Patents
Literature
2034results about "Synchronous machine details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
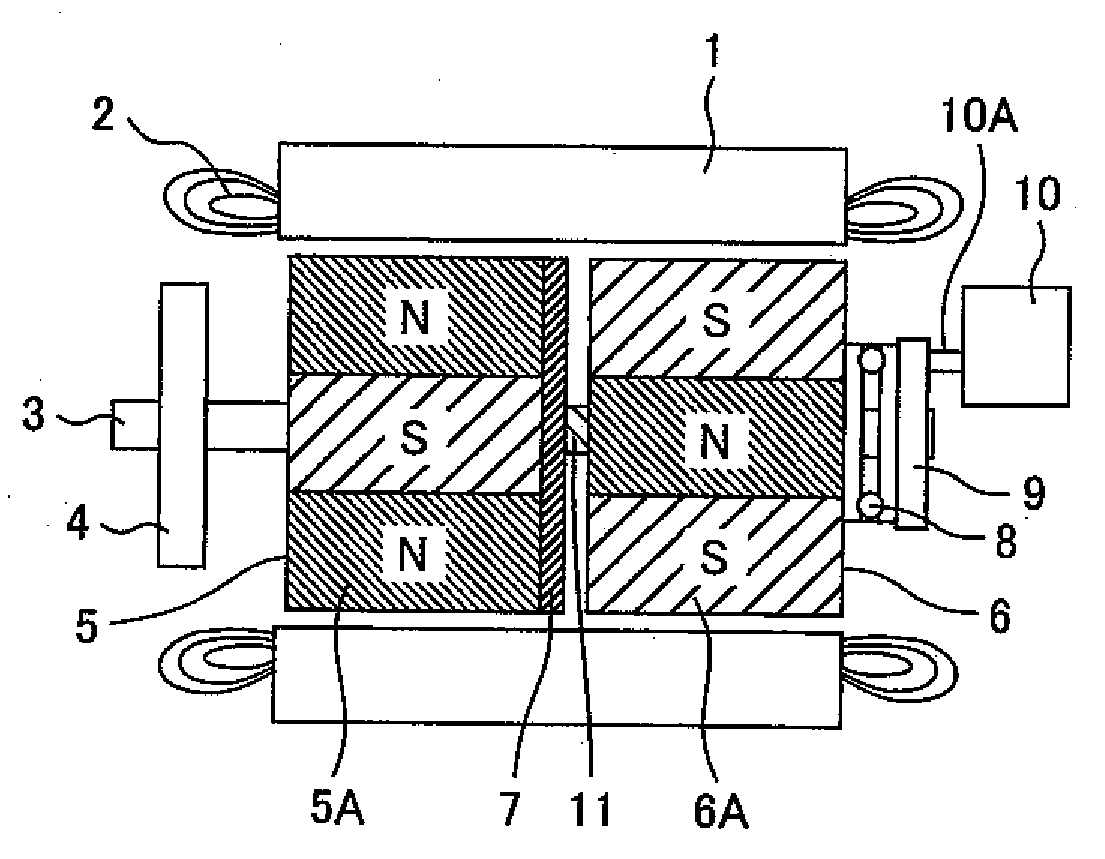
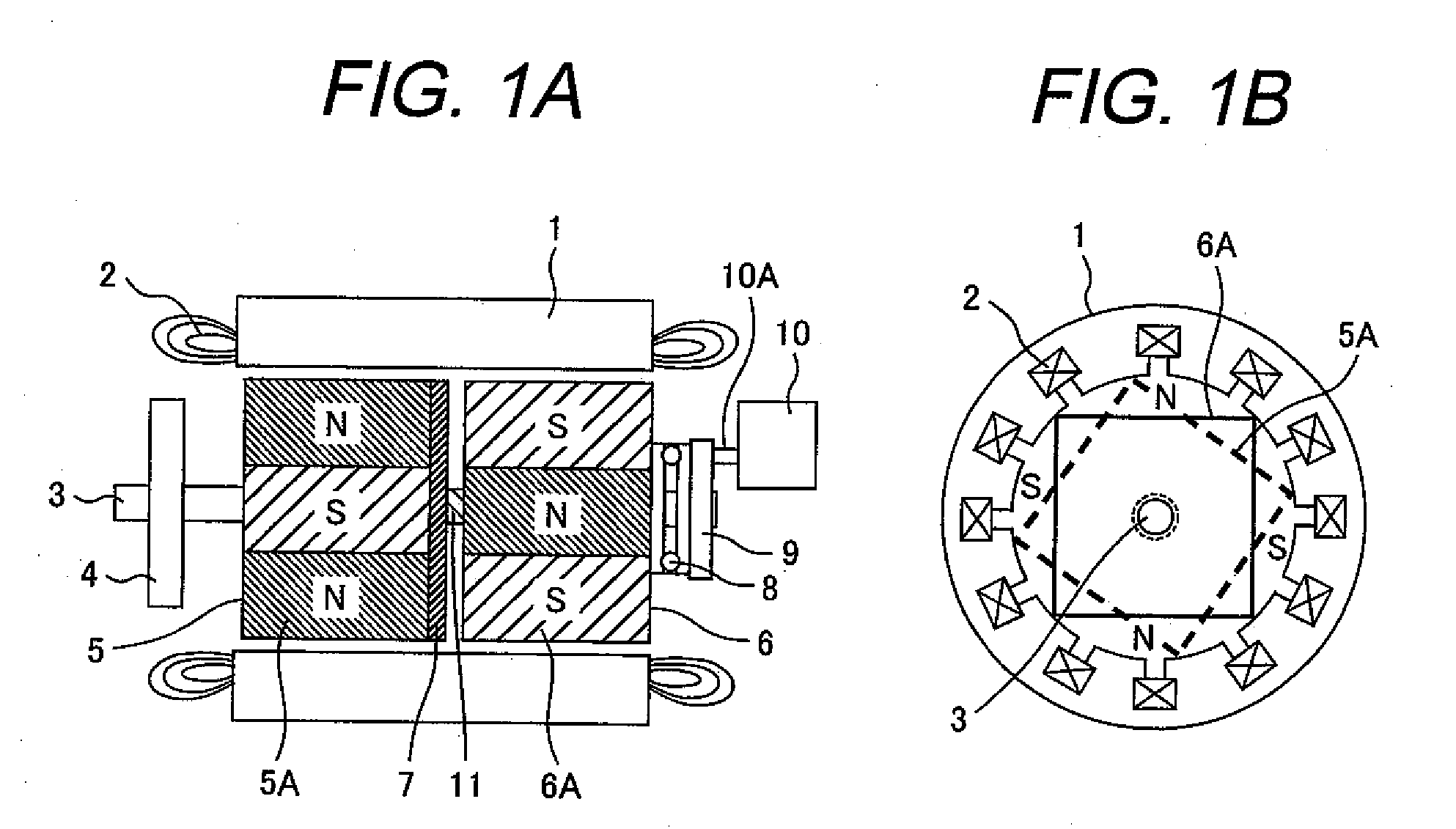
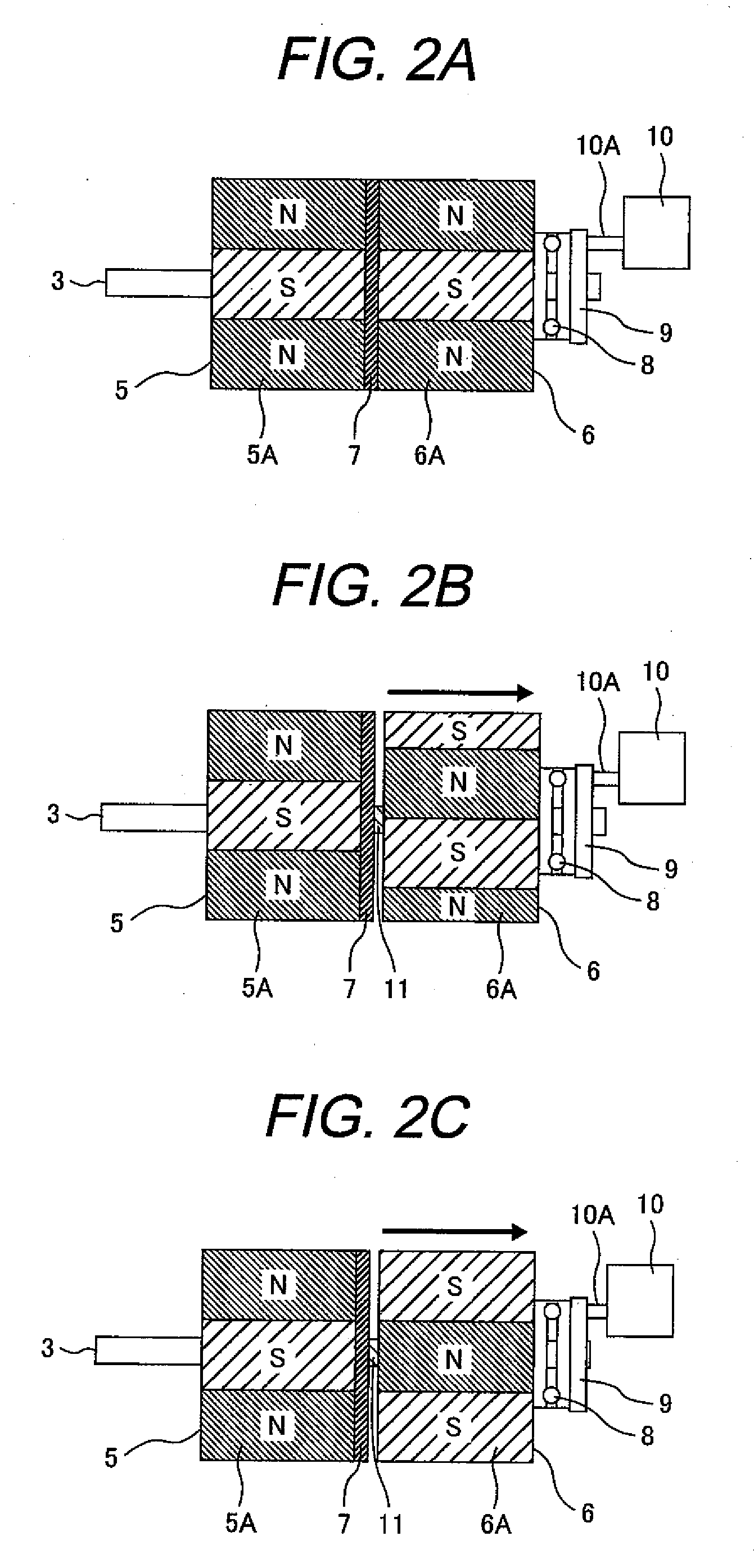
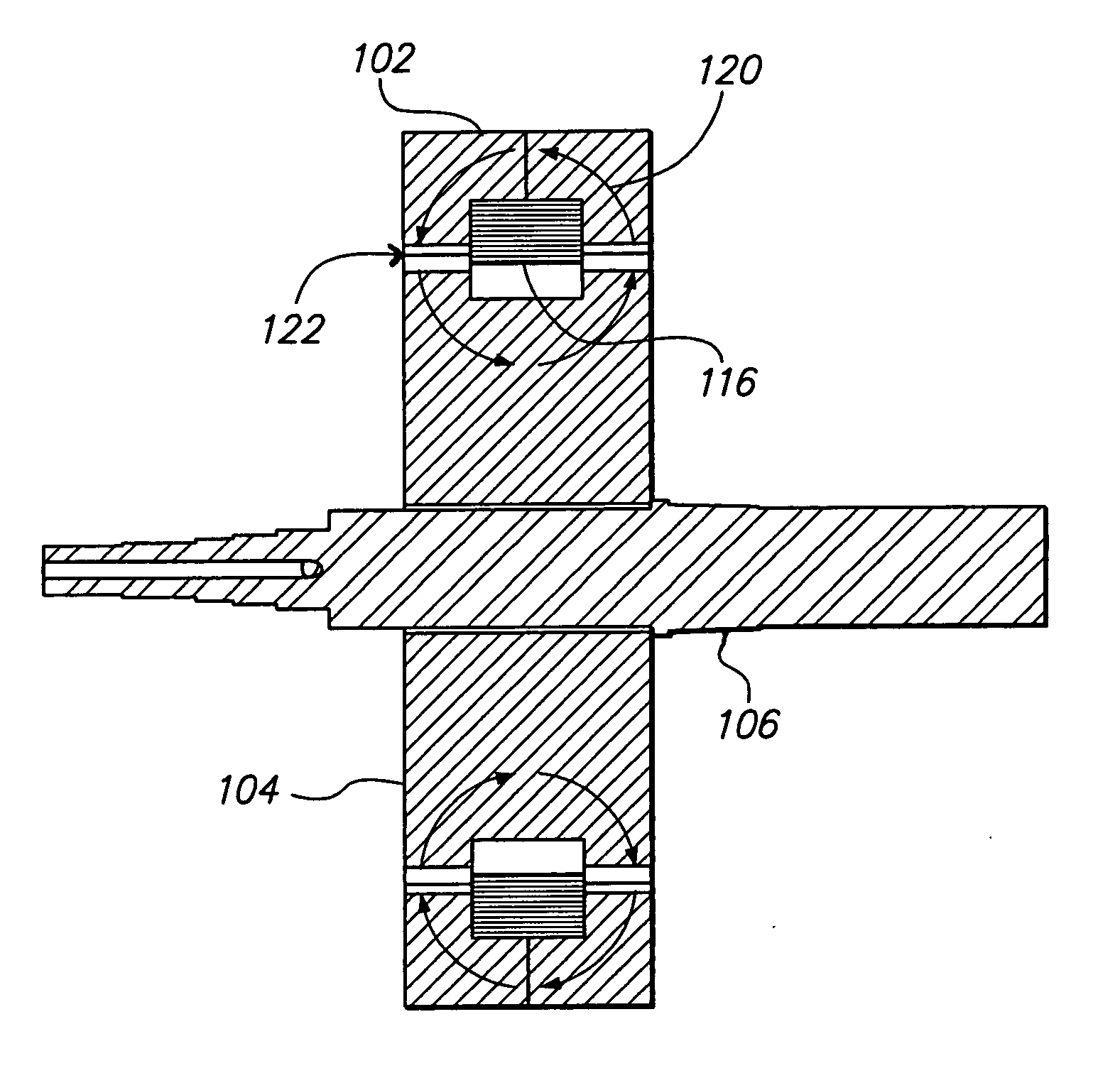
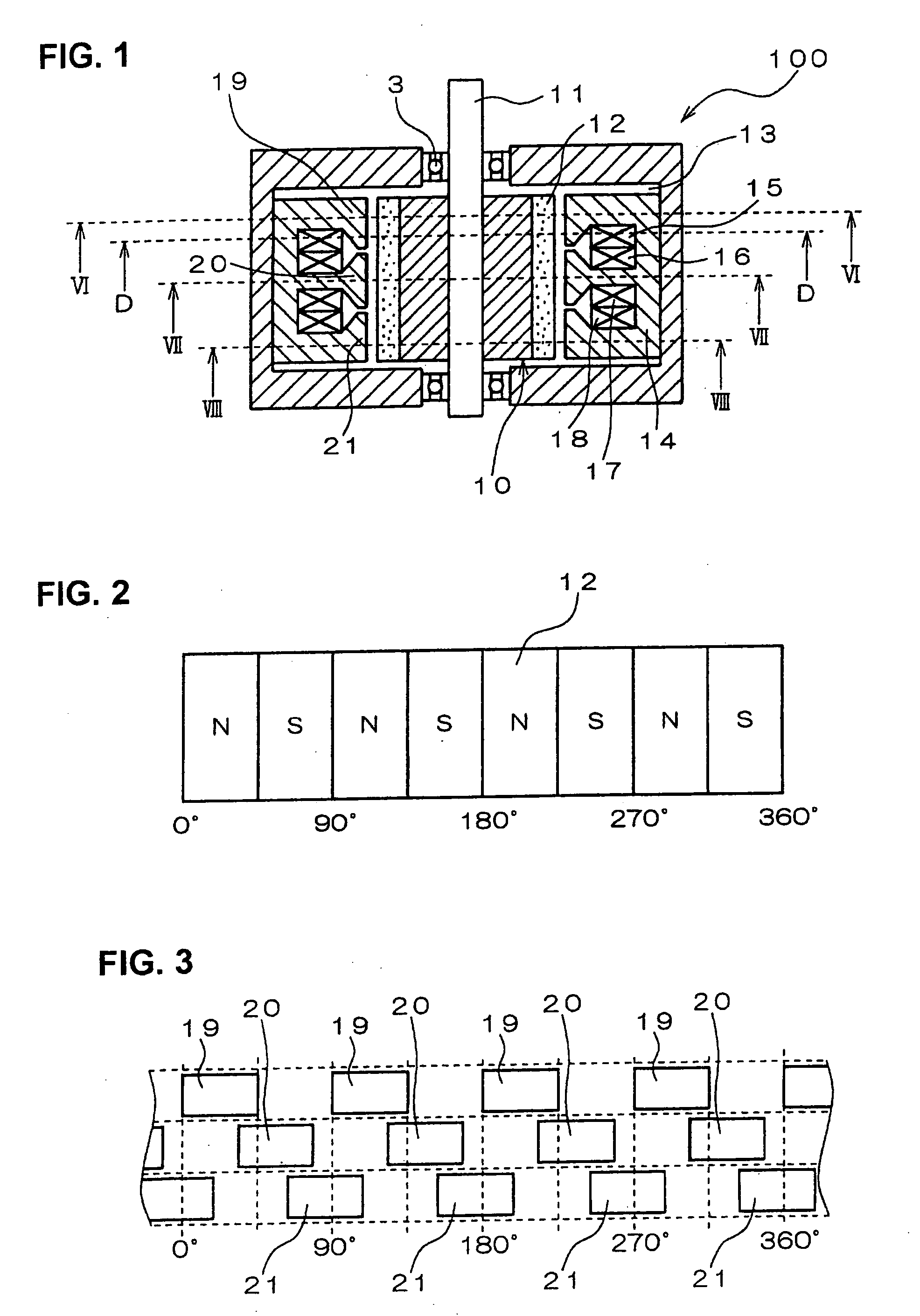
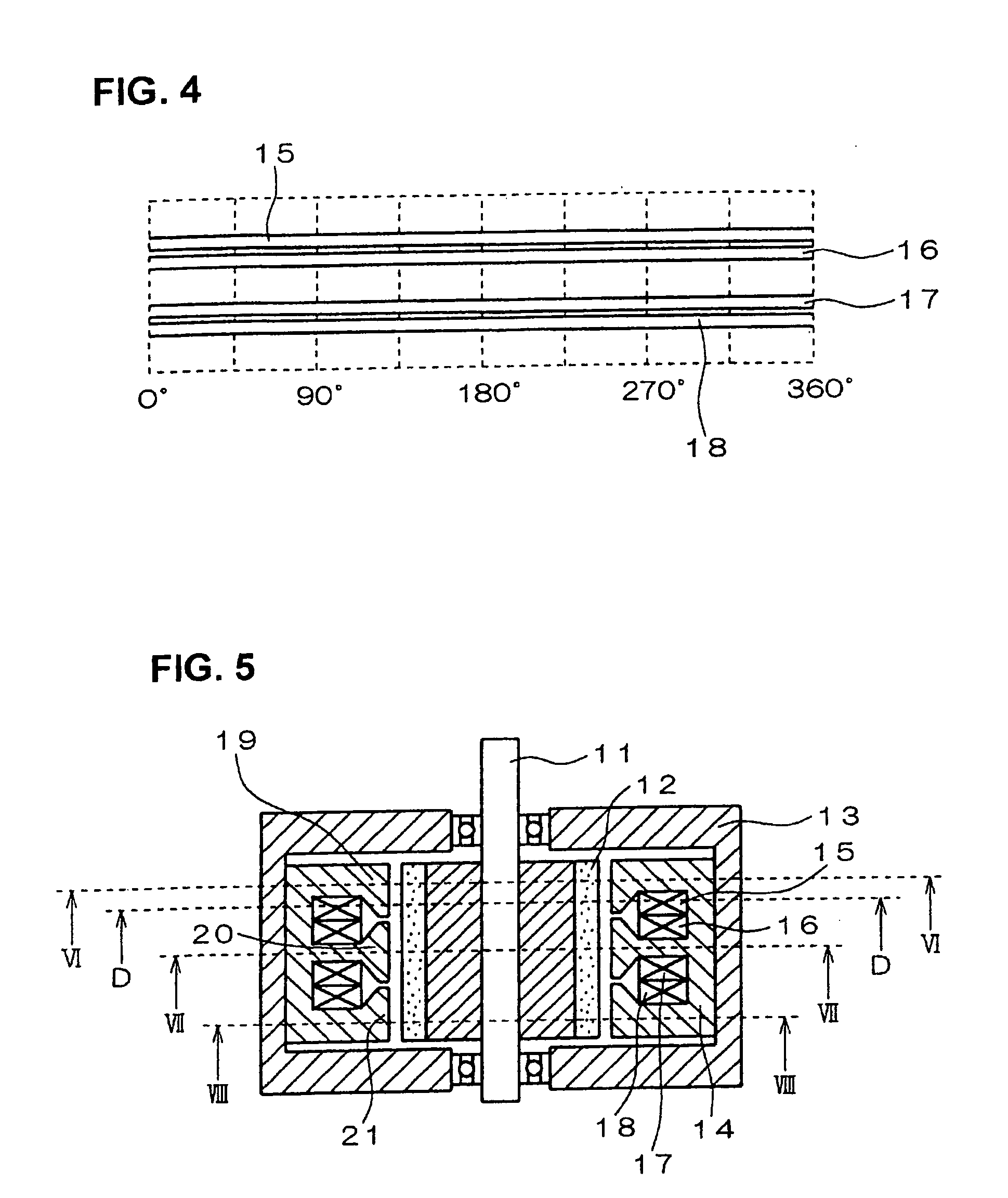
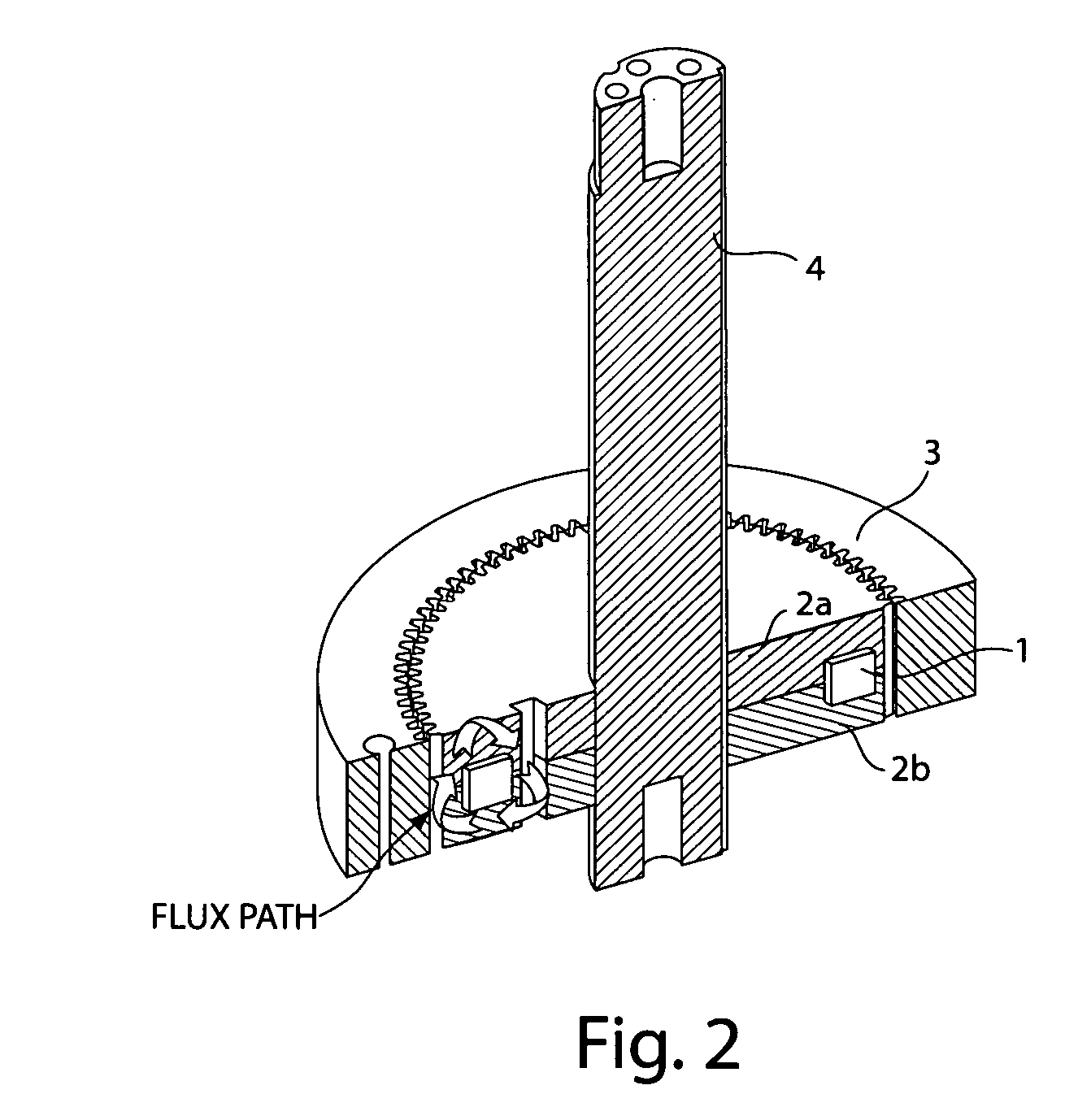
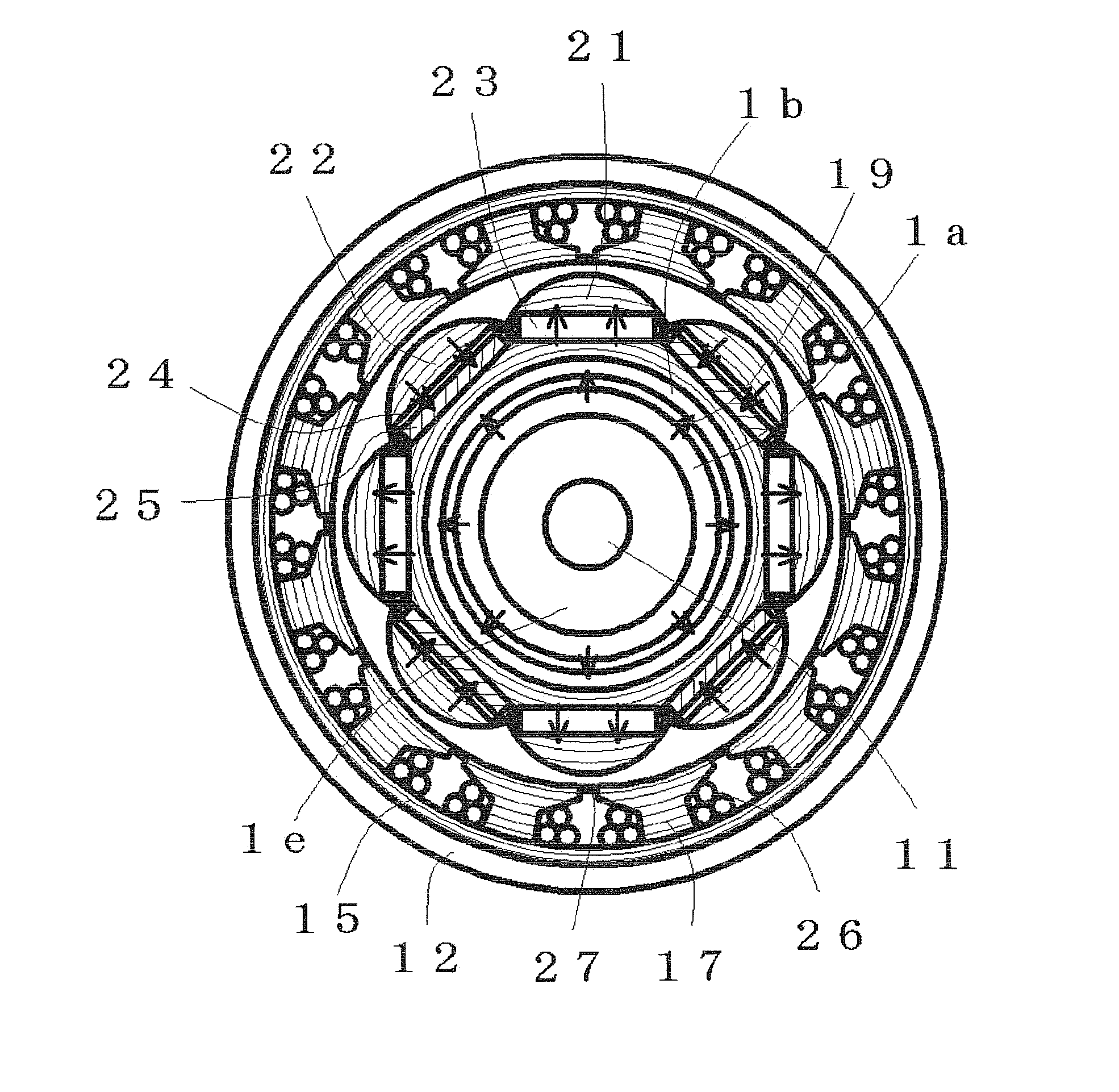
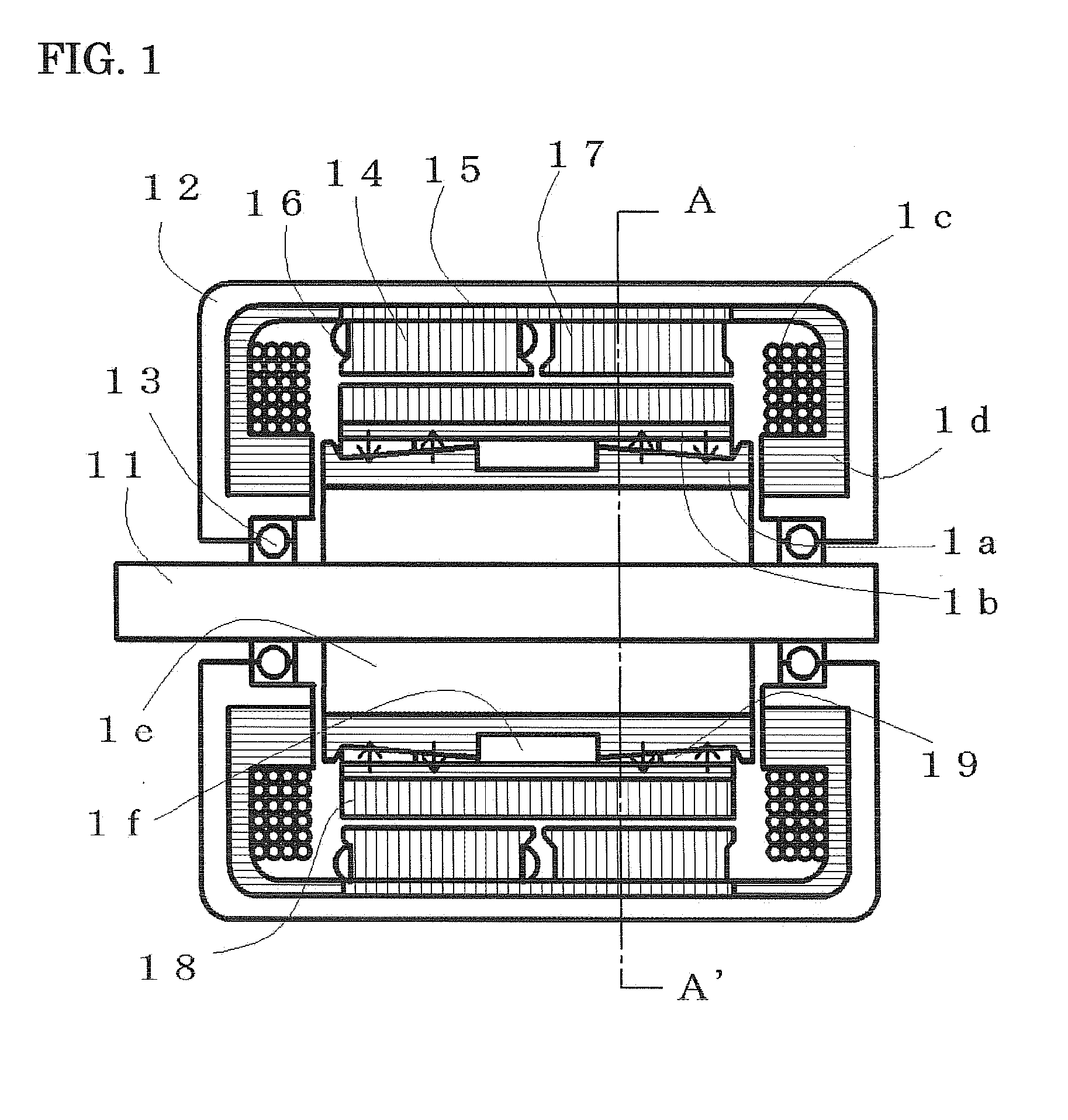
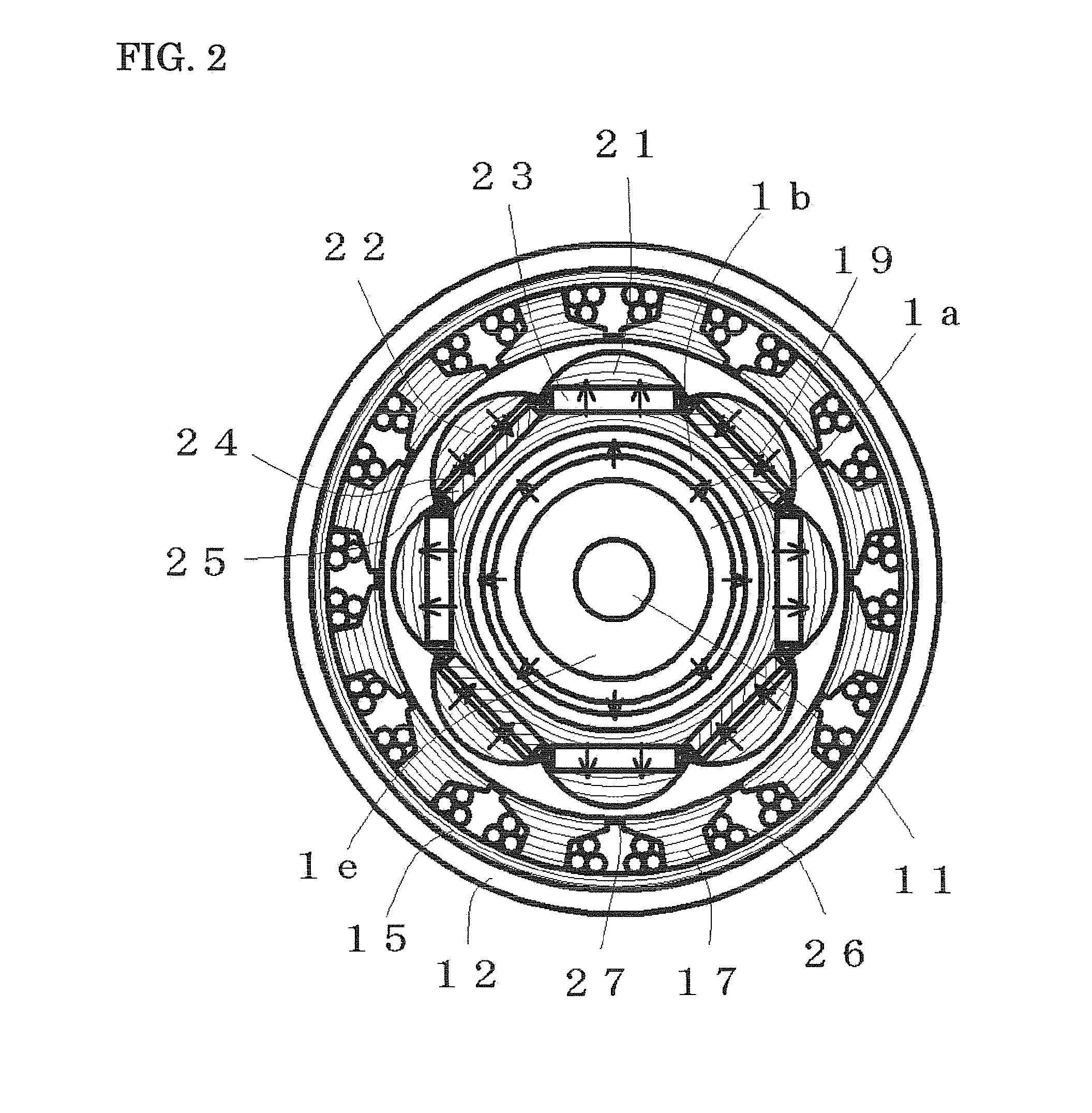
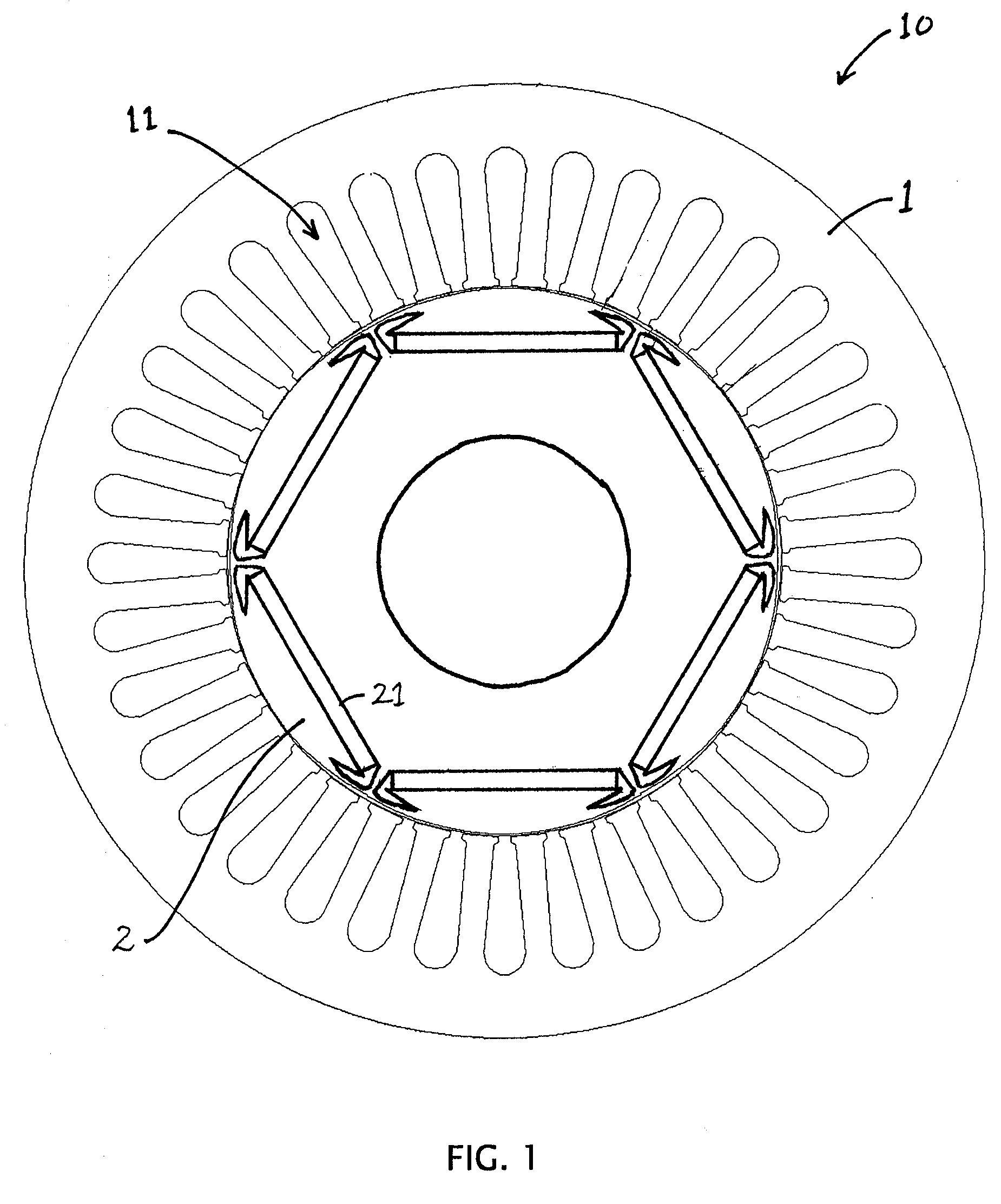
Variable magnetic flux electric rotary machine
InactiveUS20100164422A1Easy to operateWide operating speed rangeDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesElectrical polarityEngineering
An electric rotary machine is disclosed which can adjust relative angles of sub-rotors continuously and regardless of torque direction without generating an attractive force between the field magnets of the sub-rotors. The electric rotary machine includes: a stator having a winding; a dual rotor which is rotatably disposed with a gap from the stator and divided axially along a shaft into a first rotor and a second rotor each having field magnets with different polarities arranged alternately in a rotation direction; a mechanism for varying the axial position of the second rotor relative to the first rotor continuously; and a non-magnetic member located between the first rotor and the second rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
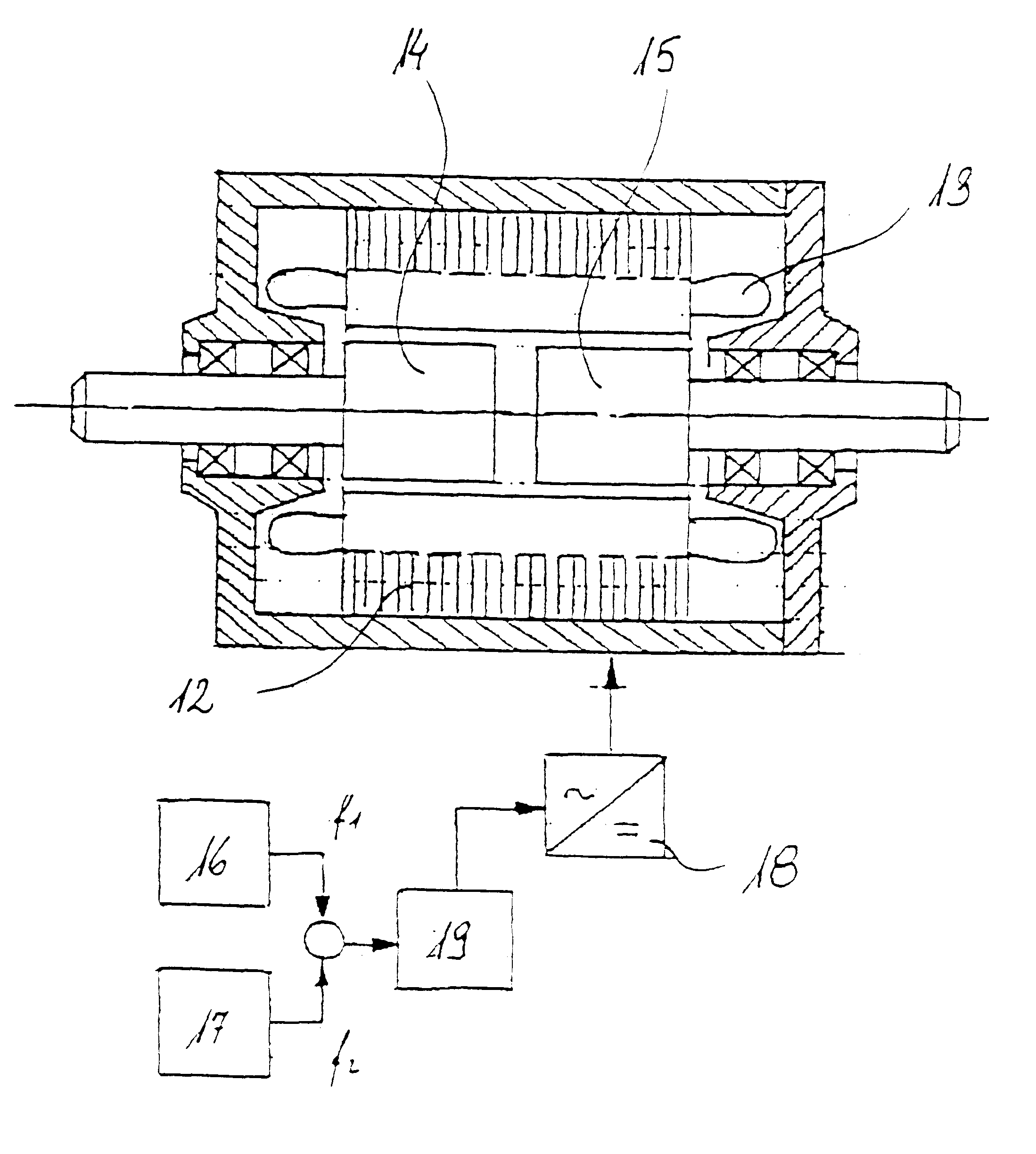
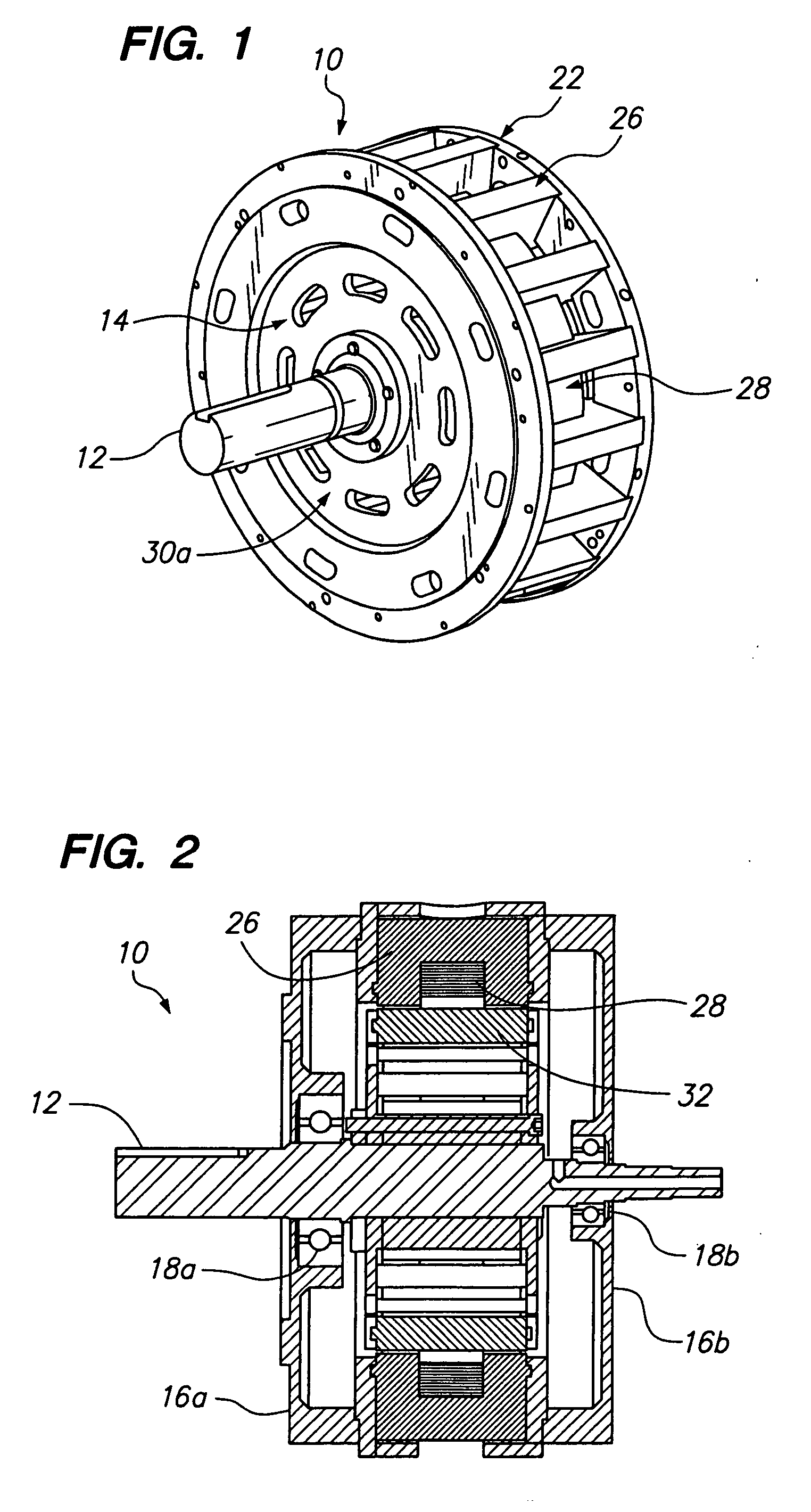
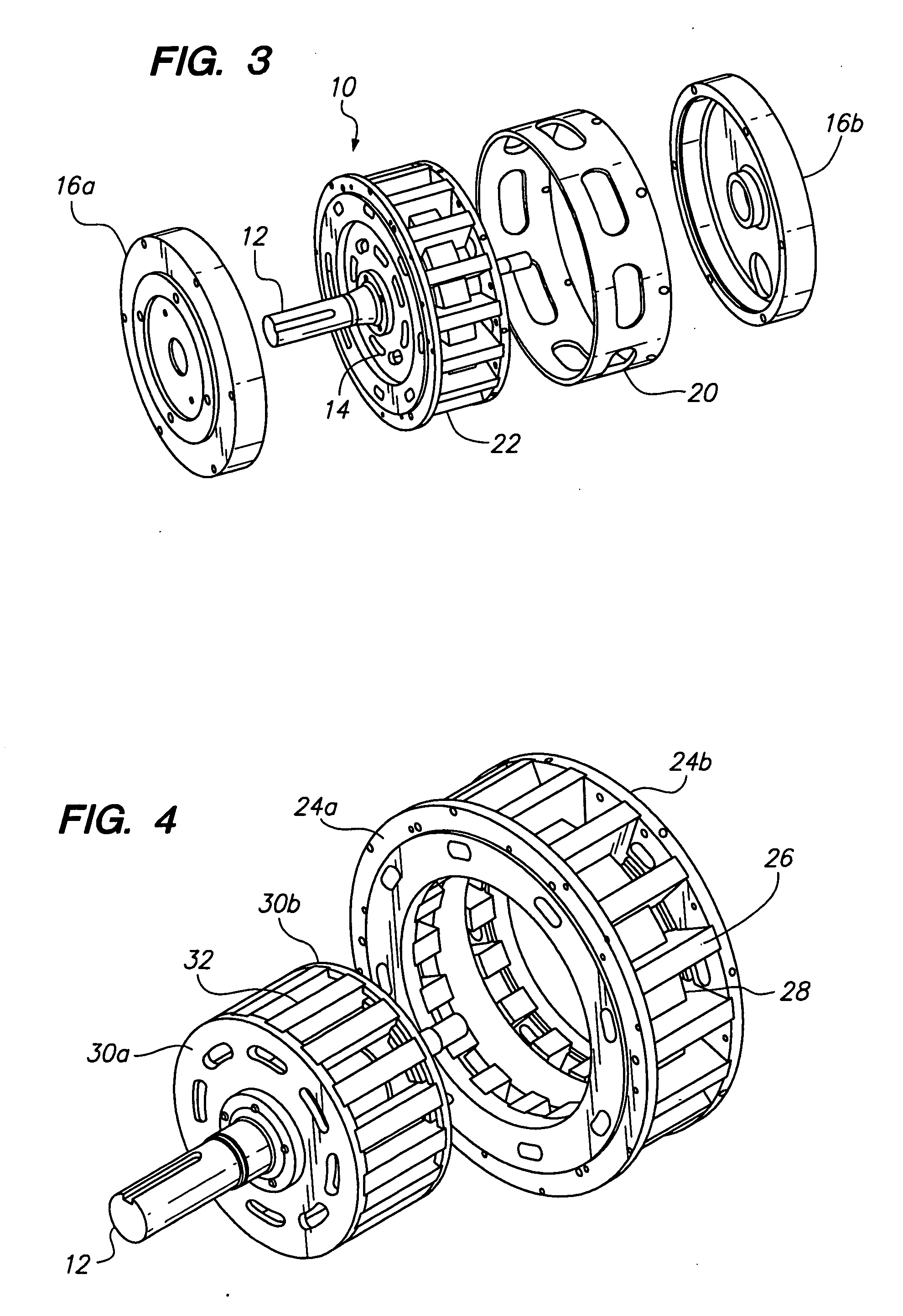
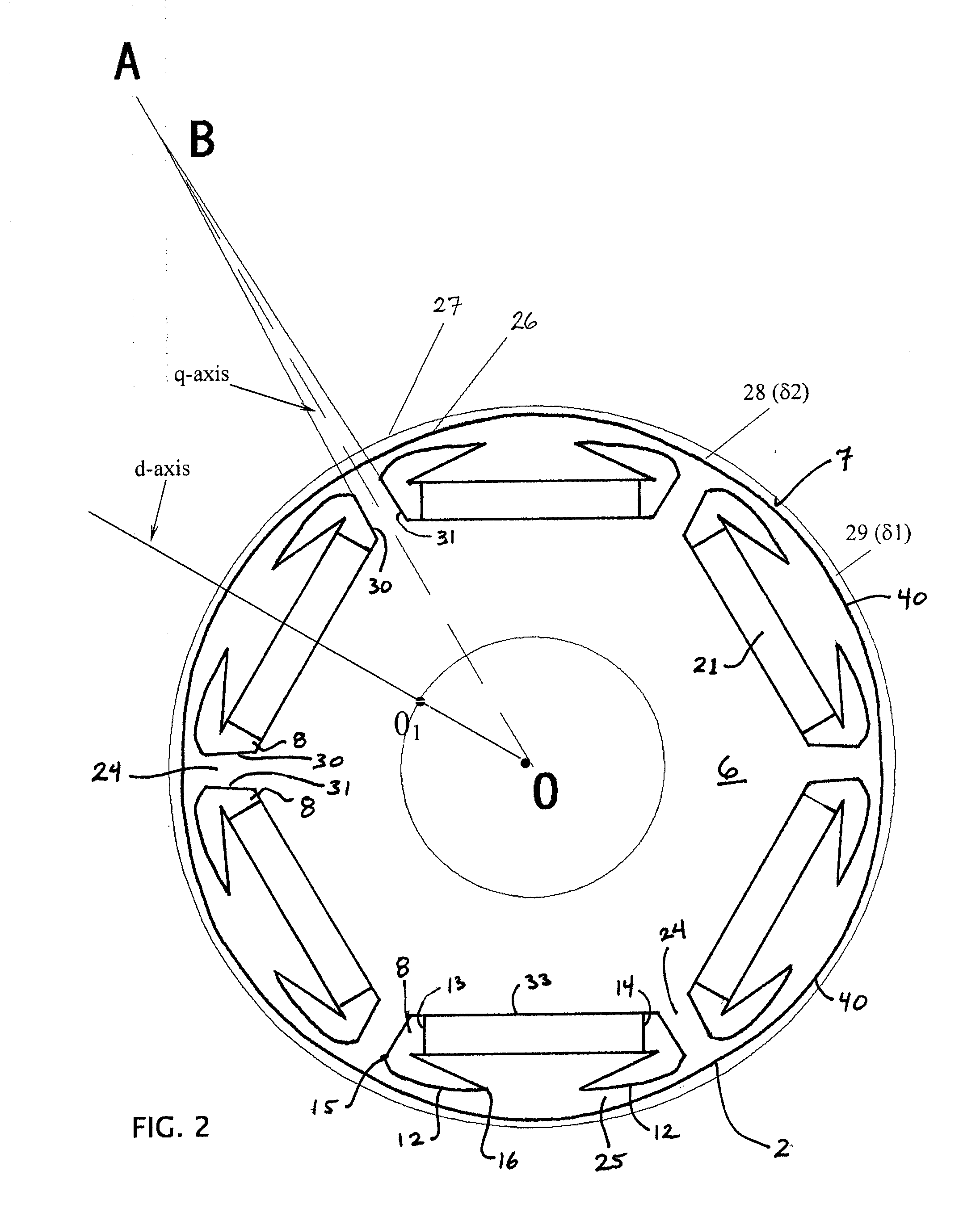
Electric machine
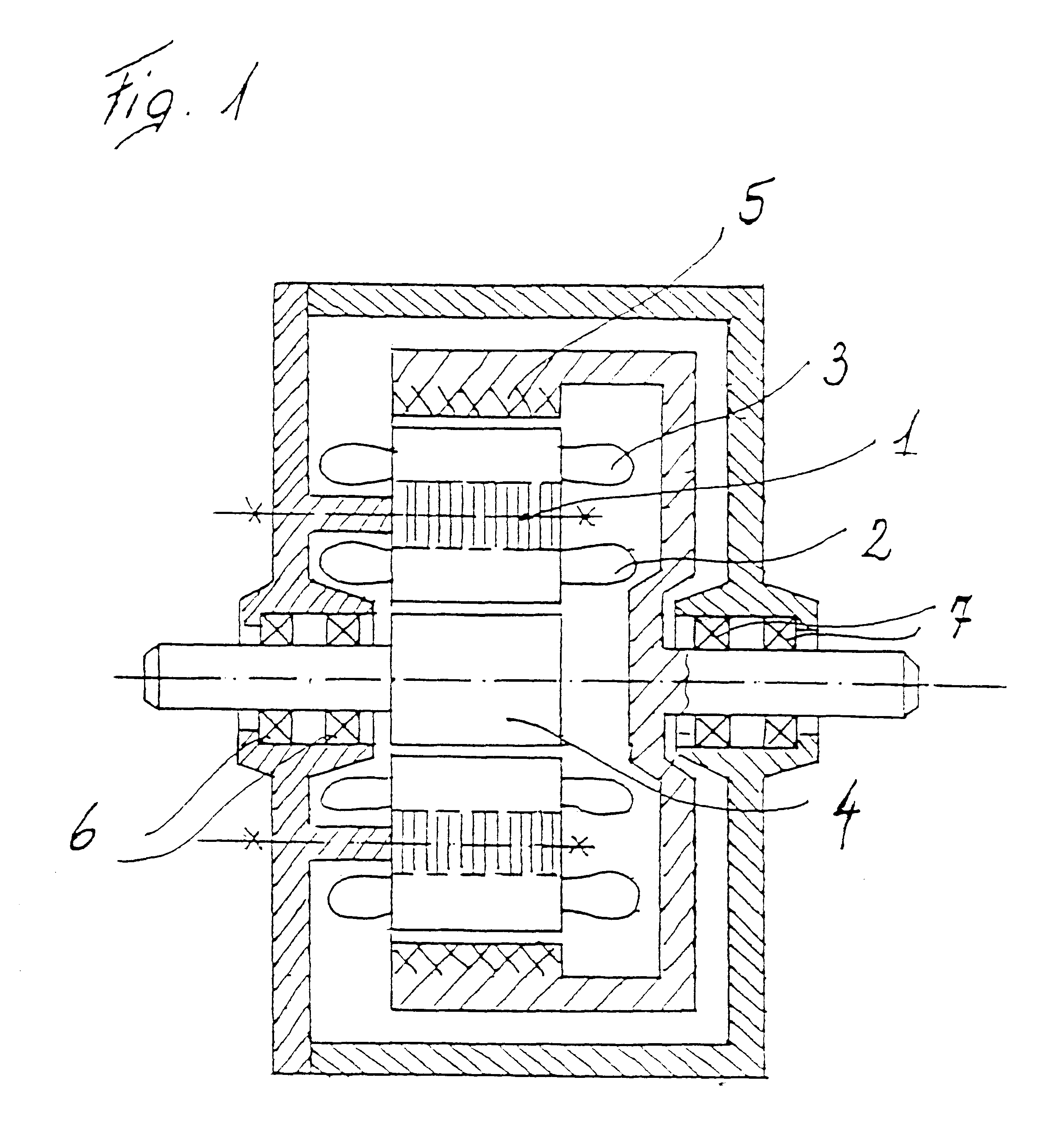
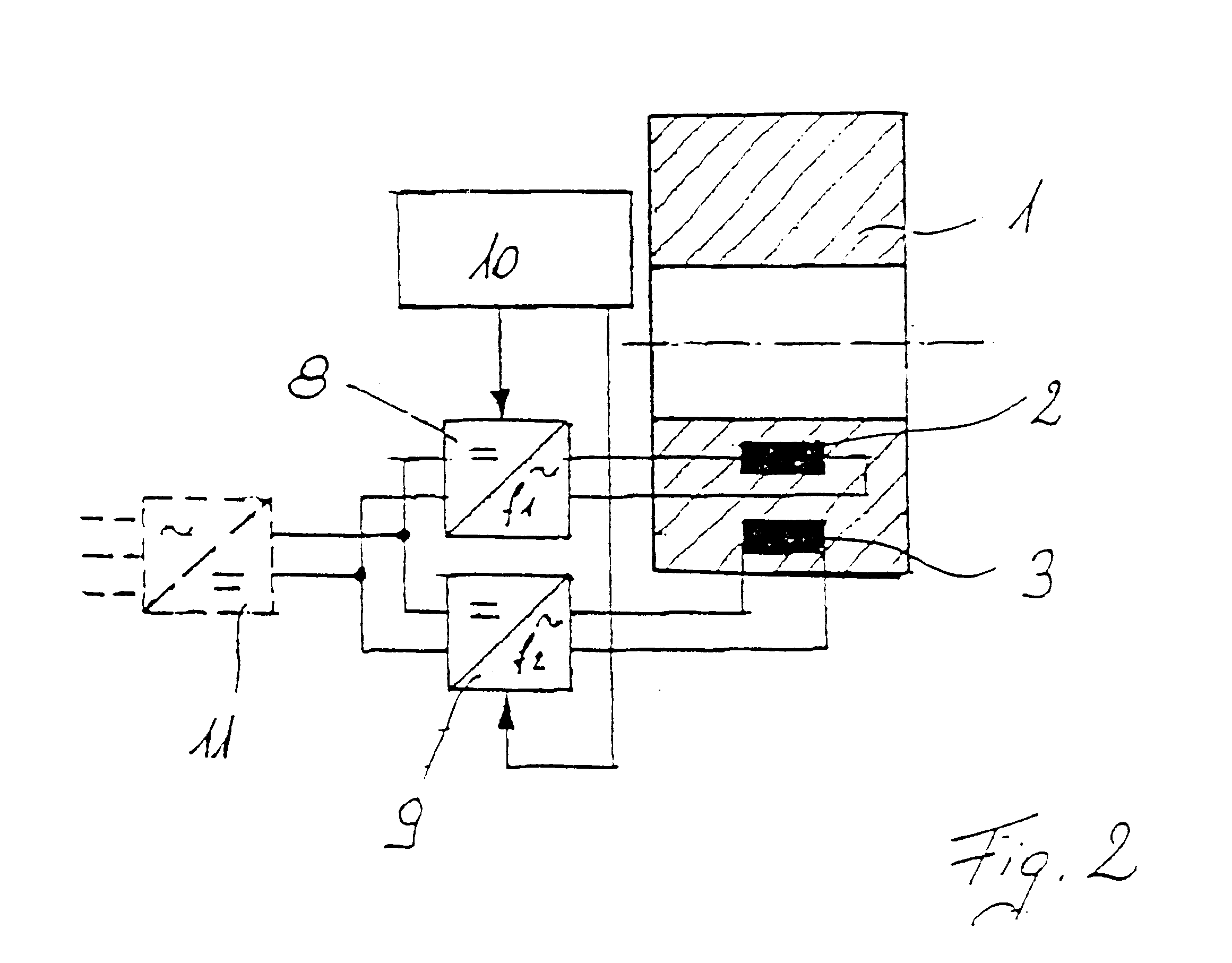
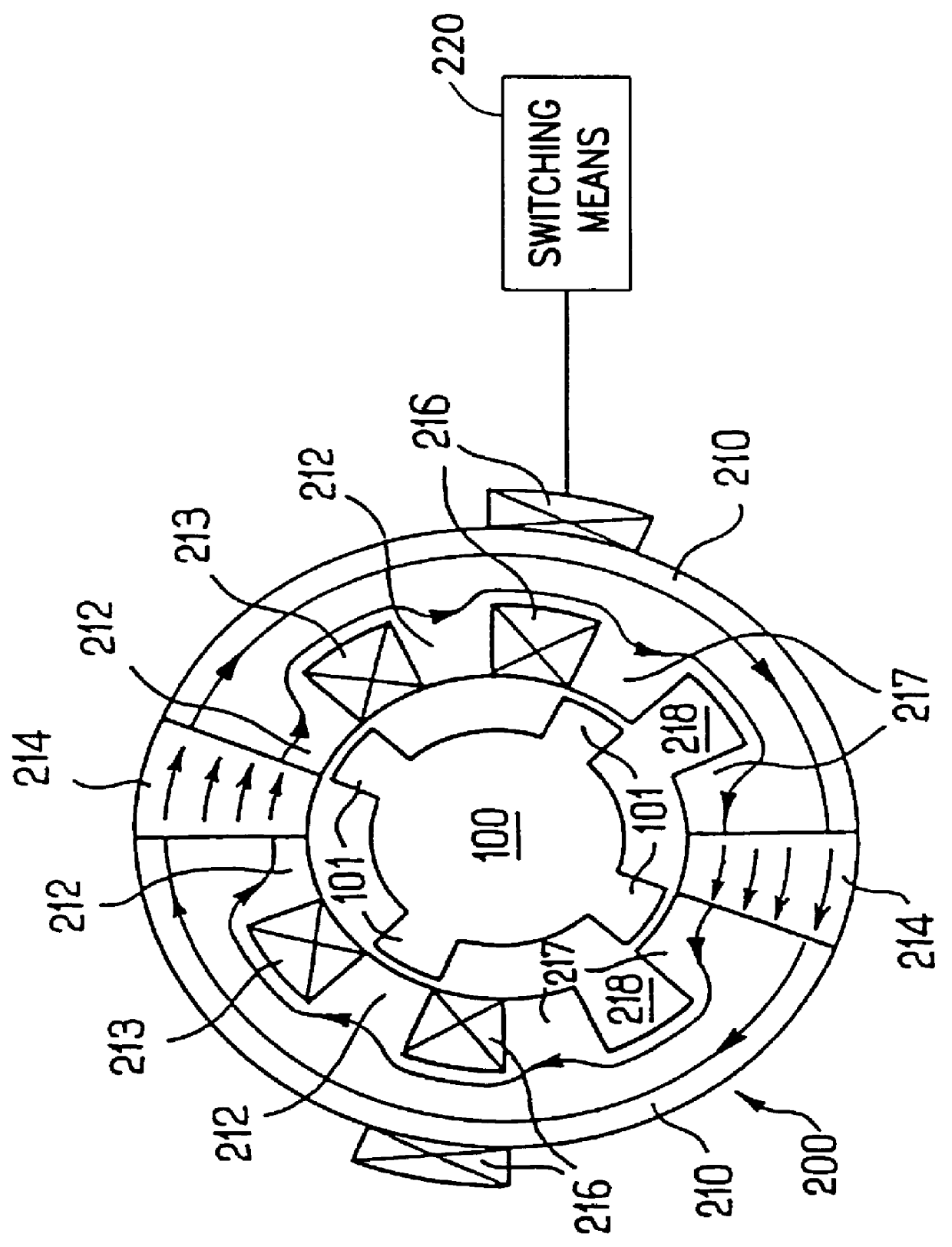
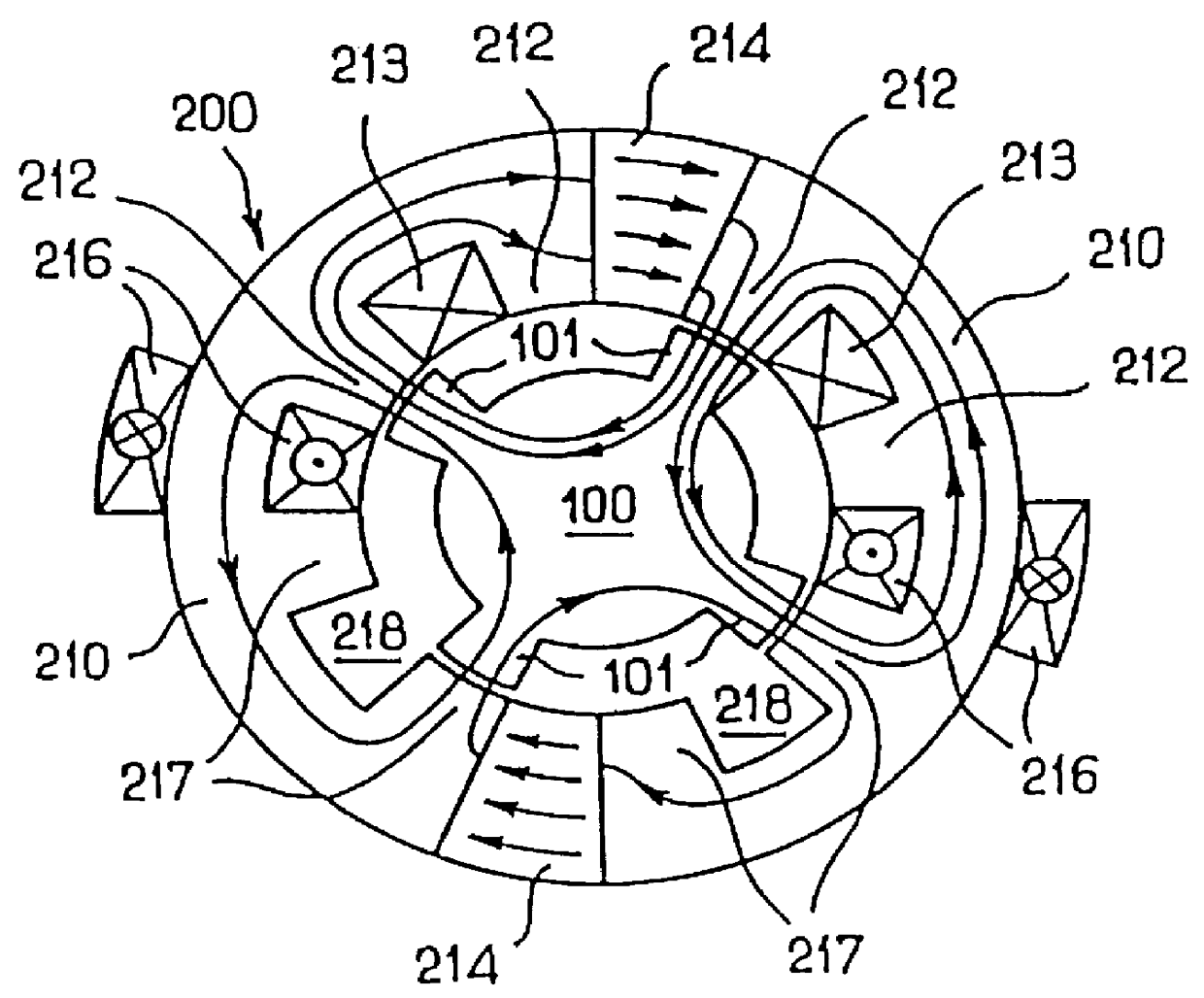
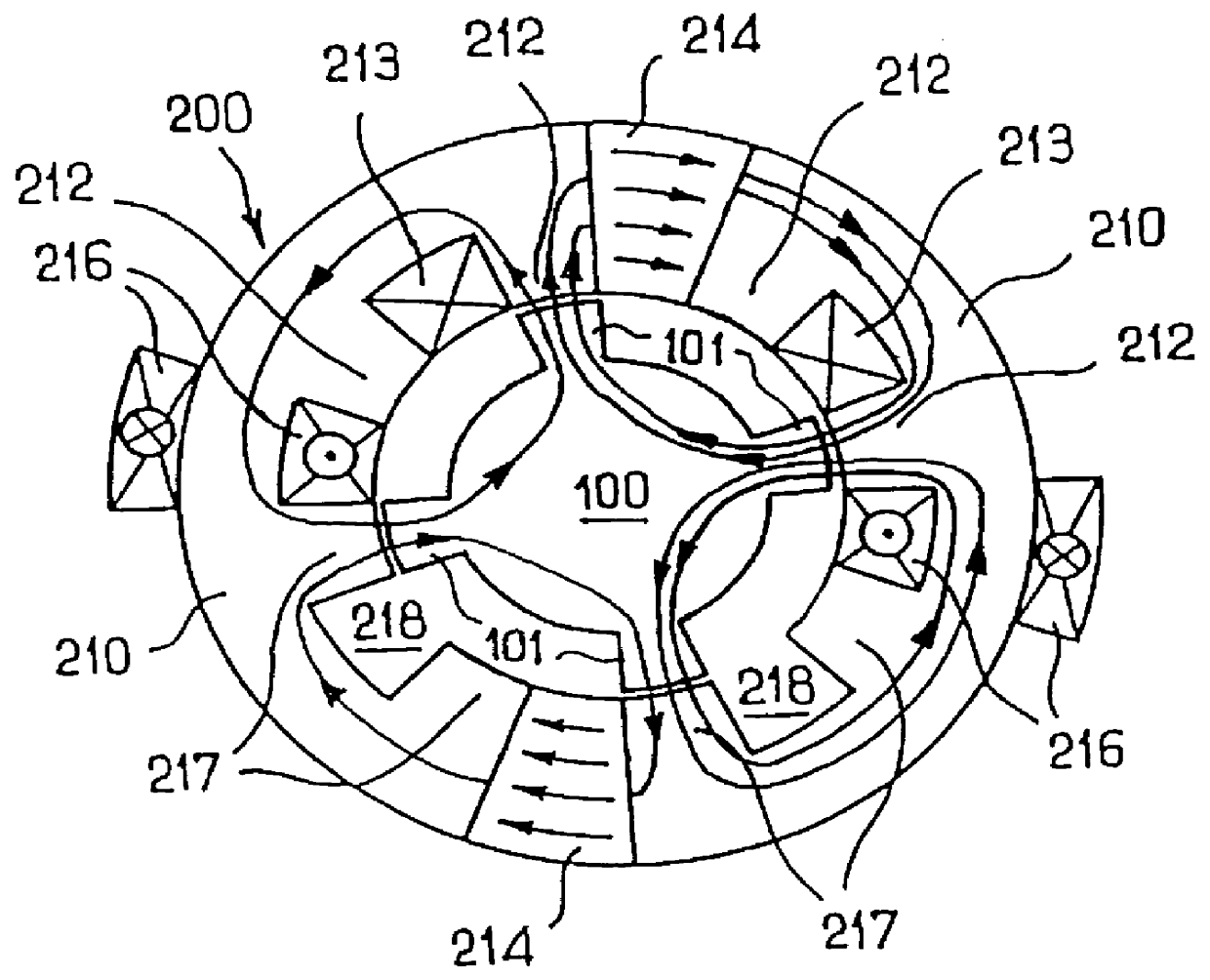
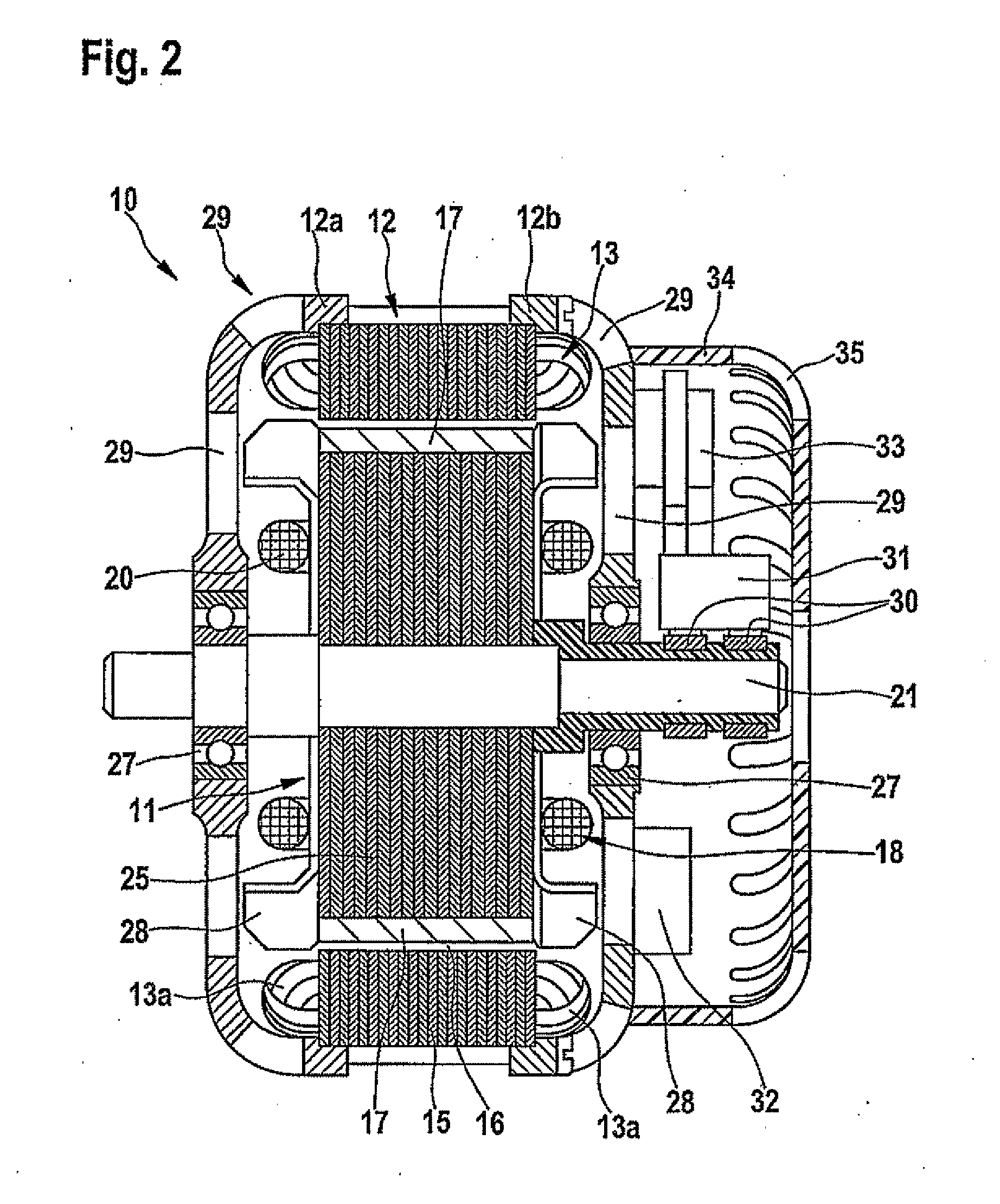
InactiveUS6373160B1Economically manufacturedEconomically usedSpeed controllerSynchronous machine detailsElectric machineEngineering
Electric rotary current machine that includes a casing and a stator fitted within the casing. The stator has at least one stator winding. At least two mechanically separate rotors are rotatably mountable within the casing and have a same axis of rotation. In this way, each rotor has electromagnetic interaction with the stator when the stator is electromagnetically active. The rotor speeds are the same or different. A motor control is arranged to control a supply to at least one of said at least one stator winding by superposition of at least two rotary field components, one for each rotor.
Owner:SCHRODL MANFRED
Magnetic drive devices, and related systems and methods
A magnetic drive device may comprise a stator comprising a plurality of windings for generating a first number of magnetic pole pairs and a rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets for generating a second number of magnetic pole pairs that differs from the first number of magnetic pole pairs. The magnetic drive device may further comprise a plurality of free-spinning interpole elements disposed within an air gap between the stator and the rotor. The interpole elements may produce a magnetomotive force and harmonically couple the magnetic pole pairs of the stator with the magnet pole pairs of the rotor.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
High-power low-RPM DC motor
InactiveUS6194799B1Increase profitIncreasing motor torqueAsynchronous induction motorsPropulsion by batteries/cellsEngineeringConductor Coil
A high power low RPM direct current electric motor is disclosed whereby the high power output is achieved in one of two ways or both. In the first case, the need for cooling is reduced simultaneously along with an increase in the utilization of the magnetic field present in the motor permanent magnets. This is achieved by wrapping the electromagnet core with windings that are capable of demagnetizing the rotor permanent magnets under stall conditions. Interlocking motor circuitry is provided which prevents the full activation of these motor windings until motor RPM values reach a safe level. This increases motor power while decreasing resistive losses in electromagnet windings. In the second case, the rotary portion consists of a large diameter relatively flat rotor containing permanent magnets and having built in vanes for moving air over the electromagnet stator windings providing forced air cooling.
Owner:MAGNETIC MOTORS
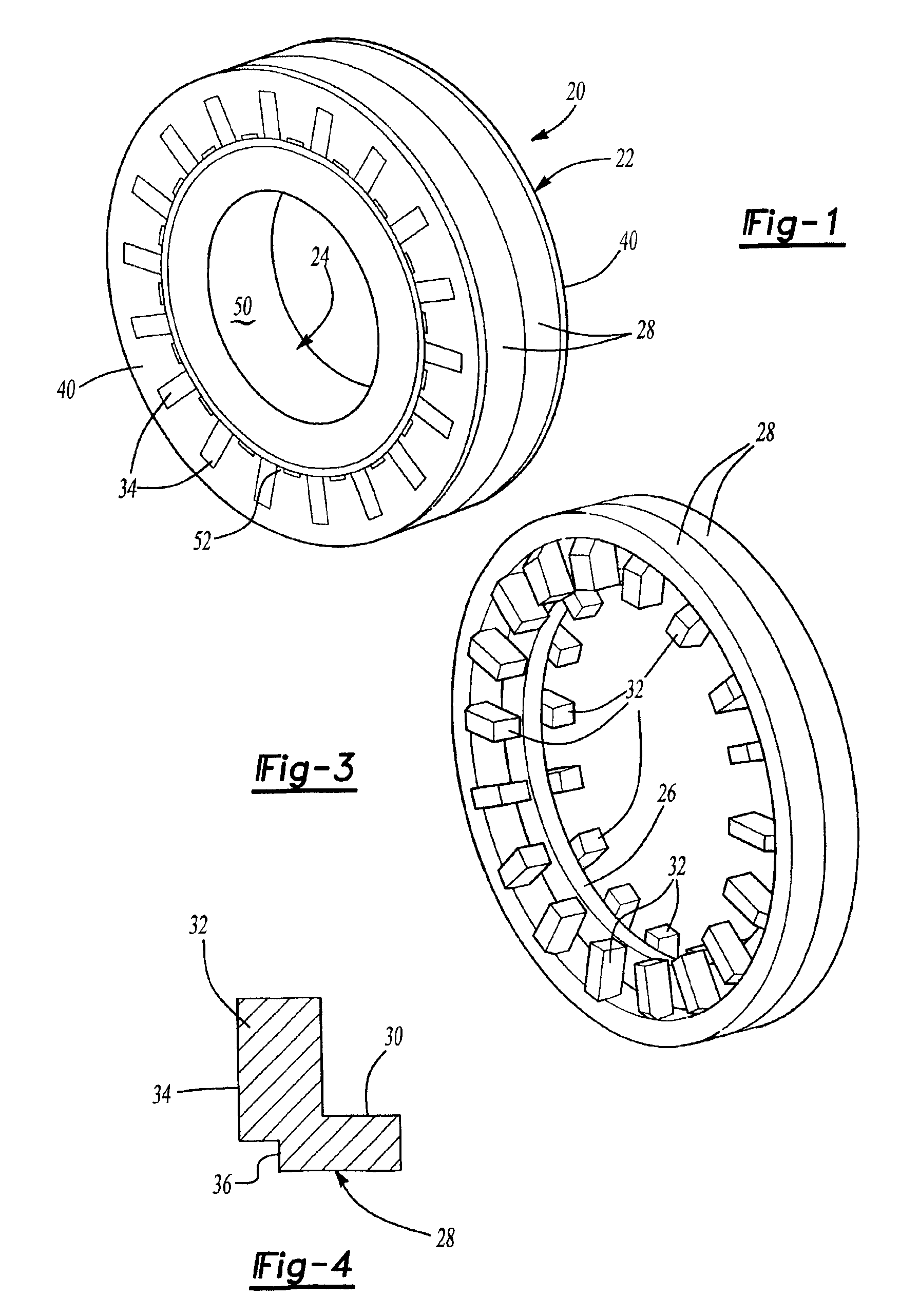
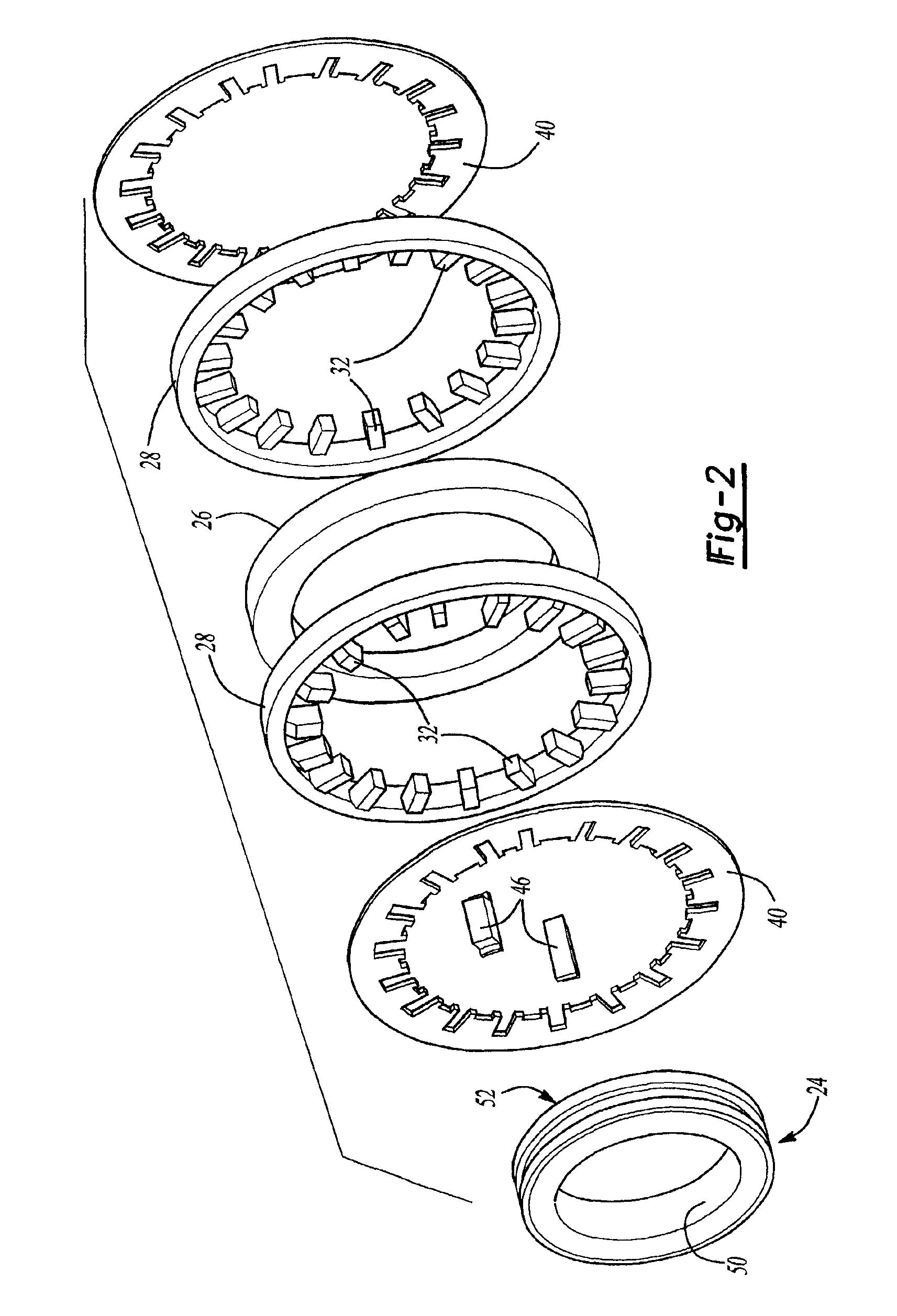
Rotating electric machine
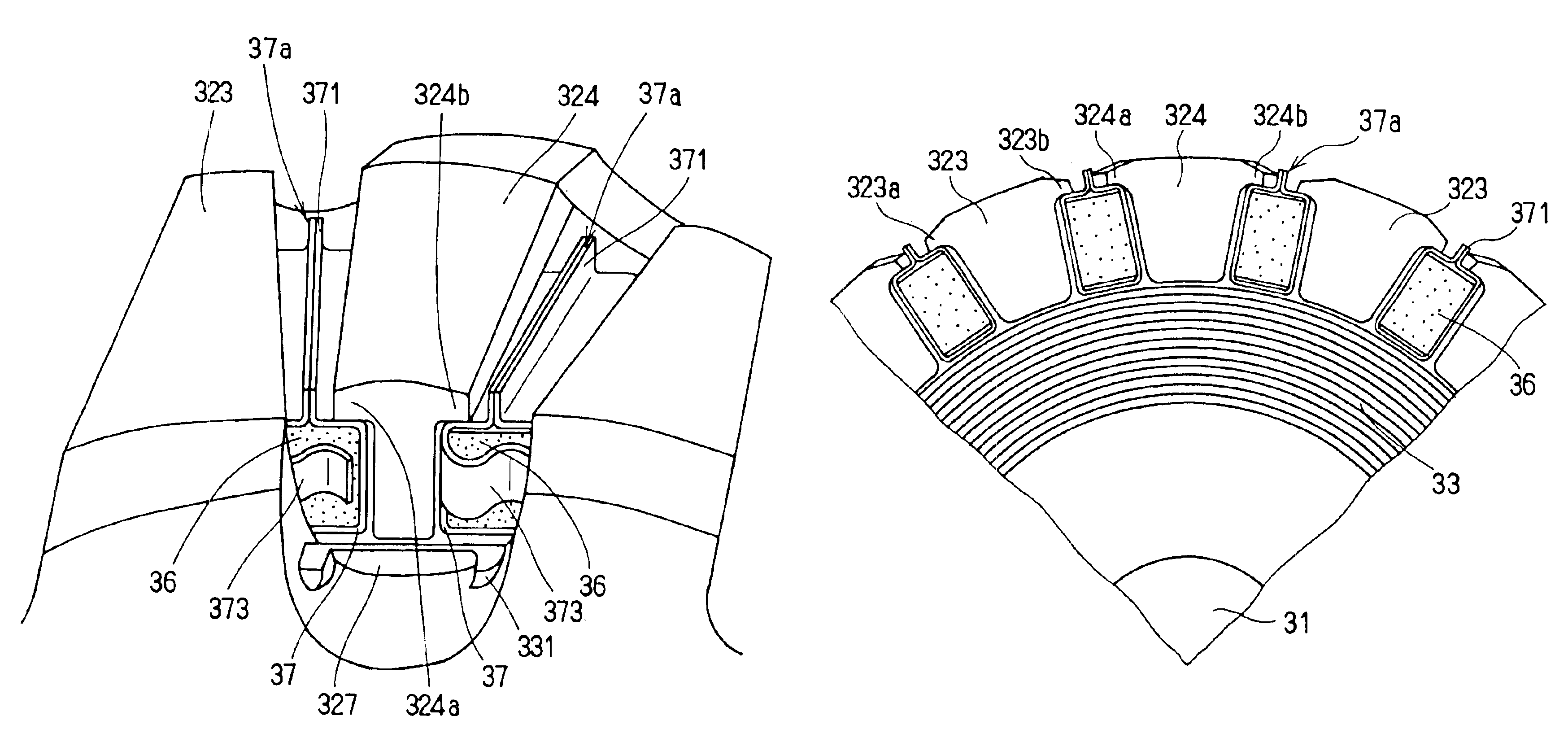
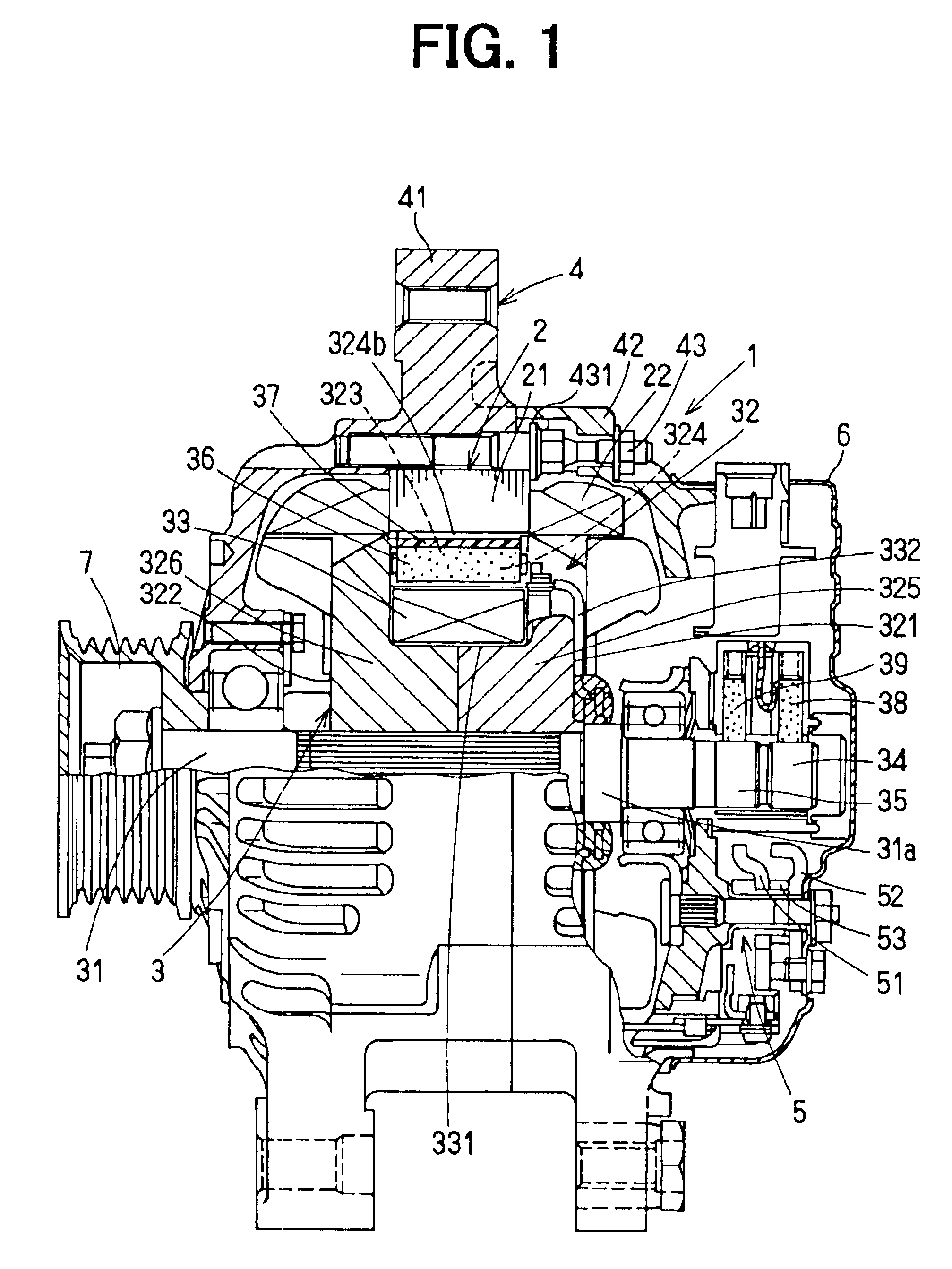
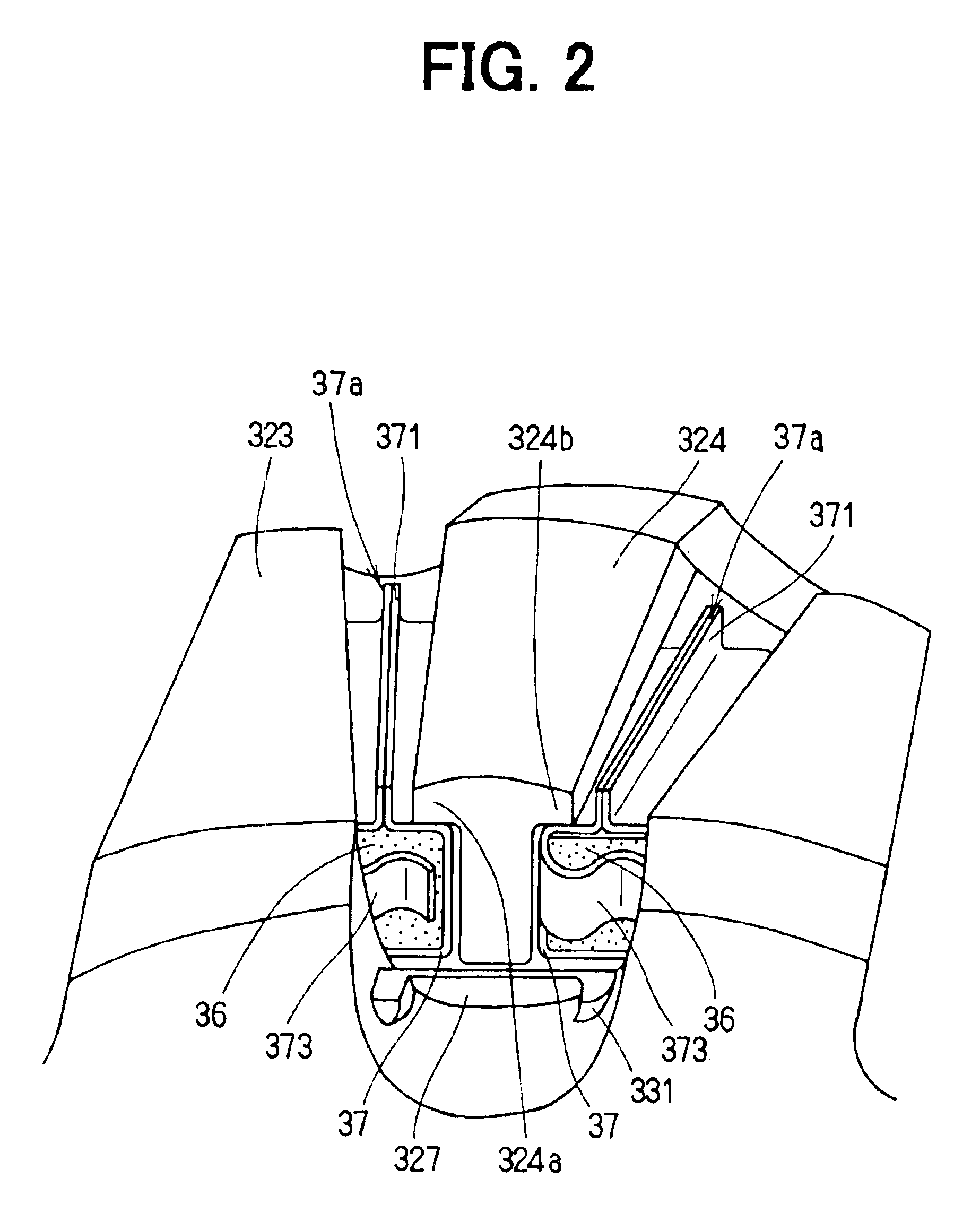
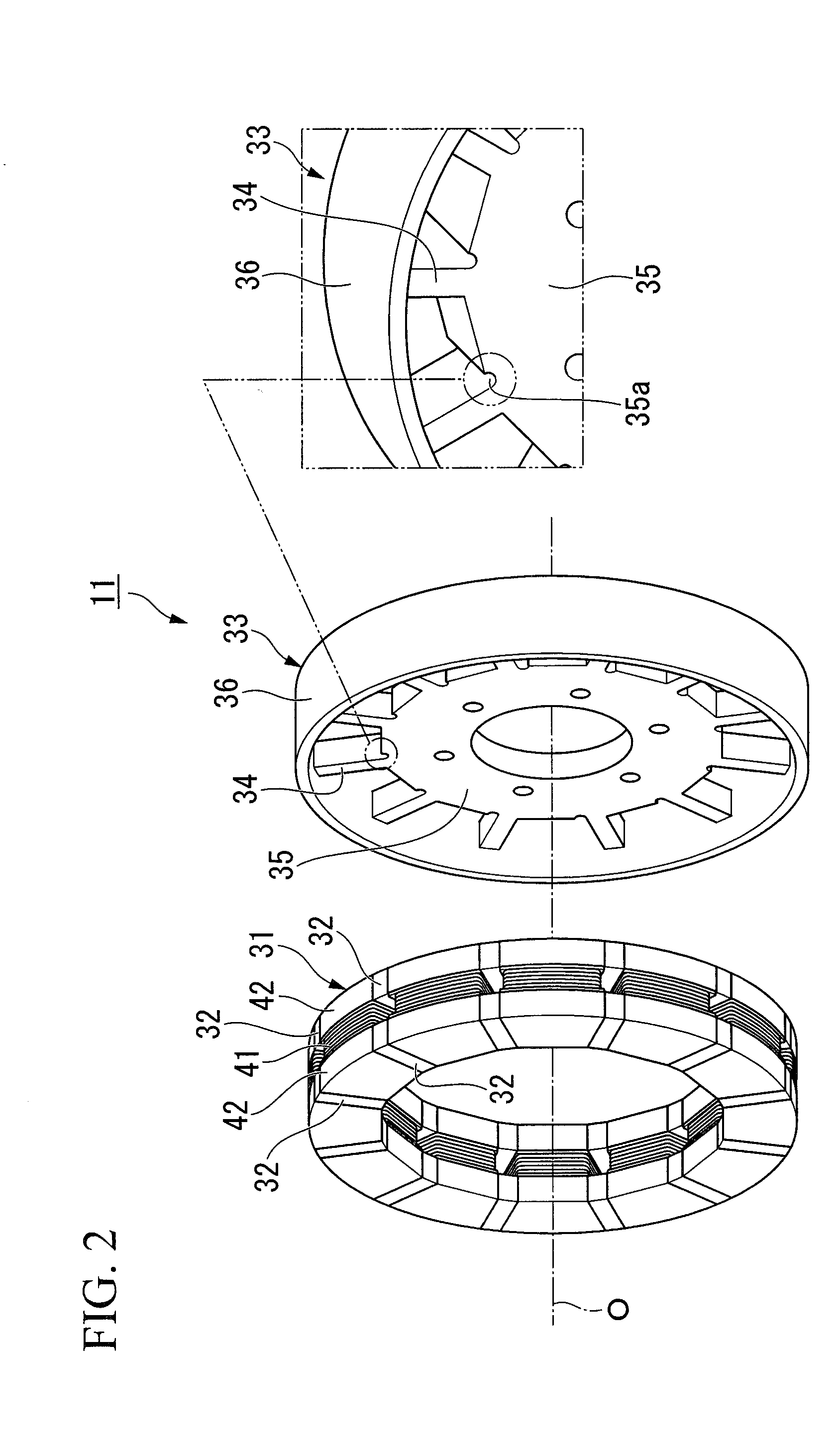
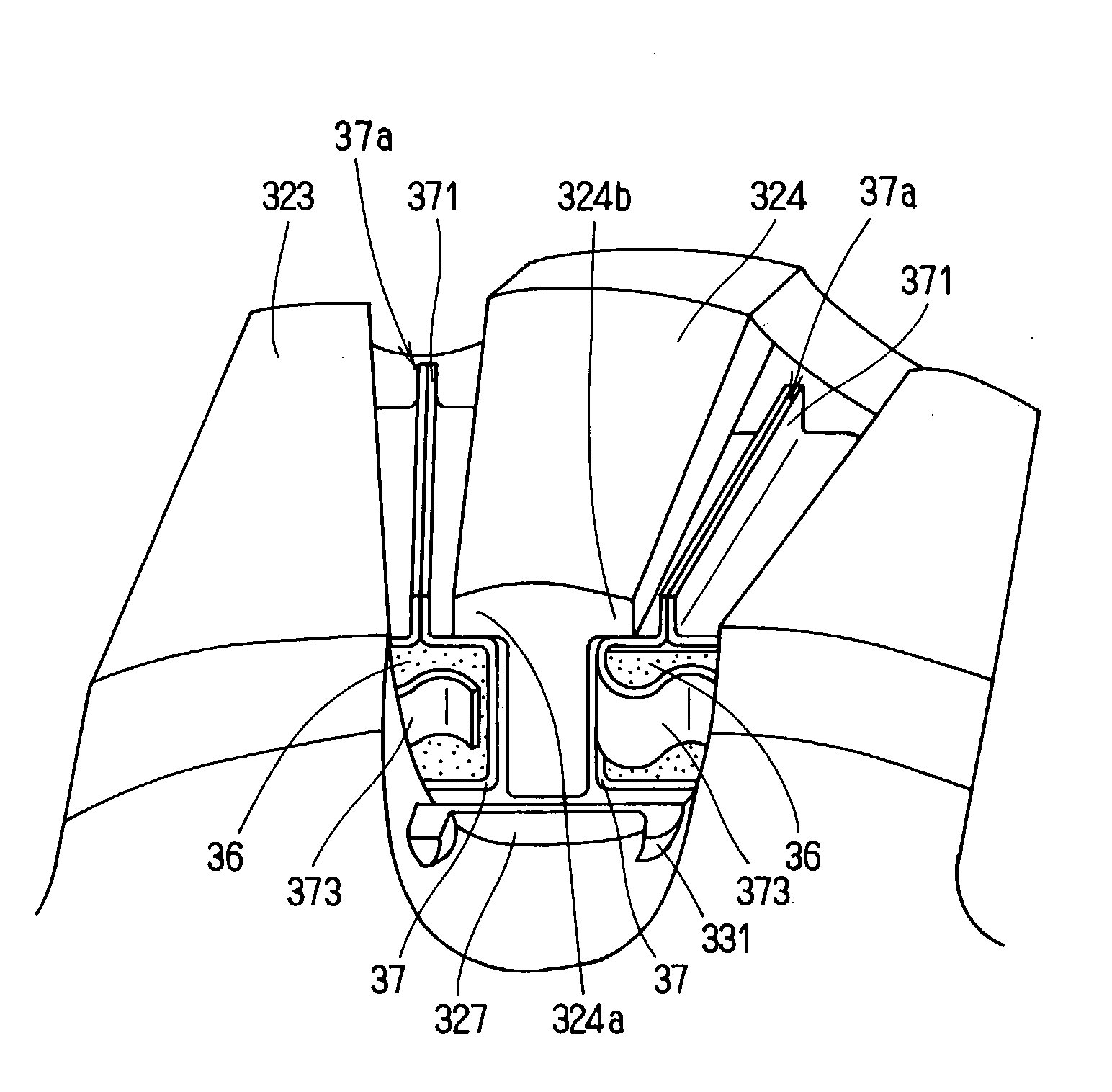
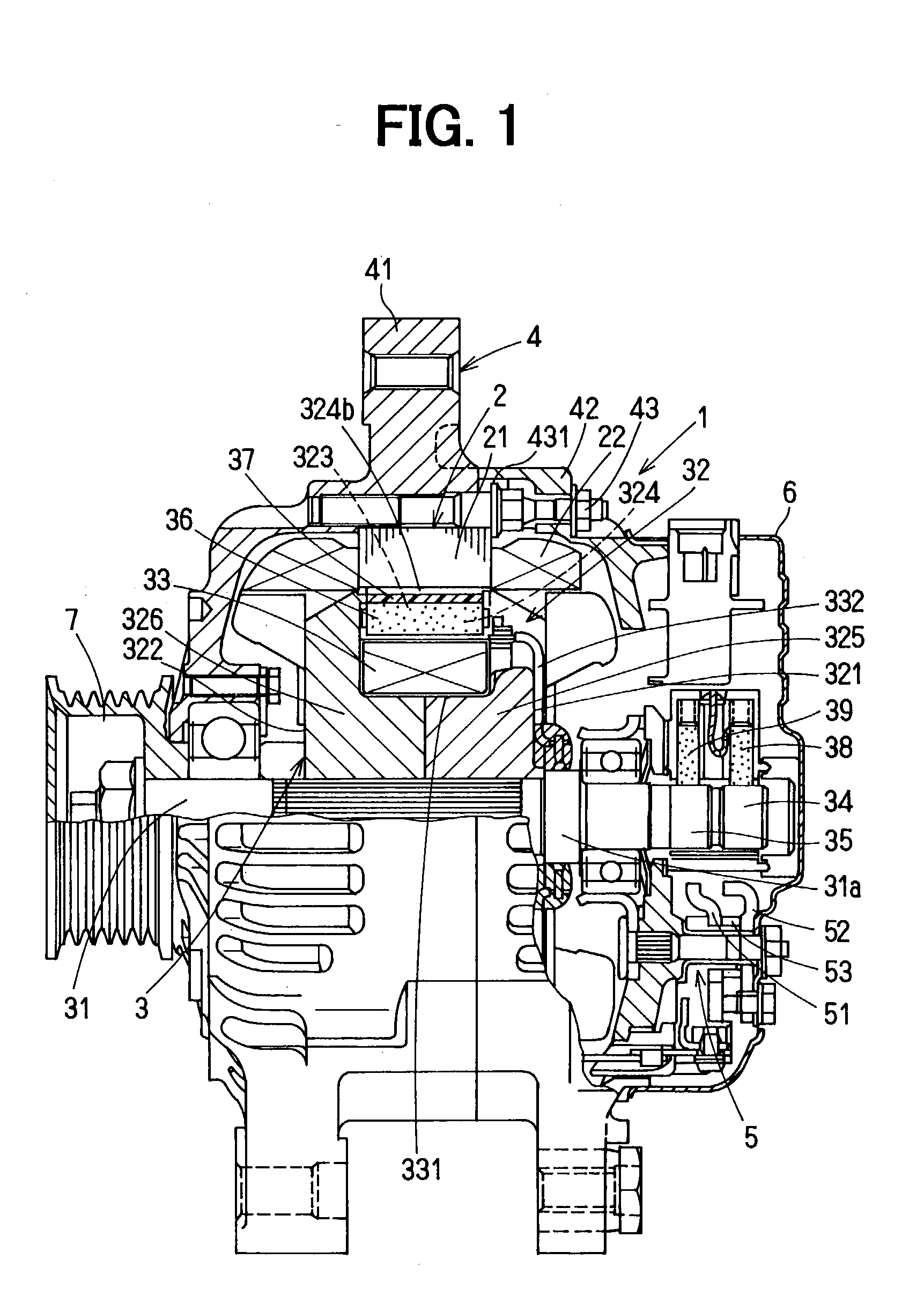
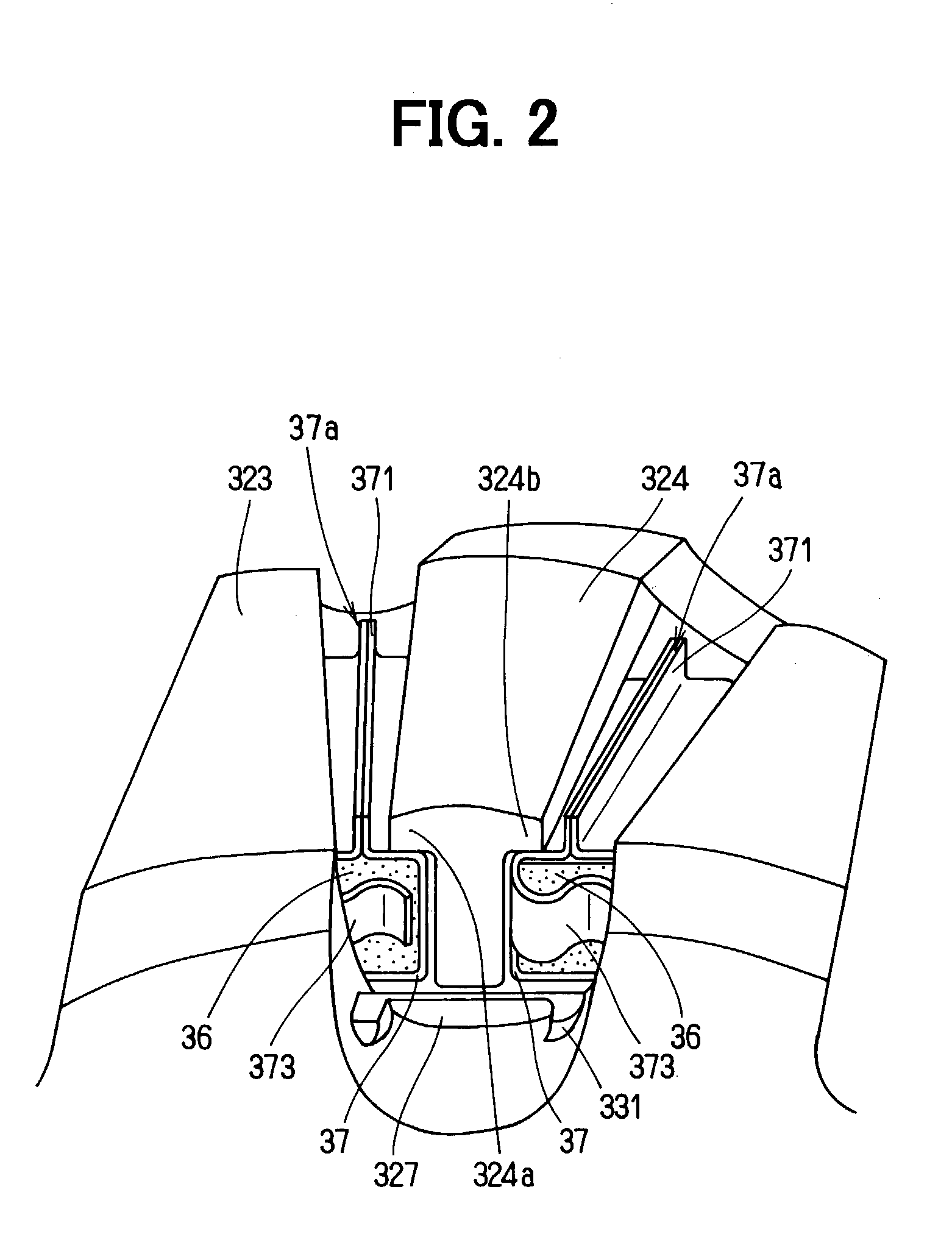
InactiveUS6853112B2Improve rigidityIncrease radial thicknessSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineMagnetic poles
A rotating electric machine for a vehicle includes magnet holders for holding permanent magnets. The magnet holder is fitted between adjacent two claw-like magnetic poles of pole cores, and plural permanent magnets are provided to be magnetized for reducing magnetic-flux leakage between the magnetic poles. The magnet holder includes a radial outer surface, and a protrusion that protrudes from the radial outer surface to a radial outside around a center in a circumferential direction. Therefore, a thickness of the radial outside surface of the magnet holder increases, and its rigidity can be increased. Accordingly, it can prevent the radial outside surface of the magnet holder from being deformed due to centrifugal force, and it can prevent the magnet holder from being damaged.
Owner:DENSO CORP
High power low RPM D.C. motor
InactiveUS6037692AIncrease motor powerHigh strengthAC motor controlAsynchronous induction motorsEngineeringConductor Coil
A high power low RPM direct current electric motor is disclosed whereby the high power output is achieved in one of two ways or both. In the first case, the need for cooling is reduced simultaneously along with an increase in the utilization of the magnetic field present in the motor permanent magnets. This is achieved by wrapping the electromagnet core with windings that are capable of demagnetizing the rotor permanent magnets under stall conditions. Interlocking motor circuitry is provided which prevents the full activation of these motor windings until motor RPM values reach a safe level. This increases motor power while decreasing resistive losses in electromagnet windings. In the second case, the rotary portion consists of a large diameter relatively flat rotor containing permanent magnets and having built in vanes for moving air over the electromagnet stator windings providing forced air cooling.
Owner:MAGNETIC MOTORS
Fabricated components of transverse flux electric motors
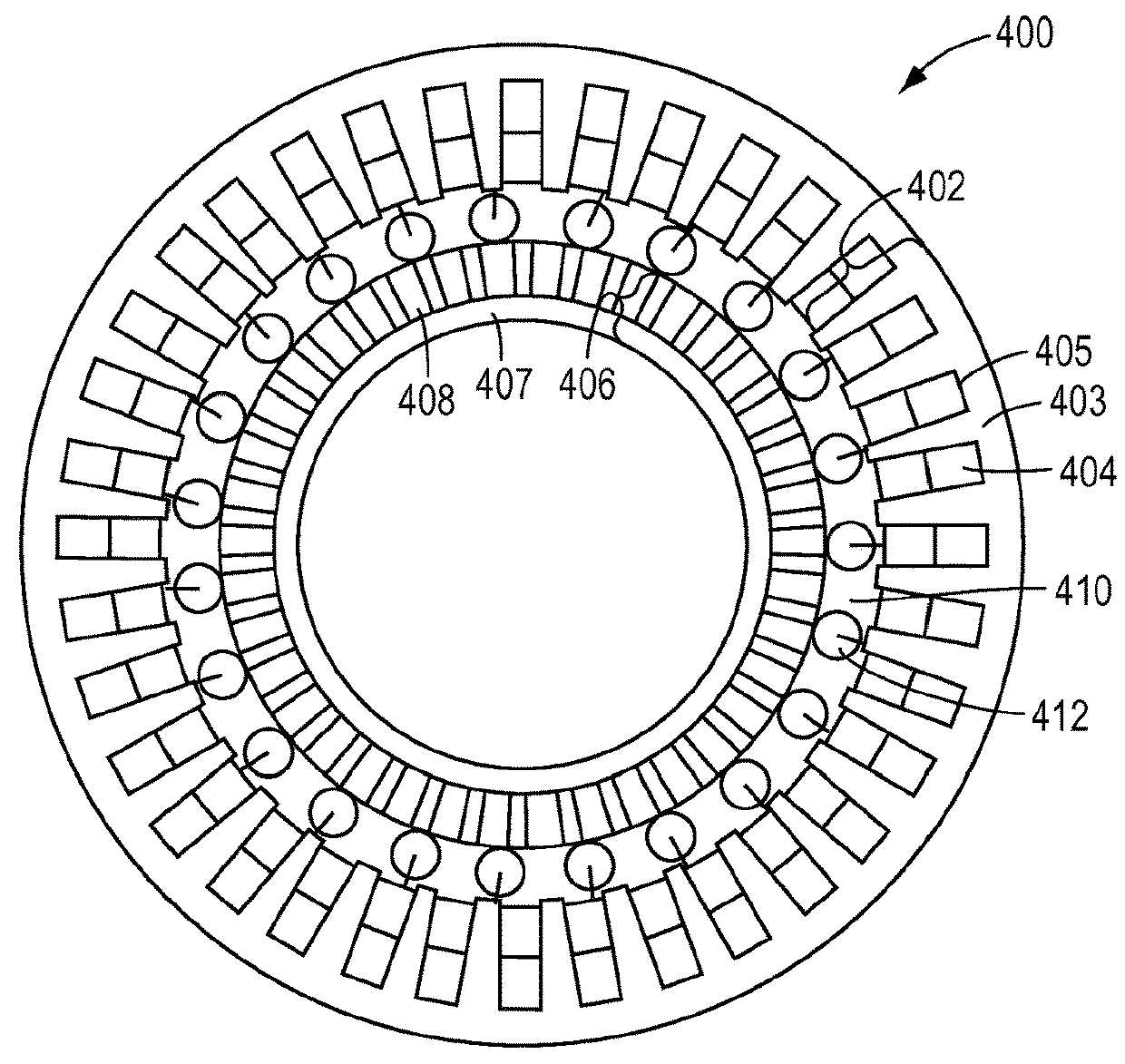
InactiveUS6952068B2Improve performanceRaise transfer toSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxEngineering
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Transverse flux electrical machine with toothed rotor
InactiveUS6949855B2Easy to produceEasy to insertMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsTransverse fluxElectrical conductor
The invention concerns a transverse flux electrical machine operating with alternating current, having a first element having an alternate arrangement of excitation cores and of flux return cores and a winding of electrical conductors, the winding of electrical conductors being wound as a toroid, inside all said excitation cores; a second element having an exciter section comprising two toothed magnetic structures, each toothed magnetic structure comprising a number of slots equal in number to the total number of excitation cores and of flux return cores, the corresponding slots of each magnetic structure being toothed by being aligned; a magnetized sub-assembly is inserted inside each indentation so that an alternating arrangement of magnetic north poles and south poles is produced in each of these magnetic toothed structures of said exciter section; an air gap between the first element and the second element; at least one of the first element and of the second element being capable of rotating around a rotation axis that is common to the first element and to the second element.
Owner:EOCYCLE TECH
Hybrid synchronous machines comprising permanent magnets and excitation windings in cylindrical element slots
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Toroidal AC motor
InactiveUS20060082237A1Longer gap lengthIncrease storage spaceSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineMagnetic poles
A toroidal motor having a generally circular rotor surrounded by an annular stator is disclosed. The rotor has a plurality of poles disposed about a circumference thereof. A shaft extends axially away from the poles and is attached to the rotor. The stator is generally annular and includes an annular winding surrounding the circumference thereof. Disposed about the winding are a plurality of stator poles. The number of stator poles is generally equal to the number of rotor poles. When the winding and hence the stator is excited, a magnetic field is produced between the stator and rotor poles that creates torque upon the shaft.
Owner:PATENT
AC motor having stator windings formed as loop coils, and control apparatus for the motor
ActiveUS20050099082A1Easy to assembleEasy constructionTorque ripple controlWindingsToroidal coilConductor Coil
A synchronous AC motor has a stator with stator poles arranged as a plurality of circumferentially extending stator pole groups, with each stator pole group having a pair of corresponding circumferentially extending loop-configuration stator windings disposed adjacent on either side or a single such winding disposed adjacent at one side, adjacent stator pole groups being mutually circumferentially displaced by a fixed amount corresponding to a specific electrical phase angle. A rotating magnetic field is produced by applying respective polyphase AC voltages to the windings, such that currents of mutually opposite direction flow in each pair.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Transverse flux switched reluctance motor and control methods
InactiveUS20060091755A1Eliminate end turn lossHigh densitySynchronous generatorsElectronic commutation motor controlTransverse fluxElectric machine
A variable reluctance motor and methods for control. The motor may include N motor phases, where N equals three or more. Each motor phase may include a coil to generate a magnetic flux, a stator and a rotor. A flux-carrying element for the rotor and / or stator may be made entirely of SMC. The stators and rotors of the N motor phases may be arranged relative to each other so that when the stator and rotor teeth of a selected phase are aligned, the stator and rotor teeth in each of the other motor phases are offset from each other, e.g., by an integer multiple of 1 / N of a pitch of the stator or rotor teeth. A fill factor of the coil relative to the space in which it is housed may be at least 60%, and up to 90% or more. The stator and rotor flux-carrying elements together may include at most three separable parts.
Owner:PRECISE AUTOMATION
Magnetic flux controllable rotating electric machine system
InactiveUS20100213885A1Easily magnetizedIncreases amount of magnetic fluxSynchronous motors startersWindingsExcitation currentWave shape
In a magnet-exciting rotating electric machine system, a rotor surface has magnetic salient poles and island-shaped magnetic poles alternately in circumferential direction, and the island-shaped magnetic poles are constituted so that magnetic flux coming from an external source does not flow through. A magnetic excitation part magnetizes the island-shaped magnetic poles and the magnetic salient poles collectively in the same direction, and then control a flux amount flowing through an armature. The armature has armature coils that face the magnetic salient pole and the island-shaped magnetic pole simultaneously so that driving torque fluctuation or power generation voltage waveform distortion is controlled. The magnetic excitation part changes magnetization state of a field magnet irreversibly, or changes an excitation current to an excitation coil to control a flux crossing the armature.
Owner:KURA LAB
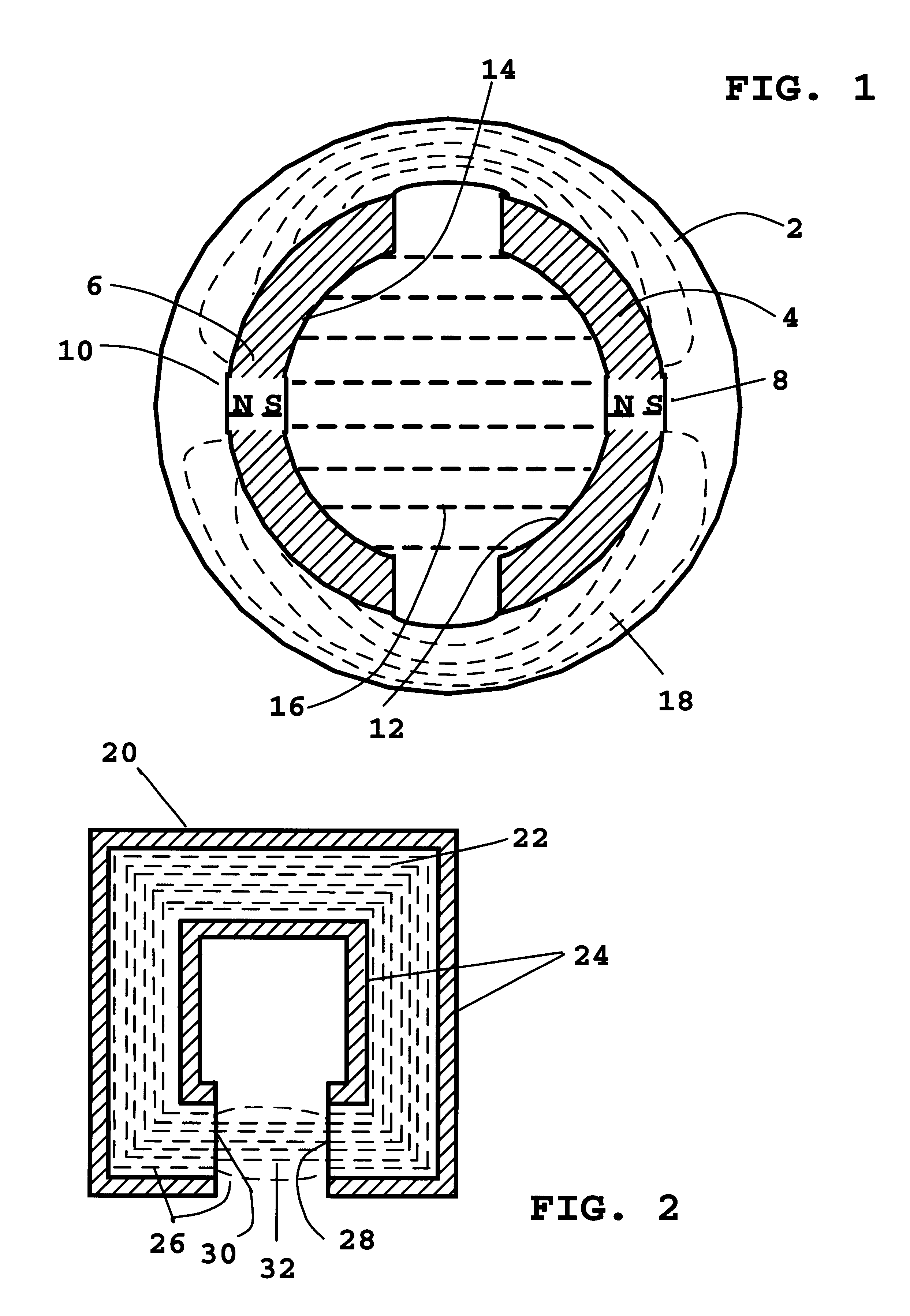
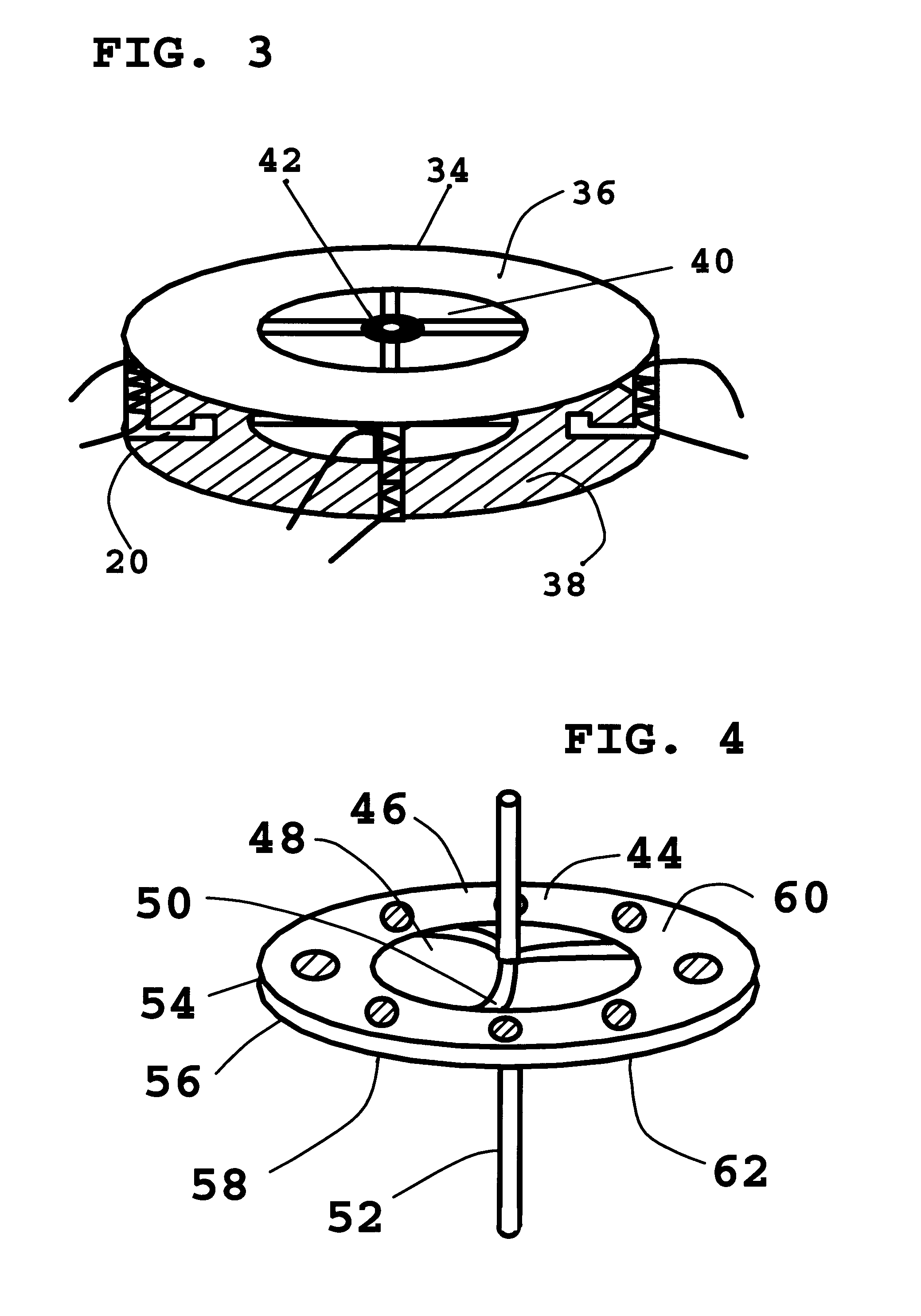
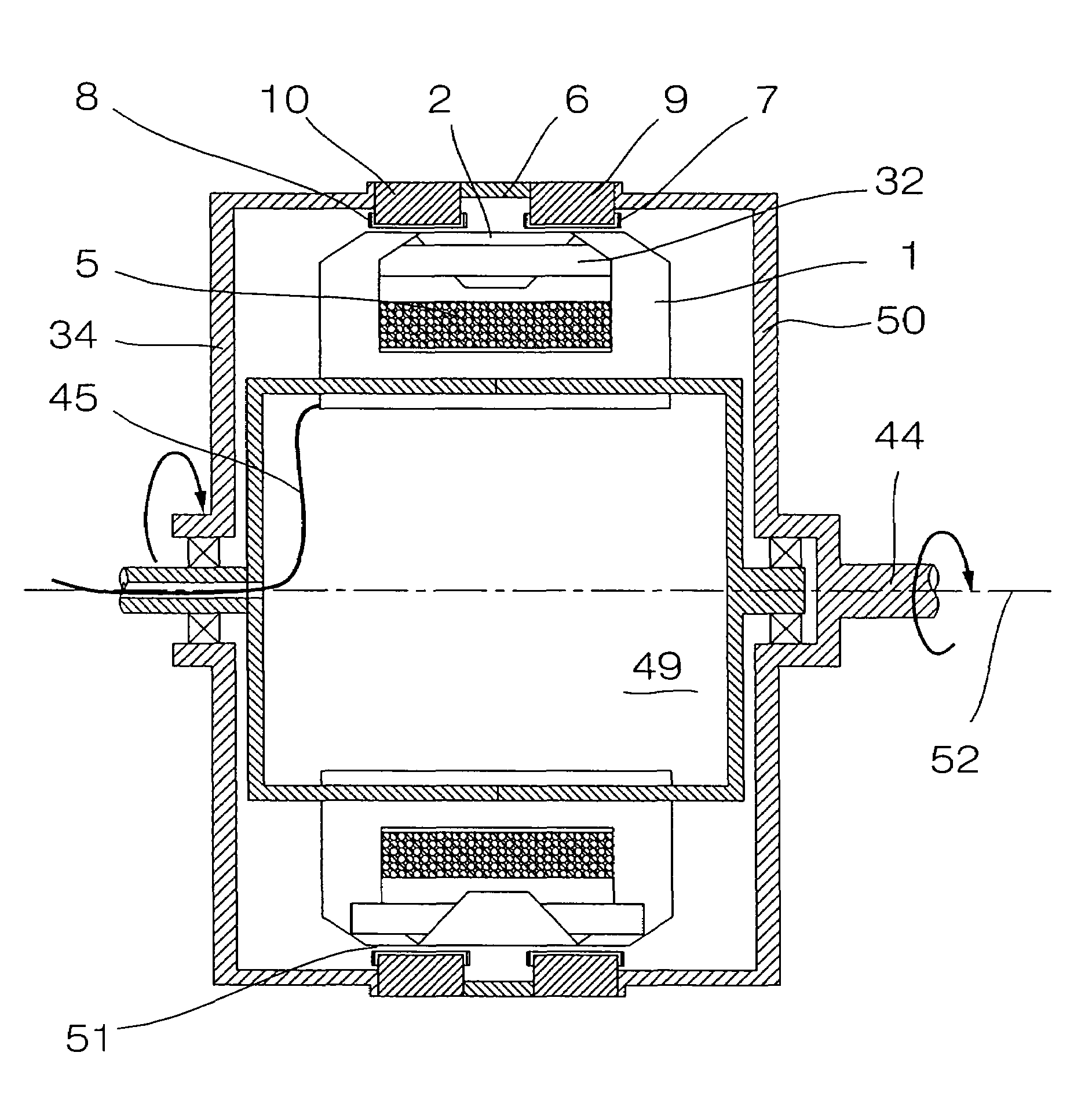
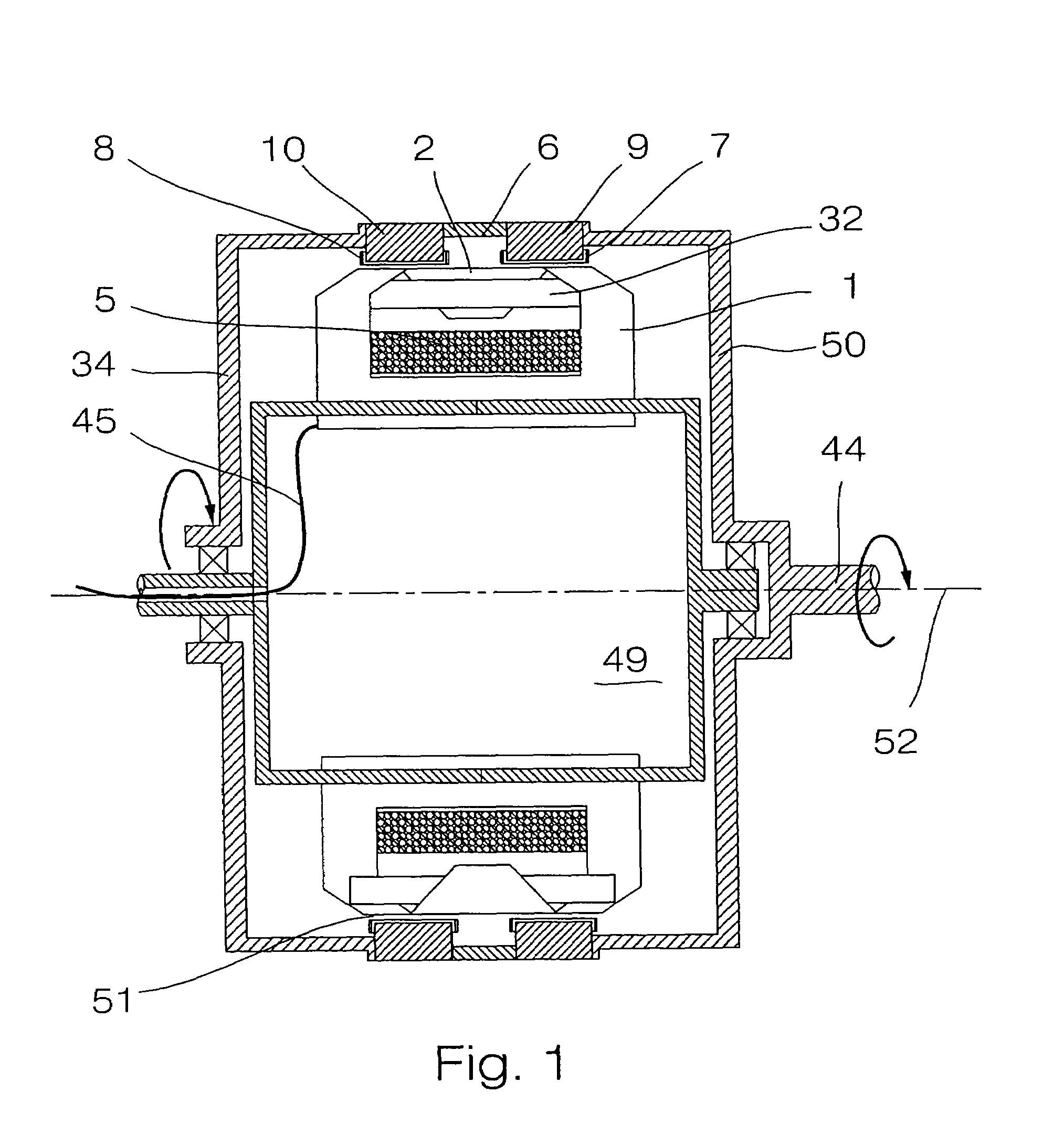
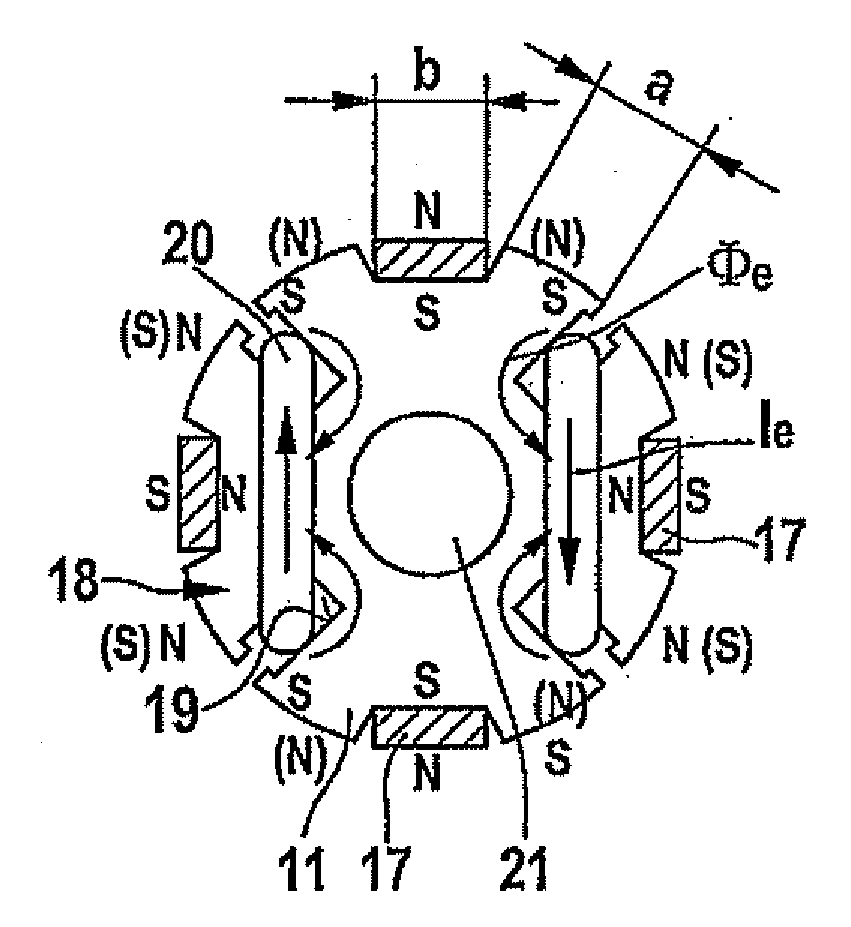
Electrical machine with double excitation, especially a motor vehicle alternator
InactiveUS6147429APromote recoveryReduce lossesSynchronous generatorsWindingsAlternatorElectric machine
A rotary electrical machine such as a motor vehicle alternator comprises a stator and a rotor. The stator has at least one armature winding in at least one pair of stator slots. The rotor includes means for selectively establishing closed magnetic circuits which pass around the turns of the armature winding or windings. The means for setting up closed magnetic circuits comprise at least two permanent excitation magnets which set up two magnetic fluxes having components in opposite directions according to the direction of displacement of the rotor; and, between each pair of successive magnets, at least one excitation winding having two wires and being arranged to produce in an adjustably way two flux components which are such as to oppose the fluxes set up in the magnets of the pair. The wires of the excitation windings are located in rotor slots, each of which lies between two successive rotor poles.
Owner:VALEO EQUIP ELECTRIC MOTEUR
Drive device of electric motor
InactiveUS20100071971A1Reduce Flux LeakageSmall sizeSynchronous motors startersWindingsExcitation currentEngineering
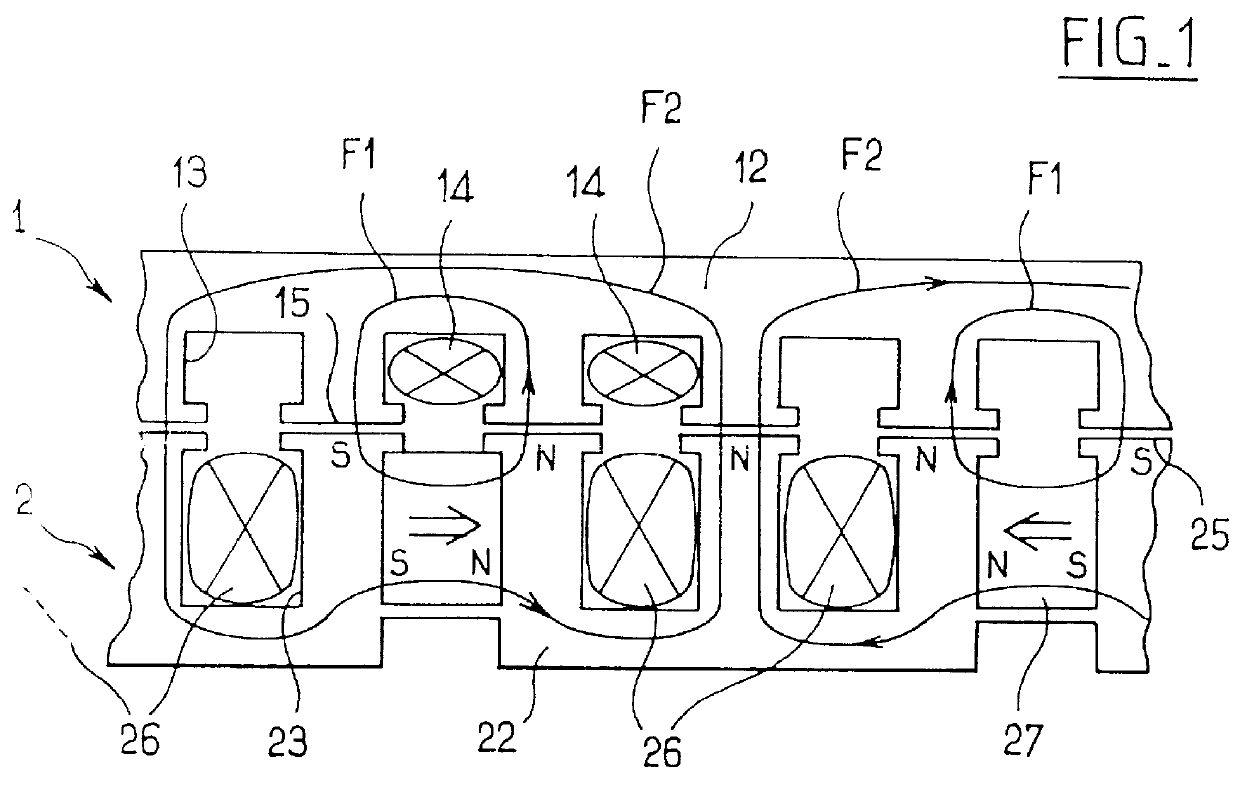
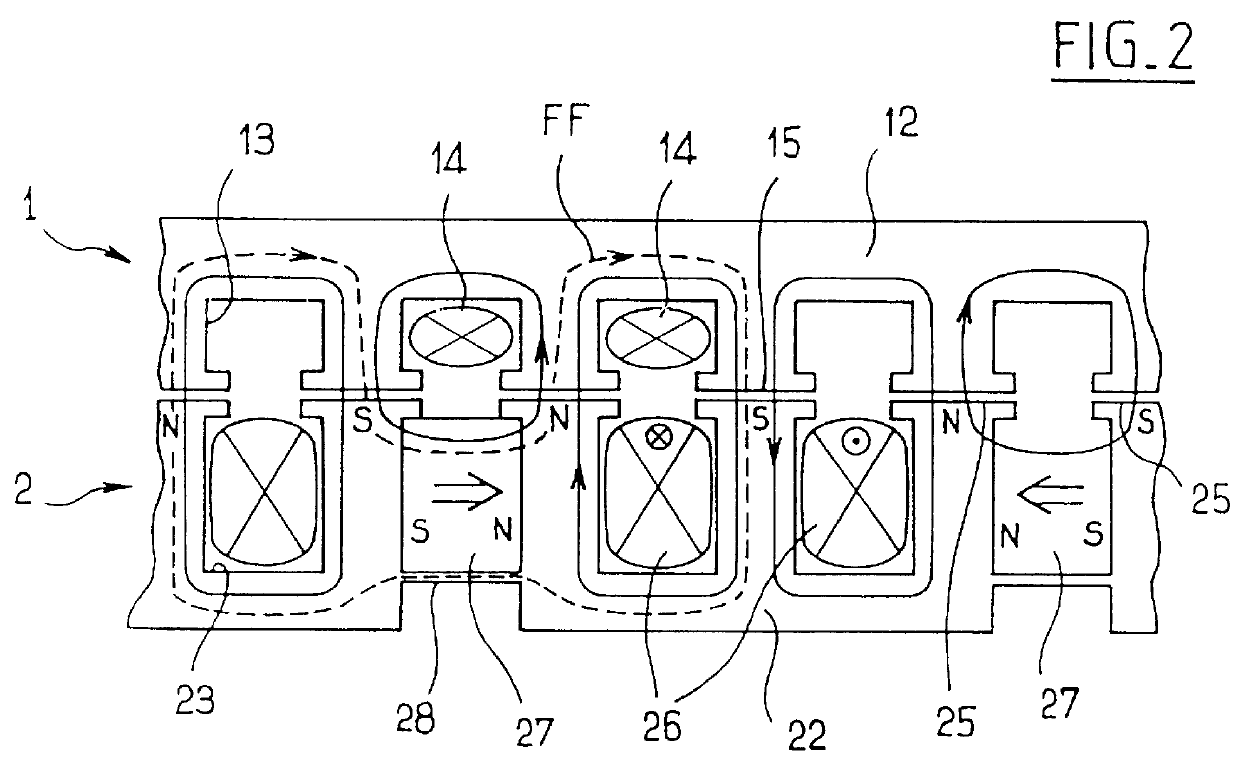
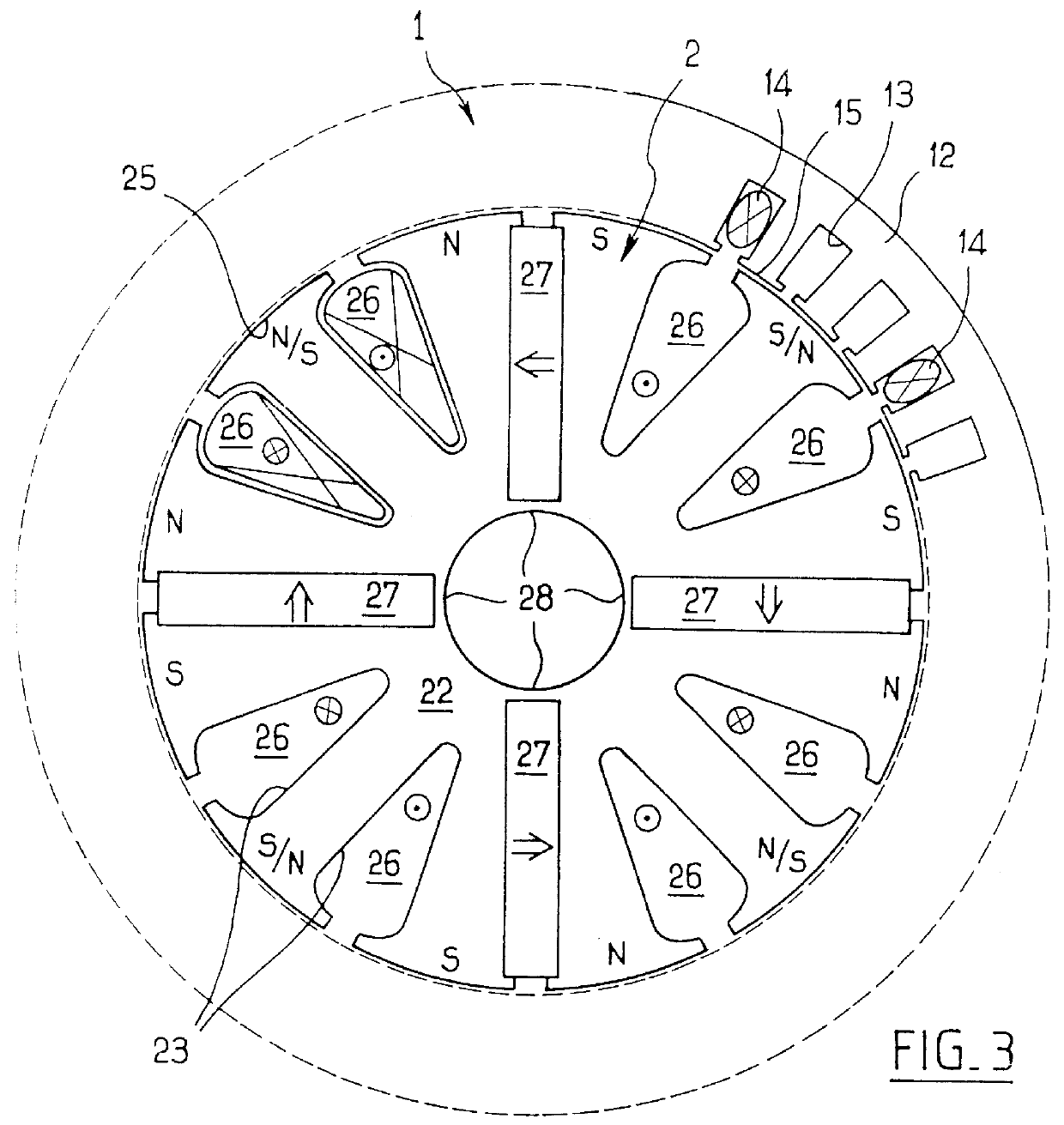
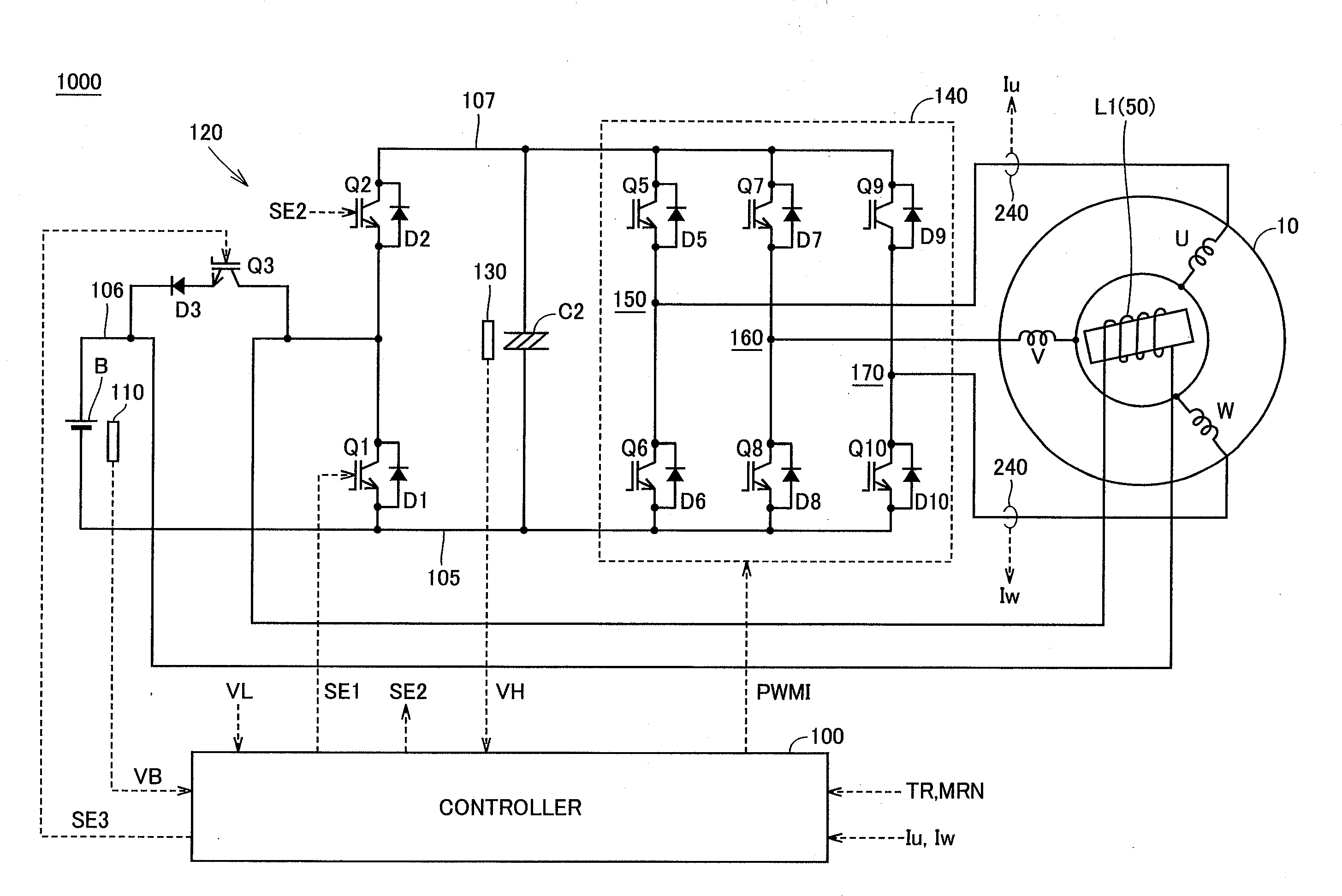
An electric motor (10) has a field pole formed by a field current passing through a field winding (50). A voltage booting converter (120) converts output voltage of a battery (B) and outputs the voltage between a power source line (107) and a grounding line (105). Field winding (50) is electrically connected onto an electric current channel between battery (B) and power source line (107) and formed so that voltage switched by a switching element (Q1) is applied to both ends. A controller (100) controls the field current so as to adjust density of magnetic flux between a rotor and a stator by performing switching control on switching element (Q1) and a switching element (Q3) connected in parallel to field winding (50) and converts the output voltage of battery (B) into voltage in accordance with a voltage command value.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Axial gap type motor
InactiveUS20080129136A1Increase heightIncreased torque rangeSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsEngineeringMagnetic flux
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Rotating electric machine
InactiveUS20040032183A1Increase radial thicknessImprove rigiditySynchronous generatorsSynchronous machine detailsElectric machineMagnetic poles
A rotating electric machine for a vehicle includes magnet holders for holding permanent magnets. The magnet holder is fitted between adjacent two claw-like magnetic poles of pole cores, and plural permanent magnets are provided to be magnetized for reducing magnetic-flux leakage between the magnetic poles. The magnet holder includes a radial outer surface, and a protrusion that protrudes from the radial outer surface to a radial outside around a center in a circumferential direction. Therefore, a thickness of the radial outside surface of the magnet holder increases, and its rigidity can be increased. Accordingly, it can prevent the radial outside surface of the magnet holder from being deformed due to centrifugal force, and it can prevent the magnet holder from being damaged.
Owner:DENSO CORP
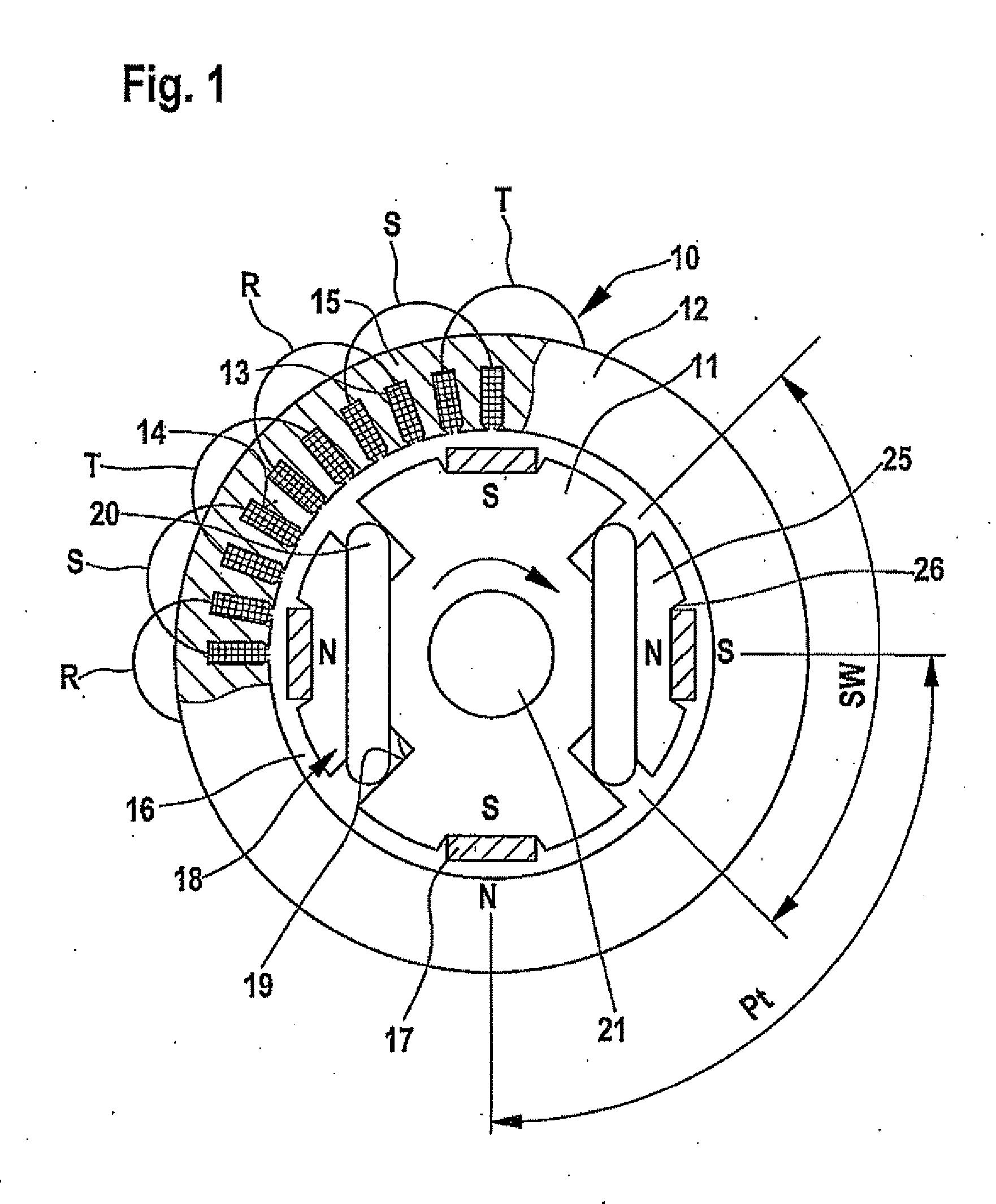
Rotary electric machine, especially an alternator for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6051904AElectronic commutation motor controlSynchronous generatorsAlternatorElectric machine
An electrical machine includes a stator and a rotor. The stator includes on its internal face at least one induction winding housed in a pair of recesses and a series of housings for excitation means. The rotor does not have windings and includes teeth for establishing variable magnetic fluxes in the induction winding. The excitation brings into play permanent magnets adapted to establish a closed circumferential magnetic flux in the stator and excitation windings locally establishing an adjustable magnetic flux in the reverse circumferential direction. The rotor teeth are adapted to effect a flux commutation in the stator and the, or each, permanent magnet occupies an angular position located between the angular positions of the two arms of a common induction winding. In this way an alternating magnetic flux is produced in the induction winding or windings during the rotation of the rotor.
Owner:VALEO EQUIP ELECTRIC MOTEUR
Flat linear vibrating motor
A flat linear oscillation motor comprises an upper cover, a base matched with the upper cover to form a holding space, a coil which contained in the holding space and positioned on the base, an elastic supporting piece connected with the base and a permanent-magnet that is hung in the holding space by the elastic supporting piece; wherein, the base is provided with a plurality of side walls and a bottom wall being vertical to the side walls, the coil is arranged on the bottom wall and positioned in the center under the permanent-magnet, a gap is arranged between the coil and the permanent-magnet, the magnetic pole of the permanent-magnet just faces the coil, and the polarization direction of the magnetic pole of the permanent-magnet facing the coil is opposite, the elastic supporting piece is provided with a fixing part connected with the base, an elastic arm that extends out from and faces the fixing part and has the elastic deformation direction to be parallel to the bottom wall of the base, and a jointing part that extends out from the elastic arm and is connected with the permanent-magnet to lead the permanent-magnet to move along the direction being parallel to the bottom wall.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD +1
Three-freedom Halback array permanent magnetism sphericity synchronous motor
InactiveCN101282070AHigh positioning accuracySimple mechanical structureMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsFixed bearingSynchronous motor
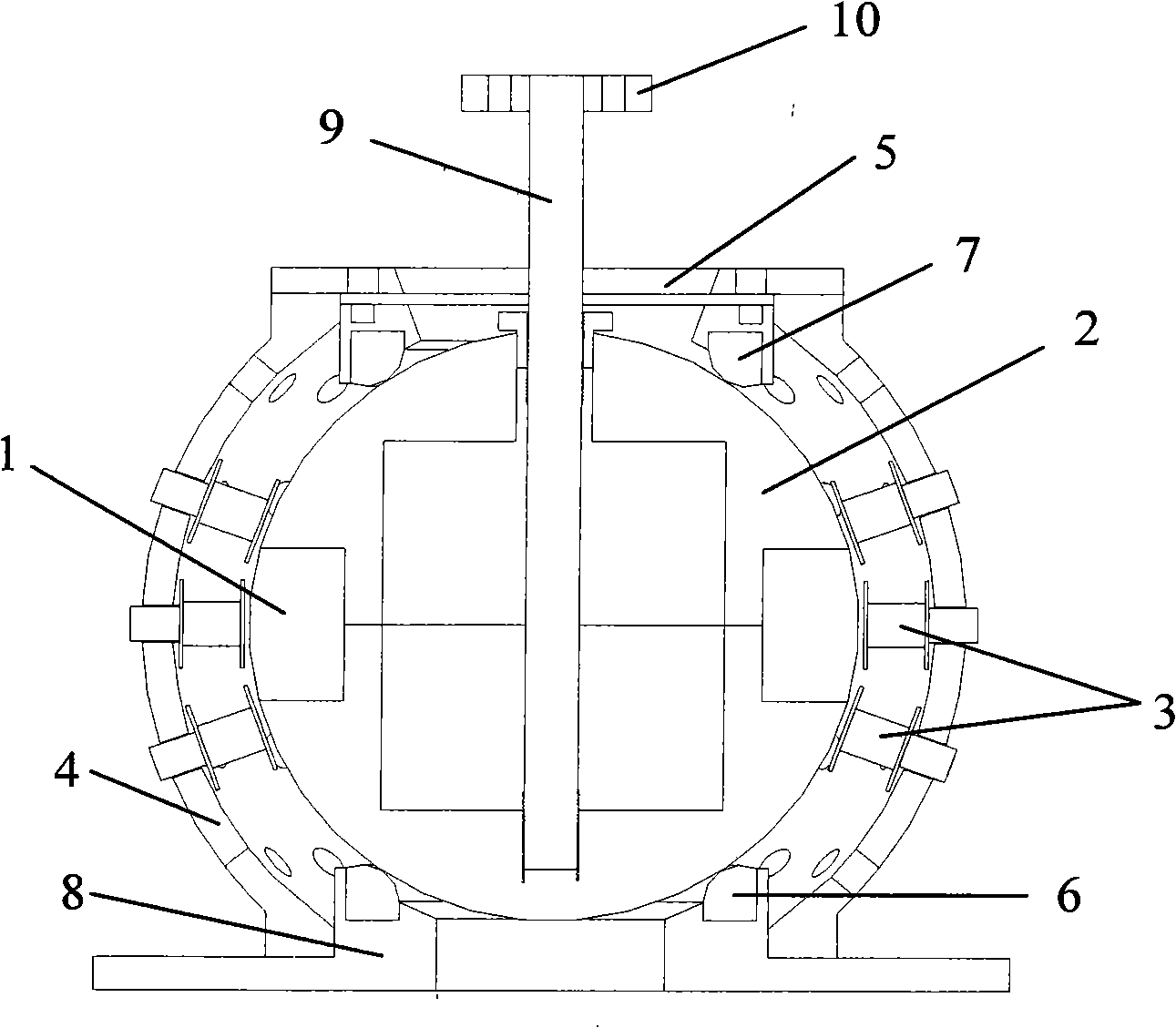
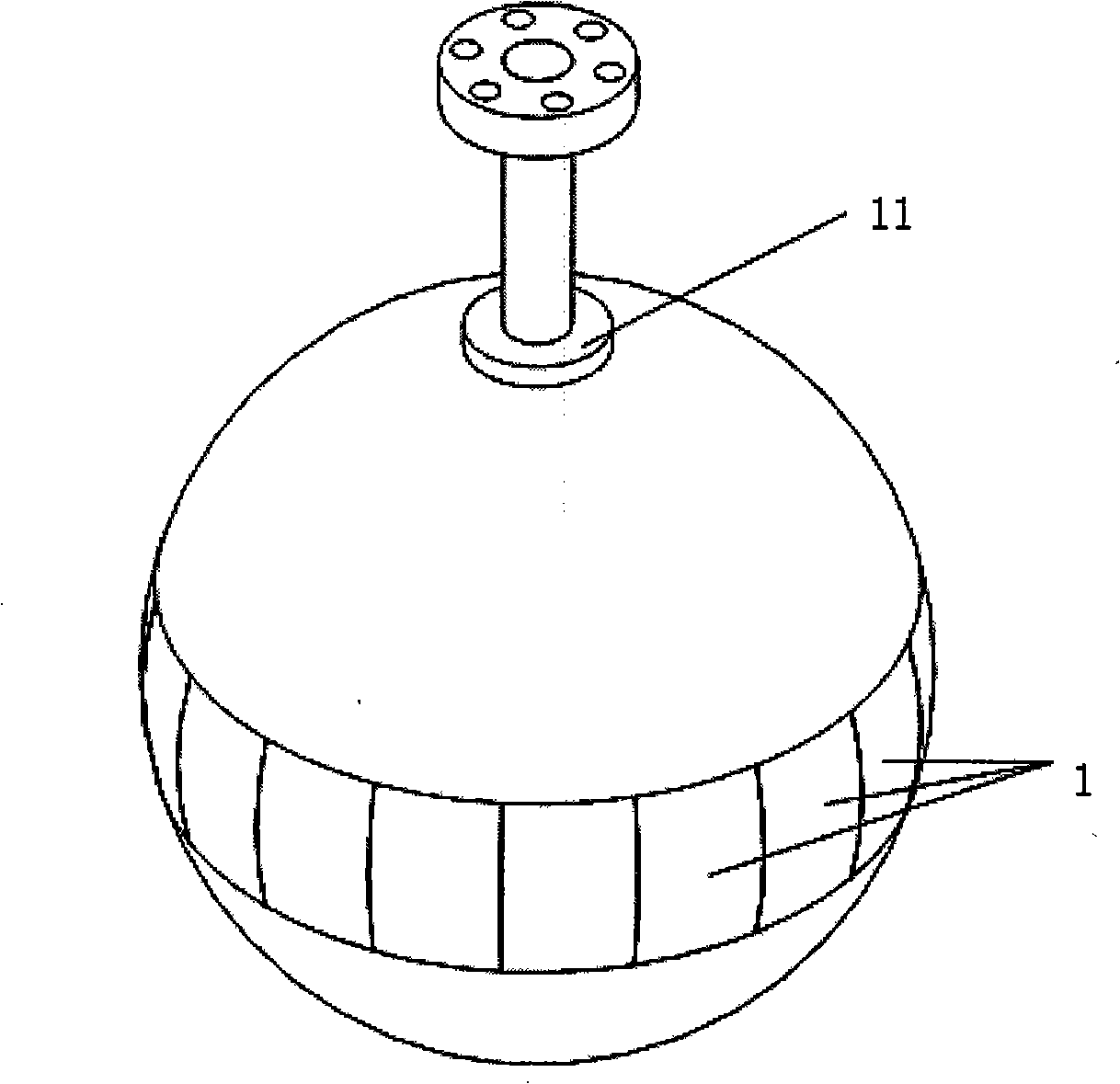
The invention relates to a three-freedom degree Halbach array permanent magnetism spherical synchronous motor, belonging to spherical electric machine manufacturing technical field, which comprises a base, a support bearing positioned on the base, a spherical rotor body, an outside stator, an output shaft, the spherical rotor body comprises a hollow spherical rotor yoke made by non-guide magnetism materials and a Halbach array permanent magnetism body, the output shaft is through the upper of the hollow spherical rotor yoke and is fixingly connected with the hollow spherical rotor yoke, column-shaped slots are provided around a cycle of the hollow spherical rotor yoke equator, the Halbach array permanent magnetism body are fixed evenly on one cycle of the rotor yoke equator along the column-shaped slots, the contact surface of the rotor yoke lower and the support bearing is ring-shaped arc surface; the outer stator comprises a stator casing and multi-row coils, an adjustable fixing bearing is provided on the lower side of the stator casing cover. The spherical synchronous motor of the invention can realize three-freedom degree movement, has simple mechanical structure and improved dynamic and static performance of the drive system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
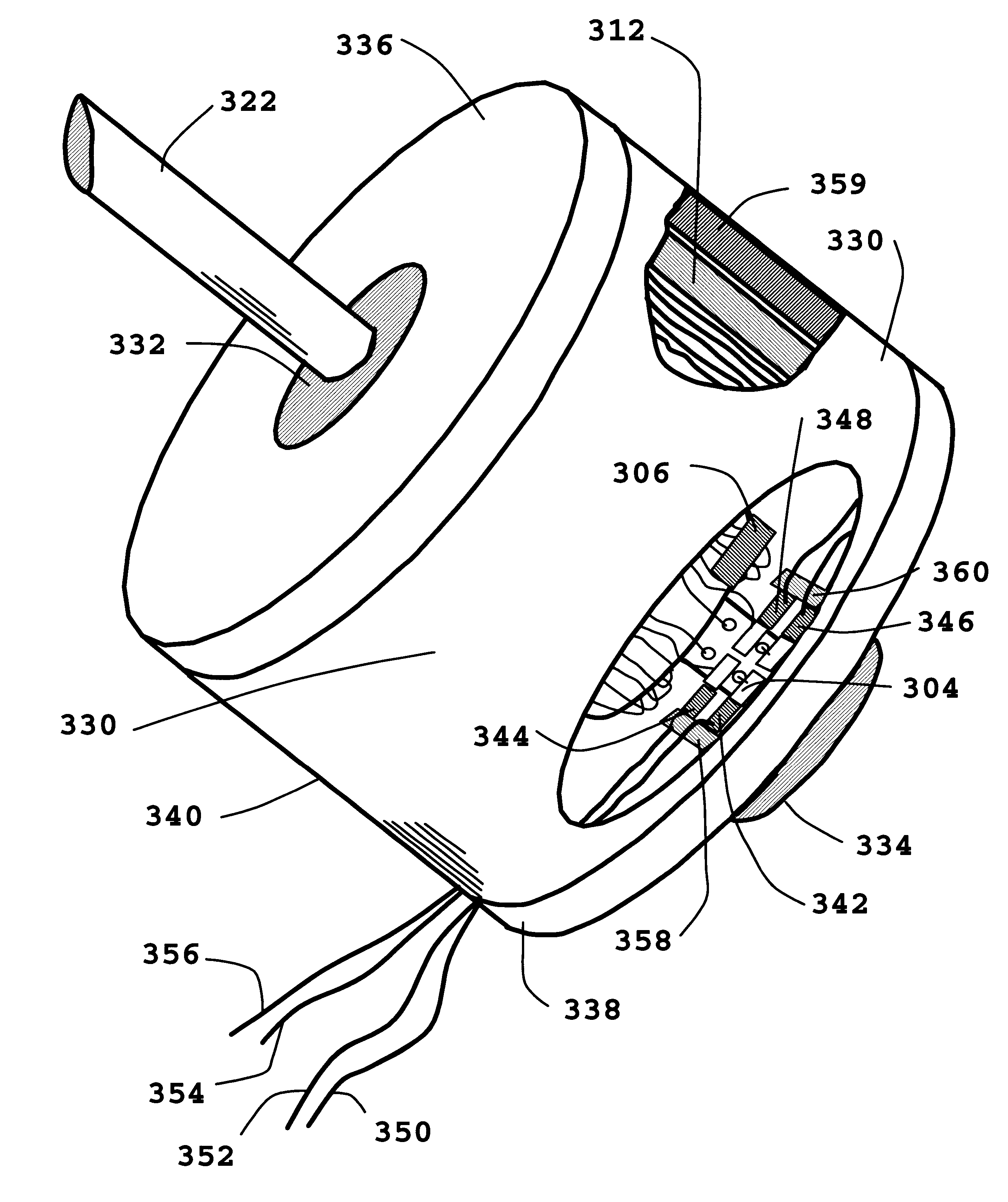
DC induction electric motor-generator
An electromagnetic apparatus has a rotating element acting as a transfer bridge between two active energetic suppliers, the rotating element providing a ferromagnetic core with plural solenoid coils having induced electric energy from external permanent magnets; the core transferring energy by induction to the inner stator's wound active permanent magnet, the energy collector and inductor acting as a generator.
Owner:CLEARWATER TECH SYST +1
Permanent-Magnet (PM) Rotors and Systems
InactiveUS20100052455A1Suitable magnetic insulation propertyImprove performanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsMagnetAerospace engineering
Owner:TECO WESTINGHOUSE MOTOR
Electric machine comprising a rotor with hybrid excitation
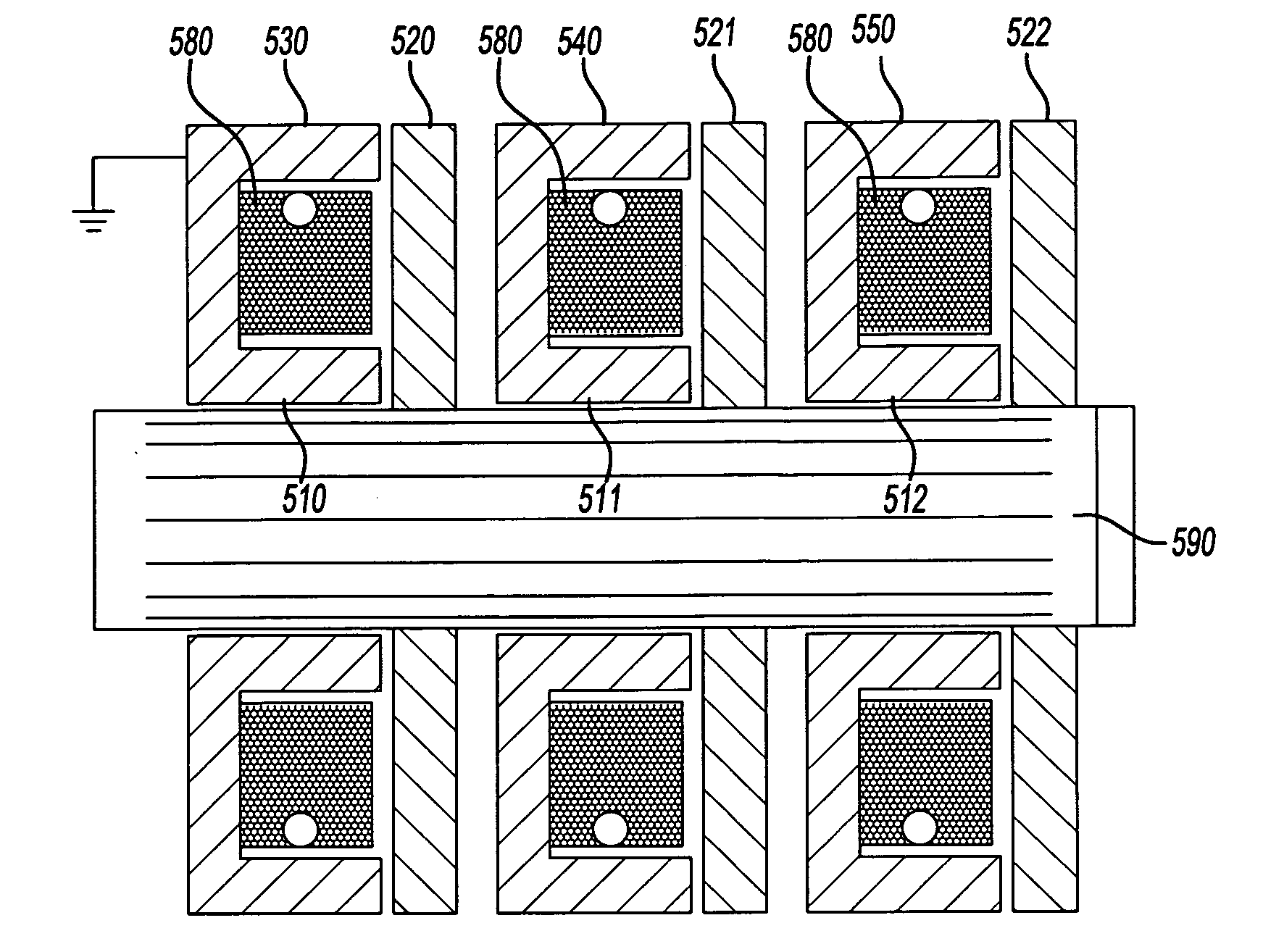
ActiveUS20100207480A1Reduced cross sectionKeep the electromagnetic losses lowSynchronous generatorsWindingsElectric machineExcitation current
A synchronous electric machine having a fixed stator, a multi-phase stator winding and having a rotor which has poles, excited in a predefined sequence, over its circumference, the number of poles being changeable as a function of the intensity and the direction of a field current in at least one field coil of the rotor. For improving the efficiency of the machine and for reducing the number of field coils and the entire coil cross section it is provided that the rotor has a laminated core, laminated in the axial direction, which has grooves on the circumference for accommodating the at least one field coil and that the at least one field coil is situated on the circumference of the rotor with a step size which corresponds to the pole pitch of the lower number of poles.
Owner:SEG AUTOMOTIVE GERMANY GMBH
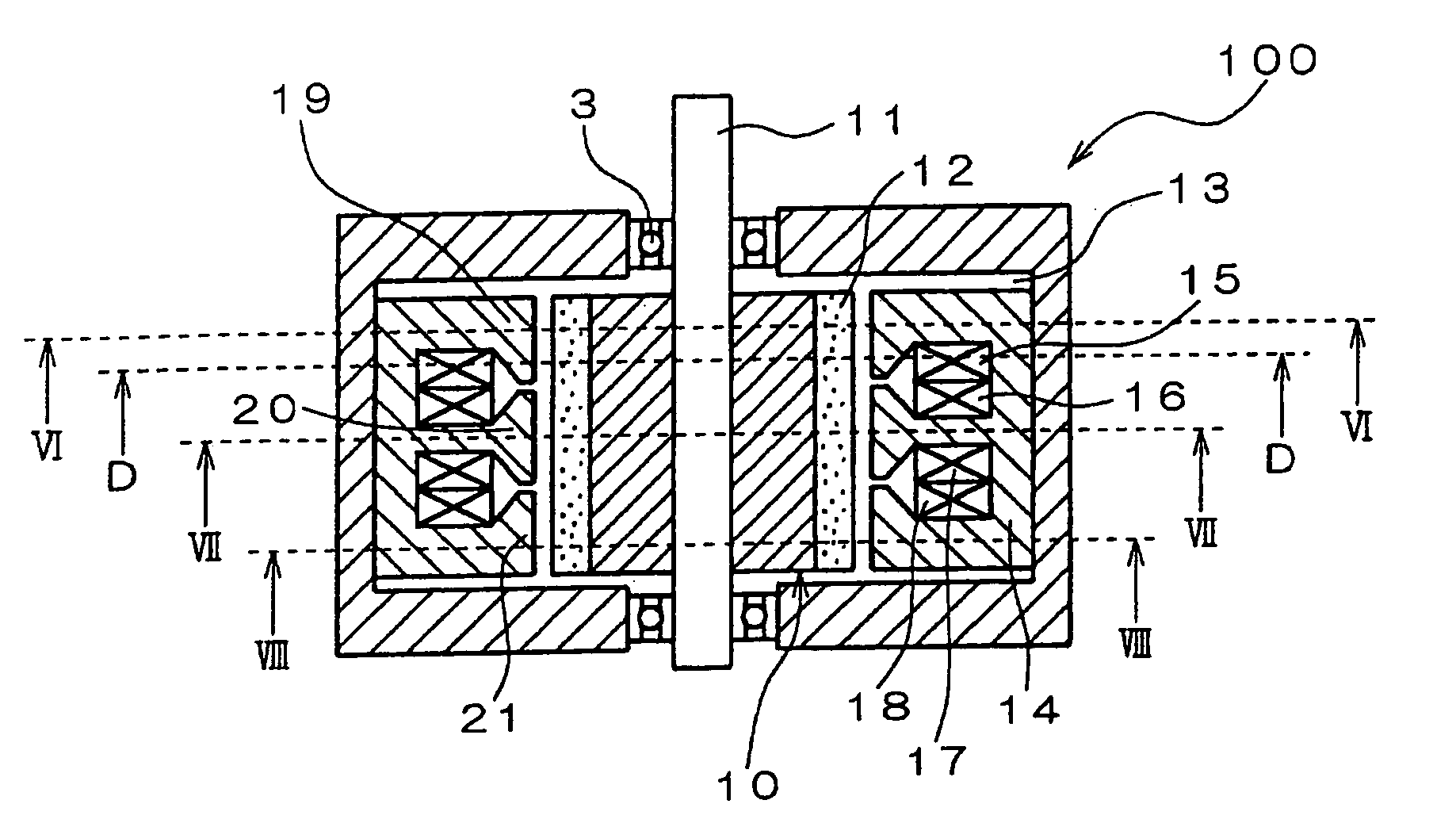
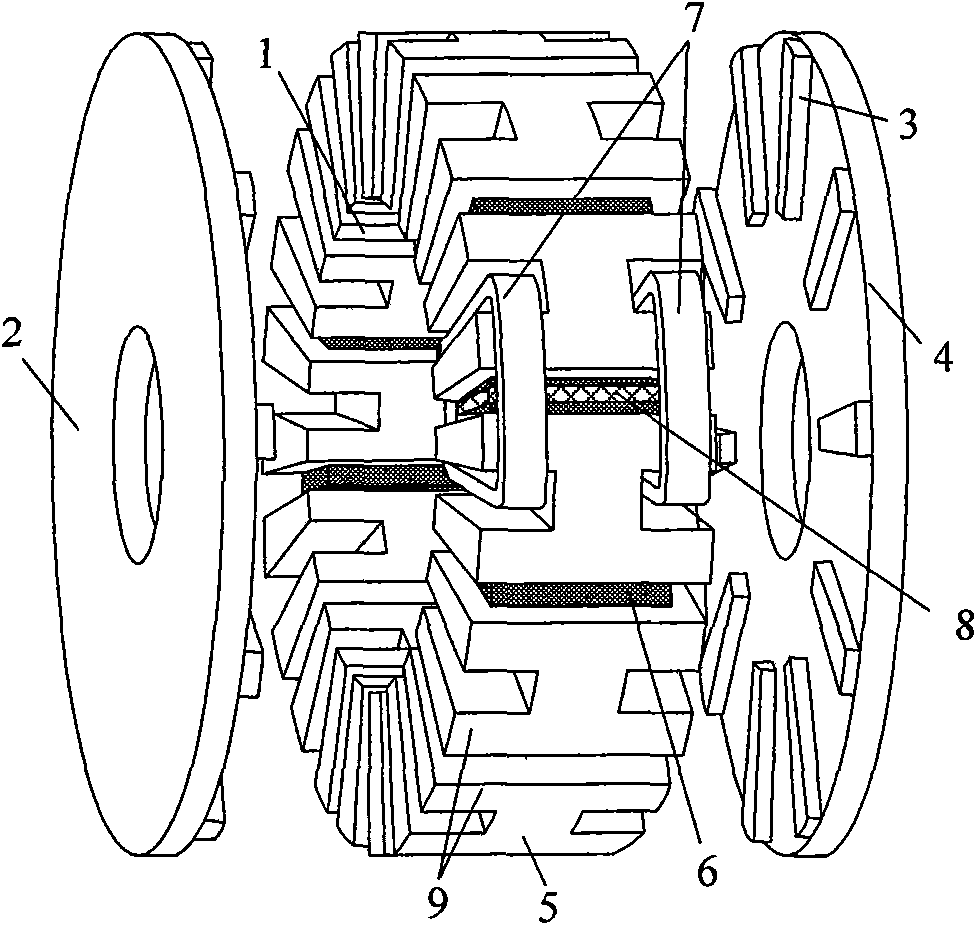
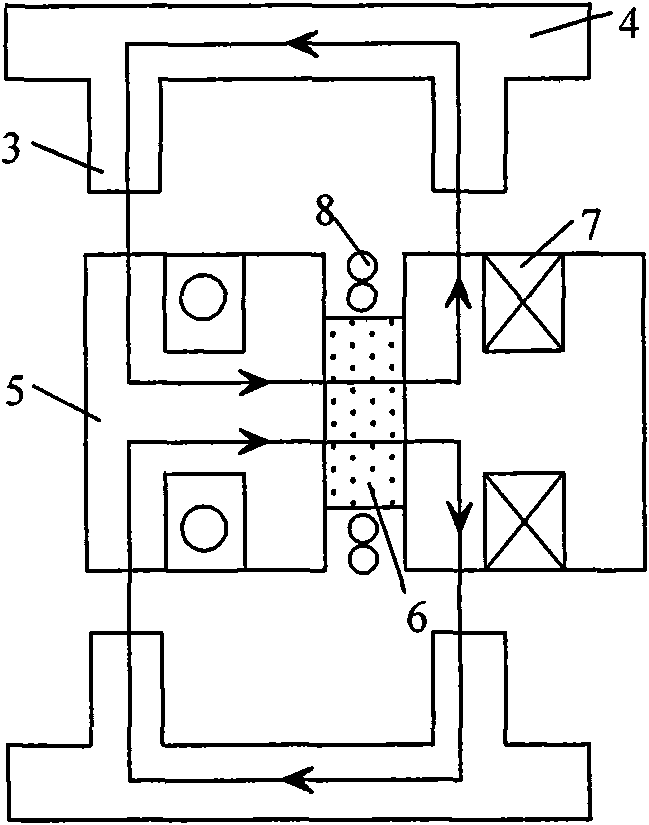
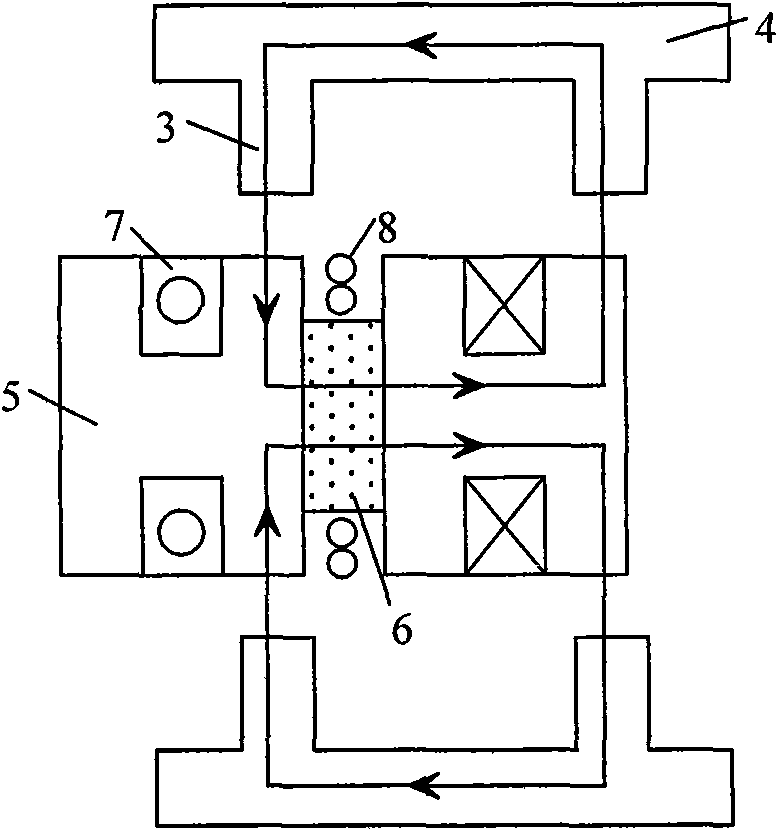
Two-rotor axial magnetic flux switching type mixed excitation synchronous generator
InactiveCN101662193AImprove cooling effectImprove efficiencySynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit stationary partsConstant frequencyVoltage regulation
The invention relates to the generator technology and in particular to a two-rotor axial magnetic flux switching type mixed excitation synchronous generator which has high efficiency, direct driving and variable speed and constant frequency; the generator comprises a stator and rotors; the stator is assembled to be round by 6a H-shaped unit stator cores, a is positive integer, an armature windingadopts a concentrated winding which is circumferentially wound on a stator tooth adjacent to the H-shaped unit stator core, permanent magnets are arrayed between the adjacent H-shaped unit stator cores in a staggering way, the permanent magnet charges the magnetism tangentially, an exciting winding is axially wound on the surface of the permanent magnet, so as to generate circumferential magneticfield by direct current in the exciting winding and enhance or weaken the permanent magnet field; the rotor comprises a rotor magnet yoke and a rotor pole fixed at the inner side of the rotor magnet yoke, the rotor and the stator are arranged axially. The invention is a novel mixed excitation synchronous generator which has high efficiency, direct driving and wide voltage regulating range.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Double-rotor flux-switching machine
ActiveUS20140049124A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsCost effectivenessRotor flux
Advantageous machines, such as flux-switching machines (FSMs) are provided. An FSM can be yokeless and can have two rotors, which can be displaced from one another (e.g., by half a pole pitch). An FSM can be a flux-switching permanent magnet machine (FSPMM), and all magnets can be magnetized in the same circumferential direction. FSMs of the subject invention are cost-effective, have high torque density, and can operate well even under fault conditions.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
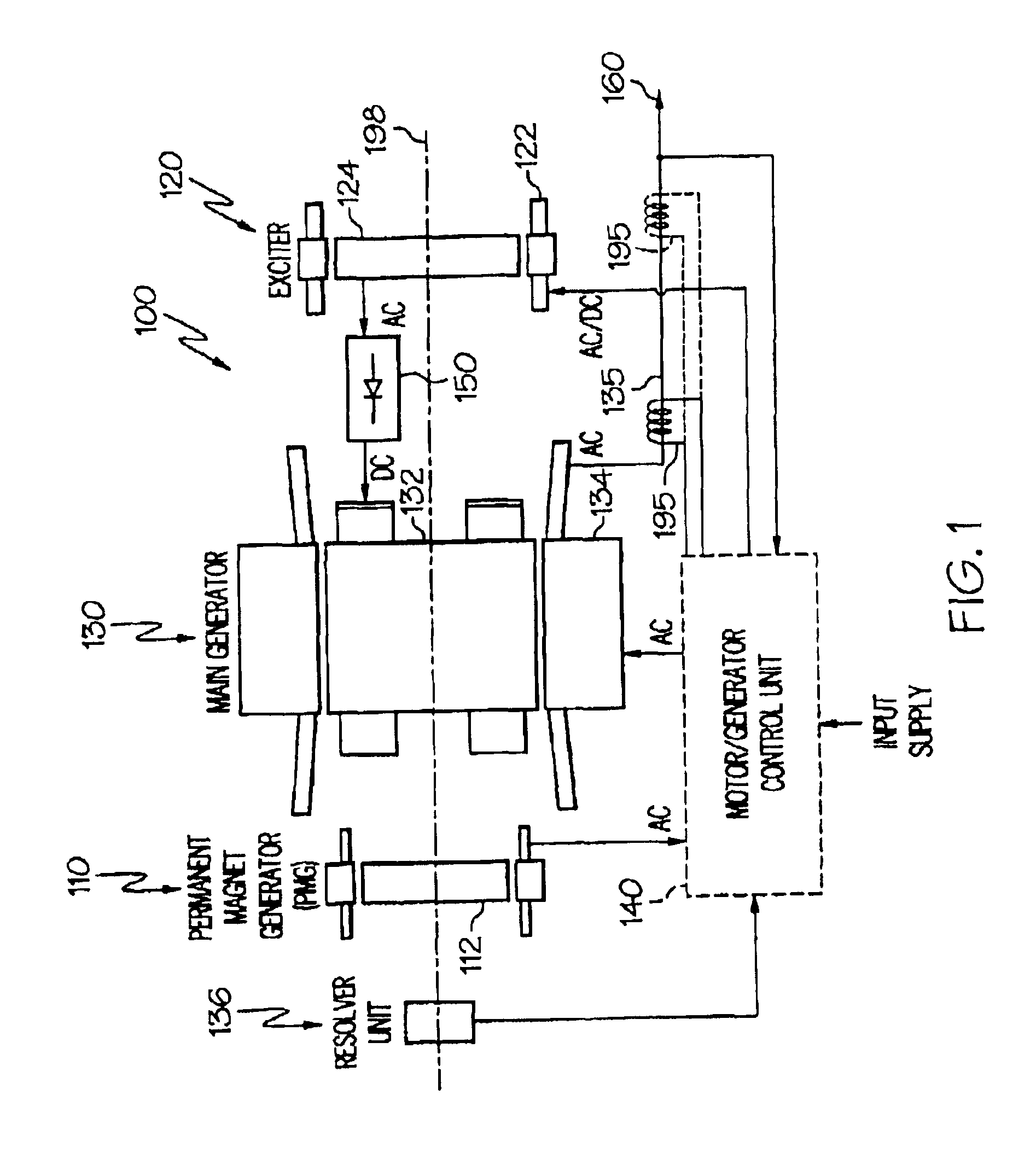
Gas turbine engine starter-generator exciter starting system and method including a capacitance circuit element
A rotating electrical machine, such as an aircraft starter-generator, that includes an exciter that has its stator windings supplied with electrical power from a power supply. One or more switches are electrically coupled between the exciter stator winding and the power supply and are configured and controlled so that a capacitance may be selectively placed electrically in series with the exciter stator windings.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
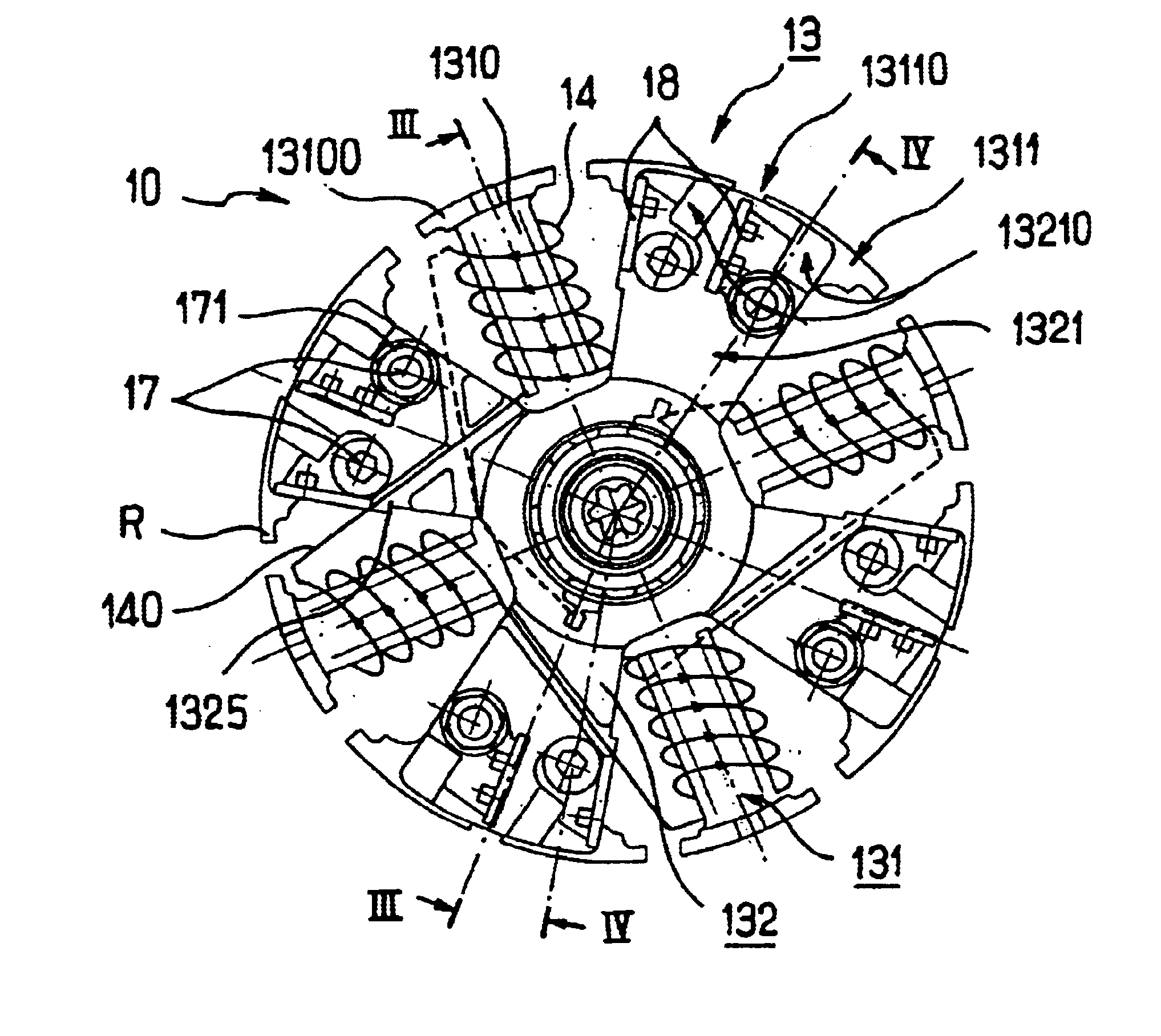
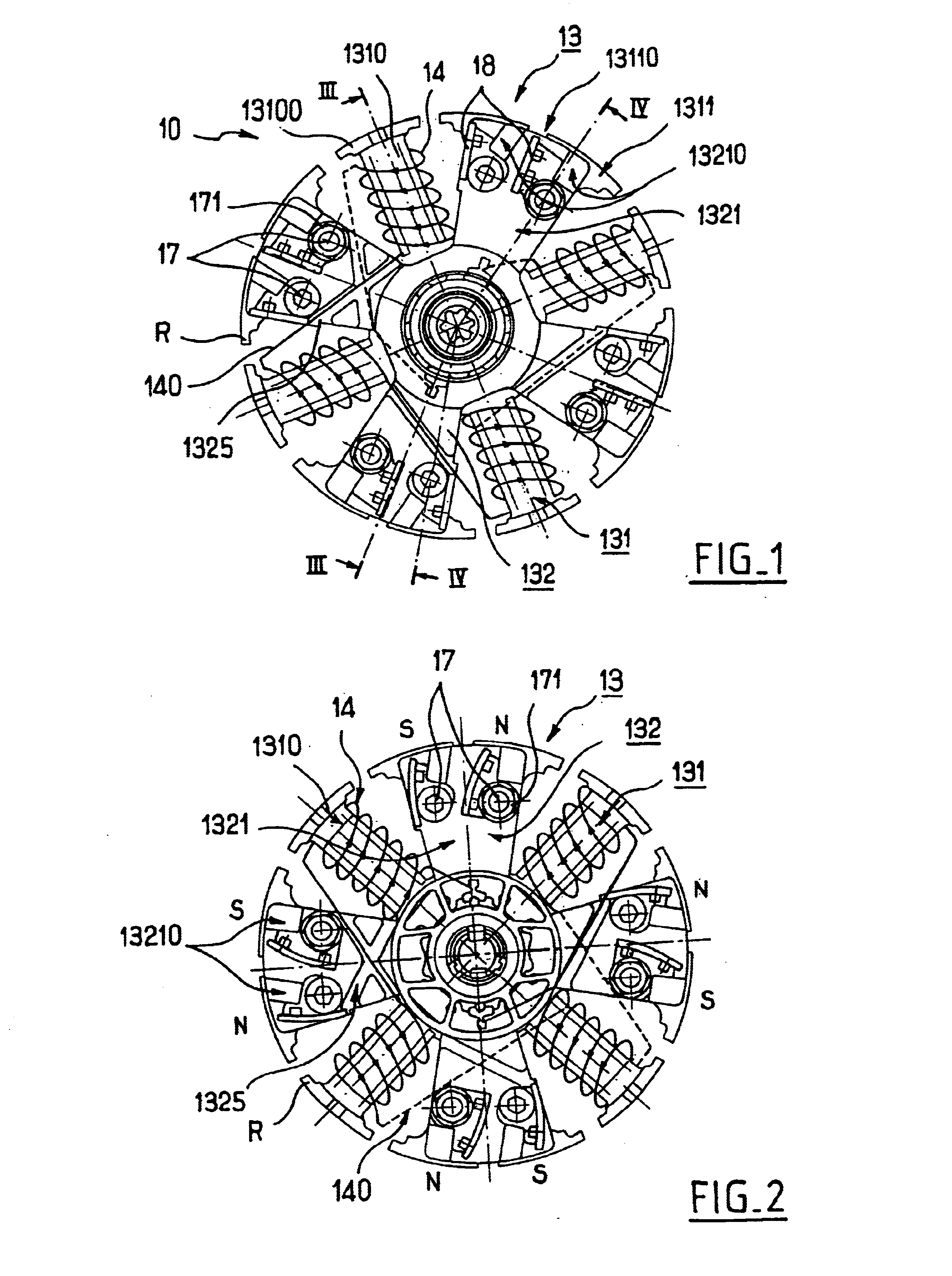
Hybrid alternator with an axial end retainer for permanent magnets
InactiveUS6784586B2Guaranteed safe operationAvoid overall overheatingSynchronous generatorsSynchronous machine detailsAlternatorElectric machine
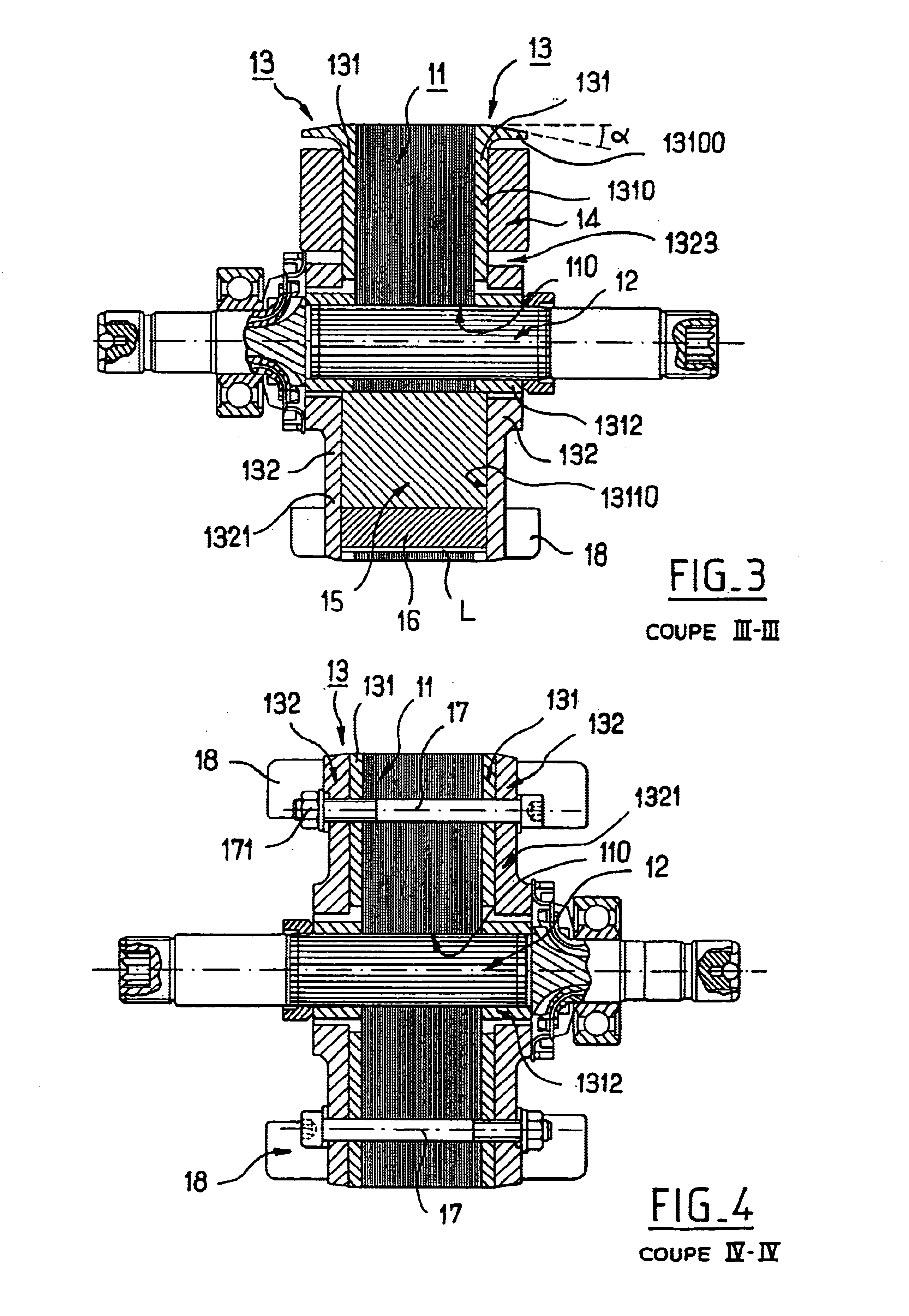
The invention relates to a rotating electric machine, especially an alternator or alternator / starter for motor vehicles, including a stator surrounding a rotor (10) equipped with a pack of metal plates, a gap between the stator and the rotor, permanent magnets integrated into the rotor and excitation coils (14) integrated into the rotor, in which the excitation coils are wound around salient poles (1310) cut out in the pack of metal plates of the rotor, and the permanent magnets are accommodated in housings (13110) formed in the pack of plates of the rotor and open towards the periphery of the rotor, characterized in that the housings (13110) are closed axially at each of their ends by a non-magnetic retaining piece (13) equipped with a part intended to come into abutment with the magnets, and in that the retaining piece features recesses for accommodations [sic] of the buns of the excitation coils (14).
Owner:VALEO EQUIP ELECTRIC MOTEUR
Underwater motor and thruster integrated apparatus
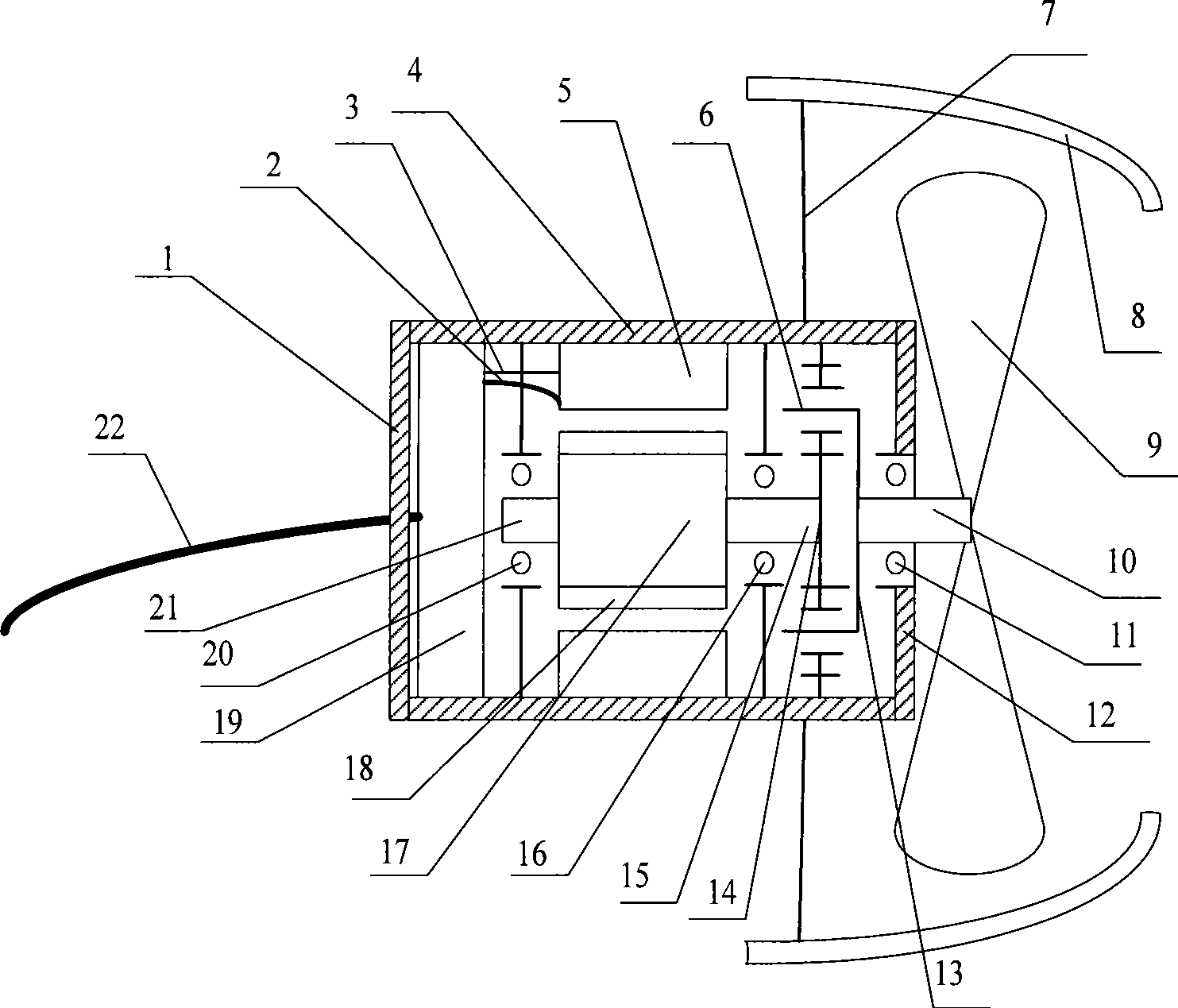
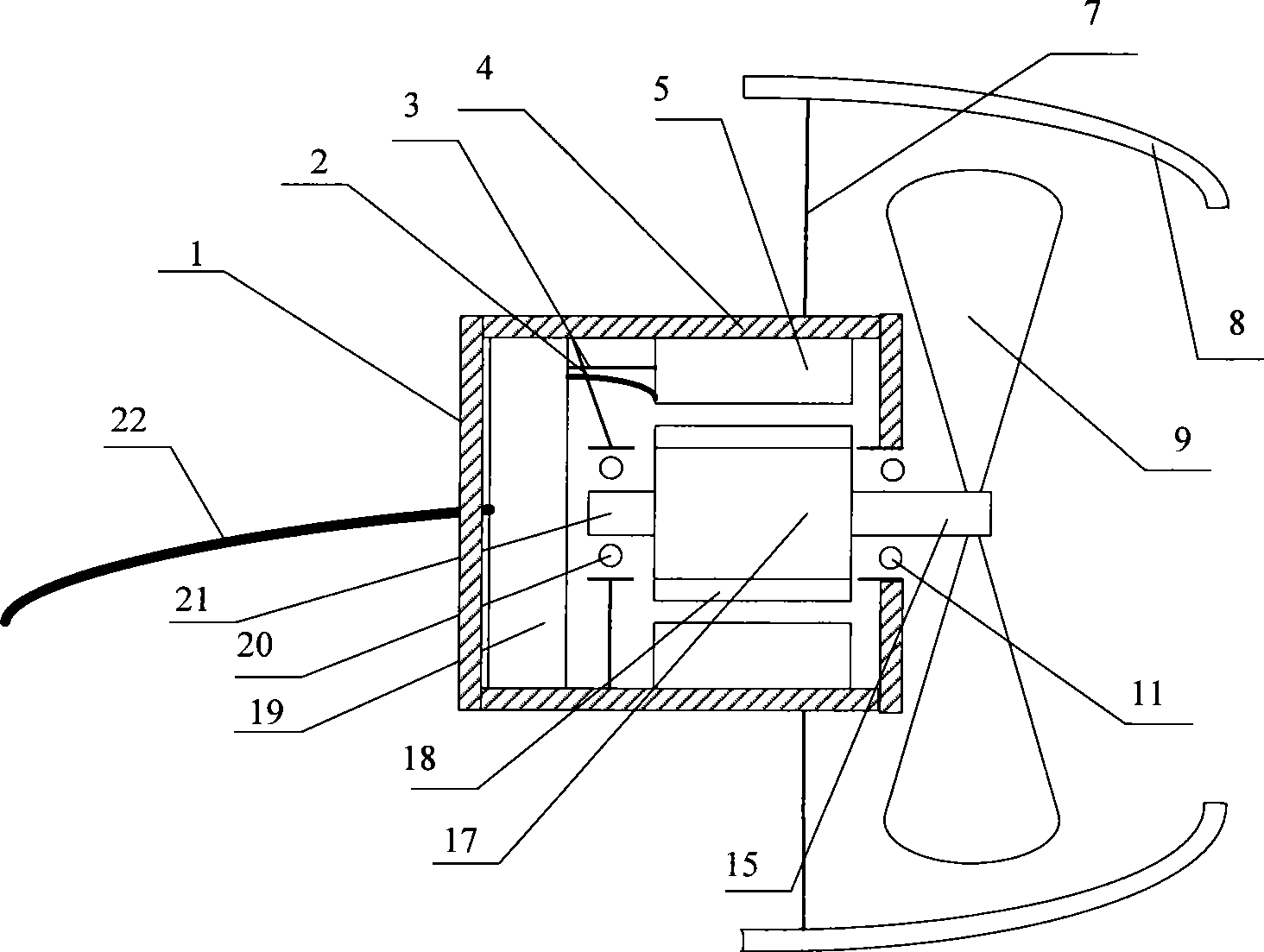
InactiveCN101417702AReduce volumeReduce weightAssociation with control/drive circuitsSynchronous machine detailsPropellerTotal efficiency
The invention provides an apparatus integrating an underwater motor and a thruster, comprising a motor casing and end covers respectively arranged at two ends of the motor casing. The clearance between the end cover and the motor casing is sealed; a stator core embedded with a three-phase winding is fixed on the inner side of the motor casing; a rotor provided with a fixing shaft at one end and a transmission shaft at the other end is arranged through a bearing inside the motor casing and the transmission shaft is extended out of the end cover and a screw propeller is fixed on the transmission shaft; the sintered NeFeB is stuck onto the rotor; a locating sensor is arranged on the stator core; a controller is arranged inside the motor casing and the three-phase winding and a controller arranged on the stator are respectively connected with the controller through lead; a control cable of the controller is derived out from the end cover of one end; and an air deflector is fixed through a bracket on the motor casing. The adoption of the high-grade sintered NeFeB as alnico largely reduces the motor volume and weight so as to lead the integral structure to become compact and enhance the total efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Transverse flux, switched reluctance, traction motor with bobbin wound coil, with integral liquid cooling loop
InactiveUS20080179982A1Light weightIncrease torqueAsynchronous induction motorsMechanical energy handlingTransverse fluxBobbin
The present invention deals with a transverse flux machine of the switched reluctance variety. The transverse flux machine consists of multiple phases where each phase is spaced axially along the shaft. Axial spacing provides many benefits including a decreased weight and a capability to use simple wound bobbin coils for the windings. An embedded cooling loop is provided within the coils themselves. This cooling loop provides internal temperature regulation for the windings and allows for a higher efficiency among other benefits.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
Methods and apparatus for increasing power of permanent magnet motors
InactiveUS6472784B2Synchronous motors startersAsynchronous induction motorsMotor speedPermanent magnet motor
A method of increasing the power output of existing permanent magnet motors along with apparatus is disclosed. Increased power output is achieved by more completely utilizing the magnetic field of motor permanent magnets during running. The apparatus is external to the motor and therefore eliminates the need for modifications to the motor itself. The method involves providing a source of power to a permanent magnet motor which is capable of demagnetizing the motor permanent magnets at stall, and reducing the power at start up to a level sufficient to prevent demagnetization. Full power to the motor is provided when the motor speed reaches a level sufficient to prevent demagnetization of the permanent magnets.
Owner:MAGNETIC MOTORS
Popular searches
Electric motor speed/torque regulation Synchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnets Dynamo-electric motors/converters starters Motor/generator/converter stoppers Electric machines Propulsion using engine-driven generators Dynamo-electric converter control DC commutator Electric generator control Electric devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com