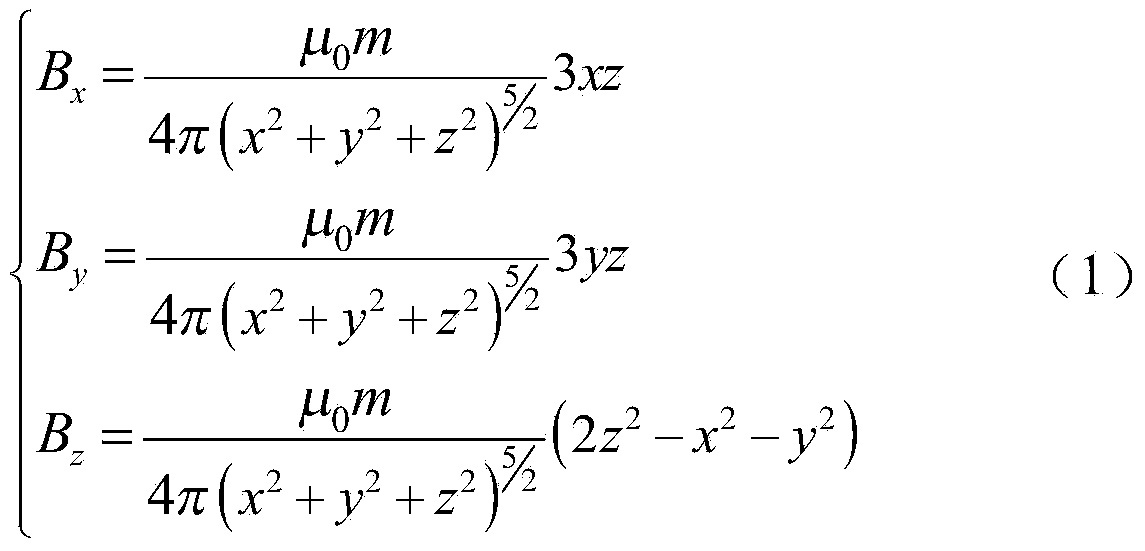Patents
Literature
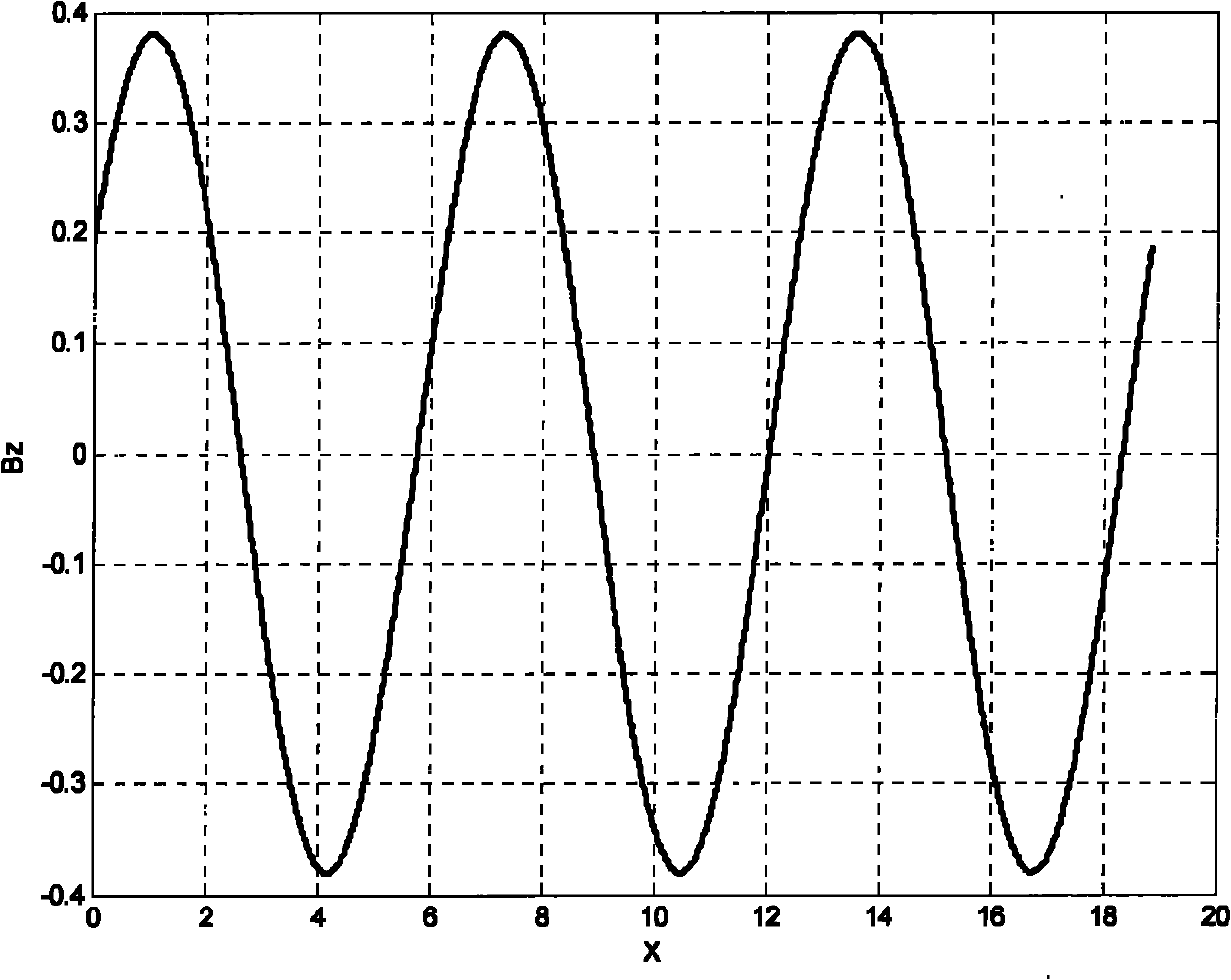
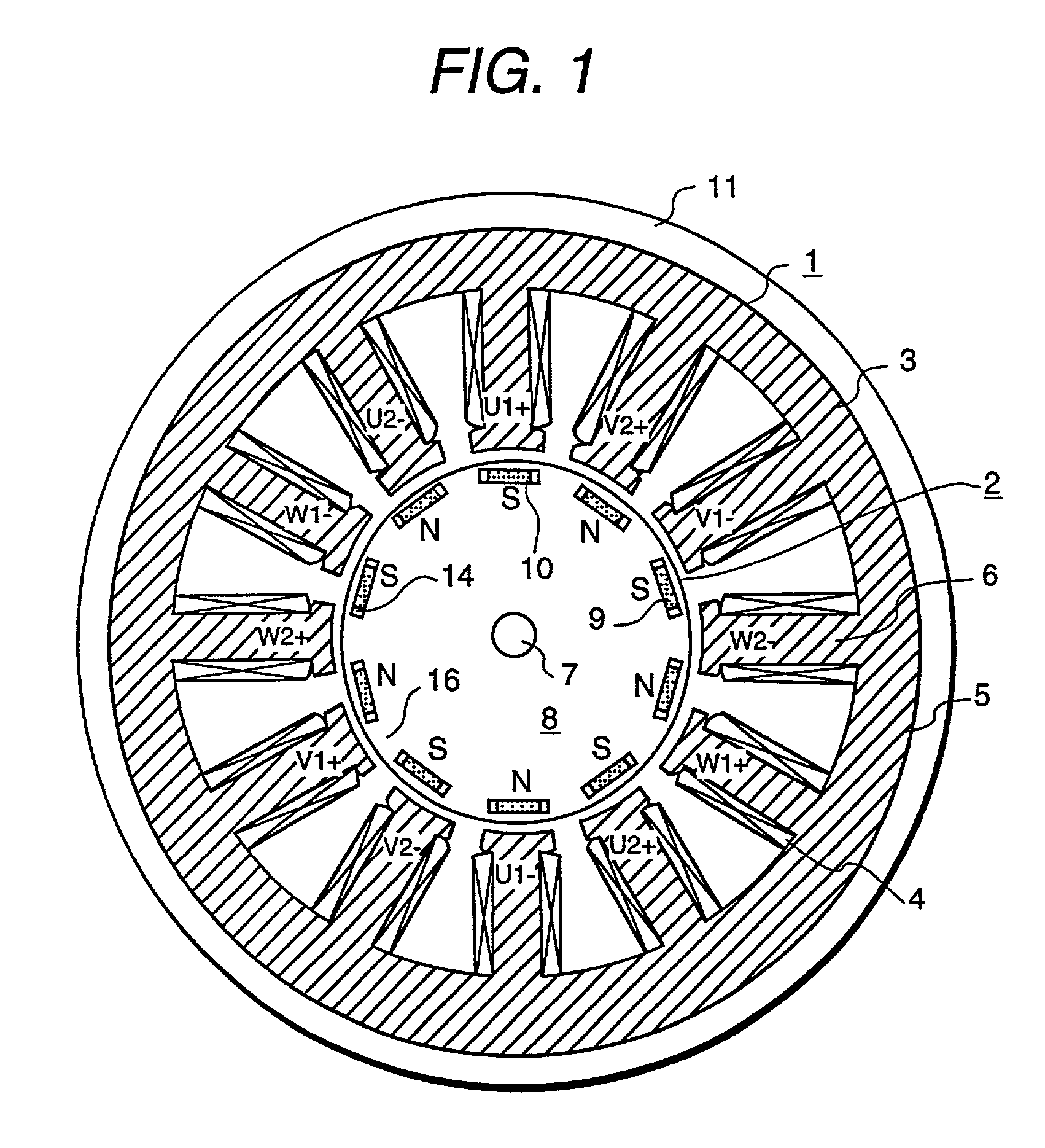
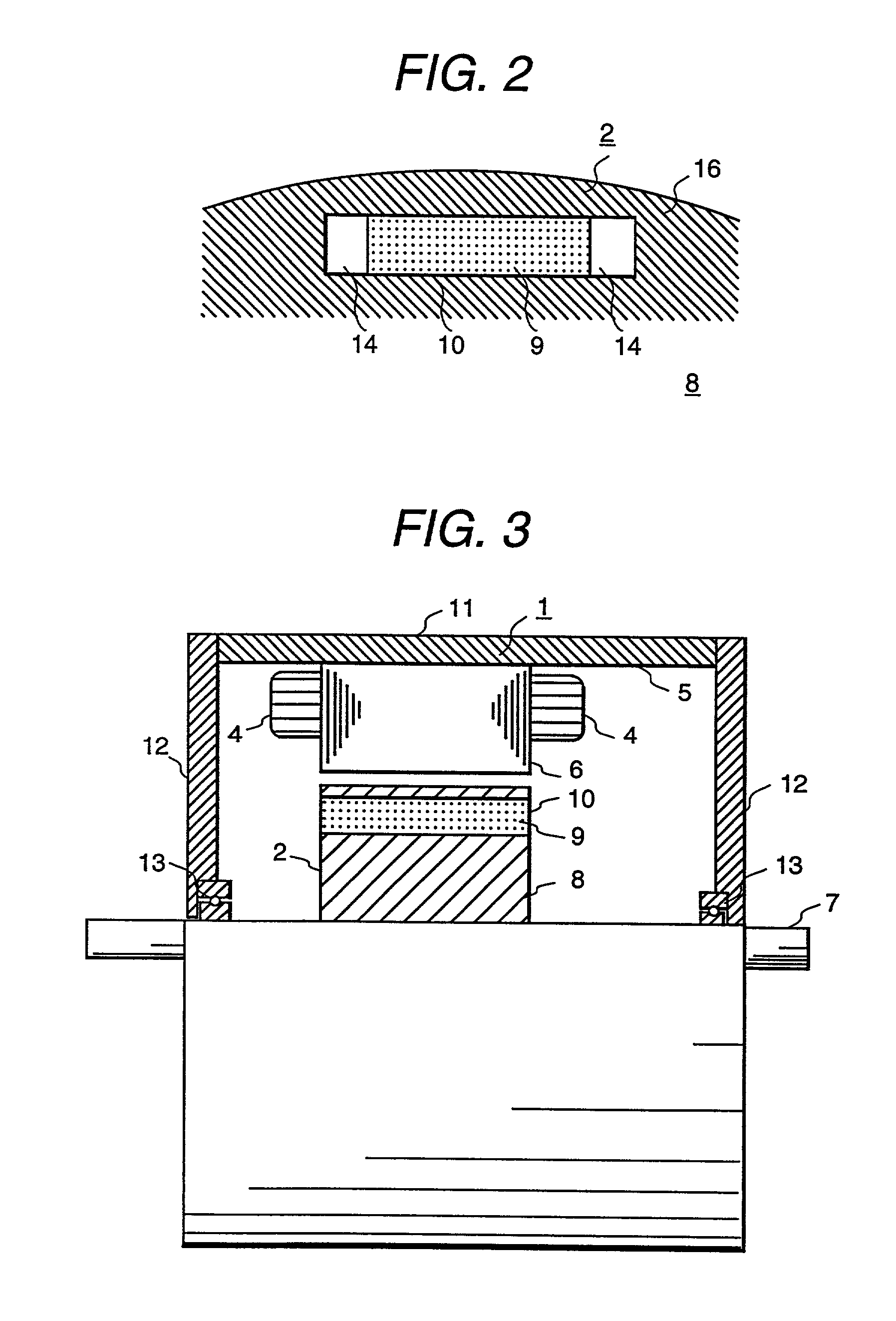
104 results about "Magnetic flux density distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
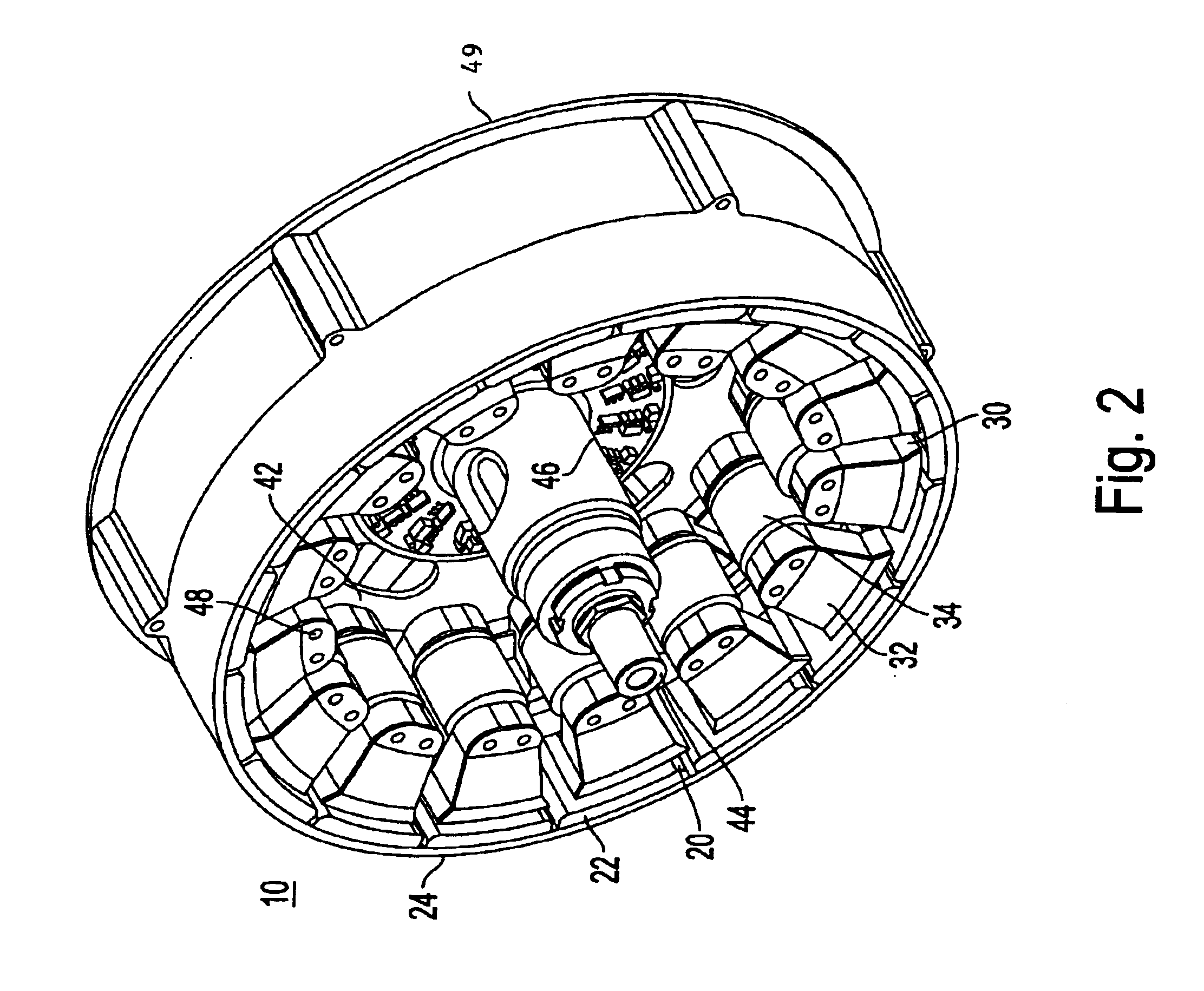
Permanent magnet electric rotating machine and electromotive vehicle using permanent magnet electric rotating machine
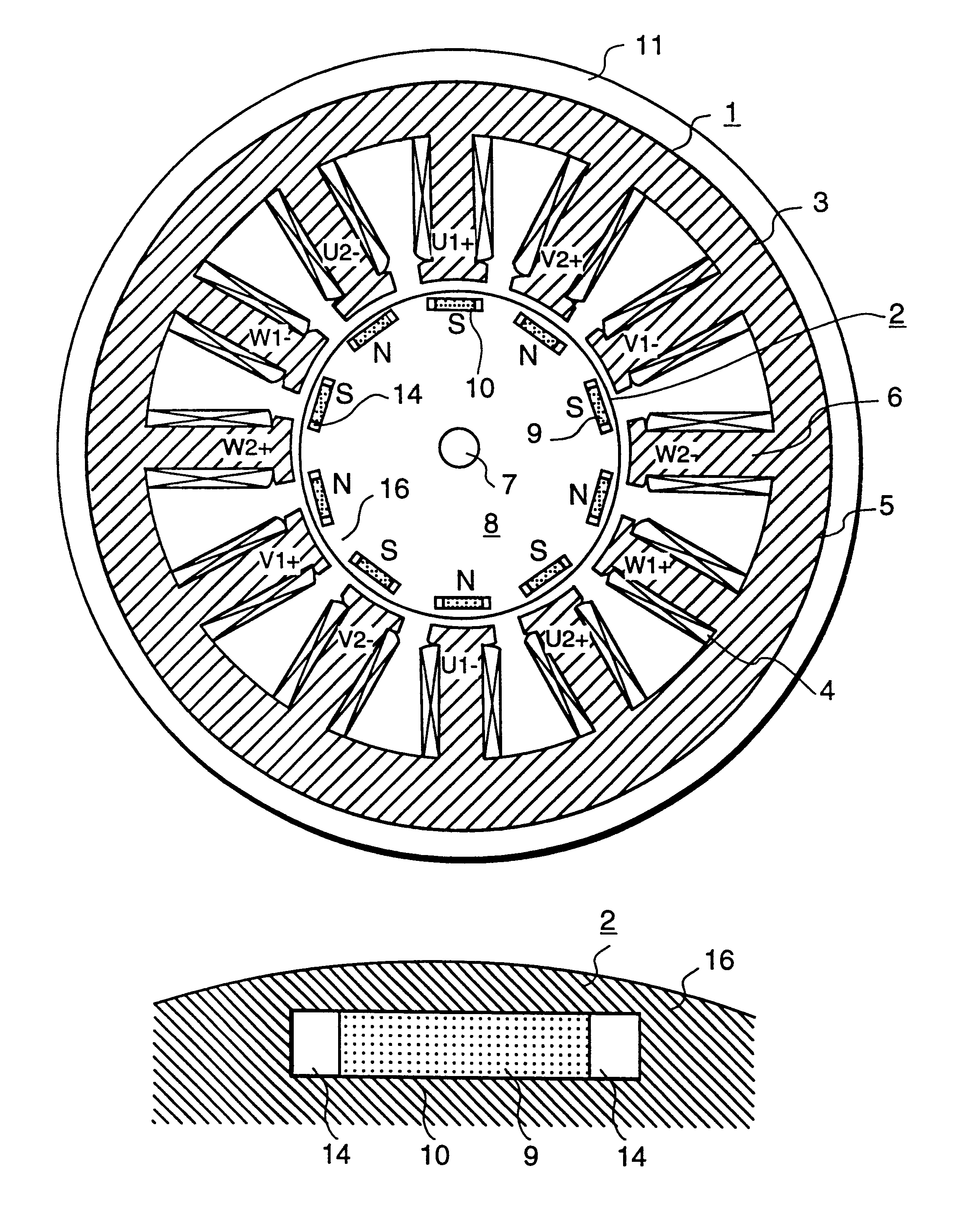
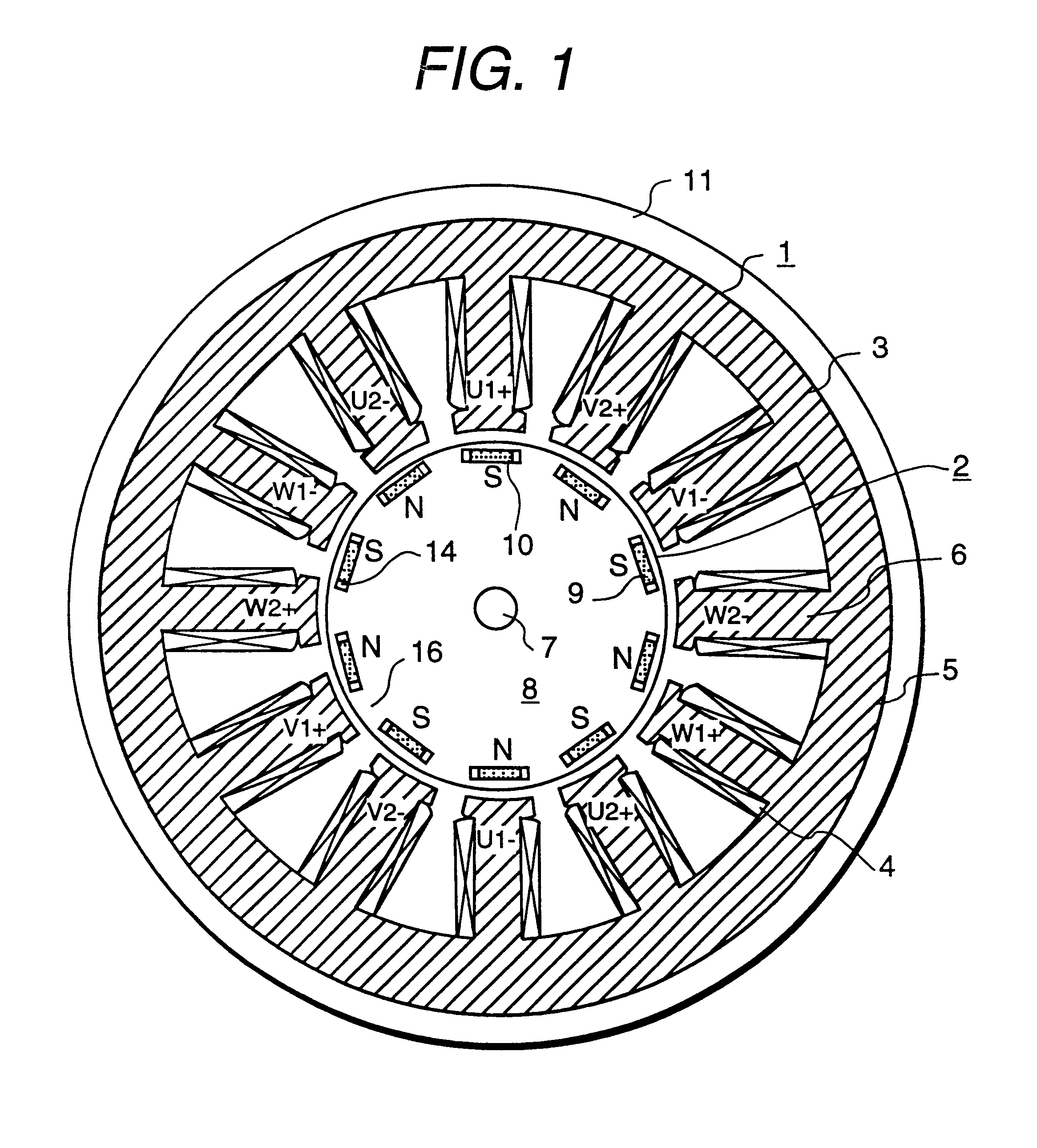
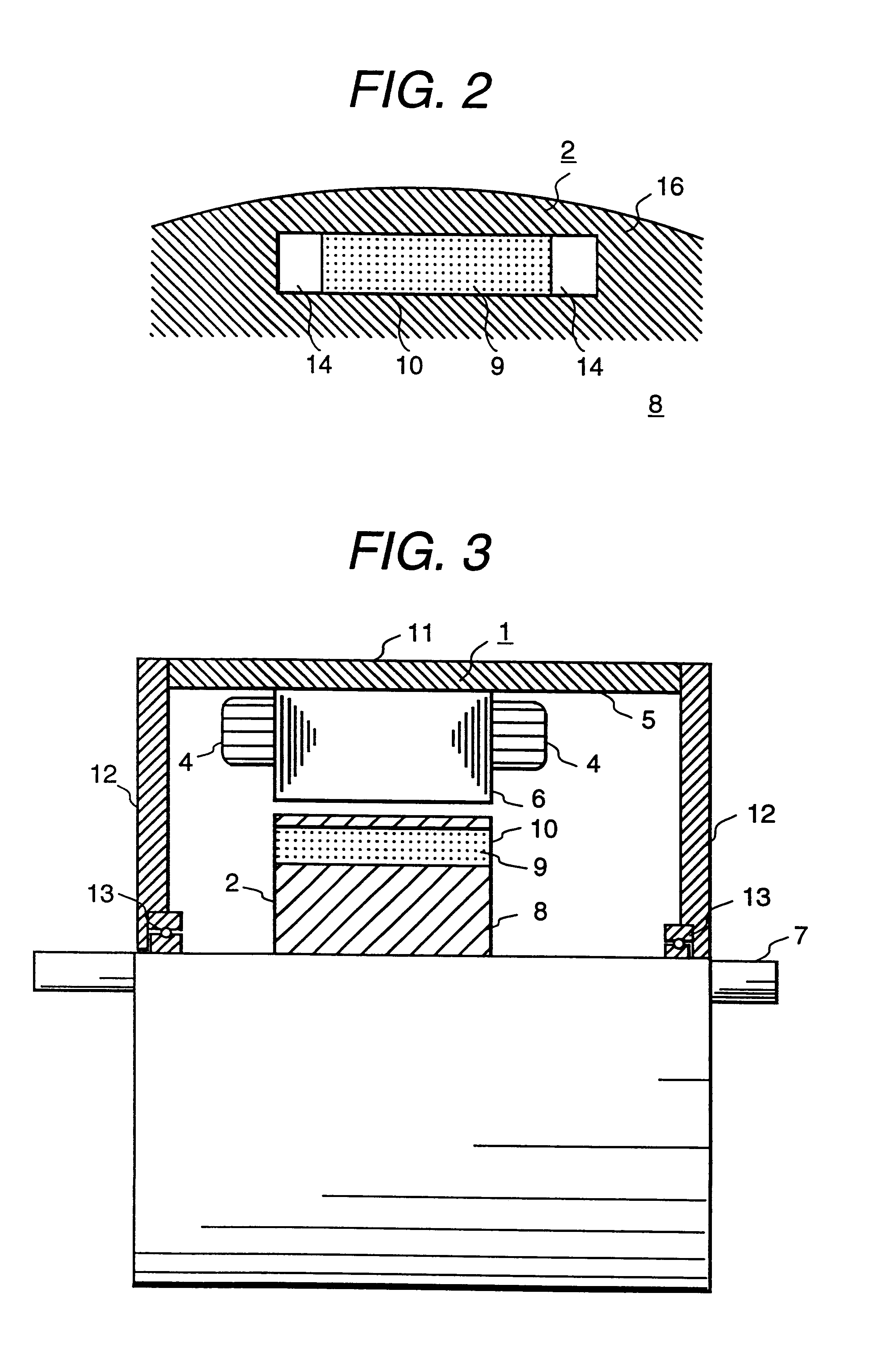
InactiveUS6208054B1Reduce pulsationMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
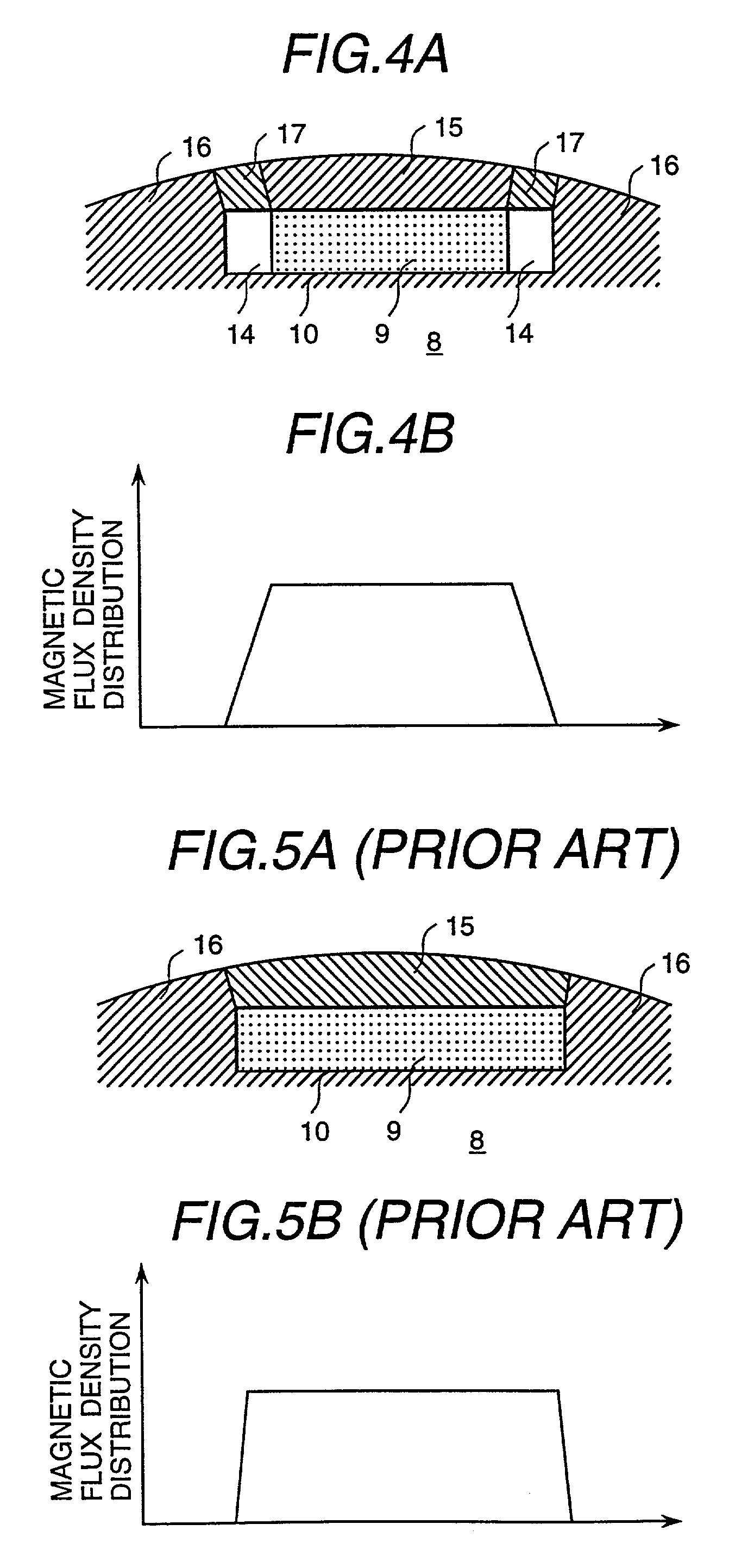
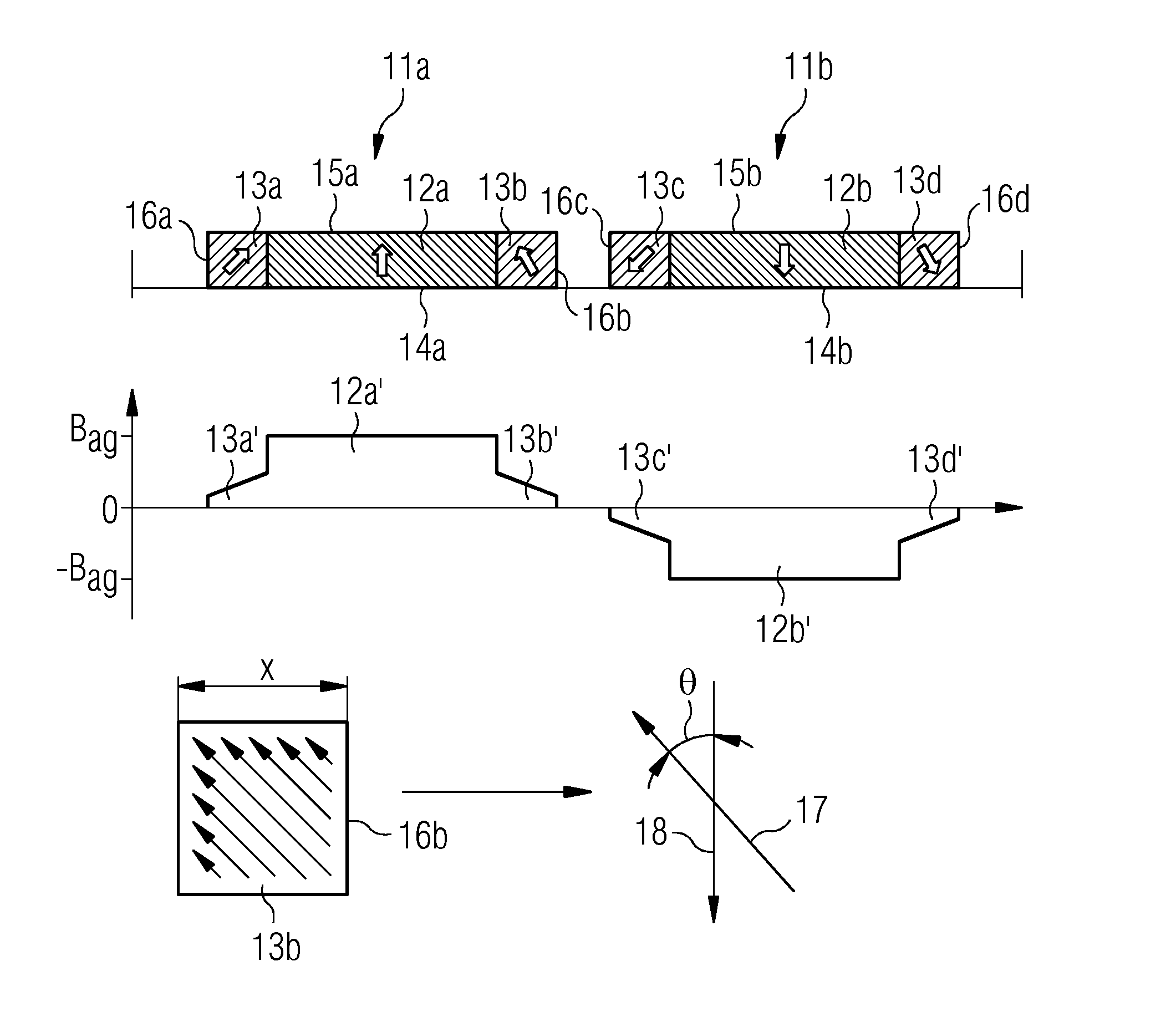
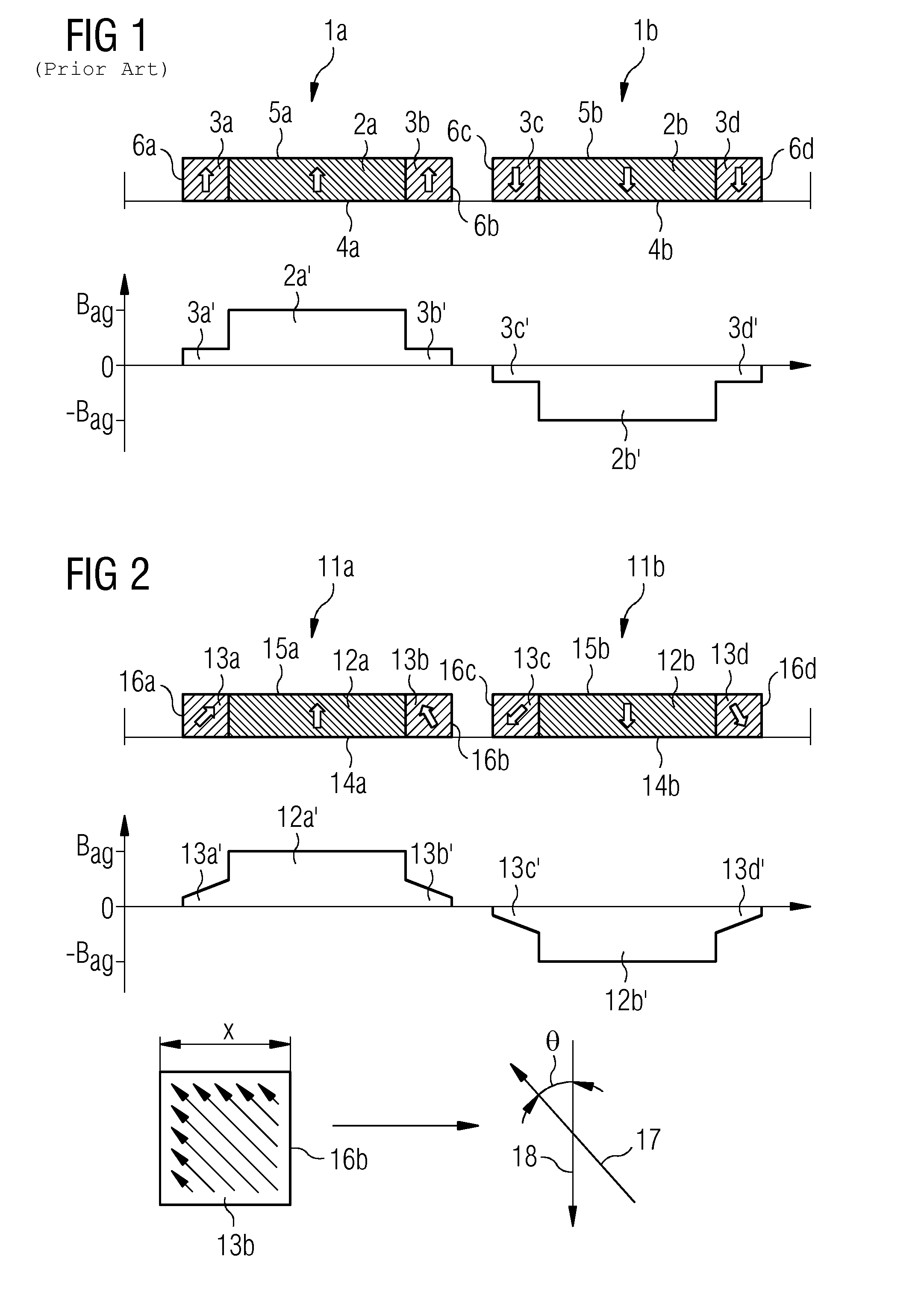
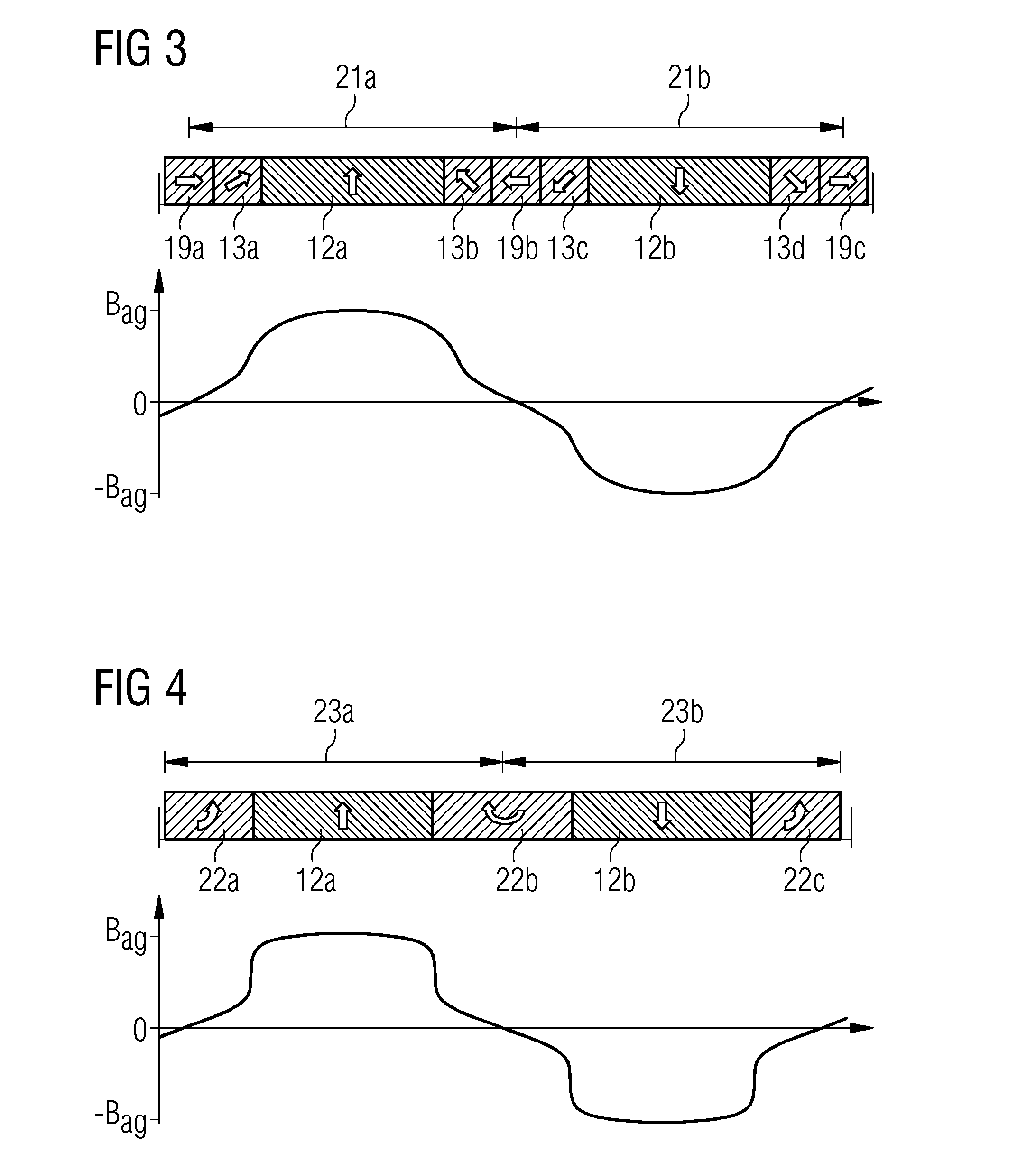
A magnetic gap is provided between a permanent magnet of a rotor and an auxiliary magnetic pole portion which is arranged adjacent to the permanent magnet in a peripheral direction. A gradual change in a magnetic flux density distribution of a surface of the rotor is obtained and a cogging torque and a torque pulsation are restrained. By obtaining a reluctance torque according to the auxiliary magnetic pole, a permanent magnet electric rotating machine in which the cogging torque and the torque pulsation are restrained can be obtained and further an electromotive vehicle having the permanent magnet electric rotating machine can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Magnetic liquid sealing device
A sealing device with magnetic liquid is prepared as forming magnetic pole ring by jacketing and superposing external and internal magnetic pole rings or by butt-joint and superposing top and bottom magnetic pole rings, setting adjacent and near permanent magnetic ring used for forming said magnetic pole ring to be at opposite polarity, sealing and erecting dual-superposed magnetic pole rings separately between coaxial gyrorotors to form seal gap for filling in magnetic liquid to realize magnetic liquid seal.
Owner:NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP CORP
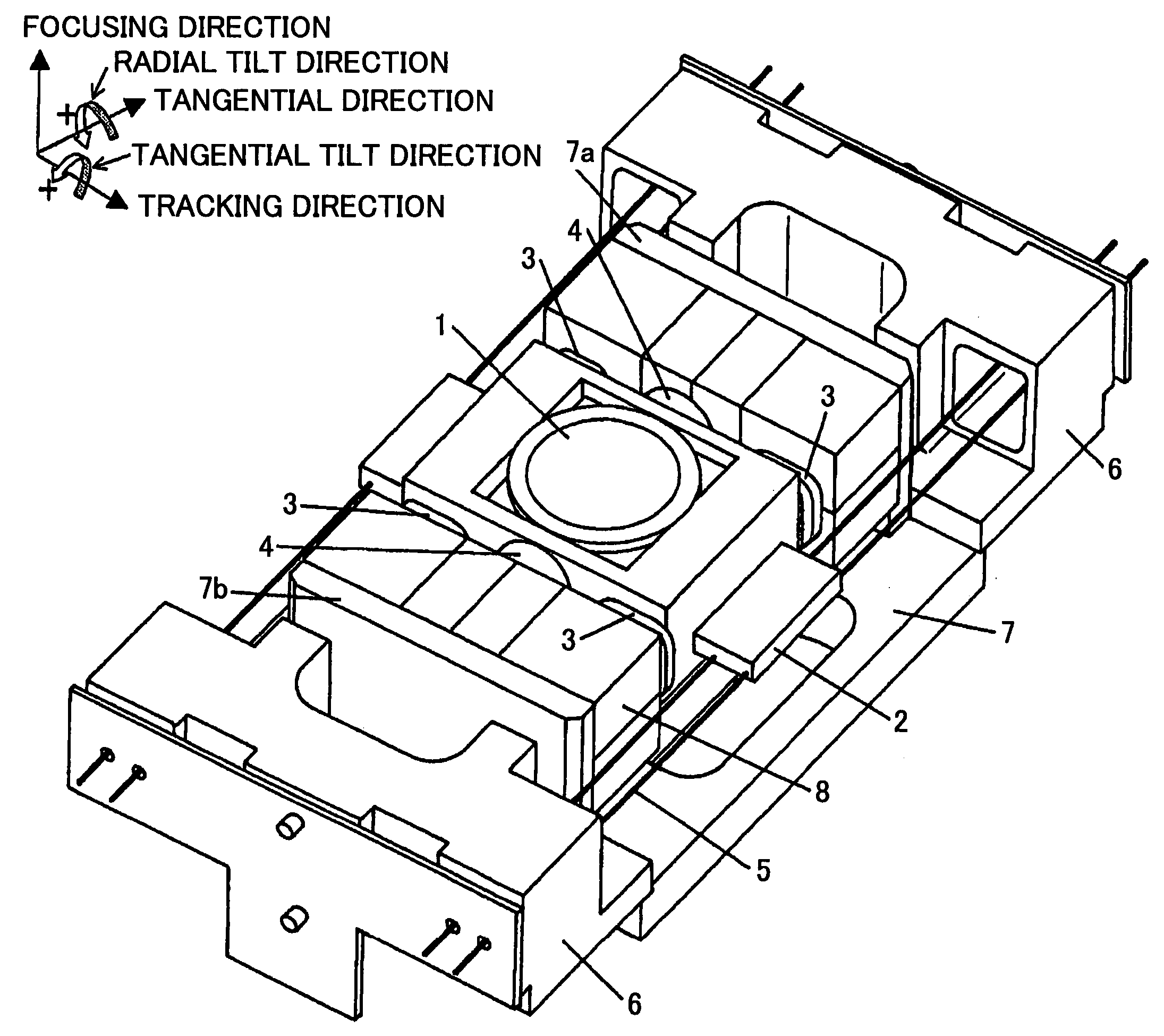
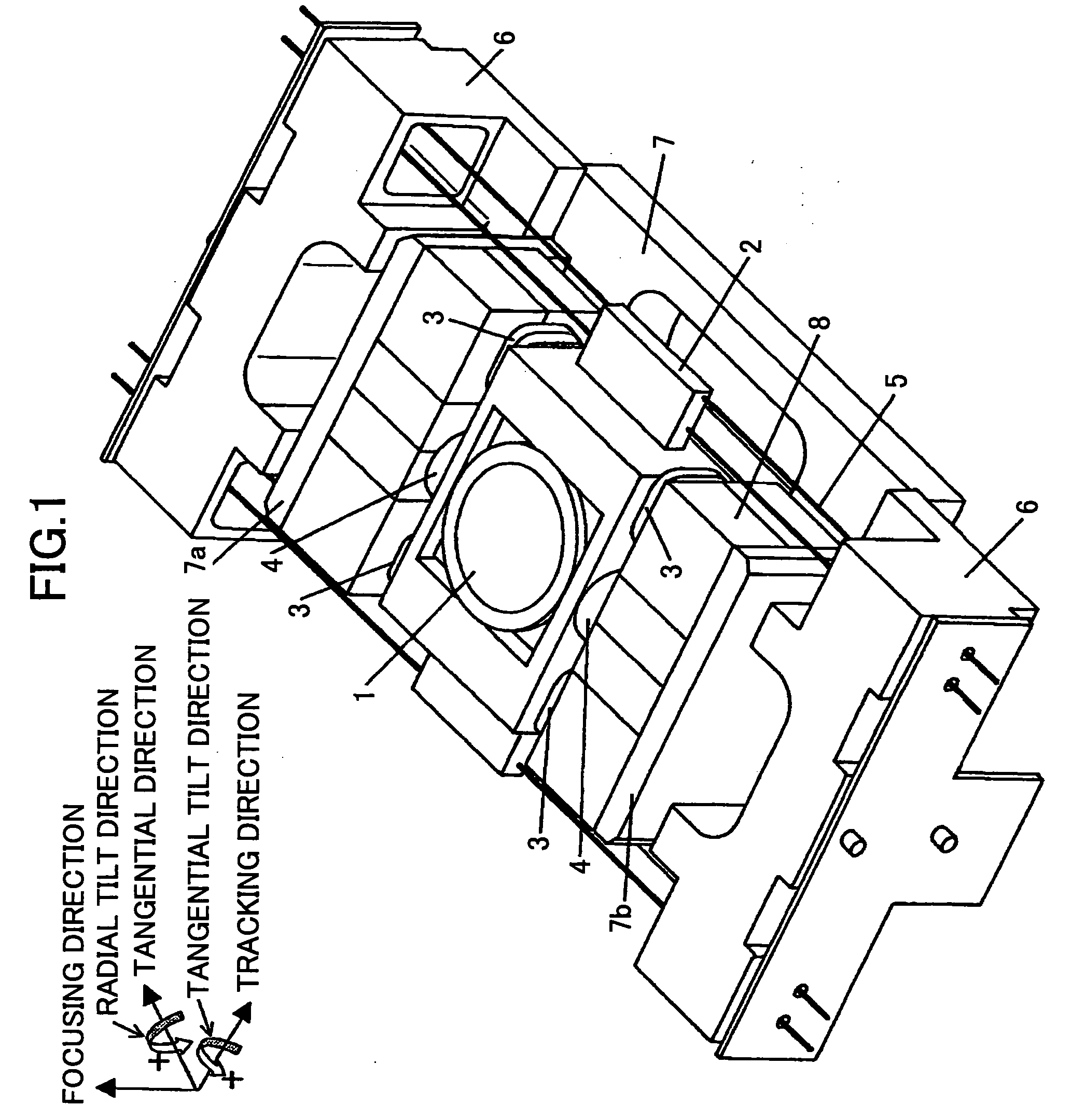
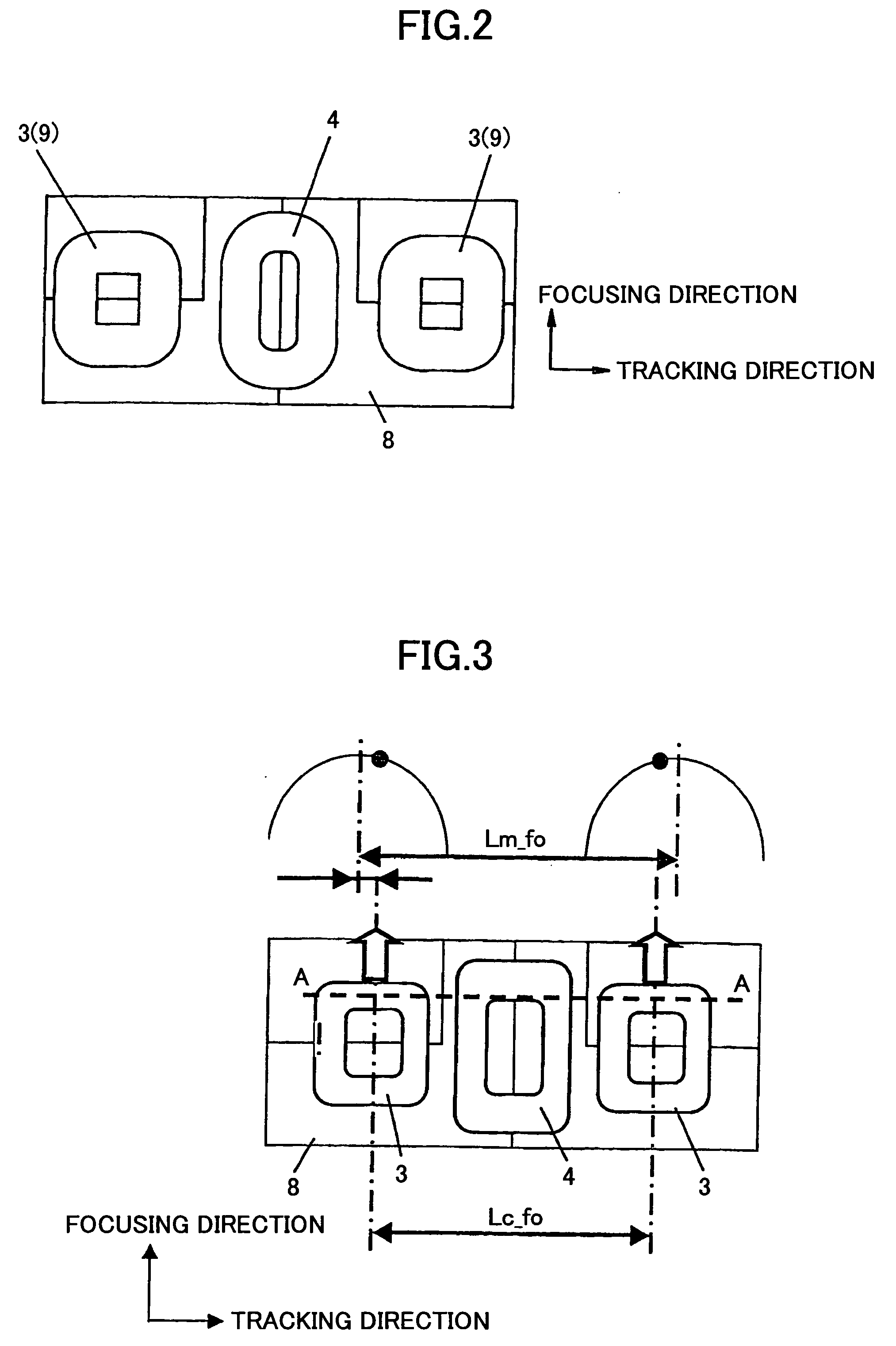
Object lens driving device, optical pickup, and optical disk drive
InactiveUS20050185530A1Reduce tiltImprove featuresRecord information storageDisposition/mounting of headsOptical pickupSupporting system
An object lens driving device is disclosed that has a small tilt even when focusing and tracking operations are performed at the same time. A movable unit including an object lens holding member with an object lens, focus coils and track coils attached thereon is supported by two sets of four wire springs, totaling eight wire springs, connected to fixed units on two sides of the object lens holding member in the tangential direction. When the movable unit is set to face a driving magnet which has a boundary line at the center portion of the magnet and parallel to the focusing direction, and boundary lines at two ends of the magnet and parallel to the tracking direction, the interval Lc_Fo between centers of the focus coils in the tracking direction is less than the interval Lm_Fo between centers of magnetic flux density distributions of the magnet. Consequently, a moment is generated to cancel out a tilt of the movable unit occurring in a supporting system when the movable unit moves in the focusing direction and the tracking direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
Modeling method of axial permanent magnetic motor equivalent magnetic circuit model
InactiveCN104063556AReduce analysis calculation timeSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMagnetization curve
The invention discloses a modeling method of an axial permanent magnetic motor equivalent magnetic circuit model. The modeling method includes the following steps of judging the topological structure which an axial permanent motor belongs to, determining the sizes of a stator, a rotor, a permanent magnet and an air gap of the motor, carrying out three-dimensional limiting element analysis on the axial permanent magnetic motor by means of limiting element simulation software to obtain magnetic flux density distribution of all portions of the motor, averagely dividing the axial permanent magnetic motor into N sections in the diameter direction, calculating equivalent magnetic resistance of the stator and the rotor according to magnetic flux density distribution obtained through limiting element analysis and magnetization curves of iron core materials of the stator and the rotor, calculating equivalent magnetic potential and equivalent magnetic resistance of the permanent magnet according to residual magnetism density of permanent magnetic materials and relative recoil permeability, dividing the air gap into a plurality of small areas according to the relative position of the stator and the rotor to calculate the equivalent magnetic resistance of all the portions, building the axial permanent magnetic motor equivalent magnetic circuit model according to modeling of all the portions. According to the modeling method, an accurate and quick magnetic circuit calculating method is provided for initialization and optimal design of the axial permanent magnetic motor.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous motor for compressor
PendingCN106712425ASmall torqueReduce noiseSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet synchronous motorMagnetic poles
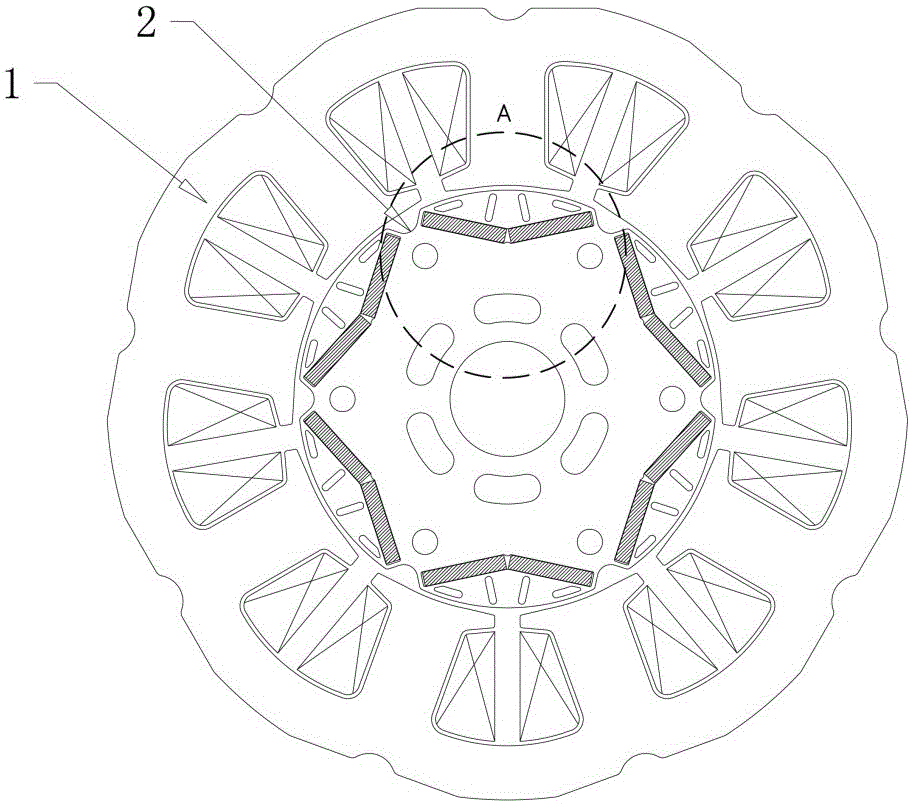
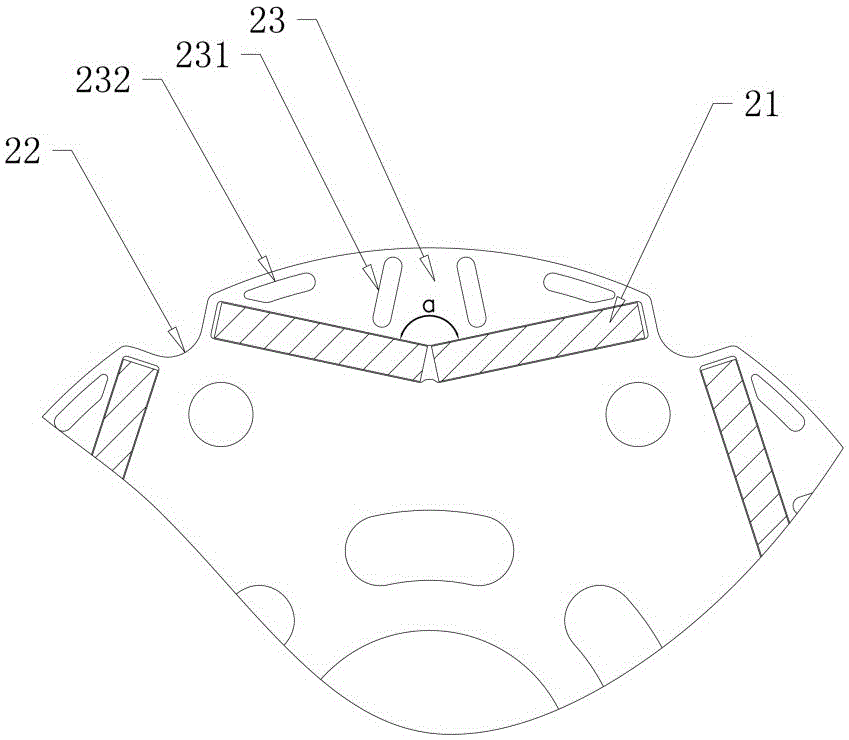
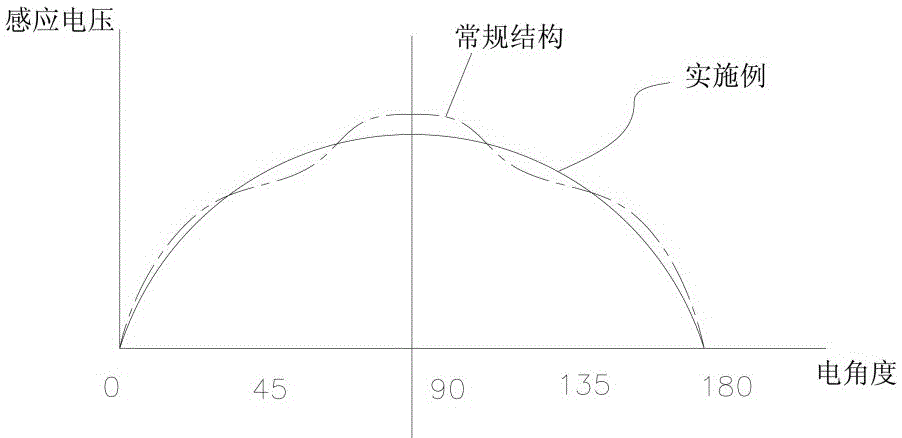
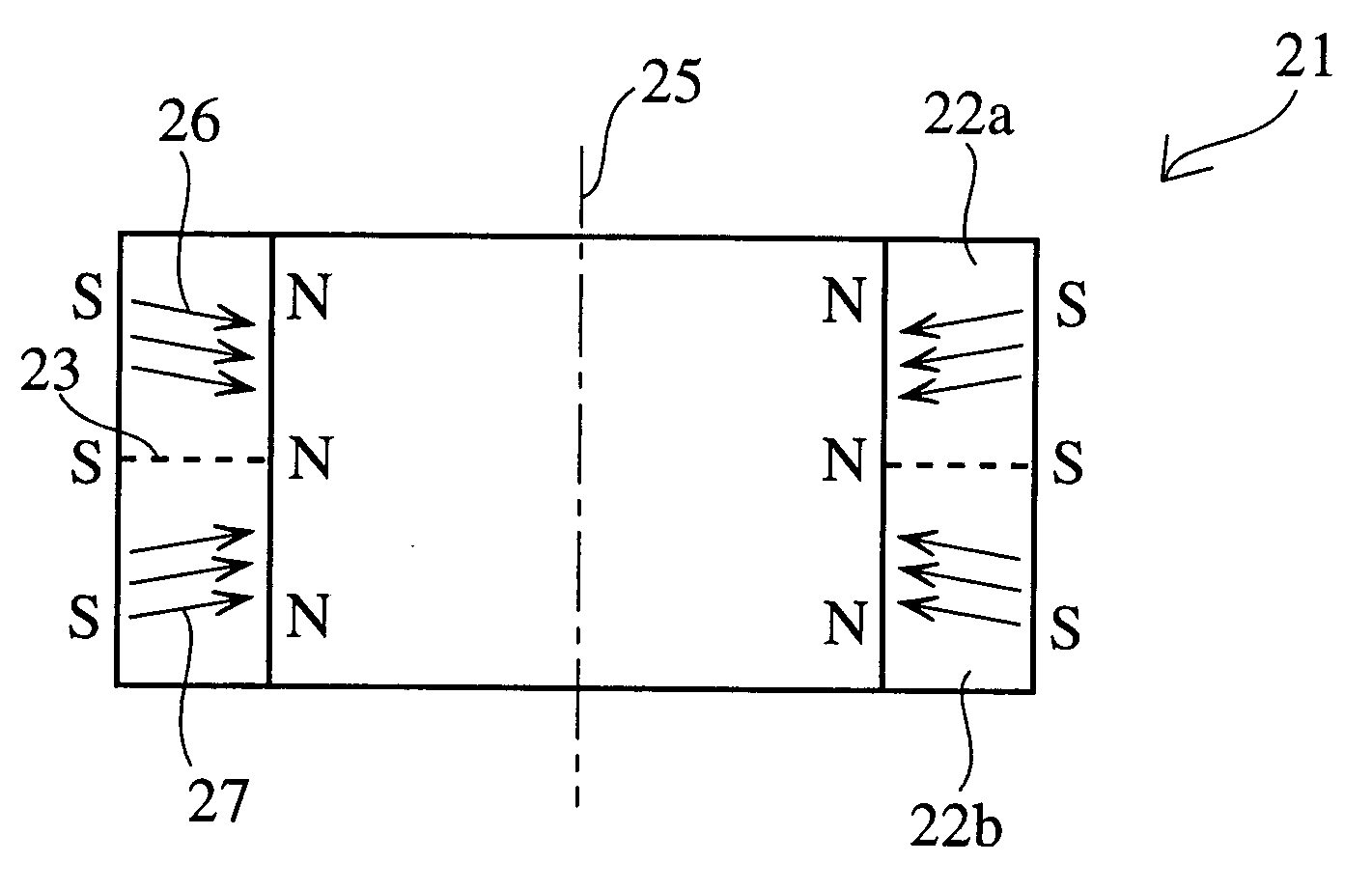
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor, comprising a stator and a rotor which are formed by laminating electromagnetic steel plates, wherein the rotor is arranged inside the stator, a plurality of magnet accommodating slots extending in the length direction of the rotor and distributed circumferentially in a V-shaped structure are formed in the end face of the rotor, permanent magnets having the same magnetic poles are arranged in the magnet accommodating slots, and meanwhile, permanent magnets having opposite magnetic poles are arranged in any two adjacent magnet accommodating slots; an arc groove extending in the length direction of the rotor is formed in the outer circumferential surface of the rotor between any two adjacent magnet accommodating slots; at least one first gap hole group and one second gap hole group extending in the length direction of the rotor are formed in a gap part between the outer side of each magnet accommodating slot and the outer circumference of the rotor; thus, the magnetic flux density distribution of the air gap part between the stator and the rotor is smoothed circumferentially, and then noise and vibration of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are reduced.
Owner:广东志高精密机械有限公司
Speaker comprising ring magnet
InactiveUS6529107B2Improve linearityIncrease valueTransducer detailsPermanent magnetsClassical mechanicsPeak value
A ring magnet having improved linearity and / or peak value in a pace magnetic flux density distribution, comprising at least one first radially anisotropic region having a radial anisotropy direction of 89° or more relative to a center axis thereof, and at least one second radially anisotropic region having a radial anisotropy direction of 40° or more and less than 89° relative to a center axis thereof, the first and second radially anisotropic regions being arranged along the center axis such that a space magnetic flux density distribution on an inner or outer surface of the ring magnet has increased linearity and / or peak value.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Apparatus for sensing angular position
InactiveUS7049808B2Cost effectiveSensor redundancySolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesData signalMagnetic flux density distribution
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Electric machine and rotor arrangement
The invention relates to an electric machine, particularly for a synchronous machine excited by a permanent magnet. The electric machine comprises a rotor arrangement (4) having buried permanent magnets (6) and a stator arrangement (2) having an inner recess (3) for rotationally movably receiving the rotor arrangement (4), the rotor arrangement (4) comprising a plurality of rotor segments (7), each having a pole shoe (10), the outer contour thereof corresponding to an arc contour having a contour radius, the contour radius being smaller than the radius of the rotor arrangement (4), thus forming a gap between two adjacent rotor segments (7), the at least one outer contour of one of the rotor segments (7) having an arc contour designed such that an air gap length ratio of the radial spacingbetween the inner recess (3) and the outer contour along a radial outer boundary of the corresponding rotor segment and the radial spacing between the inner recess and the outer contour along a radial center axis of the corresponding rotor segment (7) is optimized with regard to the distortion factor of the course of the flux density distribution of the pole shoe (10).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
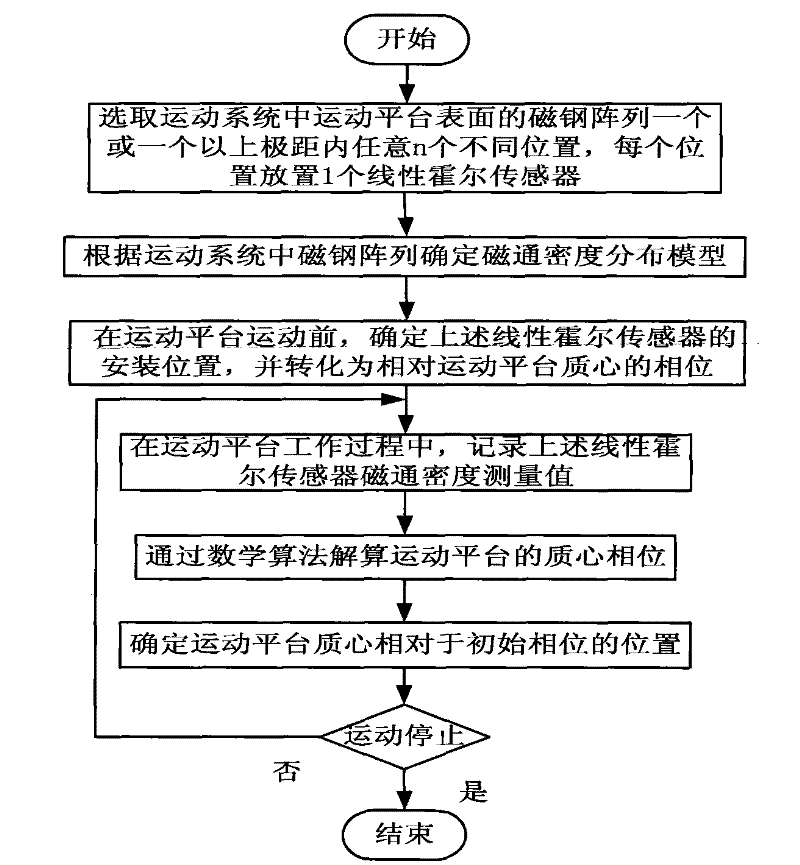
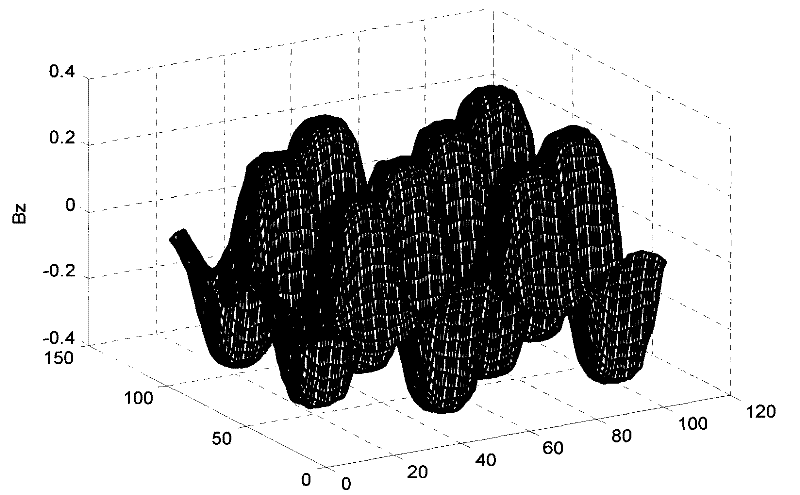
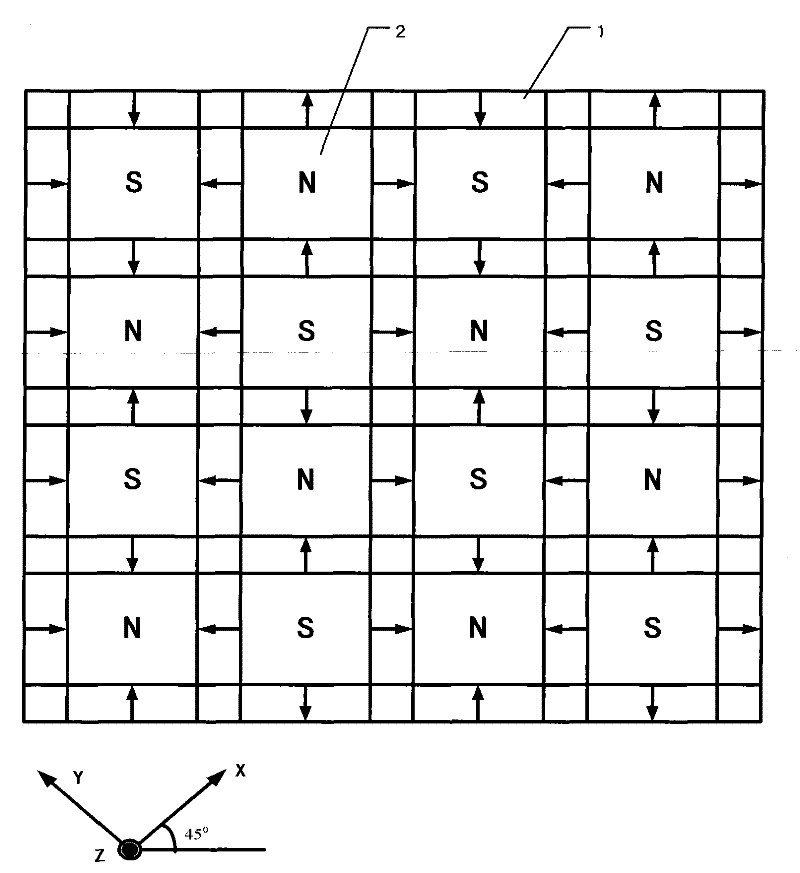
Two-dimensional location method of moving platform based on magnetic steel array
ActiveCN101750187ARealize plane two-dimensional positioningSimple Position Calculation MethodStatic/dynamic balance measurementConverting sensor outputRelative motionMagnetic flux density distribution
The invention provides a two-dimensional location method of a moving platform based on a magnetic steel array. The method comprises the following steps: putting more than four linear Hall sensors at optional different positions in one or more polar distances of the magnetic steel array on the surface of the moving platform in a moving system, determining a magnetic flux density distributed model according to the magnetic steel array, determining the mounting positions of the linear Hall sensors, converting into the phases with respect to the mass center of the moving platform, recording the magnetic flux density measured values of the linear Hall sensors in a moving process, using the measured values as observed quantities and the magnetic flux density distributed model as a computation model, resolving the phase of the mass center of the moving platform in a plane, using the phase as evidence, and determining the position of the mass center of the moving platform with respect to an initial phase to realize the planar location of the moving platform. The invention provides a simple, convenient, quick and robust computational method of the mass center position of the platform for the moving system containing the magnetic steel array.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
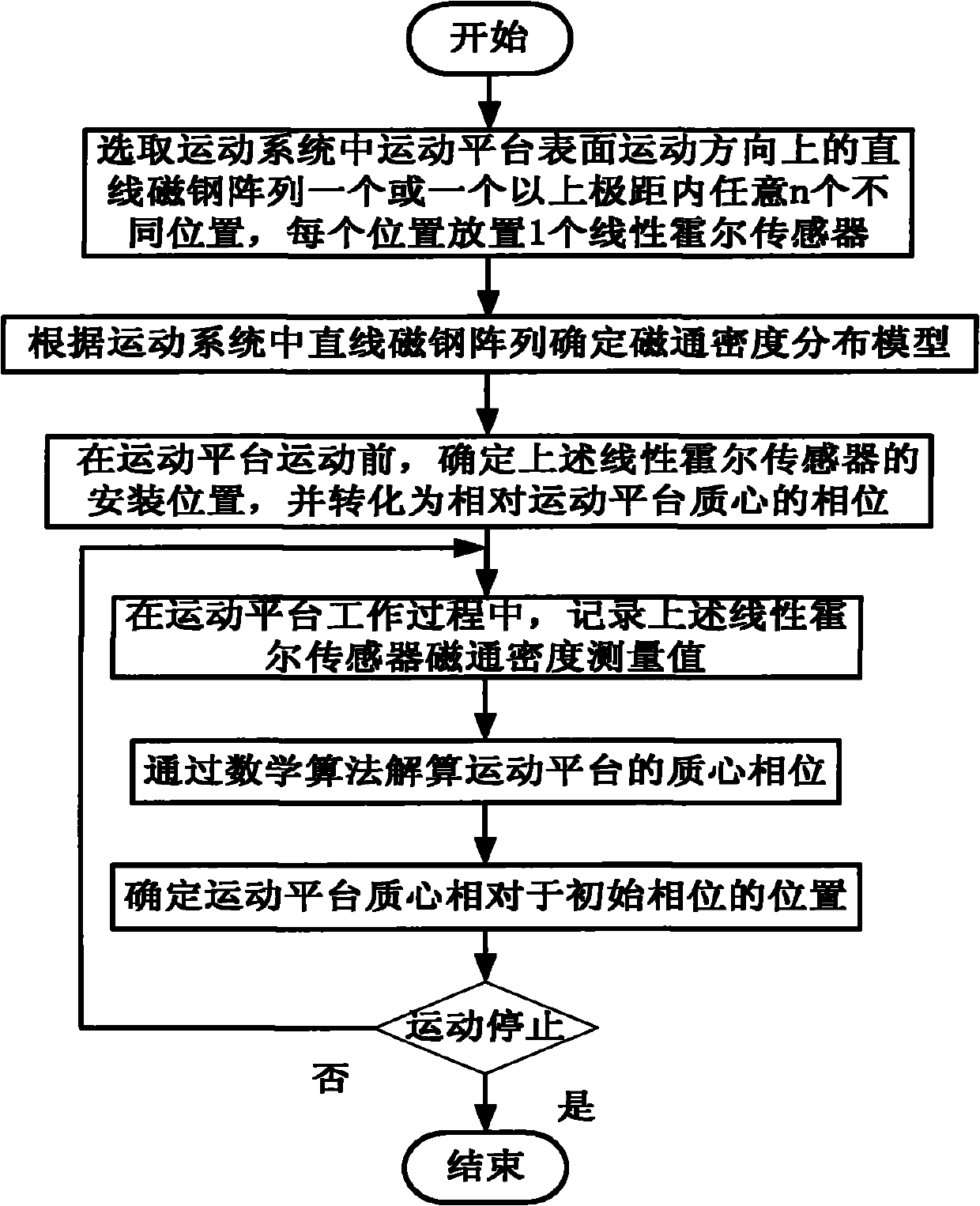
One-dimensional positioning method of motion platform based on linear magnetic steel array
ActiveCN101769764ASimple platform one-dimensional positioning methodLow costConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyRelative motionMagnetic flux density distribution
The invention discloses a one-dimensional positioning method of a motion platform based on a linear magnetic steel array, which comprises the following steps: placing more than 2 linear Hall sensors in arbitrary and different positions within one or more polar distances on the linear magnetic steel array in the motion direction of the surface of the motion platform in a motion system, determining a magnetic flux density distribution model according to the linear magnetic steel array, determining the mounting positions of the linear Hall sensors and converting into a phase relative to the mass center of the motion platform, recoding magnetic flux density measured values of the linear Hall sensors in the motion process, solving the phase of the mass core of the motion platform in the motion direction by taking the measured values as observed values and taking the magnetic flux density distribution model as a calculation value, and then determining the position of the mass core of the motion platform relative to an initial phase according to the phase, thus realizing the one-dimensional positioning of the motion platform. The invention provides the easy, convenient and robust method for calculating the position of the one-dimensional mass core of the platform for the motion system which contains the linear magnetic steel array.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Permanent magnet electric rotating machine and electomotive vehicle using permanent magnet electric rotating machine
InactiveUS20010002094A1Reduce pulsationReduce centrifugal forceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
A magnetic gap is provided between permanent magnet of a rotor and an auxiliary magnetic pole portion which is adjacently arranged to the permanent magnet to a peripheral direction. A change in a magnetic flux density distribution of a surface of the rotor is performed moderately and a cogging torque and a torque pulsation are restrained. By obtaining a reluctance torque according to the auxiliary magnetic pole, a permanent magnet electric rotating machine in which the cogging torque and the torque pulsation are restrained can be obtained and further an electromotive vehicle having the permanent magnet electric rotating machine can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Synchronous permanent magnet machine
ActiveUS20120313473A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsHigh energyMagnetization
A synchronous permanent magnet machine includes a permanent magnet arrangement for producing a magnetic field having a flux density distribution that is approximately sinusoidal. The permanent magnet arrangement includes a permanent magnet pole with both low and high energy-product magnets. The permanent magnet pole includes a low energy-product magnet and a high energy-product magnet which have different directions of magnetization, or a disposition of low / high energy-product magnets within the permanent magnet pole is asymmetric with respect to the central region of the permanent magnet pole.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Electrical machine and permanent-magnet
ActiveCN102222985AWind energy generationMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionMagnetic flux density distributionMagnet
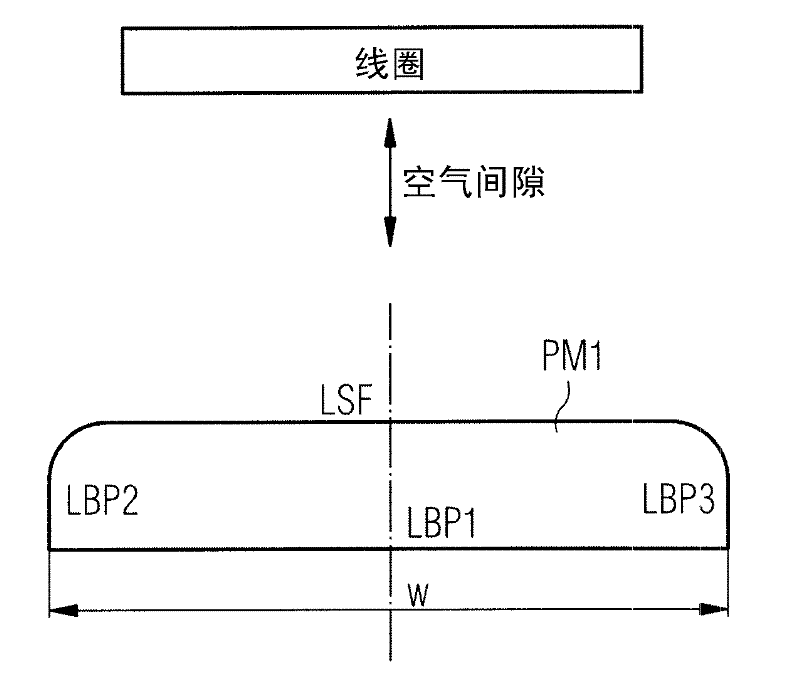
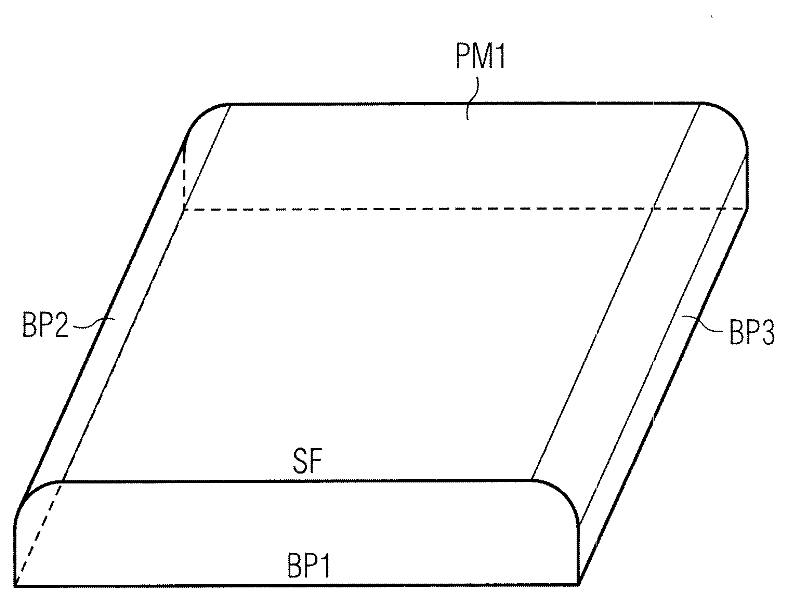
The invention relates to an electrical machine, which contains permanent magnets and to the permanent magnets being used. The invention especially relates to a synchronous machine. According to the invention the electrical machine contains a permanent magnet and a coil. The coil is arranged in a way that it interacts with the permanent magnet via an air gap, which is located between the permanent magnet and the coil. The permanent magnet and the coil are arranged in a way that electrical power is generated in the coil when the permanent magnet or the coil is moved in their relative position to each other. The permanent magnet contains a surface, which is aligned to the coil and to the air gap in a way, that magnetic forces of the permanent magnet interact via the surface and the air gap with the coil by a magnetic flux density distribution. The permanent magnet contains a surface, a base plane and a transition area. A first side of the surface is connected with the adjacent base plane via the transition area. The cross-section of the transition between the surface and the adjacent base plane is determined by a Bezier function, which is assigned to and defined by three points. A first point is assigned to the surface, while a second point is assigned to the base plane and while a third point is assigned to the transition area, which is between the surface and the base plane.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
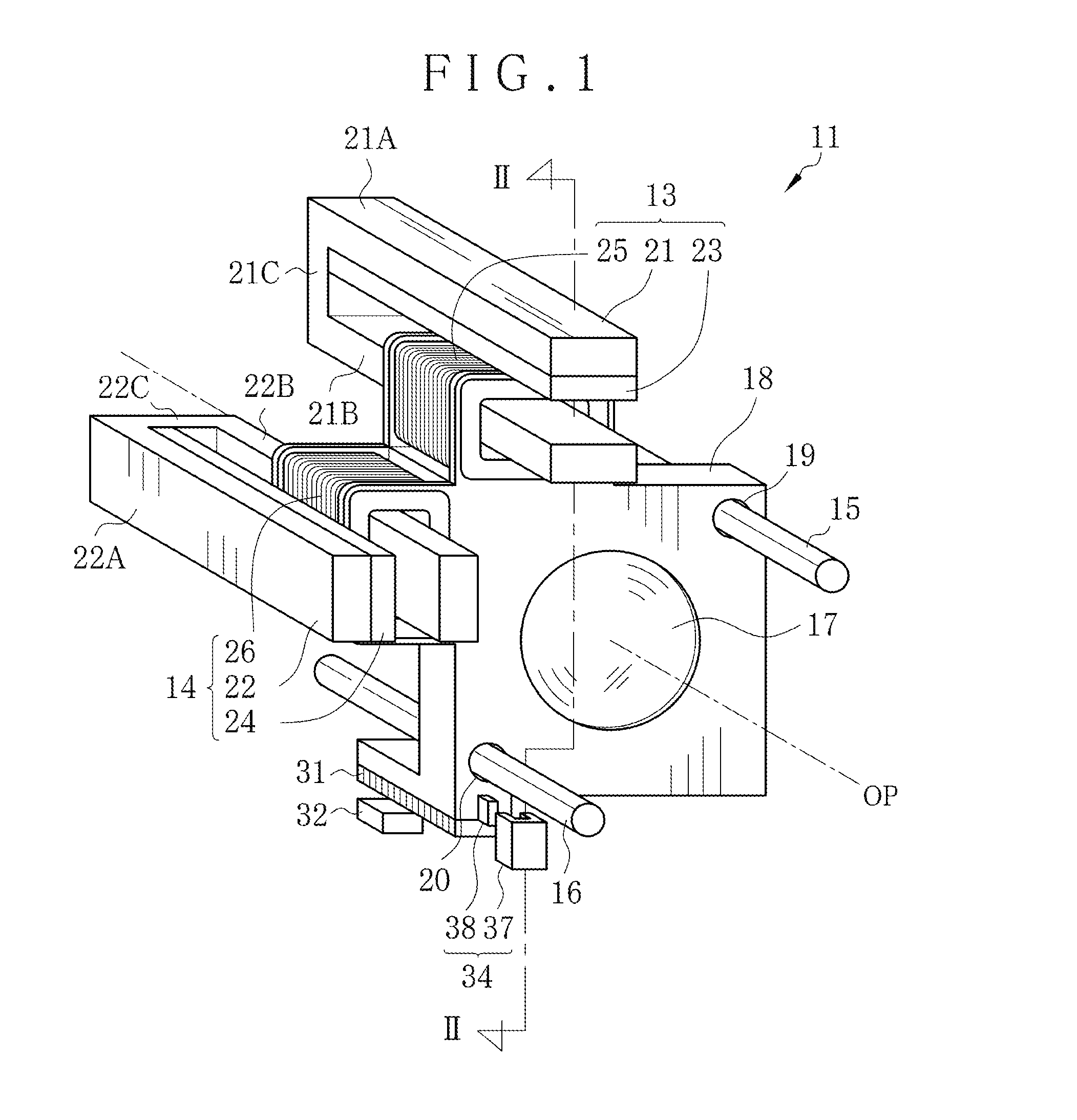
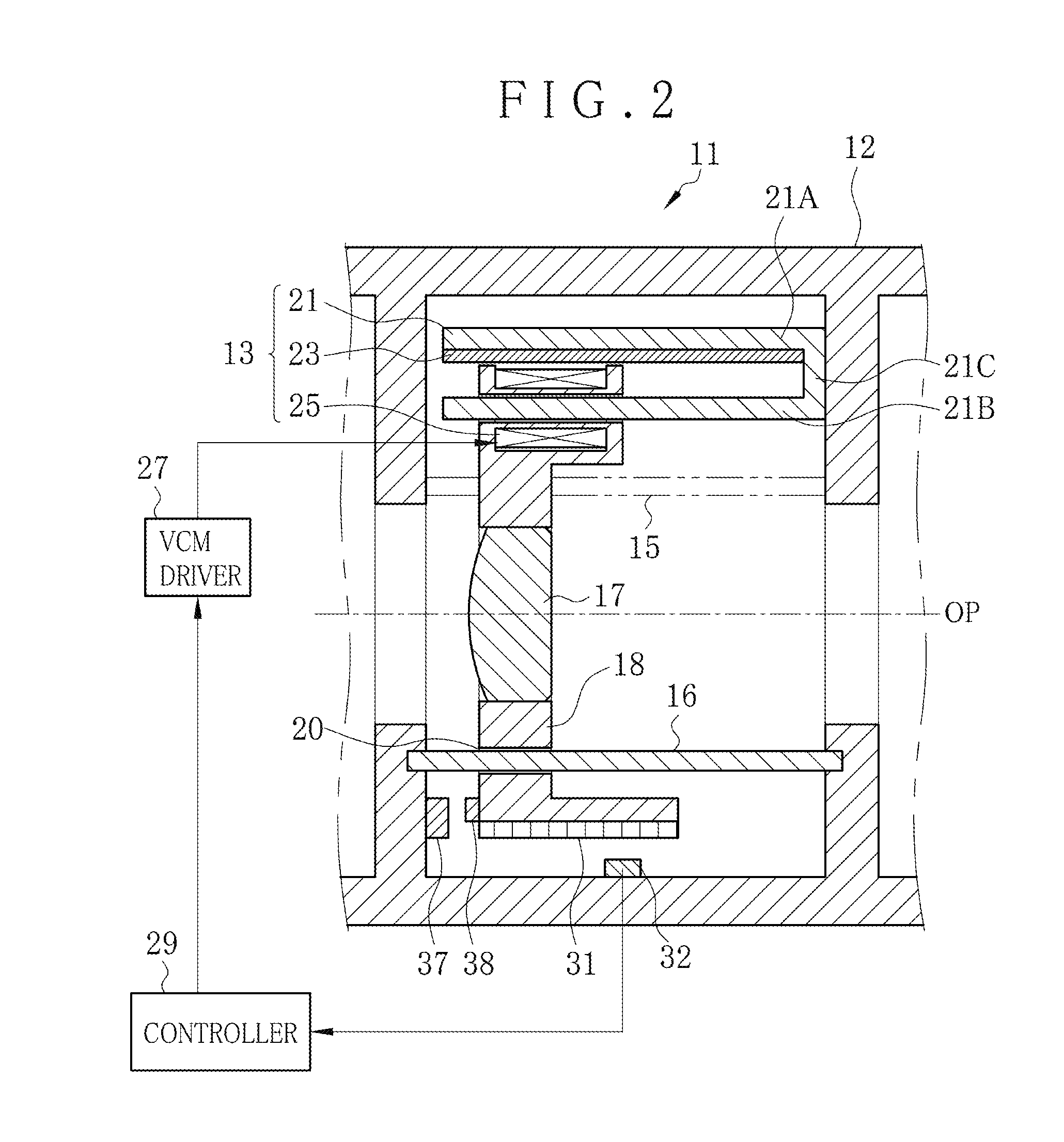
Lens driving apparatus and method
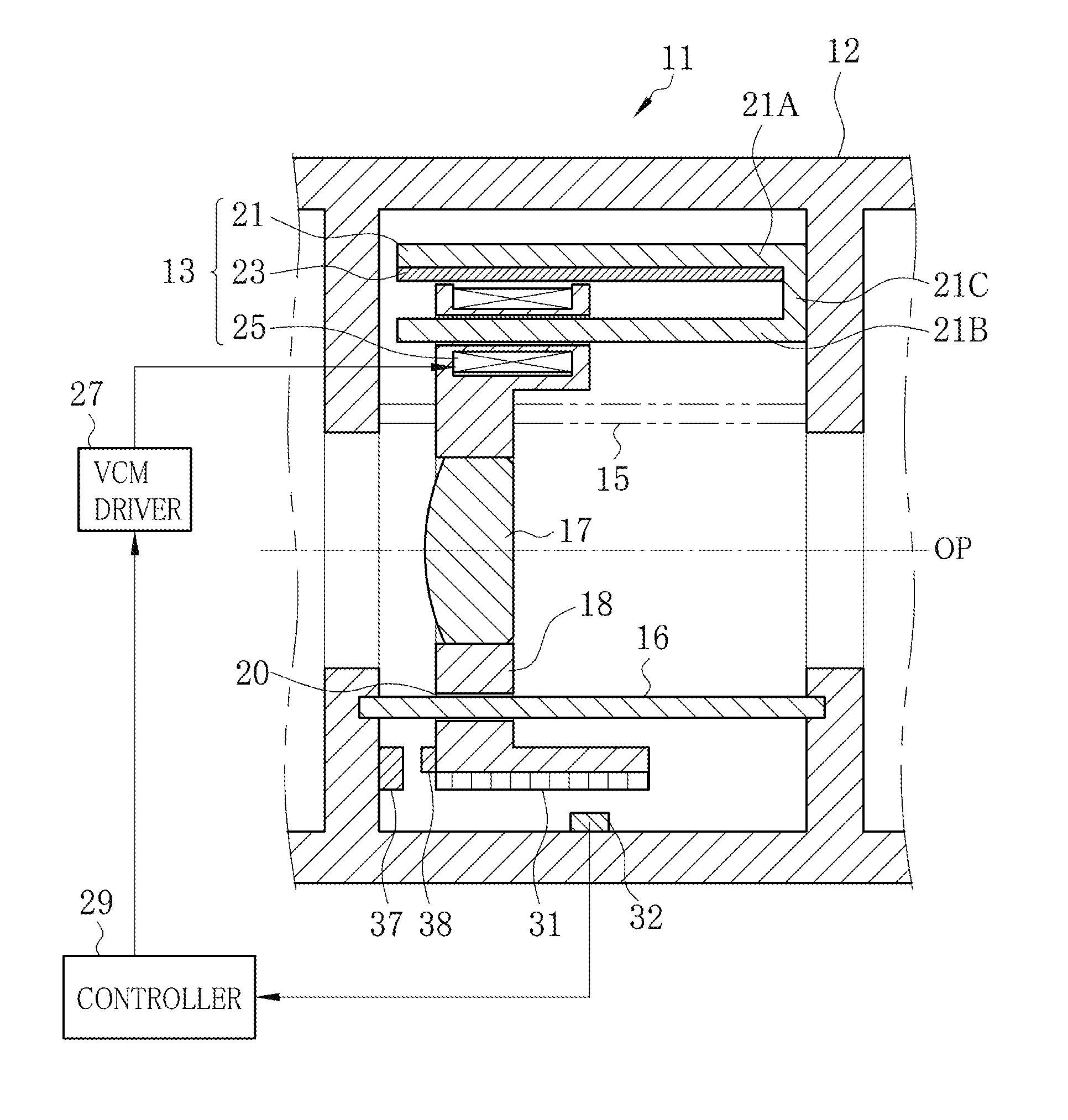
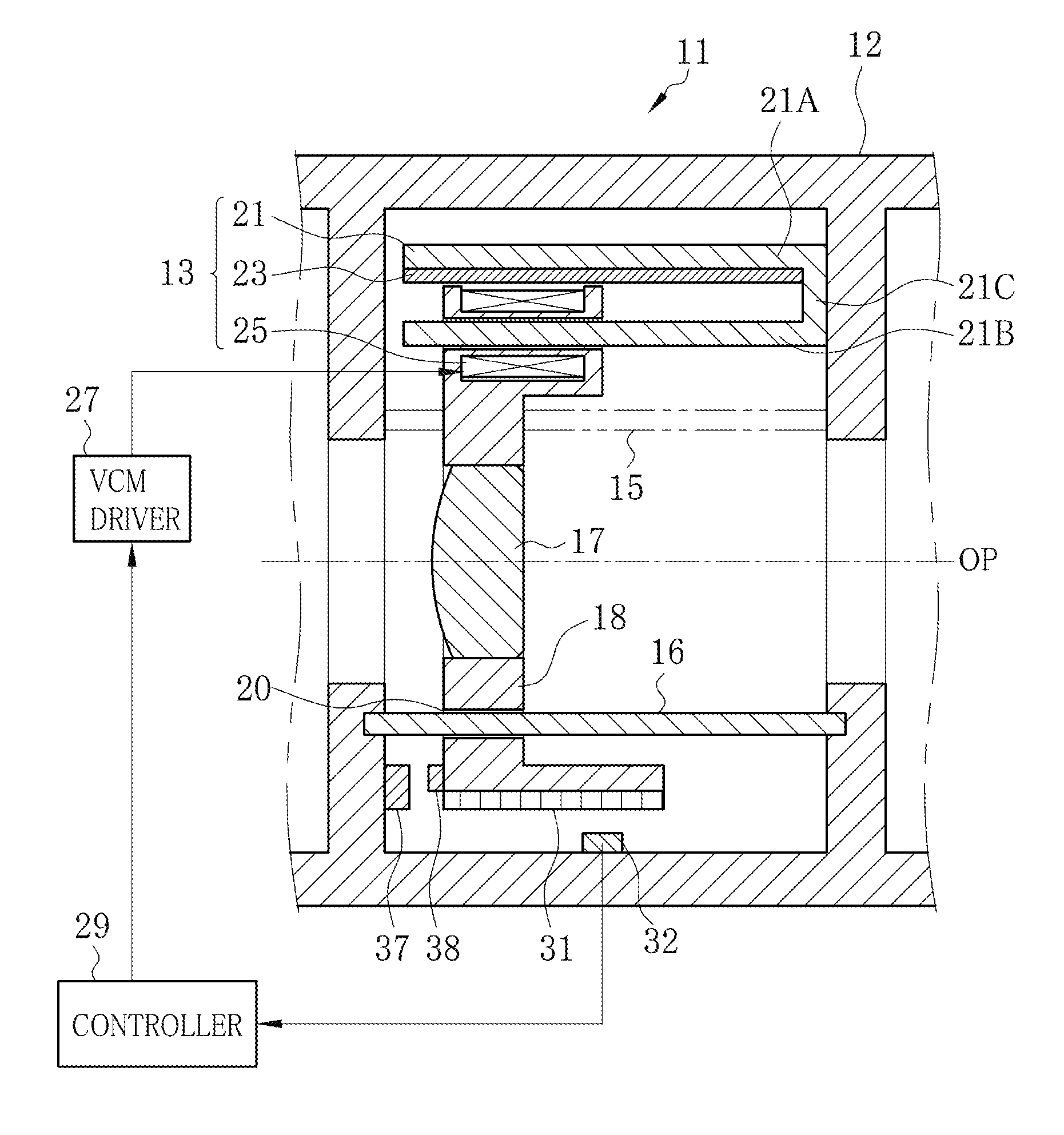
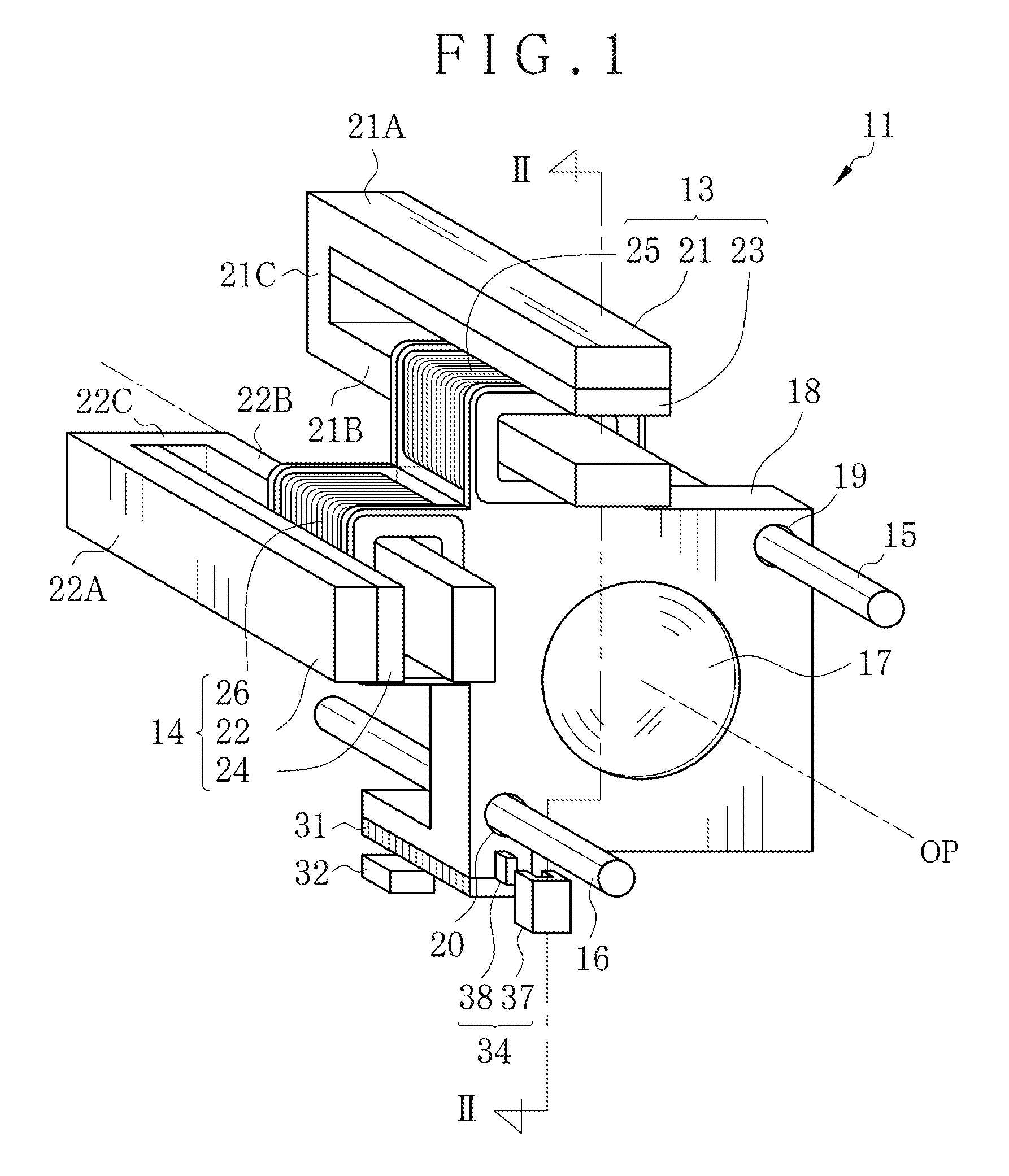
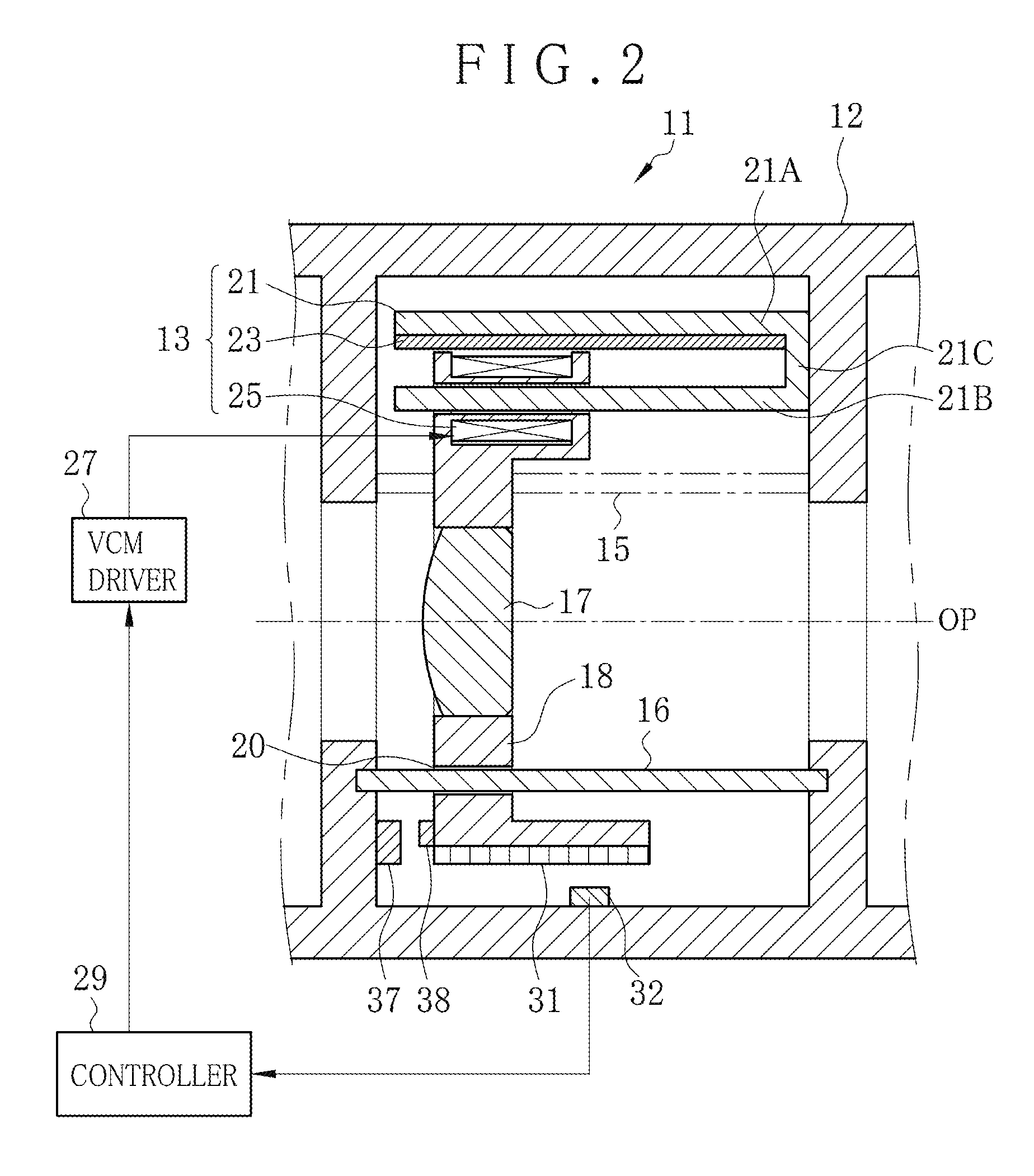
ActiveUS20150198783A1Remove unfamiliar feelingRemove unfamiliar feeling in manipulation of a userAC motor controlMountingsOptical axisMagnetic flux density distribution
A lens driving apparatus for a lens includes a voice coil motor. A coil position of a coil is detected. A table memory stores a correction factor for each one of plural values of the coil position according to flux density distribution. The correction factor is read from the table memory according to the detected coil position. A coil current is corrected by use of the correction factor for each coil position. The corrected coil current is caused to flow through the coil, with which the lens is moved together along an optical axis. Consequently, changes in a moving speed of the lens can be prevented.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
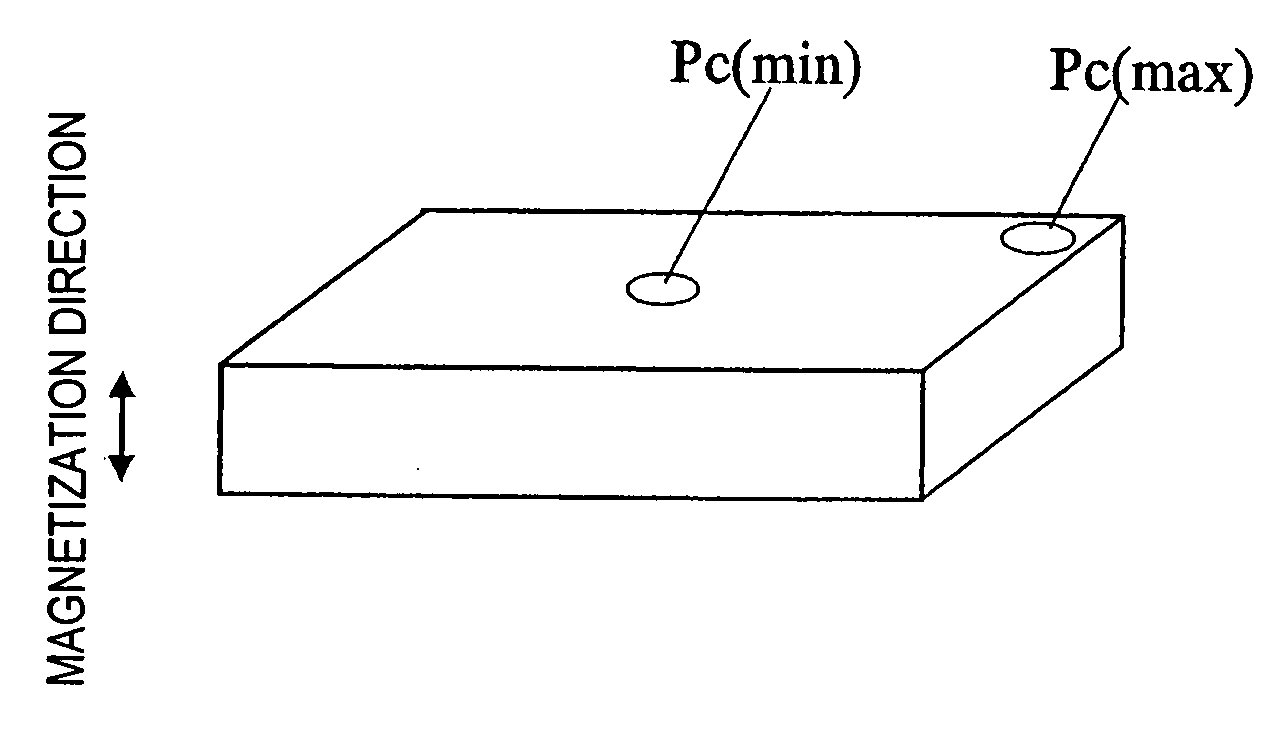
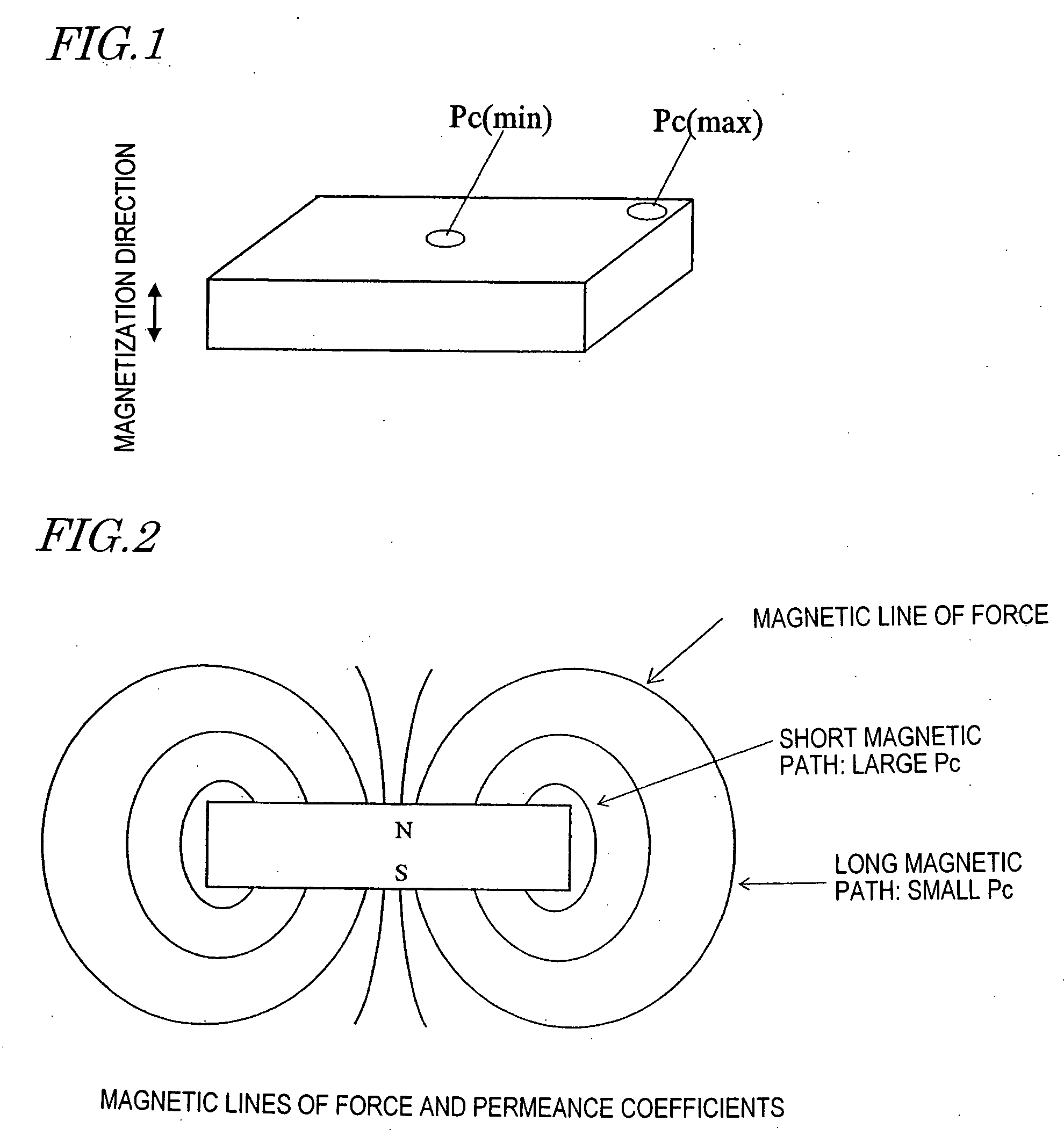
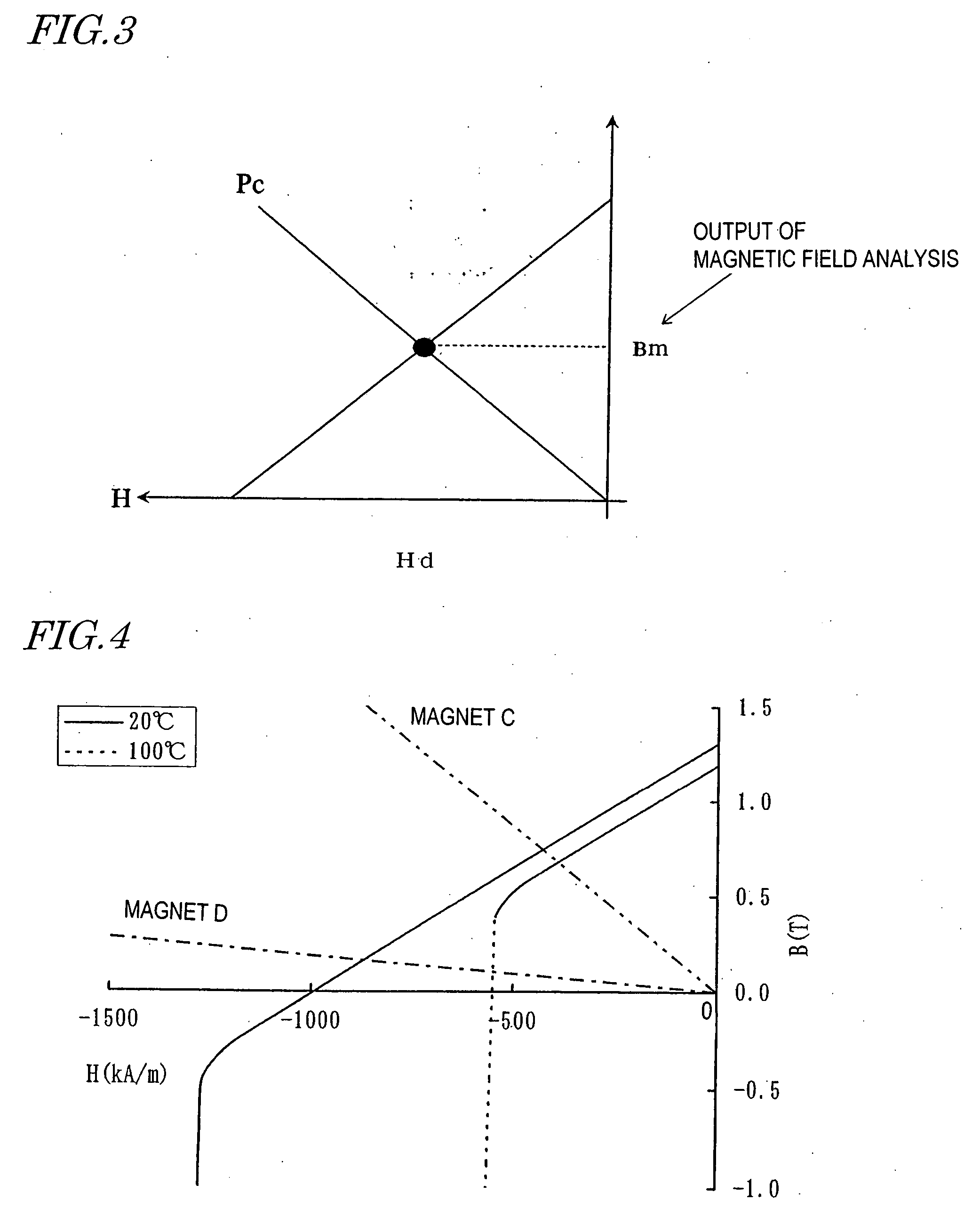
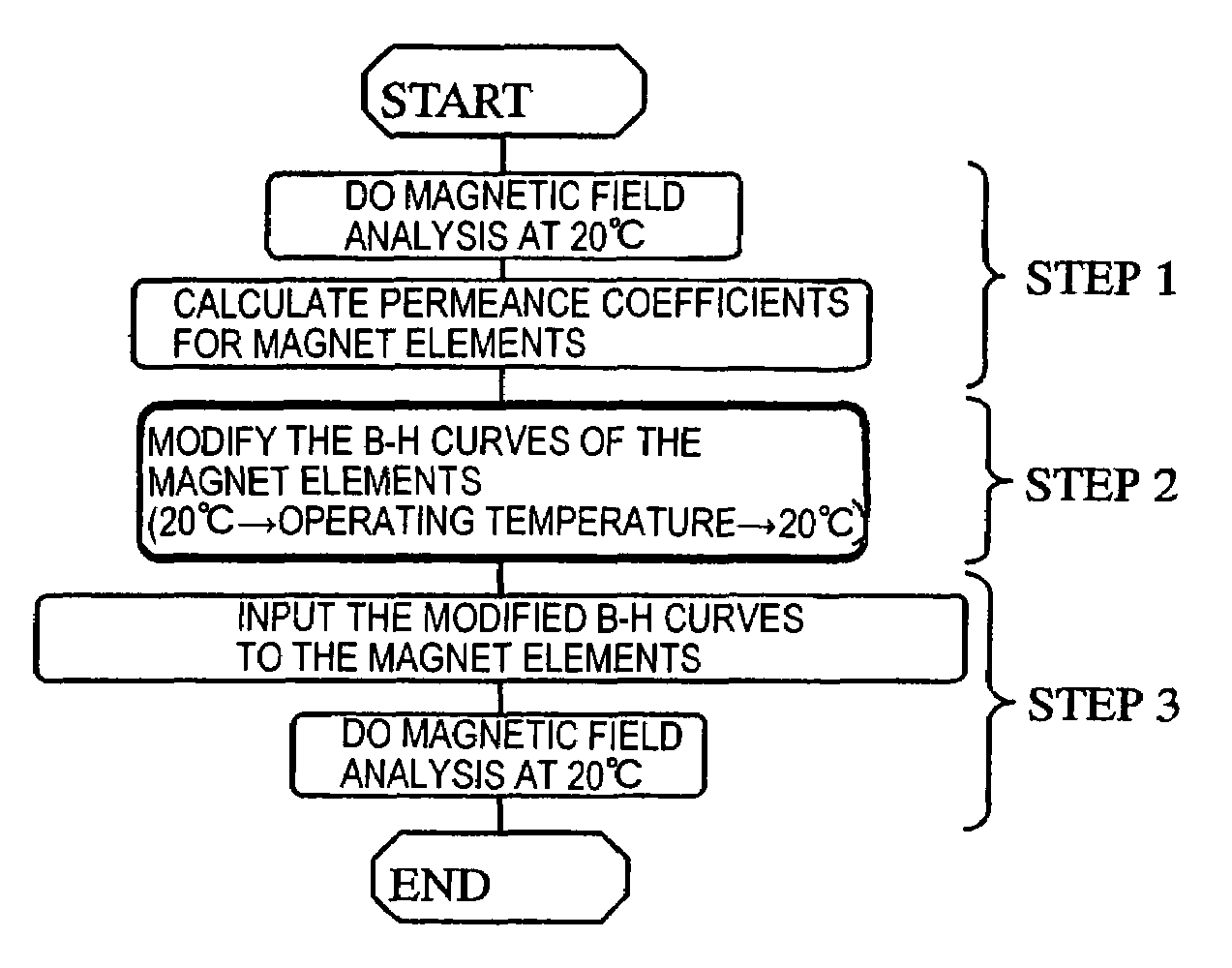
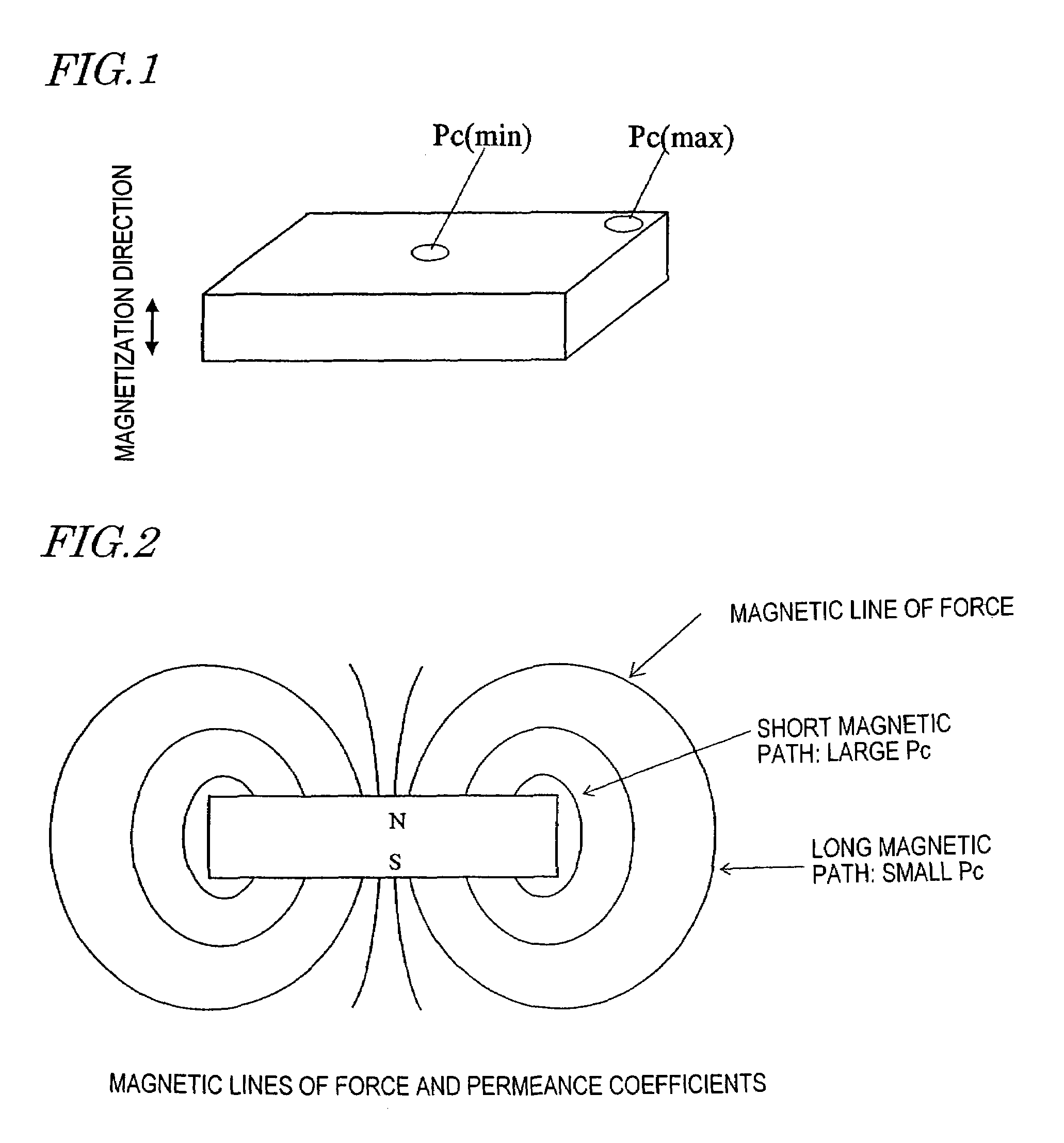
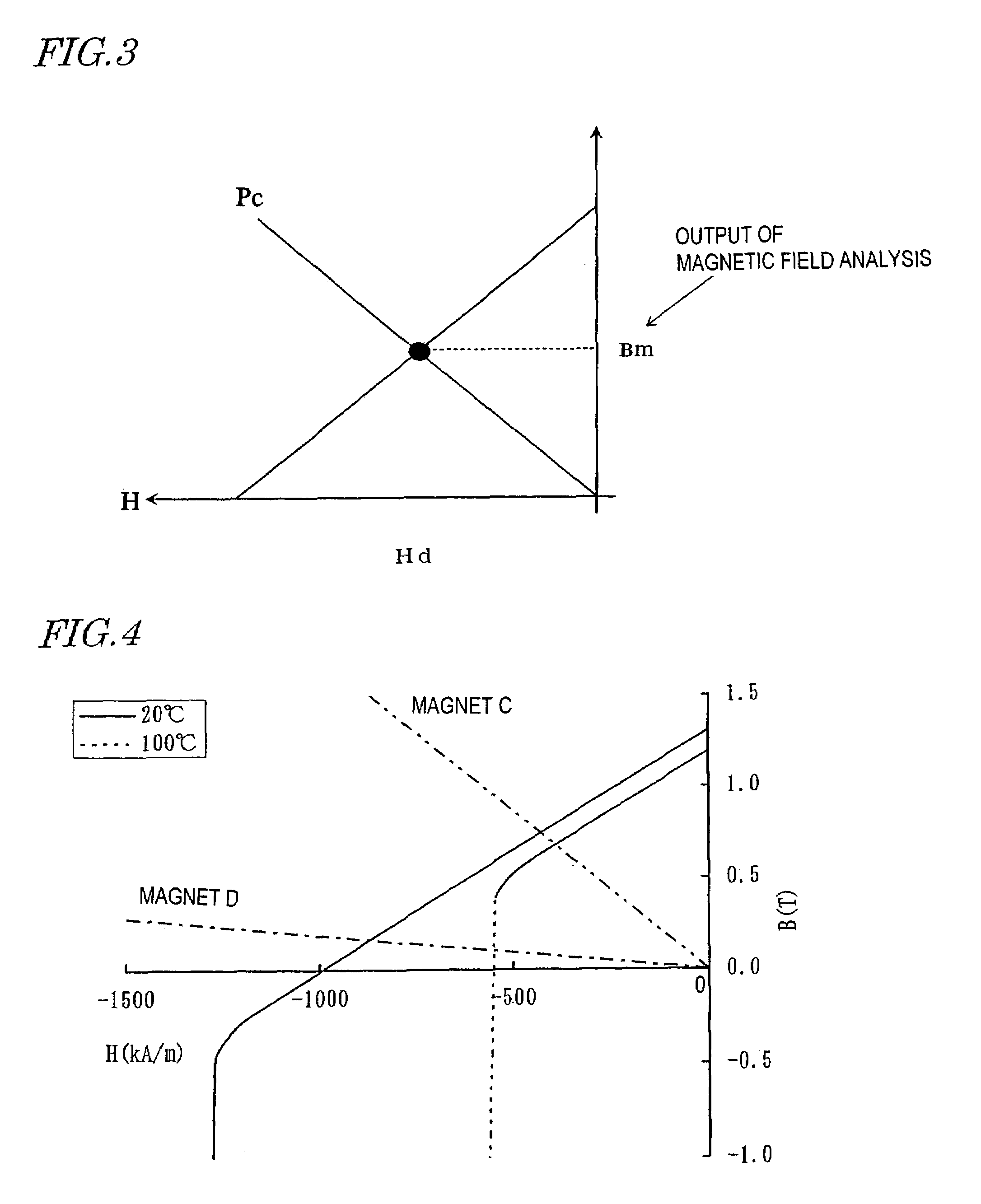
Magnetic field analyzing method and device therefor
ActiveUS20050151609A1Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetic flux density distributionAnalysis method
A method and apparatus for magnetic field analysis, contributing to not only determining whether or not demagnetization would occur in a permanent magnet but also calculating its magnetic flux density distribution after the demagnetization, is provided. In a magnetic field analysis method according to the present invention, first, permeance coefficients at multiple sites in a permanent magnet and / or numerical values that are dependent on the permeance coefficients are calculated based on B-H curve data of the permanent magnet at a first temperature T1. Next, modified B-H curve data of the permanent magnet, which has been operated at a second temperature T2 that is different from the first temperature T1, are derived for the respective sites based on B-H curve data of the permanent magnet at the second temperature T2 and the permeance coefficients or the numerical values.
Owner:SUMITOMO SPECIAL METAL CO LTD
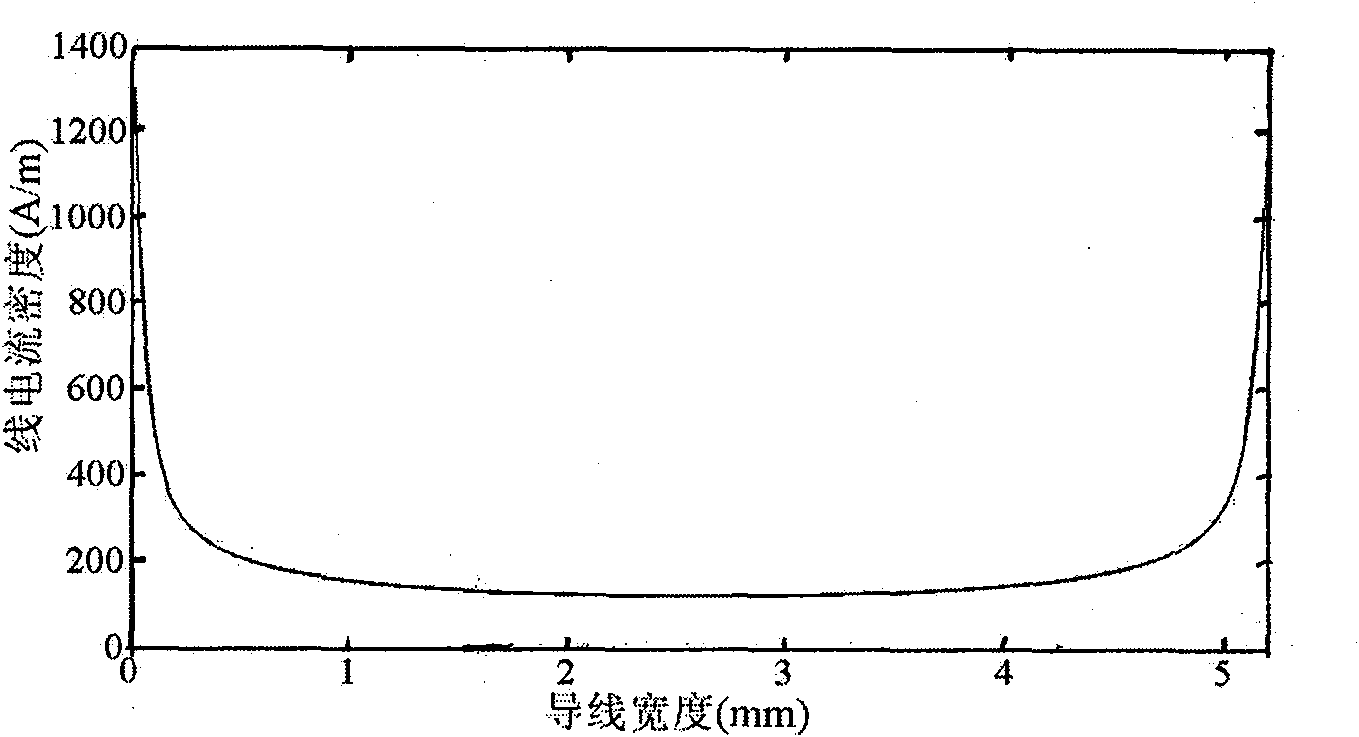
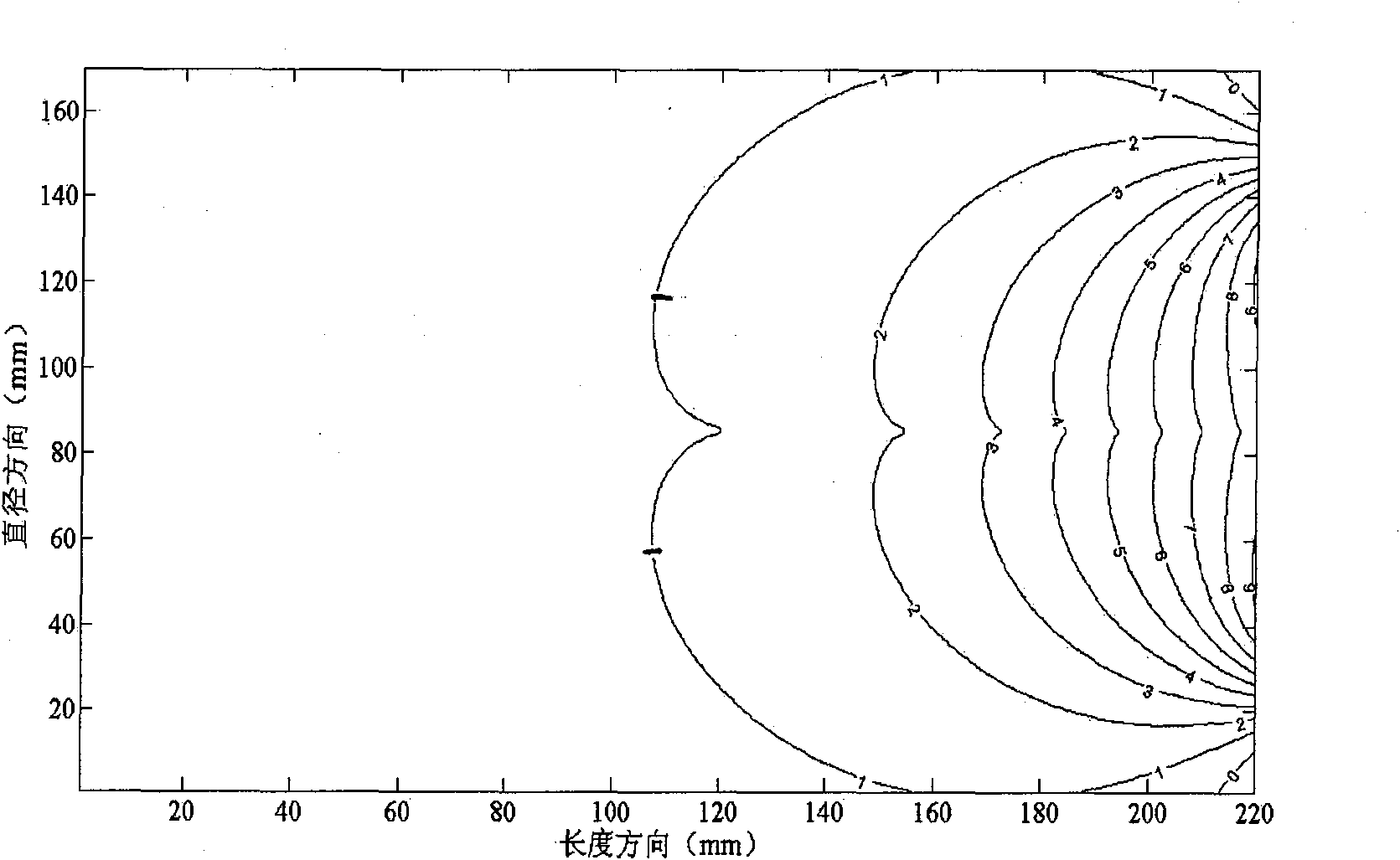
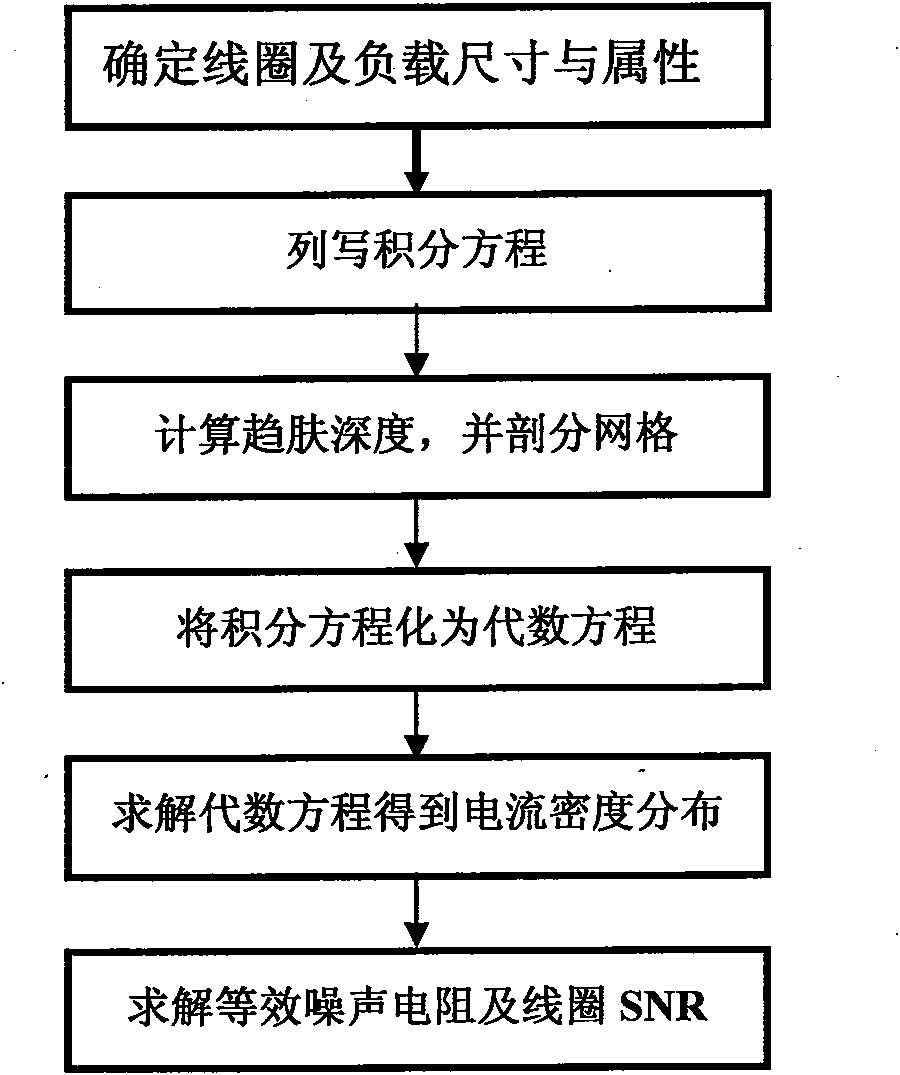
Method for calculating signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF coil
InactiveCN101794329AImprove accuracyAvoid computationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical field strengthAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses a method for calculating a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF coil, belonging to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is characterized by comprising the following steps: constructing an RF coil and a load size and material parameter model, listing integral equations satisfied by current densities, calculating skin depth and surface resistivity of a conductor and dissecting the conductor on the basis, converting the integral equations into algebraic equations, solving the algebraic equations to obtain current density distribution in the conductor, calculating magnetic flux density distribution in the load by using Biot-Savart integral, and adopting vector potential to obtain electric field strength distribution in the load, thus calculating self resistance, load eddy-current loss equivalent resistance and SNR of the RF coil. The invention improves the calculation efficiency of self resistance, load eddy-current loss and electric magnetic field space distribution of the conductor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetic field analyzing method and device therefor
InactiveUS6967551B2Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsOsmotic coefficientMagnetic flux density distribution
A method and apparatus for magnetic field analysis, contributing to not only determining whether or not demagnetization would occur in a permanent magnet but also calculating its magnetic flux density distribution after the demagnetization, is provided. In a magnetic field analysis method according to the present invention, first, permeance coefficients at multiple sites in a permanent magnet and / or numerical values that are dependent on the permeance coefficients are calculated based on B-H curve data of the permanent magnet at a first temperature T1. Next, modified B-H curve data of the permanent magnet, which has been operated at a second temperature T2 that is different from the first temperature T1, are derived for the respective sites based on B-H curve data of the permanent magnet at the second temperature T2 and the permeance coefficients or the numerical values.
Owner:SUMITOMO SPECIAL METAL CO LTD
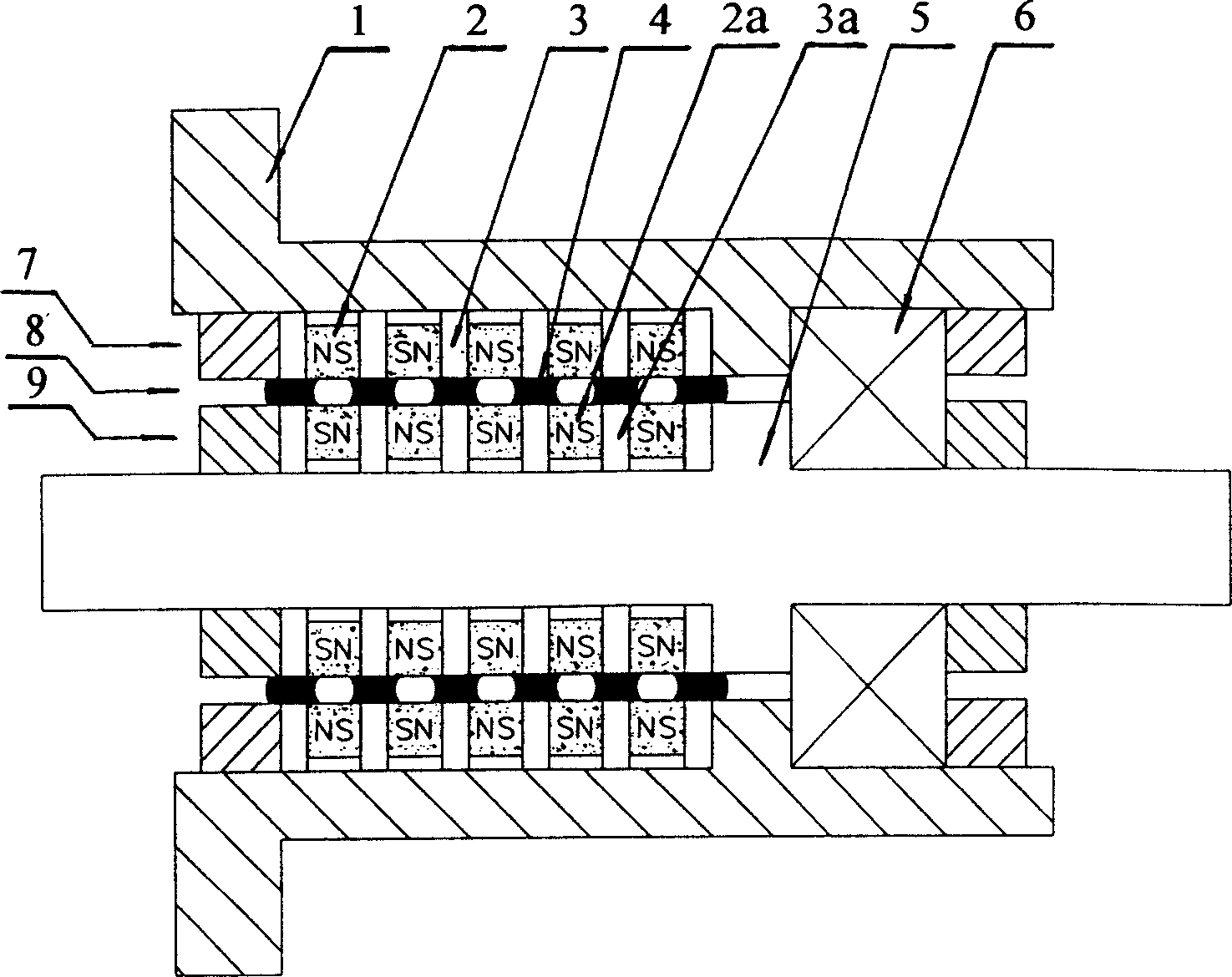
Magnetic floating device
ActiveUS7211908B2Weaken energyLarge forceLinear bearingsMagnetic circuitMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
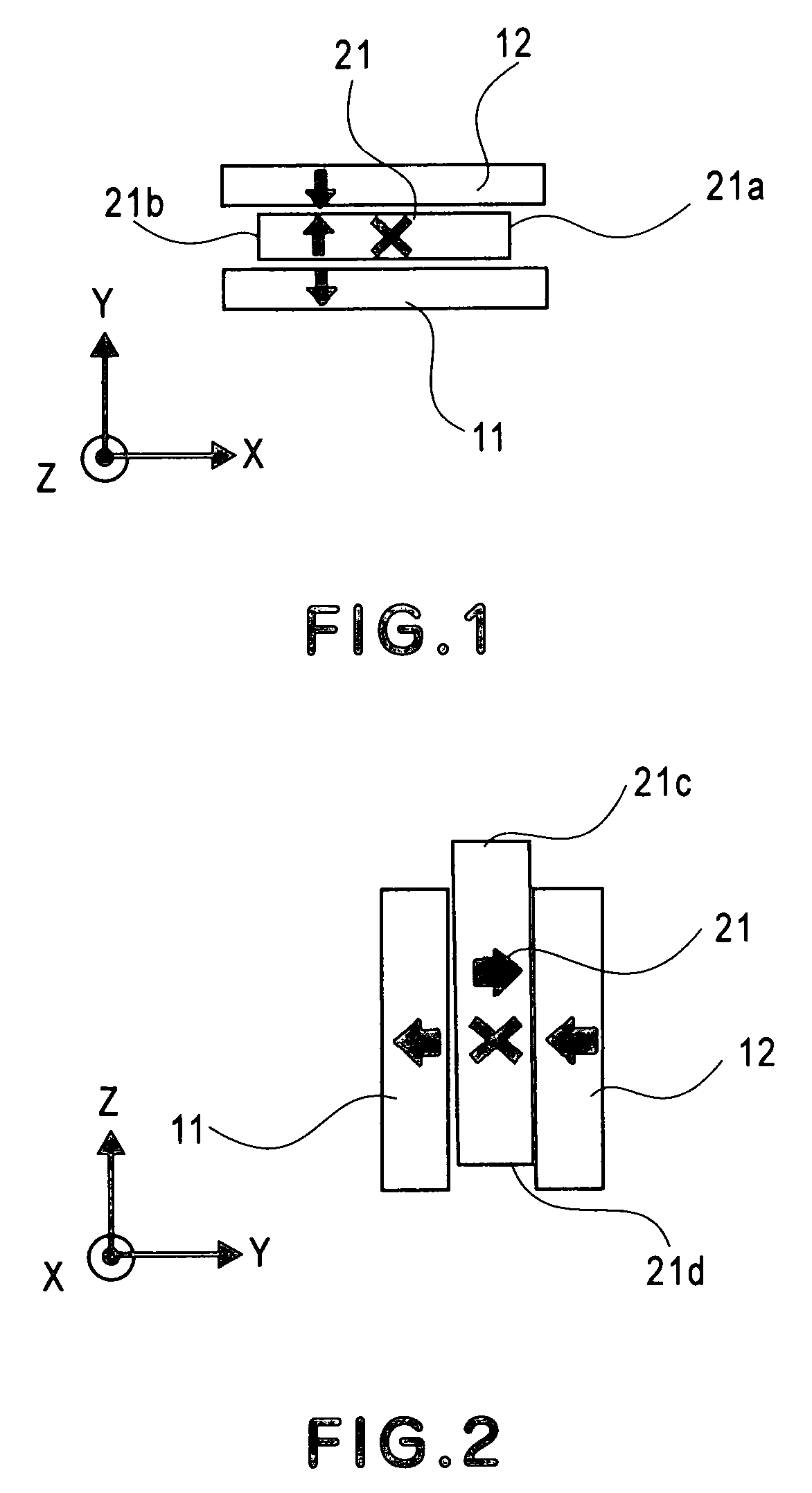
Disclosed is a magnetic floating device in which a movable magnet is sandwiched by fixed magnets in the manner that the same magnetic poles are opposed to each other, such that the movable magnet and the fixed magnets are held relatively movably in a floating direction and an intersecting direction that intersects with a polarization direction of the fixed magnets. The second magnet is placed within a range of extreme value position of a distribution of the magnetic flux density, with respect to the intersecting direction, as produced between the fixed magnets by the fixed magnets, at an opposing surface of the second magnet, being opposed to the fixed magnets. This arrangement assures a large force in the floating direction while making the force in the lateral shift direction weak. Hence, energy consumption of a lateral-direction control mechanism can be reduced significantly.
Owner:CANON KK
Brushless direct-current motor simulator
ActiveCN103607144AEasy to operateProtection securityElectronic commutation motor controlElectronic loadElectromotive force
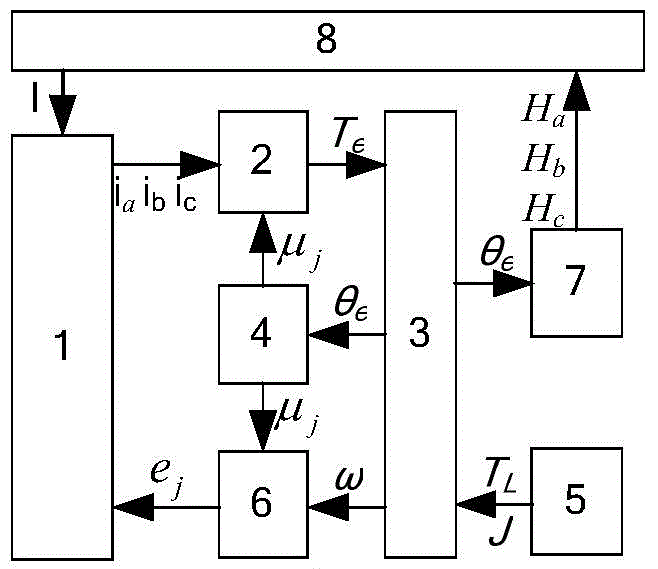
Disclosed in the invention is a brushless direct-current motor simulator. A winding subsystem simulator simulates a winding resistor, an inducer and a back electromotive force; an electromagnetic subsystem simulator simulates an electromagnetic moment of a brushless direct-current motor; a load characteristic simulator simulates a load moment; a mechanical subsystem simulator simulates a mechanical characteristic of the brushless direct-current motor; a magnetic flux density simulator simulates a distribution characteristic of the magnetic flux density of the rotor of the brushless direct-current motor; a back electromotive force subsystem simulator simulates back electromotive forces of three-phase windings of the brushless direct-current motor; and a position sensor simulator simulates an output signal of a switch hall sensor. According to the invention, the electronic load of the brushless direct-current motor body can be replaced; and the brushless direct-current motor simulator has the real electrical and mechanical characteristics of the brushless direct-current motor; important parameters like a driving voltage, a driving current, a back electromotive force and an electromagnetic moment and the like can be monitored; information including commutation errors and current abnormality and the like can be recorded; and the simulator has the fault self-diagnosis capability and the processing capability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Permanent magnet electric rotating machine and electromotive vehicle using permanent magnet electric rotating machine
InactiveUS20030102757A1Reduce pulsationReduce centrifugal forceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Development magnet roller, development device, process cartridge and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS7352983B2Improvement in trailing edge omissionInhibit adhesionPermanent magnetsElectrographic process apparatusImage formationPeak value
A development magnet roller for use in a development roller of an electrophotographic image forming apparatus is provided. The development magnet roller has a development pole to form a magnetic field causing a developer born on a surface of the development roller including the development magnet roller to rise in a form of a series of ears in a development area of the image forming apparatus where the development roller opposes an image bearing member, and in a magnetic flux density distribution in a normal line direction of the development pole, a peak magnetic flux density is 120 mT or greater, a zero gauss region width is 70° or greater, and a half-value region width is 40° or smaller.
Owner:RICOH KK
Process for preparing square deflecting magnetic core and material thereof
ActiveCN1547234AReduce manufacturing costGuaranteed performance indicatorsMagnetic deflection device manufactureInorganic material magnetismTelevision receiversElectron
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a kind of square deflection magnetism core and the materials. 1) the Fe2O3, ZnO, Mn3O4, ...MgO, and additives CuO, Bi2O3 elements are blended, prebaked, and reacted with solid phase, the compound generates the ferrite phase after being prebaked; 2) the prebaked material are grinded into pulp with particle size less than phi1.8ª–m, then the additives are added in and carries on the atomization pelleting; 3) the particles are blended and pressed, formed in the automatic presser and special model; 4) uses the flat board or bake bearing base process to carry on oriented baking. The merits of the invention are: 1) it uses cheap materials ferric oxide, with current manufacturing device and special process, it decreases the cost greatly, the key technology parameter is upgraded; 2) PF design makes the magnetic flow area and the density distributed more reasonable, it upgrades the articulation and resolution of the screen; 3)( upgrades the deflection efficiency of negative transmitting pipe of the television receiver, reduces the idle work consumption of the electron beam deflection.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
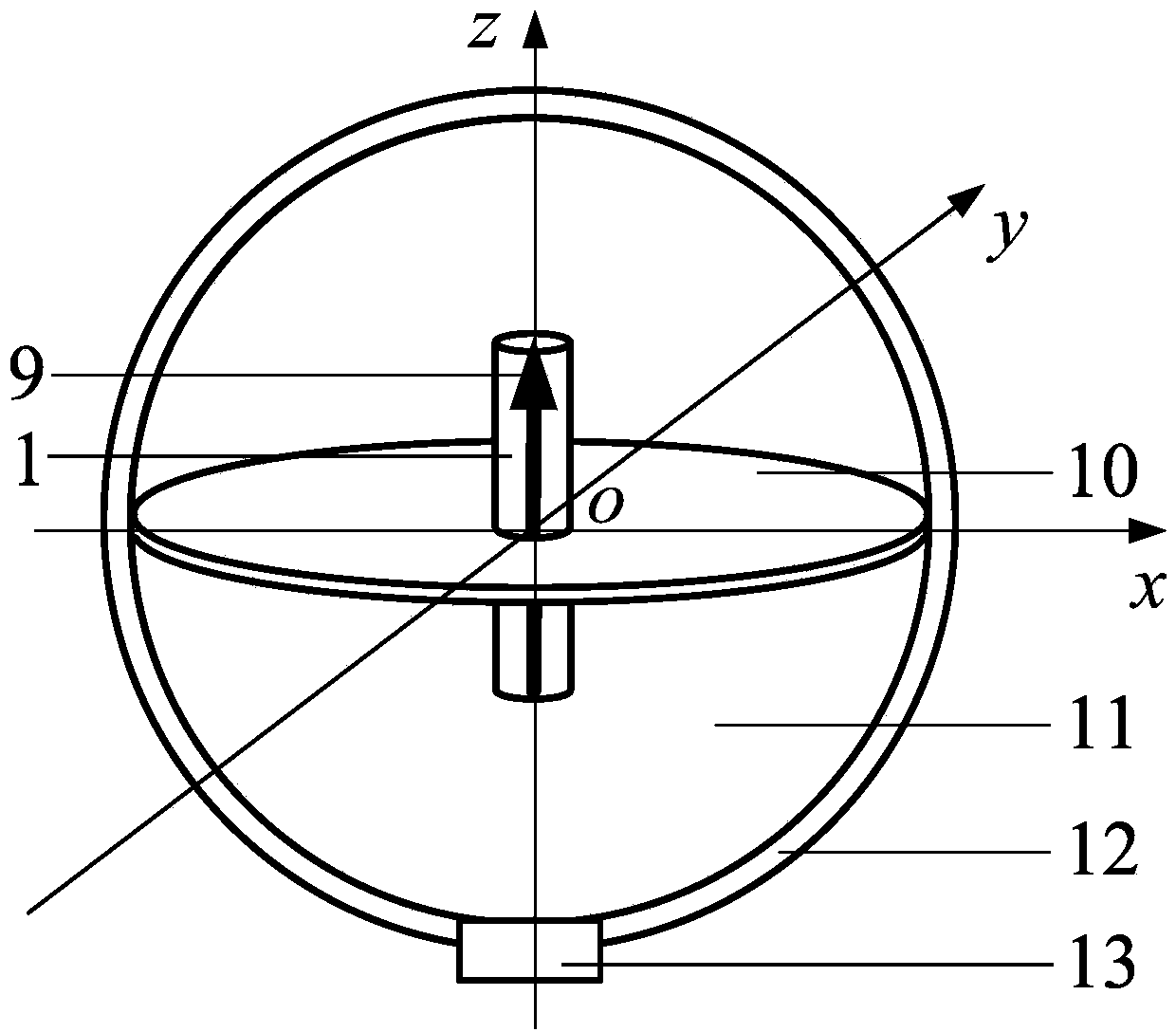
Linear positioning method based on marked magnetic source with permanent magnetic dipole moment
The invention discloses a linear positioning method based on a marked magnetic source with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. The linear positioning method based on the marked magnetic source with the permanent magnetic dipole moment comprises the steps that a space magnetic field is established by means of the marked magnetic source which has the vertically upward magnetic dipole moment all the time, and the corresponding relation between the magnetic flux density distribution intensity and the distances between measurement points and the marked magnetic source is obtained; an xyz rectangular coordinate system is established, and the magnetic flux density components, at the position of each measurement point in the space magnetic field, in all the directions of the coordinates are detected, so that the magnetic flux density distribution intensity and the distances between the measurement points and the marked magnetic source are obtained; all coordinate values at the position of the marked magnetic source are obtained according to the magnetic flux density components in all the directions of the coordinates and magnetic flux density components detected through a three-axis magnetic field measurement sensor based on a marked magnetic source magnetic coupling polaron positive model, and thus accurate positioning of a marked object is achieved. According to the linear positioning method based on the marked magnetic source with the permanent magnetic dipole moment, the solution to the location parameters of the magnetic source is achieved based on the linear model; compared with a traditional magnetic marking and positioning method, the linear positioning method has the advantages that only one three-axis magnetic sensor is needed, the solution can be achieved without the need of the non-linear iteration method, rapid positioning is achieved, the precision is high, and cost is low.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
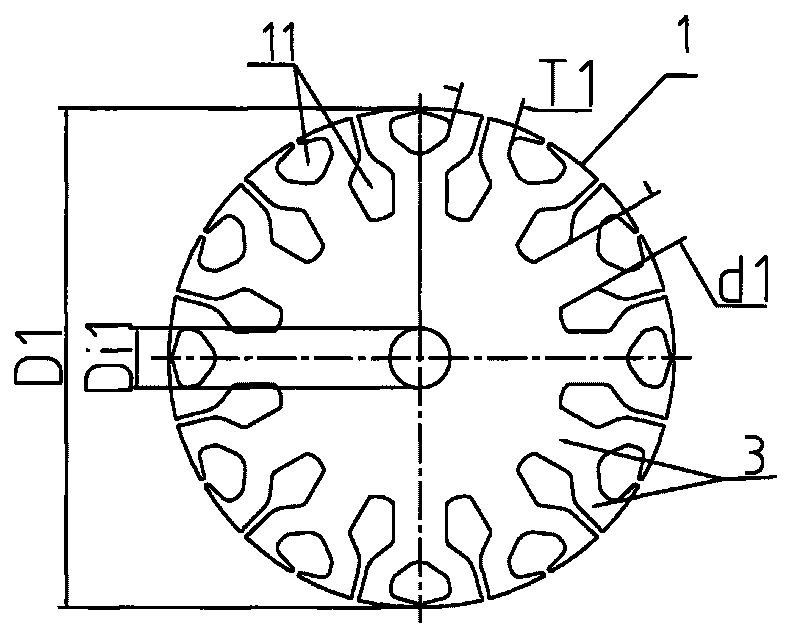
12-pole external-rotor capacitor-run asynchronous motor
The invention relates to a 12-pole external-rotor capacitor-run asynchronous motor, which comprises a motor stator arranged on a motor shaft, and a motor rotor sleeved outside the motor stator; the number of stator slots of the motor stator is 24, wherein the number of main winding slots and the number of secondary winding slots are respectively 12; the ratio of the number of the stator slots of the motor stator to the number of rotor slots of the motor rotor is 0.3-0.7; the ratio of the stator outer diameter D1 of the motor stator to the rotor outer diameter D2 of the motor rotor is 0.68-0.95. The 12-pole external-rotor capacitor-run asynchronous motor has the characteristics of small motor shock, low noise, high rotating speed and the like; in addition, in order to fully utilize the iron core punching area, the slot type is designed into a double-row slot structure, the slot area and tooth area are increased and the service efficiency of an iron core is effectively improved; moreover, the slot type adopts arc transition, the width of tooth parts and yoke parts of the rotor and the stator is uniformly designed, the distribution of magnetic flux density of the tooth parts and yoke parts of the rotor and the stator is reasonable and relative balanced, the reduction of iron consumption of the punching is facilitated, the radiation of the motor is reduced, the winding temperature rise is reduced, and the magnetic flux density and motor noise are reduced.
Owner:MIDEA GRP CO LTD
Electrical machine and permanent-magnet
ActiveCN102223039AMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesElectric machineMagnetic flux density distribution
The invention relates to an electrical machine, which contains permanent magnets and to the permanent magnets being used. The invention especially relates to a synchronous machine. The magnet and the coil interact with the permanent magnet via an air gap, which is located between the permanent magnet and the coil. The permanent magnet and the coil are arranged in a way that electrical power is generated in the coil when the permanent magnet or the coil is moved in their relative position to each other. The permanent magnet contains a surface, which is aligned to the coil and to the air gap in a way, that magnetic forces of the permanent magnet interact via the surface and the air gap with the coil by a magnetic flux density distribution. The cross sectional shape of this surface approximates at least partly to a sinusoidal-function.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Anisotropy ferrite magnet and motor
ActiveCN101055786AReduce torqueReduce torque fluctuationPermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismMagnetic anisotropyHorizontal axis
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method for computing air gap flux density of permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN103279607ASuitable designAccurate calculationSpecial data processing applicationsComputational modelPhysical model
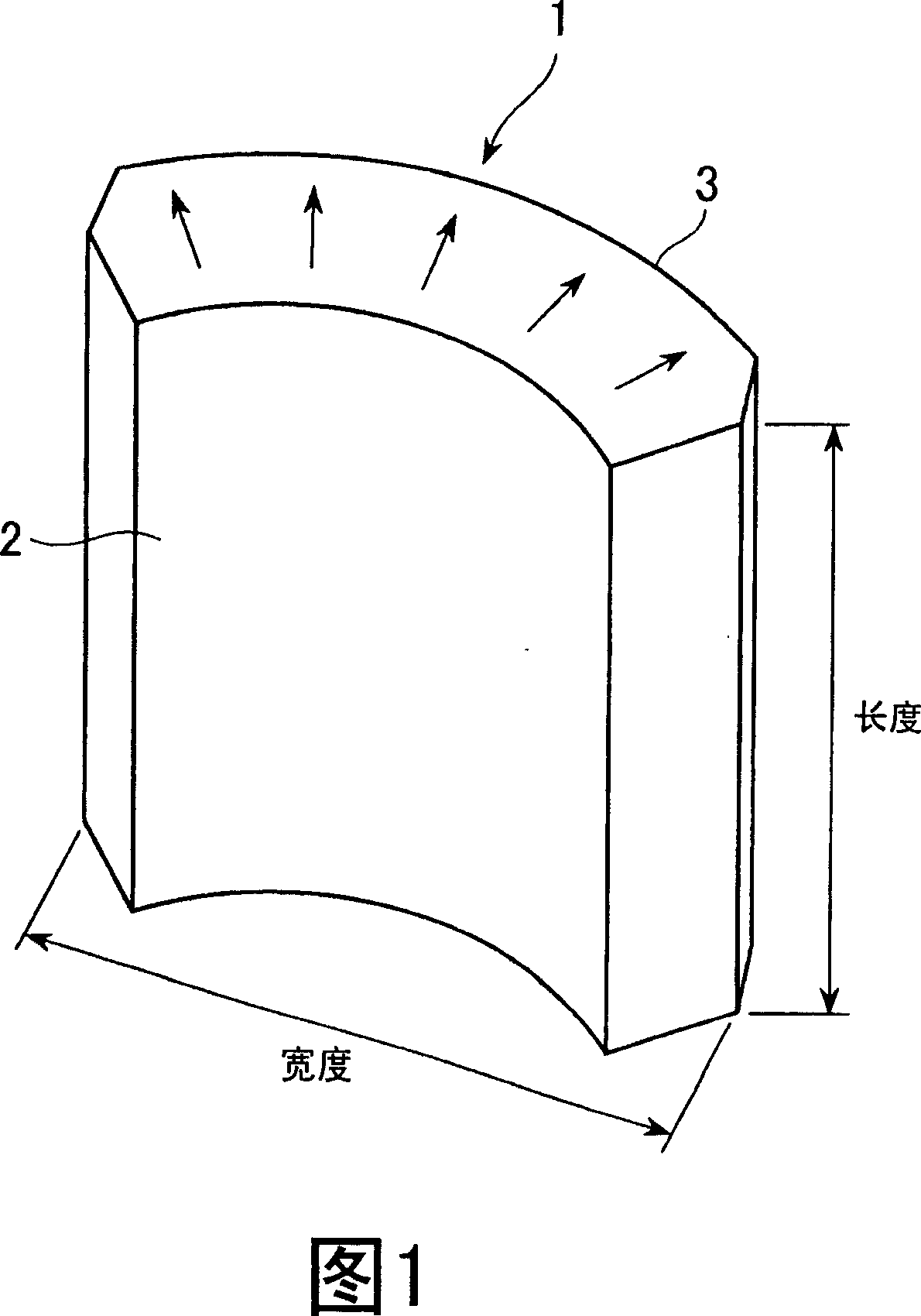
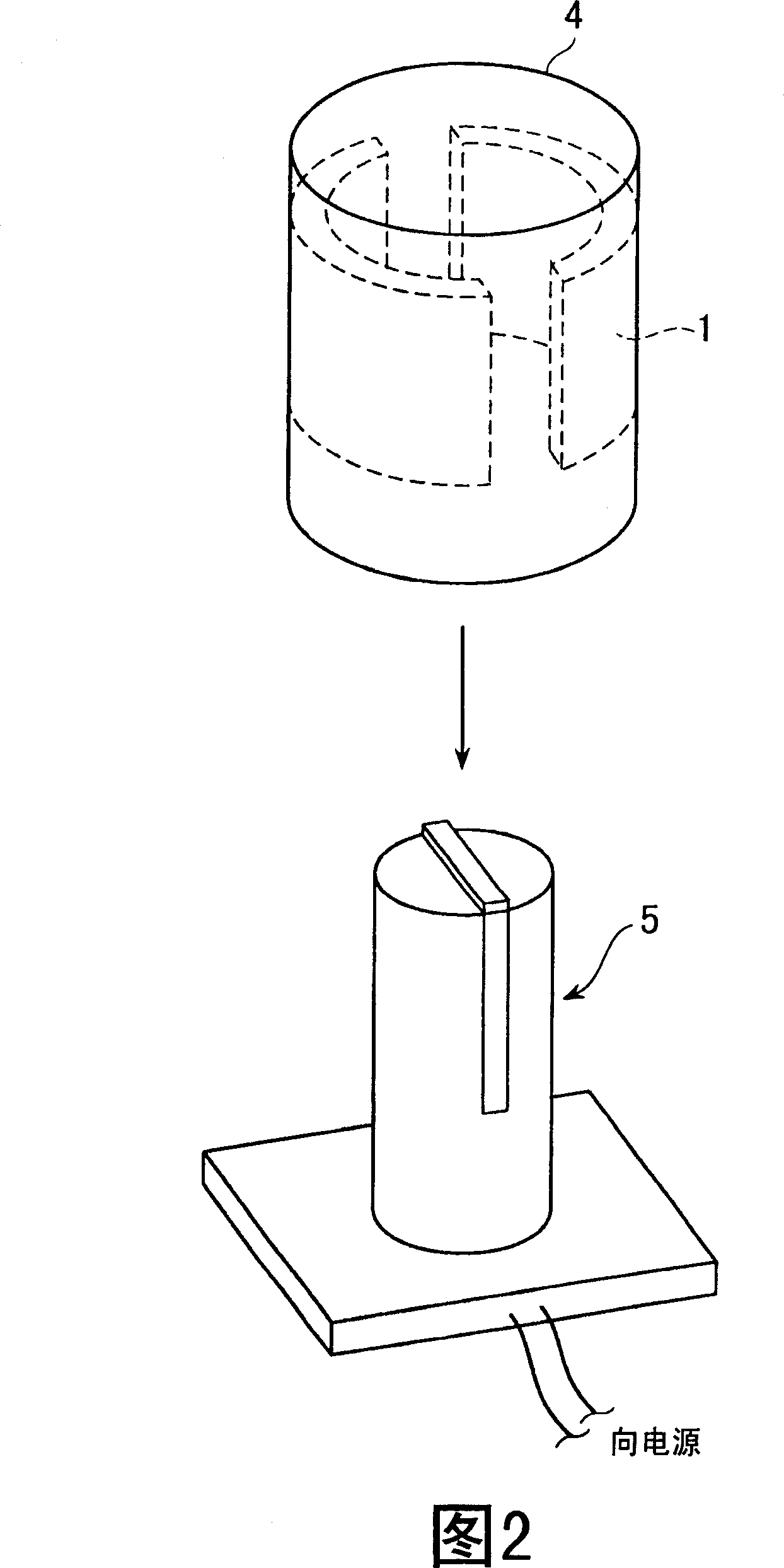
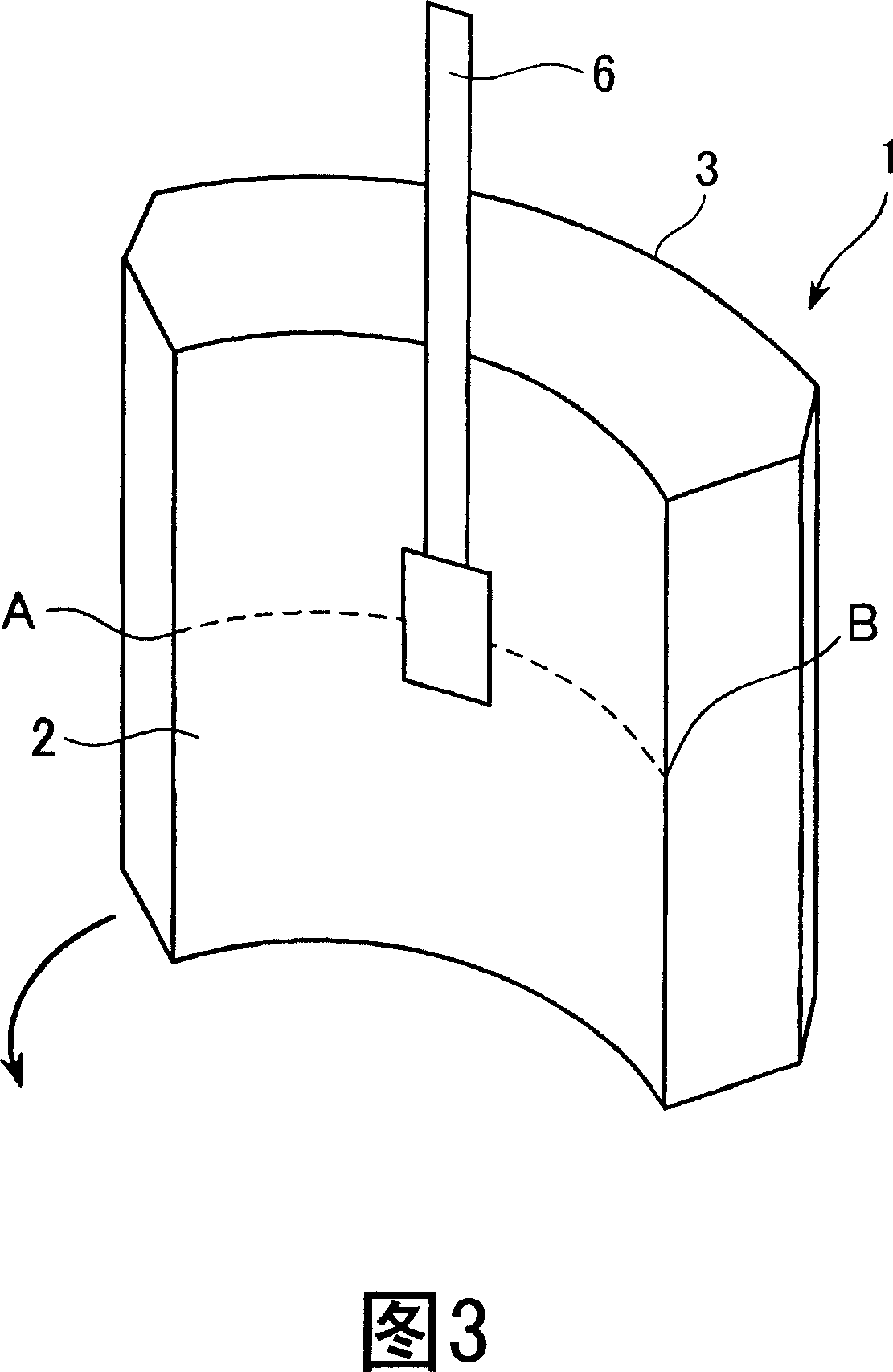
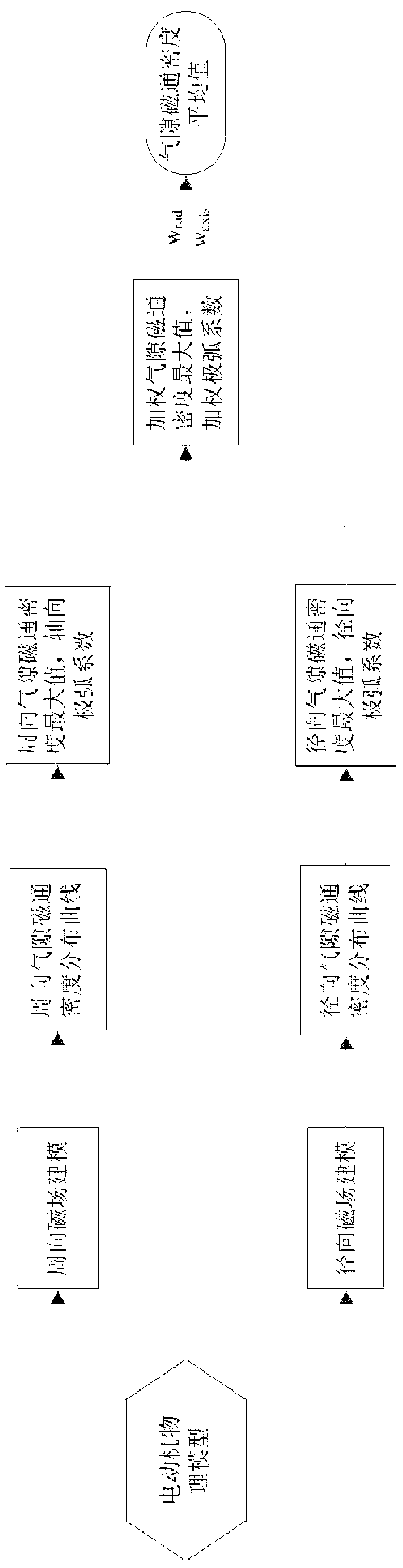
The invention relates to a method for computing the air gap flux density of a permanent magnet motor and belongs to the technical field of motors. The method comprises the steps of establishing a circumferential magnetic circuit computational model and a radial magnetic circuit computational model according to a permanent magnet motor physical model, carrying out electromagnetic field solving on the air-gap field of the circumferential magnetic circuit of the permanent magnet motor and on the air-gap field of the radial magnetic circuit of the permanent magnet motor to obtain a circumferential magnetic circuit air gap flux density distribution curve and a radial magnetic circuit air gap flux density distribution curve, introducing a circumferential weight number and a radial weight number, and computing the air gap flux density of the permanent magnet motor by means of the circumferential weight number and the radial weight number. The method for computing the air gap flux density of the permanent magnet motor is not limited by the structural style and the size of the motor, accurate in computation, and suitable for design and analysis of the permanent magnet motor.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Permanent magnet motor rotor having magnetic permeable material for enhanced flux distribution
InactiveUS6844645B2Inhibition effectIncreased torque outputMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet motorMagnetic flux density distribution
A permanent magnet motor has rotor structure that includes magnetically permeable backing material attached to magnets for enhancing flux density distribution. A plurality of permanent magnets are circumferentially distributed about an axis of rotation, adjacent magnets successively alternating in magnetic polarity. The magnetically permeable material is configured with apertures therethrough at areas of low flux density, such as at central portions of the magnets, while in contact with perimeter areas of the magnets. Additional apertures in the material may be located at spaced intersections at which no significant flux density exists. The apertures may be replaced with backing material portions of reduced radial thickness.
Owner:HANON SYST EFP BAD HOMBURG GMBH
Dried calibration method and apparatus of portable electromagnetic flowmeter
InactiveCN101377429ADry Calibration ImplementationImprove calibration efficiencyTesting/calibration apparatusMagnetic sensor arraysSensor arrayMathematical model
The invention provides a dry calibration method and the device for the portable electromagnetic flow meter. The device comprises a measuring paper which is arranged with hall sensor array, a measuring control module and a portable computer. The measuring paper is pasted to the inner wall of the electromagnetic flow meter pipe. The computer controls the measuring paper through the measuring control module to obtain the normal flux density distribution information of the pipe inner wall, and furthermore, combining with the geometries of the electrode and the pipe and the flow rate distribution information, and by using the computer program compiled based on dry calibration methematical model, the once sensor conversion coefficient can be calculated, and so the once sensor dry calibration of the electromagnetic flow meter can be realized. The size of the measuring paper can be adjusted by cutting or assembling, which leads that the device can be applied in the electromagnetic flow meter with different size. The device removes the complicate point-by-point scanning process and the bulky driving mechanism in the prior point-by-point typed dry calibration device, which makes the calibration rate improve greatly. The device is quite light and convenient, and is a portable dry calibration device for the electromagnetic flow meter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Lens driving apparatus and method
ActiveUS9500838B2Remove unfamiliar feelingRemove unfamiliar feeling in manipulation of a userAC motor controlMountingsOptical axisMagnetic flux density distribution
A lens driving apparatus for a lens includes a voice coil motor. A coil position of a coil is detected. A table memory stores a correction factor for each one of plural values of the coil position according to flux density distribution. The correction factor is read from the table memory according to the detected coil position. A coil current is corrected by use of the correction factor for each coil position. The corrected coil current is caused to flow through the coil, with which the lens is moved together along an optical axis. Consequently, changes in a moving speed of the lens can be prevented.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com