Patents
Literature
169 results about "Fluid interface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluid interfaces improve the user’s experience, making every interaction feel quick, lightweight, and meaningful. They give the user a feeling of control, which builds trust with your app and your brand. They are hard to build. A fluid interface is difficult to copy and can be a competitive advantage.
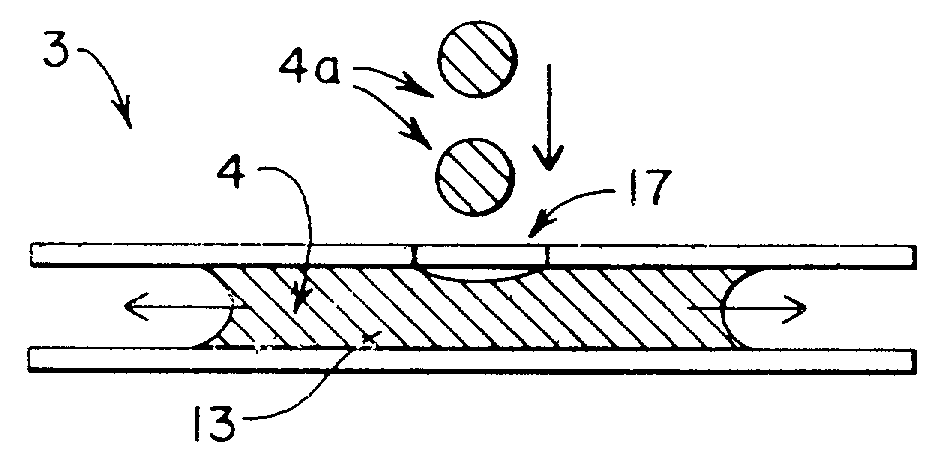
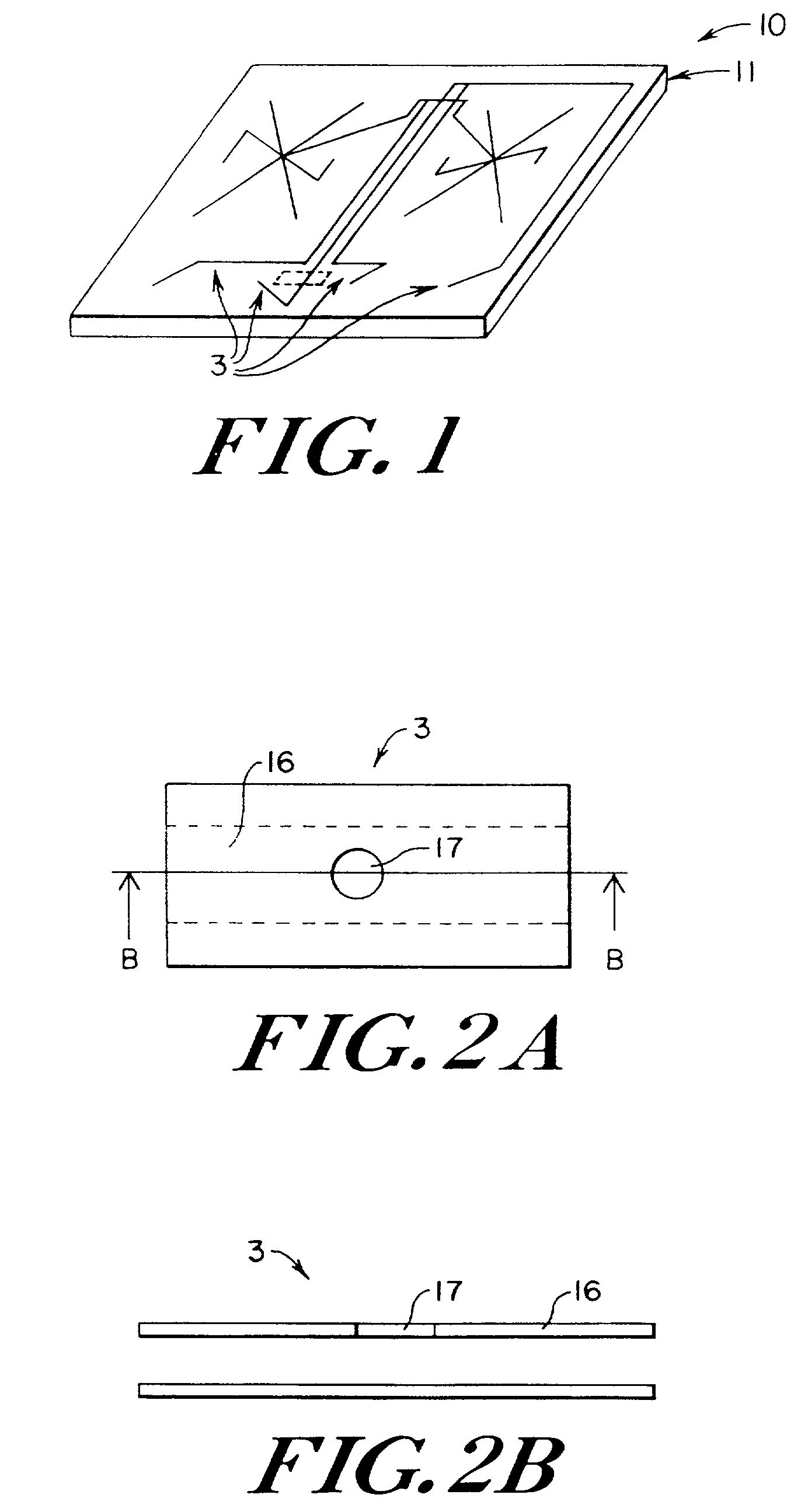
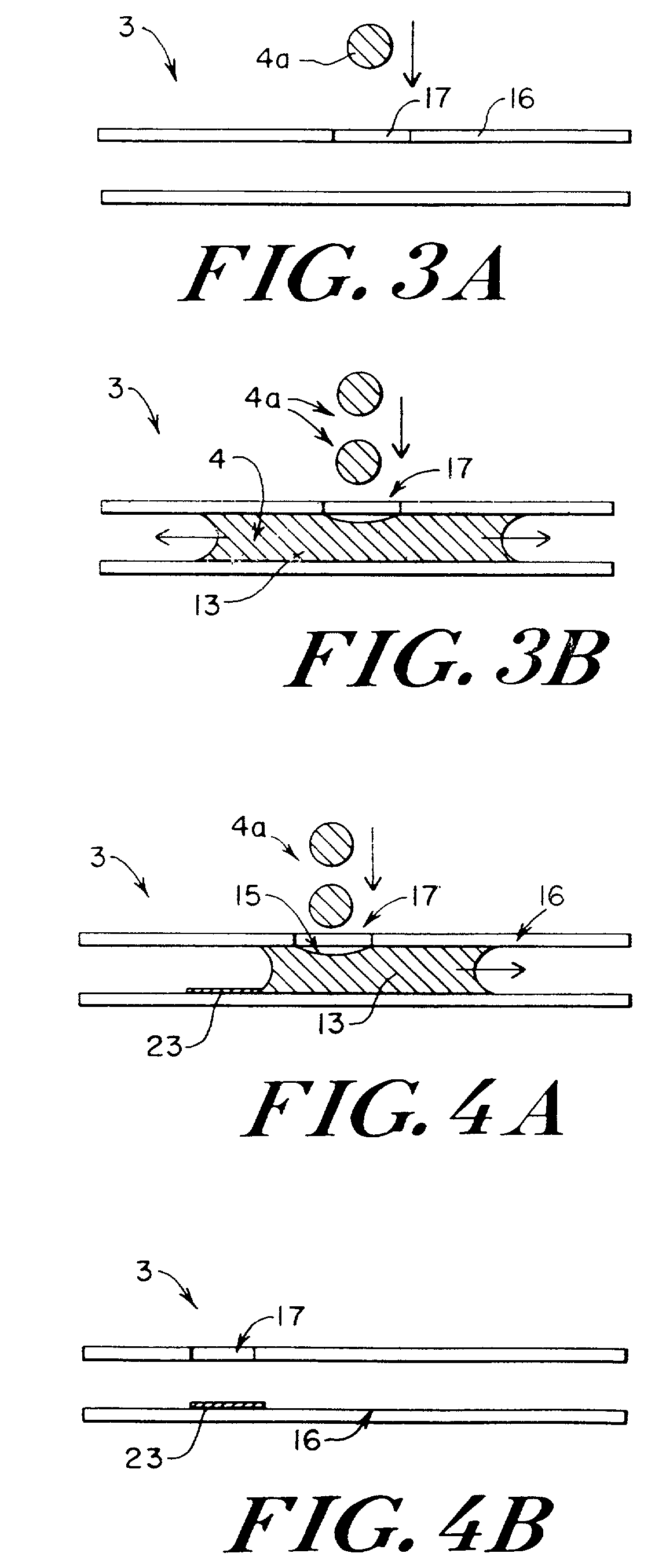
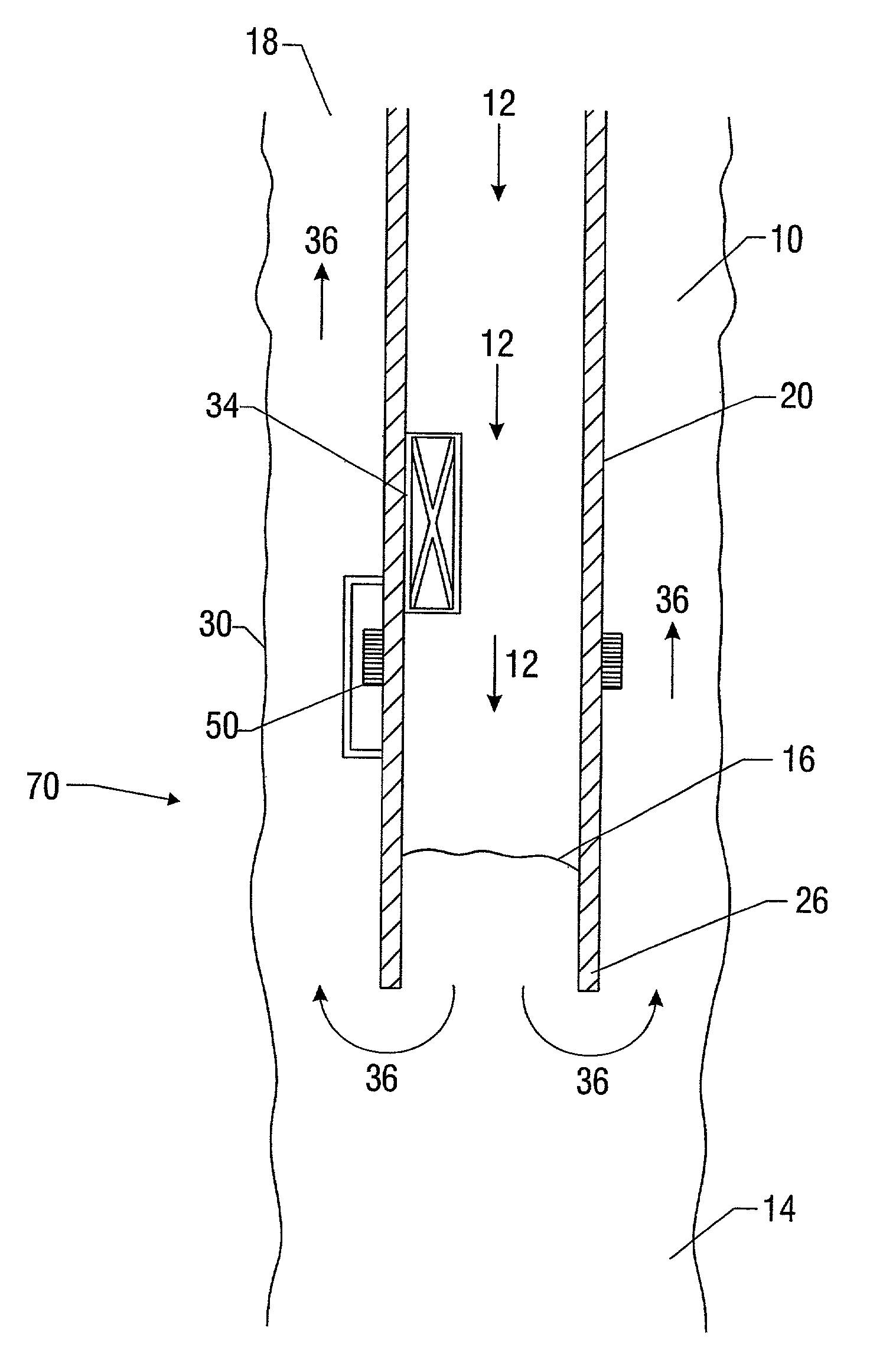
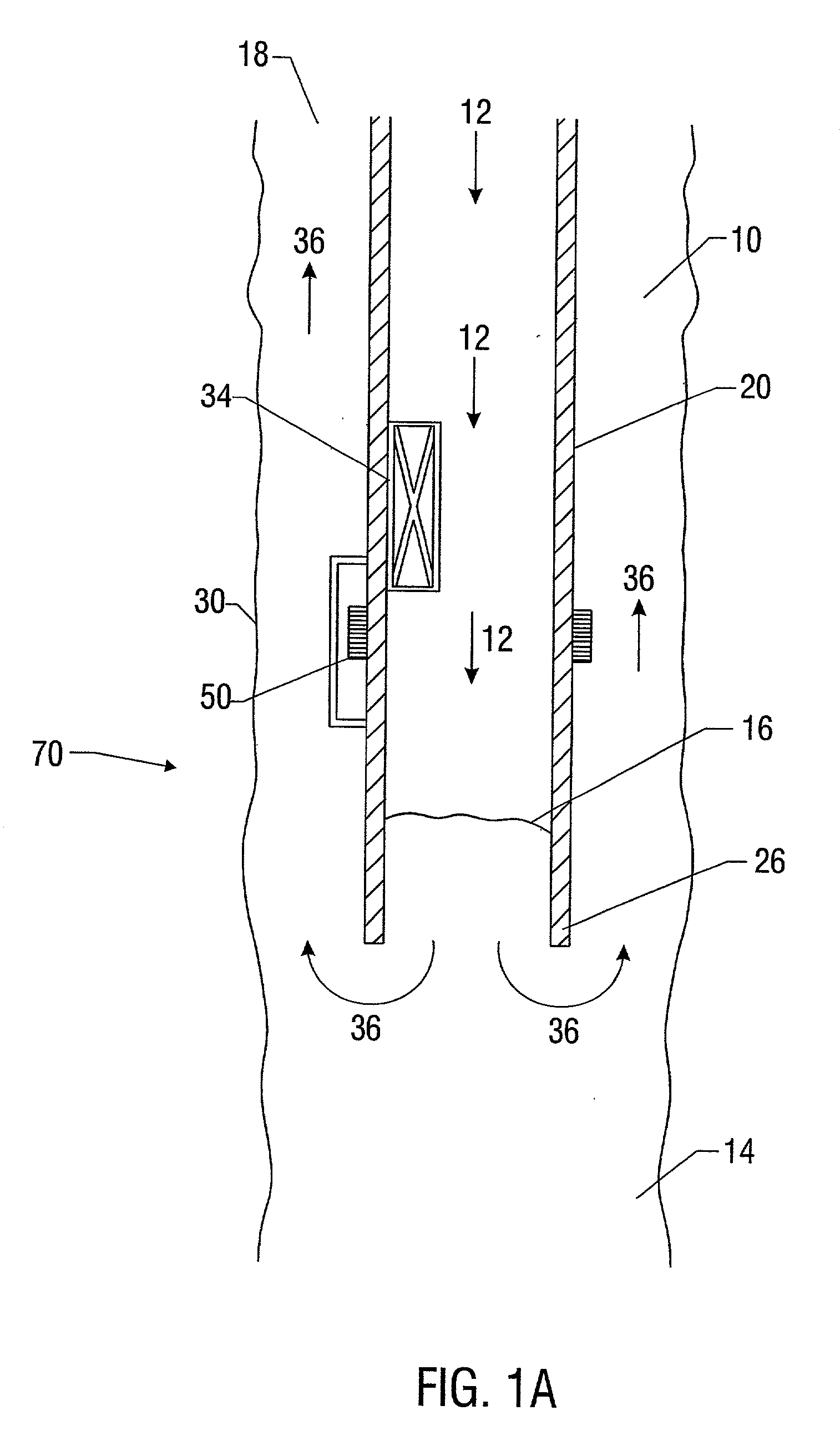
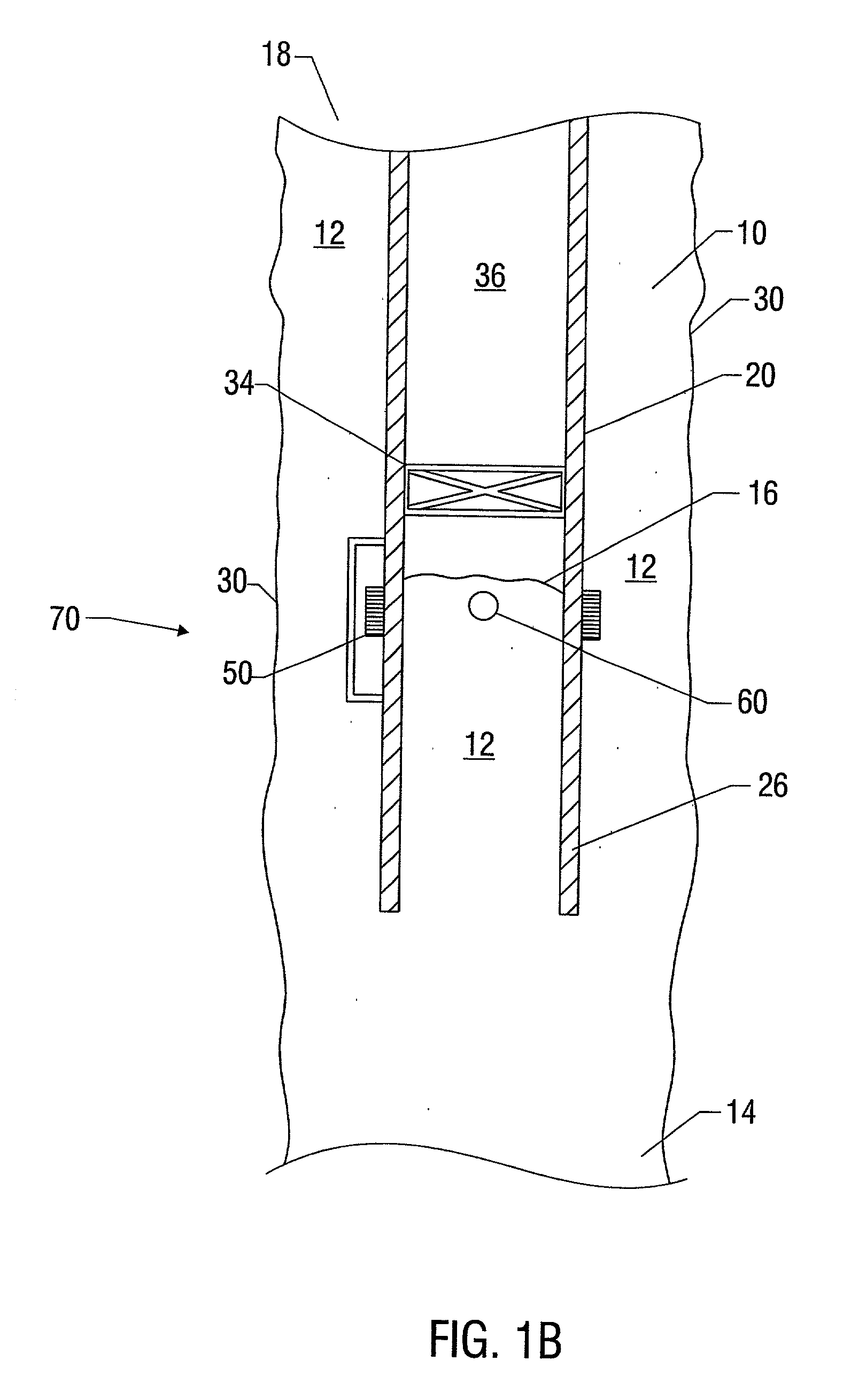
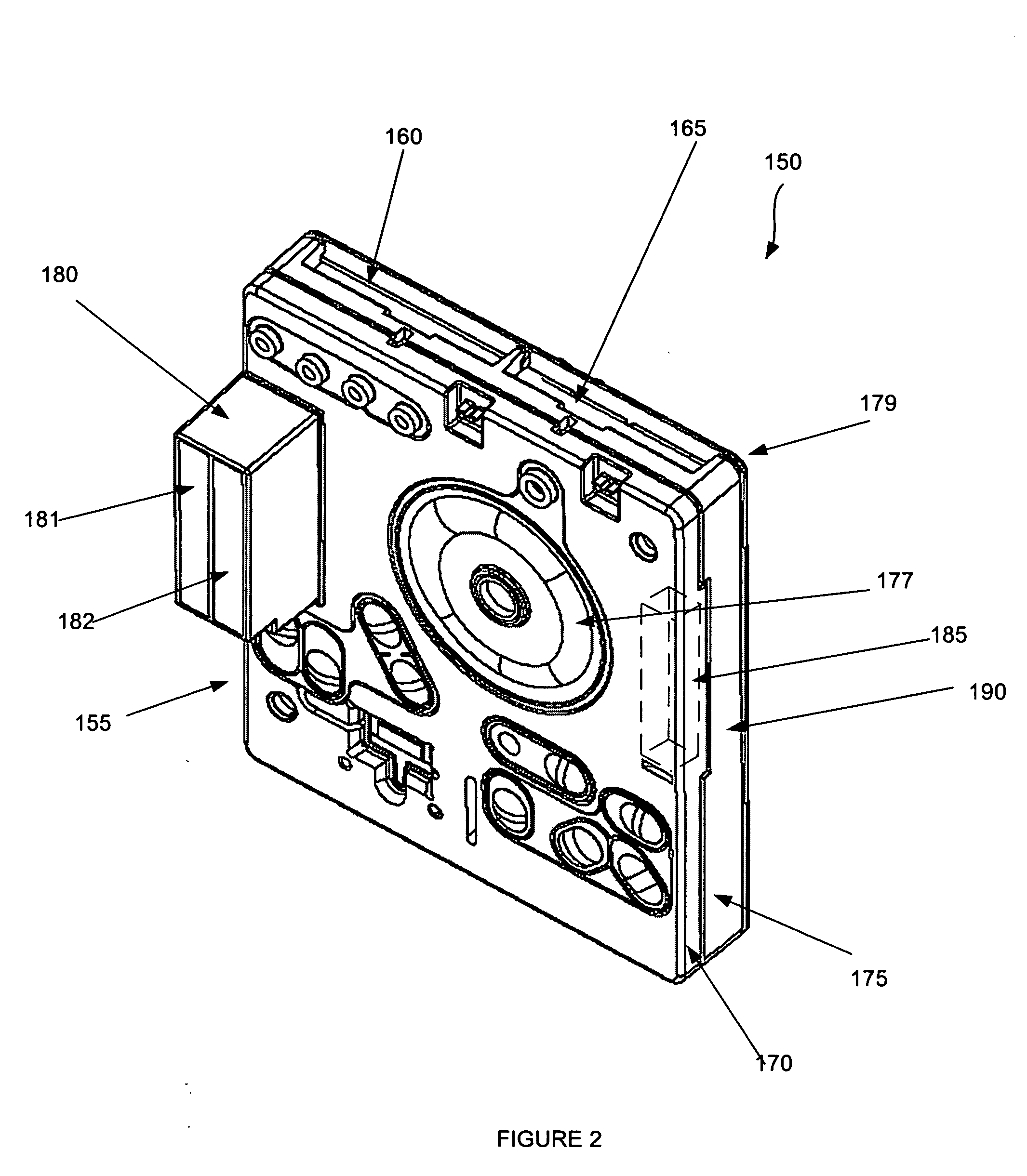
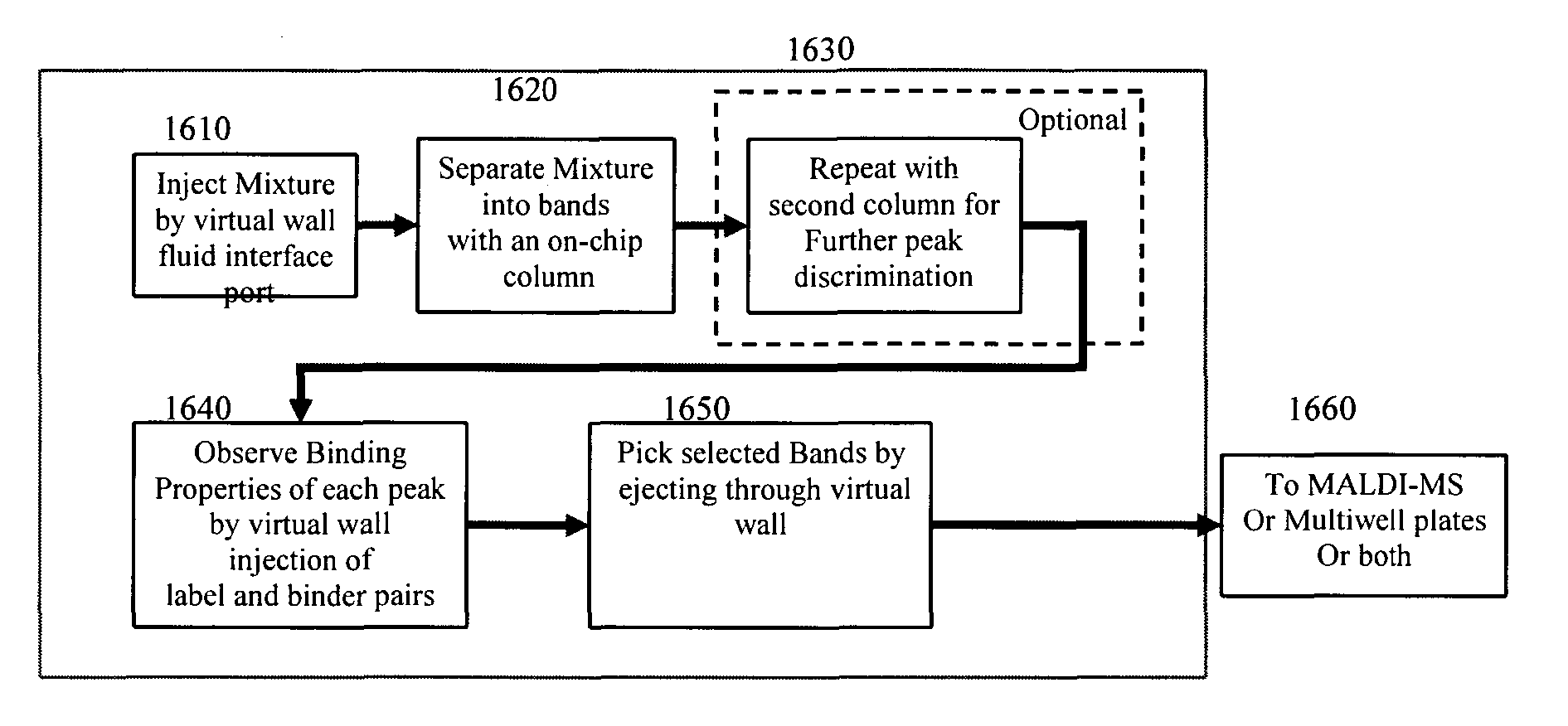
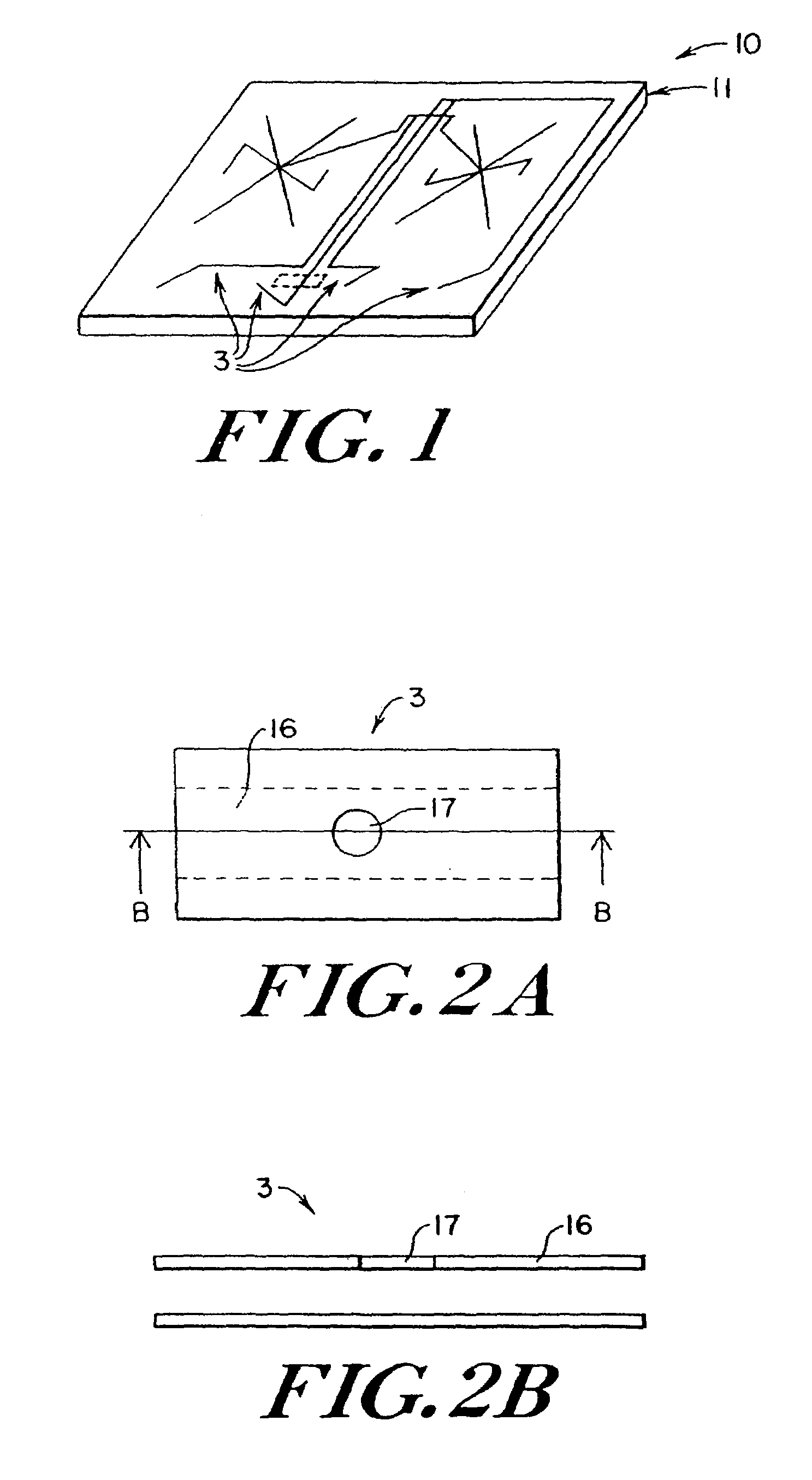
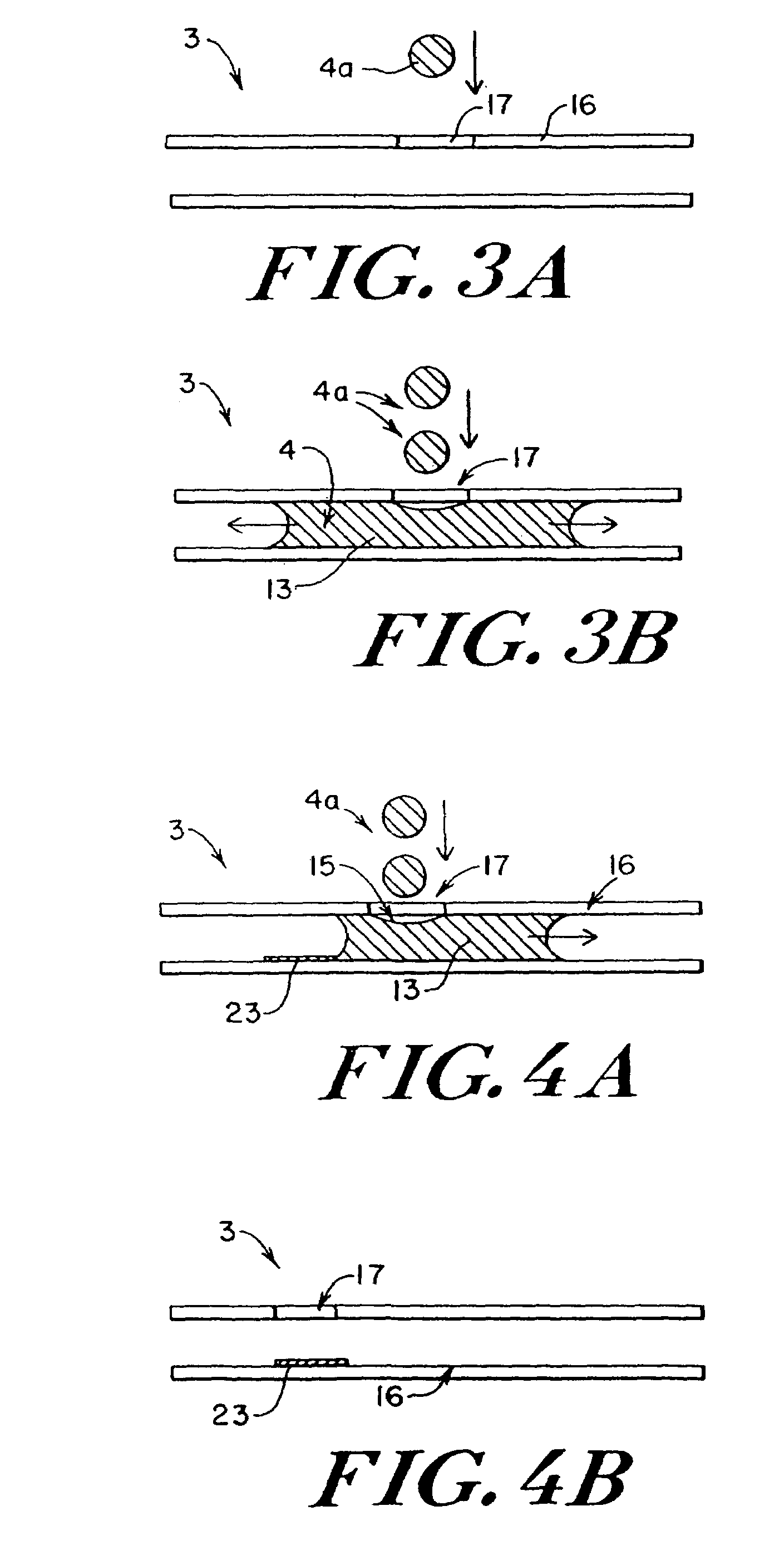
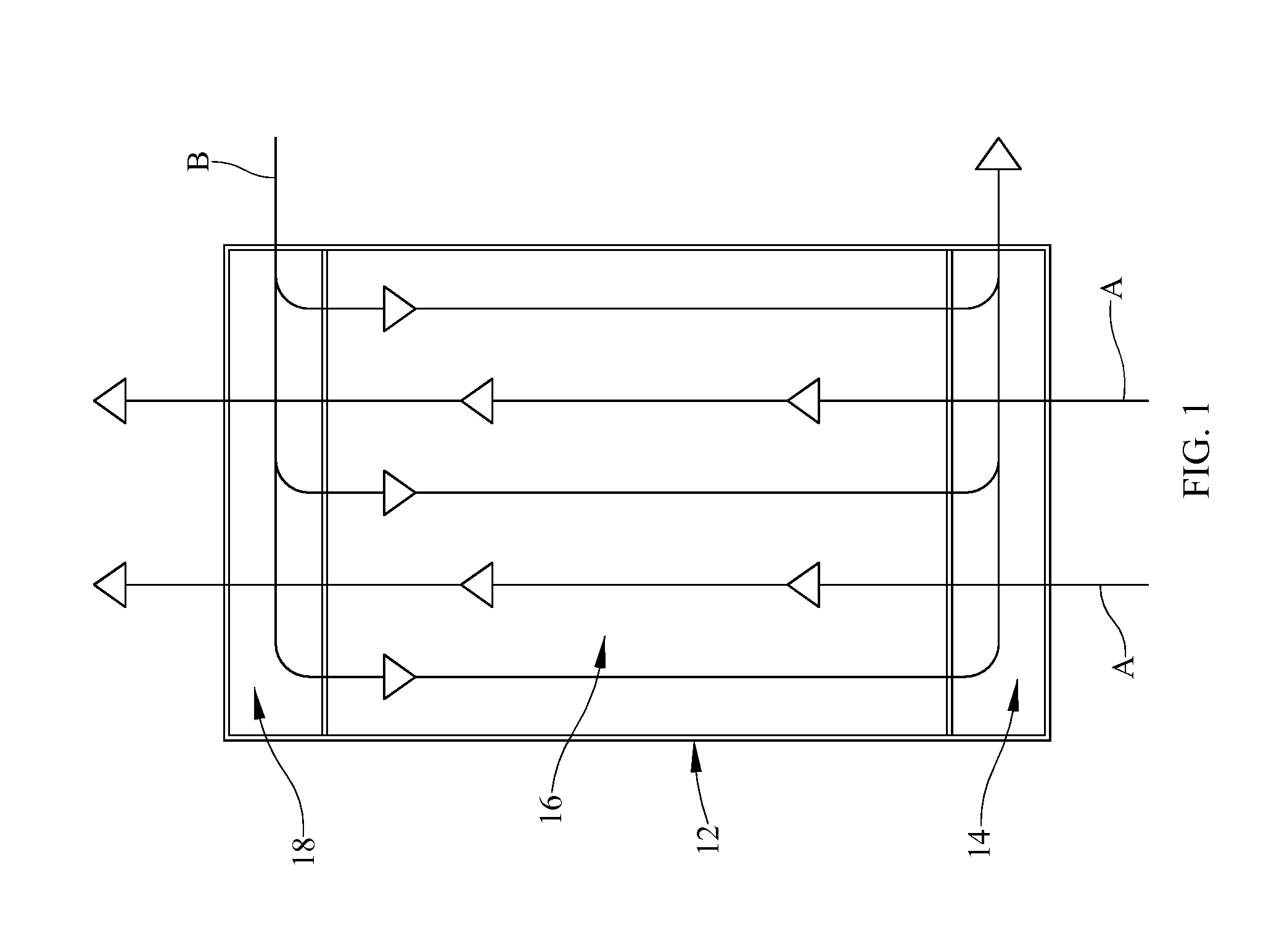
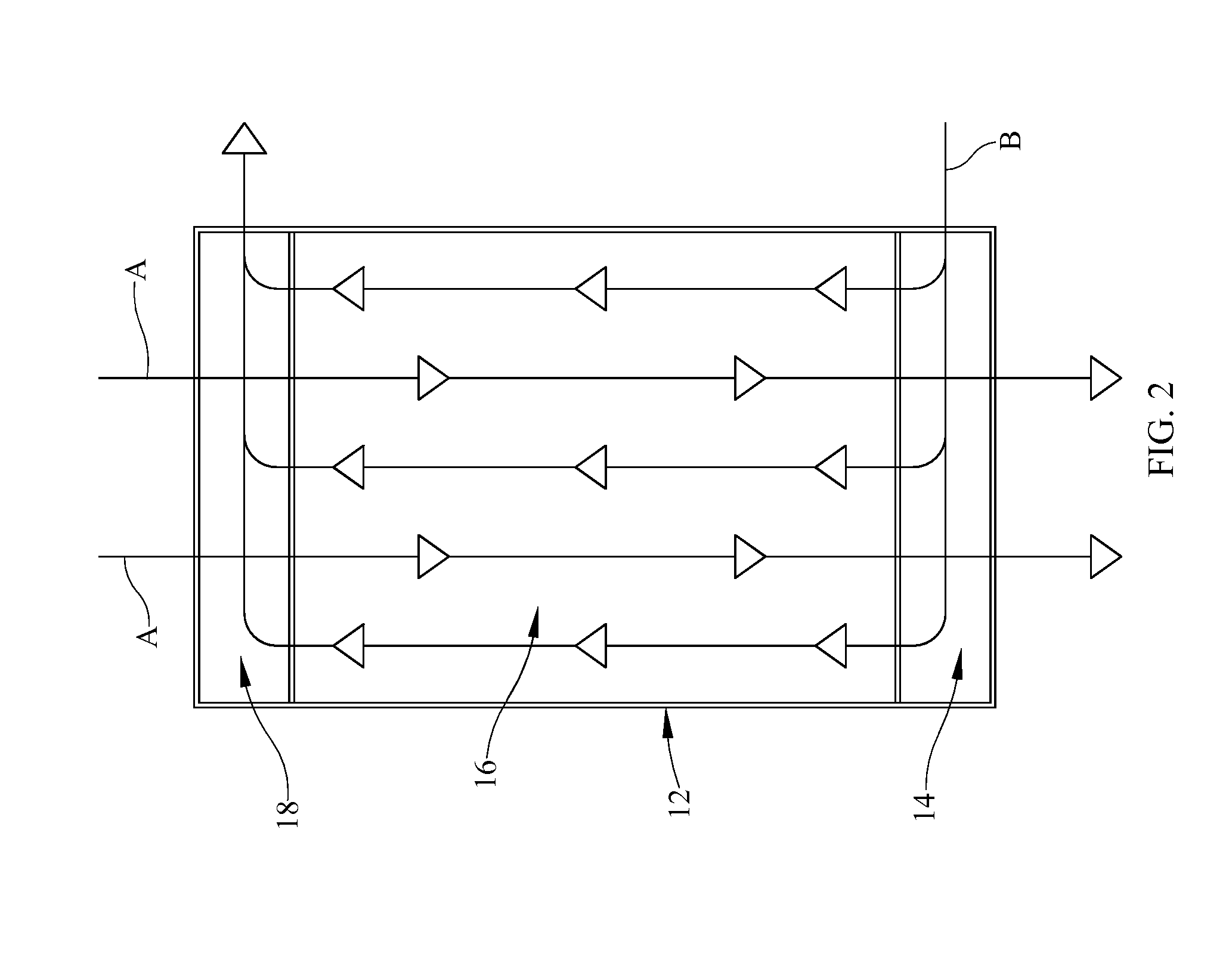
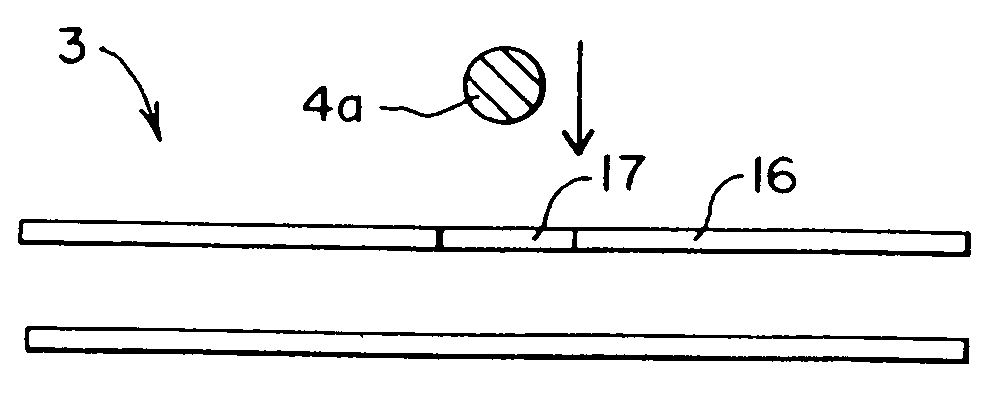
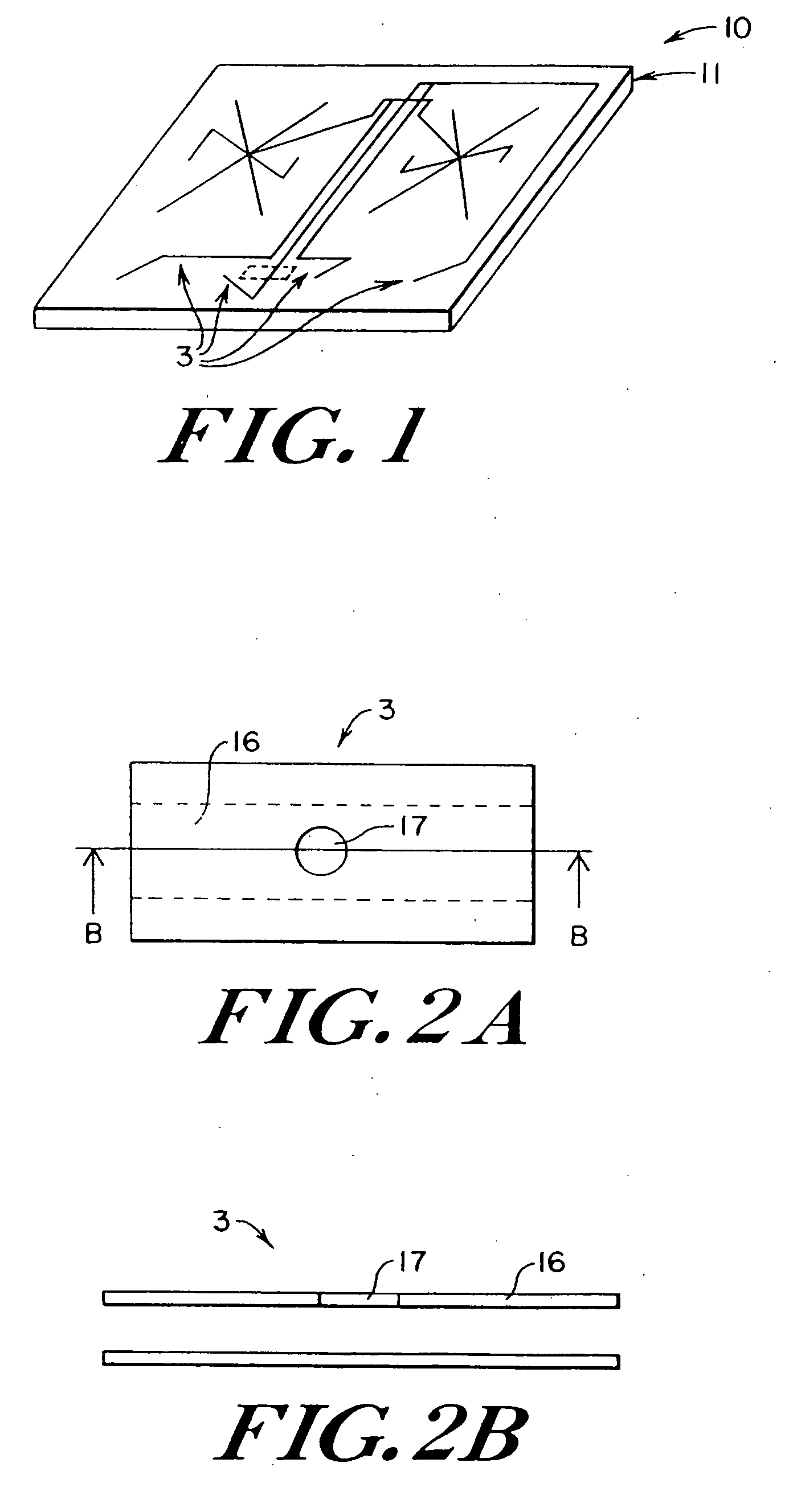
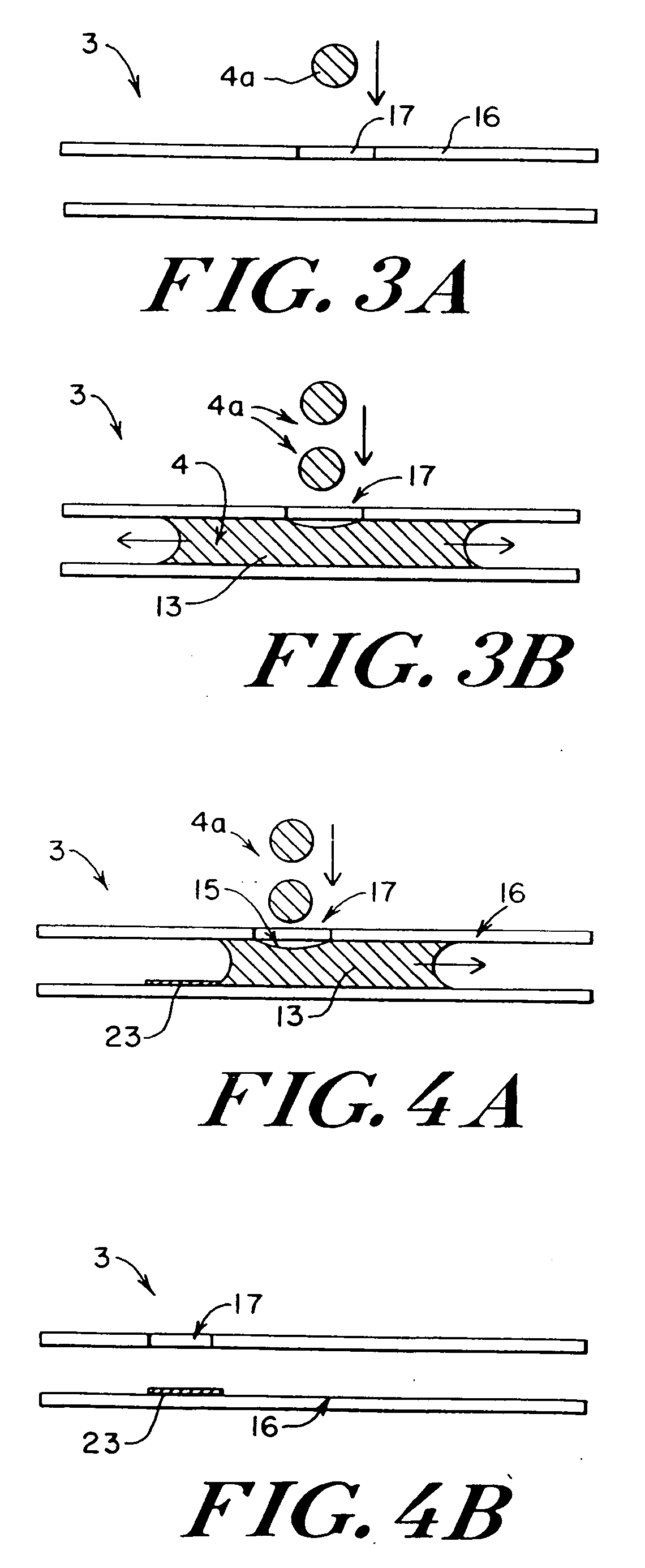
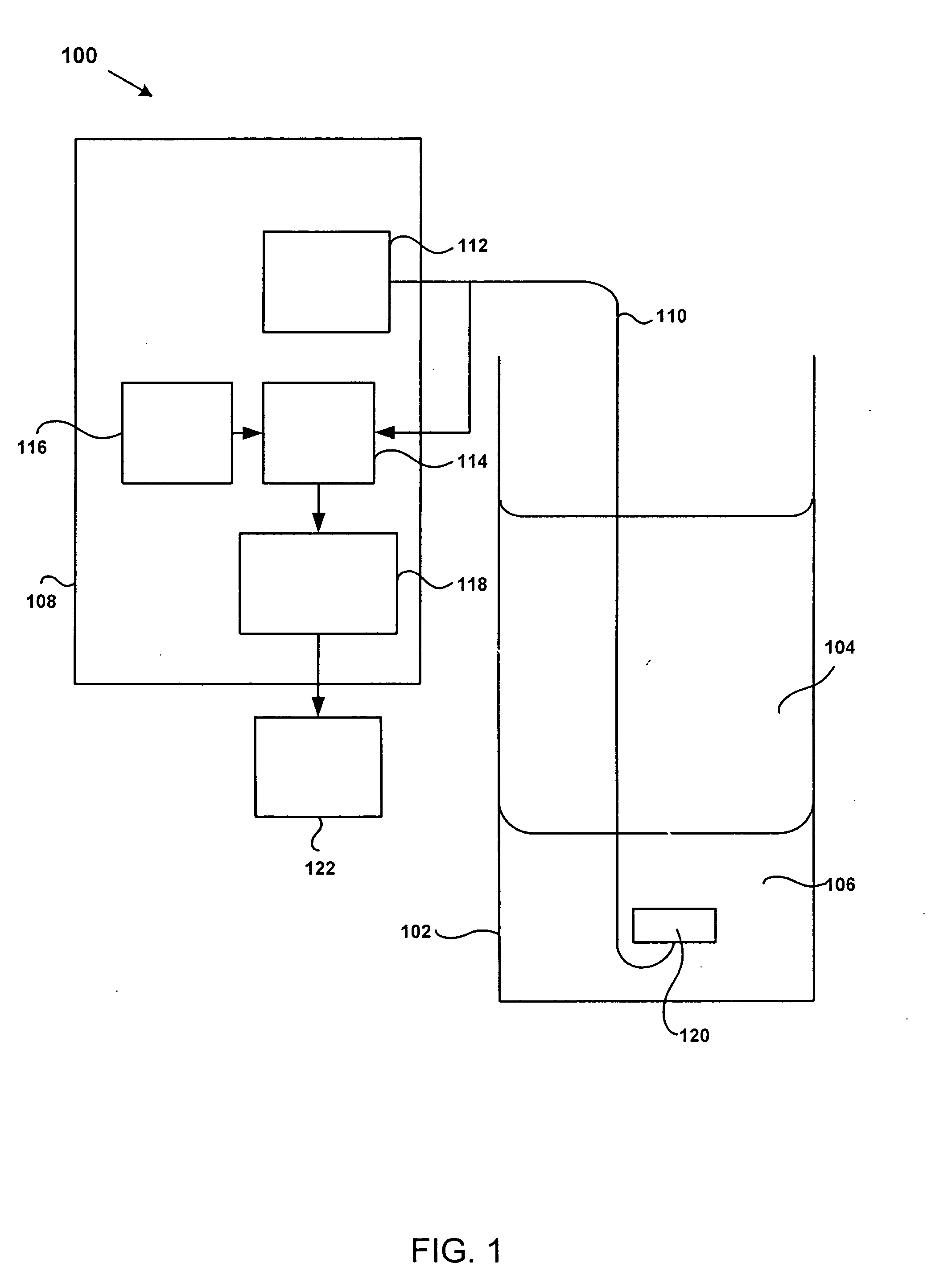
Microfluidic system including a virtual wall fluid interface port for interfacing fluids with the microfluidic system
InactiveUS7179423B2Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementFluid interfaceBiomedical engineering
A fluid interface port in a microfluidic system and a method of forming the fluid interface port is provided. The fluid interface port comprises an opening formed in the side wall of a microchannel sized and dimensioned to form a virtual wall when the microchannel is filled with a first liquid. The fluid interface port is utilized to fill the microchannel with a first liquid, to introduce a second liquid into the first liquid and to eject fluid from the microchannel.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Apparatus and method of detecting interfaces between well fluids
An apparatus for use in circulating cement in a casing in a wellbore is described having a first component such as a sensor disposed on the casing and a second component such as a detectable device disposed at a fluid interface formed between the cement and a fluid. The sensor may be a sensor coil mounted on the perimeter of the lower end of the casing, while the detectable device may be a transponder capable of emitting Radio Frequency Identification signals to the sensor to signal its arrival at the lower end of the casing. The transponder may be encased in a protective covering. Also described is a method of cementing a casing utilizing a first component such as a sensor disposed on the casing and a second component such as a detectable device disposed in the cement.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC
System and method of non-invasive continuous level sensing
ActiveUS20080066542A1High resolutionHigh sensitivity flow rate determinationSurgical furnitureEye surgerySensor arrayAir interface
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for detecting the level of a fluid in a surgical cassette by projecting light from a linear light source into a wall of a cassette. Depending on the amount a light reflected or refracted in the cassette (i.e., due to the cassette material / fluid interface or cassette material / air interface (or other interface)) various portions of a linear sensor array will be more or less illuminated. By examining the illumination of the linear sensor array, the level of fluid in the chamber can be determined.
Owner:ALCON INC
Apparatus and method of detecting interfaces between well fluids
An apparatus for use in circulating cement in a casing in a wellbore is described having a first component such as a sensor disposed on the casing and a second component such as a detectable device disposed at a fluid interface formed between the cement and a fluid. The sensor may be a sensor coil mounted on the perimeter of the lower end of the casing, while the detectable device may be a transponder capable of emitting Radio Frequency Identification signals to the sensor to signal its arrival at the lower end of the casing. The transponder may be encased in a protective covering. Also described is a method of cementing a casing utilizing a first component such as a sensor disposed on the casing and a second component such as a detectable device disposed in the cement.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC
Microfluidic system including a virtual wall fluid interface port for interfacing fluids with the microfluidic system
InactiveUS7211442B2Quick measurementTransportation and packagingChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsFluid interfaceBiomedical engineering
A fluid interface port in a microfluidic system and a method of forming the fluid interface port is provided. The fluid interface port comprises an opening formed in the side wall of a microchannel sized and dimensioned to form a virtual wall when the microchannel is filled with a first liquid. The fluid interface port is utilized to perform a labeling operation on a sample.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
System and method for cleaning a vehicle-mounted sensor
ActiveUS20170313286A1Reduce in quantityPromote quick completionFlexible member pumpsPiston pumpsFluid interfaceEngineering
An aspect of the invention refers to a system for cleaning an external vehicle-mounted sensor surface. The system comprises an air nozzle arranged to discharge air onto a sensor surface; an air pump comprising a fluid inlet, an air outlet, an air-fluid interface and a variable volume compression chamber communicated with the air outlet; an air flow control device communicated with the air nozzle and the air outlet for controlling the flow of air therethrough; and a liquid pump communicated with the fluid inlet to supply a flow of pressurized liquid such that the volume of the compression chamber varies to generate a volume of pressurized air with an absolute pressure below 10 bar.
Owner:FICO TRANSPAR
Fluid interface cartridge for a microfluidic chip
InactiveUS20110008223A1Pharmaceutical containersMaterial analysis by optical meansFluid interfaceEnvironmental engineering
An interface cartridge for a microfluidic chip, with microfluidic process channels and fluidic connection holes at opposed ends of the process channels, provides ancillary fluid structure, including fluid flow channels and input and / or waste wells, which mix and / or convey reaction fluids to the fluidic connection holes and into the process channels of the microfluidic chip.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
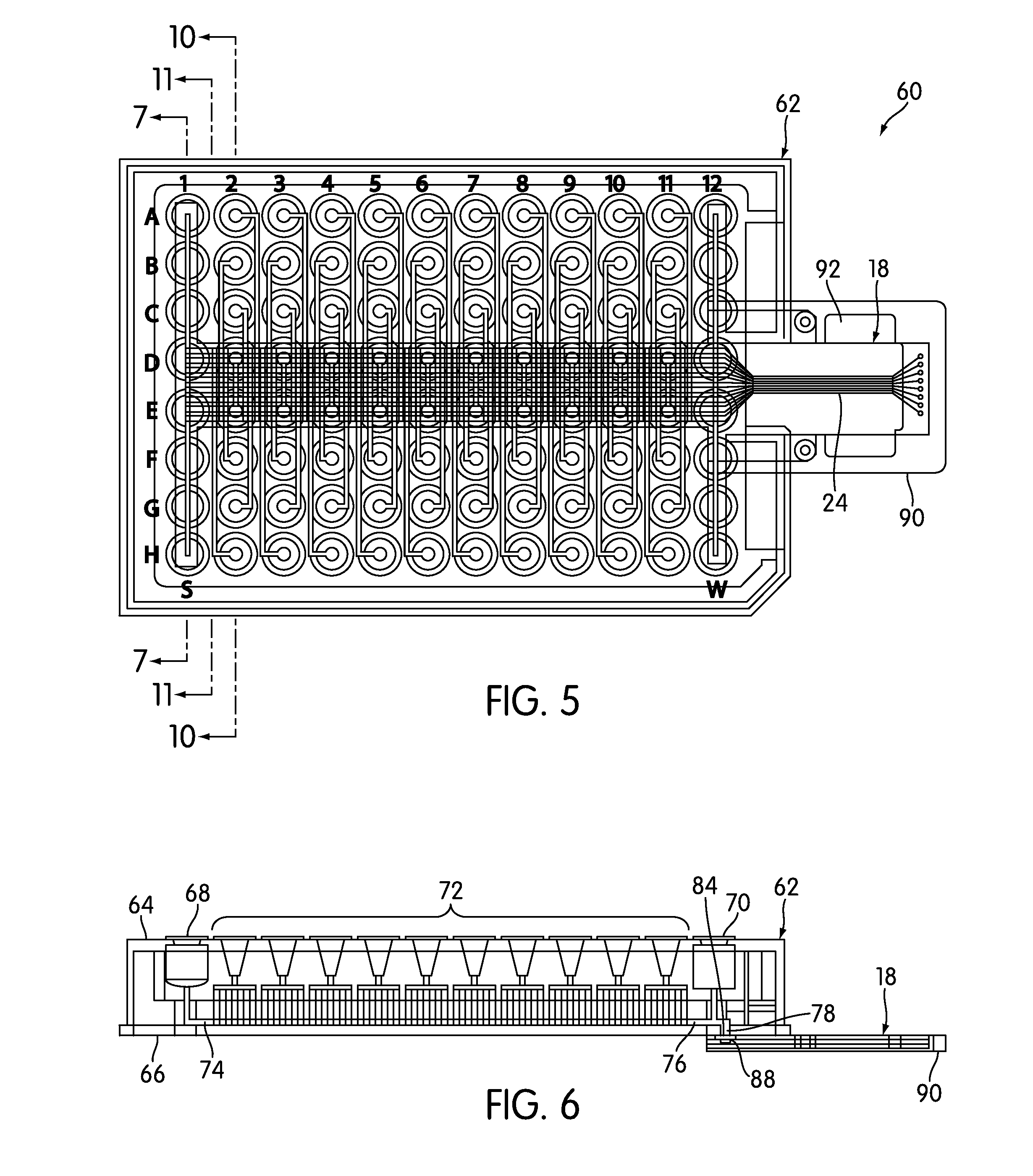
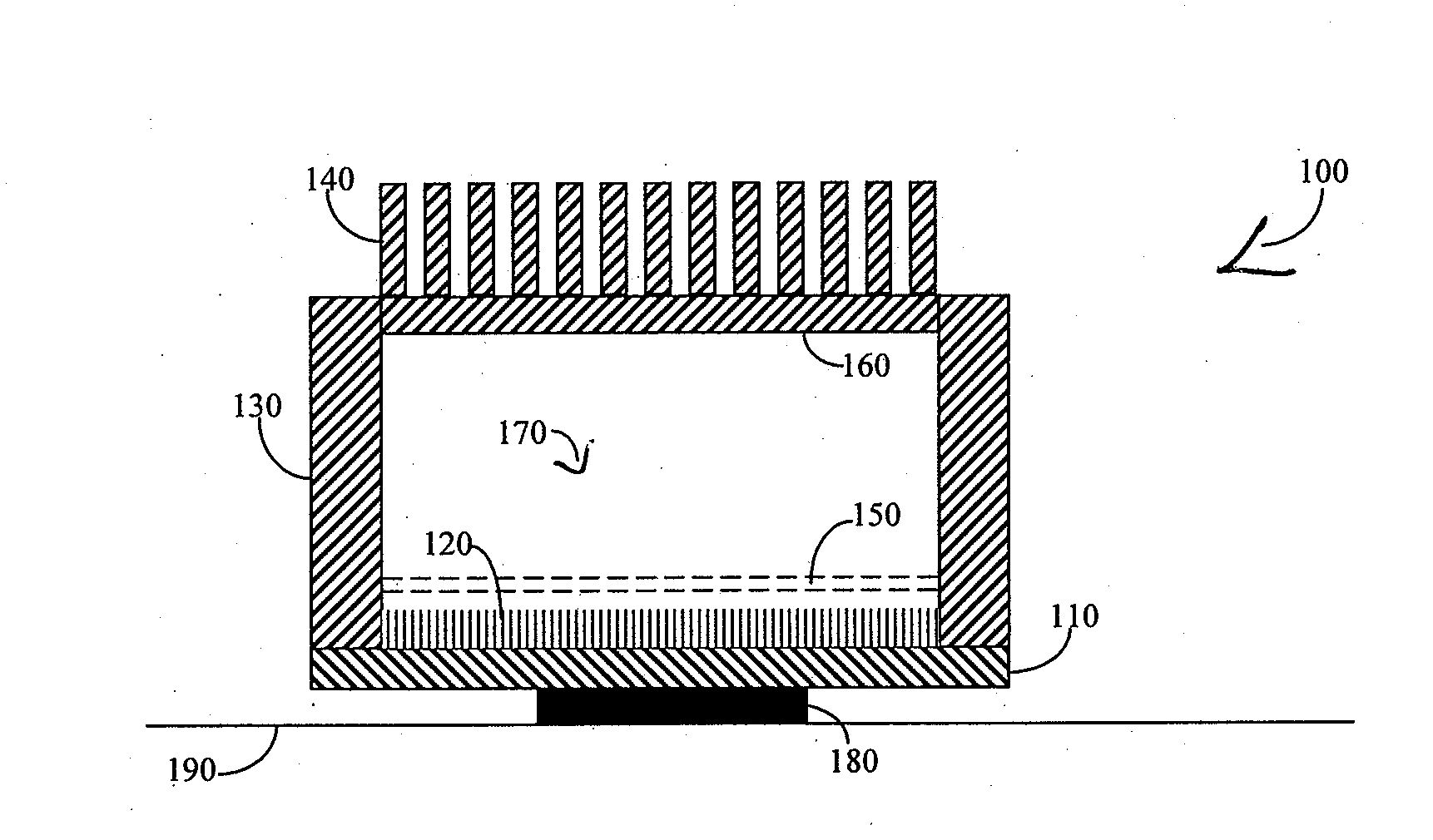
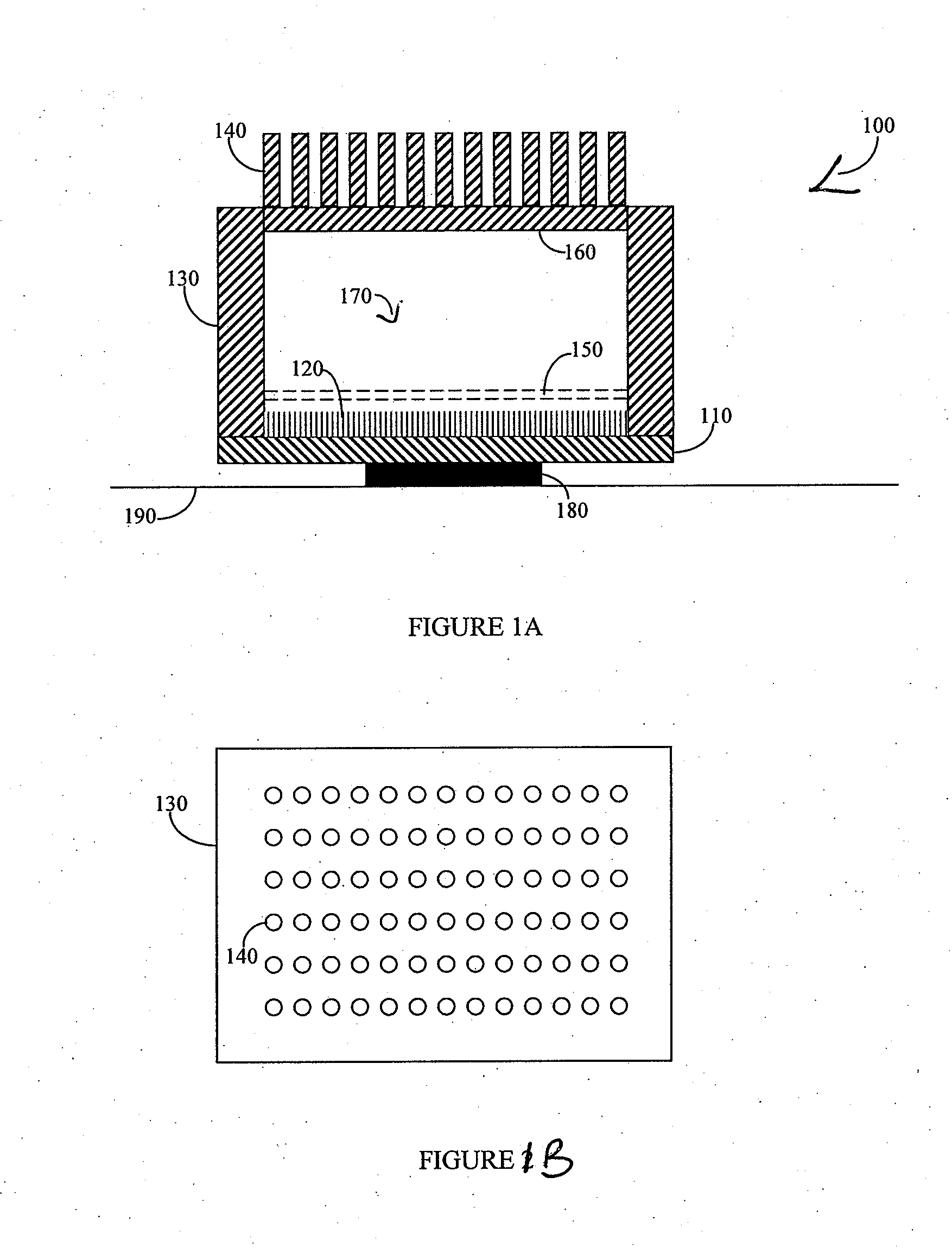
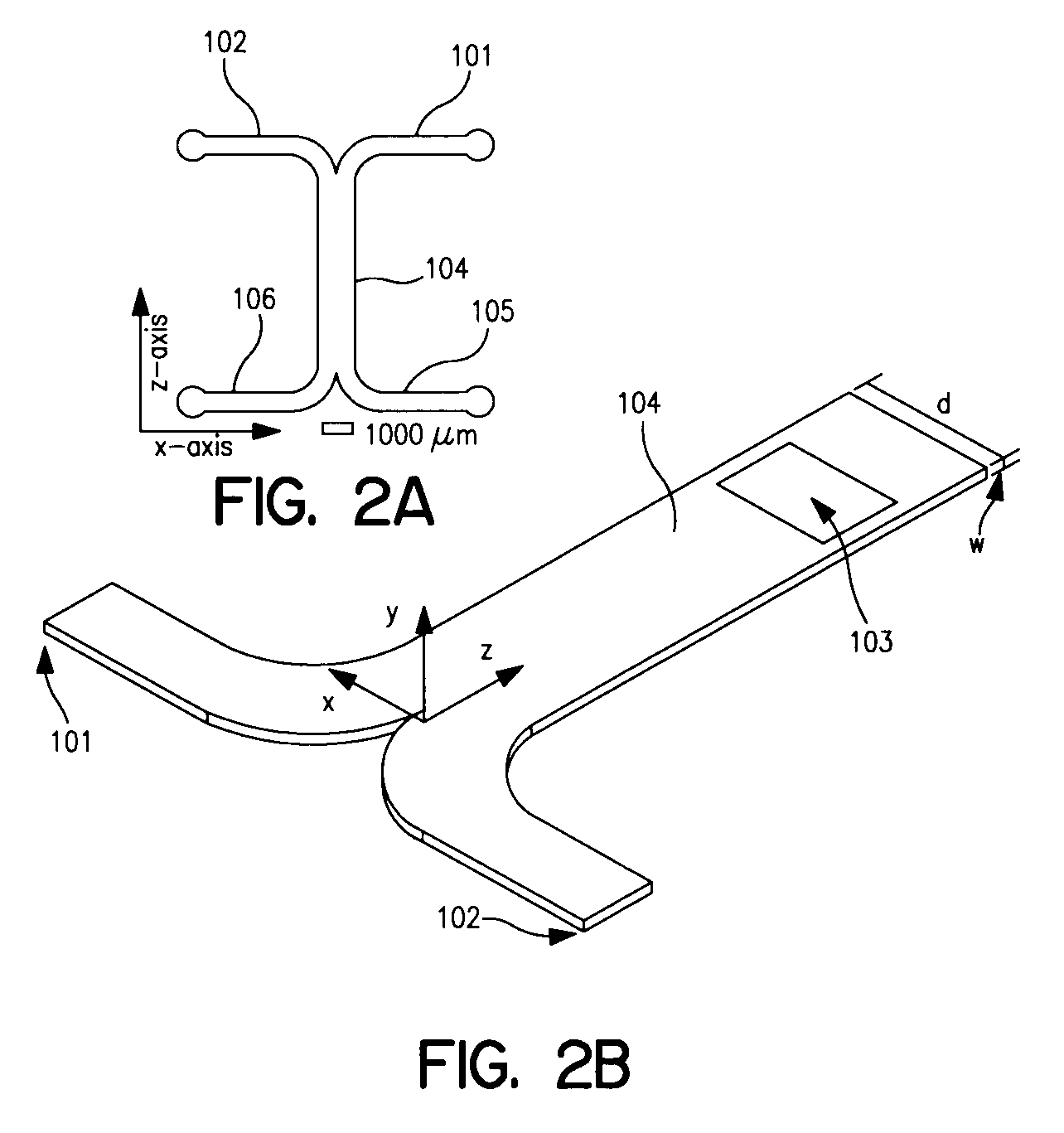
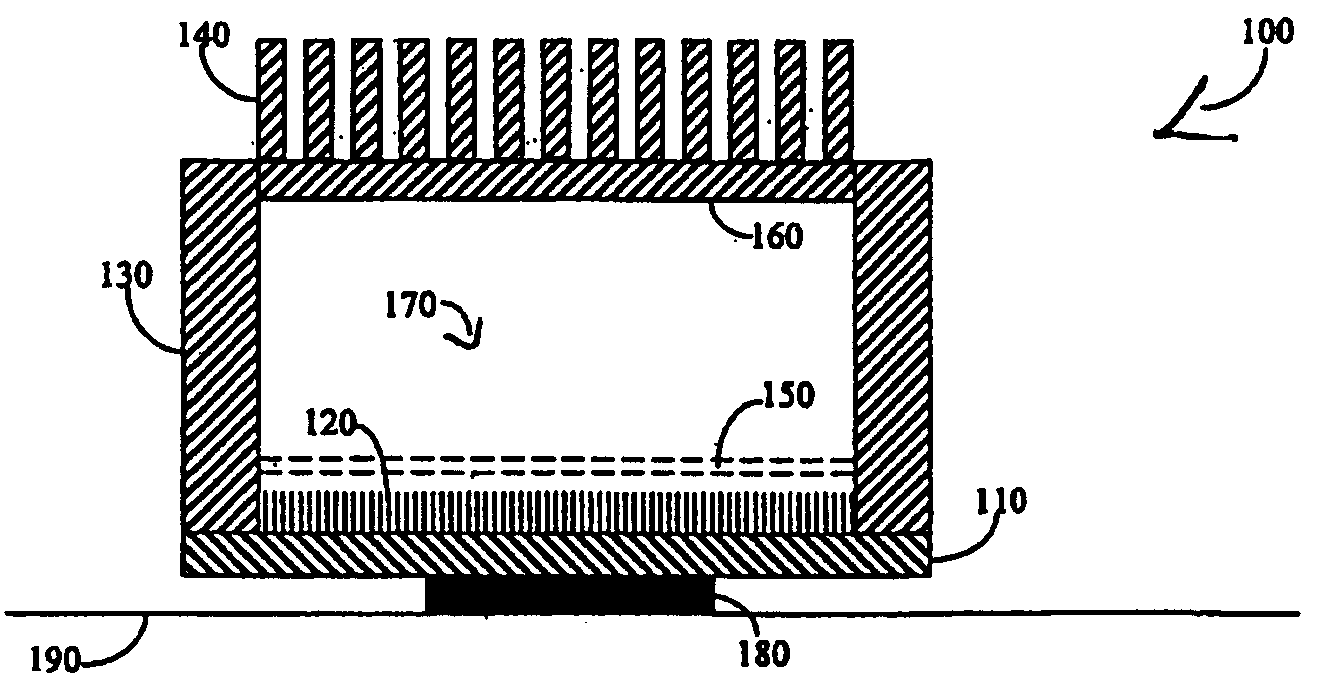
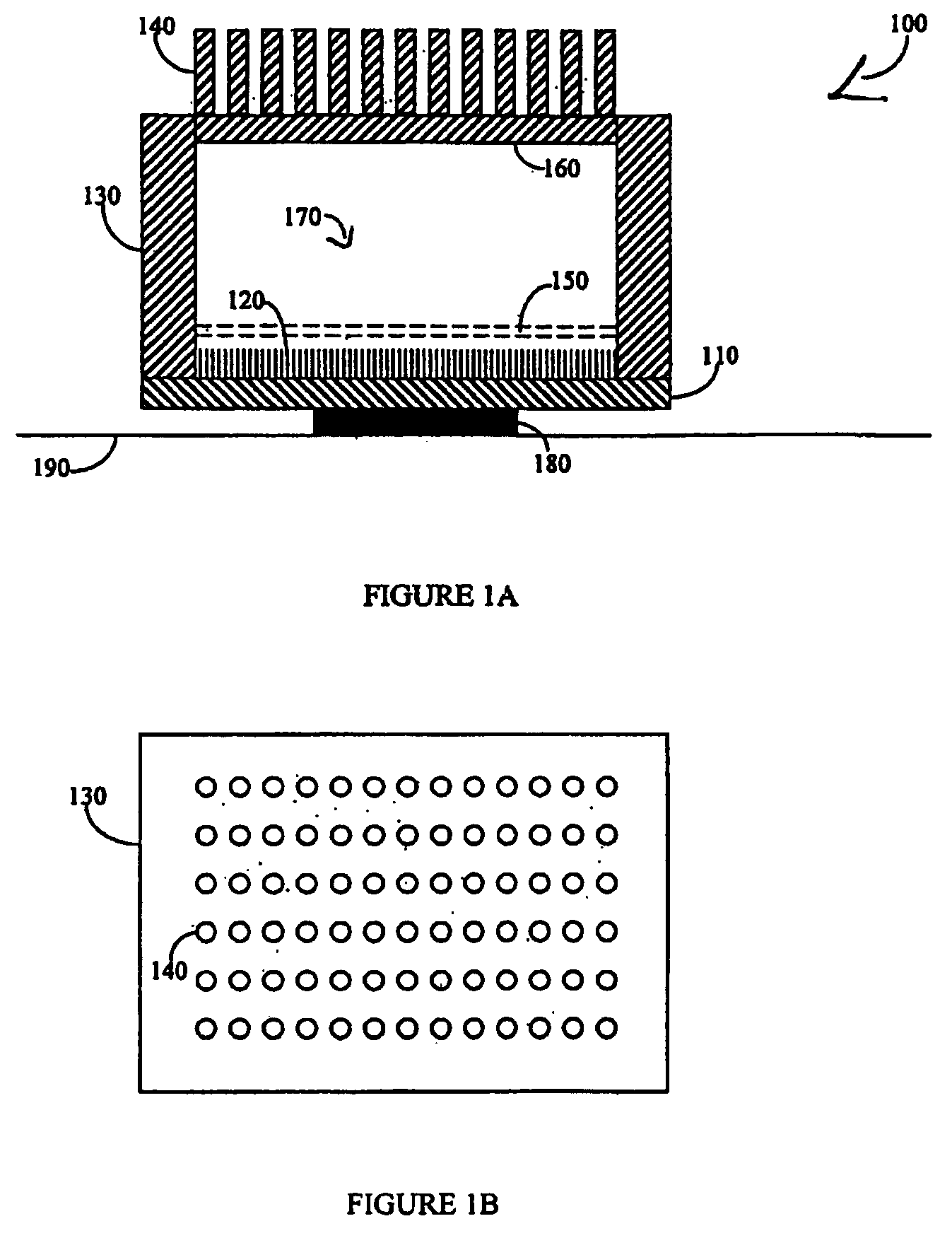
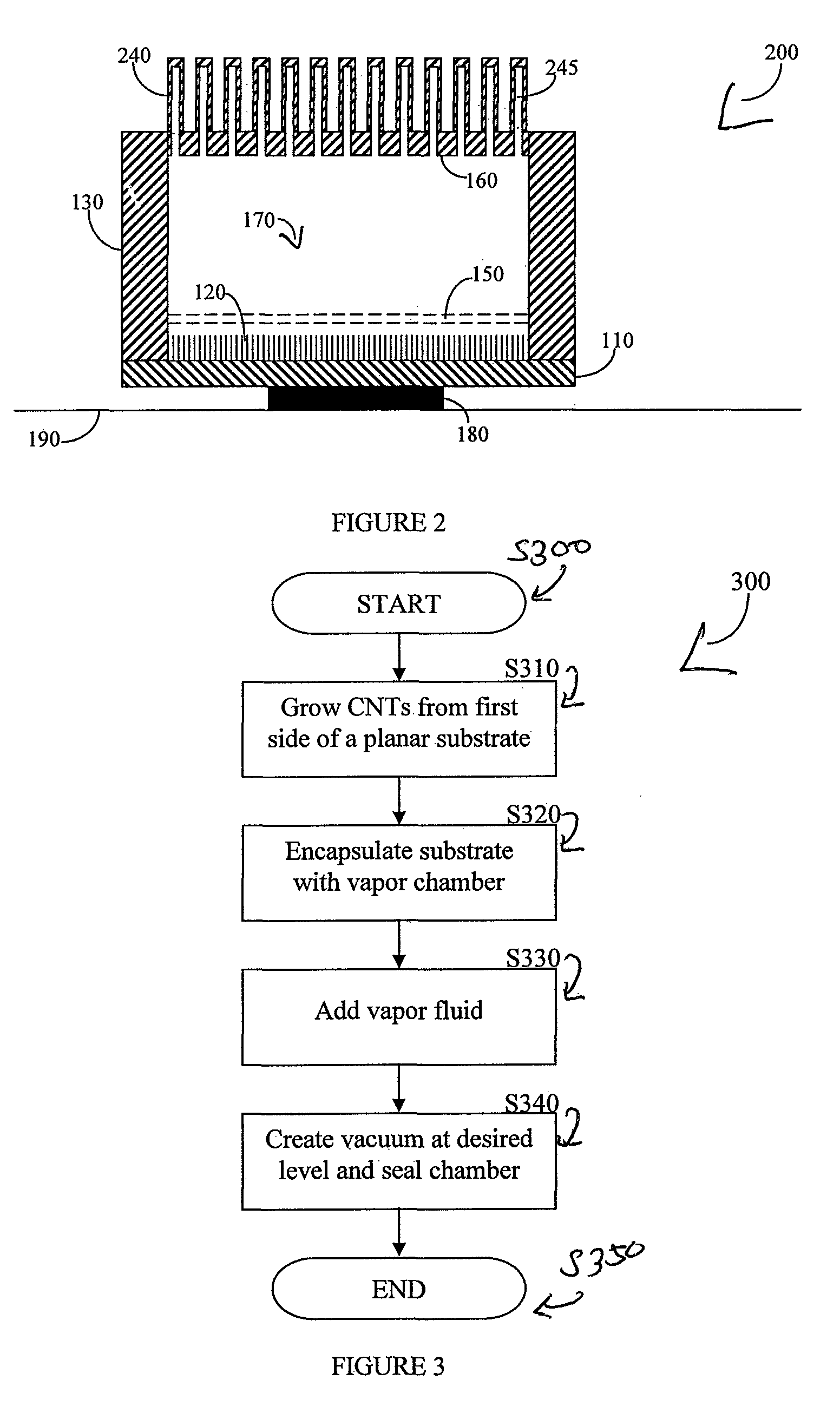
Vapor chamber heat sink having a carbon nanotube fluid interface
An enhanced heat transposer comprised is of a vapor chamber. The surface of the vapor chamber that holds the fluid comprises an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) that are grown in a way that enables the fluid to come into maximum contact with the CNTs. The fluid evaporates in the sealed vapor chamber when it is in touch with a hot surface. The vapor comes in contact with a hollow pin-fin structure that provides additional surface area for vapor cooling and heat transfer. The condensed vapor then drops back into the fluid container, and the cycle continues.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Microfluidic device wherein the liquid/fluid interface is stabilized
InactiveUS7591936B2Easy to implementIncrease contact surfaceCellsSludge treatmentFluid interfaceBiomedical engineering
The microfluidic device comprises at least one microchannel bounded by a bottom wall, side walls and a top wall and which is designed to contain at least one liquid and at least one fluid non-miscible with the liquid. The microfluidic device comprises means for stabilizing the interface between the liquid and the fluid. The means for stabilizing comprise at least one electrode arranged on at least one part of a first wall of the microchannel, over the entire length thereof, and at least one counter-electrode arranged over the entire length of the microchannel, on at least one part of a second wall, arranged facing the electrode. The electrode and counter-electrode are preferably respectively arranged on the bottom and top wall of the microchannel.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Fill material for direct-contact heat/mass exchangers
InactiveUS20150048528A1Reduced dysfunctionSmall sizeAdditive manufacturing apparatusUsing liquid separation agentFilling materialsLinear element
Fill material for a direct contact heat exchanger wherein the fill material has flow pathways bounded by an array of linear elements, namely a mesh. The invention intentionally uses surface tension and capillary action to anchor the fluid / fluid interface in a desired location. The heat exchanger is wick or collector in direct contact with the fill material (matrix) to extract fluid without formation of large droplets. The mesh is made from a neutrally wetting material.
Owner:BARTON SEAN ANDERSON
Sphero cylindrical eye refraction system using fluid focus electrostatically variable lenses
InactiveUS20060106426A1Aberration compensationEfficient use ofElectrotherapyPhoroptersSpherical powerFluid interface
Optical devices, systems, and methods can produce and / or measure cylindrical (as well as spherical) lens shapes throughout a range of both powers and cylindrical axes. Fluid focus lenses employ electrical potentials to vary the shape of a fluid / fluid interface between two immiscible fluids having differing indices of refractions by controlling localized angles between the interface and a surrounding container wall. Spherical power, cylindrical power, and cylindrical access alignment may be varied with no moving parts (other than the fluids).
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Sphero cylindrical eye refraction system using fluid focus electrostatically variable lenses
InactiveUS7413306B2Aberration compensationEfficient use ofElectrotherapyPhoroptersSpherical powerRefractive index
Optical devices, systems, and methods can produce and / or measure cylindrical (as well as spherical) lens shapes throughout a range of both powers and cylindrical axes. Fluid focus lenses employ electrical potentials to vary the shape of a fluid / fluid interface between two immiscible fluids having differing indices of refractions by controlling localized angles between the interface and a surrounding container wall. Spherical power, cylindrical power, and cylindrical access alignment may be varied with no moving parts (other than the fluids).
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Device for dispensing medical active ingredients
InactiveUS7442181B2Accurate settingAct quicklyJet injection syringesInfusion devicesLine tubingCoupling
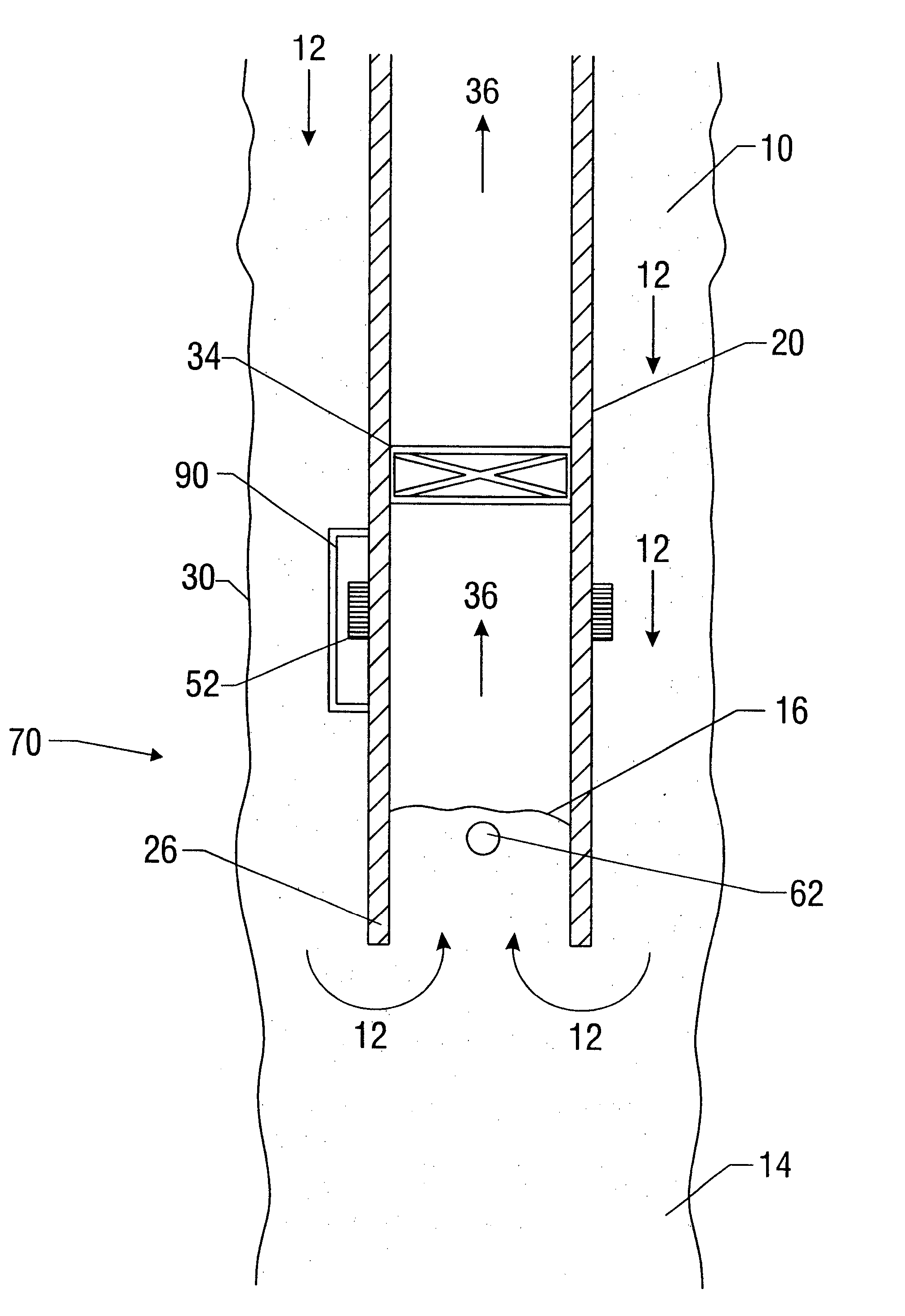
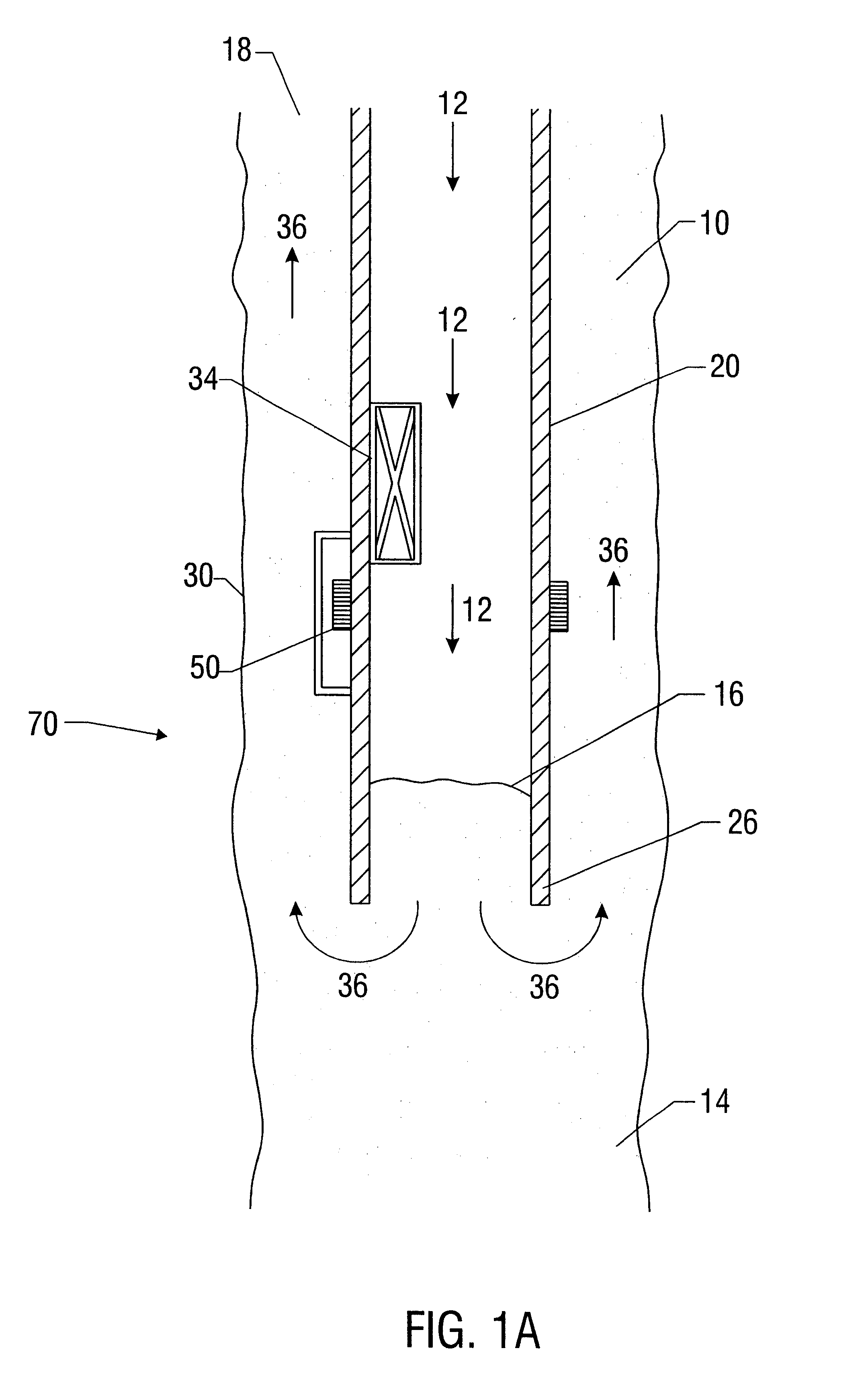
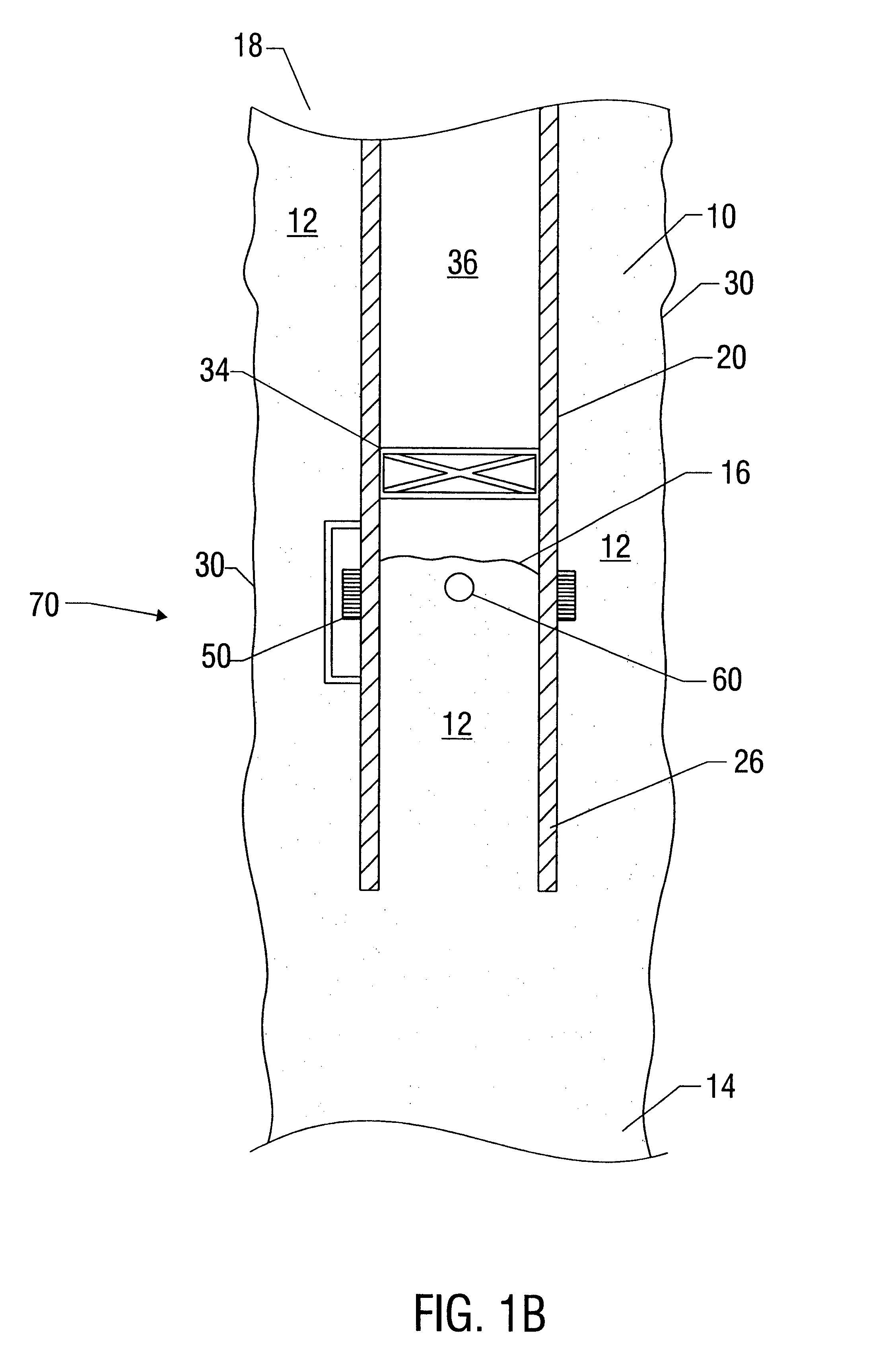
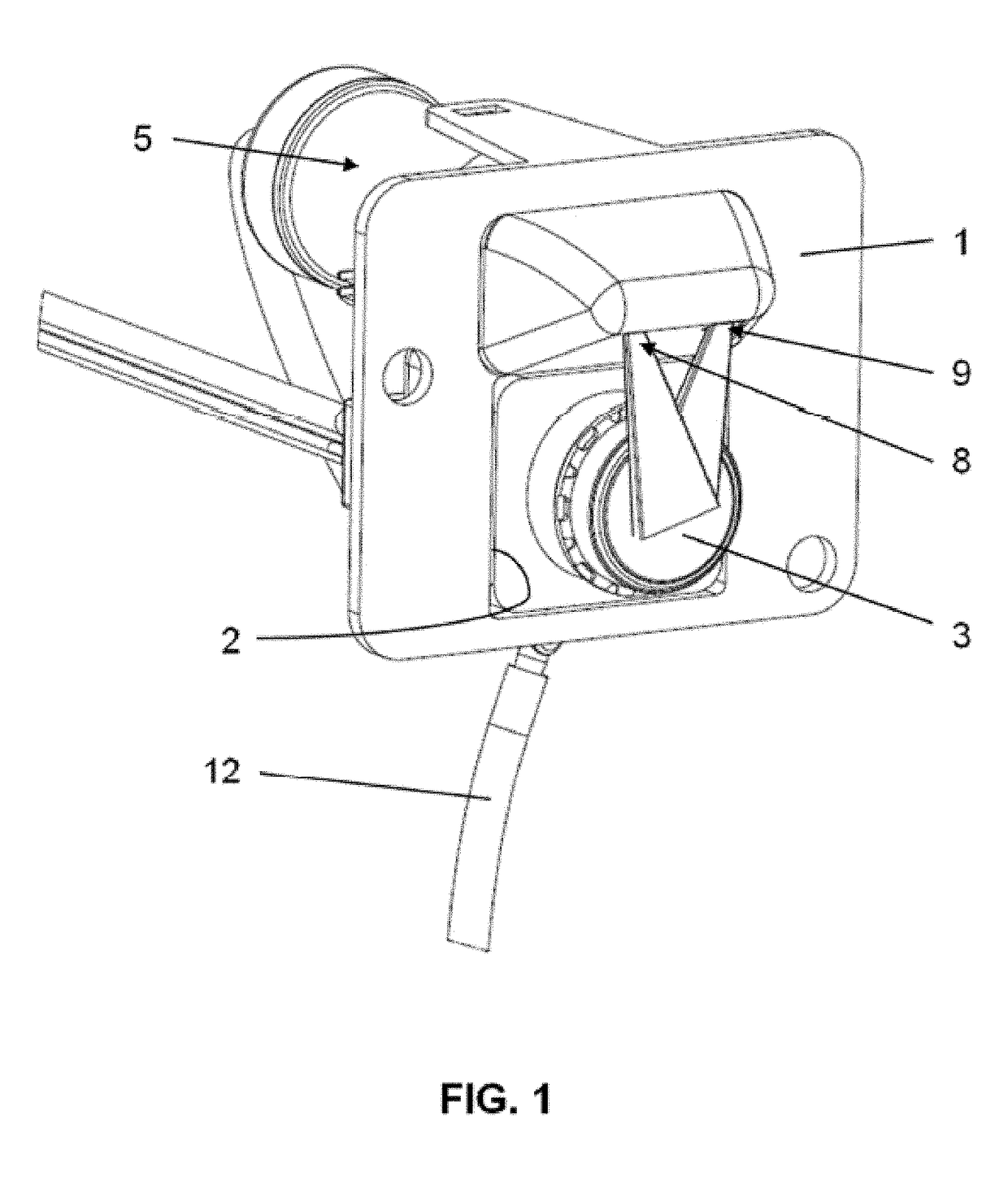
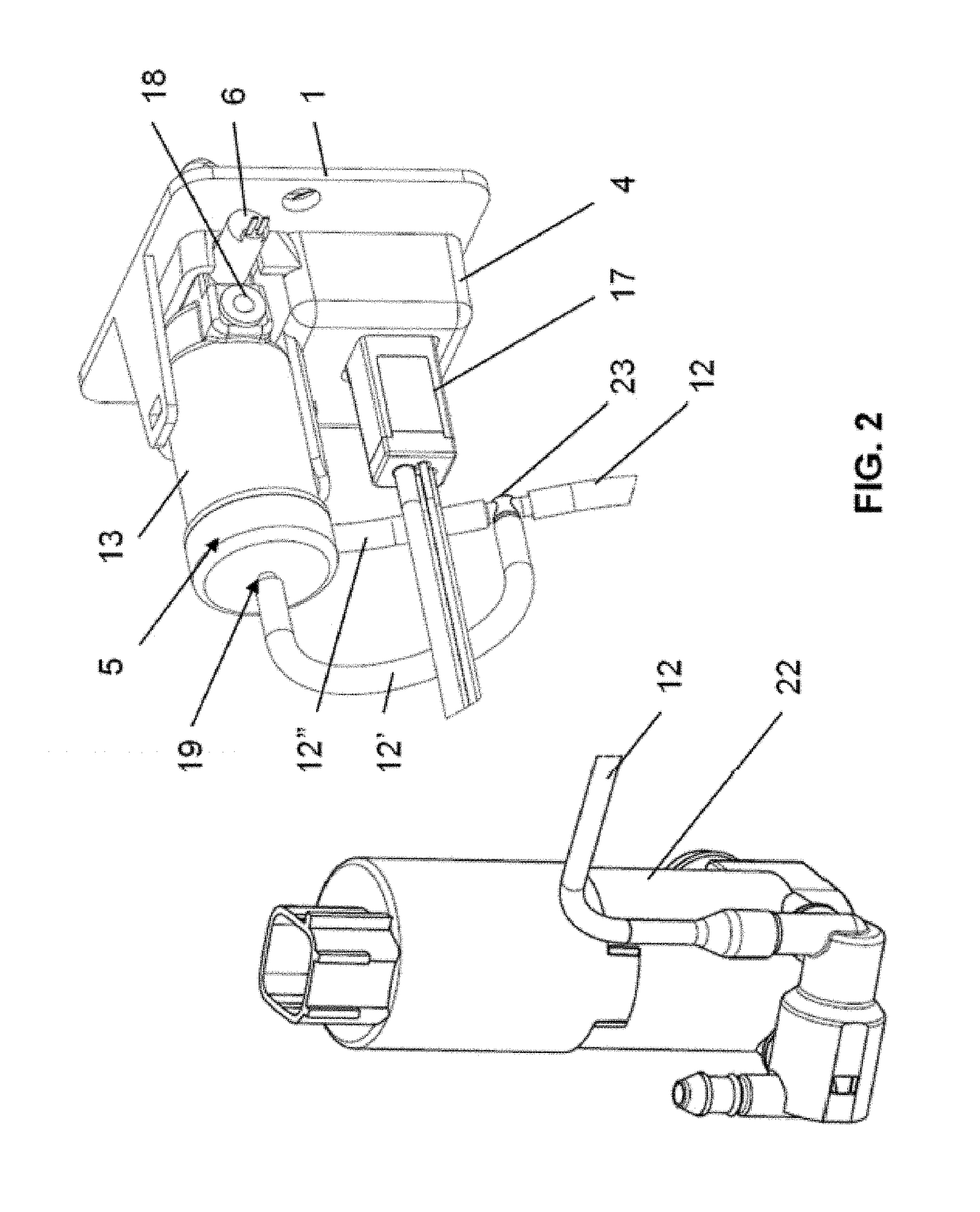
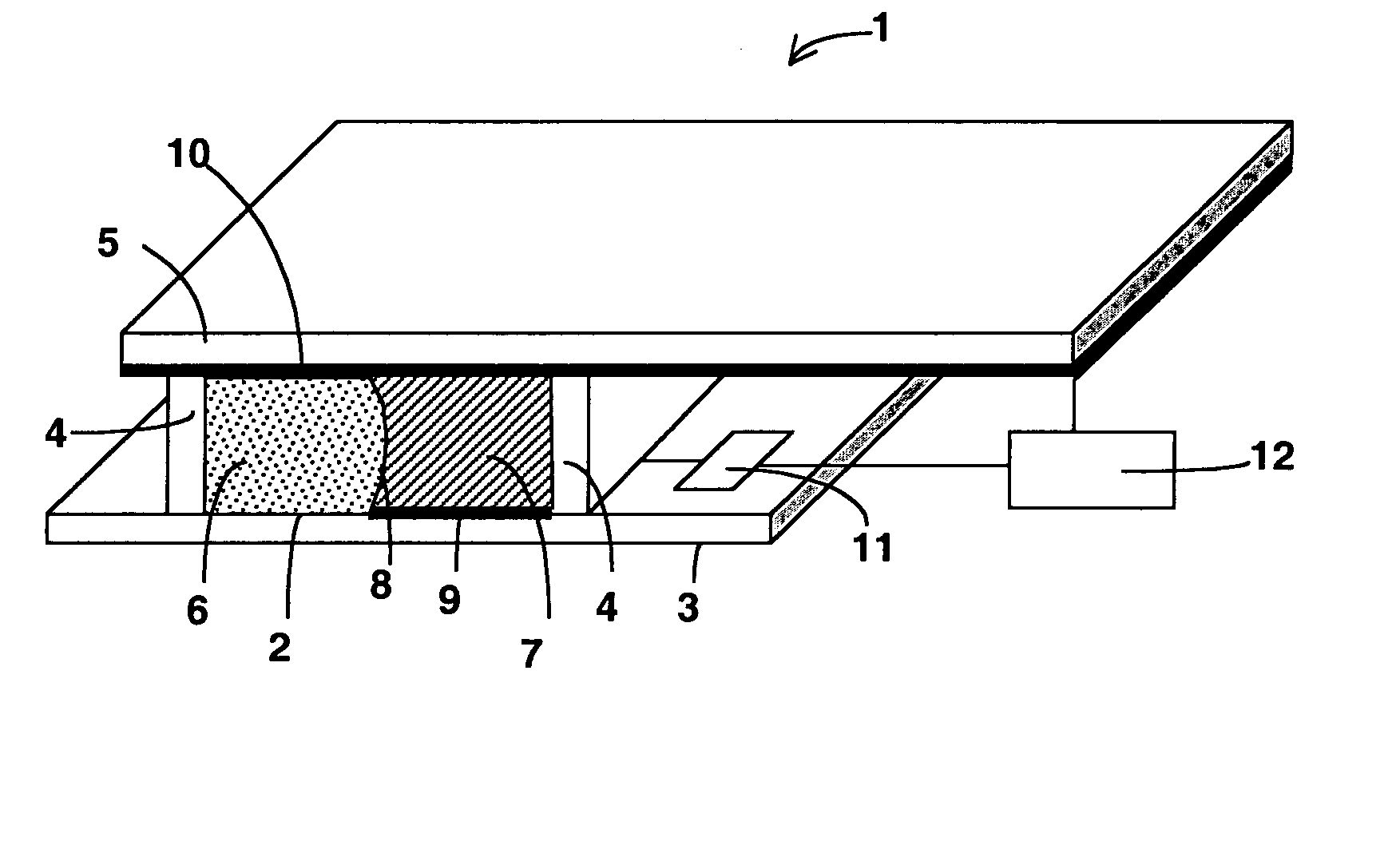
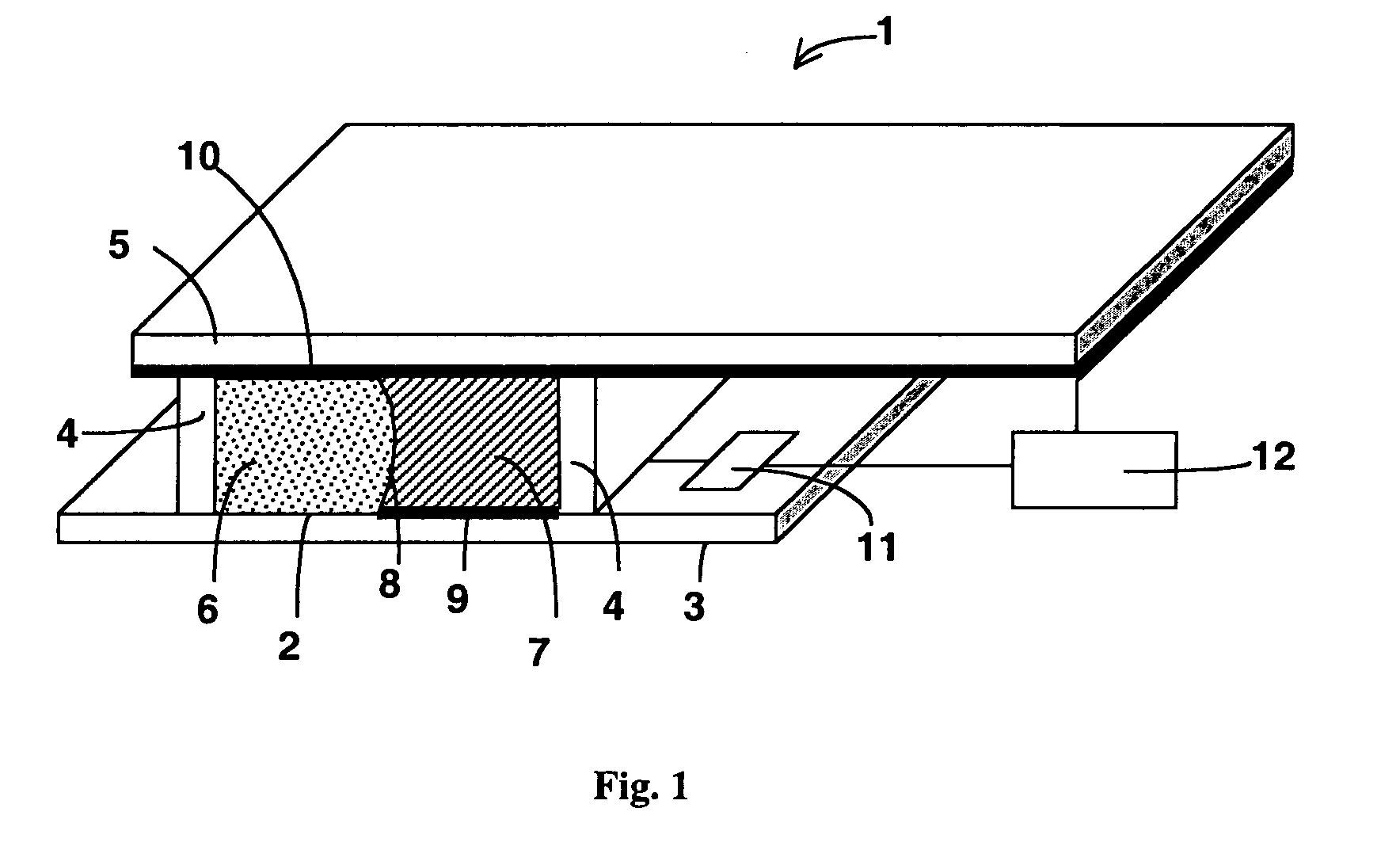
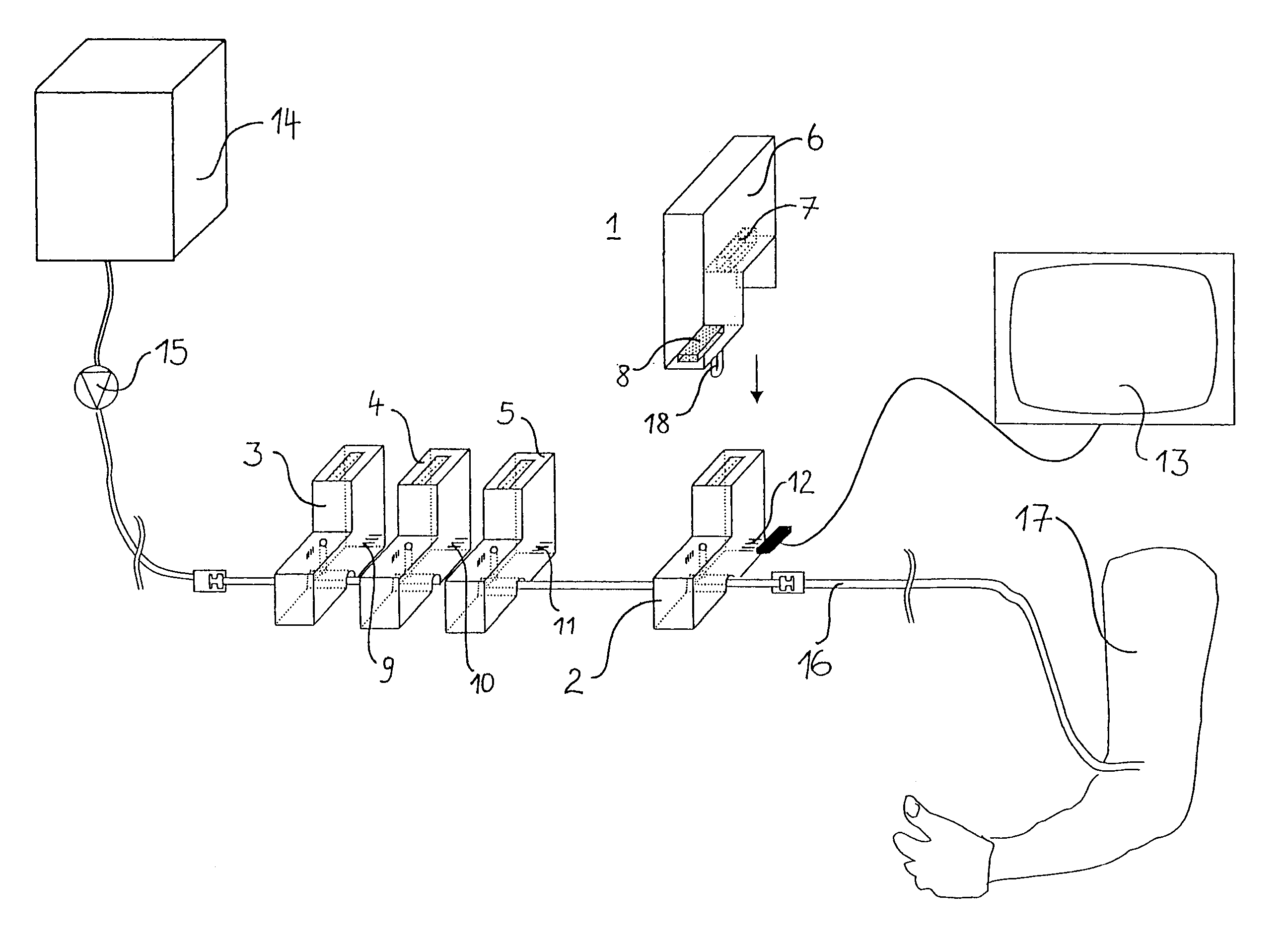
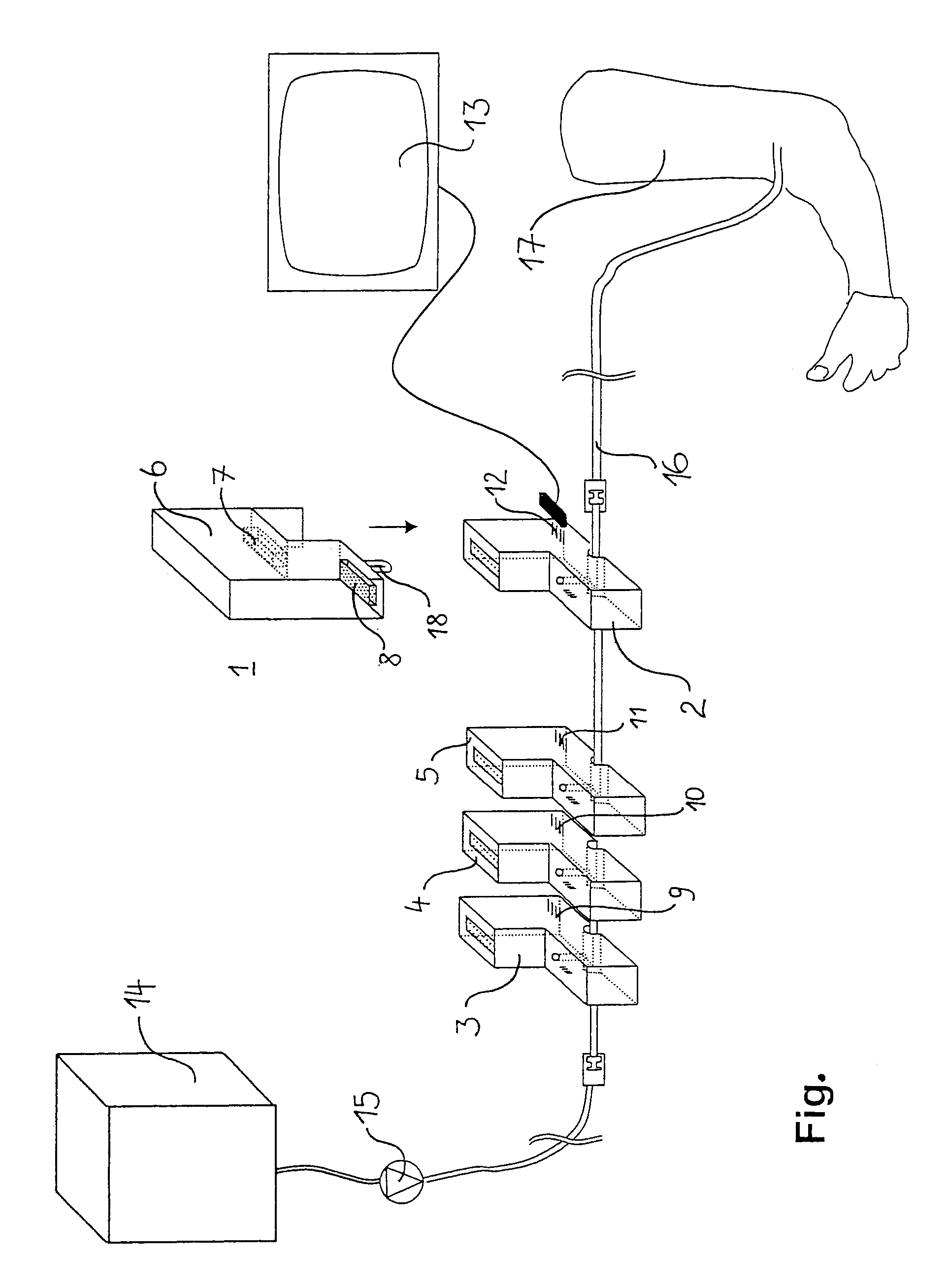
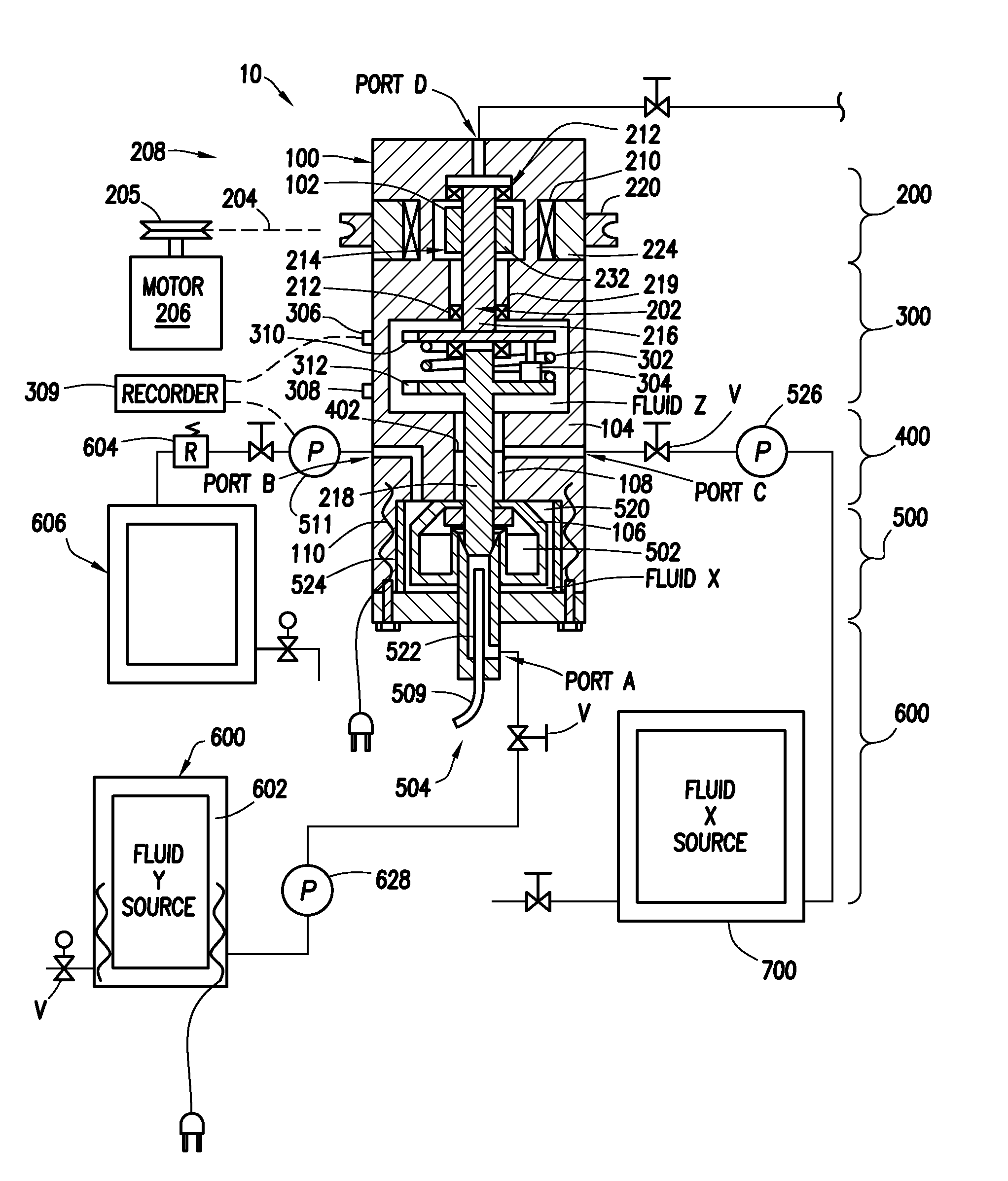
A device and system for dispensing medical active ingredients. Medical active ingredients may be, e.g., drugs or anesthetics, which enter the patient's bloodstream. Injection pumps and perfusors are usually used for their dispensing, and vapors are frequently used in the case of inhalation anesthetics. The device permits the dispensing of a plurality of medical active ingredients, in which the rates of dispensing can be set precisely and changed with rapid action. This is accomplished by the series connection of a plurality of devices according to the present invention, which are designed as modules. Each module comprises a cartridge (6) as well as a delivery device (8) for delivering the particular medical active ingredient to be administered to a fluid interface (18), which leads to a supply line (16) designed either as an infusion line or as a respiration tube. The module has a coupling means (9, 10, 11, 12).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
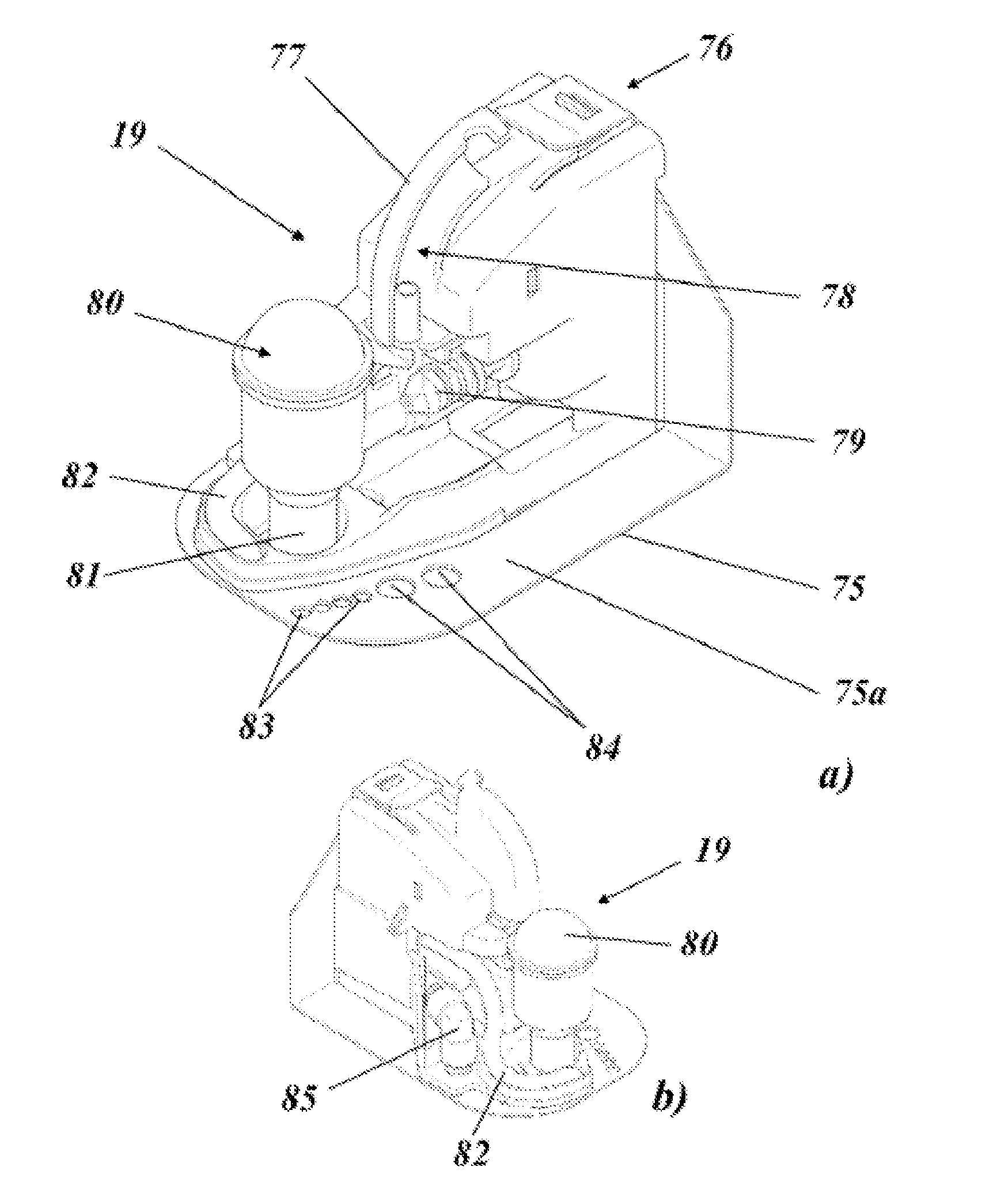
Fluid interface for bioprocessor systems
InactiveUS20070072285A1Low costFacilitates rapid, frequent, automated samplingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBioprocessorAutomatic control
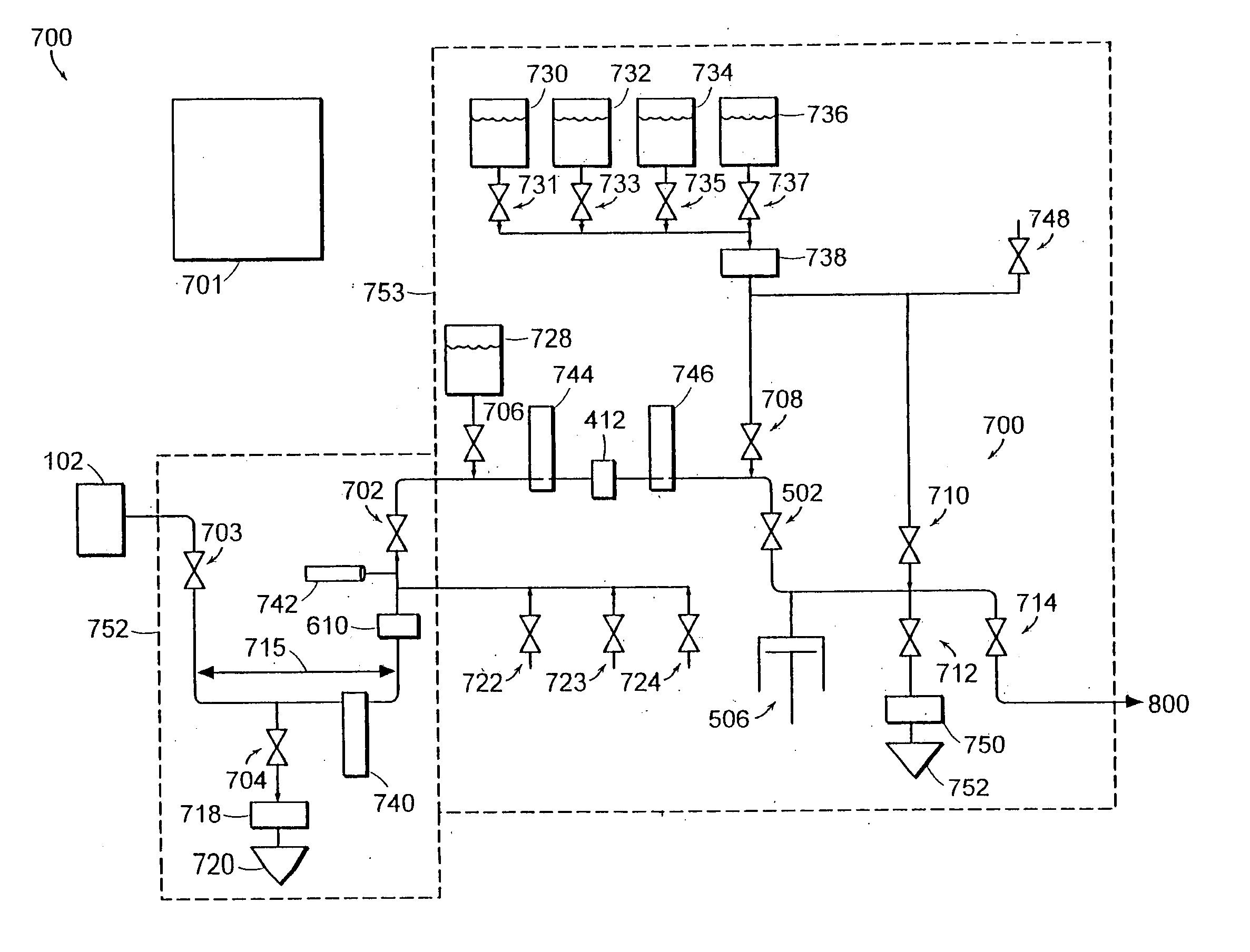
An apparatus and method for an aseptic fluidic interface between bioprocess systems is provided. The apparatus includes an inlet valve, adapted for automatic control, that is coupled to a biofluid source site. A sampling conduit extends from the inlet valve to an outlet valve. The outlet valve is adapted for automatic control and is coupled to a biofluid process site. A trap is at the sampling conduit. A waste valve, adapted for automatic control, is located at a waste conduit extending from the sampling conduit to a waste site. Also included is a wash fluid source that is coupled to at least one of the inlet or outlet valves. In the method, the sample is automatically directed to the biofluid process site by opening the outlet valve, and closing the waste valve Also included is isolating the biofluid sites by closing the inlet and outlet valves, and opening the waste valve to drain biofluid from the trap to the waste site. Another step is cleaning the sampling conduit before sample collection by directing the wash fluid through at least one valve selected from the inlet and outlet valves, and subsequently through the waste valve to the waste site.
Owner:GROTON BIOSYST
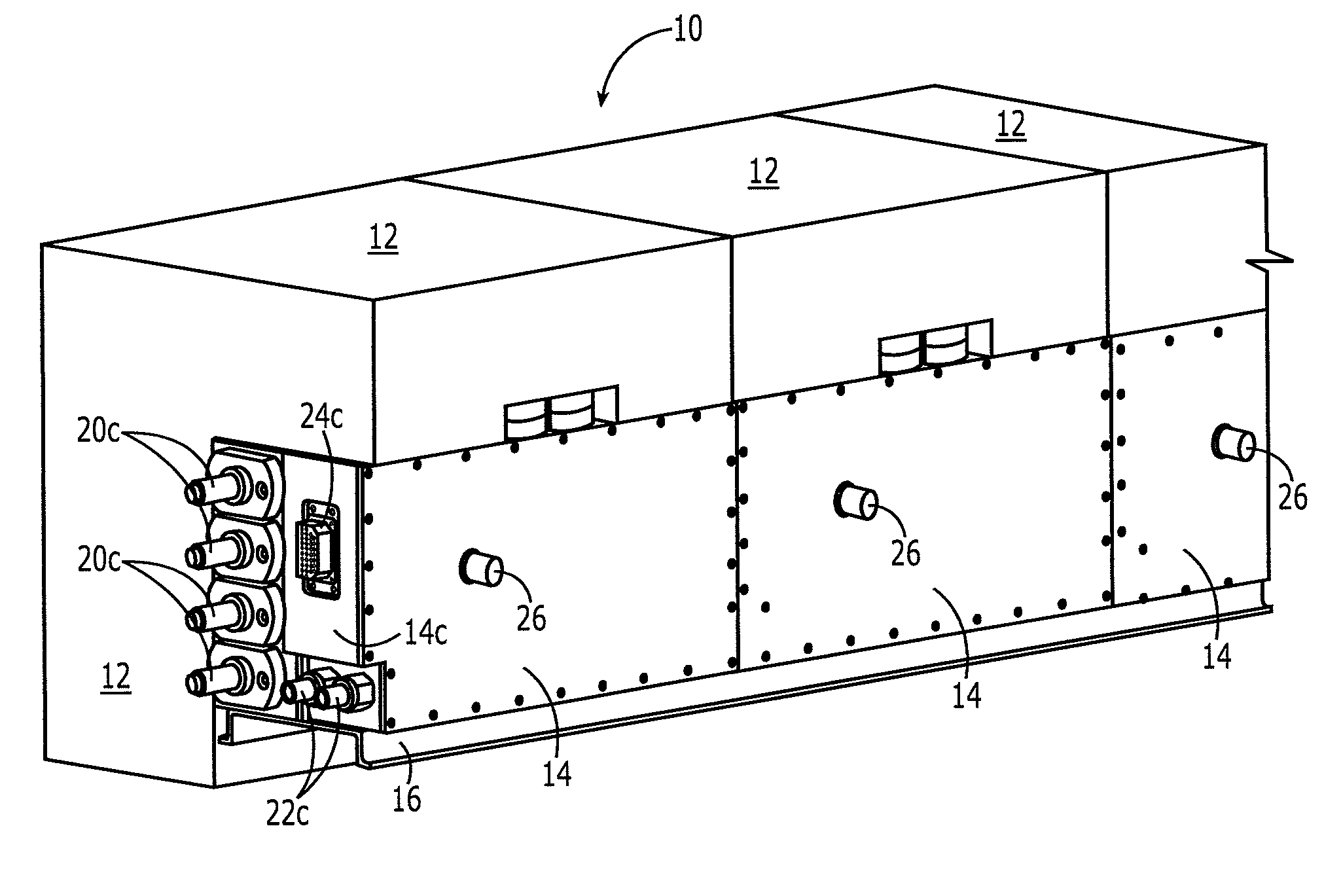
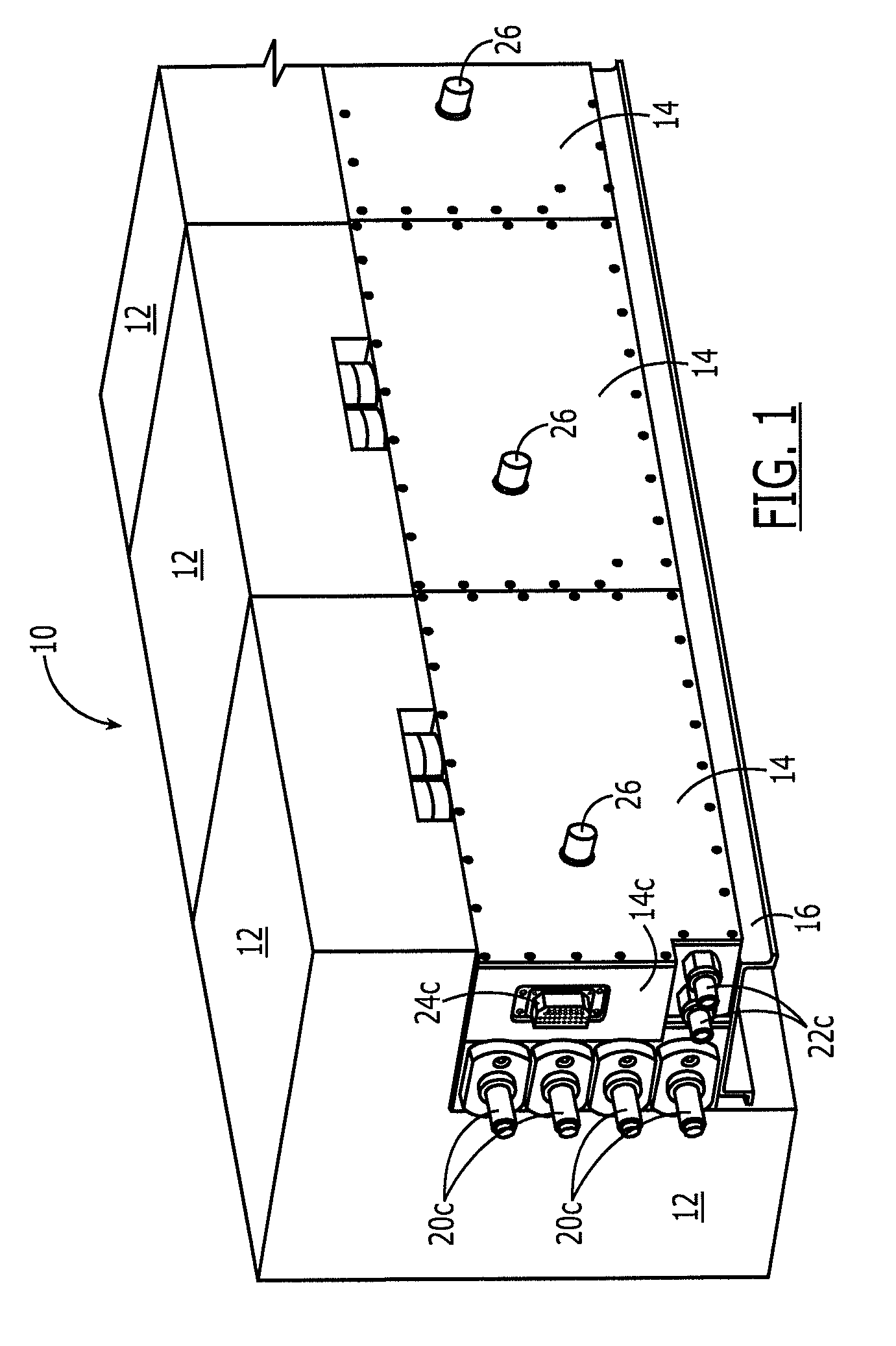
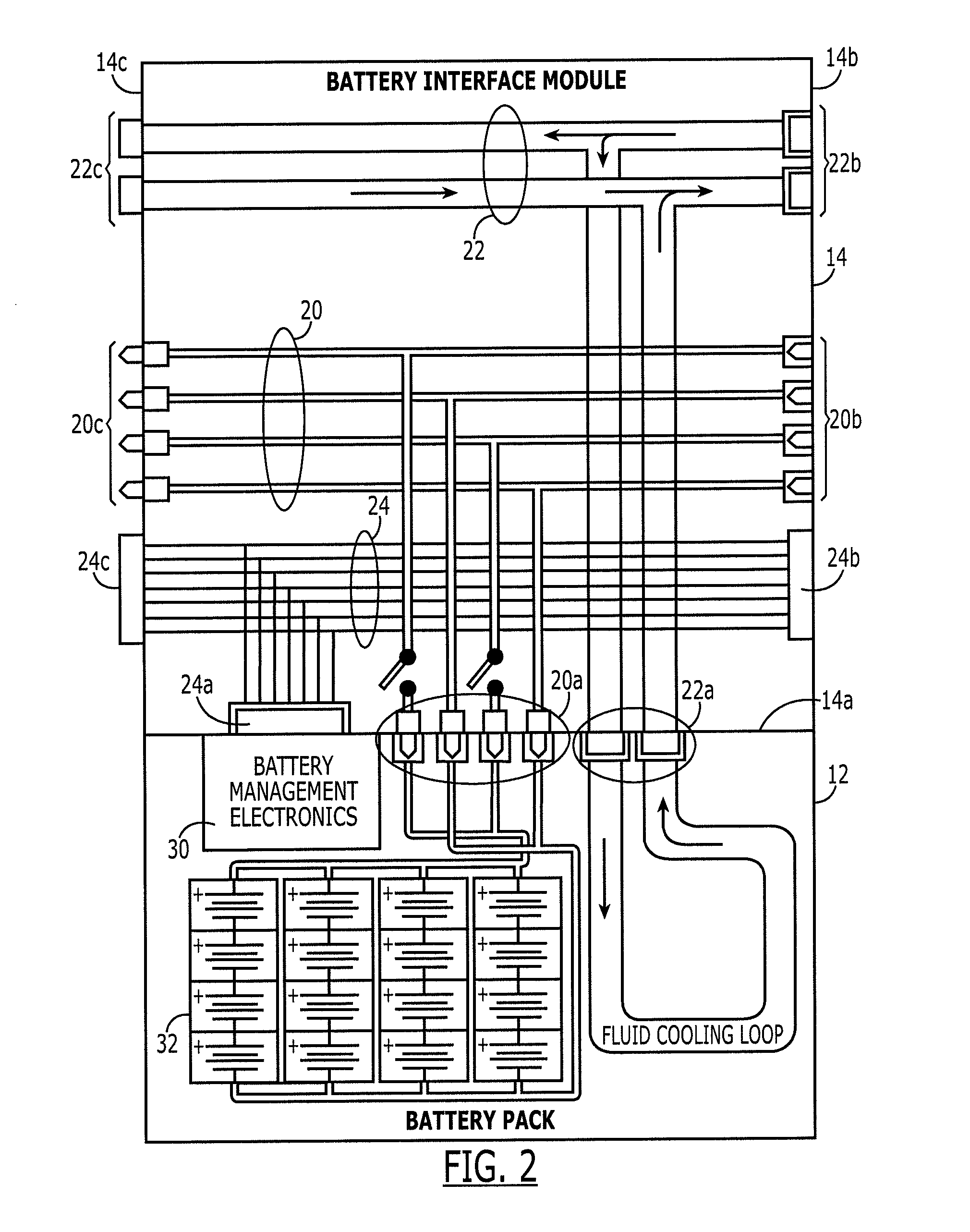
Modular vehicular power system having a battery interface module and associated method
InactiveUS8691416B1Easy maintenanceEasy to scaleElectrically conductive connectionsCurrent conducting connectionsElectricityComputer module
A battery interface module is provided that includes a housing and a battery interface carried by the housing and configured to interface with a battery. The battery interface may include a first power bus interface, a first fluid interface and a first data interface. The battery interface module may also include first and second transmission interfaces carried by the housing. At least one of the first and second transmission interfaces may be configured to interface with another battery interface module. Each transmission interface may include a second power bus interface, a second fluid interface and a second data interface. Additionally, the first and second power bus interfaces may be in electrical communication, the first and second fluid interfaces may be in fluid communication and the first and second data interfaces may be communicably connected.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Tilting rack system
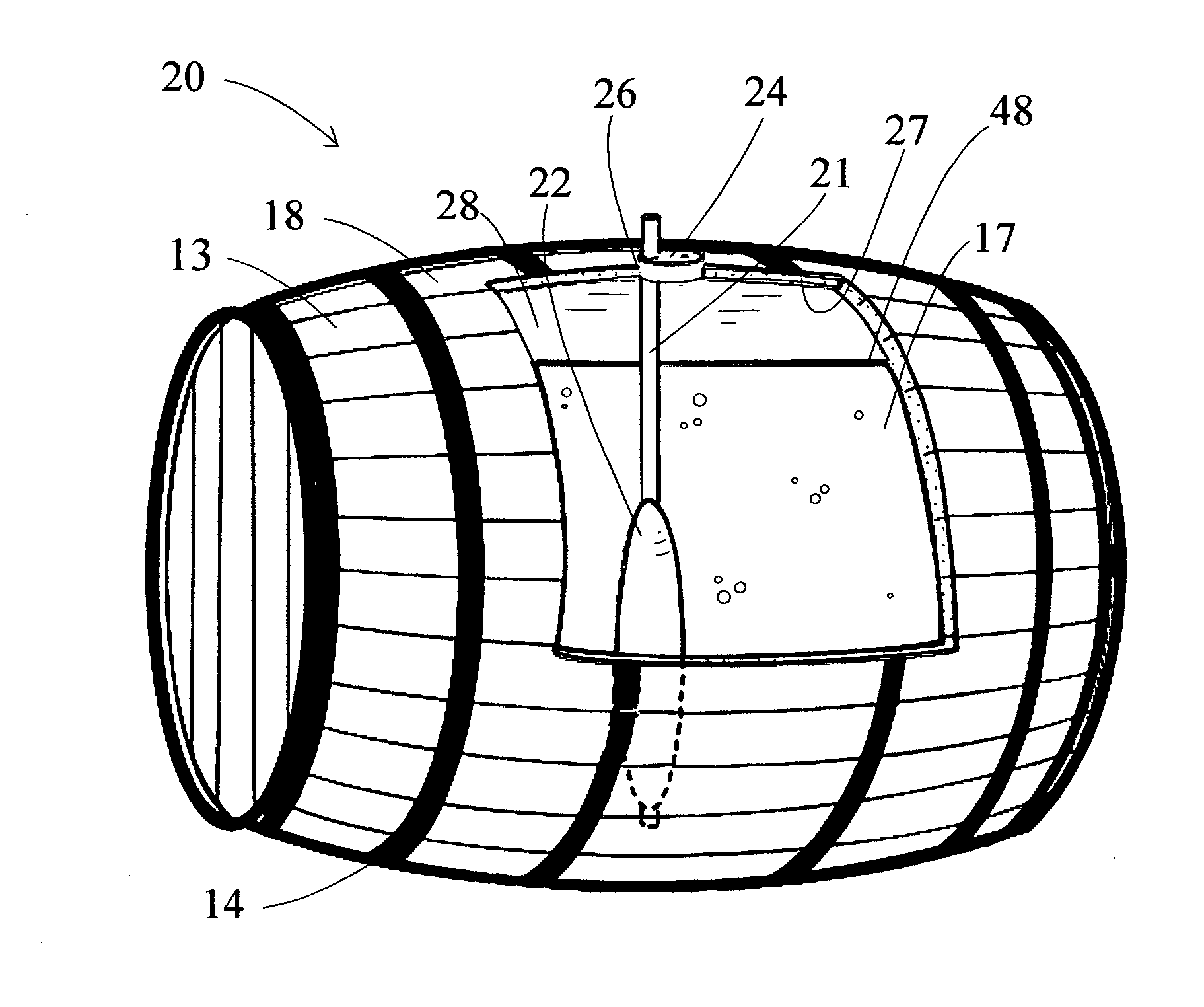
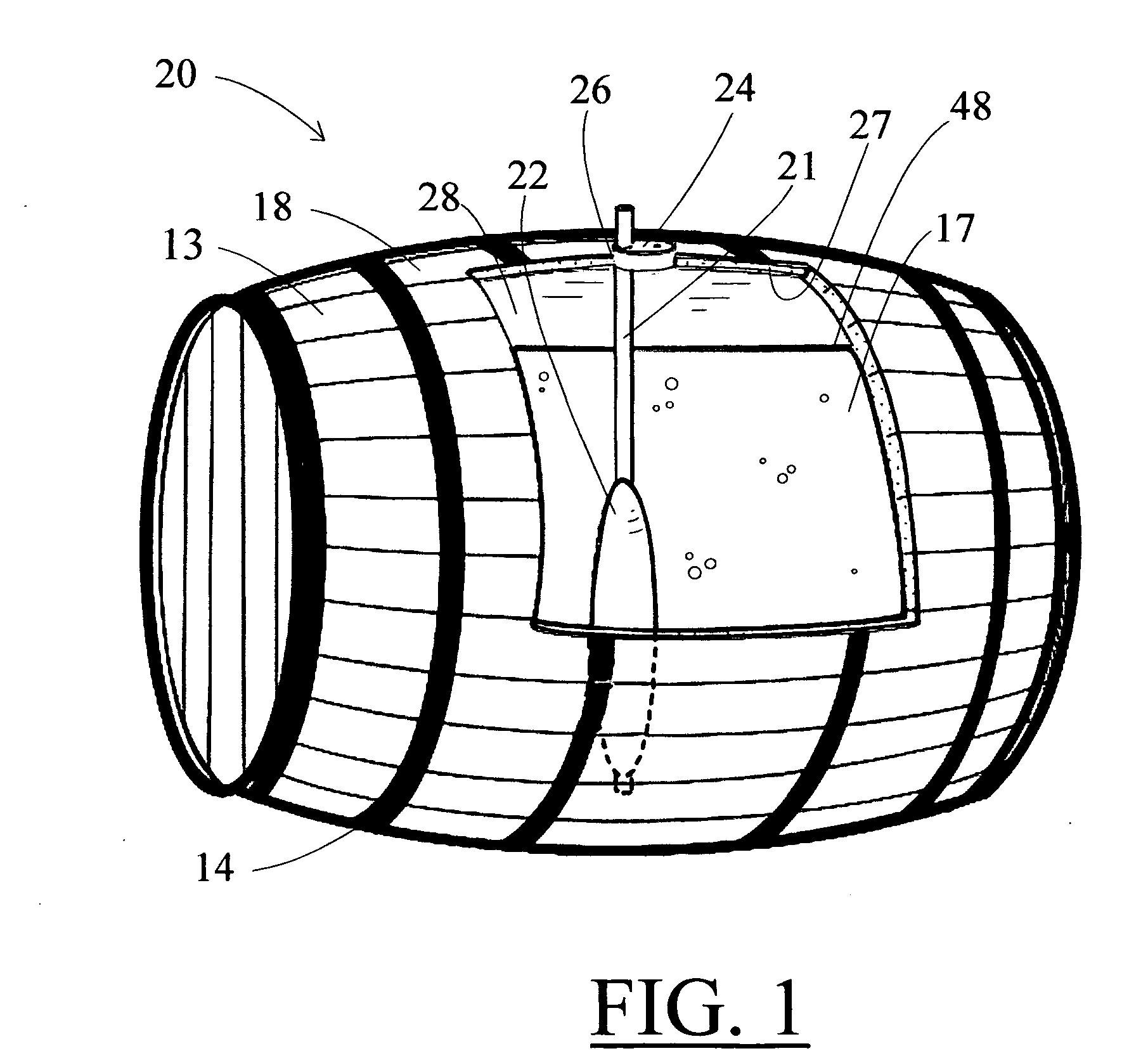
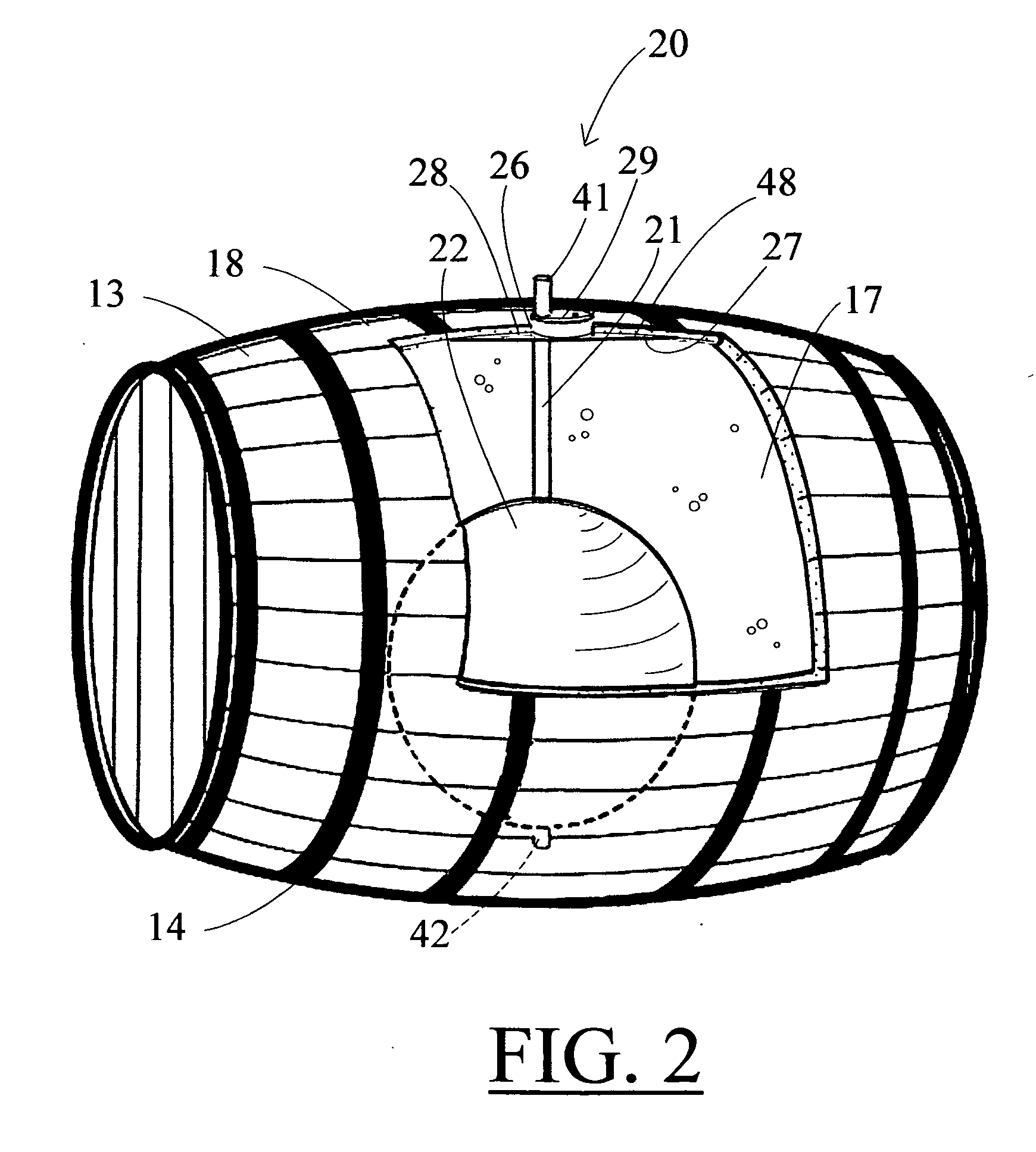
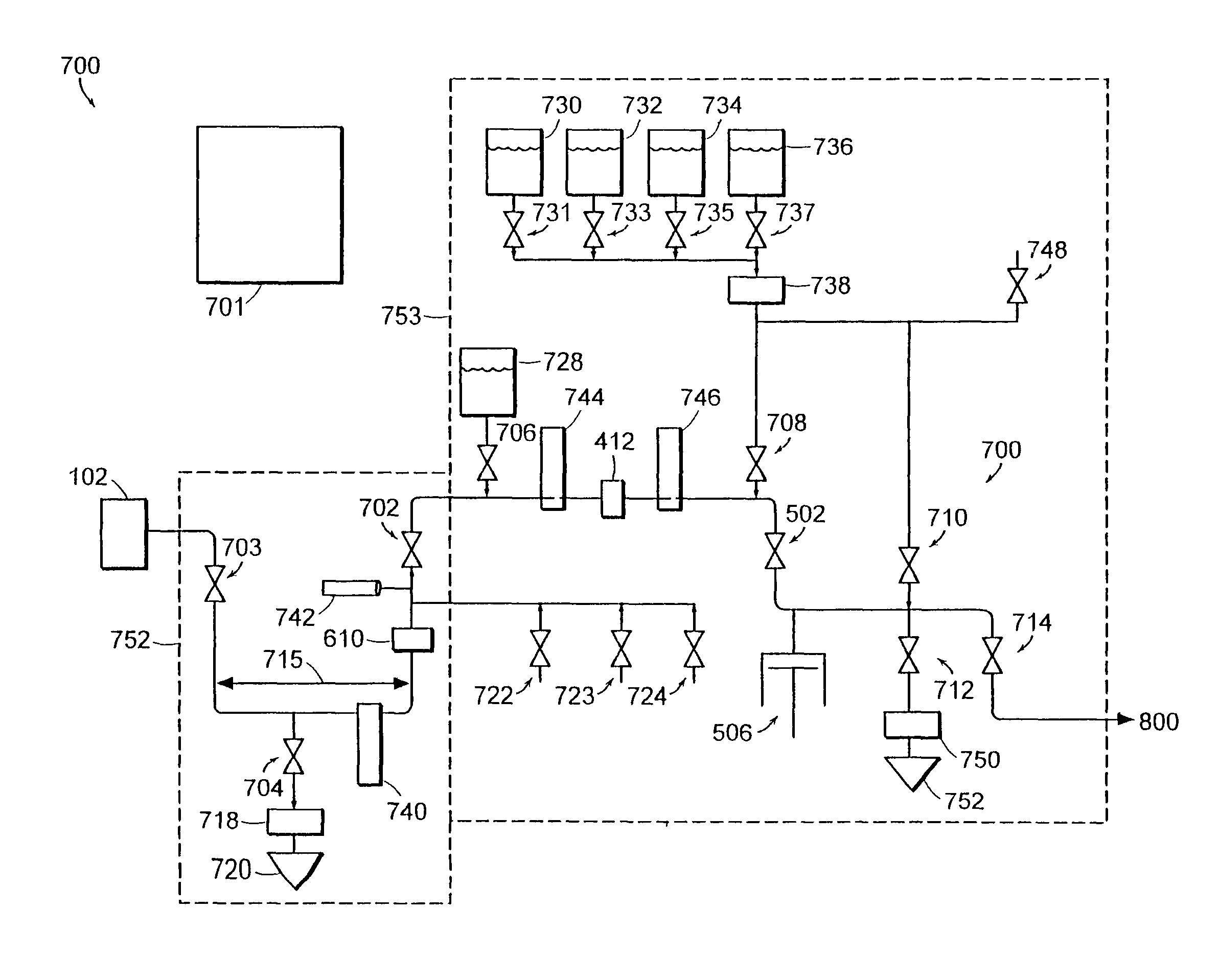
ActiveUS20110101010A1Flexible wall reciprocating enginesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEvaporationFluid interface
A bladder system and apparatus for use with a beverage barrel or container, to reduce undesirable head-space in a wooden container of a beverage, especially a fermented beverage, such as wine. The system continuously protects the beverage contained in a wooden barrel from the harmful effects of oxidation at the air-to-fluid interface in the head-space and compensates for ullage, attributable to evaporation, leakage or sampling losses. The system includes an inflation stem connected to a barrel bladder inflatable by filling with an inflation gas. The inflation stem includes a liquid level sensor and inserts into a bung opening. The fluid level is sensed and a gas valve opens to fill the bladder, reducing head-space within the barrel. The system can combine the control of several barrels and optionally with other sensors, to create a barrel monitoring and control network.
Owner:INGENIOUS BARREL INNOVATIONS LLC
Fluid interface for bioprocessor systems
InactiveUS7955843B2Low costFacilitates rapid, frequent, automated samplingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBioprocessorAutomatic control
An apparatus and method for an aseptic fluidic interface between bioprocess systems is provided. The apparatus includes an inlet valve, adapted for automatic control, that is coupled to a biofluid source site. A sampling conduit extends from the inlet valve to an outlet valve. The outlet valve is adapted for automatic control and is coupled to a biofluid process site. A trap is at the sampling conduit. A waste valve, adapted for automatic control, is located at a waste conduit extending from the sampling conduit to a waste site. Also included is a wash fluid source that is coupled to at least one of the inlet or outlet valves. In the method, the sample is automatically directed to the biofluid process site by opening the outlet valve, and closing the waste valve. Also included is isolating the biofluid sites by closing the inlet and outlet valves, and opening the waste valve to drain biofluid from the trap to the waste site. Another step is cleaning the sampling conduit before sample collection by directing the wash fluid through at least one valve selected from the inlet and outlet valves, and subsequently through the waste valve to the waste site.
Owner:GROTON BIOSYST
Use of liquid junction potentials for electrophoresis without applied voltage in a microfluidic channel
This invention provides methods for using liquid junction potentials to control the transport of charged particles in fluid streams that are in laminar flow within microfluidic channels. Applications of the methods of this invention include sample preconditioning (removal of interfering substances), electrophoretic separation (fractionation) of charged particles, enhanced or delayed mixing of charged particles across a fluid interface relative to diffusion only, focusing charged particles in a fluid stream in one or two dimensions, and concentration of charged reactants at a fluid interface.
Owner:WASHINGTON THE UNIV OF
Vapor chamber heat sink having a carbon nanotube fluid interface
An enhanced heat transposer comprised is of a vapor chamber. The surface of the vapor chamber that holds the fluid comprises an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) that are grown in a way that enables the fluid to come into maximum contact with the CNTs. The fluid evaporates in the sealed vapor chamber when it is in touch with a hot surface. The vapor comes in contact with a hollow pin-fin structure that provides additional surface area for vapor cooling and heat transfer. The condensed vapor then drops back into the fluid container, and the cycle continues.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Microfluidic system including a virtual wall fluid interface port for interfacing fluids with the microfluidic system
InactiveUS20060263264A1Suitable cross sectional dimensionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluid interfaceBiomedical engineering
A fluid interface port in a microfluidic system and a method of forming the fluid interface port is provided. The fluid interface port comprises an opening formed in the side wall of a microchannel sized and dimensioned to form a virtual wall when the microchannel is filled with a first liquid. The fluid interface port is utilized to fill the microchannel with a first liquid, to introduce a second liquid into the first liquid and to eject fluid from the microchannel.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Apparatus and methods for continuous compatibility testing of subterranean fluids and their compositions under wellbore conditions
Disclosed is a fluid testing device which utilizes a small, cross-section fluid interface to separate a test fluid chamber from a drive and measuring chamber. The test fluid chamber contains the test fluid and a paddle-type fluid test assembly. The drive and measuring chamber contains a second fluid and assemblies for moving the paddle and for determining the resistance movement. The two chambers are connected together by a narrow cross-section passageway allowing for continuous testing while test fluids are flowed through the test chamber and for successive testing of different samples without breaking down the device between tests. A pair of coaxial shafts extends between the test fluid chamber and the drive and measuring chamber. The shafts are connected together by a spring located in the drive chamber whereby the resistance to movement is determined by measuring the deflection in the spring. The shafts are magnetically coupled to a motor to rotate the shafts.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Hydrodynamic bearing device
InactiveUS6890104B2Excellently preventingSimple structureShaftsRecord information storageCapillaria obsignataFluid interface
A bearing has a thrust plate integrated with its shaft and a bearing member surrounds both. A radial pressure bearing portion and separate thrust portion generate pressure on a lubricating fluid in a gap between the shaft and bearing member. One end of the gap is closed while the other is open and has a capillary seal formed with an angle that is large at a boundary but smaller at increasing distance therefrom. The fluids fills the gap so that gas-fluid interface is where the angle is small and causes the thrust plate to float. A pressure mechanism forces the fluid from the open to the closed end and the quantity of fluid is set to fill the mechanism even if the gas-fluid interface moves.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD +1
Hydraulic control unit performance test station for stability control system in vehicle dynamics
ActiveCN101566527ARapid positioningQuick dockingVehicle testingFluid-tightness measurementHydraulic cylinderHydraulic control unit
The invention relates to a hydraulic control unit performance test station for a stability control system in vehicle dynamics and belongs to the technical field of automobile manufacturing. The test station comprises a flat workbench, an HCU fast limiting and oil circuit sealing platform which is arranged on the workbench, a controller, a sealing feeding differential hydraulic cylinder, a hydraulic test system, a vehicle braking system, and a pressure source; the controller is respectively connencted with the HCU fast limiting and oil circuit sealing platform, the differential hydraulic cylinder and the hydraulic test system by a circuit; the differential hydraulic cylinder contacts the HCU fast limiting and oil circuit sealing platform; the hydraulic test system is connencted with the HCU fast limiting and oil circuit sealing platform by a test oil circuit; the vehicle braking system is connencted with the HCU fast limiting and oil circuit sealing platform by a braking fluid interface pipeline; and the hydraulic test system and the oil circuit sealing differential hydraulic cylinder are connencted with the pressure source by a hydraulic pipeline. The invention meets the delivery inspection needs of HCU, has easy and quick operation, and achieves low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
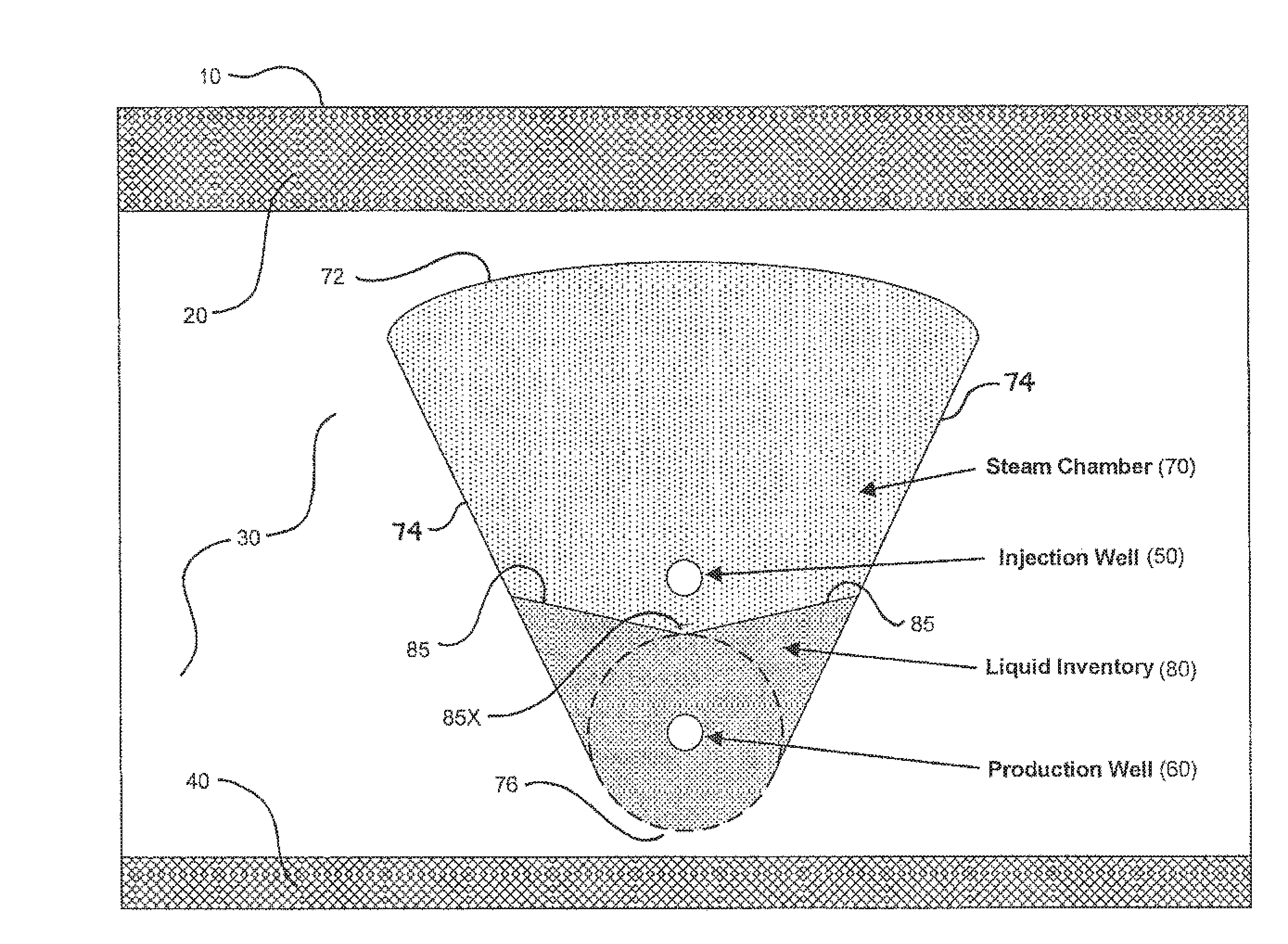
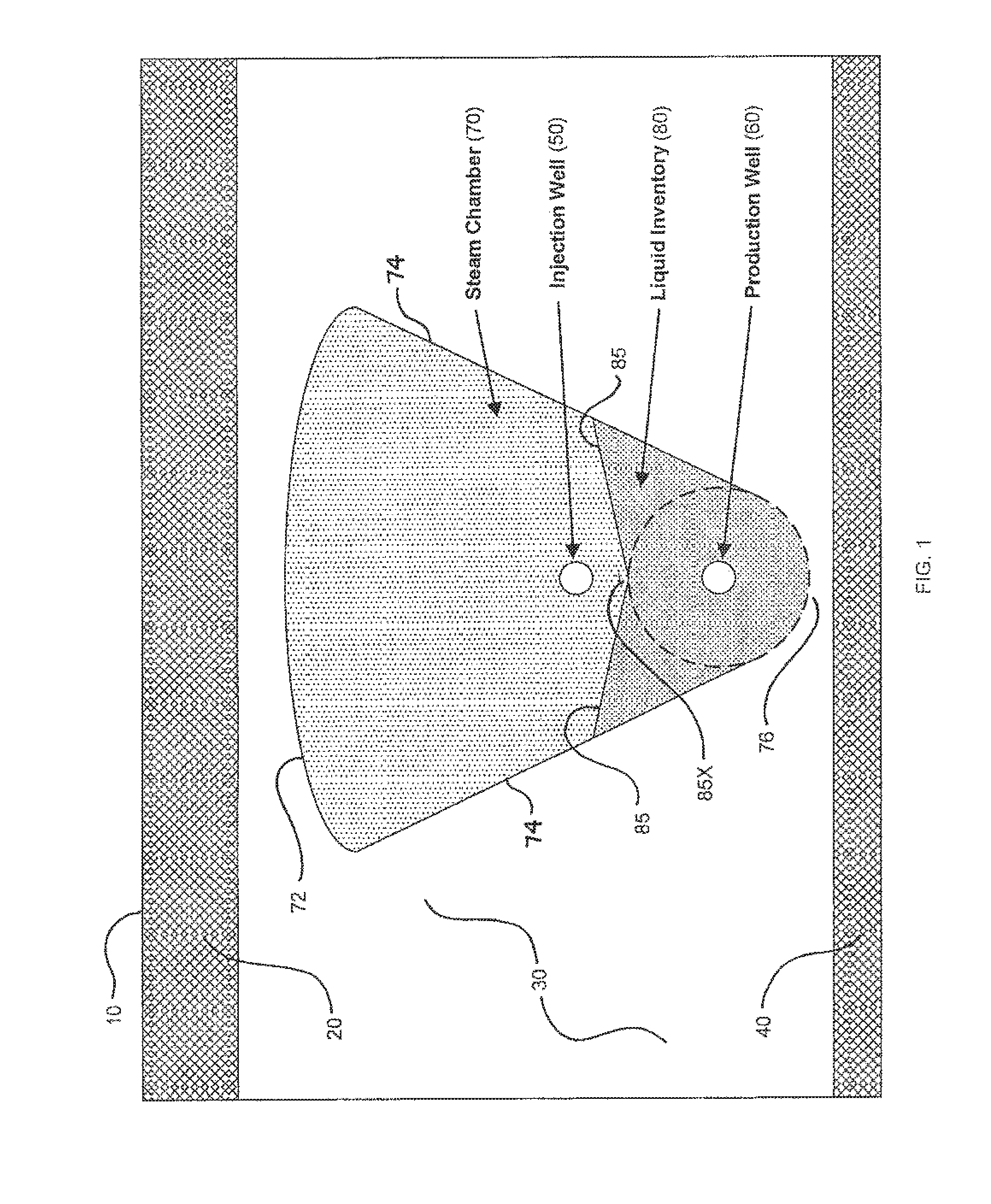
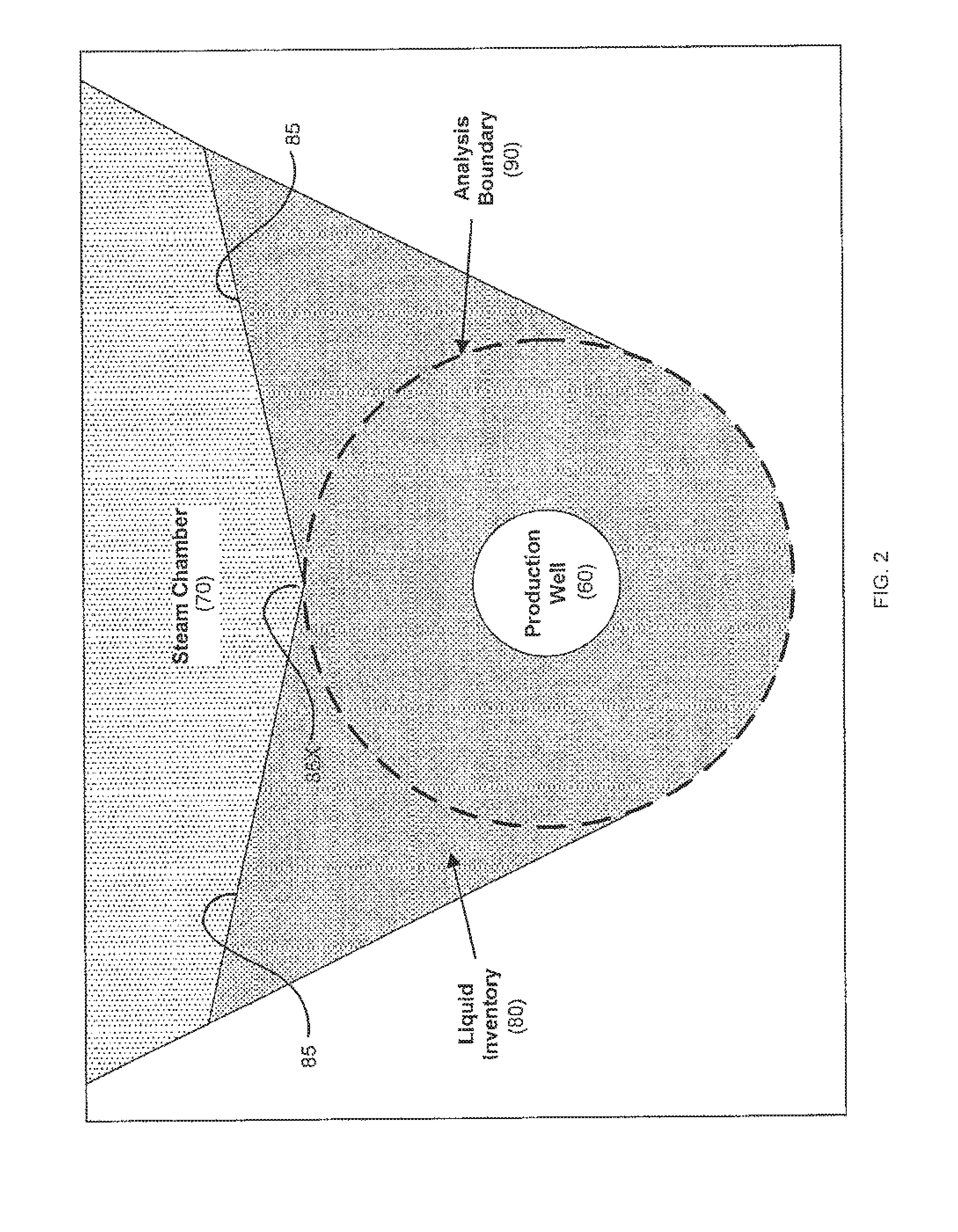
Method for controlling fluid interface level in gravity drainage oil recovery processes with crossflow
In a method for controlling the interface level between a liquid inventory and an overlying steam chamber in a subterranean petroleum-bearing formation, an inflow relationship is developed to predict the vertical position in a gravity field of the interface between two fluids with a density contrast (most commonly a water / oil emulsion and steam), relative to a horizontal producer well. The inflow relationship is applied to producer well completions by designing the completion to raise or lower sand face pressures over the horizontal length of the well. This pressure distribution will affect liquid levels according to the inflow relationship. Axial flow relationships for the liquid inventory may be developed to facilitate estimation of liquid levels at selected locations. Axial flow relationships for the steam chamber may also be developed to estimate the effect of the injector well completion on the steam chamber pressure and, in turn, the liquid level.
Owner:NOETIC TECH INC
Fluid level detection device and methods
A fluid level measurement device includes a cable arranged to penetrate fluid to be measured at least to a measurement depth. The cable has first and second conductors. The fluid imposes a dielectric constant on the cable. The device also includes a signal generating arrangement configured to introduce an input signal into the cable and a signal receiving arrangement configured to receive a reflected signal from the cable. The device also includes analysis circuitry configured to analyze the reflected signal in the time domain to thereby determine a depth of at least one fluid interface.
Owner:PCS FERGUSON
High spatial resolution fiber optic temperature sensor
ActiveUS8630816B2Thermometers using physical/chemical changesAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyFiberHigh spatial resolution
High resolution distributed temperature sensors using fiber optic distributed temperature sensing systems deployed on various carriers to significantly improve spatial resolution and provide high resolution temperature profile and detection of fluid or fluid interface levels.
Owner:SENSORTRAN
Method and system for measuring fluid level in a container
InactiveUS20060169055A1Improve accuracyMinimize the dead zoneLarge containersLiquid transferring devicesFuel tankFluid interface
The method and system for measuring a fluid level in a container according to the present invention allow measuring fluid level in confined volumes where, for example, there is no sufficient space to locate the ultrasonic transducer, where the fluid level constantly changes, such as in a vehicle gas tank, where the properties of the fluid or geometry of the tank changes with the environmental conditions, or where a high precision is required. The method composes i) emitting an ultrasound beam from a source along an ultrasound beam path generally oriented towards the bottom of the container, ii) receiving ultrasound echo values indicative of changes of environment along the ultrasound beam path; and iii) using the echo values to determine distance from the source of the changes of environment along the ultrasound beam path; whereby, a fluid level in the container is determined by associating at least one of said echo values to a fluid interface. A waveguide in the form of a pipe may be used in defining the ultrasound beam path and reduced clutter. A fixed target along the ultrasound beam path allows continuous calibration of the system to cope for environment changes in the container and for changes of properties of the fluid. A measurement window can further be used to minimize false reading and to cope with environment changes.
Owner:SENSOTECH LTD
Single wafer dryer and drying methods
In a first aspect, a first method of drying a substrate is provided. The first method includes the steps of (1) lifting a substrate through an air / fluid interface at a first rate; (2) directing a drying vapor at the air / fluid interface during lifting of the substrate; and (3) while a portion of the substrate remains in the air / fluid interface, reducing a rate at which a remainder of the substrate is lifted through the air / fluid interface to a second rate. The drying vapor may form an angle of about 23° with the air / fluid interface and / or the second rate may be about 2.5 mm / sec.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
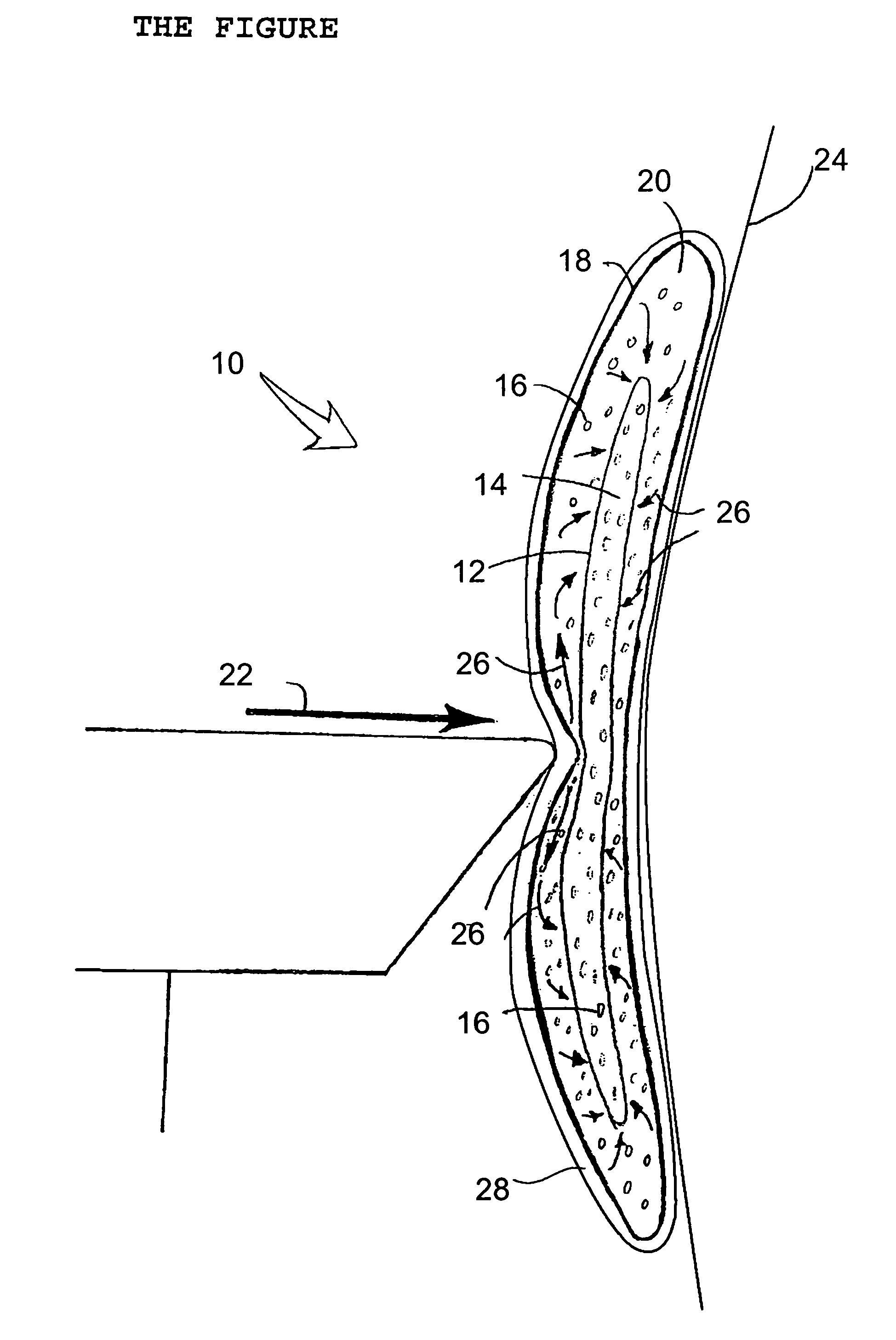
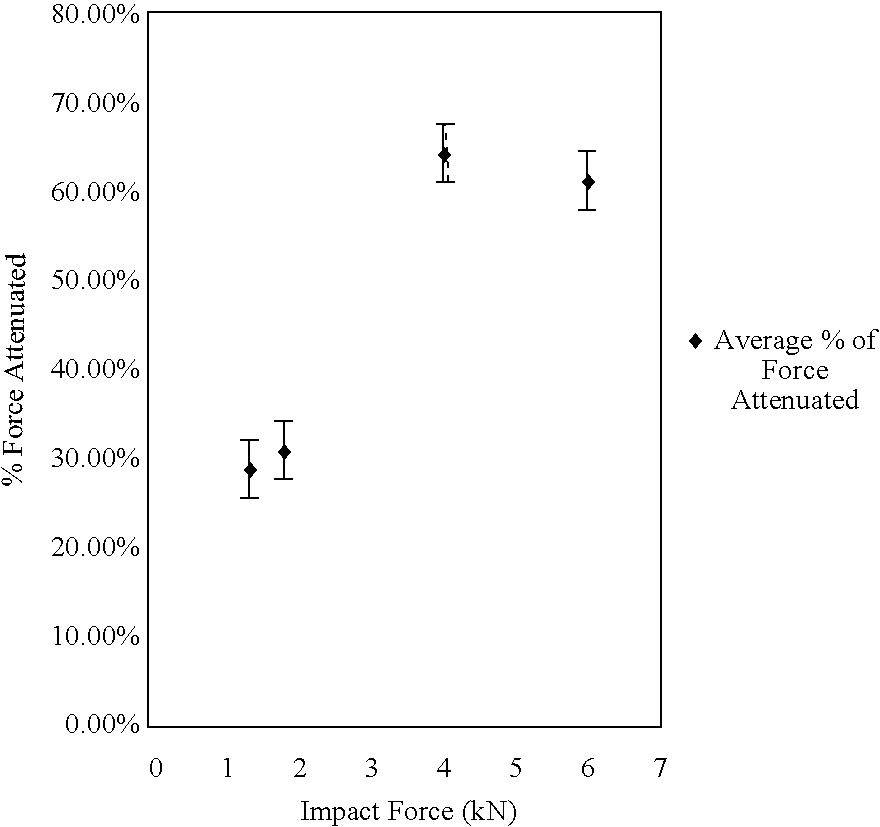
Fluid filled body padding for fall protection
InactiveUS6986170B2Effective protectionReduce weightChemical protectionHeat protectionHip protectorFluid interface
A fluid filled body padding for fall protection includes a flexible inner pouch holding a shock absorbing fluid. A flexible outer pouch encapsulates the inner pouch. A fluid interface is provided between the inner pouch and the outer pouch. The fluid interface serves to pressurize and rigidify the inner pouch containing the shock absorbing fluid when a localized force is exerted upon the outer pouch. This body padding is suitable for a variety of fall protection applications, such as hip protectors for senior citizens.
Owner:NELSON THOMAS M
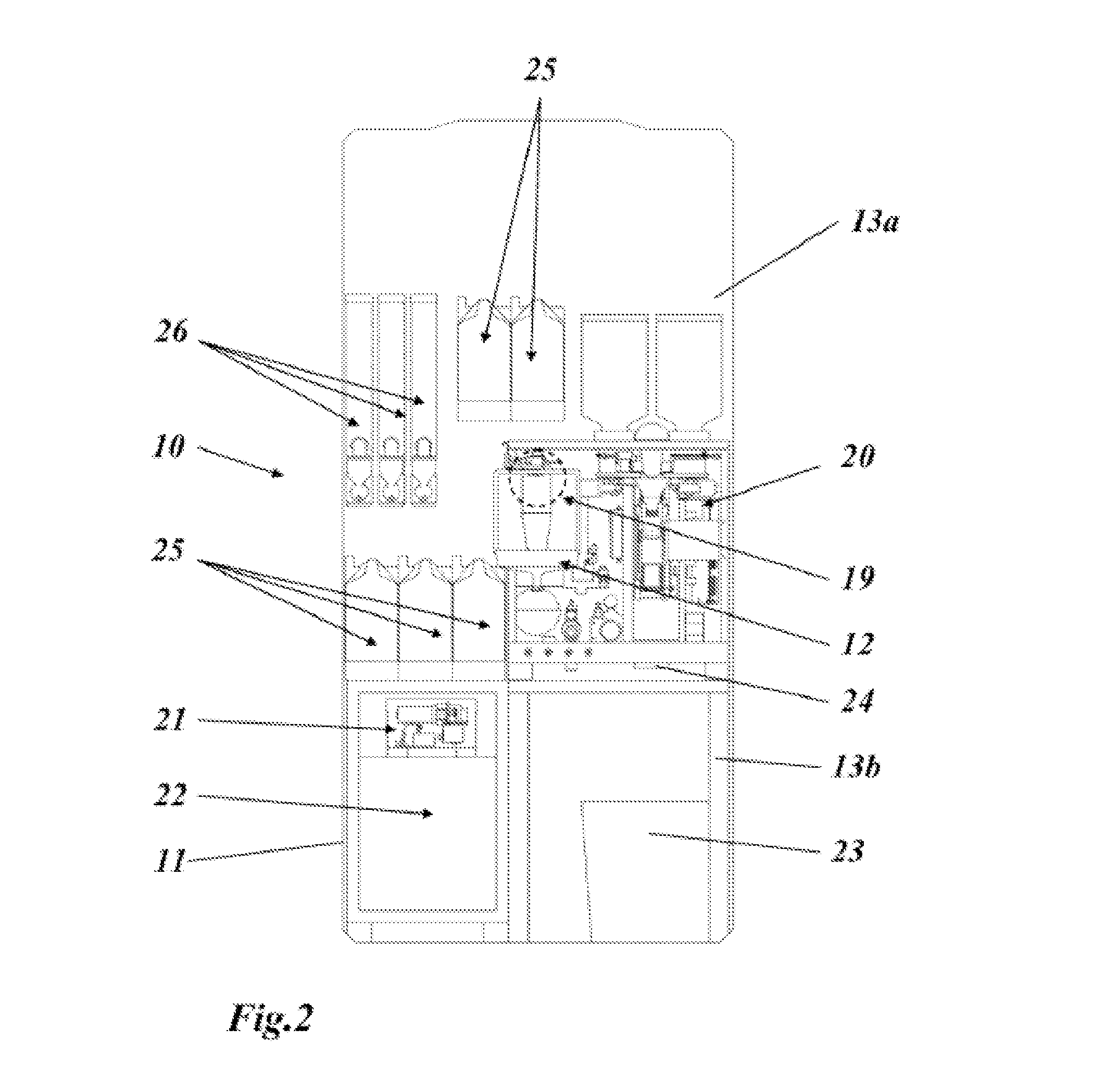
Beverage vending machine and outflow module for such a beverage vending machine
PendingUS20150013545A1Simple operation and maintenanceFlexible configurationLiquid transferring devicesBeverage vesselsFluid interfaceEngineering
A beverage vending machine has a housing, in which first means for brewing and dispensing a coffee beverage prepared using freshly ground coffee are housed. Flexible configuration is made possible in that the first means have a modular construction and comprise at least one base module for brewing the coffee beverage and a separate outflow module for dispensing the coffee beverage, which are in fluid connection with one another by means of one or more fluid interfaces.
Owner:SCHAERER AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com