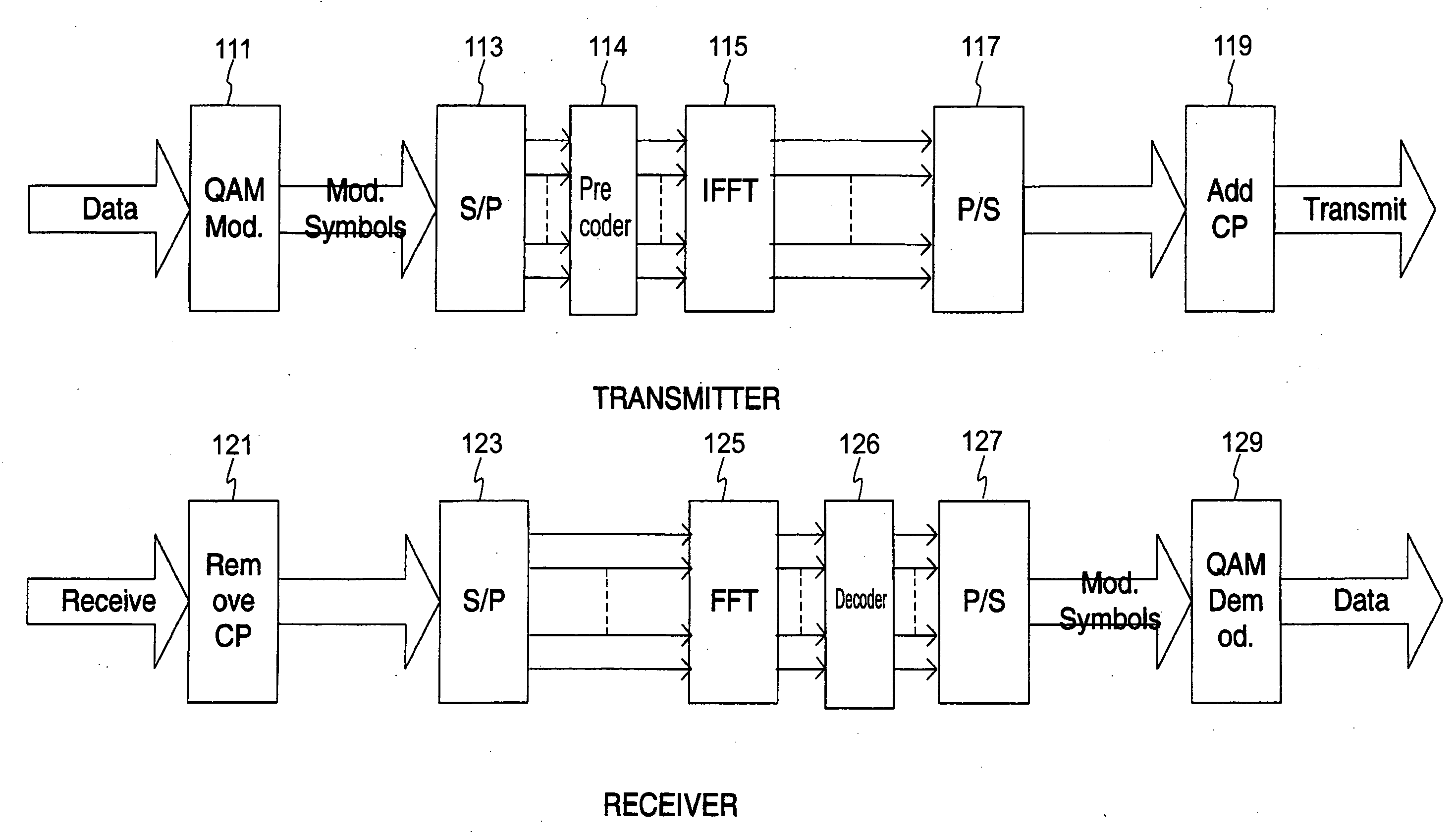
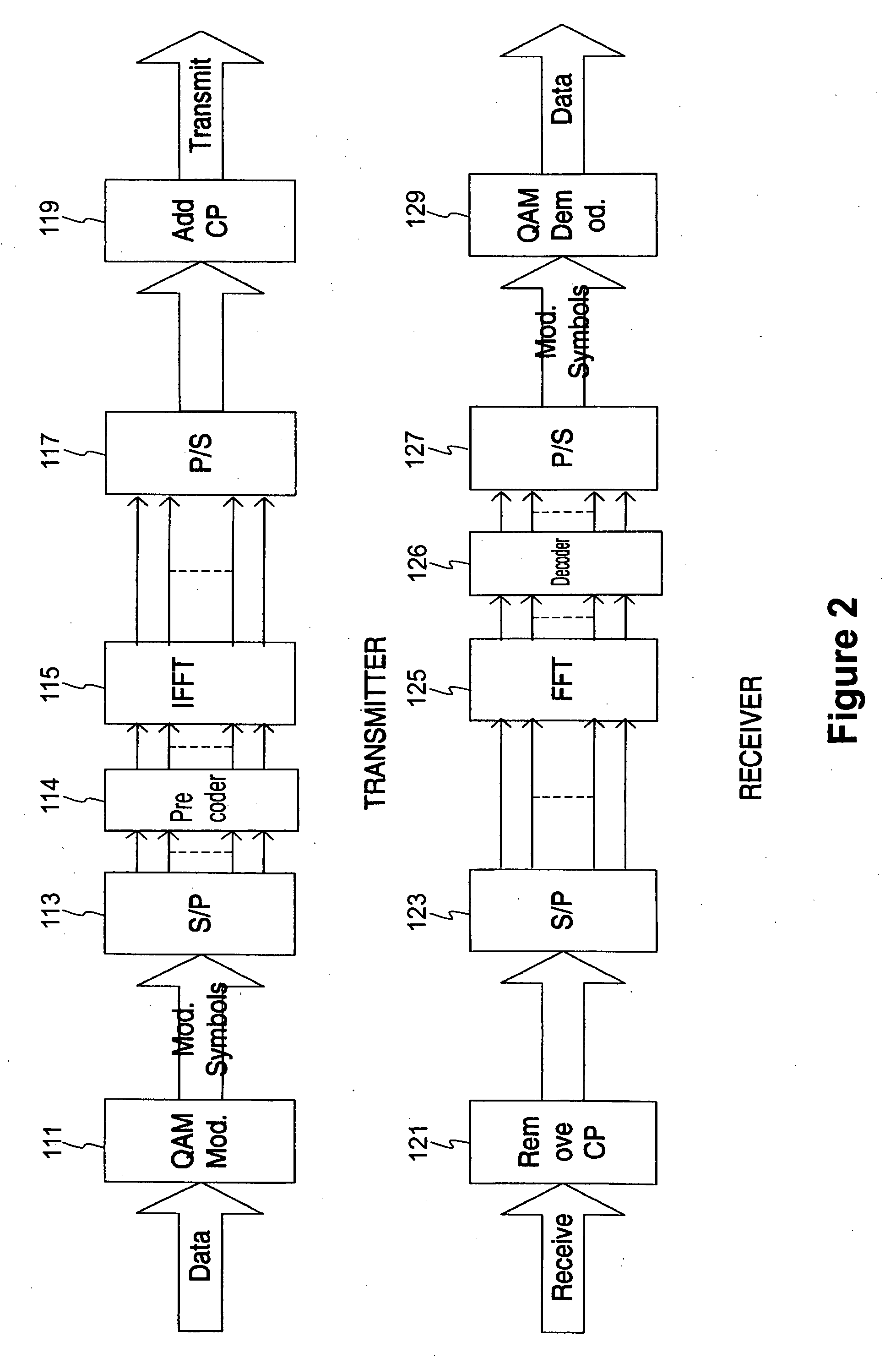
Patents
Literature
3602 results about "Transposer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
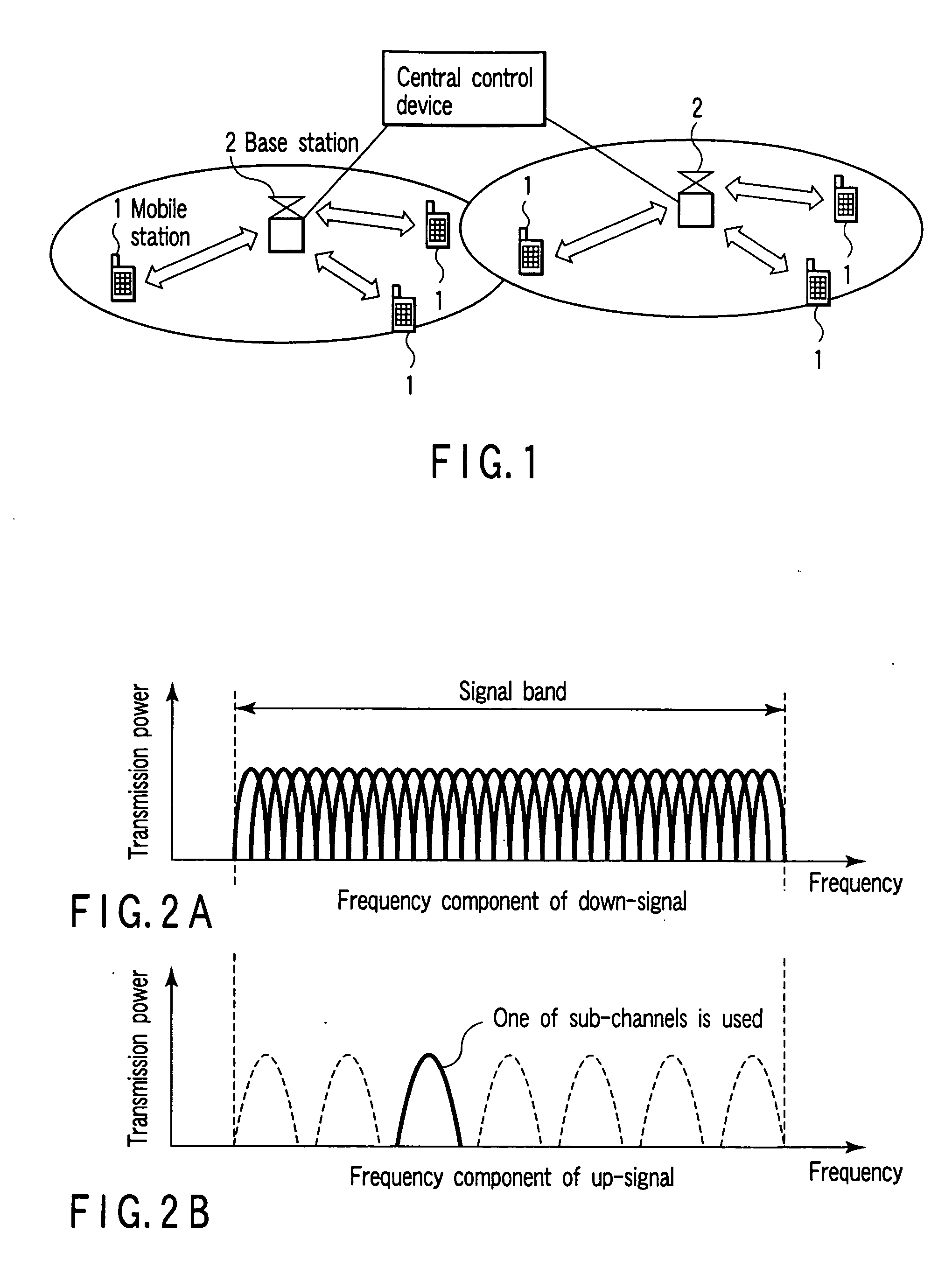
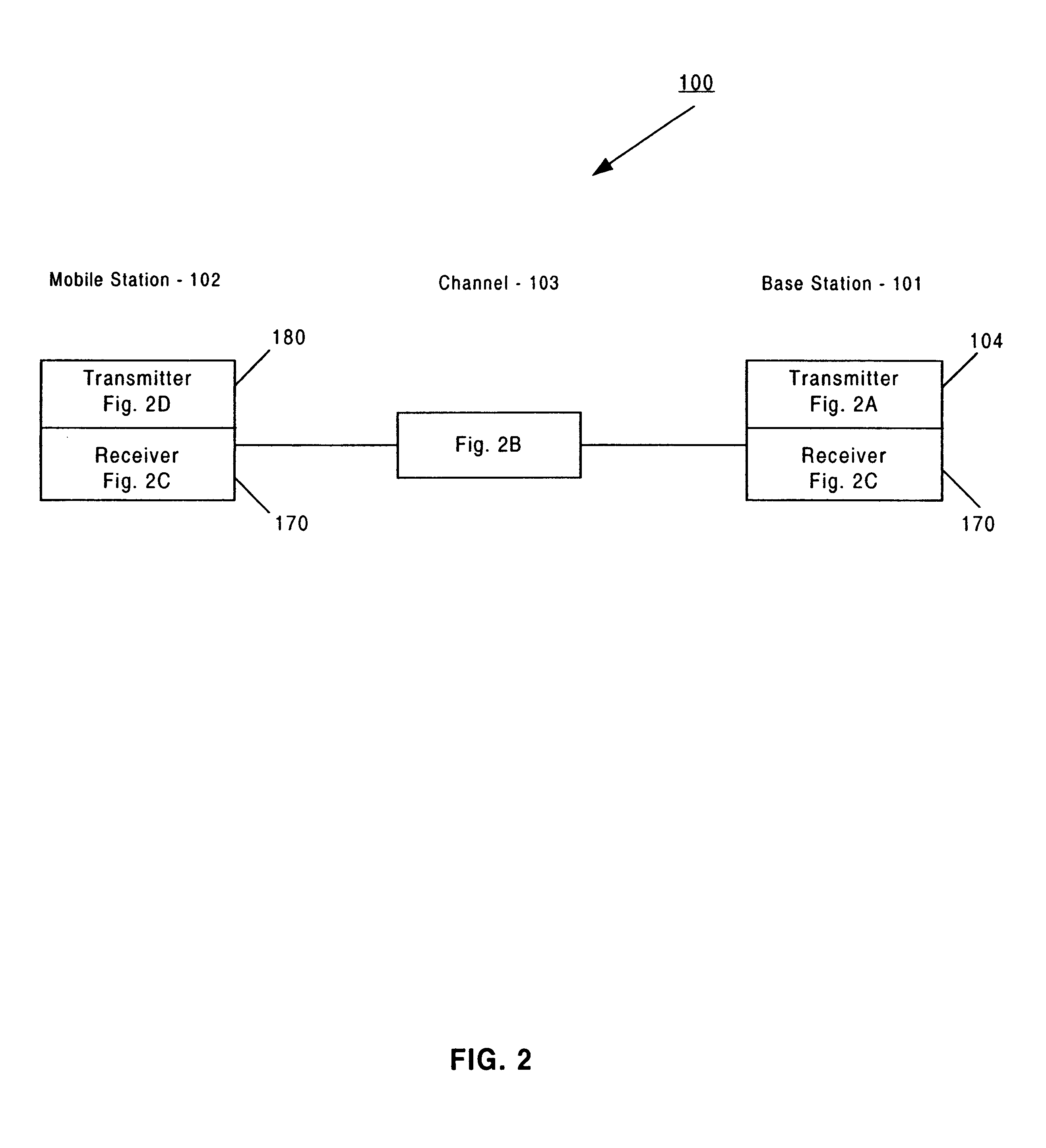
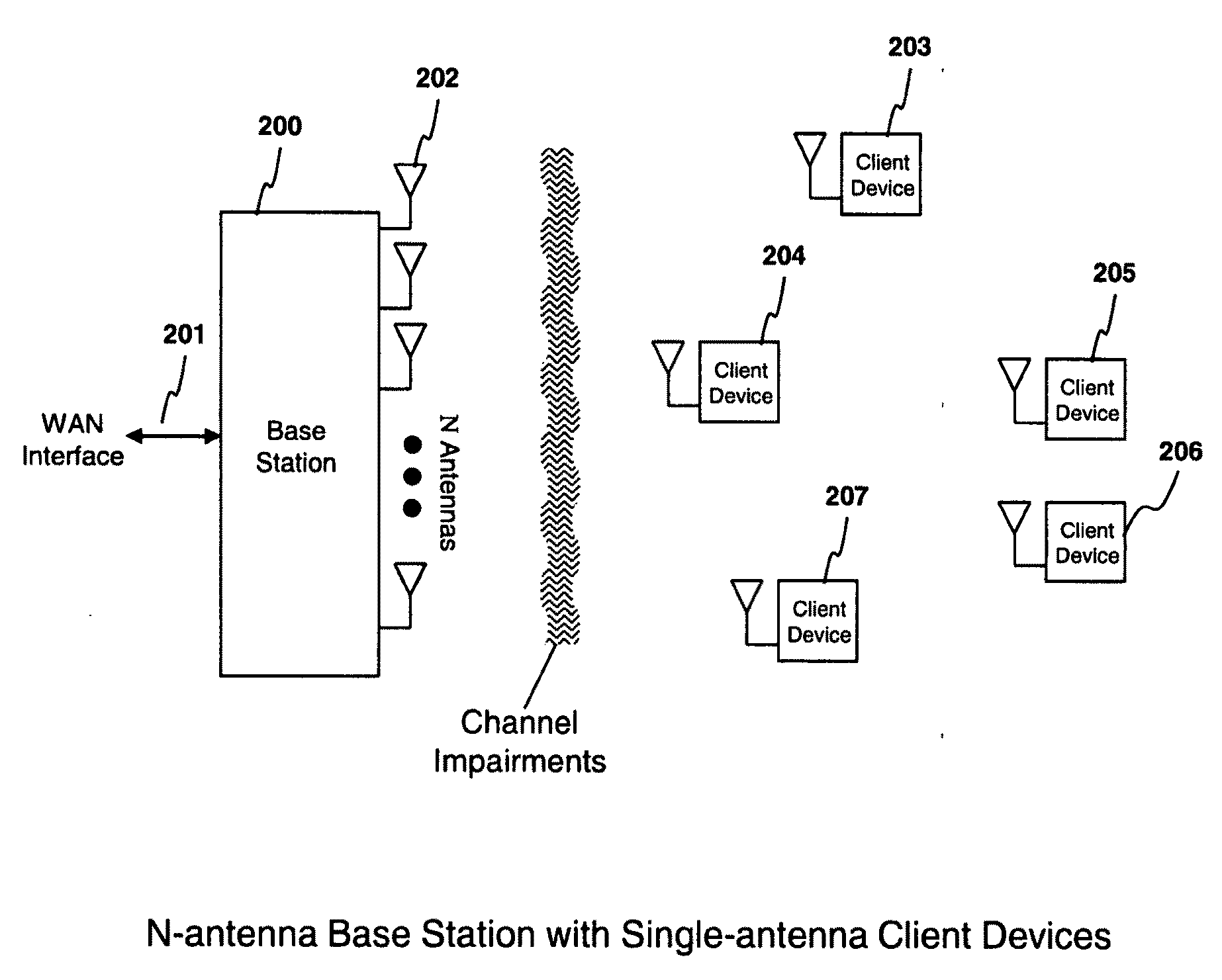
In broadcasting, a transposer or translator is a device in or beyond the service area of a radio or television station transmitter that rebroadcasts signals to receivers which can’t properly receive the signals of the transmitter because of a physical obstruction (like a hill). A translator receives the signals of the transmitter and rebroadcasts the signals to the area of poor reception. Sometimes the translator is also called a relay transmitter, rebroadcast transmitter or transposer. Since translators are used to cover a small shadowed area, their output powers are usually lower than that of the radio or television station transmitters feeding them.
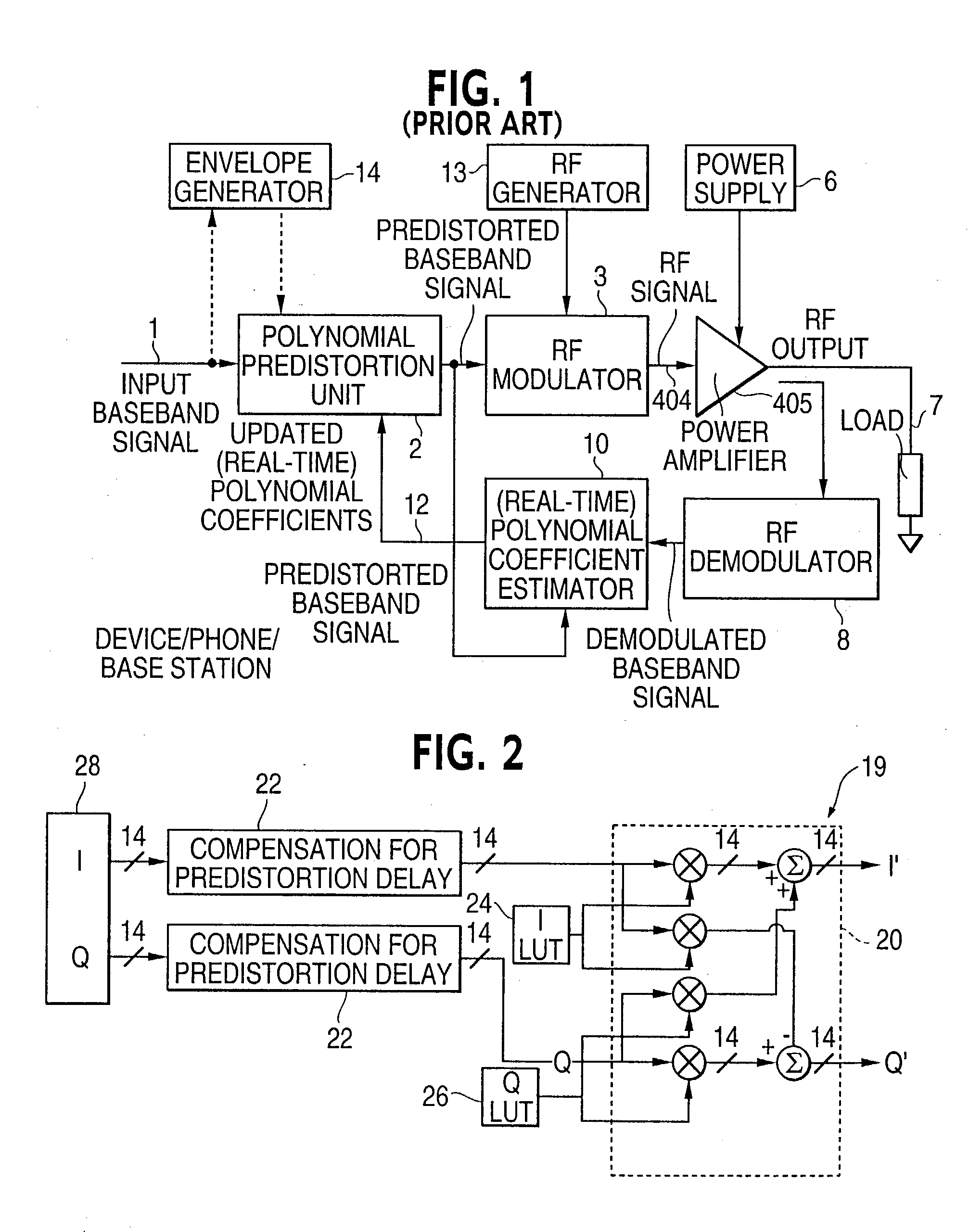
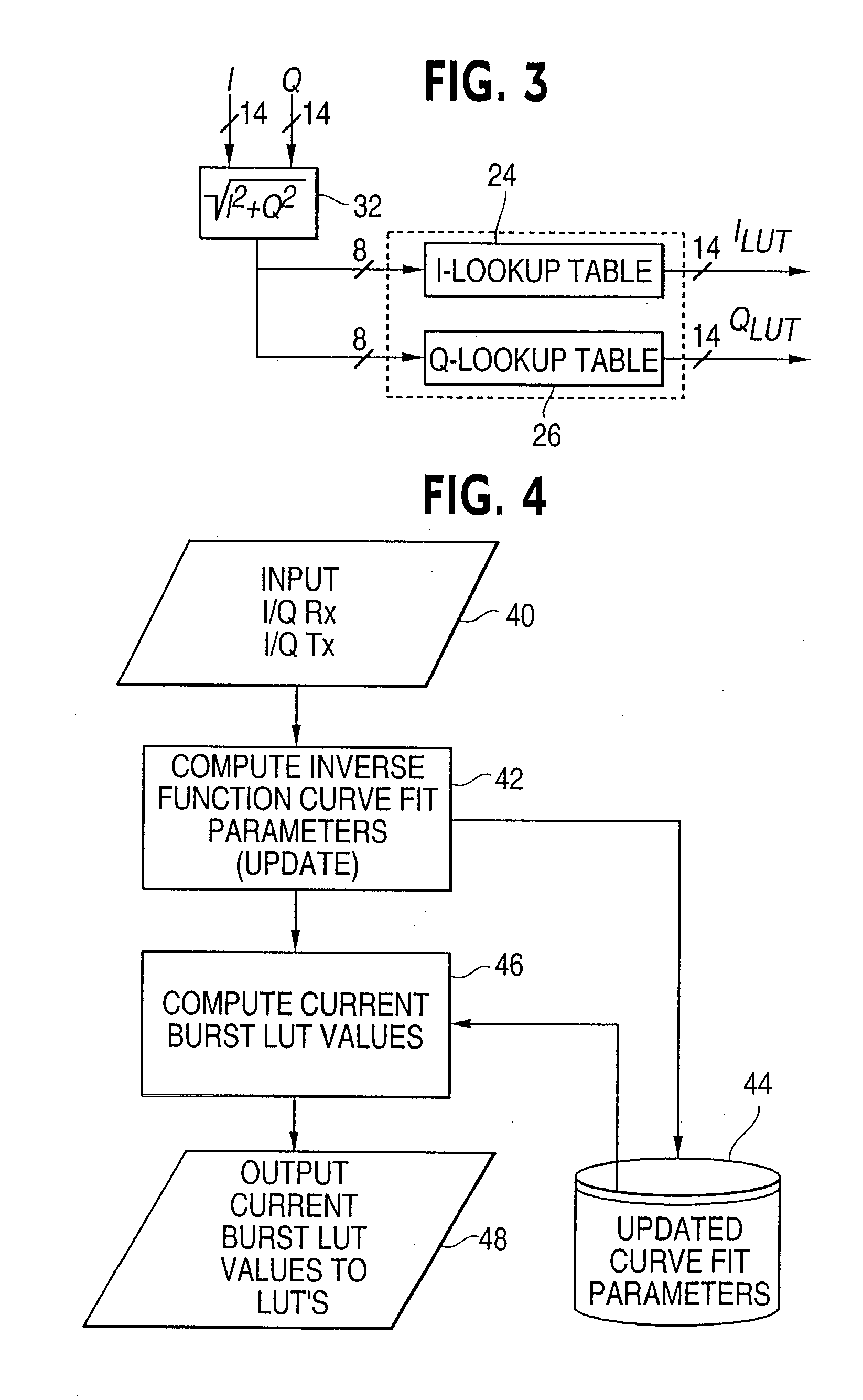
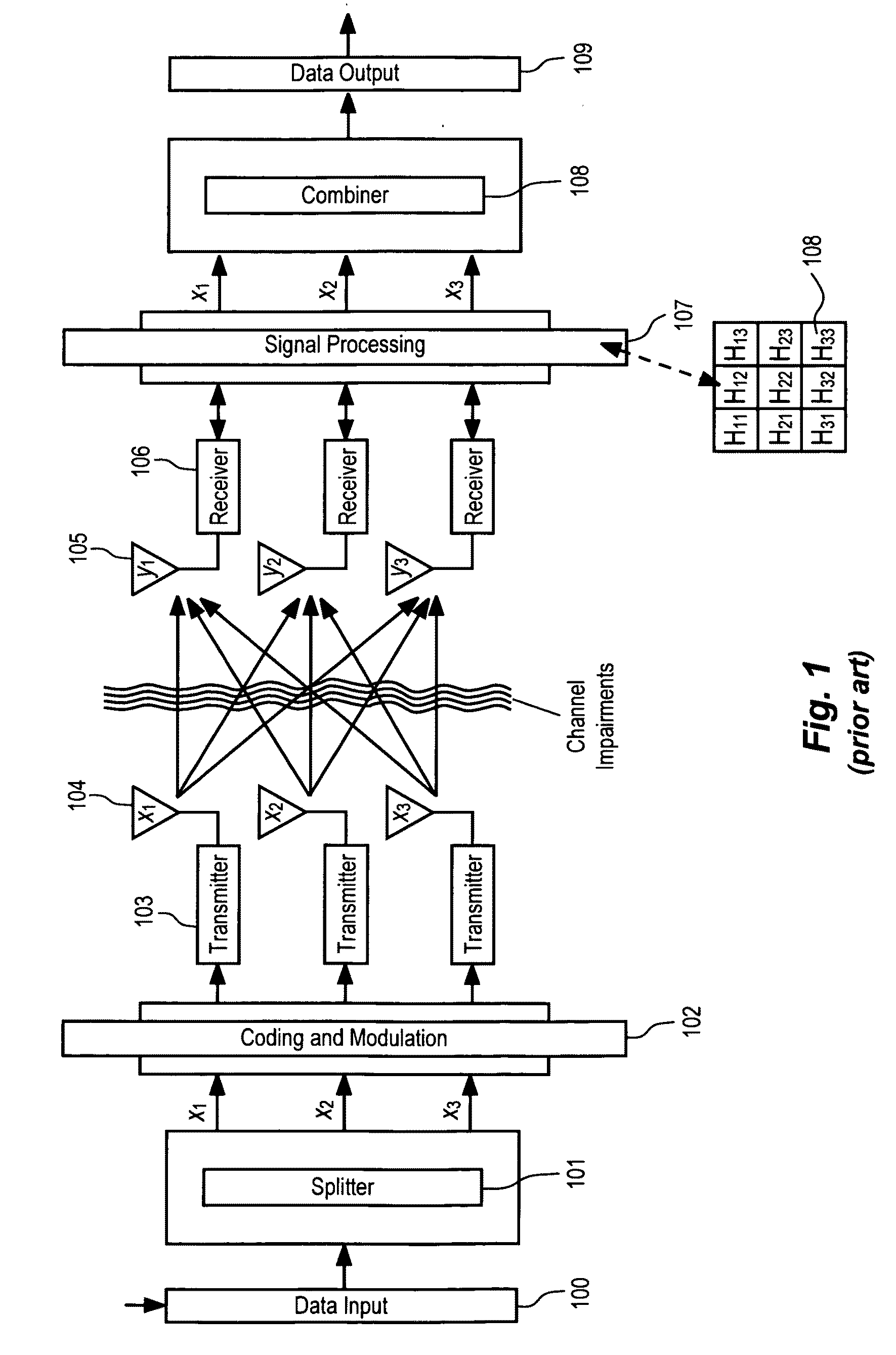
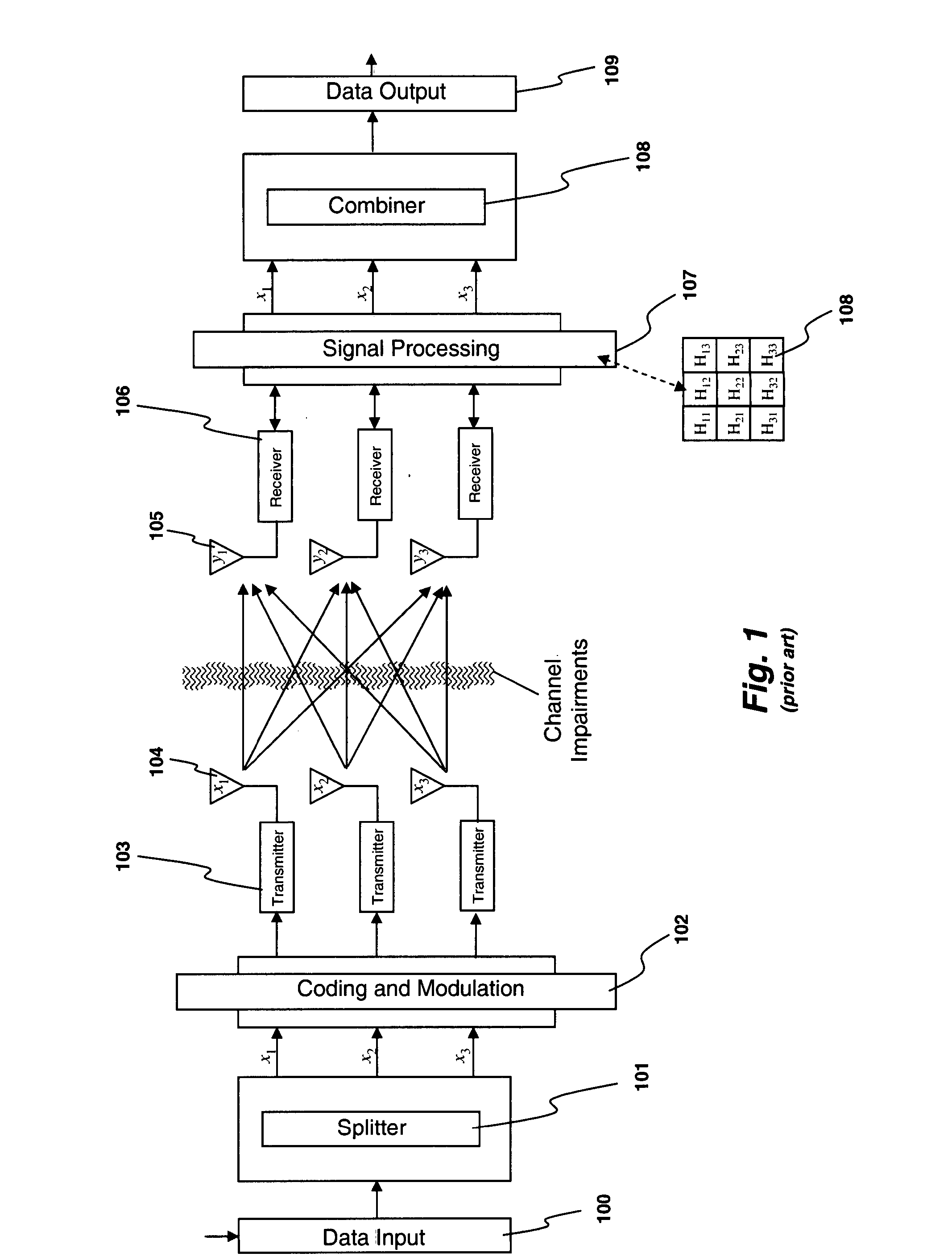
Method of correcting distortion in a power amplifier
InactiveUS20040142667A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionLookup table adaptive predistortionAudio power amplifierData signal
The invention is a method of correcting distortion in a power amplifier in a transmitter. The method includes applying an input time varying modulated data signal to the power amplifier which outputs an amplified time varying modulated data signal which is an amplification of the input time varying modulated data signal; storing samples of the input time varying modulated data signal; storing samples of the output amplified time varying data signal; using the stored input and output time varying modulated samples to provide a processor implemented model with parameters representing a non-linear characteristic of the power amplifier without the use of any polynomials; and producing predistortion coefficients.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
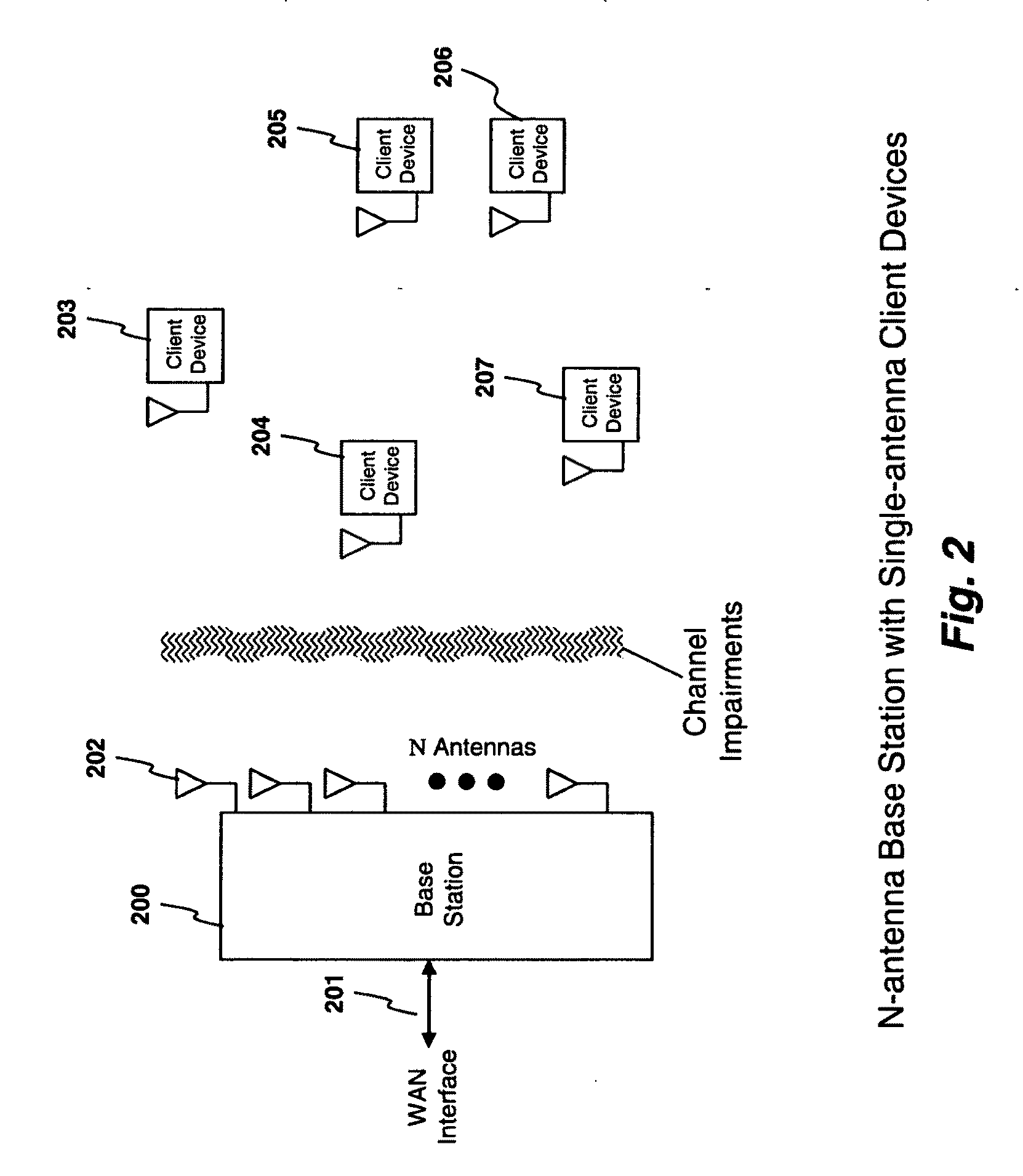
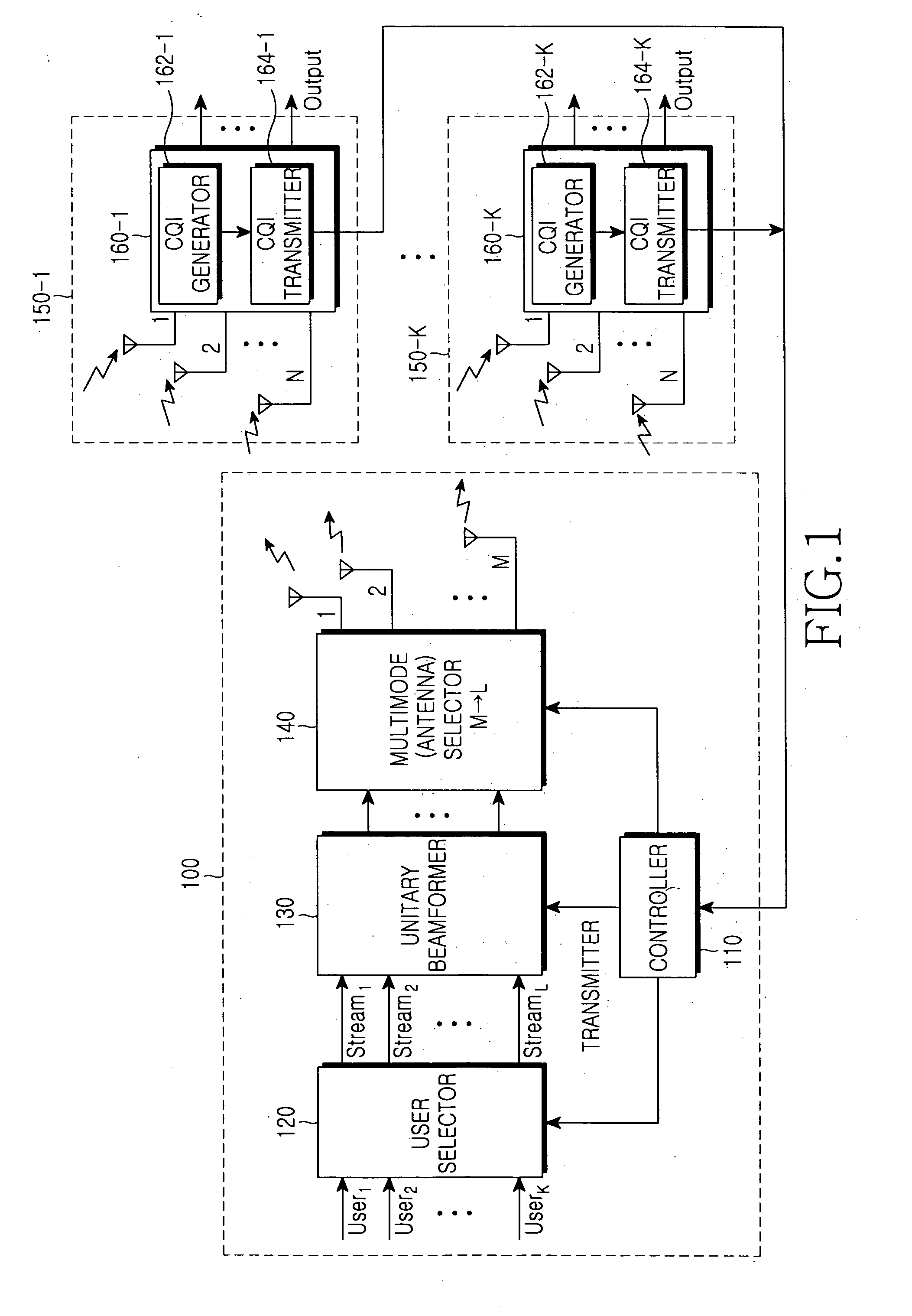
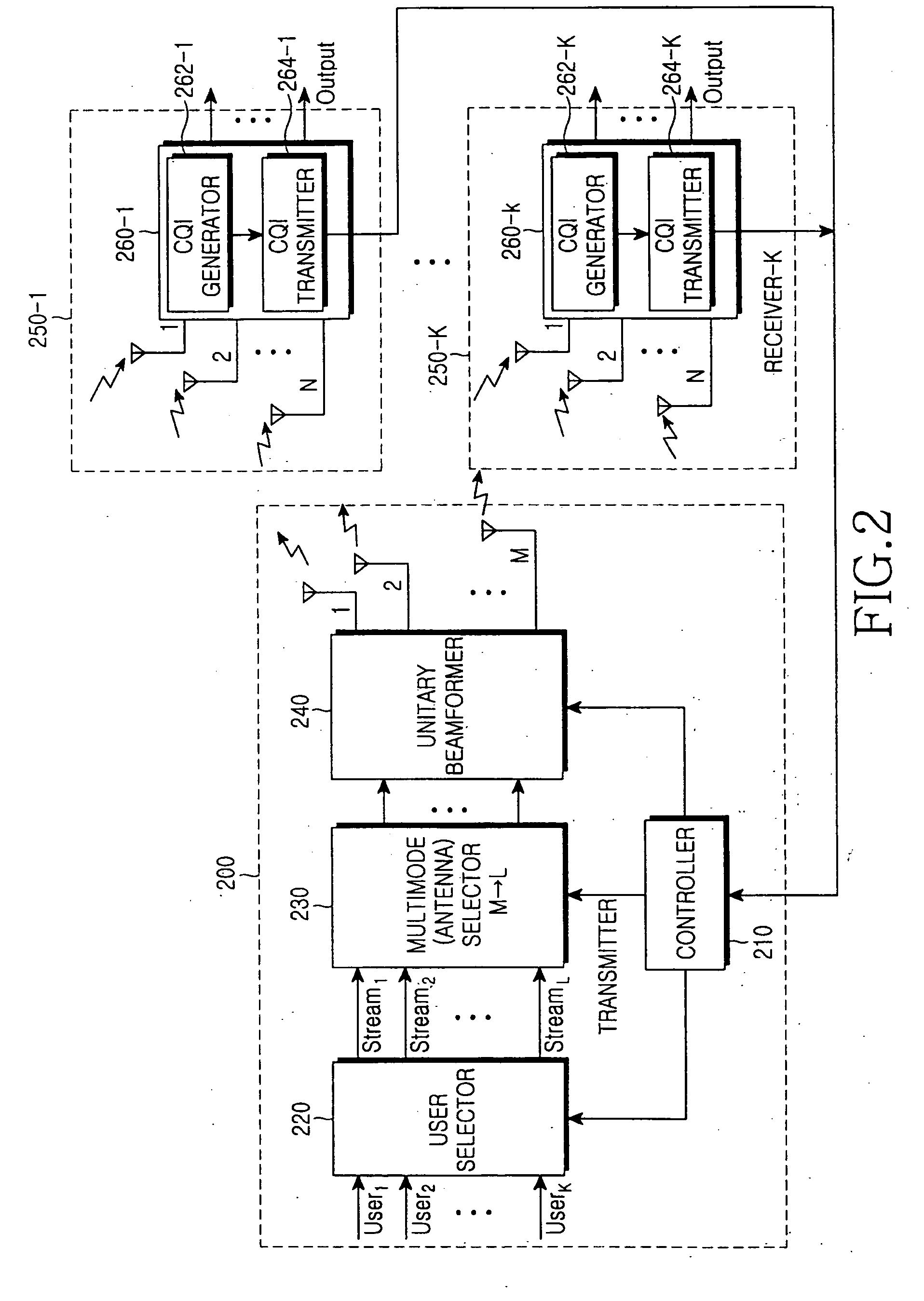
Apparatus and method for scheduling resource in a multiuser MIMO radio communication system
InactiveUS20050043031A1Maximize transfer efficiencySpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPrecodingCommunications system
In a multiuser Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) radio communication system, a transmitter receives channel quality information transmitted from receivers, schedules resource for the receivers within a corresponding scheduling epoch based on the received channel quality information. Thereafter, the transmitter pre-codes signals to be transmitted to the resource-scheduled receivers in a predetermined coding method before transmission, thereby maximizing system transmission efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Mimo-ofdm system using eigenbeamforming method
ActiveUS20070177681A1Reduce the amount requiredMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationFourier transform on finite groupsShort terms
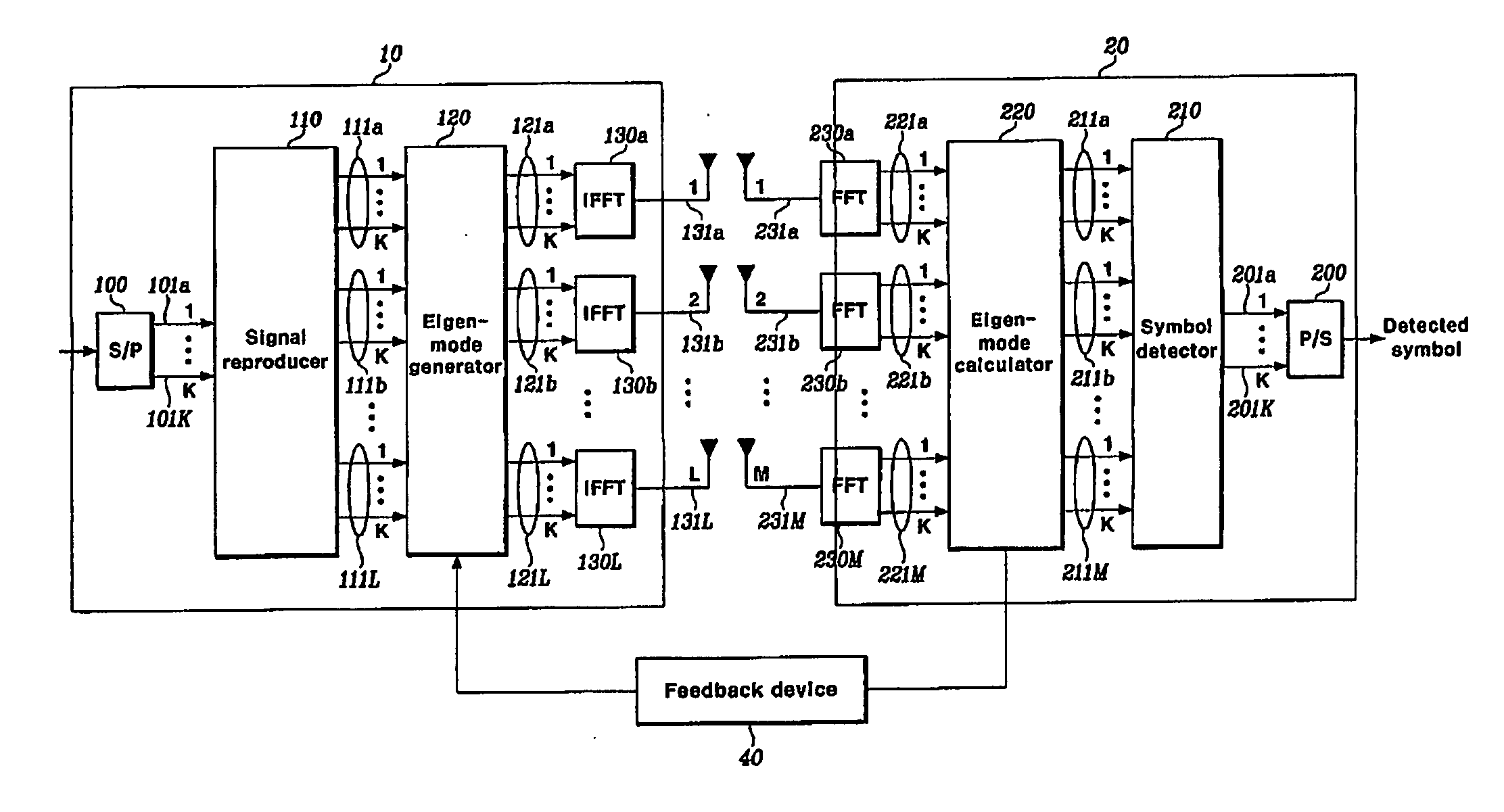
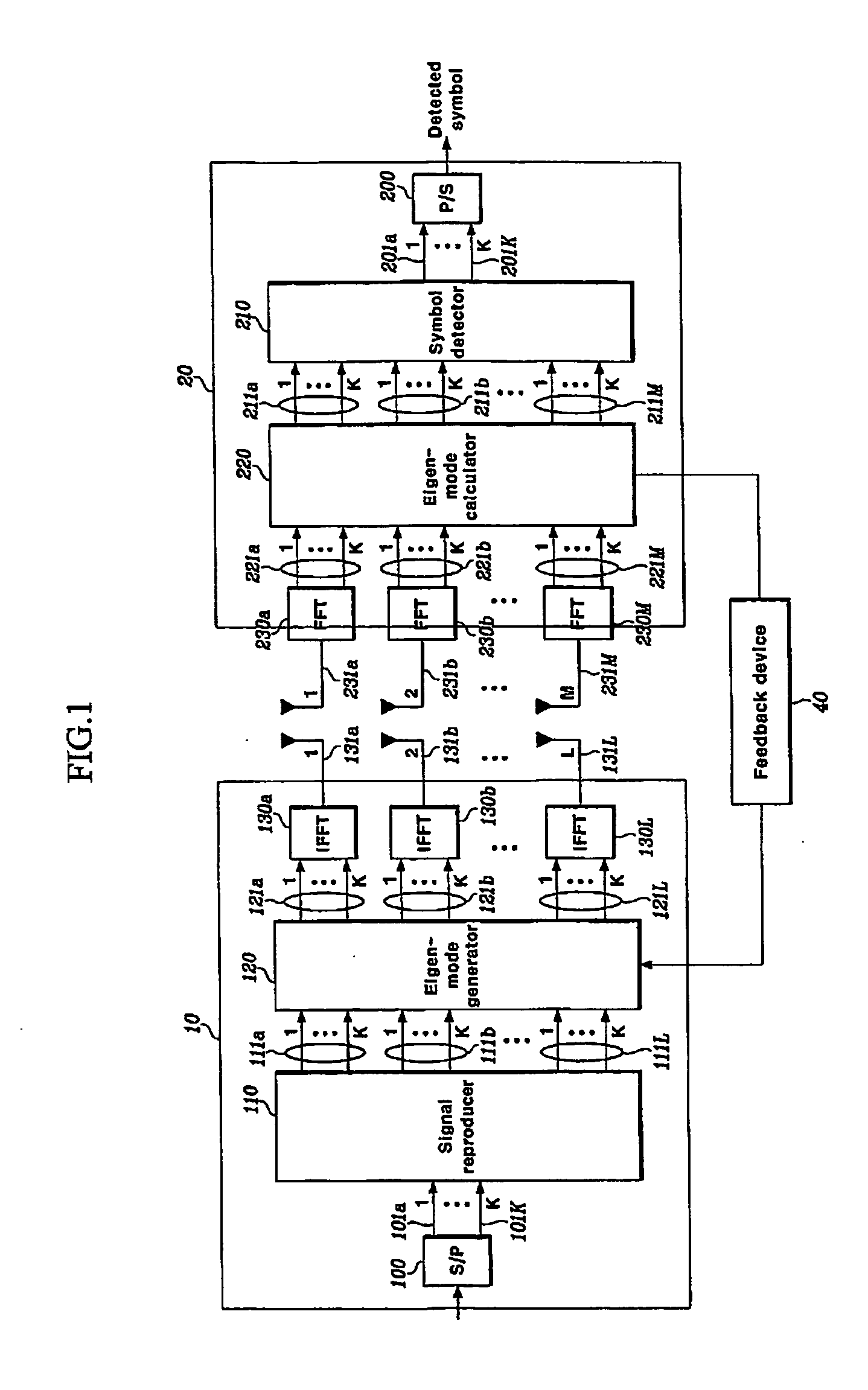
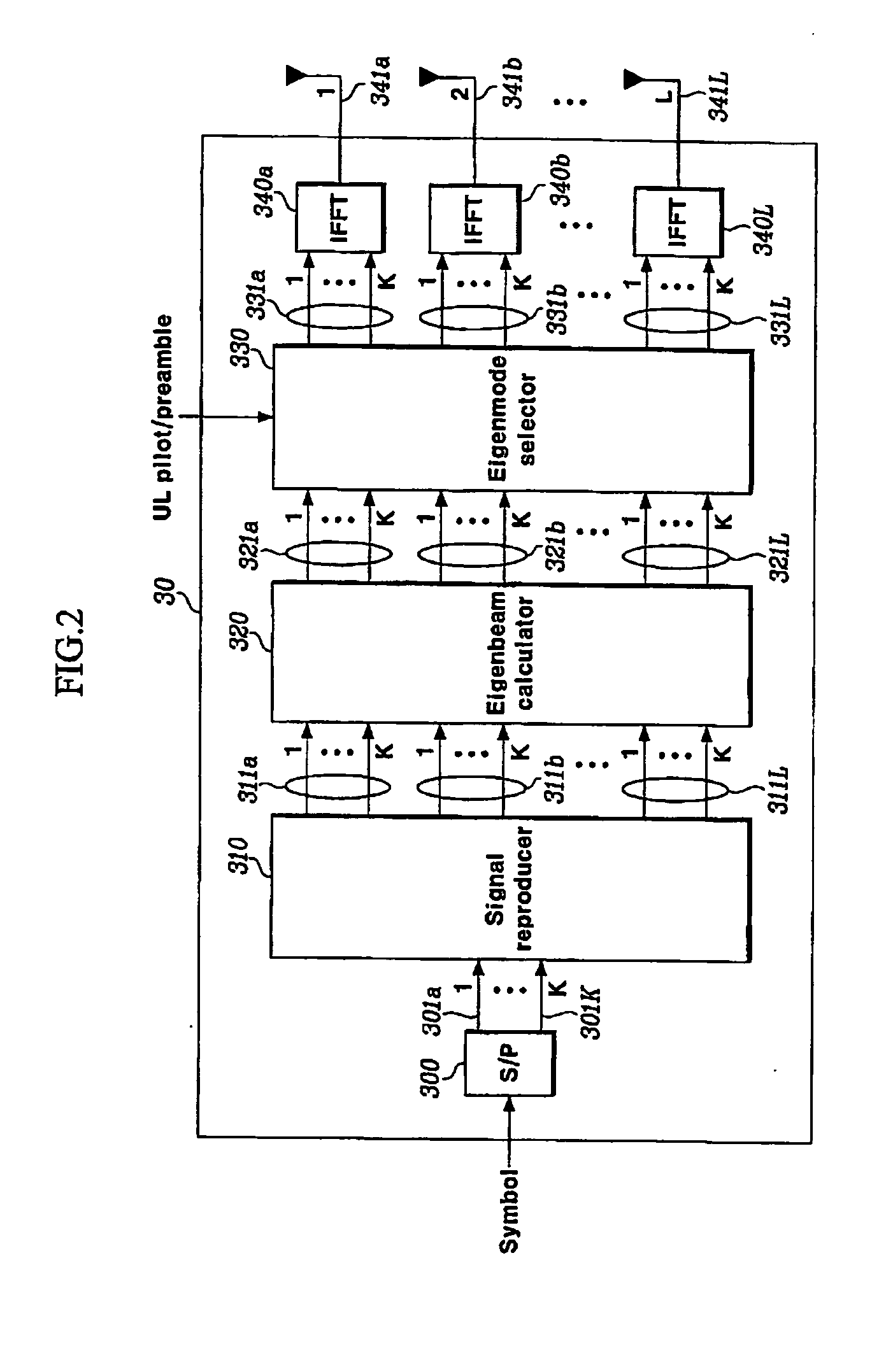
Disclosed is a MIMO-OFDM system, wherein the transmitter comprises a serial / parallel converter for converting continuously inputted symbols of the number of subcarriers to K parallel signals; a signal reproducer for reproducing K parallel signals by the number of transmit antennas L an eigenmode generator for generating eigenbeam of the reproduced signals outputted from the signal reproducer at each subcarrier, on the basis of Nf eigenbeam forming vectors which are fed back long-term and information of a best eigenbeam forming vector at each subcarrier which is fed back short-term, through the feedback device; and a plurality of inverse Fourier converters for receiving the signals outputted from the eigenmode generator and generating an OFDM symbol.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Digital broadcast transmitting and receiving system having an improved receiving performance and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20050249301A1Improve reception performanceModulation with suppressed carrierCode conversionData streamEqualization
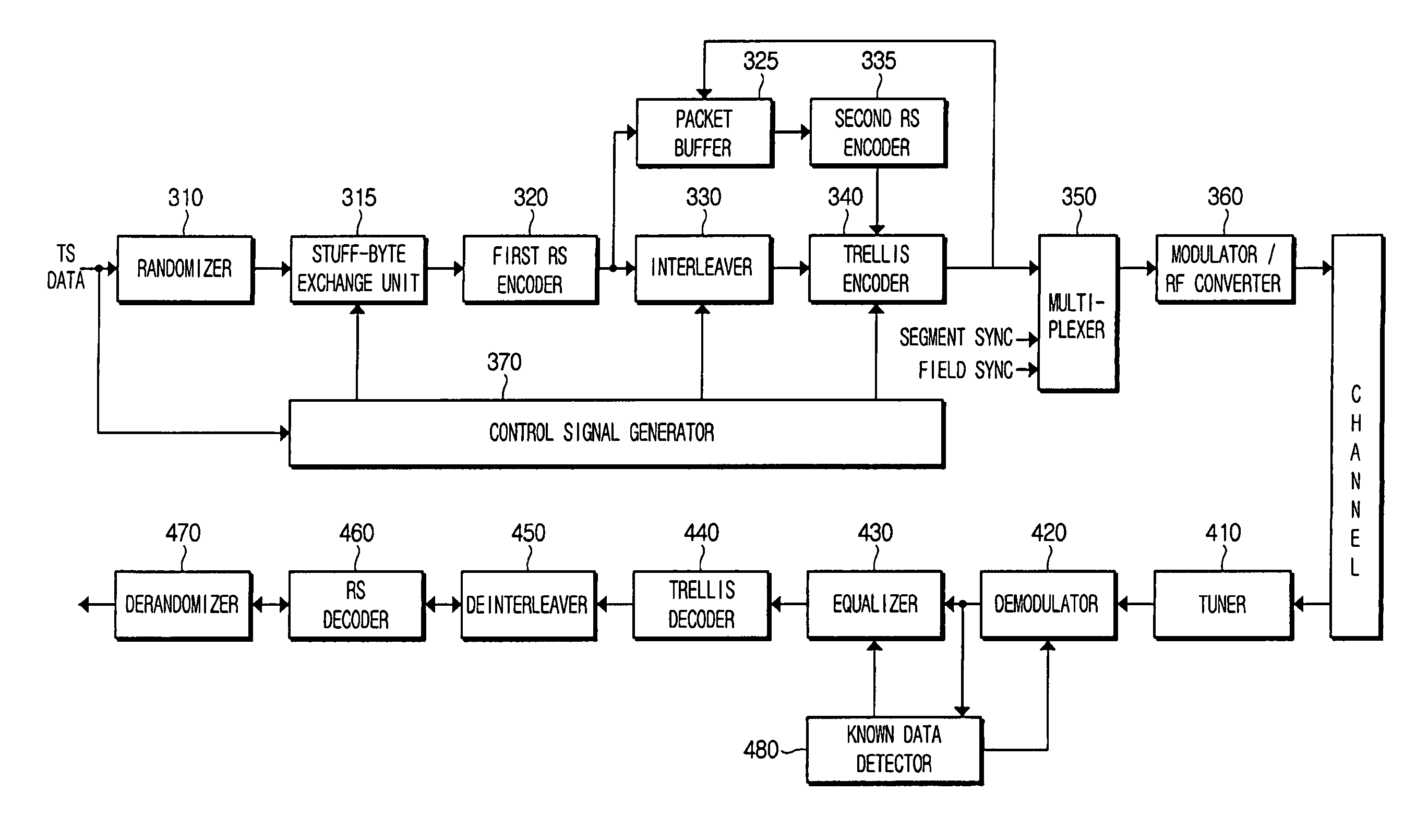
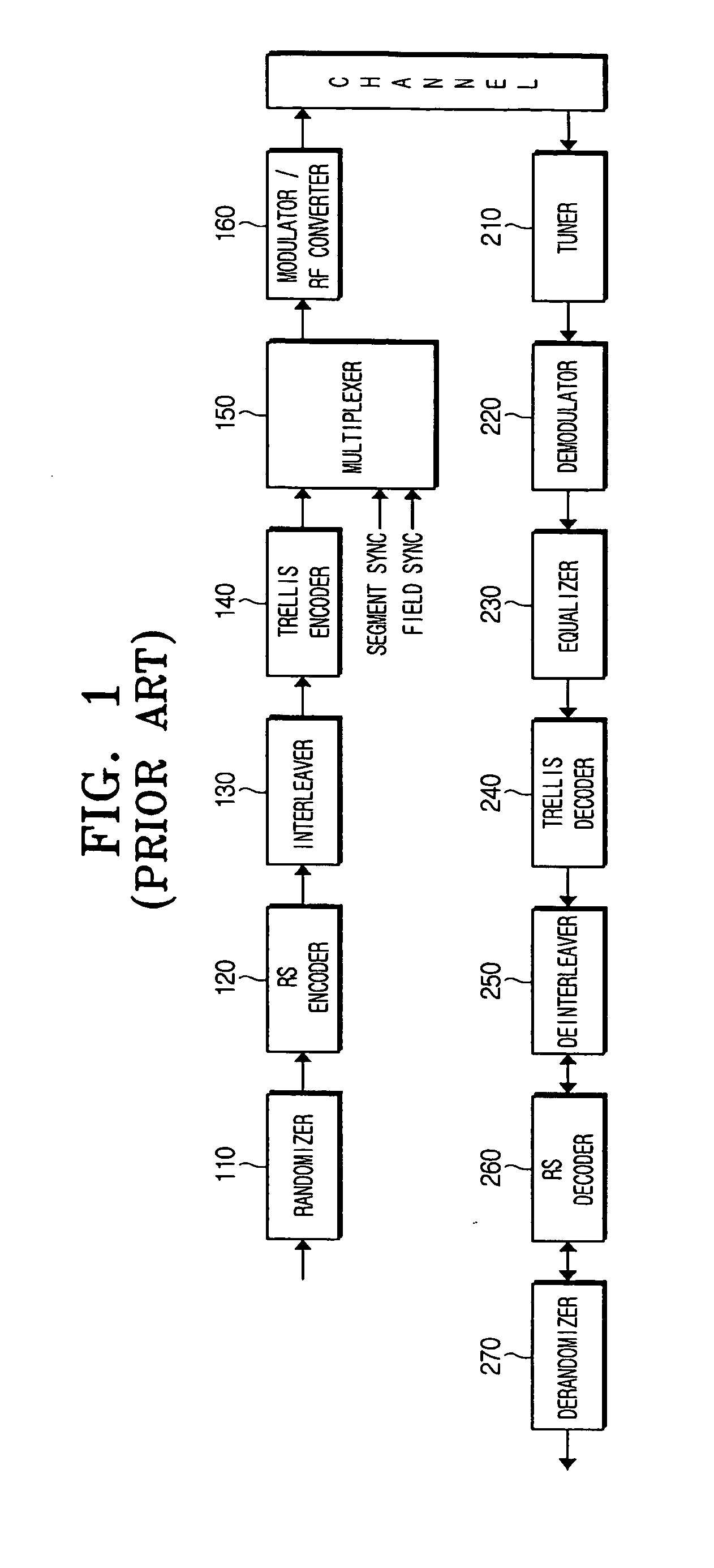
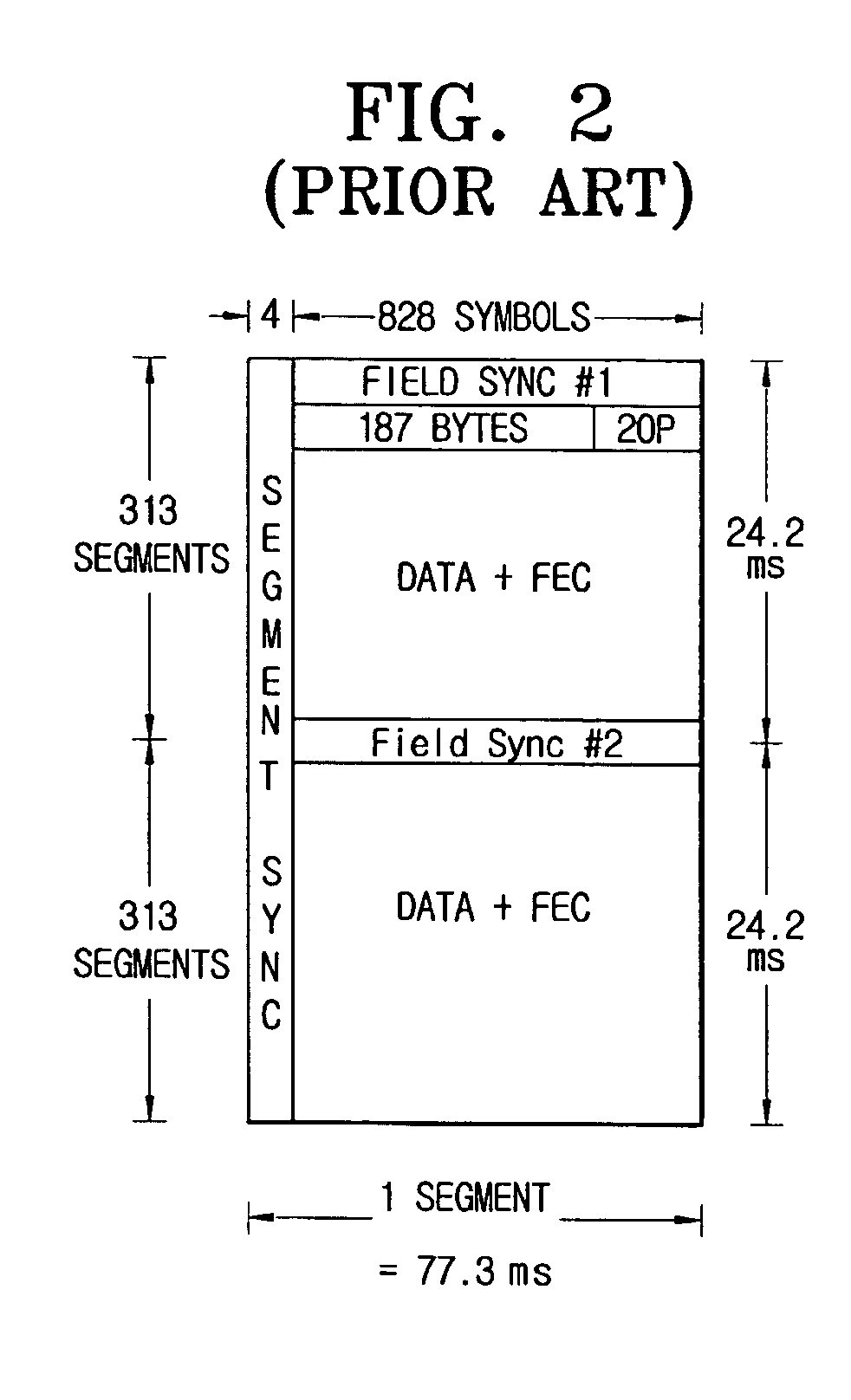
A digital broadcast transmitting and receiving system and a signal processing method thereof that improves the receiving performance of the system. A digital broadcast transmitter can include a randomizer to receive and randomize a data stream into a specified position of which stuff bytes are inserted, a stuff-byte exchange unit to generate known data having a predefined pattern and insert the known data into the specified position of the data stream into which the stuff bytes are inserted, an encoder to encode the data stream output from the stuff-byte exchange unit for an error correction, and a modulator and RF converter to modulate the encoded data stream, RF-convert the modulated data stream and transmit the RF-converted data. The digital broadcast receiving performance can be improved even in an inferior multi-path channel by detecting the known data from the received transmission and using the known data for synchronization and equalization in a digital broadcast receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scattered pilot pattern and channel estimation method for MIMO-OFDM systems
ActiveUS7248559B2Reduced scattered pilot overheadLess computationally complexPower managementSpatial transmit diversityTime domainCommunications system
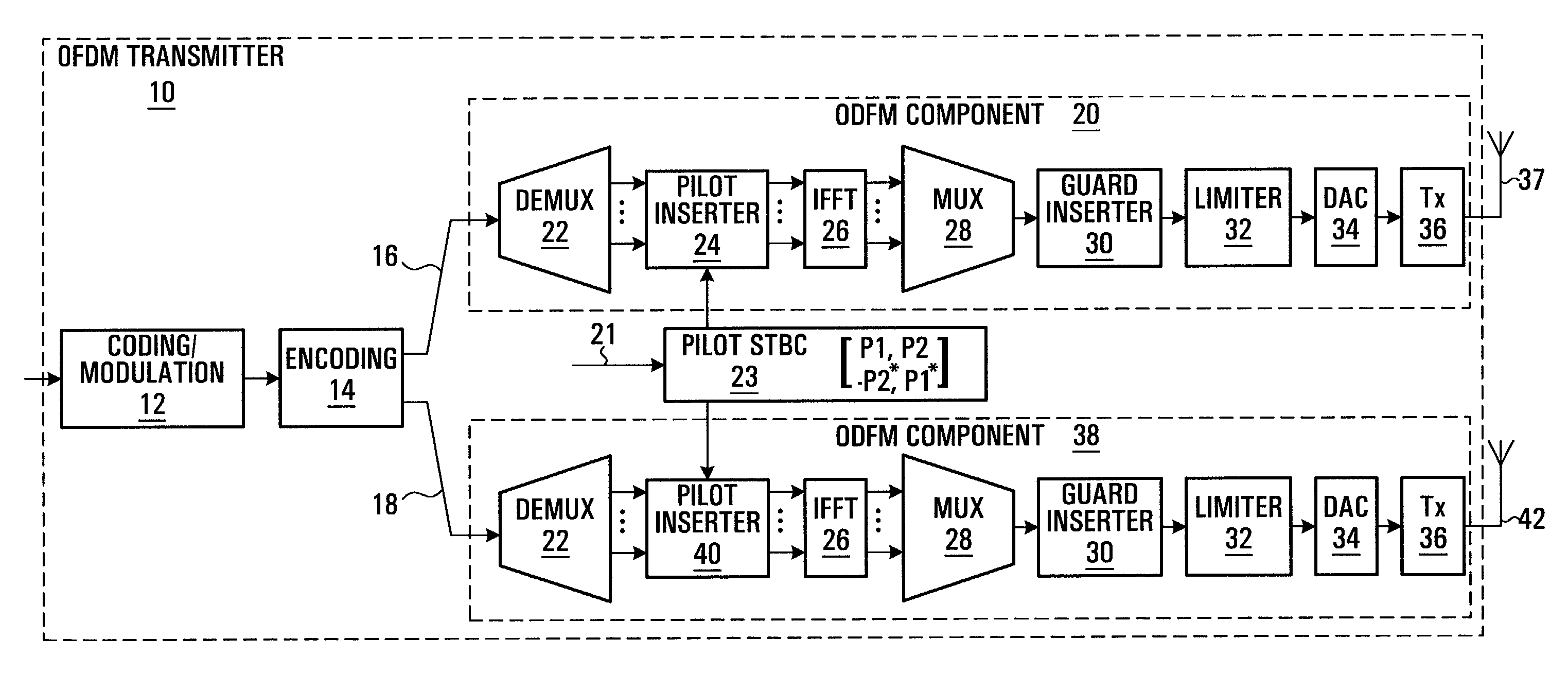
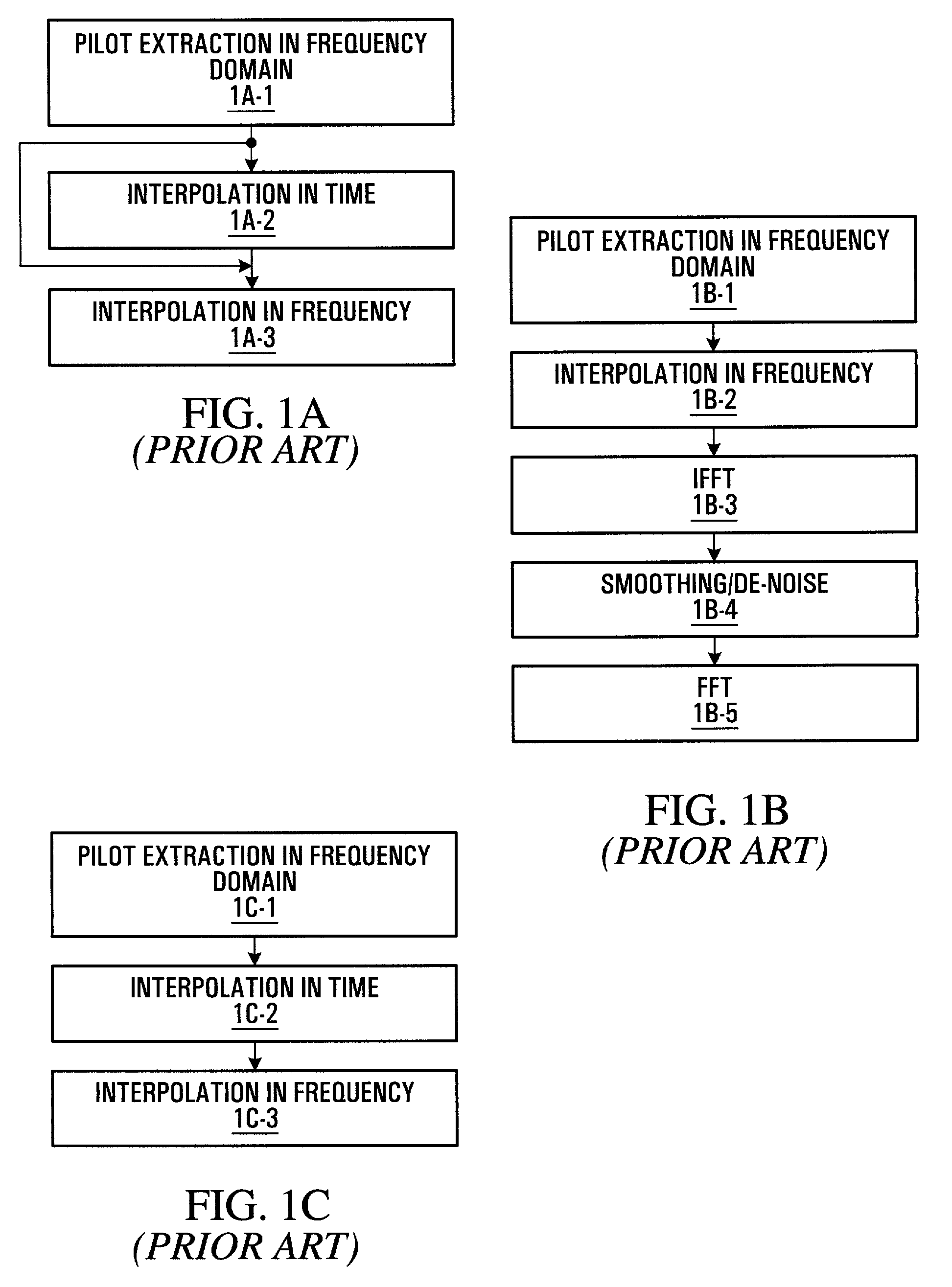
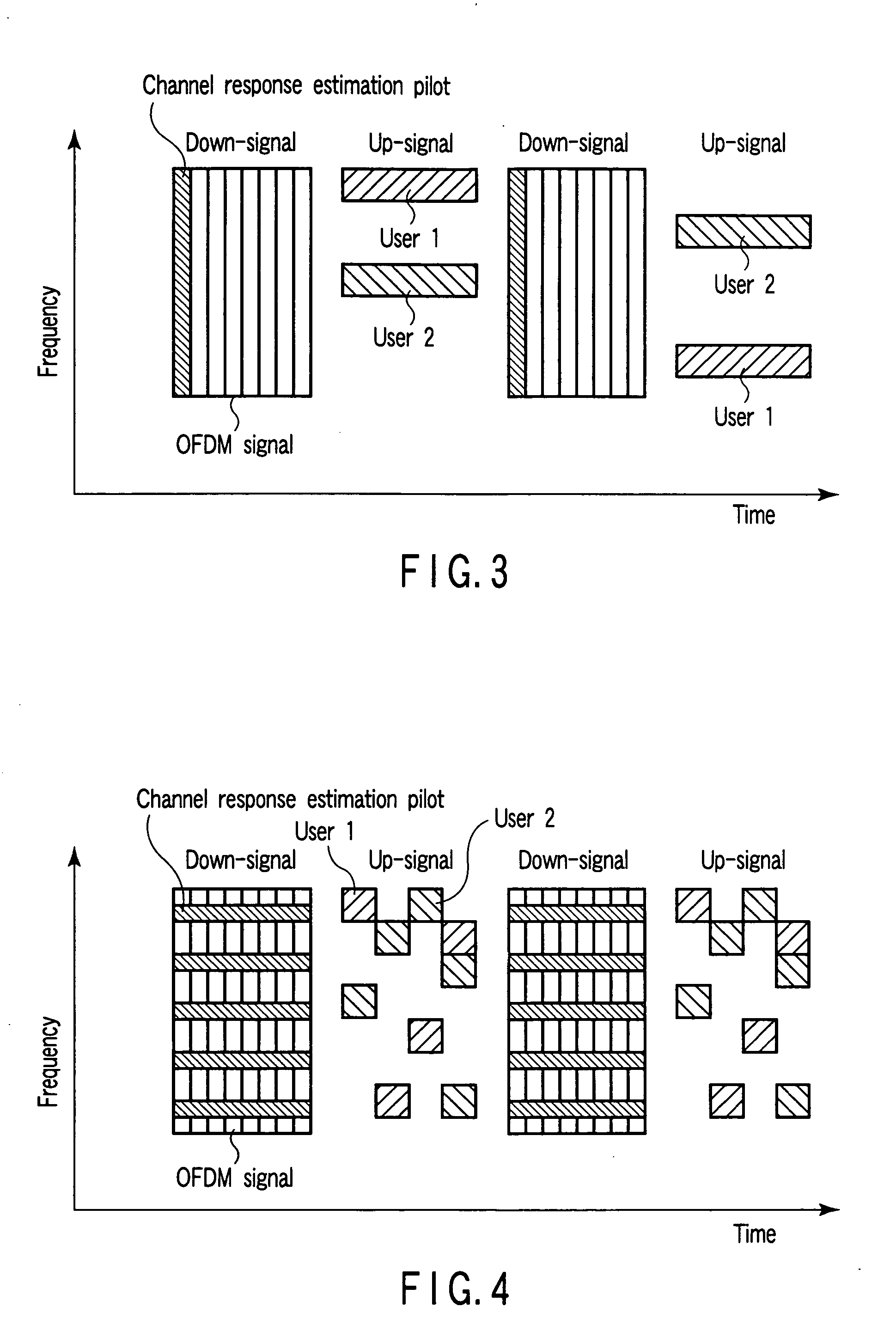
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing the number of pilot symbols within a MIMO-OFDM communication system, and for improving channel estimation within such a system. For each transmitting antenna in an OFDM transmitter, pilot symbols are encoded so as to be unique to the transmitting antenna. The encoded pilot symbols are then inserted into an OFDM frame to form a diamond lattice, the diamond lattices for the different transmitting antennae using the same frequencies but being offset from each other by a single symbol in the time domain. At the OFDM receiver, a channel response is estimated for a symbol central to each diamond of the diamond lattice using a two-dimensional interpolation. The estimated channel responses are smoothed in the frequency domain. The channel responses of remaining symbols are then estimated by interpolation in the frequency domain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
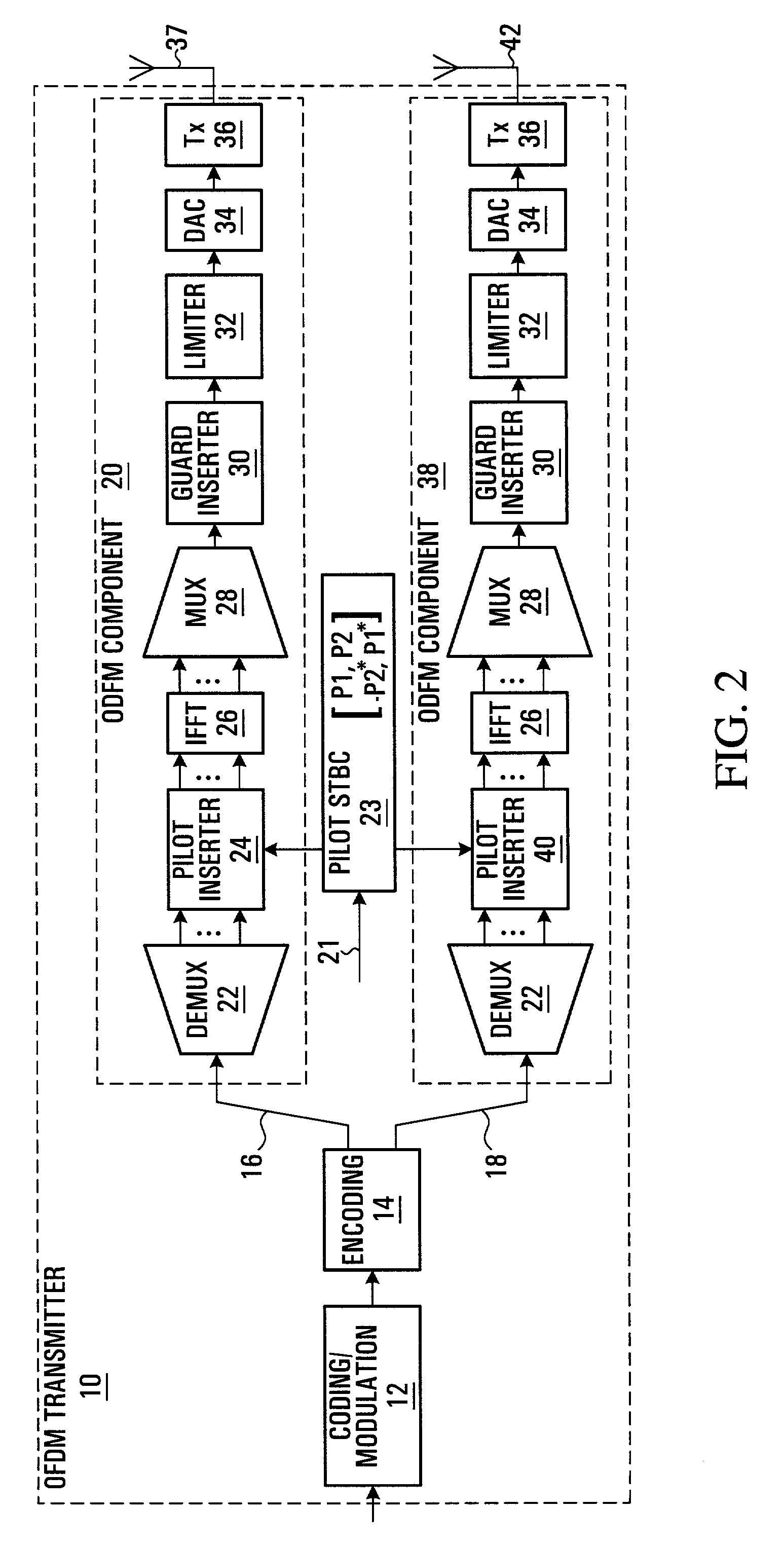
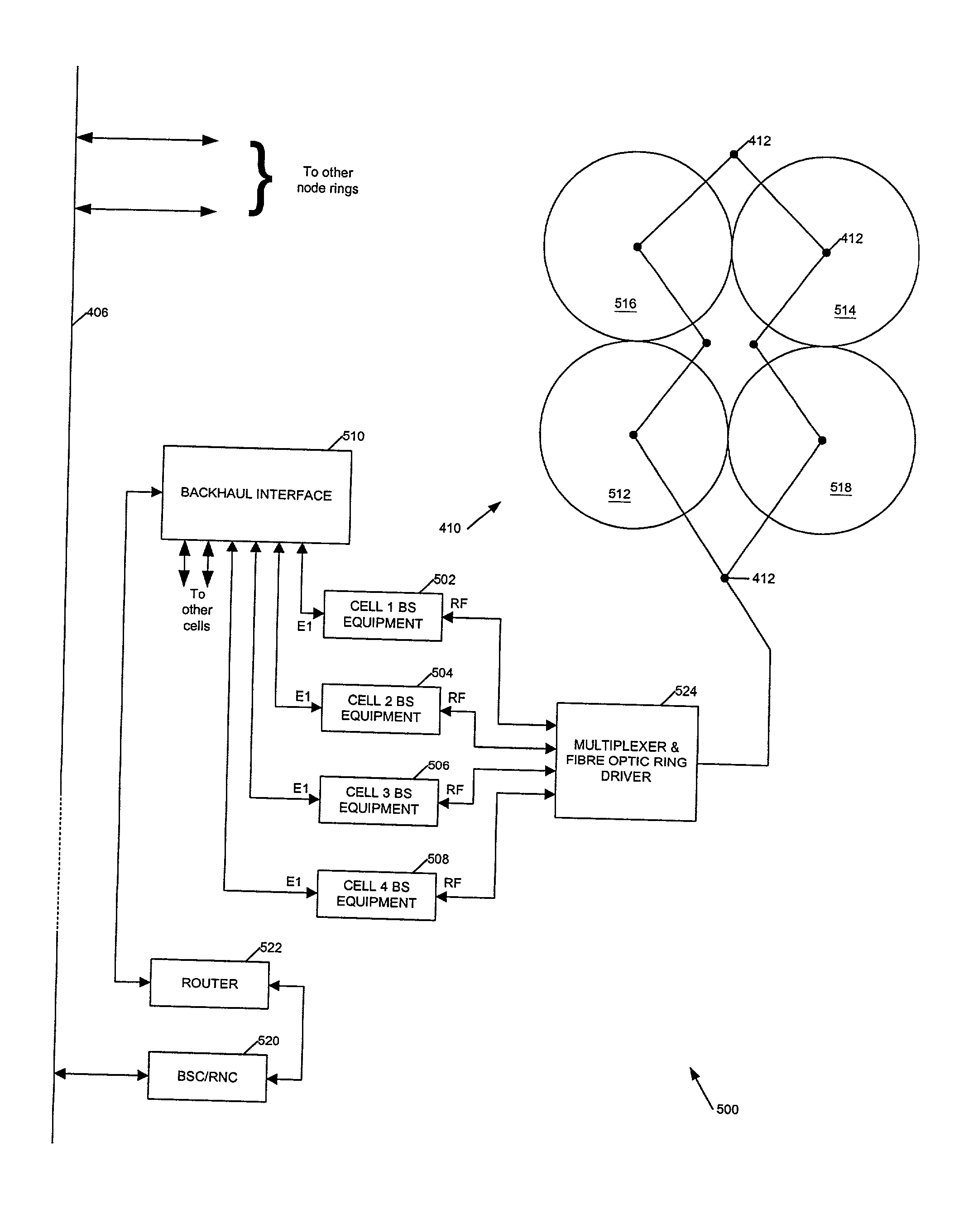
Signal transmission systems
Signal transmission systems for second and third generation mobile communications networks are described. A signal distribution system comprises a plurality of rf transmitters for serving a plurality of network cells. The system is characterised by a multiplexer coupled to the transmitters for multiplexing the transmitter outputs, a signal transporter for transporting the multiplexed signals to each of the network cells, and a multiplexed signal receiver at each cell for selecting and receiving a signal from a transmitter serving the cell. The invention also provides a complementary signal reception system, and corresponding methods. Preferably, the multiplexed signals are transported over a fibre optic network such as an existing cable TV network. The system simplifies the deployment of network infrastructure for third generation mobile communications systems.
Owner:NTL GROUP
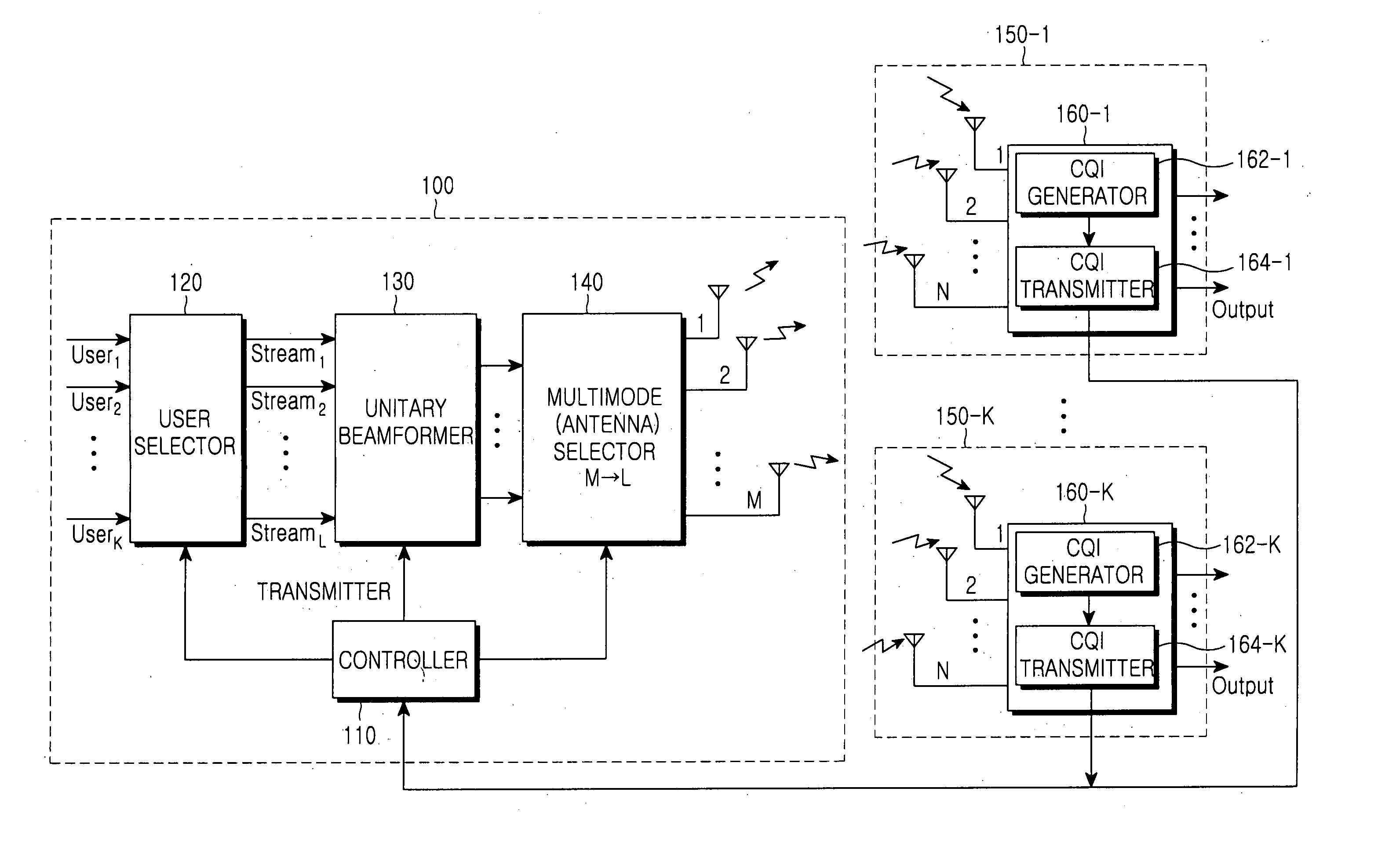
Method and apparatus of codebook-based single-user closed-loop transmit beamforming (SU-CLTB) for OFDM wireless systems
ActiveUS20090041150A1Improve throughputMaximize signal to noise ratioMultiple-port networksAntenna arraysCommunications systemClosed loop
A method includes broadcasting, at a transmitter, messages comprising antenna configuration, antenna spacing and a number of antenna of the transmitter and reference signals; generating, at a receiver, a codebook comprising a plurality of antenna beams based on the broadcasted messages; receiving, at the receiver, the broadcasted reference signals; selecting, at the receiver, an antenna beam among the plurality of antenna beams within the codebook in dependence upon a predetermined performance criteria of a data communication system and in dependence upon the broadcasted reference signals; feedbacking to the transmitter, at the receiver, information comprising the antenna beam selected by the receiver; optimizing, at the transmitter, a beamforming process by utilizing the feedback information from the receiver; transmitting, at the transmitter, data signals by utilizing the optimized beamforming process; and receiving and processing, at the receiver, the data signals in dependence upon the selected antenna beams within the codebook.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio communication apparatus, base station and system
InactiveUS20060013285A1Modulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexSignal to noise power ratioTransmitter
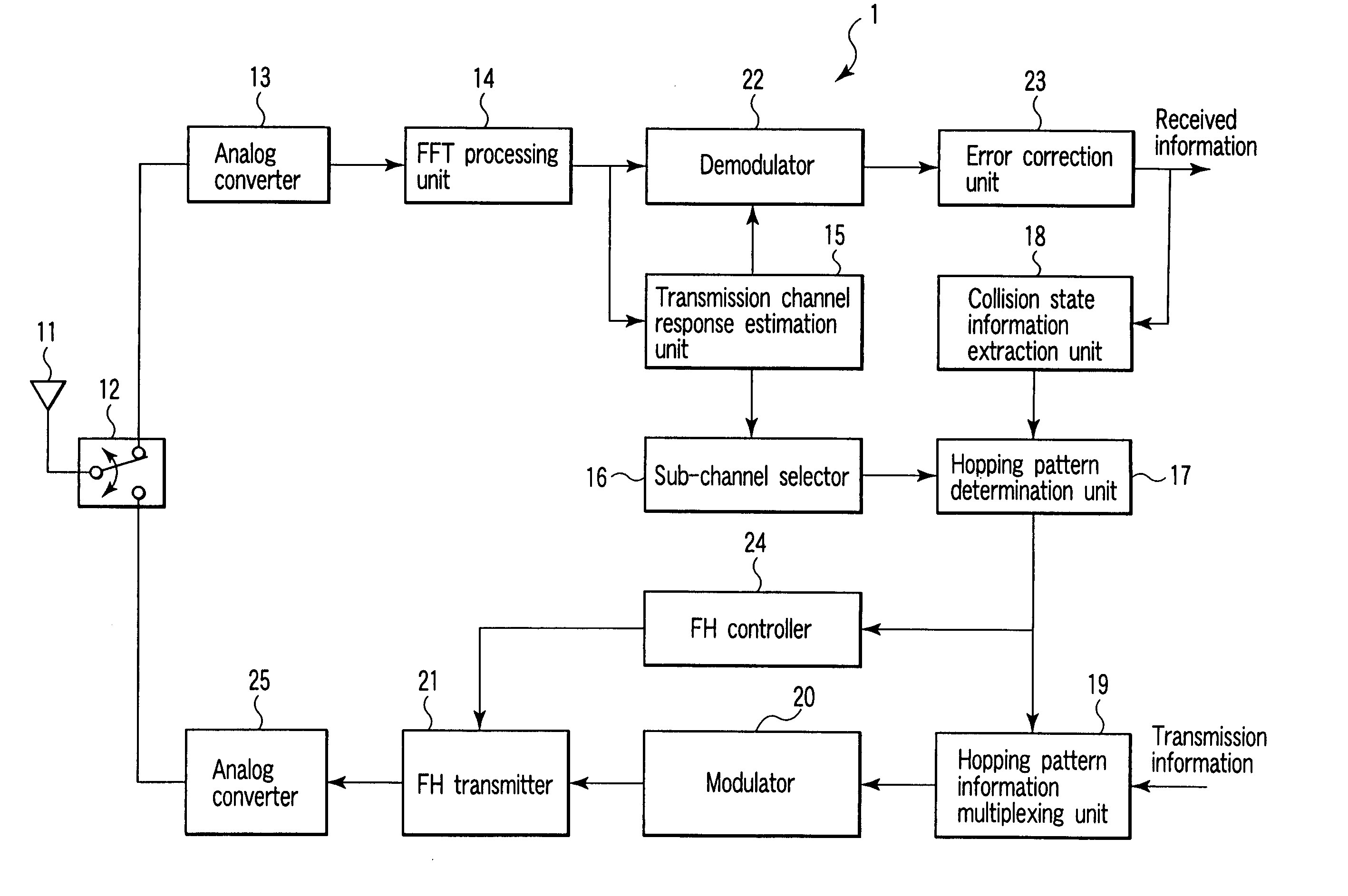
Radio communication apparatus for receiving OFDM signal from base station and transmitting FH signal to base station, using sub-channels, base station comparing hopping pattern information items indicating hopping patterns from radio communication apparatuses including radio communication apparatus, and generating collision information when hopping patterns include colliding hopping patterns, includes estimation unit configured to estimate channel response values of sub-channels based on OFDM signal, selector which selects, from sub-channels, several sub-channels which have higher channel response values than a value, each of channel response values being expressed by power level, signal-to-noise power ratio, or signal-to-interference ratio, determination unit configured to determine hopping pattern from selected sub-channels, transmitter which transmits, to base station, hopping pattern information item indicating determined hopping pattern, receiver which receives collision information from base station, and correction unit configured to correct hopping pattern based on collision information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Adaptive power control in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6690652B1Maintain conductivityMaximizes controlEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel powerControl signal
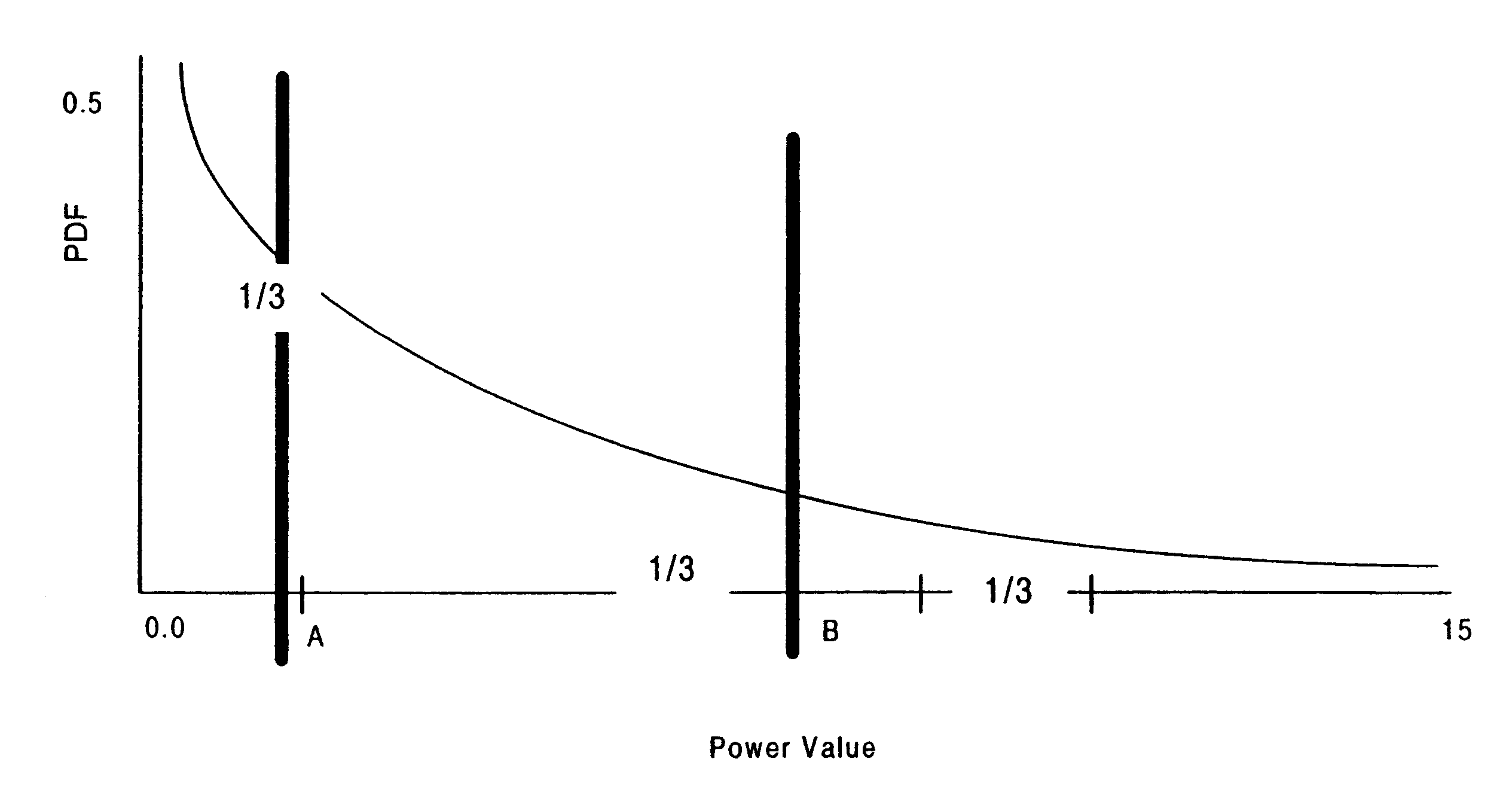
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) transmitter, or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between the BS and a Mobile Station (MS) to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver. Reconfiguration is performed according to the prediction of the channel attenuation and the threshold set at the BS or MS based on its channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. In one embodiment, Seamless Rate Change (SRC) / Transmitter Power Control (TPC) logic uses the predicted channel attenuation to signal both the transmitter and the receiver in a channel to reconfigure their transmit power level according to the power density function (pdf) of the channel power and threshold level. A transmission rate is reduced when the power level is below the threshold and increased when the channel power is above threshold. The pilot channel is used to signal the mobile station and the base station.
Owner:IBM CORP
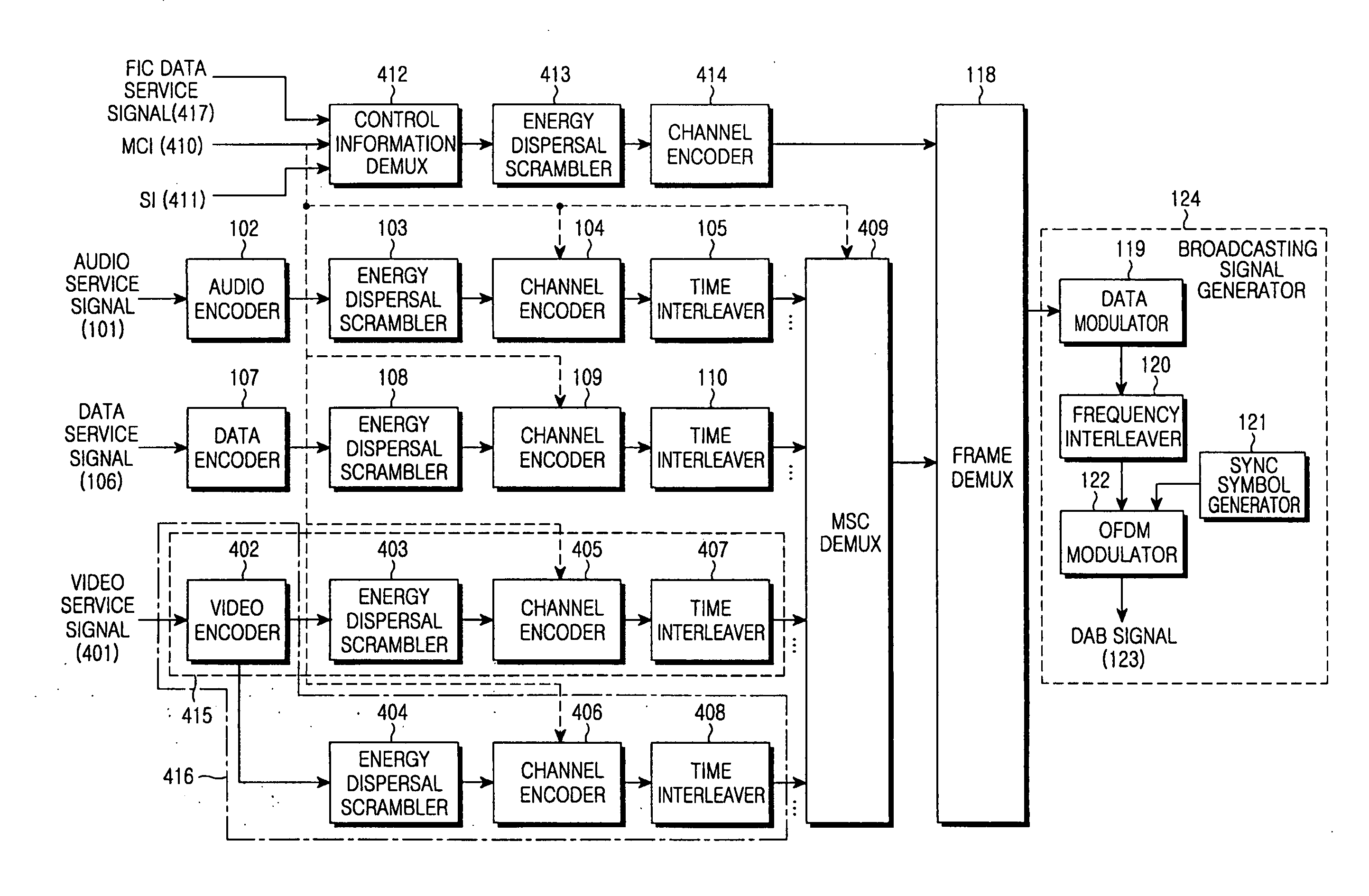
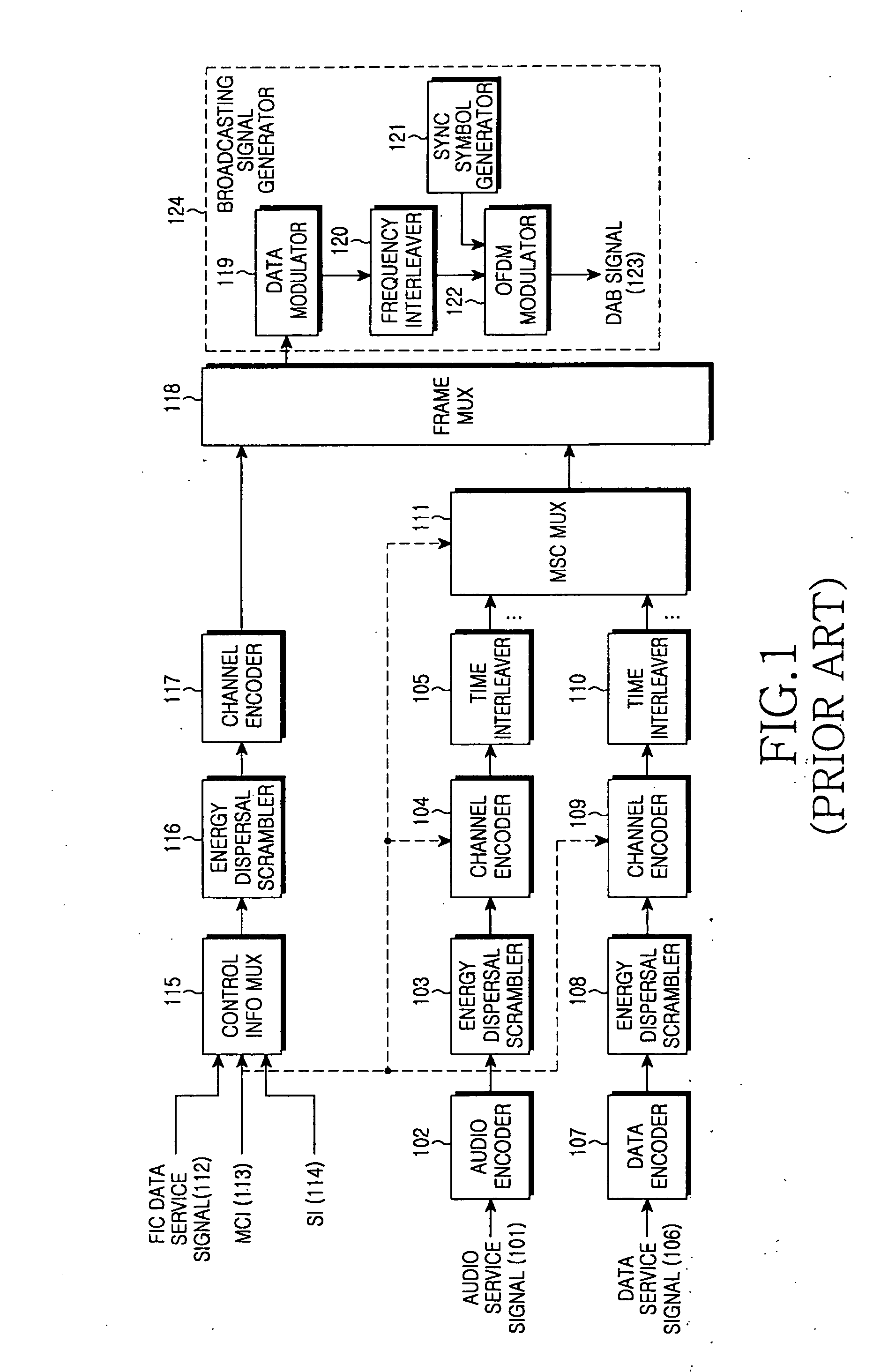
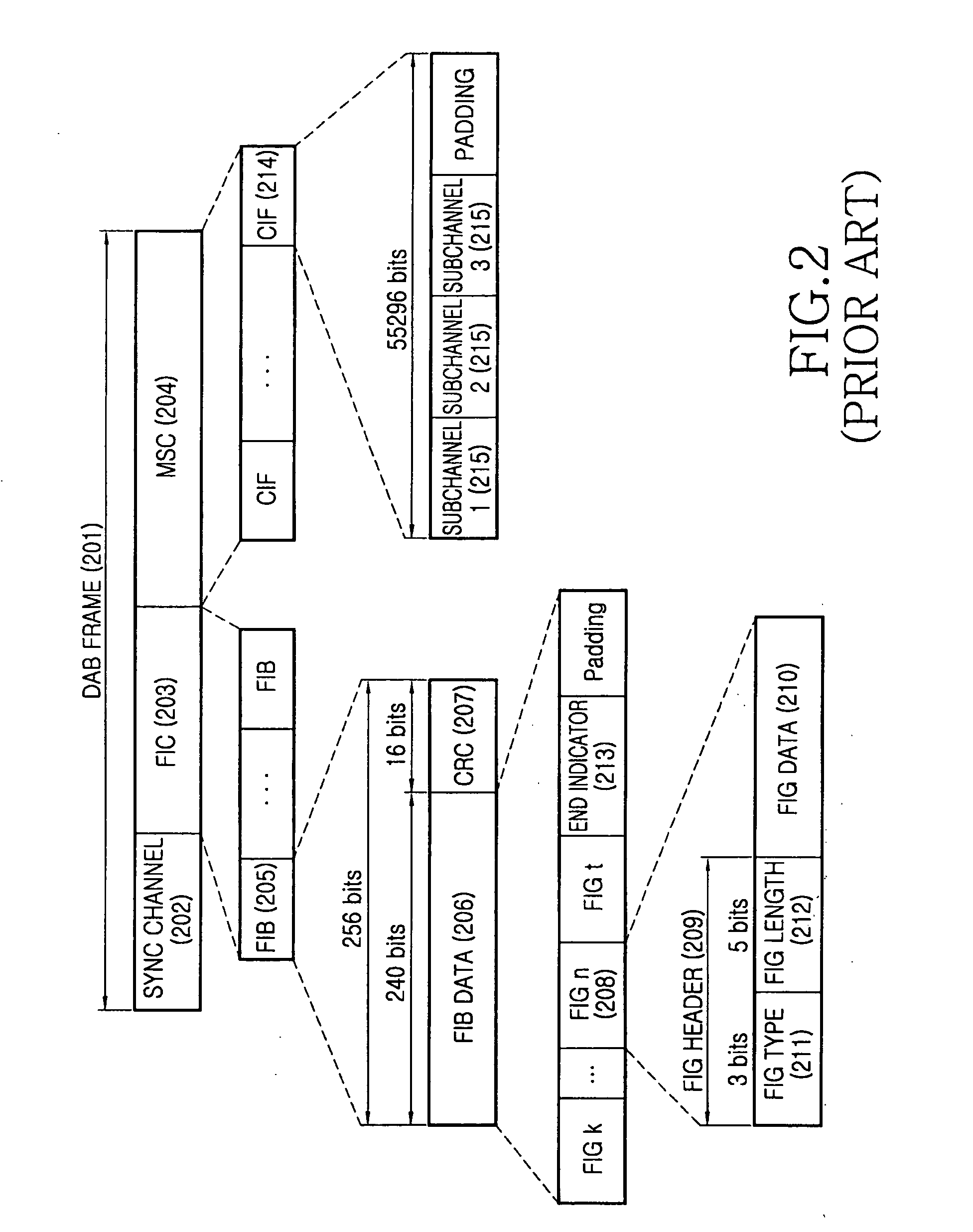
Method and apparatus for supporting a priority data transmission in a transmitter of a digital audio broadcasting system
InactiveUS20060248563A1Broadcast information characterisationResource management arrangementsData streamDigital audio broadcasting
A method and apparatus for supporting a priority transmission of broadcasting data in a transmitter of a digital broadcasting system. A determination is made as to whether a priority transmission of one broadcasting service to be provided is supported. If the service supports the priority transmission, a plurality of subchannels to be transmitted for the service are set and a priority of the data to be mapped to the plurality of subchannels is set. The data of the broadcasting service is mapped to the plurality of subchannels according to the priority. Data streams mapped to the plurality of subchannels are encoded in different encoders and the encoded data streams are transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Interference management, handoff, power control and link adaptation in distributed-input distributed-output (DIDO) communication systems
ActiveUS20110003607A1Reduce distractionsImprove downlink throughputDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission noise suppressionPrecodingCommunications system
A system and method are described herein employing a plurality of distributed transmitting antennas to create locations in space with zero RF energy. In one embodiment, when M transmit antennas are employed, it is possible to create up to (M−1) points of zero RF energy in predefined locations. In one embodiment of the invention, the points of zero RF energy are wireless devices and the transmit antennas are aware of the channel state information (CSI) between the transmitters and the receivers. In one embodiment, the CSI is computed at the receivers and fed back to the transmitters. In another embodiment, the CSI is computed at the transmitter via training from the receivers, assuming channel reciprocity is exploited. The transmitters may utilize the CSI to determine the interfering signals to be simultaneously transmitted. In one embodiment, block diagonalization (BD) precoding is employed at the transmit antennas to generate points of zero RF energy.
Owner:REARDEN
Method and system for transmitting data in a communication system
ActiveUS20070160162A1Efficient data transferModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemData transmission
A method and system are provided for transmitting data in a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication system. A receiver sets the number of sub-streams of each column of a preceding matrix with respect to all precoding matrices of channels formed between the receiver and a transmitter and measures channel states with respect to sub-stream combinations whose number is equivalent to the number of set sub-streams. The receiver transmits data according to channel states to the transmitter after measuring the channel states with respect to the sub-stream combinations and antenna combinations representing sub-streams used upon data transmission of all the precoding matrices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
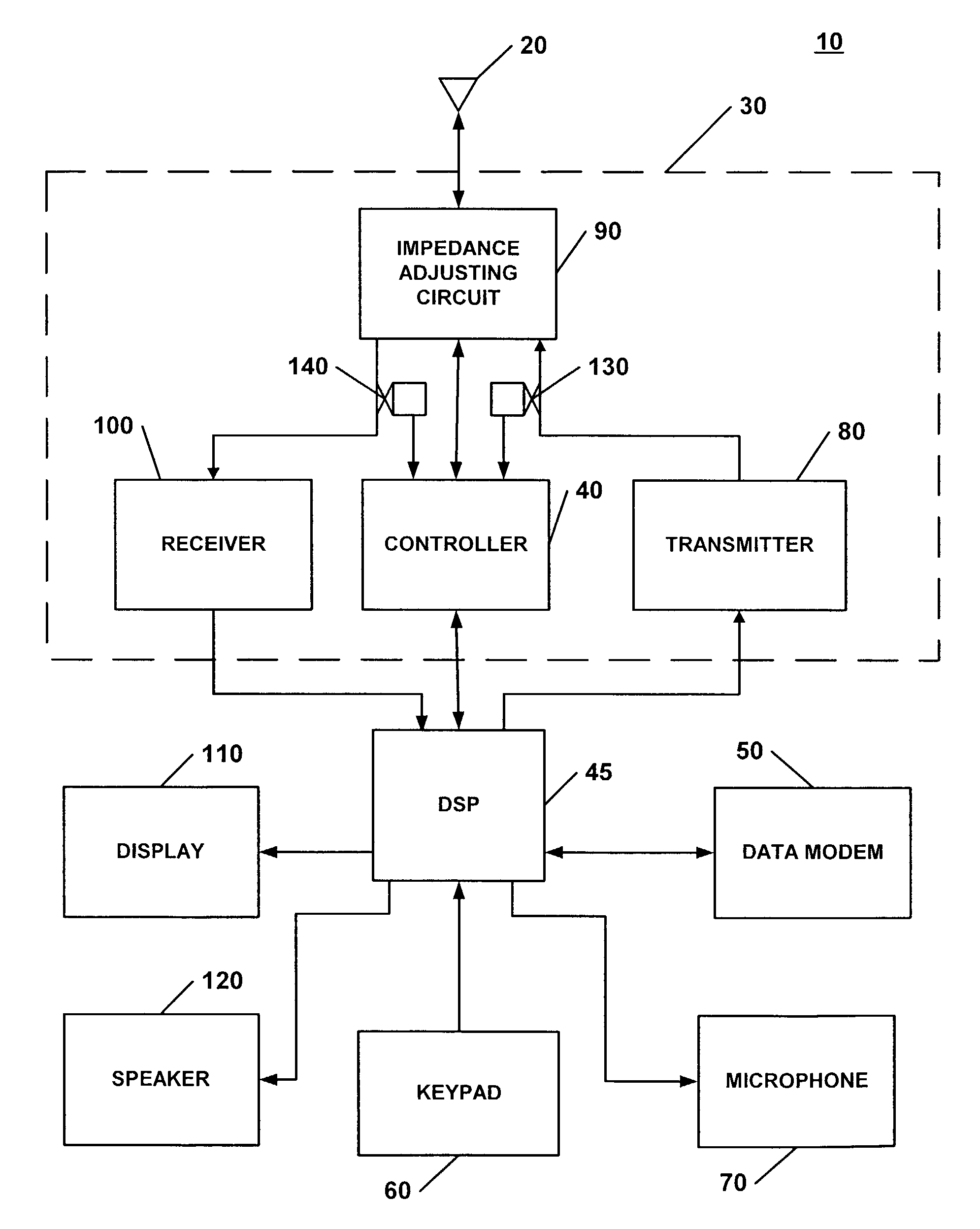
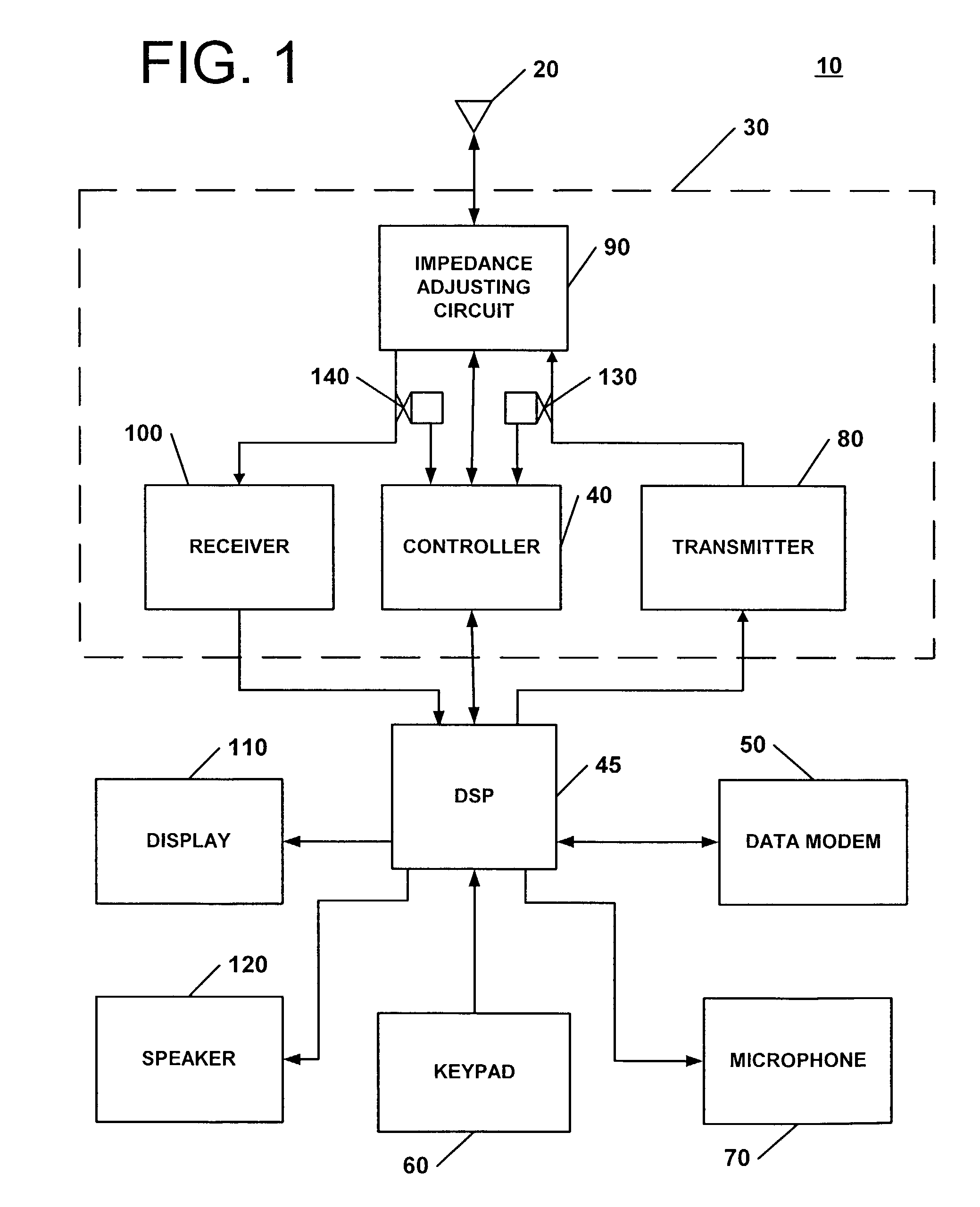
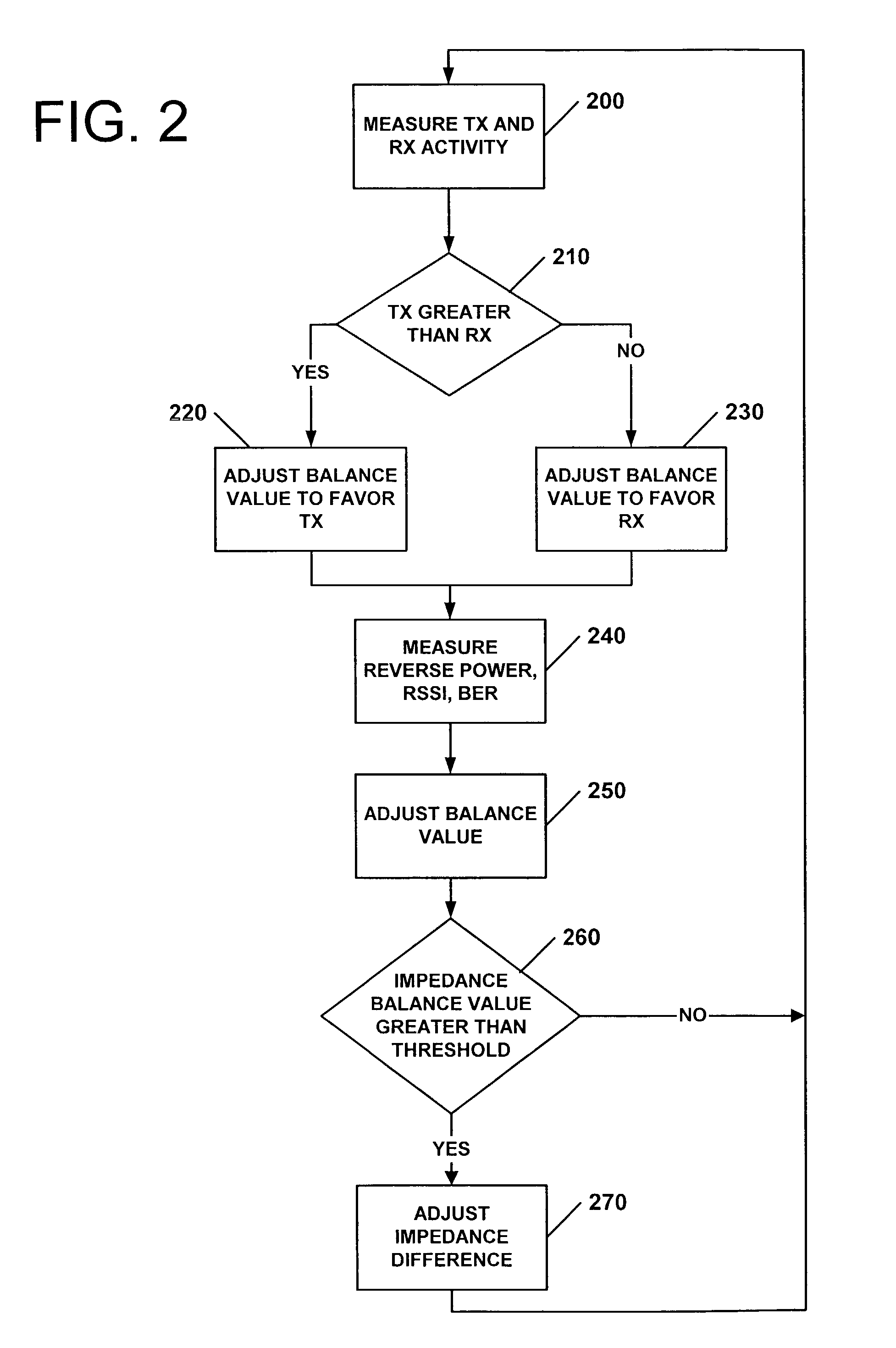
Apparatus and methods for tuning antenna impedance using transmitter and receiver parameters
InactiveUS6993297B2Reduce presented impedance differenceReduce impedance differenceMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasAntenna impedanceControl signal
According to some embodiments of the present invention, an impedance transformation circuit is provided for use with a transmitter, a receiver, and an antenna. The transmitter may provide transmission signals for transmission by the antenna. The antenna may provide received signals having an associated signal parameter to the receiver. The impedance transformation circuit includes an impedance adjusting circuit and a controller. The impedance adjusting circuit is connected between the antenna, the receiver, and the transmitter. The impedance adjusting circuit is configured to change an impedance difference presented between at least one of: 1) the transmitter and the antenna, and 2) the antenna and the receiver, in response to a control signal. The controller generates the control signal to change the presented impedance difference in response to a signal parameter.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
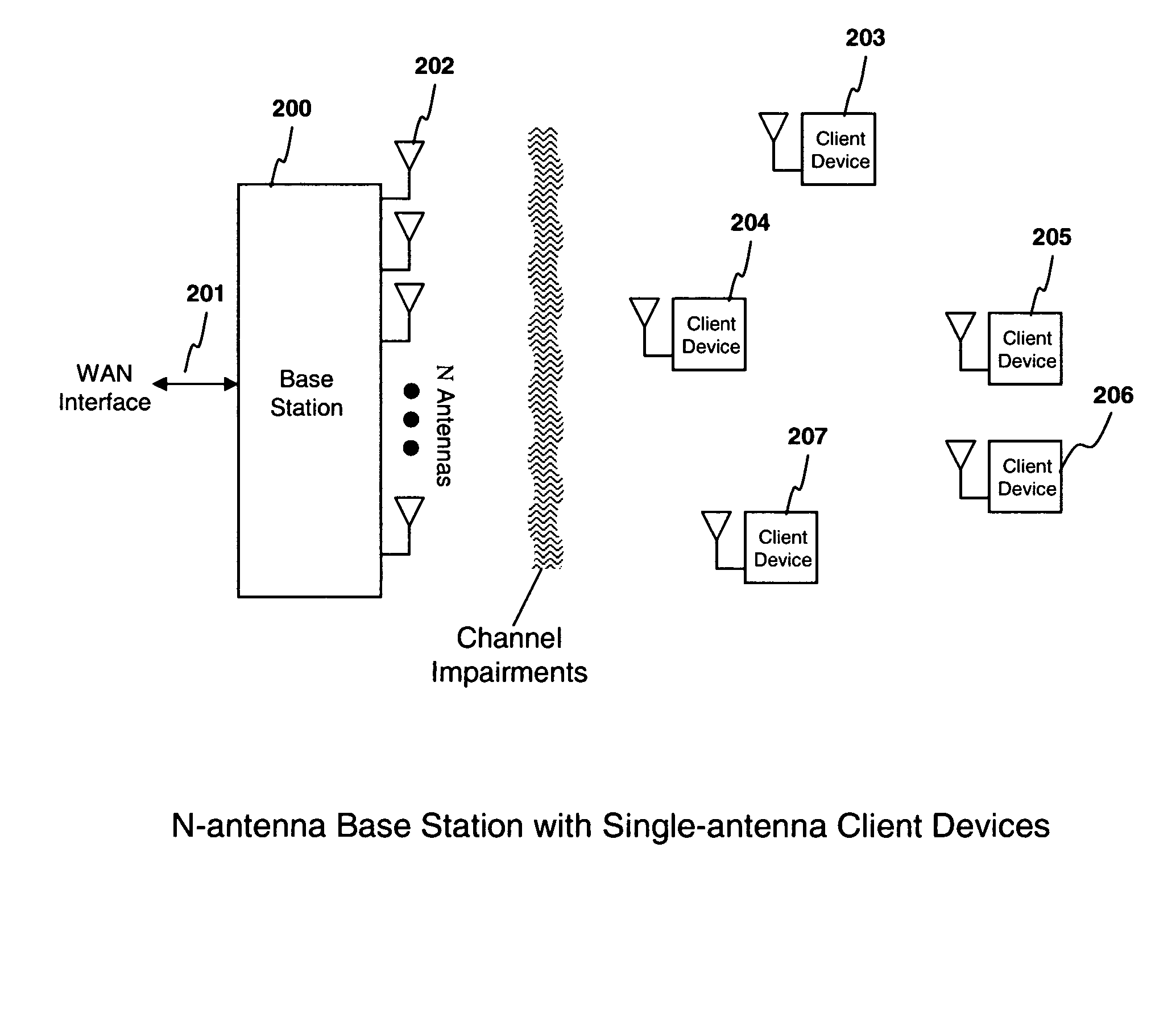
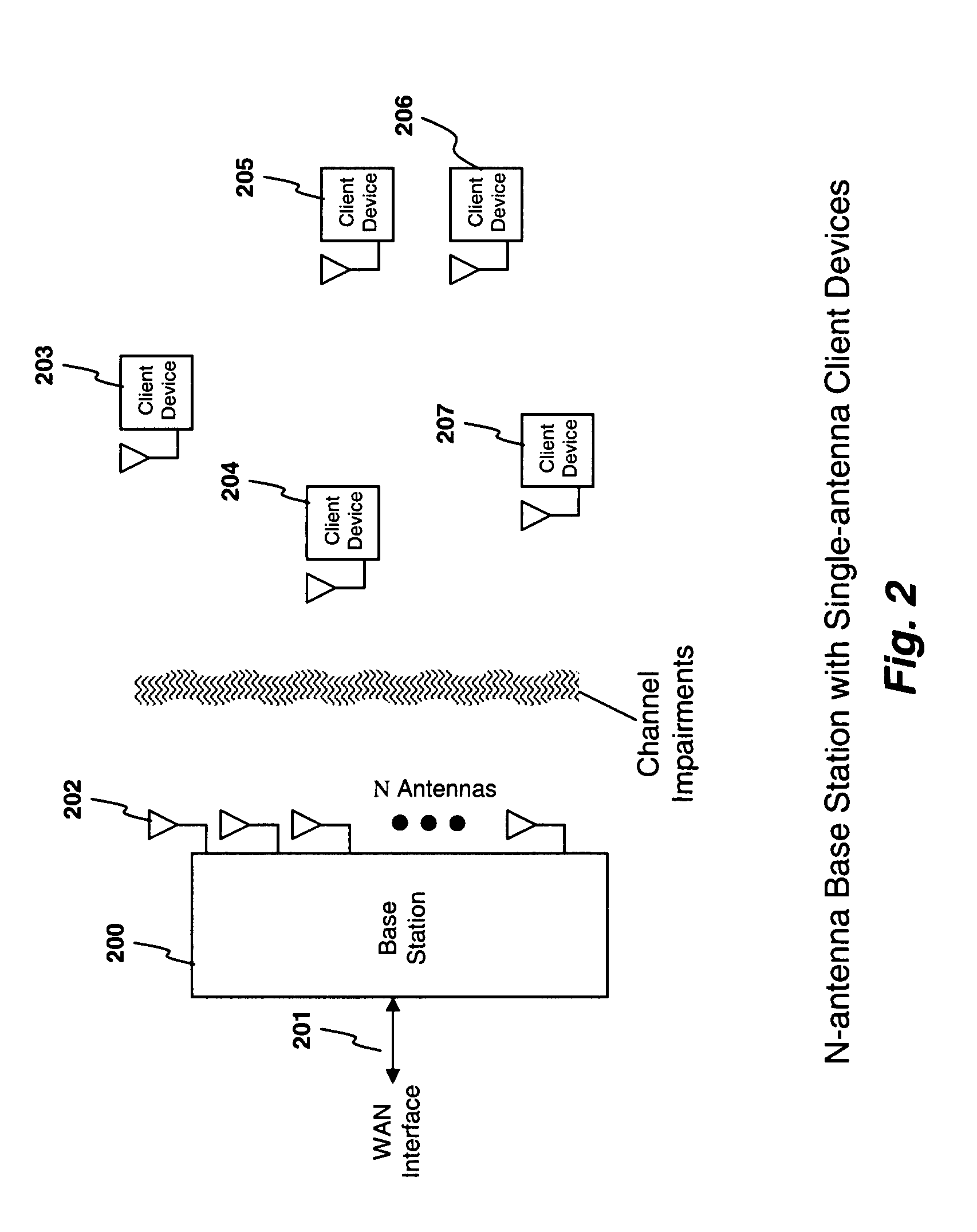
System and method for distributed input distributed output wireless communications
A system and method are described for compensating for frequency and phase offsets in a multiple antenna system (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (“MU-MAS”). For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: transmitting a training signal from each antenna of a base station to one or each of a plurality of wireless client devices, one or each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate frequency offset compensation data, and receiving the frequency offset compensation data at the base station; computing MU-MAS precoder weights based on the frequency offset compensation data to pre-cancel the frequency offset at the transmitter; precoding training signal using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded training signals for each antenna of the base station; transmitting the precoded training signal from each antenna of a base station to each of a plurality of wireless client devices, each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate channel characterization data, and receiving the channel characterization data at the base station; computing a plurality of MU-MAS precoder weights based on the channel characterization data, the MU-MAS precoder weights calculated to pre-cancel frequency and phase offset and / or inter-user interference; precoding data using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded data signals for each antenna of the base station; and transmitting the precoded data signals through each antenna of the base station to each respective client device.
Owner:REARDEN
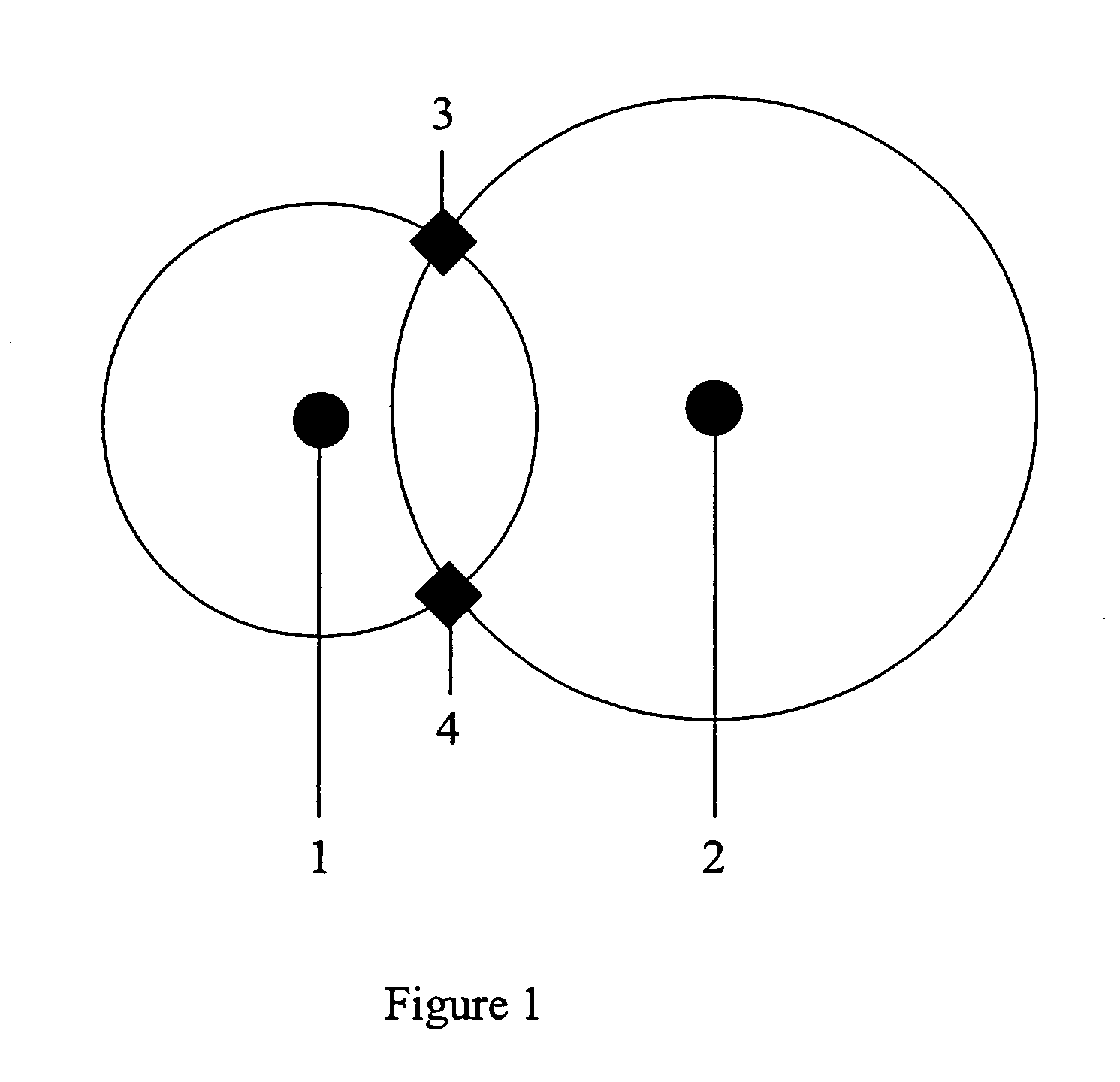
Method for RF fingerprinting
InactiveUS20050040968A1Improve accuracyAccurate locationElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEngineeringLocation determination
The invention provides a novel method for preparing a wireless environment for location determination of a wireless mobile unit, and for location determination of a wireless mobile unit. In preparing the physical environment, the invention utilizes novel techniques, including novel techniques to place transmitters, the removal of outlying data in the creation of reference RF fingerprints, and algorithms to obtain accurate reference RF fingerprints. In determining the location of a wireless mobile unit, the invention utilizes novel techniques, including novel techniques to select transmitters, the removal of outlying data in the creation of reference RF fingerprints, and algorithms to obtain accurate reference RF fingerprints.
Owner:INNERWIRELESS
Method and devices for efficient data transmission link control in mobile multicast communication systems
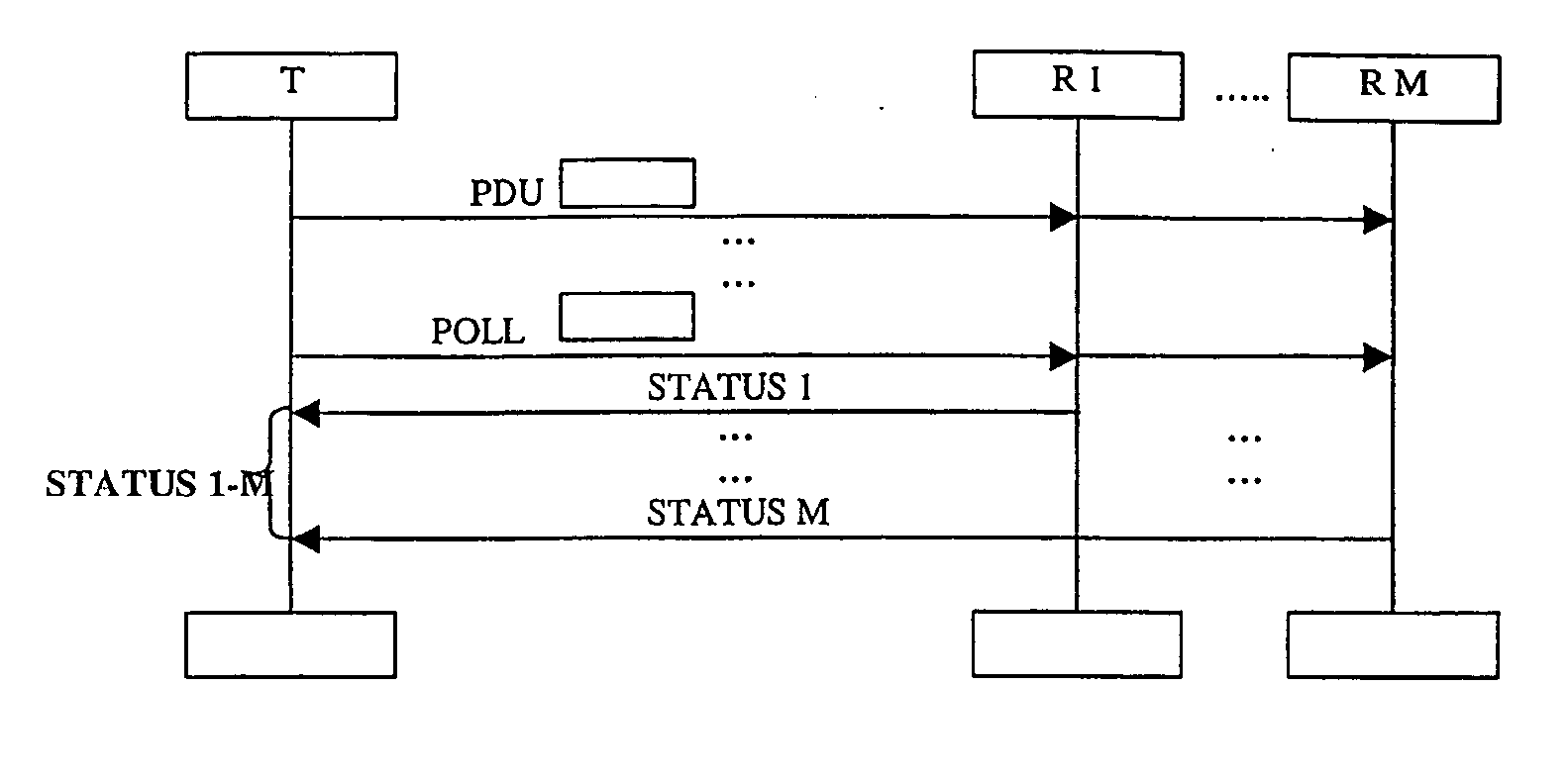
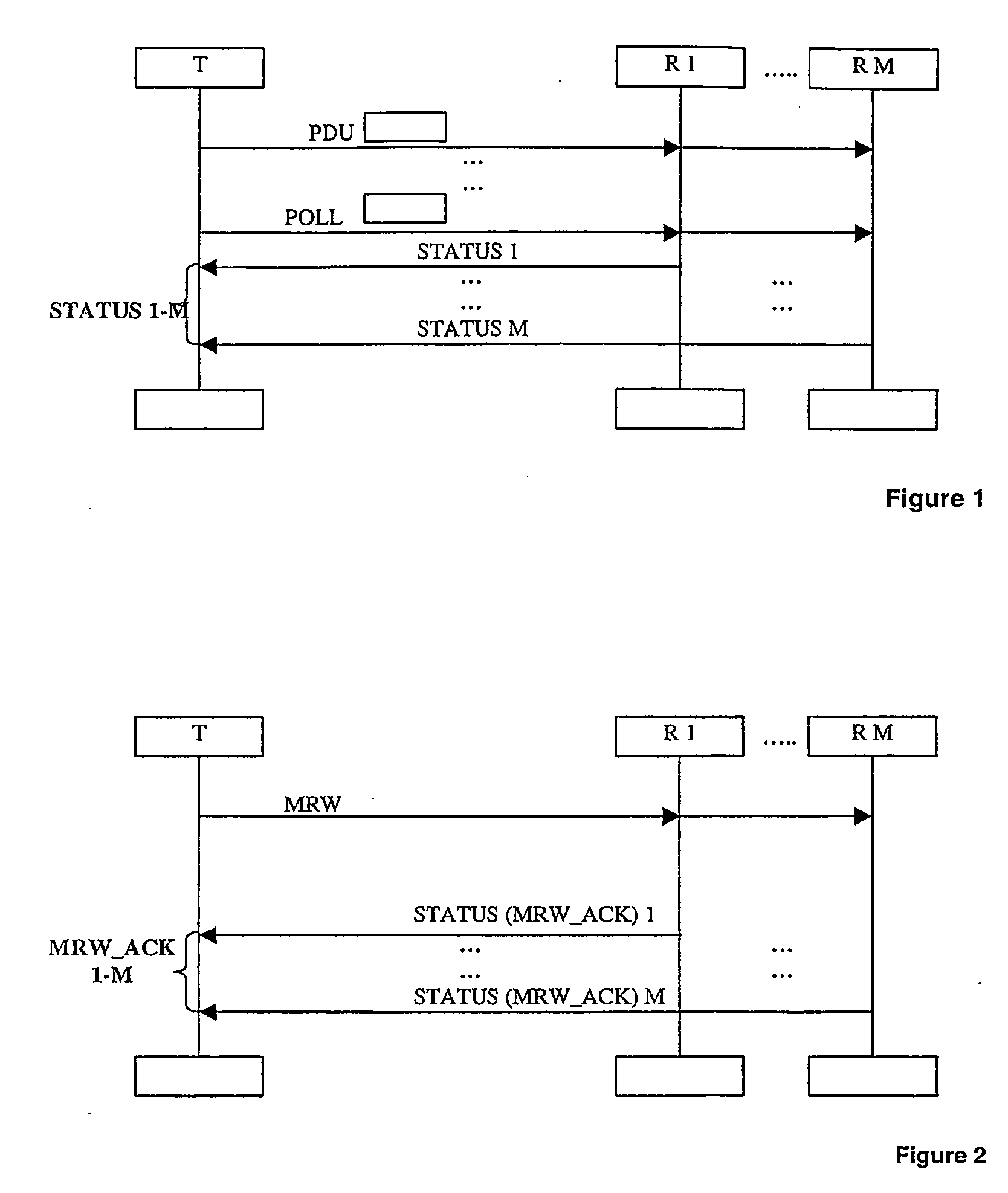
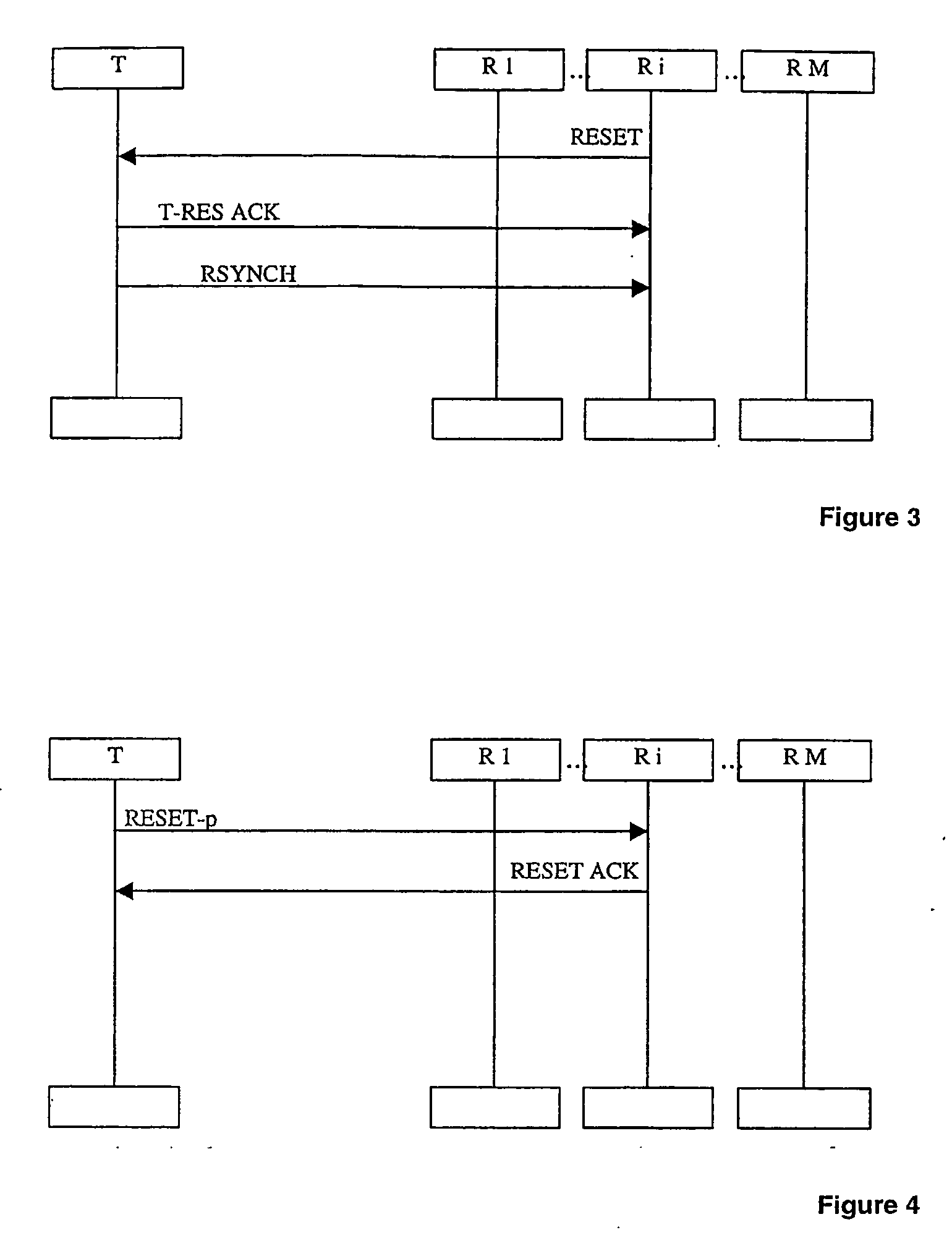
InactiveUS20060154603A1Easy to useAvoid failureSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelData transmissionTransposer
A method for a data transmission with ARQ protocol using multicast groups such as GSM, GPRS or UMTS in a mobile communication system is described. Data is transmitted in data blocks (PDU) from a transmitter (T) to a plurality of receivers (R1-RM), said data blocks (PDU) being identifiable by an identification (e.g. a sequence number). The receivers (R1-RM) send status indications to the transmitter (T) whether a data block (PDU) is correctly received. The transmitter (T) is adapted to perform retransmissions according to the status indications and has a transmission window comprising the transmission status for the data blocks (PDU) according to their identification. In the method, a synchronization to the transmitter (T) is performed for at least one first of said receivers (Ri), wherein a range of identifications of transmitted data block (PDU) is selected in said synchronization. The transmitter (T) deletes the transmission status for the selected range of identifications from the transmitter window and the first receiver (Ri) stops sending status indications for the data blocks (PDU) corresponding to the selected range of identifications. In addition, a transmitter and a computer program implementing the method are described. As an example the transmitter can be a RNC extending the RLC and MAC-HSPDA protocols standardized by 3GPP for obtaining efficient and reliable point-to-multipoint radio links.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
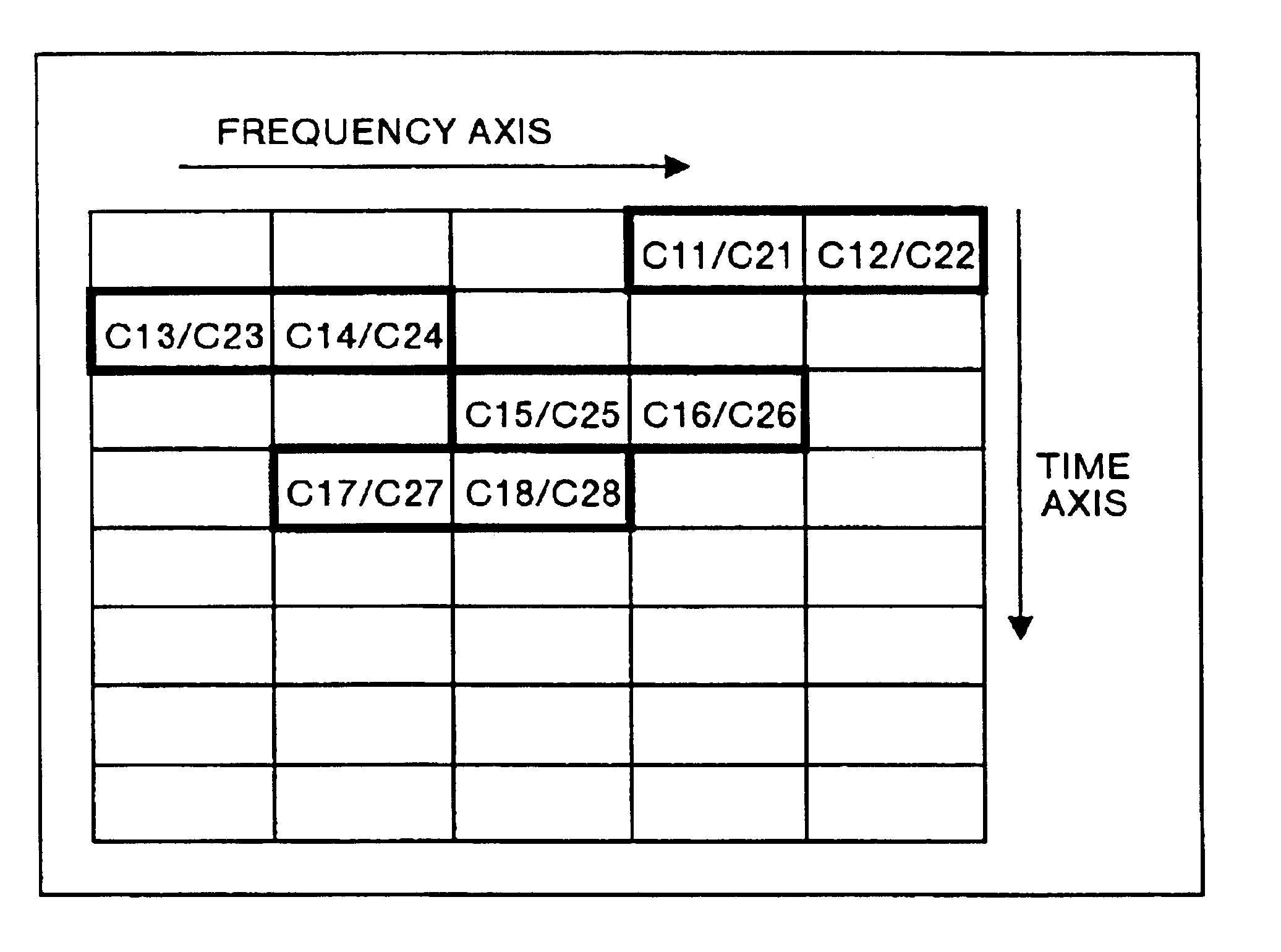
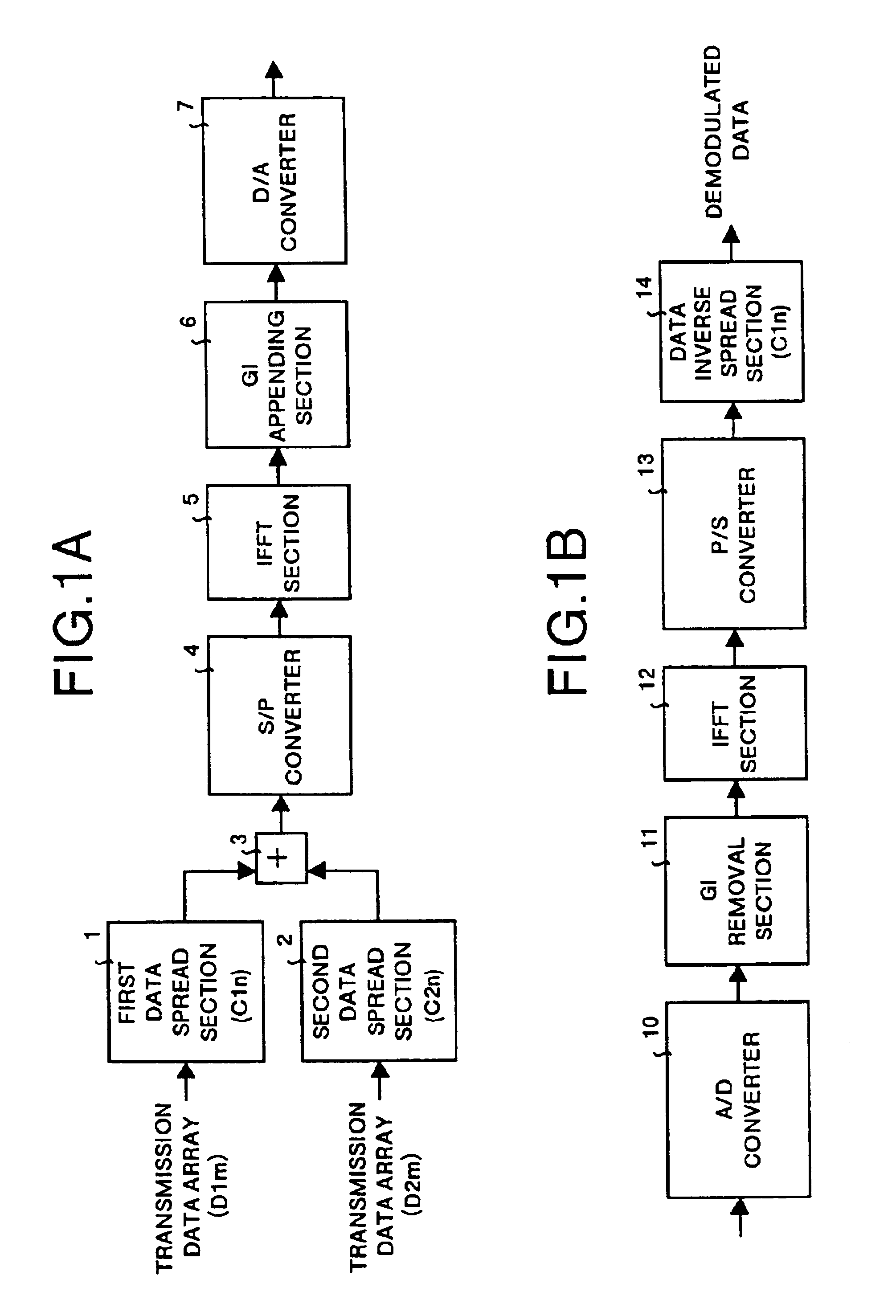
Multicarrier transfer system and multicarrier modulation method
InactiveUS6870826B1Increase the number ofNetwork traffic/resource managementModulated-carrier systemsSoftware engineeringCarrier signal
The multicarrier transfer system employing the OFDM / CDMA modulation system comprises a transmitter having an S / P converter which two-dimensionally arranges spread signals for a transmission data array on a frequency and time axes system and then rearrange the spread signals for one transmission data array arranged two-dimensionally. The transmitter transmits the signals generated in the S / P converter. A receiver receives the signals transmitted by the transmitter and demodulates the signal to reconstruct the transmission data array.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Methods and apparatus of providing transmit and/or receive diversity with multiple antennas in wireless communication systems
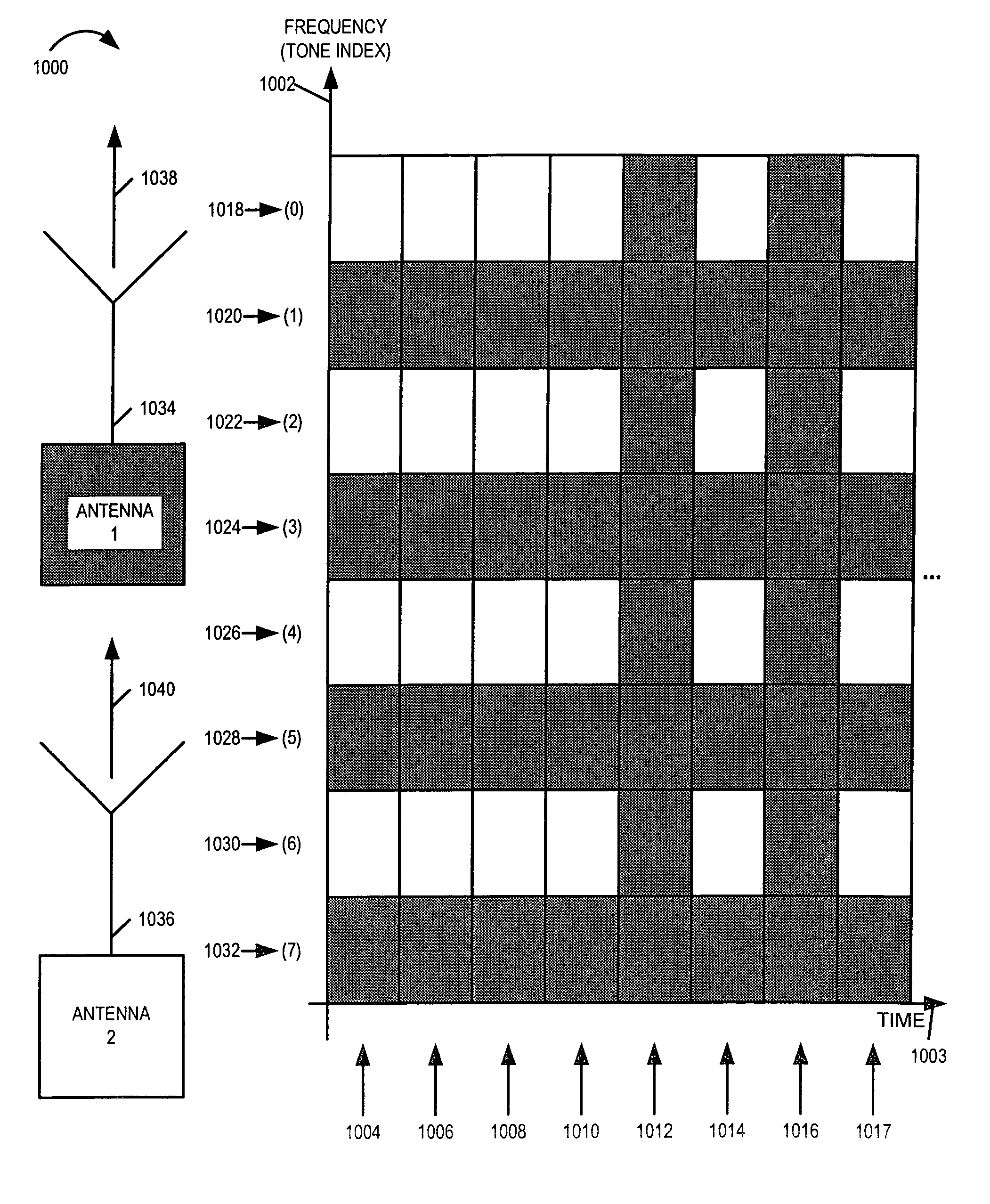
Transmit and / or receive diversity is achieved using multiple antennas. In some embodiments, a single transmitter chain within a wireless terminal is coupled over time to a plurality of transmit antennas. At any given time, a controllable switching module couples the single transmitter chain to one the plurality of transmit antennas. Over time, the switching module couples the output signals from the single transmitter chain to different transmit antennas. Switching decisions are based upon predetermined information, dwell information, and / or channel condition feedback information. Switching is performed on some dwell and / or channel estimation boundaries. In some OFDM embodiments, each of multiple transmitter chains is coupled respectively to a different transmit antenna. Information to be transmitted is mapped to a plurality of tones. Different subsets of tones are formed for and transmitted through different transmit chain / antenna sets simultaneously. The balance of tones allocated to the subsets for each antenna are changed as a function of predetermined information, dwell information, and / or channel condition feedback information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
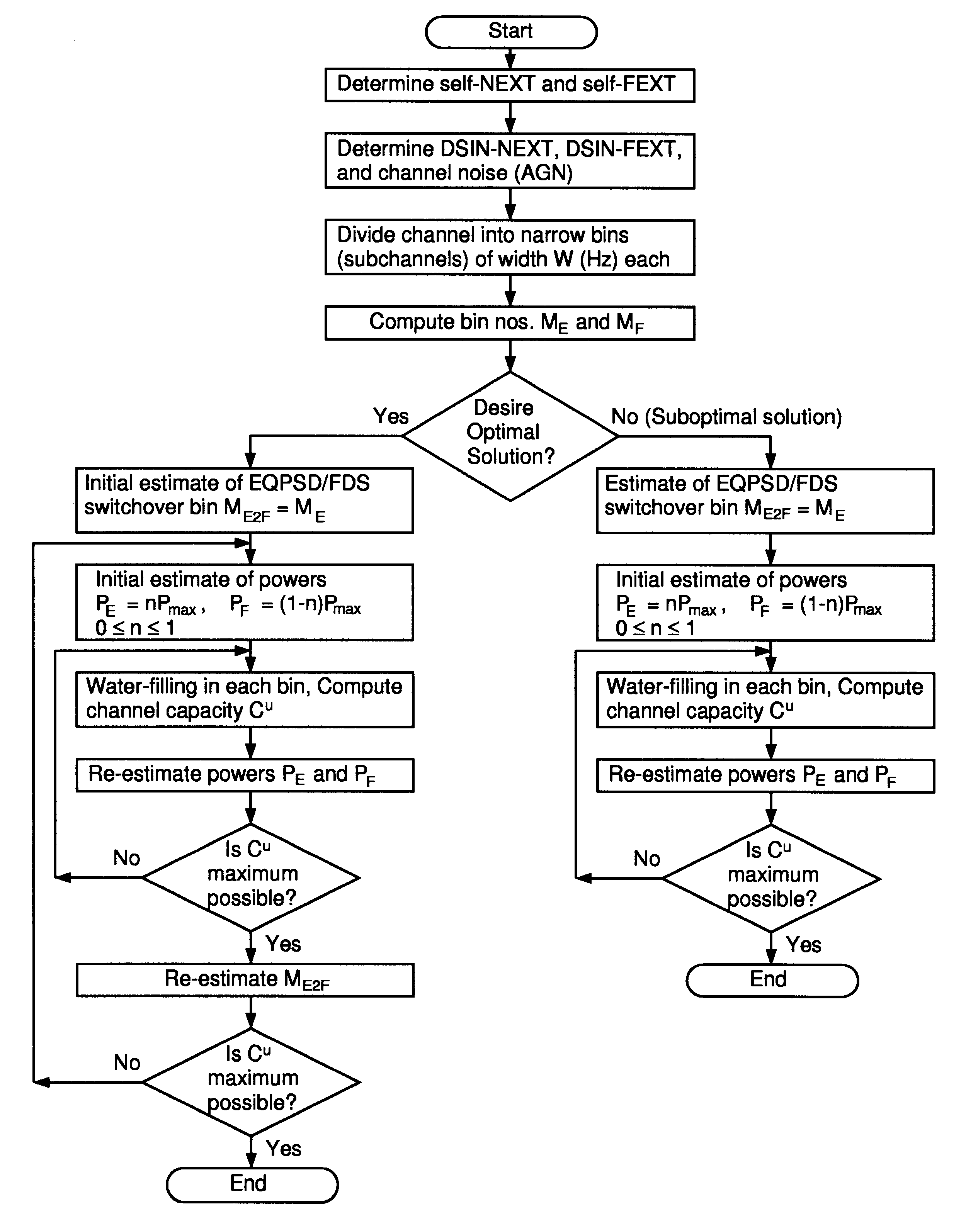
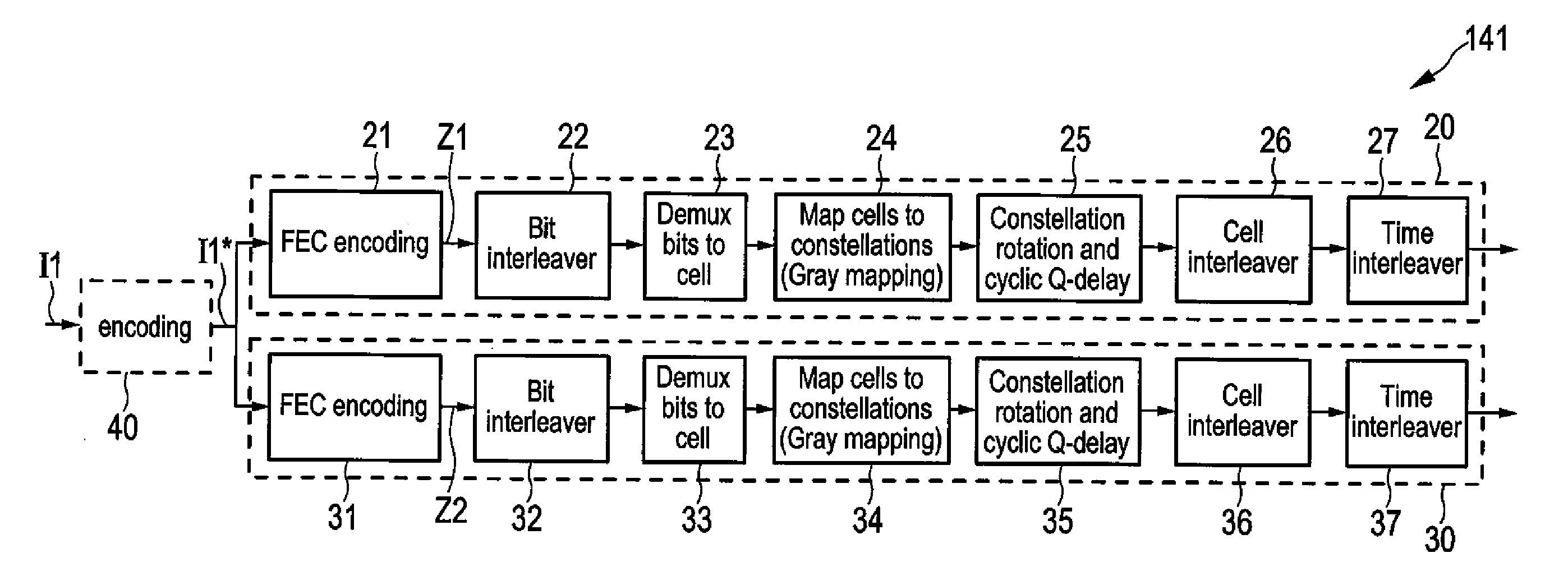
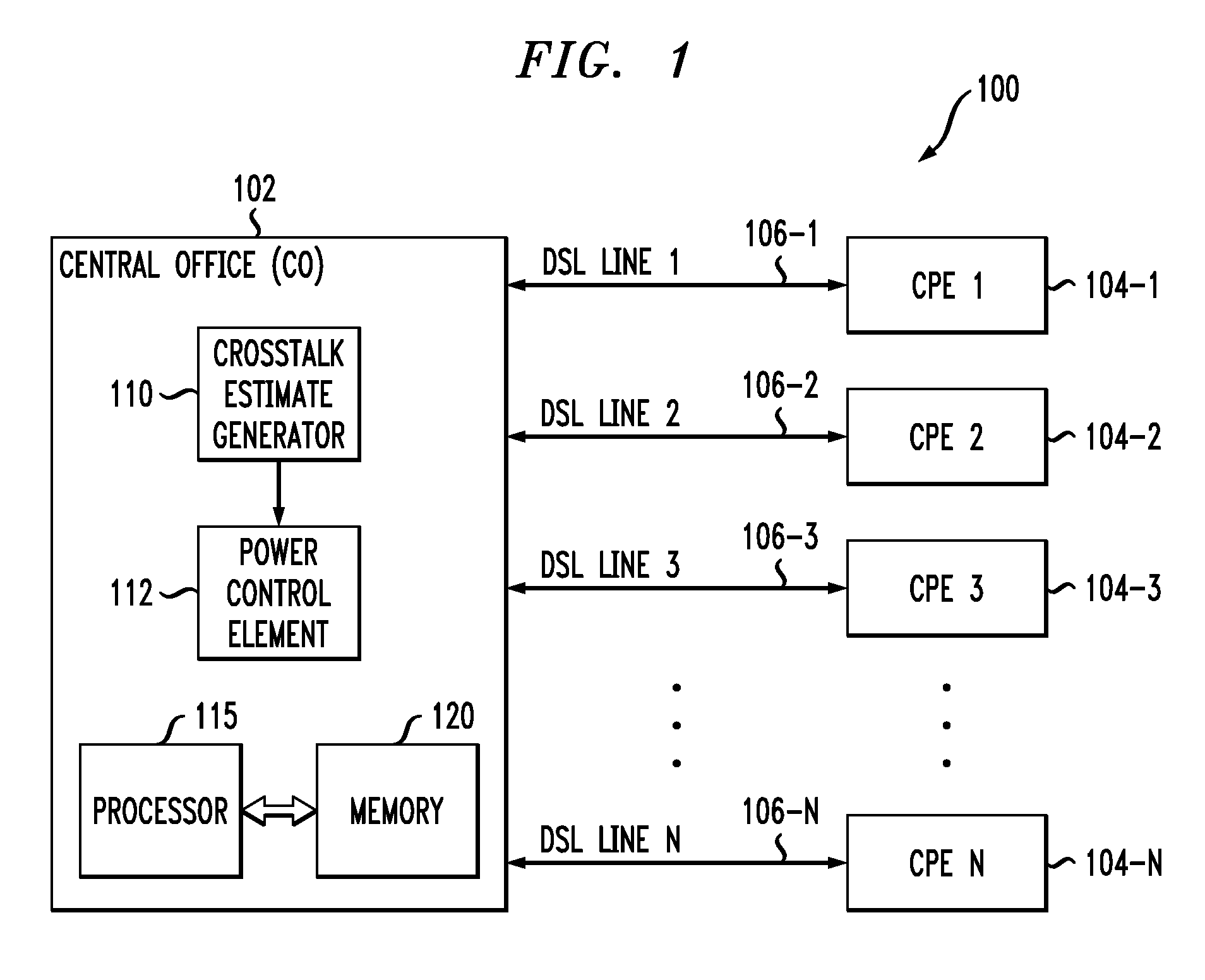
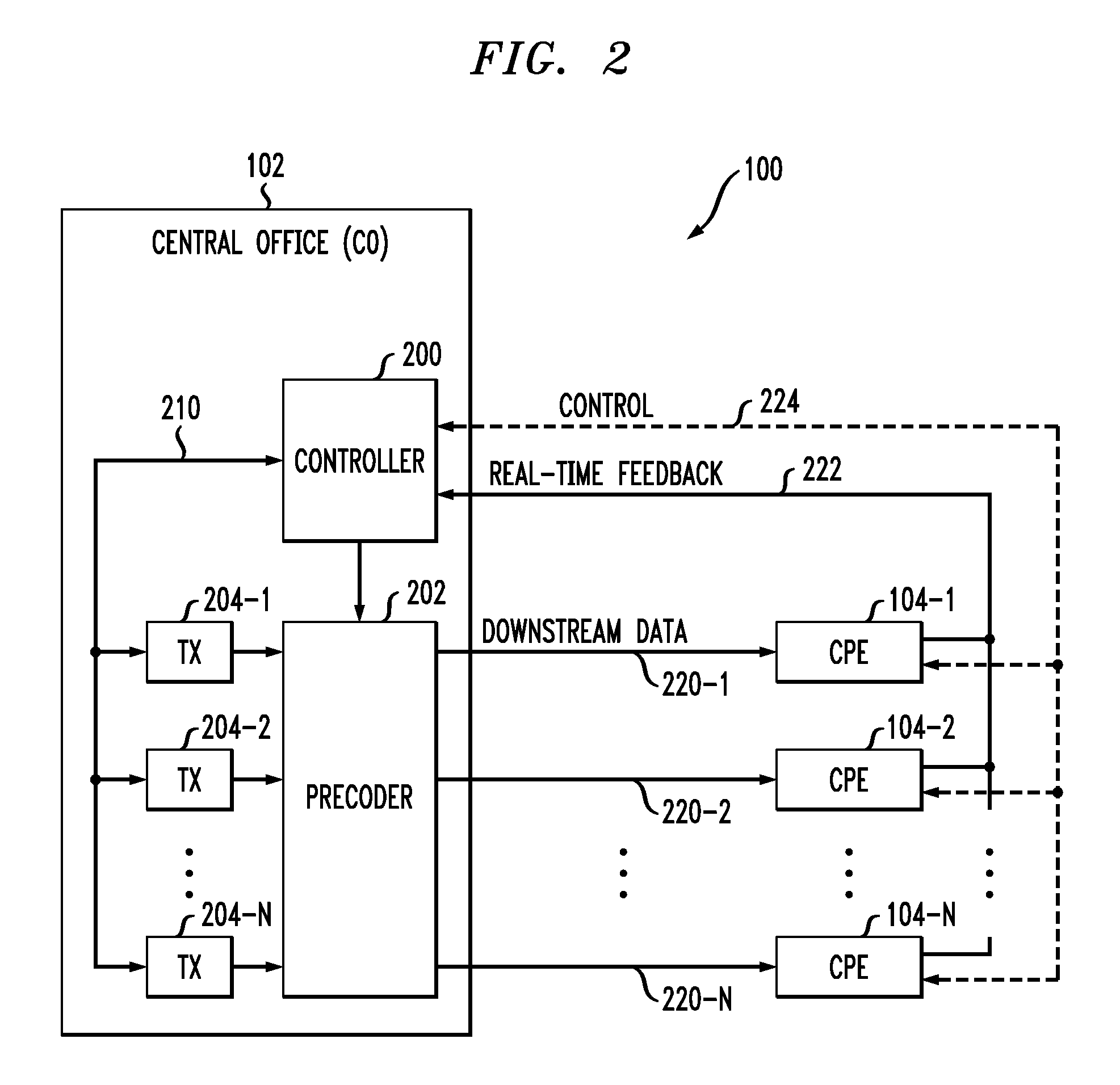
Spectral optimization and joint signaling techniques with upstream/downstream separation for communication in the presence of crosstalk
InactiveUS6292559B1Power managementSubstations coupling interface circuitsChannel transfer functionChannel capacity
A system and method for determining transmission characteristics for a communications channel and for transmitting data on the communications channel. In one embodiment, the method starts by determining the channel's transfer function and determining interference characteristics for the channel. The interference characteristics preferably include transfer functions describing the channel's susceptibility to cross talk from neighboring channels. The channel transfer function and the interference characteristics are then examined and a transmit spectrum (or power spectral density function) is constructed for the channel. The transmit spectrum preferably uses orthogonal separation of upstream and downstream communications to increase channel capacity. This method is useable in communicating data when the channel is subject to interference from one or more other communications channels, including near-end cross talk (NEXT) and far-end cross talk (FEXT), from other channels carrying the same service and / or different services. The present invention may be used in digital subscriber-line (xDSL) communications or in a variety of other applications, such as in well-logging and in systems involving multiple interfering radio transmitters.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Transmitter and receiver for broadcasting data and providing incremental redundancy
ActiveUS20120272117A1Increase probabilityImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionData streamBroadcast data
A transmitter for broadcasting data in a broadcasting system that improves the decoding quality, if needed, comprises a data input, and an encoder for error correction code encoding the input data words into codewords, a codeword comprising a basic codeword portion and an auxiliary codeword portion, wherein said encoder is adapted for generating said basic codeword portion from an input data word according to a first code and for generating said auxiliary codeword portion from an input data word according to a second code, said basic codeword portion being provided for regular decoding and said auxiliary codeword portion being provided as incremental redundancy if regular decoding of the codeword by use of the basic codeword portion is erroneous. Further, the transmitter comprises a data mapper for mapping the codewords onto frames of a transmitter output data stream, and a transmitter unit for transmitting said transmitter output data stream.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Digital branch calibrator for an RF transmitter
InactiveUS20050018787A1Significant to useImprove efficiencyResonant long antennasSecret communicationPhase imbalanceLocal oscillator
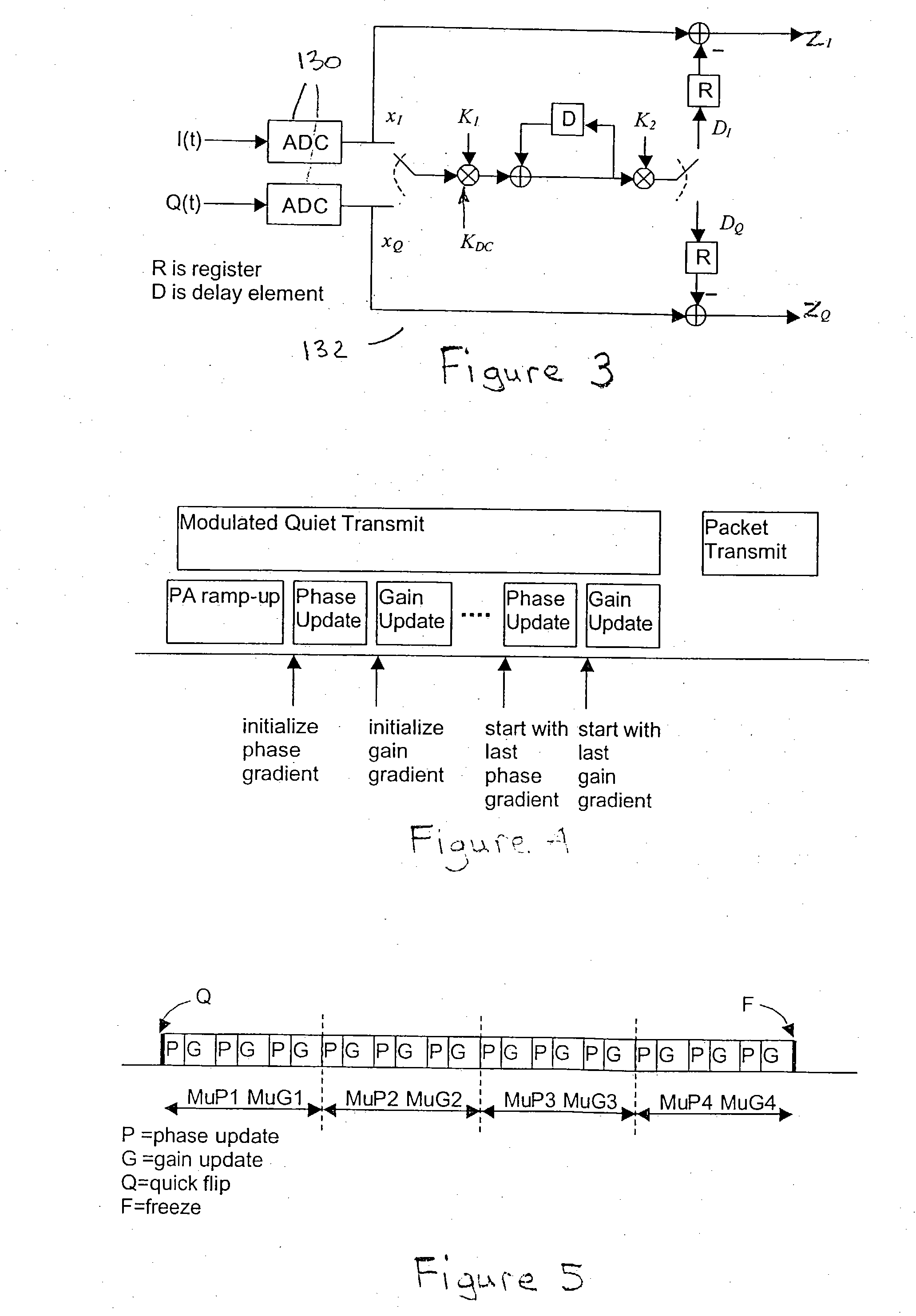
The present invention provides a digital (computational) branch calibrator which uses a feedback signal sensed from an RF transmit signal path following the combining stage of LINC circuitry of a transmitter to compensate for gain and phase imbalances occurring between branch fragment signals leading to the combiner. The calibrator feeds a quiet (zero) base band signal through the transmit path during the calibration sequence (i.e. a period when data is not transmitted) and adjusts the phase and gain of the phasor fragment signals input thereto by driving the sensed output power to zero. The calibration is performed by alternating phase and gain adjustments with predetermined (programmable) and multiple update parameters stages (speeds). A baseband modulation is preferably used to distinguish false leakage (e.g. due to local oscillator, LO, feed through and DC offset in the base band Tx) from imbalance leakage.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
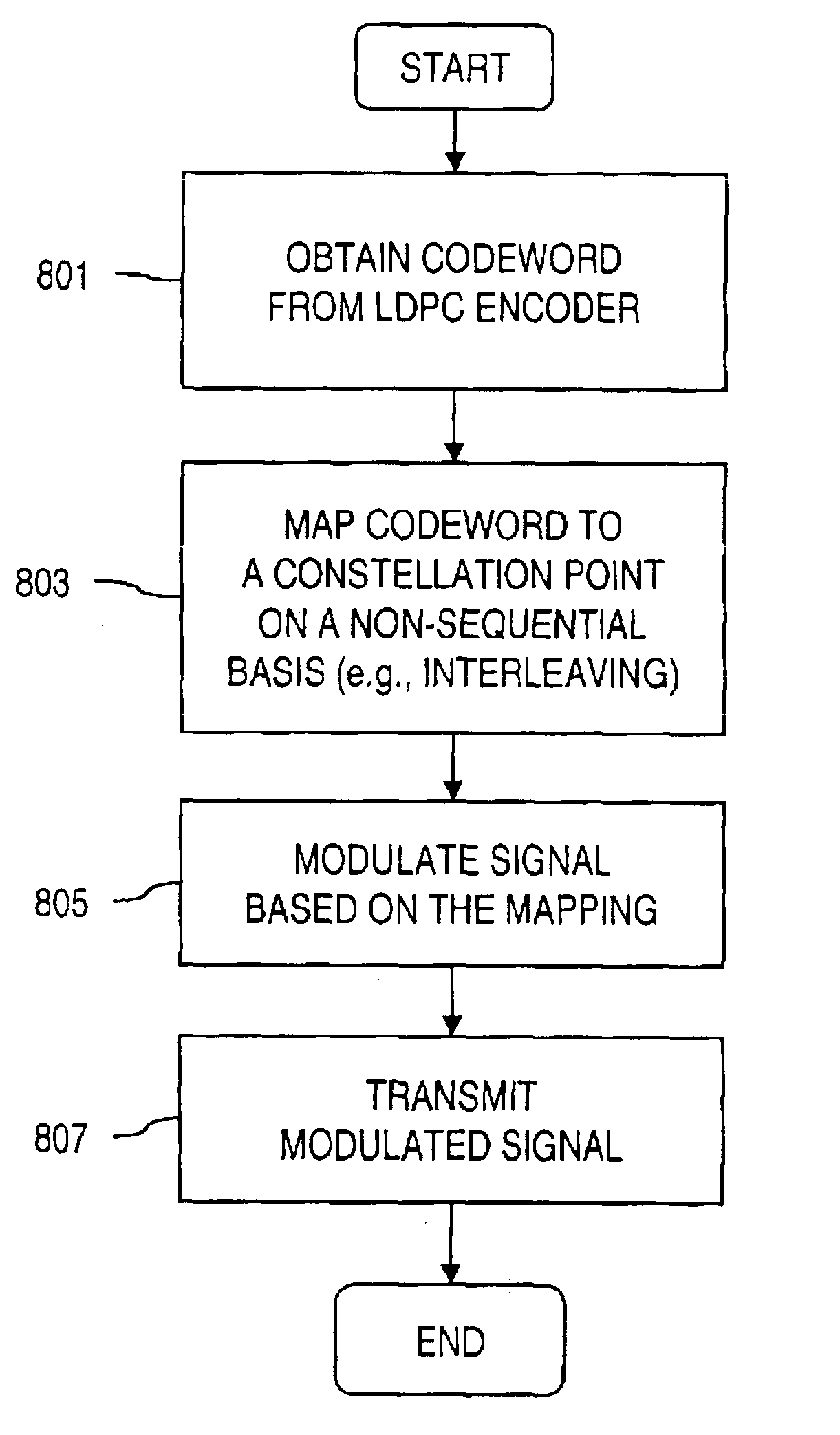
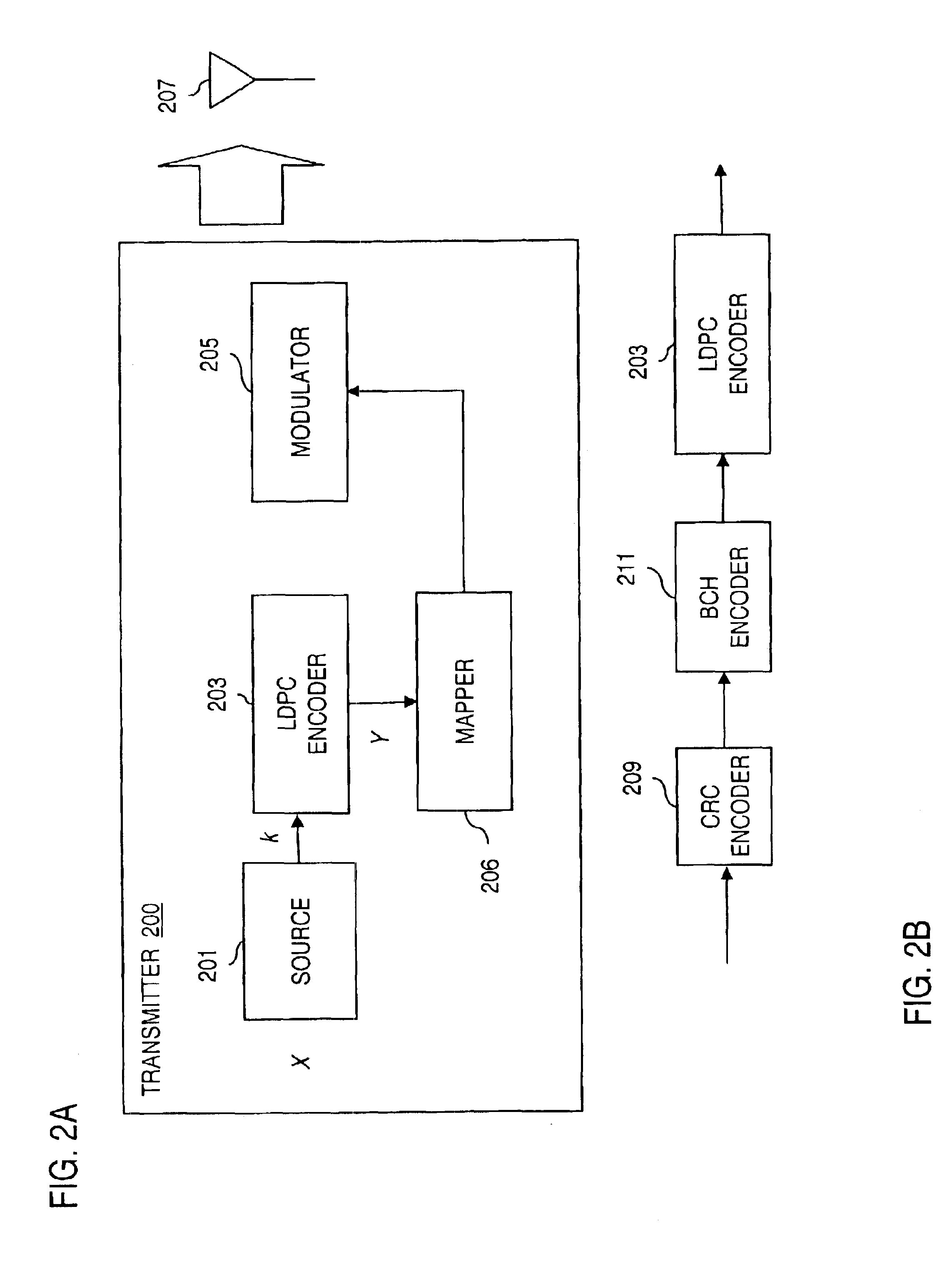
Bit labeling for amplitude phase shift constellation used with low density parity check (LDPC) codes
InactiveUS6963622B2Improve performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionParity-check matrixEngineering
An approach is provided for bit labeling of a signal constellation. A transmitter generates encoded signals using, according to one embodiment, a structured parity check matrix of a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code. The transmitter includes an encoder for transforming an input message into a codeword represented by a plurality of set of bits. The transmitter includes logic for mapping non-sequentially (e.g., interleaving) one set of bits into a higher order constellation (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), 8-PSK, 16-APSK (Amplitude Phase Shift Keying), 32-APSK, etc.), wherein a symbol of the higher order constellation corresponding to the one set of bits is output based on the mapping.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Channel Estimation in a Multi-Channel Communication System Using Pilot Signals Having Quasi-Orthogonal Subpilots
ActiveUS20100303136A1High speedLess timeCross-talk reductionSecret communicationCommunications systemData signal
An access node of a communication system comprises a plurality of transmitters adapted for communication with at least one receiver. The access node is operative to transmit pilot signals from respective associated ones of the transmitters, to estimate channel coefficients between the transmitters and the receiver, and to utilize the estimated channel coefficients to control at least one data signal sent by at least one of the transmitters. The pilot signals are partitioned into a plurality of sets of pilot signals such that pilot signals from the same set have respective subpilots that are orthogonal to one another and pilot signals from different sets have respective subpilots that are not orthogonal to one another but are instead quasi-orthogonal to one another. The pilot signals are associated with the respective transmitters based on the partitioning of the pilot signals into sets.
Owner:RPX CORP
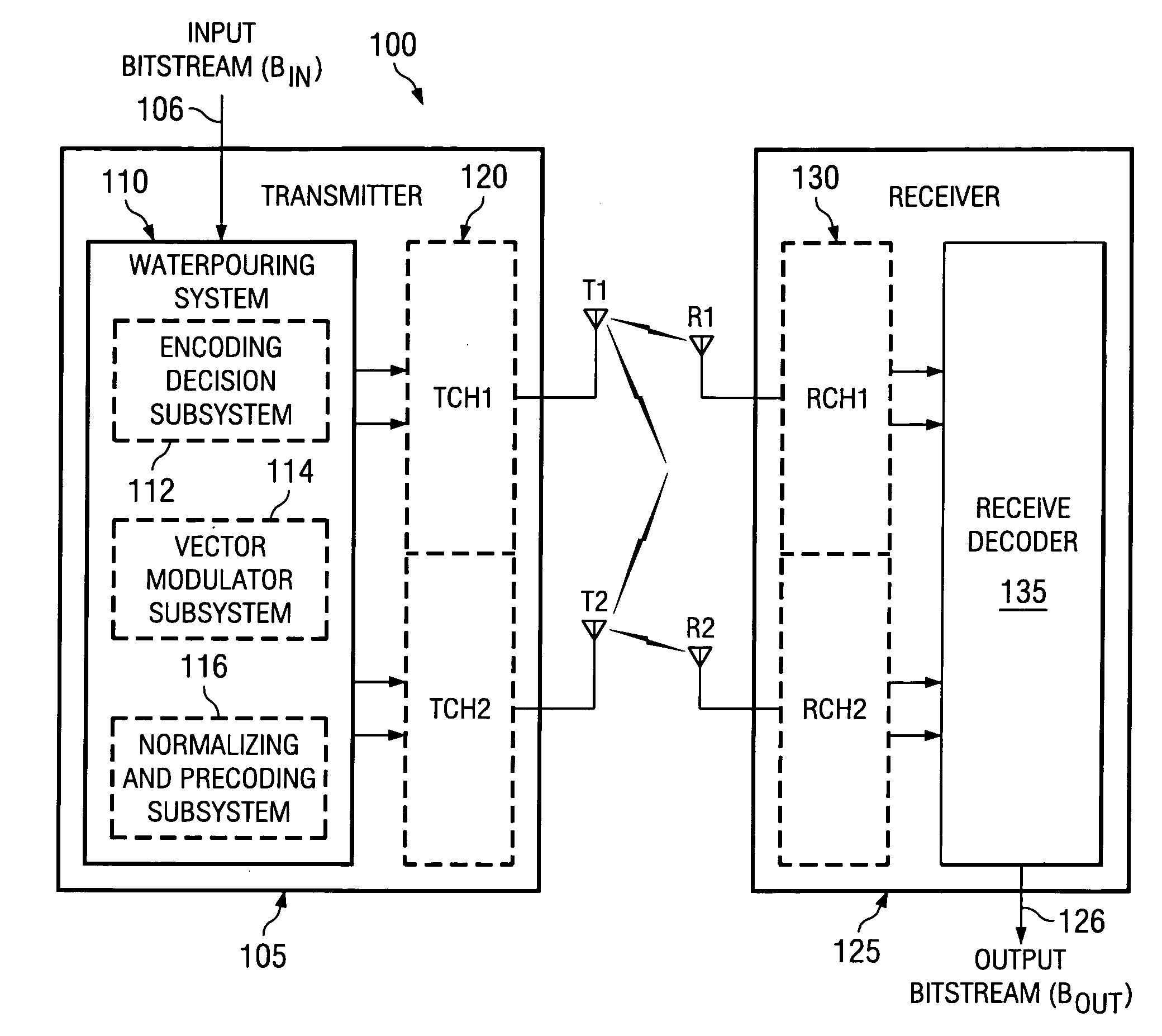
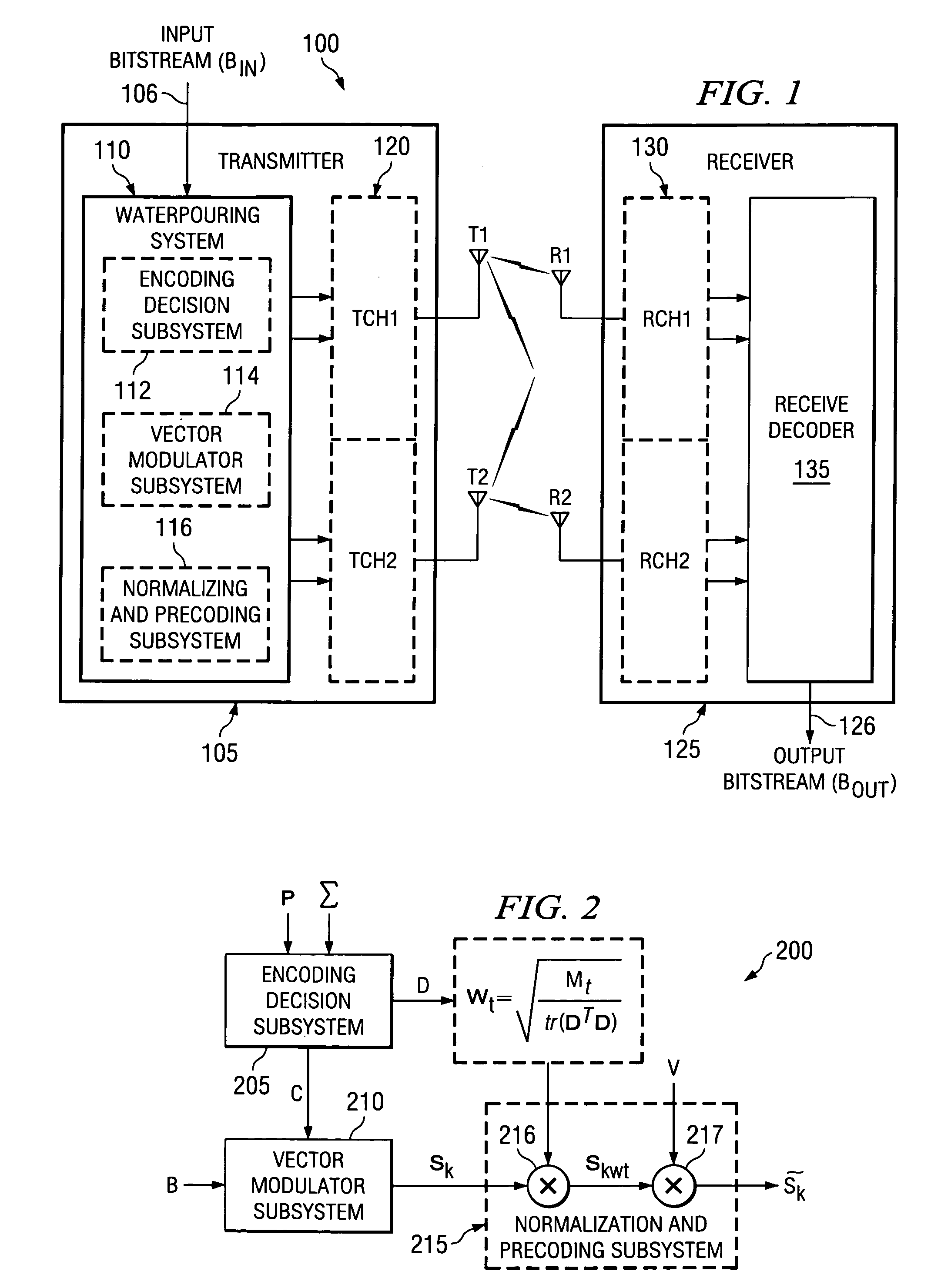
Reduced complexity transmit spatial waterpouring technique for multiple-input, multiple-output communication systems
A waterpouring system and method for use with a multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) transmitter. In one embodiment, the waterpouring system includes an encoding decision subsystem that selects a constellation combination based on gains in channels of the MIMO transmitter, and a vector modulator subsystem, coupled to the encoding decision system, that modulates a fixed number of bits in a bitstream with the constellation combination to generate a symbol vector. The waterpouring system also includes a normalization and precoding subsystem, coupled to the vector modulator subsystem, that weights the symbol vector based on the gains to yield a weighted symbol vector and distributes the weighted symbol vector among the channels.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Reconfigurable transmitter
InactiveUS20070014382A1Improve efficiencyFlexible useModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationEngineeringOperation mode
A transmission device and method are shown, wherein an amplification is implemented which can be changed between a switched operation mode and linear operation mode as desired, depending on which mode of operation best meets the needs of the radio system in use. This opens the possibility of using the same hardware for different systems.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
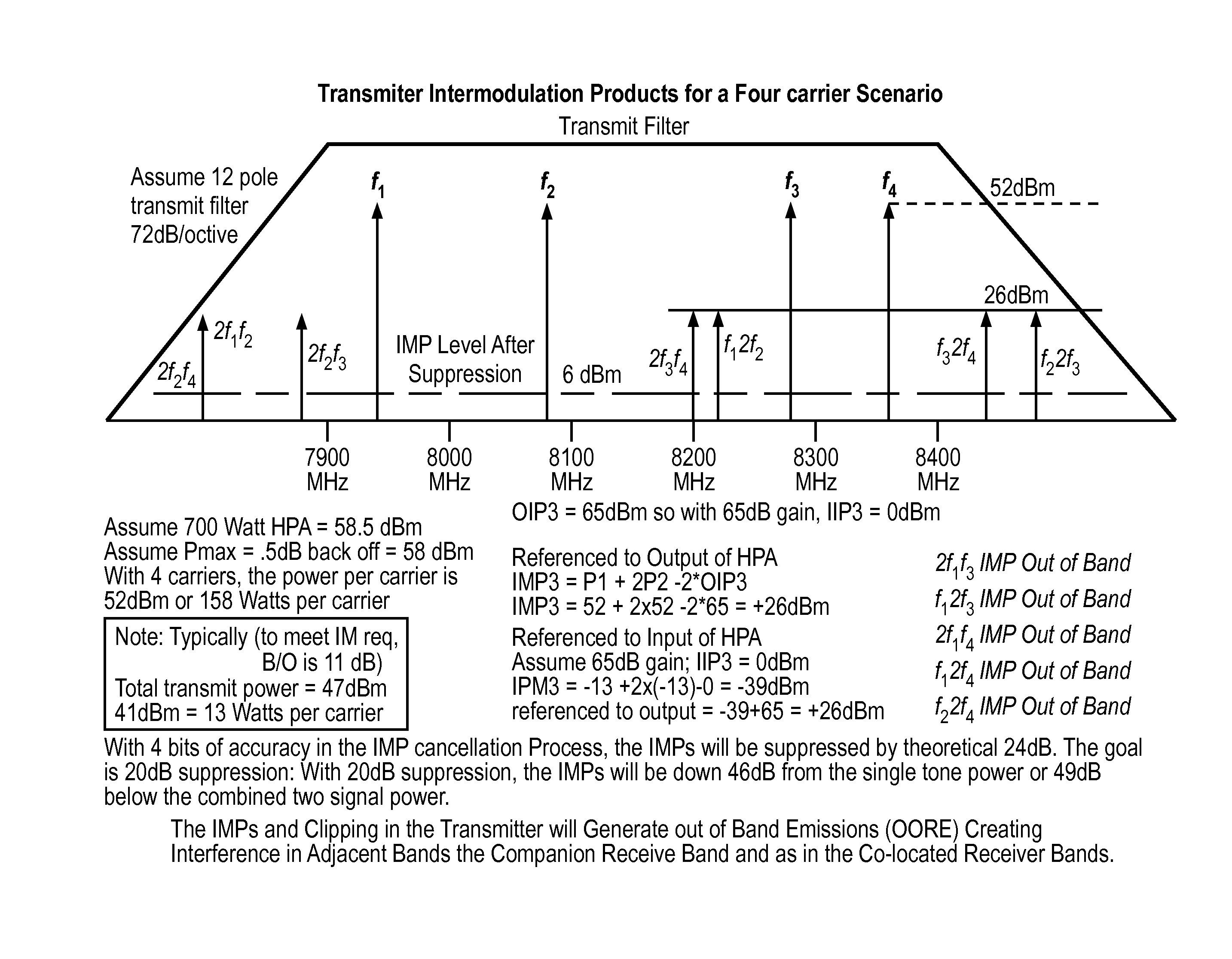
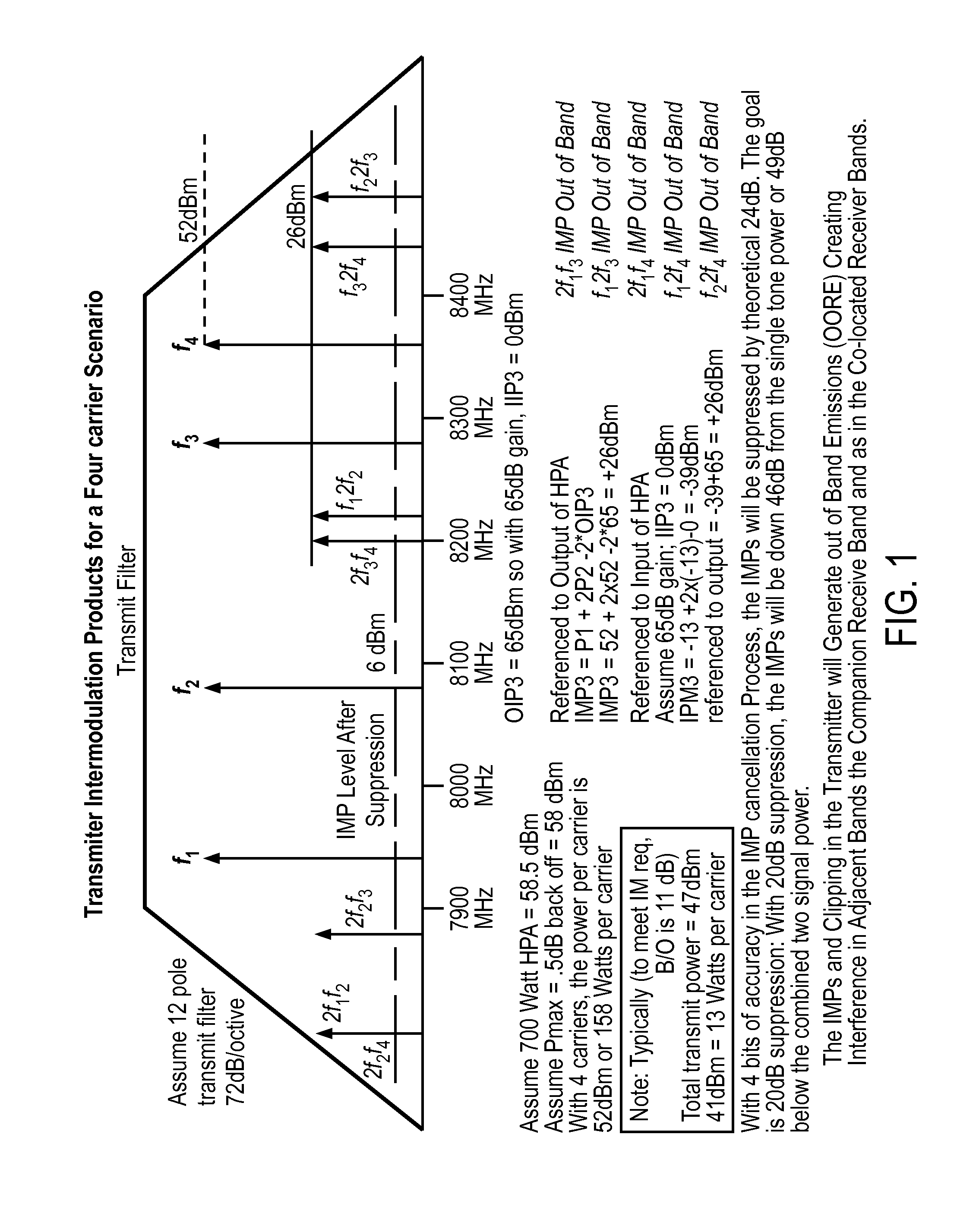
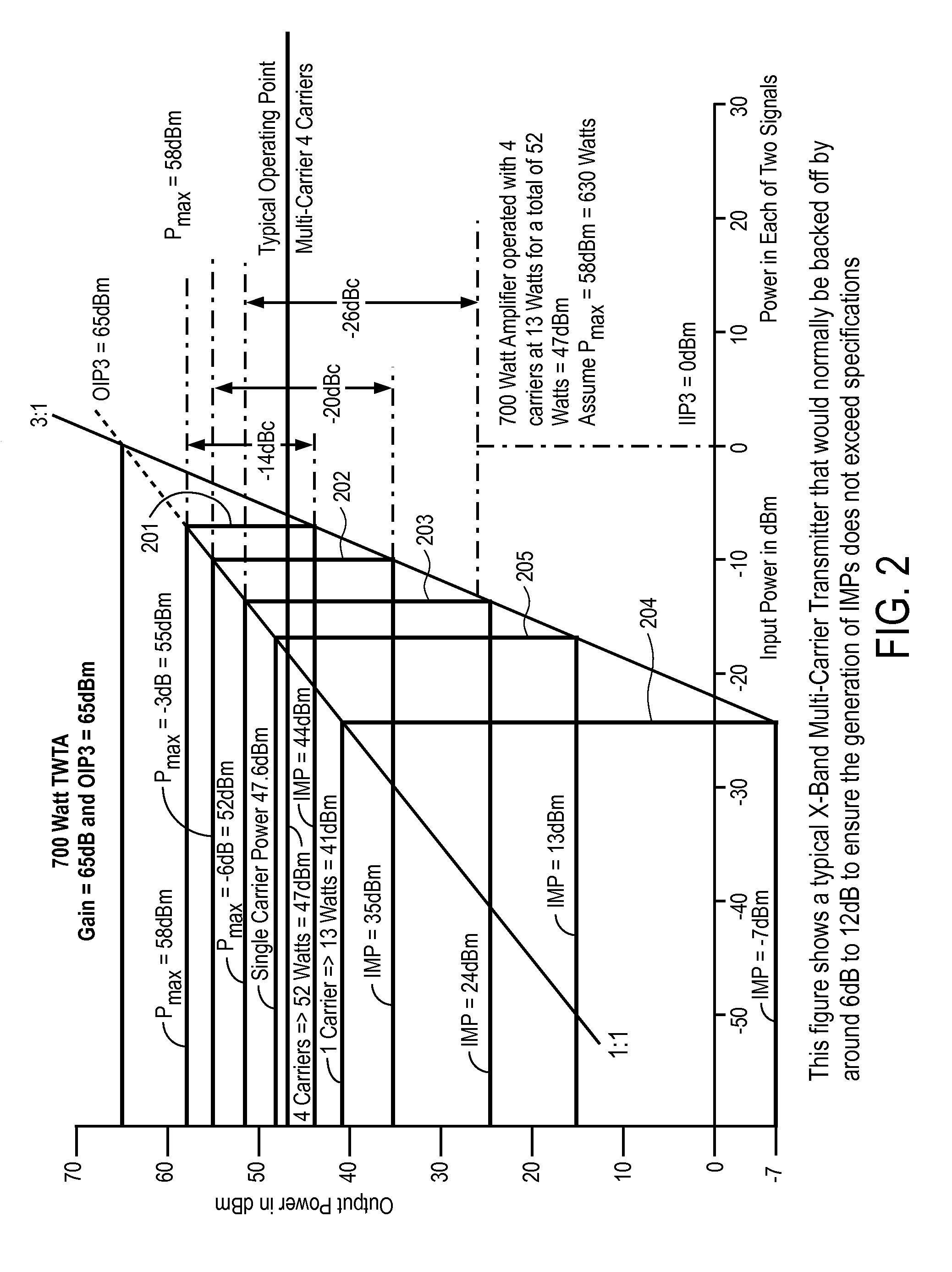
Mitigation of transmitter passive and active intermodulation products in real and continuous time in the transmitter and co-located receiver
ActiveUS20110075754A1Secret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLinear componentEngineering
A transmitter channel interference mitigation processing method for cancellation of intermodulation products are described. In one embodiment, a method comprising generating continuous and real time IMP cancellation signals (ICS) in the baseband digital signal set of the transmitter based on a transmitter signal set, combining digital IMP cancellation signals with a digital baseband transmitter signal set such that the digital cancellation signals, when converted to analog signals and transmitted as part of an analog transmitter signal set, are cancelled by and so cancel the IMPs generated by the non-linear components in the analog transmitter hardware, including digitally generating the IMP cancellation signals using a process based on a power series description of a non-linear process generating the IMPs, generating 3rd order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three signals of the transmitter signal set to create 3rd order IMP cancellation signals, generating 5th order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three or five signals of the transmitter signal set to create 5th order IMP cancellation signals, generating 7th order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three or five or seven signals of the transmitter signal set to create 7th order IMP cancellation signal, generating odd order IMP cancellation signals (ICS) by digitally multiplying an odd number of digital signals and combining multiplied digital signals with the transmitter baseband digital signals, creating IMP cancellation signals in the receiver, and cancelling one or both of active and passive IMPs generated in a transmitter path that fall within a receiver passband.
Owner:FINESSE WIRELESS LLC
System and method for positioning pulses in time using a code that provides spectral shaping
InactiveUS6937639B2Minimizing the code spectrumDifferenceBeacon systems using radio wavesFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationRadar systemsFrequency spectrum
A system, method and computer program product for positioning pulses, including positioning pulses within a specified time layout according to one or more codes to produce a pulse train having one or more predefined spectral characteristics where a difference in time position between adjacent pulses positioned to produce a spectral characteristic differs from another difference in time position between other adjacent pulses positioned to produce the spectral characteristic. The present invention may include shaping a code spectrum according to a spectral template in order to preserve a pre-defined code characteristic. A pre-defined code characteristic can include desirable correlation, or spectral properties. A transmitter incorporating the present invention can avoid transmitting at a particular frequency. Similarly, a receiver can avoid interference with a signal transmitting at a particular frequency. A radar system, can avoid a radar jammer attempting to jam a particular frequency.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
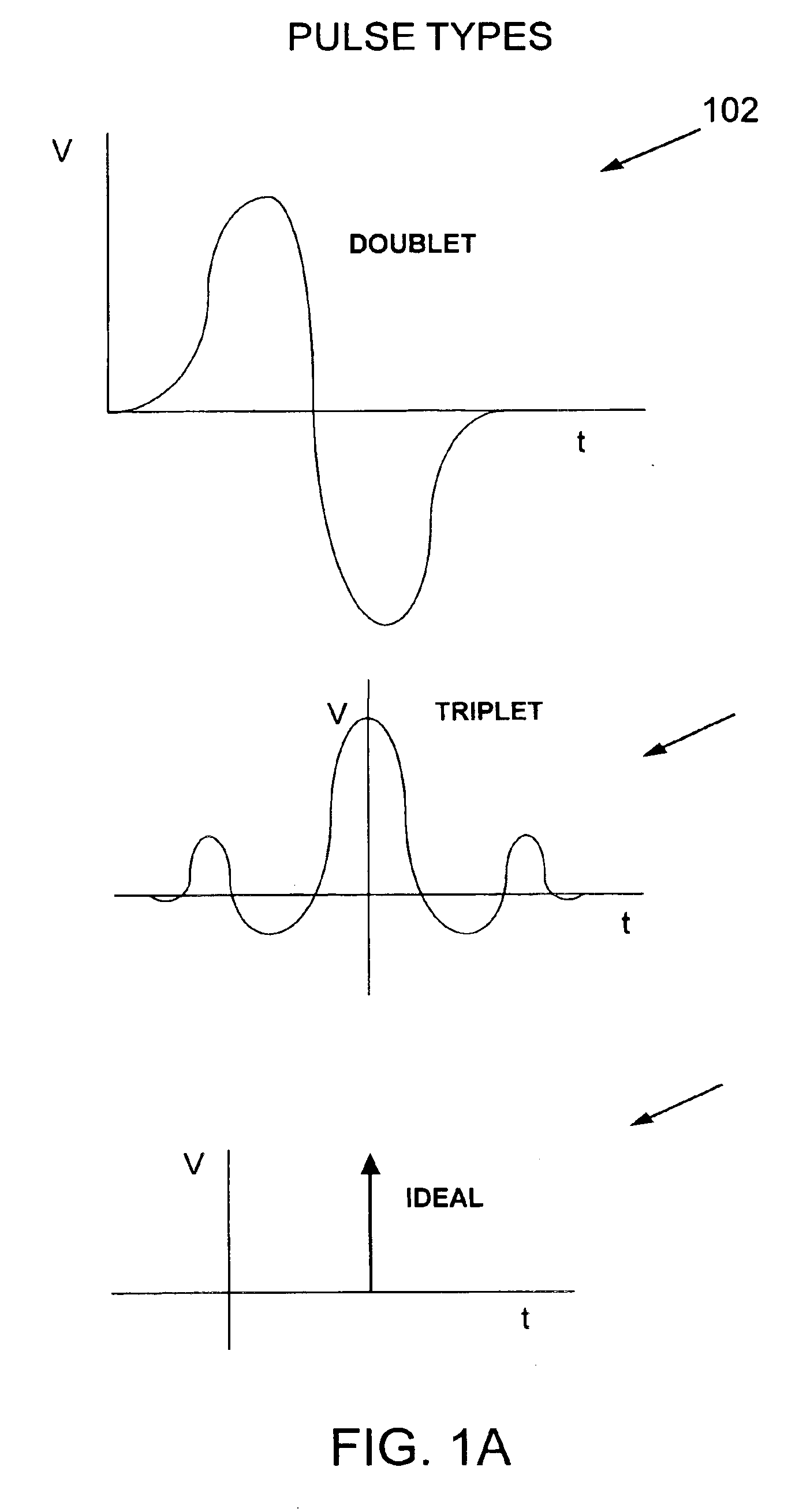
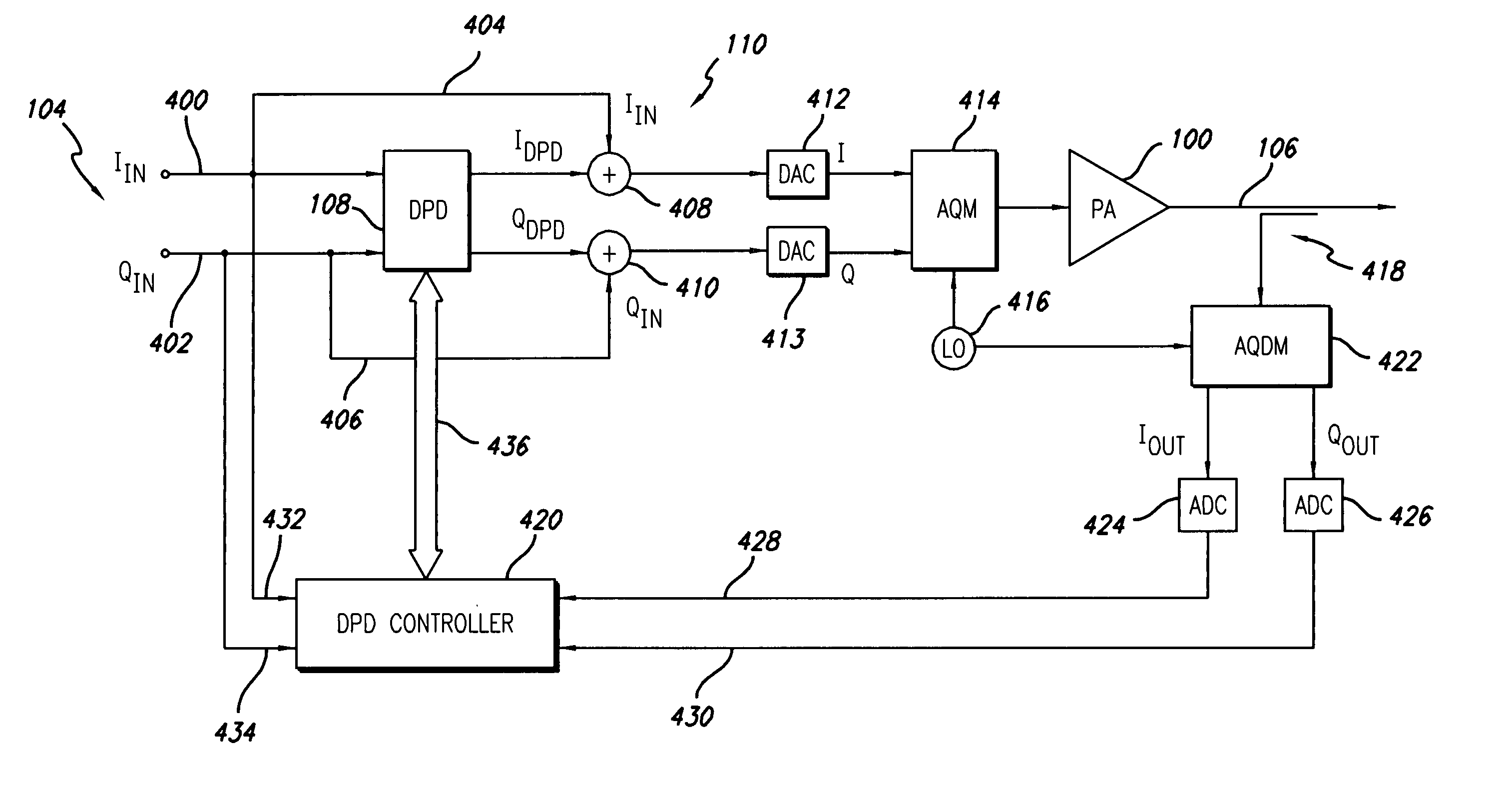
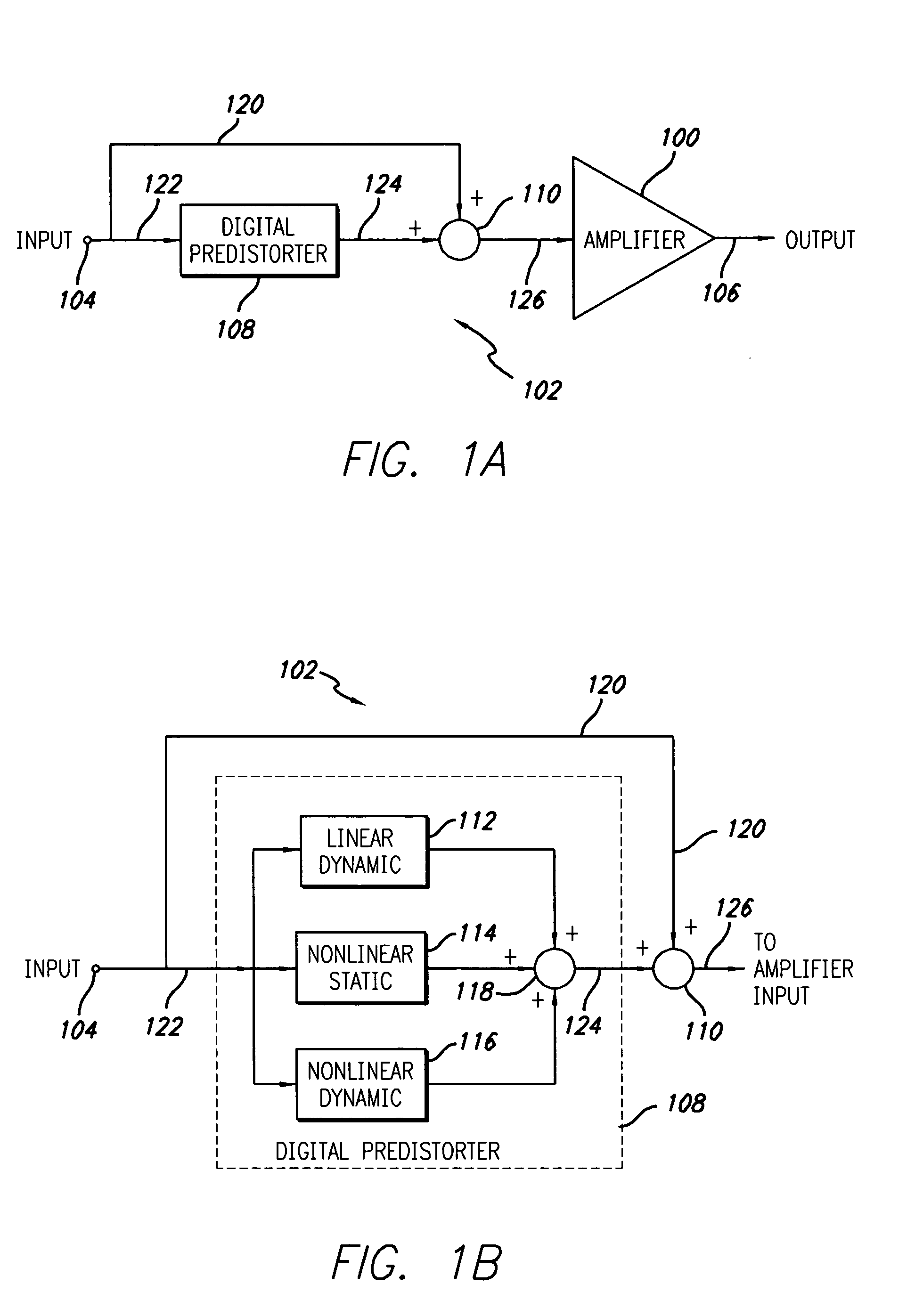
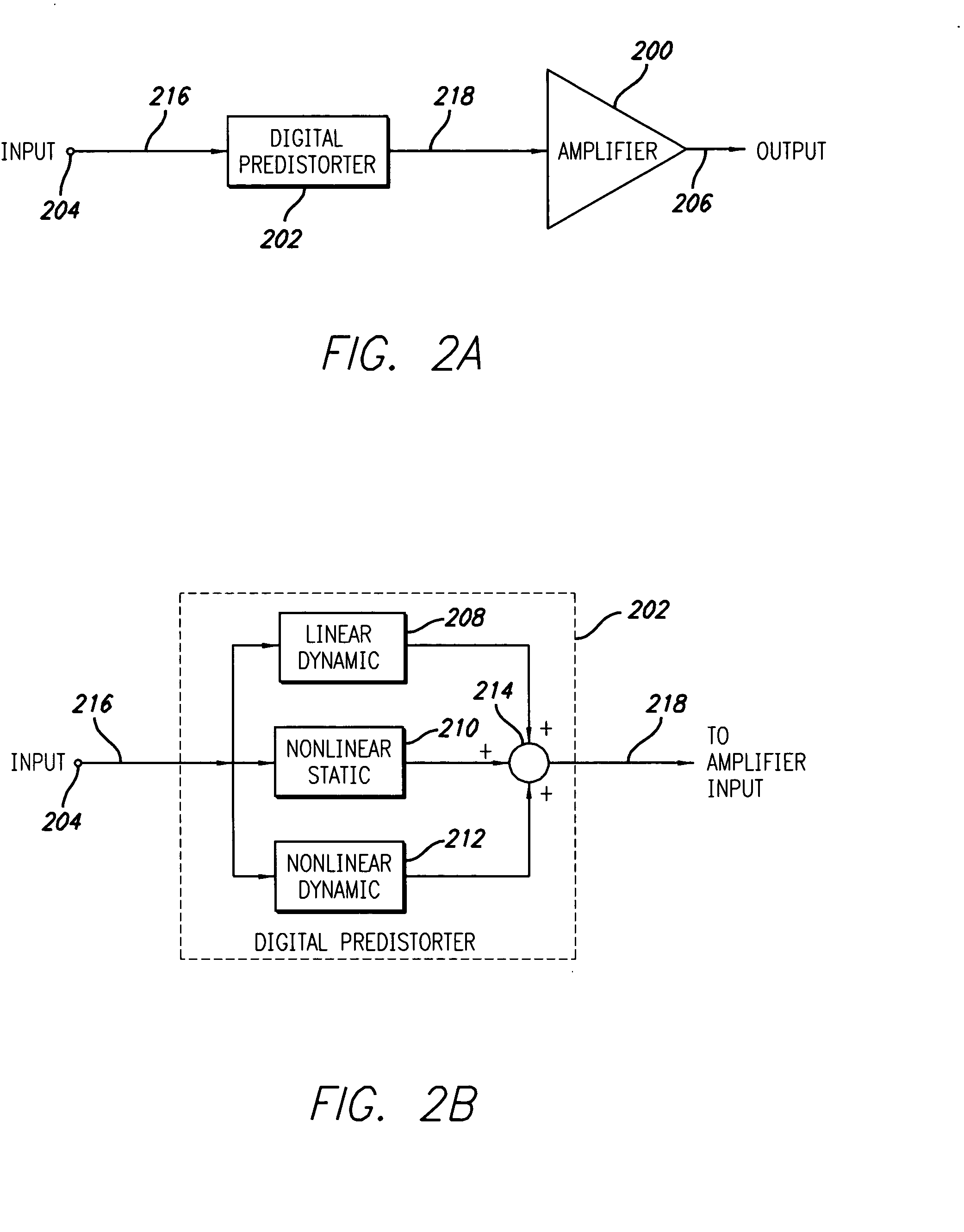
Digital predistortion system and method for high efficiency transmitters
ActiveUS20050195919A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationNon linear dynamicEngineering
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for higher order reactive and thermal memory effects is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter in an IIR filter bank. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
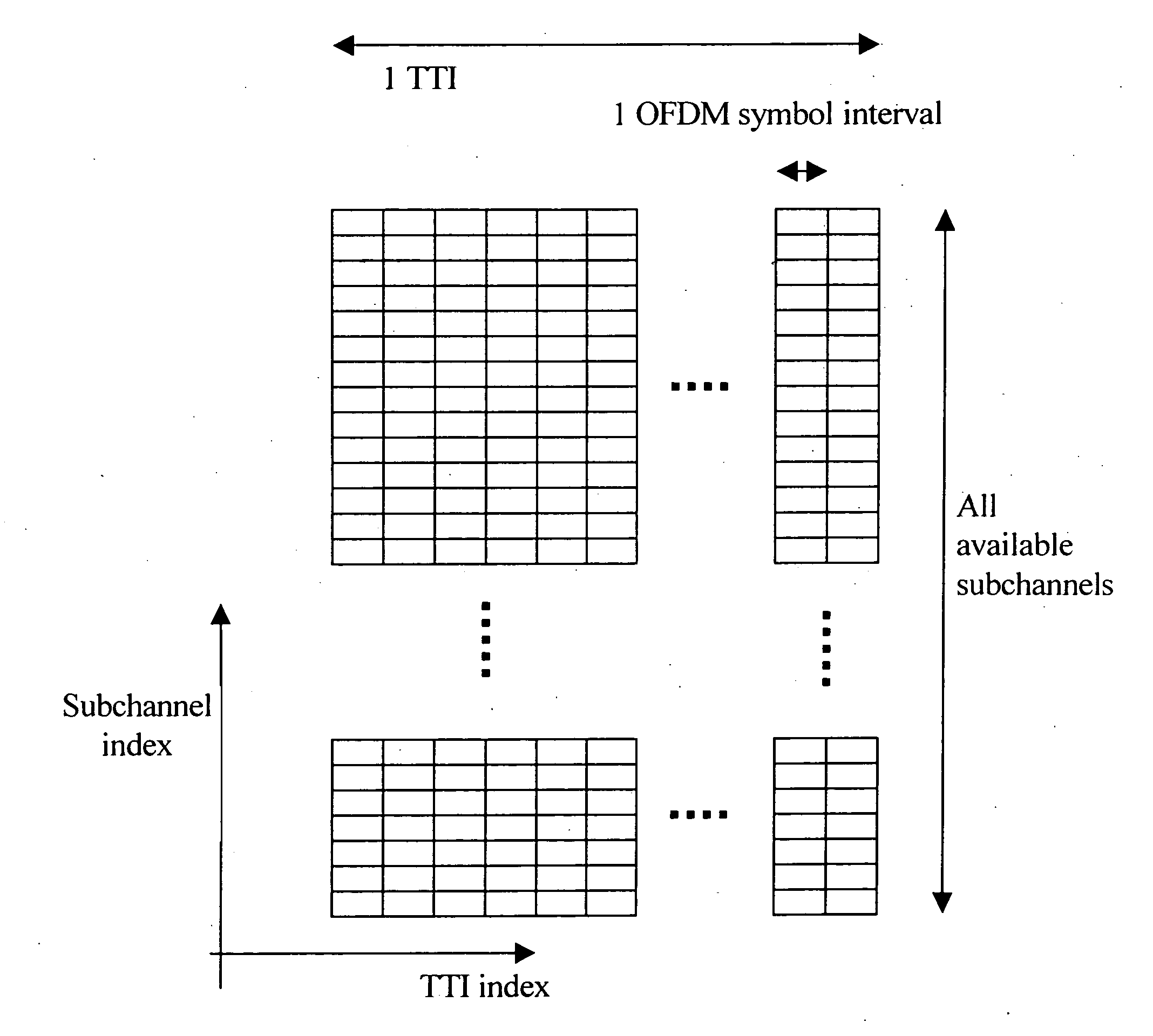
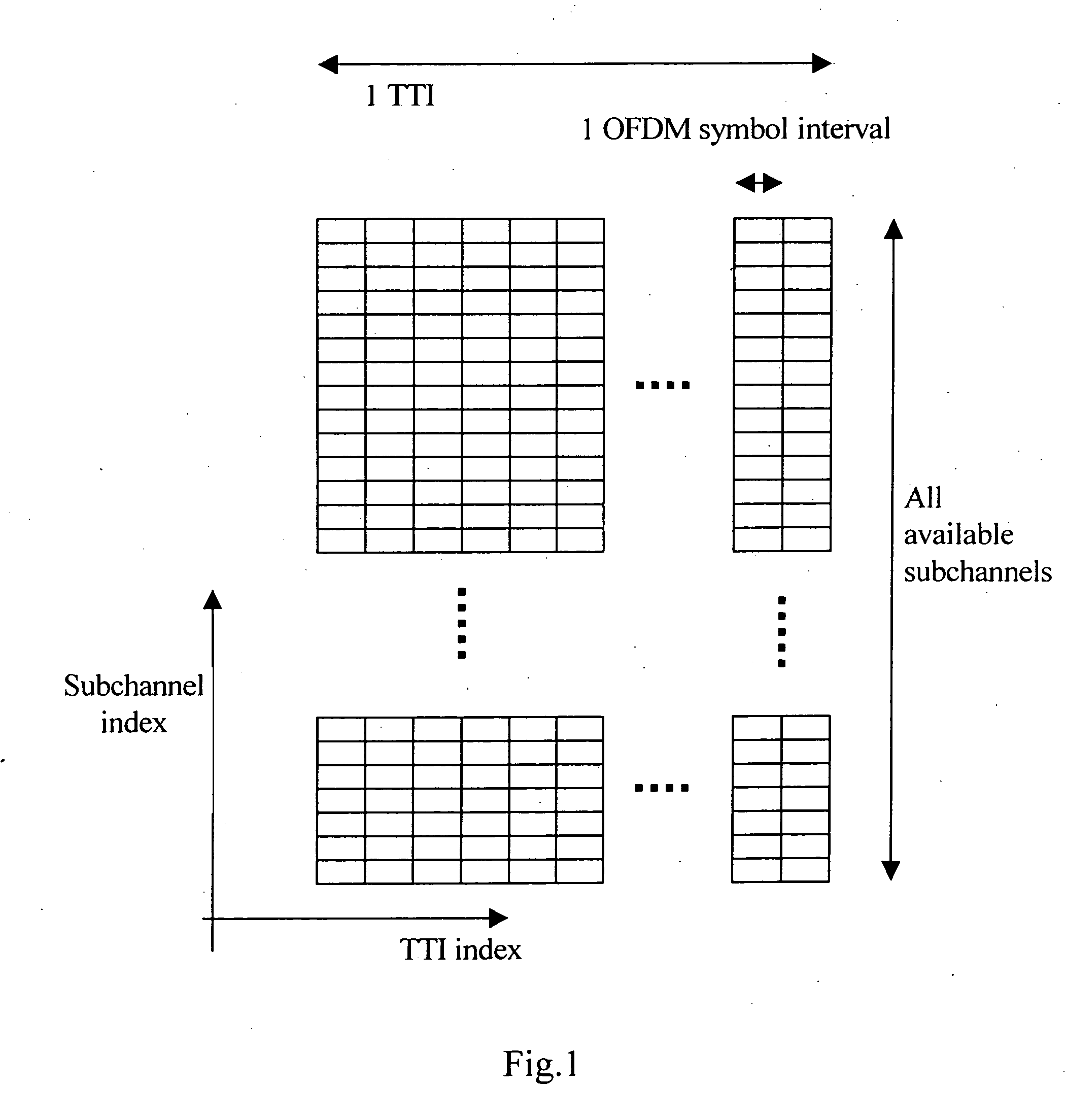
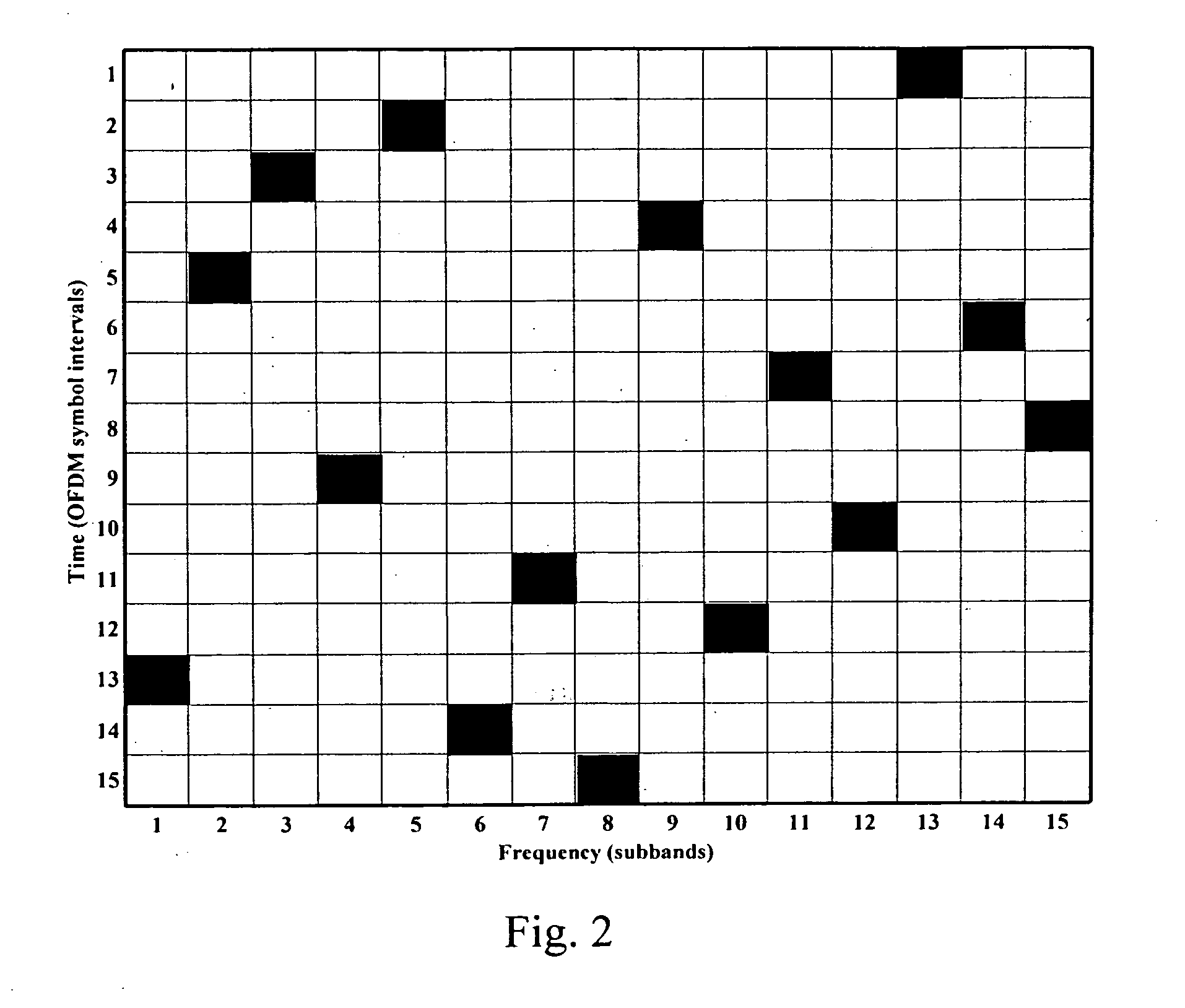
Multiplexing scheme in a communication system
ActiveUS20070177631A1Interference minimizationPerformance maximizationSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationMultiplexingCommunications system
A method for multiplexing communication resources to multiple users in a communication system having no network resource planning. The method includes the steps of: generating a generic time-frequency (T-F) mapping pattern (TFPgeneric), generating a set of orthogonal T-F mapping patterns from said generic T-F mapping pattern (TFPgeneric), performing a random variable cyclic offsetting of said set of orthogonal T-F mapping patterns in each transmission time interval (TTI), and allocating the orthogonal T-F mapping patterns to the one or more users and / or traffic channels in each TTI. A transmitter for executing said multiplexing method, and a system including such transmitters, are also disclosed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com