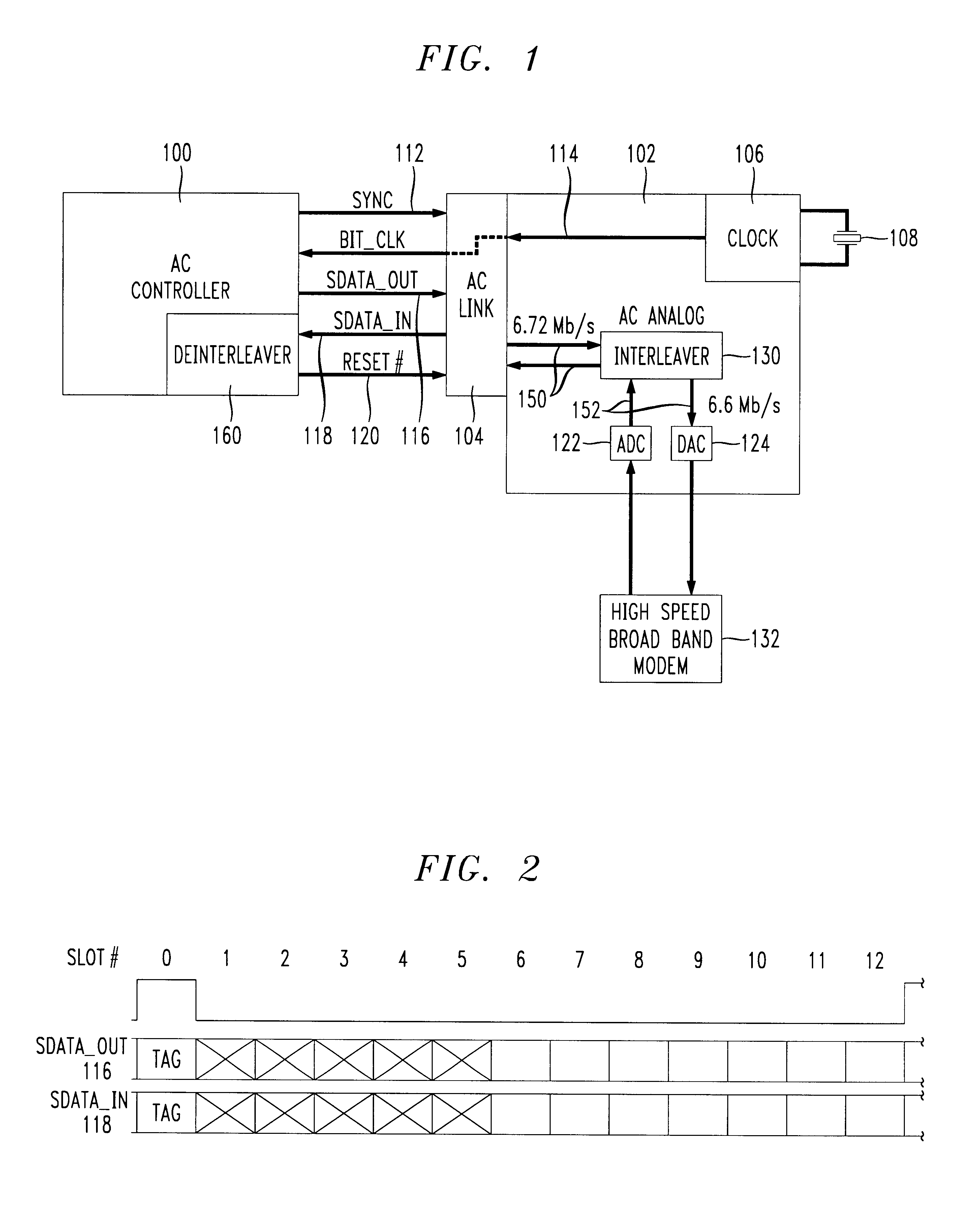Patents
Literature
58 results about "Megabit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information. The megabit has the unit symbol Mbit. The megabit is closely related to the mebibit, a unit multiple derived from the binary prefix mebi (symbol Mi) of the same order of magnitude, which is equal to 2²⁰bits = 1048576bits, or approximately 5% larger than the megabit. Despite the definitions of these new prefixes for binary-based quantities of storage by international standards organizations, memory semiconductor chips are still marketed using the metric prefix names to designate binary multiples.
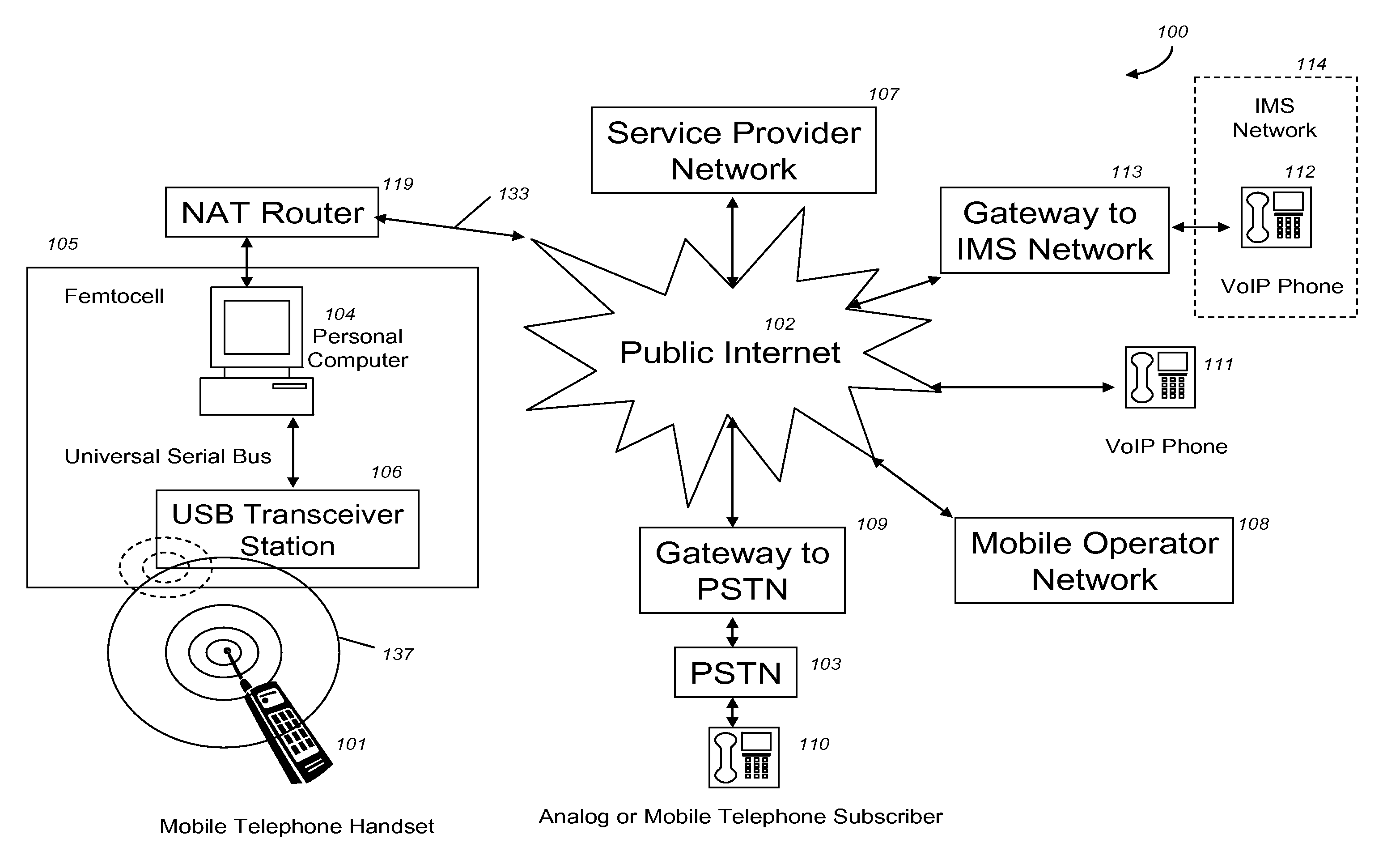
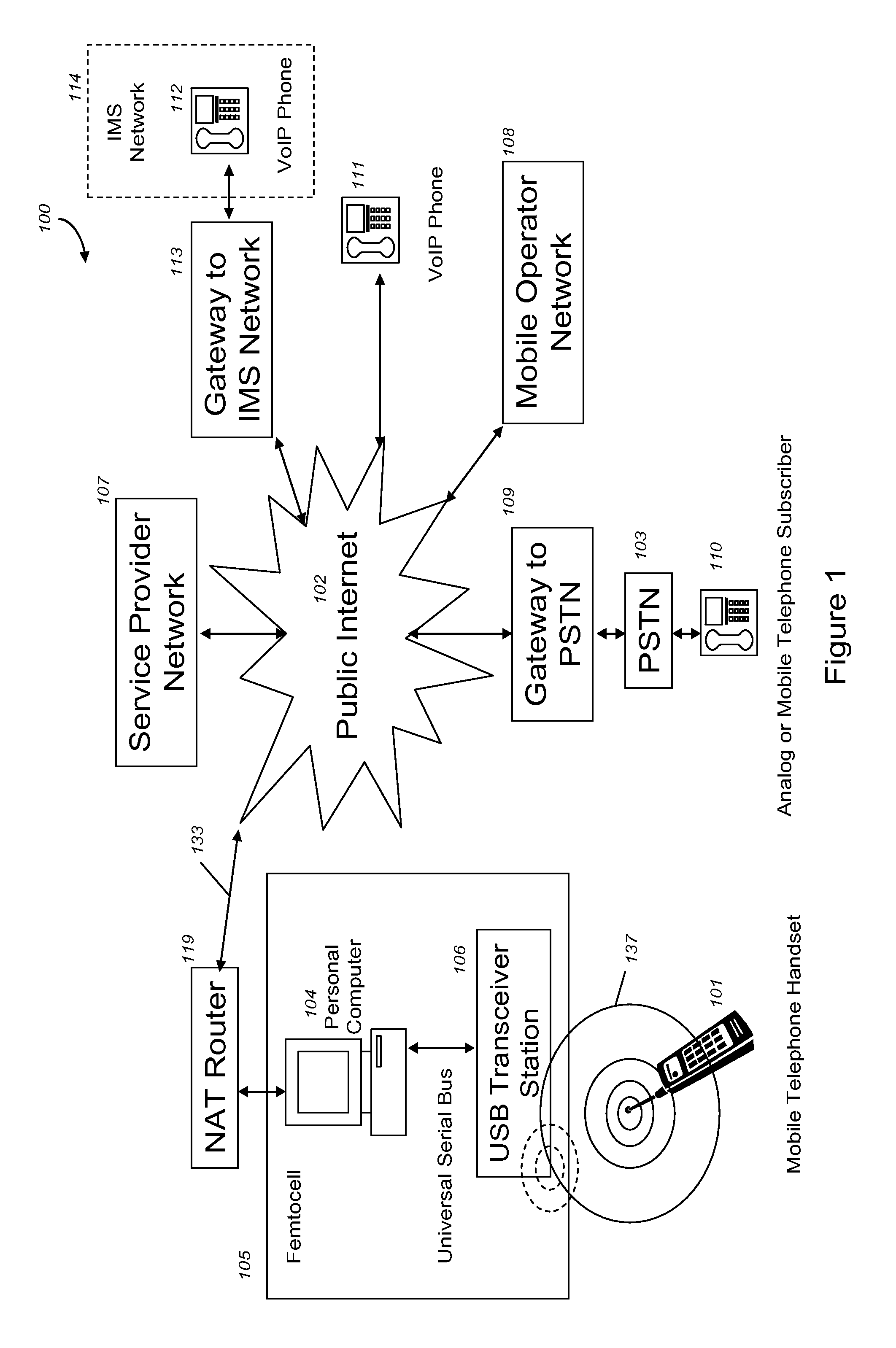
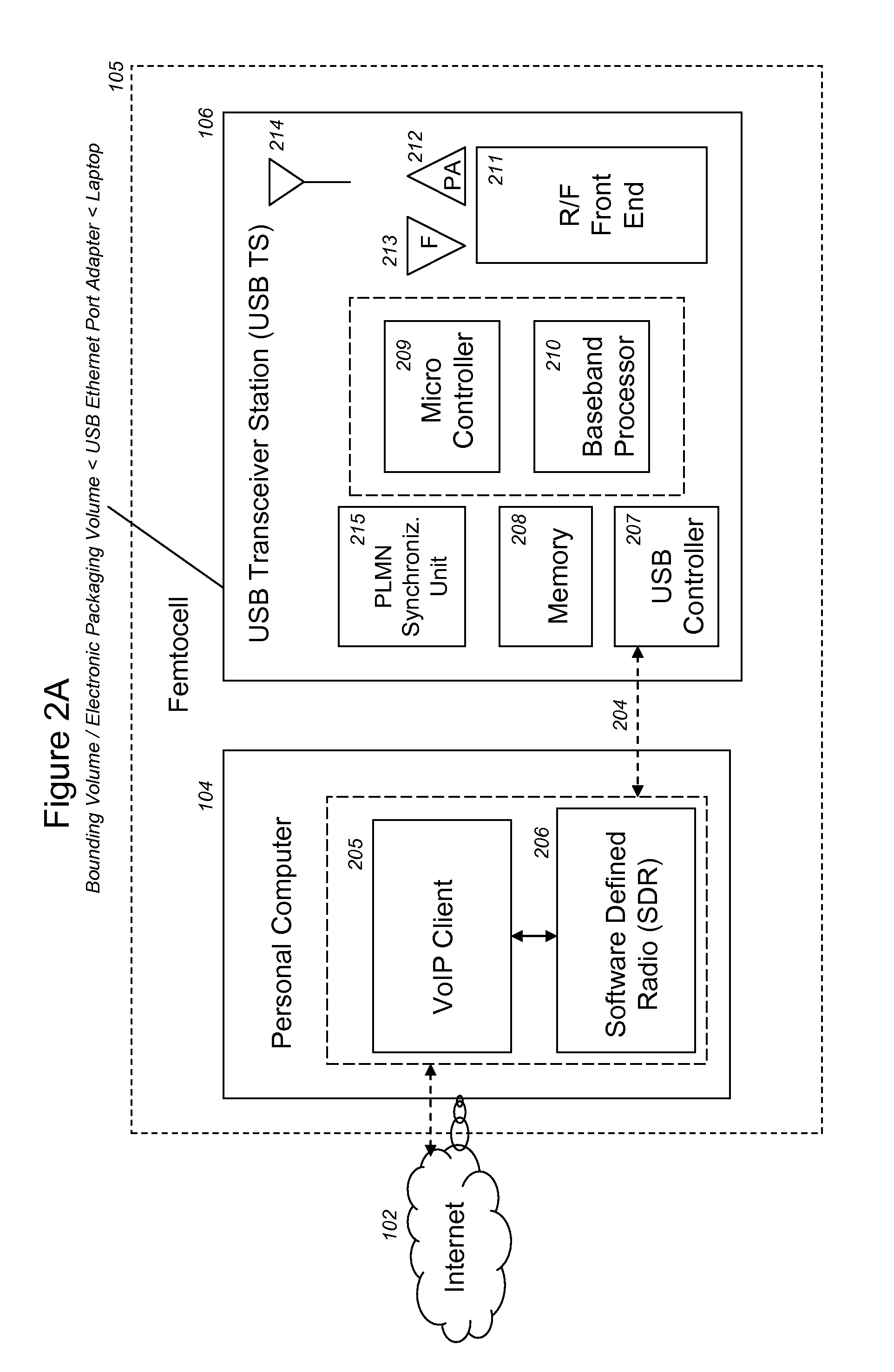
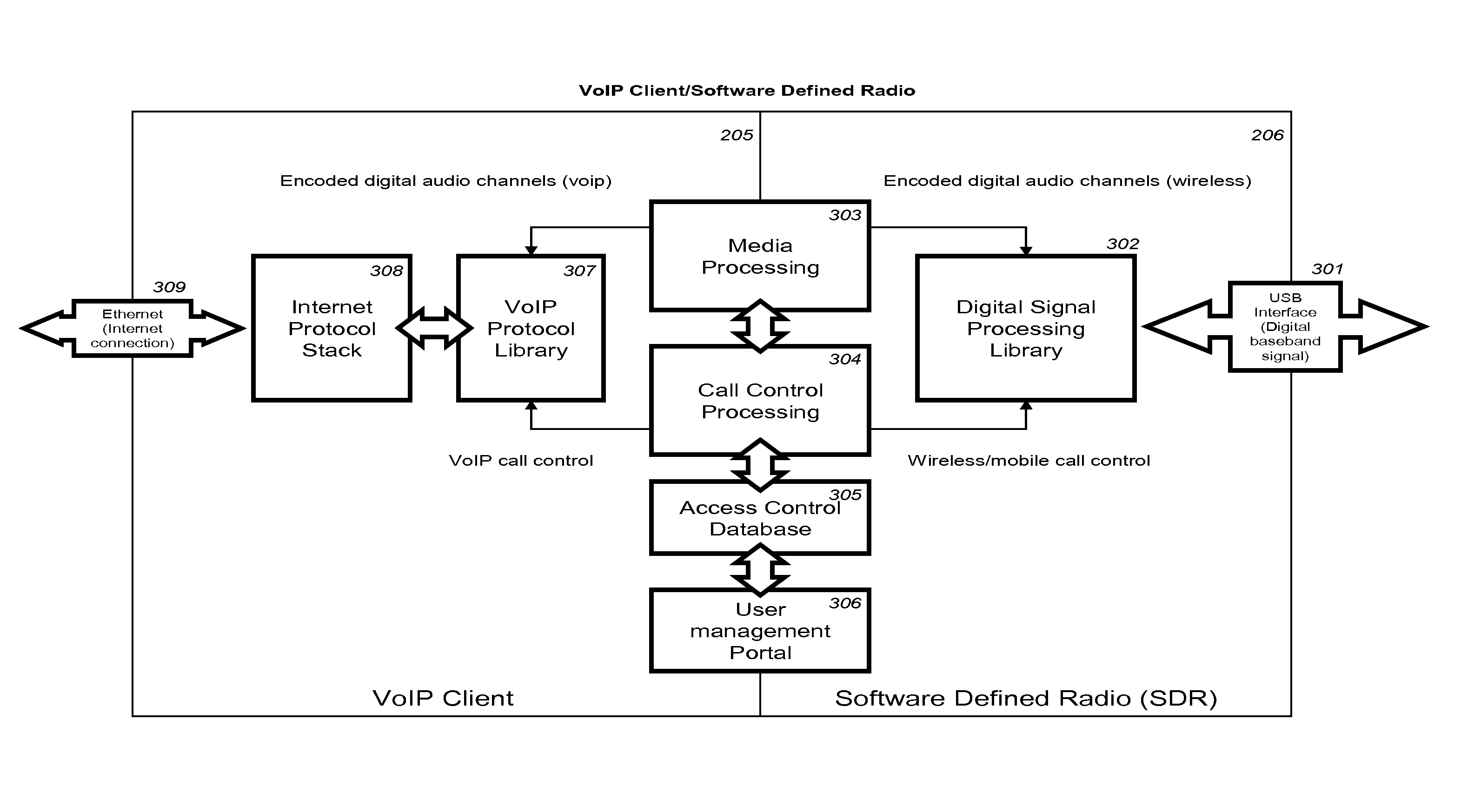
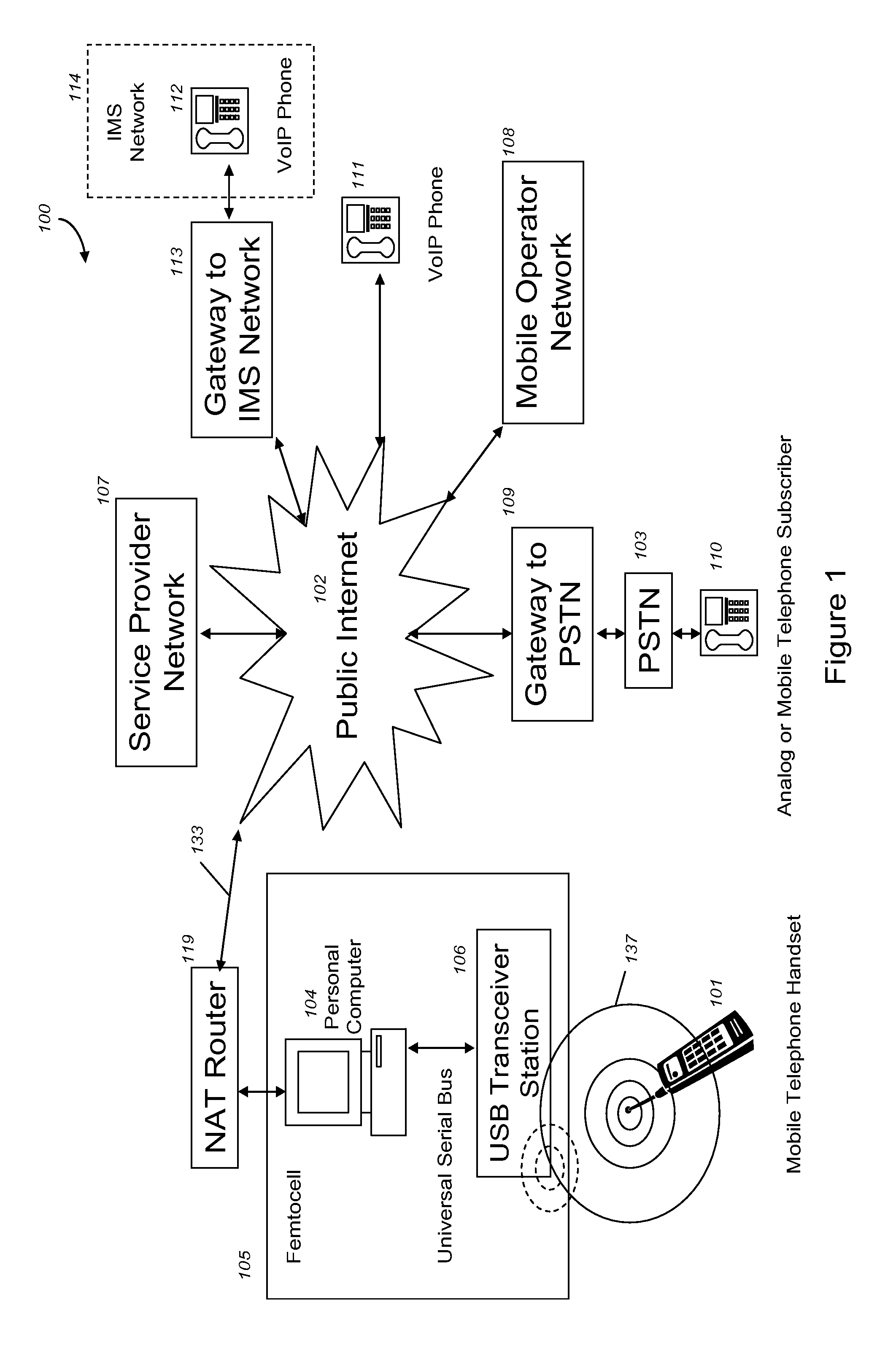
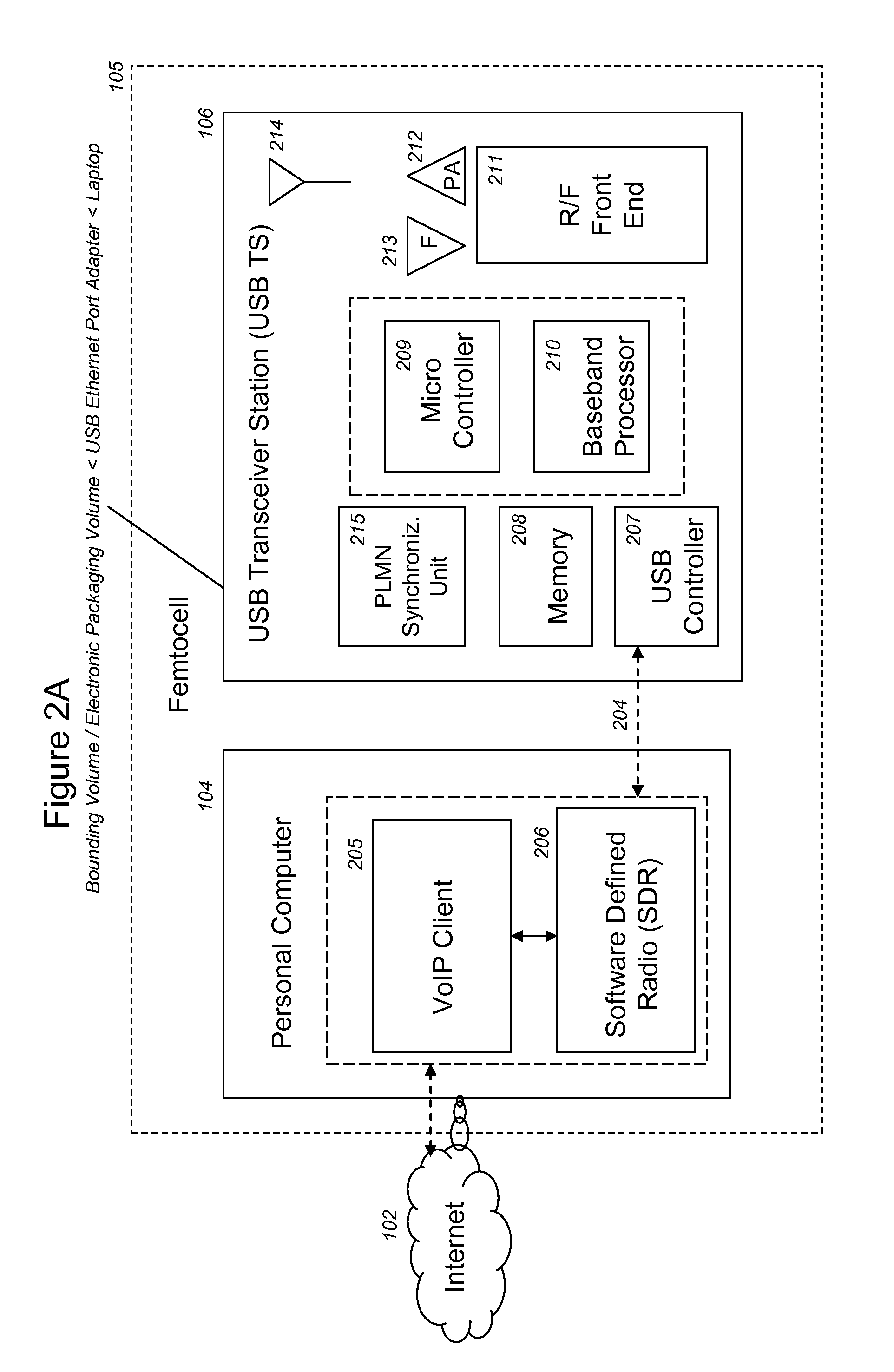
VoIP Enabled Femtocell with a USB Transceiver Station
InactiveUS20080244148A1High quality audioLow costNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentMicrocontrollerRF front end
Telephone calls between a mobile station (MS) and the mobile network or PSTN are routed through the Internet via VoIP using a femtocell, as opposed to the traditional macrocellular network. The femtocell can comprise a USB Transceiver Station that is connected to a personal computer through a universal serial bus port, which provides both power and a multi-megabit per second connection between the personal computer and the USB transceiver station. The USB transceiver station can comprise a microcontroller to manage signaling between the RF front end / baseband processor and the personal computer, as well as a precise timing mechanism to assist the synchronization of femtocell timing with the surrounding macrocellular network, if it is present. The USB transceiver station can have a compact form factor that that facilitates a high degree of portability by the subscriber, such as being readily attachable to their keychain.
Owner:SMALL CELL INNOVATIONS
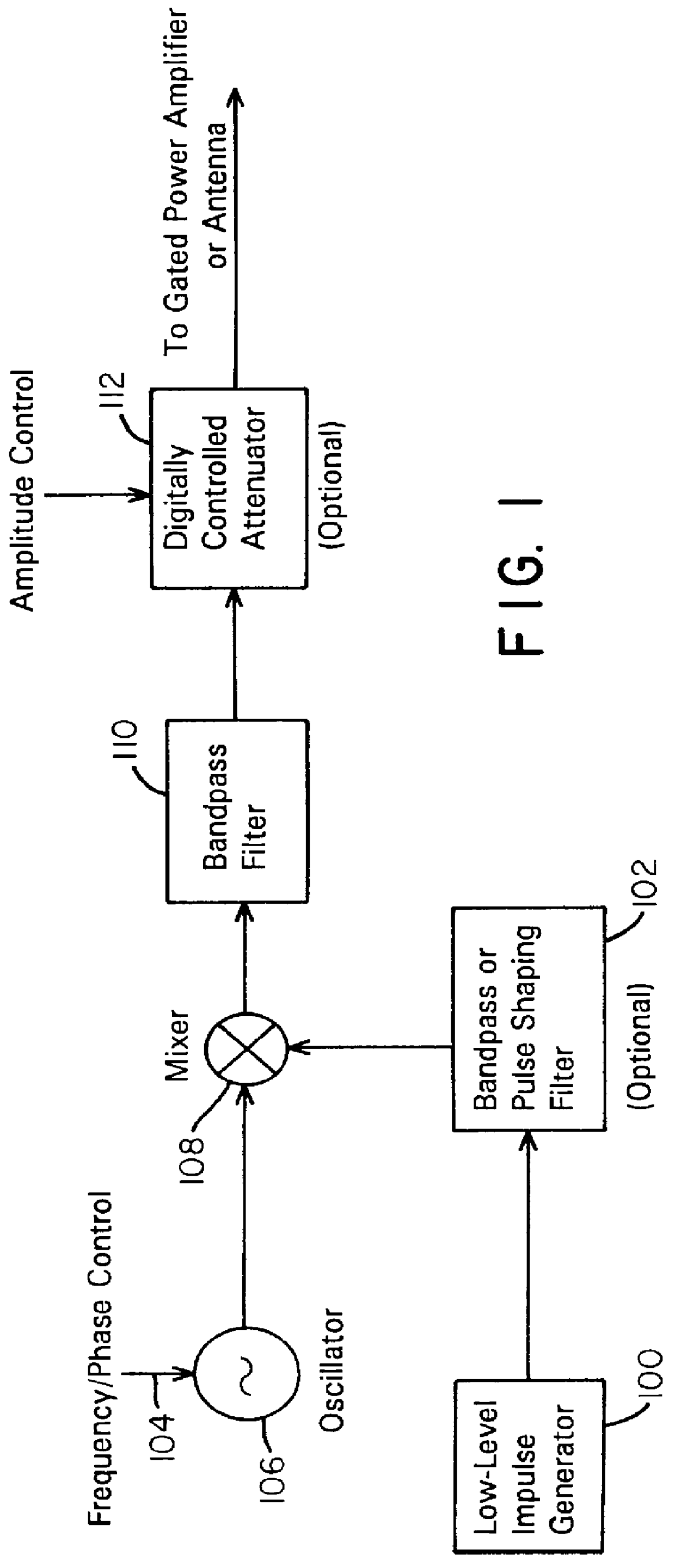
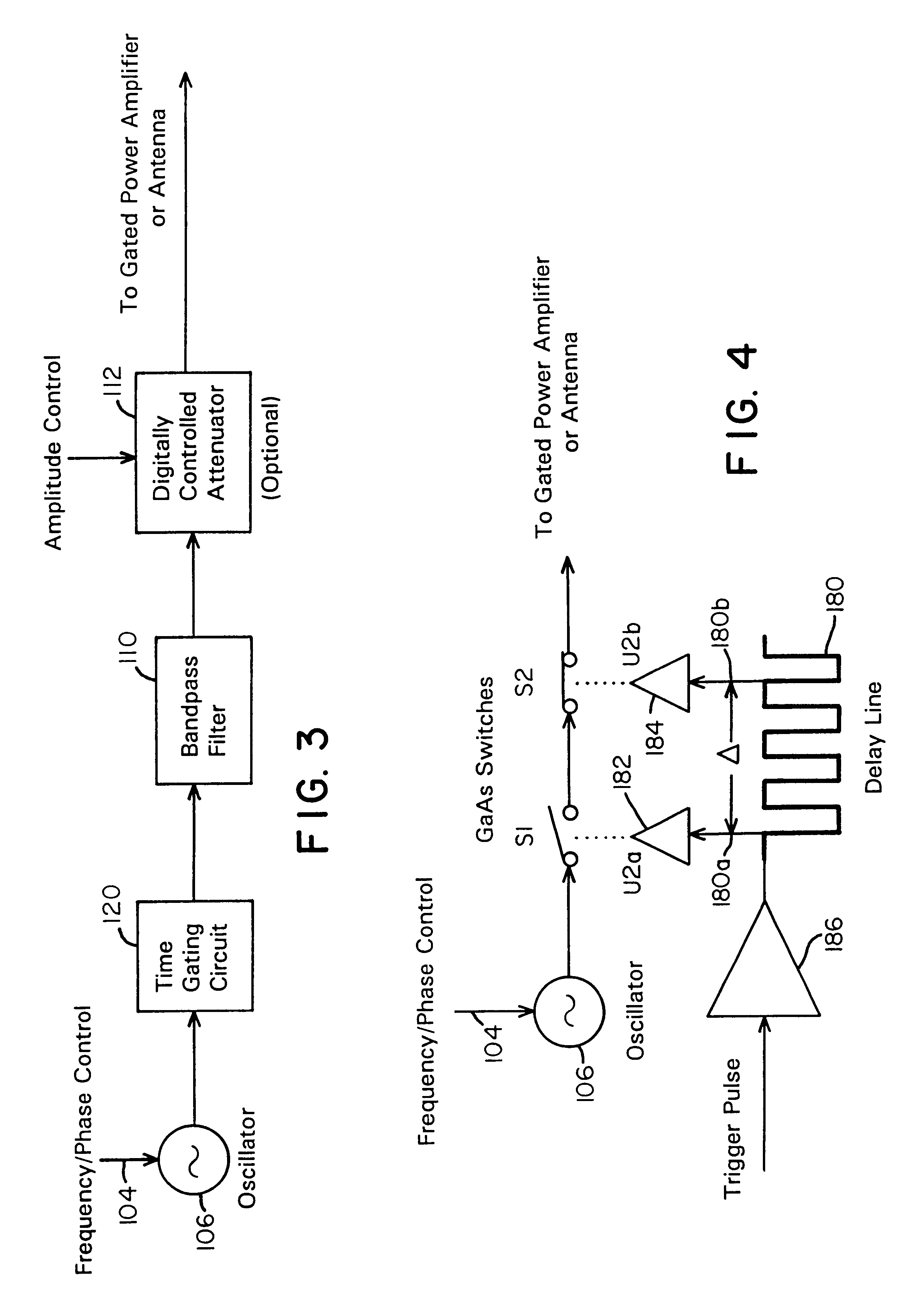
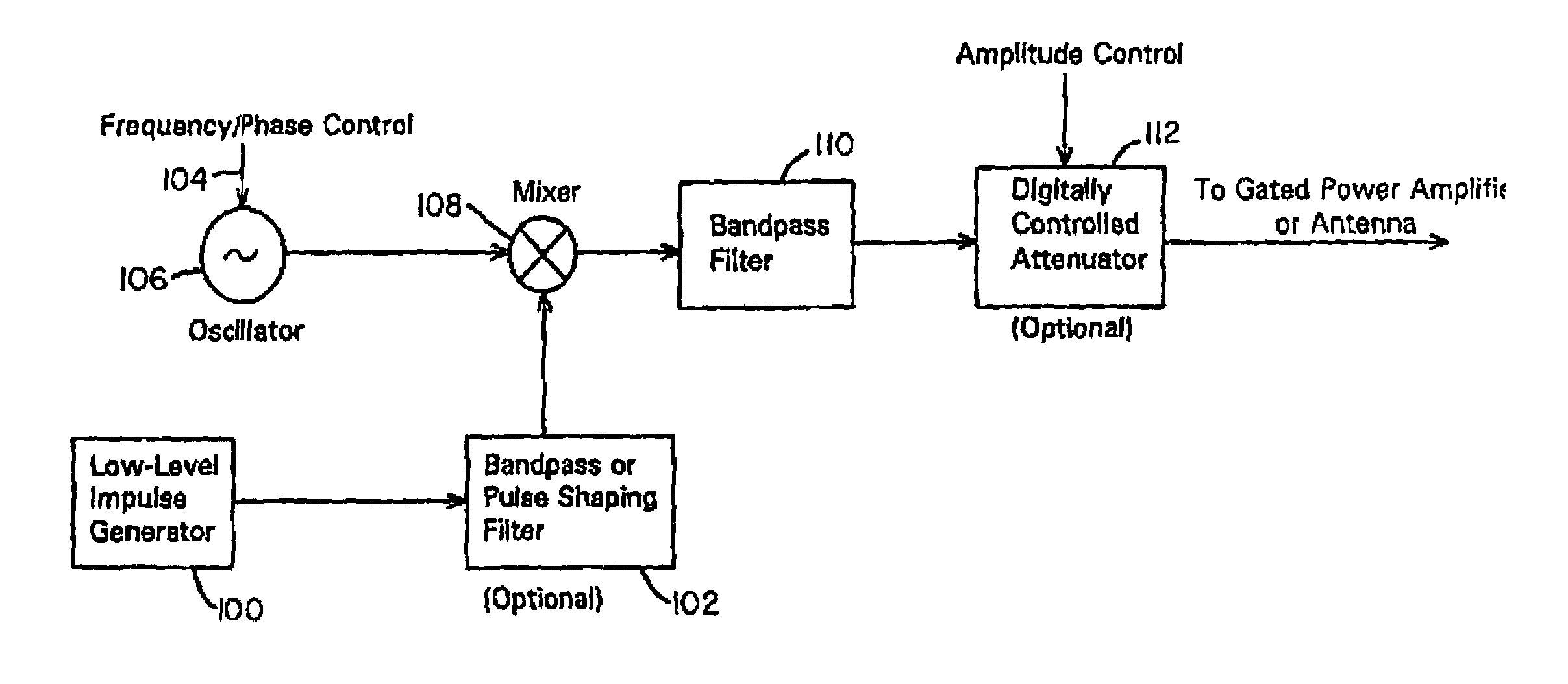
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
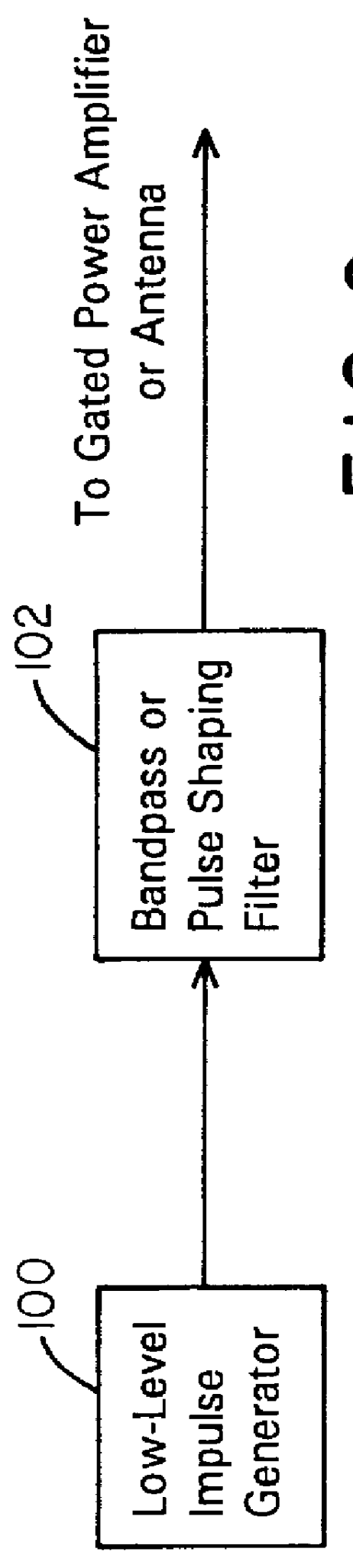
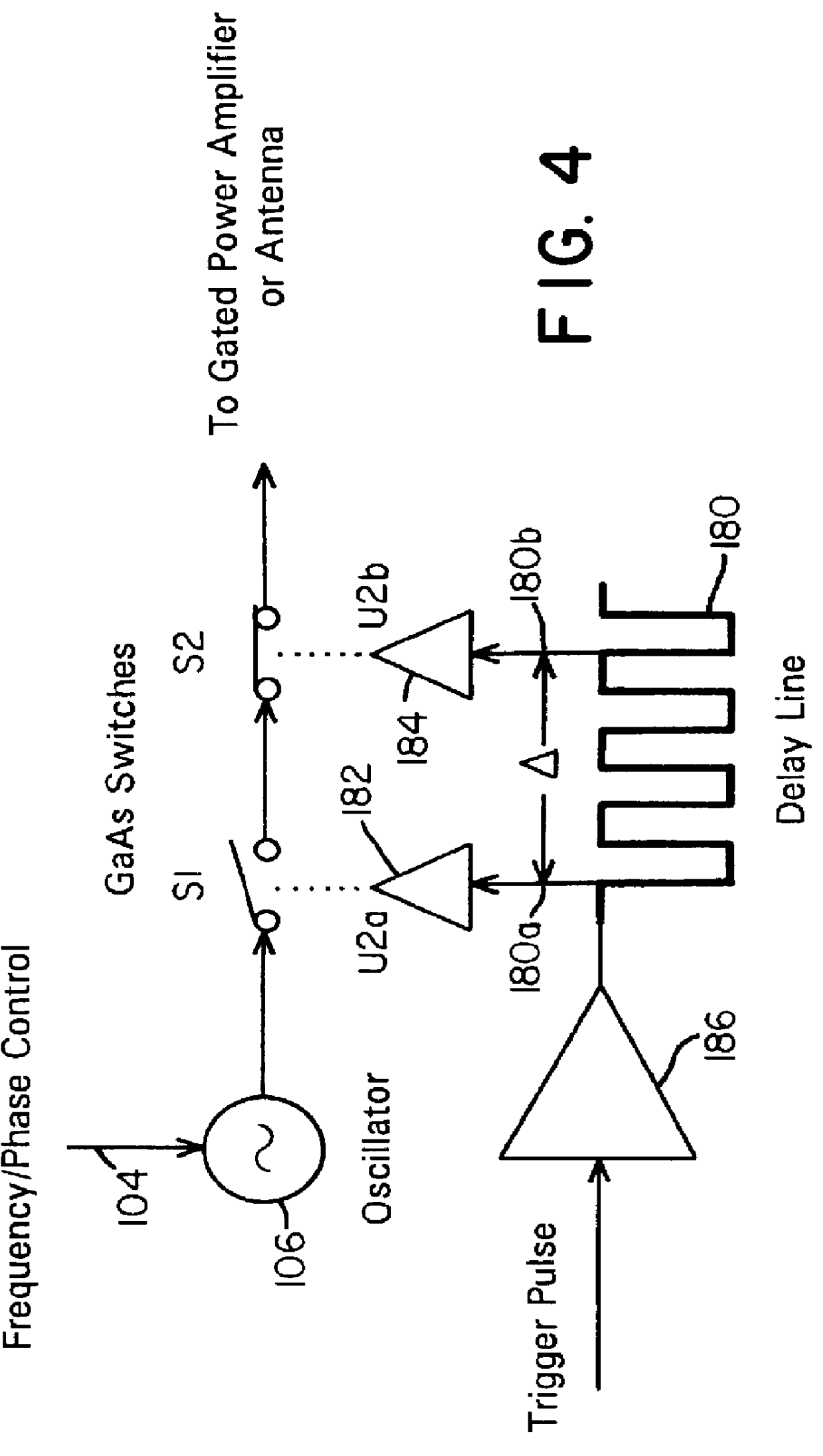
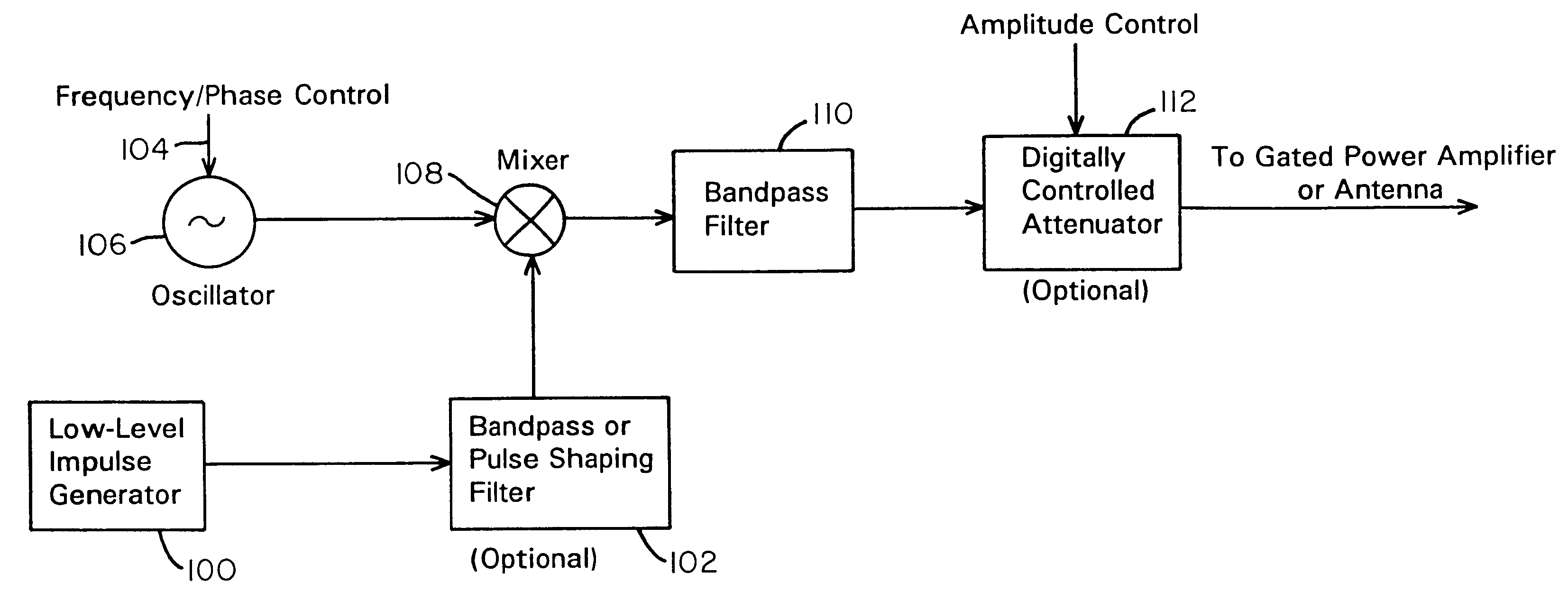
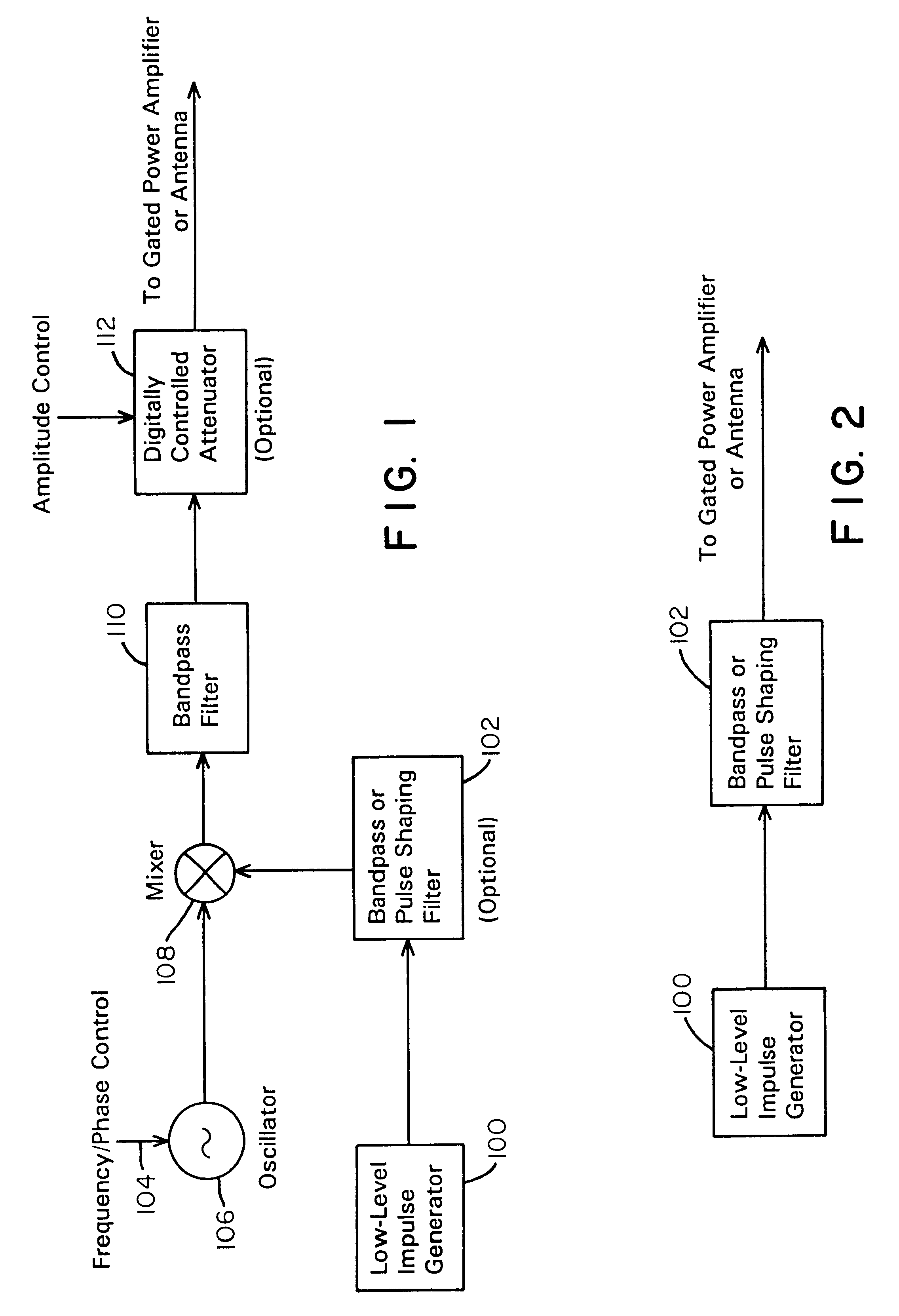
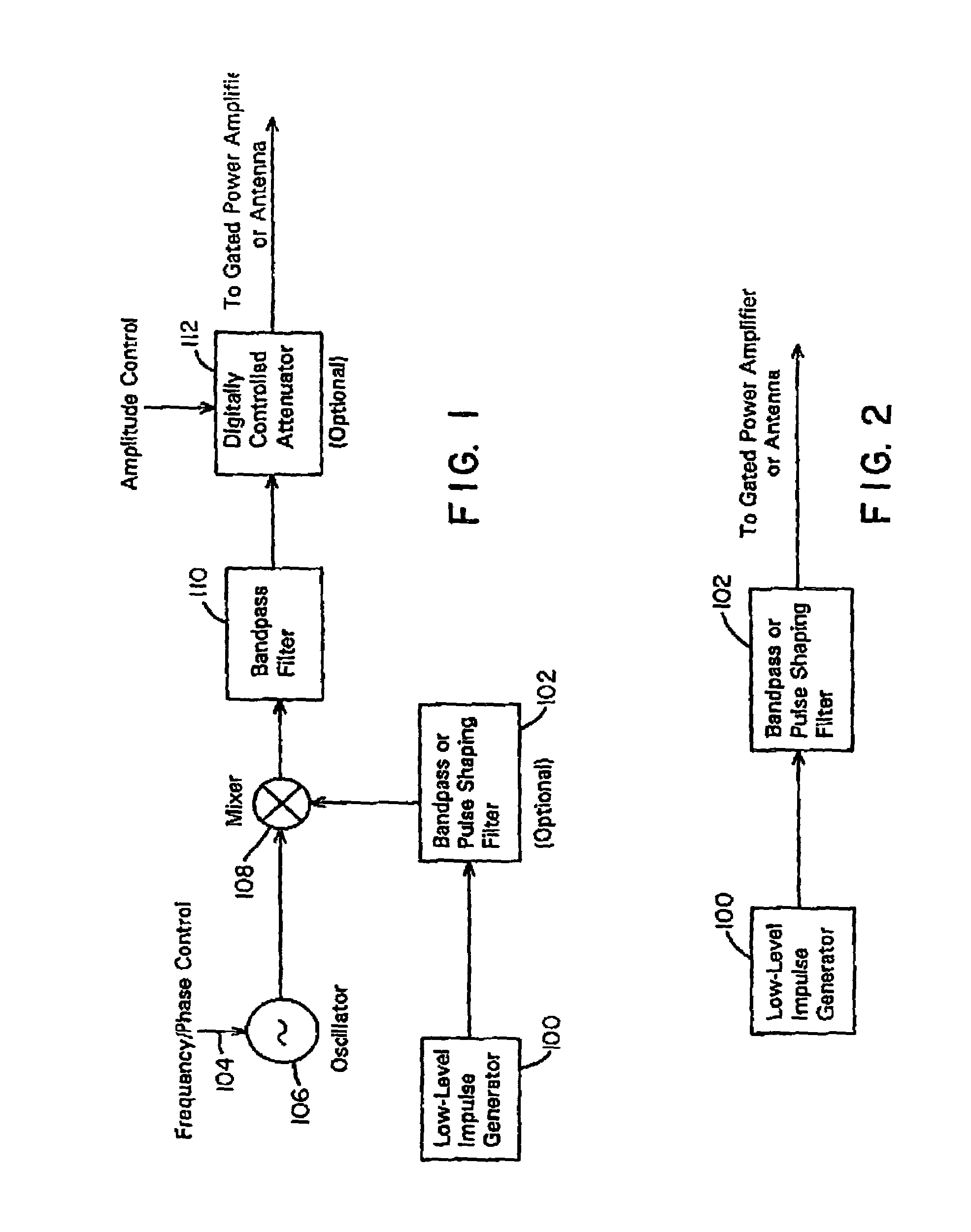
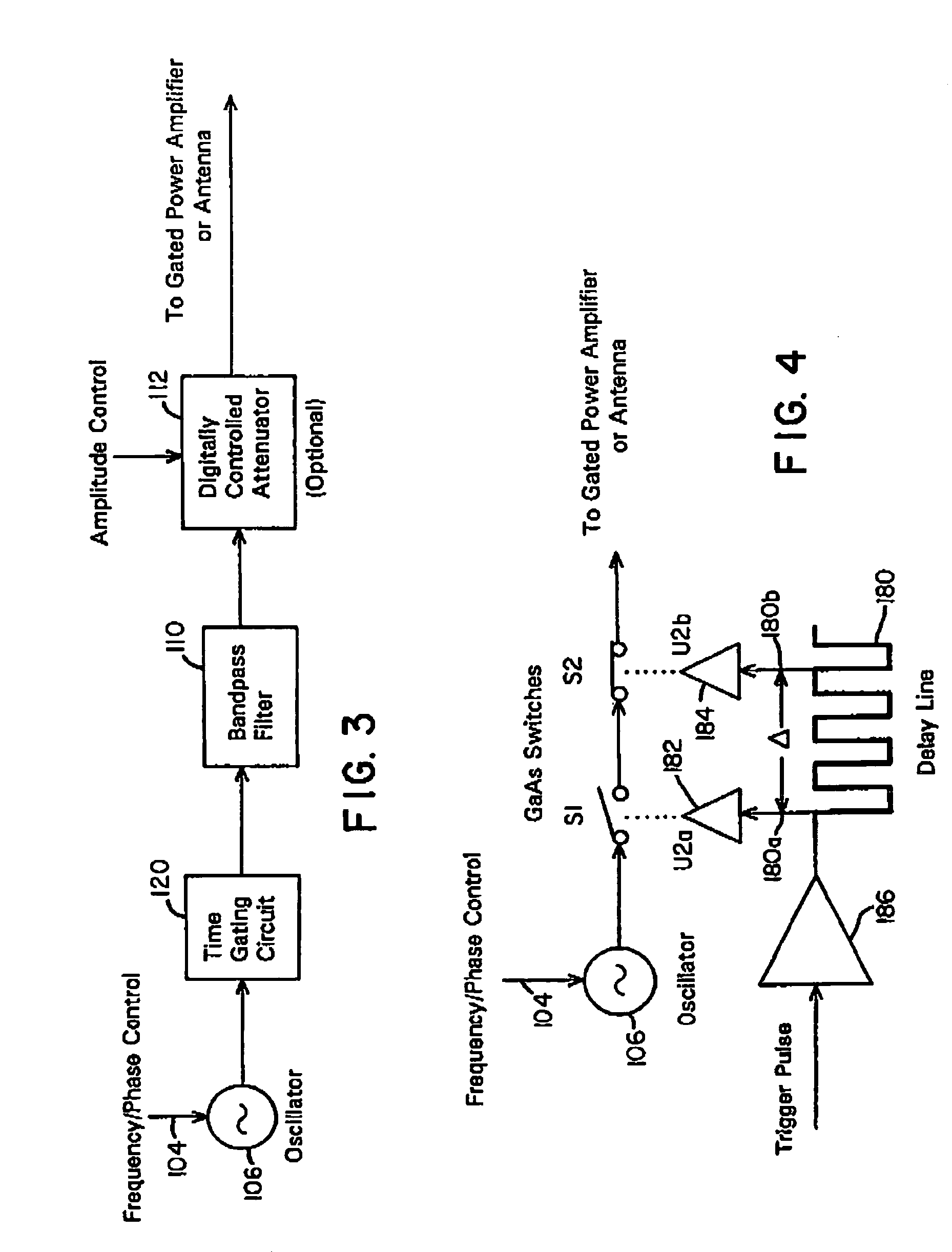
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
High-density NVRAM
High density NVRAM. An array of memory cells capable of storing at least a megabit of information, each memory cell including a memory plug that includes a memory element that switches from a first resistance state to a second resistance state upon application of a first write voltage of a first polarity and reversibly switches from the second resistance state to the first resistance state upon application of a second write voltage of polarity opposite to the first polarity.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
VoIP enabled femtocell with a USB transceiver station
InactiveUS7990912B2High degreeFirmly connectedNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentMicrocontrollerRF front end
Telephone calls between a mobile station (MS) and the mobile network or PSTN are routed through the Internet via VoIP using a femtocell, as opposed to the traditional macrocellular network. The femtocell can comprise a USB Transceiver Station that is connected to a personal computer through a universal serial bus port, which provides both power and a multi-megabit per second connection between the personal computer and the USB transceiver station. The USB transceiver station can comprise a microcontroller to manage signaling between the RF front end / baseband processor and the personal computer, as well as a precise timing mechanism to assist the synchronization of femtocell timing with the surrounding macrocellular network, if it is present. The USB transceiver station can have a compact form factor that facilitates a high degree of portability by the subscriber, such as being readily attachable to their keychain.
Owner:SMALL CELL INNOVATIONS
Ultra-wideband receiver and transmitter
InactiveUS7209523B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorExtensibilityBandpass filtering
A waveform-adaptive ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitter and noise-tracking UWB receiver for use in communications, object detection and radar applications. In one embodiment, the output of an oscillator is gated by a low-level impulse generator either directly or through an optional filter. In a special case of that embodiment wherein the oscillator is zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, the low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The low-level impulse signal can be generated digitally. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry data, or may be used in object detection or ranging applications. The power amplifier may be gated to provide a power-efficient UWB transmitter. The UWB transmitter exhibits well defined and controllable spectral characteristics. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
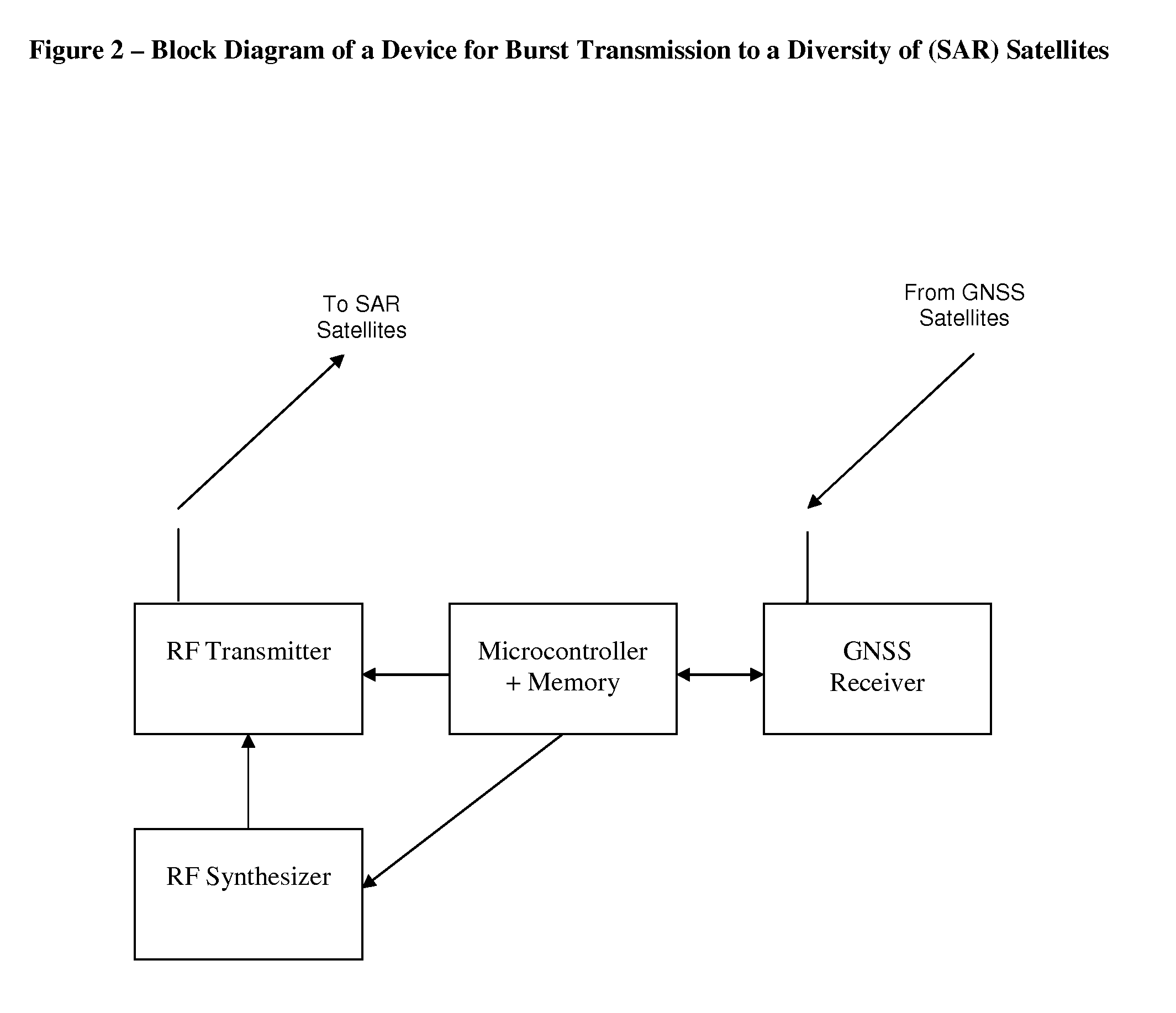
Channel Allocation for Burst Transmission to a Diversity of Satellites
ActiveUS20090274113A1Increase probabilitySharing the network resources more evenlyBroadcast transmission systemsBeacon systemsBurst transmissionTransmission channel
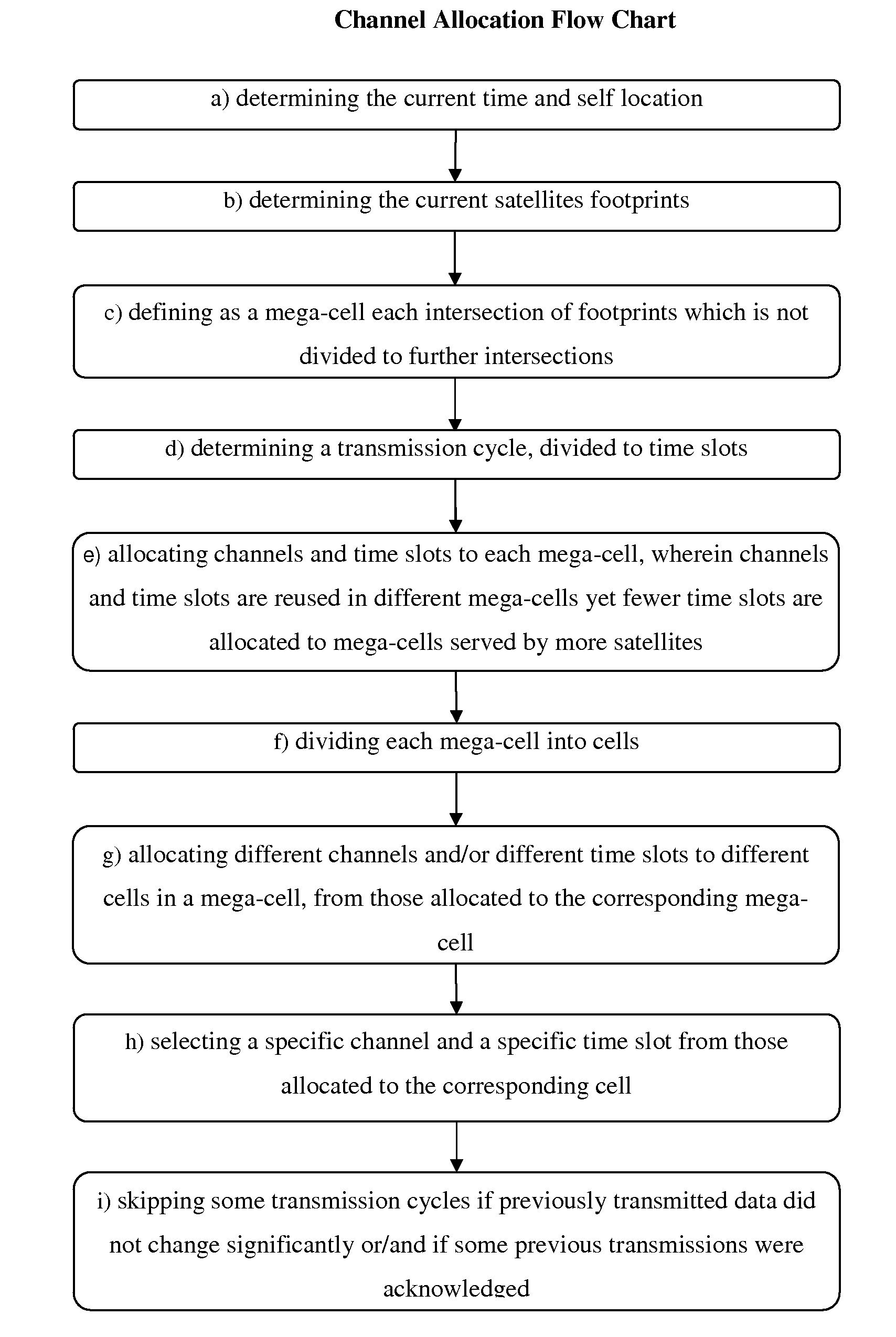
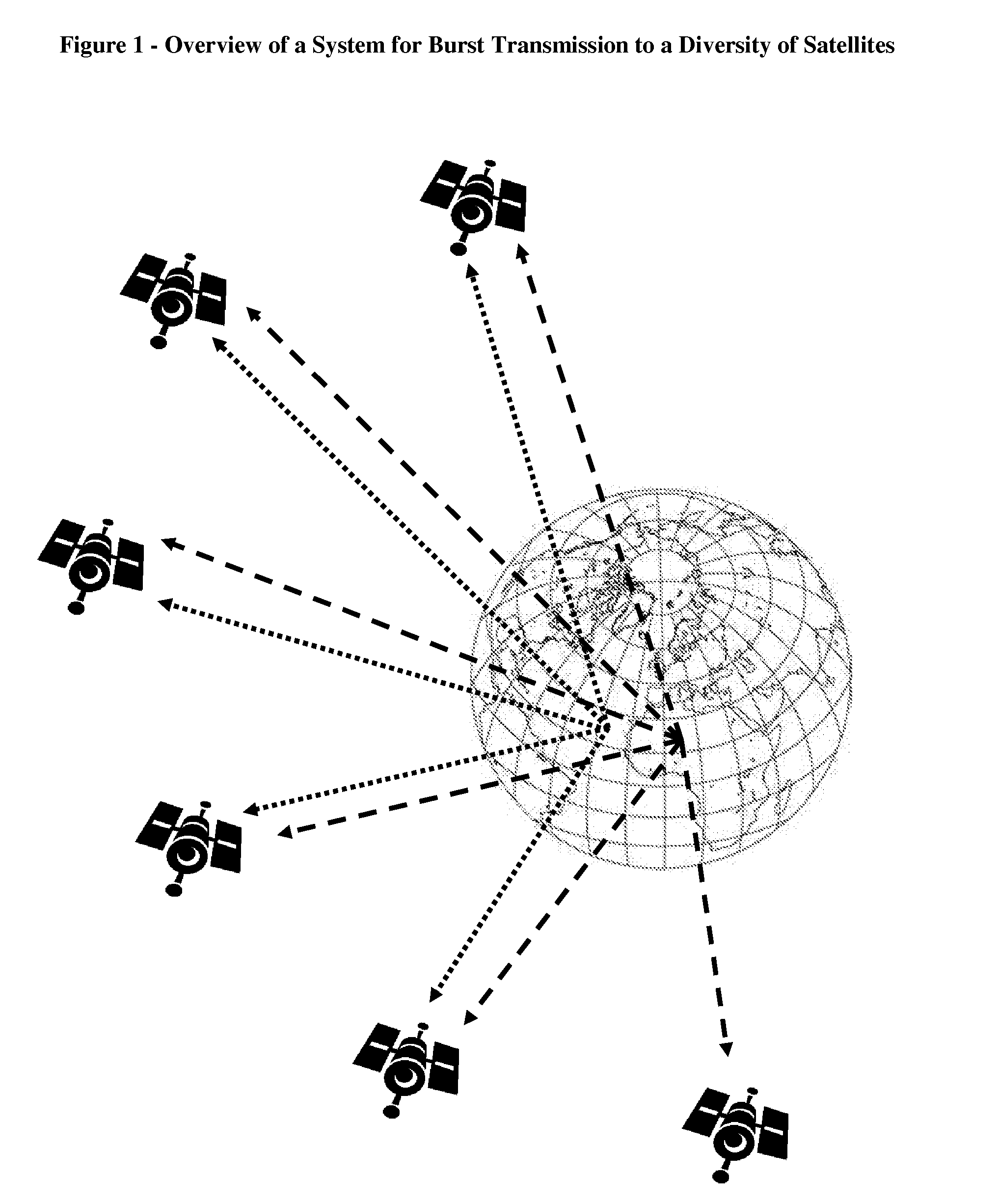
A method for allocating transmission channels to devices configured to communicate short data packets to a diversity of non geostationary satellites is disclosed hereby. The method suggests a dynamic cellular partitioning of the earth surface, based on the smallest intersections of overlapping satellite service areas (“footprints”), defined as mega-cells, and reusing channels in different mega-cells. In addition, a transmission cycle is defined and divided to time slots, synchronized at each device by GPS timing signals, and mega-cells served by more satellites are allocated with fewer time slots, in order to increase the chance of transmitters placed in mega-cells served by fewer satellites to be detected. Further, each mega-cell is divided to cells, and different channels and time slots are allocated to each cell, from those allocated to the corresponding mega-cell. Consequently, collision of transmissions from different mega-cells is reduced, and collision of transmissions from different cells in a mega-cell is avoided.
Owner:MOBIT TELECOM
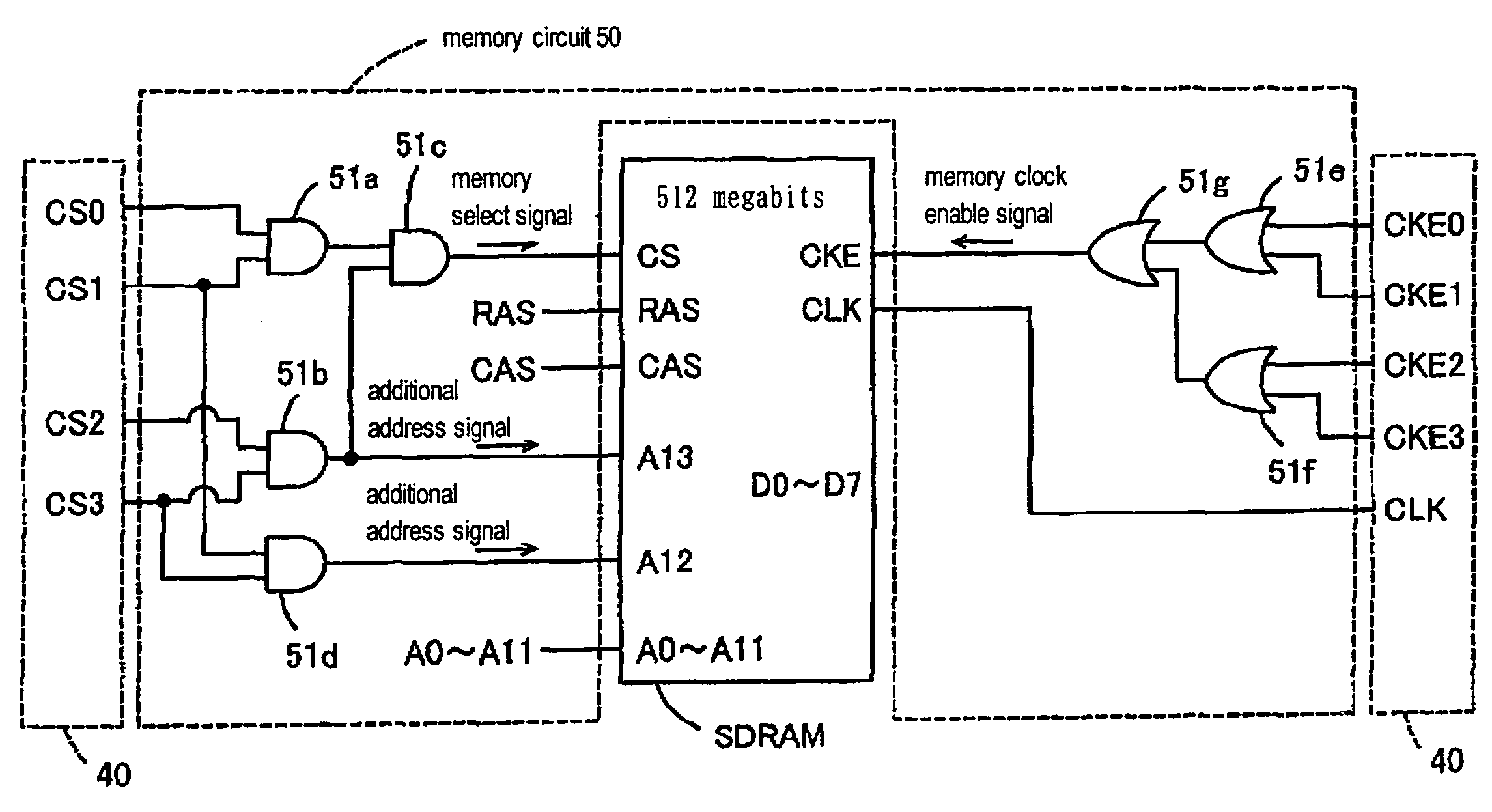
Memory module and memory-assist module
InactiveUS7167967B2Easy to useMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMegabitMemory module
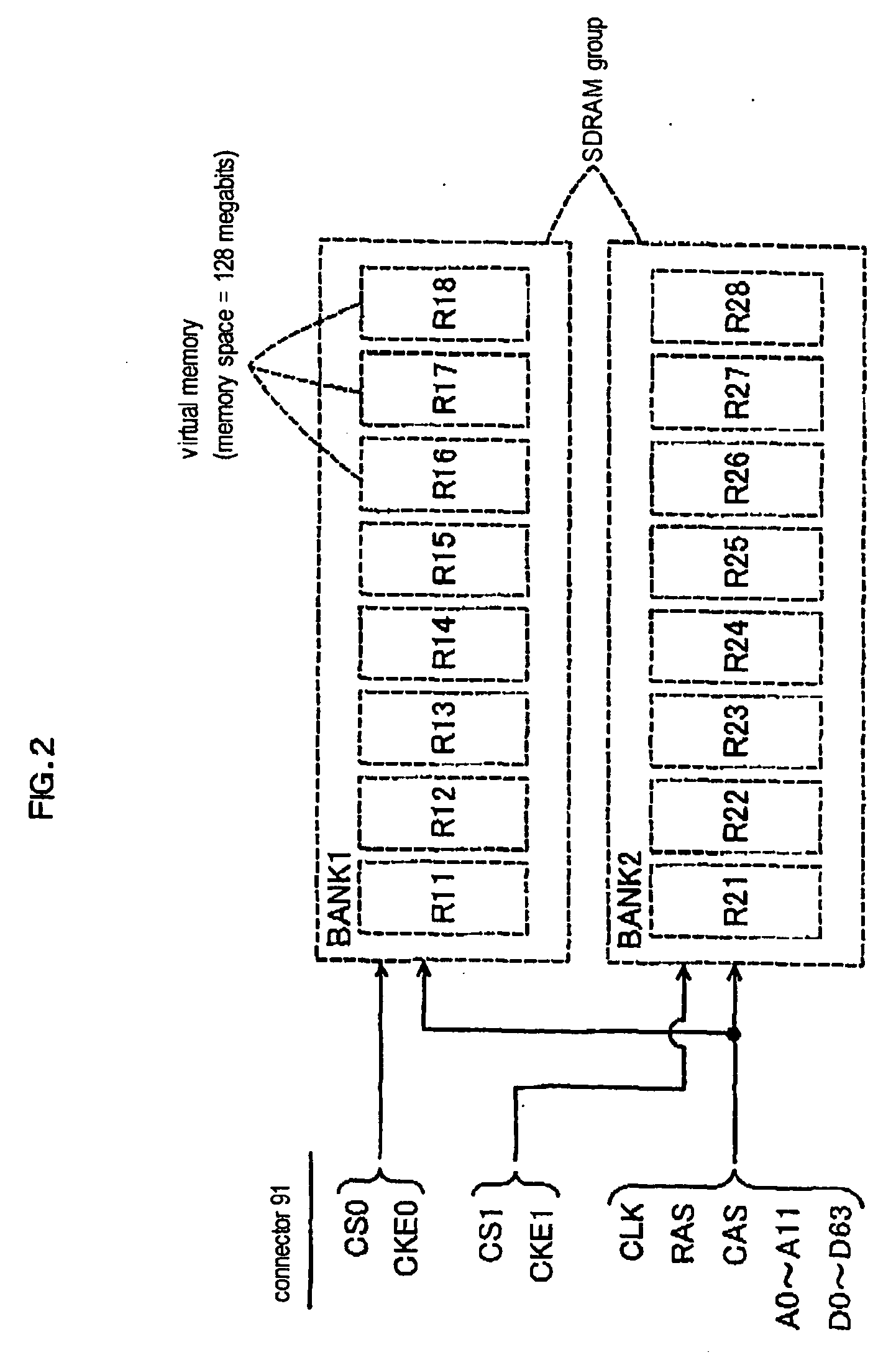
A computer body outputting a predetermined number of address signals A0 to A11 and a plurality of select signals CSO and CSI, generates a memory select signal CS and an additional address signal A12 added to the signals A0 to A11 according to the inputted signals CSO and CSI, and provides the signal CS, signal A12, and signals A0 to AI1 to a 256-megabit SDRAM (memory), so that the computer body can access the corresponding data. The computer body can access the data corresponding to the generated additional address signal A12 and predetermined number of the address signals A0 to A11.
Owner:BUFFALO CORP LTD
Galvanic isolation of a signal using capacitive coupling embeded within a circuit board
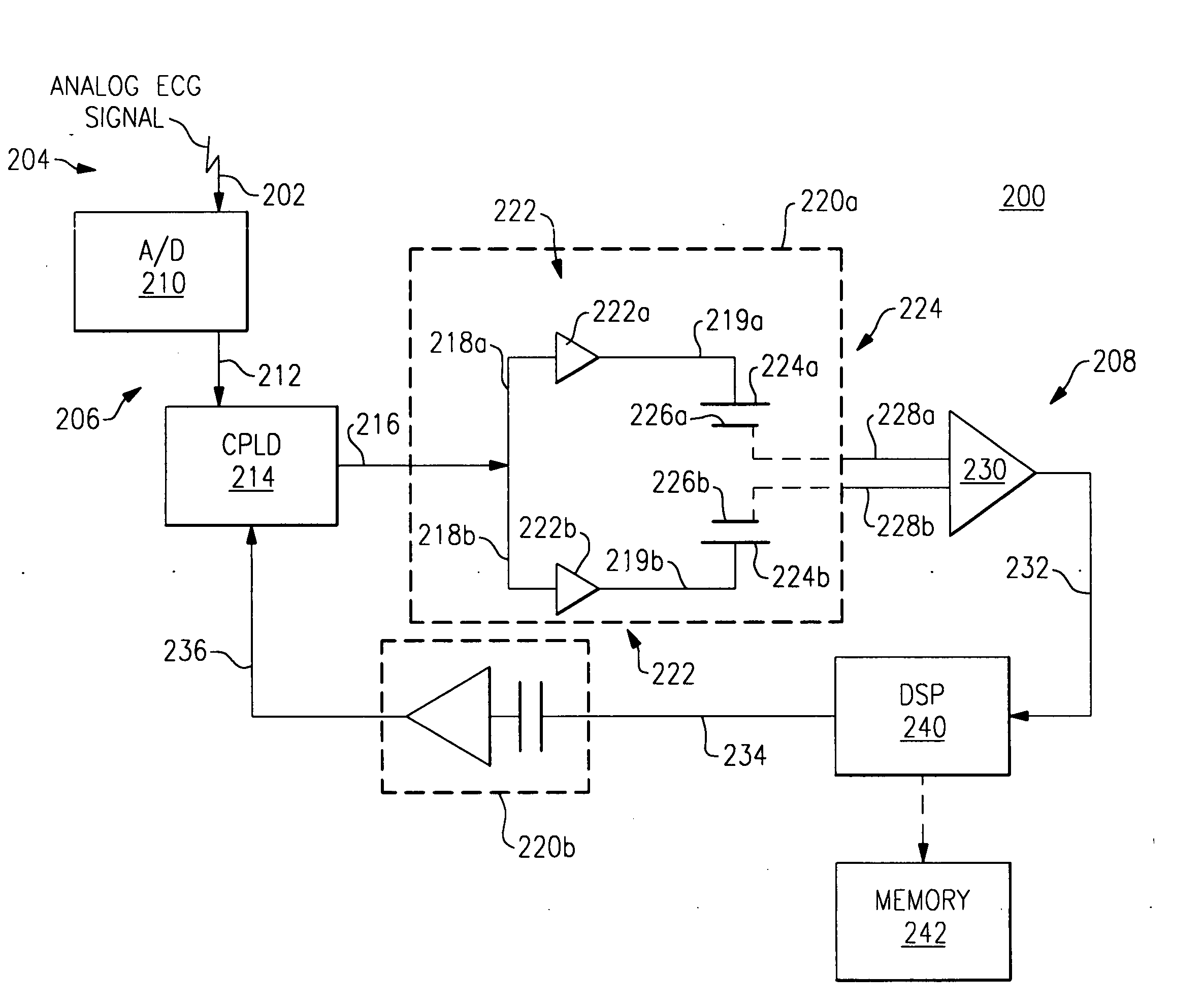
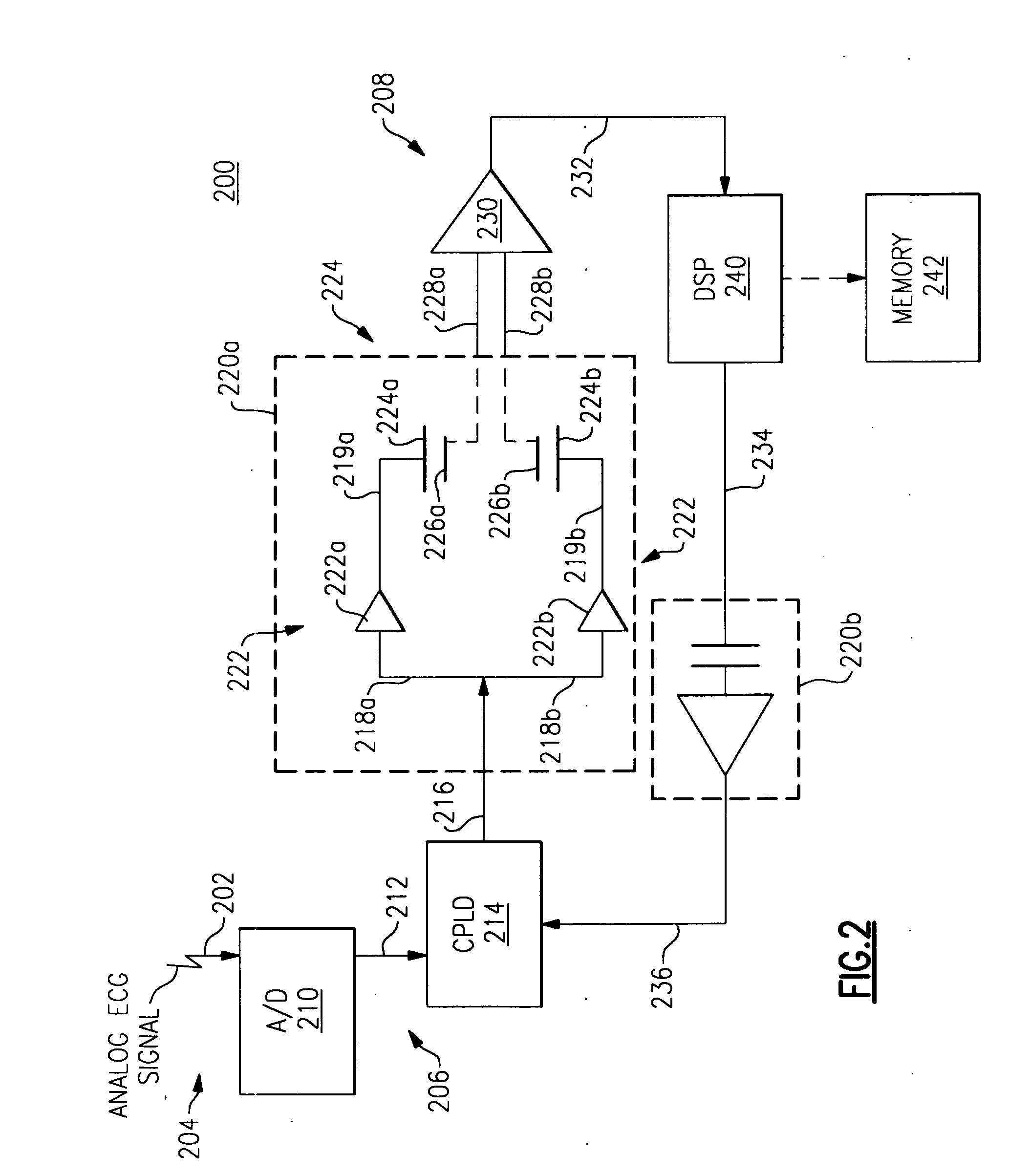
InactiveUS20070080587A1Low costSubstantial galvanic isolationElectrocardiographyMagnetic/electric field screeningCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A method and apparatus for providing galvanic isolation for signal communication between two electrical circuits via a capacitive coupler that is constructed from conductive and non-conductive layers of a printed circuit board. The invention can provide at low cost and with substantial galvanic isolation, the communication of data at rates of greater than 1 megabit per second. The galvanic isolation provided by the invention protects against common mode fields as well as limited differential mode fields. The invention makes use of pre-existing layers of a circuit board and does not require many other or expensive electrical components.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Two step oxide removal for memory cells
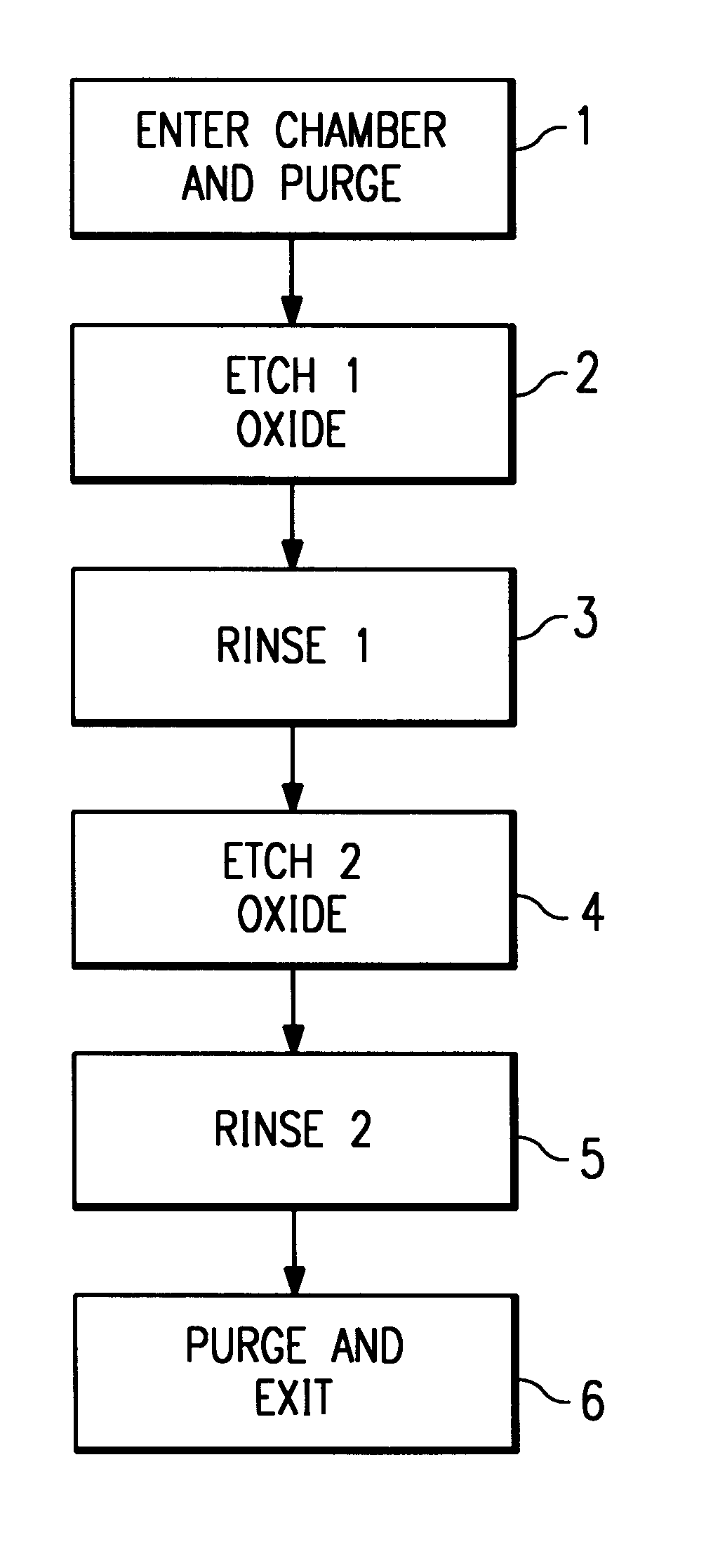
InactiveUS6174817B1Reduce particlesMinimizesTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrofluoric acidWater vapor
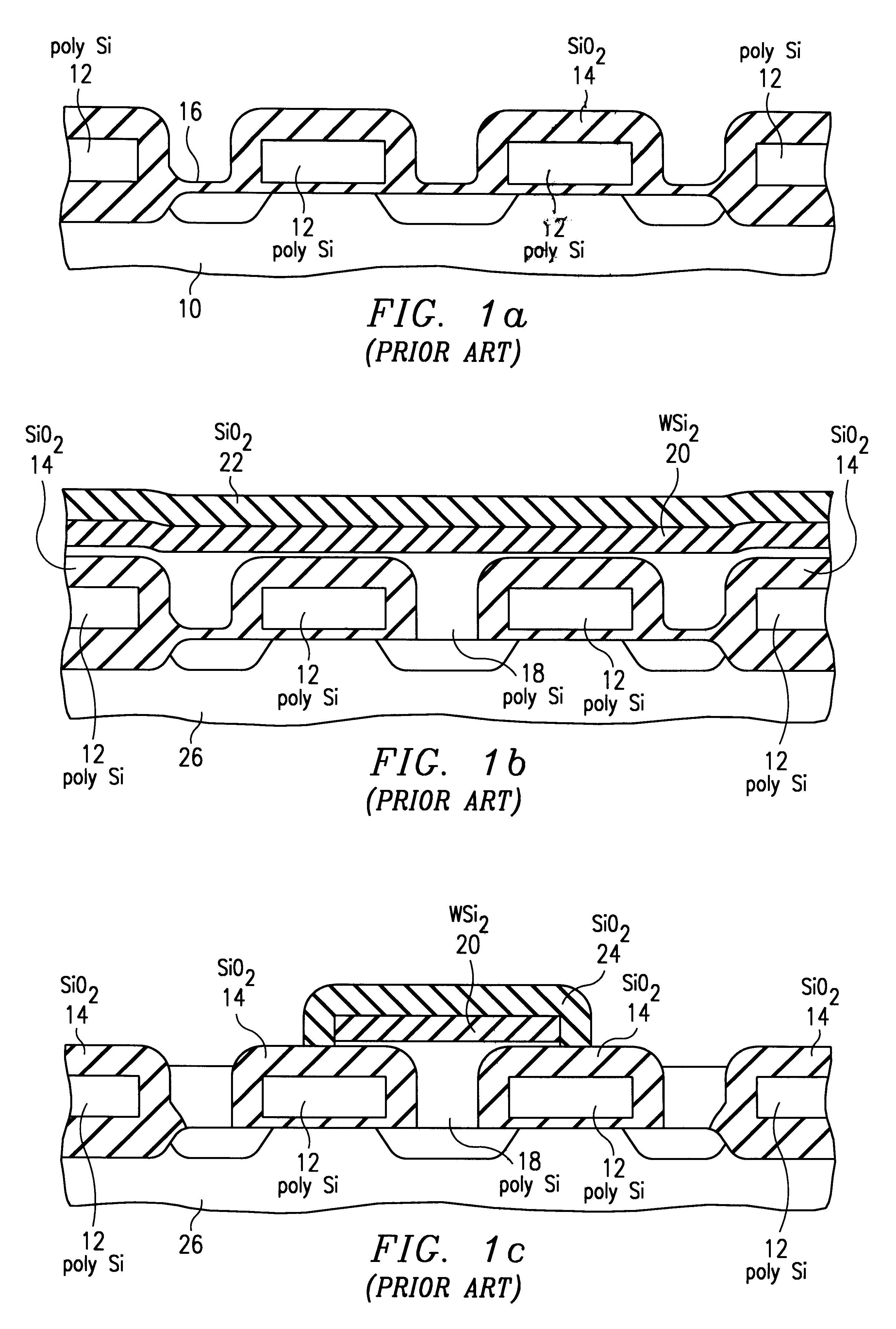
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) mixed with water and often buffered with ammonium fluoride is a standard silicon dioxide wet etchant which is followed by a rinse. An improved silicon dioxide etch is vapor HF which may be followed by a water vapor rinse. The invention discloses a further improved silicon dioxide etch. Following an initial exposure to vapor HF for oxide removal, a first insitu water rinse occurs. A second exposure to vapor HF then occurs and is followed by a second insitu water rinse. Water, rather than water vapor, aids in freeing particles from the wafer surface. During both the water rinses, the wafer may be rotated at increasing speeds to aid in sweeping particles from wafer surface. The process may be practiced in a commercially available reactor and is suitable for ULSI devices having complex topographies, such as, for example, 64 megabit DRAMs employing crown type memory cells.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
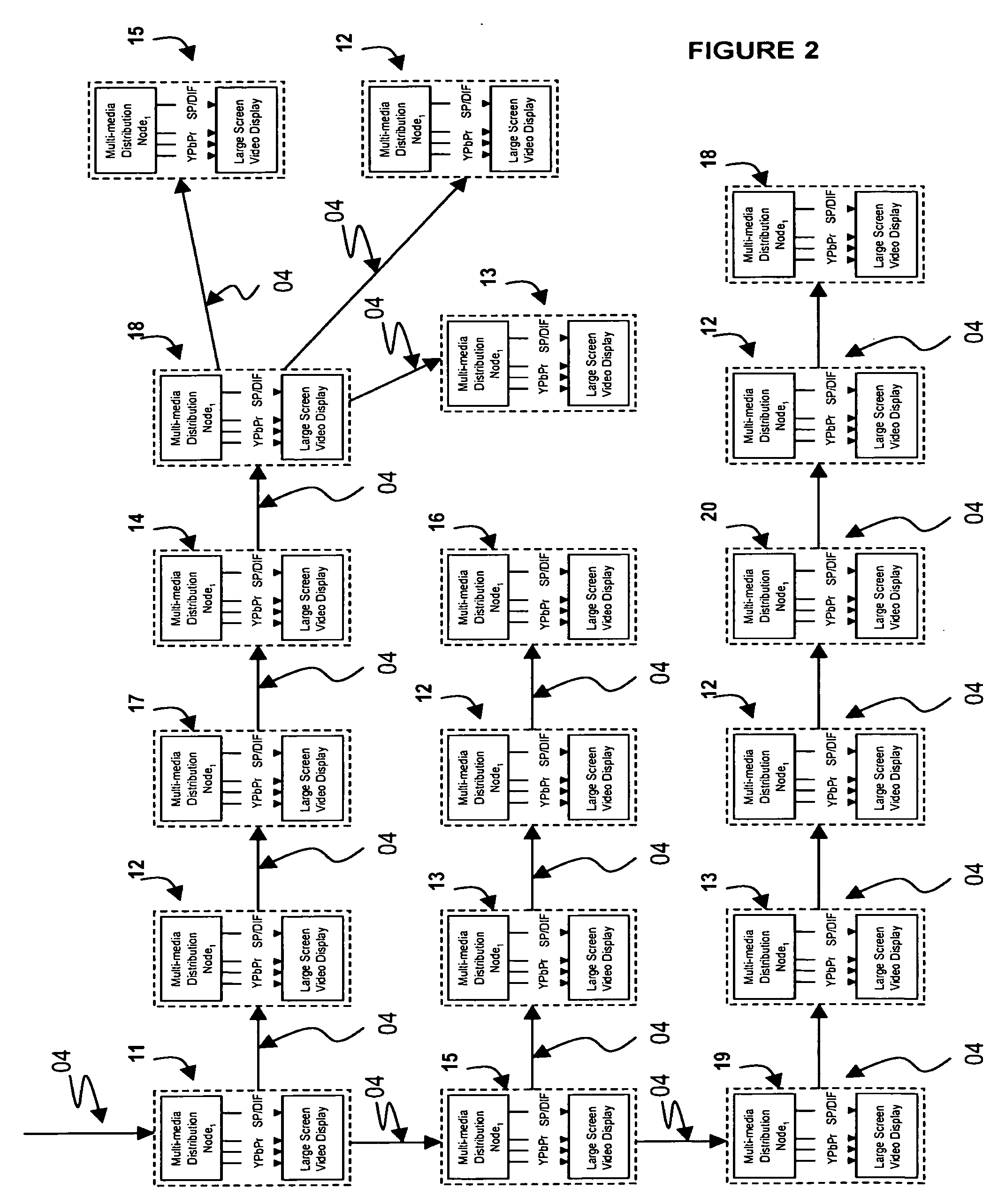
System for distribution of numerous streams of multimedia content to a multiplicity of video displays
InactiveUS20060184685A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsMultimedia streamsComputer network
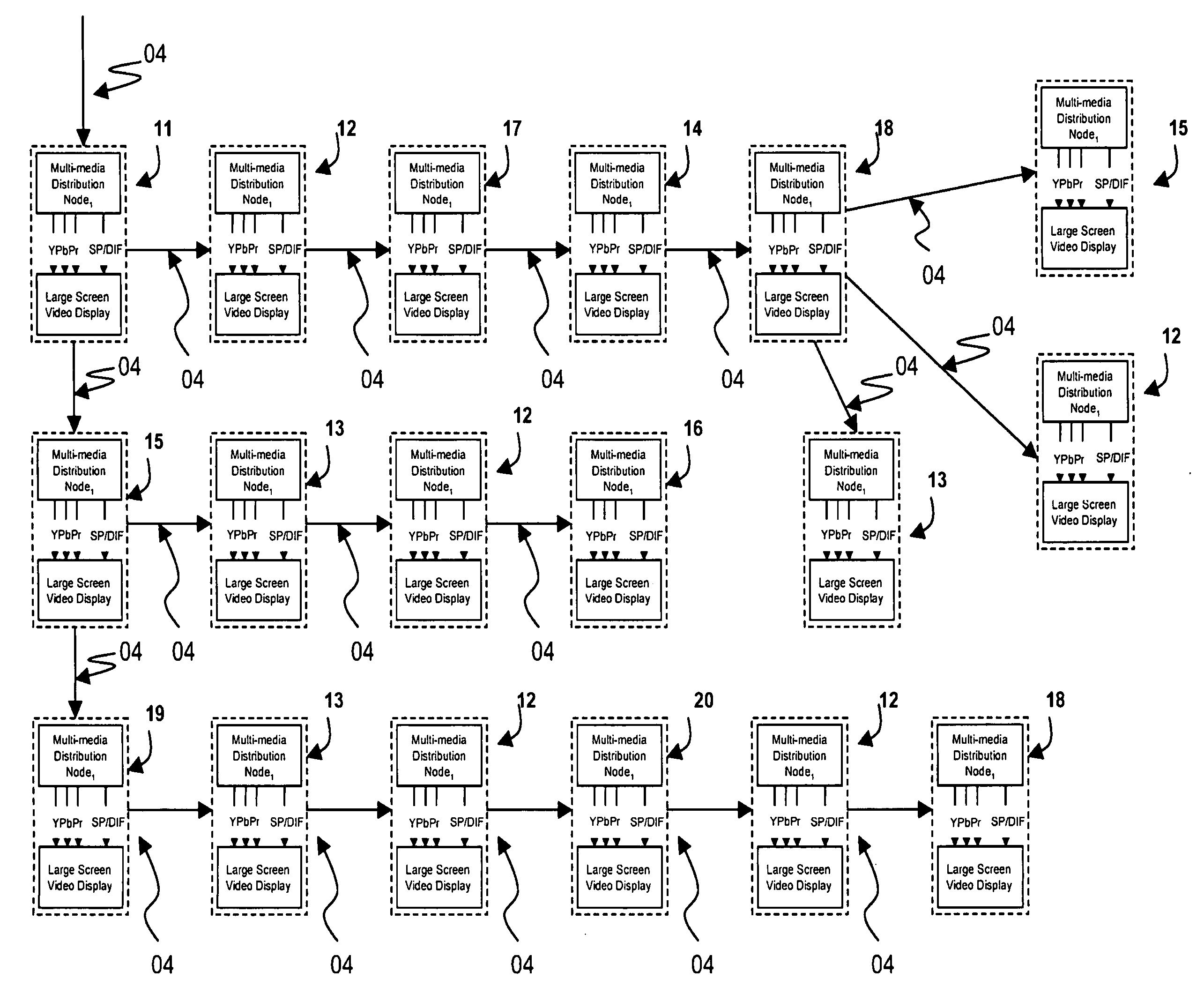
Each of a plurality of remotely located video displays, projectors or multimedia equipment receives operator scheduled and initiated streams of multimedia content. Under the control of the operator each remotely located video display may receive from one to many multimedia streams. Each remotely located video display is associated with a multimedia distribution switch node. Multimedia distribution switch nodes may be configured as feature modules integrated into video displays, optional slot-cards specific to particular varieties of video displays or as stand-alone devices. Multimedia distribution switch nodes are capable of sustaining at least two physical connections to either a copper interface 1000 megabit per second (or greater) network or a fiber-optic 1000 megabit per second (or greater) network.
Owner:LANTASM NETWORKS
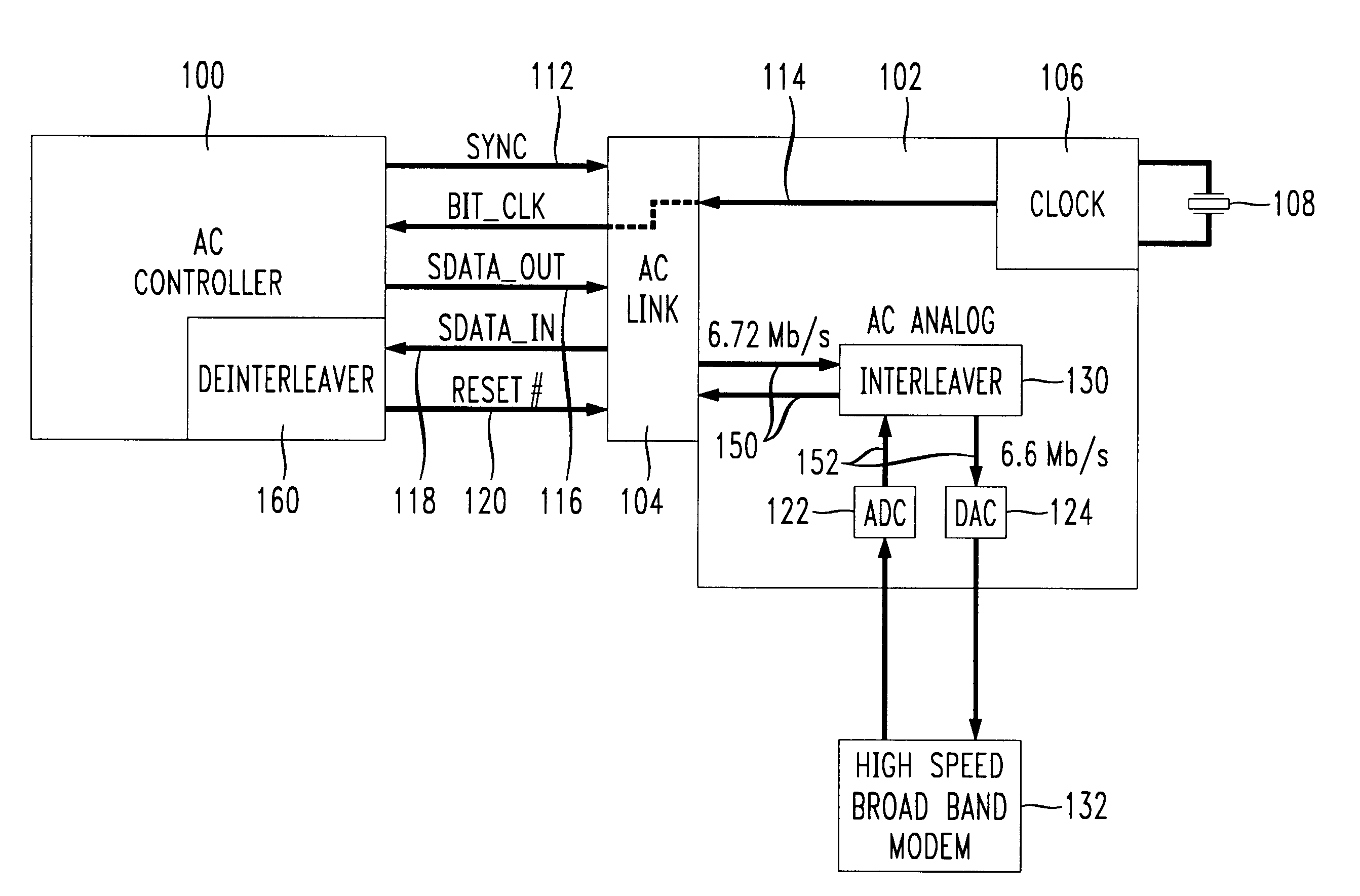
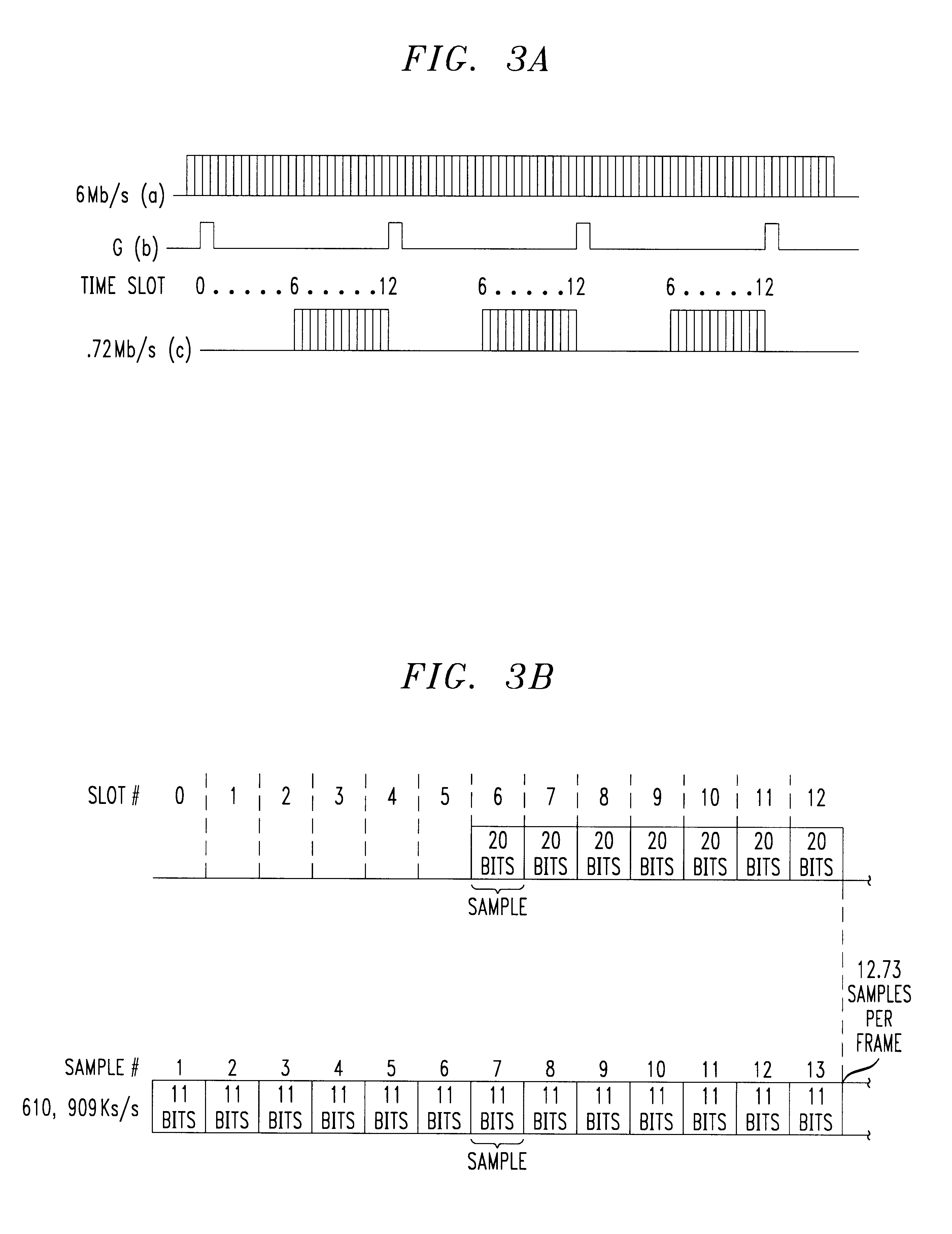
High speed data interface using TDM serial bus
InactiveUS6269103B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRandom number generatorsModem deviceData source
A split-architecture audio codec providing an interface to a high speed broad band modem or other data source device capable of multi-megabit data rates. A plurality of time slots are utilized by the broad band modem in a time division multiplexed (TDM) data bus between the controller and analog sub-systems of the audio codec. Current examples of such high speed broad band modems include HDSL, SDSL, and ADSL, collectively referred to as xDSL. An interleaver in the analog sub-system rate adapts between the data rate of the broad band modem and the fixed rate of the TDM data bus between the sub-systems based on the number of time slots assigned to the broad band modem interface. Interface capability is provided for broad band modems having data rates up to 6.72 Mb / s for split-architecture audio codecs which conform to the AC '97 specification, and higher if non-conformance is acceptable. A programmable clock in the analog sub-system has the capability to operate in several modes including a conventional AC '97 conforming mode with the clock set to divide the frequency of the external crystal in half, and an AC '97 non-conforming mode wherein the frequency of an external crystal oscillator is multiplied by one or more to correspondingly increase the speed of the TDM data bus and the capacity of the interface to the broad band modem.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
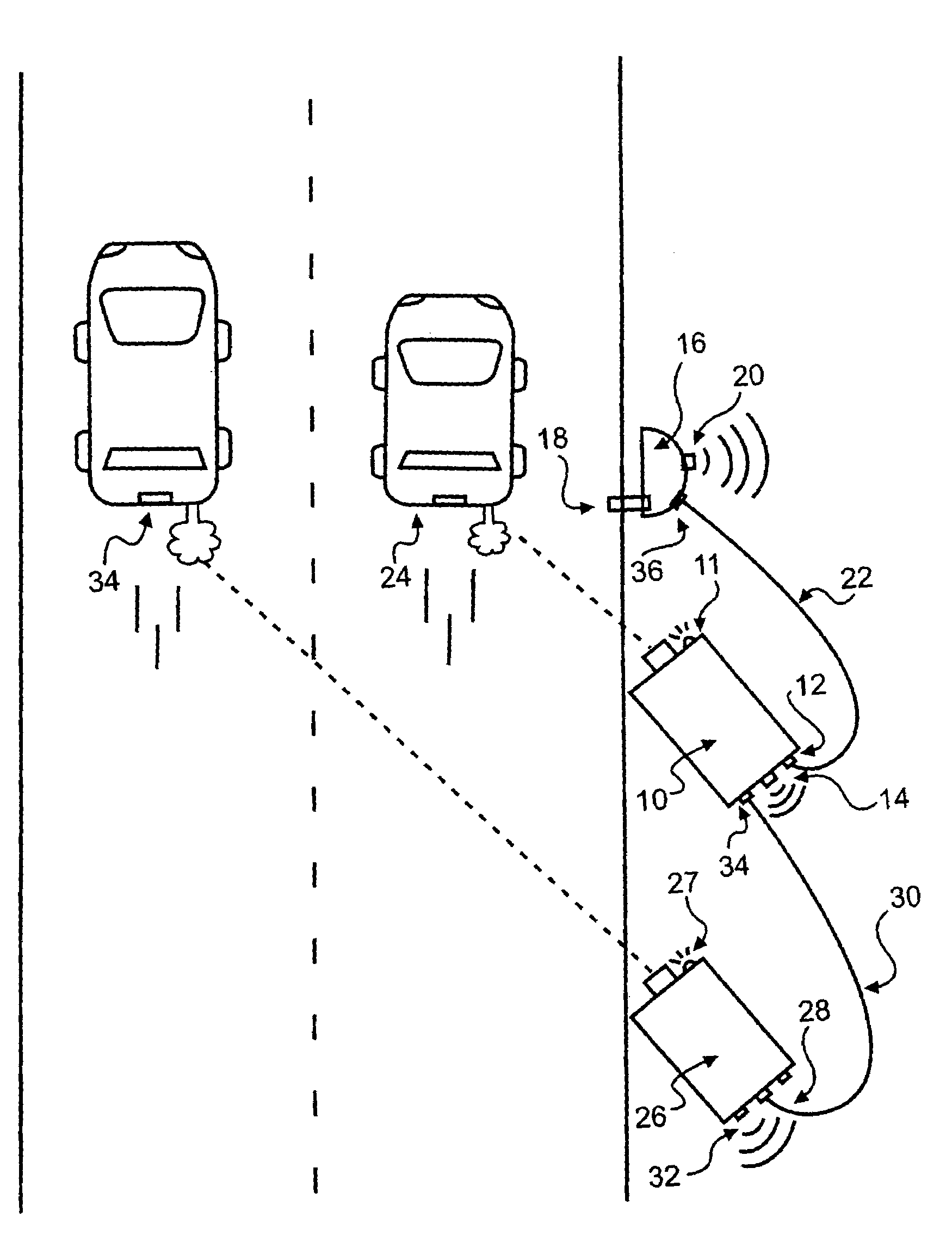
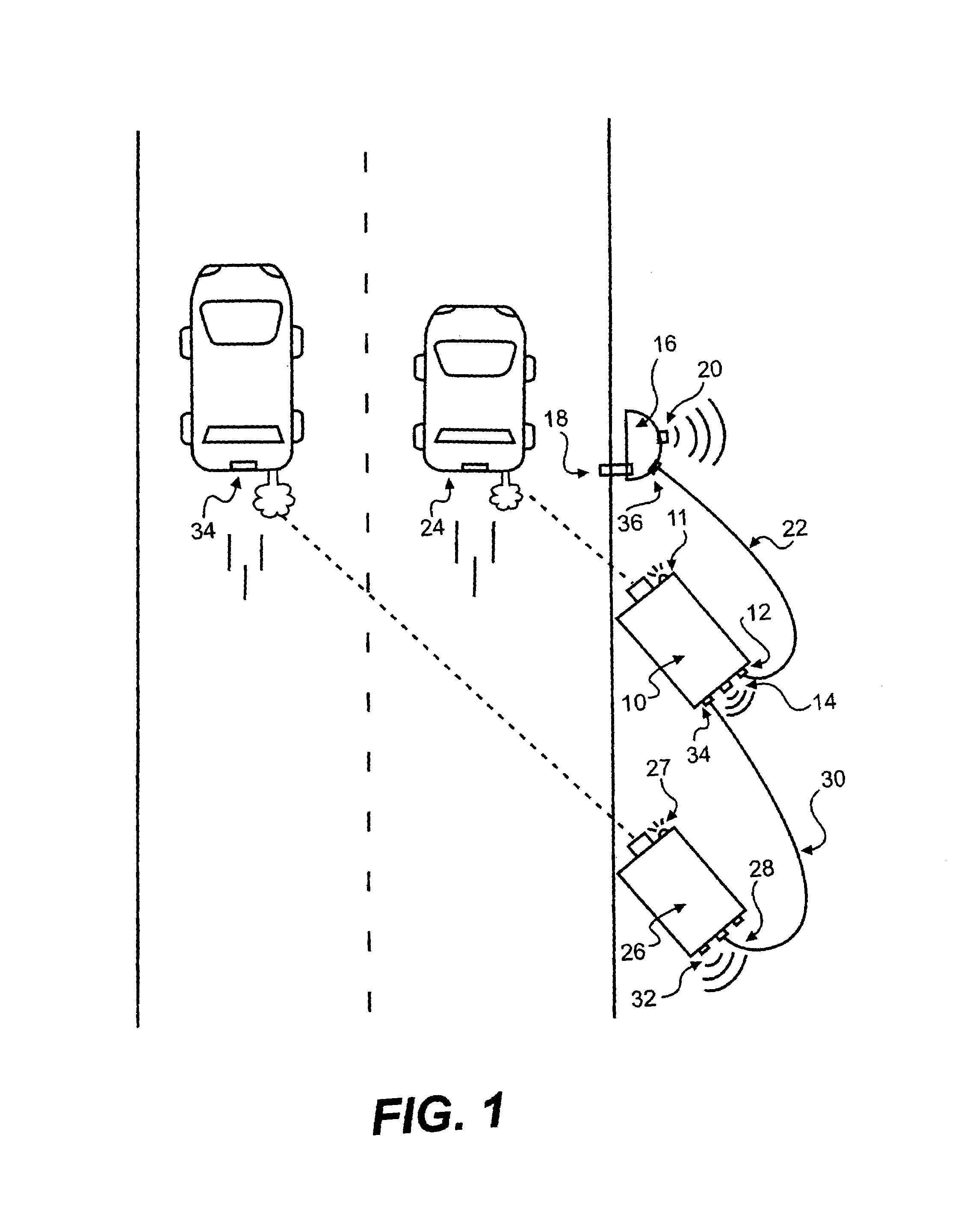
Method and system for video capture of vehicle information
ActiveUS7183945B2Improve performanceGreat contributionImage analysisTicket-issuing apparatusTelecommunications linkInformation transmission
A system for collecting and managing information relating to vehicles includes a digital image collection system positioned to capture an image of a vehicle travelling along a roadway. The captured images are delivered to a computer program memory via a communications link at a transfer rate substantially equal to 100, 200, and / or 400 megabits per second. A second device collects additional information relating to the vehicle, such as the vehicle's speed, acceleration, and / or emissions data, and also delivers such information to the memory. Alternatively, two or more video capture devices may be connected in series via communications links that are all capable of transmitting data at rates substantially equal to 100, 200, and / or 400 megabits per second, such that the images collected by all of the capture devices are delivered to the memory.
Owner:SPX CORP
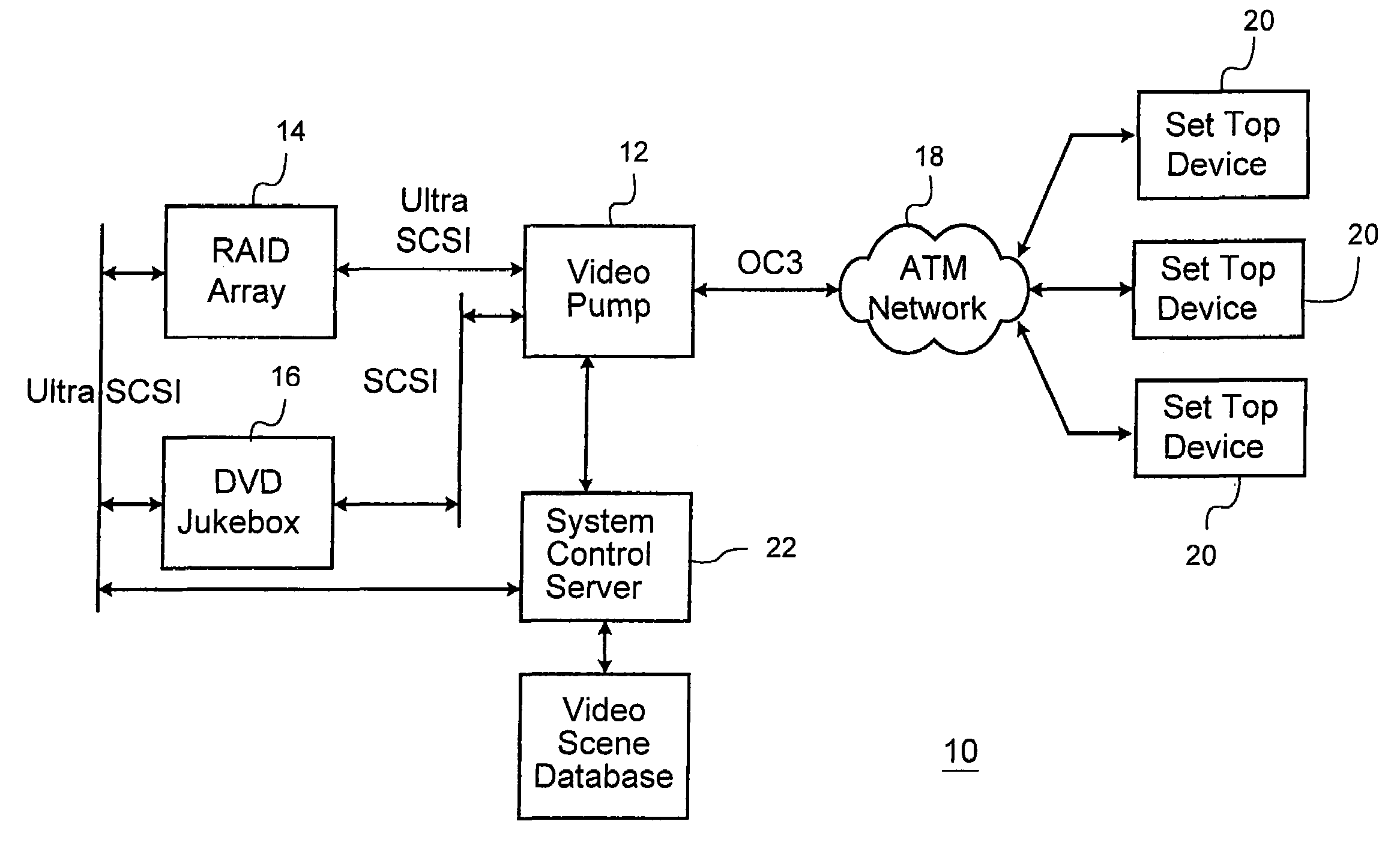
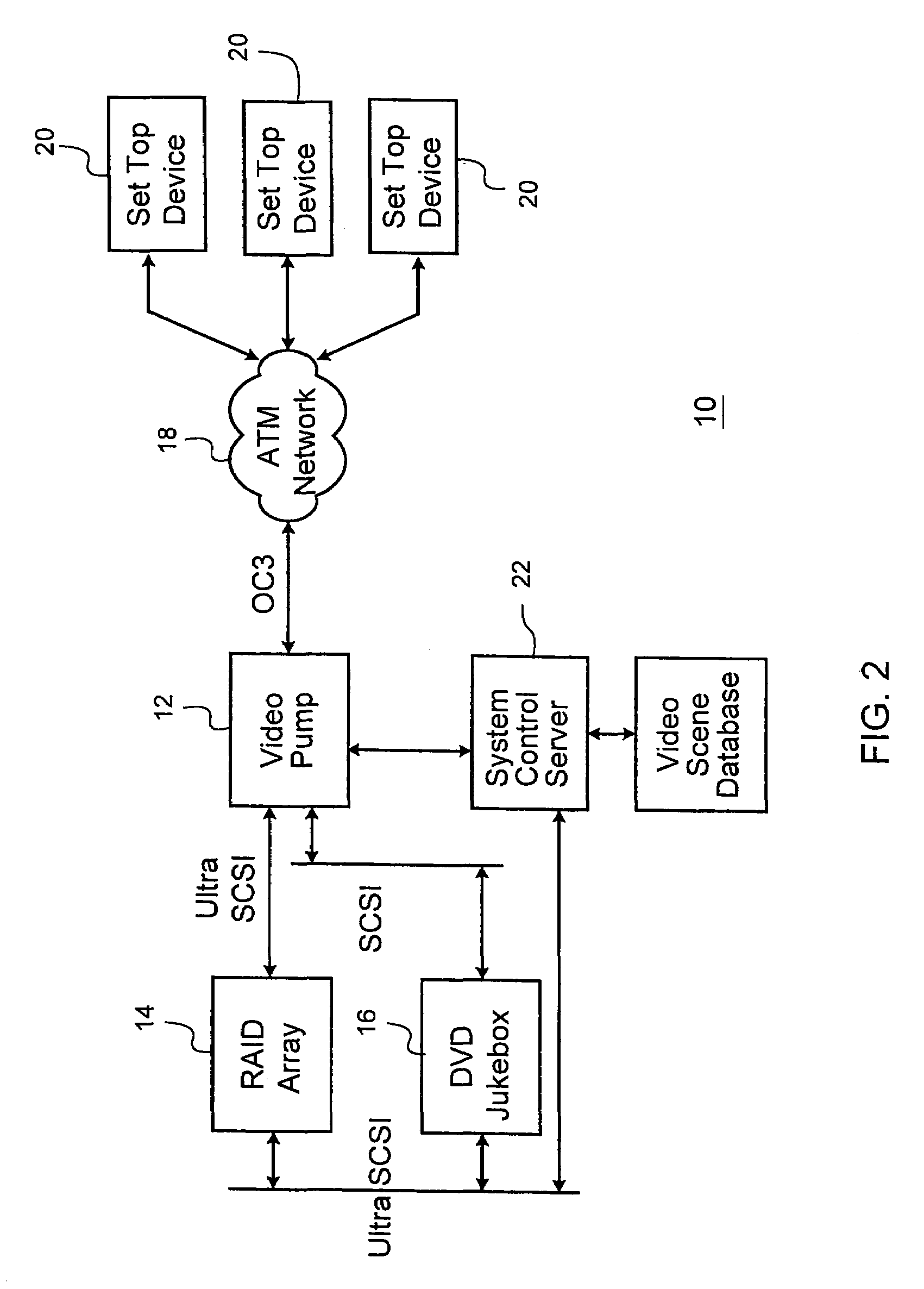
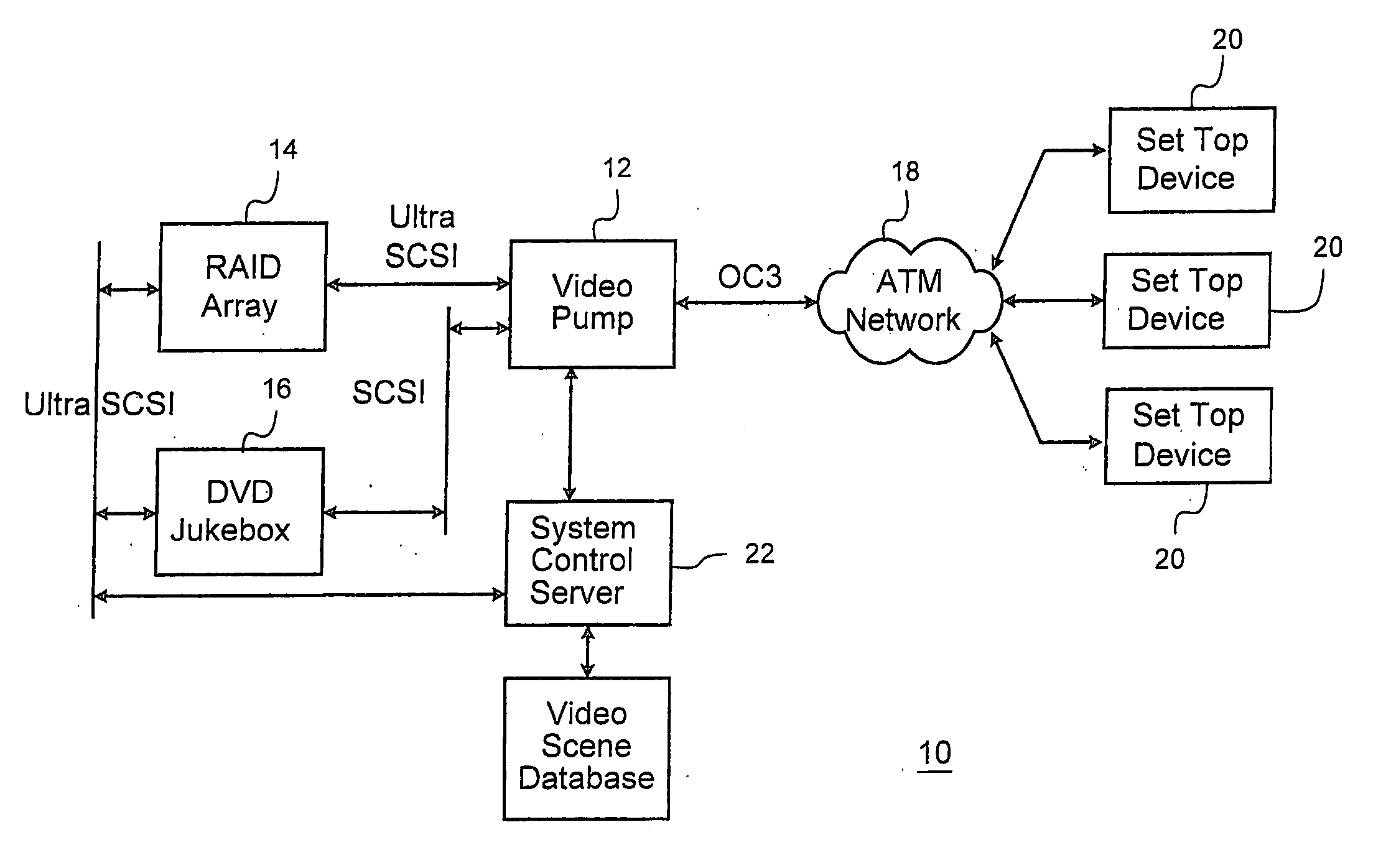
Multi-channel video pump
InactiveUS6954469B1Accurate recoveryTelevision system detailsTime-division multiplexMegabitMillisecond
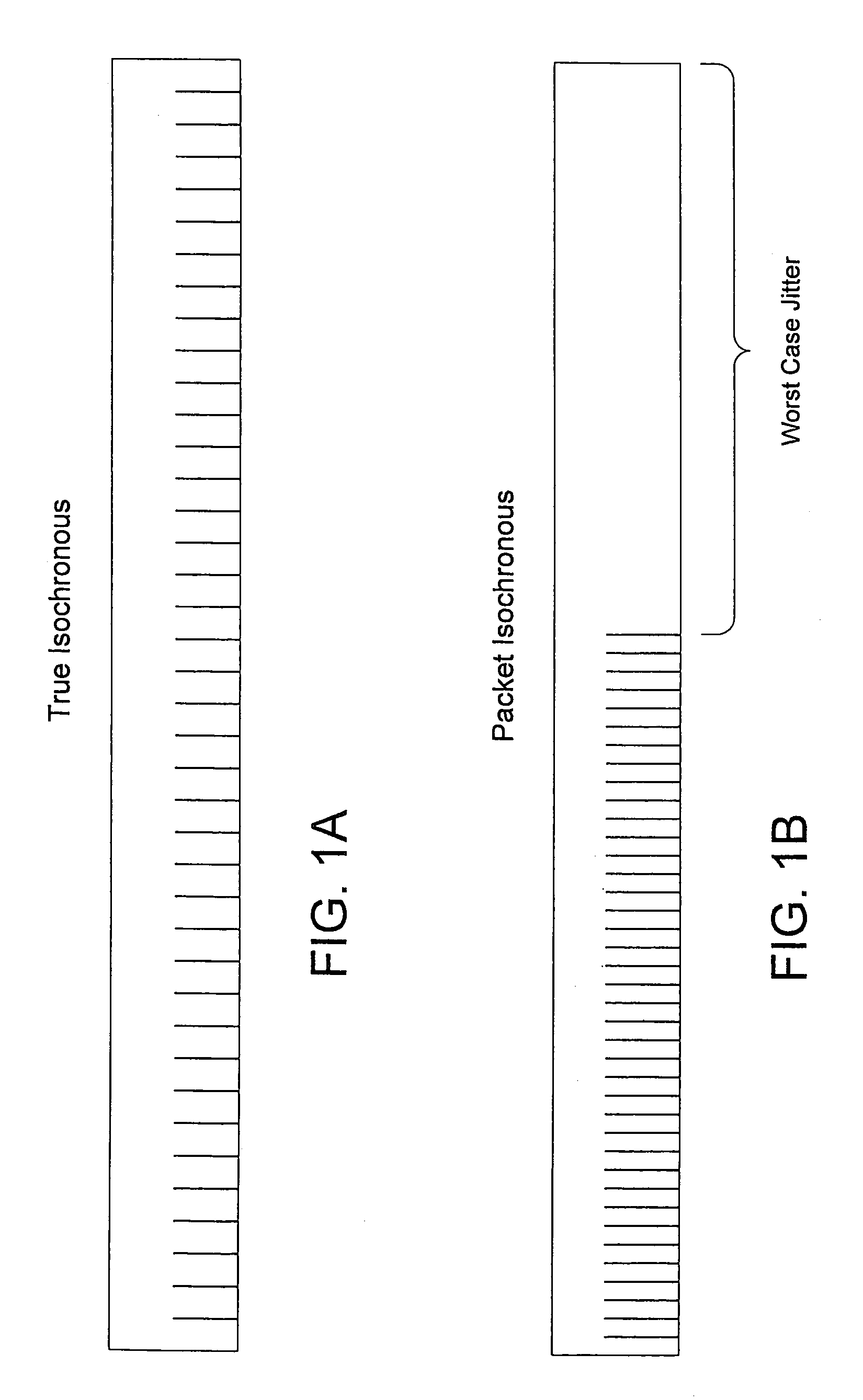
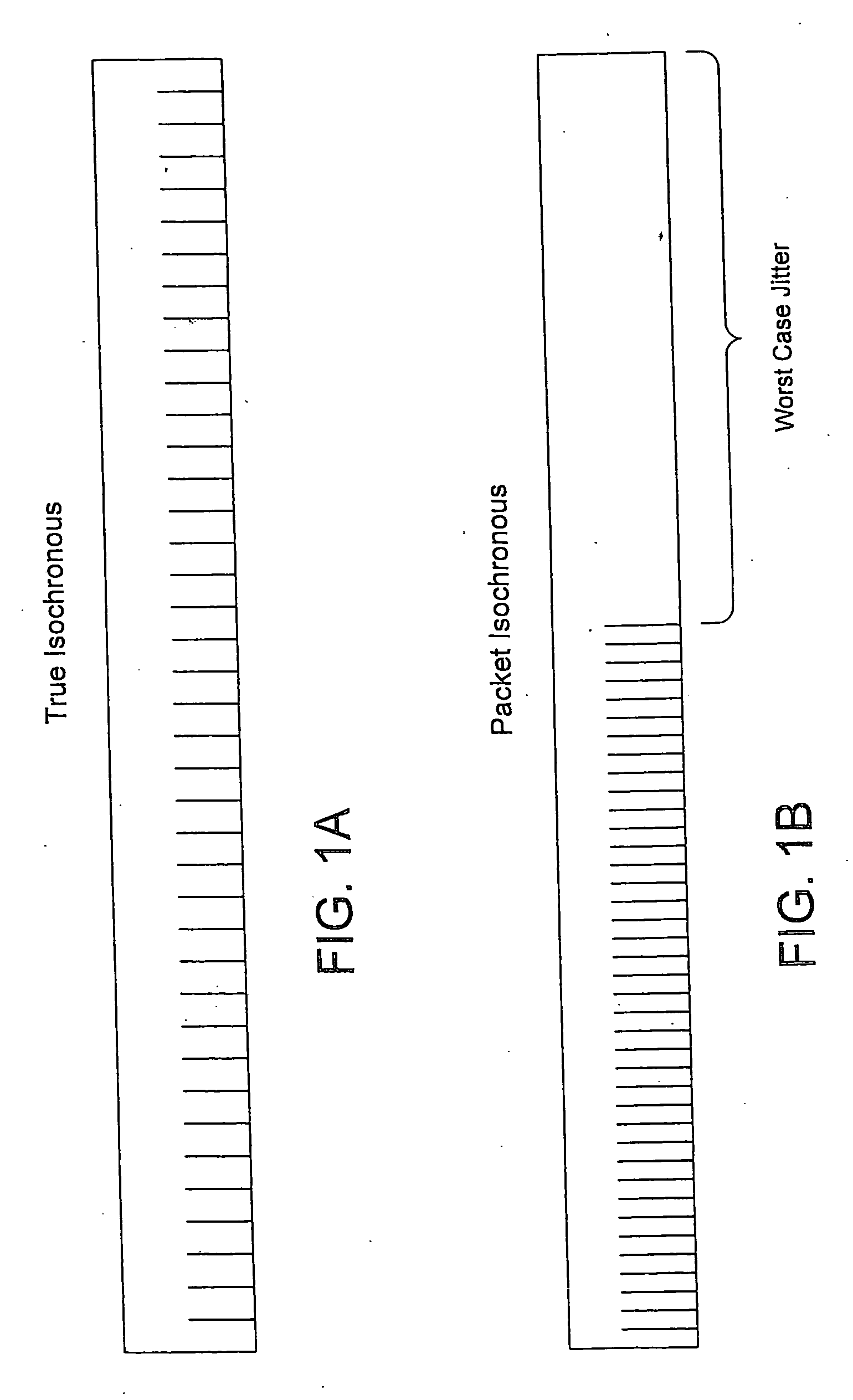
A system for streaming a plurality of video or other recorded signals from storage to receiving devices maintains each of the signal streams at their encoded bit rate. The bit rate of each stream is detected from the stored signals and a corresponding queue is set up in memory or in a network interface card for outputting data at the detected bit rate. A channel timing module in the signal streaming device contains a two-stage dithered counter for each bit rate. The first stage of the counter counts one clock cycle longer than the second stage. By adjusting the ratio of the first stage and second stage counters in a fixed number of cycles (the dither cycle) a very precise average count is achieved. The average count is calculated to achieve the desired bit rate with a given packet size. Every time either the first stage of the second counter times out, a packet of data is sent to the corresponding queue in the network interface. As a result, the network interface is able to output packet isochronous signals with an average bit rate within one bit per second of desired bit rates between one megabit / second and 20 megabit / second and with a jitter of less than two milliseconds.
Owner:ESCIENT +1
Workshop scheduling method for Job-shop discrete production
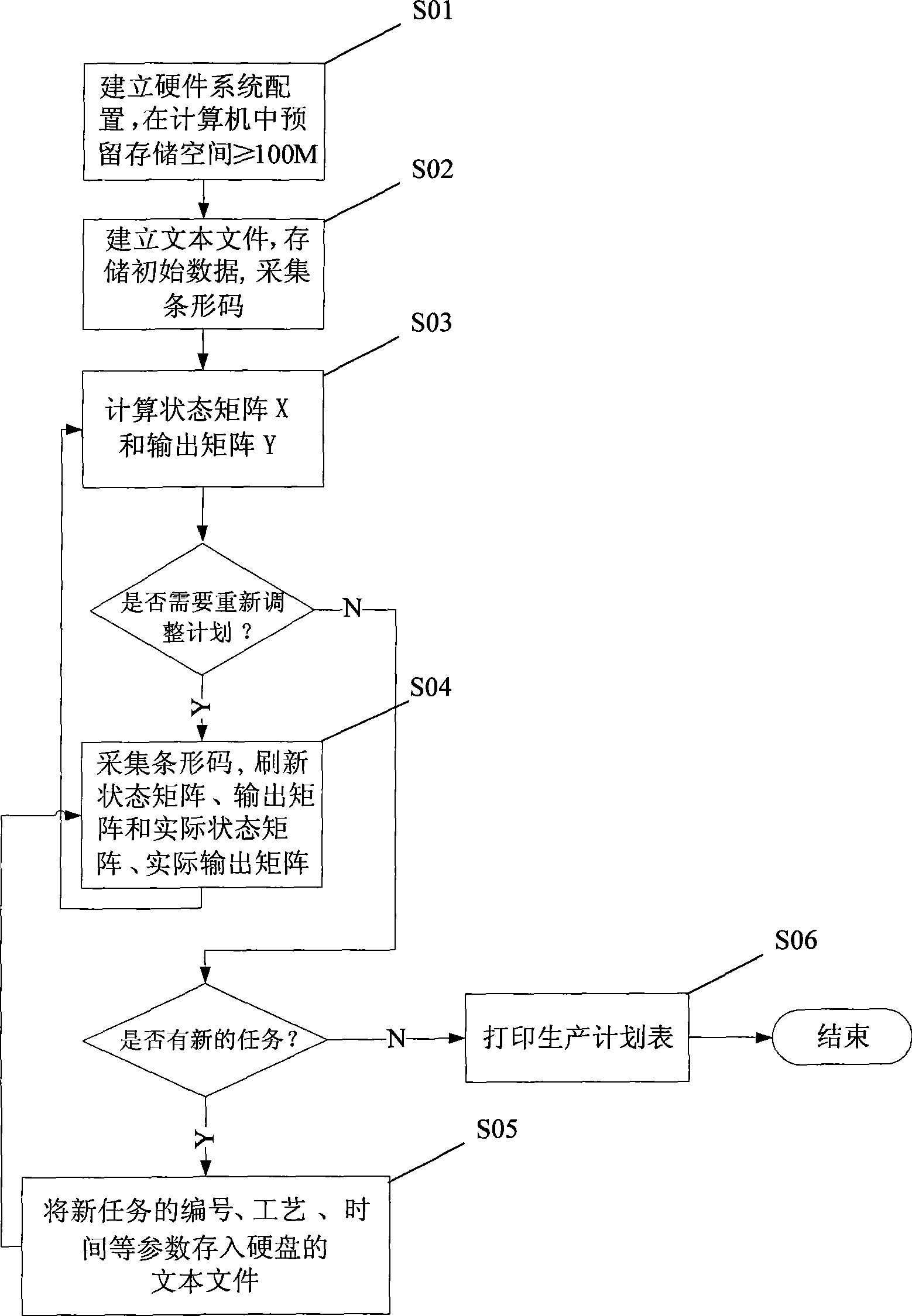
The invention relates to a workshop scheduling method for Job-shop discrete production, which comprises the following steps: reserving a memory space of more than or equal to 100 megabits on a computer hard disc, establishing a text file for storing matrix data, printing bar codes representing task numbers and bar codes representing equipment numbers of equipment required by each process step on a process flow card, assigning a value for the text file, calculating a state matrix according to a scheduling optimization algorithm, and outputting the state matrix and storing the same in the text file of the hard disc; when the ordering of a production plan needs to be adjusted, resampling the bar codes and refreshing the matrix; and when a new task needs scheduling, storing parameters of the new task into the text file in the hard disc, and printing a production plan table. The workshop scheduling method provides a set of practicable solution for optimizing the allocation of resources for industrial facilities, which not only can control the production in real time, but also can effectively shorten the processing cycle and improve the equipment utilization rate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
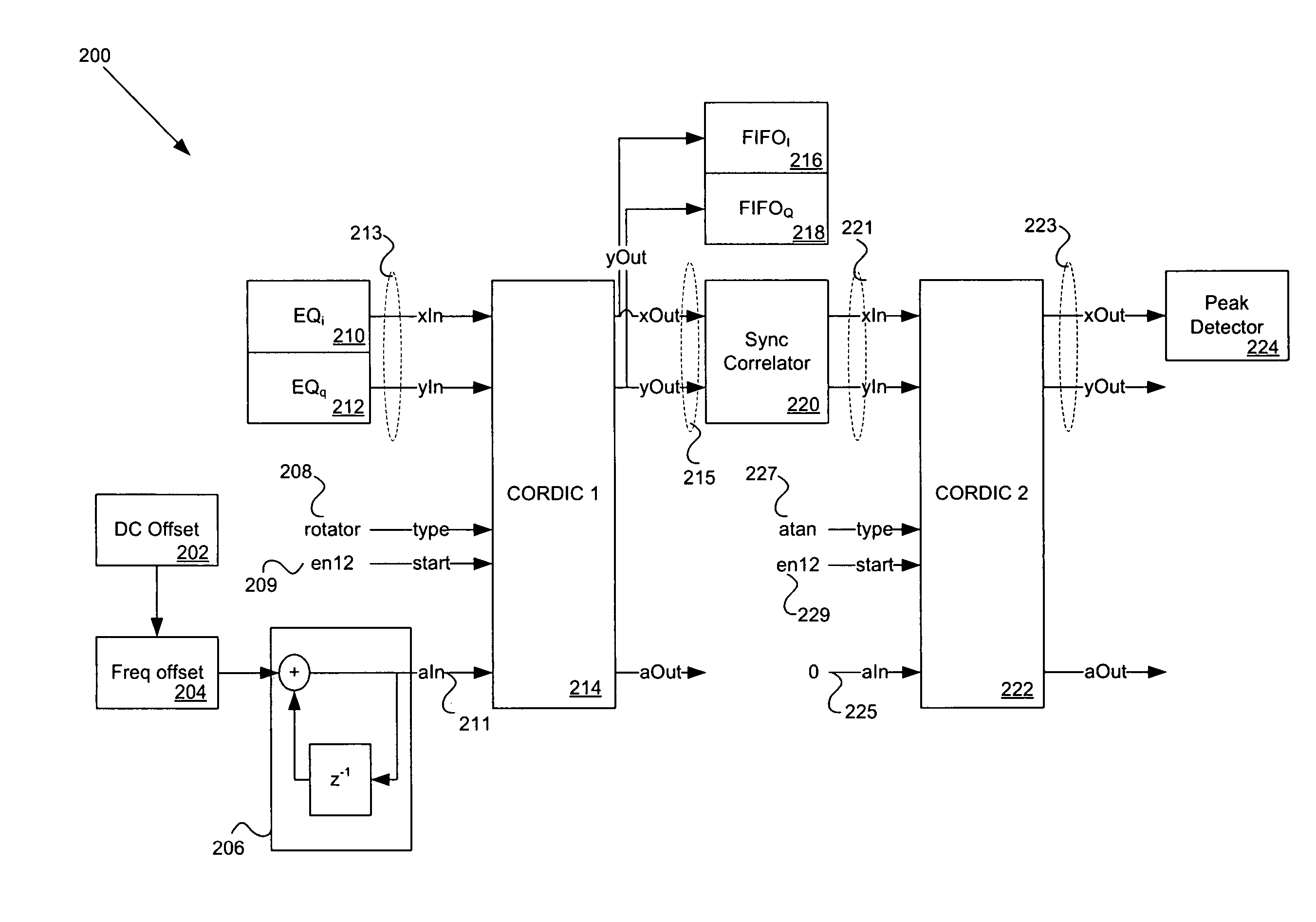
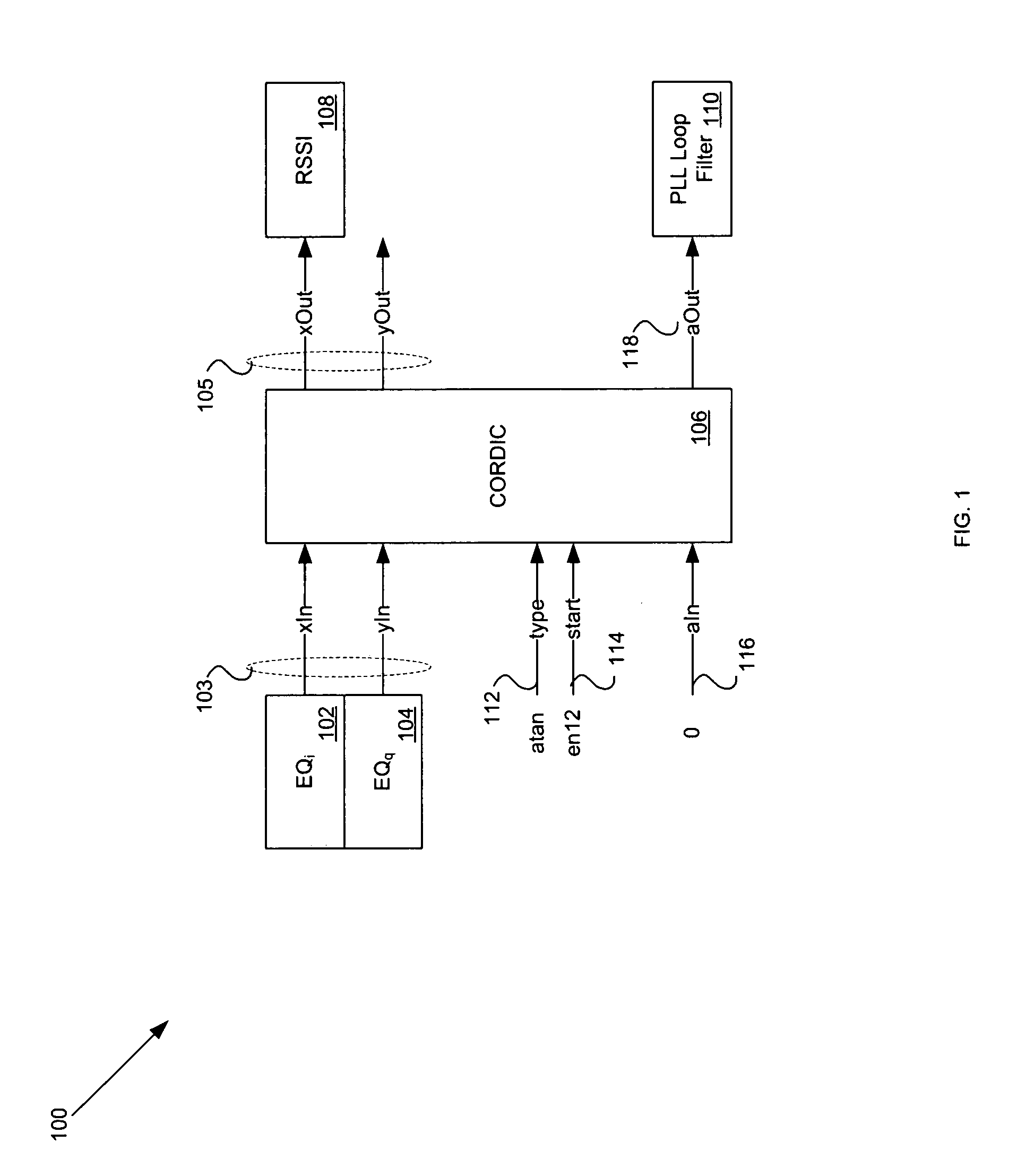
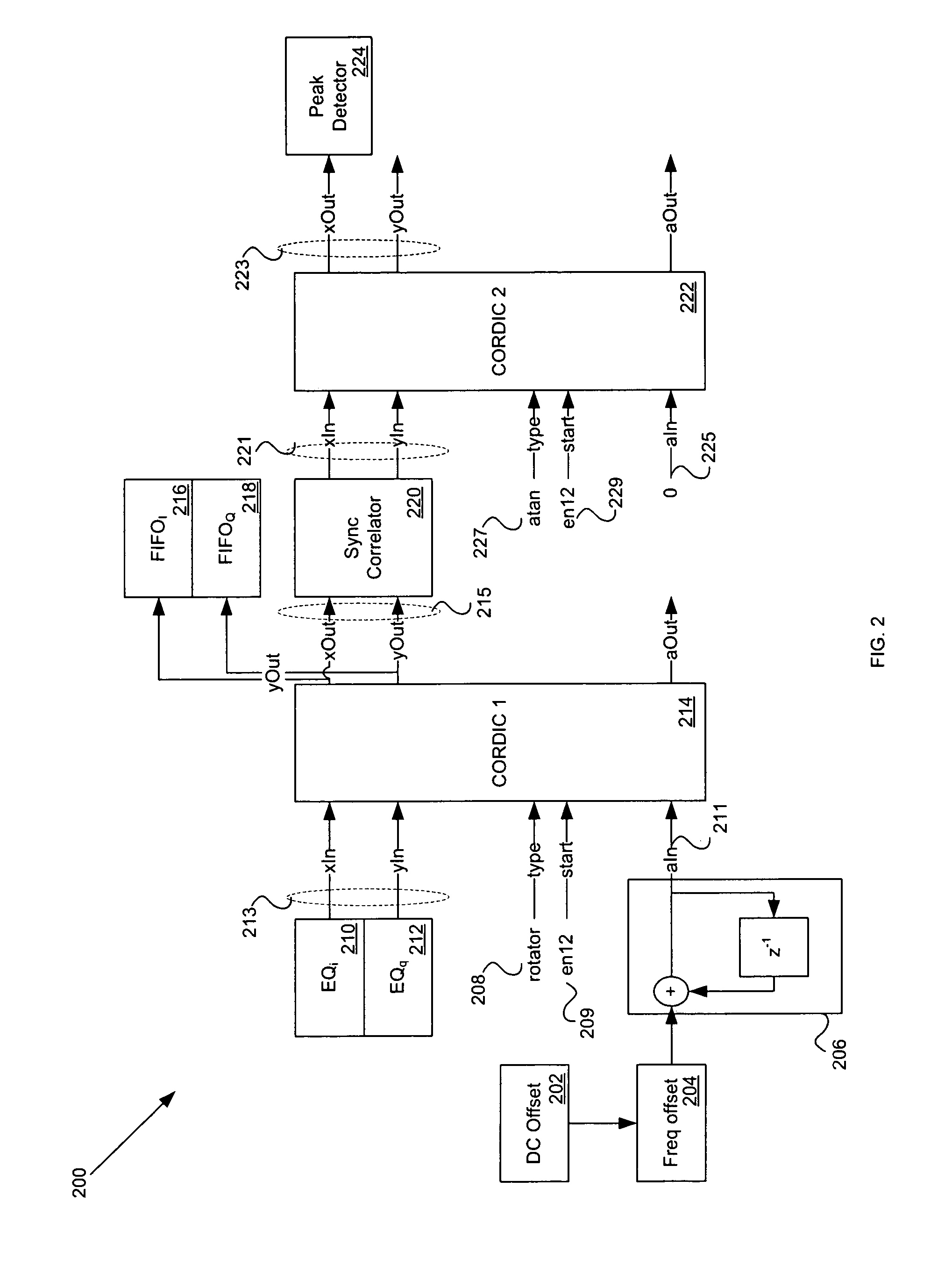
Method and system for reuse of CORDIC in an RF transceiver by reconfiguration in real time
InactiveUS20060093070A1Frequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverMegabit
Methods and systems for processing an RF signal are disclosed herein. Aspects of the method may comprise utilizing a single input CORDIC and a single output CORDIC for synchronizing and demodulating a received signal, wherein the received signal may comprise one or more bit rates. The received signal may comprise a one megabit per second (Mbps) signal. The single input CORDIC may be configured to operate in a rotating mode and the single output CORDIC may be configured to operate in a rotating mode and / or an arctangent (ARCTAN) mode. A rotated output of the single input CORDIC may be correlated with a phase shift keying (PSK) synchronization (sync) word and a portion of the correlated rotated output of the single input CORDIC may be buffered.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
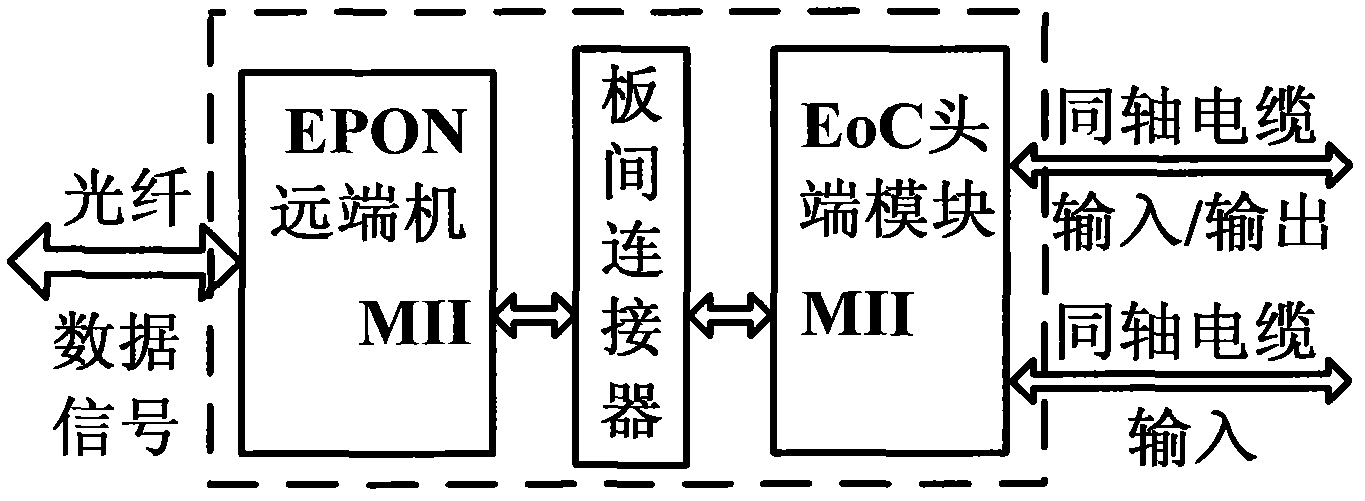
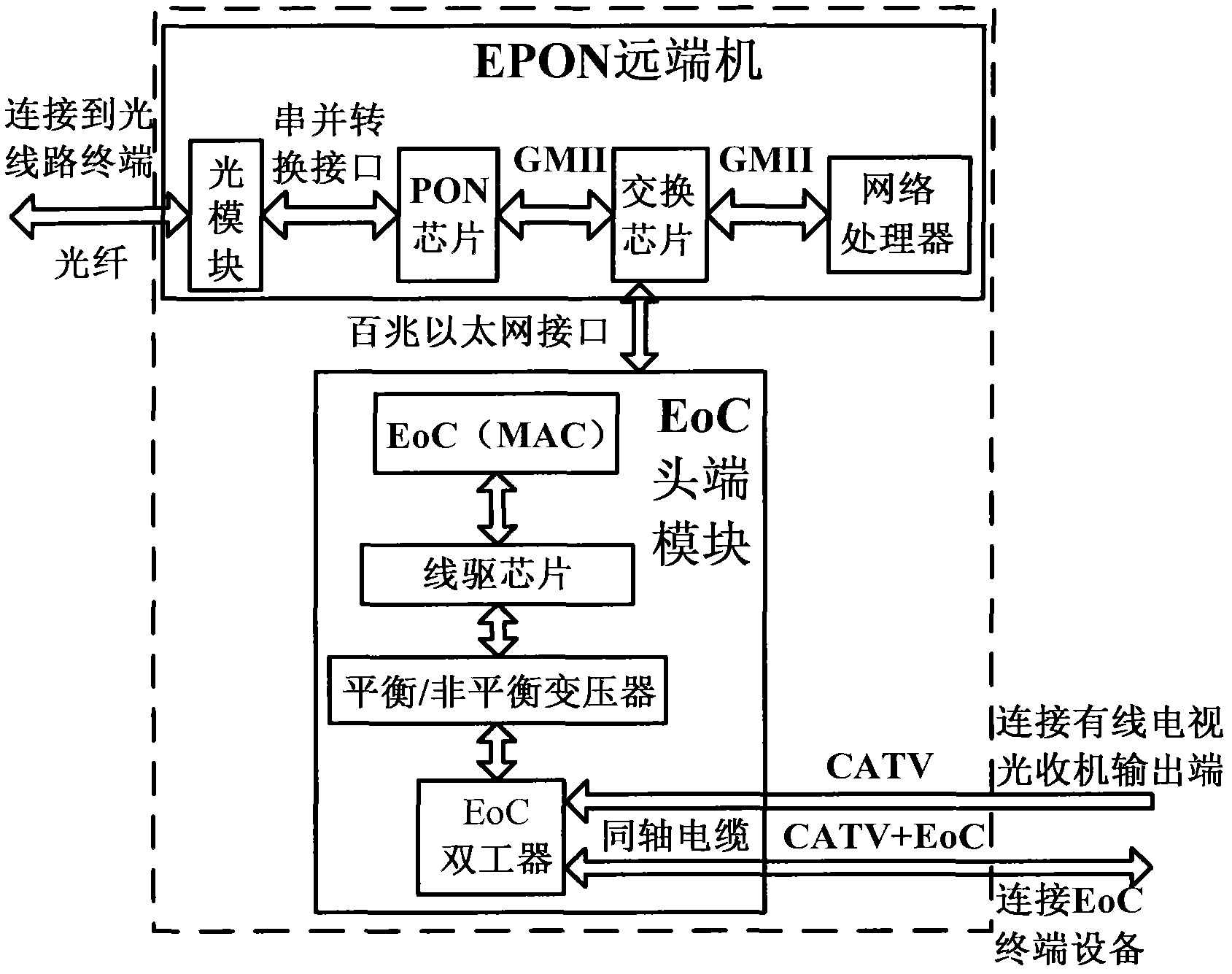
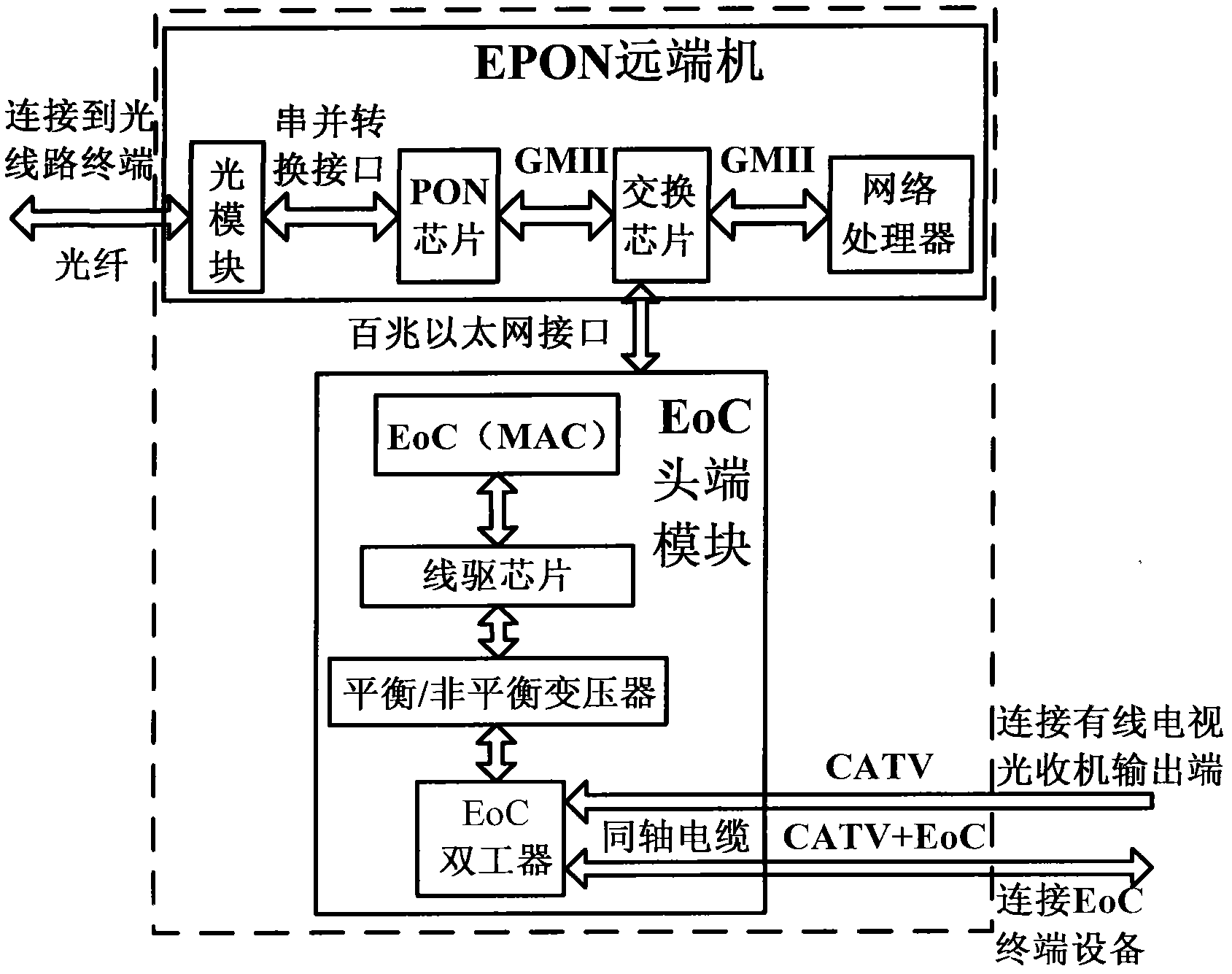
Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) optical network unit fusing Ethernet over coaxial cable (EoC) function
ActiveCN102437941ARealize integrationAchieve accessMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationAnti jammingMegabit
The invention discloses an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) optical network unit fusing an Ethernet over coaxial cable (EoC) function. The optical network unit comprises an EPON remote terminal, an EoC head end and an inter-board connector, wherein the EPON remote terminal is connected with the EoC head end through the inter-board connector, and finishes equipment configuration management and the PON access of Internet protocol (IP) data; the inter-board connector transmits megabit Ethernet data, a resetting signal and a port connection status indicator signal; and the EoC head end finishes conversion between the Ethernet data and low-frequency EoC data and the coupling of high-frequency / low-frequency EoC data. By the optical network unit, the accessing of an EoC signal can be realized on the basis of no influence of original coaxial network performance and no change of a coaxial network topology structure, the volumes and sorts of networking equipment can be decreased, a mounting procedure can be simplified, power consumption can be reduced, unified management can be realized, operation and maintenance cost can be decreased, networking flexibility and high network adaptability can be achieved, the capability of communication with terminal equipment and anti-jamming capability are high, and transmission frequency points can be flexibly selected.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Multi-channel video pump
InactiveUS20060262813A1Accurate recoveryTelevision system detailsTime-division multiplexNetwork packetMegabit
A system for streaming a plurality of video or other recorded signals from storage to receiving devices maintains each of the signal streams at their encoded bit rate. The bit rate of each stream is detected from the stored signals and a corresponding queue is set up in memory or in a network interface card for outputting data at the detected bit rate. A channel timing module in the signal streaming device contains a two-stage dithered counter for each bit rate. The first stage of the counter counts one clock cycle longer than the second stage. By adjusting the ratio of the first stage and second stage counters in a fixed number of cycles (the dither cycle) a very precise average count is achieved. The average count is calculated to achieve the desired bit rate with a given packet size. Every time either the first stage of the second counter times out, a packet of data is sent to the corresponding queue in the network interface. As a result, the network interface is able to output packet isochronous signals with an average bit rate within one bit per second of desired bit rates between one megabit / second and 20 megabit / second and with a jitter of less than two milliseconds.
Owner:DIGITAL NETWORKS NORTH AMERICA
System and method for power saving modes in high speed serial interface communication systems by utilizing selective byte synchronization
A system and method for minimizing power consumption in a transceiver circuit (500) are provided. The circuit uses a digital high-speed serial communications link between at least two devices. Comma code matching is generally used as a means for establishing byte synchronization and for determining and preventing data transfer errors. However, comma code matching, when performed in high speed serial communications links that can transfer data at rate of thousands of megabit per second, can use a significant amount of power. Thus, the system and method described herein maintain comma code matching in an off-state, and transform comma code matching from an off-state to an on-state when a substantive operational change occurs in the serial communications link.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Managed gigabit industrial Ethernet switch supporting technology for quickly recovering redundancy within 5 ms and meeting requirements of rail traffic control system
InactiveCN102223222AShorten the timeDoes not affect normal communicationError preventionData switching networksIndustrial EthernetControl system
The invention discloses a managed gigabit industrial Ethernet switch supporting a technology for quickly recovering redundancy within 5 ms and meeting requirements of a rail traffic control system. By adoption of a new redundancy algorithm, master and slave switches are selected, and a normal link and a backup link are determined; the communication state of a port is determined by using an interrupted and polling monitoring method; switching between the backup link and the normal link is realized by changing the state of the port; and the recovery time of a gigabit redundancy technology is shortened to be less than 5 ms, and the recovery time of a megabit redundancy technology is shortened to be less than 15 ms.
Owner:SUZHOU HENGQI AUTOMATION ENG
Direct comparison type FPGA-ADC device based on single carry chain
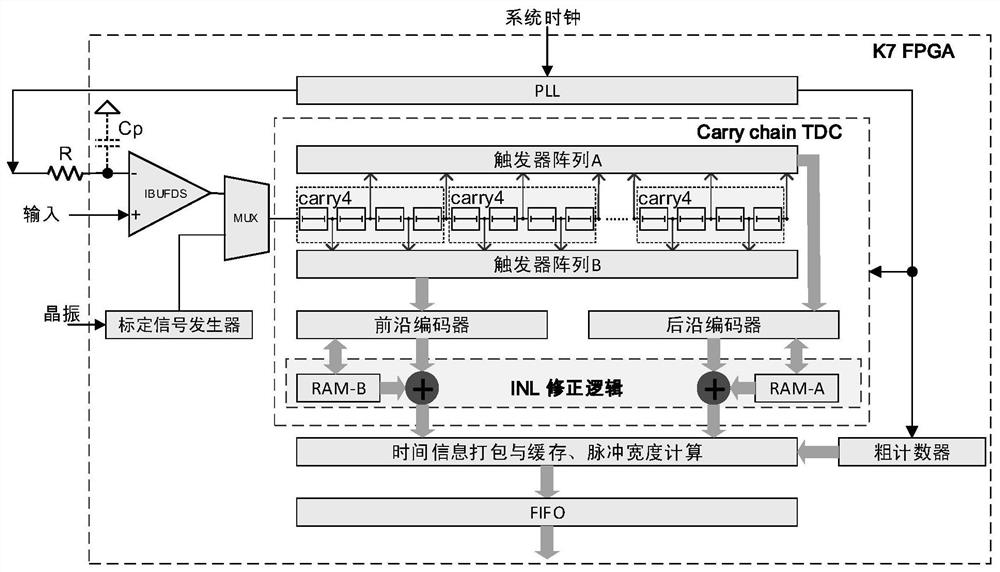
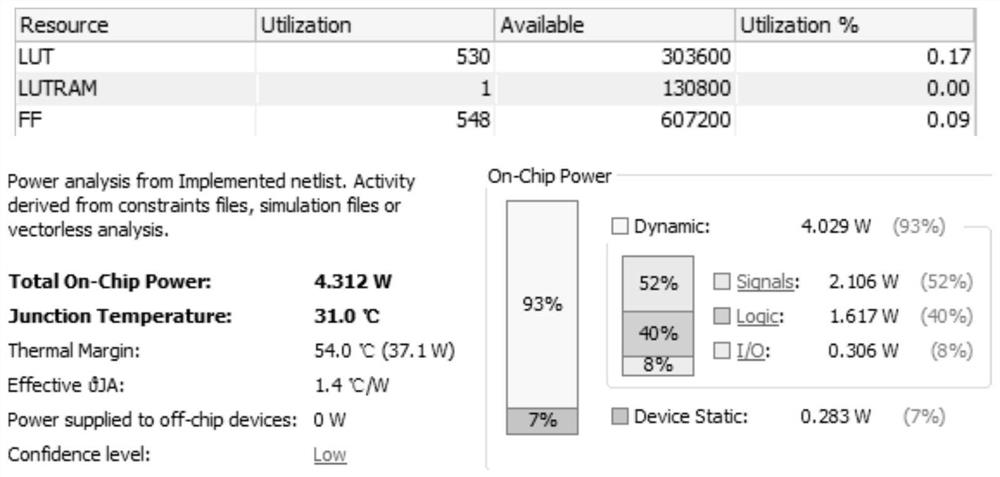
PendingCN111610549ASimple structureLow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceSoftware engineering
The invention provides a direct comparison type FPGA-ADC device based on a single carry chain, and relates to the technical field of medical imaging equipment. The device comprises a calibration signal generator, a low-pass filter circuit, a comparator, a clock generator, a carry chain time measurement module, a fine time coding circuit, a coarse time counter, a nonlinear correction circuit, a pulse width calculation circuit and the like. The clock generator generates a sampling clock, and the sampling clock is compared with an input analog signal through the FPGA internal comparator after passing through the low-pass filter circuit, thereby obtaining a to-be-measured pulse. The width of the to-be-measured pulse can be approximately proportional to the amplitude of the input analog signal,and analog-to-digital conversion can be completed by measuring the pulse width of the to-be-measured pulse. Based on FPGA chip logic codes and an off-chip simple resistance-capacitance discrete device (a low-pass filter), the ADC with low cost, low power consumption, high integration level and high performance and the 100-megabit magnitude sampling rate can be realized, and the ADC has great significance for a whole detector and even a PET system.
Owner:FMI MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Space target characteristic identification device based on image sensing technology
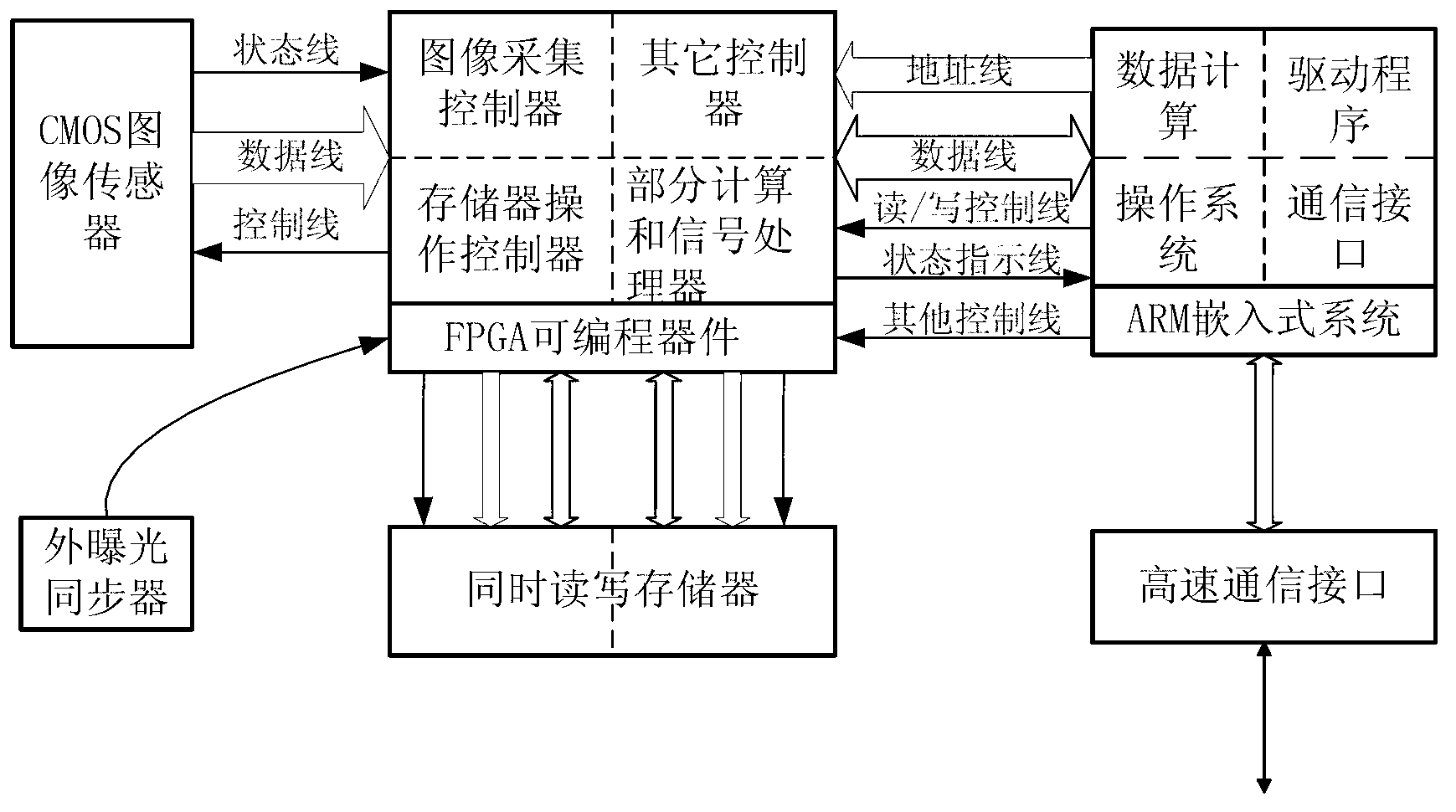
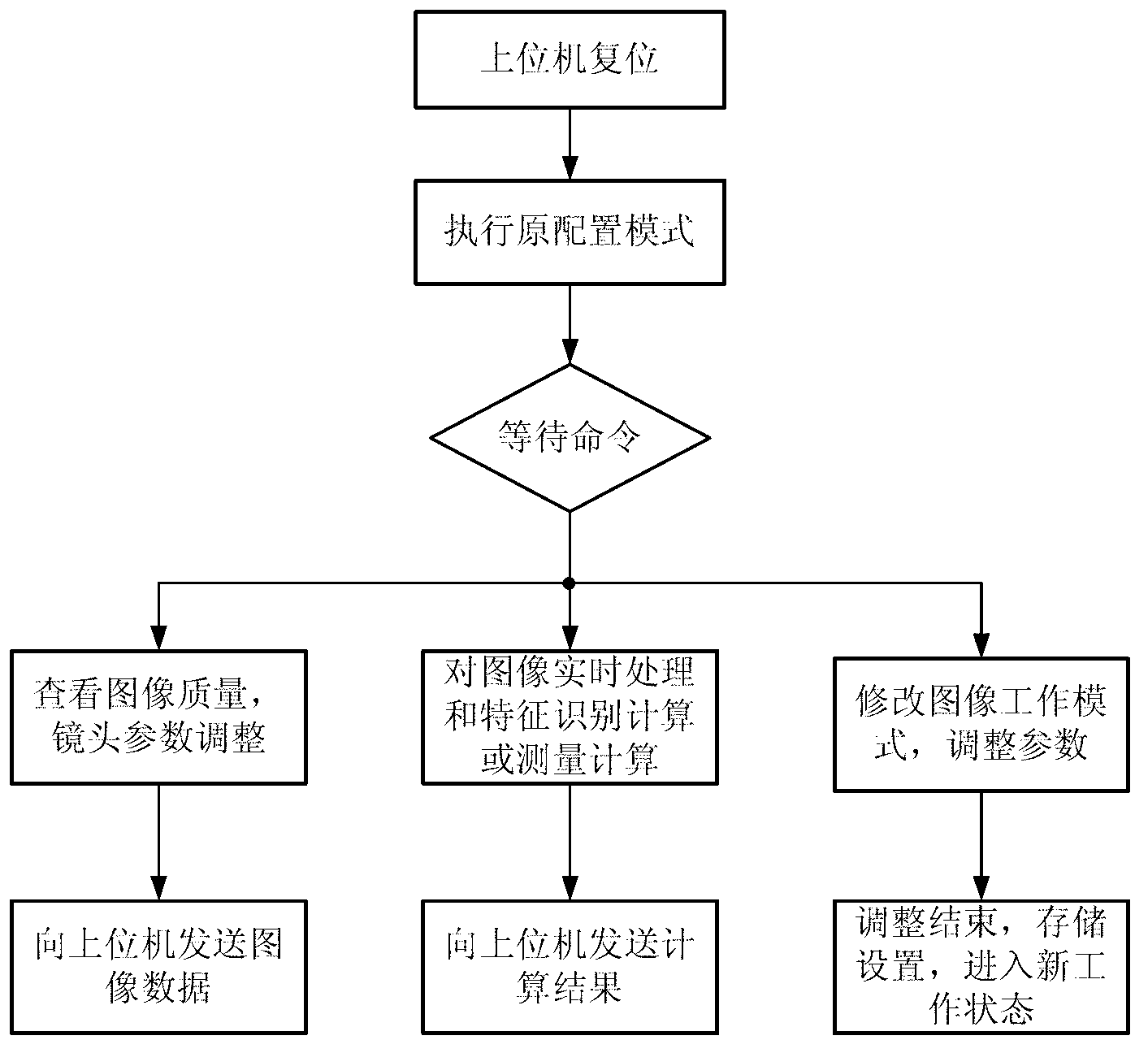
InactiveCN103226707AReduce the burden onEasy to useCharacter and pattern recognitionMicrocontrollerMeasurement device
The invention belongs to the technical field of embedded information and relates to a space target characteristic identification or measurement device based on an image sensing technology. The device is characterized in that an image sensor is a high-frame or high-density complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) device; after the image sensor is driven, a digital image signal is output; the data quantity is large and can be hundreds of megabits to thousands of megabits at each second, so a high-speed data acquisition circuit, a storage circuit and a high-speed communication circuit are necessarily adopted; and when characteristic identification or measuring calculation is performed, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) circuit and a microcontroller circuit coordinate to calculate hierarchically. Therefore, image signal acquisition, image signal processing, image characteristic identification or measuring calculation must be performed simultaneously. A high-frame or high-density image acquisition and processing complex huge structure is concentrated into a minitype industrial camera, so the device is convenient to use, in particular, when multiple devices are used simultaneously, a huge number of image data does not need to be transmitted in a network and the burden of the network is reduced. The device has a small size, saves energy and is particularly suitable for being used outdoors.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Multi-carrier light transmitting method of light access system with multi-path signal
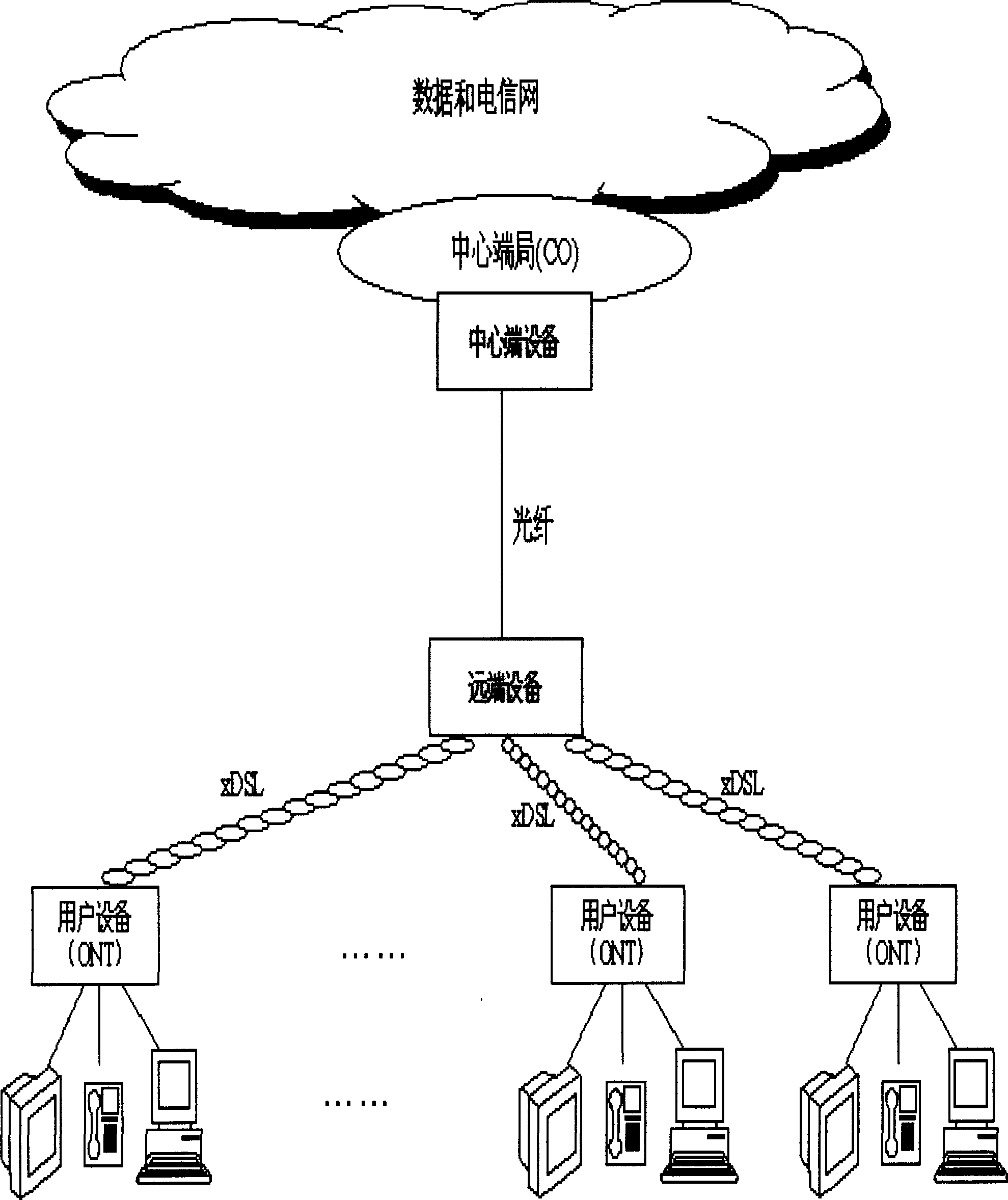
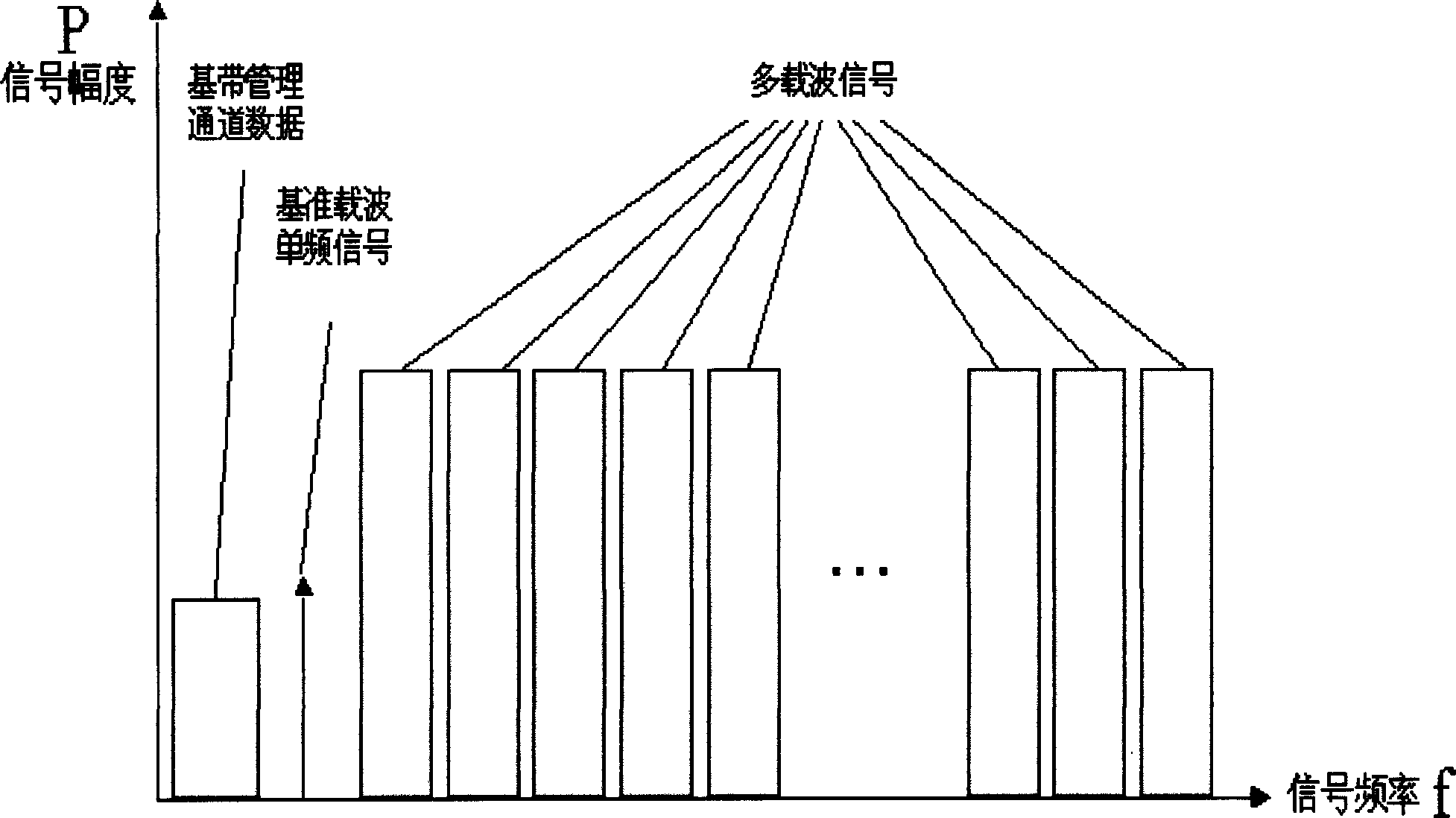
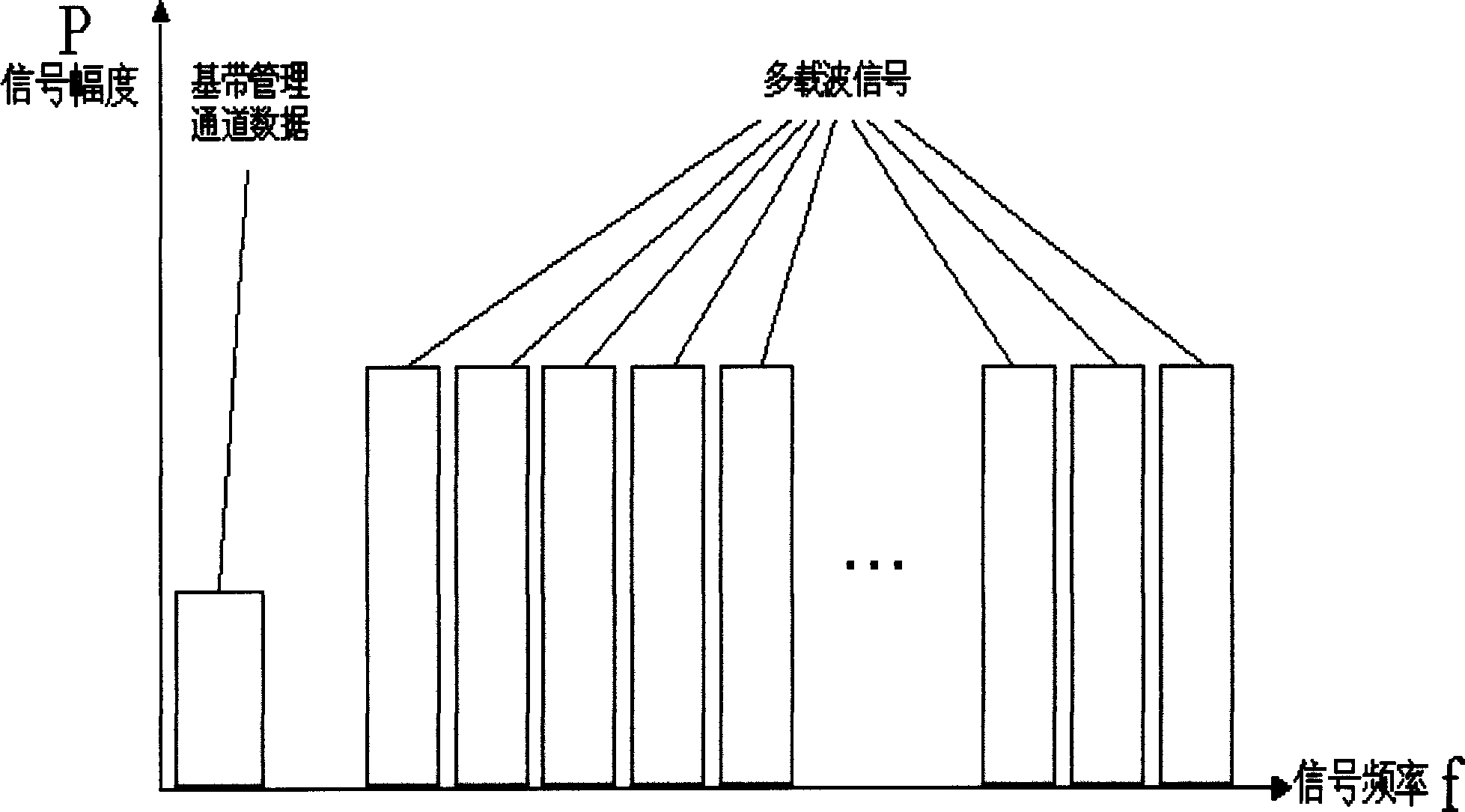
InactiveCN1819500AIncrease distanceIncrease speedOptical multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsTransceiverMegabit
Though xDSL technology takes up main share in network access market, but in company with increasing access distance the access rate drops from a few of decade megabit to hundreds kilobit. The invention can keeps maximum access rate of xDSL in a long distance access and includes: a multi-carrier modulation with different frequency is used to transparently pack multi-way xDLS signal to be transmitted, and then optical transceiver outputs the multi-way xDSL signal; the transmission reference signal is used to implement the synchronous demodulation for the multi-way modulation signal; the message interaction channel is used to implement the control and interaction for devices at accessing end and accessed end.
Owner:沈红
Large-scale service-rate regulators for ATM switching
Techniques of service-rate controls in ATM switches are described, and apparatus for their implementation are devised. The techniques fall in two categories: frequency domain controls, and time-domain controls. The regulators control the service rate on a per-class basis or on a per-connection basis. Some class regulators operate at very high speeds of the order of several gigabits per second and cover a medium number of classes, 32 for example. Other regulators operate at high speeds of the order of several-hundred megabits per second, and cover a very large number of classes, e.g., 10000. A compound regulator which combines both types of regulators is also described. The compound regulators extend the range of controllable classes considerably, covering some 200,000 classes. The main advantages of the regulators of the invention are simplicity, robustness, and high performance.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Parallel service-rate controllers in ATM switches
Techniques of service-rate controls in ATM switches are described, and apparatus for their implementation are devised. The techniques fall in two categories: frequency domain controls, and time-domain controls. The regulators control the service rate on a per-class basis or on a per-connection basis. Some class regulators operate at very high speeds of the order of several gigabits per second and cover a medium number of classes, 32 for example. Other regulators operate at high speeds of the order of several-hundred megabits per second, and cover a very large number of classes, e.g., 10000. A compound regulator which combines both types of regulators is also described. The compound regulators extend the range of controllable classes considerably, covering some 200,000 classes. The main advantages of the regulators of the invention are simplicity, robustness, and high performance.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
24-port optical switch supporting megabit optical fiber and gigabit optical fiber at the same time
InactiveCN106506406AFirmly connectedMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksMultiplexingMicrocontroller
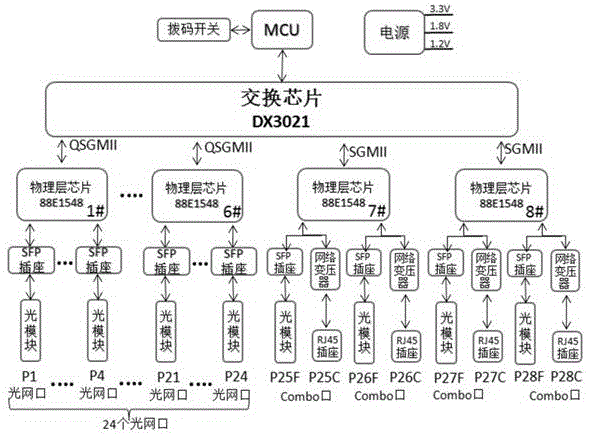
The invention discloses a 24-port optical switch supporting a Megabit optical fiber and a Gigabit optical fiber at the same time. The 24-port optical switch comprises a PCB mainboard, wherein a power supply chip, a microcontroller and a switching chip are arranged on the PCB mainboard. The microcontroller is connected with a DIP switch. The microcontroller is connected with the switching chip. The switching chip is connected with eight physical layer chips. The first to sixth physical layer chips are connected with four SFP sockets. Each SFP socket is connected with an optical module. The optical modules are connected with optical network ports, and totally, 24 optical network ports are formed. The seventh to eighth physical layer chips are respectively connected with two groups of photoelectric multiplexing modules. Each photoelectric multiplexing module comprises an SFP socket and a network transformer. The SFP sockets are connected with the optical modules. The network transformers are connected with RJ45 sockets. The optical modules and the RJ45 sockets are together connected with Combo interfaces. According to the 24-port optical switch, matched chips of the 24-port MAC switching chip 98DX3021 and the physical layer chips 88E1548 are employed; the physical layer chips 88E1548 support 1000Base-X and 100Base-FX; through selection of the DIP switch, both the Gigabit optical fiber and the Megabit optical fiber are supported; and the 24-port optical switch is very convenient.
Owner:深圳市立全鼎盛科技有限公司
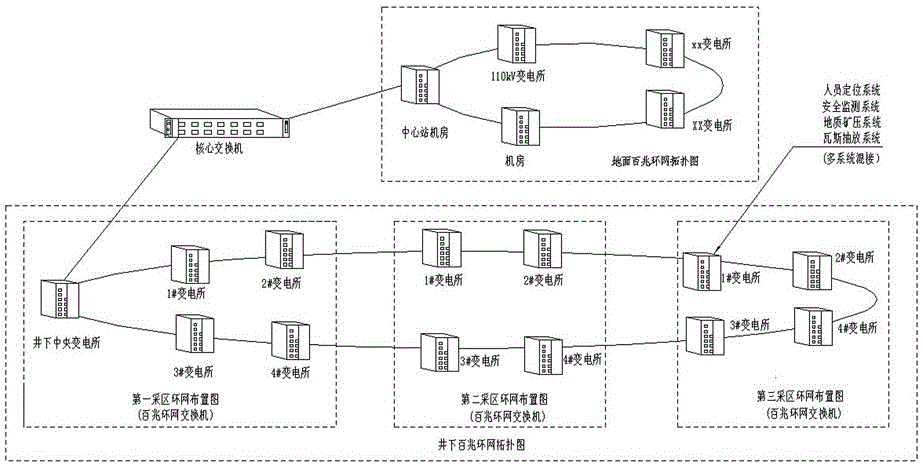
Visual mine network networking system and method
InactiveCN106301943AReduce data trafficCommunication does not affectClosed circuit television systemsNetworks interconnectionRing networkMegabit
The invention belongs to the technical field of coal mine data transmission and specifically relates to a visual mine network networking system and method, for solving the problem of providing a visual mine network operation state monitoring system and method so as to perform real-time monitoring, query and fault analysis on the operation state of a mine network system. The technical scheme employed by the invention is as follows: the visual mine network networking system comprises a remote management host, a core switch network, a ground megabit ring network, an underground gigabit ring network and an underground megabit ring network, wherein the ground megabit ring network, the underground gigabit ring network and the underground megabit ring network are connected with the remote management host through the core switch network.
Owner:YUWU COAL CO LTD OF SHANXI LUAN GRP
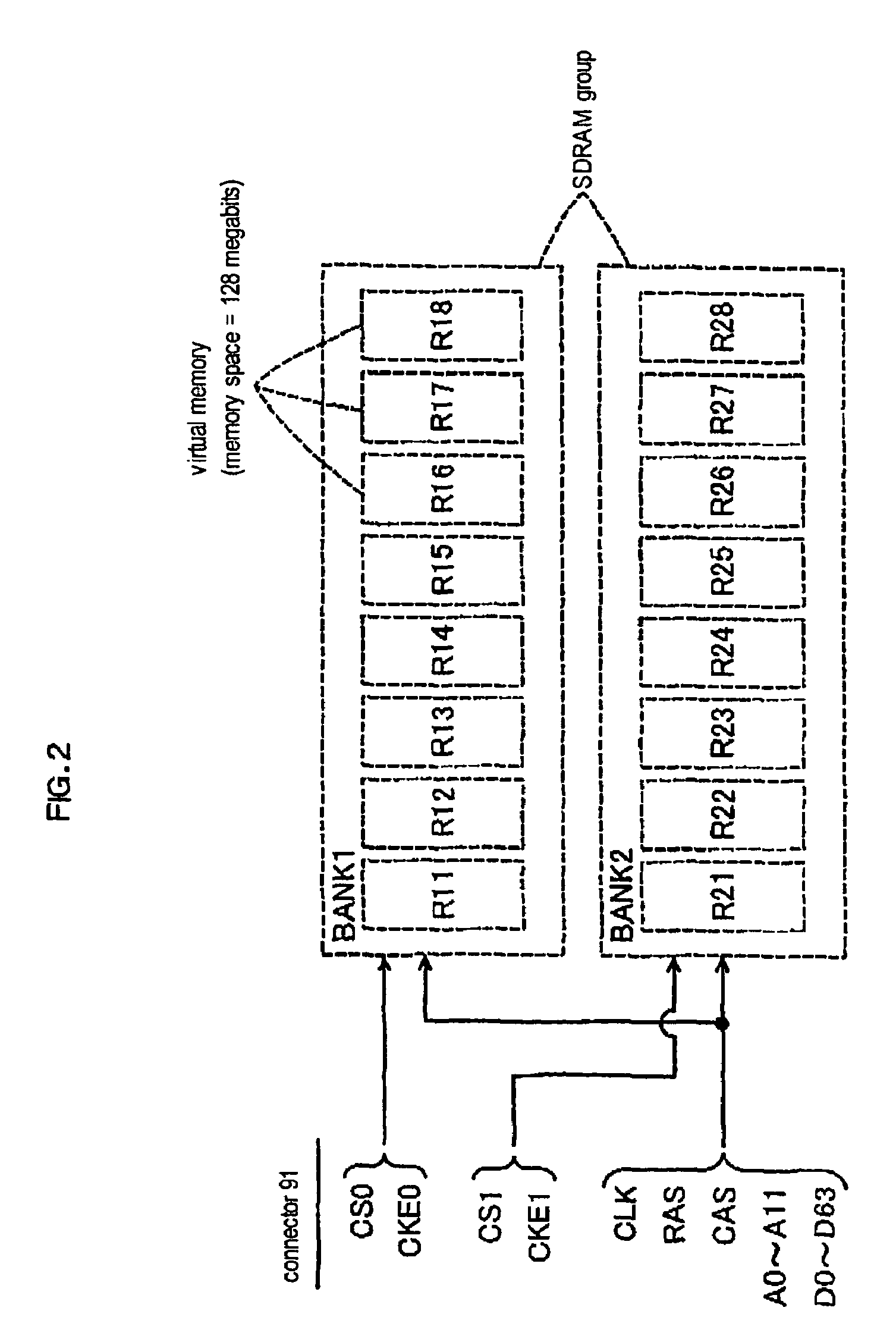
Memory module and memory-assist module
InactiveUS20050114622A1Easy to useMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMegabitMemory circuits
A computer body outputting only address signals A0 to A11 could use only a half area of a 256-megabit SDRAM. The memory circuit 30 receives a predetermined number of address signals A0 to A11 and a plurality of select signals CS0 and CS1, generates a memory select signal CS and an additional address signal A12 added to the signals A0 to A11 according to the inputted signals CS0 and CS1, and provides the signal CS, signal A12, and signals A0 to A11 to a 256-megabit SDRAM (memory), so that the computer body can access the corresponding data. The computer body can access the data corresponding to the generated additional address signal A12 and predetermined number of the address signals A0 to A11.
Owner:BUFFALO CORP LTD
Megabit protocol analysis method and megabit protocol analysis method
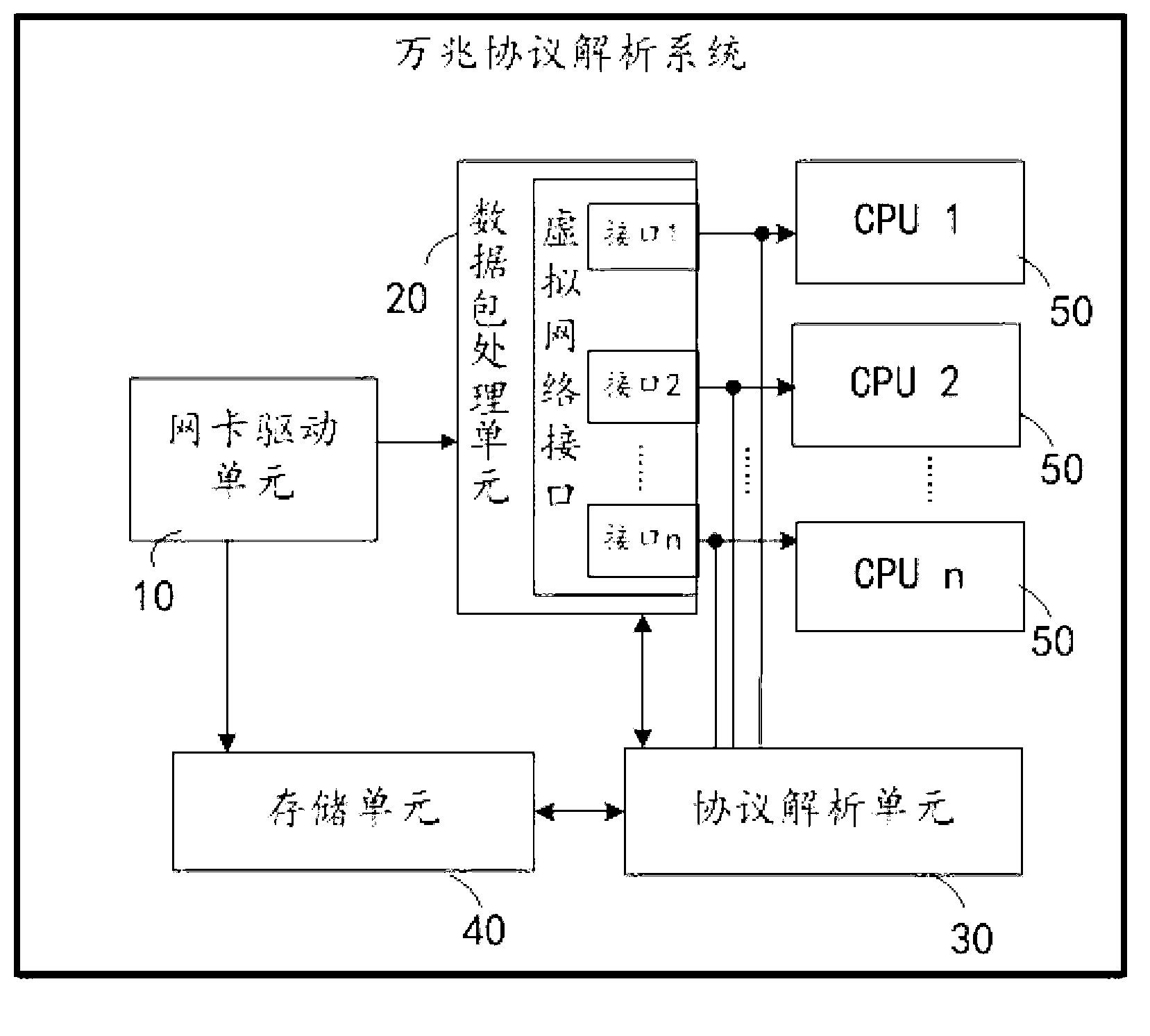
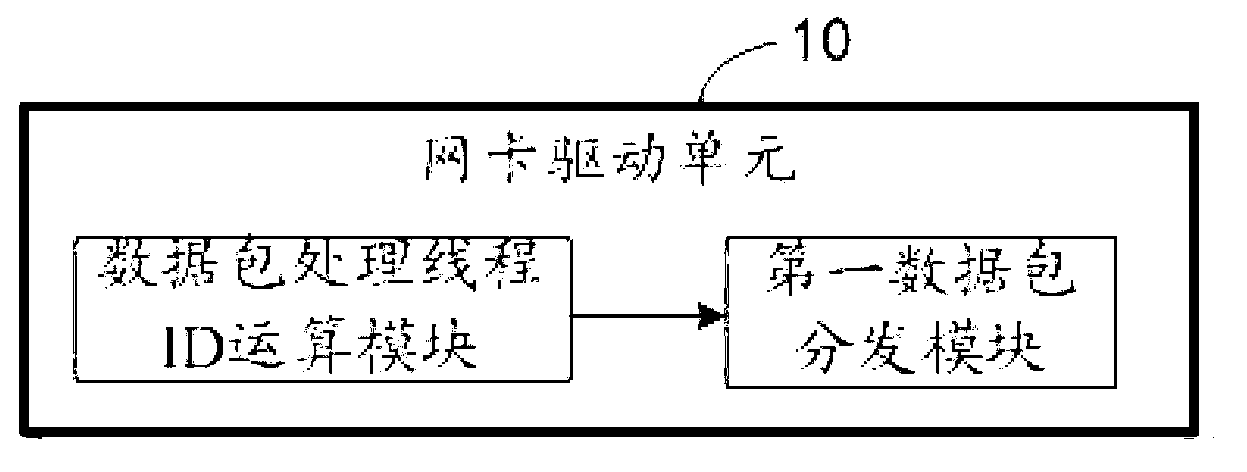
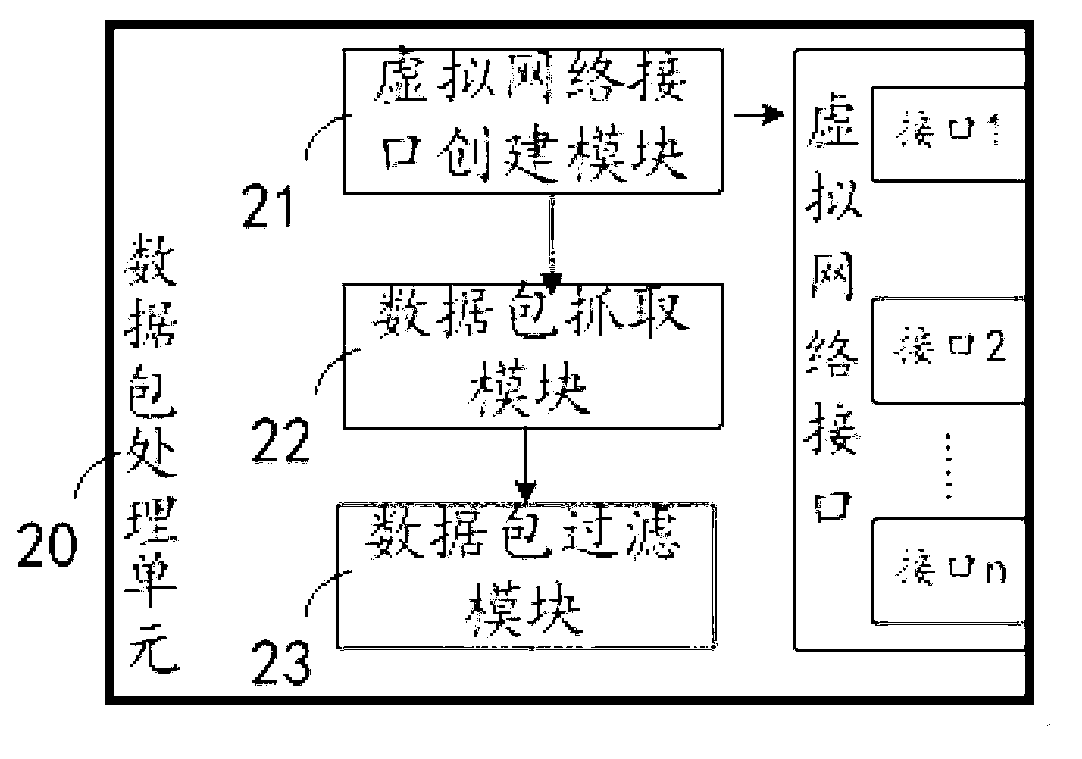
The invention discloses a megabit protocol analysis method. The megabit protocol analysis method includes steps that a network card driving unit computes first hash values of data packets and data packet processing thread IDs (identities) and distributes the data packets to data packet processing threads of corresponding CPUs (central processing units); a data packet processing unit creates a corresponding virtual network interface for each CPU, and received data packets are filtered and are transmitted to the corresponding CPUs; and after monitoring that the virtual network interfaces receive the data packets, a protocol analysis unit computes second hash values of the data packets and protocol analysis thread IDs, whether first hash values equal to the second hash values are available in a data packet distribution list or not is judged, the data packets are distributed onto protocol analysis data link lists corresponding to the protocol analysis thread IDs in a semaphore manner, and the data packets on the protocol analysis data link lists in the semaphore manner are subjected to protocol analysis, reassembling, in-storeroom and indexing operation. The invention further discloses a megabit protocol analysis system.
Owner:XIAMEN MEIYA PICO INFORMATION
Light-emitting diode (LED) screen control system
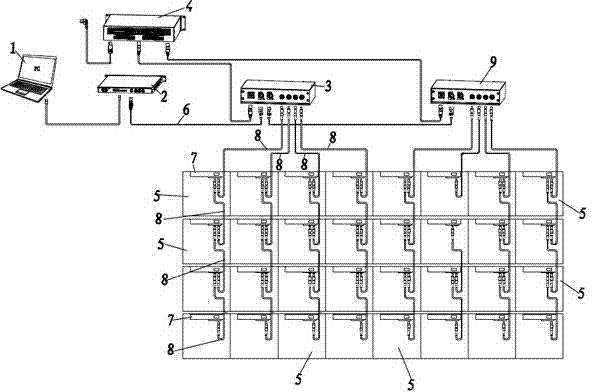
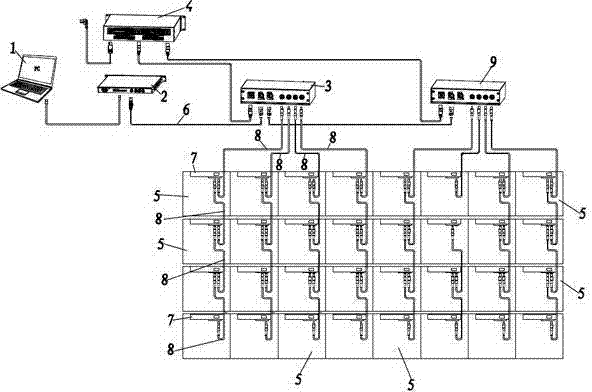
InactiveCN102419701ASimple structureFirmly connectedStatic indicating devicesDigital output to display deviceMegabitEngineering
The invention provides a light-emitting diode (LED) screen control system. Video signal output equipment is connected with a gigabit control system, the gigabit control system is connected with a first data distributor by a gigabit network line, a power supply unit is connected with the first data distributor by a power line, each LED screen unit comprises an LED display screen and a control unit which is connected with the LED display screen and comprises two interfaces, the first data distributor is connected with one interface of the control unit by a megabit network line, a plurality of LED screen units are provided and serially connected by the megabit network line to form a display module, one end of the megabit network line is inserted into one interface of the control unit, and the other end of the megabit network line is inserted into the other interface of the control unit. The megabit network line is a four-core line, two lines are the power lines, and the other two lines are data lines.
Owner:钟再柏
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com