Patents
Literature
323 results about "Motor noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
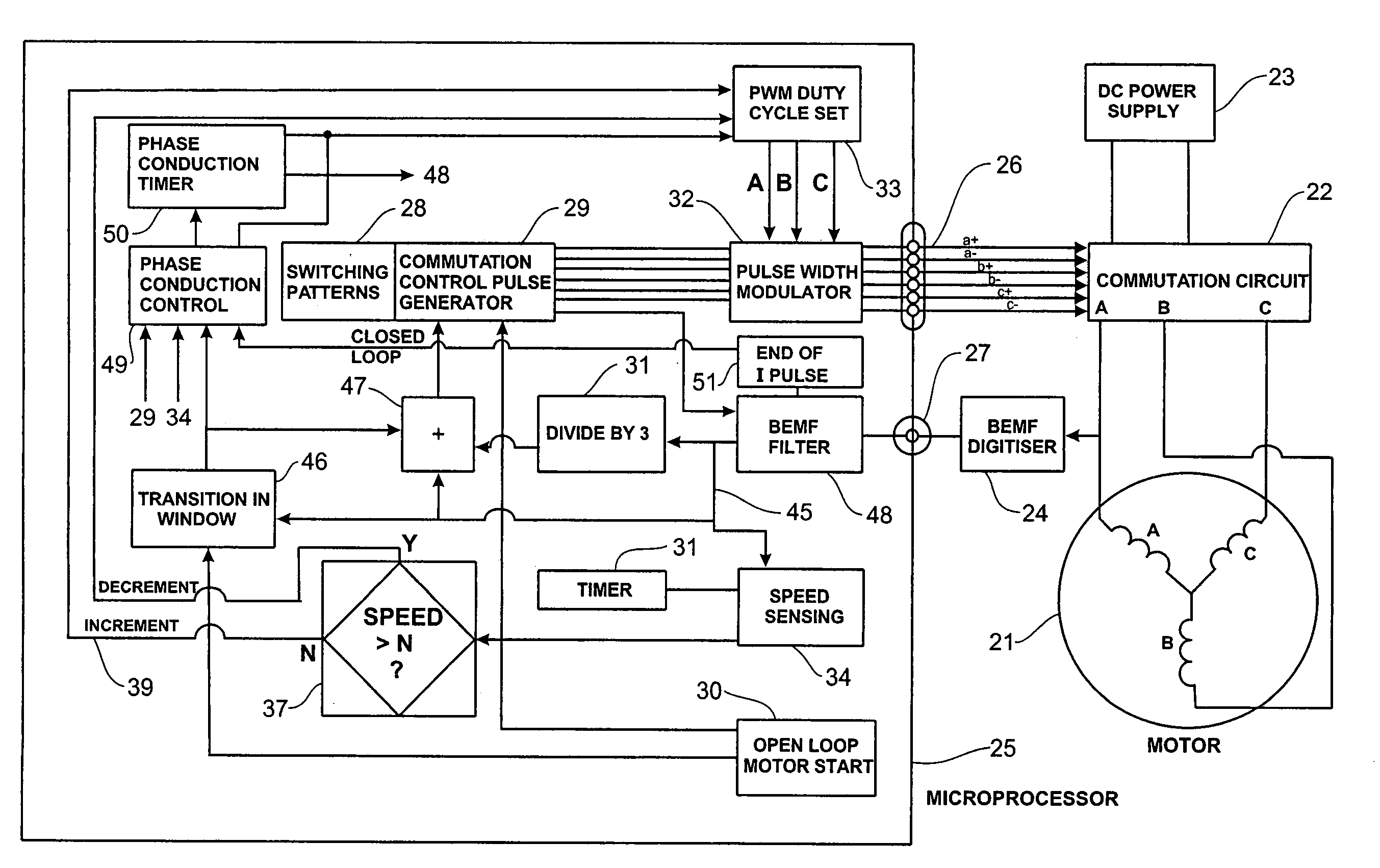
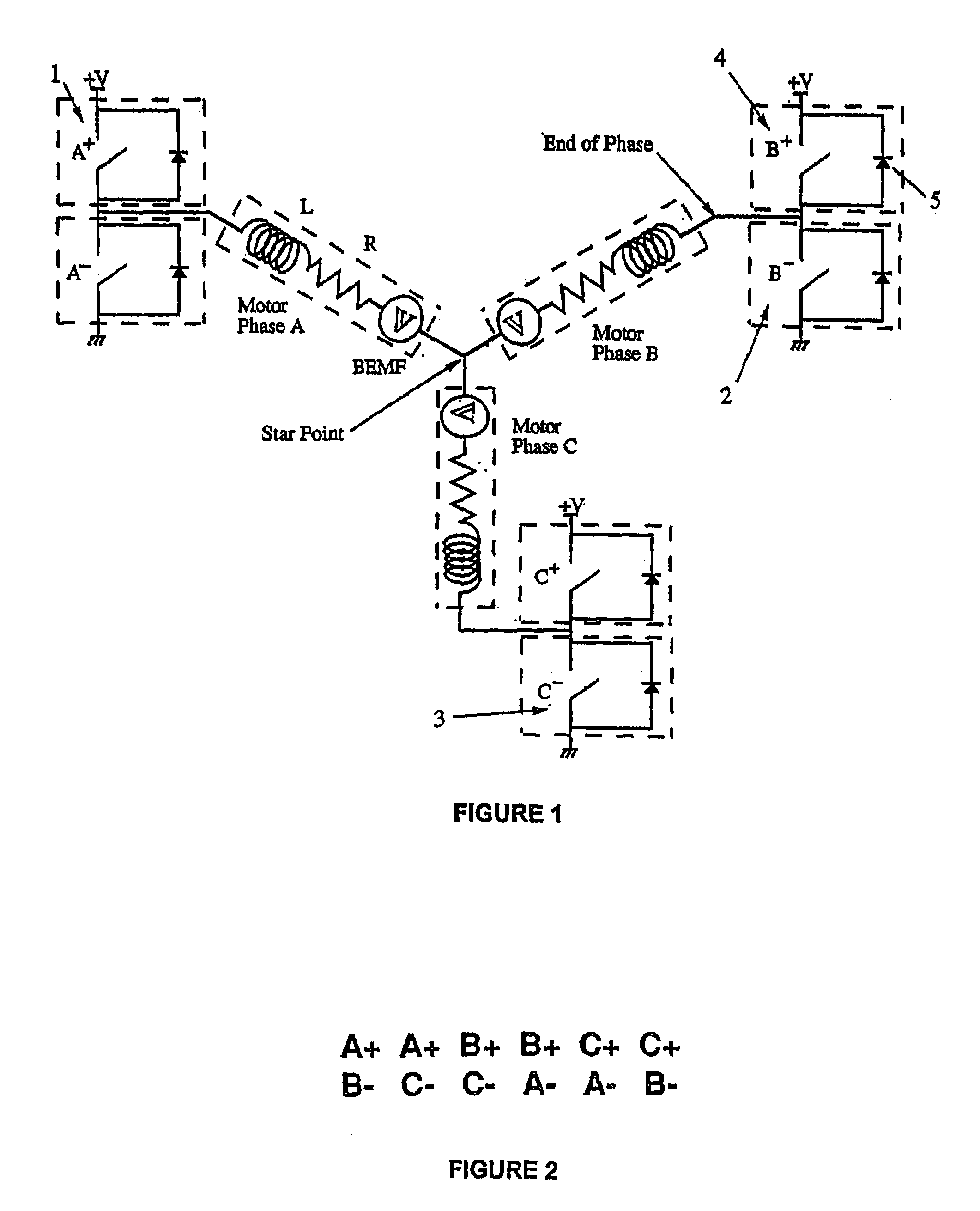
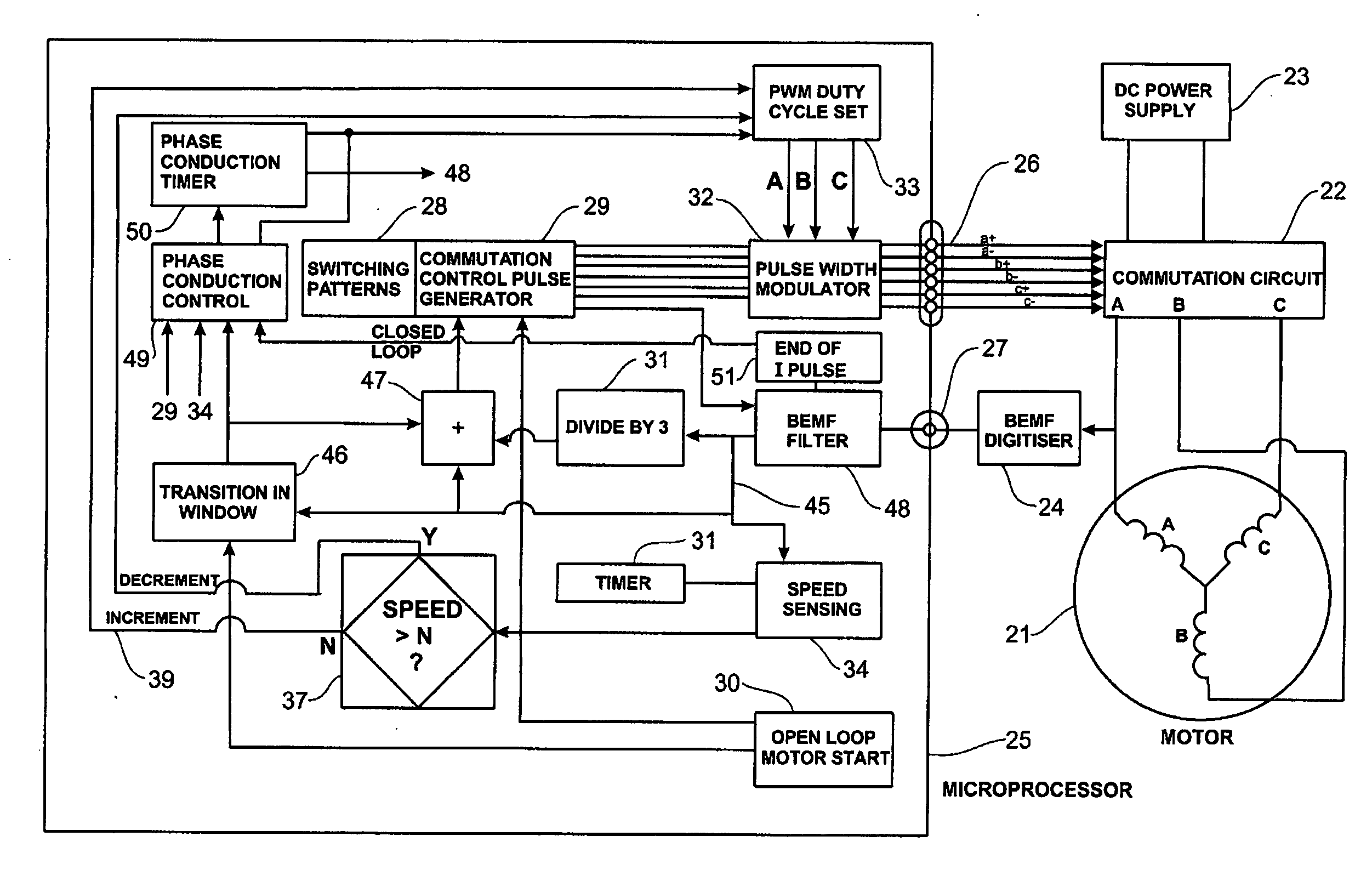
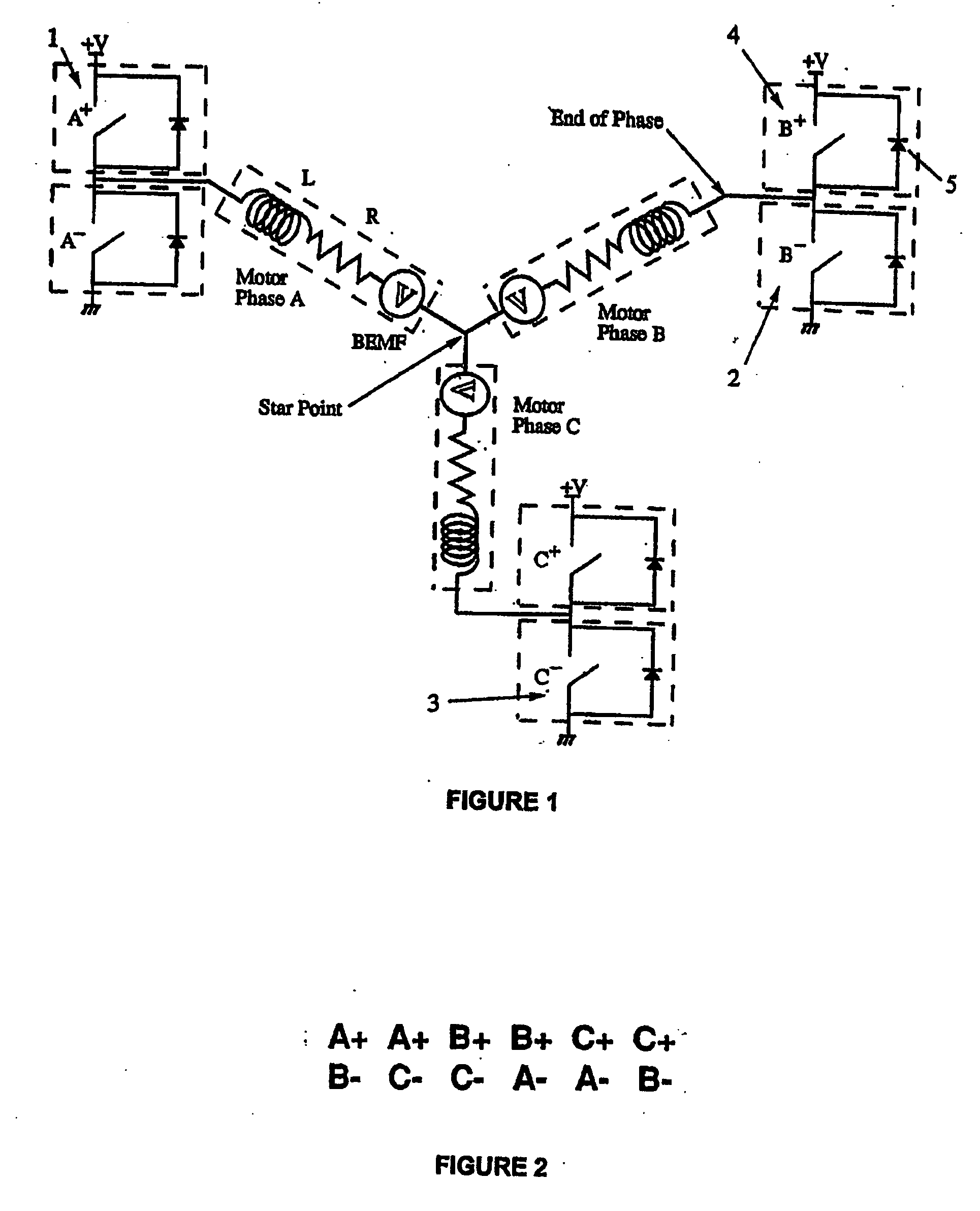
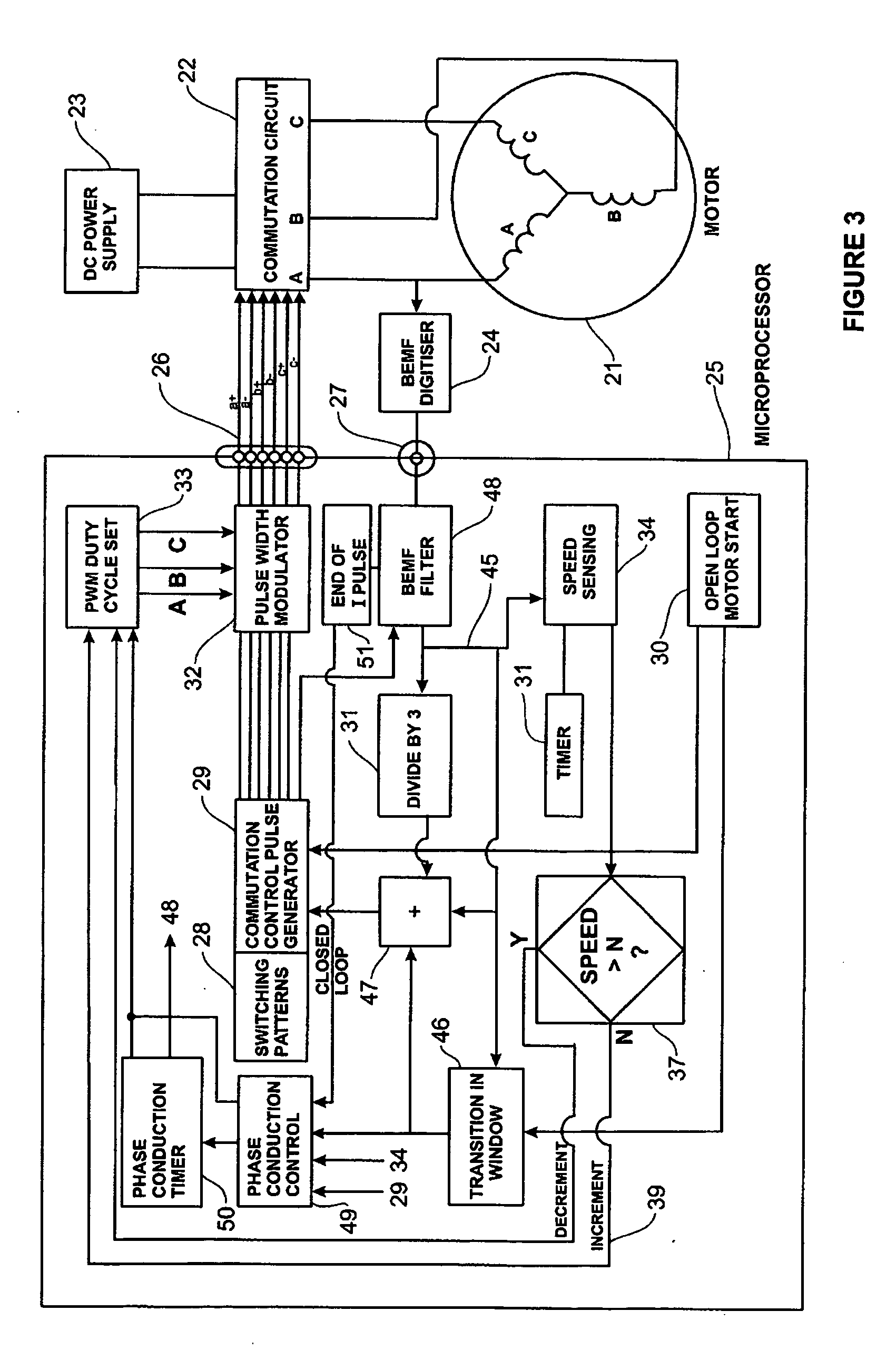
Low noise back EMF sensing brushless DC motor
InactiveUS7141949B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow noiseEngineering
A low noise electronic three phase bridge controlled brushless DC motor suitable for whiteware appliance pumps and other appliance applications. Back EMF zero crossing sensing is used to determine rotor position and thus stator winding commutation times. Motor torque and speed are controlled by pulse width modulating the operation of that bridge switching device which has just been switched from an OFF state to an ON state on each new commutation. All three stator windings have current flowing in each winding commutation to improve motor current waveform and thereby reduce motor noise, but the current in one winding is always terminated before the end of the commutation period to allow the back EMF in that winding to be sensed to zero crossing.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
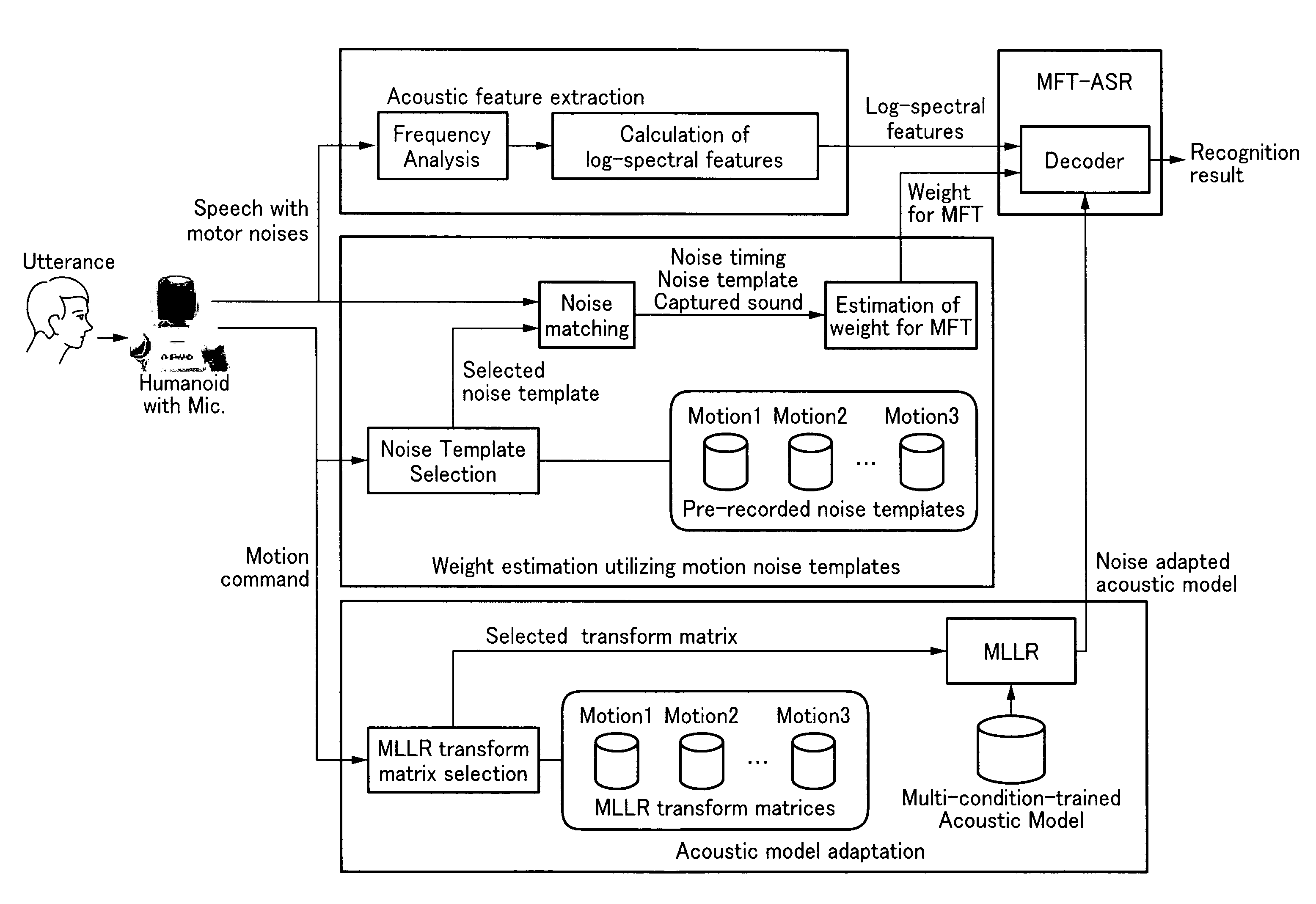
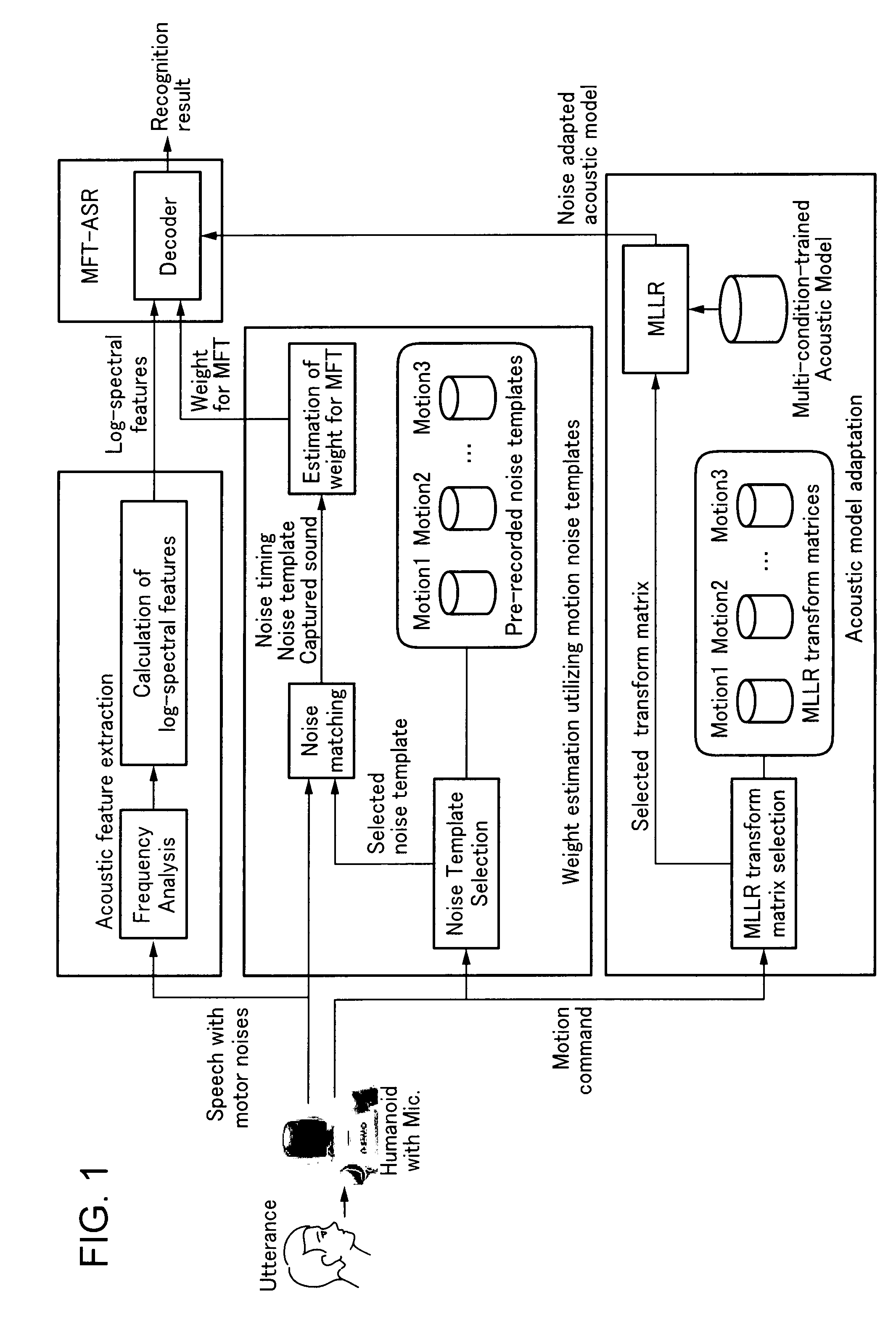
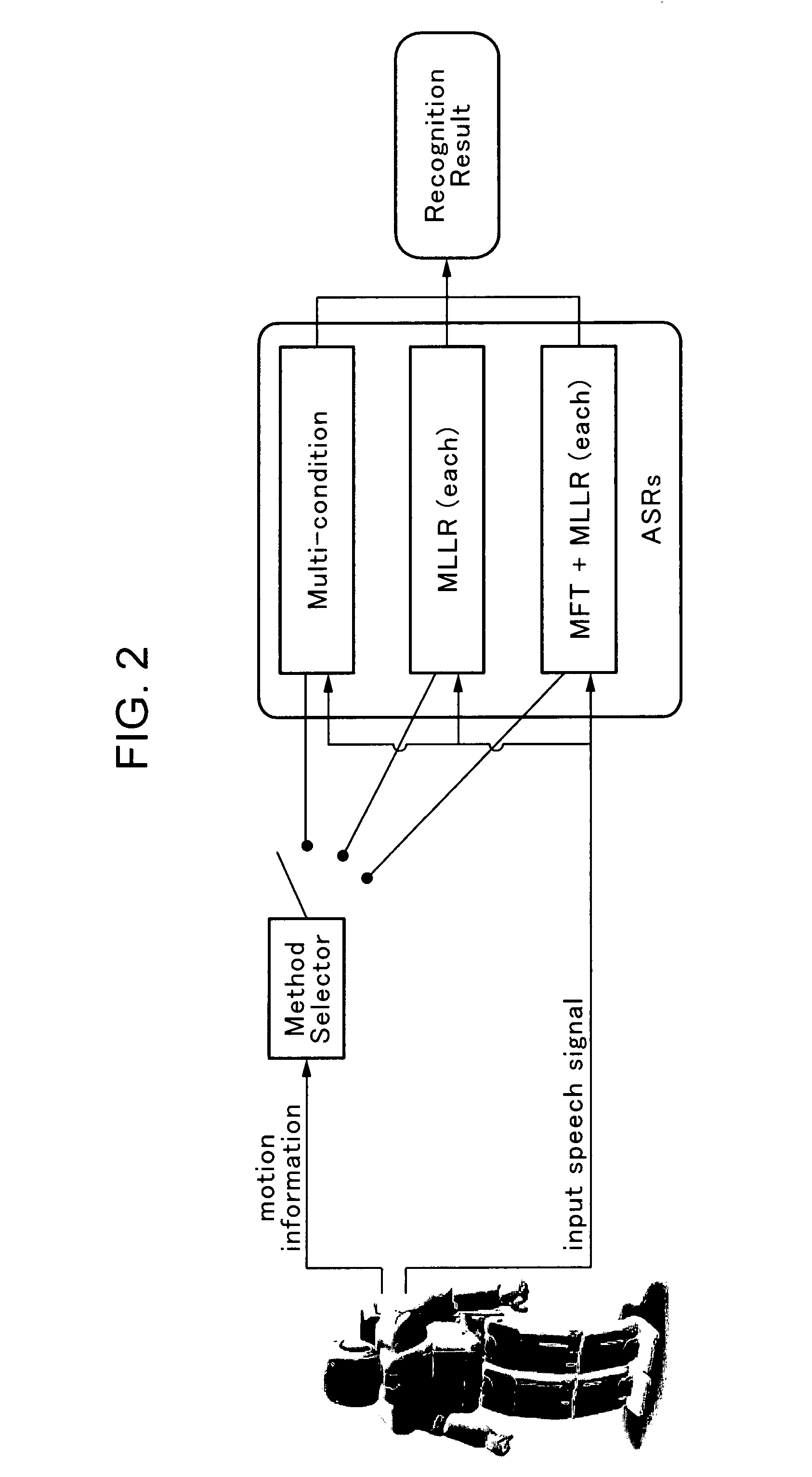
Speech recognition method for robot under motor noise thereof
A robot that recognizes speech of a person while performing predetermined motions or gestures, the robot includes: a drive unit executing the motions or gestures; a determination unit determining one of the motions or gestures being executed; a speech recognition unit having at least two recognition algorithms including a multi-condition training algorithm; and a switch unit selecting one of the recognition algorithms depending on one of the motions or gestures determined.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
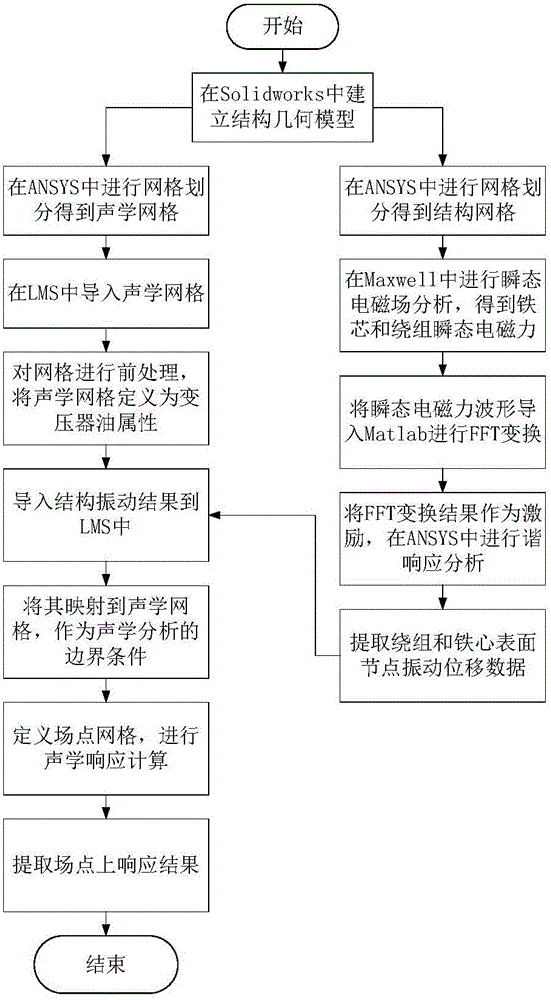
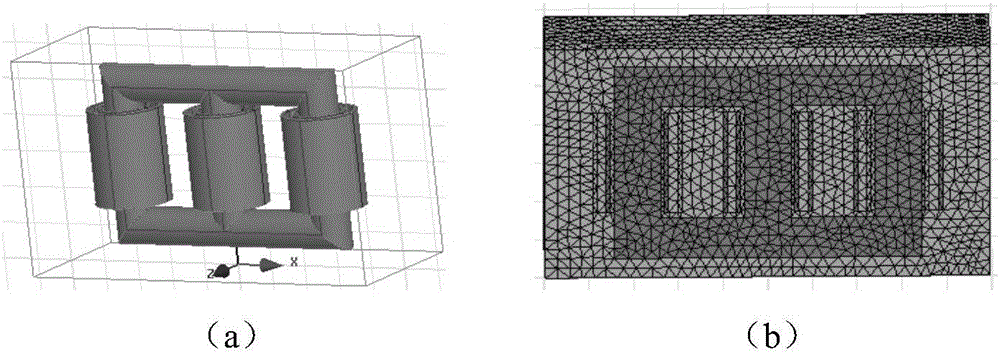
Transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method based on finite element method
InactiveCN105095609AEasy data transferCalculations are reliableSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerEngineering
The invention discloses a transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method based on the finite element method. The transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method comprises the steps of 1, establishing a structured grid model and an acoustics grid model according to a three-dimensional geometrical model of a transformer; 2, conducting transient electromagnetic simulation on the structured grid model to obtain transient electromagnetic force waves borne by each phase winding and an iron core; 3, conducting FFT on the transient electromagnetic force waves borne by each phase winding and the iron core to obtain the frequency domain distribution of electromagnetic force borne by each phase winding and the iron core; 4, conducting harmonic response analysis on the structured grid model to obtain the vibration displacement data of nodes on the surfaces of the windings and the iron core; 5, conducting sound field calculation on the acoustics grid model to obtain the radiation noise distribution of the transformer. According to the transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method, all noise influence factors are considered, and calculation results are accurate and reliable. The transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method can be used for winding short circuit vibration deformation analysis and the like and can also provide method and basis for motor noise analysis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
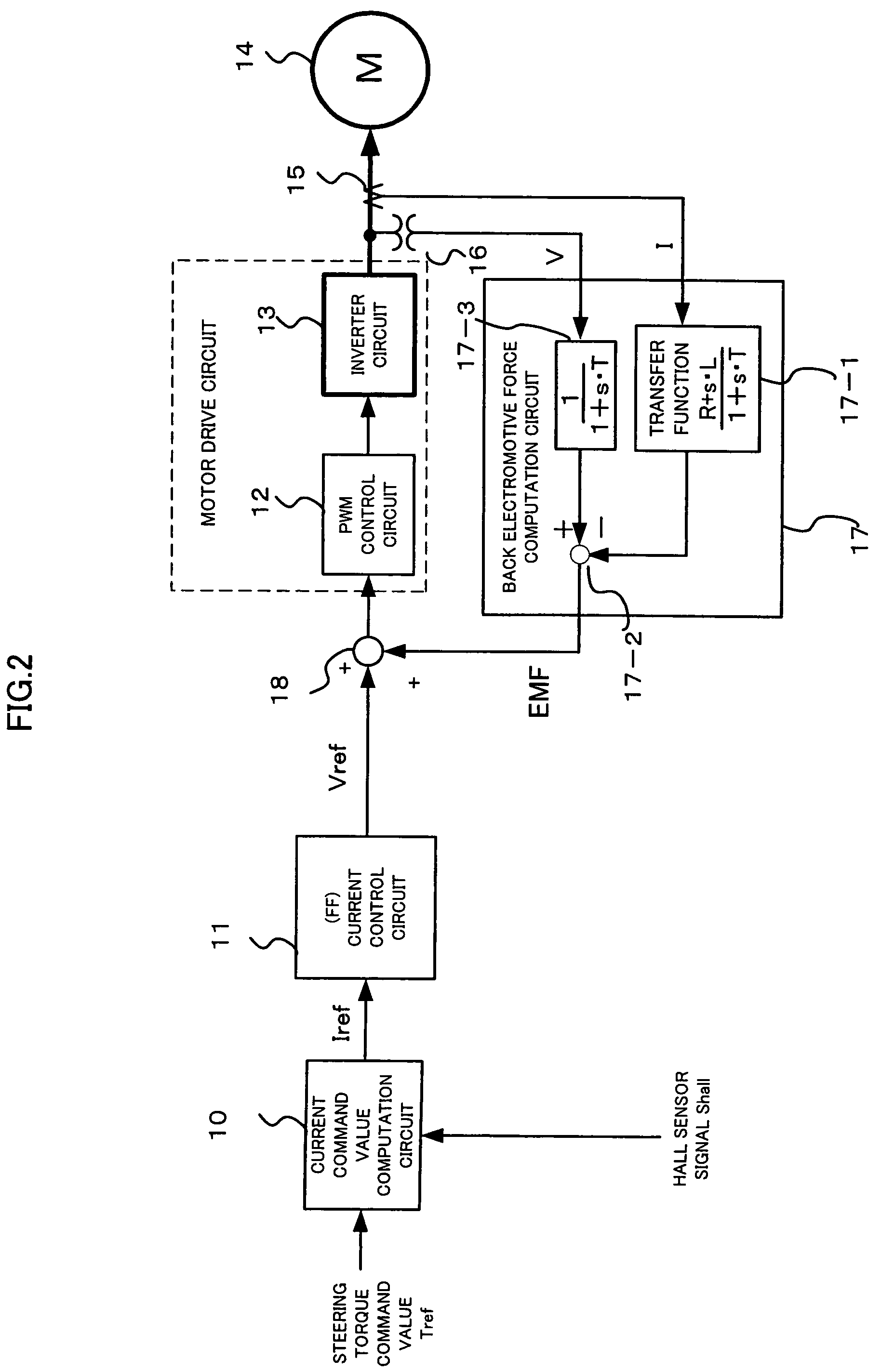
Control unit for electric power steering apparatus
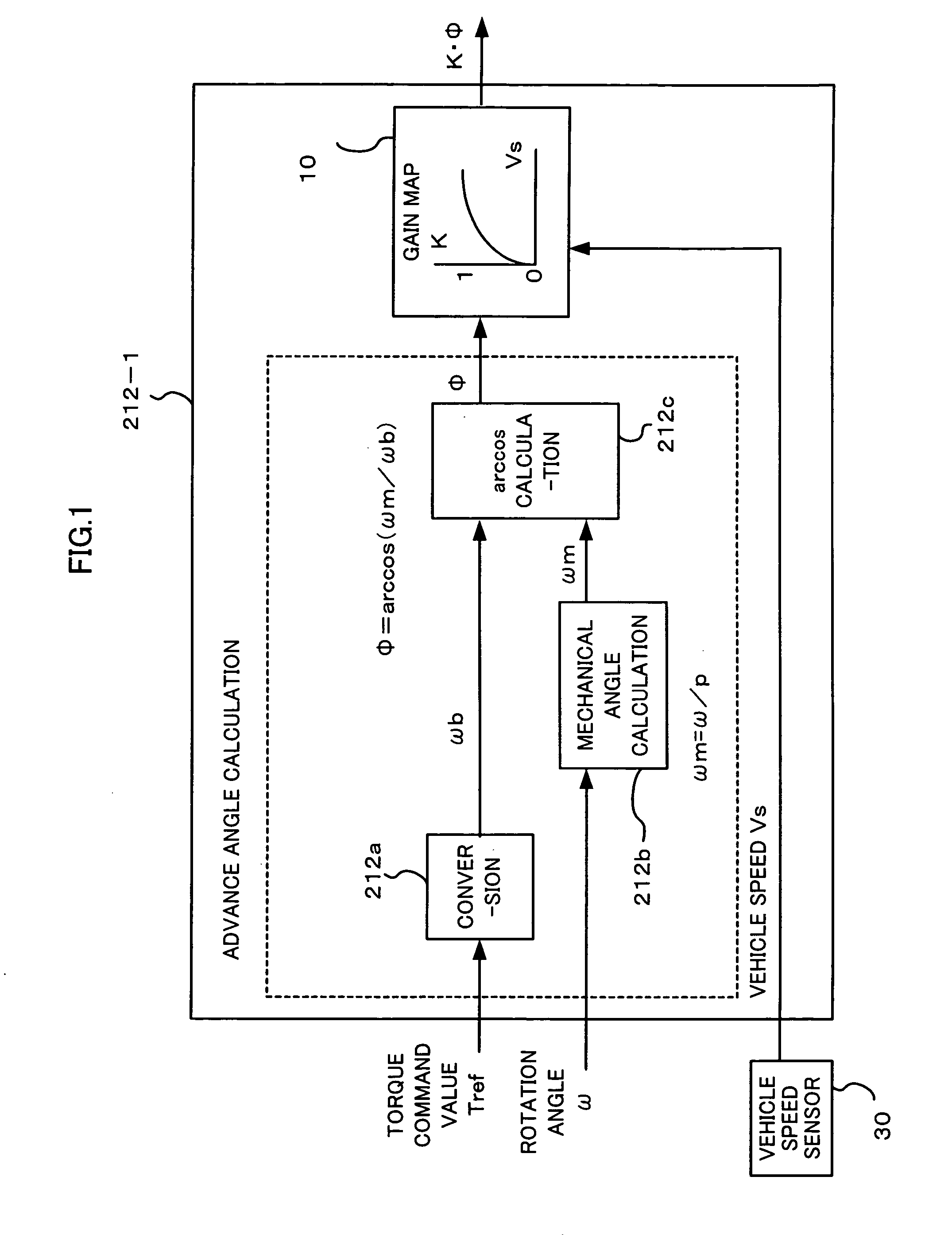
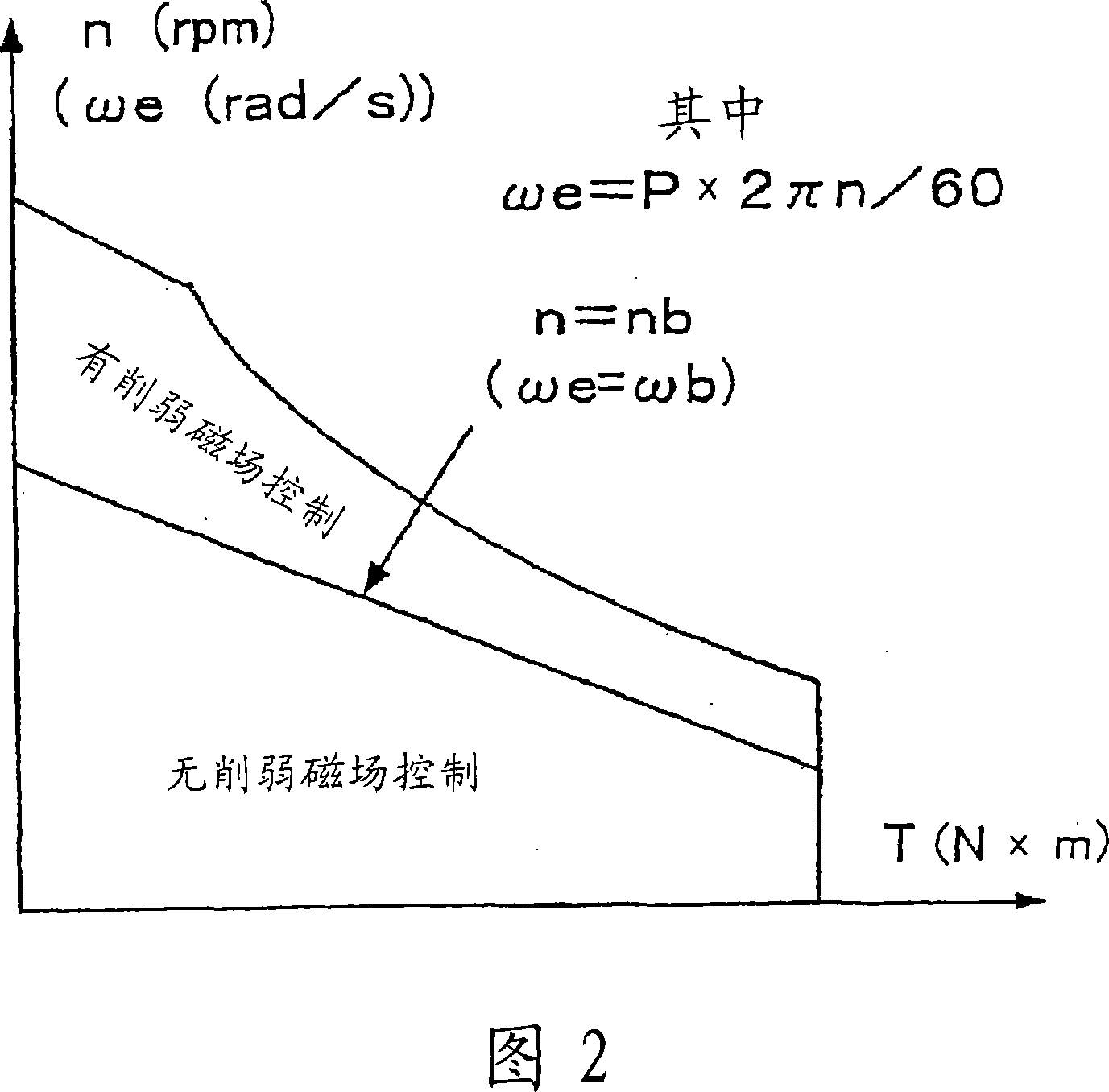
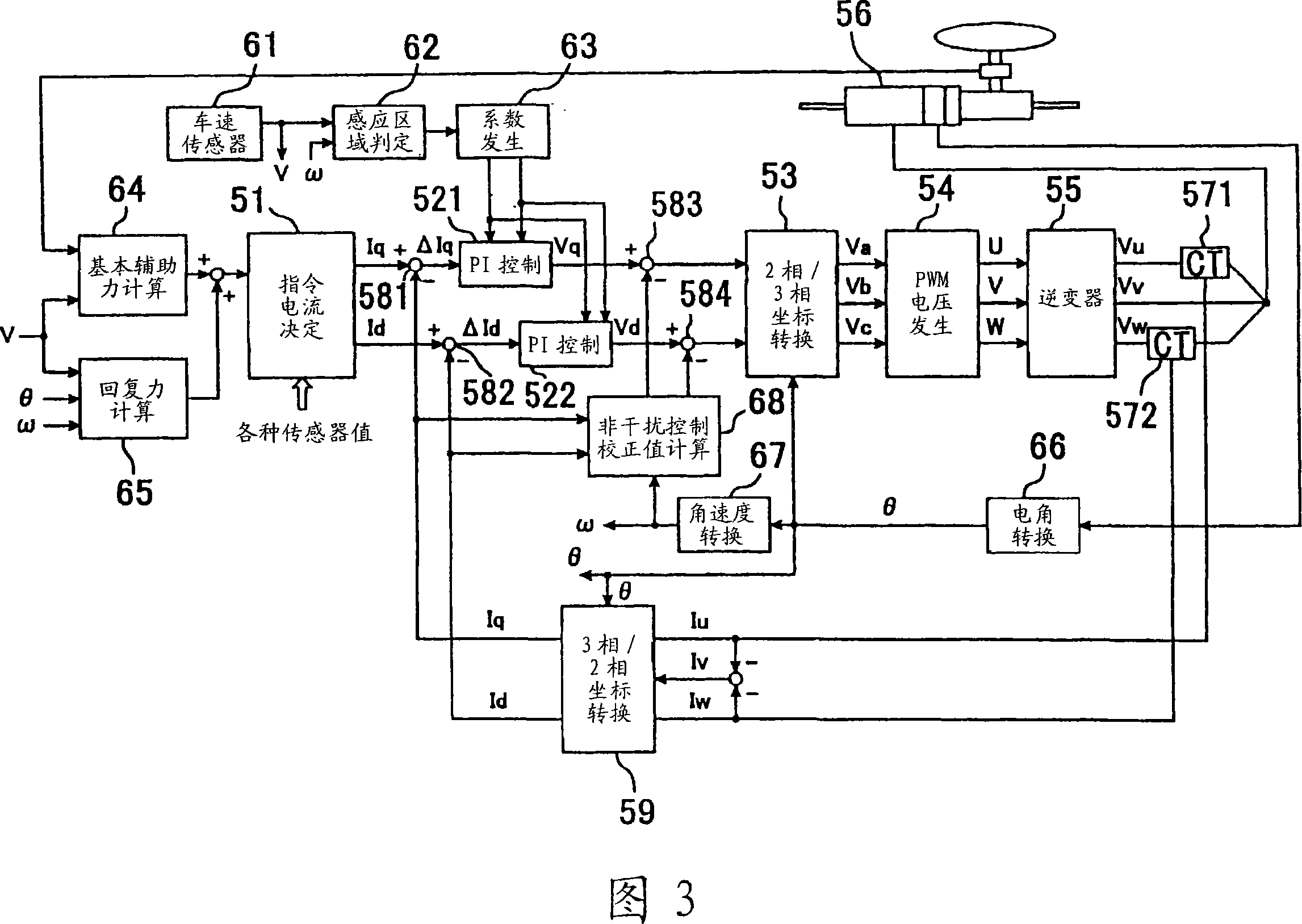
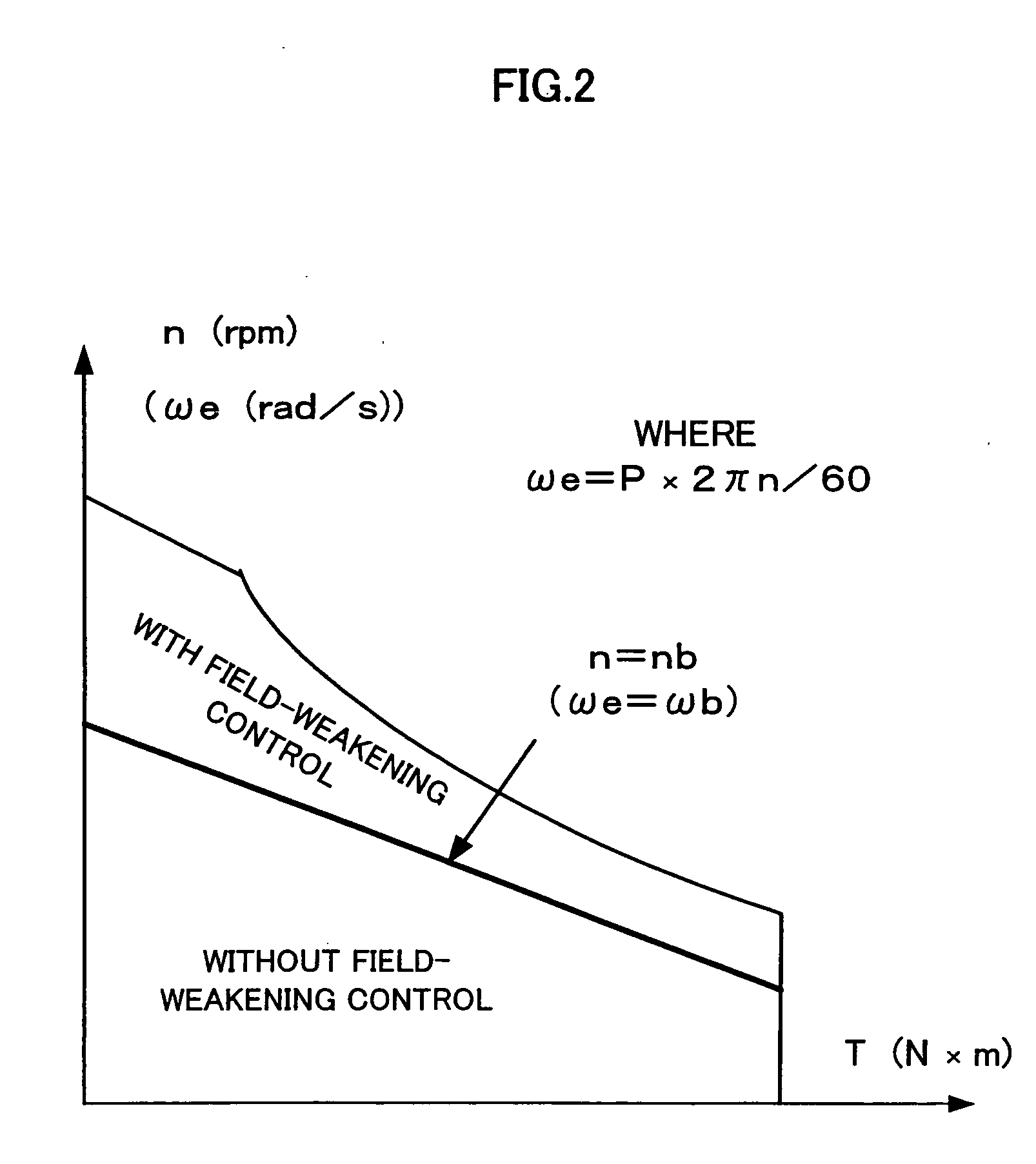
ActiveUS7394214B2Reduce motor noiseImproving a wheel steering feelDC motor speed/torque controlVector control systemsElectric power steeringRoad surface
In order to solve a problem that a motor generates a noise so as to deteriorate an environment in a vehicle if a field weakening control is executed to the motor of a electric power steering apparatus, in the case that a vehicle speed is high, the same field weakening control as the conventional one is applied to the motor because a noise generated due to a friction between a tire and a road surface and a wind noise of a vehicle body are large, and in the case that the vehicle speed is low, the field weakening control is weakly applied in comparison with the conventional one because the noise generated by the motor is felt relatively largely. Accordingly, the field weakening control can be executed in response to the vehicle speed in such a manner as to make the motor noise smaller.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
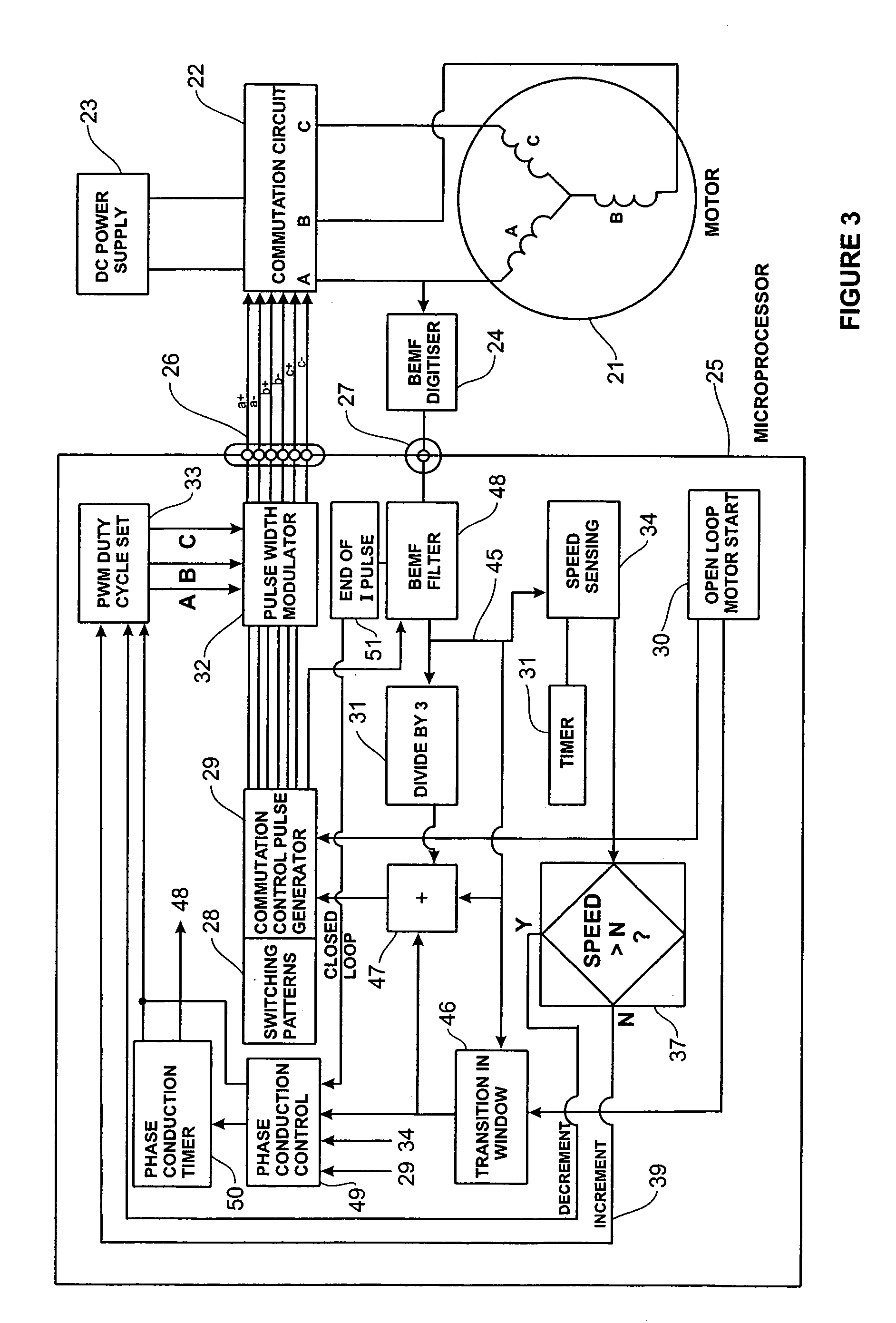
Low noise back EMF sensing brushless DC motor
InactiveUS20060197482A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow noiseWave shape
A low noise electronic three phase bridge controlled brushless DC motor suitable for whiteware appliance pumps and other appliance applications. Back EMF zero crossing sensing is used to determine rotor position and thus stator winding commutation times. Motor torque and speed are controlled by pulse width modulating the operation of that bridge switching device which has just been switched from an OFF state to an ON state on each new commutation. All three stator windings have current flowing in each winding commutation to improve motor current waveform and thereby reduce motor noise, but the current in one winding is always terminated before the end of the commutation period to allow the back EMF in that winding to be sensed to zero crossing.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Massage Machine
ActiveUS20080097260A1Small sizeIncrease productionMagnetic circuit rotating partsSingle motor speed/torque controlBrushless motorsMotor speed
A massage machine using a small size and high torque brushless DC motor includes a driving unit moved up and down along guide rails of a chair and a first motor for moving the driving unit up and down. A pair of treatment head bases are driven reciprocally in opposite directions to each other; and a second motor reciprocally drives the treatment head bases in opposite directions to each other. Treatment heads are respectively supported by the treatment head bases; and a third motor drives the treatment heads in a plane substantially perpendicular to a backrest. A control circuit drives the respective motors respectively independently of one another. Each motor is a brushless motor. A control circuit corrects, corresponding to a load imposed on the brushless DC motor, a waveform of a drive signal applied to a winding of the brushless DC motor so as to allow a current flowing through the winding of the brushless DC motor to have a substantially sinusoidal waveform making it possible to reduce discomfort due to motor noise, and to accurately control the motor rotation speed.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Controller for electric power steering device
InactiveUS7574294B2Digital data processing detailsSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringEngineering
Owner:NSK LTD +1
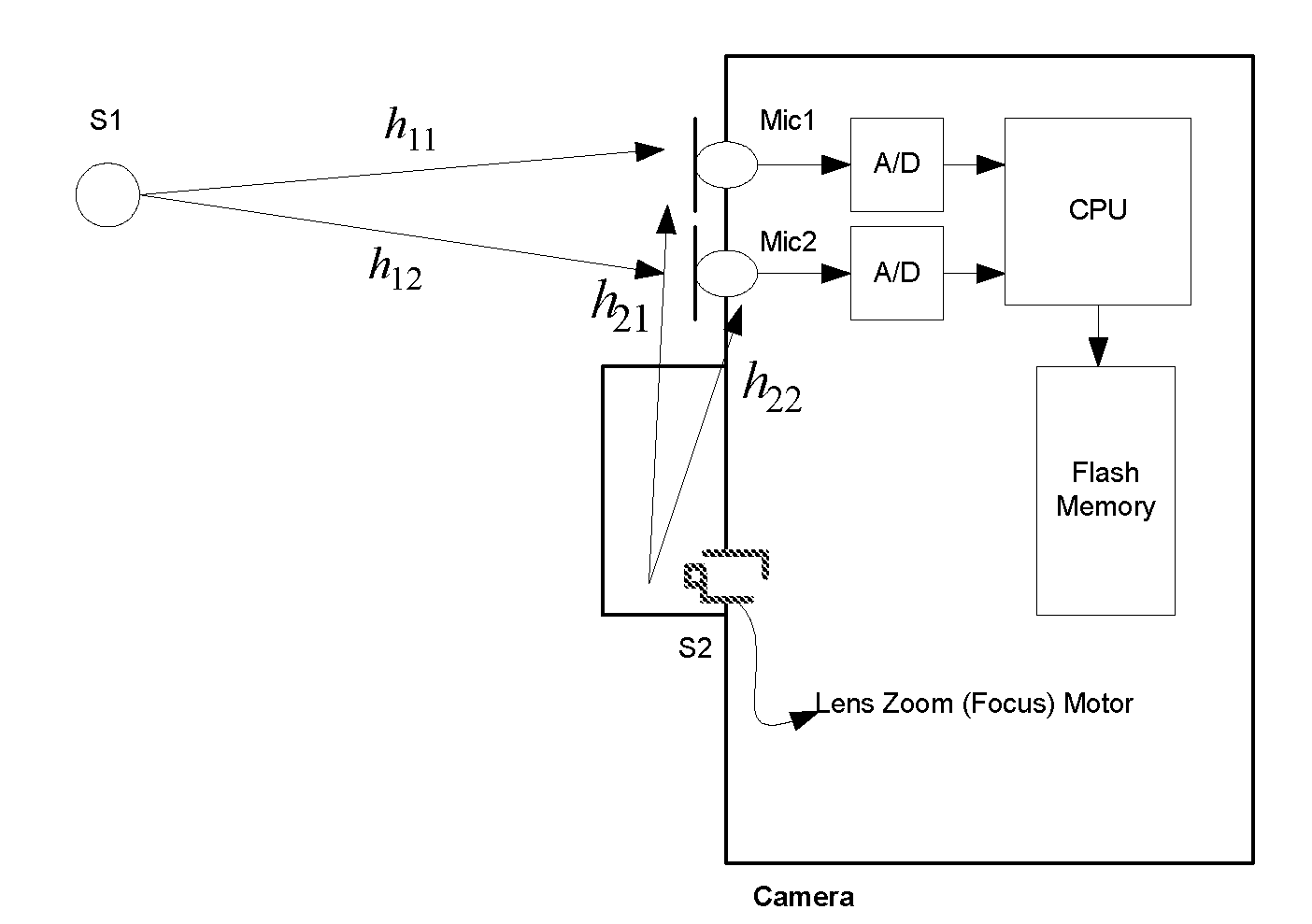
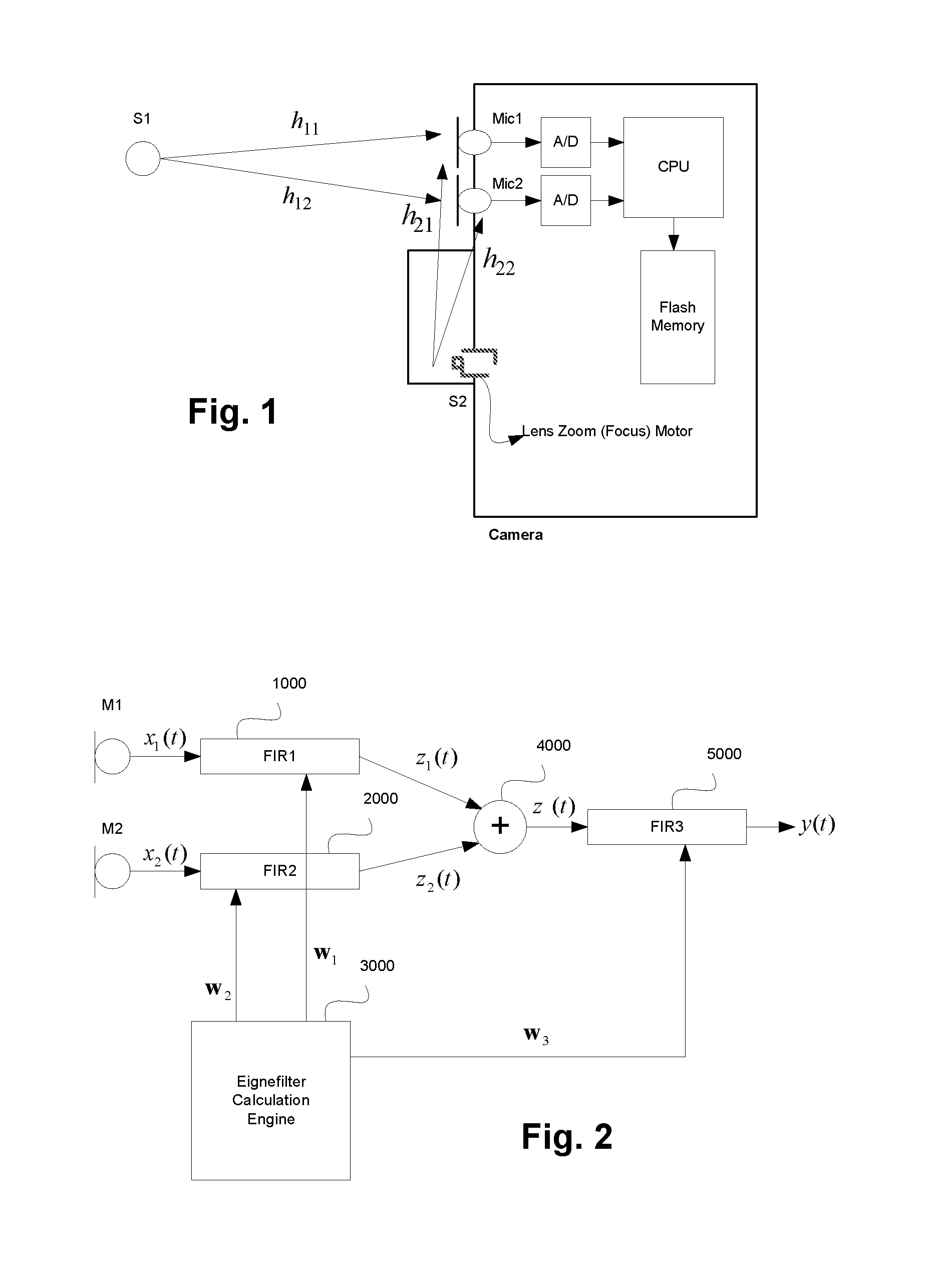
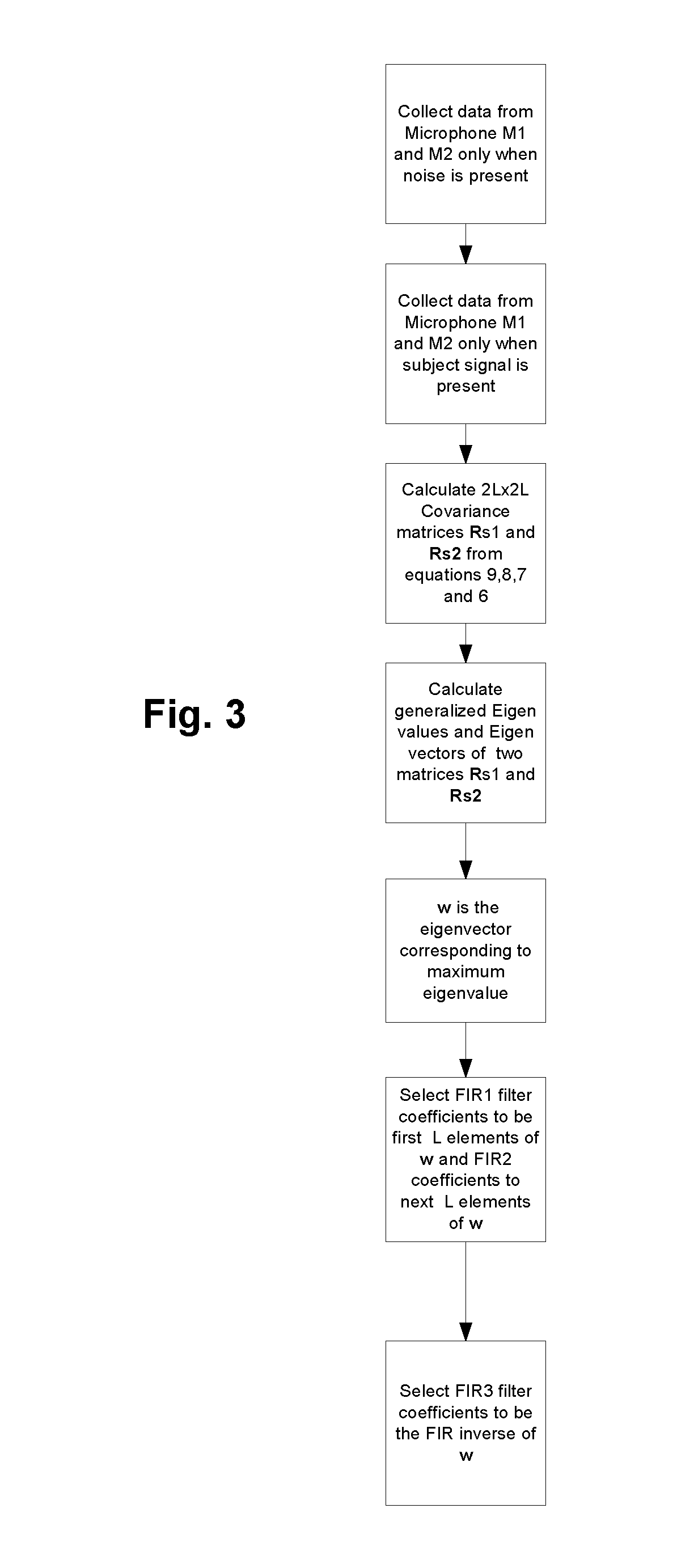
Motor noise reduction circuit
ActiveUS20120154610A1Reduce noiseMinimal degradationTelevision system detailsSignal processingLinear filterComputer science
A method of reducing noise in an environment where the noise source is in a fixed location relative to a pair of microphones, such as in a camera with a zoom motor, involves receiving signals x1(t), x2(t) from the respective microphones, and filtering each of the signals x1(t), x2(t) with respective first and second linear filters having filter coefficients obtained by computing eigenfilters corresponding to data samples from the respective microphones for noise only and signal only conditions.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON
Audible noise reduction for single current shunt platform
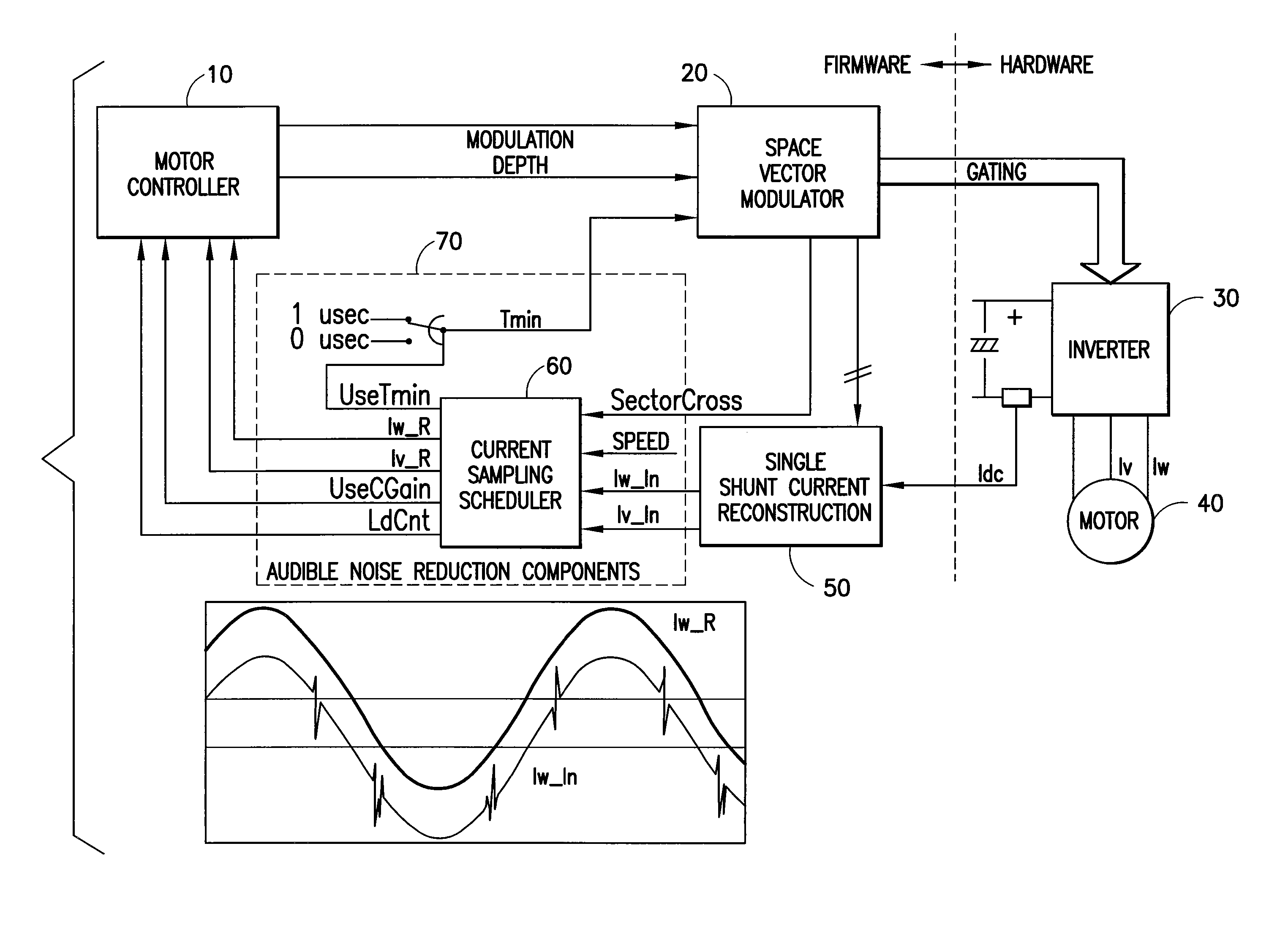
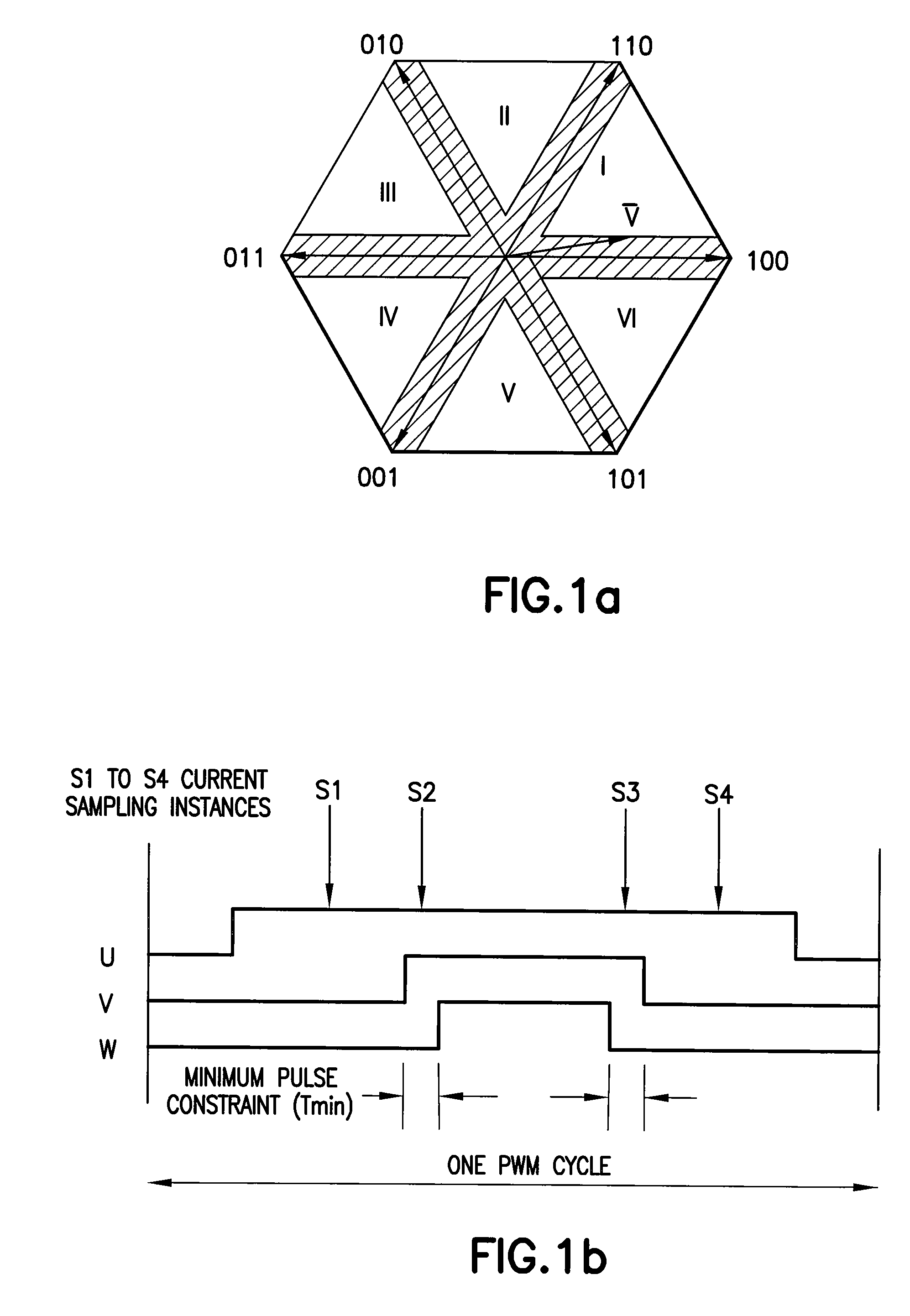
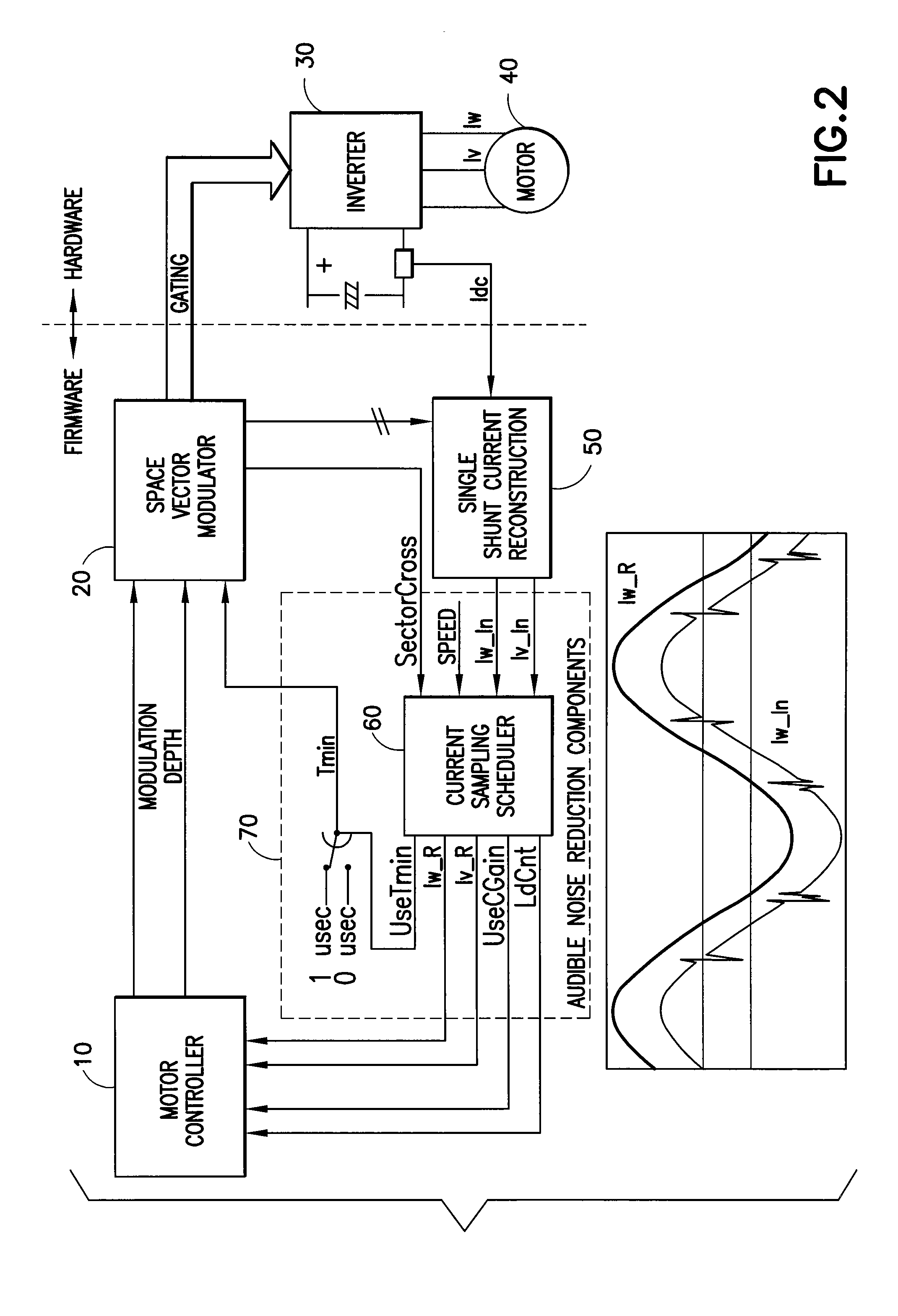
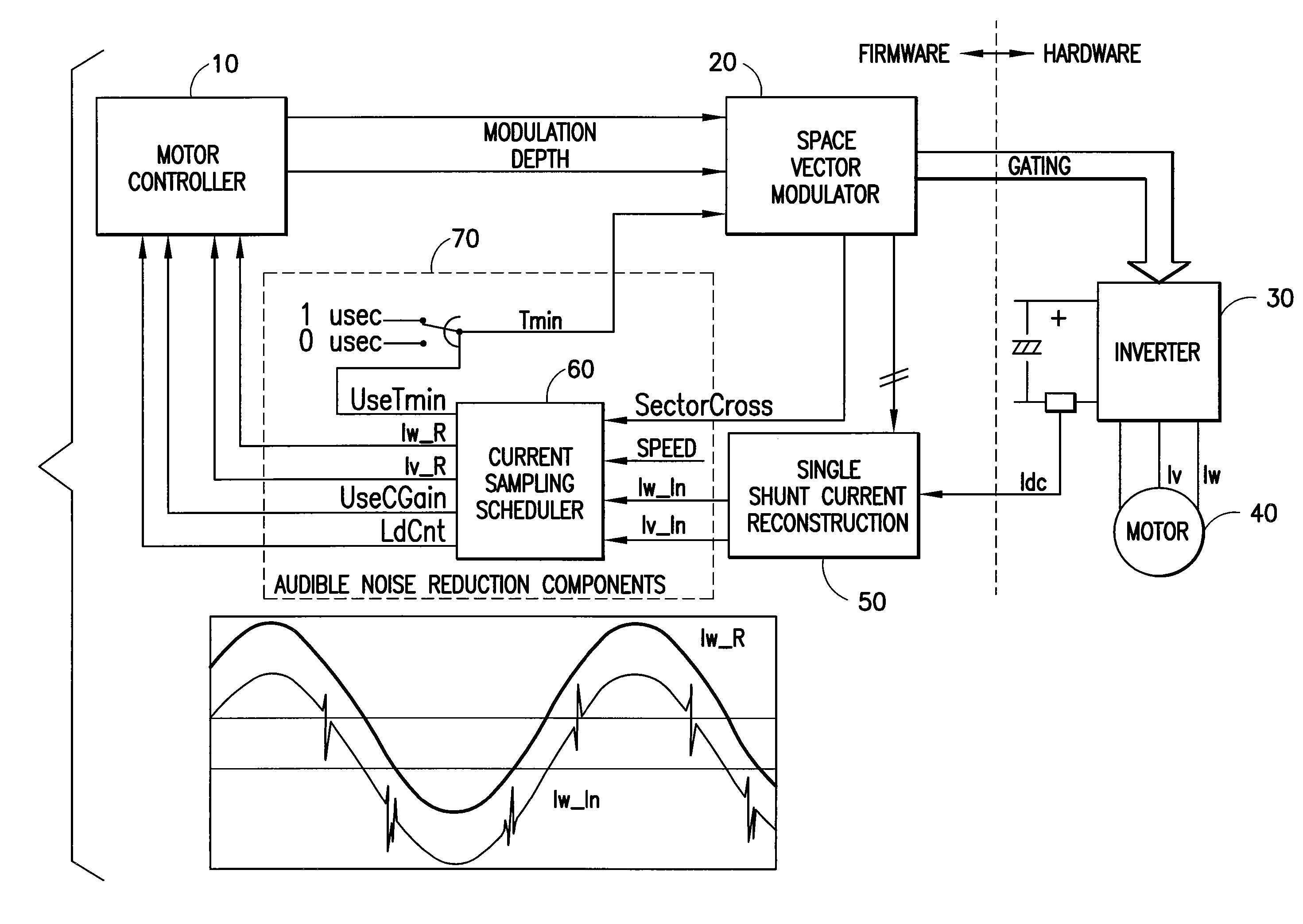
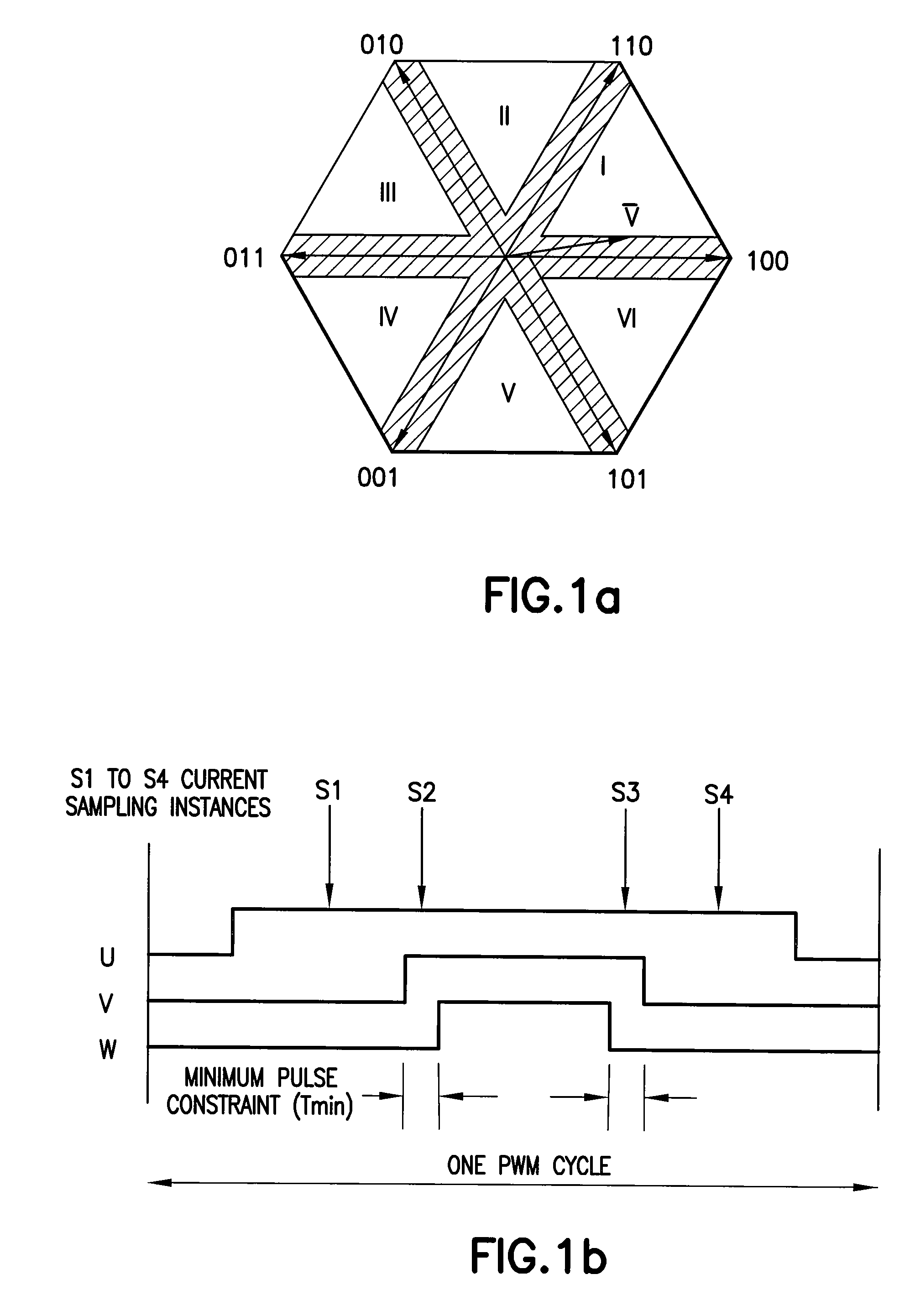
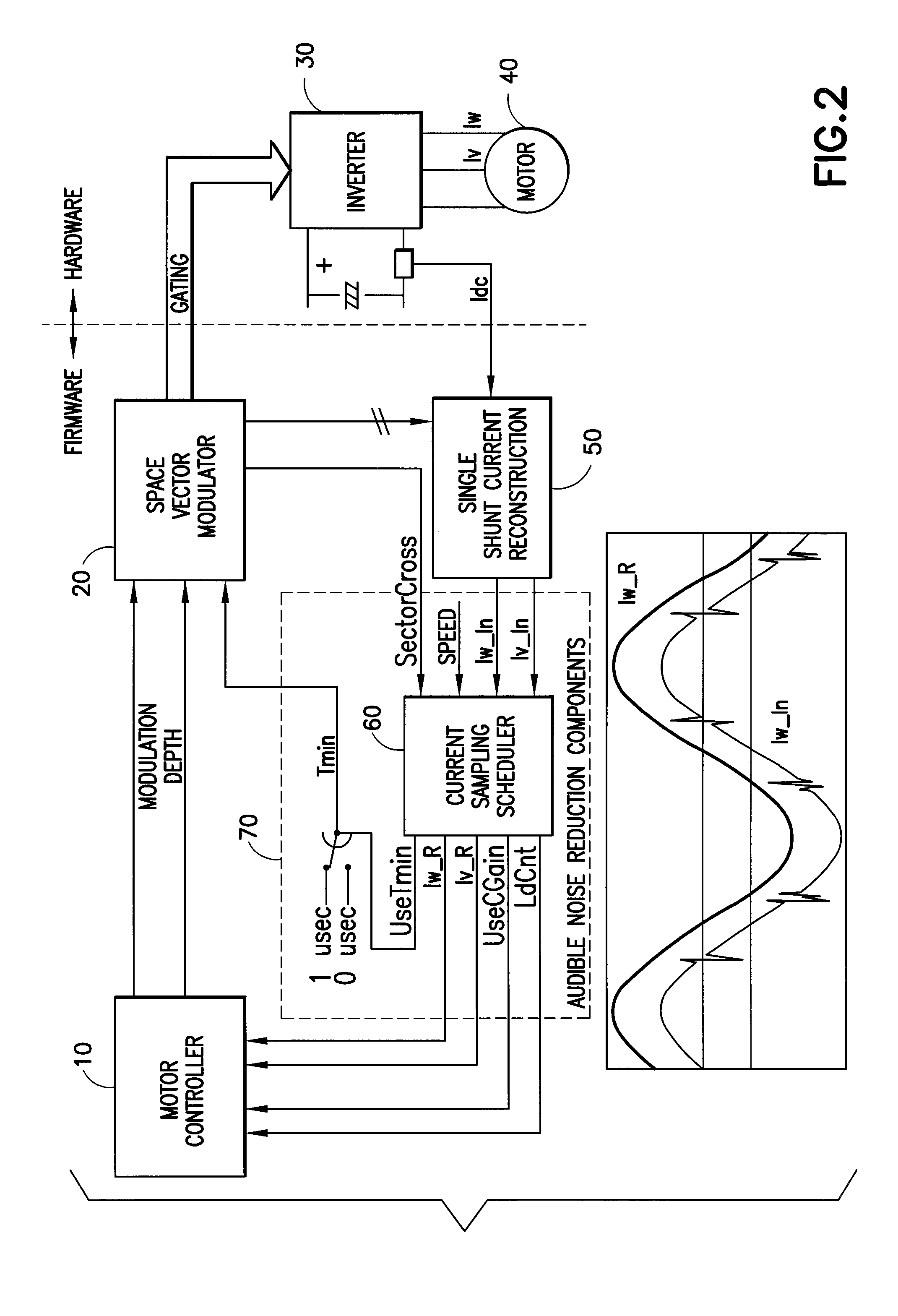
ActiveUS20070090785A1Reduce motor noiseAudible noiseMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric motor controlPhase currentsMotor speed
A method and system for reducing audible motor noise in a system for reconstructing motor phase current from a DC bus current comprising current pulses on a DC bus in a PWM inverter motor drive system having a PWM cycle, and for controlling the motor, which forms a command voltage vector according to a space vector modulation arrangement for controlling the motor; measures the DC bus current on the DC bus supplying power to the inverter to reconstruct said motor phase current; and determines when the command voltage vector results in an inverter switching state that prevents the measuring of the DC bus current from accurately indicating motor phase current. During said inverter switching state, a current sampling scheduler applies a minimum pulse width constraint to said current pulses in said DC bus current to improve reconstruction of said motor phase current based on said DC bus current; and reduces the application of said minimum pulse width constraint to less than once per PWM cycle imposed by the PWM inverter motor drive system, thereby allowing motor phase current reconstruction with reduced audible motor noise. The current sampling scheduler synchronously samples said measured motor phase current to reduce errors in said measured motor phase current caused by said reduction of said minimum pulse constraint; reduces a bandwidth of said motor controller during said inverter switching state; and is adjustable in response to motor speed for setting the number of said minimum pulse width constraints per PWM cycle.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Sensing mechanical transitions from current of motor driving hydraulic pump or other mechanism
Owner:INPOWER LLC
55KW grade electricity loading test stand for automobile gear box low noise energy-conserving type under line detection and working method thereof
InactiveCN101393076AImplement closed loadingAchieve four-quadrant workVehicle testingComputer controlLow noiseAutomatic control
The invention relates to a low-noise energy-saving test bed for the offline detection of 55KW-stage electric loading for an automobile gear-box and an operating method thereof. The test bed comprises a test bed main body, a motor box body, an electric transmission control system, a computer measuring-controlling system and an intensive oil supply hydraulic station, and is characterized in that a noise measuring device is arranged on the tested gear-box and a tray sliding table is arranged under the tested gear-box; and a gear shift device and a handle gear shift force operation measuring device are arranged on the right side of an operator who faces to the test bed. The test bed has the advantages of providing large torque up to 140Nm and meeting requirements on 30 to 100 percent of the factory detection of the loading of the gear-box with multi-specification variety types in the range of between 90 and 350Nm, reducing noise of a machine tool to be lower than 80dB through motor noise isolation and other noise reduction measurements, adjusting center distances and vertical dropping distances of input / output shafts to adapt to positioning and mounting of the gear-box with different variety specifications, adopting electric sealing power to feed back loading for energy conservation, and adopting an industrial control computer system and a measuring instrument to realize automatic control of a testing process.
Owner:天津横河电子技术有限公司
Magnetic circuit method and finite element method-based motor noise optimization method and apparatus
InactiveCN106934162AGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationVibration accelerationPermanent magnet synchronous motor
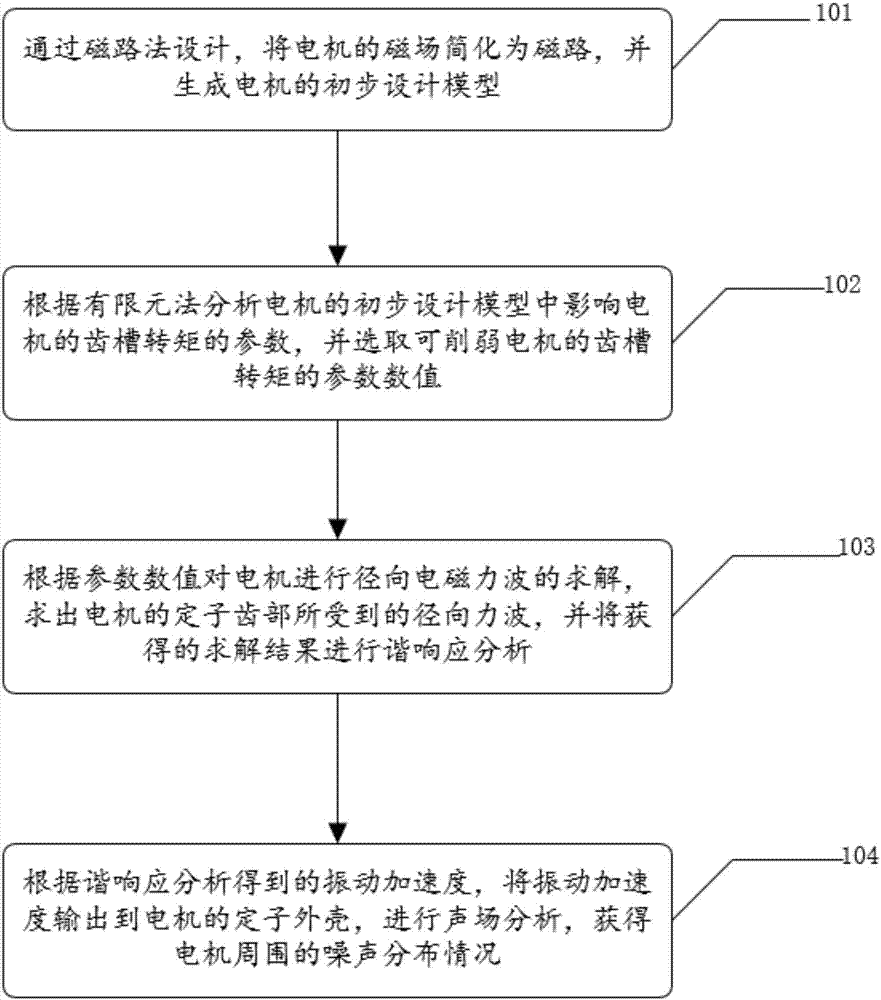
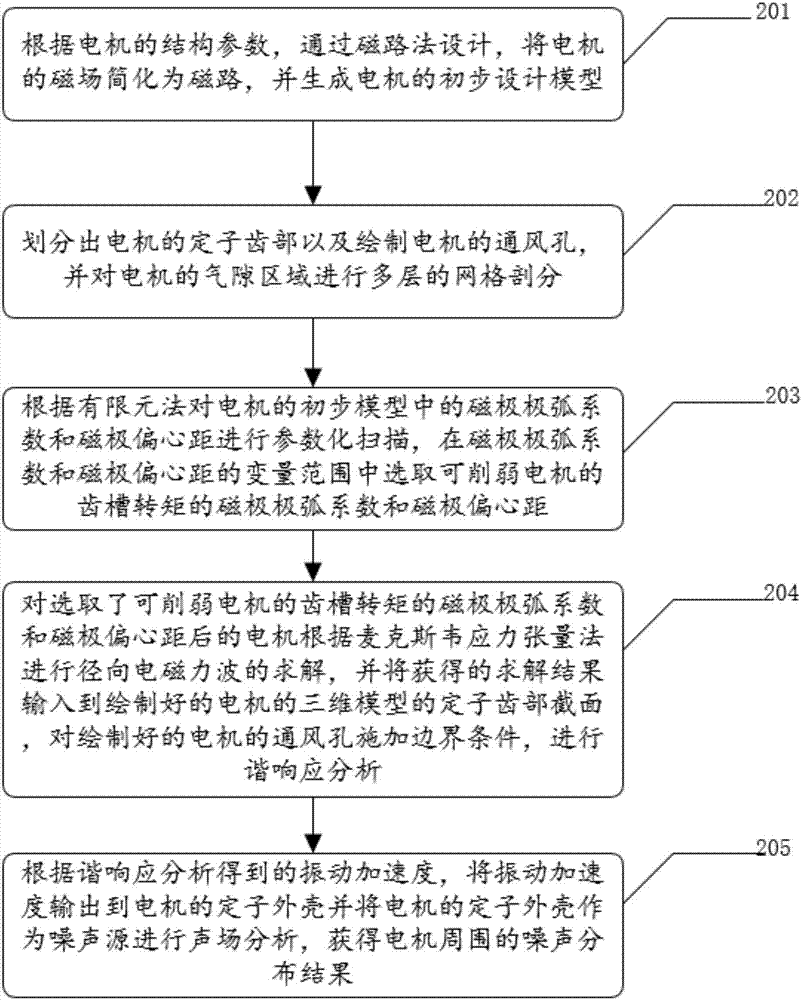
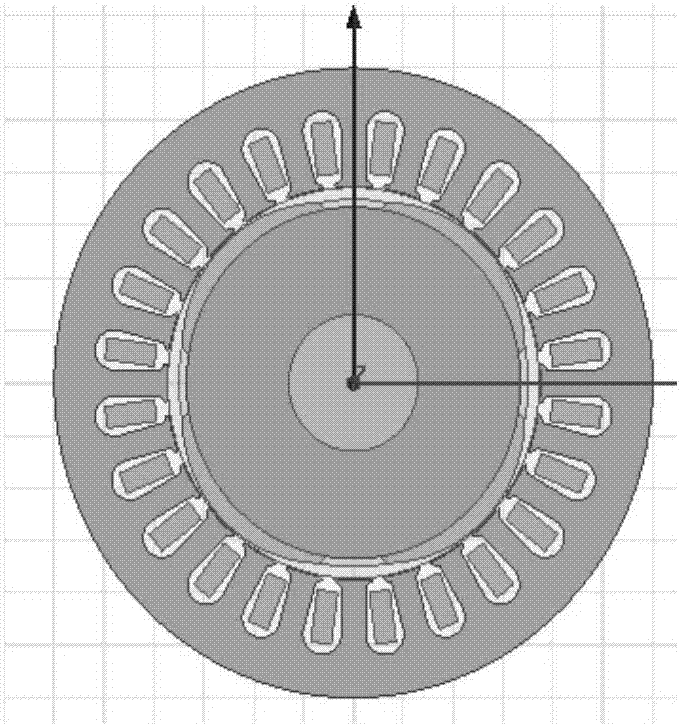
Embodiments of the invention disclose a magnetic circuit method and finite element method-based motor noise optimization method and apparatus, which is used for solving the technical problems of relatively high noise measurement precision and cost of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and difficulty in adjusting parameters of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in a measurement process to achieve the purpose of optimizing motor noises in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of simplifying a magnetic field of the motor to a magnetic circuit through magnetic circuit method design, and generating a preliminary design model of the motor; analyzing parameters influencing cogging torque of the motor in the preliminary design model of the motor according to a finite element method, and selecting numerical values of parameters capable of reducing the cogging torque of the motor; performing radial electromagnetic force wave solving on the motor, working out radial force waves on stator teeth of the motor, and performing harmonic response analysis on an obtained solving result; and outputting vibration acceleration obtained by the harmonic response analysis to a stator shell of the motor, and performing sound field analysis to obtain a noise distribution condition around the motor.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Ironclad motor cast-aluminum rotor end surface burr cleaning device
InactiveCN107370306AMeet clean upPrevent adhesionEdge grinding machinesGrinding drivesCouplingDrive motor
The invention discloses an ironclad motor cast-aluminum rotor end surface burr cleaning device, which comprises a slideway, a driving gear, a toothed belt, a driven gear, a driving motor A, a screw rod, a driving motor B, a lifting table, a high-pressure suction fan, a circular wheel and grinding heads, wherein a plurality of groups of sliding blocks are arranged on a sliding groove in a sliding mode; a rotor placement groove is opened in the upper surface of each sliding block; the output shaft of the driving motor B is connected with the screw rod through a coupler; the lifting table is arranged on the screw rod in a threaded mode; the lower side of the lifting table is provided with a fan cover; the upper side of the lifting table is provided with the high-pressure suction fan; the output shaft of a rotation motor is provided with the circular wheel in a rotating mode; and the lower side of the circular wheel is fixedly provided with a plurality of groups of grinding heads. While the device grinds rotor end surface burrs, the ground burrs can also be absorbed, burr scrap can be prevented from being attached to the surface of the rotor as much as possibly, the problem of single motor noise caused by various friction noise in the case of final assembly can be effectively avoided, and the production qualification rate of the motor can be improved.
Owner:HEFEI TOTEM LONG MACHINERY DESIGN CO LTD
Control unit for elctric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20070103105A1Reduce motor noiseImproving a wheel steering feelDC motor speed/torque controlVector control systemsElectric power steeringEngineering
In order to solve a problem that a motor generates a noise so as to deteriorate an environment in a vehicle if a field weakening control is executed to the motor of a electric power steering apparatus, in the case that a vehicle speed is high, the same field weakening control as the conventional one is applied to the motor because a noise generated due to a friction between a tire and a road surface and a wind noise of a vehicle body are large, and in the case that the vehicle speed is low, the field weakening control is weakly applied in comparison with the conventional one because the noise generated by the motor is felt relatively largely. Accordingly, the field weakening control can be executed in response to the vehicle speed in such a manner as to make the motor noise smaller.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
Audible noise reduction for single current shunt platform
ActiveUS7348758B2Audible noiseMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric motor controlMotor speedPhase currents
A method and system for reducing audible motor noise in a system for reconstructing motor phase current from a DC bus current comprising current pulses on a DC bus in a PWM inverter motor drive system having a PWM cycle, and for controlling the motor, which forms a command voltage vector according to a space vector modulation arrangement for controlling the motor; measures the DC bus current on the DC bus supplying power to the inverter to reconstruct said motor phase current; and determines when the command voltage vector results in an inverter switching state that prevents the measuring of the DC bus current from accurately indicating motor phase current. During said inverter switching state, a current sampling scheduler applies a minimum pulse width constraint to said current pulses in said DC bus current to improve reconstruction of said motor phase current based on said DC bus current; and reduces the application of said minimum pulse width constraint to less than once per PWM cycle imposed by the PWM inverter motor drive system, thereby allowing motor phase current reconstruction with reduced audible motor noise. The current sampling scheduler synchronously samples said measured motor phase current to reduce errors in said measured motor phase current caused by said reduction of said minimum pulse constraint; reduces a bandwidth of said motor controller during said inverter switching state; and is adjustable in response to motor speed for setting the number of said minimum pulse width constraints per PWM cycle.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Motor and drive control device therefor
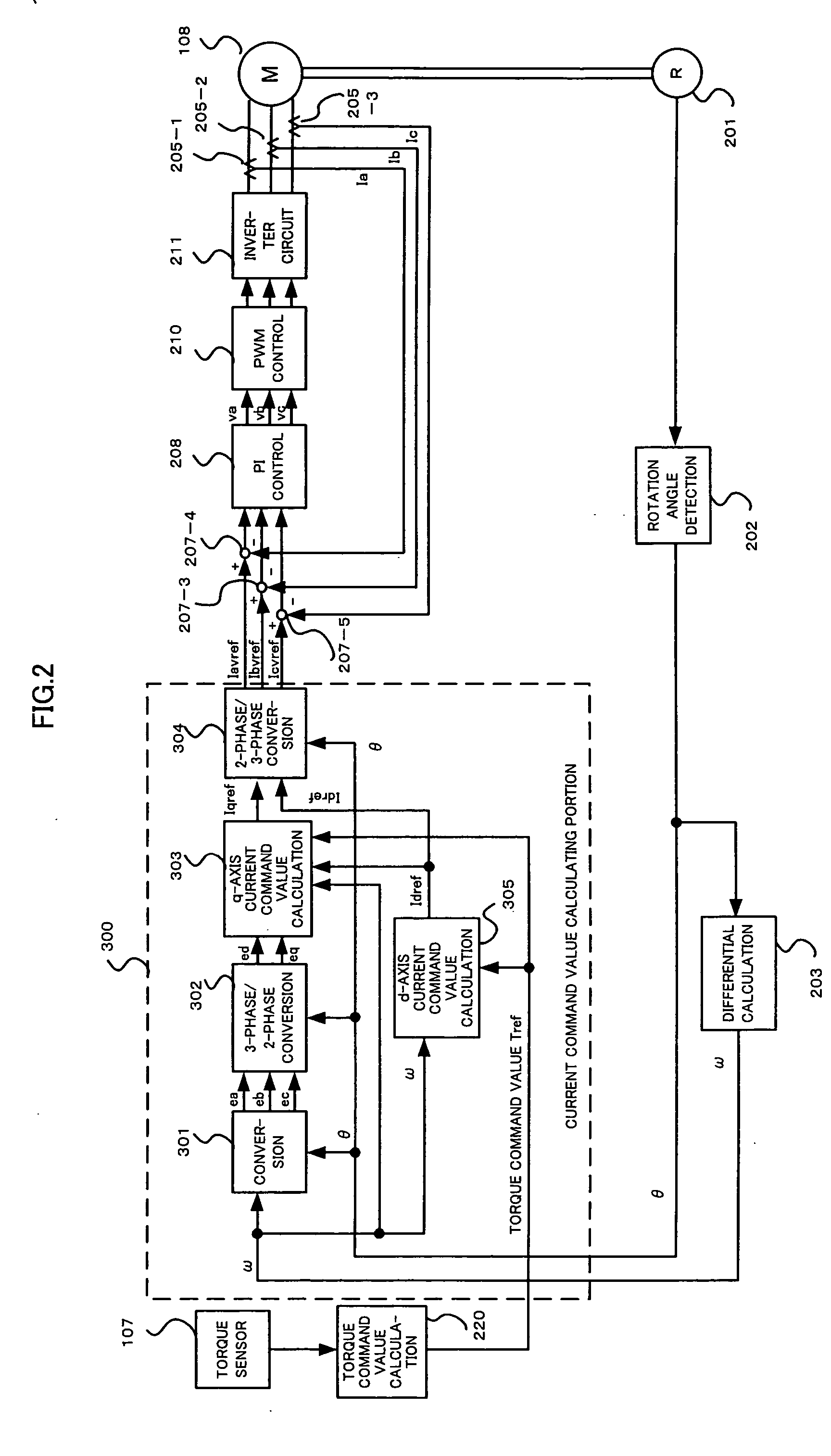
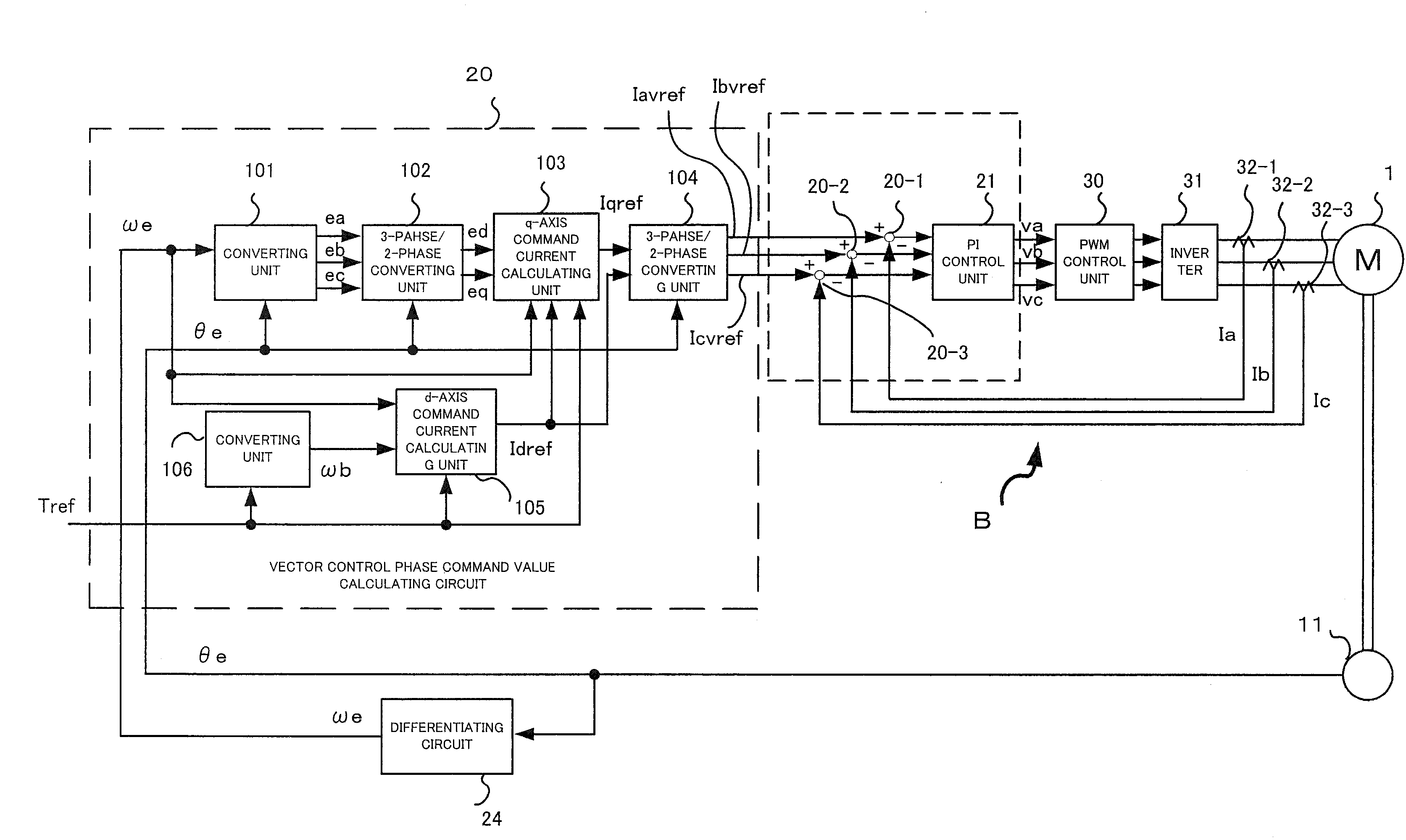
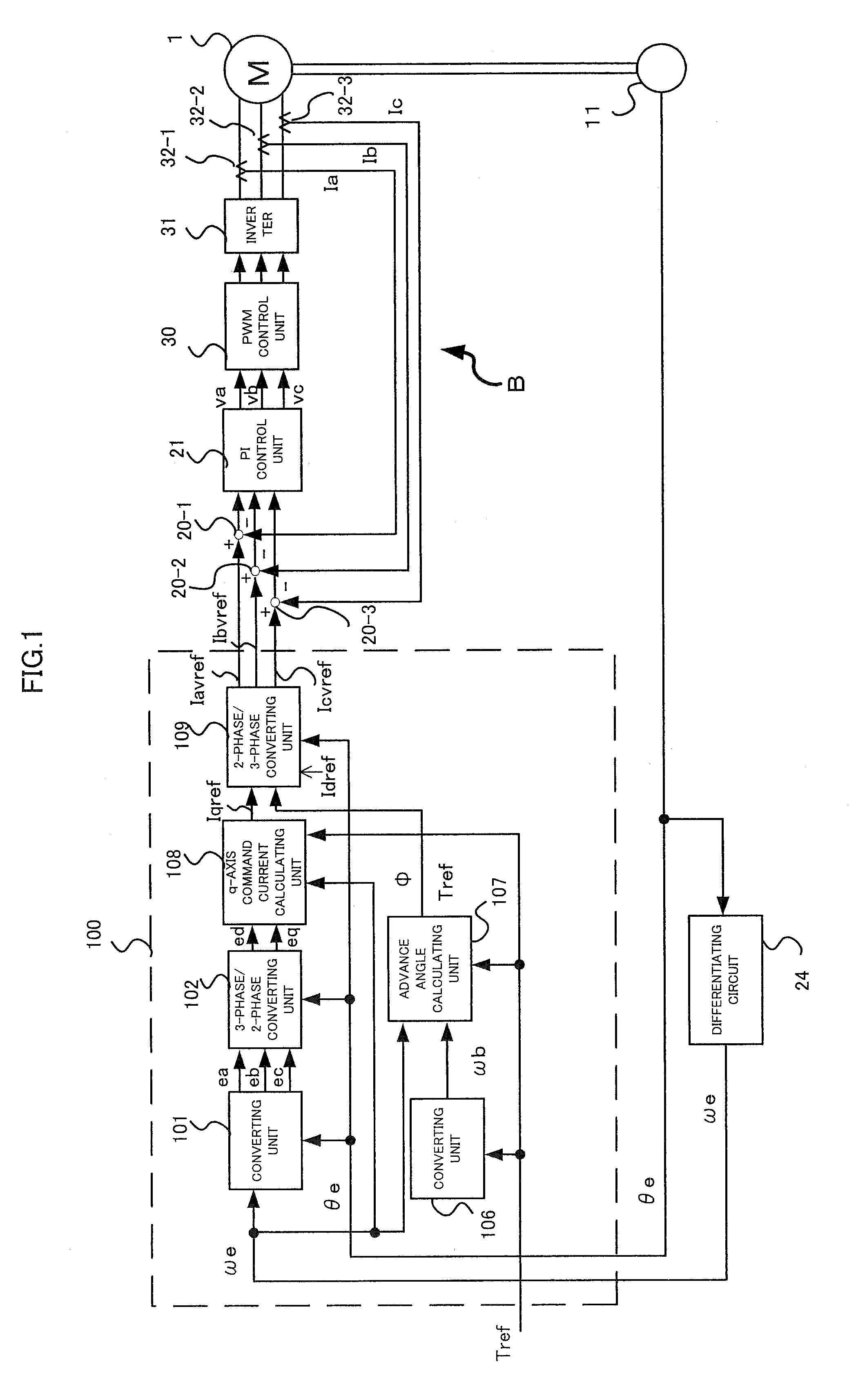
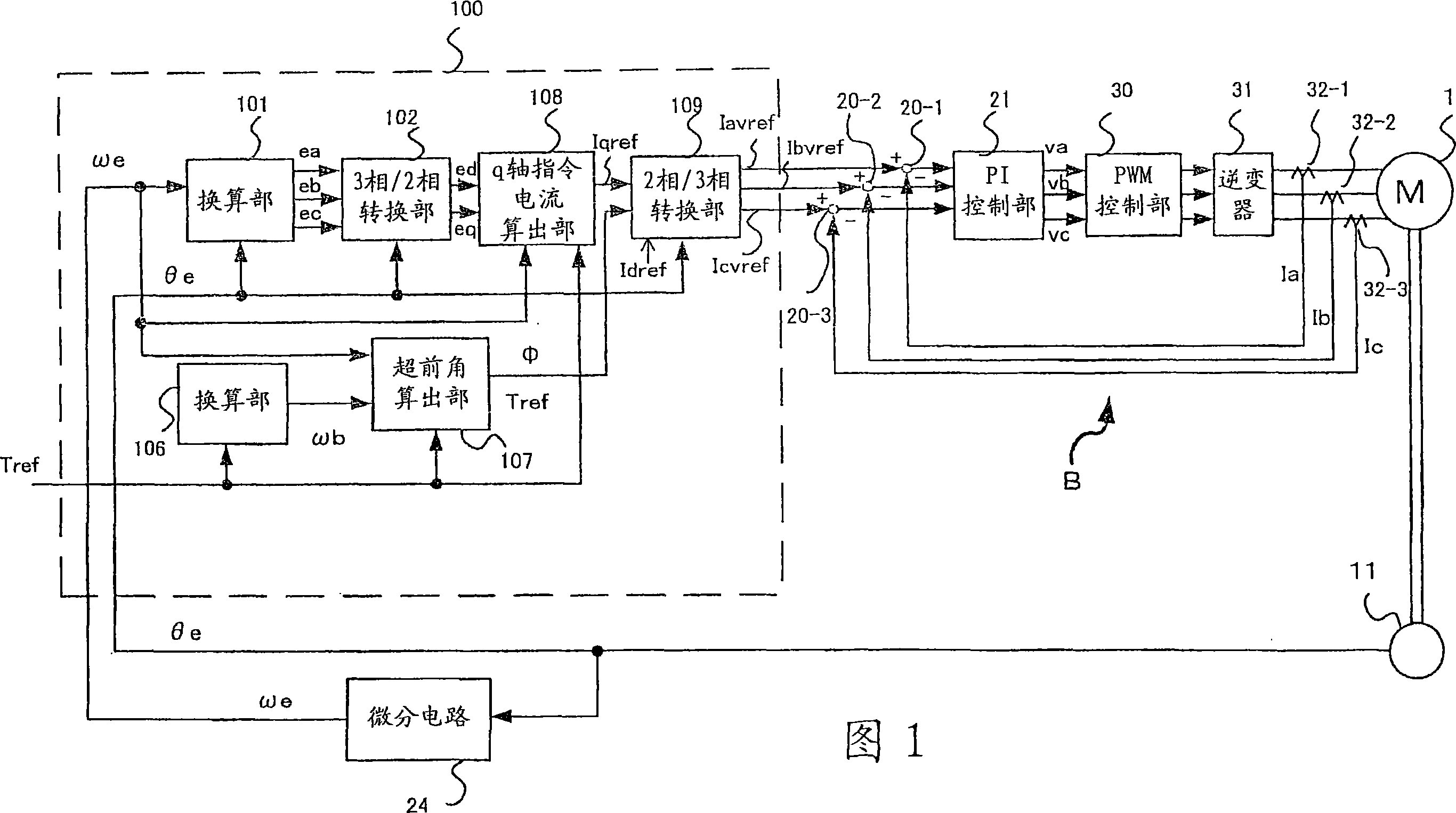
The invention provides a motor for a brushless DC motor, which has small torque ripple even if a trapezoidal wave current is supplied and has a small size and reduced motor noise. Respective phase current command values are calculated on the basis of vector control. Pseudo-vector control for controlling respective phases separately is used as current feedback control.
Owner:NSK LTD
Current decay control in switched reluctance motor
InactiveUSRE36568E1Reduce motor noiseEasy to controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringEnergy recovery
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Electric Motor
InactiveUS20030006660A1Complicated to produceAvoid easy installationMagnetic circuit stationary partsMechanical energy handlingElectric machineMotor noise
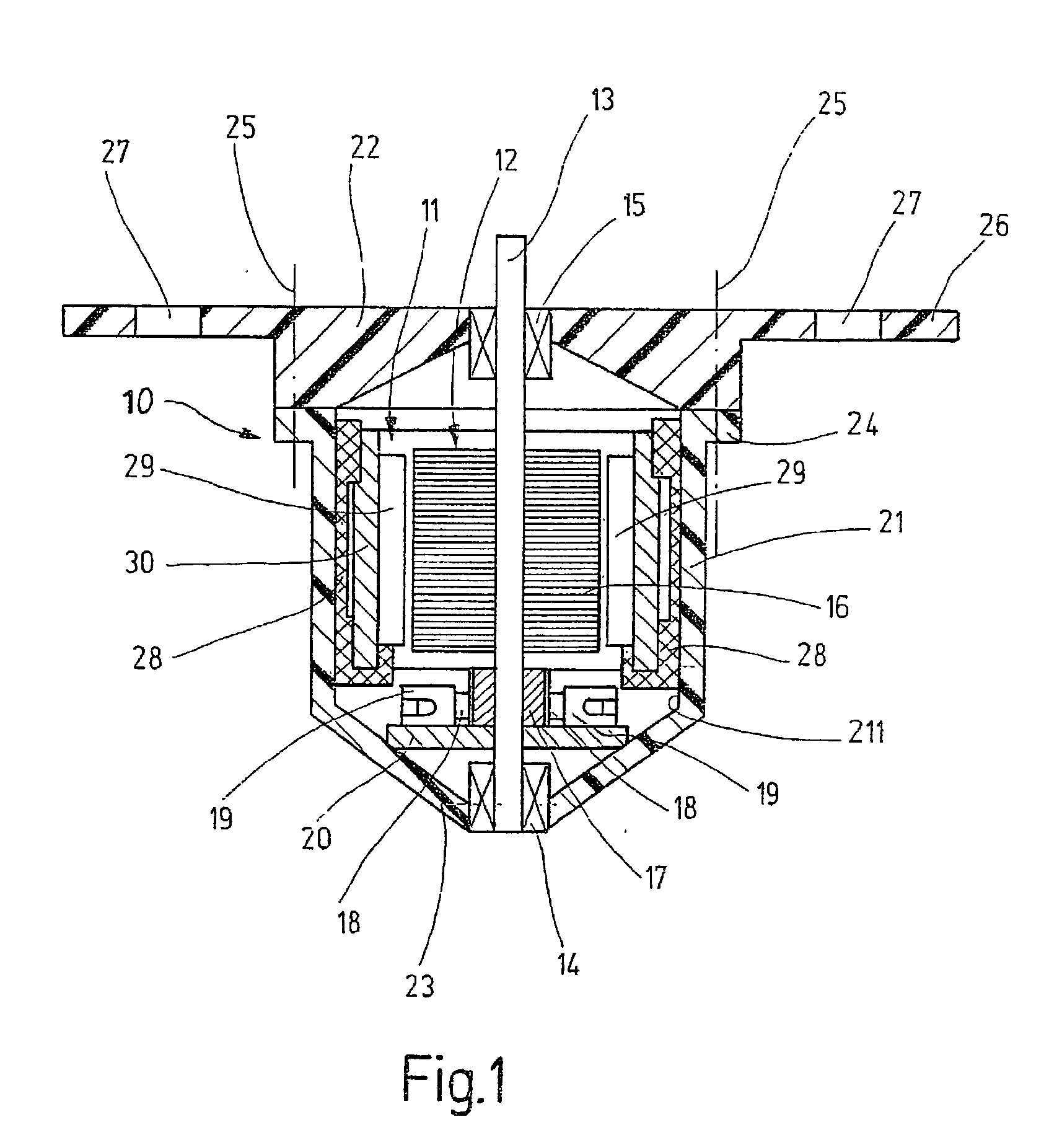
In an electric motor with a stator (11) and a rotor (12) that is received rotatably via its rotor shaft (13) in rotor bearings (14, 15), and having an effective decoupling between the stator (11) and rotor bearings (14, 15) for reducing the emission of airborne and structure-borne sound, in order to attain a structurally simple, sturdy design with markedly little motor noise, the rotor bearings (14, 15) are fixed on a housing (10) surrounding and gripping the stator (11), while the decoupling is achieved by a spring-elastic suspension of the stator (11) from the housing (10), and to that end elastic decoupling elements (28) are disposed between the stator (11) and the housing (10) (FIG. 1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fan motor noise reduction device and vacuum cleaner with the same
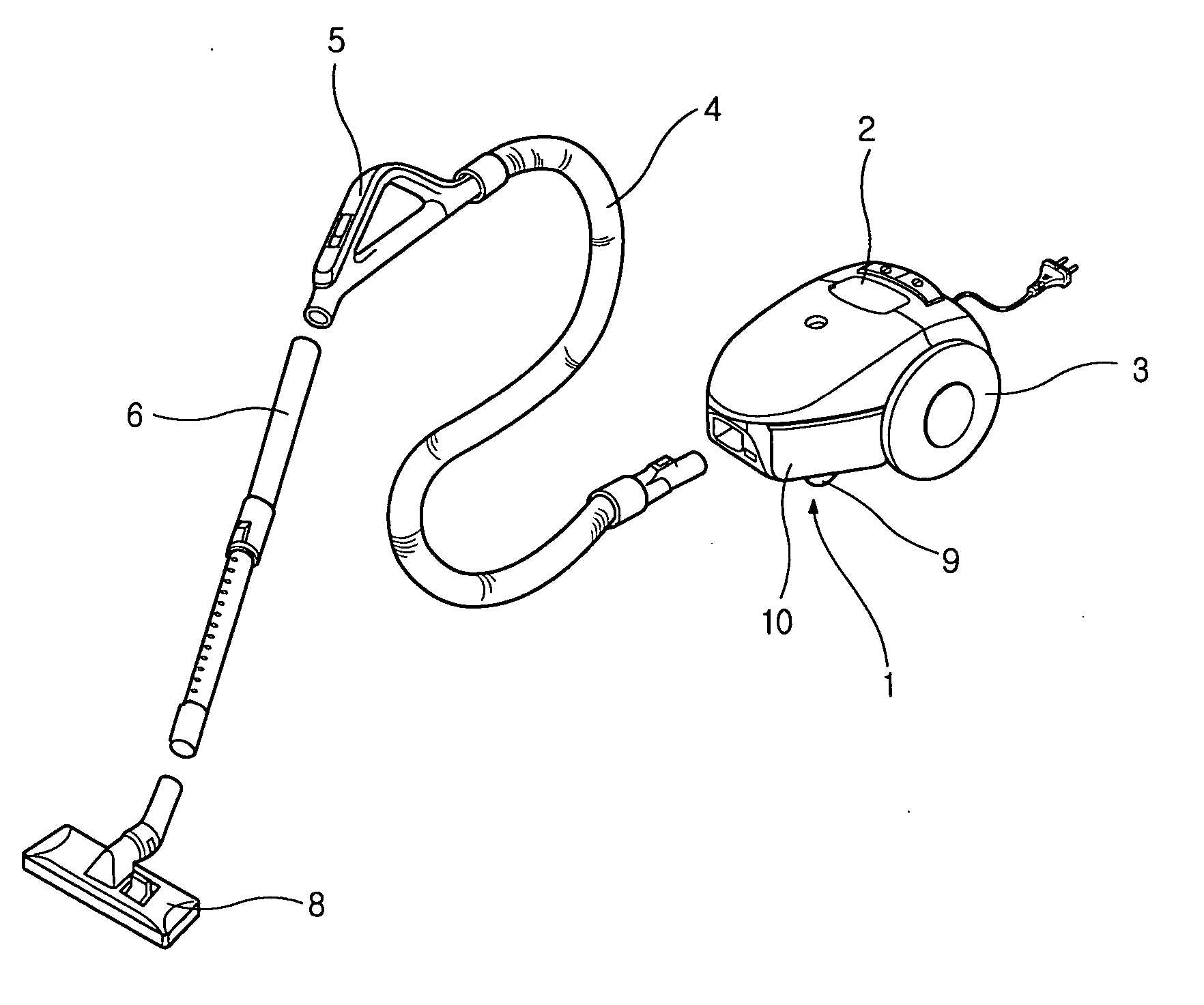
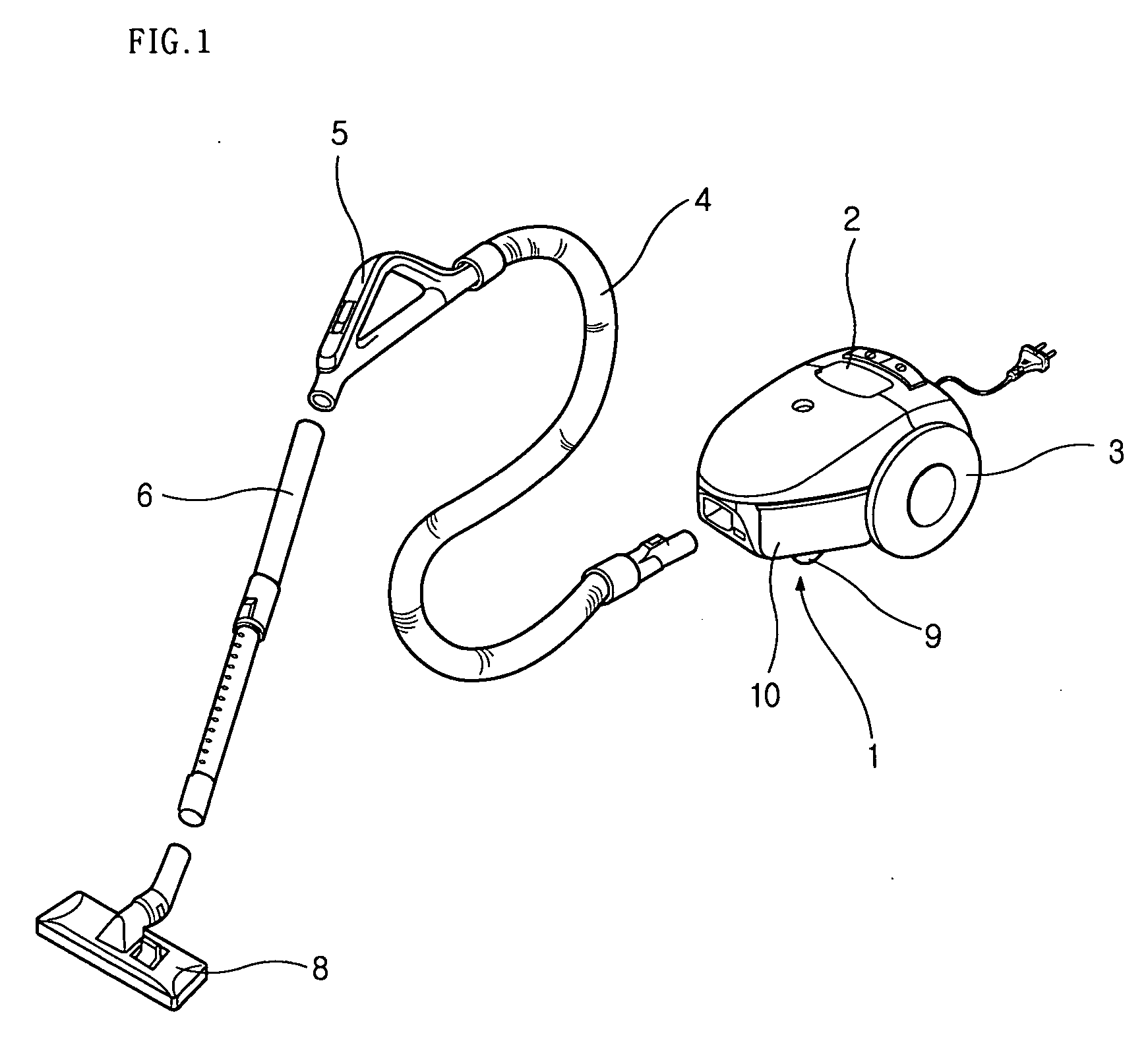
InactiveUS20060117518A1Avoid spreadingReduce the amount of noisePump componentsExhaust apparatusEngineeringVacuum cleaner
A vacuum cleaner includes a fan motor generating air current, a main body receiving the fan motor, a wheel allowing the main body to smoothly move, a flexible connecting hose extending from the main body, an expandable extending tube connected to the connecting holes, a suction nozzle connected to an end of the extending tube to suck outer air, an inner sound absorption member disposed around the fan motor to absorb noise generated by the fan motor, a casing disposed around the inner sound absorption member to enclose the fan motor, the casing being provided with an air hole through which the air is exhausted in a side direction of the fan motor, and an outer sound absorption member disposed around the casing to absorb the noise generated by the fan motor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Control apparatus for vehicular drive apparatus
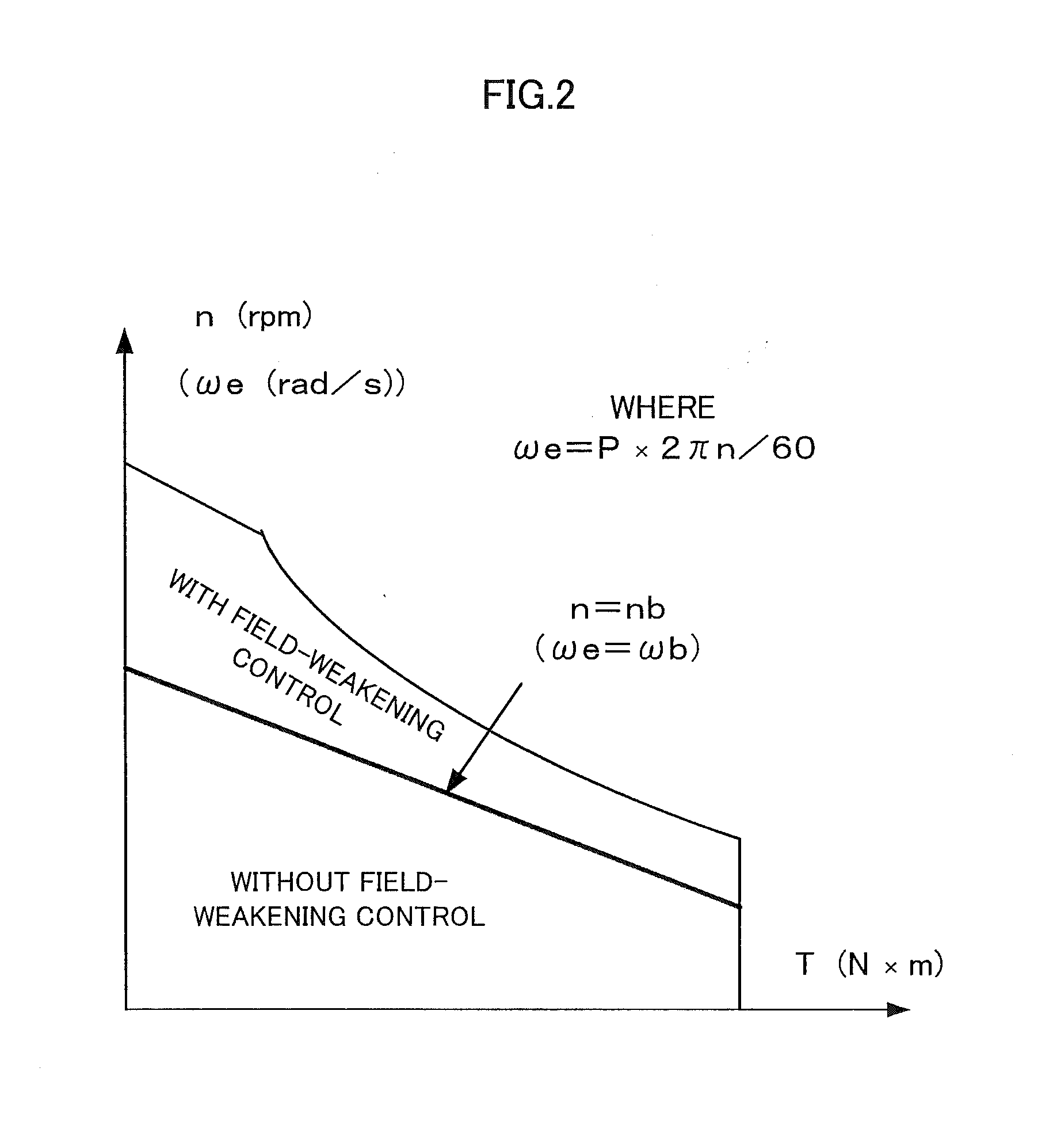
ActiveUS8167064B2InhibitionSuppress noiseHybrid vehiclesDC motor speed/torque controlOperating pointControl equipment
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive apparatus including an engine and a motor is provided. The control apparatus includes a controller that determines the operating point of the engine and the operating point of the motor based on the characteristic of the vehicular drive apparatus. When at least one of the operating point of the motor and the operating point of the engine is in at least one of a motor noise occurrence region and a gear noise occurrence region, the controller changes the at least one of the operating point of the motor and the operating point of the engine so that the at least one of the operating point of the motor and the operating point of the engine avoids the at least one of the motor noise occurrence region and the gear noise occurrence region. This suppresses at least one of motor noise and gear noise.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for detecting external acceleration to a hard disk drive by a spindle motor
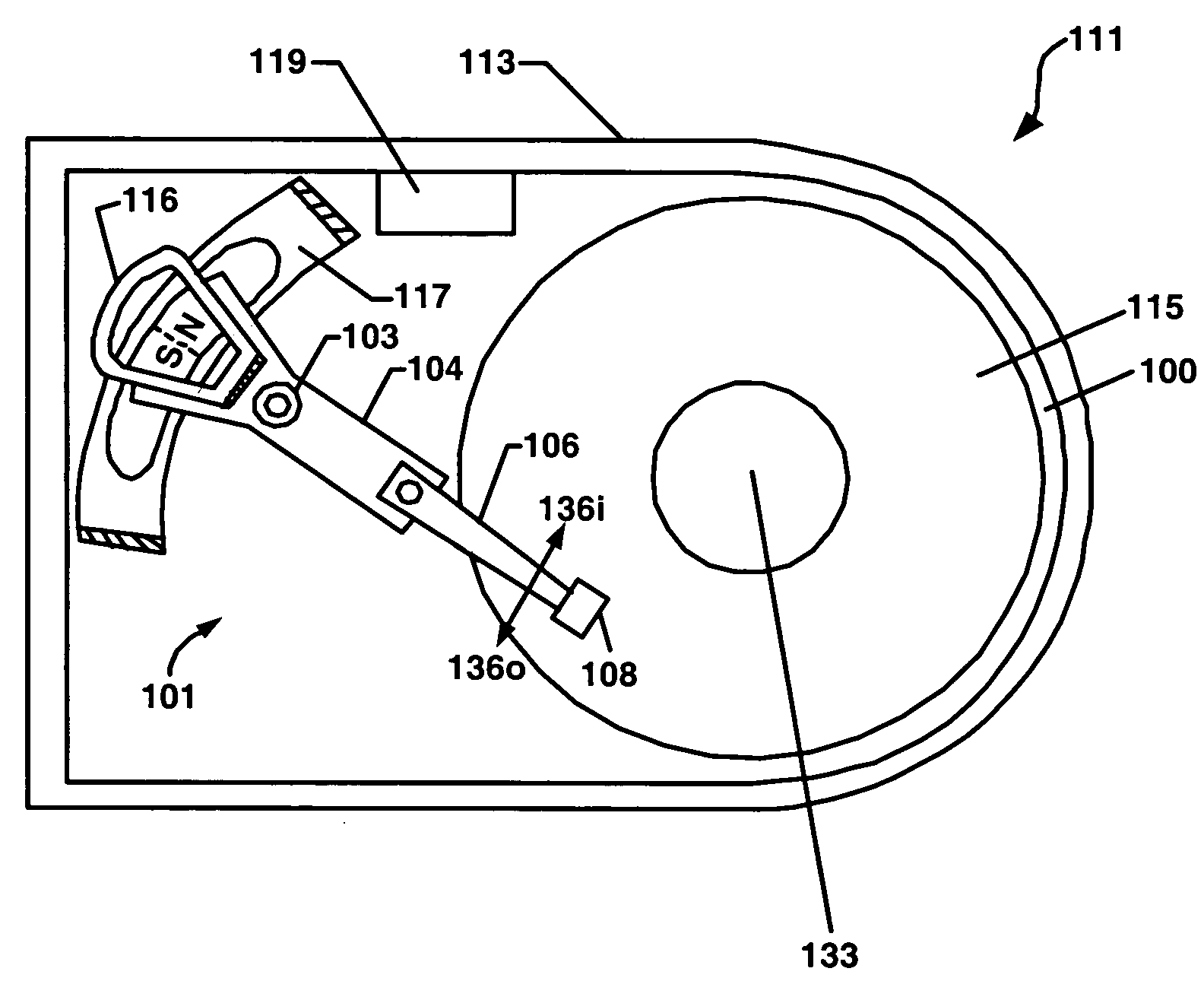
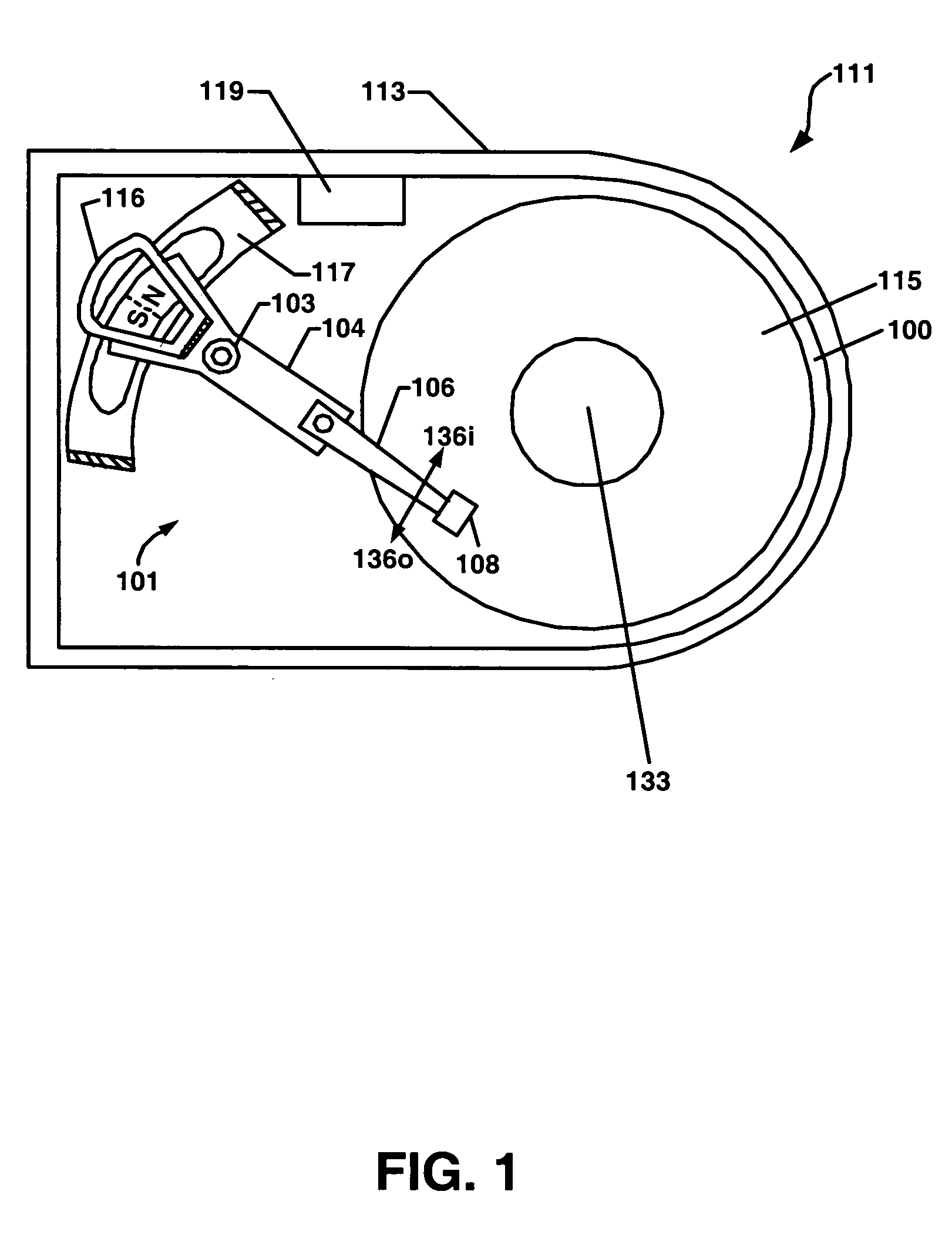
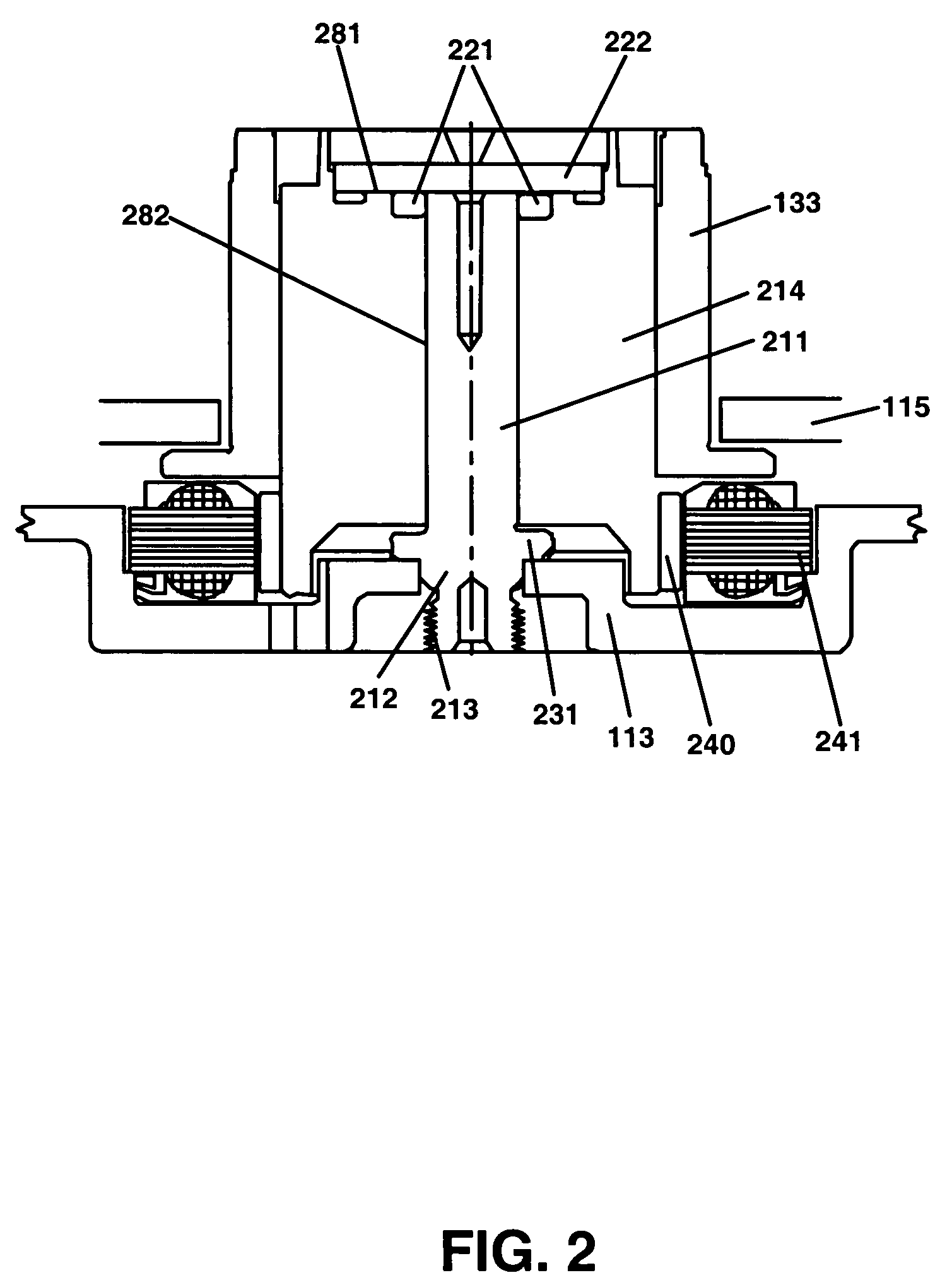
InactiveUS7143002B2Driving/moving recording headsUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionHard disc driveAcceleration amplitude
A method for detecting an external acceleration applied to a hard disk drive is described. The method includes obtaining a running current value for a spindle motor operating a hard disk drive. The running current is provided from a controller coupled with the hard disk drive. The method further includes compensating the running current value for positional orientation of a data transducer and for torque disturbance. The method also includes filtering the running current value for removal of motor noise and direct current offset which, subsequent thereto, provides an estimated external acceleration amplitude. The method also includes invoking a defensive action for preventing damage to the data transducer and the data storage disk and loss of data disposed on the data storage disk. The defensive action is triggered when the estimated external acceleration amplitude exceeds a threshold value.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Brushless DC motor
InactiveCN101102090AReduce torque fluctuationReduce noiseElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsElectricity
The invention provides a motor for a brushless DC motor, which has small torque ripple even if a trapezoidal wave current is supplied and has a small size and reduced motor noise. Respective phase current command values are calculated on the basis of vector control. Pseudo-vector control for controlling respective phases separately is used as current feedback control.
Owner:NSK LTD
Motor noise reduction structure
The invention relates to a motor noise reduction structure, in particular to a dust collector motor noise reduction structure. The structure comprises a motor cover for containing a motor. The motor cover internally comprises an impeller cavity and a sound elimination cavity in sequence from an air inlet to an air outlet. A movable impeller assembly is arranged in a movable impeller cavity. A first sound elimination part and / or a second sound elimination part are / is arranged in the sound elimination cavity, the first sound elimination part comprises an oblique grid, and the second sound elimination part comprises small dense holes formed in the air outlet and a sound elimination material arranged on the inner side of the air outlet. The air noise can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SKYBEST ELECTRIC APPLIANCE SUZHOU CO LTD
Stator mounting apparatus, stator mounting structure and fan system
InactiveCN107171466AGuaranteed installation accuracyReduce noiseMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineRadial position
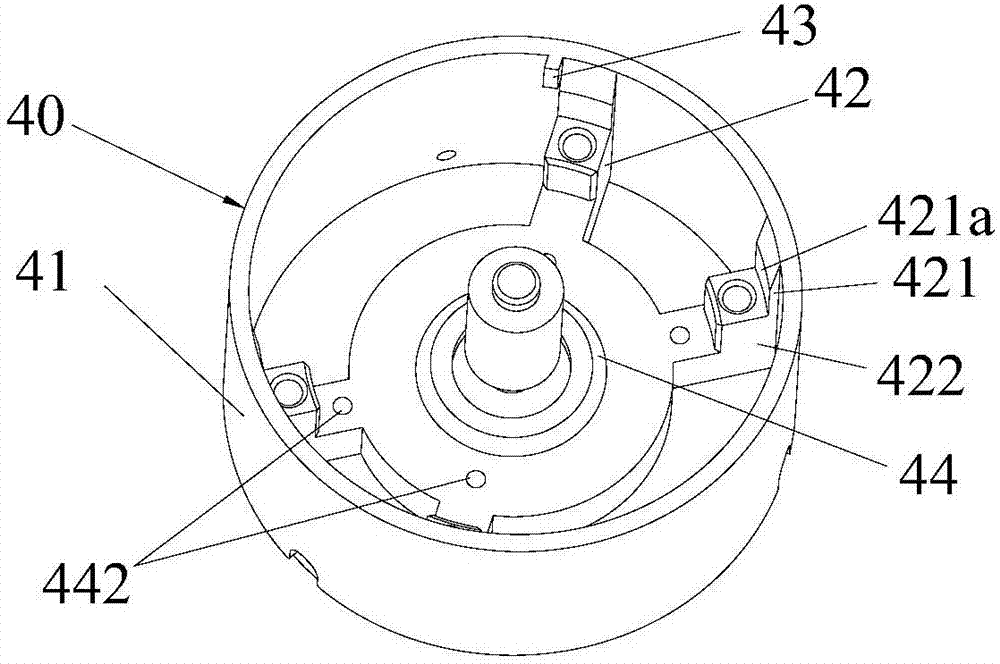
The invention relates to the field of an electric tool, and discloses a stator mounting apparatus, a stator mounting structure and a fan system. The stator mounting apparatus (40) comprises a barrel-shaped shell (41) and a connecting piece (42) mounted on the inner wall of the shell; the connecting piece comprises a first part (421) connected to the shell and a second part (42) which extends from the first part (421) towards the inner side of the shell; a stator (50) is mounted on the second part; a radial positioning part (421a) for radially limiting the mounting position of the stator is arranged on the first part; and a circumferential positioning part (43) used for circumferentially limiting the mounting position of the stator is arranged on the shell. By virtue of the stator mounting apparatus disclosed in the invention, the mounting position of the stator can be accurately positioned, thereby ensuring the mounting precision of the stator; and therefore, accurate mounting of a rotor can be matched, and higher air gap uniformity can be obtained, thereby lowering motor noise.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG +1
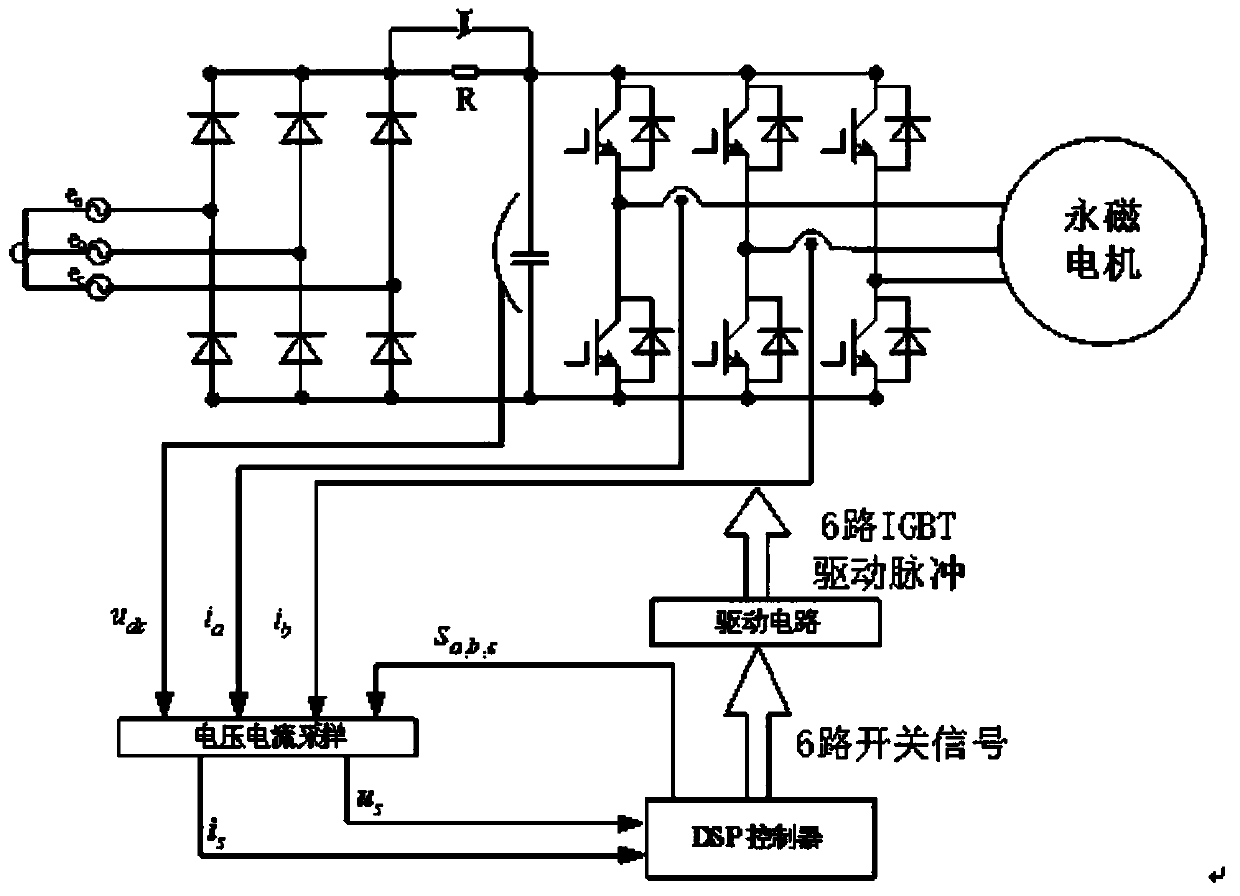
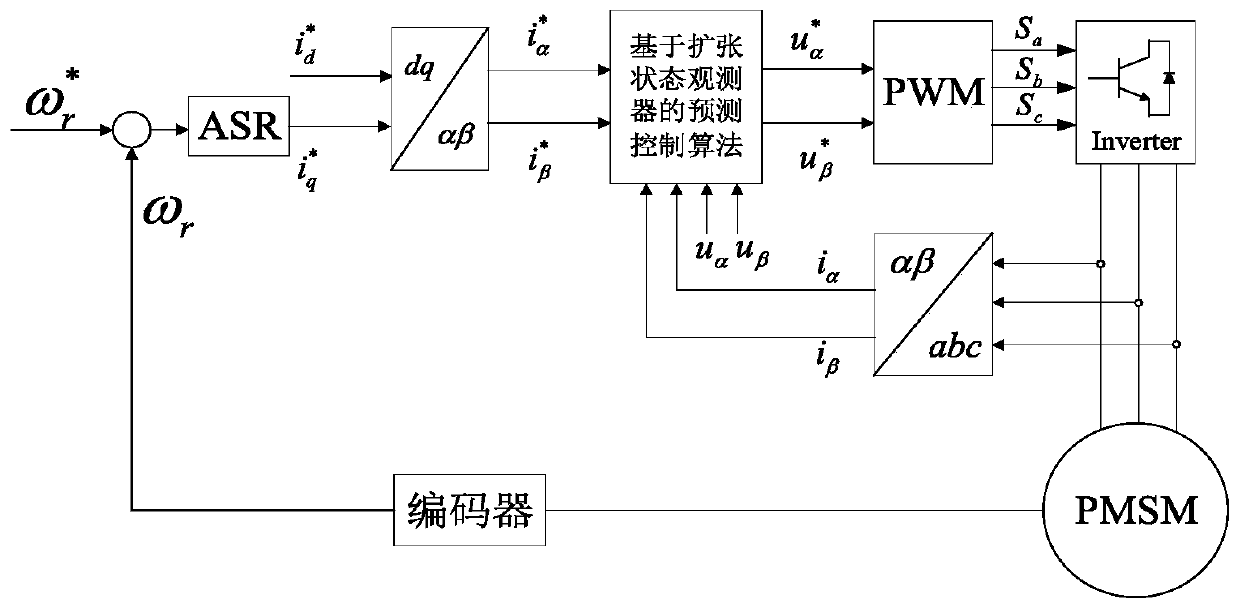
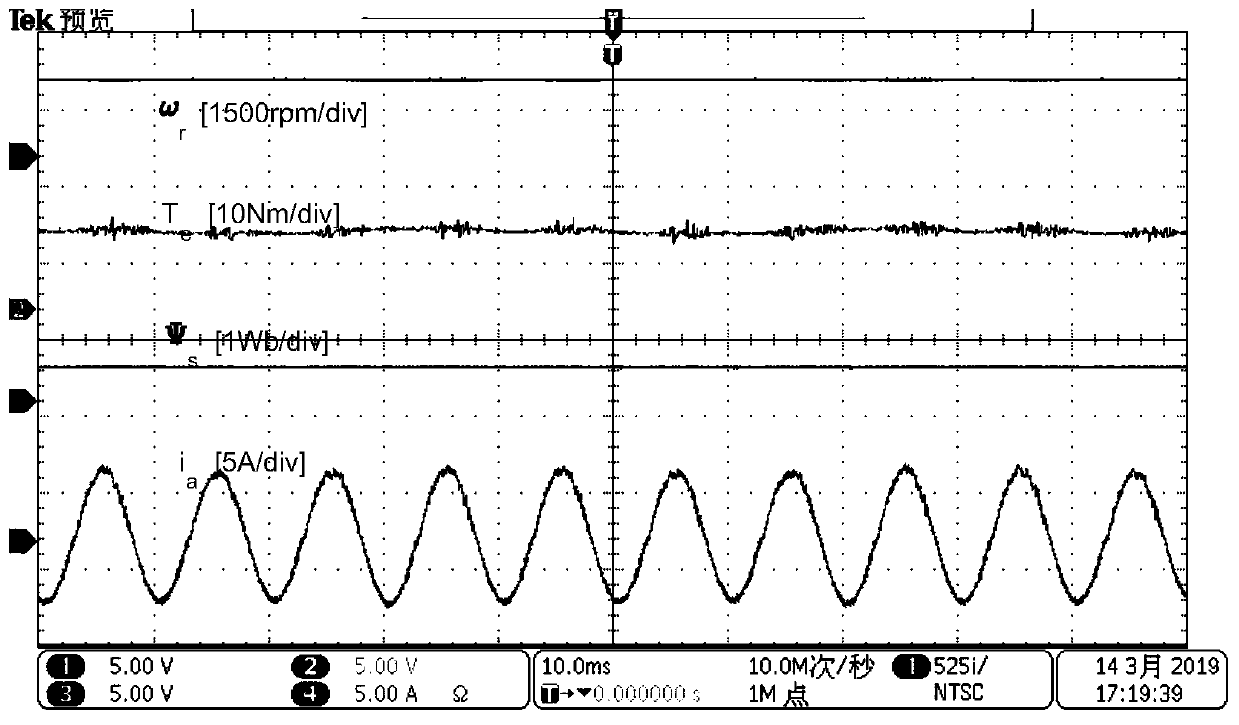
Permanent magnet synchronous motor model-free prediction control method based on extended state observer
InactiveCN110912480AImprove dynamic performanceImprove steady state performanceElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorReference current
The invention relates to a permanent magnet synchronous motor model-free prediction control method based on an extended state observer, and the method comprises the steps: A, estimating unknown and disturbance parts of a system through employing a linear extended state observer, and not relating to motor parameters; and B, enabling the motor reference current vector and the feedback current vectorto pass through a permanent magnet synchronous motor model-free controller based on an extended state observer, obtaining a reference voltage vector by using a complex vector current regulator, and obtaining six paths of switching signals of an inverter after PWM modulation, thereby realizing control of the motor. According to the invention, the problems of large motor noise, steady-state torque,large current ripple, static current difference and poor system control performance in a traditional model prediction control scheme when motor parameters are inaccurate are solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Rotating armature controller
ActiveCN101803171AReduce noiseImprove reliabilityHybrid vehiclesVector control systemsMotor driveElectric machine
A motor driving error is prevented. In concrete, disturbance in a rotation detection signal of a resolver due to motor noise is reduced. An inverter is controlled to set output torque of a rotating armature at target torque using the target torque, rotation speed and a rotation angle of the rotating armature. Three-phase / two-phase modulation takes place, wherein control of the inverter is changedfrom three-phase modulation to two-phase modulation when a modulation ratio expressed as a ratio of voltage applied to the rotating armature for voltage input to the inverter is larger than three-phase / two-phase modulation changeover boundary. Even in a three-phase modulation region where the modulation ratio is smaller than the three-phase / two-phase modulation changeover boundary, the modulationis changed over to the two-phase modulation in a specific region where torque of the rotating armature corresponding to the mentioned boundary, a torque threshold lower than the rotation speed and electric noise applied by the rotating armature exceeding the rotation speed threshold to the resolver are large. In an embodiment using step-up voltage (Vuc), the torque threshold is made to be the lower the higher the step-up voltage, to enlarge the specific region.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Motor and drive control device therefor
ActiveUS20060071628A1Reduce noiseSingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlPhase currentsElectric power steering
The invention provides a motor for a brushless DC motor, which has small torque ripple even if a trapezoidal wave current is supplied and has a small size and reduced motor noise, and a drive control device for the motor as well as an electric power steering device using the motor and the drive control device. Respective phase current command values are calculated on the basis of vector control. Pseudo-vector control for controlling respective phases separately is used as current feedback control.
Owner:NSK LTD
Sensing mechanical transitions from current of motor driving hydraulic pump or other mechanism
ActiveUS20060145651A1Single-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlBandpass filteringMotor drive
A circuit and method for detecting an operating transition of a mechanical apparatus driven by a hydraulic prime mover comprising a hydraulic pump driven by an electric motor, the operating transition causing a change in the force applied by the mechanical apparatus on the prime mover. A motor current sensing circuit is connected in a motor power supply circuit to provide a motor current signal representing motor current. A bandpass filter receives the motor current signal and provides a filtered motor current signal consisting essentially of motor current signal components in the frequency range from a lower frequency boundary greater than zero Hz to an upper frequency boundary below substantially all the motor noise frequencies. A comparison circuit compares the filtered motor current signal to a first selected threshold level and outputs a signal representing the occurrence of the operating transition when the filtered motor current signal exceeds the selected threshold level. The circuit is preferably implemented with a digital controller programmed to perform these operations.
Owner:INPOWER LLC
Motor rotor and electric motor having it
ActiveCN104600890AReduce harmonic contentReduce noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnetic poles
The invention provides a motor rotor and an electric motor having the electric motor. The motor rotor includes a rotor core, and a magnetic pole structure is arranged on the rotor core; the magnetic pole structure includes a multi-layer magnetic steel groove, wherein both ends of every layer of the magnetic steel groove are provided with magnetic isolating bridges; permanent magnetic structures, each of which is correspondingly arranged in every layer of the magnetic steel groove, and at least one permanent magnetic structure includes a plurality of magnetic steels, and a plurality of magnetic steels include a middle magnetic steel and even number of side magnetic steels; the center line of the middle magnetic steel is overlapped with the center line of the magnetic pole, the side magnetic steels are symmetrically arranged at both sides of the middle magnetic steel; a retained magnetic bridge is arranged between adjacent two magnetic steels, and the center line of every layer of the retained magnetic bridge is not located on the same one line. By adopting the motor rotor, the motor noise can be reduced.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Motor noise-reducing structure of dust collector
InactiveCN107550392AImprove sound insulationExtended delivery pathSuction cleanersNoise reductionControl theory
The invention discloses a motor noise-reducing structure of a dust collector. The motor noise-reducing structure of the dust collector comprises a motor inner cover, wherein the motor inner cover is installed at the outer side of a dust collector motor, a first airflow cavity is formed between the motor inner cover and the dust collector motor, and the first airflow cavity is internally provided with a spiral flow guide plate; a motor outer cover, wherein the motor outer cover is installed at the outer side of the motor inner cover, a second airflow cavity is formed between the motor outer cover and the motor inner cover, the motor outer cover is a double-layer structure, the motor outer cover comprises an outer cover inner ring and an outer cover outer ring, a cavity is formed between theouter cover inner ring and the outer cover outer ring, the cavity is internally provided with a plurality of separating plates, and the separating plates are used for separating the cavity to form aplurality of noise-reducing cavities; and a shock ring, wherein the shock ring is circle-shaped, the shock ring is installed between the motor outer cover and a dust collector housing. The solution uses the noise-reducing structure, has the functions of sound insulation, shock absorption and noise reduction, and is capable of solving the technical problem that the noise of a current dust collectoris larger.
Owner:SUZHOU HAIGE ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com