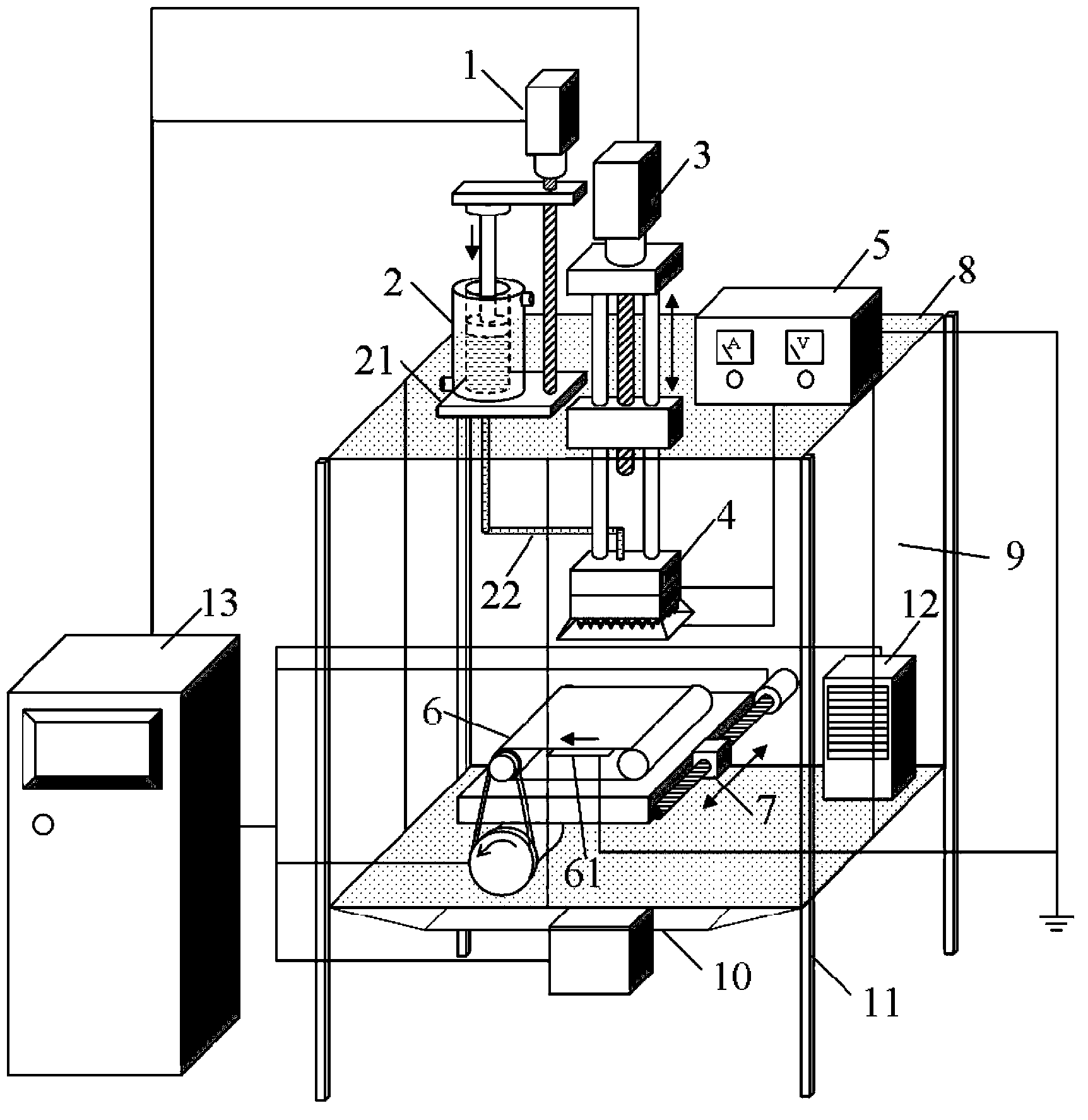
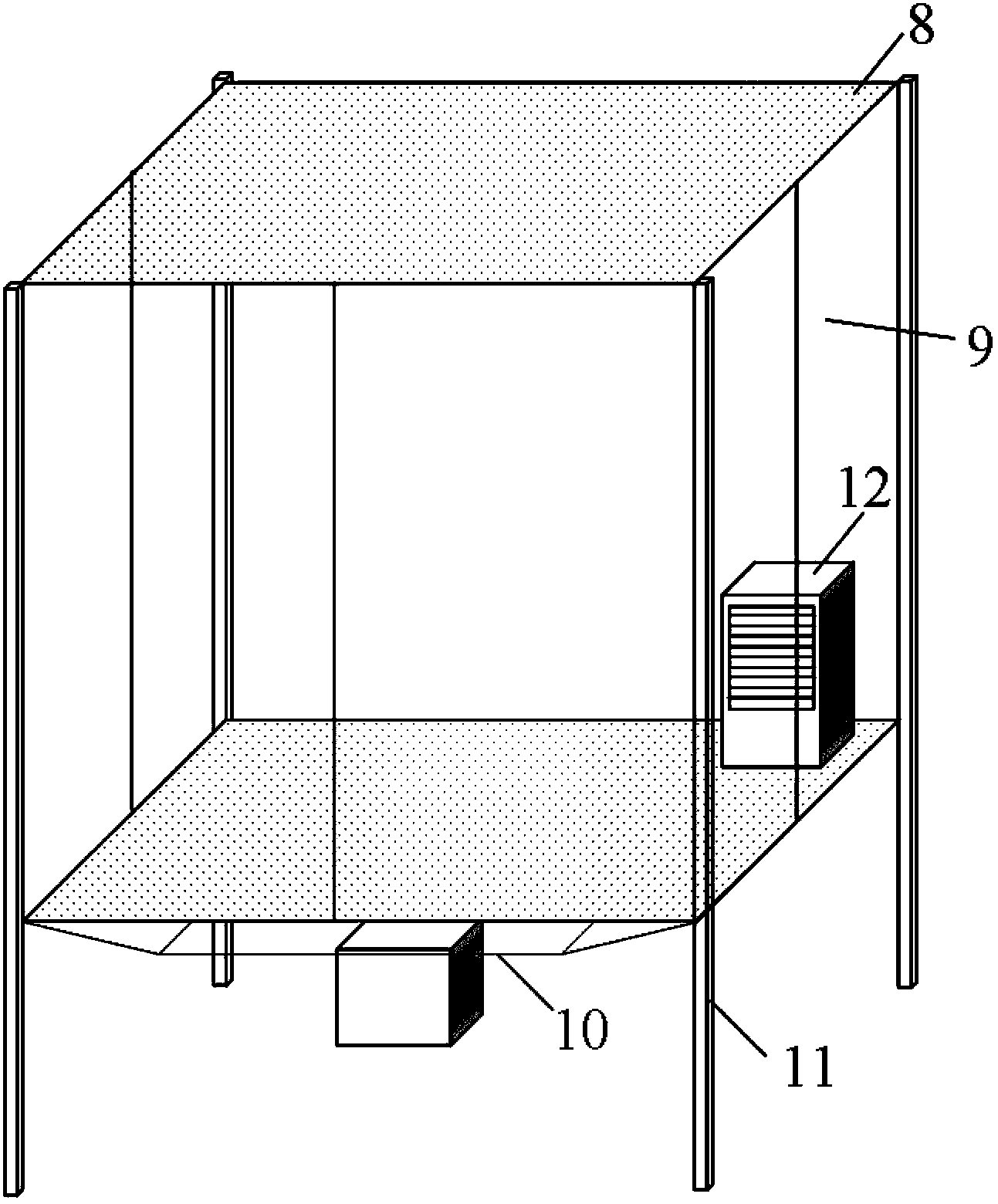
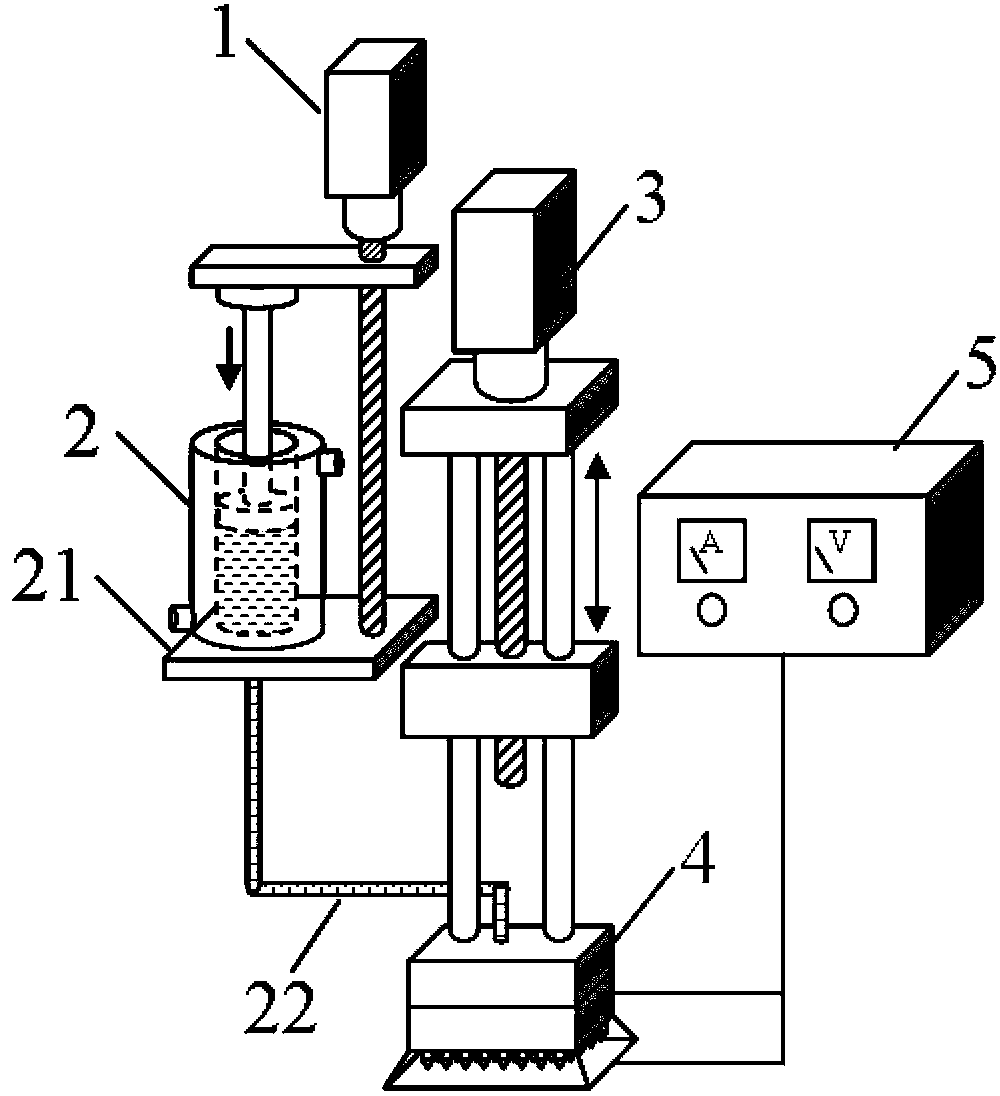
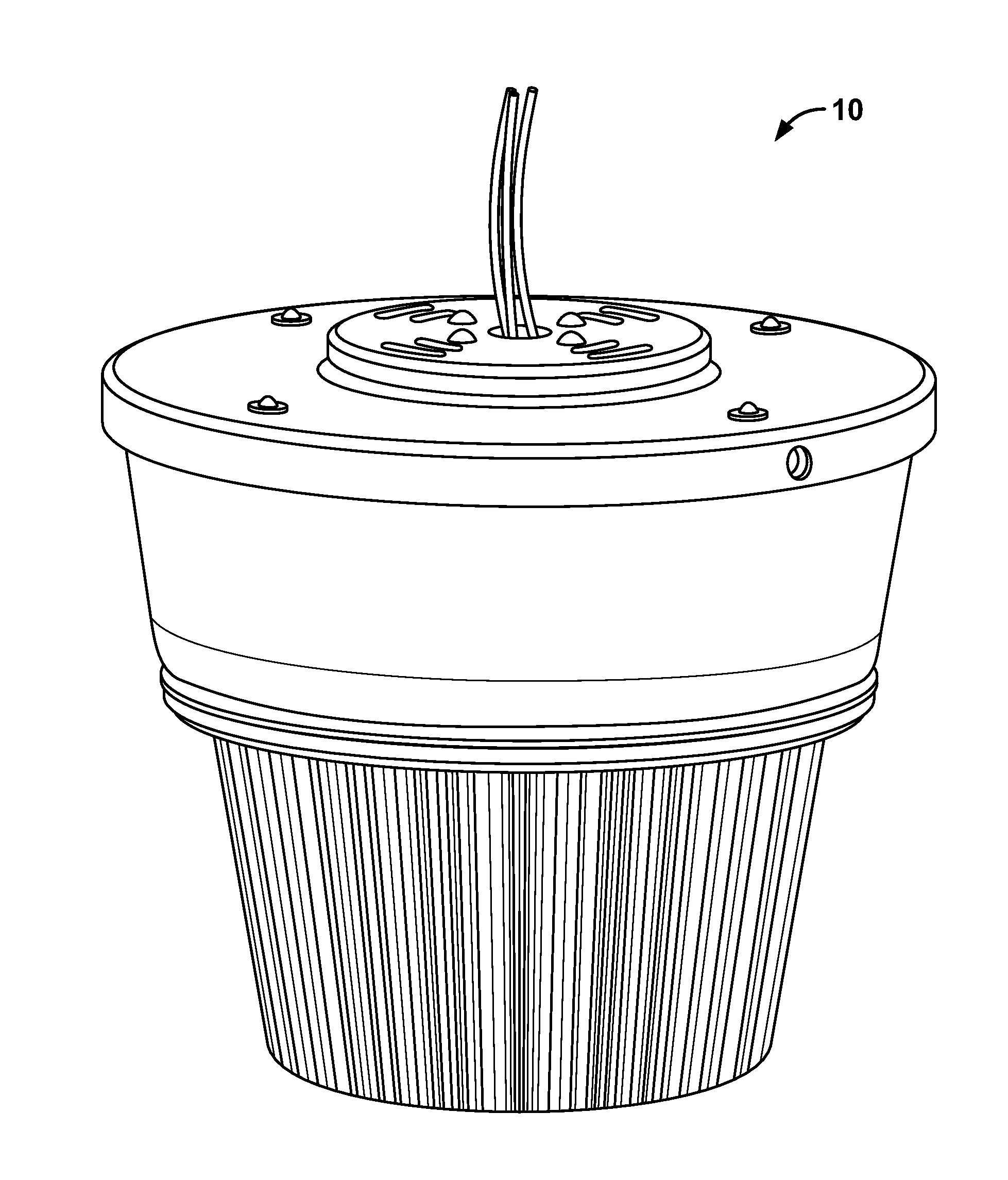
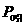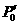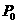Patents
Literature
940 results about "Air current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Air currents are concentrated areas of winds. They are mainly due to differences in pressure or temperature. They are divided into horizontal and vertical currents; both are present at mesoscale while horizontal ones dominate at synoptic scale. Air currents are not only found in the troposphere, but extend to the stratosphere and mesosphere.
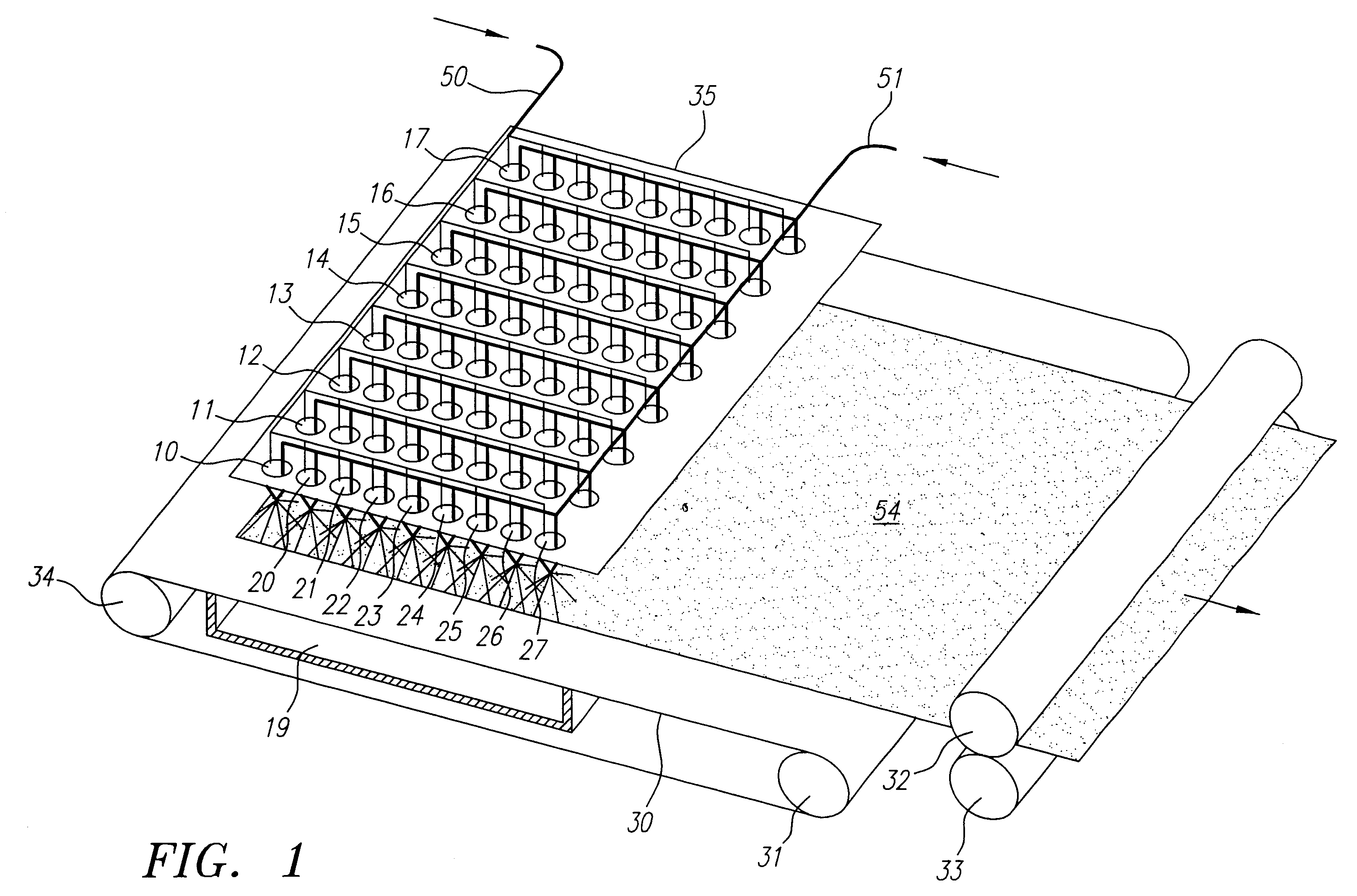
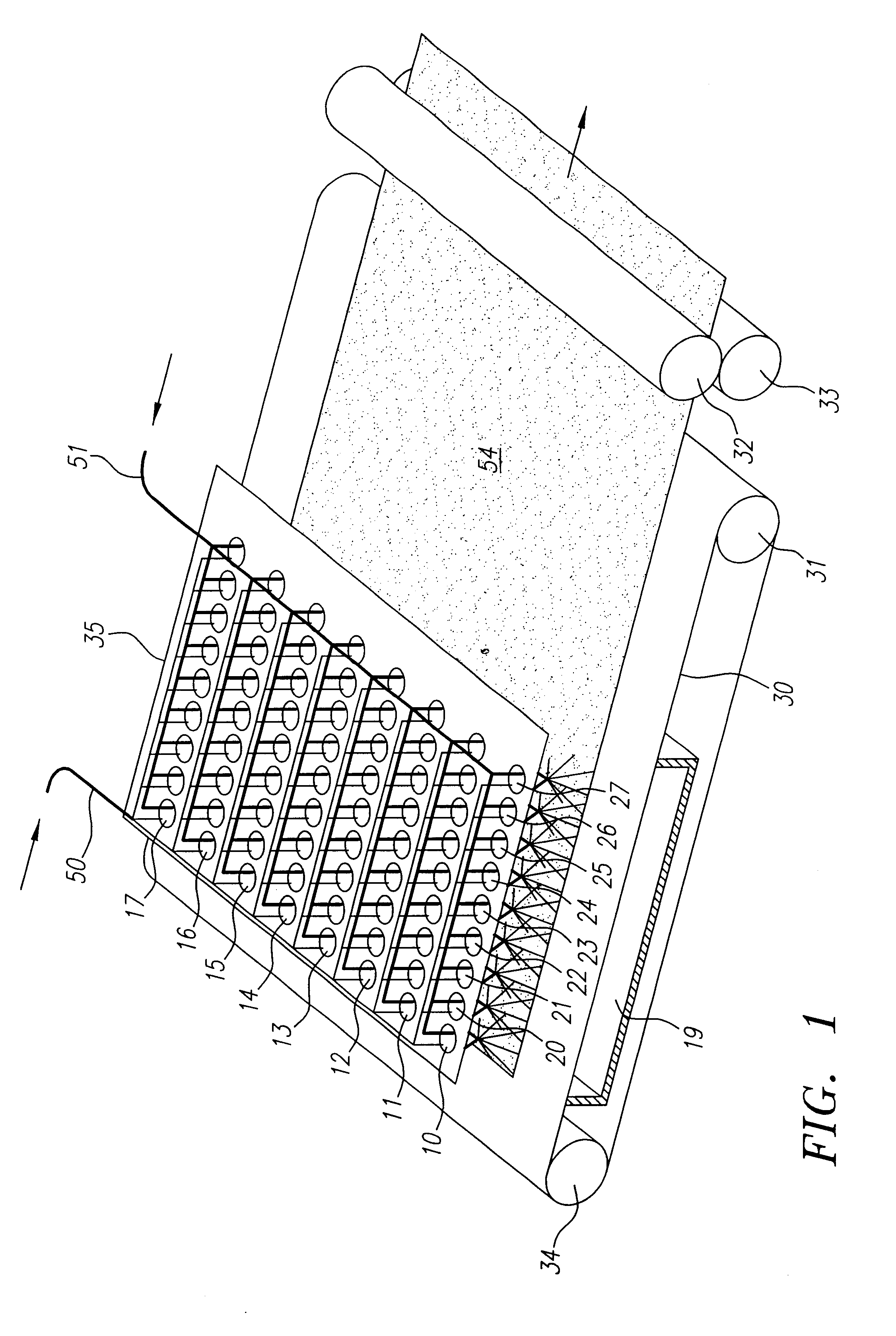
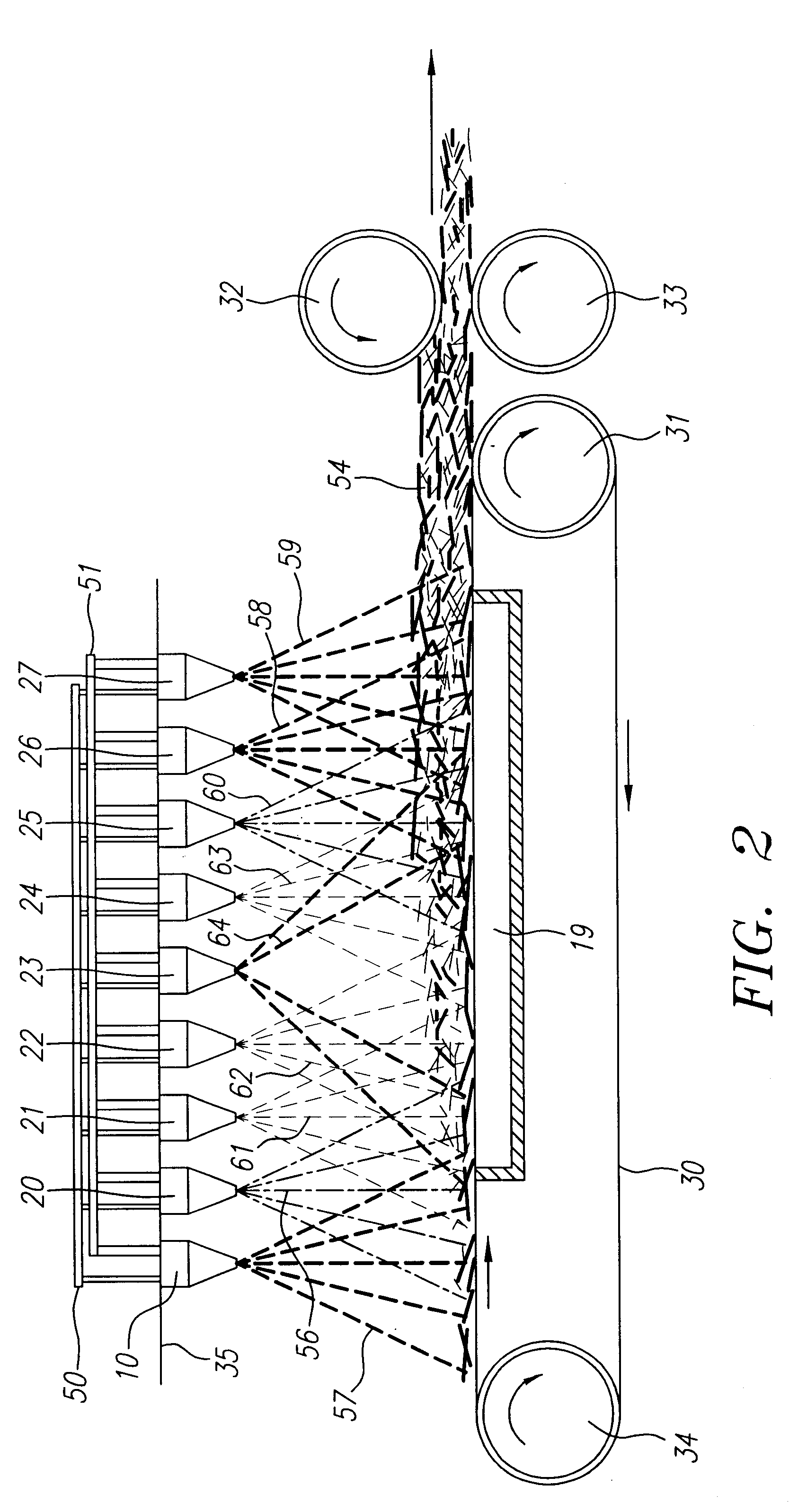
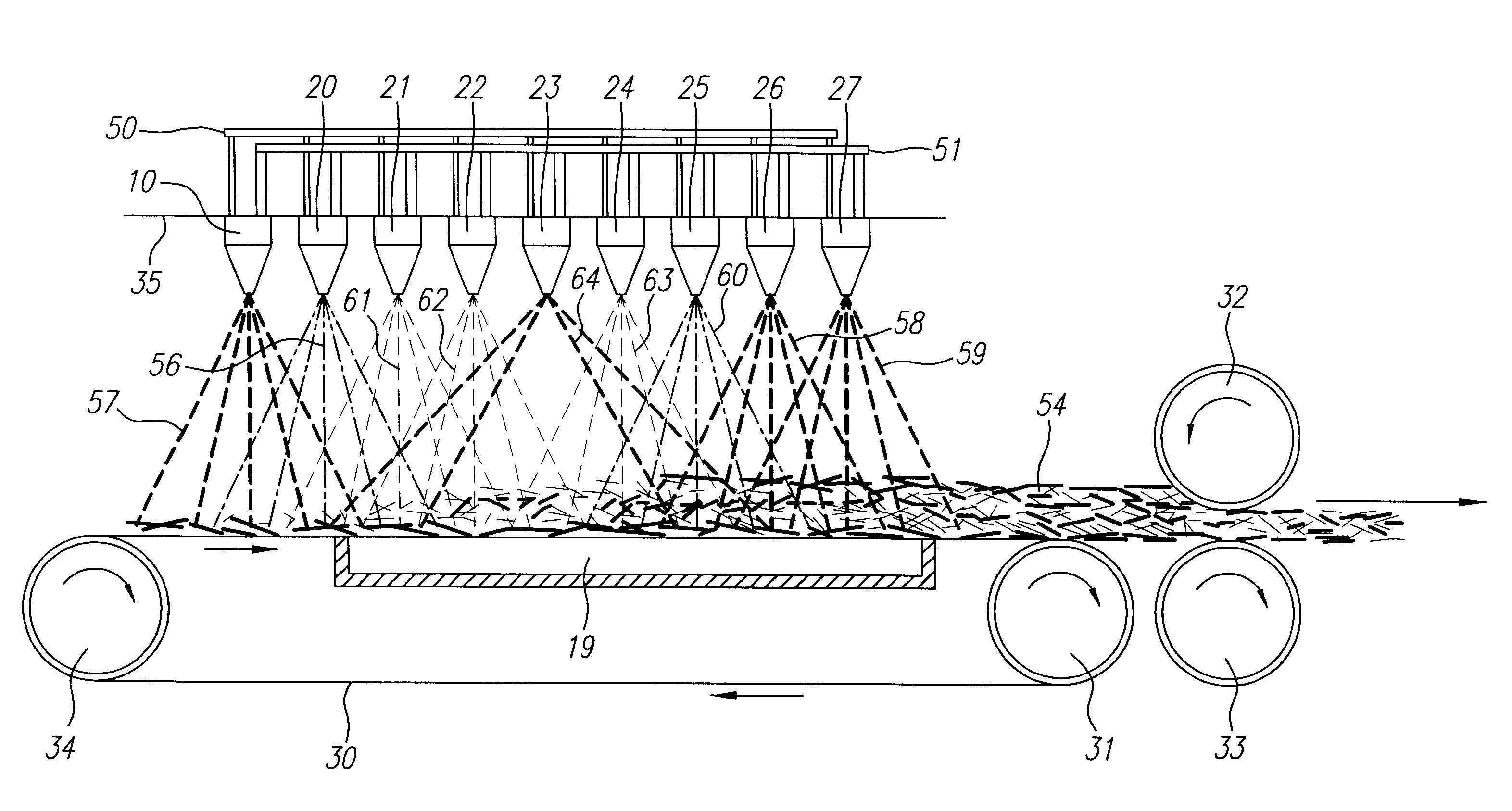
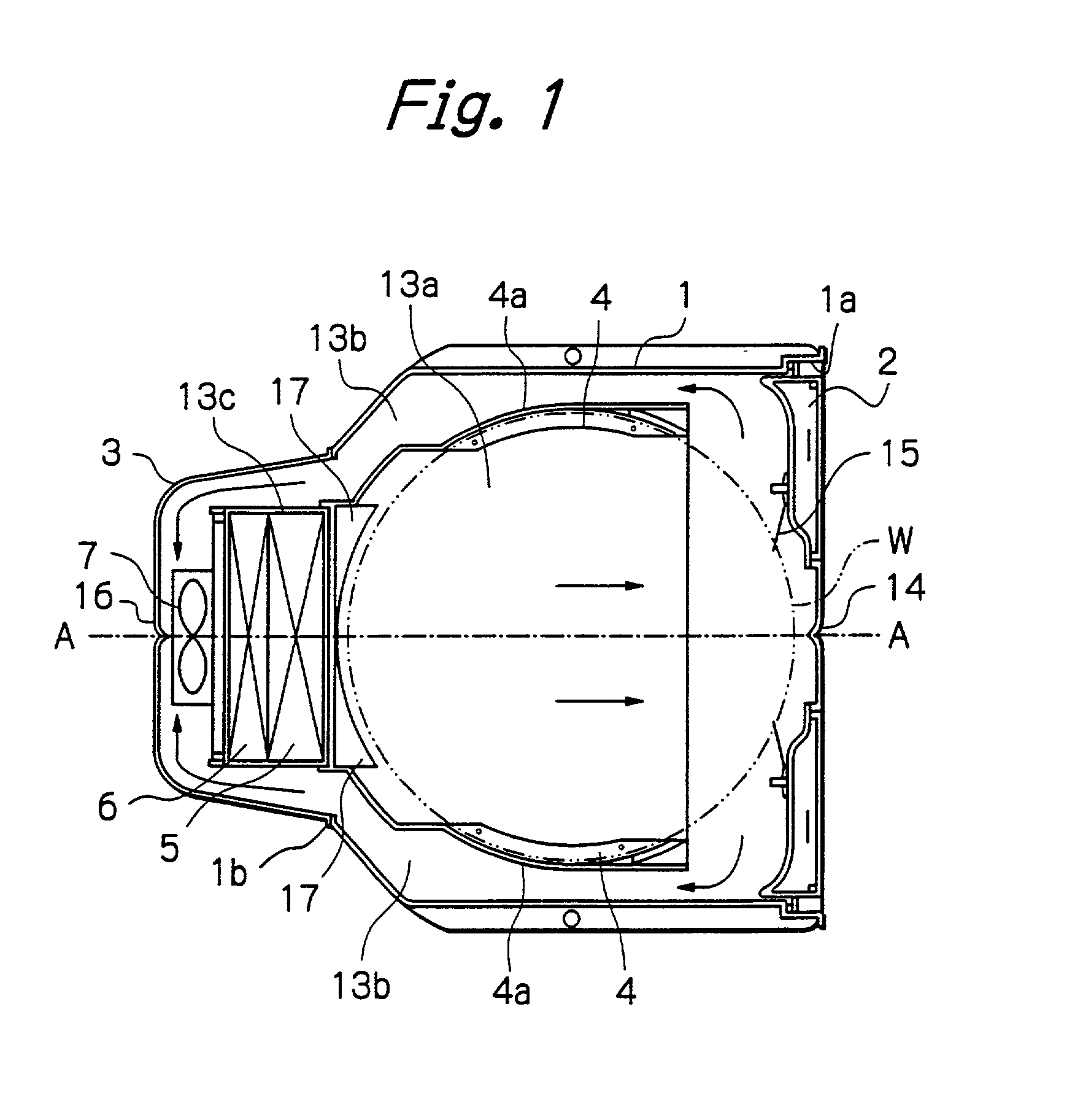
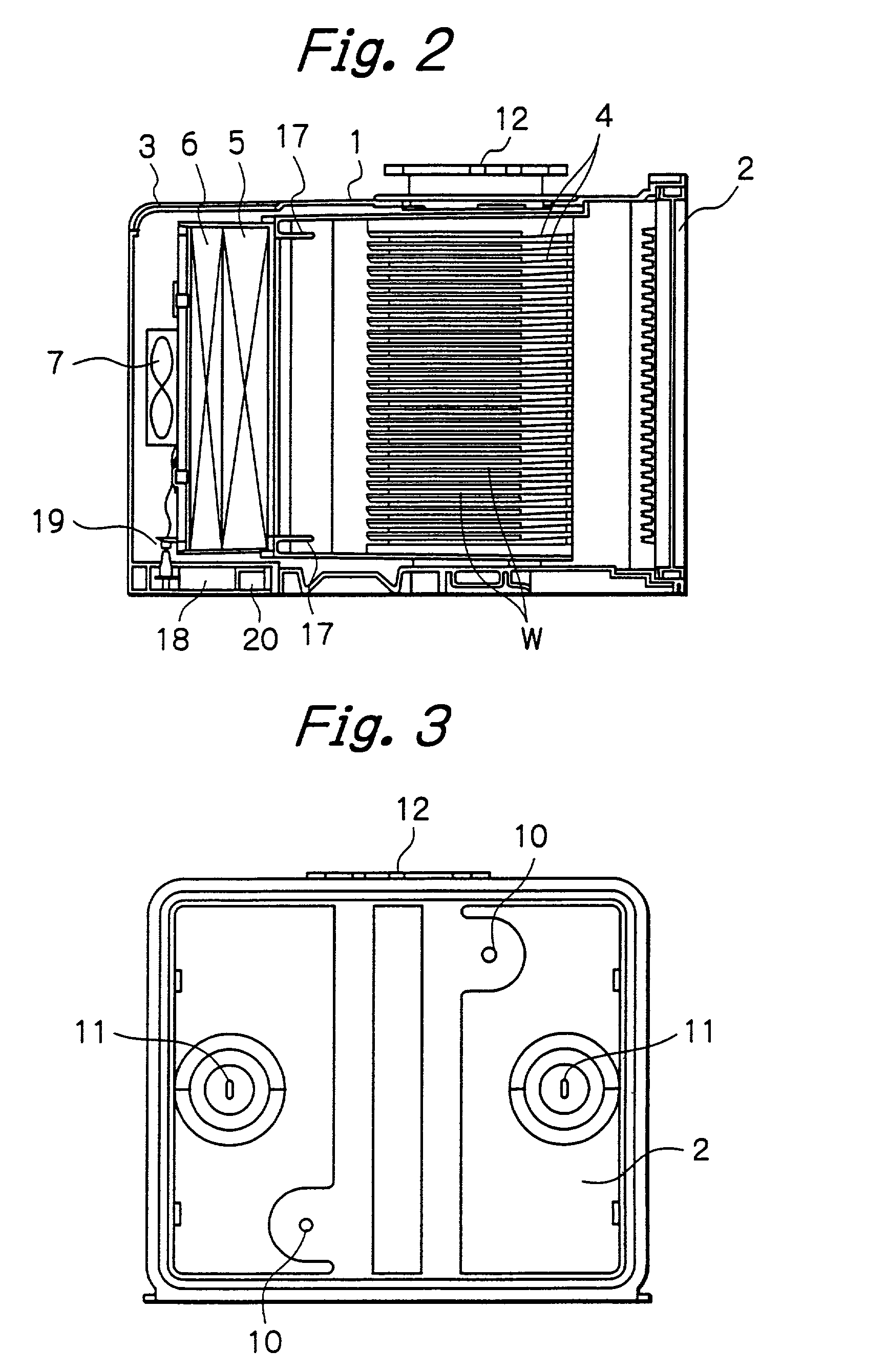
Method and apparatus for producing high efficiency fibrous media incorporating discontinuous sub-micron diameter fibers, and web media formed thereby
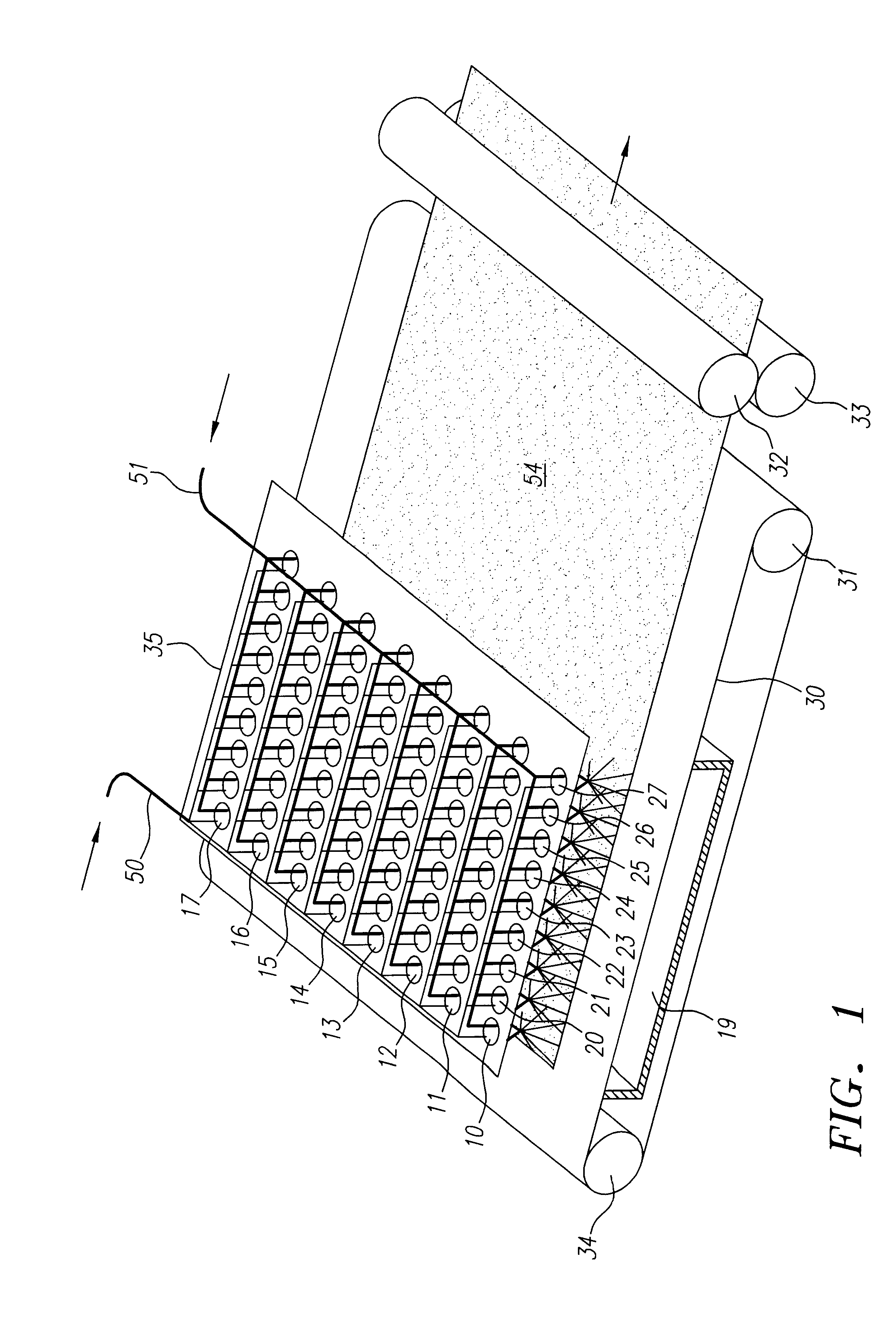
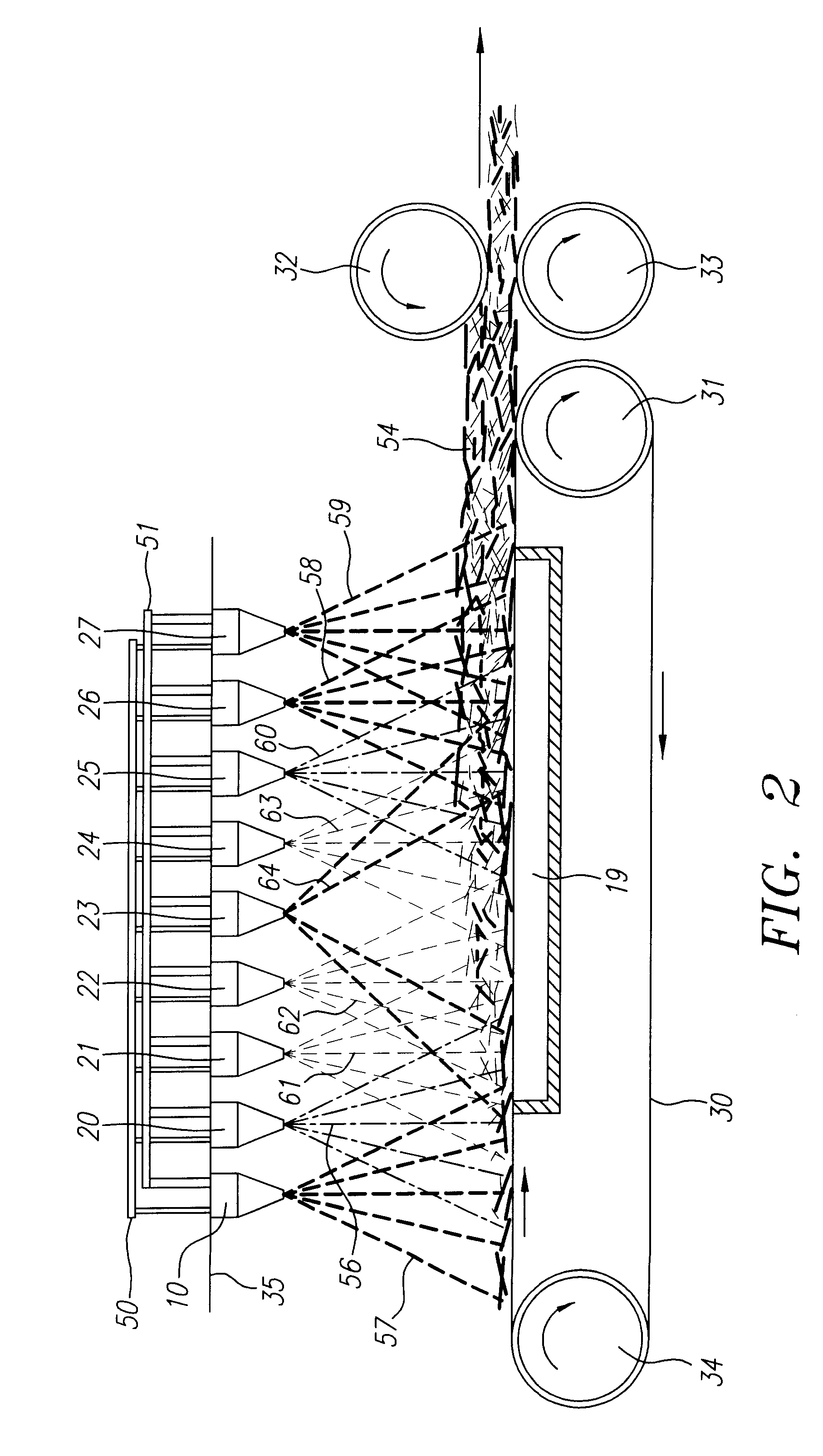
InactiveUS6315806B1Increase distanceReduce resistanceFilament/thread formingLoose filtering material filtersMean diameterFiber
A composite filtration medium web of fibers containing a controlled dispersion of a mixture of sub-micron and greater than sub-micron diameter polymeric fibers is described. The filtration medium is made by a two dimensional array of cells, each of which produces a single high velocity two-phase solids-gas jet of discontinuous fibers entrained in air. The cells are arranged so that the individual jets are induced to collide in flight with neighboring jets in their region of fiber formation, to cause the individual nascent fibers of adjacent jets to deform and become entangled with and partially wrap around each other at high velocity and in a localized fine scale manner before they have had an opportunity to cool to a relatively rigid state. The cells are individually adjusted to control the mean diameters, lengths and trajectories of the fibers they produce. Certain cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of fibers having diameters less than one micron diameter, and which are relatively shorter in length and certain other cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of structure-forming reinforcing fibers having diameters greater than one micron diameter which are relatively longer in length. By employing appropriate close positioning and orientation of the cells in the array, the sub-micron fibers are caused to promptly entangle with and partially wrap around the larger reinforcing fibers. The larger fibers thereby trap and immobilize the sub-micron diameter fibers in the region of formation, to minimize the tendency of sub-micron diameter fibers to clump, agglomerate, or rope together in flight. Also, the larger fibers in flight are made to form a protective curtain to prevent the sub-micron fibers from being carried off by stray air currents.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method and apparatus for producing high efficiency fibrous media incorporating discontinuous sub-micron diameter fibers, and web media formed thereby
InactiveUS6183670B1Increase collisionImprove compactionFilament/thread formingAuxillary shaping apparatusMean diameterFiber
A composite filtration medium web of fibers containing a controlled dispersion of a mixture of sub-micron and greater than sub-micron diameter polymeric fibers is described. The filtration medium is made by a two dimensional array of cells, each of which produces a single high velocity two-phase solids-gas jet of discontinuous fibers entrained in air. The cells are arranged so that the individual jets are induced to collide in flight with neighboring jets in their region of fiber formation, to cause the individual nascent fibers of adjacent jets to deform and become entangled with and partially wrap around each other at high velocity and in a localized fine scale manner before they have had an opportunity to cool to a relatively rigid state. The cells are individually adjusted to control the mean diameters, lengths and trajectories of the fibers they produce. Certain cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of fibers having diameters less than one micron diameter, and which are relatively shorter in length and certain other cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of structure-forming reinforcing fibers having diameters greater than one micron diameter which are relatively longer in length. By employing appropriate close positioning and orientation of the cells in the array, the sub-micron fibers are caused to promptly entangle with and partially wrap around the larger reinforcing fibers. The larger fibers thereby trap and immobilize the sub-micron diameter fibers in the region of formation, to minimize the tendency of sub-micron diameter fibers to clump, agglomerate, or rope together in flight. Also, the larger fibers in flight are made to form a protective curtain to prevent the sub-micron fibers from being carried off by stray air currents.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
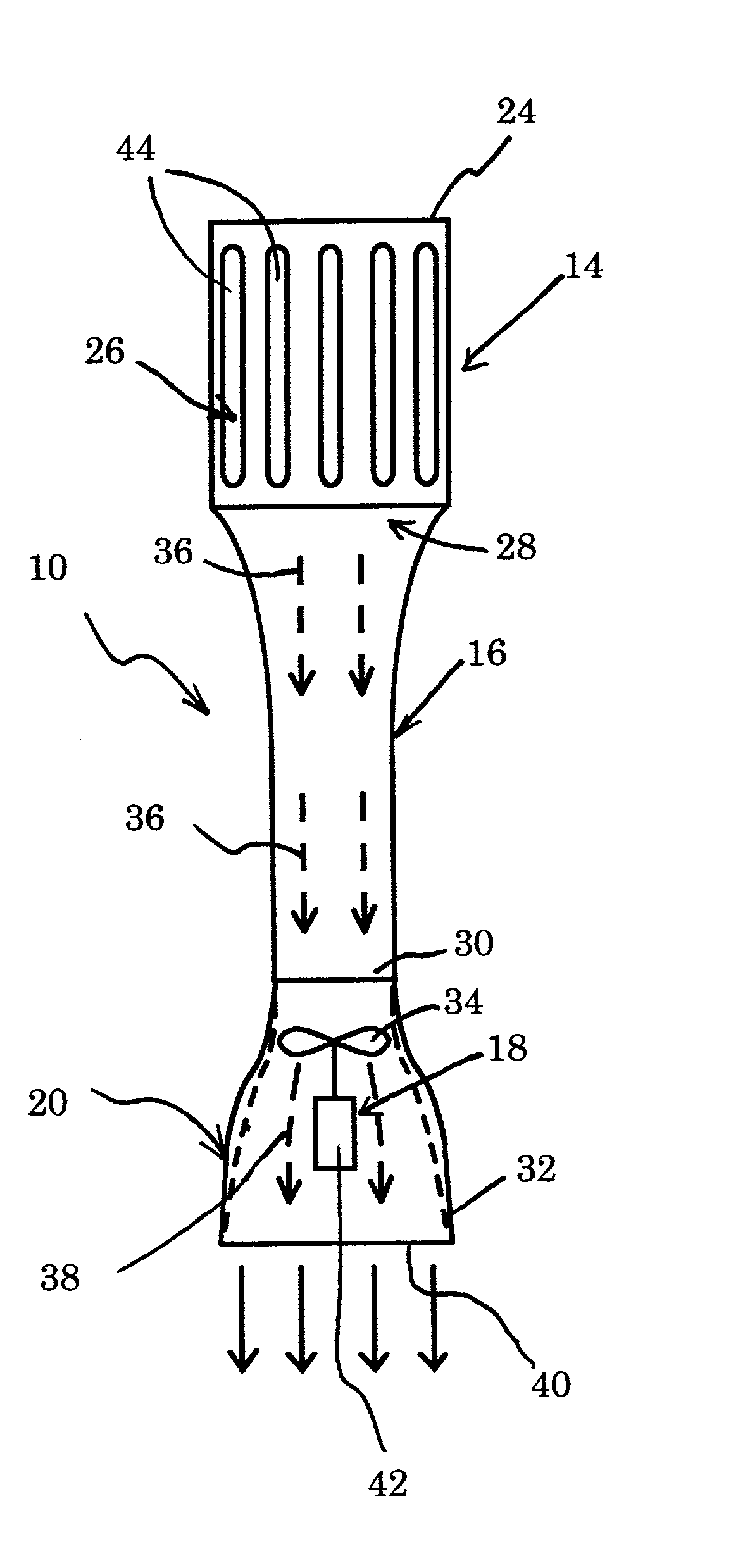
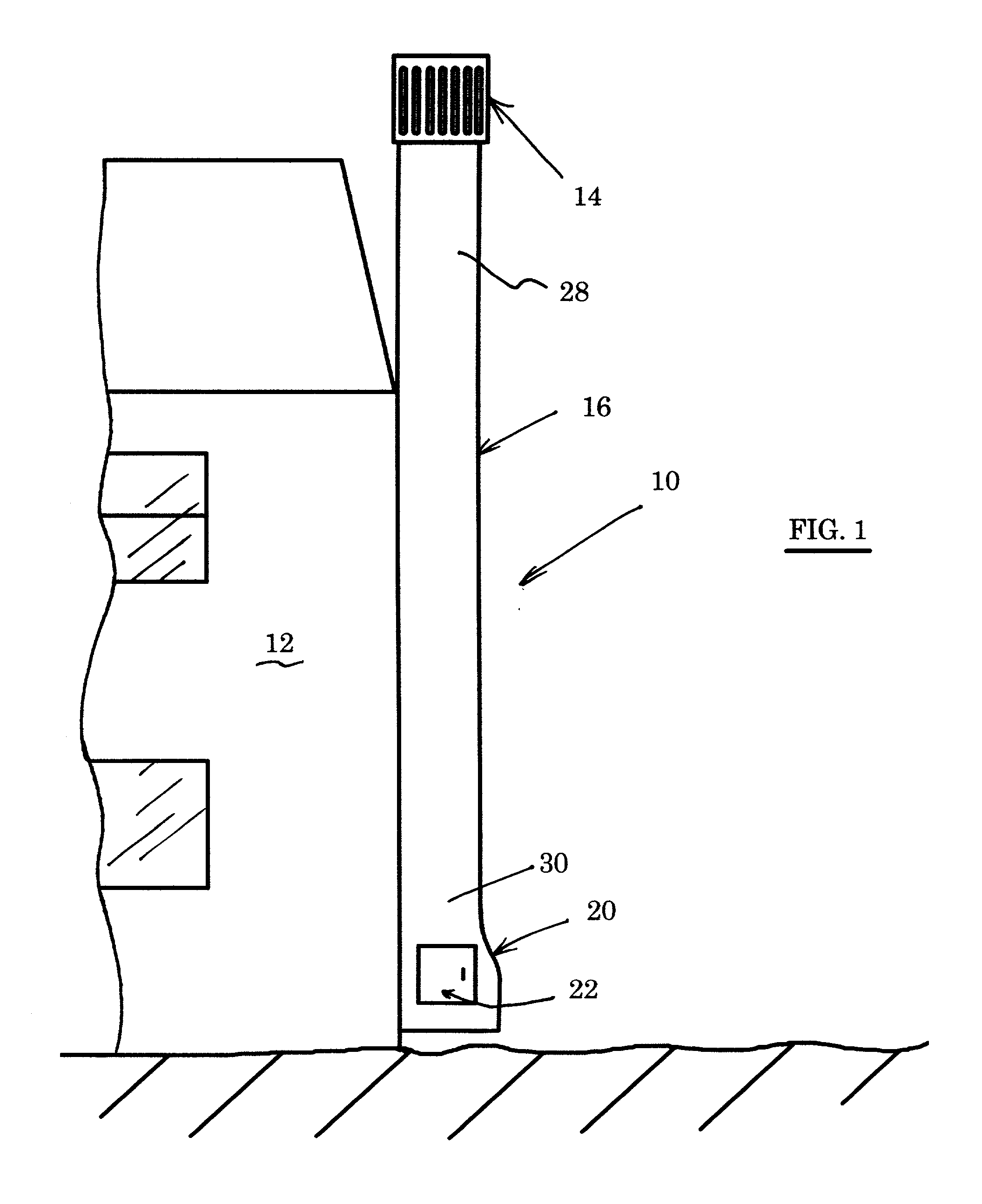
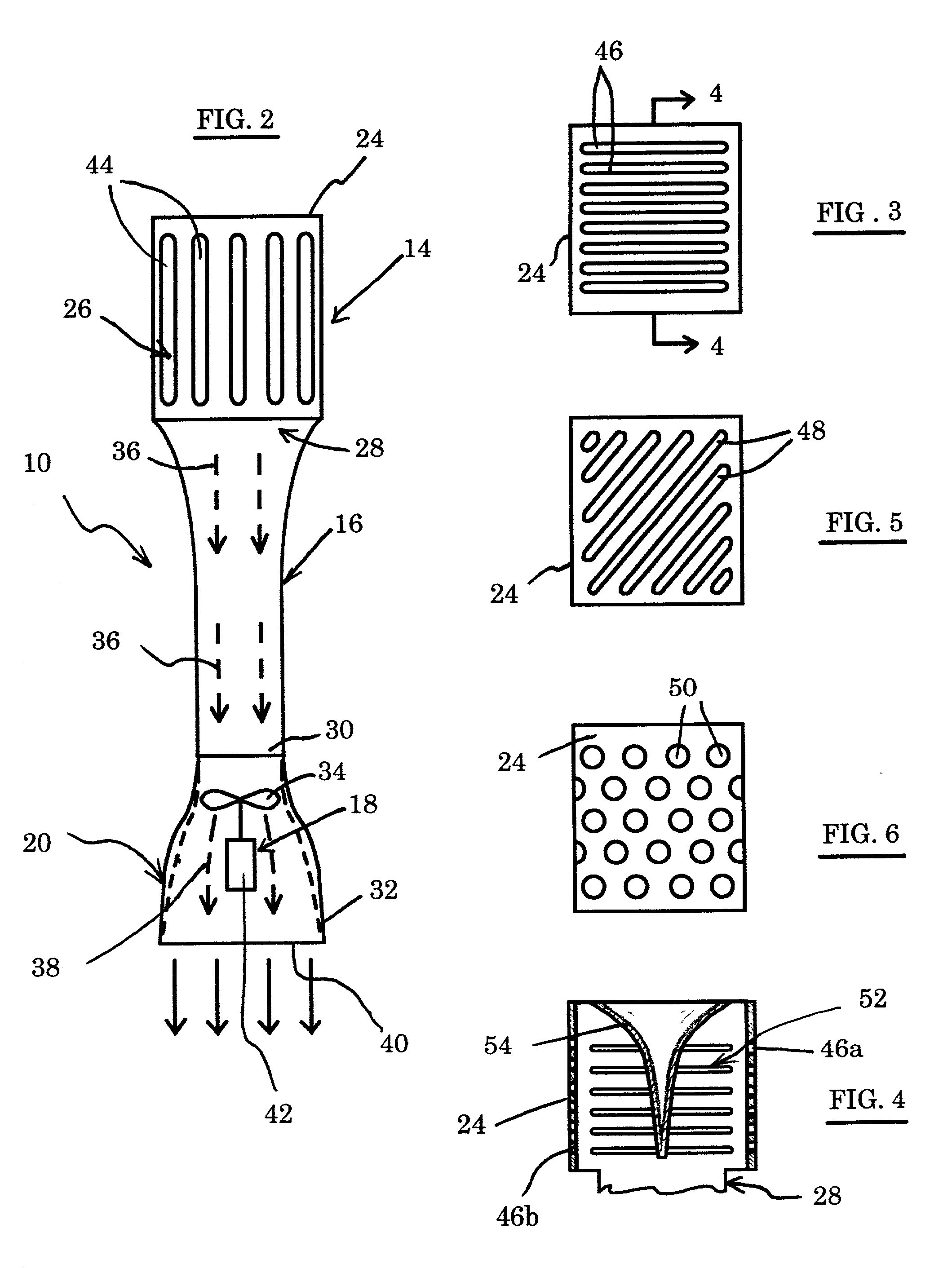
Conveyer apparatus
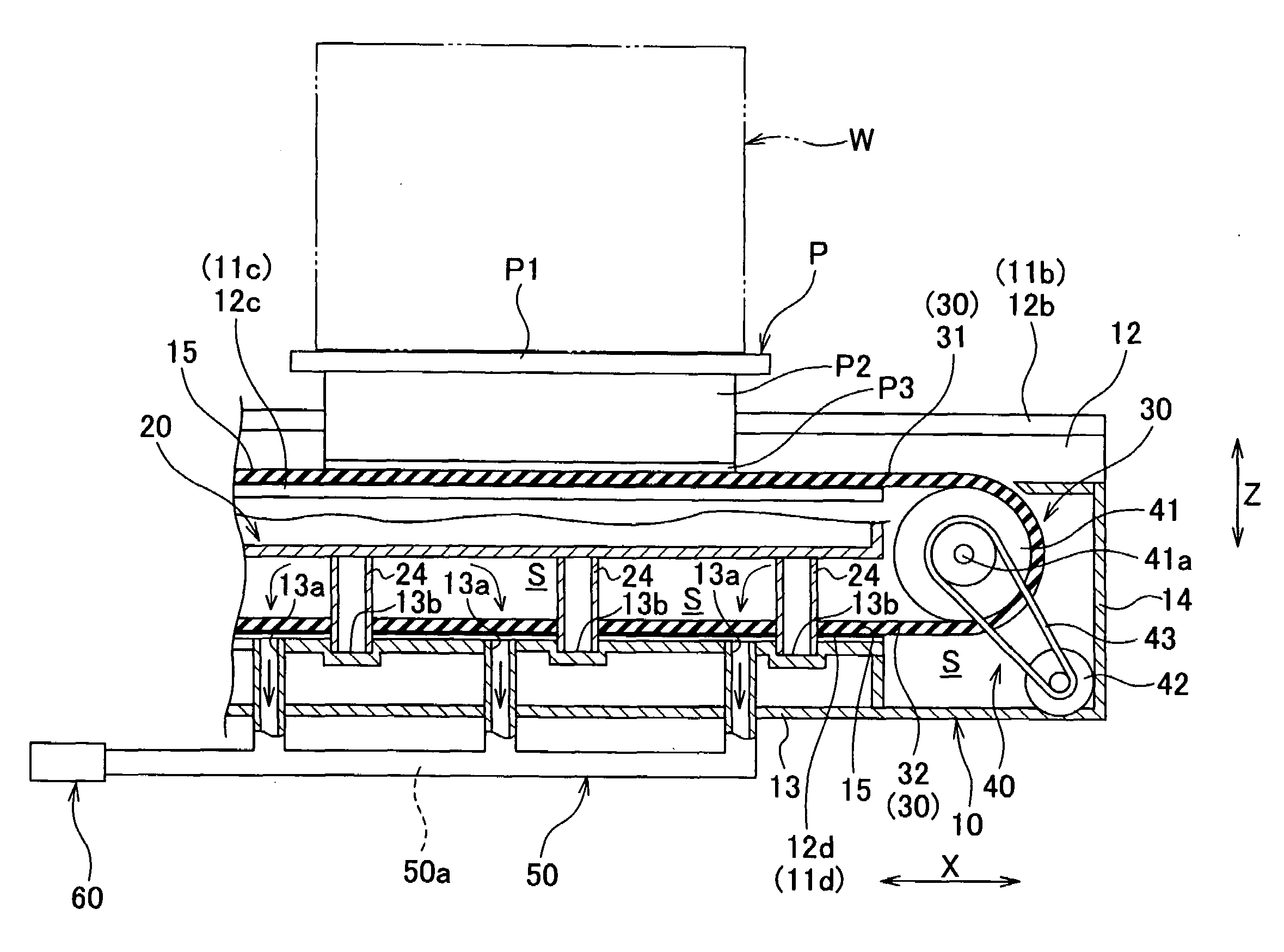
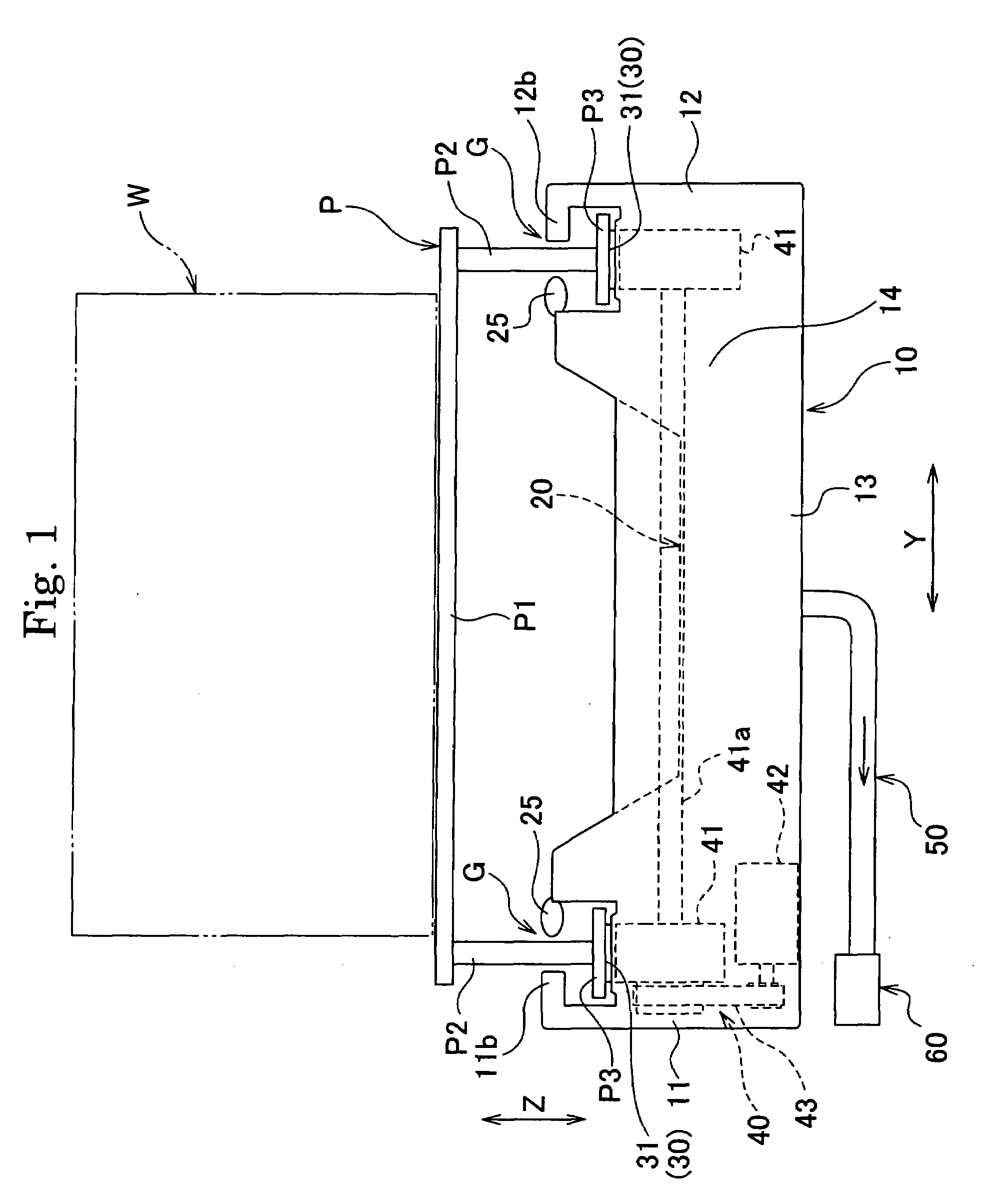
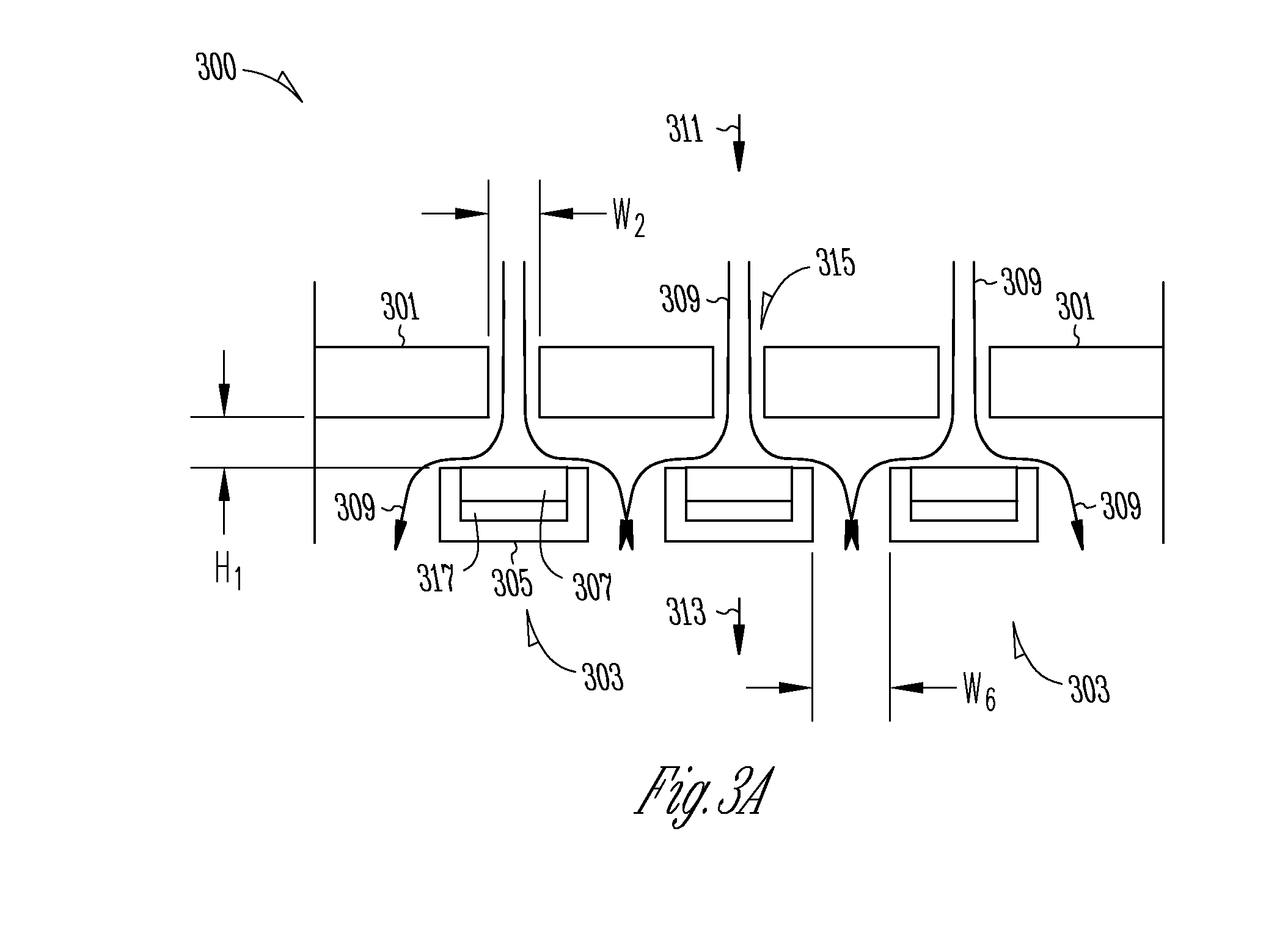
A conveyer apparatus according to the present invention includes a case that defines a pair of right and left gap portions each of which has a predetermined width and extends in a conveying direction of a conveyance object, a conveyer that is arranged near or in a region adjacent to each of the pair of right and left gap portions and supported by the case to support and convey the conveyance object, a driving mechanism that is arranged in an internal space of the case to drive each conveyer, and sucking means for sucking air in the internal space. According to this configuration, when the sucking means sucks air in the internal space in the case, an air current flowing into the internal space from the outside through each gap portion is produced, and an abrasion powder or dust generated near, e.g., each conveyer arranged near under each gap portion flows with this air current to be sucked, thus avoiding scattering toward the outside.
Owner:HIRATA & CO LTD
Cooling system for information device
ActiveUS20080232064A1Increase heatCool many racks efficientlyDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCooling coilInformation device
To cool a blade type server disposed in an air-conditioned room, the following arrangements are made. The first is at least one shell having a ventilation passage disposed in the air-conditioned room. The second is, the following are disposed in a ventilation passage: racks, in which blade type servers each composed of a case with slim boards housed therein are stacked; cooling coils each having a coolant passage and a cooling fin and cooling a passing air; and at least one fan unit having axial-flow fans placed therein and producing air currents in one direction. The third is the fan unit forces a cooling air to flow in one direction in the ventilation passage thereby to cool the servers in the racks. The cooling coils and racks are disposed alternately so that warmed cooling air after passing through the rack is cooled by the cooling coil and then cools the next rack.
Owner:FUJI FURUKAWA ENG & CONSTR +1
Air seed meter
InactiveUS20050204972A1Increase the sectionSolve fouling and cloggingPotato plantersFurrow making/coveringCircular discVisual inspection
An air seed meter for an agricultural planter includes a vacuum cover which has a central opening which exposes the central portion of the seed disc to the exterior. The central opening of the vacuum cover is centered on a location offset from the axis of rotation of the seed disc. This reduces disc wear at the disc-vacuum cover interface, and renders the disc more accessible for self-cleaning, visual inspection and verification of the proper disc. Openings in the central, open portion of the disc, the back wall of the seed housing and the side wall of the seed housing cooperate to equalize the air pressure in the seed reservoir to atmospheric pressure and reduce or eliminate reverse air currents in the discharge chute. An adjustable brush with three separate stations cooperates with an edge-release, beveled disc to apply a progressively more forceful singulation force to eliminate duplicate seeds.
Owner:KINZE MFG INC
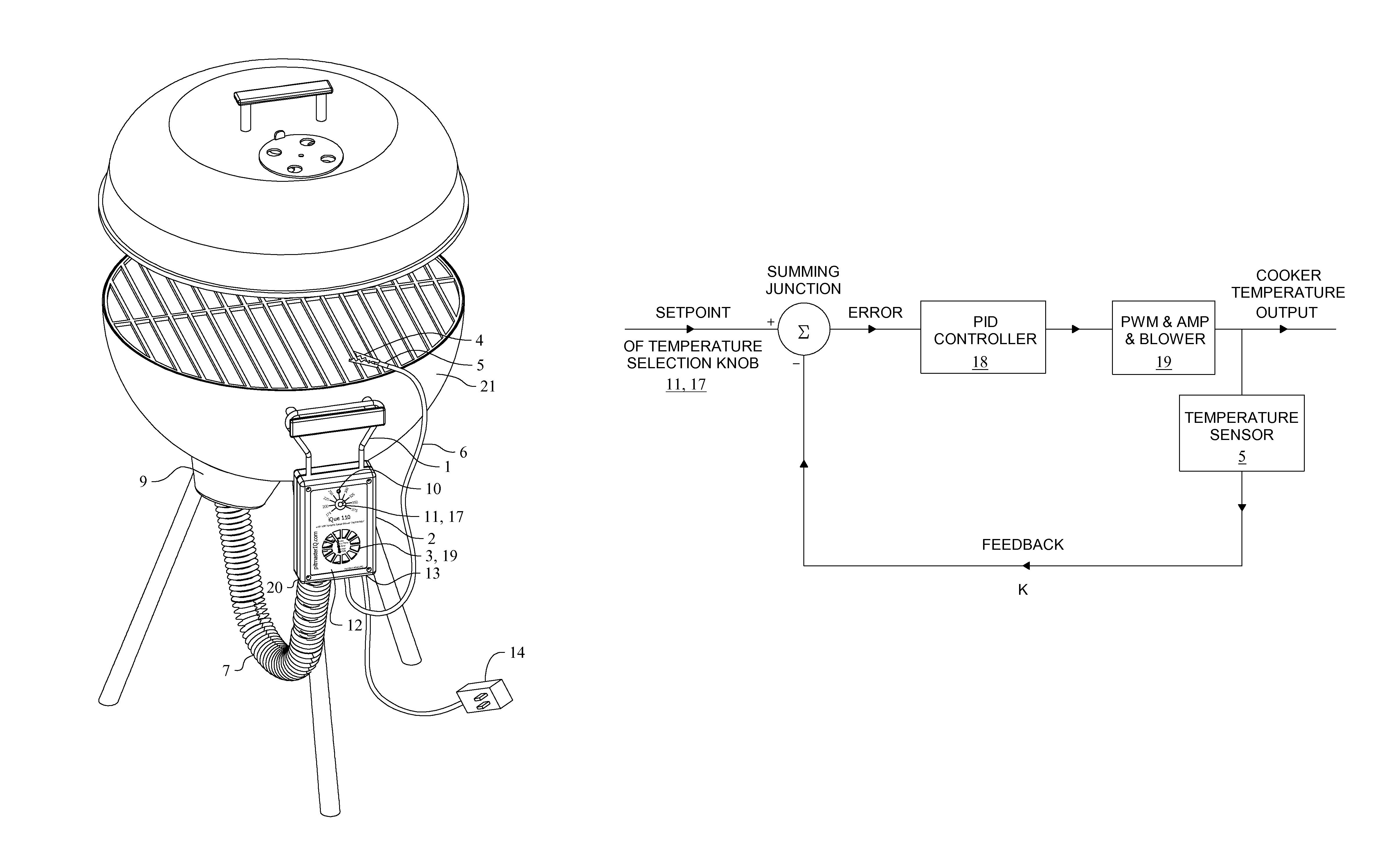
Automatic temperature control device for solid fuel fired food cooker
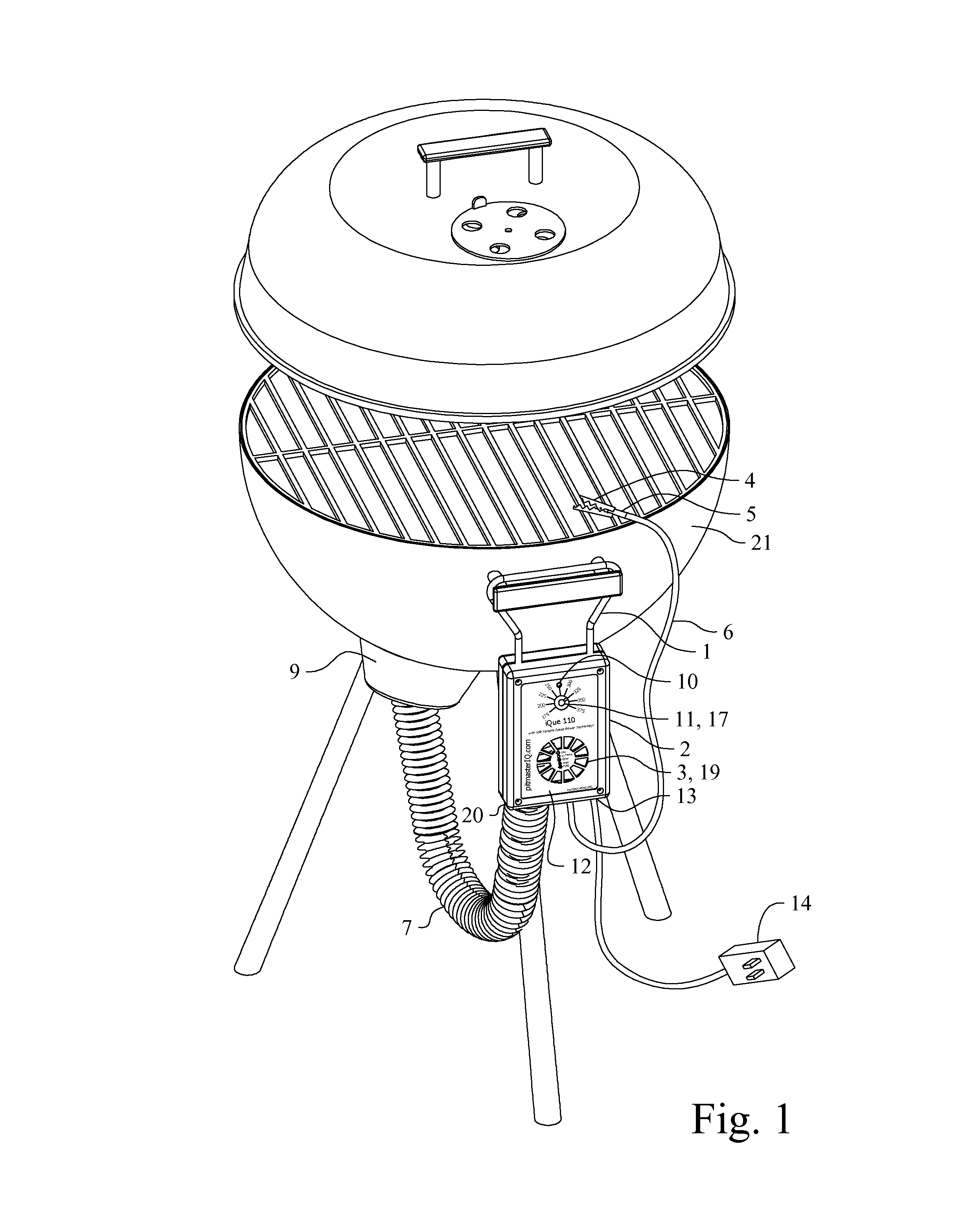
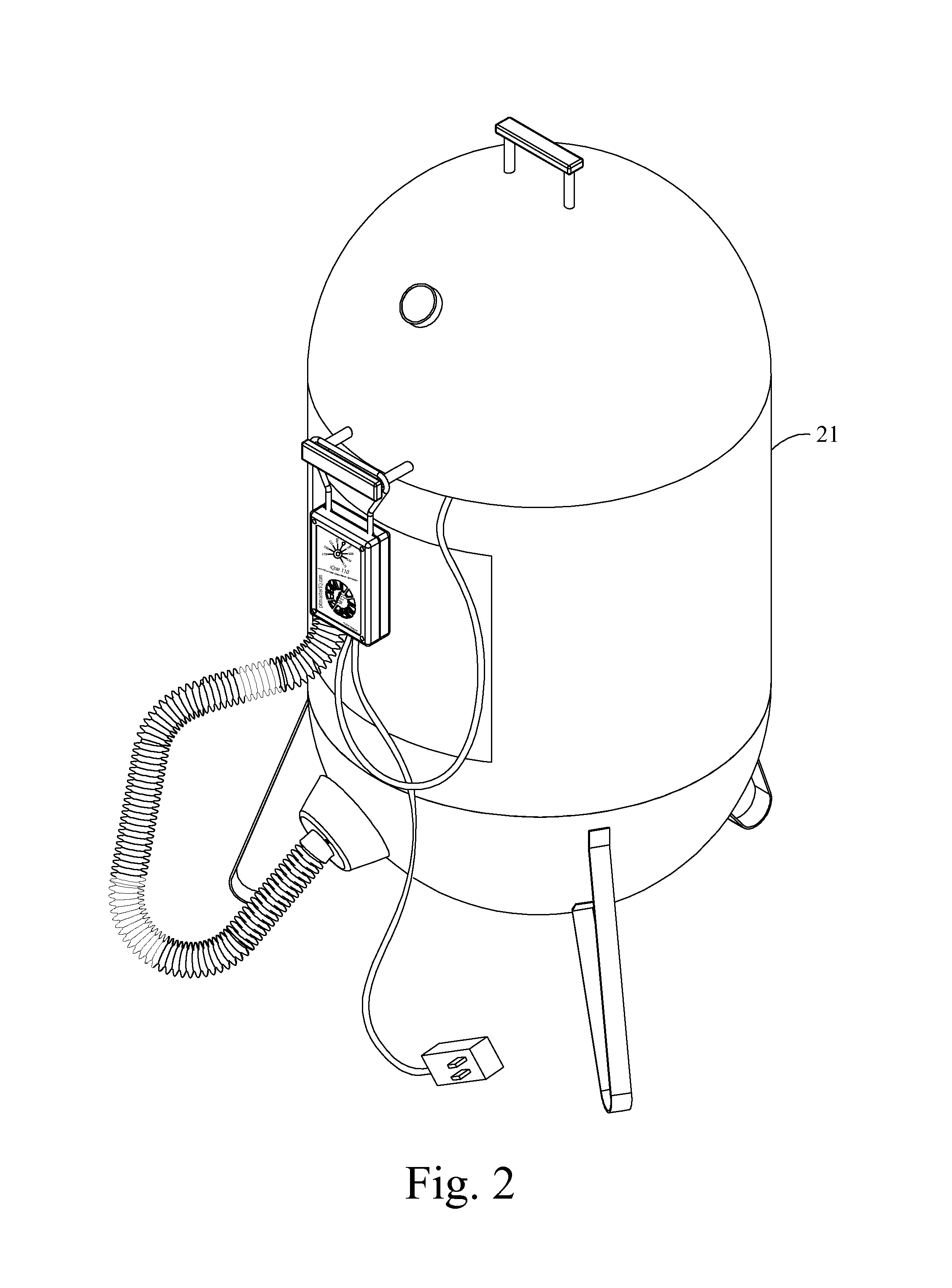
ActiveUS8800542B1The process is simple and easy to understandQuick installationDomestic stoves or rangesBoiling over preventionTemperature controlCore component
An automatic temperature control device for solid fuel fired food cooker fueled by wood, charcoal, or other solid fuels which is capable of operation with any type of cooker without utilization of different sized blowers and conserves solid fuel usage. The present invention serves to regulate cooking temperature by controlling or optimizing the amount of combustion air reaching the fuel. The present invention also allows an outdoor barbecue grill or smoker of any reasonable size to be retrofitted with the invention in order to allow a chef to cook foods at stable and precise temperatures. The core components of the invention are an air blower to provide combustion air to the burning fuel, an electronic controller to control the amount of air delivered by the air blower via a unique algorithm embedded within the electronic controller, a temperature sensor to sense the temperature inside of the cooker in the vicinity of the cooking food and provide feedback to the electronic controller, and an air tube and air manifold to get or direct the combustion air from the air blower inside the blower box to the burning fuel inside the cooker. Alternative embodiments utilize an automatic damper connected with said electronic controller whereby convection air currents may be precisely controlled.
Owner:KENNINGTON JOHN MATTHEW
Road sheltering and optimization
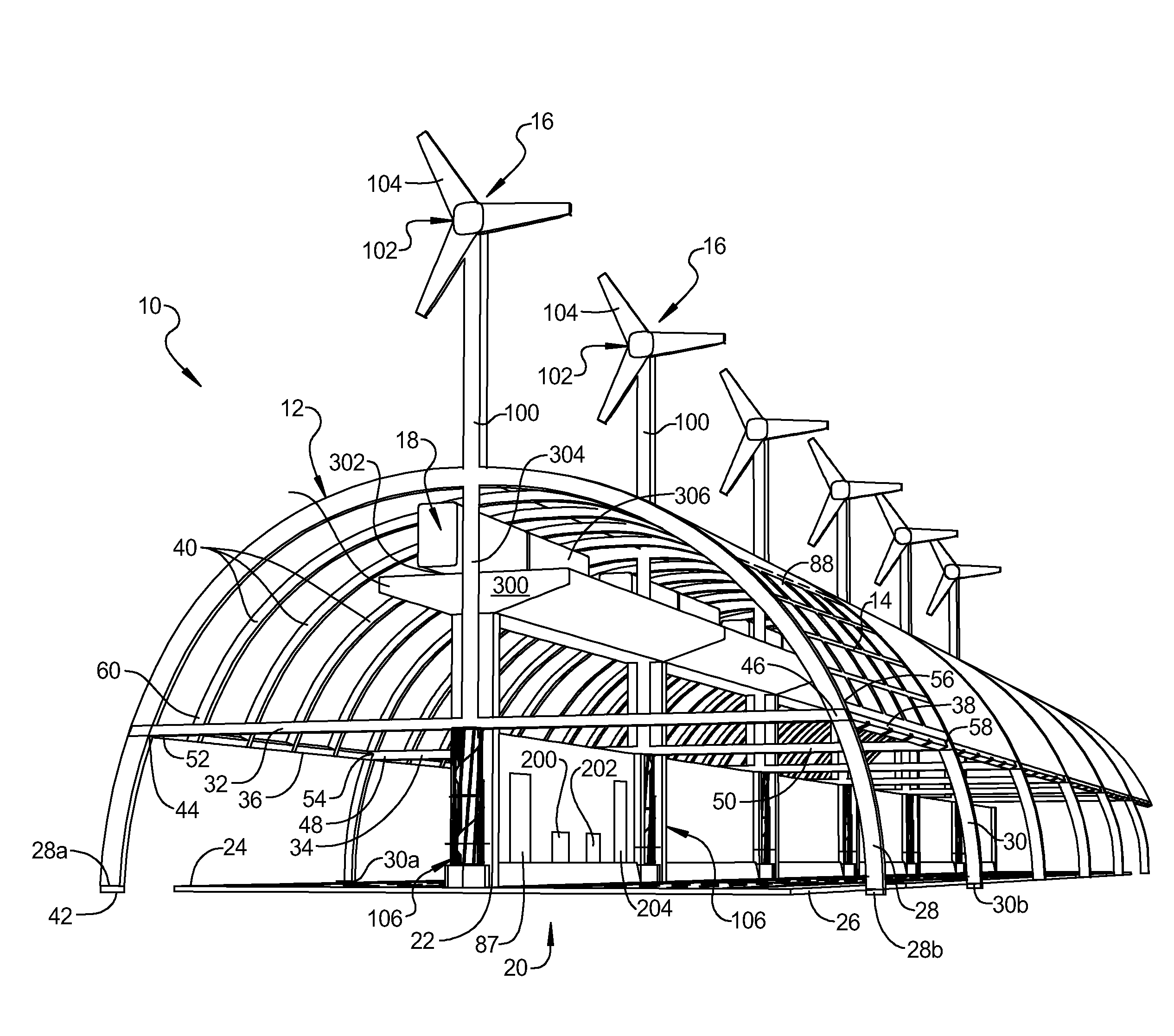
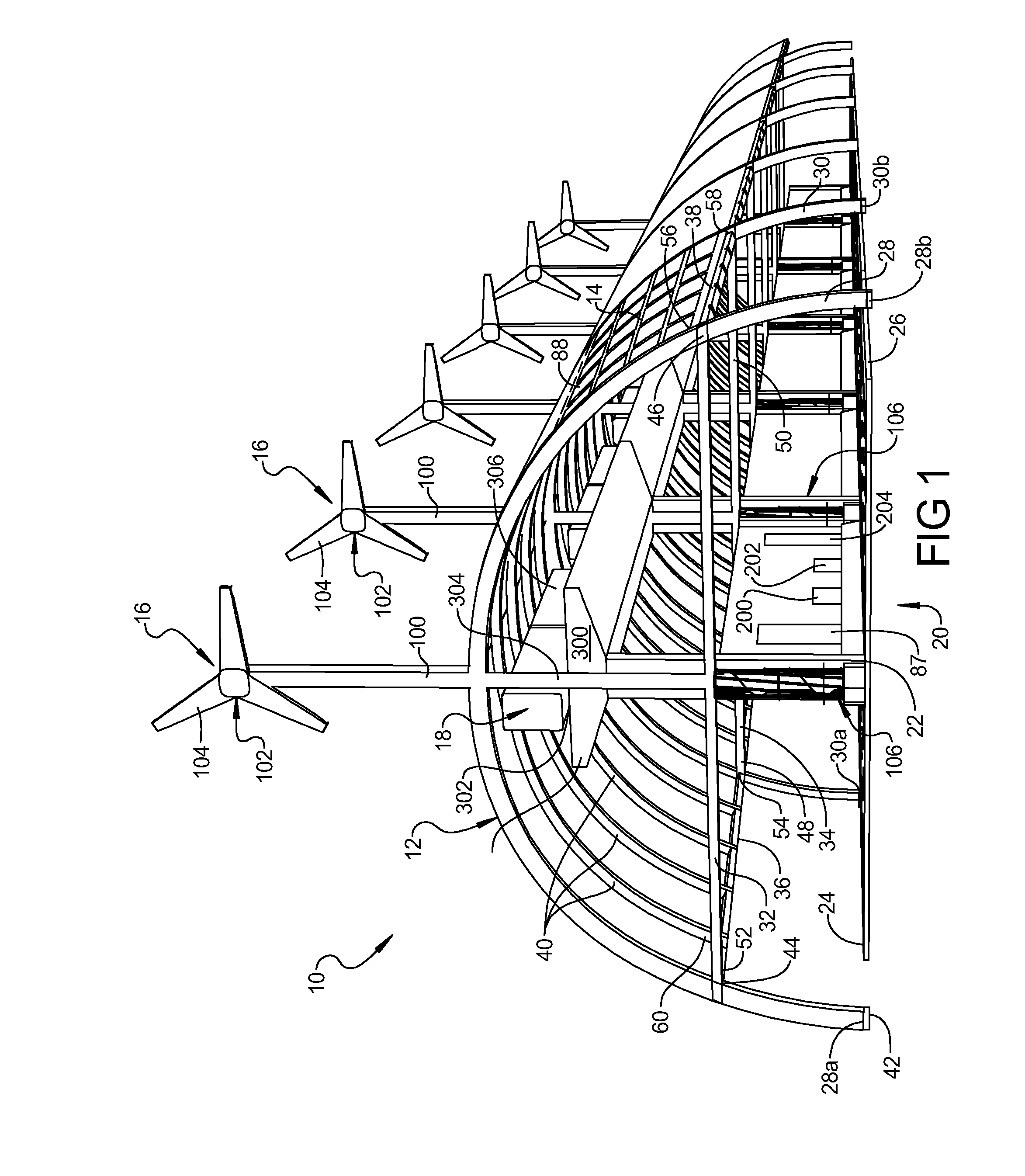
InactiveUS20110113705A1Reduce air resistanceMaximizing drawn from airPhotovoltaic supportsBuilding roofsHighway systemTurbine
A structure for sheltering and optimizing highway systems includes an arcuate structure extending over a highway and a cover over the structure to create an enclosure. The enclosure protects the highway and users of the highway from rain, snow and sun while the surrounding scenery remains visible to drivers. A number of different additions optimize use of the highway. For example, a plurality of solar panels are layered on the cover and wind turbines are used to create usable energy, an air current generation system reduces wind resistance on vehicles to increase gas mileage, and an elevated rail system transports many persons great distances along the highway.
Owner:RACZKOWSKI RAYMOND
Cyclonic separating apparatus
InactiveUS6989039B2Improved inlet arrangementImprove efficiencySuction filtersAuxillary pretreatmentCycloneCyclonic separation
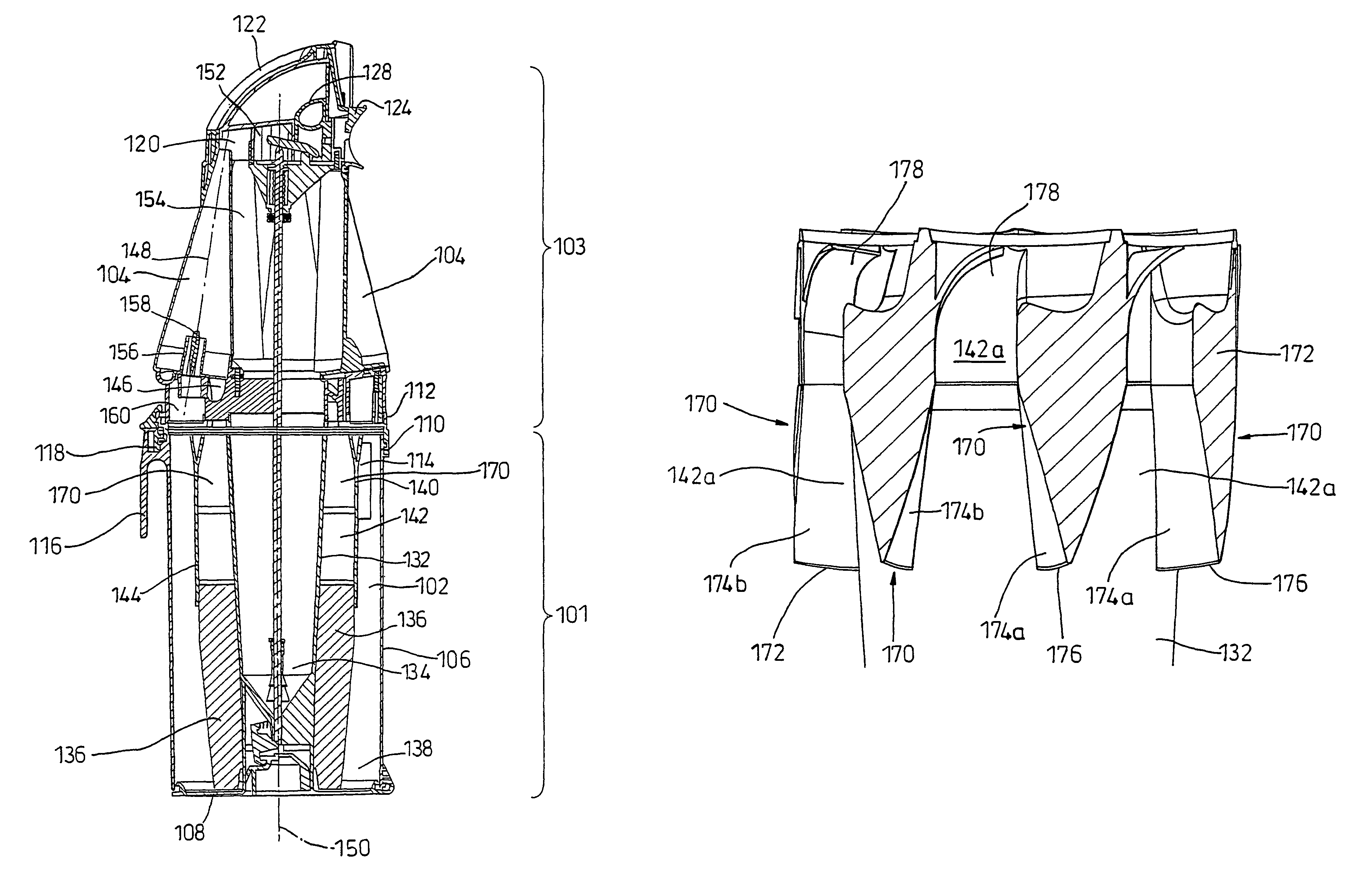
The invention provides a cyclonic separating apparatus that includes a plurality of cyclones, each having an inlet and being arranged in parallel with one another, and a passageway arranged upstream of the cyclones for carrying an airflow to the inlets of the cyclones, wherein dividers are provided in the passageway for dividing the airflow within the passageway into a number of separate flowpaths, the number of flowpaths being equal to the number of cyclones, and wherein the cross-sectional area of each flowpath (142a), decreases along the direction of air flow. The invention also provides a method of operating a cyclonic separating apparatus (100) comprising a plurality of cyclones (104), each having an inlet and being arranged in parallel with one another, and a passageway (142) arranged upstream of the cyclones (104), the method comprising the steps of:(a) introducing a flow of dirt-laden air to the passageway (142); (b) dividing the flow of dirt-laden air into a plurality of airflow portions, the number of airflow portions being equal to the number of cyclones (104); and (c) reducing the cross-sectional area of each of the airflow portions in the direction of flow of the dirt-laden air.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Multi-spraying-nozzle electrostatic spinning device with controllable spinning environment
InactiveCN103409818AControl impactImprove spinning efficiencySpinnerette packsFilament/thread formingFiberElectrospinning
The invention relates to a multi-spraying-nozzle electrostatic spinning device with the controllable spinning environment. The multi-spraying-nozzle electrostatic spinning device comprises a spinning environment control unit, an electrostatic spinning unit and a spinning connecting unit. An air current stabilization cover is arranged on the top of a spinning box body; an air suction and solvent recovery device is arranged at the bottom of the spinning box body; a constant-temperature and constant-humidity system is arranged in the spinning box body; a spinning liquid material barrel, a micro spinning solvent propelling device, a material barrel fixing support and an electrostatic generator are installed on the top of the spinning box body; the spinning solvent in the material barrel enters a three-dimensional multi-spraying-nozzle spinneret plate through a tube; a spinneret plate lifting device penetrates through the air current stabilization cover and is connected with the three-dimensional multi-spraying-nozzle spinneret plate; a continuous fiber mat receiving device and a horizontal receiving surface moving device are arranged below the spinneret plate. Due to the multi-spraying-nozzle electrostatic spinning device with the controllable spinning environment, an existing electrostatic spinning method is improved, the sealed spinning box body is additionally arranged to improve the electrostatic spinning environment, and accordingly requirements for temperature and humidity in the spinning process are satisfied; meanwhile, due to the adoption of the three-dimensional multi-spraying-nozzle spinneret plate, spinning efficiency is greatly improved and the multi-spraying-nozzle electrostatic spinning device with the controllable spinning environment can be applied to industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
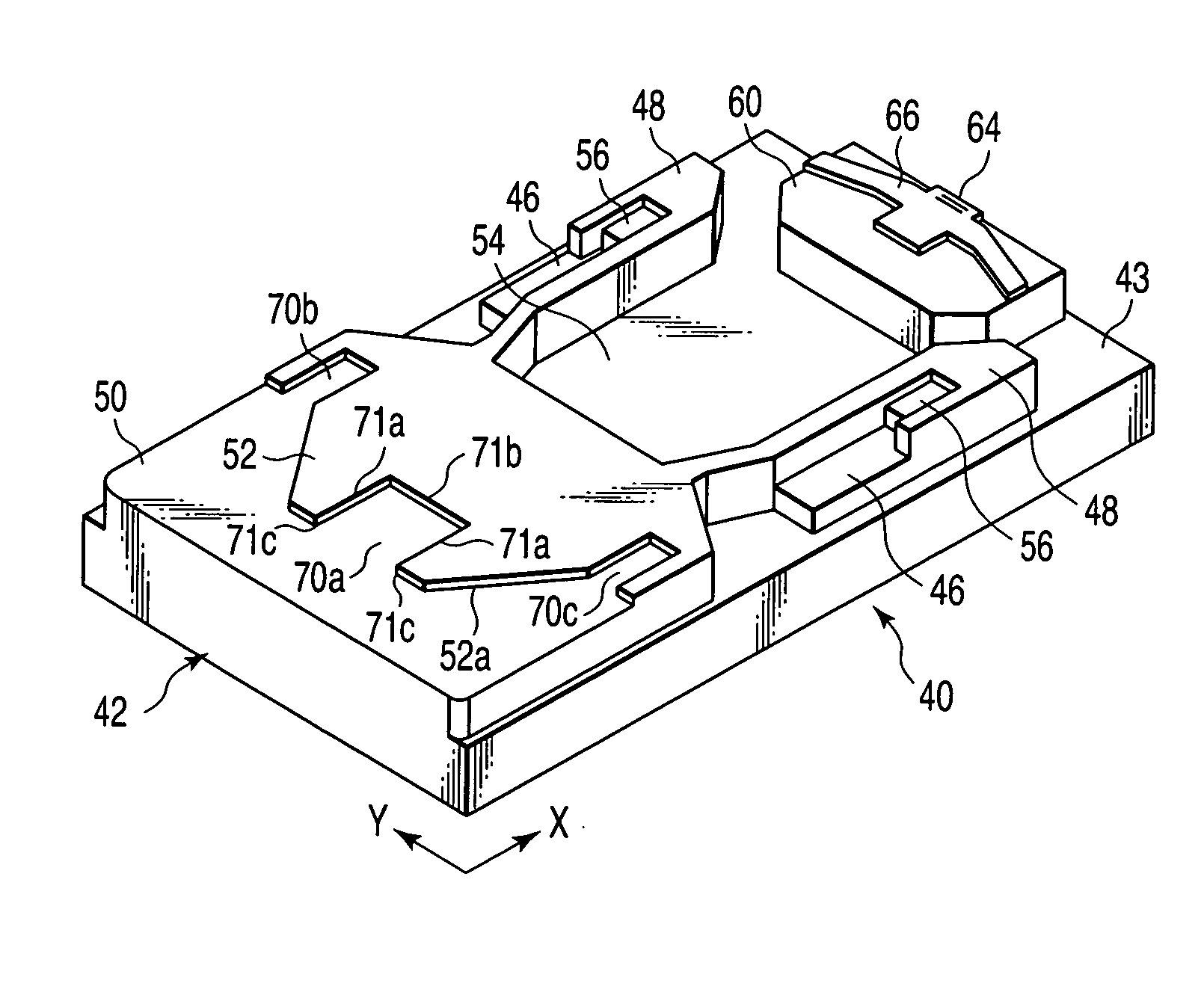
Solid state low bay light with integrated and sealed thermal management
InactiveUS20110228529A1Effective coolingIncrease airflowMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceSolid-stateAir current
A lighting fixture utilizing LED light sources for illumination of commercial, outdoor and other large area applications incorporates efficient heat dissipation and improved convective air flow. An integrated heat transfer assembly is disclosed that is configured to enhance heat dissipation by providing an efficient thermal conductive pathway for radiation of heat to an external environment. The lighting fixture body is configured with a lens body and heat sink having a chimney tube with internally facing finned heat sink arrangement for providing enhanced convective air flow through the light fixture body. When the heat sink transfers heat from the LED light sources during operation so as to create heated air surrounding the heat sink, ambient air is drawn through the chimney and the heated air is exhausted through air gaps so as to create a conductive air current with the environment. The heat sink fins are configured to enhance the natural air draw through the chimney by tapering the surface areas of the fins.
Owner:INFINILUX
Air seed meter
InactiveUS7093548B2Reduce wearSmall diameterPotato plantersFurrow making/coveringVisual inspectionEngineering
Owner:KINZE MFG INC
Solid state low bay light with integrated and sealed thermal management
InactiveUS8692444B2Efficient heat dissipationIncrease airflowMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceEngineeringAmbient air
A lighting fixture utilizing LED light sources for illumination of commercial, outdoor and other large area applications incorporates efficient heat dissipation and improved convective air flow. An integrated heat transfer assembly is disclosed that is configured to enhance heat dissipation by providing an efficient thermal conductive pathway for radiation of heat to an external environment. The lighting fixture body is configured with a lens body and heat sink having a chimney tube with internally facing finned heat sink arrangement for providing enhanced convective air flow through the light fixture body. When the heat sink transfers heat from the LED light sources during operation so as to create heated air surrounding the heat sink, ambient air is drawn through the chimney and the heated air is exhausted through air gaps so as to create a conductive air current with the environment. The heat sink fins are configured to enhance the natural air draw through the chimney by tapering the surface areas of the fins.
Owner:INFINILUX
Apparatus for capturing and harnessing the energy from environmental wind
InactiveUS20030156938A1Prevent sudden impactAvoid speed changesWind motor controlWind motor combinationsElectricityEngineering
An apparatus is disclosed for capturing and converting wind energy to electrical energy. The apparatus includes a tower member arranged in the form of an elongated conduit having first and second end portions. A wind collector is provided and is associated with the conduit first end portion. The wind collector has an air inlet to capture environmental wind originating from one or more directions and then deflect the captured wind into the conduit to create an axial airflow therein. Finally, a wind turbine device is disposed at the conduit second end portion for receiving the airflow from the conduit in order to generate electricity therefrom.
Owner:VERINI NICHOLAS A
Radiating device
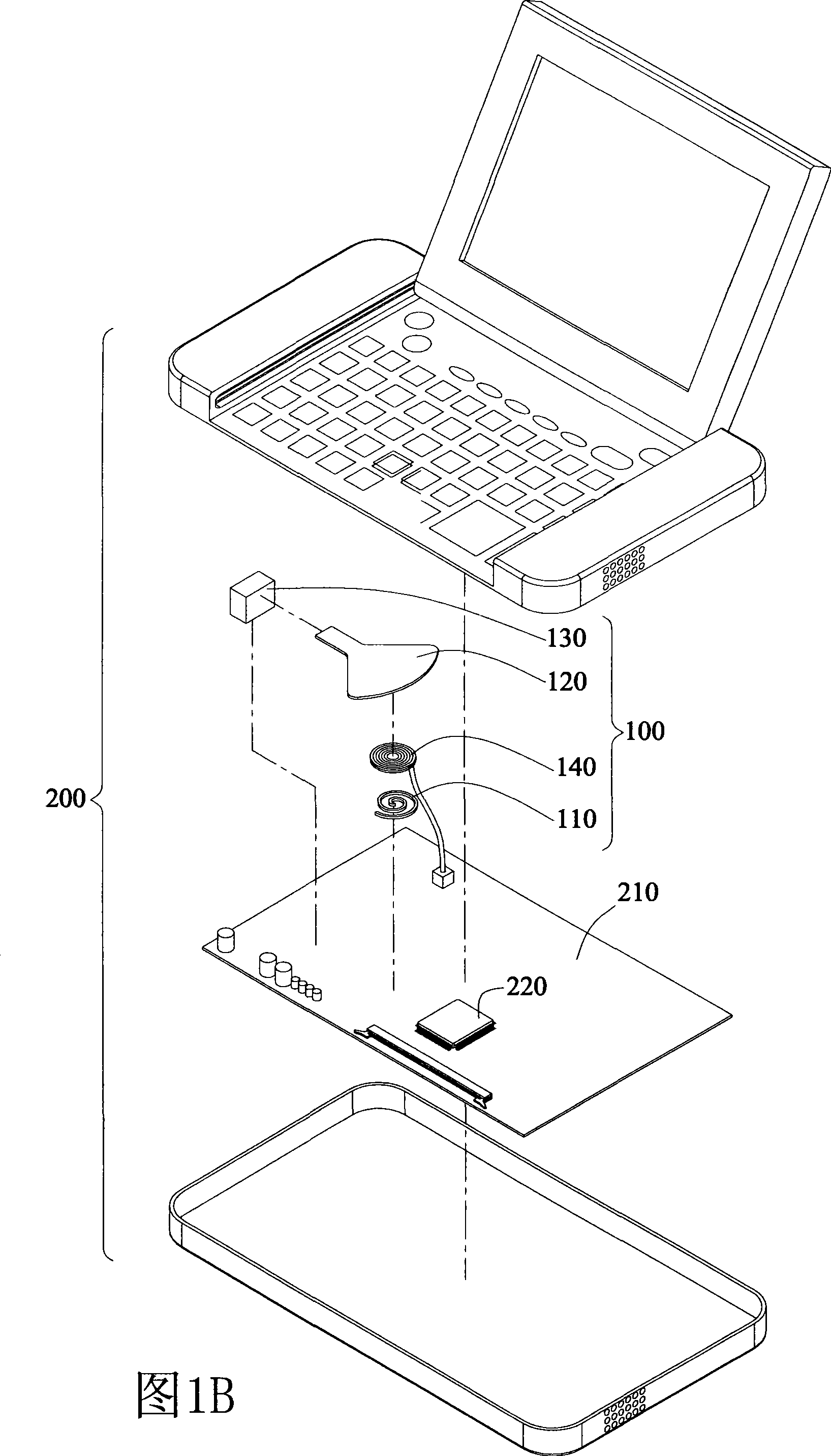
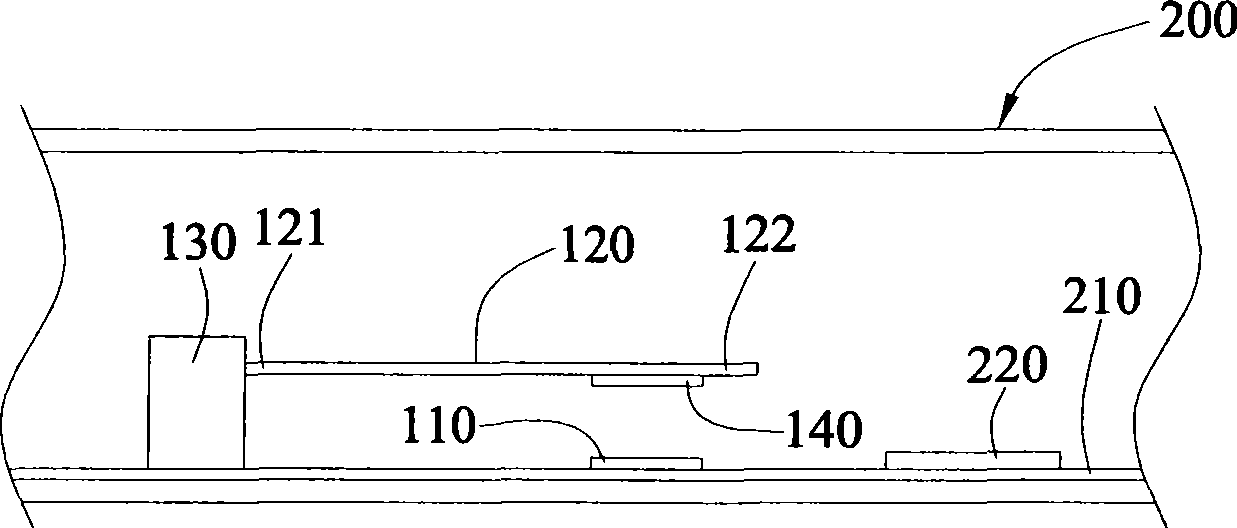
InactiveCN101370373AThin and lightVolume thinningDigital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsMagnetic tension forceAir current
The invention discloses a heat radiation device connecting with a periodic power supply for radiating for circuit board heating element. The radiation device possesses at least a coil, for receiving power supply and producing a magnetic field; and at least a swinging sheet, one end of which is fixed, and other end, suspended correspondingly to coil, wags driven by magnetic force of magnetic field to produce a air current.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
Method for controlling temporary flush type supersonic velocity wind tunnel with ejector function
ActiveCN103135624ASmall back pressureReduce the total pressure of the stable sectionAerodynamic testingFluid pressure control using electric meansEngineeringMechanics
The invention provides a method for controlling a temporary flush type supersonic velocity wind tunnel with an ejector function. The method includes that when the wind tunnel is started, firstly, the total pressure of a gas collection chamber of an ejector is adjusted to be working total pressure, then the total pressure of a stable section is adjusted to be a running total pressure value of a wind tunnel test, and then the ejector is closed for carrying out the wind tunnel test; and after specified testing items are finished, the total pressure value of the stable section maintains the same, the ejector is started to adjust the total pressure of the gas collection chamber to be a working total pressure value in a closed-loop mode, then gas flow is cut off, after the total pressure of the stable section is reduced to a preset cutoff total pressure value, the ejector is closed, and then a whole air-blowing testing process is finished. Through the method for controlling the temporary flush type supersonic velocity wind tunnel with the ejector function, the impact load in a start-up process of the wind tunnel and the impact load in a cutoff process of the wind tunnel can be reduced effectively, safety of models, a balance and a wind tunnel system can be guaranteed, requirements of the balance on strength and rigidity in a designing process of the balance can be effectively reduced, sensitivity of the balance can be improved, and the accuracy of the measurement of the balance and the quality of testing data can be improved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Dynamic pressure pneumatic bearing structure and method of manufacturing the same
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 00739 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 23, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 38433 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 3, 1998Provided is a hydrodynamic gas bearing structure which can prevent occurrence of whirl not only in high-speed rotation but also in low-speed rotation, reduces such frequency that a floating rotational frequency in starting or stoppage of rotation increases, and is capable of shifting the floating rotational frequency to a low rotational frequency side. The hydrodynamic gas bearing structure comprises a shaft body (1) and a bearing body (2). A groove (11) is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the shaft body (1). The groove (11) consists of at least two concave parts, whose depths substantially differ from each other, which are formed serially in the circumferential direction, and has a circumferentially asymmetrical shape in a cross section perpendicular to the axis. The circumferential distance a between the intersection point (15) of a line (C) connecting the deepest point (14) of the groove (11) and the center (O) of the shaft body (1) and the outer peripheral line (Q) of the shaft body (1) and one edge (16) of the groove (11) positioned downward an air current (P) generated in rotation in relation to the intersection point (15) is larger than the circumferential distance b between the intersection point (15) and the other edge (17) of the groove (11) positioned upstream the air current (P) in relation to the intersection point (15). The ratio (d2 / d1) of the mean depth d2 of a relatively shallow part of the groove (11) to the mean depth d1 of a relatively deep part of the groove (11) is less than 0.3. The hydrodynamic gas bearing structure is suitable for employment for a rotation driving part of a magnetic recording apparatus or a laser beam printer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
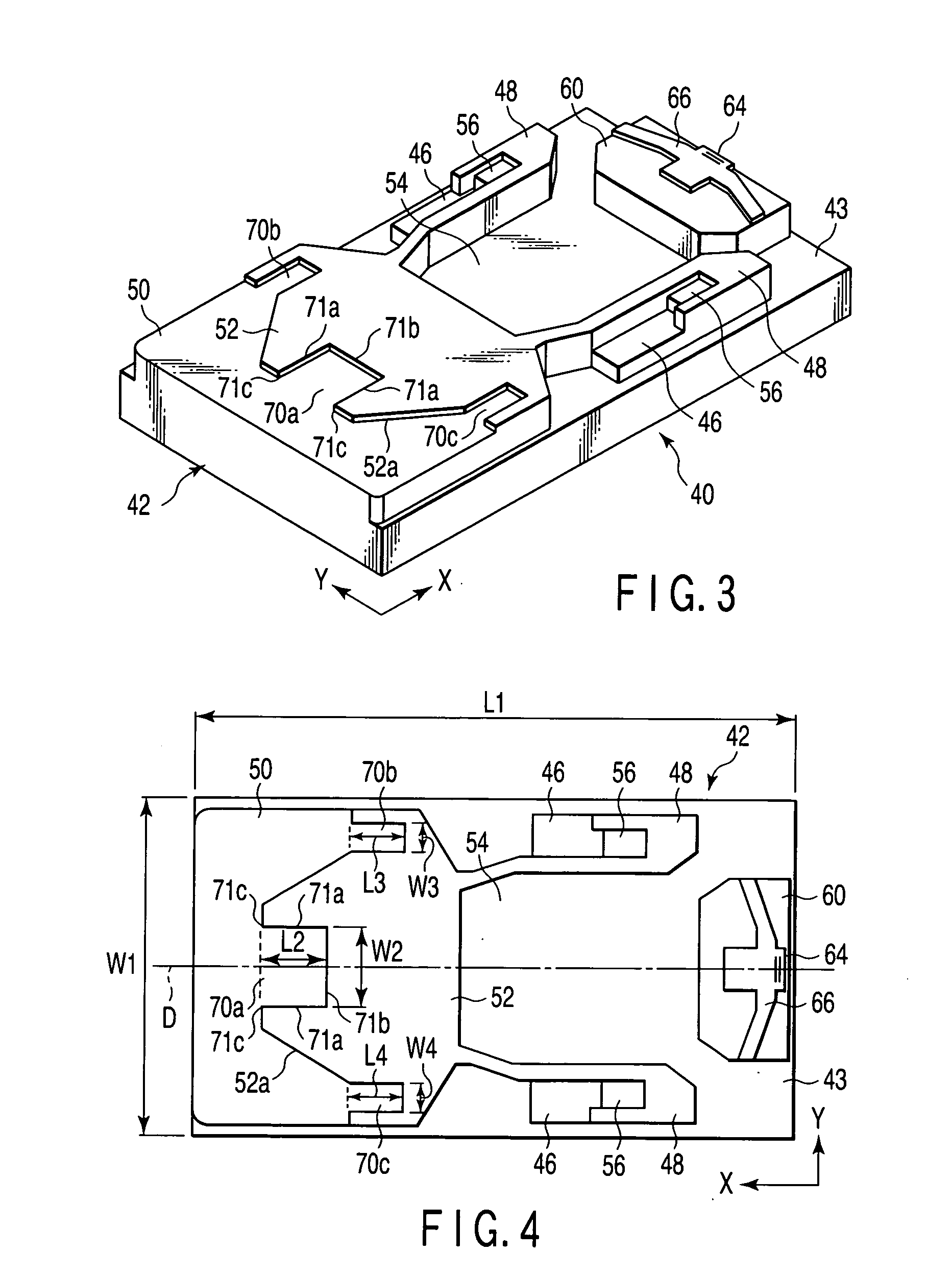
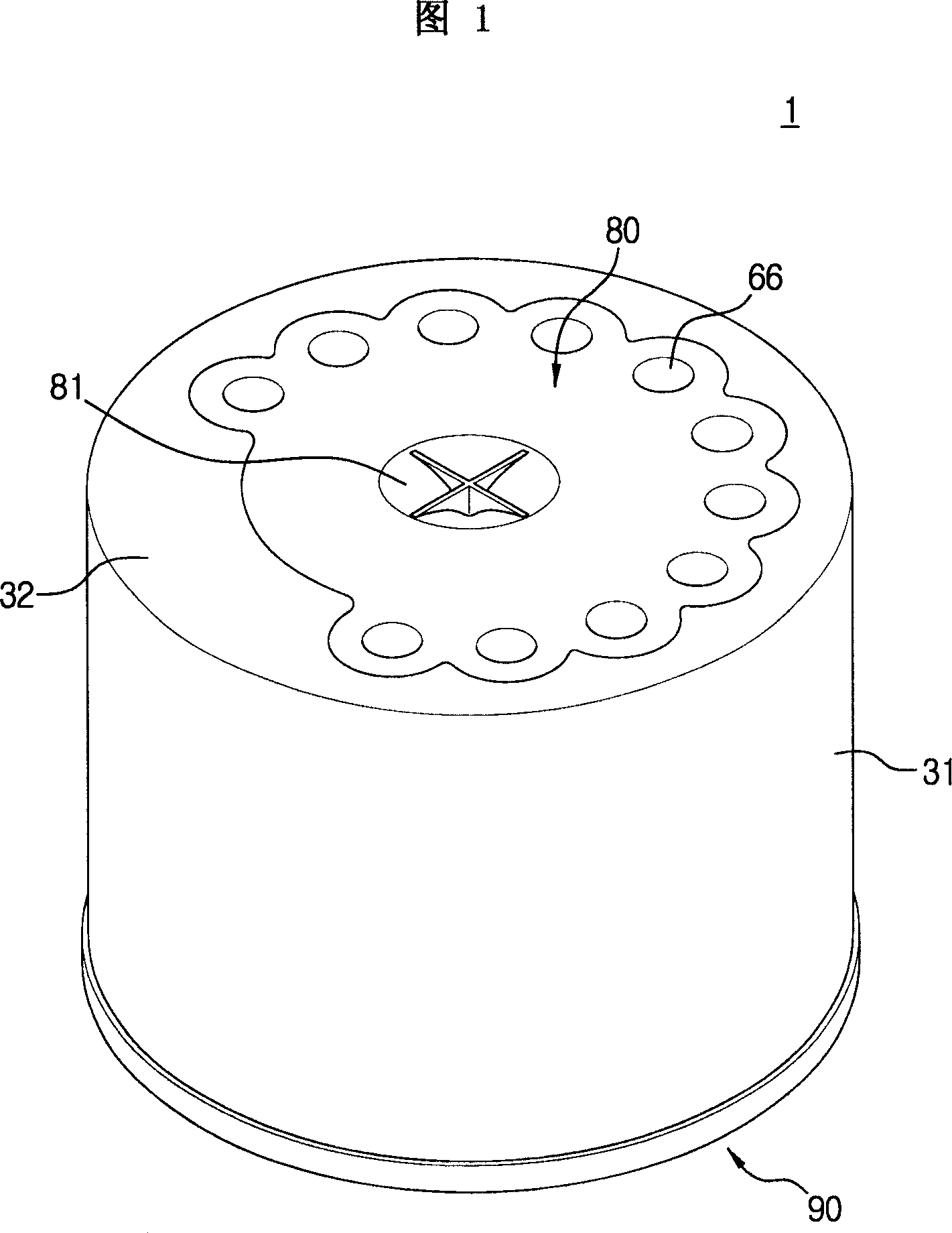
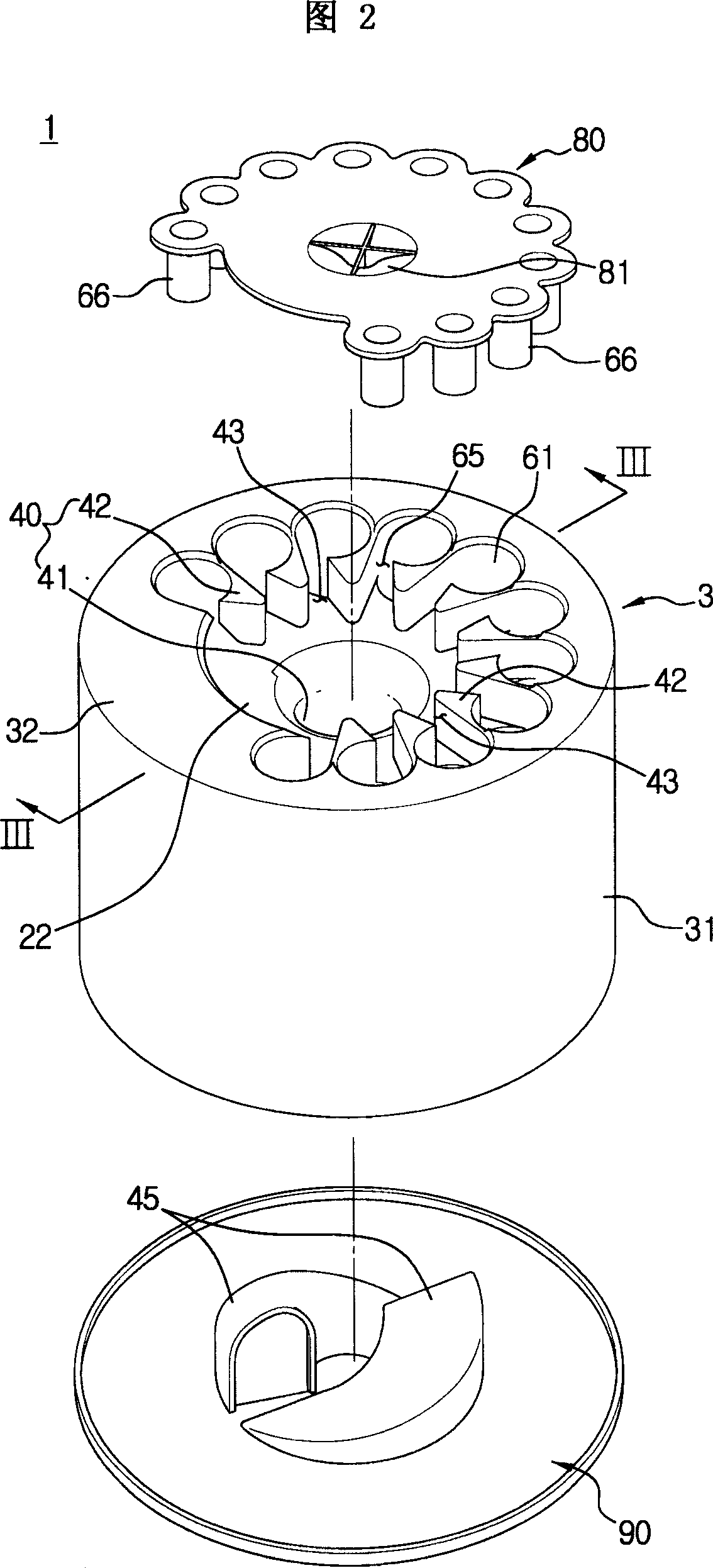
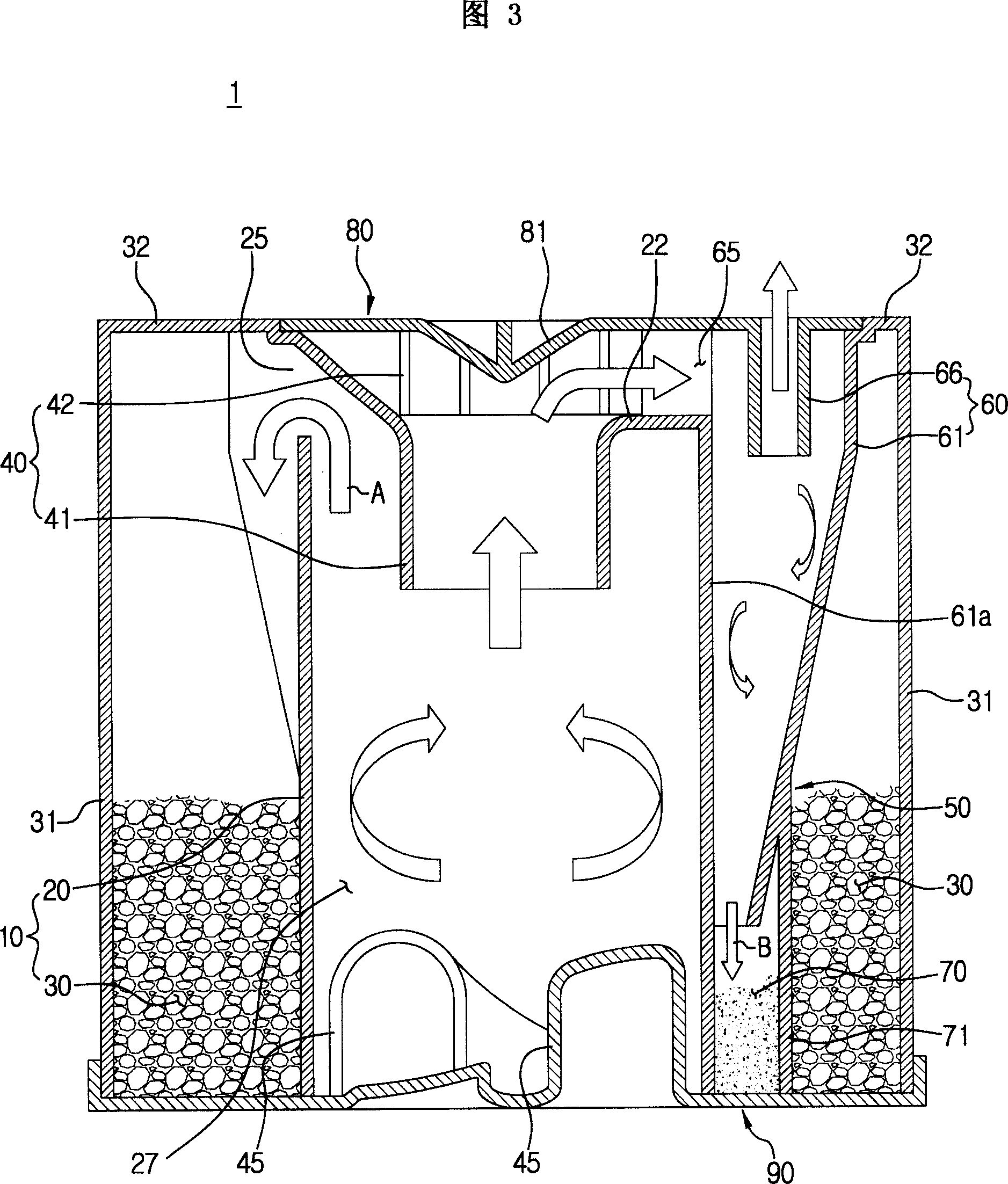
Dust-collecting apparatus and cleaner having the same
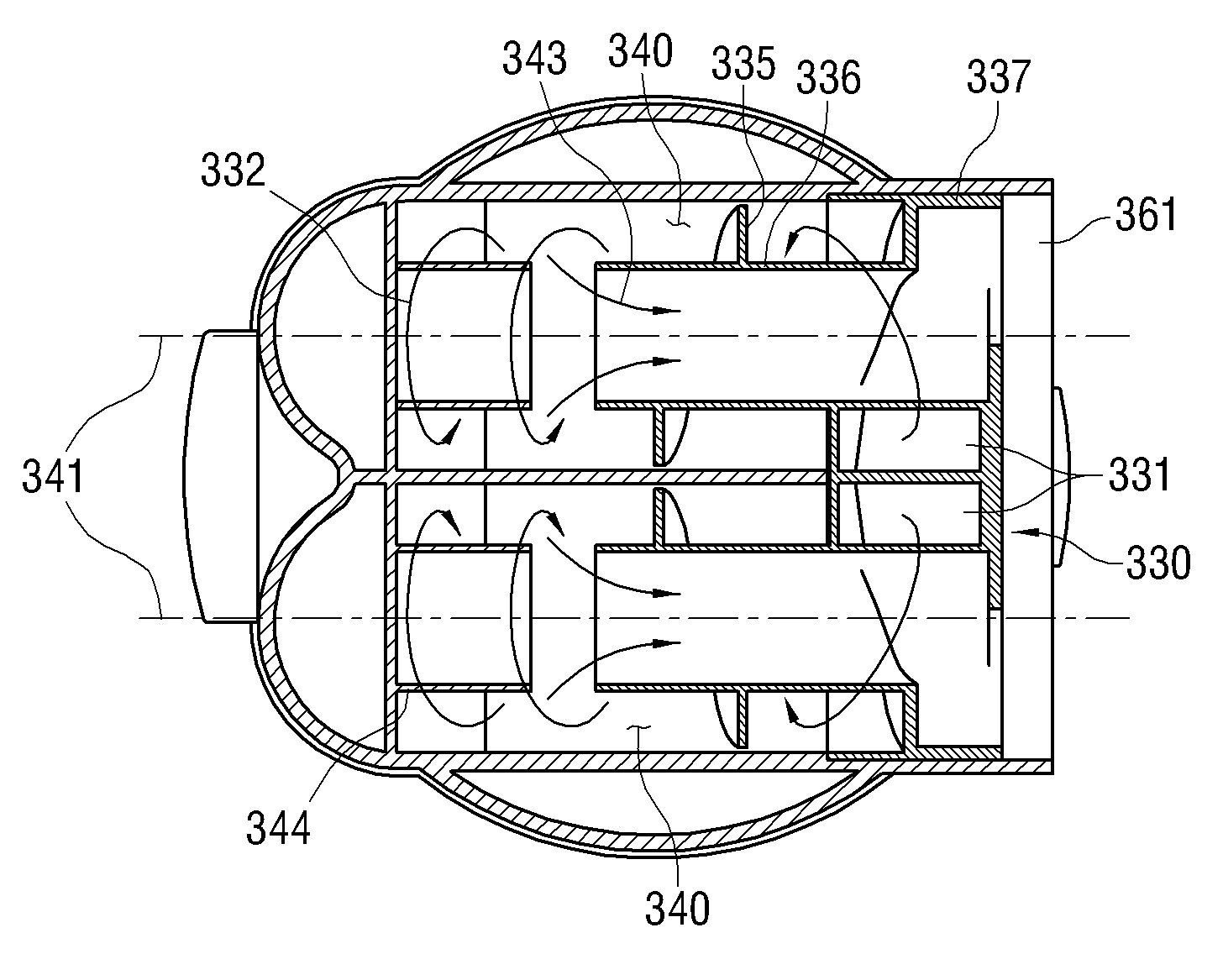
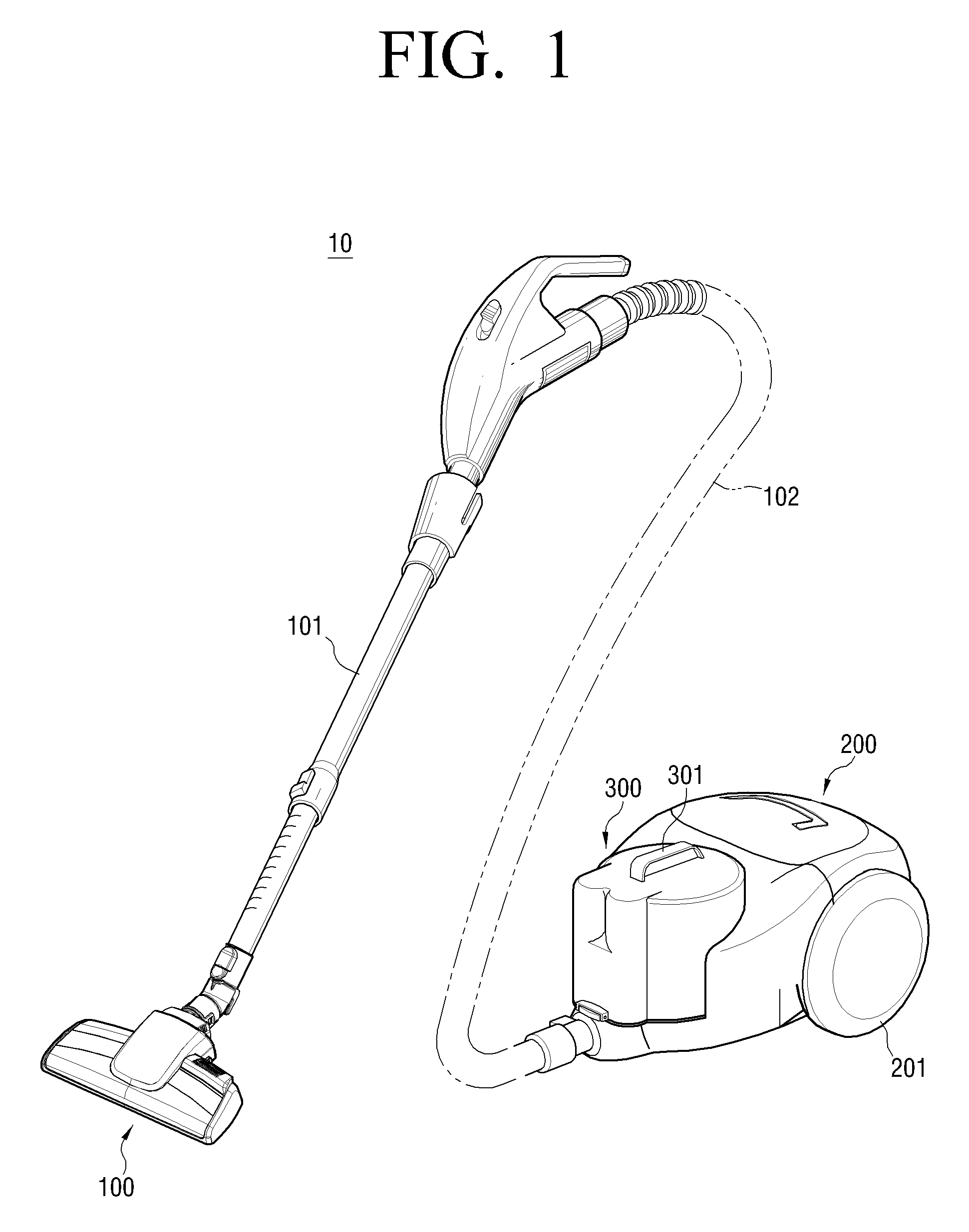
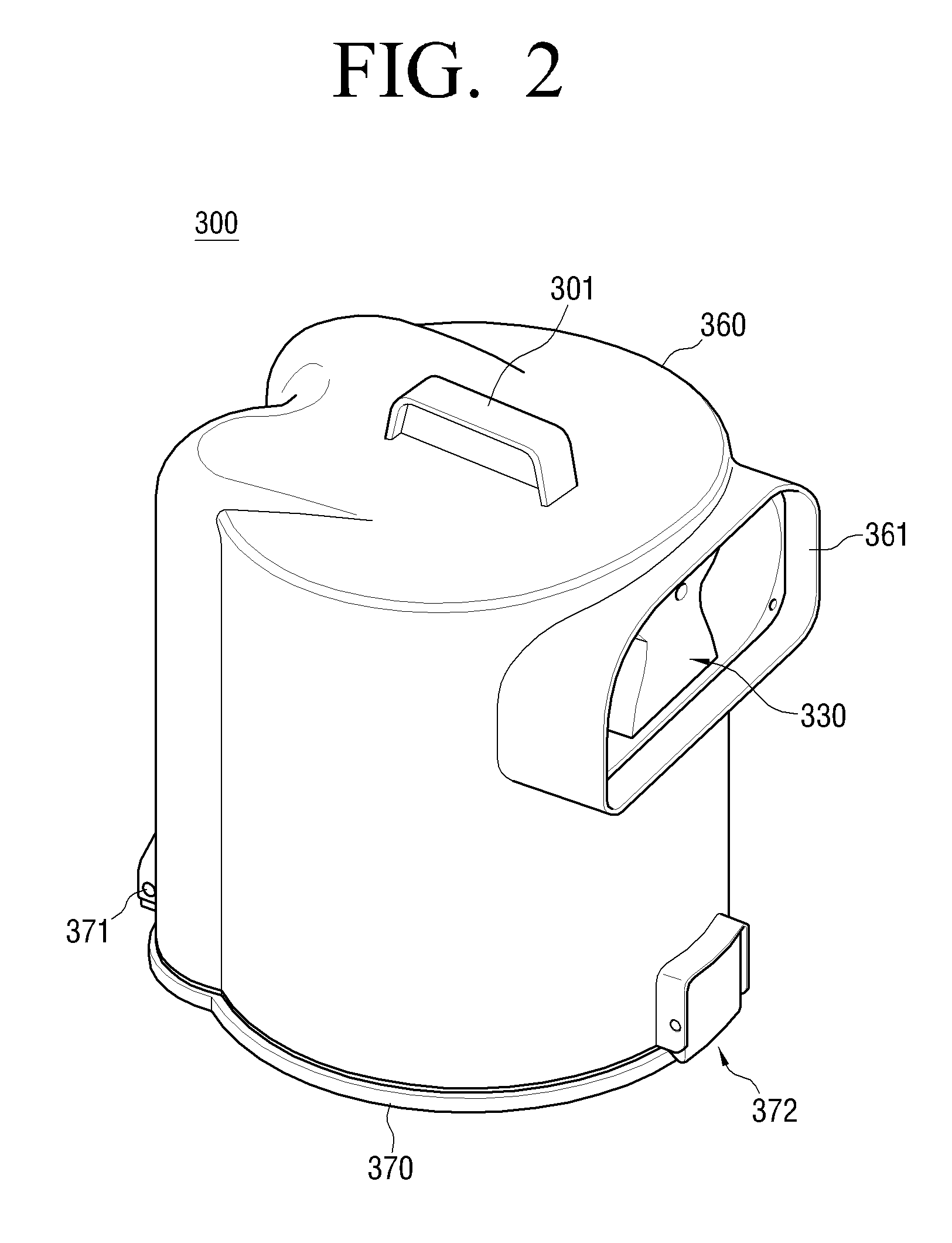
A cyclone dust-collecting apparatus is provided. The apparatus may includes a cyclone chamber configured to separate dust from air which is drawn in along with the dust, a dust receptacle configured to store the dust separated by the cyclone chamber, a transparent case configured to surround the cyclone chamber and the dust receptacle, and a colored guide unit configured to form a spiral passage so that a whirling air current is formed in the cyclone chamber.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electric heating device with heating zones
InactiveCN1525795AAchieve regulationEasy to adjustAir-treating devicesOhmic-resistance electrodesMobile vehicleElectricity
An electric heating device is adapted to be used in particular as an auxiliary electric heating for motor vehicles. The heating device comprises a plurality of PTC heating elements arranged in a plane of said heating device. The PTC heating elements are in electric contact with contact sheets for supplying current thereto and in thermal contact with radiator elements for transferring the heat produced to an air current to be heated. According to the present invention, the PTC heating elements arranged in this plane are adapted to be controlled separately in at least two groups.
Owner:CATEM
Ceiling fan capable of adjusting angles of fan blades
ActiveUS20180128277A1Optimize volumeFeel comfortablePump componentsPump controlCeiling fanDrive motor
A ceiling fan capable of adjusting angles of fan blades includes a hub, a downrod, a rotating motor selectively driving the hub to rotate relative to the downrod, multiple blade assemblies separately mounted on and arranged around the hub, and an adjusting assembly mounted in the hub and including an outer tube, an inner tube, a support, and a driving motor. A driving rod of each of the blade assemblies is mounted in a driving annular recess of the support. When a driving screw of the driving motor rotates, the driving screw drives the outer tube to rotate and drives the inner tube to move upwardly or downwardly accordingly, so as to provide an optimized volume of air current that meets power saving requirement under a constant revolution speed of the rotating motor.
Owner:ETEN TECH
Multi-gap self-swelling strong-air-current longitudinal blow-out arc anti-thunder protecting device
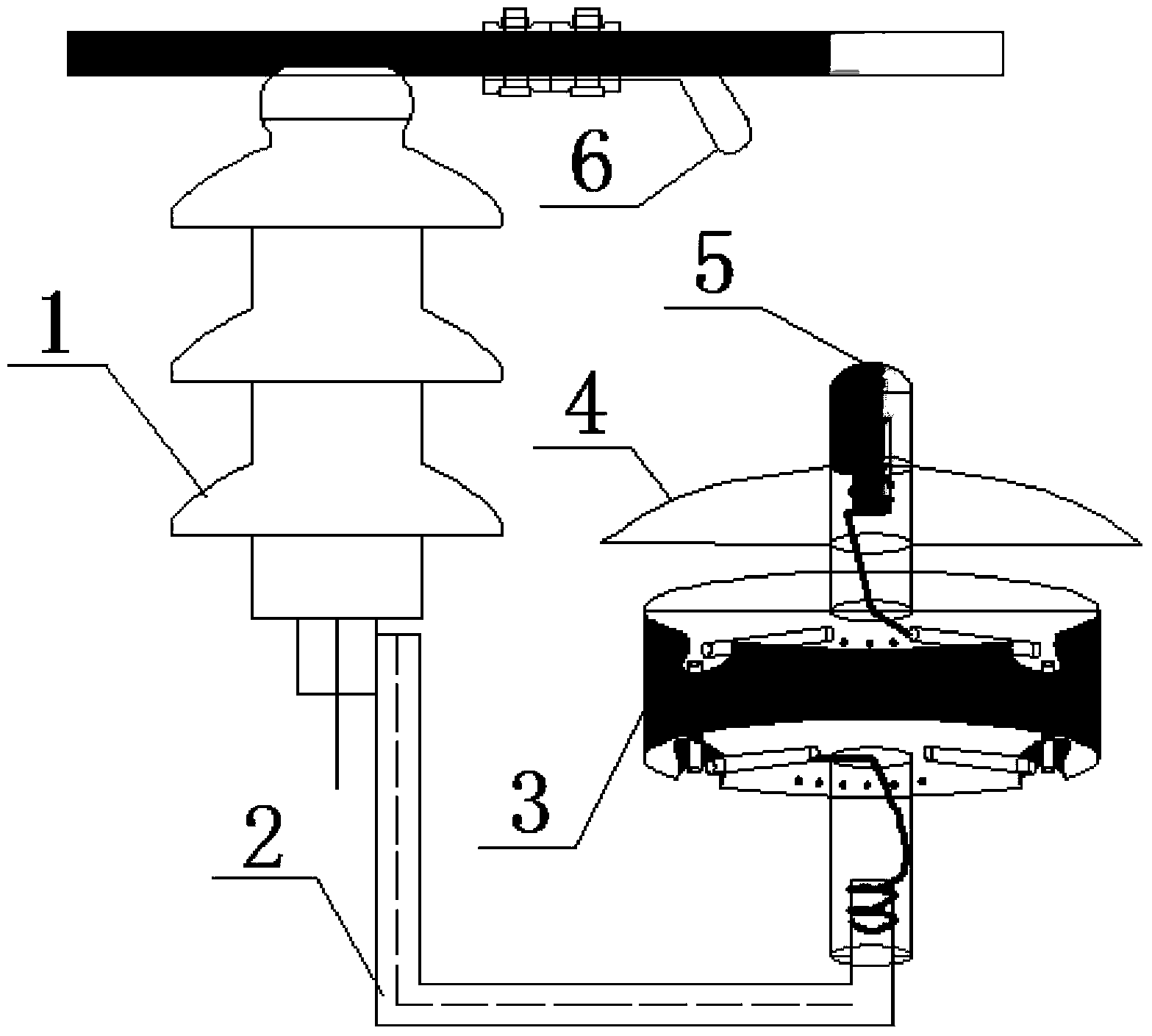
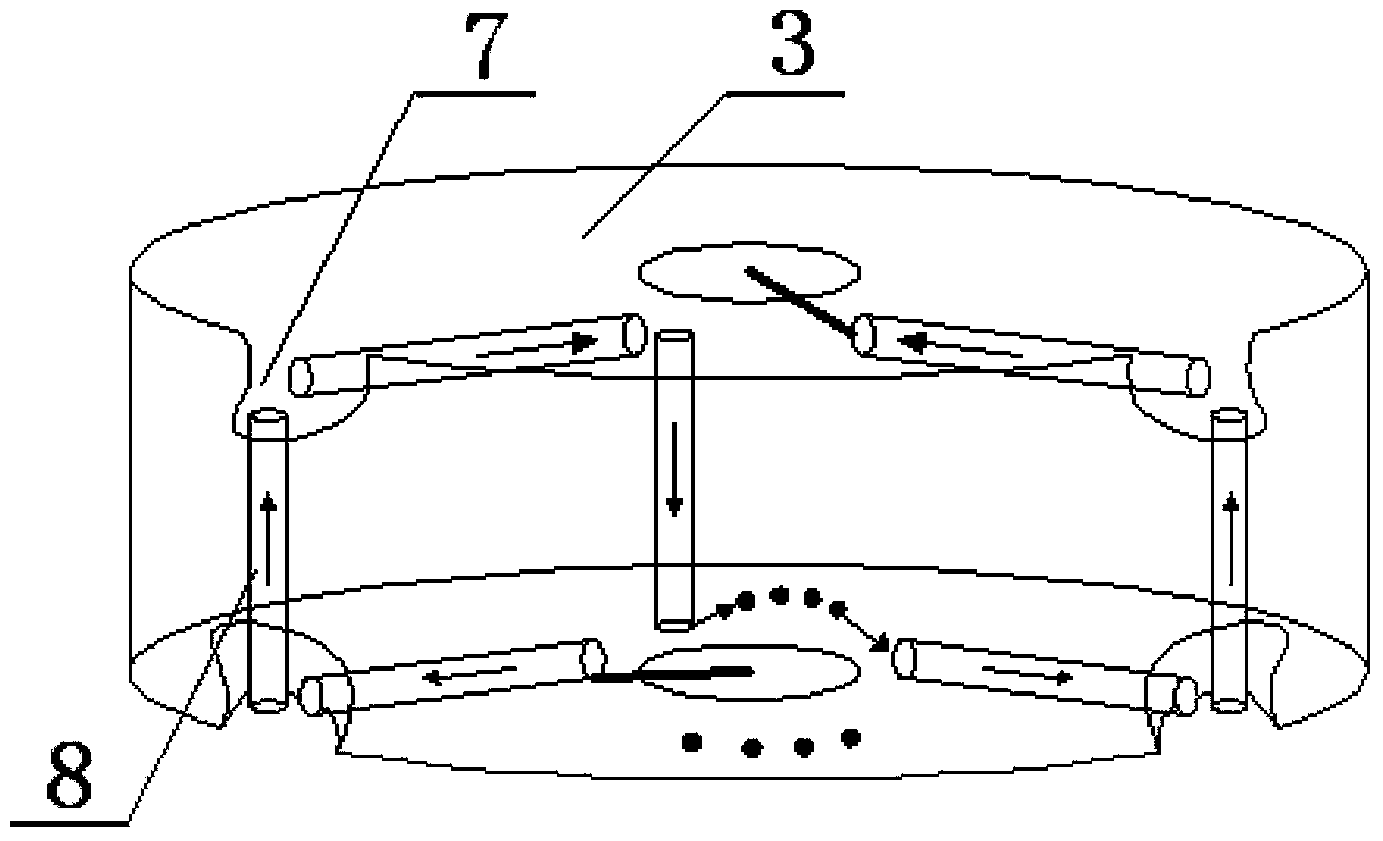
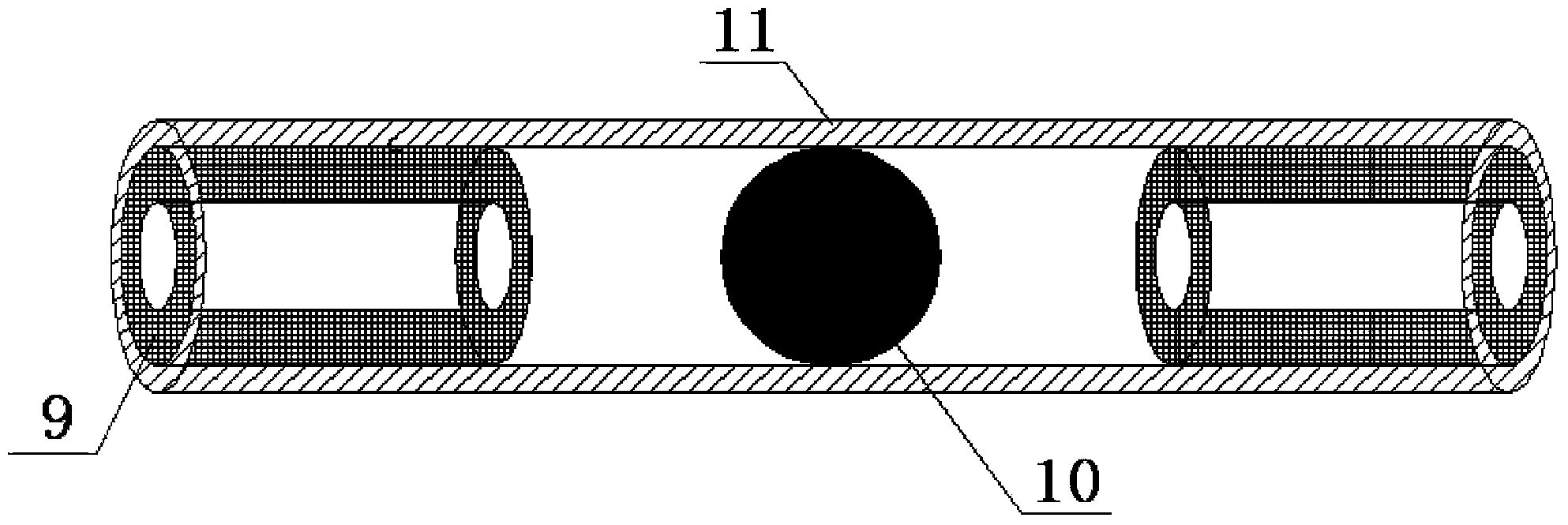
ActiveCN103594210AImprove arc extinguishing effectHigh vulnerabilityInsulatorsCorona dischargeElectricityElectric power system
The invention discloses a multi-gap self-swelling strong-air-current longitudinal blow-out arc anti-thunder protecting device which comprises a longitudinal blow-out arc device arranged at an insulator string earthing terminal through a grounding side connecting hardware fitting, a grounding side electrode arranged on the longitudinal blow-out arc device, and a guide line side electrode arranged on an off-contact guide line. A protecting gap formed by the grounding side electrode and the guide line side electrode is parallel to an insulator string. The longitudinal blow-out arc device comprises an arc extinguishing device body and arc extinguishing tubes. The arc extinguishing device body is provided with a plurality of through holes for placing the arc extinguishing tubes. An angle formed by two arc extinguishing tubes which are arranged in the arc extinguishing device body is 90 degrees, and end portions of the two arc extinguishing tubes are in contact with each other. Each arc extinguishing tube is in a spiral shape. The grounding side electrode is connected with a first arc extinguishing tube through a guide line, and the grounding side connecting hardware fitting is connected with a last arc extinguishing tube through a guide line. The device is simple in structure, low in manufacture cost, safe and reliable, effectively reduces the power system transmission line thunderstrike tripping rate and the accident rate, and improves the stability of a power system.
Owner:王巨丰 +1
Method and device for preparing silicon nanoparticles by utilizing plasma body
The invention discloses a method and a device for preparing silicon nanoparticles by utilizing a plasma body. The method comprises the following steps: introducing mixed gas containing a silicon-containing air source and inert gas into a plasma body cavity; exciting the gas in the plasma body cavity to make the silicon-containing air source converted into the silicon nanoparticles; and collecting the silicon nanoparticles by the collection device after the silicon nanoparticles are taken out of the plasma body cavity by air current. The method can use the high-power plasma body in the process of preparing the silicon nanoparticles, simultaneously avoids depositing the silicon nanoparticles on the inner wall of the plasma body cavity, and improves the collection of the silicon nanoparticles in a gas phase. The method and the device ensure that the preparation of the silicon nanoparticles meets the requirements of large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Apparatuses and methods for capturing and retaining particles
InactiveUS20120255375A1Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringAirflow
Various embodiments comprise apparatuses and methods for capturing particles from a particle-laden airstream. An embodiment of a device includes an inlet air passage to direct a particle-laden airstream, an outlet air passage, an impaction nozzle in fluid communication with and downstream of the inlet air passage, and a channel in fluid communication with and downstream of the impaction nozzle and upstream of the outlet air passage. An open portion of the channel is oriented substantially toward the inlet air passage and has a cavity at least partially covered with a substrate material. A base of the substrate material is substantially normal to an incoming direction of the particle-laden airstream. Other embodiments of the device and a method of using the device are also provided.
Owner:LMSTECH
Heavy metal cations elimination from aqueous media by nanotechnology
InactiveUS20100051557A1Easily substitutedReduced pHWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsIron oxide nanoparticlesIron nanoparticle
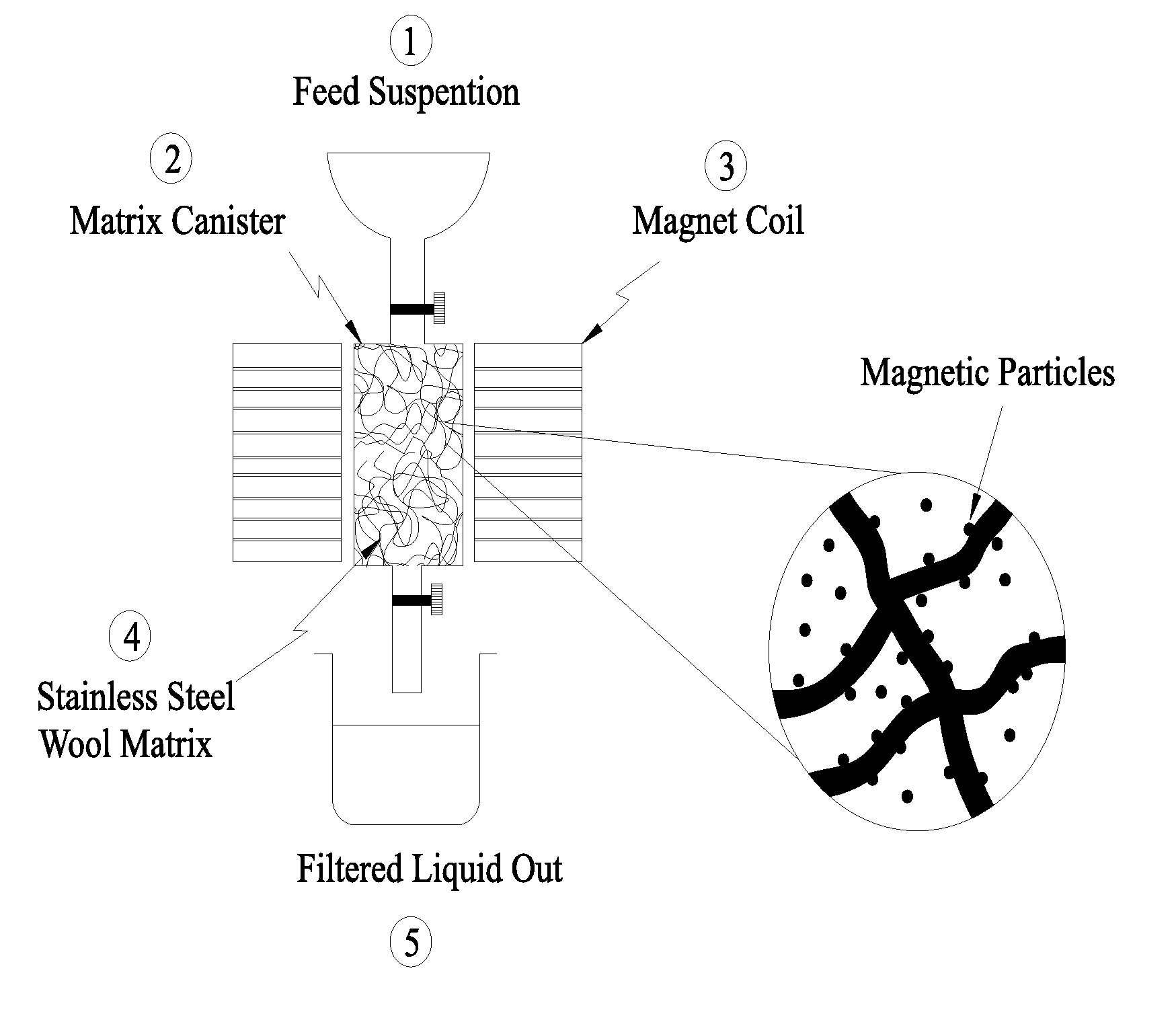
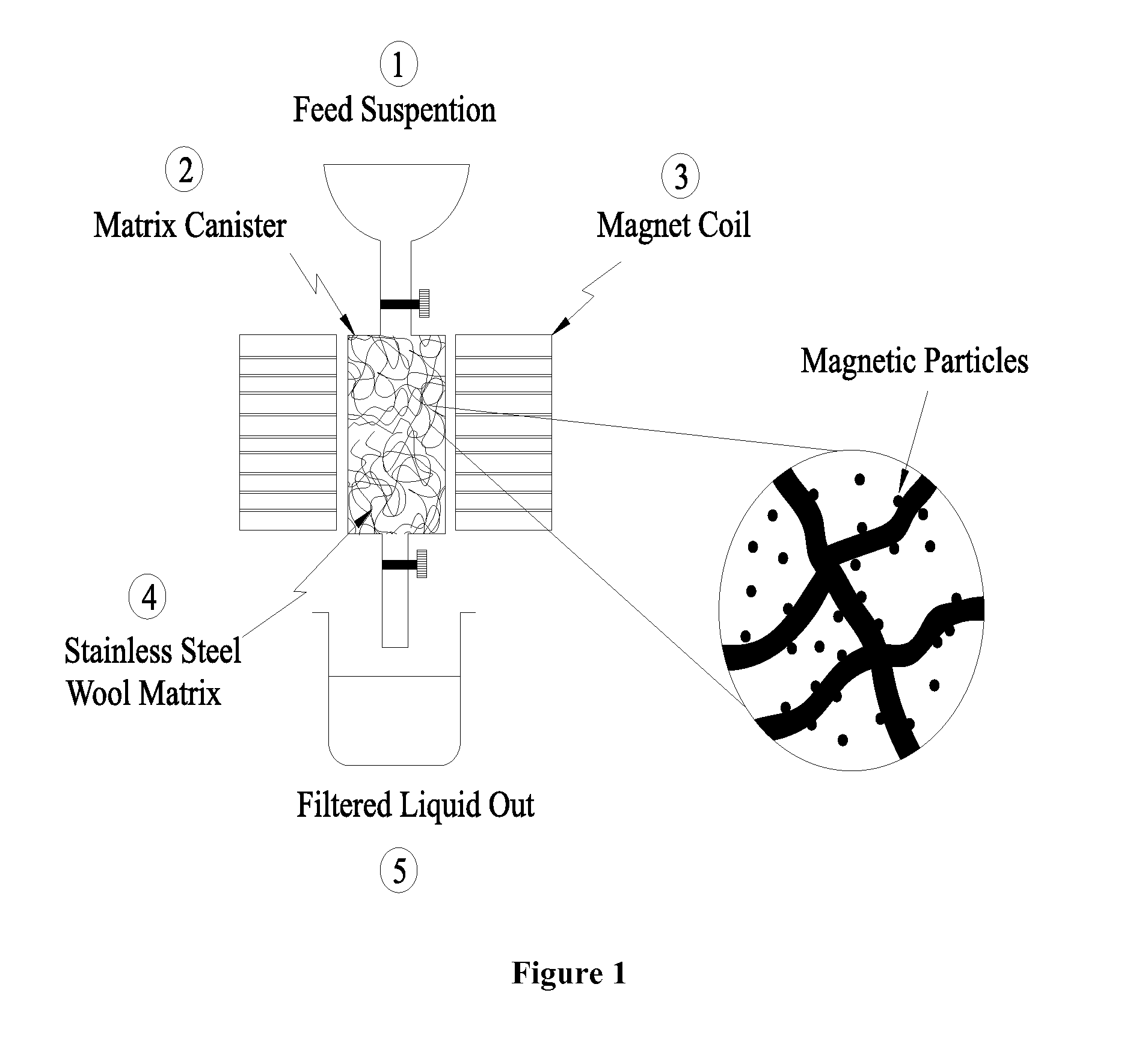
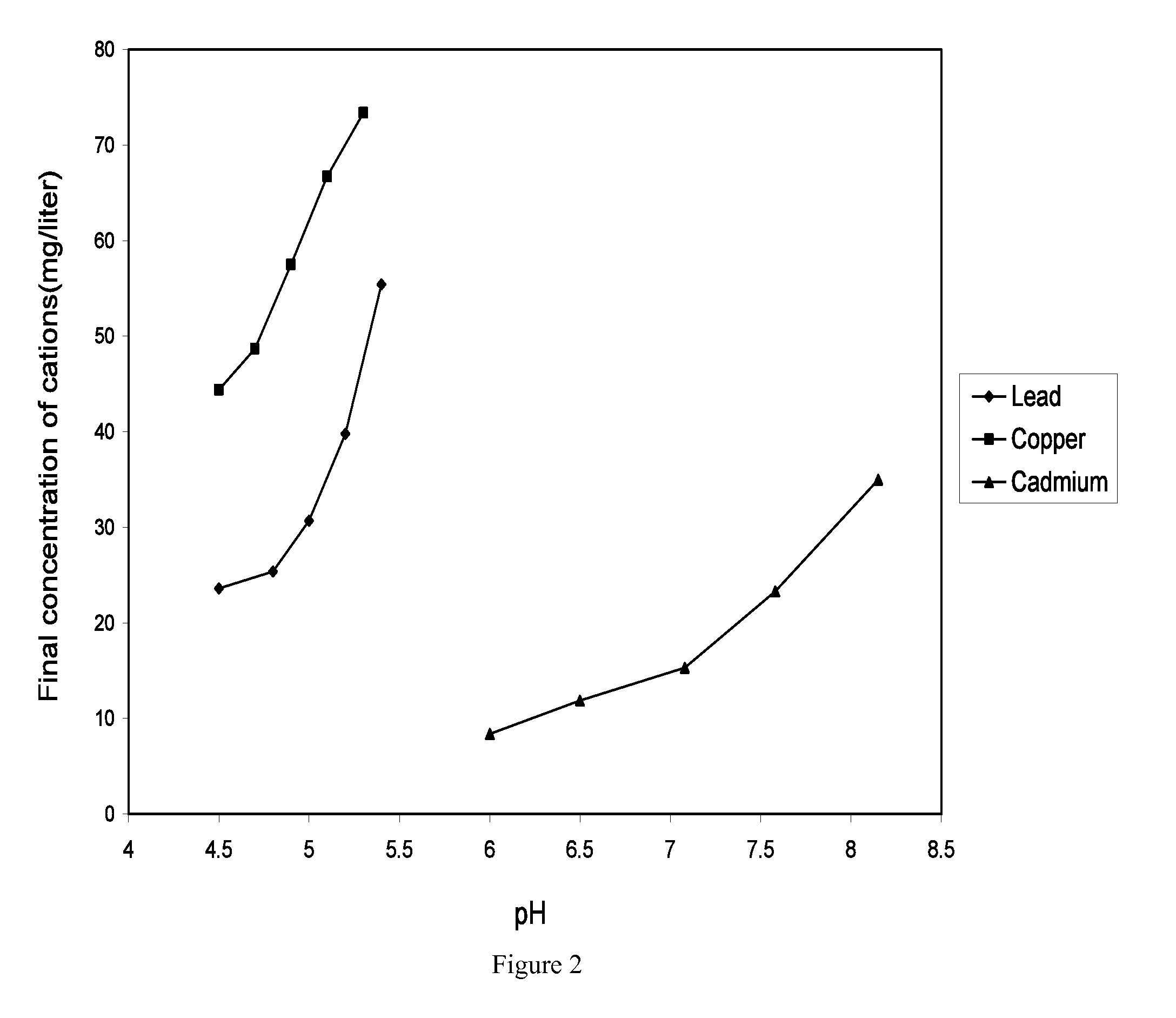
Disclosed is a process, which is used to eliminate heavy metal cations from the aqueous media, and provides a better solution for the existing problems of the separation systems like low efficiency and high costs. The heavy metal cations selected for this purpose are cadmium, lead and copper. The separation system consists of a two stage process: In the first stage, the iron oxide nanoparticles are suspended in an aqueous medium contaminated with the heavy metal cations. In the second stage, the solution is brought into contact with a ferromagnetic matrix (or a paramagnetic matrix) magnetized by the application of an outside magnetic field. The heavy metal cations are deposited on the matrix under the imposed magnetic field. This two-stage process makes it possible to separate the heavy metal cations from the aqueous medium. The wire matrices are upon the completion of separation washed away by water or air current.
Owner:ISFAHAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Air-to-air atmospheric exchanger for condensing cooling tower effluent
InactiveCN1589387AReduce weightReduce loadEfficient regulation technologiesTrickle coolersCooling towerWarm water
Heat exchanger packs having a first set of passageways for receiving a stream of ambient air and a second set of passageways for receiving a stream of warm water laden air is disclosed. The first set of passageways and second set of passageways being separate and permitting the warm water laden air stream to be cooled by the stream of ambient air so that water can condense out of the warm water laden air stream. Cooling tower configurations including the heat exchanger pack are disclosed for achieving effluent plume abatement, and capture of a portion of the effluent for replacement back into the cooling tower reservoir or as a source of purified water.
Owner:SPX COOLING TECH
Substrate transport container
InactiveUS20020129707A1Effective preventionEffectively preventCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentTrappingEngineering
A substrate transport container having a carrier box including a container body and a door hermetically sealably covering an opening provided in the front of the container body. Partitions form a circulating flow path in the carrier box. The circulating flow path has a flow path in which air flows toward substrates and a flow path in which air flows toward a fan. A substrate carrying section is disposed in the flow path in which air flows toward the substrates to carry the substrates in such a way that the principal surfaces of the substrates are approximately parallel to the flow path in which air flows toward the substrates. A particle removing filter and a gaseous impurity trapping filter are placed on the upstream side of the substrate carrying section in the flow path in which air flows toward the substrates. A fan motor for driving the fan is incorporated in the carrier box to form an air current for circulating through the circulating flow path.
Owner:EBARA CORP
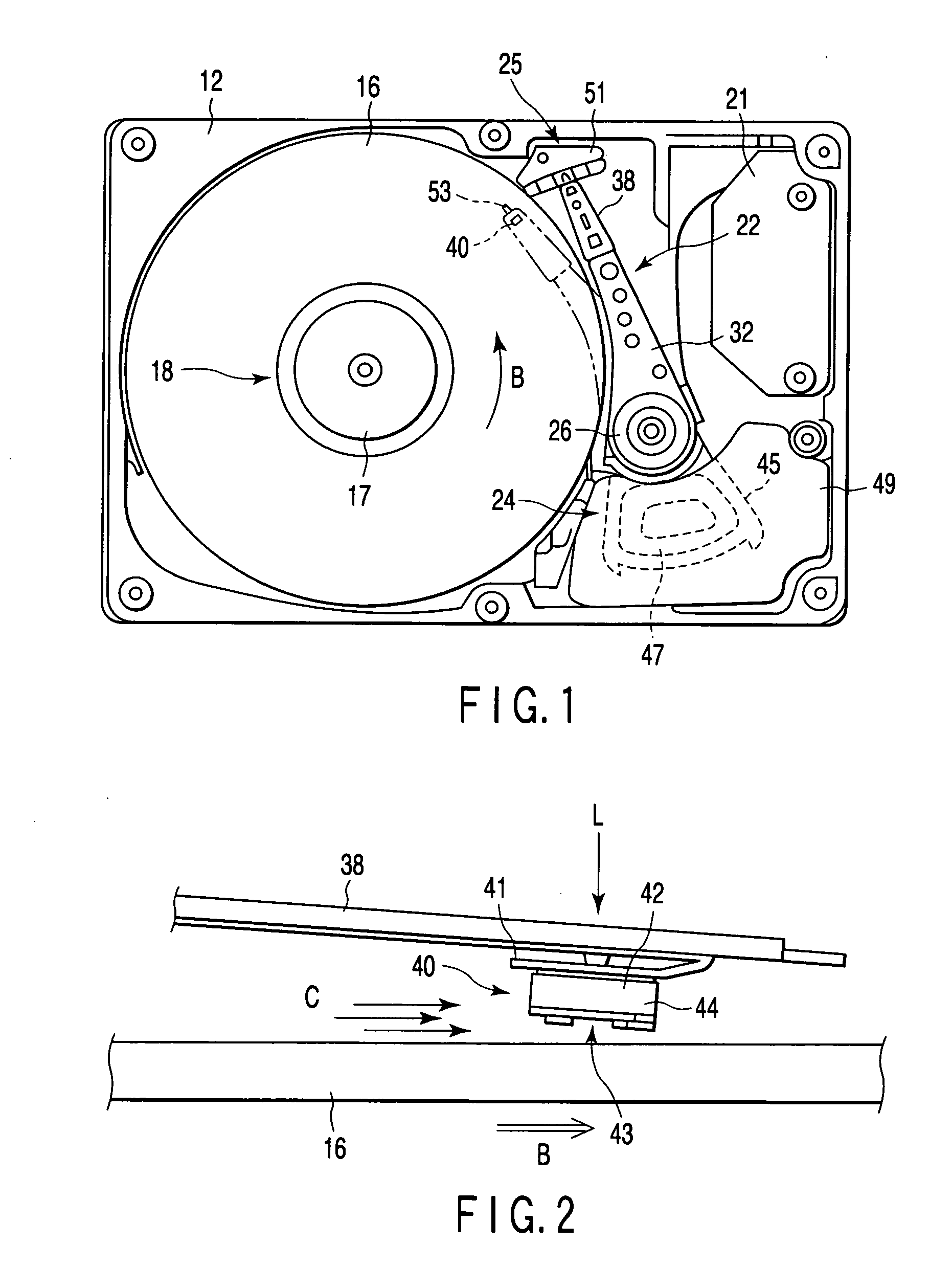
Head, head suspension assembly, and disk device provided with same
InactiveUS20060238922A1Record information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsEngineeringAir current
A slider of a head has a negative-pressure cavity which is formed in the facing surface and generates a negative pressure, a leading step portion which protrudes from the facing surface and is situated on an upstream side of the air current with respect to the negative-pressure cavity, and a leading pad which is provided on the leading step portion and faces the recording medium. The leading pad has an inlet end edge which is situated on the upstream side of the air current and extends throughout a length of the leading step portion in the transverse direction, and a plurality of recesses which individually open in the inlet end edge and extend in the longitudinal direction from the inlet end edge.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi-cyclone dust collector for vacuum cleaner
InactiveCN1951307AReduce the overall heightReduce noiseSuction filtersDispersed particle separationCycloneEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing vanadium nitride and device
InactiveCN1562769AQuality improvementSimple processing methodNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsVanadium compoundsHydrogenVanadium nitride
The invention relates to a processing method of prepn. vanadium nitride by fluidized bed technology and corresponding special device. The characteristic is to create plasma body in reaction zone of fluidized bed by ratio frequency induction, the reaction gas ammonia, nitrogen and hydrogen are excited and ionized to create active hydrogen and nitrogen particle which is made reducting and nitrating reaction with vanadium oxide particle suspensing in fluidized zone to create vanadium nitride. The special device used by this invention includes fluidized bed, radio frequency inducting coil, radio frequency power source, heater, air supply tank, air current distributor, air-extracting system, air valve, general air valve controlling and adjusting reaction gas flow and the pipe line system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Exterior sieve type bag-type dust remover and its ashing method
ActiveCN101161330AExtend your lifeNo damageDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingEngineeringAshing
The present invention relates to an external filtering bag type dust remover and a method for ash removing to the remover thereof. The inner side of the box body of the external filtering bag type remover is provided with a figure pattern card which is fixedly arranged with the filter bag of the inner inserting bag cage that tenses the filter bag, and the external filtering bag type dust remover further includes a back flushing device which provides pressure-stable back flushing air current in the ash removing. The external filtering bag type dust remover realizes the static ash removing the service lifetime is evidently prolonged at the same time the impulse blowing device is saved because that the pressure of the back flushing air current is stable and the tensioned filter bag holds still in the ash removing. The ash removing method comprise the following procedures: first blowing in the pressure-stable back flushing air current to the filter bag; and cutting off the back flushing air current after lasting a predetermined time. The external filtering bag type dust remover and the dust removing method thereof can guarantee that the filter bag is not damaged in the ash removing and prolong the service lifetime of the filter bag.
Owner:北京赫宸智慧能源科技股份有限公司
Heat-Dissipating Device For Supplying Cold Airflow
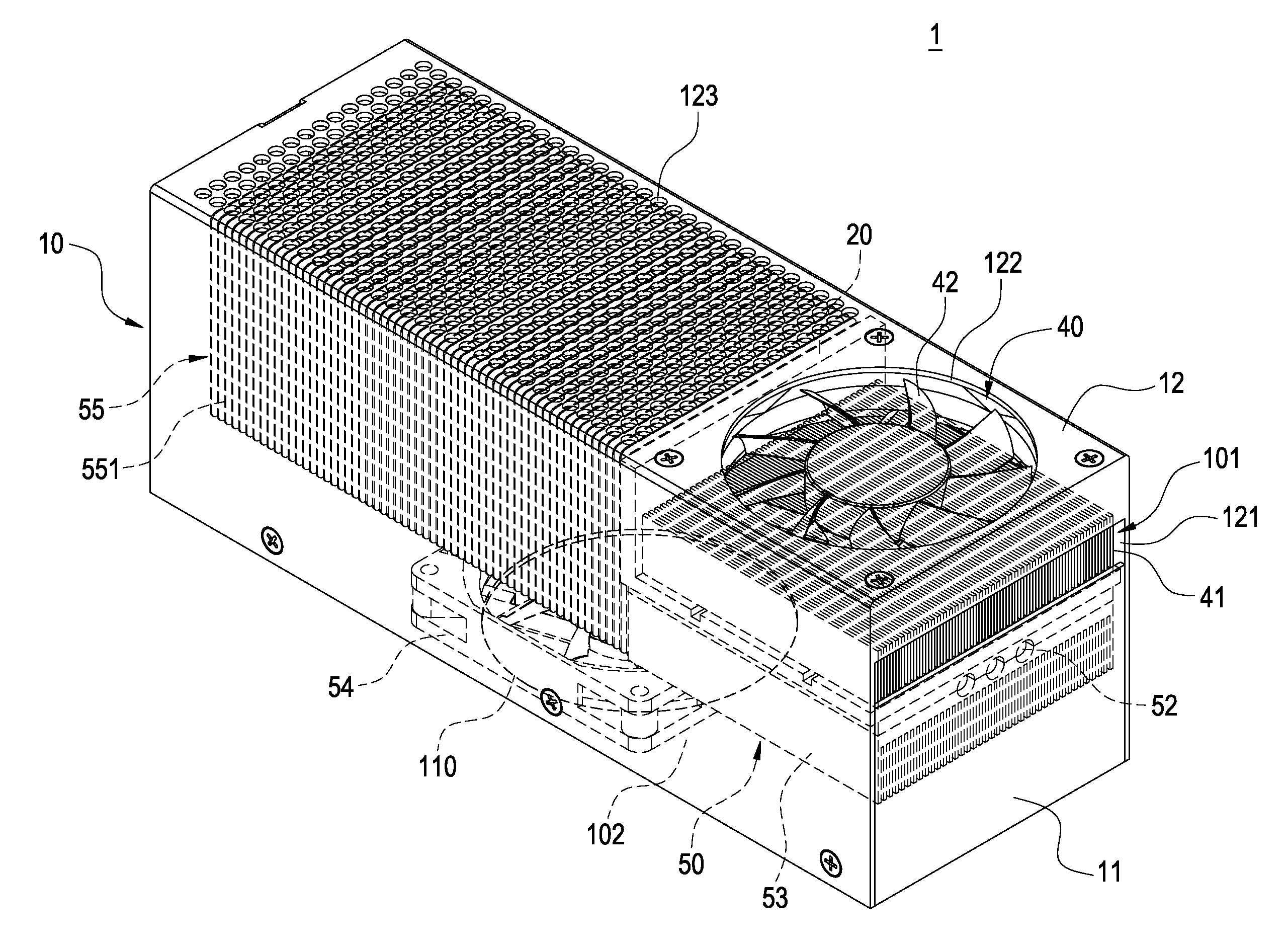
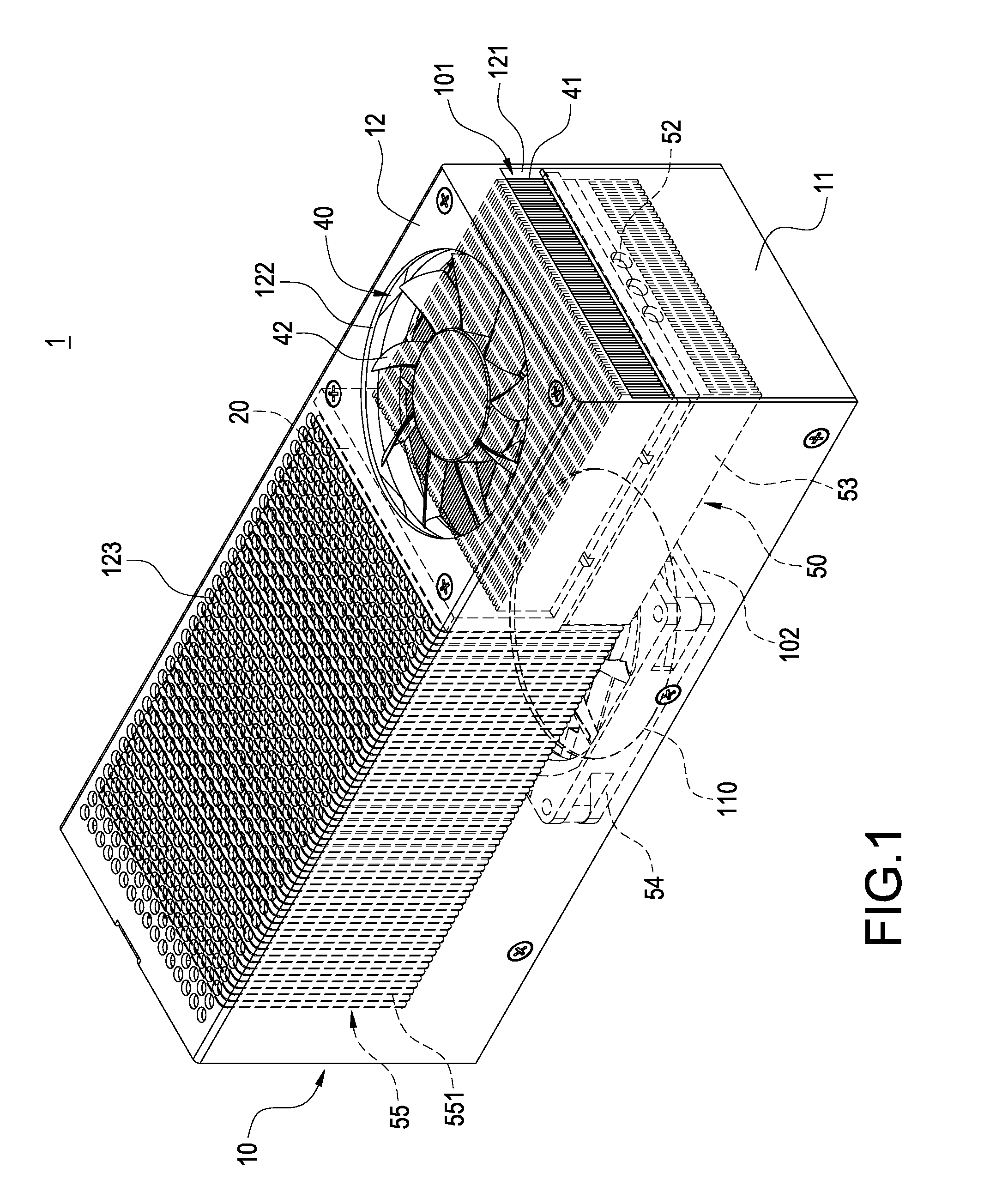
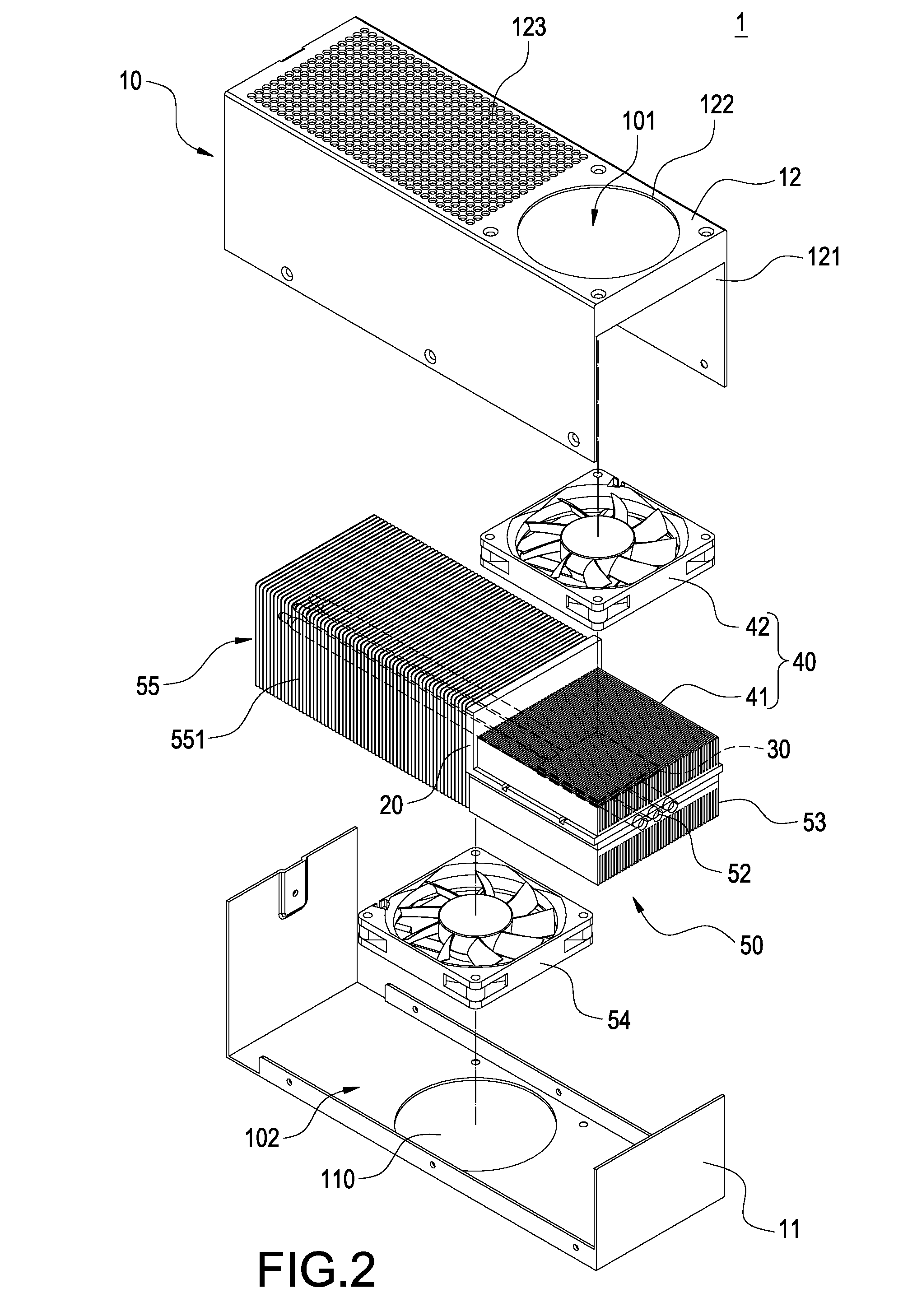
InactiveUS20110197598A1Great practicabilityImprove convenienceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermoelectric coolingCold air
A heat-dissipating device (1) includes a casing (10) and a thermal insulation plate (20) provided within the casing (10). The thermal insulating plate (20) divides the interior of the casing (10) into a first accommodating space (101) and a second accommodating space (102). A hot air outlet (121) and a first air inlet (122) of the casing (10) are in communication with the first accommodating space (101). A cold air outlet (110) and a second air inlet (123) of the casing (10) are in communication with the second accommodating space (102). A thermoelectric cooling chip (30) is disposed in a through-hole (200) of the thermal insulation plate (20) and has a hot-end surface (31) facing the first accommodating space (101) and a cold-end surface (32) facing the second accommodating space (102). A heat-dissipating module (40) is received in the first accommodating space (101). A cold-airflow supplying module (50) is received in the second accommodating space (102). The heat generated by the hot-end surface (31) is dissipated to the hot air outlet (121) by the thermal conduction of the heat-dissipating module (40). The cold generated by the cold-end surface (32) is conducted and distributed uniformly by the cold-airflow supplying module (50) to the cold air outlet (110).
Owner:GOLDEN SUN NEWS TECHN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com