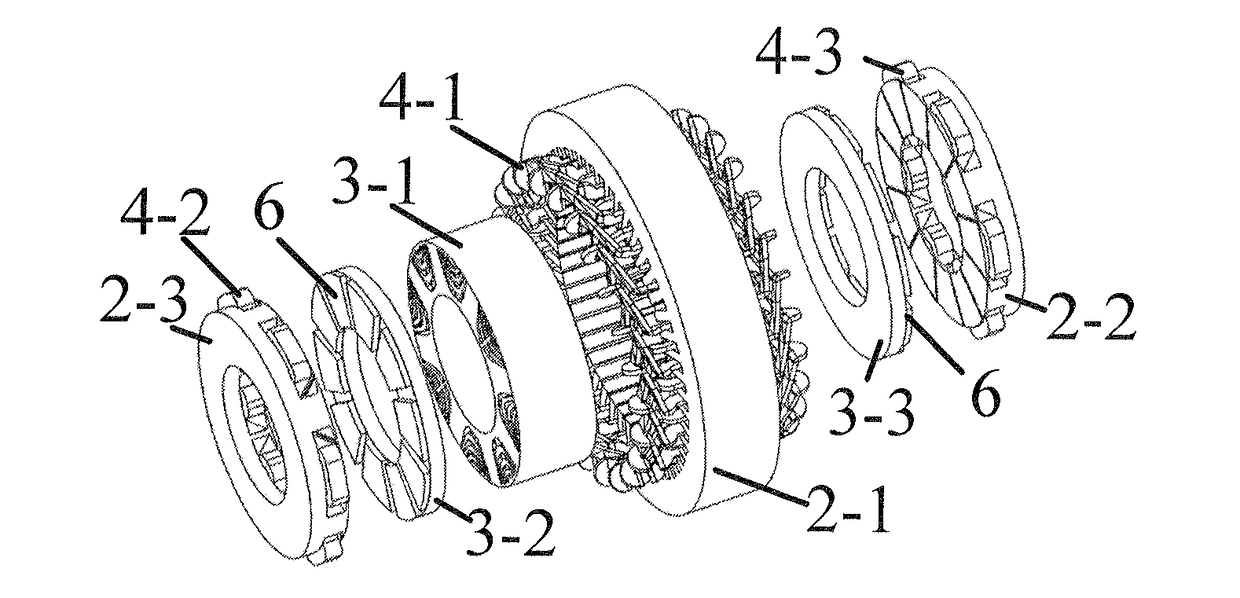
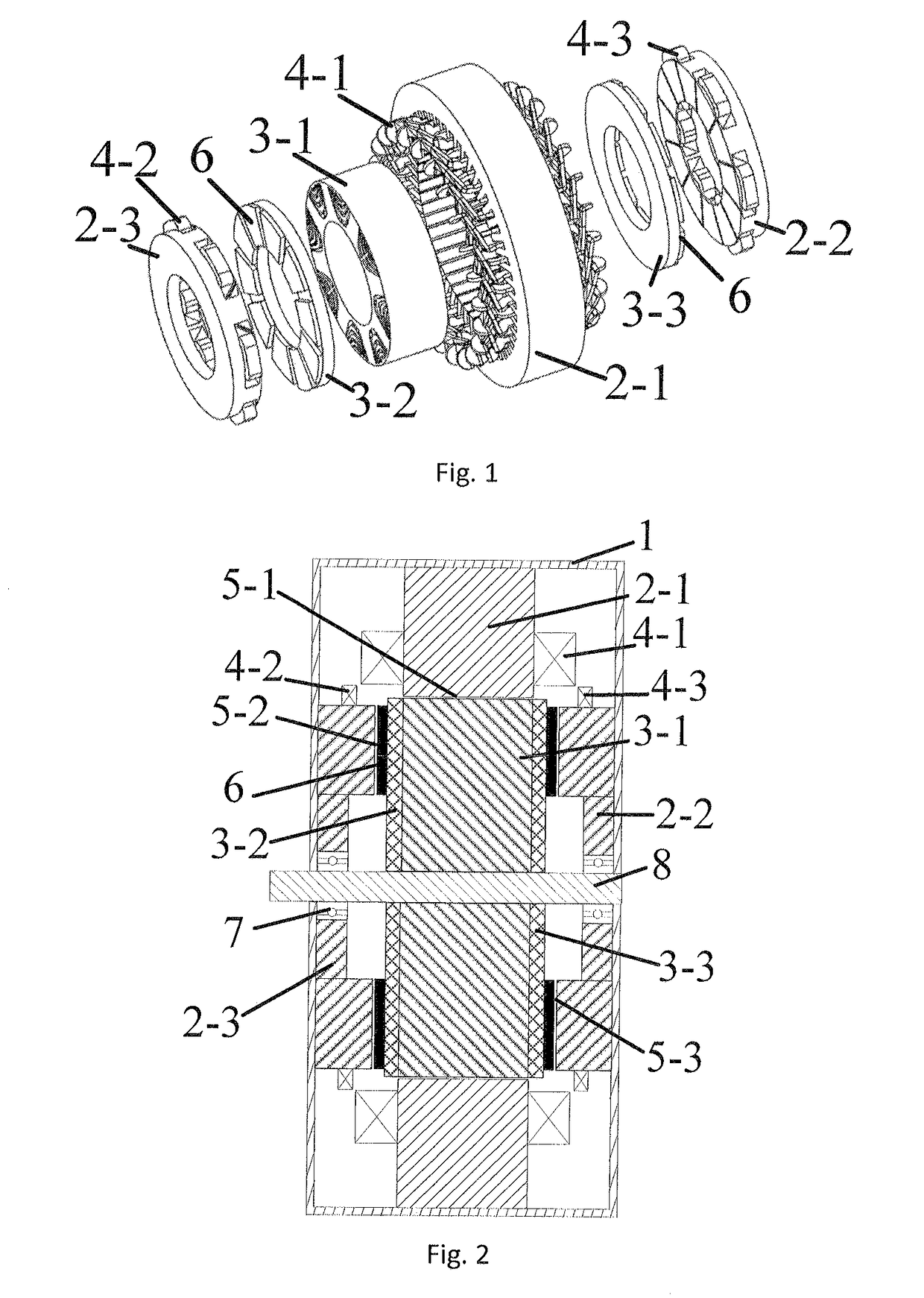
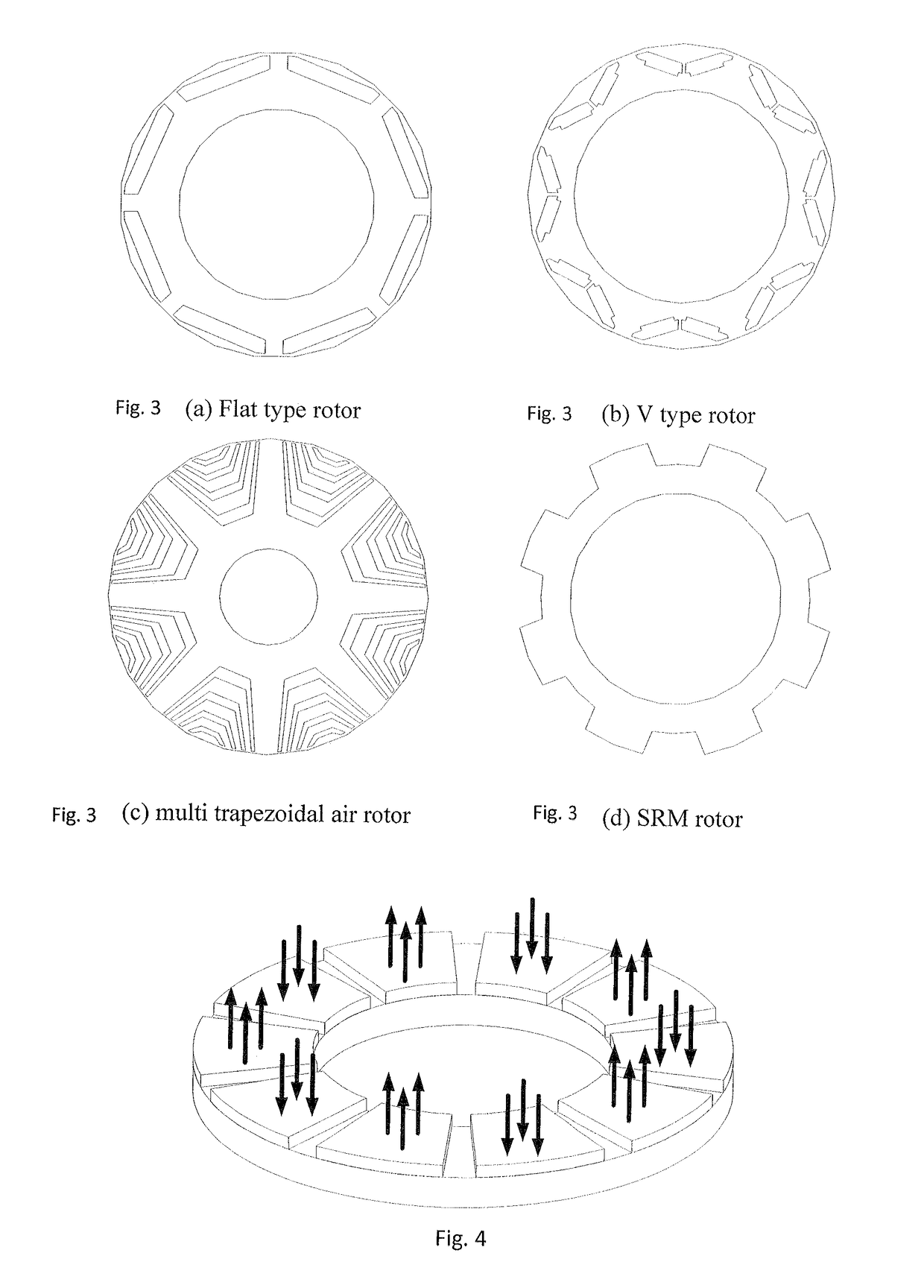
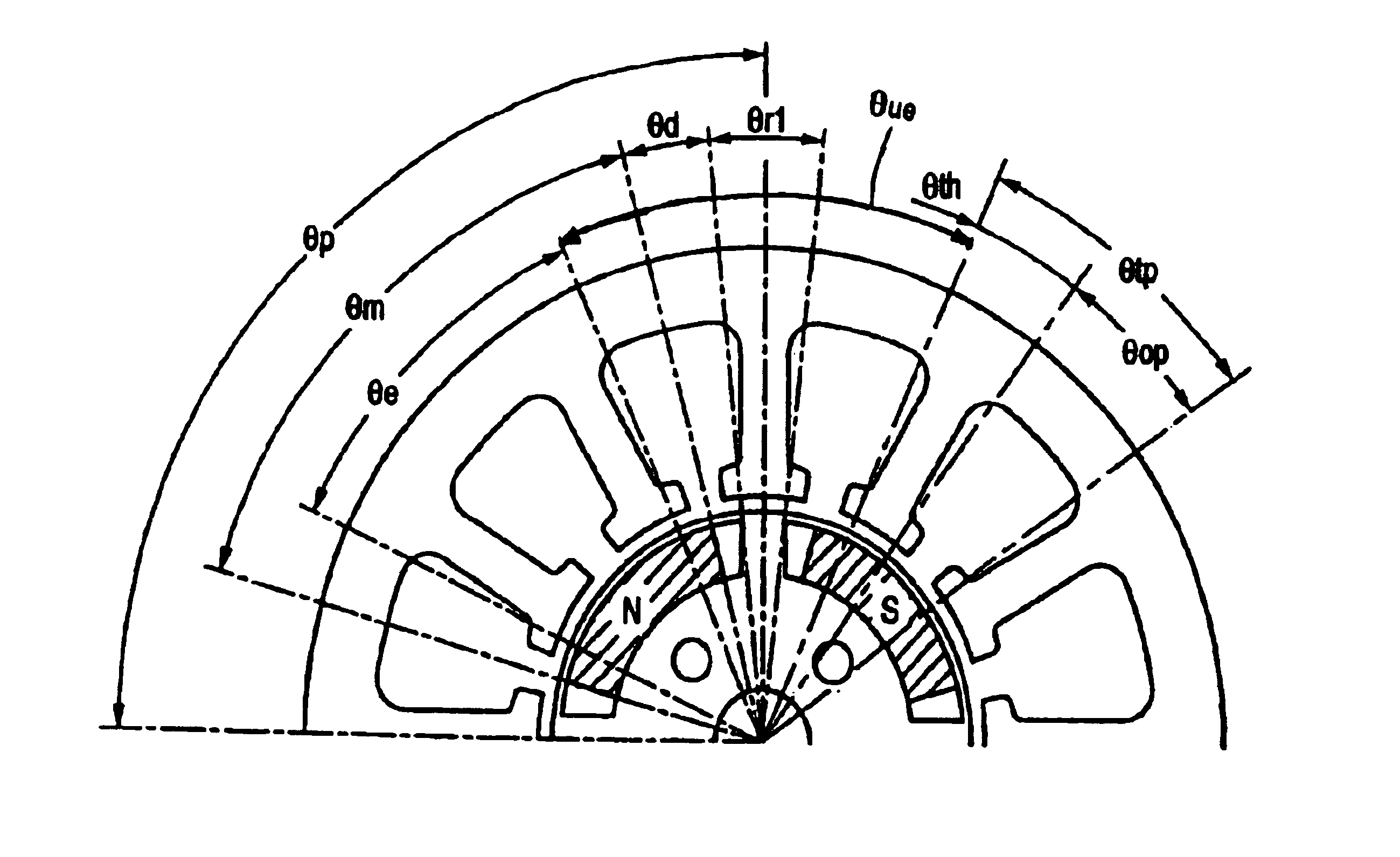
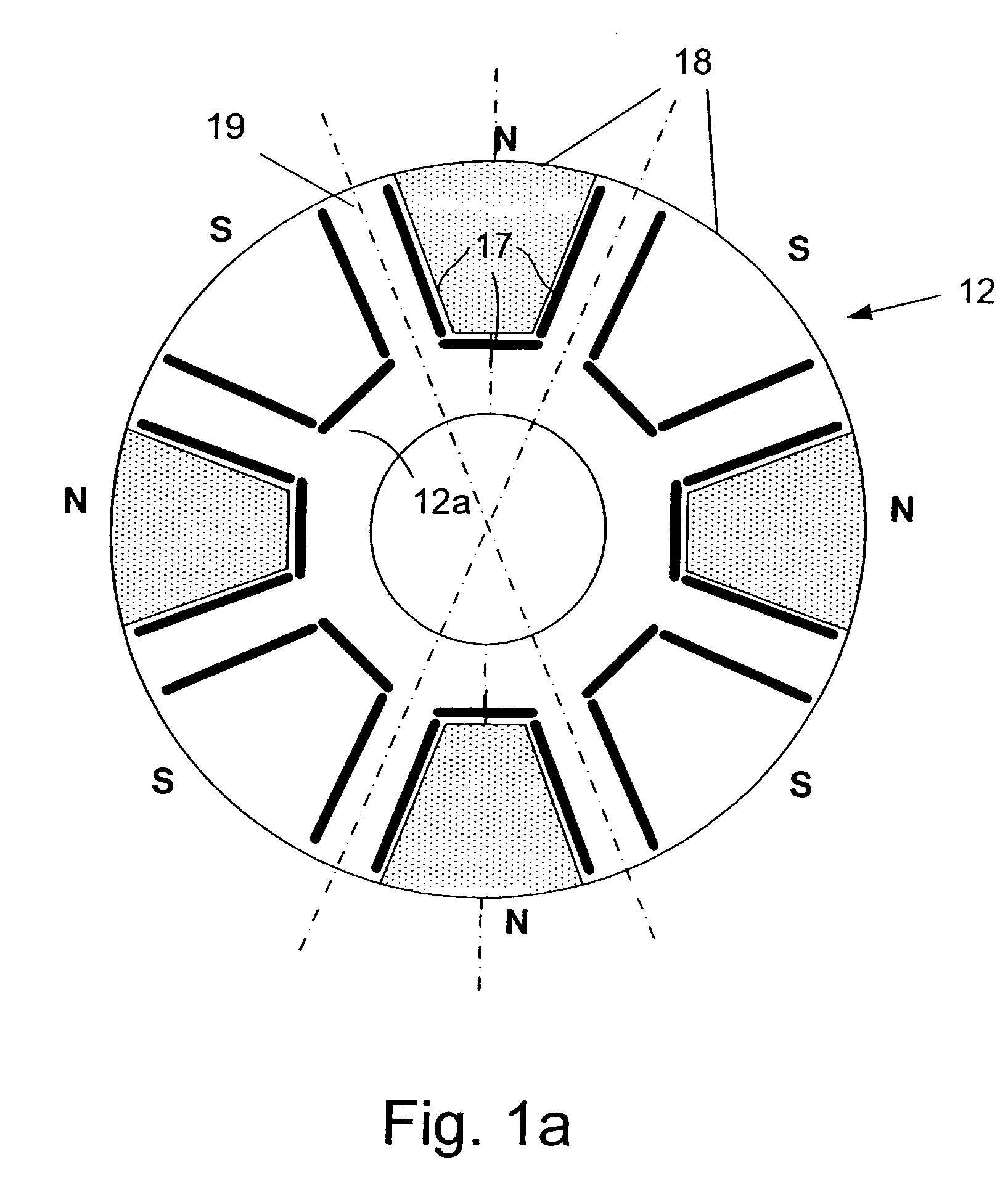
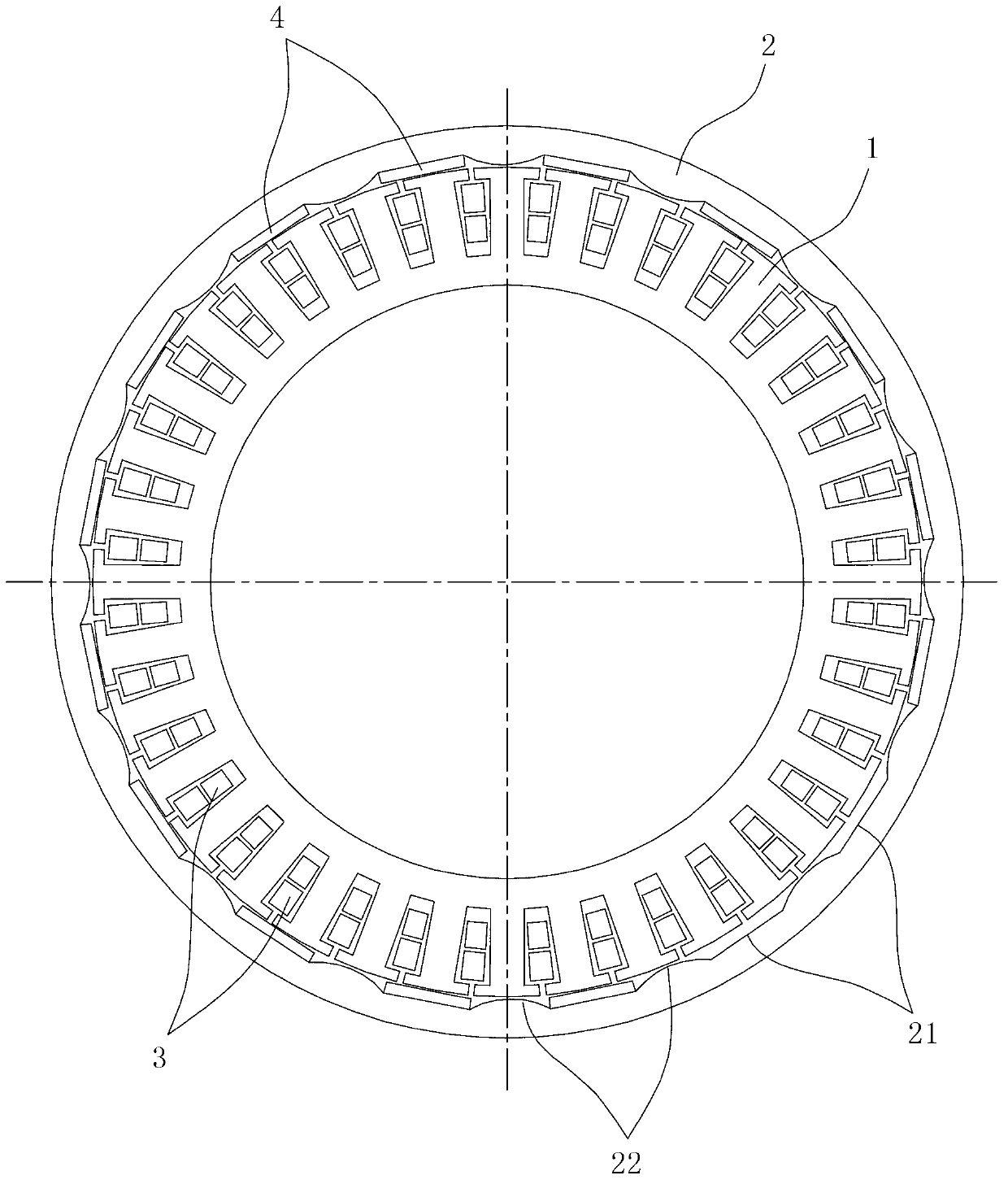
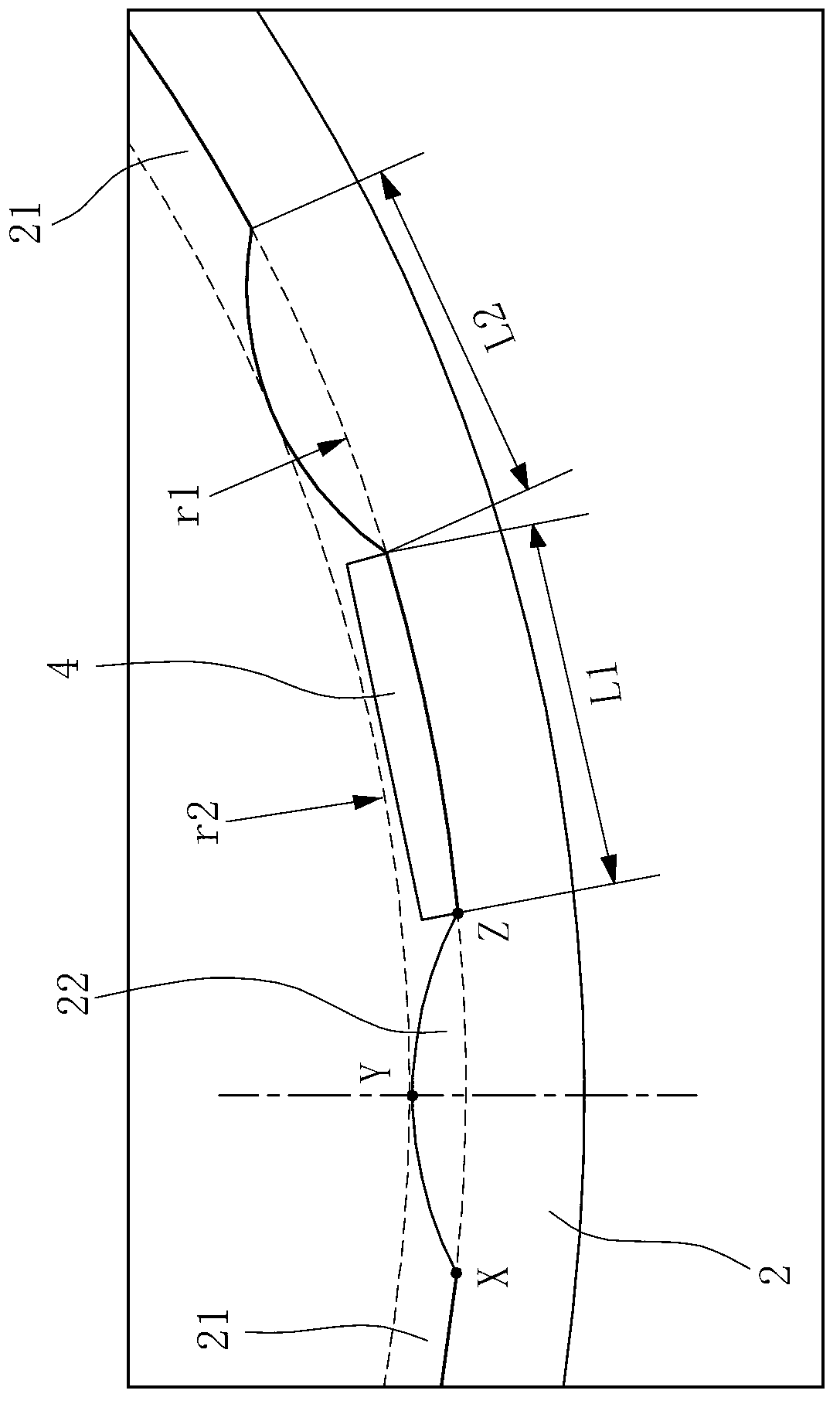
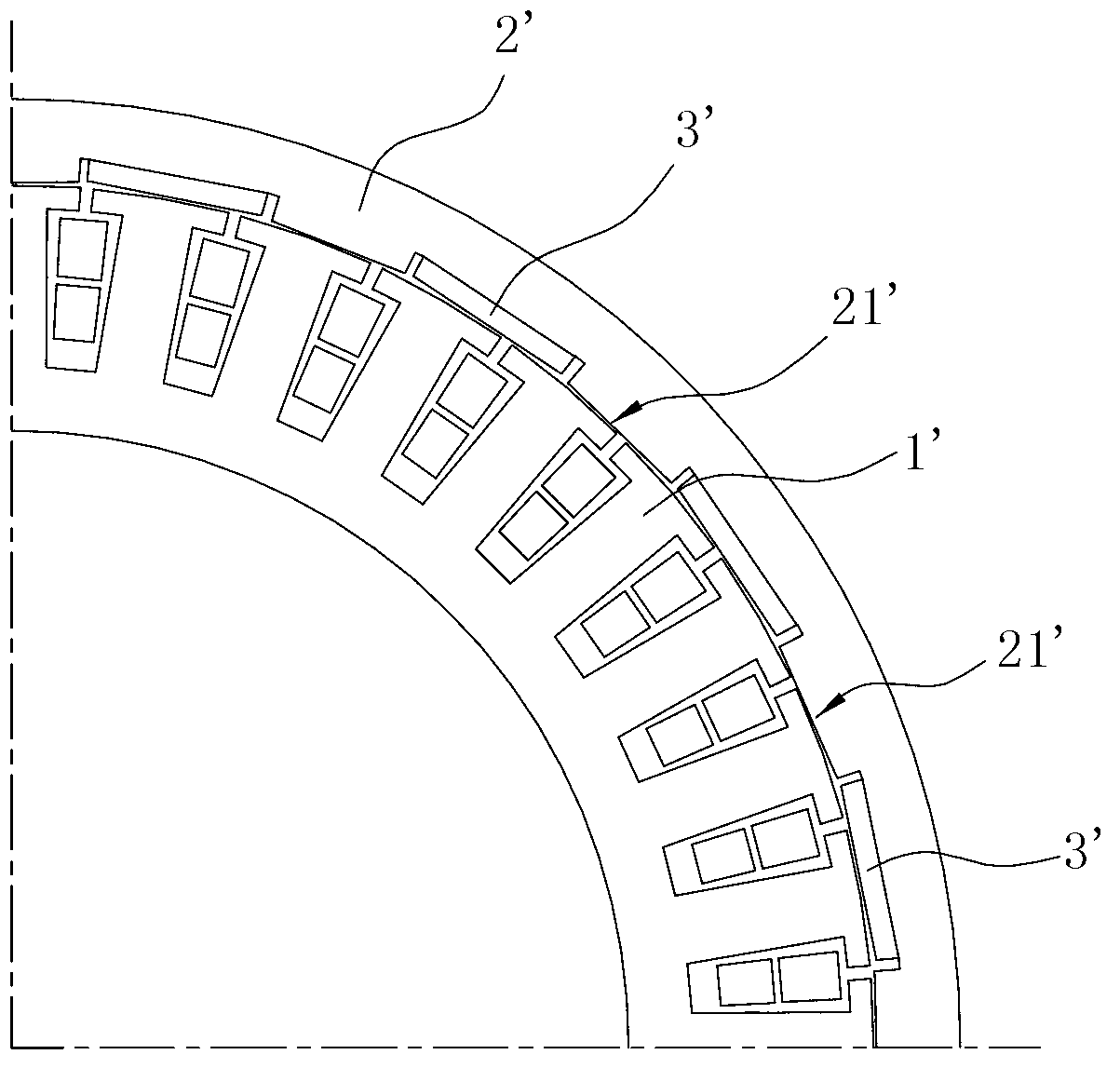
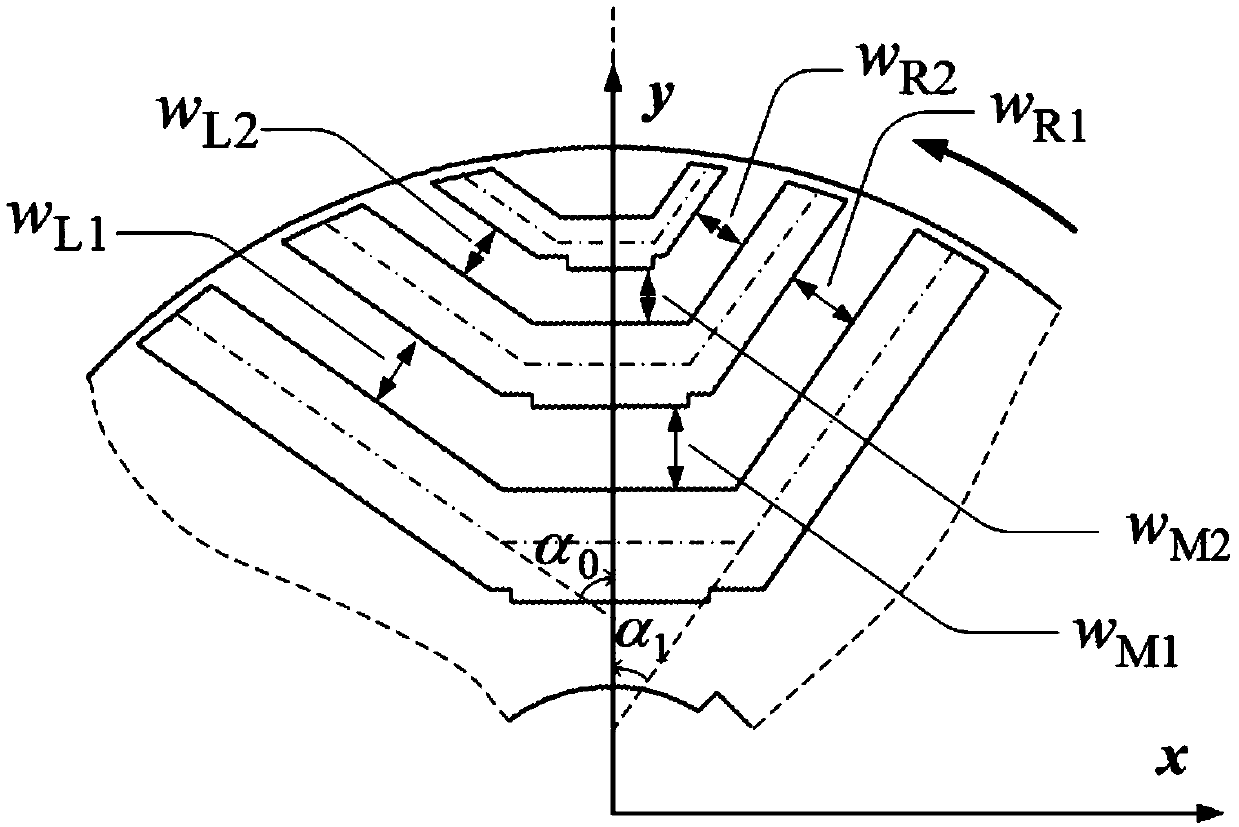
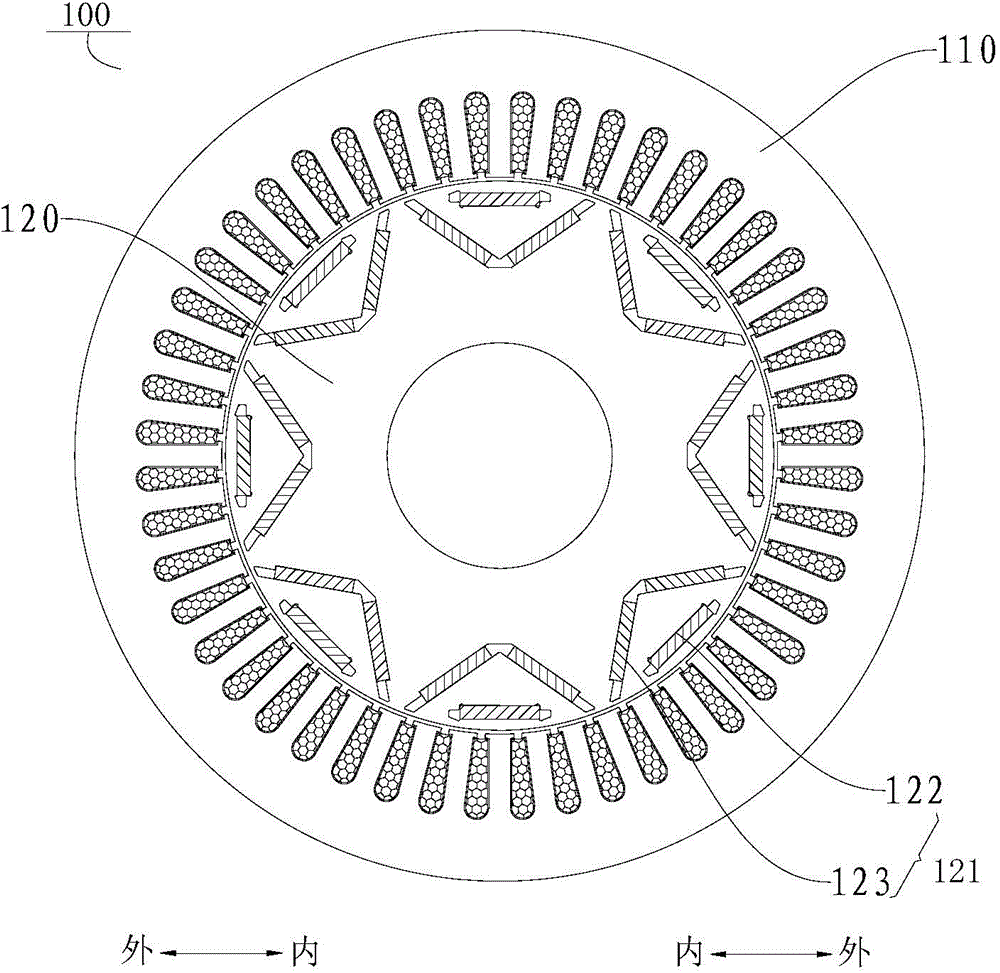
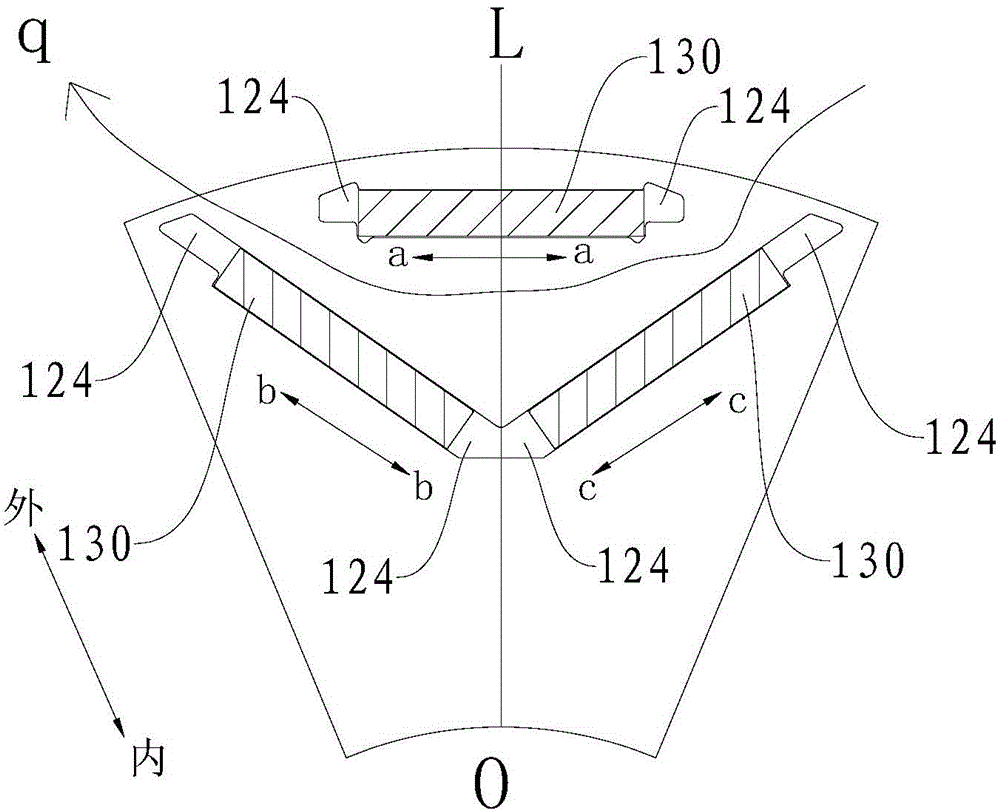
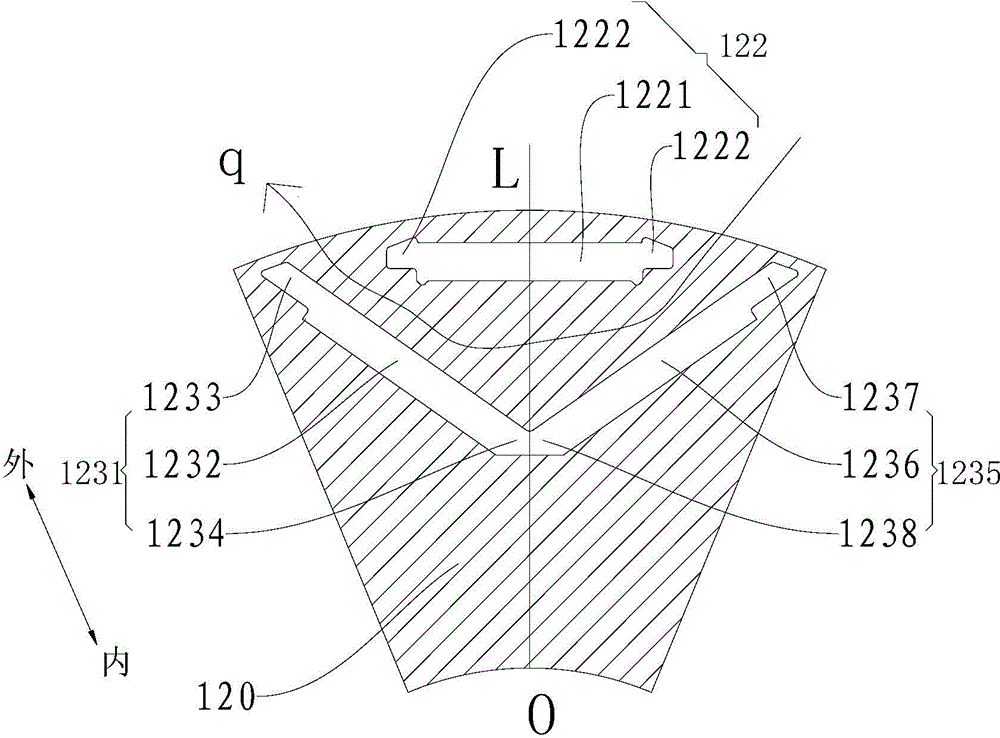
Patents
Literature
341 results about "Reluctance torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
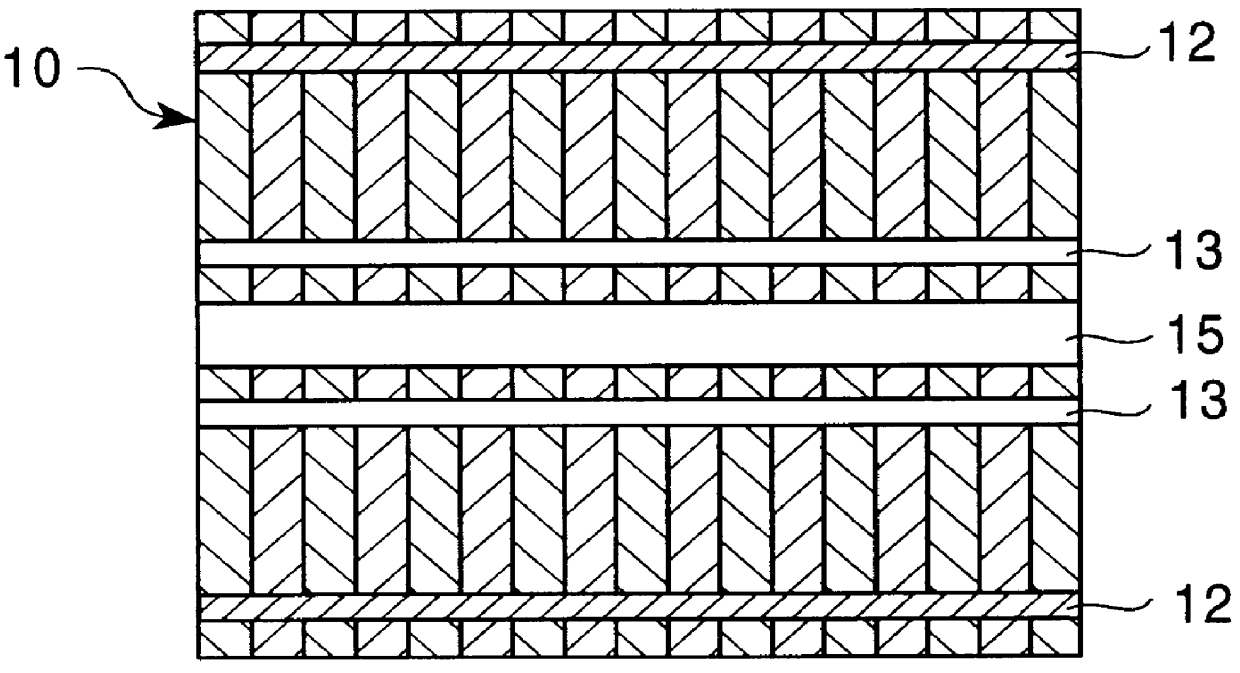
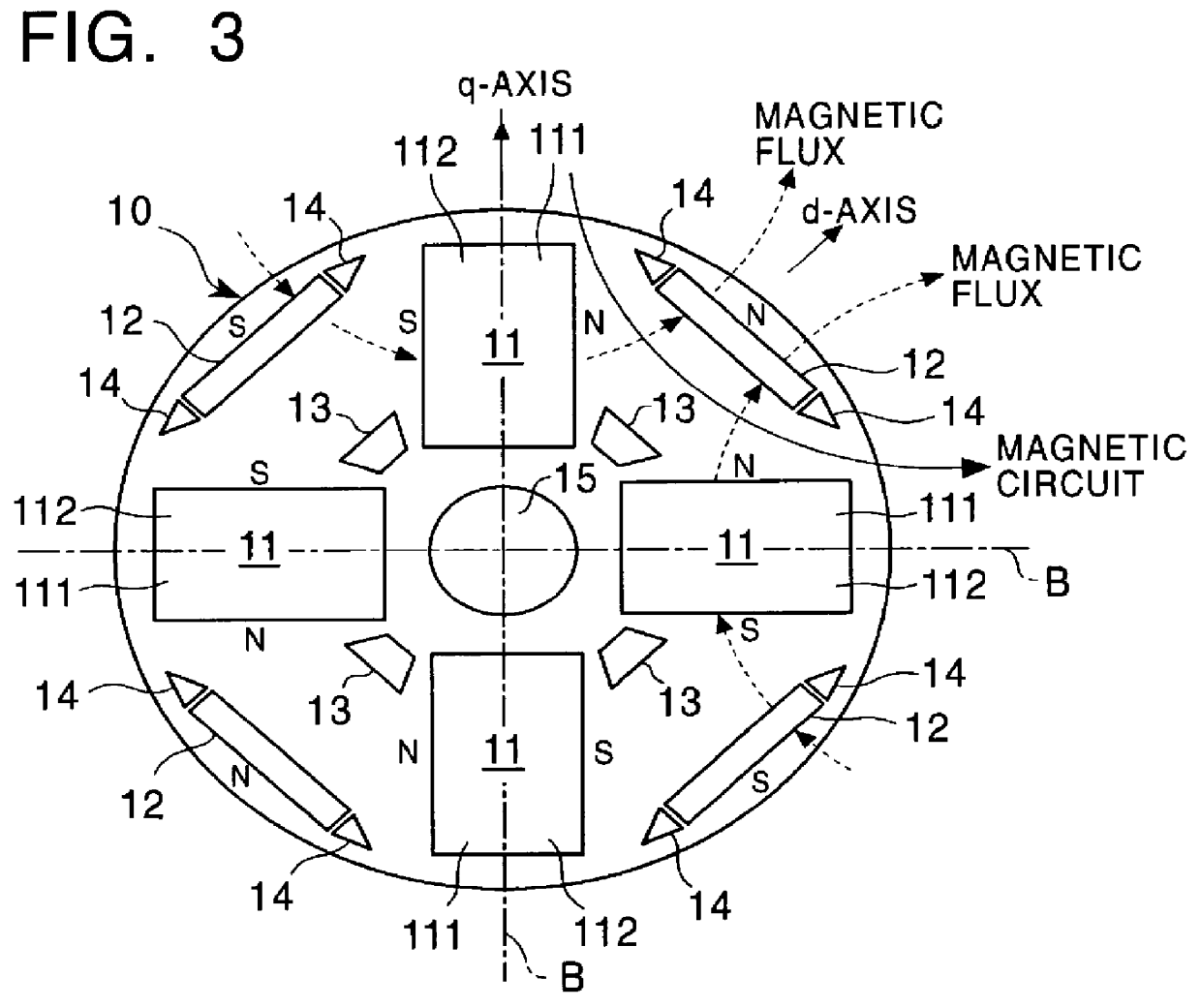
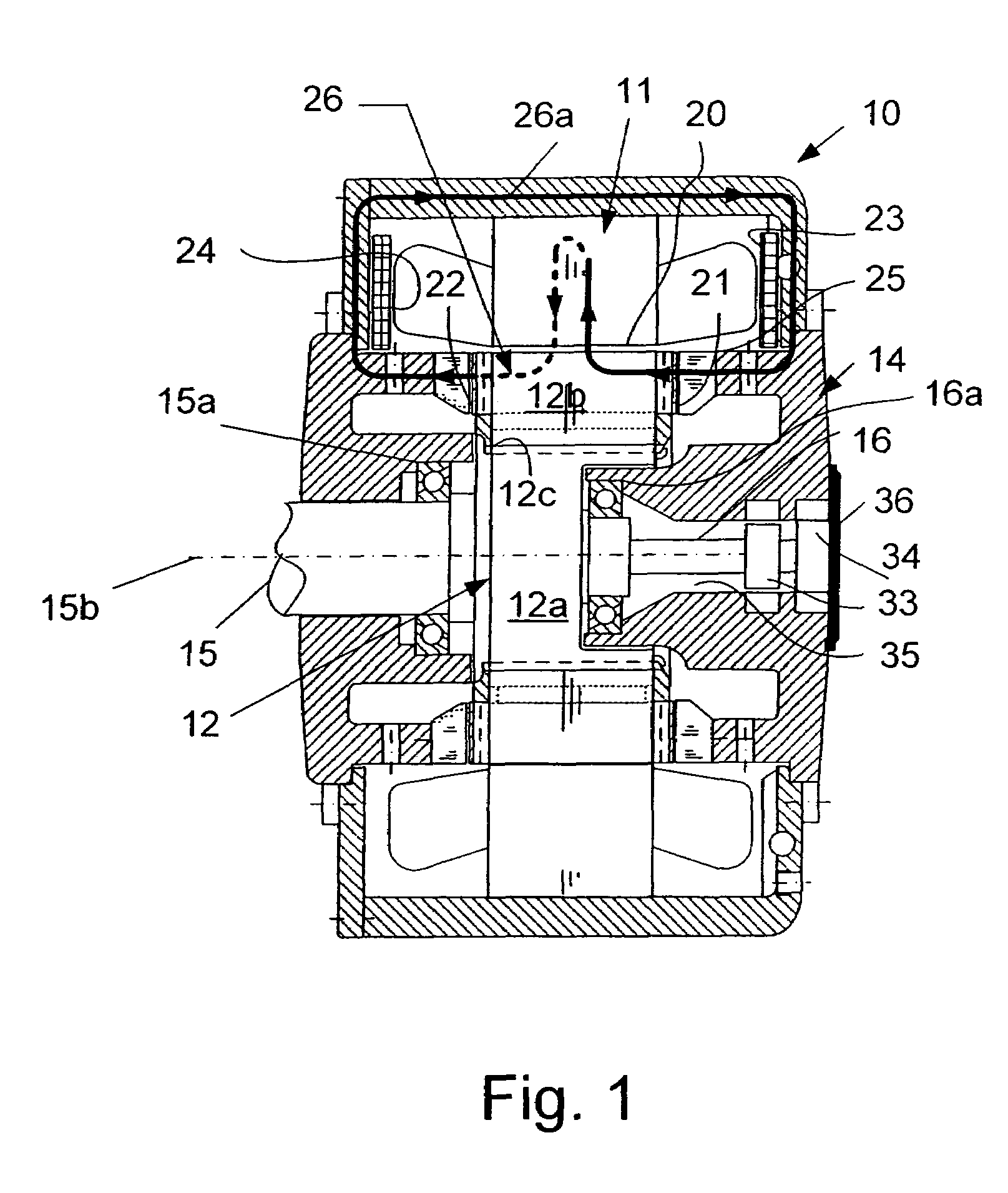
Permanent magnet electric rotating machine and electromotive vehicle using permanent magnet electric rotating machine
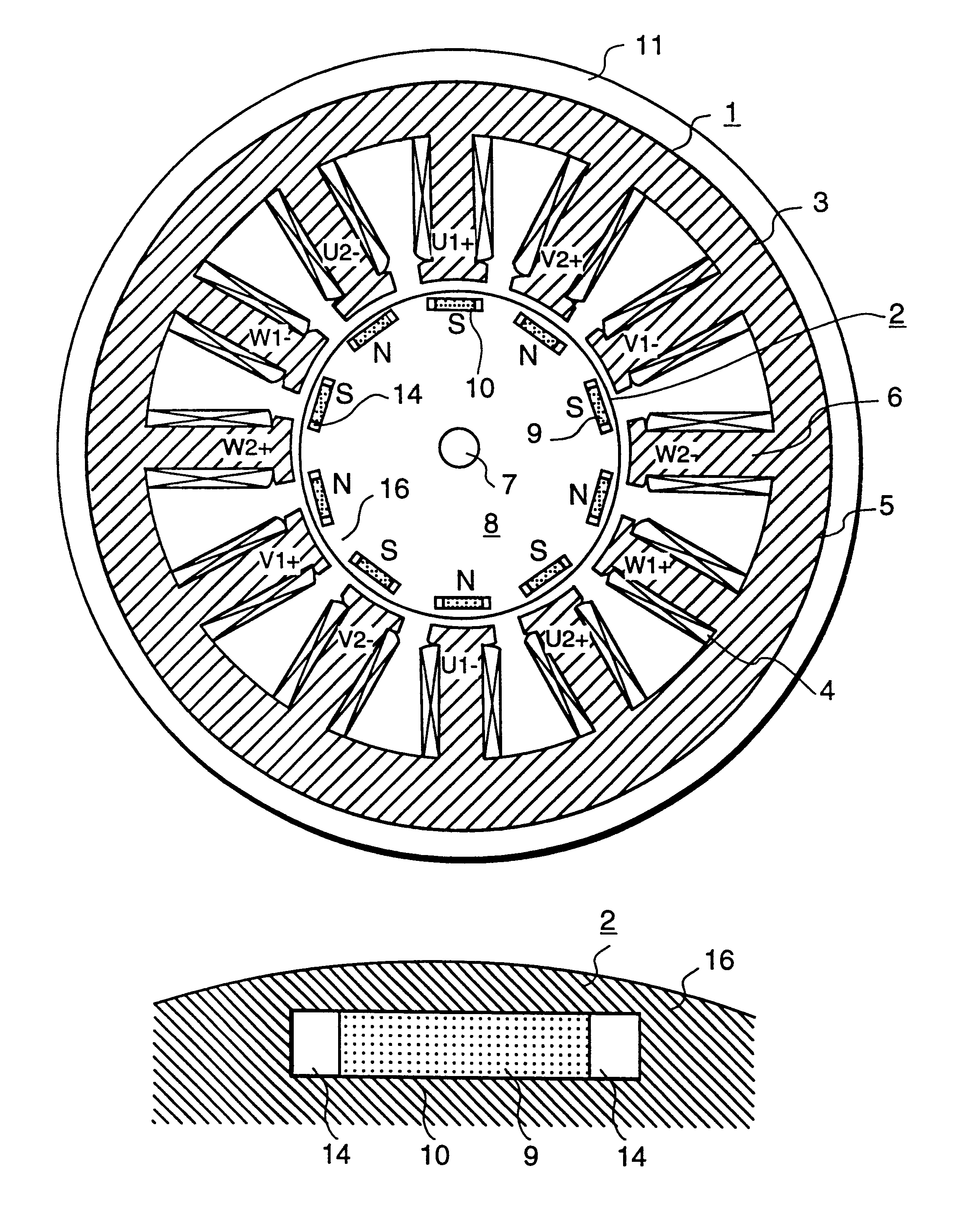
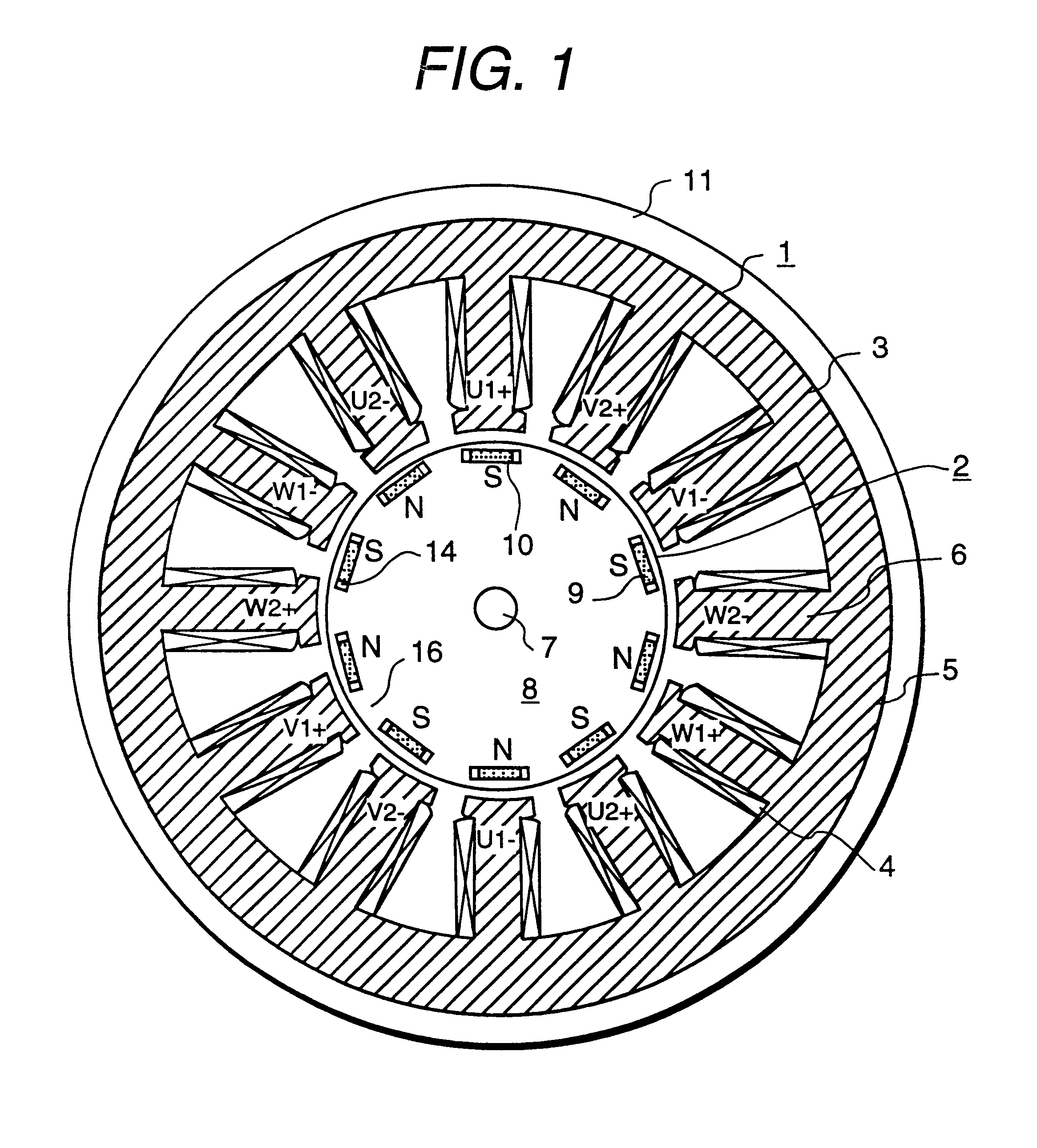
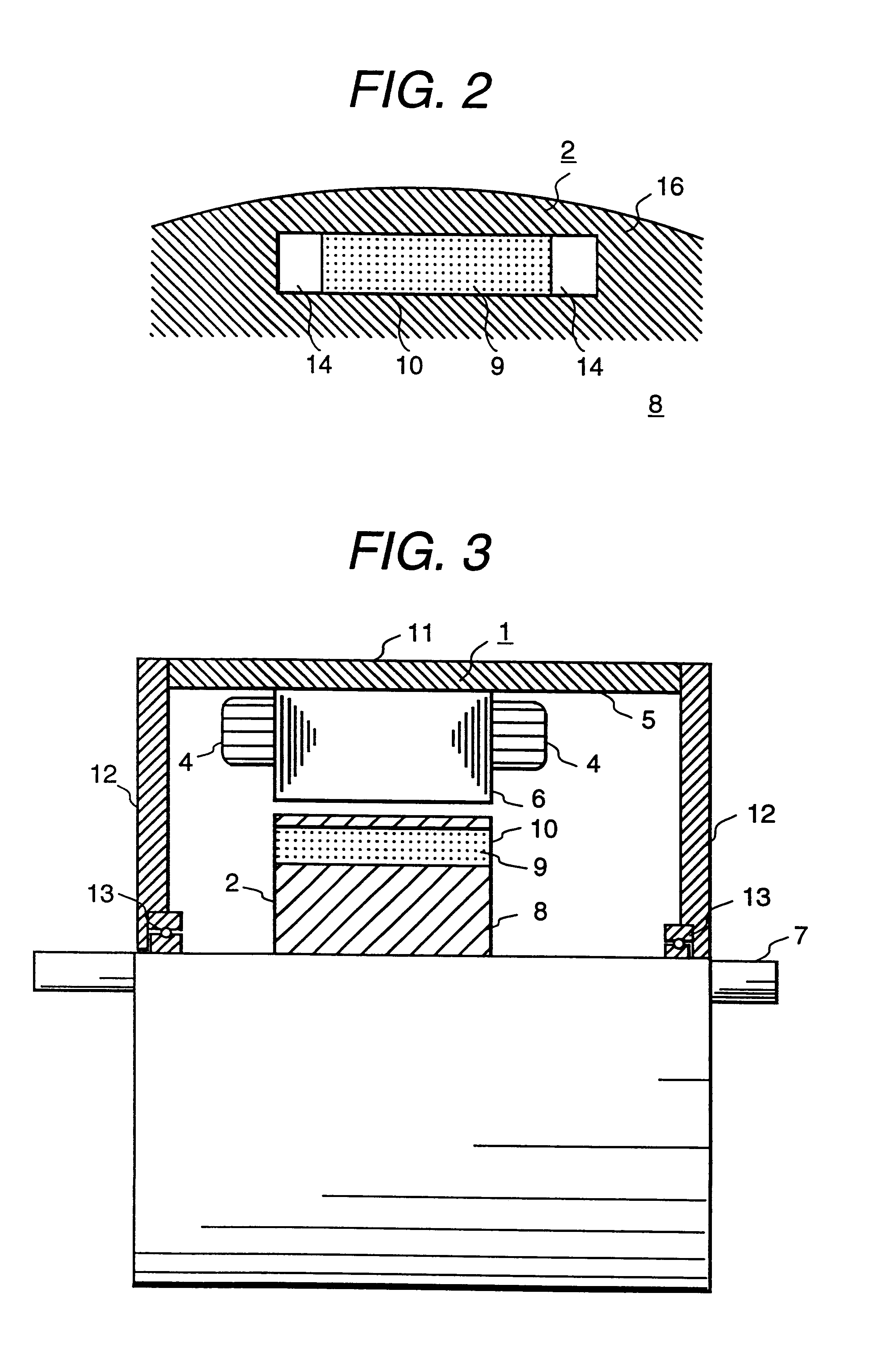
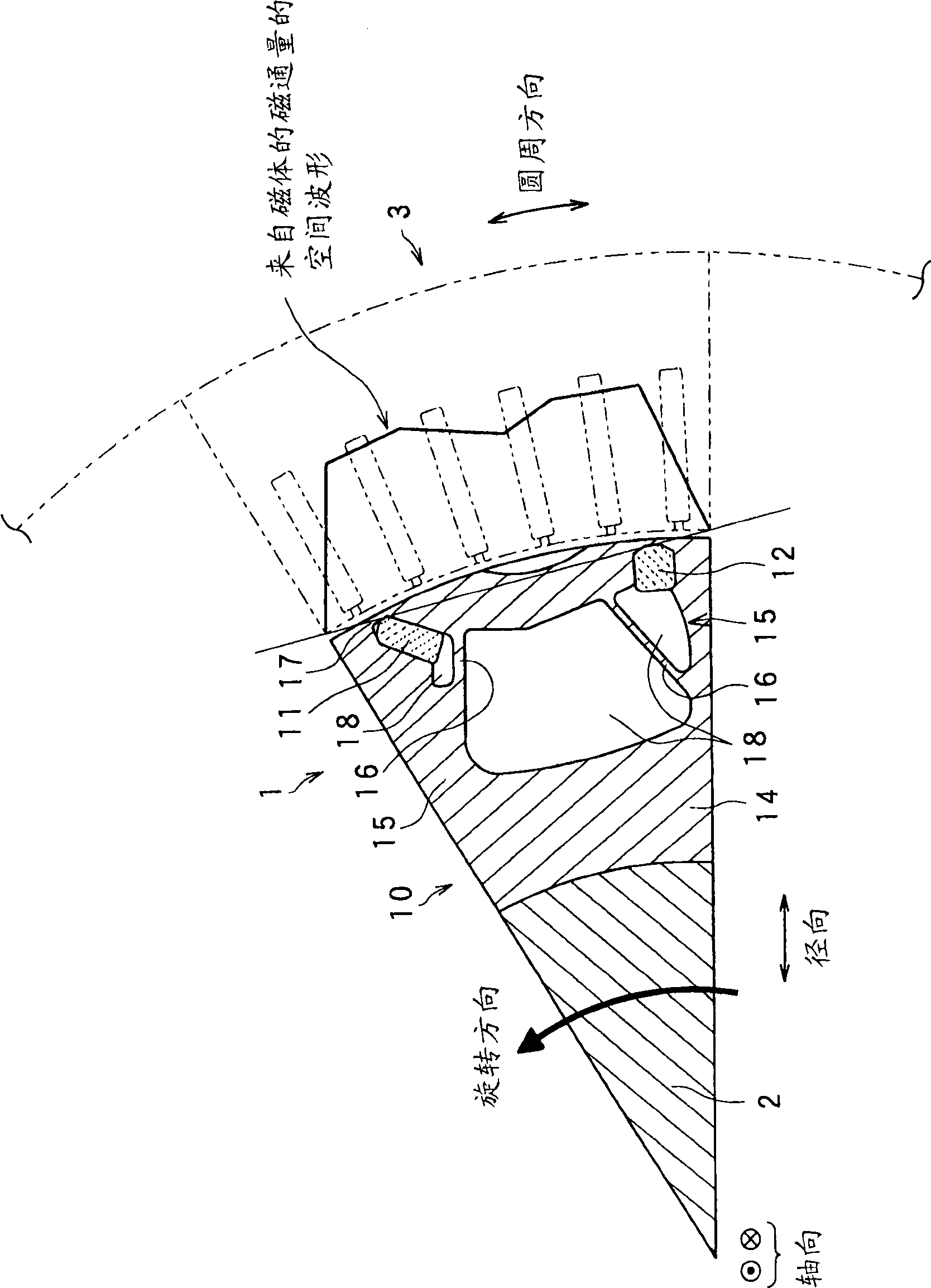
InactiveUS6208054B1Reduce pulsationMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
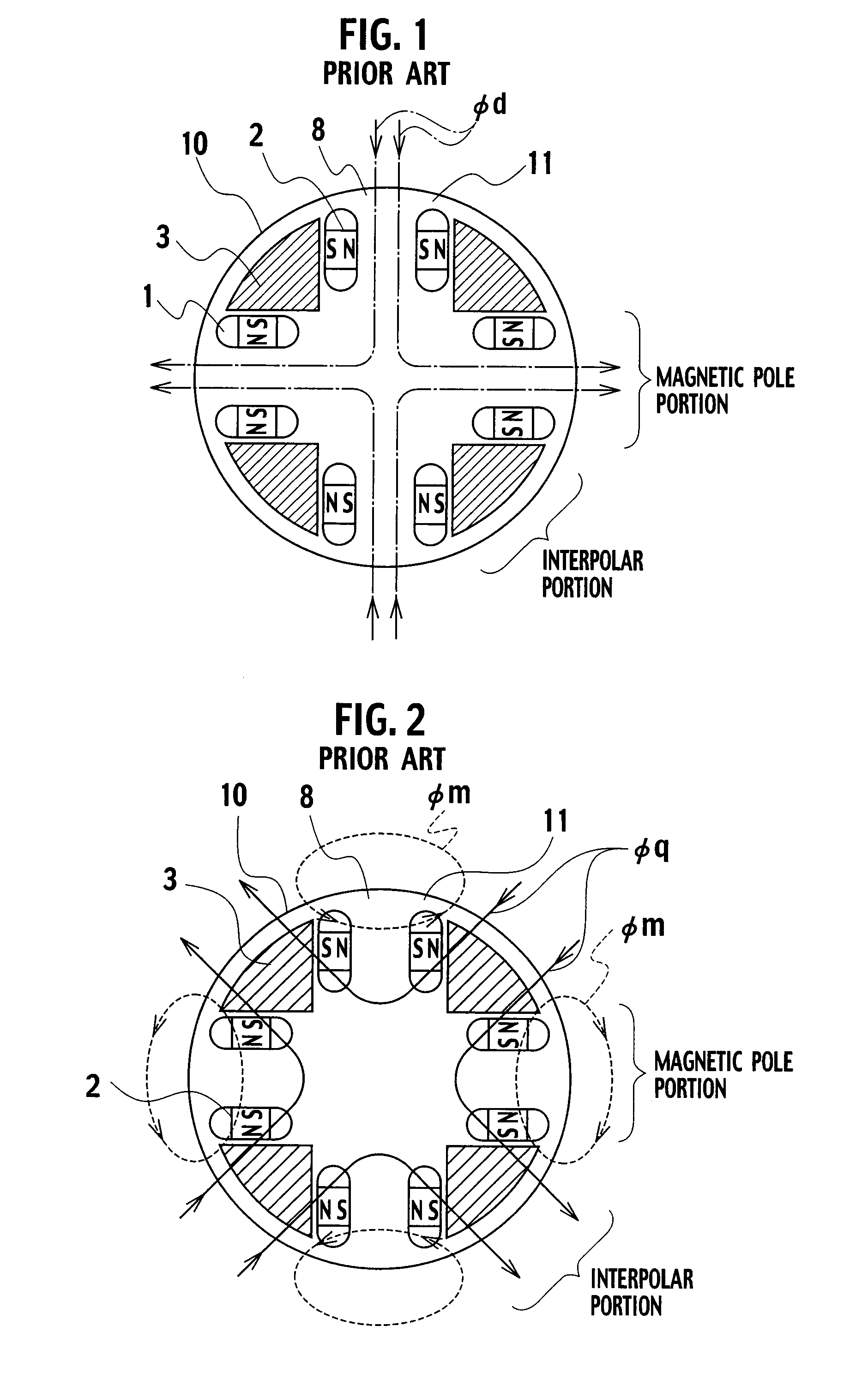
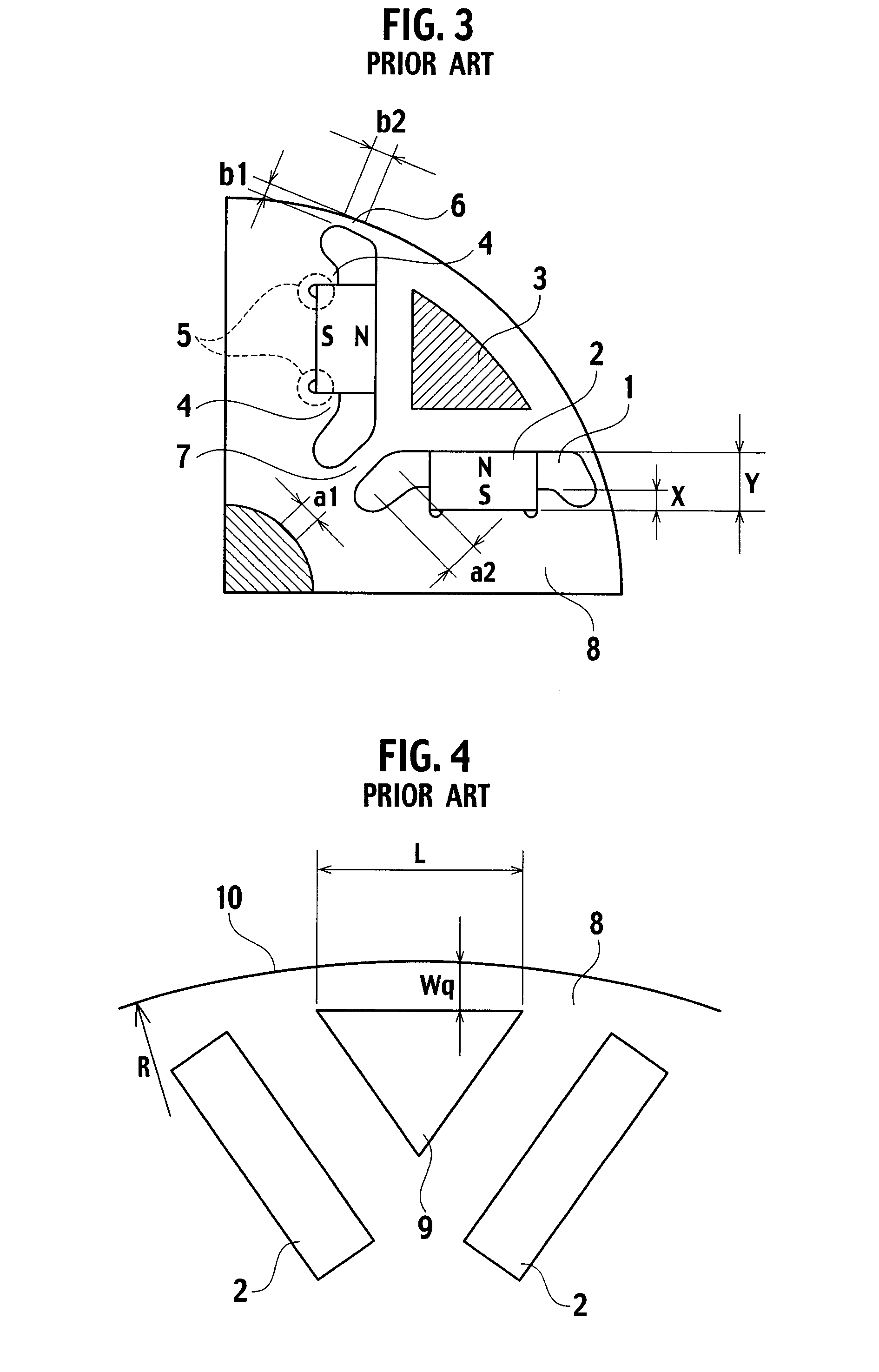
A magnetic gap is provided between a permanent magnet of a rotor and an auxiliary magnetic pole portion which is arranged adjacent to the permanent magnet in a peripheral direction. A gradual change in a magnetic flux density distribution of a surface of the rotor is obtained and a cogging torque and a torque pulsation are restrained. By obtaining a reluctance torque according to the auxiliary magnetic pole, a permanent magnet electric rotating machine in which the cogging torque and the torque pulsation are restrained can be obtained and further an electromotive vehicle having the permanent magnet electric rotating machine can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Permanent magnet rotor type electric motor with different permanent magnet materials
InactiveUS6025667AMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
In an electric motor, such as a DC brushless motor or the like, having a permanent magnet in a rotor, each magnetic pole is formed of three permanent magnets, and the permanent magnets are made of at least two kinds of magnetic materials represented by ferrite magnet and rare-earth magnet. Thus, in a permanent magnet rotor type electric motor, a reluctance torque and a magnetic flux density can be selectively established, and cost is reasonable, corresponding to the quality.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
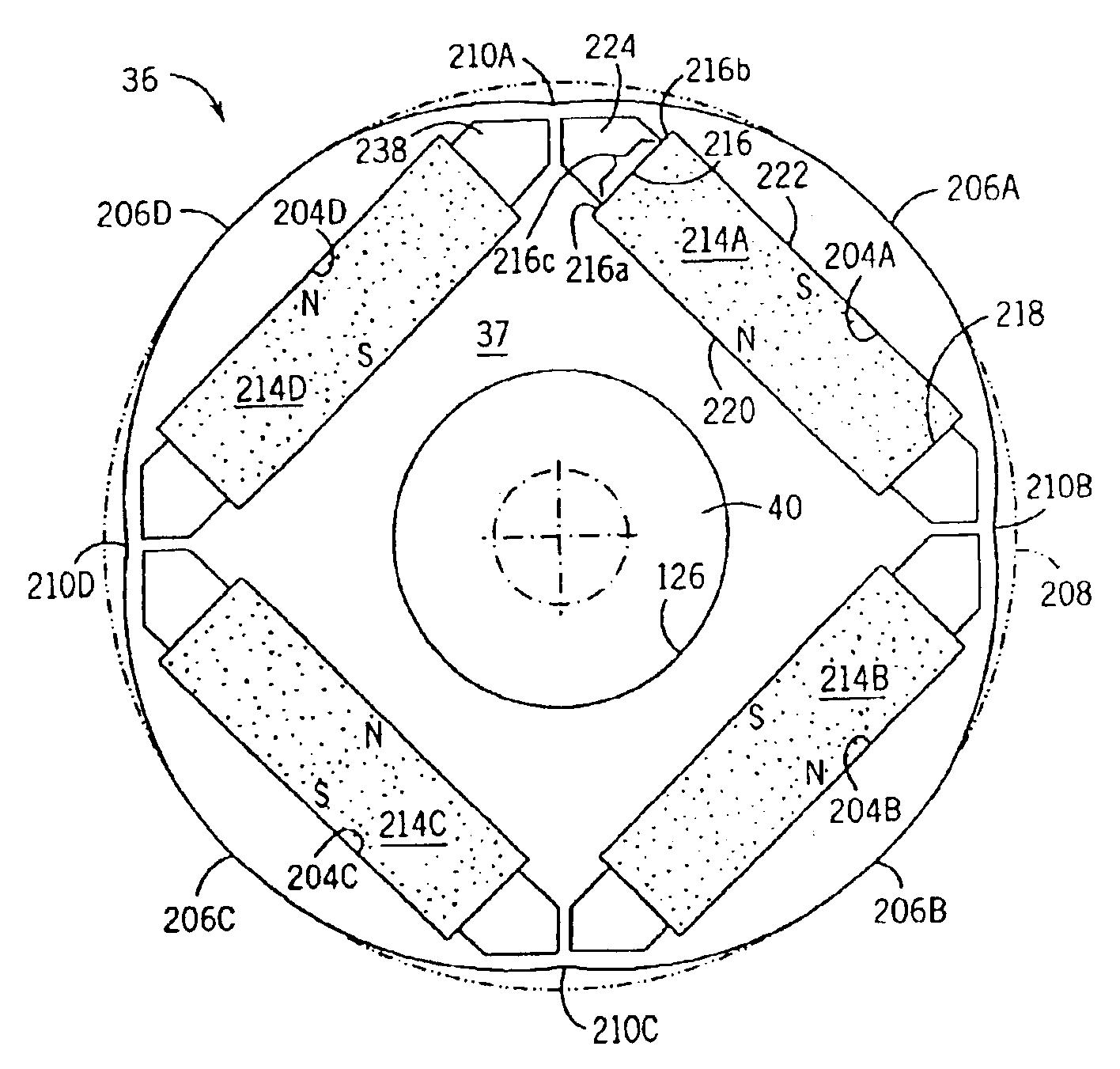
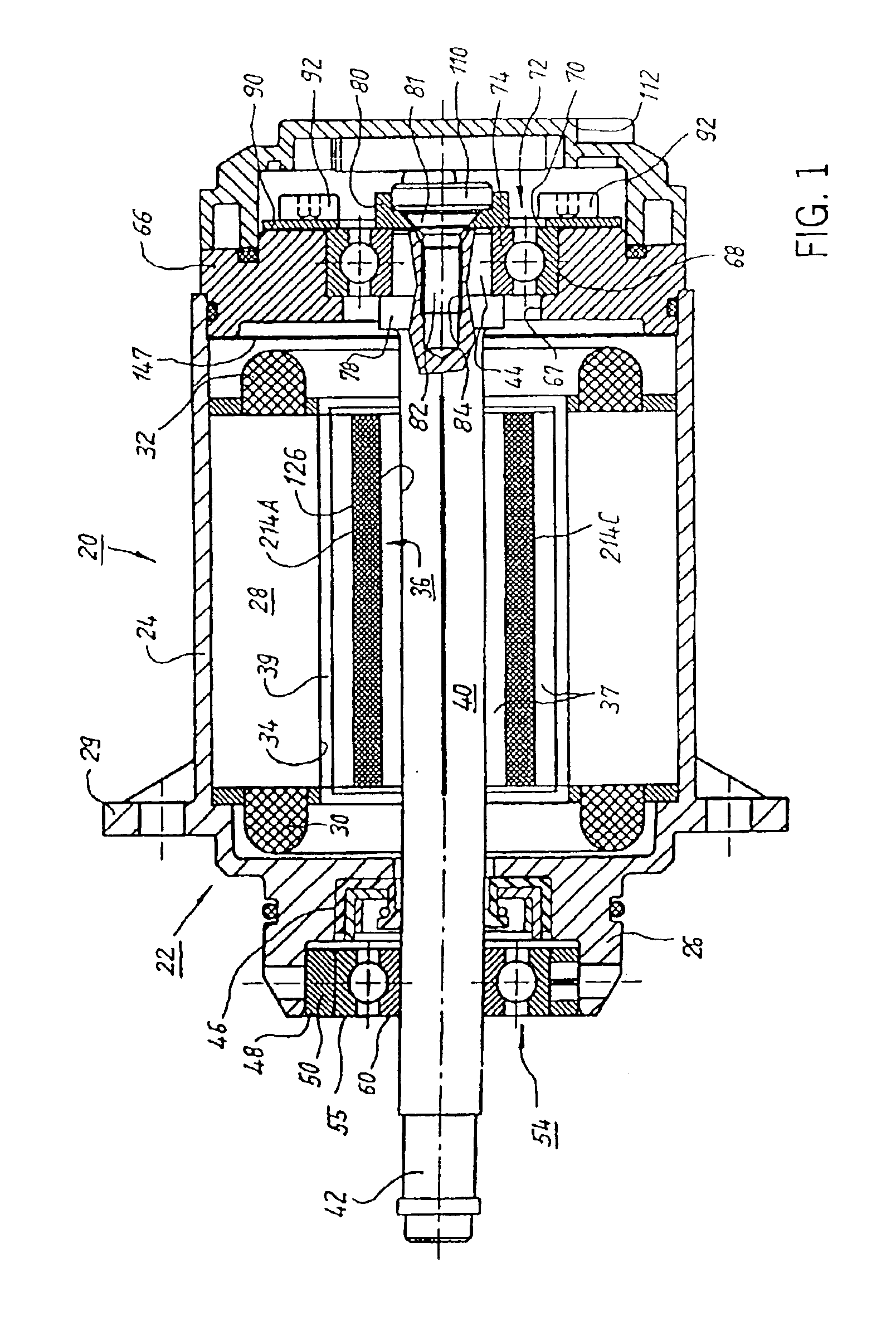
Internal rotor motor
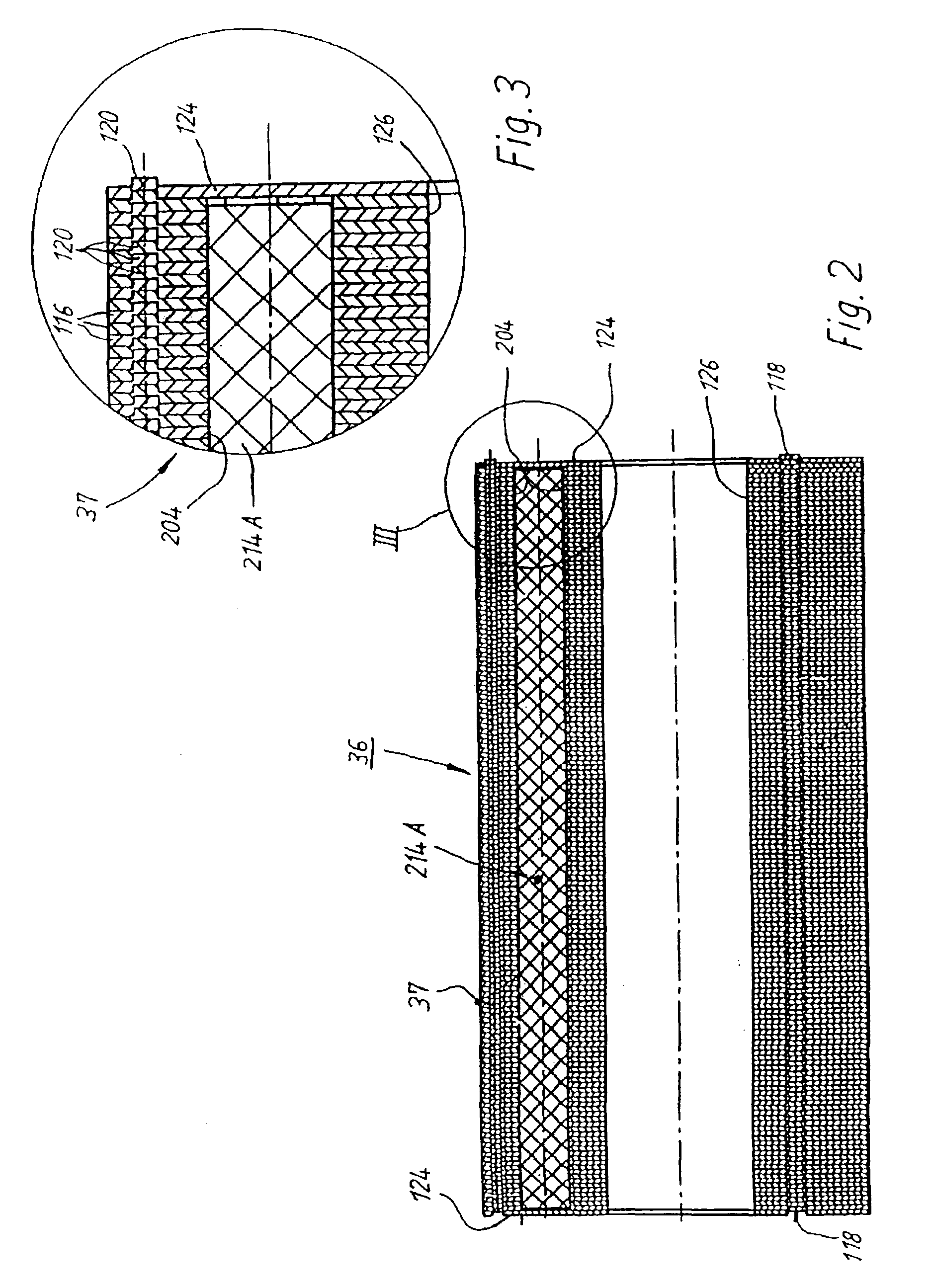
InactiveUS6919663B2Minimized cogging torqueImprove featuresMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsElectric machine
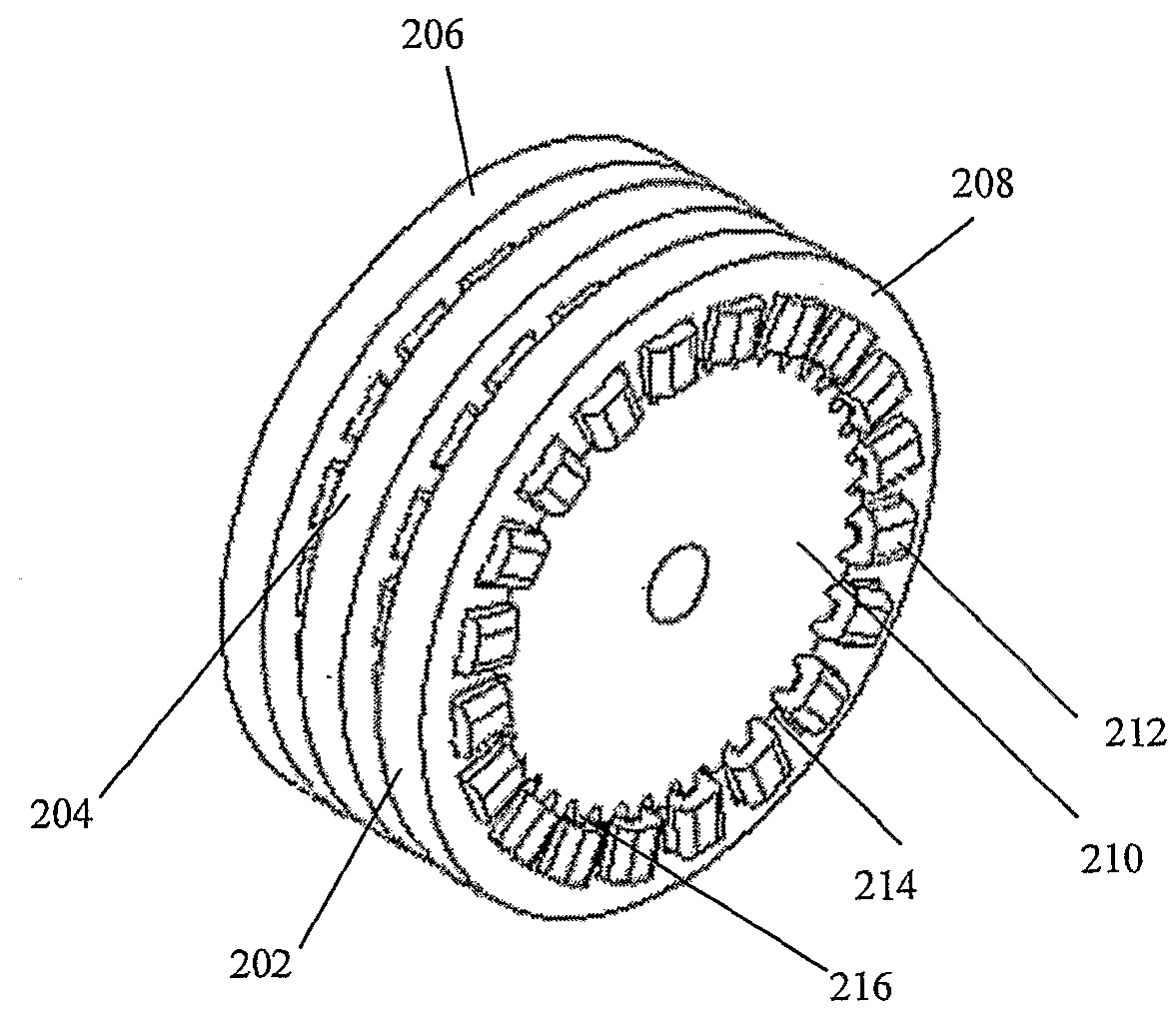
A low-ripple multi-phase internal rotor motor has a slotted stator (28) separated by an air gap (39) from a central rotor (36). The rotor has a plurality of permanent magnets (214), preferably neodymium-boron, arranged in pockets (204) formed in a lamination stack (37), thereby defining a plurality of poles (206) separated by respective gaps (210). In a preferred embodiment, the motor is three-phase, with four rotor poles and six stator poles. As a result, when the first and third rotor poles are so aligned, with respect to their opposing stator poles, as to generate a reluctance torque, the second and fourth rotor poles are aligned to generate oppositely phased reluctance torques, so that these torques cancel each other, and essentially no net reluctance torque is exerted on the rotor. In order to magnetically separate the rotor magnets from each other, a hollow space (224, 238) is formed at the interpolar-gap-adjacent end face (216, 218) of each rotor magnet. A control circuit (147) provides electronic commutation and current control, based on rotor position signals generated with the aid of a control magnet (110) on the rotor shaft (40).
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
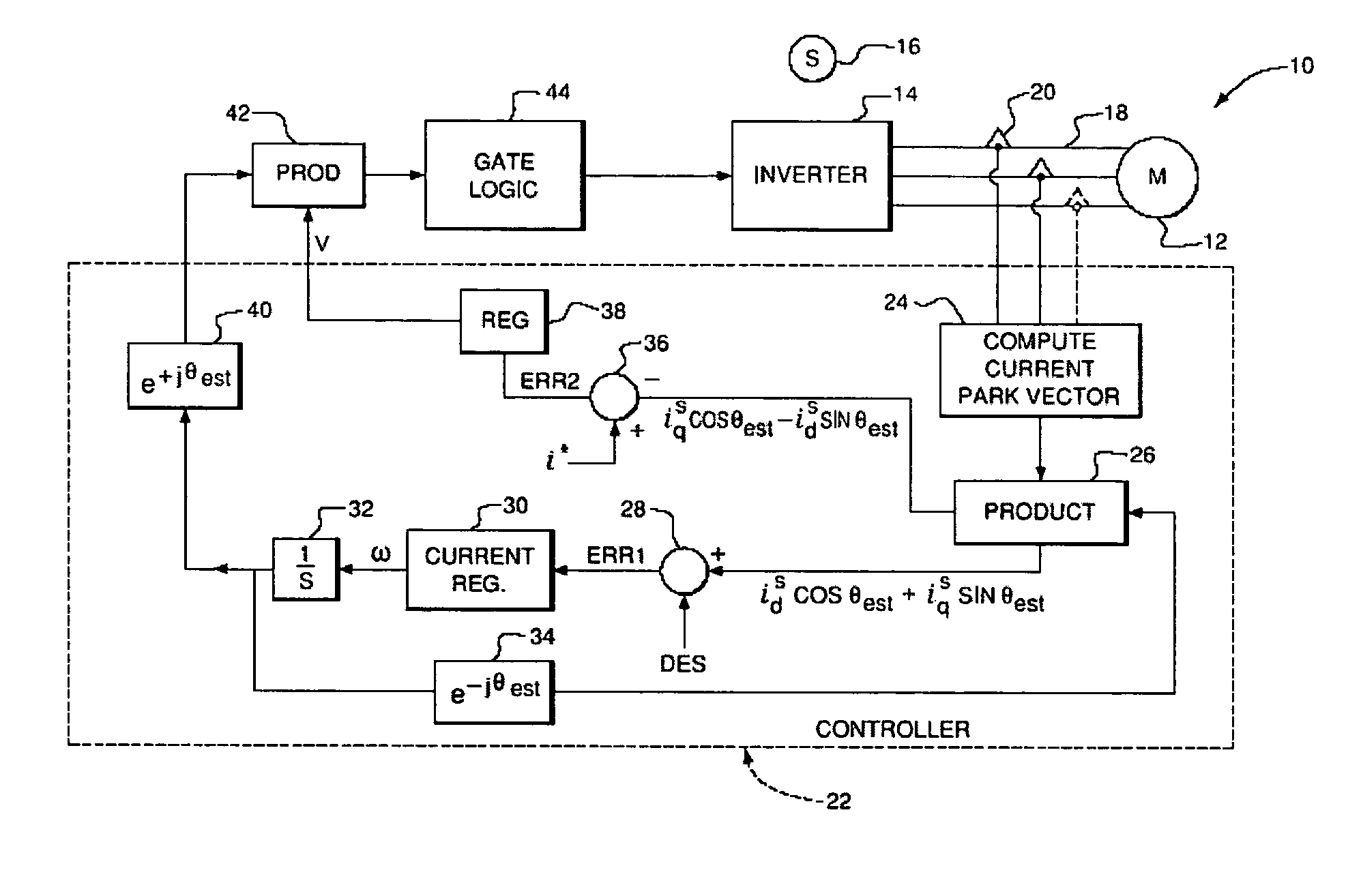
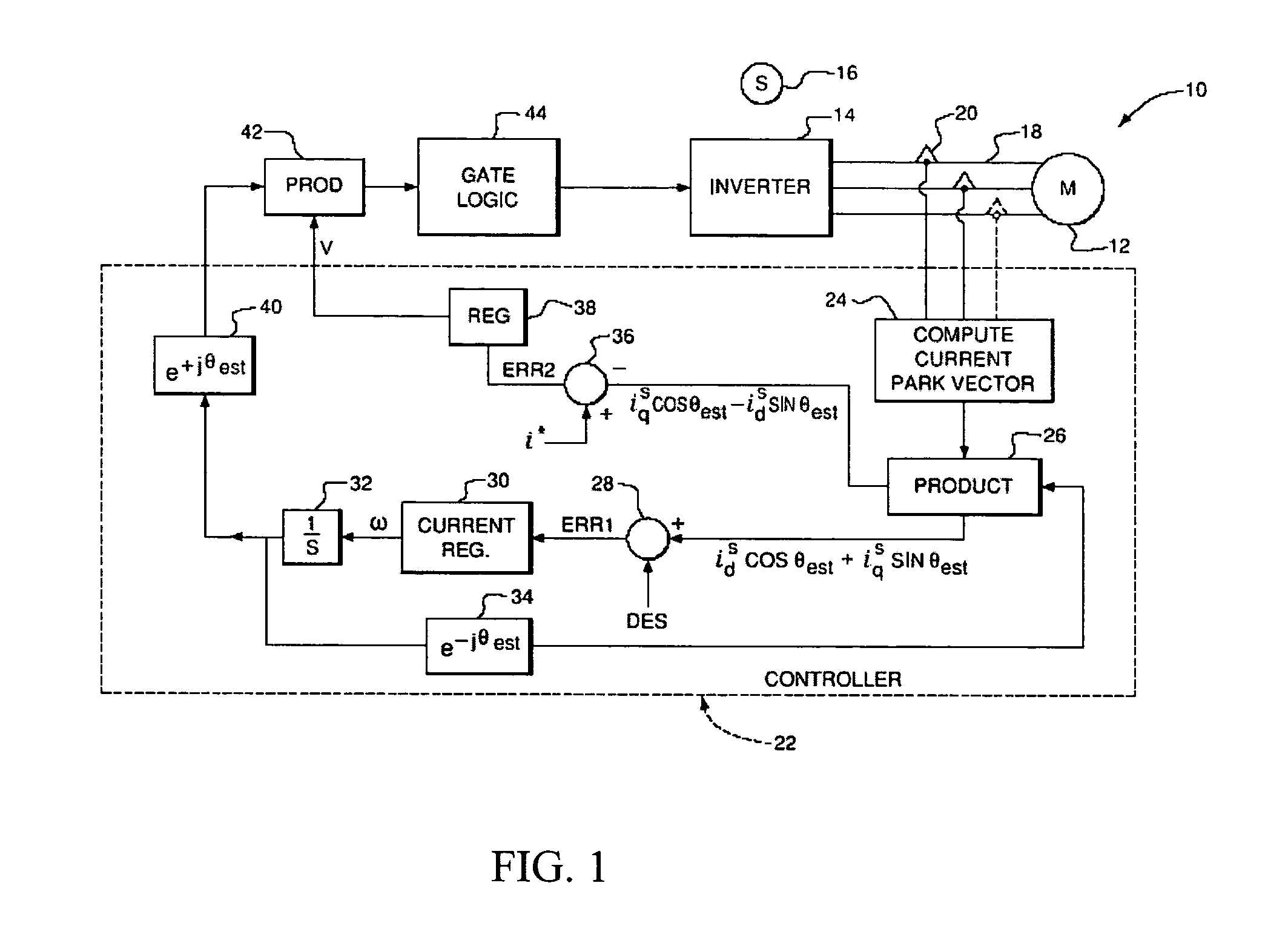
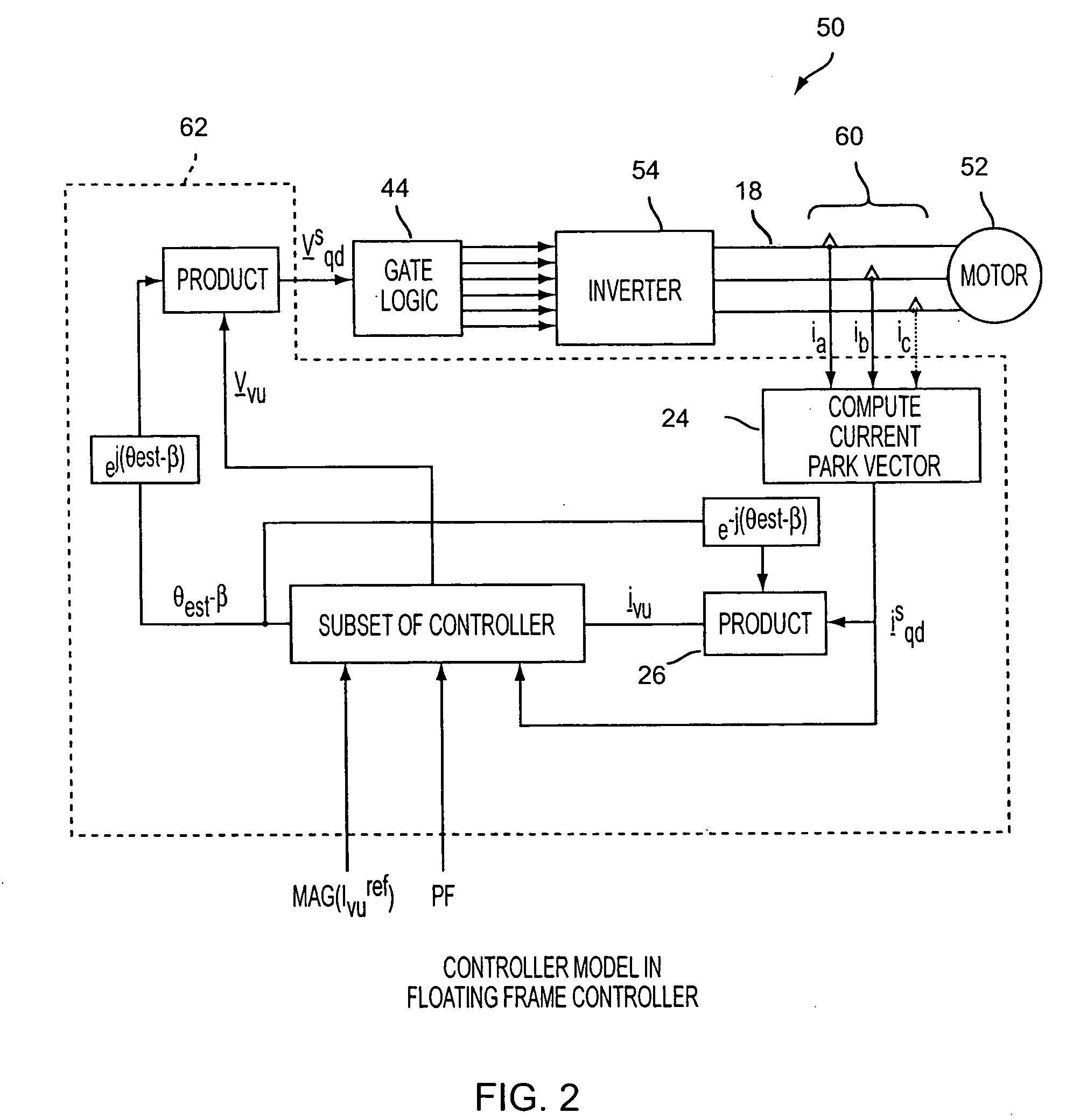
Power factor control for floating frame controller for sensorless control of synchronous machines
ActiveUS20070040524A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsControl system
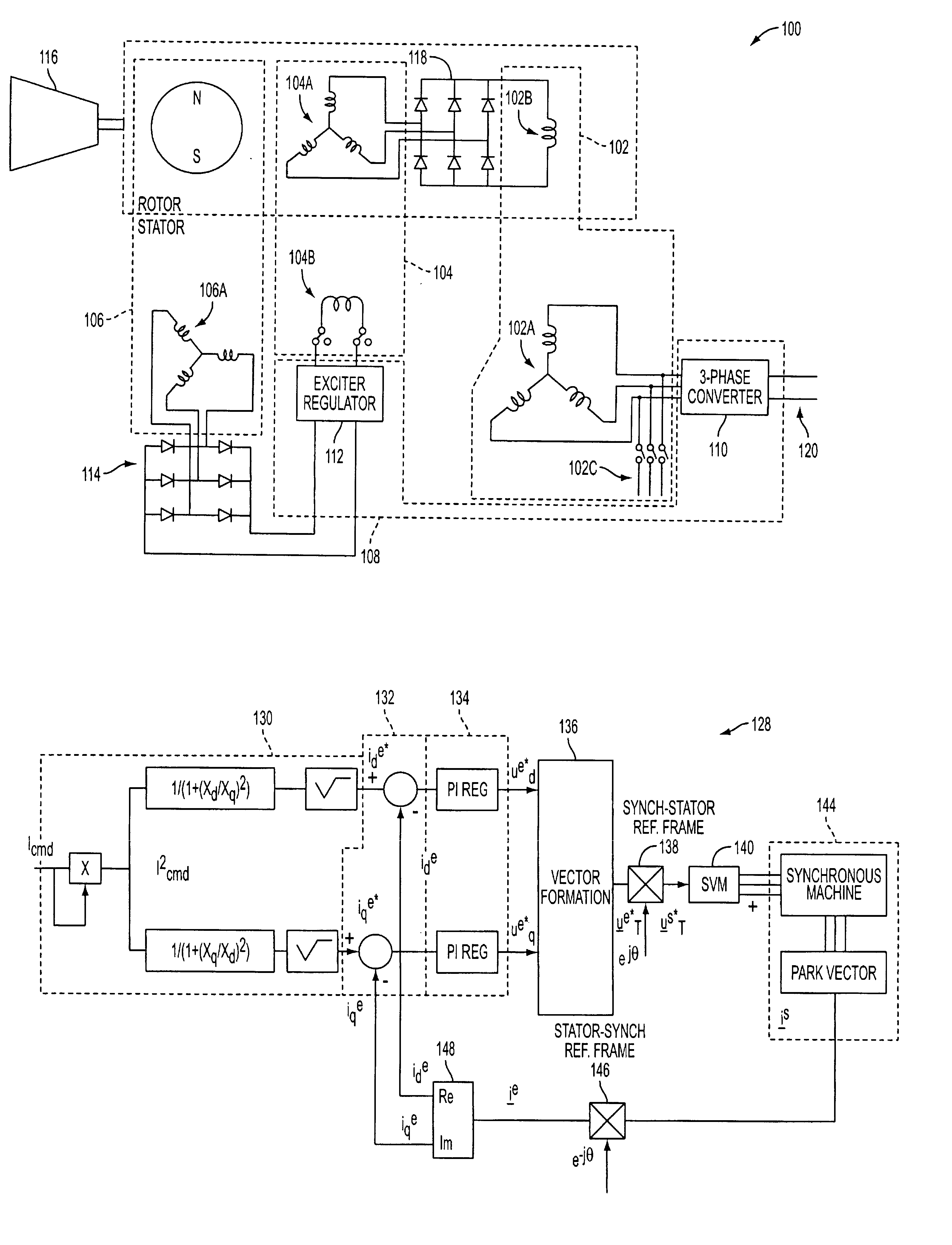
A system and method of controlling the power factor for providing either unity, leading or lagging results for the sensorless control of synchronous machines. The system and method provides an estimated angle of the phase current Park vector and uses a floating synchronous reference frame that is shifted from the estimated angle of the phase current Park vector by an angle β to allow the active control and change of the power factor during operation for applications such as producing reluctance torque of a salient pole synchronous machine during Main Engine Start (MES), and field weakening for Environmental Control Systems (ECS) and MES applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Electric start for a prime mover
InactiveUS6847194B2Increasing main field fluxIncreasing the main field fluxMotor/generator/converter stoppersTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionStart timeMagnetic reluctance
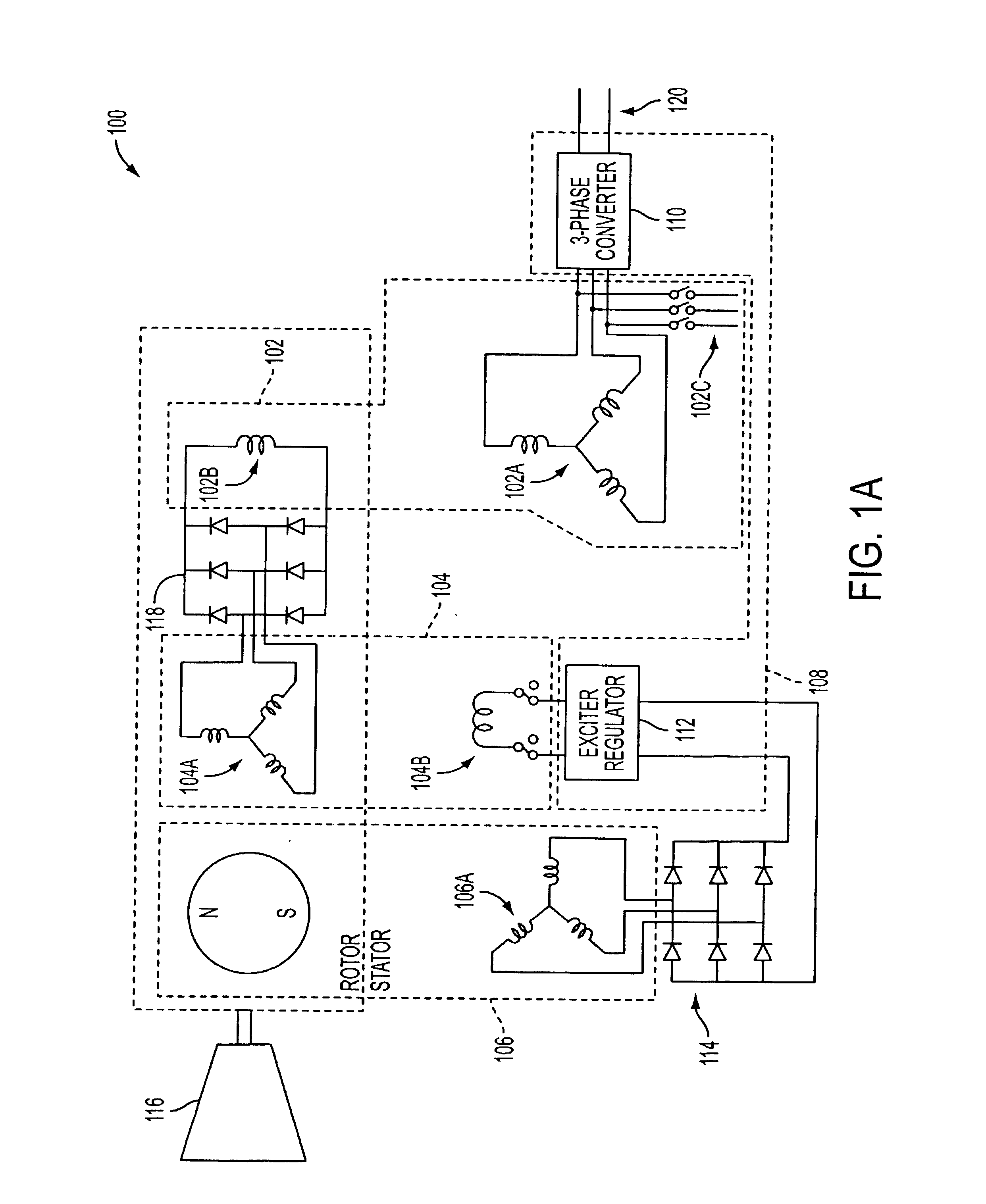
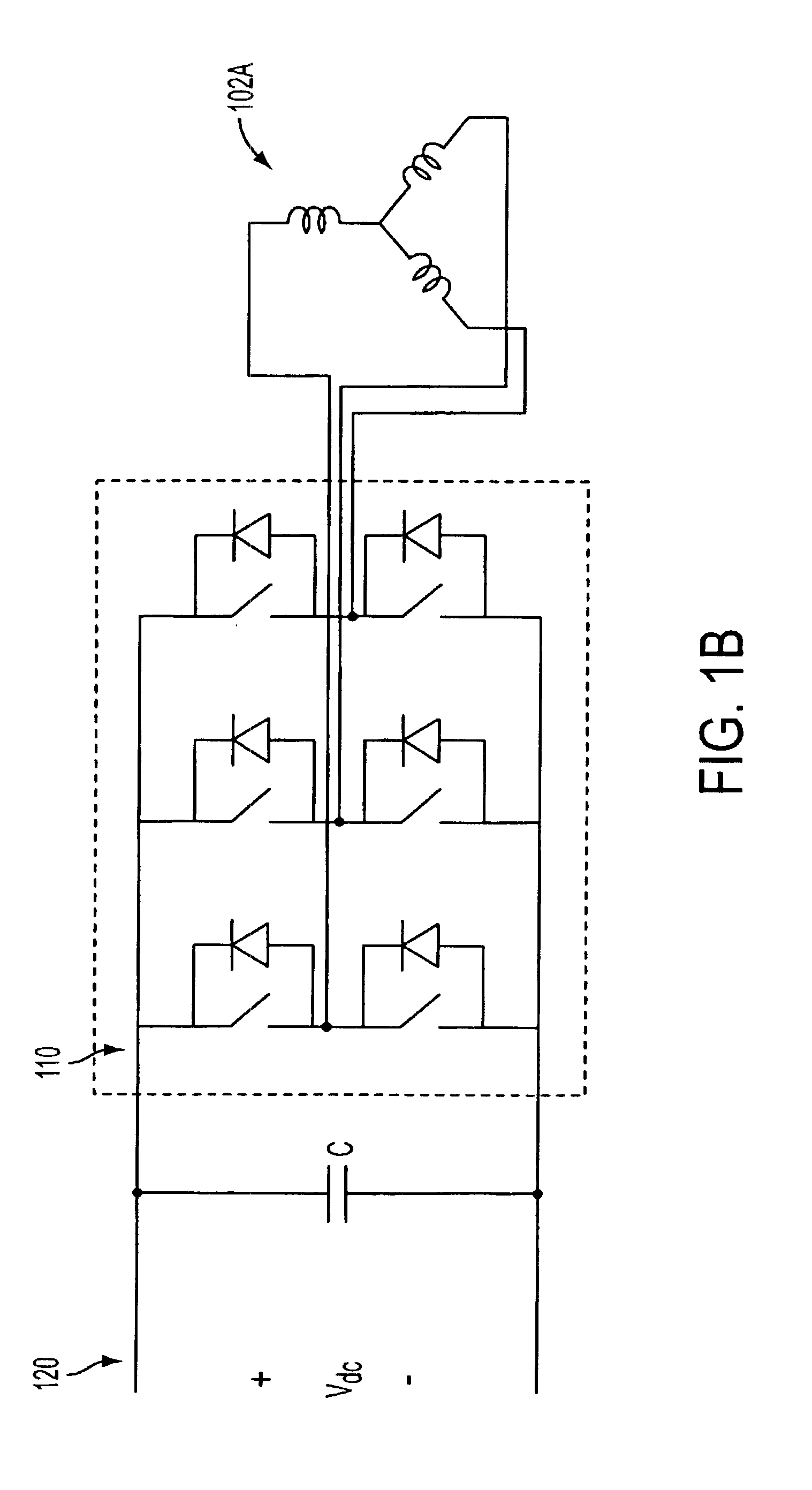
A system and method for using reluctance torque or a combination of both reluctance and reaction torque components of an attached synchronous machine (102) to accelerate a prime mover (116), such as a gas turbine engine, within a desired start time. The system selects a mode of starting operation, and thereafter applies reluctance torque through a synchronous machine (102) armature winding (102A) excitation as a single, sufficient starting force in a first mode, or staged reluctance and reaction torque through the additional excitation of the synchronous machine (102) field winding (102B) excitation in a second mode, using existing power electronics and controls.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Permanent-magnet reluctance electrical rotary machine
ActiveUS20080093944A1Improve efficiencyMotor losses to be reducedMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesConductor Coil
For an electrical reluctance rotary machine, a stator has a winding as an armature, and a rotor has permanent magnet implanting slots provided in a rotor core at lateral sides magnetic poles configured to produce reluctance torque along directions of magnetic flux passing through the magnetic poles to produce reluctance torque, and permanent magnets inserted in the permanent magnet implanting slots so as to cancel magnetic flux of the armature intersecting that magnetic flux, to control a magnetic field leaking at ends of the magnetic poles, having circumferential magnetic concavo-convex. The electrical reluctance rotary machine is configured to meet a relationship, such that1.6≤P×WpmR≤1.9where Wpm [mm] is a width of permanent magnet, R [mm] is an outer-diametrical radius of the rotor, and P is the number of poles.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
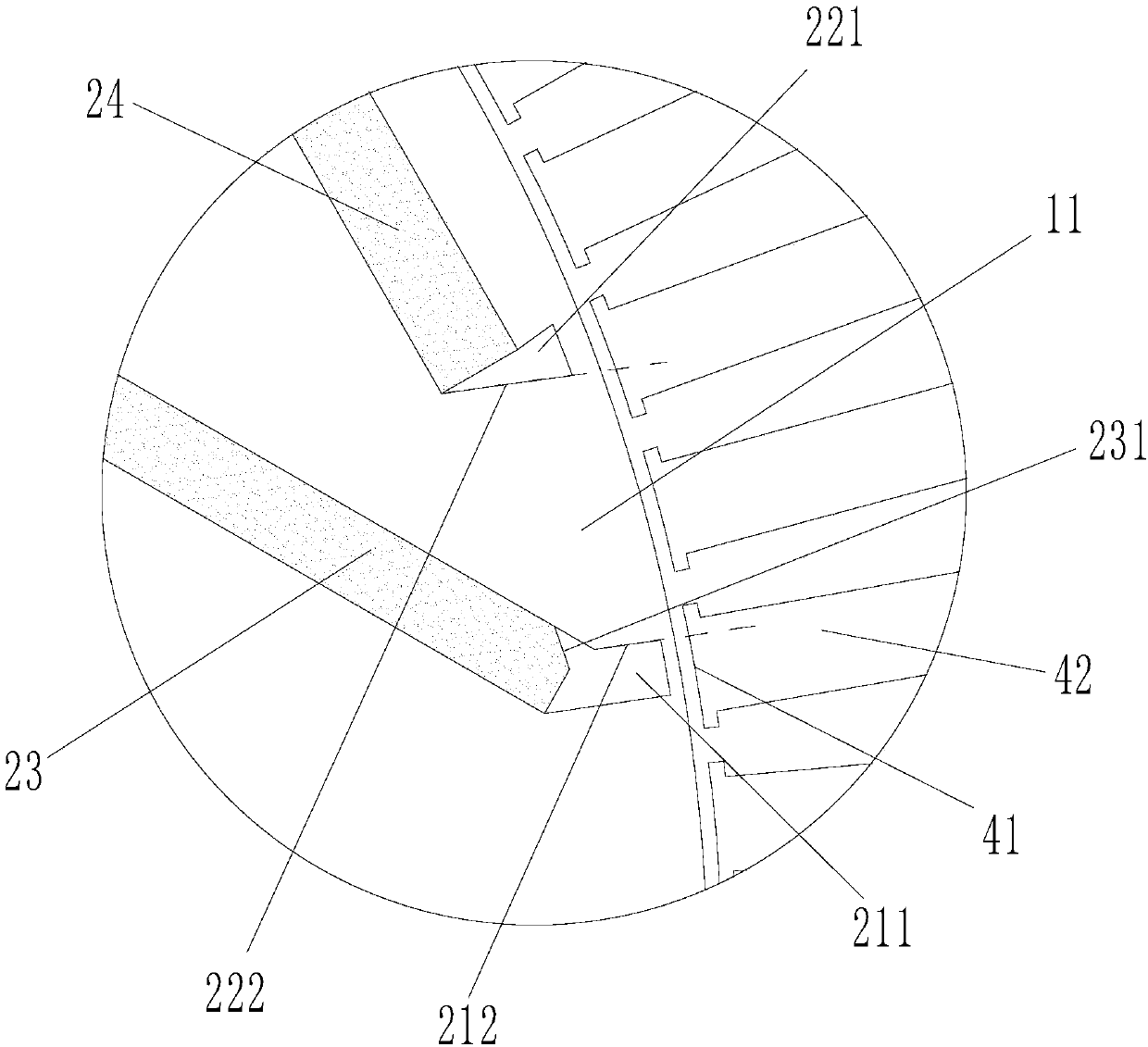
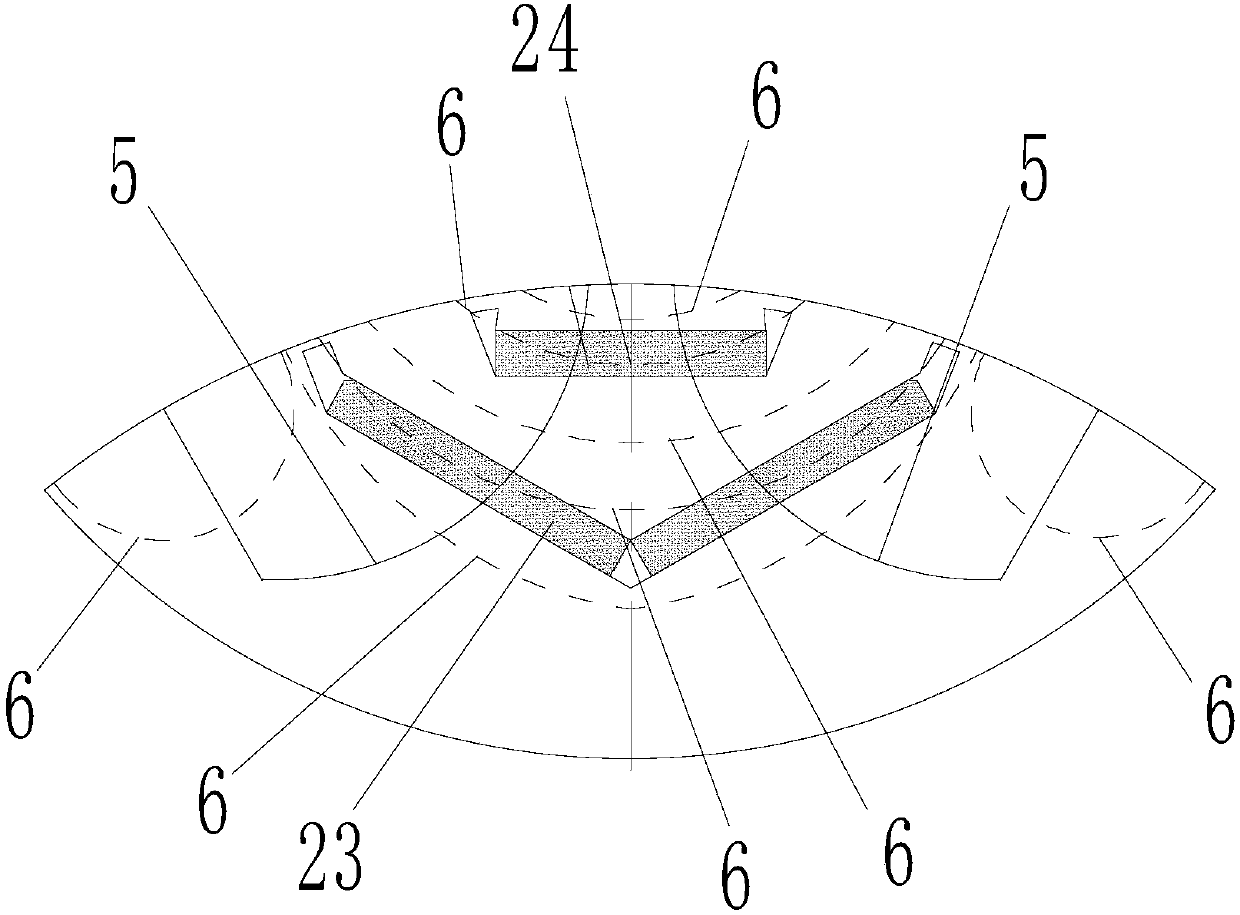
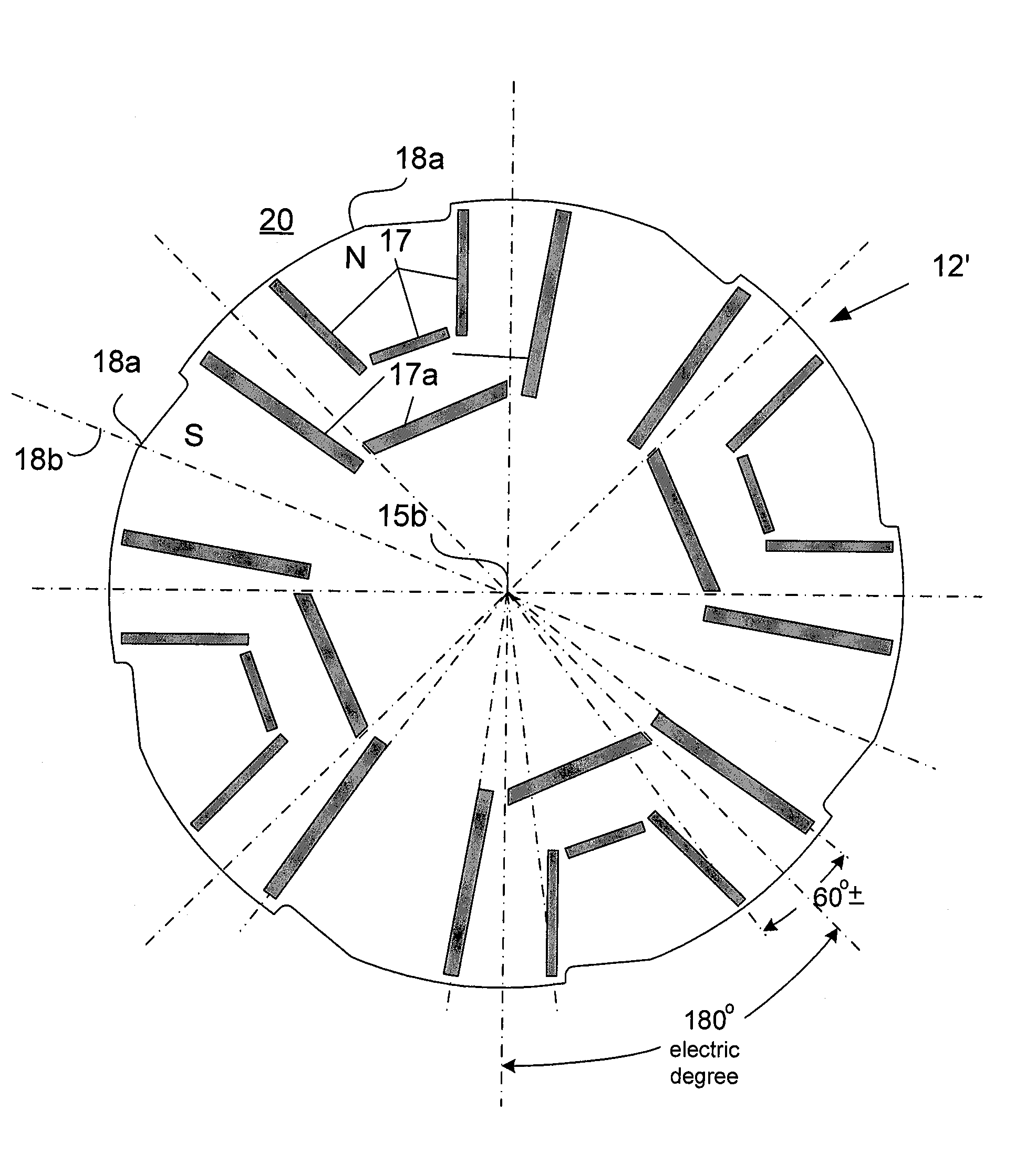
Permanent magnet machine and method with reluctance poles and non-identical PM poles for high density operation
InactiveUS20070145850A1Increase torqueHigh densitySynchronous generatorsWindingsHigh densityElectric machine
A method and apparatus in which a stator (11) and a rotor (12) define a primary air gap (20) for receiving AC flux and at least one source (23, 40), and preferably two sources (23, 24, 40) of DC excitation are positioned for inducing DC flux at opposite ends of the rotor (12). Portions of PM material (17, 17a) are provided as boundaries separating PM rotor pole portions from each other and from reluctance poles. The PM poles (18) and the reluctance poles (19) can be formed with poles of one polarity having enlarged flux paths in relation to flux paths for pole portions of an opposite polarity, the enlarged flux paths communicating with a core of the rotor (12) so as to increase reluctance torque produced by the electric machine. Reluctance torque is increased by providing asymmetrical pole faces. The DC excitation can also use asymmetric poles and asymmetric excitation sources. Several embodiments are disclosed with additional variations.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Ipm type of synchronous machine
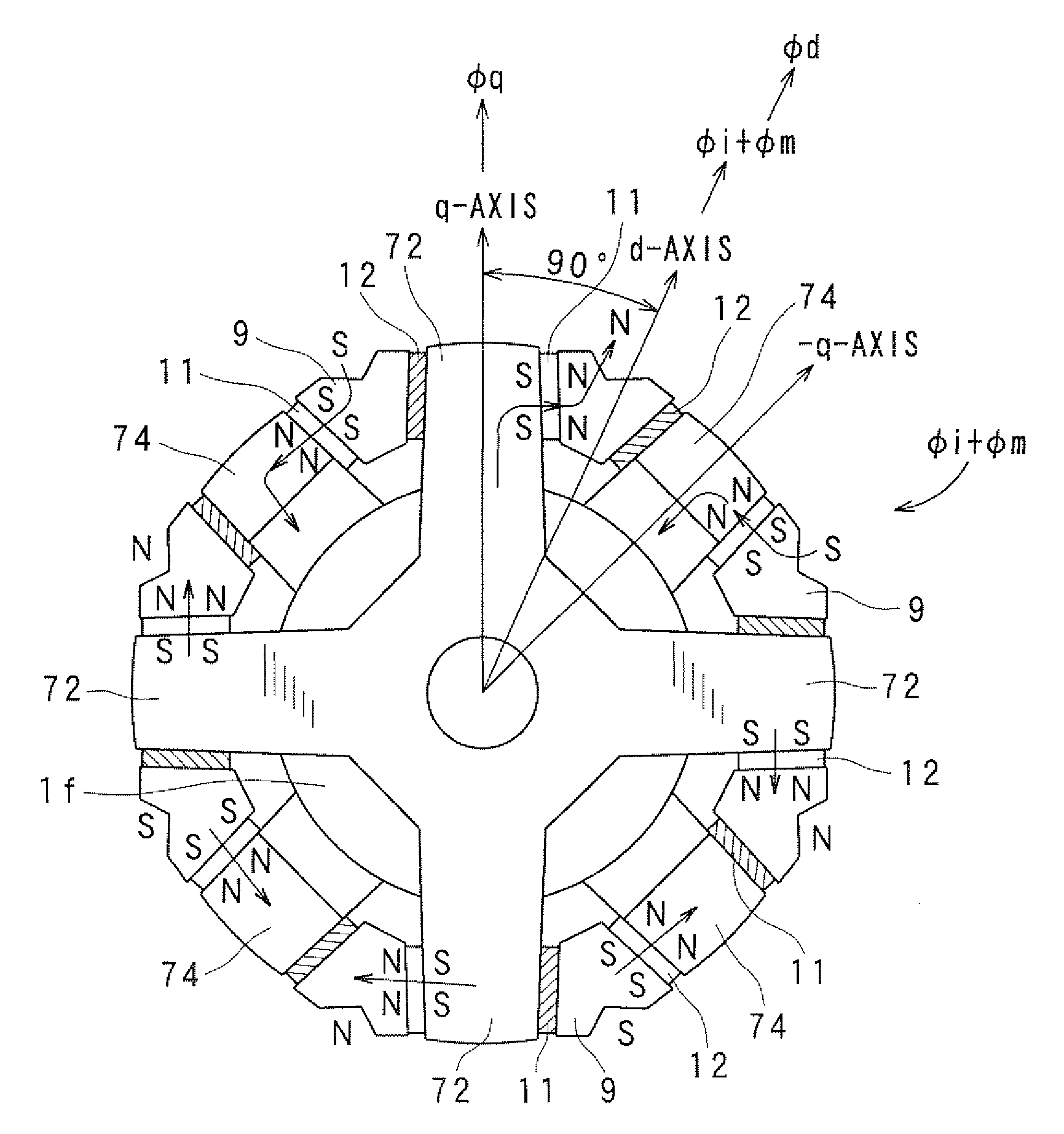
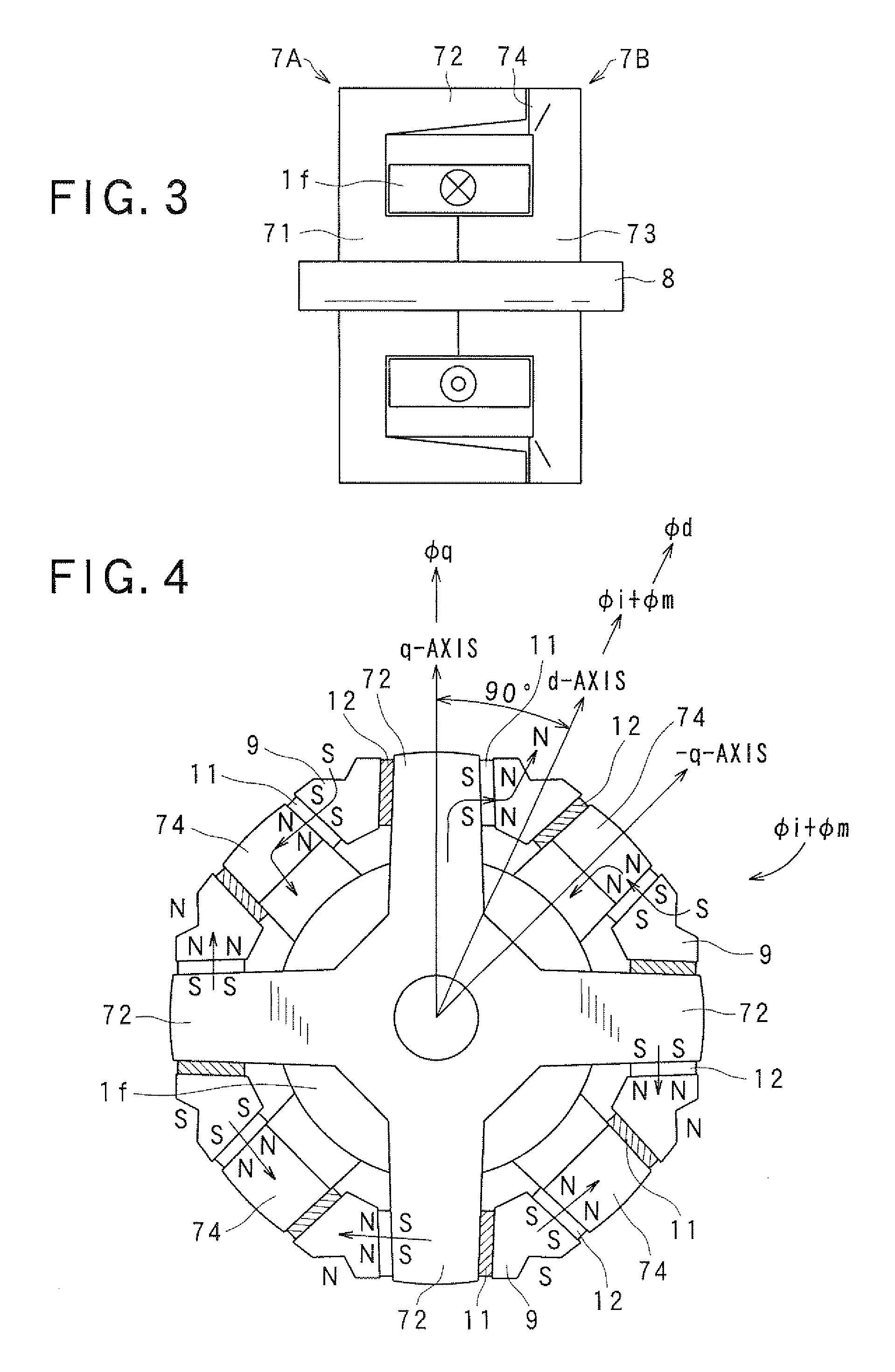
ActiveUS20090134732A1Increase output torqueMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsHarmonicMagnetic poles
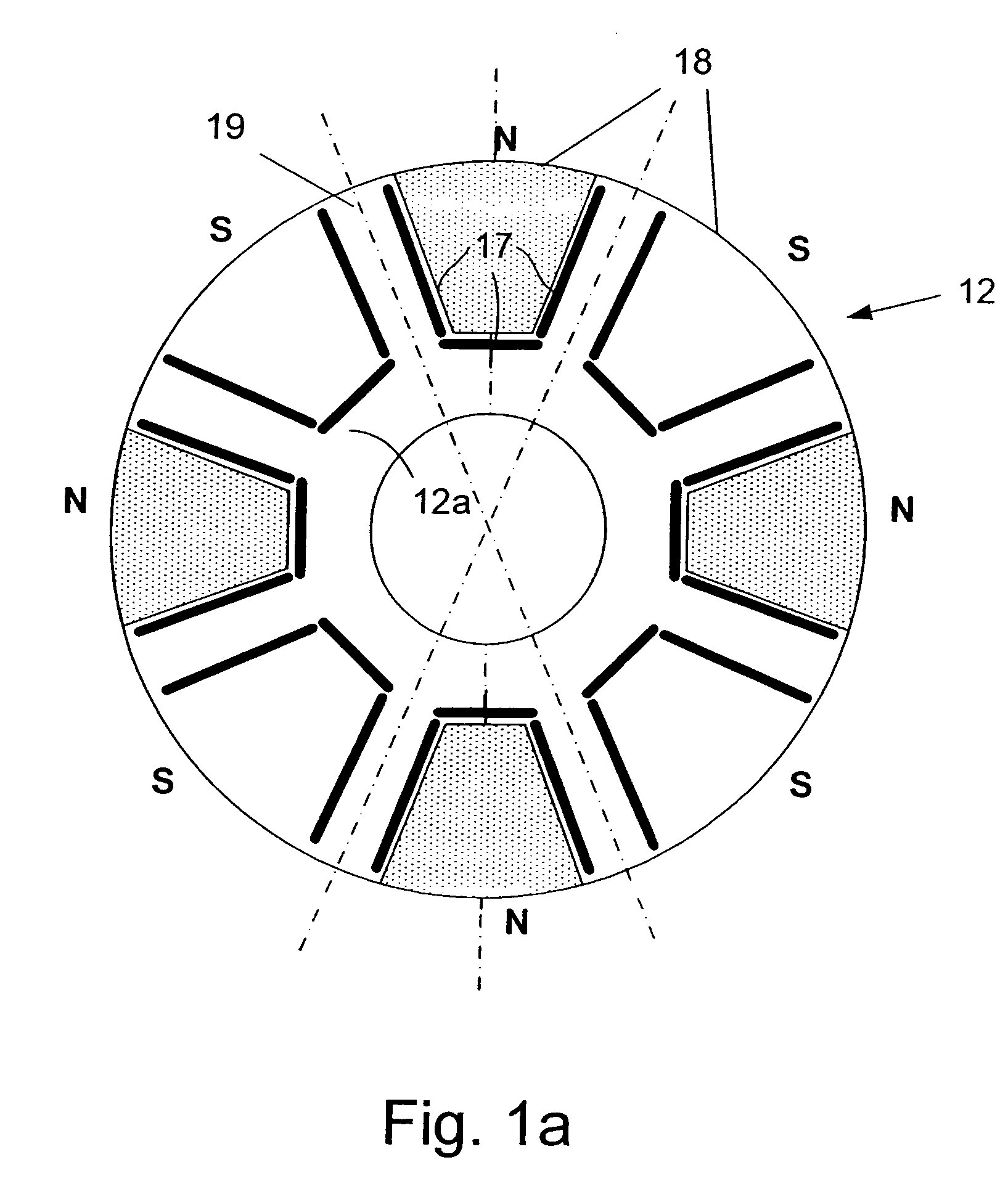
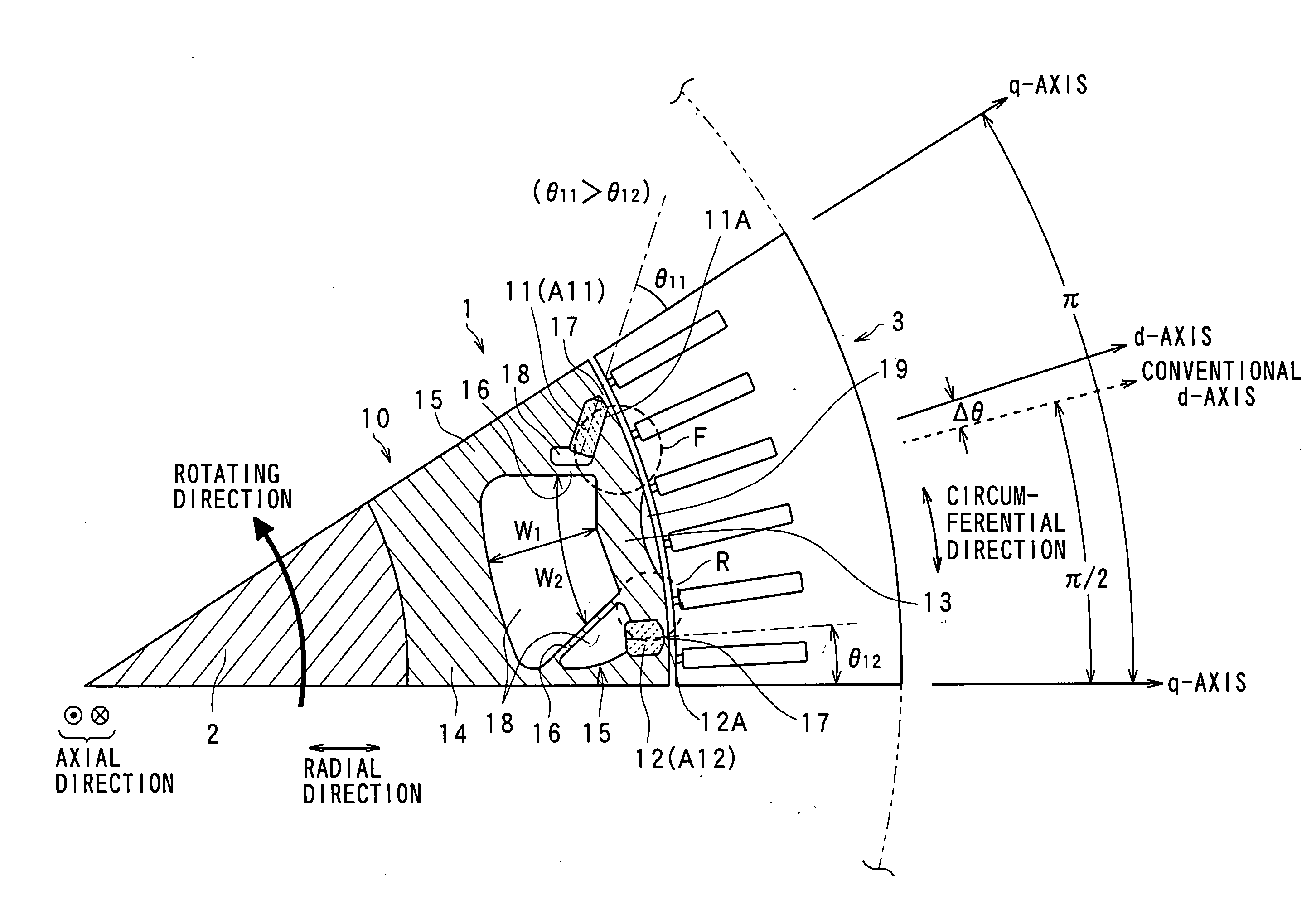
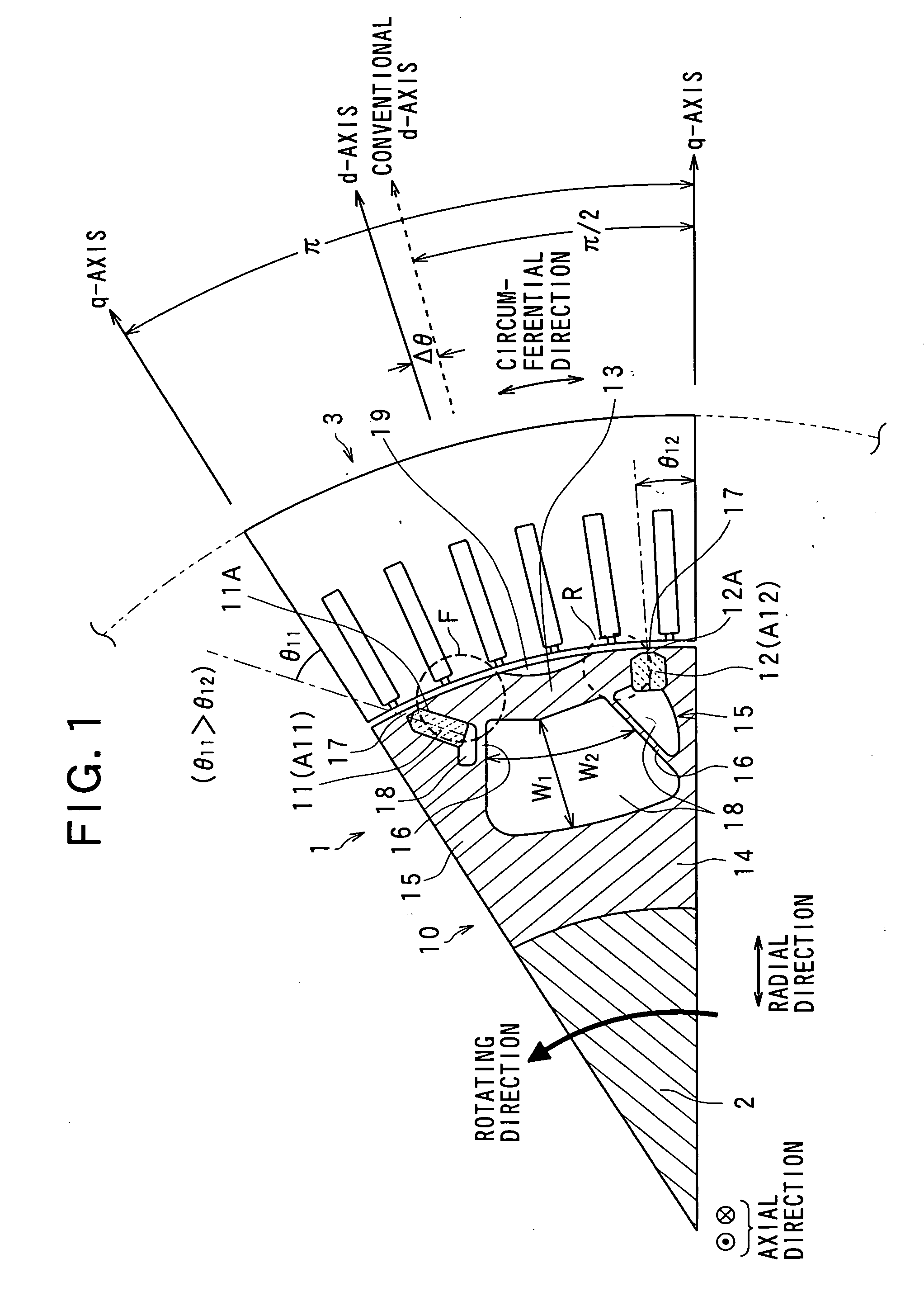
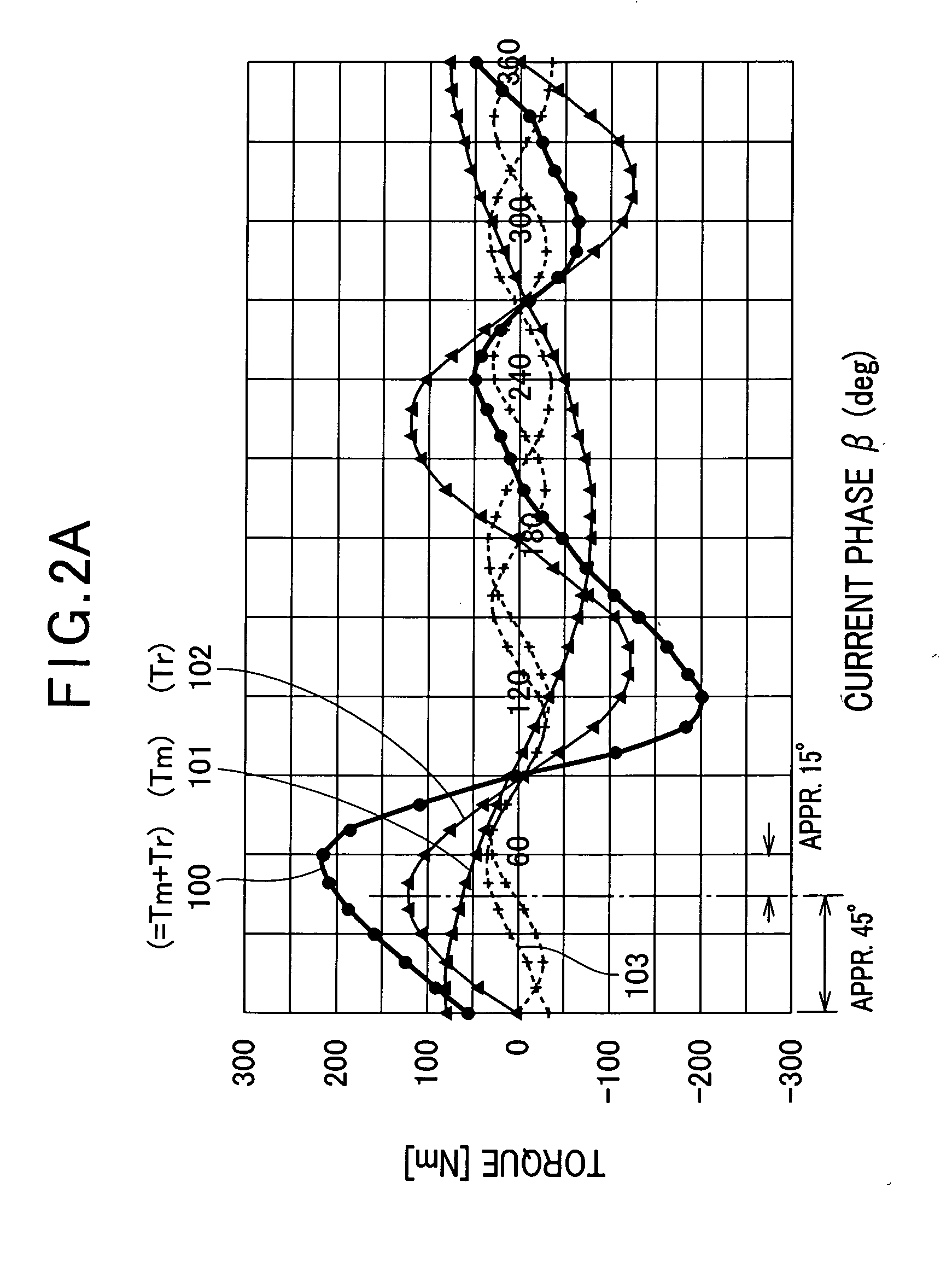
A synchronous machine comprises a stator and a rotor that faces the stator and rotates on a shaft thereof in a circumferential direction The rotor has magnetic salient poles that generate reluctance torque and magnet-originating magnetic poles that generate magnet torque by using permanent magnets embedded in the rotor, The machine comprises means for shifting a magnetically substantial central position of magnetic flux emanating from the permanent magnets in the circumferential direction, by an electrical angle π / 2 plus a predetermined angle Δθ, from a reference position taken as a central position between paired magnetic salient poles composing each magnetic pole of the machine among the magnetic salient poles. Hence a maximum amplitude of a sum between a harmonic component of the magnet torque and the reluctance torque is changed from that obtained at the reference position without the shift.
Owner:DENSO CORP
High-torque-density permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure
ActiveCN105914925AReduce manufacturing costReduce consumptionMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorTorque density
The invention discloses a high-torque-density permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure, which comprises a central rotating shaft and a rotor core, wherein P groups of through slots are evenly formed in the rotor core along the circumferential direction, each group of through slots includes three layers of U-shaped through slots formed along a radial direction of the rotor core at intervals, and a permanent magnet is embedded in each of two wings of the middle U-shaped through slot; and the middle U-shaped through slot among the three layers of U-shaped through slots is of a symmetric structure, and the outer-layer and inner-layer U-shaped through slots are each of asymmetric structure. The high-torque-density permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure can change torque characteristics of a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor, makes the maximum synthesized torque fully utilize a permanent-magnet torque component and a reluctance torque component, and increases torque density of a motor.
Owner:江苏仪能电机有限公司 +1
Brushless motor control method, brushless motor control device and electric power steering apparatus
InactiveUS20130099707A1Reducing a torque ripple of a brushless motorDiminish the torque rippleTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersBrushless motorsElectric power steering
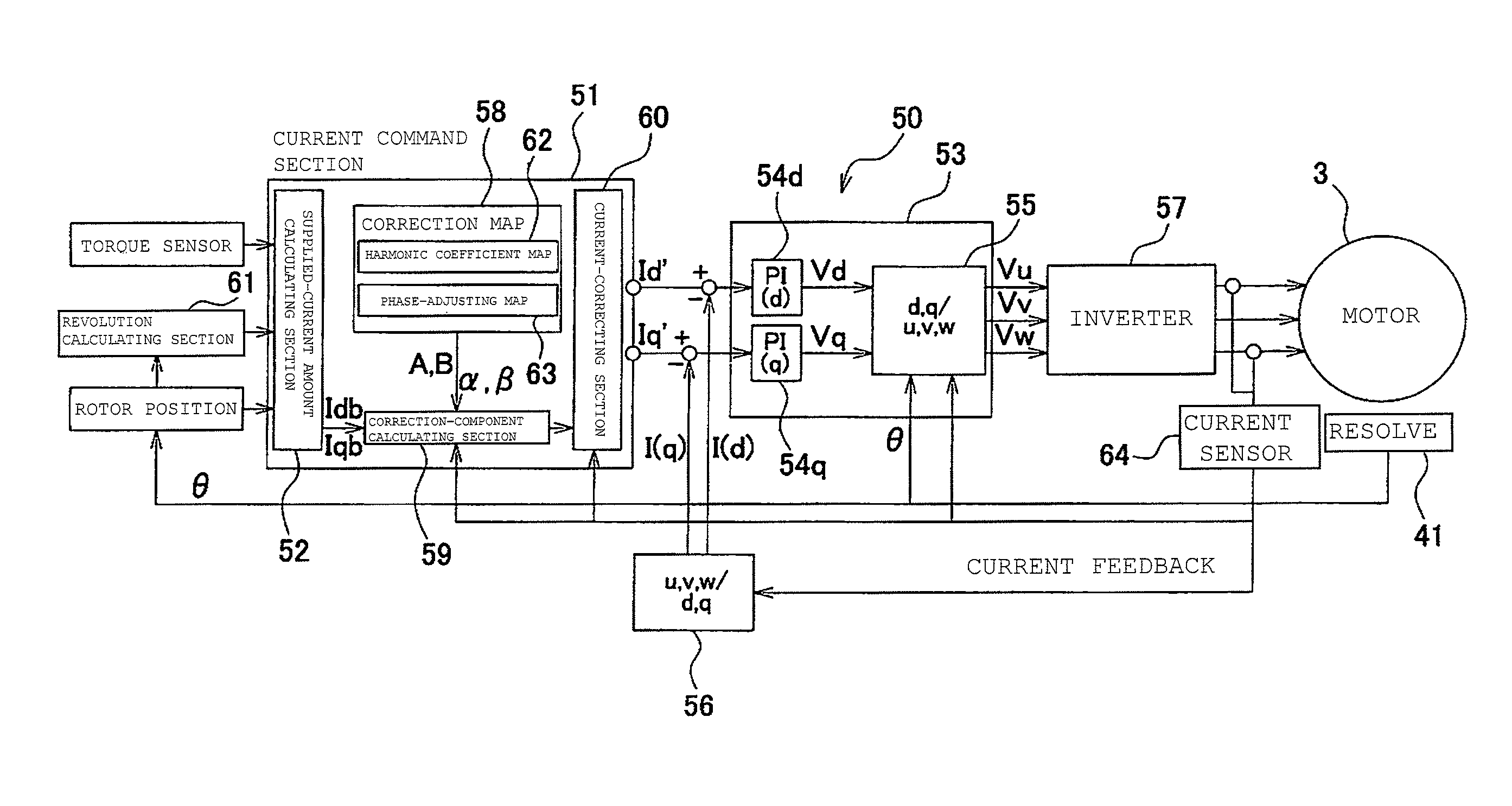
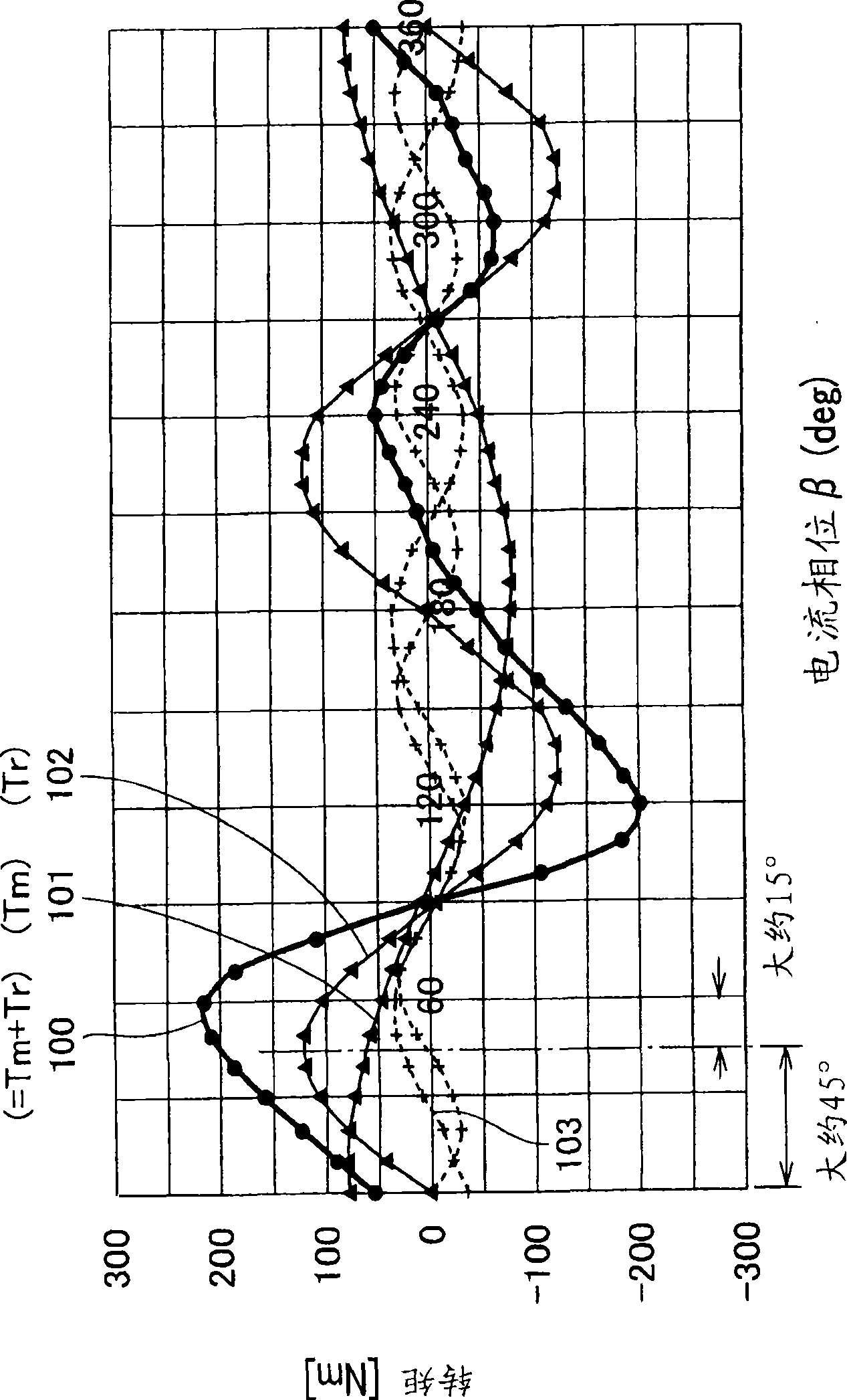
A control device (50) for an IPM-type brushless motor (3) includes a fundamental-current calculating section (52) for calculating fundamental-wave currents indicating winding current values to be set in maximum-torque control, a correction-component calculating section (59) for calculating a first harmonic component (B sin 6(θ+β)) for cancelling a torque ripple for a magnet torque and a second harmonic component (A sin 6(θ+α)) for cancelling a torque ripple for a reluctance torque based on phase-current values detected by a current sensor (64), a correction map (58) storing relationships between the phase currents and parameters (A, B, α, and β) of the first harmonic component and the second harmonic component, and a current-correcting section (60) for superimposing the first harmonic component and the second harmonic component respectively on the fundamental-wave currents to correct a current to be supplied so as to generate current command values (Id′ and Iq′).
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Synchronmaschine eines innenpermanentmagnettyps
A synchronous machine comprises a stator and a rotor that faces the stator and rotates on a shaft thereof in a circumferential direction The rotor has magnetic salient poles that generate reluctance torque and magnet-originating magnetic poles that generate magnet torque by using permanent magnets embedded in the rotor, The machine comprises means for shifting a magnetically substantial central position of magnetic flux emanating from the permanent magnets in the circumferential direction, by an electrical angle pi / 2 plus a predetermined angle Deltatheta, from a reference position taken as a central position between paired magnetic salient poles composing each magnetic pole of the machine among the magnetic salient poles. Hence a maximum amplitude of a sum between a harmonic component of the magnet torque and the reluctance torque is changed from that obtained at the reference position without the shift.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor apparatus including lundell motor having lundell-type rotor
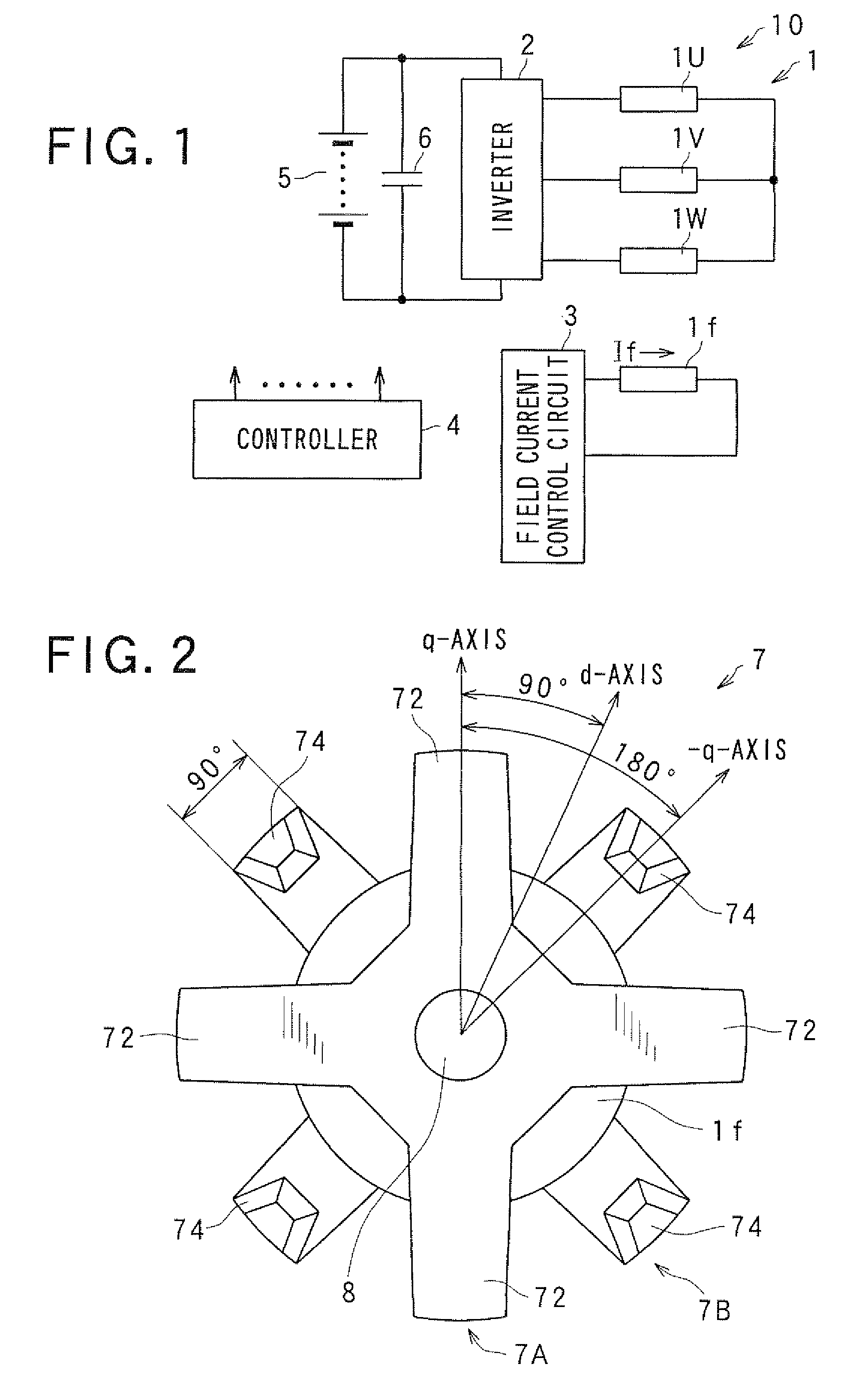
InactiveUS20090218907A1High torqueEasy to adjustSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsExcitation currentStator coil
The Lundell motor apparatus includes a controller for controlling a field current passed to a field coil of a Lundell-type rotor of a motor and an armature current passed to a stator coil of the motor in order to generate a required torque. When the field current is If, the armature current is Ia, a d-axis inductance is Ld, a q-axis inductance is Lq, a q-axis current as a q-axis component of the armature current is Iq, a d-axis current as a d-axis component of the armature current is Id, a field torque is Tf, a field flux is Φf, a reluctance torque is Tr, and a combined torque of the field torque and the reluctance torque is ΣT, the controller passes the d-axis current Id to the stator coil within a phase angle range in which the combined torque ΣT become larger than the field torque Tf in order to generate the reluctance torque Tr which is equal to (Ld−Lq)Id·Iq in addition to the field torque Tf.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Rotor for synchronous induction motor, synchronous induction motor, fan motor, compressor, air conditioner, and refrigerator
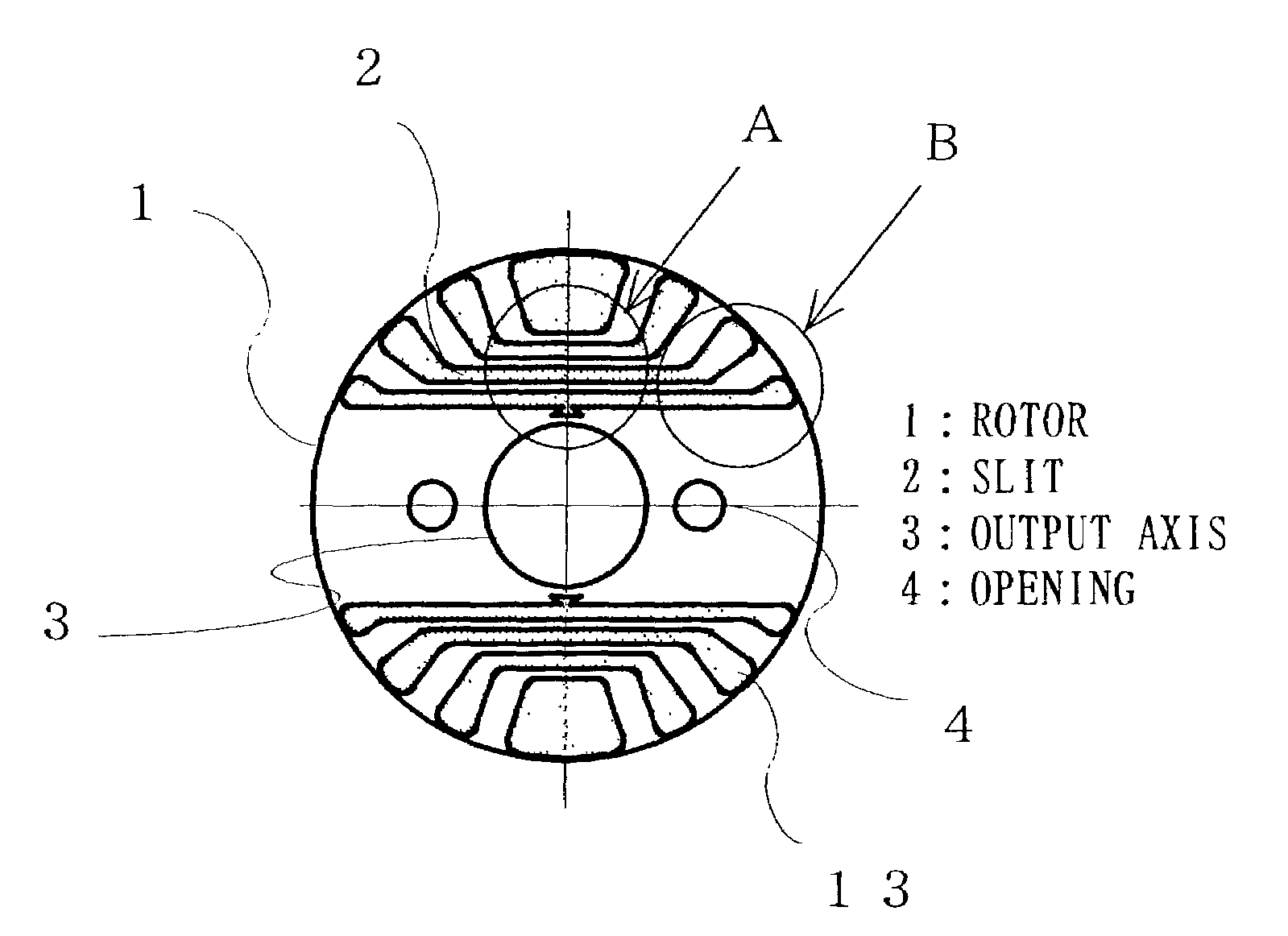
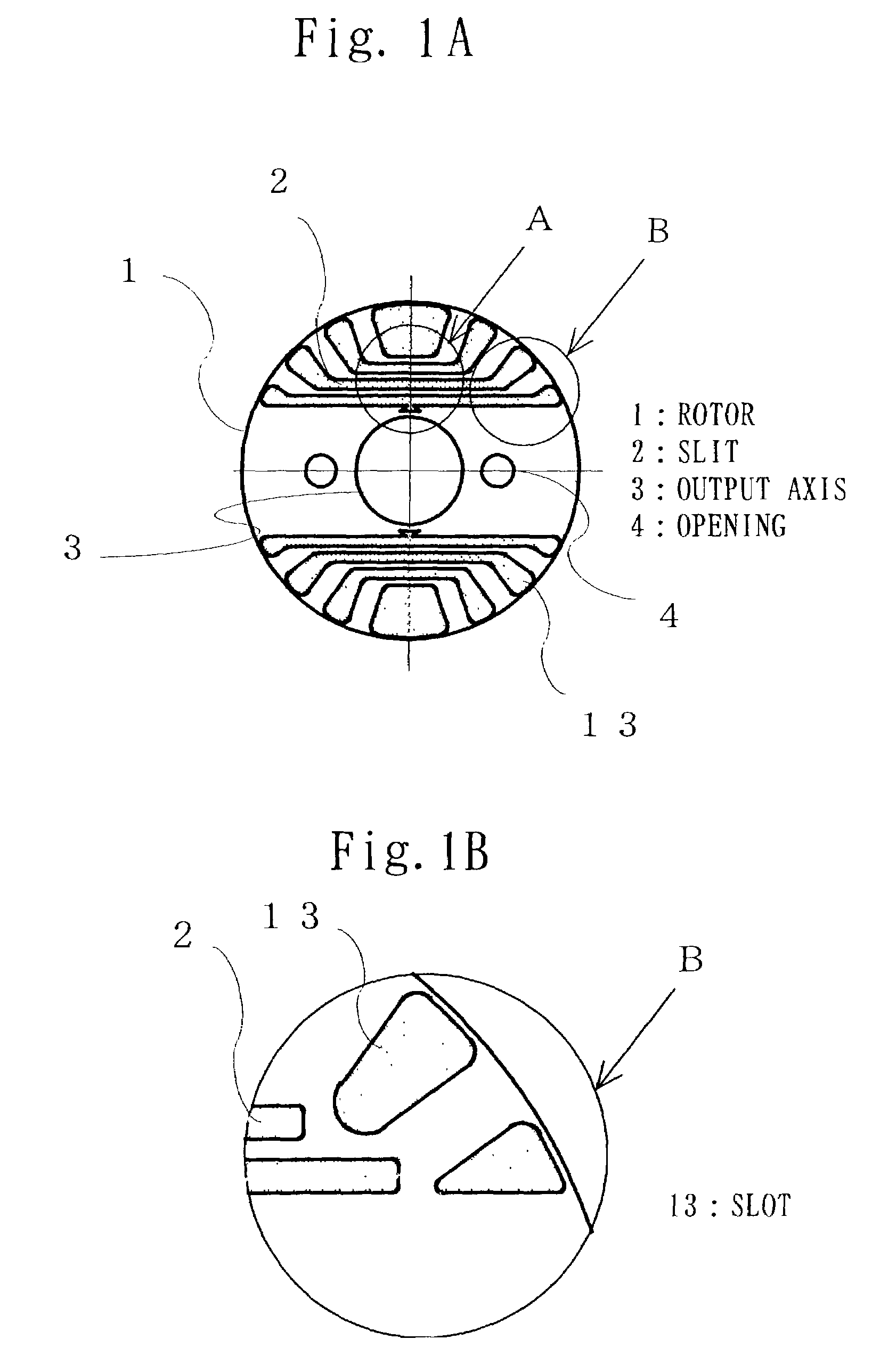
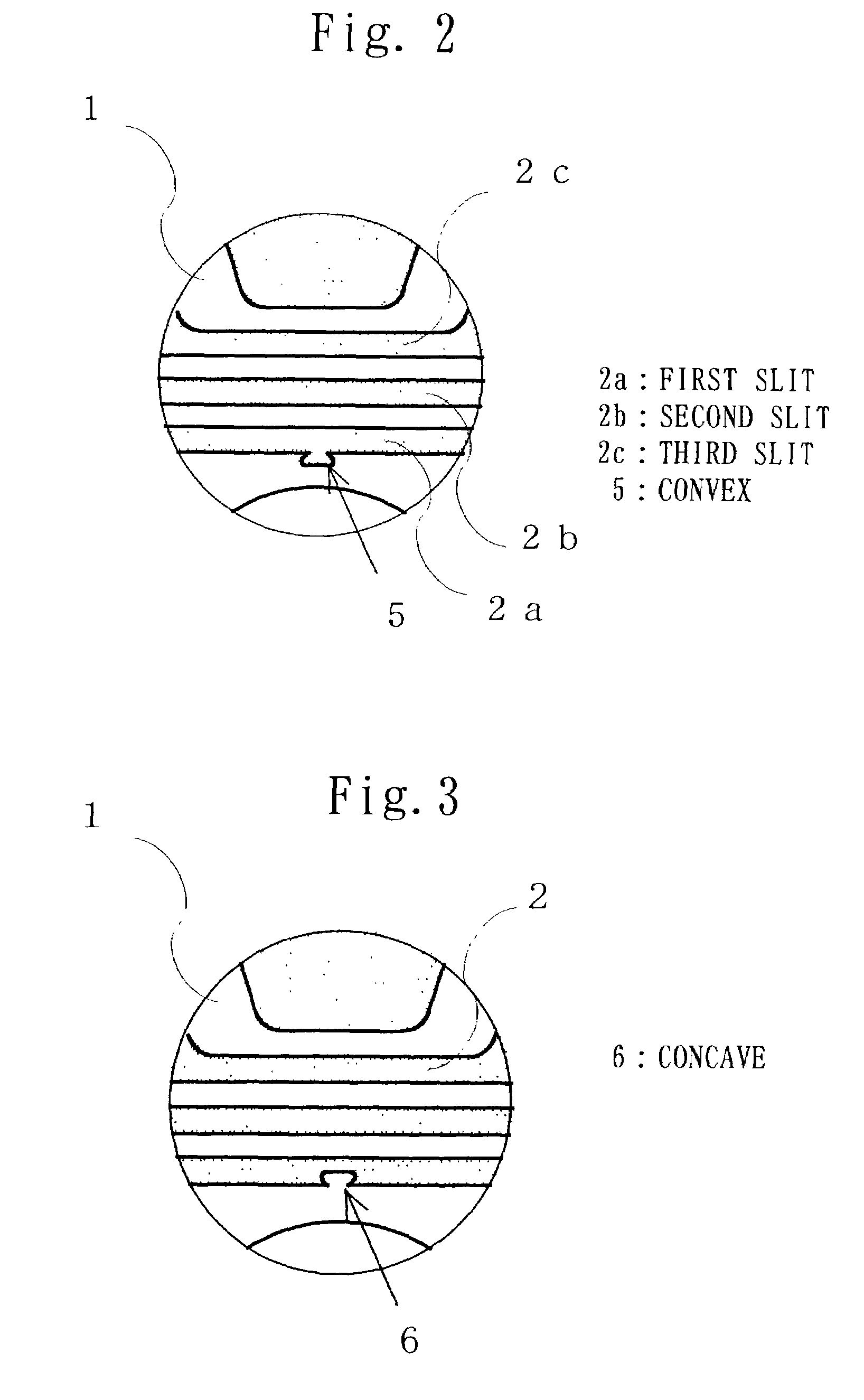
InactiveUS7112908B2Improve suppression propertiesEasy constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsPositive displacement pump componentsSynchronous motorInduction motor
There are problems in a rotor having a slit that it is difficult to increase the number of rotations of the rotor, since the centrifugal force is received at both ends of the slit, and if the connection part is made thick to increase the number of rotations, the properties of the motor is deteriorated. According to the present invention, a rotor for a synchronous motor includes a slot for generating induction torque and a slit for generating reluctance torque, the slit is filled with a filler, the slit is provided with at least one of a convex and a concave, so that the convex and the concave are formed so as to receive the centrifugal force which is generated by the rotation of the rotor and acts on a part of the rotor outside the slit and the filler so as to bulge toward the outside from the center side of the rotor by mechanical bondage of the filler and the rotor core.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Double-layer V-shaped built-in permanent magnet motor rotor for electric automobile
InactiveCN103280904AImproved air gap magnetic field waveformImprove resultant torque rippleSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsConstant powerMagnet
The invention relates to a double-layer V-shaped built-in permanent magnet motor rotor for an electric automobile. Multiple groups of permanent magnet slots which are radially arranged in an inner layer and an outer layer are uniformly arranged on the iron core of the rotor at intervals along the circumferential direction; one or more V-shaped magnetized stripy magnetic steel is embedded in each permanent magnet slot. By virtue of the optimization of structures such as the angle of polar arc of inner-layer V-shaped magnetic steel, the included angle of outer-layer V-shaped magnetic steel, the width proportion of the inner-layer magnetic steel to the outer-layer V-shaped magnetic steel and the included angle of the outer-layer forcipated permanent magnet slot and the outer-layer magnetic steel, the air-gap flux density waveform is more approximate to the sinusoidal distribution, the harmonic component is reduced, the air-gap field waveform of the motor is improved, the fundamental wave frequency of spline torque fluctuation is improved, the spline fundamental wave and the ultraharmonics torque amplitude value are reduced, the torque fluctuation caused by splines is reduced, and the synthesis torque fluctuation of the motor is greatly reduced; and meanwhile, the reluctance torque is obviously increased, the salient pole rate and flux weakening speed expanding capability of the motor are improved, a constant-power speed range wider than that of a surface-mounted permanent magnet motor can be obtained, and the driving requirement of electric and hybrid automobiles can be met.
Owner:苏州和鑫电气股份有限公司
Permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor and mounting method thereof
ActiveCN102761221AImprove efficiencyImprove utilizationManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsSynchronous reluctance motorMagnetic poles
The invention provides a permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor and a mounting method thereof. The permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor comprises a stator and a rotor, wherein the stator comprises a stator iron core and a concentrated winding, and the stator iron core comprises a plurality of convex magnetic poles; the convex magnetic poles comprise magnetic pole teeth and tooth boots, and the widths of the tooth boots are larger than the widths Lc of the magnetic pole teeth; the rotor comprises a rotor iron core and a plurality of permanent magnet groups, and a plurality of permanent magnet slot groups are uniformly distributed on the rotor iron cores; each permanent magnet slot group comprises at least two layers of permanent magnet slots, and each permanent magnet group comprises a permanent magnet arranged in a corresponding permanent magnet slot; the permanent magnets in each permanent magnet slot group have the same polarity, and the polarities of two adjacent permanent magnet groups are opposite; and a relation between a minimum interlayer distance g between two adjacent layers of permanent magnets in each permanent magnet group and the widths T of the tooth boots is disclosed in the specification. According to the permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor, the reluctance torque is maximally utilized, so that the efficiency of the motor reaches a higher level.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Brushless direct current reluctance starter generator
ActiveCN103780042ASimple structureWork reliablyDynamo-electric machinesGenerator control by field variationStarter generatorConductor Coil
The invention discloses a brushless direct current reluctance starter generator. The generator comprises a three-phase armature winding, an exciting winding, a winding series-parallel switching switch, a stator iron core, a rotor iron core, a shaft, a position sensor, a bridge converter and a controller, wherein armature coils, wound intensively, are wound on each pole of the stator iron core; excitation coils are wound by crossing three stator poles; and the armature coils in the same phase are in series or parallel connection to form a group. According to the starter generator, a reluctance structure is used; no winding is generated on the rotor; the generator is simple in structure and reliable to operate; excitation current can be adjusted to keep stability of output voltage during generating; when the generator is started, the generator rotates by means of a reluctance torque; the armature coils are connected in series; a large starting torque is achieved; the generator is applicable to operation at a low speed; the excitation winding is used for generating a magnetic field during generating; the armature coils are connected in parallel; small armature reaction is generated; and the generator is applicable to operation in a high speed. The brushless direct current reluctance starter generator is very applicable to transport tools comprising vehicles.
Owner:ANHUI ZHONGCI HI TECH
Motor with separated permanent magnet torque and reluctance torque and its optimal efficiency control
ActiveUS20180323665A1Reduce processing difficultyGreater reluctance torqueElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSurface mountingReluctance motor
The invention proposes a new motor with separated permanent magnet torque and reluctance torque. Meanwhile, the optimal efficiency control method for this motor is proposed. This invention belongs to the field of motor and its drive system. The proposed motor includes 3 stators and 1 rotor (composed of 2 axial rotors and 1 radial rotor), the radial stator employs distributed winding, the axial stator adopts concentrated winding. The distributed winding and the radial reluctance rotor structure contribute to higher reluctance torque, while the concentrated winding and the surface mount permanent magnet structure offer higher permanent magnet torque. In the view of the magnetic circuit, the axial magnetic circuit generates the permanent magnet torque, and the radial magnetic circuit generates the reluctance torque. By using the decoupling of axial and radial magnetic circuits, the separation and the independent control of the permanent magnet torque and the reluctance torque are realized. Each stator and rotor of the invention can be processed independently, and the modular installation can be processed, thereby reducing the difficulty of the motor processing.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Brushless DC motor
InactiveUS6867526B2Reduce decreaseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsBrushless motorsMagnetic reluctance
A bridge (8) in conformity with a tooth opening angle of the stator (1) is provided between a permanent magnet (5) and a permanent magnet (5) in a rotor (4), so that a magnetic flux for a reluctance torque is made to pass an inner side of the permanent magnet (5). An opening angle of each of ribs (7) on both sides of the permanent magnet (5) is set to be equal to or smaller than the teeth interval opening angle and equal to or larger than a half thereof. Thereby, reluctance of the rib (7) against a magnetic flux in a circumferential direction is increased and leakage of the magnetic flux of the permanent magnet (5) is prevented.
Owner:KOYO SEIKO CO LTD
Axial motor
InactiveUS20120104880A1Increase productionIncrease torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMiniaturizationEngineering
An axial motor includes a rotor arranged between a pair of stators with coils. In the rotor, a plurality of permanent magnets sandwiched between pairs of first magnetic materials and a plurality of second magnetic materials are alternately arranged in a rotation direction while gaps are provided therebetween. Since the permanent magnets are sandwiched by the first magnetic materials in the thus constructed axial motor, a field-weakening control can be performed. Since the second magnetic materials are provided, a reluctance torque can be generated. Further, since the gaps are provided, more magnetic fluxes generated from the permanent magnets can be caused to flow toward the coils. Therefore, the thus constructed axial motor can achieve a higher output, higher torque, higher efficiency, and miniaturization.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
Brushless DC motor
InactiveUS20050134134A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic fluxDC motor
A bridge (8) in conformity with a tooth opening angle of the stator (1) is provided between a permanent magnet (5) and a permanent magnet (5) in a rotor (4), so that a magnetic flux for a reluctance torque is made to pass an inner side of the permanent magnet (5). An opening angle of each of ribs (7) on both sides of the permanent magnet (5) is set to be equal to or smaller than the teeth interval opening angle and equal to or larger than a half thereof. Thereby, reluctance of the rib (7) against a magnetic flux in a circumferential direction is increased and leakage of the magnetic flux of the permanent magnet (5) is prevented.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Self-starting darrieus wind turbine
InactiveUS20110031756A1Low possible frictionLow starting frictionWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesElectronic controllerMagnetic bearing
A Darrieus rotor supported by a bearing system to rotate about a vertical axis for capturing wind energy has an alternator that is directly-driven by the rotor and converts rotational power from the rotor into electrical power. An electronic controller controls the electrical load applied to the alternator and the power output from the alternator to an output. The alternator is constructed having a substantially constant reluctance torque for all angular positions of rotation of the rotor. The bearing system includes upper and lower rolling element mechanical bearings that provide radial support of the rotor against wind load and axial support of the rotor, and a magnetic bearing that provides axial lift that reduces the axial load on the mechanical bearings and reduces the starting torque for rotating the rotor. The electronic controller applies minimal electrical load to the alternator until the rotor is at a rotational speed greater than a deadband for the rotor in the instantaneous wind speed, whereby the electronic controller, the alternator and the bearing system together avoid retarding forces that would otherwise prevent passive self-starting.
Owner:MARIAH POWER
Reluctance type alternating pole permanent magnet motor
PendingCN107659101ATake advantage ofIncrease the q-axis inductanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet motorInductance
The invention provides a reluctance type alternating pole permanent magnet motor, which comprises a rotor, wherein the rotor is provided with at least two permanent magnet poles which take an axis ofthe rotor as a center and are uniformly distributed along the circumferential direction of the rotor, each permanent magnet pole comprises inner-layer magnetic slots and outer-layer magnetic slots which are sequentially arranged and mutually separated along the radial direction of the rotor; and each inner-layer magnetic slot is internally provided with an inner-layer permanent magnet matched withthe inner-layer magnetic slot, and each outer-layer magnetic slot is internally provided with an outer-layer permanent magnet matched with the outer-layer magnetic slot. The reluctance type alternating pole permanent magnet motor has the advantages that the difference between q-axis inductance and d-axis inductance can be improved, thus the reluctance torque is enabled to be fully utilized, and the electromagnetic torque is enabled to be improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Permanent magnet machine and method with reluctance poles and non-identical PM poles for high density operation
InactiveUS7719153B2Increase torqueHigh densitySynchronous generatorsWindingsHigh densityElectric machine
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Permanent magnet reluctance type in-wheel motor
InactiveCN103001360AReduce torque rippleGuaranteed stabilityTorque ripple controlMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectrical polarityMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a permanent magnet reluctance type in-wheel motor, which comprises an outer rotor and an inner stator, wherein a three-phase winding is arranged on the inner stator; magnetic steel is uniformly distributed along the circumferential direction of the outer rotor; the permanent magnet reluctance type in-wheel motor is characterized in that grooves arranged at intervals are formed on the inner circumferential surface of the outer rotor; the magnetic steel is embedded inside the grooves; the cross section of the magnetic steel is rectangular; the polarity of all magnetic steel facing to the inner stator is the same; a magnetic conduction salient pole is formed between adjacent grooves; the magnetic conduction salient poles and the magnetic steel are arranged alternately at intervals; the curve of the cross section of the magnetic conduction salient pole facing to one side end of the inner stator is convex arc-shaped; and the number of grooves and the number of magnetic poles in the outer rotor adopt the combination with close grooves. The permanent magnet reluctance type in-wheel motor has the advantages that the using amount of magnetic steel can be efficiently reduced and the output of reluctance torque is improved under the precondition of not increasing process complexity; and the magnetic conduction salient poles adopt arc-shaped convex surfaces, so that the motor torque pulsation is efficiently reduced, the stability of motor running is ensured, and the product reliability is improved.
Owner:吴正林
Permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor, rotor of motor and mounting method of motor
ActiveCN102761222AImprove efficiencyImprove utilizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous reluctance motorMagnet
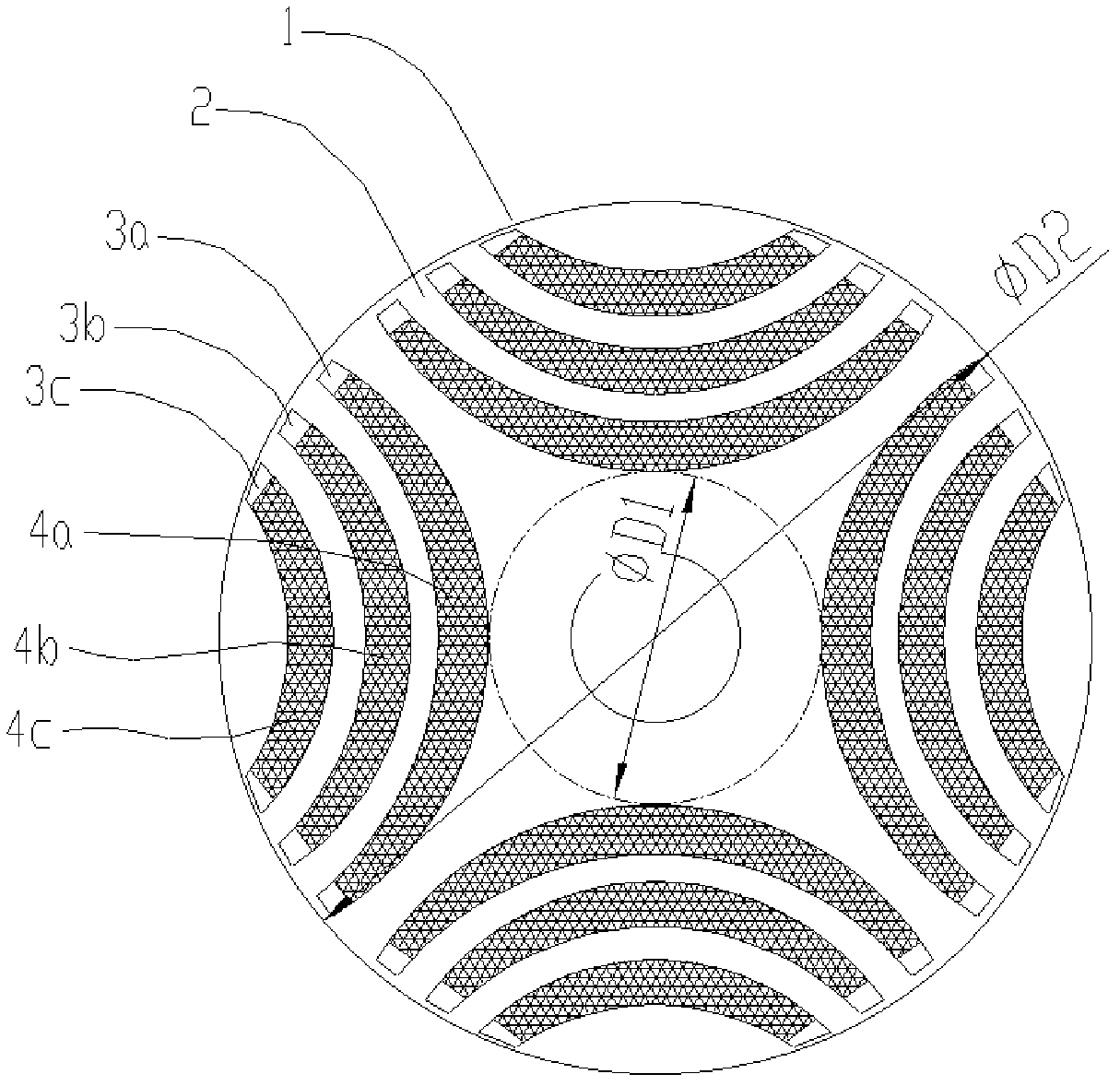
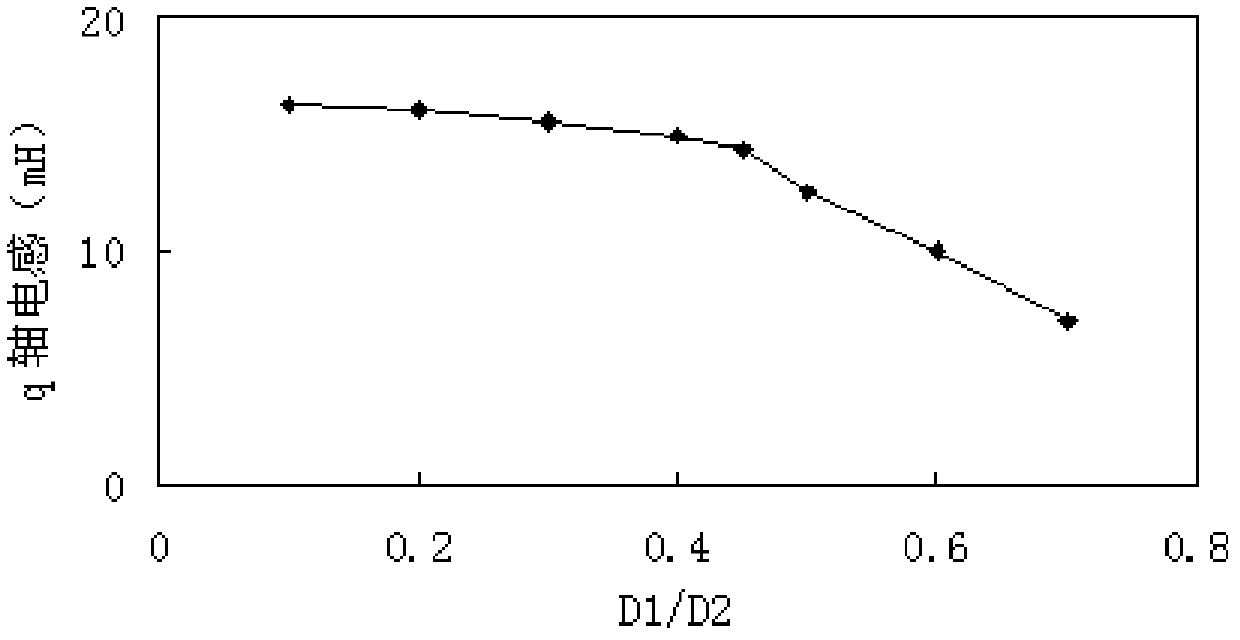
The invention provides a permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor, a rotor of the motor and a mounting method of the motor. The rotor of the permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor provided by the invention comprises a rotor iron core and four permanent magnet groups; four permanent magnet groove groups are uniformly distributed on the rotor iron core along the circumferential direction by using the rotor centre of the rotor as the centre of a circle; each permanent magnet groove group comprises at least two layers of permanent magnet grooves; each permanent magnet group comprises at least two layers of permanent magnets which are cooperatively embedded in the permanent magnet grooves of the corresponding permanent magnet groove groups, respectively; and the permanent magnets in each permanent magnet group are of the same polarity, and the polarities of two adjacent permanent magnet groups are opposite, wherein the diameter D1 of an internal circle tangential tothe vertexes, facing the rotor centre, of the innermost-layer permanent magnets in the four permanent magnet groups and the diameter D2 of the rotor meet the following relationship: D1 / D2 is not lessthan 0.3 and not more than 0.45. According to the permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor, the rotor of the motor and the mounting method of the motor, the placement depths of the permanent magnet layers of the motor rotor are designed so as to ensure that the reluctance torque of the motor is utilized to the maximum.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Switched Reluctance Machine And Method Of Operation Thereof
InactiveUS20090021192A1Eliminate the problemIncreased coil winding spaceAC motor controlMagnetic circuitControl mannerCentre of rotation
The present invention provides an S SRM (switched reluctance machine), which supports one or more phases and each phase comprises a stator, a rotor and coils. The stator is hollow, cylindrical and comprises stator poles extending inwards, such that a recess is formed between adjacent stator poles. The coils are wound on the stator poles and occupy the recess. The rotor is positioned inside the stator and has poles extending outwards. The rotor and stator poles subtend an angle having a maximum value of 0.5 electrical pole pitches at a center of rotation. The different phases are distributed along the axis of the S SRM. The rotor is rotated by a reluctance torque generated by energizing a phase in a current controlled manner until the rotor rotates through a minimum commutation angle required to maintain motion; de-energizing the phase by freewheeling it by using the energy stored in it and simultaneously energizing a second sequentially adjacent phase.
Owner:KUDLIGI SRINIVAS
Permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure having high torque density
ActiveCN105958692AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsSynchronous motorElectric machine
The invention discloses a permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure having high torque density. The permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure comprises a central rotating shaft and a rotor iron core; the rotor iron core is uniformly provided with P groups of through grooves along the circumferential direction; each group of through grooves comprises three layers of U-shaped through grooves arranged in the radial direction of the rotor iron core at intervals; and a permanent magnet is embedded in the straight bottom side of each U-shaped through groove. By means of the permanent magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure disclosed by the invention, the permanent magnet torque component and the reluctance torque component are sufficiently utilized in the synthesis torque of a motor; and thus, the torque density of the motor is increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Permanent-magnet synchronous motor and compressor with same
InactiveCN104600939AIncrease the q-axis inductanceLarge reluctance torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsPiston pumpsSynchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a permanent-magnet synchronous motor and a compressor with the same. The permanent-magnet synchronous motor comprises a stator and a rotor arranged inside the stator, the rotor is provided with a plurality of groups of magnet grooves distributed circumferentially, each group of magnet grooves comprises an outer groove and an inner groove, and on the cross section of the rotor, the outer grooves extend along the circumferential direction of the rotor, and the V-shaped inner grooves are positioned on the radial inner sides of the outer grooves. The permanent-magnet synchronous motor has the advantages that the rotor is provided with the outer grooves extending along the circumferential direction of the rotor, and the V-shaped inner grooves positioned on the radial inner sides of the outer grooves, so that q-axis inductance of the motor can be enhanced effectively, a difference value between the q-axis inductance and d-axis inductance is further increased, and reluctance torque of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor can be increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIZHI COMPRESSOR +1
Motor rotor and its mfg. method, motor, brushless motor, compressor, refrigerator and air conditioner
InactiveCN1420606AWon't burn outReduce circulationMagnetic circuit rotating partsPositive displacement pump componentsBrushless motorsInduction motor
To provide a rotor for synchronous induction motor capable of preventing the lowering of output or efficiency due to increasing magnetic resistance even if a gas venting hole is formed for using a hermetic compressor. This rotor includes slots for generating induction torque and slits for generating reluctance torque. The slot and the slits are filled with aluminum. The filling aluminum is shorted by end ring at both ends of the rotor, and a non-filling section axially passed through the slit and not filled with aluminum is provided.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Low-torque-ripple high-efficient permanent magnetic motor stator and rotor structure
ActiveCN104882978AReduce Flux LeakageIncrease profitMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEddy currentMagnetic leakage
The invention relates to a low-torque-ripple high-efficient permanent magnetic motor stator and rotor structure comprising a stator and a rotor. The stator employs pear-shaped flat-bottomed grooves. Irregular grooves are disposed on a position, corresponding to the center of a stator tooth portion, on the outer circumference of the stator. A rotor outer circumference is formed by a plurality of four-segment arcs. The rotor is provided with a plurality of grooves in which permanent magnets are embedded. The grooves are flat-bottomed V-shaped grooves. The tops of the left groove and the right groove of each V-shaped groove are provided wedge-shaped grooves for preventing the permanent magnets from moving. The permanent magnets are embedded in the left groove and the right groove. Reinforcing ribs are arranged between the tops of adjacent flat-bottomed V-shaped grooves. Compared with a conventional motor with a built-in V-shaped permanent magnet, the low-torque-ripple high-efficient permanent magnetic motor stator and rotor structure is decreased in permanent magnet magnetic leakage, increased in the utilization rate of the permanent magnets, and provided with a salient pole effect, fully utilizes reluctance torque, improves motor efficiency and power density, improves gap flux density waveform, reduces cogging torque and torque ripple, and effectively reduces core loss and eddy-current loss.
Owner:苏州德迈科电机技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com