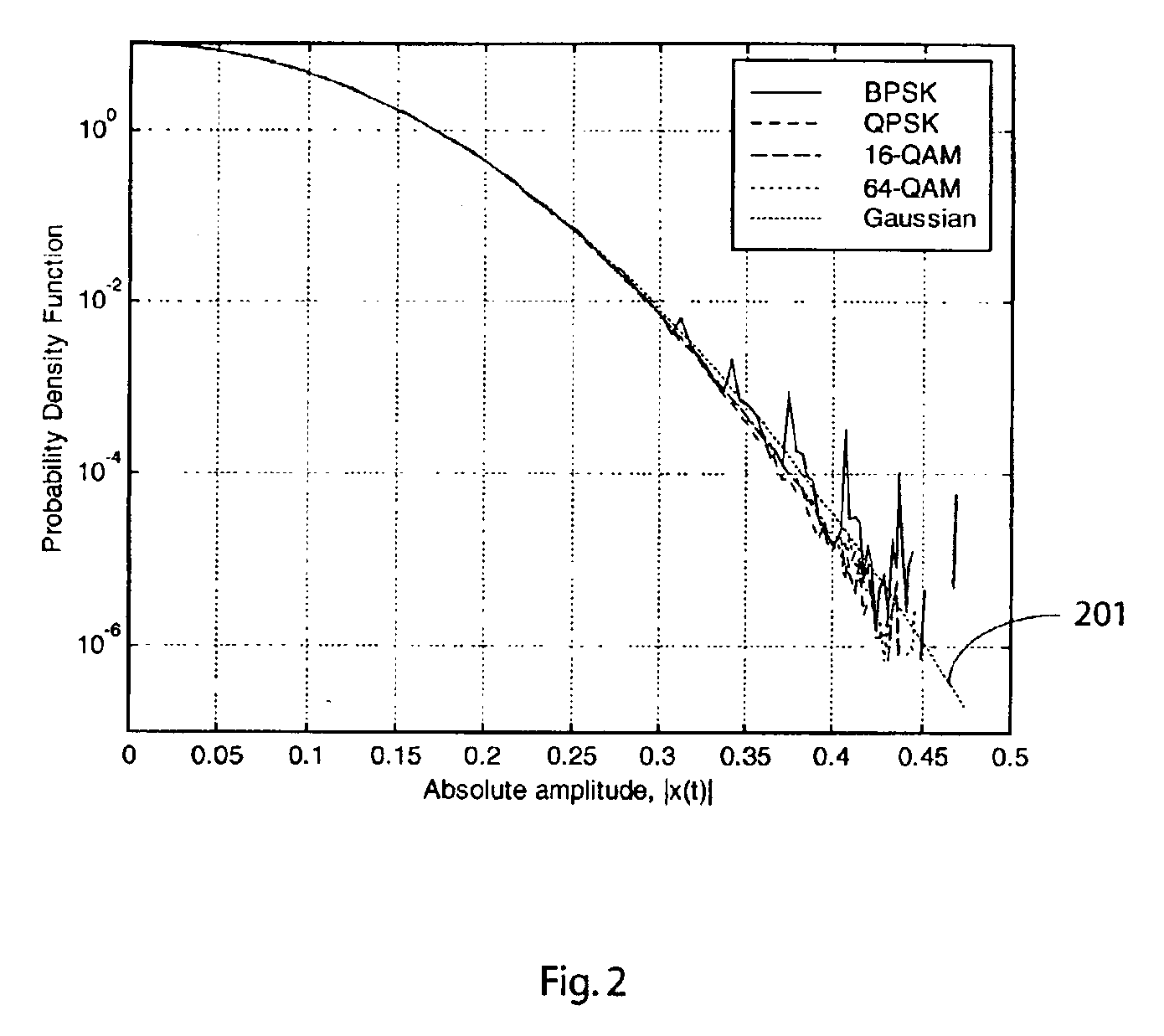
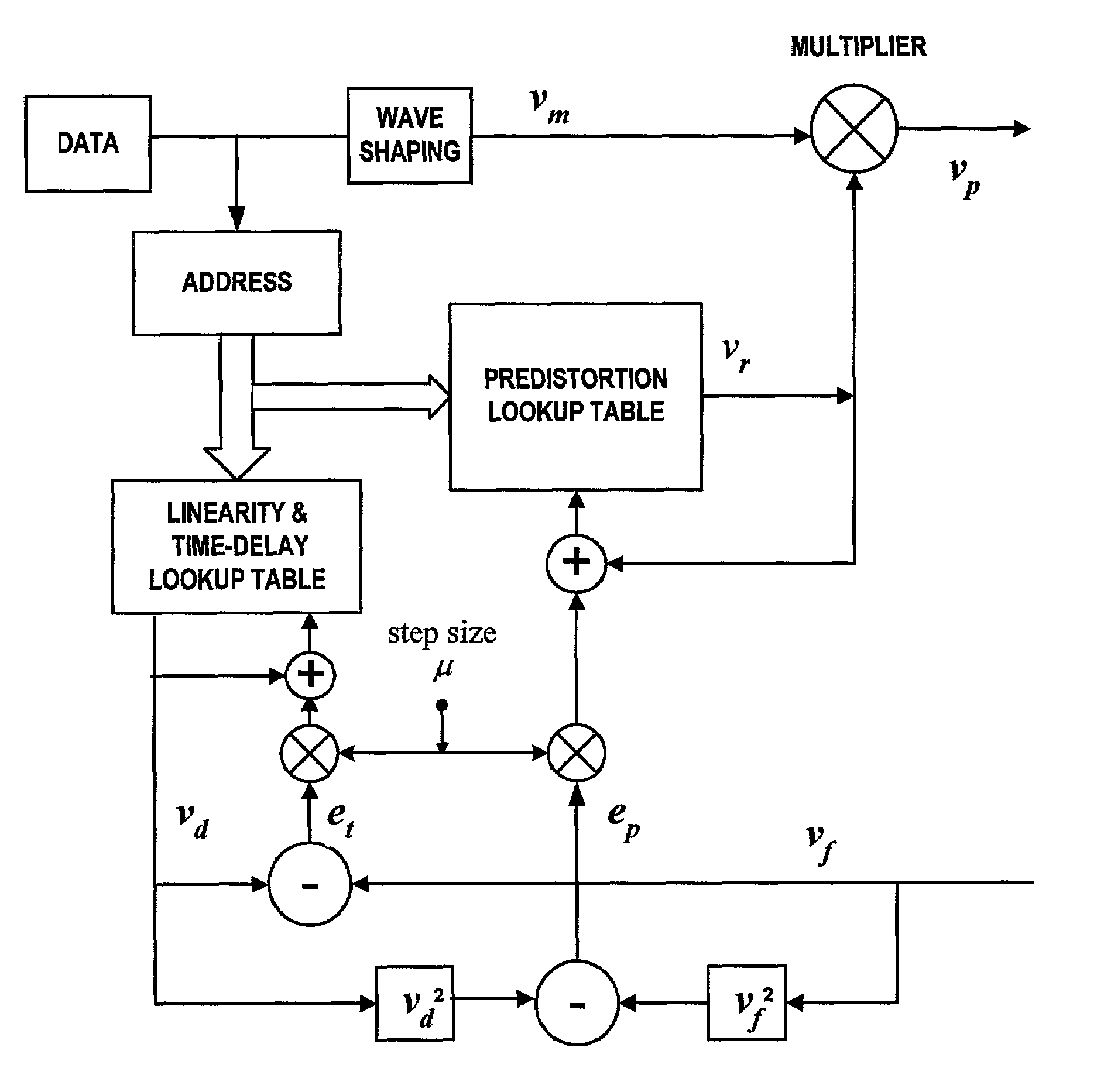
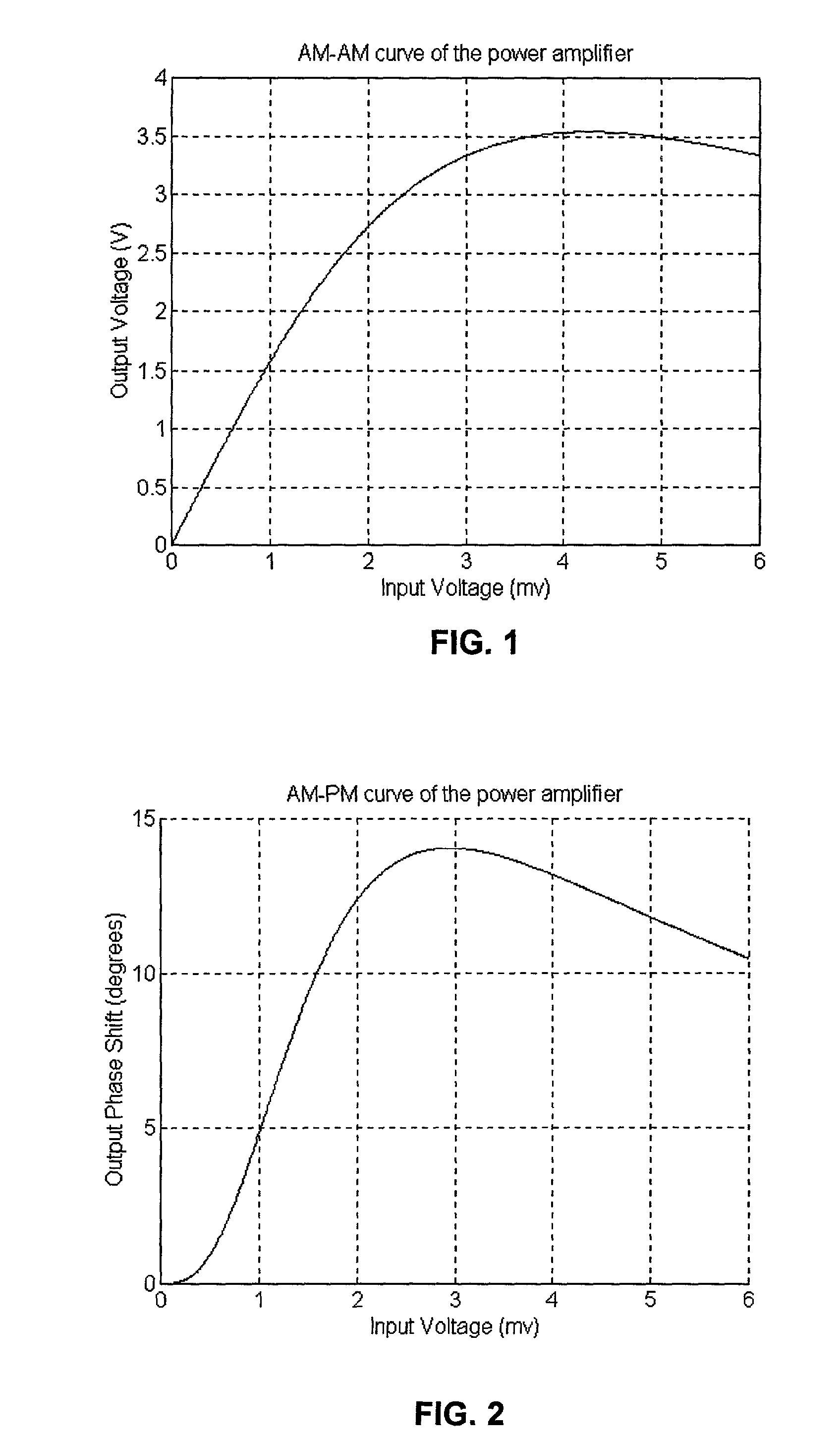
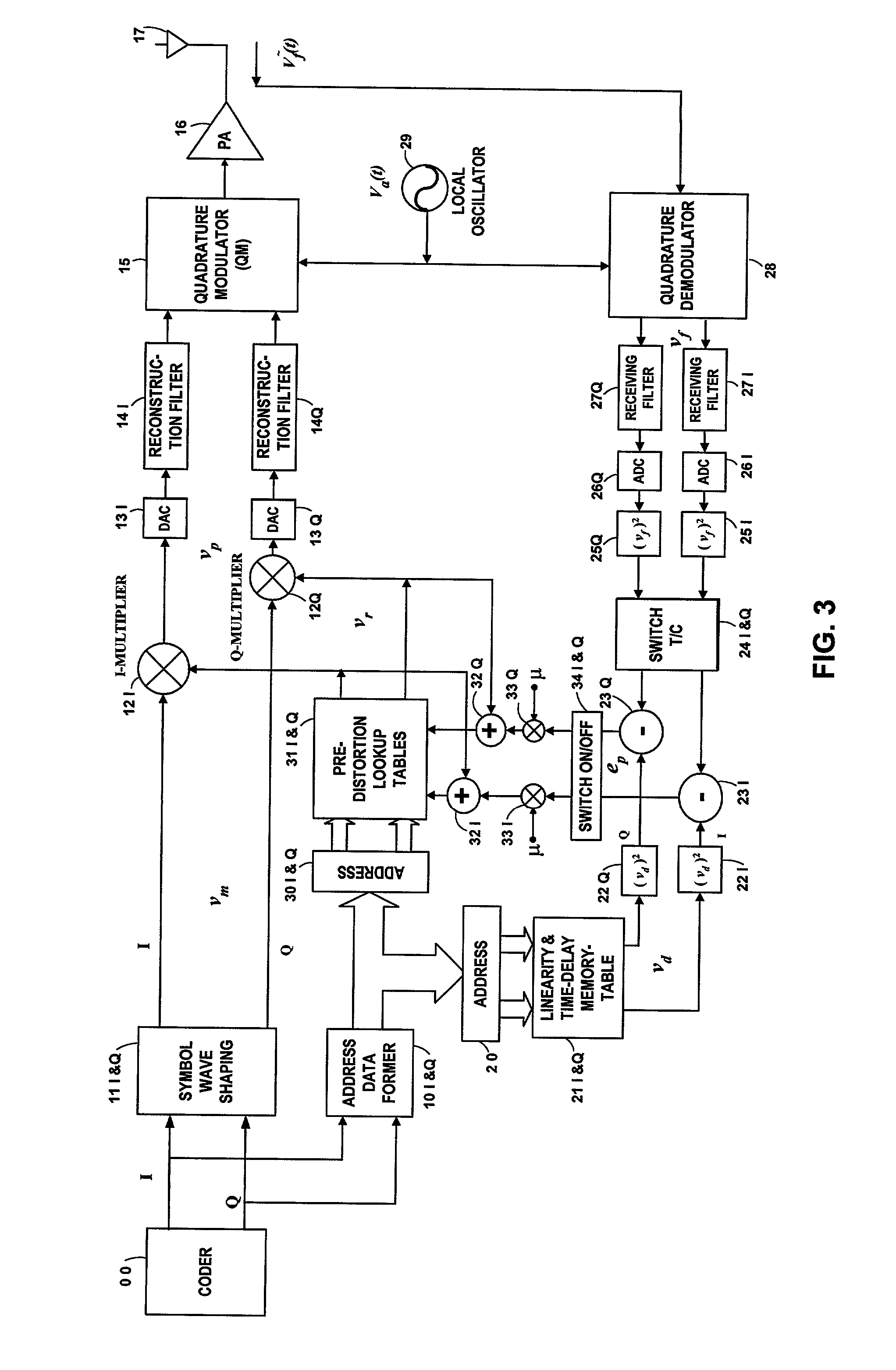
Patents
Literature
1462 results about "Predistortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
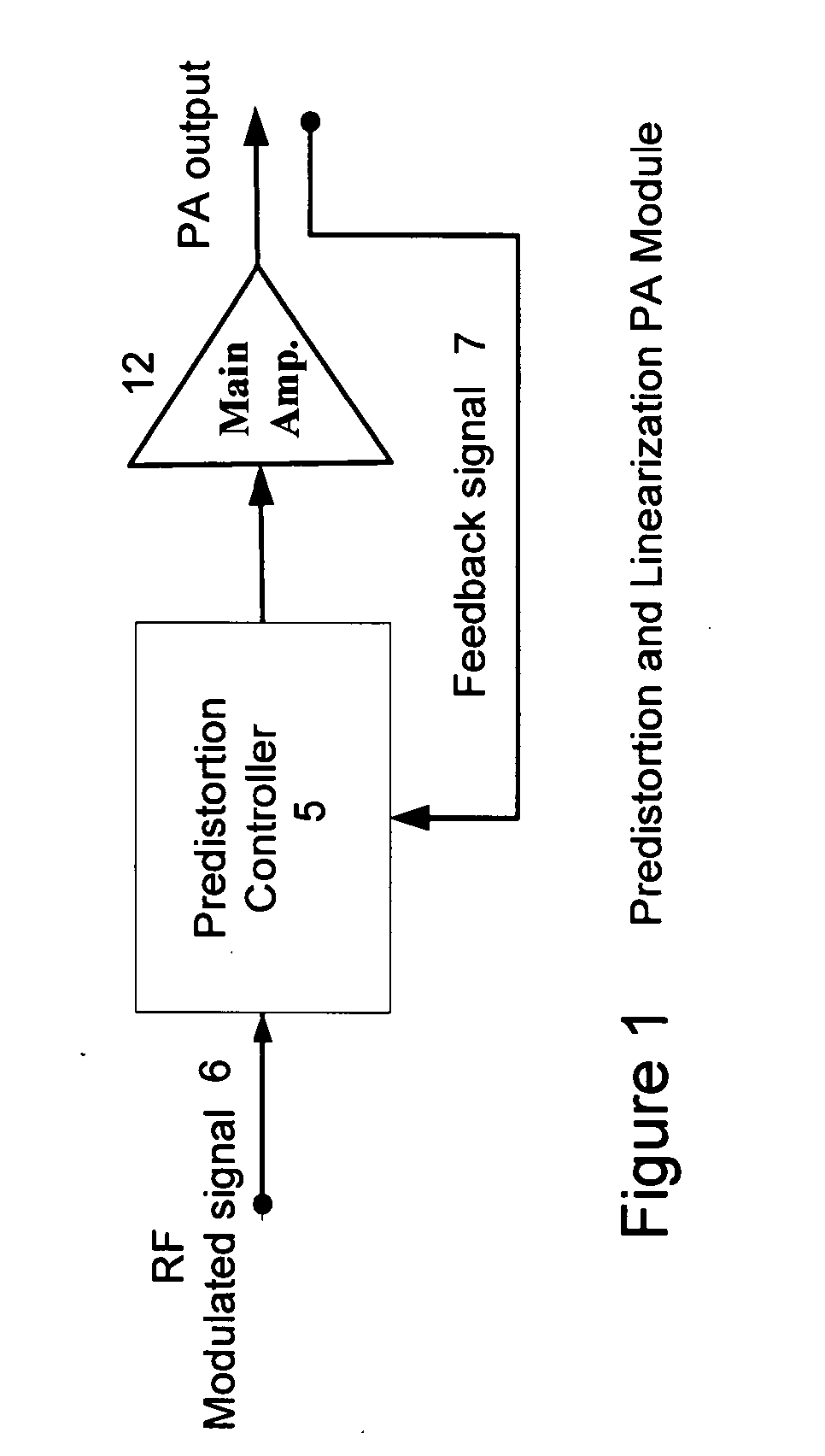
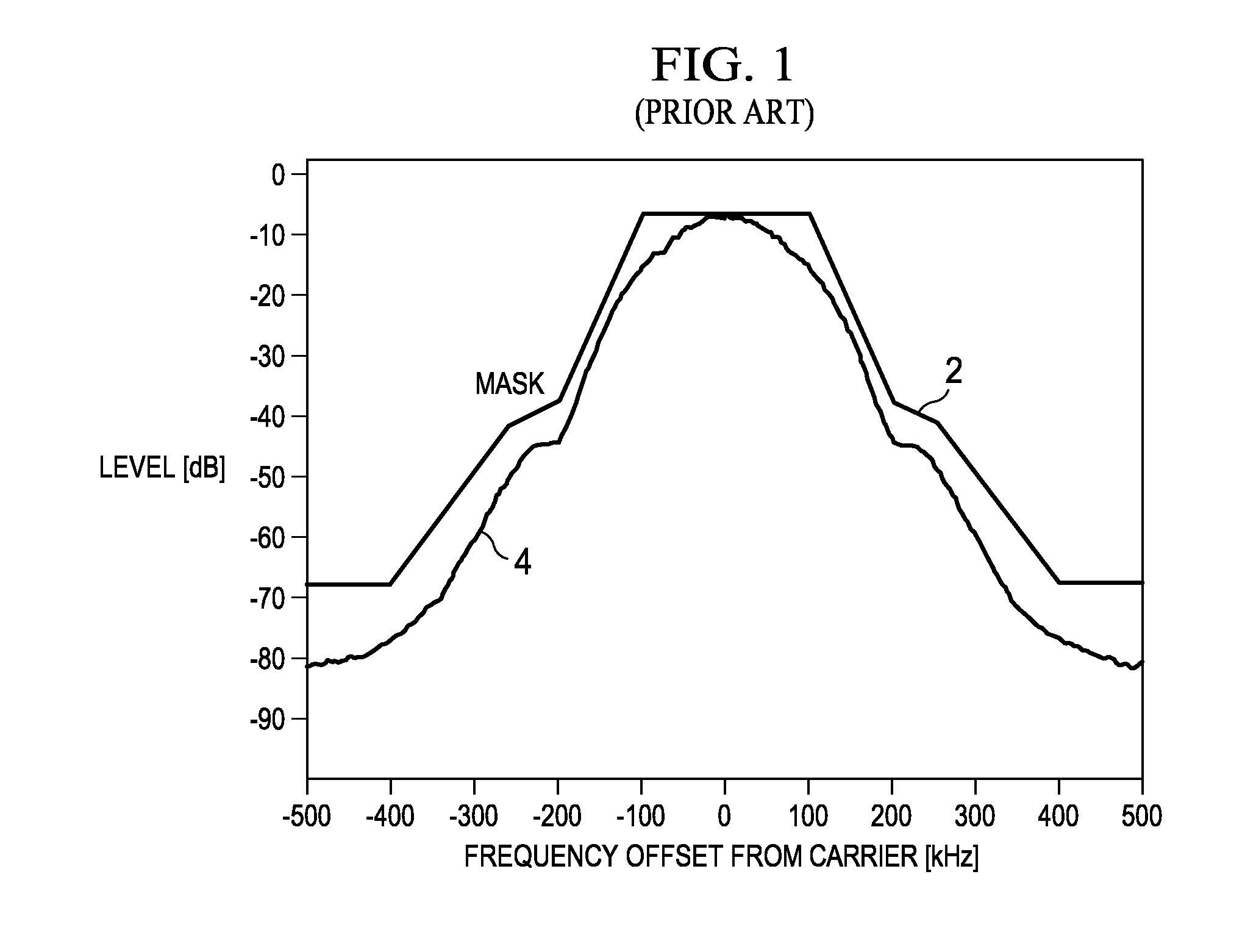
Predistortion is a technique used to improve the linearity of radio transmitter amplifiers. Radio transmitter amplifiers in most telecommunications systems are required to be "linear", in that they must accurately reproduce the signal present at their input. An amplifier that compresses its input or has a non-linear input/output relationship causes the output signal to splatter onto adjacent radio frequencies. This causes interference on other radio channels.
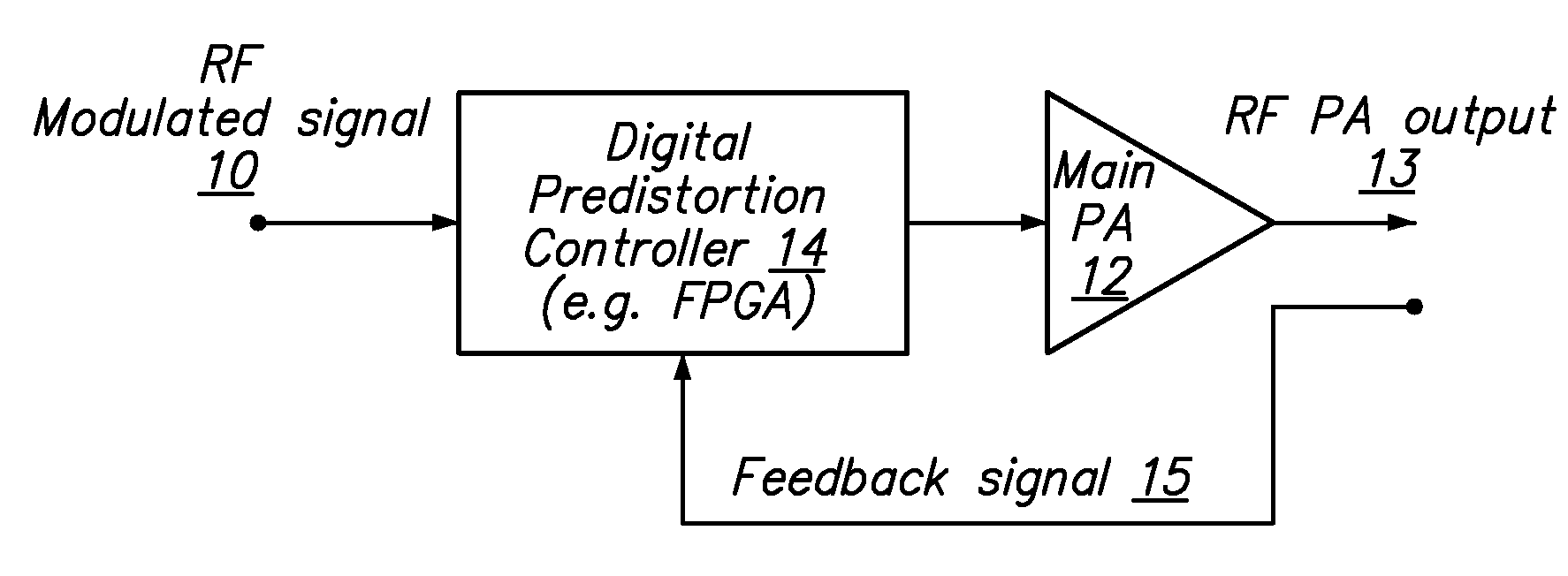
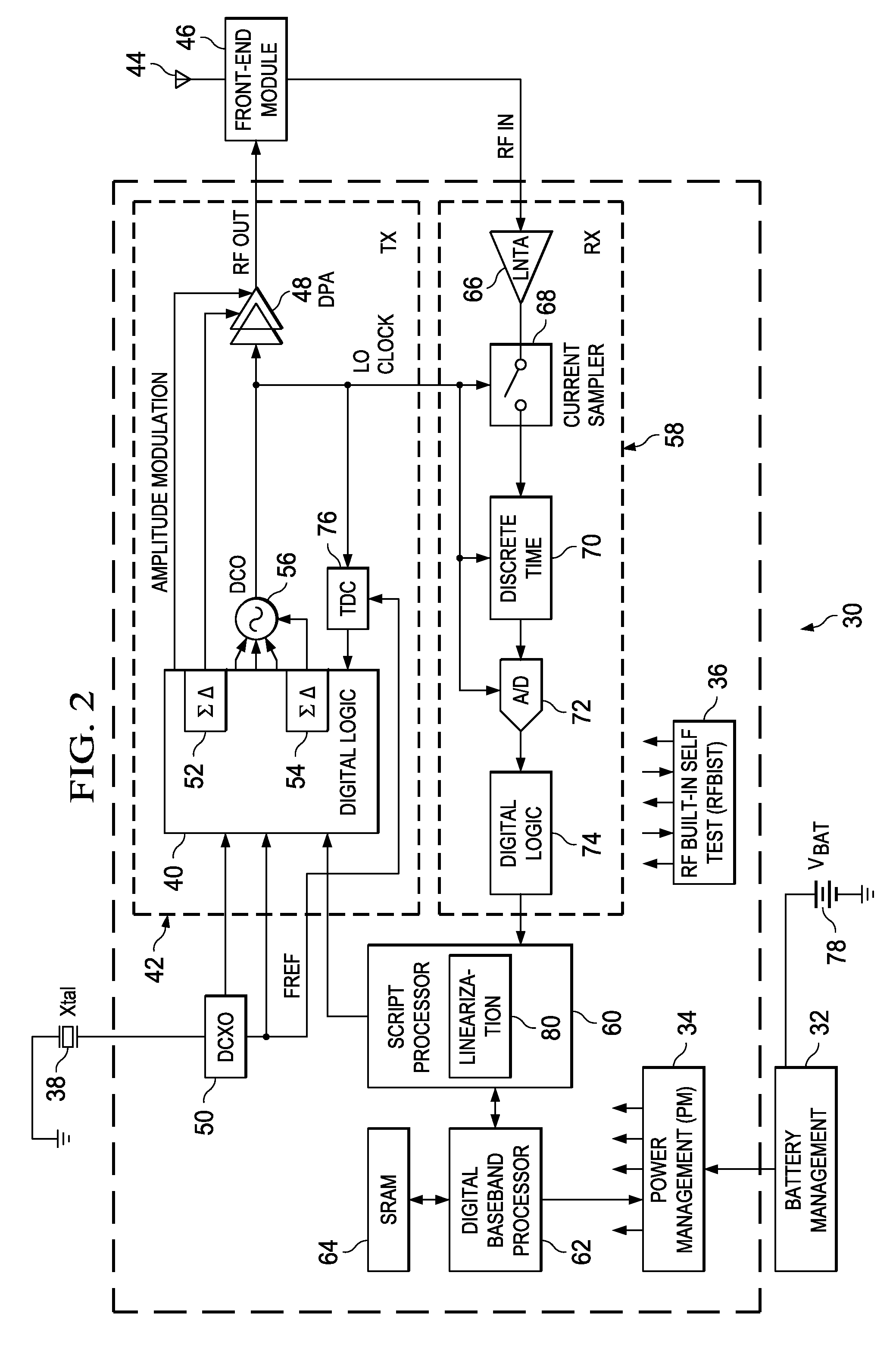
High efficiency digital transmitter incorporating switching power supply and linear power amplifier
InactiveUS20090004981A1Improve efficiencyAttenuation bandwidthResonant long antennasPower amplifiersDigital signal processingDc current
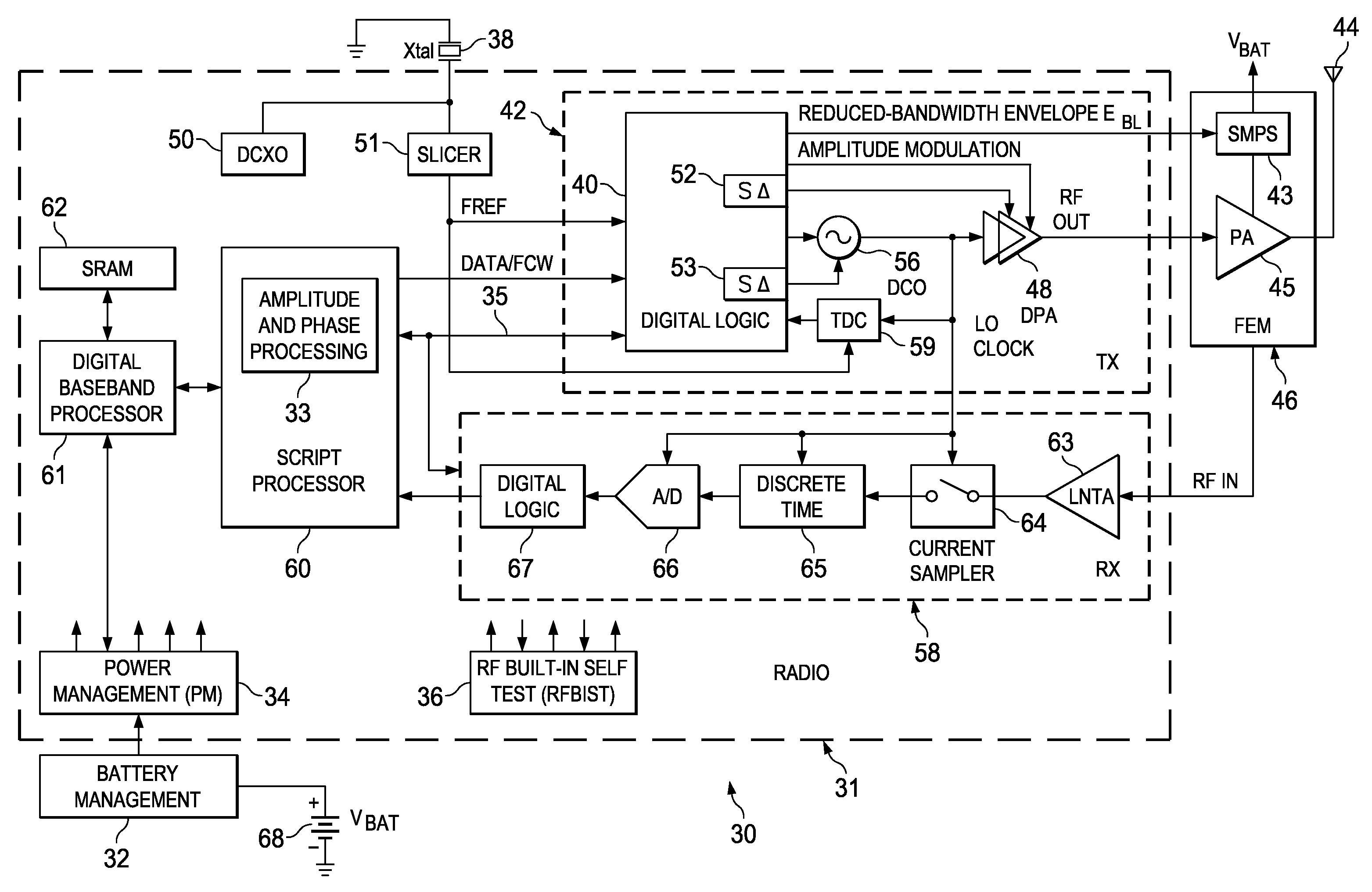
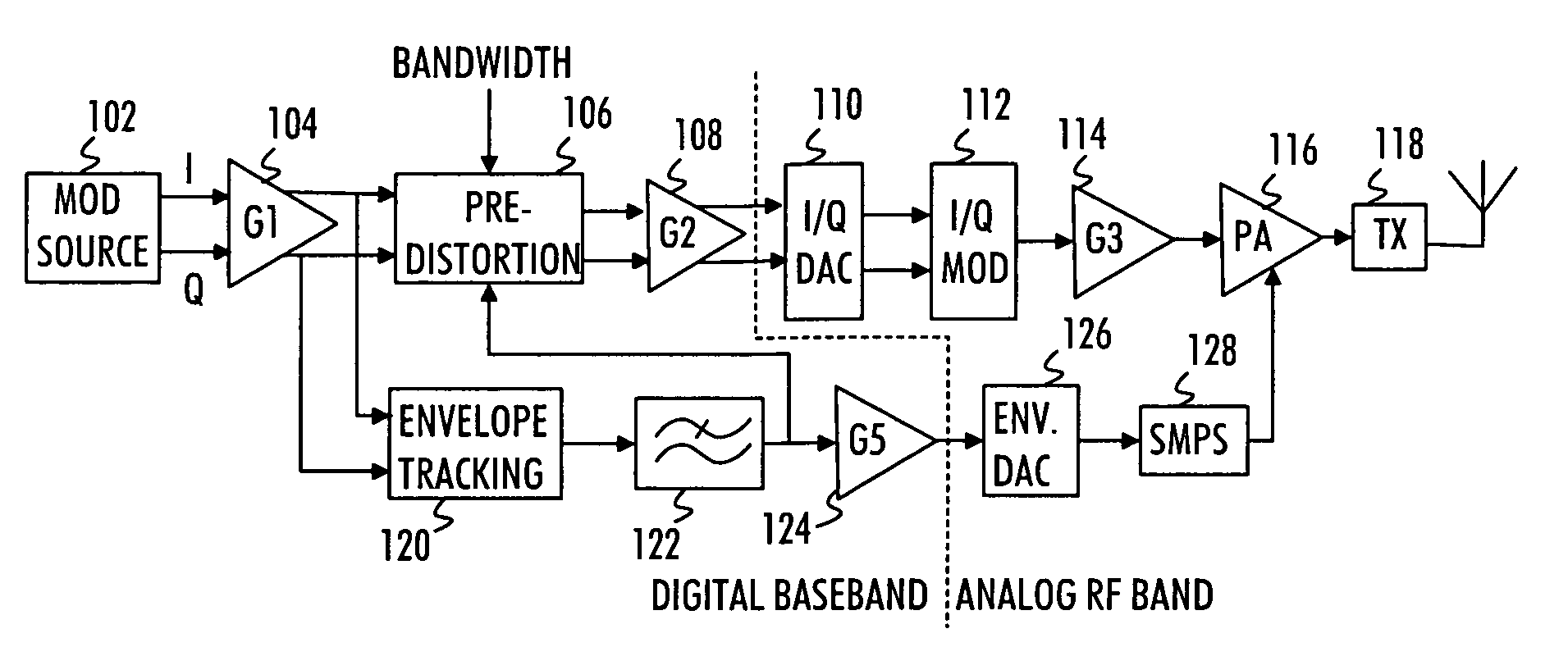
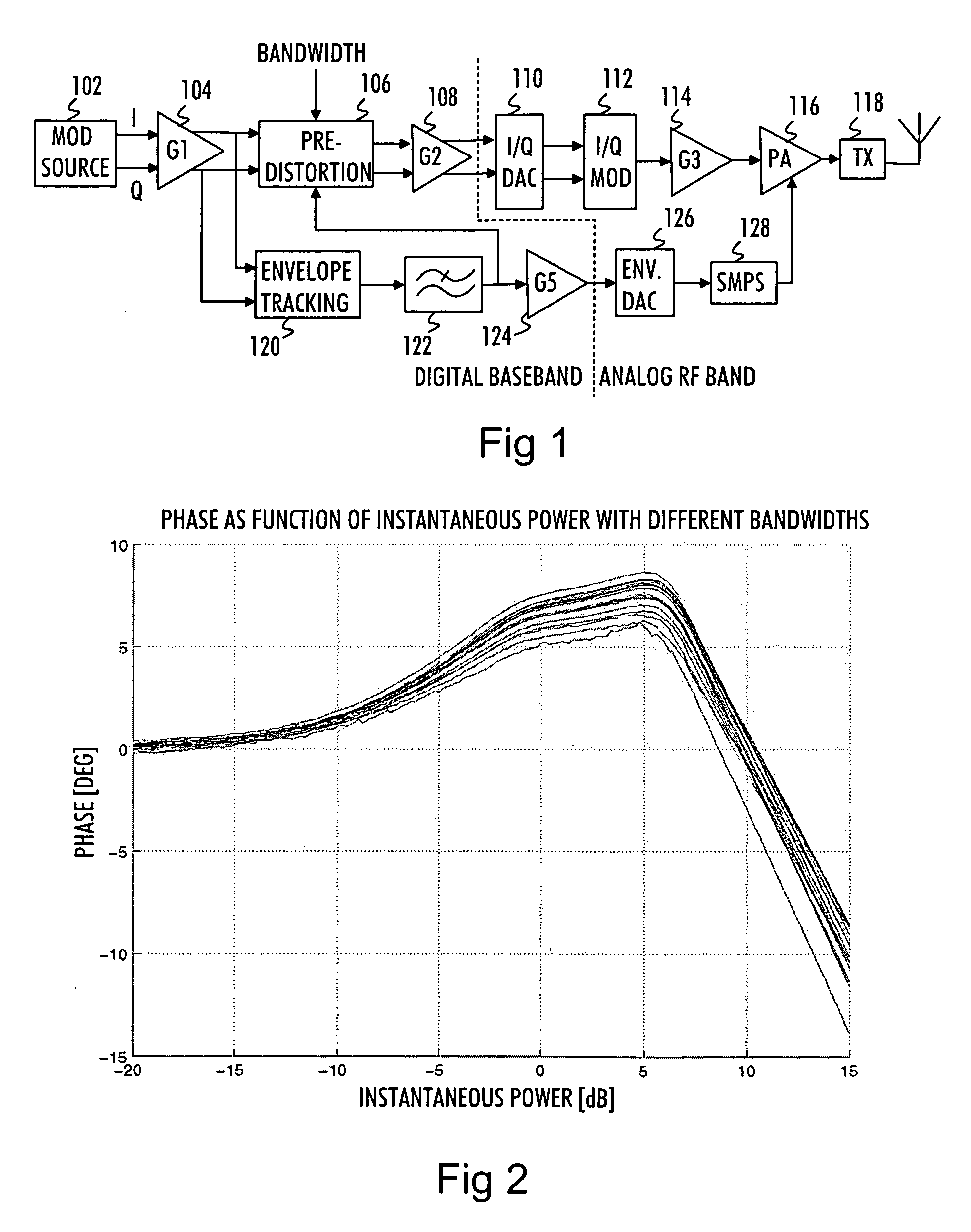
A novel apparatus and method of improving the power efficiency of a digital transmitter for non-constant-amplitude modulation schemes. The power efficiency improvement mechanism of the invention leverages the high efficiency of a switched-mode power supply (SMPS) that supplies the high DC current to the transmitter's power amplifier, while compensating for its limitations using predistortion. The predistortion may be achieved using any suitable technique such as digital signal processing, hardware techniques, etc. A switched mode power supply (i.e. switching regulator) is used to provide a slow form (i.e. reduced bandwidth) of envelope tracking (based on a narrower bandwidth distorted version of the envelope waveform) such that the switching regulator can use a lower switching rate corresponding to the lower bandwidth, thereby obtaining high efficiency in the switching regulator. The resulting AM-AM and AM-PM distortions in the power amplifier are compensated through predistortion of the digital amplitude modulating signal which dictates the envelope at the PA input. Similarly, the phase modulation is also compensated prior to the PA, such that once it undergoes the distortion in the PA, the end result is sufficiently close to the desired phase.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of correcting distortion in a power amplifier
InactiveUS20040142667A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionLookup table adaptive predistortionAudio power amplifierData signal
The invention is a method of correcting distortion in a power amplifier in a transmitter. The method includes applying an input time varying modulated data signal to the power amplifier which outputs an amplified time varying modulated data signal which is an amplification of the input time varying modulated data signal; storing samples of the input time varying modulated data signal; storing samples of the output amplified time varying data signal; using the stored input and output time varying modulated samples to provide a processor implemented model with parameters representing a non-linear characteristic of the power amplifier without the use of any polynomials; and producing predistortion coefficients.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Multicarrier distributed active antenna
InactiveUS6906681B2Antenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
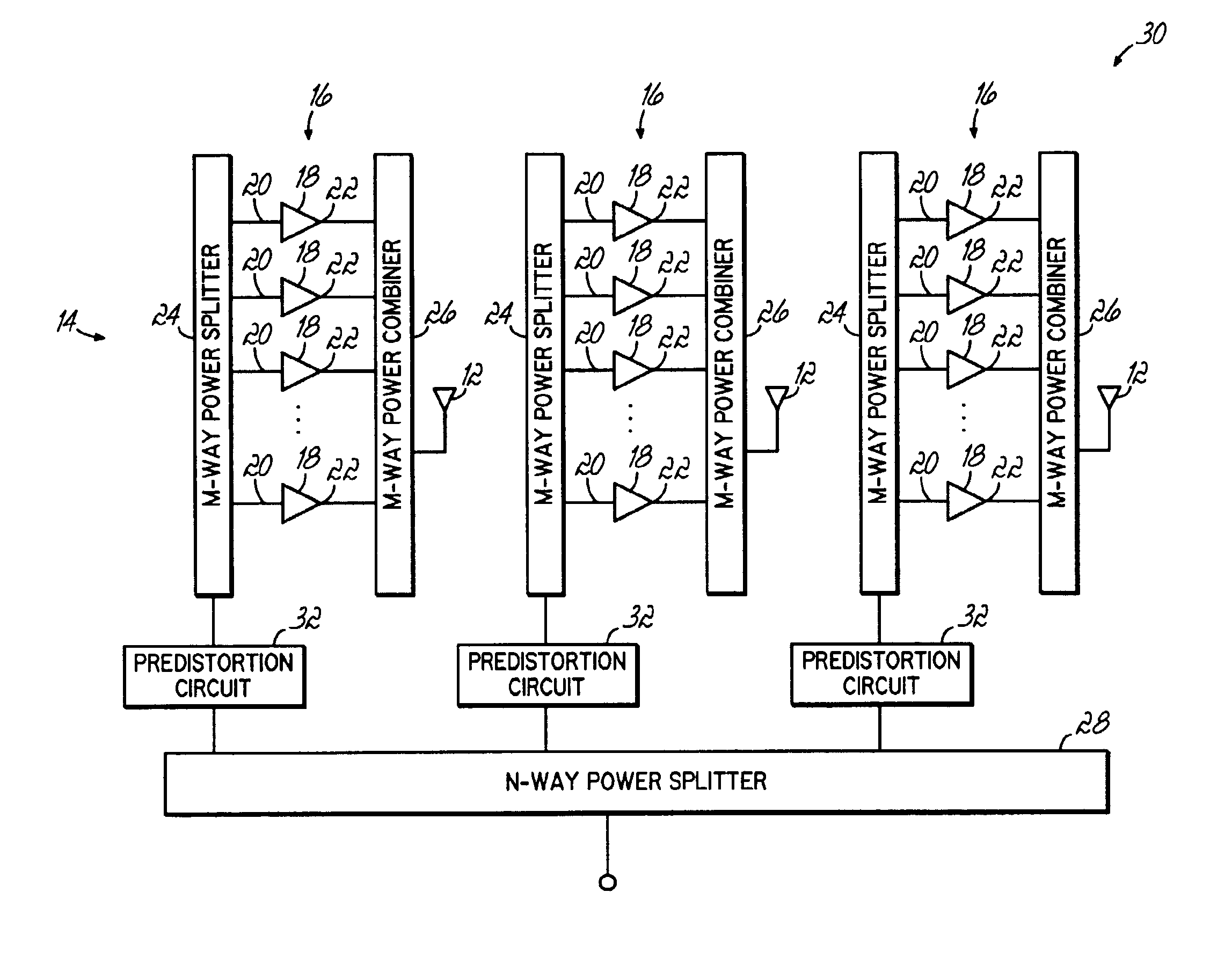
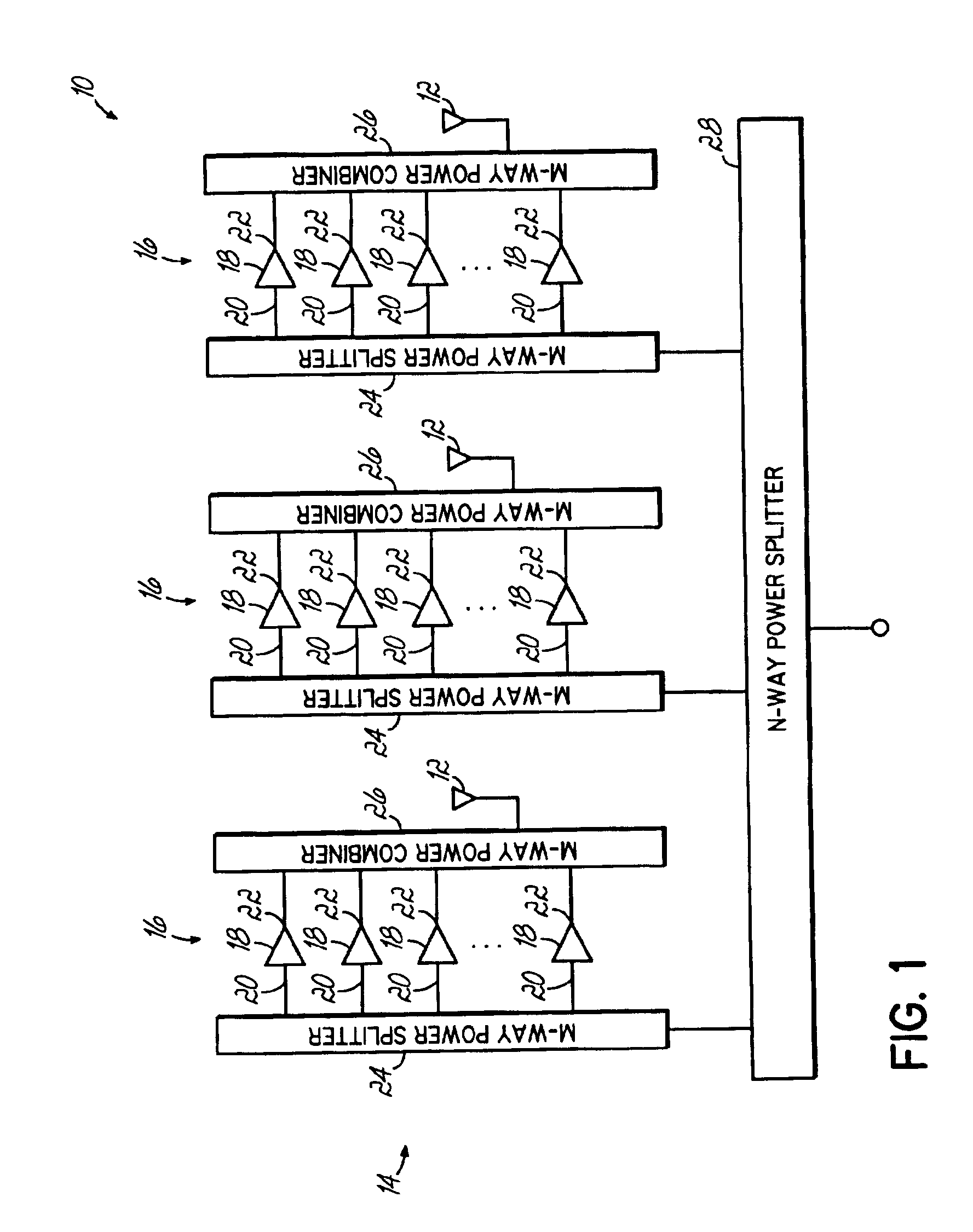
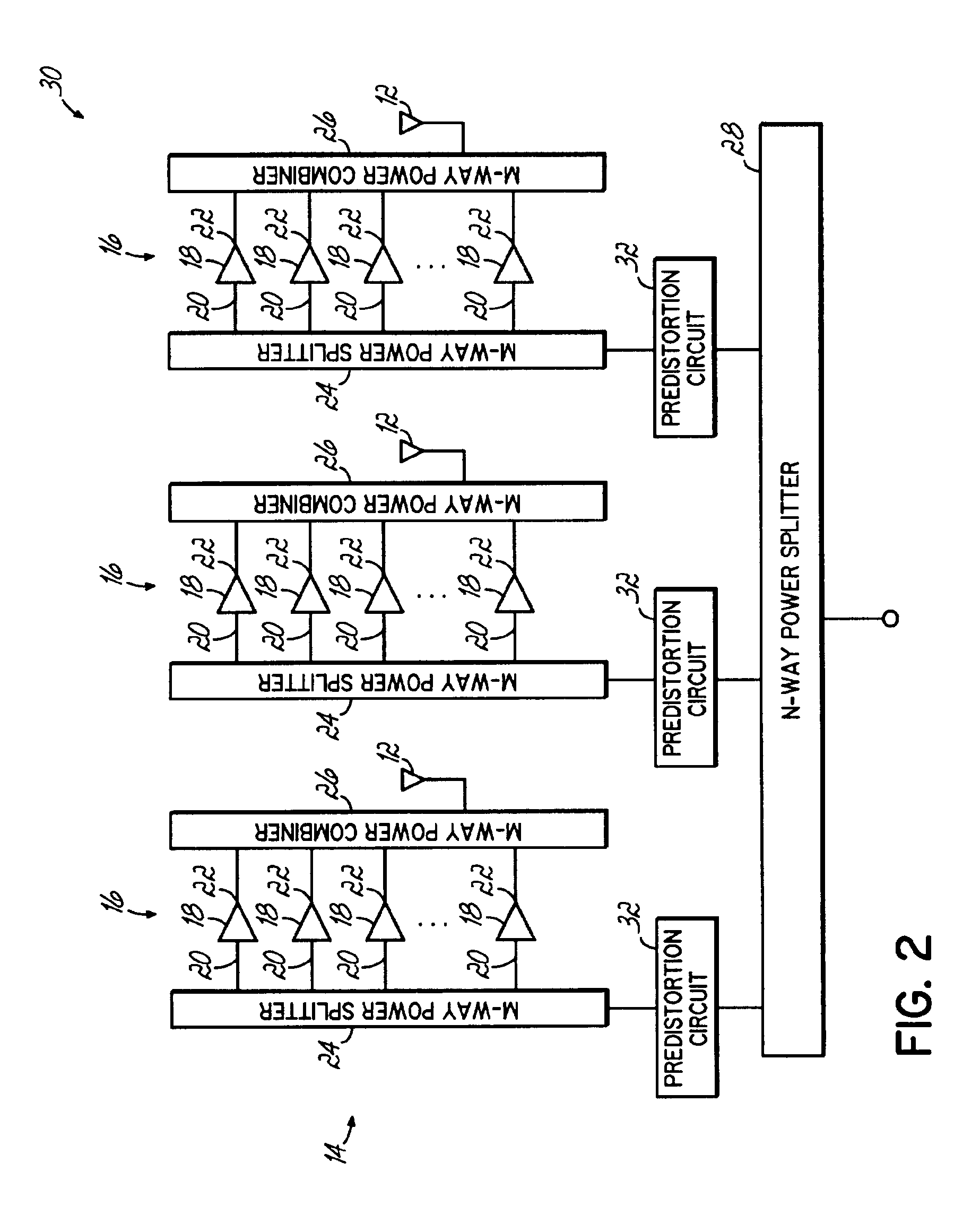
A distributed active antenna includes a power module having a parallel combination of power amplifiers for driving each antenna element of the distributed active antenna. A predistortion linearization circuit may be coupled to each power module to linearize the output of each antenna element of the distributed active antenna.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Method and system for broadband predistortion linearization
InactiveUS20060240786A1Improve linearization performanceExtends linearization bandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationTime domainRadio frequency
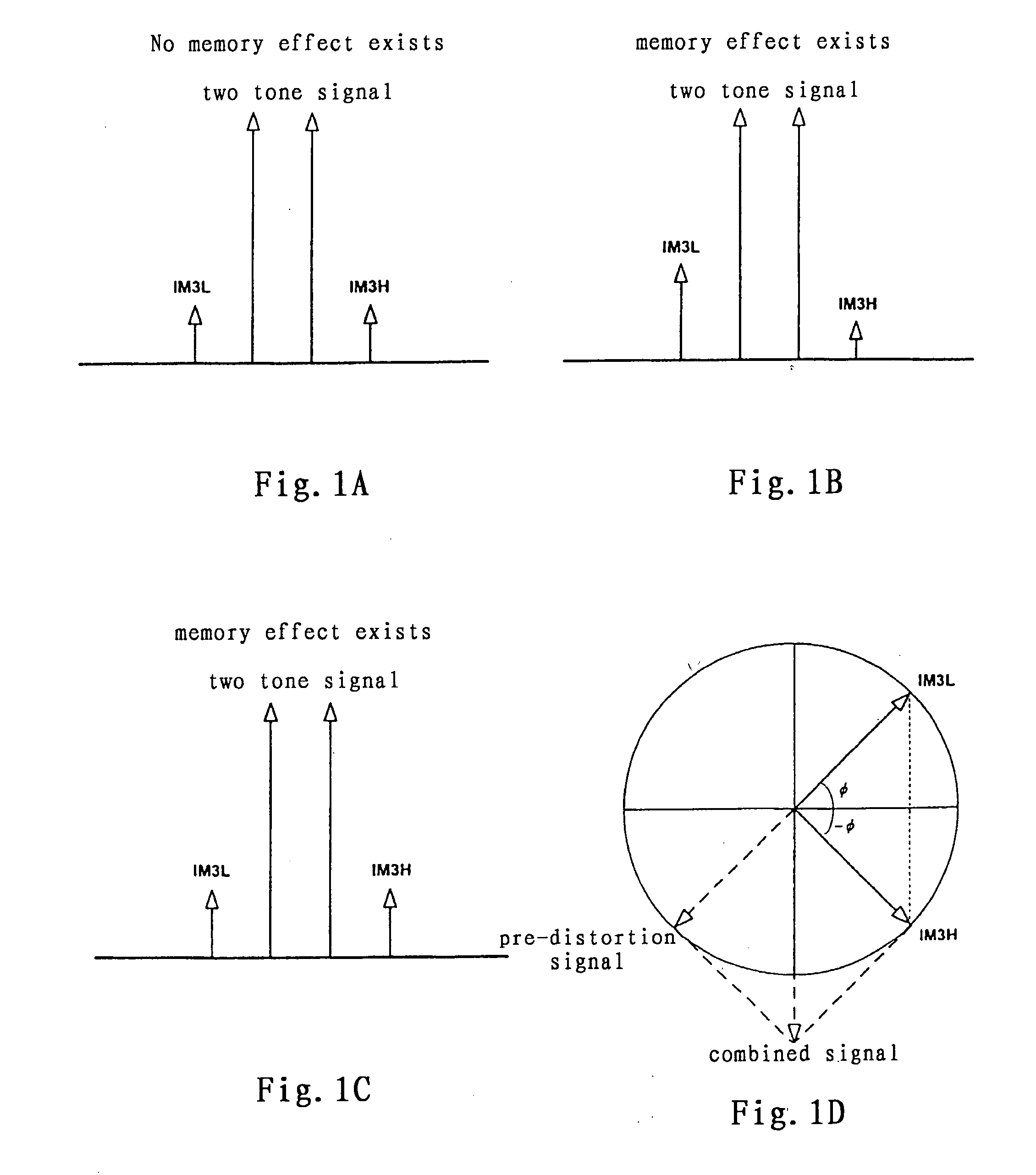
The invention relates to a method and system for wideband digital pre-distortion linearization, which is used to overcome the influence of memory effect in radio frequency power amplifier, to expand digital pre-distortion linearization bandwidth, and to improve digital pre-distortion linearization performance. The method and system can get an in-band pre-distortion signal and an out-of-band pre-distortion signal according to the characteristic parameter of the amplifier; the in-band pre-distortion signal is up-converted and the up-converted signal is added to the out-of-band pre-distortion signal, which is not up-converted, then the combined signal is inputted to the power amplifier as an input signal; a part of the output signal from the power amplifier, serving as a feedback signal, can be compared with the original input signal, and the characteristic parameter of the amplifier for generating the in-band pre-distortion signal and the out-of-band pre-distortion signal is adaptively regulated according to the comparison result, so that the waveform of time domain or the frequency domain of the feedback signal can be close to that of the original input signal as much as possible.
Owner:ZTE CORP
High efficiency linearization power amplifier for wireless communication
ActiveUS20070241812A1Improve efficiencyImprove linearityEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier details to increase power/efficiencyFrequency changerControl signal
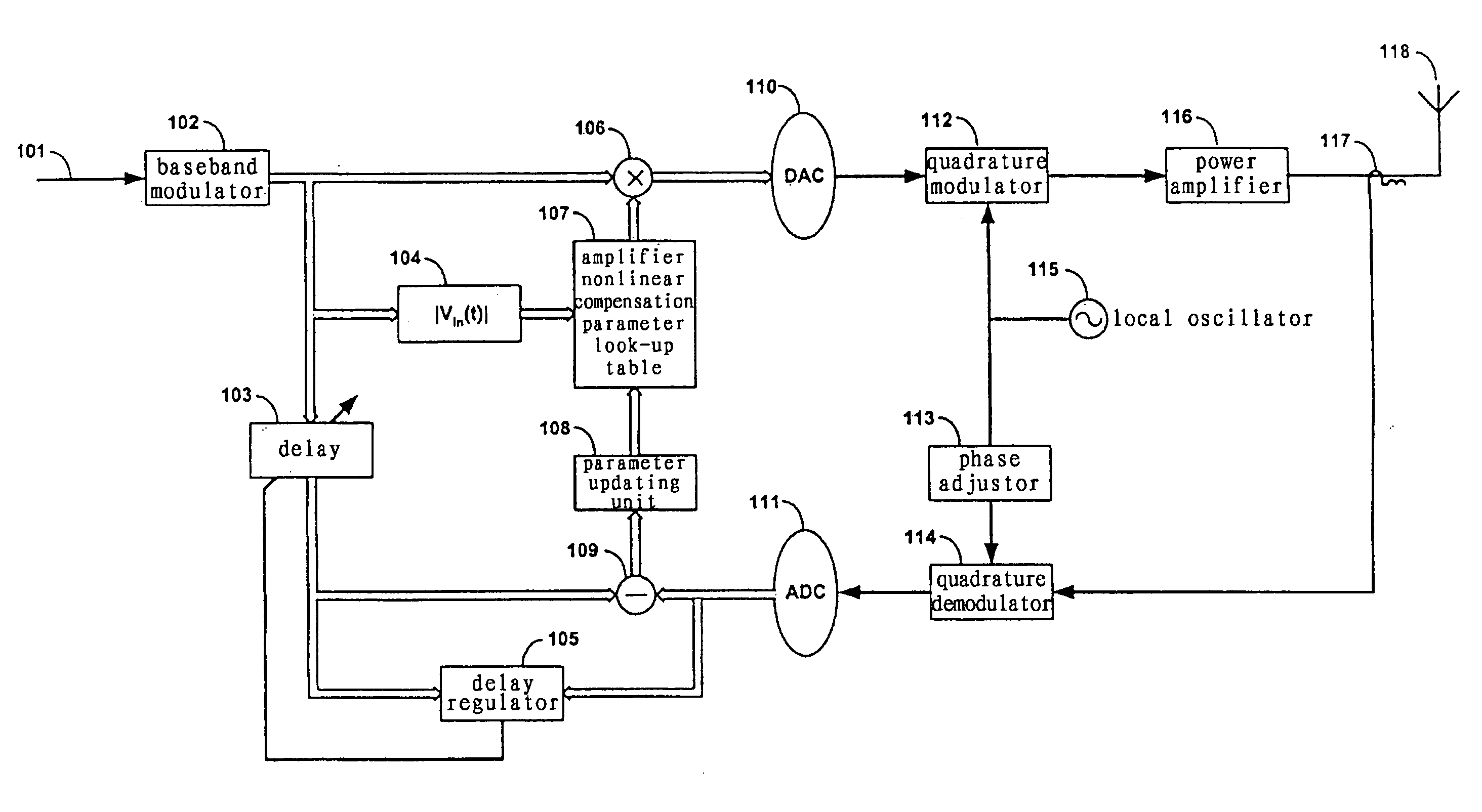
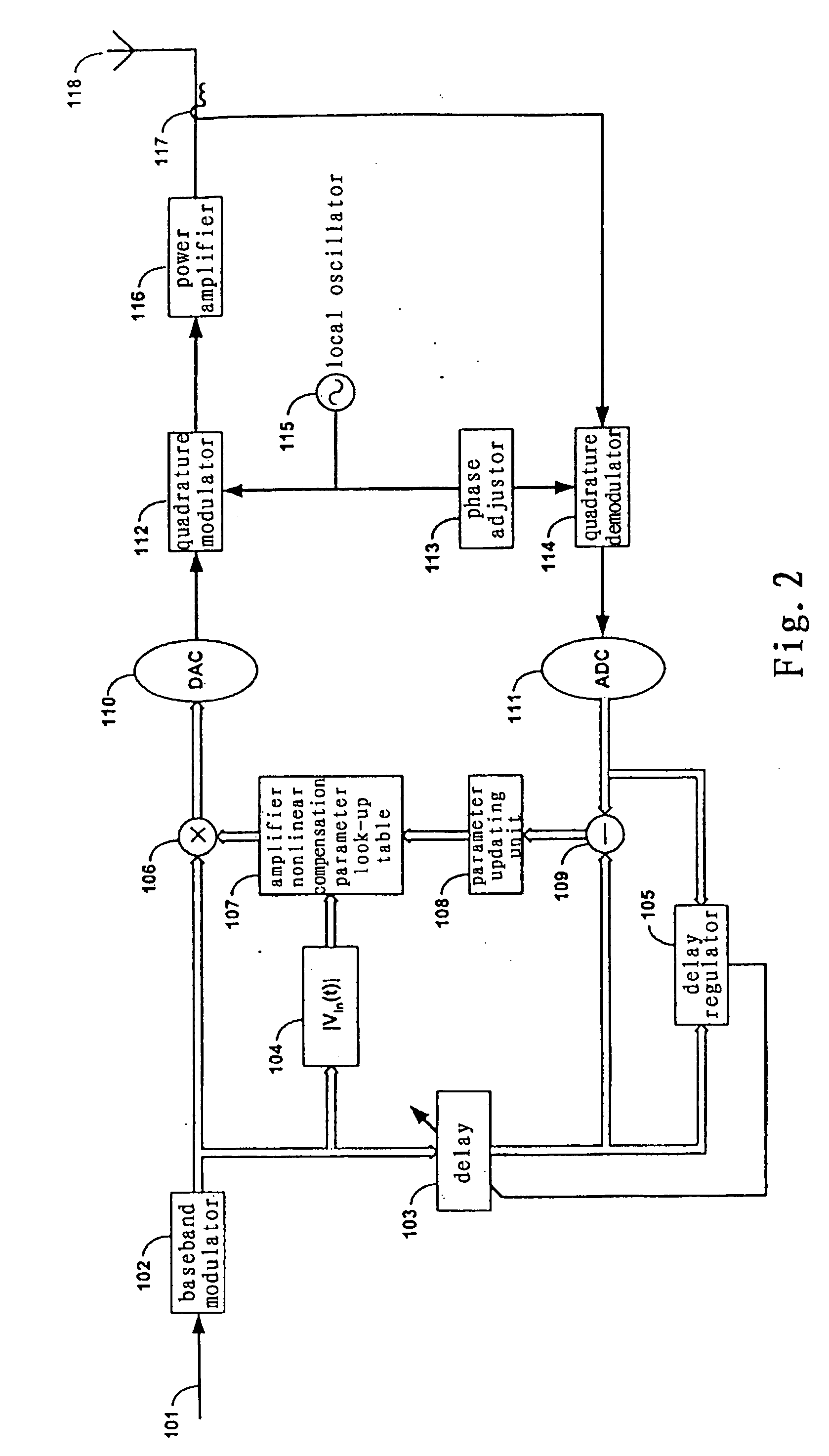
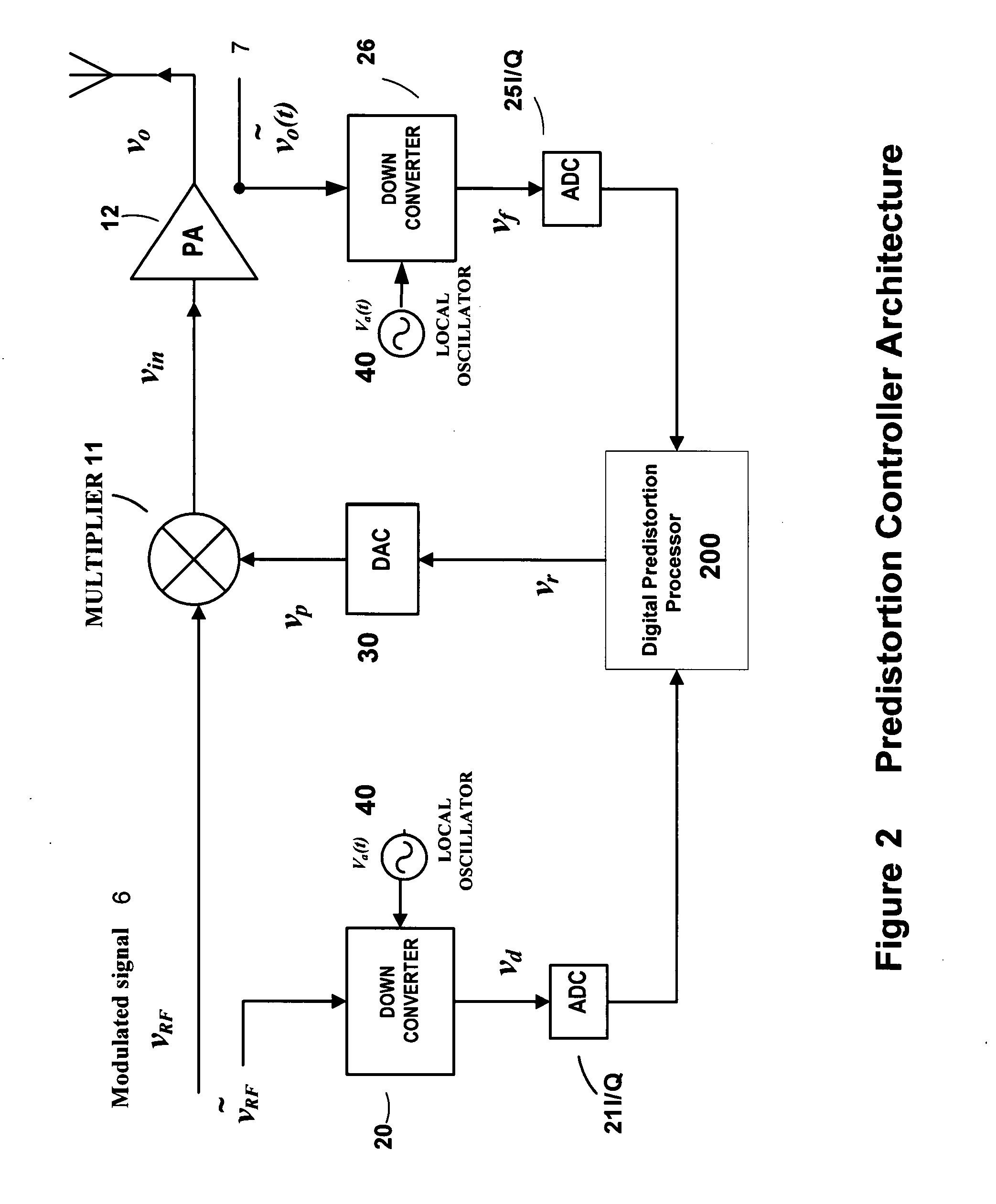
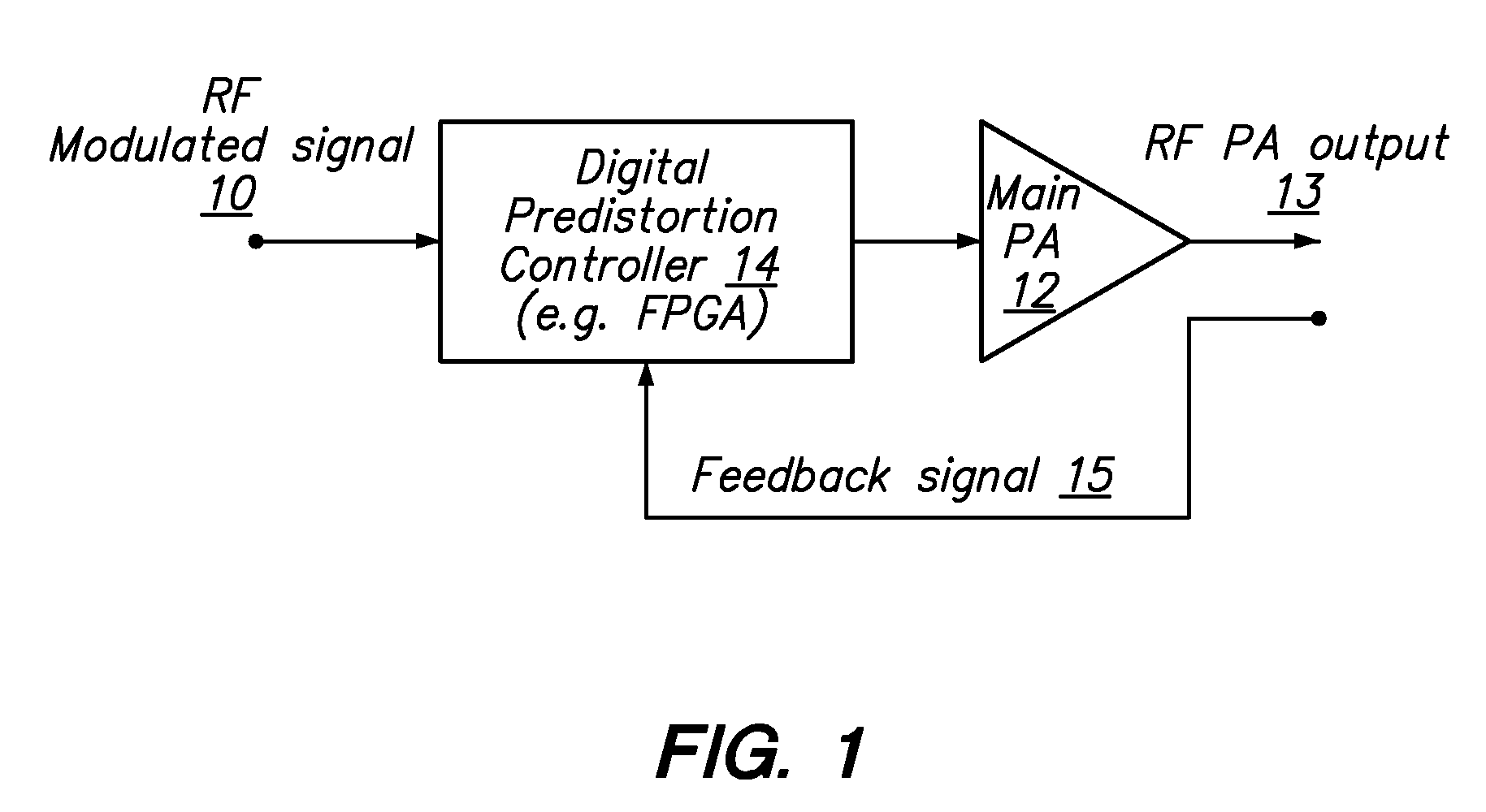
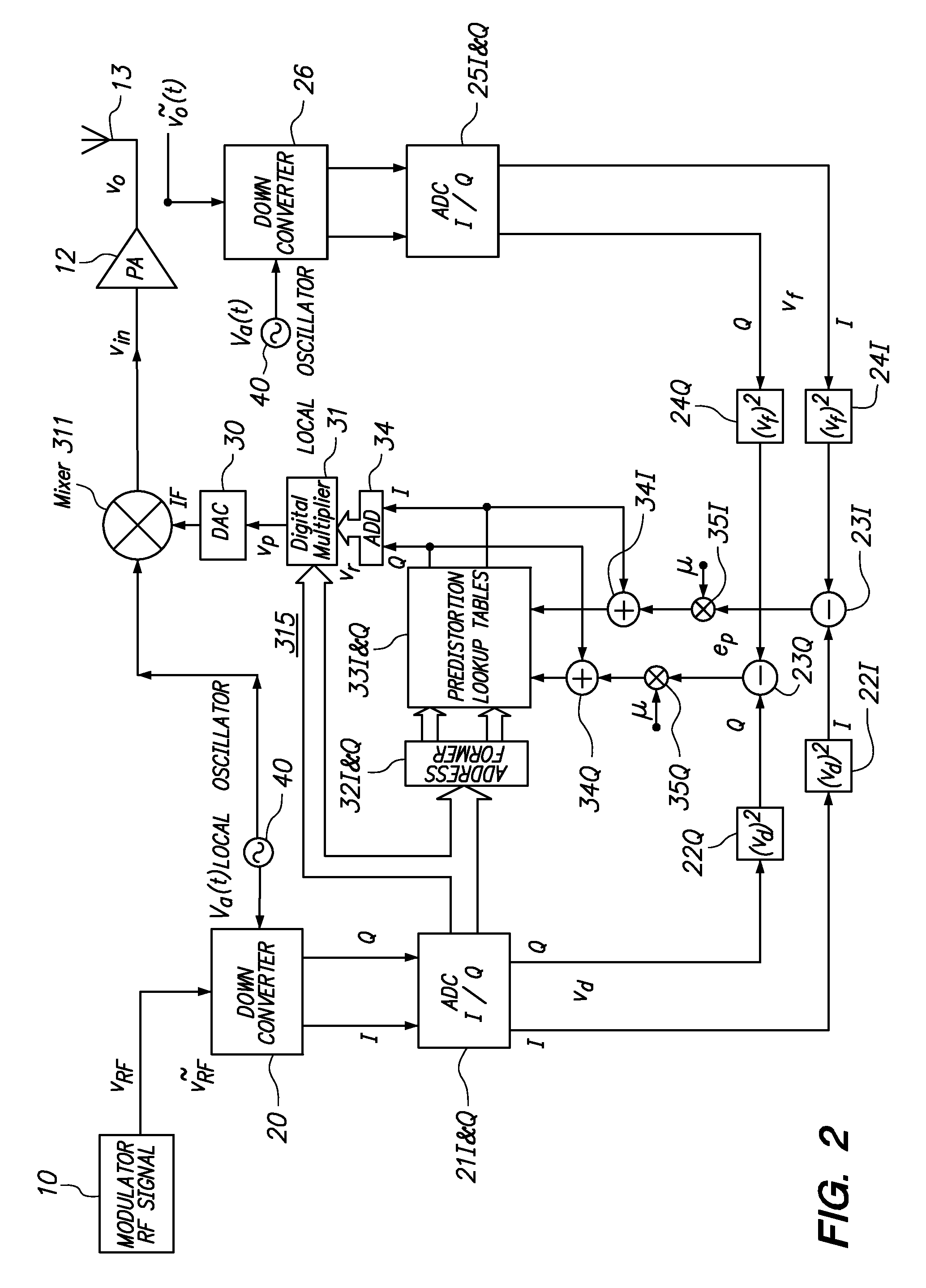
An embodiment of the invention uses a predistortion correction signal to combination the modulated RF signal by an analog multiplier for linearization of power amplifiers having nonlinear characteristics such as those used in wireless RF transmitters. A predistortion controller comprises a plurality of down converters for retrieving both the ideal non-distorted information and the feedback distorted information, together with pre-stored digitally-indexed predistortion information stored, for example, in a look-up table. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the high power amplifier, and is stored prior to processing of pre-compensation in the power amplifier. When the predistortion information is combined with the modulated RF signal in the analog multiplier, the result is a substantially linear information transmission from the power amplifier. In an embodiment of the system, the modulated RF input signal and the feedback signal from PA output are down-converted, respectively, by analog devices, such as mixers, after which the analog intermediate frequency (IF) signals are digitized by analog-to-digital converters for digital predistortion correction processing, followed by predistortion processing performed by, for example, a DSP or FPGA chip to generate a digital correction control signal, which is then converted to an analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter, followed by combining the analog correction signal with the RF modulated input signal to yield the input to the power amplifier.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Cubic spline predistortion, algorithm and training, for a wireless LAN system
InactiveUS6882217B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric devicesAudio power amplifierHiperLAN
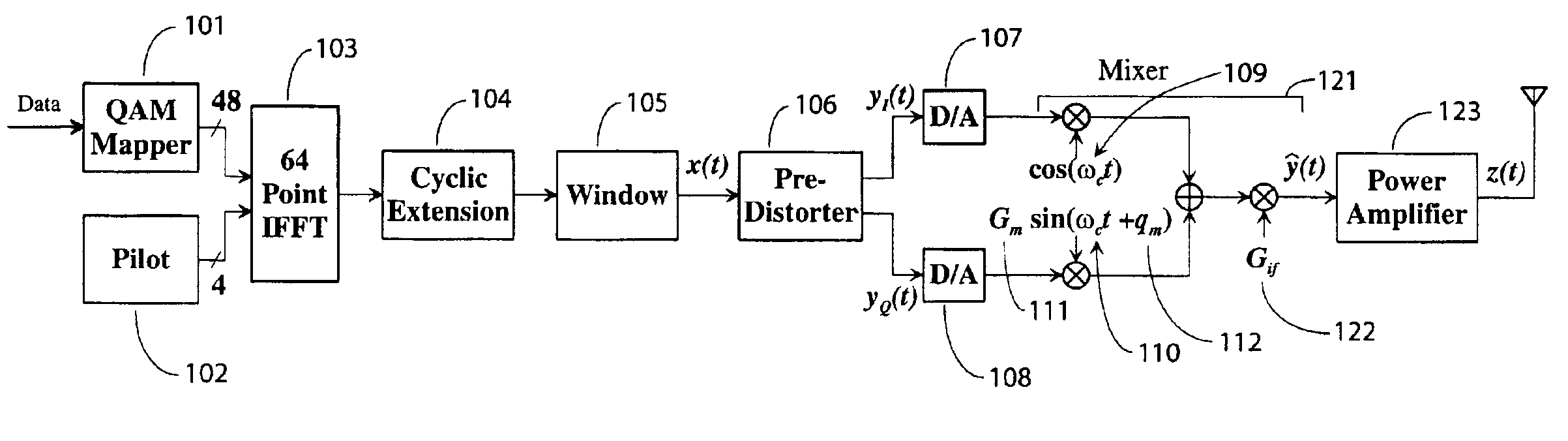
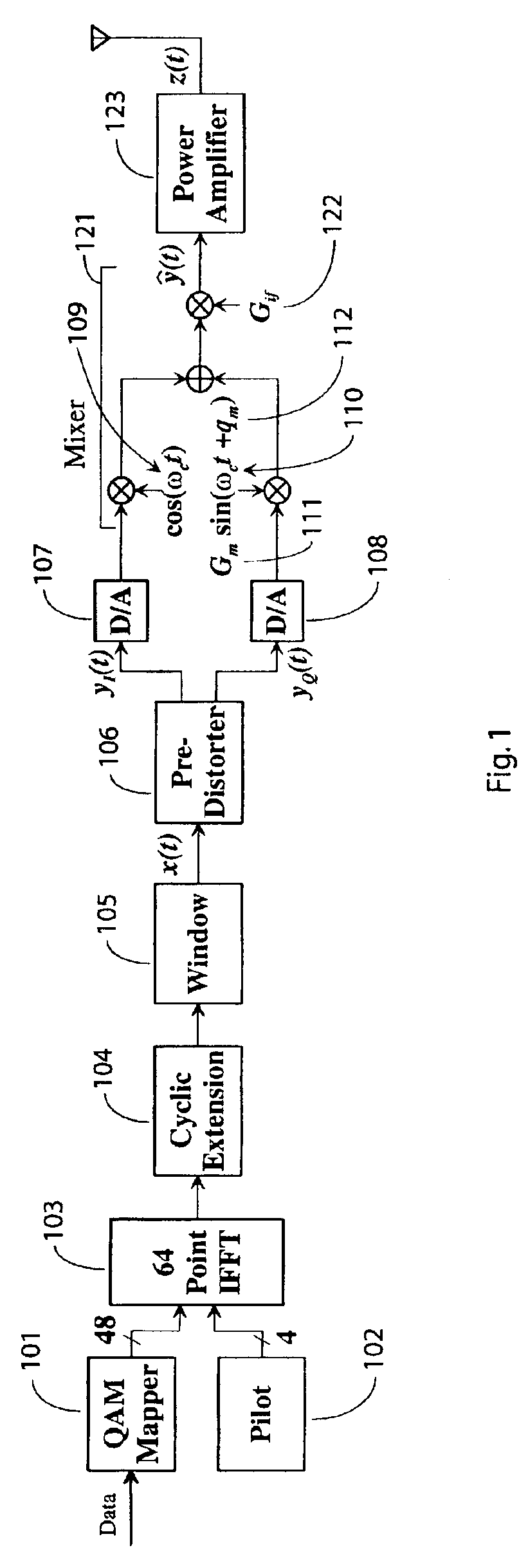
The present invention includes methods and devices to apply predistortion to correct nonlinearities of a power amplifier in an OFDM symbol transmission system. More particularly, predistortion is patterned to take into account clipping of symbols and to match an effective input range of the predistorter with an average power output of the power amplifier. This invention may be applied to a variety of standards utilizing OFDM technology, including IEEE 802.11a, Hiperlan / 2 and MMAC.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
System and method for digital memorized predistortion for wireless communication
ActiveUS6985704B2Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierWireless transmission
An embodiment of the invention is a system for signal processing in preparation for wireless transmission, the wireless transmission being from a portable wireless communication device and including use of a power amplifier having nonlinear characteristics. The system includes memory for storing digitally-indexed information. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the digitally-indexed information is stored prior to processing of a first signal that reflects information to be communicated. The system further includes first logic, configured to accept the first signal and to retrieve, based on the first signal, a portion of the digitally-indexed information stored in the memory, and second logic, configured to generate a second signal based on the portion of the digitally-accessed information and on the first signal. The second signal pre-compensates for the nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the second signal is for wireless transmission based on the second signal.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Transmitter predistortion circuit and method therefor
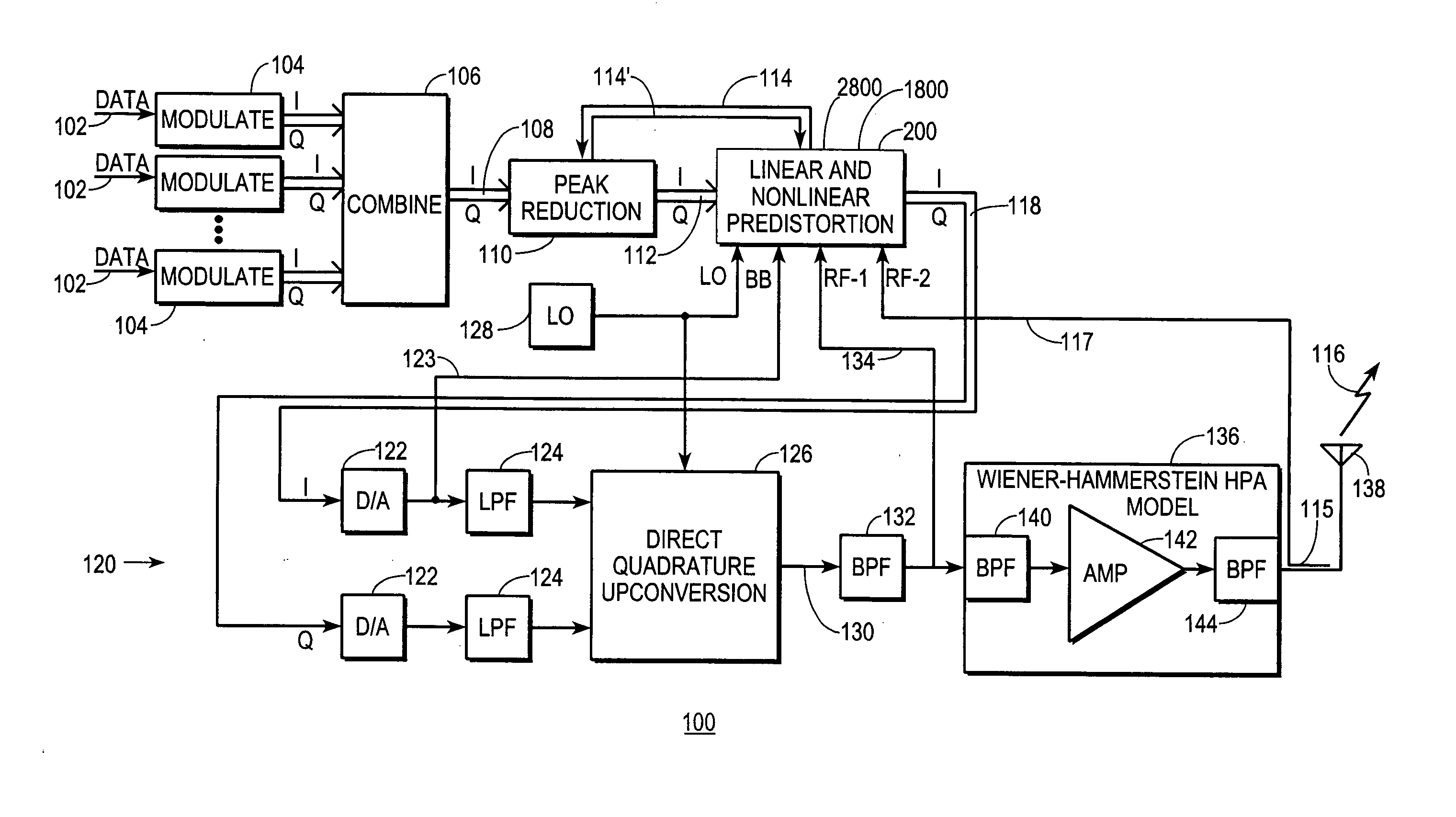
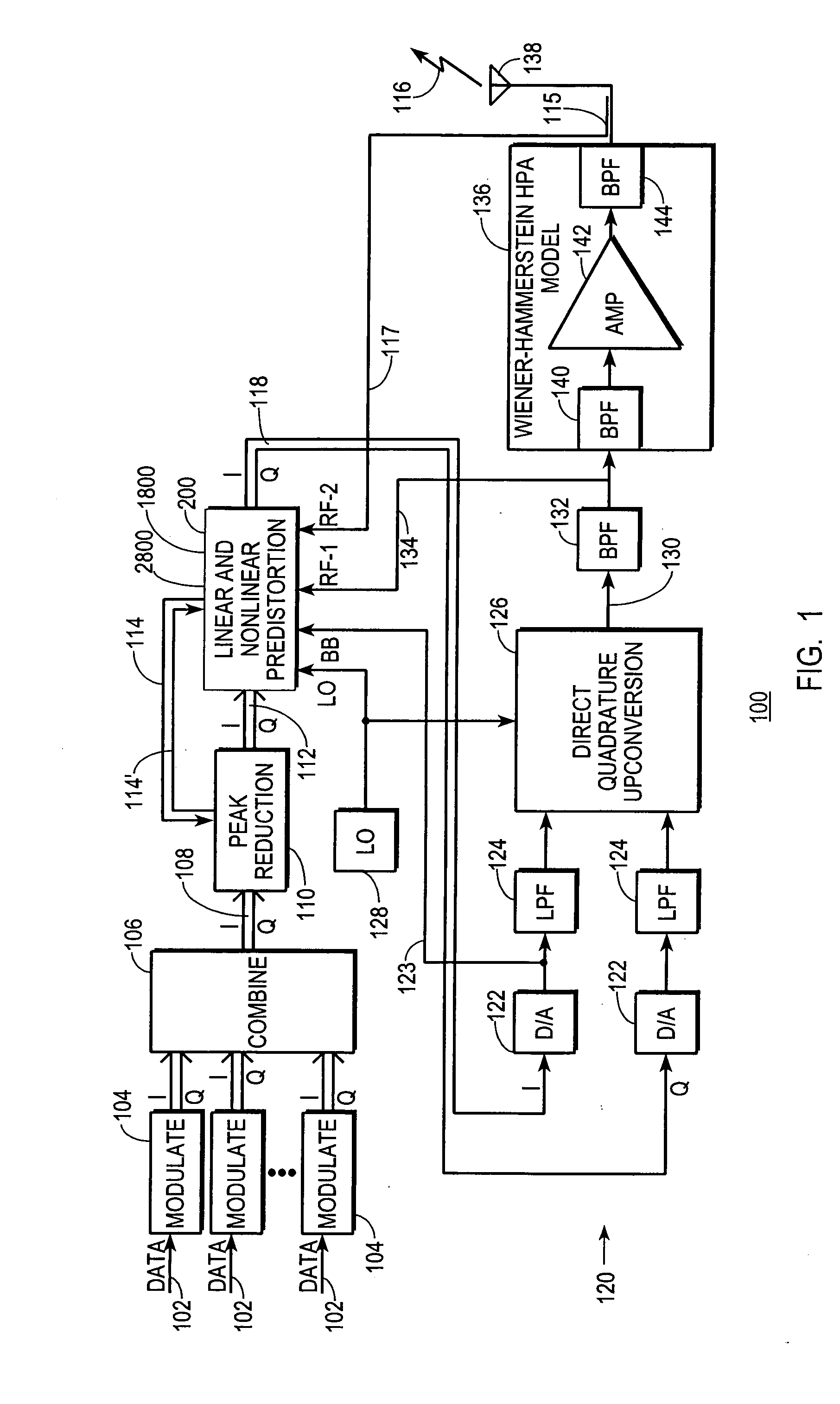
InactiveUS7469491B2Compensation DistortionMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionData stream
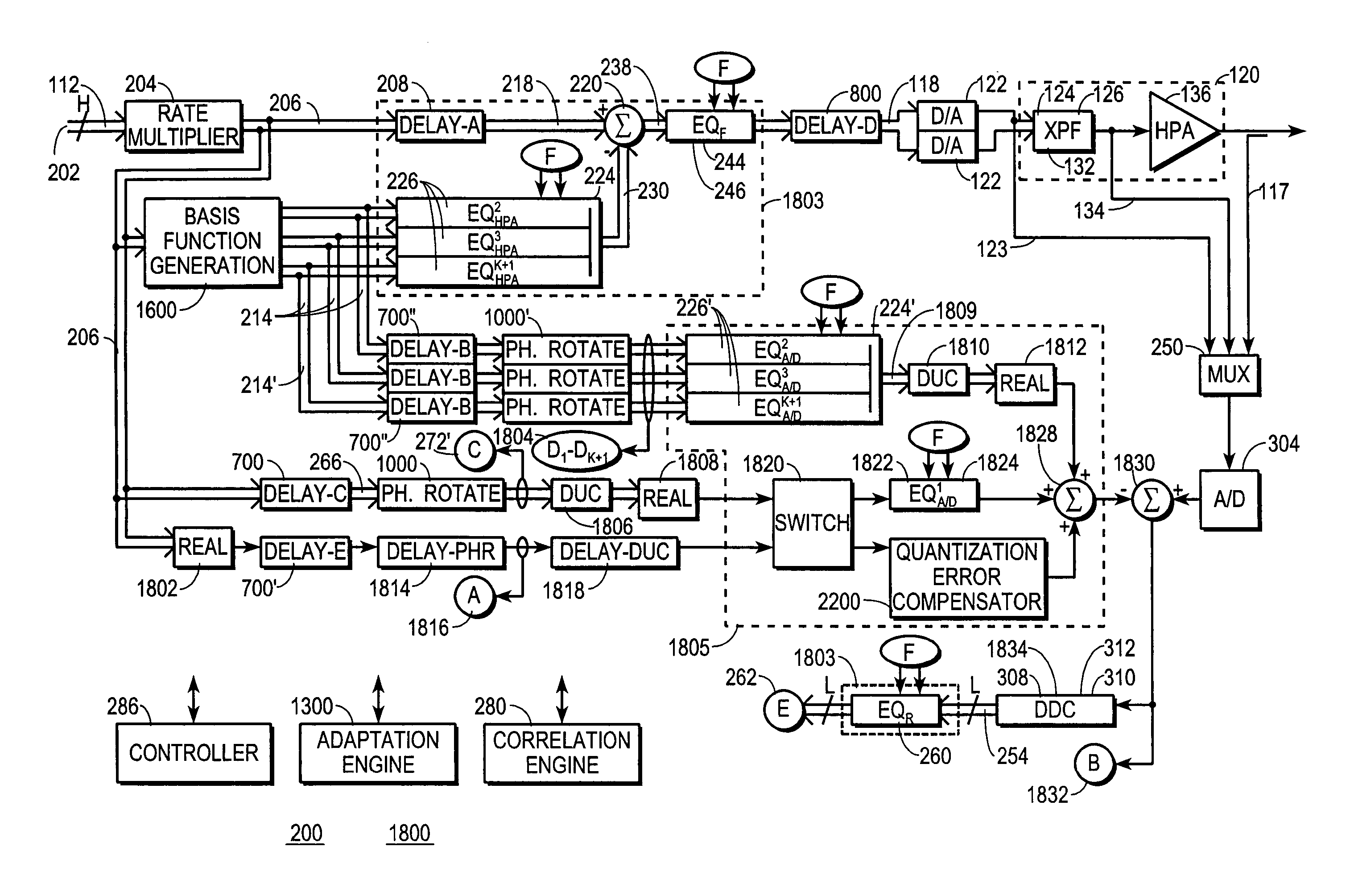
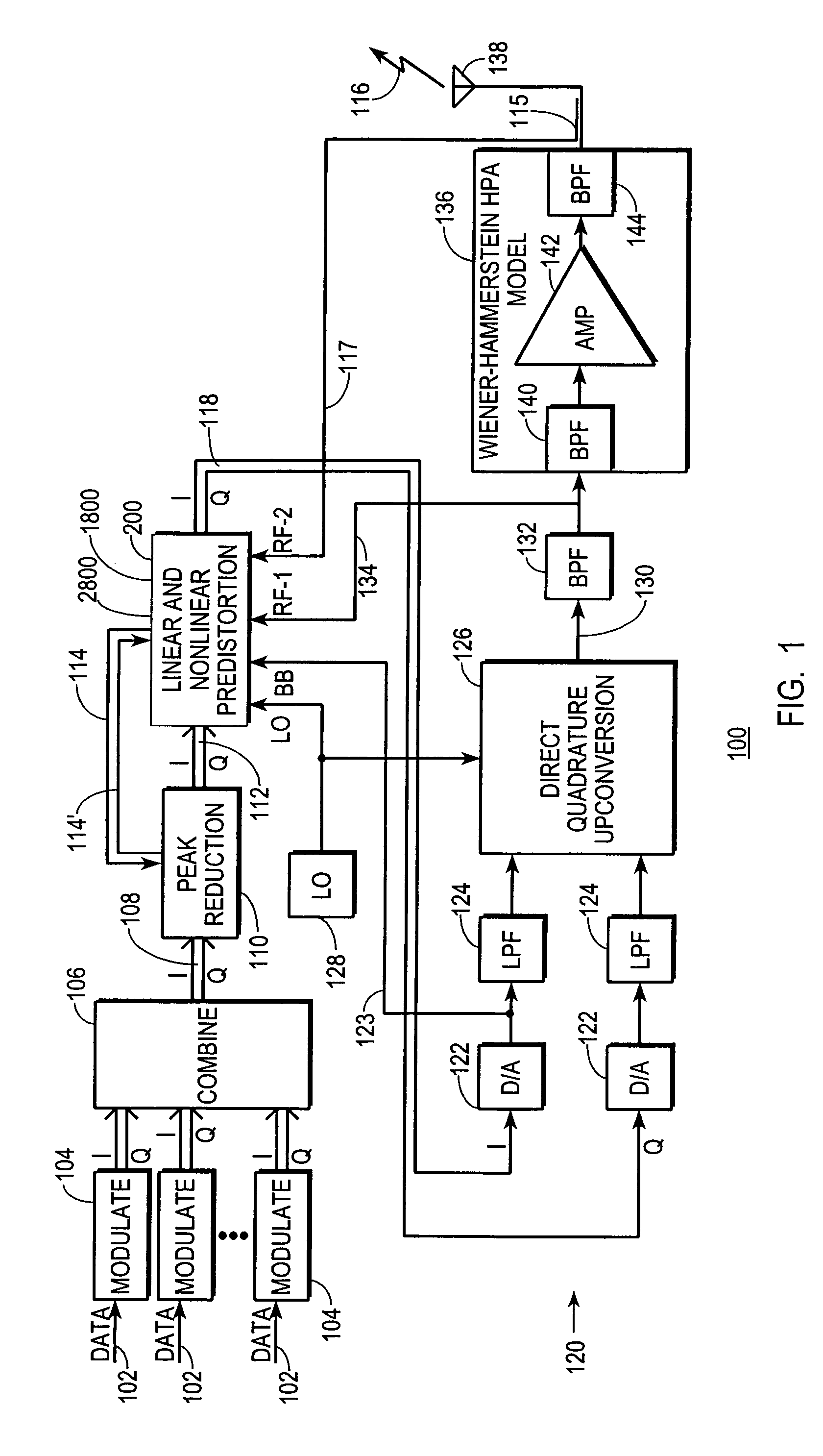
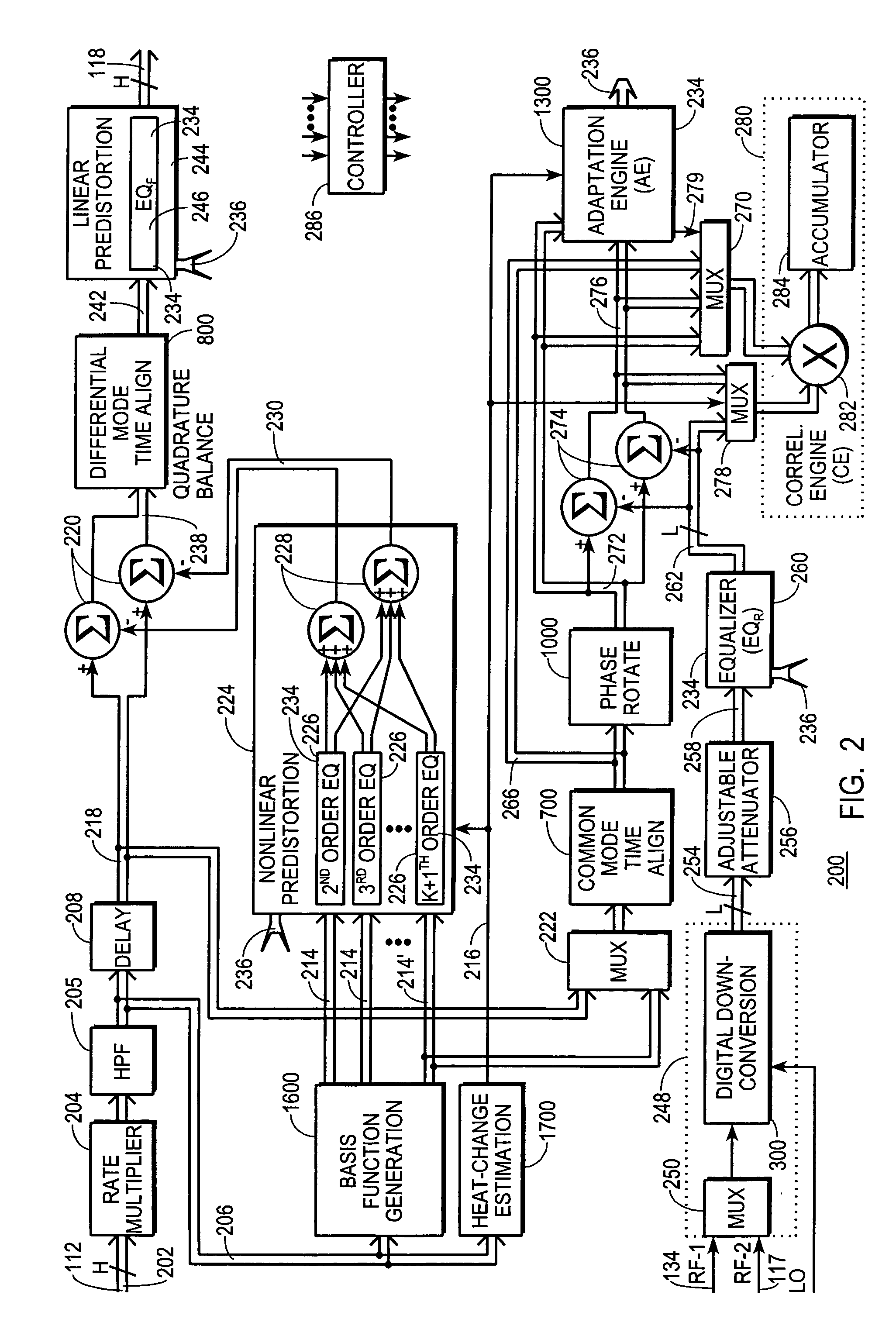
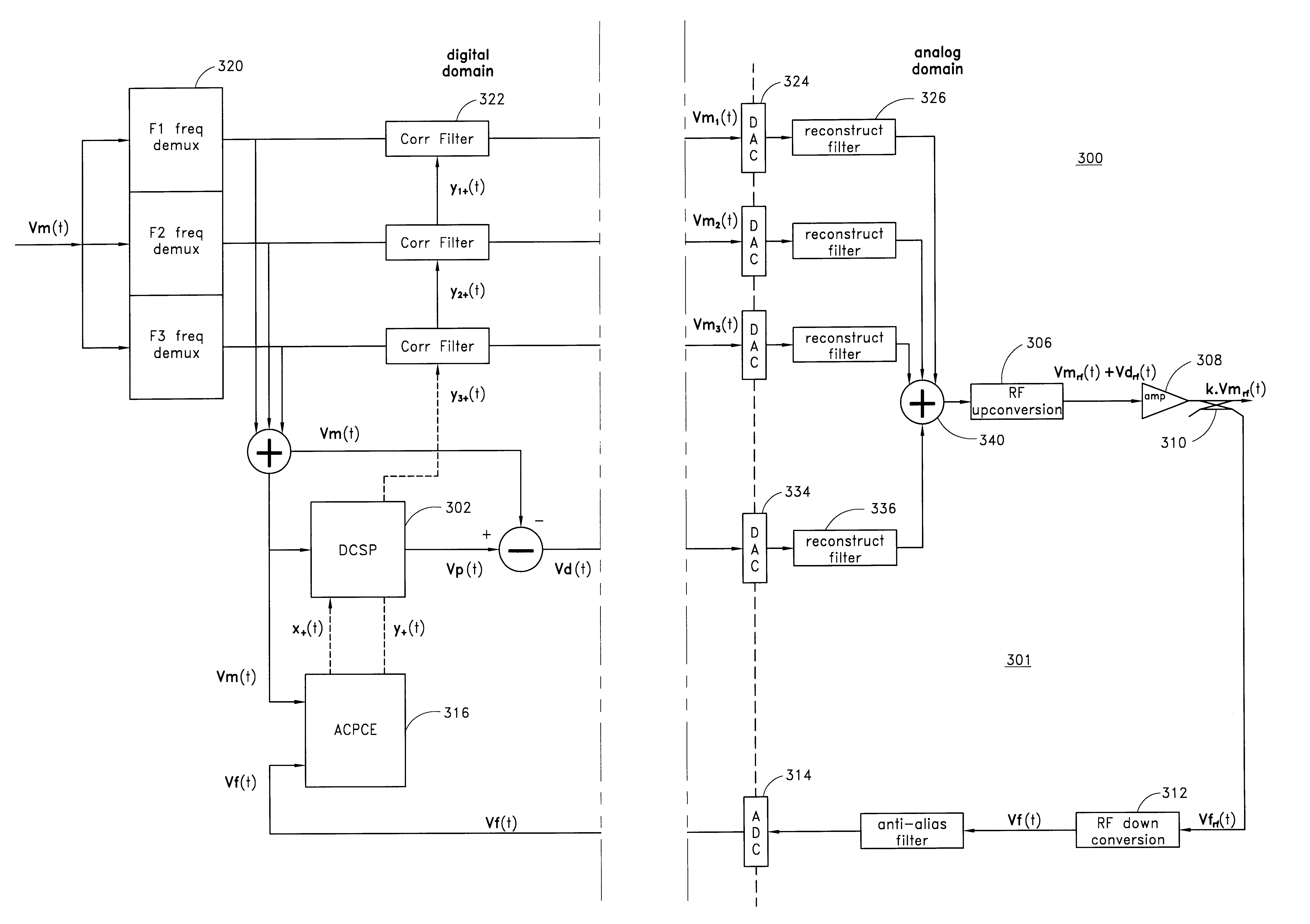
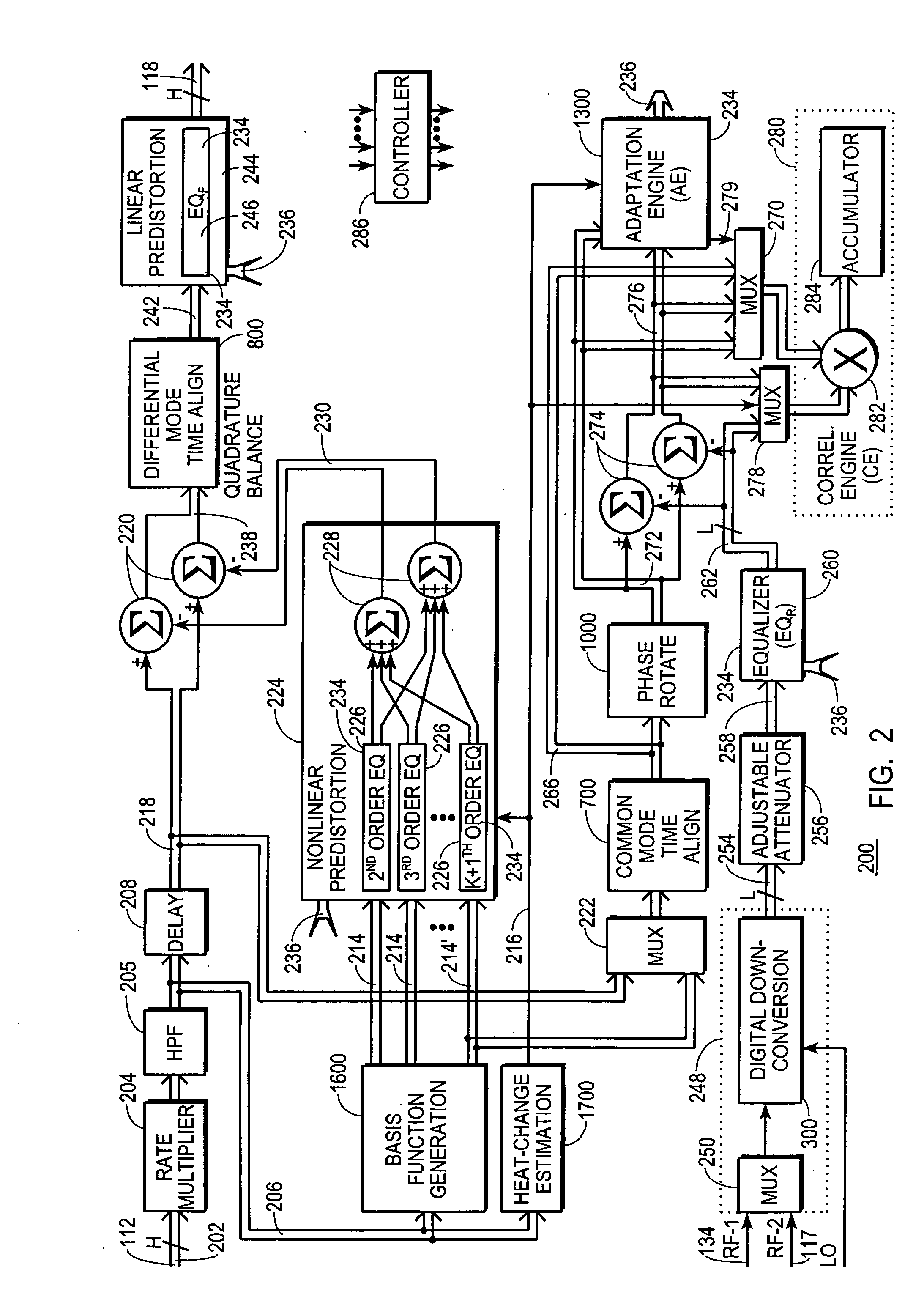
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200, 1800, 2800) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Distortion introduced by an analog-to-digital converter (304) may be compensated using a variety of adaptive techniques. Linear distortion is compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Low noise wideband digital predistortion amplifier
InactiveUS6570444B2Low bandwidthReduce total powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsLow noiseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
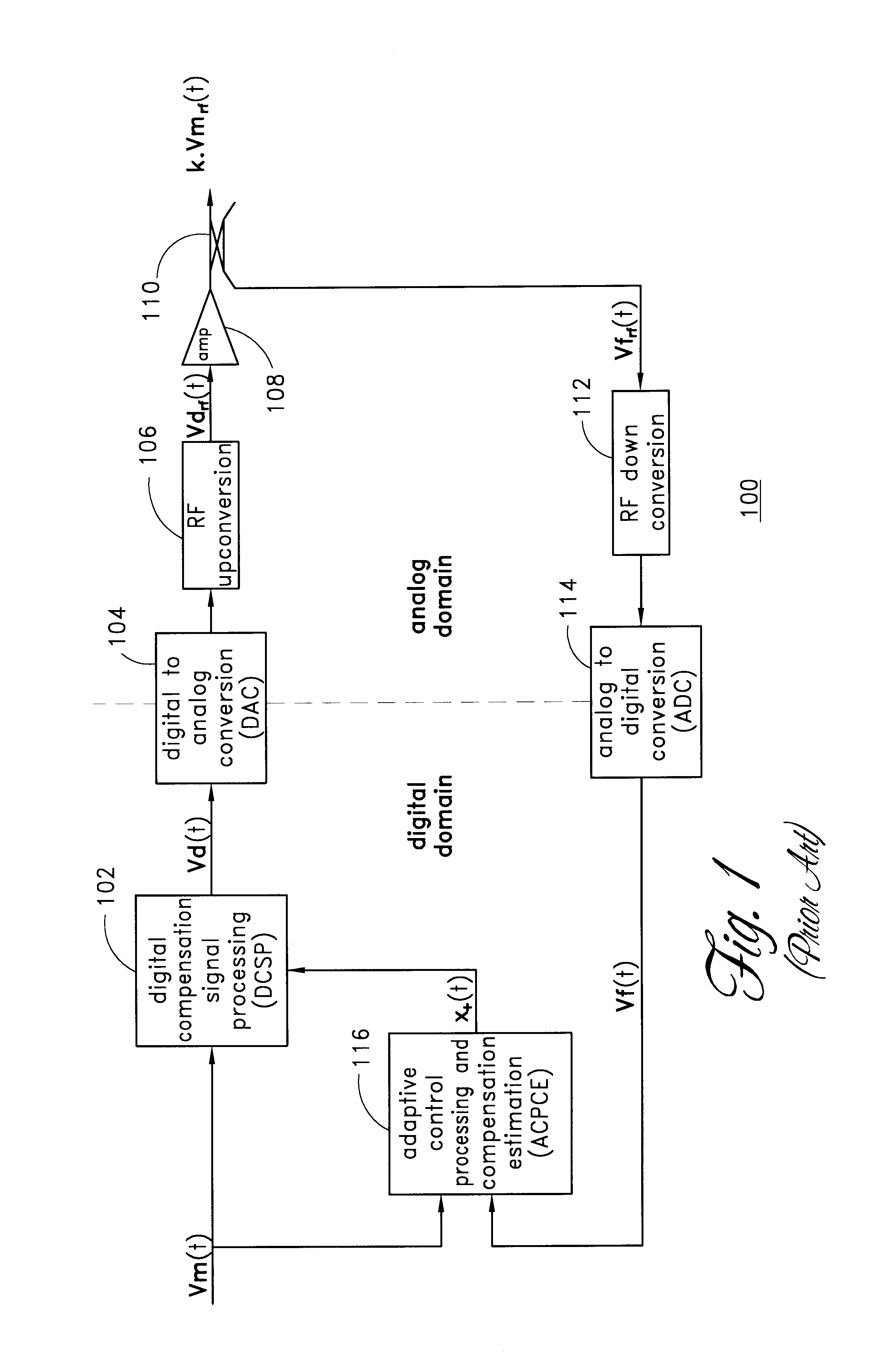
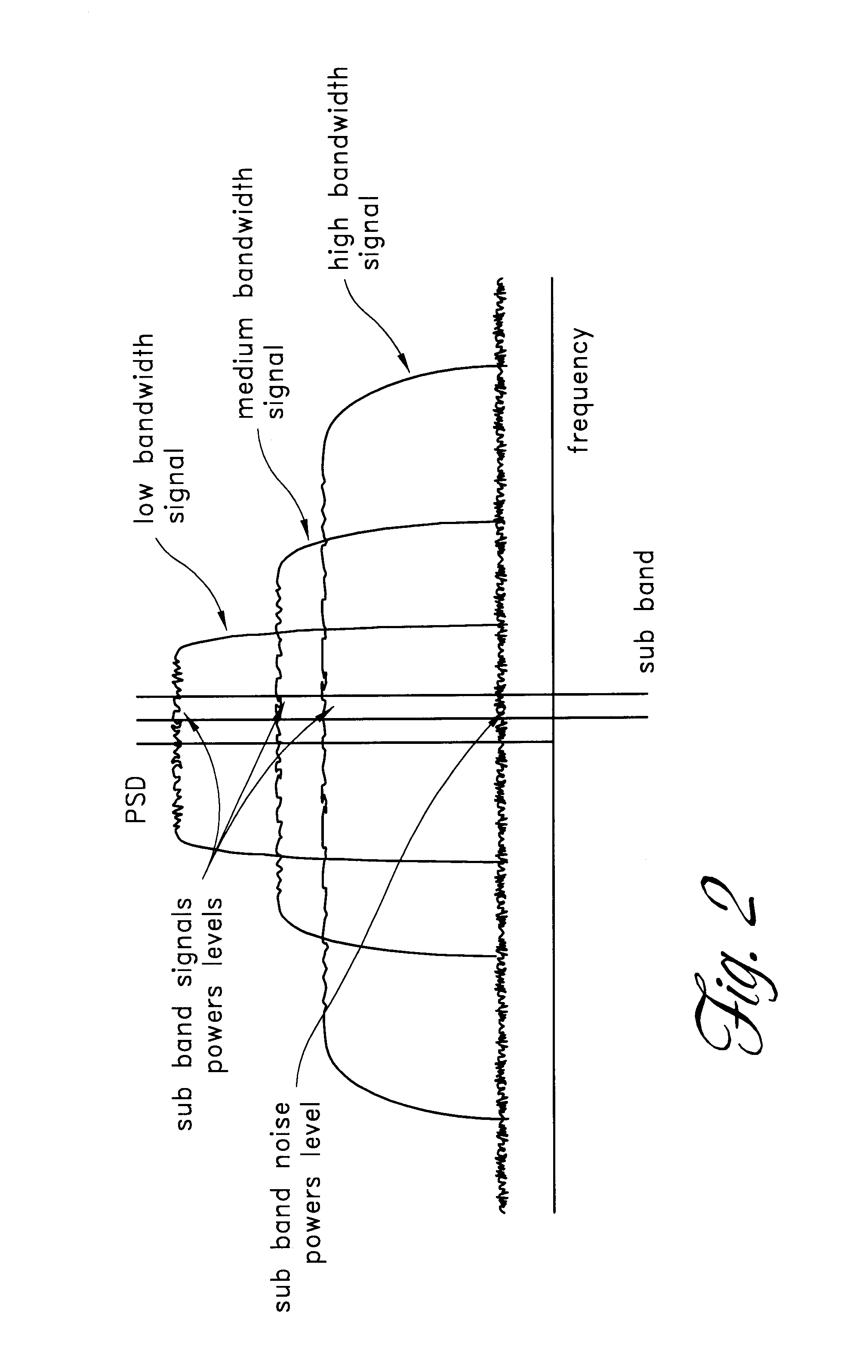
A digital predistortion amplifier design compensates for non-linear amplification of an input signal using predistortion techniques. The design provides a reduced noise floor by using separate digital to analog converters (DAC) to separately convert the input signal and an error correction signal. Furthermore, the input signal can be separated into two or more subbands of narrower bandwidth. Each of the subbands are converted to analog using a separate DAC. By reducing the power and / or bandwidth to be handled by any one DAC, the available levels of quantization of the DAC are applied to a lower power signal and therefore the signal to noise ratio resulting from the conversion process is improved. In addition, each digital subband is passed through a correction filter, which is driven by an adaptive control processing and compensation estimator to compensate for relative gain, phase, and delay inconsistencies between the different subbands.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
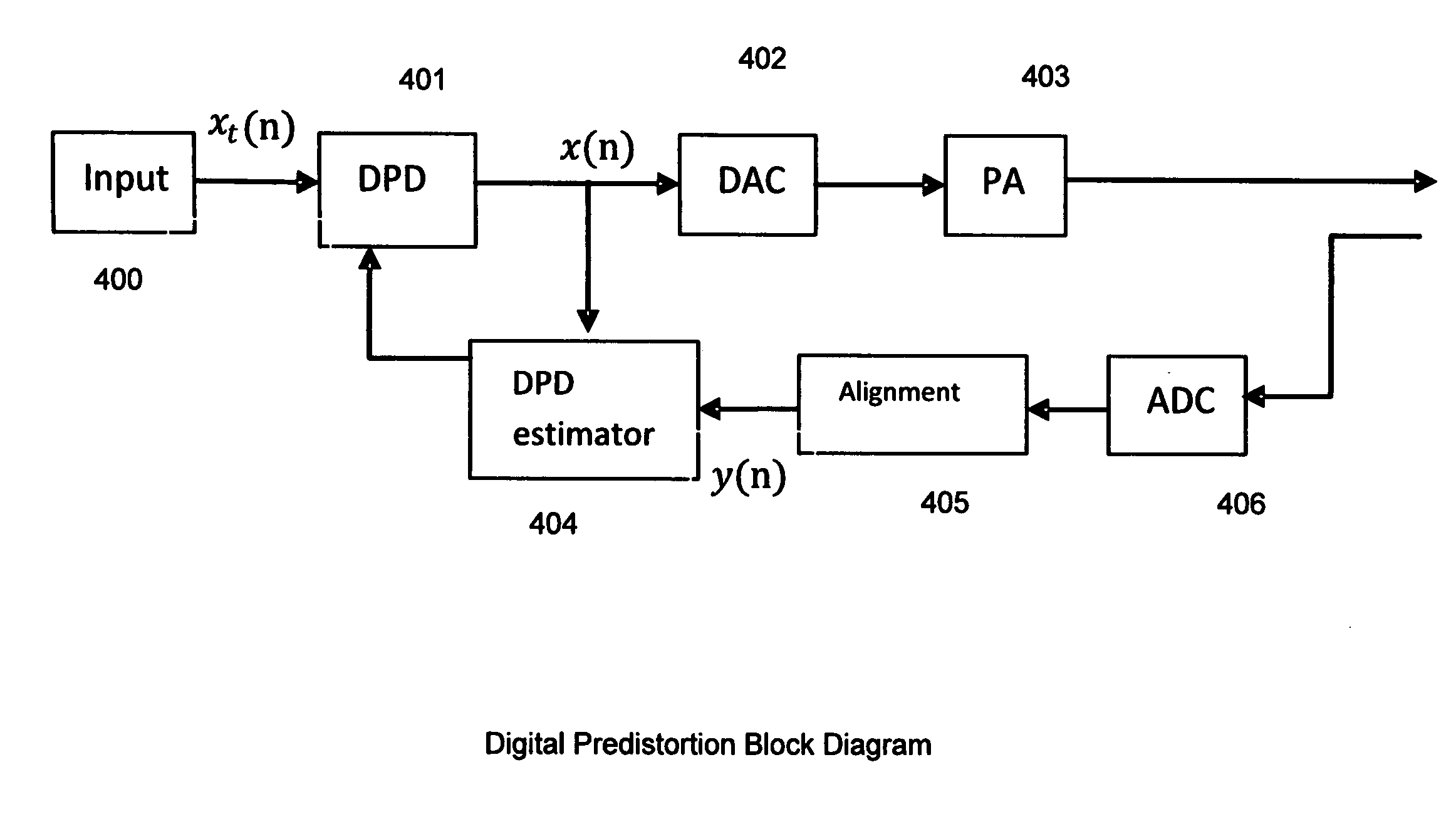
Digital predistortion system and method for high efficiency transmitters
ActiveUS20050195919A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationNon linear dynamicEngineering
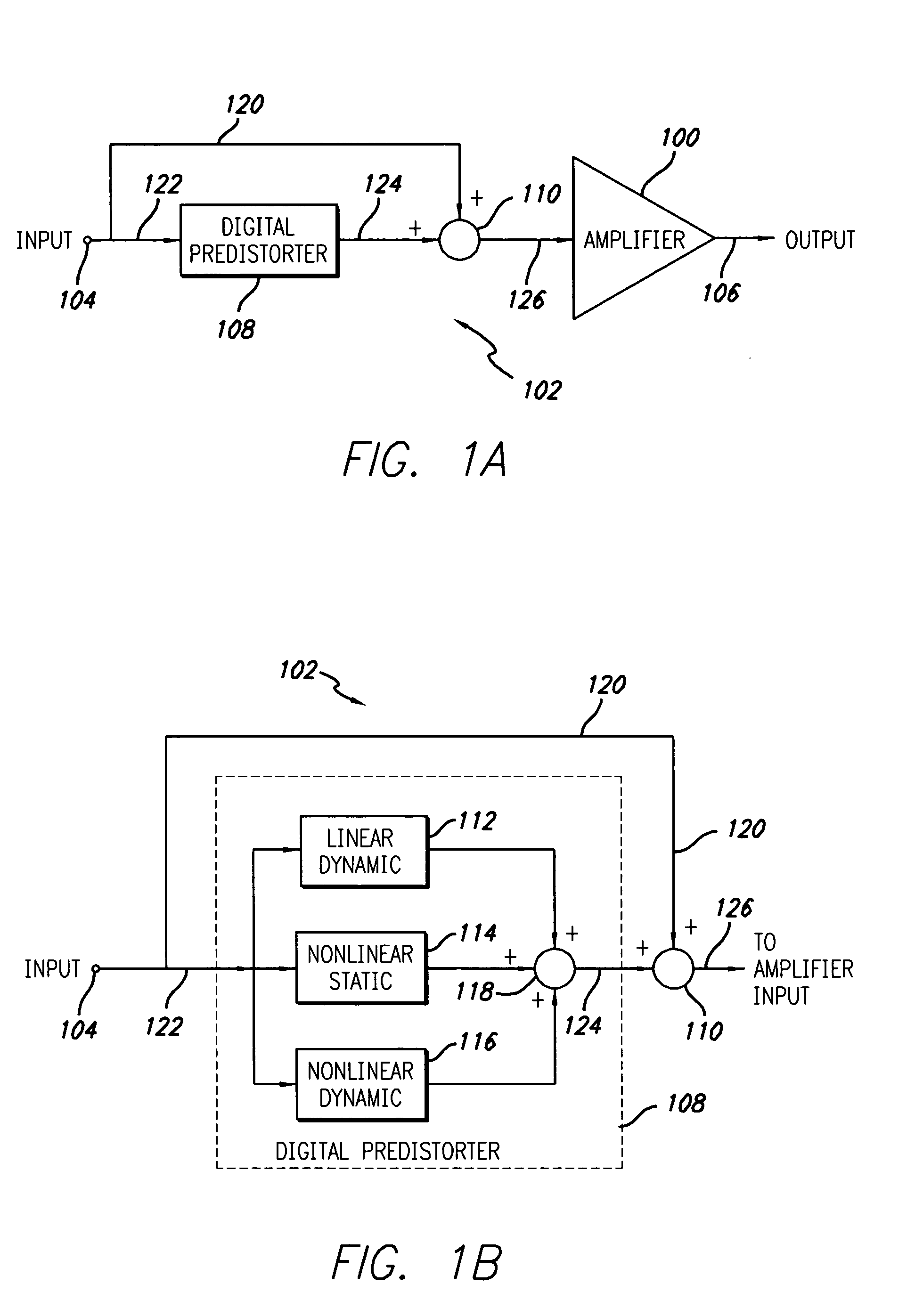
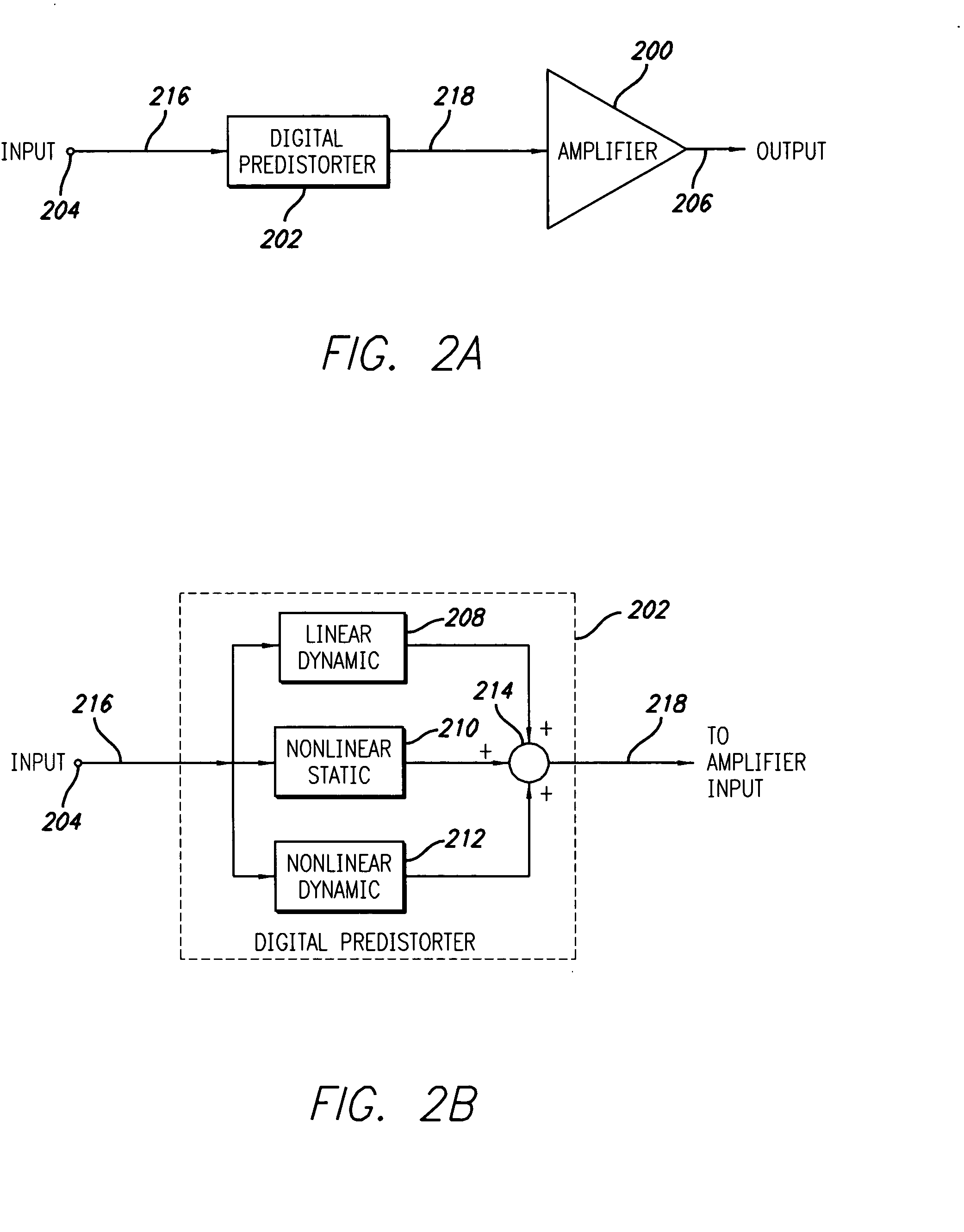
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for higher order reactive and thermal memory effects is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter in an IIR filter bank. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Method and apparatus for preparing signals to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier
InactiveUS20030156658A1Improve electricity efficiencyImprove performance efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierUnit of time
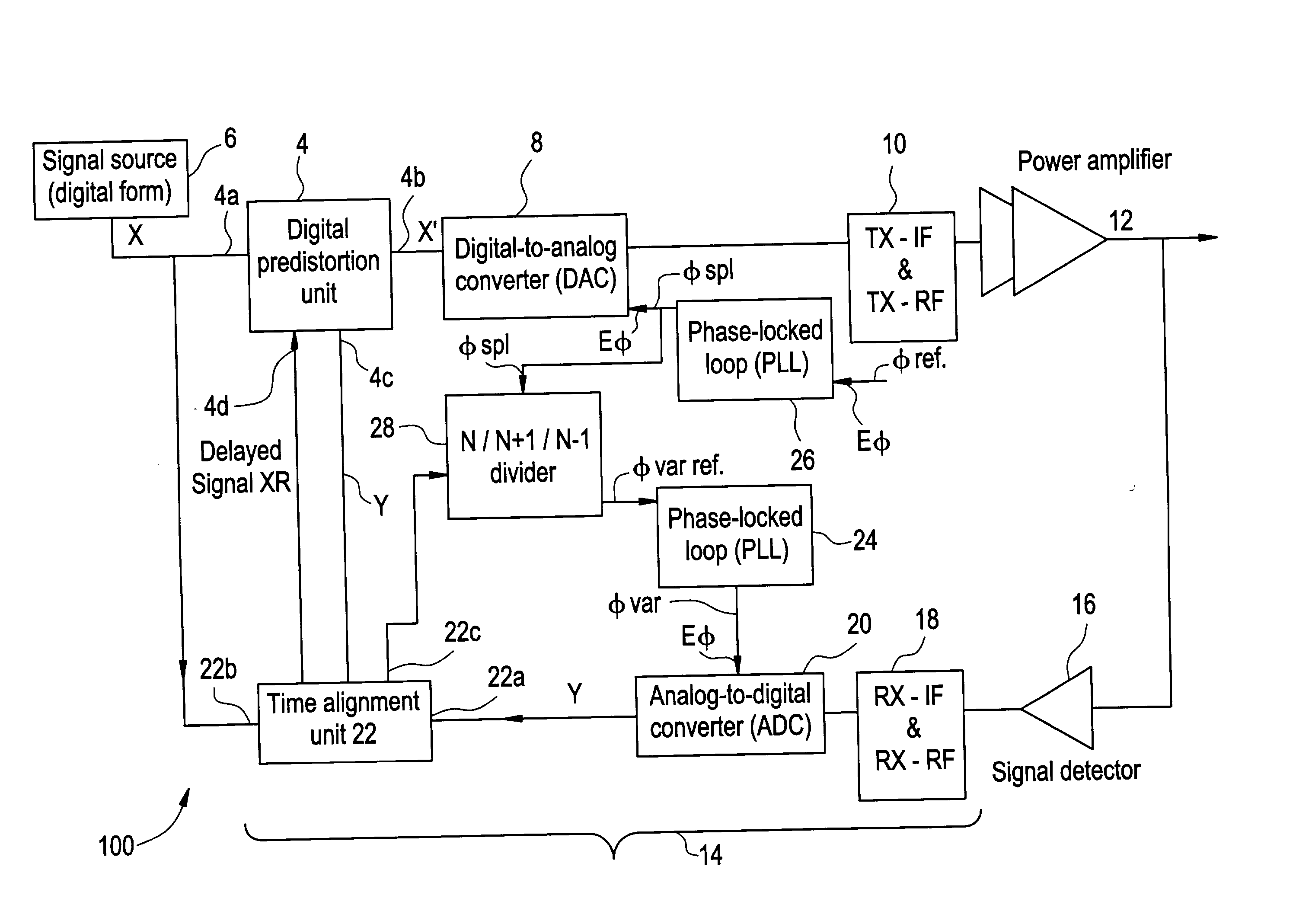
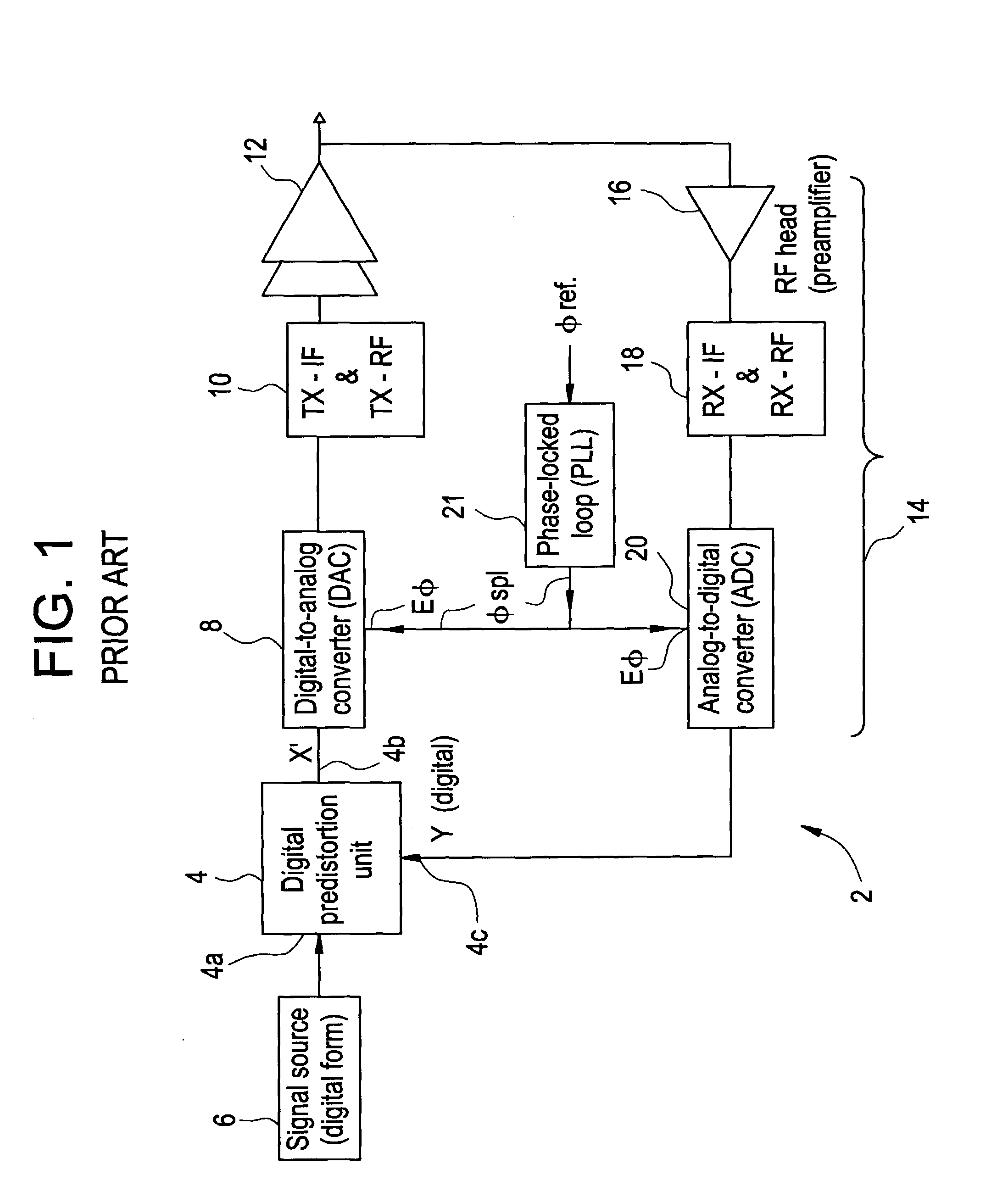
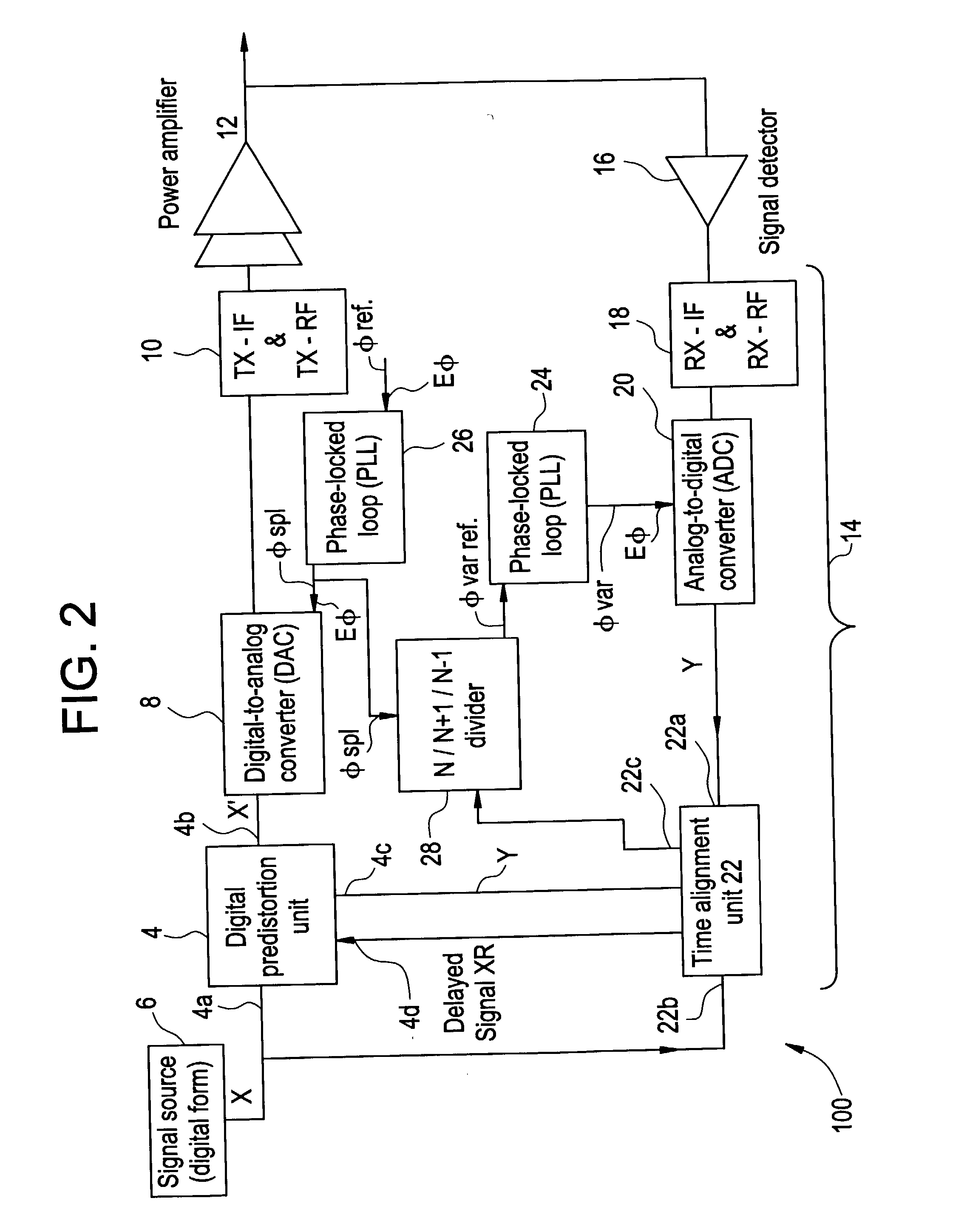
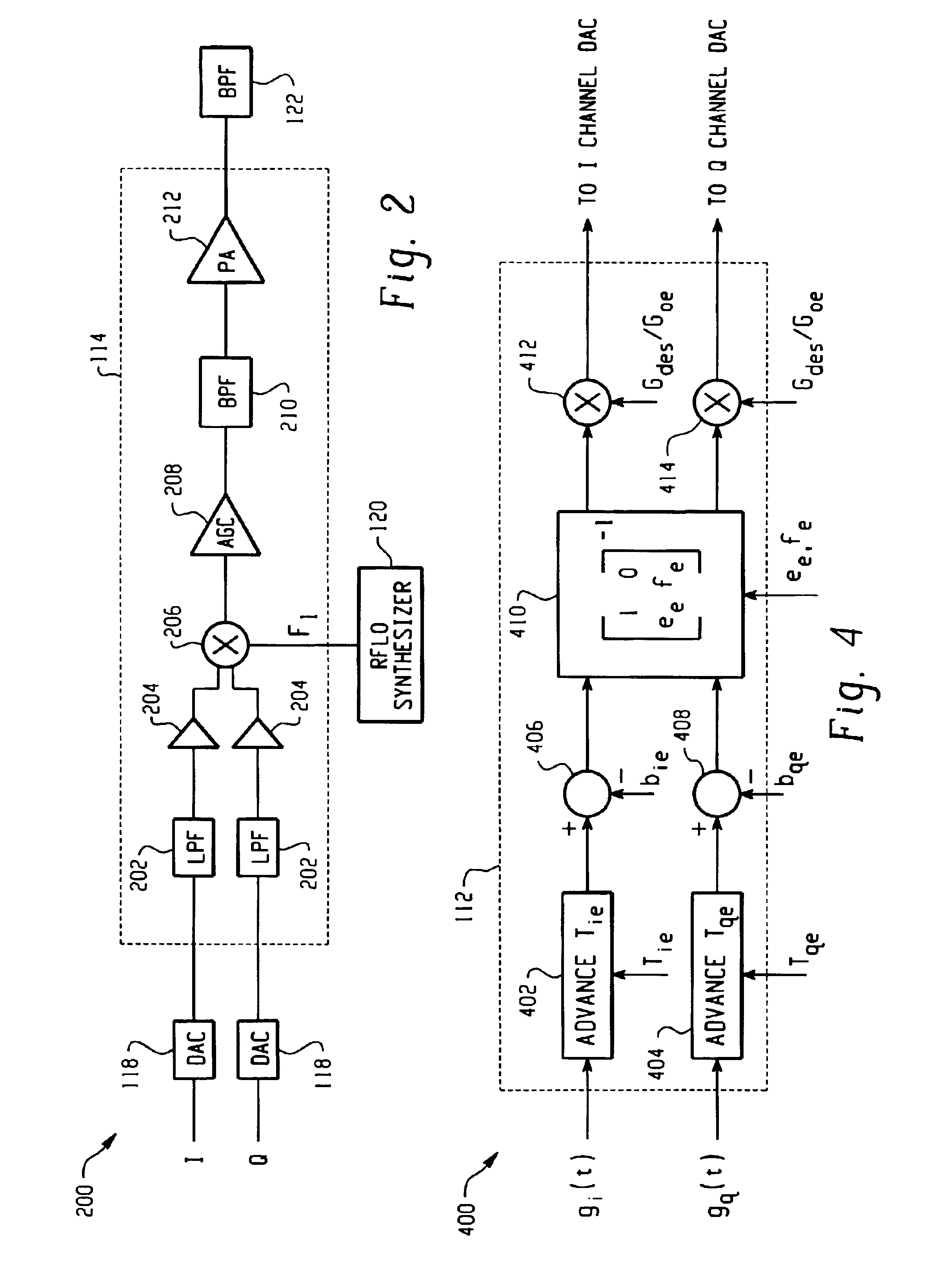
The invention relates to a method of preparing signals (X and Y) to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier (12), the signals comprising a signal (X) before amplification and a signal (Y) after amplification by said amplifier. Preparation includes time aligning (22) the signal before amplification (X) with the signal after amplification (Y) before using them to establish said predistortion. The invention preferably operates in two stages, namely a stage of coarse time alignment, in which the signal before amplification (X) is subjected to a time delay comprising an integer number of first time units, and a stage of fine time alignment, in which a delay or advance value of a fraction of the first time unit is determined.
Owner:EVOLIUM
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
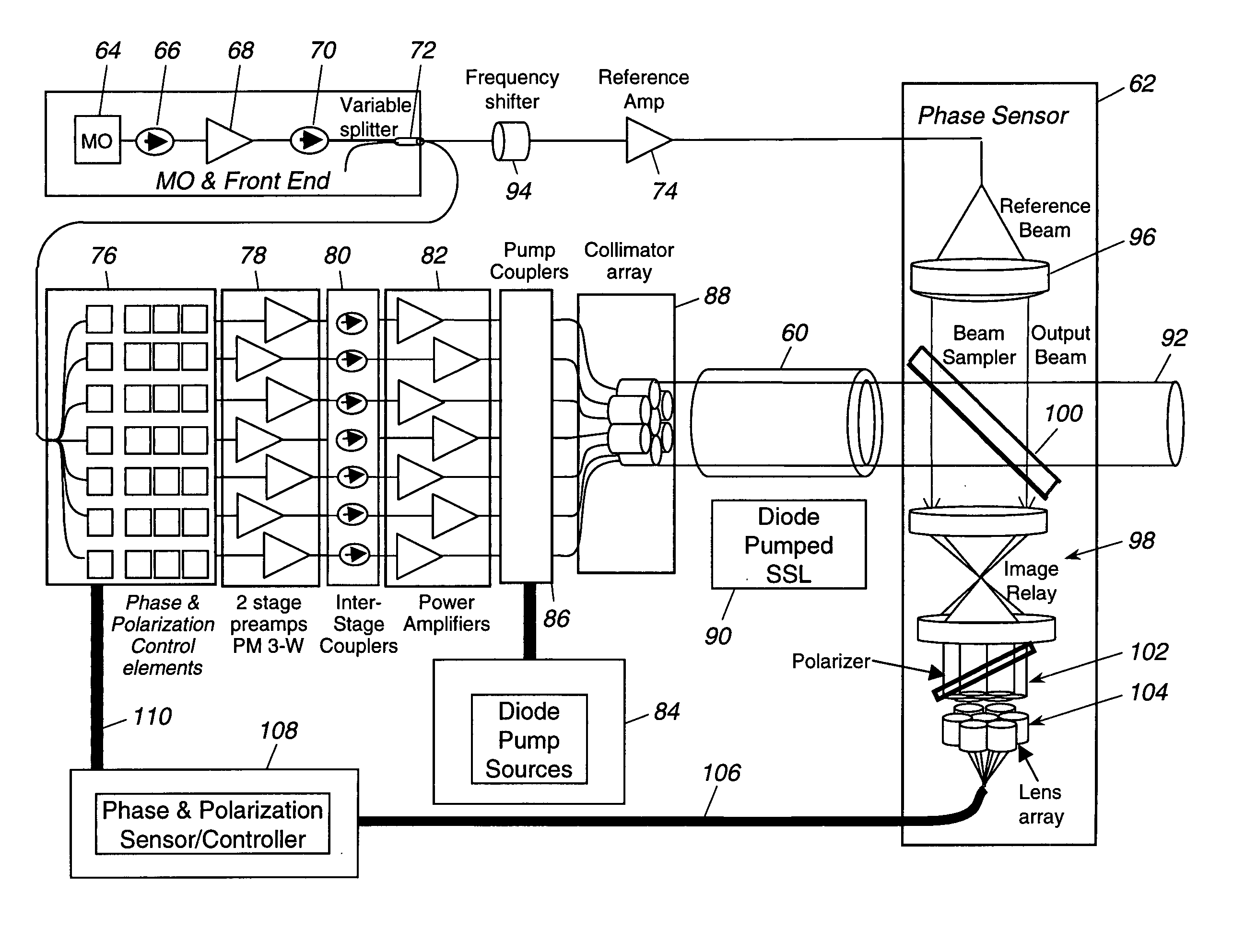
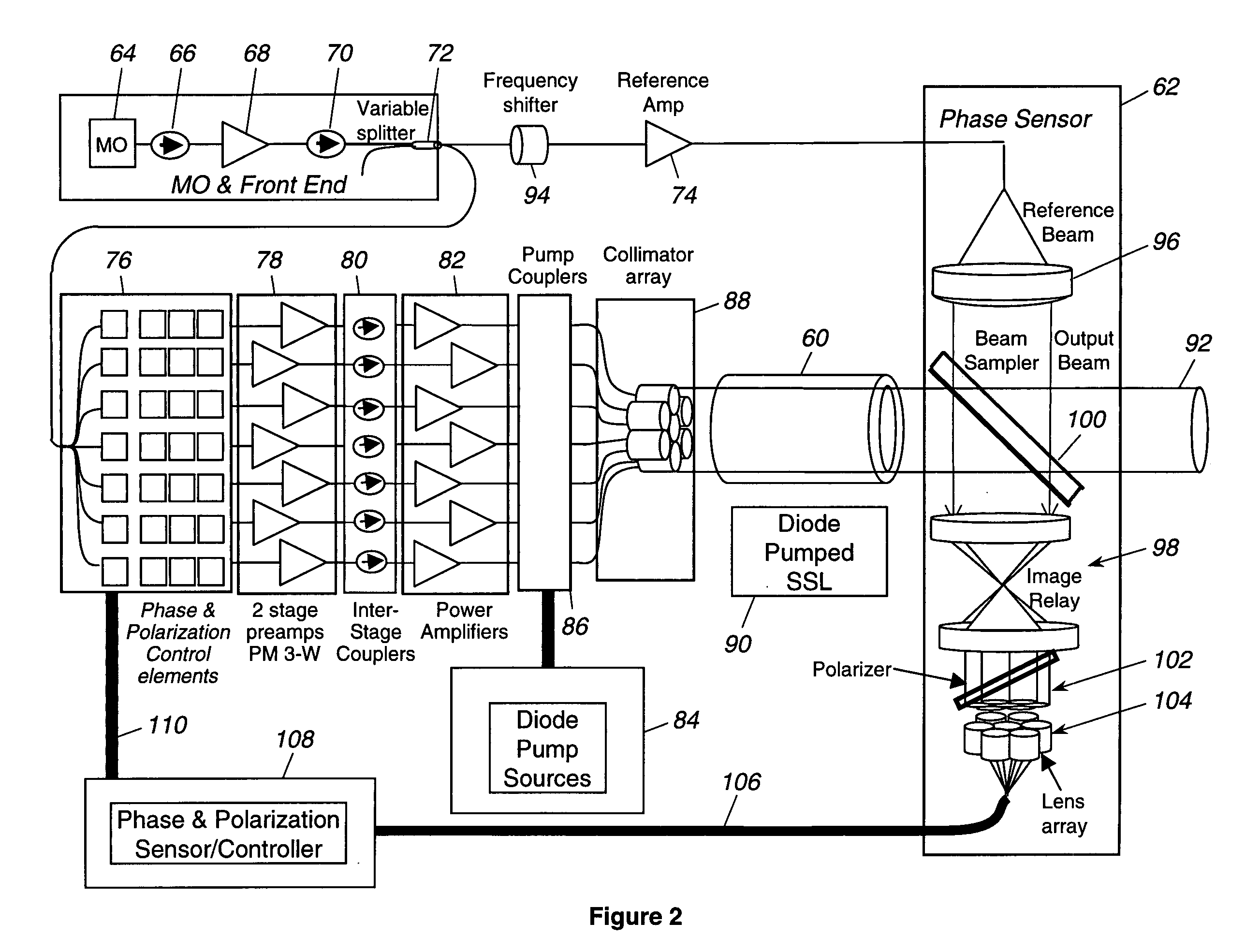
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Digital Hybrid Mode Power Amplifier System
InactiveUS20080265996A1High performance and cost-effectiveImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersPeak valueMulti carrier
A RF-digital hybrid mode power amplifier system for achieving high efficiency and high linearity in wideband communication systems is disclosed. The present invention is based on the method of adaptive digital predistortion to linearize a power amplifier in the RF domain. The power amplifier characteristics such as variation of linearity and asymmetric distortion of the amplifier output signal are monitored by the narrowband feedback path and controlled by the adaptation algorithm in a digital module. Therefore, the present invention could compensate the nonlinearities as well as memory effects of the power amplifier systems and also improve performances, in terms of power added efficiency, adjacent channel leakage ratio and peak-to-average power ratio. The present disclosure enables a power amplifier system to be field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation agnostic), multi-carriers and multi-channels. As a result, the digital hybrid mode power amplifier system is particularly suitable for wireless transmission systems, such as base-stations, repeaters, and indoor signal coverage systems, where baseband I-Q signal information is not readily available.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Transmitter predistortion circuit and method therefor
InactiveUS20050163252A1Easy to optimizeCompensation DistortionMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionData stream
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200, 1800, 2800) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Distortion introduced by an analog-to-digital converter (304) may be compensated using a variety of adaptive techniques. Linear distortion is compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Wideband enhanced digital injection predistortion system and method
ActiveUS20050157814A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSecret communicationAudio power amplifierNon linear dynamic
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for thermal memory effects also is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter and is implemented parametrically using an autoregressive dynamics tracking mechanism. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
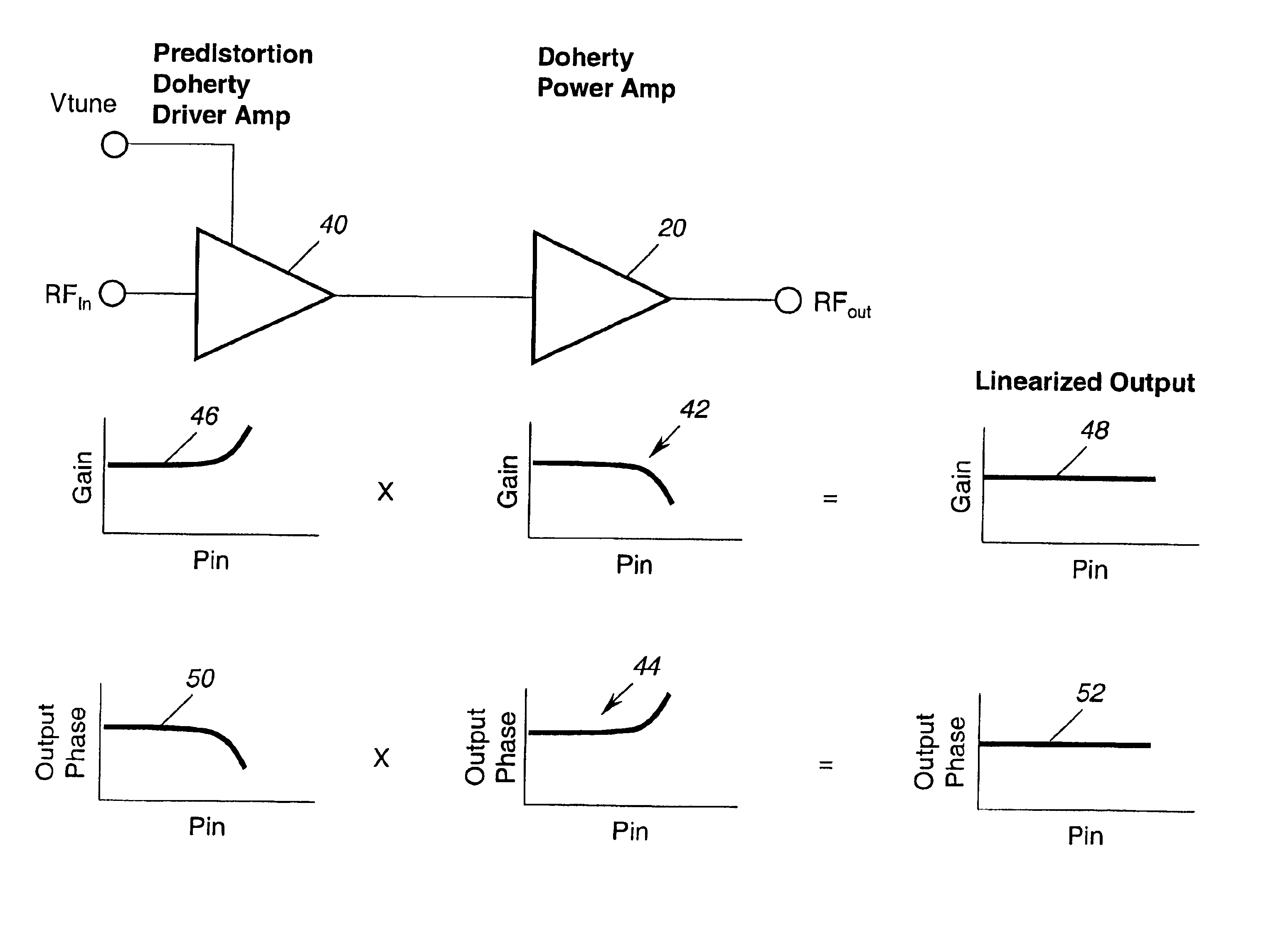
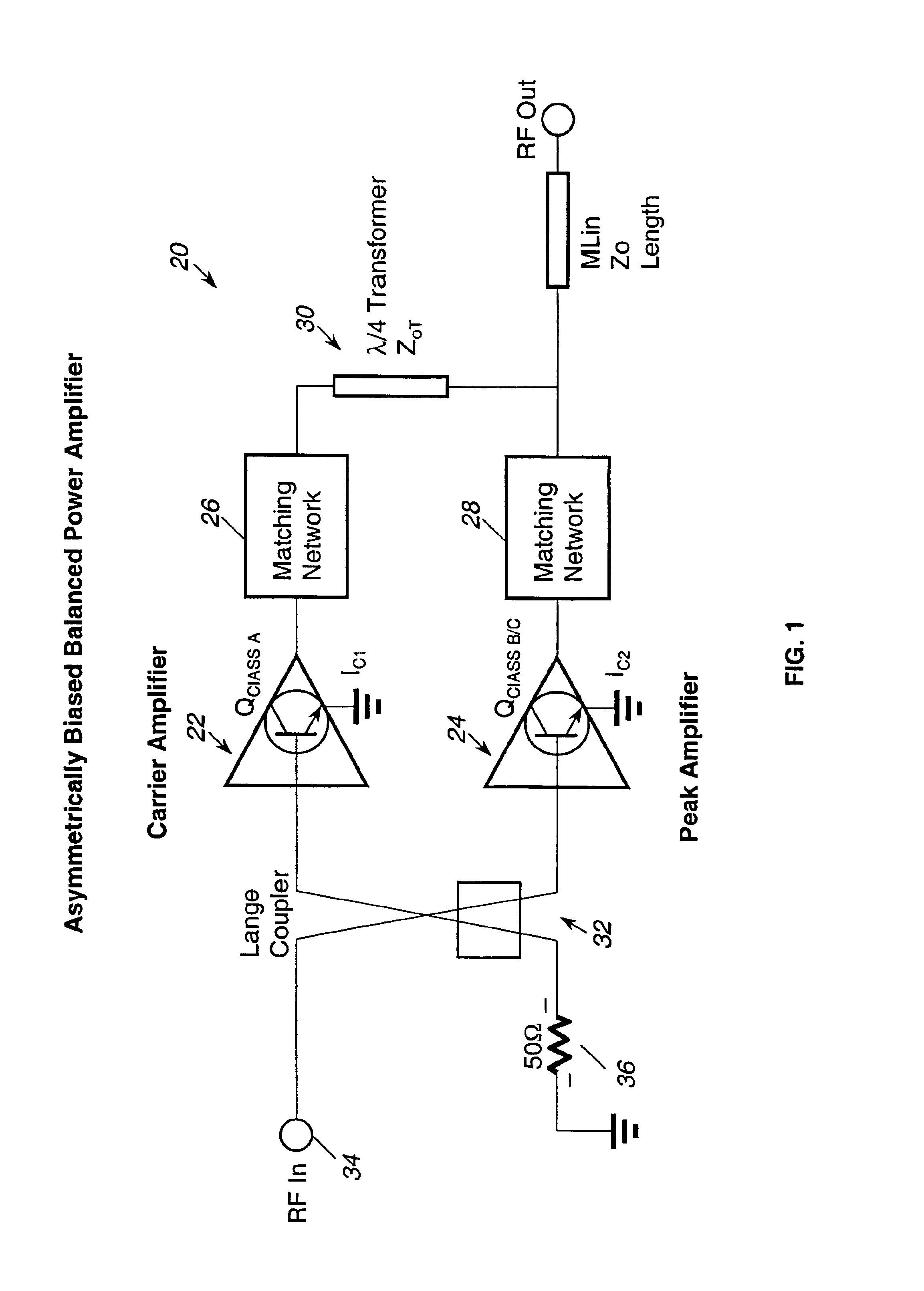
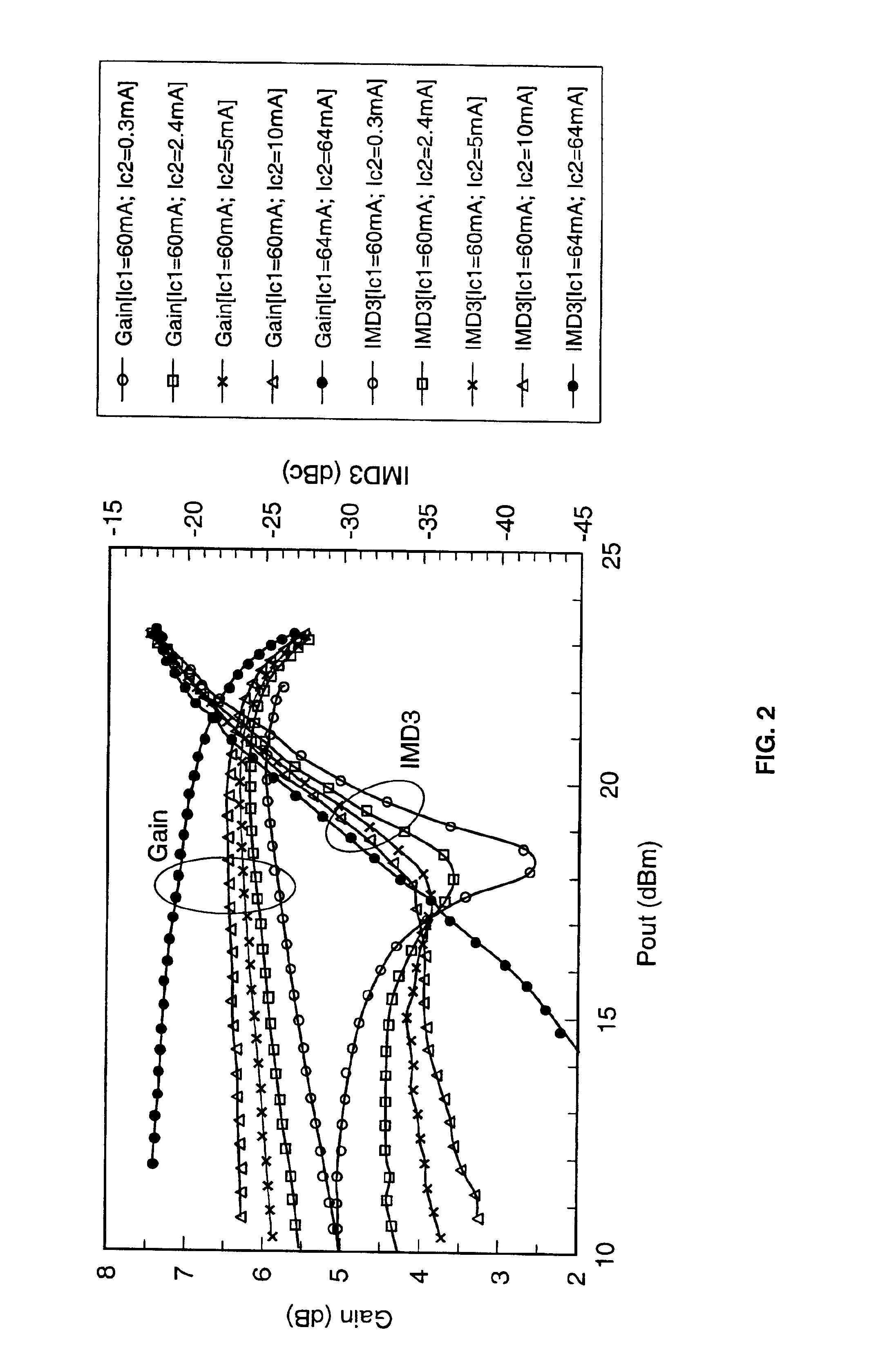
Application of the doherty amplifier as a predistortion circuit for linearizing microwave amplifiers
InactiveUS6864742B2Reducing intermodulation (IM) distortionImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A predistortion circuit for a microwave amplifier and more particularly to predistortion circuit configured as a Doherty amplifier. The predistortion circuit is adapted to be coupled to a downstream Doherty amplifier to precompensate for the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier as the input power level is increased while simultaneously reducing the intermodulation (IM) distortion. In order to provide precompensation, the precompensation circuit is operated at bias level to provide gain expansion and phase compression to cancel out the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier to provide a higher overall linear power added efficiency (PAE).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
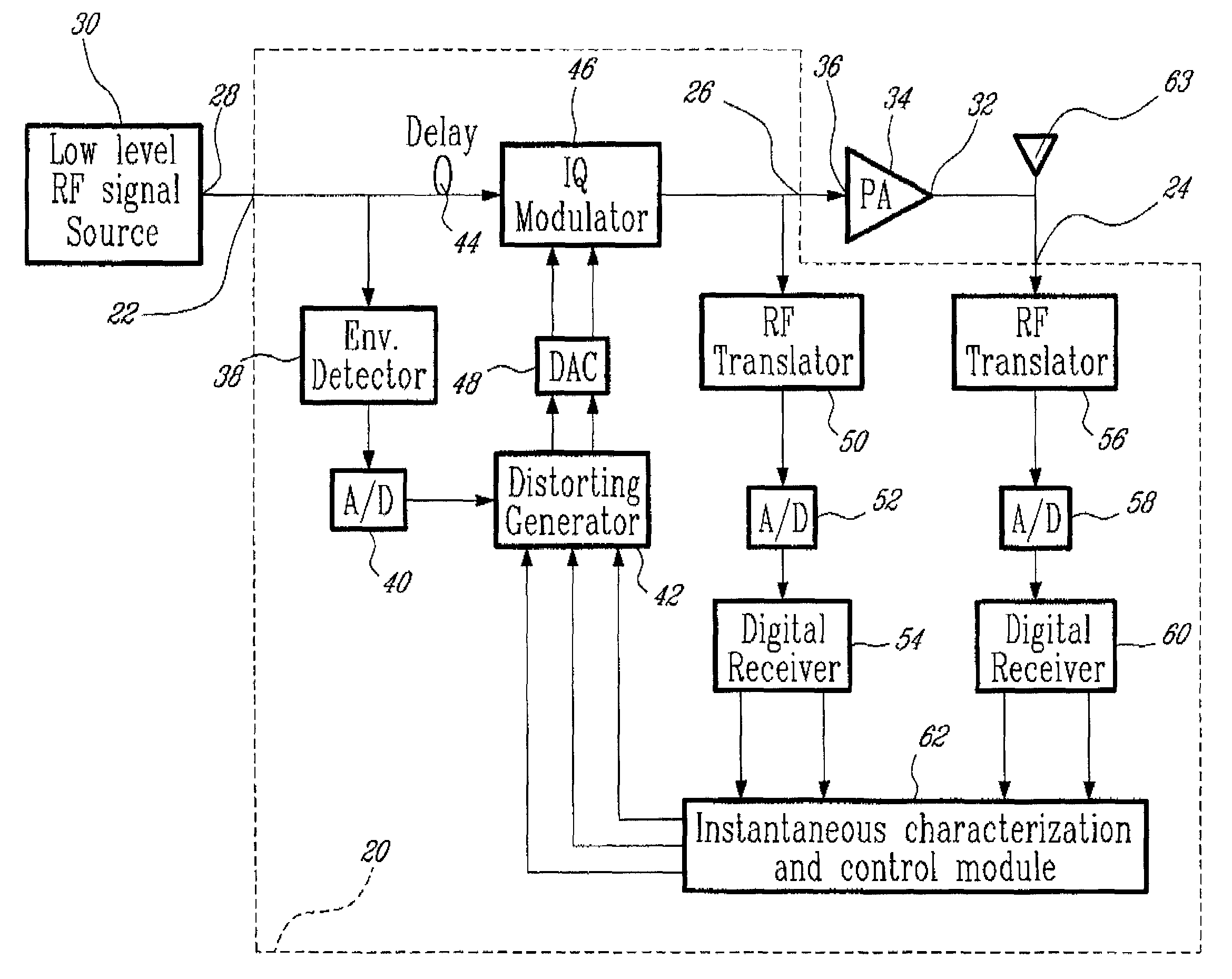
Adaptive predistortion device and method using digital receiver
InactiveUS7035345B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringSelf adaptive
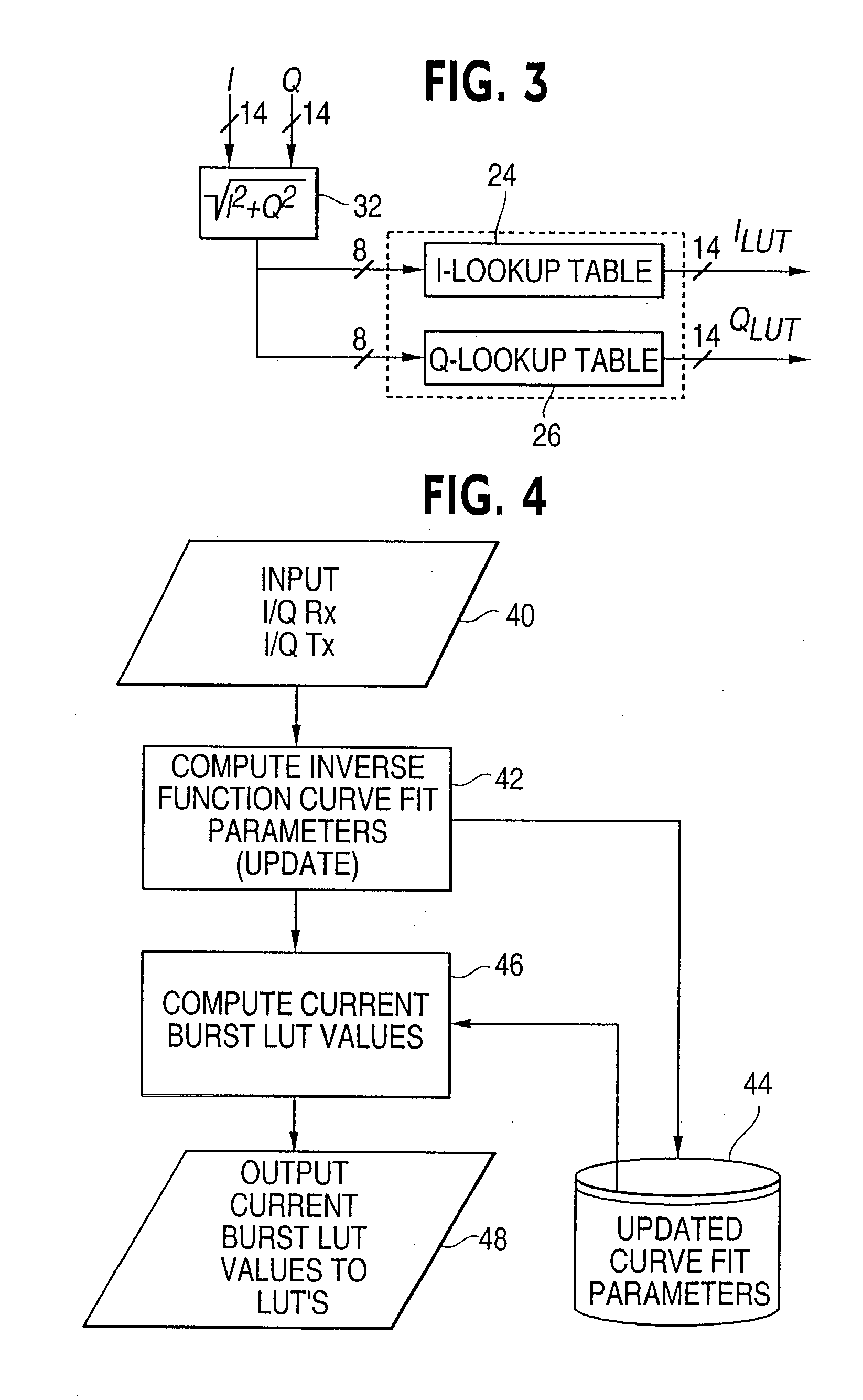
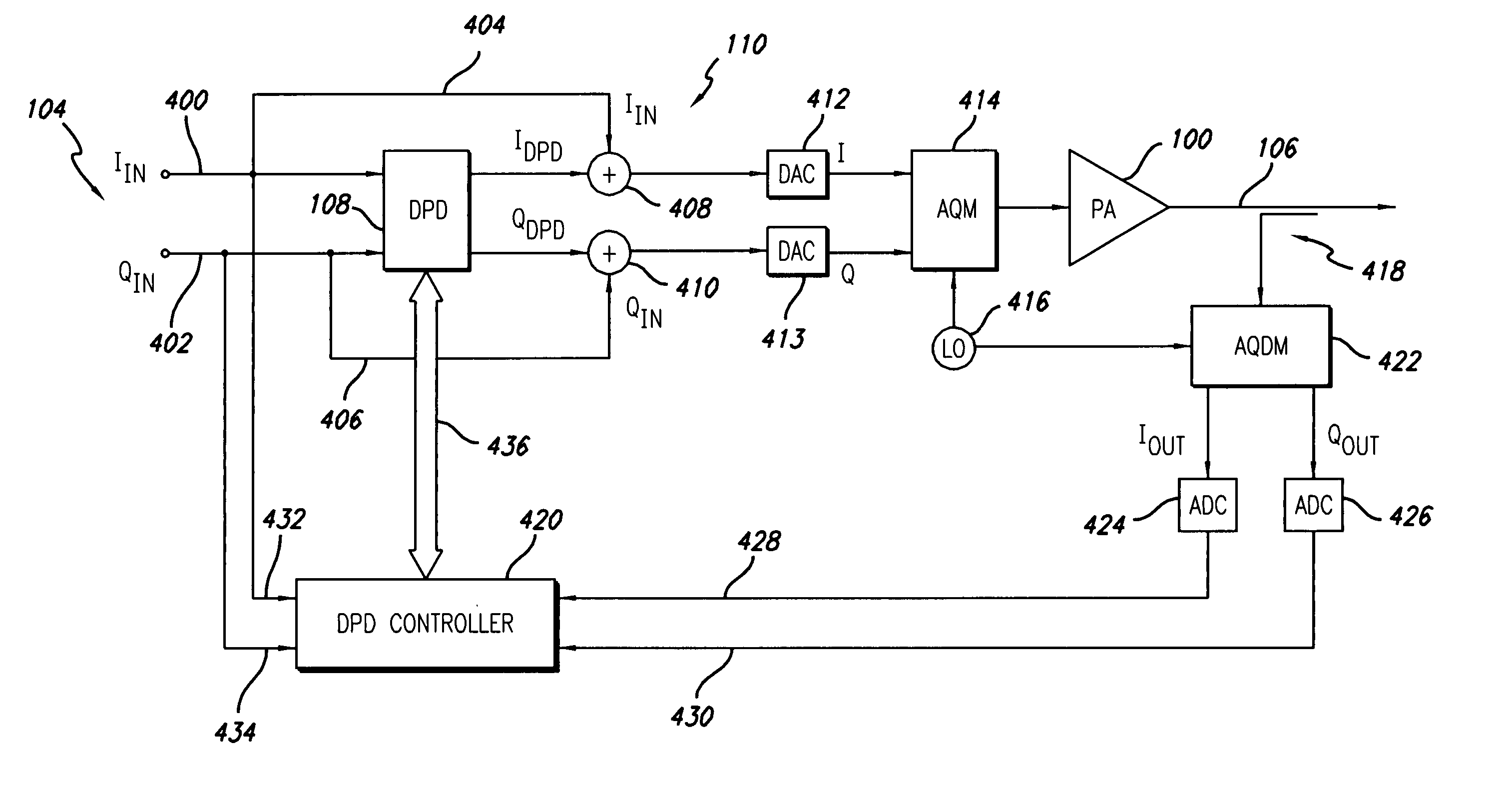
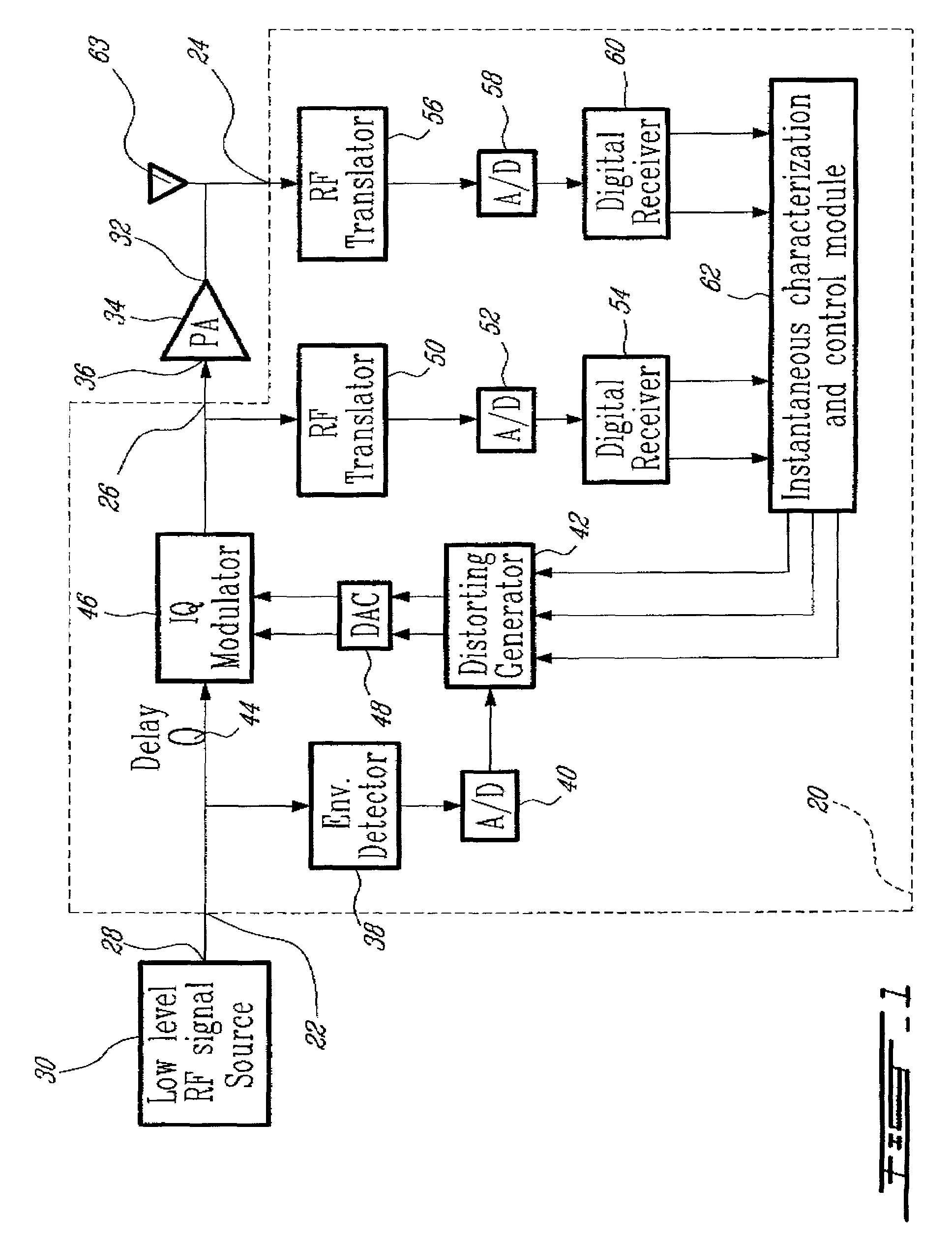
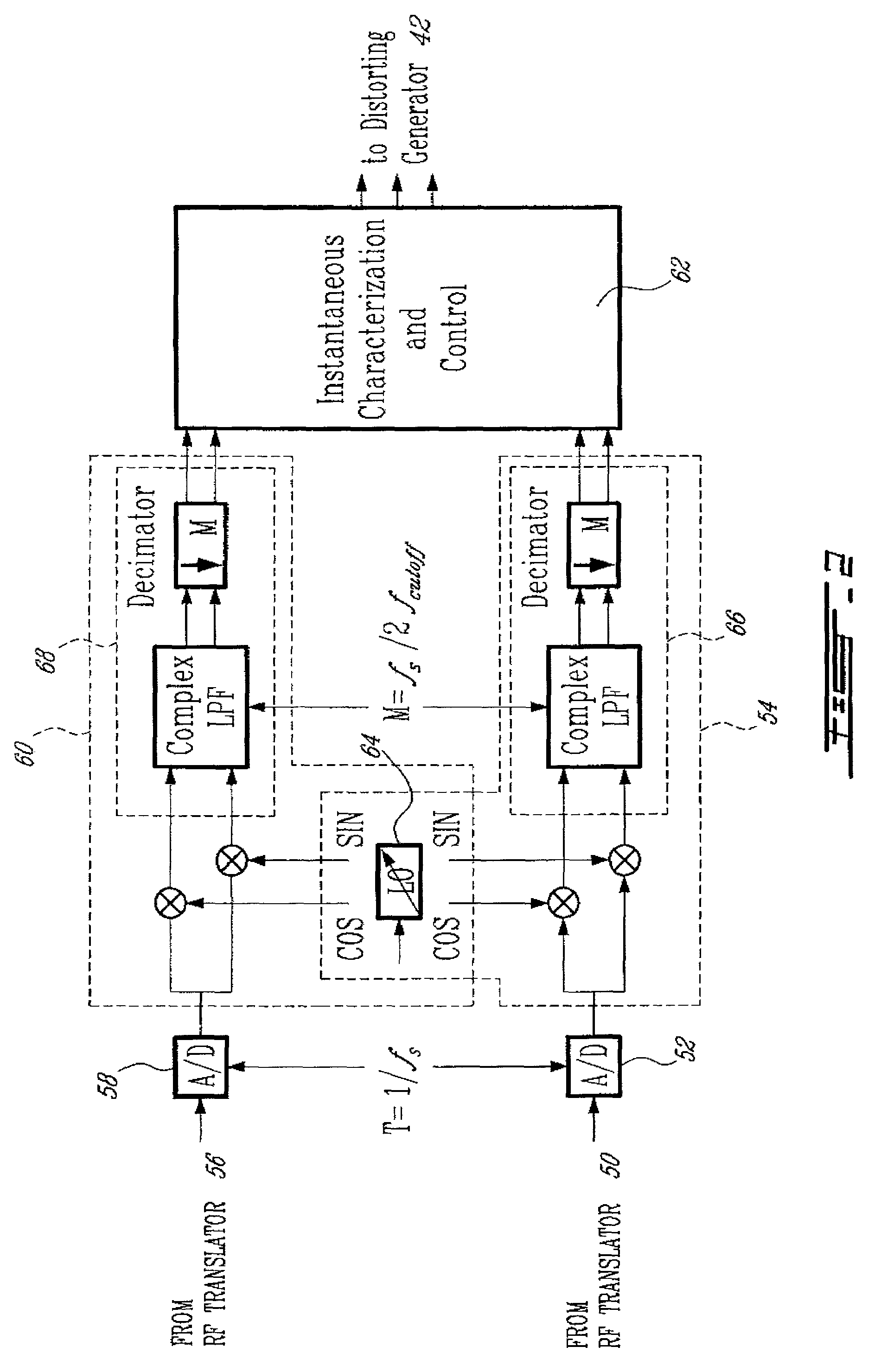
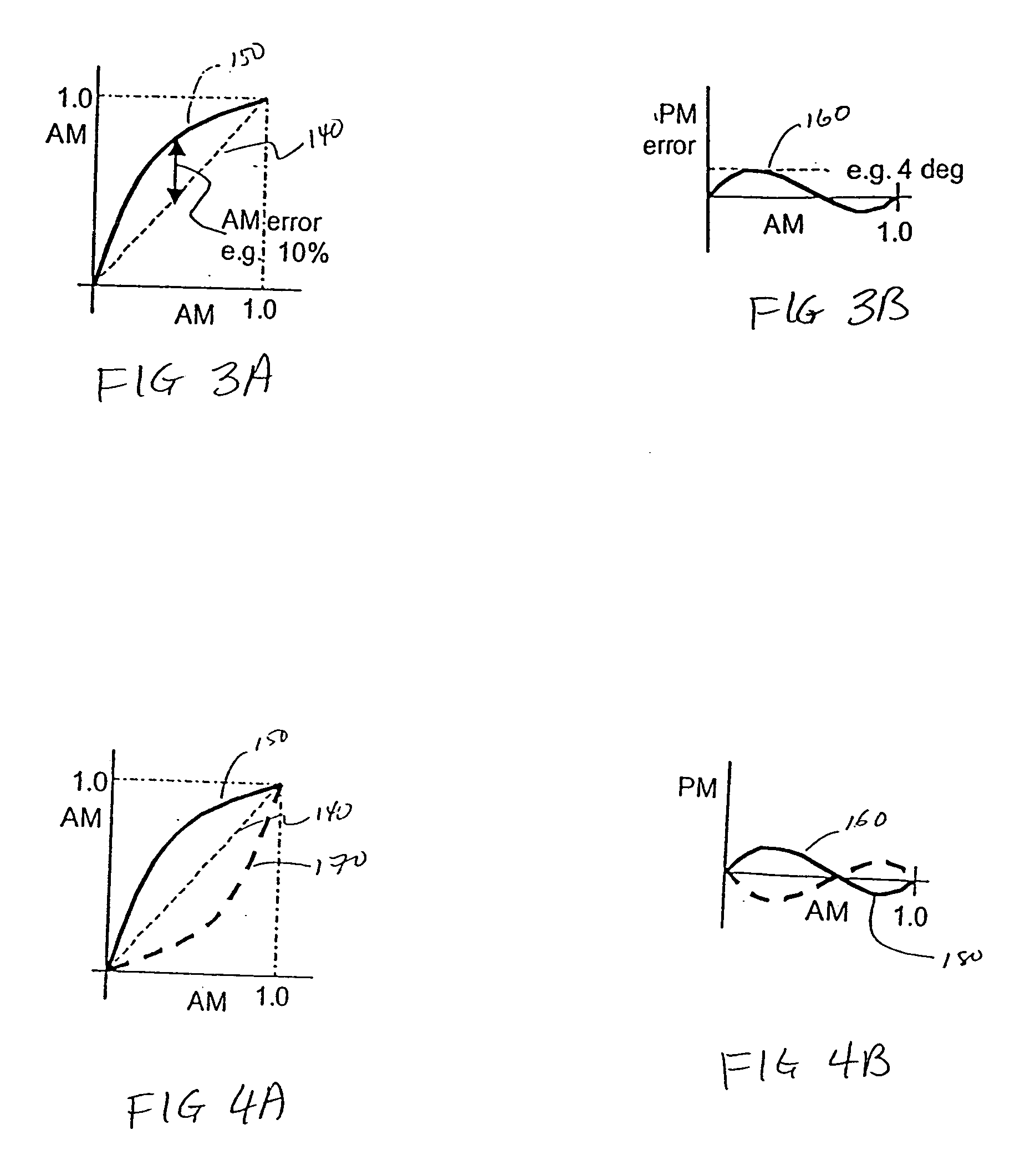
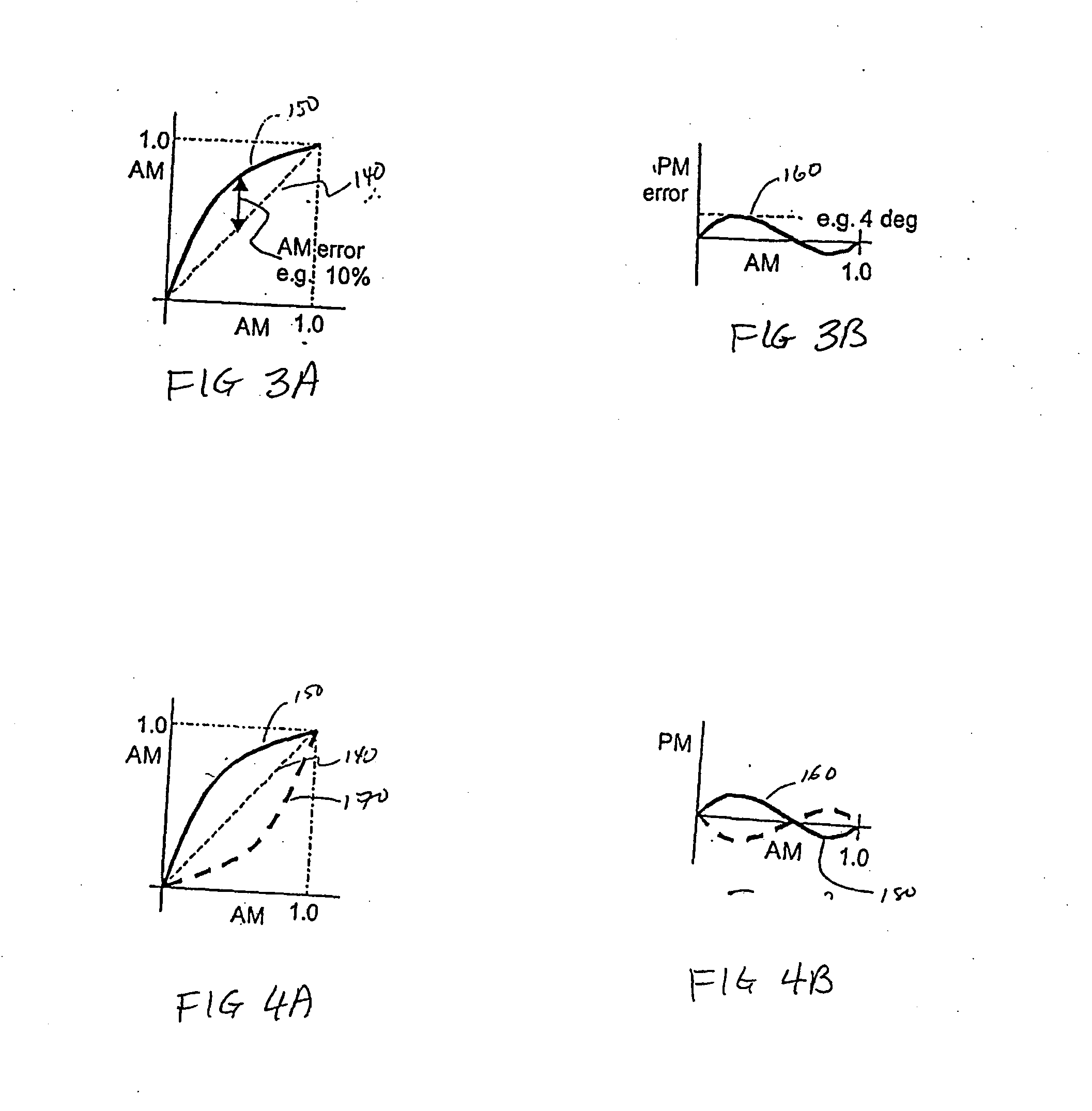
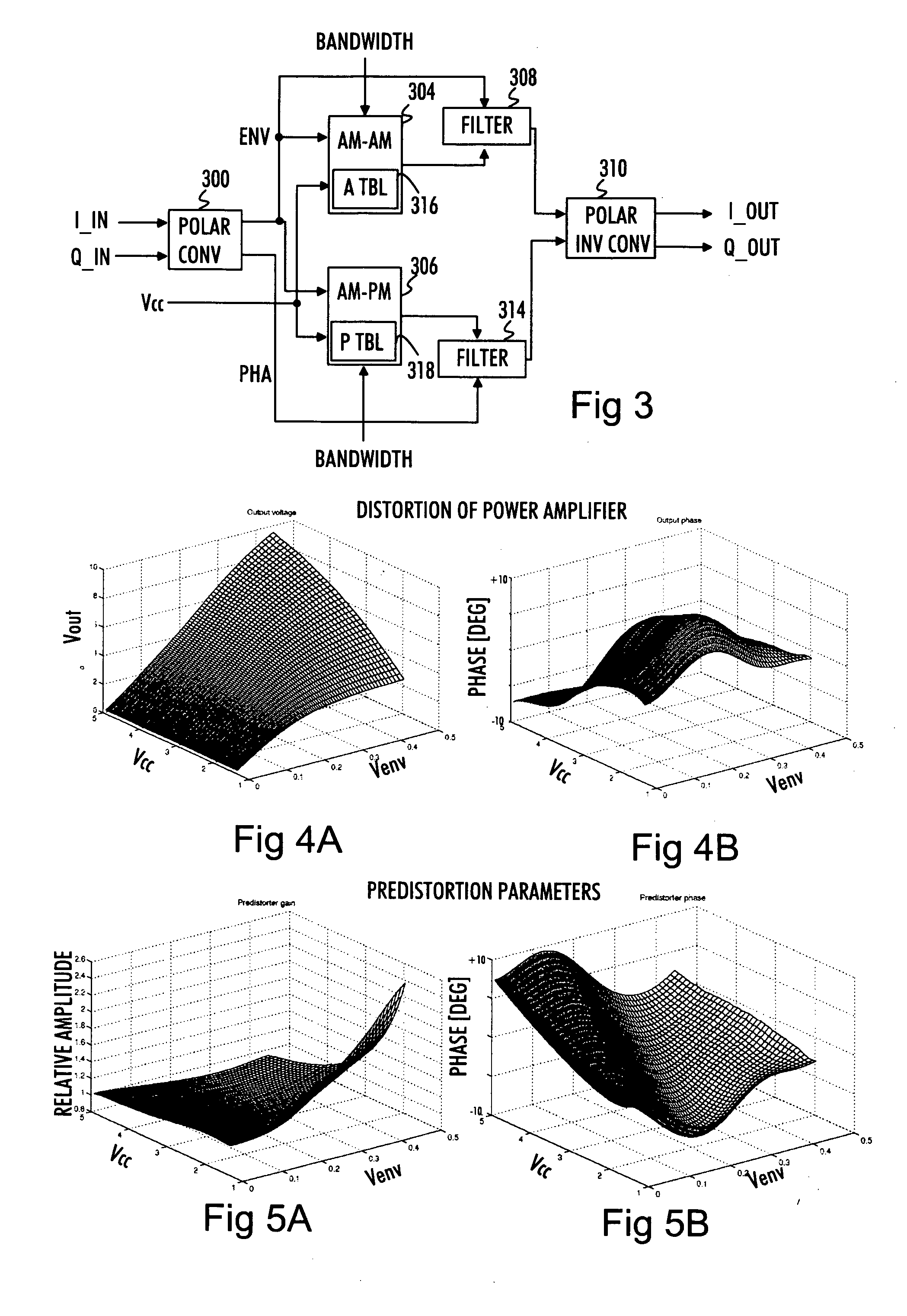
An advanced adaptive baseband / RF predistorting device, which advantageously uses the concept of digital receiver technology into power amplifier (PA) linearization area. The predistorting device performs an instantaneous characterization of the PA using two digital receivers to supply its dynamic AM-AM and AM-PM transfer functions used to synthesize Look-Up Tables (LUT) which implement the complex predistortion function in order to compensate for any non-linearity and memory effects.
Owner:POLYVALOR S E C
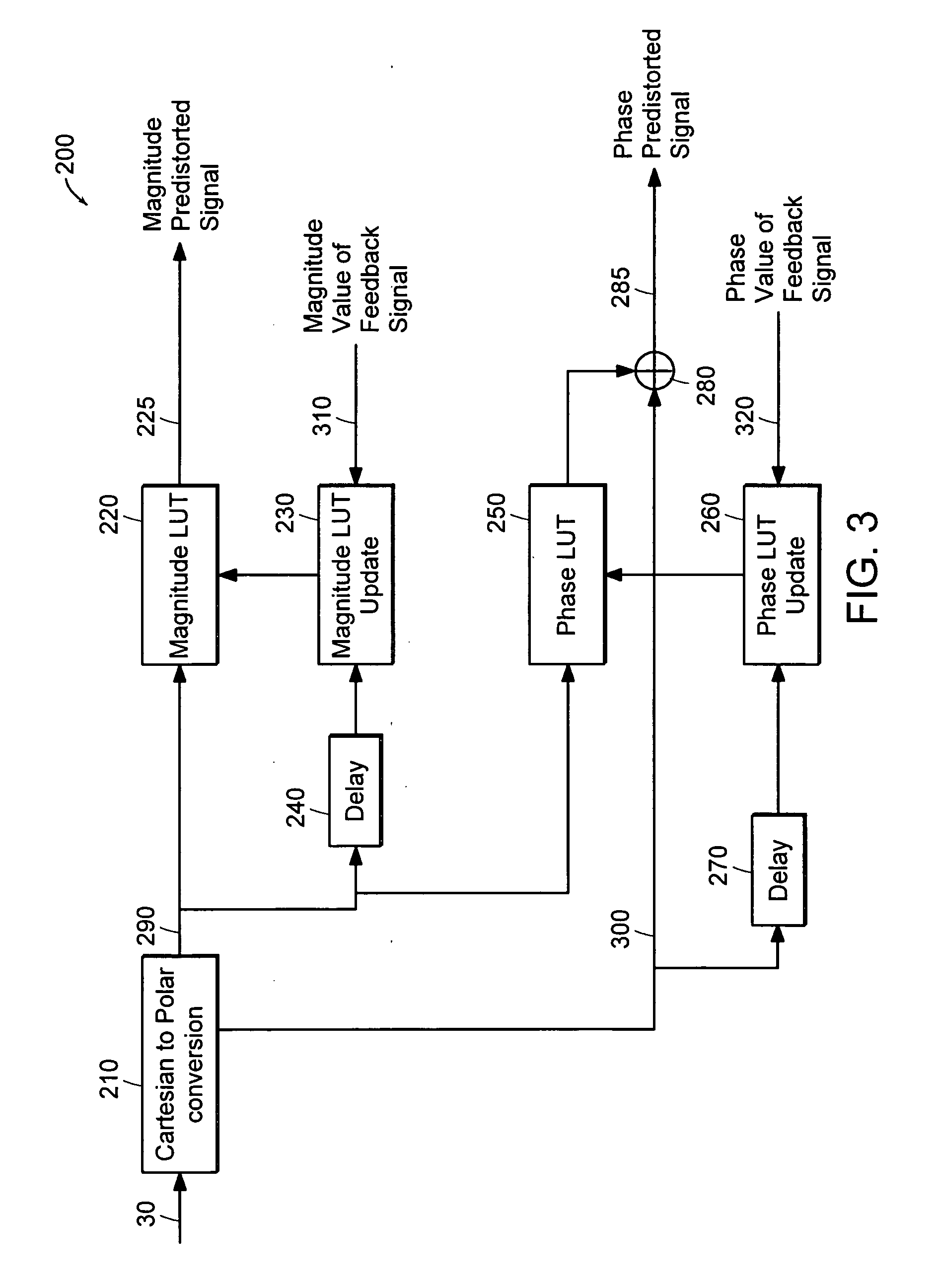
Predistortion circuit for a transmit system
ActiveUS20050002470A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSecret communicationAudio power amplifierEngineering
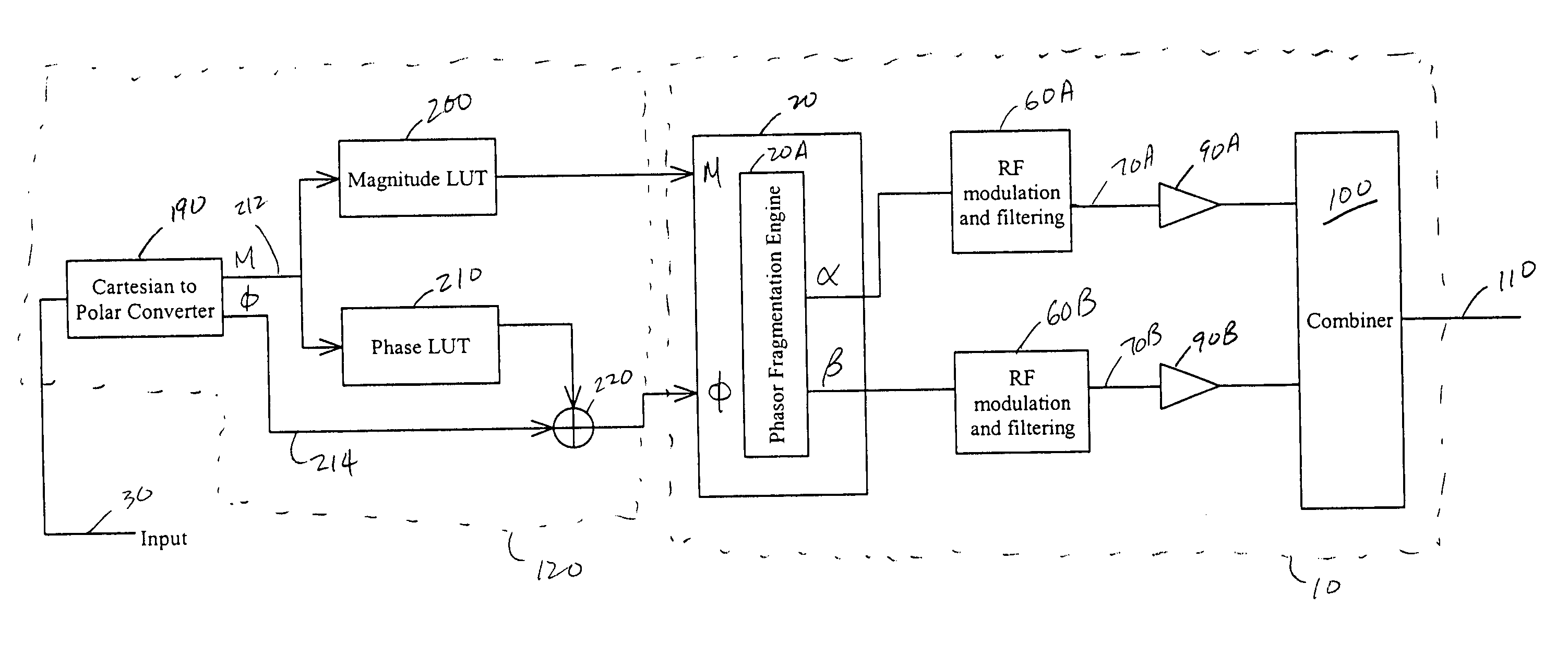
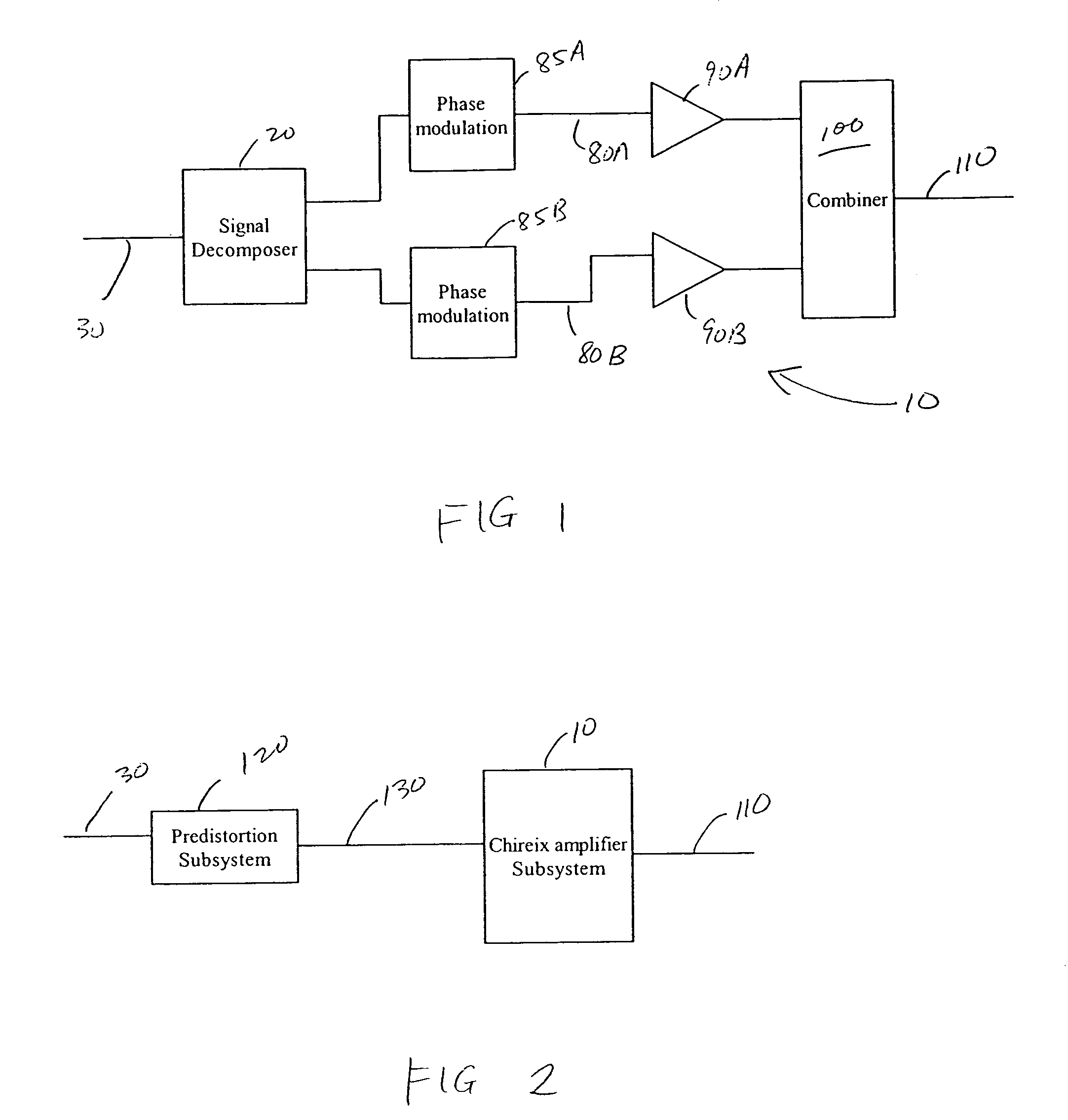
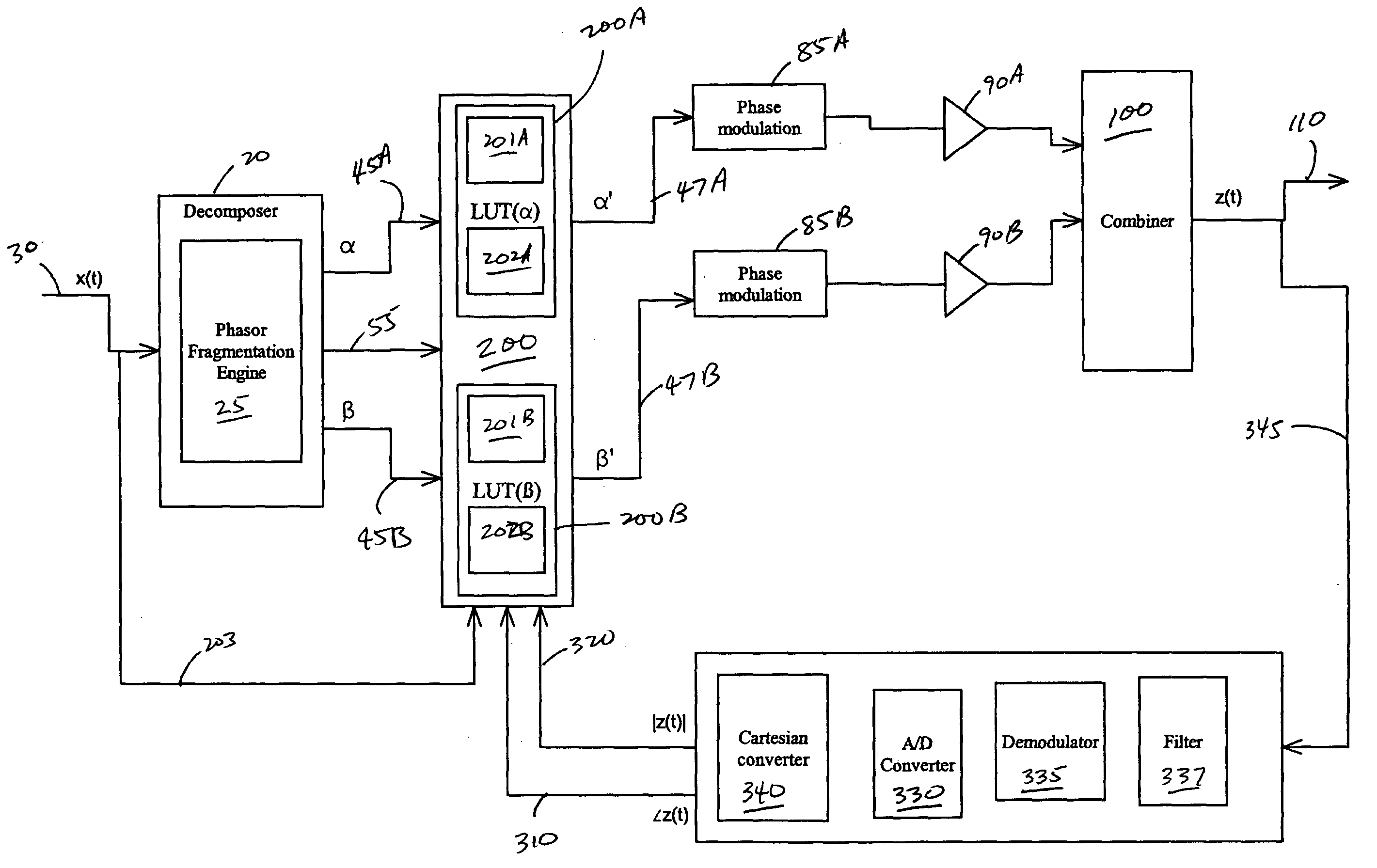
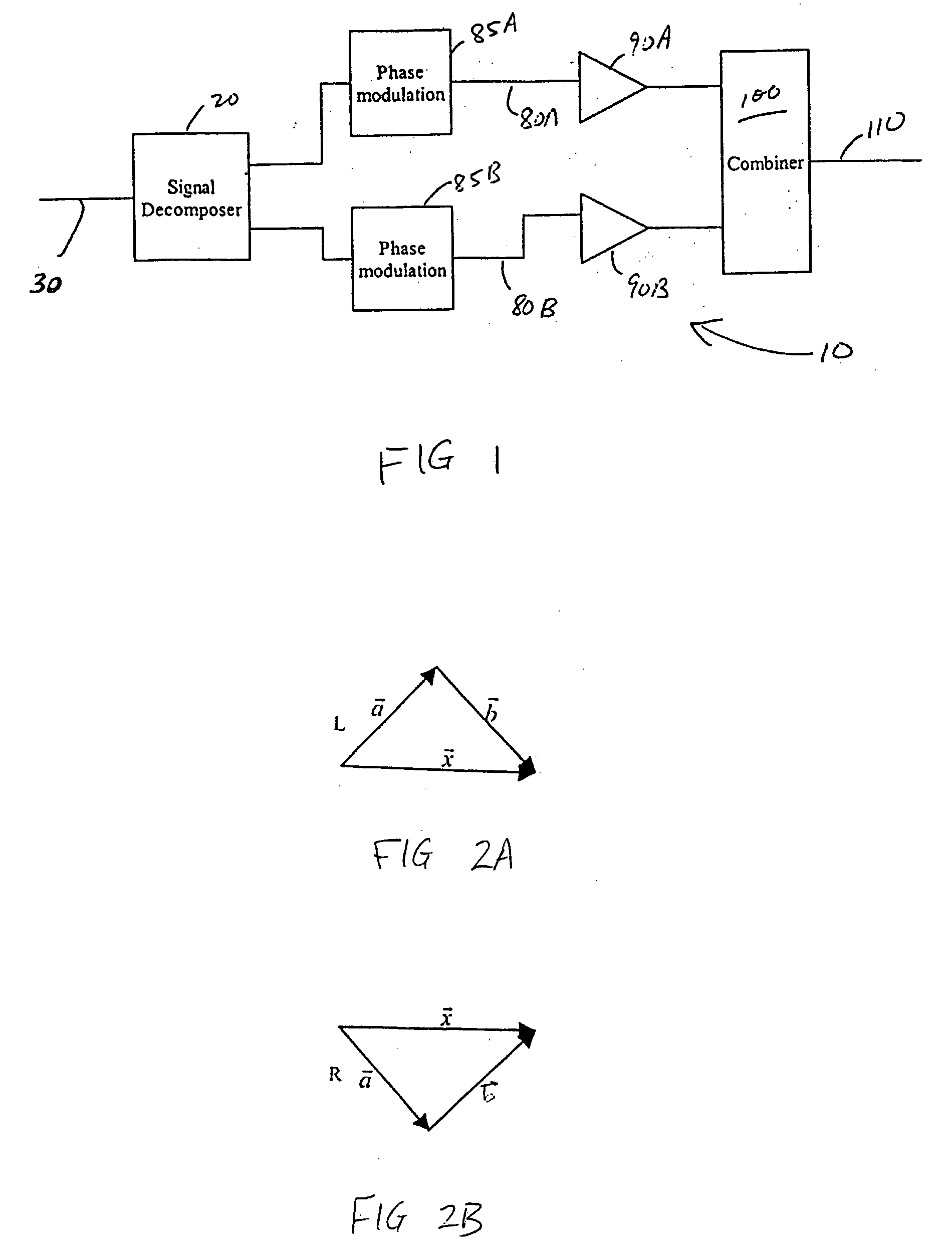
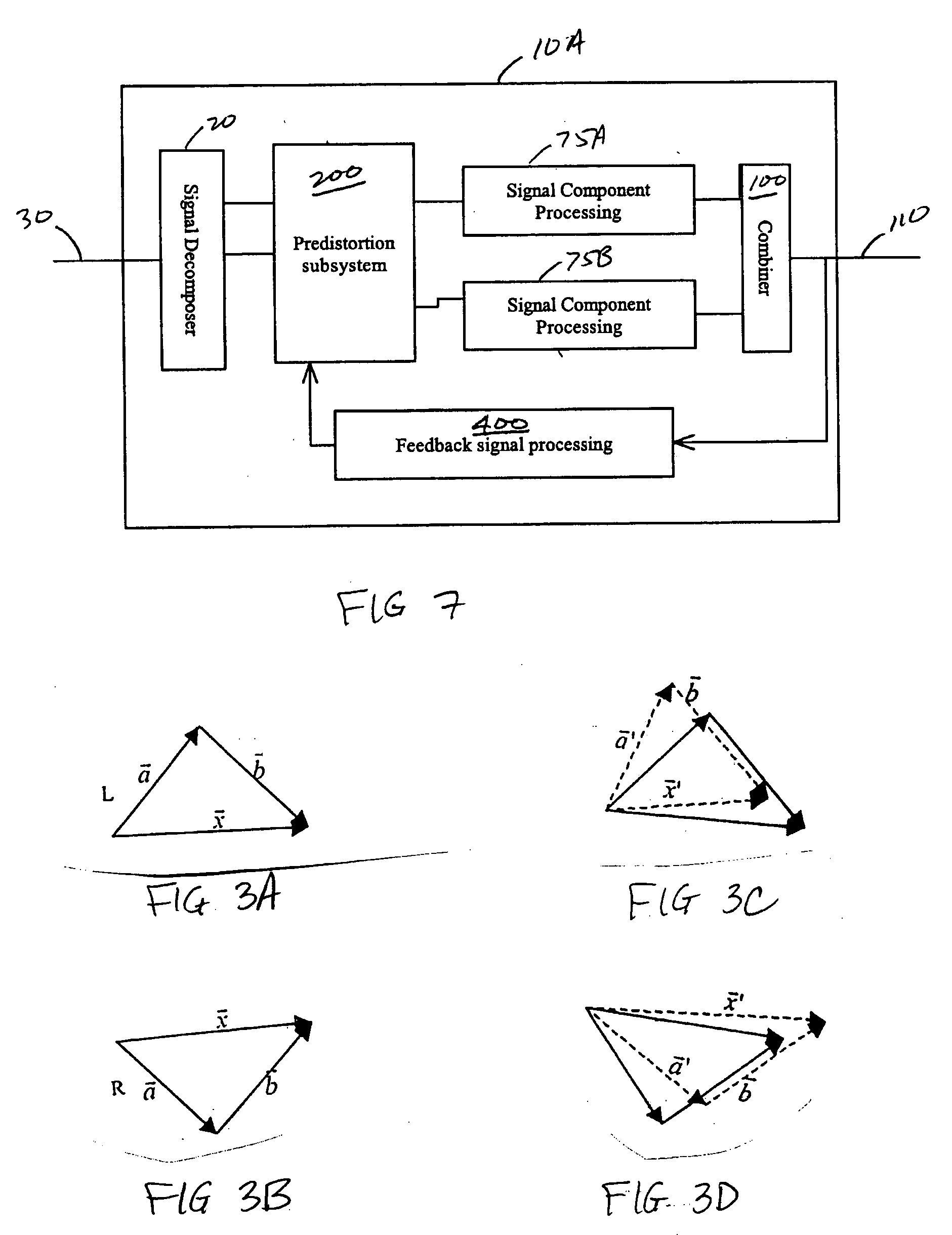
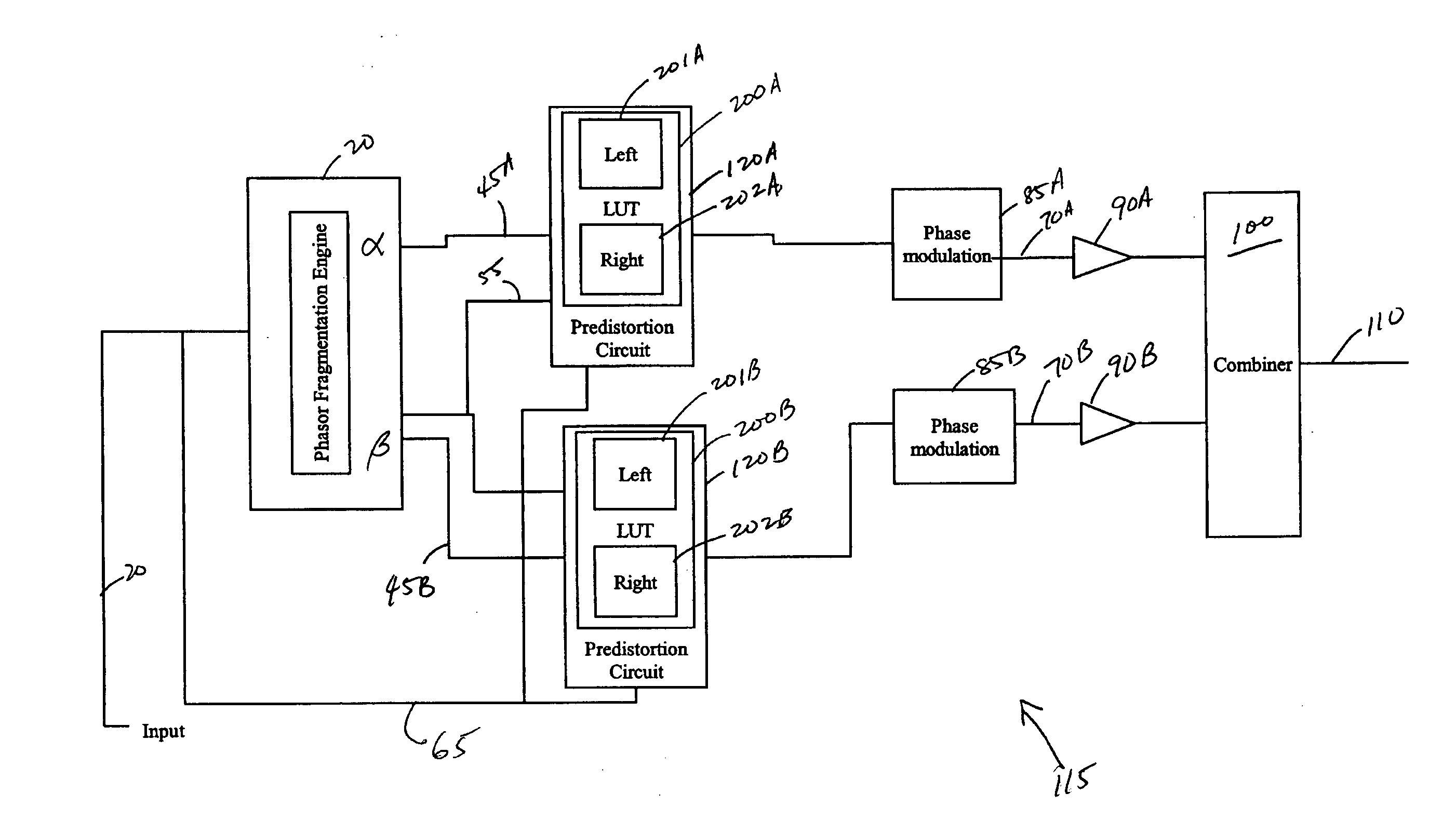
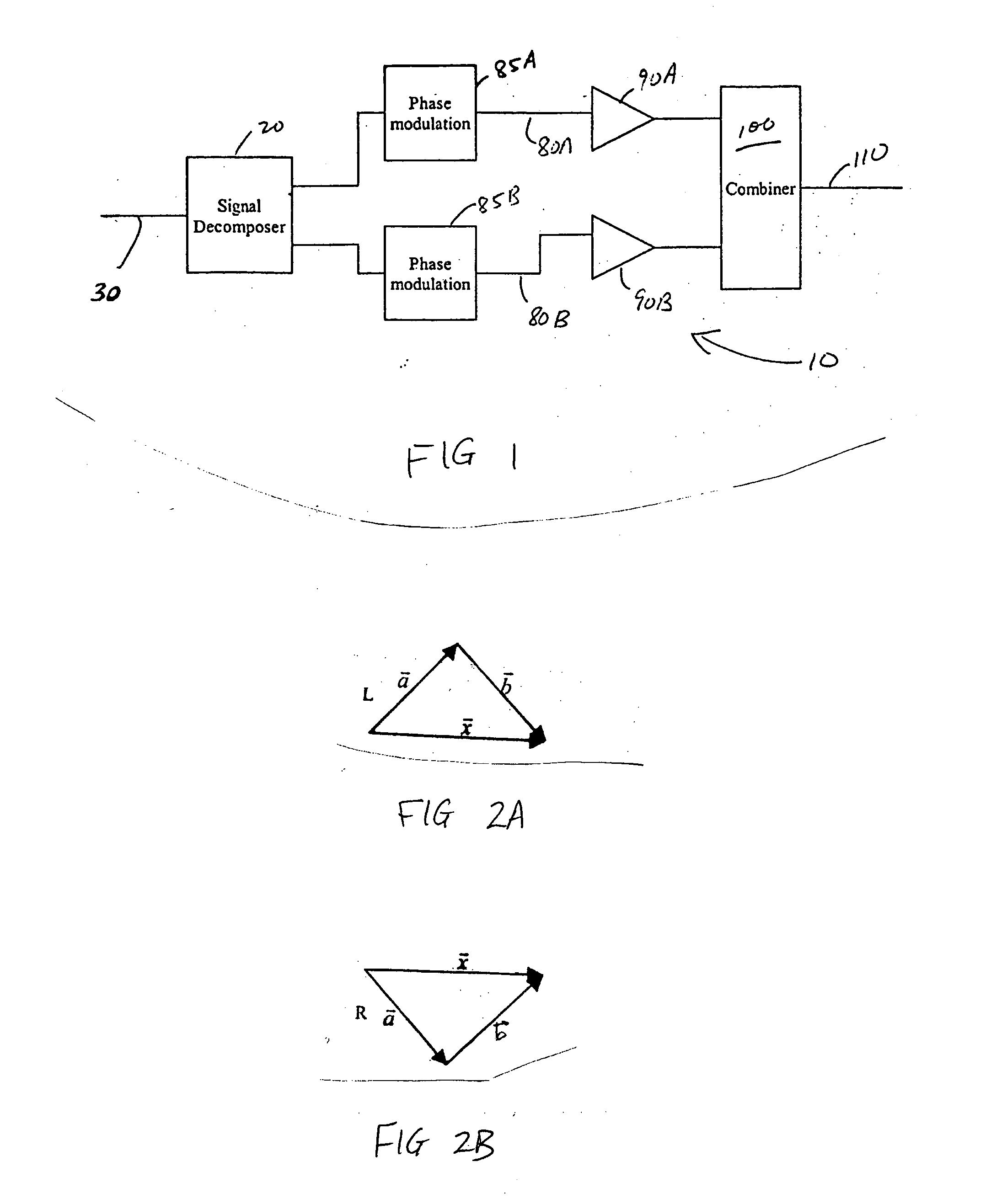
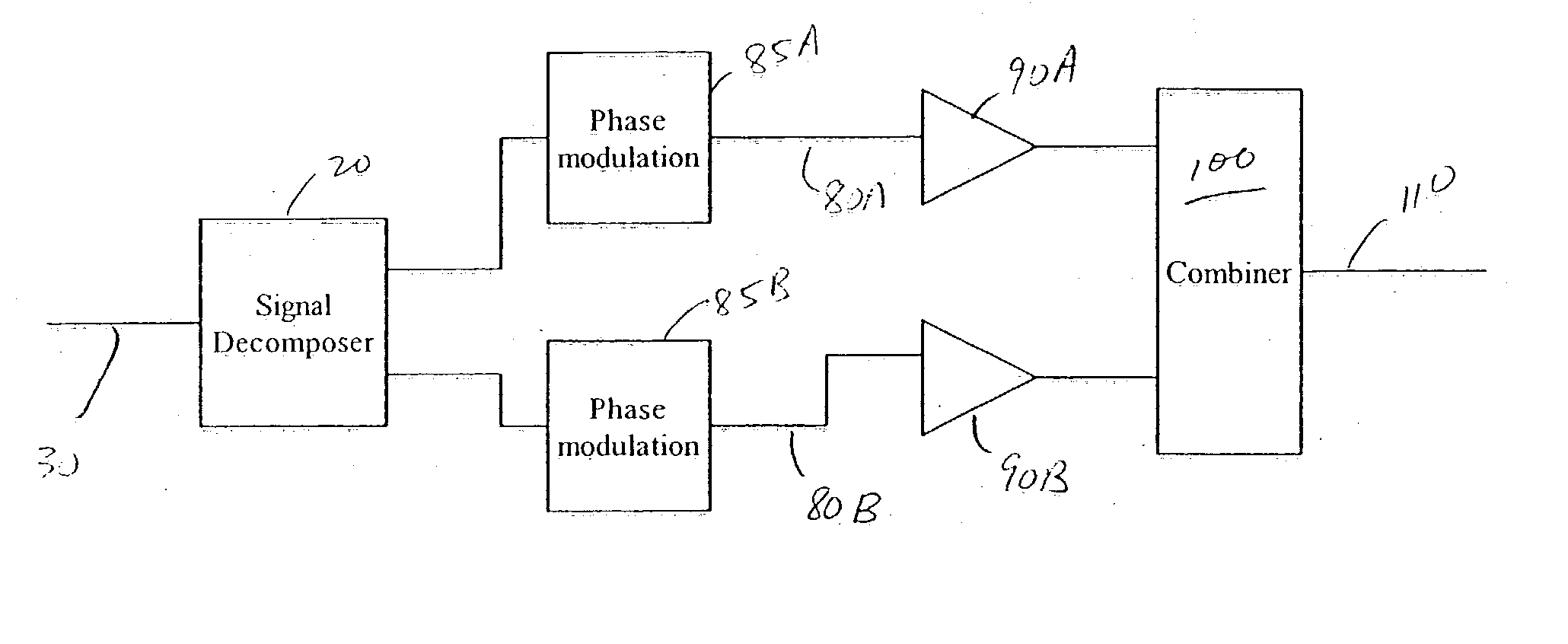
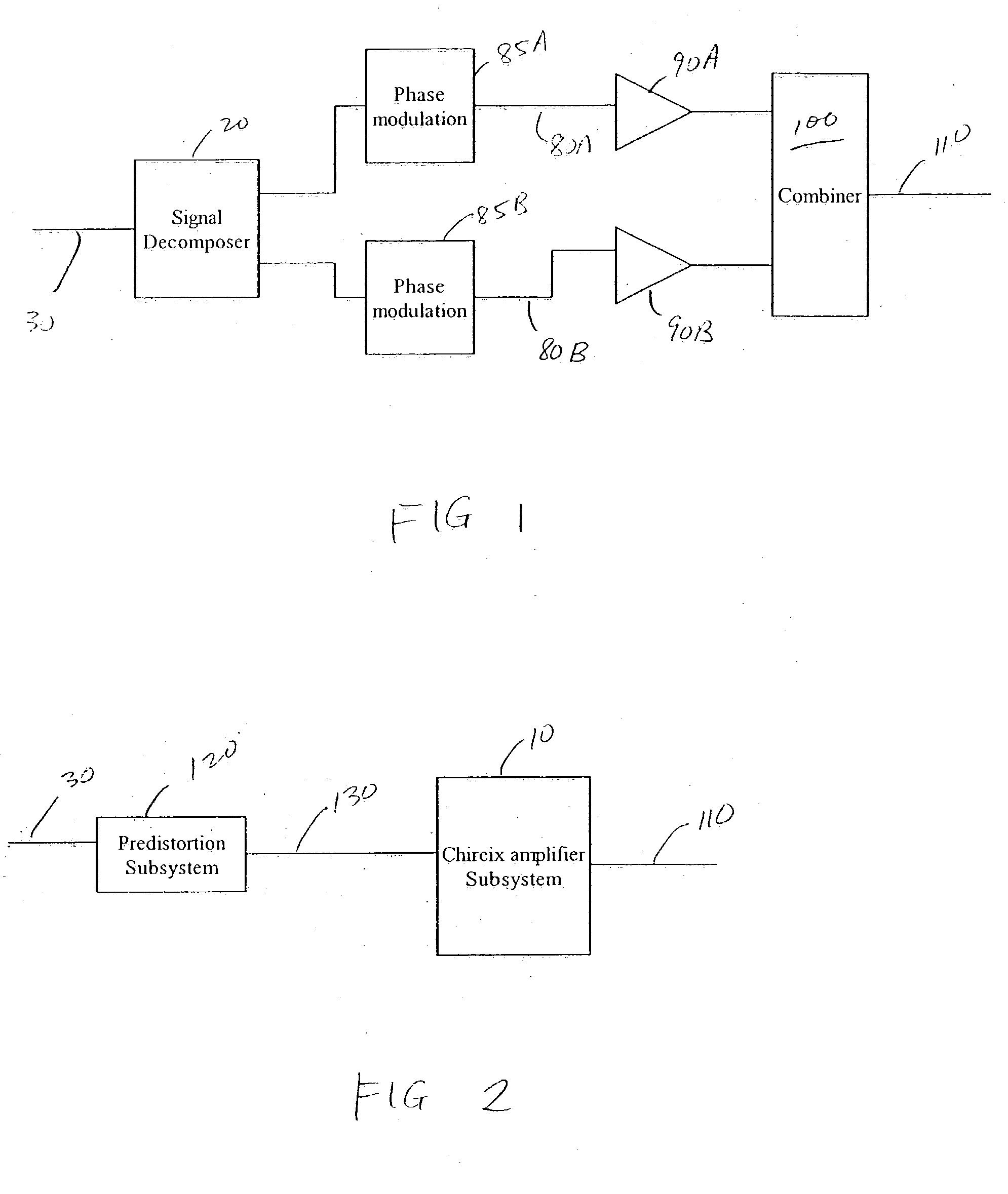
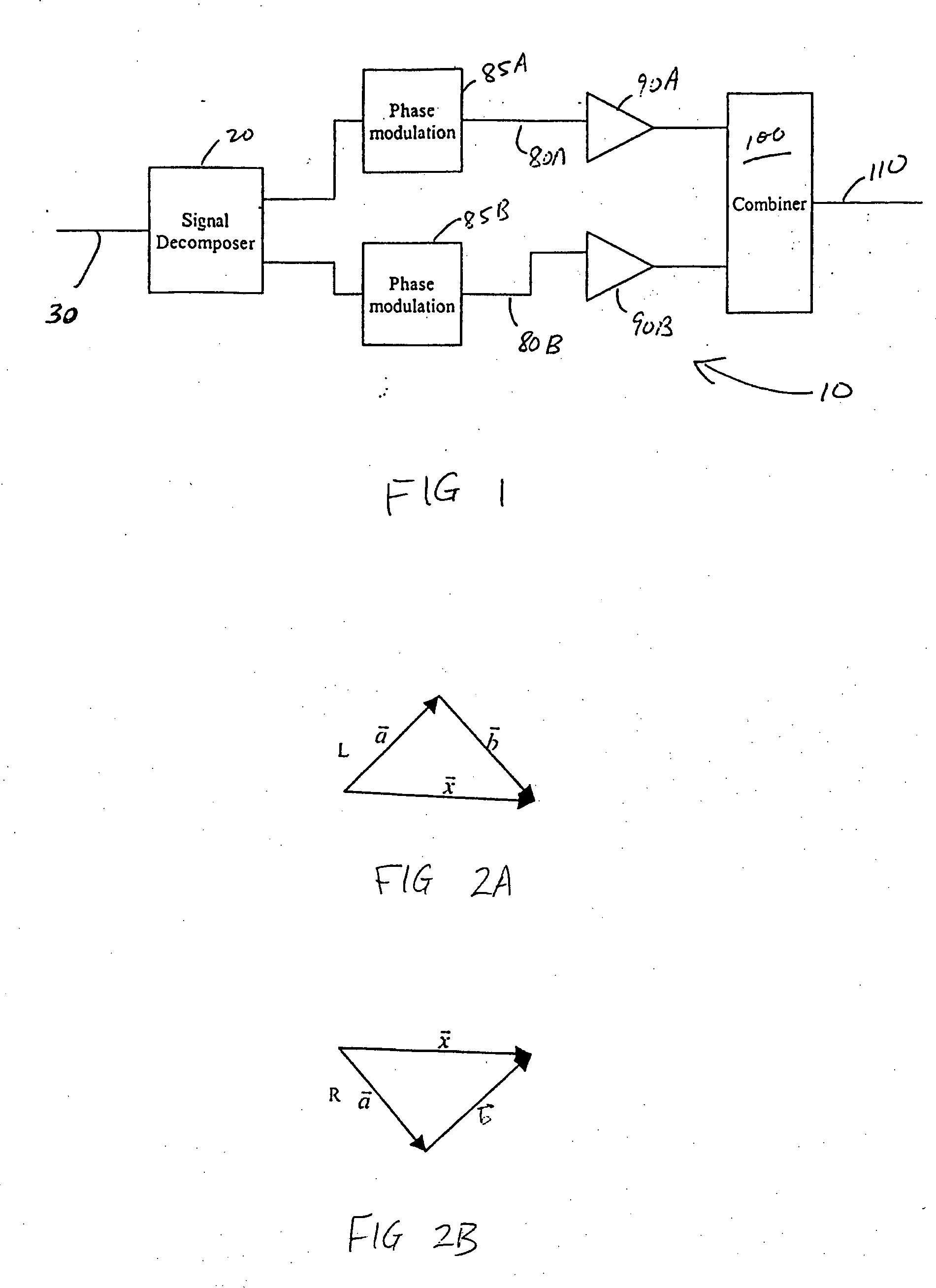
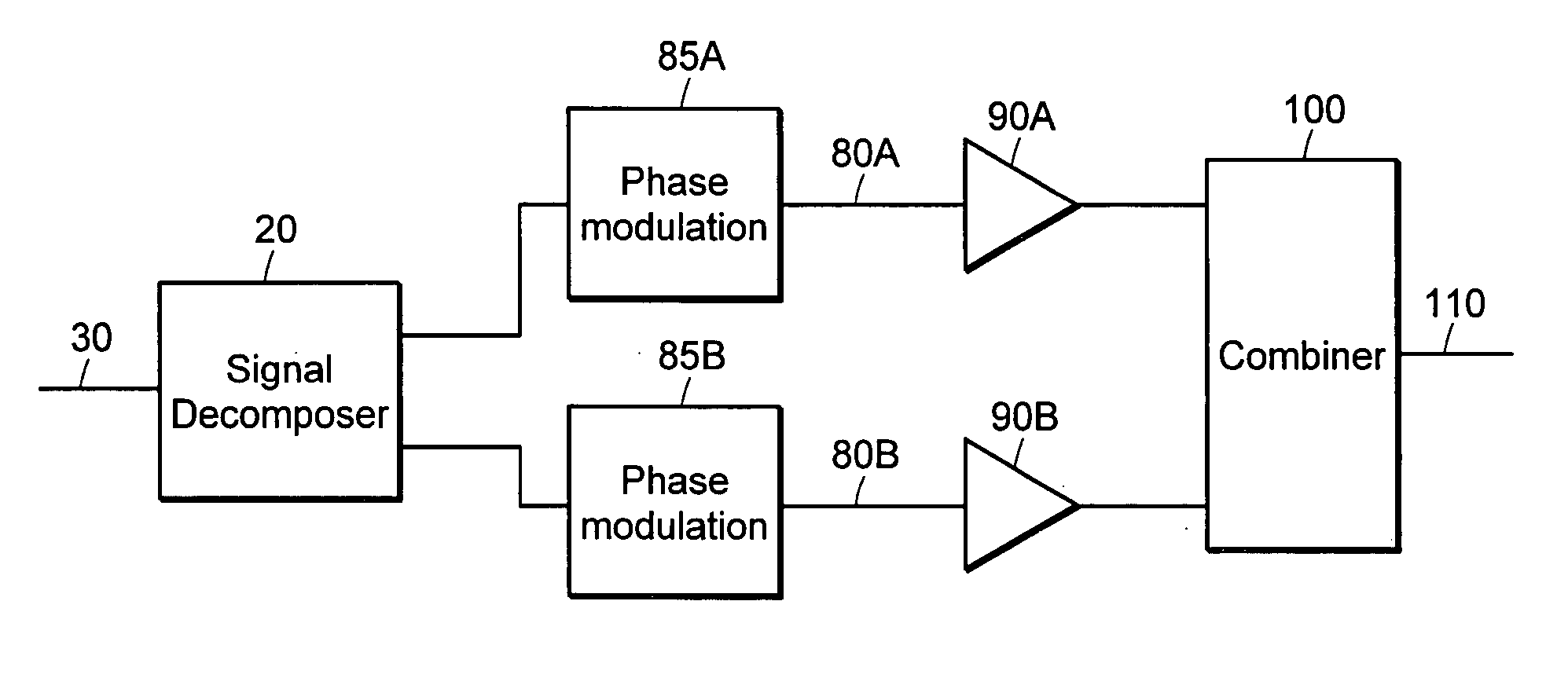
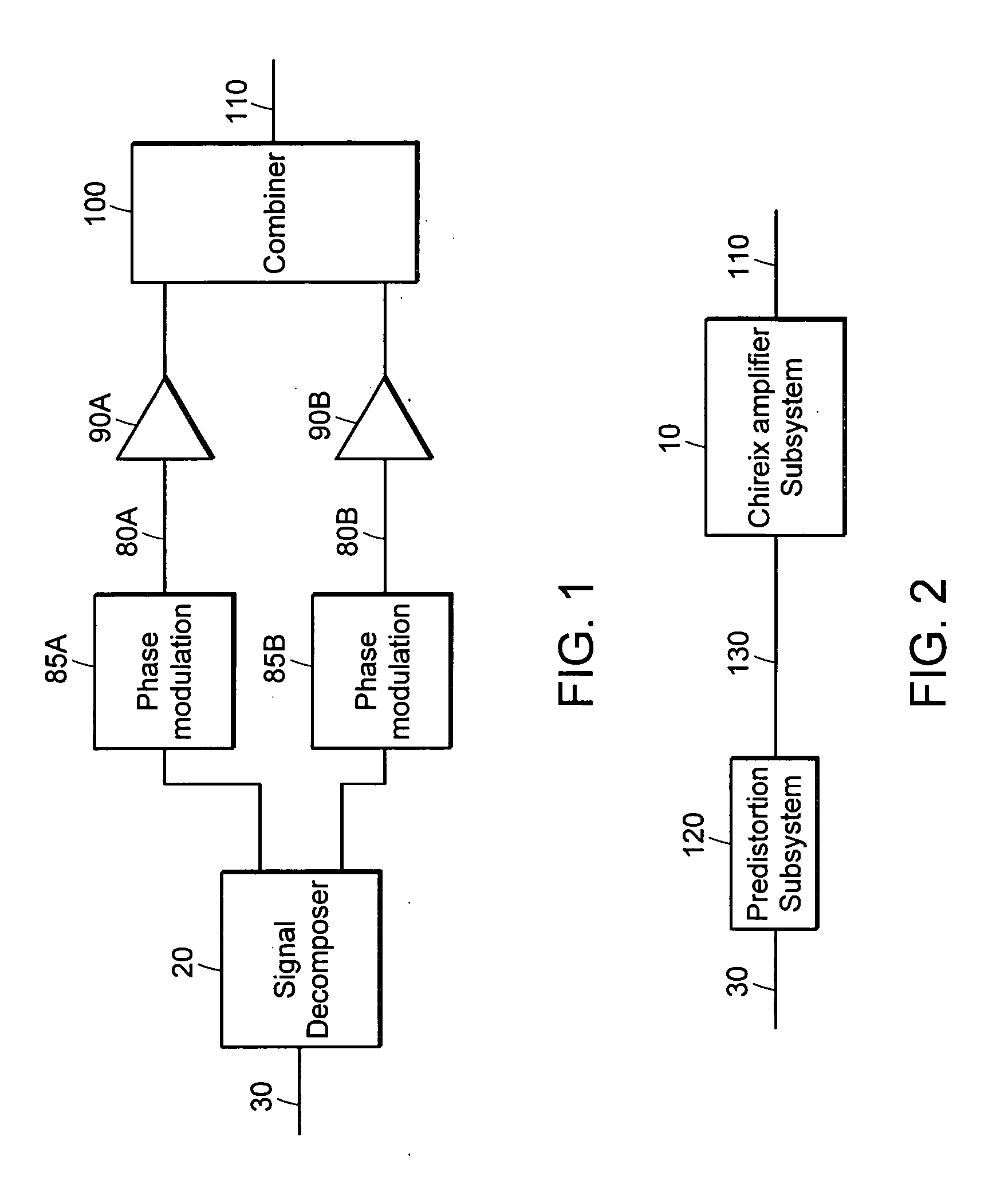
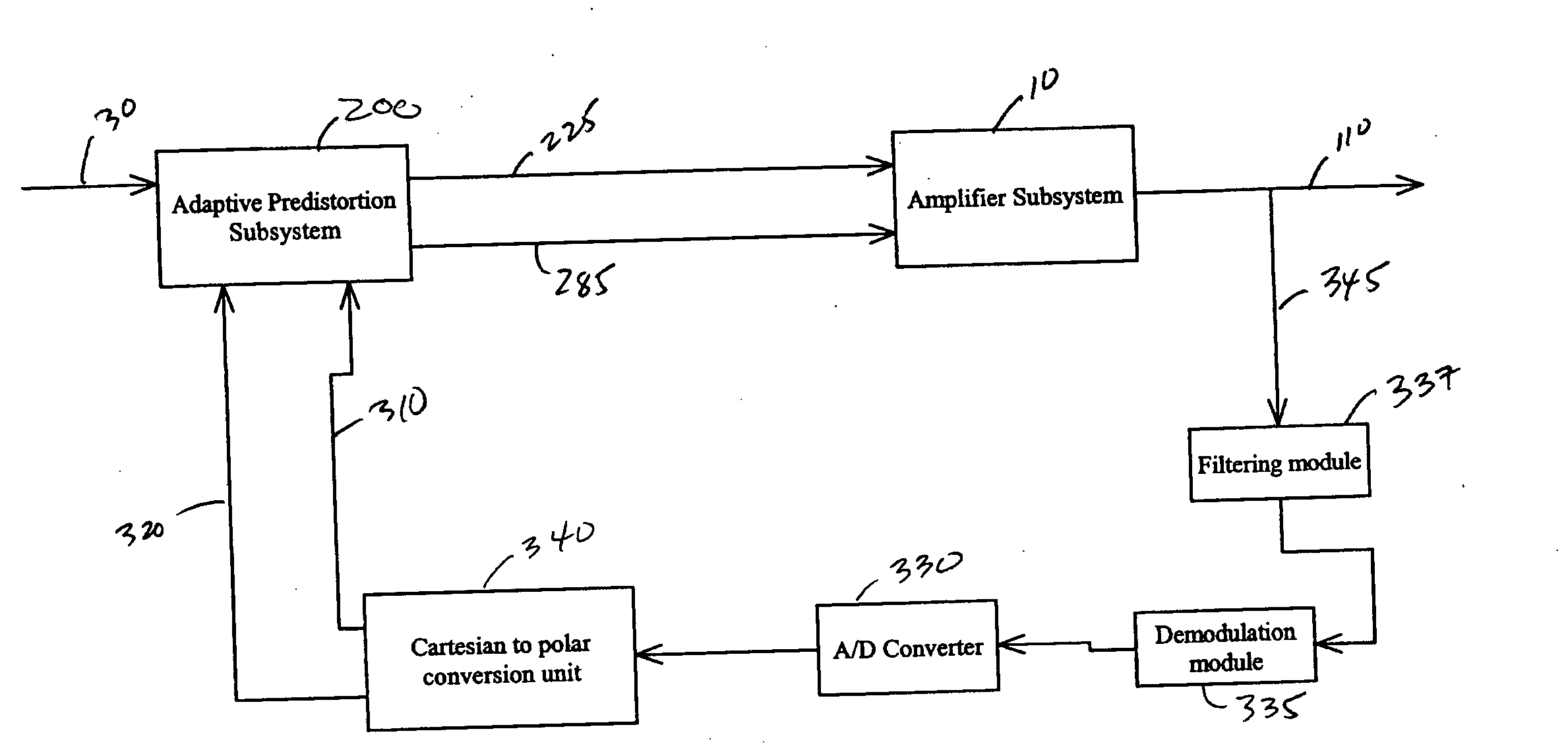
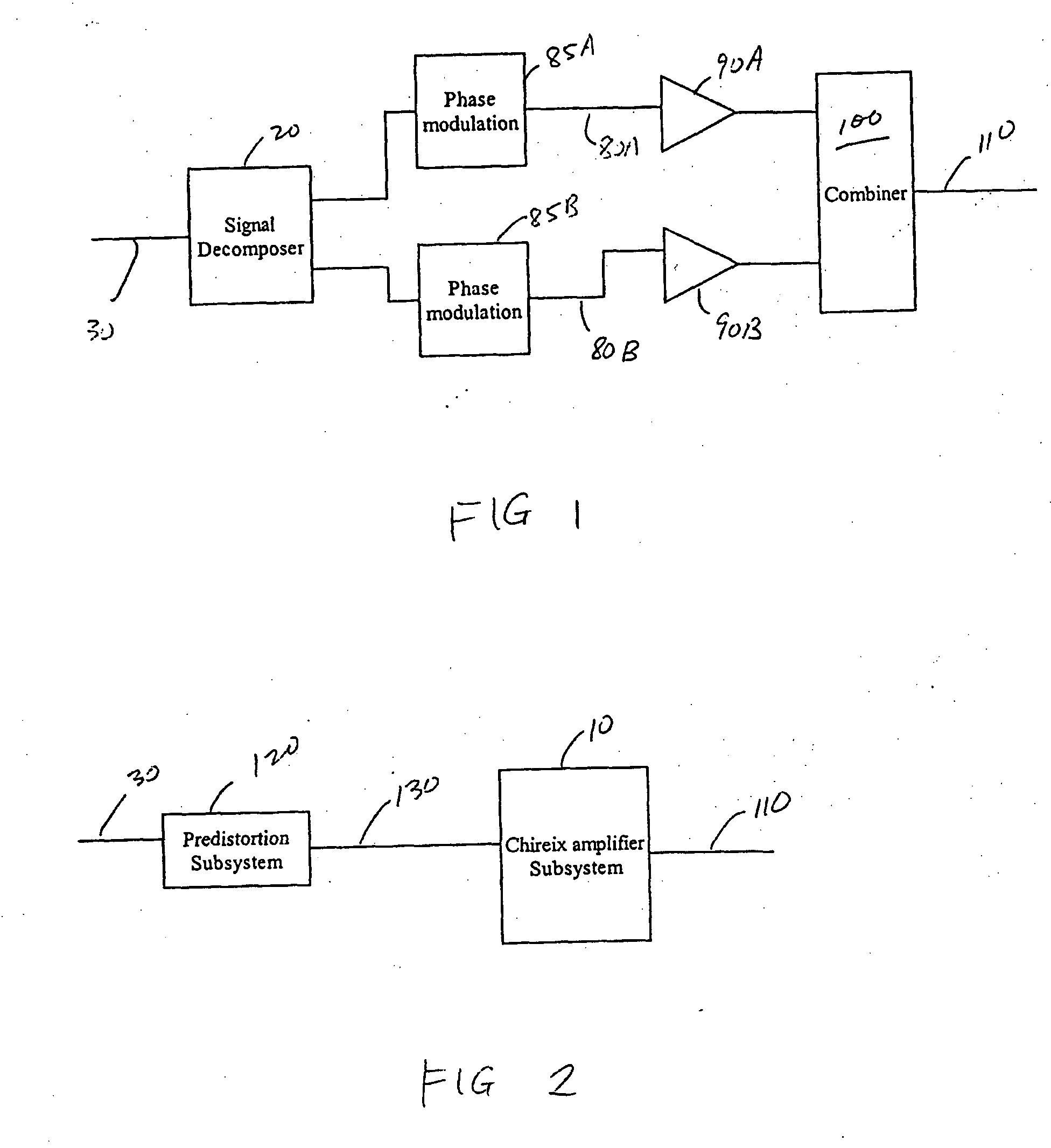
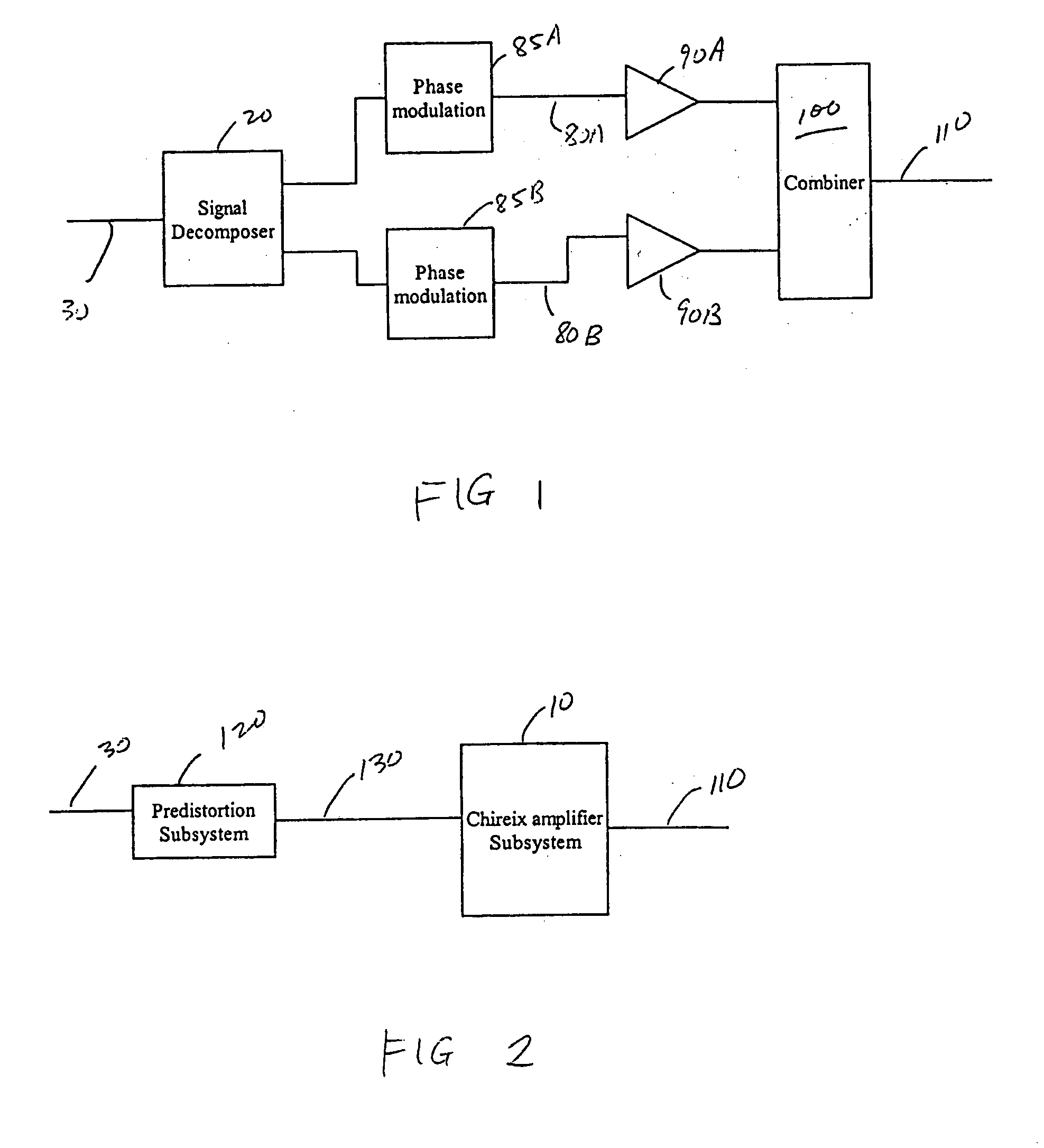
Systems and methods related to amplifier systems which use a predistortion subsystem to compensate for expected distortions in the system output signal. A predistortion subsystem receives an input signal and applies a predistortion modification to the input signal. The predistortion modification may be a phase modification, a magnitude modification, or a combination of both. The predistorted signal is then received by an amplifier subsystem. The amplifier subsystem decomposes the predistorted signal into separate components, each having a constant envelope phase modulation, and separately amplifies each component. The phase modulated and amplified components are then recombined to arrive at an amplitude and phase modulated and amplified output signal. The predistortion modification is applied to the input to compensate for distortions introduced in the signal by the amplifier subsystem.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
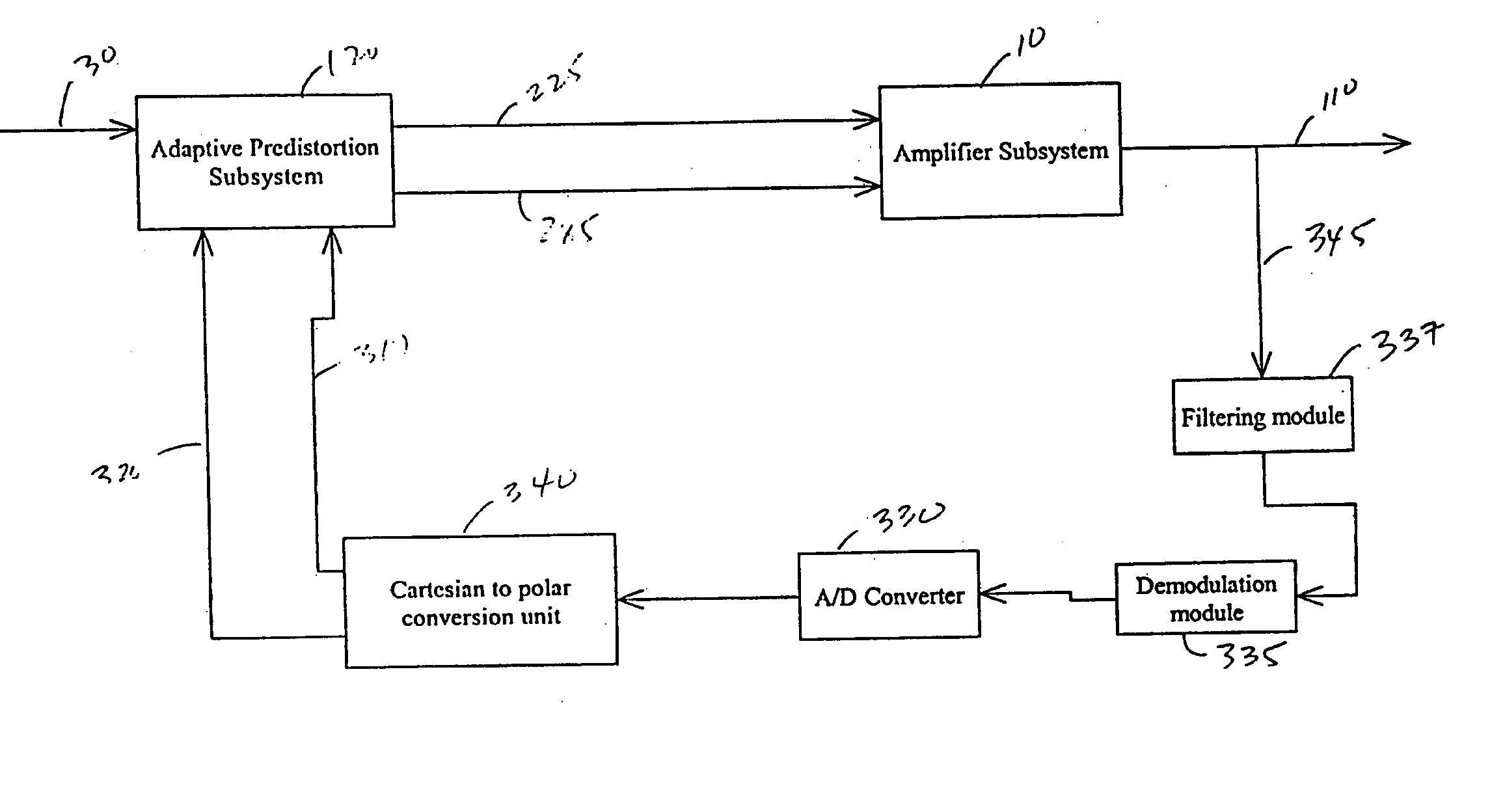
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system
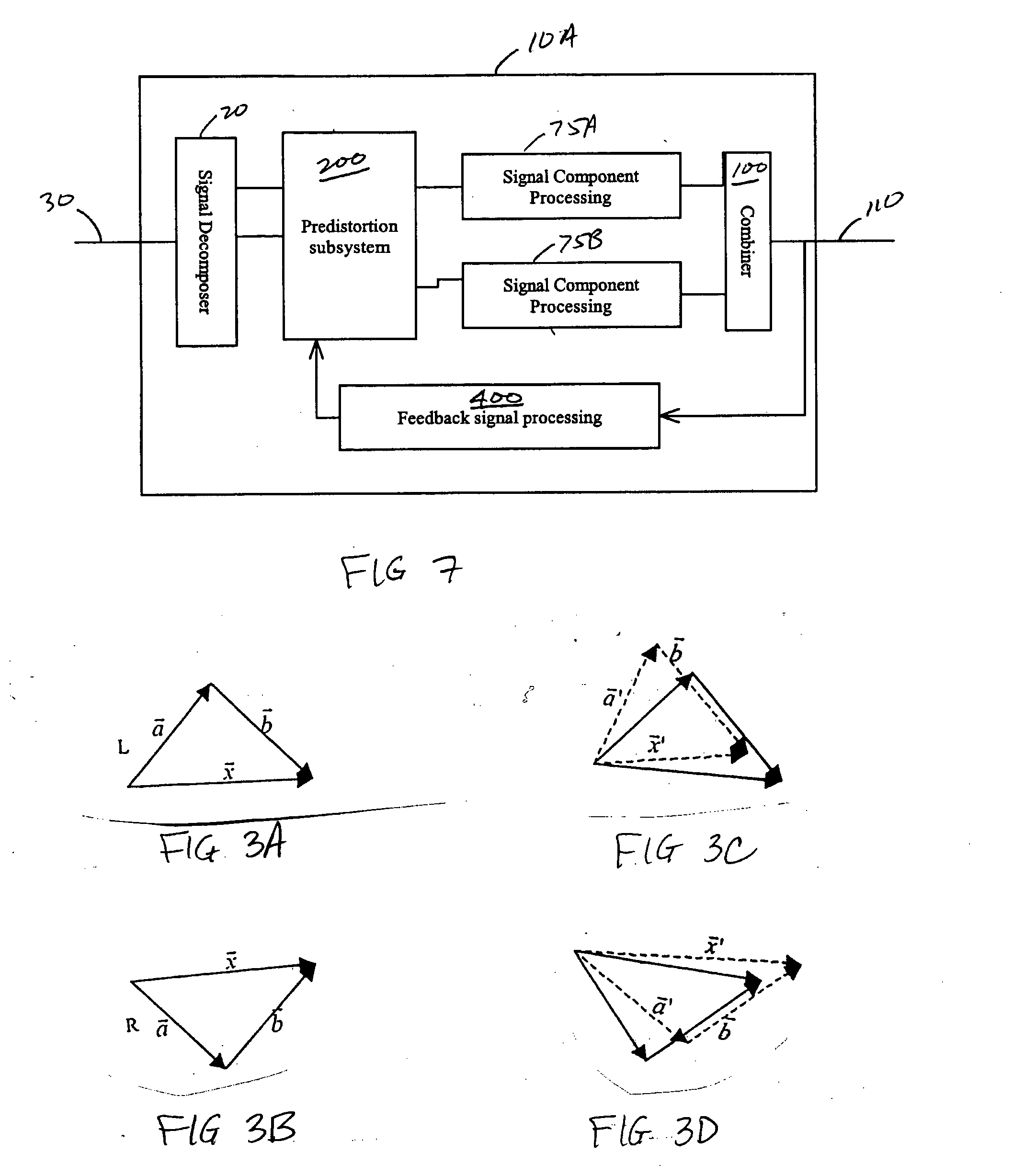
ActiveUS20050001677A1Compensation DistortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsControl systemEngineering
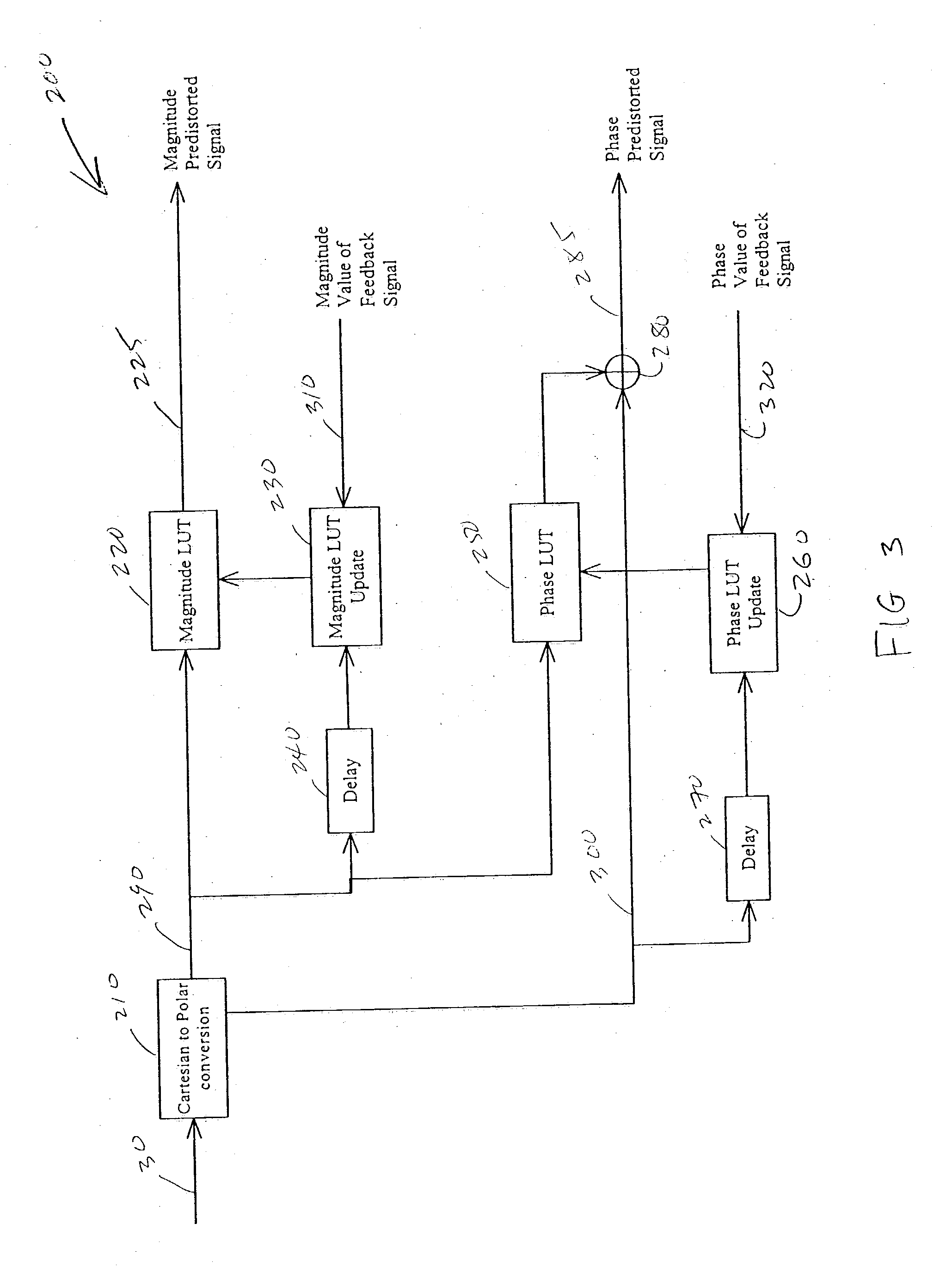
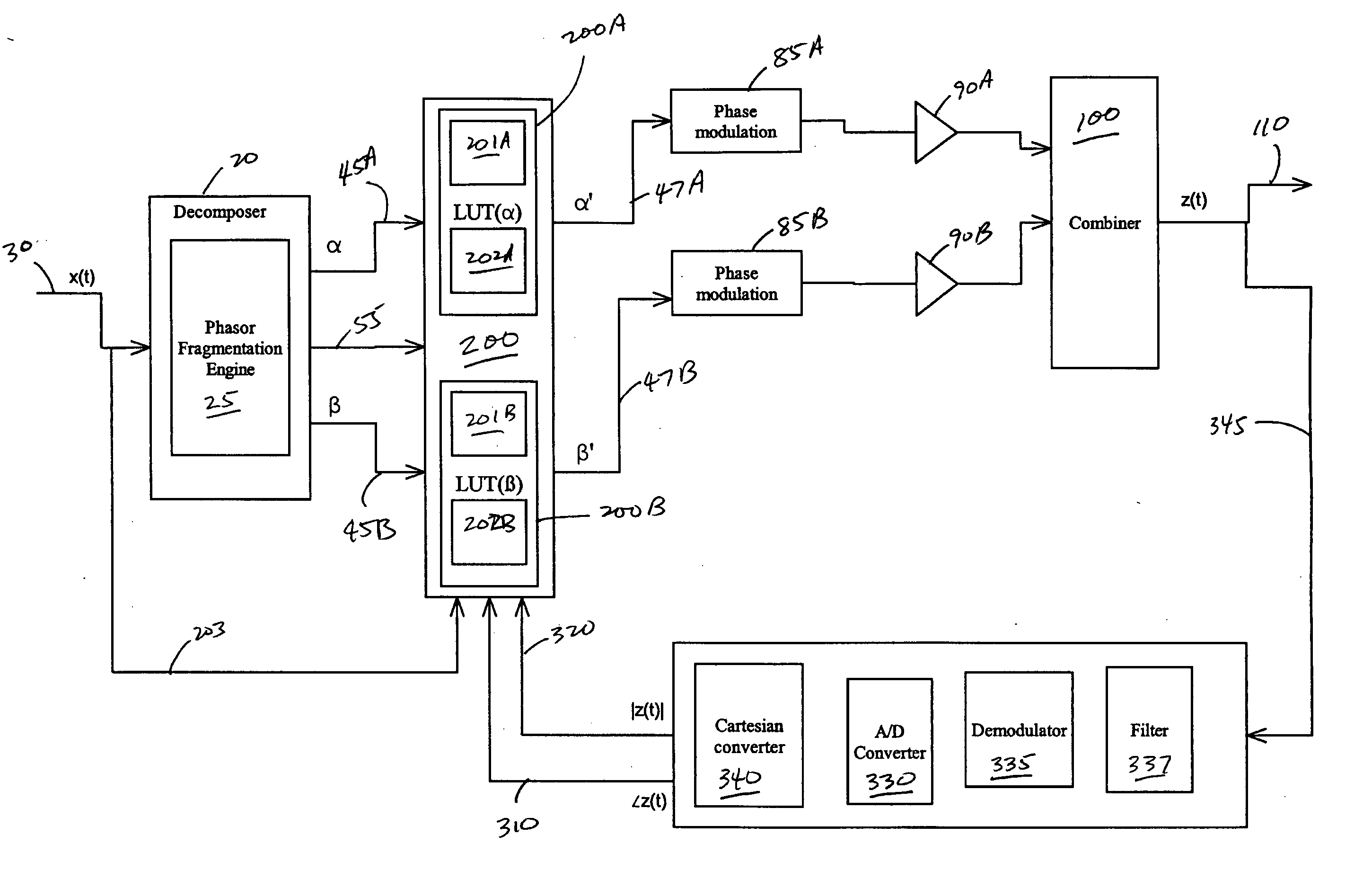
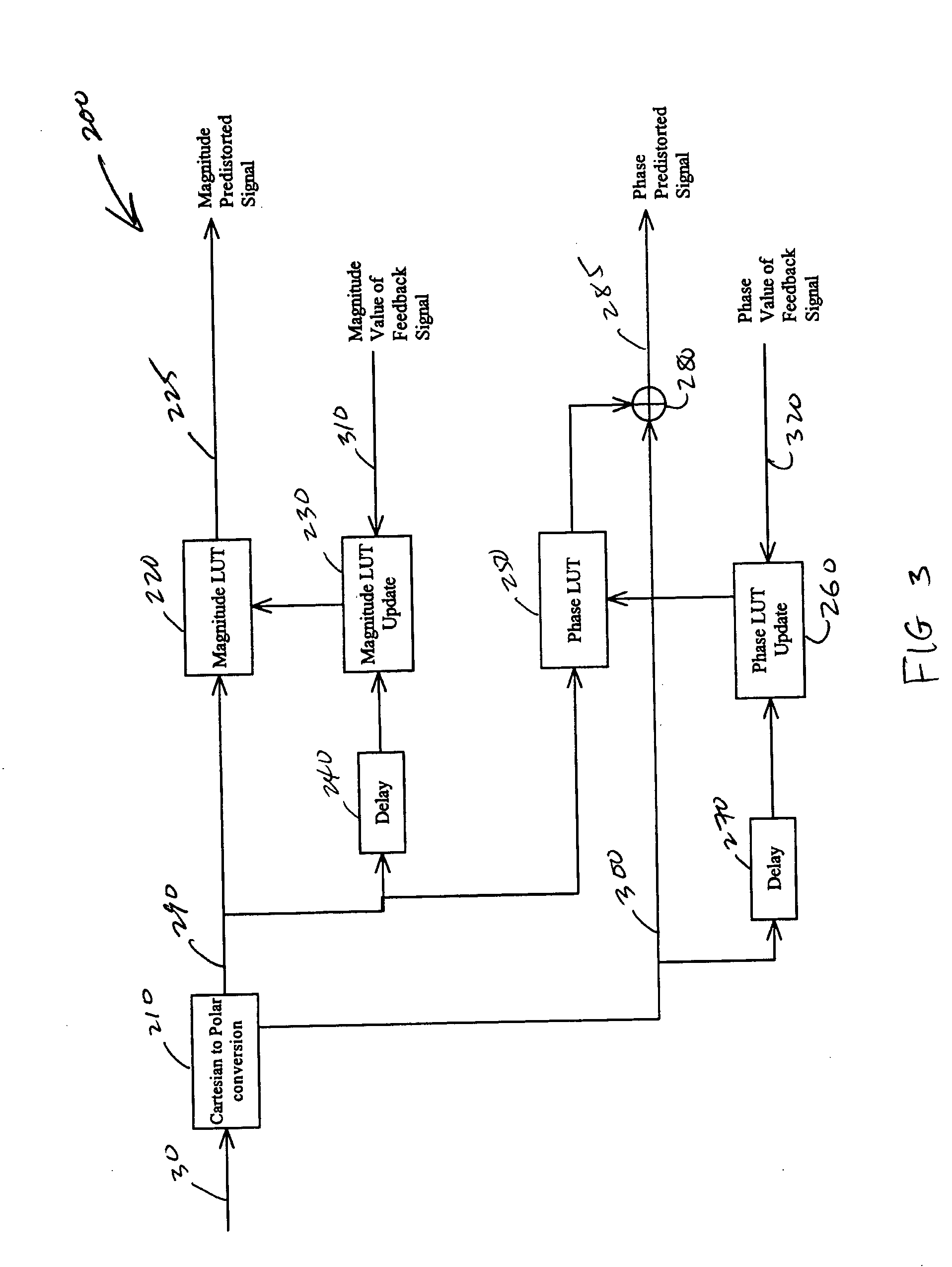
Systems, methods, and devices relating to the provision of deliberate predistortion to an input signal to compensate for distortions introduced by an amplifier subsystem. An input signal is received by a signal processing system which includes a predistortion subsystem. The input signal is decomposed and the fragments are then predistorted by the predistortion subsystem by applying a deliberate predistortion to the fragments. The predistorted fragments are then separately processed and recombined to arrive at the system output signal. The predistortion subsystem adaptively adjusts based on characteristics of the system output signal. Also, the predistortion subsystem is equipped with a control system that is state based—the state of the predistortion subsystem is dependent upon the prevailing conditions and, when required, the control system switches the state of the predistortion subsystem. A feedback signal, a replica of the system output signal, is used in updating lookup table entries used to determine the predistortion.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
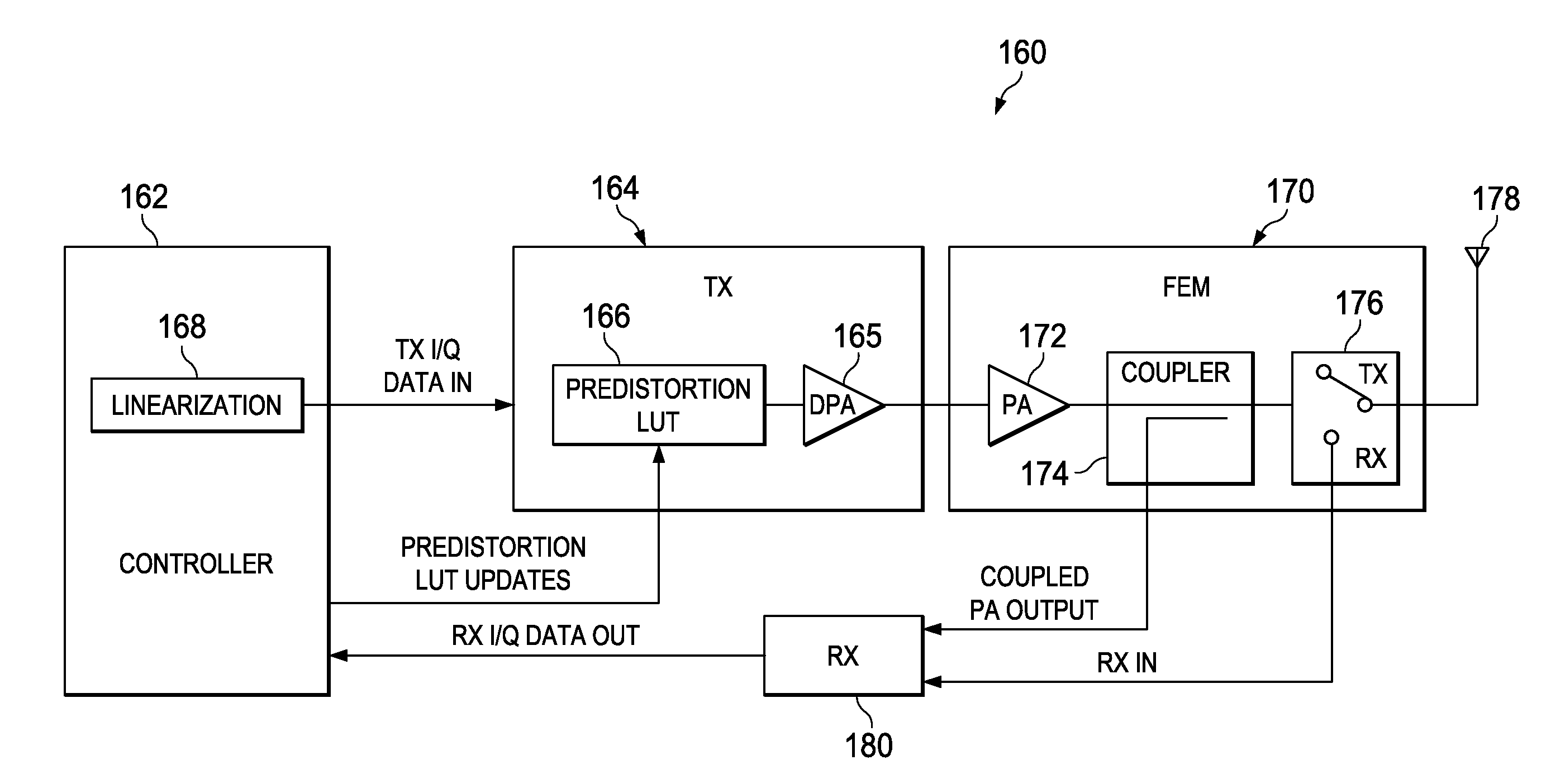
Predistortion calibration and built in self testing of a radio frequency power amplifier using subharmonic mixing
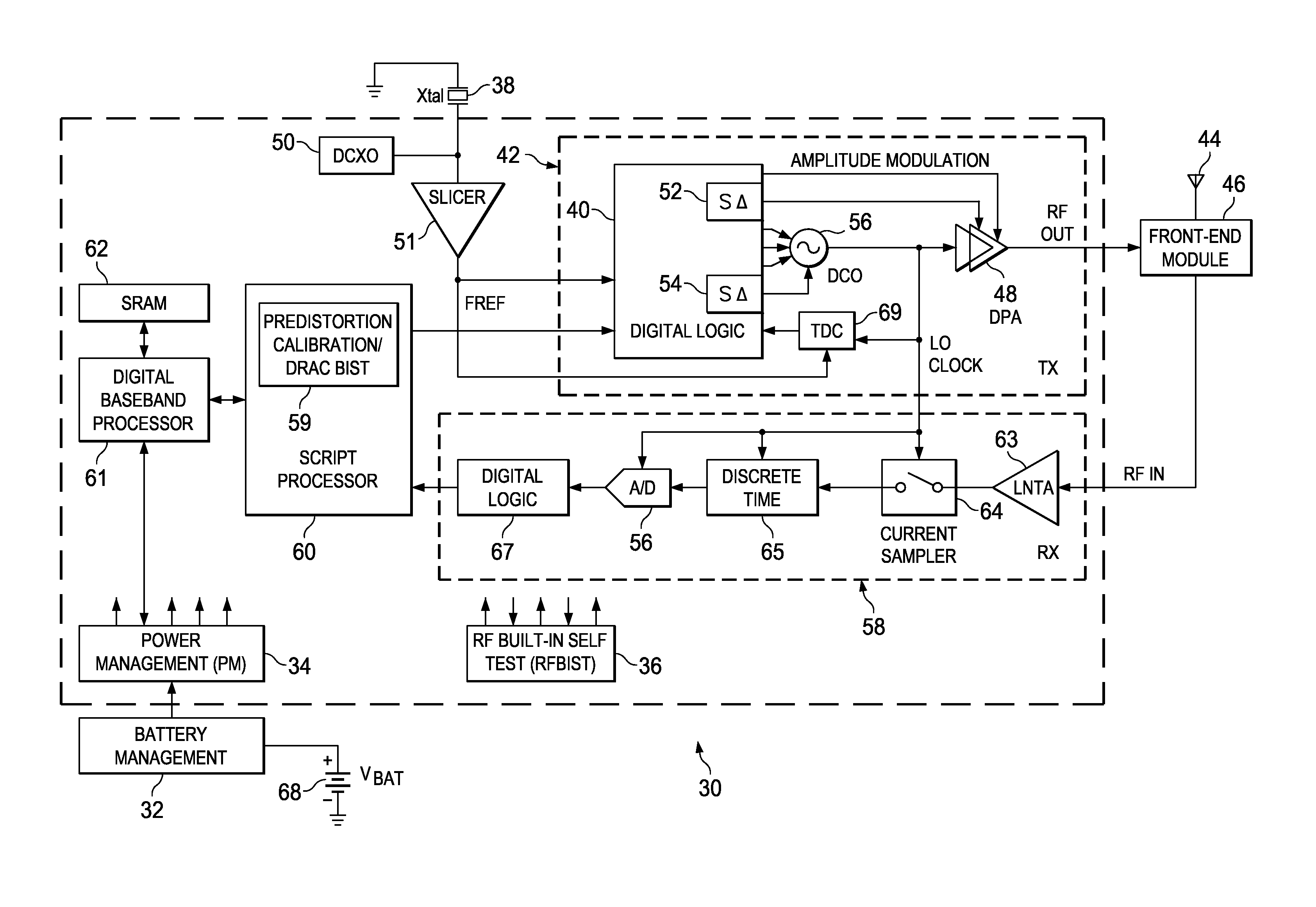
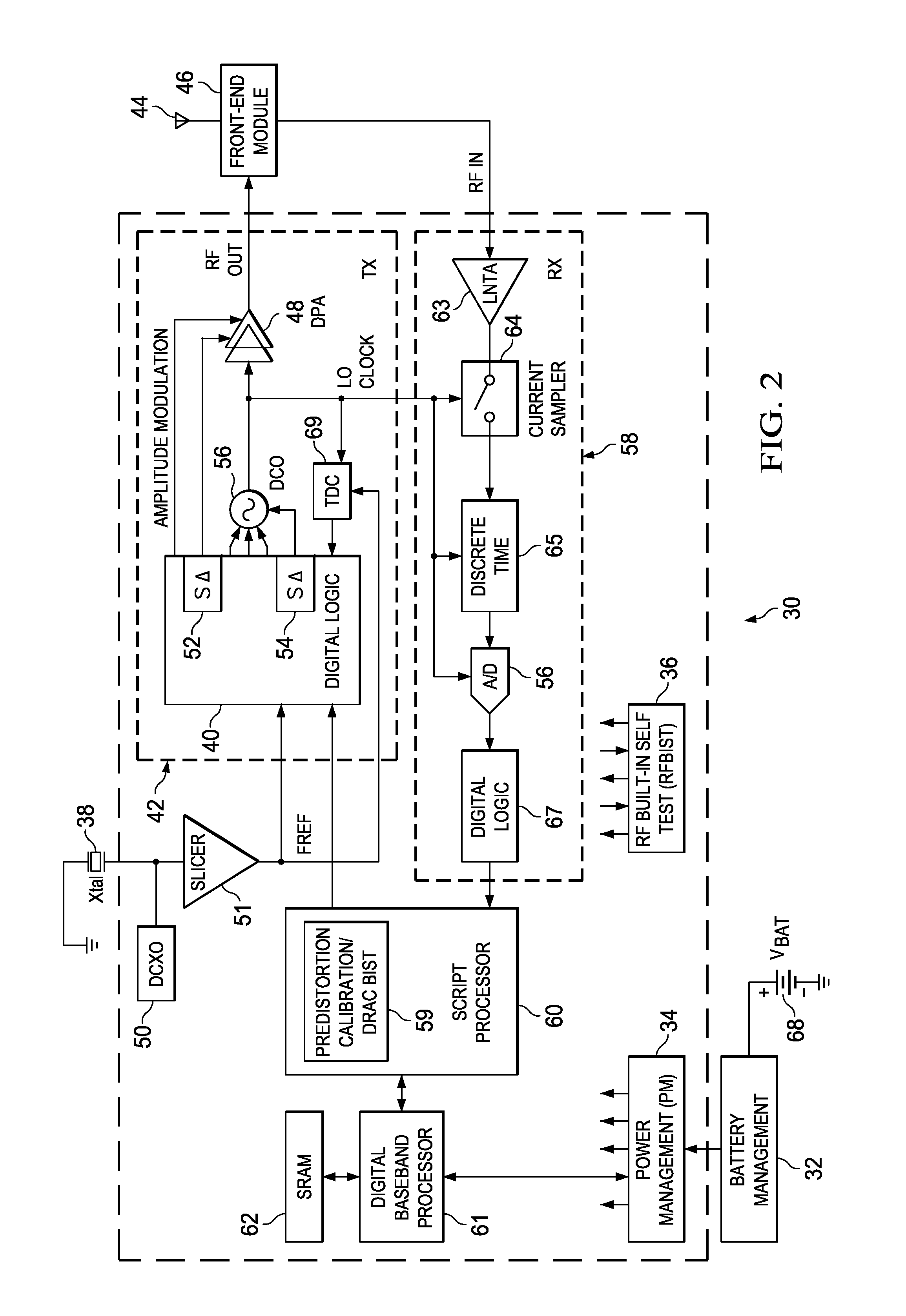
ActiveUS20120252382A1No significant hardware overheadStrain is placedTransmitters monitoringPower amplifiersHarmonicTested time
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of predistortion calibration and built-in self testing (BIST) of a nonlinear digitally-controlled radio frequency (RF) power amplifier (DPA) using subharmonic mixing. The RF power amplifier output is temporarily coupled into the frequency reference (FREF) input and the phase error samples generated in the phase locked loop (PLL) are then observed and analyzed. The digital predistortion and BIST mechanisms process the phase error samples to calibrate and test the DPA in the transmitter of the Digital RF Processor (DRP). The invention enables the characterization of nonlinearities, the configuration of internal predistortion, as well as the testing of the transmitter's analog / RF circuitry, thereby eliminating commonly employed RF performance testing using high-cost test equipment and associated extended test times.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Predistortion circuit for a transmit system
Systems and methods related to amplifier systems which use a predistortion subsystem to compensate for expected distortions in the system output signal. A signal processing subsystem receives an input signal and decomposes the input signal into multiple components. Each signal component is received by a predistortion subsystem which applies a predistortion modification to the component. The predistortion modification may be a phase modification, a magnitude modification, or a combination of both and is applied by adjusting the phase of the fragment. The predistorted component is then separately processed by the signal processing subsystem. The processing may take the form of phase modulation and amplification. The phase modulated and amplified components are then recombined to arrive at an amplitude and phase modulated and amplified output signal. The predistortion modification is applied to the components to compensate for distortions introduced in the signal by the signal processing subsystem.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
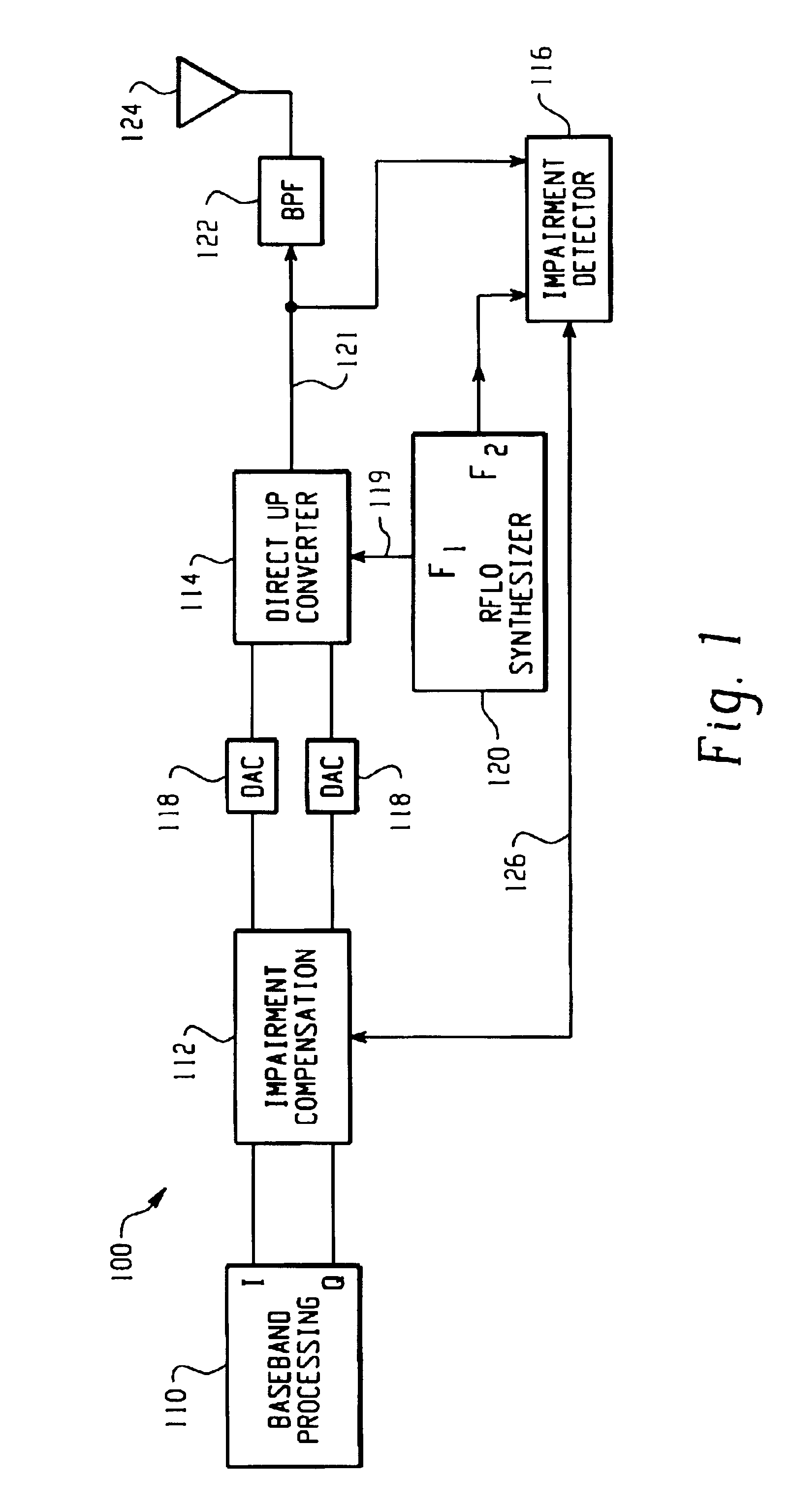
Feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter
ActiveUS6987954B2Resonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
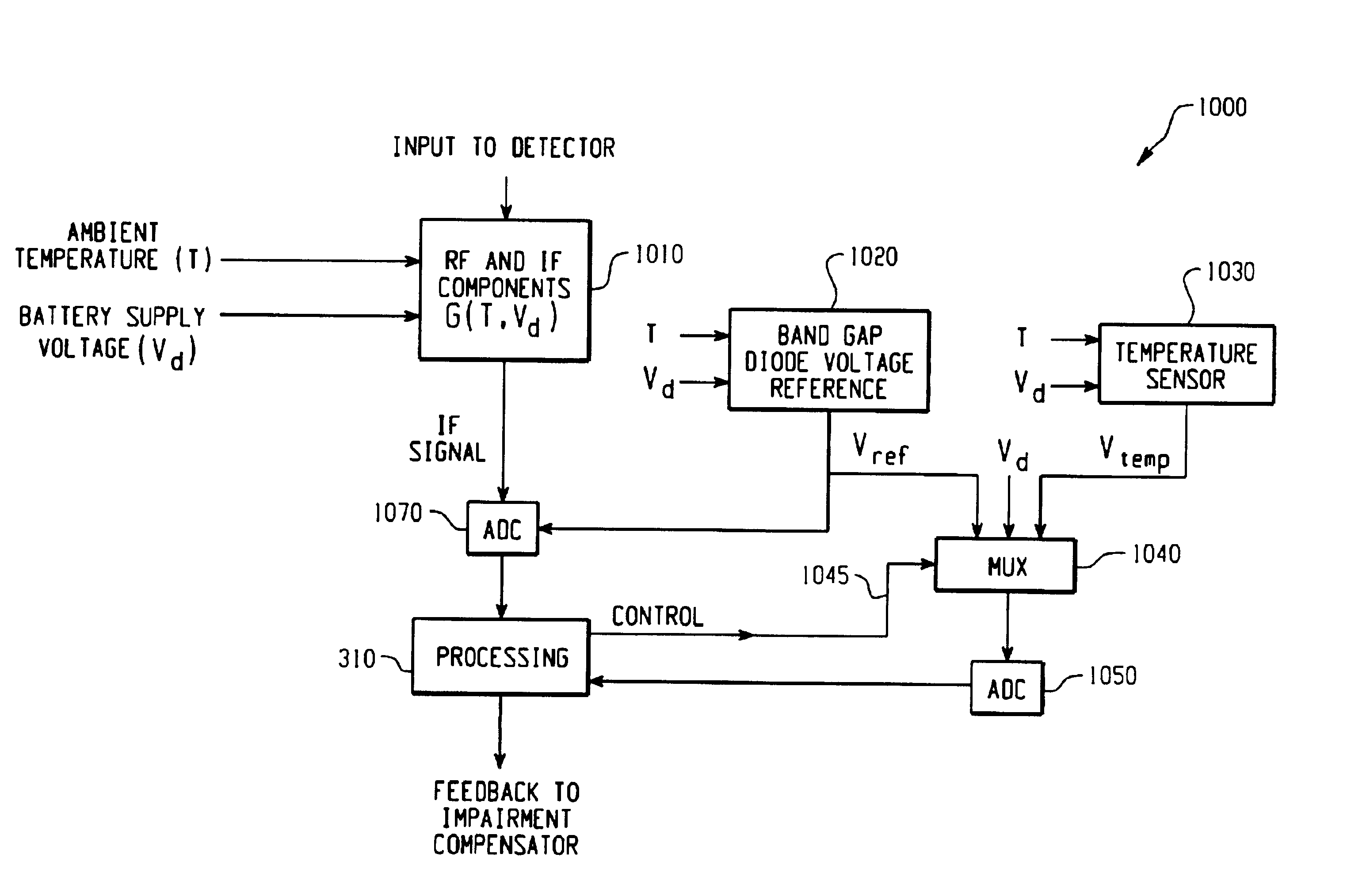
A feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter includes a baseband processor, a direct up-converter, an antenna, and an impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit. The baseband processor generates an in-phase (I) baseband signal and a quadrature-phase (Q) baseband signal. The direct up-converter is coupled to the baseband processor, and combines the I and Q baseband signals with an RF carrier signal to generate an RF output signal. The antenna is coupled to the direct up-converter, and transmits the RF output signal. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit is coupled to the RF output signal and the I and Q baseband signals. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit down-converts the RF output signal to generate an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, measures as least one signal impairment in the IF signal, and pre-distorts the I and Q baseband signals to compensate for the measured signal impairment.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
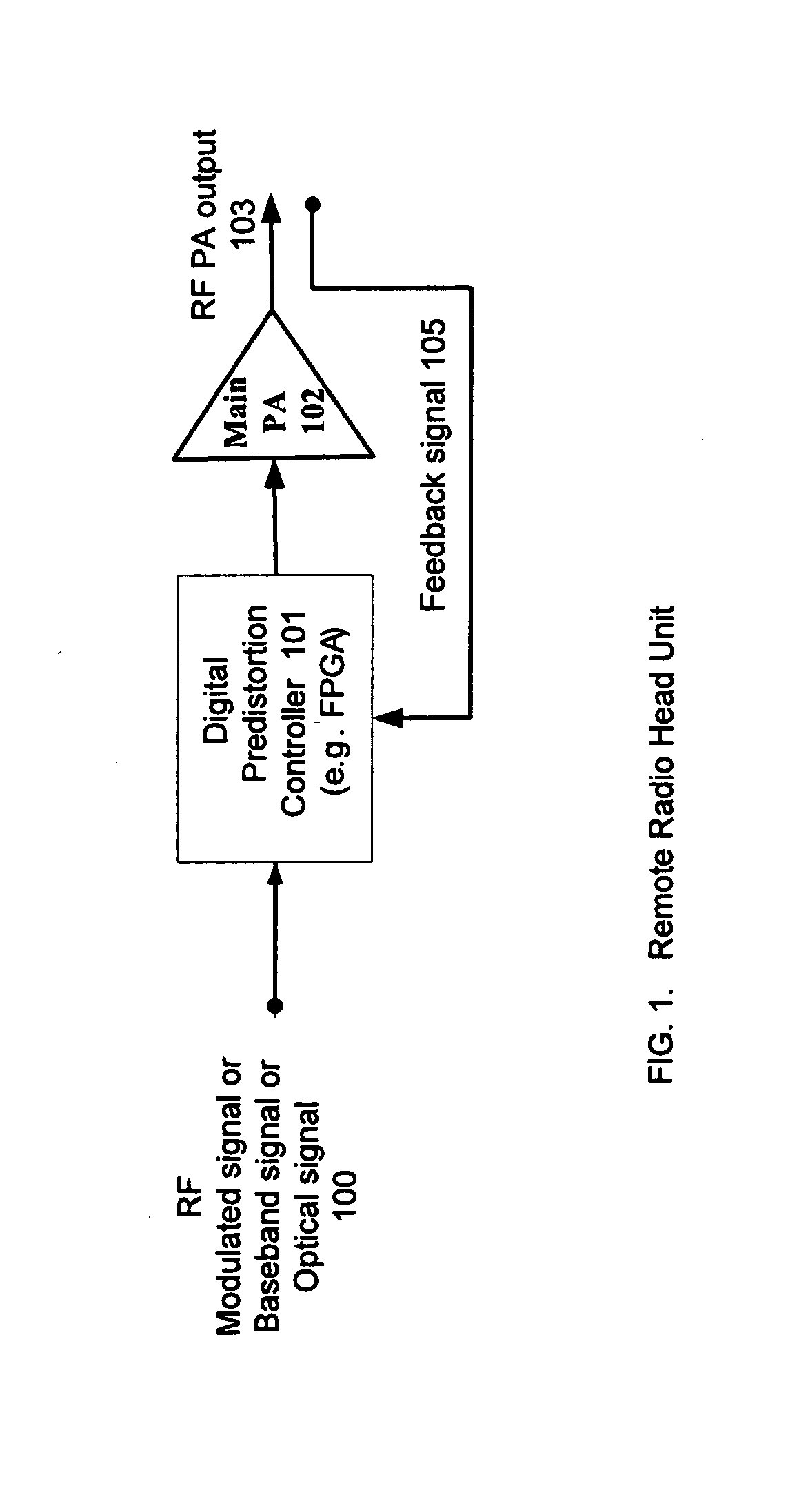
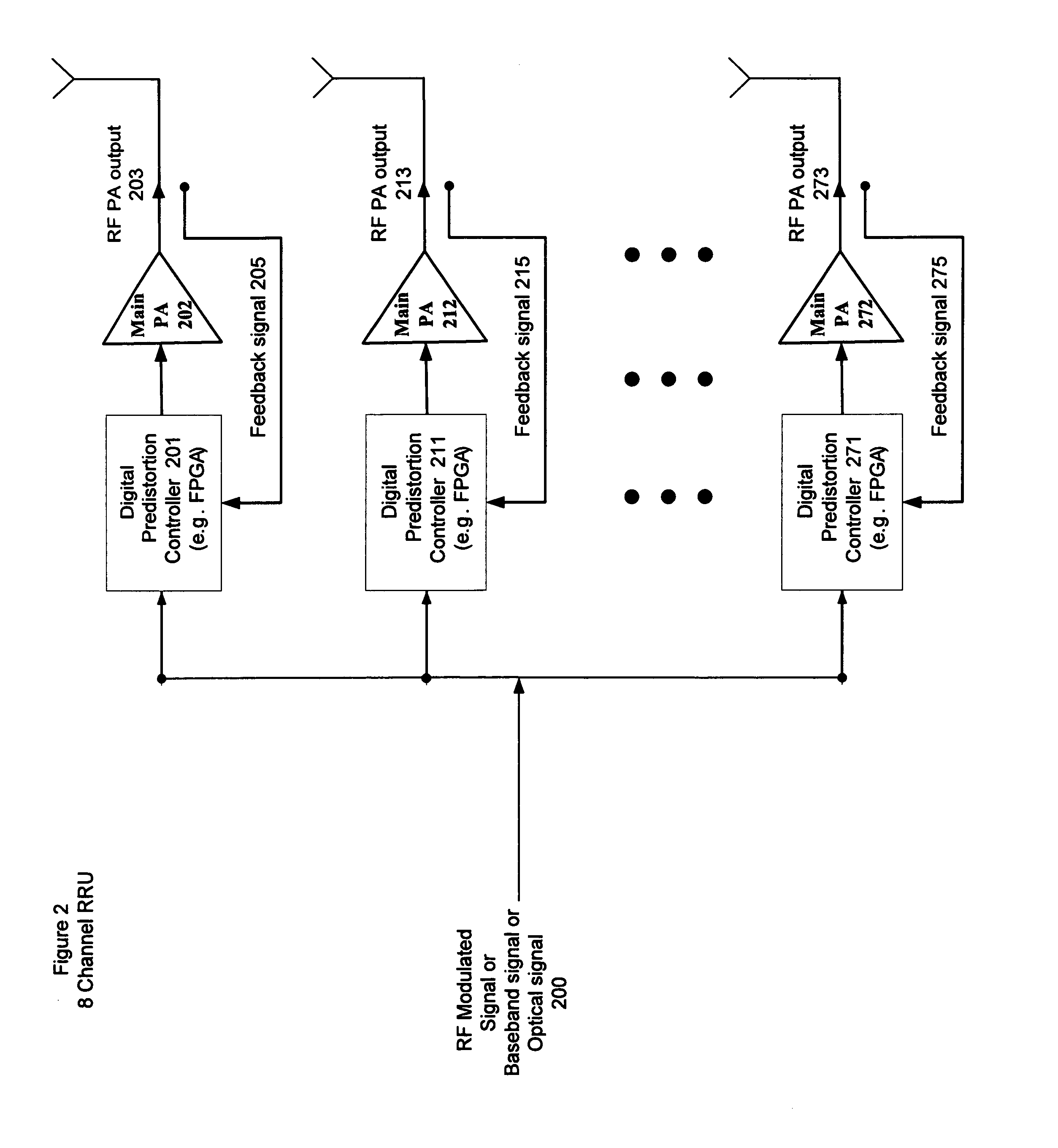
High efficiency, remotely reconfigurable remote radio head unit system and method for wireless communications
ActiveUS20120155572A1High performance and cost-effectiveImprove linearityEnergy efficient ICTPower amplifiersUnit systemEngineering
A remote radio head unit (RRU) system for achieving high efficiency and high linearity in wideband communication systems is disclosed. The present invention is based on the method of adaptive digital predistortion to linearize a power amplifier inside the RRU. The power amplifier characteristics such as variation of linearity and asymmetric distortion of the amplifier output signal are monitored by a wideband feedback path and controlled by the adaptation algorithm in a digital module. Therefore, embodiments of the present invention can compensate for the nonlinearities as well as memory effects of the power amplifier systems and also improve performance, in terms of power added efficiency, adjacent channel leakage ratio and peak-to-average power ratio. The present disclosure enables a power amplifier system to be field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation agnostic), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. As a result, the remote radio head system is particularly suitable for wireless transmission systems, such as base-stations, repeaters, and indoor signal coverage systems.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments
ActiveUS20050001675A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsEngineeringSelf adaptive
Systems and methods relating to the provision of gain, phase and delay adjustments to signals to be used by a predistortion subsystem. A portion of an input signal is delayed by delay elements prior to being received by the predistortion subsystem. The delayed input signal portion is also received by a feedback signal processing subsystem that adjusts the gain and phase of the feedback signal based on the delayed input signal portion. The adjusted feedback signal is used, along with the delayed portion of the input signal, to determine an appropriate predistortion modification to be applied to the input signal.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments.
InactiveUS20050001678A1Compensation DistortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsControl systemLookup table
Systems, methods, and devices relating to the provision of deliberate predistortion to an input signal to compensate for distortions introduced by an amplifier subsystem. An input signal is received by a signal processing system which includes a predistortion subsystem. The input signal is decomposed and the fragments are then predistorted by the predistortion subsystem by applying a deliberate predistortion to the fragments. The predistorted fragments are then separately processed and recombined to arrive at the system output signal. The predistortion subsystem adaptively adjusts based on characteristics of the system output signal. Also, the predistortion subsystem is equipped with a control system that is state based—the state of the predistortion subsystem is dependent upon the prevailing conditions and, when required, the control system switches the state of the predistortion subsystem. A feedback signal, a replica of the system output signal, is used in updating lookup table entries used to determine the predistortion.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system
ActiveUS20050001674A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsTransfer systemEngineering
Systems, methods, and devices relating to the provision of deliberate predistortion to an input signal to compensate for distortions introduced by an amplifier subsystem. An input signal is received by a predistortion subsystem which applies deliberate predistortions to the input signal to arrive at a predistorted signal. The predistorted signal is received by an amplifier subsystem which decomposes the signal, processes the decomposed signal, and then recombines the components to arrive at a system output signal. The predistortion subsystem adaptively adjusts the predistortions based on characteristics of the system output signal. A feedback signal, a replica of the system output signal, is used in updating lookup table entries used to determine the predistortion.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Linearization of a transmit amplifier
ActiveUS8195103B2Reduce sensitivitySimple calculationResonant long antennasTransmission monitoringElectricityAudio power amplifier
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Signal predistortion in radio transmitter
A transmission signal to be transmitted from a radio transmitter is predistorted in order to compensate for the signal distortion caused by a power amplifier. The predistortion parameters for at least one of envelope and phase predistortion are selected according to the bandwidth of the transmission signal. Then, the transmission signal is predistorted with the selected predistortion parameters, and the predistorted transmission signal is power-amplified in the power amplifier for transmission
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Adaptive predistortion for a transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments
InactiveUS20050001679A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSelf adaptivePredistortion
Systems and methods relating to the provision of gain, phase and delay adjustments to signals to be used by a predistortion subsystem. A portion of an input signal is delayed by delay elements prior to being received by the predistortion subsystem. The delayed input signal portion is also received by a feedback signal processing subsystem that adjusts the gain and phase of the feedback signal based on the delayed input signal portion. The adjusted feedback signal is used, along with the delayed portion of the input signal, to determine an appropriate predistortion modification to be applied to the input signal.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Adaptive predistortion for transmit system with gain, phase and delay adjustments
InactiveUS20050001676A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsEngineeringSelf adaptive
Systems and methods relating to the provision of gain, phase and delay adjustments to signals to be used by a predistortion subsystem. A portion of an input signal is delayed by delay elements prior to being received by the predistortion subsystem. The delayed input signal portion is also received by a feedback signal processing subsystem that adjusts the gain and phase of the feedback signal based on the delayed input signal portion. The adjusted feedback signal is used, along with the delayed portion of the input signal, to determine an appropriate predistortion modification to be applied to the input signal.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com