Patents
Literature
4318results about "Trickle coolers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
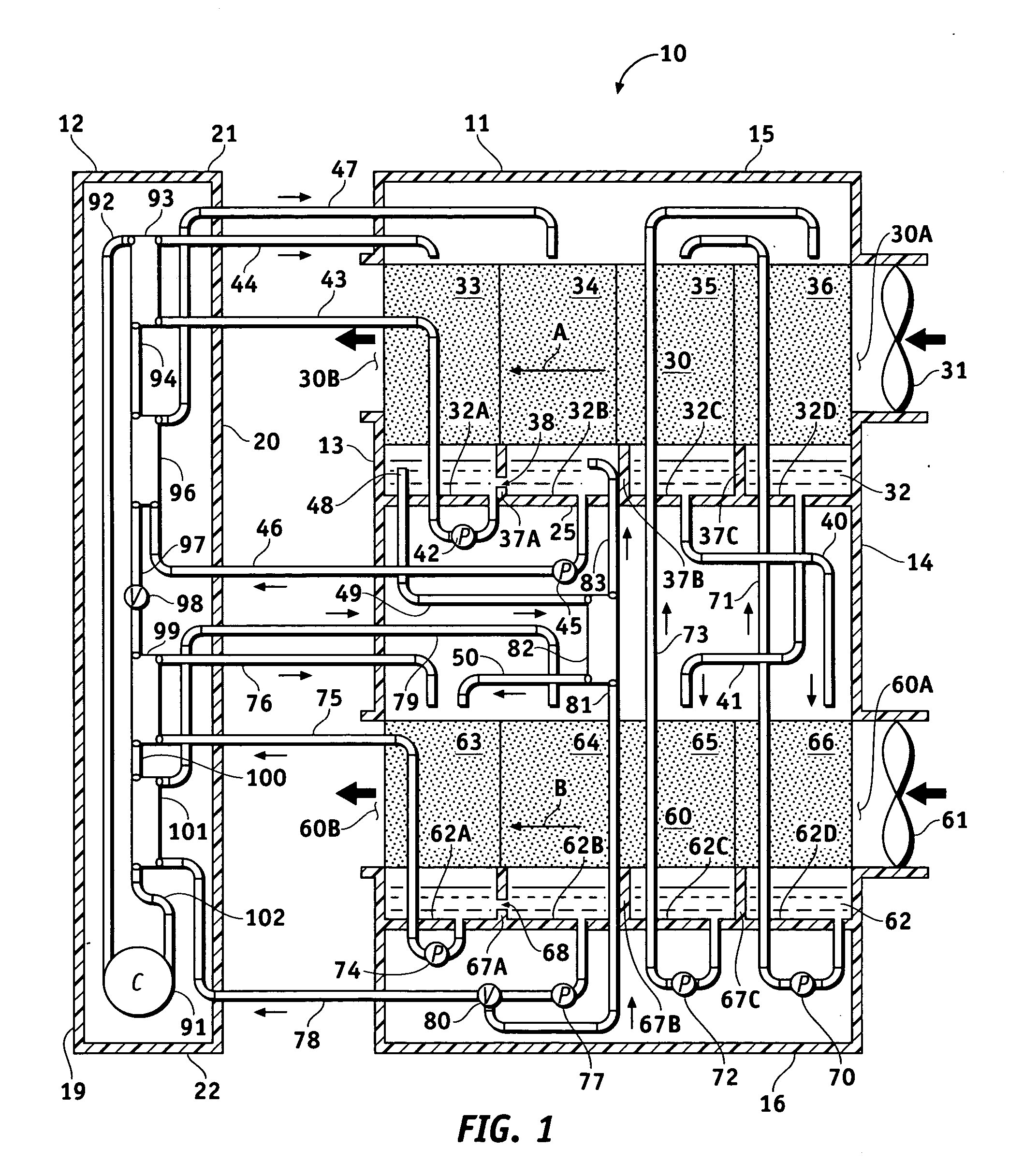
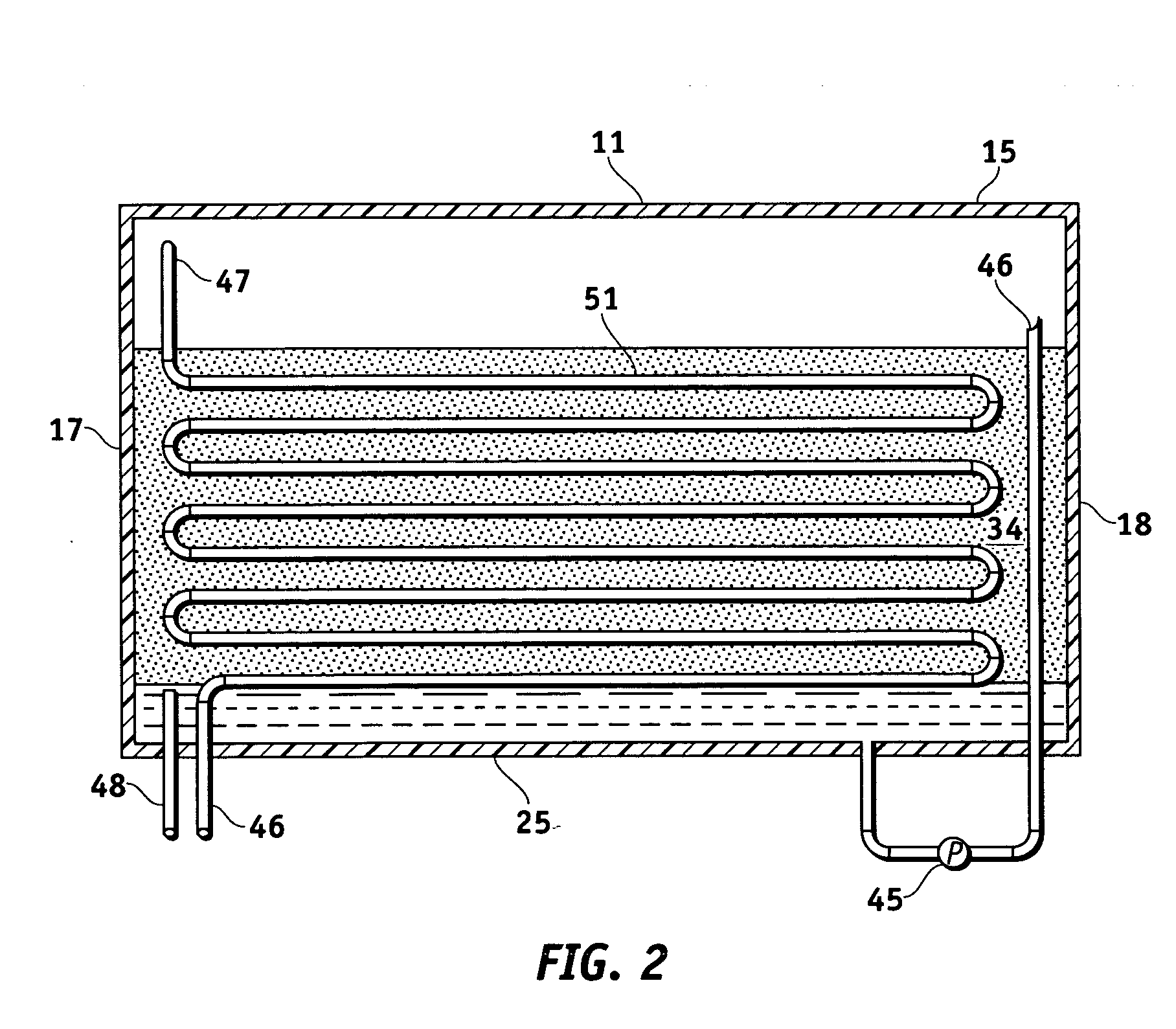
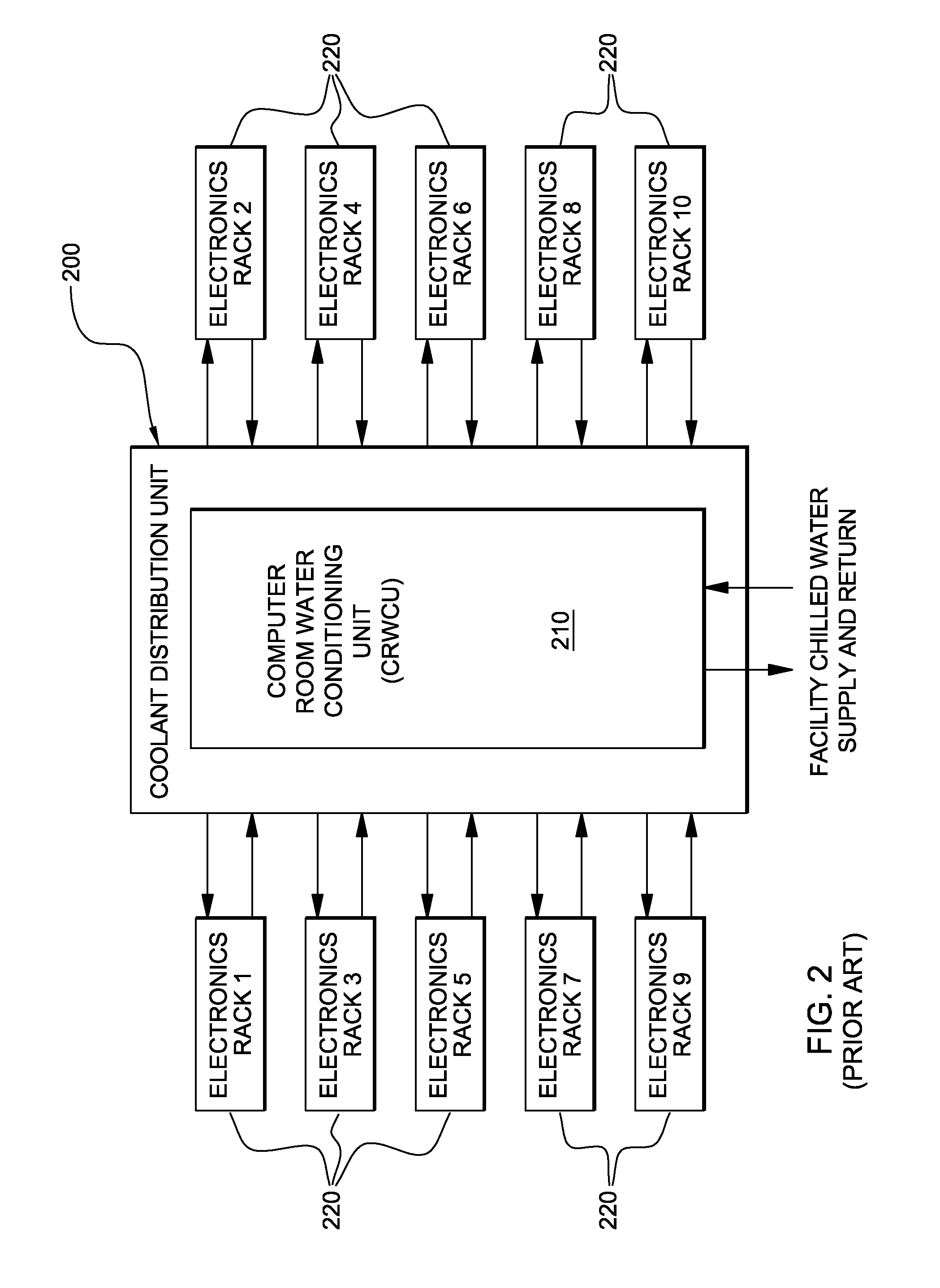
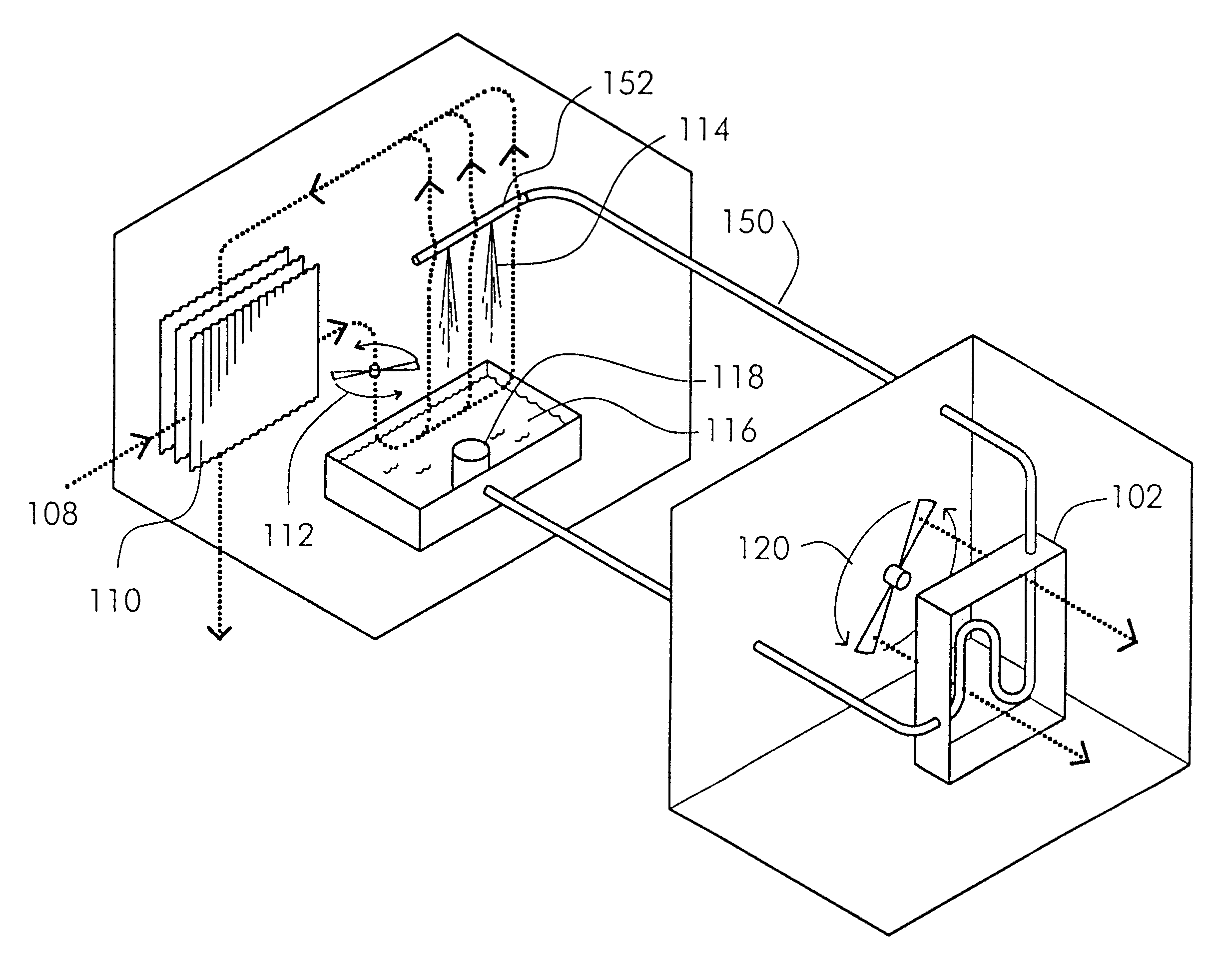
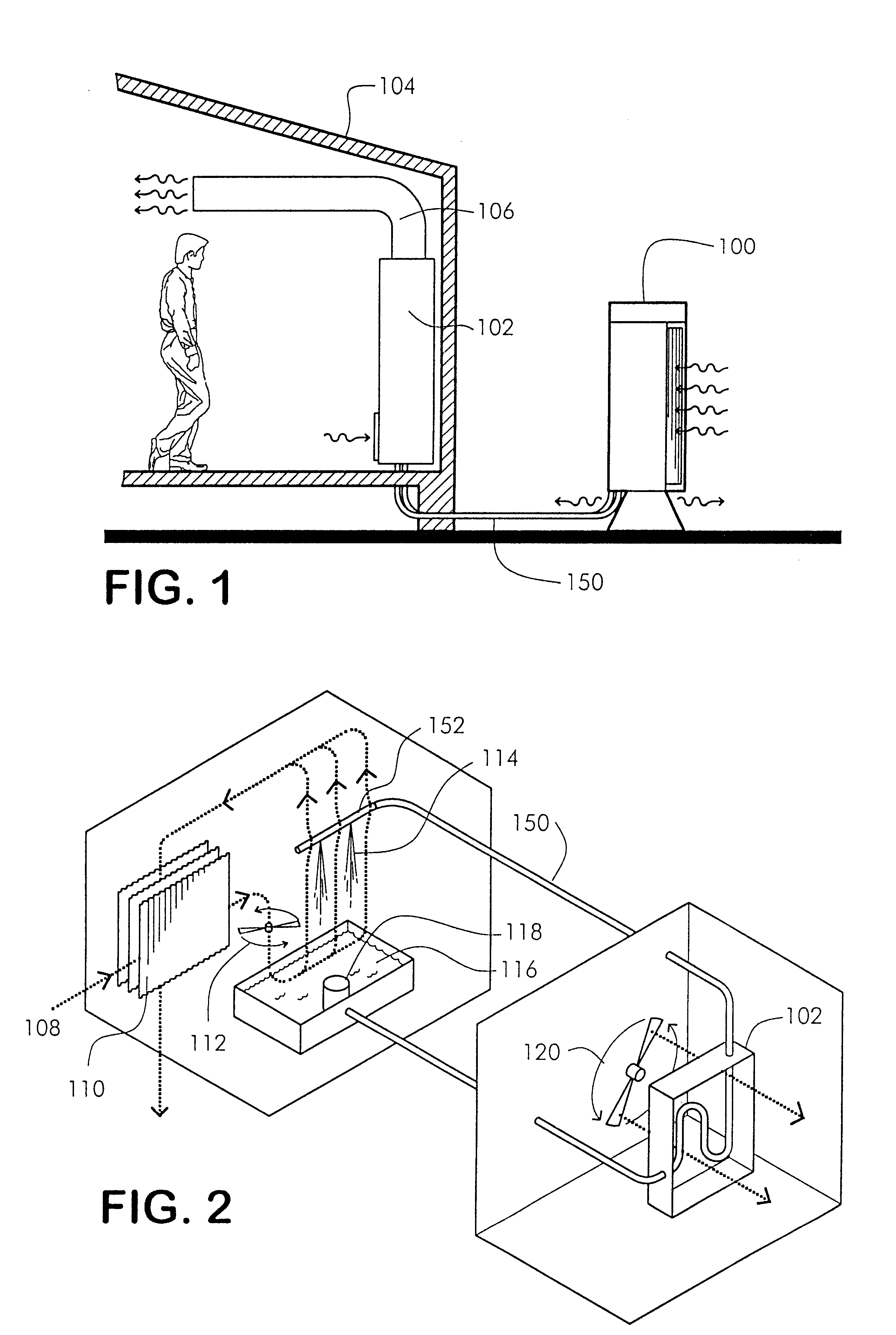
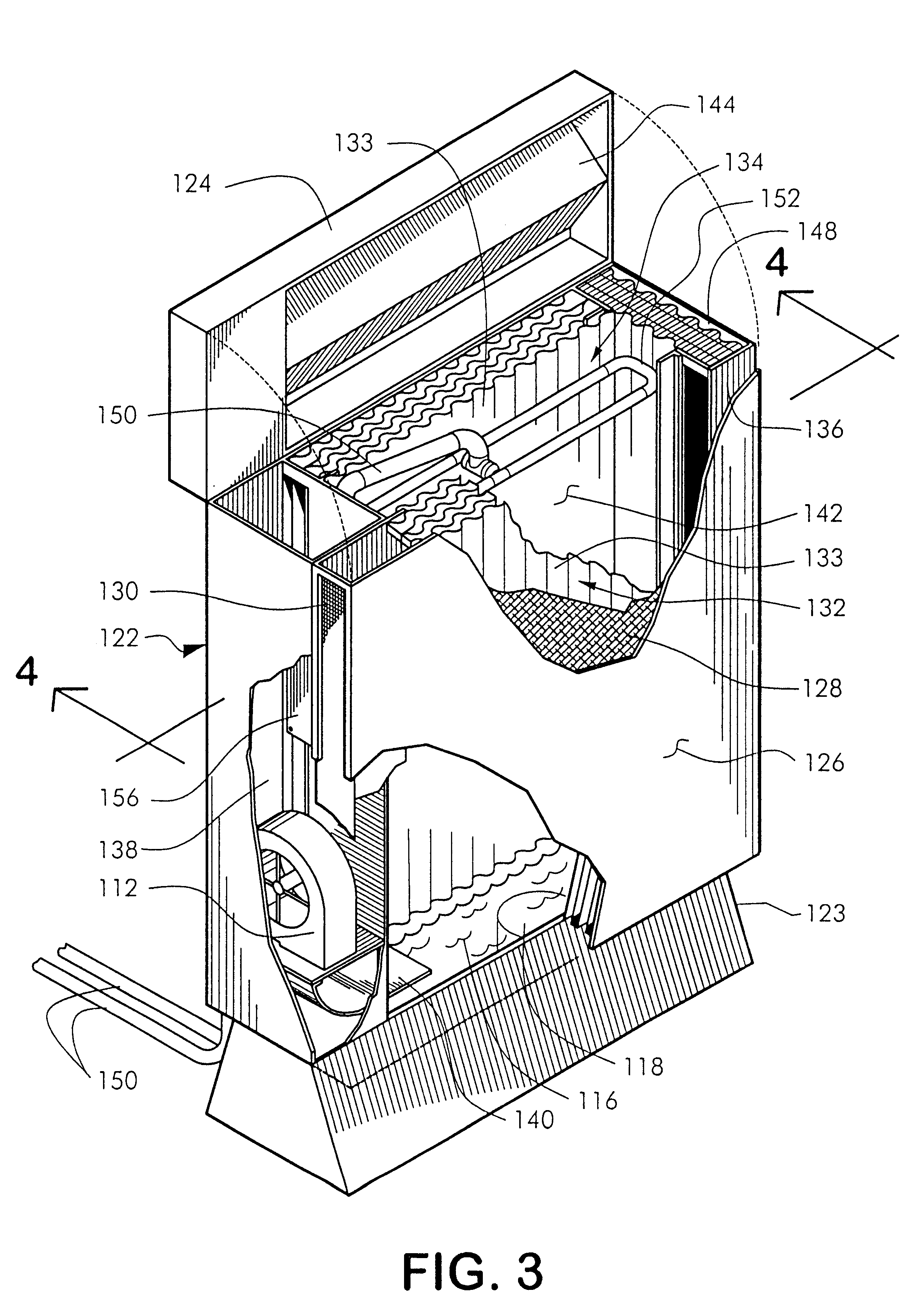
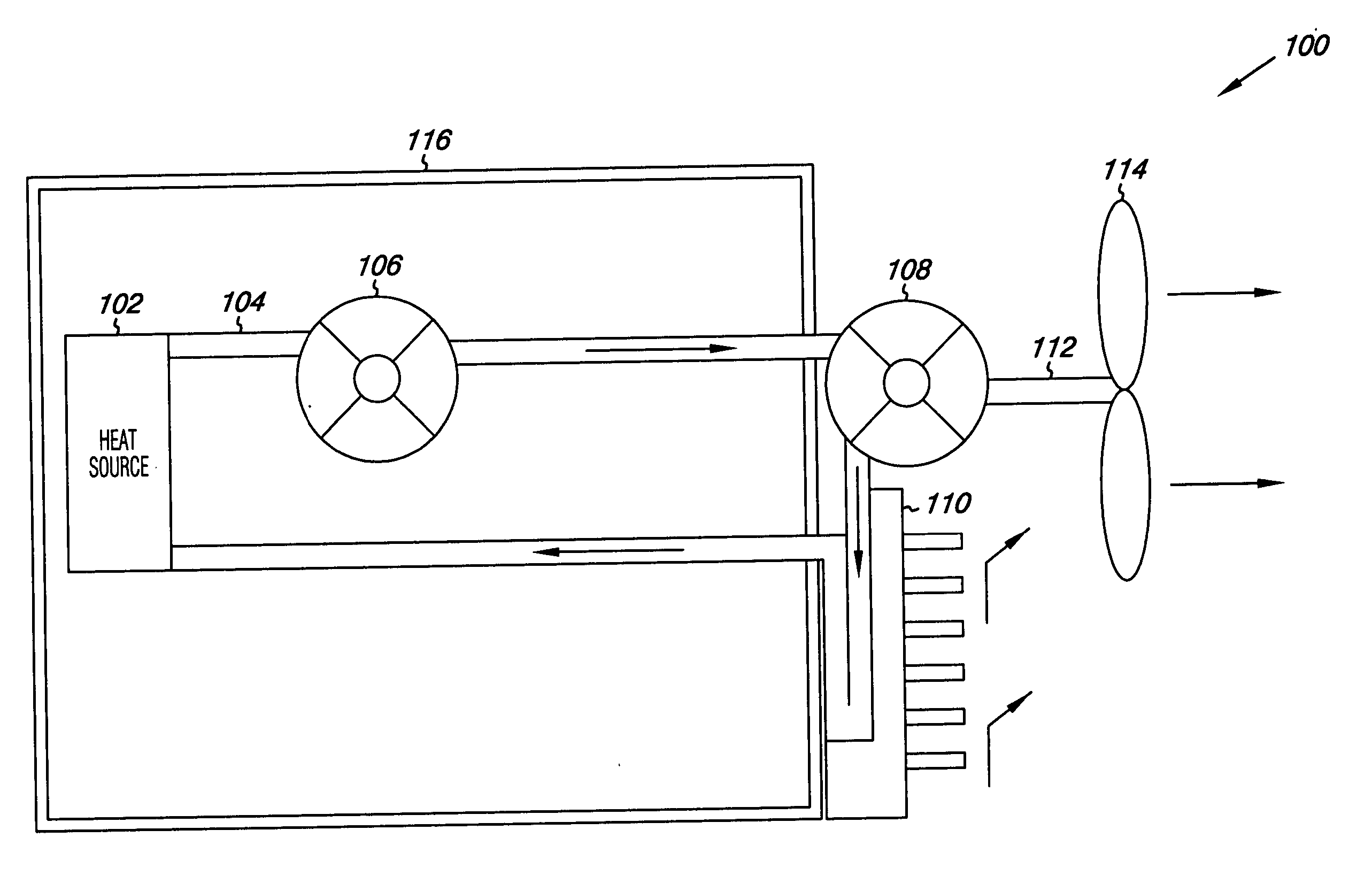
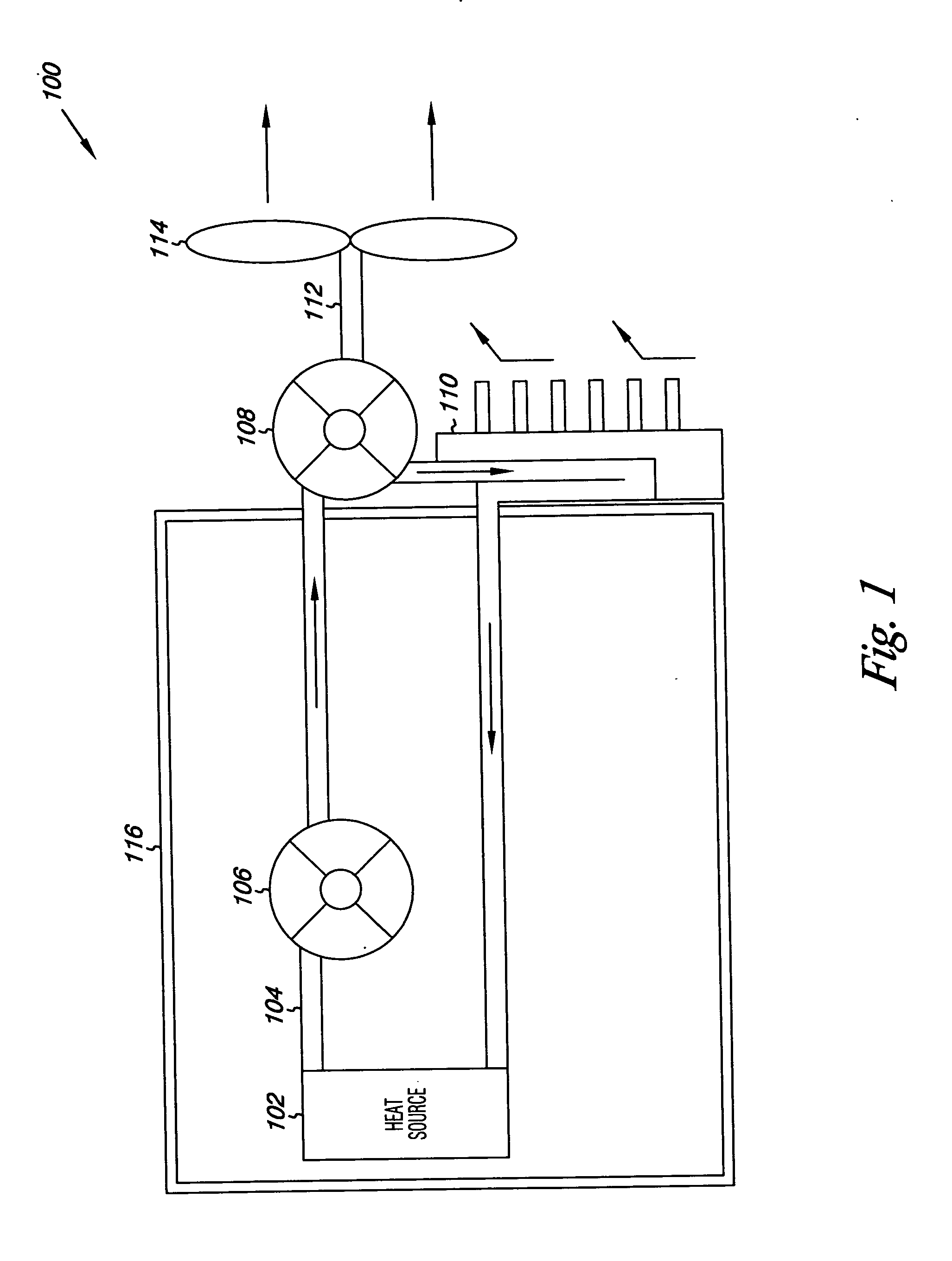
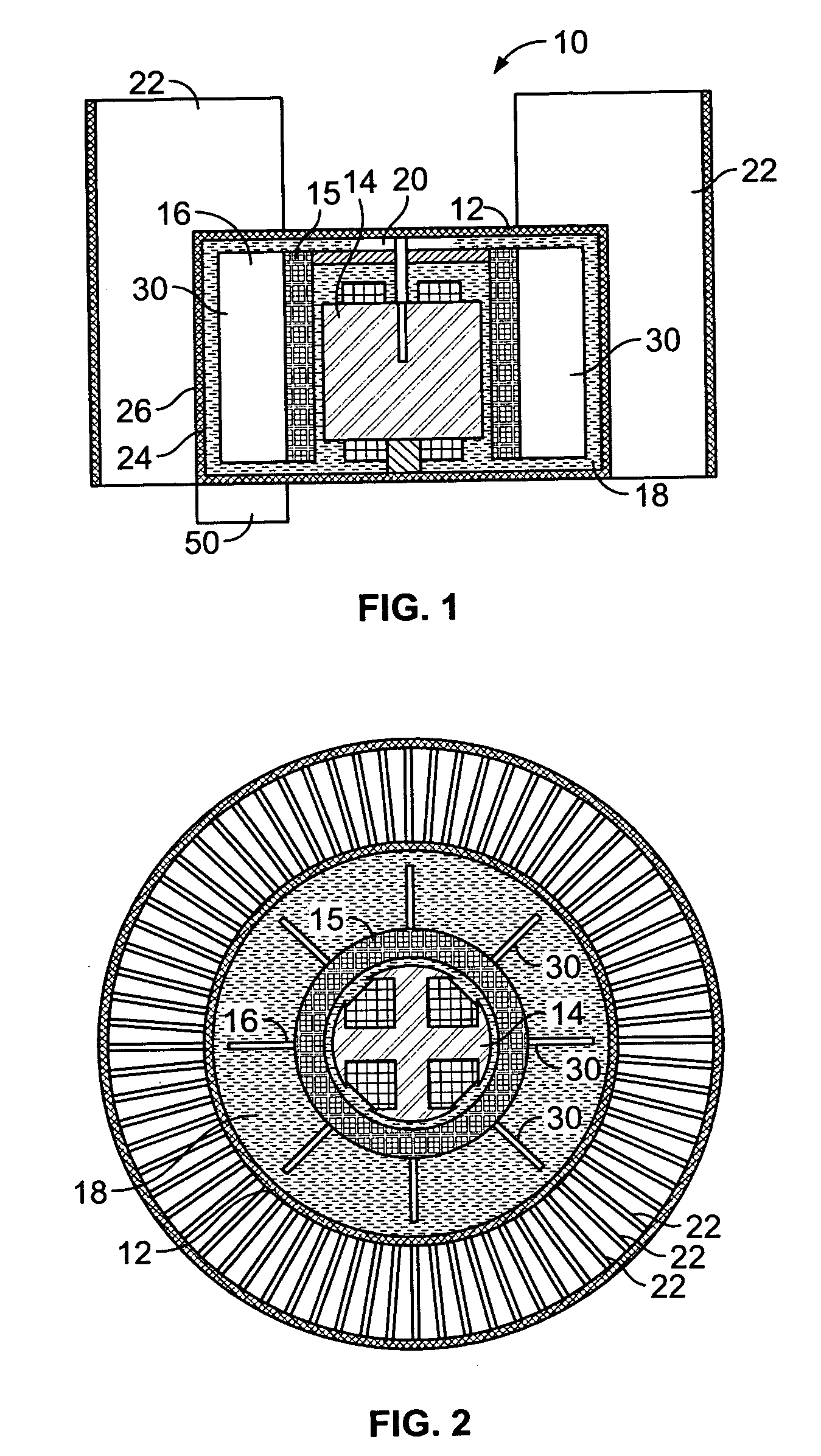
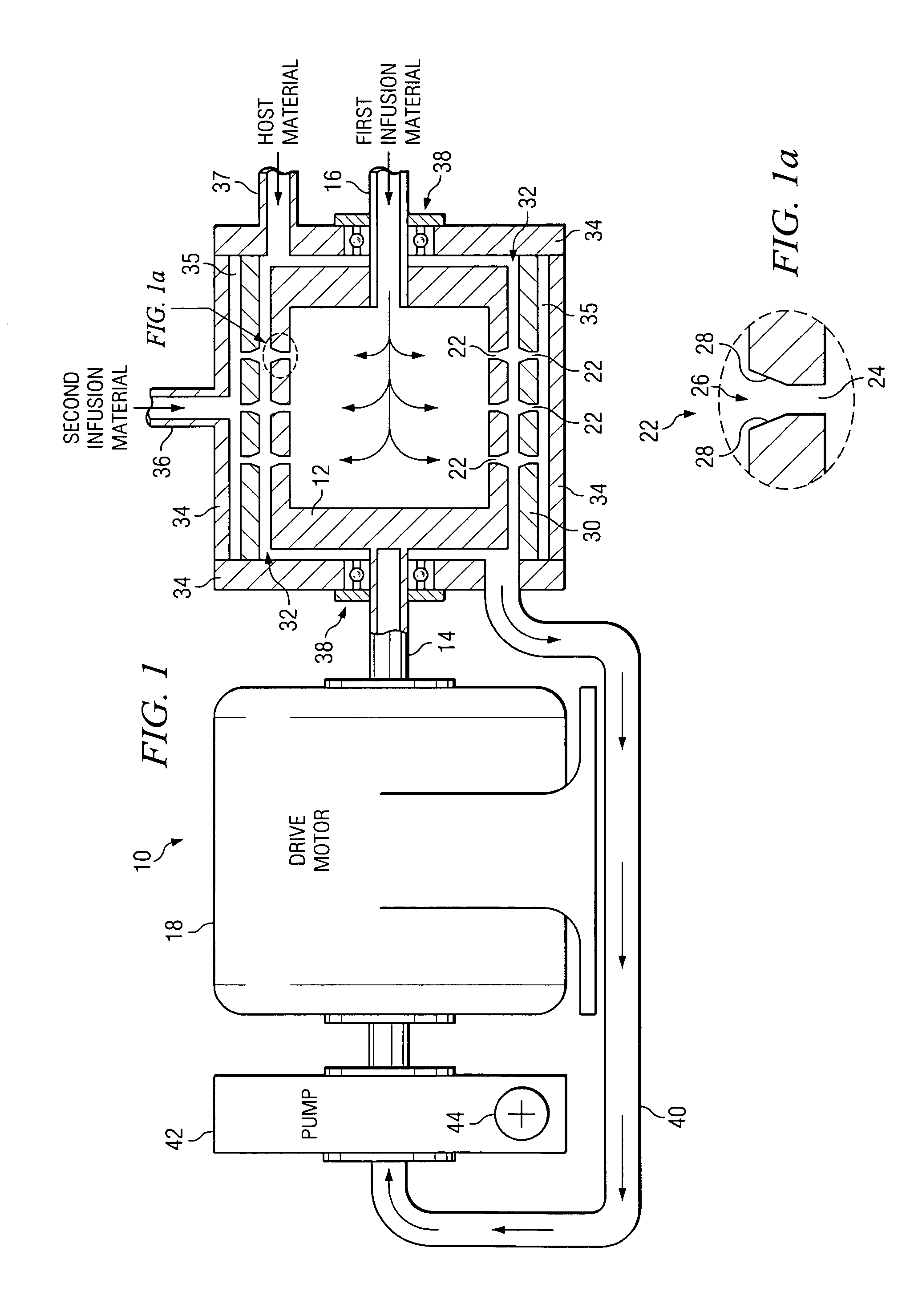
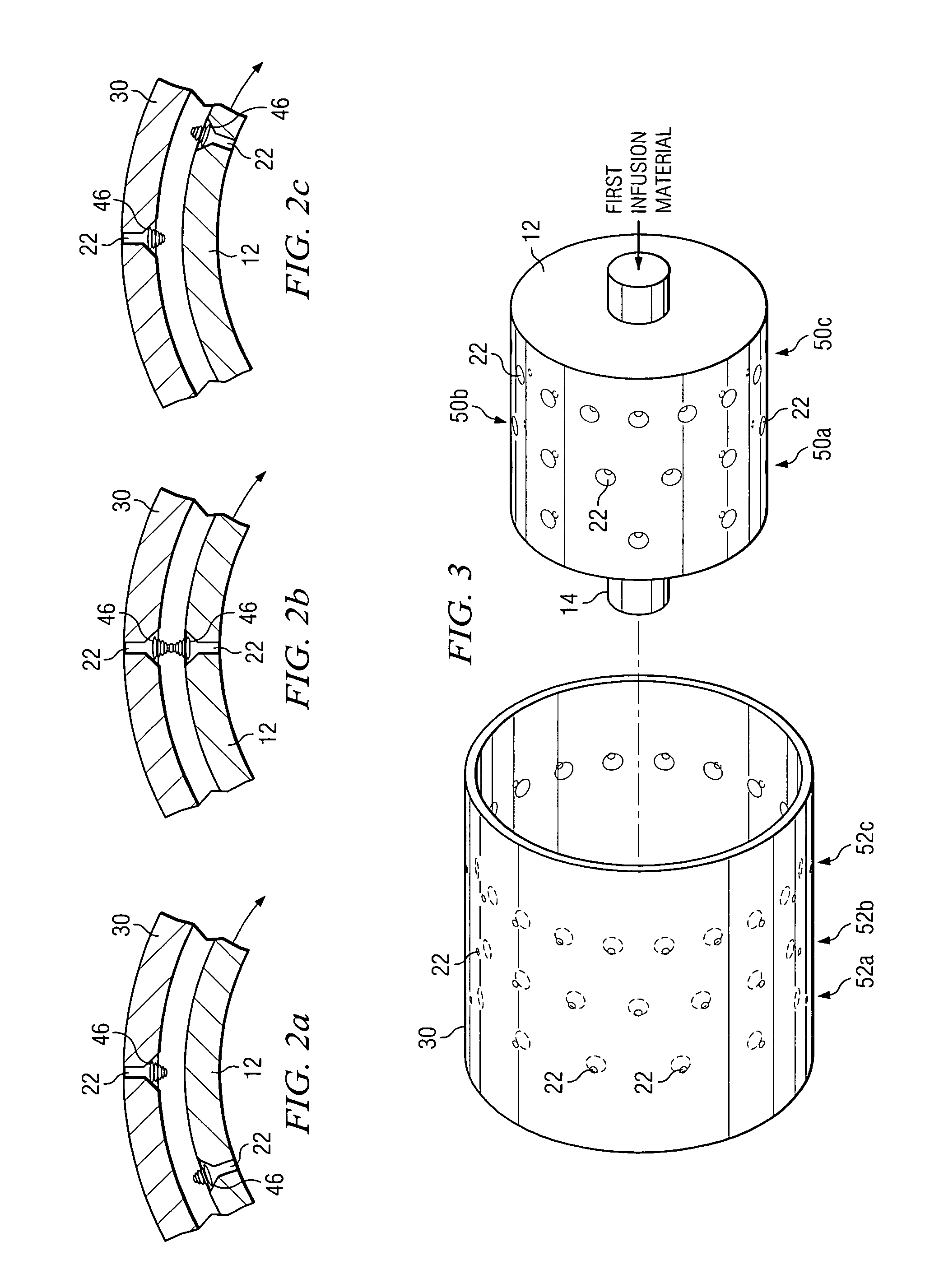
Method and apparatus of indirect-evaporation cooling
InactiveUS6497107B2Less energyHigh energy costFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesWorking fluidEvaporation
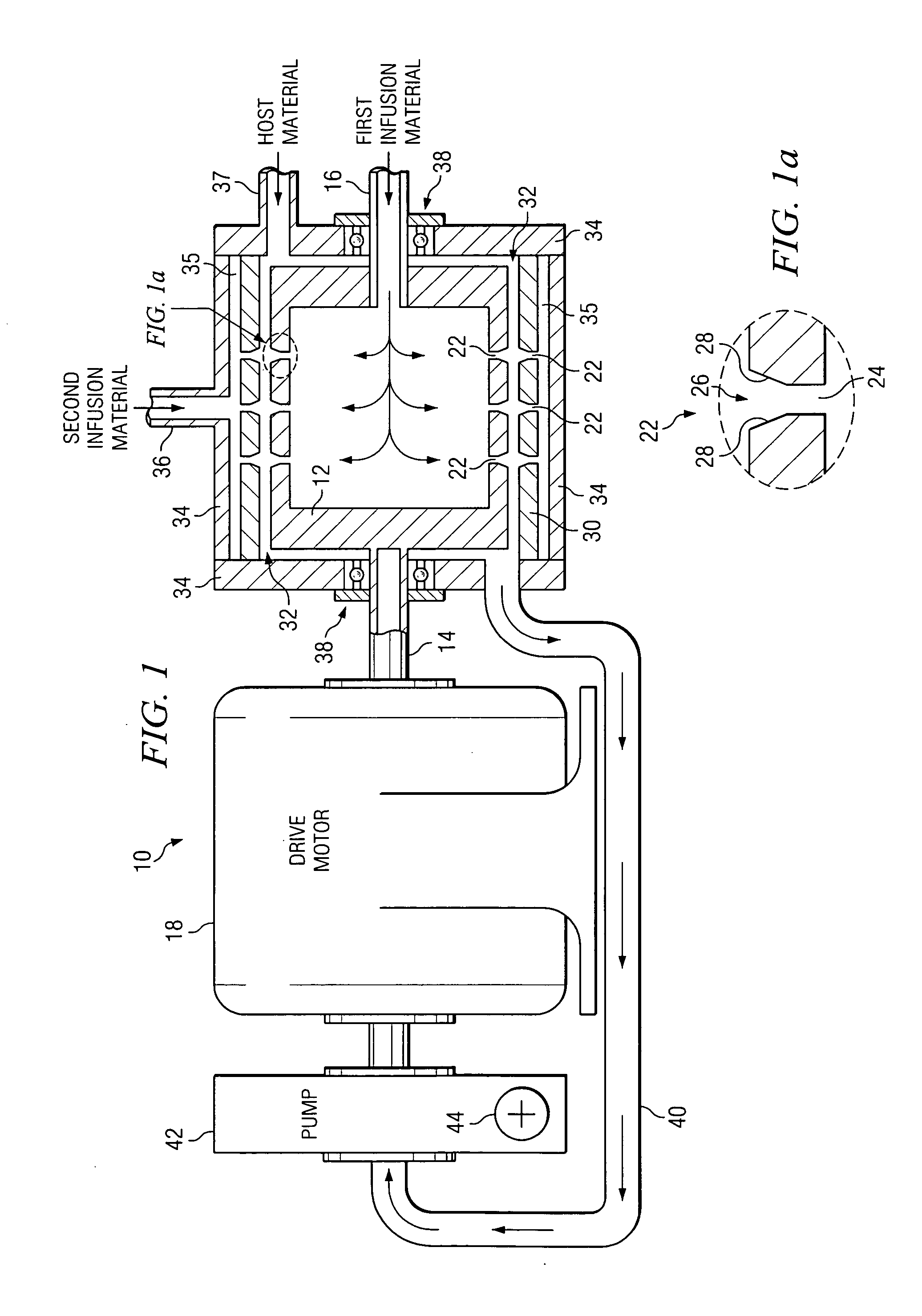
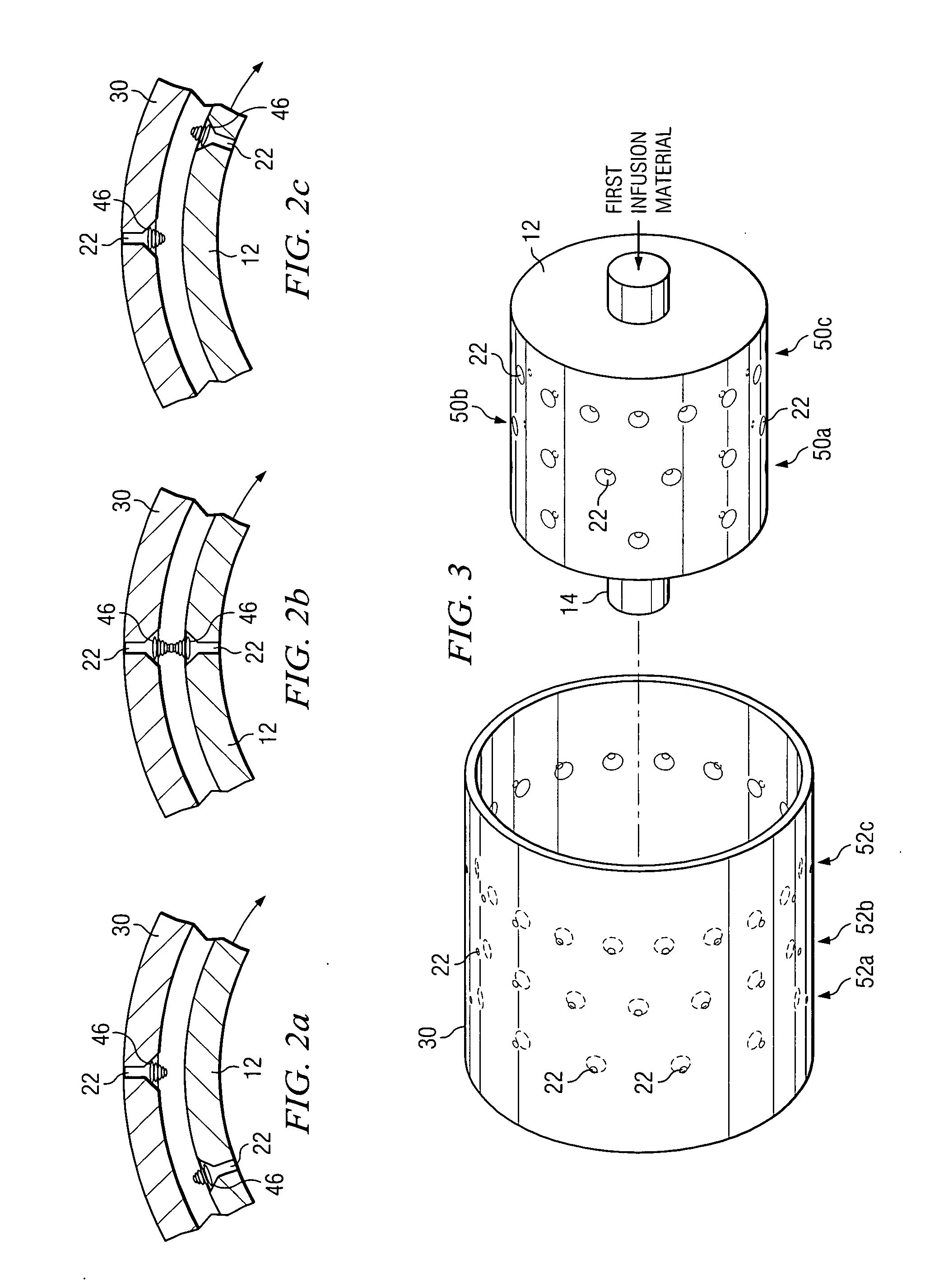
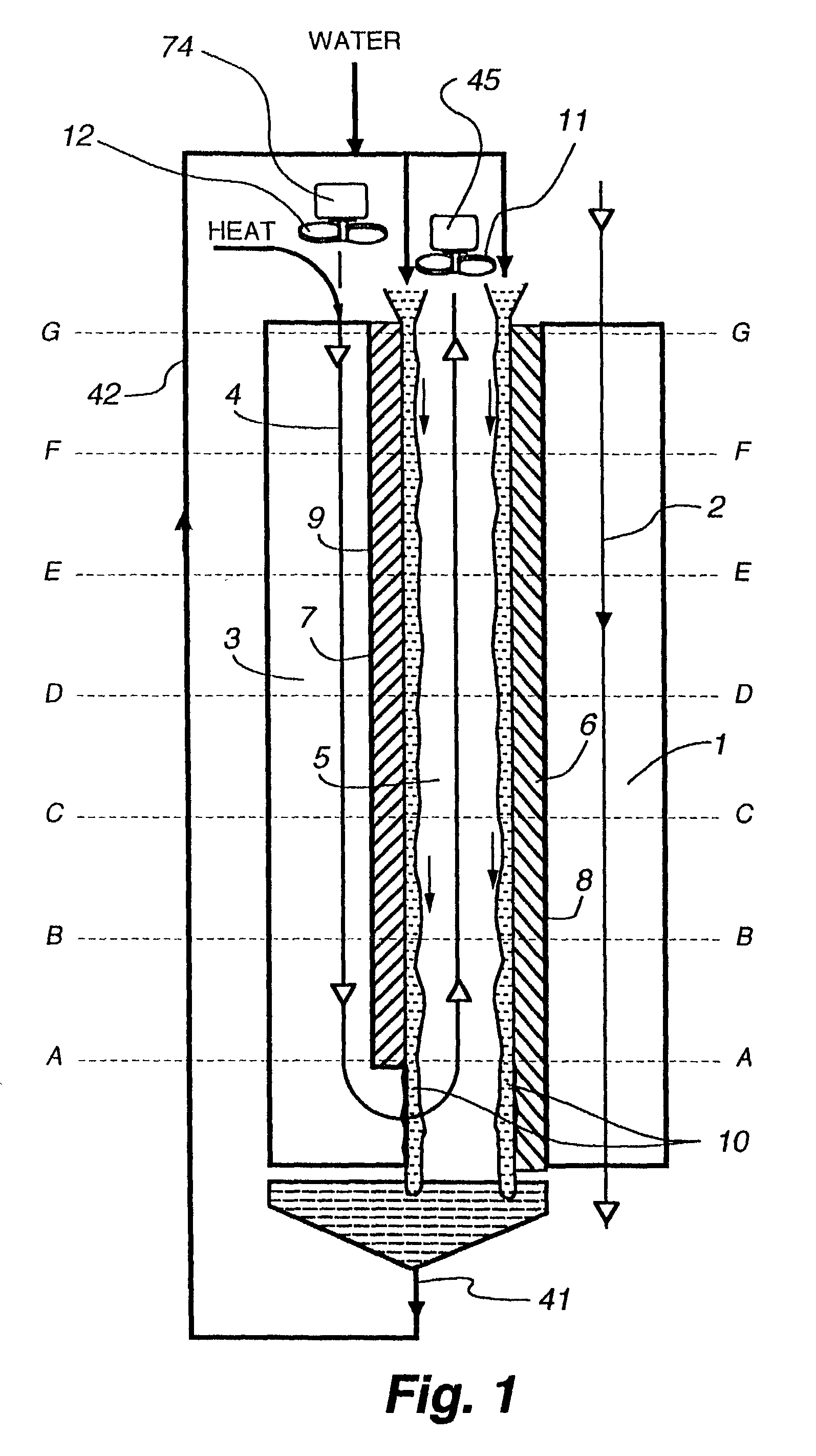
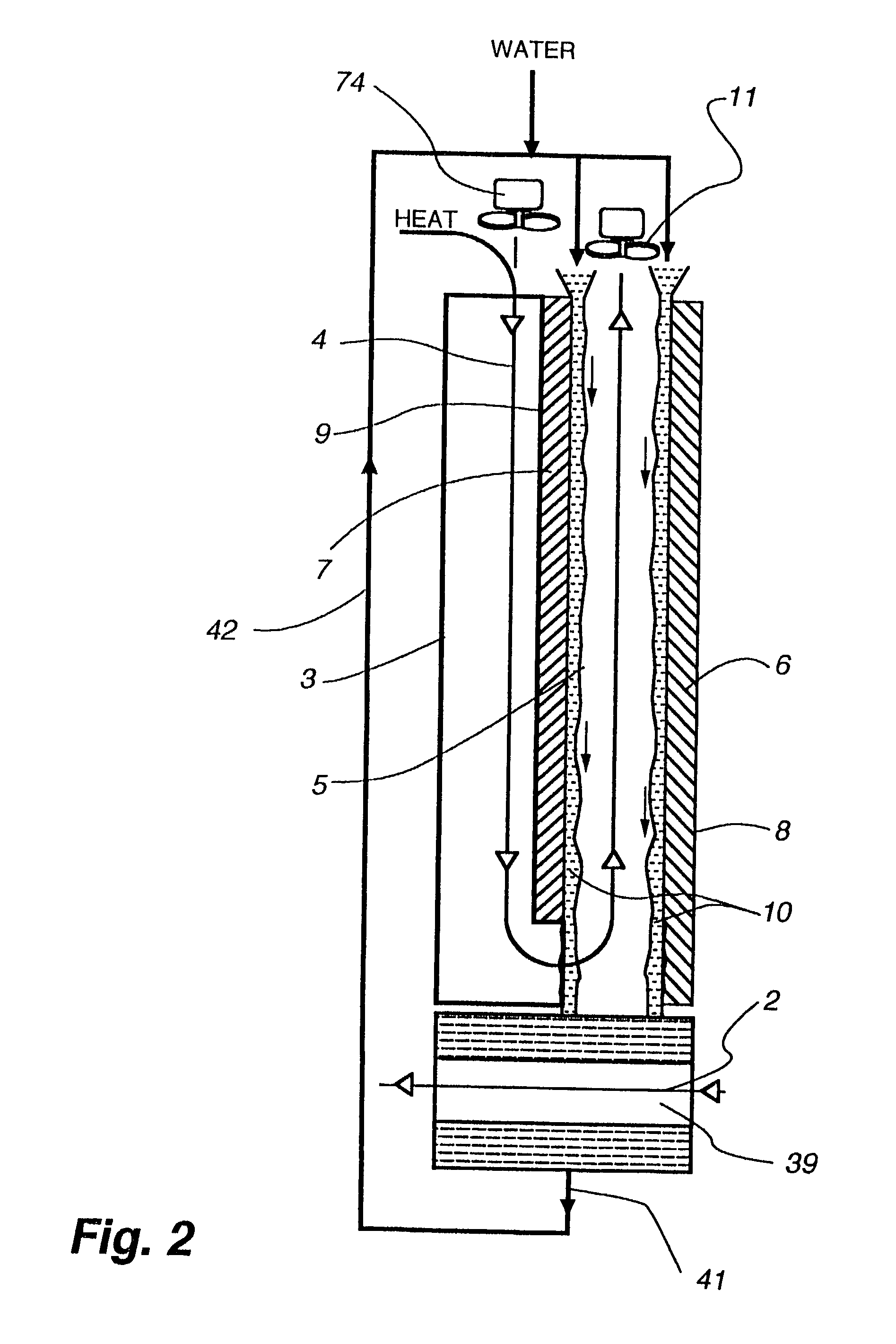
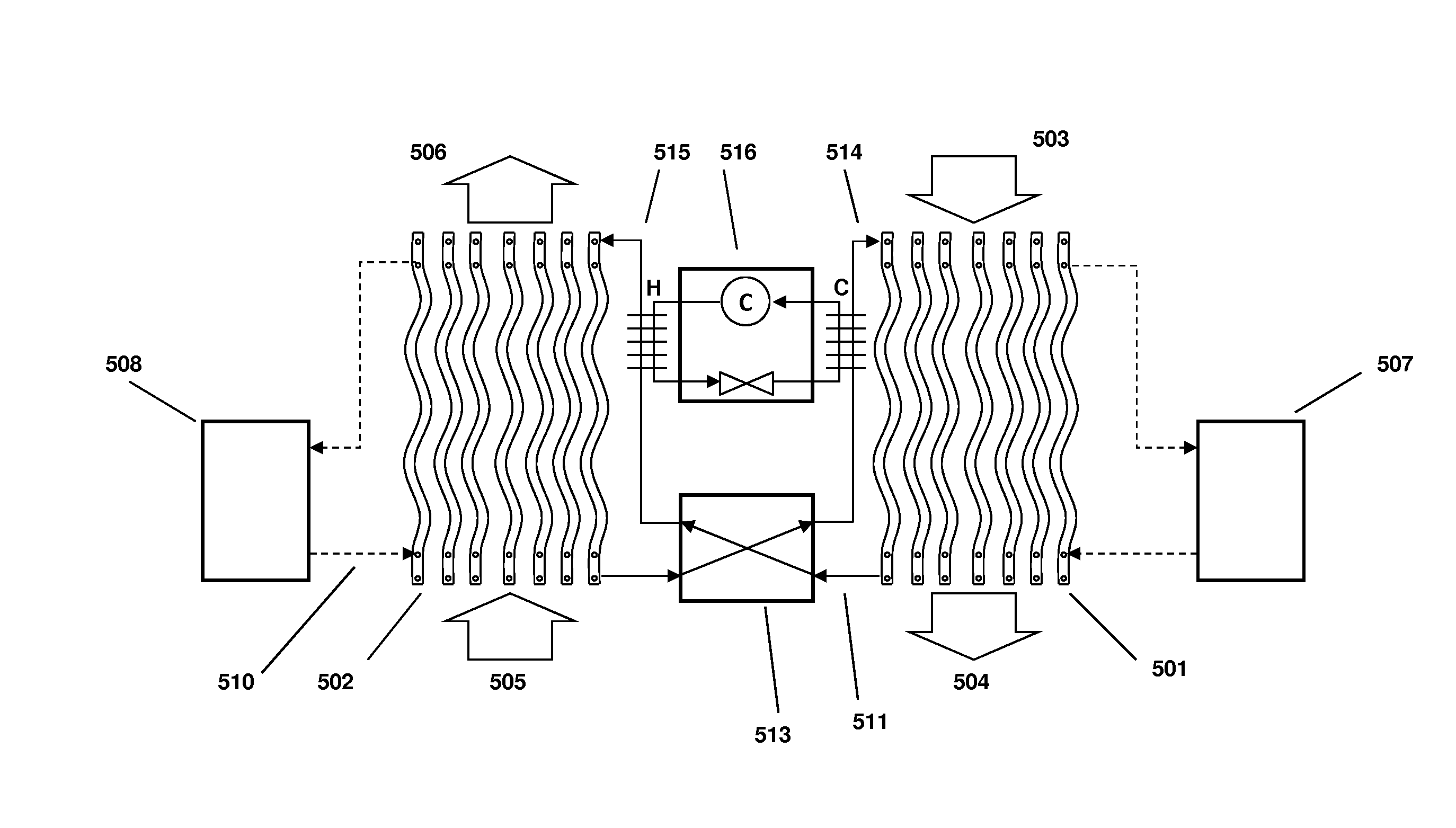
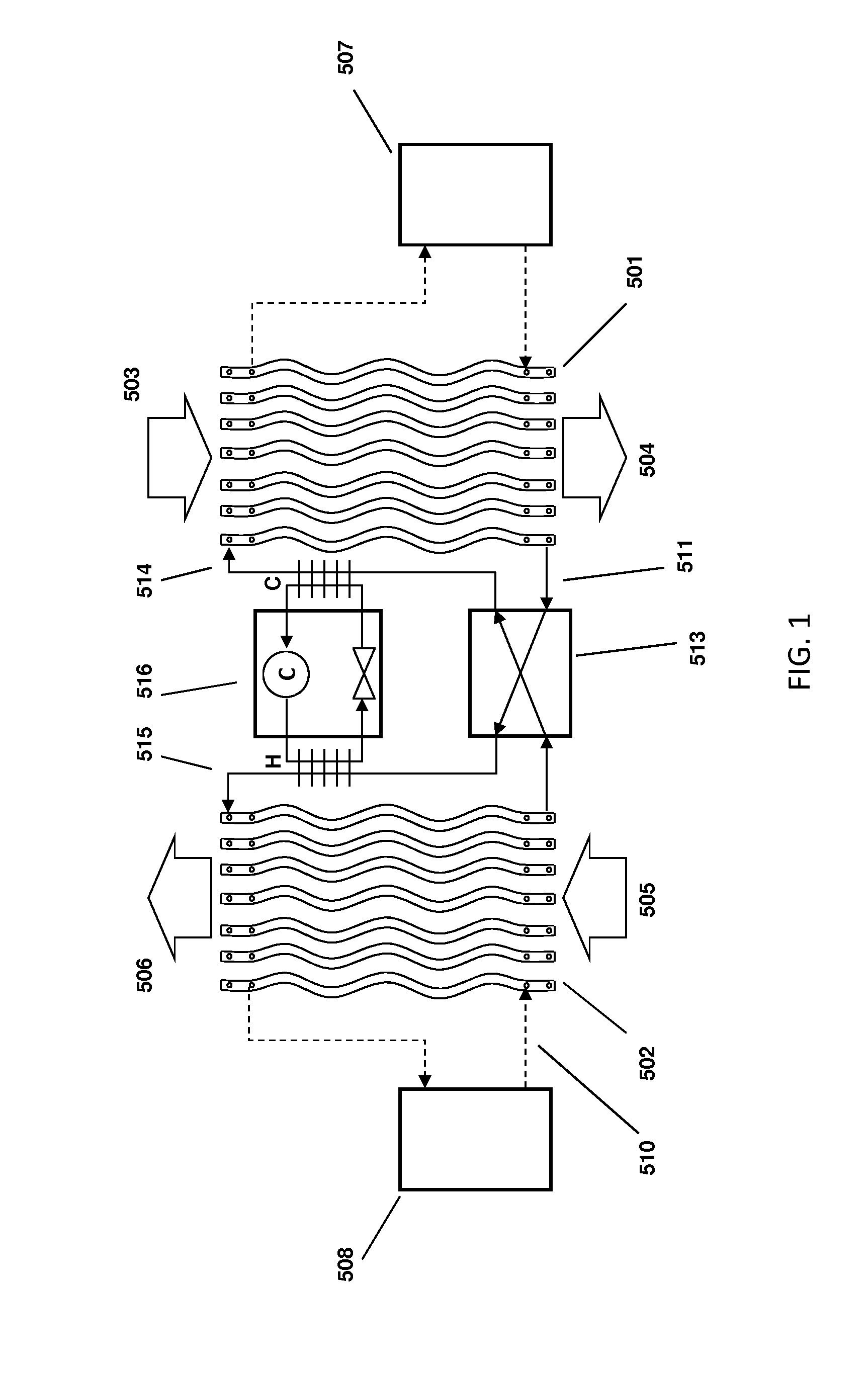
The within invention improves on the indirect evaporative cooling method and apparatus by making use of a working fluid that is pre-cooled with and without desiccants before it is passed through a Wet Channel where evaporative fluid is on the walls to take heat and store it in the working fluid as increased latent heat. The heat transfer across the membrane between the Dry Channel and the Wet Channel may have dry, solid desiccant or liquid desiccant and may have perforations, pores or capillary pathways. The evaporative fluid may be water, fuel, or any substance that has the capacity to take heat as latent heat. The Wet Channel or excess cooled fluid is in heat transfer contact with a Product Channel where Product Fluid is cooled without adding any humidity. An alternative embodiment for heat transfer between adjacent channels is with heat pipes.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
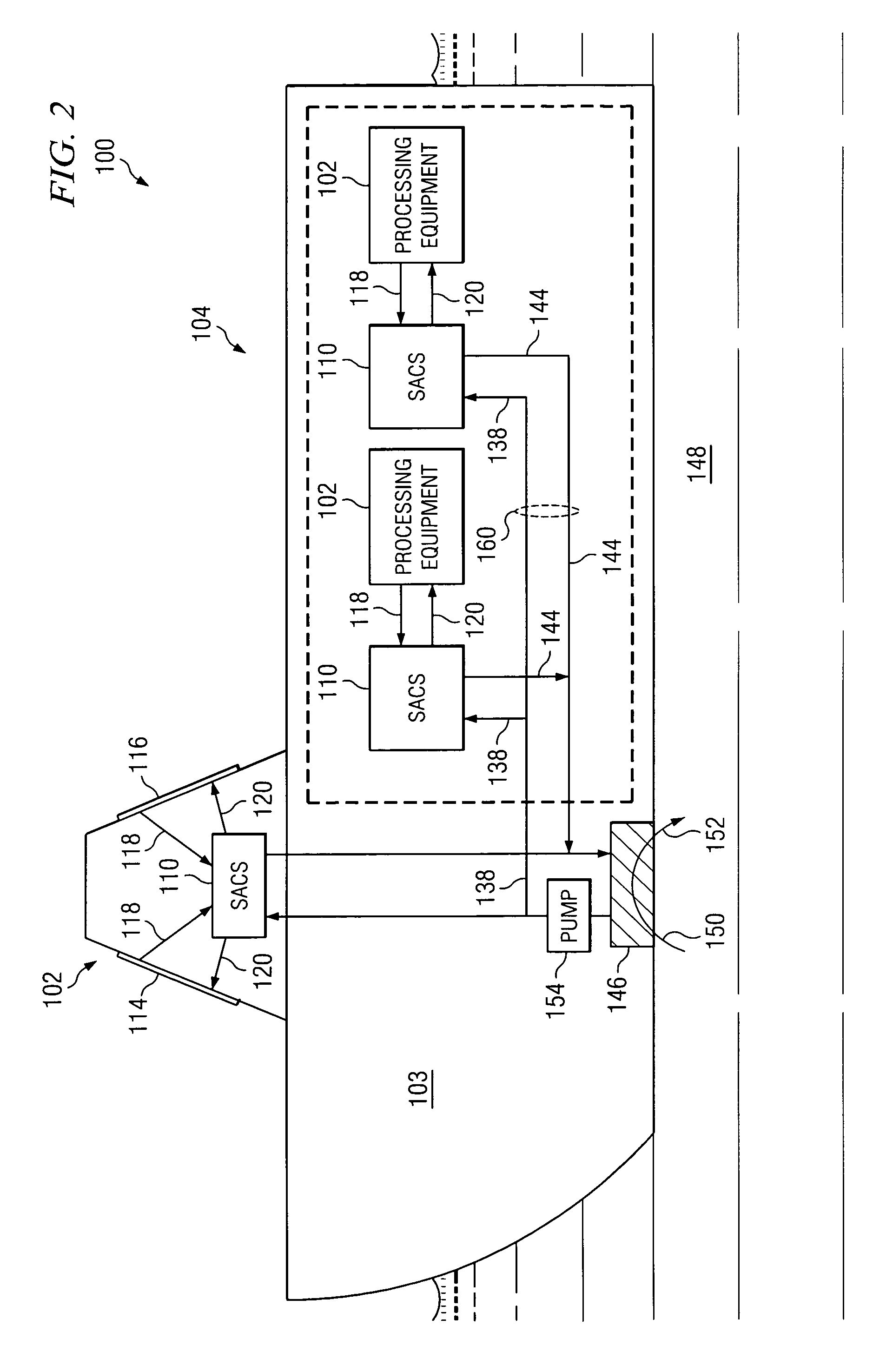
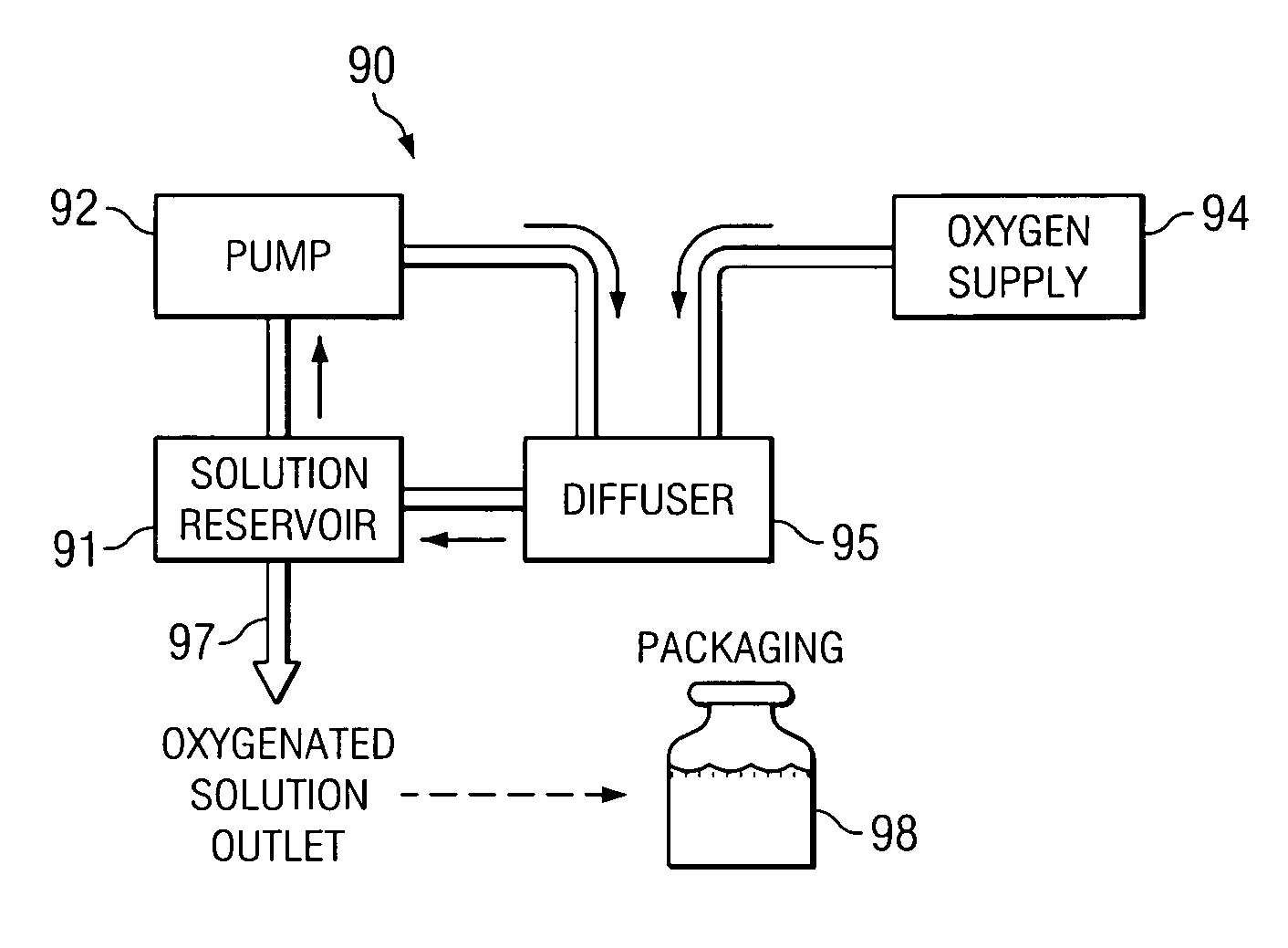
System and method for therapeutic application of dissolved oxygen
InactiveUS20050047270A1Rotary stirring mixersUsing liquid separation agentCavitationAqueous solution
A system and method for generating an oxygen enriched aqueous solution for therapeutic application includes a diffuser comprising a first diffusing member having a surface incorporating surface disturbances, and a second diffusing member positioned relative to the first diffusing member to form a channel through which an aqueous solution and oxygen gas may flow. A reservoir containing the aqueous solution is connected to a pump that draws the aqueous solution from the reservoir and inputs the aqueous solution into the diffuser. The aqueous solution is moved through the channel relative to the surface disturbances to create cavitation in the aqueous solution to diffuse the oxygen gas into the aqueous solution to produce an oxygen enriched aqueous solution.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Hydronic rooftop cooling systems
InactiveUS20050056042A1Improve RTU efficiencyEnhanced evaporative cooling effectEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsAir filterEngineering
A roof top cooling unit has an evaporative cooling section that includes at least one evaporative module that pre-cools ventilation air and water; a condenser; a water reservoir and pump that captures and re-circulates water within the evaporative modules; a fan that exhausts air from the building and the evaporative modules and systems that refill and drain the water reservoir. The cooling unit also has a refrigerant section that includes a compressor, an expansion device, evaporator and condenser heat exchangers, and connecting refrigerant piping. Supply air components include a blower, an air filter, a cooling and / or heating coil to condition air for supply to the building, and optional dampers that, in designs that supply less than 100% outdoor air to the building, control the mixture of return and ventilation air.
Owner:DAVIS ENERGY GROUP
Method of evaporative cooling of a fluid and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6854278B2Reduce the temperatureLess pressure dropMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsDesiccantMechanical engineering
The operating efficiency of indirect evaporative cooling processes and indirect evaporative cooling apparatus employing a dry side channel and a wet side channel separated by a heat exchange plate are improved by placement of holes in the heat exchange plate. Further improvements are obtained when the flow direction in the wet side channel is cross-current to the flow direction in the dry side channel. Placement of desiccant materials in the dry side channel also serve to improve the operating efficiencies of these processes and apparatus.
Owner:IDALEX TECH INC
Multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system
InactiveUS20070101746A1Improve efficiencyFree-cooling systemsEfficient regulation technologiesEngineeringRefrigeration
A multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system is described as having a direct evaporative cooling subsystem and an indirect evaporative cooling subsystem having one of a horizontal and a vertical set of heat exchanger channels. The multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system with a horizontal set of heat exchanger channels has a portion of the horizontal heat exchanger channels partially extended into a next stage of the multi-stage system. The multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system with the vertical set of heat exchanger channels includes a first set of vertical set of heat exchanger channels spanning a substantial vertical height of the stage of the hybrid evaporative cooling system, and a second set spanning approximately half the height of the stage. The multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system further includes a refrigeration system for lowering the temperature of the indirect evaporative cooling subsystem air without affecting its pressure flow.
Owner:S&T MFG CO
Direct drive fan system with variable process control
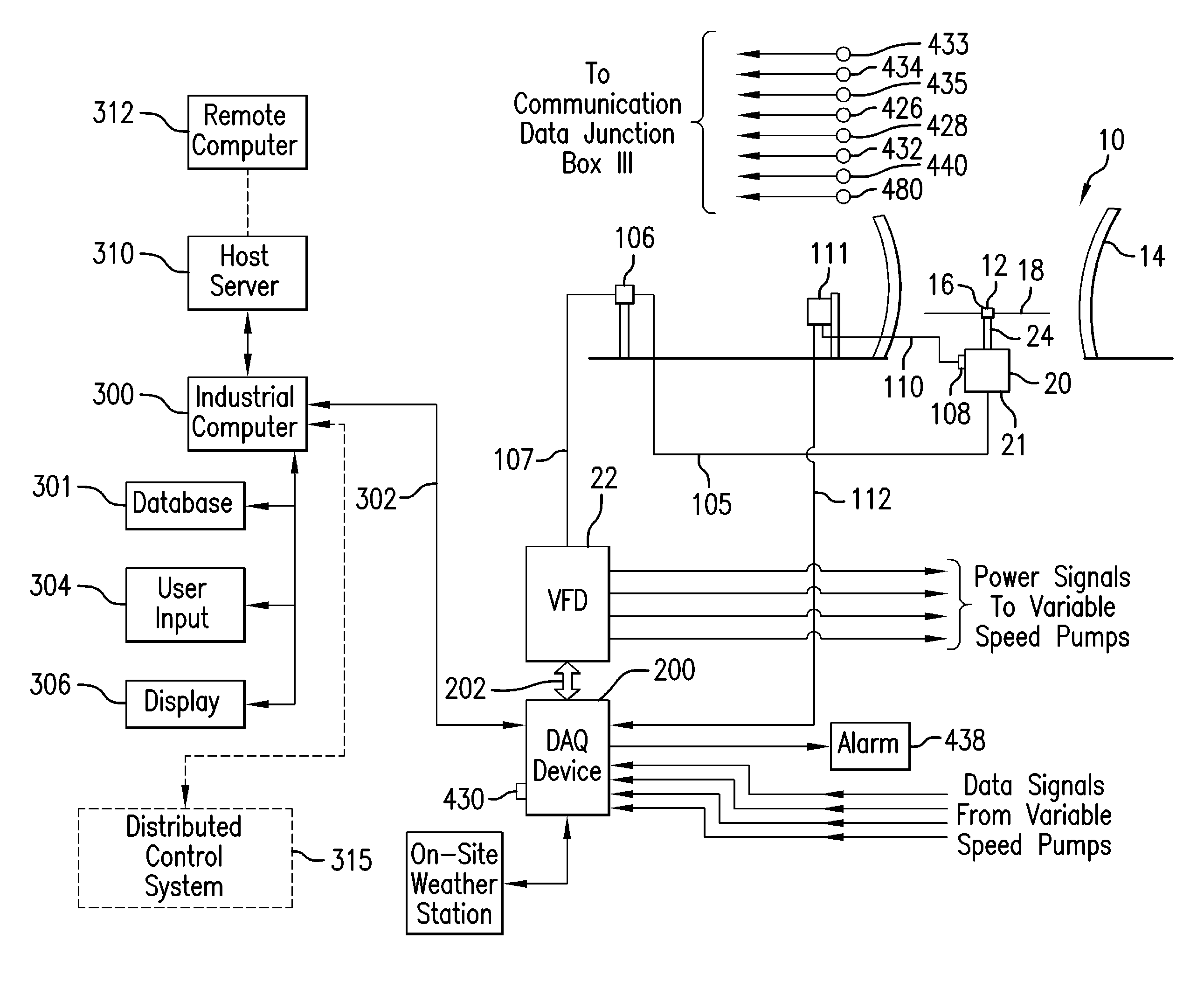
ActiveUS20140244051A1System smoothReduce vibrationTransportation and packagingEngine fuctionsCooling towerHigh torque
The present invention is directed to a direct-drive fan system and a variable process control system for efficiently managing the operation of fans in a cooling system such a as wet-cooling tower or air-cooled heat exchanger (ACHE), HVAC systems, mechanical towers or chiller systems. The present invention is based on the integration of key features and characteristics such as tower thermal performance, fan speed and airflow, motor torque, fan pitch, fan speed, fan aerodynamic properties, and pump flow. The variable process control system processes feedback signals from multiple locations in order control a high torque, variable speed, permanent magnet motor to drive the fan. Such feedback signals represent certain operating conditions including motor temperature, basin temperature, vibrations, and pump flow rates. Other data processed by the variable process control system in order to control the motor include turbine back pressure set-point, condenser temperature set-point and plant part-load setting. The variable process control system processes this data and the aforesaid feedback signals to optimize the operation of the cooling system in order to prevent disruption of the industrial process and prevent equipment (turbine) failure or trip. The variable process control system alerts the operators for the need to conduct maintenance actions to remedy deficient operating conditions such as condenser fouling. The variable process control system increases cooling for cracking crude and also adjusts the motor RPM, and hence the fan RPM, accordingly during plant part-load conditions in order to save energy.
Owner:PRIME DATUM
Electronic device cooling system
ActiveUS8223495B1Reduce dependenceLow costSolar heating energyDomestic cooling apparatusWaste treatmentOperations management
Cooling systems for providing cooled air to electronic devices are described. The systems can include large storage tanks or waste treatment systems to improve the efficiency of the plant and reduce impact on the environment.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Low profile evaporative cooler housing
InactiveUS20050000241A1Domestic cooling apparatusHeating and ventilation casings/coversEvaporative coolerLouver
A low profile evaporative cooler housing for attachment to a building includes a front panel, and an opposing rear panel that may have an extension that extends into a wall of the building. A first and second louver may extend between the front and rear panels.
Owner:CHAMPION COOLER CORP +2
Systems and methods for conditioning air and transferring heat and mass between airflows
An air conditioning system includes a first chamber having a plurality of first sectors, a second chamber having a plurality of second sectors, a first airflow device forming a first airflow through the first chamber, a second airflow device forming a second airflow through the second chamber, and a heat and mass transfer substance flowing in a plurality of the first and second sectors, the substance interacting with the first and second airflows through the first and second chambers. Thermal inducement apparatus thermally interacts with the substance establishing a thermal gradient between the first sectors and a thermal gradient between the second sectors providing a heat and mass energy gradient for the first airflow through the first sectors and a reversed heat and mass energy gradient for the second airflow through the second sectors. Plumbing is provided, which moves the substance throughout the system.
Owner:ALBERS WALTER F +1
Systems and Methods of Thermal Transfer and/or Storage
ActiveUS20110162829A1System design difficultSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringInput device
Systems, methods, and computer-implemented embodiments consistent with the inventions herein are directed to storing and / or transferring heat. In one exemplary implementation, there is provided a system for transferring / storing heat comprised of a heat exchange / storage apparatus including a chamber, and a heat input device adapted to heat / provide a vapor into the chamber. Other exemplary implementations may include one or more features consistent with a heat output device through which a working medium / fluid passes, a thermal storage medium located within the chamber, and / or a heat exchange system that delivers a heat exchange medium / fluid to the thermal storage medium.
Owner:BLUELAGOON TECH
Rapid fluid cooling and heating device and method
InactiveUS20020124576A1Increase surface areaGreat frictional contactFrozen sweetsContainer filling methodsIce creamElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method and device for rapidly changing at least one of the temperature and the state of a liquid in a container is provided. The container is rapidly rotated about its longitudinal axis. A source of a thin film of a medium having a different temperature than the liquid in the container is provided to thermally affect the container while rotating the container. The container is positioned at an angle to the horizontal of less than 45°, and the position of the container with respect to the thin film source is controlled by angling the axis of the container skewed from the axis of the rotating mechanism. The device can be used to cool liquids such as beverages, warm liquids such as infant formula, and / or make ice cream.
Owner:THE COOPER UNION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCI & ART
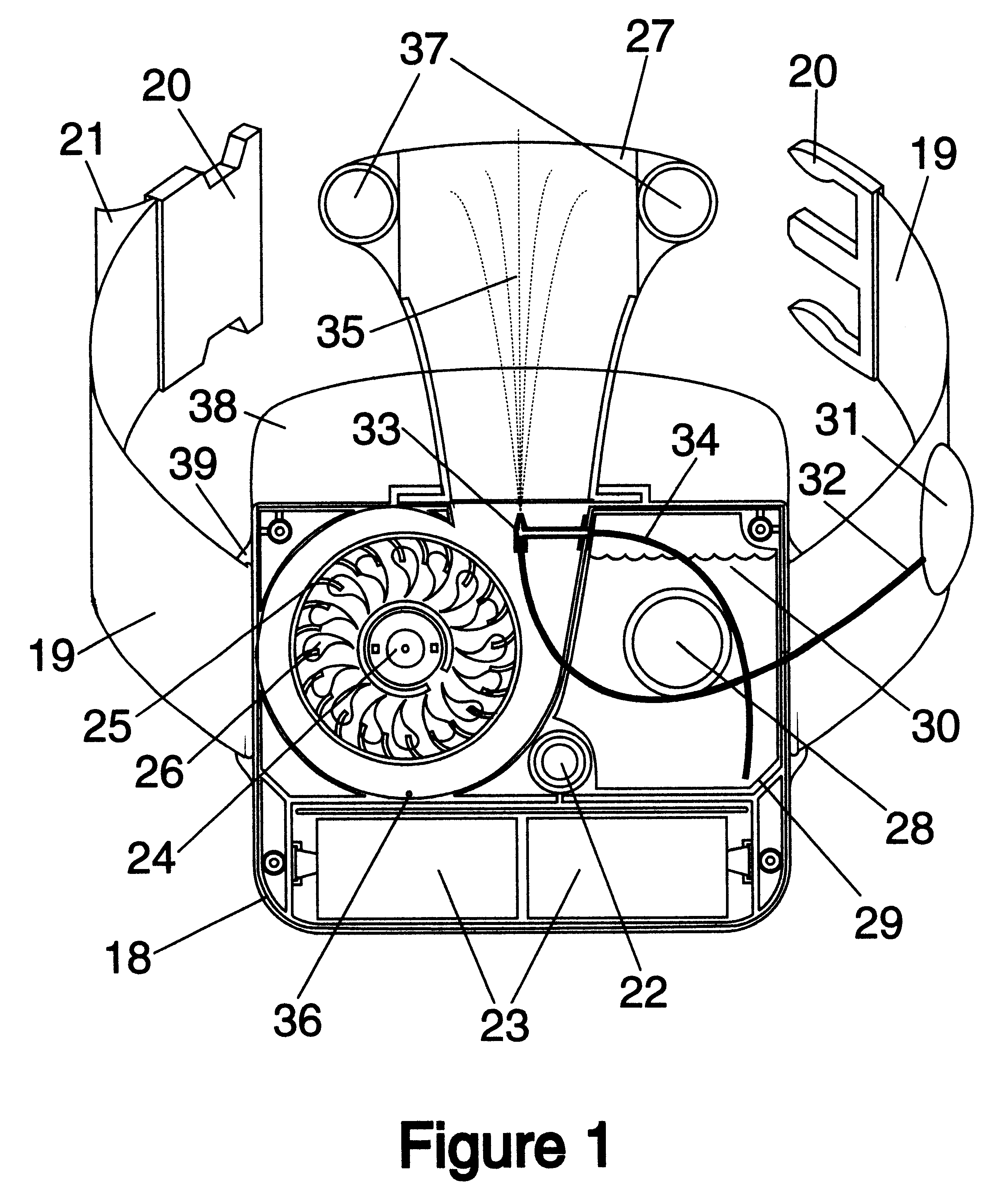
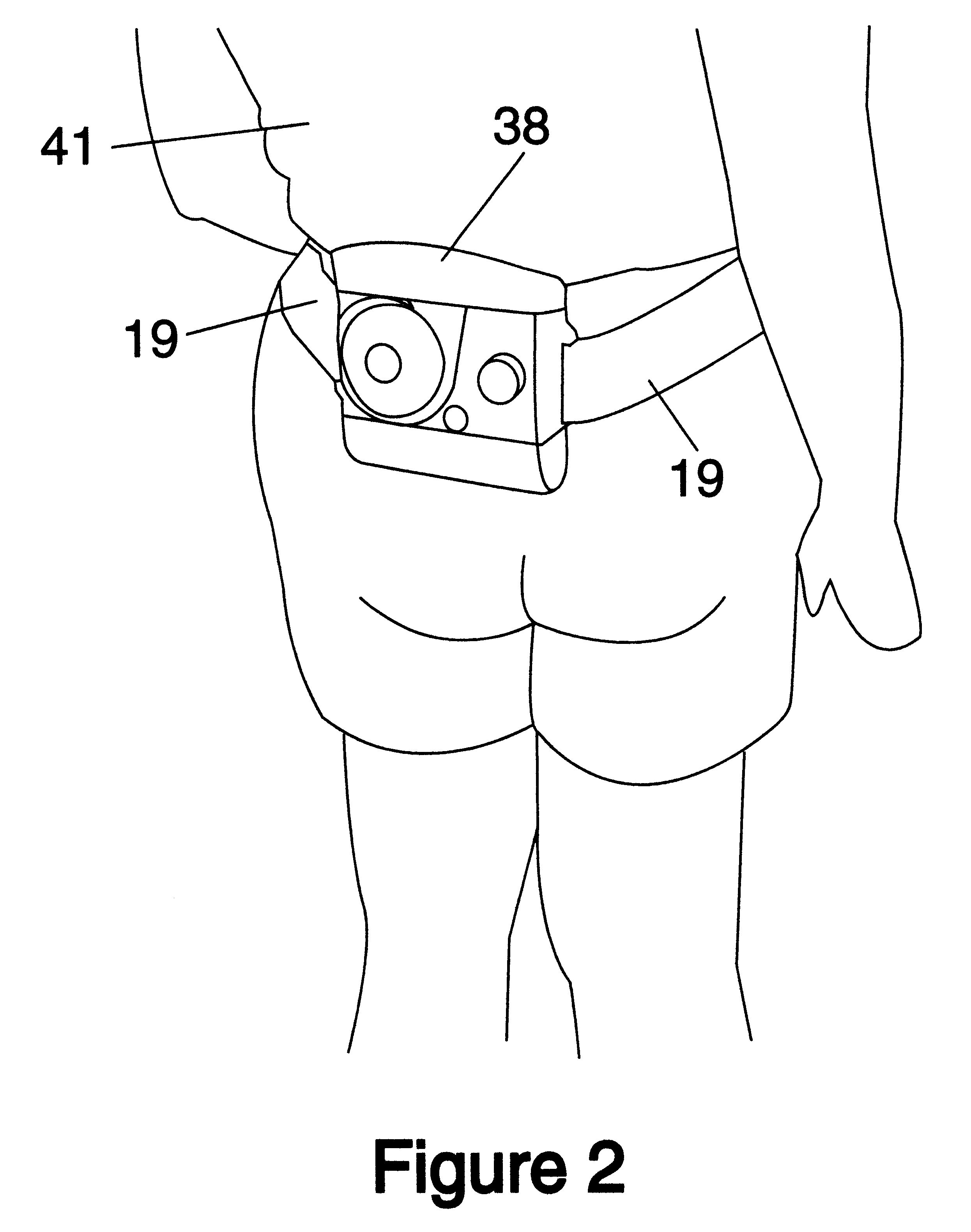
Waist-mounted evaporative personal cooler
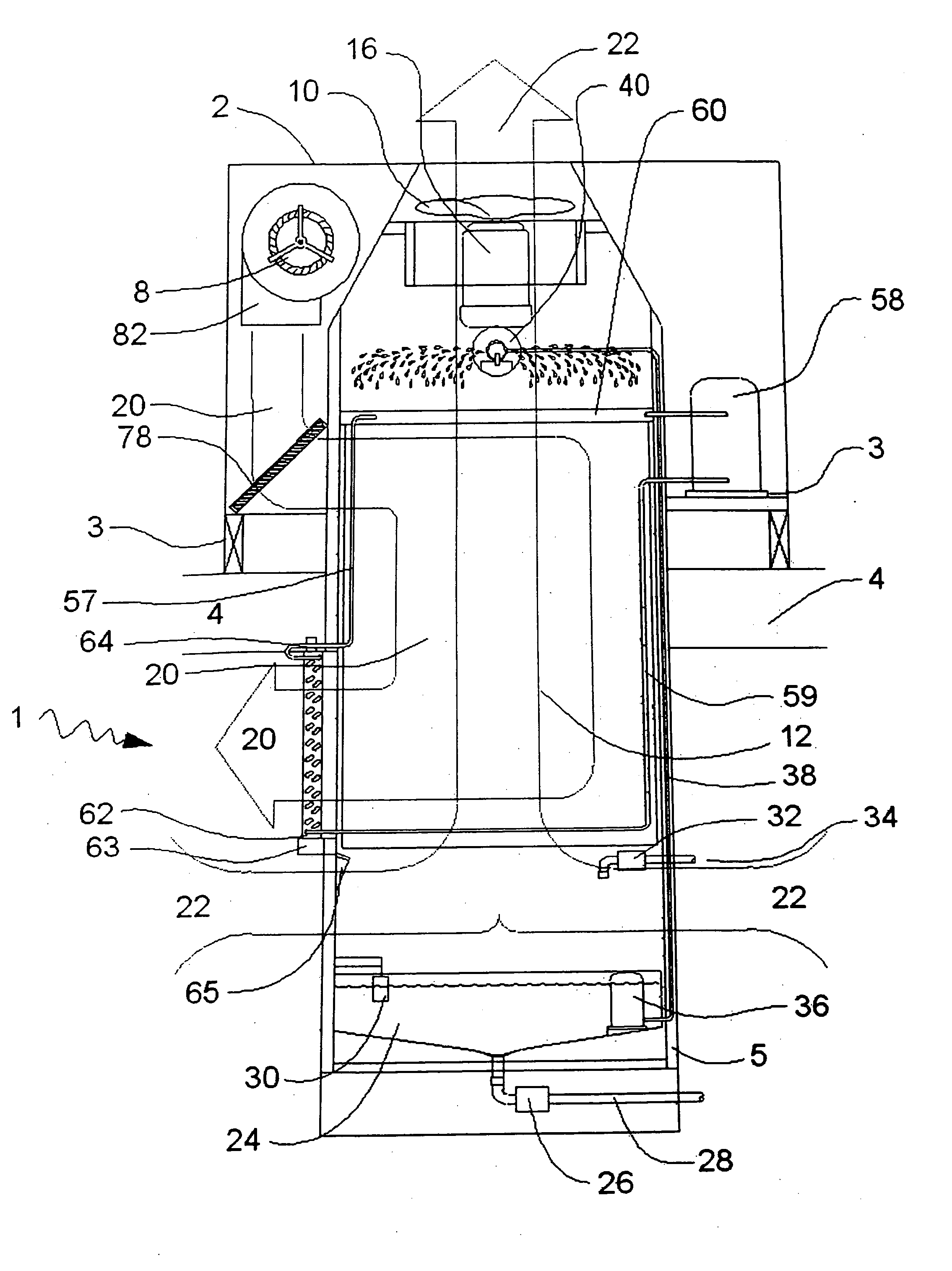
A waist-mounted evaporative personal cooling device designed to cool the back of a user, comprises a blower (25), a liquid reservoir (29), a means to deliver liquid from the reservoir a mist of droplets into blower-forced air (33) or directly onto the skin area to which the forced air will be directed (45), and a duct (27) to guide forced air under the user's shirt or blouse and directly onto or across the skin of the user's back. The device improves on prior art coolers by delivering a powerful evaporative cooling effect directly to a user's back, while being compact, comfortably wearable, and requiring the user to do little or nothing to get its benefit.
Owner:STRAUSS TED
Cooling system and method utilizing thermal capacitor unit(s) for enhanced thermal energy transfer efficiency
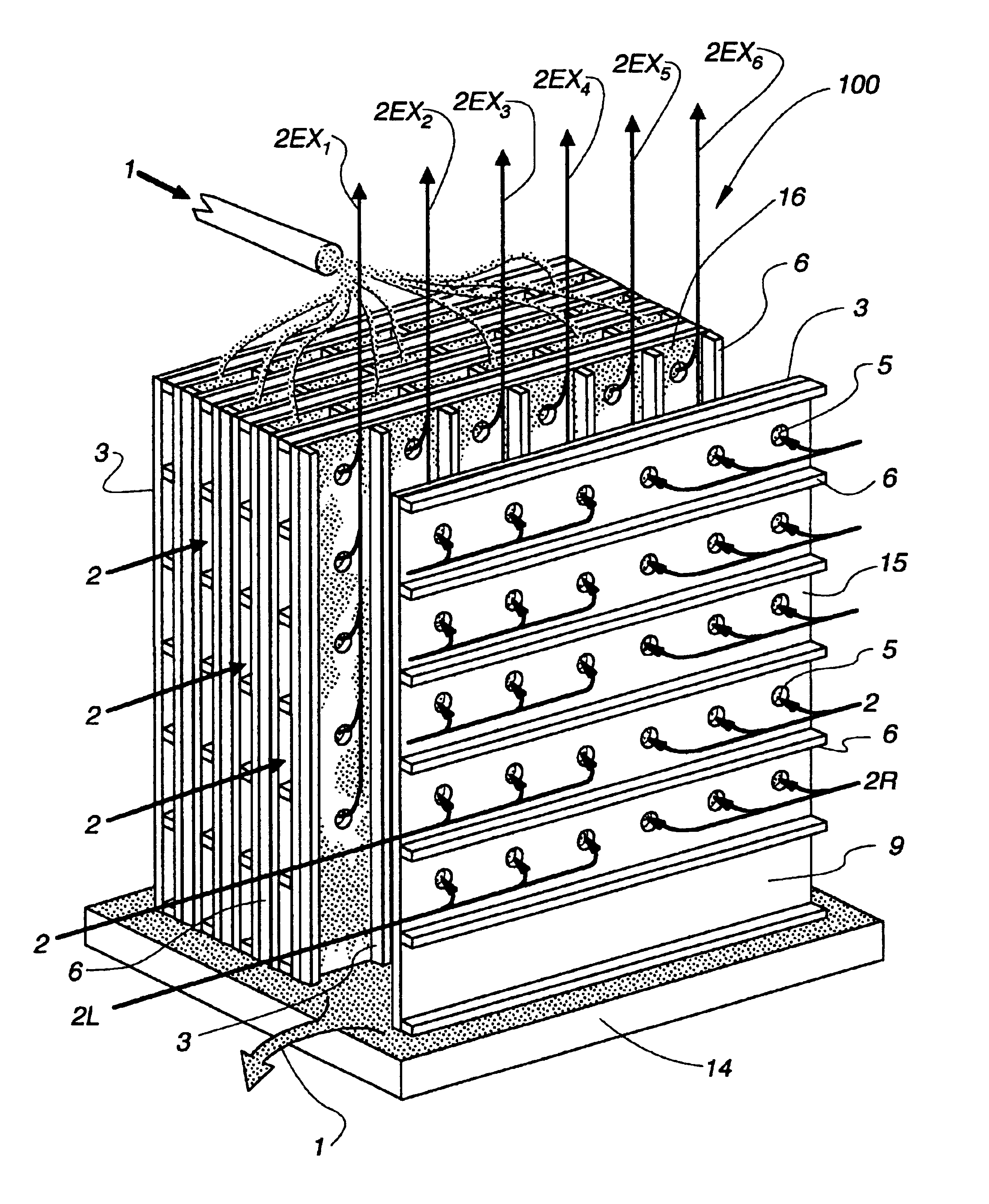
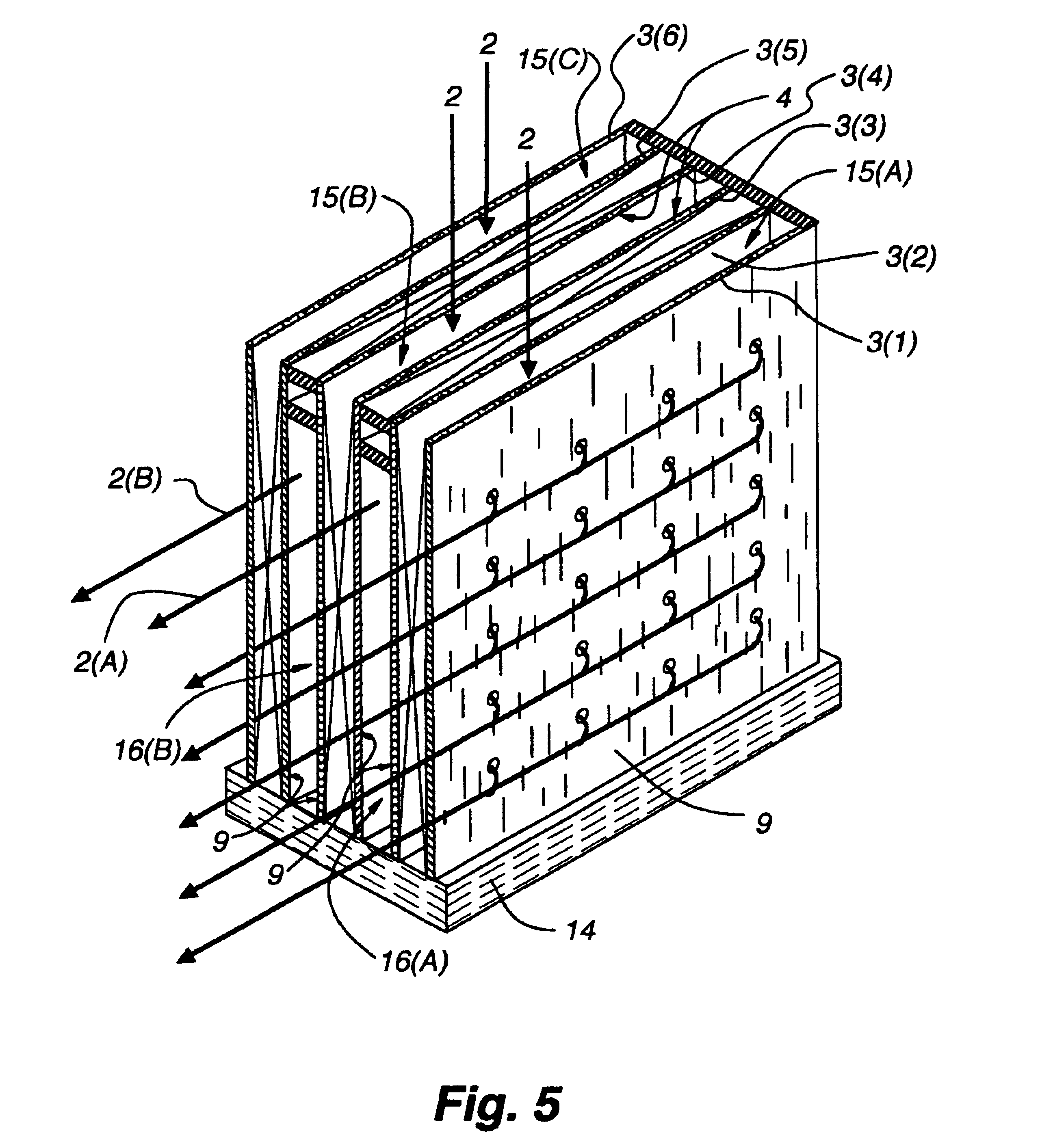
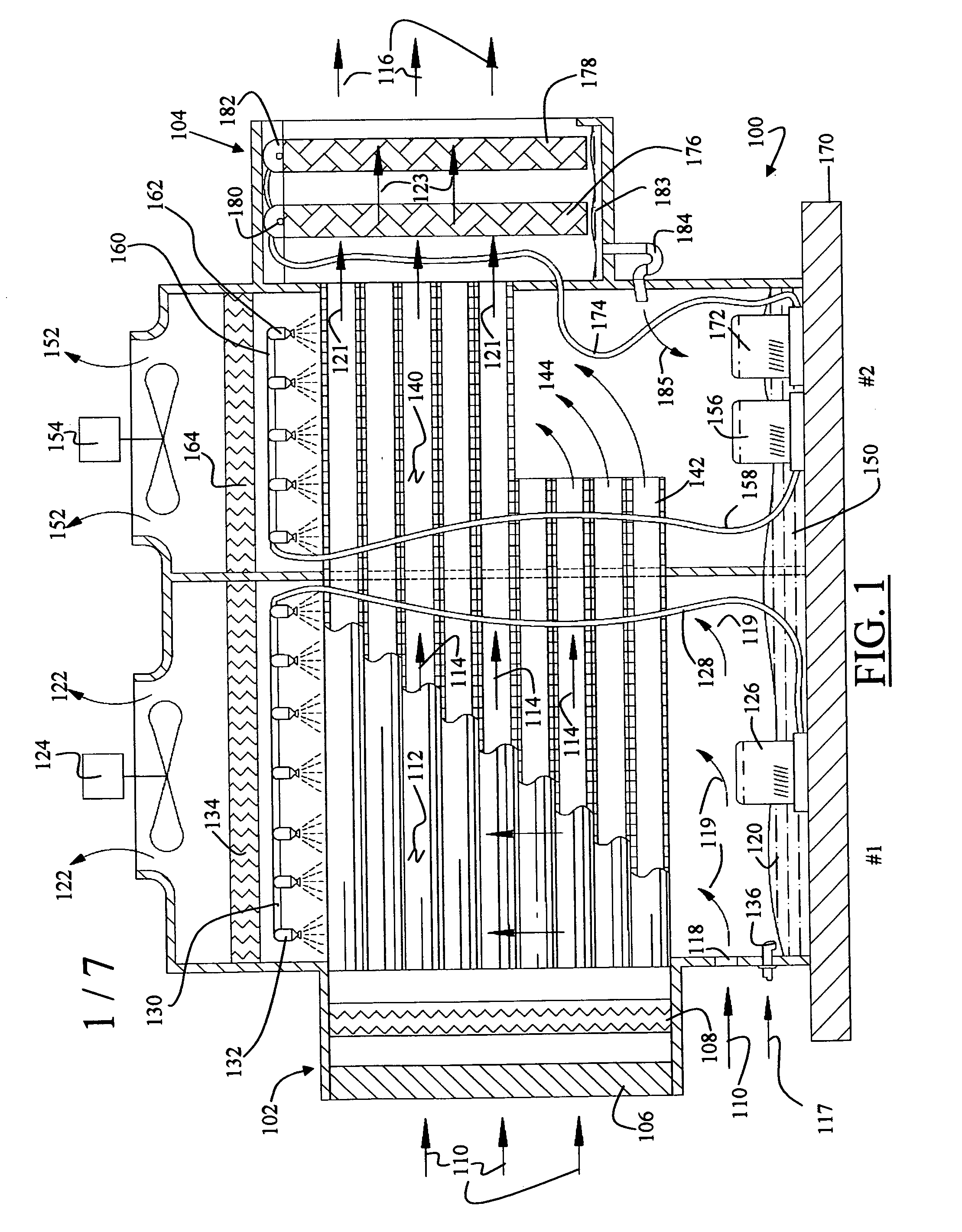
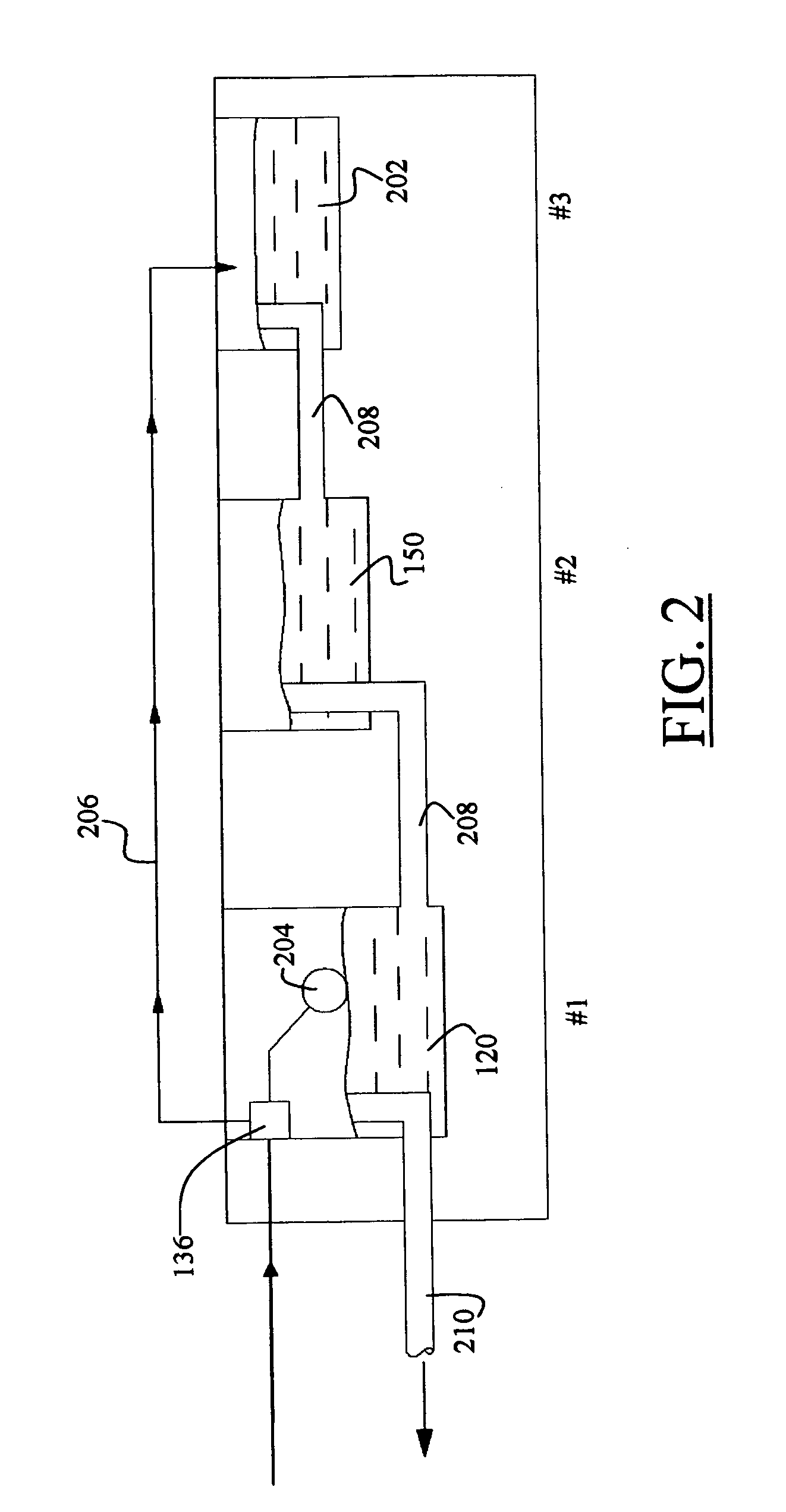
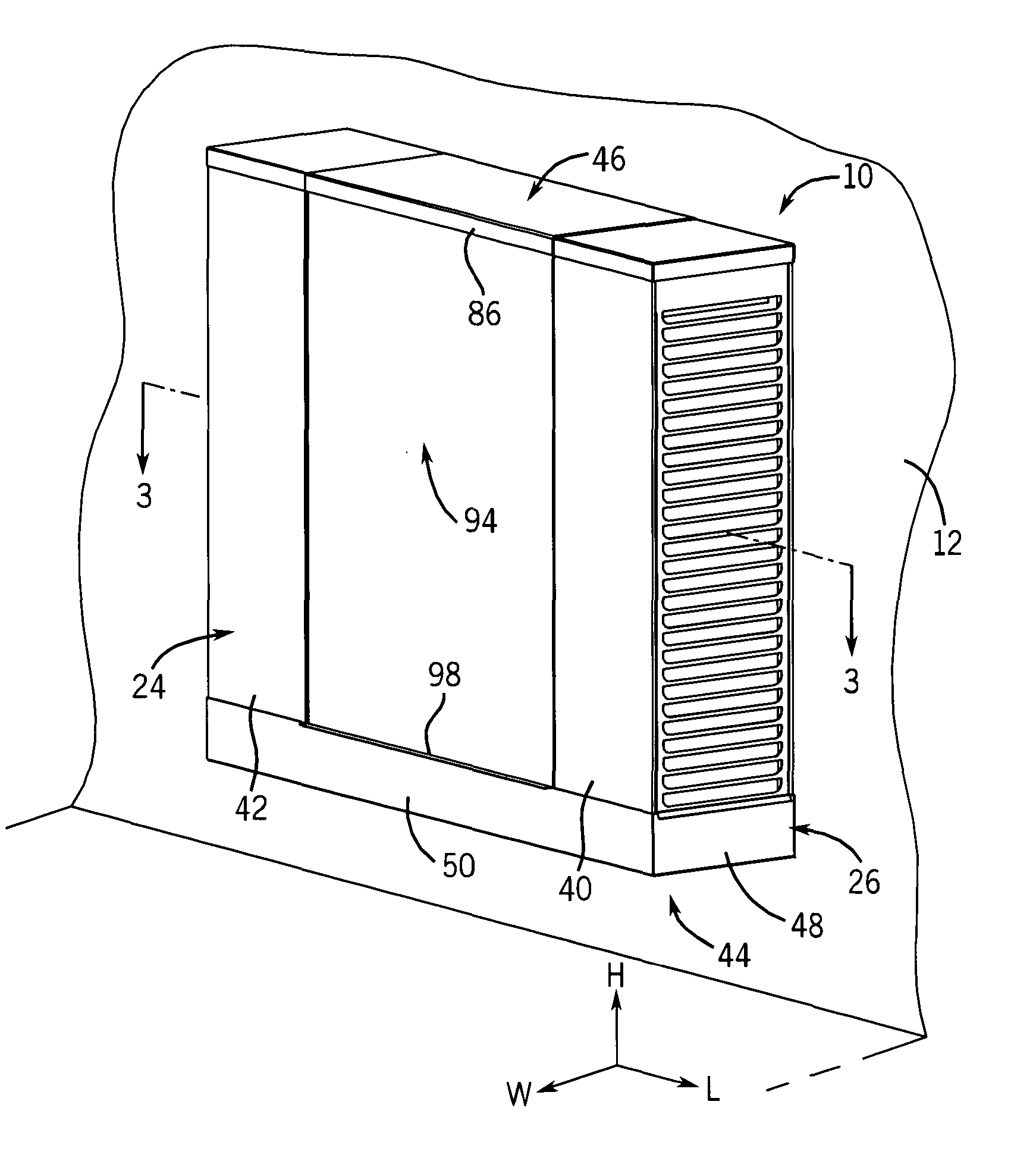
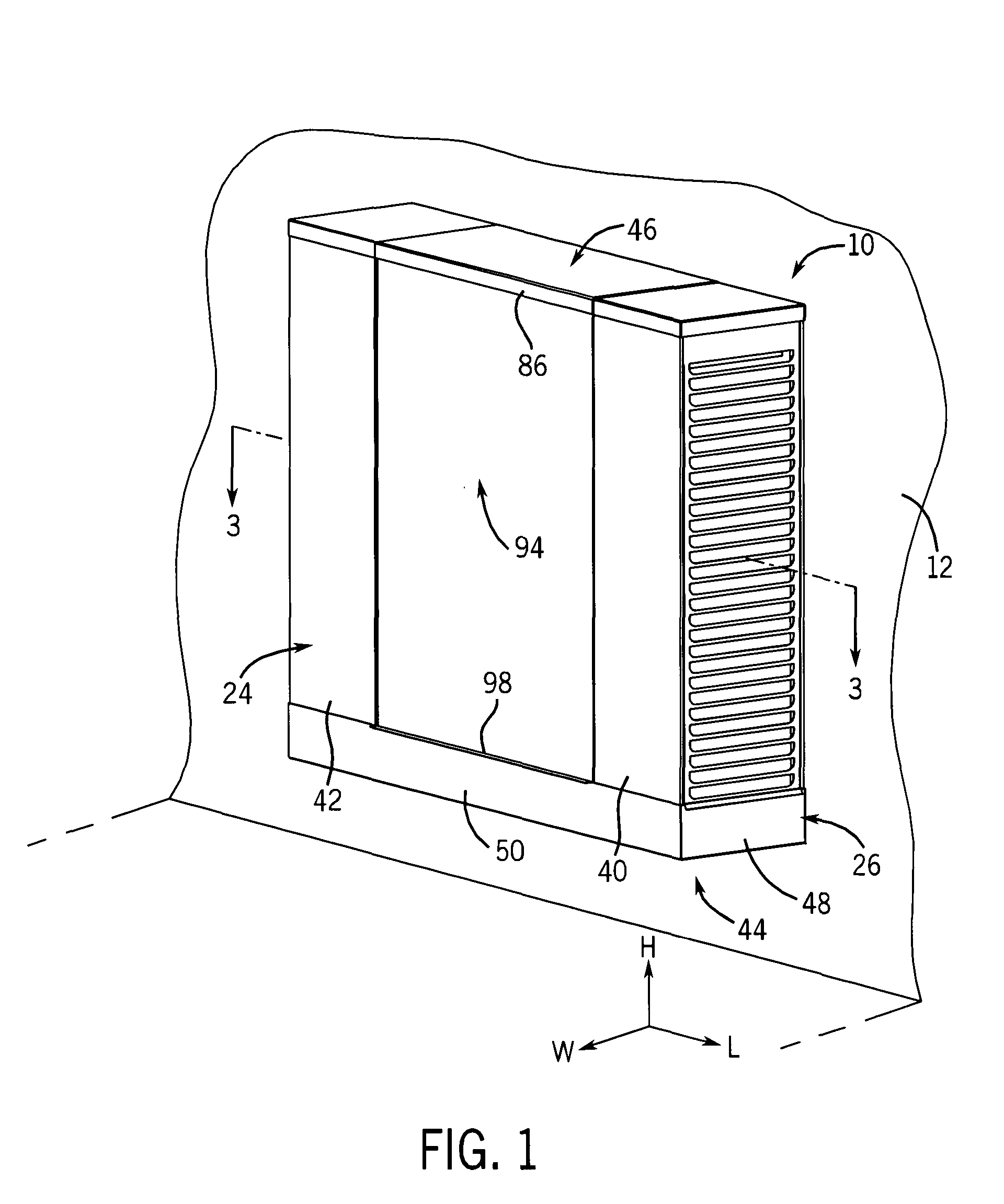
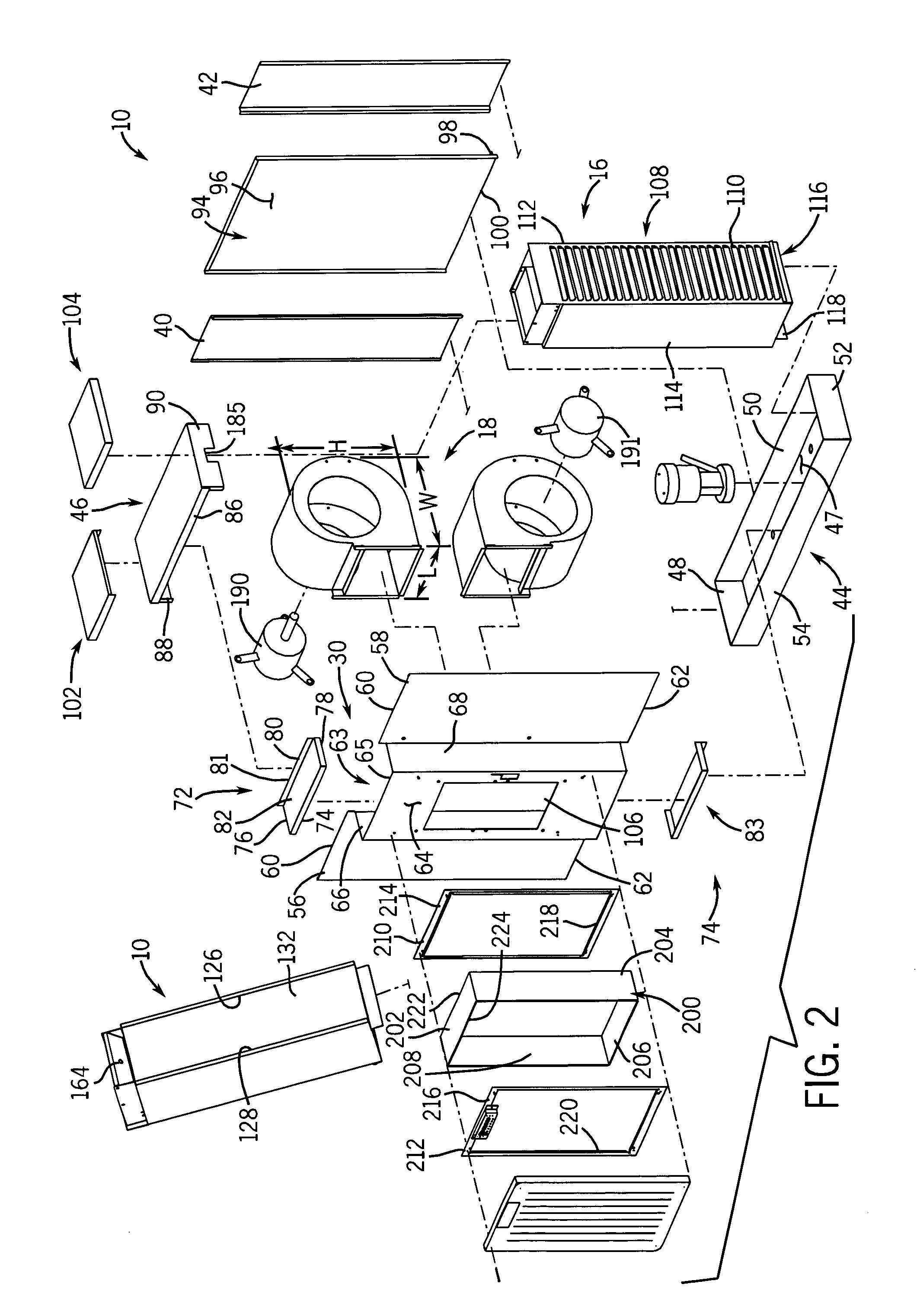
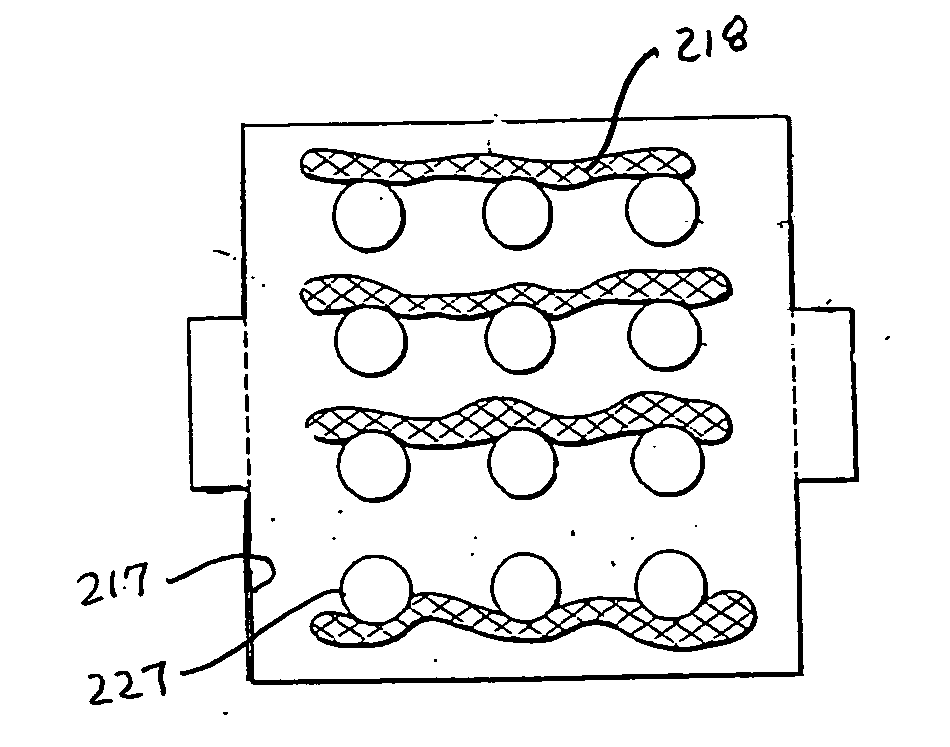
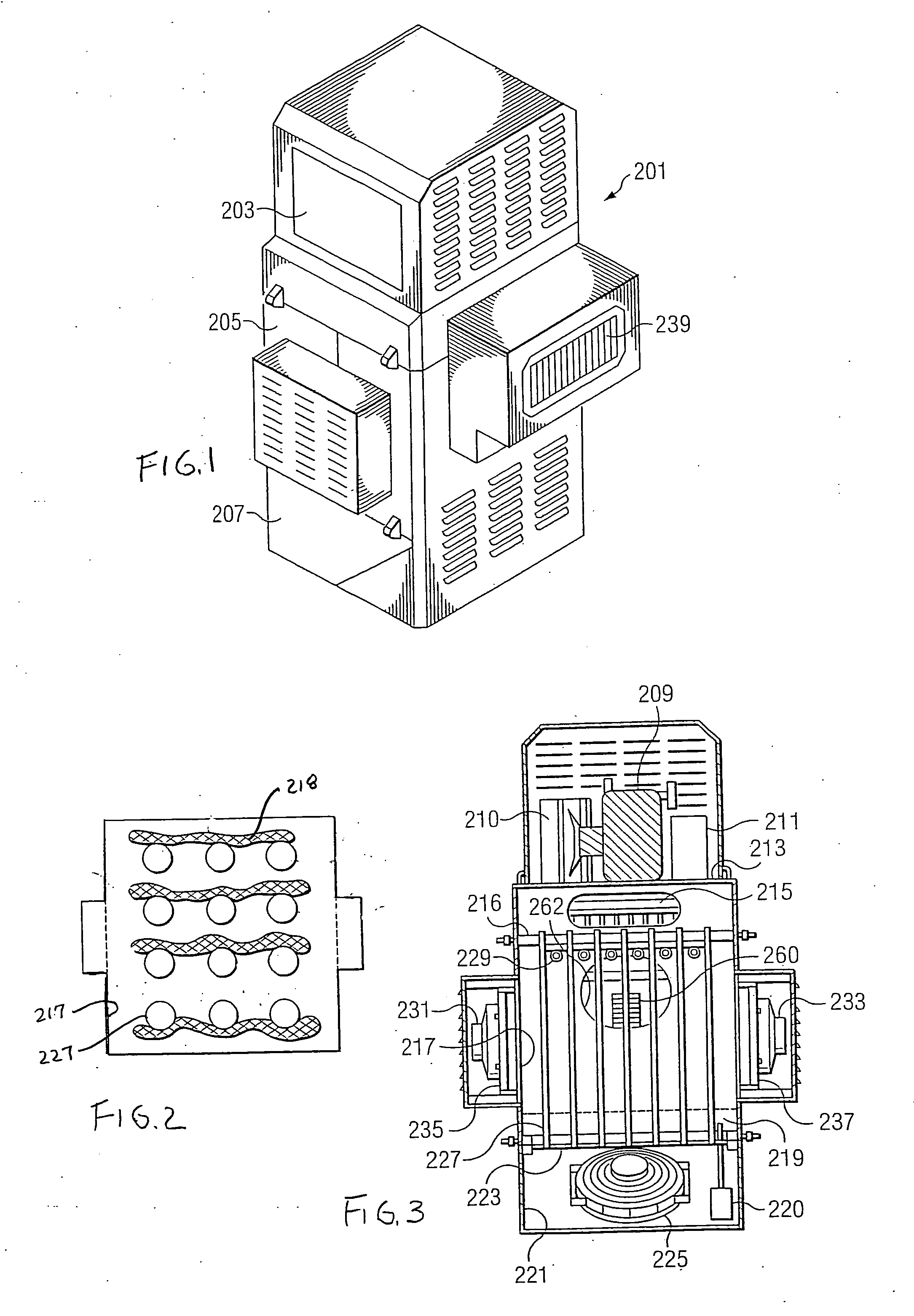
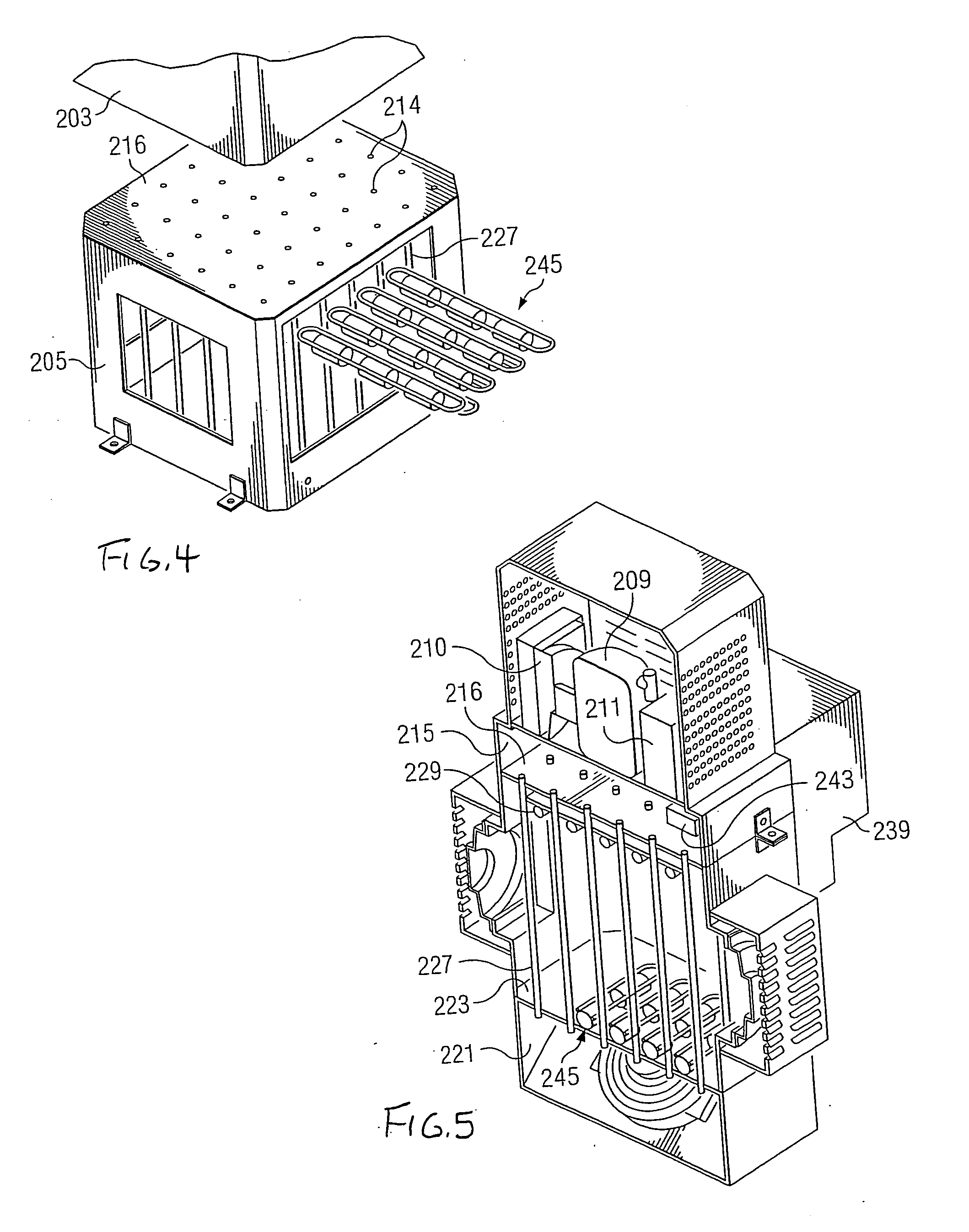
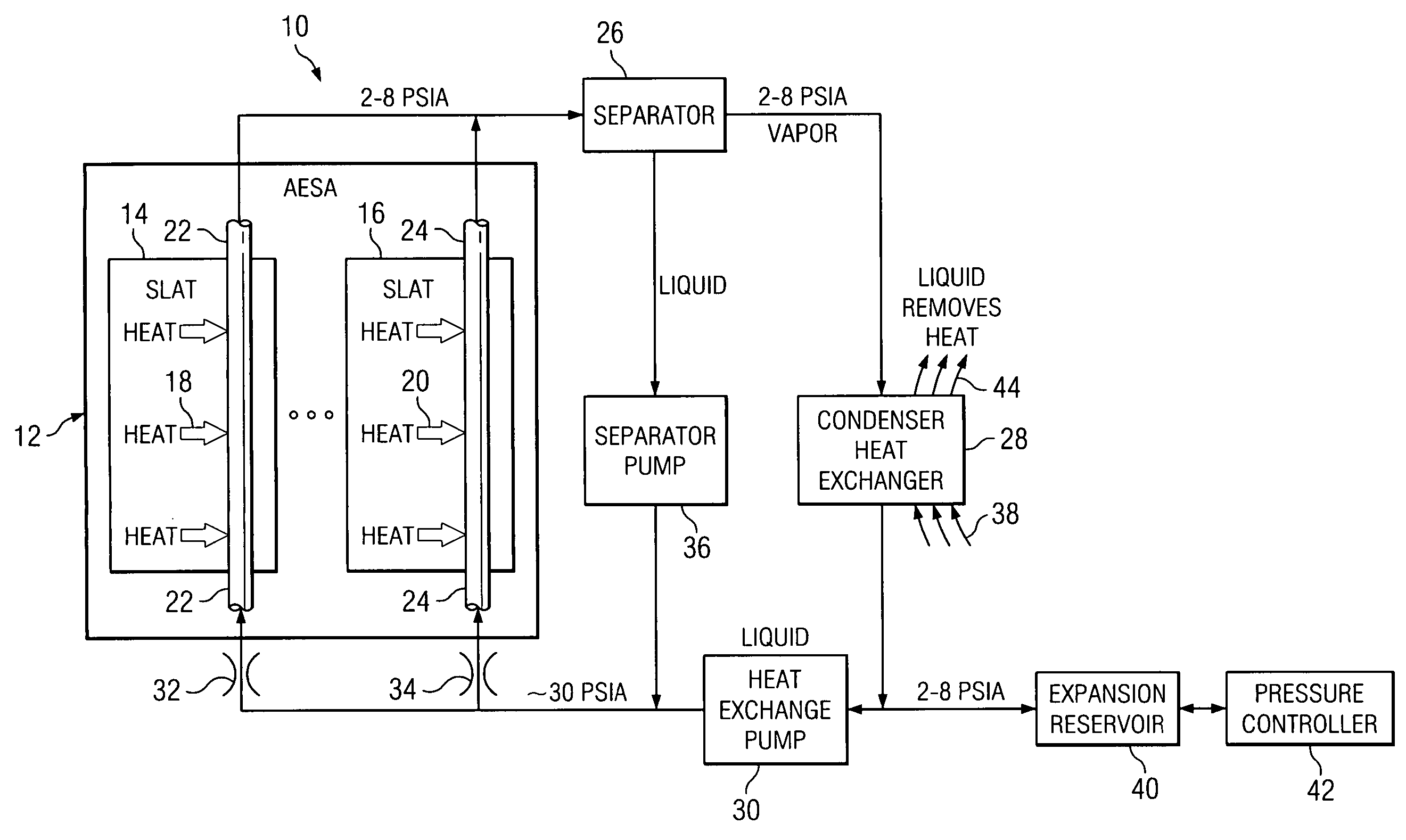
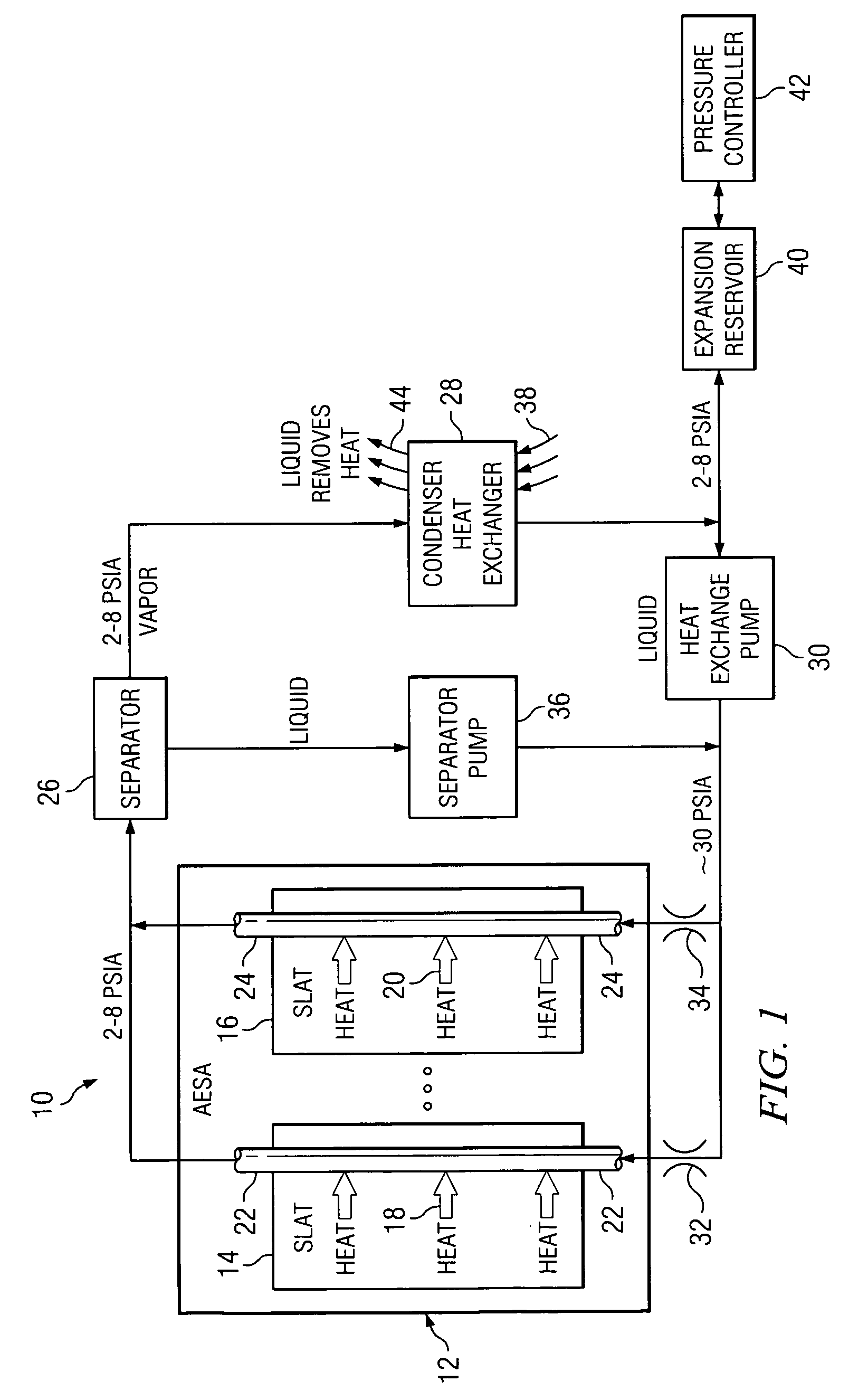
InactiveUS20080307806A1Facilitates extracting thermal energyEfficient thermal energy transferHeat storage plantsTrickle coolersThermal energyCooling tower
A cooling system and method are provided which include a facility cooling unit, a cooling tower, and one or more thermal capacitor units. The facility cooling unit, which includes a heat dissipation coolant loop, facilitates thermal energy extraction from a facility, such as a data center, for expelling of the energy to coolant within the heat dissipation coolant loop. The cooling tower is in fluid communication with the coolant loop, and includes a liquid-to-air heat exchanger for expelling thermal energy from coolant of the heat dissipation coolant loop to the surrounding environment. The thermal capacitor unit is in fluid communication with the heat dissipation coolant loop to facilitate efficient thermal energy transfer from coolant with in the coolant loop to the surrounding environment with variation in ambient temperature about the cooling tower.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cooling system
A system is disclosed that incorporates a generator for generating a liquid coolant. This invention provides a self-contained water (or similar liquid coolant) chilling system of suitable capacity to cool small to medium size structures, such as private residences and manufactured homes. The system utilizes an arrangement of heat-exchanging panels to pre-condition an ambient temperature air-stream, prior to passage through a pump-driven coolant spray. The system also provides several sub-systems for automatic coolant monitoring, chemical addition and periodic coolant replacement.
Owner:CONSOLI ART
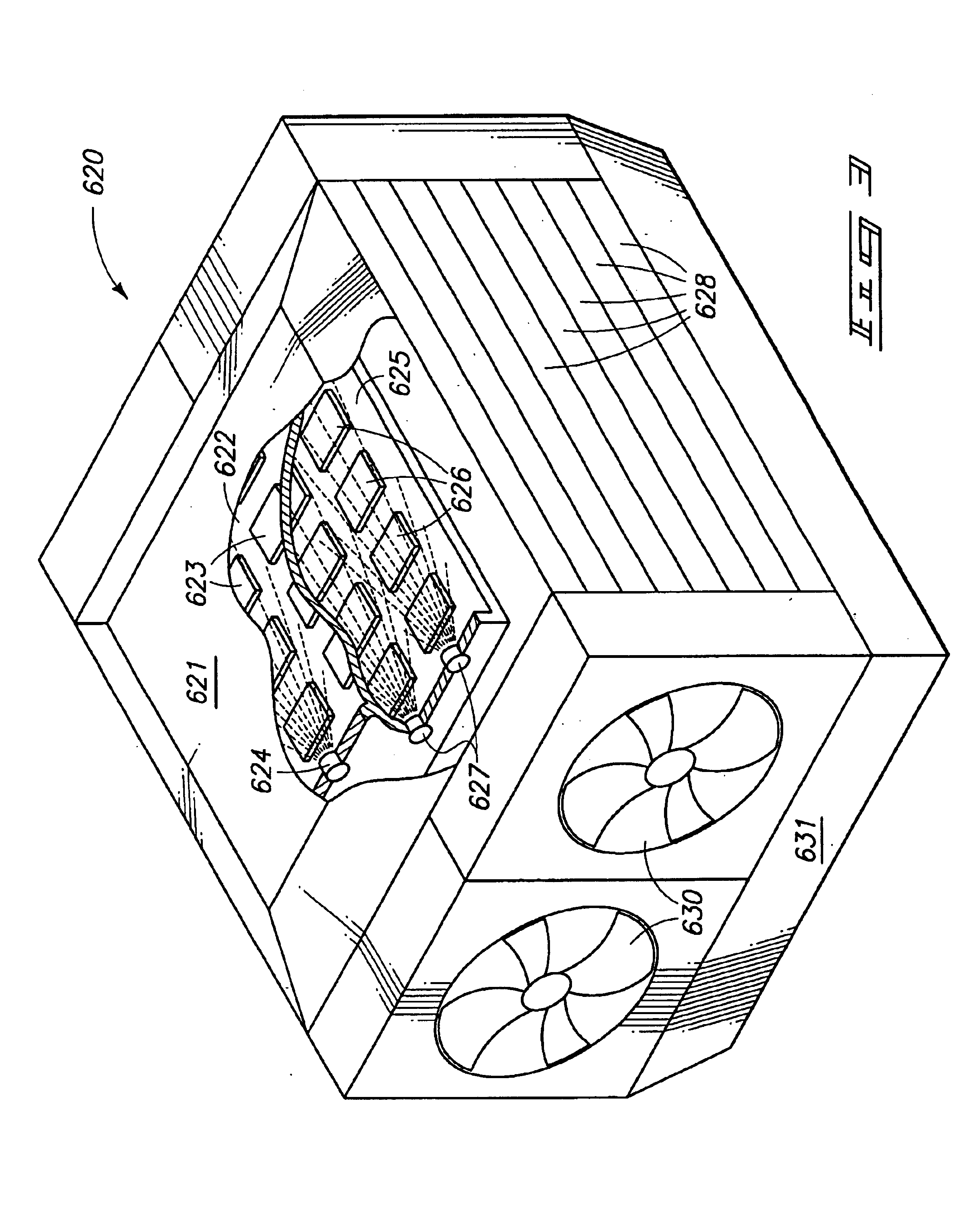
Cooling devices and systems
InactiveUS20060056994A1Reduce dust accumulationEasy to passSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringTurbine
Methods, systems, and devices are provided for cooling a heat source. One apparatus embodiment includes a housing, a fluid conduit, a pump within the housing and in communication with the fluid conduit for conveying fluid through the fluid conduit, and a turbine in communication with the fluid conduit to be driven by the fluid as it passes through the fluid conduit.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Integrated liquid cooling device with immersed electronic components
InactiveUS20060007656A1Increase surface areaImprove cooling effectDomestic cooling apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal energyEngineering
An integrated liquid cooling device for electronic components addresses the need for efficient cooling created by ever increasing power densities of electronic components. The integrated liquid cooling device has a housing enclosing the electronic component, cooling liquid contained in the housing, a motor immersed in the cooling liquid and mounted to the housing, an impeller driven by the motor, and cooling surfaces on the exterior of the housing. The motor driven impeller creates a turbulent flow in the cooling liquid and a high velocity liquid flow over the electronic component, which rapidly transfers heat from the electronic component and distributes it throughout the interior of the housing. The cooling surfaces on the exterior of the housing dissipate this heat, either by free or forced convection, into the surrounding environment. Alternately, the integrated liquid cooling device may distribute this heat energy over an equipment case by circulating cooling liquid through a baffled enclosure that provides high velocity cooling liquid flow near the heat generating electronic component. Additional cooling capacity can be gained with the described integrated liquid cooling device by selecting a cooling liquid whose boiling point is near the operating temperature of the electronic component.
Owner:SYMONS ROBERT S
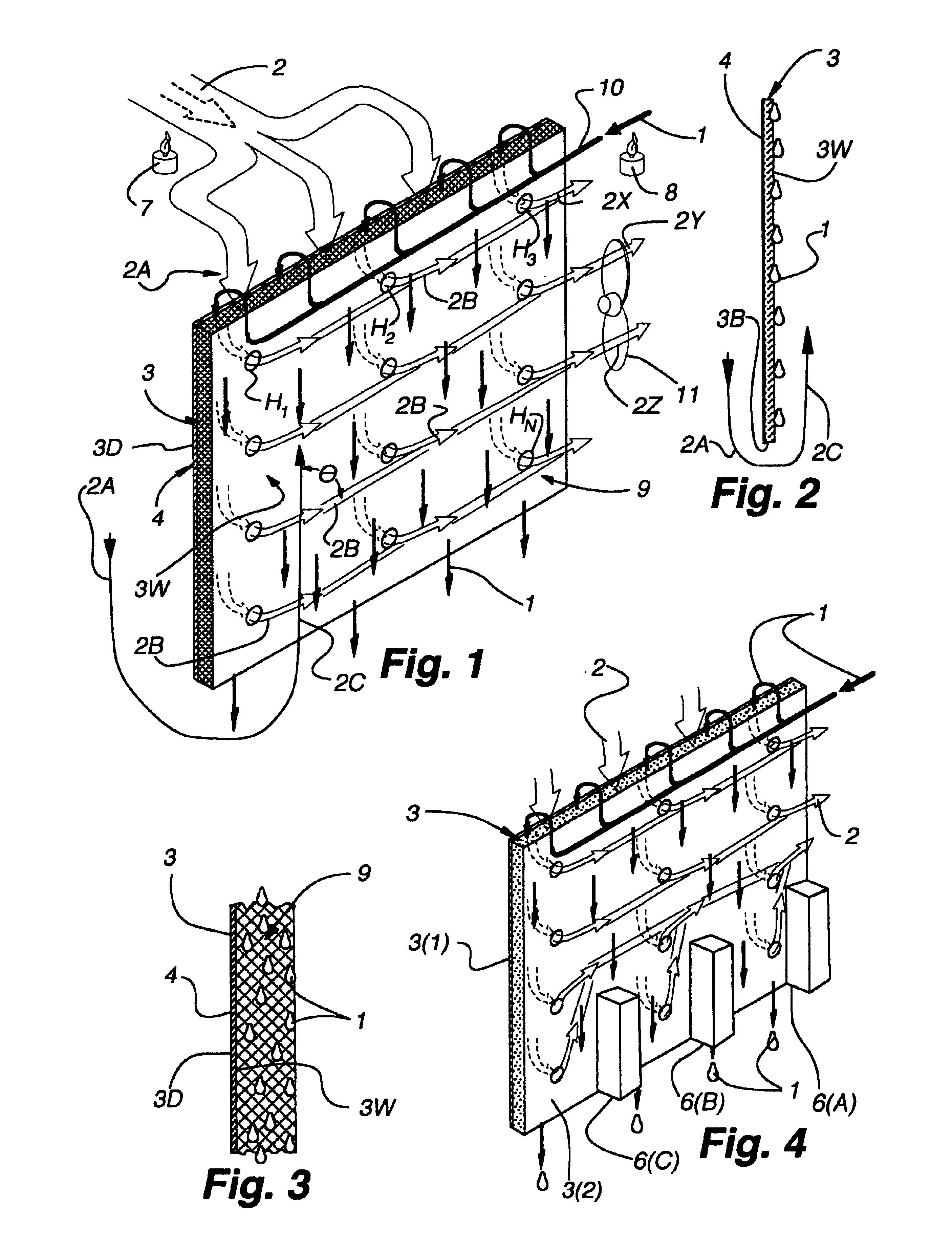
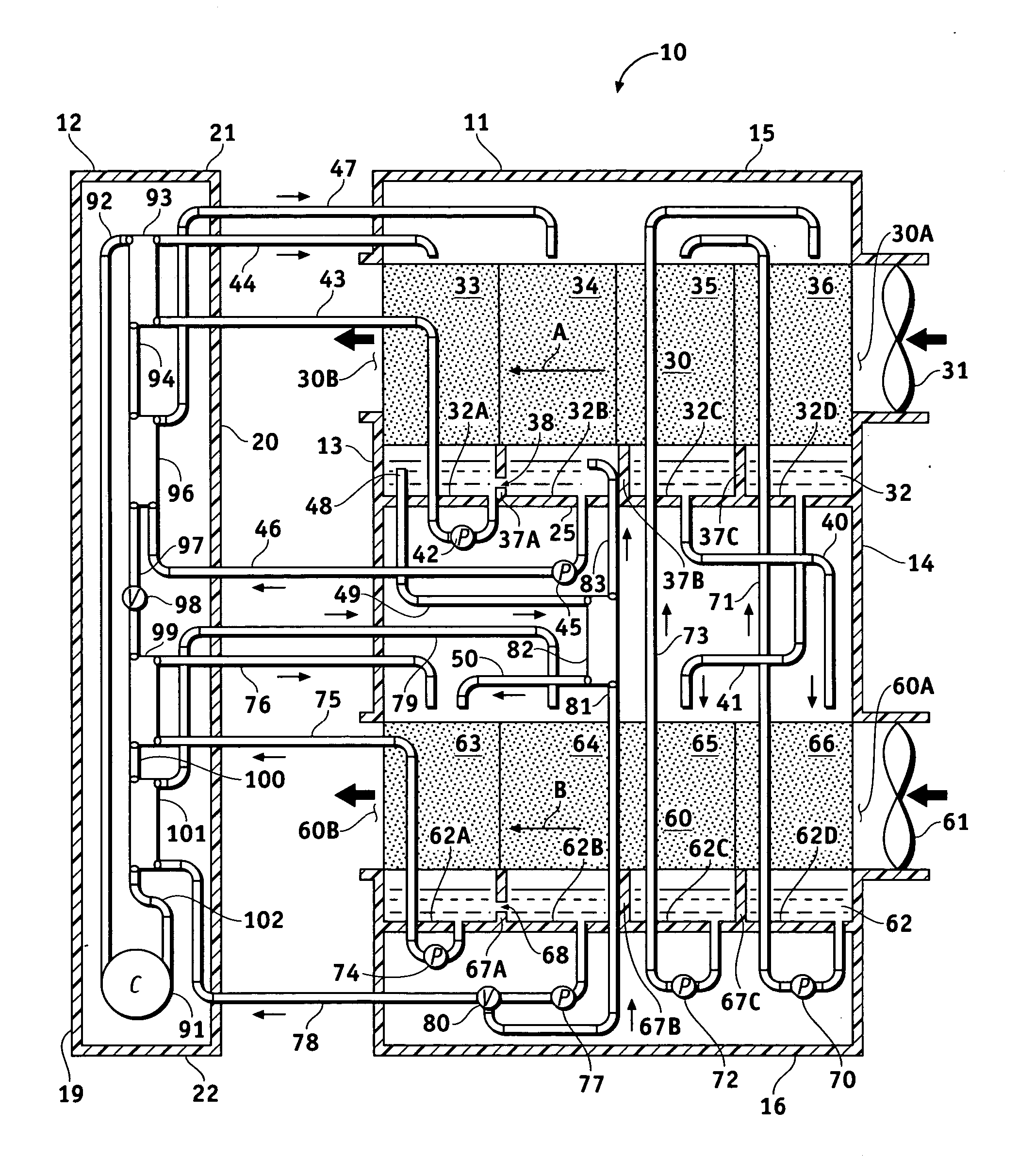
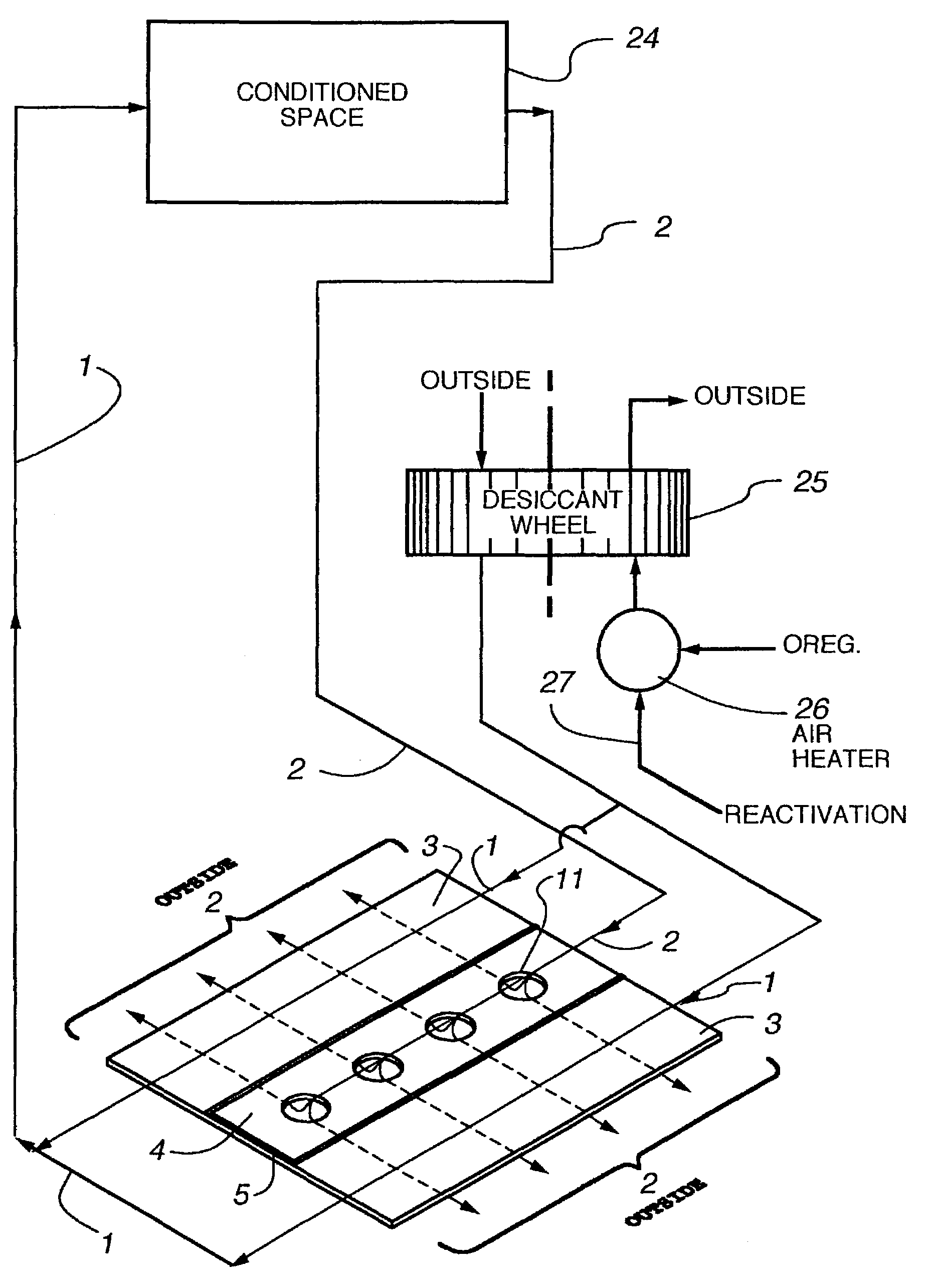
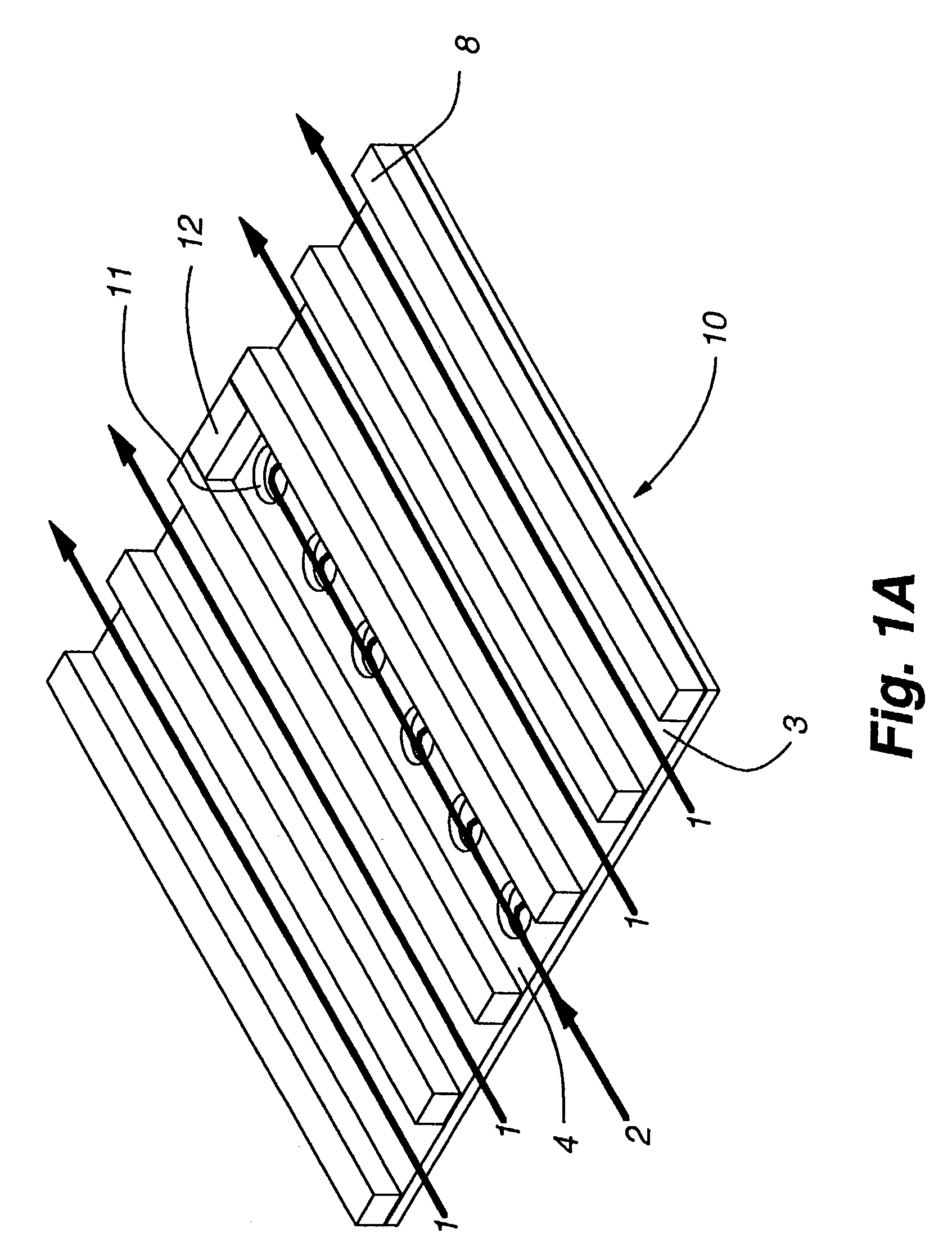
Method and plate apparatus for dew point evaporative cooler
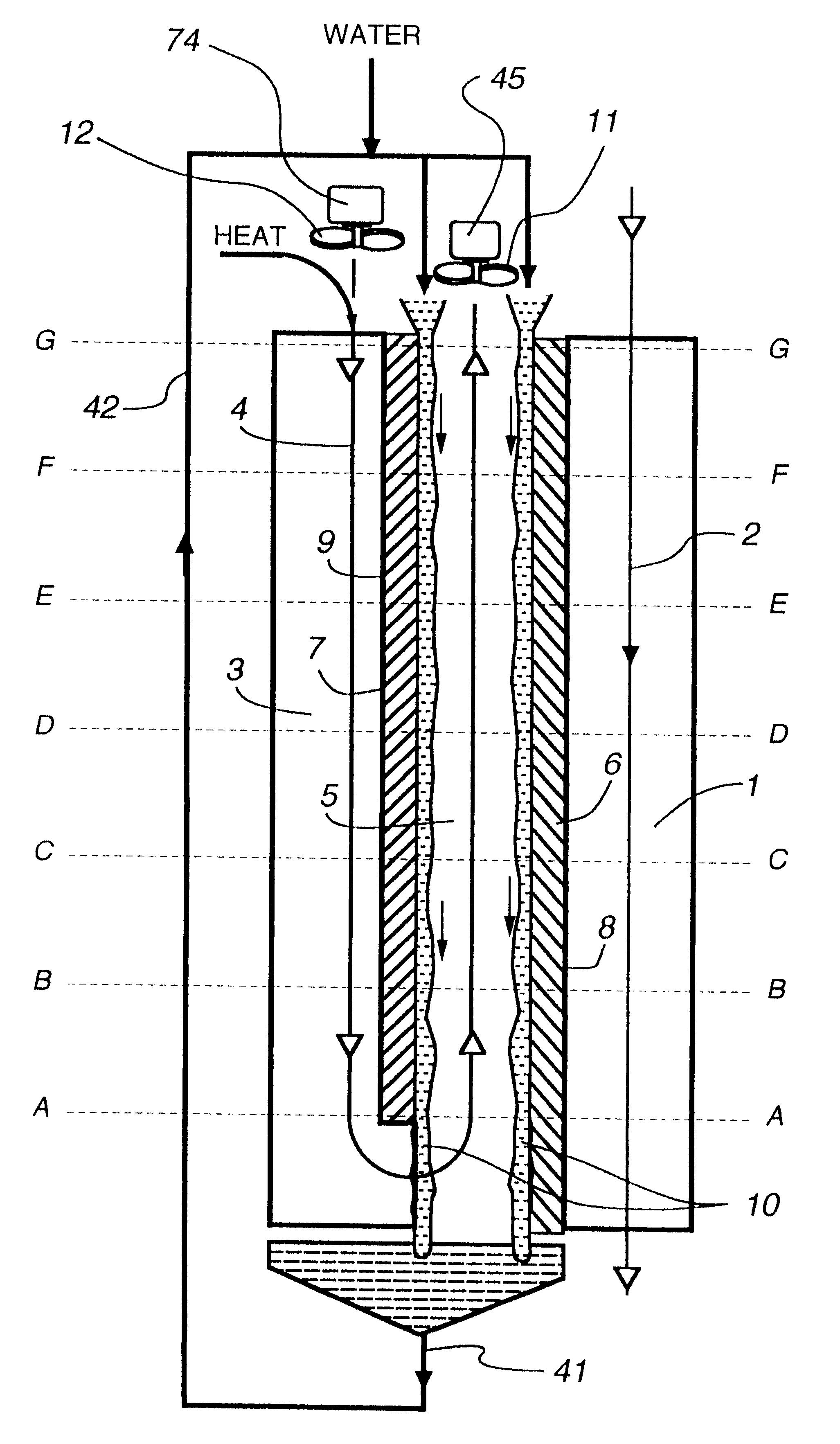
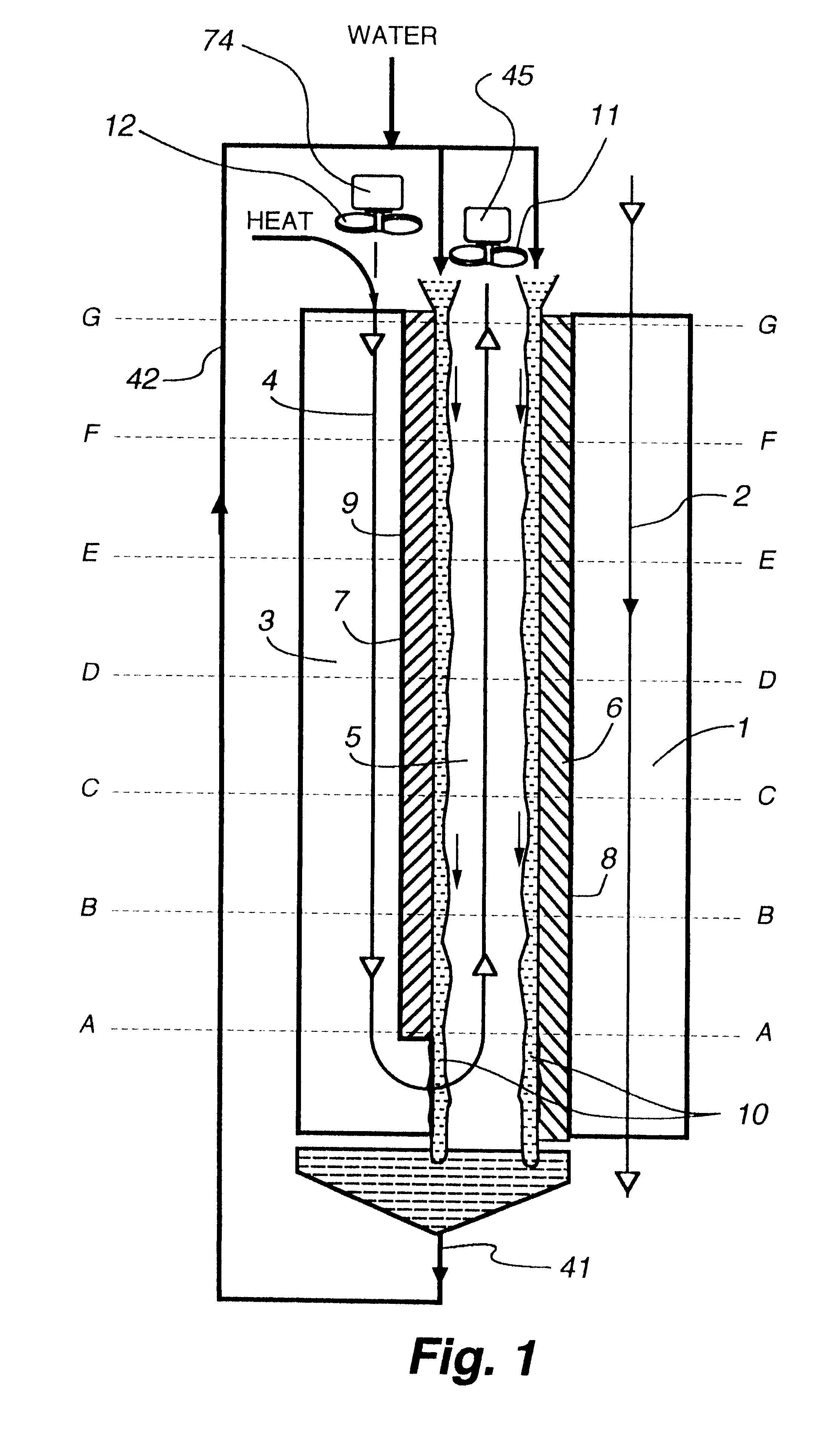
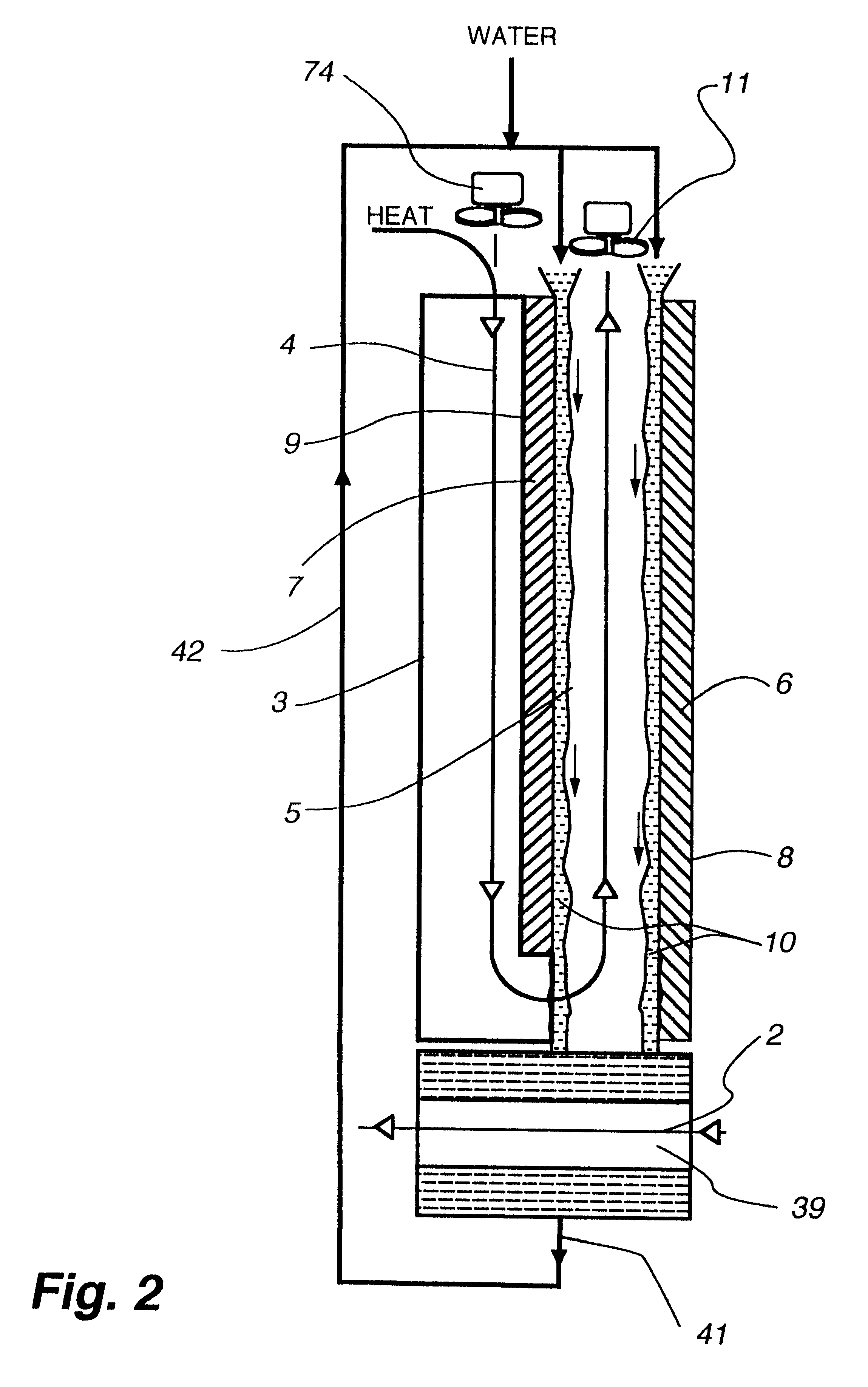
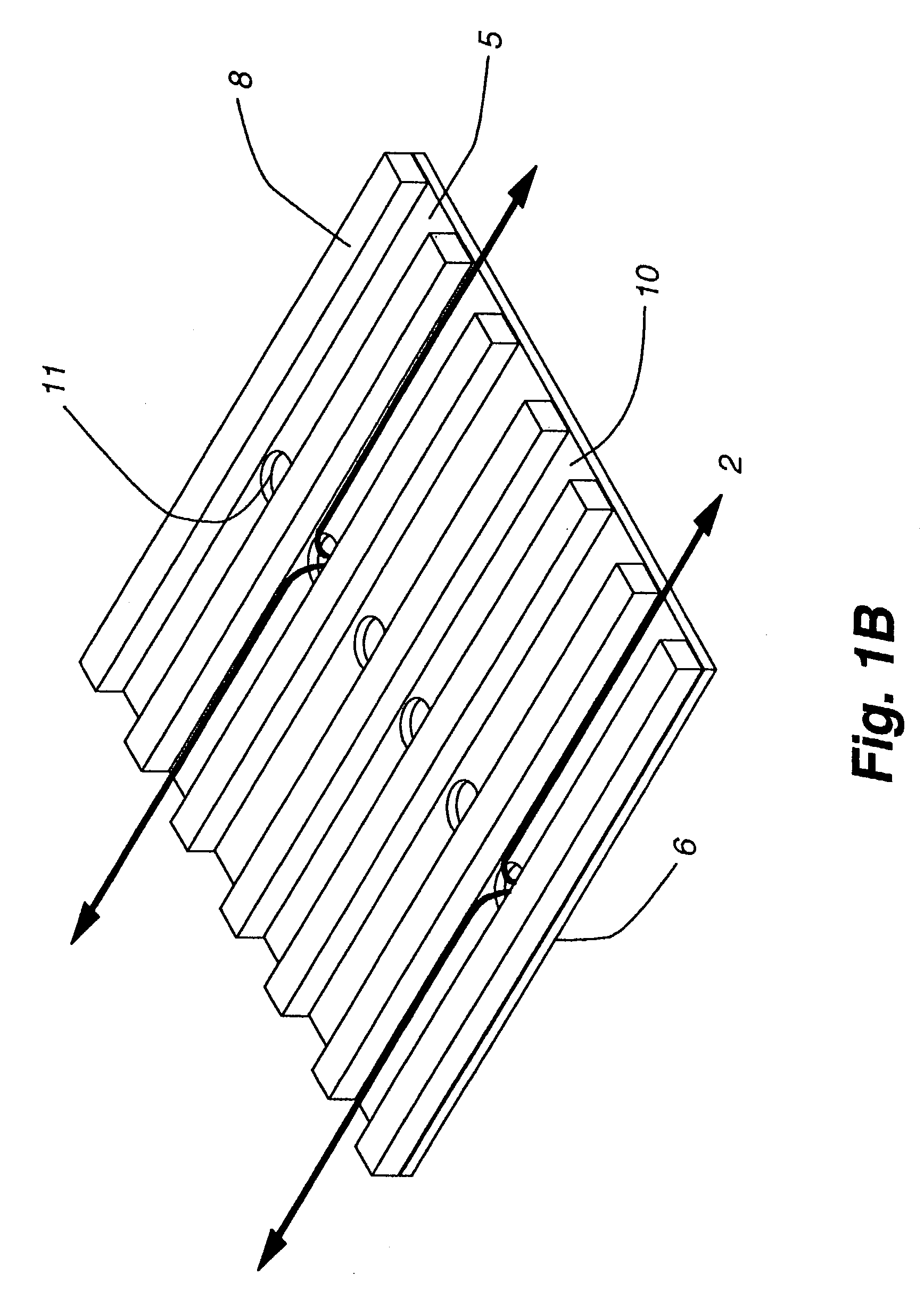
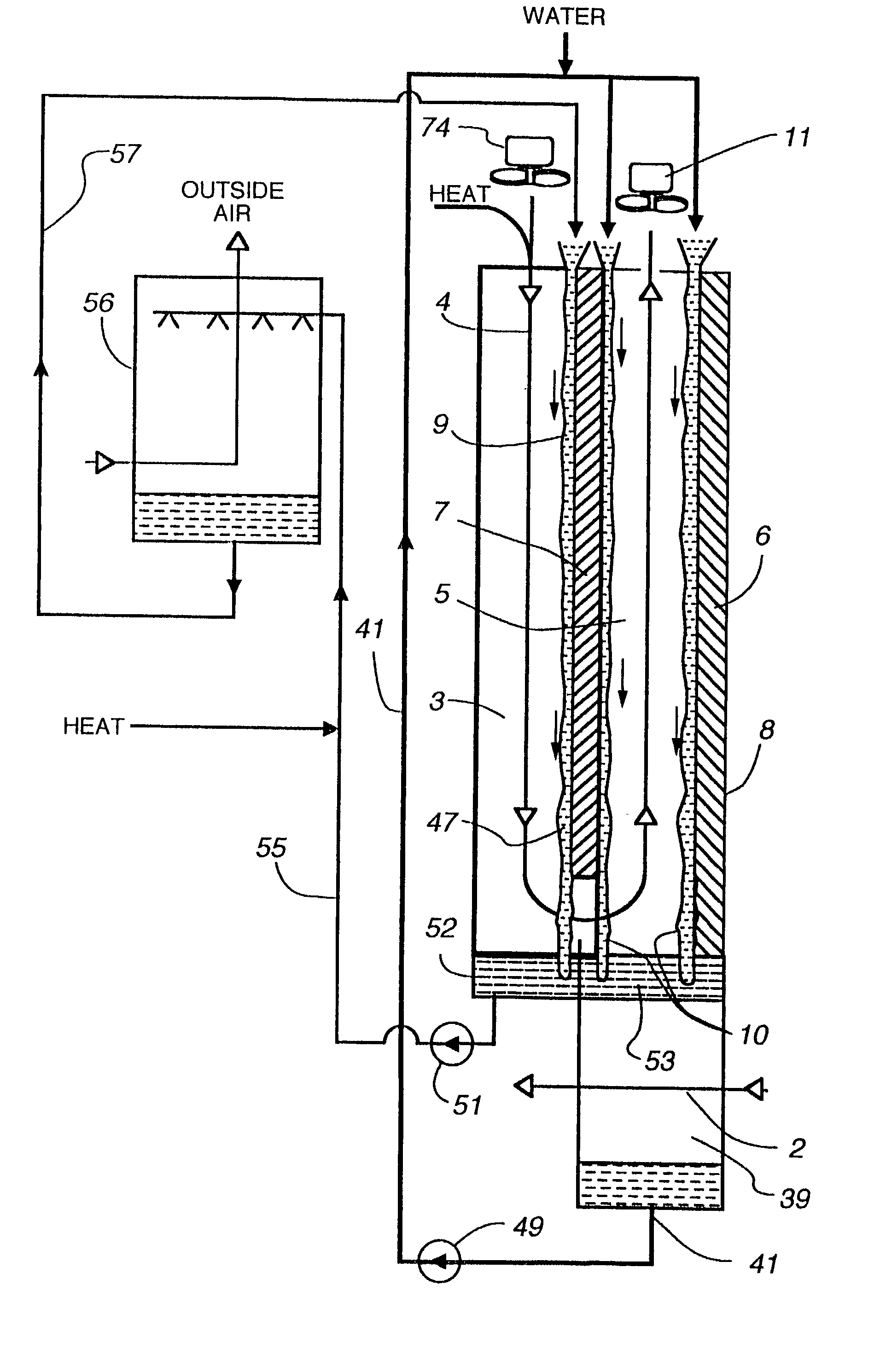
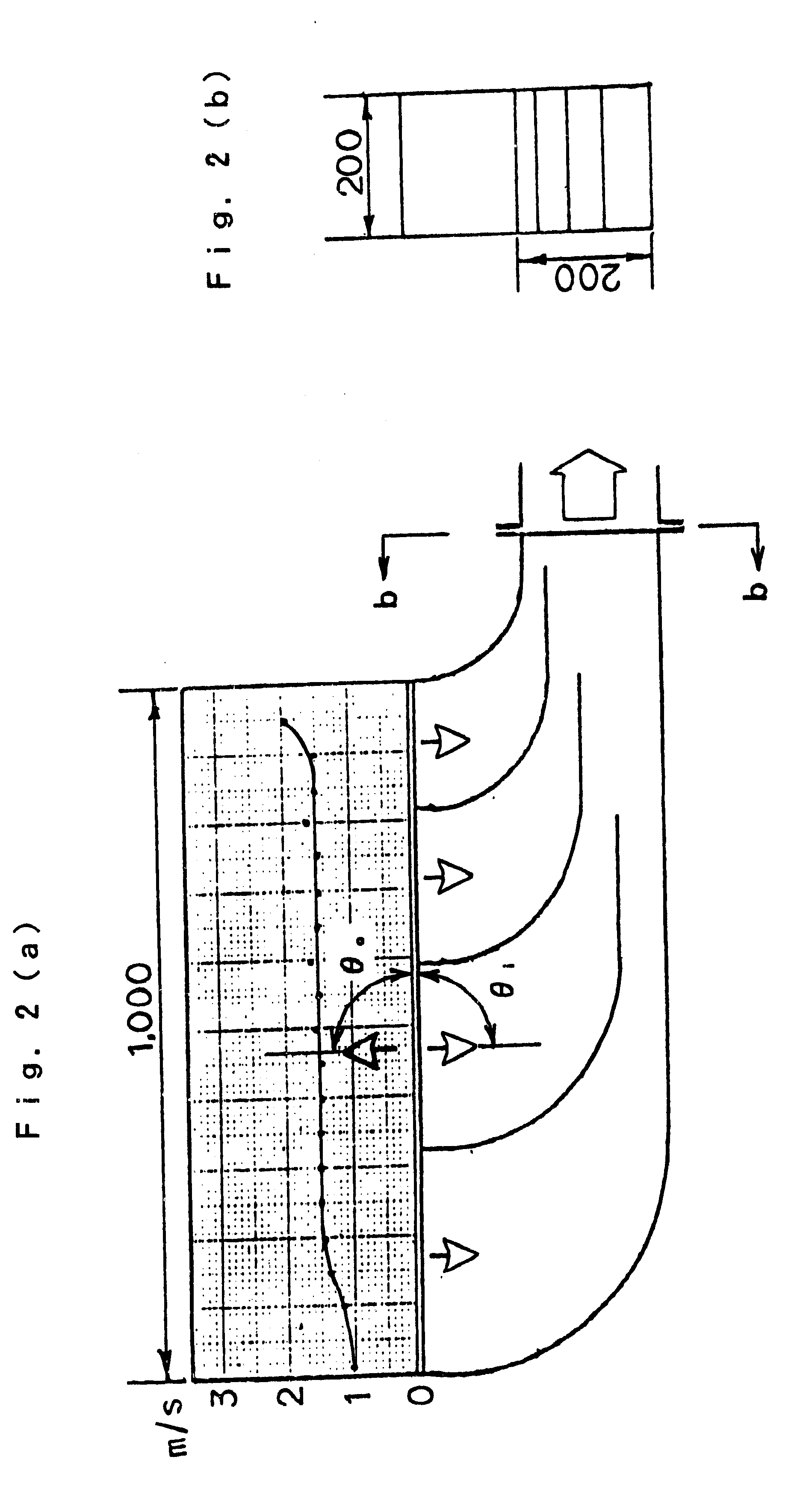
InactiveUS7197887B2Small pressure dropReduce temperature differenceAir treatment detailsFree-cooling systemsEvaporative coolerFiber
An improved method and apparatus for indirect evaporative cooling of a fluid stream to substantially its dew point temperature. Plate heat exchanger has perforations 11 and channels 3, 4 and 5 for gas or a low temperature for liquids on a dry side and wet side. Fluid streams 1 flow across the dry side 9, transferring heat to the plate. Gas stream 2 flows across the dry side and through perforations to channels 5 on wet side 10, which it then cools by evaporative cooling as well as conductive and radiative transfer of heat from plate. A wicking material provides wetting of wet side. In other embodiments, a desiccant wheel may be used to dehumidify the gas, air streams may be recirculated, feeder wicks 13 and a pump may be used to bring water from a water reservoir, and fans may be used to either force or induce a draft. The wicking material may be cellulose, organic fibers, organic based fibers, polyester, polypropylene, carbon-based fibers, silicon based fibers, fiberglass, or combinations of them. The device may be operated in winter months to scavenge heat from exhaust gases of a space and thus pre-heat fresh air, while simultaneously humidifying the fresh air.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
Sanitization system and system components
InactiveUS7767168B2Easy to adaptUsing liquid separation agentMixing methodsOzone generatorVapor–liquid separator
A multi-use sanitization system is disclosed which includes one or more containers in fluid communication with other system components. Components of the system include an ozone contacting device, such as a vortex-venturi or a sparger, for incorporating ozone into a liquid, an ozone generator to provide ozone to the vortex-venturi, a fluid transfer valve to allow simultaneous flow of liquid into and out of the container, and a pump to promote fluid flow through the system. Optionally, a gas-liquid separator with an optional integral gas release valve, an ozone destructor, an oxidation-reduction potential ozone sensor, or a pour-through type pre-filter may be incorporated into the system.
Owner:TERSANO INC
Method and apparatus for generating drinking water by condensing air humidity
InactiveUS20070175234A1Efficient workIdeal for useSteam/vapor condensersStationary conduit assembliesElectricityRural location
A system and method are shown which utilize a hybrid mechanical and evaporative air conditioning system to produce potable drinking while cooling an enclosure. The system operates on direct current, making it suitable for use in areas effected by natural disaster, power outage, or simply rural locations without access to electricity. The conditioning system includes both evaporative air conditioning and mechanical air conditioning functioning components to produce a water discharge. The system is operated to cool an enclosure. A portion of the water discharge is then drawn off and purified for use as drinking water.
Owner:GPM INC
Method and apparatus of indirect-evaporation cooling
InactiveUS20030014983A1Economic securityFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesDesiccantHeat transmission
The within invention improves on the indirect evaporative cooling method and apparatus by making use of a working fluid that is pre-cooled with and without desiccants before it is passed through a Wet Channel where evaporative fluid is on the walls to take heat and store it in the working fluid as increased latent heat. The heat transfer across the membrane between the Dry Channel and the Wet Channel may have dry, solid desiccant or liquid desiccant and may have perforations, pores or capillary pathways. The evaporative fluid may be water, fuel, or any substance that has the capacity to take heat as latent heat. The Wet Channel or excess cooled fluid is in heat transfer contact with a Product Channel where Product Fluid is cooled without adding any humidity. An alternative embodiment for heat transfer between adjacent channels is with heat pipes.
Owner:MAISOTSENKO VALERIY +3
Method and apparatus for cooling with coolant at a subambient pressure
ActiveUS7254957B2Valuable spaceImprove cooling effectDomestic cooling apparatusAuxillariesCoolant flowAmbient pressure
According to one embodiment, an apparatus includes a fluid coolant and structure which reduces a pressure of the fluid coolant through a subambient pressure at which the coolant has a cooling temperature less than a temperature of the heat-generating structure. The apparatus also includes structure that directs a flow of the fluid coolant in the form of a liquid at a subambient pressure in a manner causing the liquid coolant to be brought into thermal communication with the heat-generating structure. The heat from the heat-generating structure causes the liquid coolant to boil and vaporize so that the coolant absorbs heat from the heat-generating structure as the coolant changes state. The structure is configured to circulate the fluid coolant through a flow loop while maintaining the pressure of the fluid coolant within a range having an upper bound less than ambient pressure. The apparatus also includes a first heat exchanger for exchanging heat between the fluid coolant flowing through the loop and a second coolant in an intermediary loop so as to condense the fluid coolant flowing through the loop to a liquid. The apparatus also includes a second heat exchanger for exchanging heat between the second coolant in the intermediary cooling loop and a body of water on which the ship is disposed.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
System and method for therapeutic application of dissolved oxygen
A system and method for generating an oxygen enriched aqueous solution for therapeutic application includes a diffuser comprising a first diffusing member having a surface incorporating surface disturbances, and a second diffusing member positioned relative to the first diffusing member to form a channel through which an aqueous solution and oxygen gas may flow. A reservoir containing the aqueous solution is connected to a pump that draws the aqueous solution from the reservoir and inputs the aqueous solution into the diffuser. The aqueous solution is moved through the channel relative to the surface disturbances to create cavitation in the aqueous solution to diffuse the oxygen gas into the aqueous solution to produce an oxygen enriched aqueous solution.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
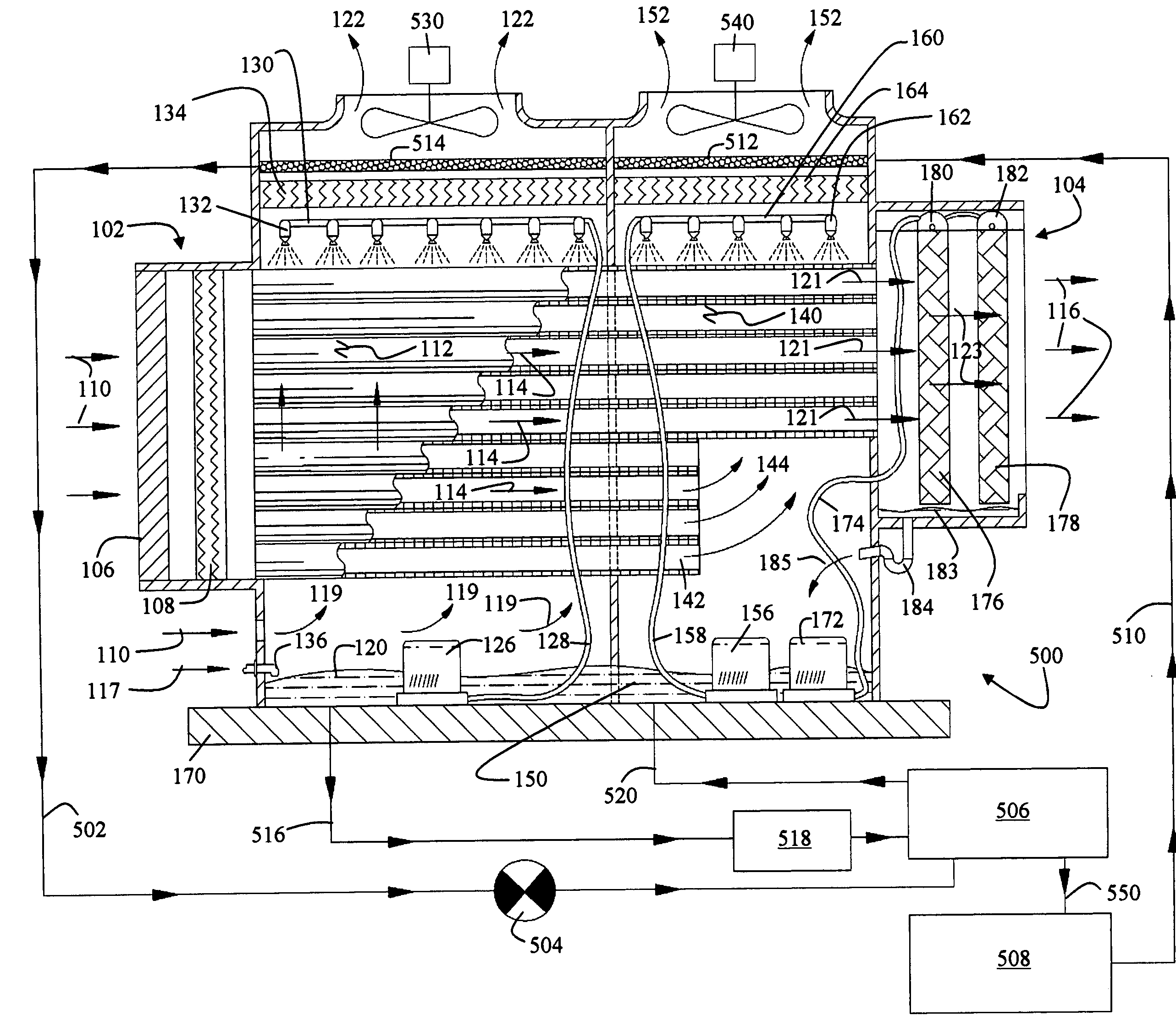
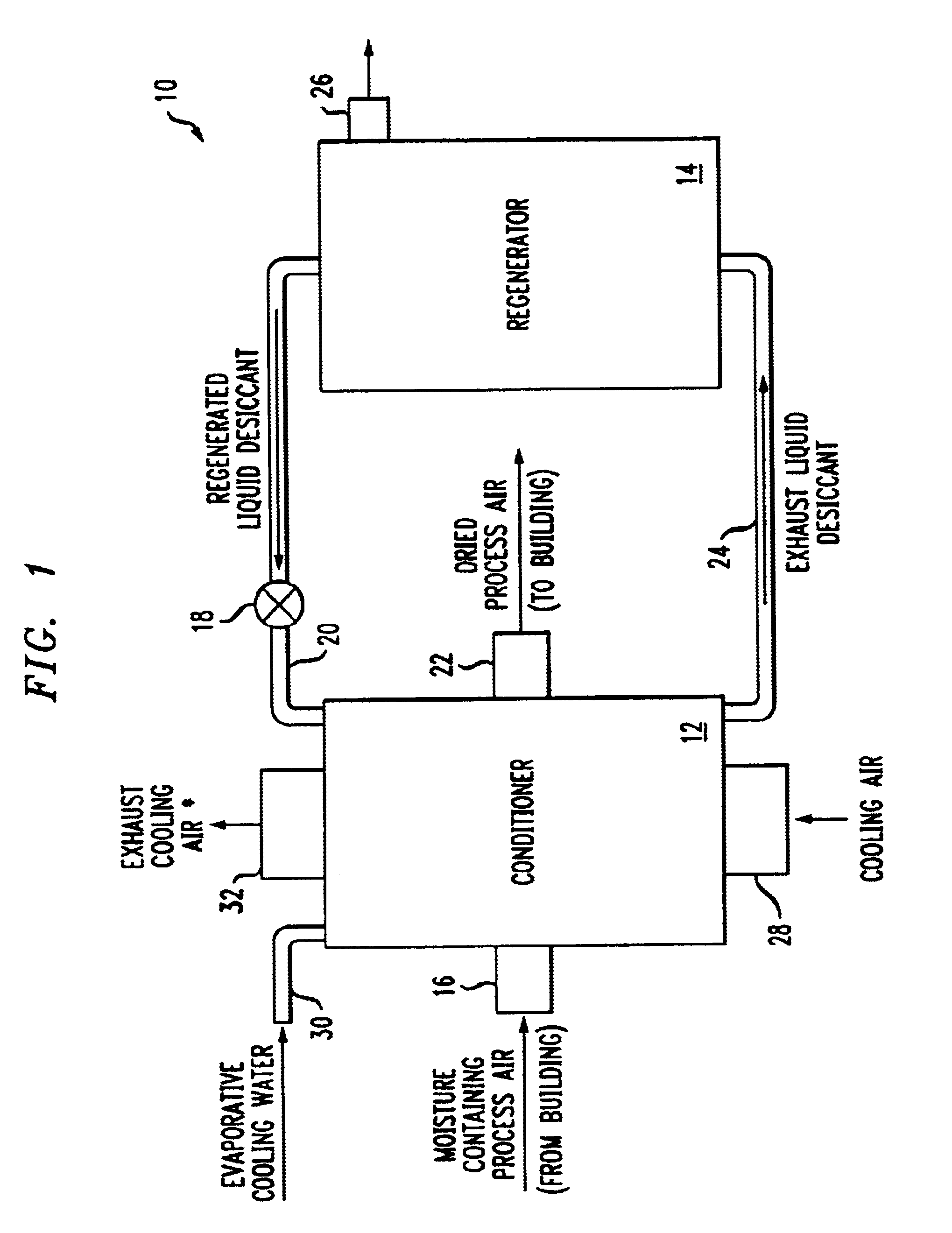
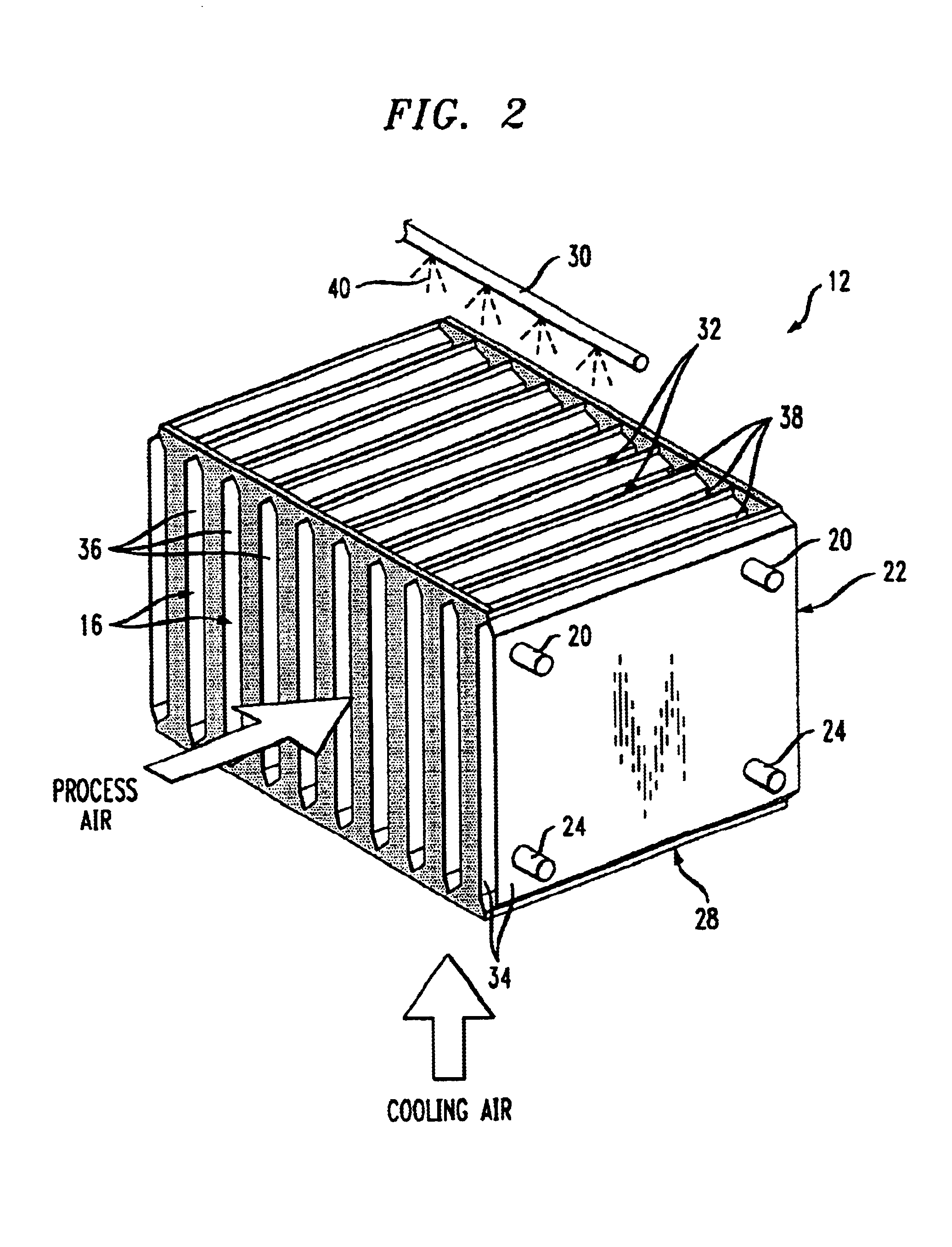
Methods and systems for cooling buildings with large heat loads using desiccant chillers
ActiveUS20140150481A1Improve cooling efficiencyDispersed particle separationEfficient regulation technologiesCooling towerDesiccant
A system for providing cooling to a building includes a cooling tower for transferring waste heat from the building to the atmosphere and a liquid desiccant system for dehumidifying an air stream entering the cooling tower to increase cooling efficiency of the cooling tower. The liquid desiccant system includes a conditioner and a regenerator. The conditioner utilizes a liquid desiccant for dehumidifying the air stream entering the cooling tower. The regenerator is connected to the conditioner for receiving dilute liquid desiccant from the conditioner, concentrating the dilute liquid desiccant using waste heat from the building, and returning concentrated liquid desiccant to the conditioner.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Method and apparatus for simultaneous heat and mass transfer utilizing a carrier-gas
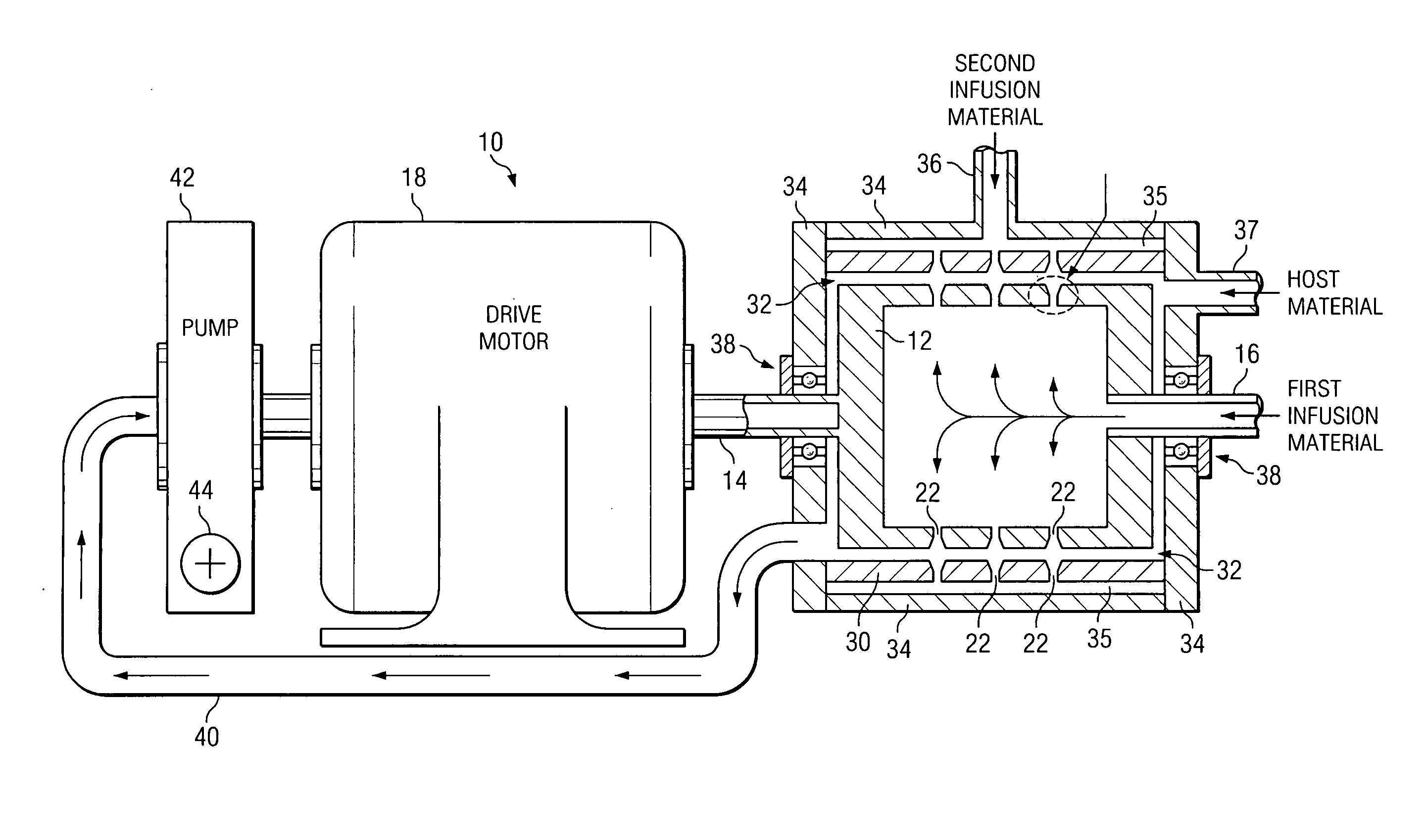
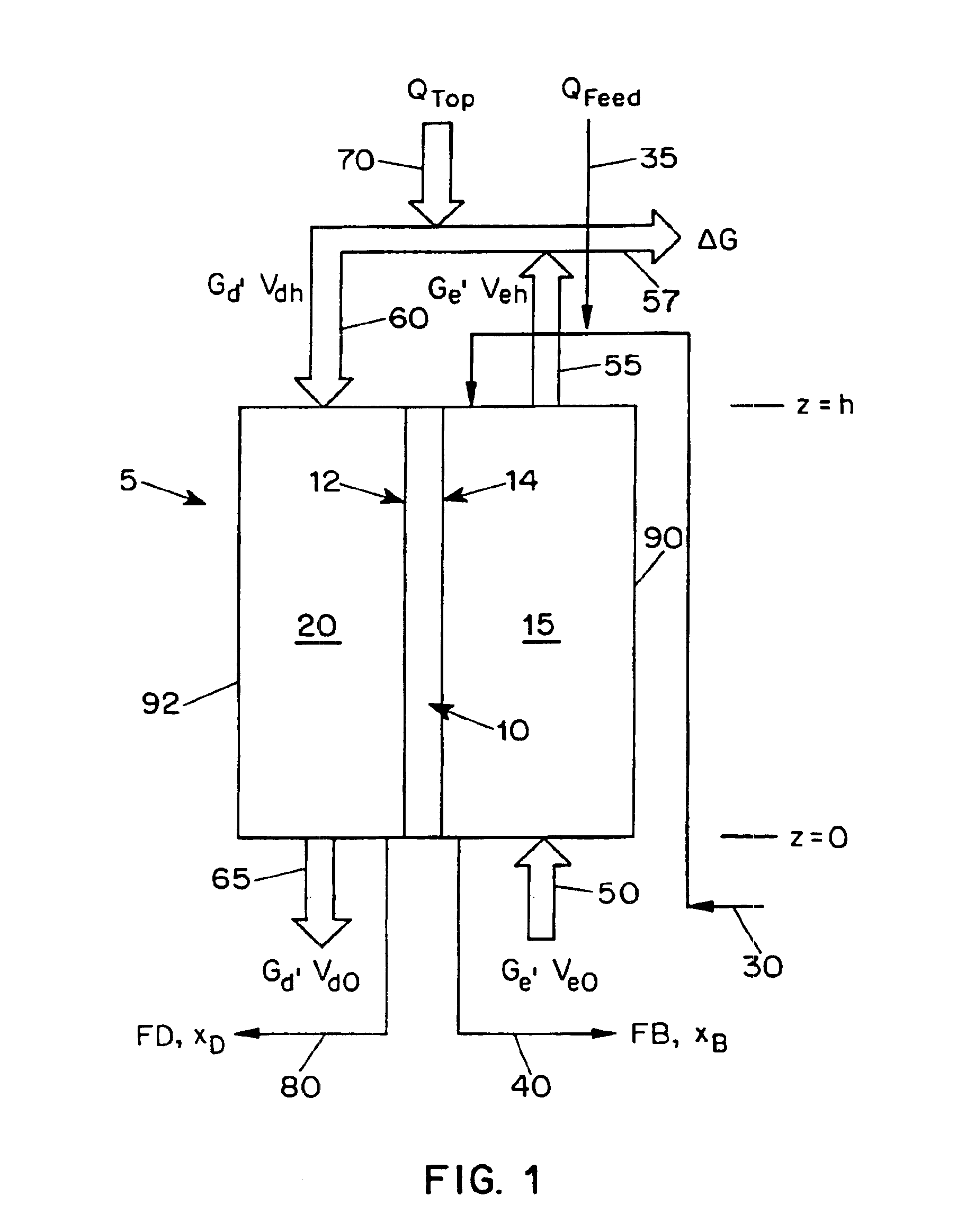
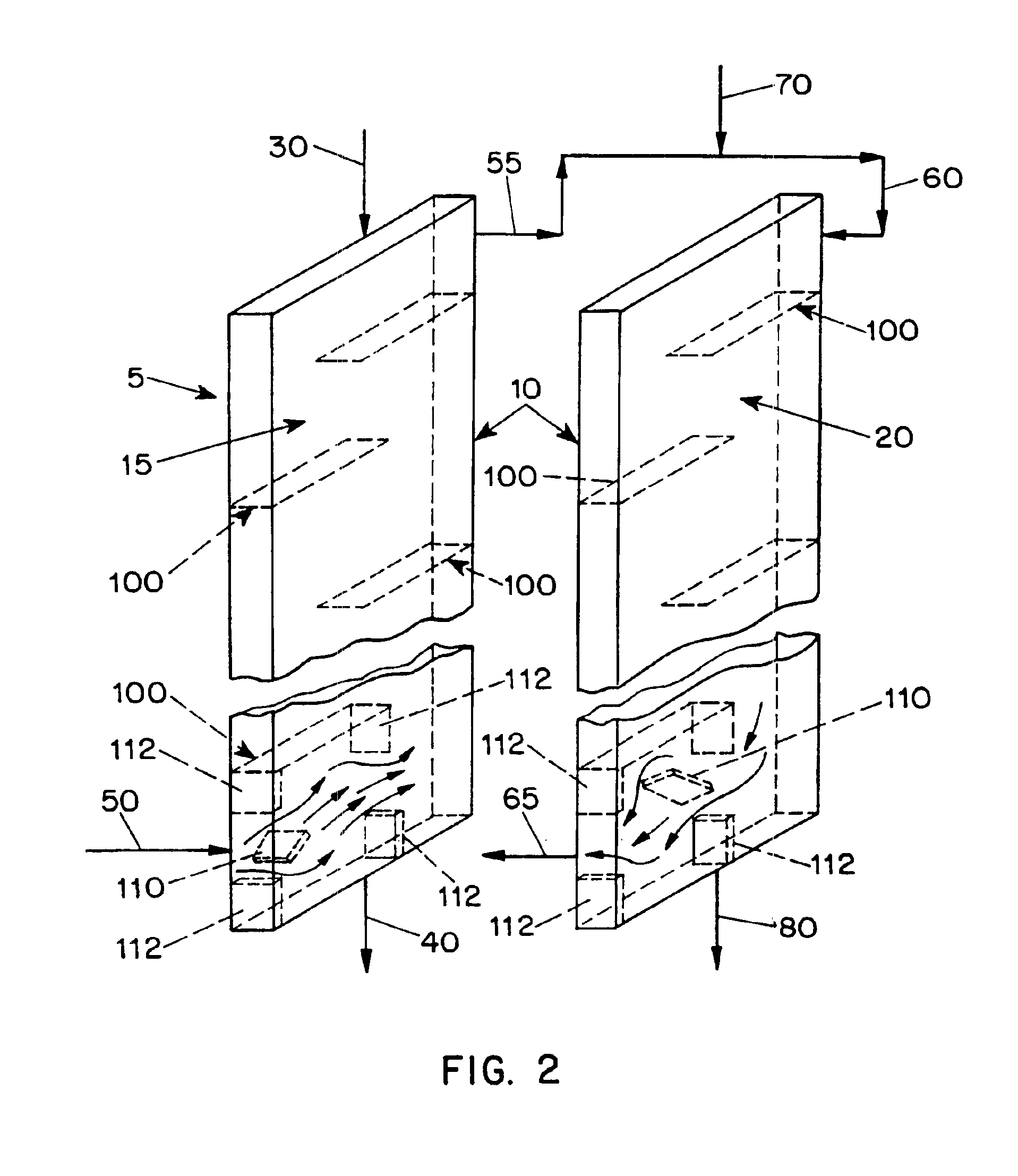
InactiveUS6911121B1Improve concentrationDistillation regulation/controlEnergy based wastewater treatmentDewEvaporation chamber
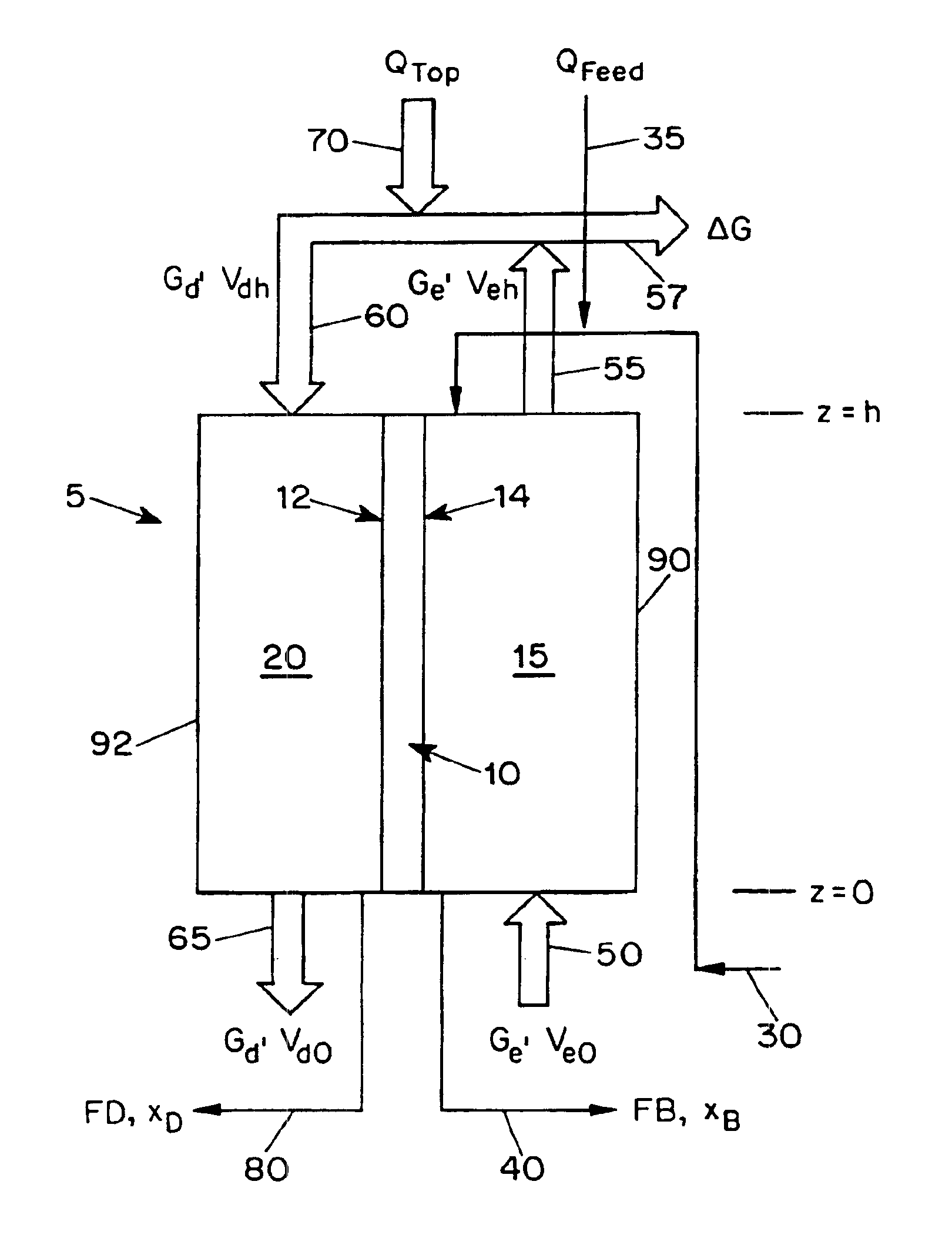
The present application is directed to a continuous contacting apparatus for separating a liquid component from a liquid mixture. The apparatus comprises: (i) an evaporation chamber (15) having first and second ends, an inlet (50) and an outlet (55) for a carrier gas, and an inlet (30) and an outlet (40) for a liquid mixture, wherein the inlet (30) for the liquid mixture and the outlet (55) of the carrier gas are located on the first end of the evaporation chamber (15); (ii) a dew-formation chamber (20) having an inlet (60) and an outlet (65) for a carrier gas and an outlet for the separable liquid component (80), wherein the inlet for the carrier gas (60) of the dew-formation chamber (20) is situated in a countercurrent manner to the inlet for the carrier gas of the evaporation chamber; (iii) a common heat transfer wall (10) providing thermal communication between the evaporation chamber (15) and the dew-formation chamber (20); (iv) a feeding device for providing the liquid mixture onto the evaporation side of the heat transfer wall; (v) an air mover for controlling a flow of a carrier gas through the chambers, wherein the gas flow in the evaporation chamber is countercurrent to the gas flow in the dew-formation chamber; and (vi) a heating apparatus for heating the carrier gas from the outlet of the evaporation chamber, wherein the heated carrier gas is directed to flow into the inlet of the dew-formation chamber. Also described is a process for separating a liquid component from a liquid mixture in a continuous contacting manner comprising employing such an apparatus for such separation.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
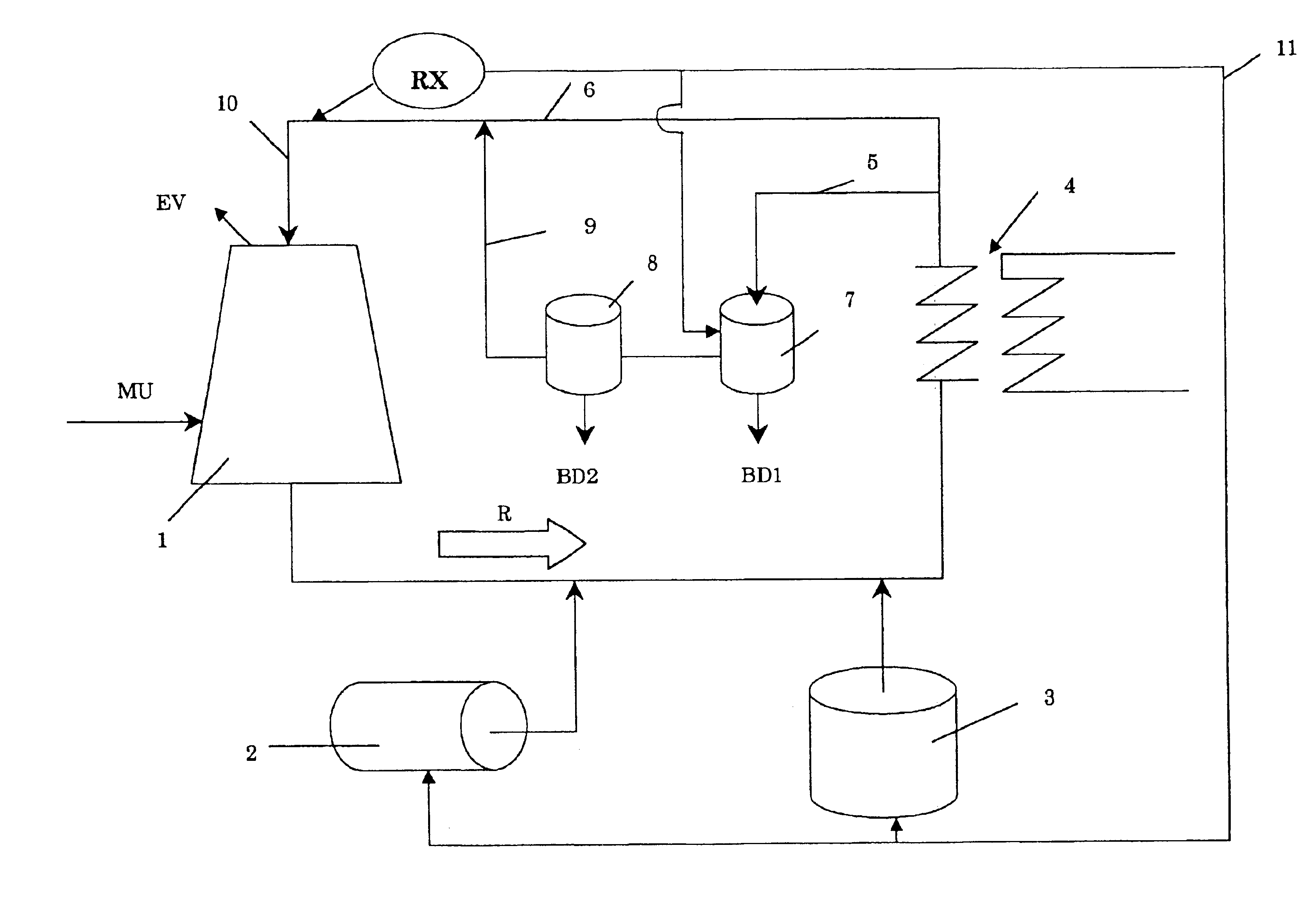
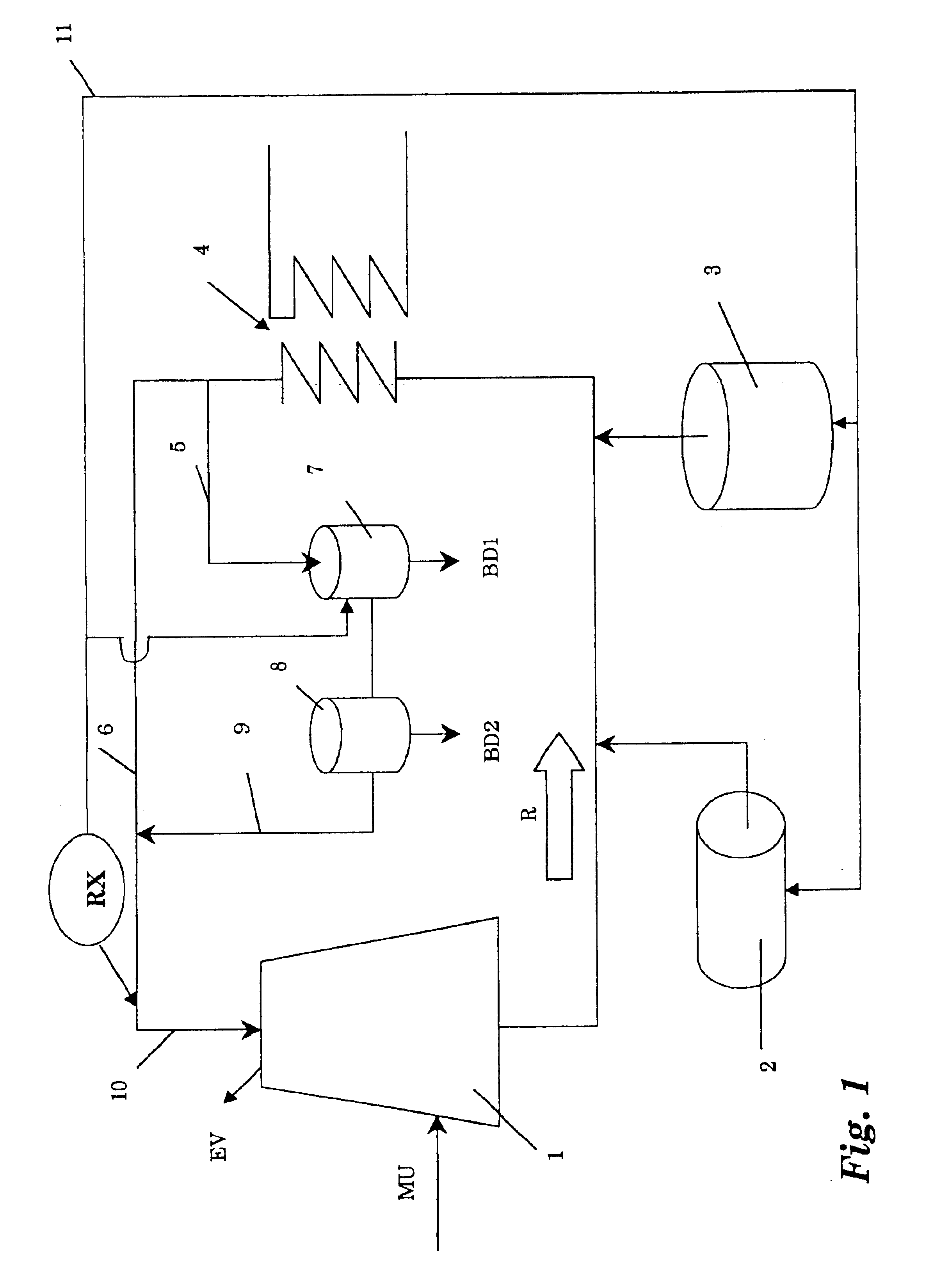
Water treatment method and apparatus
InactiveUS6733654B1Water treatment parameter controlNature of treatment waterCooling towerWater flow
A method of operating a cooling tower comprises feeding to the cooling tower a make-up stream of water containing organic and / or biological contaminants, causing a side stream taken from the recirculating stream to pass through an electrolytic cell, removing solids precipitating by the action of the cell, and remixing the treated side stream with the main stream, before feeding them to the cooling tower.
Owner:ARGAD EYAL
Fill material for direct-contact heat/mass exchangers
InactiveUS20150048528A1Reduced dysfunctionSmall sizeAdditive manufacturing apparatusUsing liquid separation agentFilling materialsLinear element
Fill material for a direct contact heat exchanger wherein the fill material has flow pathways bounded by an array of linear elements, namely a mesh. The invention intentionally uses surface tension and capillary action to anchor the fluid / fluid interface in a desired location. The heat exchanger is wick or collector in direct contact with the fill material (matrix) to extract fluid without formation of large droplets. The mesh is made from a neutrally wetting material.
Owner:BARTON SEAN ANDERSON
Air conditioning system
InactiveUS6848265B2Less complicated to fabricateLow costSpacing meansFree-cooling systemsContinuous flowEngineering
An air conditioner comprises a plurality of plates arranged in a successively stacked configuration with portions thereof having a spaced apart arrangement, and defining between successive adjacent pairs of plates at the spaced apart portions a first and second series of discrete alternating passages wherein a first air stream is passed through the first series of passages and a second air stream is passed through the second series of passages; and said stacked configuration of plates forming integrally therewith a liquid delivery means for delivering from a source a sufficient quantity of a liquid to the inside surfaces of the first series of fluid passages in a manner which provides a continuous flow of the liquid from a first end to a second end of the plurality of plates while in contact with the first air stream.
Owner:AIL RES
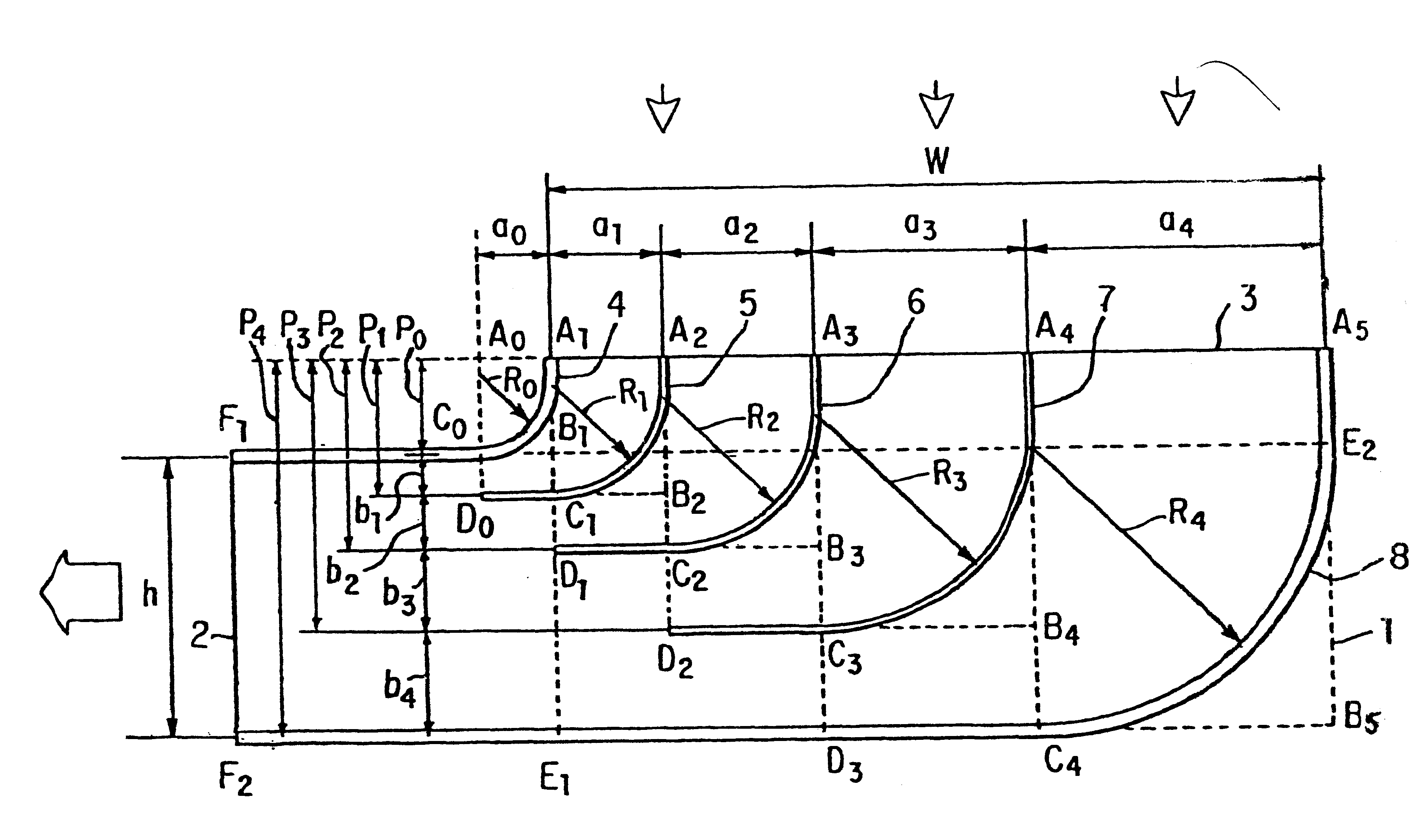
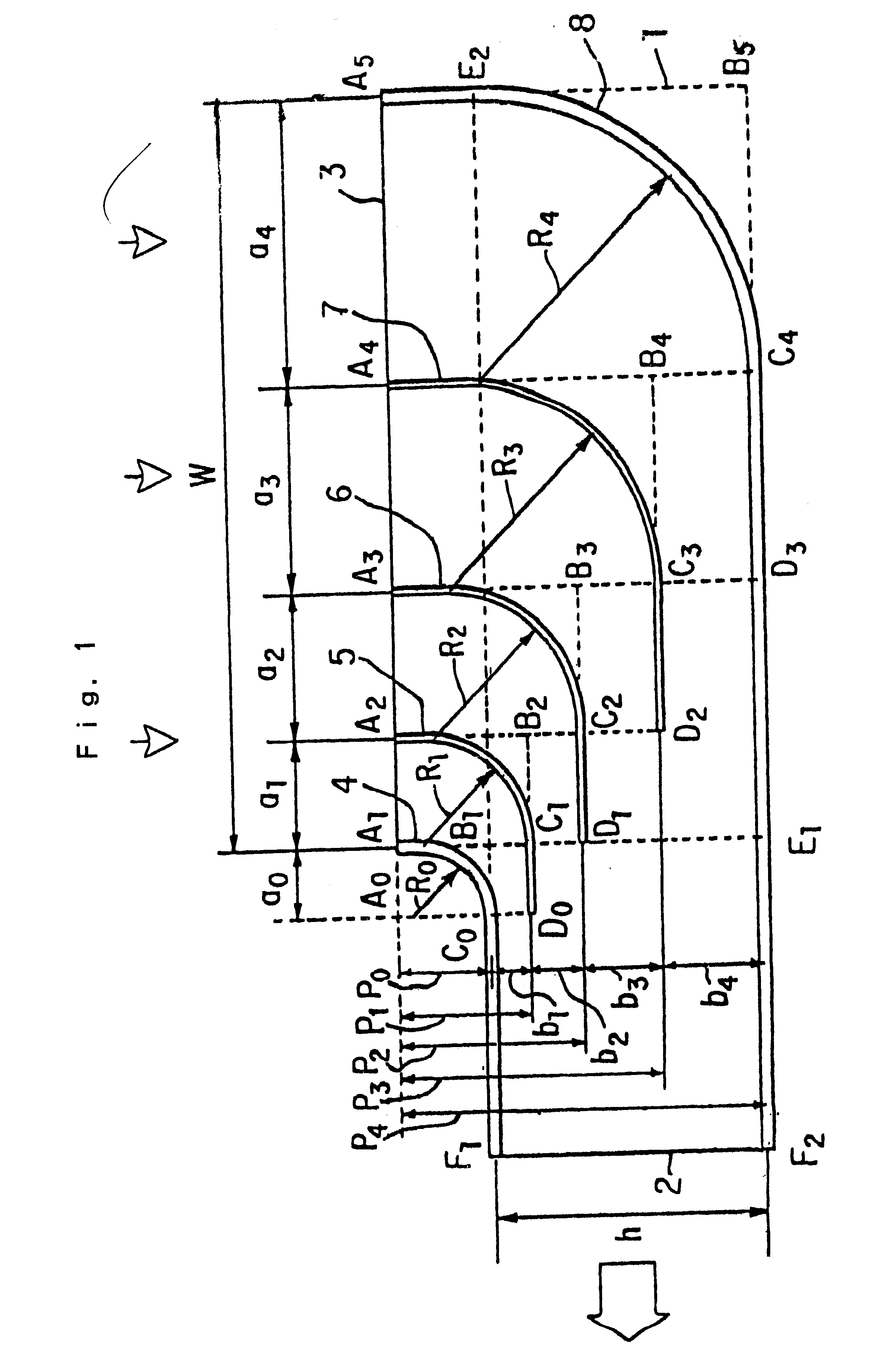
Suction elbow provided with built-in guide blades
InactiveUS6290266B1Evenly distributedSmall pressure lossPipeline expansion-compensationPump componentsEngineeringElbow
A suction elbow is divided in a plurality of sub-channels similar to each other by one or more guide vanes made of a curved plate and flat plates connected to the curved plate based on the following formulas.p0: overhang length at the inlet of the elbowh: outlet breadth of the elbowf: reduction ratio of the elbow (f=W / h)W: inlet breadth of the elbowm: number of sub-channels (m>=2)an: inlet breadth of n-th sub-channel (a0 indicates the radius of curvature of the inner side wall and am indicates the radius of curvature of the outer side wall)r: aspect ratio of the sub-channelsbn: outlet breadth of n-th sub-channel
Owner:KAWANO MICHIHIKO
Installation element of an installed packing
ActiveUS8834058B2Avoid high forceEasy to lockSnap fastenersFasteningsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:GEA 2H WATER TECH GMBH
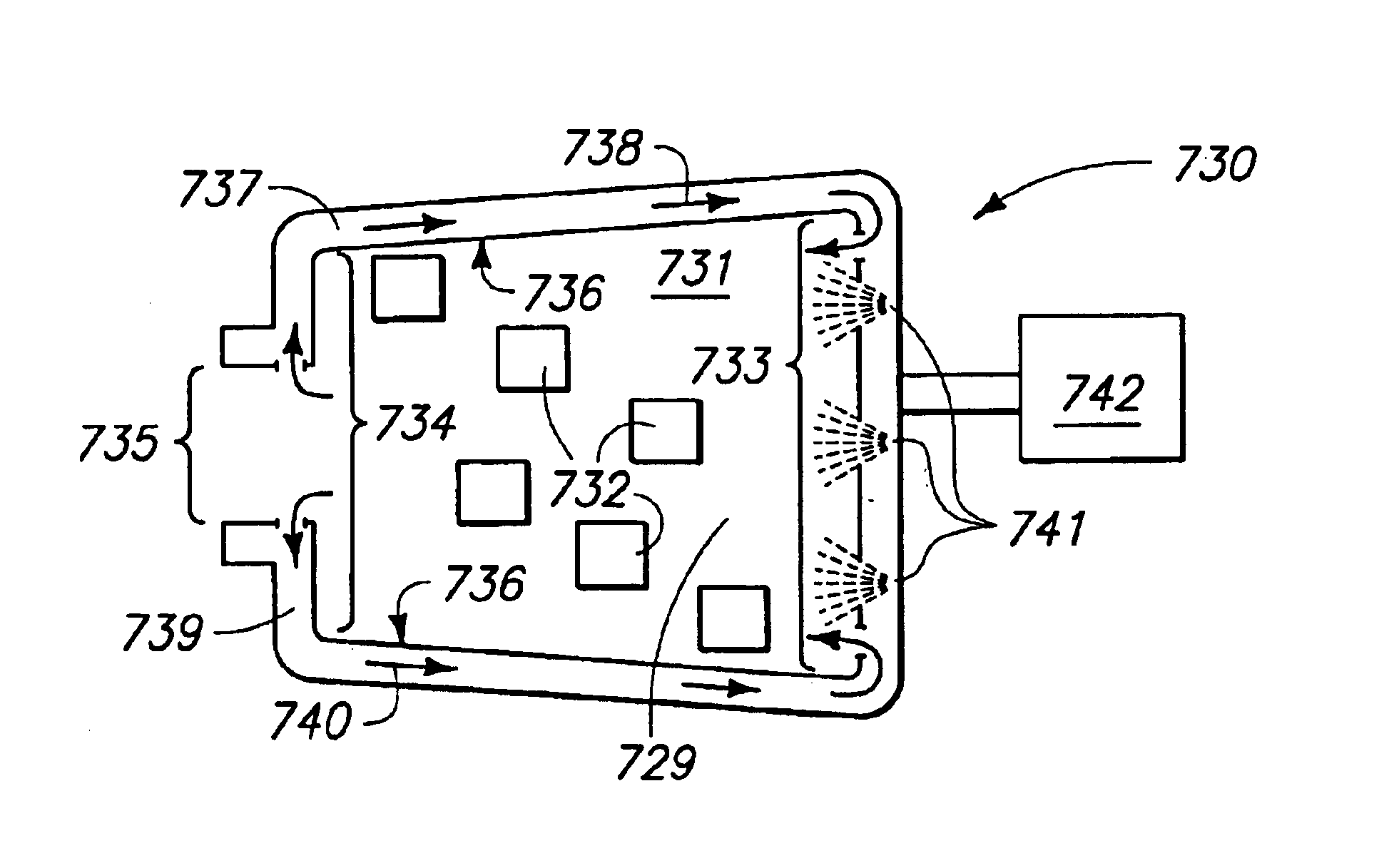
Spray cooling system for transverse thin-film evaporative spray cooling
InactiveUS6955062B2Domestic cooling apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringElectronic component
A spray cooling system for transverse thin-film evaporative spray cooling in a narrow gap which generally includes a framework, a cooling cavity, a plurality of atomizers oriented to transversely spray coolant across the electronic components to be cooled, and preferably a vapor recirculation system and a reduction in cross section from the inlet or spray side to the exit side.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com