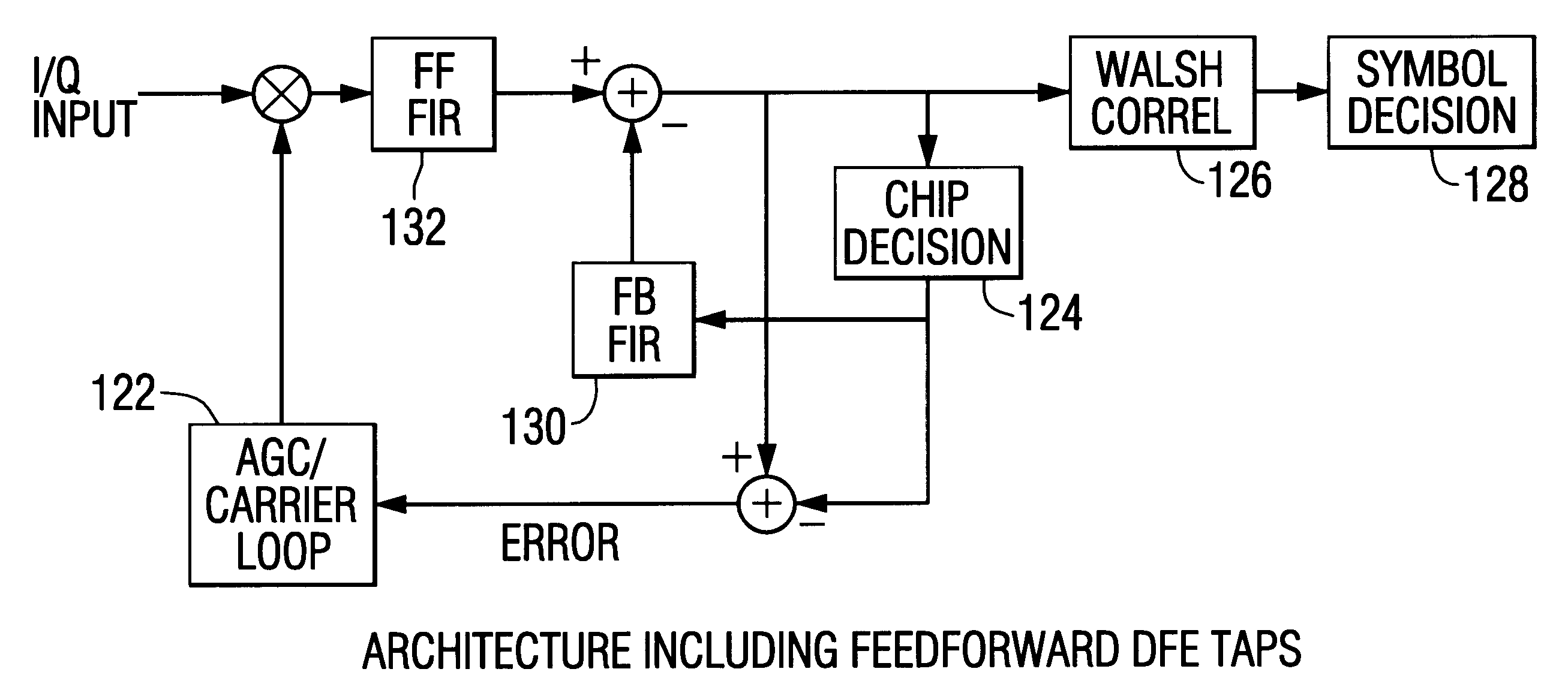
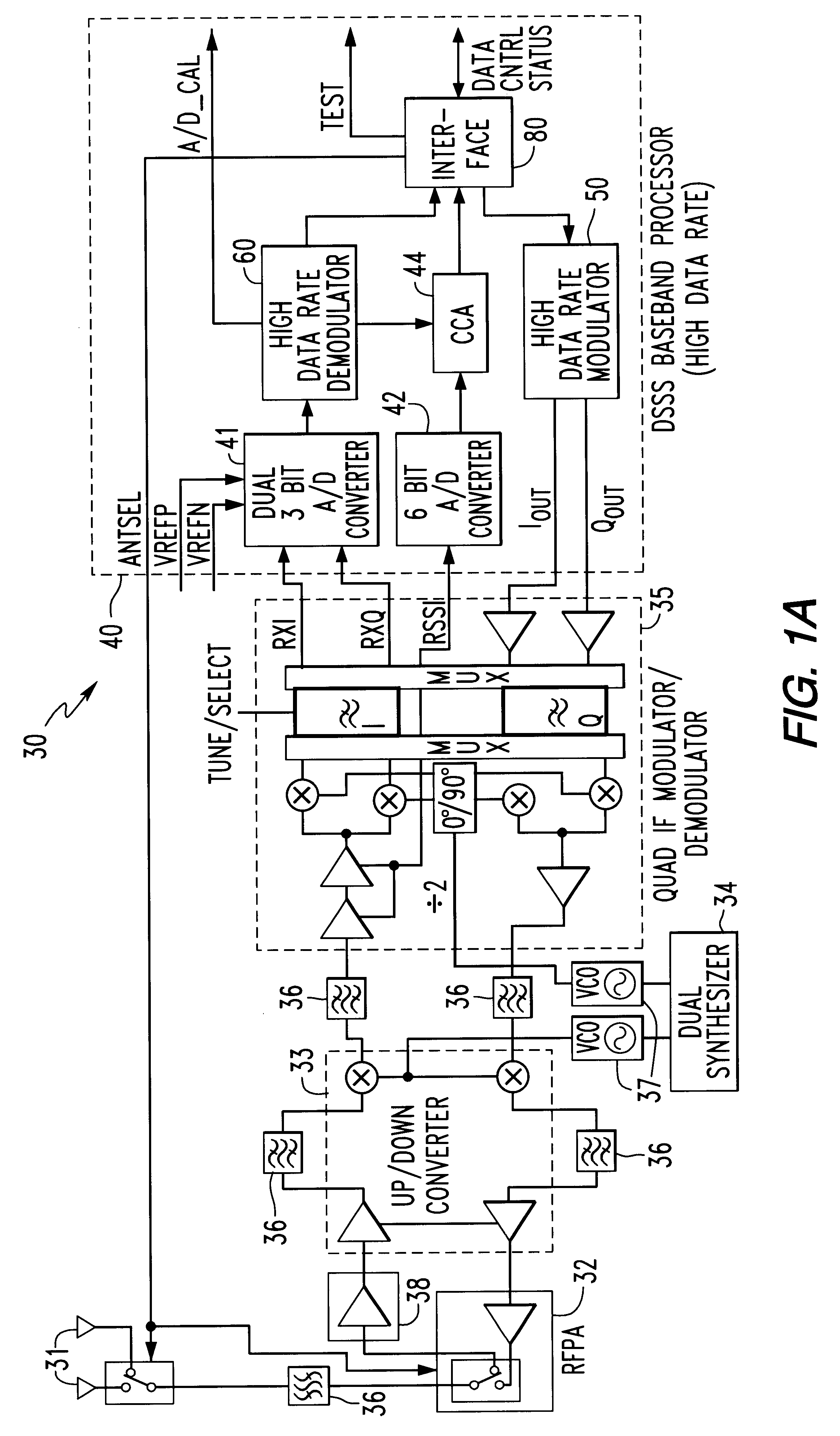
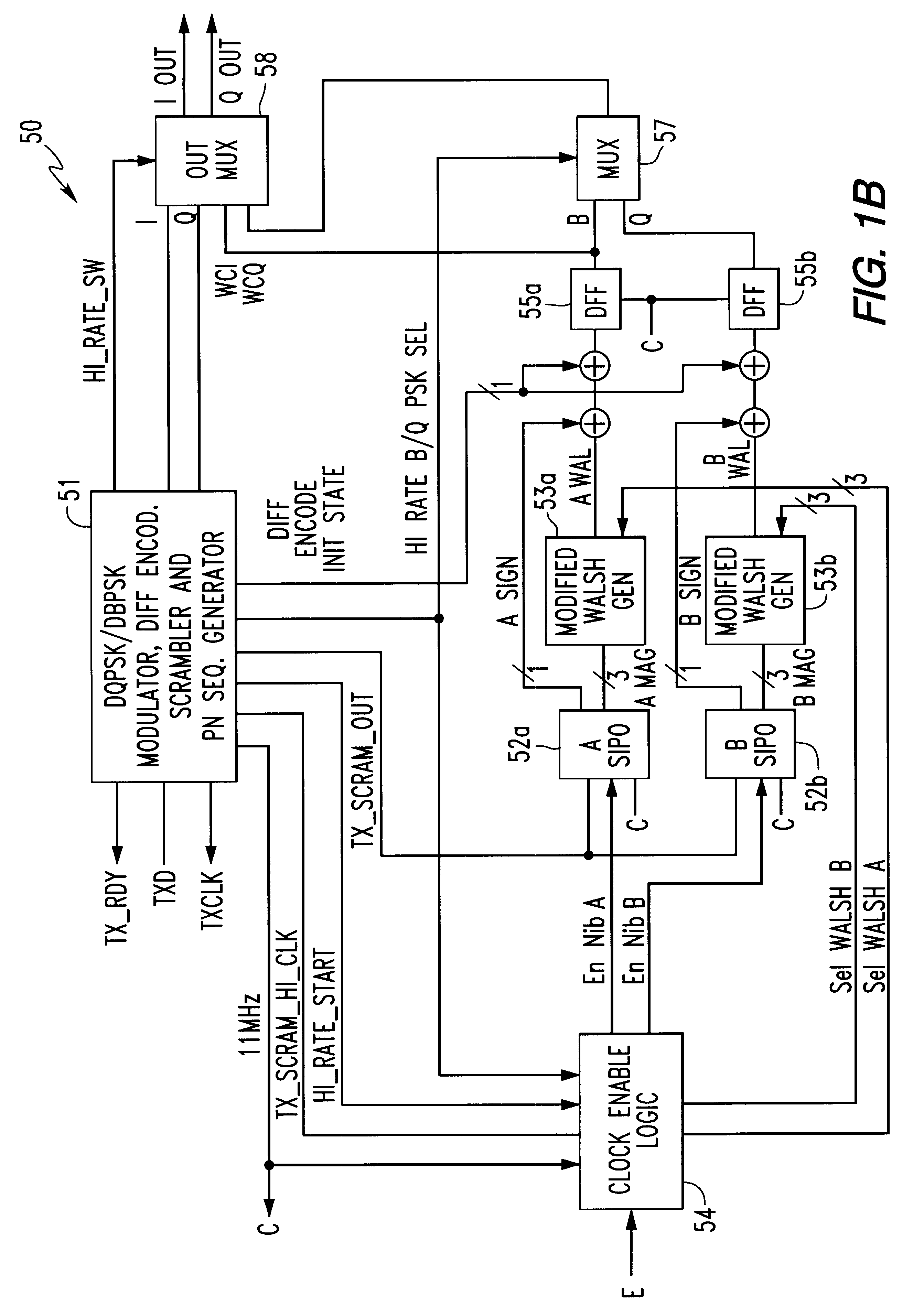
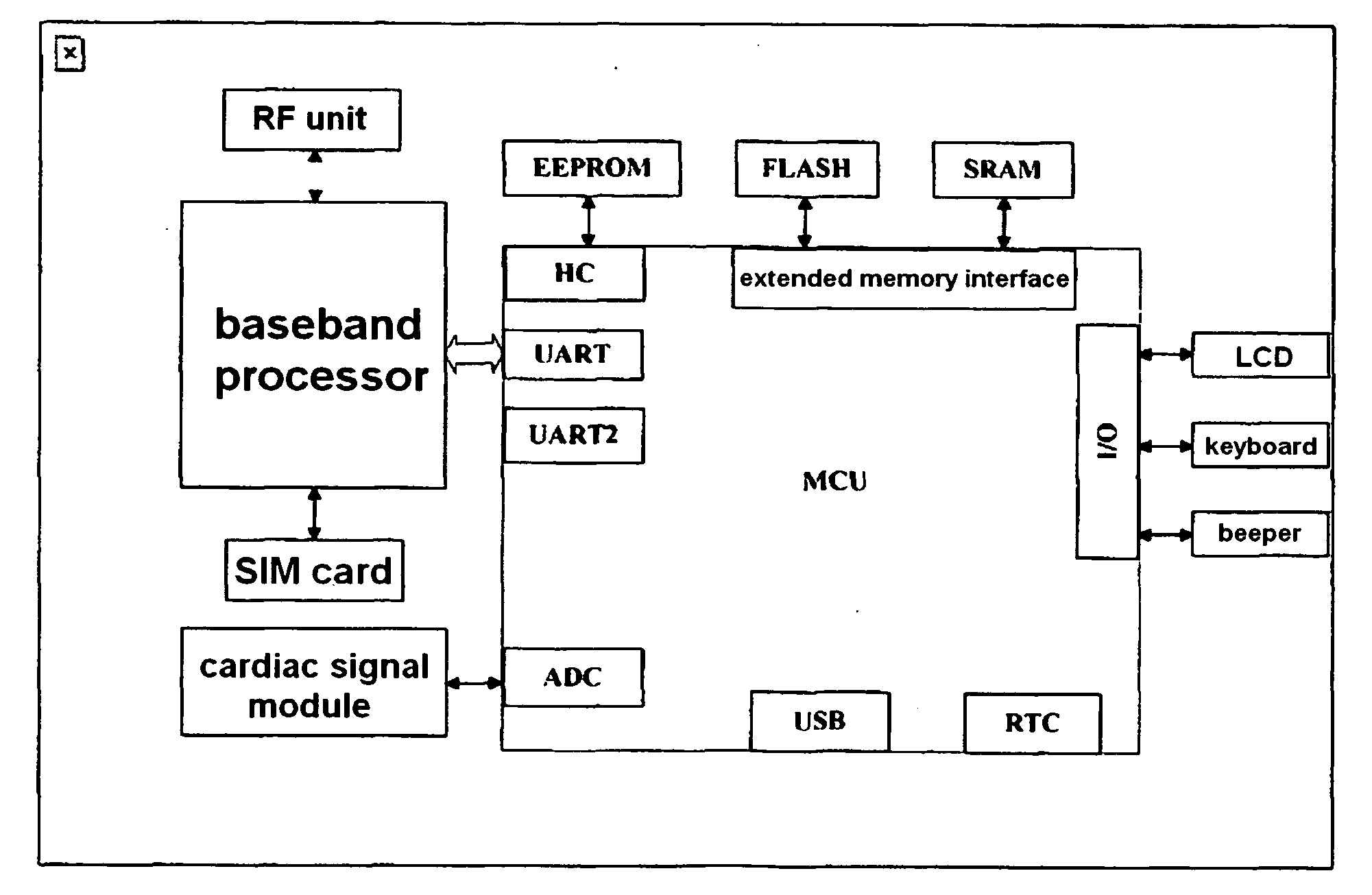
Patents
Literature
981 results about "Baseband processor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
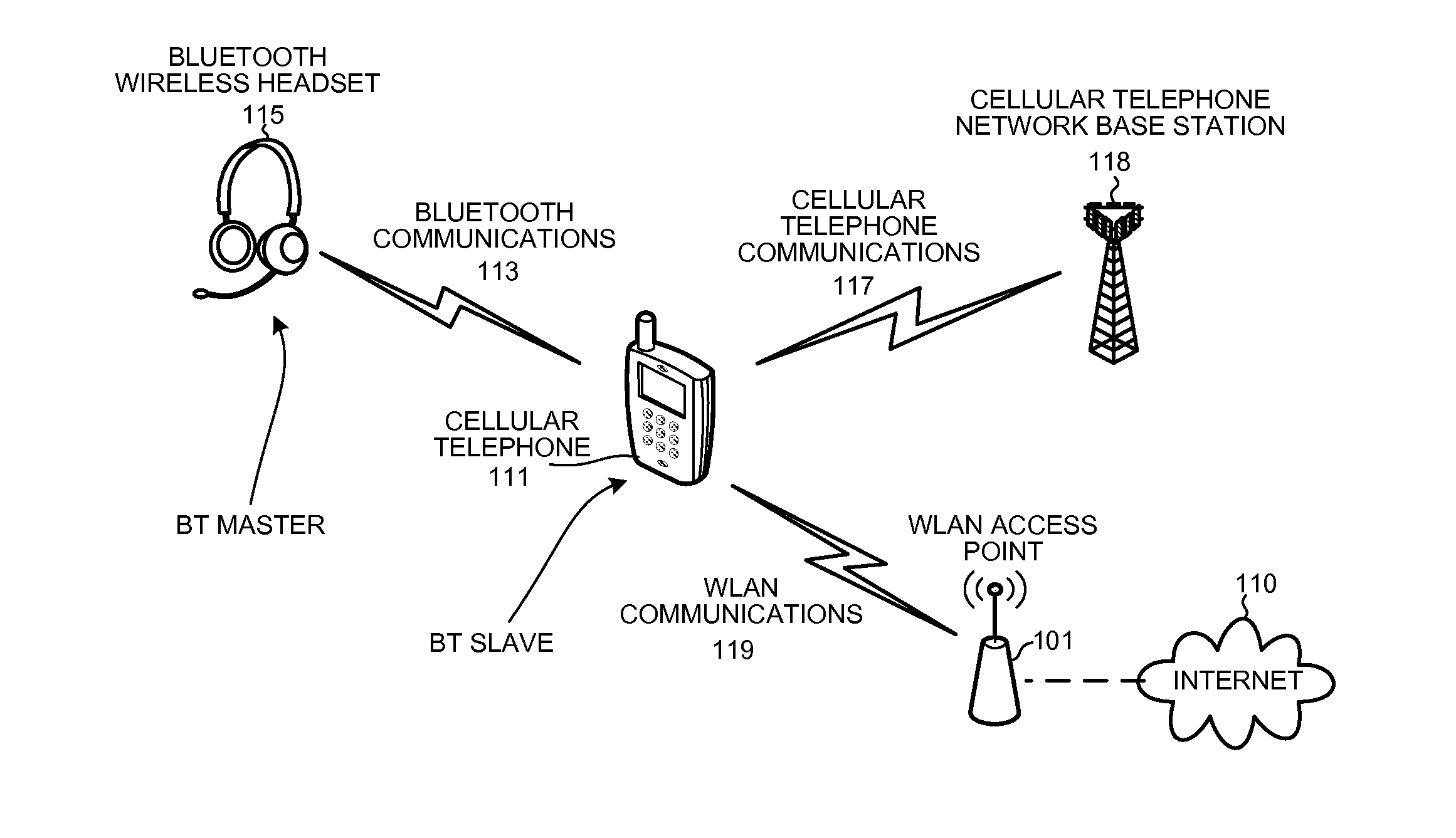
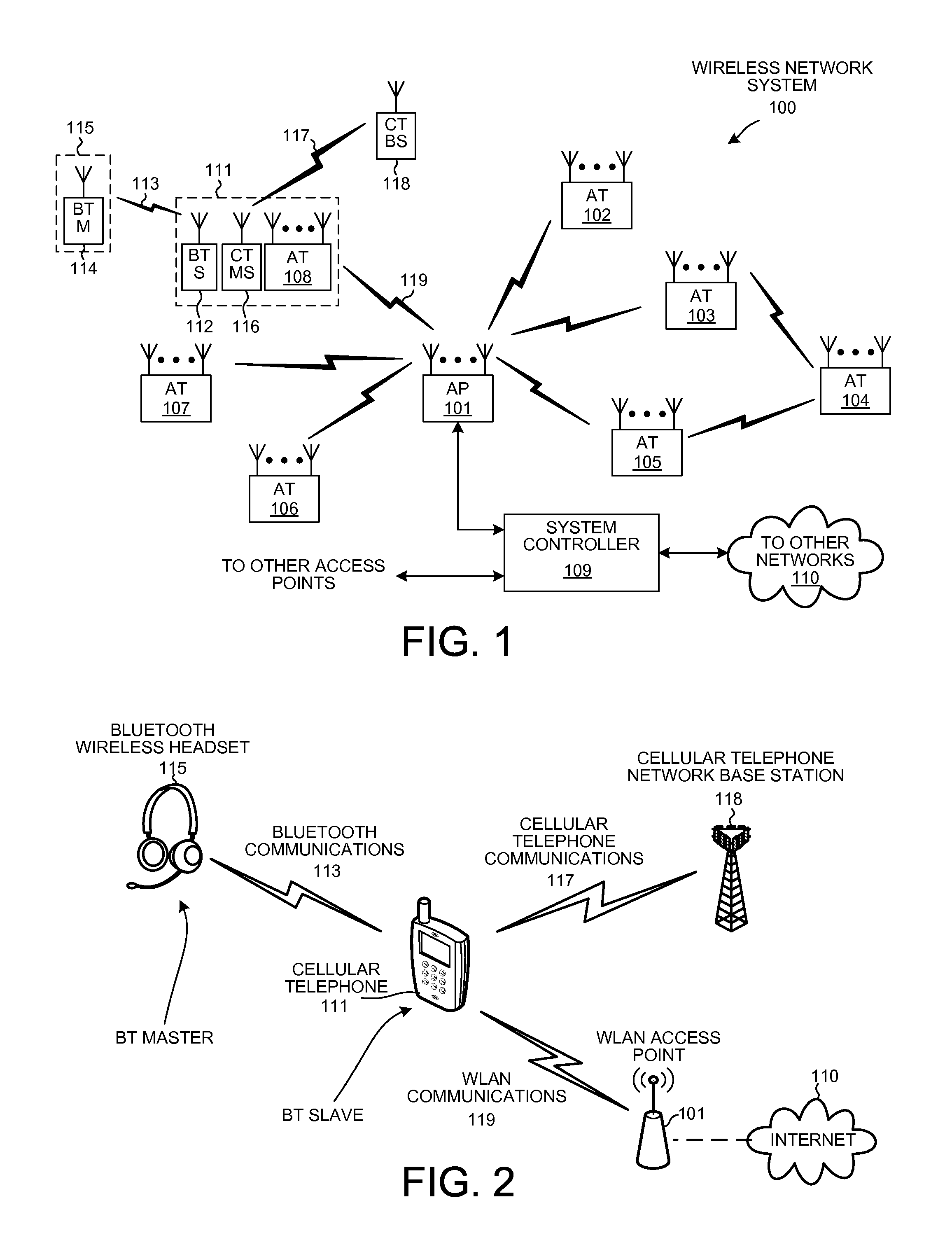
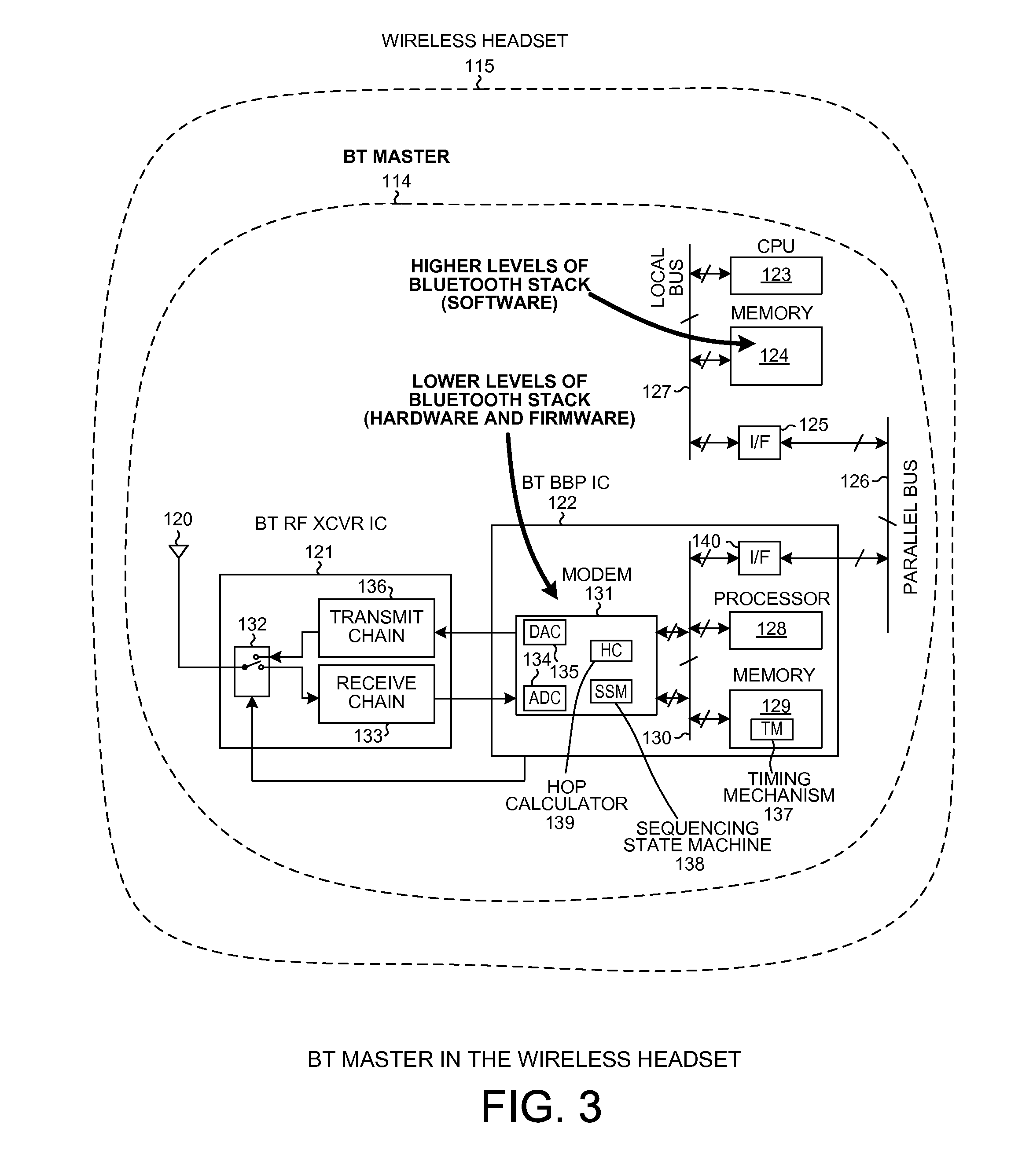
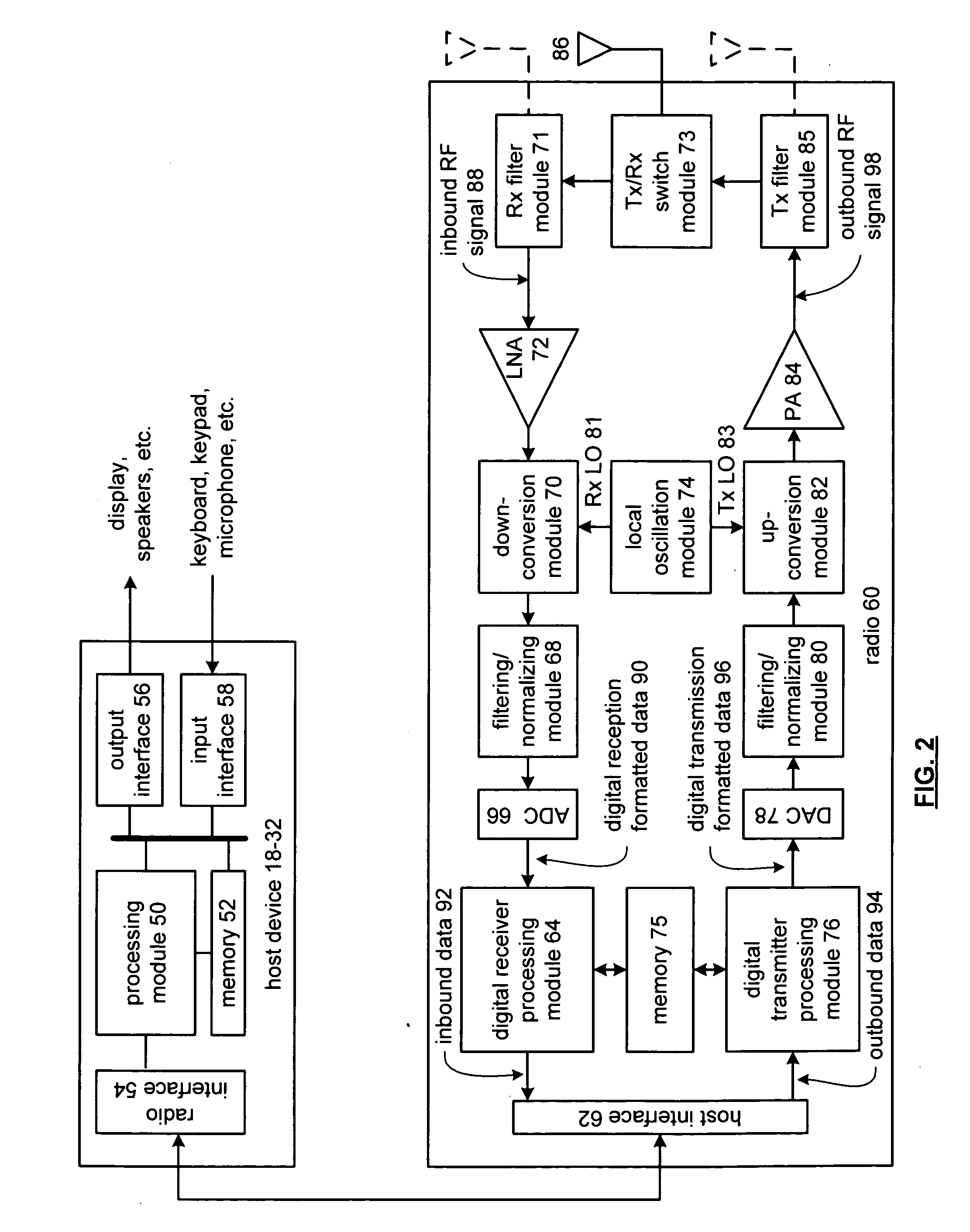
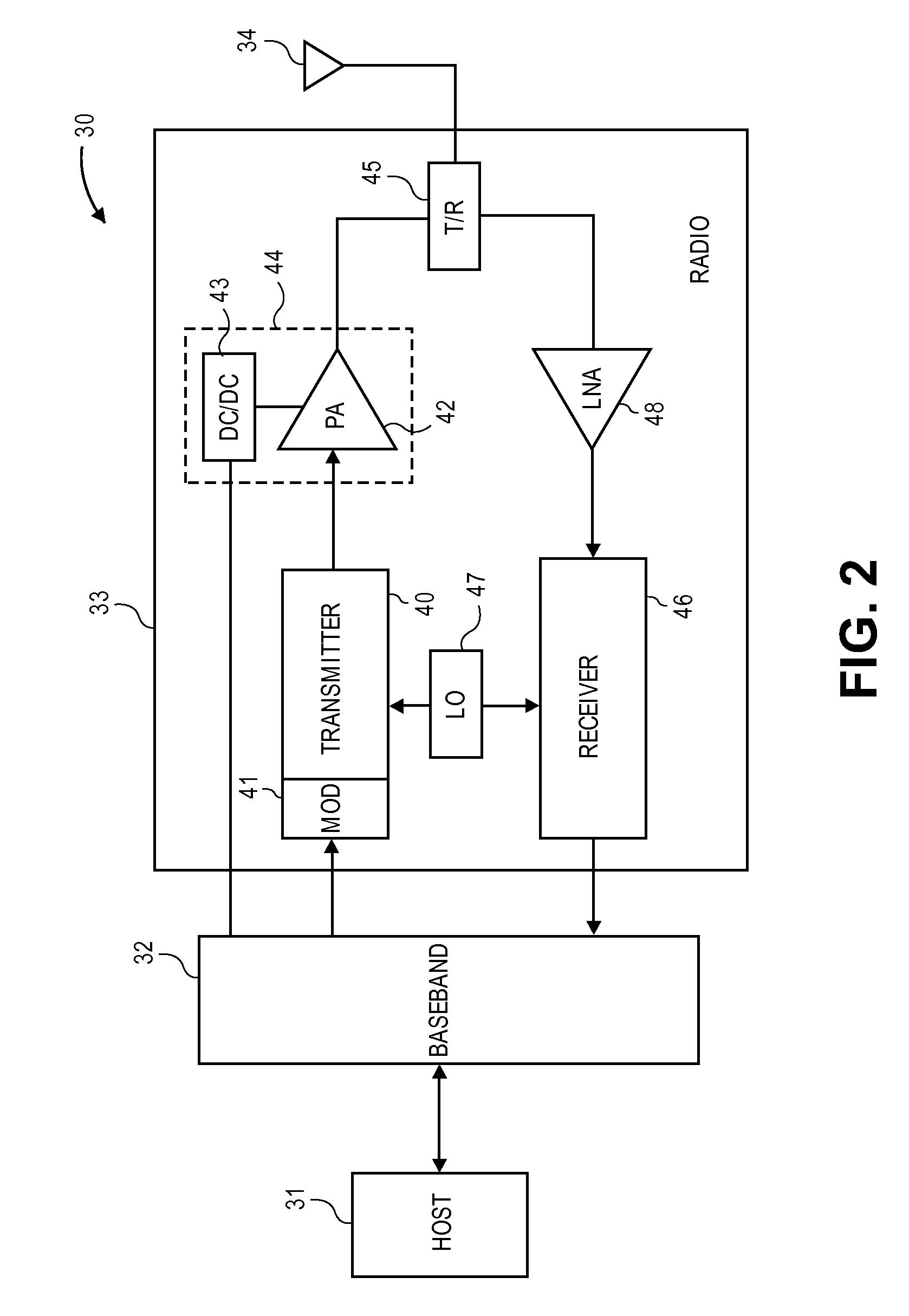
A baseband processor (also known as baseband radio processor, BP, or BBP) is a device (a chip or part of a chip) in a network interface that manages all the radio functions (all functions that require an antenna); however, this term is generally not used in reference to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth radios. A baseband processor typically uses its own RAM and firmware.
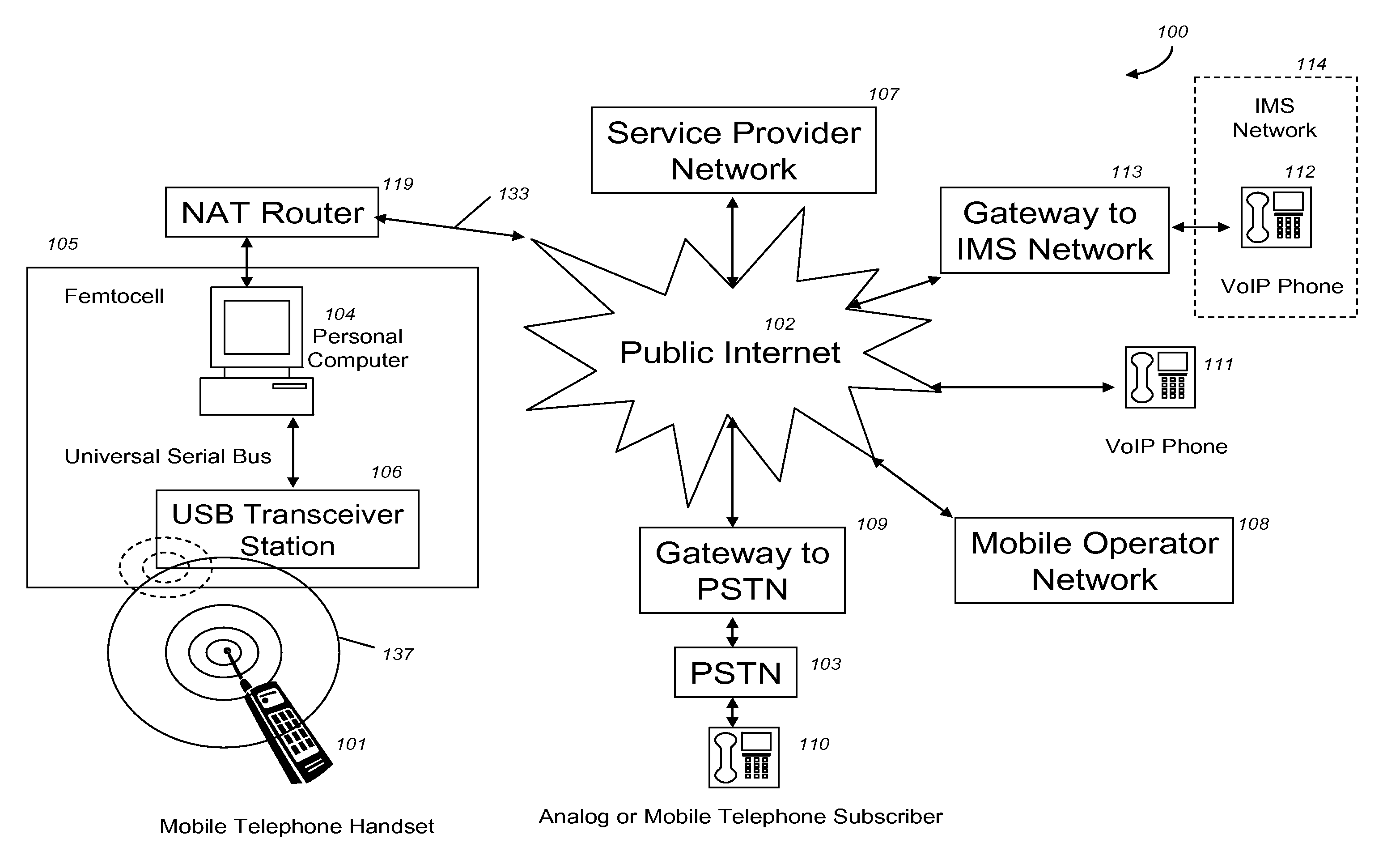
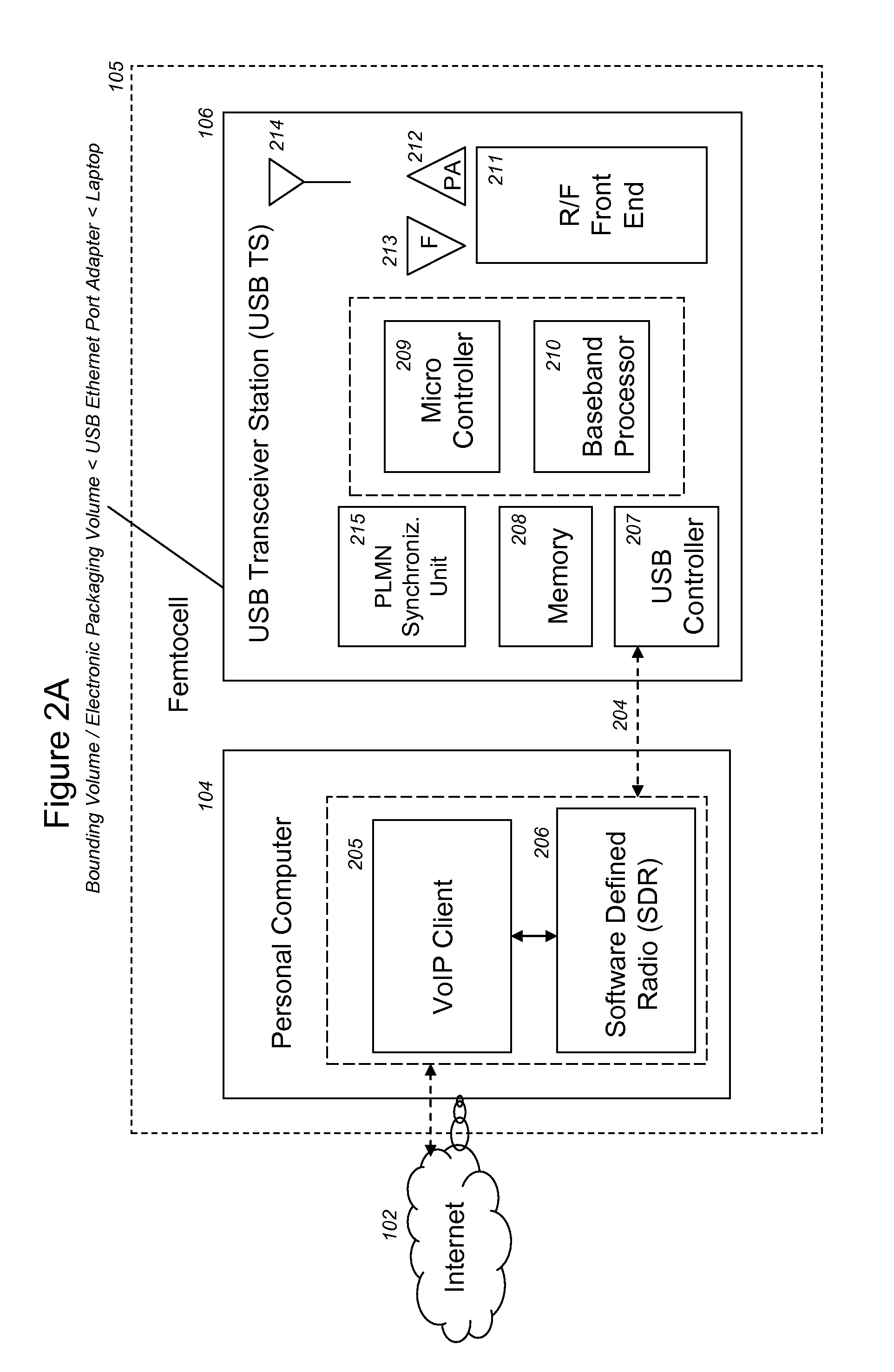
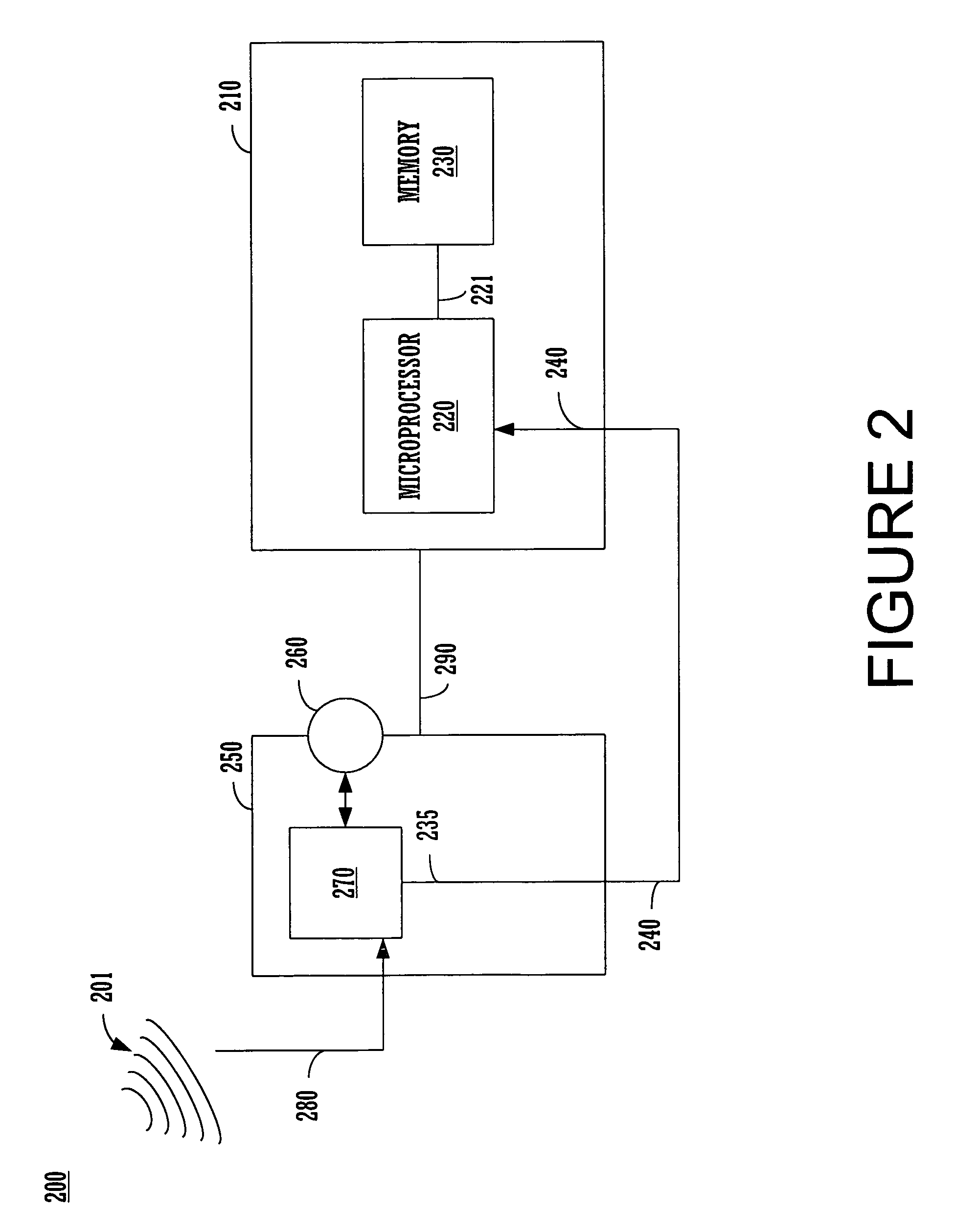
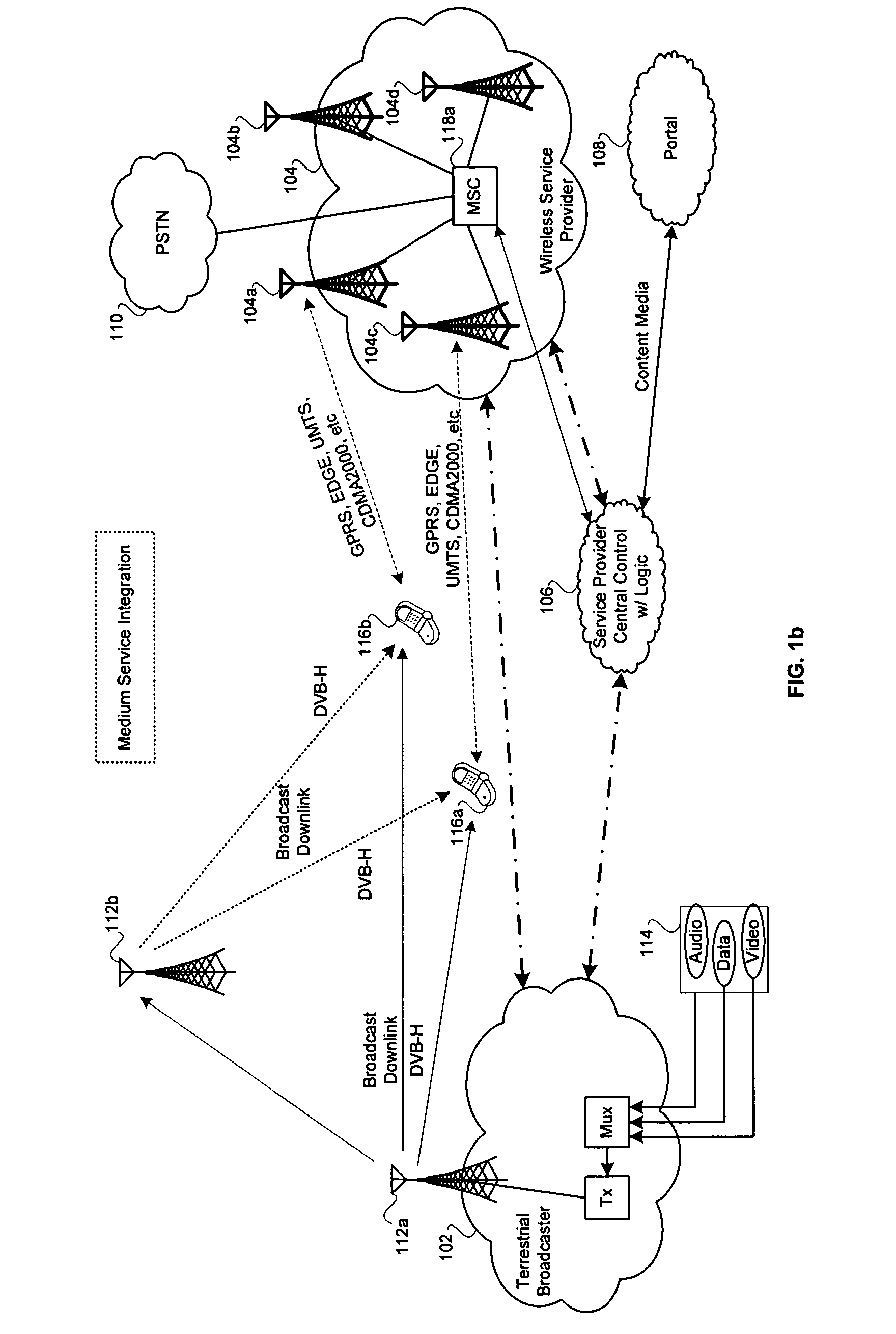
VoIP Enabled Femtocell with a USB Transceiver Station
InactiveUS20080244148A1High quality audioLow costNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentMicrocontrollerRF front end
Telephone calls between a mobile station (MS) and the mobile network or PSTN are routed through the Internet via VoIP using a femtocell, as opposed to the traditional macrocellular network. The femtocell can comprise a USB Transceiver Station that is connected to a personal computer through a universal serial bus port, which provides both power and a multi-megabit per second connection between the personal computer and the USB transceiver station. The USB transceiver station can comprise a microcontroller to manage signaling between the RF front end / baseband processor and the personal computer, as well as a precise timing mechanism to assist the synchronization of femtocell timing with the surrounding macrocellular network, if it is present. The USB transceiver station can have a compact form factor that that facilitates a high degree of portability by the subscriber, such as being readily attachable to their keychain.
Owner:SMALL CELL INNOVATIONS
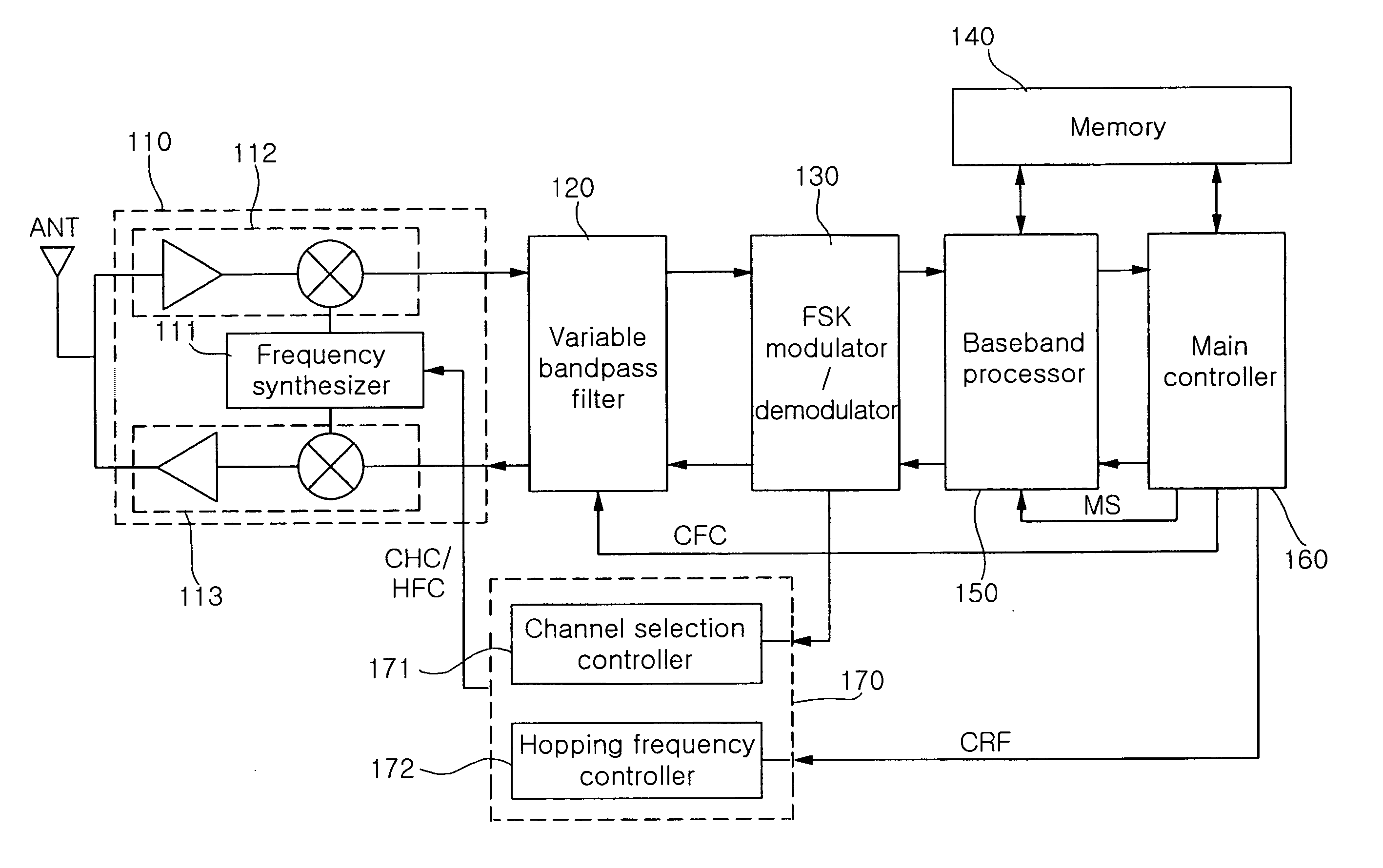
Transceiver for zigbee and bluetooth communications
InactiveUS20060193375A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsSewerage structuresBandpass filteringTransceiver
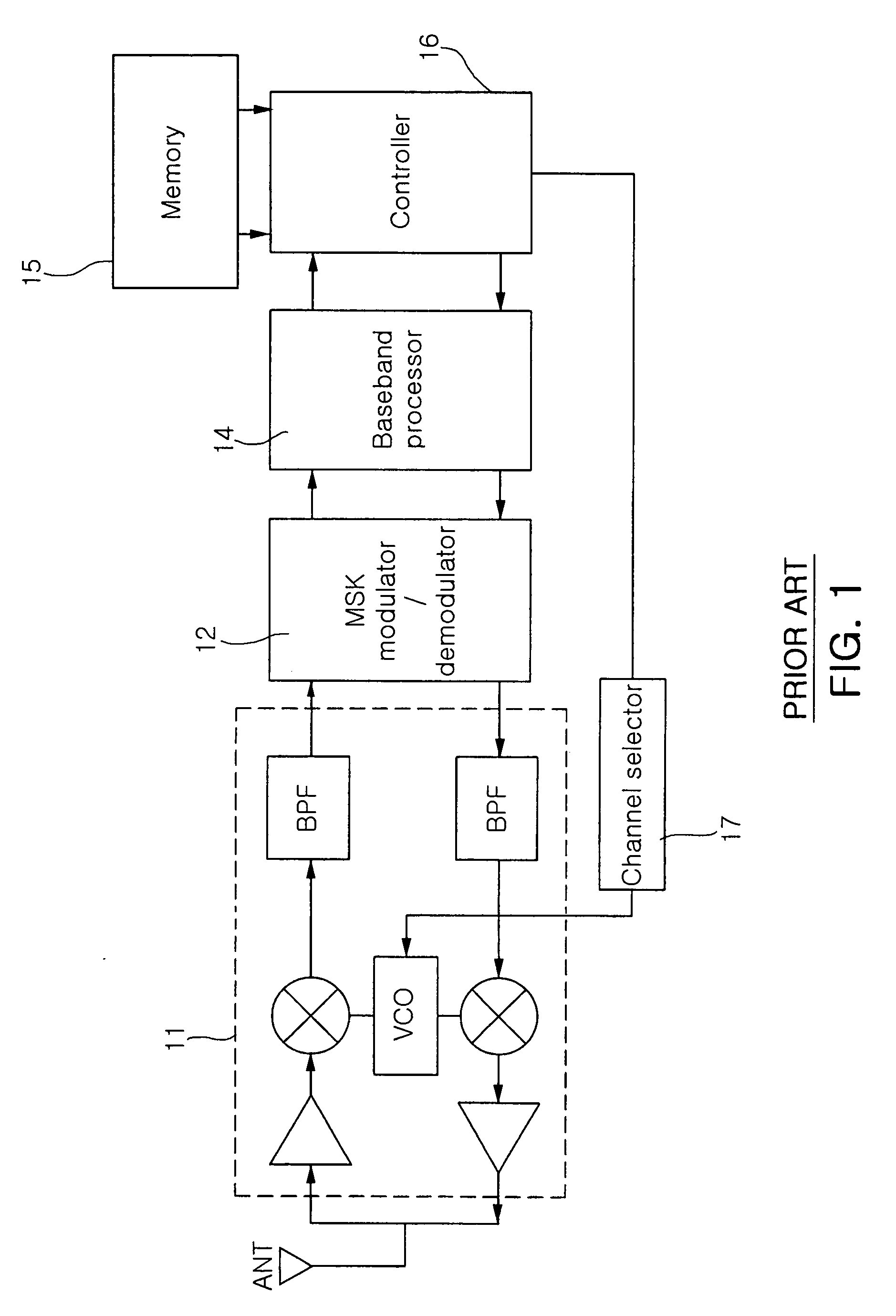
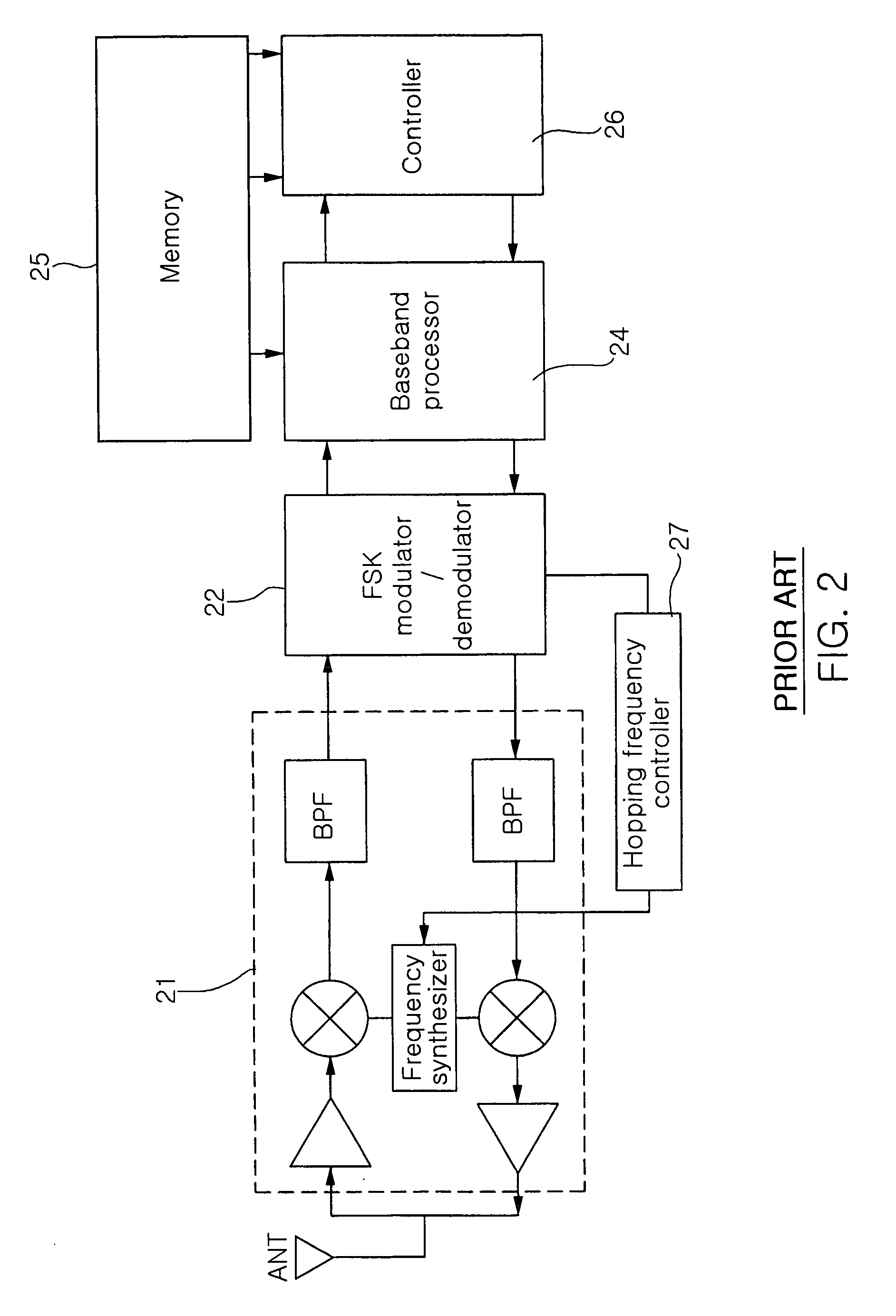
The invention provides a transceiver for Zigbee and Bluetooth communications integrating a Zigbee transceiver and a Bluetooth transceiver. The transceiver includes an RF processor 110, a variable bandpass filter 120, an FSK modulator / demodulator 130, a memory 140, a baseband processor 150, a main controller 160, and a channel selection / frequency hopping controller 170. The invention integrates the Zigbee transceiver and the Bluetooth transceiver so as to partially make common use of a higher layer application and a physical layer of the Zigbee transceiver and the Bluetooth transceiver. As a result, the invention has the advantage of functioning as a transceiver for Zigbee and Bluetooth communications, without causing a significant increase in size and unit price.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
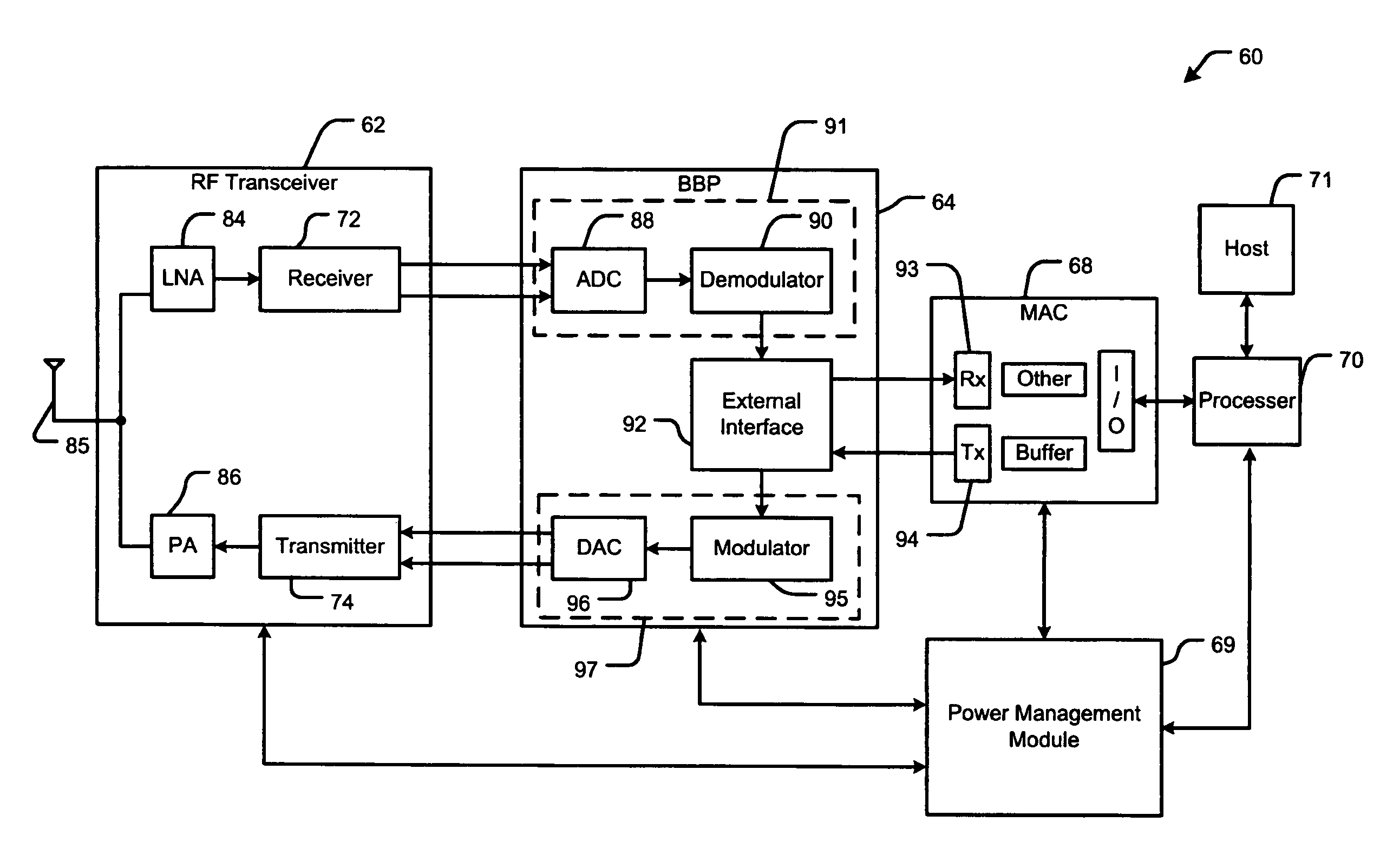
Wireless LAN power savings
A network device includes a base band processor (BBP) receiver to detect a frame in a signal. A media access controller (MAC) receiver identifies a destination address in the frame. A power management module transitions the BBP receiver to an active mode based on an estimated energy level of the signal before transitioning the MAC receiver, a processor, a MAC transmitter, and a BBP transmitter to the active mode; transitions the MAC receiver to the active mode when the frame is present after transitioning the BBP receiver to the active mode and before transitioning the processor, the MAC transmitter, and the BBP transmitter to the active mode; and transitions the processor to the active mode based on the destination address after transitioning the BBP receiver and the MAC receiver to the active mode and before transitioning the MAC transmitter and the BBP transmitter to the active mode.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
OFDM signal processing in a base transceiver system
ActiveUS20120250740A1Removing unnecessary processing stepSimple designModulated-carrier systemsCode conversionTransceiverDigital down conversion
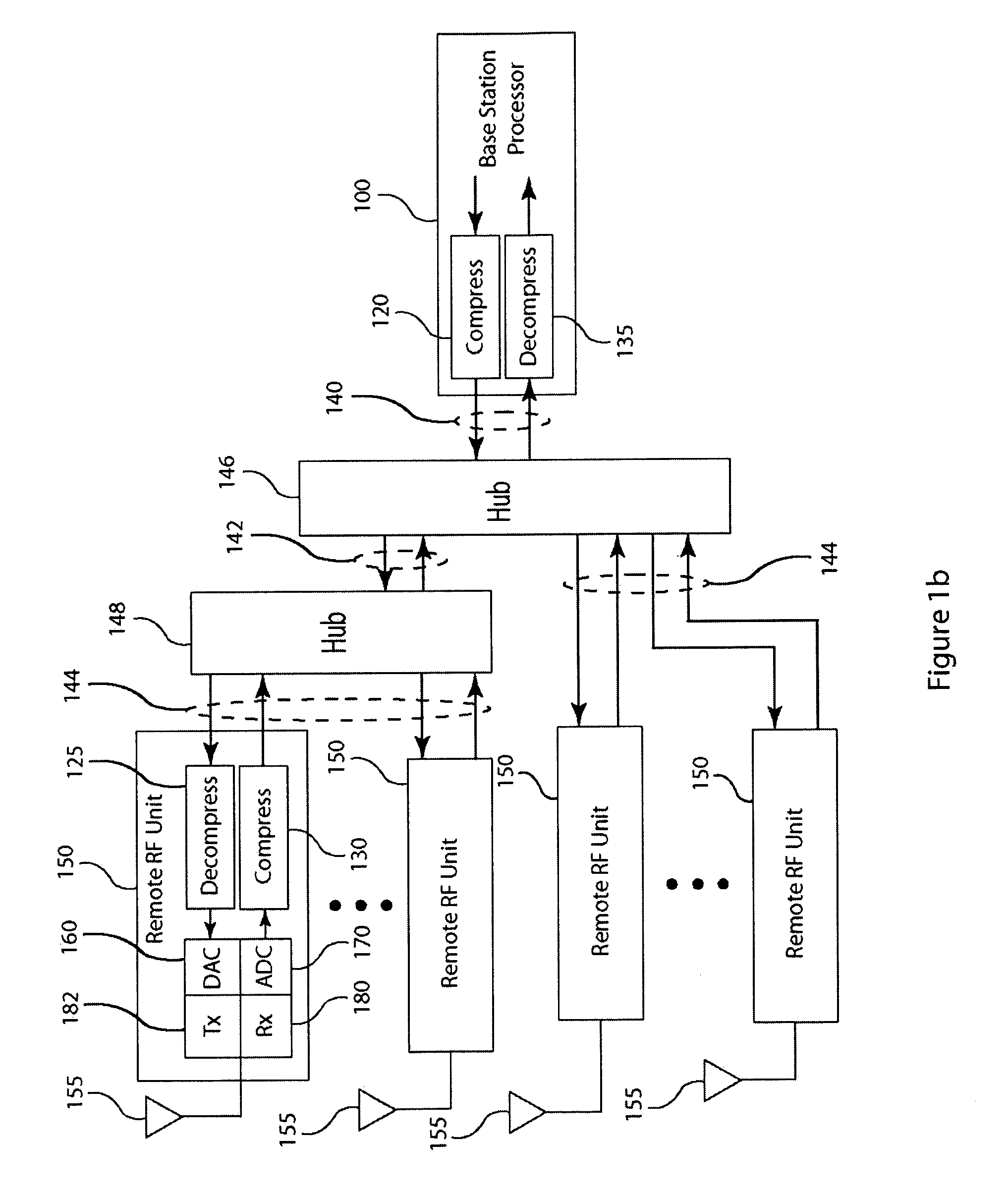
A method and apparatus provides OFDM signal compression for transfer over serial data links in a base transceiver system (BTS) of a wireless communication network. For the uplink, an RF unit of the BTS applies OFDM cyclic prefix removal and OFDM frequency transformation of the baseband signal samples followed by frequency domain compression of the baseband signal samples, resulting from analog to digital conversion of received analog signals followed by digital downconversion, forming compressed coefficients. After transfer over the serial data link, the baseband processor applies frequency domain decompression to the compressed coefficients prior to further signal processing. For the downlink, the RF unit performs frequency domain decompression of the compressed coefficients and applies OFDM inverse frequency transformation of the decompressed coefficients and OFDM cyclic prefix insertion prior to digital upconversion and digital to analog conversion, generating the analog signal for transmission over the antenna.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Detecting a WLAN signal using a bluetooth receiver during bluetooth scan activity
InactiveUS20110274021A1Reduce resolutionSignal bandwidthPower managementEnergy efficient ICTTransceiverRF front end
A BT receiver RF front end receives RF energy in a sequence of BT scan windows. Throughout a scan window, the front end is tuned to one hop frequency. Before and after the window the front end is in a disabled state. A WLAN energy detector processes an output of the front end during the window and determines whether more than a predetermined amount of RF energy was received onto the front end during the window. A BT baseband processor attempts to demodulate the output of the front end. If the WLAN energy detector determines that the predetermined amount of RF energy was received and if a BT signal could not be demodulated, then a WLAN wake-up signal is asserted, thereby causing a WLAN transceiver to be powered up to receive WLAN signals. BT scan intervals are varied in duration to facilitate a BT scan window overlapping a WLAN beacon.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
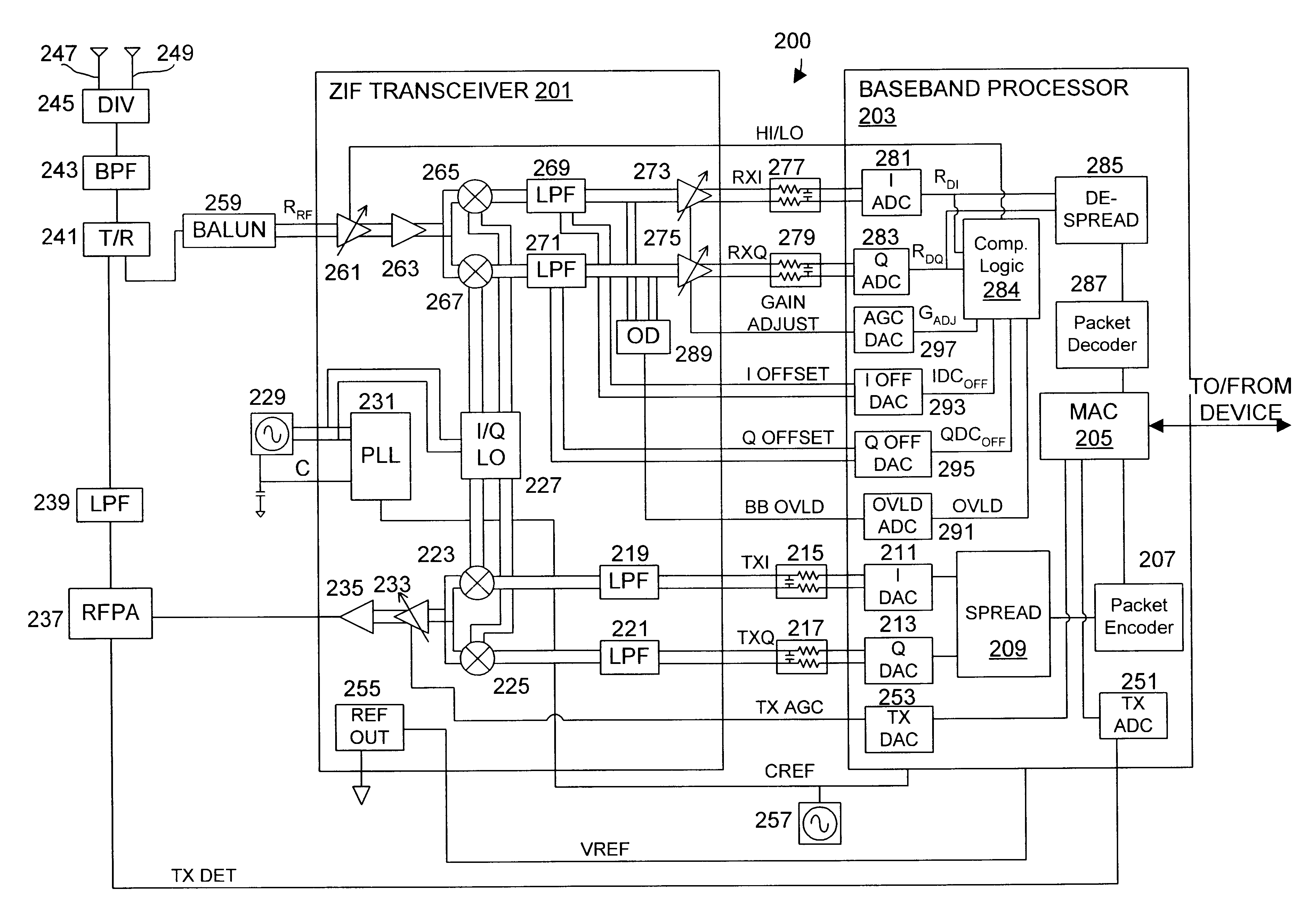
DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6560448B1Low costMaximum performanceGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverAudio power amplifier
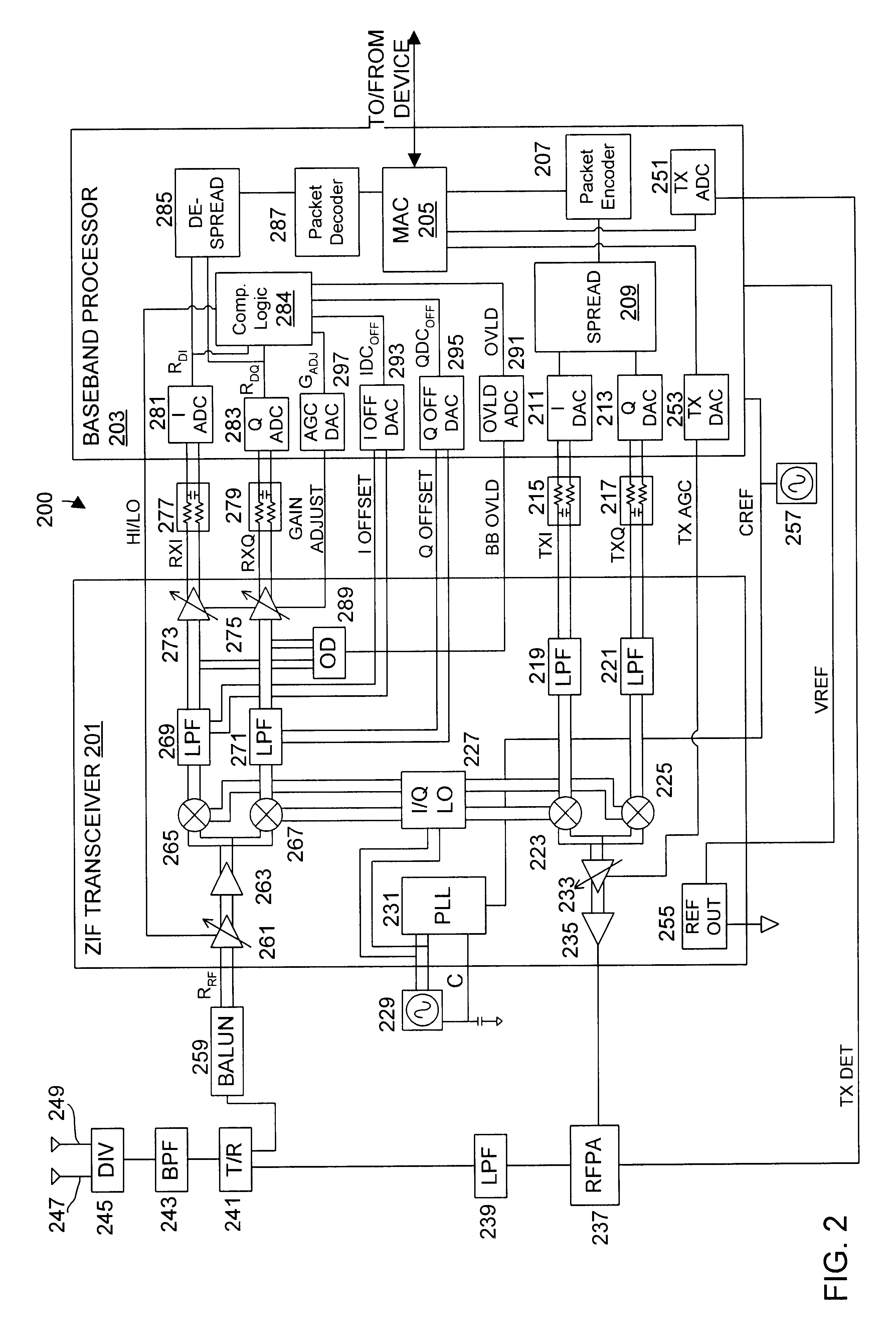
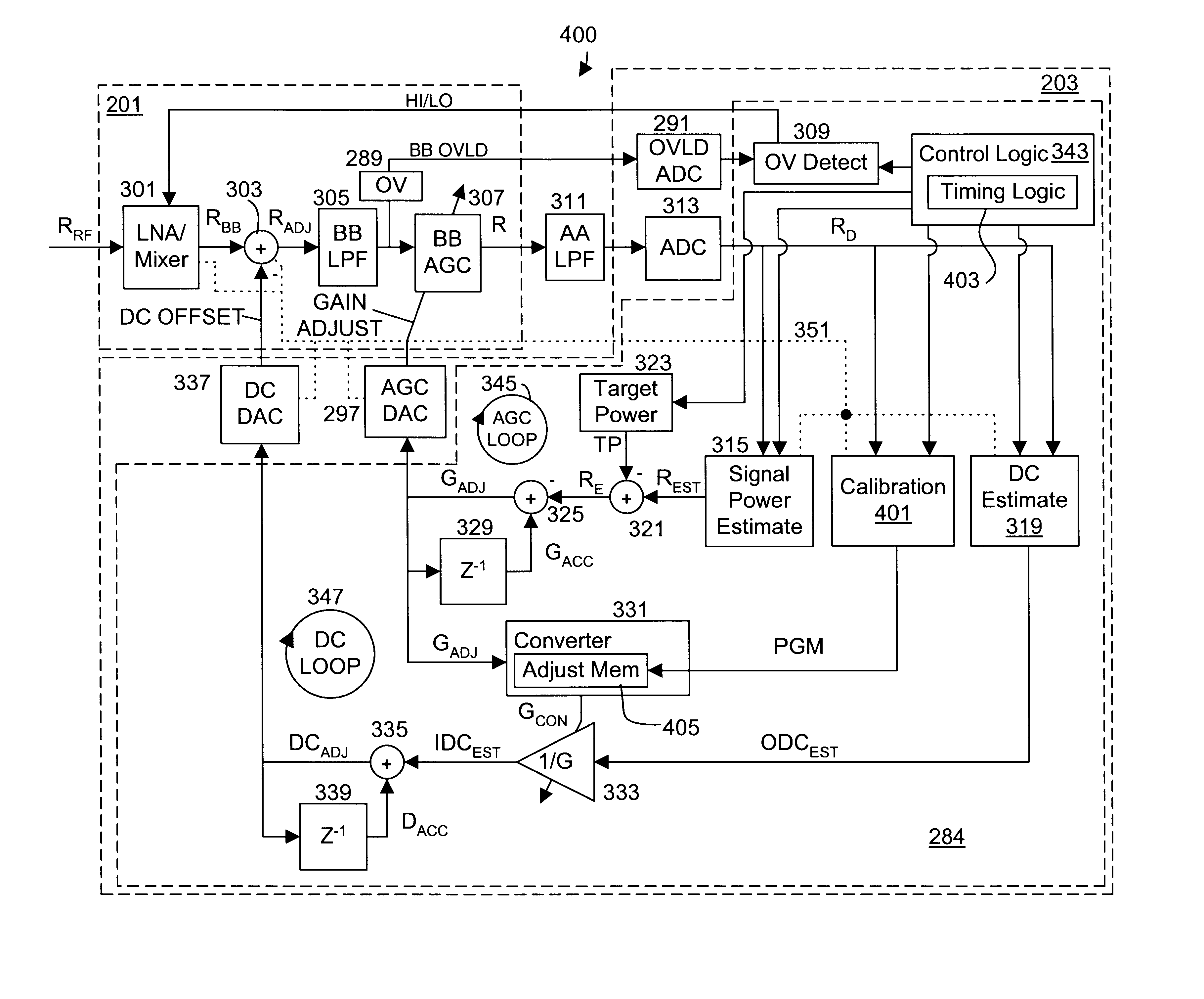
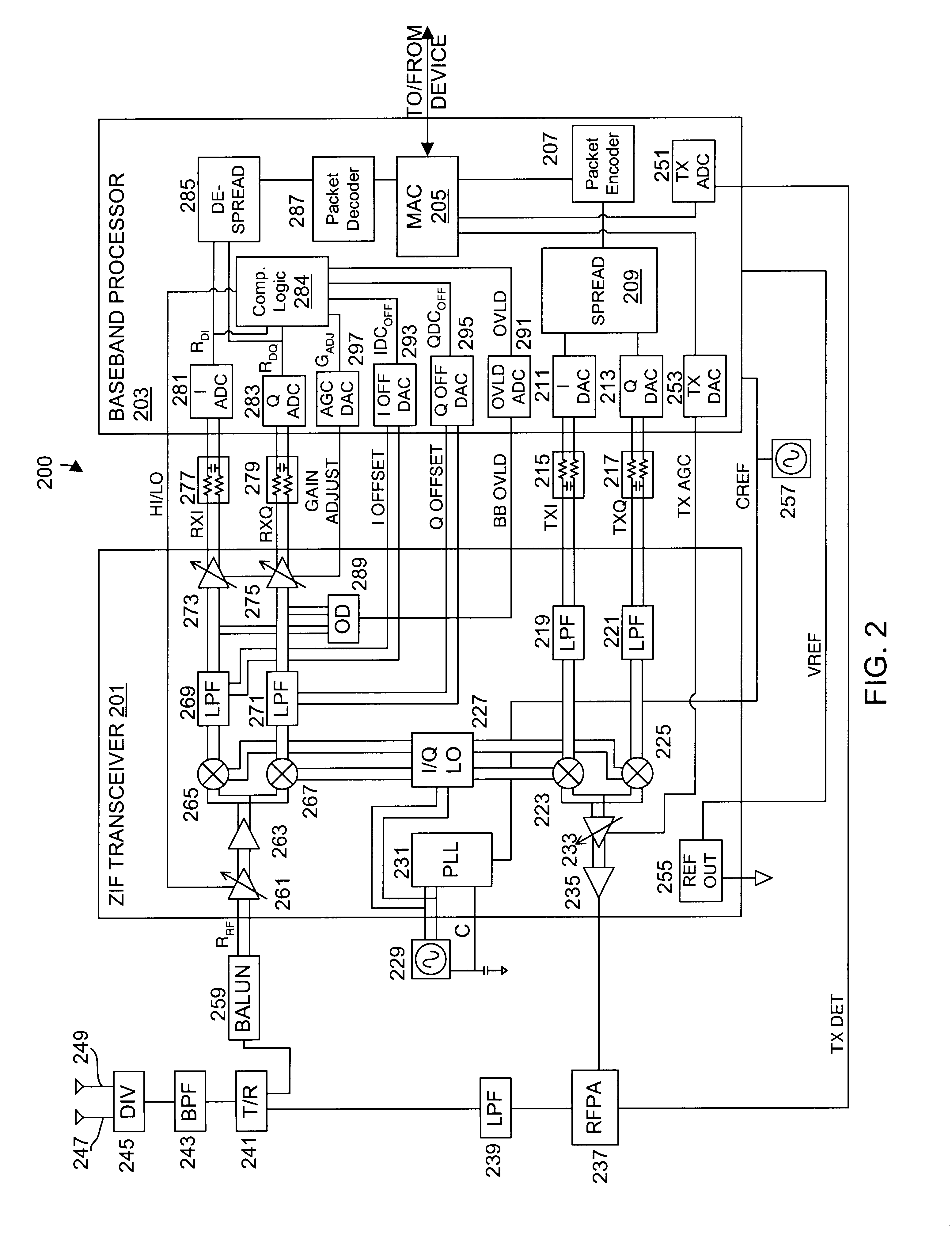
A wireless communication device including a radio frequency (RF) circuit, a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor. The ZIF transceiver includes an RF mixer circuit that converts the RF signal to a baseband input signal, a summing junction that subtracts a DC offset from the baseband input signal to provide an adjusted baseband input signal, and a baseband amplifier that receives the adjusted baseband input signal and that asserts an amplified input signal based on a gain adjust signal. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic and a gain interface. The gain control logic receives the amplified input signal, estimates input signal power and asserts the gain adjust signal in an attempt to keep the input signal power at a target power level. The DC control logic estimates an amount of DC in the amplified input signal and provides the DC offset in an attempt to reduce DC in the amplified input signal. The gain interface converts gain levels between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The RF signal may include in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) portions, where the RF mixer circuit splits I and Q baseband input signals from the RF signal. Operation is substantially identical for both I and Q channels. The DC control logic operates to remove or otherwise eliminate DC from the received signal that is provided to decoders in the baseband processor.
Owner:M RED INC
Orthogonal normalization for a radio frequency integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050157778A1Reduce noiseImprove accuracyCarrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAudio power amplifierRadio frequency
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6735422B1Low costMaximum performancePulse automatic controlGain controlTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency (ZIF) architecture. The device includes a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor, which further includes a calibrator that periodically performs a calibration procedure. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic, a gain converter and the calibrator. The gain converter converts gain between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The calibrator programs the gain converter with values determined during the calibration procedure. The gain converter may be a lookup table that stores gain conversion values based on measured gain of a baseband gain amplifier of the ZIF transceiver. The gain control logic may further include a gain adjust limiter that limits change of a gain adjust signal during operation based on a maximum limit or on one or more gain change limits. A second lookup table stores a plurality of DC adjust values, which are added during operation to further reduce DC offset. The calibration procedure includes sampling an output signal for each gain step of the baseband amplifier at two predetermined range values and corresponding DC offsets using successive approximation. The data is used to calculate gain, DC offset and DC differential values, which are used to determine the conversion values programmed into the lookup tables or the gain adjust limiter.
Owner:M RED INC
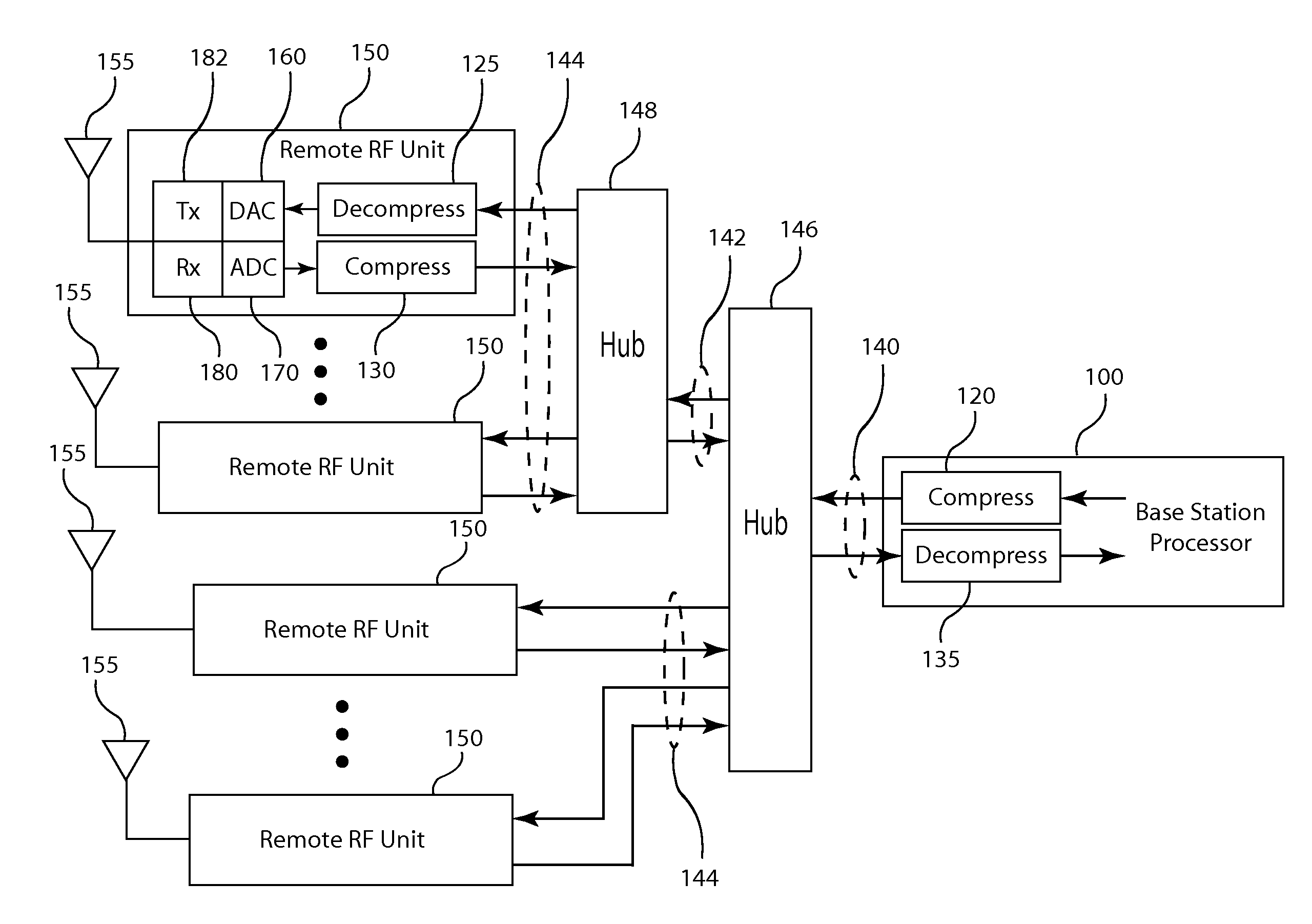
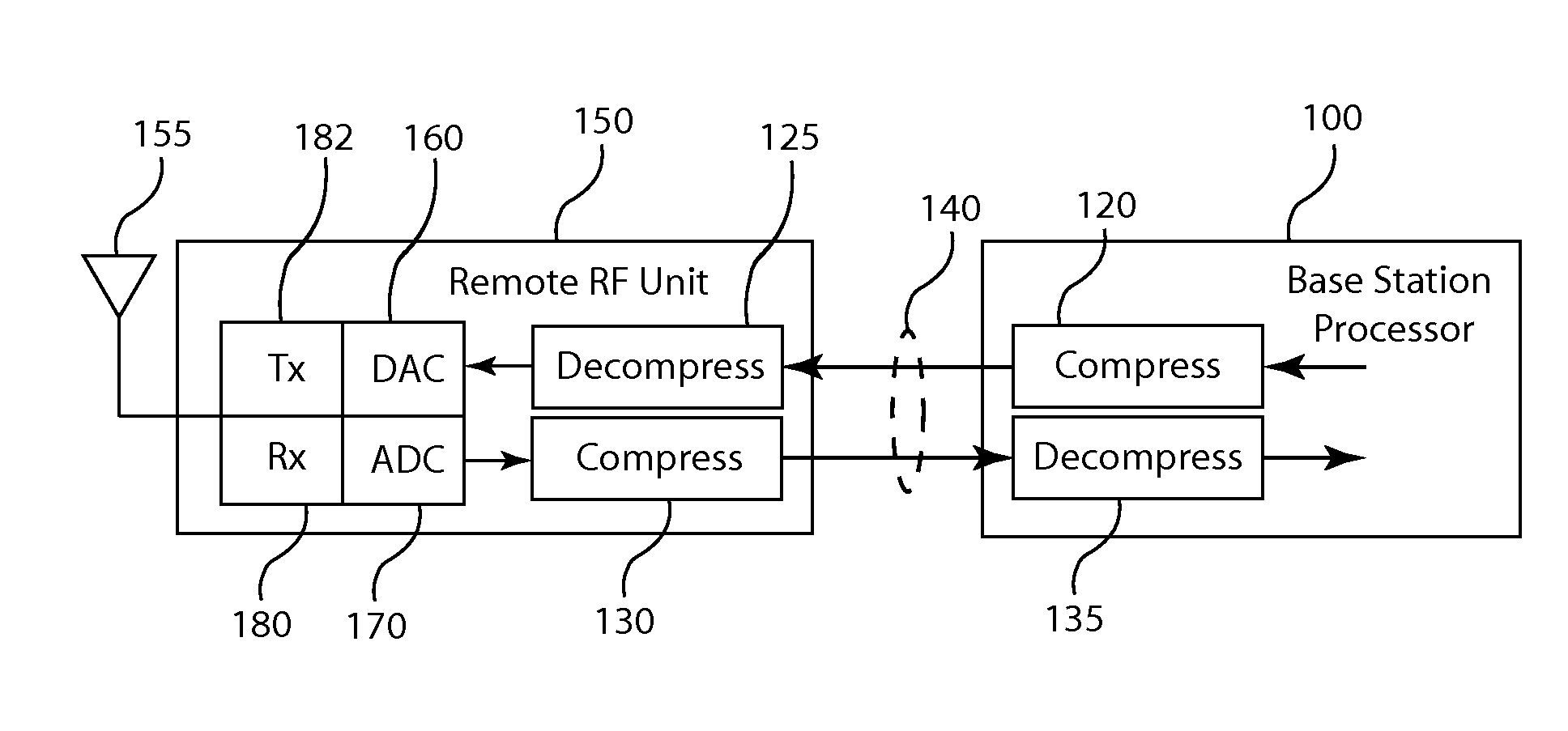
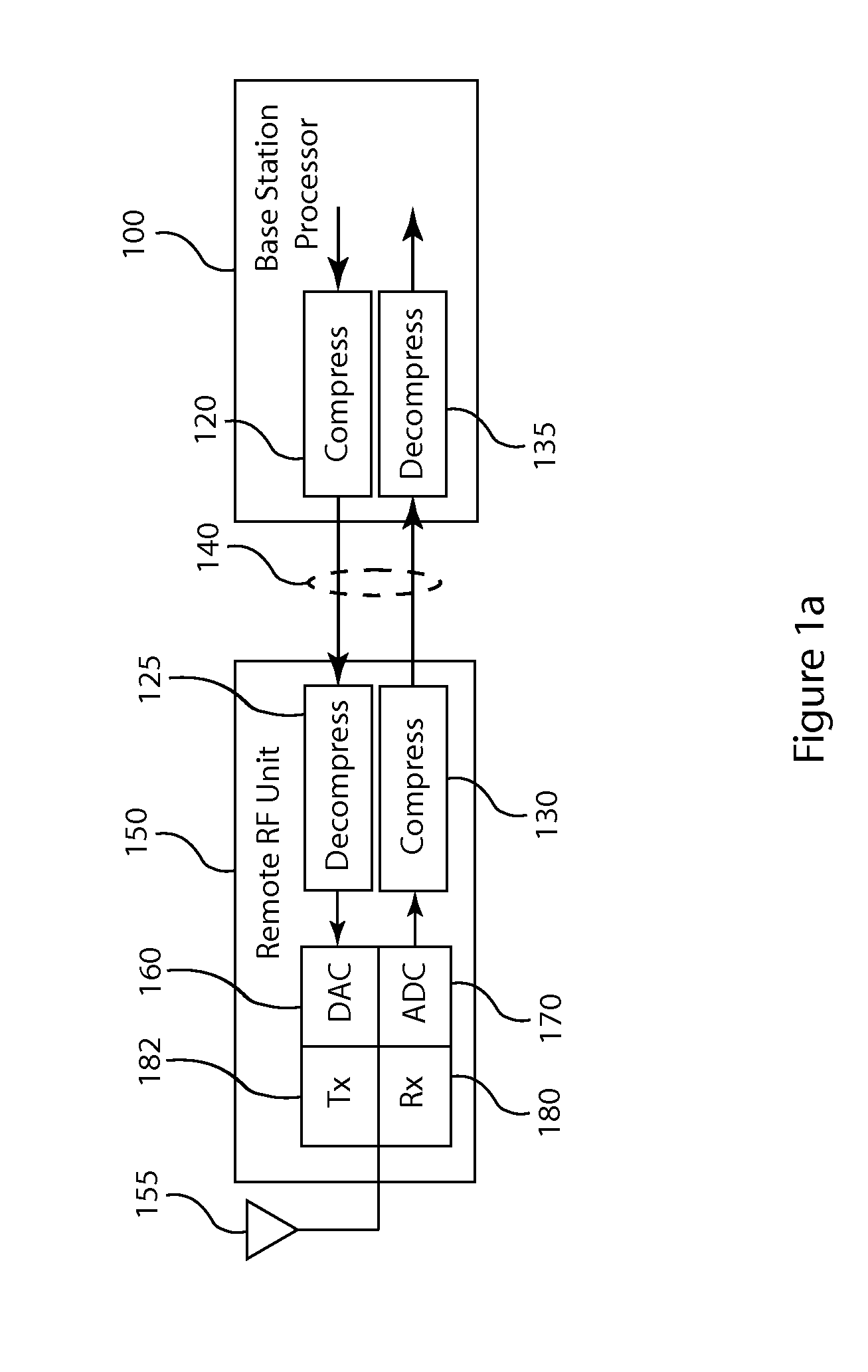
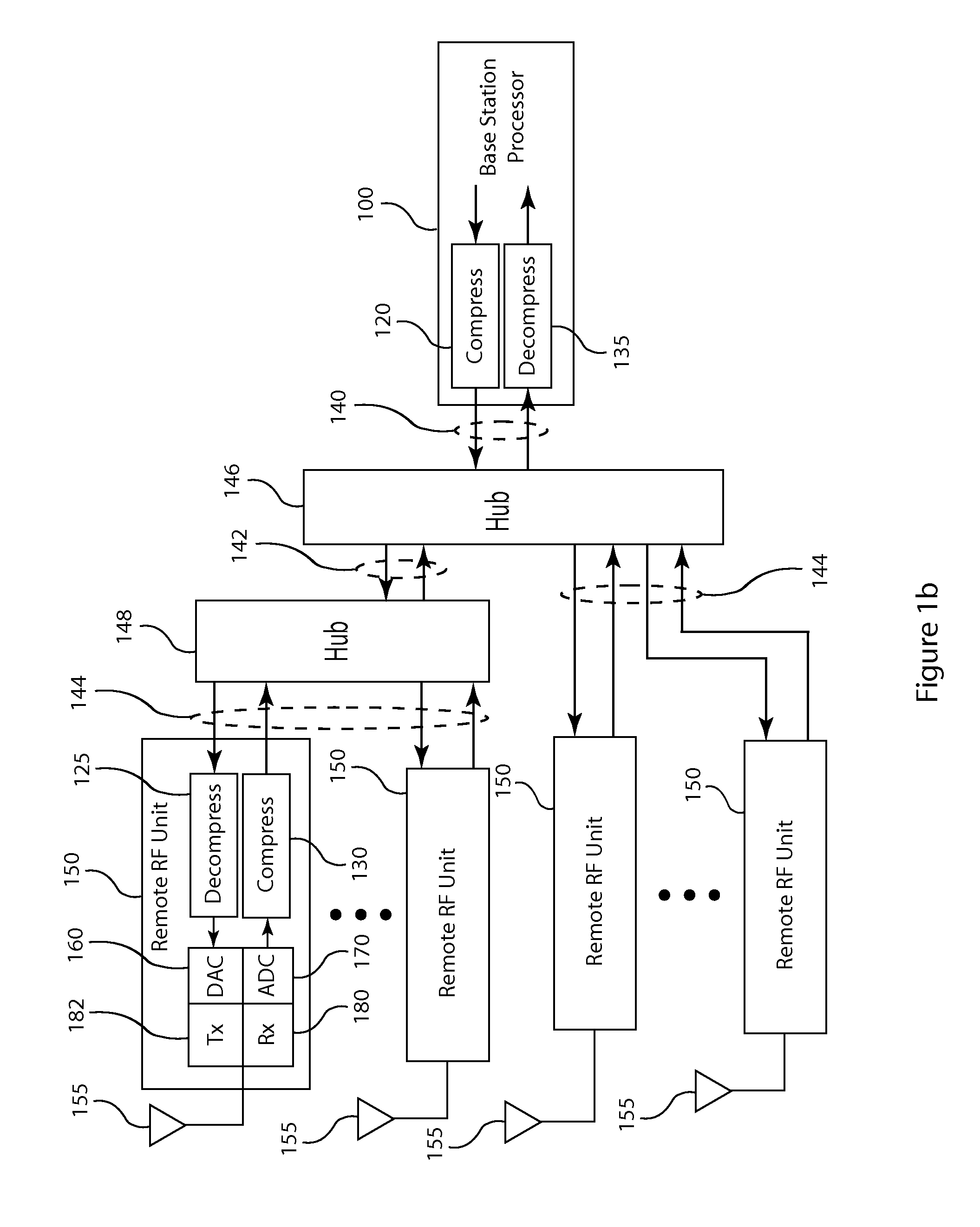
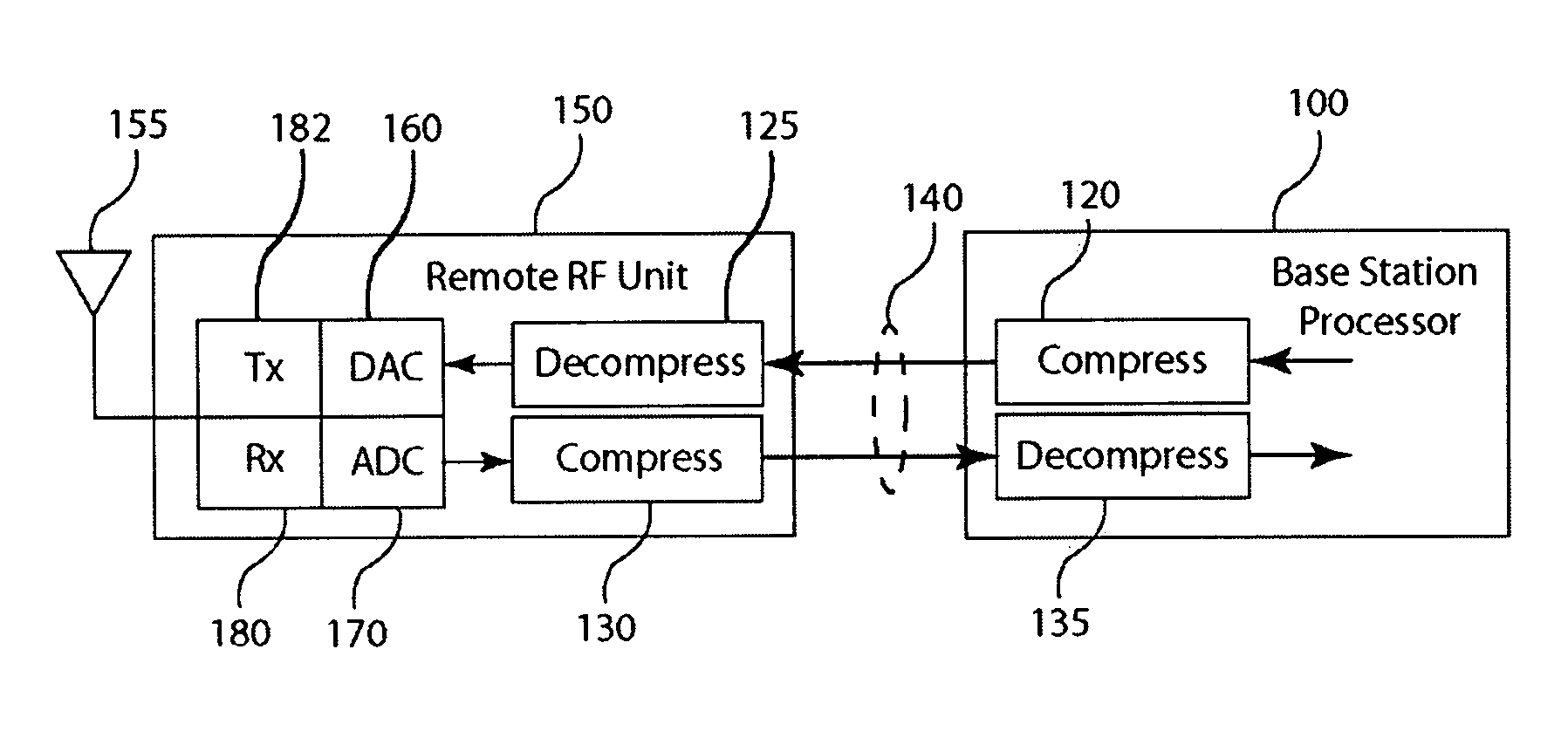
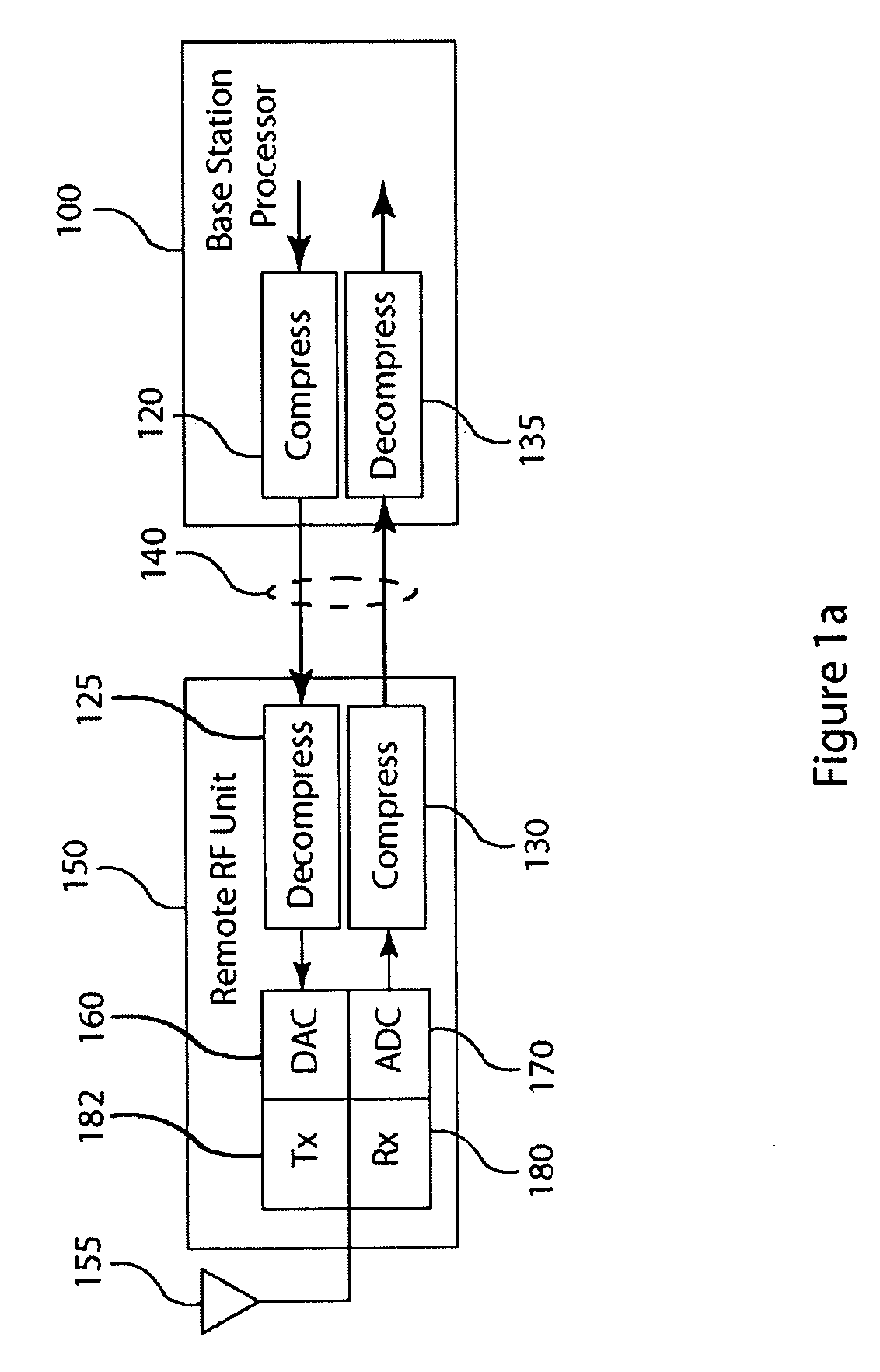
Frequency domain compression in a base transceiver system
ActiveUS20120176966A1Significant compressionReduce processing overheadModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTransceiverImage compression
A method and apparatus provide signal compression for transfer over serial data links in a base transceiver system (BTS) of a wireless communication network. For the uplink, an RF unit of the BTS applies frequency domain compression of baseband signal samples, resulting from analog to digital conversion of received analog signals followed by digital downconversion, forming compressed coefficients. After transfer over the serial data link, the baseband processor then applies frequency domain decompression to the compressed coefficients prior to normal signal processing. For the downlink, the baseband processor applies frequency domain compression of baseband signal samples and transfers the compressed coefficients to the RF unit. The RF unit applies frequency domain decompression to the compressed coefficients prior to digital upconversion and digital to analog conversion, generating the analog signal for transmission over the antenna. This abstract does not limit the scope of the invention as described in the claims.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
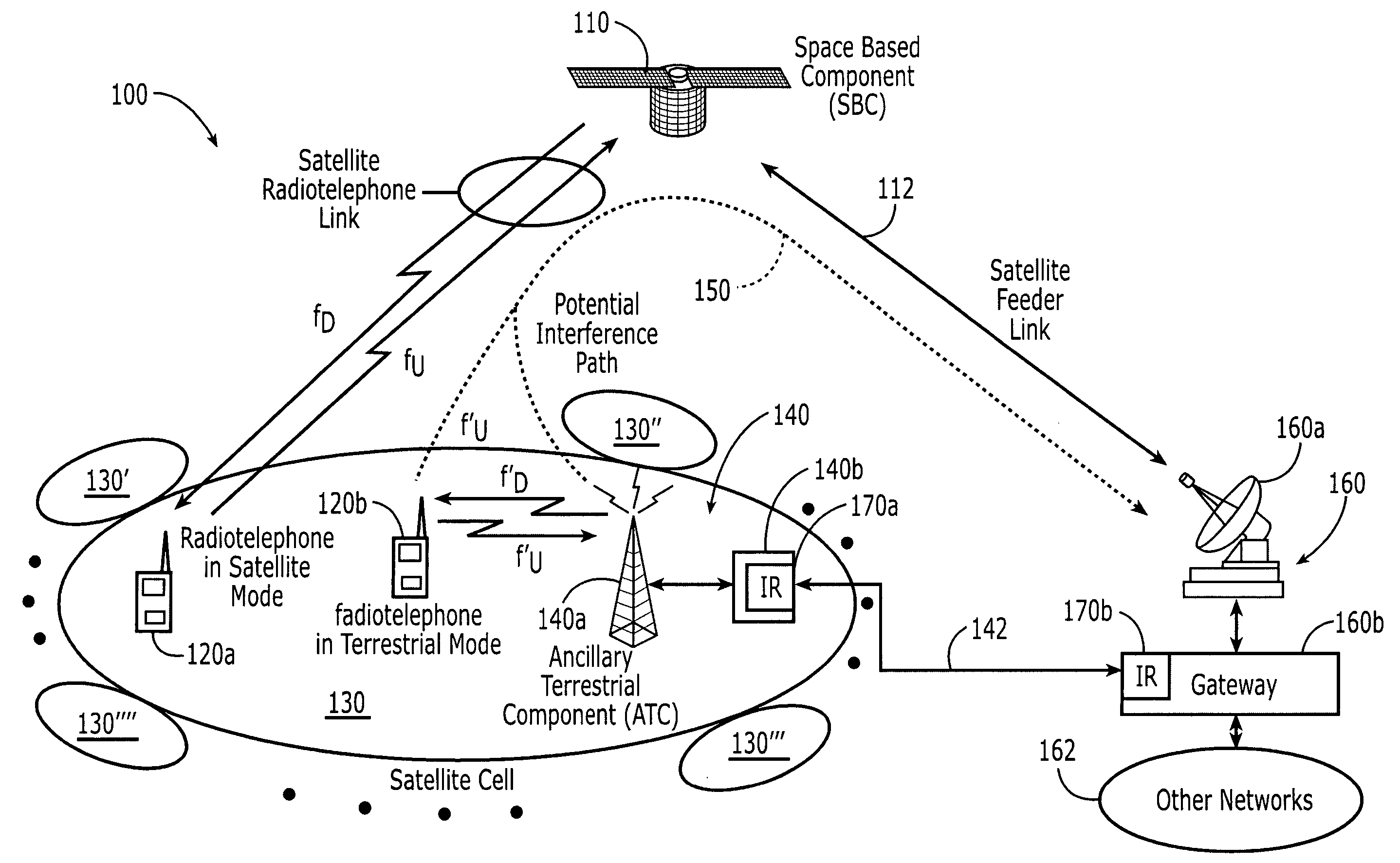
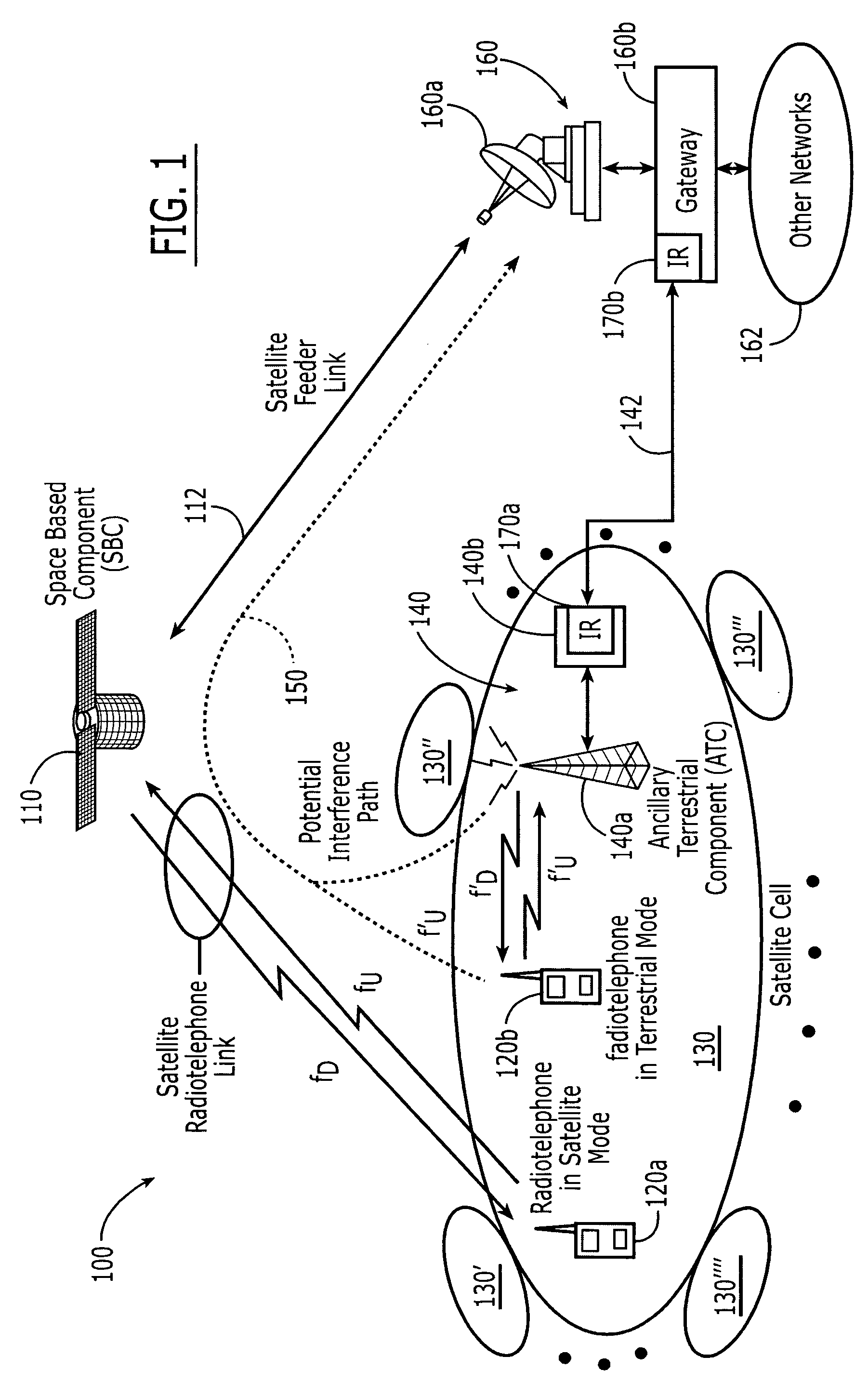
Radiotelephones and operating methods that use a single radio frequency chain and a single baseband processor for space-based and terrestrial communications
InactiveUS20050245192A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsBeacon systemsAir interfaceRadio frequency
A radiotelephone includes a single radio frequency chain and a single baseband processor that is connected thereto. The single radio frequency chain and the single baseband processor are configured to communicate with a space-based system using frequencies of a satellite band and an air interface, and to communicate with a terrestrial wireless network using frequencies of the satellite band and substantially the air interface.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
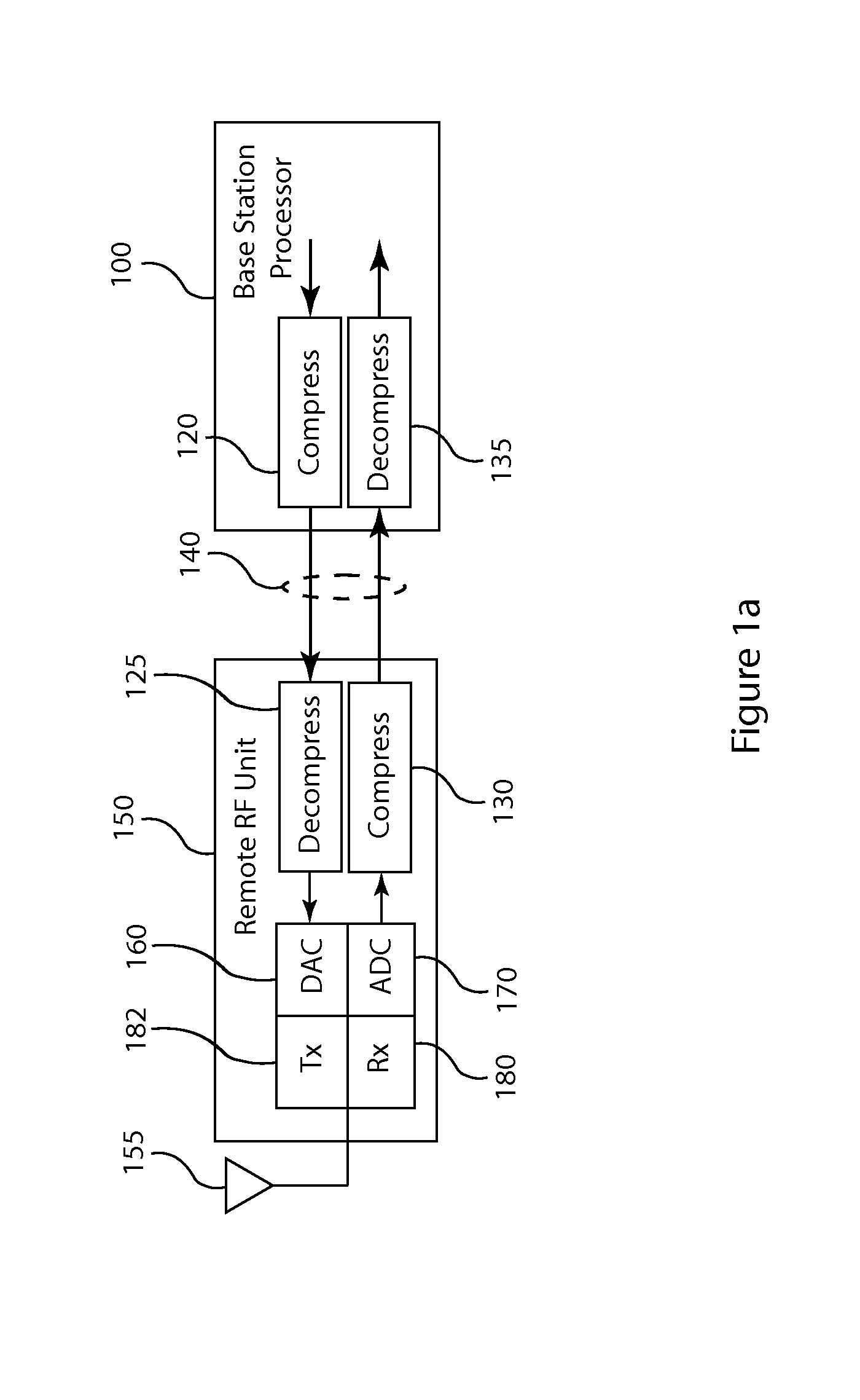
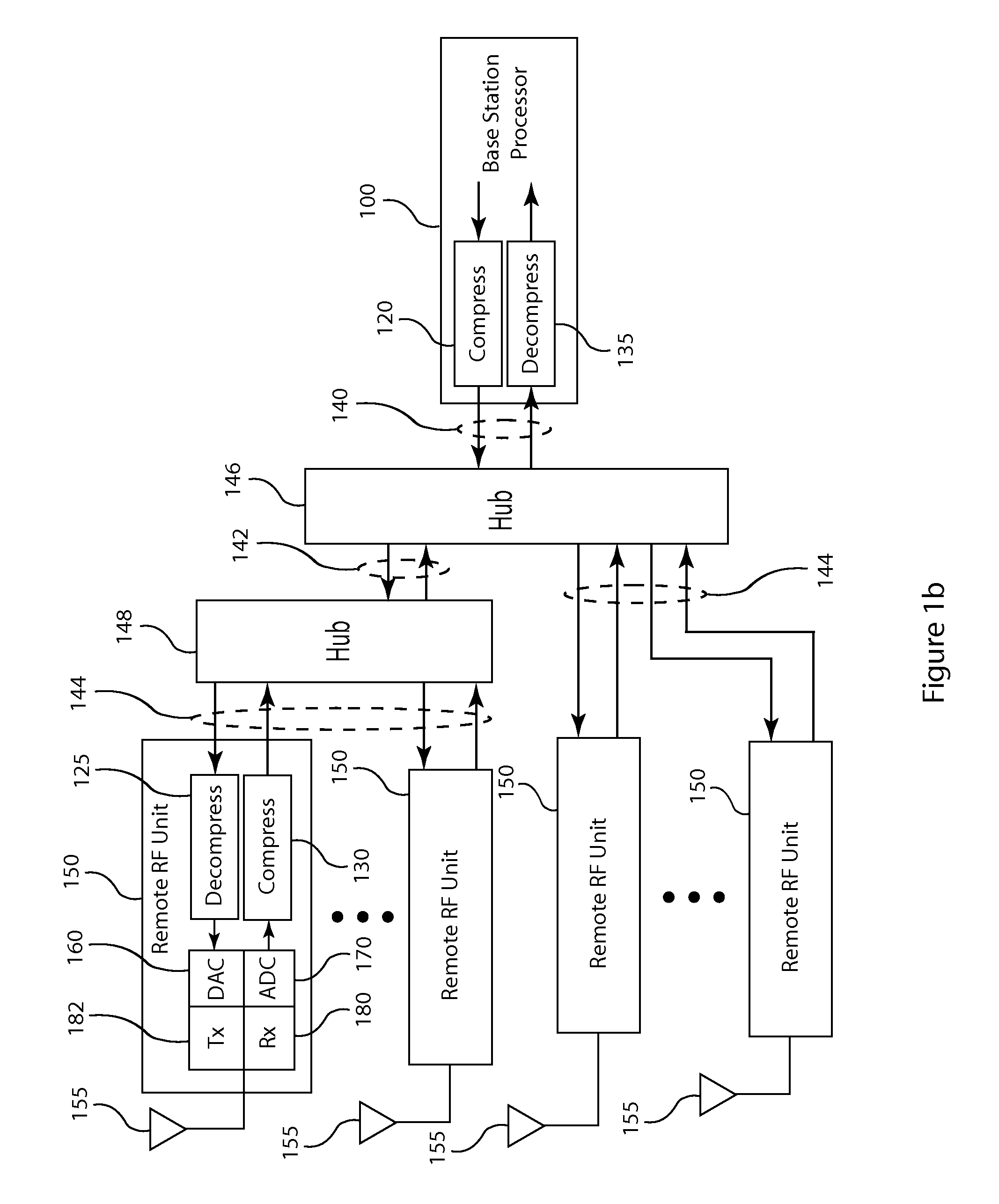
Compression of baseband signals in base transceiver systems
ActiveUS20110135013A1Increase data transfer capacity of dataIncrease capacityCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverDistributed antenna system
A signal compression method and apparatus for a base transceiver system (BTS) in a wireless communication network provides efficient transfer of compressed signal samples over serial data links in the system. For the uplink, an RF unit of the BTS compresses baseband signal samples resulting from analog to digital conversion of a received analog signal followed by digital downconversion. The compressed signal samples are transferred over the serial data link to the baseband processor then decompressed prior to normal signal processing. For the downlink, the baseband processor compresses baseband signal samples and transfers the compressed signal samples to the RF unit. The RF unit decompresses the compressed samples prior to digital upconversion and digital to analog conversion to form an analog signal for transmission over an antenna. Compression and decompression can be incorporated into operations of conventional base stations and distributed antenna systems, including OBSAI or CPRI compliant systems.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
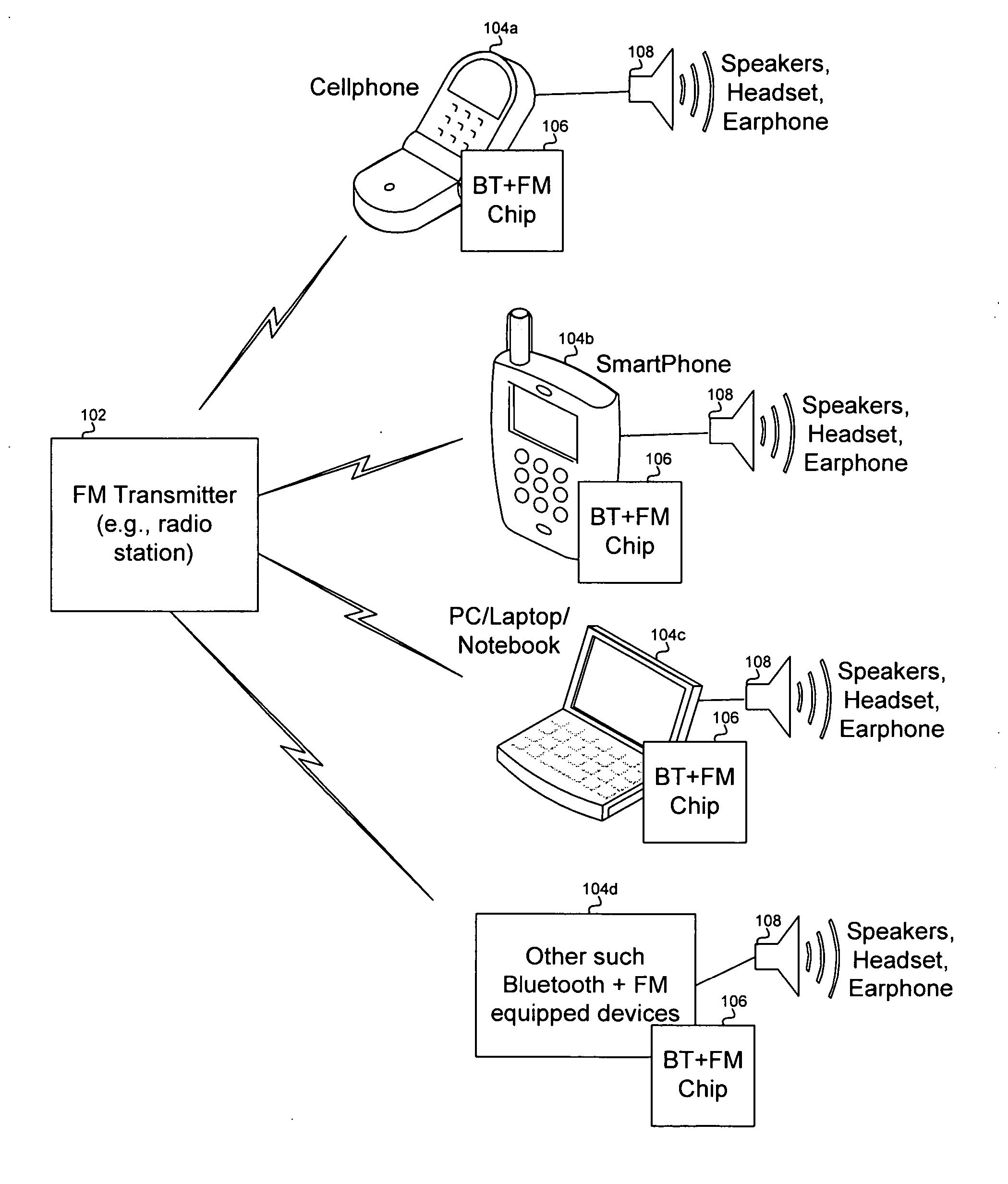
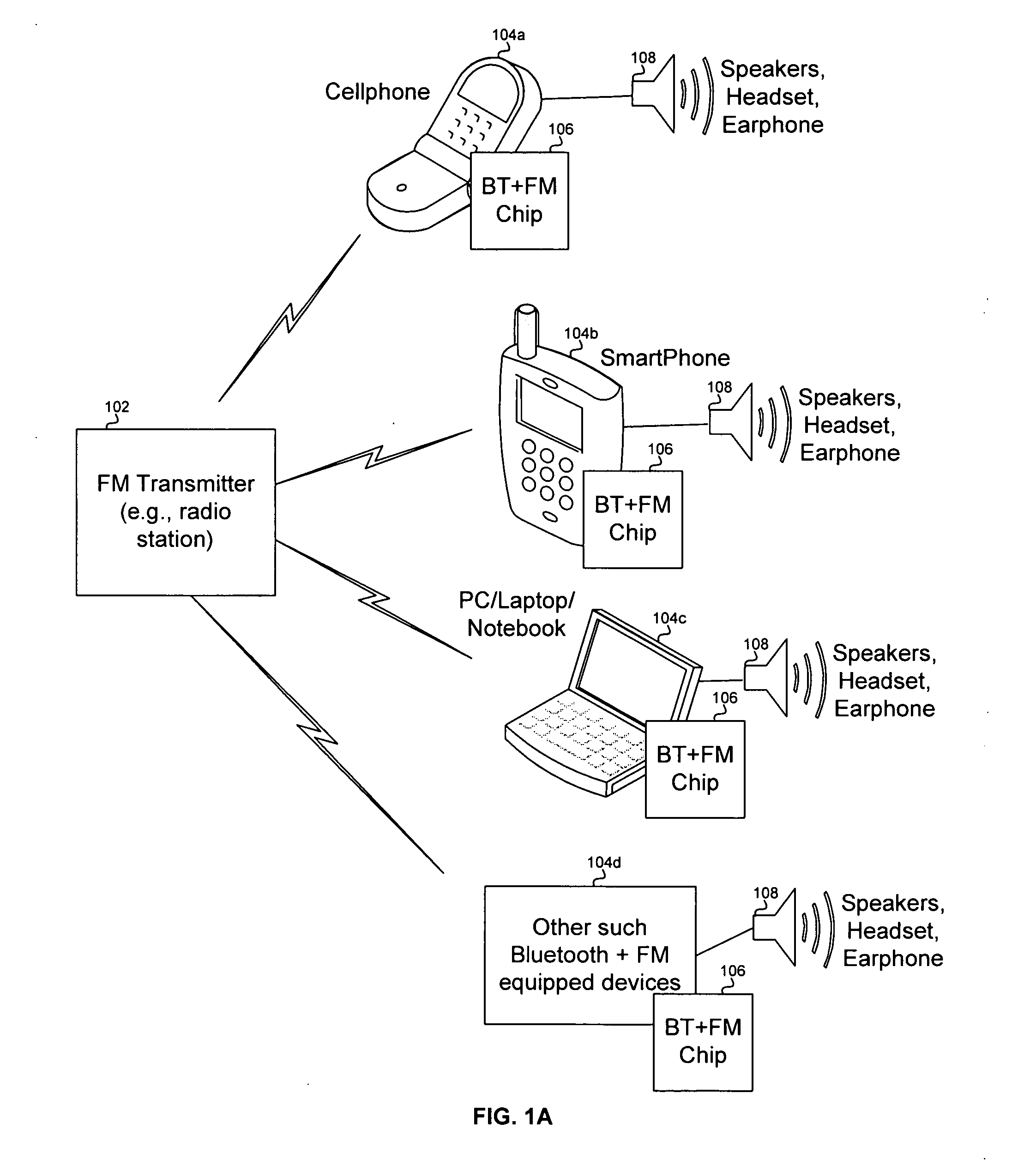
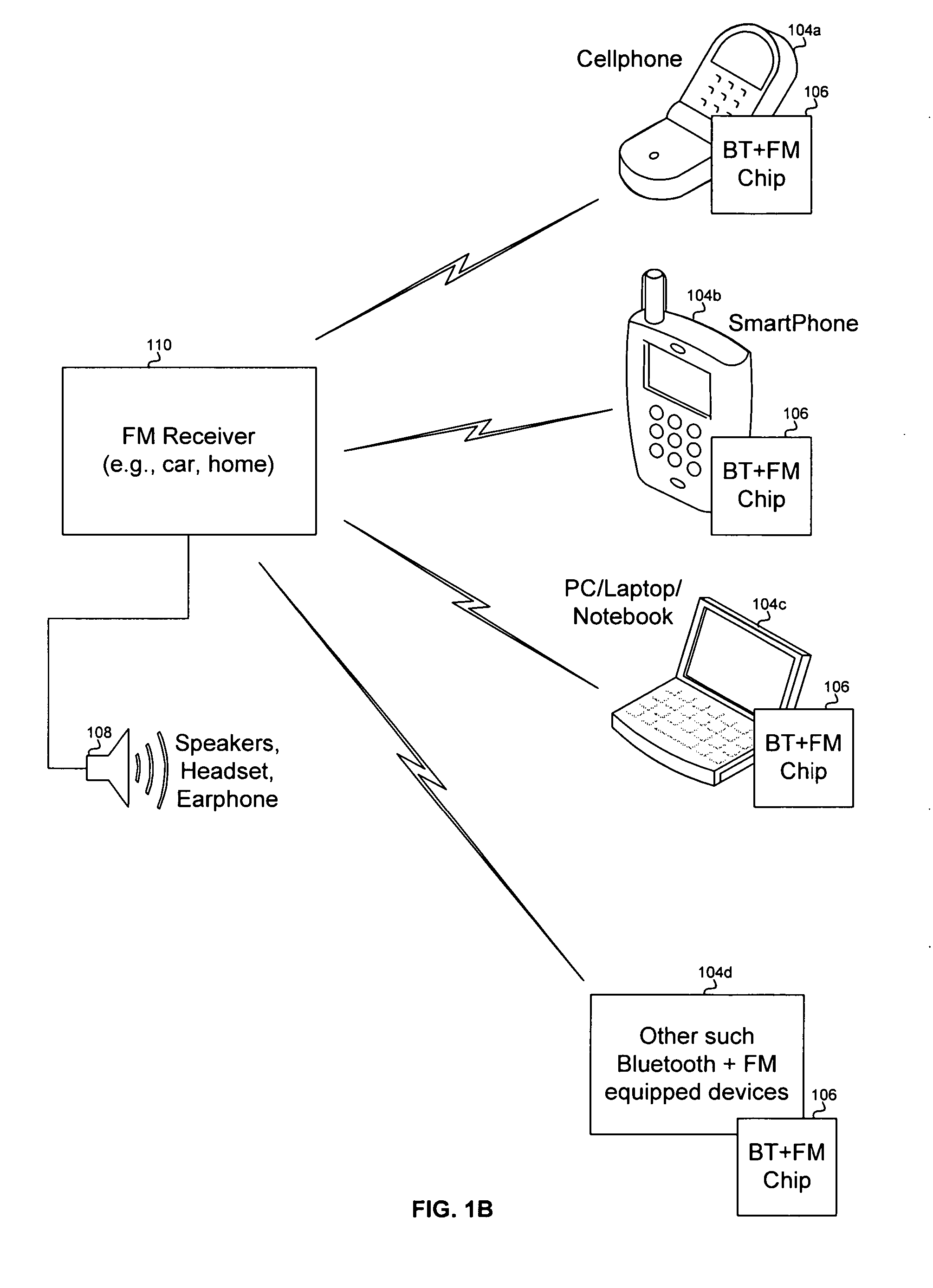
Method and system for a single chip integrated Bluetooth and FM transceiver and baseband processor
A method and system for a single chip integrated Bluetooth and FM transceiver and baseband processor are provided. The single chip may comprise a Bluetooth radio, an FM radio, a processor system, and a peripheral transport unit (PTU). FM data may be received and / or transmitted via the FM radio and Bluetooth data may be received and / or transmitted via the Bluetooth radio. The FM radio may receive radio data system (RDS) data. The PTU may support digital and analog interfaces. A processor in the processor system may time-multiplex processing of FM data and processing of Bluetooth data. The single chip may operate in an FM-only, a Bluetooth-only, and an FM-Bluetooth mode. The single chip may reduce power consumption by disabling portions of the Bluetooth radio during FM-only mode and / or disabling analog circuitry when performing digital processing. Communication between Bluetooth and FM channels may be enabled via the single chip.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter
ActiveUS6987954B2Resonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
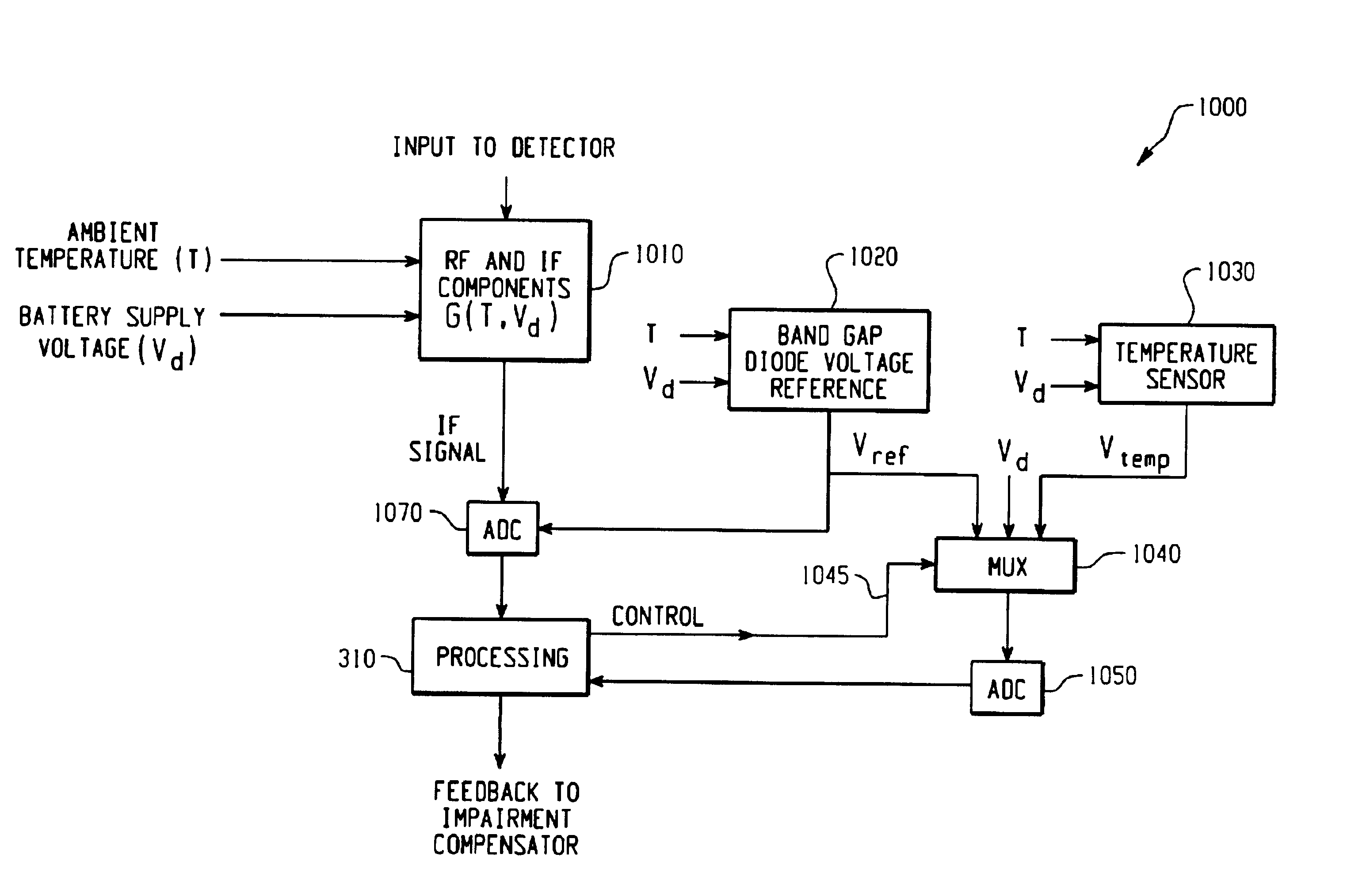
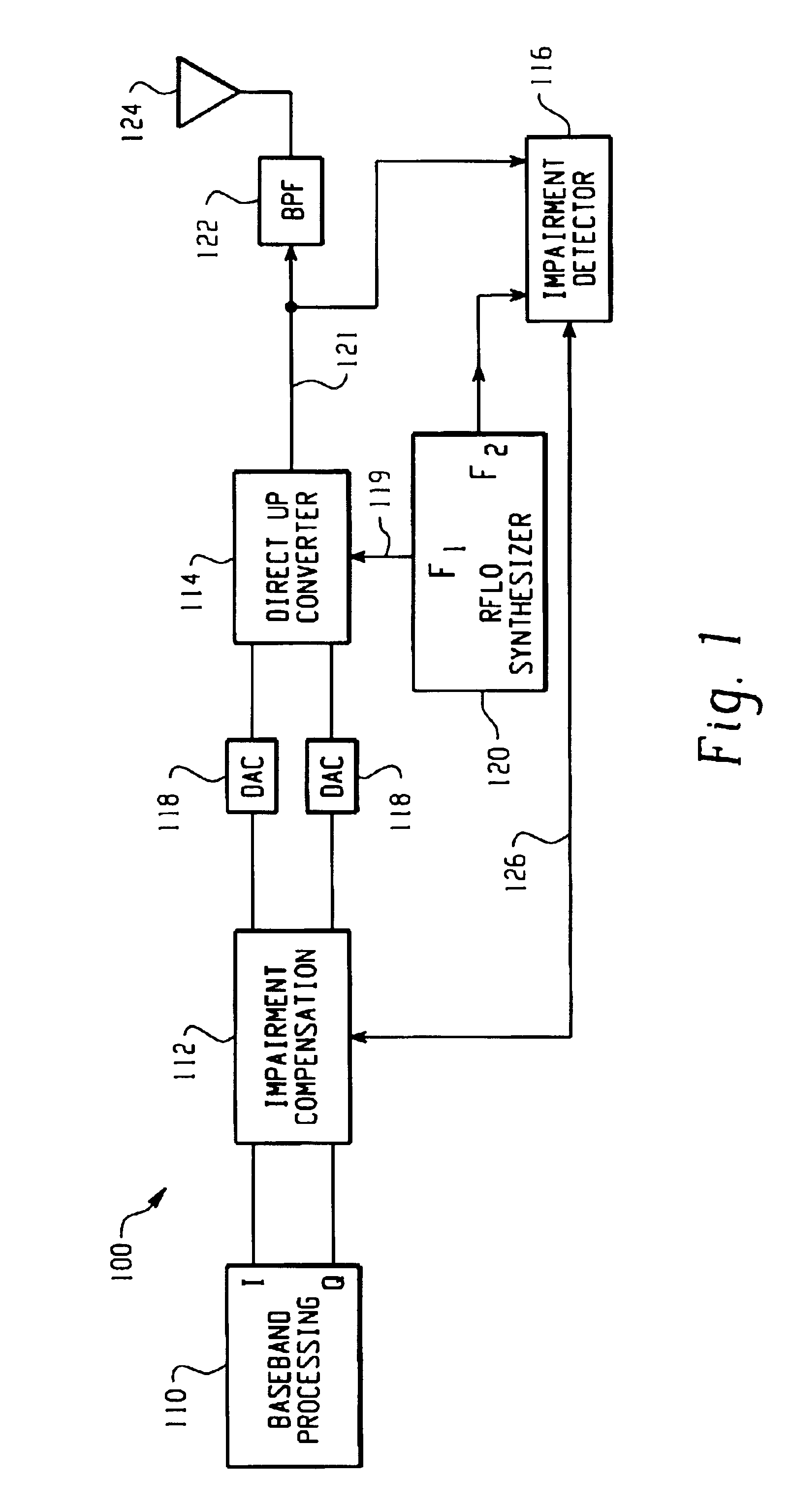
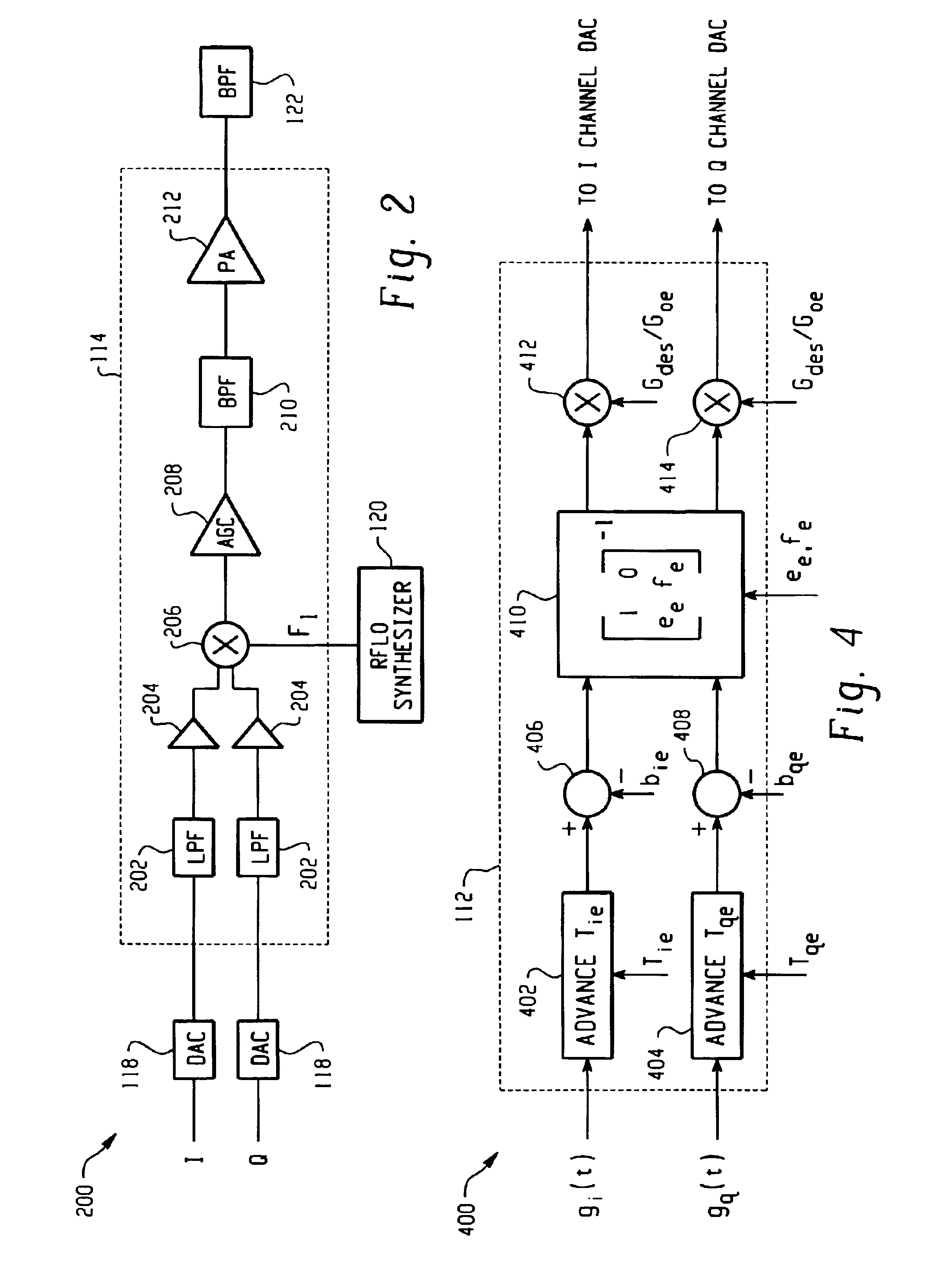
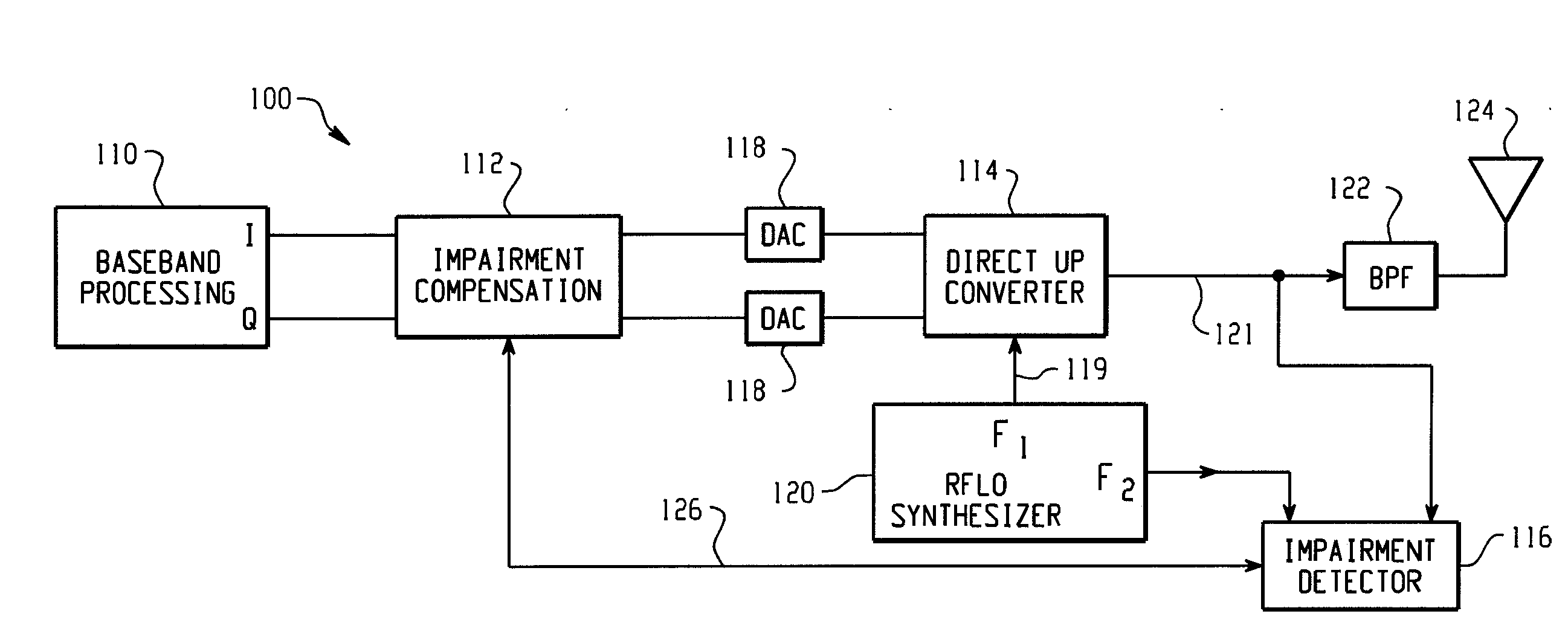
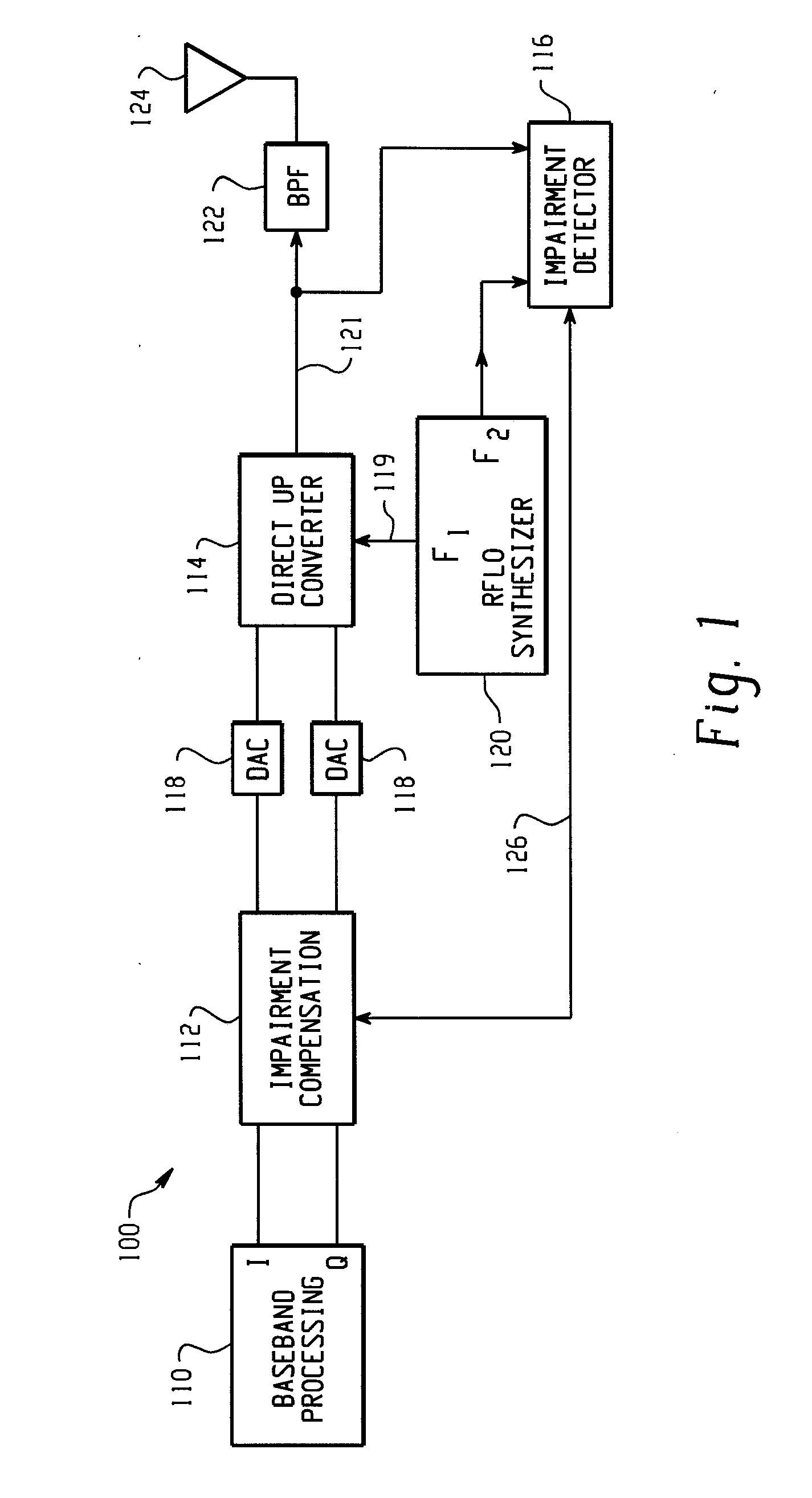
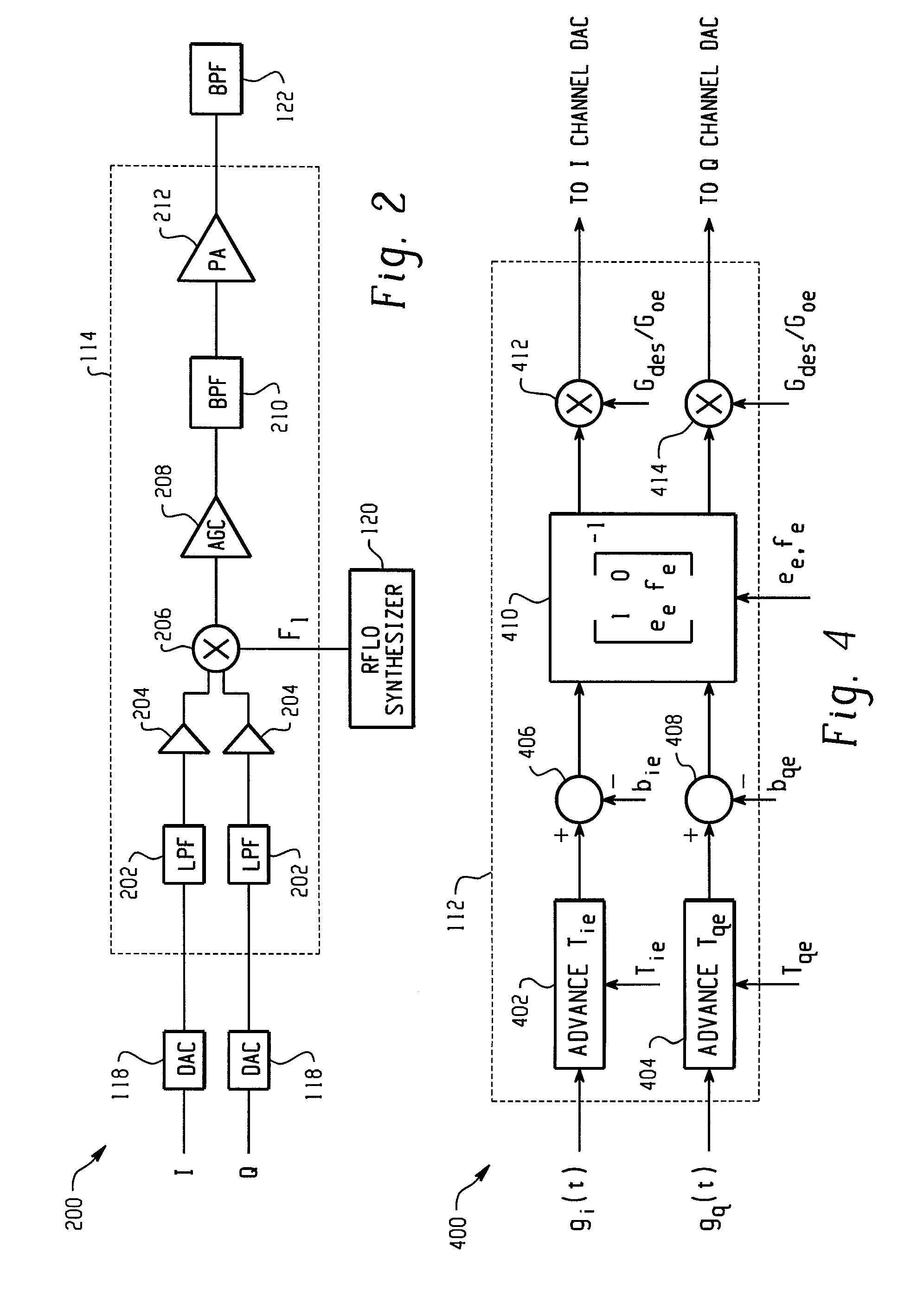
A feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter includes a baseband processor, a direct up-converter, an antenna, and an impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit. The baseband processor generates an in-phase (I) baseband signal and a quadrature-phase (Q) baseband signal. The direct up-converter is coupled to the baseband processor, and combines the I and Q baseband signals with an RF carrier signal to generate an RF output signal. The antenna is coupled to the direct up-converter, and transmits the RF output signal. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit is coupled to the RF output signal and the I and Q baseband signals. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit down-converts the RF output signal to generate an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, measures as least one signal impairment in the IF signal, and pre-distorts the I and Q baseband signals to compensate for the measured signal impairment.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
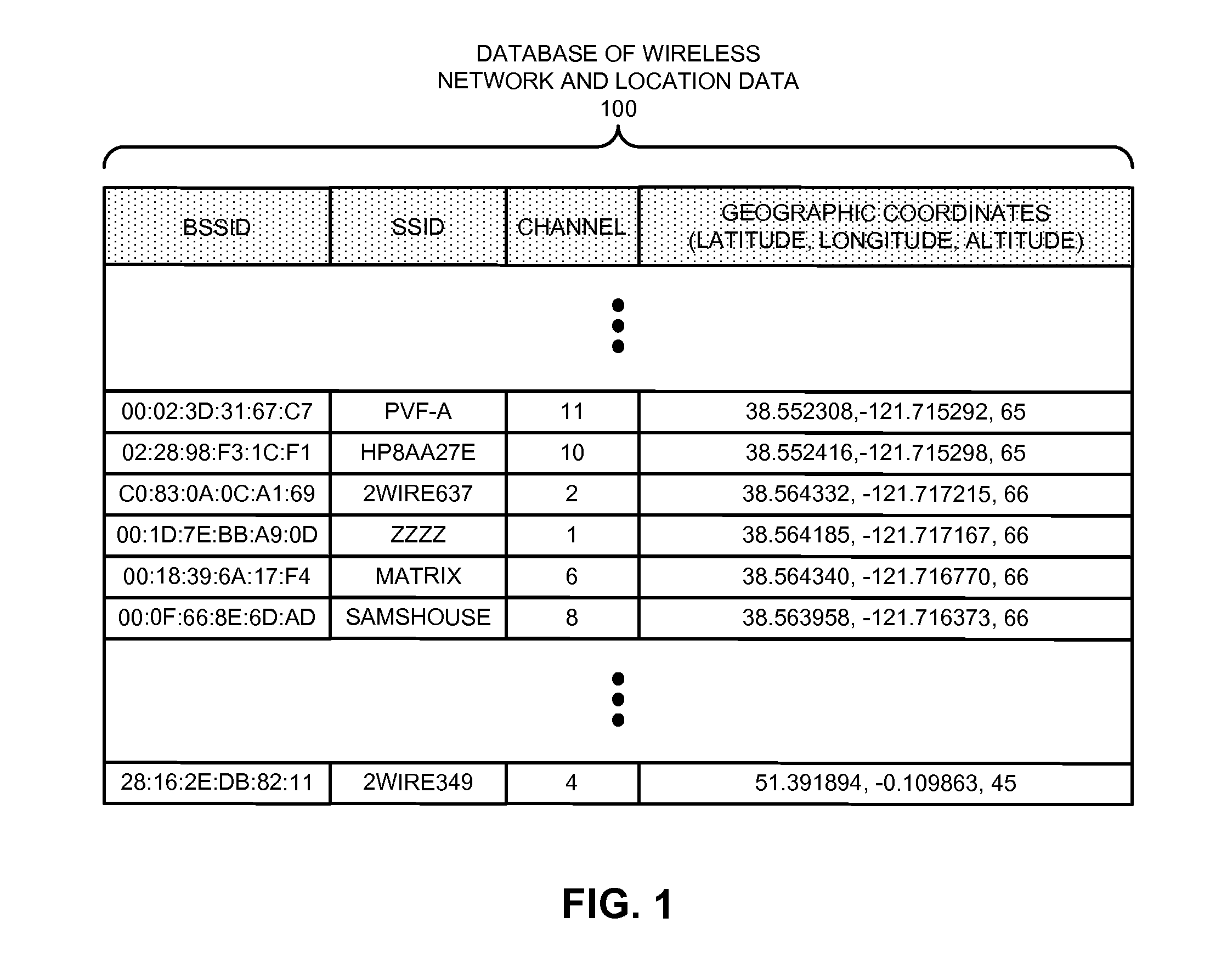
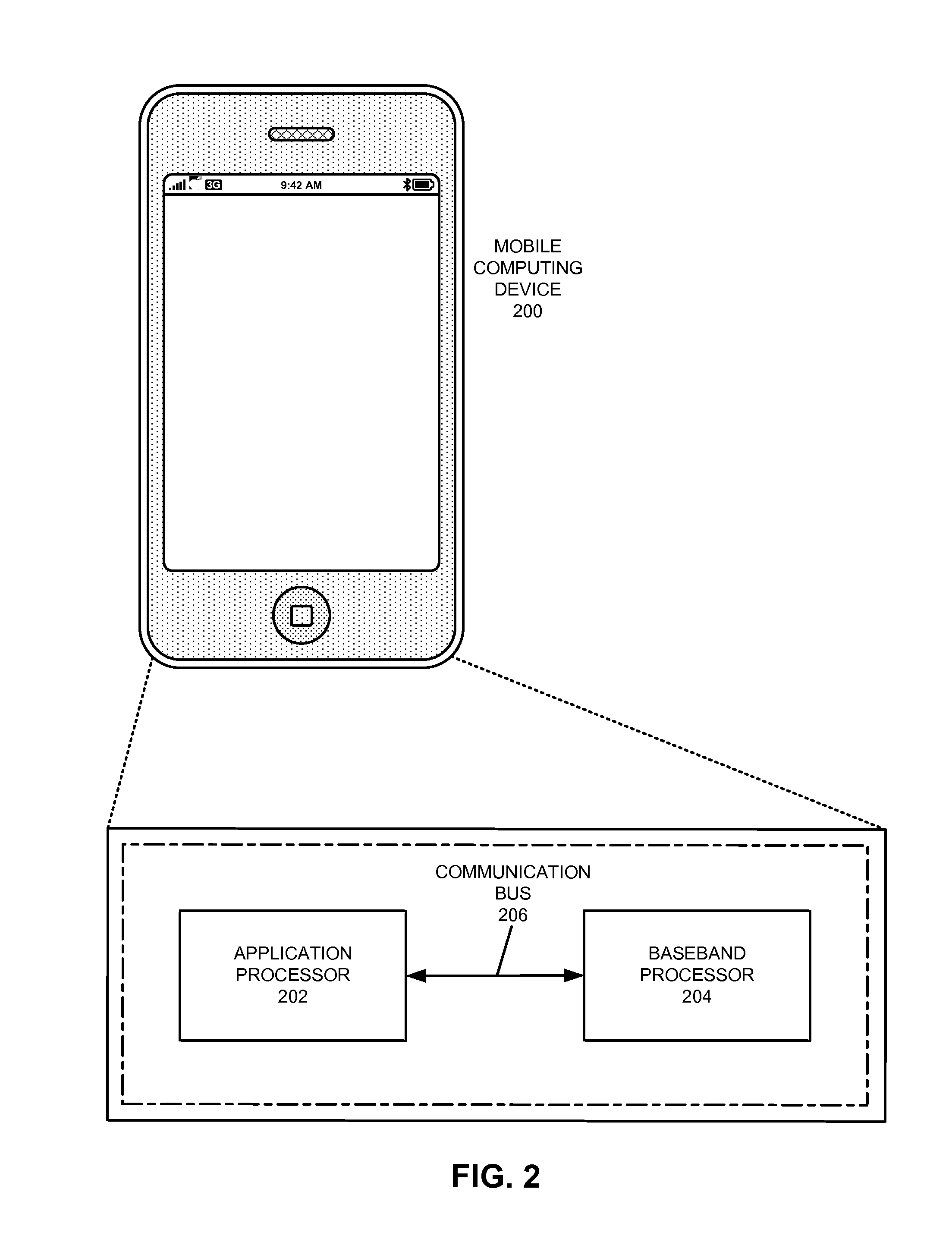
Performing enhanced background location scans to facilitate location-based geo-fencing
The disclosed embodiments facilitate location awareness in mobile computing devices while also reducing power consumption. A baseband processor performs background scanning of wireless networks, tracking the status of surrounding wireless networks while a primary application processor operates in a lower-power sleep state. Upon detecting a wireless network of interest, the baseband processor notifies (and wakes up) the application processor. The baseband processor can also be configured to track a subset of the wireless networks detected from previous scans to facilitate trajectory tracing.
Owner:APPLE INC
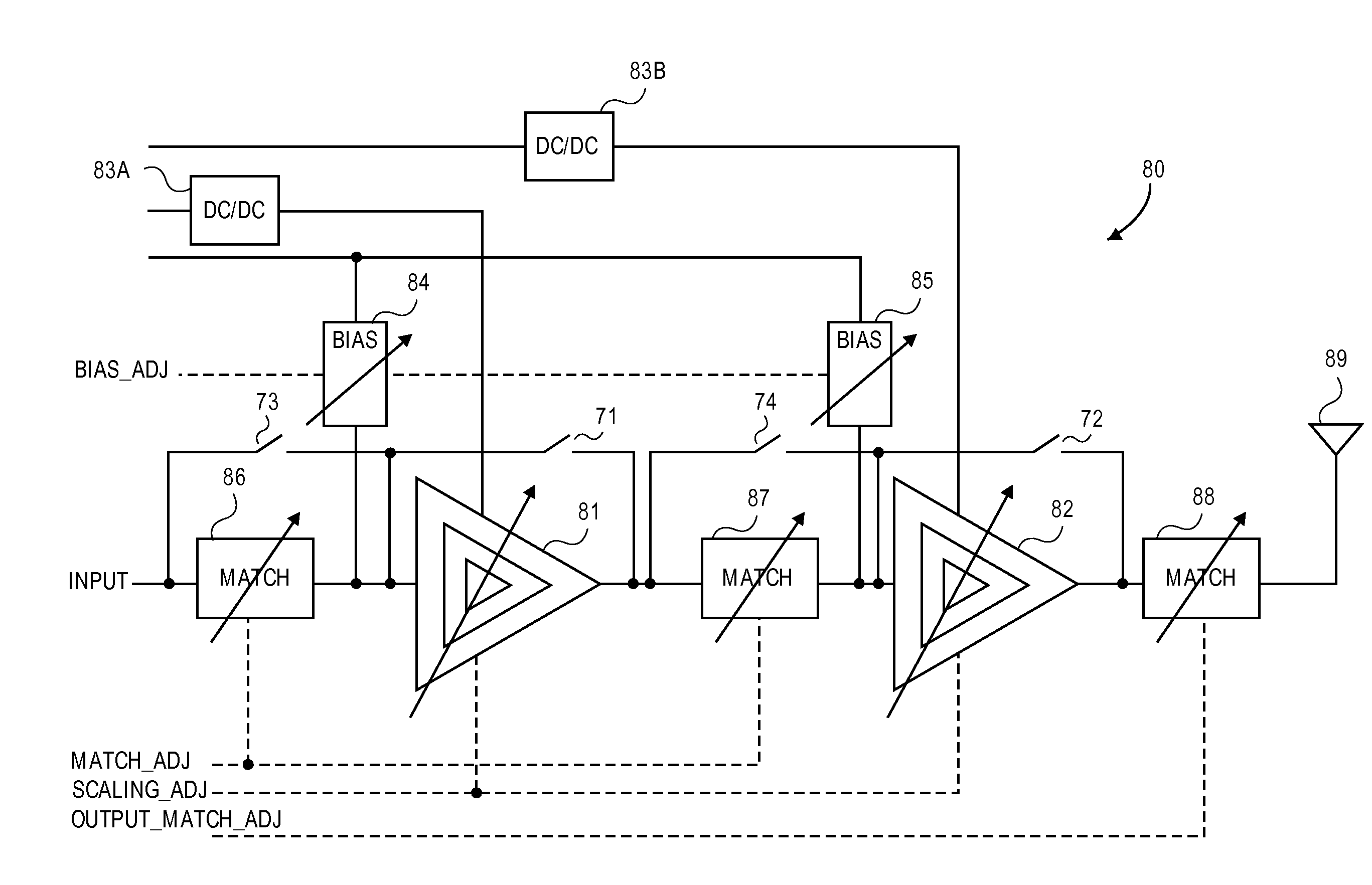
Dynamic stability, gain, efficiency and impedance control in a linear/non-linear CMOS power amplifier
A power amplifier (PA) provides dynamic stability and gain control for linear and non-linear operation. The PA operates with a baseband processor and a transmitter, in which the PA receives a signal from the transmitter for power amplification prior to transmission of the signal. The PA is configured to select between the linear mode of operation and the non-linear mode of operation, in which device scaling within the PA is achieved by changing a device sizing of at least one stage of the PA. Further to changing the device size, the PA changes biasing resistance and impedance of a matching network in response to the changing of the device size to control power output and stability for the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for centralized distributed transceiver management
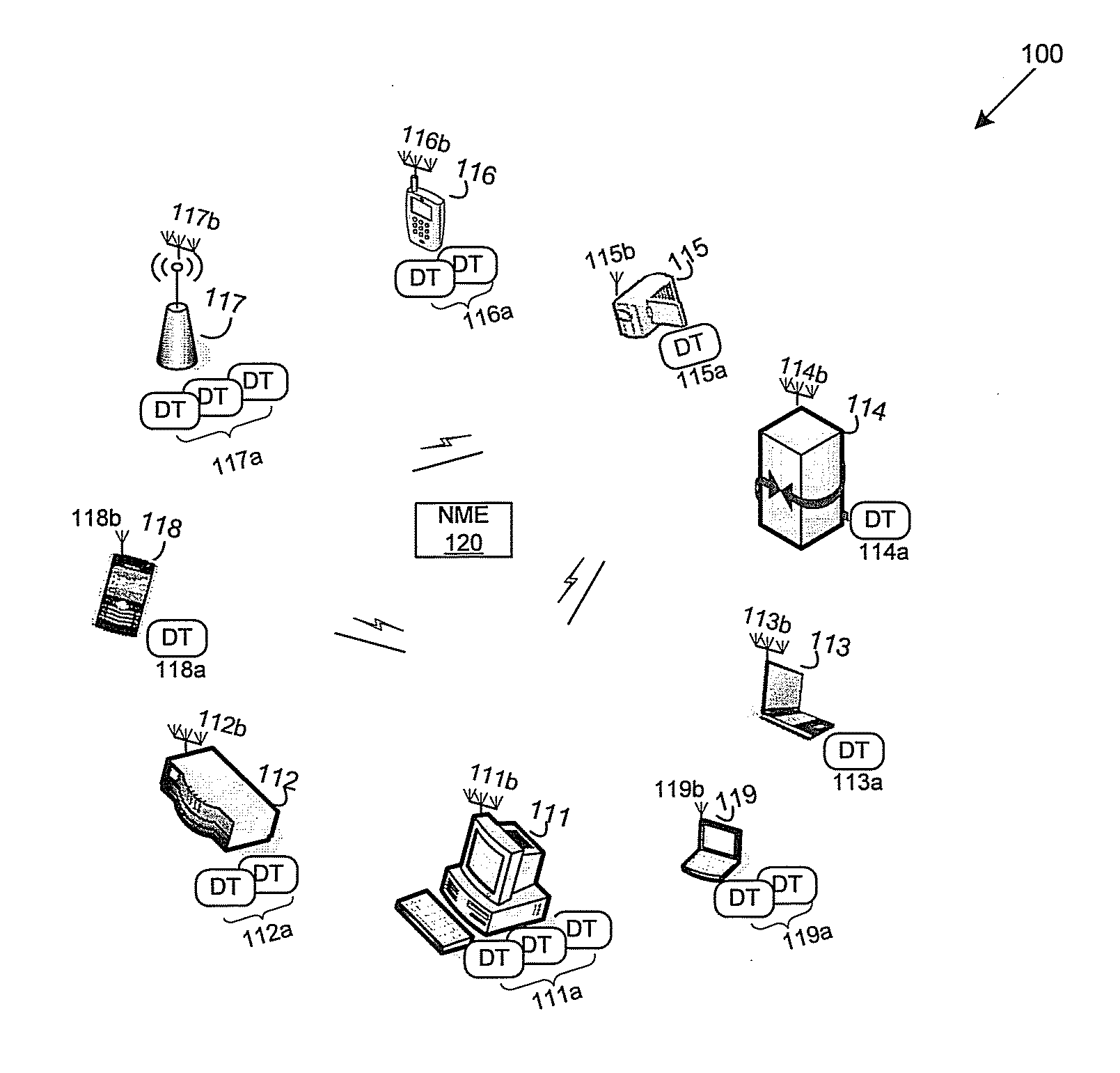
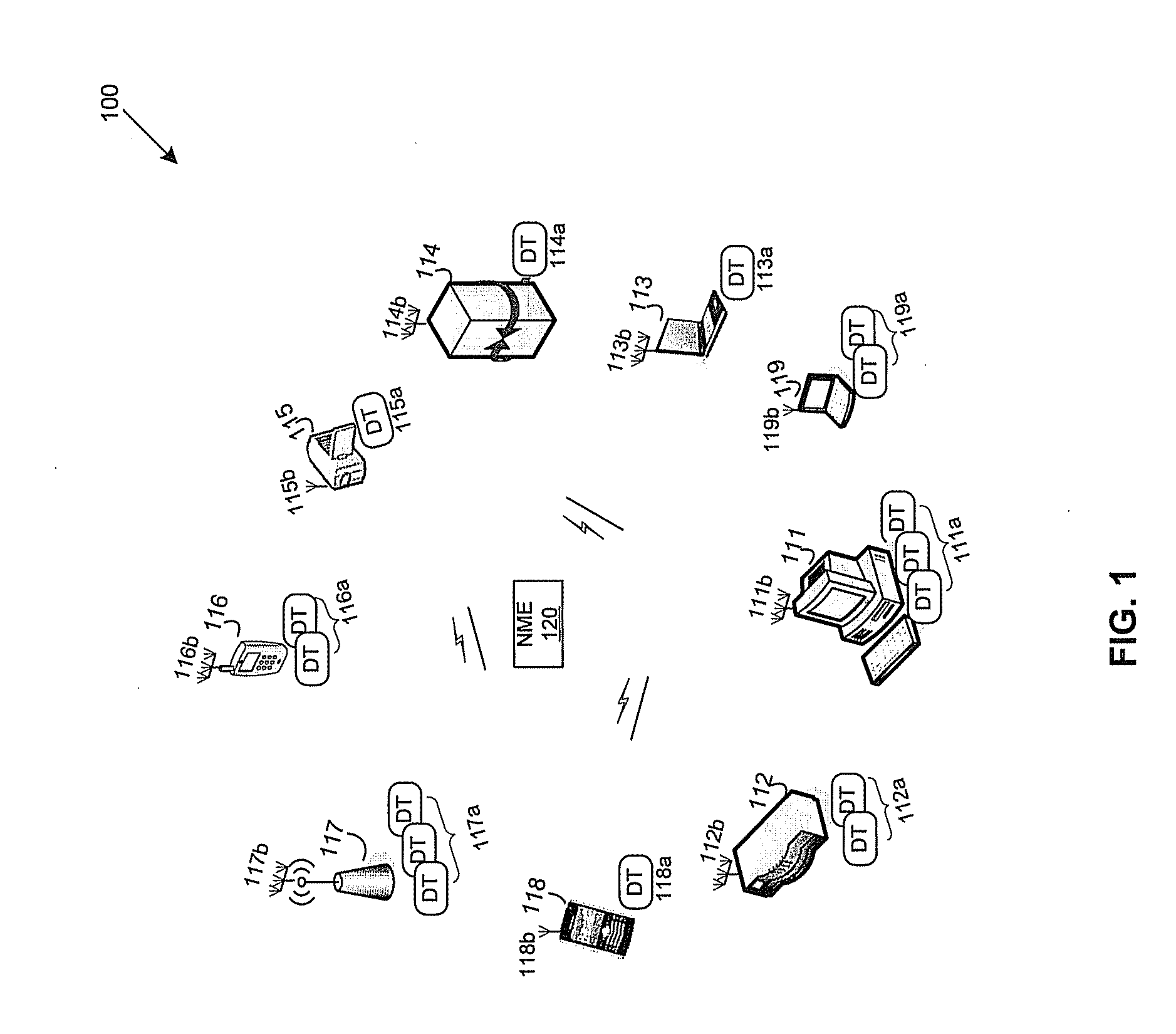
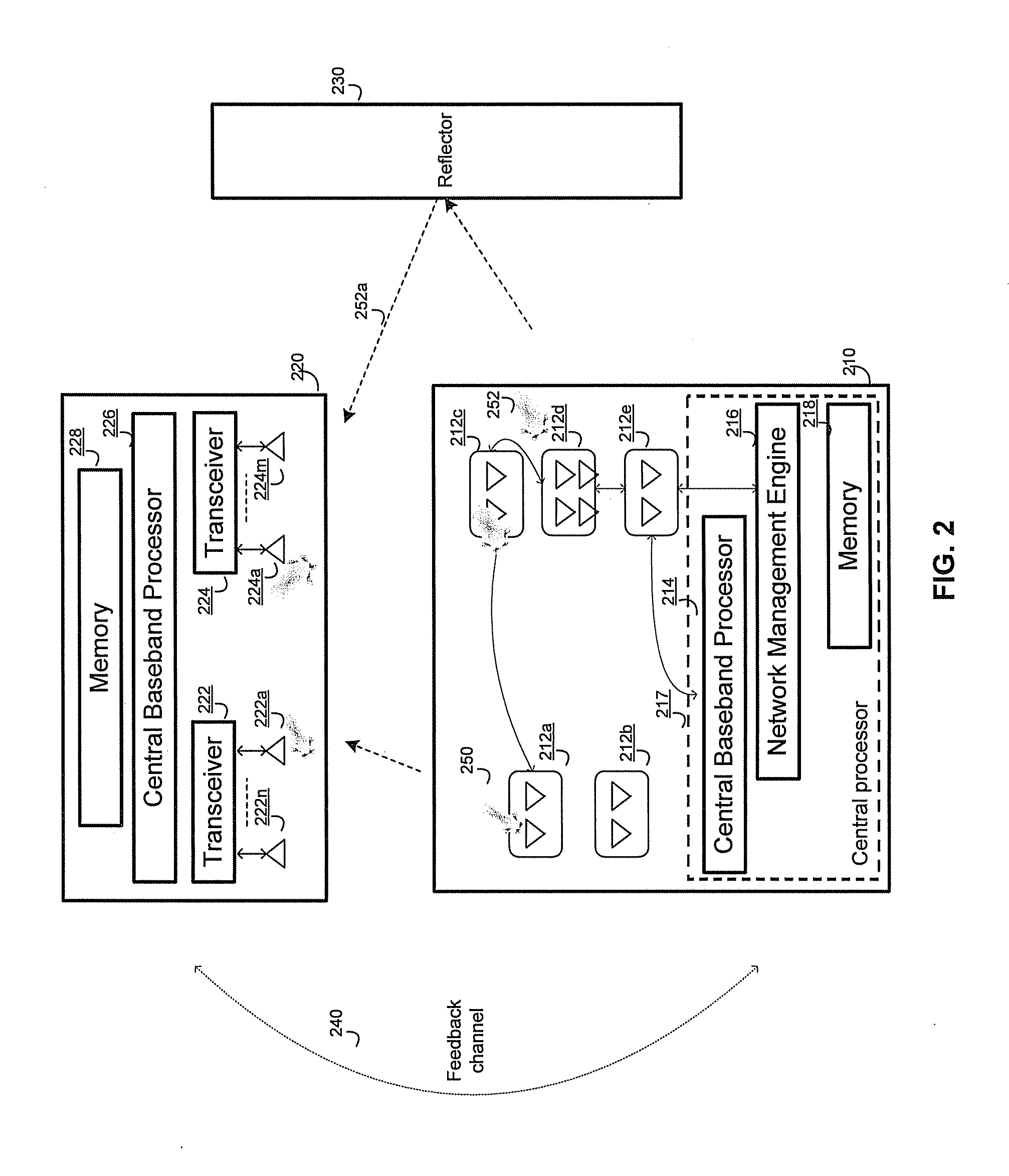
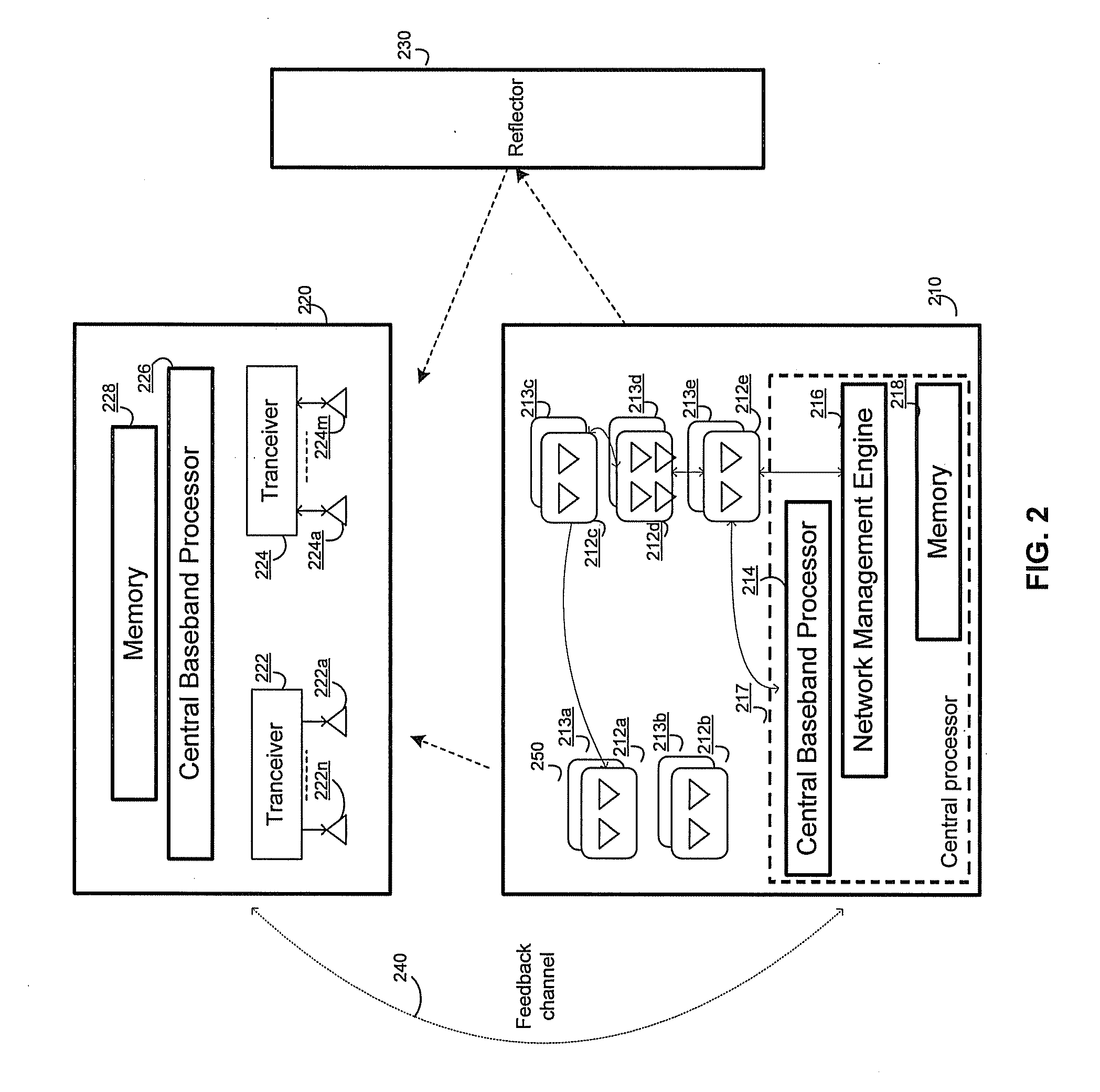
A master application device comprises a plurality of distributed transceivers, a central baseband processor, and a network management engine that manages operation of the master application device and end-user application devices. The master application device communicates data streams to the end-user devices utilizing one or more distributed transceivers selected from the plurality of distributed transceivers. The selected distributed transceivers are dynamically configured to switch between spatial diversity mode, frequency diversity mode, multiplexing mode and MIMO mode based on corresponding link quality and propagation environment. Digital signal processing needed for the selected distributed transceivers is performed by the central baseband processor. The network management engine continuously monitors communication environment information to configure beamforming settings and / or antenna arrangement for the selected distributed transceivers. Connection types, communication protocols, and / or transceiver operation modes are determined for the selected distributed transceivers. Resources are allocated to the selected distributed transceivers to continue subsequent data communication.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
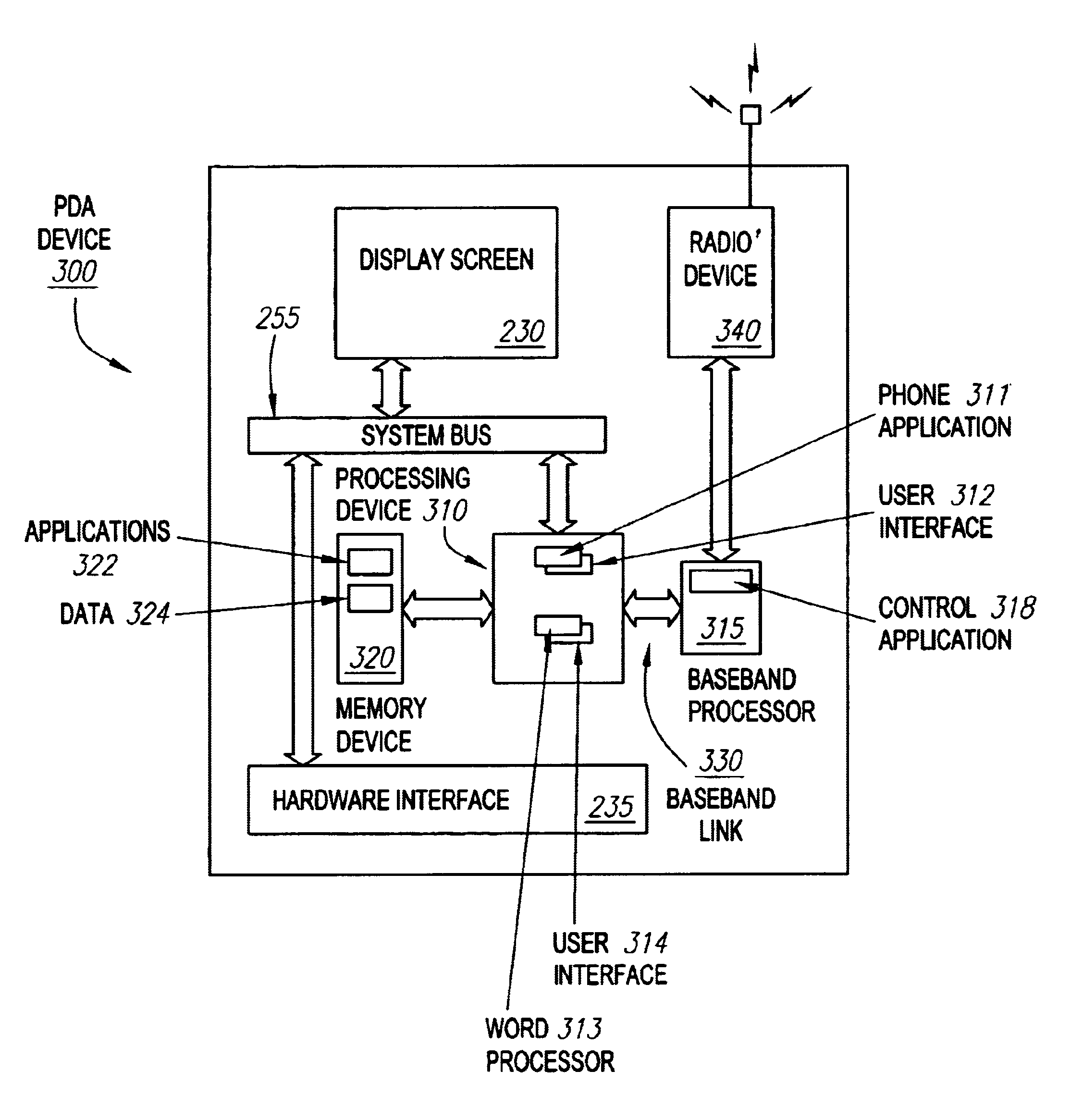
Method and apparatus for integrating phone and PDA user interface on a single processor
InactiveUS6976217B1Conveniently implementedSubstation equipmentTransmissionGraphical user interfaceApplication software
Separate processors, a PDA processor, and a baseband processor are maintained in a PDA having an integrated telephone device. The PDA processor runs PDA related programs and a user interface for the telephone device. A link between the PDA processor and baseband processor transfers data and commands from the user interface to a phone control program executing on the baseband processor. The base band processor is connected to the telephone device, and the phone control program controls operation of the telephone device. The separation of processors reduces vulnerability of the telephone device to hacker rogue applications that invade or program crashes that occur on the PDA processor.
Owner:ACCESS
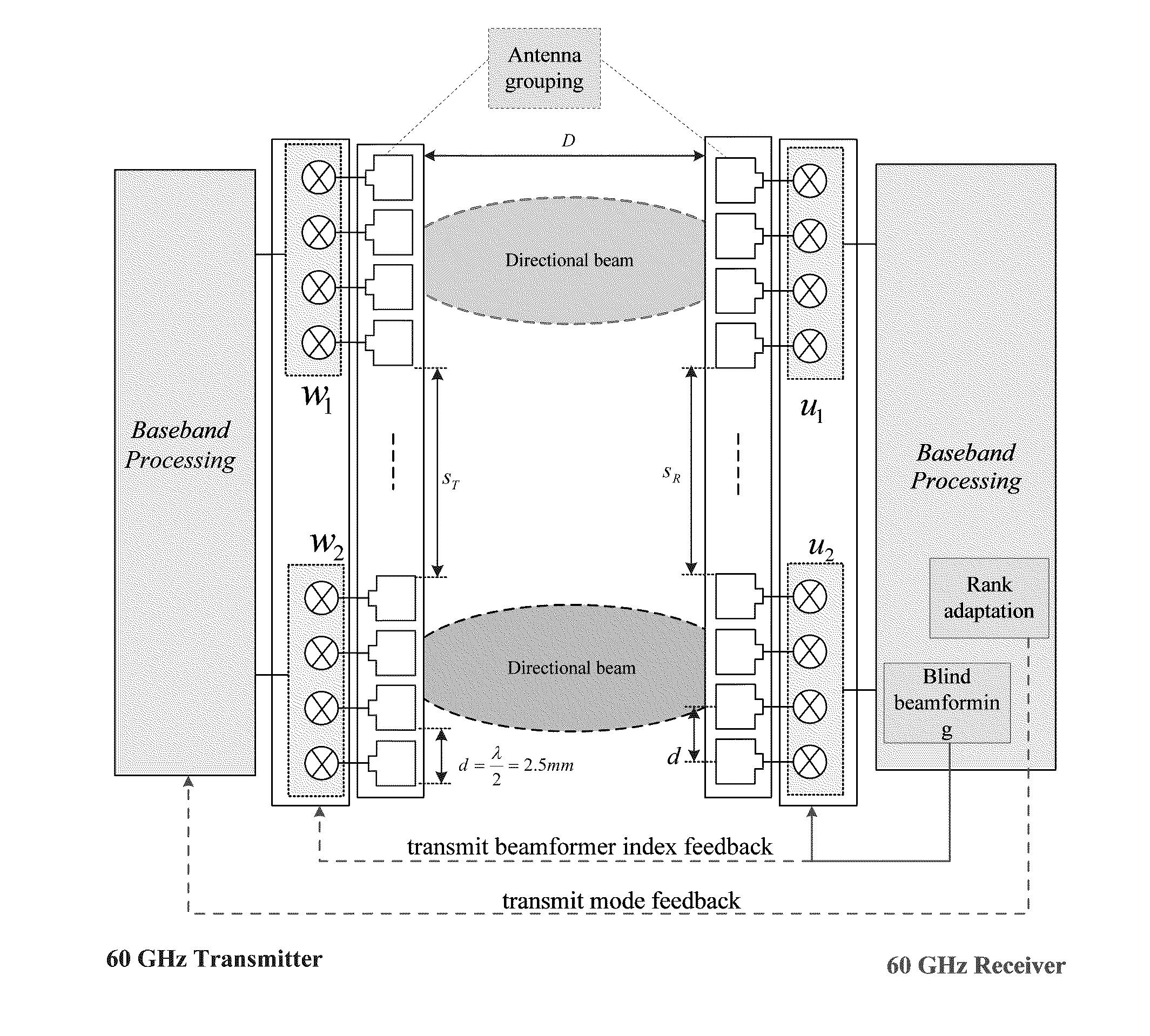
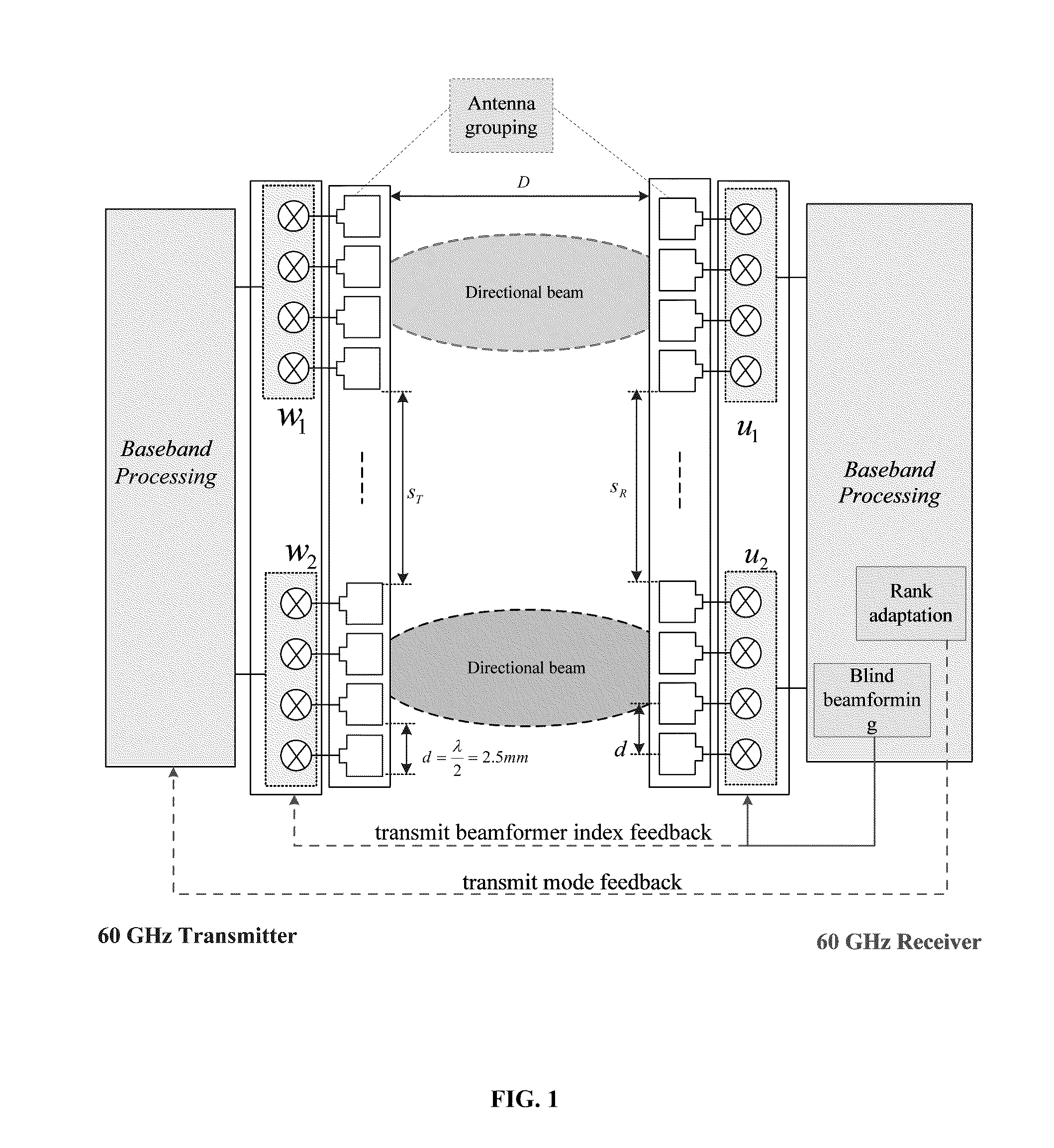
MIMO Transmission with Rank Adaptation for Multi-Gigabit 60 GHz Wireless
ActiveUS20110222616A1Reduce complexityImprove accuracySecret communicationRadio transmissionMimo transmissionGigabit
A wireless system includes a transmitter with a baseband processor responsive to groups of transmitter antenna arrays for communicating over directional beams; and a receiver with a baseband processor responsive to groups of receiver antenna rays for communicating with the transmitter over the directional beams, the receiver including both a rank adaptation providing a transmit mode feedback to the transmitter and a blind beamforming providing a transmit beamformer index feedback to the transmitter and receiver groups of antenna arrays.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for waking a device in response to a wireless network activity
InactiveUS6943667B1Error detection/correctionSignalling system detailsWireless transceiverTransceiver
A method and a system for data transmission between a first electronic device and a second electronic device, wherein the second electronic device is in a sleep mode. Transmission of data between the first electronic device and the second electronic device occurs while a microprocessor in the second device is in sleep mode and the wireless transceiver is in a wake mode. The first electronic device transmits data signals and the second electronic device detects the transmitted signal. A base band processor in the second electronic device optionally determines if the signal is from a known source. If the first electronic device is a known electronic device, an interrupt signal is generated to wake up the microprocessor in the second electronic device. The wakened microprocessor opens a communication port and disables the wake-up interrupt. In yet another embodiment of the present invention, the data receive line is directly coupled to a line that triggers an interrupt when a signal is detected. The received message is then stored in memory for subsequent use.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
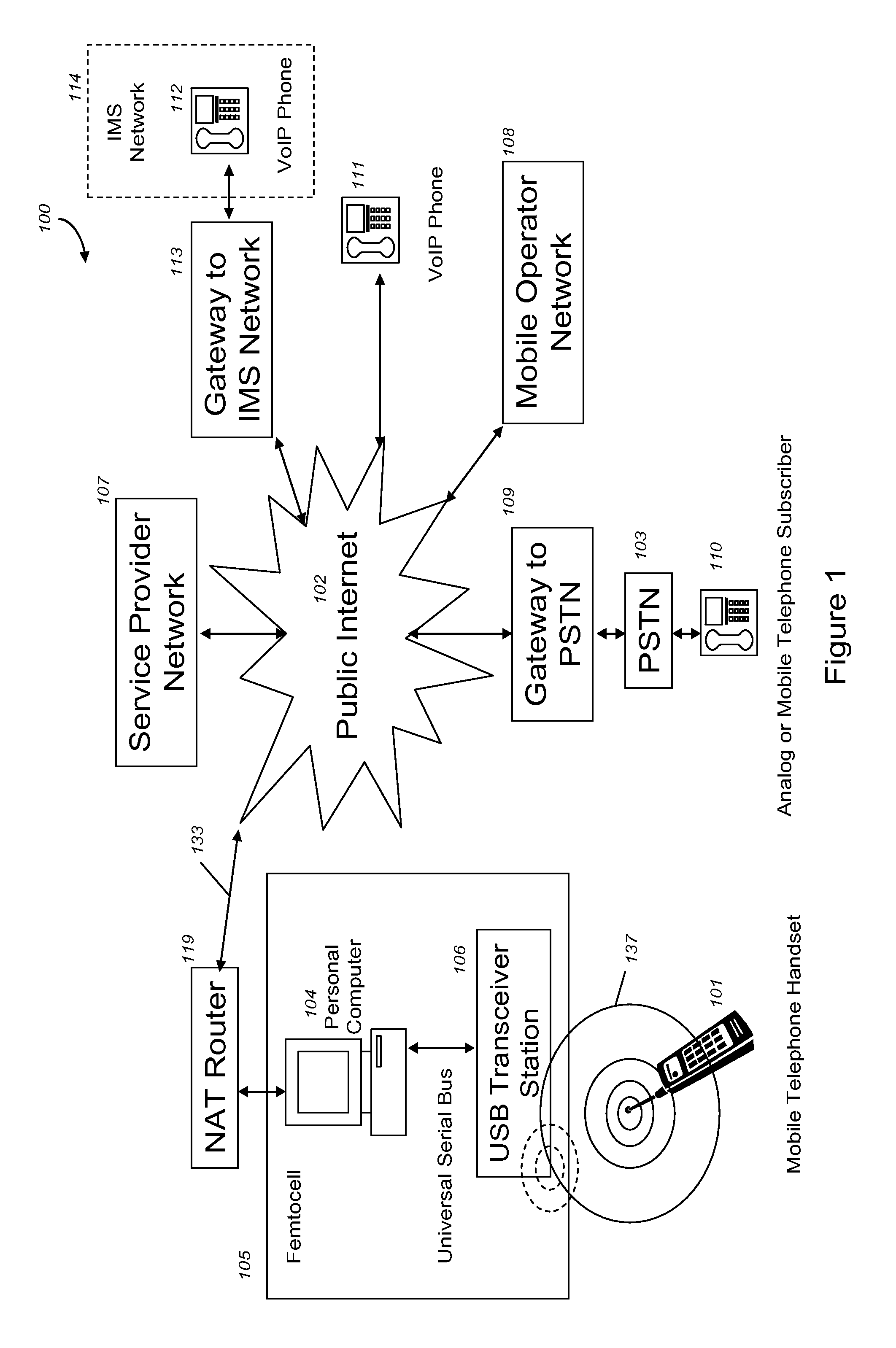
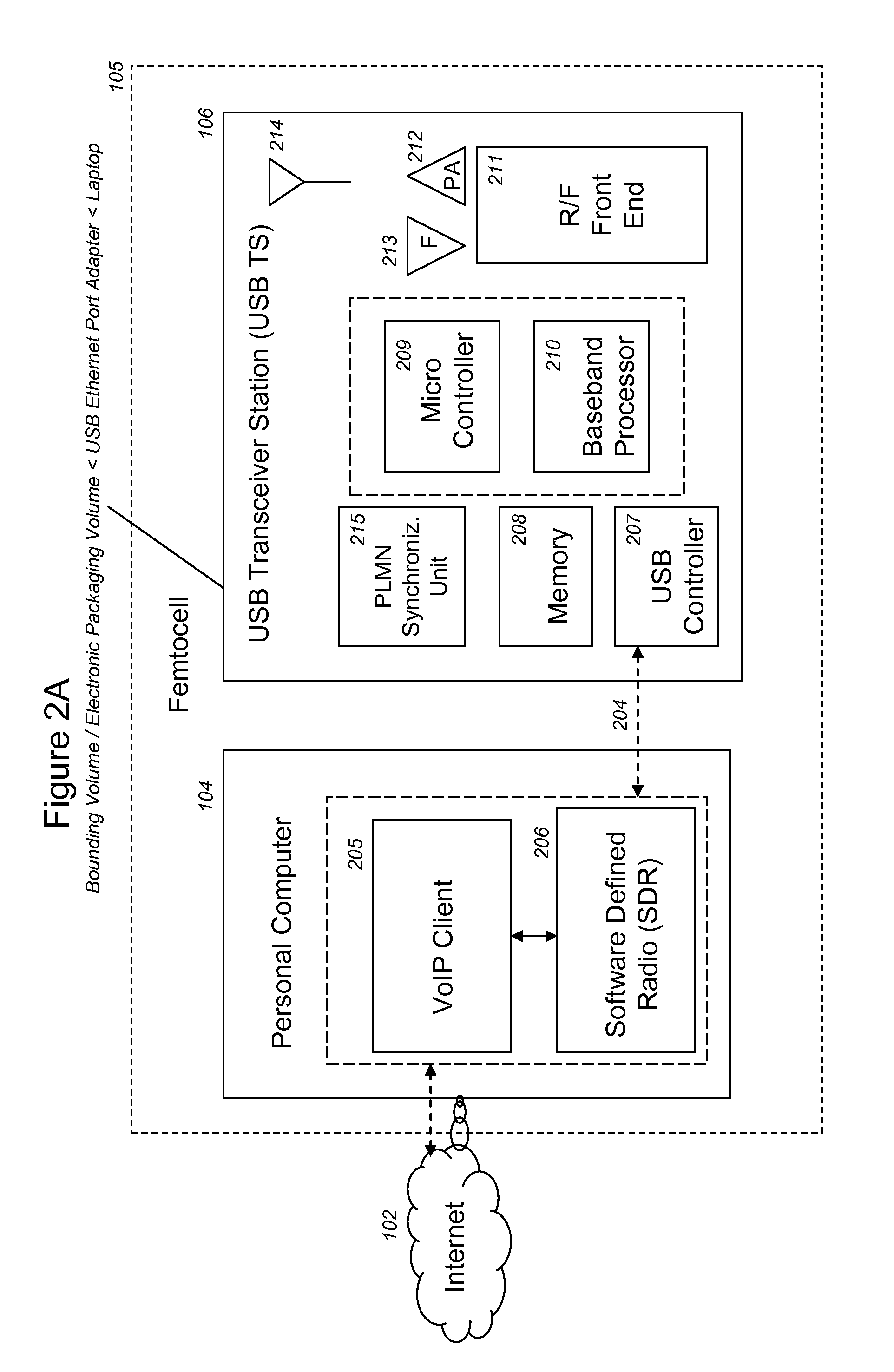
VoIP enabled femtocell with a USB transceiver station
InactiveUS7990912B2High degreeFirmly connectedNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentMicrocontrollerRF front end
Telephone calls between a mobile station (MS) and the mobile network or PSTN are routed through the Internet via VoIP using a femtocell, as opposed to the traditional macrocellular network. The femtocell can comprise a USB Transceiver Station that is connected to a personal computer through a universal serial bus port, which provides both power and a multi-megabit per second connection between the personal computer and the USB transceiver station. The USB transceiver station can comprise a microcontroller to manage signaling between the RF front end / baseband processor and the personal computer, as well as a precise timing mechanism to assist the synchronization of femtocell timing with the surrounding macrocellular network, if it is present. The USB transceiver station can have a compact form factor that facilitates a high degree of portability by the subscriber, such as being readily attachable to their keychain.
Owner:SMALL CELL INNOVATIONS
Wireless local area network spread spectrum transceiver with multipath mitigation
InactiveUS6678310B1Spatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementFinite impulse responseHigh rate
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
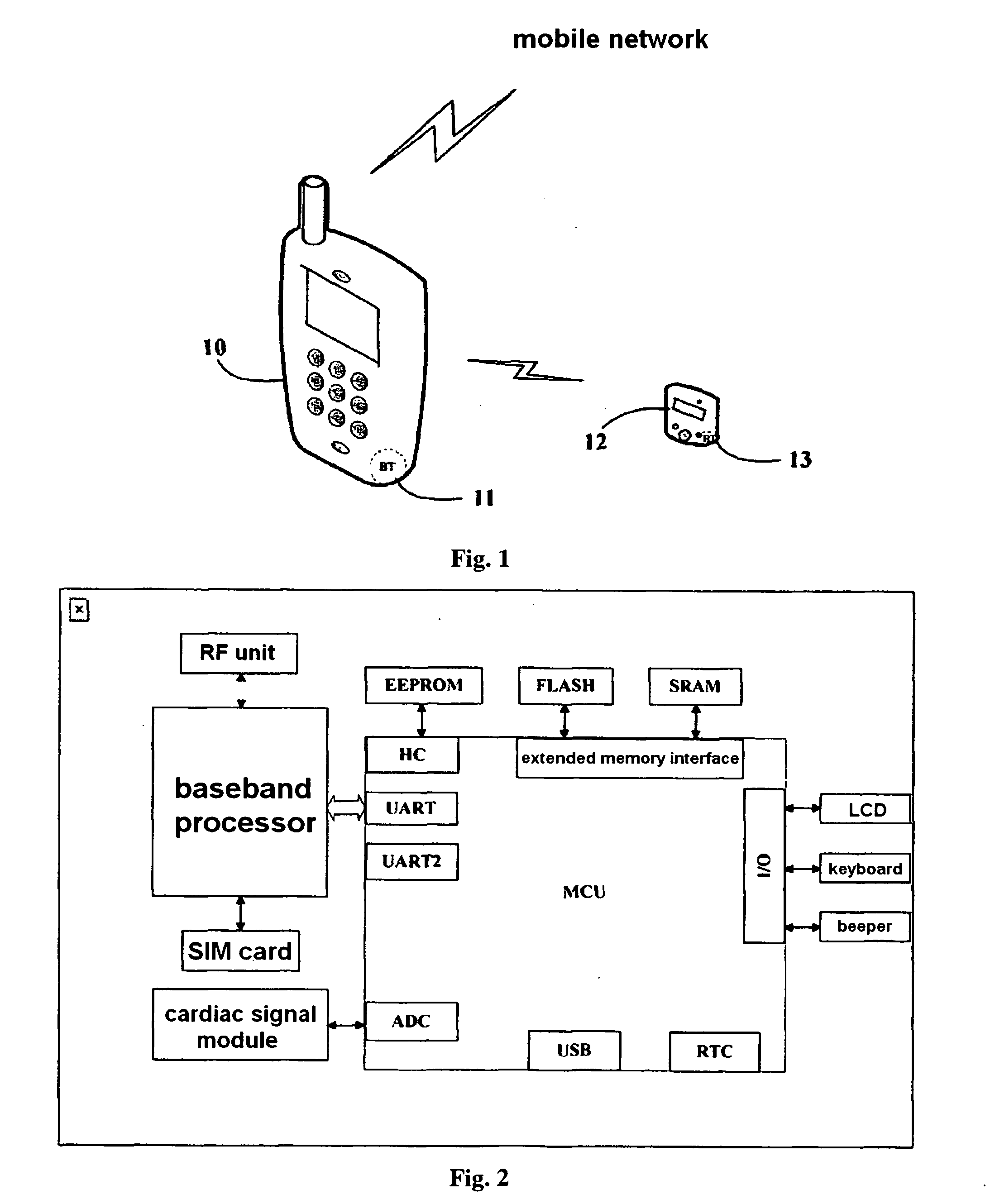
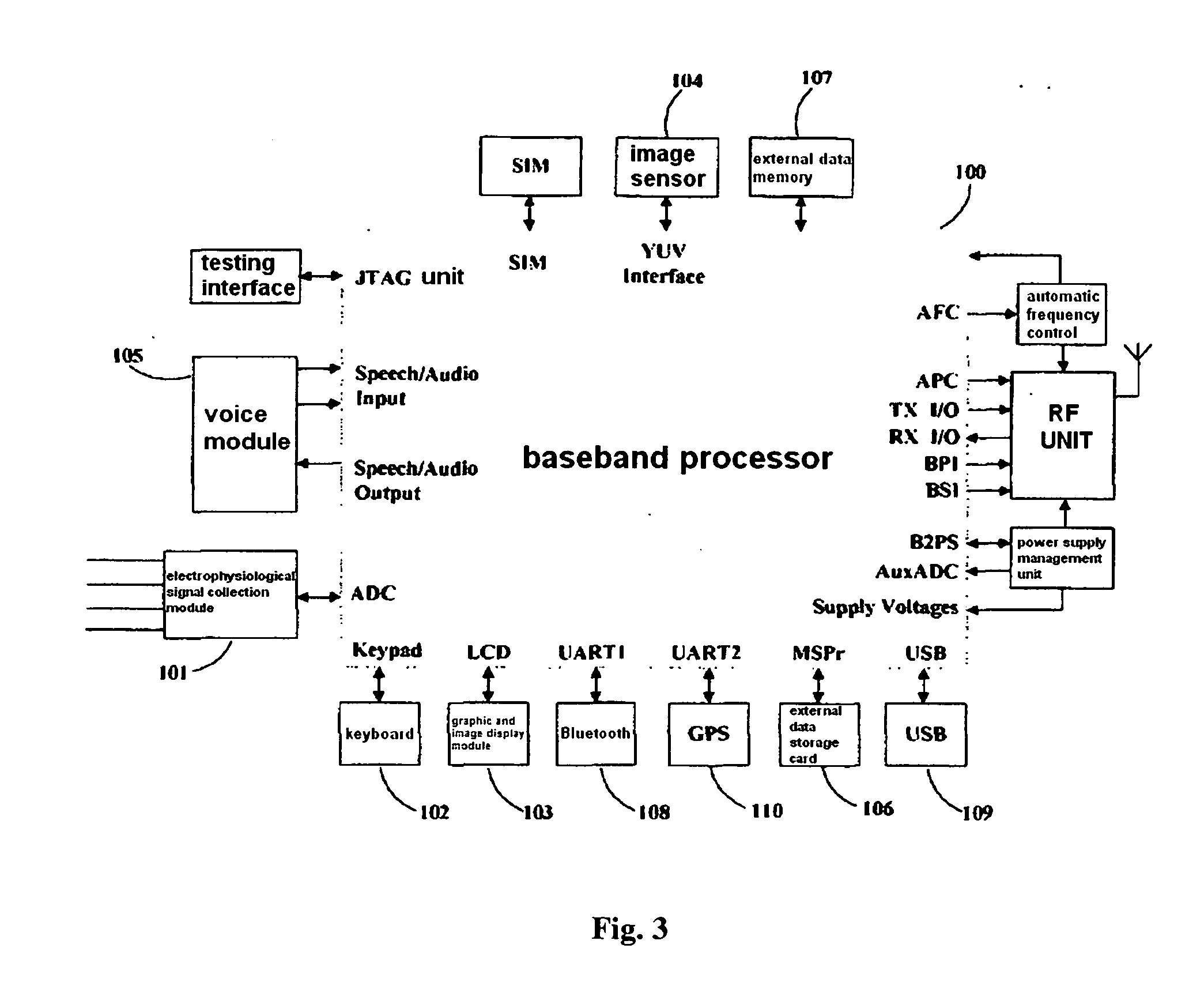
Mobile network terminal device and method for monitoring electrophysiological data and pathological image
ActiveUS20110273309A1Reduce extra spacePoor reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsVoice communicationHeart pacemakers
A mobile network terminal device and method for monitoring the electrophysiological data and a pathological image are provided, including: a baseband processor module, an electrophysiological data collection module, a keyboard module, a graphics and image display module, an image and picture sensor, a voice communication module, an external data memory card, an external data memory, a Bluetooth module, a USB interface module, a GPS receiver module, an application module set and run in the operation system of the baseband processor; an electrophysiological data remote mobile monitoring, a heart pacemaker remote mobile monitoring, a remote consultation appointment, a pathological image remote mobile monitoring, a data exchange, a medical advisory VoIP communication and a network emergency call being performed by the mobile network terminal device under the control of the application module.
Owner:SHANGHAI LEPU CLOUDMED CO LTD
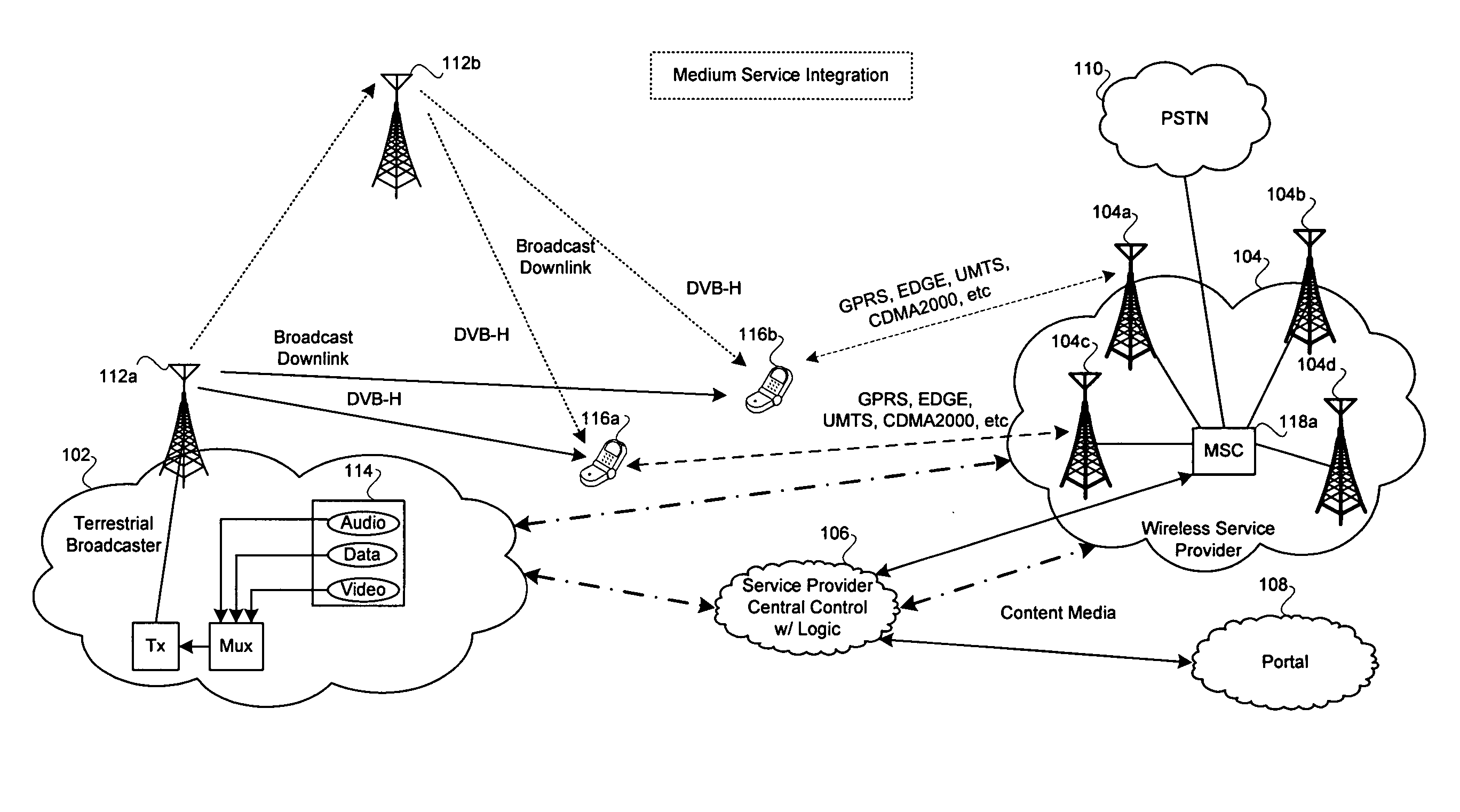
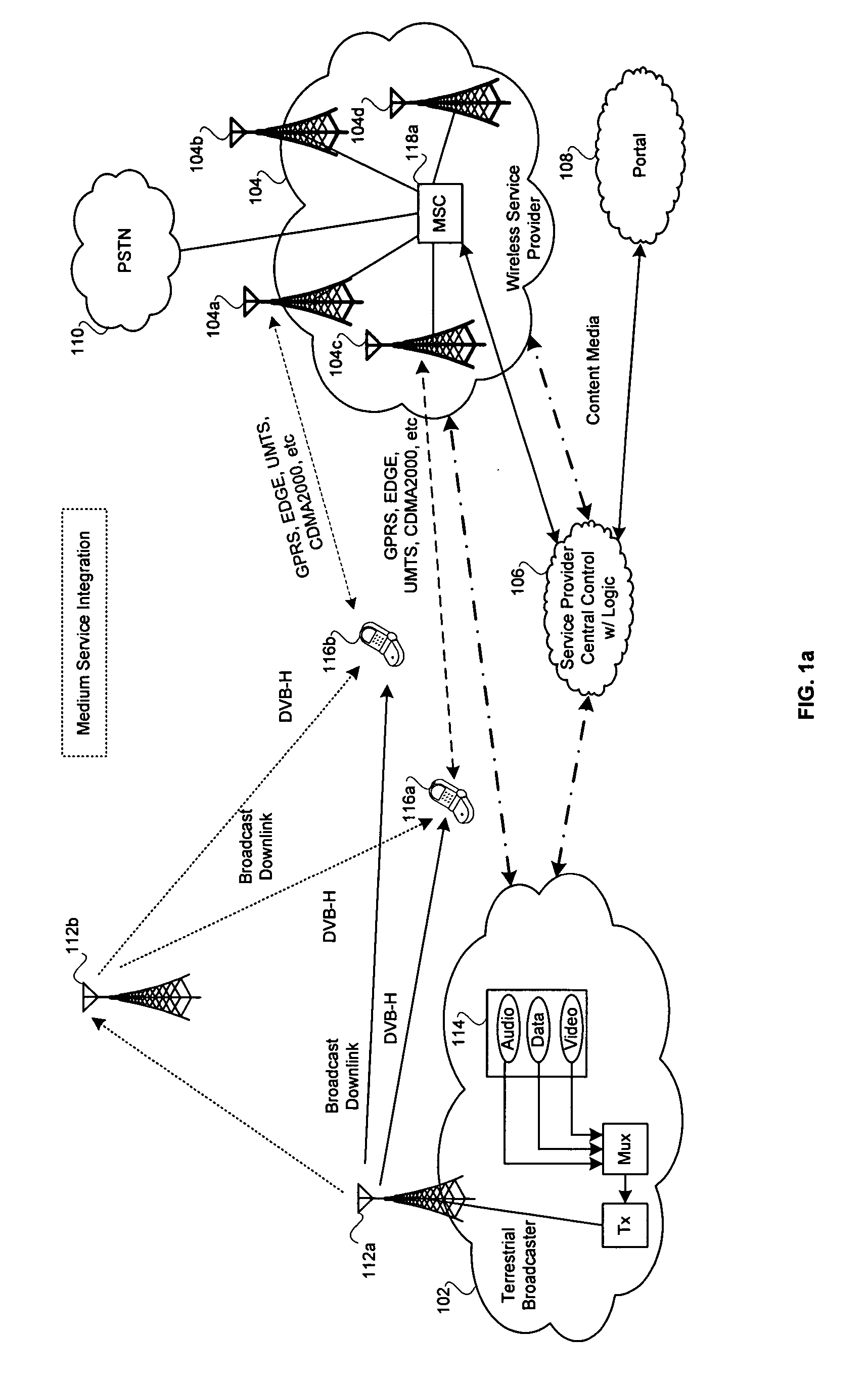
Method and system for a mobile architecture that supports a cellular or wireless network and broadcast utilizing an integrated single chip cellular and broadcast silicon solution
ActiveUS20060128428A1High data rateBroadcast specific applicationsBroadcast-related systemsCommunications systemSingle chip
In an RF communication system, aspects for supporting cellular or wireless network and broadcast utilizing an integrated single chip cellular and broadcast silicon solution may comprise receiving in a mobile terminal, a plurality of cellular frequency band communications services and VHF / UHF band broadcast services in a single baseband processor IC within a mobile terminal. Cellular information associated with the cellular frequency band communications service, and VHF / UHF broadcast information associated with the VHF / UHF broadcast service may be processed by a cellular processing module and a VHF / UHF broadcast processing module, respectively, integrated within a single integrated circuit within the mobile terminal. The cellular processing module and the VHF / UHF broadcast processing module within the mobile terminal may operate independently of each other to separately process the cellular information and the VHF / UHF broadcast information without exchanging related information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
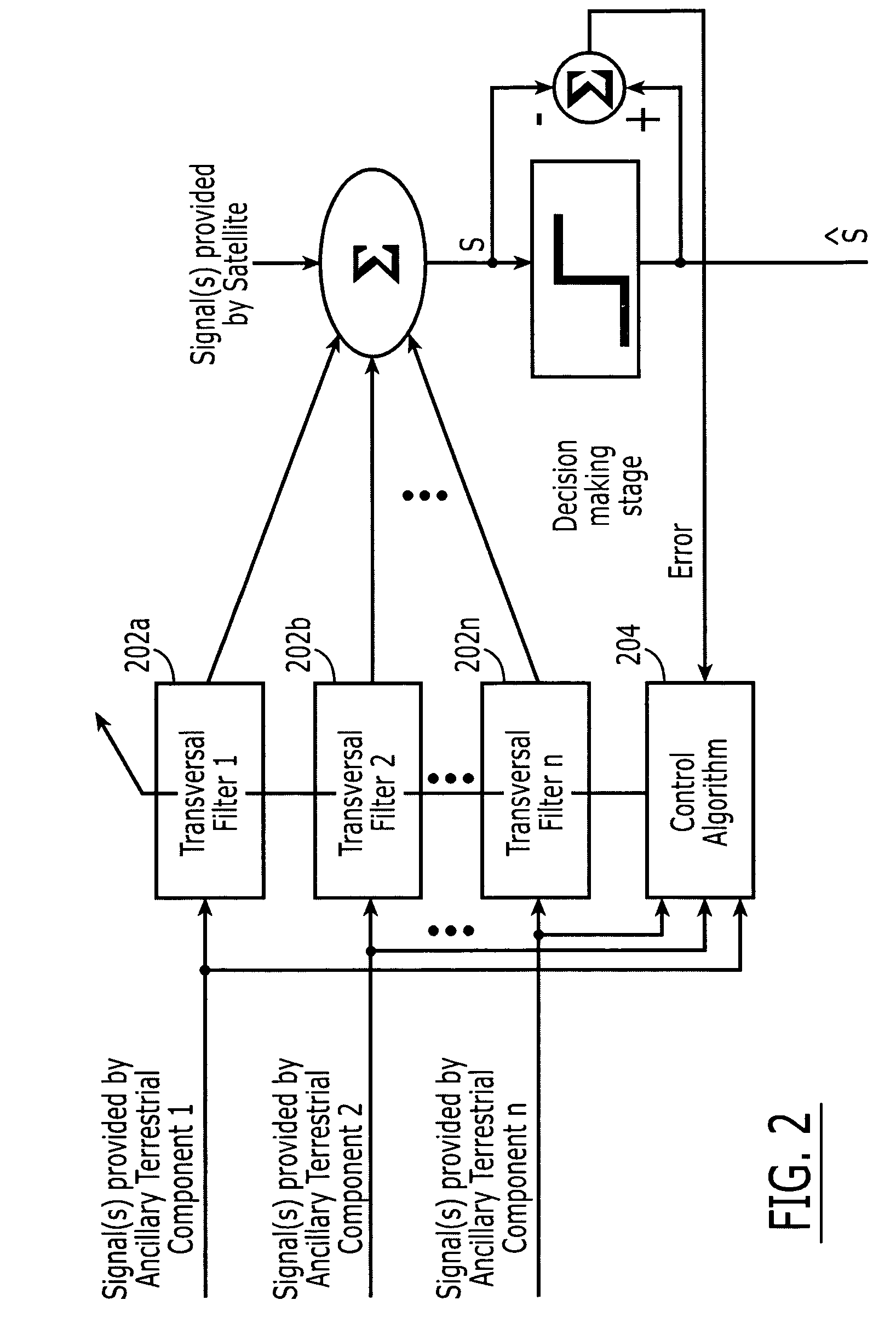
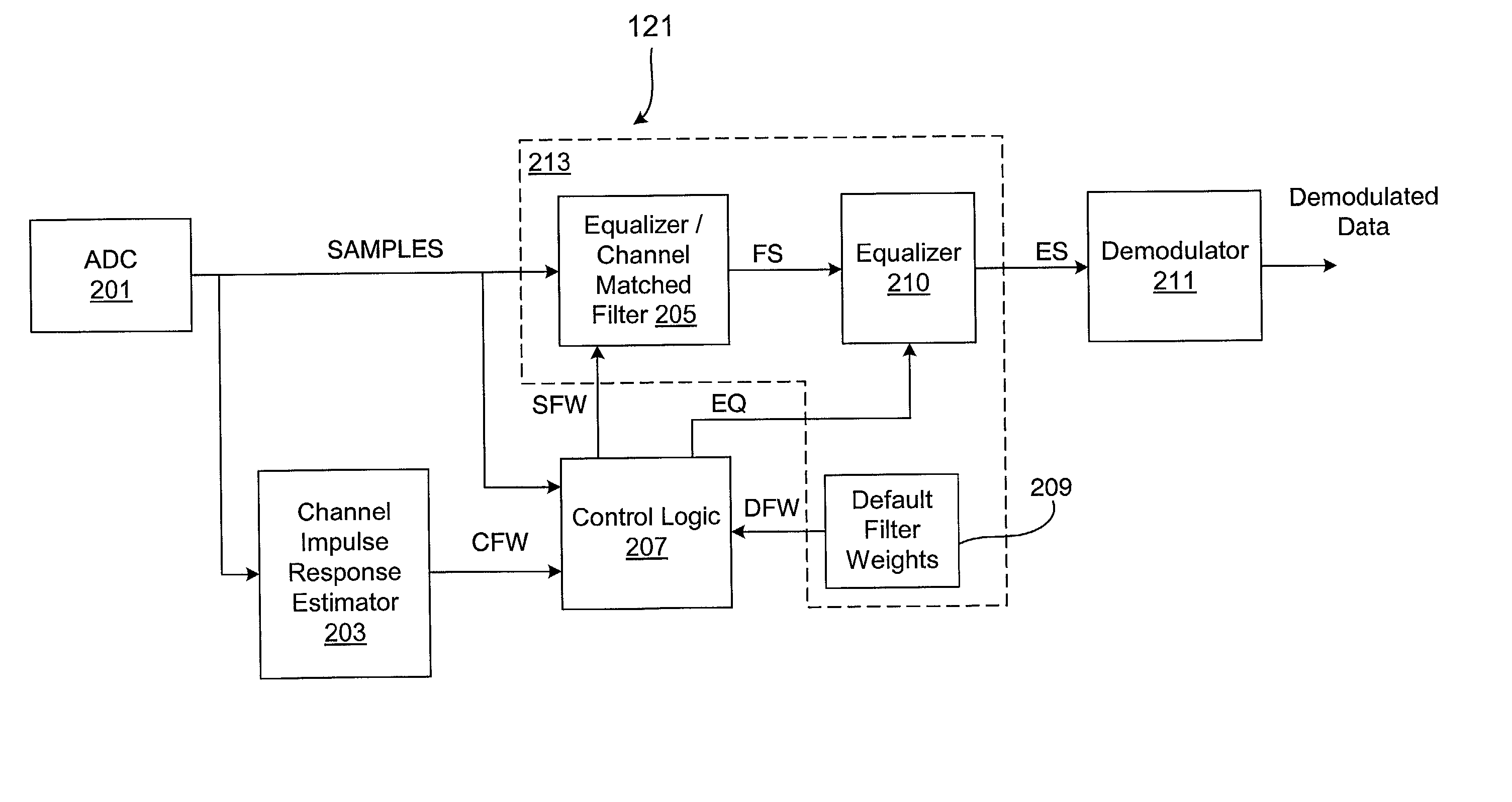
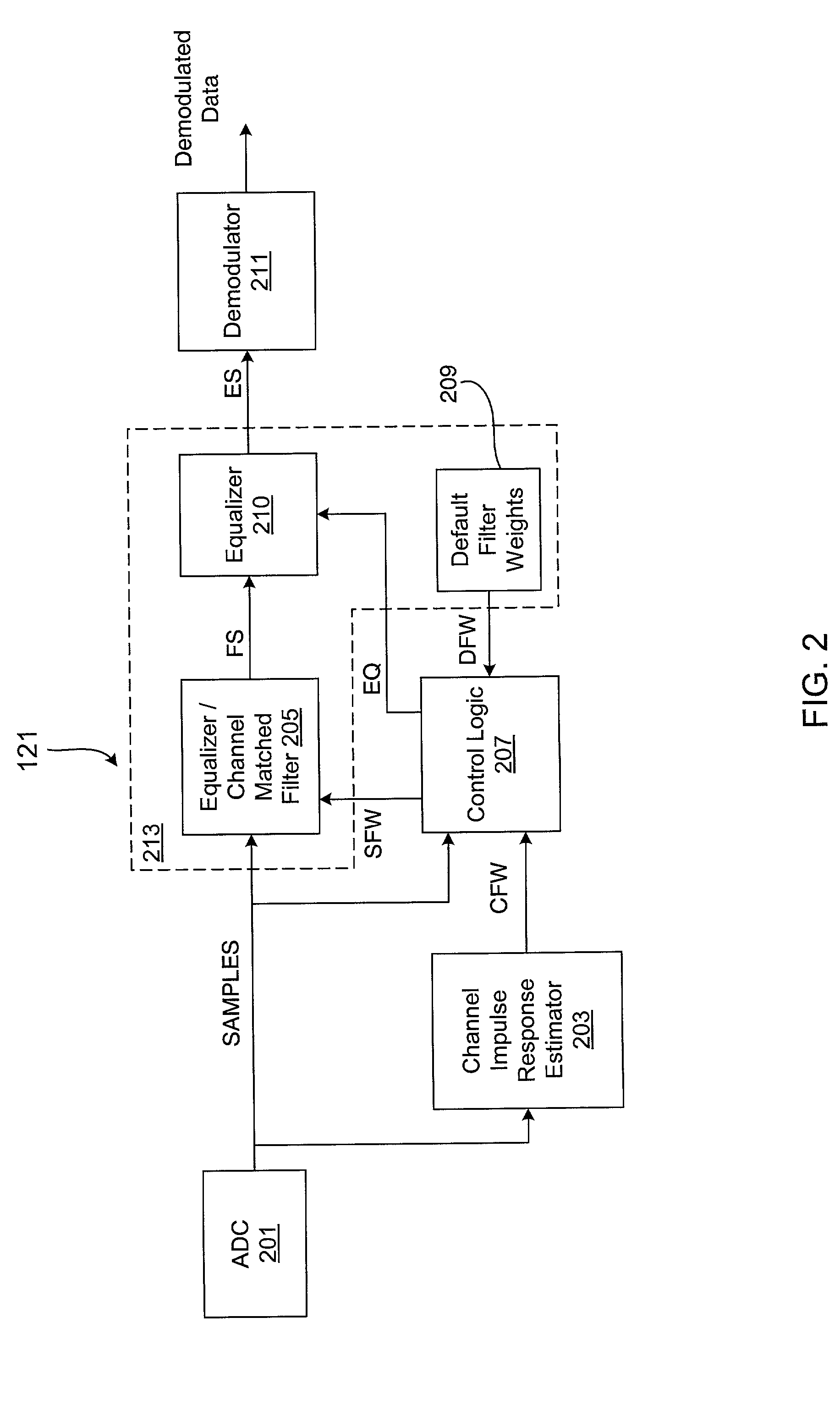
Intelligent control system and method for compensation application in a wireless communications system
ActiveUS20030058962A1Multiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemOperating point
A wireless receiver including a baseband processor that includes a compensation system that selectively includes an equalizer and a CMF that process received digital samples from a wireless medium, and a CIR estimator that calculates filter weights based on the samples. A memory stores default filter weights and select logic selects between calculated filter weights of the CIR estimator and the default filter weights from the memory. An SNR estimator receives the samples and provides an SNR metric and a multipath estimator receives the calculated filter weights and provides a multipath metric. The decision logic determines an operating point of the receiver using the SNR and multipath metrics, makes a decision based on the determined operating point according to a predetermined packet error rate (PER) performance mapping, and controls the select logic to select between the default and calculated filter weights and selectively enables the equalizer.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system
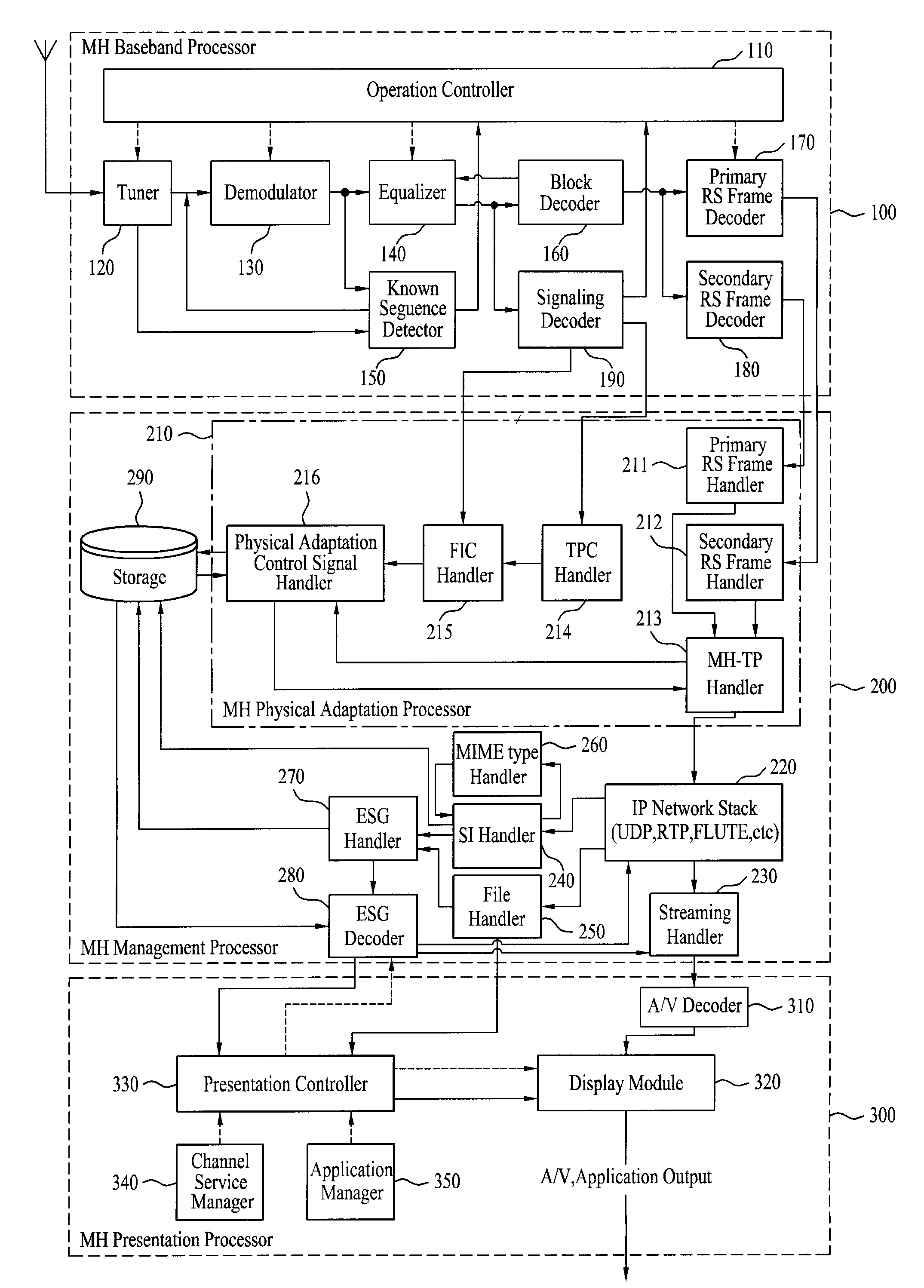
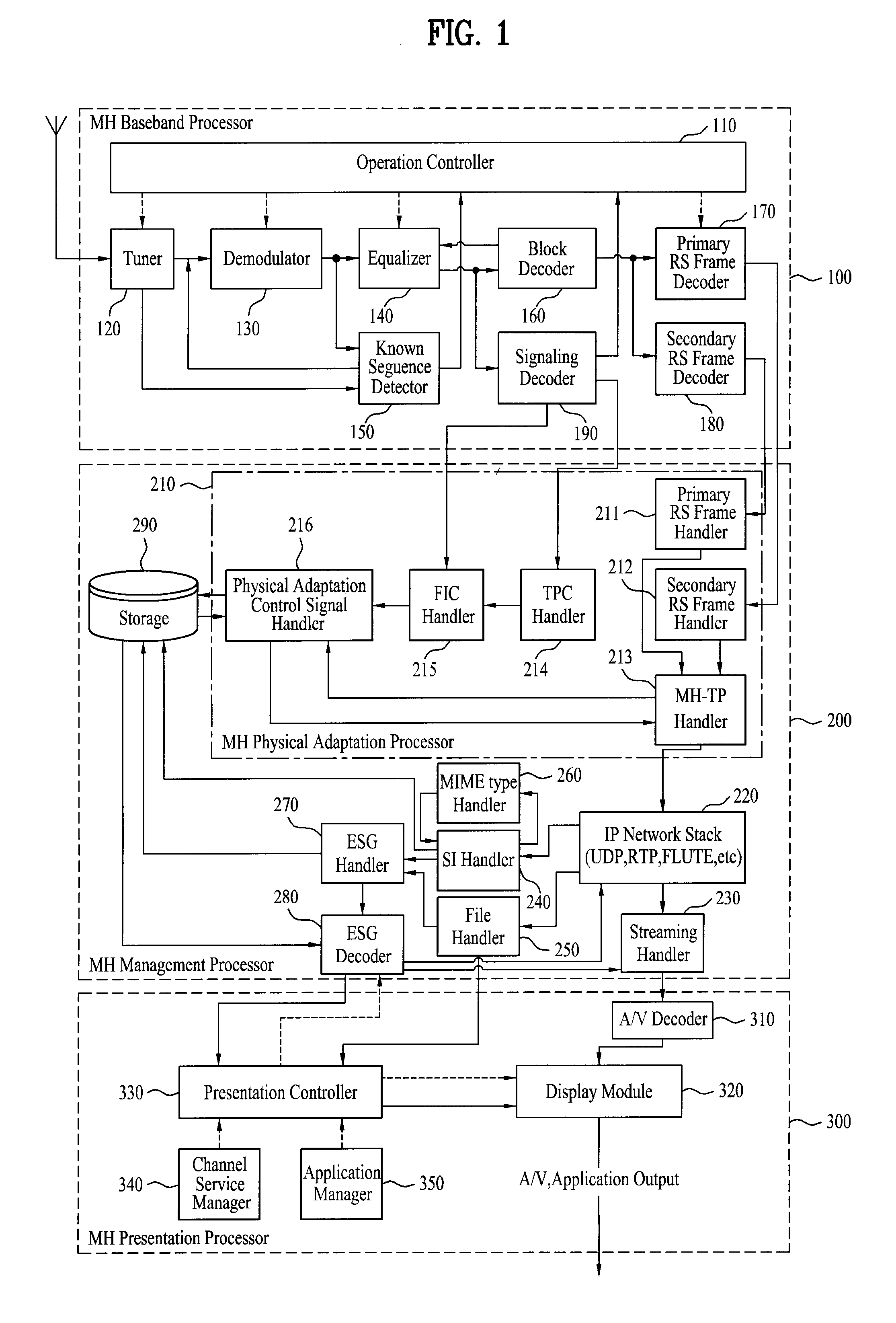
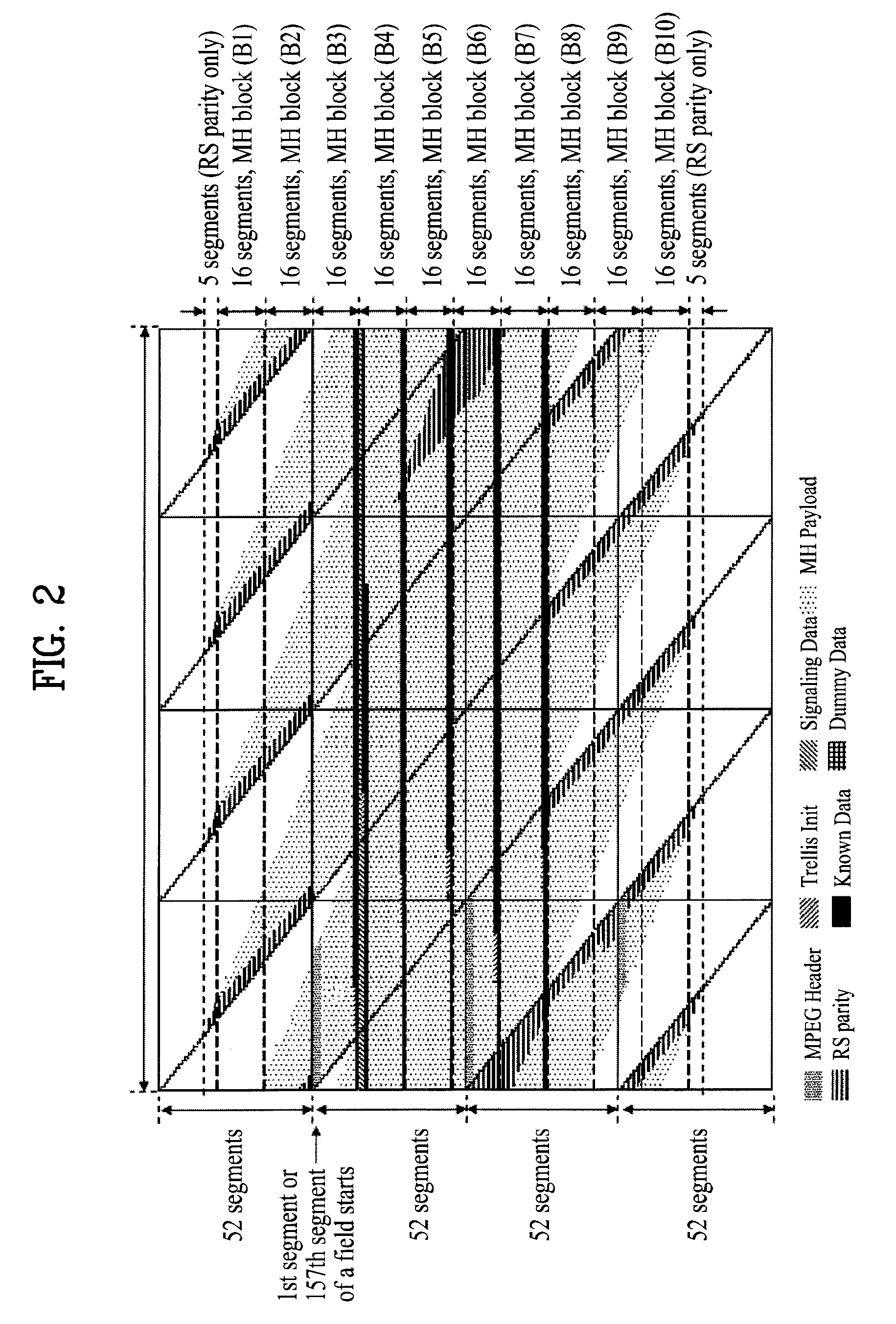
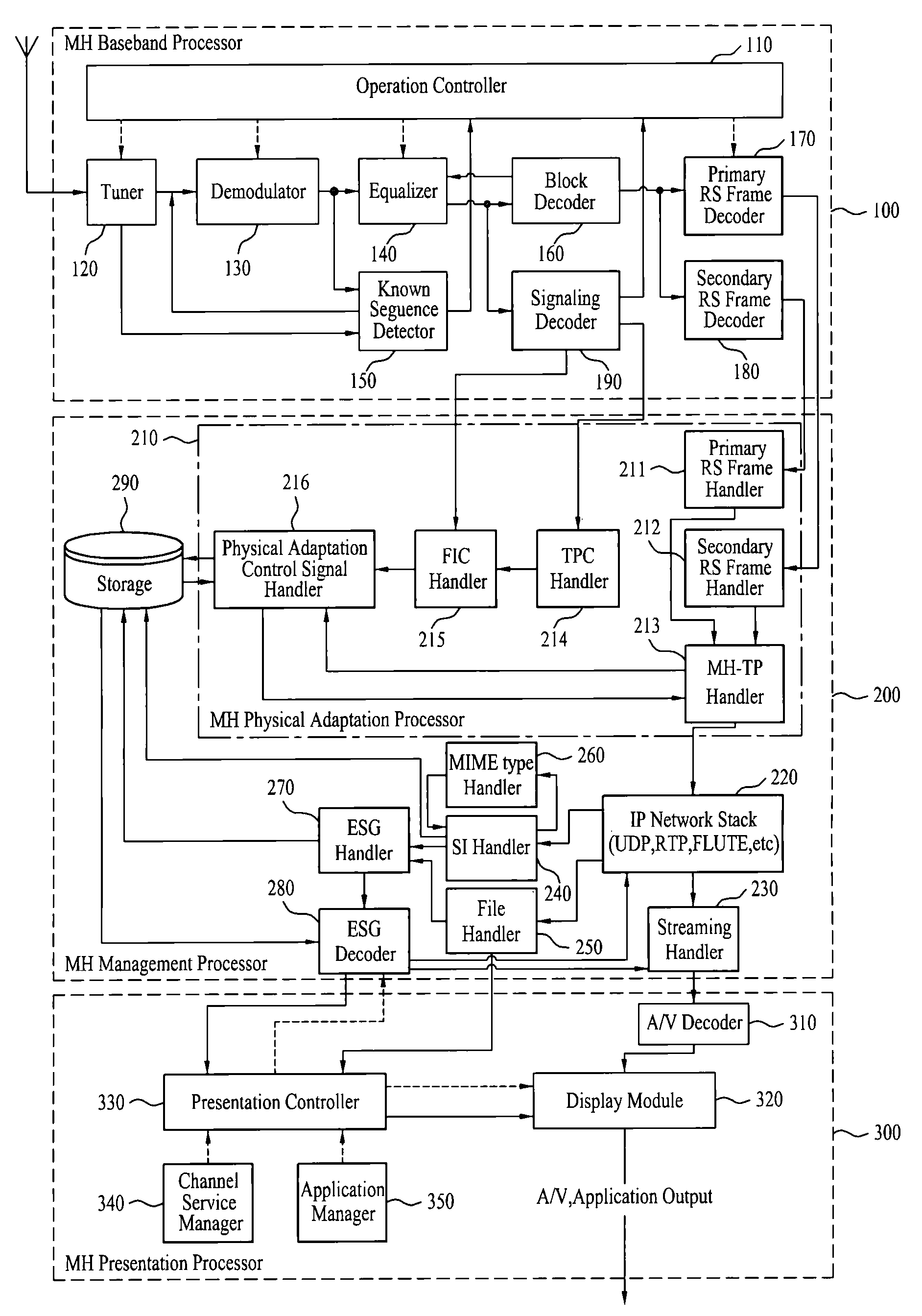
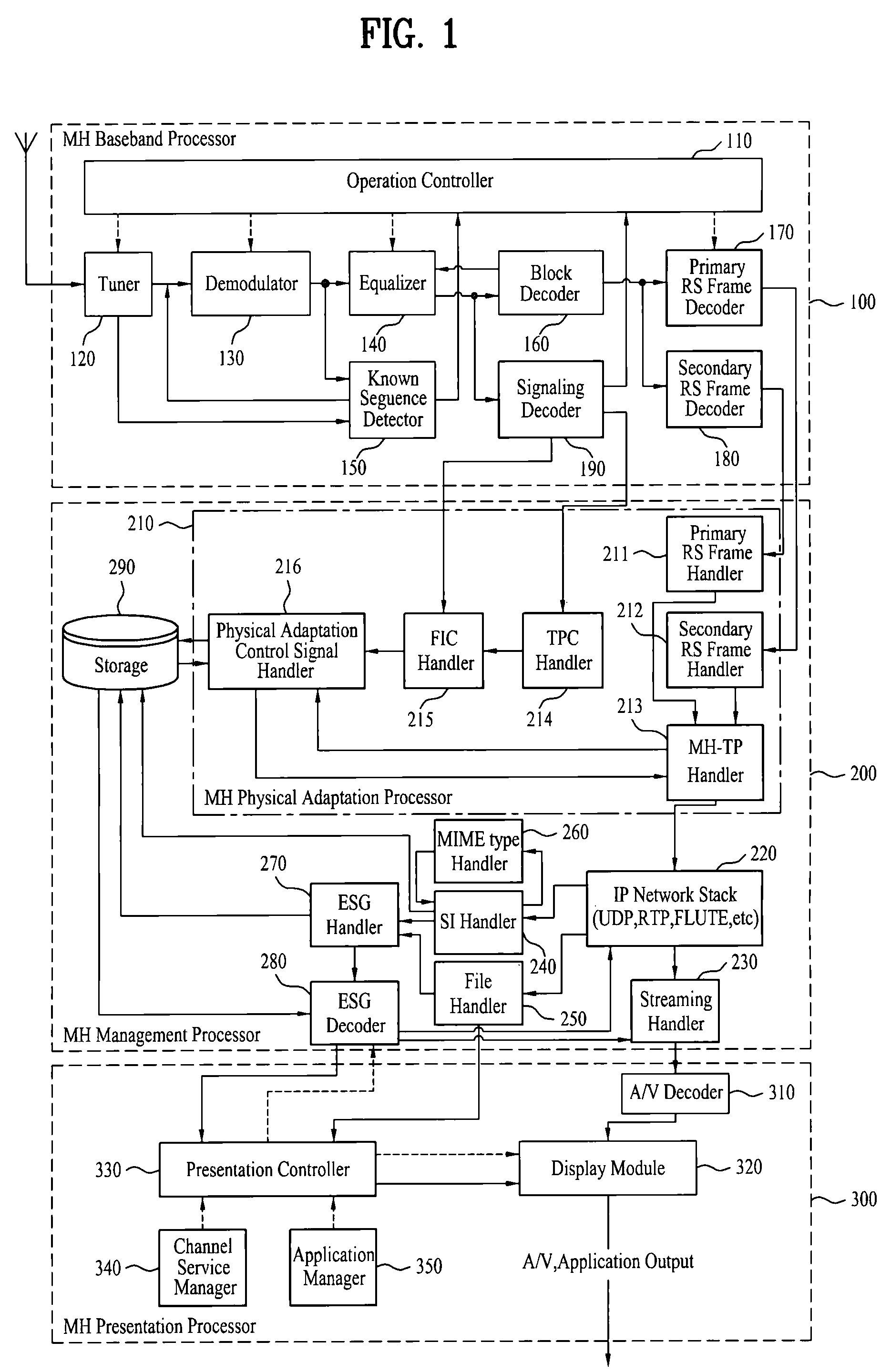
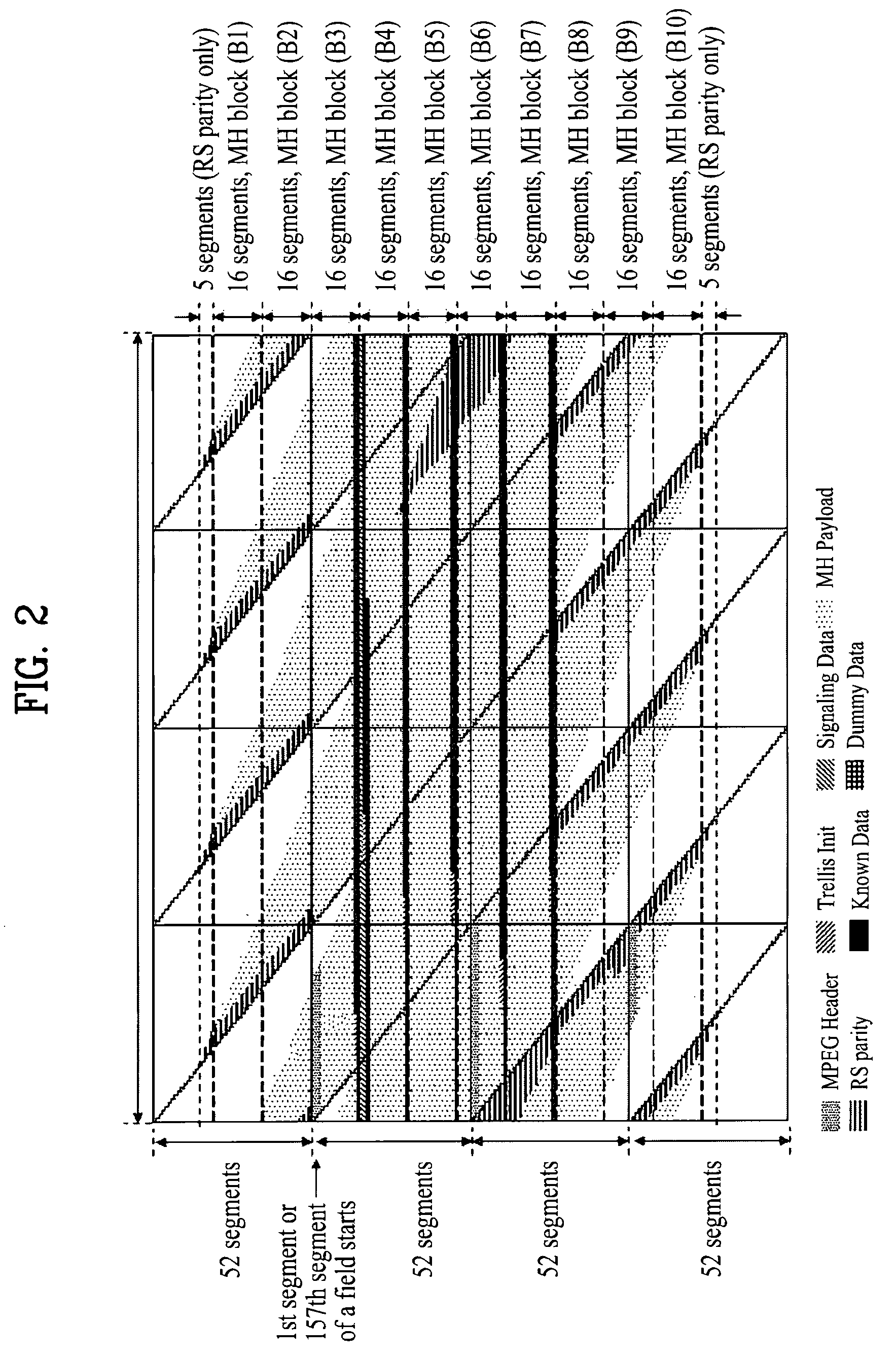
InactiveUS7646828B2Modulation type identificationBroadcast transmission systemsMobile businessData element
A digital broadcasting system and a data processing method are disclosed. The receiving system of the digital broadcasting system includes a baseband processor, a first handler, a second handler, and a storage unit. The baseband processor receives a broadcast signal including mobile service data and main service data. Herein, the mobile service data may configure an RS frame, and the RS frame may include the mobile service data and first signaling information of a first data type on the mobile service data. The first handler parses the first signaling information received from the RS frame, converts parsed data elements of the first data type to a second data type, and merges multiple identification information of the parsed first data type, thereby generating identification information of the second data type. The second handler receives second signaling information of the second data type on the mobile service data, the second signaling information including at least one fragment, uses the identification information of the second data type included in the first handler to search at least one fragment within the second signaling information, and maps data elements received through the searched fragment with the data elements converted to the second data type.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system
InactiveUS7733820B2Broadcast specific applicationsBroadcast transmission systemsDigital broadcastingMobile service
A digital broadcasting system and a data processing method are disclosed. A receiving system of the digital broadcasting system comprises a baseband processor, a management processor and a presentation processor. The baseband processor receives a broadcast signal including mobile service data and main service data, wherein the mobile service data configure a Reed-Solomon (RS) frame. The RS frame includes at least one of the mobile service data and notification messages. The notification messages are packetized in accordance with any one of a first transport protocol and a second transport protocol. The management processor decodes the notification messages from the RS frame in accordance with any one of the first transport protocol and the second transport protocol. The presentation processor directly outputs the decoded notification messages to an output unit in accordance with a channel which transmits the decoded notification messages, or outputs the decoded notification messages to the output unit only if a user selects the notification messages.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
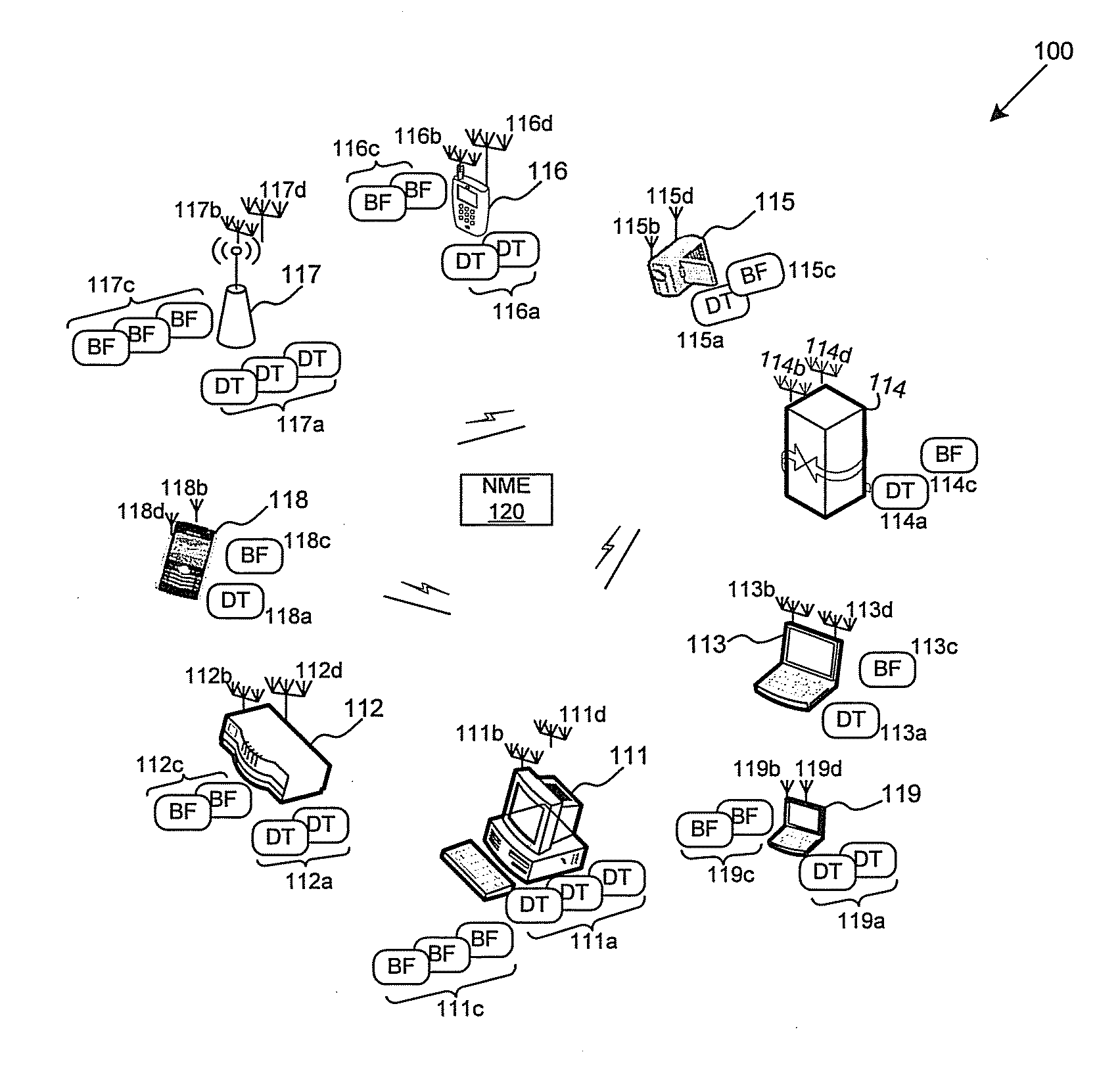
Method and system for high-throughput and low-power communication links in a distributed transceiver network
A device comprises a plurality of distributed transceivers, a plurality of distributed beamformers, a baseband processor, and a network management engine. The distributed transceivers perform beamforming in a radio frequency band. The distributed beamformers, however, performs beamforming in an intermediate frequency band. Each of the distributed transceivers is coupled to a corresponding one of the distributed beamformers. Each transceiver-beamformer pair is coupled to the baseband processor utilizing a same communication medium such as a cable. For transmission, a data stream generated at baseband is converted to intermediate frequencies. With a low-power transmission, the distributed beamformers transmit the data stream wirelessly in the intermediate frequencies to a receiving device. With a normal-power transmission, the distributed transceivers transmit the data stream to the receiving device in the radio frequency band. The transceivers and the beamformers are turned OFF whenever not being used. A high-throughput communication link may be established through resource sharing.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
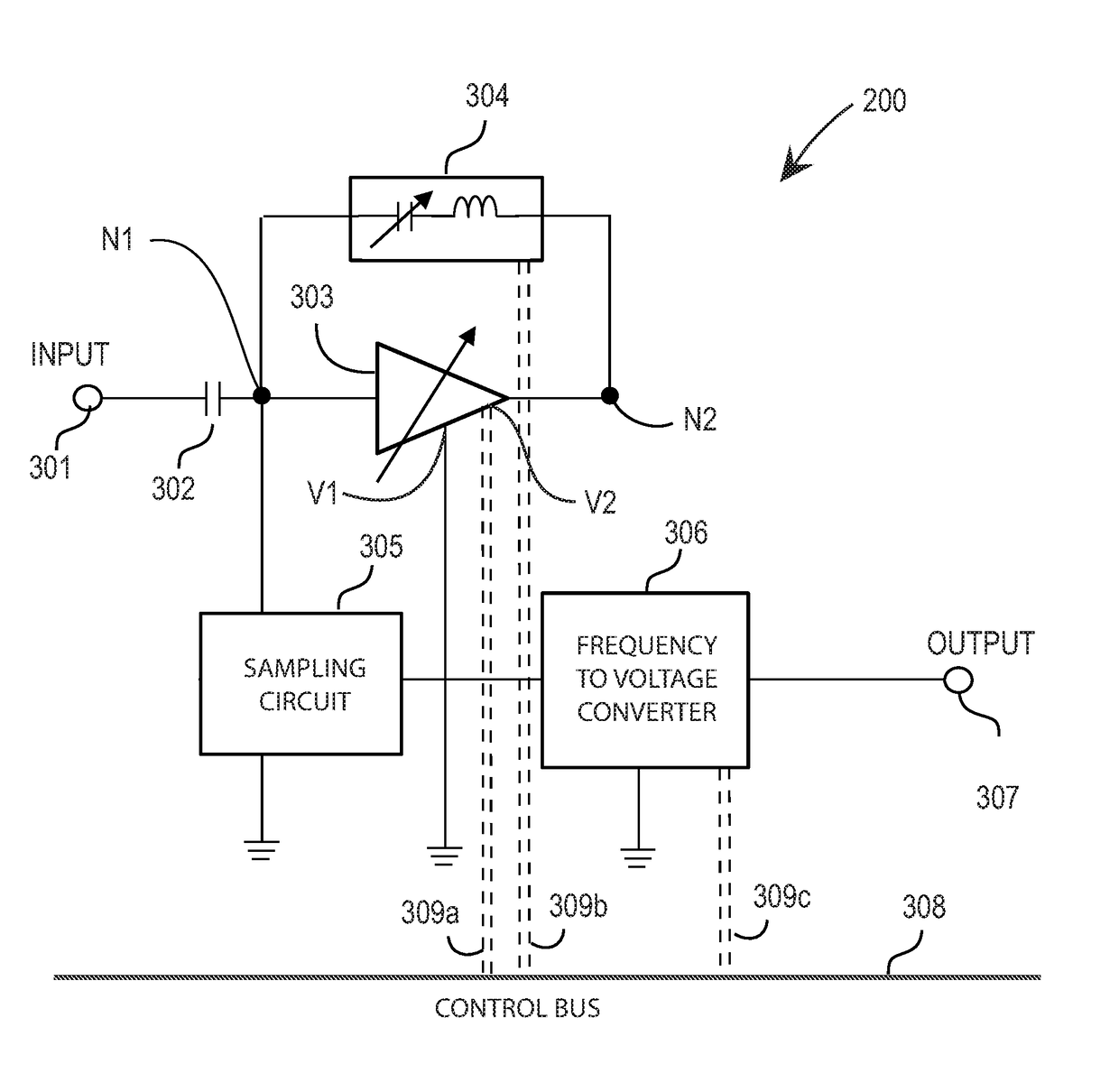
Tunable logarithmic amplifier
ActiveUS9755580B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Feedback Compensation Detector For A Direct Conversion Transmitter
InactiveUS20090262861A1Secret communicationTransmission monitoringFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
A feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter includes a baseband processor, a direct up-converter, an antenna, and an impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit. The baseband processor generates an in-phase (I) baseband signal and a quadrature-phase (Q) baseband signal. The direct up-converter is coupled to the baseband processor, and combines the I and Q baseband signals with an RF carrier signal to generate an RF output signal. The antenna is coupled to the direct up-converter, and transmits the RF output signal. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit is coupled to the RF output signal and the I and Q baseband signals. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit down-converts the RF output signal to generate an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, measures as least one signal impairment in the IF signal, and pre-distorts the I and Q baseband signals to compensate for the measured signal impairment.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Signal configuration based transmitter adjustment in wireless communication devices
ActiveUS20060068830A1Power managementAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyWireless communication systemsBaseband processor
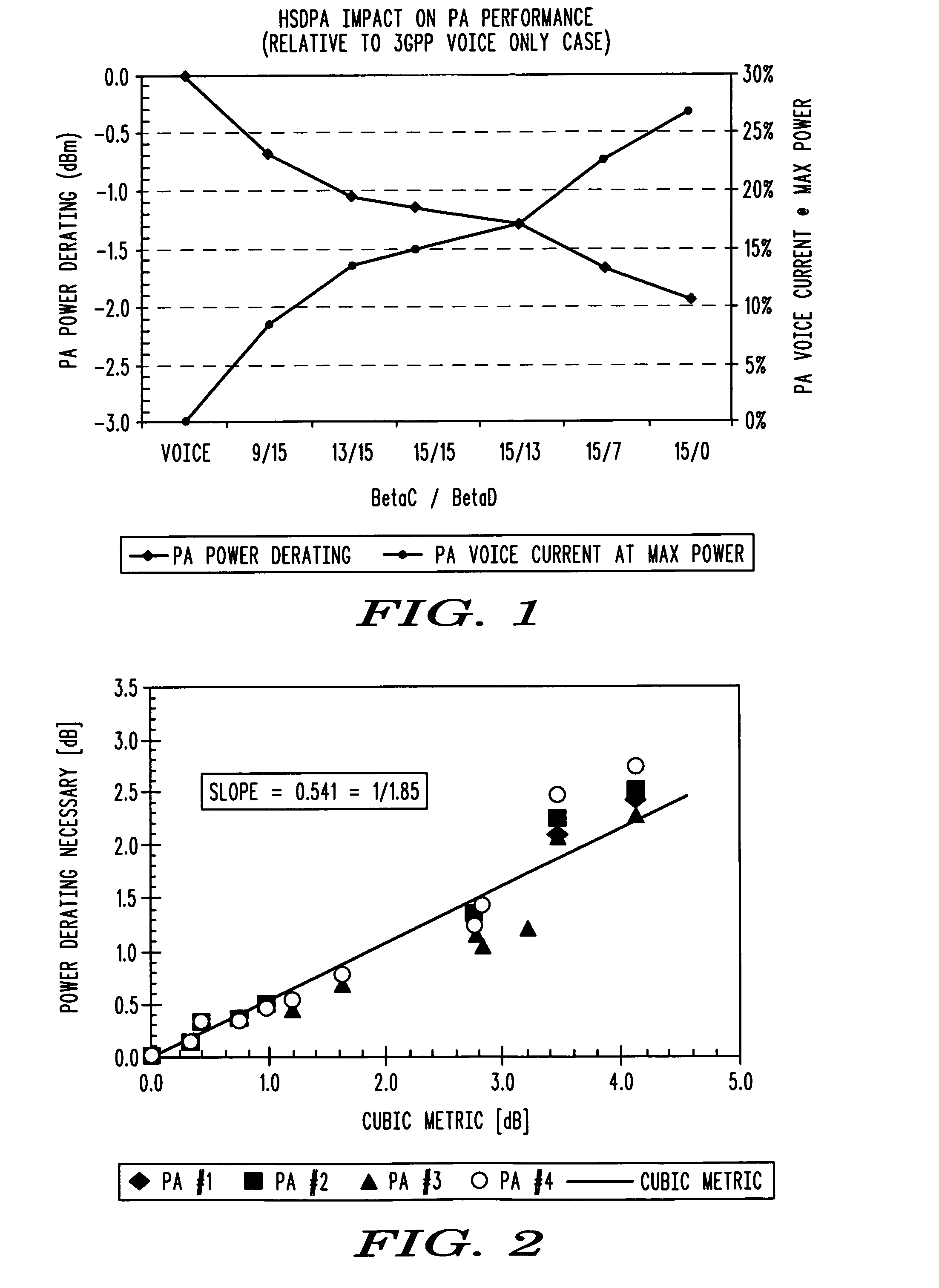
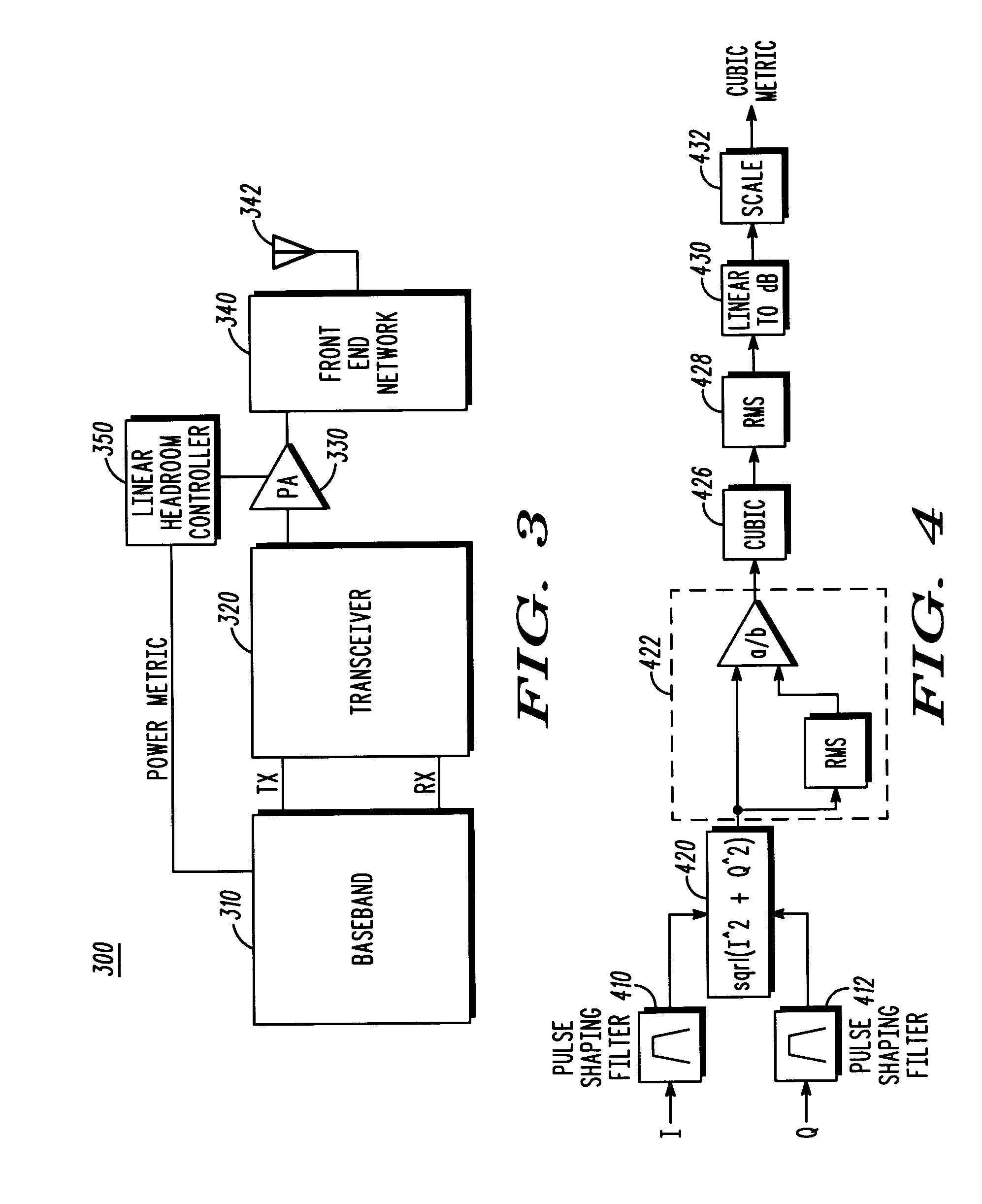
A method in a wireless communication transmitter including a baseband processor (310) that dynamically configures the transmitter for a particular signal configuration, and a headroom controller (350) for adjusting transmitter headroom based on the particular signal configuration. In one embodiment, the PA headroom is controlled based on a power metric, for example, a 3rd order polynomial or peak to average ratio (PAR) metric, that is a function of the signal configuration. In another embodiment the PA headroom is adjusted using information in a look up table.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com