Patents
Literature
692 results about "Stator poles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
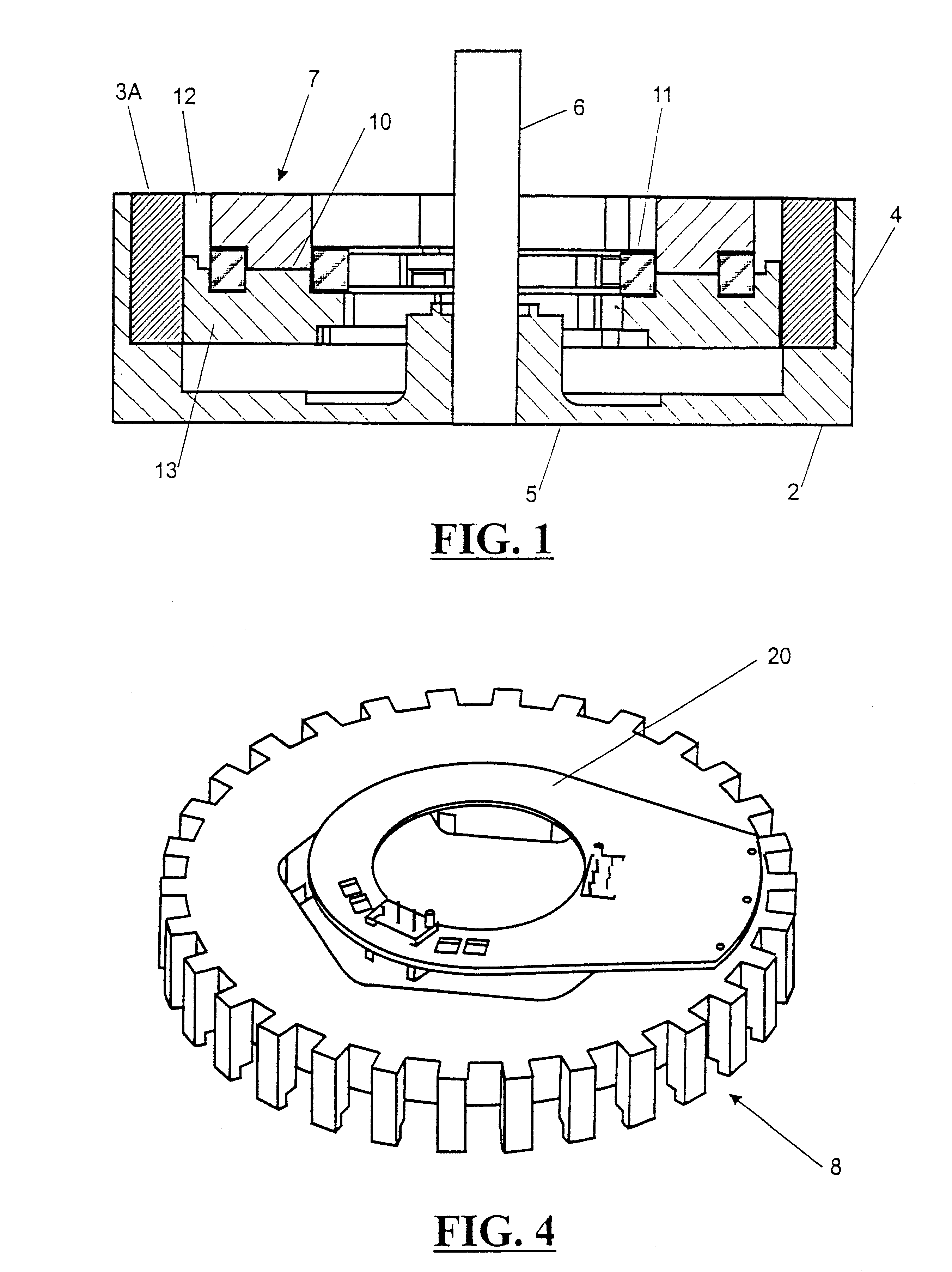
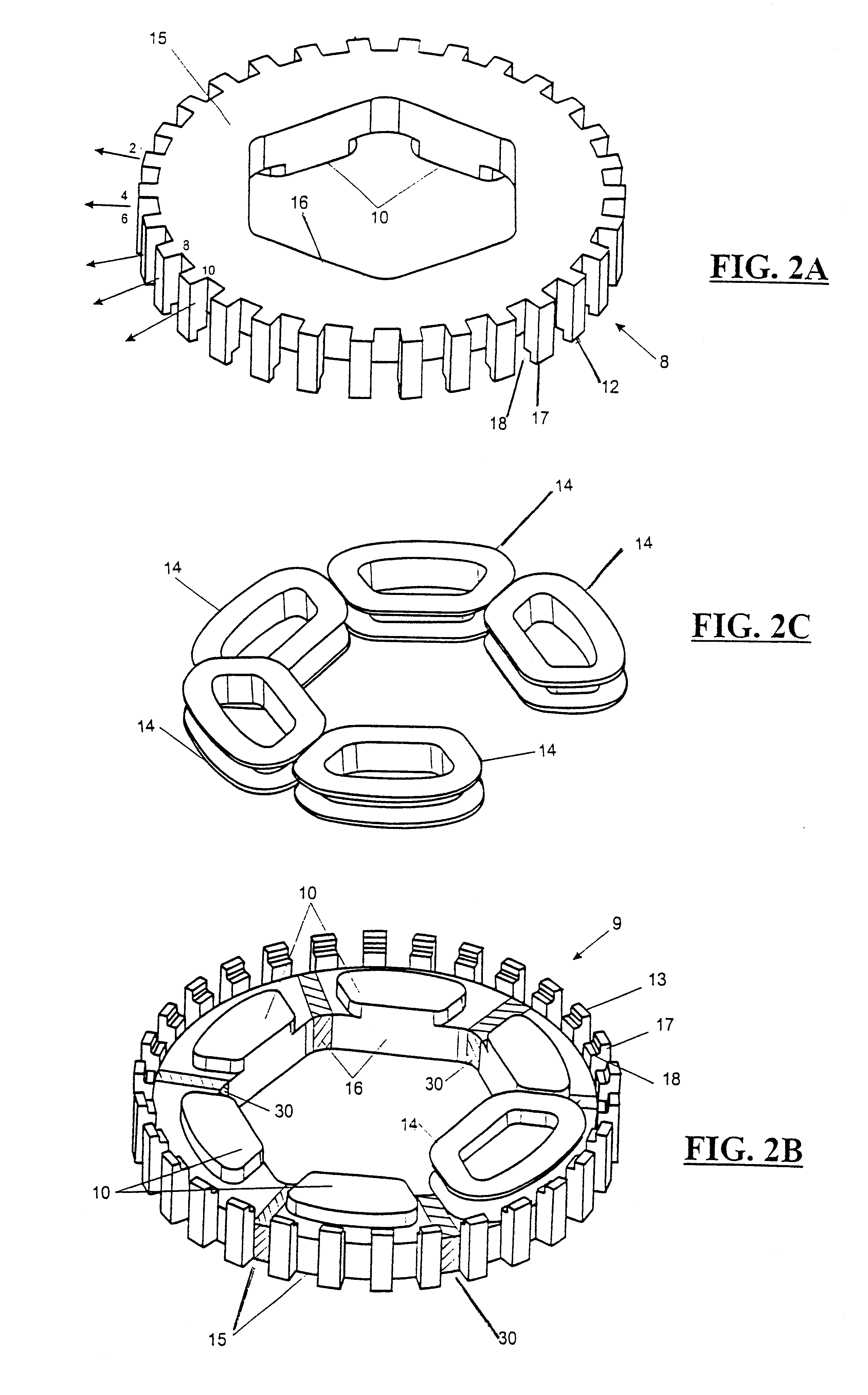
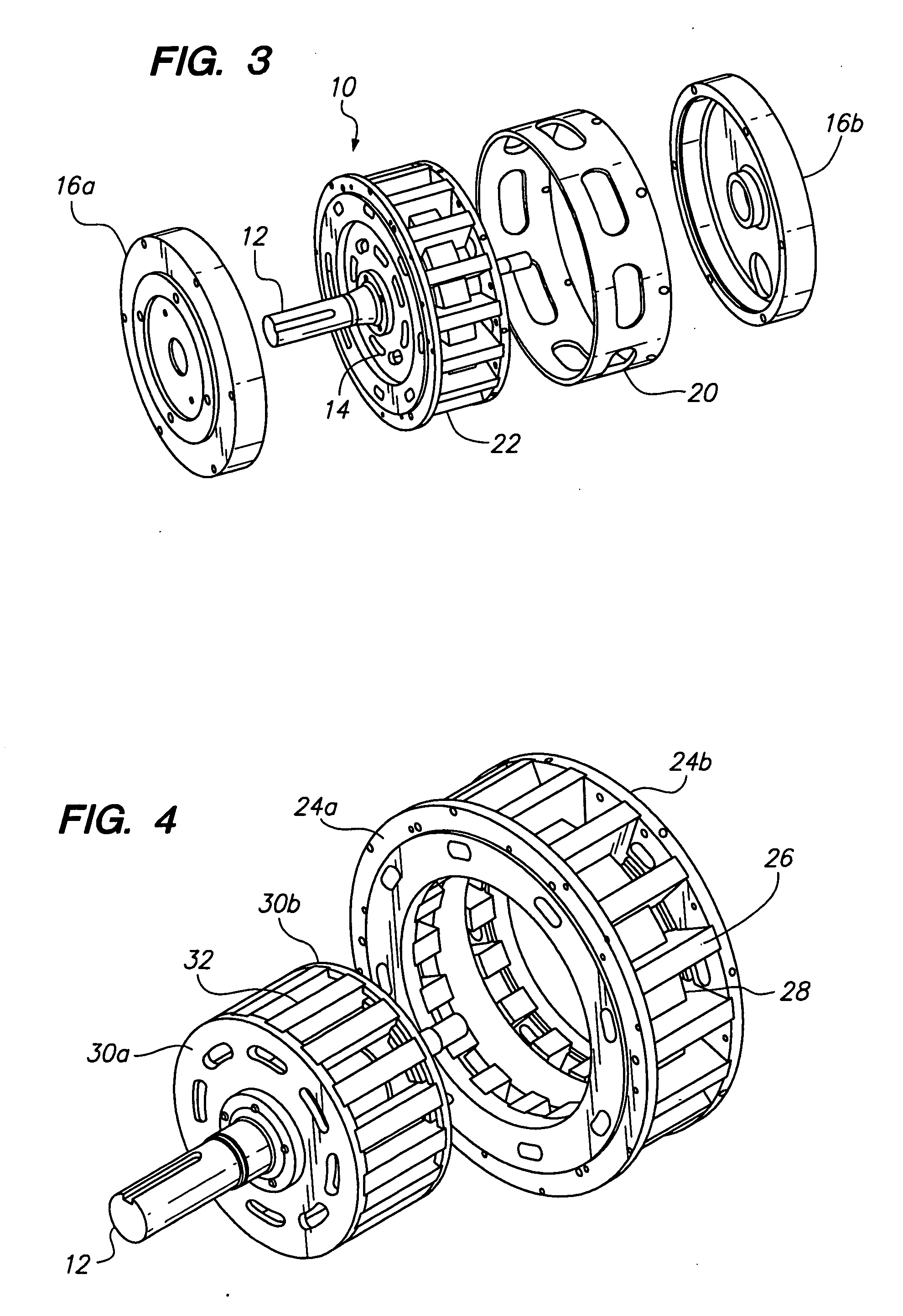
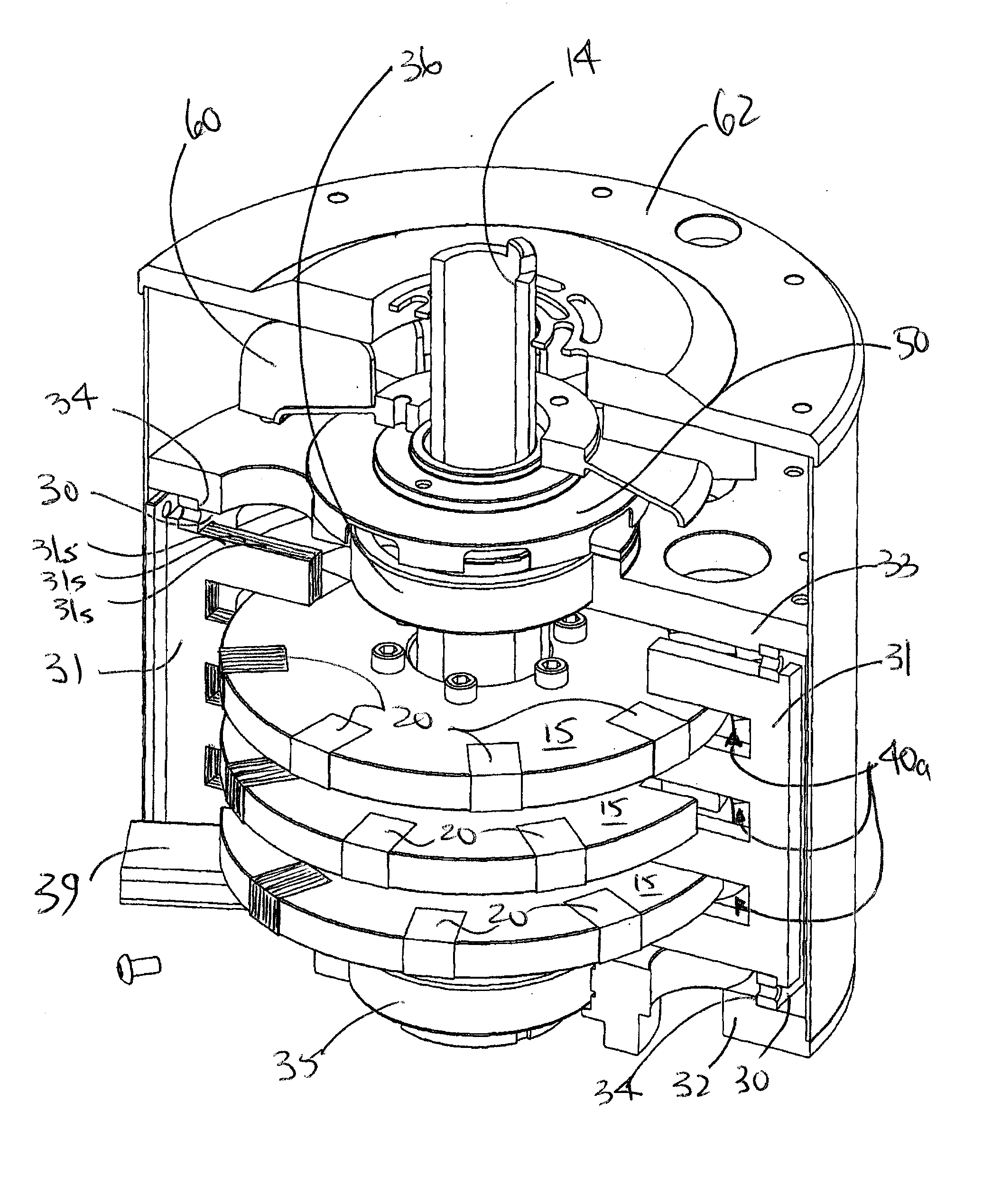
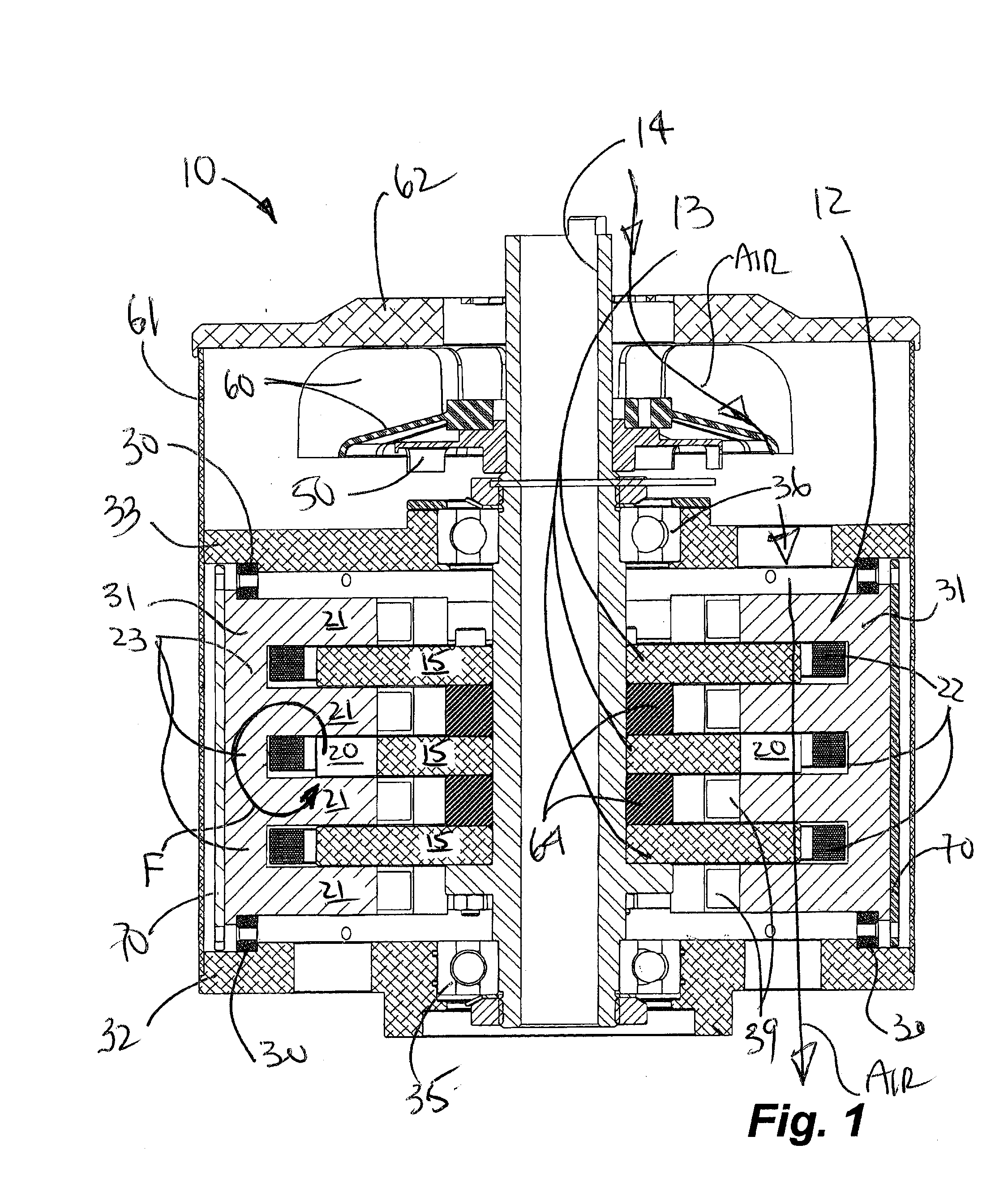
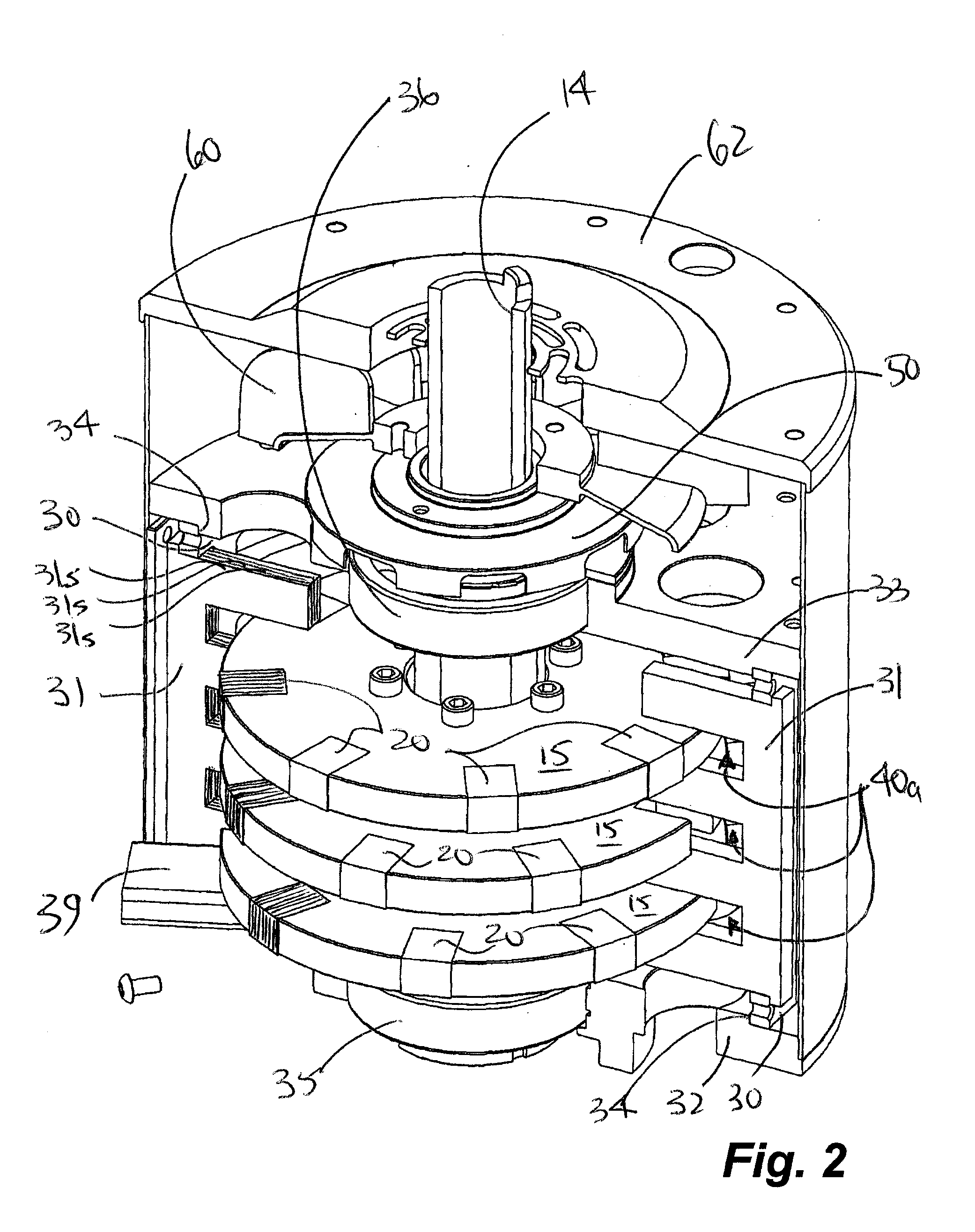
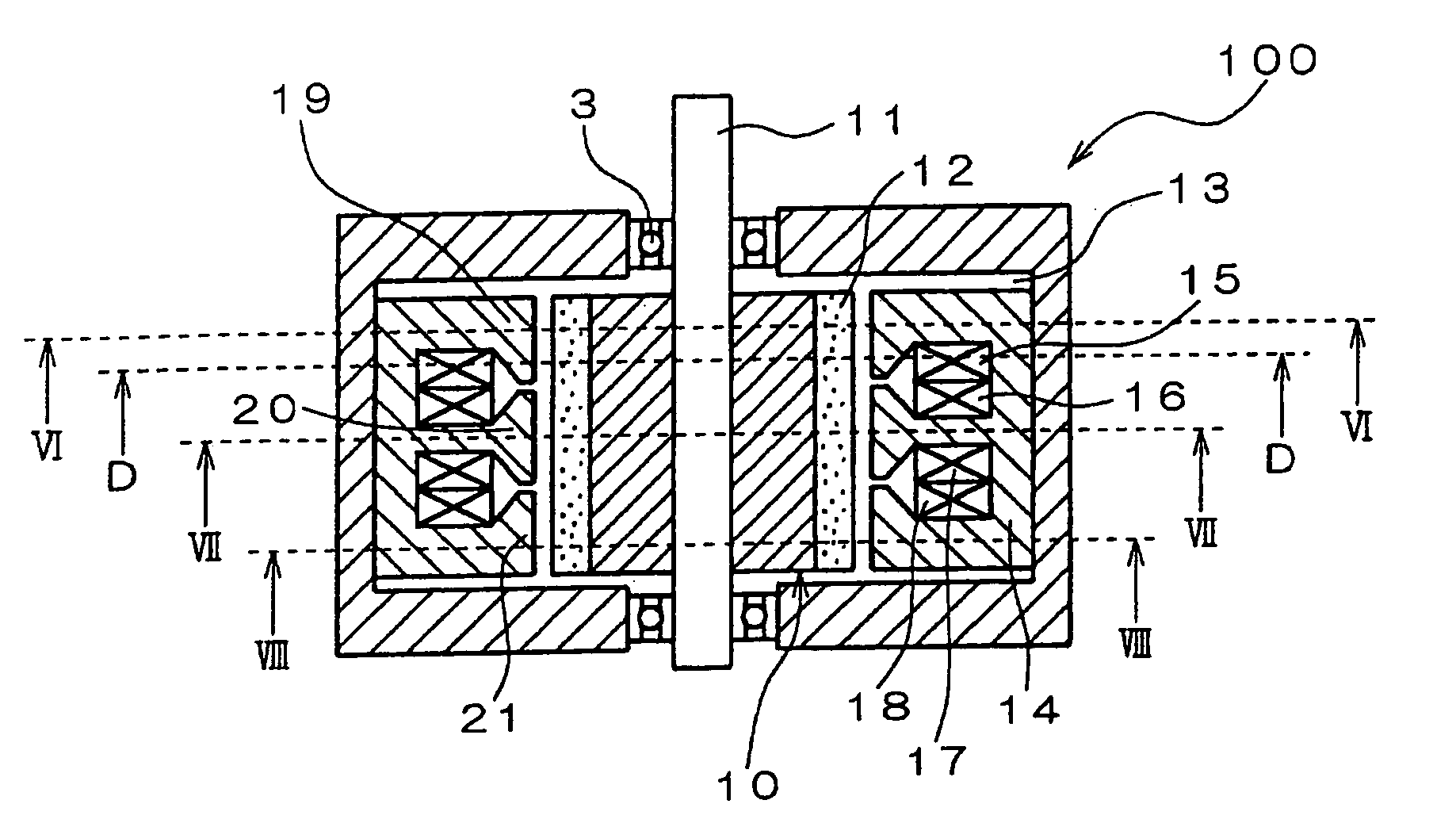
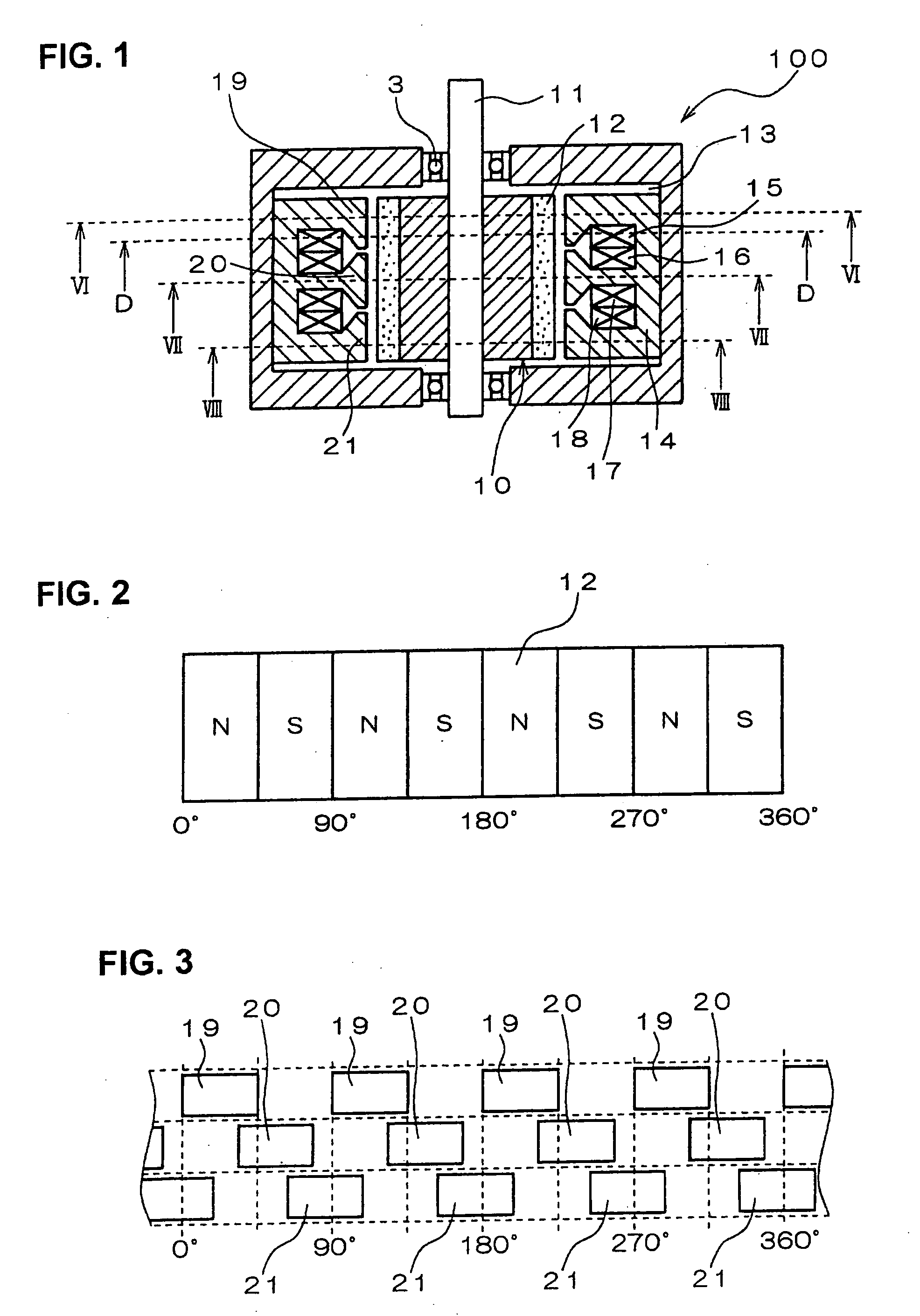
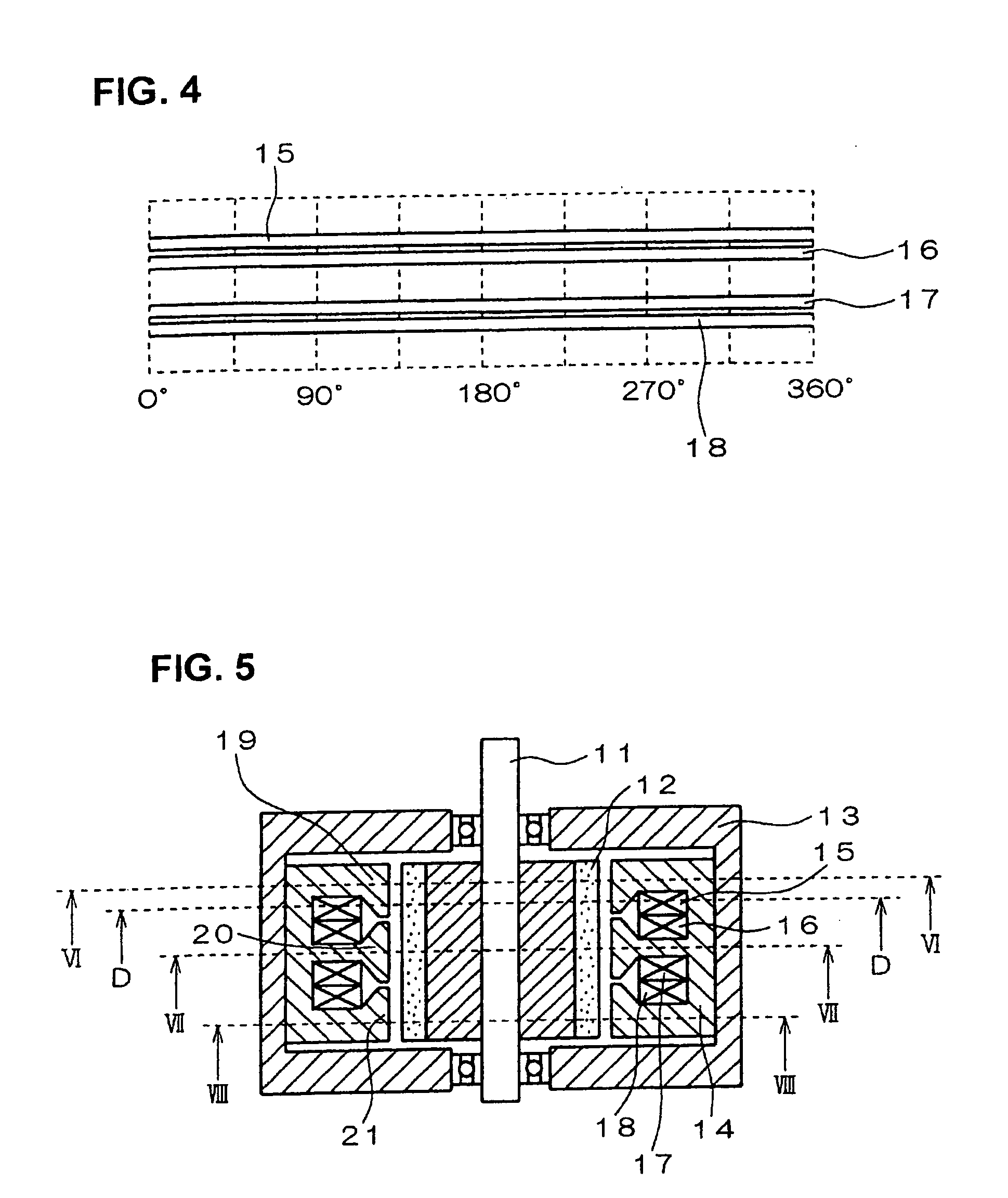
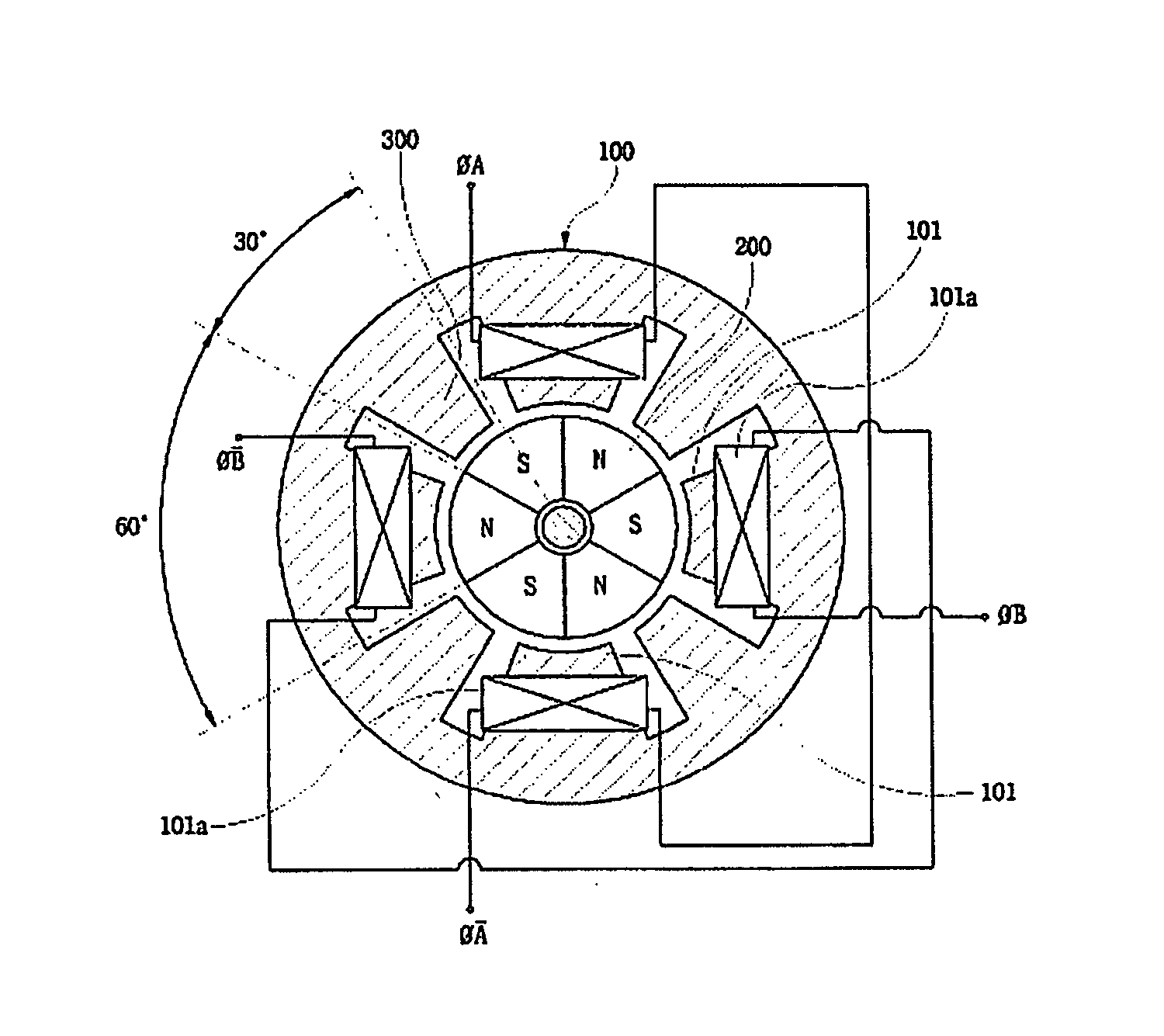
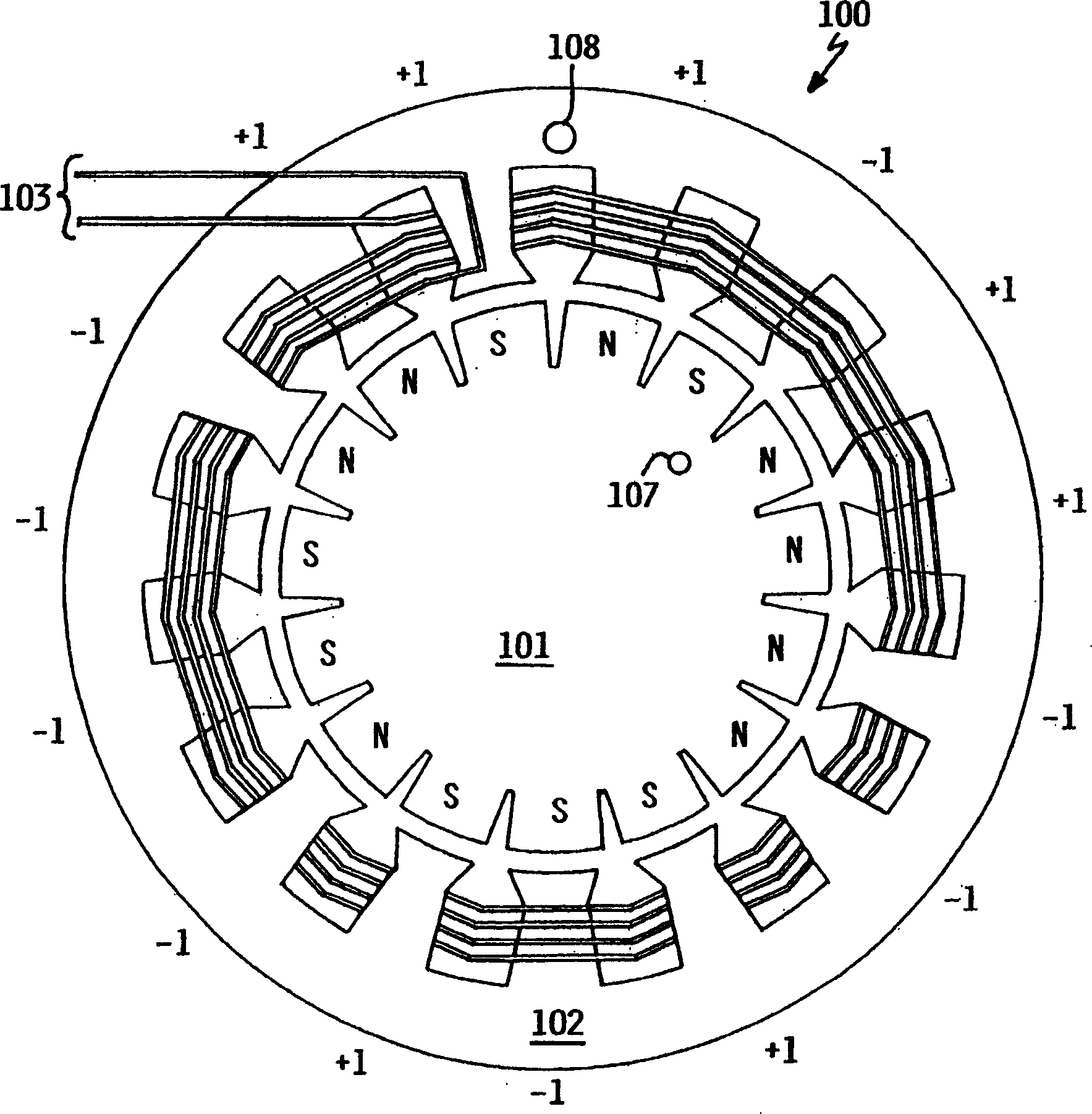
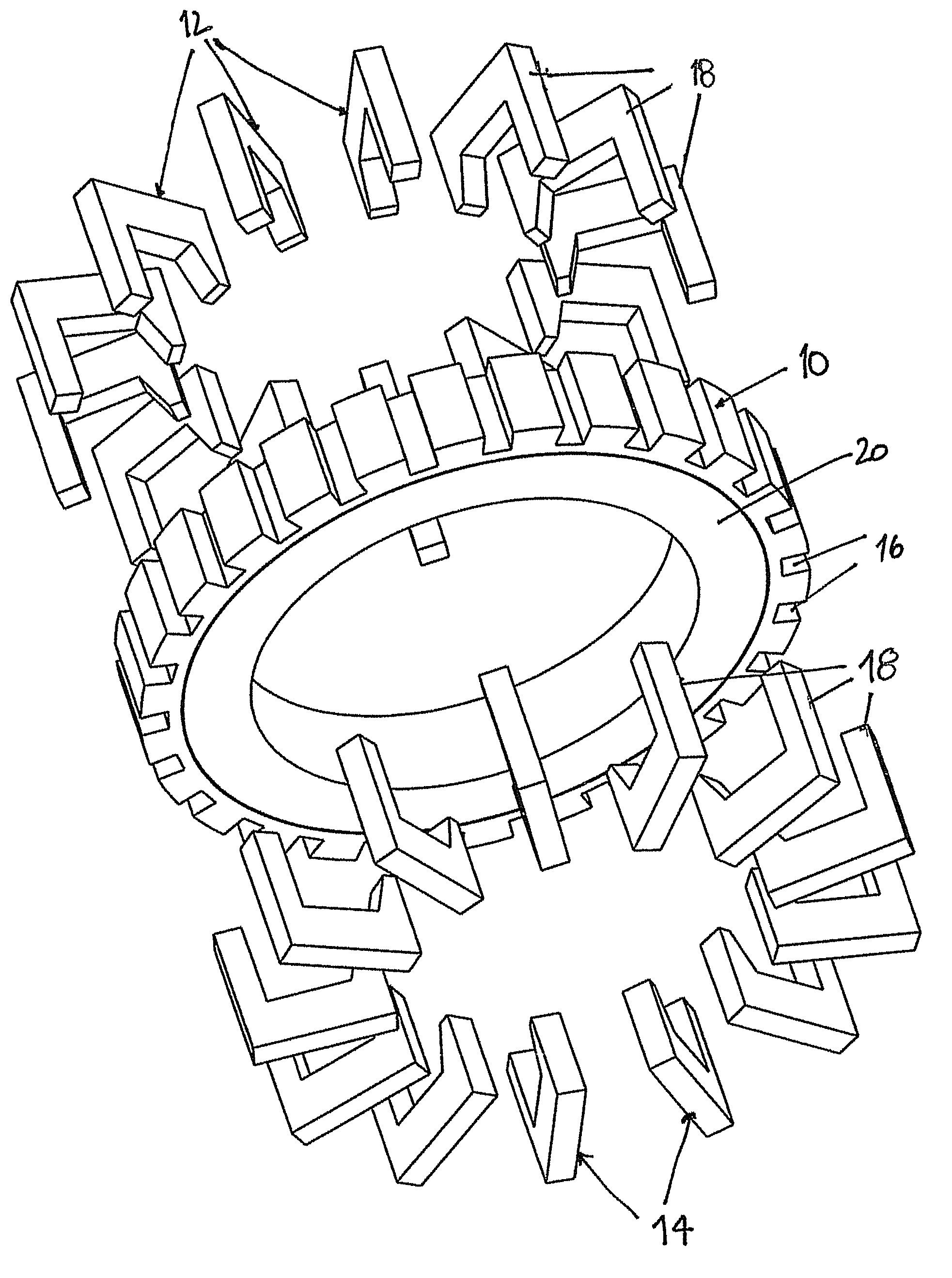
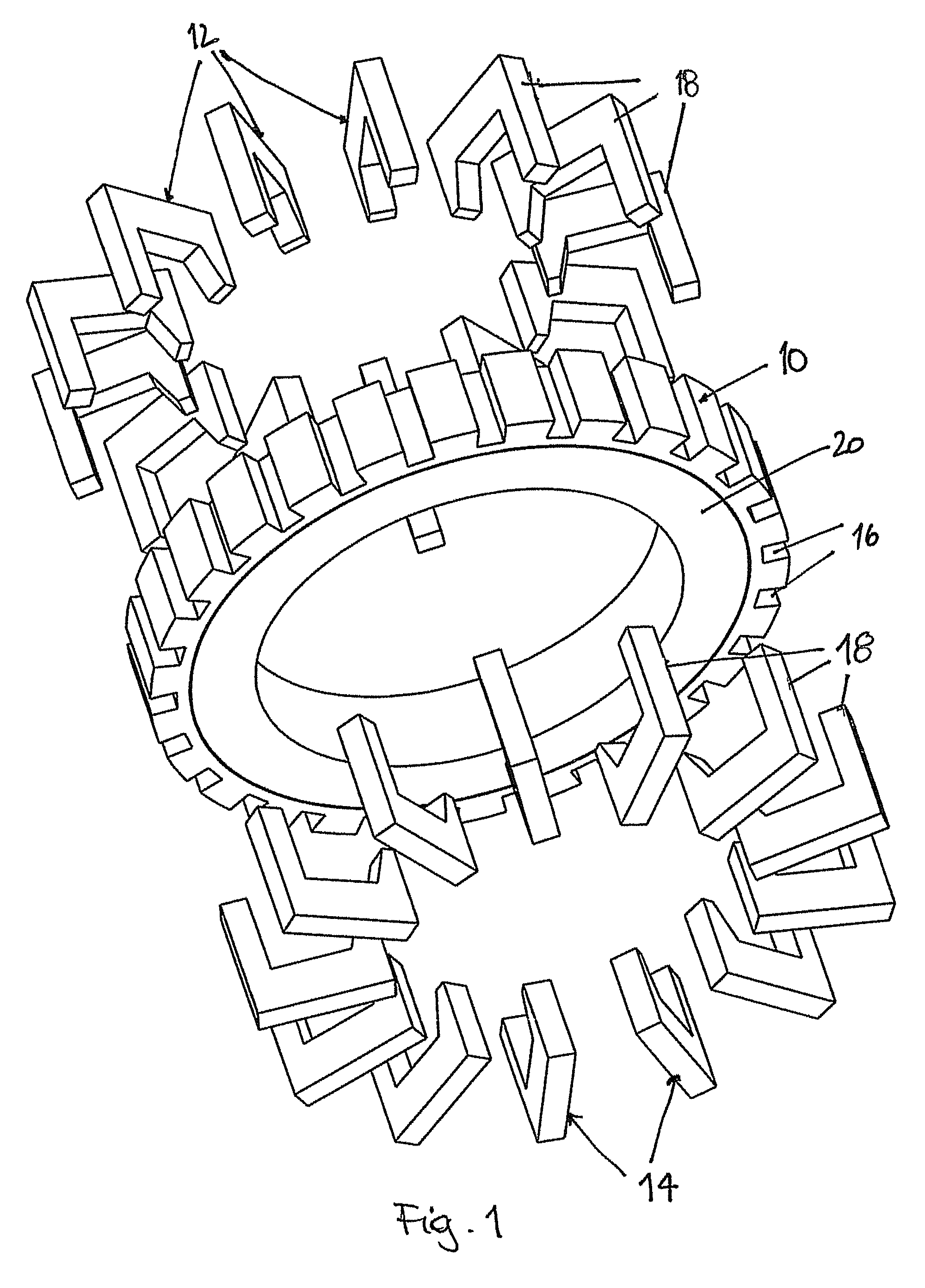
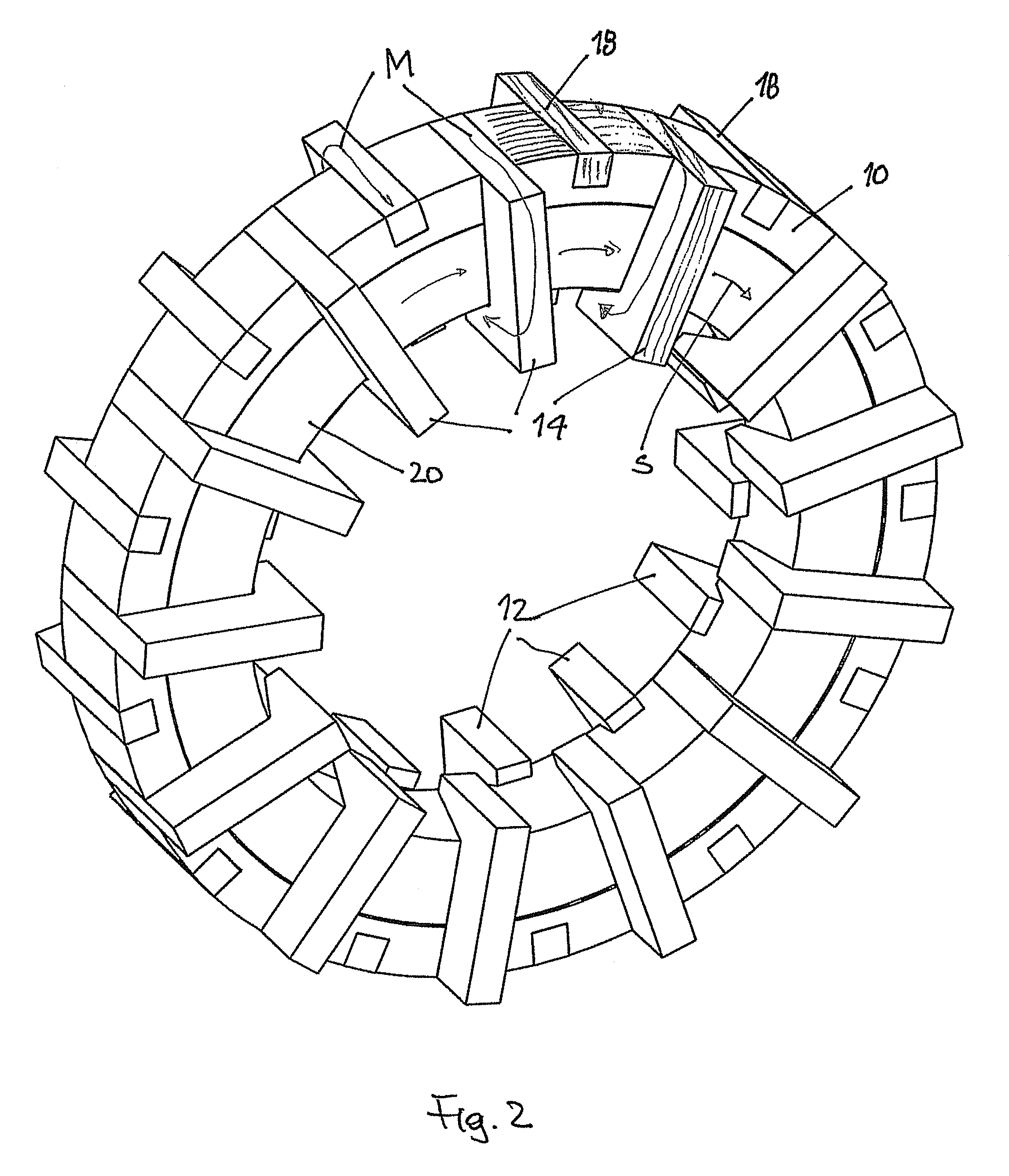
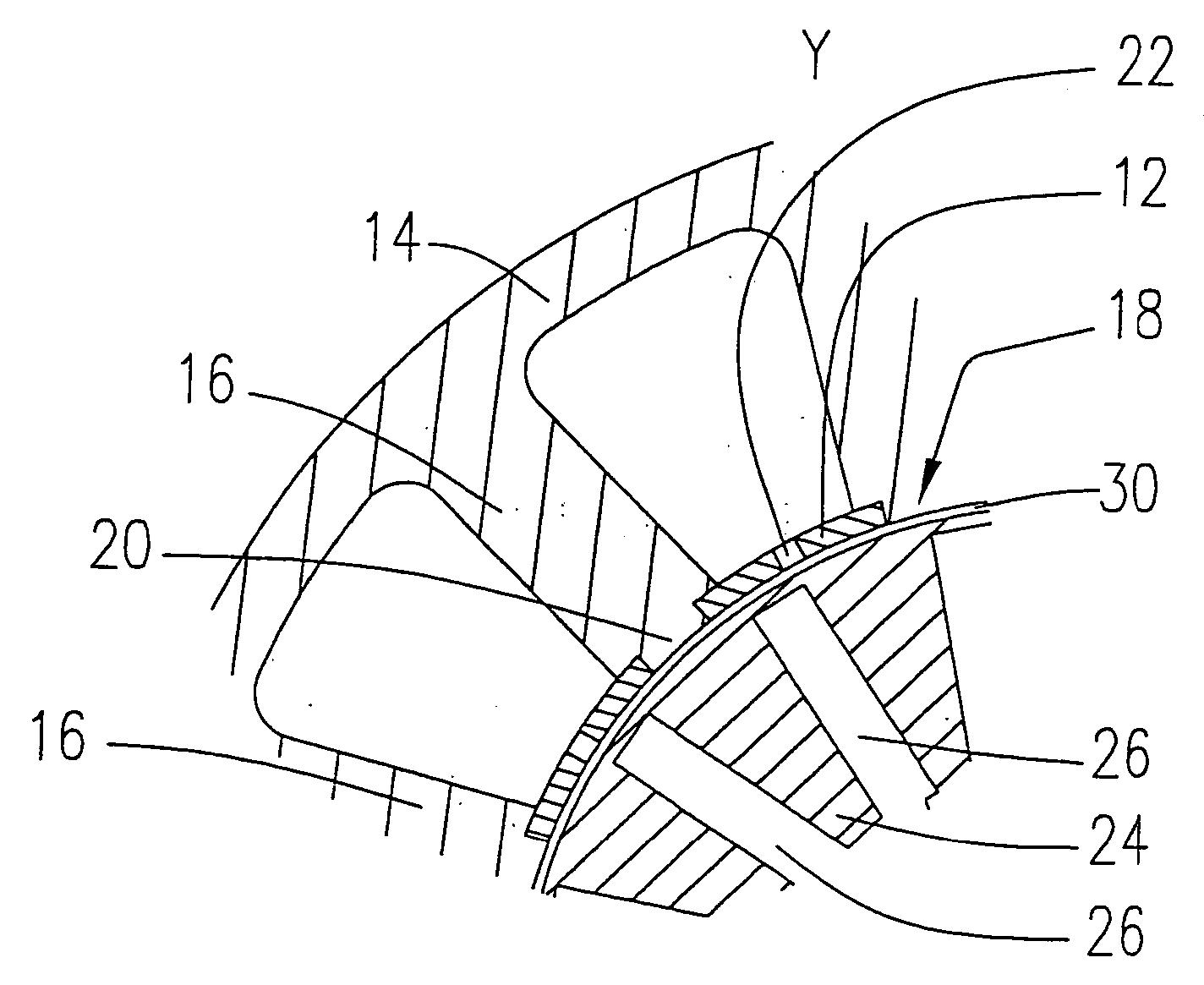
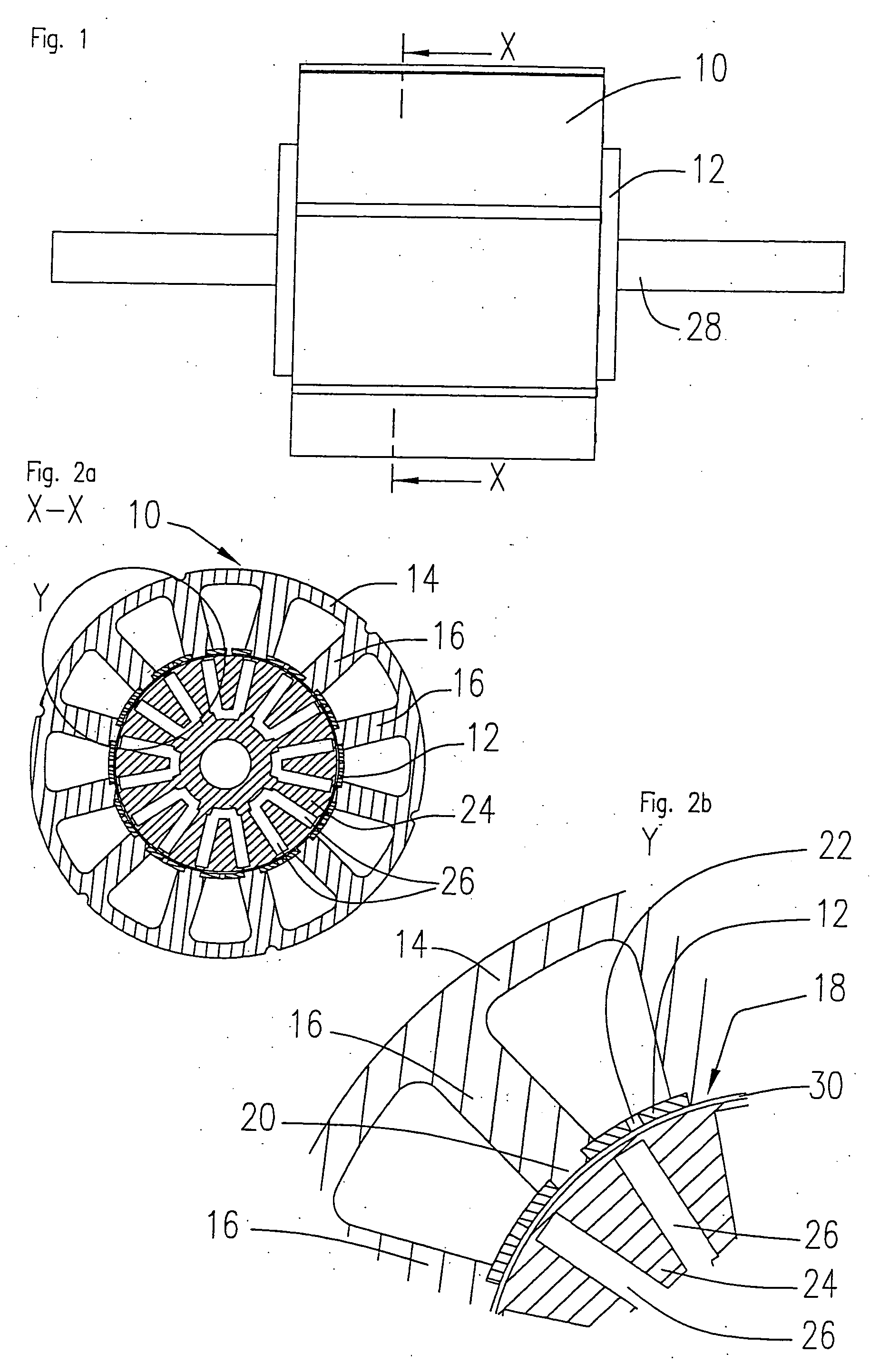
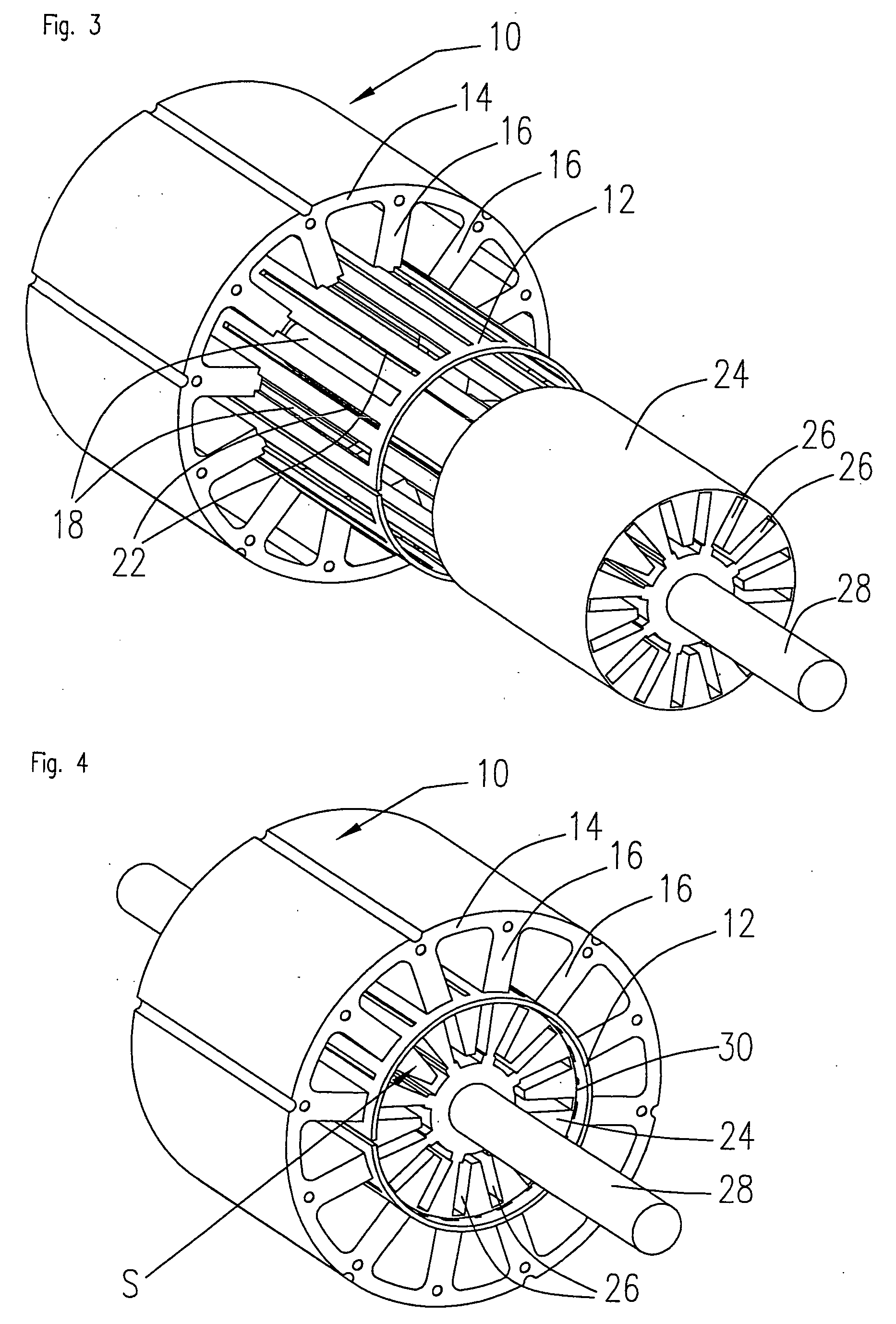
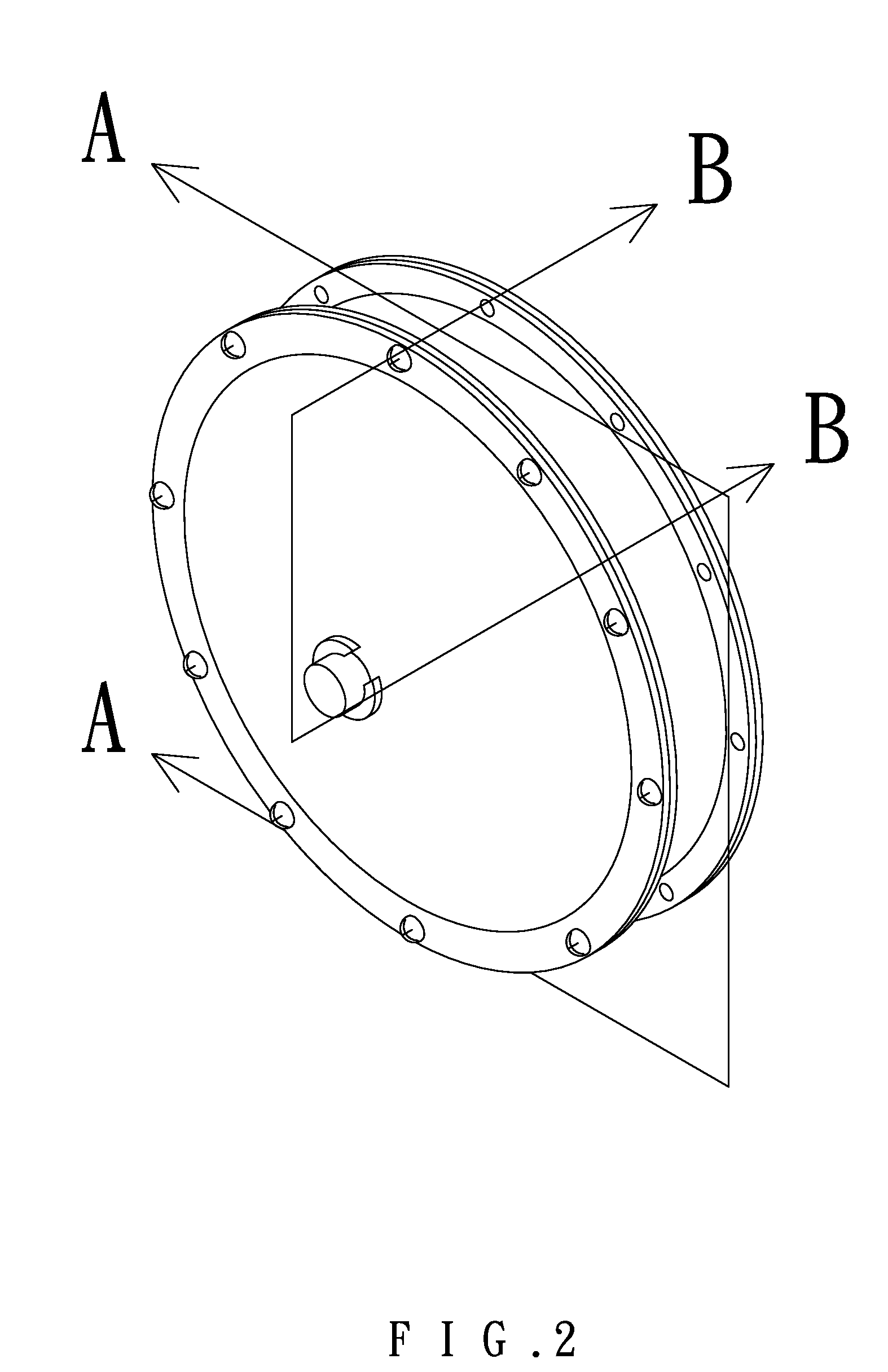
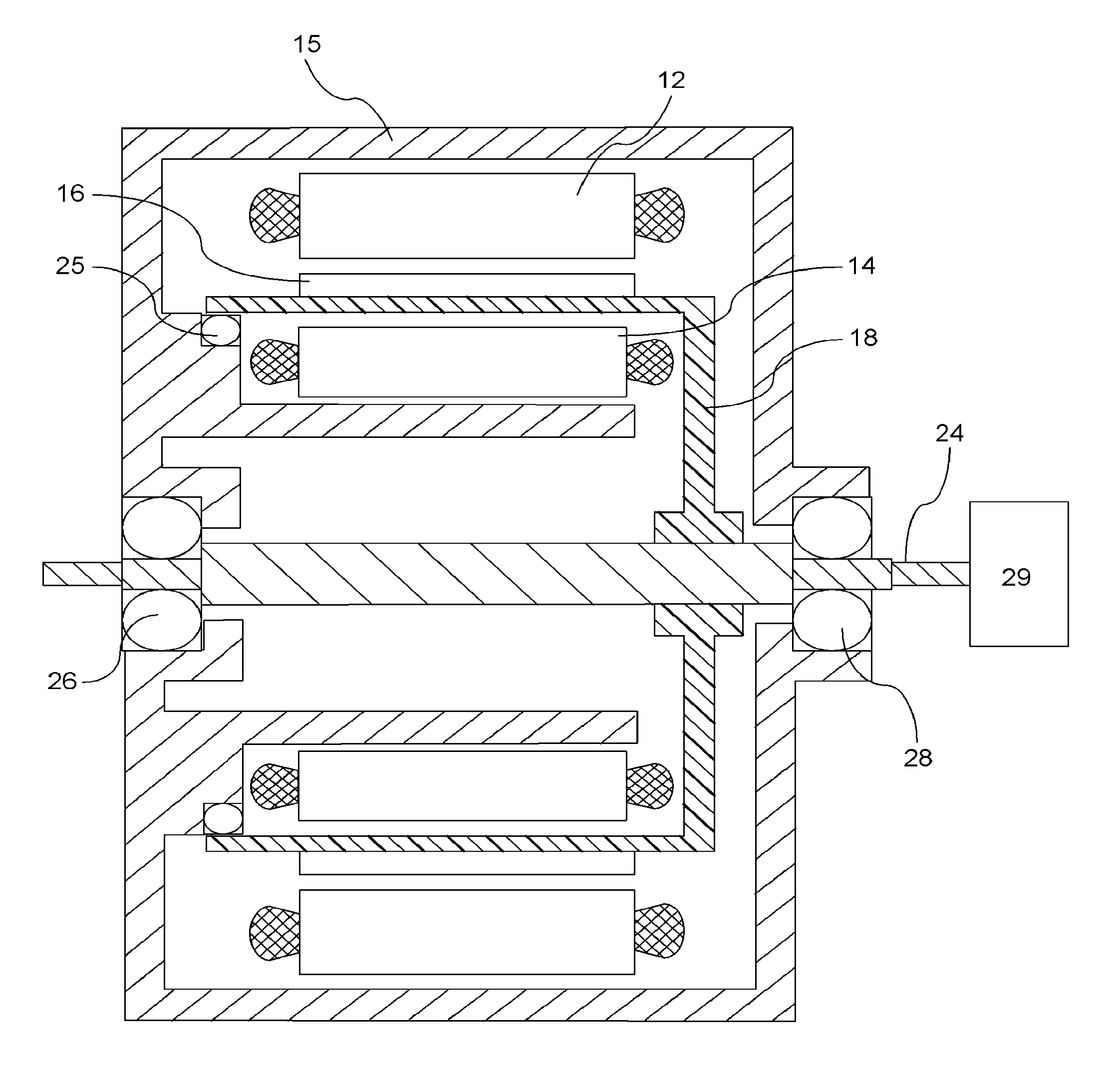
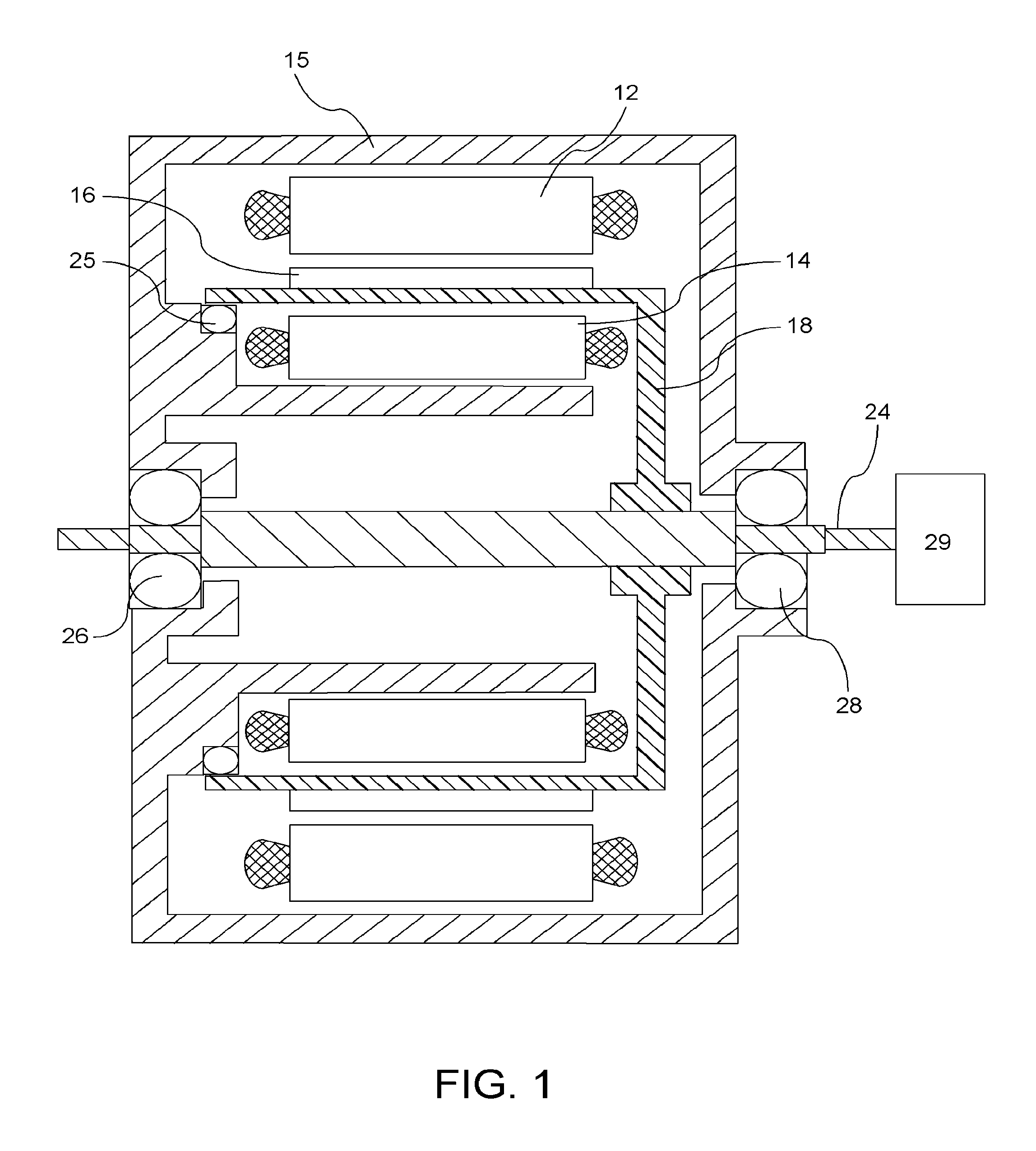
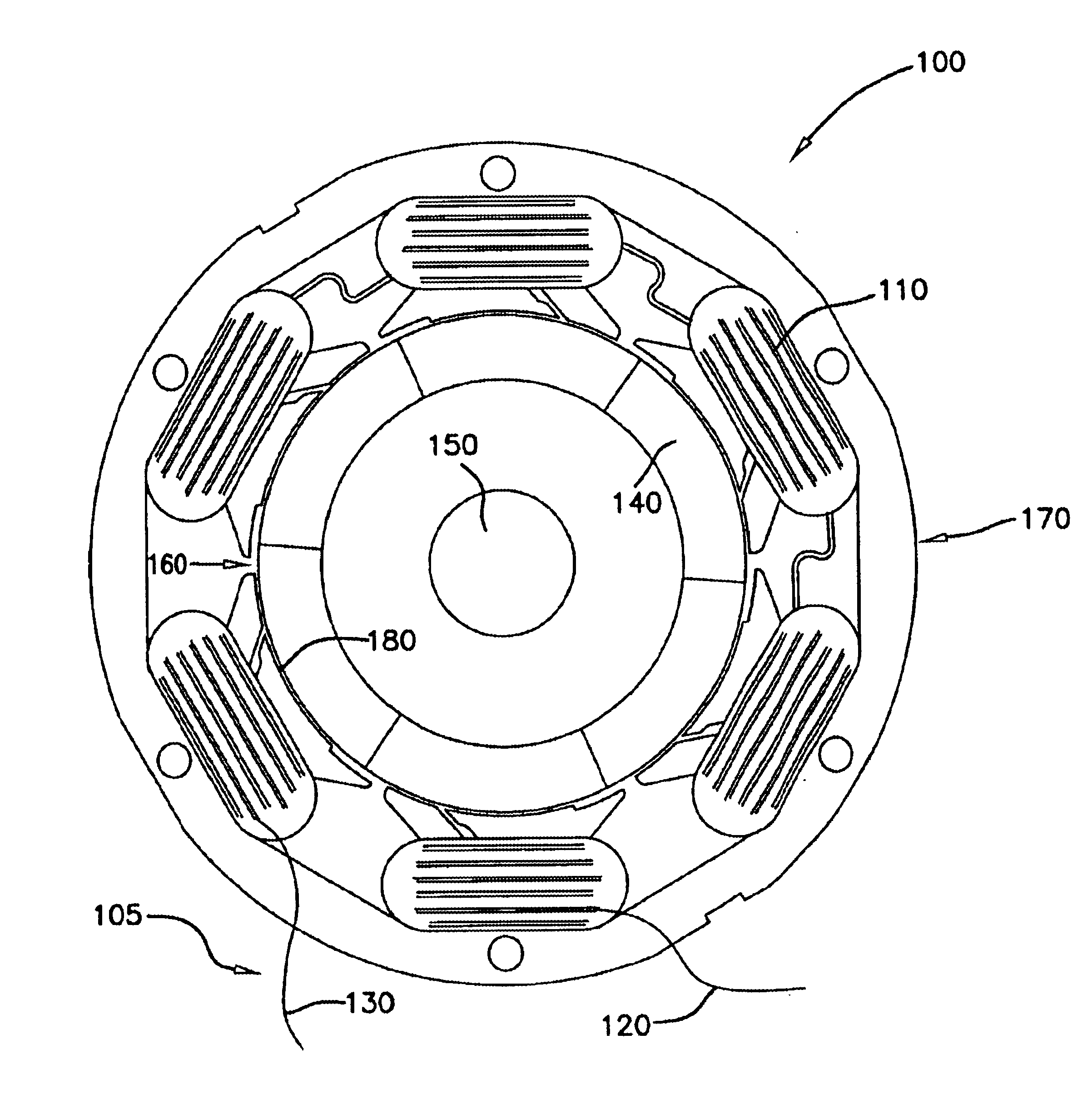
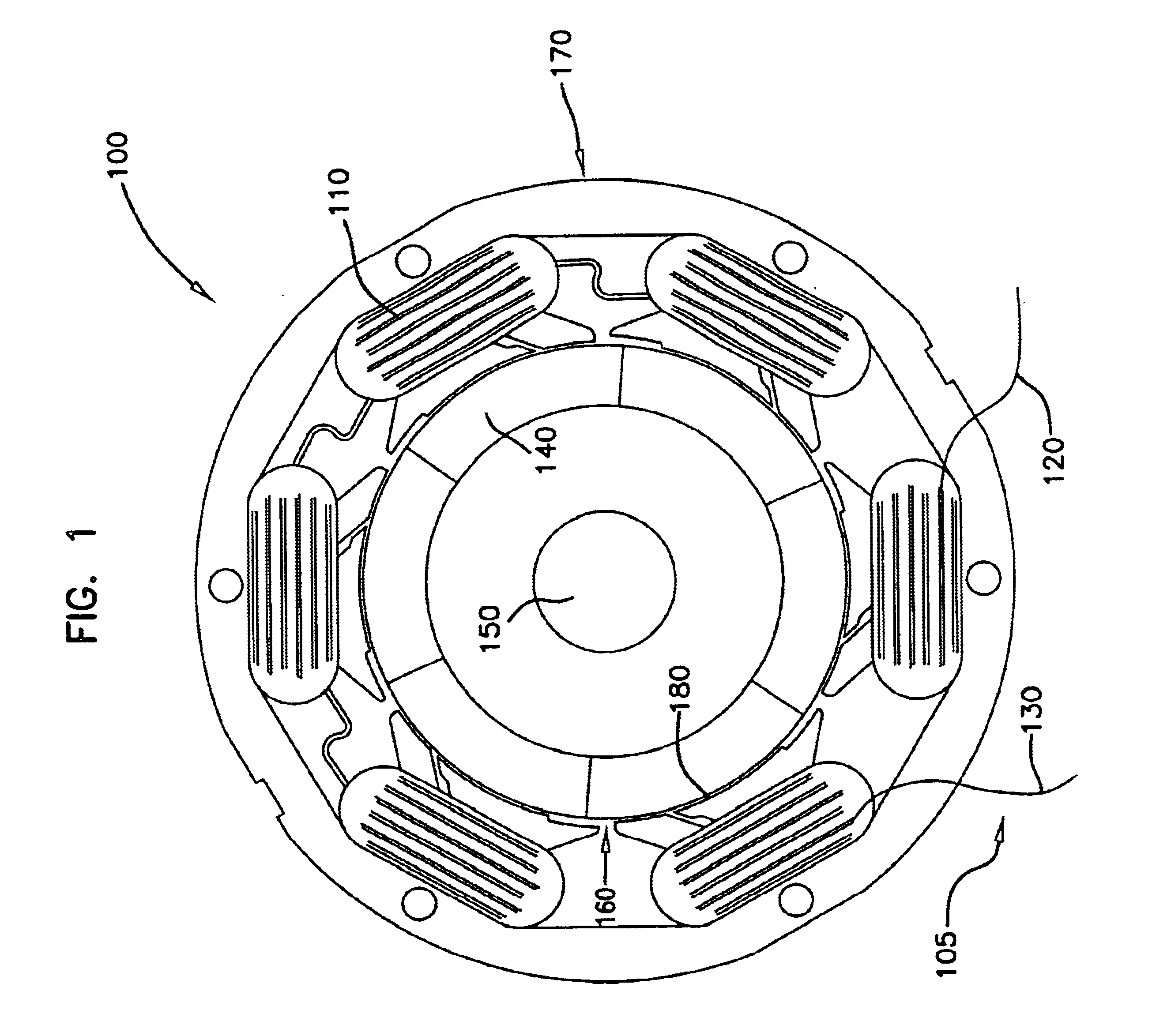
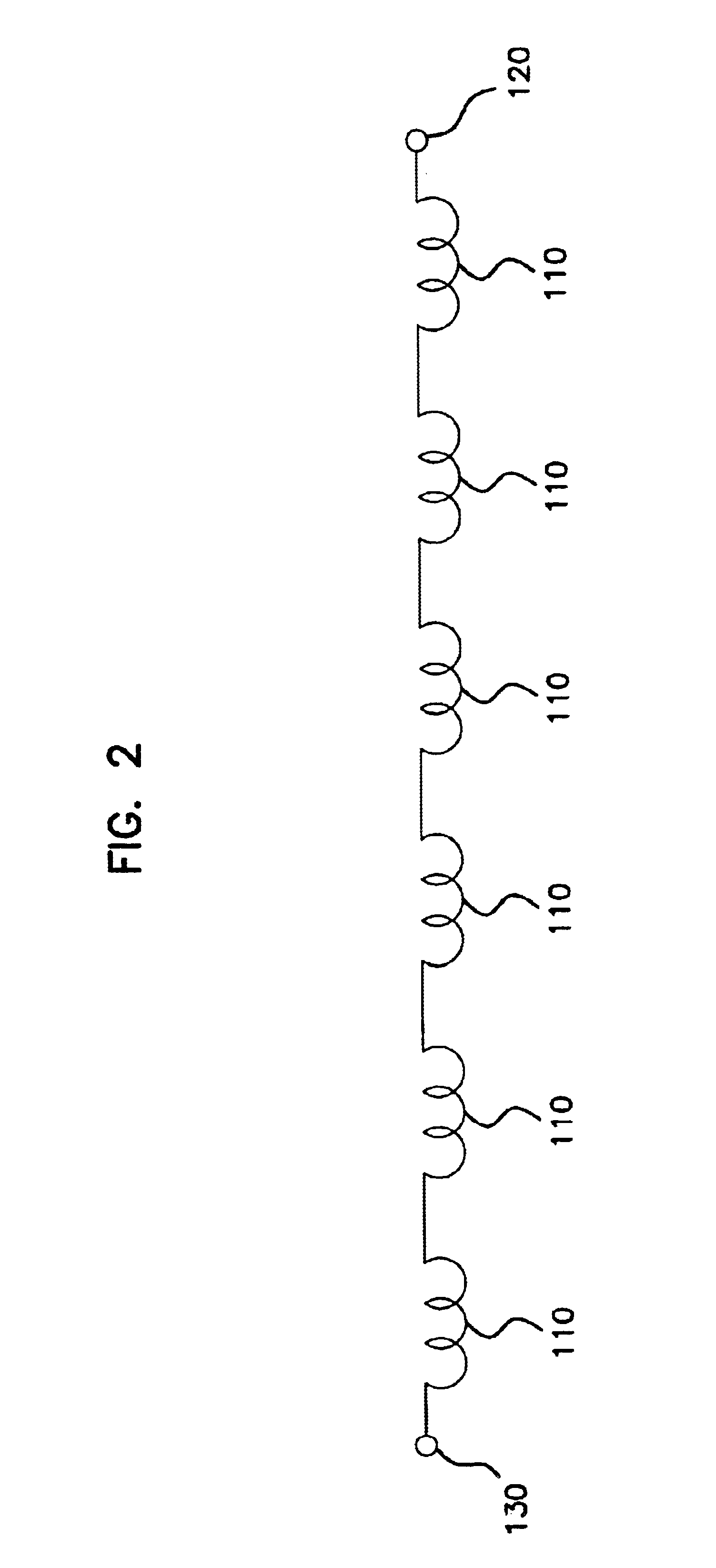
Rotary electric motor having both radial and axial air gap flux paths between stator and rotor segments
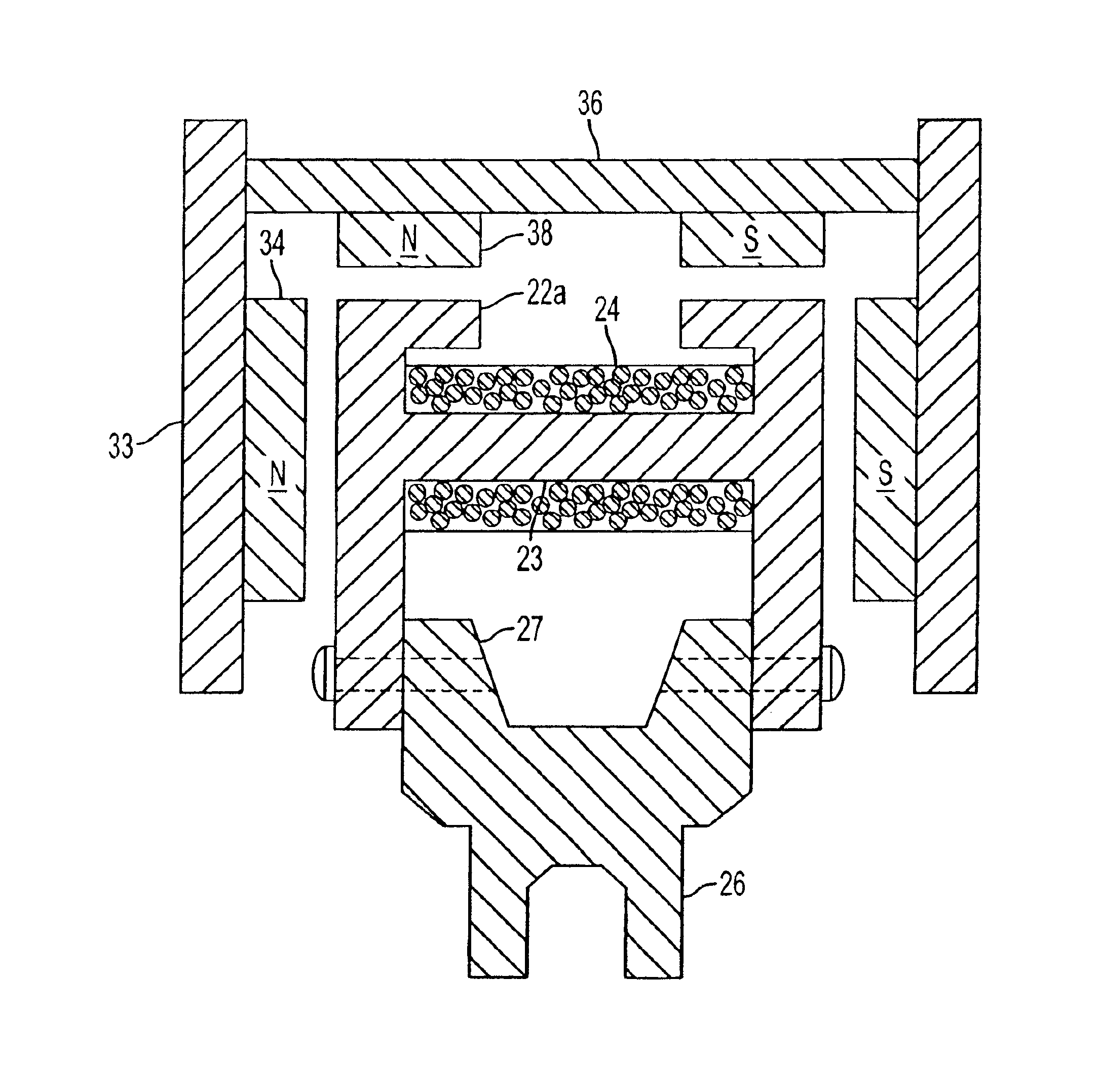
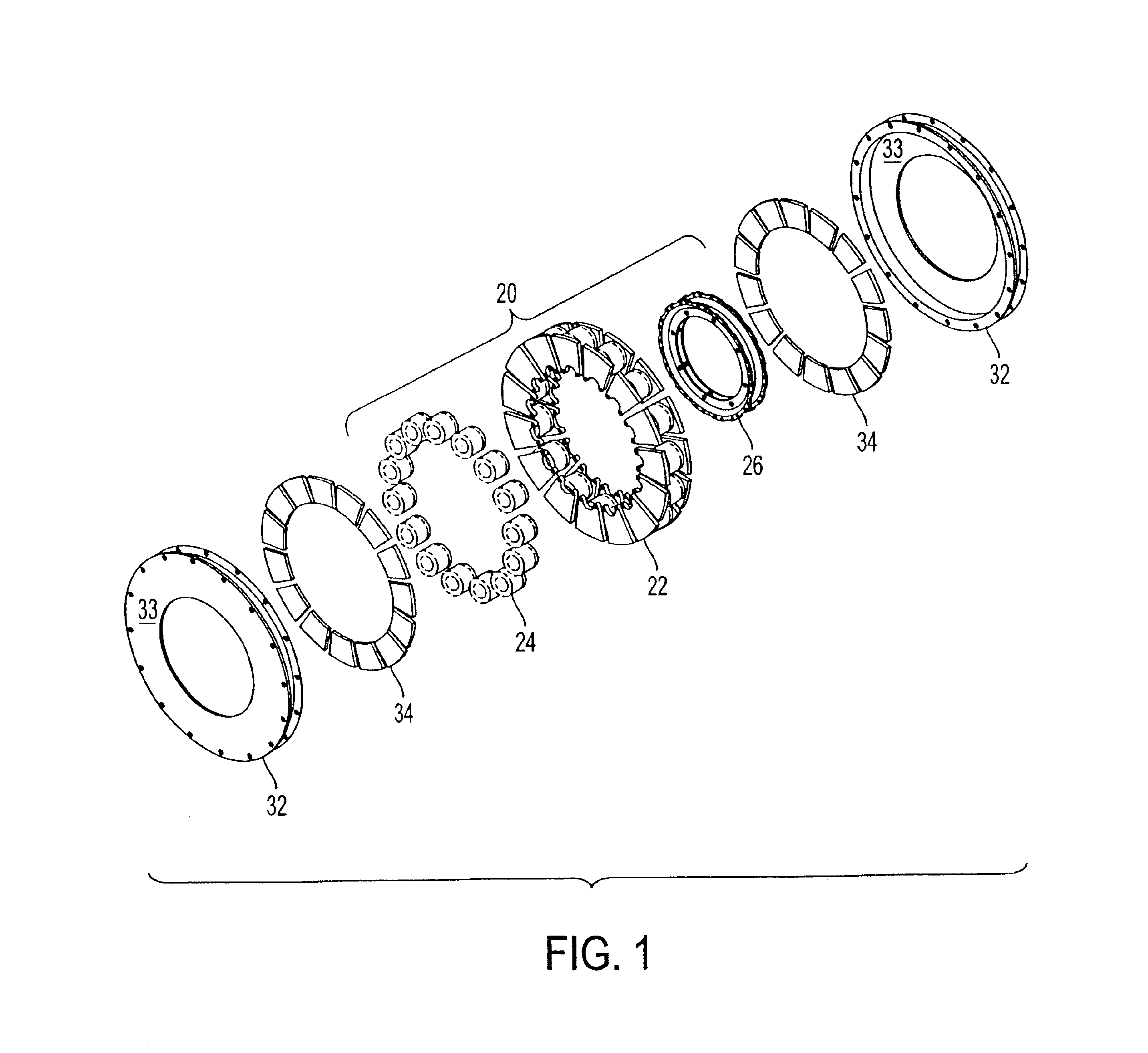
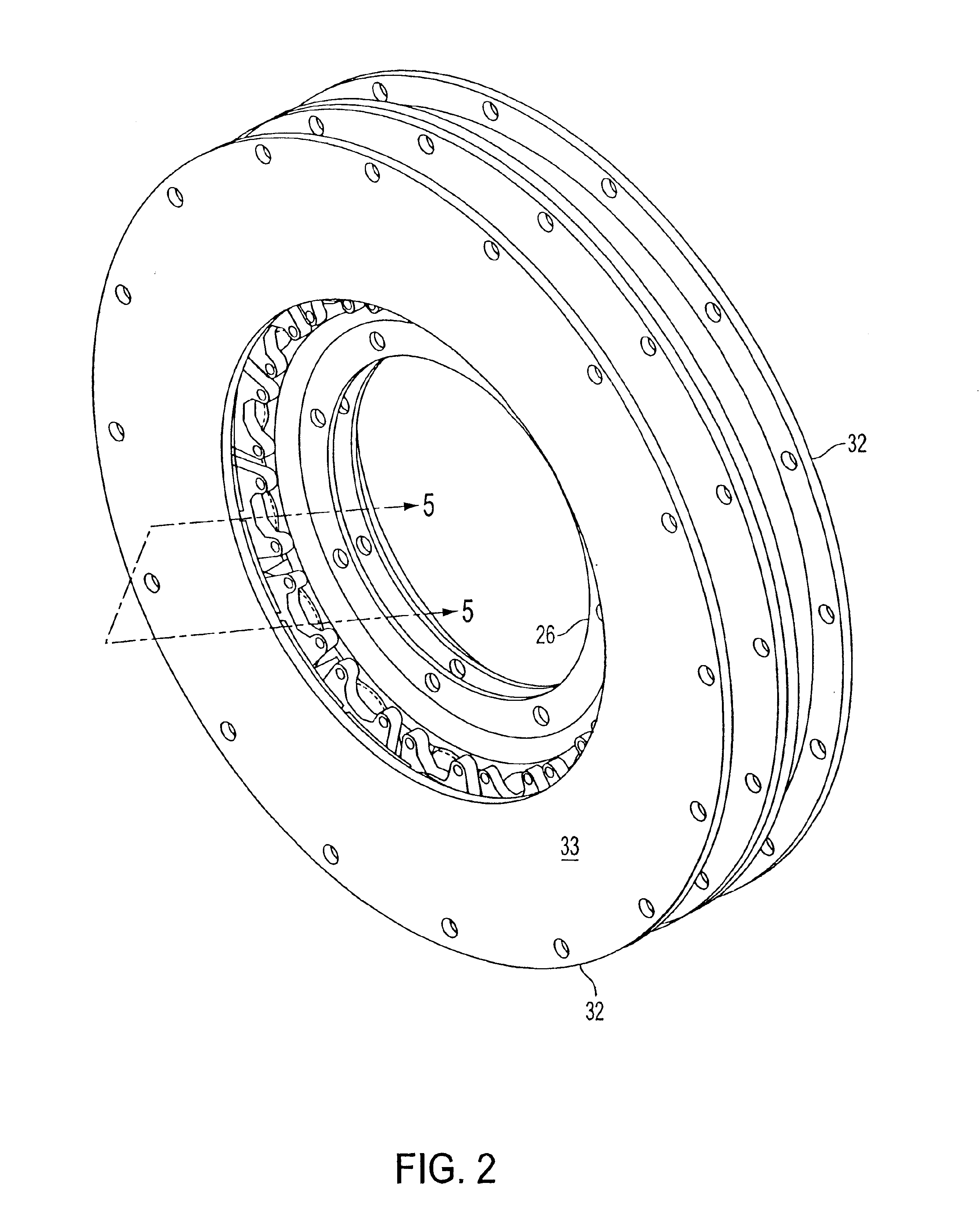
InactiveUS6891306B1Low flux lossEliminate the effects ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesElectrical polarity
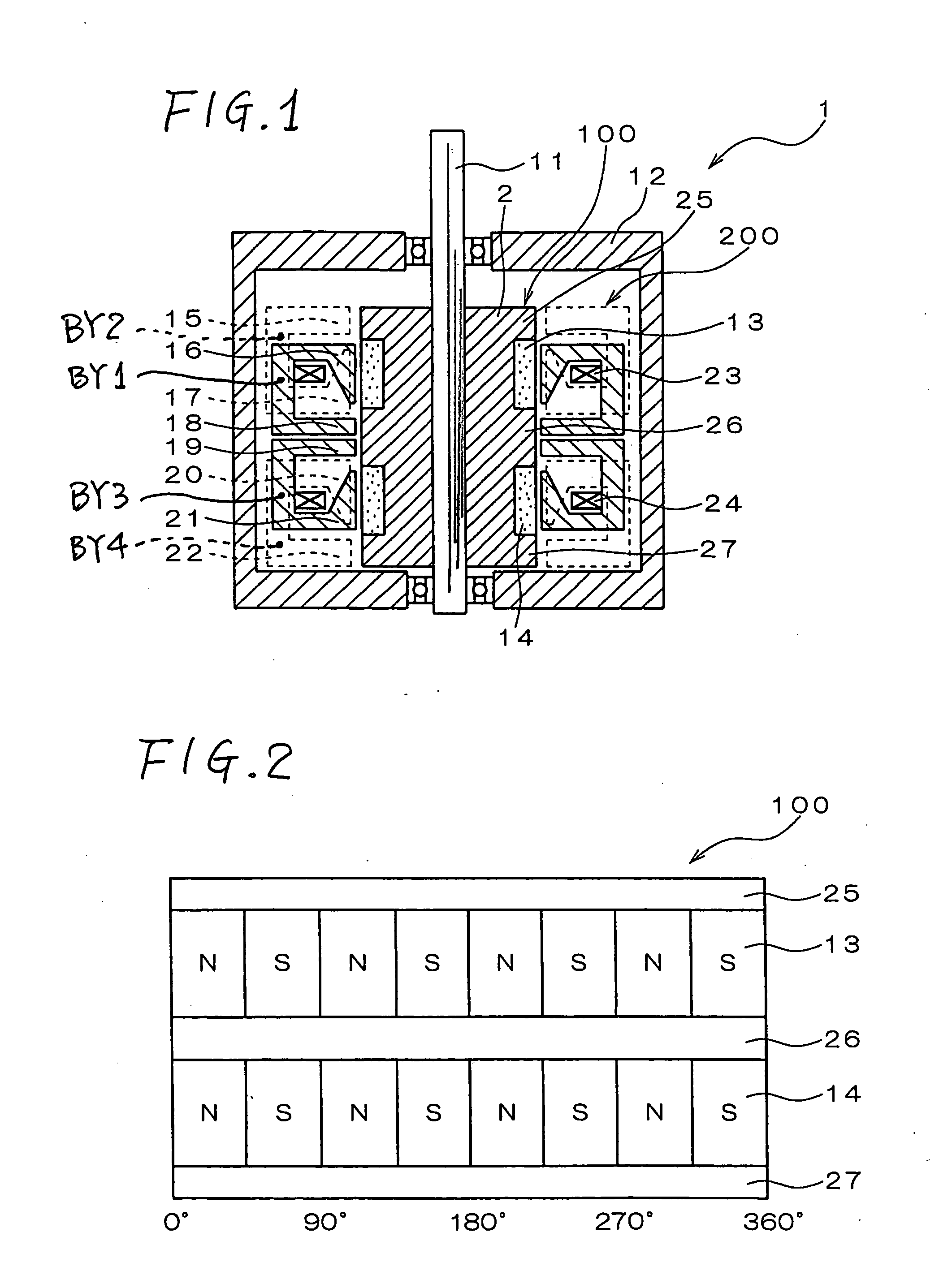
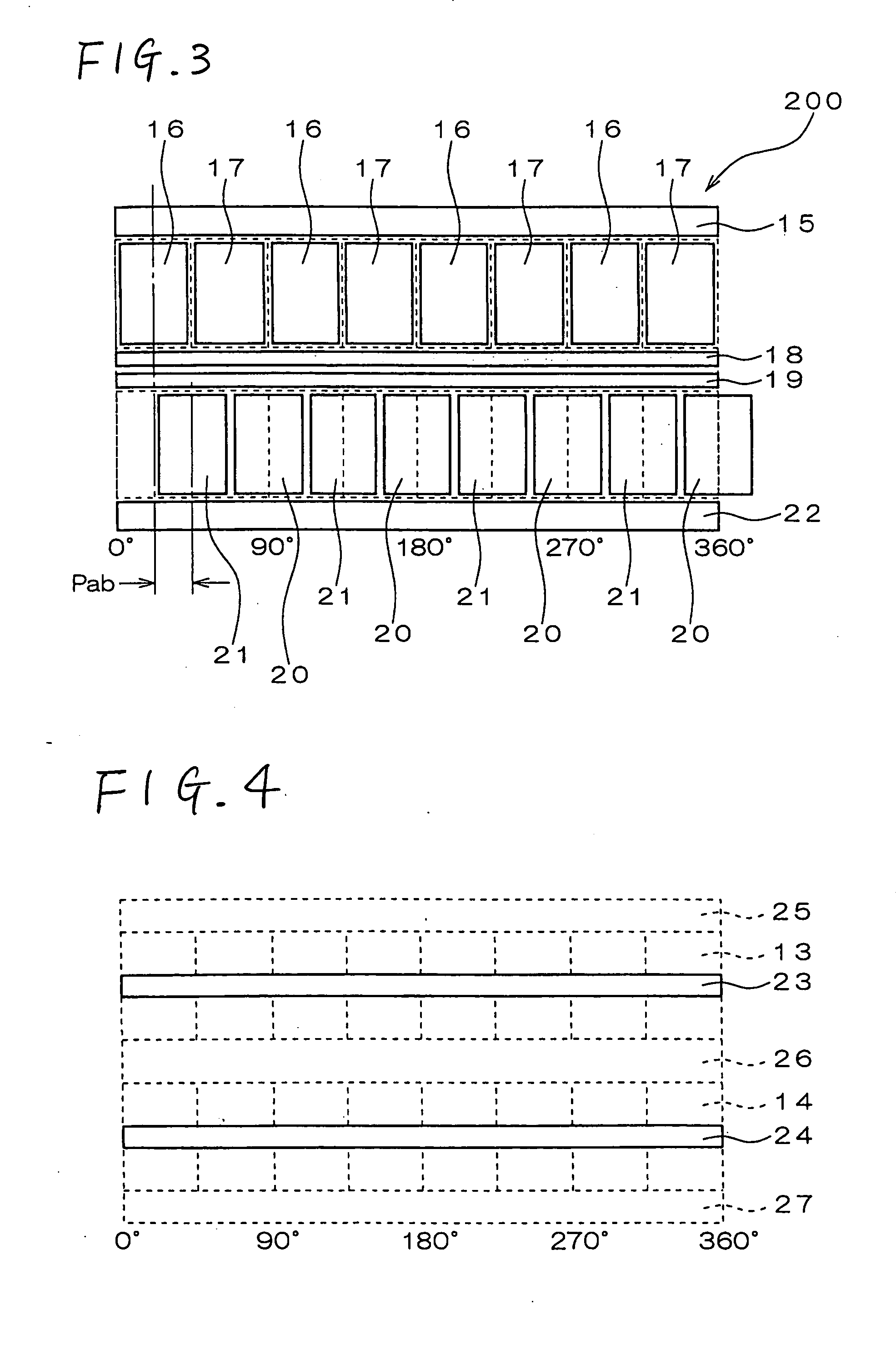
In a rotary electric motor, a stator contains a plurality of separate electromagnet core segments disposed coaxially about an axis of rotation. The core segments are affixed, without ferromagnetic contact with each other, to a non-ferromagnetic support structure. The rotor is configured in a U-shaped annular ring that at least partially surrounds the annular stator to define two parallel axial air gaps between the rotor and stator respectively on opposite axial sides of the stator and at least one radial air gap. Permanent magnets are distributed on each inner surface of the U-shaped rotor annular ring that faces an air gap. A winding is formed on a core portion that links axially aligned stator poles to produce, when energized, magnetic poles of opposite polarity at the pole faces.
Owner:BLUWAV SYST LLC
Polyphase transverse flux motor
InactiveUS6492758B1Synchronous motorsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet rotorTransverse flux
A tranverse flux motor having multiple stator phase windings which are electronically commutated to produce a rotating flux to drive a permanent magnet rotor located externally of the stator. The stator is formed by two complementary facing pieces each carrying half the stator poles, the latter preferably being of claw pole configuration. The stator windings are sandwiched between the stator pieces and wound about cores which magnetically couple the stator pieces. Preferably the number of motor phases (P) is selected from the series 2, 3, . . . , N, the number of windings per phase (W) is selected from the series 1, 2, . . . , M, the number of poles per winding (PW) is selected from the series 2, 4, . . . , L, and the number of stator poles (SP) is equal to the product P*WP*PW and the number of rotor poles is SP±W.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Permanent magnet electro-mechanical device providing motor/generator functions
InactiveUS20080272664A1DC commutatorSynchronous machines with rotating armatures and stationary magnetsMagnetic reluctanceCooling temperature
Owner:QM POWER
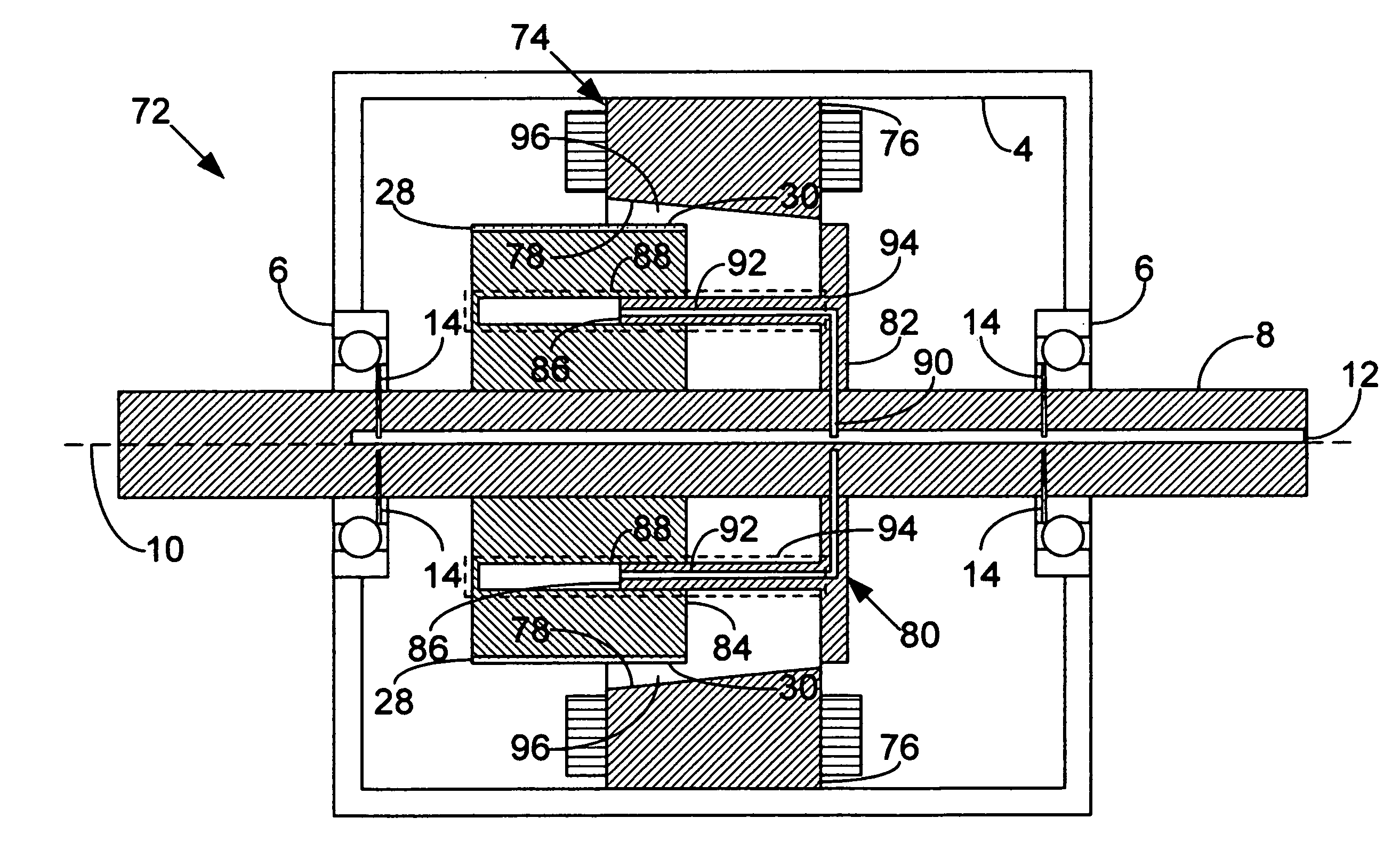
Internal rotor motor
InactiveUS6919663B2Minimized cogging torqueImprove featuresMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsElectric machine
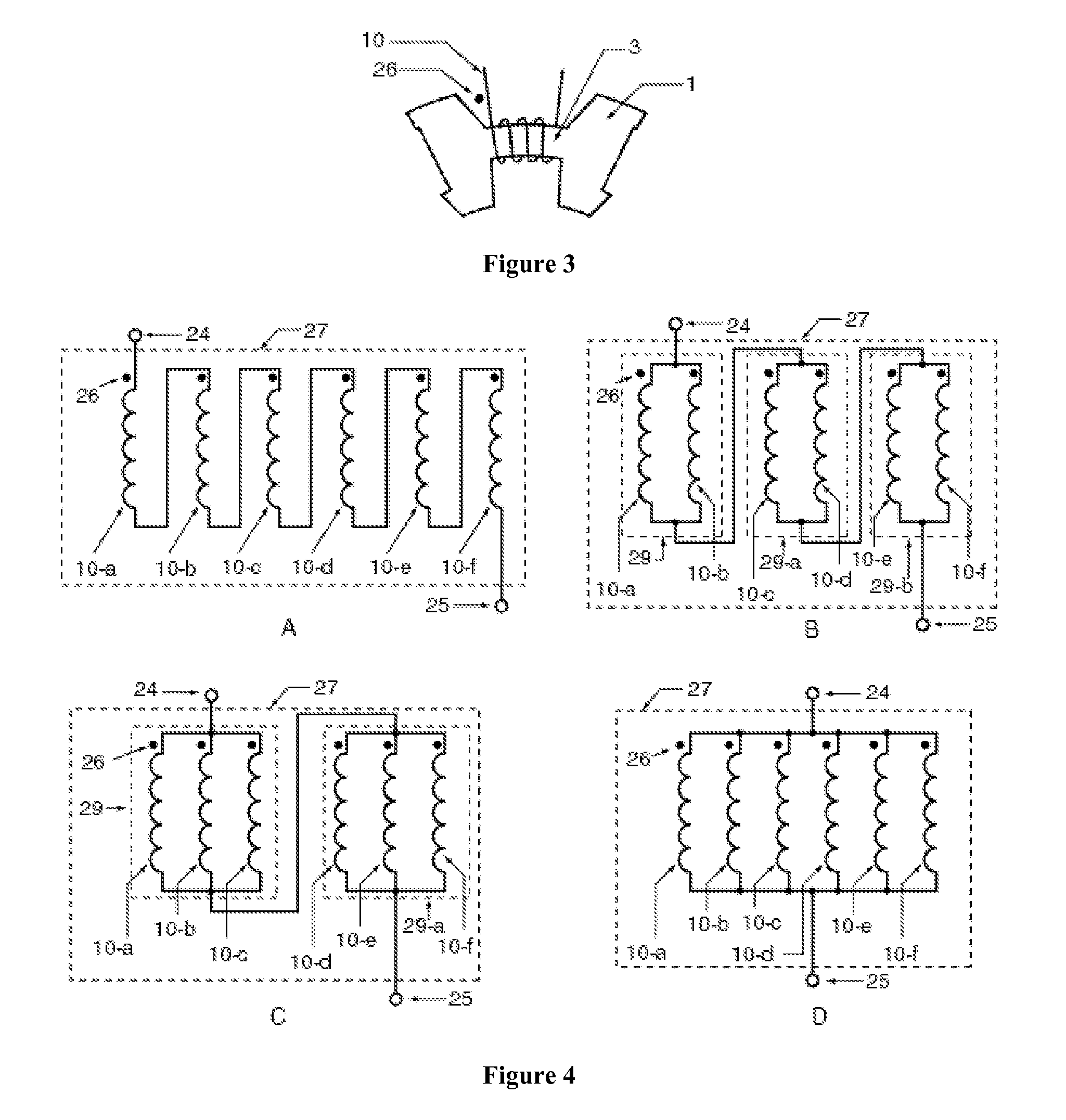
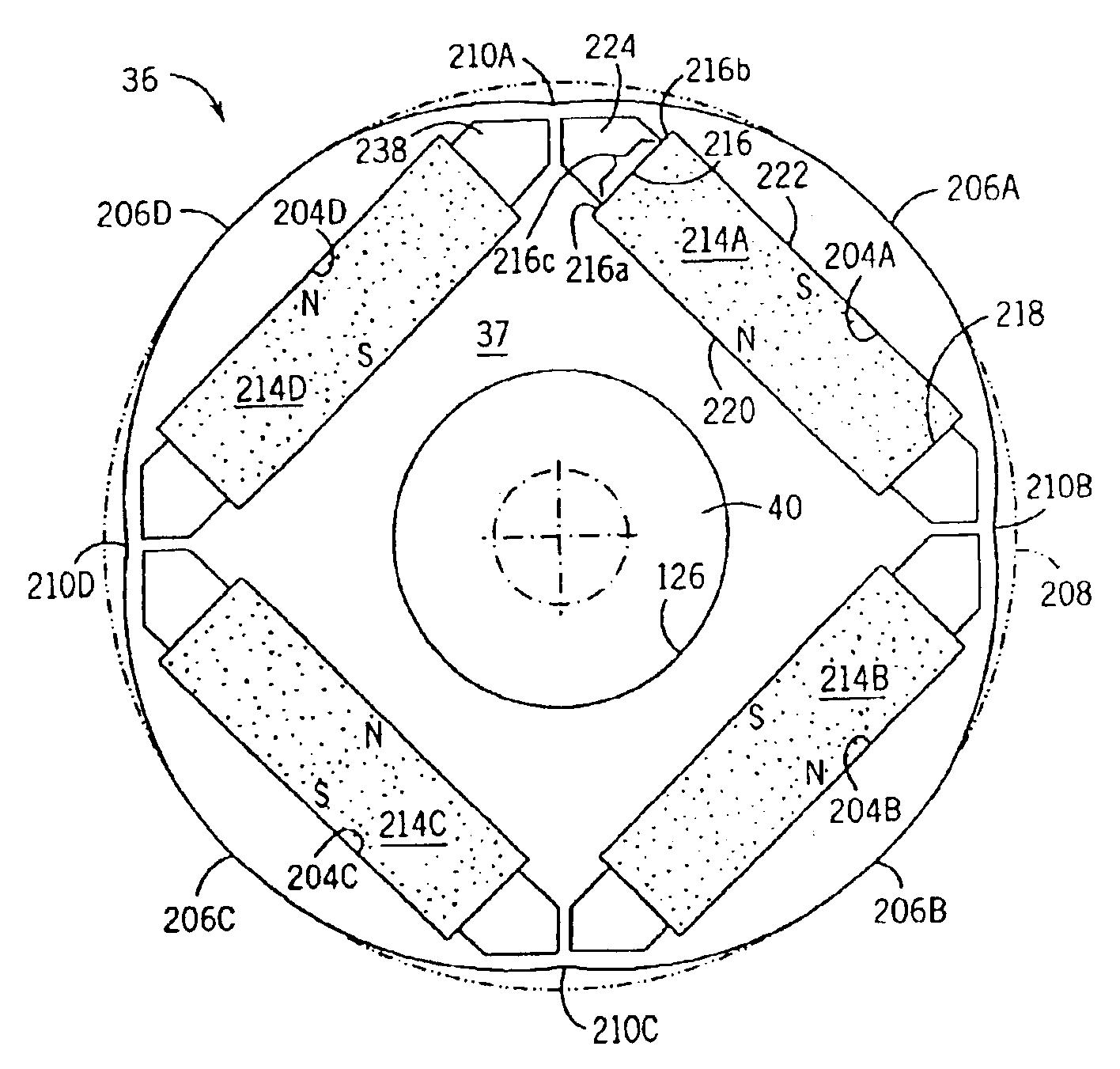
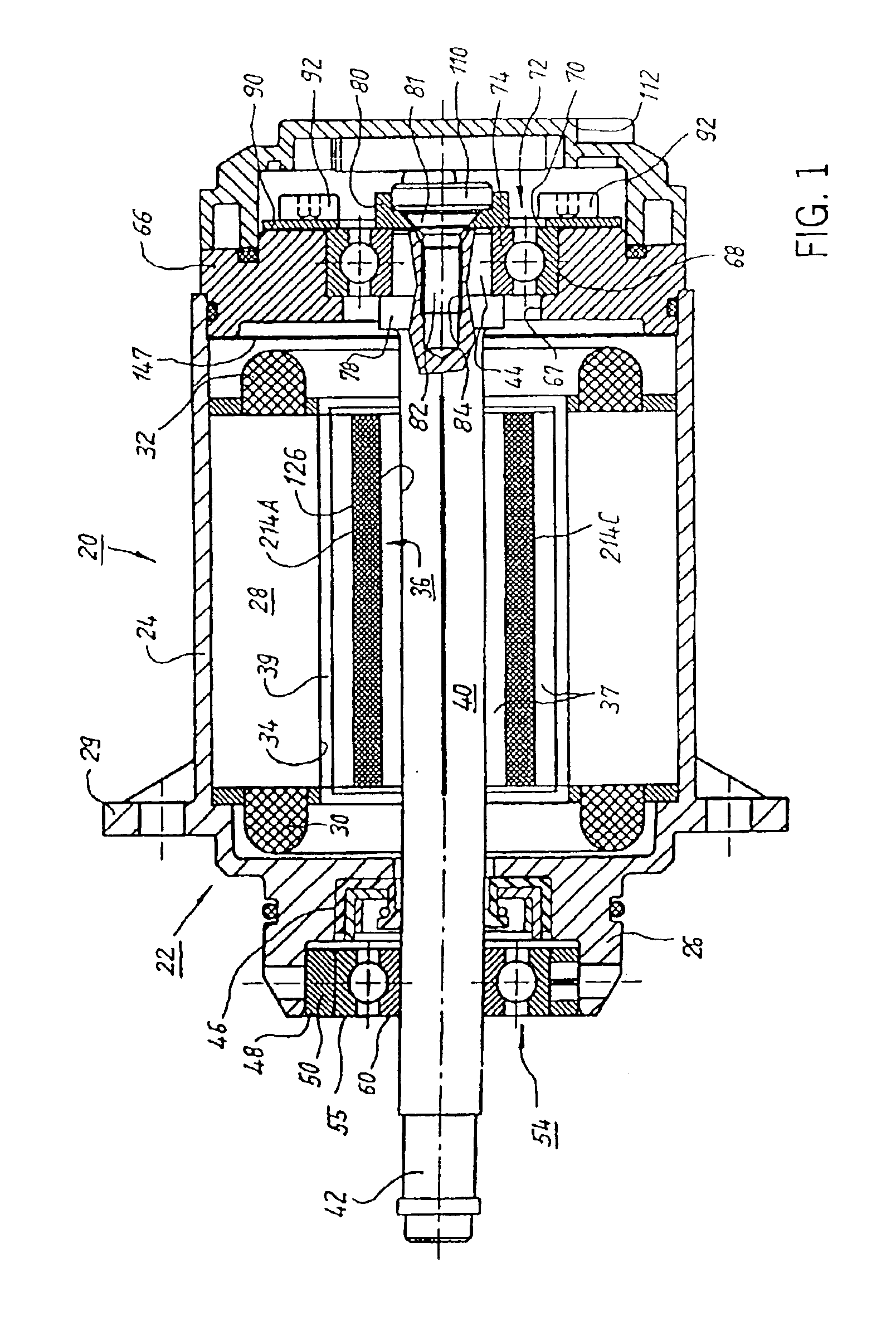
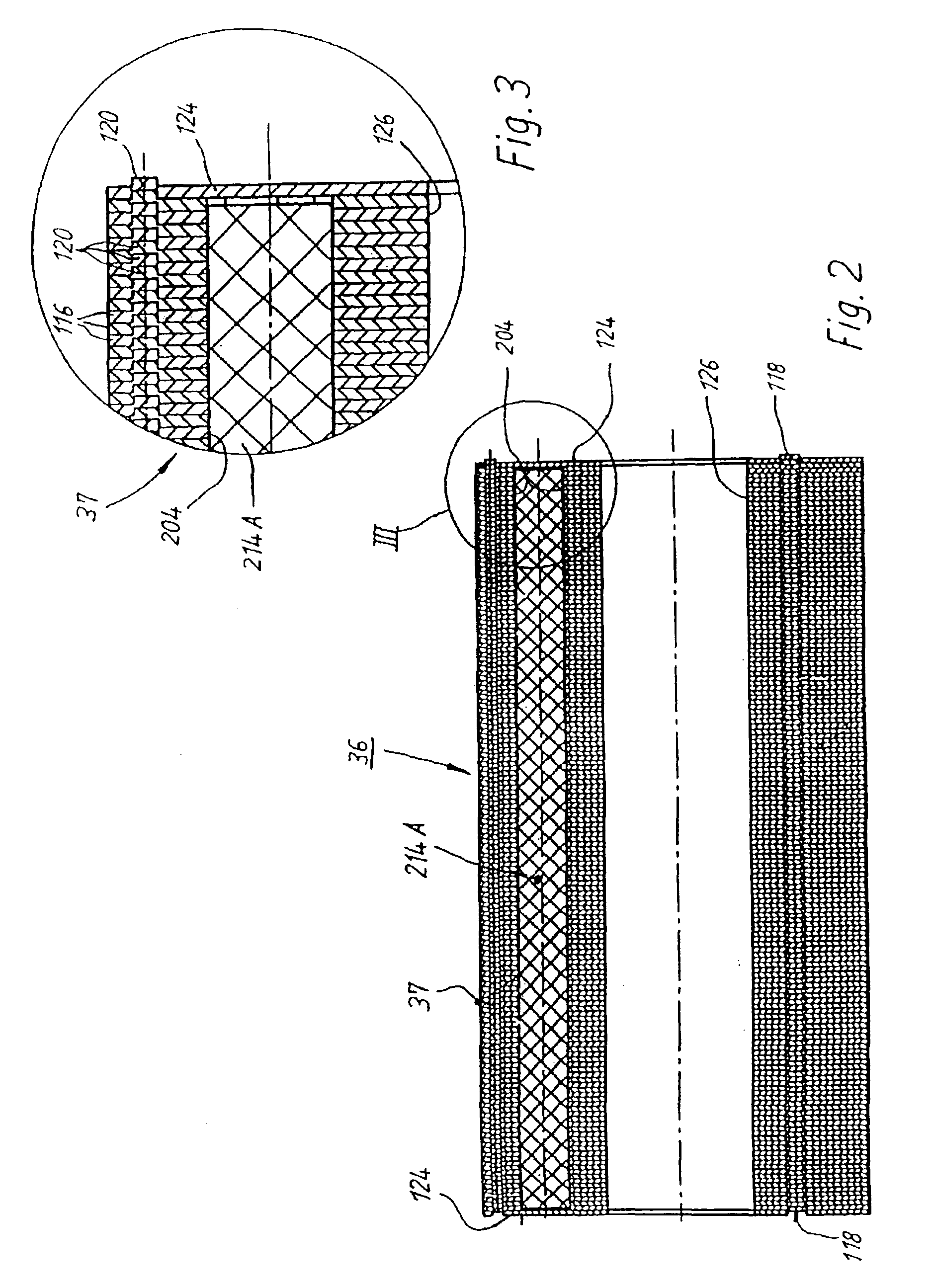
A low-ripple multi-phase internal rotor motor has a slotted stator (28) separated by an air gap (39) from a central rotor (36). The rotor has a plurality of permanent magnets (214), preferably neodymium-boron, arranged in pockets (204) formed in a lamination stack (37), thereby defining a plurality of poles (206) separated by respective gaps (210). In a preferred embodiment, the motor is three-phase, with four rotor poles and six stator poles. As a result, when the first and third rotor poles are so aligned, with respect to their opposing stator poles, as to generate a reluctance torque, the second and fourth rotor poles are aligned to generate oppositely phased reluctance torques, so that these torques cancel each other, and essentially no net reluctance torque is exerted on the rotor. In order to magnetically separate the rotor magnets from each other, a hollow space (224, 238) is formed at the interpolar-gap-adjacent end face (216, 218) of each rotor magnet. A control circuit (147) provides electronic commutation and current control, based on rotor position signals generated with the aid of a control magnet (110) on the rotor shaft (40).
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Speed control of brushless DC motors
InactiveUS7259531B1Convenient speed adjustmentEliminate degradationAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersEngineeringControl circuit
The speed control apparatus comprises a plurality of Hall sensors, a plurality of switches, a turn-on control circuit, and a gate drive logic. The Hall sensors are configured to detect magnetic rotor sections of a poly-phase brushless DC motor at different positions. The switches apply voltages on a plurality of windings to respectively produce magnetic north or south on stator poles of the poly-phase BLDC motor. The turn-on control circuit generates a conduction time reduction after each output transition of the Hall sensors. The gate drive logic separately turns on or turns off the switches according to different output transitions of the Hall sensors to respectively apply voltages on the windings with the conduction time reduction.
Owner:GREEN MARK TECH
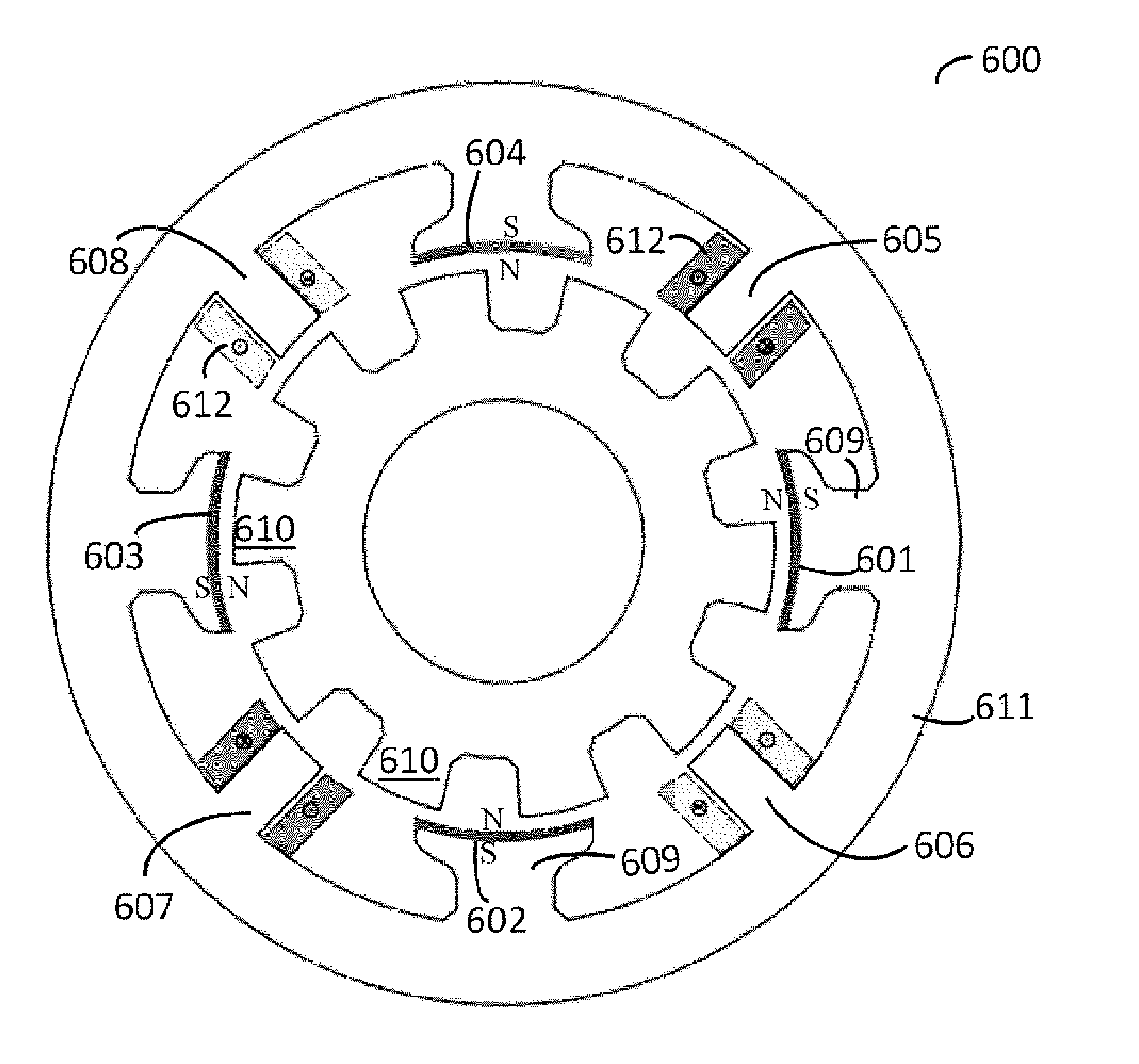
Multi-phase reluctance machine
ActiveCN104218763AReduce copper consumptionAchieve vibrationMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineTorque density
The invention belongs to the technical field of motors, discloses a multi-phase reluctance machine and solves the problem that only works for a half electric cycle, the conventional switch reluctance machine can acquire the one-way torque, thus the torque density of the motor is low. An armature core is in a cylinder shape. A plurality of axial slots are formed in the side surface of an airspace of the armature core to form a structure in which stator poles and stator slots are spaced along a peripheral direction. Each stator pole is wounded by an armature coil. Along the peripheral direction of the armature core, co-phasal armature coils are sequentially connected to for a phase armature winding, and a multi-phase winding, composed of the phase armature windings, is an armature winding. Excitation units are arranged on a yoke portion of the armature core or the stator poles. A rotator comprises a rotator core. A plurality of axial slots are formed in the side surface of an air gap of the rotator core to form a structure in which rotator poles and rotator slots are spaced along the peripheral direction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
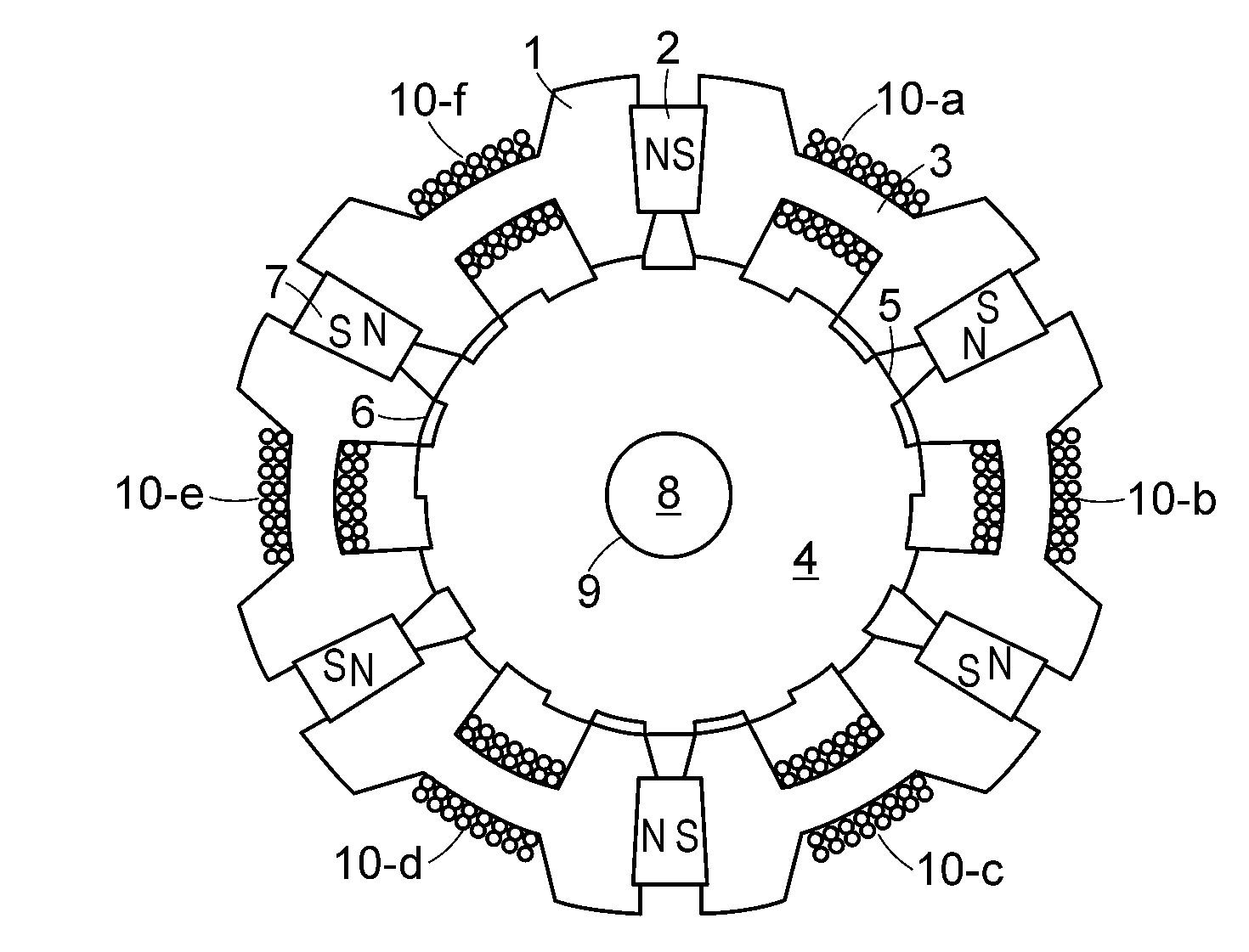
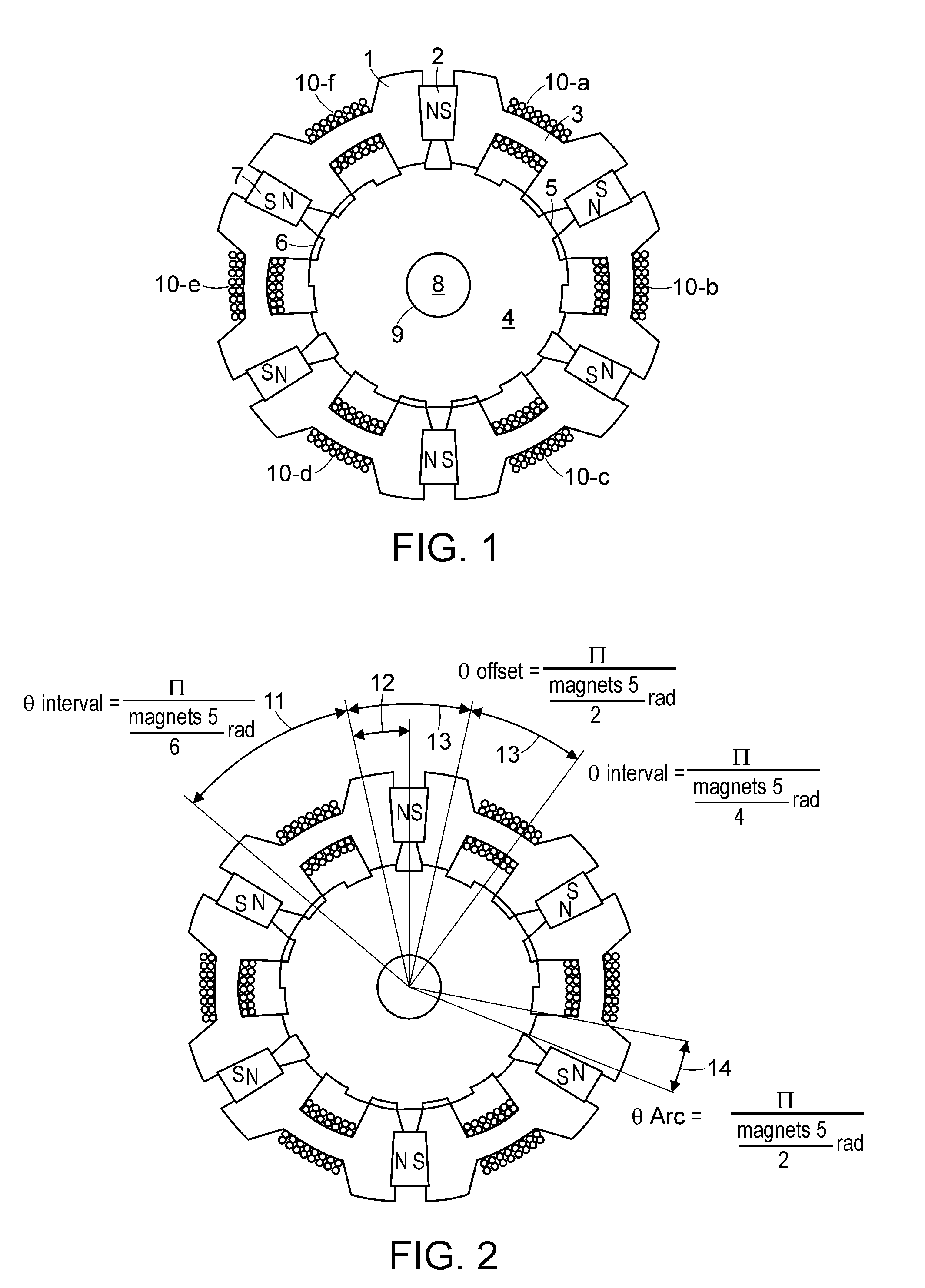
Toroidal AC motor
InactiveUS20060082237A1Longer gap lengthIncrease storage spaceSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineMagnetic poles
A toroidal motor having a generally circular rotor surrounded by an annular stator is disclosed. The rotor has a plurality of poles disposed about a circumference thereof. A shaft extends axially away from the poles and is attached to the rotor. The stator is generally annular and includes an annular winding surrounding the circumference thereof. Disposed about the winding are a plurality of stator poles. The number of stator poles is generally equal to the number of rotor poles. When the winding and hence the stator is excited, a magnetic field is produced between the stator and rotor poles that creates torque upon the shaft.
Owner:PATENT
Axial flux switched reluctance motor and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20100295389A1Use minimizedIron and copper lossMagnetic circuitSynchronous motorsStator coilReluctance motor
An axial flux switched reluctance motor utilizes one or more rotor discs spaced along a rotor shaft, each rotor disc having a plurality of rotor poles spaced along the periphery thereof. Stator elements are distributed circumferentially about the rotor discs and form pairs of radially extending stator poles for axially straddling the rotor discs. Stator coils as switched on to energize pairs of stator poles for forming an axial and radially inward flux path for rotating the rotor poles for minimizing the flux path before switching off the stator coil. Two or more rotor discs can be rotationally indexed for providing two or more motor phases. In manufacture, rotor discs and circumferentially extending stator coils about the periphery of each rotor disc are fit to a stator housing. Each stator element is then fit radially through the stator housing and secured thereto for straddling the rotor discs.
Owner:MSI MACHINEERING SOLUTIONS
AC motor having stator windings formed as loop coils, and control apparatus for the motor
ActiveUS20050099082A1Easy to assembleEasy constructionTorque ripple controlWindingsToroidal coilConductor Coil
A synchronous AC motor has a stator with stator poles arranged as a plurality of circumferentially extending stator pole groups, with each stator pole group having a pair of corresponding circumferentially extending loop-configuration stator windings disposed adjacent on either side or a single such winding disposed adjacent at one side, adjacent stator pole groups being mutually circumferentially displaced by a fixed amount corresponding to a specific electrical phase angle. A rotating magnetic field is produced by applying respective polyphase AC voltages to the windings, such that currents of mutually opposite direction flow in each pair.
Owner:DENSO CORP
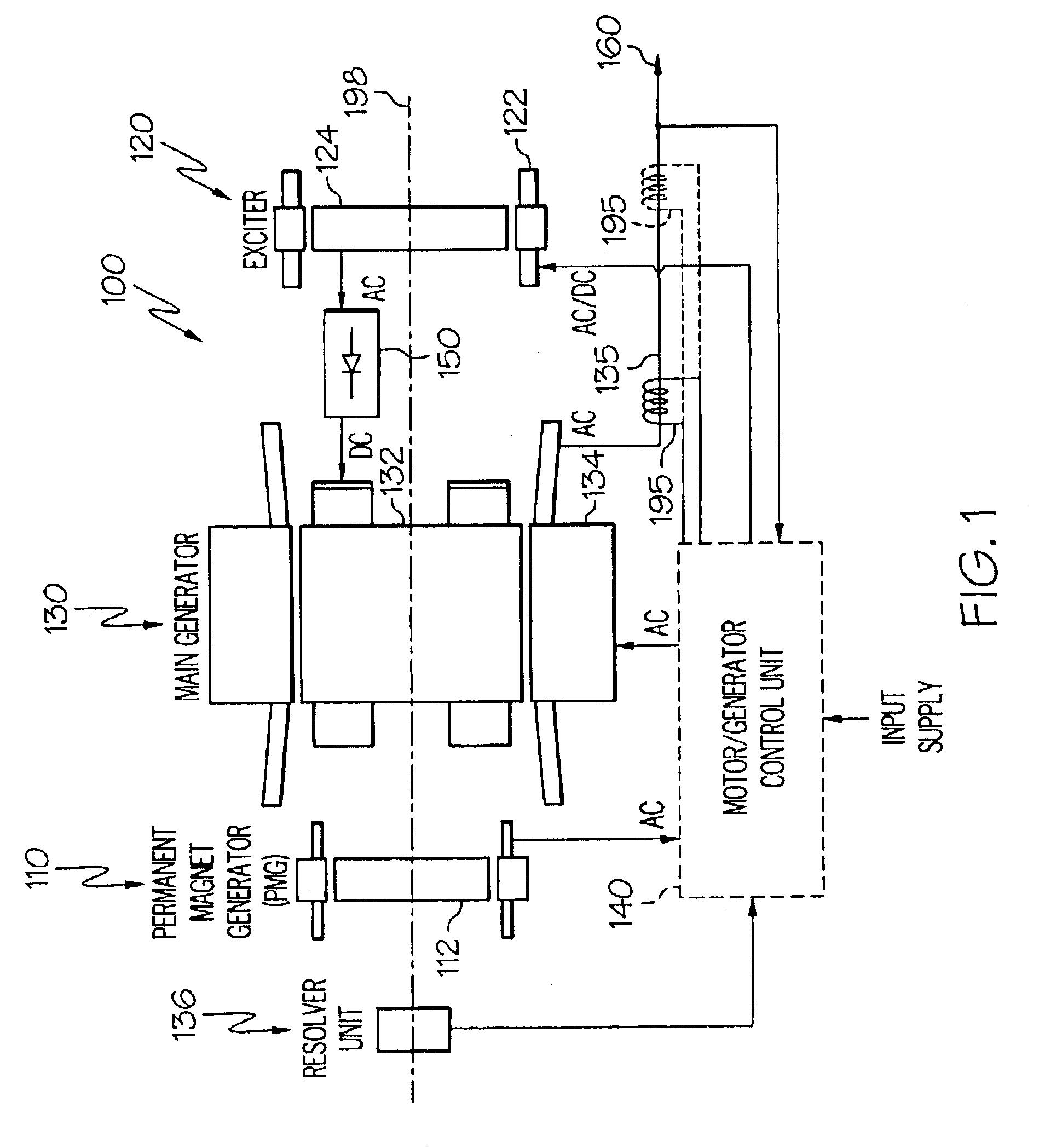
Permanent magnet dynamoelectric machine with axially displaceable permanent magnet rotor assembly
A dynamoelectric machine comprises: a stator that comprises a plurality of stator poles arranged around a stator surface of revolution with a stator axis for the stator surface of revolution; at least one rotor that comprises a plurality of permanent rotor magnets arranged around a rotor surface of revolution with a rotor axis for the rotor surface of revolution that is coincident with the stator axis and with the rotor surface of revolution adjacent the stator surface of revolution; a drive shaft with a drive shaft axis of rotation that is substantially coincident with the stator axis coupled to the rotor for rotating the rotor relative to the stator about the drive shaft axis of rotation; and a at least one actuator for axially displacing the rotor surface of revolution along the drive shaft relative to the stator surface of revolution to change magnetic flux interaction between the stator poles and the rotor magnets; wherein at least one of the surfaces of revolution tilts with respect to the drive shaft axis of rotation.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
High frequency electric motor or generator
Owner:GREEN RAY TECH
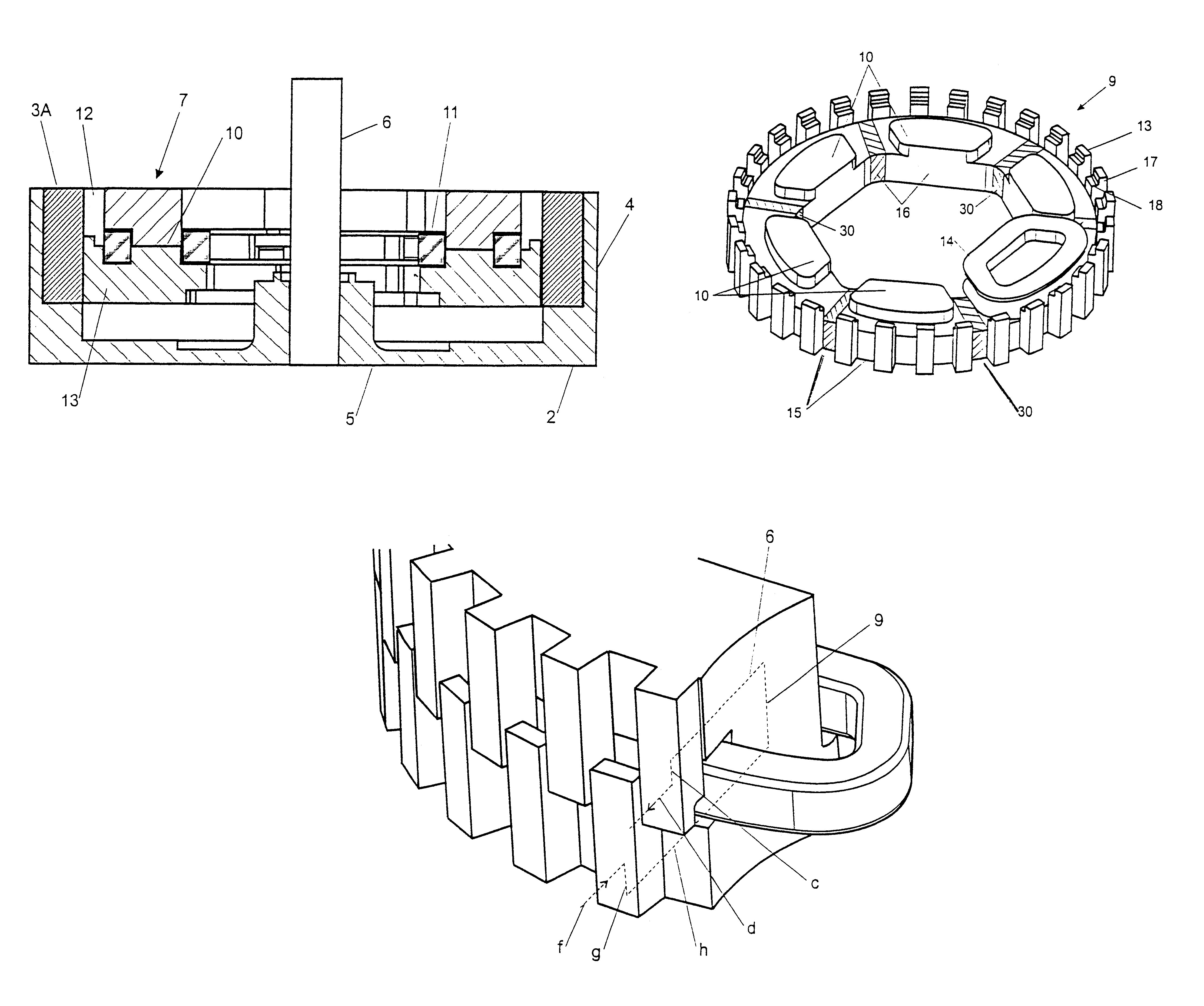
Segmented stator switched reluctance machine
InactiveUS20020125782A1Facilitate the improvement of precisionReduce usageElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersConductor CoilMechanical engineering
A switched reluctance machine includes a stator with a plurality of circumferentially-spaced stator segment assemblies that include salient stator poles and inter-polar stator slots. Each of the stator segment assemblies includes a stack of stator plates forming a stator segment core, an end cap assembly, and winding wire wound around the stator segment core and the end cap assembly. The rotor defines a plurality of rotor poles. The rotor tends to rotate relative to the stator to maximize the inductance of an energized winding. A drive circuit energizes the winding wire around the stator segment assemblies based on a rotational position of the rotor. Each stator plate includes a first radially outer rim section and a tooth section that extends radially inwardly from a first center portion of the first radially outer rim section.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Two-phase brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20060244333A1Improve large rotation torque featureImprove efficiencyAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersBrushless motorsElectric machine
The present invention relates to a two-phase brushless DC motor which can increase a pemerance coefficient of a rotor to the maximum to thereby improve efficiency and starting feature of the motor, and to reduce torque ripple and noise thereof. The brushless motor of the present invention includes a two-phase winding stator having 4×n winding poles and auxiliary poles provided between the winding poles, and a rotor constituted by 6×n permanent magnet rotating poles having divided angle. Auxiliary poles between the stator poles can be provided. The two-phase brushless motor of the present invention can be driven by a control device for the two-phase motor which can transform electric power and rectify electronically.
Owner:BLUFFTON MOTOR WORKS
AC motor and control device therefor
InactiveUS20060006744A1Small sizeLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsDynamo-electric converter controlConductor CoilAC motor
A rotor, which is rotatable about a rotor shaft, comprises N poles and S poles alternately disposed in the circumferential direction, and rotor-side neutral poles disposed adjacent to the N poles and the S poles along the axial direction of the rotor, being magnetically connected to their back yoke. A stator comprises two modules which are adjacently disposed in the axial direction of the rotor. Each of these two modules comprises a winding wound, in a loop shape, around the rotor shaft, stator-side neutral poles disposed at positions opposed to the rotor-side neutral poles, stator poles each of which is disposed at a position opposed to either the N pole or the S pole, and a back yoke which connects the stator-side neutral poles and the stator poles to surround the winding.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electrical pulse generator using pseudo-random pole distribution
InactiveCN1615573ALow power outputElectrical output does not generateElectric ignition installationMachines/enginesHigh energyElectrical polarity
A multi-pole electric pulse generator containing magnetic poles having a pseudo-random distribution. Preferably, the magnetic poles are equal in size and interval, and the polarity conforms to a pseudo-noise binary sequence, which sequence is specifically a primitive polynomial m-sequence. At one position in the rotor rotation, all rotor poles are aligned with corresponding stator poles to provide maximum net magnetic flux through the armature windings. At all other rotor positions, the poles are misaligned and the net magnetic flux through the armature windings is small. In operation, rotation through these misaligned rotor positions produces substantially no change in magnetic flux and thus no electrical energy. When the rotor reaches this alignment position, a sudden, large change in magnetic flux produces a high-energy electrical pulse. An exemplary application is for generating an ignition spark for an internal combustion engine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Permanent magnet dynamoelectric machine with axially displaceable permanent magnet rotor assembly
A dynamoelectric machine comprises: a stator that comprises a plurality of stator poles arranged around a stator surface of revolution with a stator axis for the stator surface of revolution; at least one rotor that comprises a plurality of permanent rotor magnets arranged around a rotor surface of revolution with a rotor axis for the rotor surface of revolution that is coincident with the stator axis and with the rotor surface of revolution adjacent the stator surface of revolution; a drive shaft with a drive shaft axis of rotation that is substantially coincident with the stator axis coupled to the rotor for rotating the rotor relative to the stator about the drive shaft axis of rotation; and a at least one actuator for axially displacing the rotor surface of revolution along the drive shaft relative to the stator surface of revolution to change magnetic flux interaction between the stator poles and the rotor magnets; wherein at least one of the surfaces of revolution tilts with respect to the drive shaft axis of rotation.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Stator arrangement and rotor arrangement for a transverse flux machine
InactiveUS7638919B2Easily magnetized unipolarGreat magnet volumeMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxMetal sheet
A stator arrangement and a rotor arrangement for a transverse flux machine. The stator arrangement comprises an annular stator back yoke having a number of stator poles designed in the manner of claw poles. The rotor arrangement includes number of rotor poles designed in the manner of claw poles and connected to each other to form an annular rotor body enclosing a unipolar ring magnet magnetized in an axial direction. In the stator arrangement, the stator back yoke includes a first laminated stack of metal sheets whose laminations are stacked in an axial direction, and the stator poles include a second laminated stack of metal sheets whose laminations are stacked in a tangential direction. In the rotor arrangement, the rotor poles include laminated stacks of metal sheets whose laminations are stacked in a tangential direction.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Stator arrangement for an electric machine, a method for the manufacture of a stator arrangement and a direct current motor
InactiveUS20060108890A1Minimizes problemPrevent materialWindingsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineConductor Coil
The invention relates to a stator arrangement for an electric machine, particularly a DC motor, comprising a stator body having a stator back yoke ring and a number of stator teeth between which stator slots to receive stator windings are formed, the stator teeth extending radially from the stator back yoke ring and stator poles being formed at the free ends of the stator teeth, the stator teeth being coupled to a sleeve, which extends coaxially to the stator body, at their free ends. The invention also relates to a method for the manufacture of a stator arrangement of this kind and a direct current motor that employs such a stator arrangement.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
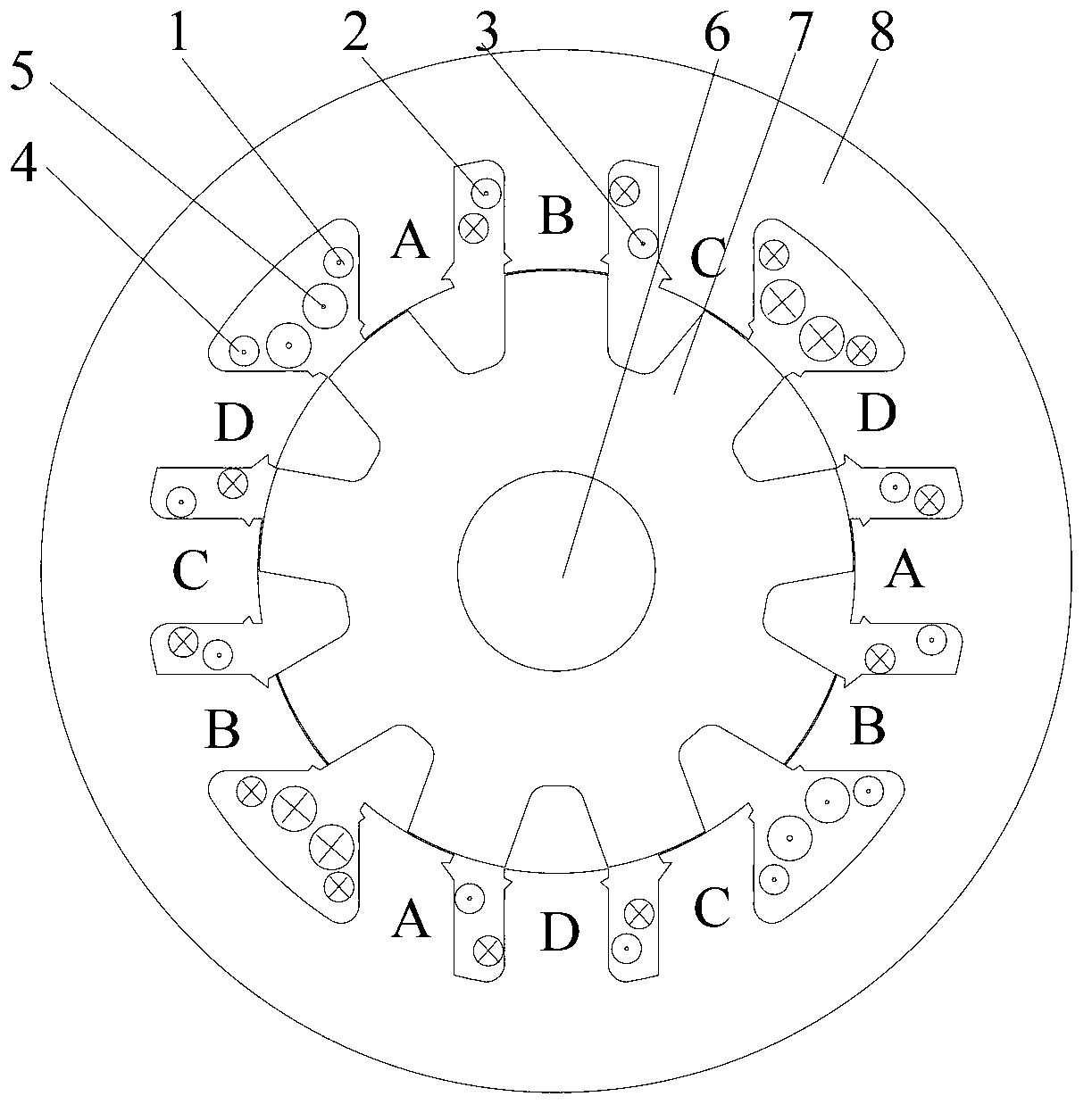
Four-phase and double-salient brushless direct current motor with symmetrical phase inductances
ActiveCN103187846AReduce torque rippleSmall positioning torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsFault toleranceStator coil
The invention discloses a four-phase and double-salient brushless direct current motor with symmetrical phase inductances. According to the four-phase and double-salient brushless direct current motor, a unit motor is of a novel 12 / 9 salient structure or a novel 12 / 15 salient structure, each excitation element is wound after spanning three stator poles, each stator coil of each phase stator winding is distributed at different positions, and the symmetry of the phase inductances is achieved by a mode of symmetrically distributing the four phase stator windings; the pole-arc coefficient matching size of motor stators and rotors is determined by theoretical analysis and emulation verification methods, so that the phase inductances of the motor are hoisted and decreased by an electrical angle of 180 degrees, the total permeance of exciting windings remain basically unchanged, the positioning torque of the motor is small, and the four phases are electrified at the same time to operate. In addition, the four phase stator windings are independent in pairs, so that the motor can operate by only using the two phases after one phase is in fault, and the fault tolerance performance is favorable. Moreover, the total permeance of the exciting windings is unchangeable, so that the four-phase and double-salient brushless direct current motor has the advantages of small positioning torque and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Full-pitch windings switched reluctance motor
InactiveUS20120169267A1Increase speedSimple circuitMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringThree-phase
A full-pitch winding switched reluctance motor is provided. In this motor, one set of current components are estimated, which electromagnetically act on only one set of stator poles for one phase. Based on the estimated one set of current components, current components for respective three phases are controlled, resulting in accurate current control with no electromagnetic interactions with other phases. This current control allows a control circuit to be made compact, and a motor with effective field means can be provided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
High frequency electric motor or generator including magnetic cores formed from thin film soft magnetic material
InactiveUS6879080B2Magnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsElectric generatorStator poles
Owner:GREEN RAY TECH
Gas turbine engine starter generator with multiple windings on each exciter stator pole
InactiveUS6906479B2Sufficient electricityGenerate torque that is sufficiently highAC motor controlMultiple dynamo-motor startersAC powerGas turbines
A rotating electrical machine, such as an aircraft starter-generator, includes an exciter that has its stator windings divided into a number of sections. A plurality of switches are electrically coupled to the exciter stator winding sections and are configured and controlled so that the exciter stator winding sections may be selectively coupled in series or in parallel with one another, and selectively coupled to receive either DC or AC power.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Brushless electric machine
InactiveUS20090102305A1Improve efficiencyTorque pulsation can be reducedWheelchairs/patient conveyancePropulsion by batteries/cellsBrushless motorsElectric machine
A brushless electric machine includes a rotor and a stator. Each of the twin poles of the stator electromagnetic members corresponds to one of the two magnetic poles of the rotor magnetic assembles. Two radial component air-gaps are arranged between the stator and the rotor to separate the stator and the rotor. Axial component air-gaps axially corresponding are arranged between the stator poles and the corresponding rotor poles to separate the stator poles and the rotor poles. The stator wheel-shaped ring is partly surrounded by the rotor wheel-shaped ring.
Owner:UNION PLASTIC HANGZHOU MACHINERY +2
Optimized electric machine for smart actuators
InactiveUS7791245B1Optimal operating characteristicRaise the ratioSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineEngineering
An electric machine includes a plurality of magnets for generating a first magnetic field. A magnet holder retains the plurality of magnets. A first stator is disposed radially outward from the magnet holder for generating a second magnetic field. The first stator includes a plurality of stator poles separated by slots with each of the stator poles having a concentrated winding with a respective number of turns formed around each respective stator pole. A second stator is disposed radially inward from the magnet for generating a third magnetic field. The second stator has a plurality of stator poles separated by slots with each of the stator poles having a concentrated winding with a respective number of turns formed around each respective stator pole. The magnet holder and magnets retained therein are rotatable between the first stator and second stator.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Rotor gravity unloading type magnetic bearing composite motor
ActiveCN107222131ASolve the coupling problemReduce weightMagnetic holding devicesMagnetic bearingElectric machine
The invention discloses a rotor gravity unloading type magnetic bearing composite motor comprising an external stator, an armature winding, a permanent magnet, a rotor, a magnetic isolation aluminum ring, an internal stator and a suspension control winding. The armature winding is wound in external stator slots. The magnetic isolation aluminum ring is embedded in the rotor. A Halbach type permanent magnet array is surface-mounted on the surface of the rotor. The internal stator has seven internal stator poles including two opposite bias flux magnetic poles, four radial suspension control poles and one gravity direction rotor weight unloading pole. Radial magnetized permanent magnets are surface-mounted on the surface of the bias flux magnetic poles. The suspension control winding is wound on the four suspension control poles. Coupling between the suspension winding and the armature winding in the conventional magnetic suspension motor can be eliminated, and the influence of the rotor weight on suspension control in the conventional suspension motor can also be greatly solved so that the rotor is enabled to stably work at the central balance position without increasing suspension control current, and low power consumption and stable suspension of the magnetic bearing composite motor can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Signaling and reduced torque ripple in brushless repulsion motors
InactiveUS7166984B1Improving ability selectively controlAdditional costTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersRepulsion motorSwitching signal
Brushless repulsion motors are presented, in which rotor coils switching signal detectors are selectively located in spaced angular relationship on the rotor and signaling sources are distributed around all or most of the stator circumference to allow looser tolerances for motor manufacturing and improved controllability of rotor coil actuation during operation. Asymmetric stator poles are also provided for brushless repulsion motors to mitigate torque ripple and vibration, in which the shape of the stator pole tips is tailored by varying the angular length of the pole section.
Owner:DYNAMOTORS
Single coil, direct current permanent magnet brushless motor with voltage boost
InactiveUS6850019B2Provide protectionSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlBrushless motorsSwitching signal
A single coil, direct current permanent magnet brushless motor including a stator including six alternately-wound coils connected into a single coil having first and second ends, the oppositely-wound coils forming stator poles, and six magnets of alternating polarity coupled to a rotor and rotatably journaled in the stator. A sensor, such as a dual output Hall sensor, is used for sensing rotation of the rotor. A drive circuit, such as an H-bridge circuit, is coupled to the first and second ends of the single coil to drive the motor. The H-bridge circuit includes two high-side switches for alternately receiving signals from the Hall sensor, and two low-side switches alternately receiving signals from the Hall sensor. A high-side switching signal can be controlled by an inverted low-side switching signal. A voltage boost circuit is also provided, having capacitors to provide a boosted voltage to alternately turn on the high-side switches of the H-bridge. The capacitors can be charged by an unregulated bus voltage.
Owner:MCMILLAN ELECTRIC
High power density switched reluctance machines with hybrid excitation
ActiveUS20110260672A1Increase productionElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersHigh power densityConductor Coil
A switched reluctance machine having salient stator and rotor poles. Alternating ones of the stator poles having windings and the others having permanent magnets attached on their pole faces. The alternate stator pole windings are provided with polarities that are suitable for unidirectional and bidirectional current operation of the switched reluctance machine. The alternate poles with permanent magnets in the switched reluctance machines can have also concentric windings placed on them and excited with currents to further augment the flux linkages in the stator poles. The windings on the poles with permanent magnets can be excited from the same source as the windings on the poles without permanent magnets to enhance power output or provide power factor correction.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Sectional type switch reluctance motor
ActiveCN102983694AImprove energy efficiencyReduce distractionsDynamo-electric machinesCapacitanceRectifier diodes
The invention discloses a sectional type switch reluctance motor, belonging to the field of magnetic circuit components. The sectional type switch reluctance motor comprises a main shaft, at least two sections of stators, at least two sections of rotors and magnetic isolating plates arranged on the main shaft, wherein each section of the stators and each section of the rotors are respectively provided with magnetic isolating plates, and each section of the stators and each section of the rotors are uniformly distributed around 360 degrees in the axial direction respectively. Stator poles of each phase of each section of the stators are respectively connected in series and are connected with a one-way guide circuit; the one-way guide circuit comprises four rectifier diodes, energy storage capacitors, main control thyristor switches and guide thyristor switches which are connected in series two by two; series circuits of each stator pole are mutually connected in parallel; one ends of the series circuits are respectively connected with the main control thyristor switches and guide thyristor switches; and the middles of two series circuits of the rectifier diodes are respectively connected with two output ends of the alternative current. By utilizing the sectional type switch reluctance motor, output torque pulse can be effectively reduced, and by guiding the induced current among the sections, the energy consumption efficiency of a system is improved, the impact of the induced current to the components is reduced, and the service life of the system is prolonged.
Owner:费赛恩流体技术(合肥)有限公司
High reliability motor system
InactiveUS6885162B2Reduced risk of phase to phase shortageFull powerAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical conductorPower switching
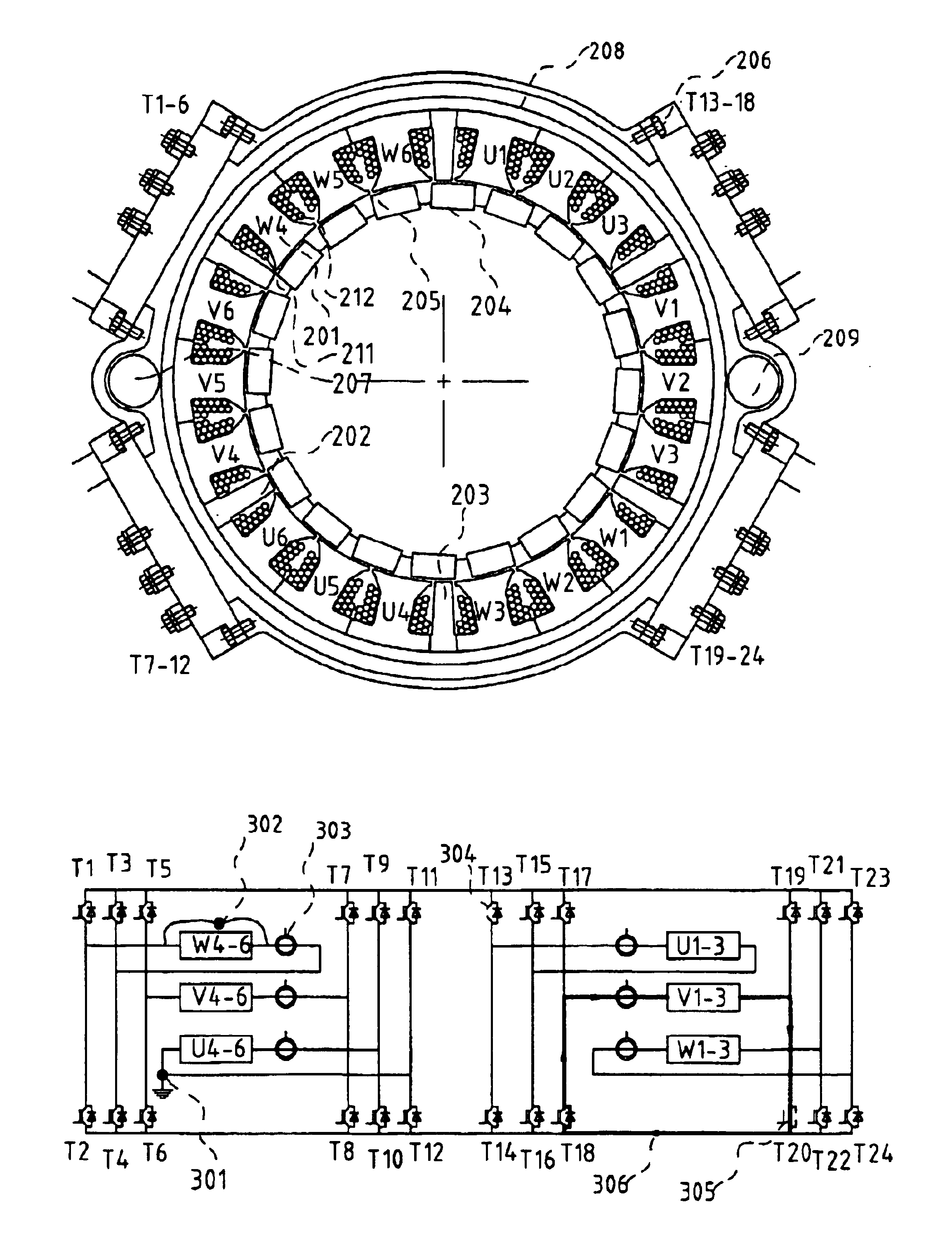
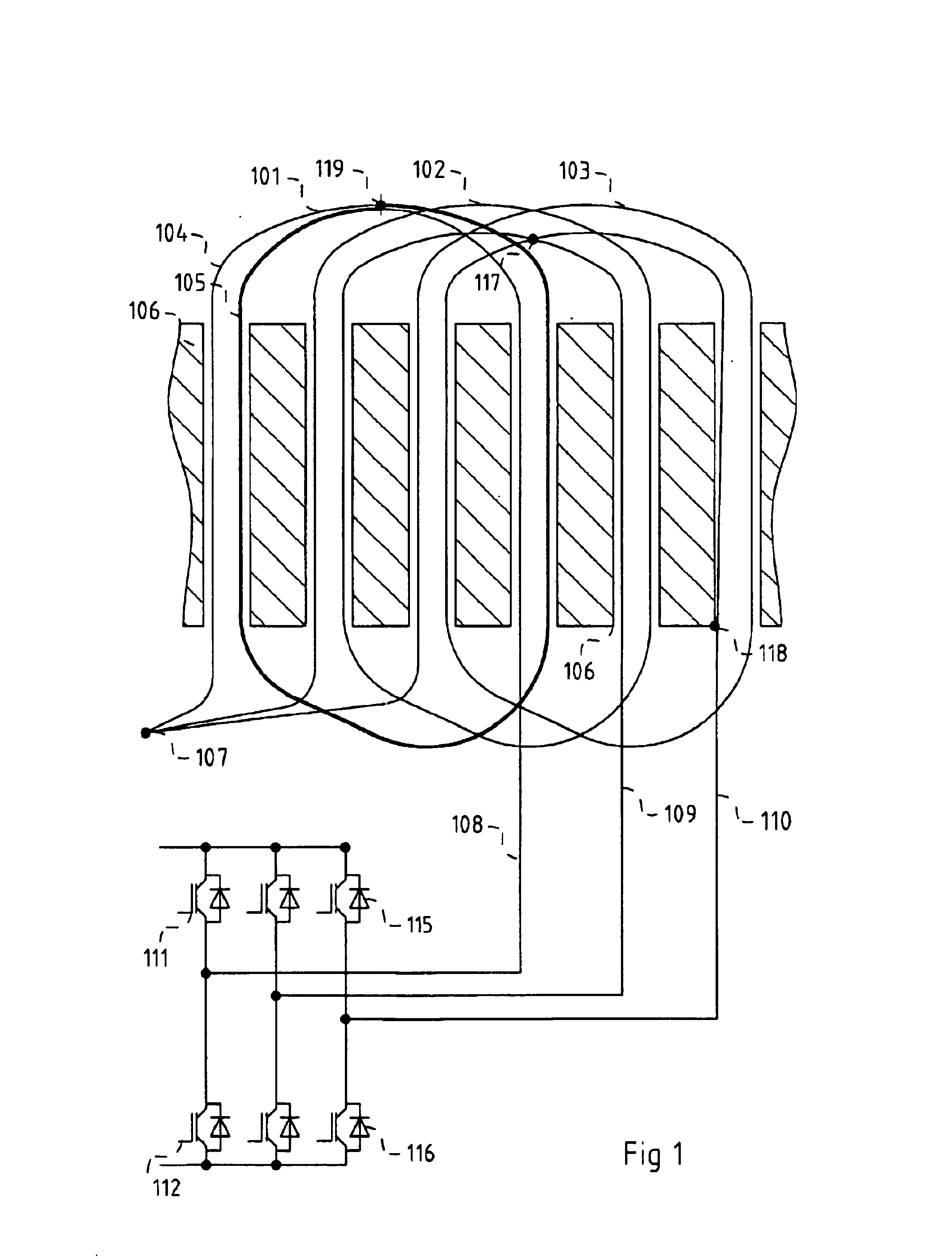
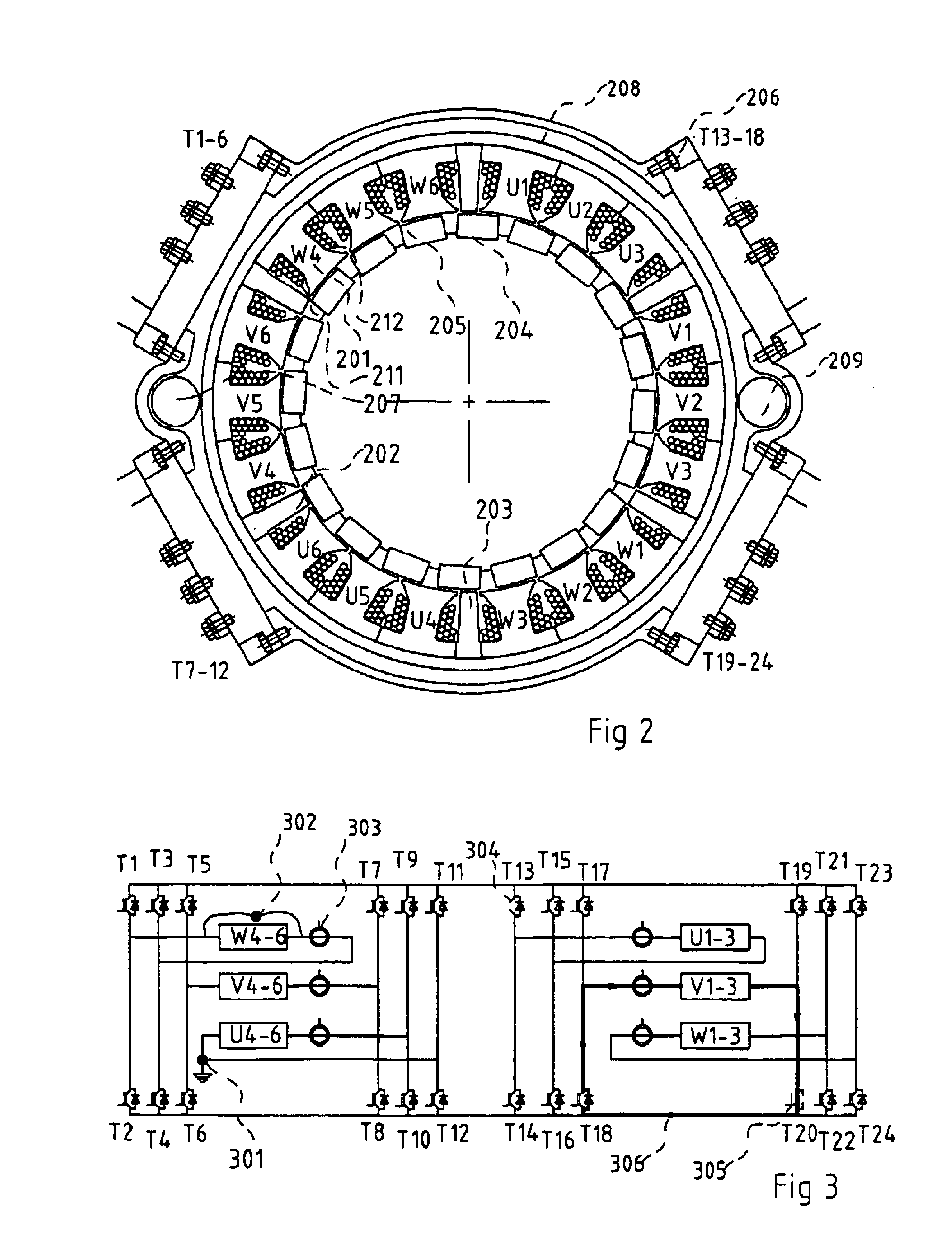
A brushless electric motor system comprises a rotor and a stator comprising poles. Electrical phase windings have coils (U1-6, V1-6, W1-6) wound around the poles. Power switches (T1-24) controlled by a control device supply electric current the windings from positive and negative rails connected to power supply. For each phase at least one group of four power switches arranged in a H-bridge configuration is provided. The coils of each phase winding are preferably divided into winding group (U1-3, Ua-6, V1-3, V4-6, W1-3, W4-6) and the electric conductor of each winding group is then electrically conductor of the other winding groups. Then four power switches arranged in an H-configuration is provided for each winding group. The use of power switches in H-bridge configurations allows the faulty windings or winding groups to be disabled and that the rest of the windings or coils can be used for driving the rotor, this giving the motor system a high reliability. The current supplied to other windings or winding groups can then be increased to compensate for the faulty group. The coil groups can be separated from other coil groups by unwound stator poles. Current sensors (303) can sense the current in each winding group and be used to detect whether the currents are too high. The sensed currents can be used to identify fault conditions in the system so that then suitable switches can be disabled, disconnecting a faulty winding group.
Owner:STRIDSBERG LICENSING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com