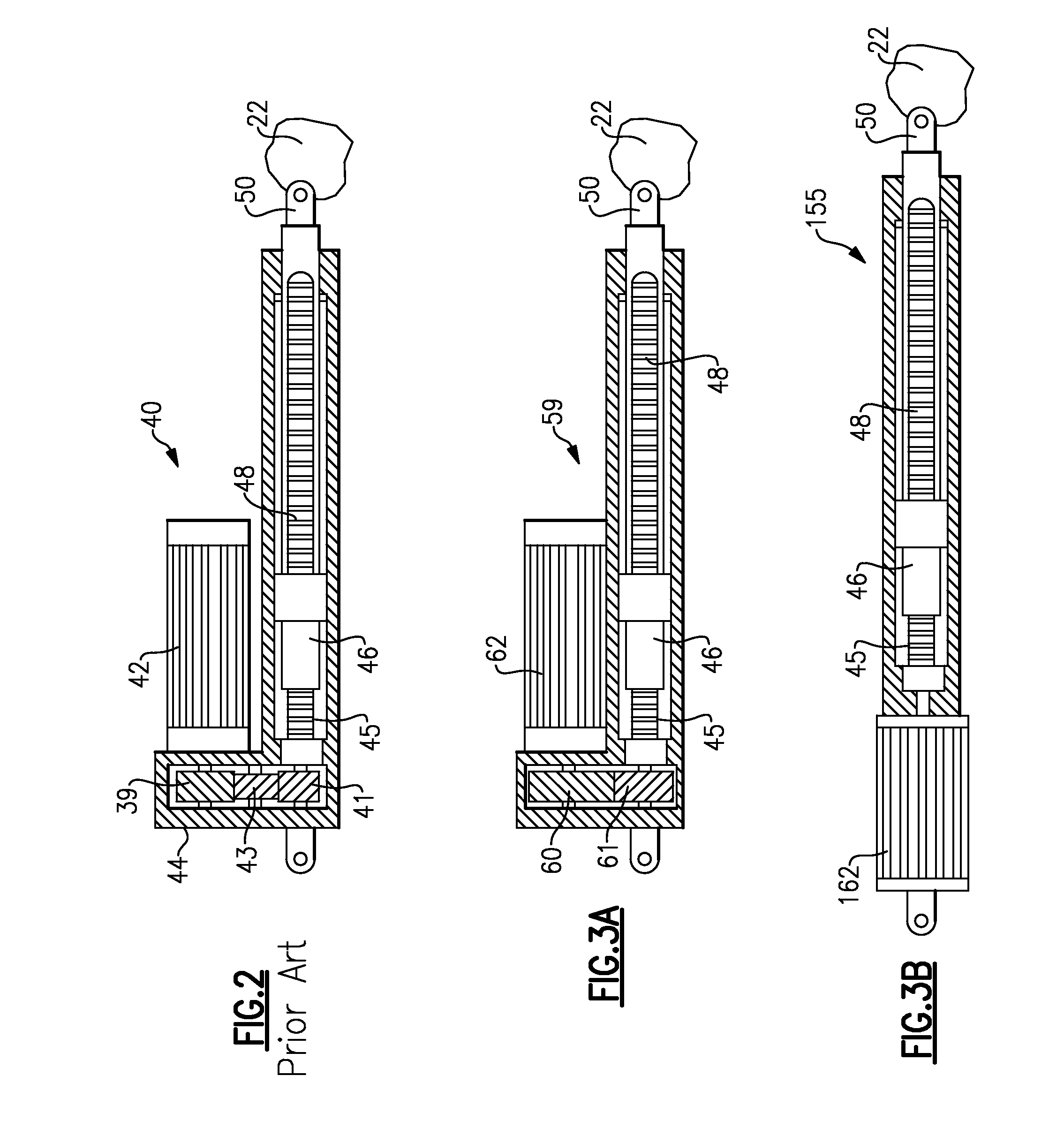
Compact electromechanical actuator
An electromechanical actuator for controlling the position of an aircraft component has a linear actuator to be driven to position a component. A transverse flux motor drives the linear actuator to move in a linear direction and control the position of the component
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Electric machine with soft magnetic teeth
InactiveUS6960862B2Decrease of winding lossIncrease the areaSynchronous motorsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectrical conductorDirect effects
Electric machines operating according to the reluctance principle have toothed air gap surfaces between their moving and fixed parts. The magnetizability of these teeth directly affects the performance of the machine. According to the invention, the teeth projecting into the air gap consist of a material which in relation to the remaining soft-magnetic body presents better magnetizability and / or greater magnetic saturation flux density. This material is preferably a grain-oriented electric steel sheet or a cobalt / iron alloy. Alternatively or in addition thereto, the soft-magnetic body in which the conductor coils are positioned can be made entirely of a grain-oriented material by appropriate segmentation. In this case, every other pole is non-spooled and consists of two halves separated by a non-magnetic holding element. The use of steel sheets rolled at an angle also contributes to the improved utilization of space and material in rotating machines, especially in transverse flux machines. The characteristics of the construction provided for in the invention result in the production of little cutting waste and thus raise the performance of electric machines with soft-magnetic teeth at the air gap surface and reduce losses.
Owner:HILL WOLFGANG
Transverse flux electrical machine with toothed rotor
InactiveUS20050040720A1Shorten production timeSimple processMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxElectrical conductor
The invention concerns a transverse flux electrical machine operating with alternating current, having a first element having an alternate arrangement of excitation cores and of flux return cores and a winding of electrical conductors, the winding of electrical conductors being wound as a toroid, inside all said excitation cores; a second element having an exciter section comprising two toothed magnetic structures, each toothed magnetic structure comprising a number of slots equal in number to the total number of excitation cores and of flux return cores, the corresponding slots of each magnetic structure being toothed by being aligned; a magnetized sub-assembly is inserted inside each indentation so that an alternating arrangement of magnetic north poles and south poles is produced in each of these magnetic toothed structures of said exciter section; an air gap between the first element and the second element; at least one of the first element and of the second element being capable of rotating around a rotation axis that is common to the first element and to the second element.
Owner:EOCYCLE TECH
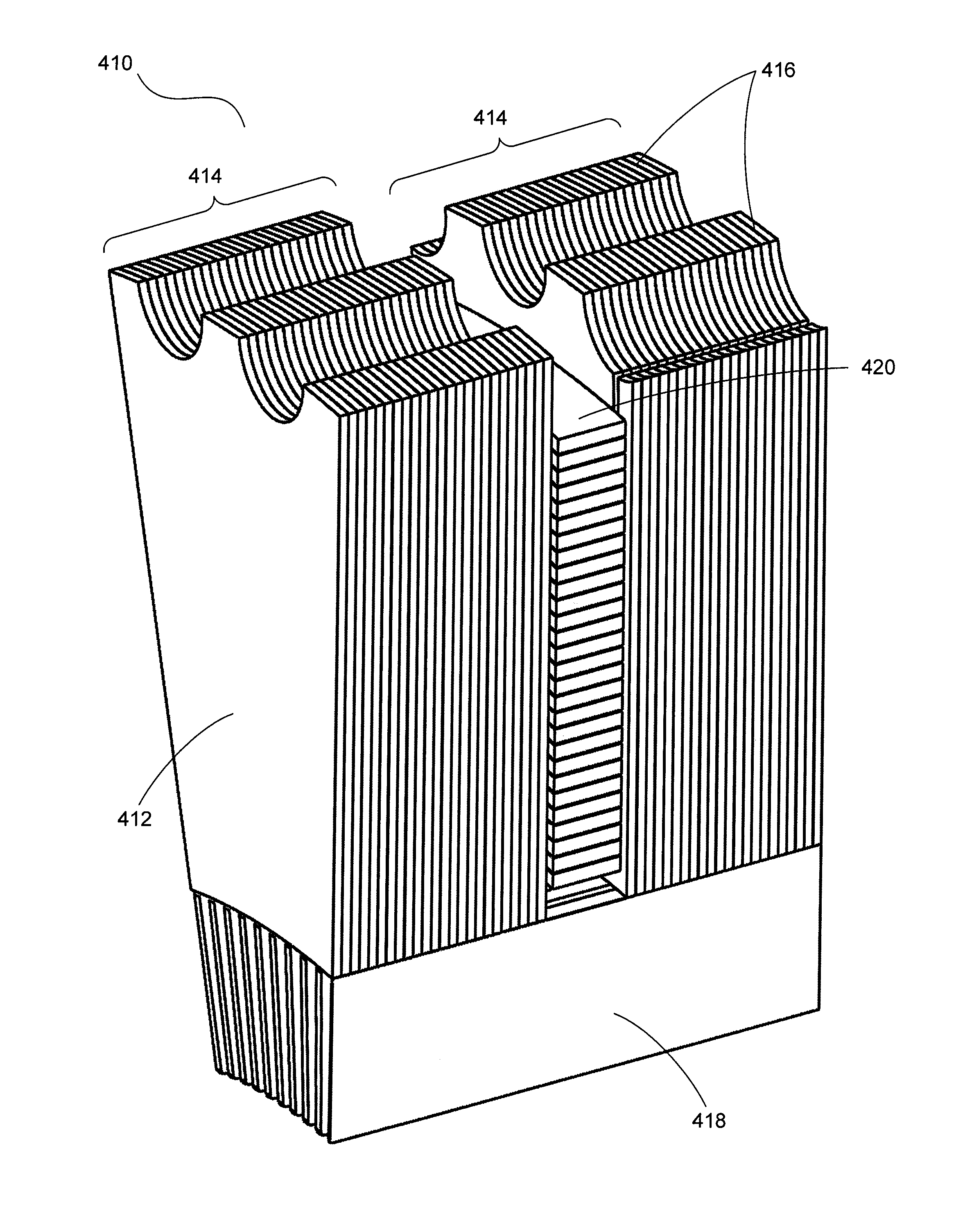
Transverse and/or commutated flux systems having segmented stator laminations
ActiveUS8405275B2Manufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsTransverse fluxEngineering
Electrical machines, for example transverse flux machines and / or commutated flux machines, may be configured to achieve increased efficiency, increased output torque, and / or reduced operating losses via use of laminated materials, for example laminated materials configured with cuts and / or segmentations. Segmentations may also assist with manufacturability, mechanical retention of components, and the like.
Owner:ELECTRIC TORQUE MASCH INC
Transverse regulated flux machine
ActiveUS20110133485A1Magnetic circuitMultiple ac dynamo-electric motors controlTransverse fluxPole piece
A machine has a rotor to be associated with a shaft. The rotor is provided with permanent magnets. A stator has pole pieces, including a main winding and flux diverters separating the main winding from a control coil. Control is provided for controlling the power passing through the control coil. The machine is a transverse flux machine. The machine may be utilized as a generator, an electric motor, or for other application.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
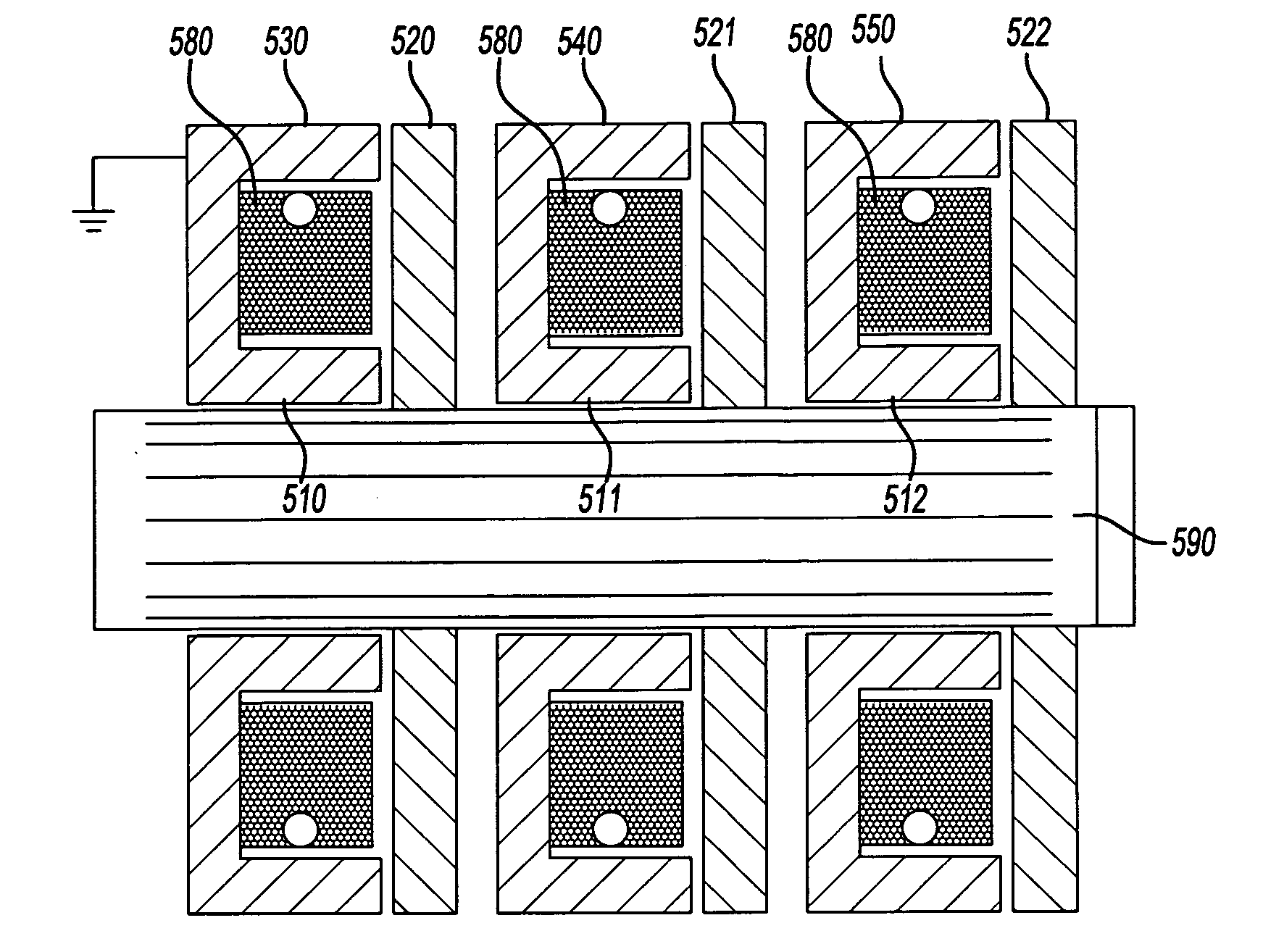
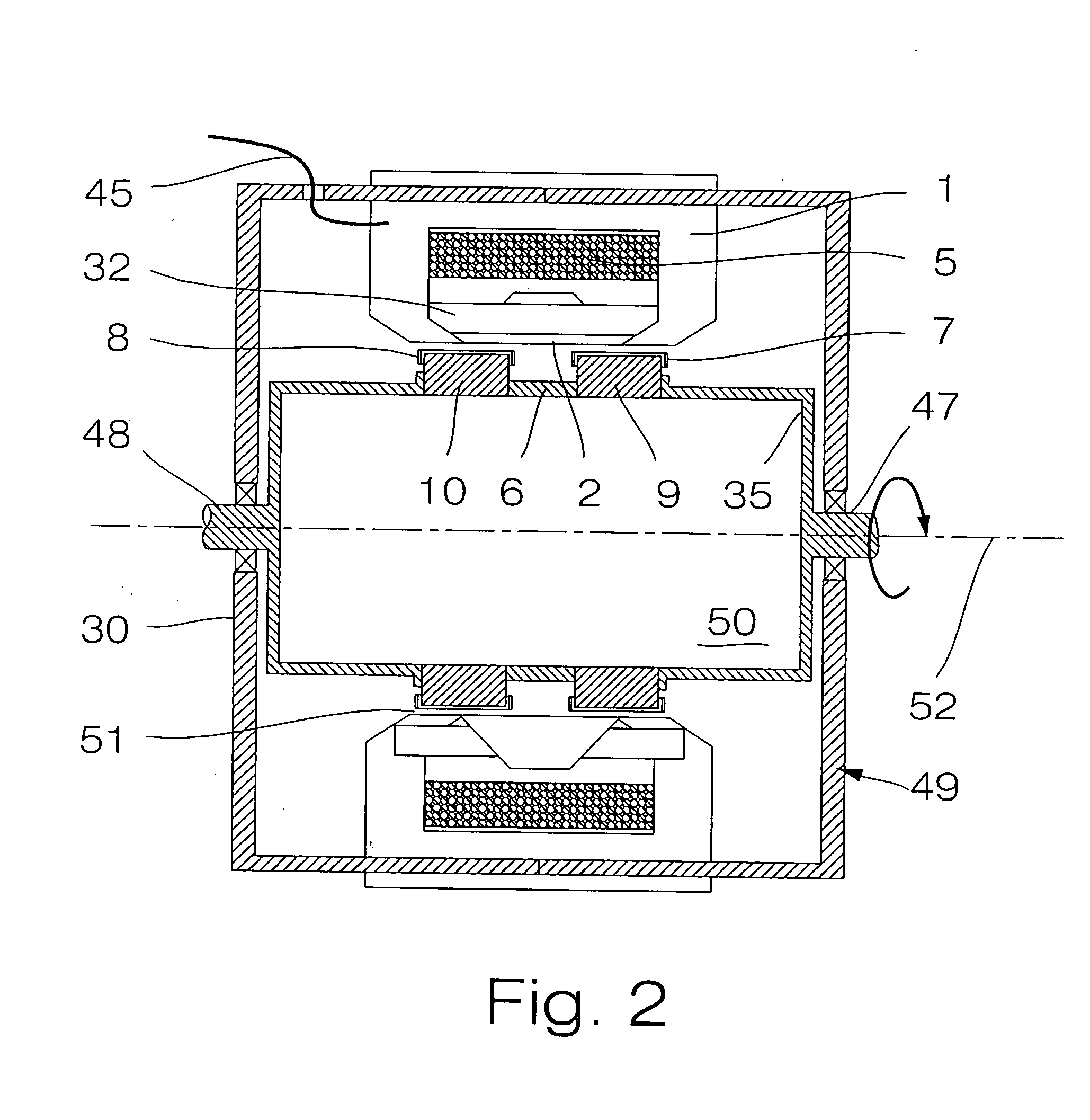
Electric Induction Heat Treatment of Electrically Conductive Thin Strip Material
Apparatus and method are provided for electric induction heat treatment of electrically conductive thin strip material. Multiple series-connected coil loops, each having a pole pair, are provided in each of a top and bottom induction coil, which are positioned mirror image to each other. The top and bottom induction coils form a transverse flux induction heat treatment apparatus. A separate flux concentrator is provided over and on the side of each pole. The thin strip material passes between the poles of the top and bottom induction coils and the flux concentrators associated with each of the poles.
Owner:RADYNE CORP
Flux switching type magnetic-concentration transverse flux permanent magnetic wind generator
InactiveCN101741197AAvoid the situation that only corresponds to one stator coreIncreased torque densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxElectric machine
The invention relates to a flux switching type magnetic-concentration transverse flux permanent magnetic wind generator, in particular to a novel high-performance and direct-driving type transverse flux permanent magnetic wind generator. The generator comprises a stator, a rotor, permanent magnets and a winding. The stator consists of a plurality of stator cores (1) and an armature winding (5), wherein the stator cores (2) are distributed around the rotor. Two adjacent stator cores (1) in the circumferential direction are arranged in bilateral symmetry, and the stator cores are arranged on a casing (7) made from non-magnetic conductive material. Rotor cores (4) are arranged on a barrel (8) made from the non-magnetic conductive material. The barrel is connected with a motor rotary shaft (6), and is connected with a motor casing (7) through a bearing (9). Both sides of the rotor cores (4) are respectively embedded into permanent magnets (2) and (3), and the pole directions are opposite. The pole directions of the permanent magnets (2) and (3) of two adjacent rotor cores (4) in the peripheral direction are opposite. According to the motor structure, the single-phase generator can be manufactured, and the multiple-phase generator also can be manufactured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com